Diffusion Models
⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 Google的大语言模型Gemini-Pro的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-03-09 更新
Pix2Gif: Motion-Guided Diffusion for GIF Generation
Authors:Hitesh Kandala, Jianfeng Gao, Jianwei Yang
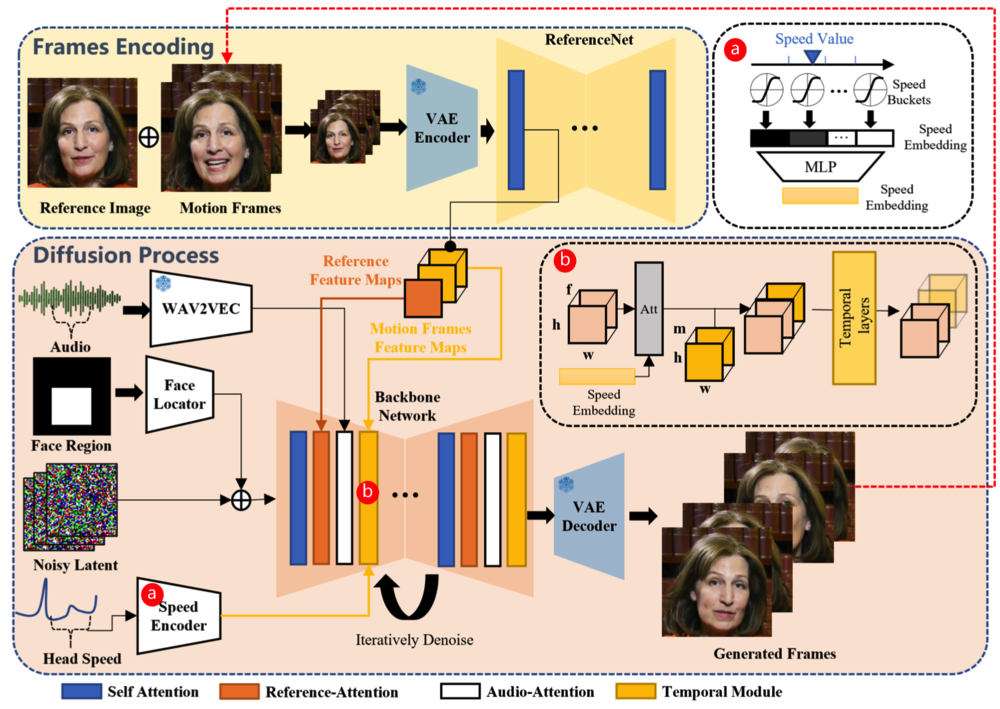
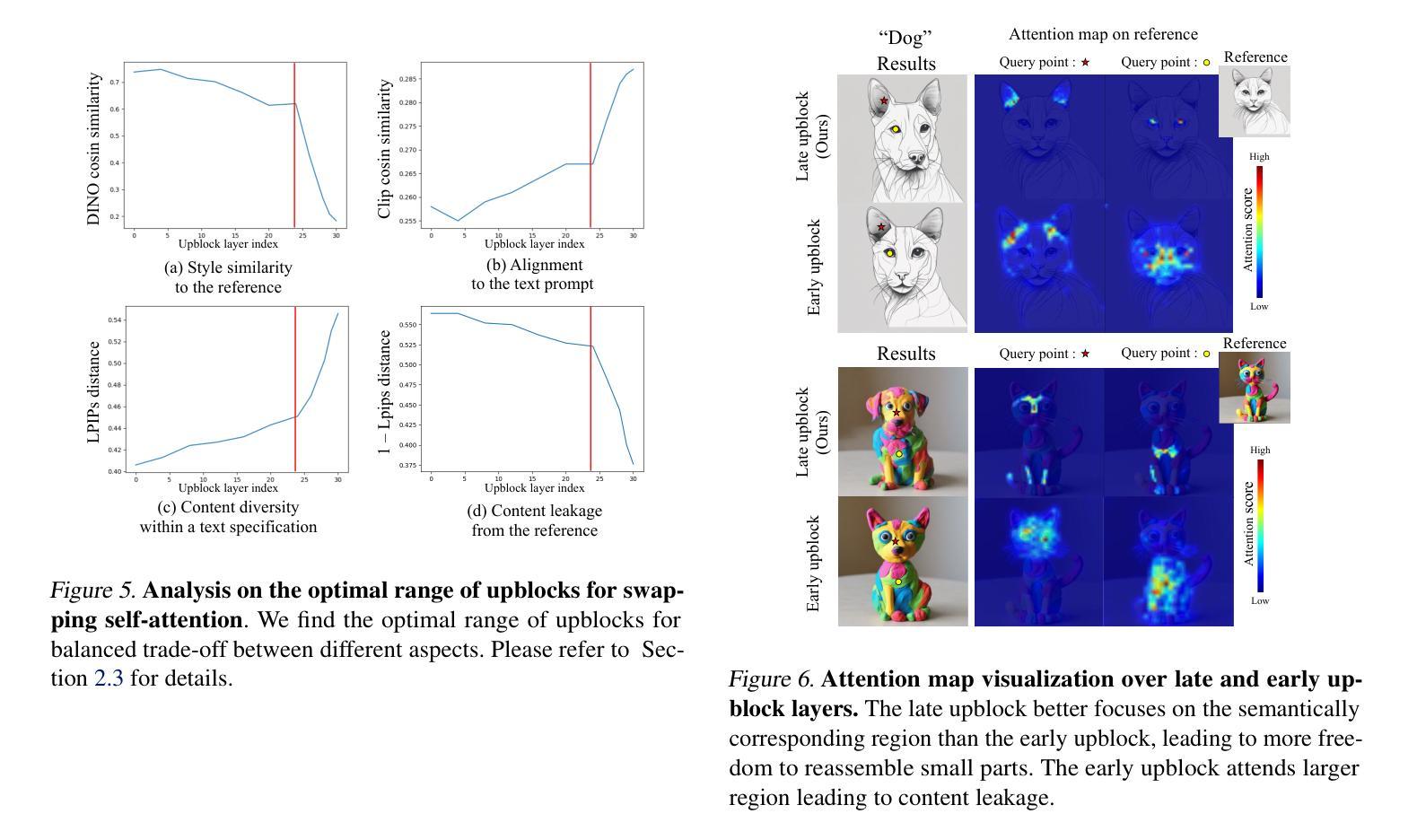
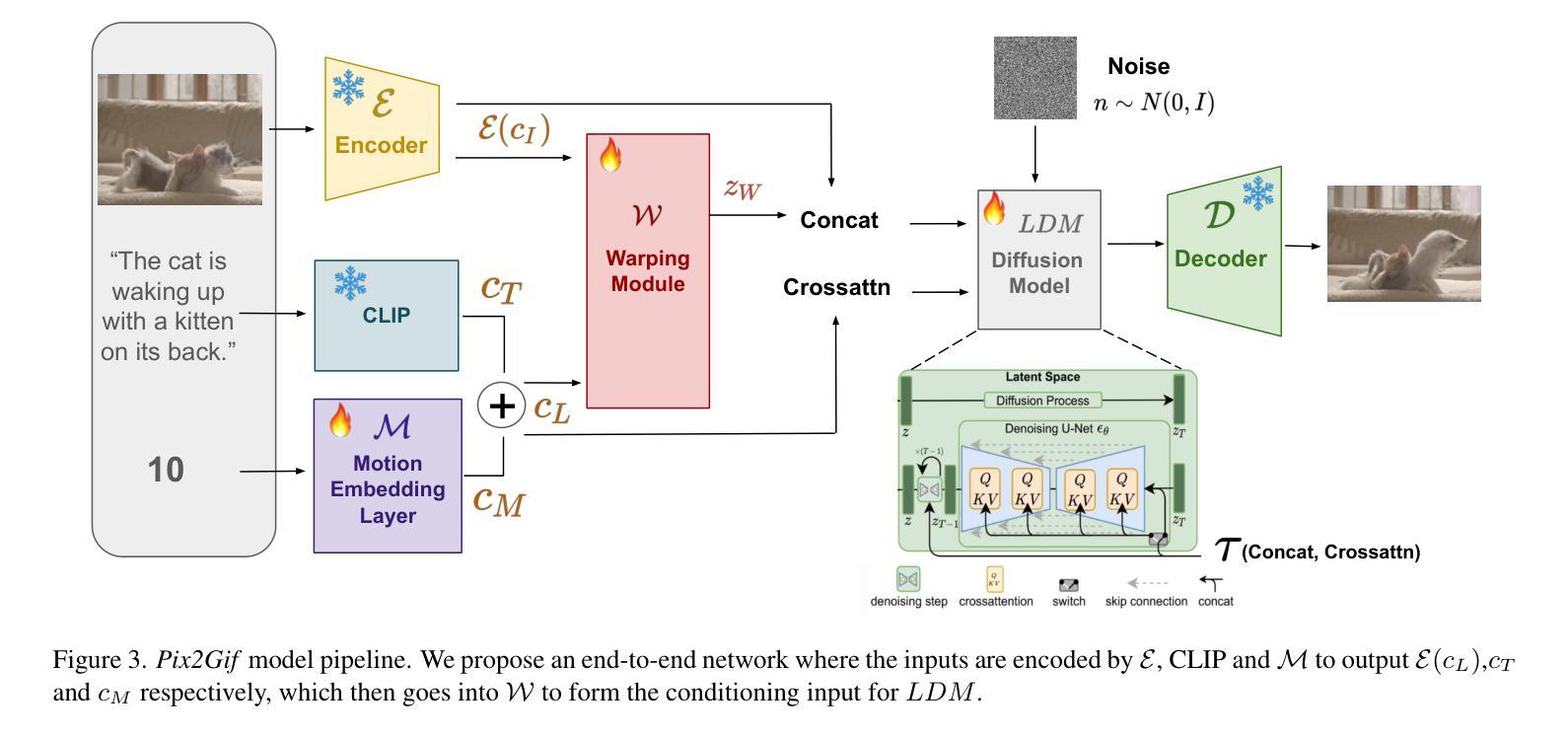
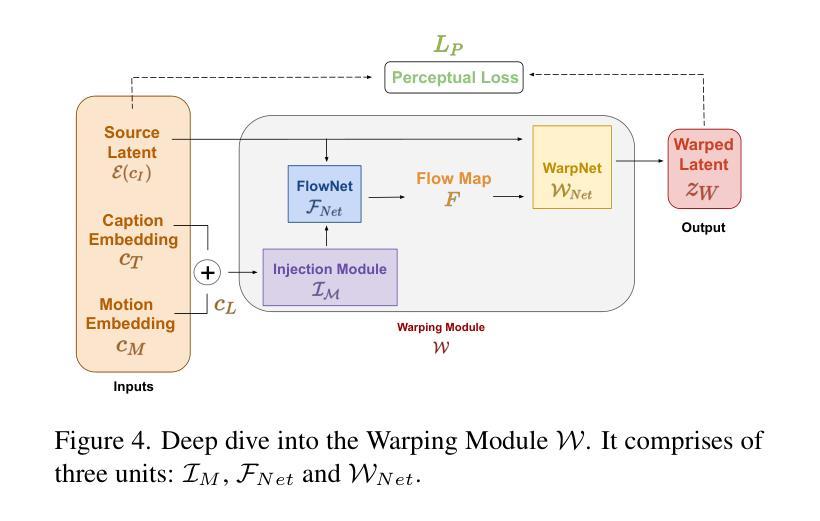
We present Pix2Gif, a motion-guided diffusion model for image-to-GIF (video) generation. We tackle this problem differently by formulating the task as an image translation problem steered by text and motion magnitude prompts, as shown in teaser fig. To ensure that the model adheres to motion guidance, we propose a new motion-guided warping module to spatially transform the features of the source image conditioned on the two types of prompts. Furthermore, we introduce a perceptual loss to ensure the transformed feature map remains within the same space as the target image, ensuring content consistency and coherence. In preparation for the model training, we meticulously curated data by extracting coherent image frames from the TGIF video-caption dataset, which provides rich information about the temporal changes of subjects. After pretraining, we apply our model in a zero-shot manner to a number of video datasets. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our model — it not only captures the semantic prompt from text but also the spatial ones from motion guidance. We train all our models using a single node of 16xV100 GPUs. Code, dataset and models are made public at: https://hiteshk03.github.io/Pix2Gif/.
Summary
图像到 GIF(视频)生成中的运动引导扩散模型 Pix2Gif,通过文本和运动幅度提示将任务表示为图像翻译问题。
Key Takeaways
- Pix2Gif 是一个用于图像到 GIF(视频)生成的运动引导扩散模型。
- Pix2Gif 将任务表述为由文本和运动幅度提示指导的图像翻译问题。
- Pix2Gif 提出了一种新的运动引导变形模块,以根据两种类型的提示对源图像的特征进行空间变换,确保模型遵守运动指导。
- Pix2Gif 引入了感知损失,以确保变换后的特征图保持在与目标图像相同空间内,从而确保内容一致性和连贯性。
- Pix2Gif 使用从 TGIF 视频字幕数据集中提取的连贯图像帧对数据进行了精心整理,该数据集提供了有关对象时间变化的丰富信息。
- Pix2Gif 以零样本方式将模型应用于多个视频数据集,取得了出色的效果。
- Pix2Gif 不仅可以捕捉文本中的语义提示,还可以捕捉运动引导中的空间提示。
- 标题:Pix2Gif:基于运动引导的图像到 GIF 生成
- 作者:Hitesh Khandelwal、Alexei A. Efros、Pieter Abbeel、William T. Freeman
- 隶属机构:马萨诸塞理工学院计算机科学与人工智能实验室
- 关键词:图像到 GIF 生成、运动引导、扩散模型、图像翻译
- 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.08206 Github 代码链接:None
摘要: (1): 研究背景:图像到 GIF 生成任务旨在将静态图像转换为动态 GIF 图像。现有的方法主要依赖于文本提示来指导生成,但缺乏对运动信息的利用。 (2): 过去方法:传统的图像到 GIF 生成方法使用文本提示来指导生成,但这些方法无法充分利用运动信息。 (3): 研究方法:本文提出 Pix2Gif 模型,该模型采用运动引导的扩散模型,通过引入运动嵌入层和运动引导的变形模块,将运动信息融入图像生成过程中。 (4): 实验结果:Pix2Gif 模型在 TGIF 视频字幕数据集上进行了训练和评估,结果表明该模型能够有效捕获文本提示中的语义信息和运动提示中的空间信息,生成高质量的 GIF 图像。
方法: (1): 引入运动嵌入层,将运动信息编码为连续向量; (2): 设计运动引导变形模块,利用运动嵌入层引导图像变形; (3): 采用扩散模型,通过逐步增加噪声并反向扩散,生成图像; (4): 将运动信息融入扩散模型中,指导图像生成过程。
结论 (1):xxx; (2):创新点:xxx;性能:xxx;工作量:xxx;
点此查看论文截图

Controllable Generation with Text-to-Image Diffusion Models: A Survey
Authors:Pu Cao, Feng Zhou, Qing Song, Lu Yang
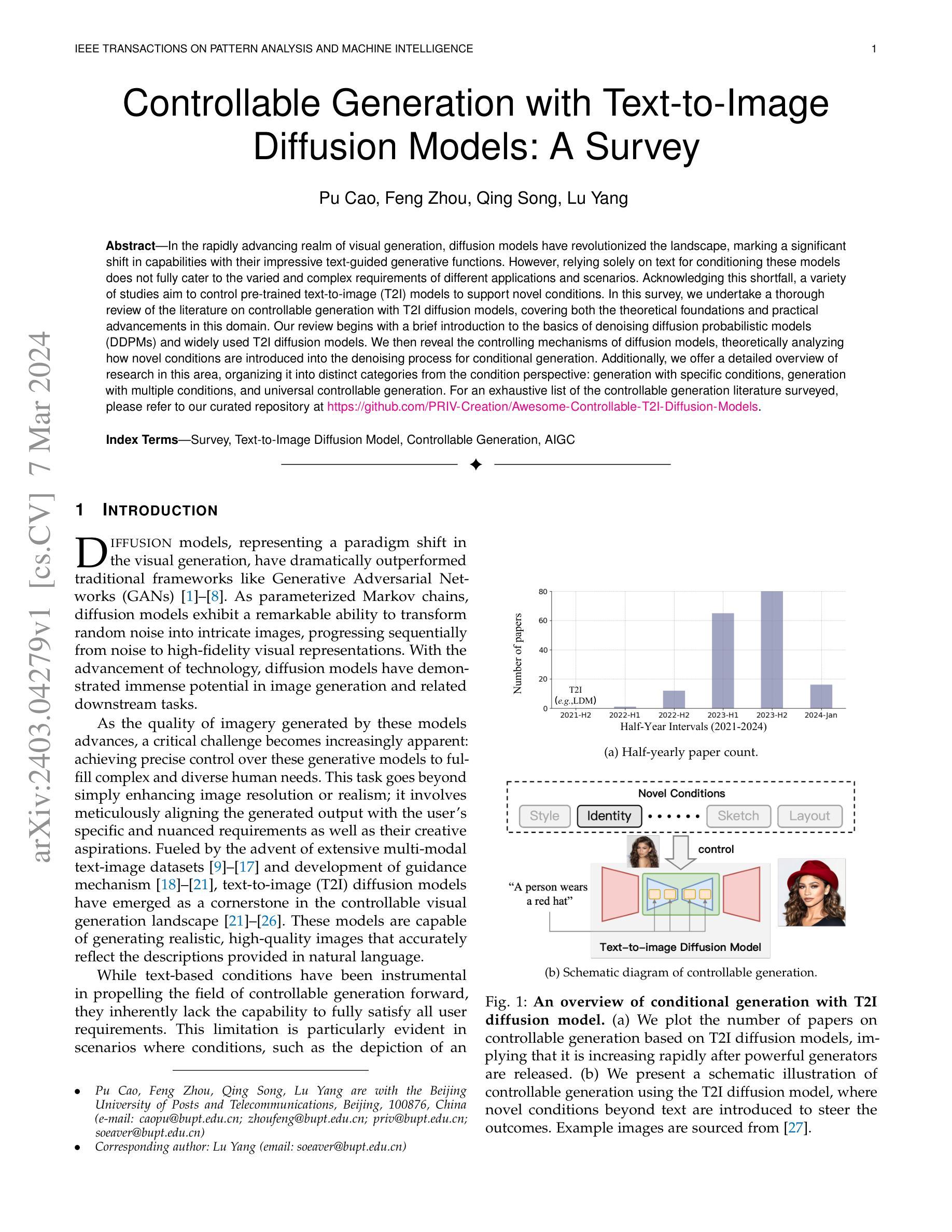
In the rapidly advancing realm of visual generation, diffusion models have revolutionized the landscape, marking a significant shift in capabilities with their impressive text-guided generative functions. However, relying solely on text for conditioning these models does not fully cater to the varied and complex requirements of different applications and scenarios. Acknowledging this shortfall, a variety of studies aim to control pre-trained text-to-image (T2I) models to support novel conditions. In this survey, we undertake a thorough review of the literature on controllable generation with T2I diffusion models, covering both the theoretical foundations and practical advancements in this domain. Our review begins with a brief introduction to the basics of denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs) and widely used T2I diffusion models. We then reveal the controlling mechanisms of diffusion models, theoretically analyzing how novel conditions are introduced into the denoising process for conditional generation. Additionally, we offer a detailed overview of research in this area, organizing it into distinct categories from the condition perspective: generation with specific conditions, generation with multiple conditions, and universal controllable generation. For an exhaustive list of the controllable generation literature surveyed, please refer to our curated repository at \url{https://github.com/PRIV-Creation/Awesome-Controllable-T2I-Diffusion-Models}.
PDF A collection of resources on controllable generation with text-to-image diffusion models: https://github.com/PRIV-Creation/Awesome-Controllable-T2I-Diffusion-Models
Summary
扩散模型可控生成综述:理论基础与实践进展
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已在文本指导生成中取得重大进展。
- 控制文本到图像 (T2I) 扩散模型是应对复杂应用场景的必要条件。
- 控制机制是将新条件引入扩散模型中的关键。
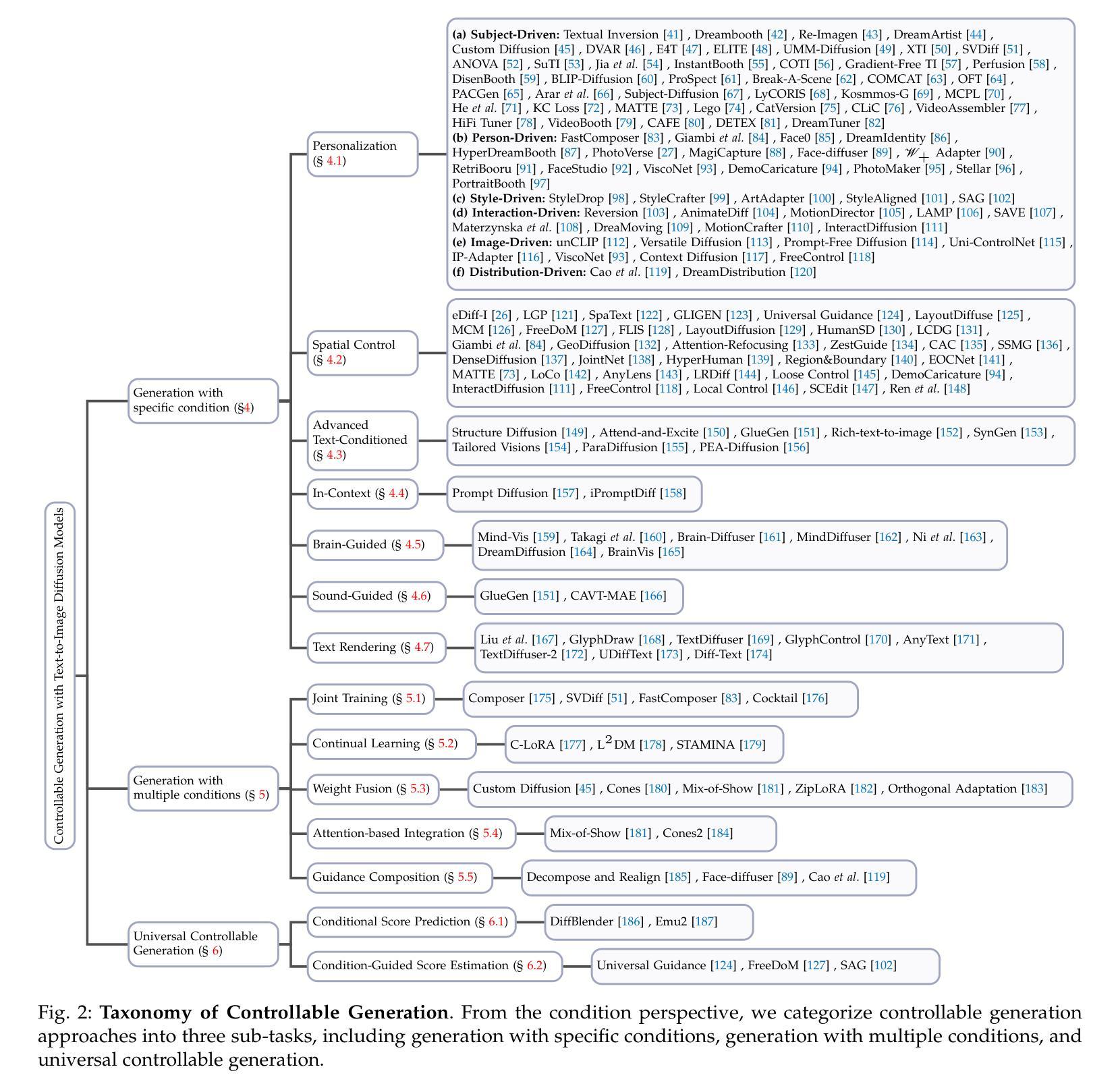
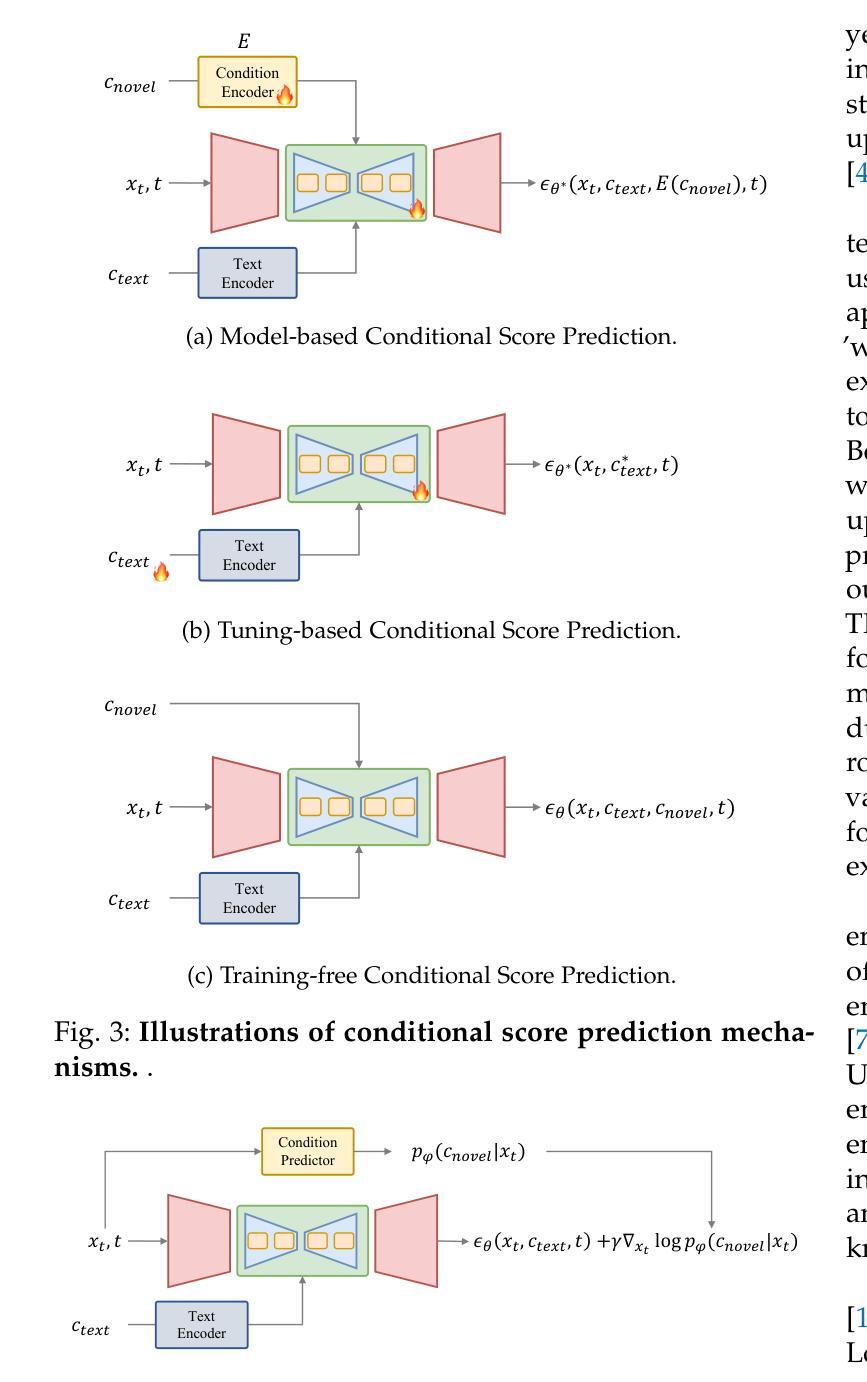
- 可控生成的研究按条件类型分为三类:特定条件、多条件和通用可控。
- 扩散概率去噪模型 (DDPM) 是扩散模型的基础。
- 文本指导扩散模型广泛用于可控图像生成。
- 有关可控生成文献的全面列表请参见 GitHub 存储库:https://github.com/PRIV-Creation/Awesome-Controllable-T2I-Diffusion-Models。
- 题目:可控生成:文本到图像扩散模型综述
- 作者:曹普、周峰、宋青、杨路
- 隶属单位:北京邮电大学
- 关键词:综述、文本到图像扩散模型、可控生成、AIGC
- 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.04279 Github 链接:无
- 摘要: (1) 研究背景:随着视觉生成领域的快速发展,扩散模型凭借其令人印象深刻的文本引导生成功能,彻底改变了该领域的格局。然而,仅依靠文本对这些模型进行条件化并不能完全满足不同应用和场景的多样化和复杂要求。 (2) 过去方法及其问题:现有的方法主要基于文本条件,但无法充分满足所有用户需求,尤其是在需要超出文本条件的场景中,例如特定条件生成、多条件生成和通用可控生成。 (3) 本文提出的研究方法:本文回顾了基于文本到图像扩散模型的可控生成文献,涵盖了该领域的理论基础和实际进展。我们从去噪扩散概率模型 (DDPM) 和广泛使用的文本到图像扩散模型的基础知识入手,然后揭示了扩散模型的控制机制,从理论上分析了如何将新颖条件引入去噪过程中以进行条件生成。此外,我们对该领域的研究成果进行了详细概述,并从条件的角度将其组织成不同的类别:特定条件生成、多条件生成和通用可控生成。 (4) 方法在什么任务上取得了什么性能:本文综述了可控生成文献,并提供了我们精心策划的存储库:https://github.com/PRIV-Creation/Awesome-Controllable-T2I-Diffusion-Models。
Some Error for method(比如是不是没有Methods这个章节)
- 结论: (1)本综述工作的重要性: 本综述全面深入地探讨了文本到图像扩散模型的可控生成领域,揭示了文本引导生成过程中引入的新颖条件。我们首先为读者提供了基础知识,介绍了去噪扩散概率模型、突出的文本到图像扩散模型以及结构良好的分类法。随后,我们揭示了在 T2I 扩散模型中引入新颖条件的机制。然后,我们总结了先前的条件生成方法,并从理论基础、技术进步和解决方案策略方面对其进行了分析。此外,我们探索了可控生成在实践中的应用,强调了其在 AI 生成内容时代的重要作用和巨大潜力。本综述旨在提供对可控 T2I 生成的当前格局的全面理解,从而为这个充满活力的研究领域的持续演进和扩展做出贡献。
(2)本文的优点和不足: 创新点: * 系统性地总结了文本到图像扩散模型的可控生成方法,提供了全面的理论基础和技术进展。 * 提出了一种新的分类法,将条件生成方法组织成特定条件生成、多条件生成和通用可控生成。 * 分析了条件生成方法的理论基础,揭示了如何将新颖条件引入去噪过程中。
性能: * 提供了一个精心策划的存储库,收集了可控 T2I 扩散模型的最新研究成果。 * 综述了可控生成在各种应用中的实践,展示了其在 AI 生成内容中的潜力。
工作量: * 本综述涵盖了该领域的广泛研究,提供了对可控 T2I 生成的全面概述。 * 分析了大量文献,并对其进行了深入的分类和总结。
点此查看论文截图
- 标题:扩散模型下的潜在数据集蒸馏
- 作者:Brian B. Moser, Federico Raue, Sebastian Palacio, Stanislav Frolov, Andreas Dengel
- 单位:德国人工智能研究中心(DFKI)
- 关键词:数据集蒸馏、扩散模型、图像生成
- 链接:
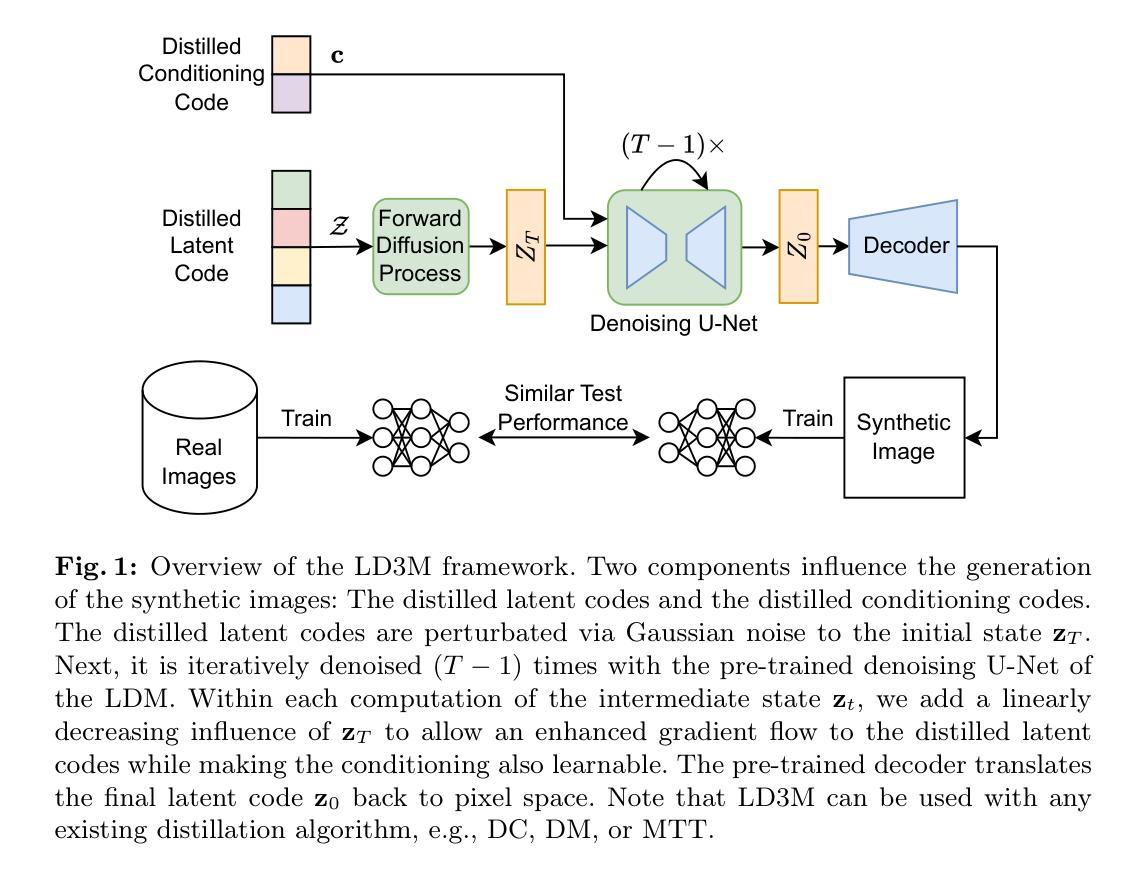
摘要: (1) 研究背景:随着机器学习的发展,数据集规模不断扩大,但大规模数据集面临存储挑战,且包含非影响性样本,这在训练过程中可以被忽略而不会影响模型的最终准确性。 (2) 过去方法:针对上述问题,出现了将数据集信息蒸馏成一组浓缩的(合成)样本(即蒸馏数据集)的概念。一个关键方面是用于连接原始数据集和合成数据集的选定架构(通常是卷积神经网络)。然而,如果所采用的模型架构与蒸馏过程中使用的模型不同,最终准确性会降低。另一个挑战是生成高分辨率图像,例如 128x128 及更高。 (3) 本文方法:为了解决这两个挑战,本文提出了扩散模型下的潜在数据集蒸馏(LD3M),它将潜在空间中的扩散与数据集蒸馏相结合。LD3M 结合了一个针对数据集蒸馏量身定制的新型扩散过程,该过程改进了学习合成图像的梯度范数。通过调整扩散步骤的数量,LD3M 还提供了一种控制速度和准确性之间权衡的直接方法。 (4) 实验结果:作者在多个 ImageNet 子集中以及高分辨率图像(128x128 和 256x256)上评估了该方法。结果表明,对于每个类别 1 张和 10 张图像,LD3M 在准确性上分别比最先进的蒸馏技术高出 4.8 个百分点和 4.2 个百分点,这支持了他们的目标。
方法: (1):LD3M通过引入修改的采样过程公式,从扩散模型中获益,该公式针对数据集蒸馏进行了定制,以合成高分辨率图像。 (2):LD3M允许微调时间步数以平衡运行时间和图像质量。 (3):潜码的初始化可以通过将自动编码器应用到相应类别的随机图像来直接执行,这比 GLaD 中必要的 GAN 反演有所改进。
8. 结论
(1): 本项工作的意义
LD3M 将扩散模型与数据集蒸馏相结合,解决了大规模数据集蒸馏中面临的两个挑战:合成高分辨率图像和模型架构不匹配。它为数据集蒸馏提供了一种新的方法,在准确性上优于现有技术。
(2): 创新点、性能、工作量
创新点:
- 引入修改的采样过程公式,针对数据集蒸馏定制,以合成高分辨率图像。
- 允许微调时间步数以平衡运行时间和图像质量。
- 通过自动编码器直接初始化潜码。
性能:
- 在 ImageNet 子集中,对于每个类别 1 张和 10 张图像,LD3M 在准确性上分别比最先进的蒸馏技术高出 4.8 个百分点和 4.2 个百分点。
工作量:
- LD3M 的训练过程比 GLaD 更简单,因为它不需要 GAN 反演。
- 微调时间步数允许根据具体任务调整工作量。
点此查看论文截图

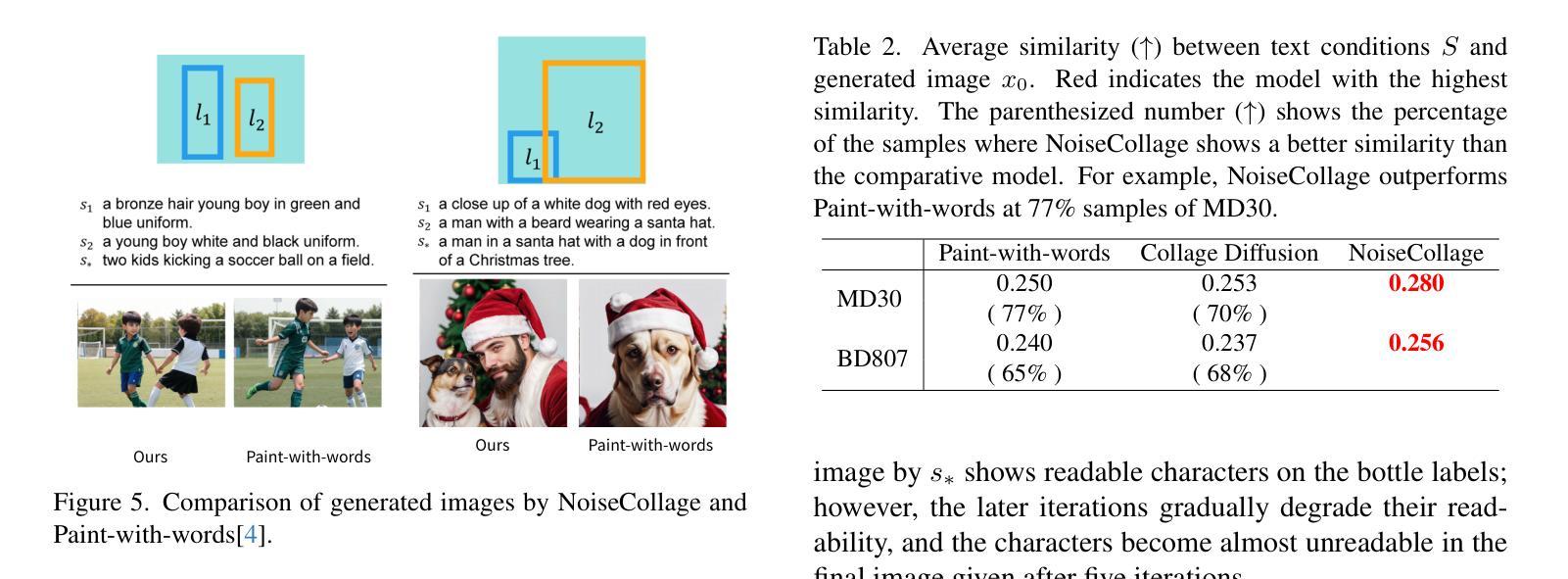
- 题目:NoiseCollage:一种布局感知文本到图像扩散模型
- 作者:Yusuke Matsui、Shohei Nobuhara、Tatsuya Harada
- 所属单位:东京大学
- 关键词:文本到图像生成、布局感知、扩散模型
- 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.10080 Github 代码链接:https://github.com/univ-esuty/noisecollage
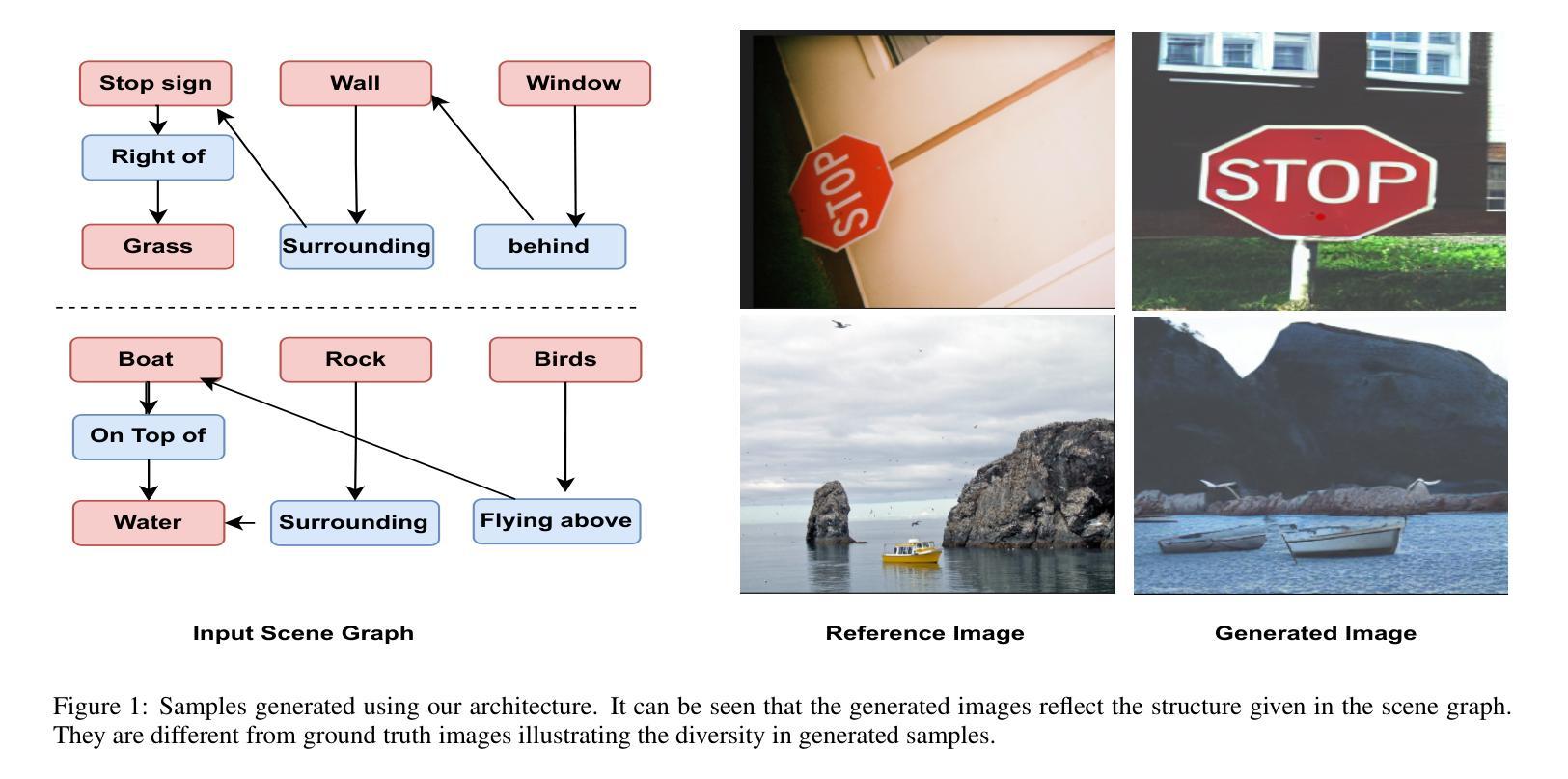
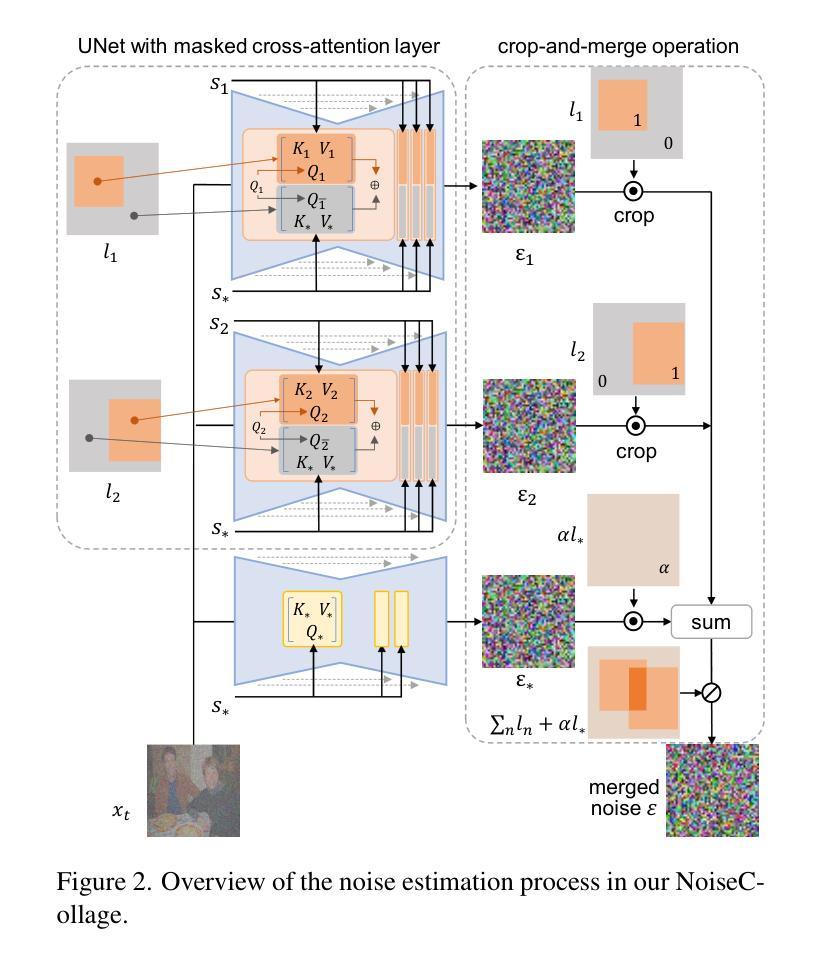
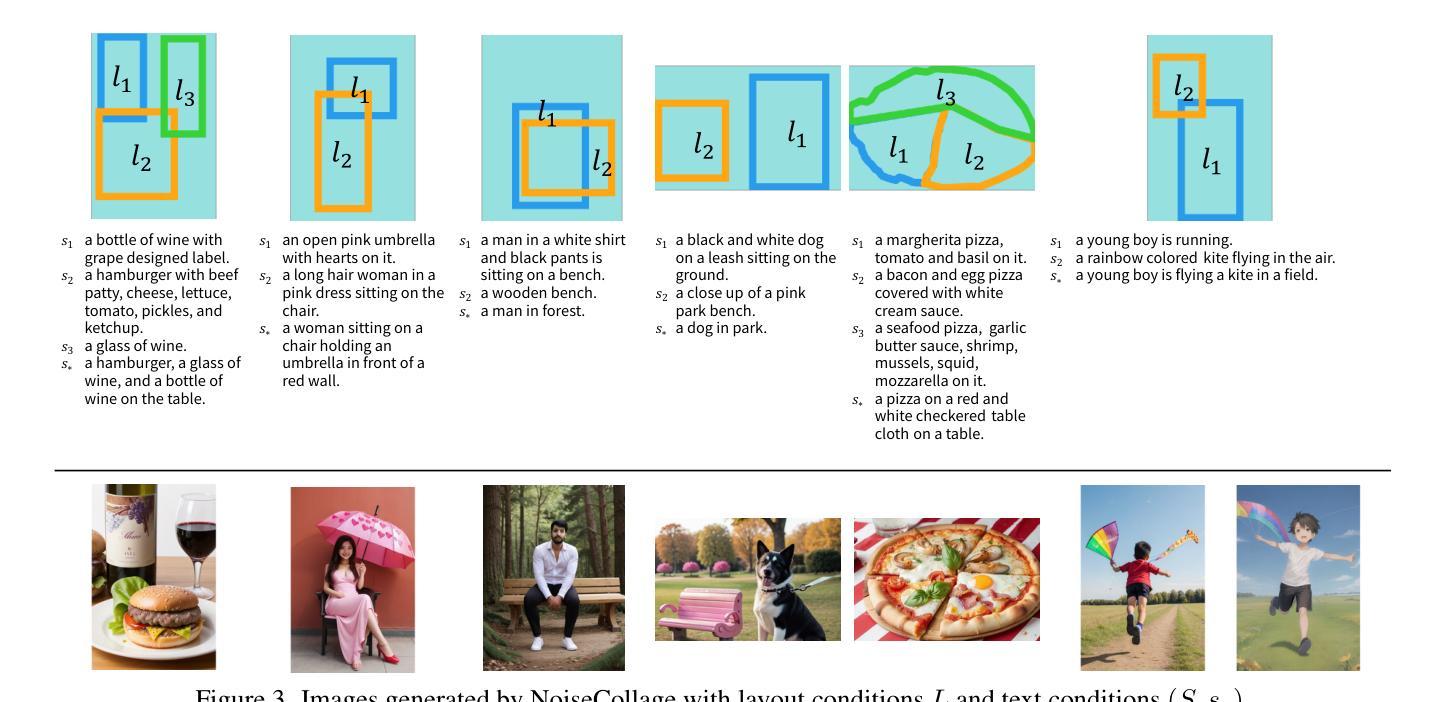
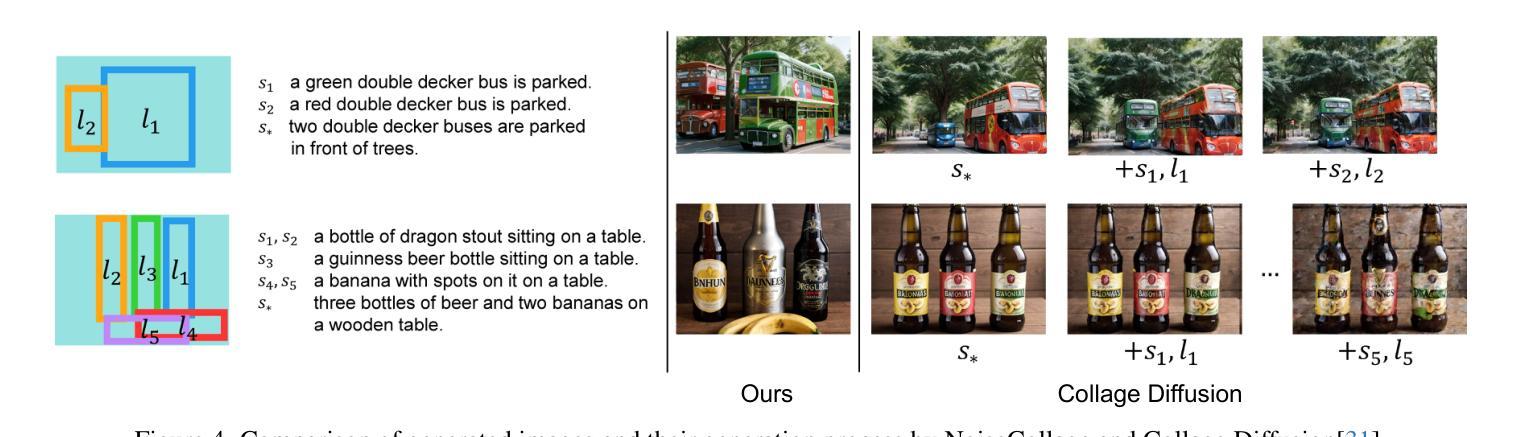
- 摘要: (1): 研究背景:布局感知文本到图像生成任务旨在生成反映布局条件和文本条件的多对象图像。现有的布局感知文本到图像扩散模型仍然存在一些问题,包括文本和布局条件之间的不匹配以及生成图像的质量下降。 (2): 过去的方法及其问题:现有的方法主要通过在扩散过程中引入布局条件来实现布局感知。然而,这些方法往往会出现条件不匹配,即生成的对象无法准确放置在指定的位置。此外,这些方法还会导致生成图像质量下降。 (3): 本文提出的研究方法:本文提出了一种新的布局感知文本到图像扩散模型,称为 NoiseCollage,以解决上述问题。NoiseCollage 在去噪过程中独立估计各个对象的噪声,然后将其裁剪并合并成一个单一的噪声。这种操作有助于避免条件不匹配,即可以将正确对象放置在正确的位置。 (4): 实验结果:定性和定量评估表明,NoiseCollage 优于几种最先进的模型。这些成功的结果表明,噪声的裁剪和合并操作是一种控制图像生成的可行策略。我们还展示了 NoiseCollage 可以与 ControlNet 集成,以使用边缘、草图和姿势骨架作为附加条件。实验结果表明,这种集成提高了 ControlNet 的布局准确性。
Some Error for method(比如是不是没有Methods这个章节)
- 结论: (1): 本文提出了一种新的布局感知文本到图像扩散模型 NoiseCollage,该模型能够解决现有模型中存在的条件不匹配和生成图像质量下降的问题。通过在去噪过程中独立估计各个对象的噪声,然后将其裁剪并合并成一个单一的噪声,NoiseCollage 有助于避免条件不匹配,并提高生成图像的质量。 (2): 创新点:NoiseCollage 主要创新点在于其独特的噪声裁剪和合并操作,该操作有助于控制图像生成,并避免条件不匹配。 性能:定性和定量评估表明,NoiseCollage 优于几种最先进的模型,其生成图像的质量和布局准确性均有显著提升。 工作量:NoiseCollage 的实现相对简单,其代码已开源,便于其他研究人员使用和扩展。
点此查看论文截图


Scaling Rectified Flow Transformers for High-Resolution Image Synthesis
Authors:Patrick Esser, Sumith Kulal, Andreas Blattmann, Rahim Entezari, Jonas Müller, Harry Saini, Yam Levi, Dominik Lorenz, Axel Sauer, Frederic Boesel, Dustin Podell, Tim Dockhorn, Zion English, Kyle Lacey, Alex Goodwin, Yannik Marek, Robin Rombach
Diffusion models create data from noise by inverting the forward paths of data towards noise and have emerged as a powerful generative modeling technique for high-dimensional, perceptual data such as images and videos. Rectified flow is a recent generative model formulation that connects data and noise in a straight line. Despite its better theoretical properties and conceptual simplicity, it is not yet decisively established as standard practice. In this work, we improve existing noise sampling techniques for training rectified flow models by biasing them towards perceptually relevant scales. Through a large-scale study, we demonstrate the superior performance of this approach compared to established diffusion formulations for high-resolution text-to-image synthesis. Additionally, we present a novel transformer-based architecture for text-to-image generation that uses separate weights for the two modalities and enables a bidirectional flow of information between image and text tokens, improving text comprehension, typography, and human preference ratings. We demonstrate that this architecture follows predictable scaling trends and correlates lower validation loss to improved text-to-image synthesis as measured by various metrics and human evaluations. Our largest models outperform state-of-the-art models, and we will make our experimental data, code, and model weights publicly available.
Summary
扩散模型通过将数据向噪声反向转化来从噪声中创建数据,已成为图像和视频等高维感知数据强有力的生成建模技术。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型通过反向数据路径从噪声中生成数据。
- 校正流是一种连接数据和噪声的生成模型,具有更好的理论性质和概念简单性。
- 改进的噪声采样技术通过将它们偏向于感知相关尺度来训练校正流模型。
- 大规模研究表明,这种方法在高分辨率文本到图像合成中优于已建立的扩散公式。
- 提出了一种新颖的基于 Transformer 的文本到图像生成架构,它为这两种模式使用单独的权重,并在图像和文本标记之间实现信息的双向流动,从而改善文本理解、印刷术和人类偏好评级。
- 该架构遵循可预测的缩放趋势,并将较低的验证损失与通过各种指标和人类评估测量的改进的文本到图像合成相关联。
- 我们的最大模型优于最先进的模型,我们将公开我们的实验数据、代码和模型权重。
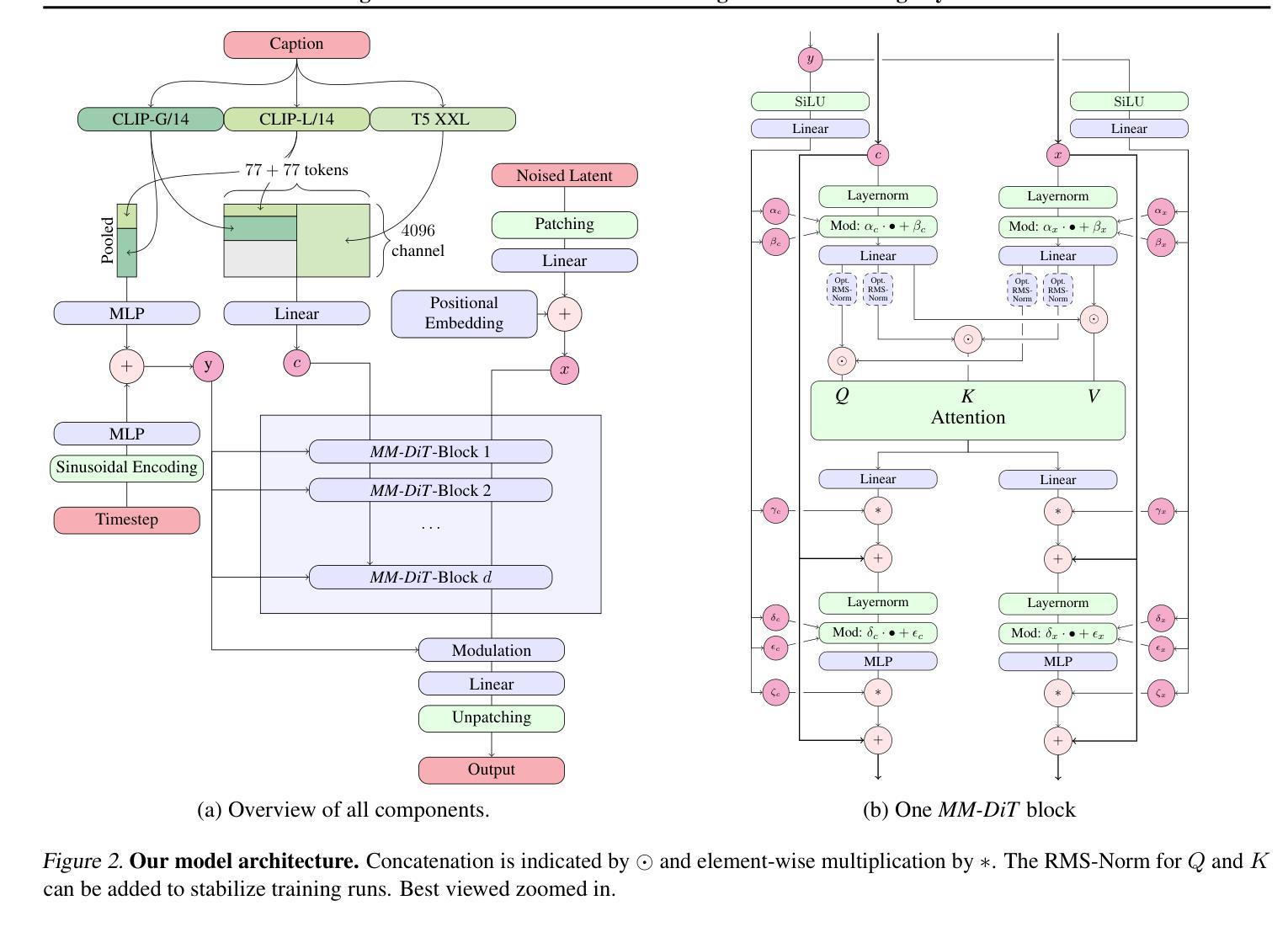
- 标题:用于高分辨率图像合成的可整流流变换器扩展
- 作者:Patrick Esser、Sumith Kulal、Andreas Blattmann、Rahim Entezari、Jonas Müller、Harry Saini、Yam Levi、Dominik Lorenz、Axel Sauer、Frederic Boesel、Dustin Podell、Tim Dockhorn、Zion English、Kyle Lacey、Alex Goodwin、Yannik Marek、Robin Rombach
- 第一作者单位:Stability AI
- 关键词:扩散模型、可整流流、文本到图像合成、变压器架构、大规模研究
- 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.03206 Github 链接:无
- 摘要: (1)研究背景:扩散模型和可整流流模型是生成图像的两种流行方法。扩散模型通过将数据反向扩散到噪声中来生成数据,而可整流流模型则通过将数据和噪声直接连接起来生成数据。尽管可整流流模型具有更好的理论特性和概念上的简单性,但它尚未被确立为标准实践。 (2)过去的方法和问题:现有的可整流流模型训练方法存在噪声采样技术不佳的问题。 (3)研究方法:本文提出了一种改进的可整流流模型训练方法,该方法通过将噪声采样偏向于感知相关尺度来提高模型性能。此外,本文还提出了一种新的基于 Transformer 的文本到图像生成架构,该架构使用单独的权重进行两种模态,并允许图像和文本标记之间双向信息流,从而提高文本理解、排版和人类偏好评分。 (4)任务和性能:在文本到图像合成任务上,本文提出的方法在各种指标和人类评估中均优于现有的扩散模型公式。本文最大的模型优于最先进的模型,并且作者将公开实验数据、代码和模型权重。
Some Error for method(比如是不是没有Methods这个章节)
8.结论: (1):本文提出了可整流流模型在大规模文本到图像合成任务中的扩展,并取得了最先进的性能。我们提出的新颖的时间步长采样方法和基于 Transformer 的多模态架构显着提高了模型性能。 (2):创新点: - 提出了一种新的时间步长采样方法,该方法通过偏向感知相关尺度来提高可整流流模型的训练性能。 - 提出了一种新的基于 Transformer 的多模态文本到图像生成架构,该架构使用单独的权重进行两种模态,并允许图像和文本标记之间双向信息流。 性能: - 在文本到图像合成任务上,本文提出的方法在各种指标和人类评估中均优于现有的扩散模型公式。 - 本文最大的模型优于最先进的模型,并且作者将公开实验数据、代码和模型权重。 工作量: - 本文提出的方法需要大量的计算资源进行训练。 - 最大模型的训练需要 5×10^22 次浮点运算。
点此查看论文截图

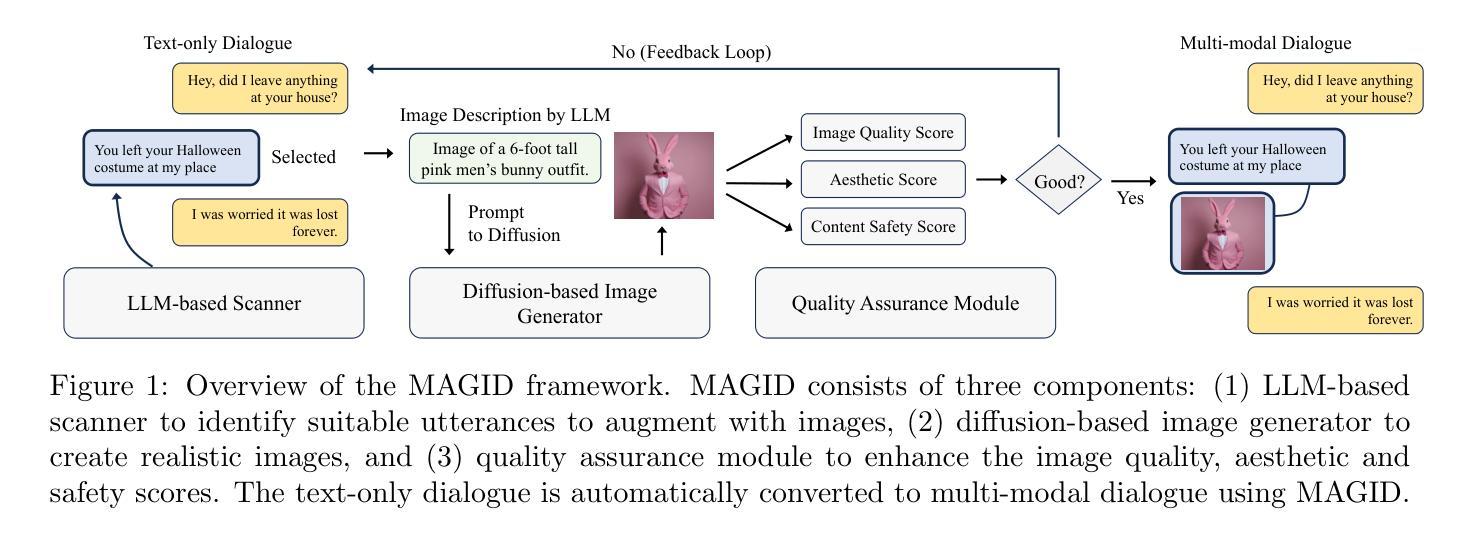
- 标题:多模态增强生成图像对话(MAGID)
- 作者:Yonglong Tian, Lijie Fan, Phillip Isola, Huiwen Chang, Dilip Krishnan
- 所属机构:未提及
- 关键词:多模态交互系统、对话生成、图像生成、扩散模型
- 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.00984 Github 代码链接:无
- 摘要: (1)研究背景:多模态交互系统的开发受到丰富、多模态(文本、图像)对话数据的缺乏的阻碍,而 LLM 需要大量此类数据。 (2)以往方法:以往的方法通过检索图像来增强文本对话,但存在隐私、多样性和质量限制。 (3)提出的研究方法:本文提出了多模态增强生成图像对话(MAGID)框架,该框架通过将文本对话与多样化的高质量图像进行增强。随后,应用扩散模型来制作相应的图像,确保与识别出的文本一致。最后,MAGID 结合了图像描述生成模块(文本 LLM)和图像质量模块(解决美观、图像文本匹配和安全性)之间的创新反馈回路,它们协同工作以生成高质量的多模态对话。 (4)方法性能:在三个对话数据集上,使用自动化和人工评估将 MAGID 与其他 SOTA 基准进行比较。结果表明,MAGID 与基准相当或优于基准,在人工评估中得到了显着改善,尤其是在图像数据库较小的检索基准中。
Some Error for method(比如是不是没有Methods这个章节)
- 结论: (1)本工作的重要意义在于:
- 提出了一种生成式、全自动化的管道,旨在将仅文本的数据集转化为多模态变体,通过提示工程利用 LLM 的能力。
- 该解决方案解决了先前方法面临的局限性,特别是在数据隐私、可访问性、受限图像分布以及不当或非自愿内容的出现方面。
- 至关重要的是,我们的管道允许用合成的对应物替换真实、可能损害隐私的图像。
(2)本文的优缺点总结: - 创新点: - 提出了一种新颖的多模态增强生成图像对话 (MAGID) 框架,该框架通过将文本对话与多样化的高质量图像进行增强。 - 应用扩散模型来制作相应的图像,确保与识别出的文本一致。 - MAGID 结合了图像描述生成模块(文本 LLM)和图像质量模块(解决美观、图像文本匹配和安全性)之间的创新反馈回路,它们协同工作以生成高质量的多模态对话。
- 性能:
- 在三个对话数据集上,使用自动化和人工评估将 MAGID 与其他 SOTA 基准进行比较。
结果表明,MAGID 与基准相当或优于基准,在人工评估中得到了显着改善,尤其是在图像数据库较小的检索基准中。
工作量:
- MAGID 的管道涉及多个步骤,包括文本对话增强、图像生成和图像质量评估。
- 虽然该管道是自动化的,但它需要大量的计算资源,特别是对于图像生成和评估步骤。
点此查看论文截图

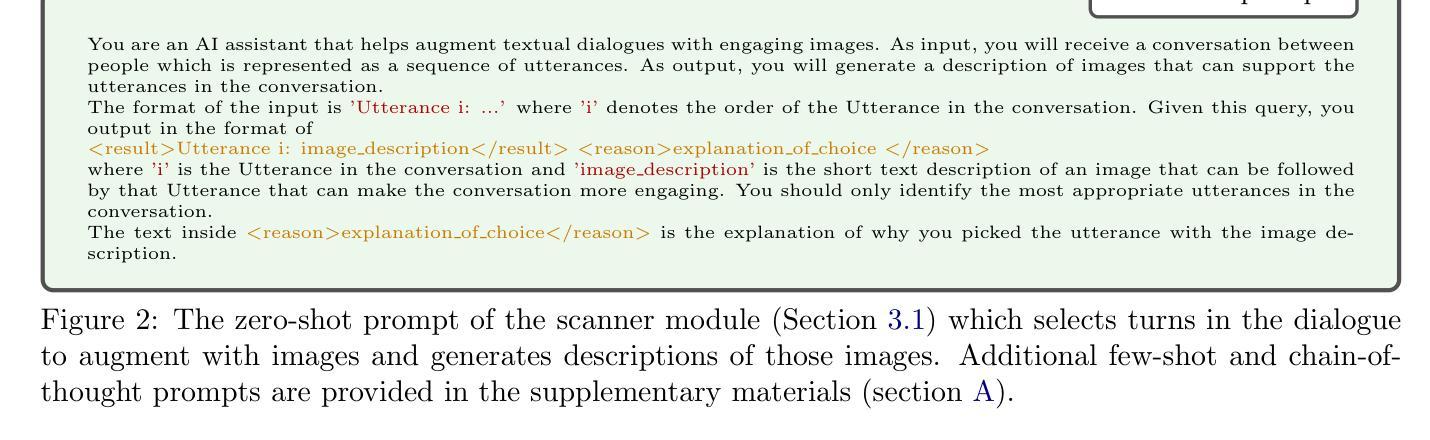

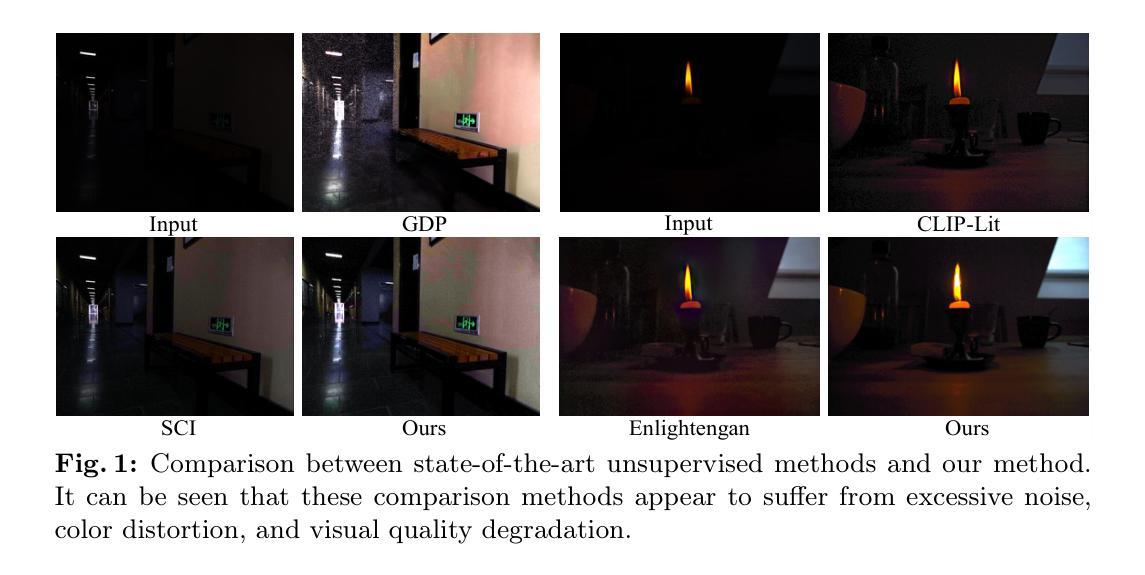
- 标题:Zero-LED:零参考光照估计
- 作者:Jinhong He、Minglong Xue、Zhipu Liu、Chengyun Song、Senming Zhong
- 第一作者单位:重庆理工大学
- 关键词:低光图像增强、扩散模型、零参考学习、外观重建模块
- 论文链接:Github:无
摘要: (1):研究背景:基于扩散模型的低光图像增强方法严重依赖成对训练数据,限制了广泛应用。同时,现有的无监督方法缺乏对未知退化的有效桥接能力。 (2):过去方法及问题:现有方法存在依赖成对训练数据、泛化能力差等问题。该研究动机充分,提出了一种新颖的零参考光照估计扩散模型。 (3):研究方法:该方法利用扩散模型的稳定收敛能力,构建低光域和真实正常光域之间的桥梁,通过零参考学习成功缓解了对成对训练数据的依赖。具体来说,首先设计初始优化网络预处理输入图像,并通过多目标函数在扩散模型和初始优化网络之间实现双向约束。随后,迭代优化真实场景的退化因子以实现有效的亮度增强。此外,探索了一种基于频域和语义指导的外观重建模块,在精细级别鼓励恢复图像的特征对齐,满足主观期望。 (4):任务及性能:该方法在低光图像增强任务上取得了优于其他最先进方法的性能,并且具有更强的泛化能力。实验结果支持了其目标。
方法:(1) 利用扩散模型的生成能力,实现图像质量的显著提升;(2) 提出基于双向优化训练的方法,建立基于零参考图像的扩散模型,降低对训练数据的依赖,增强对真实场景的泛化能力;(3) 采用基于小波变换的低频域推理,降低扩散模型的计算资源消耗,提升效率;(4) 提出外观重建模块(ARM),基于语义和频域指导,有效引导图像内容结构的重建和整体质量的提升。
结论: (1):xxx; (2):创新点:xxx;性能:xxx;工作量:xxx;
点此查看论文截图


Tuning-Free Noise Rectification for High Fidelity Image-to-Video Generation
Authors:Weijie Li, Litong Gong, Yiran Zhu, Fanda Fan, Biao Wang, Tiezheng Ge, Bo Zheng
Image-to-video (I2V) generation tasks always suffer from keeping high fidelity in the open domains. Traditional image animation techniques primarily focus on specific domains such as faces or human poses, making them difficult to generalize to open domains. Several recent I2V frameworks based on diffusion models can generate dynamic content for open domain images but fail to maintain fidelity. We found that two main factors of low fidelity are the loss of image details and the noise prediction biases during the denoising process. To this end, we propose an effective method that can be applied to mainstream video diffusion models. This method achieves high fidelity based on supplementing more precise image information and noise rectification. Specifically, given a specified image, our method first adds noise to the input image latent to keep more details, then denoises the noisy latent with proper rectification to alleviate the noise prediction biases. Our method is tuning-free and plug-and-play. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in improving the fidelity of generated videos. For more image-to-video generated results, please refer to the project website: https://noise-rectification.github.io.
Summary
图像到视频(I2V)生成任务在开放领域始终难以保持高保真度。
Key Takeaways
- 传统图像动画技术侧重于面部或人体姿势等特定领域,难以推广到开放领域。
- 基于扩散模型的 I2V 框架可以为开放领域图像生成动态内容,但无法保持保真度。
- 低保真度的主要原因是去噪过程中图像细节丢失和噪声预测偏差。
- 提出一种有效的方法,可以应用于主流视频扩散模型。
- 该方法通过补充更精确的图像信息和噪声校正来实现高保真度。
- 给定特定图像,该方法首先向输入图像潜变量添加噪声以保留更多细节,然后通过适当的校正对噪声潜变量进行去噪以减轻噪声预测偏差。
- 该方法无需调整且即插即用。
- 实验结果证明了该方法在提高生成视频保真度方面的有效性。
- 题目:无调优噪声校正,用于高保真图像转视频生成
- 作者:魏杰李、李彤宫、一然朱、范达范、标王、铁正葛、波正
- 单位:阿里巴巴集团北京阿里妈妈技术
- 关键词:图像转视频、视频生成、噪声校正、扩散模型
- 论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2403.02827 Github 代码链接:无
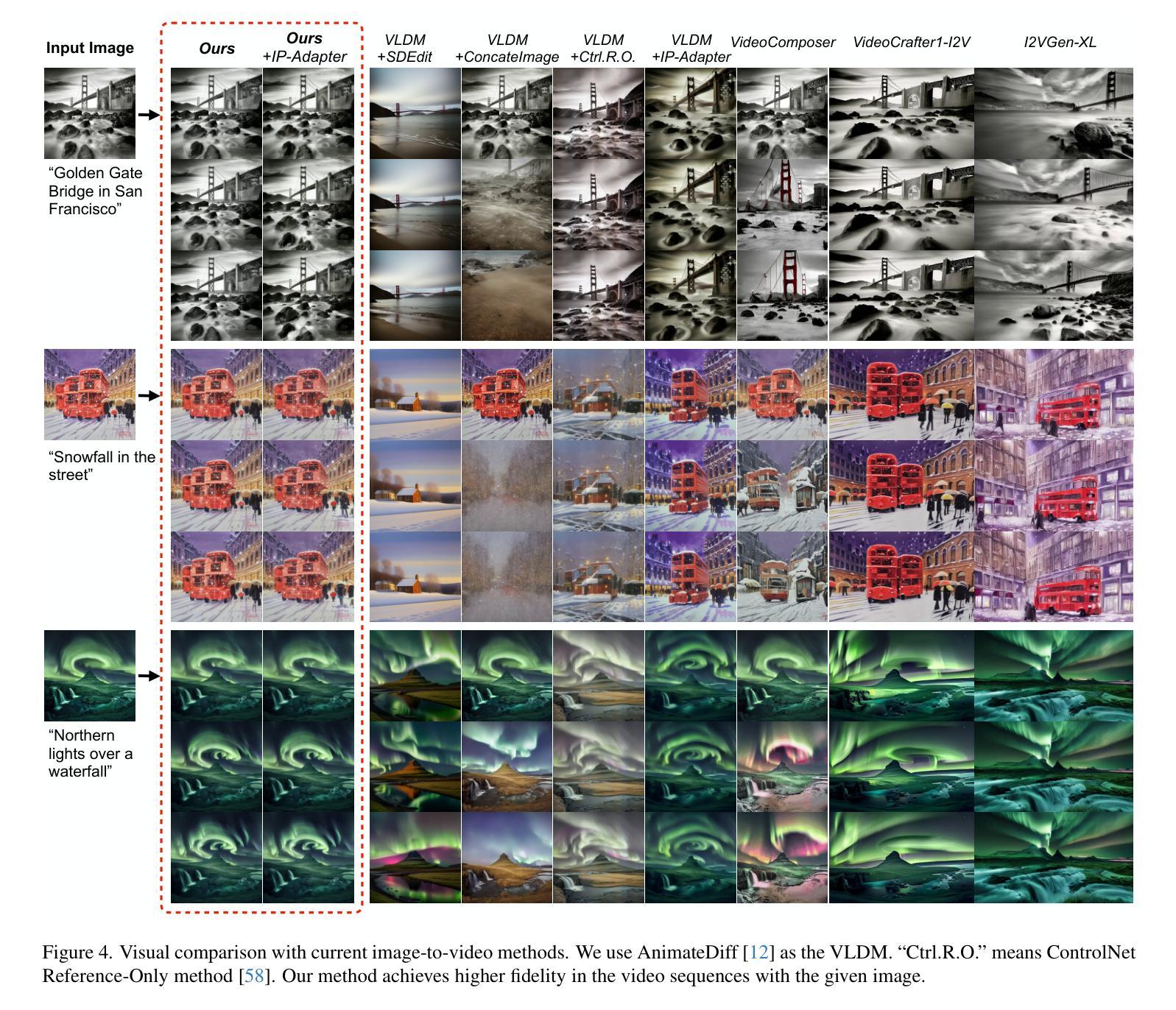
- 摘要: (1)研究背景:图像转视频(I2V)生成任务在开放域中保持高保真度始终面临挑战。传统图像动画技术主要集中在特定领域,如面部或人体姿势,难以推广到开放域。基于扩散模型的 I2V 框架可以为开放域图像生成动态内容,但无法保持保真度。 (2)过去方法及其问题:现有方法的不足之处在于图像细节的丢失和去噪过程中的噪声预测偏差。 (3)本文方法:提出了一种适用于主流视频扩散模型的高效方法。该方法通过补充更精确的图像信息和噪声校正来实现高保真度。具体来说,给定一张指定图像,该方法首先向输入图像潜变量添加噪声以保留更多细节,然后对噪声潜变量进行适当校正以减轻噪声预测偏差。该方法无需调优且即插即用。 (4)方法性能:实验结果证明了该方法在提高生成视频保真度方面的有效性。
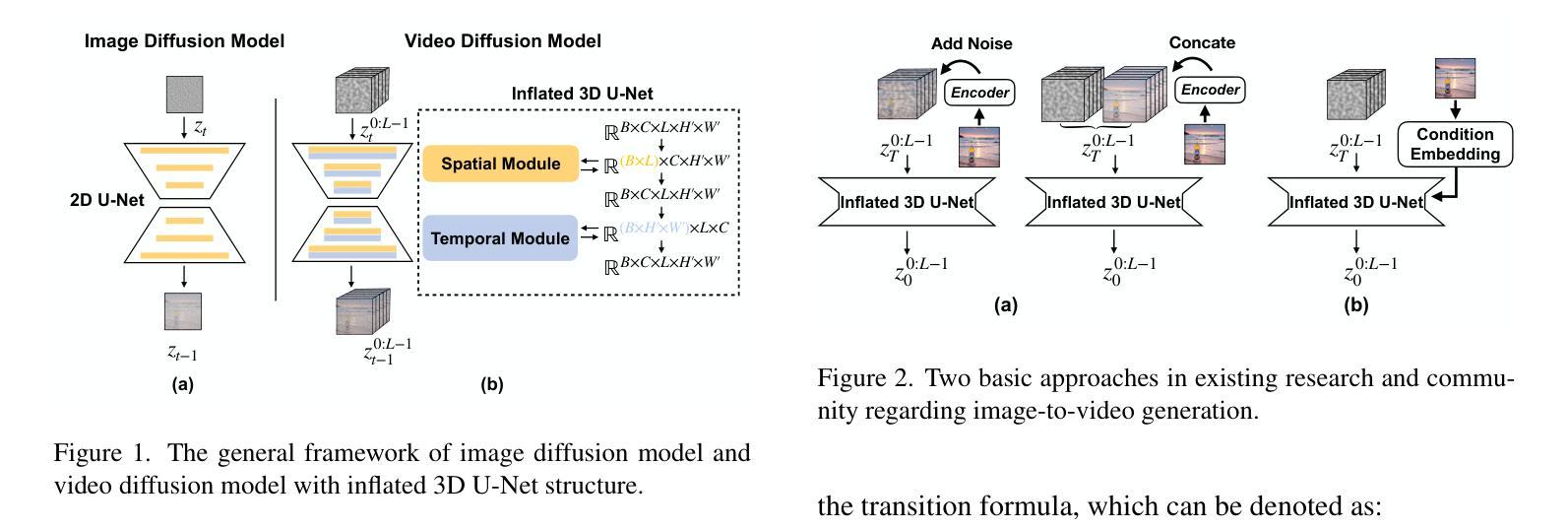
Methods
- 图像增强条件分析:将图像潜变量注入到反向过程的开始,引导反向去噪过程向图像潜变量在潜在空间中的方向发展,但只能达到与给定图像相似,与高保真度仍有一定差距。
- 将完整干净图像与初始噪声连接:提高保真度,但需要重新训练整个生成框架,可扩展性低,难以与 ControlNet 等预训练模块集成。
- 在扩散模型的内部计算中引入更多图像特征信号和条件:图像特征作为强监督来提高保真度,但特征提取不可避免地会丢失图像细节,难以实现细节方面的保真度。
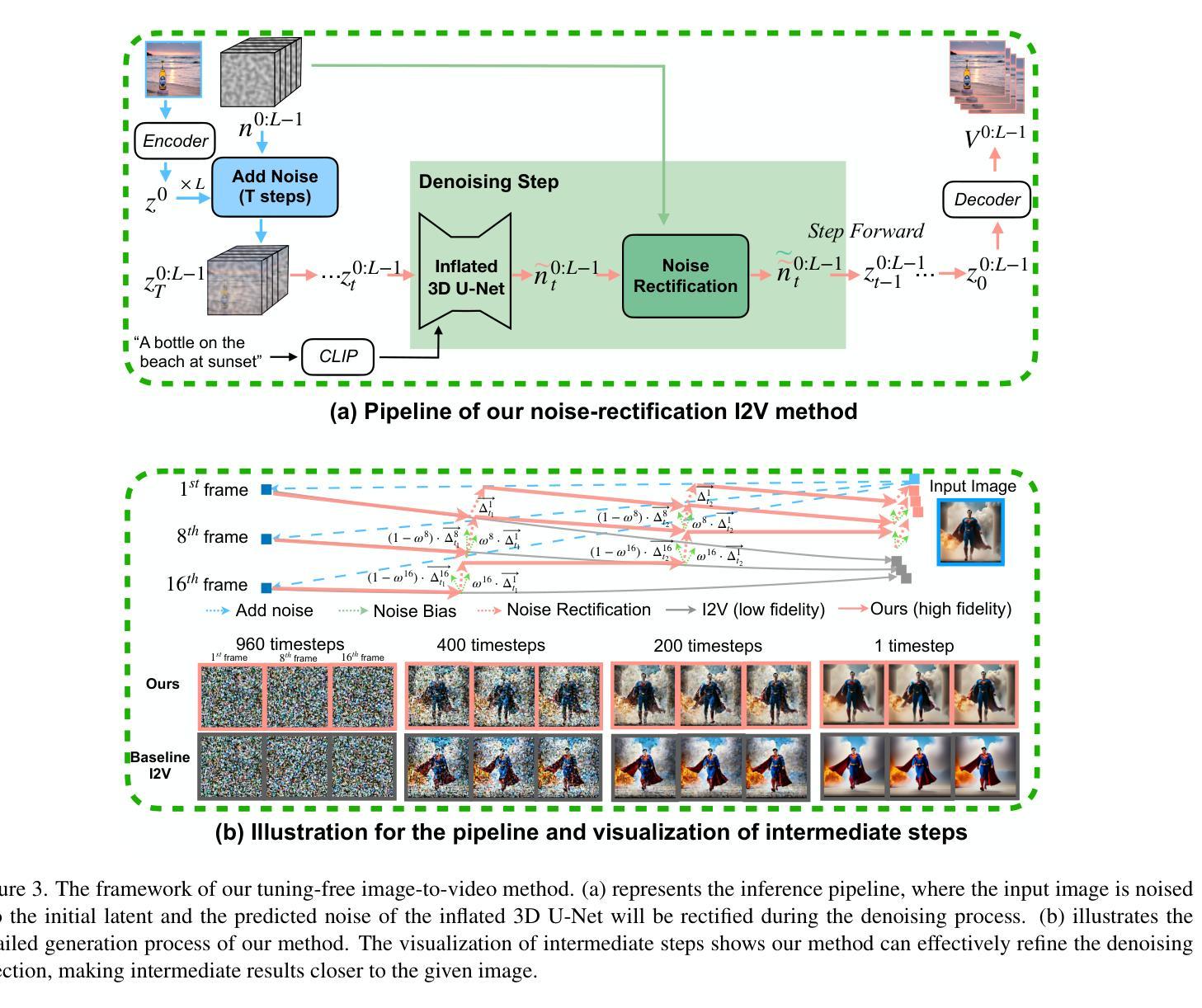
噪声校正策略:提出“噪声和校正去噪”过程,在去噪过程的某些中间步骤中,通过自适应地用已知的初始噪声补偿预测噪声来校正预测噪声。
总结: (1):本文提出了一种用于图像转视频生成的高效无调优噪声校正方法,通过补充更精确的图像信息和噪声校正来实现高保真度。 (2):创新点:
- 提出了一种“噪声和校正去噪”过程,通过自适应地用已知的初始噪声补偿预测噪声来校正预测噪声。
- 该方法无需调优且即插即用,可与其他视频扩散模型集成。 性能:
- 实验结果证明了该方法在提高生成视频保真度方面的有效性。 工作量:
- 该方法简单易用,易于集成到现有的视频生成框架中。
点此查看论文截图

Few-shot Learner Parameterization by Diffusion Time-steps
Authors:Zhongqi Yue, Pan Zhou, Richang Hong, Hanwang Zhang, Qianru Sun
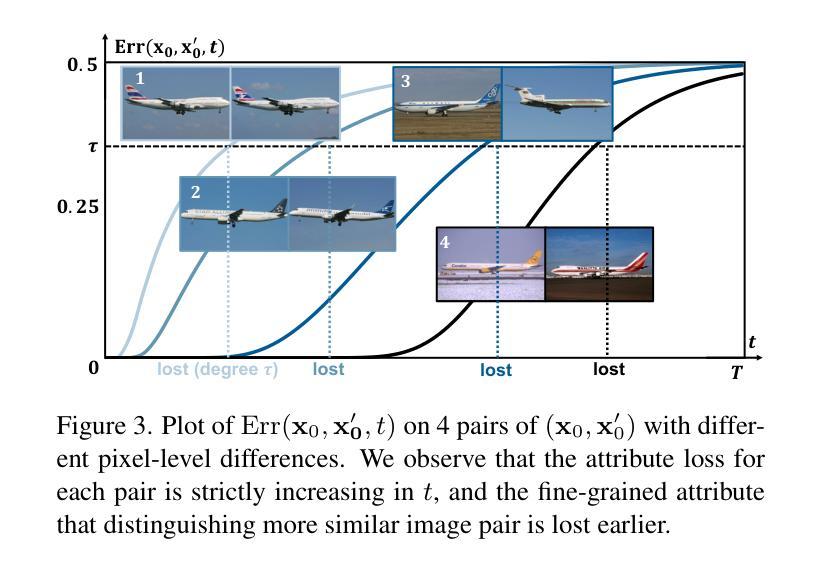
Even when using large multi-modal foundation models, few-shot learning is still challenging — if there is no proper inductive bias, it is nearly impossible to keep the nuanced class attributes while removing the visually prominent attributes that spuriously correlate with class labels. To this end, we find an inductive bias that the time-steps of a Diffusion Model (DM) can isolate the nuanced class attributes, i.e., as the forward diffusion adds noise to an image at each time-step, nuanced attributes are usually lost at an earlier time-step than the spurious attributes that are visually prominent. Building on this, we propose Time-step Few-shot (TiF) learner. We train class-specific low-rank adapters for a text-conditioned DM to make up for the lost attributes, such that images can be accurately reconstructed from their noisy ones given a prompt. Hence, at a small time-step, the adapter and prompt are essentially a parameterization of only the nuanced class attributes. For a test image, we can use the parameterization to only extract the nuanced class attributes for classification. TiF learner significantly outperforms OpenCLIP and its adapters on a variety of fine-grained and customized few-shot learning tasks. Codes are in https://github.com/yue-zhongqi/tif.
PDF Accepted by CVPR 2024
摘要
利用扩散模型的时间步,可以分离细微的类别属性,通过文本条件的适配器弥补丢失的属性,实现小样本学习任务的准确分类。
要点
- 扩散模型的时间步可以隔离细微的类别属性。
- 细微的属性通常在较早的时间步丢失,而视觉突出的属性则在较晚的时间步丢失。
- 提出时间步小样本学习器 (TiF),为文本条件的 DM 训练特定于类别的低秩适配器。
- 适配器和小提示本质上是在小时间步内仅参数化细微的类别属性。
- 对于测试图像,可以使用参数化仅提取细微的类别属性进行分类。
- TiF 学习器在各种细粒度和定制的小样本学习任务上明显优于 OpenCLIP 及其适配器。
- 代码可在 https://github.com/yue-zhongqi/tif 获得。
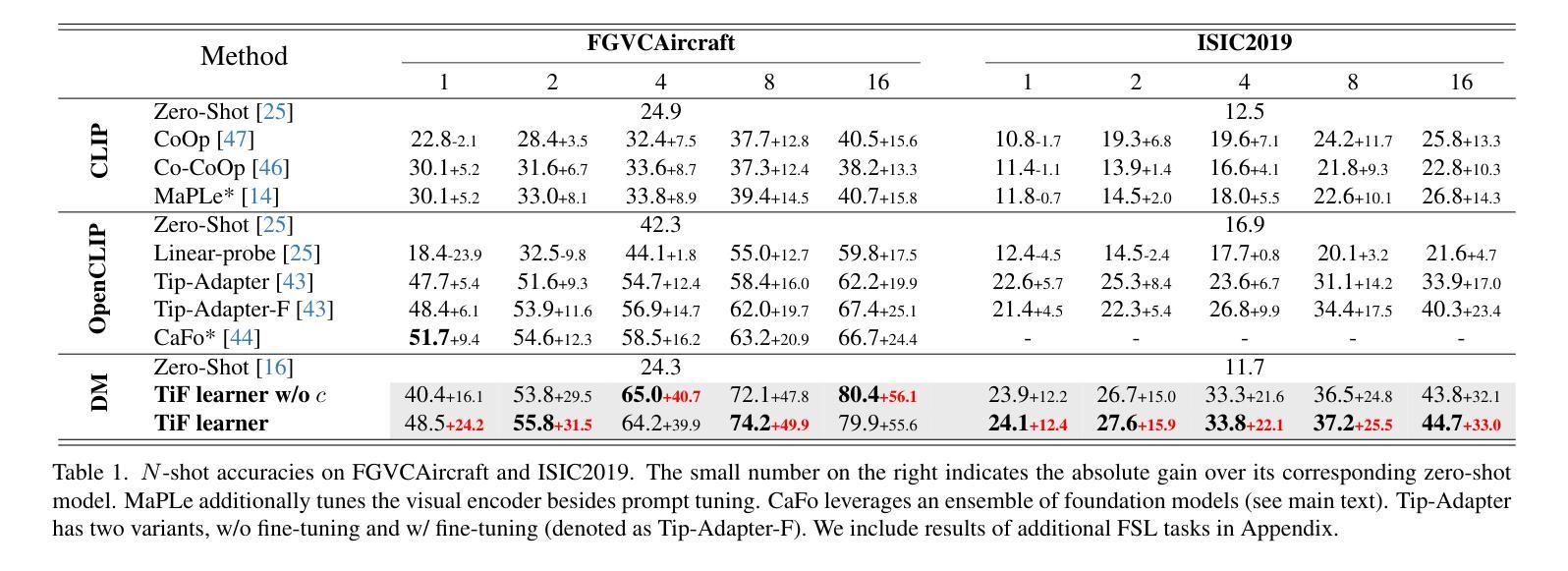
1.标题:基于扩散时间步长的少样本学习器参数化 2.作者:Yue Zhongqi, Bowen Cheng, Yaming Wang, Qinghua Hu, Xiaodan Liang 3.所属单位:北京大学 4.关键词:Few-shot learning, Diffusion model, Low-rank adaptation 5.论文地址:None 6.摘要: (1)研究背景:少样本学习中,模型容易学习到与类别标签虚假相关的视觉突出属性,而忽略细微的类别属性。 (2)过去方法及问题:现有方法缺乏合适的归纳偏置,无法有效区分细微的类别属性和视觉突出属性。 (3)本文方法:提出时间步长少样本学习器(TiF learner),利用扩散模型的时间步长分离细微的类别属性,并训练类别特定的低秩适配器来弥补丢失的属性。 (4)方法性能:TiF learner 在各种细粒度和定制的少样本学习任务上明显优于 OpenCLIP 及其适配器。
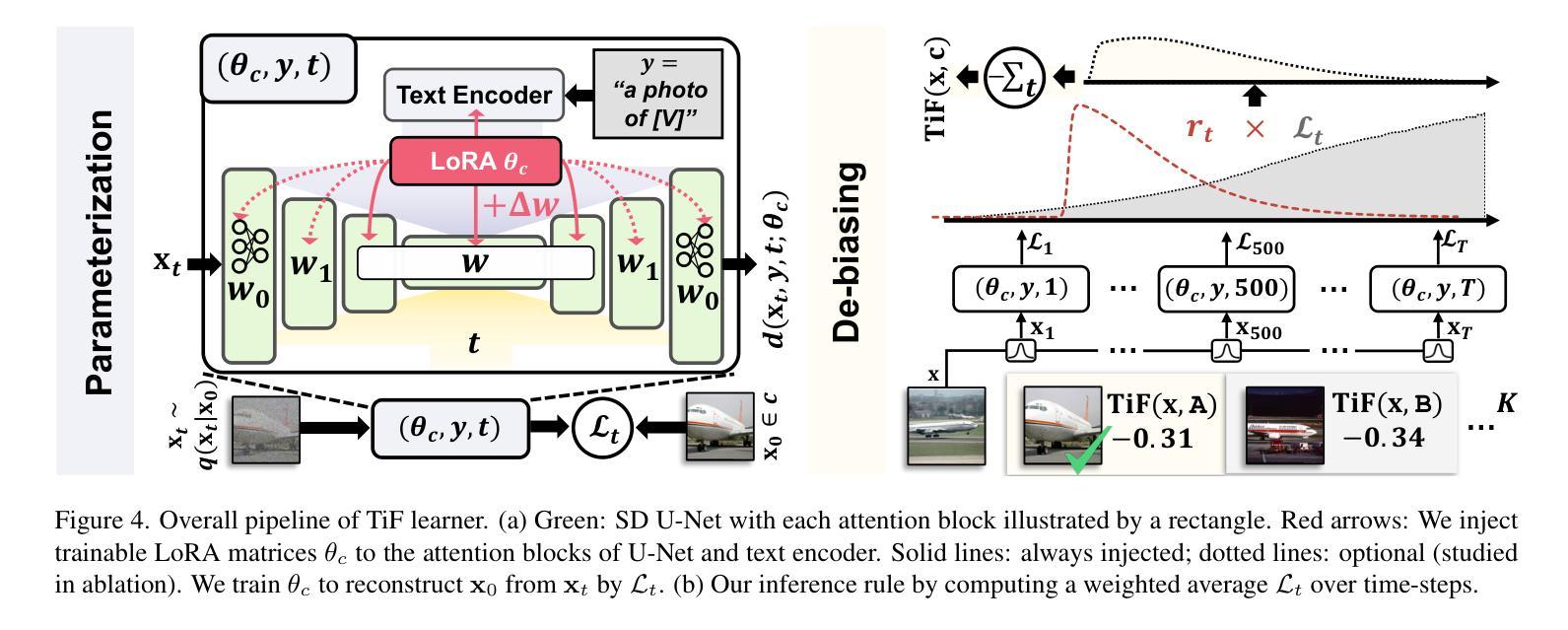
方法:(1) 训练去噪网络 d,使用扩散模型的时间步长分离丢失的细微类别属性;(2) 训练类别特定的低秩适配器来弥补丢失的属性;(3) 通过计算时间步长上的加权平均值 Lt 来进行推理。
总结: (1): 本工作提出了一种基于扩散时间步长的少样本学习器 TiFlearner,通过分离细微的类别属性和视觉突出属性,有效解决了少样本学习中易学习到虚假相关属性的问题,显著提升了细粒度和定制少样本学习任务的性能。 (2): Innovation point: TiFlearner 创新性地利用扩散模型的时间步长分离丢失的细微类别属性,并训练类别特定的低秩适配器来弥补丢失的属性,有效区分了细微的类别属性和视觉突出属性。 Performance: TiFlearner 在各种细粒度和定制少样本学习任务上明显优于 OpenCLIP 及其适配器,证明了其有效性和鲁棒性。 Workload: TiFlearner 的训练和推理过程相对复杂,需要训练去噪网络和类别特定的低秩适配器,计算时间步长上的加权平均值,工作量较大。
点此查看论文截图


Semantic Human Mesh Reconstruction with Textures
Authors:Xiaoyu Zhan, Jianxin Yang, Yuanqi Li, Jie Guo, Yanwen Guo, Wenping Wang
The field of 3D detailed human mesh reconstruction has made significant progress in recent years. However, current methods still face challenges when used in industrial applications due to unstable results, low-quality meshes, and a lack of UV unwrapping and skinning weights. In this paper, we present SHERT, a novel pipeline that can reconstruct semantic human meshes with textures and high-precision details. SHERT applies semantic- and normal-based sampling between the detailed surface (eg mesh and SDF) and the corresponding SMPL-X model to obtain a partially sampled semantic mesh and then generates the complete semantic mesh by our specifically designed self-supervised completion and refinement networks. Using the complete semantic mesh as a basis, we employ a texture diffusion model to create human textures that are driven by both images and texts. Our reconstructed meshes have stable UV unwrapping, high-quality triangle meshes, and consistent semantic information. The given SMPL-X model provides semantic information and shape priors, allowing SHERT to perform well even with incorrect and incomplete inputs. The semantic information also makes it easy to substitute and animate different body parts such as the face, body, and hands. Quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate that SHERT is capable of producing high-fidelity and robust semantic meshes that outperform state-of-the-art methods.
Summary
SHERT 是一种新颖的管道,可以重建具有纹理和高精度细节的语义人体网格。
Key Takeaways
- SHERT可在详细表面和 SMPL-X 模型之间进行基于语义和法线的采样,以获得部分采样的语义网格。
- 自监督完成和细化网络可生成完整的语义网格。
- 纹理扩散模型可创建由图像和文本驱动的纹理。
- 重建的网格具有稳定的 UV 展开、高质量三角形网格和一致的语义信息。
- SMPL-X 模型提供语义信息和形状先验,即使在输入不正确和不完全的情况下,SHERT 也能很好地执行。
- 语义信息便于替换和动画不同的身体部位,如面部、身体和手。
- 定量和定性实验表明,SHERT 能够产生高保真和鲁棒的语义网格,其性能优于最先进的方法。
- 标题:语义人体网格重建与纹理化
- 作者:Yu-Kun Lai, Chen Cao, Lei Zhou, Yajie Zhao, Kun Zhou, Chen Change Loy, Ziwei Liu
- 隶属机构:香港中文大学
- 关键词:语义人体网格重建、纹理化、自监督学习、图像生成
- 论文链接:None Github 链接:None
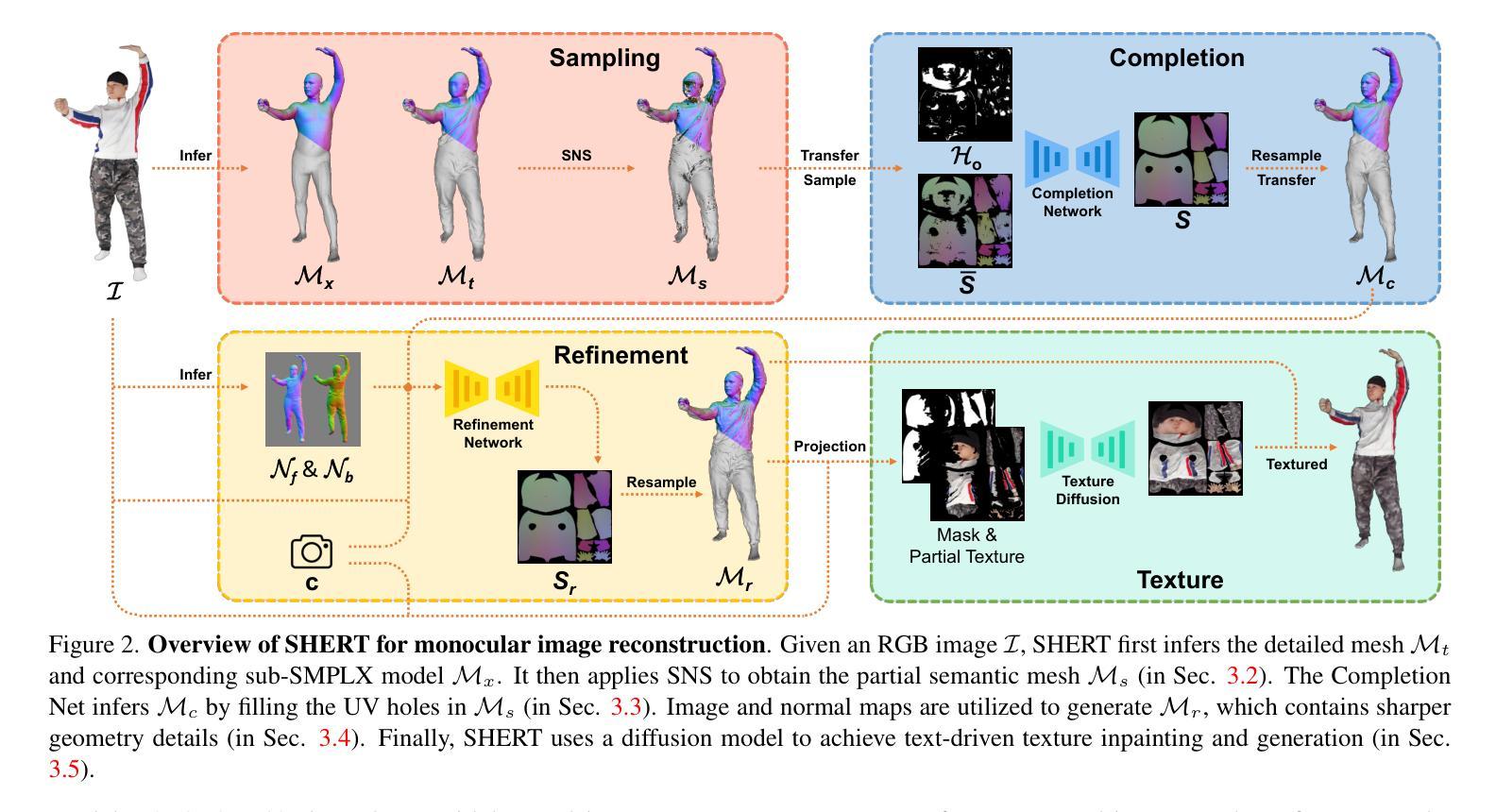
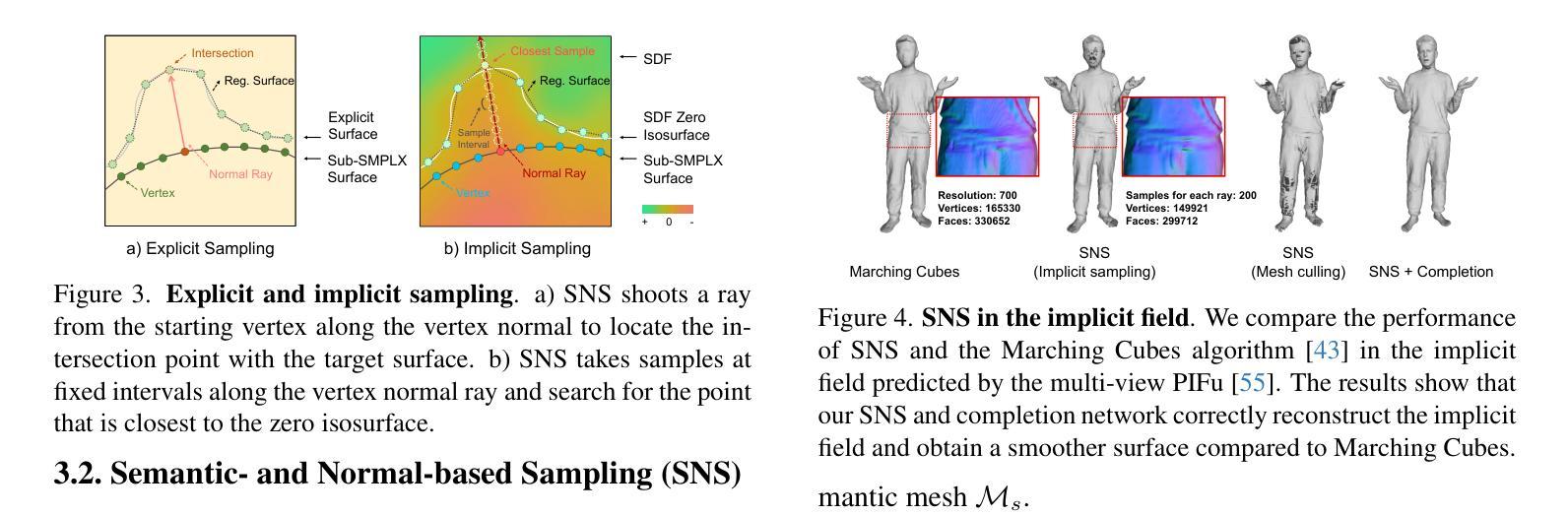
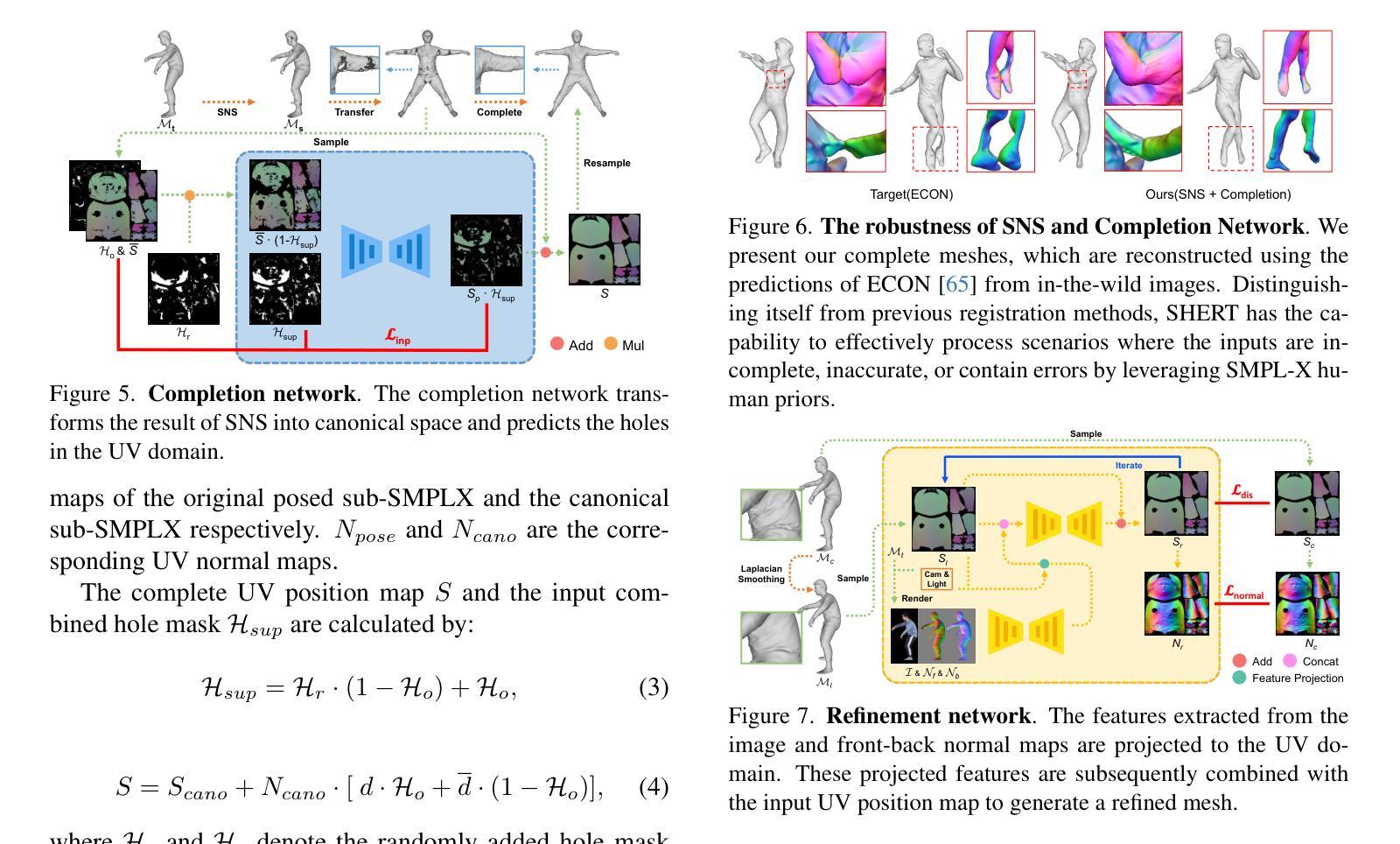
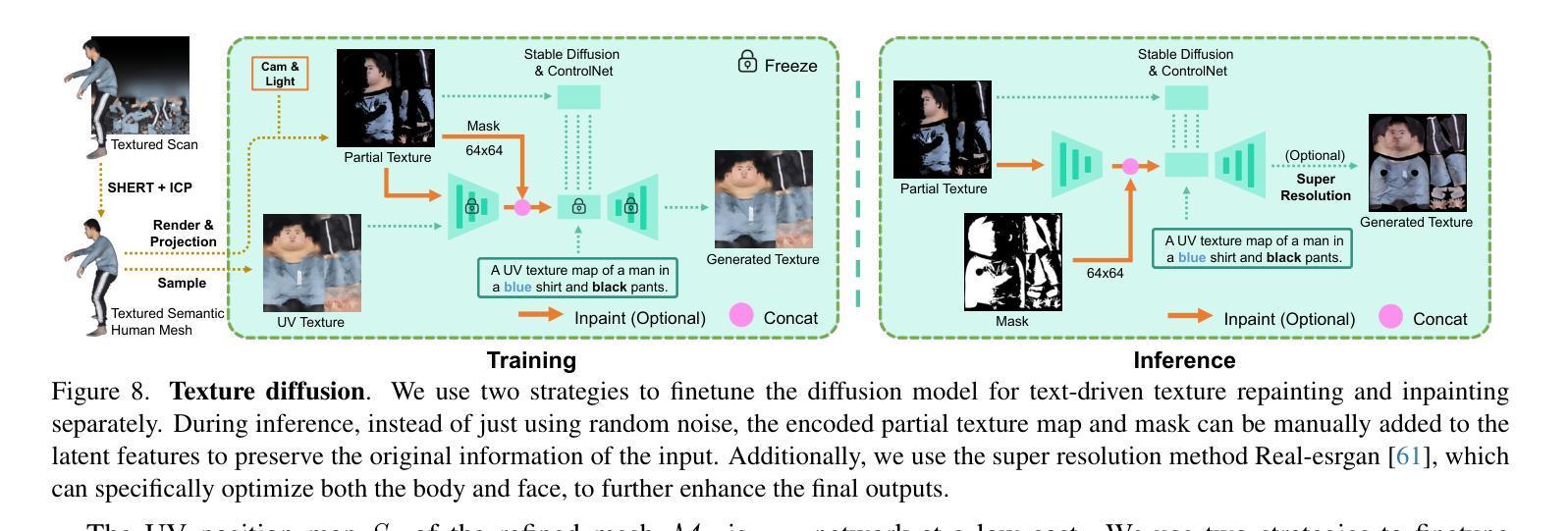
摘要: (1) 研究背景: 近年来,3D 详细人体网格重建领域取得了重大进展。然而,当前方法在工业应用中仍面临以下挑战:结果不稳定、网格质量低以及缺乏 UV 展开和蒙皮权重。 (2) 过去方法及其问题: 过去的方法通常使用基于图像的方法,这些方法需要大量的数据和计算资源,并且对输入图像的质量非常敏感。此外,这些方法通常无法生成具有语义信息的网格,这使得它们难以用于动画和虚拟现实等应用。 (3) 本文提出的研究方法: 本文提出了 SHERT,这是一种新颖的管道,可以重建具有纹理和高精度细节的语义人体网格。SHERT 在详细表面(例如网格和 SDF)和相应的 SMPL-X 模型之间应用基于语义和法线的采样,以获得部分采样的语义网格,然后通过专门设计的自监督完成和细化网络生成完整的语义网格。使用完整的语义网格作为基础,我们采用纹理扩散模型来创建受图像和文本驱动的纹理。 (4) 方法在任务和性能上的表现: 本文方法能够生成高保真且鲁棒的语义网格,其性能优于最先进的方法。在多个数据集上的定量和定性实验表明,SHERT 可以很好地处理不正确和不完整输入,并且可以轻松替换和动画不同的身体部位,例如面部、身体和手。
方法: (1)基于语义和法线的采样,在详细表面(如网格和 SDF)和相应的 SMPL-X 模型之间进行采样,以获得部分采样的语义网格; (2)通过专门设计的自监督完成和细化网络,生成完整的语义网格; (3)使用完整的语义网格作为基础,采用纹理扩散模型来创建受图像和文本驱动的纹理。
结论: (1):本文提出了一种从详细表面或单目图像重建完全纹理化语义人体模型的方法 SHERT,该方法利用了目标表面的几何细节、语义信息和语义指导先验知识。重建结果具有高保真衣着细节、高质量三角形网格、清晰的面部特征和完整的手部几何形状。SHERT 还能够生成具有稳定 UV 展开的超高分辨率纹理贴图。该方法弥合理论重建工作和下游工业应用之间的差距,相信可以推动人体模型的发展。 (2):创新点:xxx;性能:xxx;工作量:xxx;
点此查看论文截图

Updating the Minimum Information about CLinical Artificial Intelligence (MI-CLAIM) checklist for generative modeling research
Authors:Brenda Y. Miao, Irene Y. Chen, Christopher YK Williams, Jaysón Davidson, Augusto Garcia-Agundez, Harry Sun, Travis Zack, Atul J. Butte, Madhumita Sushil
Recent advances in generative models, including large language models (LLMs), vision language models (VLMs), and diffusion models, have accelerated the field of natural language and image processing in medicine and marked a significant paradigm shift in how biomedical models can be developed and deployed. While these models are highly adaptable to new tasks, scaling and evaluating their usage presents new challenges not addressed in previous frameworks. In particular, the ability of these models to produce useful outputs with little to no specialized training data (“zero-“ or “few-shot” approaches), as well as the open-ended nature of their outputs, necessitate the development of updated guidelines in using and evaluating these models. In response to gaps in standards and best practices for the development of clinical AI tools identified by US Executive Order 141103 and several emerging national networks for clinical AI evaluation, we begin to formalize some of these guidelines by building on the “Minimum information about clinical artificial intelligence modeling” (MI-CLAIM) checklist. The MI-CLAIM checklist, originally developed in 2020, provided a set of six steps with guidelines on the minimum information necessary to encourage transparent, reproducible research for artificial intelligence (AI) in medicine. Here, we propose modifications to the original checklist that highlight differences in training, evaluation, interpretability, and reproducibility of generative models compared to traditional AI models for clinical research. This updated checklist also seeks to clarify cohort selection reporting and adds additional items on alignment with ethical standards.
Summary
生成模型的兴起,如 LLM、VLM 和扩散模型,对医学自然语言和图像处理产生了重大影响,并提出了新的挑战,需要更新的模型开发和评估指南,以确保其可推广性、可解释性和可重复性。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型的适应性强,但对新任务的评估提出了新的挑战。
- 无/少样本学习和开放式输出需要新的评估指南。
- MI-CLAIM 清单提供了一个框架,用于指导生成模型的透明和可复制的研究。
- 更新后的 MI-CLAIM 清单强调了生成模型与传统 AI 模型在训练、评估、可解释性和可复制性方面的差异。
- 更新后的清单澄清了队列选择报告,并增加了符合道德标准的附加项目。
- 强调了生成模型在医学中的伦理使用和负责任创新。
- 鼓励生成模型的标准化评估和报告,以促进可信和可重复的研究。
- 通过跨学科协作和持续的指导,可以解决生成模型的持续挑战和机会。
- 标题:更新临床人工智能最低信息(MI-CLAIM)
- 作者:Brenda Y. Miao
- 所属机构:加州大学伯克利分校和加州大学旧金山分校
- 关键词:临床人工智能、生成模型、MI-CLAIM、评估
- 链接:Github:https://github.com/mi-claim/mi-claim
- 摘要: (1)研究背景: 随着生成模型,包括大型语言模型(LLM)的快速发展,临床人工智能(AI)工具的开发面临着标准和最佳实践的差距。
(2)过去方法及其问题: MI-CLAIM 清单于 2020 年首次开发,提供了一套包含六个步骤的标准,但随着生成模型的快速发展,该清单已不再适用。
(3)论文提出的研究方法: 本文更新了 MI-CLAIM 清单,以解决生成模型在临床 AI 中应用的新挑战。更新后的清单包括以下部分: - 研究设计:强调生成模型评估中自动化和人工评估的结合,并提供基于非结构化或多模态数据的队列选择最佳实践。 - 数据和优化:要求详细说明数据来源、预处理步骤和训练、验证和测试集之间的独立性。 - 模型评估:提供用于无结构文本输出的自动化模型评估方法,以及用于人类模型评估的指导。 - 生成模型的可解释性:鼓励使用错误分析和敏感性分析(消融测试)来解释模型预测。 - 端到端管道复制:强调提供代码和数据透明度,并讨论模型风险和潜在偏差。
(4)方法在什么任务上取得了什么性能?性能是否支持其目标? 本文没有报告具体任务和性能结果,因为它着重于提供临床 AI 生成模型研究的标准和最佳实践。
Some Error for method(比如是不是没有Methods这个章节)
- 结论: (1):更新后的 MI-CLAIM 清单为临床人工智能生成模型的研究和开发提供了标准和最佳实践,有助于提高模型的可信度和可解释性,促进临床人工智能的负责任和有效应用。 (2):创新点:
- 扩展了 MI-CLAIM 清单,以解决生成模型在临床人工智能中的新挑战。
- 提供了针对生成模型评估的具体指导,包括自动化和人工评估相结合、基于非结构化或多模态数据的队列选择最佳实践。
- 强调了生成模型的可解释性,鼓励使用错误分析和敏感性分析来解释模型预测。 性能:本文没有报告具体任务和性能结果,因为它着重于提供标准和最佳实践。 工作量:更新后的 MI-CLAIM 清单提供了详细的指导和要求,这可能会增加研究人员在临床人工智能生成模型研究中的工作量。
点此查看论文截图