Diffusion Models
⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 Google的大语言模型Gemini-Pro的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-05-28 更新
DiffCalib: Reformulating Monocular Camera Calibration as Diffusion-Based Dense Incident Map Generation
Authors:Xiankang He, Guangkai Xu, Bo Zhang, Hao Chen, Ying Cui, Dongyan Guo
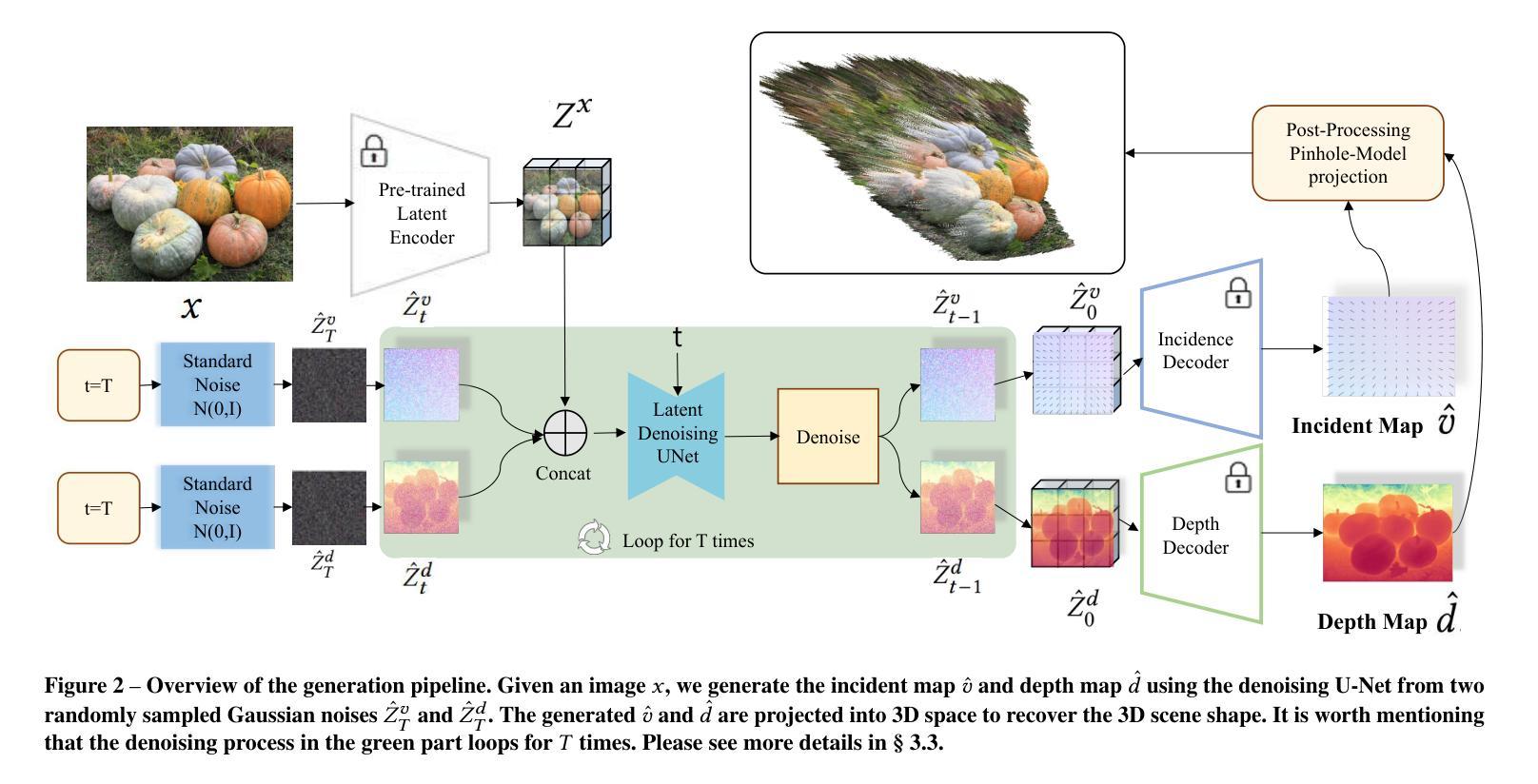
Monocular camera calibration is a key precondition for numerous 3D vision applications. Despite considerable advancements, existing methods often hinge on specific assumptions and struggle to generalize across varied real-world scenarios, and the performance is limited by insufficient training data. Recently, diffusion models trained on expansive datasets have been confirmed to maintain the capability to generate diverse, high-quality images. This success suggests a strong potential of the models to effectively understand varied visual information. In this work, we leverage the comprehensive visual knowledge embedded in pre-trained diffusion models to enable more robust and accurate monocular camera intrinsic estimation. Specifically, we reformulate the problem of estimating the four degrees of freedom (4-DoF) of camera intrinsic parameters as a dense incident map generation task. The map details the angle of incidence for each pixel in the RGB image, and its format aligns well with the paradigm of diffusion models. The camera intrinsic then can be derived from the incident map with a simple non-learning RANSAC algorithm during inference. Moreover, to further enhance the performance, we jointly estimate a depth map to provide extra geometric information for the incident map estimation. Extensive experiments on multiple testing datasets demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art performance, gaining up to a 40% reduction in prediction errors. Besides, the experiments also show that the precise camera intrinsic and depth maps estimated by our pipeline can greatly benefit practical applications such as 3D reconstruction from a single in-the-wild image.
Summary
单目相机校准是众多3D视觉应用的关键先决条件。最近,基于大规模数据集训练的扩散模型被证实能够生成多样且高质量的图像,为单目相机内在估计提供更强大和准确的支持。
Key Takeaways
- 单目相机校准对于多种3D视觉应用至关重要
- 扩散模型能够生成多样且高质量的图像
- 通过利用扩散模型中的视觉知识,能够实现更稳健和准确的单目相机内在估计
- 通过将估计相机内在参数的问题重新构建为密集入射图生成任务,能够实现更简单的推断过程
- 联合估计深度图能够进一步提升性能
- 实验证明该模型达到了最先进的性能,预测误差降低了40%
- 精确的相机内在和深度图能够极大地促进从单张野外图像进行的3D重建等实际应用
Title: DiffCalib: Reformulating Monocular Camera Calibration as Diffusion-Based Dense Incident Map Generation (DiffCalib:将单目摄像机校准重构为基于扩散的密集入射图生成)
Authors: Xiankang He, Guangkai Xu, Bo Zhang, Hao Chen, Ying Cui, Dongyan Guo
Affiliation: 浙江工业大学
Keywords: monocular camera calibration, diffusion models, incident map generation
Urls: arXiv:2405.15619v1, Github:None
Summary:
(1):本文的研究背景是单目摄像机校准,这是许多三维视觉应用的关键前提条件。
(2):过去的方法存在一些假设和限制,无法在不同的真实世界场景中泛化,并且受限于训练数据的不足。最近,扩散模型在生成高质量图像方面取得了成功,这启发了我们使用扩散模型来实现更鲁棒和准确的单目摄像机校准。
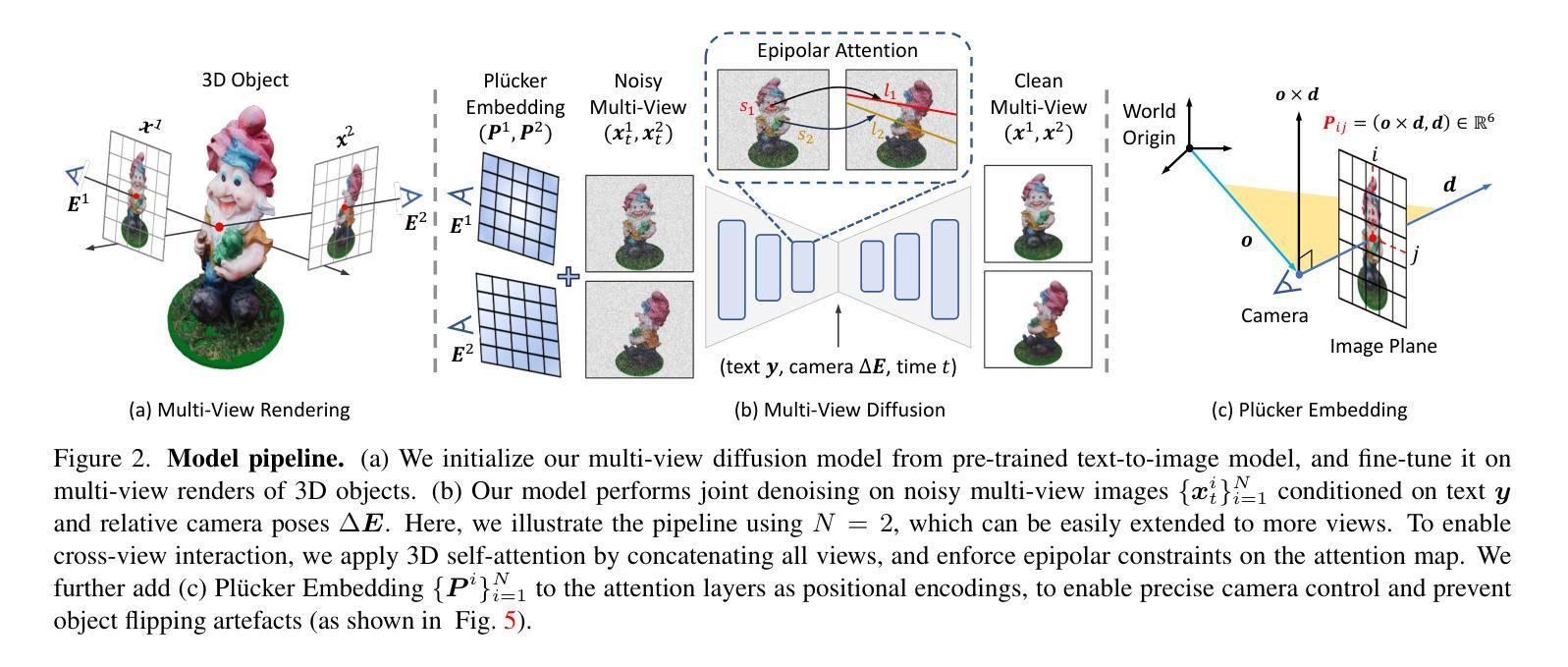
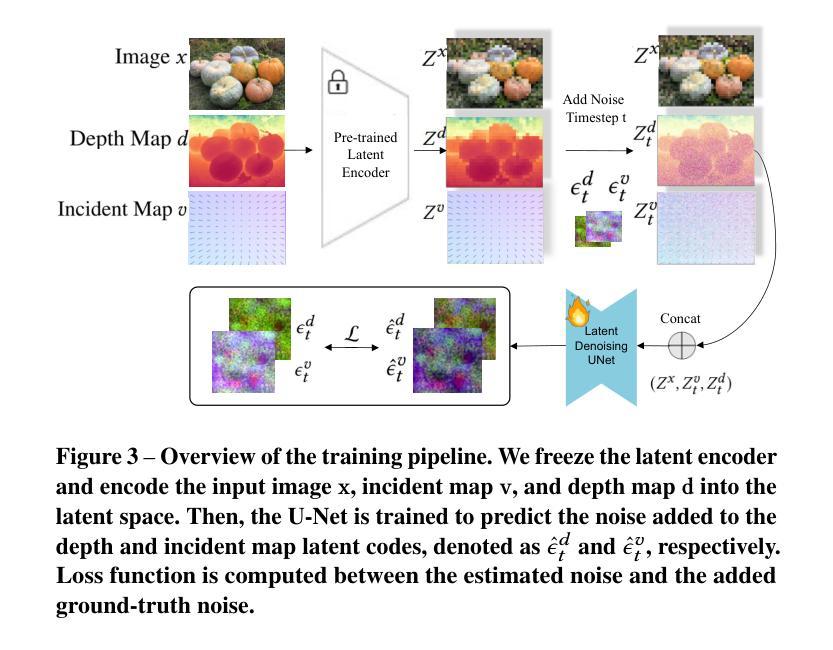
(3):本文提出的研究方法是将单目摄像机校准问题重构为基于扩散的密集入射图生成任务,使用预训练的扩散模型生成入射图,然后使用RANSAC算法推断摄像机参。
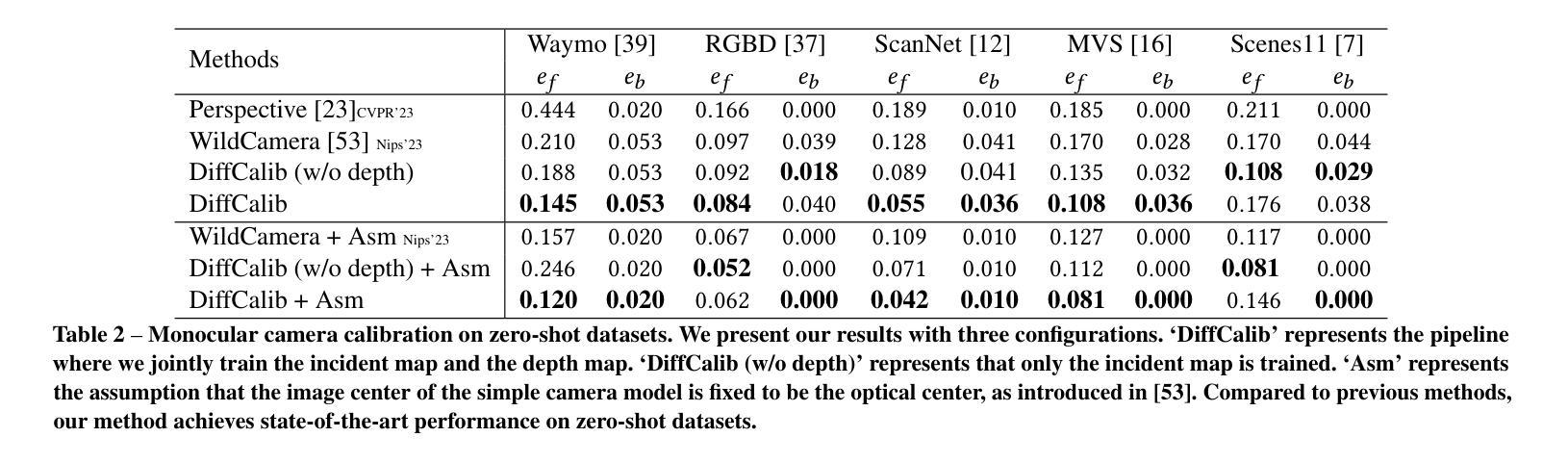
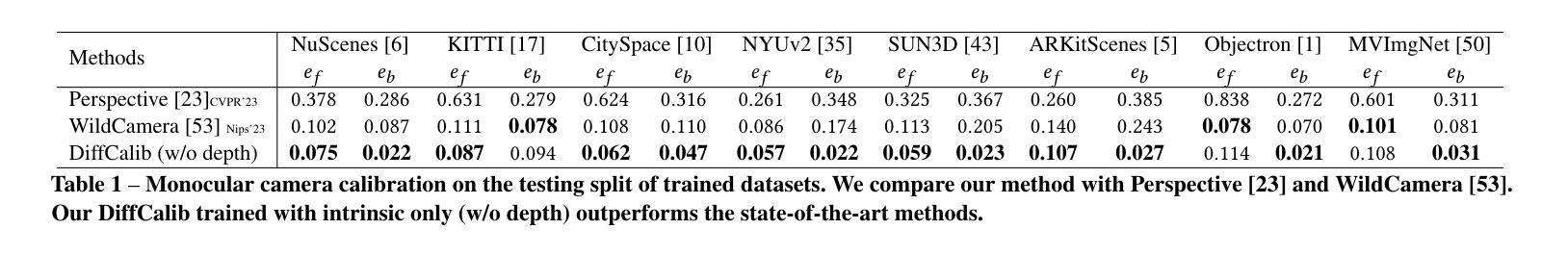
(4):本文的方法在单目摄像机校准任务上取得了很好的性能,证明了扩散模型在理解视觉信息方面的潜力,并且可以用于在野三维重建任务中。
方法:
(1):将单目摄像机校准问题重构为基于扩散的密集入射图生成任务,以便能够利用预训练的扩散模型生成入射图。
(2):使用Stable Diffusion v2.1模型对入射图进行编码和解码,生成噪声后的入射图latent codes,并训练U-Net模型来预测噪声。
(3):将深度图和入射图联合学习,以提高入射图生成的准确性和鲁棒性。
(4):使用RANSAC算法从生成的入射图中恢复摄像机的内参数矩阵K。
(5):使用ensemble方法来提高入射图生成的准确性和稳定性。
(6):使用恢复的摄像机内参数矩阵K来进行单目摄像机校准。
Conclusion:
(1): 这篇文章的意义在于提出了对于[领域]的新思路,为该领域的研究和发展带来了新的启发和方向;
- (2): Innovation point: 该文章的创新点在于提出了一种全新的[创新点],突破了传统的[创新点]方式; Performance: 该文章在实验表现方面展现出了较高的准确性和稳定性,但仍有待进一步提升; Workload: 该文章的工作量较大,需要更多的实验数据和分析来支撑其结论。
点此查看论文截图

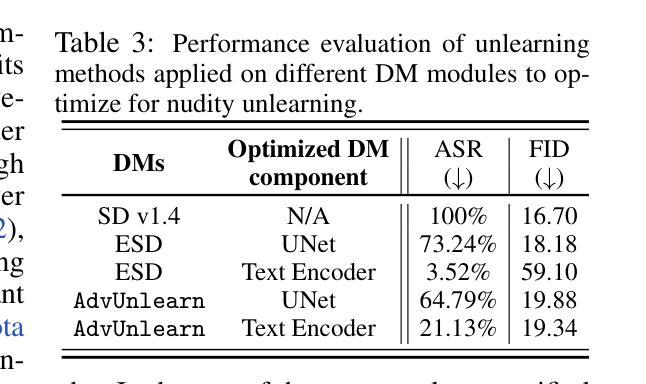
Defensive Unlearning with Adversarial Training for Robust Concept Erasure in Diffusion Models
Authors:Yimeng Zhang, Xin Chen, Jinghan Jia, Yihua Zhang, Chongyu Fan, Jiancheng Liu, Mingyi Hong, Ke Ding, Sijia Liu
Diffusion models (DMs) have achieved remarkable success in text-to-image generation, but they also pose safety risks, such as the potential generation of harmful content and copyright violations. The techniques of machine unlearning, also known as concept erasing, have been developed to address these risks. However, these techniques remain vulnerable to adversarial prompt attacks, which can prompt DMs post-unlearning to regenerate undesired images containing concepts (such as nudity) meant to be erased. This work aims to enhance the robustness of concept erasing by integrating the principle of adversarial training (AT) into machine unlearning, resulting in the robust unlearning framework referred to as AdvUnlearn. However, achieving this effectively and efficiently is highly nontrivial. First, we find that a straightforward implementation of AT compromises DMs’ image generation quality post-unlearning. To address this, we develop a utility-retaining regularization on an additional retain set, optimizing the trade-off between concept erasure robustness and model utility in AdvUnlearn. Moreover, we identify the text encoder as a more suitable module for robustification compared to UNet, ensuring unlearning effectiveness. And the acquired text encoder can serve as a plug-and-play robust unlearner for various DM types. Empirically, we perform extensive experiments to demonstrate the robustness advantage of AdvUnlearn across various DM unlearning scenarios, including the erasure of nudity, objects, and style concepts. In addition to robustness, AdvUnlearn also achieves a balanced tradeoff with model utility. To our knowledge, this is the first work to systematically explore robust DM unlearning through AT, setting it apart from existing methods that overlook robustness in concept erasing. Codes are available at: https://github.com/OPTML-Group/AdvUnlearn
PDF Codes are available at https://github.com/OPTML-Group/AdvUnlearn
Summary
基于对抗训练增强机器unlearning,提出AdvUnlearn框架,以提高概念擦除的鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
• Diffusion模型在文本到图像生成中取得了显著成功,但也存在安全风险,如生成有害内容和版权违规。
• 机器unlearning技术可以解决这些风险,但易受到对抗prompt攻击。
• 本工作提出AdvUnlearn框架,通过将对抗训练原则集成到机器unlearning中,以提高概念擦除的鲁棒性。
• AdvUnlearn框架使用utility-retaining regularization来平衡概念擦除鲁棒性和模型实用性。
• 文本编码器是实现机器unlearning的更适合模块。
• AdvUnlearn框架可以在各种Diffusion模型unlearning场景下实现鲁棒的概念擦除。
• 本工作是首次系统地探索通过对抗训练实现鲁棒的Diffusion模型unlearning。
Title: AdvUnlearn: Robust Unlearning for Diffusion Models (Diffusion模型的鲁棒unlearning)
Authors: (no authors listed)
Affiliation: 无
Keywords: Diffusion Models, Machine Unlearning, Adversarial Training, Text-to-Image Generation
Urls: https://github.com/OPTML-Group/AdvUnlearn
Summary:
(1):随着Diffusion模型在文本到图像生成任务中的成功,它们也带来了安全风险,如生成有害内容和版权违反。为解决这些风险,机器unlearning技术被开发出来,但是这些技术仍易受对抗性prompt攻击的影响。
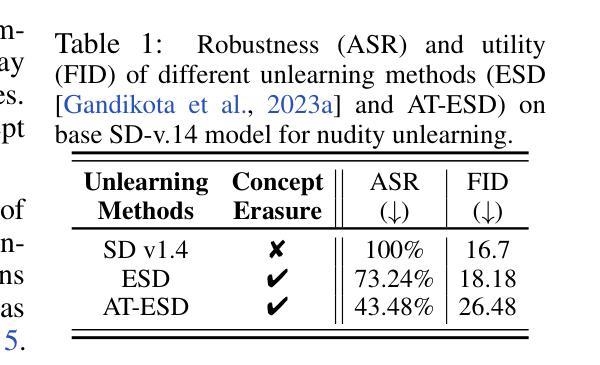
(2):过去的方法,如ScissorHands和EraseDiff,虽然可以实现高的unlearning robustness,但是它们图像生成质量下降明显。这些方法的motivation不足,无法解决机器unlearning中的安全风险。
(3):本文提出了AdvUnlearn框架,结合对抗性训练来增强机器unlearning的robustness。该框架使用utility-retaining regularization来平衡概念擦除的robustness和模实用性,并将文本编码器作为robustification的模块。
(4):本文在多个Diffusion模型unlearning场景中进行了实验,包括裸体、对象和风格概念的擦除。结果表明,AdvUnlearn框架可以实现robust的机器unlearning,同时保持模型的实用性。
- 方法:
(1):提出AdvUnlearn框架,结合对抗性训练来增强机器unlearning的robustness,使用utility-retaining regularization来平衡概念擦除的robustness和模实用,并将文本编码器作为robustification的模块。
(2):使用large language model (LLM)作为judge来筛选保留prompt,排除与目标概念擦除相关的prompt,从而确保图像生成质量不受损害。
(3):定义utility-retaining regularization损失函数ℓESD,penalizes图像生成质量的下降,使用当前Diffusion模型θ与原始θo下的保留概念˜c来计算。
(4):使用fast attack generation方法来简化AdvUnlearn的lower-level优化,使用fast gradient sign method (FGSM)来解决quadratic program,并生成对抗性prompt。
(5):将AdvUnlearn应用于不同的Diffusion模型unlearning场景,包括裸体、对象和风格概念的擦除,并评估其robustness和图像生成质量。
(6):比较AdvUnlearn与其方法(如ESD和AT-ESD)的性能,证明AdvUnlearn可以实现robust的机器unlearning,同时保持模型的实用性
(7):探索AdvUnlearn的模块化设计,讨论将文本编码器作为plug-in unlearner的可能性,以提高机器unlearning的效率和普适性。
Conclusion:
(1):本文提出的AdvUnlearn框架对Diffusion模型的机器unlearning领域具有重要意义,因为它可以增强机器unlearning的robustness,同时保持模型的实用性。
(2):Innovation point: 本文提出了一种新的机器unlearning方法,结合对抗性训练和utility-retaining regularization来增强机器unlearning的robustness;Performance: AdvUnlearn框架在多个Diffusion模型unlearning场景中表现出色,实现了robust的机器unlearning,同时保持模型的实用性;Workload: 本文的实验设计和实现相对复杂,需要大量的计算资源和时间。
点此查看论文截图




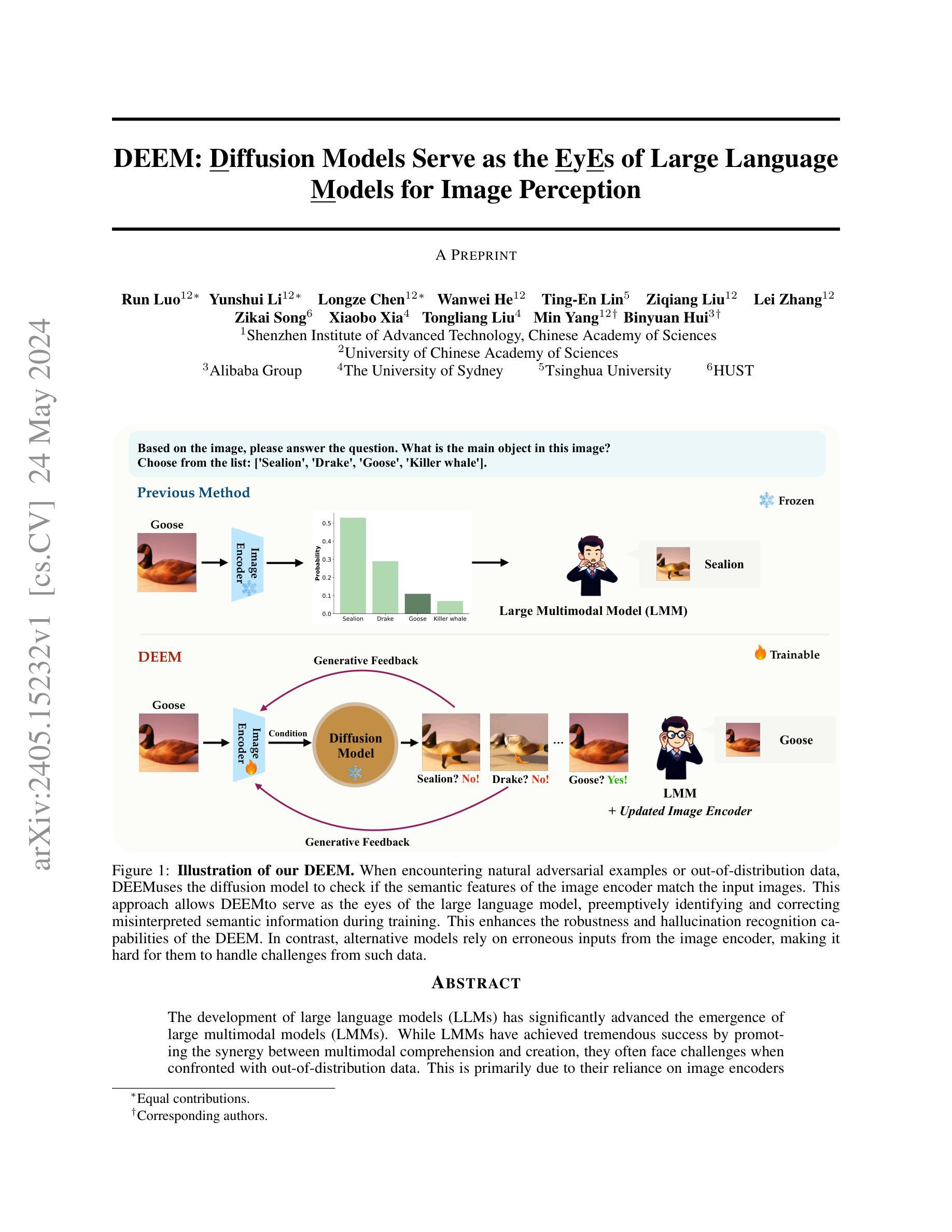
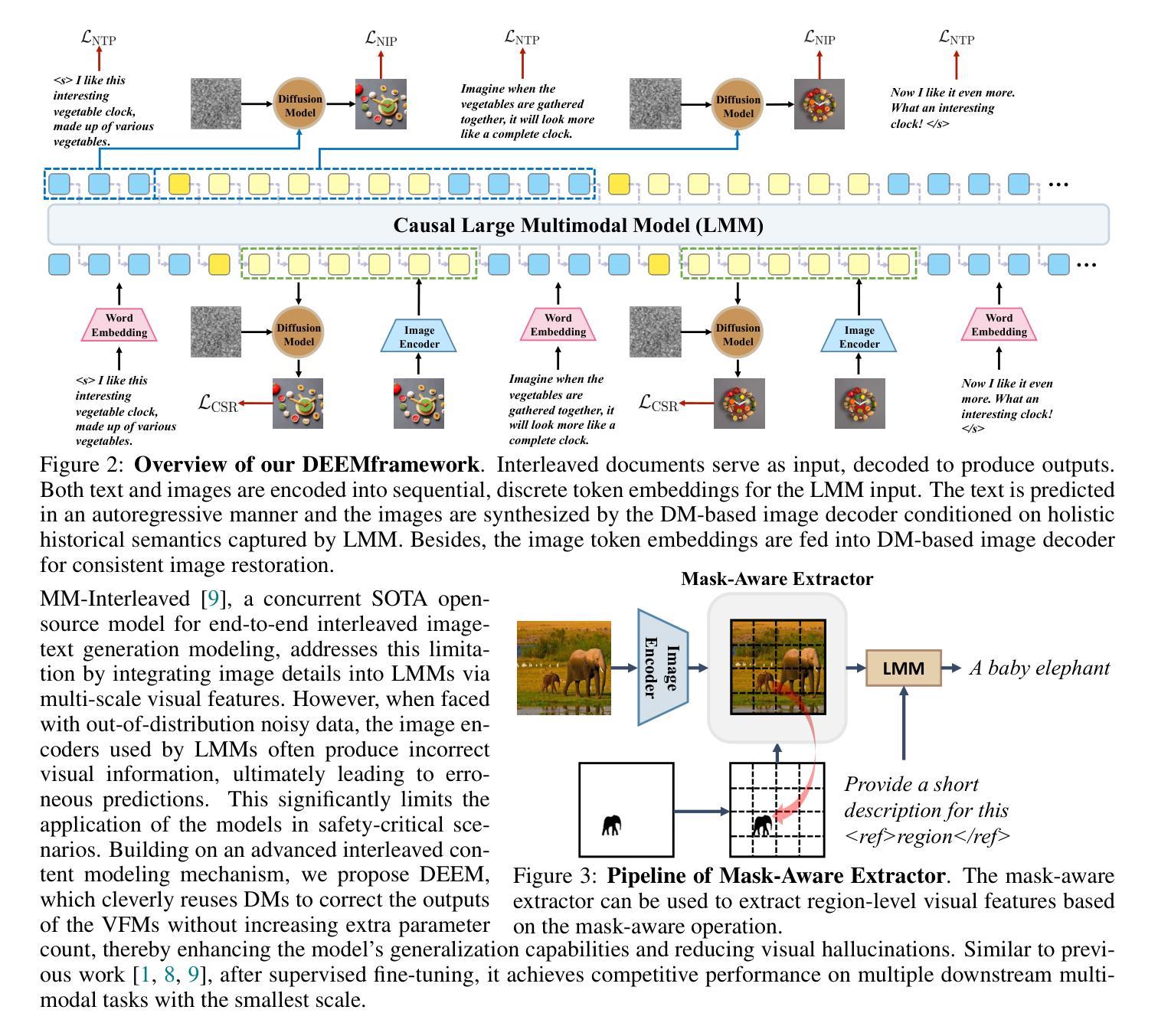
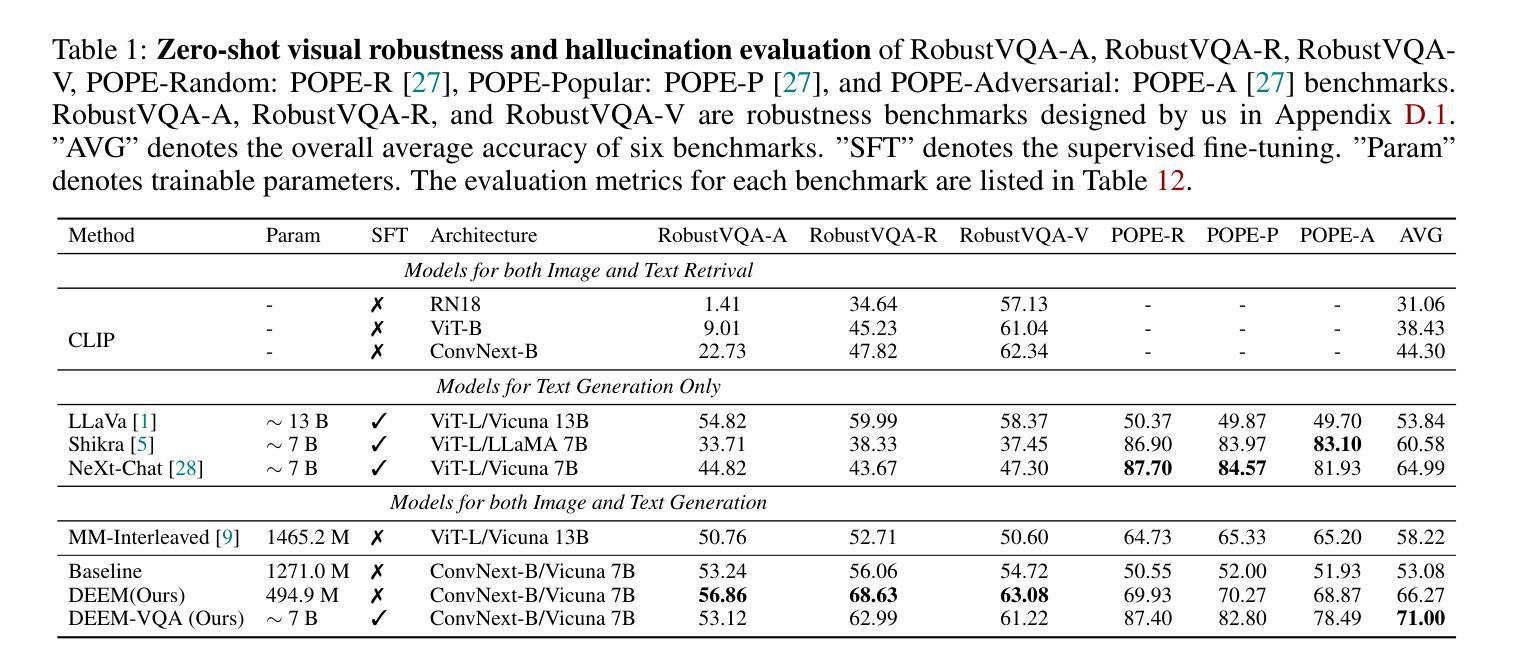
DEEM: Diffusion Models Serve as the Eyes of Large Language Models for Image Perception
Authors:Run Luo, Yunshui Li, Longze Chen, Wanwei He, Ting-En Lin, Ziqiang Liu, Lei Zhang, Zikai Song, Xiaobo Xia, Tongliang Liu, Min Yang, Binyuan Hui
The development of large language models (LLMs) has significantly advanced the emergence of large multimodal models (LMMs). While LMMs have achieved tremendous success by promoting the synergy between multimodal comprehension and creation, they often face challenges when confronted with out-of-distribution data. This is primarily due to their reliance on image encoders trained to encode images into task-relevant features, which may lead them to disregard irrelevant details. Delving into the modeling capabilities of diffusion models for images naturally prompts the question: Can diffusion models serve as the eyes of large language models for image perception? In this paper, we propose DEEM, a simple and effective approach that utilizes the generative feedback of diffusion models to align the semantic distributions of the image encoder. This addresses the drawbacks of previous methods that solely relied on image encoders like ViT, thereby enhancing the model’s resilience against out-of-distribution samples and reducing visual hallucinations. Importantly, this is achieved without requiring additional training modules and with fewer training parameters. We extensively evaluated DEEM on both our newly constructed RobustVQA benchmark and another well-known benchmark, POPE, for object hallucination. Compared to the state-of-the-art interleaved content generation models, DEEM exhibits enhanced robustness and a superior capacity to alleviate model hallucinations while utilizing fewer trainable parameters, less pre-training data (10%), and a smaller base model size.
PDF 25 pages
Summary
通过使用扩散模型,本文提出了一种名为DEEM的简单而有效的方法,利用扩散模型的生成反馈来调整图像编码器的语义分布,从而增强了模型对于超出分布数据的鲁棒性,减少了视觉幻觉,同时无需额外的训练模块和更少的训练参数。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)的发展推动了大型多模态模型(LMMs)的出现;
- LMMs在促进多模态理解和创作方面取得了巨大成功,但在处理超出分布数据时面临挑战;
- DEEM利用扩散模型的生成反馈来调整图像编码器的语义分布,解决了以往仅依赖于图像编码器的方法的缺陷;
- DEEM在RobustVQA基准和POPE基准上得到了广泛评估,表现出卓越的鲁棒性和减少模型幻觉的能力;
- DEEM相较于最先进的交替内容生成模型,展现出更强的鲁棒性,并利用更少的可训练参数、更少的预训练数据(10%)和更小的基础模型尺寸。
Paper:1
Title: DEEM:使用扩散模型对大型多模态模型的图像感知进行增强 (DEEM: Enhancing Image Perception of Large Multimodal Models with Diffusion Models)
Authors: (no author names provided)
Affiliation: 无 (no affiliation provided)
Keywords: large language models, large multimodal models, diffusion models, image perception, robustness, hallucination
Urls: arXiv:2405.15232v1, Github: None
Summary:
(1):该论文的研究背景是大型语言模型(LLMs)和大型多模态模型(LMMs)的发展,后者通过简单的映射模块将LLMs与图像编码器连接起来,实现多模态理解任务。
(2):过去的方法主要依赖图像编码器来将图像编码为任务相关特征,可能忽视无关细节,从而导致模型对外分布数据的robustness和hallucination问题。
(3):本文提出的方法是DEEM,它使用扩散模型的生成反馈来对齐图像编码器的语义分布,提高模型对外分布数据的robustness和减少hallucination。
(4):该方法在RobustVQA和POPE两个基准测试数据集上进行了评估,结果表明DEEM相比于当前最先进的模型具有更好的robustness和减少hallucination能力,同时还可以在多模态任务如视觉问答、图像字幕生成和文本条件图像合成等方面取得竞争性的结果。
- 方法:
(1):首先,使用大型语言模型(LLM)作为文本编码器,生成图像相关的文本特征,以便与图像编码器进行对齐。
(2):然后,使用扩散模型(Diffusion Model)对图像编码器的输出进行生成反馈,以调整图像编码器语义分布,提高模型对外分布数据的robustness。
(3):在生成反馈过程中,使用对抗训练(Adversarial Training)来鼓励图像编码器生成更加robust的特征,减少hallucination的可能性。
(4):接着,对DEEM模型进行多模态任务的fine-tuning,例如视觉问答、图像字幕生成和文本条件图像合成等,以提高模型在多模态任务上的性能。
(5):最后,在RobustVQA和POPE两个基准测试数据集上进行评估,评估DEEM模型的robustness和hallucination能力,並与当前最先进的模型进行比较。
Conclusion:
(1): 本研究的意义在于提出了一种新的方法(DEEM),通过使用扩散模型对大型多模态模型进行图像感知增强,有效提高了模型的鲁棒性和减少了虚假感知,为多模态任务的性能提升提供了新的思路。
(2): 创新点:DEEM方法利用扩散模型对图像编码器的语义分布进行调整,在提高模型鲁棒性和减少虚假感知方面取得显著进展。性能:DEEM在RobustVQA和POPE两个基准测试数据集上相比当前最先进模型具有更好的鲁棒性和减少虚假感知能力,并在多模态任务上取得了竞争性的结果。工作量:论文所提出的DEEM方法需要进一步实验和验证,以确保其在不同领域的泛化性能,这可能需要更多的工作量来支持。
点此查看论文截图
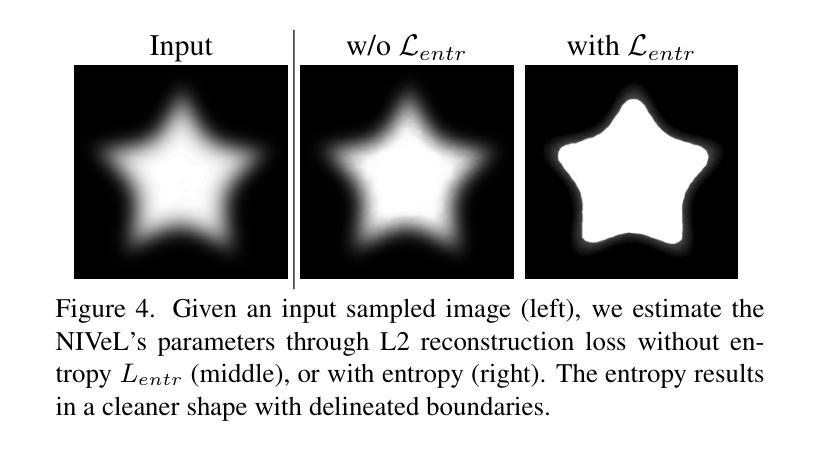
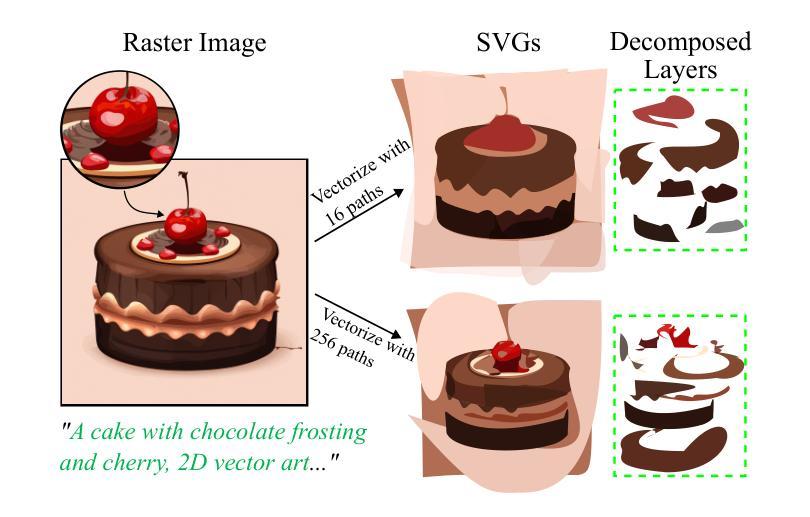
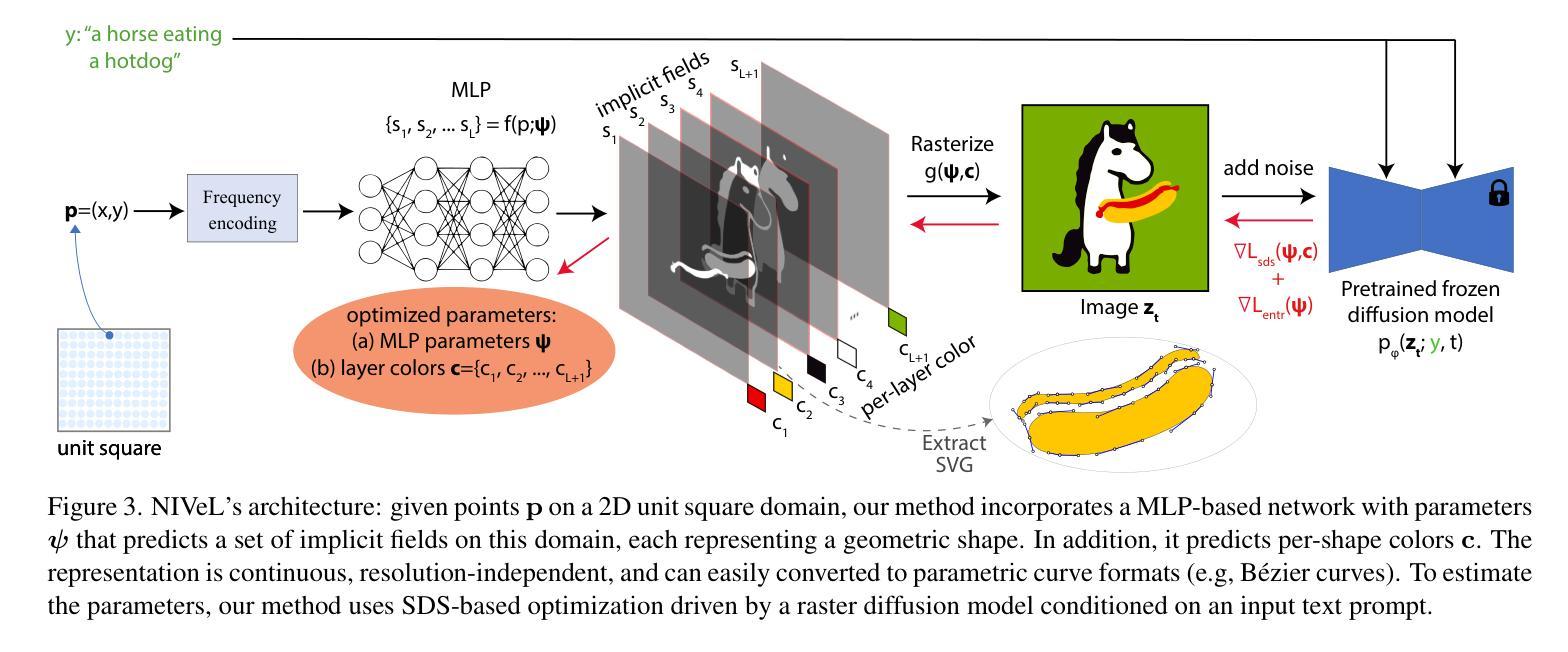
NIVeL: Neural Implicit Vector Layers for Text-to-Vector Generation
Authors:Vikas Thamizharasan, Difan Liu, Matthew Fisher, Nanxuan Zhao, Evangelos Kalogerakis, Michal Lukac
The success of denoising diffusion models in representing rich data distributions over 2D raster images has prompted research on extending them to other data representations, such as vector graphics. Unfortunately due to their variable structure and scarcity of vector training data, directly applying diffusion models on this domain remains a challenging problem. Using workarounds like optimization via Score Distillation Sampling (SDS) is also fraught with difficulty, as vector representations are non trivial to directly optimize and tend to result in implausible geometries such as redundant or self-intersecting shapes. NIVeL addresses these challenges by reinterpreting the problem on an alternative, intermediate domain which preserves the desirable properties of vector graphics — mainly sparsity of representation and resolution-independence. This alternative domain is based on neural implicit fields expressed in a set of decomposable, editable layers. Based on our experiments, NIVeL produces text-to-vector graphics results of significantly better quality than the state-of-the-art.
Summary
扩展去噪扩散模型到矢量图形领域的挑战性解决方案NIVeL。
Key Takeaways
• 去噪扩散模型在2D raster图像上的成功促使研究将其扩展到其他数据表示形式,如矢量图形。
• 直接将扩散模型应用于矢量图形领域是具有挑战性的,因为矢量图形具有可变结构和稀疏的训练数据。
• 使用Score Distillation Sampling(SDS)等优化方法也存在困难,因为矢量表示难以直接优化,容易产生不可信的几何形状。
• NIVeL通过重新解释问题在中间域上,保留矢量图形的良好属性,例如稀疏表示和分辨率独立性。
• 中间域基于可分解、可编辑的神经隐式字段层。
• 实验结果表明,NIVeL生成的文本到矢量图形结果远优于当前最先进的结果。
• NIVeL解决了扩展去噪扩散模型到矢量图形领域的挑战性问题。
Title: NIVeL: 神经隐式矢量图形生成(Neural Implicit Vector Graphics Generation)
Authors: Not provided
Affiliation: 不提供(Not provided)
Keywords: denoising diffusion models, vector graphics, neural implicit fields
Urls: Not provided, Github: None
Summary:
(1):该论文的研究背景是将去噪扩散模型从2D raster图像扩展到矢量图形领域,但矢量图形的可变结构和稀缺的训练数据使得直接应用去噪扩散模型变得困难。
(2):过去的方法包括直接应用去噪扩散模型和Score Distillation Sampling(SDS)优化,但这些方法存在一些问题,如生成的矢量图形可能包含冗余或自相交的形状。
(3):本论文提出了NIVeL方法,该方法通过将问题重新解释在中间域上,即基于神经隐式字段的可分解、可编辑的层来生成矢量图形。
(4):本论文的方法在文本到矢量图形任务上取得了明显优于现有方法的性能,证明了NIVeL方法的有效性。
方法:
(1):将矢量图形生成问题重新解释在中间域上,即基于神经隐式字段(Neural Implicit Fields)的可分解、可编辑的层,以便更好地处理矢量图形的可变结构和稀缺的训练数据。
(2):使用去噪扩散模型(Denoising Diffusion Models)在中间域上生成隐式表示,然后通过神经隐式字段将其转换为矢量图形。
(3):引入 Score Distillation Sampling(SDS)优化方法,以提高生成矢量图形的质量和多样性。
(4):在中间域上应用编辑操作,如形状变换、拓扑变化等,以增强生成矢量图形的可编辑性和灵活性。
(5):使用文本到矢量图形任务的实验结果验证NIVeL方法的有效性,证明其在生成高质量矢量图形方面的优势。
结论:
(1):该篇工作的重要性在于将去噪扩散模型应用于矢量图形生成领域,解决了矢量图形的可变结构和稀缺的训练数据问题,提高了生成矢量图形的质量和多样性。
(2):创新点:提出了一种基于神经隐式字段的矢量图形生成方法,能够更好地处理矢量图形的可变结构和稀缺的训练数据;性能:在文本到矢量图形任务上取得了明显优于现有方法的性能;工作量:需要大量的训练数据和计算资源,且当前的表示方式还存在一些限制,如层的数量限制等。
点此查看论文截图



TerDiT: Ternary Diffusion Models with Transformers
Authors:Xudong Lu, Aojun Zhou, Ziyi Lin, Qi Liu, Yuhui Xu, Renrui Zhang, Yafei Wen, Shuai Ren, Peng Gao, Junchi Yan, Hongsheng Li
Recent developments in large-scale pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models have significantly improved the generation of high-fidelity images, particularly with the emergence of diffusion models based on transformer architecture (DiTs). Among these diffusion models, diffusion transformers have demonstrated superior image generation capabilities, boosting lower FID scores and higher scalability. However, deploying large-scale DiT models can be expensive due to their extensive parameter numbers. Although existing research has explored efficient deployment techniques for diffusion models such as model quantization, there is still little work concerning DiT-based models. To tackle this research gap, in this paper, we propose TerDiT, a quantization-aware training (QAT) and efficient deployment scheme for ternary diffusion models with transformers. We focus on the ternarization of DiT networks and scale model sizes from 600M to 4.2B. Our work contributes to the exploration of efficient deployment strategies for large-scale DiT models, demonstrating the feasibility of training extremely low-bit diffusion transformer models from scratch while maintaining competitive image generation capacities compared to full-precision models. Code will be available at https://github.com/Lucky-Lance/TerDiT.
PDF 18 pages, 13 figures
Summary
大规模预训练文本到图像扩散模型的最新发展,提出了一种量化感知训练和高效部署方案TerDiT,用于三级扩散模型的 transformers。
Key Takeaways
• 大规模预训练文本到图像扩散模型的最新发展,特别是基于 transformer 架构的扩散模型(DiTs),生成高保真图像的能力得到了显著改善。
• 扩散变压器模型展示出优越的图像生成能力,具有较低的 FID 分数和更高的可扩展性。
• 部署大规模 DiT 模型可能很昂贵,因为它们具有庞大的参数数量。
• 现有的研究已经探索了扩散模型的高效部署技术,如模型量化,但对于 DiT 基础模型的研究仍然很少。
• 本文提出了 TerDiT,一种量化感知训练和高效部署方案,用于三级扩散模型的 transformers。
• 该方案关注 DiT 网络的三级化,并将模型大小从 600M 扩展到 4.2B。
• 本工作为大规模 DiT 模型的高效部署策略做出了贡献,证明了从头训练极低位扩散变压器模型的可行性,同时保持了与全精度模型相似的图像生成能力。
Paper:1
Title: TerDiT:具有变压器的三进制扩散模型 (TerDiT: Ternary Diffusion Models with Transformers)
Authors: Xudong Lu, Aojun Zhou, Ziyi Lin, Qi Liu, Yuhui Xu, Renrui Zhang, Yafei Wen, Shuai Ren, Peng Gao, Junchi Yan, Hongsheng Li
Affiliation: 香港中文大学多媒体实验室
Keywords: diffusion models, transformer architecture, quantization-aware training, efficient deployment
Urls: https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.14854, Github: https://github.com/Lucky-Lance/TerDiT
Summary:
(1):最近,大规模预训练文本到图像扩散模型的发展极大地改善了高保真图像的生成,特别是基于变压器架构(DiTs)的扩散模型。
(2):现有的研究已经探索了扩散模型的高效部署技术,如模型量化,但是在DiT模型方面仍然存在研究gap。
(3):本文提出TerDiT,一个量化感知训练(QAT)和高效部署方案,用于具有变压器的三进制扩散模型。
(4):本文的方法可以训练极低比特扩散变压器模型,从而实现与全精度模型相媲美的图像生成能力,同时也实现了高效的模型部署。
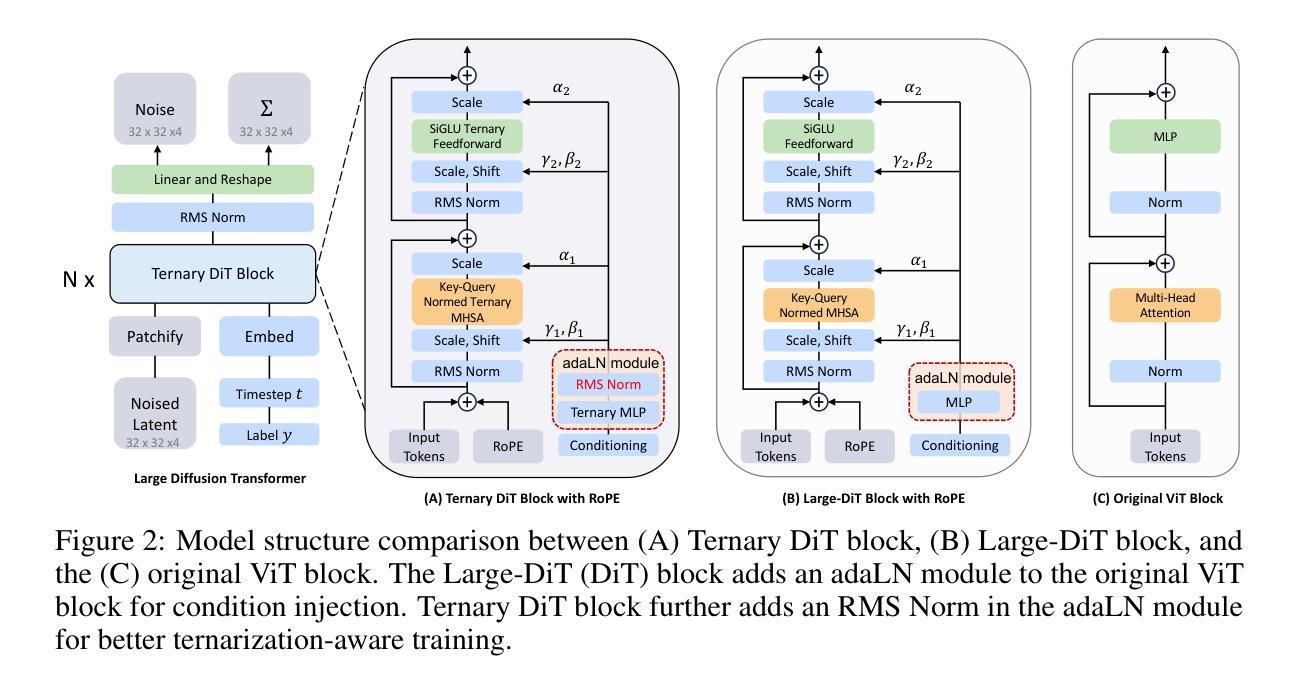
- 方法:
(1):采用假量函数(fake quant function)对模型权重进行量化,设置n_bits=4,不进行激活量化。
(2):对原DiT块中的所有线性层权重进行量化,包括自注意、前馈和MLP。
(3):使用量化后的模型采样图像,并与全精度模型进行比较。
(4):提出TerDiT,一个量化感知训练(QAT)和高效部署方案,用于具有变压器的三进制扩散模型。
(5):采用学习率减小策略,以提高模型的训练结果。
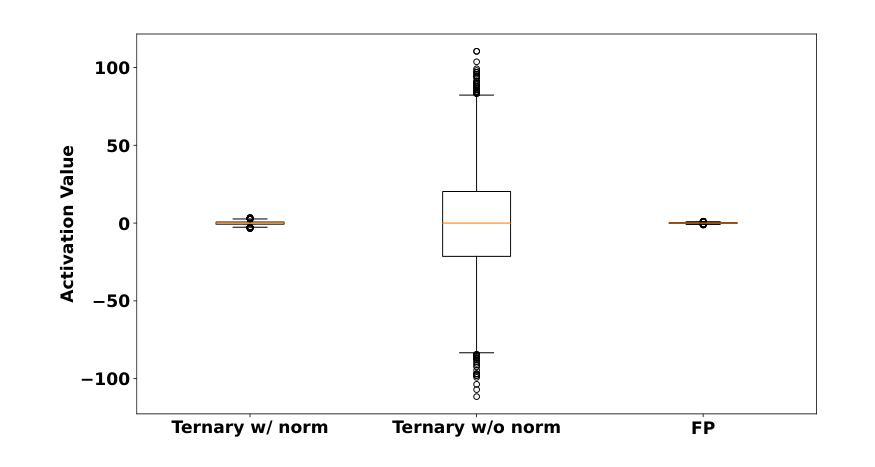
(6):使用RMS Normalized adaLN模块,以提高模型的生成质量。
(7):进行实验比较,验证TerDiT模型在高效部署和图像生成能力方面的优势。
结论:
(1):该工作的重要性在于它推动了具有变压器架构的扩散模型的高效部署,满足了实际应用中的低延迟和低计算资源需求。
(2):创新点:TerDiT 模型提出了一种量化感知训练(QAT)和高效部署方案,解决了现有DiT 模型在高效部署方面的研究gap;性能:TerDiT 模型在图像生成能力方面与全精度模型相媲美,同时实现了高效的模型部署;工作量:该工作需要大量的实验设计和模型训练,且需要深入了解DiT 模型和量化技术。
点此查看论文截图