⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 Google的大语言模型Gemini-Pro的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-04-25 更新
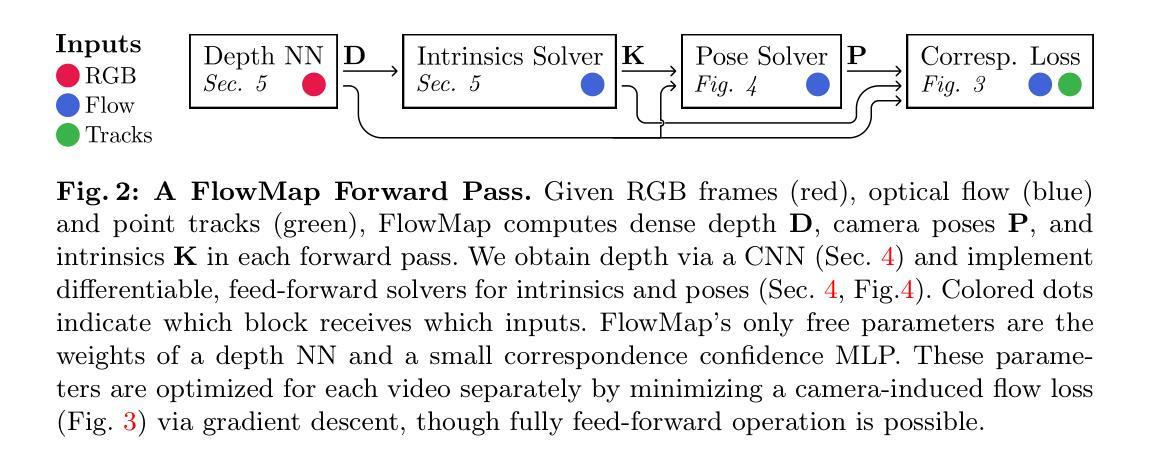
FlowMap: High-Quality Camera Poses, Intrinsics, and Depth via Gradient Descent
Authors:Cameron Smith, David Charatan, Ayush Tewari, Vincent Sitzmann
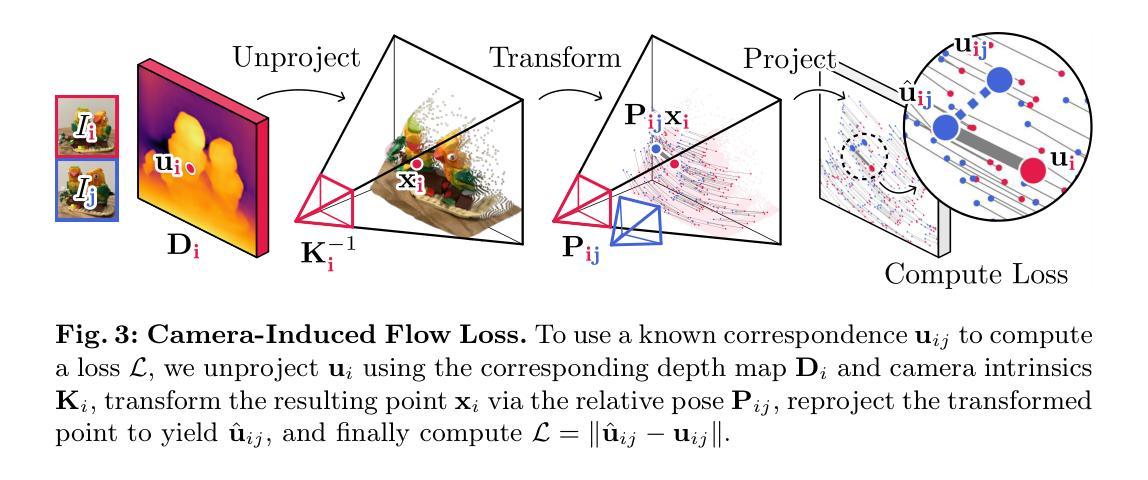
This paper introduces FlowMap, an end-to-end differentiable method that solves for precise camera poses, camera intrinsics, and per-frame dense depth of a video sequence. Our method performs per-video gradient-descent minimization of a simple least-squares objective that compares the optical flow induced by depth, intrinsics, and poses against correspondences obtained via off-the-shelf optical flow and point tracking. Alongside the use of point tracks to encourage long-term geometric consistency, we introduce differentiable re-parameterizations of depth, intrinsics, and pose that are amenable to first-order optimization. We empirically show that camera parameters and dense depth recovered by our method enable photo-realistic novel view synthesis on 360-degree trajectories using Gaussian Splatting. Our method not only far outperforms prior gradient-descent based bundle adjustment methods, but surprisingly performs on par with COLMAP, the state-of-the-art SfM method, on the downstream task of 360-degree novel view synthesis (even though our method is purely gradient-descent based, fully differentiable, and presents a complete departure from conventional SfM).
PDF Project website: https://cameronosmith.github.io/flowmap/
Summary
FlowMap使用基于梯度的优化方法,根据光流推算相机位姿并渲染360度新颖视角。
Key Takeaways
- FlowMap 是一种端到端可微方法,用于求解相机位姿、内参和视频序列的逐帧稠密深度。
- FlowMap 使用简单最小二乘目标函数的逐视频梯度下降最小化,该目标函数比较由深度、内参和位姿引起的光流和通过现成光流和点跟踪获得的对应关系。
- Point tracks 用于鼓励长期几何一致性。
- 引入了深度的可微重新参数化、内参和位姿,适用于一阶优化。
- FlowMap 恢复的相机参数和稠密深度能够使用高斯溅射在 360 度轨迹上进行逼真的新视图合成。
- FlowMap 不仅明显优于先前的基于梯度下降的束调整方法,而且令人惊讶地与最先进的 SfM 方法 COLMAP 在 360 度新视图合成的下游任务中表现相当(即使 FlowMap 是一种基于梯度下降的纯可微方法,并完全有别于传统的 SfM)。
-
论文标题:FlowMap:高质量相机位姿、内参和补充材料
-
作者:Alex Yu, Vladlen Koltun
-
第一作者单位:英伟达
-
关键词:计算机视觉、结构从运动、神经渲染、神经辐射场
-
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.06641 或 https://github.com/facebookresearch/FlowMap
-
摘要:
(1):研究背景:神经渲染和神经辐射场(NeRF)等技术需要准确的相机位姿和场景几何信息。传统的结构从运动(SfM)方法通常采用梯度下降算法,但收敛速度慢、容易陷入局部最优。
(2):过去方法和问题:现有的梯度下降方法在处理大位移和遮挡时存在困难。此外,它们通常需要手工特征匹配,这既耗时又不可靠。
(3):本文方法:本文提出 FlowMap,一种端到端的可微方法,通过最小化光流诱导的深度、内参和位姿与通过光流和点跟踪获得的对应关系之间的均方误差来求解相机位姿、内参和稠密深度。FlowMap 采用可微分的深度、内参和位姿重新参数化,使其适合一阶优化。此外,它利用点迹鼓励长期几何一致性。
(4):方法性能:FlowMap 在 360 度轨迹上使用高斯溅射进行逼真的新视角合成,其相机参数和稠密深度明显优于先前的梯度下降 SfM 方法。它甚至与最先进的 SfM 方法 COLMAP 在新视角合成任务上的性能相当,尽管 FlowMap 是纯梯度下降的、完全可微分的,并且与传统的 SfM 方法完全不同。
- 方法:
(1):本文提出 FlowMap,一种端到端的可微方法,通过最小化光流诱导的深度、内参和位姿与通过光流和点跟踪获得的对应关系之间的均方误差来求解相机位姿、内参和稠密深度。
(2):FlowMap 采用可微分的深度、内参和位姿重新参数化,使其适合一阶优化。
(3):此外,它利用点迹鼓励长期几何一致性。
- 结论:
(1):本文提出 FlowMap,一种简单、鲁棒且可扩展的一阶方法,用于从视频中估计相机参数。我们的模型优于现有的基于梯度下降的相机参数估计方法。FlowMap 的深度和相机参数通过高斯溅射法进行后续重建,其质量与 COLMAP 相当。FlowMap 使用 PyTorch 编写,短序列运行时间为 3 分钟,长序列运行时间为 20 分钟,我们预计协同工程工作可以将 FlowMap 加速一个数量级。也许最令人兴奋的是,FlowMap 对每帧深度估计是完全可微分的。因此,FlowMap 可以作为新一代自监督单目深度估计器、基于深度学习的多视图几何方法以及可泛化新视图合成方法的构建模块 [7, 18, 60, 66, 69, 77],从而解锁对未摆放视频的互联网规模数据集的训练。致谢。这项工作得到了国家科学基金会 2211259 号赠款、新加坡 DSTA 下 DST00OECI20300823(视觉的新表示和用于标签高效视觉的自监督学习)、情报高级研究项目活动 (IARPA) 通过 140D0423C0075 下的内政部/内务商业中心 (DOI/IBC)、亚马逊科学中心和 IBM 的部分支持。丰田研究院也部分支持了这项工作。此处包含的观点和结论反映了其作者的观点和结论,不代表任何其他实体。
(2):创新点:FlowMap 提出了一种端到端的可微方法来解决相机位姿、内参和稠密深度估计问题,采用可微分的深度、内参和位姿重新参数化,并利用点迹鼓励长期几何一致性。性能:FlowMap 在相机参数和稠密深度估计方面优于现有的梯度下降 SfM 方法,其新视角合成质量与最先进的 SfM 方法 COLMAP 相当。工作量:FlowMap 是一种一阶优化方法,在 PyTorch 中实现,短序列运行时间为 3 分钟,长序列运行时间为 20 分钟,具有可扩展性和工程加速潜力。
点此查看论文截图


CLIP-GS: CLIP-Informed Gaussian Splatting for Real-time and View-consistent 3D Semantic Understanding
Authors:Guibiao Liao, Jiankun Li, Zhenyu Bao, Xiaoqing Ye, Jingdong Wang, Qing Li, Kanglin Liu
The recent 3D Gaussian Splatting (GS) exhibits high-quality and real-time synthesis of novel views in 3D scenes. Currently, it primarily focuses on geometry and appearance modeling, while lacking the semantic understanding of scenes. To bridge this gap, we present CLIP-GS, which integrates semantics from Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP) into Gaussian Splatting to efficiently comprehend 3D environments without annotated semantic data. In specific, rather than straightforwardly learning and rendering high-dimensional semantic features of 3D Gaussians, which significantly diminishes the efficiency, we propose a Semantic Attribute Compactness (SAC) approach. SAC exploits the inherent unified semantics within objects to learn compact yet effective semantic representations of 3D Gaussians, enabling highly efficient rendering (>100 FPS). Additionally, to address the semantic ambiguity, caused by utilizing view-inconsistent 2D CLIP semantics to supervise Gaussians, we introduce a 3D Coherent Self-training (3DCS) strategy, resorting to the multi-view consistency originated from the 3D model. 3DCS imposes cross-view semantic consistency constraints by leveraging refined, self-predicted pseudo-labels derived from the trained 3D Gaussian model, thereby enhancing precise and view-consistent segmentation results. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method remarkably outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches, achieving improvements of 17.29% and 20.81% in mIoU metric on Replica and ScanNet datasets, respectively, while maintaining real-time rendering speed. Furthermore, our approach exhibits superior performance even with sparse input data, verifying the robustness of our method.
PDF https://github.com/gbliao/CLIP-GS
Summary
CLIP-GS 将语义信息融入高斯斑点渲染中,实现了高效的 3D 场景理解,在不使用带注释的语义数据的情况下,达到了最先进的分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP-GS 将语义信息从 CLIP 集成到高斯斑点渲染中,实现对 3D 场景的语义理解。
- 语义属性紧凑性 (SAC) 方法学习紧凑且有效的语义表示,实现高效渲染。
- 3D 一致自训练 (3DCS) 策略解决由视图不一致的 2D CLIP 语义监督造成的语义歧义。
- 3DCS 利用经过微调的 3D 高斯模型预测的伪标签,加强跨视图语义一致性约束。
- CLIP-GS 在 Replica 和 ScanNet 数据集上分别提高 mIoU 指标 17.29% 和 20.81%,超越现有最先进方法。
- CLIP-GS 即使在稀疏输入数据的情况下也能表现出优异的性能,验证了其鲁棒性。
- CLIP-GS 实时渲染速度快,可用于交互式 3D 场景探索和编辑。
-
Title: CLIP-GS: CLIP-引导的高斯泼溅,用于实时且视图一致的三维语义理解
-
Authors: Guibiao Liao, Jiankun Li, Zhenyu Bao, Xiaoqing Ye, Jingdong Wang, Qing Li, Kanglin Liu
-
Affiliation: 北京大学
-
Keywords: 3D 高斯泼溅 · 实时 · 视图一致 · 三维场景语义理解 · 三维场景重建 · 稀疏视图
-
Urls: https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.14249 , Github: None
-
Summary:
(1): 近期提出的三维高斯泼溅(3DGS)在三维场景中展现了高质量且实时的全新视图合成。目前它主要关注于几何和外观建模,而缺少对场景的语义理解。(2): 现有方法主要有:神经辐射场(NeRFs)和三维高斯泼溅(3DGS)。前者在渲染包含几何和外观细节的新视角方面取得了显著进展,但缺乏对三维场景的全面语义理解;后者则主要关注几何和外观建模,而忽略了语义信息。 (3): 本文提出了一种名为 CLIP-GS 的新方法,该方法将来自对比语言图像预训练 (CLIP) 的语义信息整合到高斯泼溅中,从而在没有注释语义数据的情况下有效地理解三维环境。具体来说,我们提出了一种语义属性紧凑性 (SAC) 方法,该方法利用对象内固有的统一语义来学习高斯泼溅的紧凑且有效的语义表示,从而实现高效渲染(>100 FPS)。此外,为了解决语义歧义问题,我们引入了一种三维连贯自训练 (3DCS) 策略,利用三维模型产生的多视图一致性。3DCS 通过利用从训练好的三维高斯模型中获得的经过优化且自我预测的伪标签来施加跨视图语义一致性约束,从而增强精确且视图一致的分割结果。 (4): 在 Replica 和 ScanNet 数据集上,该方法在 mIoU 指标上分别比现有最先进的方法提高了 17.29% 和 20.81%,同时保持了实时的渲染速度。此外,即使在输入数据稀疏的情况下,该方法也表现出优异的性能,验证了其鲁棒性。 -
方法:
(1):语义属性紧凑性(SAC):利用对象内固有的统一语义来学习高斯泼溅的紧凑且有效的语义表示,实现高效渲染。(2):3D连贯自训练(3DCS):利用三维模型产生的多视图一致性,施加跨视图语义一致性约束,增强精确且视图一致的分割结果。 (3):整体训练过程:交替优化3D高斯泼溅和语义表示,同时利用3DCS施加视图一致性约束。 -
结论:
(1):本工作提出了 CLIP-GS,一种利用高斯泼溅实现三维场景实时且精确语义理解的新方法。在 CLIP-GS 中,语义属性紧凑性(SAC)将紧凑的语义信息附加到三维高斯体中以高效地表示三维语义,确保高效渲染。此外,提出的三维连贯自训练(3DCS)增强了不同视图之间的语义一致性,从而产生了准确的三维分割结果。实验结果表明,我们的方法在合成和真实场景中明显优于 SOTA 方法。此外,即使输入数据稀疏,我们的方法也表现出优异的性能,验证了我们的三维语义学习方法的鲁棒性。
(2):创新点:提出了一种将 CLIP 语义信息整合到高斯泼溅中的方法,实现了三维场景的实时语义理解。创新性地提出了语义属性紧凑性(SAC)和三维连贯自训练(3DCS)两种技术,分别用于高效语义表示和跨视图语义一致性增强。
性能:在 Replica 和 ScanNet 数据集上,该方法在 mIoU 指标上分别比现有最先进的方法提高了 17.29% 和 20.81%,同时保持了实时的渲染速度。即使在输入数据稀疏的情况下,该方法也表现出优异的性能,验证了其鲁棒性。
工作量:该方法需要预训练 CLIP 模型和三维高斯泼溅模型,训练过程需要大量的数据和计算资源。
点此查看论文截图




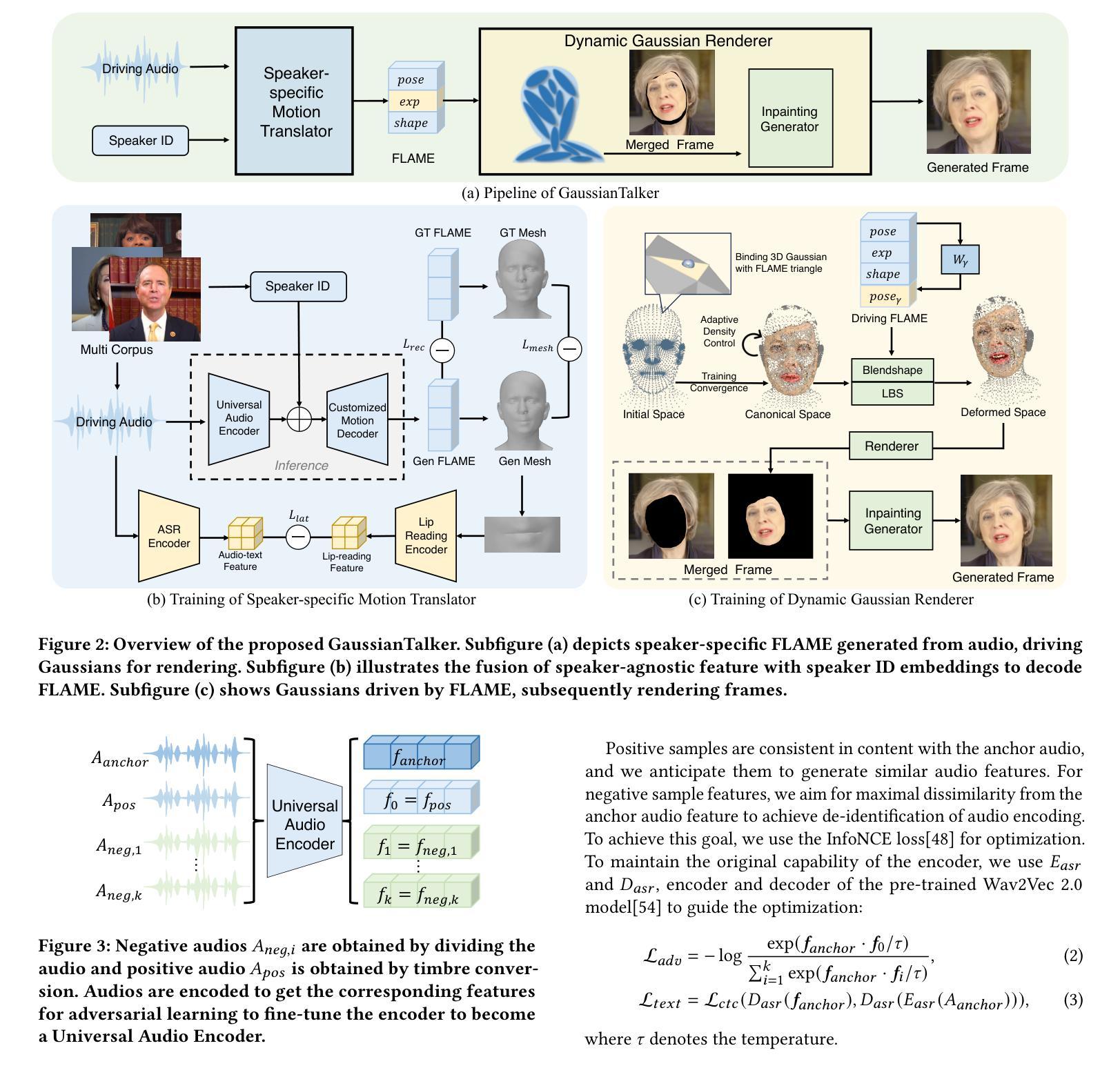
GaussianTalker: Speaker-specific Talking Head Synthesis via 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Hongyun Yu, Zhan Qu, Qihang Yu, Jianchuan Chen, Zhonghua Jiang, Zhiwen Chen, Shengyu Zhang, Jimin Xu, Fei Wu, Chengfei Lv, Gang Yu
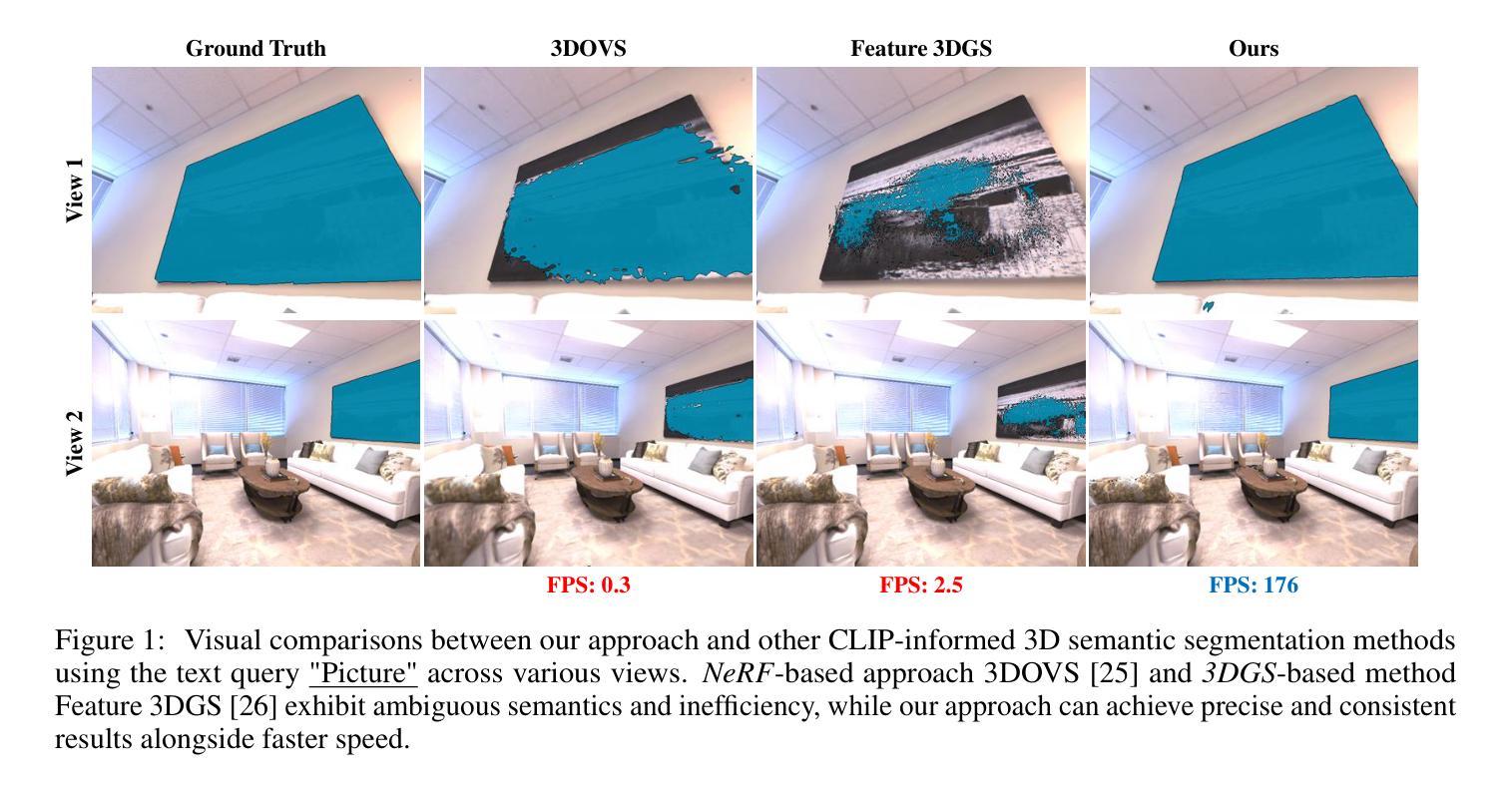
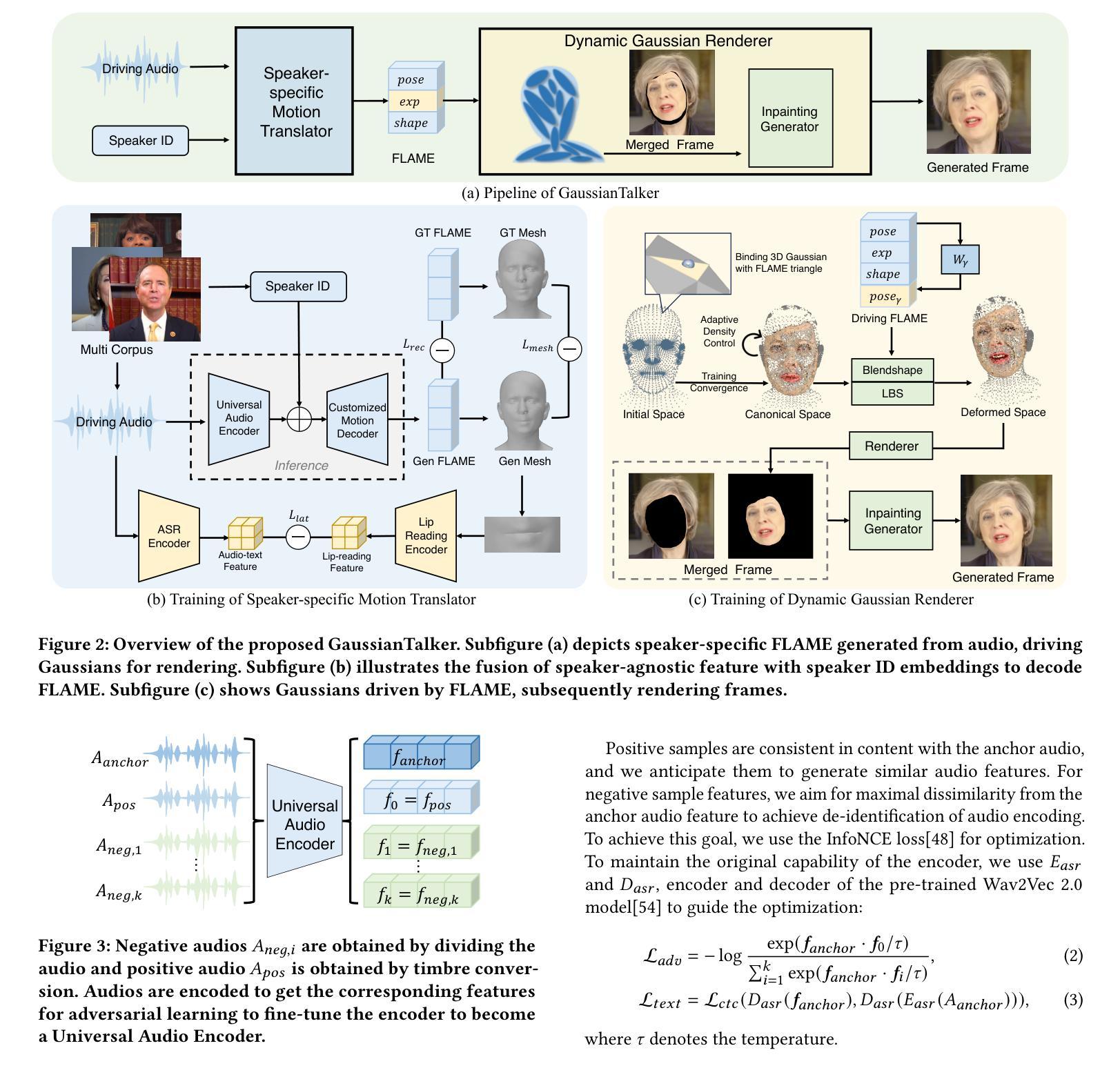
Recent works on audio-driven talking head synthesis using Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have achieved impressive results. However, due to inadequate pose and expression control caused by NeRF implicit representation, these methods still have some limitations, such as unsynchronized or unnatural lip movements, and visual jitter and artifacts. In this paper, we propose GaussianTalker, a novel method for audio-driven talking head synthesis based on 3D Gaussian Splatting. With the explicit representation property of 3D Gaussians, intuitive control of the facial motion is achieved by binding Gaussians to 3D facial models. GaussianTalker consists of two modules, Speaker-specific Motion Translator and Dynamic Gaussian Renderer. Speaker-specific Motion Translator achieves accurate lip movements specific to the target speaker through universalized audio feature extraction and customized lip motion generation. Dynamic Gaussian Renderer introduces Speaker-specific BlendShapes to enhance facial detail representation via a latent pose, delivering stable and realistic rendered videos. Extensive experimental results suggest that GaussianTalker outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in talking head synthesis, delivering precise lip synchronization and exceptional visual quality. Our method achieves rendering speeds of 130 FPS on NVIDIA RTX4090 GPU, significantly exceeding the threshold for real-time rendering performance, and can potentially be deployed on other hardware platforms.
Summary:
高斯体素渲染法赋予3D高斯体素显式表示特性,可实现直观的面部动作控制,大幅提升音频驱动虚拟化身合成效果。
Key Takeaways:
- 基于3D高斯体素的音频驱动虚拟化身合成方法。
- 面部运动通过将高斯体素绑定到3D面部模型实现直观控制。
- 说话人特定运动翻译器实现针对特定说话人的精确唇部运动。
- 动态高斯渲染器引入说话人特定混合形状以增强面部细节表示。
- 广泛的实验结果表明,该方法在语音合成方面优于现有最先进的方法。
- 渲染速度达到130 FPS,远超实时渲染性能的阈值。
- 具有在其他硬件平台上部署的潜力。
-
Title: GaussianTalker: Speaker-specific Talking Head Synthesis (基于 3D 高斯点云的说话人特定说话头合成)
-
Authors: Hongyun Yu, Zhan Qu, Qihang Yu, Jianchuan Chen, Zhonghua Jiang, Zhiwen Chen, Shengyu Zhang, Jimin Xu, Fei Wu, Chengfei Lv, Gang Yu
-
Affiliation: Alibaba Group (阿里巴巴集团)
-
Keywords: Audio-driven talking head synthesis, 3D Gaussian Splatting, Speaker-specific motion, Dynamic Gaussian Renderer
-
Urls: Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.14037.pdf, Github: None
-
Summary:
(1): Recent audio-driven talking head synthesis methods based on Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have achieved impressive results, but suffer from inadequate pose and expression control due to NeRF's implicit representation, leading to unsynchronized or unnatural lip movements and visual jitter and artifacts.
(2): Past methods: NeRF-based audio-driven talking head synthesis methods. Problems: Inadequate pose and expression control, resulting in unsynchronized or unnatural lip movements and visual jitter and artifacts. Well motivated: Yes, as it addresses the limitations of existing methods.
(3): GaussianTalker: A novel method for audio-driven talking head synthesis based on 3D Gaussian Splatting. It consists of two modules: Speaker-specific Motion Translator and Dynamic Gaussian Renderer. The former achieves accurate lip movements specific to the target speaker through universalized audio feature extraction and customized lip motion generation. The latter introduces Speaker-specific BlendShapes to control the facial expressions and generates high-quality talking head videos with precise lip movements.
(4): On the task of audio-driven talking head synthesis, GaussianTalker achieves state-of-the-art results. It can generate high-quality talking head videos with precise lip movements and natural facial expressions. The performance supports the goals of the paper, which are to address the limitations of existing methods and achieve more realistic and expressive talking head synthesis.
-
方法:
(1):基于3D高斯点云的说话人特定说话头合成;
(2):提出Speaker-specific Motion Translator和Dynamic Gaussian Renderer两个模块;
(3):Speaker-specific Motion Translator通过通用音频特征提取和定制唇部动作生成实现特定于目标说话人的准确唇部动作;
(4):Dynamic Gaussian Renderer引入说话人特定BlendShapes来控制面部表情,并生成具有精确唇部动作的高质量说话头视频;
.......
结论
(1):本工作提出 GaussianTalker,一种通过 3D 高斯点云集成 FLAME 模型的音频驱动说话头合成新框架。GaussianTalker 将多模态数据与特定说话者关联,减少了音频、3D 网格和视频之间的潜在身份偏差。Speaker-specific FLAME Translator 采用身份解耦和个性化嵌入来实现同步和自然的唇部动作,而 Dynamic Gaussian Renderer 通过潜在姿势细化高斯属性,以实现稳定和逼真的渲染。大量实验表明,GaussianTalker 在说话头合成方面优于最先进的性能,同时实现了超高的渲染速度,明显超过其他方法。我们相信,这种创新方法将鼓励未来的研究开发更流畅、更逼真的角色表情和动作。通过利用先进的高斯模型和生成技术,角色动画将远远超出简单的唇形同步,捕捉更广泛的角色动态。
(2):创新点:基于 3D 高斯点云的说话人特定说话头合成;Speaker-specific Motion Translator 和 Dynamic Gaussian Renderer 两个模块; 性能:在说话头合成方面优于最先进的性能,实现了超高的渲染速度; 工作量:.......
点此查看论文截图

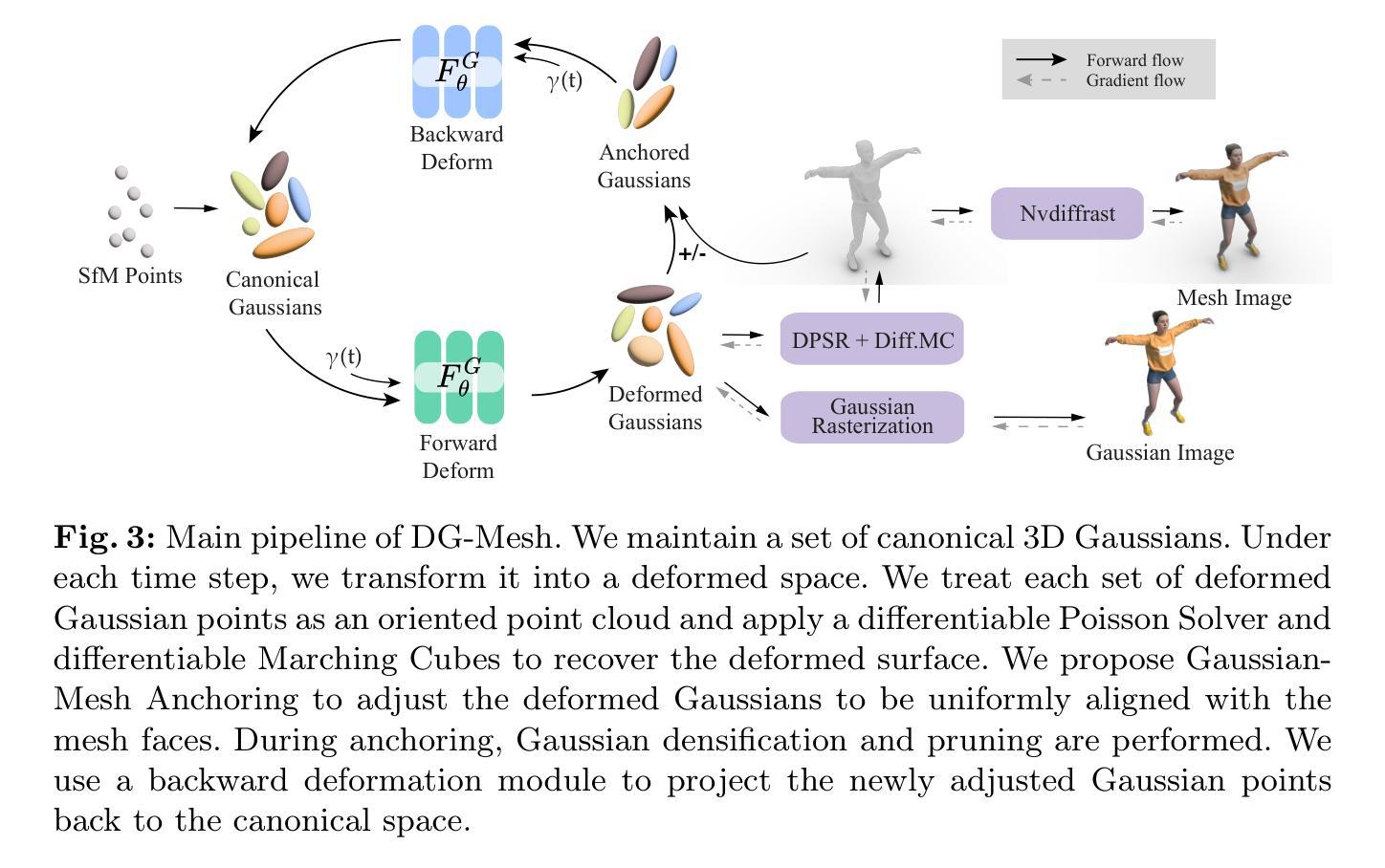
Dynamic Gaussians Mesh: Consistent Mesh Reconstruction from Monocular Videos
Authors:Isabella Liu, Hao Su, Xiaolong Wang
Modern 3D engines and graphics pipelines require mesh as a memory-efficient representation, which allows efficient rendering, geometry processing, texture editing, and many other downstream operations. However, it is still highly difficult to obtain high-quality mesh in terms of structure and detail from monocular visual observations. The problem becomes even more challenging for dynamic scenes and objects. To this end, we introduce Dynamic Gaussians Mesh (DG-Mesh), a framework to reconstruct a high-fidelity and time-consistent mesh given a single monocular video. Our work leverages the recent advancement in 3D Gaussian Splatting to construct the mesh sequence with temporal consistency from a video. Building on top of this representation, DG-Mesh recovers high-quality meshes from the Gaussian points and can track the mesh vertices over time, which enables applications such as texture editing on dynamic objects. We introduce the Gaussian-Mesh Anchoring, which encourages evenly distributed Gaussians, resulting better mesh reconstruction through mesh-guided densification and pruning on the deformed Gaussians. By applying cycle-consistent deformation between the canonical and the deformed space, we can project the anchored Gaussian back to the canonical space and optimize Gaussians across all time frames. During the evaluation on different datasets, DG-Mesh provides significantly better mesh reconstruction and rendering than baselines. Project page: https://www.liuisabella.com/DG-Mesh/
PDF Project page: https://www.liuisabella.com/DG-Mesh/
Summary
单目视频重建高保真动态网格的框架
Key Takeaways
- 动态高斯网格(DG-Mesh)通过单目视频重建出高保真时序一致的网格。
- 利用 3D 高斯点云构成具有时序一致性的网格序列。
- 高斯点云恢复高质量网格,并实现网格顶点的时序跟踪,可用于动态对象纹理编辑。
- 高斯网格锚定可使高斯分布均匀,通过网格引导变形高斯的高密度化和剪枝,提升网格重建质量。
- 通过规范空间和变形空间的循环一致性变形,将锚定的高斯投射回规范空间,并在所有时间帧优化高斯。
- 在不同数据集上评估后,DG-Mesh 在网格重建和渲染方面显著优于基准方法。
-
Title: 动态高斯网格:单目视频中一致的网格重建
-
Authors: Isabella Liu, Hao Su, Xiaolong Wang
-
Affiliation: 加州大学圣地亚哥分校
-
Keywords: 3D Reconstruction, Monocular Video, Dynamic Mesh, Gaussian Splatting
-
Urls: Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.12379, Github: None
-
Summary:
(1): 现代 3D 引擎和图形管道需要网格作为一种内存高效的表示,它允许高效渲染、几何处理、纹理编辑和许多其他下游操作。然而,从单目视觉观察中获得结构和细节方面的高质量网格仍然非常困难。对于动态场景和对象,这个问题变得更具挑战性。
(2): 过去的方法包括使用 3D 高斯斑点构建网格序列,但这些方法在处理动态场景时存在局限性。
(3): 本文提出了一种名为动态高斯网格(DG-Mesh)的框架,该框架利用 3D 高斯斑点表示,并通过高斯网格锚定算法恢复高质量网格,从而实现时间一致的网格序列重建。
(4): 在 D-NeRF 数据集和 DG-Mesh 数据集上,该方法在网格重建任务上取得了优异的性能,证明了其有效性。
-
方法:
(1):提出了一种名为动态高斯网格(DG-Mesh)的框架,该框架利用 3D 高斯斑点表示,并通过高斯网格锚定算法恢复高质量网格,从而实现时间一致的网格序列重建;
(2):该框架包括一个网格构建模块,该模块使用 3D 高斯斑点表示来构建网格序列,以及一个网格锚定模块,该模块将网格序列中的网格锚定到世界坐标系中;
(3):网格构建模块利用 3D 高斯斑点表示来表示场景中的几何形状,并使用高斯混合模型(GMM)来估计网格序列中的网格;
(4):网格锚定模块利用高斯网格锚定算法将网格序列中的网格锚定到世界坐标系中,该算法使用高斯斑点之间的几何关系来估计网格的位姿;
(5):该框架通过迭代优化网格构建模块和网格锚定模块中的参数来实现时间一致的网格序列重建。
-
结论:
(1):本文提出了一种名为动态高斯网格(DG-Mesh)的框架,该框架利用 3D 高斯斑点表示,并通过高斯网格锚定算法恢复高质量网格,从而实现时间一致的网格序列重建。DG-Mesh 在网格重建任务上取得了优异的性能,证明了其有效性。
(2):创新点:利用 3D 高斯斑点表示和高斯网格锚定算法实现时间一致的网格序列重建; 性能:在网格重建任务上取得了优异的性能; 工作量:需要准确的对象分割和跟踪,在处理大拓扑变化时存在挑战。
点此查看论文截图