3DGS
⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 Google的大语言模型Gemini-Pro的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-05-13 更新
OneTo3D: One Image to Re-editable Dynamic 3D Model and Video Generation
Authors:Jinwei Lin
One image to editable dynamic 3D model and video generation is novel direction and change in the research area of single image to 3D representation or 3D reconstruction of image. Gaussian Splatting has demonstrated its advantages in implicit 3D reconstruction, compared with the original Neural Radiance Fields. As the rapid development of technologies and principles, people tried to used the Stable Diffusion models to generate targeted models with text instructions. However, using the normal implicit machine learning methods is hard to gain the precise motions and actions control, further more, it is difficult to generate a long content and semantic continuous 3D video. To address this issue, we propose the OneTo3D, a method and theory to used one single image to generate the editable 3D model and generate the targeted semantic continuous time-unlimited 3D video. We used a normal basic Gaussian Splatting model to generate the 3D model from a single image, which requires less volume of video memory and computer calculation ability. Subsequently, we designed an automatic generation and self-adaptive binding mechanism for the object armature. Combined with the re-editable motions and actions analyzing and controlling algorithm we proposed, we can achieve a better performance than the SOTA projects in the area of building the 3D model precise motions and actions control, and generating a stable semantic continuous time-unlimited 3D video with the input text instructions. Here we will analyze the detailed implementation methods and theories analyses. Relative comparisons and conclusions will be presented. The project code is open source.
PDF 24 pages, 13 figures, 2 tables
Summary
一个图像到可编辑动态 3D 模型和视频生成是图像到 3D 表示或图像 3D 重建研究领域的新颖方向和变革。
Key Takeaways
- 采用高斯溅射法,可实现隐式 3D 重建,并优于原始神经辐射场。
- 借助技术和原理的快速发展,人们尝试使用稳定扩散模型通过文本指令生成目标模型。
- 然而,使用常规隐式机器学习方法难以获得精确的动作和动作控制,且难以生成内容长且语义连续的 3D 视频。
- 研究者提出 OneTo3D 方法,使用单张图像生成可编辑 3D 模型和目标语义连续且时间无限的 3D 视频。
- 研究者采用普通基本高斯溅射模型从单张图像生成 3D 模型,该模型对视频内存和计算机运算能力要求较低。
- 研究者针对对象骨架设计了自动生成和自适应绑定机制。
- 结合研究者提出的可重新编辑的动作和动作分析控制算法,在 3D 模型精确动作和动作控制以及根据输入文本指令生成稳定的语义连续且时间无限的 3D 视频方面取得了优于 SOTA 项目的性能。
- 研究者分析了详细的实现方法和理论分析,并将给出相关的比较和结论。
- 该项目代码开源。
论文标题:OneTo3D:单幅图像生成可编辑动态 3D 模型和视频
作者:JINWEI LIN
第一作者单位:莫纳什大学
关键词:3D、单幅图像、可编辑、动态、生成、自动化、视频、自适应、骨架
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.06547,Github 链接:无
摘要:
(1):研究背景:3D 表征或 3D 重建是计算机视觉领域长期以来的挑战。目前实现 3D 重建的方法可分为两类:传统显式方法和机器学习隐式方法。近年来,神经辐射场 (NeRF) 作为一种突出的隐式方法,在渲染和表示真实场景视图方面取得了优异的性能。
(2):过去方法:基于 NeRF,出现了各种隐式 3D 表征或重建的研究项目。然而,现有的方法在精确运动和动作控制以及生成连续语义 3D 视频方面存在困难。
(3):本文方法:本文提出 OneTo3D 方法,利用单幅图像生成可编辑 3D 模型和连续语义 3D 视频。该方法使用基本的 Gaussian Splatting 模型从单幅图像生成 3D 模型,并设计了一种自动生成和自适应绑定机制来创建对象骨架。结合可编辑运动和动作分析控制算法,OneTo3D 在 3D 模型精确运动和动作控制以及根据文本指令生成稳定连续的语义 3D 视频方面取得了优于现有技术的性能。
(4):任务和性能:本文方法在生成可编辑动态 3D 模型和视频的任务上取得了以下性能: - 实现了精确的运动和动作控制,超越了现有技术。 - 能够根据文本指令生成稳定连续的语义 3D 视频。 - 这些性能支持了本文提出的目标。
- 方法:
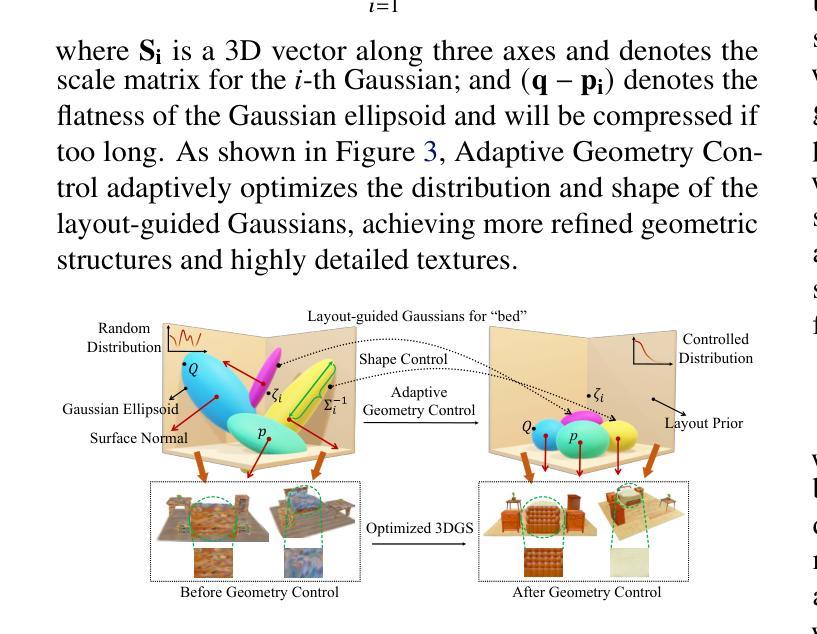
(1):生成初始 3D 模型:利用 Gaussian Splatting 模型从输入图像生成初始 3D 模型,不包含动态或可编辑因素。
(2):生成并绑定自适应骨架:分析初始 3D 模型的几何参数信息,构建适合的骨架,并根据输入图像中的姿态、形状和关键点信息微调骨架参数,使其与物体身体贴合。
(3):文本到动作:分析用户文本指令的命令意图,提取相对骨骼的特定运动和修改数据,控制特定骨骼在 Blender 中实现相对运动,考虑运动量化、运动次数、运动方向和运动范围等参数。
(4):可重新编辑运动控制:配合 Blender 界面实现运动可重新编辑控制,将当前姿态作为关键帧插入,结合连续关键帧生成最终 3D 视频,Blender 文件保存为可重新编辑的 3D 编辑文件。
- 结论:
(1):本文提出了一种生成可编辑动态 3D 模型和视频的新方法 OneTo3D。该方法具有以下优点: - 实现了精确的运动和动作控制,超越了现有技术。 - 能够根据文本指令生成稳定连续的语义 3D 视频。 - 这些性能支持了本文提出的目标。
(2):创新点: - 利用单幅图像生成可编辑 3D 模型和视频。 - 设计了一种自动生成和自适应绑定机制来创建对象骨架。 - 结合可编辑运动和动作分析控制算法,实现精确的运动和动作控制。
性能: - 在生成可编辑动态 3D 模型和视频的任务上取得了优异的性能。 - 超越了现有技术在精确运动和动作控制方面的性能。
工作量: - 该方法需要大量的训练数据和计算资源。 - 生成可编辑动态 3D 模型和视频的过程需要大量的时间。
点此查看论文截图

- Title: MGS-SLAM: 单目稀疏跟踪和高斯映射与深度平滑正则化
- Authors: Pengcheng Zhu, Yaoming Zhuang, Baoquan Chen, Li Li, Chengdong Wu, Zhanlin Liu
- Affiliation: 东北大学机器人科学与工程学院
- Keywords: Visual SLAM, Gaussian Splatting, Sparse Visual Odometry, Multi-View Stereo, Depth Smooth Regularization
- Urls: Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.06241, Github: None
- Summary:
(1):该文章的研究背景是:随着深度学习的快速发展,一种利用可微渲染的新型 SLAM 技术应运而生。基于可微渲染的 SLAM 技术最初使用神经辐射场 (NeRF) 作为其基础构建方法。NeRF 利用神经网络表示 3D 场景,能够合成高质量图像并从多视图中恢复密集的几何结构。基于 NeRF 的 SLAM 系统在制图过程中保留了详细的场景信息,增强了对后续导航和路径规划的支持。然而,NeRF 的方法在图像渲染过程中需要对每个像素进行多次前向预测,导致大量的计算冗余。因此,这种低效性阻碍了基于 NeRF 的 SLAM 实时运行,从而限制了其在直接下游任务中的实用性。
(2):过去的方法是基于高斯散射的 SLAM 系统依赖于 RGB-D 相机的深度图输入,这限制了它们的应用范围。问题是跟踪能力弱。该方法的动机很好,它将基于高斯散射的技术与稀疏视觉里程计相结合,消除了对基于高斯散射的 SLAM 系统中典型的深度图的依赖性,并增强了跟踪鲁棒性。
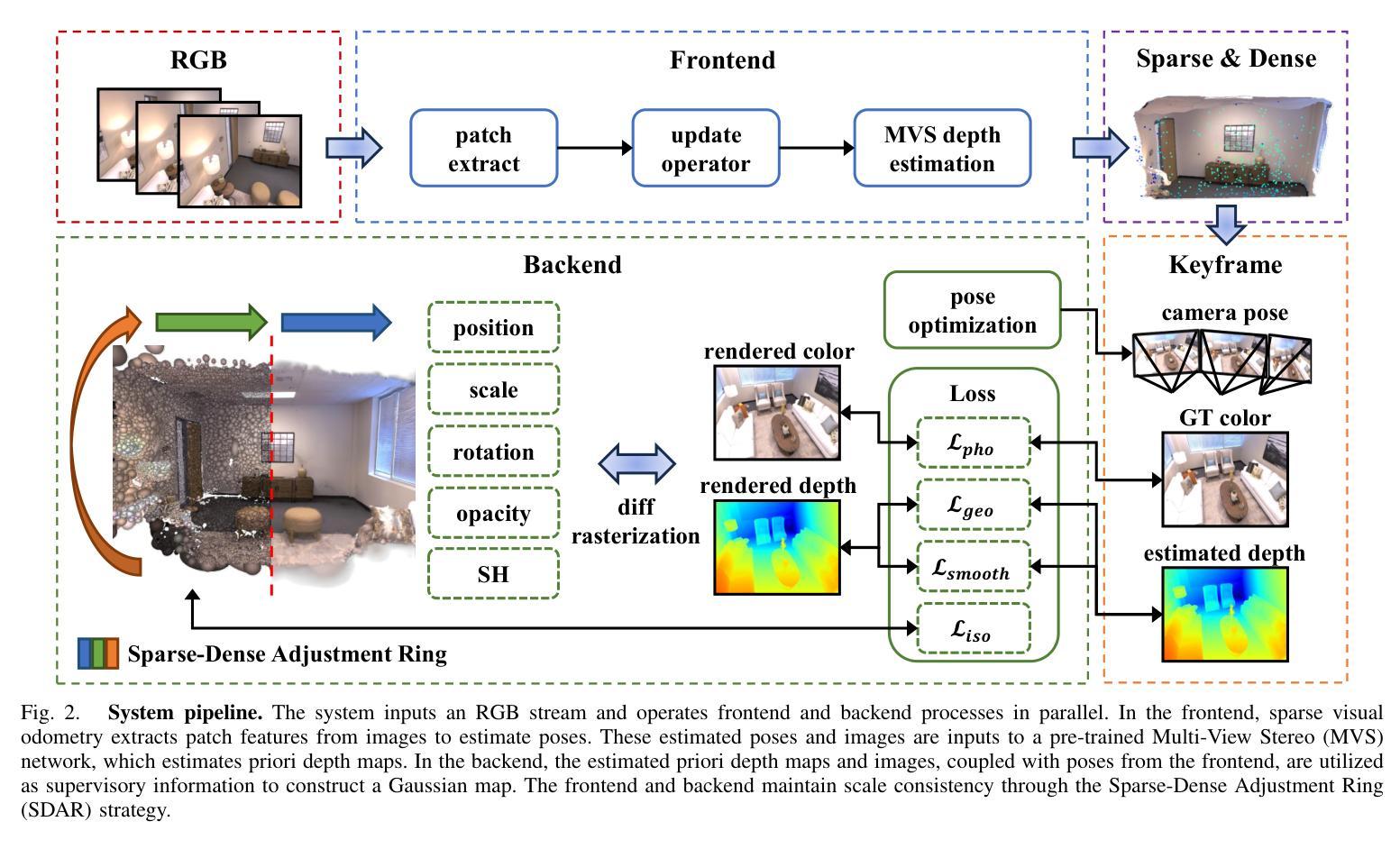
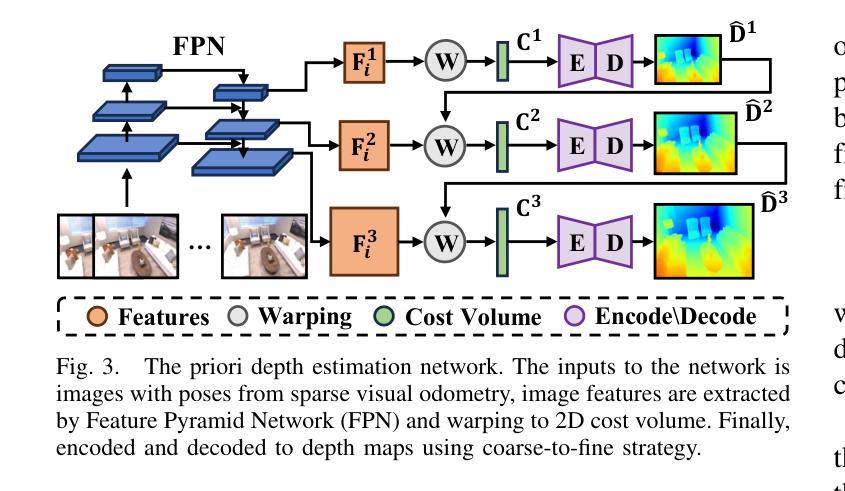
(3):本文提出的研究方法是:提出了一种新颖的单目高斯散射 SLAM 系统 MGS-SLAM。该工作在 SLAM 领域引入了多项突破性进展,包括将基于高斯散射的技术与稀疏视觉里程计相结合,采用预训练的多视图立体 (MVS) 深度估计网络,开创了一种几何平滑深度损失,并开发了稀疏 -密集调整环 (SDAR) 以确保尺度一致性。这些创新共同显着提高了仅依赖 RGB 图像输入的 SLAM 系统的准确性和功能性。
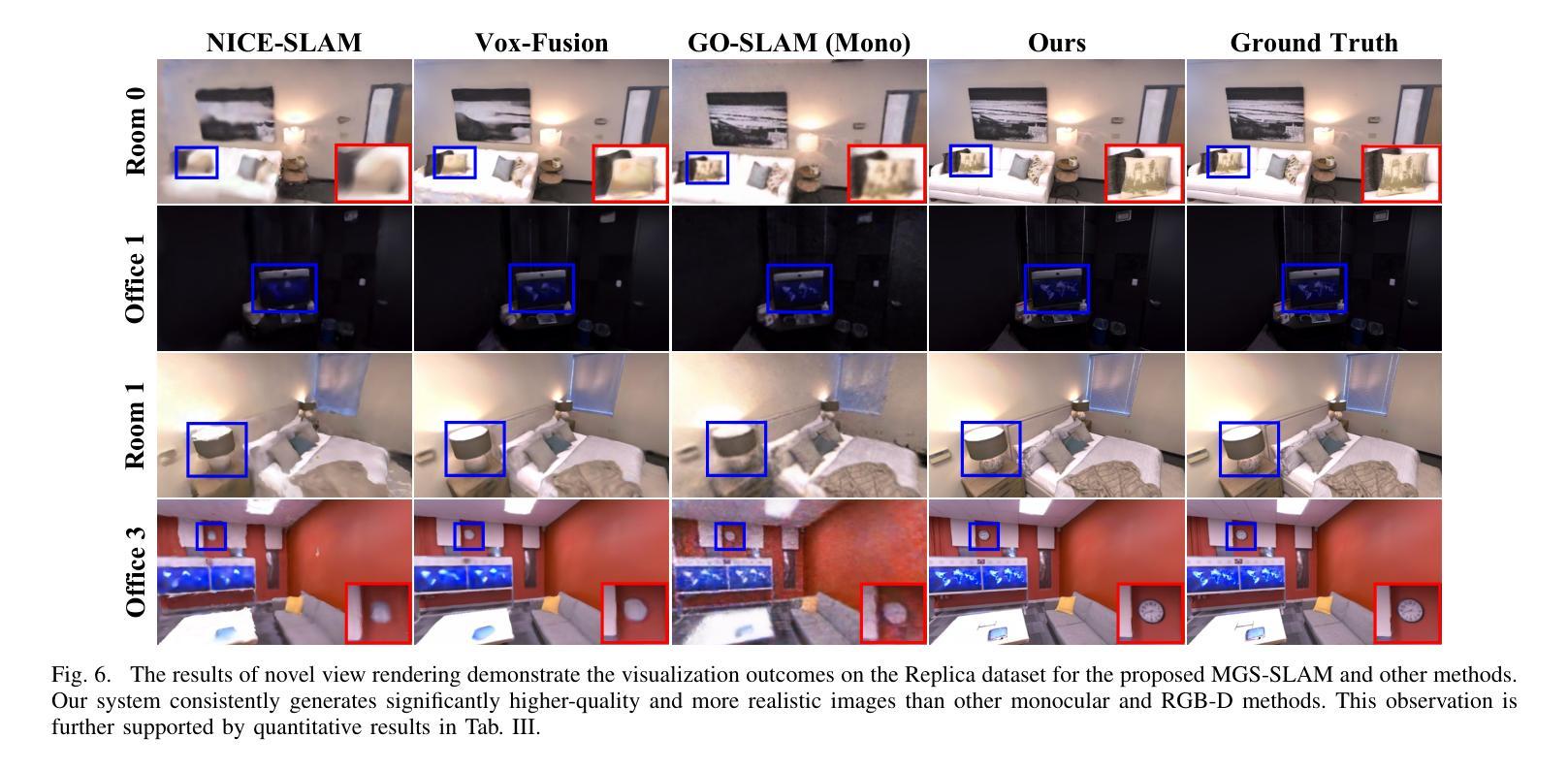
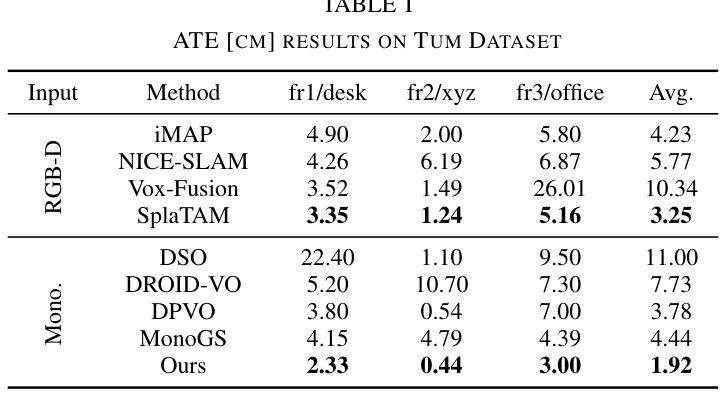
(4):本文的方法在以下任务和性能上取得了成就:在各种合成和真实世界数据集上对我们的系统进行了评估。我们的位姿估计的准确度超过了现有方法,并取得了最先进的性能。此外,它在新的视图合成保真度方面优于之前的单目方法,与利用 RGB-D 输入的神经 SLAM 系统的结果相匹配。
- 方法:
(1):提出了一种新颖的单目高斯散射 SLAM 系统 MGS-SLAM,将基于高斯散射的技术与稀疏视觉里程计相结合,消除了对基于高斯散射的 SLAM 系统中典型的深度图的依赖性,并增强了跟踪鲁棒性;
(2):采用预训练的多视图立体(MVS)深度估计网络,为后端密集映射提供几何深度监督;
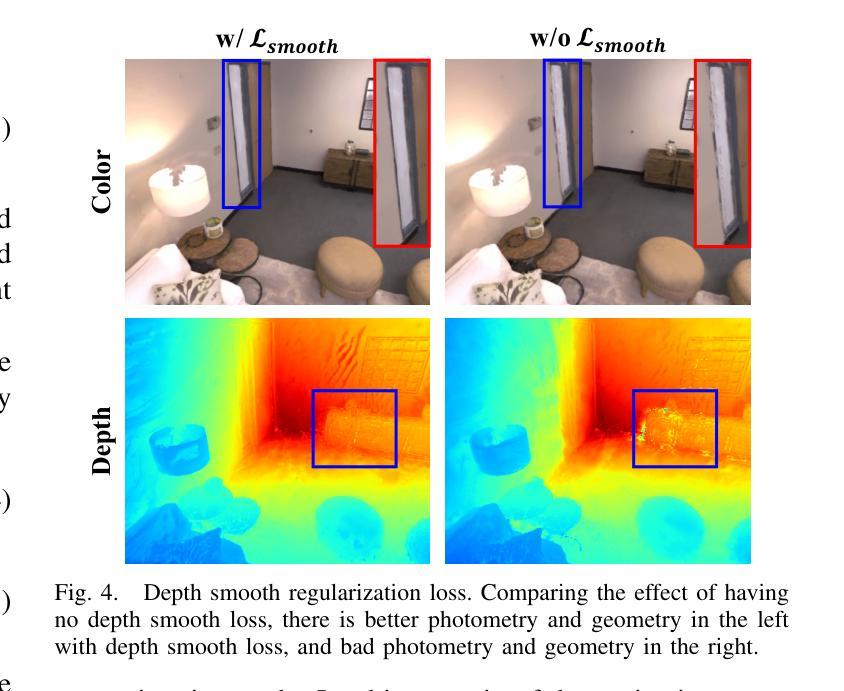
(3):开创了一种几何平滑深度损失,以减轻先验深度图误差对高斯地图几何重建的影响;
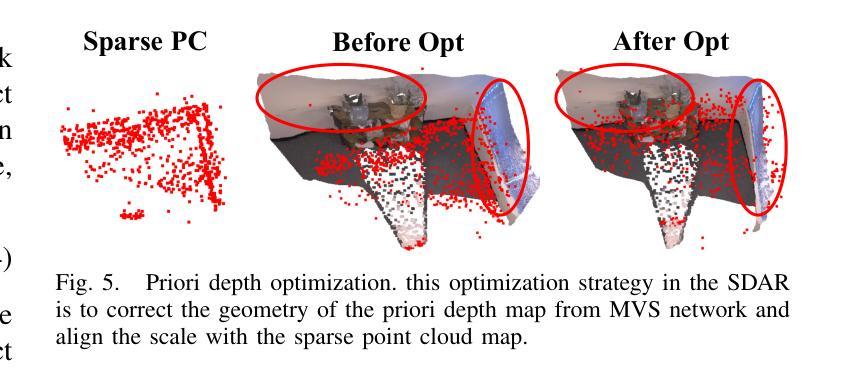
(4):开发了稀疏-密集调整环(SDAR),以确保稀疏点云地图和密集高斯地图之间的尺度一致性。
- 结论:
(1):该工作提出了一种新颖的单目高斯散射 SLAM 系统 MGS-SLAM,该系统将基于高斯散射的技术与稀疏视觉里程计相结合,消除了对基于高斯散射的 SLAM 系统中典型的深度图的依赖性,并增强了跟踪鲁棒性。此外,该工作还采用预训练的多视图立体(MVS)深度估计网络,开创了一种几何平滑深度损失,并开发了稀疏-密集调整环(SDAR),以确保稀疏点云地图和密集高斯地图之间的尺度一致性。这些创新共同显着提高了仅依赖 RGB 图像输入的 SLAM 系统的准确性和功能性。
(2):创新点:将基于高斯散射的技术与稀疏视觉里程计相结合,消除了对深度图的依赖性,并增强了跟踪鲁棒性;采用预训练的多视图立体(MVS)深度估计网络,为后端密集映射提供几何深度监督;开创了一种几何平滑深度损失,以减轻先验深度图误差对高斯地图几何重建的影响;开发了稀疏-密集调整环(SDAR),以确保稀疏点云地图和密集高斯地图之间的尺度一致性。
性能:在各种合成和真实世界数据集上对我们的系统进行了评估。我们的位姿估计的准确度超过了现有方法,并取得了最先进的性能。此外,它在新的视图合成保真度方面优于之前的单目方法,与利用 RGB-D 输入的神经 SLAM 系统的结果相匹配。
工作量:该方法需要预训练的多视图立体(MVS)深度估计网络,并且需要开发稀疏-密集调整环(SDAR)来确保稀疏点云地图和密集高斯地图之间的尺度一致性。
点此查看论文截图


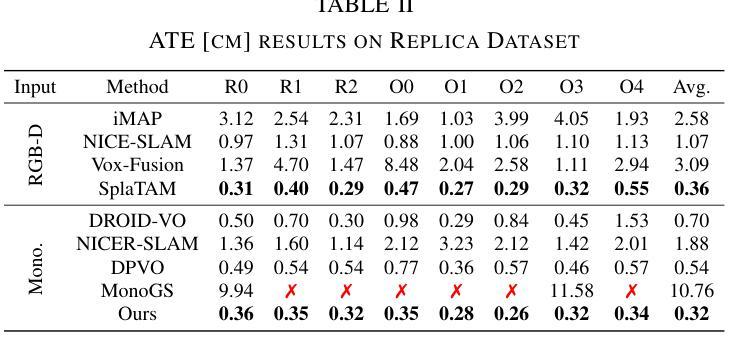
标题:FastScene:文本驱动的快速 3D 室内场景生成
作者:Yikun Ma,Dandan Zhan,Zhi Jin
单位:中山大学
关键词:文本驱动的 3D 场景生成,全景图,高斯体素渲染
论文链接:Paper_info,Github 链接:None
摘要:
(1):研究背景:文本驱动的 3D 室内场景生成在游戏、智能家居、AR/VR 等领域有着广泛的应用。快速、高保真的场景生成对于确保用户友好的体验至关重要。然而,现有方法的特点是生成过程冗长或需要复杂的手动指定运动参数,给用户带来不便。此外,这些方法通常依赖于窄视场视点迭代生成,影响了全局一致性和整体场景质量。
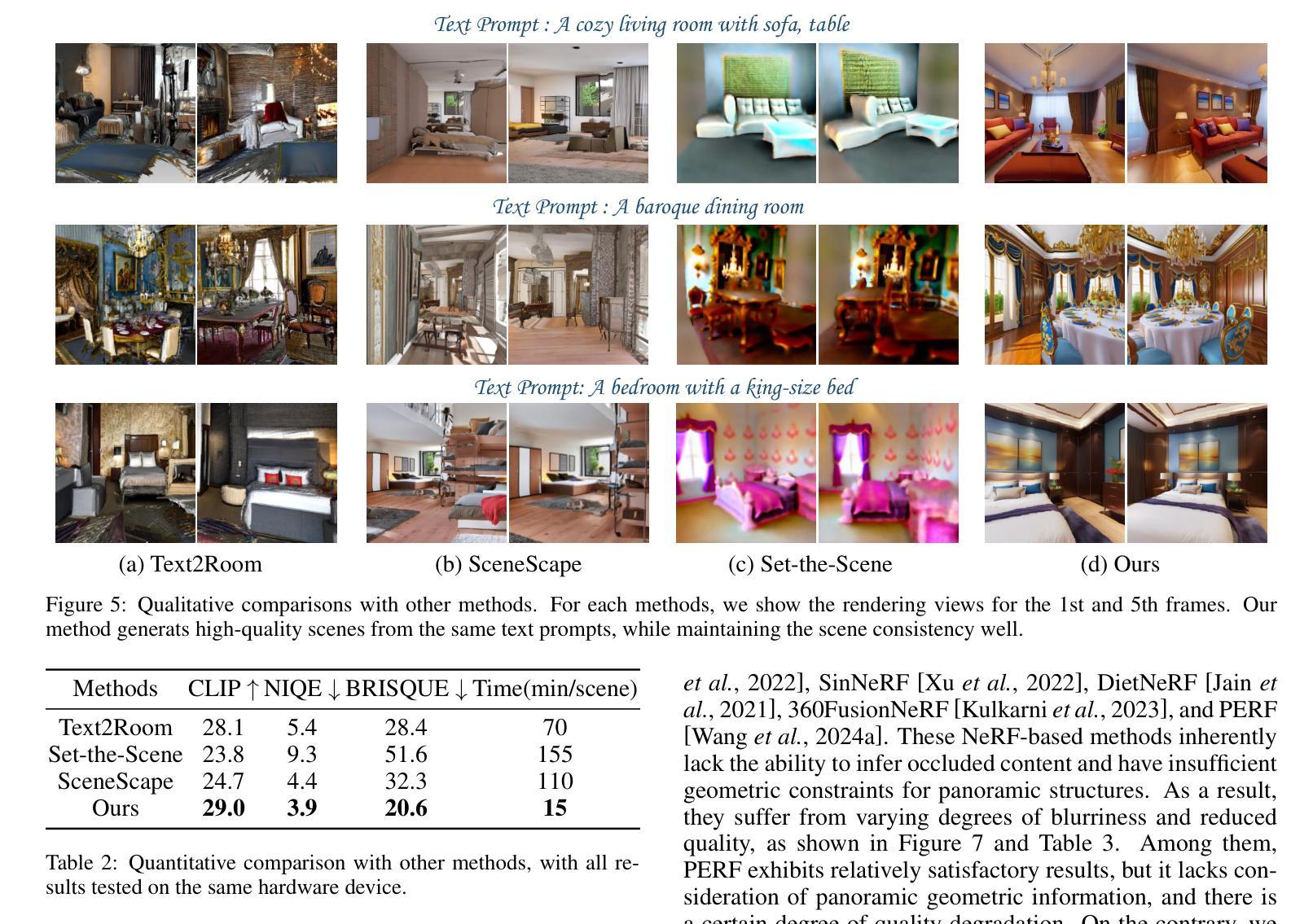
(2):过去的方法及问题:Set-the-Scene 从文本提示和 3D 对象代理进行全局局部训练,生成可控场景。但由于缺乏相应的几何信息,生成场景的质量和分辨率不佳。SceneScape 生成长距离视图,生成风格多样。但由于内绘和深度估计误差的积累,其视图质量会随着时间的推移而降低。Text2Room 和 Text2NeRF 逐步生成透视新视图。但其增量局部操作难以保证场景一致性和连贯性。Ctrl-Room 对 ControlNet 进行微调以生成可编辑的全景图,然后执行网格重建。但由于 Ctrl-Room 难以生成多视图图像,因此它倾向于将 3D 模型扁平化,场景质量有限。
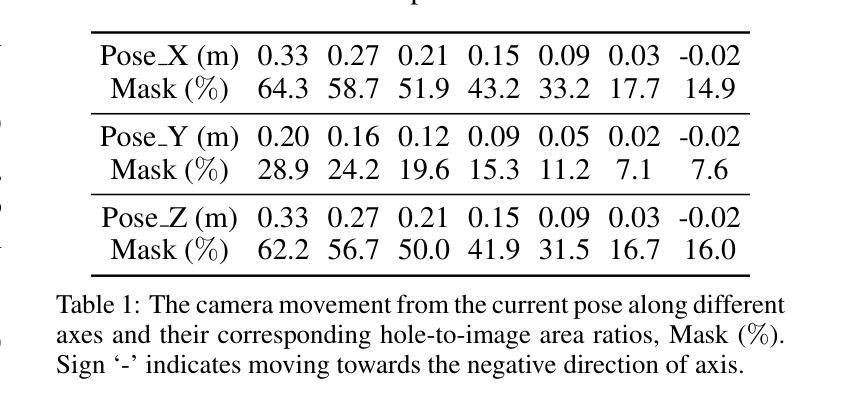
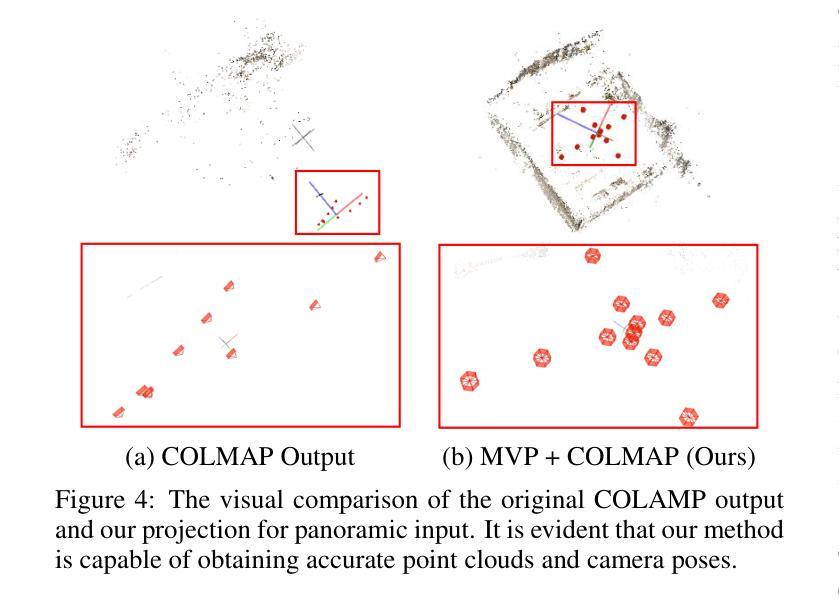
(3):提出的研究方法:本文提出了一种新颖的文本到 3D 场景框架,称为 FastScene,旨在快速生成一致、真实且高质量的场景。如图 1 所示,我们的方法主要包括三个阶段。1)在第一阶段,给定一个文本提示,我们利用预训练的 Diffusion360 生成全景图。选择全景图是因为它能够捕获全局信息并表现出明确的几何约束。2)在第二阶段,我们利用全景图及其深度估计来生成粗略视图。然后,我们引入粗略视图合成 (CVS) 和渐进式新视图内绘 (PNVI) 策略来细化粗略视图,同时确保场景一致性和视图质量。3)在第三阶段,我们利用多视图投影 (MVP) 形成透视视图,并应用 3D 高斯体素渲染 (3DGS) 进行场景重建。
(4):方法在什么任务上取得了什么性能:综合实验表明,FastScene 在生成速度和质量方面都优于其他方法,并且场景一致性更好。值得注意的是,FastScene 仅在文本提示的指导下,可以在短短 15 分钟内生成一个 3D 场景,这比最先进的方法至少快一个小时,使其成为用户友好场景生成的一个典范。
- 方法:
(1):Diffusion360生成全景图,EGformer估计深度图;
(2):CVS生成带有孔洞的新全景图,PNVI逐步修复孔洞;
(3):MVP生成透视视图,3DGS进行场景重建。
- 结论:
(1):本文提出了一种快速文本到 3D 室内场景生成框架 FastScene,展示了令人满意的场景质量和一致性。对于用户而言,FastScene 只需要一个文本提示,无需设计运动参数,即可在短短 15 分钟内提供一个完整的高质量 3D 场景。提出的 PNVI 与 CVS 可以生成一致的新全景视图,而 MVP 将其投影到透视视图,促进了 3DGS 重建。大量的实验证明了我们方法的有效性。FastScene 提供了一个用户友好的场景生成范例,我们相信它具有广泛的潜在应用。在未来的工作中,我们将重点关注 3D 场景编辑和多模态学习。致谢 本工作得到了国家自然科学基金(No.62071500)和深圳市科技计划(Grant No. JCYJ20230807111107015)的支持。
(2):创新点:提出了一种基于全景图的快速文本到 3D 室内场景生成框架 FastScene;性能:FastScene 在生成速度和质量方面均优于其他方法,并且场景一致性更好;工作量:FastScene 仅在文本提示的指导下,可以在短短 15 分钟内生成一个 3D 场景,这比最先进的方法至少快一个小时。
点此查看论文截图


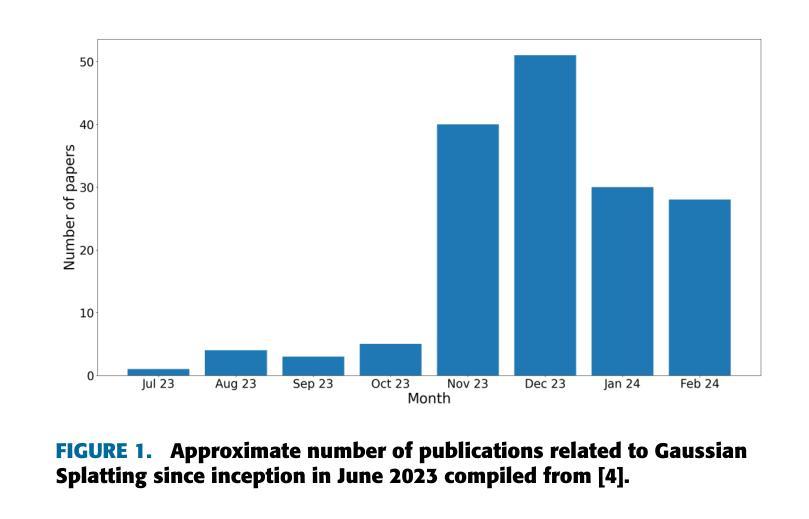
Title: Gaussian Splatting: 3D Reconstruction and Novel View Synthesis, a Review
Authors: Anurag Dalal, Daniel Hagen, Kjell G. Robbersmyr, Kristian Muri Knausgård
Affiliation: Department of Engineering Sciences, University of Agder, Grimstad, Norway
Keywords: 3D Reconstruction, Computer Vision, Deep Learning, Gaussian Splatting, Novel view synthesis, Optimization, Rendering
Urls: Paper_info:Date of publication xxxx 00, 0000, date of current version xxxx 00, 0000. Digital Object Identifier xxxx
Summary:
(1):Image-based 3D reconstruction is a challenging task that involves inferring the 3D shape of an object or scene from a set of input images. Learning-based methods have gained attention for their ability to directly estimate 3D shapes. This review paper focuses on state-of-the-art techniques for 3D reconstruction, including the generation of novel, unseen views. An overview of recent developments in the Gaussian Splatting method is provided, covering input types, model structures, output representations, and training strategies. Unresolved challenges and future directions are also discussed. Given the rapid progress in this domain and the numerous opportunities for enhancing 3D reconstruction methods, a comprehensive examination of algorithms appears essential. Consequently, this study offers a thorough overview of the latest advancements in Gaussian Splatting.; (2):Traditional approaches to 3D reconstruction, such as photogrammetry and multi-view stereo (MVS) algorithms, often suffer from artifacts, failure cases, and slow training times. Gaussian Splatting is a novel method that addresses these limitations by representing 3D objects as a collection of Gaussians. This representation allows for efficient rendering and interpolation, resulting in high-quality novel views.; (3):The Gaussian Splatting method involves an iterative refinement process, where multiple Gaussians are optimized to match the input images. The model is trained using a combination of supervised and unsupervised losses, which encourage consistency with the input images and smoothness in the 3D space. The output of the model is a volumetric point cloud, where each point represents a Gaussian with parameters such as color, spread, and location.; (4):Gaussian Splatting has been shown to achieve state-of-the-art results on a variety of 3D reconstruction and novel view synthesis tasks. The method outperforms previous approaches in terms of rendering quality, training time, and robustness to challenging scenes. These results demonstrate the potential of Gaussian Splatting for a wide range of applications, including virtual reality, augmented reality, and computer-aided design.方法:
(1):本文首先介绍了高斯散点法,这是一种使用高斯函数集合表示 3D 物体的创新方法。这种表示形式允许高效渲染和插值,从而产生高质量的新颖视图; (2):高斯散点法涉及一个迭代细化过程,其中优化多个高斯函数以匹配输入图像。模型使用监督和无监督损失的组合进行训练,这鼓励与输入图像的一致性和 3D 空间中的平滑度。模型的输出是体积点云,其中每个点表示一个具有颜色、扩展和位置等参数的高斯函数; (3):高斯散点法已被证明在各种 3D 重建和新颖视图合成任务上实现了最先进的结果。该方法在渲染质量、训练时间和对具有挑战性场景的鲁棒性方面优于以前的方法。这些结果证明了高斯散点法在广泛的应用中的潜力,包括虚拟现实、增强现实和计算机辅助设计。结论:
(1):本文从功能和应用角度对高斯散点法在三维重建和新颖视图合成中的应用进行了全面的综述,涵盖了动态建模、变形建模、运动跟踪、非刚性/可变形物体、表情/情绪变化、基于文本的生成扩散、降噪、优化、虚拟形象、可动画对象、头部建模、同步定位与规划、网格提取与物理、优化技术、编辑能力、渲染方法、压缩等方面。特别是,本文深入探讨了图像三维重建中的挑战和进展,学习型方法在三维形状估计中的作用,以及高斯散点法在三维重建中的优势和局限性。
(2):创新点:高斯散点法是一种使用高斯函数集合表示三维物体的创新方法,这种表示形式允许高效渲染和插值,从而产生高质量的新颖视图;性能:高斯散点法在三维重建和新颖视图合成方面取得了最先进的结果,在渲染质量、训练时间和对具有挑战性场景的鲁棒性方面优于以前的方法;工作量:高斯散点法涉及一个迭代细化过程,其中优化多个高斯函数以匹配输入图像,训练过程需要较大的计算资源。
点此查看论文截图


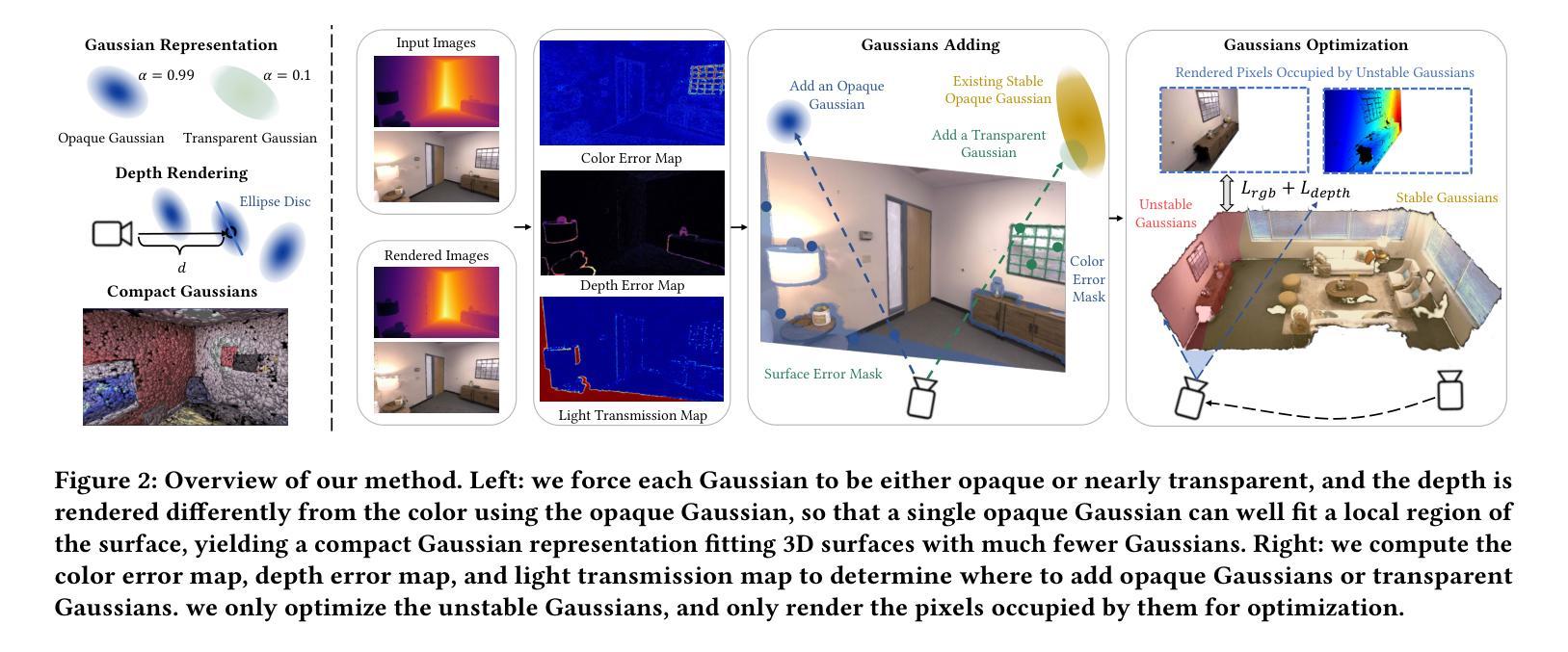
Title: RTG-SLAM:使用高斯渲染的大规模实时三维重建
Authors: Zhexi Peng, Tianjia Shao, Yong Liu, Jingke Zhou, Yin Yang, Jingdong Wang, Kun Zhou
Affiliation: 浙江大学计算机辅助设计与图形学国家重点实验室
Keywords: RGBD SLAM, 3D reconstruction, Gaussian splatting
Urls: Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.19706, Github: None
Summary:
(1): 该文章的研究背景是随着 RGBD 相机的发展,实时三维重建技术得到了广泛应用。然而,现有的方法在处理大规模环境时,往往面临内存消耗大、计算成本高的问题。
(2): 过去的方法主要使用神经辐射场(NeRF)来表示三维场景,但 NeRF 需要大量的高斯体素来拟合表面,导致内存消耗大。
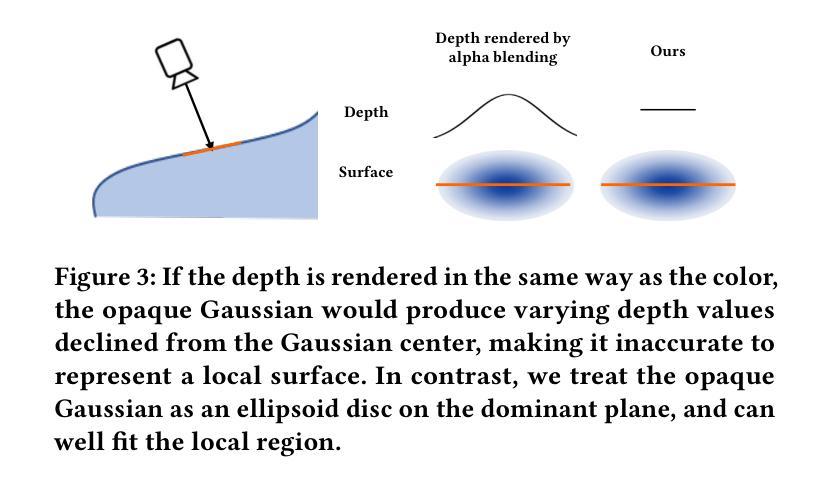
(3): 该文章提出了一种基于高斯渲染的实时三维重建系统 RTG-SLAM。RTG-SLAM 使用高斯体素来表示三维场景,并通过强制每个高斯体素要么不透明要么近乎透明,来减少内存消耗。此外,RTG-SLAM 采用了一种高效的在线高斯优化方案,只优化不稳定的高斯体素,进一步降低了计算成本。
(4): 在大规模环境重建任务上,RTG-SLAM 实现了与 NeRF-SLAM 相当的重建质量,但速度提高了约两倍,内存消耗减少了一半。
方法:
(1): 该方法使用高斯体素表示三维场景,并通过强制每个高斯体素要么不透明要么近乎透明,来减少内存消耗。 (2): 该方法采用了一种高效的在线高斯优化方案,只优化不稳定的高斯体素,进一步降低了计算成本。 (3): 该方法在大规模环境重建任务上,实现了与 NeRF-SLAM 相当的重建质量,但速度提高了约两倍,内存消耗减少了一半。结论:
(1):本文提出了一种基于高斯渲染的大规模实时三维重建系统 RTG-SLAM,该系统通过使用高斯体素表示三维场景,并强制每个高斯体素要么不透明要么近乎透明,来减少内存消耗,并采用了一种高效的在线高斯优化方案,只优化不稳定的高斯体素,进一步降低了计算成本,在保证重建质量的情况下,提高了重建速度,降低了内存消耗。 (2):创新点:提出了一种基于高斯渲染的大规模实时三维重建系统,该系统通过使用高斯体素表示三维场景,并强制每个高斯体素要么不透明要么近乎透明,来减少内存消耗,并采用了一种高效的在线高斯优化方案,只优化不稳定的高斯体素,进一步降低了计算成本。 性能:在保证重建质量的情况下,提高了重建速度,降低了内存消耗。 工作量:需要对不稳定的高斯体素进行优化,需要渲染不稳定的高斯体素占据的像素。
点此查看论文截图