⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-11 更新
Exploring Depth Information for Detecting Manipulated Face Videos
Authors:Haoyue Wang, Sheng Li, Ji He, Zhenxing Qian, Xinpeng Zhang, Shaolin Fan
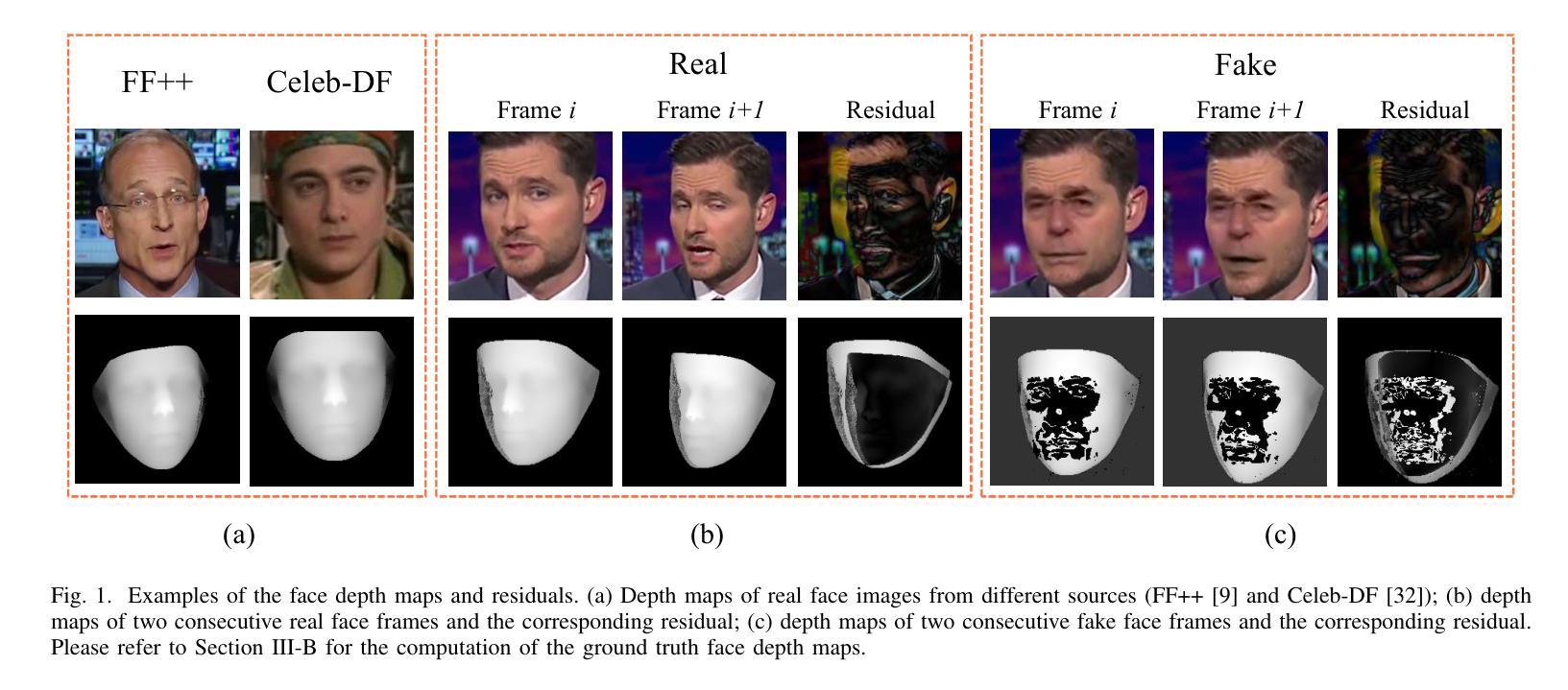
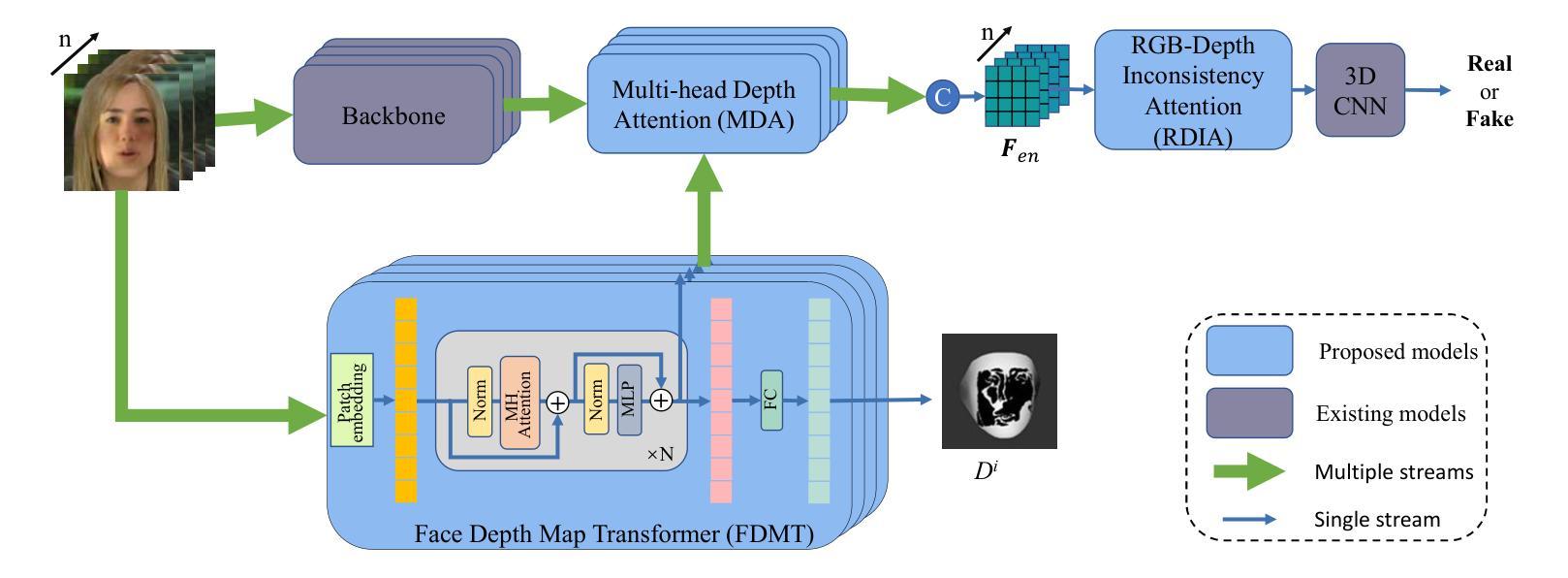
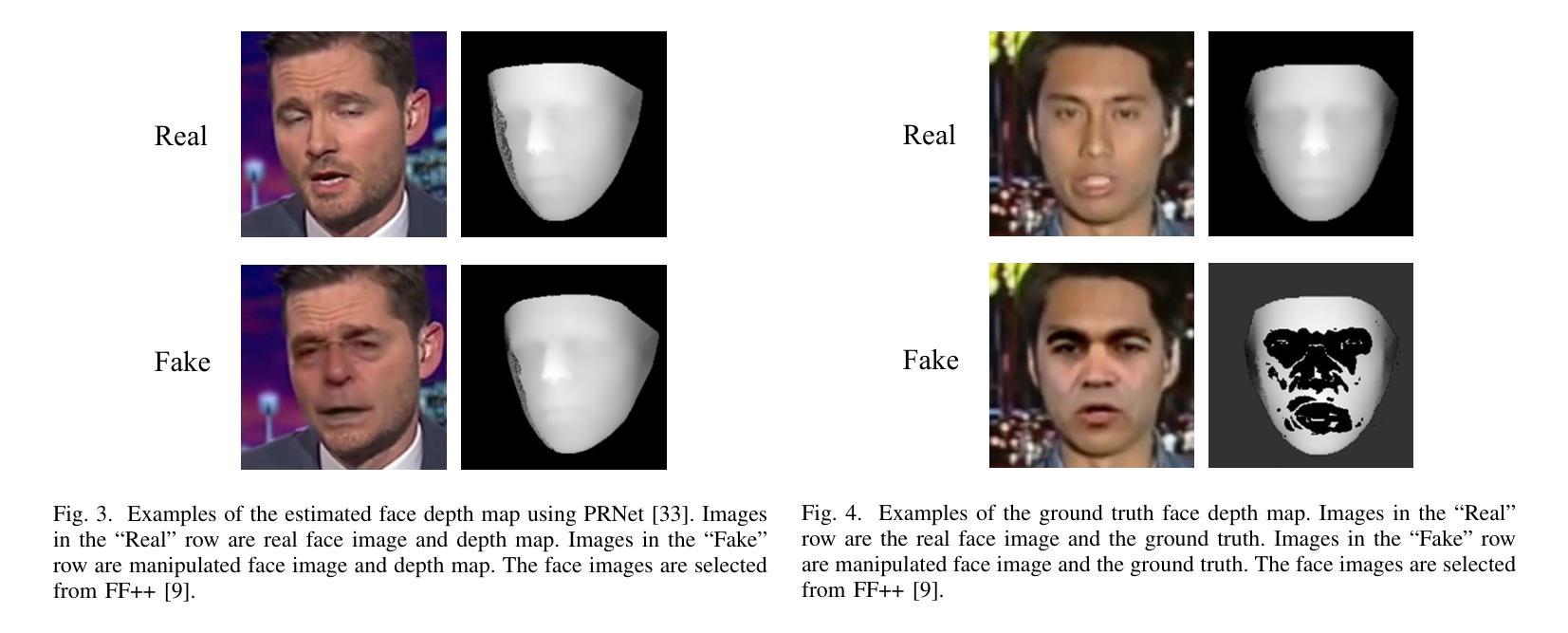
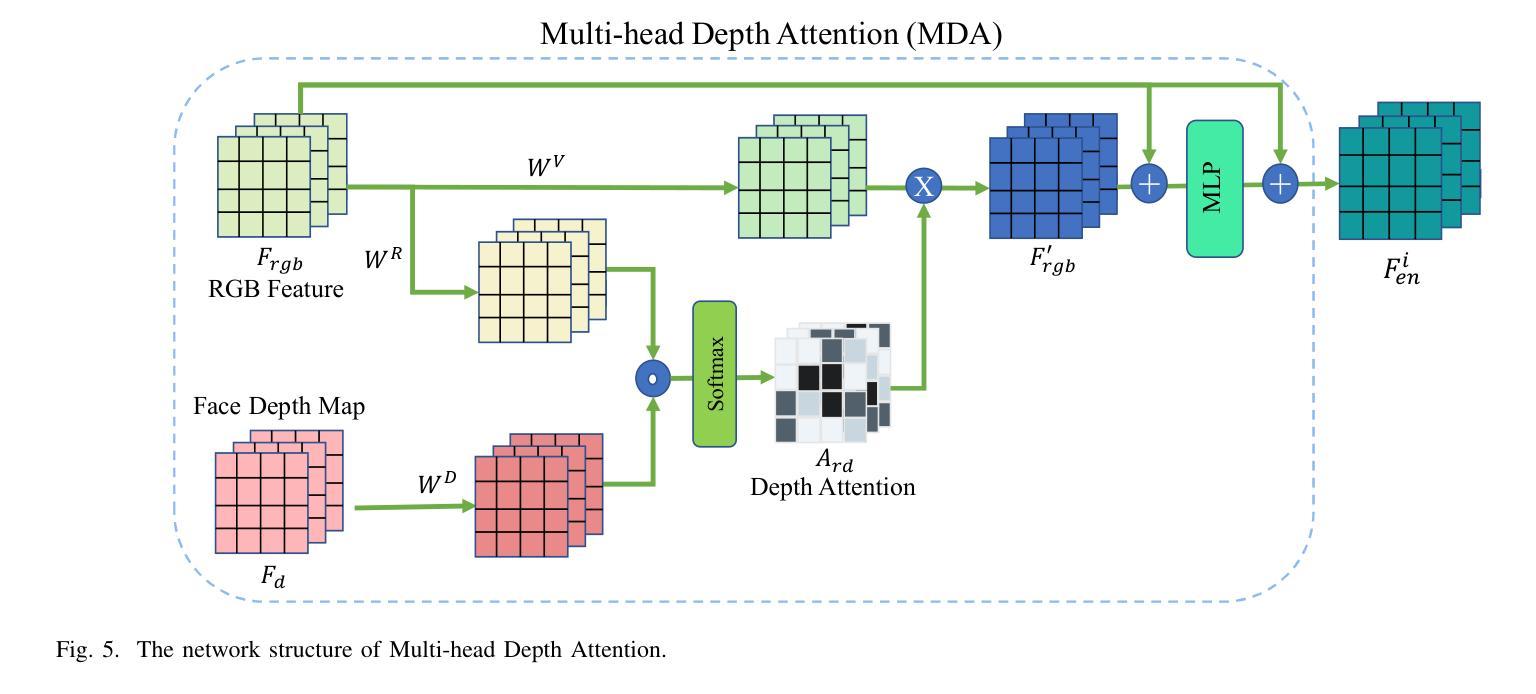
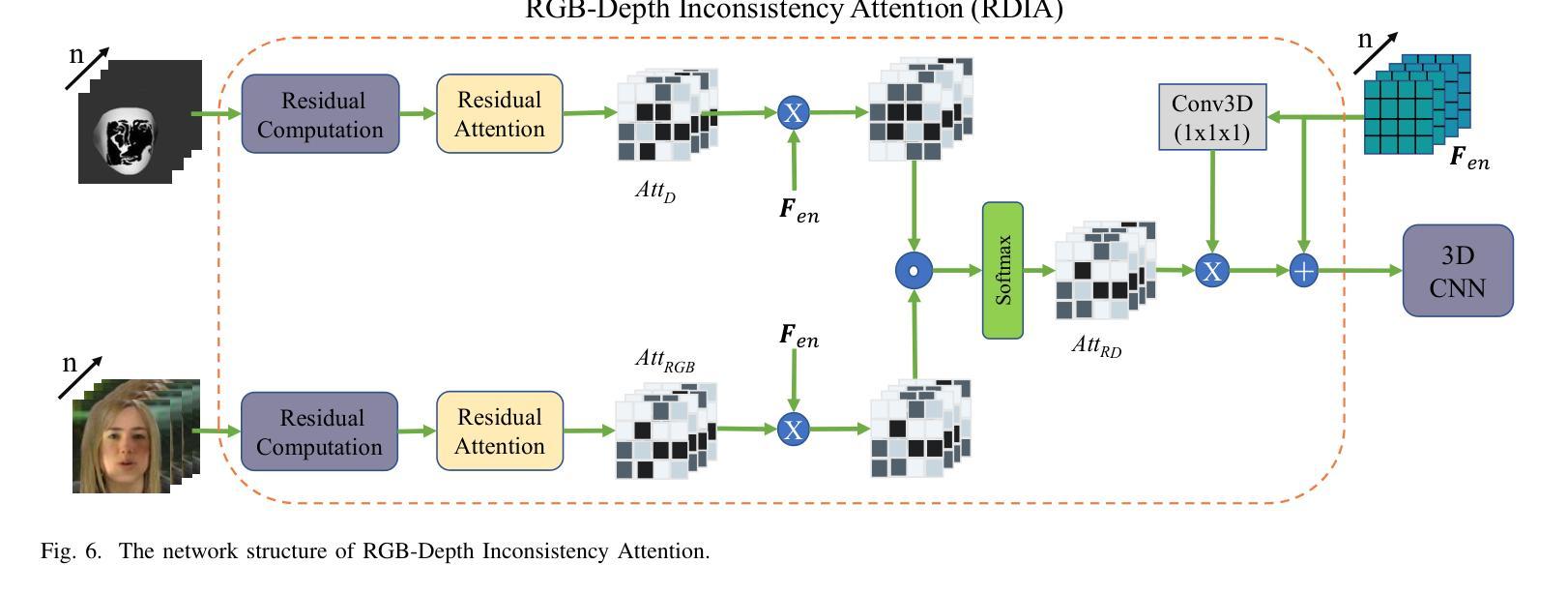
Face manipulation detection has been receiving a lot of attention for the reliability and security of the face images/videos. Recent studies focus on using auxiliary information or prior knowledge to capture robust manipulation traces, which are shown to be promising. As one of the important face features, the face depth map, which has shown to be effective in other areas such as face recognition or face detection, is unfortunately paid little attention to in literature for face manipulation detection. In this paper, we explore the possibility of incorporating the face depth map as auxiliary information for robust face manipulation detection. To this end, we first propose a Face Depth Map Transformer (FDMT) to estimate the face depth map patch by patch from an RGB face image, which is able to capture the local depth anomaly created due to manipulation. The estimated face depth map is then considered as auxiliary information to be integrated with the backbone features using a Multi-head Depth Attention (MDA) mechanism that is newly designed. We also propose an RGB-Depth Inconsistency Attention (RDIA) module to effectively capture the inter-frame inconsistency for multi-frame input. Various experiments demonstrate the advantage of our proposed method for face manipulation detection.
人脸识别技术中的图像/视频操纵检测因其可靠性和安全性而受到广泛关注。近期的研究主要集中在利用辅助信息或先验知识来捕捉稳健的操纵痕迹,这显示出了一定的前景。作为人脸特征的重要组成部分之一,人脸深度图在人脸识别或人脸检测等领域已经展现出其有效性,但在人脸操纵检测的文献中却鲜有研究涉及。在本文中,我们探讨了将人脸深度图作为辅助信息用于稳健的人脸操纵检测的可能性。为此,我们首先提出了一种Face Depth Map Transformer(FDMT)方法,能够从RGB人脸图像中逐块估计人脸深度图,该方法能够捕捉到由于操纵而产生的局部深度异常。然后,我们将估计的人脸深度图视为辅助信息,使用新设计的Multi-head Depth Attention(MDA)机制将其与主干特征进行融合。我们还提出了一种RGB-Depth Inconsistency Attention(RDIA)模块,以有效地捕捉多帧输入的帧间不一致性。各种实验证明了我们在人脸操纵检测方面提出的方法的优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 10 figures. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2212.14230
Summary
人脸识别技术面临着操控性问题,人们亟需提升相关可靠性及安全性。针对深度图的探讨一直被忽视的问题,本文通过深度图捕捉局部深度异常进行人脸识别检测研究。文章提出了一种Face Depth Map Transformer模型(FDMT)进行人脸深度图的获取与分析,并用Multi-head Depth Attention机制将结果引入原有模型提升识别效果。同时,设计RGB-Depth Inconsistency Attention模块,用于捕捉多帧输入间的帧间不一致性。实验证明,该方法在人脸识别检测中具有优势。
Key Takeaways
- 人脸操控问题在人脸识别技术中至关重要,对人脸图像和视频的安全性和可靠性提出挑战。
- 人脸深度图作为辅助信息对于人脸识别操控检测具有潜力,但相关研究较为匮乏。
- 提出Face Depth Map Transformer(FDMT)模型用于从RGB人脸图像中估计人脸深度图,捕捉因操控产生的局部深度异常。
- 采用Multi-head Depth Attention机制集成估计得到的人脸深度图与主干特征。
- 设计RGB-Depth Inconsistency Attention模块用以有效捕捉多帧输入间的帧间不一致性,以增强对动态操纵的检测能力。
- 实验结果显示所提出的方法在人脸识别检测方面具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

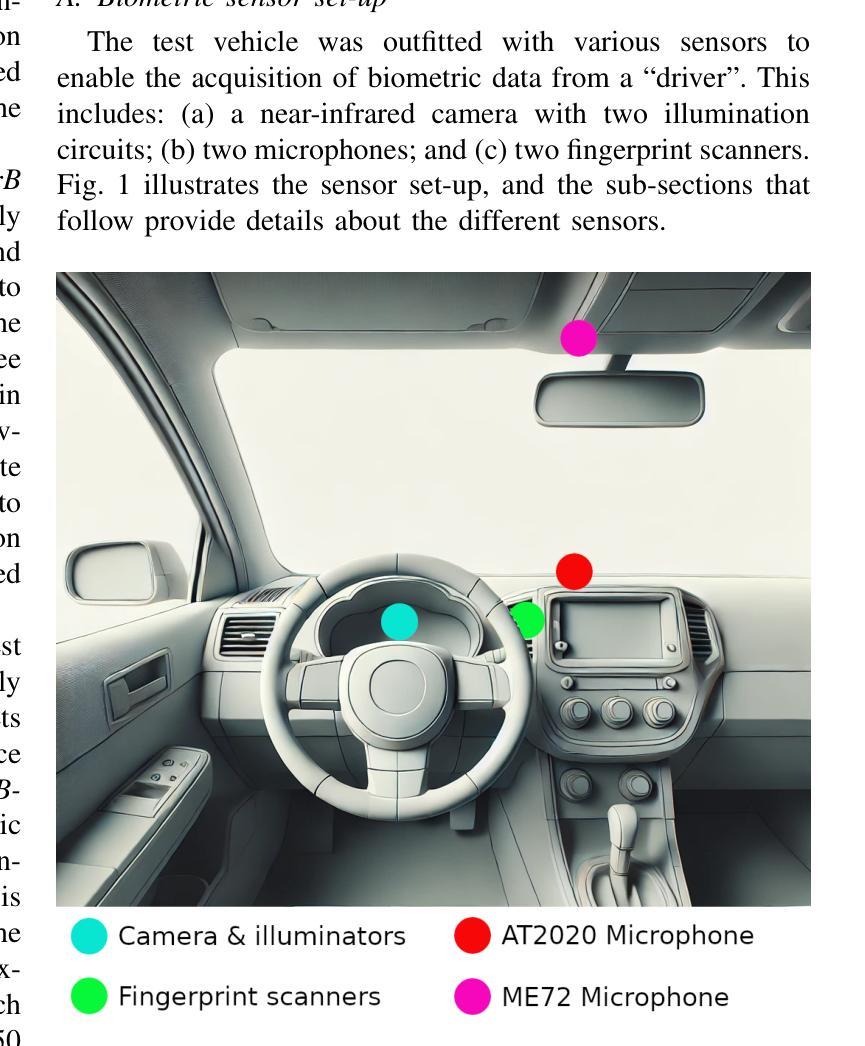
in-Car Biometrics (iCarB) Datasets for Driver Recognition: Face, Fingerprint, and Voice
Authors:Vedrana Krivokuca Hahn, Jeremy Maceiras, Alain Komaty, Philip Abbet, Sebastien Marcel
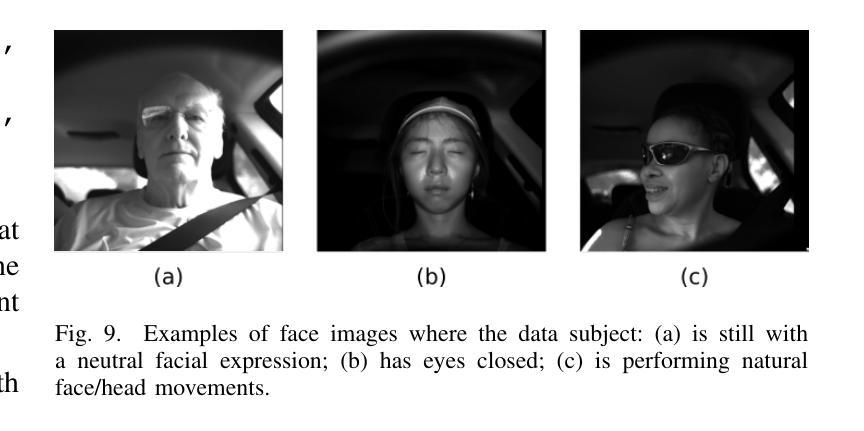
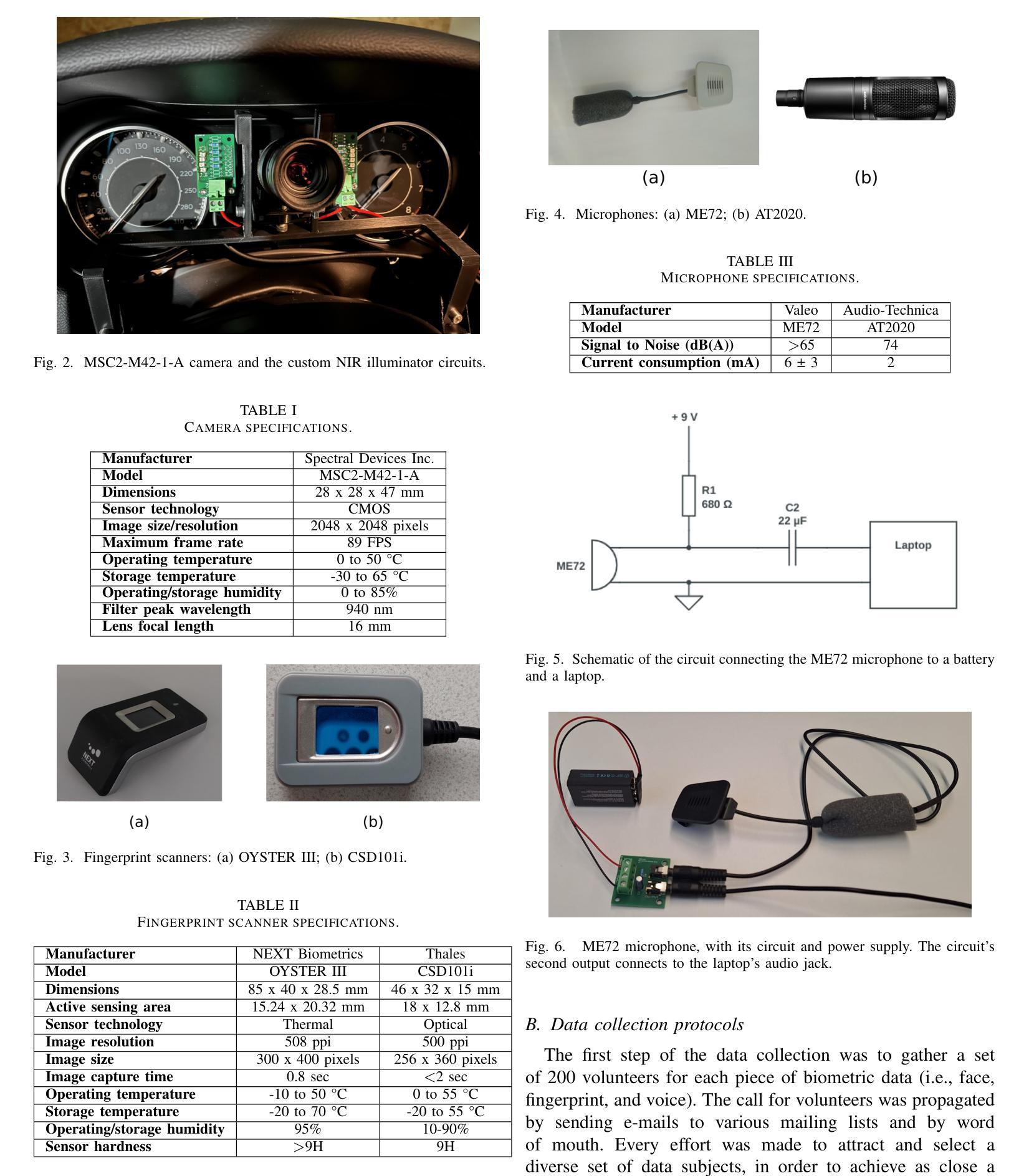
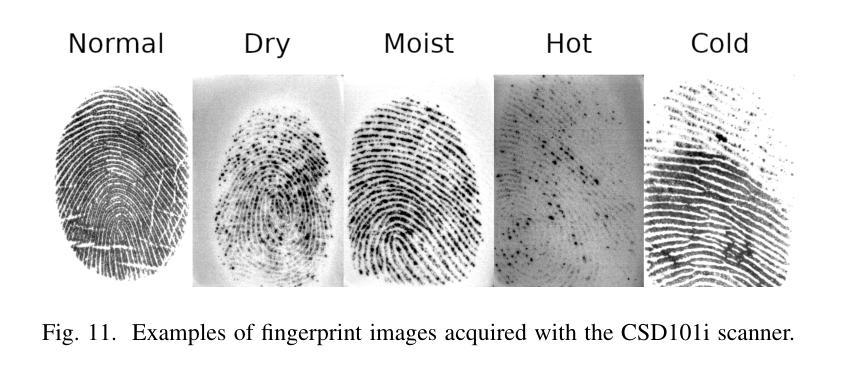
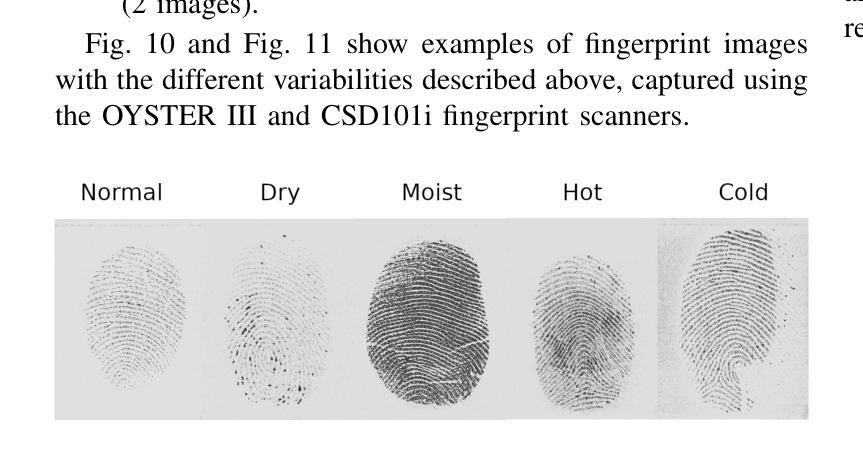
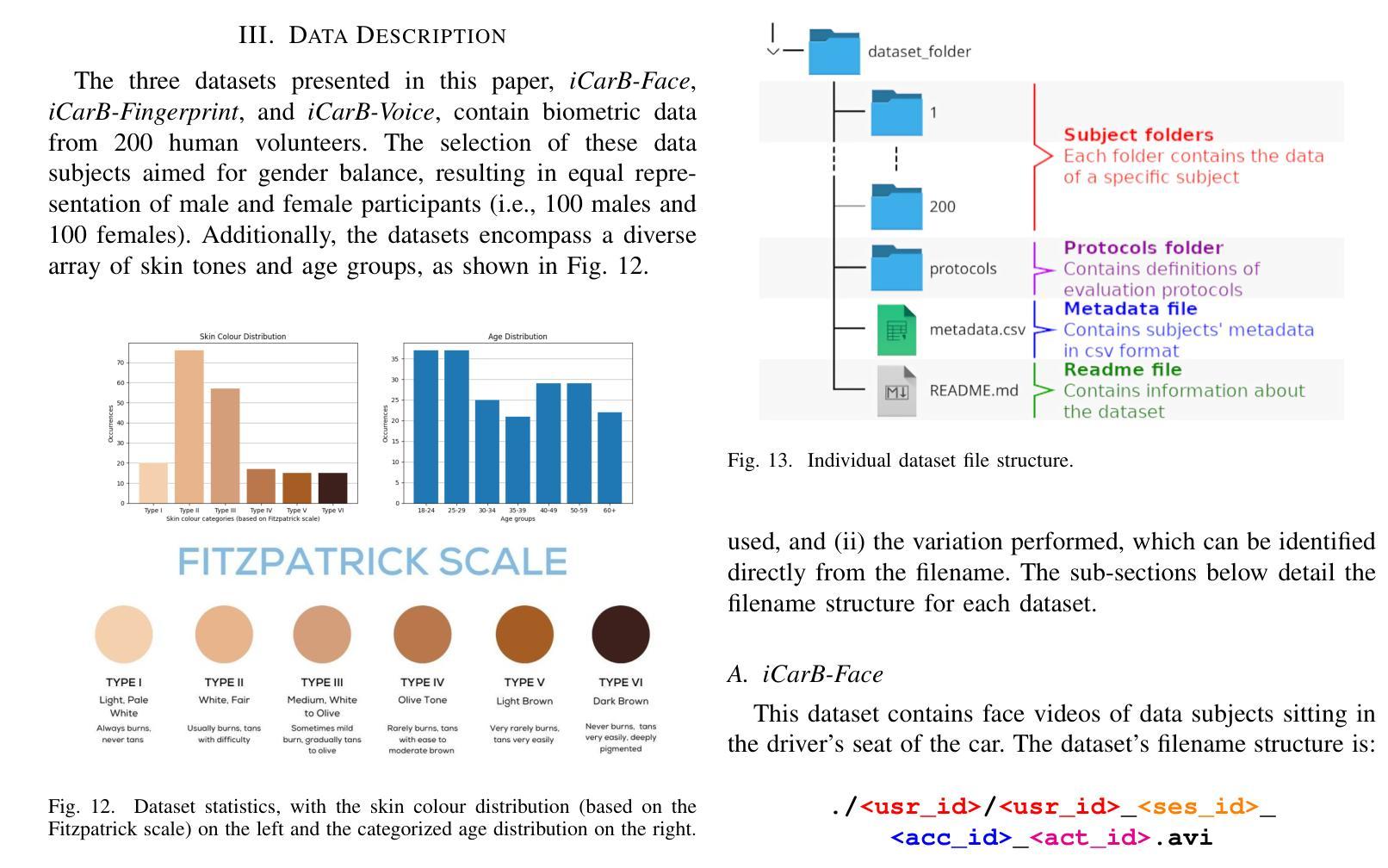
We present three biometric datasets (iCarB-Face, iCarB-Fingerprint, iCarB-Voice) containing face videos, fingerprint images, and voice samples, collected inside a car from 200 consenting volunteers. The data was acquired using a near-infrared camera, two fingerprint scanners, and two microphones, while the volunteers were seated in the driver’s seat of the car. The data collection took place while the car was parked both indoors and outdoors, and different “noises” were added to simulate non-ideal biometric data capture that may be encountered in real-life driver recognition. Although the datasets are specifically tailored to in-vehicle biometric recognition, their utility is not limited to the automotive environment. The iCarB datasets, which are available to the research community, can be used to: (i) evaluate and benchmark face, fingerprint, and voice recognition systems (we provide several evaluation protocols); (ii) create multimodal pseudo-identities, to train/test multimodal fusion algorithms; (iii) create Presentation Attacks from the biometric data, to evaluate Presentation Attack Detection algorithms; (iv) investigate demographic and environmental biases in biometric systems, using the provided metadata. To the best of our knowledge, ours are the largest and most diverse publicly available in-vehicle biometric datasets. Most other datasets contain only one biometric modality (usually face), while our datasets consist of three modalities, all acquired in the same automotive environment. Moreover, iCarB-Fingerprint seems to be the first publicly available in-vehicle fingerprint dataset. Finally, the iCarB datasets boast a rare level of demographic diversity among the 200 data subjects, including a 50/50 gender split, skin colours across the whole Fitzpatrick-scale spectrum, and a wide age range (18-60+). So, these datasets will be valuable for advancing biometrics research.
我们提供了三个生物识别数据集(iCarB-Face、iCarB-Fingerprint、iCarB-Voice),其中包含从200名同意参与的志愿者在车内收集的面部视频、指纹图像和语音样本。数据使用近红外相机、两个指纹扫描仪和两个麦克风在志愿者坐在汽车驾驶座时采集。数据收集在汽车室内和室外停放时进行,并添加了不同的“噪音”来模拟在真实生活中可能会遇到的不理想的生物识别数据采集情况。尽管这些数据集特别针对车内生物识别设计,但其用途不限于汽车环境。iCarB数据集对研究群体开放使用,可用于:(i)评估和基准测试面部、指纹和语音识别系统(我们提供了多个评估协议);(ii)创建多模态伪身份,以训练和测试多模态融合算法;(iii)从生物识别数据中创建呈现攻击,以评估呈现攻击检测算法;(iv)使用提供的元数据研究生物识别系统中的种族和环境偏见。据我们所知,我们的数据集是最大且最多元化的公开可用车内生物识别数据集。其他大多数数据集只包含一种生物识别模式(通常是面部),而我们的数据集包含三种模式,均在同一汽车环境中采集。此外,iCarB-Fingerprint似乎是首个公开可用的车内指纹数据集。最后,iCarB数据集在200个数据主体之间具有罕见的种族多样性,包括50/50的性别分布、跨越整个Fitzpatrick谱的皮肤颜色和广泛的年龄范围(18-60+)。因此,这些数据集对于推动生物识别研究将具有宝贵价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 13 figures, 4 tables
摘要
本文介绍了三个车载生物识别数据集(iCarB-Face、iCarB-Fingerprint、iCarB-Voice),包含面部视频、指纹图像和语音样本,是在车内从200名志愿者身上收集的。数据使用近红外相机、两个指纹扫描仪和两个麦克风在志愿者坐在驾驶座上时采集。数据收集在室内和室外停放的汽车中进行,并添加了不同的“噪音”以模拟现实驾驶识别中可能遇到的不理想的生物识别数据捕获情况。iCarB数据集虽然专为车内生物识别设计,但其用途不限于汽车环境。这些数据集对于推进生物识别研究具有价值,可用于评估和面授面部、指纹和语音识别系统(我们提供多个评估协议);创建多模态伪身份,以训练/测试多模态融合算法;从生物识别数据中创建呈现攻击,以评估呈现攻击检测算法;使用提供的元数据研究生物识别系统中的人口统计和环境偏见。据我们所知,我们的数据集是目前最大且最多元的车内生物识别数据集。其他大多数数据集只包含一种生物识别模式(通常是面部),而我们的数据集包含三种模式,都是在相同的汽车环境中收集的。此外,iCarB-Fingerprint似乎是首个公开可用的车内指纹数据集。最后,iCarB数据集的数据主体具有罕见的民族多样性,包括50/50的性别比例、跨越整个Fitzpatrick尺度的肤色以及广泛的年龄范围(18-60+)。
要点
- 介绍了三个车载生物识别数据集iCarB-Face、iCarB-Fingerprint和iCarB-Voice。
- 数据集包含面部视频、指纹图像和语音样本,在真实的驾驶环境中从志愿者身上收集。
- 数据集可用于评估面部、指纹和语音识别系统,提供多个评估协议。
- 可用于创建多模态伪身份、呈现攻击检测算法的研究以及生物识别系统中的偏见研究。
- 与其他数据集相比,iCarB数据集包含多种生物识别模式,并在相同的汽车环境中收集。
- iCarB-Fingerprint是首个公开可用的车内指纹数据集。
点此查看论文截图



Local and Global Feature Attention Fusion Network for Face Recognition
Authors:Wang Yu, Wei Wei
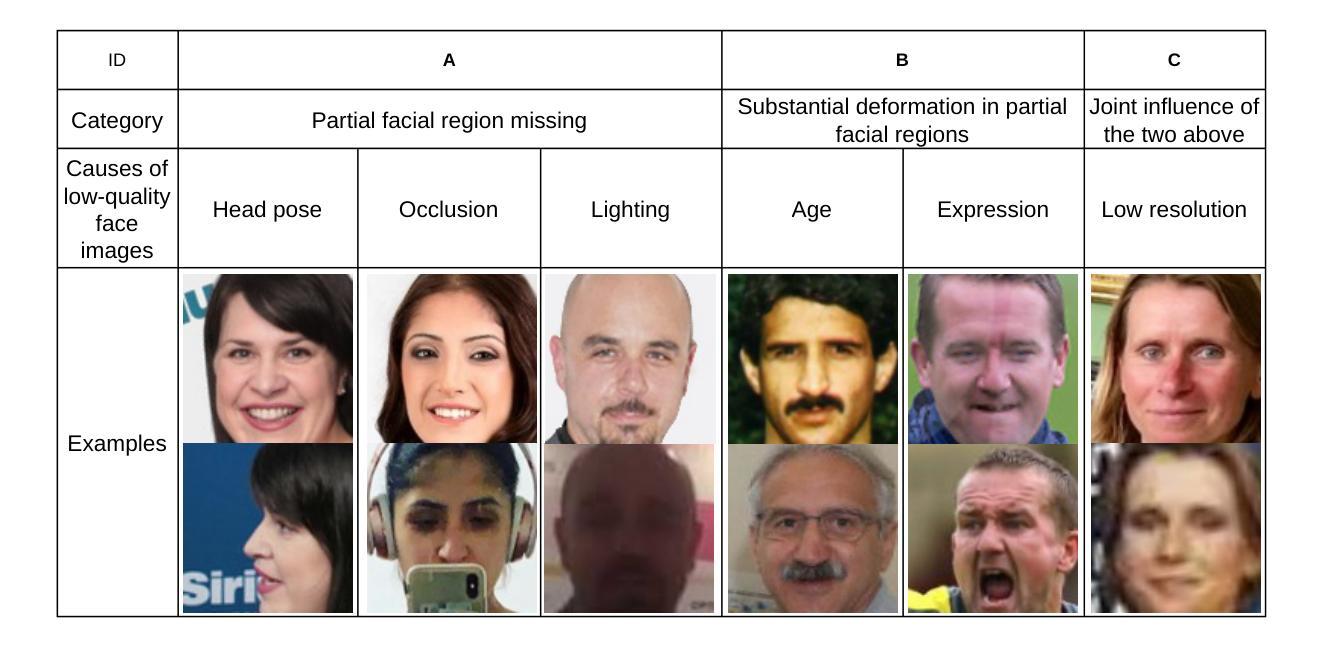
Recognition of low-quality face images remains a challenge due to invisible or deformation in partial facial regions. For low-quality images dominated by missing partial facial regions, local region similarity contributes more to face recognition (FR). Conversely, in cases dominated by local face deformation, excessive attention to local regions may lead to misjudgments, while global features exhibit better robustness. However, most of the existing FR methods neglect the bias in feature quality of low-quality images introduced by different factors. To address this issue, we propose a Local and Global Feature Attention Fusion (LGAF) network based on feature quality. The network adaptively allocates attention between local and global features according to feature quality and obtains more discriminative and high-quality face features through local and global information complementarity. In addition, to effectively obtain fine-grained information at various scales and increase the separability of facial features in high-dimensional space, we introduce a Multi-Head Multi-Scale Local Feature Extraction (MHMS) module. Experimental results demonstrate that the LGAF achieves the best average performance on $4$ validation sets (CFP-FP, CPLFW, AgeDB, and CALFW), and the performance on TinyFace and SCFace outperforms the state-of-the-art methods (SoTA).
针对低质量人脸图像的识别仍然是一个挑战,这主要是由于部分面部区域存在不可见或变形的情况。对于以缺失部分面部区域为主的低质量图像,局部区域相似性对人脸识别(FR)的贡献更大。相反,在局部面部变形占主导的情况下,过度关注局部区域可能导致误判,而全局特征表现出更好的鲁棒性。然而,大多数现有的FR方法忽视了不同因素导致的低质量图像特征质量的偏差。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种基于特征质量的局部和全局特征注意力融合(LGAF)网络。该网络根据特征质量自适应地分配局部和全局特征之间的注意力,并通过局部和全局信息的互补性获得更具区分性和高质量的人脸特征。此外,为了有效地获取各种尺度的精细信息,并在高维空间中增加面部特征的可分性,我们引入了多头多尺度局部特征提取(MHMS)模块。实验结果表明,LGAF在CFP-FP、CPLFW、AgeDB和CALFW四个验证集上的平均性能最佳,并且在TinyFace和SCFace上的性能超过了当前最前沿的方法(SoTA)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对低质量人脸图像识别中的局部区域缺失或变形问题,提出一种基于特征质量的局部与全局特征注意力融合(LGAF)网络。该网络根据特征质量自适应分配局部和全局特征的注意力,通过局部和全局信息的互补性,获取更具判别力和高质量的人脸特征。同时,引入多头多尺度局部特征提取(MHMS)模块,以获取多尺度精细信息,提高高维空间中面部特征的可分性。实验结果在多个验证集上表现出最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 低质量人脸图像识别面临挑战,主要表现为局部面部区域的缺失或变形。
- 局部区域相似性对缺失部分面部区域的低质量图像识别更重要,而局部面部变形时过度关注局部可能导致误判,全局特征更具鲁棒性。
- 现有的人脸识别方法忽视了由不同因素引起的低质量图像特征质量的偏差。
- 提出的LGAF网络基于特征质量自适应分配局部和全局特征的注意力。
- LGAF网络通过局部和全局信息的互补性,获得更具判别力和高质量的人脸特征。
- MHMS模块用于获取多尺度精细信息,提高面部特征在高维空间中的可分性。
点此查看论文截图


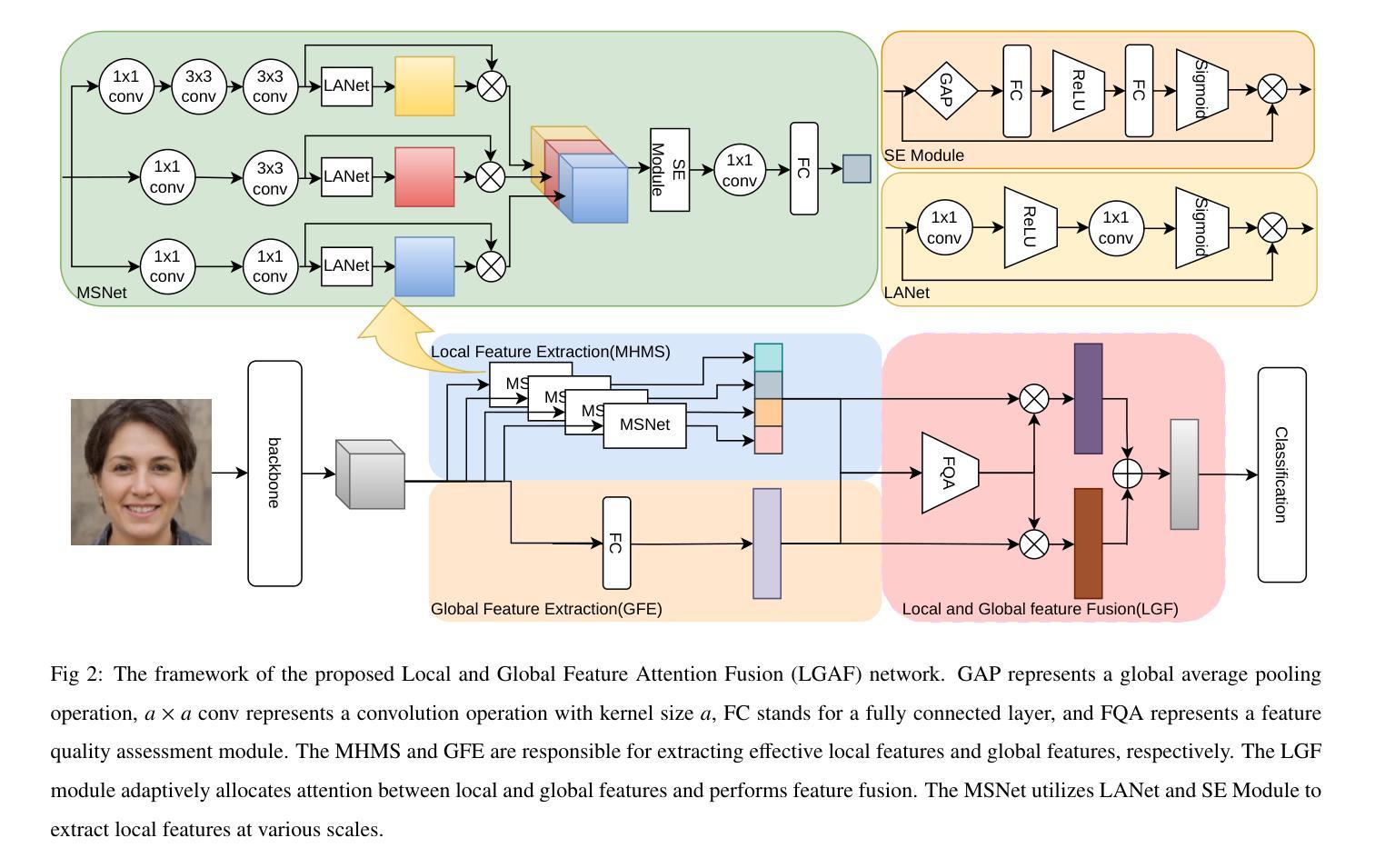
Enhancing the Transferability of Adversarial Attacks on Face Recognition with Diverse Parameters Augmentation
Authors:Fengfan Zhou, Bangjie Yin, Hefei Ling, Qianyu Zhou, Wenxuan Wang
Face Recognition (FR) models are vulnerable to adversarial examples that subtly manipulate benign face images, underscoring the urgent need to improve the transferability of adversarial attacks in order to expose the blind spots of these systems. Existing adversarial attack methods often overlook the potential benefits of augmenting the surrogate model with diverse initializations, which limits the transferability of the generated adversarial examples. To address this gap, we propose a novel method called Diverse Parameters Augmentation (DPA) attack method, which enhances surrogate models by incorporating diverse parameter initializations, resulting in a broader and more diverse set of surrogate models. Specifically, DPA consists of two key stages: Diverse Parameters Optimization (DPO) and Hard Model Aggregation (HMA). In the DPO stage, we initialize the parameters of the surrogate model using both pre-trained and random parameters. Subsequently, we save the models in the intermediate training process to obtain a diverse set of surrogate models. During the HMA stage, we enhance the feature maps of the diversified surrogate models by incorporating beneficial perturbations, thereby further improving the transferability. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed attack method can effectively enhance the transferability of the crafted adversarial face examples.
人脸识别(FR)模型容易受到对抗样本的影响,这些对抗样本会微妙地操作良性的人脸图像,这突显了提高对抗攻击转移性的迫切需求,以暴露这些系统的盲点。现有的对抗攻击方法往往忽视了用多种初始化增强代理模型的潜在优势,从而限制了生成对抗样本的迁移性。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新的方法,称为多样性参数增强(DPA)攻击方法,通过融入多种参数初始化来增强代理模型,从而产生更广泛、更多样化的代理模型集合。具体来说,DPA包括两个关键阶段:多样参数优化(DPO)和硬模型聚合(HMA)。在DPO阶段,我们使用预训练参数和随机参数来初始化代理模型的参数。随后,我们在中间训练过程中保存模型,以获得多样化的代理模型集合。在HMA阶段,我们通过融入有益的扰动来增强多样化代理模型的特征映射,从而进一步提高迁移性。实验结果表明,我们提出的攻击方法可以有效地提高构建对抗面部样本的迁移性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人脸识别模型易受对抗样本攻击,为此需改进对抗攻击的迁移性。现有攻击方法忽略利用多样化初始化增强替代模型的潜力,限制了对抗样本的迁移性。为解决此问题,提出一种名为DPA(多样化参数增强)的新型攻击方法。它采用两个阶段——多样化参数优化和硬模型聚合——利用预训练参数和随机参数初始化替代模型,从而获取更全面、多样的模型集,增强了对抗样本的迁移性。实验结果表明该方法可有效提升构造的对抗性面部示例的迁移性。
Key Takeaways
- 人脸识别模型易受对抗样本攻击,需要加强其对抗攻击的迁移性以暴露系统盲点。
- 现有攻击方法忽略了利用多样化初始化增强替代模型的潜力。
- DPA攻击方法通过结合预训练参数和随机参数初始化增强替代模型,获取更全面、多样的模型集。
- DPA方法包括两个阶段:多样化参数优化(DPO)和硬模型聚合(HMA)。
- 在DPO阶段,模型参数进行多样化初始化,并在中间训练过程中保存模型,以获取多样的替代模型集。
- 在HMA阶段,通过融入有益扰动增强了多样化替代模型的特性映射,进一步提高迁移性。
点此查看论文截图
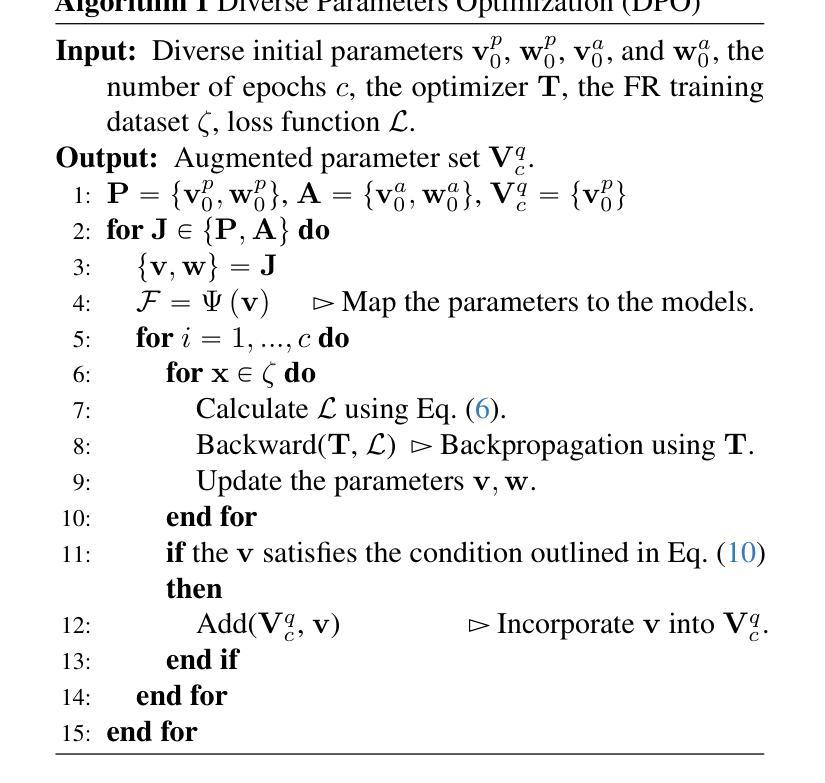
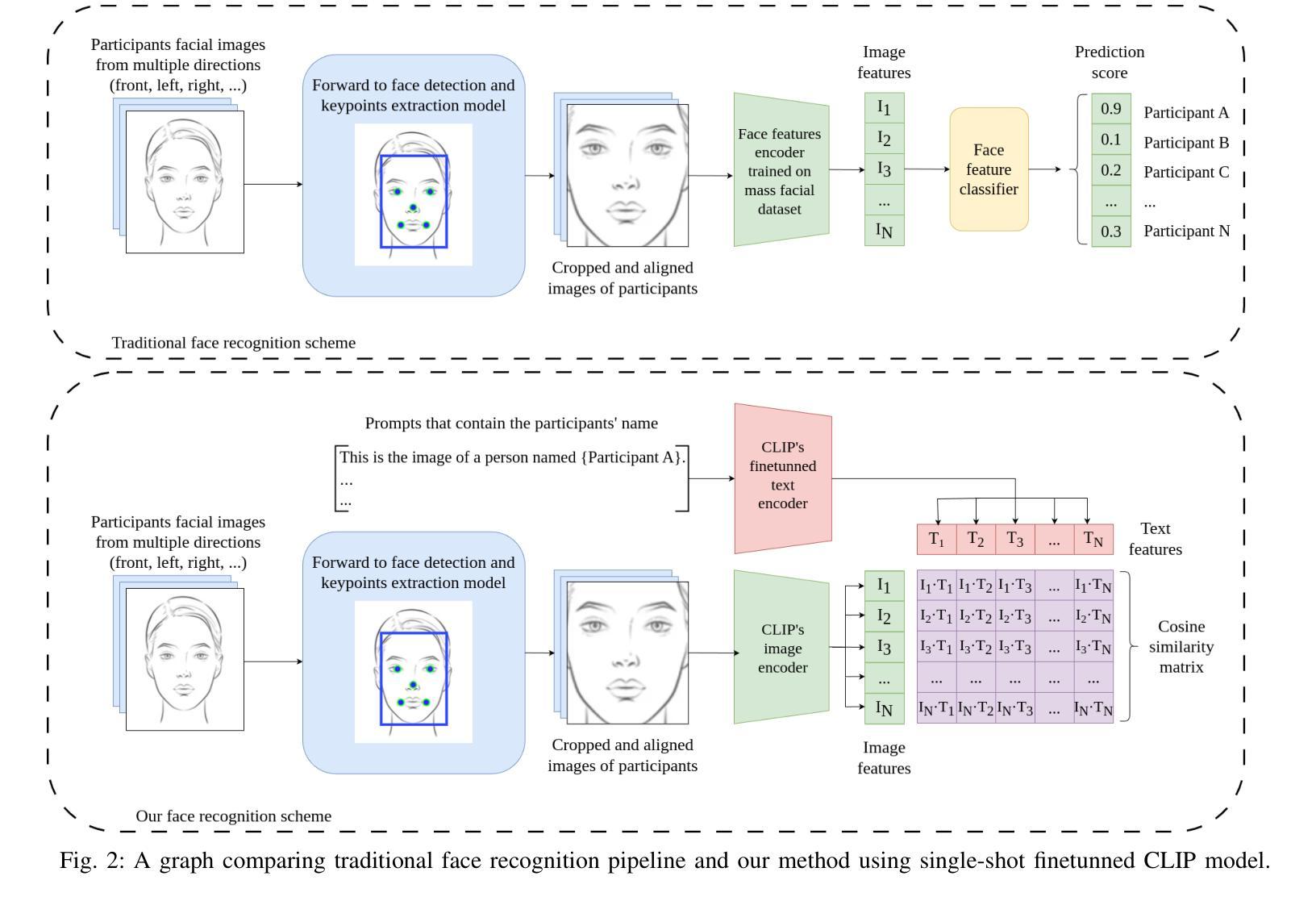
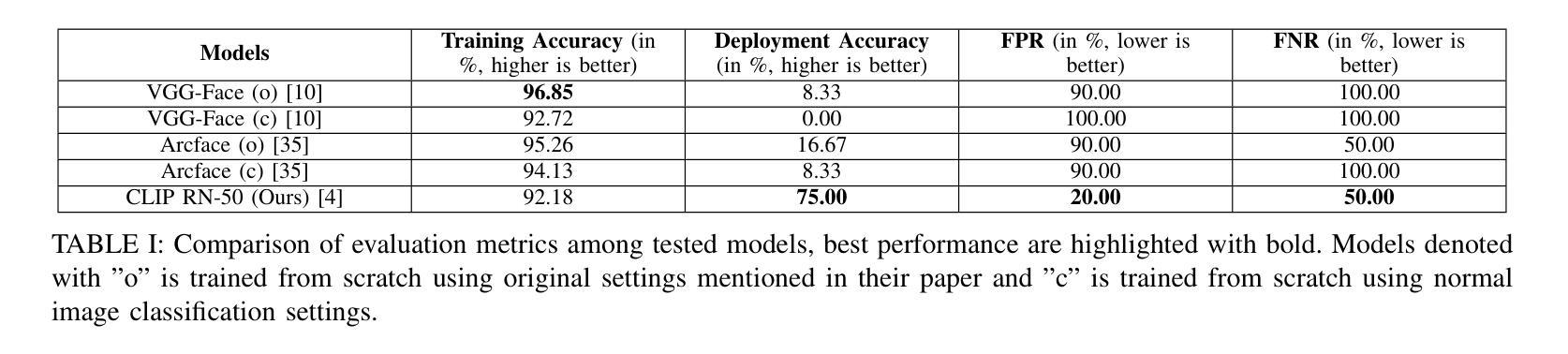
CLIP Unreasonable Potential in Single-Shot Face Recognition
Authors:Nhan T. Luu
Face recognition is a core task in computer vision designed to identify and authenticate individuals by analyzing facial patterns and features. This field intersects with artificial intelligence image processing and machine learning with applications in security authentication and personalization. Traditional approaches in facial recognition focus on capturing facial features like the eyes, nose and mouth and matching these against a database to verify identities. However challenges such as high false positive rates have persisted often due to the similarity among individuals facial features. Recently Contrastive Language Image Pretraining (CLIP) a model developed by OpenAI has shown promising advancements by linking natural language processing with vision tasks allowing it to generalize across modalities. Using CLIP’s vision language correspondence and single-shot finetuning the model can achieve lower false positive rates upon deployment without the need of mass facial features extraction. This integration demonstrating CLIP’s potential to address persistent issues in face recognition model performance without complicating our training paradigm.
人脸识别是计算机视觉中的一项核心任务,通过分析和识别面部模式和特征来识别和验证个人身份。这个领域与人工智能图像处理和机器学习有交集,在身份认证和安全个性化方面有着广泛的应用。传统的面部识别方法主要关注捕捉眼睛、鼻子和嘴巴等面部特征,并与数据库中的信息进行匹配以验证身份。然而,由于个体之间面部特征的相似性,一直存在高误报率等挑战。最近,OpenAI开发的Contrastive Language Image Pretraining(CLIP)模型通过将自然语言处理与视觉任务相联系,展示了在跨模态泛化方面的巨大潜力。通过使用CLIP的视觉语言对应关系和单次微调技术,模型可以在部署时实现较低的误报率,而无需进行大规模的面部特征提取。这种集成展示了CLIP解决人脸识别模型性能持续问题的潜力,而不会使训练模式复杂化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人脸识别是计算机视觉中的核心任务,通过分析面部模式特征来识别和验证个人身份。此领域与人工智能图像处理及机器学习相结合,在身份验证及个性化应用方面有着广泛的应用。传统人脸识别方法侧重于捕捉眼部、鼻子和嘴巴等面部特征,并与数据库进行匹配以验证身份。然而,由于个体面部特征的相似性,一直存在高误报率的问题。最近,OpenAI开发的CLIP模型通过连接自然语言处理和视觉任务,展现出跨模态的通用性潜力。CLIP的视觉语言对应和单次微调能够实现较低的部署误报率,无需大量面部特征提取。这表明CLIP模型具有解决人脸识别模型持久性问题,同时简化训练模式的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 人脸识别是计算机视觉的核心任务,涉及身份识别和验证。
- 传统人脸识别方法主要关注面部特征的捕捉和数据库匹配。
- 挑战之一是高误报率,这源于个体间面部特征的相似性。
- CLIP模型结合自然语言处理和视觉任务,展现出跨模态潜力。
- CLIP通过视觉语言对应和单次微调,降低部署时的误报率,减少对面部特征提取的需求。
- CLIP模型具有解决人脸识别模型持久性问题的能力。
点此查看论文截图

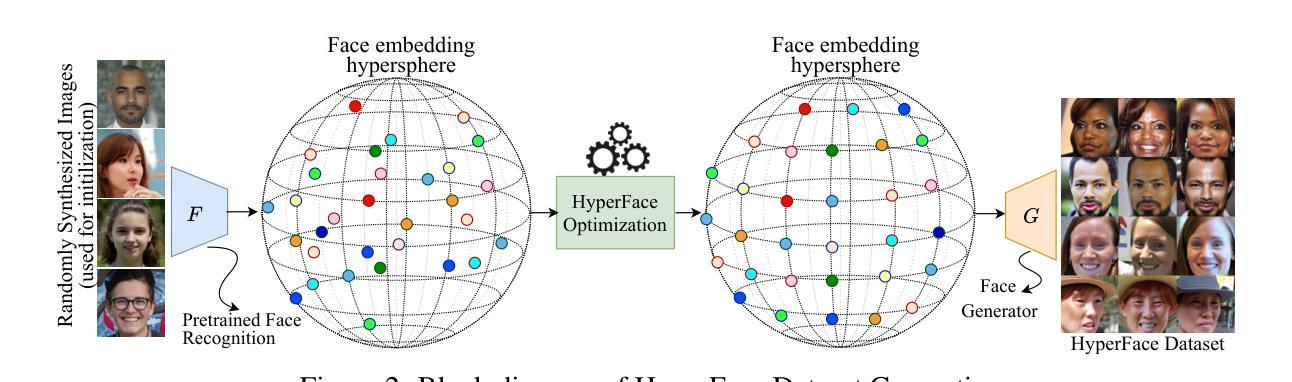
HyperFace: Generating Synthetic Face Recognition Datasets by Exploring Face Embedding Hypersphere
Authors:Hatef Otroshi Shahreza, Sébastien Marcel
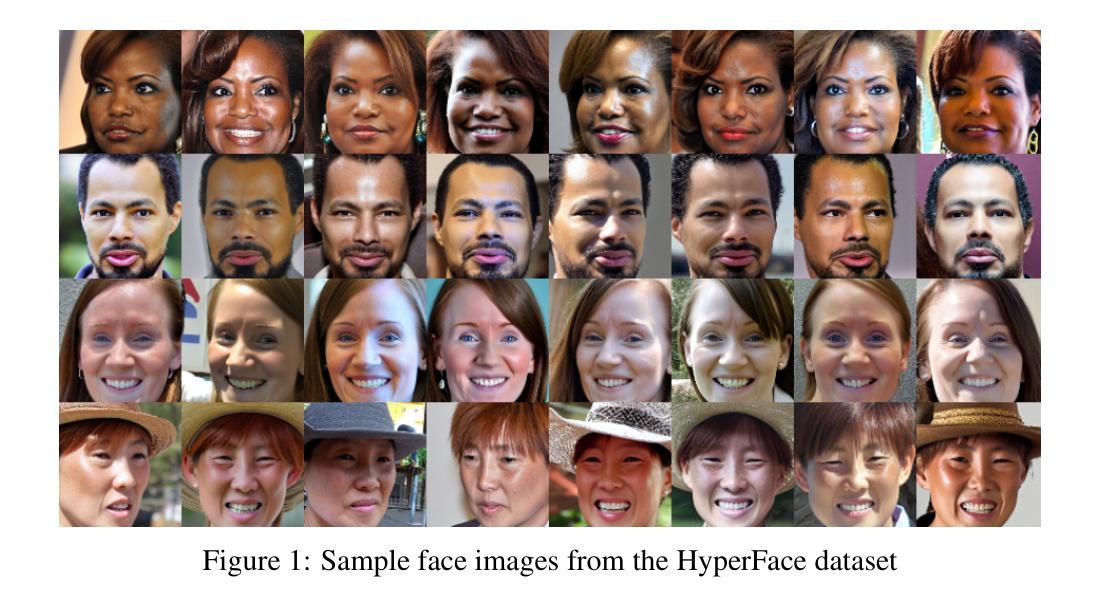
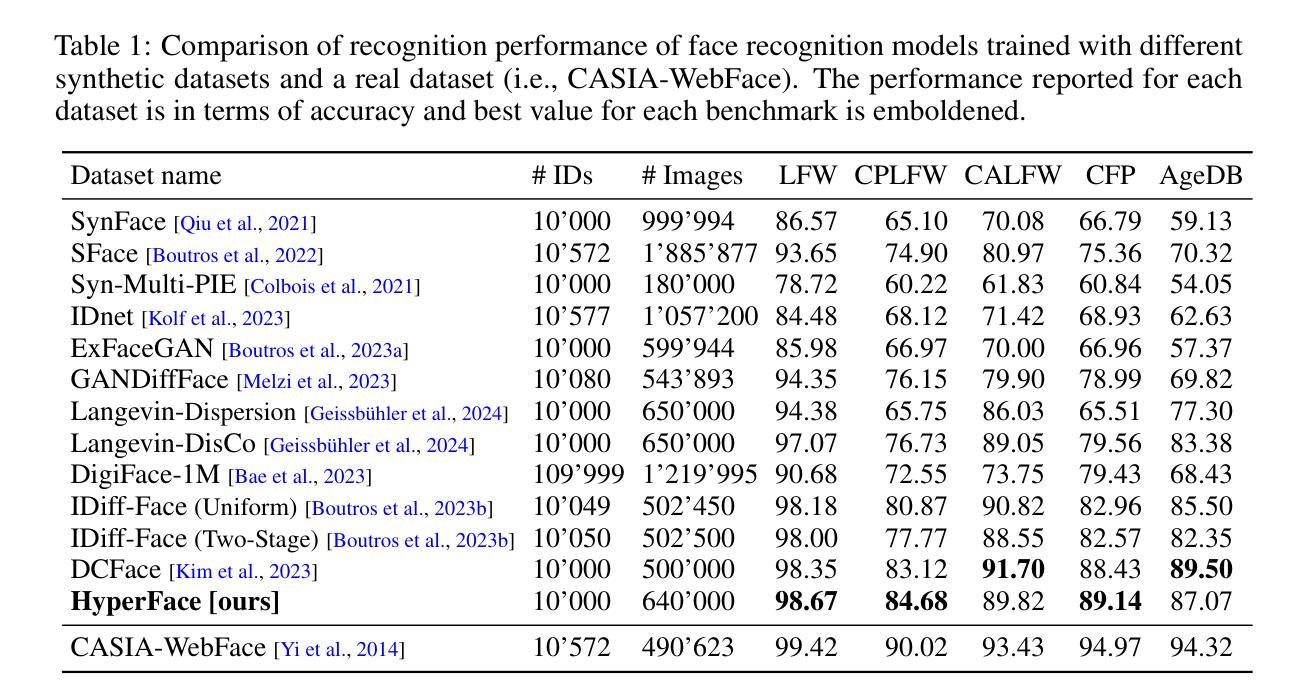
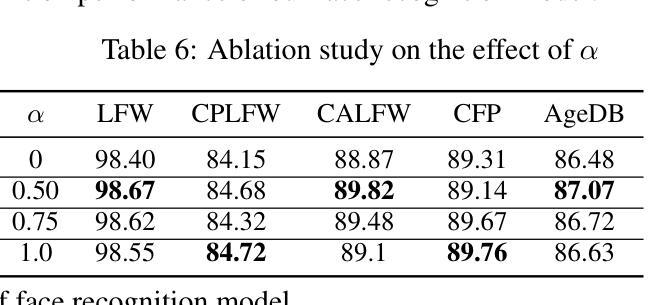
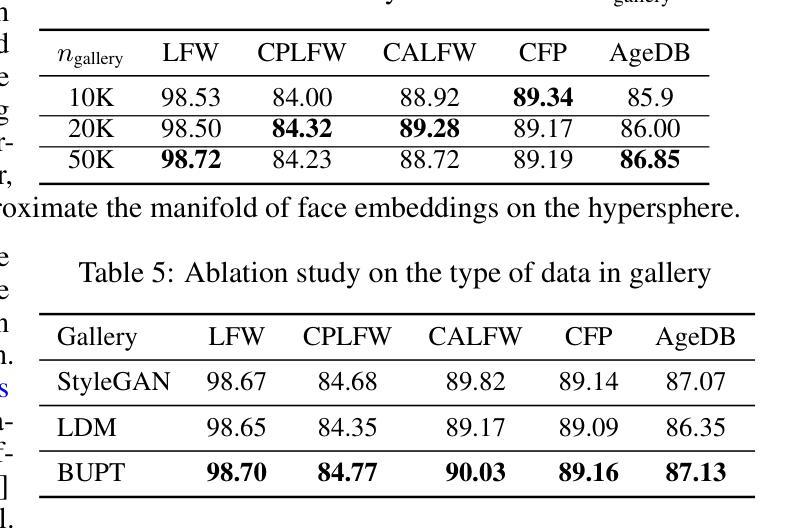
Face recognition datasets are often collected by crawling Internet and without individuals’ consents, raising ethical and privacy concerns. Generating synthetic datasets for training face recognition models has emerged as a promising alternative. However, the generation of synthetic datasets remains challenging as it entails adequate inter-class and intra-class variations. While advances in generative models have made it easier to increase intra-class variations in face datasets (such as pose, illumination, etc.), generating sufficient inter-class variation is still a difficult task. In this paper, we formulate the dataset generation as a packing problem on the embedding space (represented on a hypersphere) of a face recognition model and propose a new synthetic dataset generation approach, called HyperFace. We formalize our packing problem as an optimization problem and solve it with a gradient descent-based approach. Then, we use a conditional face generator model to synthesize face images from the optimized embeddings. We use our generated datasets to train face recognition models and evaluate the trained models on several benchmarking real datasets. Our experimental results show that models trained with HyperFace achieve state-of-the-art performance in training face recognition using synthetic datasets.
人脸识别数据集通常通过网上爬虫收集,并且未经个人同意,引发了伦理和隐私问题。使用合成数据集来训练人脸识别模型已成为一种前景广阔的方法。然而,生成合成数据集仍然具有挑战性,因为这需要足够的类间和类内变化。虽然生成模型的进步使得增加人脸数据集内的类内变化变得更加容易(如姿态、照明等),但生成足够的类间变化仍然是一项艰巨的任务。在本文中,我们将数据集生成问题转化为人脸识别模型嵌入空间(表示为超球体)上的打包问题,并提出了一种新的合成数据集生成方法,称为HyperFace。我们将打包问题形式化为优化问题,并采用基于梯度下降的方法来解决。然后,我们使用条件人脸生成器模型从优化后的嵌入中合成人脸图像。我们使用生成的数据集来训练人脸识别模型,并在几个基准真实数据集上评估训练好的模型。我们的实验结果表明,使用HyperFace训练模型在利用合成数据集训练人脸识别方面达到了最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in NeurIPS 2024 Safe Generative AI Workshop
Summary
本文探讨面部识别数据集收集过程中存在的伦理和隐私问题,并介绍了一种新型合成数据集生成方法——HyperFace。该方法将数据集生成问题表述为嵌入空间的排列问题,并利用基于梯度的优化方法进行求解。通过合成面部图像优化嵌入,进而训练面部识别模型,并在多个真实数据集上评估其性能。实验结果表明,使用HyperFace训练的模型在合成数据集上取得了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 面部识别数据集的收集常涉及伦理和隐私问题,使用合成数据集作为训练面部识别模型的替代方案备受关注。
- 生成合成数据集面临挑战,需要足够的类间和类内变化。
- 现有技术易于增加类内变化,但生成足够的类间变化仍然困难。
- 本文将数据集生成表述为嵌入空间的排列问题,并提出HyperFace方法。
- HyperFace方法通过优化嵌入空间解决排列问题,并使用基于梯度的下降方法进行求解。
- 使用条件面部生成器模型从优化的嵌入中合成面部图像。
点此查看论文截图


A Real-time Face Mask Detection and Social Distancing System for COVID-19 using Attention-InceptionV3 Model
Authors:Abdullah Al Asif, Farhana Chowdhury Tisha
One of the deadliest pandemics is now happening in the current world due to COVID-19. This contagious virus is spreading like wildfire around the whole world. To minimize the spreading of this virus, World Health Organization (WHO) has made protocols mandatory for wearing face masks and maintaining 6 feet physical distance. In this paper, we have developed a system that can detect the proper maintenance of that distance and people are properly using masks or not. We have used the customized attention-inceptionv3 model in this system for the identification of those two components. We have used two different datasets along with 10,800 images including both with and without Face Mask images. The training accuracy has been achieved 98% and validation accuracy 99.5%. The system can conduct a precision value of around 98.2% and the frame rate per second (FPS) was 25.0. So, with this system, we can identify high-risk areas with the highest possibility of the virus spreading zone. This may help authorities to take necessary steps to locate those risky areas and alert the local people to ensure proper precautions in no time.
当前世界正在发生一场由COVID-19引起的致命大流行病。这种传染病病毒正在全球范围内如野火般蔓延。为了尽量减少这种病毒的传播,世界卫生组织(WHO)制定了强制佩戴口罩和保持六英尺物理距离的规定。在本文中,我们开发了一个系统,可以检测人们是否遵守这一距离规定并正确使用口罩。我们采用了定制的注意力机制inceptionv3模型来识别这两个组成部分。我们使用了两个不同的数据集,共包含10,800张图像,其中包括戴口罩和不戴口罩的图像。训练准确率达到了98%,验证准确率达到了99.5%。该系统的精度值可达约98.2%,每秒帧率(FPS)为25.0。因此,借助此系统,我们可以识别病毒传播可能性最高的高风险区域。这可以帮助当局采取措施迅速定位这些危险区域,并提醒当地居民确保采取适当的预防措施。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人脸识别技术在抗疫中发挥重要作用,一研究通过定制化的attention-inceptionv3模型检测人们是否佩戴口罩以及保持社交距离的情况,利用两个数据集共10,800张图像进行训练,准确率达98%,可帮助识别高风险区域并采取措施防止病毒传播。
Key Takeaways
- COVID-19疫情成为当前全球最严重的流行病之一。
- 世界卫生组织(WHO)为减少病毒传播制定了戴口罩和保持六英尺距离的规定。
- 研究团队利用定制的attention-inceptionv3模型开发了可检测人们是否遵守戴口罩和保持社交距离的系统。
- 系统使用两个数据集共包含超过一万张图像进行训练,包括戴口罩和不戴口罩的图像。
- 训练准确率达到了98%,验证准确率达到了99.5%。系统的精度值约为98.2%,每秒帧速率为25。
- 该系统能够识别病毒传播可能性最高的高风险区域。
点此查看论文截图

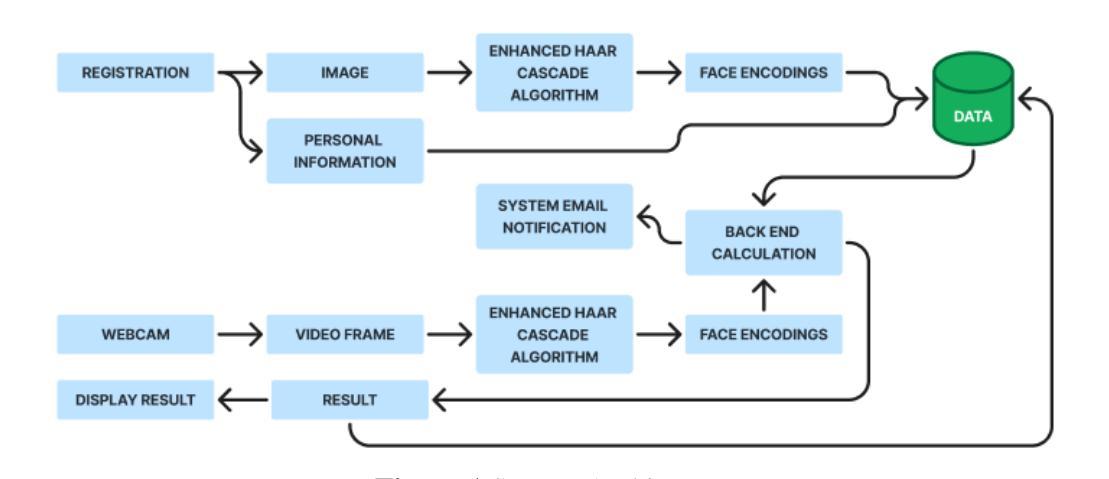
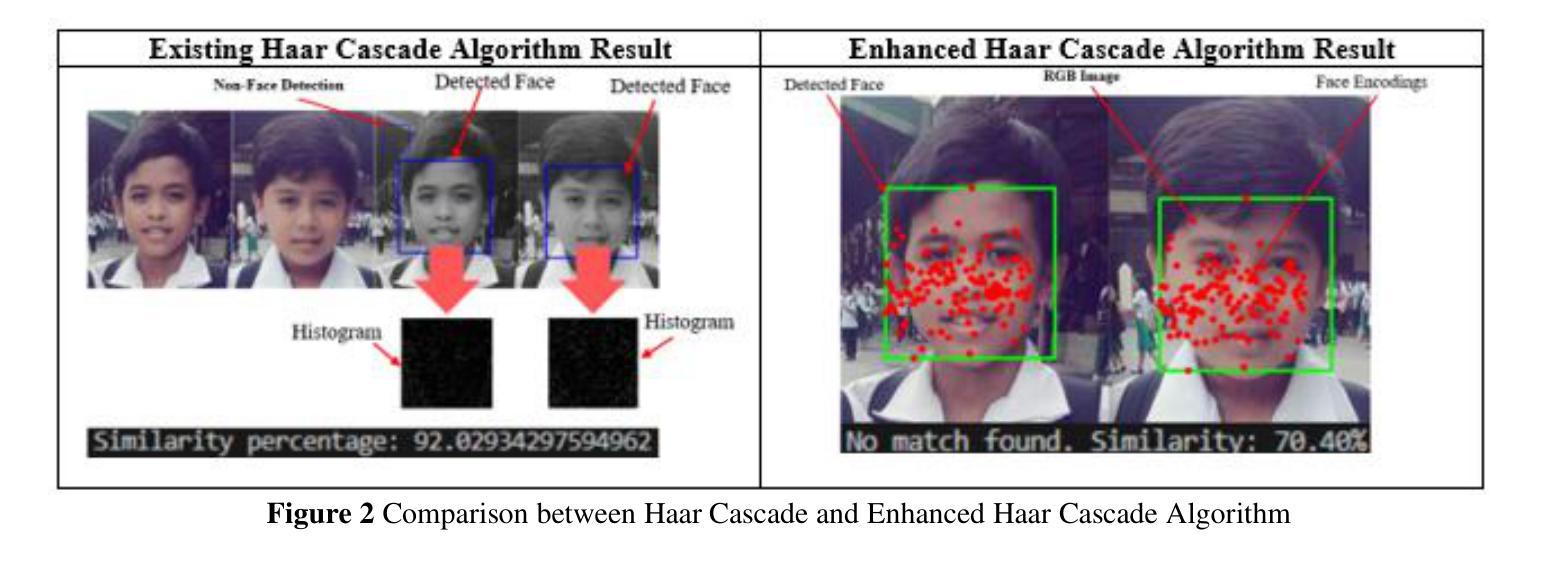
An Enhancement of Haar Cascade Algorithm Applied to Face Recognition for Gate Pass Security
Authors:Clarence A. Antipona, Romeo R. Magsino, Raymund M. Dioses, Khatalyn E. Mata
This study is focused on enhancing the Haar Cascade Algorithm to decrease the false positive and false negative rate in face matching and face detection to increase the accuracy rate even under challenging conditions. The face recognition library was implemented with Haar Cascade Algorithm in which the 128-dimensional vectors representing the unique features of a face are encoded. A subprocess was applied where the grayscale image from Haar Cascade was converted to RGB to improve the face encoding. Logical process and face filtering are also used to decrease non-face detection. The Enhanced Haar Cascade Algorithm produced a 98.39% accuracy rate (21.39% increase), 63.59% precision rate, 98.30% recall rate, and 72.23% in F1 Score. In comparison, the Haar Cascade Algorithm achieved a 46.70% to 77.00% accuracy rate, 44.15% precision rate, 98.61% recall rate, and 47.01% in F1 Score. Both algorithms used the Confusion Matrix Test with 301,950 comparisons using the same dataset of 550 images. The 98.39% accuracy rate shows a significant decrease in false positive and false negative rates in facial recognition. Face matching and face detection are more accurate in images with complex backgrounds, lighting variations, and occlusions, or even those with similar attributes.
本研究致力于改进Haar Cascade算法,旨在降低人脸匹配和人脸检测中的误报和漏报率,从而提高人脸识别的准确率,即使面对具有挑战性的条件也是如此。人脸识别库采用Haar Cascade算法实现,其中使用128维向量对人脸的独特特征进行编码。应用了一个子处理过程,将Haar Cascade的灰度图像转换为RGB图像,以改善人脸编码。还使用了逻辑过程和面部过滤来减少非面部检测。增强型Haar Cascade算法达到了98.39%的准确率(提高了21.39%),精确度为63.59%,召回率为98.3%,F1分数为72.23%。相比之下,Haar Cascade算法的准确率为46.7%至77%,精确度为44.15%,召回率为98.6%,F1分数为47%。两种算法都使用混淆矩阵测试进行比对,使用同一数据集进行30万多次比较,涉及图像达550张。98.39%的准确率表明面部识别中的误报和漏报率显著降低。人脸匹配和人脸检测在具有复杂背景、光照变化和遮挡的图像中更为准确,甚至对于具有相似特征的图像也是如此。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:该研究改进了Haar Cascade算法,以提高人脸识别准确性,特别是在挑战性条件下,包括背景复杂、光线变化及遮挡等情况。该算法提高了准确率,降低了误报和漏报率。改进后的算法在面部匹配和检测方面表现更为出色。此外,使用逻辑过程和面部过滤技术减少了非面部检测。经过测试验证,增强后的Haar Cascade算法表现出更高的性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究旨在改进Haar Cascade算法以提高面部识别的准确性。
- 通过将灰度图像转换为RGB图像改善了面部编码过程。
- 使用逻辑过程和面部过滤技术来减少非面部检测的错误率。
- 增强后的Haar Cascade算法显著提高了准确性,达到了98.39%,与原始算法相比有显著的提升。
- 该算法在复杂背景、光线变化及遮挡等条件下表现出更高的准确性。
- 算法测试使用了混淆矩阵测试,与原始数据集进行了大量比较,证明了算法的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

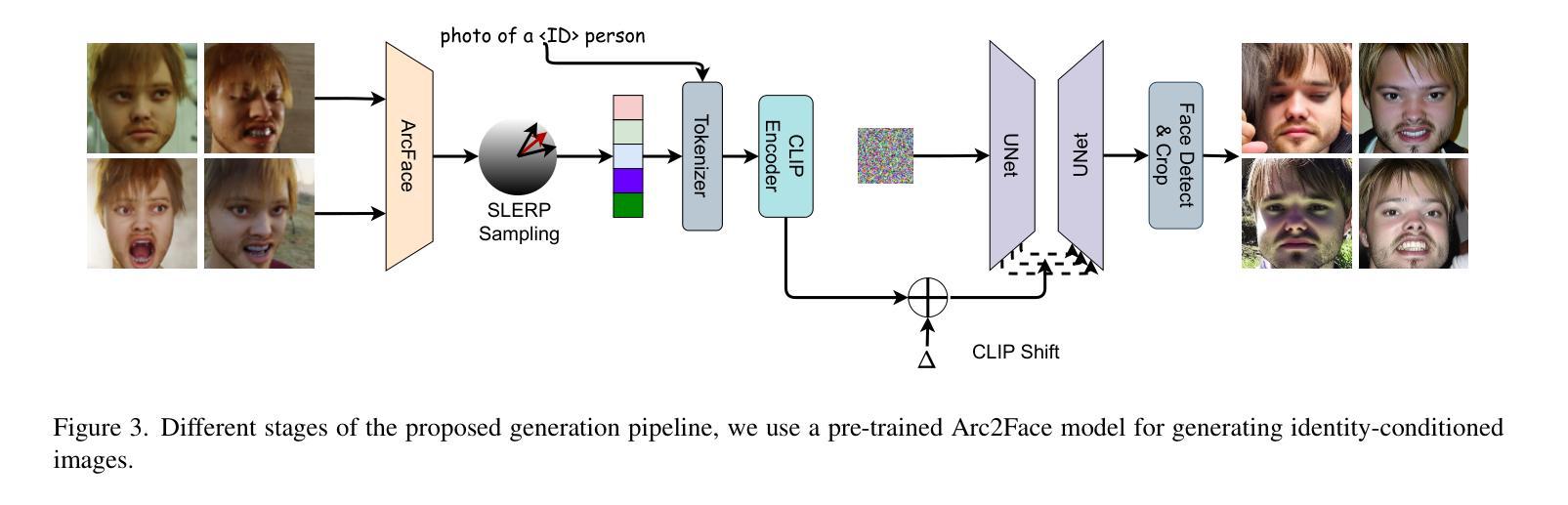
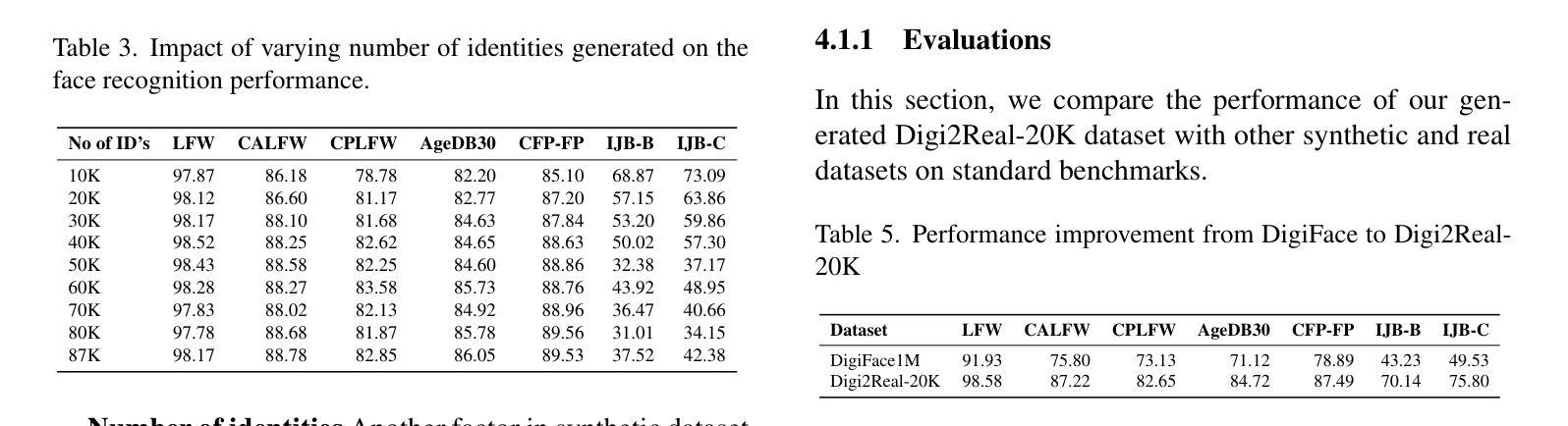
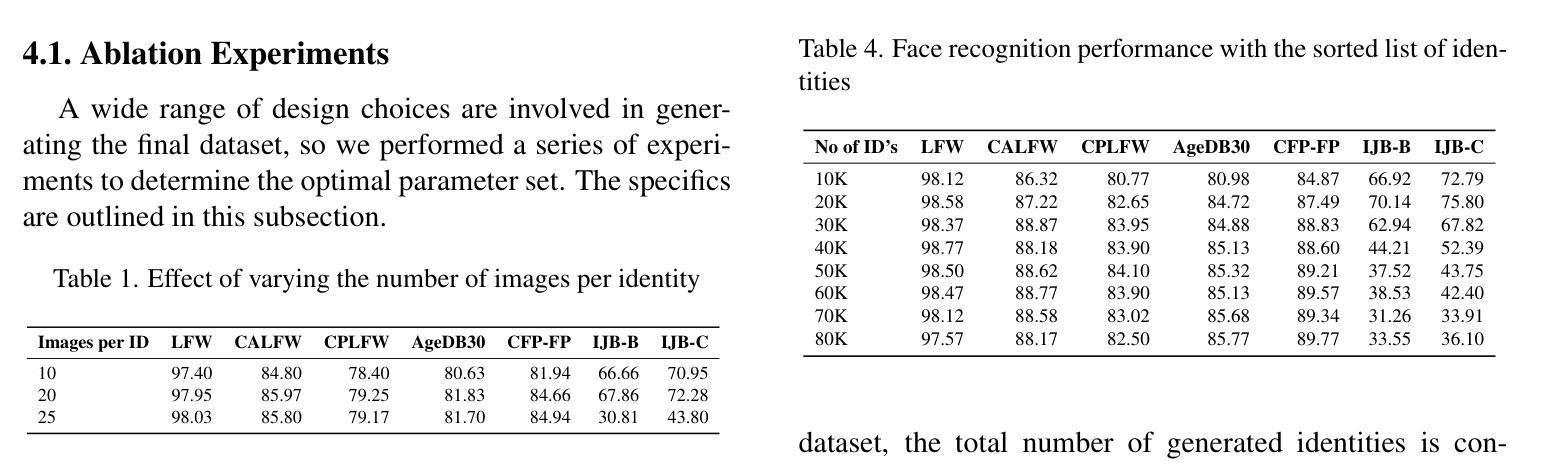
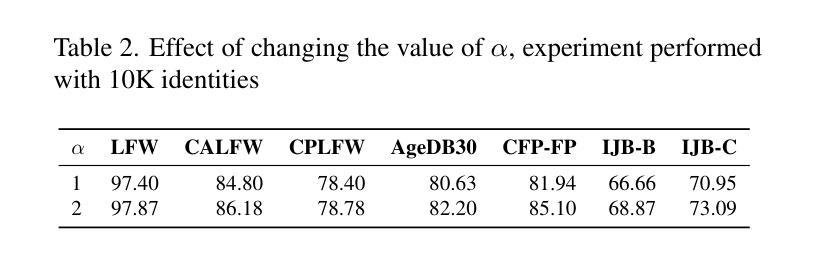
Digi2Real: Bridging the Realism Gap in Synthetic Data Face Recognition via Foundation Models
Authors:Anjith George, Sebastien Marcel
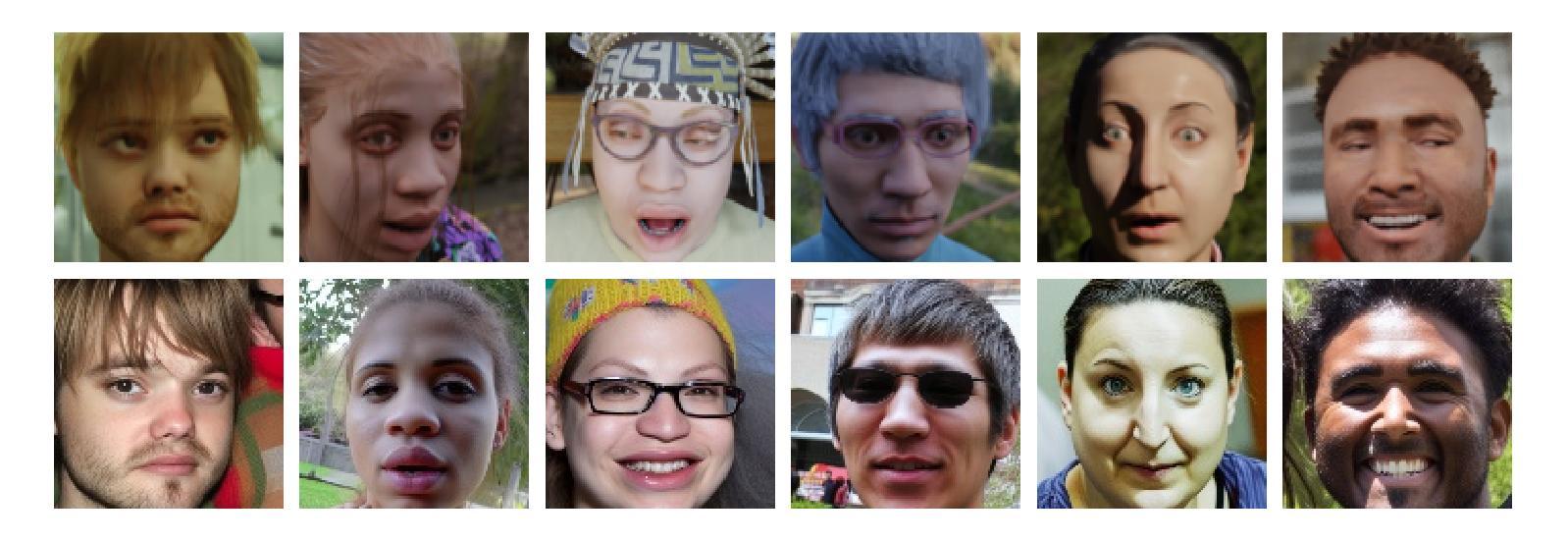
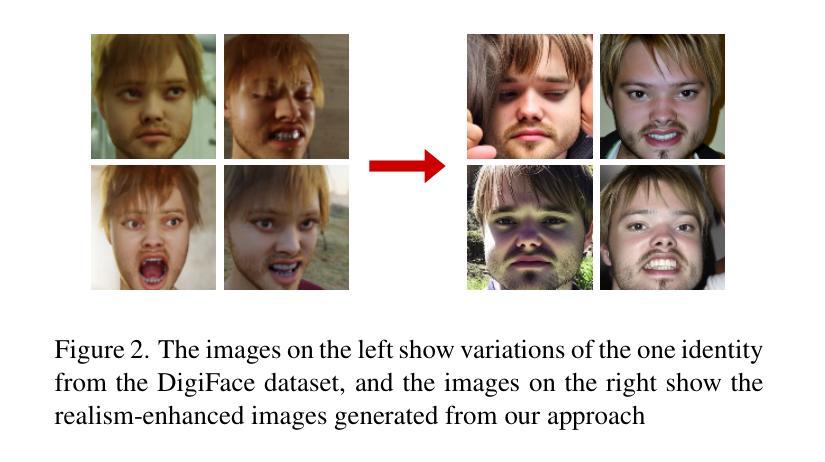
The accuracy of face recognition systems has improved significantly in the past few years, thanks to the large amount of data collected and the advancement in neural network architectures. However, these large-scale datasets are often collected without explicit consent, raising ethical and privacy concerns. To address this, there have been proposals to use synthetic datasets for training face recognition models. Yet, such models still rely on real data to train the generative models and generally exhibit inferior performance compared to those trained on real datasets. One of these datasets, DigiFace, uses a graphics pipeline to generate different identities and different intra-class variations without using real data in training the models. However, the performance of this approach is poor on face recognition benchmarks, possibly due to the lack of realism in the images generated from the graphics pipeline. In this work, we introduce a novel framework for realism transfer aimed at enhancing the realism of synthetically generated face images. Our method leverages the large-scale face foundation model, and we adapt the pipeline for realism enhancement. By integrating the controllable aspects of the graphics pipeline with our realism enhancement technique, we generate a large amount of realistic variations-combining the advantages of both approaches. Our empirical evaluations demonstrate that models trained using our enhanced dataset significantly improve the performance of face recognition systems over the baseline. The source code and datasets will be made available publicly: https://www.idiap.ch/paper/digi2real
近几年来,由于收集了大量的数据以及神经网络架构的进展,人脸识别系统的准确性得到了显著提高。然而,这些大规模数据集往往是在没有明确同意的情况下收集的,引发了伦理和隐私的担忧。为了解决这一问题,已经有人提议使用合成数据集来训练人脸识别模型。然而,这些模型仍然需要真实数据来训练生成模型,并且与在真实数据集上训练的模型相比,通常表现出较差的性能。其中之一的DigiFace数据集使用图形管道生成不同的身份和不同的类内变化,而无需在训练模型时使用真实数据。然而,该方法在人脸识别基准测试上的表现不佳,可能是由于图形管道生成的图像缺乏真实感所致。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新型的现实主义转移框架,旨在提高合成生成的人脸图像的真实性。我们的方法利用大规模人脸基础模型,并调整管道以增强现实感。通过将图形管道的可控方面与我们的增强现实技术相结合,我们生成了大量逼真的变化,结合了这两种方法的优点。我们的经验评估表明,使用我们增强的数据集训练的模型在人脸识别系统的性能上显著超过了基线。源代码和数据集将公开提供:https://www.idiap.ch/paper/digi2real
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The dataset would be available here: https://www.idiap.ch/paper/digi2real
Summary:
人脸识别系统的准确度近年来显著提升,主要得益于大量数据的收集与神经网络架构的进步。然而,数据收集常缺乏明确同意,引发伦理与隐私问题。为应对此问题,已有提议使用合成数据集进行人脸识别模型训练。尽管如此,这些模型仍依赖真实数据训练生成模型,且总体表现通常不如在真实数据集上训练的模型。本文介绍了一种新型现实感迁移框架,旨在提高合成人脸图像的现实感。新方法利用大规模人脸基础模型,并调整管道以进行现实感增强。通过结合图形管道的可控性与现实感增强技术,生成了大量逼真的变化,结合了两种方法的优点。实证评估表明,使用增强数据集训练的模型在人脸识别系统性能上显著优于基线。
Key Takeaways:
- 人脸识别系统准确度因数据收集和神经网络进步而显著提高。
- 数据收集缺乏明确同意引发伦理和隐私问题。
- 合成数据集用于人脸识别模型训练存在依赖真实数据和性能问题。
- 新型现实感迁移框架提高合成人脸图像的现实感。
- 结合图形管道可控性与现实感增强技术生成大量逼真变化。
- 使用增强数据集训练的模型在人脸识别系统性能上显著优于基线。
- 公开提供源代码和数据集。
点此查看论文截图



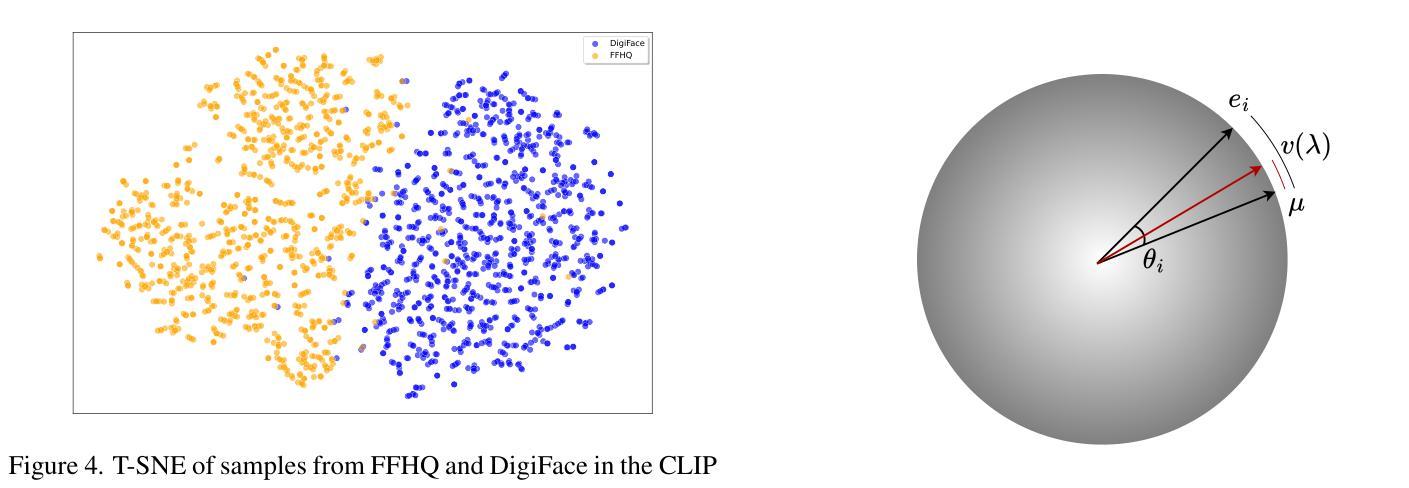
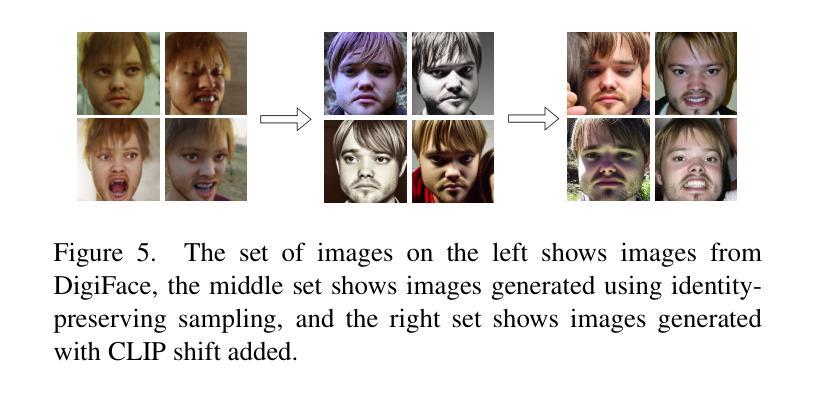
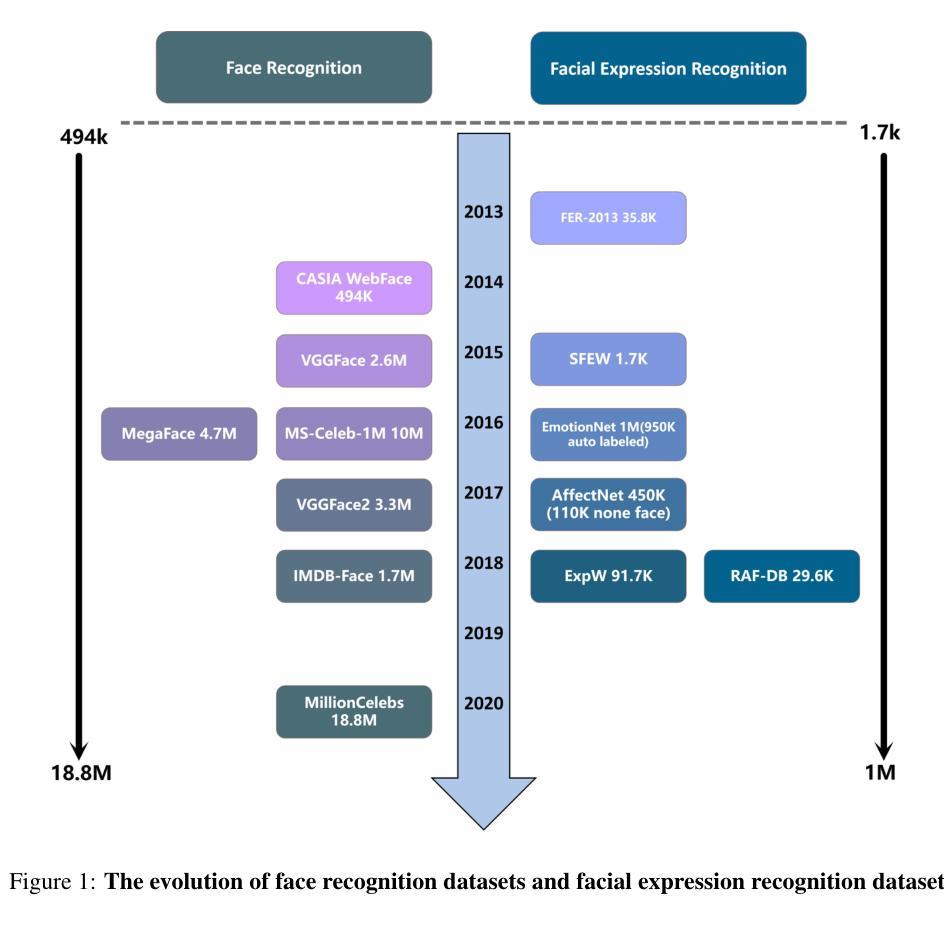
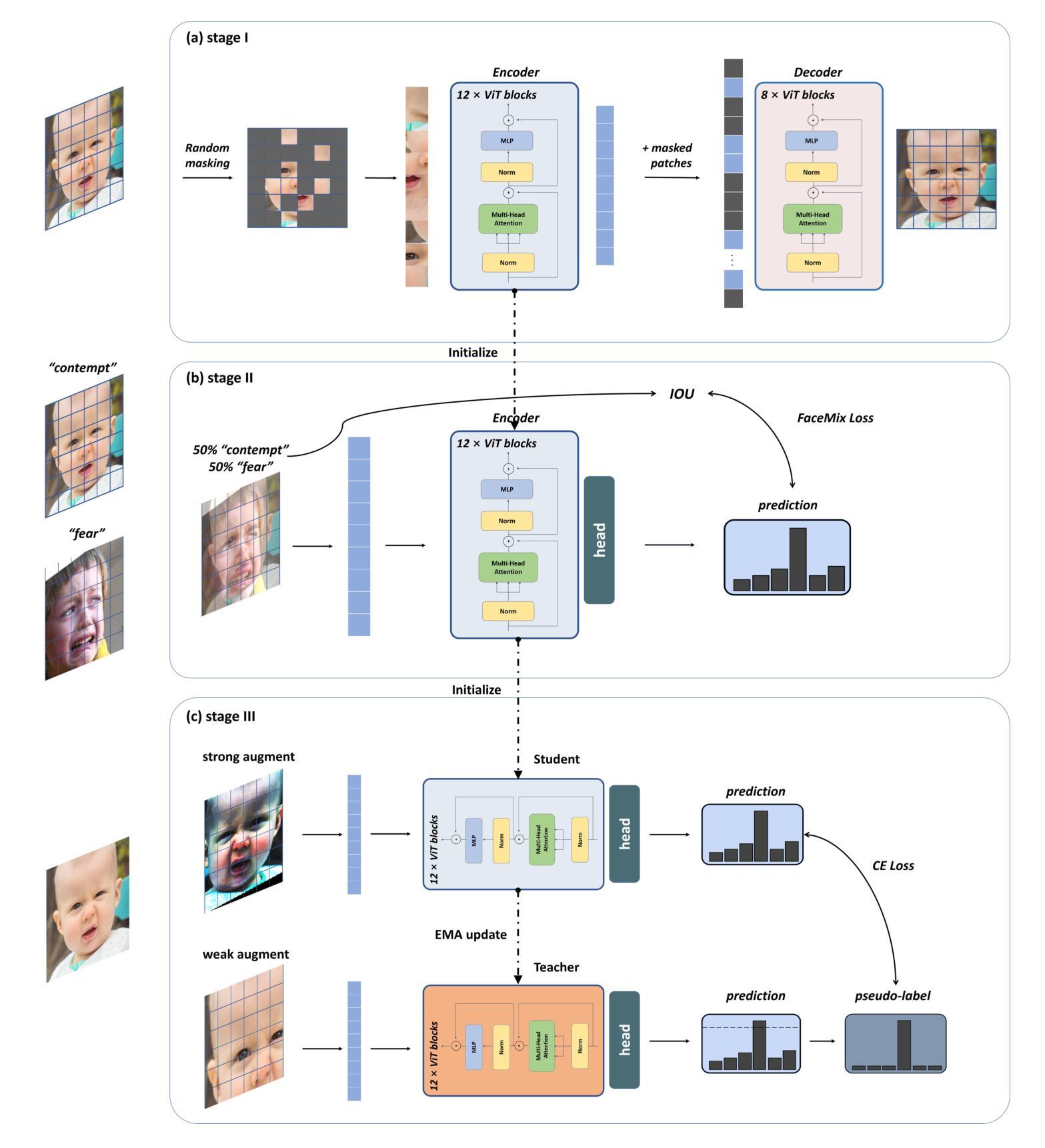
Bridging the Gaps: Utilizing Unlabeled Face Recognition Datasets to Boost Semi-Supervised Facial Expression Recognition
Authors:Jie Song, Mengqiao He, Jinhua Feng, Bairong Shen
In recent years, Facial Expression Recognition (FER) has gained increasing attention. Most current work focuses on supervised learning, which requires a large amount of labeled and diverse images, while FER suffers from the scarcity of large, diverse datasets and annotation difficulty. To address these problems, we focus on utilizing large unlabeled Face Recognition (FR) datasets to boost semi-supervised FER. Specifically, we first perform face reconstruction pre-training on large-scale facial images without annotations to learn features of facial geometry and expression regions, followed by two-stage fine-tuning on FER datasets with limited labels. In addition, to further alleviate the scarcity of labeled and diverse images, we propose a Mixup-based data augmentation strategy tailored for facial images, and the loss weights of real and virtual images are determined according to the intersection-over-union (IoU) of the faces in the two images. Experiments on RAF-DB, AffectNet, and FERPlus show that our method outperforms existing semi-supervised FER methods and achieves new state-of-the-art performance. Remarkably, with only 5%, 25% training sets,our method achieves 64.02% on AffectNet,and 88.23% on RAF-DB, which is comparable to fully supervised state-of-the-art methods. Codes will be made publicly available at https://github.com/zhelishisongjie/SSFER.
近年来,面部表情识别(FER)越来越受到关注。目前的大多数工作都集中在监督学习上,这需要大量有标签和多样化的图像。然而,FER面临着大型多样化数据集缺乏和标注困难的问题。为了解决这些问题,我们专注于利用大型无标签的人脸识别(FR)数据集来促进半监督的FER。具体来说,我们首先在无注释的大规模面部图像上进行面部重建预训练,以学习面部几何和表情区域的特征,然后利用有限的标签在FER数据集上进行两阶段微调。此外,为了进一步缓解有标签和多样化图像的稀缺性,我们提出了一种基于Mixup的数据增强策略,该策略专为面部图像定制。真实和虚拟图像的损失权重是根据两张图中面部交并比(IoU)来确定的。在RAF-DB、AffectNet和FERPlus上的实验表明,我们的方法优于现有的半监督FER方法,并达到了最新的性能水平。值得注意的是,仅使用5%、25%的训练集,我们的方法在AffectNet上达到了64.02%,在RAF-DB上达到了88.23%,这与全监督的先进方法相当。代码将在[https://github.com/zhelishisongjie/SSFER上公开提供。]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期,面部表情识别(FER)受到广泛关注。为了解决数据稀缺和标注困难的问题,研究重点利用无标签的大规模人脸识别(FR)数据集促进半监督FER。先进行面部重建预训练,学习面部几何和表情区域的特征,再进行有限标签的FER数据集的两阶段微调。此外,提出基于Mixup的面部图像数据增强策略,根据两张图像中面部的交集比(IoU)确定真实和虚拟图像的损失权重。实验表明,该方法优于现有半监督FER方法,达到最新性能水平。仅使用5%、25%的训练集,该方法在AffectNet上达到64.02%,在RAF-DB上达到88.23%,与全监督的先进方法相当。
Key Takeaways
- 面部表情识别(FER)近年来受到关注,但仍面临数据集大和标注困难的问题。
- 研究利用无标签的大规模人脸识别(FR)数据集来促进半监督FER。
- 先进行面部重建预训练,学习面部几何和表情区域的特征。
- 采用两阶段微调,利用有限标签的FER数据集。
- 提出基于Mixup的面部图像数据增强策略,根据面部交集比(IoU)确定损失权重。
- 该方法在多个数据集上的性能优于其他半监督FER方法,达到最新水平。
点此查看论文截图

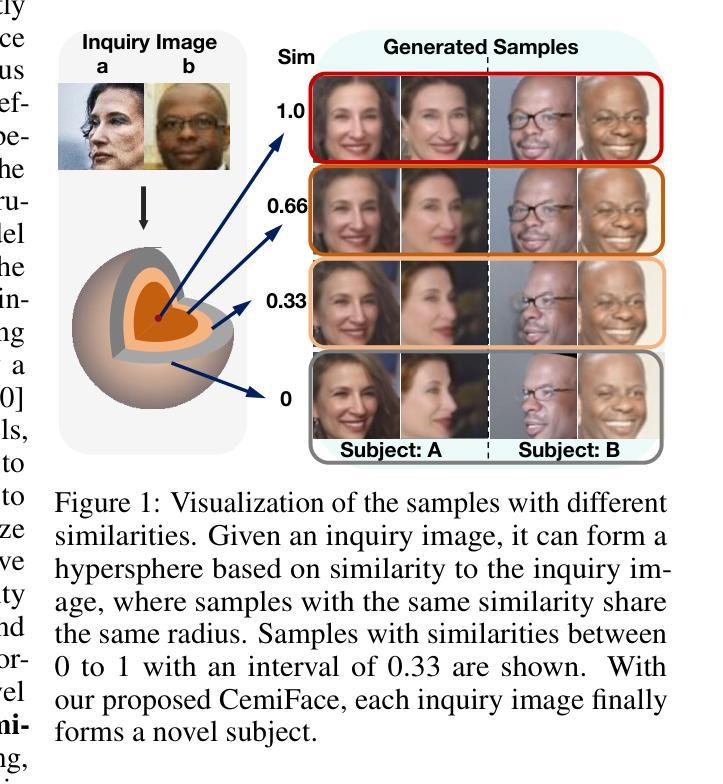
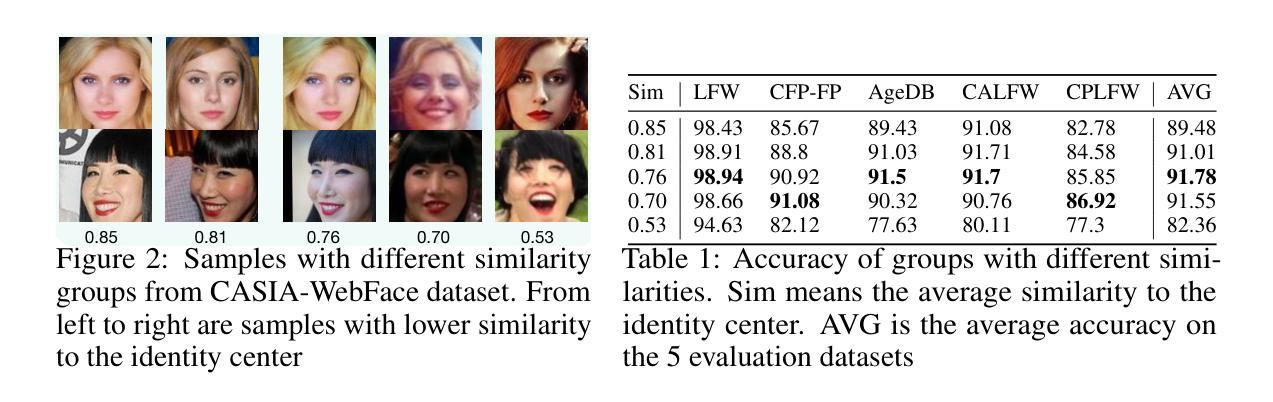
CemiFace: Center-based Semi-hard Synthetic Face Generation for Face Recognition
Authors:Zhonglin Sun, Siyang Song, Ioannis Patras, Georgios Tzimiropoulos
Privacy issue is a main concern in developing face recognition techniques. Although synthetic face images can partially mitigate potential legal risks while maintaining effective face recognition (FR) performance, FR models trained by face images synthesized by existing generative approaches frequently suffer from performance degradation problems due to the insufficient discriminative quality of these synthesized samples. In this paper, we systematically investigate what contributes to solid face recognition model training, and reveal that face images with certain degree of similarities to their identity centers show great effectiveness in the performance of trained FR models. Inspired by this, we propose a novel diffusion-based approach (namely Center-based Semi-hard Synthetic Face Generation (CemiFace)) which produces facial samples with various levels of similarity to the subject center, thus allowing to generate face datasets containing effective discriminative samples for training face recognition. Experimental results show that with a modest degree of similarity, training on the generated dataset can produce competitive performance compared to previous generation methods.
人脸识别技术的开发过程中,隐私问题是主要关注点之一。尽管合成人脸图像可以在保持有效的人脸识别(FR)性能的同时,部分缓解潜在的法律风险,但由现有生成方法合成的人脸图像训练FR模型时,经常出现性能下降问题,原因是这些合成样本的辨别能力不足。在本文中,我们系统地研究了哪些因素有助于训练稳固的人脸识别模型,并发现与身份中心有一定程度相似性的面部图像在训练FR模型的性能方面表现出极大有效性。受此启发,我们提出了一种基于扩散的新型方法(称为基于中心的半硬合成人脸生成(CemiFace)),该方法可以生成具有不同程度相似性的面部样本,从而能够生成包含有效判别样本的人脸数据集,用于训练人脸识别。实验结果表明,在适度的相似性下,在生成的数据集上进行训练可以产生与以前的方法相比具有竞争力的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted to NeurIPS 2024. Camera-ready version
摘要
基于隐私担忧,本文探索了如何通过合成面部图像技术进行人脸识别,降低法律风险的同时保证良好的识别性能。当前采用现有生成技术生成的面部图像质量难以鉴别,导致人脸识别模型性能下降。本研究发现与身份中心相似度较高的面部图像对人脸识别模型训练至关重要。基于此,我们提出了一种基于扩散的新型合成面部图像方法——中心化半硬合成面部生成(CemiFace),能够生成不同相似度水平的面部样本,从而构建包含有效鉴别样本的训练数据集。实验结果表明,在适度相似度下,使用CemiFace生成的训练数据集训练的人脸识别模型性能表现优异。
关键见解
- 合成面部图像技术可以缓解人脸识别技术中的隐私问题和法律风险。
- 当前人脸识别模型因生成样本的鉴别能力不足而面临性能下降问题。
- 与身份中心有一定相似度的面部图像对人脸识别模型训练至关重要。
- 提出的CemiFace方法基于扩散技术生成面部样本,具备不同层次的相似性。
- CemiFace方法生成的训练数据集能有效提升人脸识别模型的性能表现。
- 在适度相似度条件下,CemiFace生成的数据集训练模型表现可与传统方法竞争。
- 本研究为人脸识别技术带来了新的合成数据集生成方法和思考方向。
点此查看论文截图

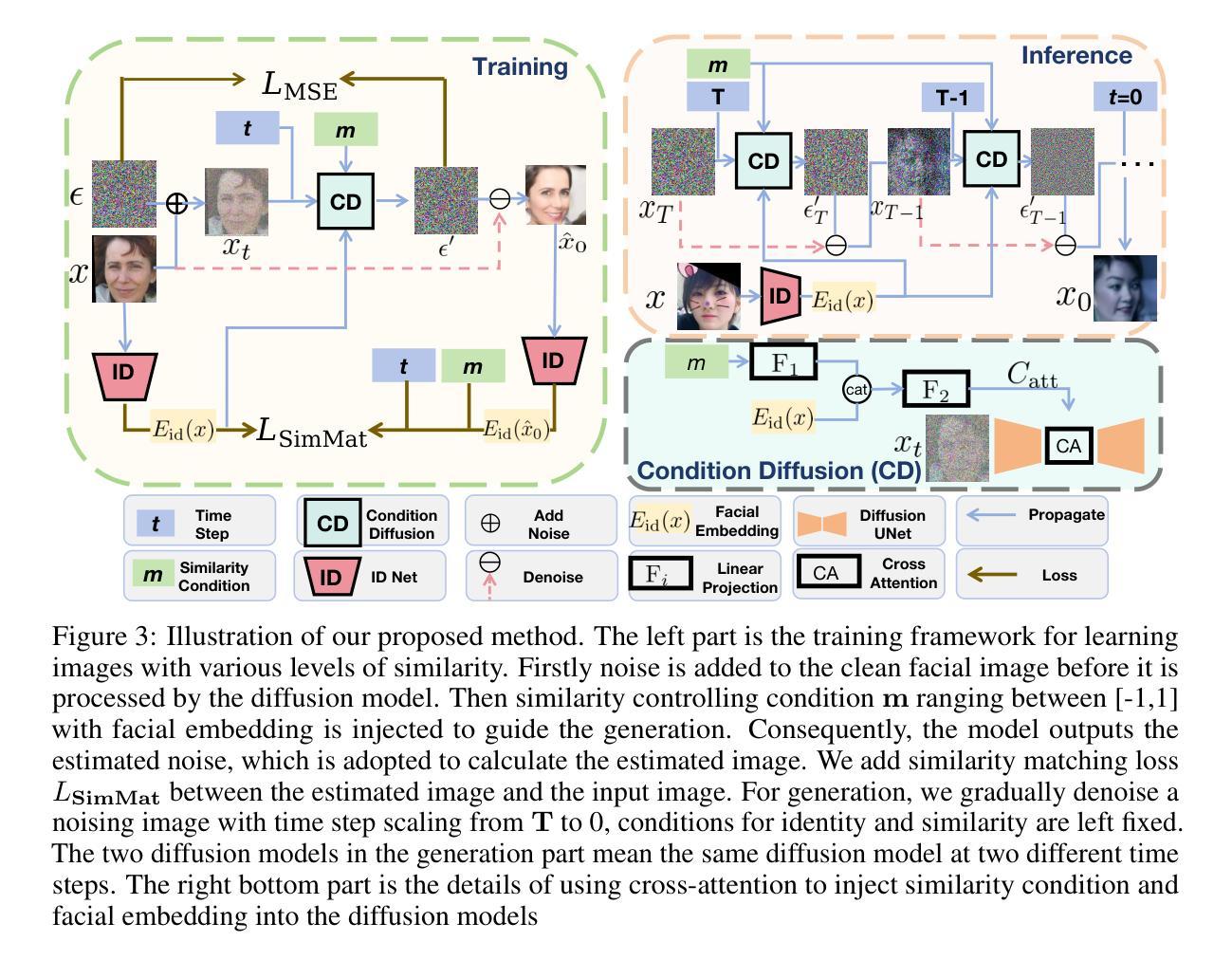
ID$^3$: Identity-Preserving-yet-Diversified Diffusion Models for Synthetic Face Recognition
Authors:Shen Li, Jianqing Xu, Jiaying Wu, Miao Xiong, Ailin Deng, Jiazhen Ji, Yuge Huang, Wenjie Feng, Shouhong Ding, Bryan Hooi
Synthetic face recognition (SFR) aims to generate synthetic face datasets that mimic the distribution of real face data, which allows for training face recognition models in a privacy-preserving manner. Despite the remarkable potential of diffusion models in image generation, current diffusion-based SFR models struggle with generalization to real-world faces. To address this limitation, we outline three key objectives for SFR: (1) promoting diversity across identities (inter-class diversity), (2) ensuring diversity within each identity by injecting various facial attributes (intra-class diversity), and (3) maintaining identity consistency within each identity group (intra-class identity preservation). Inspired by these goals, we introduce a diffusion-fueled SFR model termed $\text{ID}^3$. $\text{ID}^3$ employs an ID-preserving loss to generate diverse yet identity-consistent facial appearances. Theoretically, we show that minimizing this loss is equivalent to maximizing the lower bound of an adjusted conditional log-likelihood over ID-preserving data. This equivalence motivates an ID-preserving sampling algorithm, which operates over an adjusted gradient vector field, enabling the generation of fake face recognition datasets that approximate the distribution of real-world faces. Extensive experiments across five challenging benchmarks validate the advantages of $\text{ID}^3$.
人脸识别合成(SFR)旨在生成模拟真实人脸数据分布的人脸合成数据集,从而以隐私保护的方式训练人脸识别模型。尽管扩散模型在图像生成方面具有显著潜力,但当前的基于扩散的SFR模型在推广到现实世界人脸时仍存在困难。为了解决这一局限性,我们为SFR概述了三个关键目标:(1)促进身份间的多样性(类间多样性),(2)通过注入各种面部特征确保每个身份内的多样性(类内多样性),以及(3)保持每个身份组内身份的一致性(类内身份保留)。受这些目标的启发,我们引入了一个由扩散驱动的SFR模型,称为ID³。ID³采用了一种保身份损失的方法,以生成多样且身份一致的面部外观。从理论上讲,我们证明了最小化这种损失等同于最大化保身份数据调整条件对数似然的下界。这种等价性激发了一种保身份的采样算法,该算法在调整后的梯度矢量场上进行操作,能够生成模拟现实世界人脸分布的假冒人脸识别数据集。在五个具有挑战性的基准测试上的广泛实验验证了ID³的优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NeurIPS 2024
Summary
人脸识别领域中,合成人脸识别(SFR)旨在生成模拟真实人脸数据分布的人脸数据集,实现隐私保护下的人脸识别模型训练。当前基于扩散模型的SFR存在泛化到真实世界人脸的问题。为解决此问题,提出了三个关键目标:促进身份间的多样性、确保同一身份内不同面部特征的多样性和维持同一身份组内的身份一致性。基于此,我们引入了名为ID³的扩散驱动的SFR模型。ID³采用身份保持损失来生成多样且身份一致的面部外观。理论上,我们证明了最小化此损失等同于最大化调整后的身份保持数据的条件对数似然的下界。这推动了身份保持采样算法的发展,该算法在调整后的梯度矢量场上进行操作,能够生成模拟真实世界人脸分布的虚假人脸识别数据集。在五个具有挑战性的基准测试上的实验验证了ID³的优势。
Key Takeaways
- 合成人脸识别(SFR)关注生成模拟真实人脸数据分布的数据集,实现隐私保护下的人脸识别模型训练。
- 当前扩散模型在SFR中存在泛化问题,需要促进身份间的多样性、确保同一身份内的多样性以及维持身份一致性。
- 引入名为ID³的扩散驱动的SFR模型,采用身份保持损失生成多样且一致的面部外观。
- 最小化身份保持损失等同于最大化调整后的条件对数似然的下界。
- 开发了身份保持采样算法,在调整后的梯度矢量场上操作,生成模拟真实世界人脸分布的虚假数据集。
- ID³模型在五个具有挑战性的基准测试上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图
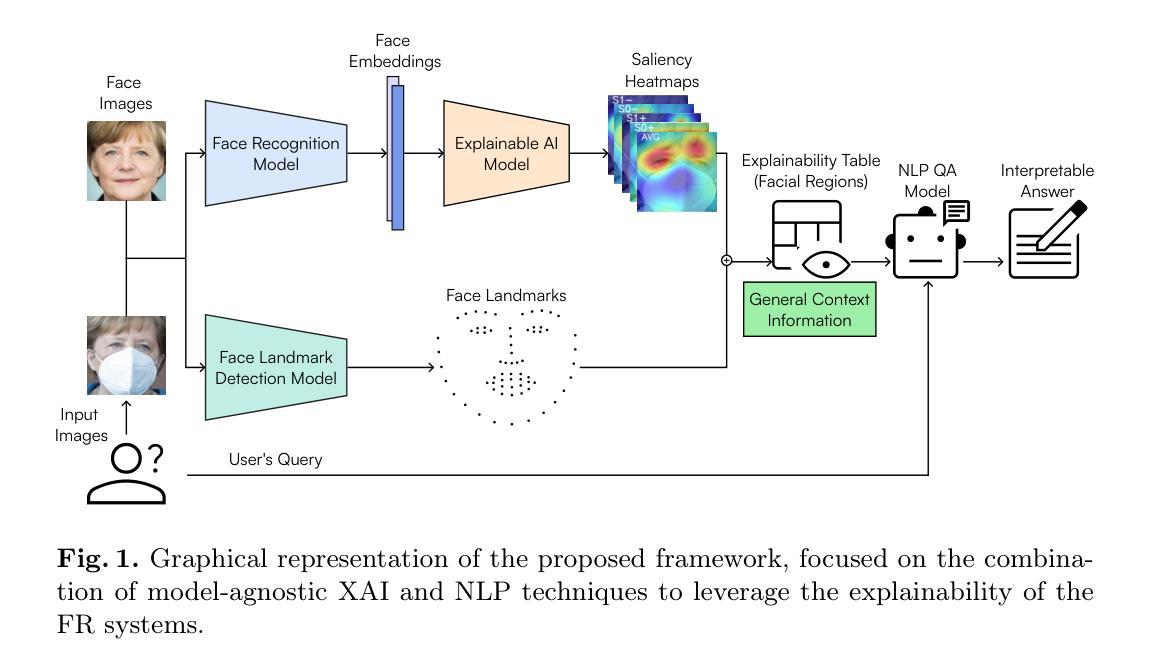
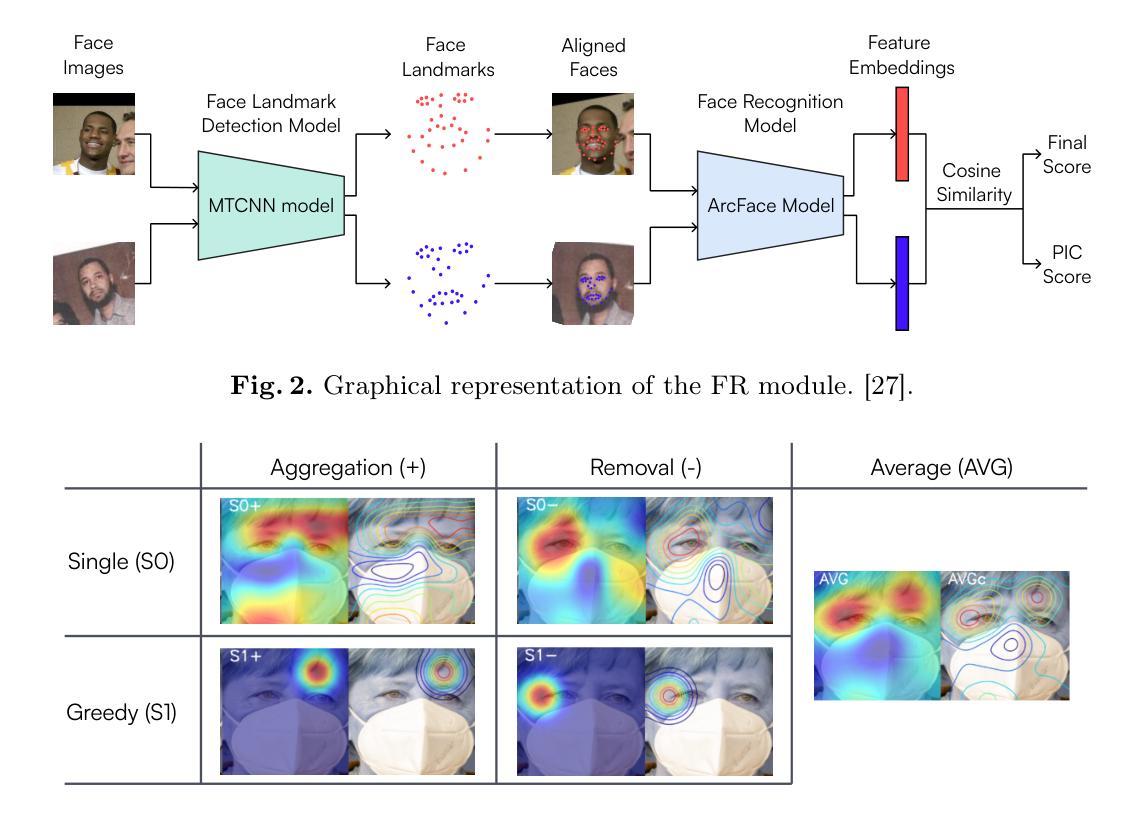
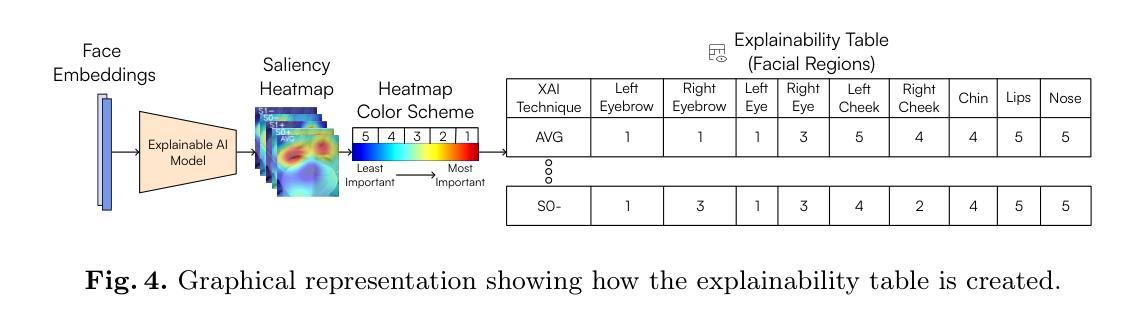
From Pixels to Words: Leveraging Explainability in Face Recognition through Interactive Natural Language Processing
Authors:Ivan DeAndres-Tame, Muhammad Faisal, Ruben Tolosana, Rouqaiah Al-Refai, Ruben Vera-Rodriguez, Philipp Terhörst
Face Recognition (FR) has advanced significantly with the development of deep learning, achieving high accuracy in several applications. However, the lack of interpretability of these systems raises concerns about their accountability, fairness, and reliability. In the present study, we propose an interactive framework to enhance the explainability of FR models by combining model-agnostic Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques. The proposed framework is able to accurately answer various questions of the user through an interactive chatbot. In particular, the explanations generated by our proposed method are in the form of natural language text and visual representations, which for example can describe how different facial regions contribute to the similarity measure between two faces. This is achieved through the automatic analysis of the output’s saliency heatmaps of the face images and a BERT question-answering model, providing users with an interface that facilitates a comprehensive understanding of the FR decisions. The proposed approach is interactive, allowing the users to ask questions to get more precise information based on the user’s background knowledge. More importantly, in contrast to previous studies, our solution does not decrease the face recognition performance. We demonstrate the effectiveness of the method through different experiments, highlighting its potential to make FR systems more interpretable and user-friendly, especially in sensitive applications where decision-making transparency is crucial.
随着深度学习的不断发展,人脸识别(FR)已经取得了显著的进步,在多个应用中实现了较高的准确性。然而,这些系统缺乏可解释性,引发了人们对其责任、公平和可靠性的关注。在本研究中,我们提出了一种交互式框架,通过结合模型无关的可解释人工智能(XAI)和自然语言处理(NLP)技术,增强人脸识别模型的解释性。所提出的框架能够通过交互式聊天机器人准确回答用户的各种问题。特别是,由我们提出的方法生成的解释以自然语言文本和视觉表示的形式出现,例如,可以描述不同面部区域如何贡献于两张脸之间的相似度测量。这是通过自动分析面部图像输出的显著性热图和使用BERT问答模型实现的,为用户提供一种界面,促进对人脸识别决策的全面理解。所提出的方法是交互式的,允许用户提出问题以获得基于用户背景知识的更精确信息。更重要的是,与以前的研究相比,我们的解决方案并不会降低人脸识别性能。我们通过不同的实验证明了方法的有效性,突显其在使人脸识别系统更具解释性和用户友好性方面的潜力,特别是在决策透明性至关重要的敏感应用中。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人脸识别技术结合深度学习取得了显著进展,但缺乏解释性引发关注。本研究提出一种交互式框架,通过结合模型无关的XAI和NLP技术增强人脸识别模型的解释性。框架可准确回答用户问题,以自然语言文本和视觉形式解释面部识别决策过程,包括不同面部区域对相似度度量的贡献等。方法互动性强,可根据用户背景知识提供精确信息。实验证明,该方法不降低人脸识别性能,具有潜力使FR系统更可解释和用户友好。
Key Takeaways
- 人脸识别技术结合深度学习取得显著进展。
- 缺乏解释性的人脸识别系统引发对责任性、公平性和可靠性的关注。
- 本研究提出一种交互式框架,增强人脸识别模型的解释性。
- 框架结合模型无关的XAI和NLP技术。
- 框架可准确回答用户问题,以自然语言文本和视觉形式提供解释。
- 方法具有强大的互动性,可根据用户背景知识提供精确信息。
- 实验证明该方法不降低人脸识别性能,有助于使FR系统更可解释和用户友好。
点此查看论文截图

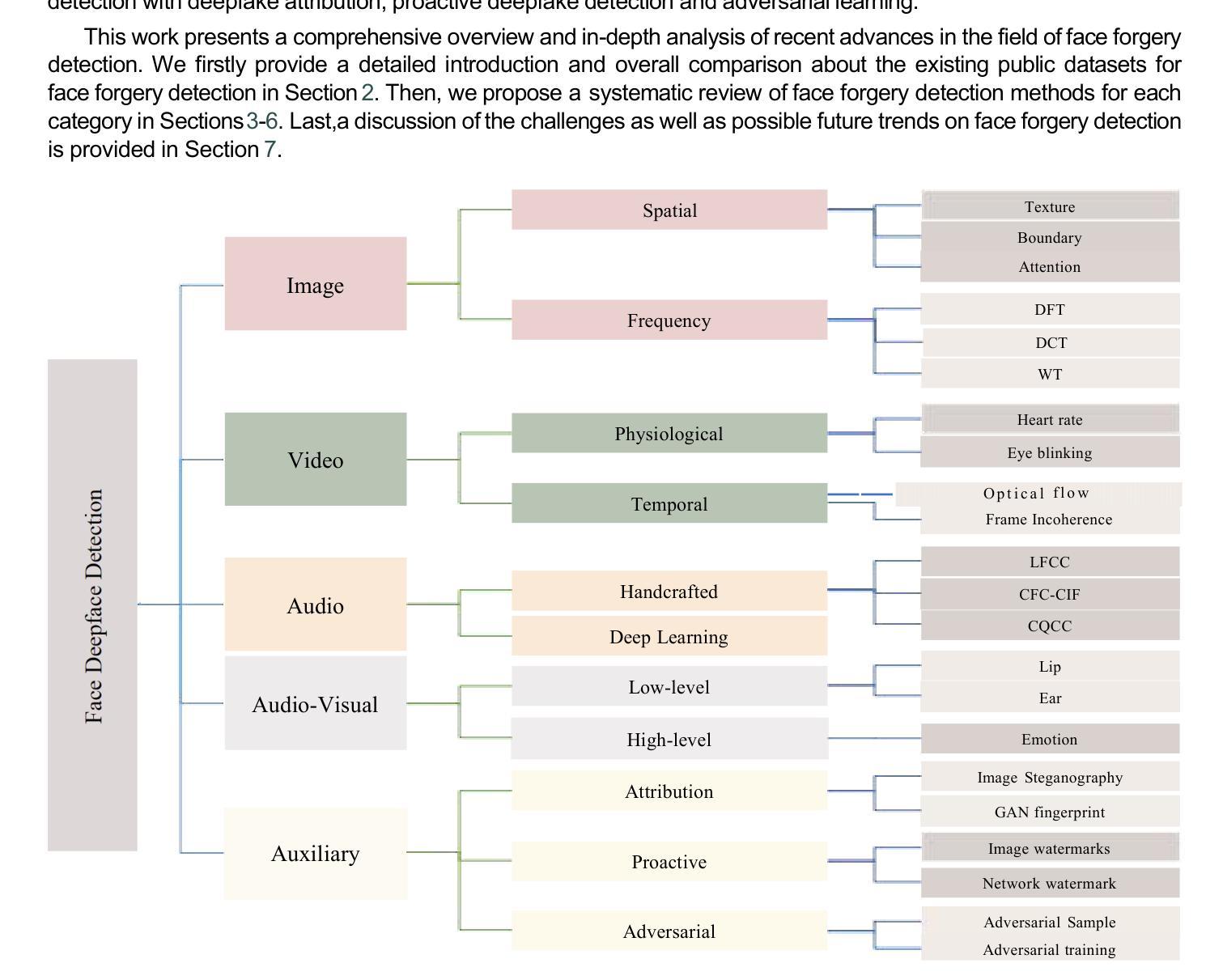
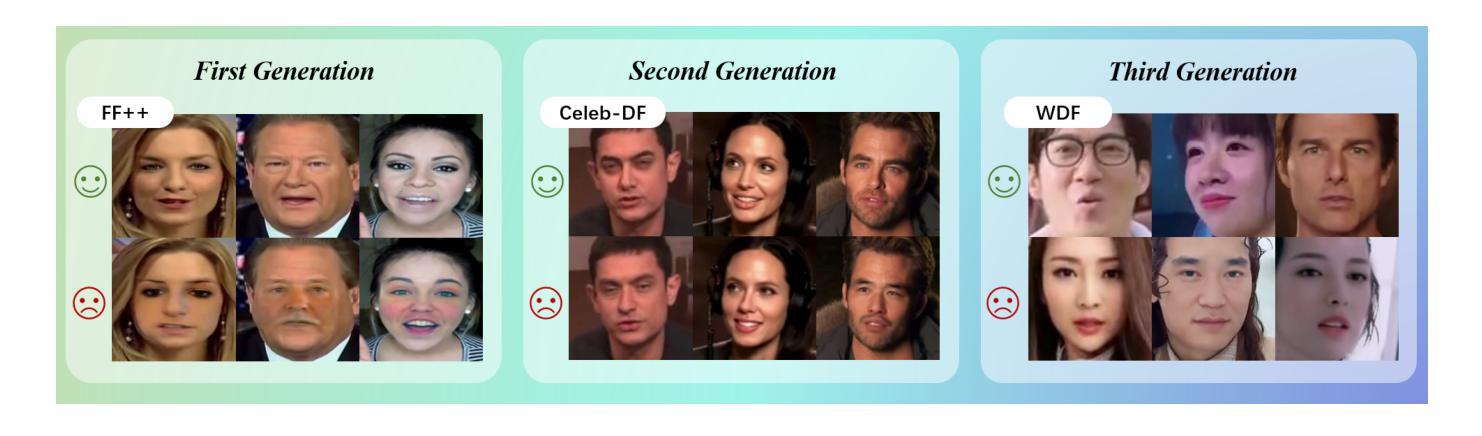
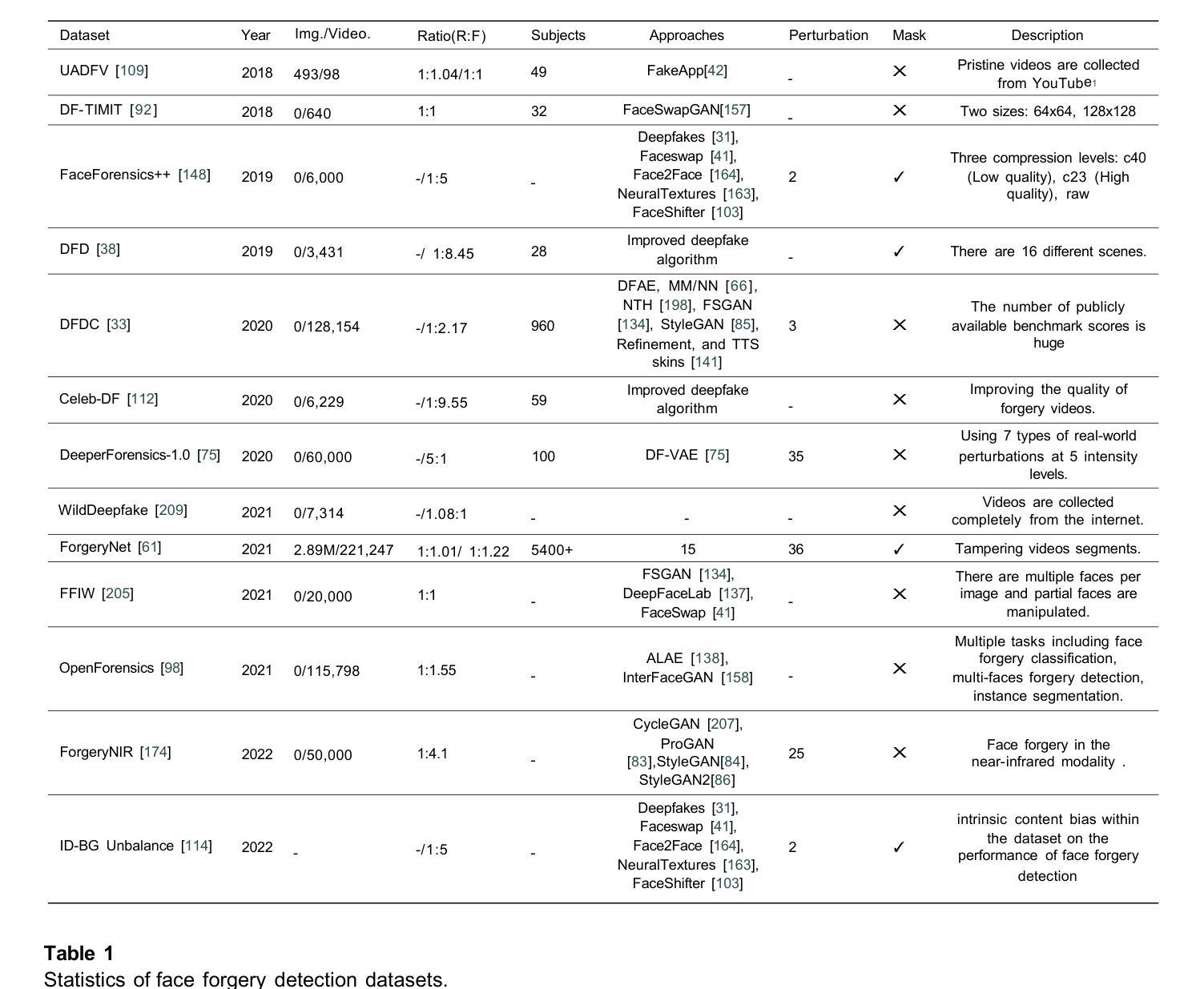
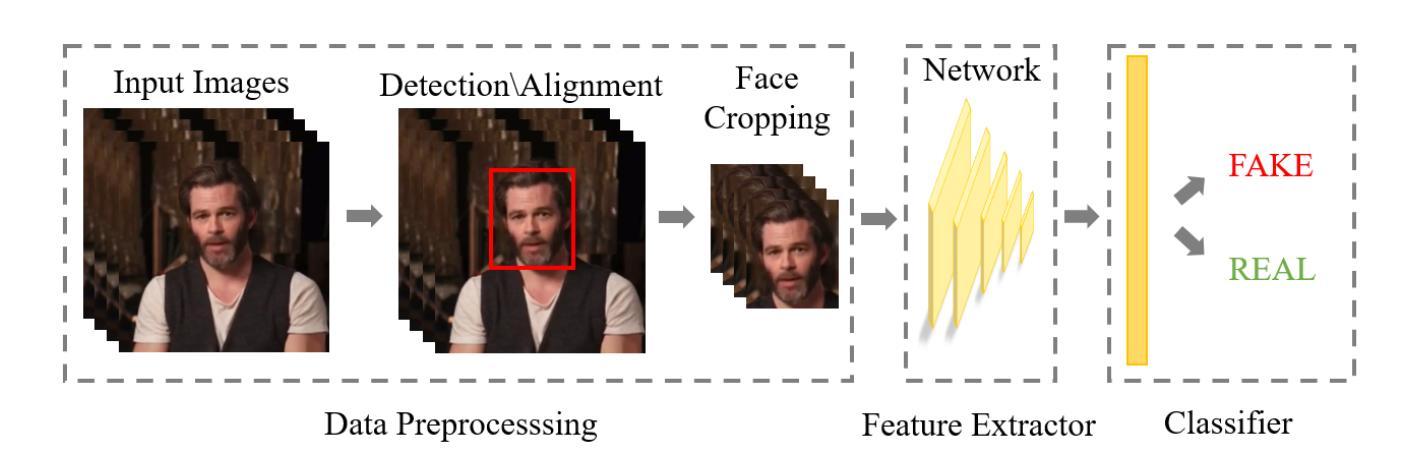
Deep Learning Technology for Face Forgery Detection: A Survey
Authors:Lixia Ma, Puning Yang, Yuting Xu, Ziming Yang, Peipei Li, Huaibo Huang
Currently, the rapid development of computer vision and deep learning has enabled the creation or manipulation of high-fidelity facial images and videos via deep generative approaches. This technology, also known as deepfake, has achieved dramatic progress and become increasingly popular in social media. However, the technology can generate threats to personal privacy and national security by spreading misinformation. To diminish the risks of deepfake, it is desirable to develop powerful forgery detection methods to distinguish fake faces from real faces. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of recent deep learning-based approaches for facial forgery detection. We attempt to provide the reader with a deeper understanding of the current advances as well as the major challenges for deepfake detection based on deep learning. We present an overview of deepfake techniques and analyse the characteristics of various deepfake datasets. We then provide a systematic review of different categories of deepfake detection and state-of-the-art deepfake detection methods. The drawbacks of existing detection methods are analyzed, and future research directions are discussed to address the challenges in improving both the performance and generalization of deepfake detection.
当前,计算机视觉和深度学习的快速发展使得通过深度生成方法创建或操作高保真面部图像和视频成为可能。这项技术也被称为深度伪造技术,已经取得了巨大的进步,并在社交媒体上越来越受欢迎。然而,该技术可以通过传播错误信息对个人隐私和国家安全构成威胁。为了减少深度伪造技术的风险,开发强大的伪造检测方法来区分真假面孔是非常必要的。本文对基于深度学习的面部伪造检测最新方法进行了全面综述。我们试图为读者提供对当前进展以及基于深度学习进行深度伪造检测的主要挑战的更深入理解。本文介绍了深度伪造技术概况,分析了各种深度伪造数据集的特点。然后,我们对不同类型的深度伪造检测方法和最新深度伪造检测方法进行了系统回顾。分析了现有检测方法的不足,并讨论了未来研究方向,以解决提高深度伪造检测性能和泛化能力的挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The paper “Deep Learning Technology for Face Forgery Detection: A Survey” is hereby formally withdrawn. The reason for this withdrawal is that I did not adequately consult and obtain proper authorization from the corresponding author during the submission process. I sincerely apologize for any inconvenience this may have caused the journal, reviewers, and readers
Summary
本文综述了基于深度学习的面部伪造检测方法的最新进展,介绍了深度伪造技术的特点以及当前面临的挑战。文章概述了深度伪造技术,分析了不同深度伪造数据集的特点,并对现有的检测方法的缺点进行了讨论,同时提出了改进性能和泛化能力的未来研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 深度伪造技术发展迅速,已成为社交媒体中的热门技术。
- 深度伪造技术对个人隐私和国家安全构成威胁,需要开发强大的伪造检测方法来区分真实和伪造的面孔。
- 当前存在多种基于深度学习的面部伪造检测方法,但仍然存在挑战,如性能提升和泛化能力的问题。
- 文章概述了深度伪造技术的特点,并分析了不同深度伪造数据集的特性。
- 文章对现有的检测方法进行系统评价,并指出了它们的缺点。
- 为了提高检测性能和泛化能力,需要进一步研究和发展新的检测方法和策略。
点此查看论文截图

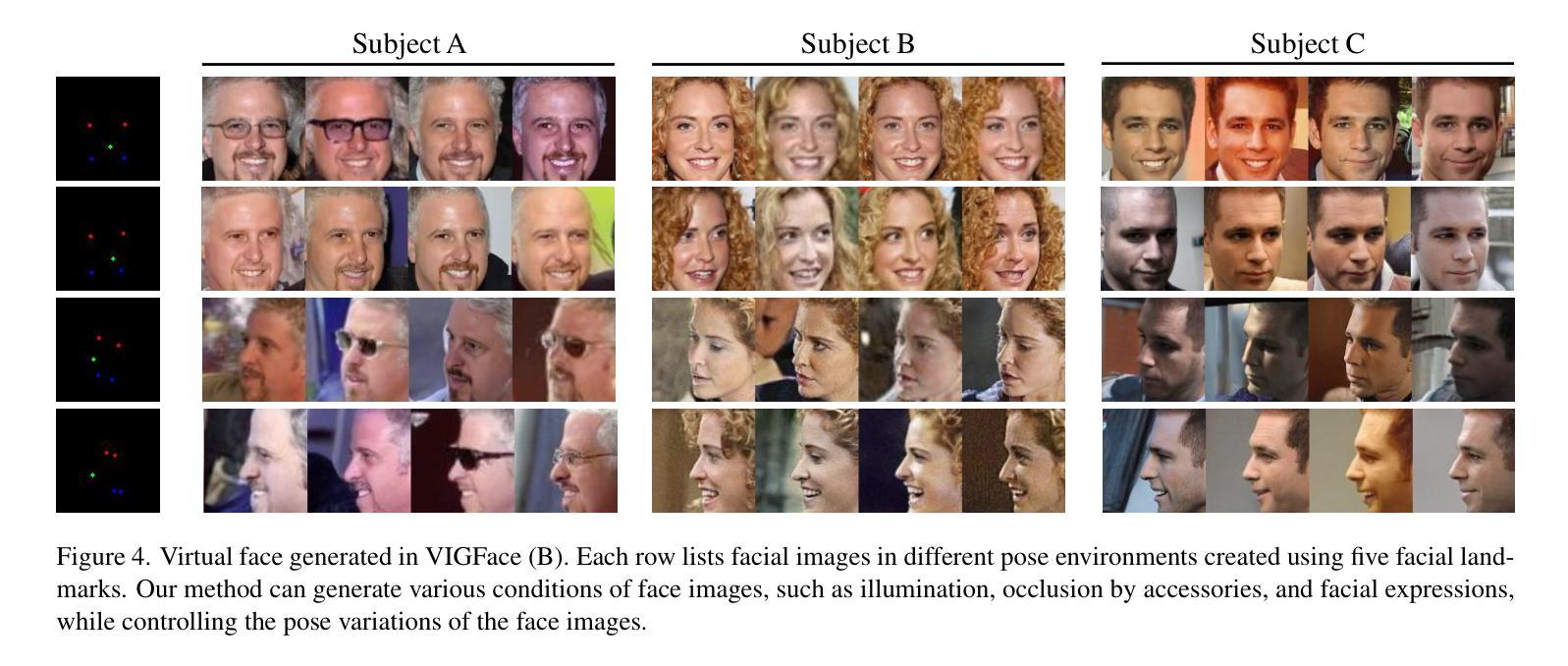
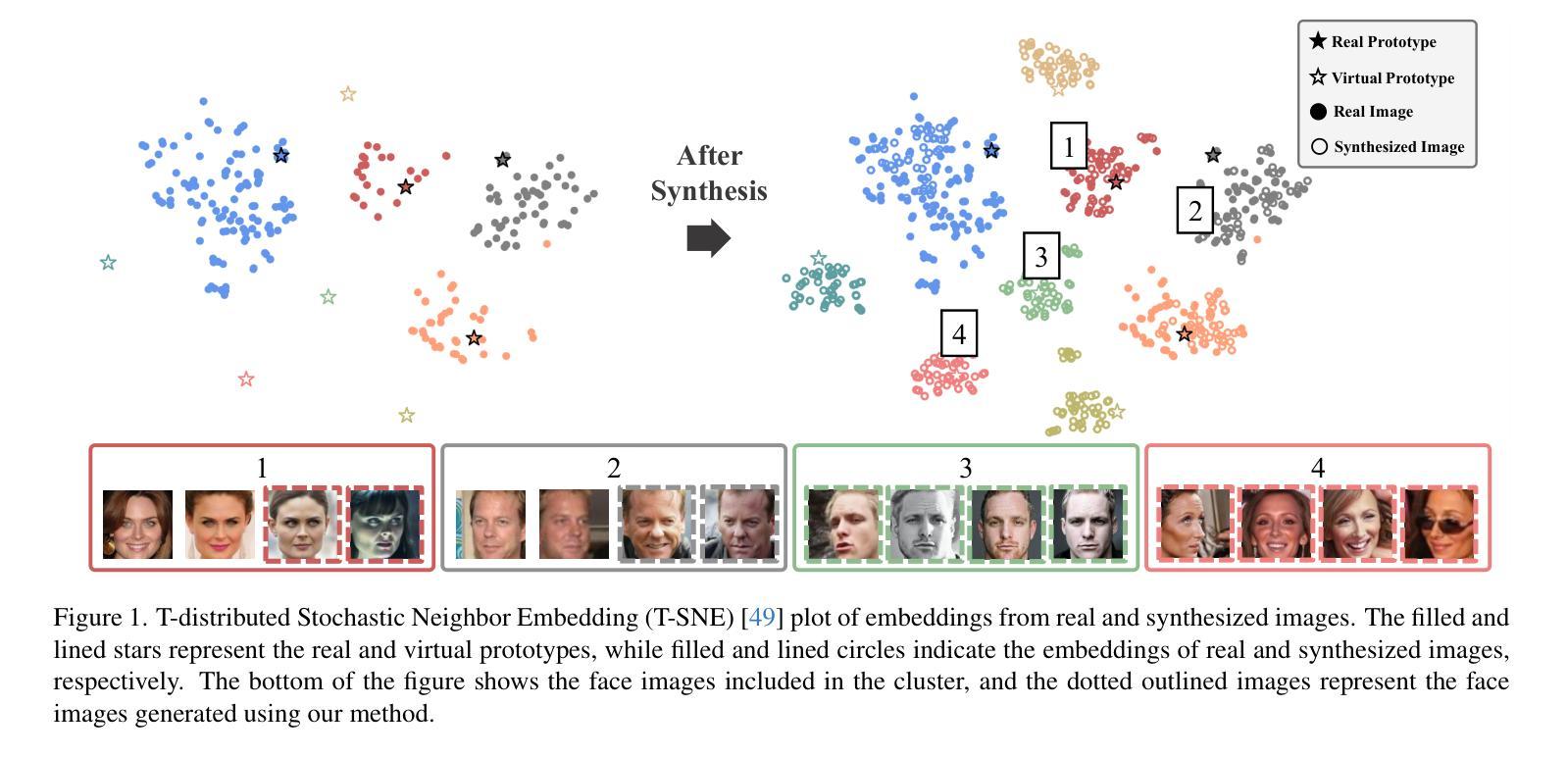
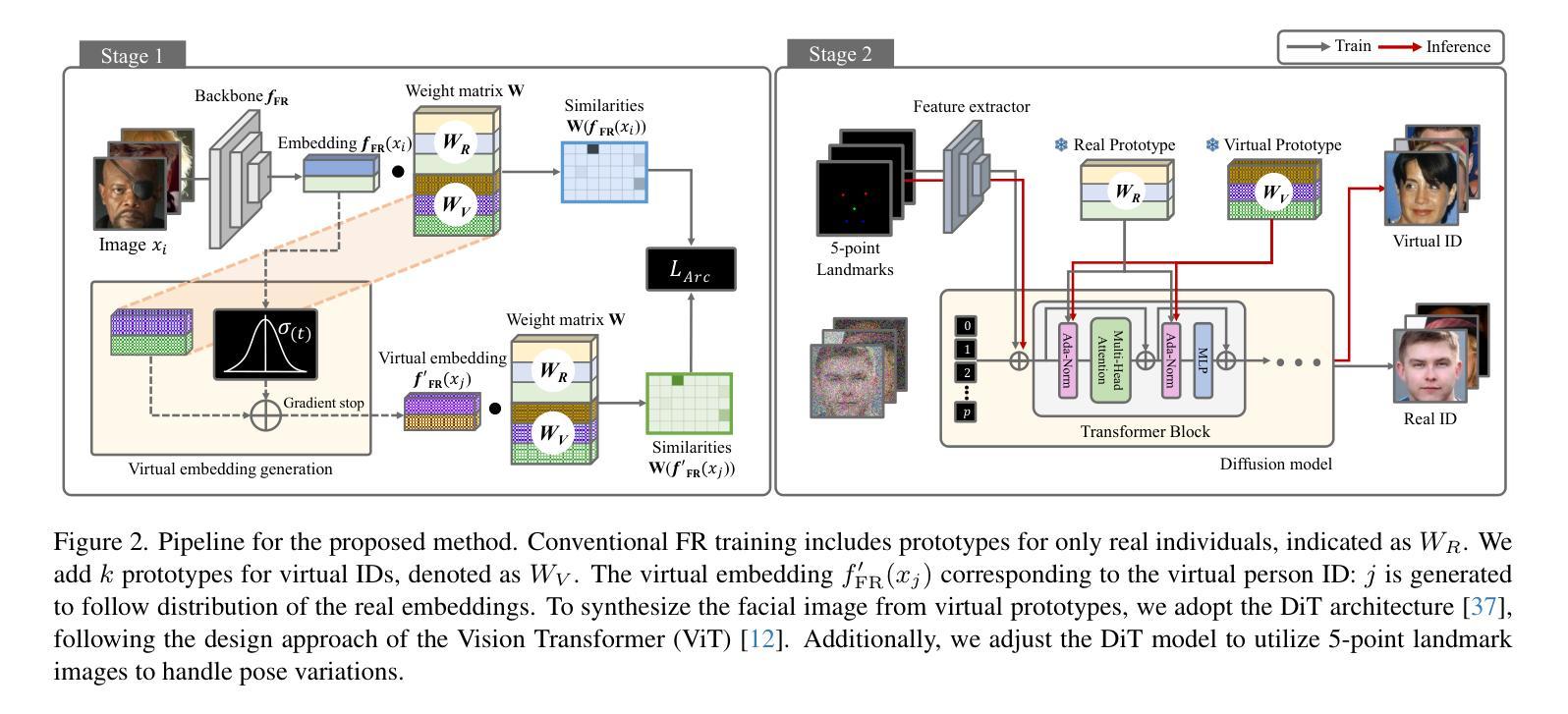
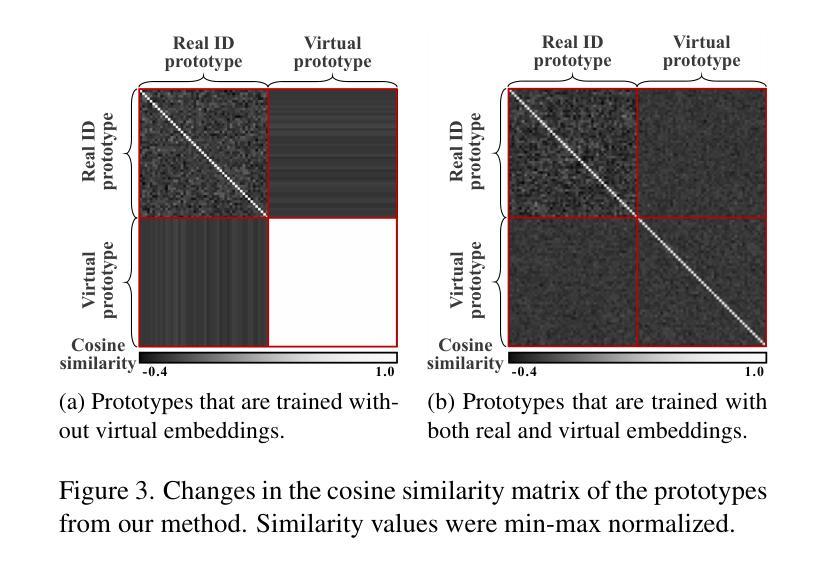
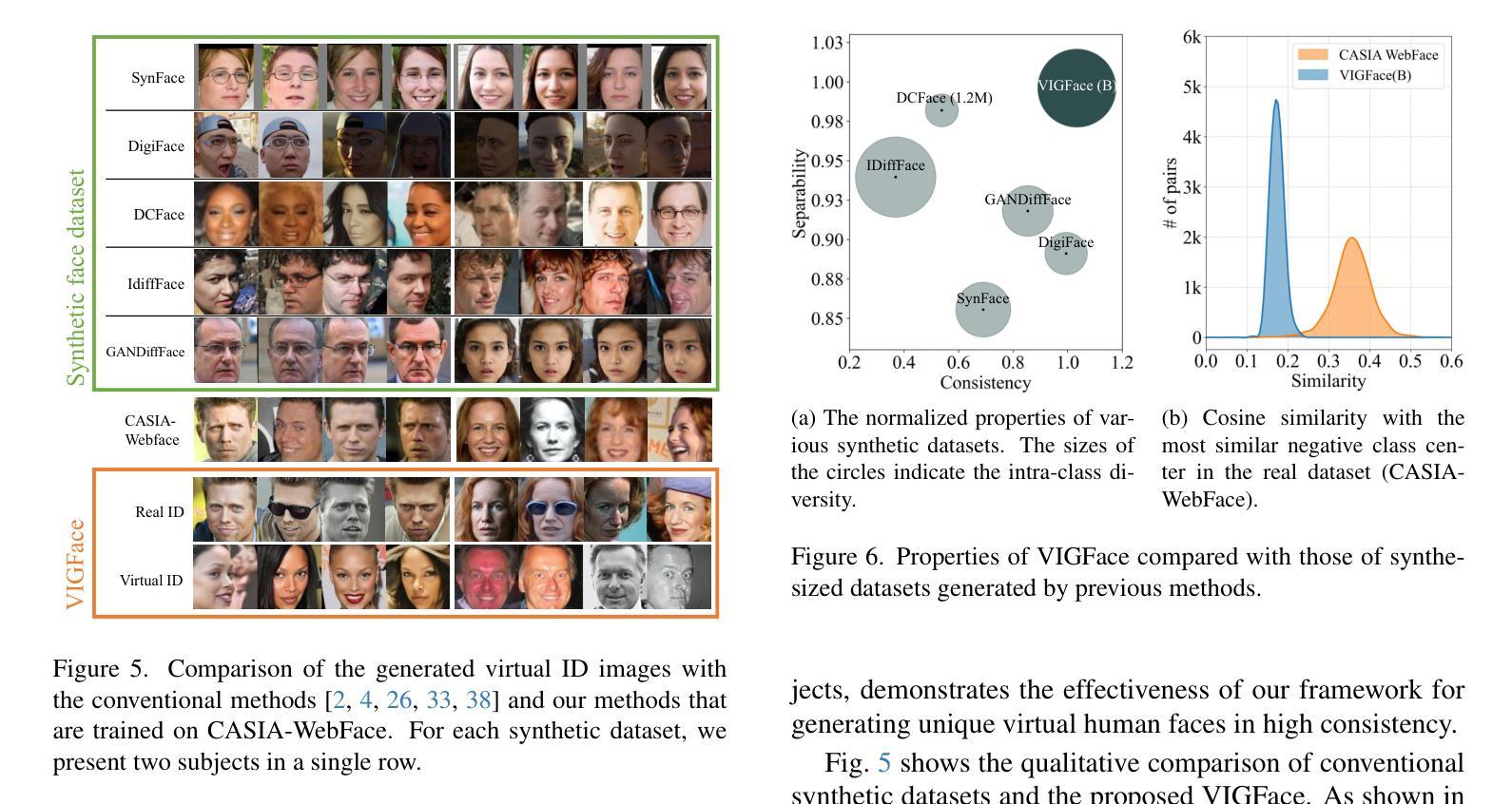
VIGFace: Virtual Identity Generation for Privacy-Free Face Recognition
Authors:Minsoo Kim, Min-Cheol Sagong, Gi Pyo Nam, Junghyun Cho, Ig-Jae Kim
Deep learning-based face recognition continues to face challenges due to its reliance on huge datasets obtained from web crawling, which can be costly to gather and raise significant real-world privacy concerns. To address this issue, we propose VIGFace, a novel framework capable of generating synthetic facial images. Our idea originates from pre-assigning virtual identities in the feature space. Initially, we train the face recognition model using a real face dataset and create a feature space for both real and virtual identities, where virtual prototypes are orthogonal to other prototypes. Subsequently, we generate synthetic images by using the diffusion model based on the feature space. The diffusion model is capable of reconstructing authentic human facial representations from established real prototypes, while synthesizing virtual entities from devised virtual prototypes. Our proposed framework provides two significant benefits. Firstly, it allows one to create virtual facial images without concerns about privacy and portrait rights, guaranteeing that the generated virtual face images are clearly differentiated from existing individuals. Secondly, it serves as an effective augmentation method by incorporating real existing images. Further experiments demonstrate the superiority of our virtual face dataset and framework, outperforming the previous state-of-the-art on various face recognition benchmarks.
基于深度学习的人脸识别仍然面临着挑战,这主要是因为其依赖于从网络爬虫获得的大量数据集,这些数据集的收集成本高昂,并引发了现实世界中的隐私担忧。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了VIGFace这一新型框架,能够生成合成面部图像。我们的灵感来源于在特征空间中进行虚拟身份的预先分配。首先,我们使用真实面部数据集训练人脸识别模型,并为真实和虚拟身份创建特征空间,其中虚拟原型与其他原型正交。随后,我们基于特征空间使用扩散模型生成合成图像。扩散模型能够从既定的真实原型重建出真实的人脸表示,同时根据设定的虚拟原型合成虚拟实体。我们提出的框架提供了两大重要优势。首先,它使人们能够创建无需担心隐私和肖像权的虚拟面部图像,保证生成的虚拟面部图像与现有个体明确区分开来。其次,它作为一种有效的增强方法,结合了现有的真实图像。进一步的实验表明,我们的虚拟面部数据集和框架优于以前的最先进技术,在各种人脸识别基准测试中表现卓越。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
人脸识别领域面临数据采集成本高昂和隐私问题的挑战。为解决这些问题,我们提出VIGFace框架,通过生成合成面部图像来解决这些问题。框架利用特征空间预分配虚拟身份的方式,训练模型并创建包含真实和虚拟身份的特征空间。利用扩散模型基于特征空间生成合成图像,能够重建真实人脸表示并从设定的虚拟原型中合成虚拟实体。此框架不仅解决了隐私和肖像权问题,还作为一种有效的数据增强方法。实验证明,我们的虚拟面部数据集和框架优于当前最佳水平的人脸识别基准测试。
Key Takeaways
- 人脸识别面临的挑战包括数据采集的高成本和对隐私的担忧。
- VIGFace框架通过生成合成面部图像来解决这些问题。
- 框架利用特征空间预分配虚拟身份来训练模型。
- 扩散模型用于基于特征空间生成合成图像。
- 框架能够重建真实人脸表示并合成虚拟实体。
- 框架解决了隐私和肖像权问题,并作为一种有效的数据增强方法。
点此查看论文截图


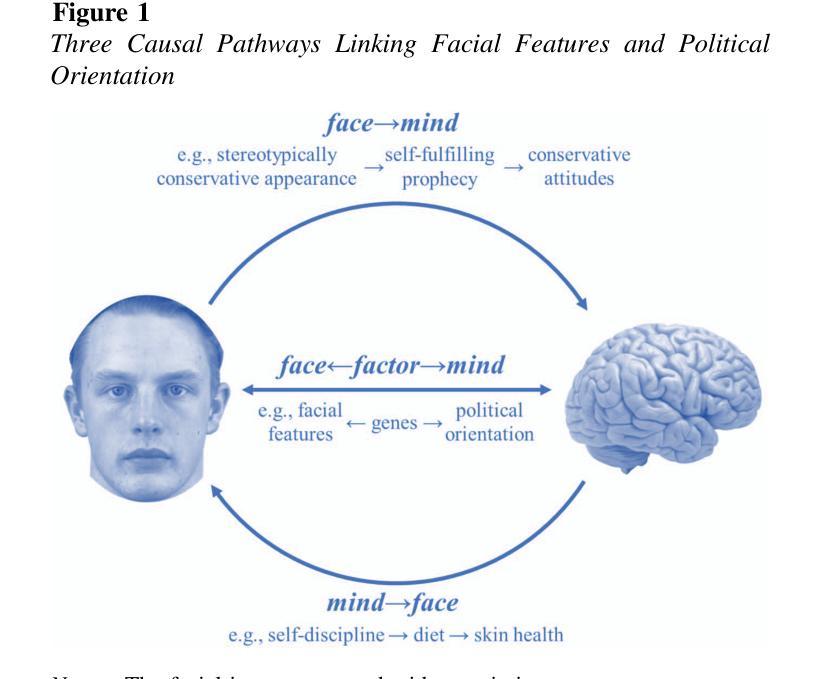
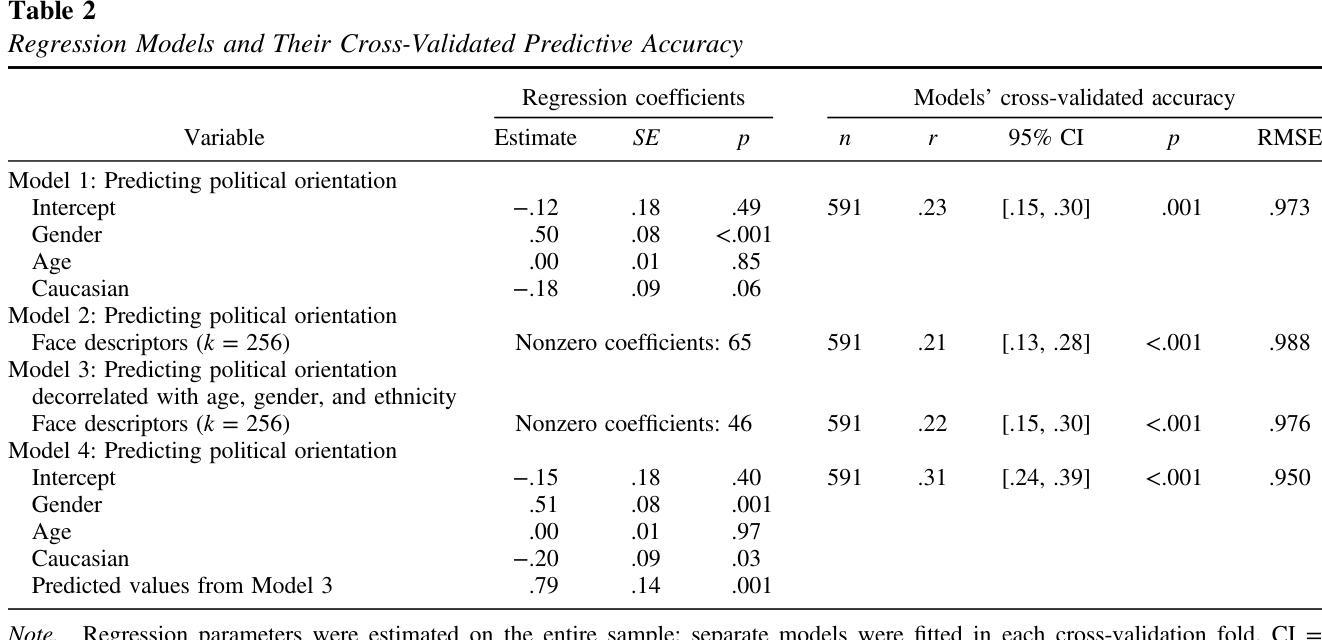
Facial recognition technology and human raters can predict political orientation from images of expressionless faces even when controlling for demographics and self-presentation
Authors:Michal Kosinski, Poruz Khambatta, Yilun Wang
Carefully standardized facial images of 591 participants were taken in the laboratory, while controlling for self-presentation, facial expression, head orientation, and image properties. They were presented to human raters and a facial recognition algorithm: both humans (r=.21) and the algorithm (r=.22) could predict participants’ scores on a political orientation scale (Cronbach’s alpha=.94) decorrelated with age, gender, and ethnicity. These effects are on par with how well job interviews predict job success, or alcohol drives aggressiveness. Algorithm’s predictive accuracy was even higher (r=.31) when it leveraged information on participants’ age, gender, and ethnicity. Moreover, the associations between facial appearance and political orientation seem to generalize beyond our sample: The predictive model derived from standardized images (while controlling for age, gender, and ethnicity) could predict political orientation (r=.13) from naturalistic images of 3,401 politicians from the U.S., UK, and Canada. The analysis of facial features associated with political orientation revealed that conservatives tended to have larger lower faces. The predictability of political orientation from standardized images has critical implications for privacy, the regulation of facial recognition technology, and understanding the origins and consequences of political orientation.
在实验室里,我们对591名参与者的面部图像进行了细致的标准化采集,同时控制了自我呈现、面部表情、头部朝向和图像属性。这些图像被展示给人类评分者和一个面部识别算法:人类(r=.21)和算法(r=.22)都能预测参与者在政治倾向量表上的得分(Cronbach的alpha=.94),并且与年龄、性别和种族无关。这些效果与面试预测工作成功的程度,或酒精引发攻击行为的程度相当。当算法利用参与者的年龄、性别和种族信息时,其预测精度甚至更高(r=.31)。此外,面部外观与政治倾向之间的联系似乎可以推广到我们的样本之外:从标准化图像中得出的预测模型(在控制年龄、性别和种族的同时)可以预测来自美国、英国和加拿大的3401名政治家的政治倾向(r=.13)。对与政治倾向相关的面部特征的分析显示,保守主义者往往具有较大的下脸部。从标准化图像预测政治倾向具有关键的隐私意义,对面部识别技术的监管和对政治倾向起源和后果的理解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Now published at American Psychologist (2024)
Summary
该研究通过实验室标准化采集的面部图像,探讨了面部外观与政治倾向之间的关系。研究结果显示,人类和面部识别算法都能根据面部特征预测参与者的政治倾向,且算法的预测准确性较高。此外,这种关联似乎可以推广到自然状态下的政治人物图像上。该研究还发现保守派的面部特征有所不同。该研究对于隐私、面部识别技术的监管以及政治倾向的起源和后果的理解具有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- 研究通过控制实验室环境中的自我呈现、面部表情、头部方向和图像属性等因素,采集了591名参与者的面部图像。
- 人类和面部识别算法都能根据面部特征预测参与者的政治倾向。这种预测的准确度类似于其他领域的预测准确性,例如面试预测工作成功与否或酒精影响攻击性等方面。
- 算法的预测准确性更高,特别是当它利用参与者的年龄、性别和种族信息时,其预测相关性达到r=.31。
- 政治人物的自然状态下的面部图像也可以用来预测其政治倾向。这种关联不仅仅适用于样本范围,还可以在更大的范围内进行推广。
- 研究发现保守派的面部特征表现为下脸部分较大。
点此查看论文截图





Learning to mask: Towards generalized face forgery detection
Authors:Jianwei Fei, Yunshu Dai, Huaming Wang, Zhihua Xia
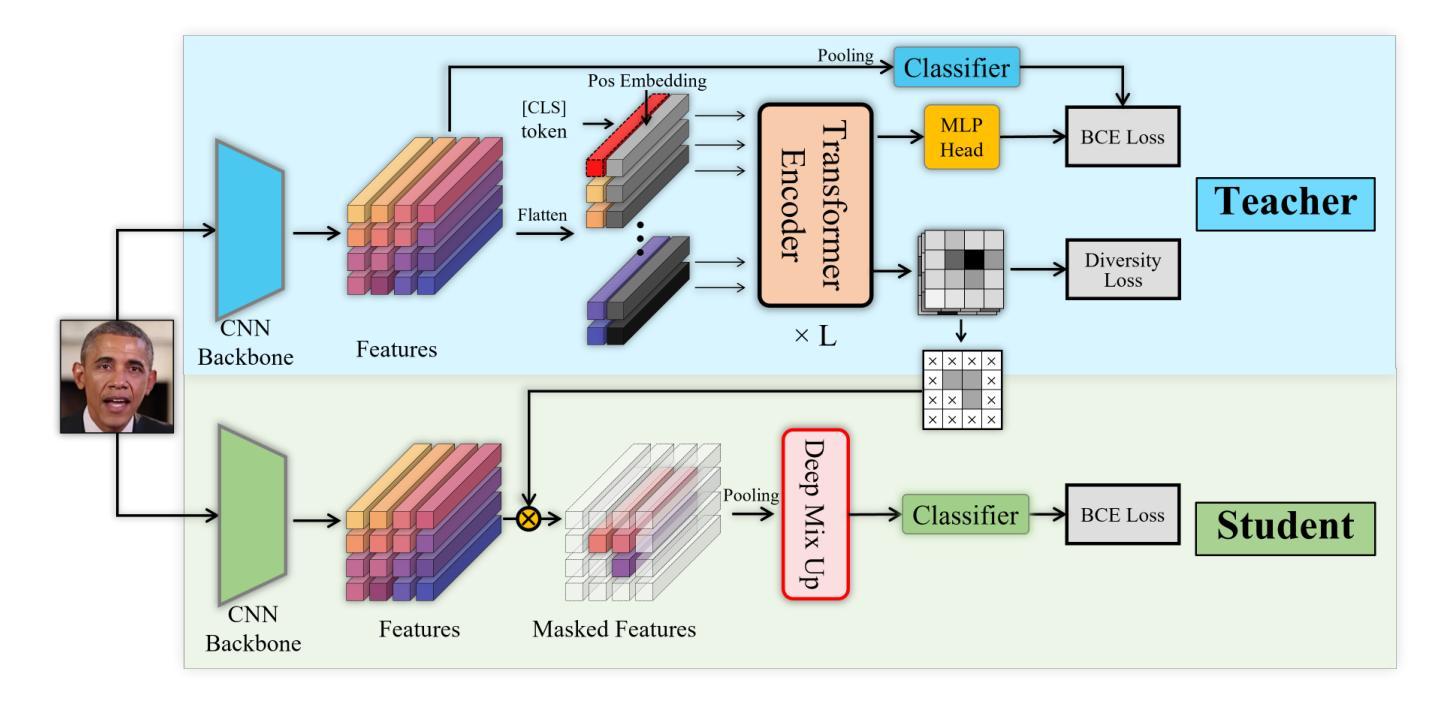
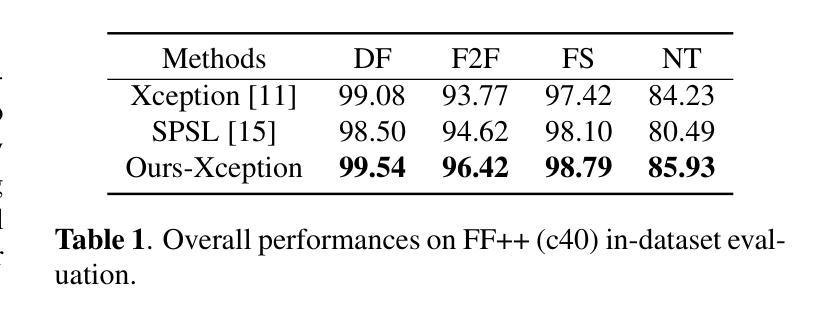
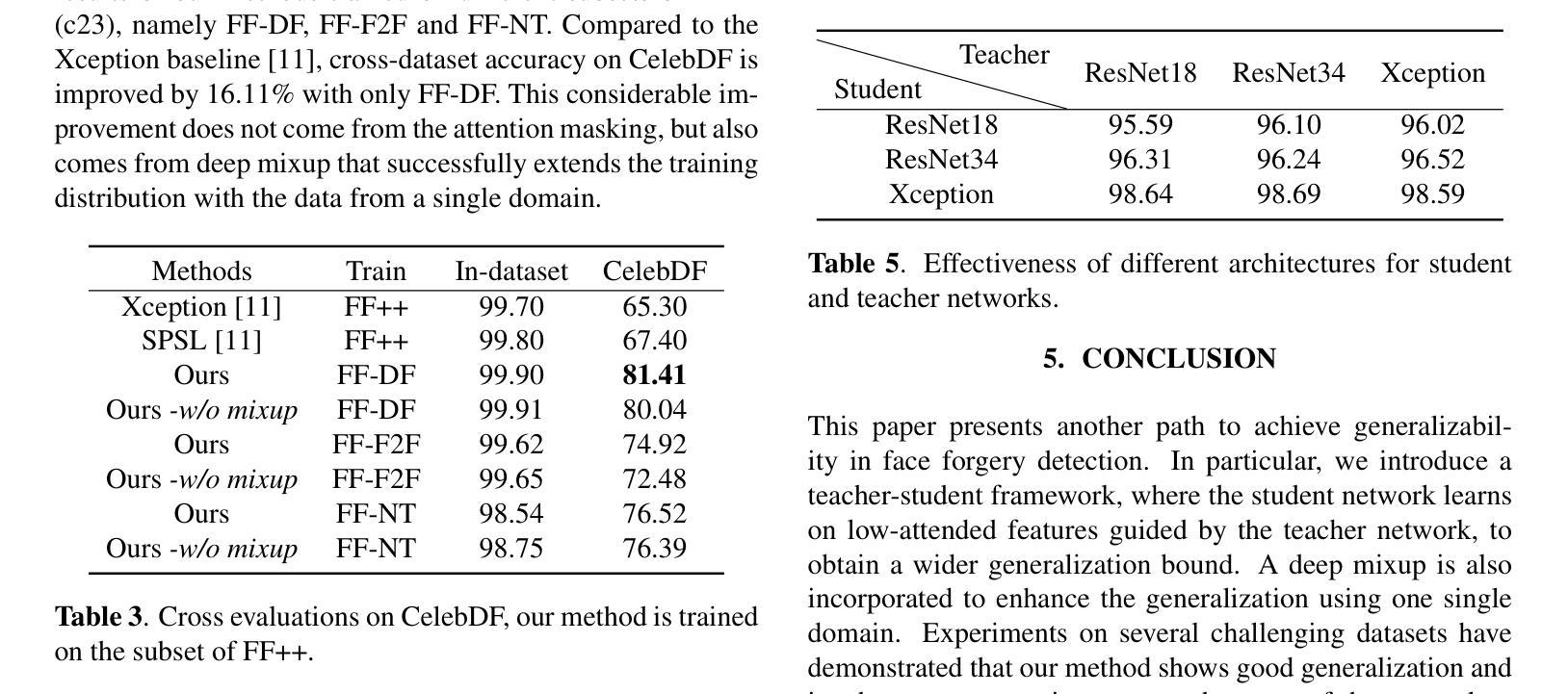
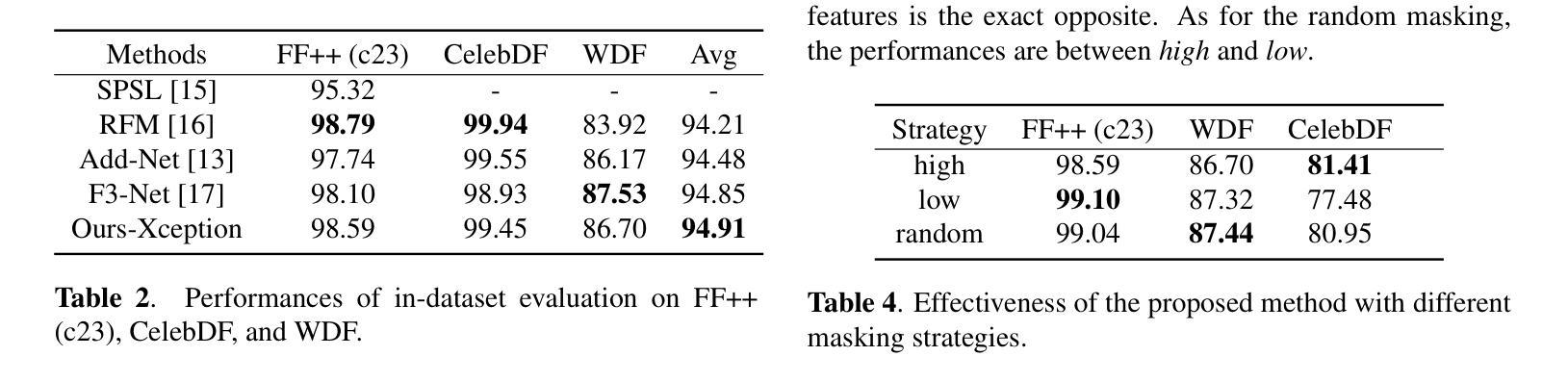
Generalizability to unseen forgery types is crucial for face forgery detectors. Recent works have made significant progress in terms of generalization by synthetic forgery data augmentation. In this work, we explore another path for improving the generalization. Our goal is to reduce the features that are easy to learn in the training phase, so as to reduce the risk of overfitting on specific forgery types. Specifically, in our method, a teacher network takes as input the face images and generates an attention map of the deep features by a diverse multihead attention ViT. The attention map is used to guide a student network to focus on the low-attended features by reducing the highly-attended deep features. A deep feature mixup strategy is also proposed to synthesize forgeries in the feature domain. Experiments demonstrate that, without data augmentation, our method is able to achieve promising performances on unseen forgeries and highly compressed data.
对于人脸伪造检测器来说,对未见过的伪造类型的泛化能力至关重要。近期的工作通过合成伪造数据增强方法,在泛化方面取得了显著进展。在这项工作中,我们探索了另一条提高泛化的路径。我们的目标是减少那些在训练阶段容易学习的特征,以降低对特定伪造类型过度拟合的风险。具体来说,在我们的方法中,教师网络以人脸图像为输入,通过多样化的多头注意力ViT生成深度特征的注意力图。注意力图被用来引导学生网络关注低关注度特征,通过减少高度关注的深度特征来实现。还提出了一种深度特征混合策略,用于在特征域中合成伪造数据。实验表明,在不进行数据增强的情况下,我们的方法能够在未见过的伪造数据和高度压缩的数据上实现有前景的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Incorrect experimental setting
总结
对于人脸伪造检测器而言,实现对新类型伪造的通用性是至关重要的。近期的研究通过合成伪造数据增强技术取得了显著的进展。本研究旨在探索另一条提高通用性的路径。我们的目标是减少在训练阶段易于学习的特征,从而降低对特定伪造类型过度拟合的风险。具体来说,在我们的方法中,教师网络以人脸图像为输入,通过多样化的多头注意力视觉转换器生成深度特征的注意力图。注意力图被用来引导学生网络关注低关注度的特征,通过减少高度关注的深度特征来实现这一点。还提出了一种深度特征混合策略,用于在特征域中合成伪造数据。实验表明,即使不使用数据增强技术,我们的方法也能在未见过的伪造和高度压缩的数据上取得令人鼓舞的性能。
关键见解
- 人脸伪造检测器对新类型伪造的通用性至关重要。
- 通过降低易于学习的特征来增强伪造检测器的通用性。
- 教师网络使用多样化的多头注意力视觉转换器生成深度特征的注意力图。
- 注意力图用于指导学生网络关注低关注度特征。
- 提出一种深度特征混合策略,用于在特征域中合成伪造数据。
- 方法在无需数据增强的情况下,在未见过的伪造和高度压缩的数据上表现良好。
- 该研究为提高人脸伪造检测器的性能和泛化能力提供了新的思路和方法。
点此查看论文截图