NeRF
⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 Google的大语言模型Gemini-Pro的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-08-28 更新
TranSplat: Generalizable 3D Gaussian Splatting from Sparse Multi-View Images with Transformers
Authors:Chuanrui Zhang, Yingshuang Zou, Zhuoling Li, Minmin Yi, Haoqian Wang
Compared with previous 3D reconstruction methods like Nerf, recent Generalizable 3D Gaussian Splatting (G-3DGS) methods demonstrate impressive efficiency even in the sparse-view setting. However, the promising reconstruction performance of existing G-3DGS methods relies heavily on accurate multi-view feature matching, which is quite challenging. Especially for the scenes that have many non-overlapping areas between various views and contain numerous similar regions, the matching performance of existing methods is poor and the reconstruction precision is limited. To address this problem, we develop a strategy that utilizes a predicted depth confidence map to guide accurate local feature matching. In addition, we propose to utilize the knowledge of existing monocular depth estimation models as prior to boost the depth estimation precision in non-overlapping areas between views. Combining the proposed strategies, we present a novel G-3DGS method named TranSplat, which obtains the best performance on both the RealEstate10K and ACID benchmarks while maintaining competitive speed and presenting strong cross-dataset generalization ability. Our code, and demos will be available at: https://xingyoujun.github.io/transplat.
Summary
开发了一种名为TranSplat的新G-3DGS方法,通过预测深度置信图和结合单目深度估计模型来提高稀疏视角下的3D重建效率。
Key Takeaways
- G-3DGS方法在稀疏视角下表现优异。
- 现有方法依赖精确的多视图特征匹配,具有挑战性。
- TranSplat通过深度置信图引导局部特征匹配。
- 利用单目深度估计模型知识作为先验来提升深度估计。
- TranSplat在RealEstate10K和ACID基准测试中表现最佳。
- 保持竞争性速度,具有强跨数据集泛化能力。
- 提供了代码和演示。
Title: TranSplat: Generalizable 3D Gaussian Splatting from Sparse Multi-View Images with Transformers (基于Transformer的稀疏多视图图像3D高斯散点重建)
Authors: Chuanrui Zhang, Yingshuang Zou, Zhuoling Li, Minmin Yi, Haoqian Wang
Affiliation: 清华大学
Keywords: 3D重建,高斯散点重建,Transformer,多视图图像,稀疏场景
Urls: https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.13770 or https://xingyoujun.github.io/transplat
Summary:
(1): 该文章的研究背景是稀疏多视图图像的3D重建,即从少量图像中恢复场景的3D结构,这在虚拟现实等领域非常重要。
(2): 过去的方法如NeRF和3D高斯散点重建(3DGS)在稀疏视图场景下表现出色,但它们依赖于精确的多视图特征匹配,这在具有大量非重叠区域和相似区域的场景中非常具有挑战性。现有方法的匹配性能较差,重建精度有限。该方法具有很好的动机。
(3): 该文章提出了TranSplat方法,利用预测的深度置信图来引导精确的局部特征匹配,并利用现有单目深度估计模型的知识作为先验来提高非重叠区域的深度估计精度。
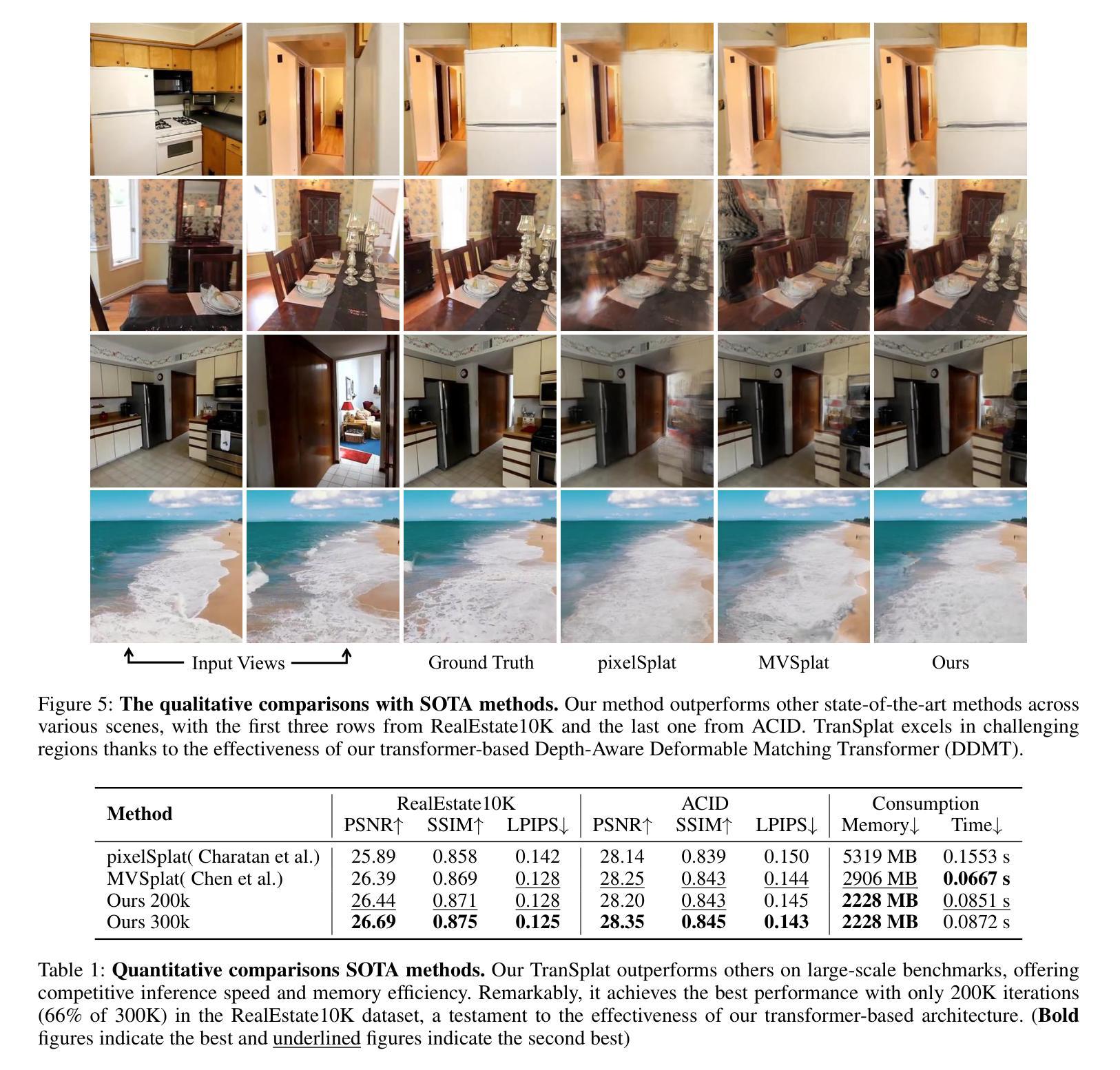
(4): 该方法在RealEstate10K和ACID基准测试上取得了最佳性能,同时保持了有竞争力的速度和强大的跨数据集泛化能力,证明了其有效性和性能。
Methods:
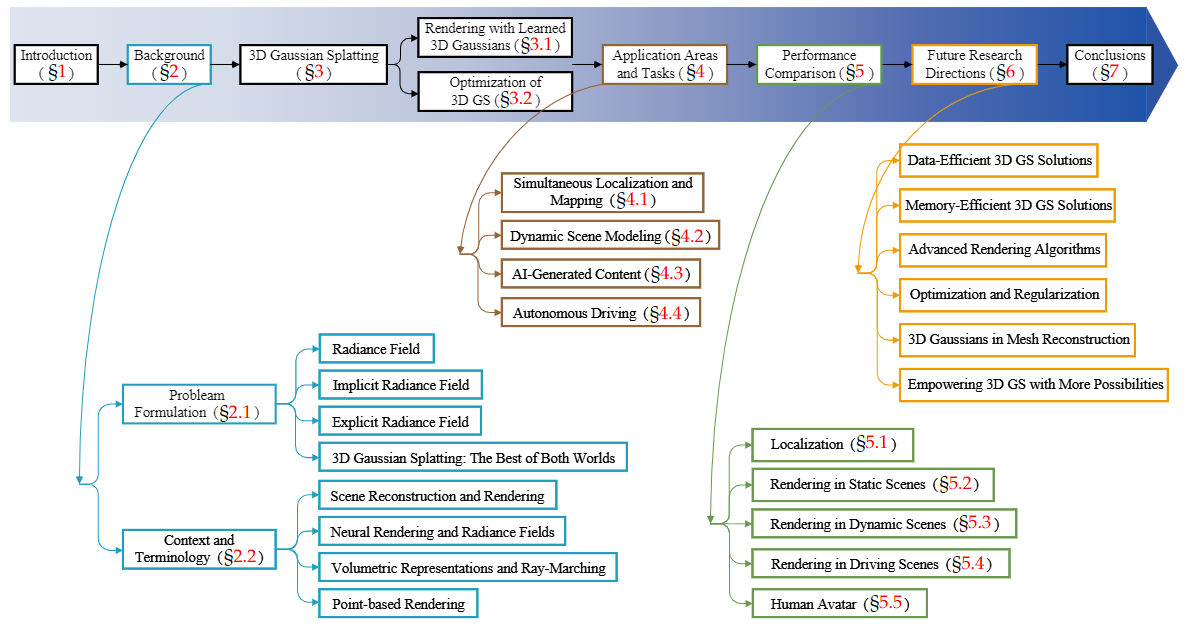
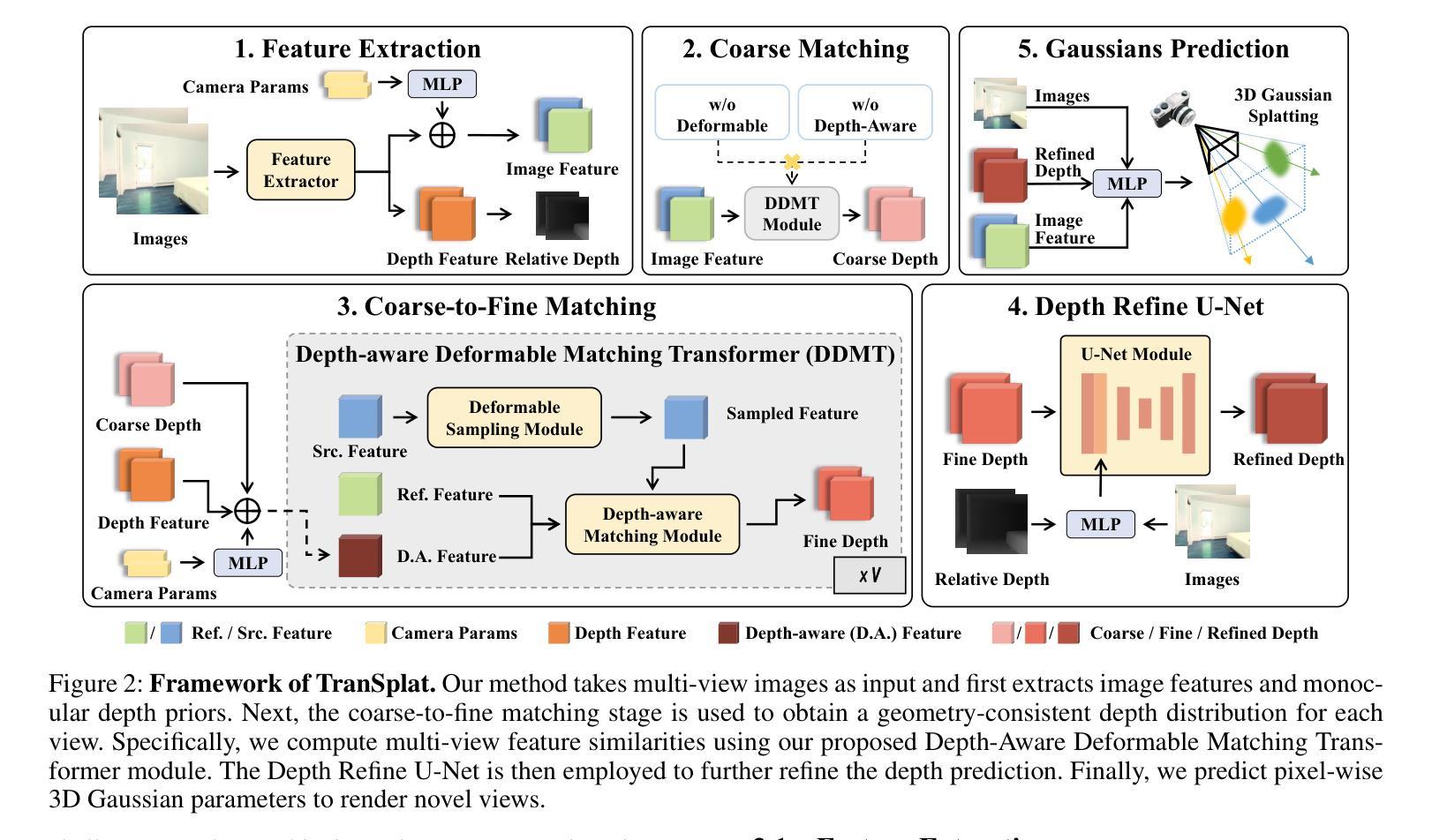
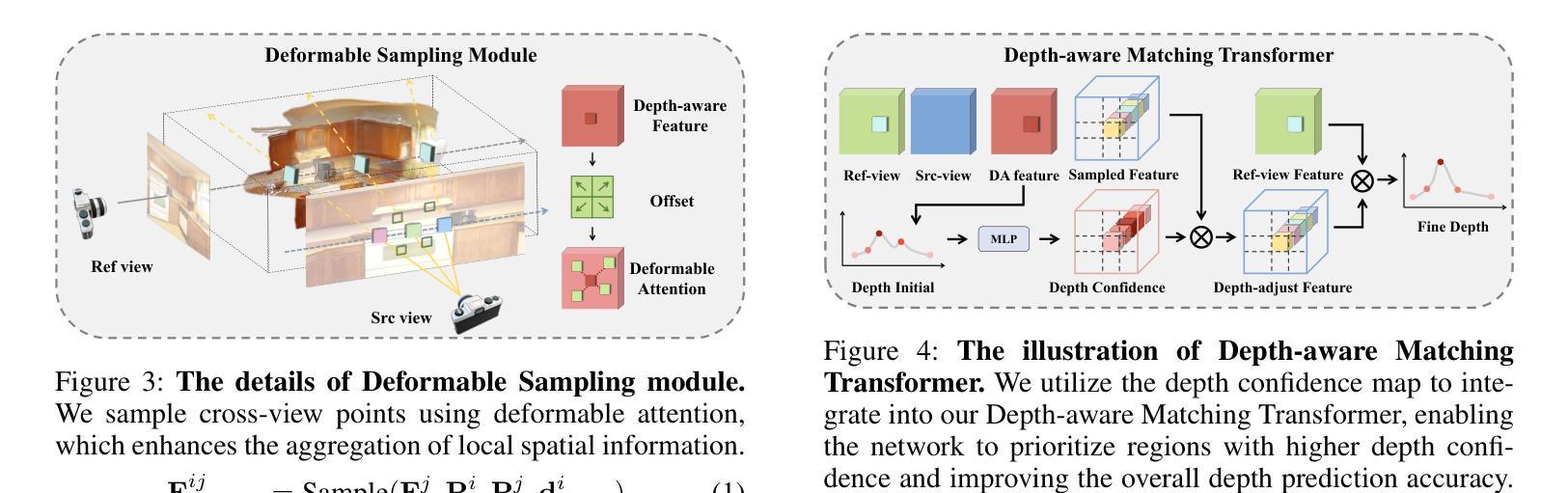
(1): TranSplat 采用 Transformer 架构来处理稀疏多视图图像的3D重建任务,通过自编码器学习图像的深度置信图(Depth Confidence Map, DCM)。
(2): 利用深度置信图来引导局部特征匹配,提高特征匹配的准确性。
(3): 结合单目深度估计模型的知识作为先验信息,优化非重叠区域的深度估计。
(4): 通过端到端训练,使模型能够在RealEstate10K和ACID等基准数据集上实现高效的3D重建。
(5): 采用自监督学习策略,提高模型在跨数据集上的泛化能力。
(6): 评估模型性能时,考虑重建精度、速度和跨数据集泛化能力等多个指标。
Conclusion:
- (1): 这项工作的意义在于为稀疏多视图图像的3D重建提供了一个创新的方法,即基于Transformer的TranSplat网络,该方法能够有效地从少量图像中恢复场景的3D结构,为虚拟现实等应用领域提供了新的技术支持。 - (2): Innovation point: TranSplat引入了Transformer架构,通过自编码器学习深度置信图,实现了对稀疏场景的高精度3D重建,是一个创新性的研究点;Performance: 在RealEstate10K和ACID基准测试中,TranSplat取得了最佳性能,同时保持了有竞争力的速度和跨数据集泛化能力;Workload: TranSplat使用了端到端训练和自监督学习策略,虽然需要较高的计算资源,但通过预训练和迁移学习,能够在一定程度上减轻训练负担。
点此查看论文截图

G3DST: Generalizing 3D Style Transfer with Neural Radiance Fields across Scenes and Styles
Authors:Adil Meric, Umut Kocasari, Matthias Nießner, Barbara Roessle
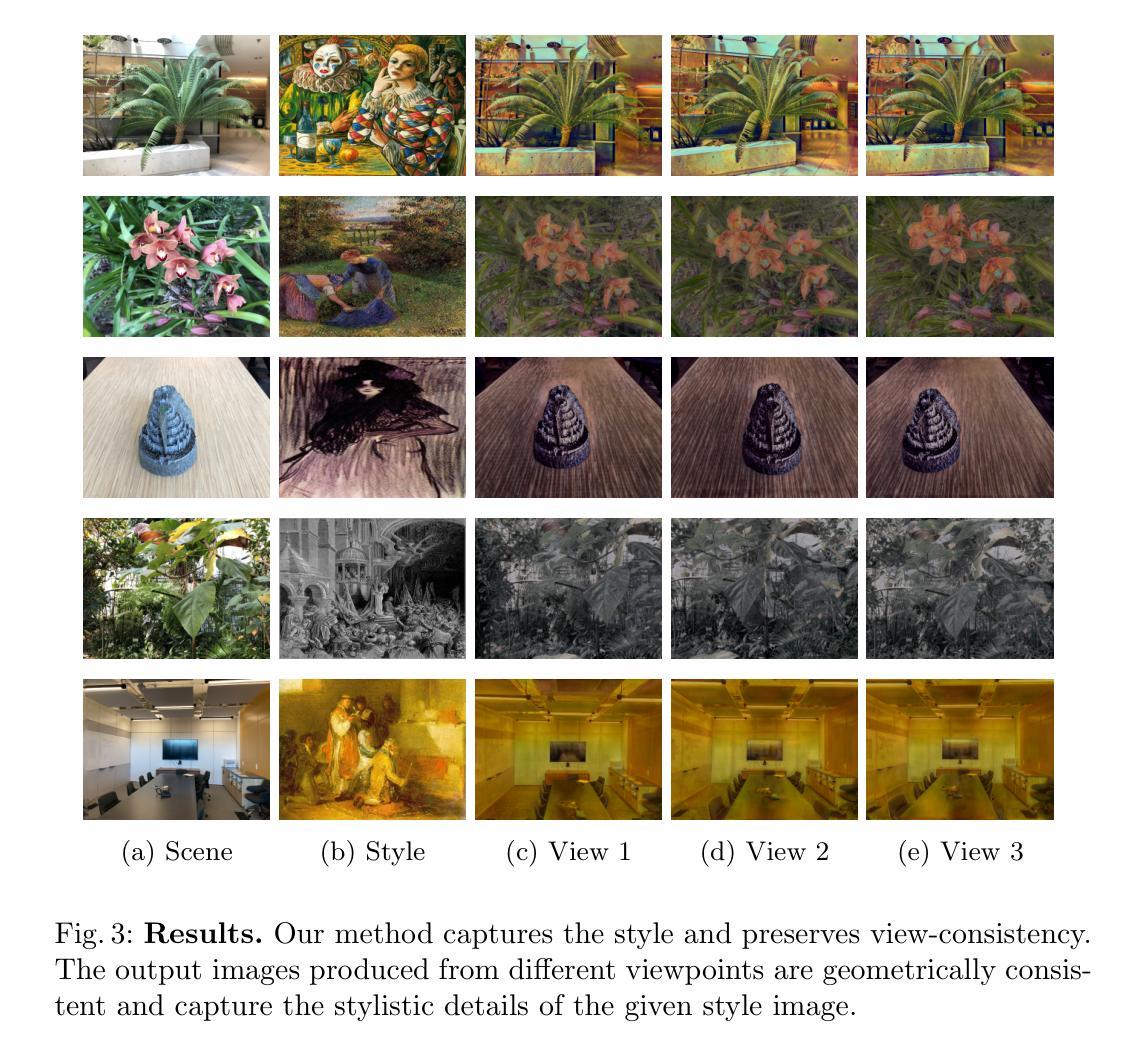
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have emerged as a powerful tool for creating highly detailed and photorealistic scenes. Existing methods for NeRF-based 3D style transfer need extensive per-scene optimization for single or multiple styles, limiting the applicability and efficiency of 3D style transfer. In this work, we overcome the limitations of existing methods by rendering stylized novel views from a NeRF without the need for per-scene or per-style optimization. To this end, we take advantage of a generalizable NeRF model to facilitate style transfer in 3D, thereby enabling the use of a single learned model across various scenes. By incorporating a hypernetwork into a generalizable NeRF, our approach enables on-the-fly generation of stylized novel views. Moreover, we introduce a novel flow-based multi-view consistency loss to preserve consistency across multiple views. We evaluate our method across various scenes and artistic styles and show its performance in generating high-quality and multi-view consistent stylized images without the need for a scene-specific implicit model. Our findings demonstrate that this approach not only achieves a good visual quality comparable to that of per-scene methods but also significantly enhances efficiency and applicability, marking a notable advancement in the field of 3D style transfer.
PDF GCPR 2024, Project page: https://mericadil.github.io/G3DST/
Summary
利用可泛化NeRF模型实现无需场景或风格优化的3D风格迁移,显著提高效率和适用性。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF在创建高细节、逼真场景方面表现出色。
- 现有NeRF风格迁移方法需大量优化,限制效率。
- 本研究通过可泛化NeRF模型实现无需优化。
- 引入超网络实现即时风格化视图生成。
- 介绍基于流的视图一致性损失,保证多视角一致性。
- 方法在多场景和风格中表现良好,无需场景特定模型。
- 实现视觉质量与场景方法相当,效率更高,应用更广。
- Title: G3DST: Generalizing 3D Style Transfer with Neural Radiance Fields across Scenes and Styles (G3DST:基于场景和风格跨场景的3D风格迁移与神经辐射场)
- Authors: Adil Meric, Umut Kocasari, Matthias Nießner, and Barbara Roessle
- Affiliation: Technical University of Munich (慕尼黑工业大学)
- Keywords: 3D Style Transfer, Generalization, Neural Radiance Fields
- Urls: arXiv:2408.13508v1 [cs.CV], Github: None
Summary:
(1):该文的研究背景是神经网络辐射场(NeRF)在创建高度详细和逼真的场景方面的强大能力。然而,现有的基于NeRF的3D风格迁移方法需要对每个场景进行大量的优化,限制了3D风格迁移的应用和效率。
(2):过去的方法需要针对单个或多个风格进行每个场景的优化,这限制了3D风格迁移的应用和效率。该方法的动机在于通过不进行场景或风格的优化来渲染风格化的新视图,从而克服现有方法的局限性。
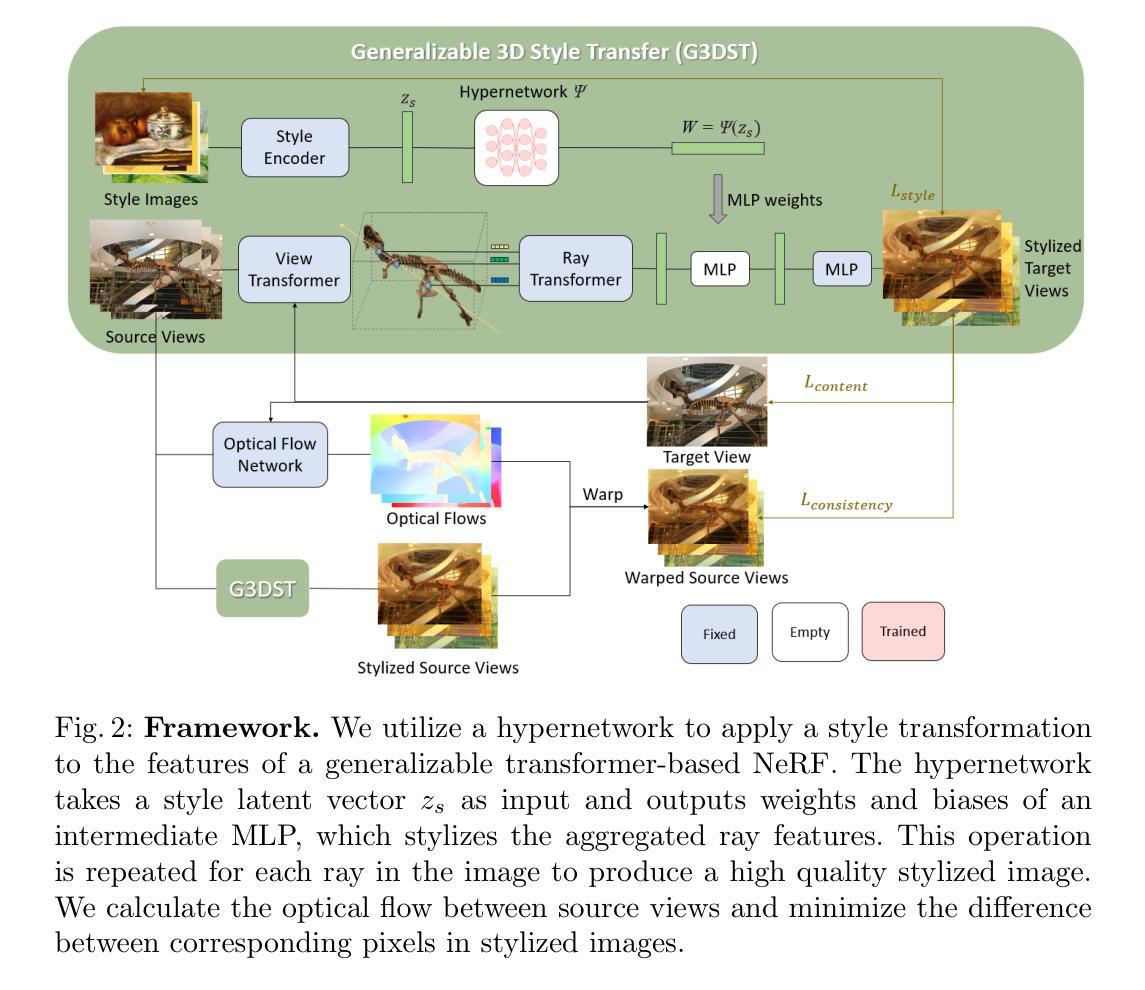
(3):该文提出的方法利用可泛化的NeRF模型来促进3D中的风格迁移,从而使得单个学习模型可以跨越各种场景使用。此外,通过将超网络集成到可泛化的NeRF中,该方法可以实时生成风格化的新视图,并引入了一种基于流的视图一致性损失,以保持多个视图的一致性。
(4):该文的方法在各种场景和艺术风格上进行了评估,展示了其在生成高质量和多视图一致的风格化图像方面的性能,无需为特定场景的隐式模型进行优化。该方法的性能不仅与场景特定方法相当,而且显著提高了效率和适用性,标志着3D风格迁移领域的重大进步。
Methods:
(1): 该方法以神经网络辐射场(NeRF)为基础,提出了一种通用的3D风格迁移框架G3DST,旨在通过学习一个可泛化的NeRF模型,实现场景和风格之间的风格迁移。
(2): 将超网络集成到可泛化的NeRF中,通过学习场景和风格的潜在空间,使得模型能够生成具有特定风格的新场景视图。
(3): 引入基于流的视图一致性损失,确保生成的多个视图在视觉上保持一致性和连贯性。
(4): 使用多个风格化的NeRF模型,通过优化超网络参数,实现风格化的新视图生成。
(5): 在多个场景和艺术风格上进行实验,验证了G3DST方法的有效性和泛化能力。
Conclusion:
- (1):该研究工作的重要性在于提出了一种通用的3D风格迁移方法,能够跨越场景和风格的限制,实现高效且高质量的3D风格化图像生成。 - (2):Innovation point: 创新点在于结合了神经网络辐射场和超网络结构,通过学习场景和风格的潜在空间,实现了对多种场景和风格的泛化风格迁移;Performance: 性能方面,该方法在多个场景和艺术风格上表现优异,生成的图像质量高,多视图一致性良好;Workload: 工作量方面,该方法仅需进行一次场景无关的预训练,即可应用于新的场景和风格,无需针对特定场景或风格进行额外的训练。
点此查看论文截图


SIn-NeRF2NeRF: Editing 3D Scenes with Instructions through Segmentation and Inpainting
Authors:Jiseung Hong, Changmin Lee, Gyusang Yu
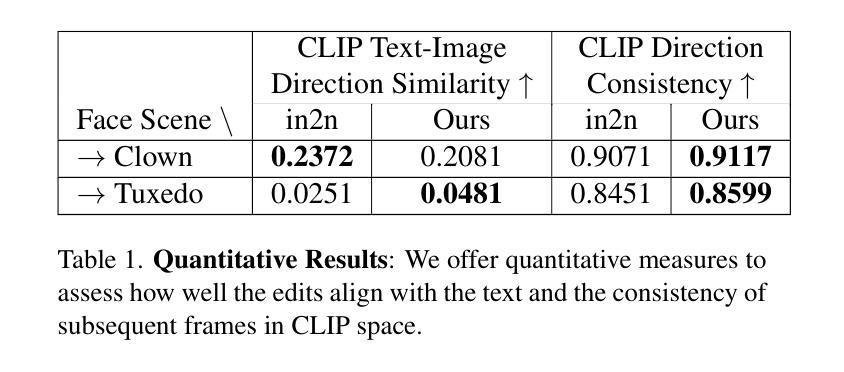
TL;DR Perform 3D object editing selectively by disentangling it from the background scene. Instruct-NeRF2NeRF (in2n) is a promising method that enables editing of 3D scenes composed of Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) using text prompts. However, it is challenging to perform geometrical modifications such as shrinking, scaling, or moving on both the background and object simultaneously. In this project, we enable geometrical changes of objects within the 3D scene by selectively editing the object after separating it from the scene. We perform object segmentation and background inpainting respectively, and demonstrate various examples of freely resizing or moving disentangled objects within the three-dimensional space.
PDF Code is available at: https://github.com/KAISTChangmin/SIn-NeRF2NeRF
Summary
通过选择性编辑分离对象,实现3D对象编辑。
Key Takeaways
- 使用Instruct-NeRF2NeRF (in2n)通过文本提示编辑NeRF场景。
- 面临同时修改背景和对象几何形状的挑战。
- 通过对象分割和背景修复实现对象几何变化。
- 支持在三维空间中自由调整分离对象的尺寸和位置。
- 方法能处理缩小、缩放或移动等几何修改。
- 提供了多种编辑示例。
- 改进了对3D场景中对象的编辑能力。
- Title: SIn-NeRF2NeRF: 通过分割进行3D场景编辑的指令学习
- Authors: Jiseung Hong, Changmin Lee, Gyusang Yu
- Affiliation: 韩国KAIST(Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology)
- Keywords: 3D场景编辑,神经网络辐射场(NeRF),分割,图像修复,指令学习
- Urls: https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.13285v1 or Github: None
Summary:
(1):本文的研究背景是3D场景编辑在虚拟现实和增强现实应用中的重要性,特别是如何通过文本指令编辑由神经网络辐射场(NeRF)构成的3D场景。
(2):过去的方法包括Instruct-NeRF2NeRF(in2n),它允许用户通过文本提示编辑3D场景,但难以同时对背景和对象进行几何修改,如缩放、平移等。这种方法虽然有效,但在处理几何变化时存在局限性。本文提出的解决方案是合理的,因为它解决了现有方法的不足。
(3):本文提出的方法SIn-NeRF2NeRF通过分割和图像修复技术,将对象从场景中分离出来,然后分别编辑对象和背景。首先进行对象分割,然后进行背景图像修复,最后对分割出的对象进行编辑。
(4):该方法在自定义数据集上进行了验证,展示了其在自由缩放和移动对象方面的能力。性能表明,该方法能够有效地实现3D场景的精确编辑,支持其目标。
Conclusion:
- (1):这项工作的意义在于,它为3D场景编辑提供了一种新的方法,通过指令学习和图像修复技术,实现了对NeRF场景中对象的精确编辑,尤其是在几何变换方面,如缩放和平移,这对于虚拟现实和增强现实等应用领域具有重要意义。 - (2): Innovation point: SIn-NeRF2NeRF通过分割和图像修复技术,实现了对3D场景中对象的独立编辑,是一个创新点;Performance: 在自定义数据集上的验证表明,该方法在自由缩放和移动对象方面表现出色,但在迭代数据集更新时,对象编辑的效果存在显著差异,性能有待提升;Workload: 该方法涉及复杂的NeRF学习和图像修复过程,计算和存储资源需求较高,工作负载较大。
点此查看论文截图