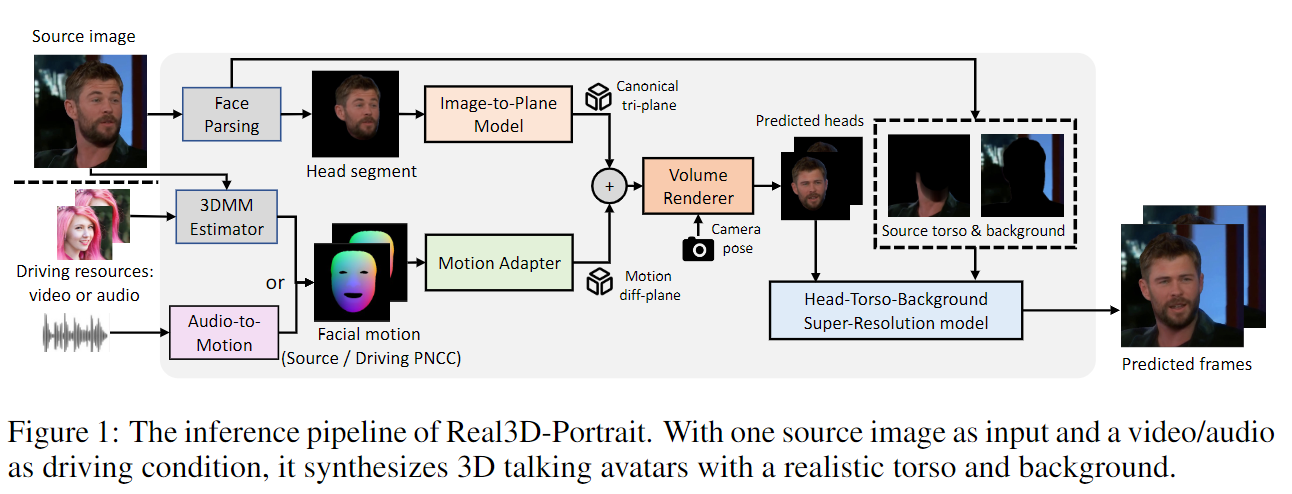
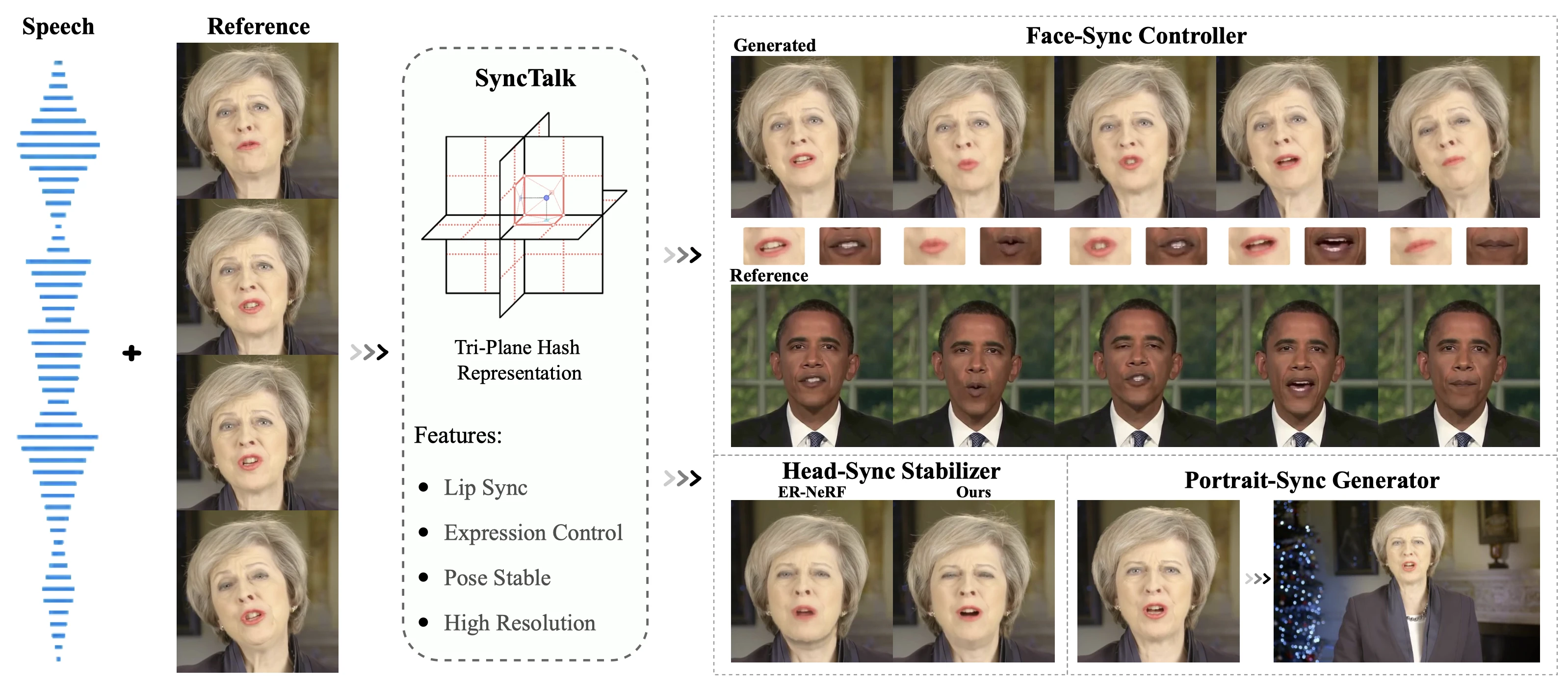
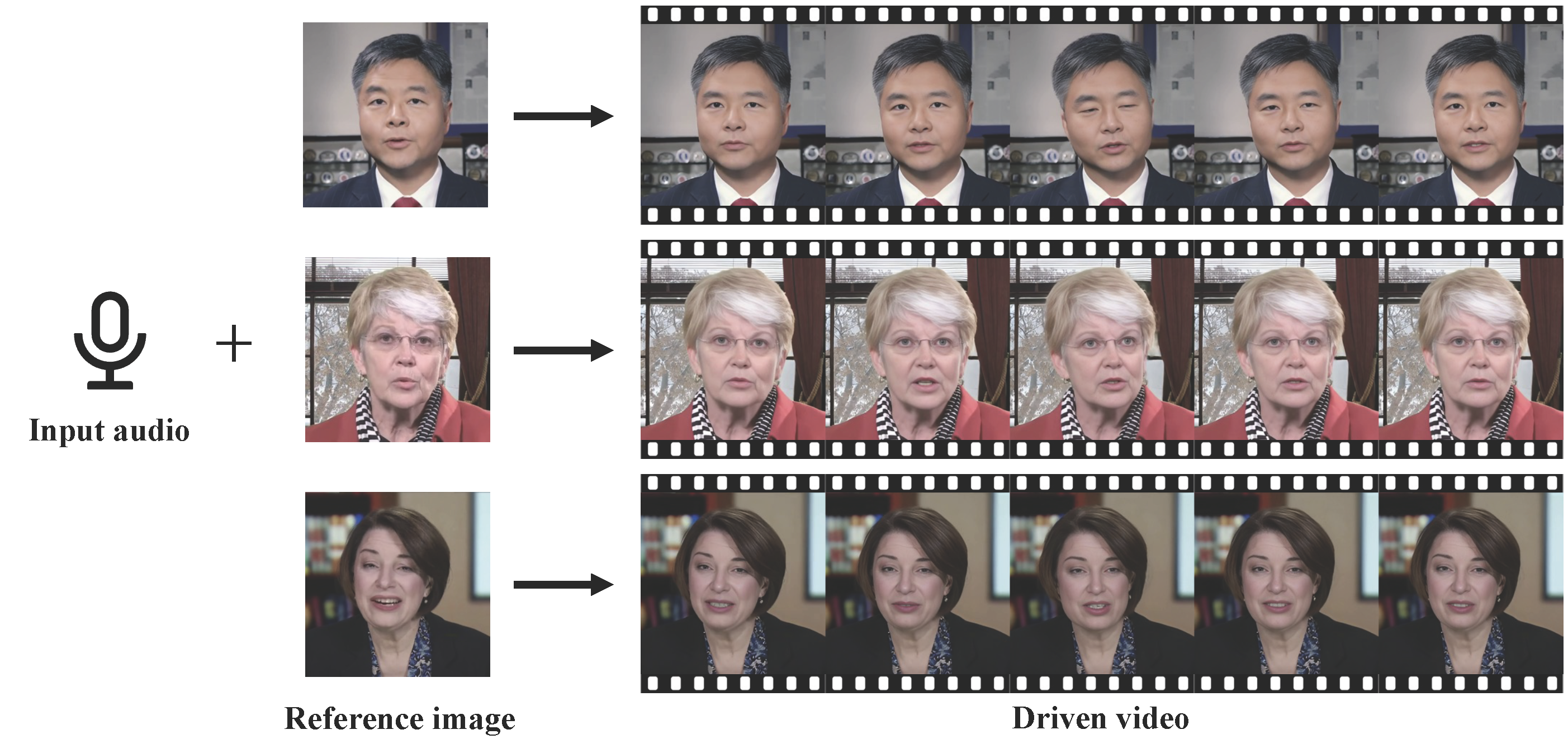
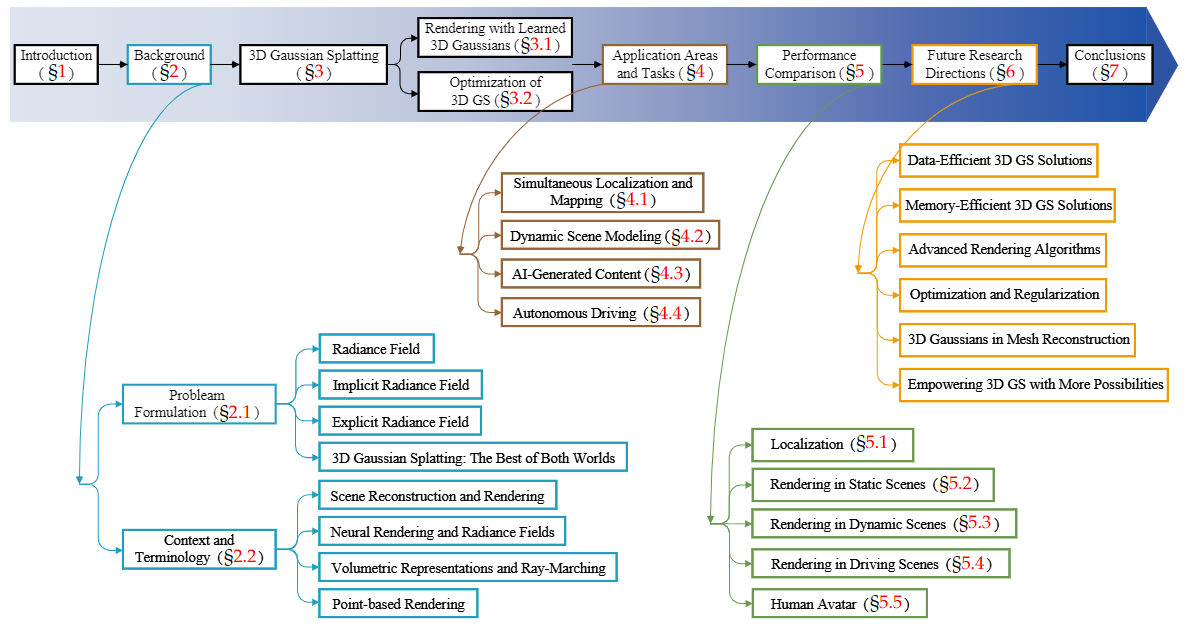
NeRF
⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 Google的大语言模型Gemini-Pro的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-05-28 更新
NeRF-Casting: Improved View-Dependent Appearance with Consistent Reflections
Authors:Dor Verbin, Pratul P. Srinivasan, Peter Hedman, Ben Mildenhall, Benjamin Attal, Richard Szeliski, Jonathan T. Barron
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) typically struggle to reconstruct and render highly specular objects, whose appearance varies quickly with changes in viewpoint. Recent works have improved NeRF’s ability to render detailed specular appearance of distant environment illumination, but are unable to synthesize consistent reflections of closer content. Moreover, these techniques rely on large computationally-expensive neural networks to model outgoing radiance, which severely limits optimization and rendering speed. We address these issues with an approach based on ray tracing: instead of querying an expensive neural network for the outgoing view-dependent radiance at points along each camera ray, our model casts reflection rays from these points and traces them through the NeRF representation to render feature vectors which are decoded into color using a small inexpensive network. We demonstrate that our model outperforms prior methods for view synthesis of scenes containing shiny objects, and that it is the only existing NeRF method that can synthesize photorealistic specular appearance and reflections in real-world scenes, while requiring comparable optimization time to current state-of-the-art view synthesis models.
PDF Project page: http://nerf-casting.github.io
Summary
NeRF方法通过光线追踪技术解决了高度光滑物体的渲染问题,实现了逼真的镜面效果和反射。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF方法改进了渲染远处环境光照细节的能力,但无法合成较近内容的一致反射。
- 采用光线追踪技术,从点上投射反射光线并跟踪它们通过NeRF表示,以呈现特征向量,并使用小型廉价网络将其解码为颜色,解决了大规模神经网络的优化和渲染速度受限的问题。
- 该模型在合成含有光亮物体场景的视图合成方面优于先前方法,是唯一可以在现实场景中合成逼真的镜面效果和反射的NeRF方法,且所需优化时间与当前最先进的视图合成模型相当。
Title: NeRF-Casting:Improved View-Dependent Appearance with Consistent Reflections(NeRF-Casting:具有consistent反射的视图相关外观改进)
Authors: DOR VERBIN, PRATUL P. SRINIVASAN, PETER HEDMAN, BEN MILDENHALL, BENJAMIN ATTAL, RICHARD SZELISKI, JONATHAN T. BARRON
Affiliation: 谷歌美国
Keywords: View synthesis, neural radiance fields, reflections
Urls: https://nerf-casting.github.io, Github:None
Summary:
(1):该论文的研究背景是Neural Radiance Fields(NeRF)在视图合成任务中的应用,特别是处理具有高频视图相关外观的镜面对象。
(2):过去的方法使用大型神经网络来模拟视图相关的radiance,但是这些方法存在两个问题:一是只能合成远距离环境照明的反射,二是计算开销很大。本文的方法motivated by这些问题。
(3):本文提出的方法是基于ray tracing的NeRF-Casting,通过casting反射光线并将其追踪到NeRF表示中,生成特征向量,然后使用小型神经网络解码成颜色。
(4):本文的方法在视图合成任务中取得了state-of-the-art的性能,能够合成具有高频视图相关外观的镜面对象的反射,且计算开销与当前最先进的视图合成模型相当。
- Conclusion:
(1):该篇工作的意义在于解决了Neural Radiance Fields(NeRF)在视图合成任务中的反射问题,提高了视图相关外观的合成质量和效率。
(2):创新点:提出了一种基于ray tracing的NeRF-Casting方法,能够生成高频视图相关外观的镜面对象反射;性能:取得了state-of-the-art的视图合成性能,能够合成具有高频视图相关外观的镜面对象反射;工作负载:计算开销与当前最先进的视图合成模型相当,具有良好的实时性和可扩展性。
点此查看论文截图


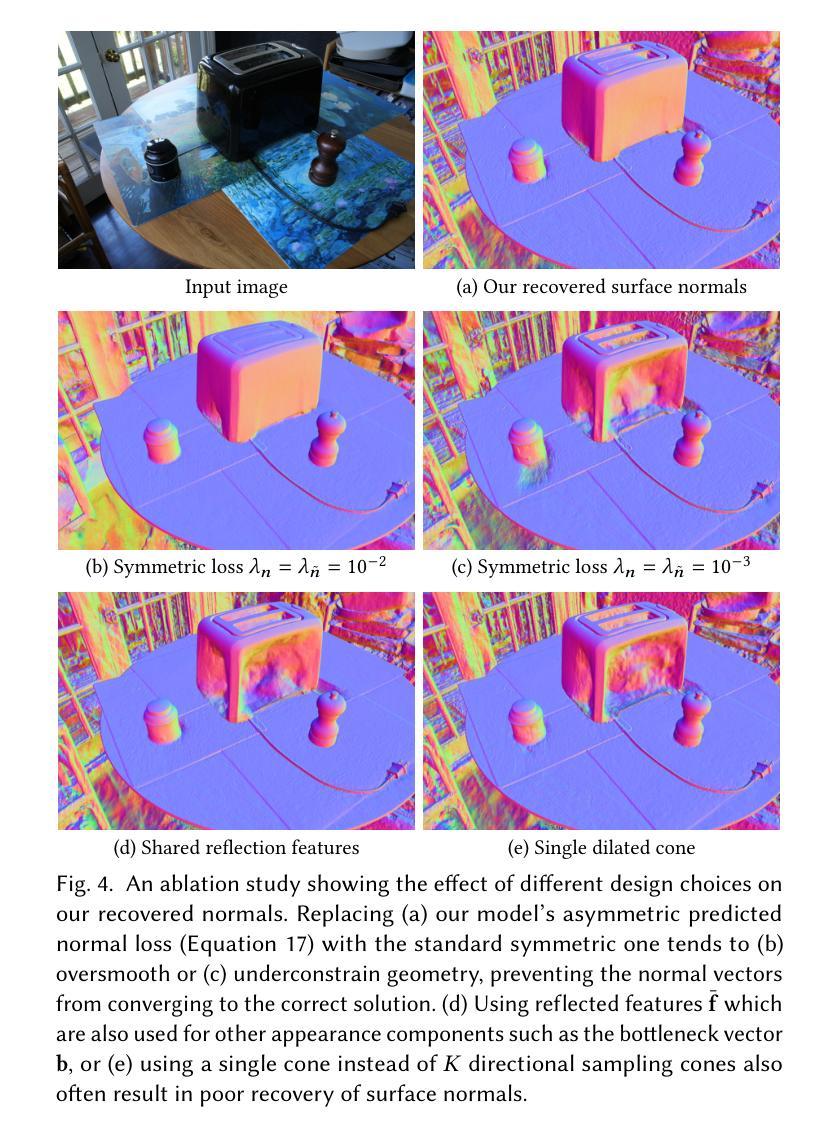
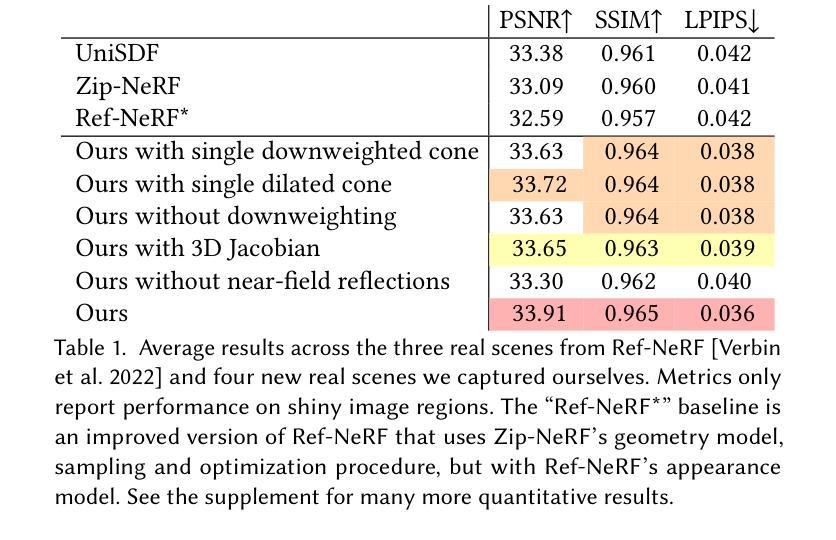
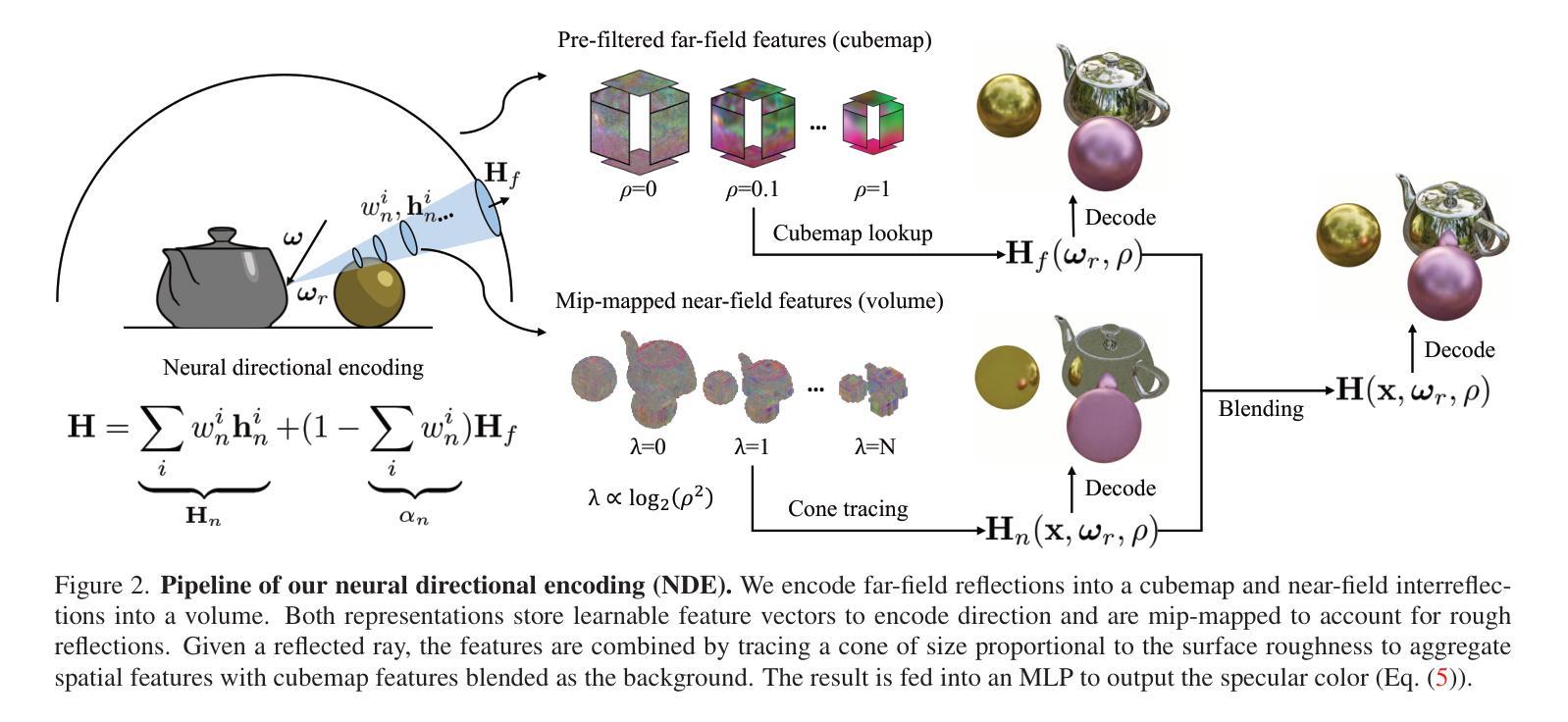
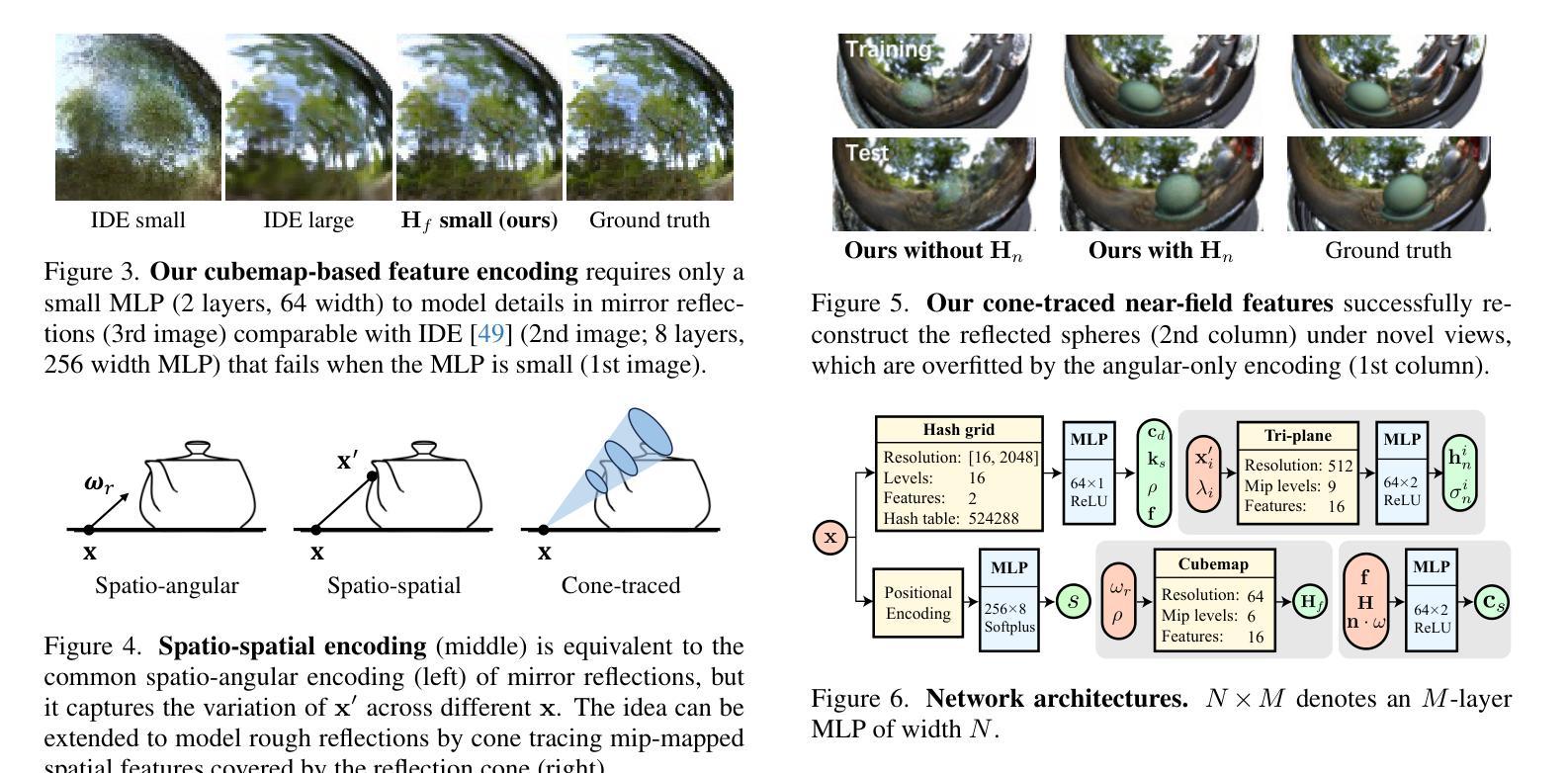
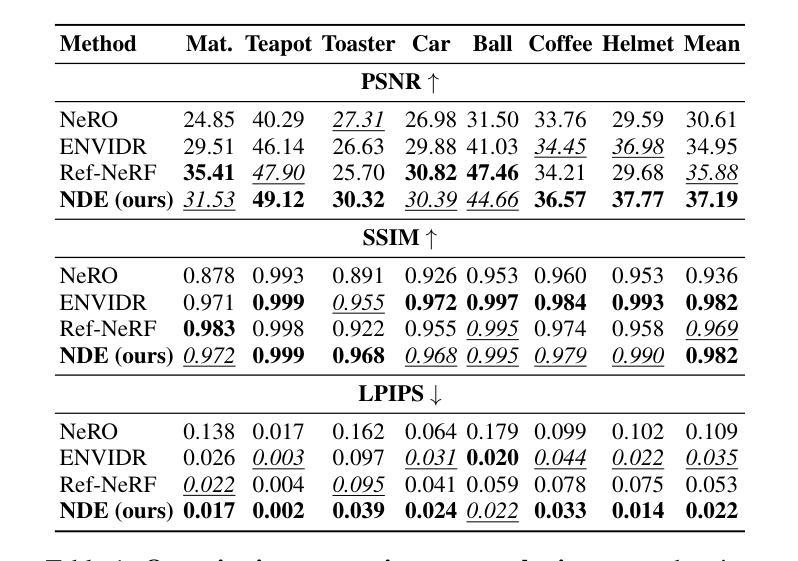
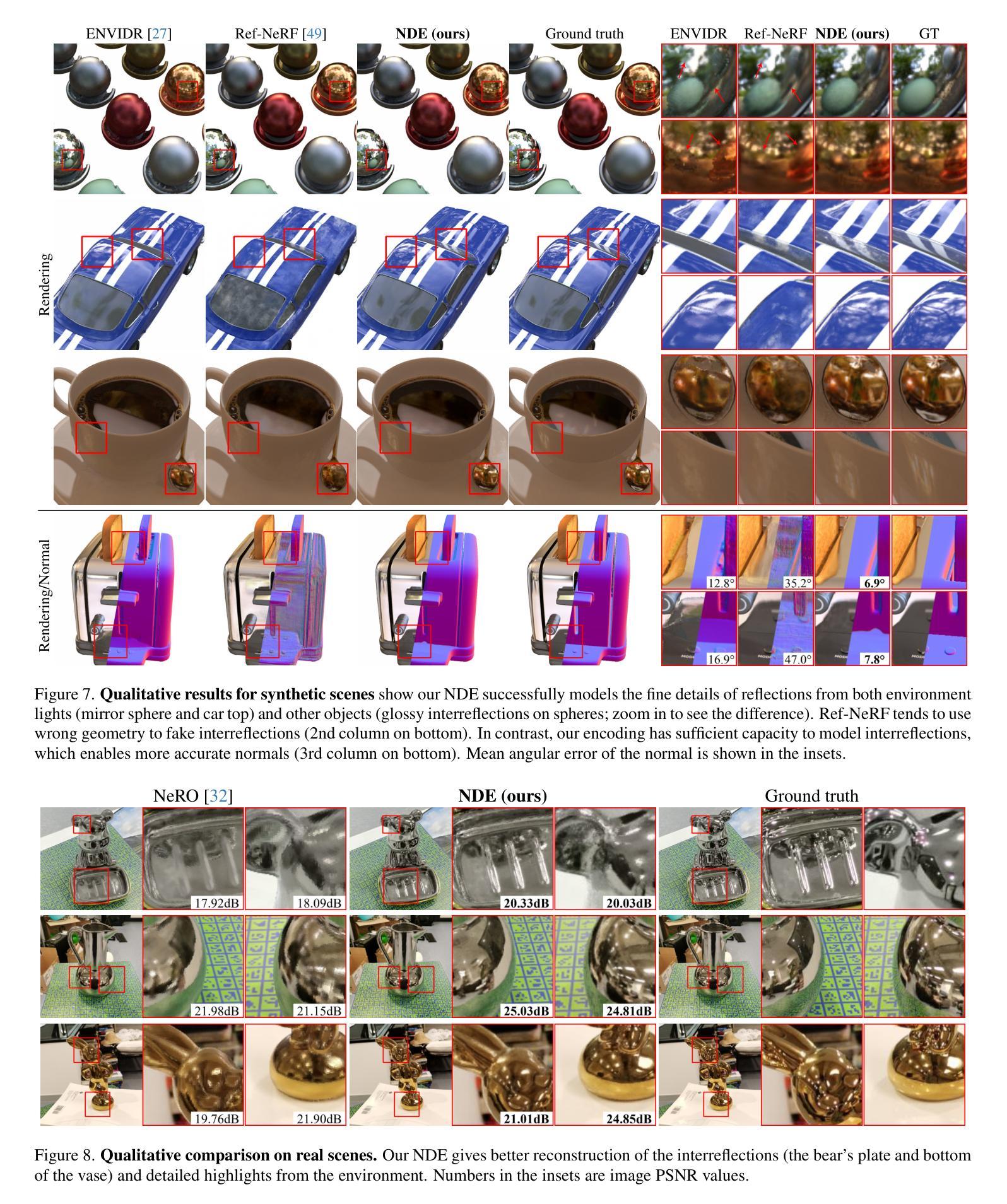
Neural Directional Encoding for Efficient and Accurate View-Dependent Appearance Modeling
Authors:Liwen Wu, Sai Bi, Zexiang Xu, Fujun Luan, Kai Zhang, Iliyan Georgiev, Kalyan Sunkavalli, Ravi Ramamoorthi
Novel-view synthesis of specular objects like shiny metals or glossy paints remains a significant challenge. Not only the glossy appearance but also global illumination effects, including reflections of other objects in the environment, are critical components to faithfully reproduce a scene. In this paper, we present Neural Directional Encoding (NDE), a view-dependent appearance encoding of neural radiance fields (NeRF) for rendering specular objects. NDE transfers the concept of feature-grid-based spatial encoding to the angular domain, significantly improving the ability to model high-frequency angular signals. In contrast to previous methods that use encoding functions with only angular input, we additionally cone-trace spatial features to obtain a spatially varying directional encoding, which addresses the challenging interreflection effects. Extensive experiments on both synthetic and real datasets show that a NeRF model with NDE (1) outperforms the state of the art on view synthesis of specular objects, and (2) works with small networks to allow fast (real-time) inference. The project webpage and source code are available at: \url{https://lwwu2.github.io/nde/}.
PDF Accepted to CVPR 2024
Summary
提出了一种名为Neural Directional Encoding(NDE)的视图相关外观编码方法,用于神经辐射场(NeRF)渲染镜面对象,提高了对高频角信号的建模能力。
Key Takeaways
• 镜面对象的新视图合成仍然是一个挑战性的问题,需要考虑全球照明效果和其他对象的反射。
• 提出了Neural Directional Encoding(NDE),一种视图相关的外观编码方法,用于NeRF渲染镜面对象。
• NDE将特征网格基于的空间编码概念转移到角域,提高了对高频角信号的建模能力。
• NDE使用角输入和空间特征来获得空间变化的方向编码,解决了挑战性的交叉反射效果。
• 实验结果表明,使用NDE的NeRF模型在镜面对象的视图合成方面优于当前最先进的方法。
• 使用小网络可以实现快速(实时)推理。
• 项目网页和源代码已经公开,网址为https://lwwu2.github.io/nde/。
Title: 神经方向编码(Neural Directional Encoding)
Authors: Liwen Wu, Sai Bi, Zexiang Xu, Fujun Luan, Kai Zhang, Iliyan Georgiev, Kalyan Sunkavalli, Ravi Ramamoorthi
Affiliation: 加州大学圣地亚哥分校(UC San Diego)
Keywords: Neural Radiance Fields, View-Dependent Appearance, Specular Objects, Novel-View Synthesis
Urls: https://lwwu2.github.io/nde/, Github:None
Summary:
(1):本文研究背景是新视图合成领域,特别是 specular 对象的新视图合成,旨在恢复物体的高频视图依赖外观和全球照明效果。
(2):过去的方法使用分析函数对视图方向进行编码,需要大型多层感知器(MLP),收敛速度慢,无法模拟复杂的反射效果。这些方法也忽视了空间特征对视图依赖外观的影响。
(3):本文提出了一种神经方向编码(NDE)方法,将特征网格编码概念应用于角度域,通过 مخروط追踪空间特征获取空间变化的方向编码,解决了 interreflection 效果的挑战。
(4):本文方法在合成 specular 对象的新视图任务上取得了 state-of-the-art 的性能,并且可以使用小型网络实现实时推理,满足了快速合成的需求。
Methods:
(1): 该方法使用神经方向编码(NDE)来对特征网格进行角度域的编码,通过مخروط追踪空间特征获取空间变化的方向编码。
(2): NDE方法能够有效解决interreflection效果的挑战,恢复物体的高频视图依赖外观和全球照明效果,而无需使用大型多层感知器(MLP)。
(3): 该方法具有实时推理的能力,可以使用小型网络实现快速合成,并在合成specular对象的新视图任务上取得了state-of-the-art的性能。
Conclusion:
(1):This piece of work is significant in advancing the field of novel-view synthesis, particularly in the synthesis of specular objects, by introducing a novel method, Neural Directional Encoding (NDE), which efficiently models complex reflections and achieves state-of-the-art performance.
(2):Innovation point: The article innovatively introduces the NDE method to efficiently model complex reflections for novel-view synthesis, addressing the limitations of previous methods.
Performance: The proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance in synthesizing specular objects with the ability for real-time inference using a small network.
Workload: The workload is reduced as the method eliminates the need for large multi-layer perceptrons and enables real-time synthesis.
点此查看论文截图

Camera Relocalization in Shadow-free Neural Radiance Fields
Authors:Shiyao Xu, Caiyun Liu, Yuantao Chen, Zhenxin Zhu, Zike Yan, Yongliang Shi, Hao Zhao, Guyue Zhou
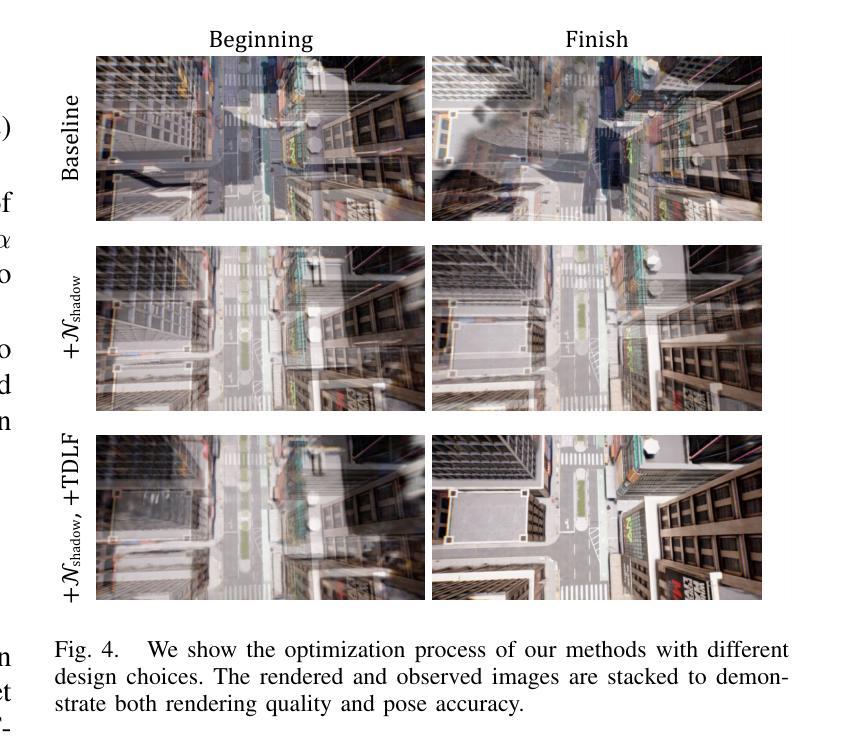
Camera relocalization is a crucial problem in computer vision and robotics. Recent advancements in neural radiance fields (NeRFs) have shown promise in synthesizing photo-realistic images. Several works have utilized NeRFs for refining camera poses, but they do not account for lighting changes that can affect scene appearance and shadow regions, causing a degraded pose optimization process. In this paper, we propose a two-staged pipeline that normalizes images with varying lighting and shadow conditions to improve camera relocalization. We implement our scene representation upon a hash-encoded NeRF which significantly boosts up the pose optimization process. To account for the noisy image gradient computing problem in grid-based NeRFs, we further propose a re-devised truncated dynamic low-pass filter (TDLF) and a numerical gradient averaging technique to smoothen the process. Experimental results on several datasets with varying lighting conditions demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art results in camera relocalization under varying lighting conditions. Code and data will be made publicly available.
PDF Accepted by ICRA 2024. 8 pages, 5 figures, 3 tables. Codes and dataset: https://github.com/hnrna/ShadowfreeNeRF-CameraReloc
Summary
本文提出了一种两阶段流水线,用于规范具有不同光照和阴影条件的图像,以改善相机重定位,实现了在不同光照条件下相机重定位的最新成果。
Key Takeaways
- 相机重定位在计算机视觉和机器人领域是一个关键问题。
- 近期关于神经辐射场(NeRFs)的进展显示出合成逼真图像的潜力。
- 之前的工作利用NeRFs优化相机姿态,但未考虑可能影响场景外观和阴影区域的光照变化,导致姿态优化过程下降。
- 该论文提出了一种基于哈希编码的NeRF来实现场景表示,显著提升了姿态优化过程。
- 为解决网格型NeRF中的噪声图像梯度计算问题,进一步提出了重新设计的截断动态低通滤波器(TDLF)和数值梯度平均技术来平滑处理。
- 在多个具有不同光照条件的数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在不同光照条件下的相机重定位中取得了最新的成果。
- 代码和数据将公开发布。
Title: 相机重定位在无阴影神经辐射场中(Camera Relocalization in Shadow-free Neural Radiance Fields)
Authors: Shiyao Xu, Caiyun Liu, Yuantao Chen, Zhenxin Zhu, Zike Yan, Yongliang Shi, Hao Zhao, Guyue Zhou
Affiliation: 清华大学人工智能产业研究院
Keywords: Camera Relocalization, Neural Radiance Fields, Shadow Removal
Urls: arXiv:2405.14824v1, Github: None
Summary:
(1):本文研究的背景是计算机视觉和机器人学领域中的相机重定位问题,目标是从给定的图像中恢复摄像机的位姿。
(2):过去的方法使用判别网络或NeRF来refine摄像机位姿,但是这些方法不能处理光照变化和阴影区域对场景外观的影响,导致位姿优化过程不稳定。
(3):本文提出的方法是一个两阶段的pipeline,首先使用阴影移除网络对图像进行 normalization,然后使用hash编码的NeRF来refine摄像机位姿,并提出了一种改进的梯度计算方法来平滑优化过程。
(4):实验结果表明,本文的方法在多个数据集上取得了 state-of-the-art 的结果,证明了其在相机重定位任务中的有效性。
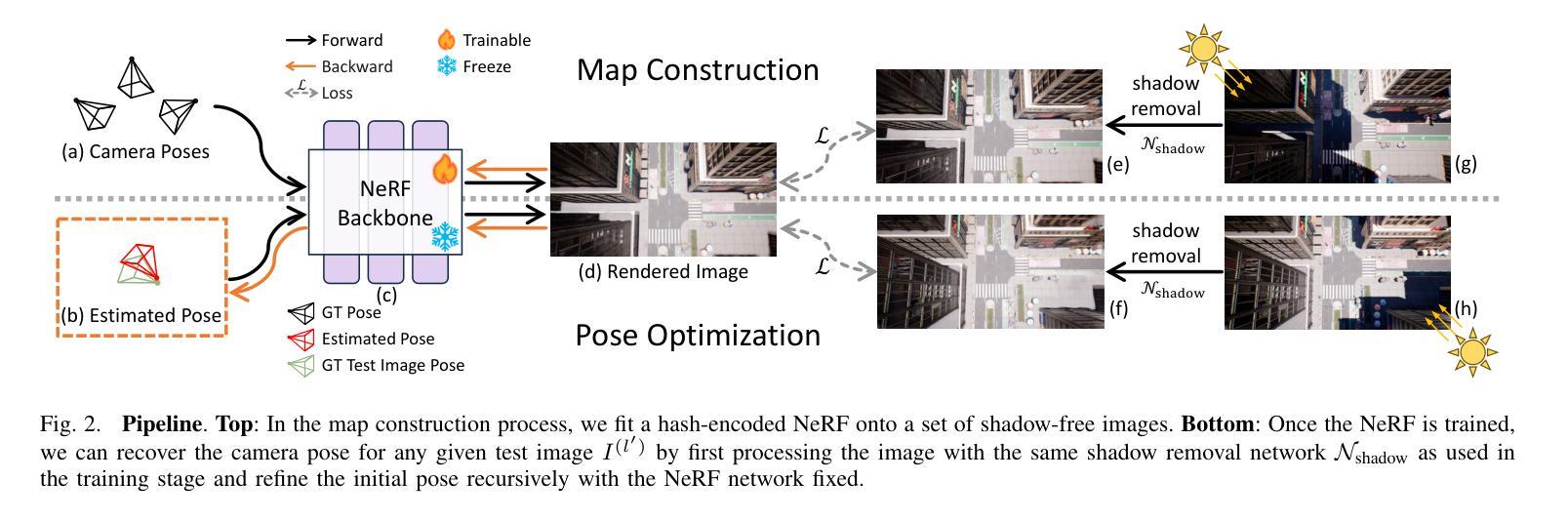
- 方法:
(1):本文提出的方法是一个两阶段的pipeline,首先使用阴影移除网络(Shadow Removal Network,Nshadow)对图像进行 normalization,得到阴影-free图像I(l0)。
(2):然后,使用hash编码的NeRF(Neural Radiance Fields)模型对阴影-free图像I(l0)进行场景重建,得到三维神经场景图F。
(3):在pose优化阶段,使用同样的阴影移除网络Nshadow对测试图像进行阴影移除,得到阴影-free测试图像I(l0),然后使用梯度下降算法优化摄像机pose,直到渲染图像ˆI(l0)与阴影-free测试图像I(l0)之间的光度loss达到最小。
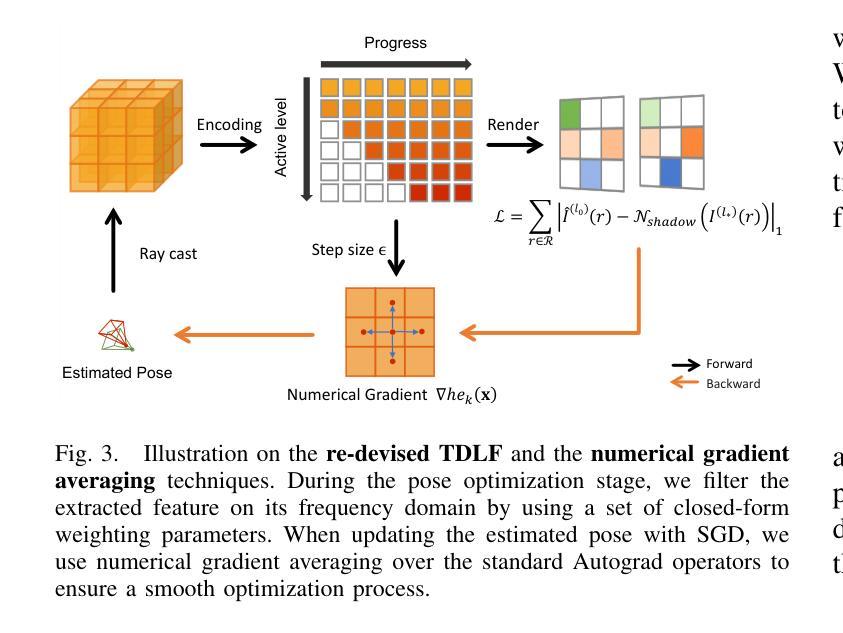
(4):为了提高pose优化的稳定性,本文提出了一种改进的梯度计算方法,使用numerical gradient averaging技术来平滑优化过程。
(5):在pose优化过程中,文还使用了一种粗到细的优化策略,使用truncated dynamic low-pass filter(TDLF)来分离高频和低频图像组件,并逐渐增加高频组件的权重,以避免局部最优解。
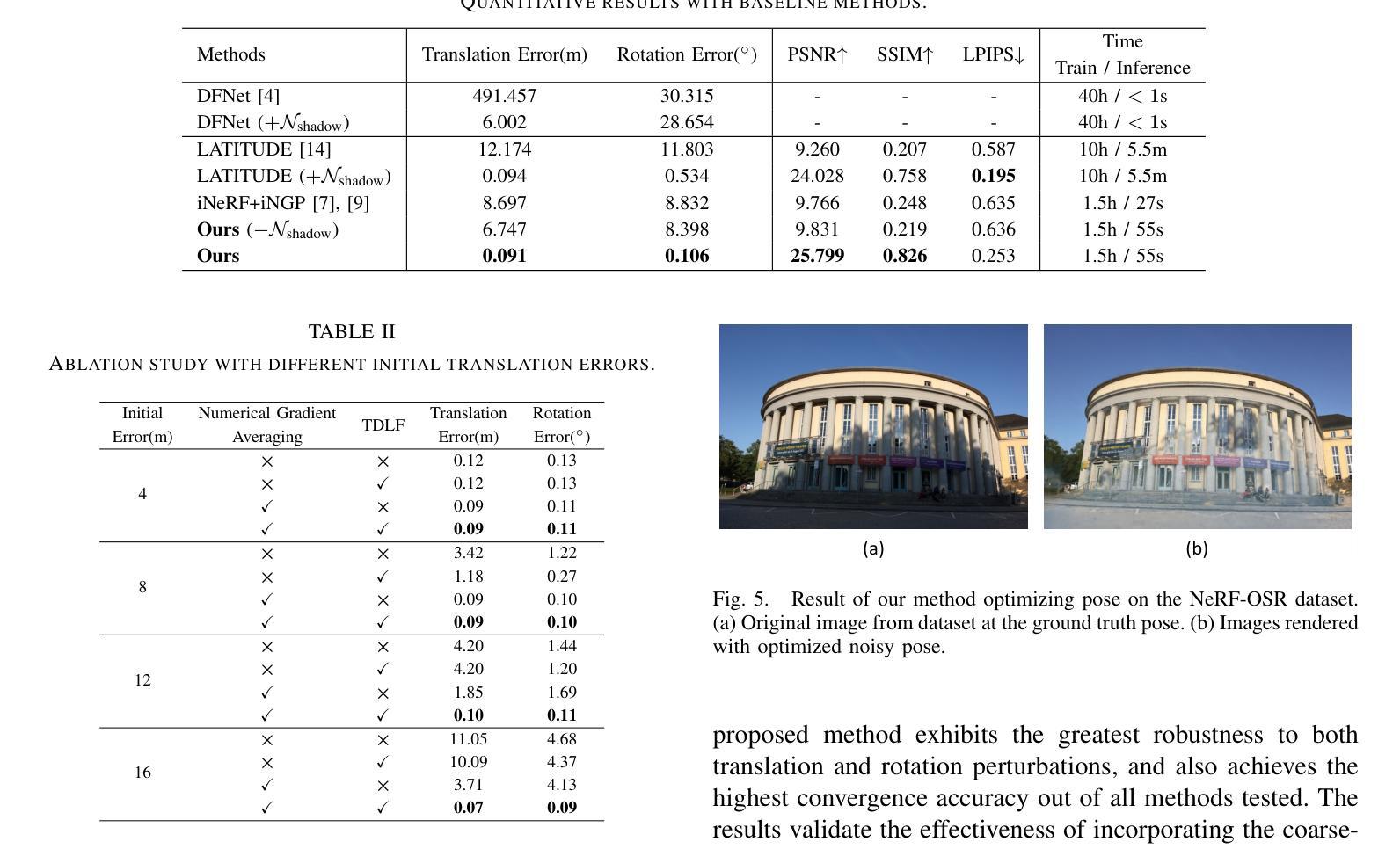
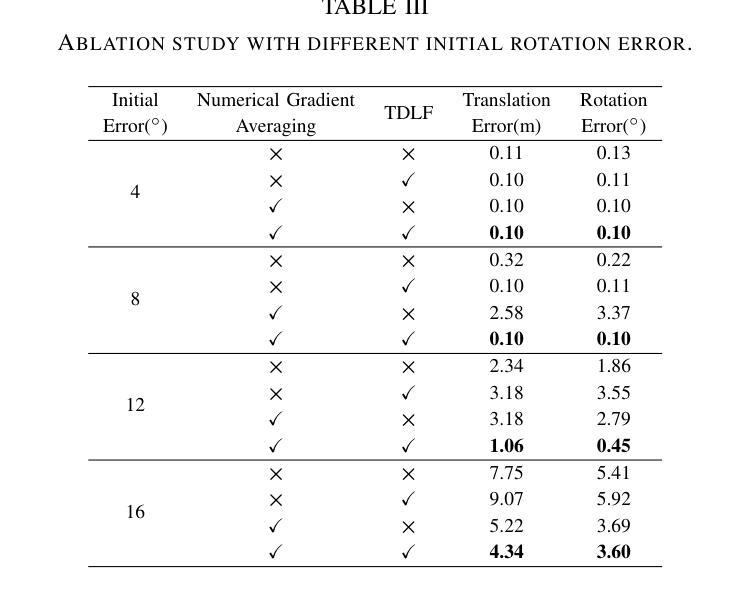
(6):实验结果表明,本文的方法在多个数据集上取得了state-of-the-art的结果,证明了其在相机重定位任务中的有效性。
- Conclusion:
(1):本文的工作对于计算机视觉和机器人学领域中的相机重定位问题具有重要意义,因为它能够在无阴影神经辐射场中实现高精度的摄像机重定位,从而提高机器人的导航和定位能力。
(2):Innovation point: 本文提出了一种新的两阶段pipeline,首先使用阴影移除网络对图像进行 normalization,然后使用hash编码的NeRF模型对阴影-free图像进行场景重建,这种方法能够有效地处理光照变化和阴影区域对场景外观的影响Performance: 实验结果表明,本文的方法在多个数据集上取得了 state-of-the-art 的结果,证明了其在相机重定位任务中的有效性;Workload: 本文的方法需要在训练和测试阶段进行大量的计算和优化,需要高性能的计算设备和大量的数据集支持。
点此查看论文截图