⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-11 更新
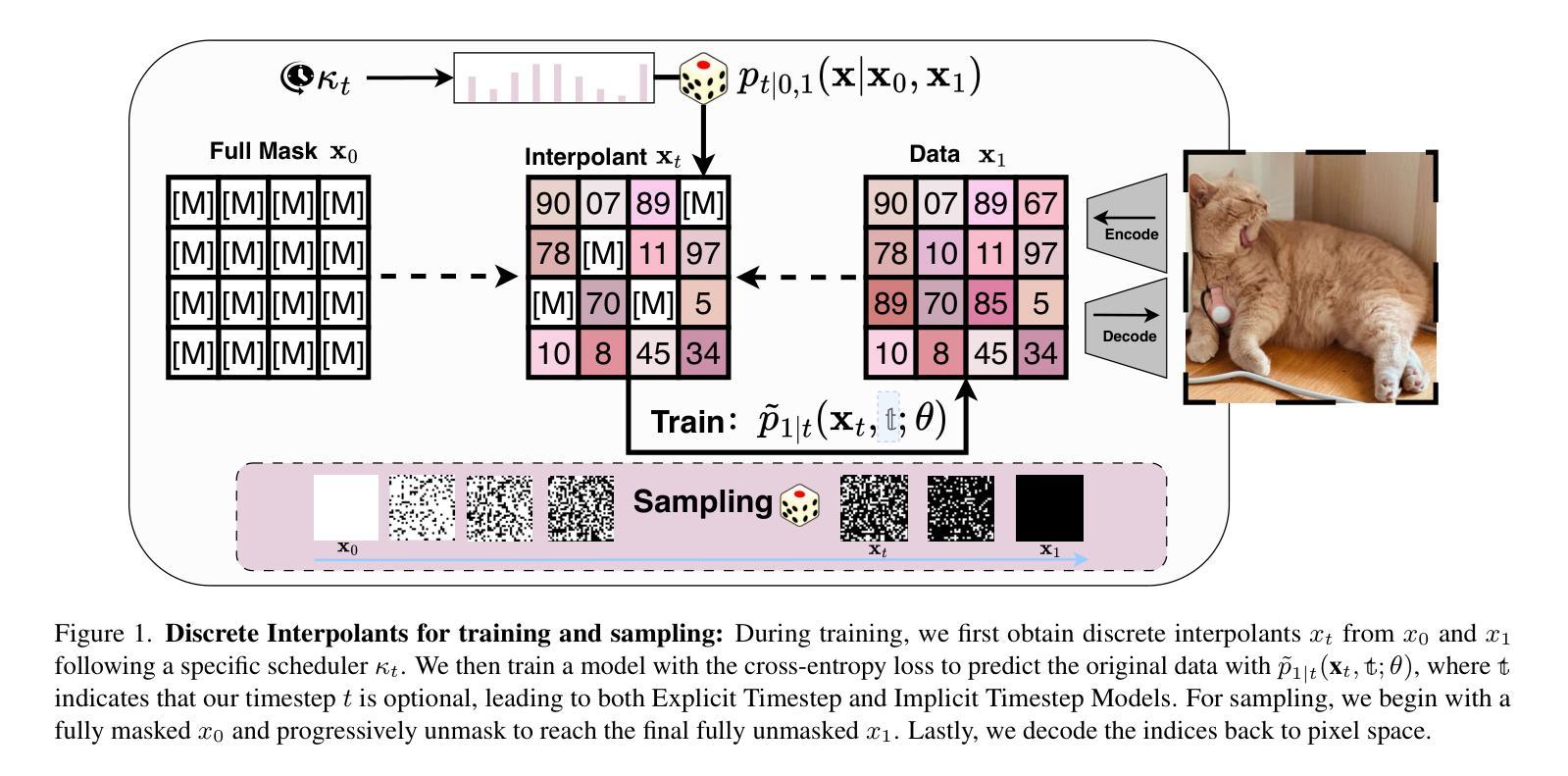
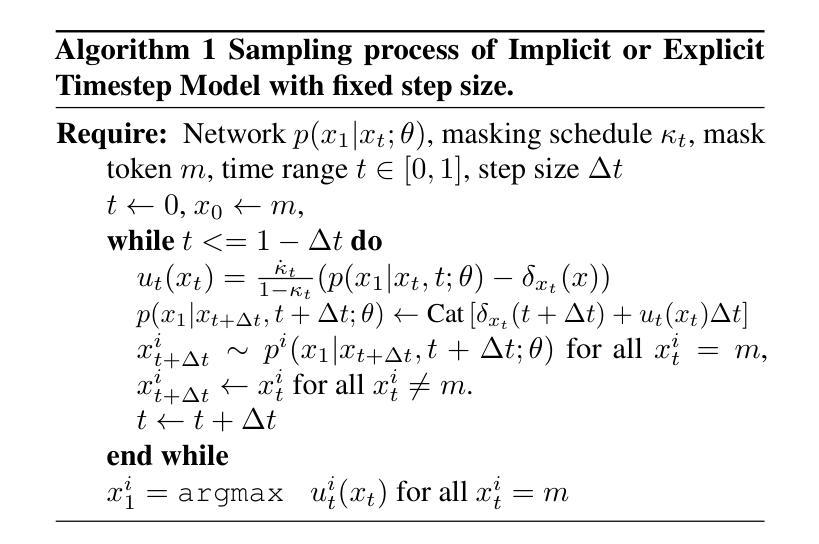
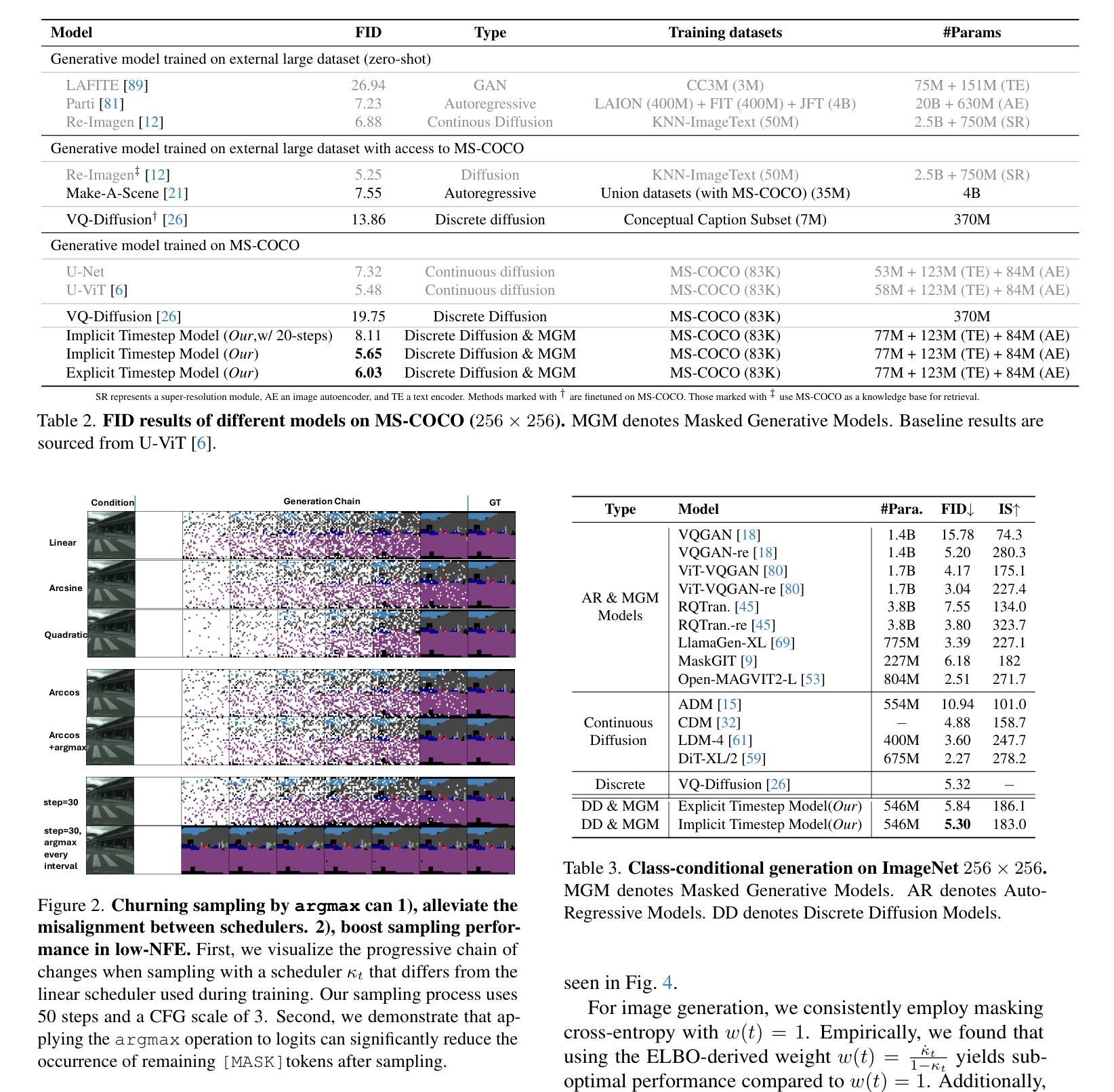
[MASK] is All You Need
Authors:Vincent Tao Hu, Björn Ommer
In generative models, two paradigms have gained attraction in various applications: next-set prediction-based Masked Generative Models and next-noise prediction-based Non-Autoregressive Models, e.g., Diffusion Models. In this work, we propose using discrete-state models to connect them and explore their scalability in the vision domain. First, we conduct a step-by-step analysis in a unified design space across two types of models including timestep-independence, noise schedule, temperature, guidance strength, etc in a scalable manner. Second, we re-cast typical discriminative tasks, e.g., image segmentation, as an unmasking process from [MASK]tokens on a discrete-state model. This enables us to perform various sampling processes, including flexible conditional sampling by only training once to model the joint distribution. All aforementioned explorations lead to our framework named Discrete Interpolants, which enables us to achieve state-of-the-art or competitive performance compared to previous discrete-state based methods in various benchmarks, like ImageNet256, MS COCO, and video dataset FaceForensics. In summary, by leveraging [MASK] in discrete-state models, we can bridge Masked Generative and Non-autoregressive Diffusion models, as well as generative and discriminative tasks.
在生成模型中,两种范式在各种应用中受到了关注:基于下一集预测的掩码生成模型和基于下一噪声预测的非自回归模型,例如扩散模型。在这项工作中,我们提出使用离散状态模型来连接它们,并探索其在视觉领域的可扩展性。首先,我们在统一的设计空间内以分阶段的方式对这两种模型进行分析,包括时间步独立性、噪声调度、温度、引导强度等,并以可扩展的方式处理。其次,我们将典型的判别任务(如图像分割)重新定义为离散状态模型上的[MASK]标记的去掩码过程。这使得我们能够执行各种采样过程,包括通过仅一次训练对联合分布进行建模来实现灵活的条件采样。所有上述探索都引领我们构建了名为“离散插值”的框架,该框架使我们能够在各种基准测试中达到或保持与以前基于离散状态的方法相比的先进或竞争性能,如ImageNet256、MS COCO和视频数据集FaceForensics。总之,通过利用离散状态模型中的[MASK],我们可以架起掩码生成和非自回归扩散模型之间的桥梁,以及生成和判别任务之间的桥梁。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report (WIP), Project Page(code, model, dataset): https://compvis.github.io/mask/
Summary
基于离散状态模型的生成模型研究,通过连接Masked Generative模型和Non-Autoregressive模型(如Diffusion Models),探索其在视觉领域的可扩展性。研究包括统一设计空间内的逐步分析、典型判别任务的重新构建以及新的框架Discrete Interpolants的提出,该框架在多个基准测试中实现了卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型中的两个范式:基于下一组预测的Masked Generative模型和基于下一噪声预测的非自回归模型(如Diffusion Models)受到关注。
- 离散状态模型被用来连接这两种模型,并在视觉领域探索其可扩展性。
- 在统一设计空间内,对两种模型进行了逐步分析,包括时间步独立性、噪声时间表、温度、指导强度等。
- 将典型的判别任务(如图像分割)重新构建为离散状态模型上的去遮掩过程。
- 提出了名为Discrete Interpolants的框架,实现了与之前的离散状态方法相比在多个基准测试中的卓越或竞争性能。
- 利用离散状态模型中的[MASK],能够架起Masked Generative和Non-autoregressive Diffusion模型之间的桥梁。
点此查看论文截图

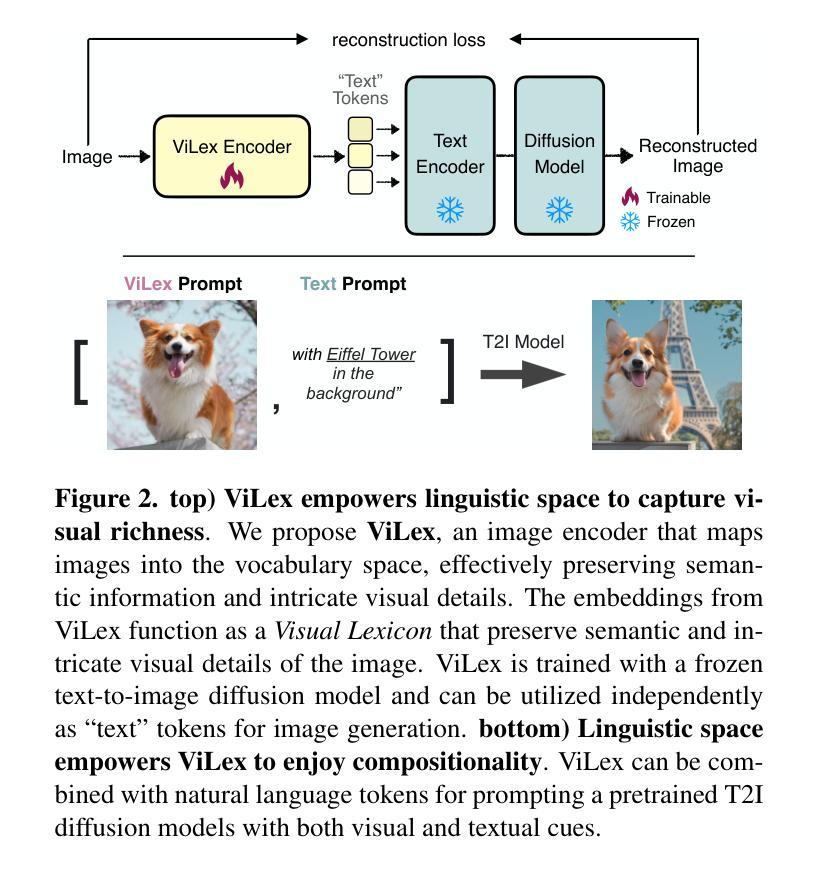
Visual Lexicon: Rich Image Features in Language Space
Authors:XuDong Wang, Xingyi Zhou, Alireza Fathi, Trevor Darrell, Cordelia Schmid
We present Visual Lexicon, a novel visual language that encodes rich image information into the text space of vocabulary tokens while retaining intricate visual details that are often challenging to convey in natural language. Unlike traditional methods that prioritize either high-level semantics (e.g., CLIP) or pixel-level reconstruction (e.g., VAE), ViLex simultaneously captures rich semantic content and fine visual details, enabling high-quality image generation and comprehensive visual scene understanding. Through a self-supervised learning pipeline, ViLex generates tokens optimized for reconstructing input images using a frozen text-to-image (T2I) diffusion model, preserving the detailed information necessary for high-fidelity semantic-level reconstruction. As an image embedding in the language space, ViLex tokens leverage the compositionality of natural languages, allowing them to be used independently as “text tokens” or combined with natural language tokens to prompt pretrained T2I models with both visual and textual inputs, mirroring how we interact with vision-language models (VLMs). Experiments demonstrate that ViLex achieves higher fidelity in image reconstruction compared to text embeddings–even with a single ViLex token. Moreover, ViLex successfully performs various DreamBooth tasks in a zero-shot, unsupervised manner without fine-tuning T2I models. Additionally, ViLex serves as a powerful vision encoder, consistently improving vision-language model performance across 15 benchmarks relative to a strong SigLIP baseline.
我们提出了一种名为Visual Lexicon的新型视觉语言。它能够将丰富的图像信息编码成词汇令牌的文本空间,同时保留复杂的视觉细节,这些视觉细节在自然语言传达时常常具有挑战性。与传统的优先关注高级语义(例如CLIP)或像素级重建(例如VAE)的方法不同,ViLex能够同时捕获丰富的语义内容和精细的视觉细节,从而实现高质量图像生成和全面的视觉场景理解。通过自监督学习管道,ViLex生成了针对输入图像重建而优化的令牌,使用冻结的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型,保留用于高保真语义级重建的详细信息。作为语言空间中的图像嵌入,ViLex令牌利用自然语言的组合性,可以独立用作“文本令牌”,也可以与自然语言令牌结合,提示预训练的T2I模型进行视觉和文本输入,这反映了我们与视觉语言模型(VLM)的交互方式。实验表明,即使在单个ViLex令牌的情况下,ViLex在图像重建方面也比文本嵌入实现了更高的保真度。此外,ViLex成功地在零样本、无监督的方式下执行各种DreamBooth任务,无需微调T2I模型。另外,ViLex作为一种强大的视觉编码器,相对于强大的SigLIP基准测试,在15个基准测试中不断改进视觉语言模型的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Tech report. 16 pages, 10 figures
Summary
视觉词汇是一种新型视觉语言,能将丰富的图像信息编码成词汇符号,同时保留复杂的视觉细节。不同于传统方法,ViLex可捕捉丰富的语义内容和精细的视觉细节,实现高质量图像生成和全面的视觉场景理解。通过自监督学习生成优化的符号,用于重建图像,并可在语言空间中作为独立的“文本符号”使用或结合自然语言符号。实验证明,ViLex在图像重建方面具有更高的保真度,并在各种任务中表现优秀。同时作为强大的视觉编码器,它改进了视觉语言模型的性能。
Key Takeaways
- ViLex是一种视觉语言,能将图像信息编码成词汇符号。
- ViLex可捕捉丰富的语义内容和精细的视觉细节。
- ViLex通过自监督学习生成优化的符号用于重建图像。
- ViLex可实现高质量图像生成和全面的视觉场景理解。
- ViLex符号可在语言空间中独立使用或结合自然语言符号使用。
- ViLex在图像重建任务中具有高保真度,表现出优秀性能。
点此查看论文截图




3D Graph Attention Networks for High Fidelity Pediatric Glioma Segmentation
Authors:Harish Thangaraj, Diya Katariya, Eshaan Joshi, Sangeetha N
Pediatric brain tumors, particularly gliomas, represent a significant cause of cancer related mortality in children with complex infiltrative growth patterns that complicate treatment. Early, accurate segmentation of these tumors in neuroimaging data is crucial for effective diagnosis and intervention planning. This study presents a novel 3D UNet architecture with a spatial attention mechanism tailored for automated segmentation of pediatric gliomas. Using the BraTS pediatric glioma dataset with multiparametric MRI data, the proposed model captures multi-scale features and selectively attends to tumor relevant regions, enhancing segmentation precision and reducing interference from surrounding tissue. The model’s performance is quantitatively evaluated using the Dice similarity coefficient and HD95, demonstrating improved delineation of complex glioma structured. This approach offers a promising advancement in automating pediatric glioma segmentation, with the potential to improve clinical decision making and outcomes.
儿童脑肿瘤,特别是胶质瘤,是导致儿童癌症相关死亡的重要原因,其复杂的浸润性生长模式使治疗变得复杂。在神经影像数据中早期、准确地分割这些肿瘤对于有效诊断和治疗干预计划至关重要。本研究提出了一种新型的3D UNet架构,结合空间注意力机制,专门用于儿童胶质瘤的自动分割。该研究使用BraTS儿童胶质瘤数据集和多参数MRI数据,所提出模型能够捕捉多尺度特征,并选择性关注肿瘤相关区域,提高分割精度,减少周围组织的干扰。该模型的性能通过Dice相似系数和HD95进行定量评估,证明了其在复杂胶质瘤结构描绘上的改进。该方法在小儿胶质瘤分割自动化方面取得了有希望的进展,有望改善临床决策和治疗效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 9 figures
Summary
研究采用新型3D UNet架构结合空间注意力机制,实现儿童胶质瘤的自动分割。利用BraTS儿童胶质瘤数据集和多参数MRI数据,模型捕捉多尺度特征,选择性关注肿瘤相关区域,提高分割精度,减少周围组织的干扰。此研究为自动化儿童胶质瘤分割提供了有前景的进展,有望改善临床决策和结果。
Key Takeaways
- 儿童脑肿瘤(特别是胶质瘤)是儿童癌症死亡的重要原因,其复杂浸润性生长模式使治疗变得复杂。
- 早期、准确的脑肿瘤神经影像数据分割对有效诊断和治疗干预至关重要。
- 研究提出了一种新型的3D UNet架构,结合空间注意力机制,用于自动分割儿童胶质瘤。
- 使用BraTS儿童胶质瘤数据集和多参数MRI数据来训练模型。
- 模型能够捕捉多尺度特征,并选择性关注肿瘤相关区域,提高分割精度。
- 模型通过Dice相似系数和HD95进行了定量评估,显示出在复杂胶质瘤结构上的改进。
点此查看论文截图


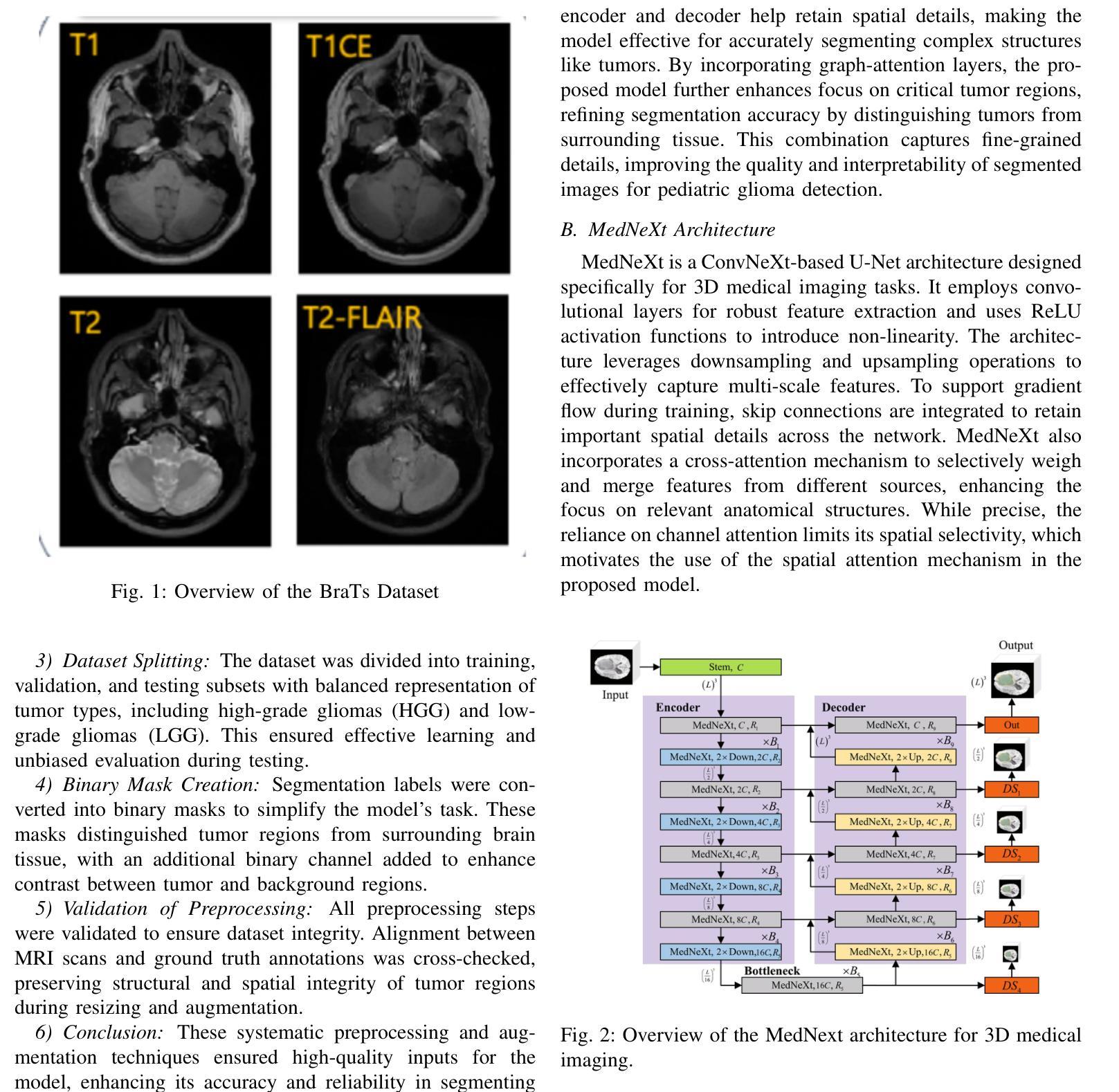
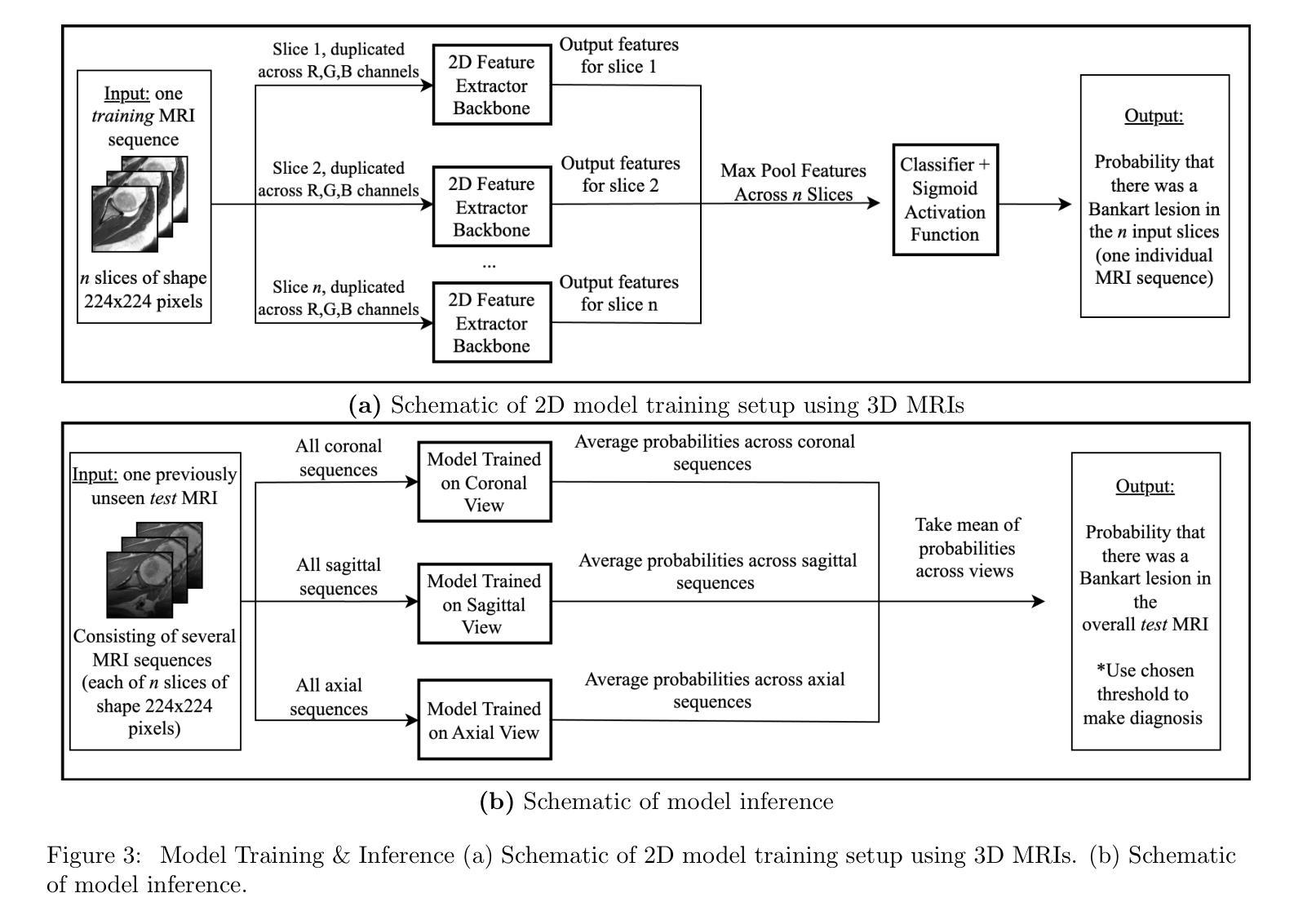
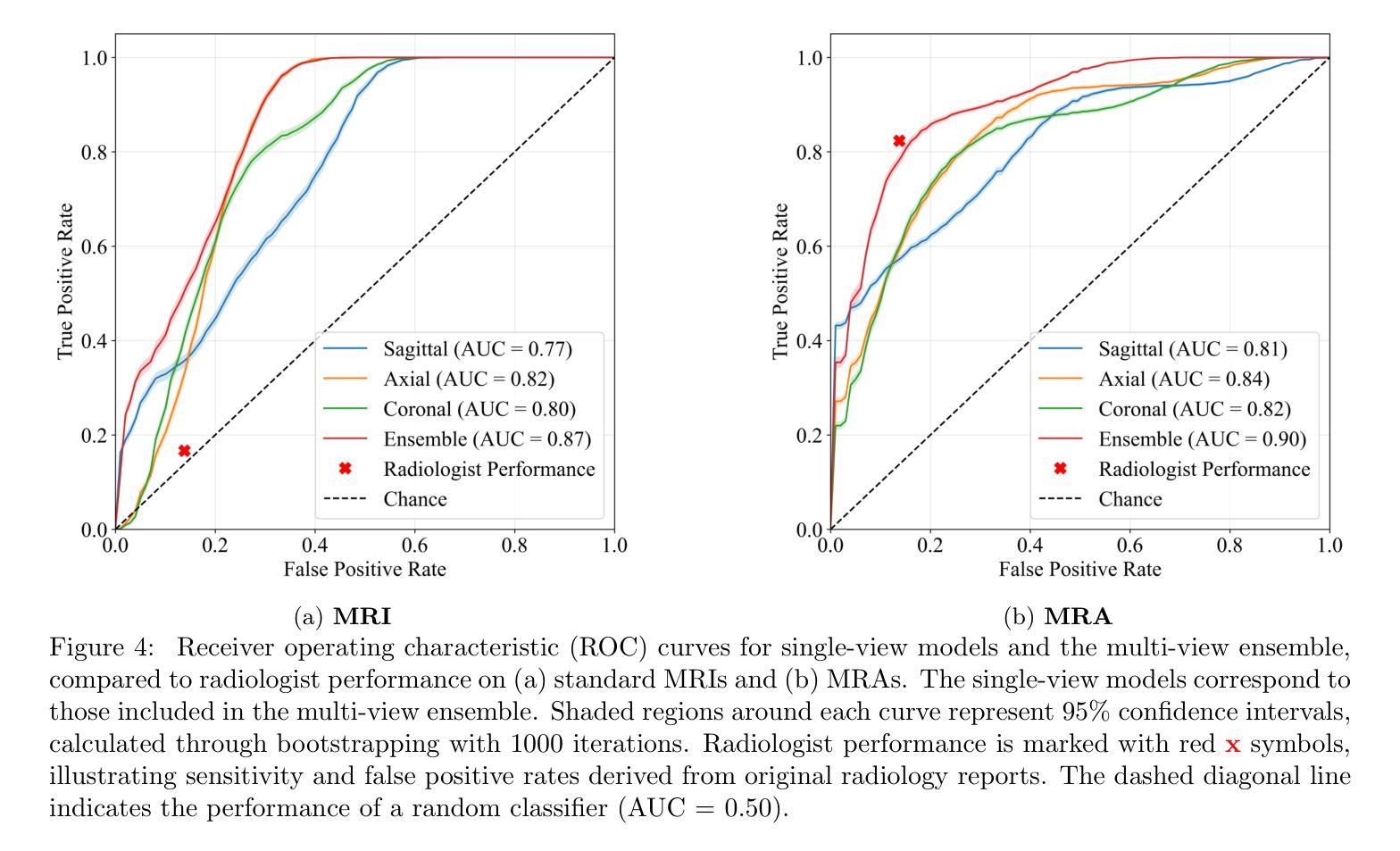
Toward Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Bankart Lesions with Deep Learning
Authors:Sahil Sethi, Sai Reddy, Mansi Sakarvadia, Jordan Serotte, Darlington Nwaudo, Nicholas Maassen, Lewis Shi
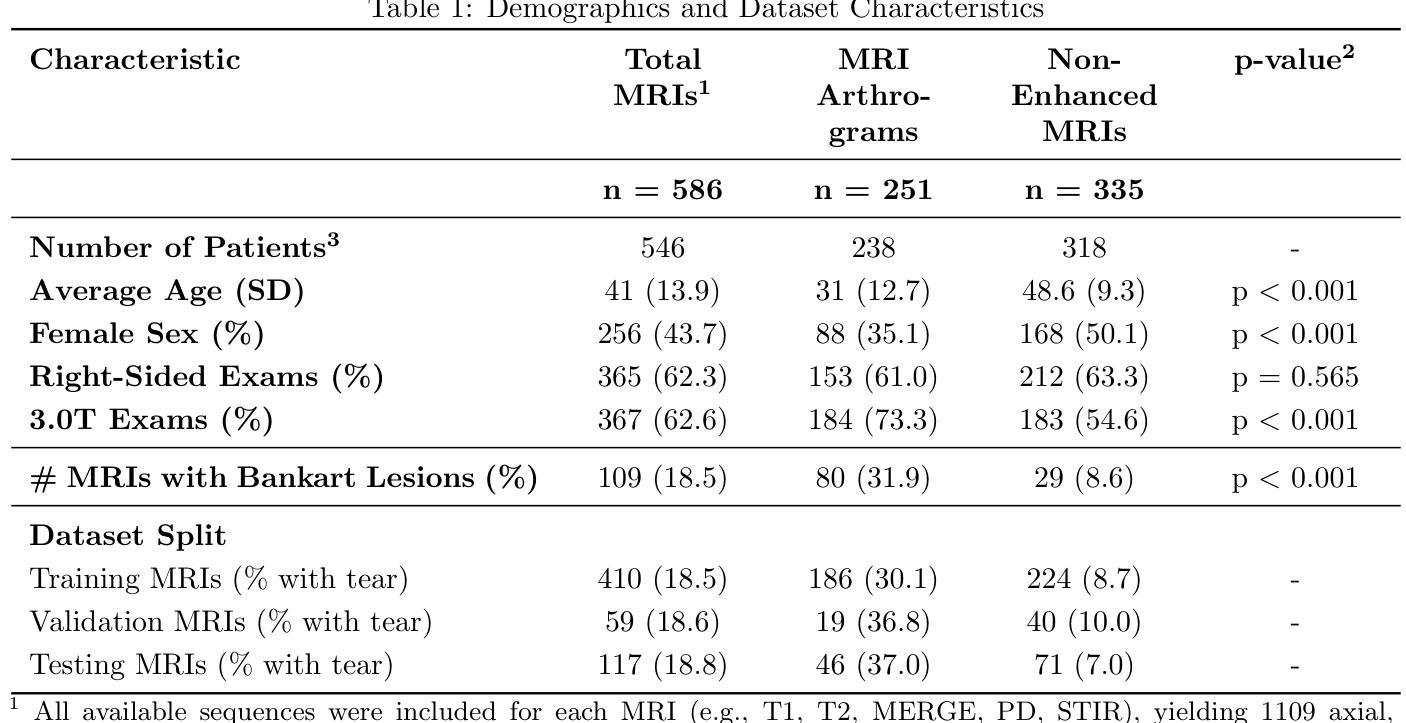
Bankart lesions, or anterior-inferior glenoid labral tears, are diagnostically challenging on standard MRIs due to their subtle imaging features-often necessitating invasive MRI arthrograms (MRAs). This study develops deep learning (DL) models to detect Bankart lesions on both standard MRIs and MRAs, aiming to improve diagnostic accuracy and reduce reliance on MRAs. We curated a dataset of 586 shoulder MRIs (335 standard, 251 MRAs) from 558 patients who underwent arthroscopy. Ground truth labels were derived from intraoperative findings, the gold standard for Bankart lesion diagnosis. Separate DL models for MRAs and standard MRIs were trained using the Swin Transformer architecture, pre-trained on a public knee MRI dataset. Predictions from sagittal, axial, and coronal views were ensembled to optimize performance. The models were evaluated on a 20% hold-out test set (117 MRIs: 46 MRAs, 71 standard MRIs). Bankart lesions were identified in 31.9% of MRAs and 8.6% of standard MRIs. The models achieved AUCs of 0.87 (86% accuracy, 83% sensitivity, 86% specificity) and 0.90 (85% accuracy, 82% sensitivity, 86% specificity) on standard MRIs and MRAs, respectively. These results match or surpass radiologist performance on our dataset and reported literature metrics. Notably, our model’s performance on non-invasive standard MRIs matched or surpassed the radiologists interpreting MRAs. This study demonstrates the feasibility of using DL to address the diagnostic challenges posed by subtle pathologies like Bankart lesions. Our models demonstrate potential to improve diagnostic confidence, reduce reliance on invasive imaging, and enhance accessibility to care.
Bankart损伤,也称为肩关节前下盂唇撕裂,在标准MRI上的诊断具有挑战性,因为其细微的成像特征通常需要侵入性的MRI关节造影术(MRAs)。本研究开发了深度学习(DL)模型,可在标准MRI和MRAs上检测Bankart损伤,旨在提高诊断准确性并减少对MRAs的依赖。我们从接受关节镜检查的558例患者中精心挑选了一个包含586个肩关节MRI(335个标准MRI,251个MRAs)的数据集。真实标签来自术中检查结果,这是诊断Bankart损伤的金标准。针对MRAs和标准MRI的单独DL模型使用Swin Transformer架构进行训练,该架构在公共膝关节MRI数据集上进行预训练。将从矢状面、轴面和冠状面得到的预测结果进行组合,以优化性能。模型在20%的保留测试集(117个MRI:46个MRAs,71个标准MRI)上进行了评估。在MRAs中检测出Bankart损伤的占31.9%,在标准MRI中检测出Bankart损伤的占8.6%。模型在标准MRI和MRAs上的AUC值分别为0.87(准确率86%,灵敏度83%,特异度86%)和0.90(准确率85%,灵敏度82%,特异度86%)。这些结果在我们的数据集和报告的文献指标上与放射科医生的性能相匹配或更高。值得注意的是,我们的模型在非侵入性标准MRI上的性能与解读MRAs的放射科医生相匹配或更高。该研究证明了使用深度学习解决由细微病理变化引起的诊断挑战(如Bankart损伤)的可行性。我们的模型有潜力提高诊断信心,减少对侵入性成像的依赖,并提高护理可及性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for presentation at SPIE Medical Imaging 2025: Computer-Aided Diagnosis. The manuscript is expected to appear in the conference proceedings
Summary
本研究利用深度学习模型检测Bankart病变的标准MRI和MRI关节造影术(MRAs)图像,旨在提高诊断准确性并减少对MRAs的依赖。研究使用肩部的MRI数据集进行训练,模型采用Swin Transformer架构,并在公共膝关节MRI数据集上进行预训练。模型在测试集上的表现良好,对标准MRI和MRAs的识别能力均达到较高水平。研究证明了使用深度学习解决细微病变诊断挑战的可行性,有望提升诊断信心、减少侵入性成像的依赖,并提高医疗服务可及性。
Key Takeaways
- Bankart病变在标准MRI上的诊断具有挑战性,常需借助侵入性的MRI关节造影术(MRAs)。
- 本研究使用深度学习模型来检测Bankart病变,旨在提高诊断准确性并减少MRAs的依赖。
- 研究采用Swin Transformer架构的深度学习模型,并在公共膝关节MRI数据集上进行预训练。
- 模型结合了矢状面、轴面和冠状面的预测来优化性能。
- 模型在测试集上的表现良好,对Bankart病变的识别能力较高。
- 模型性能与放射科医生的表现相当,甚至在非侵入性的标准MRI上表现更佳。
点此查看论文截图

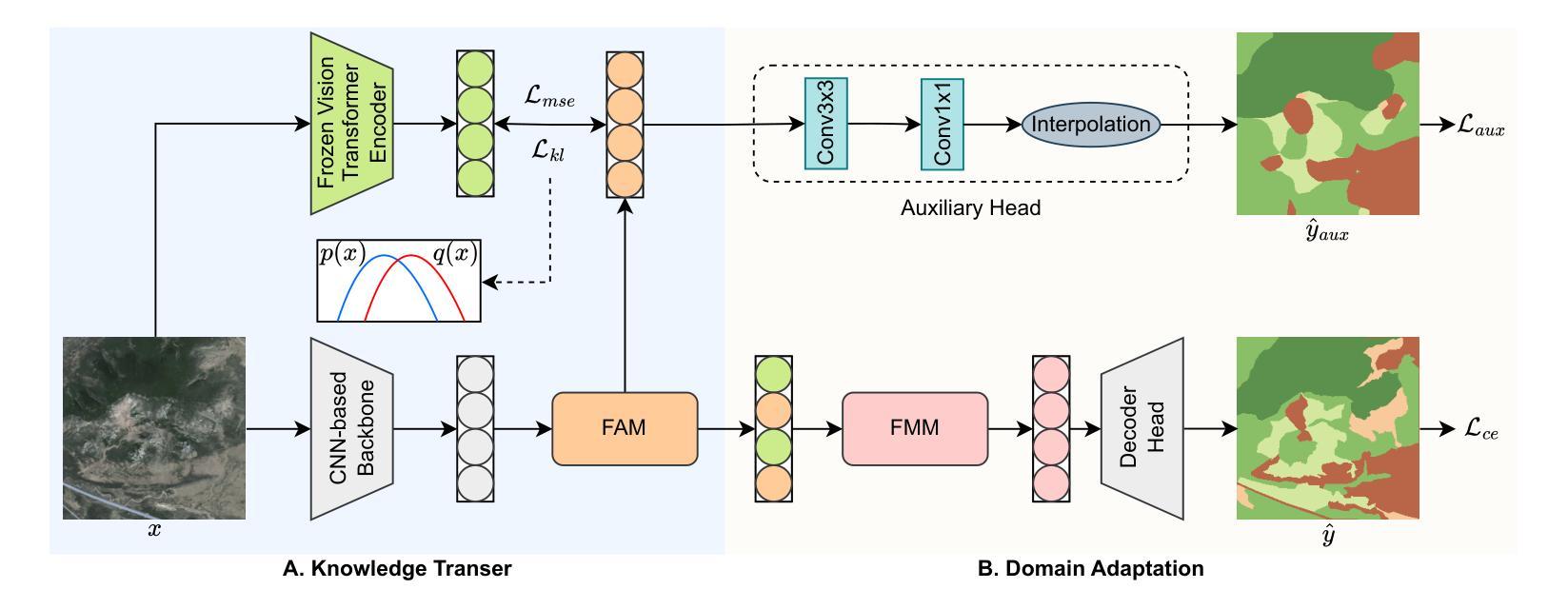
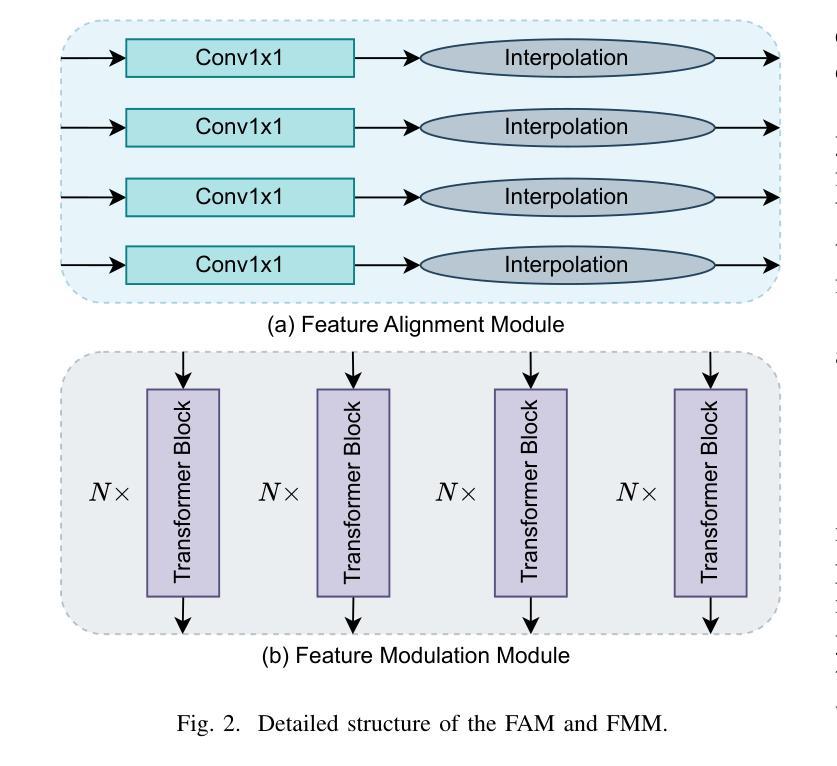
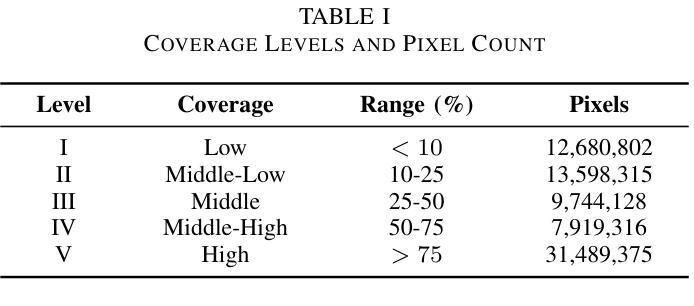
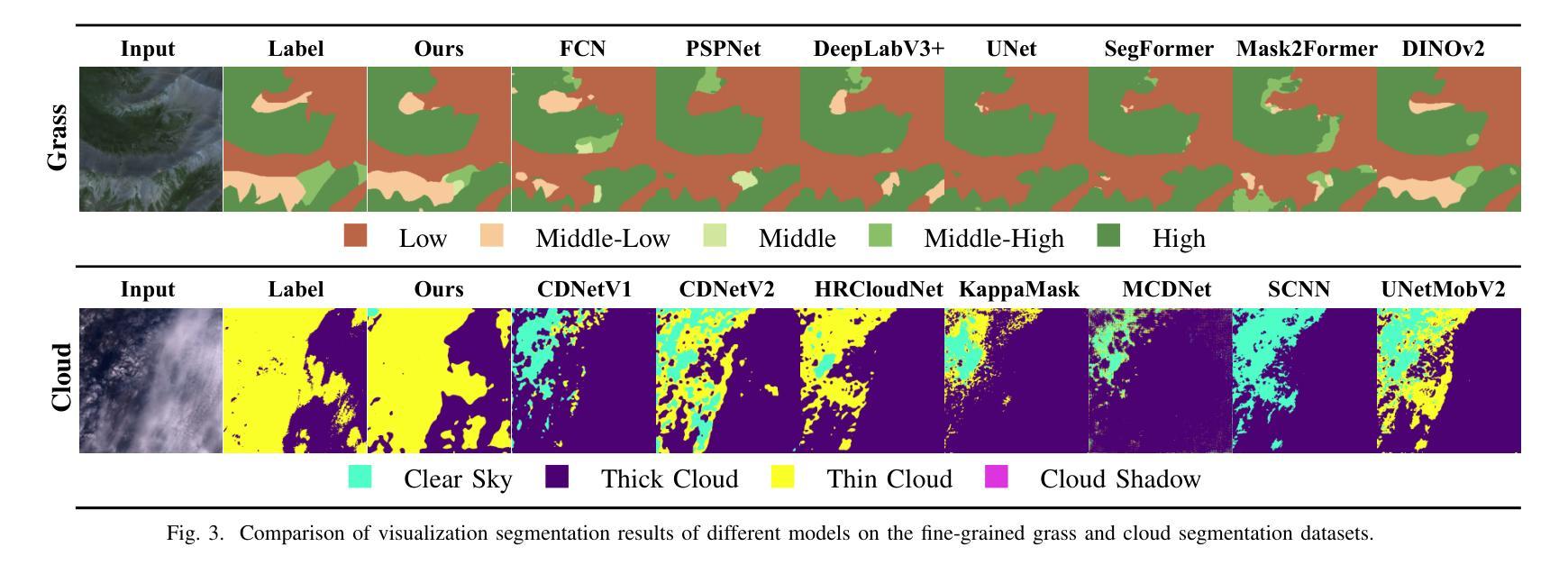
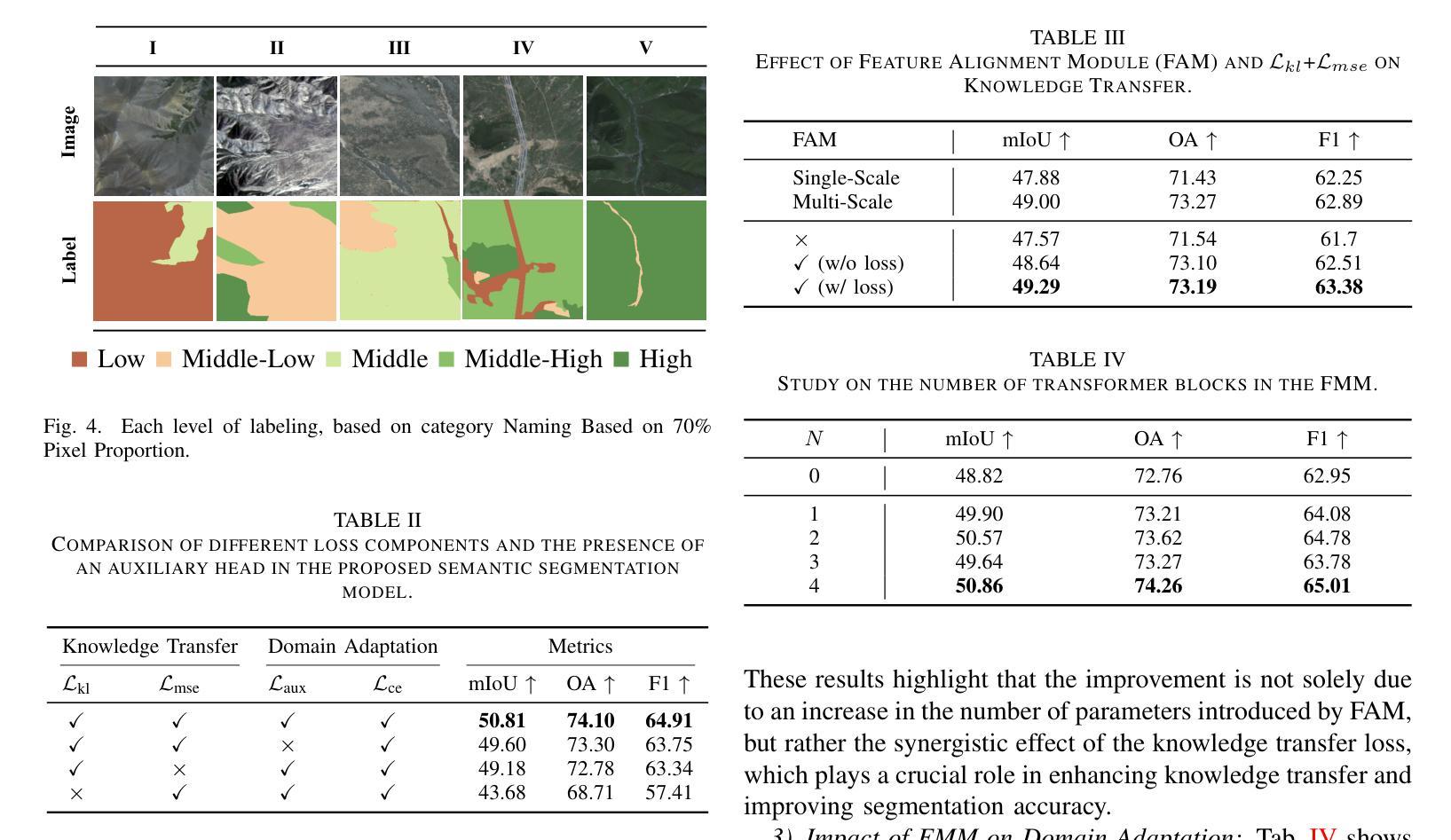
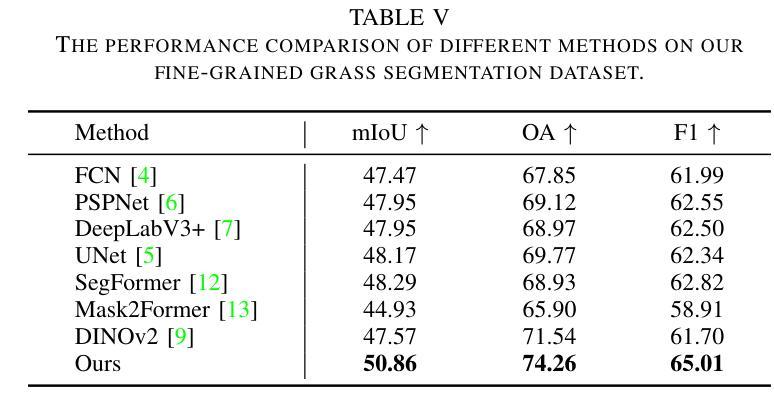
Knowledge Transfer and Domain Adaptation for Fine-Grained Remote Sensing Image Segmentation
Authors:Shun Zhang, Xuechao Zou, Kai Li, Congyan Lang, Shiying Wang, Pin Tao, Tengfei Cao
Fine-grained remote sensing image segmentation is essential for accurately identifying detailed objects in remote sensing images. Recently, vision transformer models (VTM) pretrained on large-scale datasets have shown strong zero-shot generalization, indicating that they have learned the general knowledge of object understanding. We introduce a novel end-to-end learning paradigm combining knowledge guidance with domain refinement to enhance performance. We present two key components: the Feature Alignment Module (FAM) and the Feature Modulation Module (FMM). FAM aligns features from a CNN-based backbone with those from the pretrained VTM’s encoder using channel transformation and spatial interpolation, and transfers knowledge via KL divergence and L2 normalization constraint. FMM further adapts the knowledge to the specific domain to address domain shift. We also introduce a fine-grained grass segmentation dataset and demonstrate, through experiments on two datasets, that our method achieves a significant improvement of 2.57 mIoU on the grass dataset and 3.73 mIoU on the cloud dataset. The results highlight the potential of combining knowledge transfer and domain adaptation to overcome domain-related challenges and data limitations. The project page is available at https://xavierjiezou.github.io/KTDA/.
精细遥感图像分割对于准确识别遥感图像中的详细对象至关重要。最近,在大型数据集上预训练的视觉转换器模型(VTM)表现出强大的零样本泛化能力,这表明它们已经学习了对象理解的一般知识。我们引入了一种结合知识引导和领域精化的新型端到端学习范式,以提高性能。我们提出了两个关键组件:特征对齐模块(FAM)和特征调制模块(FMM)。FAM通过对CNN骨干网络与预训练VTM编码器的特征进行通道变换和空间插值来对齐特征,并通过KL散度和L2归一化约束进行知识转移。FMM进一步将知识适应到特定领域以解决领域偏移问题。我们还引入了一个精细的草分割数据集,并通过两个数据集的实验证明,我们的方法在草数据集上实现了2.57 mIoU的显著改进,在云数据集上实现了3.73 mIoU的改进。结果突出了结合知识转移和领域适应以克服领域相关挑战和数据限制的潜力。项目页面可在https://xavierjiezou.github.io/KTDA/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 4 figures, 6 tables
Summary
基于遥感图像的精细粒度分割对于准确识别遥感图像中的详细对象至关重要。本研究引入了一种结合知识引导和域精化的新型端到端学习范式,并设计了两个关键组件:特征对齐模块(FAM)和特征调制模块(FMM)。FAM通过对通道变换和空间插值,将对来自CNN主干网的特征与预训练VTM编码器的特征对齐,并通过KL散度和L2归一化约束进行知识转移。FMM进一步调整知识以适应特定领域,以解决领域偏移问题。实验表明,该方法在草类数据集上提高了2.57 mIoU,在云数据集上提高了3.73 mIoU。结果突显了结合知识转移和领域适应以克服领域相关挑战和数据限制的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 精细粒度遥感图像分割对于识别图像中的详细对象非常重要。
- 引入了一种结合知识引导和域精化的新型端到端学习范式。
- 设计了特征对齐模块(FAM)和特征调制模块(FMM)两个关键组件。
- FAM通过对通道变换和空间插值实现特征对齐,并通过KL散度和L2归一化约束进行知识转移。
- FMM能够调整知识以适应特定领域,解决领域偏移问题。
- 在草类数据集和云数据集上的实验表明,该方法显著提高性能,分别提高了2.57 mIoU和3.73 mIoU。
点此查看论文截图

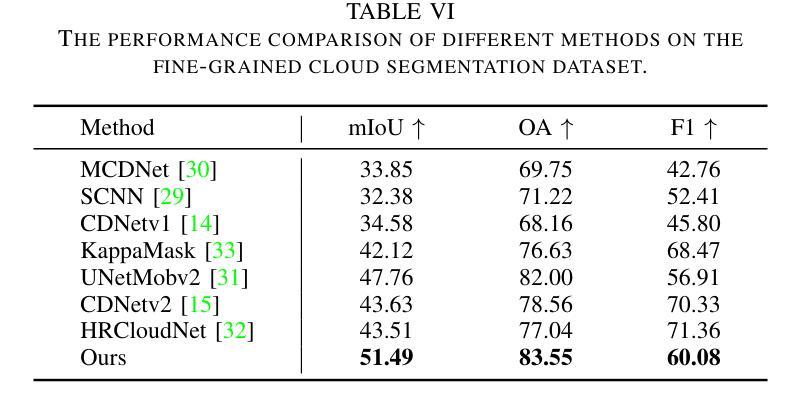
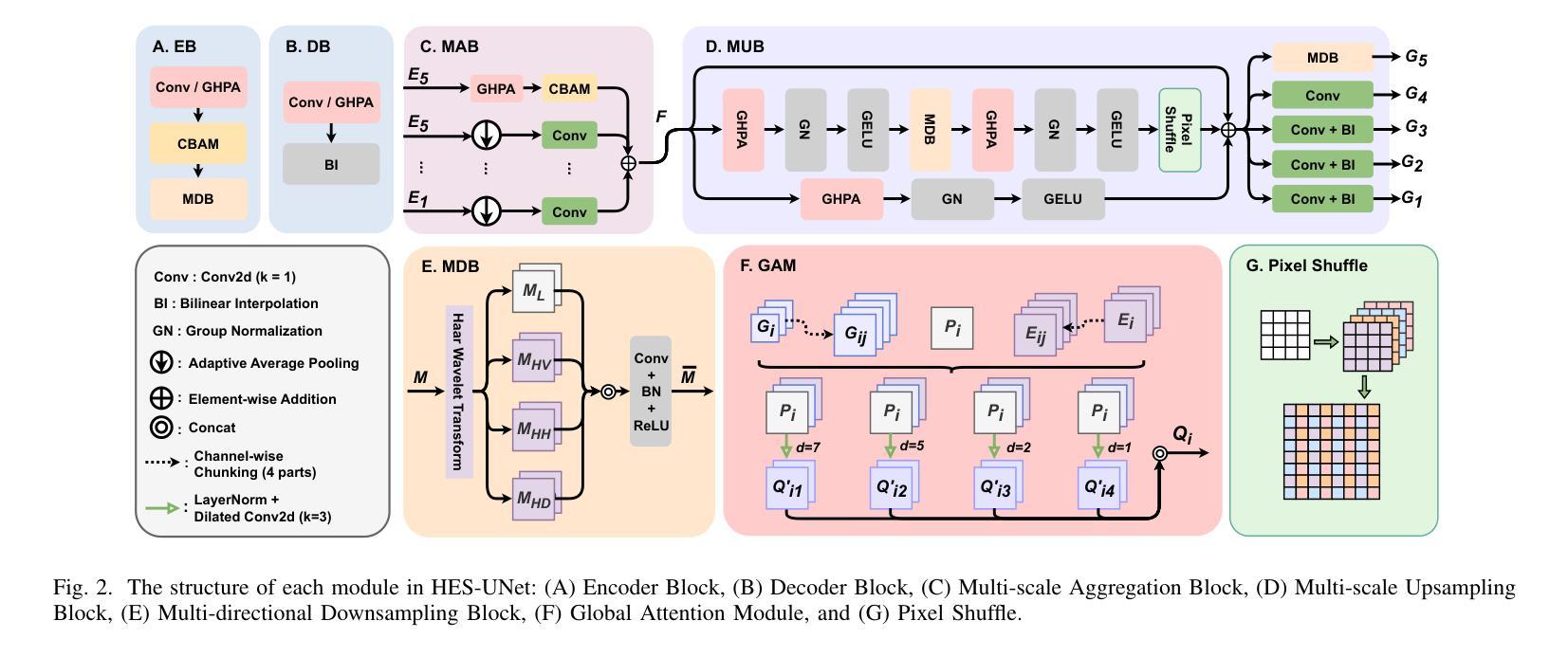
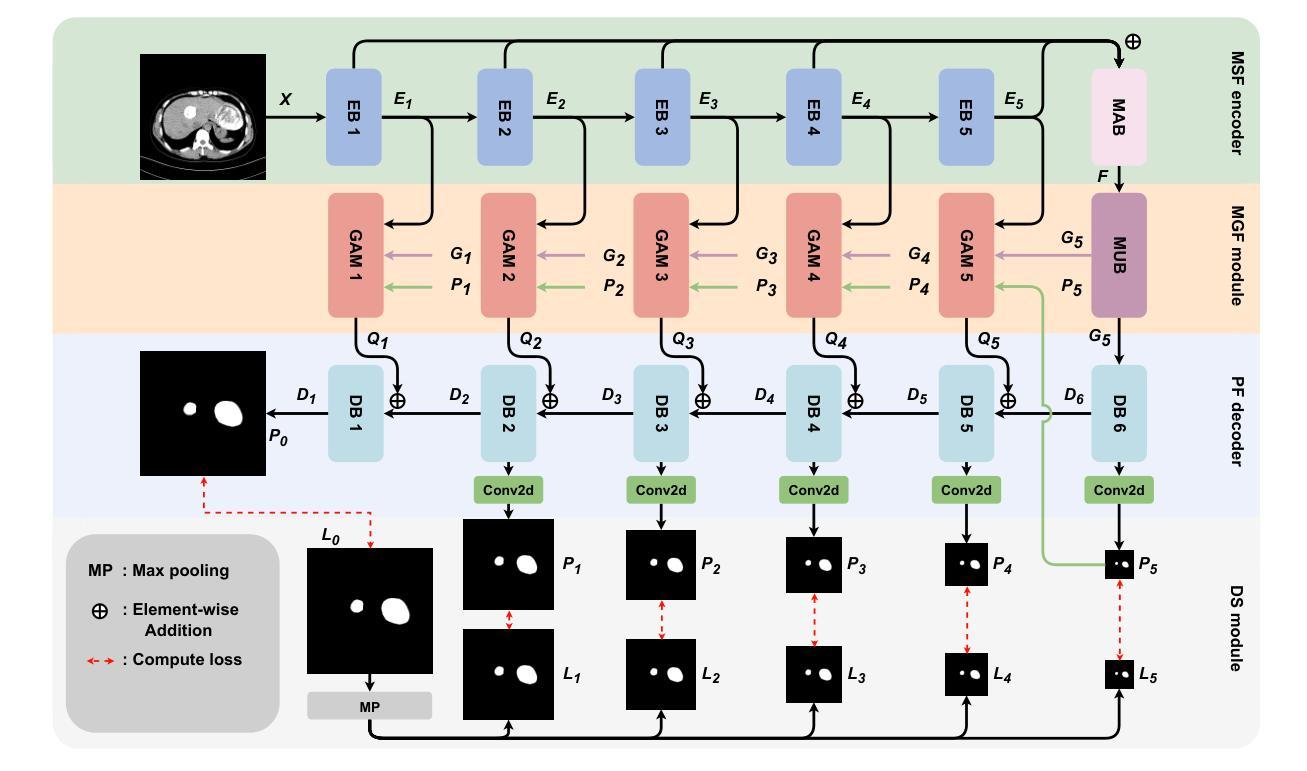
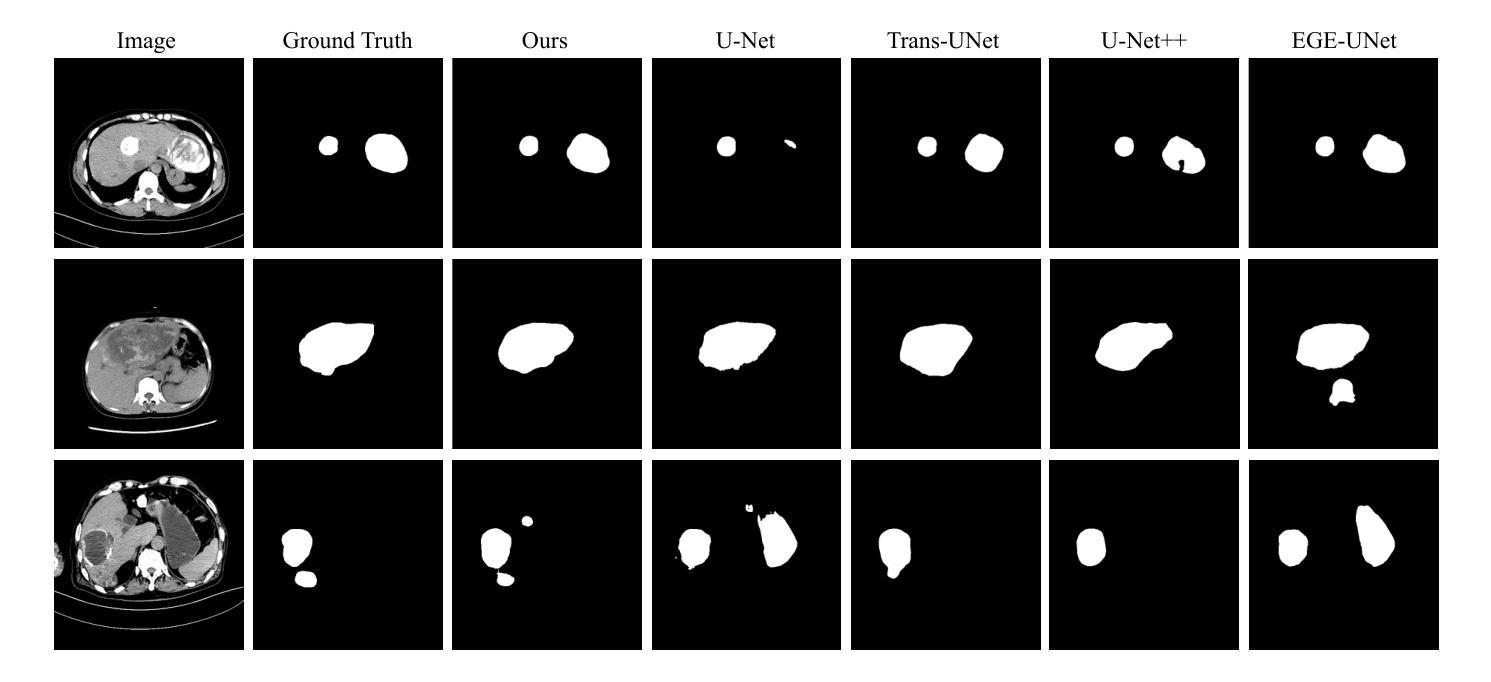
HES-UNet: A U-Net for Hepatic Echinococcosis Lesion Segmentation
Authors:Jiayan Chen, Kai Li, Zhanjin Wang, Zhan Wang, Jianqiang Huang
Hepatic echinococcosis (HE) is a prevalent disease in economically underdeveloped pastoral areas, where adequate medical resources are usually lacking. Existing methods often ignore multi-scale feature fusion or focus only on feature fusion between adjacent levels, which may lead to insufficient feature fusion. To address these issues, we propose HES-UNet, an efficient and accurate model for HE lesion segmentation. This model combines convolutional layers and attention modules to capture local and global features. During downsampling, the multi-directional downsampling block (MDB) is employed to integrate high-frequency and low-frequency features, effectively extracting image details. The multi-scale aggregation block (MAB) aggregates multi-scale feature information. In contrast, the multi-scale upsampling Block (MUB) learns highly abstract features and supplies this information to the skip connection module to fuse multi-scale features. Due to the distinct regional characteristics of HE, there is currently no publicly available high-quality dataset for training our model. We collected CT slice data from 268 patients at a certain hospital to train and evaluate the model. The experimental results show that HES-UNet achieves state-of-the-art performance on our dataset, achieving an overall Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) of 89.21%, which is 1.09% higher than that of TransUNet. The project page is available at https://chenjiayan-qhu.github.io/HES-UNet-page.
肝棘球虫病(HE)在经济欠发达的牧区是一种常见疾病,这些地区通常缺乏足够的医疗资源。现有方法常常忽略多尺度特征融合,或者只关注相邻级别之间的特征融合,这可能导致特征融合不足。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了HES-UNet,这是一个高效且准确的HE病变分割模型。该模型结合卷积层和注意力模块来捕捉局部和全局特征。在下采样过程中,采用多方向下采样块(MDB)来融合高频和低频特征,有效地提取图像细节。多尺度聚合块(MAB)聚合多尺度特征信息。相比之下,多尺度上采样块(MUB)学习高度抽象的特征,并将这些信息供应到跳过连接模块以融合多尺度特征。由于HE具有独特的区域特征,目前尚无公开的高质量数据集可供训练我们的模型。我们从某医院的268名患者那里收集了CT切片数据来训练和评估模型。实验结果表明,HES-UNet在我们的数据集上达到了最先进的性能,总体Dice相似系数(DSC)为89.21%,比TransUNet高出1.09%。项目页面可在https://chenjiayan-qhu.github.io/HES-UNet-page访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 3 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对肝棘球蚴病(HE)病变分割的高效且准确的模型HES-UNet。该模型结合卷积层和注意力模块捕捉局部和全局特征,并采用多方向下采样块(MDB)、多尺度聚合块(MAB)和多尺度上采样块(MUB)进行多尺度特征融合。使用来自268名患者的CT切片数据训练和评估模型,实验结果显示HES-UNet在数据集上达到了最先进的性能,总体Dice相似度系数为89.21%,比TransUNet高出1.09%。
Key Takeaways
- HES-UNet模型被提出用于解决肝棘球蚴病(HE)的病变分割问题。
- 模型结合了卷积层和注意力模块,以捕捉局部和全局特征。
- 采用多方向下采样块(MDB)进行图像细节的有效提取。
- 多尺度聚合块(MAB)用于聚合多尺度特征信息。
- 多尺度上采样块(MUB)学习高度抽象的特征,并将其与多尺度特征融合。
- 由于HE的独特区域特性,模型使用的是自行收集的高质量的CT切片数据。
点此查看论文截图

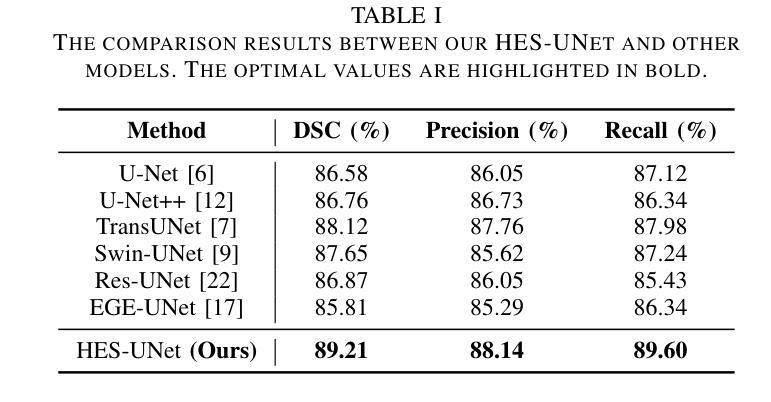
Improving text-conditioned latent diffusion for cancer pathology
Authors:Aakash Madhav Rao, Debayan Gupta
The development of generative models in the past decade has allowed for hyperrealistic data synthesis. While potentially beneficial, this synthetic data generation process has been relatively underexplored in cancer histopathology. One algorithm for synthesising a realistic image is diffusion; it iteratively converts an image to noise and learns the recovery process from this noise [Wang and Vastola, 2023]. While effective, it is highly computationally expensive for high-resolution images, rendering it infeasible for histopathology. The development of Variational Autoencoders (VAEs) has allowed us to learn the representation of complex high-resolution images in a latent space. A vital by-product of this is the ability to compress high-resolution images to space and recover them lossless. The marriage of diffusion and VAEs allows us to carry out diffusion in the latent space of an autoencoder, enabling us to leverage the realistic generative capabilities of diffusion while maintaining reasonable computational requirements. Rombach et al. [2021b] and Yellapragada et al. [2023] build foundational models for this task, paving the way to generate realistic histopathology images. In this paper, we discuss the pitfalls of current methods, namely [Yellapragada et al., 2023] and resolve critical errors while proposing improvements along the way. Our methods achieve an FID score of 21.11, beating its SOTA counterparts in [Yellapragada et al., 2023] by 1.2 FID, while presenting a train-time GPU memory usage reduction of 7%.
过去十年生成模型的发展使得超真实数据合成成为可能。尽管具有潜在优势,但这种合成数据生成过程在癌症组织病理学方面相对被研究得较少。合成逼真图像的一种算法是扩散法,它将图像逐步转换为噪声,并从这种噪声中学习恢复过程(Wang and Vastola, 2023)。虽然有效,但对于高分辨率图像来说,它的计算成本非常高,使得它在组织病理学中不可行。变分自动编码器(VAEs)的发展使我们能够在潜在空间中学习复杂高分辨率图像的代表。这的一个重要副产品是能够压缩高分辨率图像并无损恢复它们。扩散和VAEs的结合使我们能够在自动编码器的潜在空间中进行扩散,使我们能够利用扩散的逼真生成能力,同时保持合理的计算要求。Rombach等人(2021b)和Yellapragada等人(2023)为这项任务建立了基础模型,为生成逼真的组织病理图像铺平了道路。在本文中,我们讨论了当前方法的不足(尤其是Yellapragada等人(2023)的工作),并提出了解决关键错误的方法以及在过程中提出改进。我们的方法取得了FID分数为21.11的成绩,比Yellapragada等人(2023)的最佳同行高出1.2 FID,同时实现了训练时GPU内存使用减少7%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
生成模型的发展使得超真实数据合成成为可能。在癌症组织病理学领域,扩散算法(如迭代式噪声图像复原)是合成现实图像的有效方法,但其对高分辨率图像的计算需求过高,使得实际应用受限。变分自编码器(VAEs)的提出,可以在潜在空间内学习复杂高分辨率图像的表现,并可进行图像无损压缩。结合扩散和VAEs,可在潜在空间内实现扩散过程,以利用扩散的真实生成能力同时保持合理的计算需求。本文讨论了当前方法的缺陷并提出了改进方案,实现了FID分数为21.11的效果,超过了之前的研究成果。通过本文研究可进一步推进医学图像处理领域的技术发展与应用实践。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型的发展推动了超真实数据合成技术的进步。
- 扩散算法是一种有效的合成现实图像的方法,但对计算资源的需求较高,限制了其在高分辨率图像中的应用。
- 变分自编码器(VAEs)能够在潜在空间内学习复杂高分辨率图像的表现,并支持图像无损压缩。
- 结合扩散和VAEs技术,可以在潜在空间内实现扩散过程,从而提高计算效率并保留生成图像的真实性。
点此查看论文截图

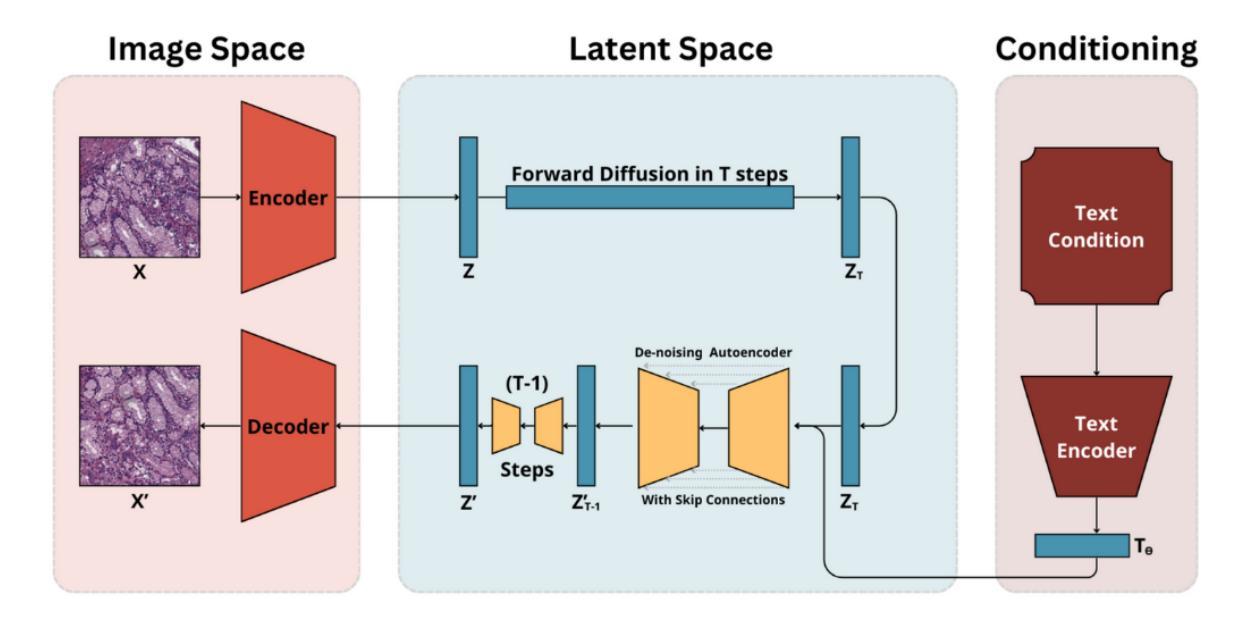
How Certain are Uncertainty Estimates? Three Novel Earth Observation Datasets for Benchmarking Uncertainty Quantification in Machine Learning
Authors:Yuanyuan Wang, Qian Song, Dawood Wasif, Muhammad Shahzad, Christoph Koller, Jonathan Bamber, Xiao Xiang Zhu
Uncertainty quantification (UQ) is essential for assessing the reliability of Earth observation (EO) products. However, the extensive use of machine learning models in EO introduces an additional layer of complexity, as those models themselves are inherently uncertain. While various UQ methods do exist for machine learning models, their performance on EO datasets remains largely unevaluated. A key challenge in the community is the absence of the ground truth for uncertainty, i.e. how certain the uncertainty estimates are, apart from the labels for the image/signal. This article fills this gap by introducing three benchmark datasets specifically designed for UQ in EO machine learning models. These datasets address three common problem types in EO: regression, image segmentation, and scene classification. They enable a transparent comparison of different UQ methods for EO machine learning models. We describe the creation and characteristics of each dataset, including data sources, preprocessing steps, and label generation, with a particular focus on calculating the reference uncertainty. We also showcase baseline performance of several machine learning models on each dataset, highlighting the utility of these benchmarks for model development and comparison. Overall, this article offers a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners working in artificial intelligence for EO, promoting a more accurate and reliable quality measure of the outputs of machine learning models. The dataset and code are accessible via https://gitlab.lrz.de/ai4eo/WG_Uncertainty.
不确定性量化(UQ)对于评估地球观测(EO)产品的可靠性至关重要。然而,在地球观测中广泛使用的机器学习模型引入了一个额外的复杂性层面,因为这些模型本身具有固有的不确定性。虽然针对机器学习模型存在各种不确定性量化方法,但它们在地球观测数据集上的性能在很大程度上尚未得到评估。社区面临的一个关键挑战是缺乏不确定性的真实基准,即除了图像/信号的标签外,不确定性的估计有多确定。本文通过引入三个专门用于地球观测机器学习模型中的不确定性量化的基准数据集来填补这一空白。这些数据集涵盖了地球观测中的三种常见类型问题:回归、图像分割和场景分类。它们能够透明地比较不同的地球观测机器学习模型的不确定性量化方法。我们描述了每个数据集的创建和特征,包括数据来源、预处理步骤和标签生成,特别侧重于计算参考不确定性。我们还展示了几个机器学习模型在每个数据集中的基准性能,突出了这些基准对于模型开发和比较的有用性。总体而言,本文为从事地球观测人工智能的研究人员和实践者提供了宝贵的资源,促进了机器学习模型输出质量的更准确和可靠度量。数据集和代码可通过https://gitlab.lrz.de/ai4eo/WG_Uncertainty访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine
Summary
本文介绍了不确定性量化在地球观测产品评估中的重要性,并针对机器学习模型在地球观测中的应用所带来的不确定性问题,提出了三个专门用于地球观测机器学习模型不确定性量化的基准数据集。这些数据集涵盖了回归、图像分割和场景分类三种常见问题类型,为不同不确定性量化方法在地球观测机器学习模型中的透明比较提供了可能。文章还介绍了每个数据集的创建和特性,包括数据来源、预处理步骤和标签生成,并特别强调了参考不确定性的计算。此外,文章展示了几个机器学习模型在这些基准数据集上的基准性能,强调了这些基准对于模型开发和比较的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 不确定性量化在评估地球观测产品可靠性方面至关重要。
- 机器学习模型在地球观测中的使用引入了一层额外的不确定性。
- 现有不确定性量化方法在地球观测数据集上的性能尚未得到充分评估。
- 文中介绍了三个专门用于地球观测机器学习模型不确定性量化的基准数据集。
- 这些数据集涵盖回归、图像分割和场景分类三种常见问题类型。
- 文章强调了参考不确定性的计算和数据集的创建特性。
点此查看论文截图

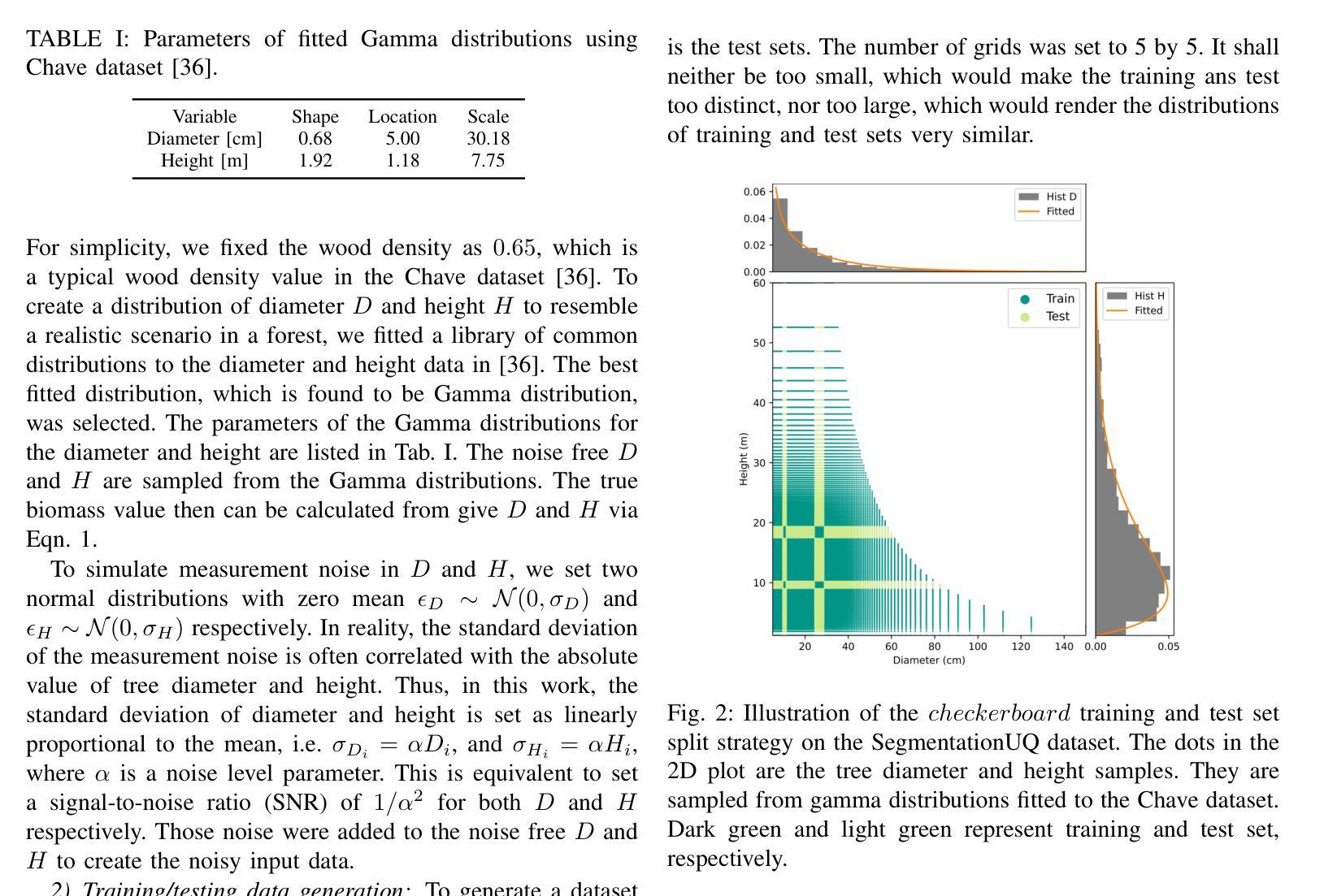

High-throughput computational screening of small, eco-friendly, molecular crystals for sustainable piezoelectric materials
Authors:Shubham Vishnoi, Geetu Kumari, Robert Guest, Pierre-André Cazade, Sarah Guerin
Organic molecular crystals are ideally placed to become next-generation piezoelectric materials due to their diverse chemistries that can be used to engineer tailor-made solid-state assemblies. Using crystal engineering principles, and techniques such as co-crystallisation, these materials can be engineered to have a wide range of electromechanical properties. For materials that have been structurally characterised by methods such as X-Ray Diffraction, computational chemistry is an effective tool to predict their electromechanical properties, allowing researchers to screen these molecular crystals and identify materials best suited to their chosen application. Here we present our database of small molecular crystals, and their Density Functional Theory (DFT) predicted electromechanical properties, CrystalDFT (https://actuatelab.ie/CrystalDFT). We highlight the broad range of electromechanical properties amongst this primary dataset, and in particular, the high number of crystals that have a naturally occurring longitudinal d33 constant. This longitudinal electromechanical coupling is a prerequisite for several conventional sensing and energy harvesting applications, the presence of which is notably rare amongst the literature on biomolecular crystal piezoelectricity to date.
有机分子晶体因其丰富的化学特性,可定制工程化固态组装结构,有望成为下一代压电材料。利用晶体工程原理和共结晶等技术,可以设计这些材料具有广泛的机电性能。对于通过X射线衍射等方法进行结构表征的材料,计算化学是预测其机电性能的有效工具,使研究人员能够筛选这些分子晶体,并确定最适合其选择应用的材料。在此,我们介绍了小分子晶体的数据库及其基于密度泛函理论(DFT)预测的机电性能CrystalDFT(https://actuatelab.ie/CrystalDFT)。我们强调了此主要数据集中机电性能的广泛范围,尤其是具有高自然纵向d33常数的晶体数量之多。这种纵向机电耦合是多种传统传感和能量收集应用的前提条件,在迄今为止的生物分子晶体压电性能的文献中极为罕见。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
有机分子晶体因其丰富的化学特性,成为下一代压电材料的理想选择。通过晶体工程原理和共结晶等技术,可以定制固态组装,使其具有广泛的机械电子特性。结构特征明确的材料,通过如X射线衍射等方法进行研究,计算化学成为预测其机械电子特性的有效工具。本文介绍了小分子晶体数据库及其密度泛函理论预测的机械电子特性——CrystalDFT。特别强调了这些晶体广泛的机械电子特性范围,特别是自然状态下具有高纵向d33常数的晶体数量众多。这种纵向机械电子耦合是许多传统传感和能量采集应用的前提条件,这在生物分子晶体压电性的文献中极为罕见。
Key Takeaways
- 有机分子晶体因其丰富的化学特性成为下一代压电材料的理想选择。
- 通过晶体工程原理和共结晶技术,可以定制固态组装以具有广泛的机械电子特性。
- 结构特征明确的材料可以通过X射线衍射方法进行研究。
- 计算化学是预测材料机械电子特性的有效工具。
- 本文介绍了小分子晶体数据库——CrystalDFT。
- 这些晶体具有广泛的机械电子特性范围。
点此查看论文截图

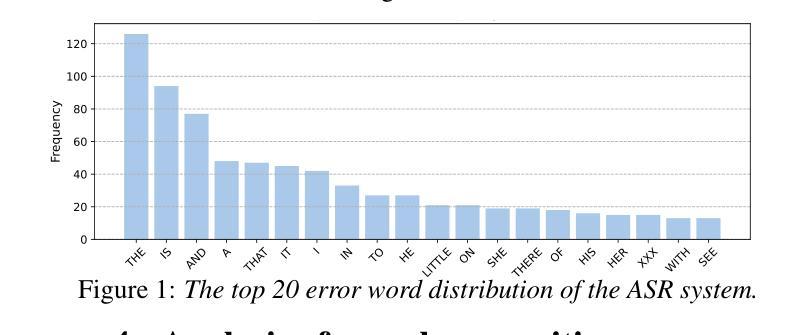
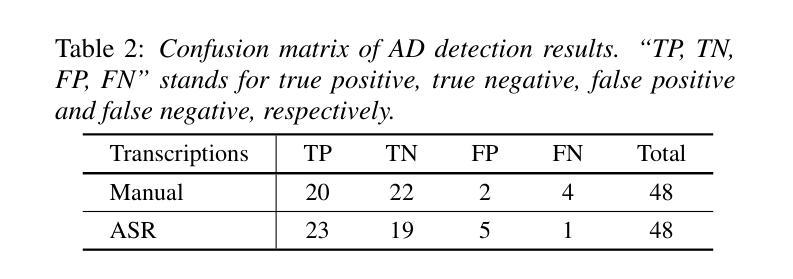
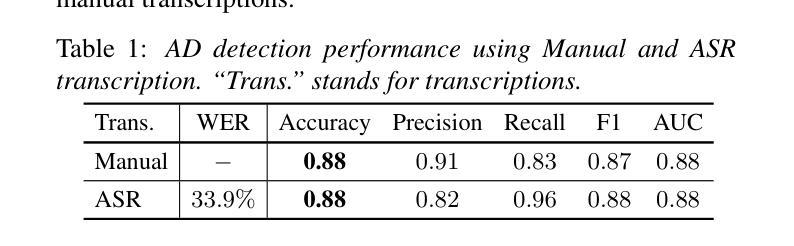
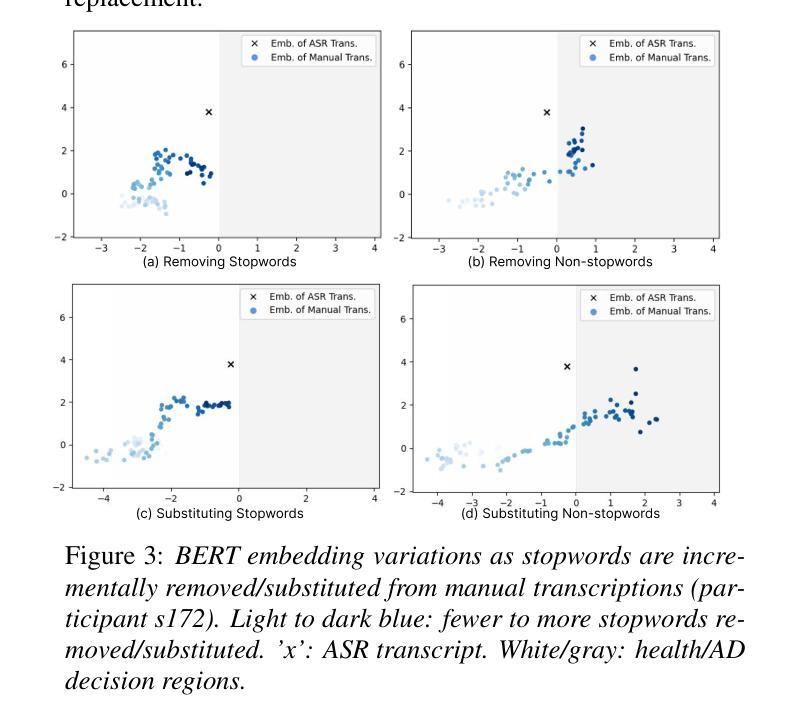
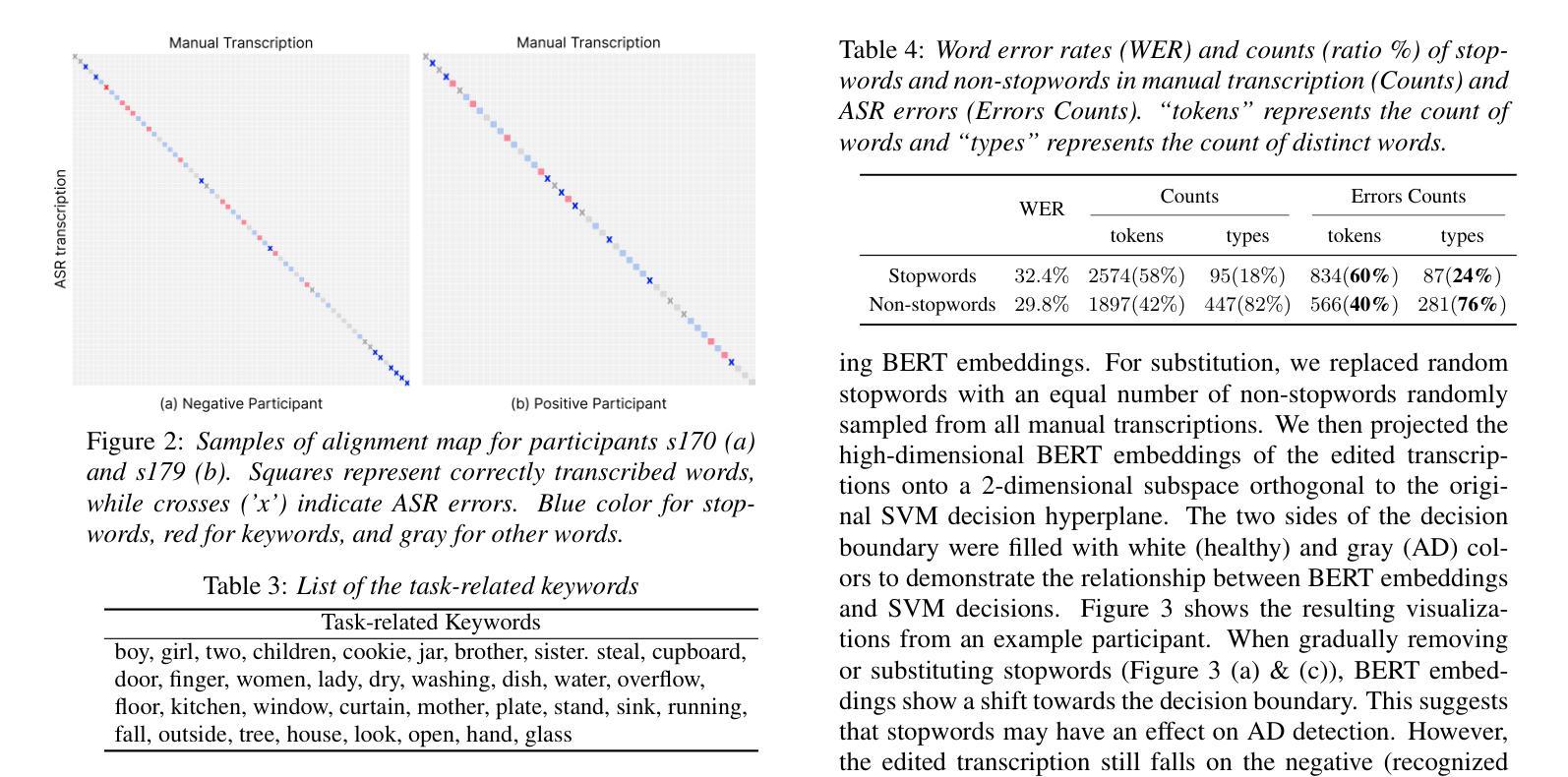
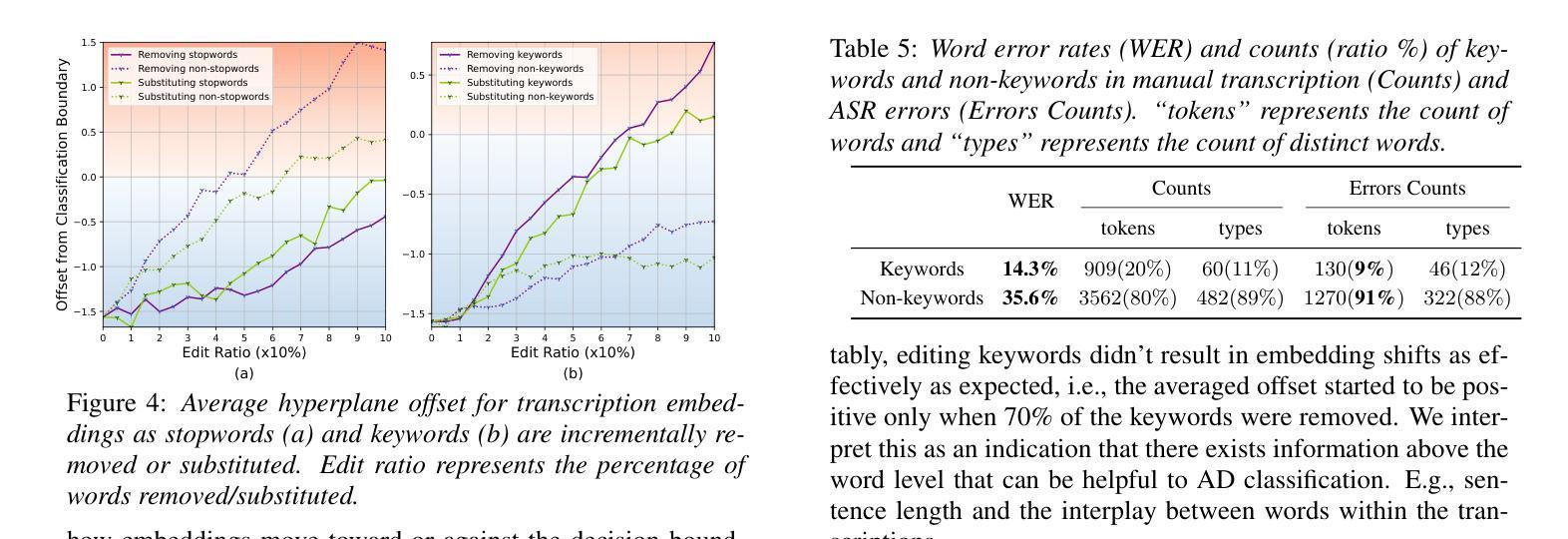
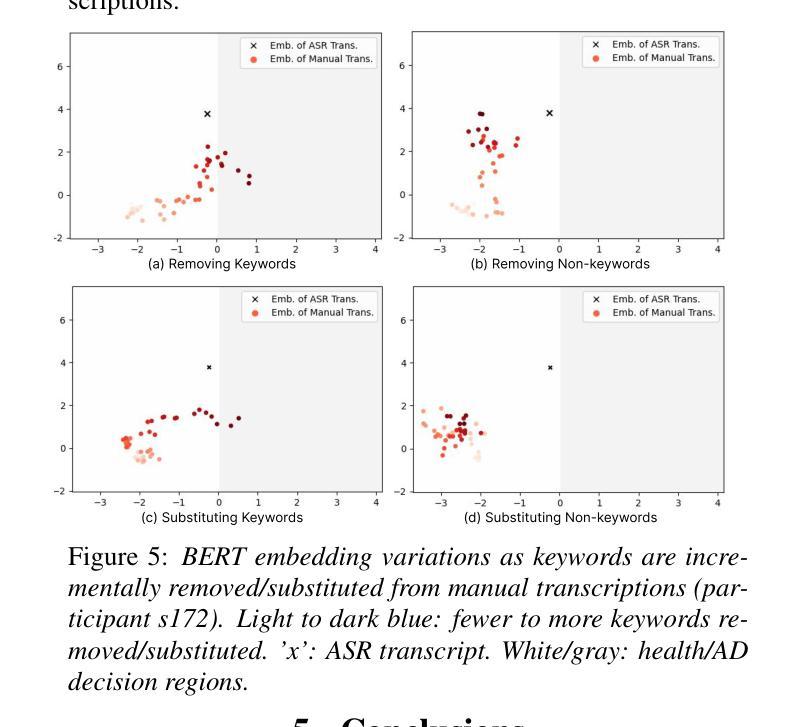
Not All Errors Are Equal: Investigation of Speech Recognition Errors in Alzheimer’s Disease Detection
Authors:Jiawen Kang, Junan Li, Jinchao Li, Xixin Wu, Helen Meng
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) plays an important role in speech-based automatic detection of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, recognition errors could propagate downstream, potentially impacting the detection decisions. Recent studies have revealed a non-linear relationship between word error rates (WER) and AD detection performance, where ASR transcriptions with notable errors could still yield AD detection accuracy equivalent to that based on manual transcriptions. This work presents a series of analyses to explore the effect of ASR transcription errors in BERT-based AD detection systems. Our investigation reveals that not all ASR errors contribute equally to detection performance. Certain words, such as stopwords, despite constituting a large proportion of errors, are shown to play a limited role in distinguishing AD. In contrast, the keywords related to diagnosis tasks exhibit significantly greater importance relative to other words. These findings provide insights into the interplay between ASR errors and the downstream detection model.
自动语音识别(ASR)在基于语音的自动检测阿尔茨海默病(AD)中发挥着重要作用。然而,识别错误可能会传播至下游,可能影响检测决策。最近的研究揭示了词错误率(WER)与AD检测性能之间的非线性关系,其中ASR转录的显著错误仍然可能产生与手动转录相当的AD检测精度。这项工作提供了一系列分析,以探讨ASR转录错误对基于BERT的AD检测系统的影响。我们的调查表明,并非所有的ASR错误都对检测性能产生同等影响。某些词语,如停用词,虽然构成了大量的错误,但在区分AD方面的作用有限。相比之下,与诊断任务相关的关键词相对于其他词语表现出显著的重要性。这些发现提供了ASR错误与下游检测模型之间相互作用的重要见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE ISCSLP 2024
Summary
语音识别在基于语音的自动检测阿尔茨海默病中扮演重要角色,但识别错误可能影响下游检测决策。研究表明,词错误率与阿尔茨海默病检测性能之间存在非线性关系。本研究探讨了自动语音识别转录错误对基于BERT的阿尔茨海默病检测系统的性能影响,发现并非所有ASR错误对检测性能产生同样的影响。对于任务无关停用词产生大量错误对检测区分度影响有限,而诊断关键词的重要性显著大于其他词汇。这为ASR错误与下游检测模型之间的相互作用提供了见解。
Key Takeaways
- 自动语音识别(ASR)在基于语音的阿尔茨海默病(AD)检测中发挥着重要作用。
- ASR识别错误可能影响下游检测决策。
- 词错误率(WER)与AD检测性能之间存在非线性关系。
- 在BERT为基础的AD检测系统中,并非所有ASR转录错误均对检测性能产生重大影响。
- 诊断任务无关停用词虽然产生大量错误但对AD检测区分度影响有限。
- 与诊断相关的关键词在区分阿尔茨海默病方面表现出显著的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

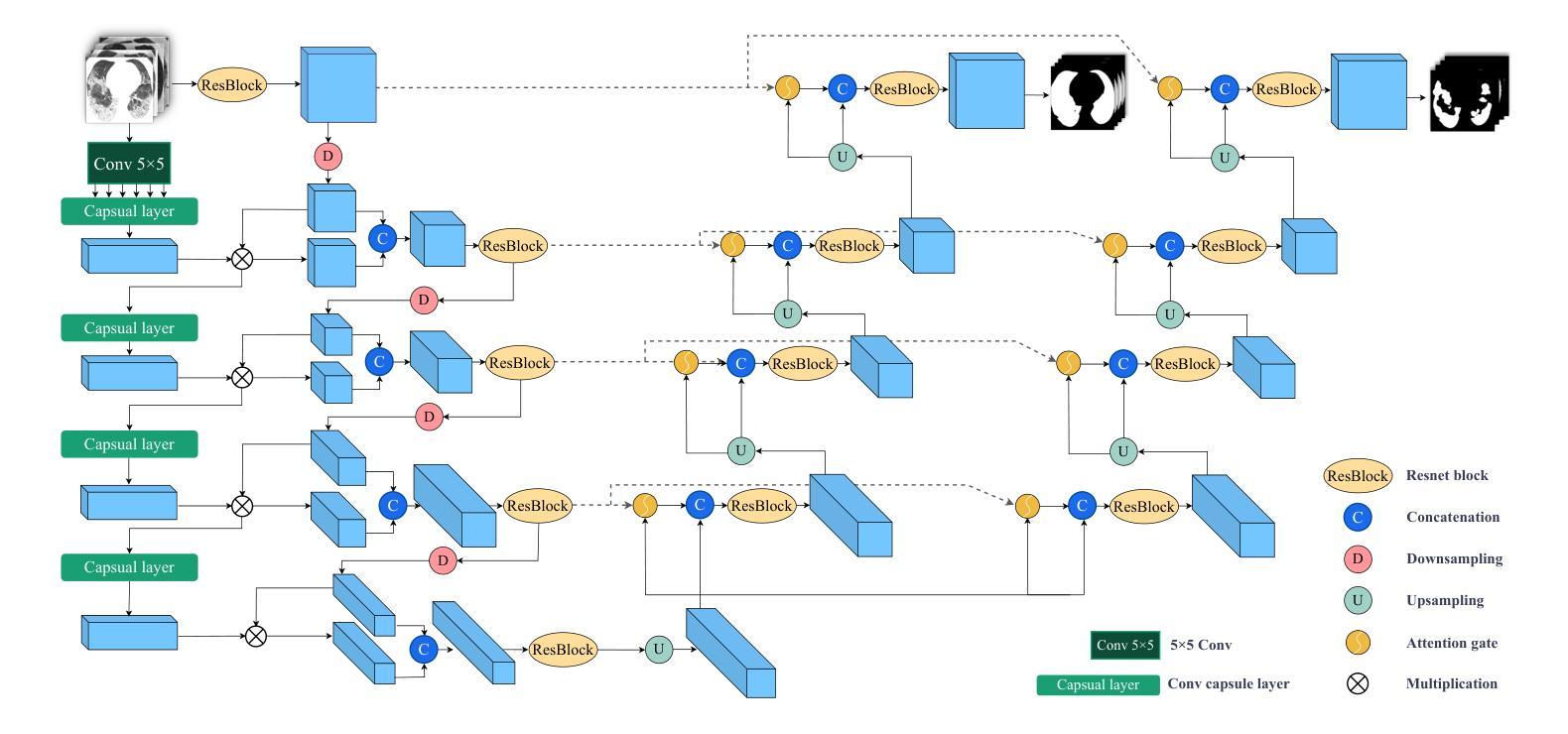
CAD-Unet: A Capsule Network-Enhanced Unet Architecture for Accurate Segmentation of COVID-19 Lung Infections from CT Images
Authors:Yijie Dang, Weijun Ma, Xiaohu Luo
Since the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2019, medical imaging has emerged as a primary modality for diagnosing COVID-19 pneumonia. In clinical settings, the segmentation of lung infections from computed tomography images enables rapid and accurate quantification and diagnosis of COVID-19. Segmentation of COVID-19 infections in the lungs poses a formidable challenge, primarily due to the indistinct boundaries and limited contrast presented by ground glass opacity manifestations. Moreover, the confounding similarity between infiltrates, lung tissues, and lung walls further complicates this segmentation task. To address these challenges, this paper introduces a novel deep network architecture, called CAD-Unet, for segmenting COVID-19 lung infections. In this architecture, capsule networks are incorporated into the existing Unet framework. Capsule networks represent a novel network architecture that differs from traditional convolutional neural networks. They utilize vectors for information transfer among capsules, facilitating the extraction of intricate lesion spatial information. Additionally, we design a capsule encoder path and establish a coupling path between the unet encoder and the capsule encoder. This design maximizes the complementary advantages of both network structures while achieving efficient information fusion. \noindent Finally, extensive experiments are conducted on four publicly available datasets, encompassing binary segmentation tasks and multi-class segmentation tasks. The experimental results demonstrate the superior segmentation performance of the proposed model. The code has been released at: https://github.com/AmanoTooko-jie/CAD-Unet.
自2019年COVID-19疫情爆发以来,医学成像已成为诊断COVID-19肺炎的主要方式。在临床环境中,从计算机断层扫描图像中对肺部感染的分割能够实现COVID-19的快速和准确量化及诊断。对肺部COVID-19感染的分割构成了一项艰巨的挑战,主要是因为磨玻璃样浑浊表现所呈现的边界模糊和对比度有限。此外,浸润、肺组织和肺壁之间的混淆相似性进一步加剧了这一分割任务的复杂性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新冠疫情爆发以来,医学成像成为诊断新冠肺炎的主要手段之一。针对肺部CT影像中新冠肺炎感染病灶分割的挑战,本文提出了一种新型的深度网络架构——CAD-Unet。该架构结合了胶囊网络与现有的Unet框架,通过矢量传递信息的方式,更精确地提取病灶的空间信息。经过四项公开数据集的实验验证,该模型在二元及多元分割任务上表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像成为诊断新冠肺炎的主要手段之一。
- 肺部CT影像中新冠肺炎感染病灶分割具有挑战性。
- CAD-Unet是一种结合了胶囊网络与Unet的新型深度网络架构。
- 胶囊网络通过矢量传递信息,更精确地提取病灶的空间信息。
- CAD-Unet模型在二元及多元分割任务上表现出卓越的性能。
- 该模型通过融合两种网络结构的优势,实现了高效的信息融合。
点此查看论文截图

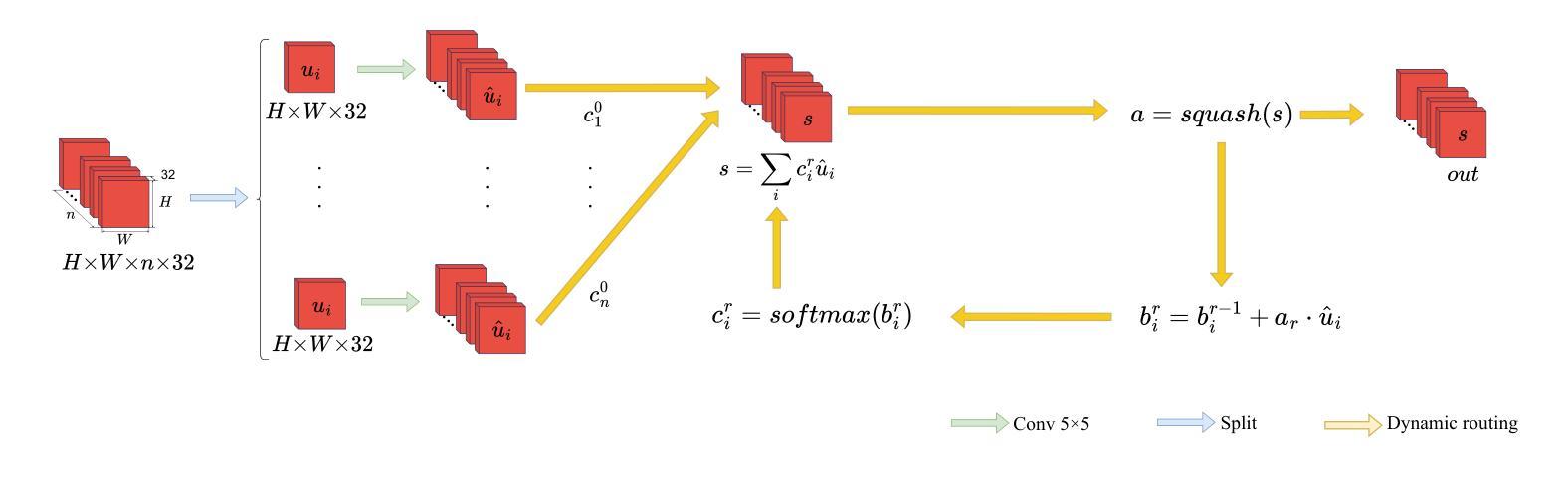
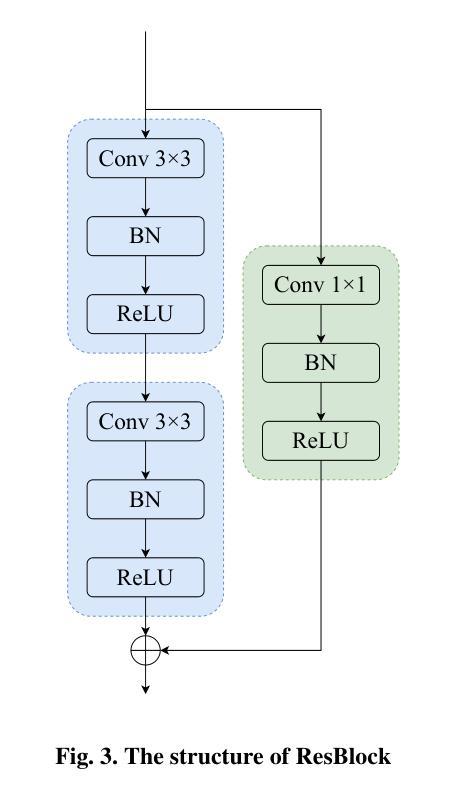
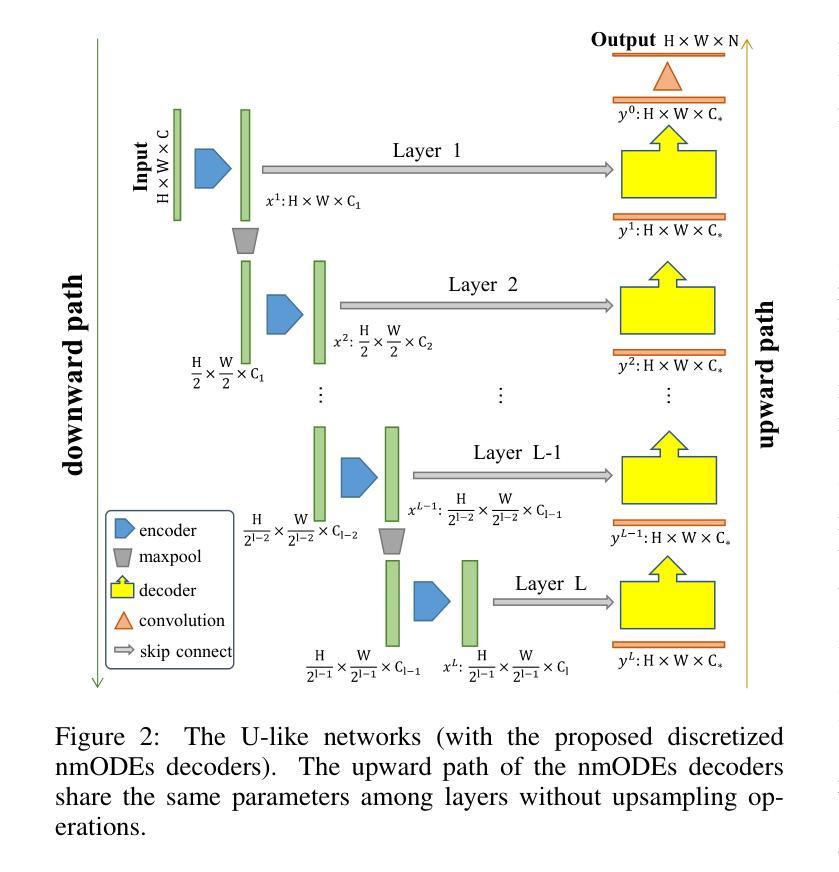
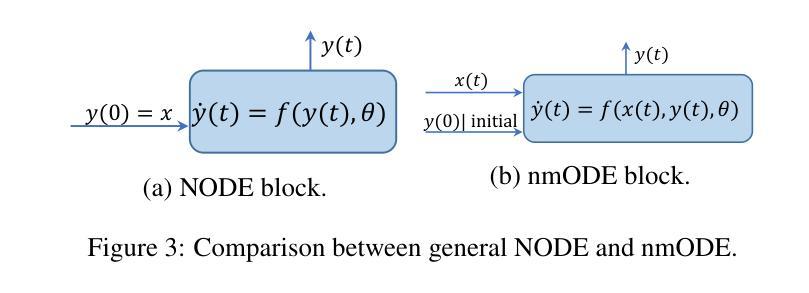
A Lightweight U-like Network Utilizing Neural Memory Ordinary Differential Equations for Slimming the Decoder
Authors:Quansong He, Xiaojun Yao, Jun Wu, Zhang Yi, Tao He
In recent years, advanced U-like networks have demonstrated remarkable performance in medical image segmentation tasks. However, their drawbacks, including excessive parameters, high computational complexity, and slow inference speed, pose challenges for practical implementation in scenarios with limited computational resources. Existing lightweight U-like networks have alleviated some of these problems, but they often have pre-designed structures and consist of inseparable modules, limiting their application scenarios. In this paper, we propose three plug-and-play decoders by employing different discretization methods of the neural memory Ordinary Differential Equations (nmODEs). These decoders integrate features at various levels of abstraction by processing information from skip connections and performing numerical operations on upward path. Through experiments on the PH2, ISIC2017, and ISIC2018 datasets, we embed these decoders into different U-like networks, demonstrating their effectiveness in significantly reducing the number of parameters and FLOPs while maintaining performance. In summary, the proposed discretized nmODEs decoders are capable of reducing the number of parameters by about 20% ~ 50% and FLOPs by up to 74%, while possessing the potential to adapt to all U-like networks. Our code is available at https://github.com/nayutayuki/Lightweight-nmODE-Decoders-For-U-like-networks.
近年来,先进的U型网络在医学图像分割任务中表现出卓越的性能。然而,它们的缺点,包括参数过多、计算复杂性高和推理速度慢,为在有限计算资源的场景中实际应用带来了挑战。现有的轻量级U型网络已经缓解了一些这些问题,但它们通常具有预先设计的结构和不可分离的模块,限制了其应用场景。在本文中,我们通过采用神经记忆普通微分方程(nmODEs)的不同离散化方法,提出了三种即插即用的解码器。这些解码器通过处理来自跳过连接的信息并在向上路径上进行数值运算,来整合不同抽象层次的特征。我们在PH2、ISIC2017和ISIC2018数据集上进行了实验,将这些解码器嵌入不同的U型网络,证明了它们在显著减少参数和FLOPs的同时保持性能的有效性。总的来说,所提出的离散化nmODEs解码器能够减少约20%~50%的参数和最多达74%的FLOPs,同时有潜力适应所有U型网络。我们的代码可在[https://github.com/nayutayuki/Lightweight-nmODE-Decoders-For-U-like-networks找到。]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出利用神经记忆常微分方程(nmODEs)的不同离散化方法设计三款即插即用解码器,用于医学图像分割。这些解码器能够集成不同层次的特征,减少参数和计算量,同时保持性能。实验证明,这些解码器可嵌入各种U形网络,减少约20%-50%的参数和最多74%的计算量。
Key Takeaways
- U形网络在医学图像分割中表现出卓越性能,但其参数过多、计算复杂度高和推理速度慢等缺点限制了实际应用。
- 现有轻量化U形网络虽缓解了部分问题,但预设计结构和不可分离模块限制了其应用场景。
- 本文提出利用nmODEs的不同离散化方法设计即插即用解码器,以集成不同层次的特征。
- 这些解码器通过处理跳跃连接的信息和向上路径上的数值运算,实现了参数和计算量的显著减少。
- 实验证明,这些解码器可嵌入不同的U形网络,并在PH2、ISIC2017和ISIC2018数据集上展示了效果。
- 解码器可减少约20%-50%的参数和最多74%的计算量,同时保持性能。
- 代码已公开,可适应所有U形网络。
点此查看论文截图

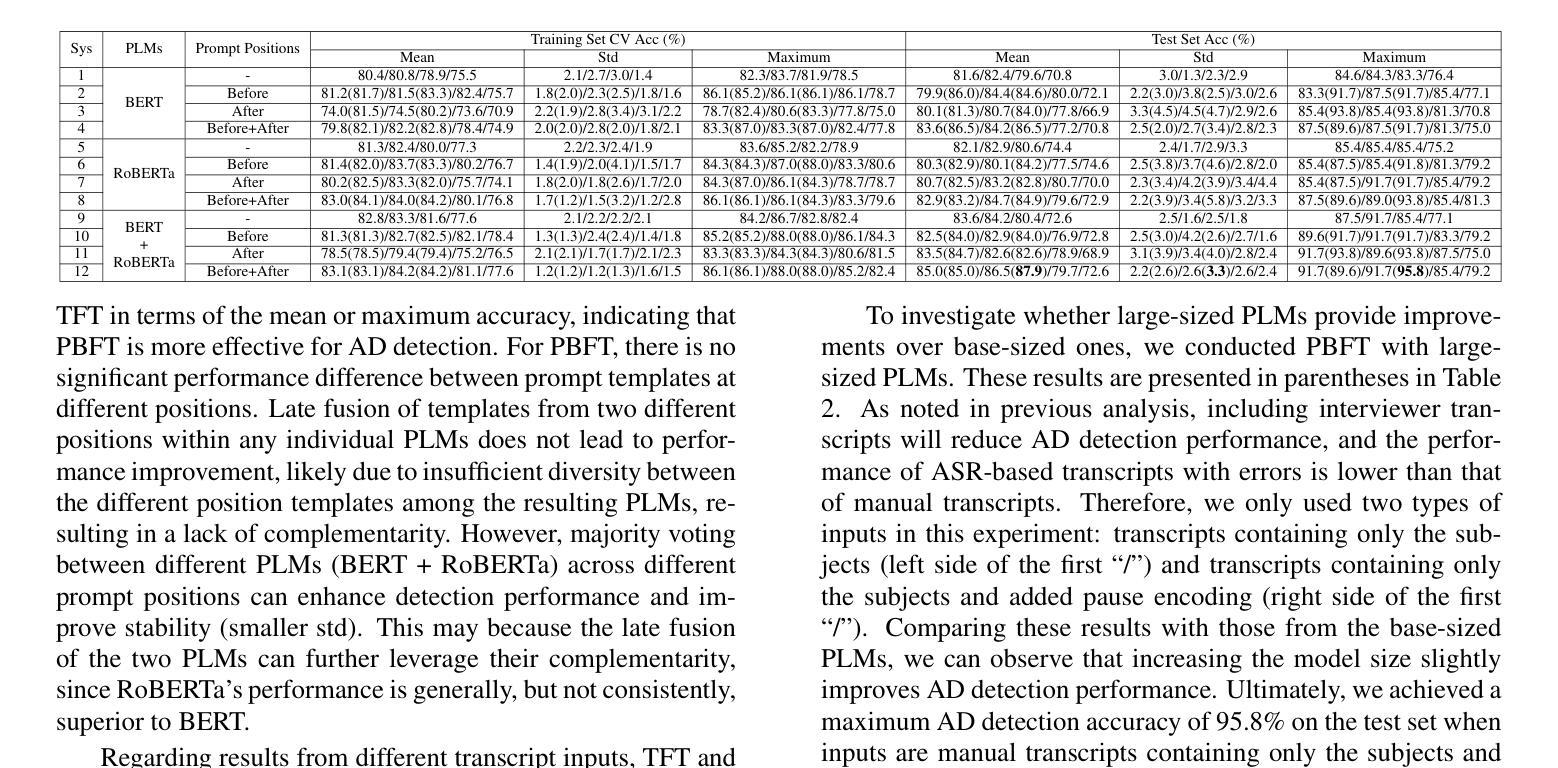
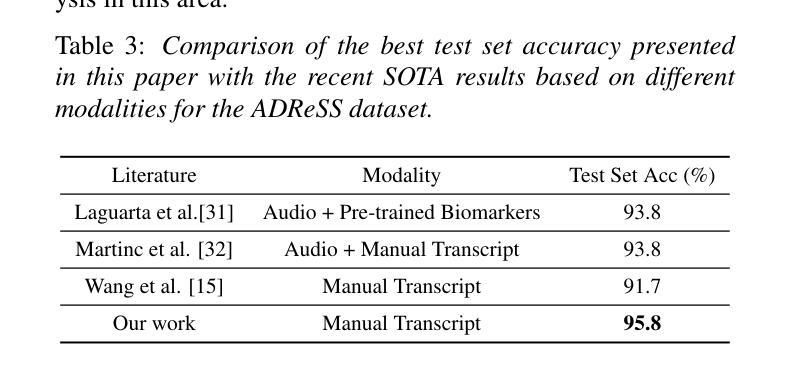
Leveraging Prompt Learning and Pause Encoding for Alzheimer’s Disease Detection
Authors:Yin-Long Liu, Rui Feng, Jia-Hong Yuan, Zhen-Hua Ling
Compared to other clinical screening techniques, speech-and-language-based automated Alzheimer’s disease (AD) detection methods are characterized by their non-invasiveness, cost-effectiveness, and convenience. Previous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of fine-tuning pre-trained language models (PLMs) for AD detection. However, the objective of this traditional fine-tuning method, which involves inputting only transcripts, is inconsistent with the masked language modeling (MLM) task used during the pre-training phase of PLMs. In this paper, we investigate prompt-based fine-tuning of PLMs, converting the classification task into a MLM task by inserting prompt templates into the transcript inputs. We also explore the impact of incorporating pause information from forced alignment into manual transcripts. Additionally, we compare the performance of various automatic speech recognition (ASR) models and select the Whisper model to generate ASR-based transcripts for comparison with manual transcripts. Furthermore, majority voting and ensemble techniques are applied across different PLMs (BERT and RoBERTa) using different random seeds. Ultimately, we obtain maximum detection accuracy of 95.8% (with mean 87.9%, std 3.3%) using manual transcripts, achieving state-of-the-art performance for AD detection using only transcripts on the ADReSS test set.
与其他临床筛查技术相比,基于语音和语言的自动化阿尔茨海默病(AD)检测方法具有非侵入性、成本效益和便利性等特点。以往的研究已经证明了预训练语言模型(PLM)进行微调对AD检测的有效性。然而,这种传统微调方法的目标仅涉及输入文本,与预训练阶段使用的语言模型中的掩码语言建模(MLM)任务不一致。在本文中,我们研究了基于提示的PLM微调方法,通过将提示模板插入到文本输入中,将分类任务转换为MLM任务。我们还探讨了将强制对齐中的停顿信息融入手动文本的影响。此外,我们比较了不同自动语音识别(ASR)模型的性能,选择了Whisper模型来生成基于ASR的文本,以便与手动文本进行比较。同时,通过应用多数投票和集成技术,结合使用不同随机种子的不同PLM(BERT和RoBERTa)。最终,我们使用手动文本获得了最高95.8%(平均87.9%,标准差3.3%)的检测准确率,在仅使用文本进行AD检测的ADReSS测试集上达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ISCSLP 2024
Summary
本研究探索了基于语音和语言的自动化阿尔茨海默病(AD)检测方法的优势,包括其非侵入性、成本效益和便利性。研究通过微调预训练语言模型(PLM)进行AD检测,提出基于提示的微调方法,将分类任务转化为掩码语言建模任务,并在转录输入中插入提示模板。此外,研究还纳入了来自强制对齐的停顿信息,并对比了不同自动语音识别(ASR)模型的性能。最终,使用手动转录本获得最高95.8%的检测准确率,达到仅使用转录本进行AD检测的领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 语音和基于语言的自动化方法用于阿尔茨海默病检测具有非侵入性、成本效益和便利性的特点。
- 传统微调方法专注于输入转录,与预训练阶段的掩码语言建模任务不一致。
- 研究提出了基于提示的微调方法,将分类任务转化为掩码语言建模任务。
- 停顿信息被纳入研究,来自强制对齐技术,增强了手动转录的信息价值。
- 对比了多种自动语音识别模型的性能,选择了Whisper模型进行比较。
- 使用手动转录本获得最高检测准确率95.8%,达到领先水平。
点此查看论文截图

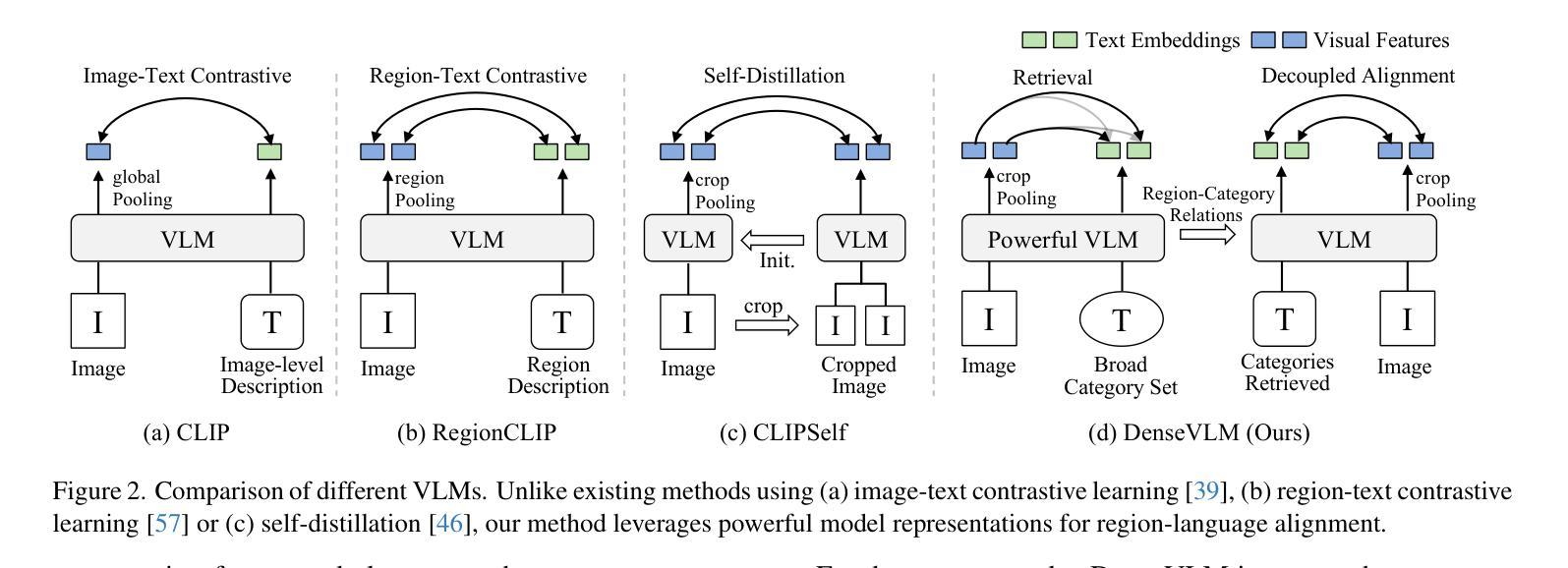
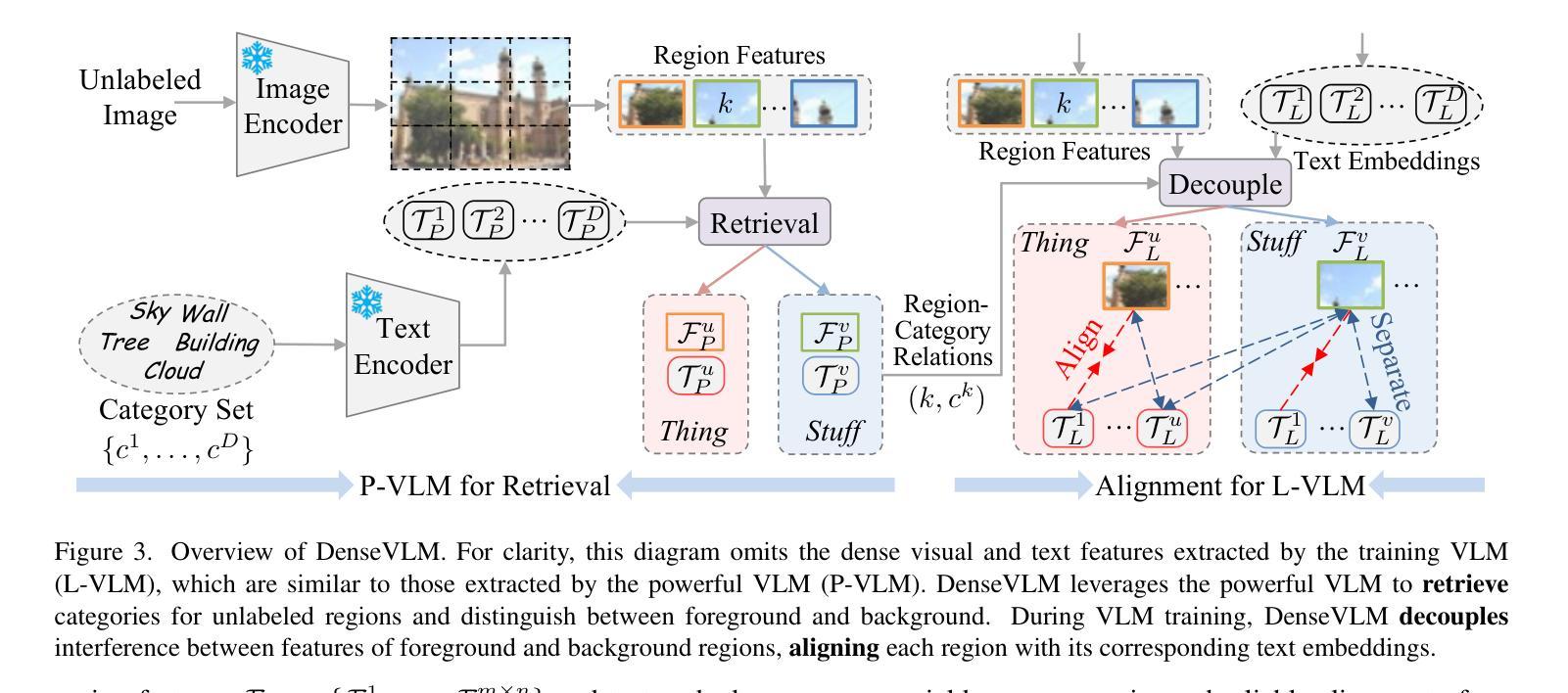
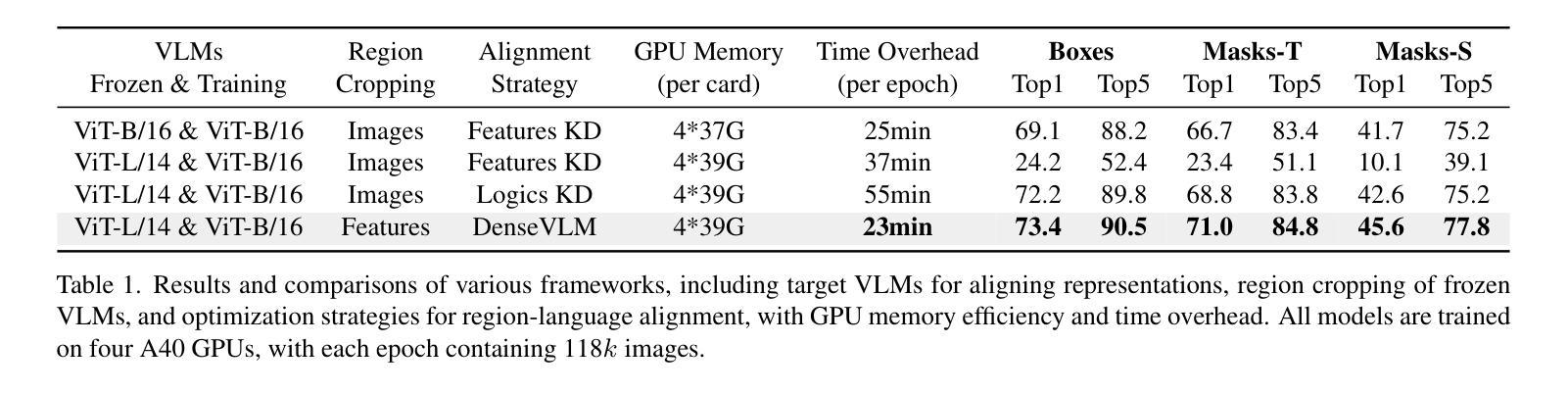
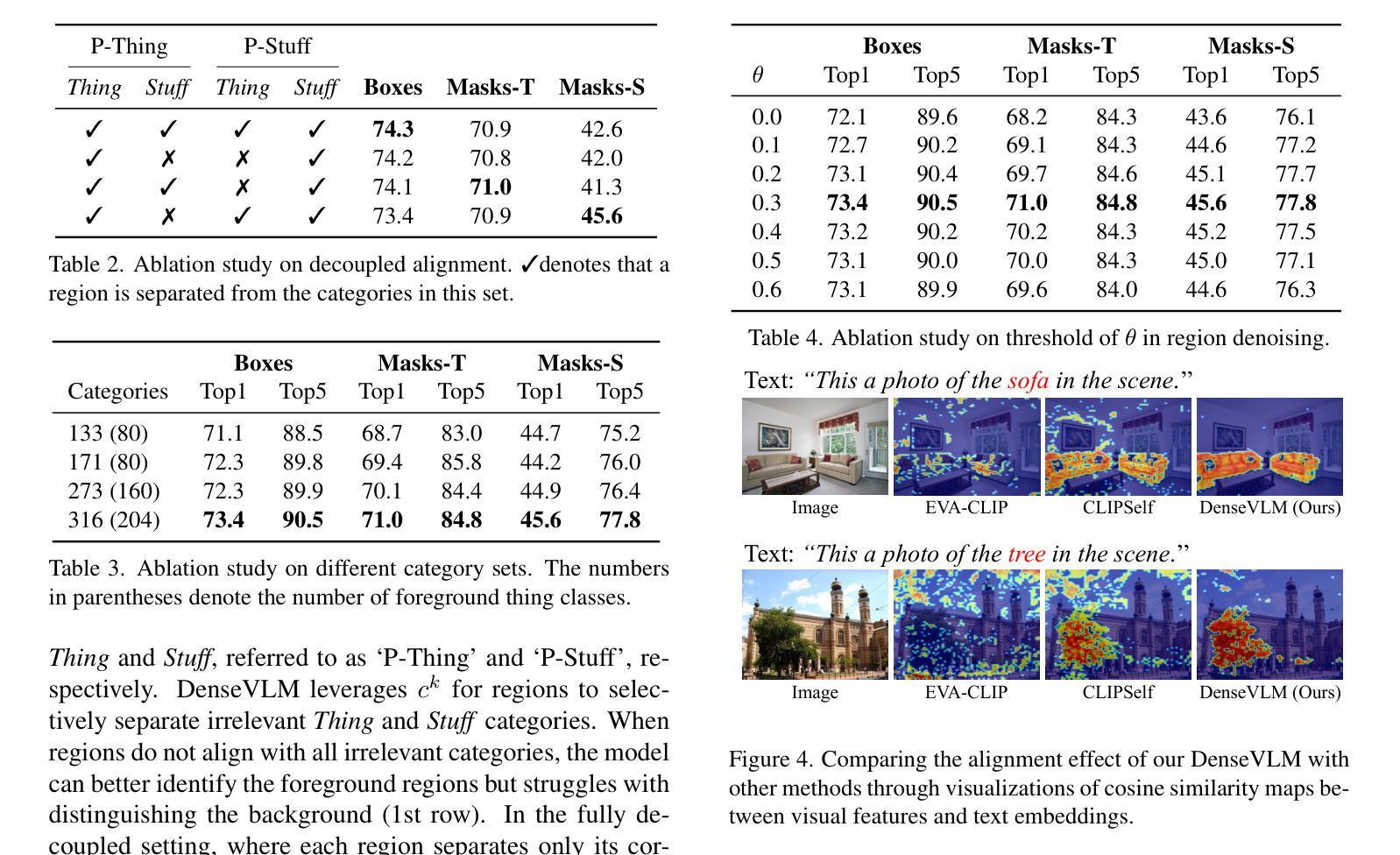
DenseVLM: A Retrieval and Decoupled Alignment Framework for Open-Vocabulary Dense Prediction
Authors:Yunheng Li, Yuxuan Li, Quansheng Zeng, Wenhai Wang, Qibin Hou, Ming-Ming Cheng
Pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs), such as CLIP, have demonstrated impressive zero-shot recognition capability, but still underperform in dense prediction tasks. Self-distillation recently is emerging as a promising approach for fine-tuning VLMs to better adapt to local regions without requiring extensive annotations. However, previous state-of-the-art approaches often suffer from significant `foreground bias’, where models tend to wrongly identify background regions as foreground objects. To alleviate this issue, we propose DenseVLM, a framework designed to learn unbiased region-language alignment from powerful pre-trained VLM representations. By leveraging the pre-trained VLM to retrieve categories for unlabeled regions, DenseVLM effectively decouples the interference between foreground and background region features, ensuring that each region is accurately aligned with its corresponding category. We show that DenseVLM can be seamlessly integrated into open-vocabulary object detection and image segmentation tasks, leading to notable performance improvements. Furthermore, it exhibits promising zero-shot scalability when training on more extensive and diverse datasets.
预训练的视觉语言模型(如CLIP)已展现出令人印象深刻的零样本识别能力,但在密集预测任务中表现仍然不佳。最近,自蒸馏法作为一种有前途的方法出现,可以微调视觉语言模型,使其更好地适应局部区域,而无需大量注释。然而,之前的最先进方法往往受到严重的“前景偏见”的影响,模型往往错误地将背景区域识别为前景对象。为了缓解这一问题,我们提出了DenseVLM框架,旨在从强大的预训练视觉语言模型表示中学习无偏见区域-语言对齐。通过利用预训练的视觉语言模型为未标记区域检索类别,DenseVLM有效地消除了前景和背景区域特征之间的干扰,确保每个区域都能与其相应的类别准确对齐。我们展示了DenseVLM可以无缝集成到开放词汇表的目标检测和图像分割任务中,从而带来显著的性能改进。此外,它在更大、更多样化的数据集上进行训练时,表现出有希望的零样本可扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)如CLIP具有出色的零样本识别能力,但在密集预测任务中表现不佳。近期自蒸馏法成为了一种有前景的方法,可以更好地微调VLMs以适应局部区域而无需大量注释。然而,先前的方法常常受到前景偏见的影响,模型倾向于错误地将背景区域识别为前景物体。为解决这一问题,我们提出了DenseVLM框架,旨在从强大的预训练VLM表示中学习无偏区域语言对齐。通过利用预训练的VLM检索未标记区域的类别,DenseVLM有效地解除了前景和背景区域特征之间的干扰,确保每个区域都能与其对应的类别准确对齐。我们的实验显示,DenseVLM可以无缝集成开放式词汇表目标检测和图像分割任务,带来显著的性能提升。此外,在更大和更多样化的数据集上进行训练时,它表现出良好的零样本可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- 预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)在密集预测任务中表现不足。
- 自蒸馏法是一种微调VLMs以更好地适应局部区域的方法,且不需要大量注释。
- 现有方法常常受到前景偏见的影响,即模型可能错误地将背景区域识别为前景物体。
- DenseVLM框架旨在学习无偏区域语言对齐,通过利用预训练的VLM检索未标记区域的类别来解决这一问题。
- DenseVLM能有效解除前景和背景区域特征之间的干扰,确保每个区域都能准确对齐其对应的类别。
- DenseVLM可以集成开放式词汇表目标检测和图像分割任务,带来性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

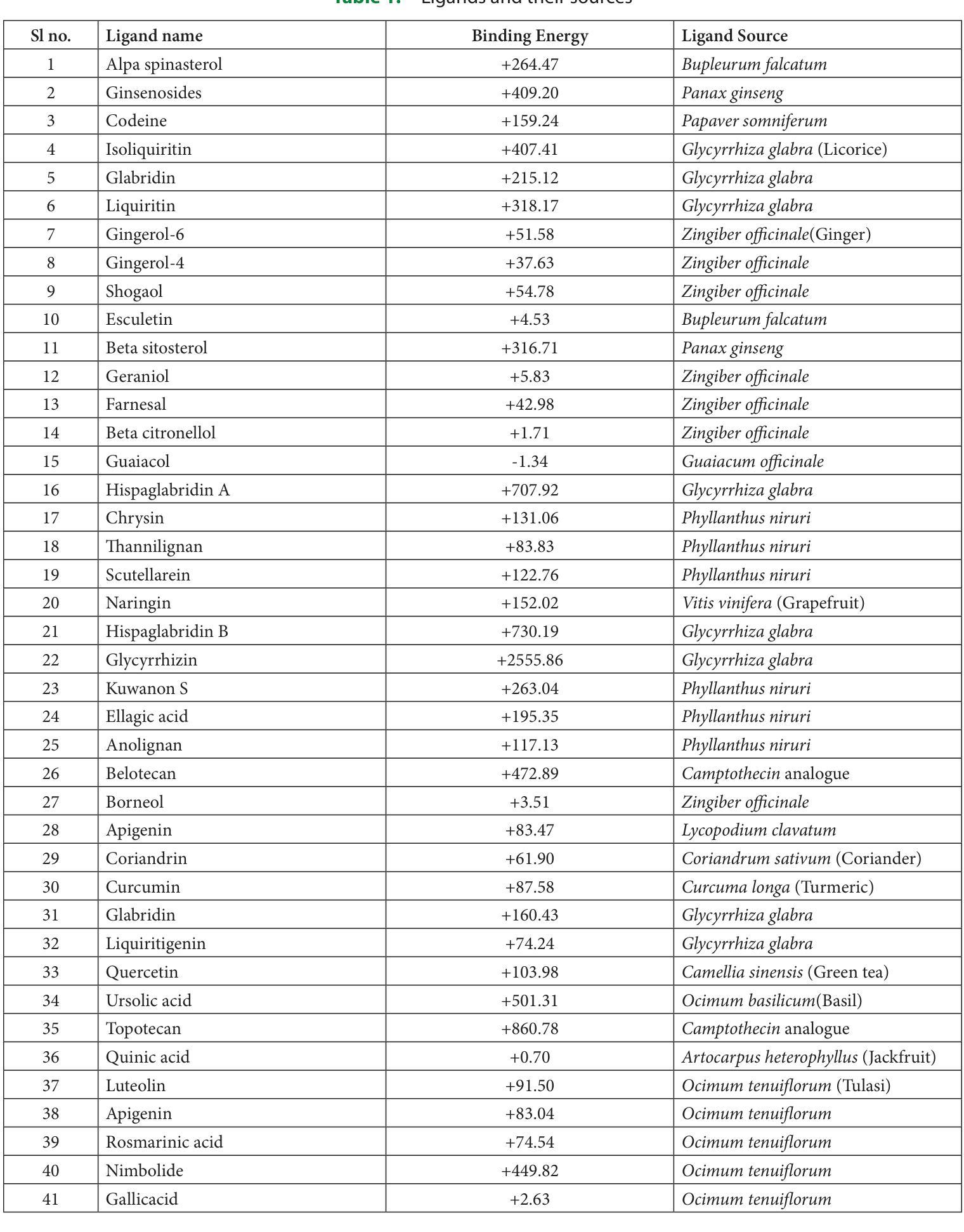
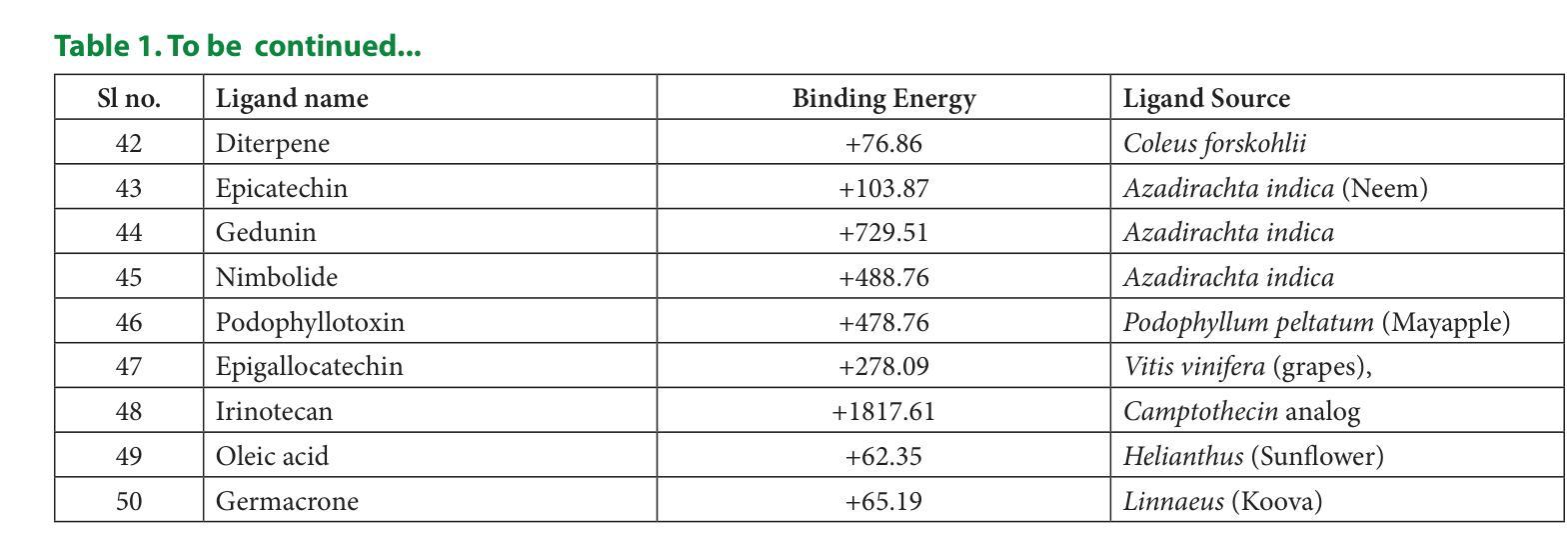
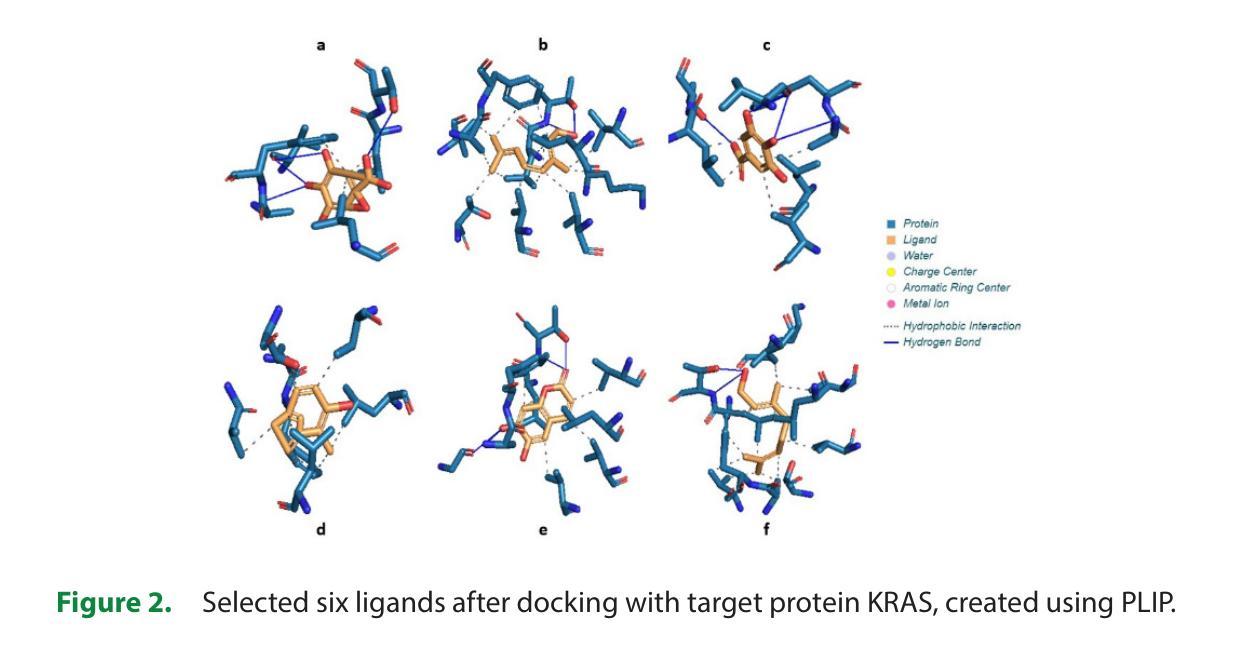
In Silico Pharmacokinetic and Molecular Docking Studies of Natural Plants against Essential Protein KRAS for Treatment of Pancreatic Cancer
Authors:Marsha Mariya Kappan, Joby George
A kind of pancreatic cancer called Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is anticipated to be one of the main causes of mortality during past years. Evidence from several researches supported the concept that the oncogenic KRAS (Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene) mutation is the major cause of pancreatic cancer. KRAS acts as an on-off switch that promotes cell growth. But when the KRAS gene is mutated, it will be in one position, allowing the cell growth uncontrollably. This uncontrollable multiplication of cells causes cancer growth. Therefore, KRAS was selected as the target protein in the study. Fifty plant-derived compounds are selected for the study. To determine whether the examined drugs could bind to the KRAS complex’s binding pocket, molecular docking was performed. Computational analyses were used to assess the possible ability of tested substances to pass the Blood Brain Barrier (BBB). To predict the bioactivity of ligands a machine learning model was created. Five machine learning models were created and have chosen the best one among them for analyzing the bioactivity of each ligand. From the fifty plant-derived compounds the compounds with the least binding energies are selected. Then bioactivity of these six compounds is analyzed using Random Forest Regression model. Adsorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion (ADME) properties of compounds are analyzed. The results showed that borneol has powerful effects and acts as a promising agent for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. This suggests that borneol found in plants like mint, ginger, rosemary, etc., is a successful compound for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
一种名为胰腺导管腺癌(PDAC)的胰腺癌预计是过去几年里导致死亡的主要原因之一。来自多项研究证据表明,致癌KRAS(Ki-ras2 Kirste鼠肉瘤病毒致癌基因)突变是胰腺癌的主要原因。KRAS充当开关,促进细胞生长。但当KRAS基因发生突变时,它将处于某一位置,使细胞无法控制地增长。这种无法控制的细胞增殖导致癌症增长。因此,KRAS被选为该研究中的目标蛋白。该研究选择了50种植物衍生的化合物进行研究。为了确定所测试的药物是否能够结合到KRAS复合物的结合口袋,进行了分子对接。使用计算分析评估了测试物质通过血脑屏障(BBB)的可能能力。创建了一个机器学习模型来预测配体的生物活性。创建了五个机器学习模型,并从中选择了最佳模型来分析每个配体的生物活性。从五十种植物衍生的化合物中选择了结合能最低的化合物。然后使用随机森林回归模型分析这些化合物的生物活性。还分析了化合物的吸附、分布、代谢、排泄(ADME)特性。结果表明,冰片具有强大的功效,并且作为治疗胰腺癌的有前途的药物。这表明冰片存在于薄荷、姜、迷迭香等植物中,是治疗胰腺癌的成功化合物。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
胰腺癌中的一种类型——胰管腺癌(PDAC)预计将成为过去几年内主要的死亡原因之一。研究表明,致癌KRAS基因突变是胰腺癌的主要原因。研究选择了五十种植物衍生的化合物进行研究,并通过分子对接、计算分析和机器学习模型等方法筛选出了具有潜在活性的化合物。最终发现薄荷醇等植物中的成分具有治疗胰腺癌的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 胰腺癌是一种严重的致死性疾病,其中胰管腺癌(PDAC)是主要的类型。
- KRAS基因突变是胰腺癌的主要诱因,它控制着细胞的生长,当其突变时,会导致细胞无控制地增殖,进而引发癌症。
- 研究采用了五十种植物衍生的化合物作为潜在的治疗药物。
- 通过分子对接、计算分析和机器学习模型等方法,筛选出能够与KRAS复合体结合并具有潜在活性的化合物。
- 薄荷醇等植物成分被筛选出具有强大的抗癌效果。
- 筛选出的化合物还需要进一步分析其在生物体内的吸附、分布、代谢和排泄(ADME)等特性。
点此查看论文截图

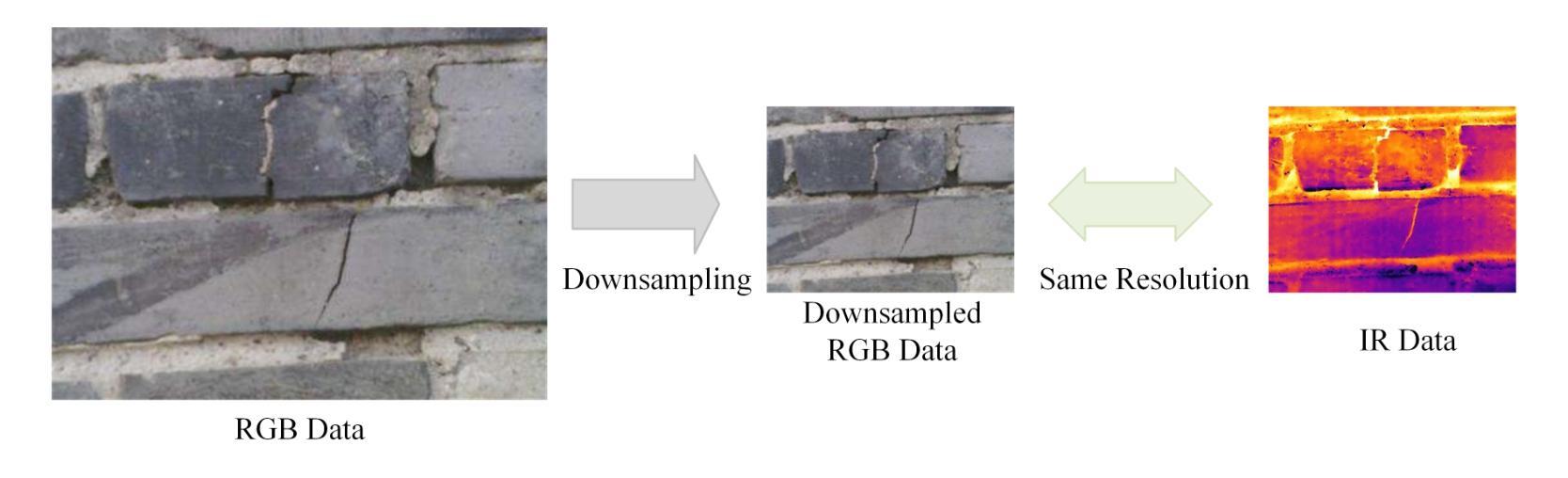
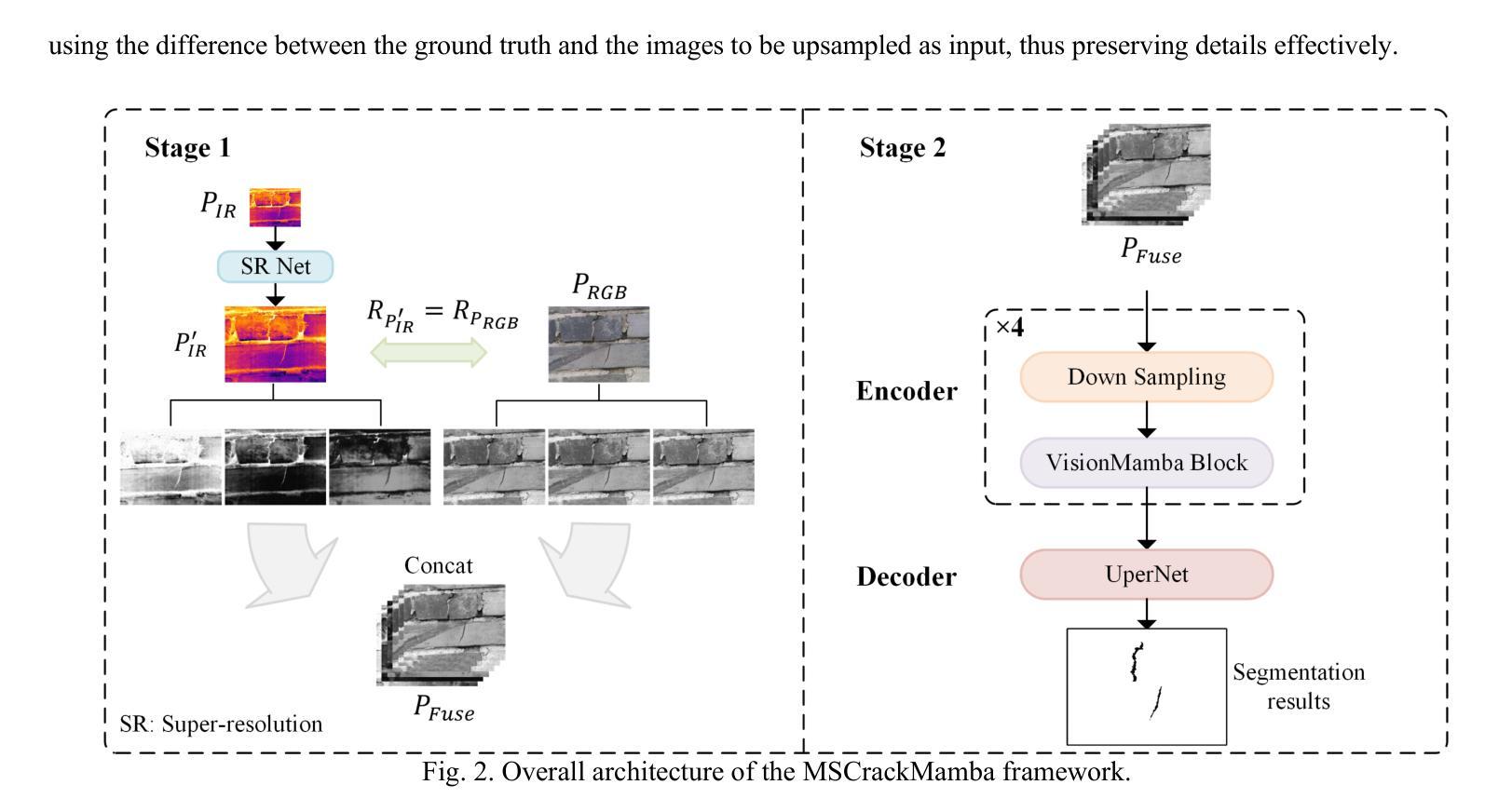
MSCrackMamba: Leveraging Vision Mamba for Crack Detection in Fused Multispectral Imagery
Authors:Qinfeng Zhu, Yuan Fang, Lei Fan
Crack detection is a critical task in structural health monitoring, aimed at assessing the structural integrity of bridges, buildings, and roads to prevent potential failures. Vision-based crack detection has become the mainstream approach due to its ease of implementation and effectiveness. Fusing infrared (IR) channels with red, green and blue (RGB) channels can enhance feature representation and thus improve crack detection. However, IR and RGB channels often differ in resolution. To align them, higher-resolution RGB images typically need to be downsampled to match the IR image resolution, which leads to the loss of fine details. Moreover, crack detection performance is restricted by the limited receptive fields and high computational complexity of traditional image segmentation networks. Inspired by the recently proposed Mamba neural architecture, this study introduces a two-stage paradigm called MSCrackMamba, which leverages Vision Mamba along with a super-resolution network to address these challenges. Specifically, to align IR and RGB channels, we first apply super-resolution to IR channels to match the resolution of RGB channels for data fusion. Vision Mamba is then adopted as the backbone network, while UperNet is employed as the decoder for crack detection. Our approach is validated on the large-scale Crack Detection dataset Crack900, demonstrating an improvement of 3.55% in mIoU compared to the best-performing baseline methods.
裂缝检测是结构健康监测中的一项关键任务,旨在评估桥梁、建筑和道路的结构完整性,以防止潜在故障。基于视觉的裂缝检测已成为主流方法,因其易于实施且效果显著。将红外(IR)通道与红绿蓝(RGB)通道融合可以增强特征表示,从而提高裂缝检测效果。然而,IR和RGB通道在分辨率上经常存在差异。为了对齐它们,通常需要将军用级RGB图像的分辨率降低以匹配IR图像,这导致了精细细节的丢失。此外,裂缝检测性能还受到传统图像分割网络受限的感受野和高计算复杂度的限制。本研究受到最近提出的Mamba神经网络架构的启发,引入了一种名为MSCrackMamba的两阶段范式,该范式利用Vision Mamba和超分辨率网络来解决这些挑战。具体来说,为了对齐IR和RGB通道,我们首先应用超分辨率技术来提高IR通道的分辨率,以匹配RGB通道进行数据融合。然后采用Vision Mamba作为骨干网络,同时采用UperNet作为裂缝检测的解码器。我们在大规模裂缝检测数据集Crack900上验证了我们的方法,相较于最佳基线方法,在mIoU方面提高了3.55%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一种基于红外(IR)和红色、绿色和蓝色(RGB)双通道融合的裂缝检测新方法MSCrackMamba。为解决IR和RGB通道分辨率不匹配问题,采用超分辨率技术对齐IR通道分辨率。利用Vision Mamba作为主干网络,UperNet作为解码器进行裂缝检测。在大型裂缝检测数据集Crack900上的实验表明,该方法与最佳基线方法相比,平均交并比提高了3.55%。
关键要点
- 裂缝检测是结构健康监测中的关键任务,旨在评估桥梁、建筑和道路的结构完整性,预防潜在故障。
- 视觉基于的裂缝检测已成为主流方法,因其易于实施且有效。
- 红外(IR)与红、绿、蓝(RGB)通道的融合能增强特征表示,从而提高裂缝检测性能。
- IR和RGB通道分辨率的不匹配问题通过超分辨率技术解决,以实现数据融合。
- 采用Vision Mamba作为主干网络,UperNet作为解码器进行裂缝检测。
- 方法在大型裂缝检测数据集Crack900上进行了验证,平均交并比(mIoU)有所提高。
- 与最佳基线方法相比,MSCrackMamba方法在mIoU上提高了3.55%。
点此查看论文截图


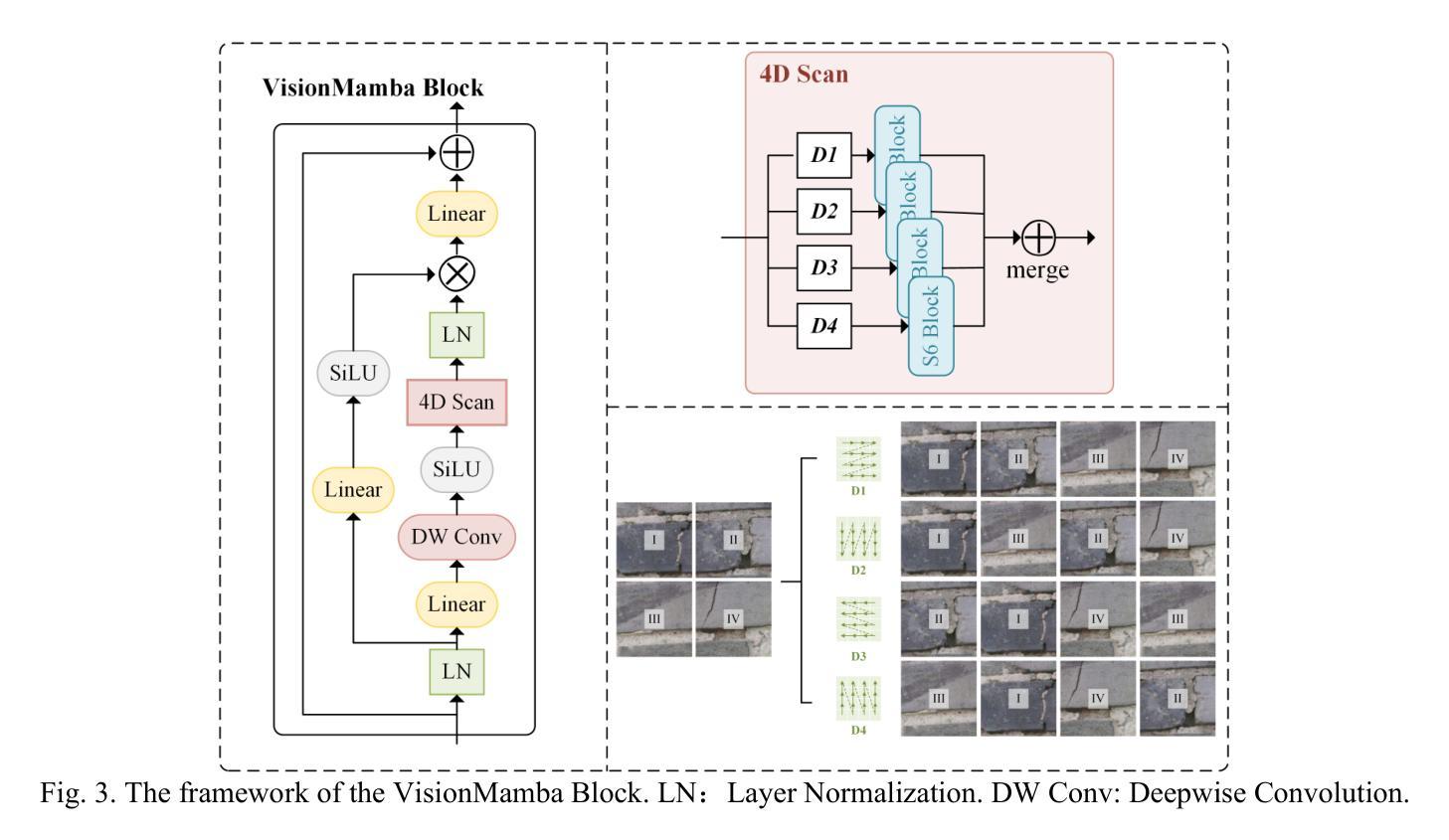
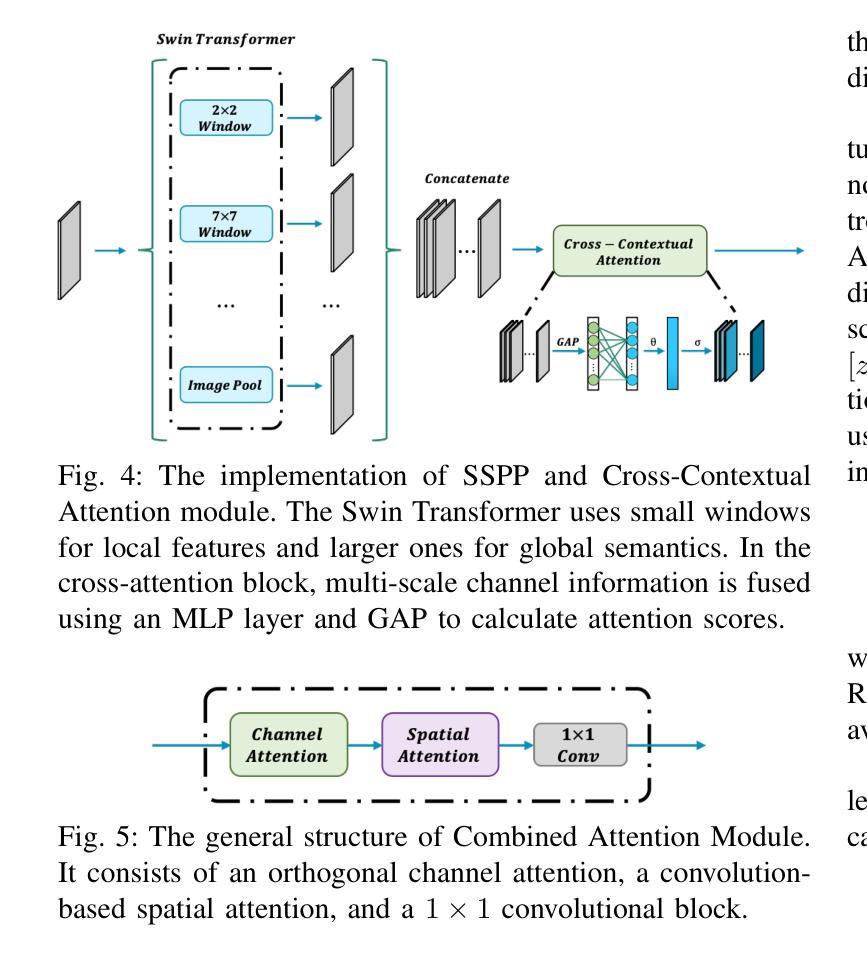
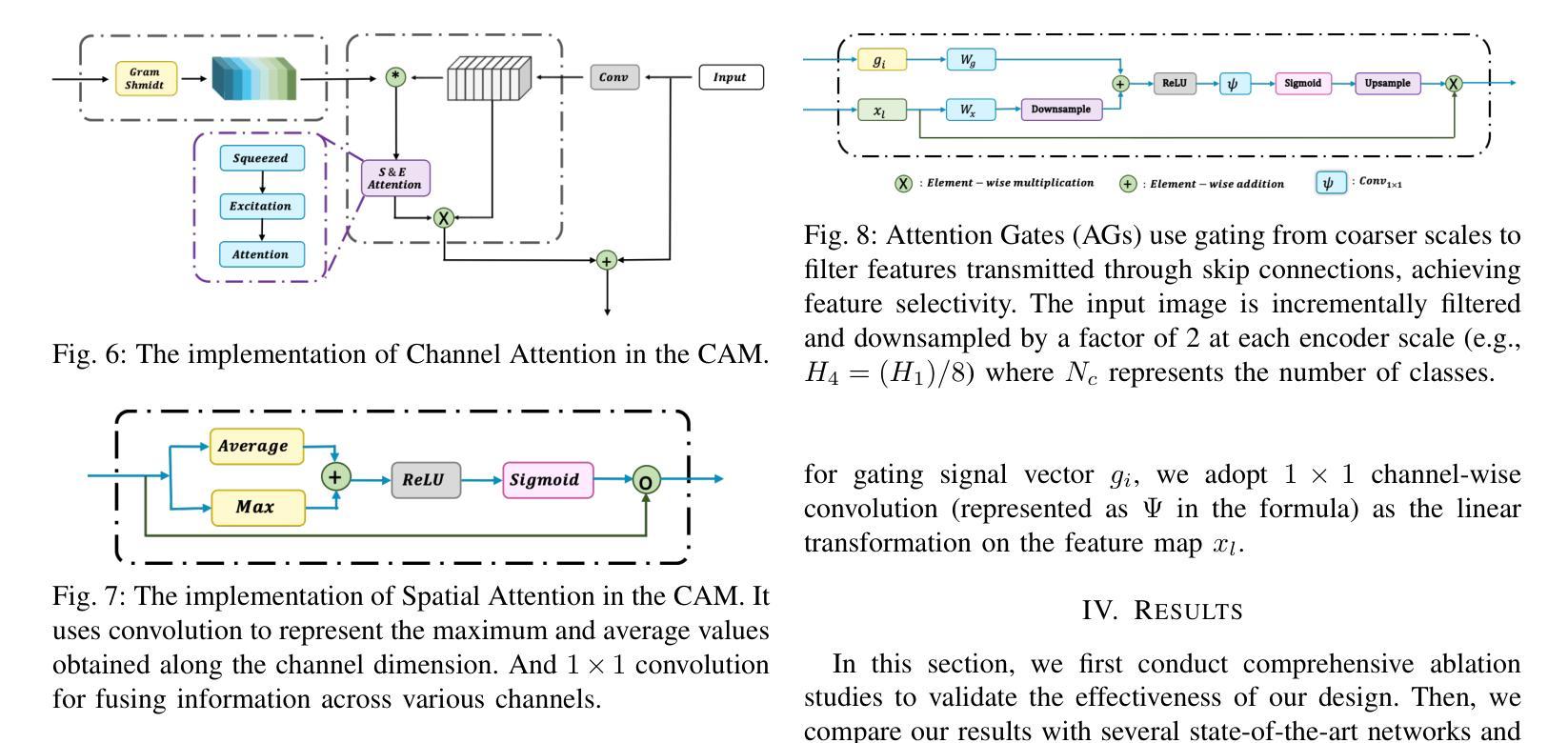
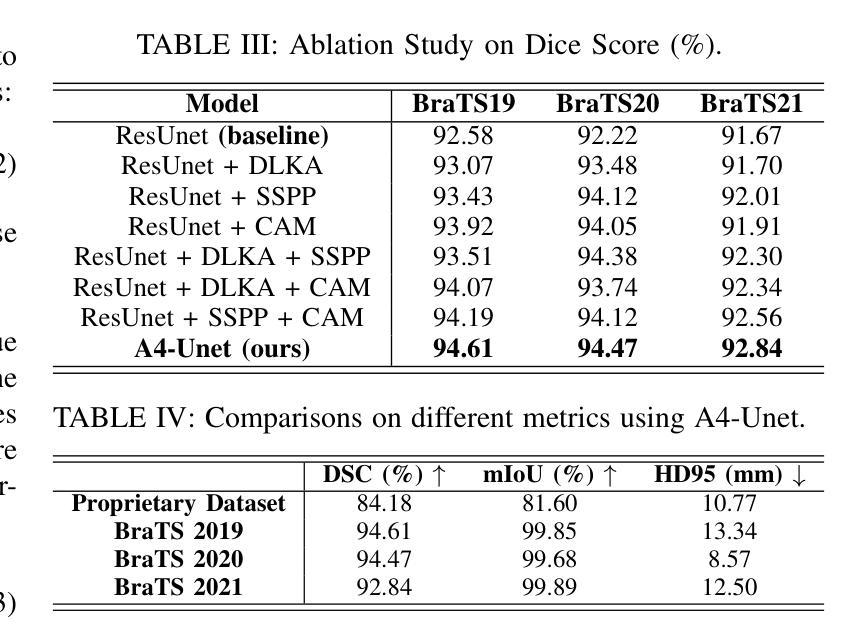
A4-Unet: Deformable Multi-Scale Attention Network for Brain Tumor Segmentation
Authors:Ruoxin Wang, Tianyi Tang, Haiming Du, Yuxuan Cheng, Yu Wang, Lingjie Yang, Xiaohui Duan, Yunfang Yu, Yu Zhou, Donglong Chen
Brain tumor segmentation models have aided diagnosis in recent years. However, they face MRI complexity and variability challenges, including irregular shapes and unclear boundaries, leading to noise, misclassification, and incomplete segmentation, thereby limiting accuracy. To address these issues, we adhere to an outstanding Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) design paradigm and propose a novel network named A4-Unet. In A4-Unet, Deformable Large Kernel Attention (DLKA) is incorporated in the encoder, allowing for improved capture of multi-scale tumors. Swin Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SSPP) with cross-channel attention is employed in a bottleneck further to study long-distance dependencies within images and channel relationships. To enhance accuracy, a Combined Attention Module (CAM) with Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) orthogonality for channel weighting and convolutional element-wise multiplication is introduced for spatial weighting in the decoder. Attention gates (AG) are added in the skip connection to highlight the foreground while suppressing irrelevant background information. The proposed network is evaluated on three authoritative MRI brain tumor benchmarks and a proprietary dataset, and it achieves a 94.4% Dice score on the BraTS 2020 dataset, thereby establishing multiple new state-of-the-art benchmarks. The code is available here: https://github.com/WendyWAAAAANG/A4-Unet.
近年来,脑肿瘤分割模型在诊断中起到了辅助作用。然而,它们面临着磁共振成像(MRI)的复杂性和变异性挑战,包括形状不规则和边界不清,导致噪声、误分类和分割不完全,从而限制了准确性。为了解决这些问题,我们遵循卓越的卷积神经网络(CNN)设计范式,并提出了一种新型网络,名为A4-Unet。在A4-Unet中,我们在编码器中加入了可变形大内核注意力(DLKA),能够改进多尺度肿瘤的捕获。我们还在瓶颈处采用了带有跨通道注意力的Swin空间金字塔池化(SSPP),进一步研究图像内的长距离依赖关系和通道关系。为了提高准确性,我们在解码器中引入了一个结合注意力模块(CAM),该模块具有离散余弦变换(DCT)正交性用于通道加权和卷积元素级乘法以实现空间加权。我们还在跳跃连接中添加了注意力门(AG),以突出前景并抑制无关的背景信息。该网络在三个权威的MRI脑肿瘤基准测试和一个专有数据集上进行了评估,在BraTS 2020数据集上实现了94.4%的Dice得分,从而建立了多个新的最新技术基准。代码可在https://github.com/WendyWAAAAANG/A4-Unet获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 14 figures, IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM) 2024
Summary
近年来,脑肿瘤分割模型通过采用卷积神经网络设计范例来辅助诊断。为了解决MRI的复杂性和差异性所带来的噪音、误分类和不完整分割问题,提出了一个名为A4-Unet的新型网络。该网络在编码器中加入了大内核变形注意力机制,以更好地捕捉多尺度肿瘤;在瓶颈部分采用了带有跨通道注意力的空间金字塔池化模块,研究图像内的长距离依赖关系和通道关系;并结合了注意力模块和离散余弦变换以增强准确性。在三个权威的MRI脑肿瘤基准测试集和一个专有数据集上评估,A4-Unet在BraTS 2020数据集上实现了94.4%的Dice得分,树立了新的基准线。相关代码可在链接中获取:https://github.com/WendyWAAAAANG/A4-Unet。
Key Takeaways
- 脑肿瘤分割模型辅助诊断,面临MRI复杂性和差异性挑战。
- A4-Unet网络通过加入大内核变形注意力机制捕捉多尺度肿瘤。
- 瓶颈部分采用空间金字塔池化和跨通道注意力机制研究图像的长距离依赖关系和通道关系。
- 引入注意力模块和离散余弦变换以增强准确性。
- A4-Unet在多个基准测试集上表现优异,特别是在BraTS 2020数据集上实现了高Dice得分。
点此查看论文截图

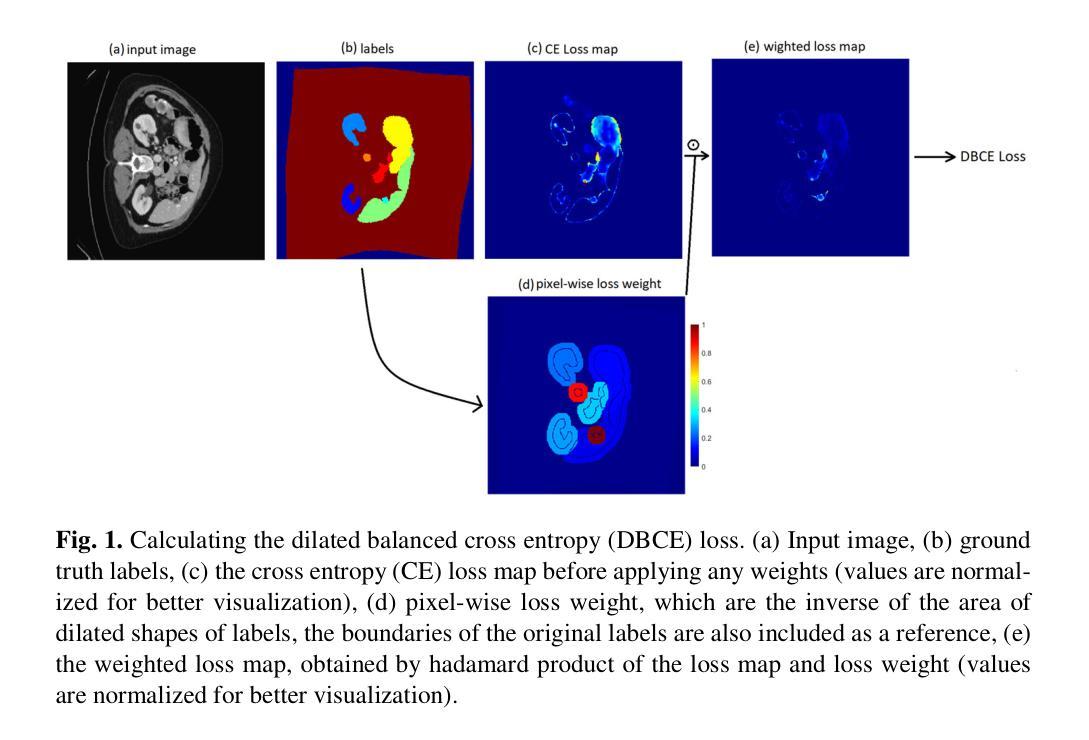
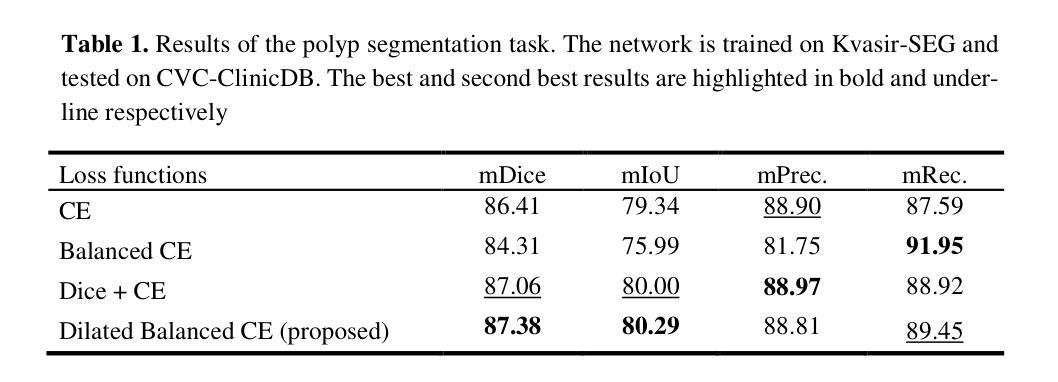
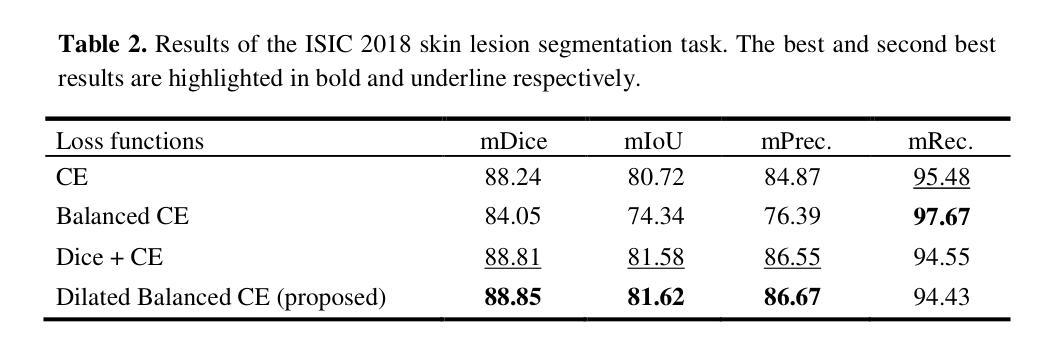
Dilated Balanced Cross Entropy Loss for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Seyed Mohsen Hosseini, Mahdieh Soleymani Baghshah
A novel method for tackling the problem of imbalanced data in medical image segmentation is proposed in this work. In balanced cross entropy (CE) loss, which is a type of weighted CE loss, the weight assigned to each class is the in-verse of the class frequency. These balancing weights are expected to equalize the effect of each class on the overall loss and prevent the model from being biased towards the majority class. But, as it has been shown in previous studies, this method degrades the performance by a large margin. Therefore, balanced CE is not a popular loss in medical segmentation tasks, and usually a region-based loss, like the Dice loss, is used to address the class imbalance problem. In the pro-posed method, the weighting of cross entropy loss for each class is based on a dilated area of each class mask, and balancing weights are assigned to each class together with its surrounding pixels. The goal of this study is to show that the performance of balanced CE loss can be greatly improved my modifying its weighting strategy. Experiments on different datasets show that the proposed dilated balanced CE (DBCE) loss outperforms the balanced CE loss by a large margin and produces superior results compared to CE loss, and its performance is similar to the performance of the combination of Dice and CE loss. This means that a weighted cross entropy loss with the right weighing strategy can be as effective as a region-based loss in handling the problem of class imbalance in medical segmentation tasks.
本文提出了一种解决医学图像分割中数据不平衡问题的新方法。在平衡交叉熵(CE)损失中,它是一种加权CE损失,分配给每个类的权重是类频率的倒数。这些平衡权重预计会对每个类对总体损失的影响进行平衡,防止模型偏向于多数类。但是,如先前研究所示,此方法会降低性能,幅度较大。因此,平衡CE在医学分割任务中并不流行,通常使用区域性的损失,如Dice损失,来解决类别不平衡问题。在提出的方法中,每个类的交叉熵损失的权重基于每个类掩码的膨胀区域,并且为每个类及其周围像素分配平衡权重。本研究的目标表明,通过修改其加权策略,可以大大提高平衡CE损失的性能。在不同数据集上的实验表明,所提出的膨胀平衡CE(DBCE)损失在很大程度上优于平衡CE损失,并且与CE损失相比产生了更好的结果,其性能与Dice和CE损失组合的性能相似。这意味着采用正确加权策略的加权交叉熵损失在处理医学分割任务中的类别不平衡问题时,可以像基于区域的损失一样有效。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种解决医学图像分割中类别不平衡问题的新方法。该方法基于膨胀平衡交叉熵(DBCE)损失,通过修改权重策略,改进了平衡交叉熵损失的性能。实验表明,DBCE损失在多个数据集上的表现均优于平衡交叉熵损失和传统的交叉熵损失,其性能与结合Dice和交叉熵损失的方案相当。这表明采用适当权重策略的加权交叉熵损失在处理医学图像分割中的类别不平衡问题时,可以像基于区域的损失一样有效。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割中存在类别不平衡问题。
- 平衡交叉熵损失通过为每个类别分配权重来解决此问题,但这种方法可能导致模型性能下降。
- 新提出的膨胀平衡交叉熵(DBCE)损失考虑到了每个类别的膨胀区域及其周围像素来分配权重。
- DBCE损失在多个数据集上的表现优于平衡交叉熵损失和传统的交叉熵损失。
- DBCE损失的性能与结合Dice和交叉熵损失的方案相当。
点此查看论文截图

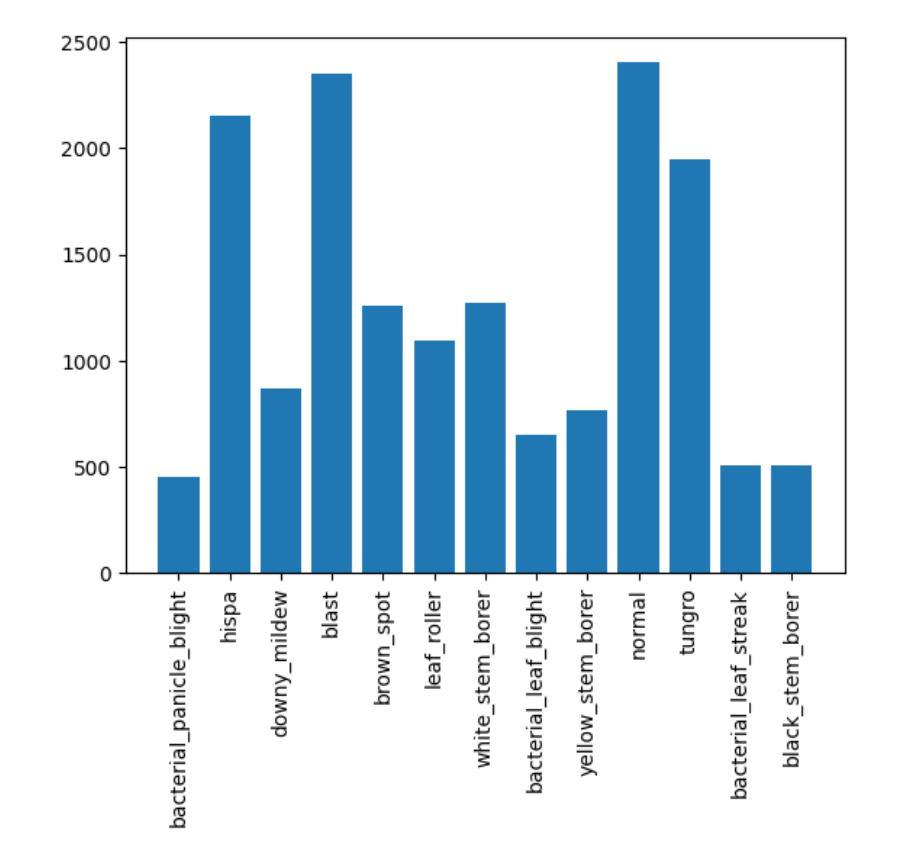
Paddy Disease Detection and Classification Using Computer Vision Techniques: A Mobile Application to Detect Paddy Disease
Authors:Bimarsha Khanal, Paras Poudel, Anish Chapagai, Bijan Regmi, Sitaram Pokhrel, Salik Ram Khanal
Plant diseases significantly impact our food supply, causing problems for farmers, economies reliant on agriculture, and global food security. Accurate and timely plant disease diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and minimizing yield losses. Despite advancements in agricultural technology, a precise and early diagnosis remains a challenge, especially in underdeveloped regions where agriculture is crucial and agricultural experts are scarce. However, adopting Deep Learning applications can assist in accurately identifying diseases without needing plant pathologists. In this study, the effectiveness of various computer vision models for detecting paddy diseases is evaluated and proposed the best deep learning-based disease detection system. Both classification and detection using the Paddy Doctor dataset, which contains over 20,000 annotated images of paddy leaves for disease diagnosis are tested and evaluated. For detection, we utilized the YOLOv8 model-based model were used for paddy disease detection and CNN models and the Vision Transformer were used for disease classification. The average mAP50 of 69% for detection tasks was achieved and the Vision Transformer classification accuracy was 99.38%. It was found that detection models are effective at identifying multiple diseases simultaneously with less computing power, whereas classification models, though computationally expensive, exhibit better performance for classifying single diseases. Additionally, a mobile application was developed to enable farmers to identify paddy diseases instantly. Experiments with the app showed encouraging results in utilizing the trained models for both disease classification and treatment guidance.
植物疾病显著影响我们的粮食供应,给农民、依赖农业的经济和全球粮食安全带来问题。准确及时的植物疾病诊断对于有效治疗和减少产量损失至关重要。尽管农业技术取得了进展,但精确的早期诊断仍然是一个挑战,特别是在农业至关重要但农业专家稀缺的欠发达地区。然而,采用深度学习应用可以在不需要植物病理学家的情况下,帮助准确识别疾病。本研究评估了多种计算机视觉模型在检测水稻疾病方面的有效性,并提出了最佳的基于深度学习的疾病检测系统。使用Paddy Doctor数据集对分类和检测进行了测试和评估,该数据集包含超过2万张用于疾病诊断的水稻叶片注释图像。对于检测,我们使用了YOLOv8模型进行水稻疾病检测,并使用CNN模型和视觉转换器进行疾病分类。检测任务的平均mAP50达到69%,视觉转换器分类准确率为99.38%。研究结果表明,检测模型在识别多种疾病方面非常有效,且计算功率较低,而分类模型虽然计算成本较高,但在单一疾病分类方面表现更好。此外,还开发了一个移动应用程序,使农民能够立即识别水稻疾病。该应用程序的实验结果表明,在疾病分类和治疗指导方面利用训练模型具有令人鼓舞的效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages,12 figures and 2 tables
Summary
本文探讨了深度学习在稻谷疾病诊断中的应用。研究评估了多种计算机视觉模型在检测水稻疾病方面的有效性,并提出了最佳的水稻疾病检测体系。通过使用YOLOv8模型、CNN模型和视觉转换器进行试验和评估,发现检测模型可有效识别多种疾病且计算功率较低,而分类模型虽计算成本较高,但在单一疾病分类方面表现较好。此外,还开发了一款移动应用程序,使农民能够即时识别水稻疾病并进行治疗指导。
Key Takeaways
- 植物疾病对全球粮食供应安全构成严重影响,早期准确诊断对于有效治疗和减少产量损失至关重要。
- 在农业技术不断进步的背景下,精确的早期诊断仍然是一个挑战,特别是在农业至关重要而农业专家稀缺的地区。
- 深度学习在植物疾病诊断中具有潜力,能够协助准确识别疾病而无需植物病理学家的参与。
- 研究评估了多种计算机视觉模型在检测水稻疾病方面的有效性,并开发了一个移动应用程序用于即时识别水稻疾病并进行治疗指导。
- 检测模型能够有效识别多种疾病且计算功率较低,而分类模型则在单一疾病分类方面表现出较高的性能。
- YOLOv8模型被用于水稻疾病的检测,而CNN模型和视觉转换器则用于分类任务。
点此查看论文截图


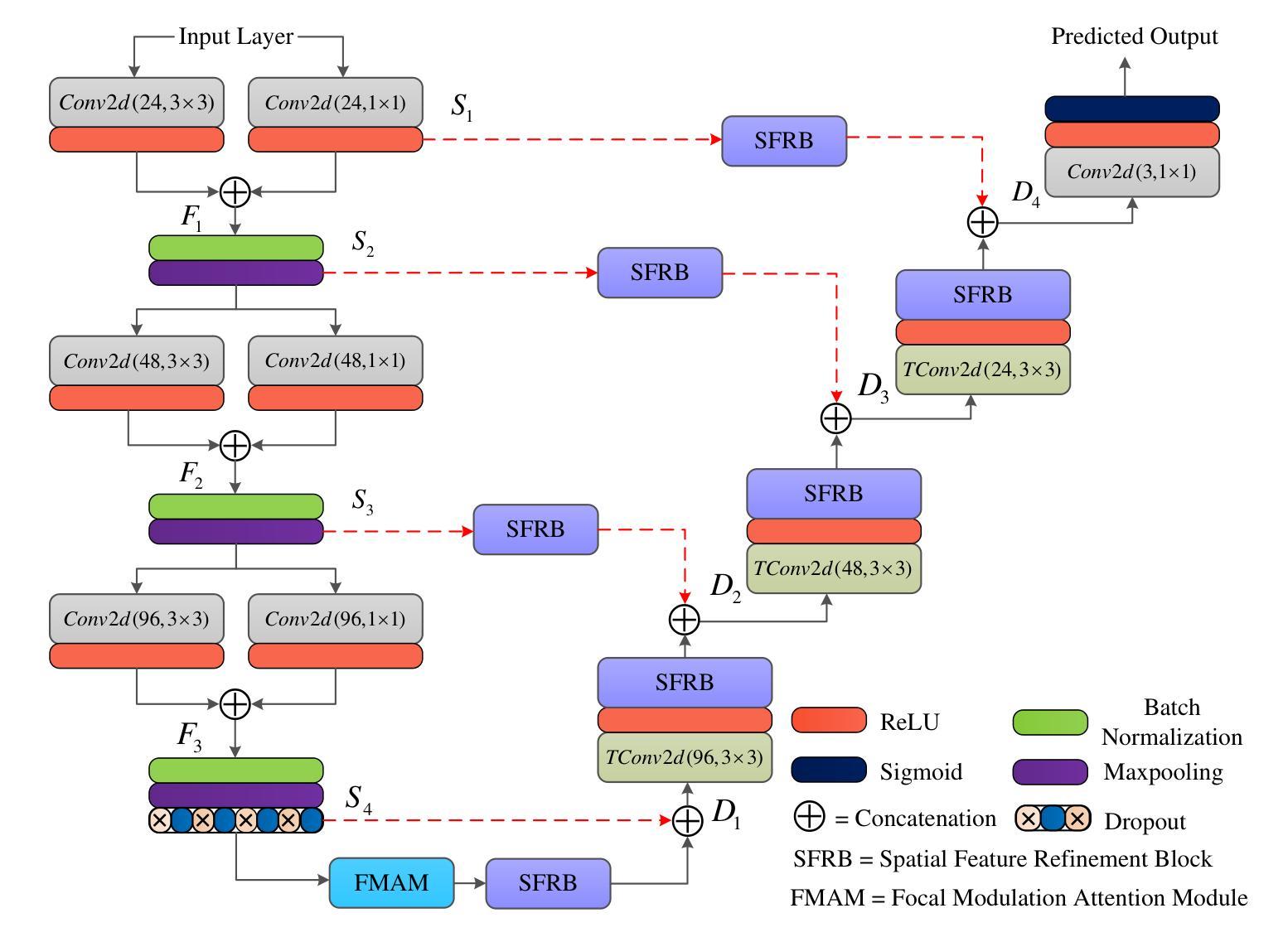
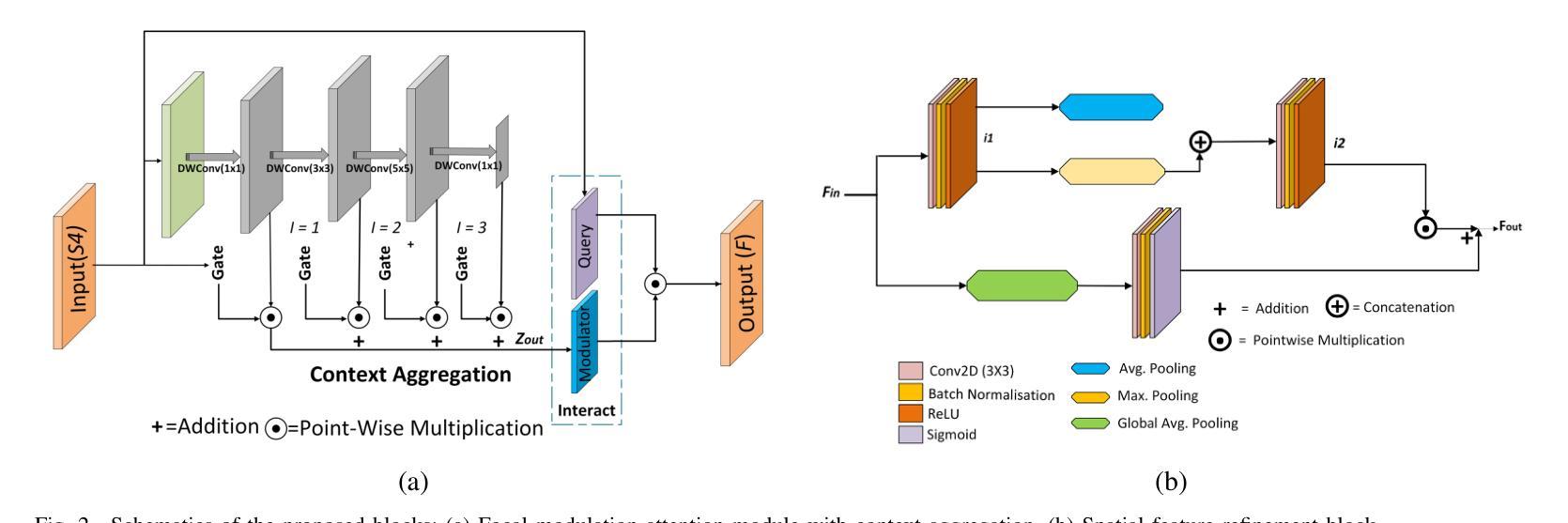
LVS-Net: A Lightweight Vessels Segmentation Network for Retinal Image Analysis
Authors:Mehwish Mehmood, Shahzaib Iqbal, Tariq Mahmood Khan, Ivor Spence, Muhammad Fahim
The analysis of retinal images for the diagnosis of various diseases is one of the emerging areas of research. Recently, the research direction has been inclined towards investigating several changes in retinal blood vessels in subjects with many neurological disorders, including dementia. This research focuses on detecting diseases early by improving the performance of models for segmentation of retinal vessels with fewer parameters, which reduces computational costs and supports faster processing. This paper presents a novel lightweight encoder-decoder model that segments retinal vessels to improve the efficiency of disease detection. It incorporates multi-scale convolutional blocks in the encoder to accurately identify vessels of various sizes and thicknesses. The bottleneck of the model integrates the Focal Modulation Attention and Spatial Feature Refinement Blocks to refine and enhance essential features for efficient segmentation. The decoder upsamples features and integrates them with the corresponding feature in the encoder using skip connections and the spatial feature refinement block at every upsampling stage to enhance feature representation at various scales. The estimated computation complexity of our proposed model is around 29.60 GFLOP with 0.71 million parameters and 2.74 MB of memory size, and it is evaluated using public datasets, that is, DRIVE, CHASE_DB, and STARE. It outperforms existing models with dice scores of 86.44%, 84.22%, and 87.88%, respectively.
视网膜图像分析以诊断各种疾病是新兴研究领域之一。最近,研究方向倾向于研究包括痴呆在内的多种神经障碍患者的视网膜血管变化。该研究旨在通过提高视网膜血管分割模型的性能来早期检测疾病,使用较少的参数,从而降低计算成本并支持更快处理速度。本文提出了一种新型的轻量级编码器-解码器模型,用于分割视网膜血管,以提高疾病检测的效率。该模型在编码器中引入了多尺度卷积块,以准确识别各种大小和厚度的血管。该模型的瓶颈结合了焦点调制注意力和空间特征细化块,以精炼和增强重要特征,实现高效分割。解码器对特征进行上采样,并在每个上采样阶段使用跳跃连接和空间特征细化块将其与编码器中的对应特征相结合,以增强不同尺度的特征表示。所提出模型的估算计算复杂度约为29.60 GFLOP,具有0.71百万个参数和2.74 MB的内存大小。它使用公共数据集(即DRIVE、CHASE_DB和STARE)进行评估,表现出优于现有模型的表现,其Dice得分分别为86.44%、84.22%和87.88%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要介绍了视网膜图像分析在疾病诊断中的新兴研究趋势。针对神经疾病如痴呆症患者视网膜血管变化的调查已成为研究焦点。为提高疾病检测效率,本文提出了一种新型的轻量级编码解码模型,用于视网膜血管分割。该模型通过引入多尺度卷积块、焦点调制注意力和空间特征细化块等结构,提高了对不同大小和厚度血管的准确识别能力。此外,该模型计算复杂度低,参数和内存占用较小,且在公开数据集上的表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 视网膜图像分析在疾病诊断中是新兴研究领域。
- 研究重点是通过改进模型性能来早期检测疾病,特别关注视网膜血管变化在神经疾病中的应用。
- 提出了一种新型的轻量级编码解码模型,用于视网膜血管分割,以提高疾病检测效率。
- 模型通过引入多尺度卷积块,能够准确识别不同大小和厚度的血管。
- 模型集成了焦点调制注意力和空间特征细化块,以优化和改进重要特征,提高分割效率。
- 模型计算复杂度低,参数和内存占用较小。
点此查看论文截图

MCP-MedSAM: A Powerful Lightweight Medical Segment Anything Model Trained with a Single GPU in Just One Day
Authors:Donghang Lyu, Ruochen Gao, Marius Staring
Medical image segmentation involves partitioning medical images into meaningful regions, with a focus on identifying anatomical structures or abnormalities. It has broad applications in healthcare, and deep learning methods have enabled significant advancements in automating this process. Recently, the introduction of the Segmentation Anything Model (SAM), the first foundation model for segmentation task, has prompted researchers to adapt it for the medical domain to improve performance across various tasks. However, SAM’s large model size and high GPU requirements hinder its scalability and development in the medical domain. To address these challenges, research has increasingly focused on lightweight adaptations of SAM to reduce its parameter count, enabling training with limited GPU resources while maintaining competitive segmentation performance. In this work, we propose MCP-MedSAM, a powerful and lightweight medical SAM model designed to be trainable on a single GPU within one day while delivering superior segmentation performance. Our method was trained and evaluated using a large-scale challenge dataset\footnote{\url{https://www.codabench.org/competitions/1847}\label{comp}}, compared to top-ranking methods on the challenge leaderboard, MCP-MedSAM achieved superior performance while requiring only one day of training on a single GPU. The code is publicly available at \url{https://github.com/dong845/MCP-MedSAM}.
医学图像分割是将医学图像分割成有意义的区域,重点关注解剖结构或异常的识别。它在医疗保健领域有着广泛的应用,而深度学习的方法已经能够实现这个过程的自动化,并推动了显著的进步。最近,分割任务首个基础模型——Segmentation Anything Model(SAM)的引入,促使研究者将其适应医学领域,以提高各种任务的性能。然而,SAM的大型模型尺寸和高GPU要求阻碍了其在医学领域的可扩展性和开发。为了解决这些挑战,研究越来越多地关注SAM的轻型适配,以减少其参数数量,在有限的GPU资源上进行训练,同时保持竞争性的分割性能。在这项工作中,我们提出了MCP-MedSAM,这是一个强大而轻型的医学SAM模型,旨在能够在单GPU上一天内完成训练,同时提供卓越的分割性能。我们的方法使用大规模挑战赛数据集进行了训练和评估^[数据集链接:https://www.codabench.org/competitions/1847]^,与排行榜上的顶尖方法相比,MCP-MedSAM在单个GPU上仅需要一天的训练时间就取得了优越的性能。代码公开可用在https://github.com/dong845/MCP-MedSAM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医疗图像分割是医学图像的重要应用领域,通过识别解剖结构或异常来将图像分割成有意义的区域。深度学习在自动化这一过程中发挥了重要作用。最近引入的分割模型SAM为医学领域带来了机会,但其在医疗图像分割领域的大规模应用仍面临模型体积大、GPU需求高等挑战。针对这些挑战,研究者致力于开发SAM的轻量级版本,以降低其参数数量,实现在有限GPU资源下的训练,同时保持良好的分割性能。本文提出了一个强大的轻量级医学SAM模型MCP-MedSAM,能够在单个GPU上训练一天时间即可获得优越的分割性能。该方法已经在大型挑战赛数据集上进行了训练和评估,并且与排行榜上的顶尖方法相比表现出了优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像分割是医学图像处理的重要分支,涉及将图像划分为有意义的区域以识别解剖结构或异常。
- 深度学习在医疗图像分割中起到了关键作用,促进了自动化进程的发展。
- Segmentation Anything Model (SAM) 的引入为医疗图像分割带来了新的机会,但其在医学领域的应用面临模型体积大和GPU需求高的挑战。
- 为应对这些挑战,研究者正在开发SAM的轻量级版本,以降低参数数量并提高训练效率。
- MCP-MedSAM是一个强大的轻量级医学SAM模型,能在单个GPU上一天内完成训练并表现出卓越的分割性能。
- MCP-MedSAM已经在大型挑战赛数据集上进行了验证,并与排行榜上的顶尖方法相比具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

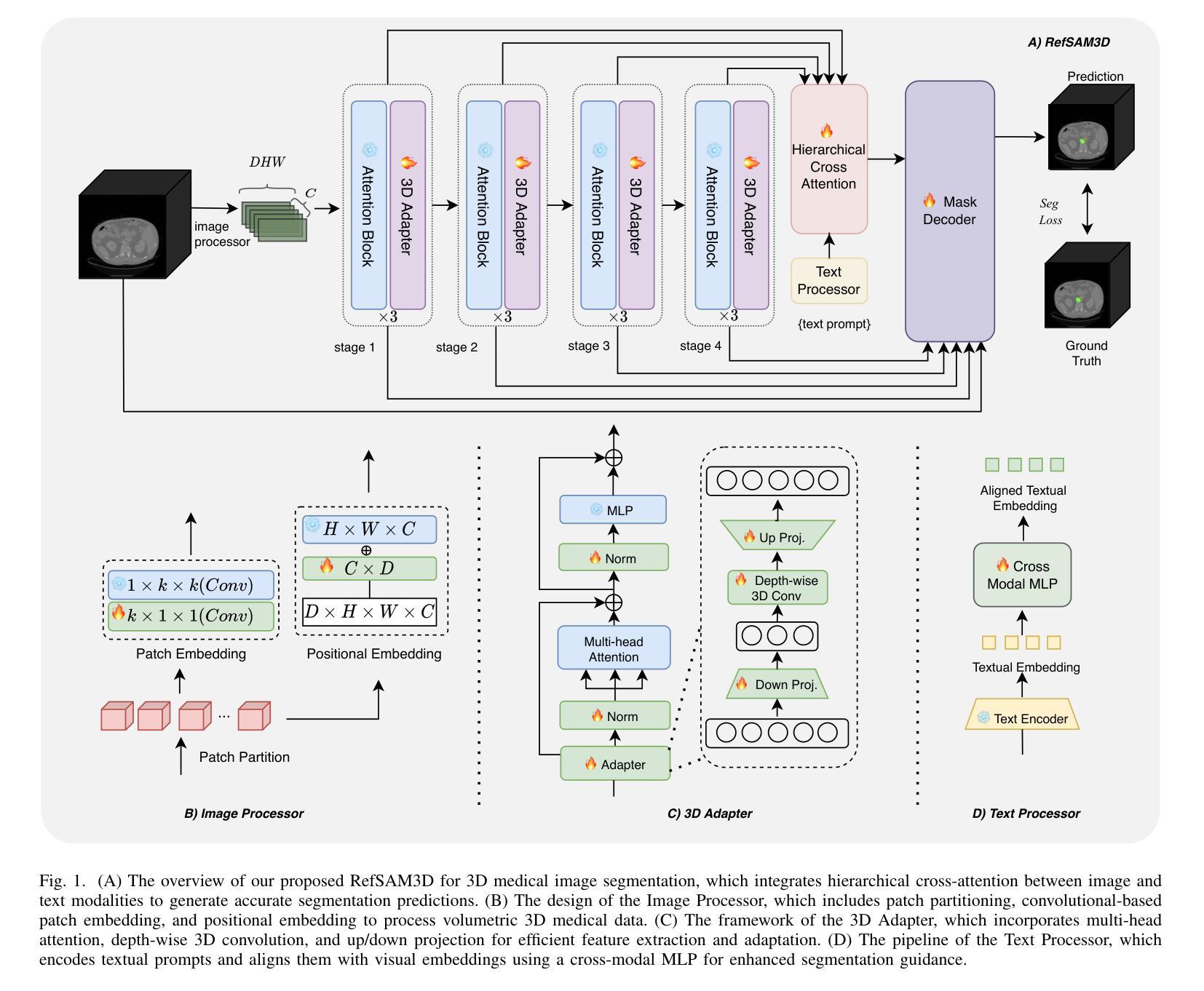
RefSAM3D: Adapting SAM with Cross-modal Reference for 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Xiang Gao, Kai Lu
The Segment Anything Model (SAM), originally built on a 2D Vision Transformer (ViT), excels at capturing global patterns in 2D natural images but struggles with 3D medical imaging modalities like CT and MRI. These modalities require capturing spatial information in volumetric space for tasks such as organ segmentation and tumor quantification. To address this challenge, we introduce RefSAM3D, which adapts SAM for 3D medical imaging by incorporating a 3D image adapter and cross-modal reference prompt generation. Our approach modifies the visual encoder to handle 3D inputs and enhances the mask decoder for direct 3D mask generation. We also integrate textual prompts to improve segmentation accuracy and consistency in complex anatomical scenarios. By employing a hierarchical attention mechanism, our model effectively captures and integrates information across different scales. Extensive evaluations on multiple medical imaging datasets demonstrate the superior performance of RefSAM3D over state-of-the-art methods. Our contributions advance the application of SAM in accurately segmenting complex anatomical structures in medical imaging.
Segment Anything Model(SAM)最初是建立在2D Vision Transformer(ViT)之上,擅长捕捉2D自然图像中的全局模式,但在处理如CT和MRI等3D医学成像模式时却面临困难。这些模式需要捕获体积空间中的空间信息,以完成器官分割和肿瘤量化等任务。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了RefSAM3D,它通过融入3D图像适配器和跨模态参考提示生成,将SAM改编为适用于3D医学影像。我们的方法修改了视觉编码器以处理3D输入,并增强了掩膜解码器以进行直接的3D掩膜生成。我们还整合了文本提示,以提高复杂解剖场景中的分割精度和一致性。通过采用分层注意力机制,我们的模型能够有效地捕捉并整合不同尺度的信息。在多个医学成像数据集上的广泛评估表明,RefSAM3D的性能优于最新方法。我们的贡献推动了SAM在医学成像中准确分割复杂解剖结构的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
SAM模型在二维自然图像上表现优异,但在三维医学影像如CT和MRI上表现不佳。为解决此挑战,我们推出RefSAM3D,它通过融入三维图像适配器和跨模态参考提示生成,让SAM适应三维医学影像。该方法调整视觉编码器以处理三维输入,增强掩膜解码器以实现直接的三维掩膜生成。此外,它还结合了文本提示以提高复杂解剖场景的分割精度和一致性。通过分层注意力机制,我们的模型在不同尺度上有效地捕捉并整合信息。在多个医学影像数据集上的广泛评估表明,RefSAM3D的性能优于最新技术。
Key Takeaways
- SAM模型擅长捕捉二维自然图像中的全局模式,但在处理三维医学影像时面临挑战。
- RefSAM3D旨在解决SAM在三维医学影像上的不足,通过融入三维图像适配器等方法使其适应医学影像分析。
- RefSAM3D能够直接生成三维掩膜,提高了医学影像的分割能力。
- 通过结合文本提示,RefSAM3D在复杂解剖场景的影像分割中表现出更高的精度和一致性。
- 采用分层注意力机制,使模型在不同尺度上更有效地捕捉和整合信息。
- 在多个医学影像数据集上的评估显示,RefSAM3D性能优于现有先进技术。
- 此研究为SAM模型在医学影像分割领域的应用提供了新的发展方向。
点此查看论文截图

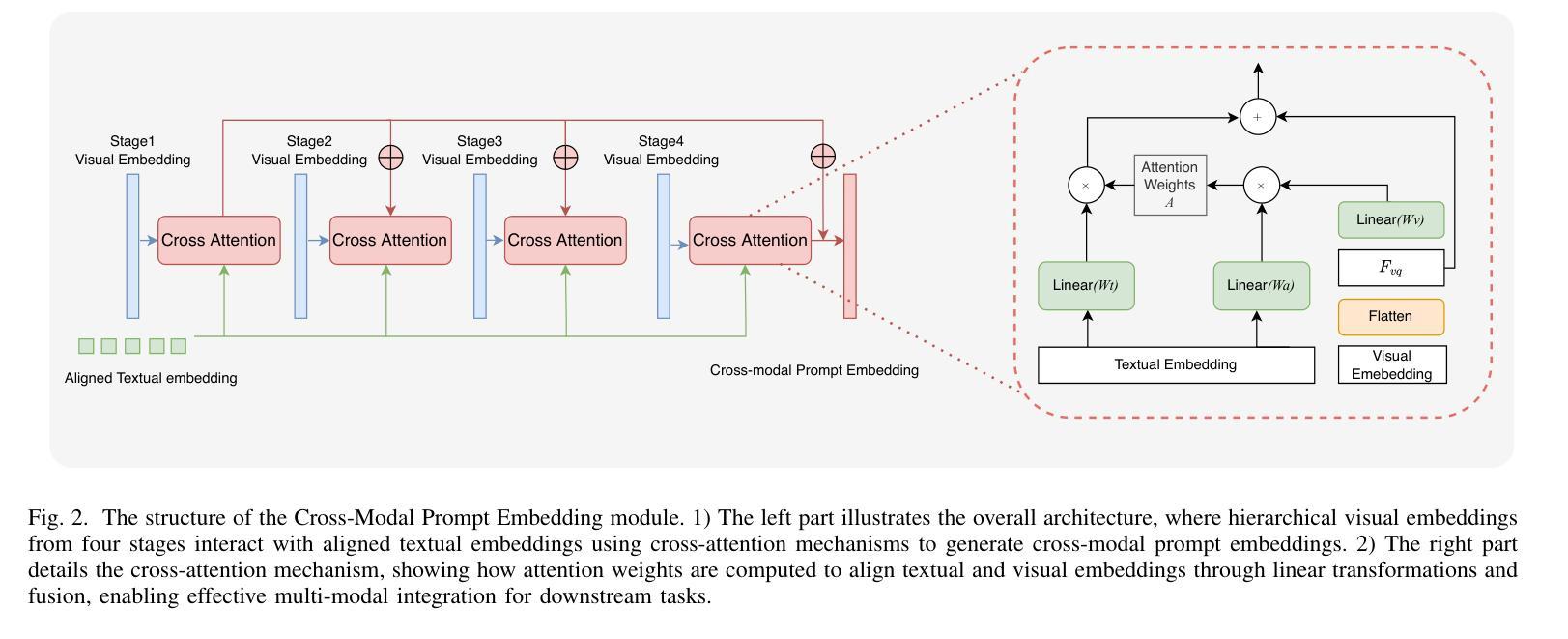
UNet++ and LSTM combined approach for Breast Ultrasound Image Segmentation
Authors:Saba Hesaraki, Morteza Akbari, Ramin Mousa
Breast cancer stands as a prevalent cause of fatality among females on a global scale, with prompt detection playing a pivotal role in diminishing mortality rates. The utilization of ultrasound scans in the BUSI dataset for medical imagery pertaining to breast cancer has exhibited commendable segmentation outcomes through the application of UNet and UNet++ networks. Nevertheless, a notable drawback of these models resides in their inattention towards the temporal aspects embedded within the images. This research endeavors to enrich the UNet++ architecture by integrating LSTM layers and self-attention mechanisms to exploit temporal characteristics for segmentation purposes. Furthermore, the incorporation of a Multiscale Feature Extraction Module aims to grasp varied scale features within the UNet++. Through the amalgamation of our proposed methodology with data augmentation on the BUSI with GT dataset, an accuracy rate of 98.88%, specificity of 99.53%, precision of 95.34%, sensitivity of 91.20%, F1-score of 93.74, and Dice coefficient of 92.74% are achieved. These findings demonstrate competitiveness with cutting-edge techniques outlined in existing literature.
乳腺癌是全球女性死亡的常见原因之一,而及早发现对于降低死亡率起着至关重要的作用。在医疗图像相关的乳腺癌超声扫描数据集(BUSI)中,通过应用UNet和UNet++网络,展现出了令人称赞的分割效果。然而,这些模型的一个明显缺点是对图像中嵌入的暂时方面的忽视。本研究旨在通过集成LSTM层和自注意力机制来丰富UNet++架构,以利用时间特征进行分割。此外,引入多尺度特征提取模块的目的是为了捕获UNet++内的不同尺度特征。通过将本研究提出的方法与BUSI-GT数据集上的数据增强相结合,实现了准确率98.88%,特异性99.53%,精确度95.34%,敏感度91.20%,F1分数93.74%,以及Dice系数92.74%。这些发现表明与现有文献中前沿技术的竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了乳腺癌医学影像的分割问题,利用超声扫描数据集的医学图像数据,探讨了使用改进后的UNet++网络结合LSTM层和自注意力机制进行图像分割的方法。该研究通过引入多尺度特征提取模块和数据增强技术,取得了较高的准确率和良好的性能指标。这些发现与现有文献中的先进技术相比具有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌是全球女性常见的致命疾病,及时检测对降低死亡率至关重要。
- UNet和UNet++网络在BUSI数据集上的医学图像分割表现出良好的结果。
- 现有模型忽略图像中的时间特性是一个显著缺点。
- 研究通过整合LSTM层和自注意力机制来丰富UNet++架构,以利用时间特性进行分割。
- 引入的多尺度特征提取模块旨在捕获不同尺度的特征。
- 结合提出的方法和数据增强技术,在BUSI with GT数据集上取得了高准确率(98.88%)、高特异性(99.53%)、精准度(95.34%)、敏感性(91.2%)和F1分数(93.74%)以及Dice系数(92.74%)。
点此查看论文截图

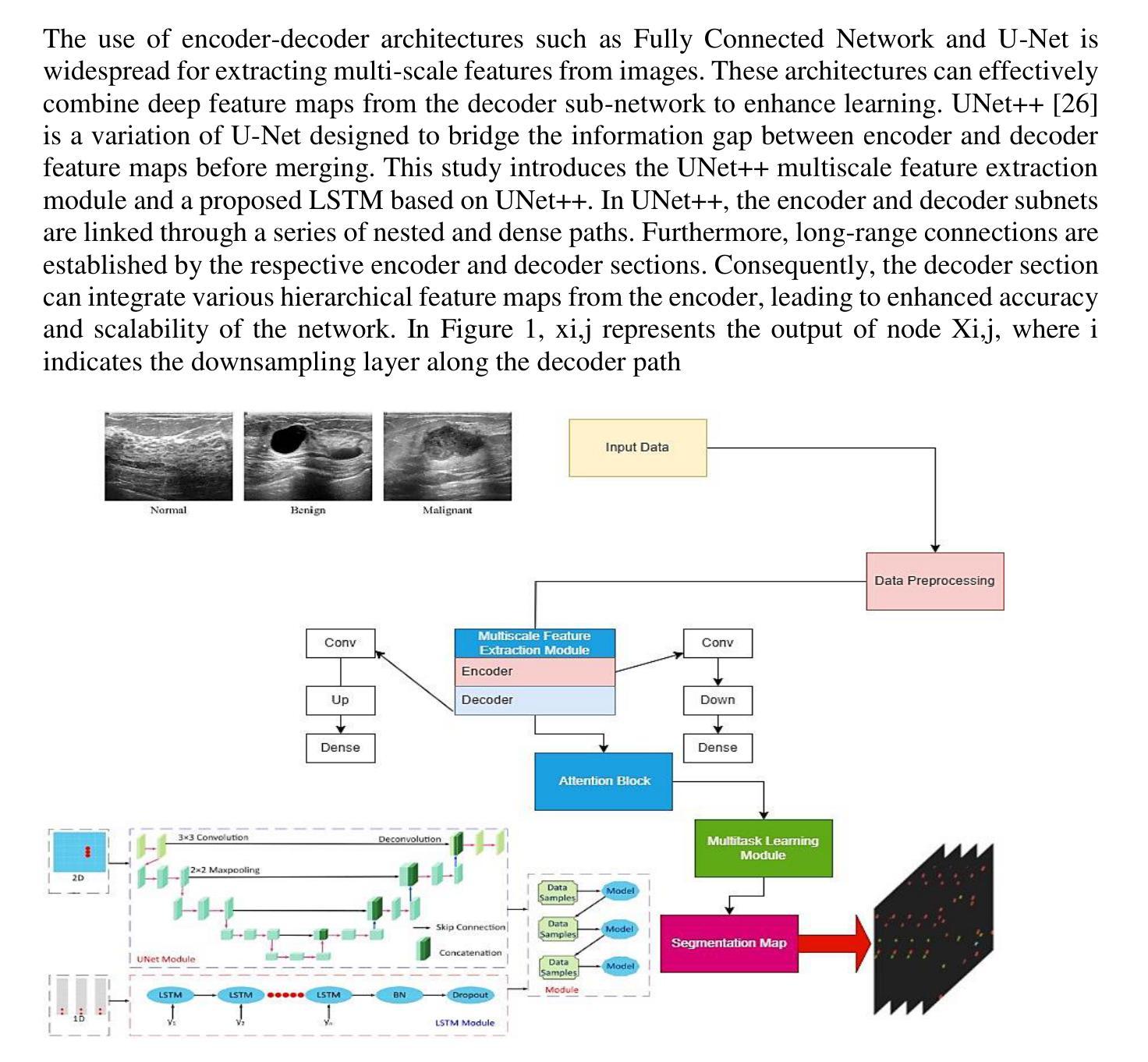
From Deterministic to Probabilistic: A Novel Perspective on Domain Generalization for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yuheng Xu, Taiping Zhang
Traditional domain generalization methods often rely on domain alignment to reduce inter-domain distribution differences and learn domain-invariant representations. However, domain shifts are inherently difficult to eliminate, which limits model generalization. To address this, we propose an innovative framework that enhances data representation quality through probabilistic modeling and contrastive learning, reducing dependence on domain alignment and improving robustness under domain variations. Specifically, we combine deterministic features with uncertainty modeling to capture comprehensive feature distributions. Contrastive learning enforces distribution-level alignment by aligning the mean and covariance of feature distributions, enabling the model to dynamically adapt to domain variations and mitigate distribution shifts. Additionally, we design a frequency-domain-based structural enhancement strategy using discrete wavelet transforms to preserve critical structural details and reduce visual distortions caused by style variations. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework significantly improves segmentation performance, providing a robust solution to domain generalization challenges in medical image segmentation.
传统领域泛化方法通常依赖于领域对齐来减少跨域分布差异并学习领域不变的表示。然而,领域偏移本质上难以消除,这限制了模型的泛化能力。针对这一问题,我们提出了一种创新框架,通过概率建模和对比学习提高数据表示质量,减少对领域对齐的依赖,并在领域变化下提高稳健性。具体来说,我们将确定性特征与不确定性建模相结合,以捕捉全面的特征分布。对比学习通过对特征分布的均值和协方差进行对齐,实现分布级别的对齐,使模型能够动态适应领域变化并缓解分布偏移。此外,我们利用离散小波变换设计了一种基于频域的结构增强策略,以保留关键的结构细节,并减少由风格变化引起的视觉失真。实验结果表明,该框架显著提高了分割性能,为医学图像分割中的领域泛化挑战提供了稳健的解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 3 figures
Summary
该文本介绍了一种新颖的框架,它通过概率建模和对比学习提升数据表现质量,减少了对领域对齐的依赖,提高了模型在不同领域下的稳健性。结合确定性特征和不确定性建模,该框架能够捕捉全面的特征分布。对比学习通过对特征分布的均值和协方差进行对齐,使模型能够动态适应领域变化并缓解分布偏移问题。此外,该框架还设计了一种基于频域的结构增强策略,使用离散小波变换保留关键结构细节,减少由风格变化引起的视觉失真。实验结果表明,该框架显著提高了分割性能,为医学图像分割中的领域泛化挑战提供了稳健的解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新颖的框架,旨在提高数据表现质量以增强模型在不同领域的泛化能力。
- 该框架结合概率建模和对比学习,减少了对领域对齐的依赖。
- 通过结合确定性特征和不确定性建模,全面捕捉特征分布。
- 对比学习通过分布层面的对齐,使模型能够适应领域变化并缓解分布偏移。
- 设计了一种基于频域的结构增强策略,使用离散小波变换保留关键结构细节。
- 框架能够减少由风格变化引起的视觉失真。
点此查看论文截图

Automated Dynamic Image Analysis for Particle Size and Shape Classification in Three Dimensions
Authors:Sadegh Nadimi, Vasileios Angelidakis, Sadaf Maramizonouz, Chao Zhang
We introduce OCULAR, an innovative hardware and software solution for three-dimensional dynamic image analysis of fine particles. Current state-of-the art instruments for dynamic image analysis are largely limited to two-dimensional imaging. However, extensive literature has demonstrated that relying on a single two-dimensional projection for particle characterisation can lead to inaccuracies in many applications. Existing three-dimensional imaging technologies, such as computed tomography, laser scanning, and orthophotography, are limited to static objects. These methods are often not statistically representative and come with significant post-processing requirements, as well as the need for specialised imaging and computing resources. OCULAR addresses these challenges by providing a cost-effective solution for imaging continuous particle streams using a synchronised array of optical cameras. Particle shape characterisation is achieved through the reconstruction of their three-dimensional surfaces. This paper details the OCULAR methodology, evaluates its reproducibility, and compares its results against X-ray micro computed tomography, highlighting its potential for efficient and reliable particle analysis.
我们介绍了OCULAR,这是一种用于微粒三维动态图像分析的创新软硬件解决方案。当前动态图像分析的最先进仪器大多仅限于二维成像。然而,大量文献表明,依赖单一二维投影进行颗粒表征会导致许多应用中的不准确。现有的三维成像技术,如计算机断层扫描、激光扫描和正射摄影,仅限于静态物体。这些方法往往不具有统计代表性,并且需要大量的后期处理要求,以及需要专门的成像和计算资源。OCULAR通过提供使用同步光学相机阵列对连续颗粒流进行成像的成本效益解决方案来解决这些挑战。通过重建颗粒的三维表面来实现颗粒形状表征。本文详细介绍了OCULAR的方法论,评估了其可重复性,并与X射线显微计算机断层扫描进行了比较,突出了其高效可靠的颗粒分析潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 5 figures
Summary
OCULAR是一种创新的硬件和软件解决方案,用于对微粒进行三维动态图像分析。相较于当前二维成像的技术,OCULAR更能准确分析粒子特性,特别是在对连续粒子流进行成像时具有优势。该方法采用同步的光学相机阵列进行拍摄,并通过重建粒子三维表面实现形状特征描述。此方法具有成本效益,且与X射线微计算机断层扫描相比,具有高效可靠的粒子分析潜力。
Key Takeaways
- OCULAR是一种用于微粒三维动态图像分析的创新硬件和软件解决方案。
- 当前二维成像技术在粒子特性分析方面存在局限性。
- OCULAR通过采用同步光学相机阵列对连续粒子流进行成像。
- 该技术通过重建粒子的三维表面来实现形状特征描述。
- OCULAR具有成本效益,无需特殊的成像和计算资源。
- OCULAR与X射线微计算机断层扫描相比,具有高效可靠的粒子分析潜力。
点此查看论文截图


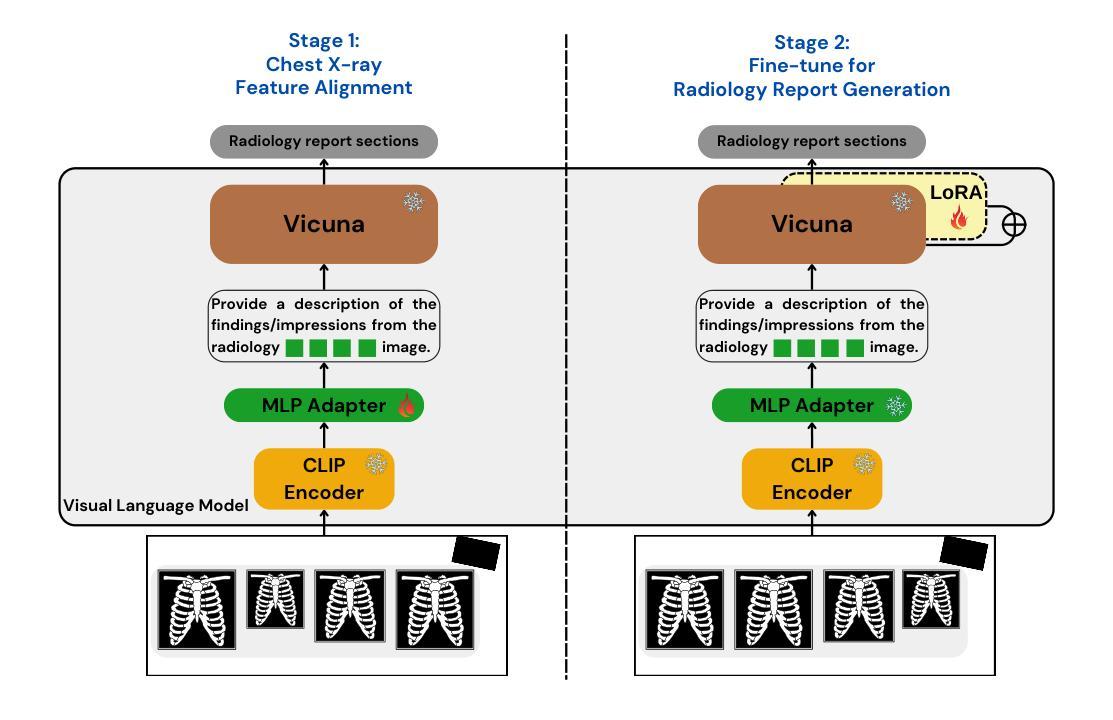
Gla-AI4BioMed at RRG24: Visual Instruction-tuned Adaptation for Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Xi Zhang, Zaiqiao Meng, Jake Lever, Edmond S. L. Ho
We introduce a radiology-focused visual language model designed to generate radiology reports from chest X-rays. Building on previous findings that large language models (LLMs) can acquire multimodal capabilities when aligned with pretrained vision encoders, we demonstrate similar potential with chest X-ray images. This integration enhances the ability of model to understand and describe chest X-ray images. Our model combines an image encoder with a fine-tuned LLM based on the Vicuna-7B architecture, enabling it to generate different sections of a radiology report with notable accuracy. The training process involves a two-stage approach: (i) initial alignment of chest X-ray features with the LLM (ii) followed by fine-tuning for radiology report generation.
我们引入了一款专注于放射学的视觉语言模型,该模型旨在从胸部X光片中生成放射学报告。在大型语言模型(LLM)可以与预训练的视觉编码器对齐从而获取多模态能力的前期研究基础上,我们对胸部X射线图像展示了类似的潜力。这种融合增强了模型理解和描述胸部X射线图像的能力。我们的模型结合了图像编码器和基于Vicuna-7B架构的微调LLM,使其能够准确生成放射学报告的不同部分。训练过程包括两个阶段:(i)胸部X射线特征与LLM的初步对齐,(ii)随后进行针对放射学报告生成的微调。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by BioNLP@ACL 2024
Summary
基于先前大型语言模型(LLM)与预训练视觉编码器相结合的多模态能力研究成果,我们针对放射学领域开发了一种视觉语言模型,用于从胸部X光片中生成放射学报告。通过结合图像编码器和基于Vicuna-7B架构的微调LLM,该模型能够准确生成不同部分的放射学报告。其训练过程包括两个阶段:一是初步对齐胸部X光特征与LLM,二是针对放射学报告生成进行微调。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种针对放射学的视觉语言模型,可从胸部X光片中生成放射学报告。
- 模型结合图像编码器和基于Vicuna-7B架构的LLM,展示多模态潜力。
- 训练过程采用两阶段方法:初期对齐胸部X光特征到LLM,随后针对报告生成进行微调。
- 模型能够理解并描述胸部X光图像,生成报告的不同部分具有显著准确性。
- 此模型为放射学报告自动生成提供了新的可能性,可能改变放射学报告的生成方式。
- 该模型的训练方法和性能为医学影像领域的AI应用提供了新的思路。
点此查看论文截图

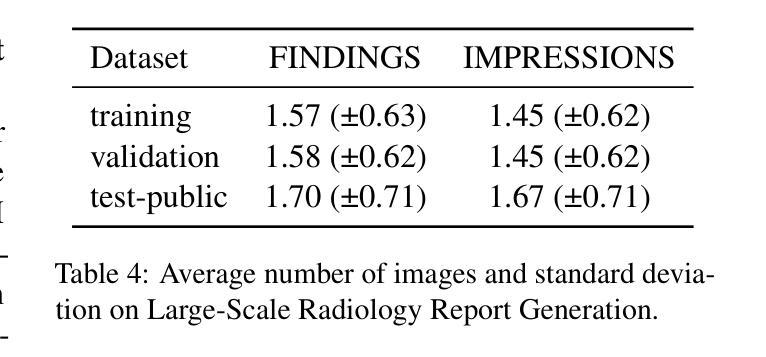
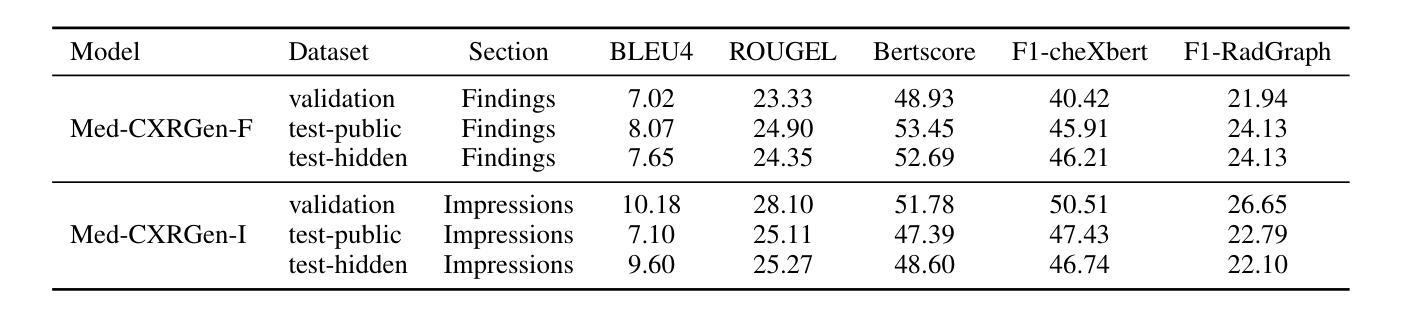
DAug: Diffusion-based Channel Augmentation for Radiology Image Retrieval and Classification
Authors:Ying Jin, Zhuoran Zhou, Haoquan Fang, Jenq-Neng Hwang
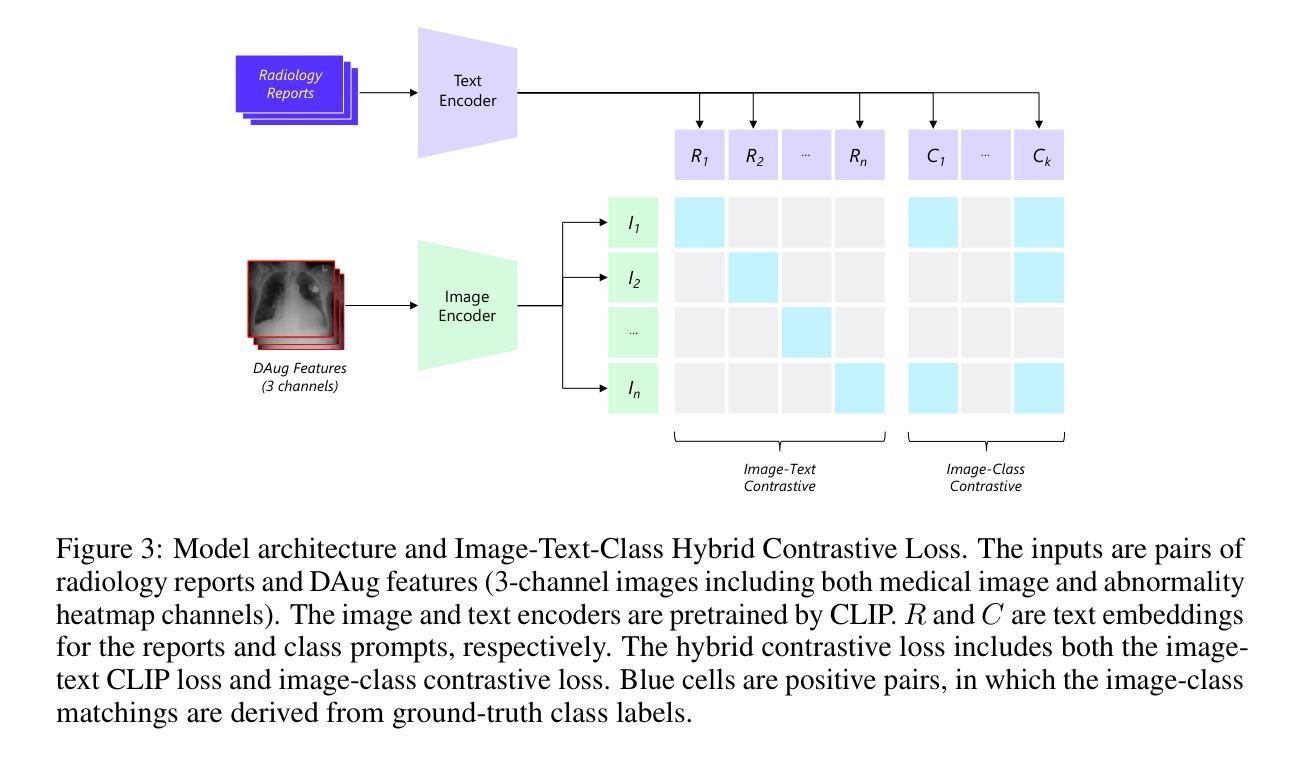
Medical image understanding requires meticulous examination of fine visual details, with particular regions requiring additional attention. While radiologists build such expertise over years of experience, it is challenging for AI models to learn where to look with limited amounts of training data. This limitation results in unsatisfying robustness in medical image understanding. To address this issue, we propose Diffusion-based Feature Augmentation (DAug), a portable method that improves a perception model’s performance with a generative model’s output. Specifically, we extend a radiology image to multiple channels, with the additional channels being the heatmaps of regions where diseases tend to develop. A diffusion-based image-to-image translation model was used to generate such heatmaps conditioned on selected disease classes. Our method is motivated by the fact that generative models learn the distribution of normal and abnormal images, and such knowledge is complementary to image understanding tasks. In addition, we propose the Image-Text-Class Hybrid Contrastive learning to utilize both text and class labels. With two novel approaches combined, our method surpasses baseline models without changing the model architecture, and achieves state-of-the-art performance on both medical image retrieval and classification tasks.
医学图像理解需要对细微的视觉细节进行细致的检查,特定区域需要额外的关注。虽然放射科医生通过多年的经验积累获得了这样的专业知识,但对于人工智能模型来说,在有限的训练数据下学习应该关注的地方却是一个挑战。这种局限性导致了医学图像理解的稳健性不佳。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了基于扩散的特征增强(DAug)方法,该方法利用生成模型的输出提高感知模型的性能。具体来说,我们将放射学图像扩展到多个通道,额外的通道是疾病倾向发展区域的热图。我们使用基于扩散的图像到图像翻译模型来根据选定的疾病类别生成这样的热图。我们的方法受到以下事实的启发:生成模型学习正常和异常图像的分布,这些知识对于图像理解任务是互补的。此外,我们提出了图像文本类别混合对比学习,以利用文本和类别标签。通过结合两种新方法,我们的方法在不需要改变模型架构的情况下超越了基线模型,并在医学图像检索和分类任务上达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于扩散的特征增强(DAug)方法,通过结合生成模型的输出,提高感知模型在医学图像理解方面的性能。通过扩展放射图像到多个通道,并生成疾病的潜在热图,增强模型对关键区域的关注。结合图像文本分类混合对比学习,该方法在不改变模型架构的前提下,超越了基线模型,实现了医学图像检索和分类任务的最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像理解需要精细的视觉细节分析,特定区域需重点关注。
- AI模型在医学图像理解中面临训练数据有限、稳健性不足的挑战。
- 提出扩散特征增强(DAug)方法,通过生成模型的输出提高感知模型性能。
- 将医学图像扩展到多个通道,包括疾病的潜在热图。
- 采用基于扩散的图像到图像翻译模型,根据选定疾病类别生成热图。
- 借助生成模型学习正常和异常图像分布的知识,补充图像理解任务。
点此查看论文截图

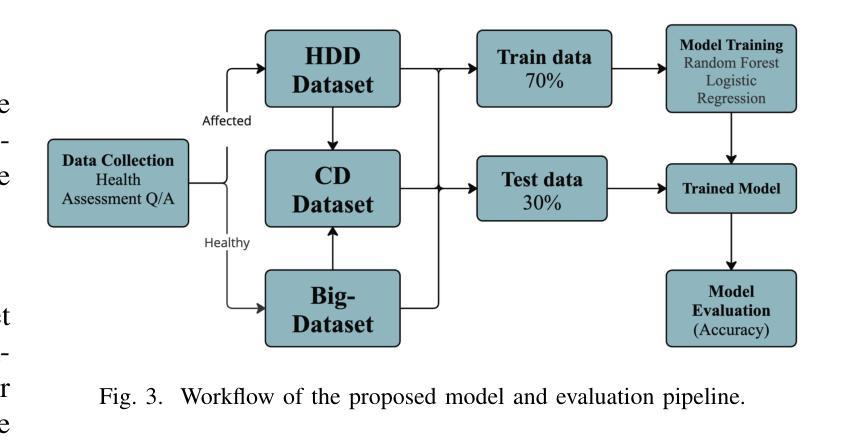
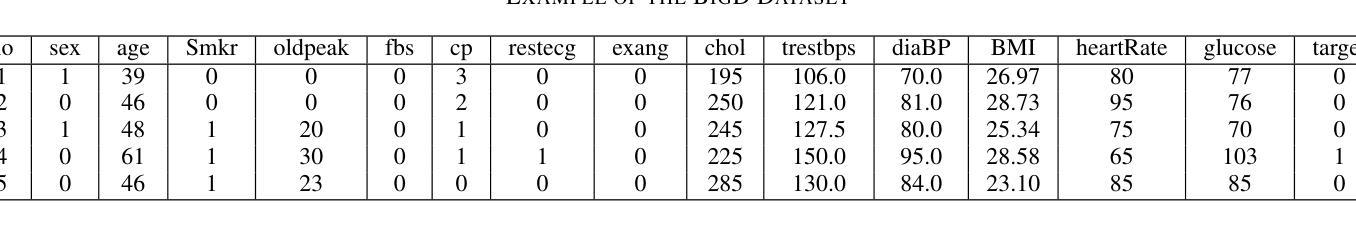
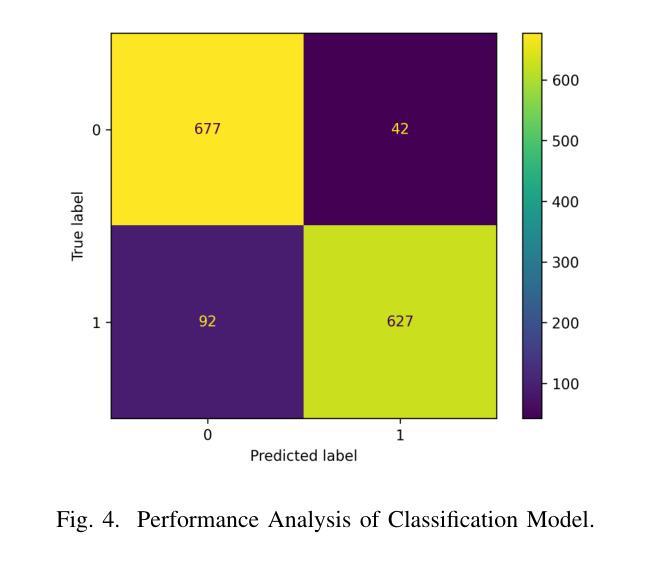
Multi-class heart disease Detection, Classification, and Prediction using Machine Learning Models
Authors:Mahfuzul Haque, Abu Saleh Musa Miah, Debashish Gupta, Md. Maruf Al Hossain Prince, Tanzina Alam, Nusrat Sharmin, Mohammed Sowket Ali, Jungpil Shin
Heart disease is a leading cause of premature death worldwide, particularly among middle-aged and older adults, with men experiencing a higher prevalence. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), non-communicable diseases, including heart disease, account for 25% (17.9 million) of global deaths, with over 43,204 annual fatalities in Bangladesh. However, the development of heart disease detection (HDD) systems tailored to the Bangladeshi population remains underexplored due to the lack of benchmark datasets and reliance on manual or limited-data approaches. This study addresses these challenges by introducing new, ethically sourced HDD dataset, BIG-Dataset and CD dataset which incorporates comprehensive data on symptoms, examination techniques, and risk factors. Using advanced machine learning techniques, including Logistic Regression and Random Forest, we achieved a remarkable testing accuracy of up to 96.6% with Random Forest. The proposed AI-driven system integrates these models and datasets to provide real-time, accurate diagnostics and personalized healthcare recommendations. By leveraging structured datasets and state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms, this research offers an innovative solution for scalable and effective heart disease detection, with the potential to reduce mortality rates and improve clinical outcomes.
心脏病是全球范围内,尤其是中老年男性群体中的主要早逝原因。根据世界卫生组织(WHO)的数据,包括心脏病在内的非传染性疾病占全球死亡人数的25%(1790万人),其中孟加拉国每年有超过43,204人因此丧生。然而,由于缺乏基准数据集,以及过度依赖手动或有限数据的方法,针对孟加拉国人口定制的心脏病检测(HDD)系统的开发仍然被较少探索。本研究通过引入新的、道德来源的HDD数据集——BIG数据集和CD数据集,该数据集包含了症状、检查技术和风险因素的全面数据,来解决这些挑战。使用先进的机器学习技术,包括逻辑回归和随机森林,我们利用随机森林达到了高达96.6%的测试准确率。所提出的AI驱动系统集成了这些模型和数据集,以提供实时、准确的诊断和个性化的医疗建议。通过利用结构化数据集和最新的机器学习算法,这项研究为可伸缩和有效的心脏病检测提供了创新的解决方案,具有降低死亡率、改善临床治疗效果的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
心脏病是全球尤其是中老年男性早逝的主要原因之一。世界卫生组织表示,非传染性疾病(包括心脏病)占全球死亡人数的四分之一,孟加拉国每年有超过四万三千人死亡于此。然而,针对孟加拉国人口的心脏病检测(HDD)系统发展仍然欠缺研究,由于缺乏基准数据集以及依赖于手动或有限数据方法。本研究通过引入新的合法获取HDD数据集和CD数据集来解决这些挑战,该数据集包含了症状、检查技术和风险因素的综合数据。通过逻辑回归和随机森林等先进机器学习技术,我们取得了高达96.6%的测试准确率。所提出的AI驱动系统集成了这些模型和数据集,可实时准确地诊断和个性化医疗保健建议。该研究提供了一个可规模扩展且有效的创新心脏病检测解决方案,有望降低死亡率并改善临床结果。
Key Takeaways
- 心脏病是全球性的主要健康问题,尤其在中年和老年人中更为常见,对男性影响更大。
- 非传染性疾病,包括心脏病,占全球死亡人数的四分之一,孟加拉国的年度死亡人数超过四万三千人。
- 针对孟加拉国人口的心脏病检测系统发展仍然不足,缺乏基准数据集和依赖手动或有限数据方法的问题突出。
- 本研究引入了新的合法获取HDD数据集和CD数据集,包括症状、检查技术和风险因素的综合数据。
- 通过逻辑回归和随机森林等机器学习技术,测试准确率高达96.6%。
- AI驱动的系统集成了这些模型和数据集,可实时提供准确的诊断和个性化医疗建议。
点此查看论文截图


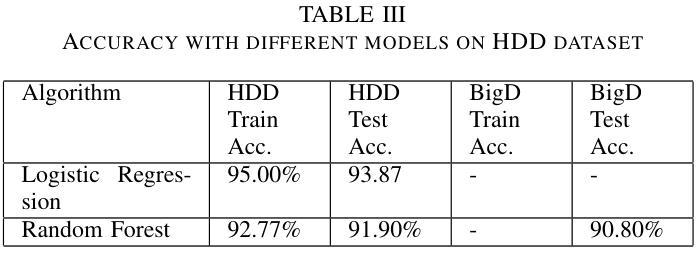
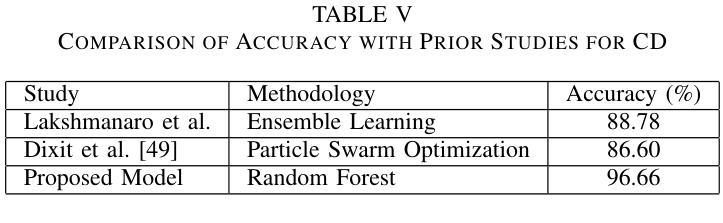
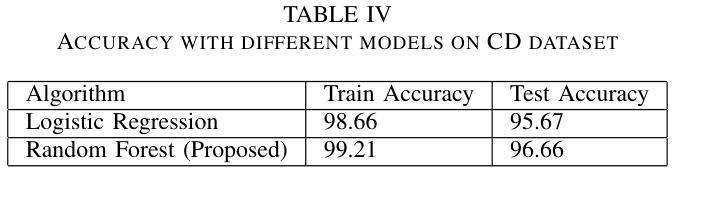
Unsupervised Segmentation by Diffusing, Walking and Cutting
Authors:Daniela Ivanova, Marco Aversa, Paul Henderson, John Williamson
We propose an unsupervised image segmentation method using features from pre-trained text-to-image diffusion models. Inspired by classic spectral clustering approaches, we construct adjacency matrices from self-attention layers between image patches and recursively partition using Normalised Cuts. A key insight is that self-attention probability distributions, which capture semantic relations between patches, can be interpreted as a transition matrix for random walks across the image. We leverage this by first using Random Walk Normalized Cuts directly on these self-attention activations to partition the image, minimizing transition probabilities between clusters while maximizing coherence within clusters. Applied recursively, this yields a hierarchical segmentation that reflects the rich semantics in the pre-trained attention layers, without any additional training. Next, we explore other ways to build the NCuts adjacency matrix from features, and how we can use the random walk interpretation of self-attention to capture long-range relationships. Finally, we propose an approach to automatically determine the NCut cost criterion, avoiding the need to tune this manually. We quantitatively analyse the effect incorporating different features, a constant versus dynamic NCut threshold, and incorporating multi-node paths when constructing the NCuts adjacency matrix. We show that our approach surpasses all existing methods for zero-shot unsupervised segmentation, achieving state-of-the-art results on COCO-Stuff-27 and Cityscapes.
我们提出了一种利用预训练文本到图像扩散模型的特性进行无监督图像分割的方法。该方法受到经典谱聚类方法的启发,我们构建了图像补丁间的自注意力层的邻接矩阵,并使用归一化切割进行递归划分。我们的关键见解是,自注意力概率分布能够捕捉补丁之间的语义关系,可以被解释为图像上随机游走的转移矩阵。我们首次利用这一点,直接在自注意力激活值上使用随机游走归一化切割来划分图像,以最小化集群之间的过渡概率,同时最大化集群内的连贯性。递归应用这种方法会产生反映预训练注意力层丰富语义的层次分割,无需任何额外的训练。接下来,我们探索了从特征构建NCuts邻接矩阵的其他方法,以及如何使用自注意力的随机游走解释来捕捉长距离关系。最后,我们提出了一种自动确定NCut成本标准的方法,避免了需要手动调整这一参数。我们定量分析了融入不同特性、常数与动态NCut阈值、在构建NCuts邻接矩阵时融入多节点路径的影响。我们展示,我们的方法在零样本无监督分割上超越了所有现有方法,并在COCO-Stuff-27和Cityscapes上达到了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
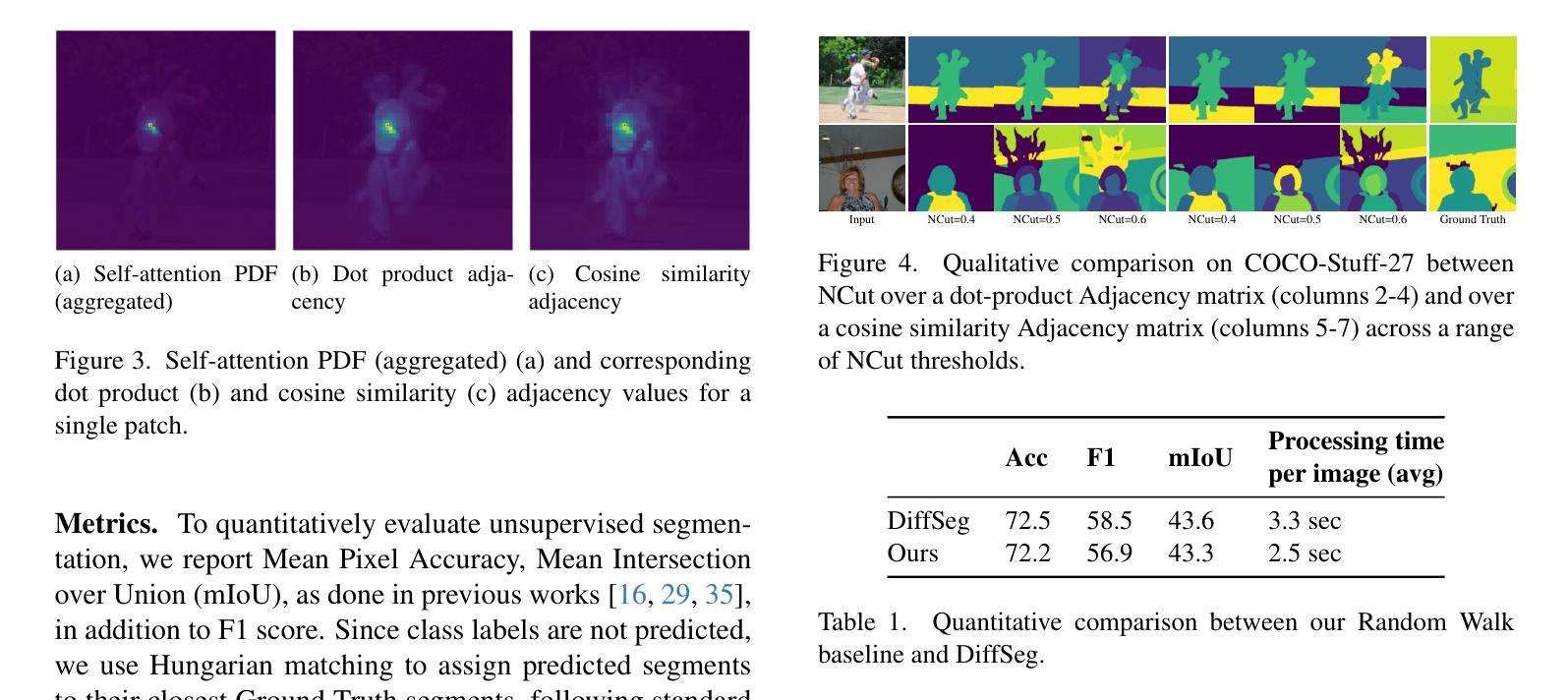
Summary
本研究提出了一种利用预训练文本到图像扩散模型特征进行无监督图像分割的方法。该方法结合经典谱聚类思想,构建图像补丁间的自注意力层邻接矩阵,采用归一化切割进行递归分割。研究关键见解是自注意力概率分布能够解释为图像内随机游走的转移矩阵,并以此为基础直接在自注意力激活上应用随机游走归一化切割,实现图像分割,反映预训练注意层中的丰富语义,无需任何额外训练。此外,研究还探讨了构建NCuts邻接矩阵的方法和自动确定NCut成本标准的方式,并进行定量分析。实验表明,该方法在COCO-Stuff-27和Cityscapes上超越现有零监督分割方法,达到最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种基于预训练文本到图像扩散模型特征的无监督图像分割方法。
- 结合谱聚类思想,利用自注意力层构建邻接矩阵。
- 通过归一化切割递归分割图像,基于自注意力概率分布进行随机游走解释。
- 提出直接在自注意力激活上应用随机游走归一化切割的方法,反映预训练注意层中的丰富语义。
- 探讨构建NCuts邻接矩阵的多种方法和利用随机游走解释自注意力的方式以捕捉长期关系。
- 实现自动确定NCut成本标准的方法,避免手动调整。
- 在COCO-Stuff-27和Cityscapes等数据集上达到零监督分割的领先水平。
点此查看论文截图

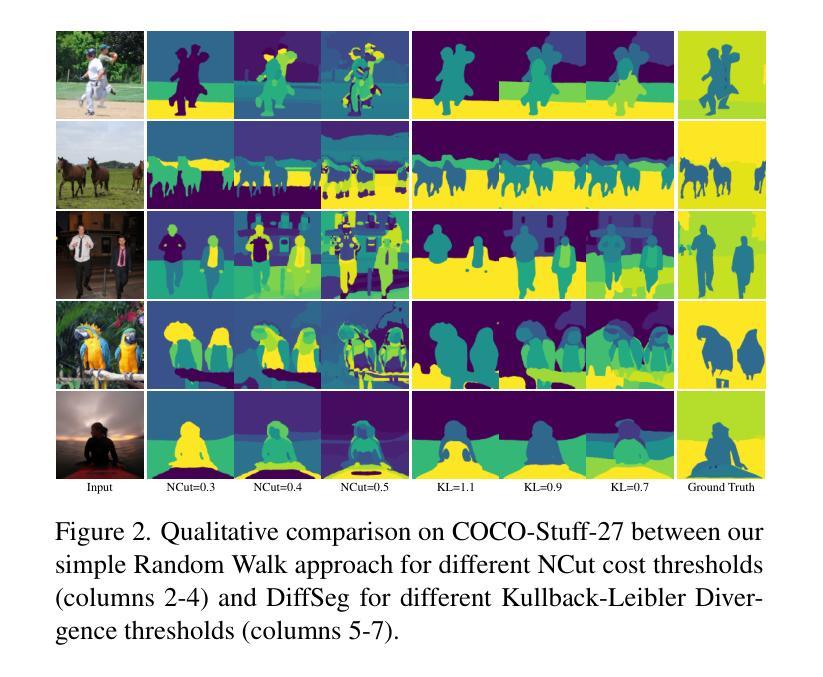
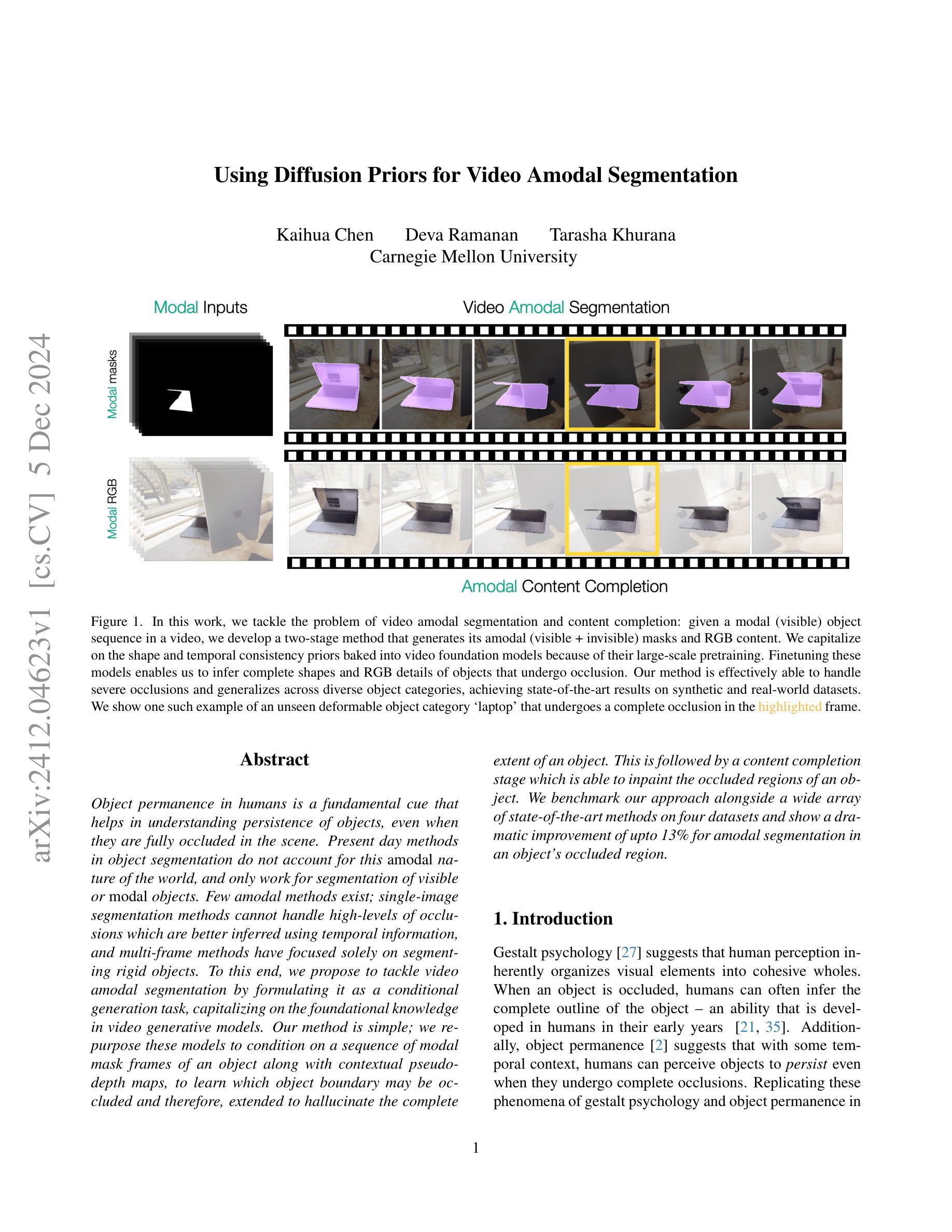
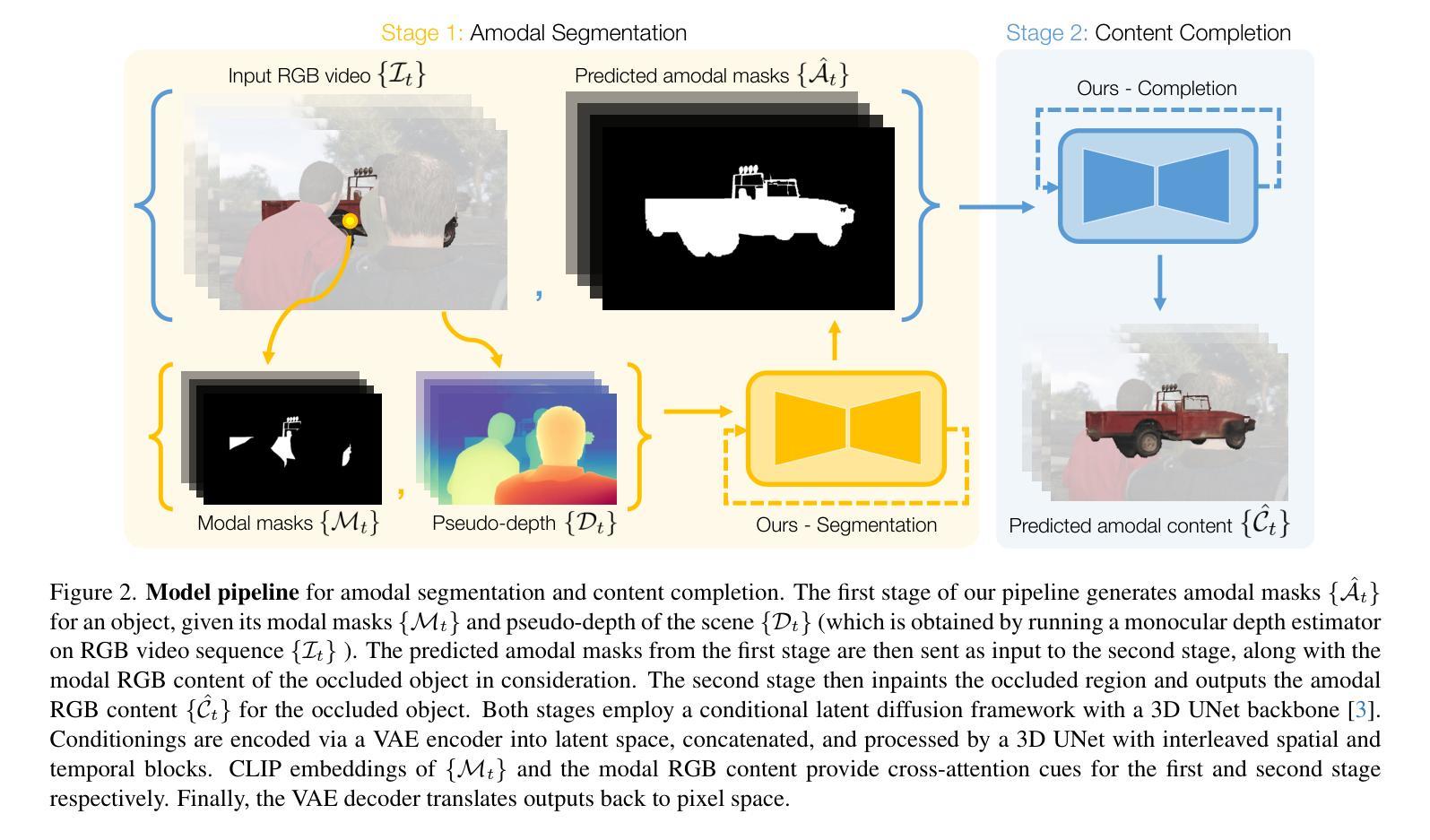
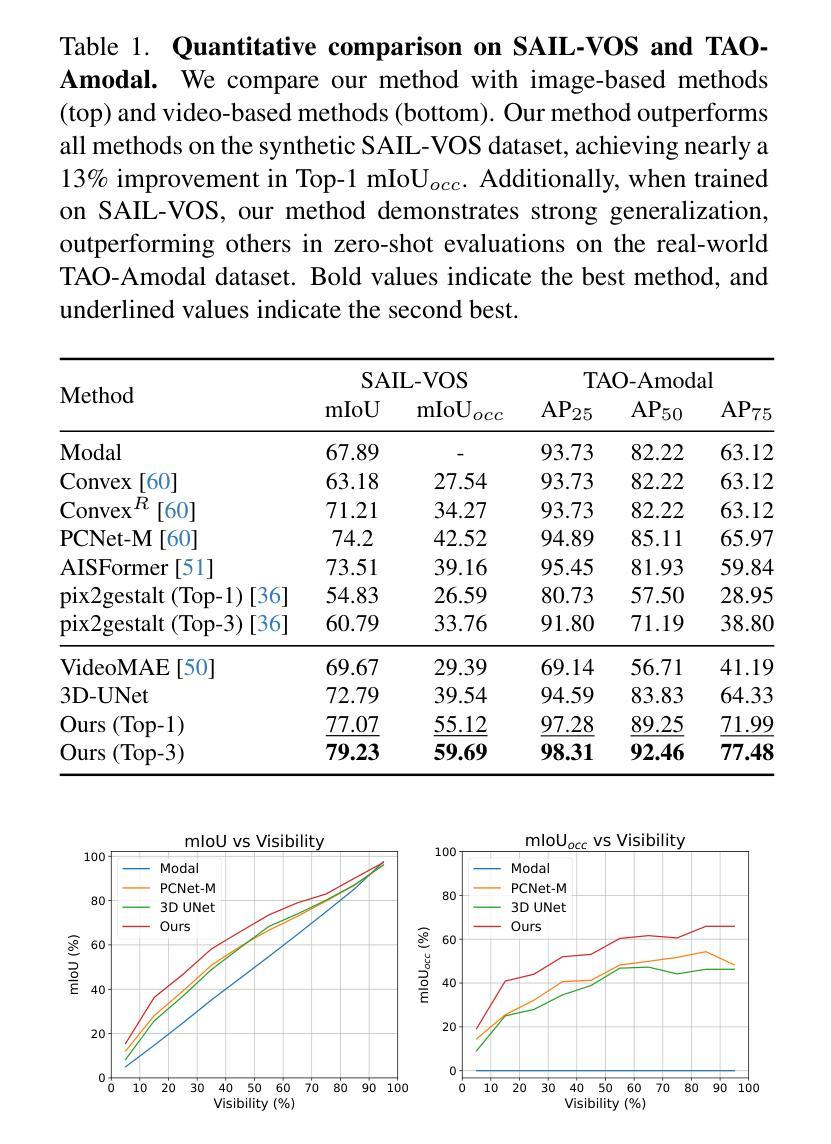
Using Diffusion Priors for Video Amodal Segmentation
Authors:Kaihua Chen, Deva Ramanan, Tarasha Khurana
Object permanence in humans is a fundamental cue that helps in understanding persistence of objects, even when they are fully occluded in the scene. Present day methods in object segmentation do not account for this amodal nature of the world, and only work for segmentation of visible or modal objects. Few amodal methods exist; single-image segmentation methods cannot handle high-levels of occlusions which are better inferred using temporal information, and multi-frame methods have focused solely on segmenting rigid objects. To this end, we propose to tackle video amodal segmentation by formulating it as a conditional generation task, capitalizing on the foundational knowledge in video generative models. Our method is simple; we repurpose these models to condition on a sequence of modal mask frames of an object along with contextual pseudo-depth maps, to learn which object boundary may be occluded and therefore, extended to hallucinate the complete extent of an object. This is followed by a content completion stage which is able to inpaint the occluded regions of an object. We benchmark our approach alongside a wide array of state-of-the-art methods on four datasets and show a dramatic improvement of upto 13% for amodal segmentation in an object’s occluded region.
人类的对象恒定性是一个基本线索,有助于理解对象在完全遮挡时的持久性。现有的对象分割方法并没有考虑到世界的非模态性质,只能对可见或模态对象进行分割。虽然存在一些非模态方法,但单图像分割方法无法处理高水平的遮挡,而这些遮挡更适合通过时间信息进行推断,而多帧方法则只专注于对刚性对象的分割。为此,我们提出将视频非模态分割作为条件生成任务来解决,利用视频生成模型的基础知识。我们的方法很简单:我们重新利用这些模型,以对象的模态掩膜帧序列和上下文伪深度图作为条件,学习哪些对象边界可能被遮挡,因此可以扩展到想象对象的完整程度。接下来是内容完成阶段,能够填充对象被遮挡的区域。我们在四个数据集上评估了我们的方法与一系列最新方法的表现,并在对象的遮挡区域进行非模态分割时显示出高达13%的显著改善。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF project page: https://diffusion-vas.github.io
Summary
本摘要提出一种视频的无模态分割方法,采用基于视频生成模型的先验知识,通过条件生成任务处理视频的无模态分割问题。该方法通过序列的模态掩膜帧和上下文伪深度图来预测对象的边界是否被遮挡,从而推断出对象的完整范围,并填充遮挡区域。在四个数据集上与其他先进方法相比,该方法在对象遮挡区域的无模态分割方面提高了高达13%。
Key Takeaways
- 人类物体永久性的概念是理解物体持久性的基本线索,尤其在物体被完全遮挡时。
- 现有物体分割方法忽略了世界无模态(非局部遮挡)特性,只能处理可见或模态物体的分割。
- 提出一种基于视频生成模型的条件生成任务来处理视频的无模态分割问题。
- 方法通过序列的模态掩膜帧和上下文伪深度图来预测对象边界是否被遮挡。
- 通过学习这种先验知识,方法可以推断出对象的完整范围并填充遮挡区域。
- 方法包括内容完成阶段,能够填充对象的遮挡区域。
点此查看论文截图

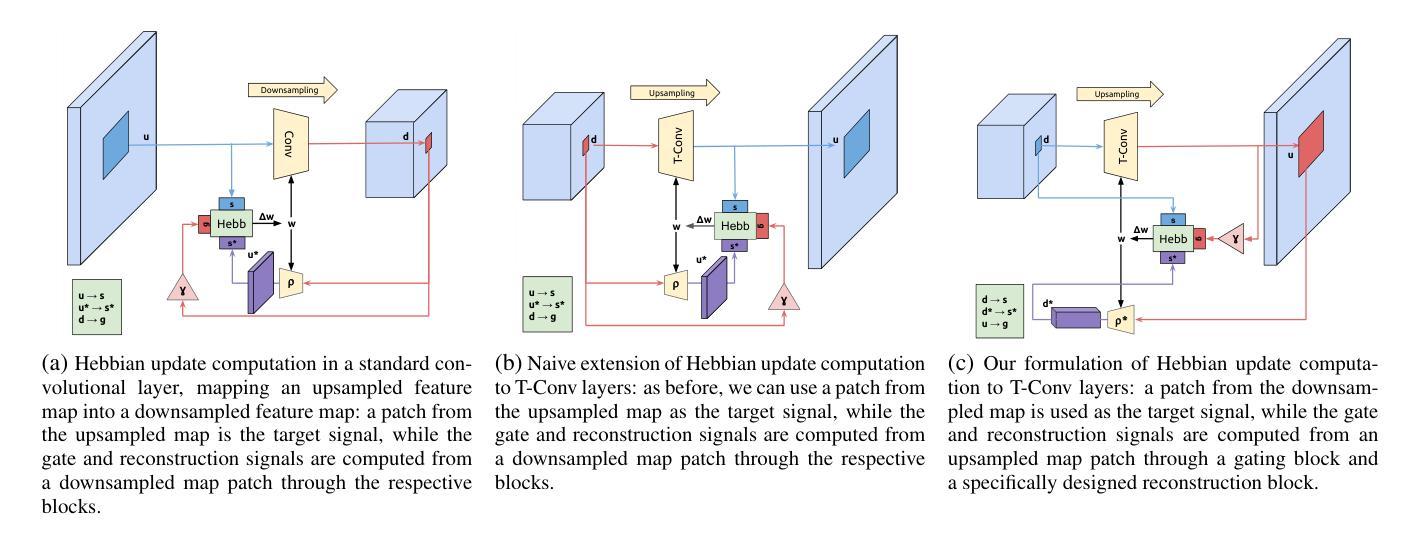
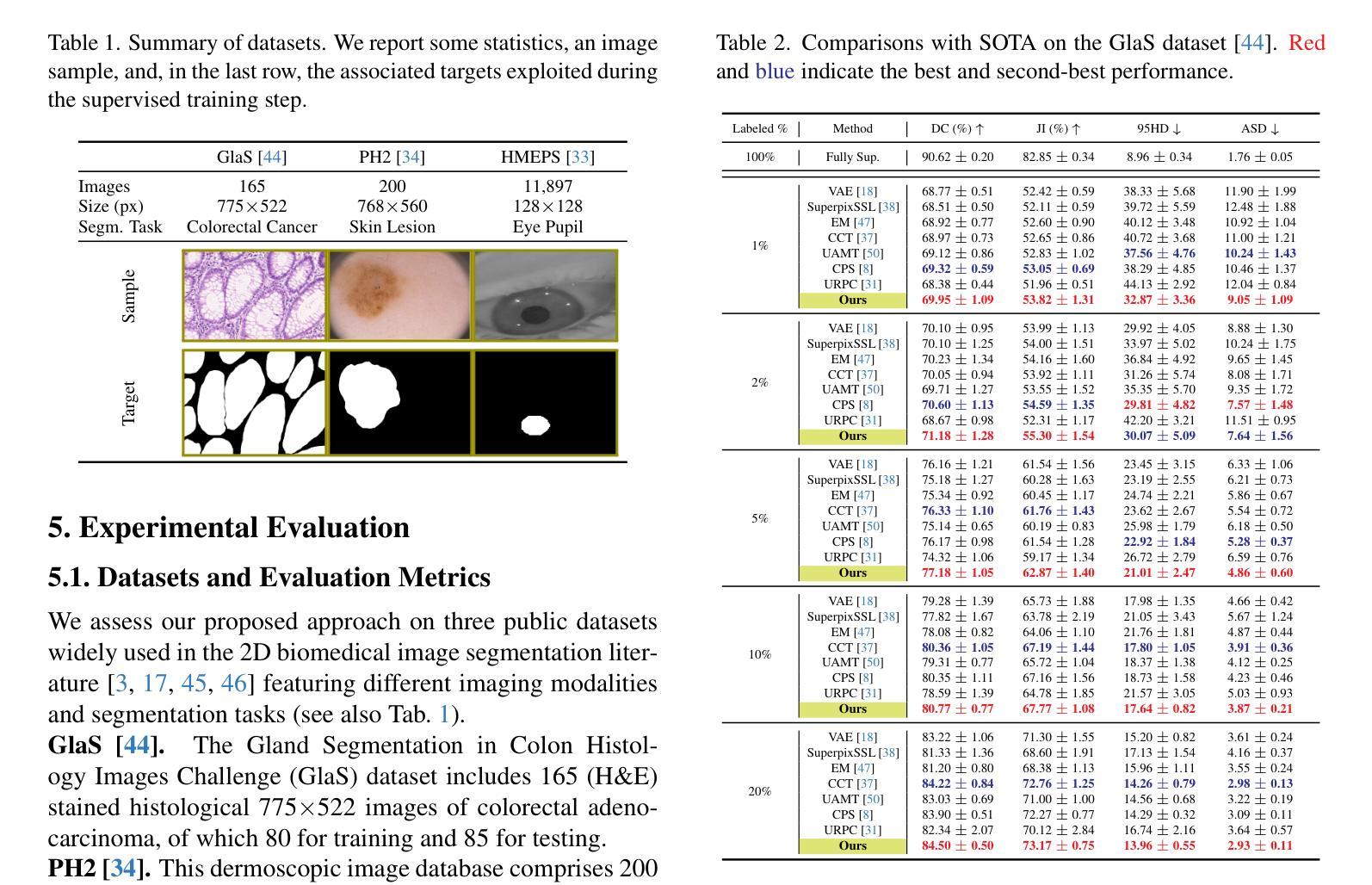
Biologically-inspired Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation for Biomedical Imaging
Authors:Luca Ciampi, Gabriele Lagani, Giuseppe Amato, Fabrizio Falchi
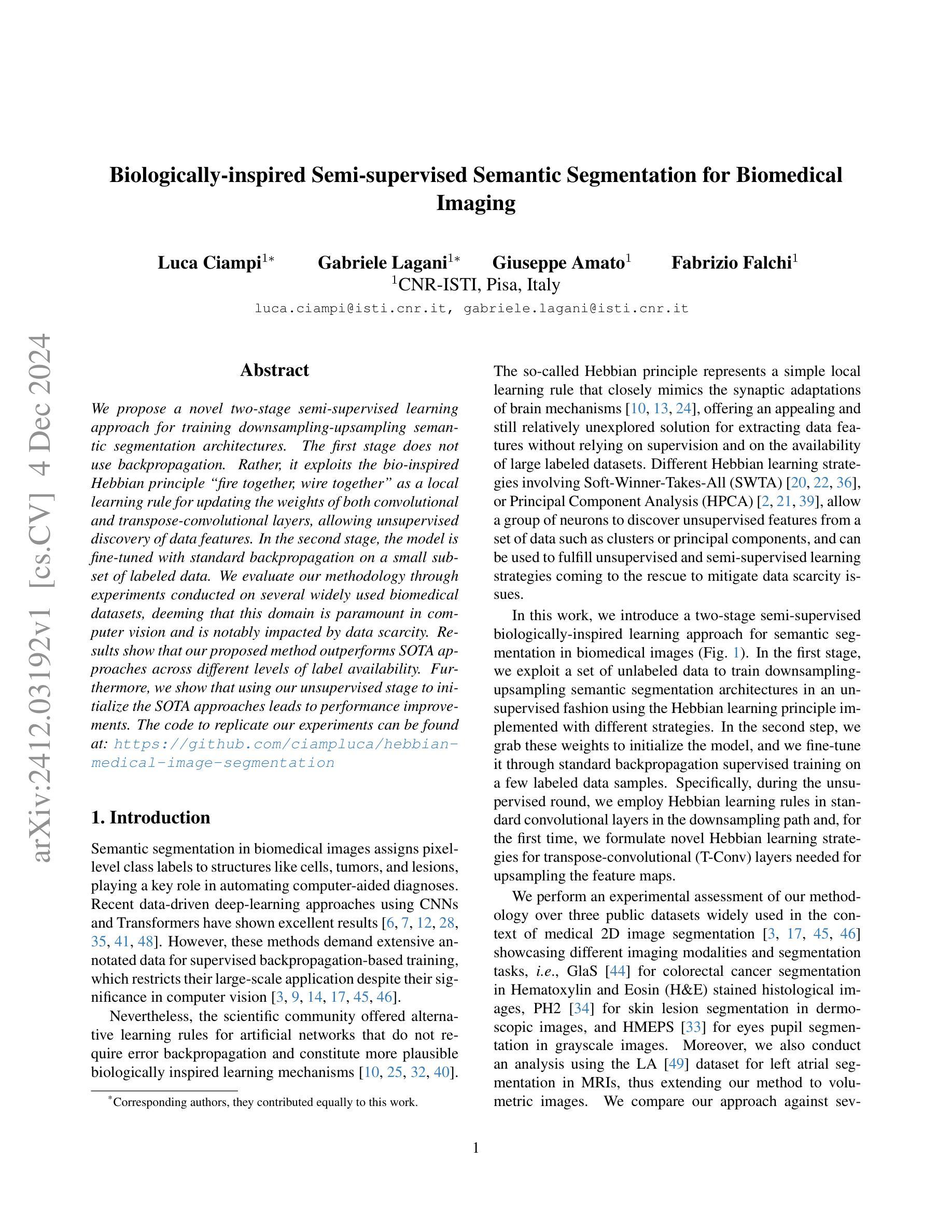
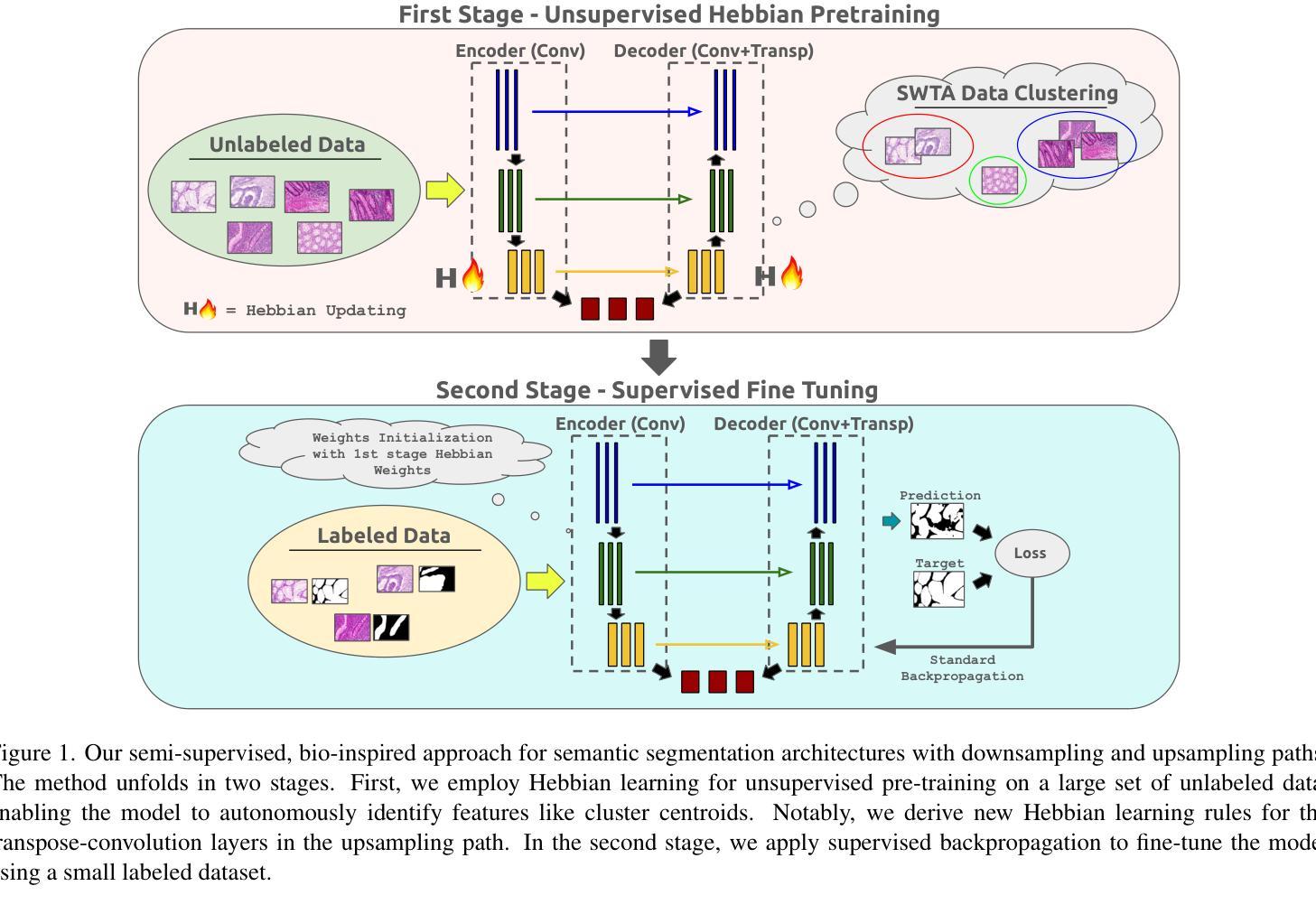
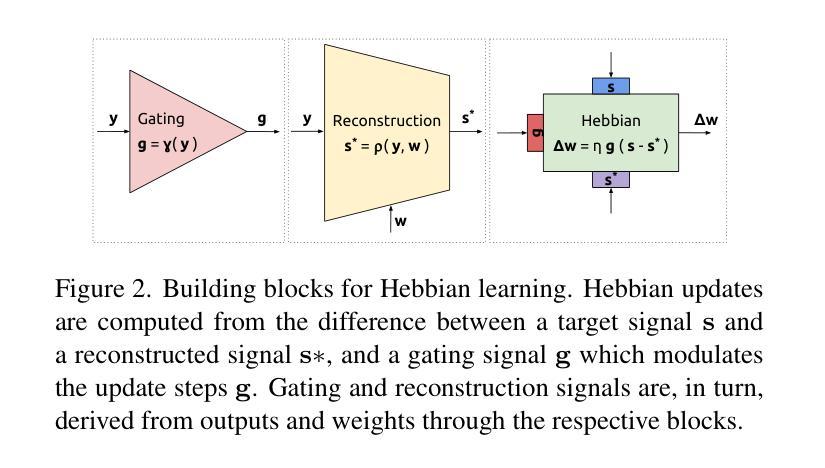
We propose a novel two-stage semi-supervised learning approach for training downsampling-upsampling semantic segmentation architectures. The first stage does not use backpropagation. Rather, it exploits the bio-inspired Hebbian principle “fire together, wire together” as a local learning rule for updating the weights of both convolutional and transpose-convolutional layers, allowing unsupervised discovery of data features. In the second stage, the model is fine-tuned with standard backpropagation on a small subset of labeled data. We evaluate our methodology through experiments conducted on several widely used biomedical datasets, deeming that this domain is paramount in computer vision and is notably impacted by data scarcity. Results show that our proposed method outperforms SOTA approaches across different levels of label availability. Furthermore, we show that using our unsupervised stage to initialize the SOTA approaches leads to performance improvements. The code to replicate our experiments can be found at: https://github.com/ciampluca/hebbian-medical-image-segmentation
我们提出了一种新颖的两阶段半监督学习方法,用于训练下采样-上采样语义分割架构。第一阶段不使用反向传播。相反,它利用生物启发的赫布原则“一起开火,一起连线”作为局部学习规则,以更新卷积层和转置卷积层的权重,从而实现数据特征的无监督发现。在第二阶段,模型在少量标记数据子集上利用标准反向传播进行微调。我们通过实验评估了我们的方法,实验是在几个广泛使用的生物医学数据集上进行的,我们认为这个领域在计算机视觉领域中至关重要,而且受到数据稀缺的显著影响。结果表明,在标签可用性不同的情况下,我们的方法优于其他前沿方法。此外,我们还展示了使用我们的无监督阶段来初始化前沿方法可以提高性能。复制我们实验的代码可以在以下网址找到:https://github.com/ciampluca/hebbian-medical-image-segmentation
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种两阶段半监督学习方法,用于训练下采样上采样语义分割架构。第一阶段采用生物启发的学习规则,不依赖反向传播,利用赫布原则更新权重,进行特征的无监督发现。第二阶段采用标准反向传播对小量标记数据进行微调。实验证明该方法在多个生物医学数据集上的表现优于现有技术,特别是在标签稀缺的情况下。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种两阶段半监督学习方法进行语义分割架构的训练。
- 第一阶段不依赖反向传播,利用赫布原则进行权重的无监督更新。
- 第二阶段采用标准反向传播对模型进行微调。
- 方法在多个生物医学数据集上的表现优于现有技术。
- 方法在标签稀缺的情况下表现尤为出色。
- 使用无监督阶段初始化现有技术可提高性能。
点此查看论文截图
MRNet: Multifaceted Resilient Networks for Medical Image-to-Image Translation
Authors:Hyojeong Lee, Youngwan Jo, Inpyo Hong, Sanghyun Park
We propose a Multifaceted Resilient Network(MRNet), a novel architecture developed for medical image-to-image translation that outperforms state-of-the-art methods in MRI-to-CT and MRI-to-MRI conversion. MRNet leverages the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to exploit frequency-based features to build a powerful method for advanced medical image transformation. The architecture extracts comprehensive multiscale features from diverse datasets using a powerful SAM image encoder and performs resolution-aware feature fusion that consistently integrates U-Net encoder outputs with SAM-derived features. This fusion optimizes the traditional U-Net skip connection while leveraging transformer-based contextual analysis. The translation is complemented by an innovative dual-mask configuration incorporating dynamic attention patterns and a specialized loss function designed to address regional mapping mismatches, preserving both the gross anatomy and tissue details. Extensive validation studies have shown that MRNet outperforms state-of-the-art architectures, particularly in maintaining anatomical fidelity and minimizing translation artifacts.
我们提出了一种多面弹性网络(MRNet)的新型架构,该架构针对医学图像到图像的翻译任务而开发,并在MRI到CT和MRI到MRI的转换中表现出超越现有方法的效果。MRNet利用分段任何模型(SAM)来开发基于频率的特征,以建立先进的医学图像转换方法。该架构使用强大的SAM图像编码器从各种数据集中提取全面的多尺度特征,并执行具有分辨率感知的特征融合,该融合始终将U-Net编码器的输出与SAM衍生的特征结合在一起。这种融合优化了传统的U-Net跳过连接,同时利用基于变压器的上下文分析。翻译由创新的双掩膜配置补充,该配置结合了动态注意力模式,并设计了一种专门的损失函数,以解决区域映射不匹配的问题,同时保留整体解剖结构和组织细节。广泛的验证研究表明,MRNet优于最先进的架构,特别是在保持解剖保真度和最小化翻译伪影方面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
摘要
本文提出了一种多面抗网络(MRNet),这是一种为医学图像到图像转换开发的新型架构,它在MRI到CT和MRI到MRI转换中表现出超越最新技术的性能。MRNet利用分割任何东西模型(SAM)挖掘基于频率的特征,建立了一种先进的医学图像转换方法。该架构使用强大的SAM图像编码器从各种数据集中提取全面的多尺度特征,并执行具有分辨率感知的特征融合,该融合始终将U-Net编码器的输出与SAM衍生的特征相结合。这种融合优化了传统的U-Net跳跃连接,同时利用基于变压器的上下文分析。翻译通过创新的双掩模配置进行补充,该配置结合了动态注意力模式,并设计了一个专门的损失函数,以解决区域映射不匹配的问题,同时保留总体解剖结构和组织细节。广泛的验证研究表明,MRNet在保持解剖保真度和最小化翻译伪影方面优于最新的架构。
要点
- MRNet是一种针对医学图像到图像转换的新型架构。
- 它利用Segment Anything Model (SAM) 提取频率特征为基础进行医学图像转换。
- MRNet能够全面提取多尺度特征并进行分辨率感知的特征融合。
- MRNet将SAM和U-Net结合,优化了传统的跳跃连接并使用基于变压器的上下文分析。
- MRNet具有创新的双掩模配置,结合动态注意力模式来处理区域映射不匹配的问题。
- MRNet设计了一种专门的损失函数来保持解剖结构的完整性和组织细节。
点此查看论文截图
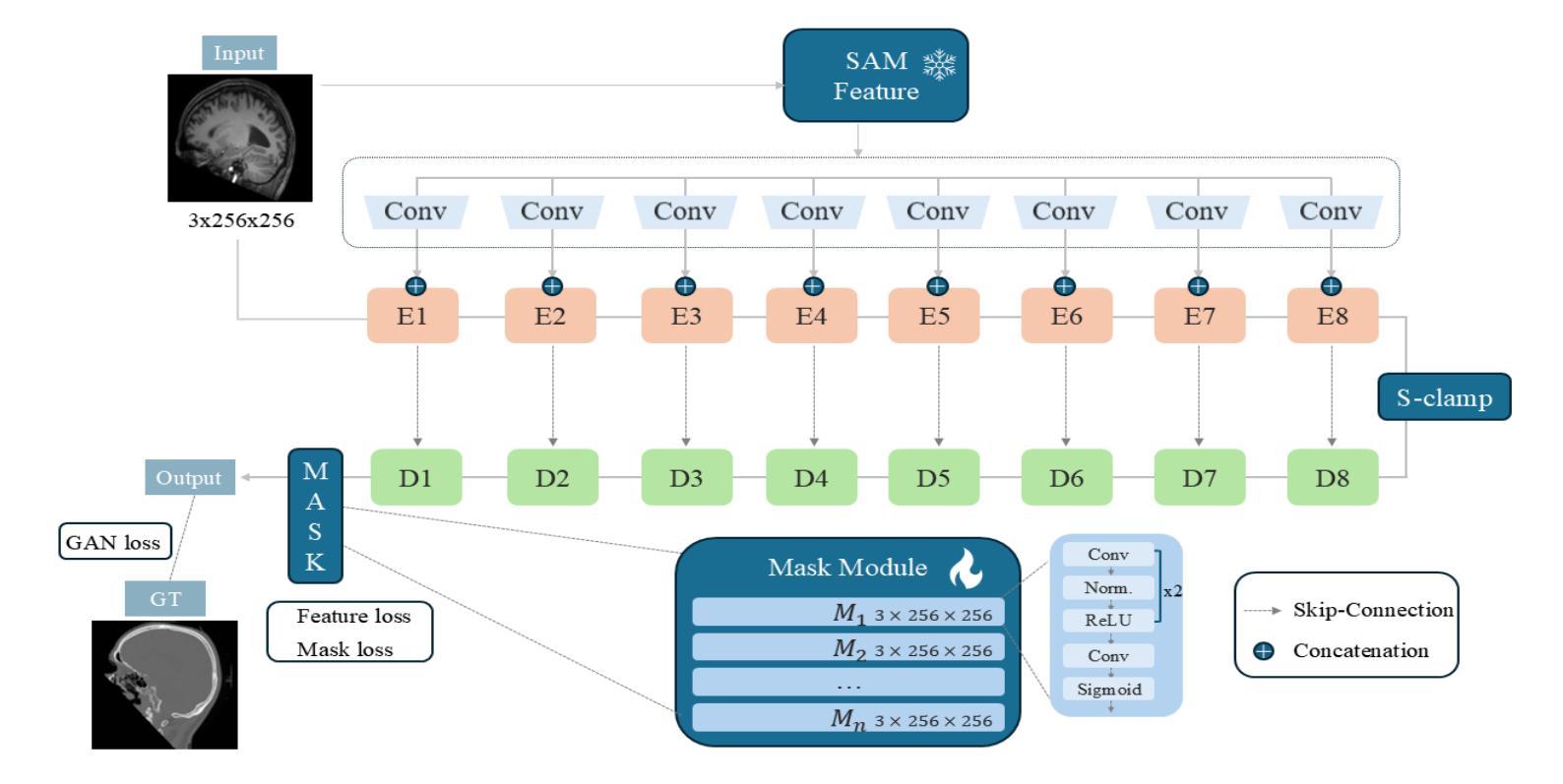
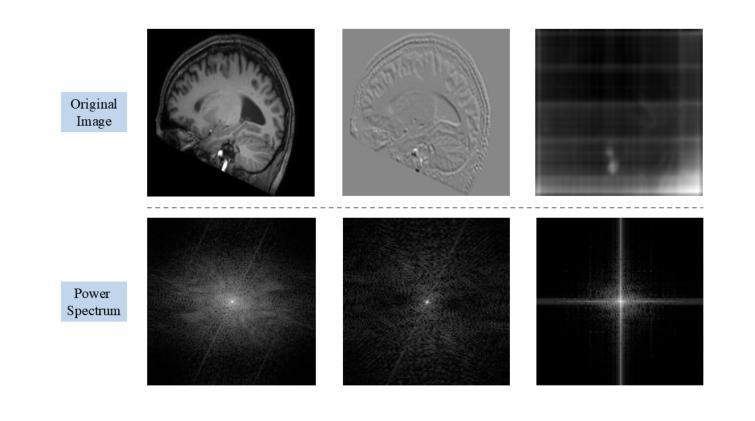
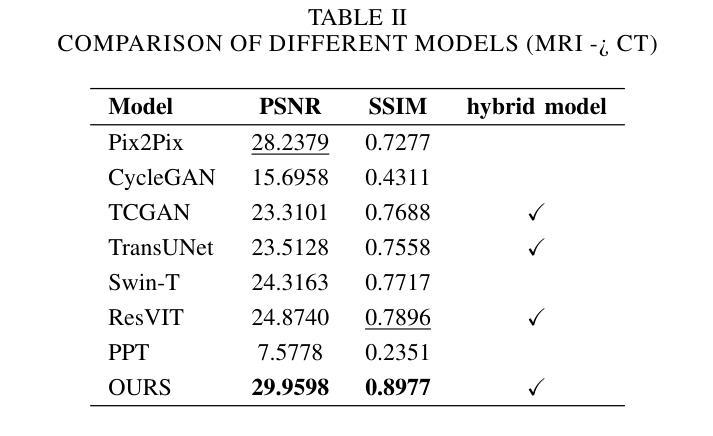
Is Foreground Prototype Sufficient? Few-Shot Medical Image Segmentation with Background-Fused Prototype
Authors:Song Tang, Chunxiao Zu, Wenxin Su, Yuan Dong, Mao Ye, Yan Gan, Xiatian Zhu
Few-shot Semantic Segmentation(FSS)aim to adapt a pre-trained model to new classes with as few as a single labeled training sample per class. The existing prototypical work used in natural image scenarios biasedly focus on capturing foreground’s discrimination while employing a simplistic representation for background, grounded on the inherent observation separation between foreground and background. However, this paradigm is not applicable to medical images where the foreground and background share numerous visual features, necessitating a more detailed description for background. In this paper, we present a new pluggable Background-fused prototype(Bro)approach for FSS in medical images. Instead of finding a commonality of background subjects in support image, Bro incorporates this background with two pivot designs. Specifically, Feature Similarity Calibration(FeaC)initially reduces noise in the support image by employing feature cross-attention with the query image. Subsequently, Hierarchical Channel Adversarial Attention(HiCA)merges the background into comprehensive prototypes. We achieve this by a channel groups-based attention mechanism, where an adversarial Mean-Offset structure encourages a coarse-to-fine fusion. Extensive experiments show that previous state-of-the-art methods, when paired with Bro, experience significant performance improvements. This demonstrates a more integrated way to represent backgrounds specifically for medical image.
少量语义分割(FSS)旨在将预训练模型适应于新类别,每类只需一个标记的训练样本。现有的原型工作在自然图像场景中偏重于捕获前景的区分度,同时对背景采用简单的表示方式,基于前景和背景之间的固有观察分离。然而,这种模式并不适用于医学图像,因为前景和背景共享许多视觉特征,需要对背景进行更详细的描述。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的可插入式背景融合原型(Bro)方法,用于医学图像的FSS。Bro不需要在支持图像中寻找背景主题共性,而是与两个枢轴设计相结合融入背景。具体来说,特征相似性校准(FeaC)首先通过采用特征交叉注意力与查询图像相结合来减少支持图像中的噪声。随后,层次化通道对抗注意力(HiCA)将背景合并到综合原型中。我们通过基于通道组的注意力机制实现这一点,其中对抗性均值偏移结构鼓励从粗糙到精细的融合。大量实验表明,当与Bro配对时,以前的最先进方法性能得到了显著改善。这证明了一种更为整合的方式来表示医学图像中的背景。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文针对医学图像中的小样本语义分割问题,提出了一种新的可插入背景融合原型(Bro)方法。该方法通过特征相似性校准(FeaC)和层次化通道对抗注意力(HiCA)机制,将背景信息融入原型表示中。实验表明,与之前的方法相比,Bro方法能够显著提高性能,为医学图像分割提供更全面的背景表示方式。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文关注医学图像中的小样本语义分割问题,即使用极少量有标签的训练样本对预训练模型进行适应。
- 现有方法在自然图像场景中使用的原型工作偏向于捕捉前景的判别信息,而对背景采用简单的表示方式。
- 医学图像中的前景和背景具有许多共享的视觉特征,需要更详细的背景描述。
- 论文提出了一种新的背景融合原型(Bro)方法,适用于医学图像的FSS。
- Bro方法通过特征相似性校准(FeaC)减少支持图像中的噪声,通过层次化通道对抗注意力(HiCA)将背景融入综合原型表示。
- 实验结果表明,与最先进的方法相比,Bro方法能够显著提高性能。
点此查看论文截图

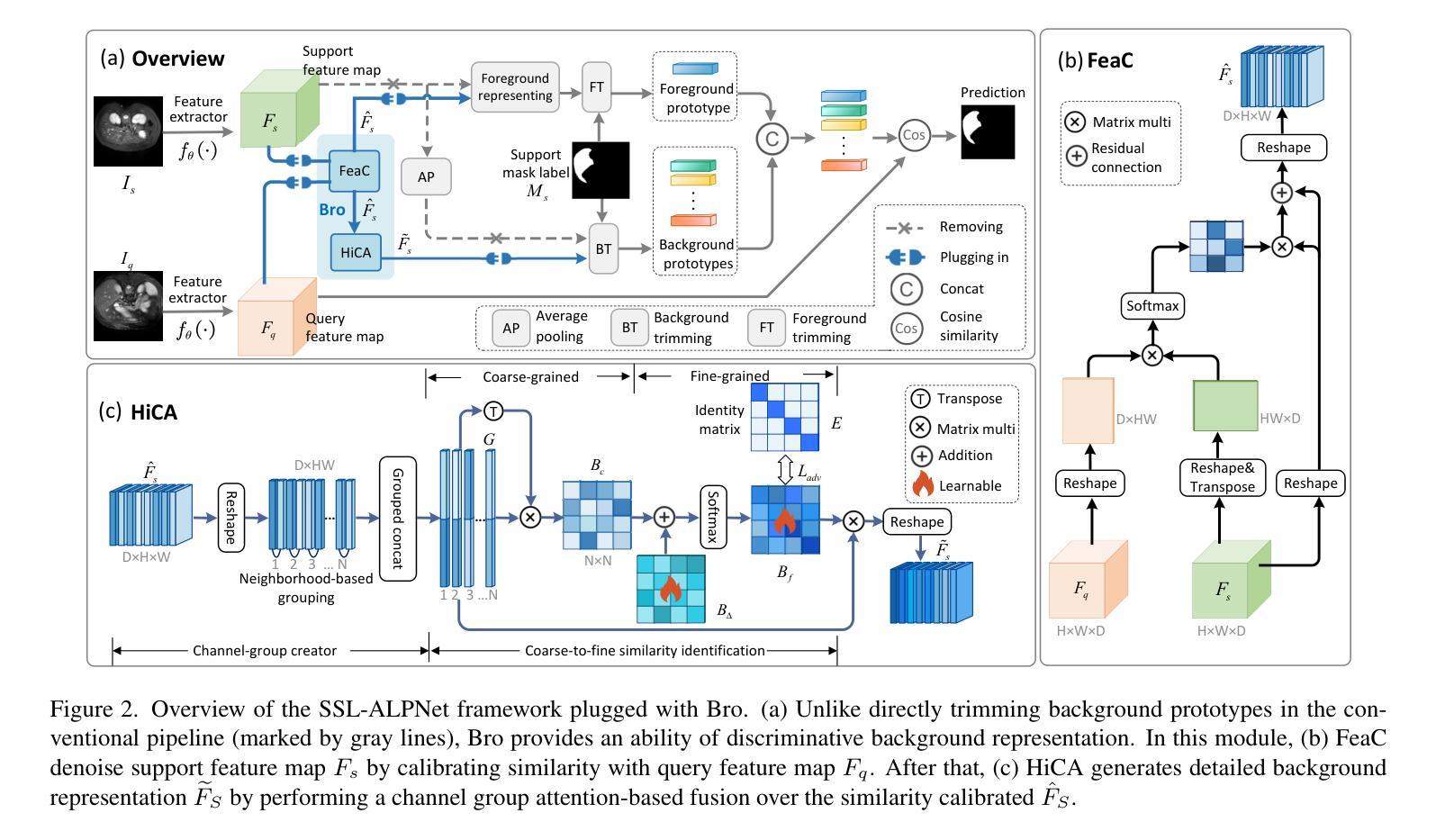
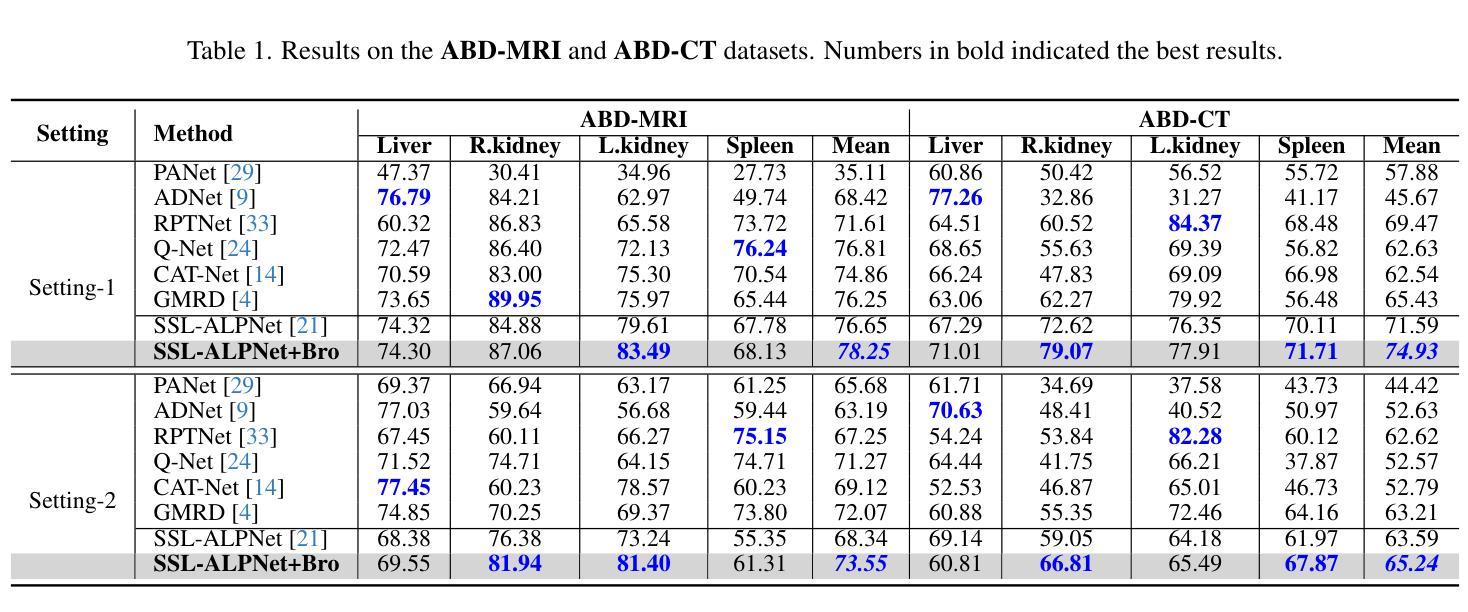
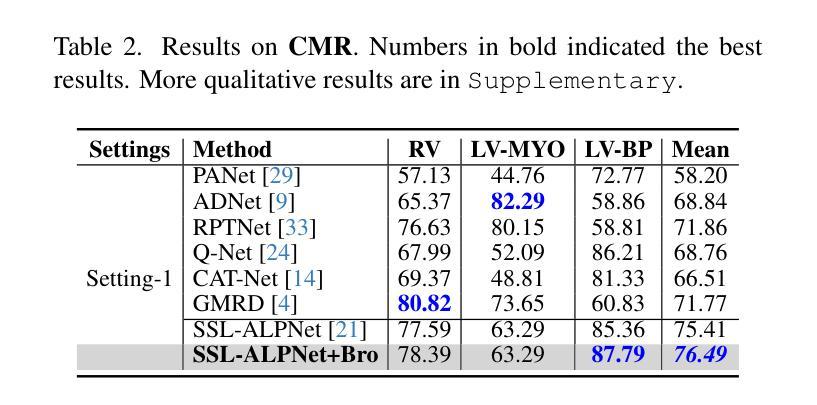
RaD: A Metric for Medical Image Distribution Comparison in Out-of-Domain Detection and Other Applications
Authors:Nicholas Konz, Yuwen Chen, Hanxue Gu, Haoyu Dong, Yaqian Chen, Maciej A. Mazurowski
Determining whether two sets of images belong to the same or different domain is a crucial task in modern medical image analysis and deep learning, where domain shift is a common problem that commonly results in decreased model performance. This determination is also important to evaluate the output quality of generative models, e.g., image-to-image translation models used to mitigate domain shift. Current metrics for this either rely on the (potentially biased) choice of some downstream task such as segmentation, or adopt task-independent perceptual metrics (e.g., FID) from natural imaging which insufficiently capture anatomical consistency and realism in medical images. We introduce a new perceptual metric tailored for medical images: Radiomic Feature Distance (RaD), which utilizes standardized, clinically meaningful and interpretable image features. We show that RaD is superior to other metrics for out-of-domain (OOD) detection in a variety of experiments. Furthermore, RaD outperforms previous perceptual metrics (FID, KID, etc.) for image-to-image translation by correlating more strongly with downstream task performance as well as anatomical consistency and realism, and shows similar utility for evaluating unconditional image generation. RaD also offers additional benefits such as interpretability, as well as stability and computational efficiency at low sample sizes. Our results are supported by broad experiments spanning four multi-domain medical image datasets, nine downstream tasks, six image translation models, and other factors, highlighting the broad potential of RaD for medical image analysis.
确定两组图像是否属于同一领域或不同领域是现代医学图像分析和深度学习中的一项关键任务,领域偏移是一个常见的问题,通常会导致模型性能下降。这个决定对于评估生成模型的输出质量也很重要,例如用于缓解领域偏移的图像到图像翻译模型。当前的指标要么依赖于某些下游任务(如分割)的选择(可能存在偏见),要么采用自然成像的任务独立感知指标(如FID),这些指标不足以捕捉医学图像中的解剖一致性和真实性。我们针对医学图像引入了一种新的感知指标:放射学特征距离(RaD),它利用标准化、临床有意义和可解释的图像特征。我们证明,在各种实验中,RaD在其他指标中表现出卓越的跨领域(OOD)检测性能。此外,RaD在下游任务性能以及与解剖一致性和真实性的相关性方面,表现优于之前的感知指标(如FID、KID等),在图像到图像翻译任务中表现更为出色,并在无条件图像生成评估中显示出类似的实用性。RaD还提供了可解释性、稳定性以及小样本计算效率等额外优势。我们的结果得到了广泛的实验支持,这些实验涵盖了四个多领域医学图像数据集、九个下游任务、六个图像翻译模型以及其他因素,突出了RaD在医学图像分析中的广阔潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在医学图像分析和深度学习领域中,判断两组图像是否属于同一域的重要性。针对现有度量指标的不足,如倾向于下游任务的潜在偏见或自然成像中的感知指标不足以捕捉医学图像的解剖一致性和逼真度,本文提出了一种新的感知指标——放射学特征距离(RaD)。该指标利用标准化、临床意义重大且可解释的医学图像特征进行评估。实验表明,RaD在多种实验中的离群检测表现优于其他指标,对于图像到图像的翻译任务能够更强烈地与下游任务性能和解剖一致性与逼真度相关,并展示了在无条件图像生成中的评价能力。此外,RaD还具有可解释性、稳定性和计算效率等额外优势。实验结果广泛支持了RaD在医学图像分析中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 确定医学图像是否属于同一域对于医学图像分析和深度学习至关重要,因为域偏移是一个常见问题,可能导致模型性能下降。
- 当前度量指标存在缺陷,可能倾向于下游任务的偏见或不足以捕捉医学图像的解剖一致性和逼真度。
- 引入了一种新的感知指标——放射学特征距离(RaD),用于评估医学图像。
- RaD利用标准化、临床意义重大且可解释的图像特征进行评估。
- RaD在多种实验中表现出优异的离群检测性能,相较于其他指标更具优势。
- RaD在图像到图像翻译任务中表现出强烈的下游任务性能相关性,同时具备良好的解剖一致性与逼真度评估能力。
点此查看论文截图

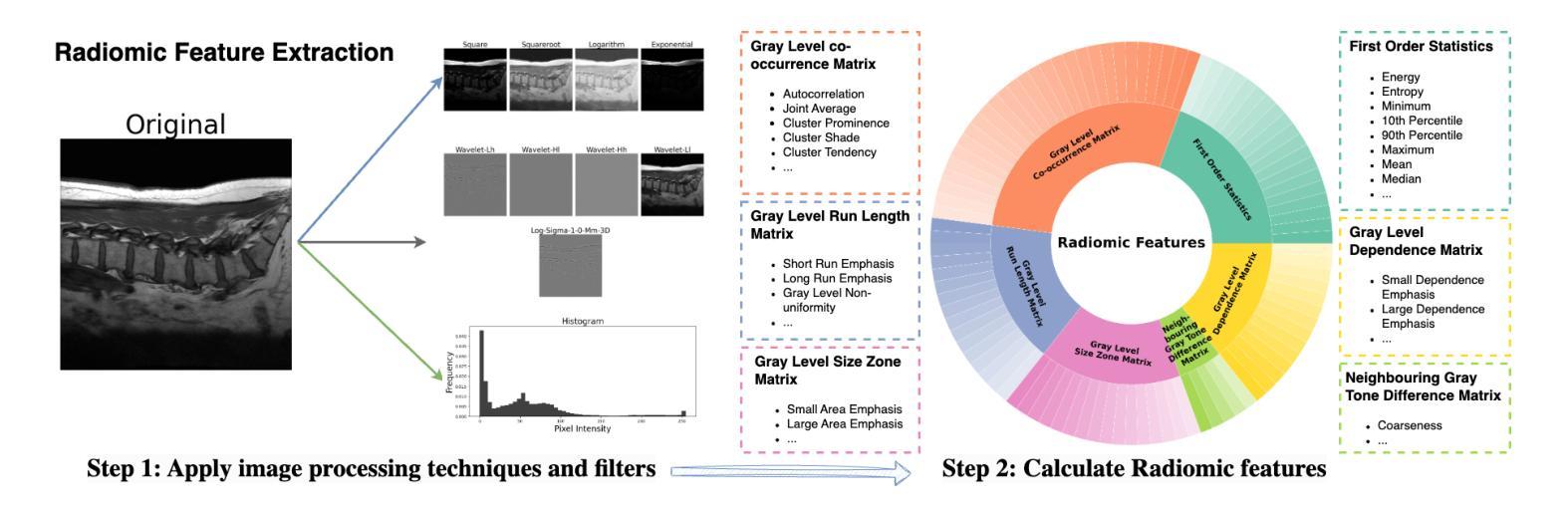
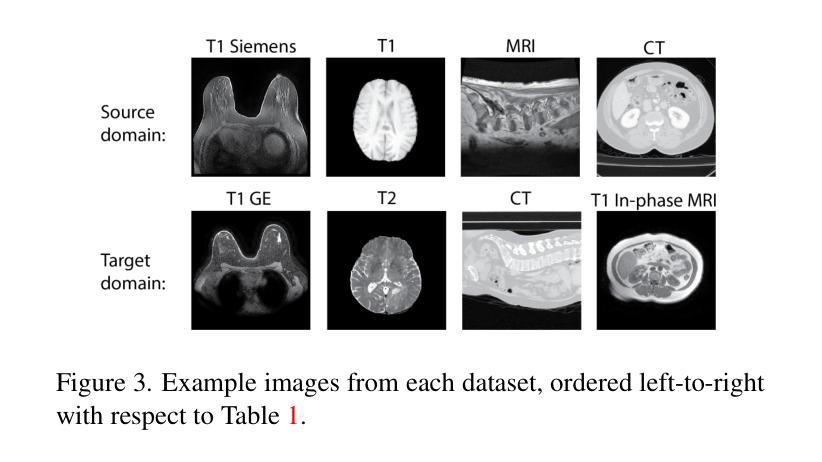
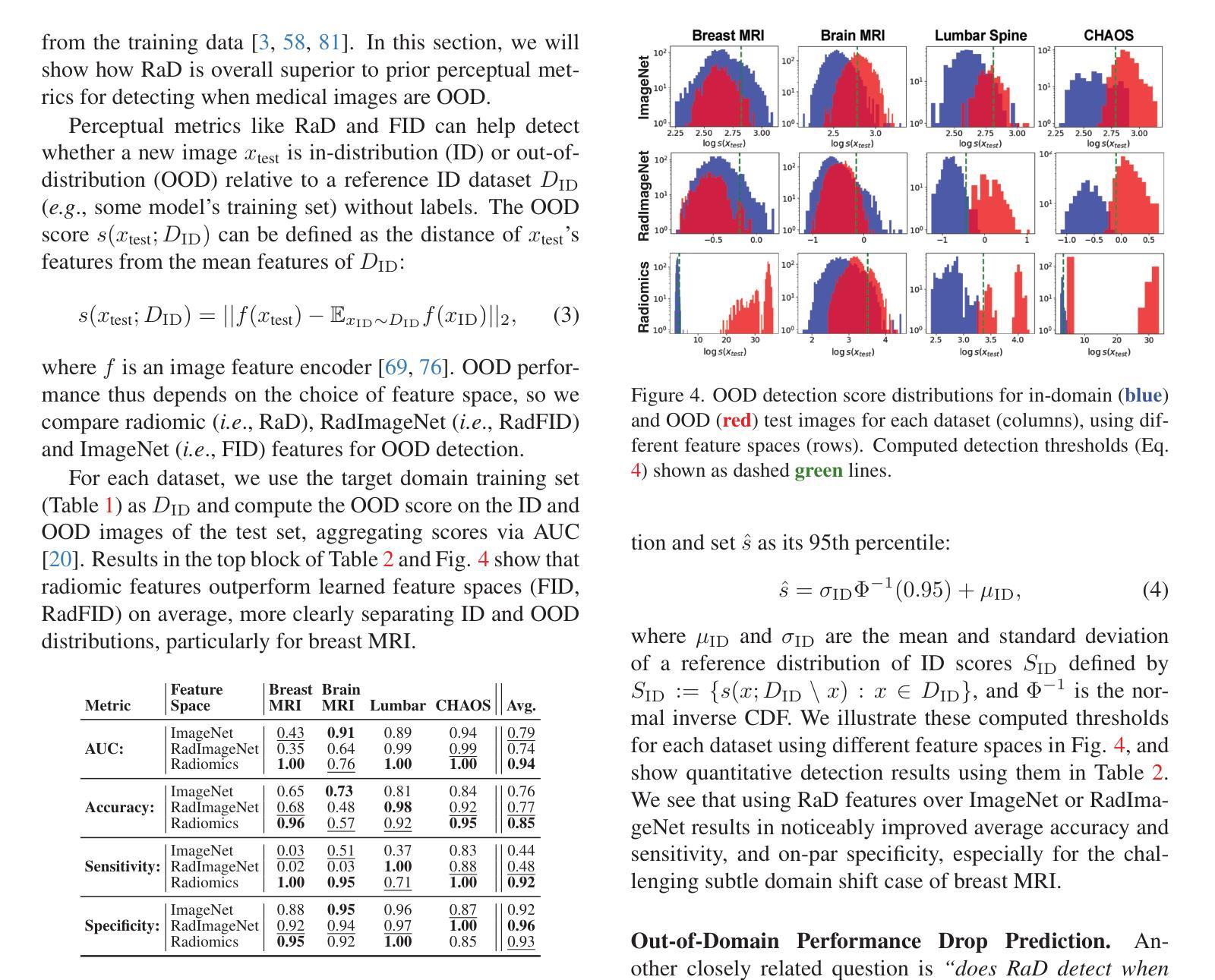
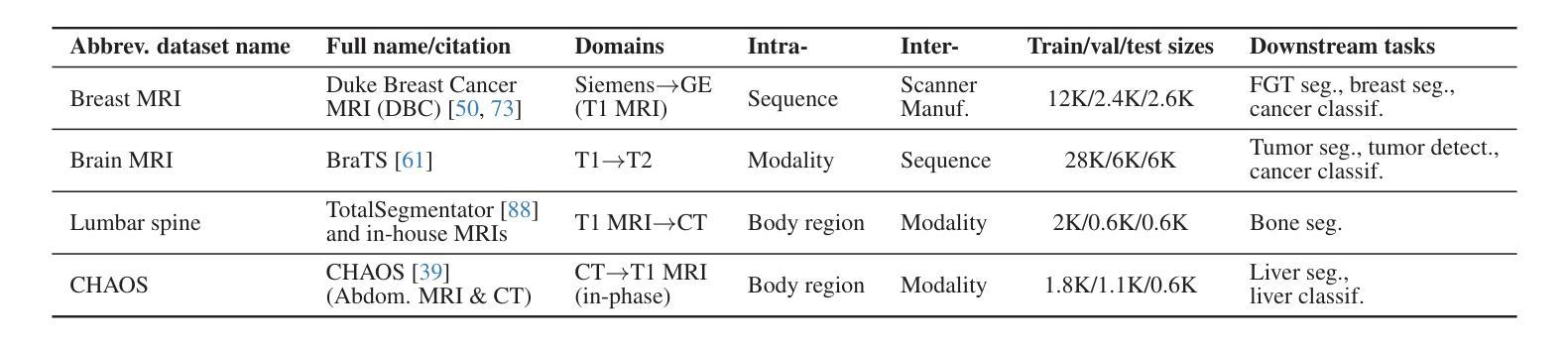
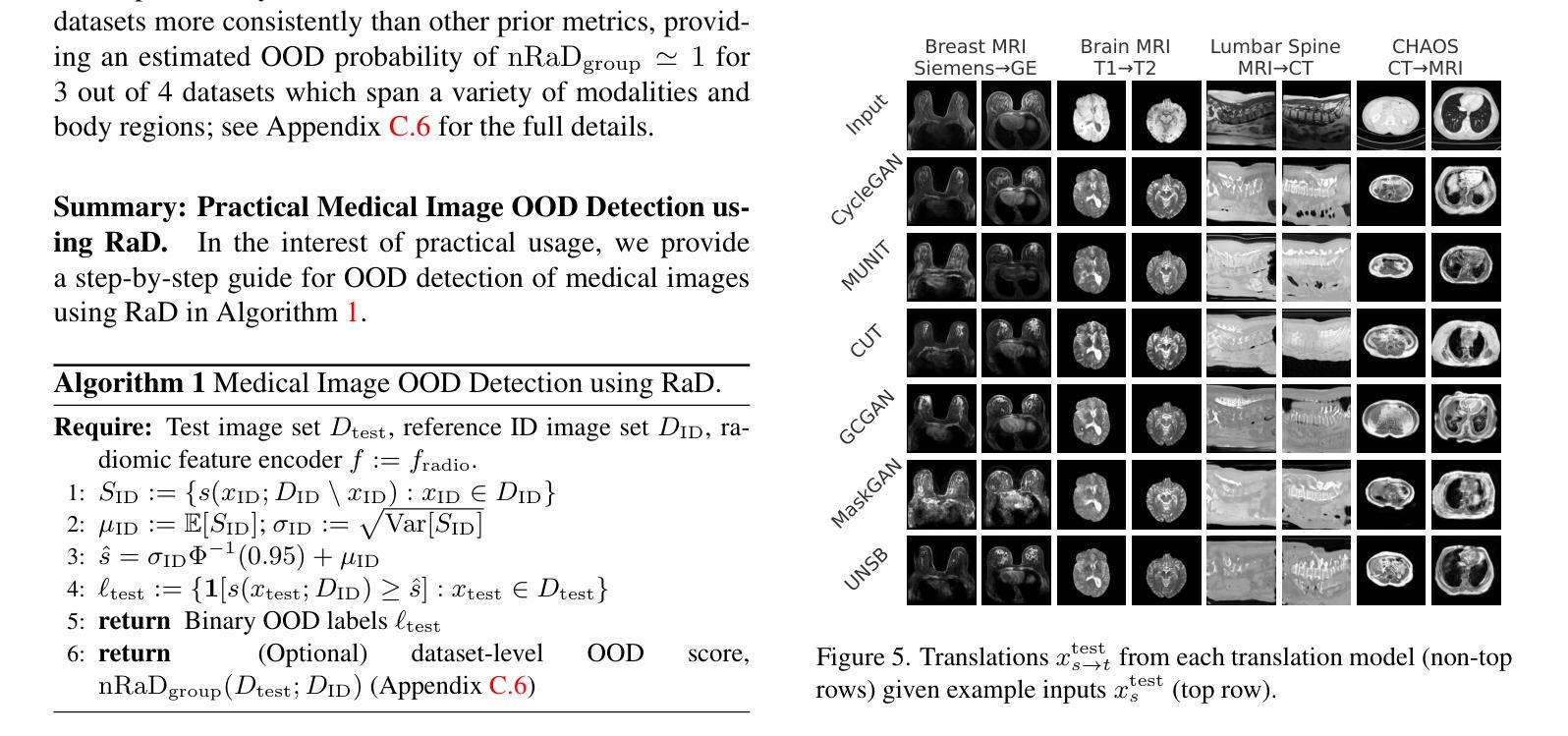
Exploiting Precision Mapping and Component-Specific Feature Enhancement for Breast Cancer Segmentation and Identification
Authors:Pandiyaraju V, Shravan Venkatraman, Pavan Kumar S, Santhosh Malarvannan, Kannan A
Breast cancer is one of the leading causes of death globally, and thus there is an urgent need for early and accurate diagnostic techniques. Although ultrasound imaging is a widely used technique for breast cancer screening, it faces challenges such as poor boundary delineation caused by variations in tumor morphology and reduced diagnostic accuracy due to inconsistent image quality. To address these challenges, we propose novel Deep Learning (DL) frameworks for breast lesion segmentation and classification. We introduce a precision mapping mechanism (PMM) for a precision mapping and attention-driven LinkNet (PMAD-LinkNet) segmentation framework that dynamically adapts spatial mappings through morphological variation analysis, enabling precise pixel-level refinement of tumor boundaries. Subsequently, we introduce a component-specific feature enhancement module (CSFEM) for a component-specific feature-enhanced classifier (CSFEC-Net). Through a multi-level attention approach, the CSFEM magnifies distinguishing features of benign, malignant, and normal tissues. The proposed frameworks are evaluated against existing literature and a diverse set of state-of-the-art Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architectures. The obtained results show that our segmentation model achieves an accuracy of 98.1%, an IoU of 96.9%, and a Dice Coefficient of 97.2%. For the classification model, an accuracy of 99.2% is achieved with F1-score, precision, and recall values of 99.1%, 99.3%, and 99.1%, respectively.
乳腺癌是全球主要的死亡原因之一,因此迫切需要早期和准确的诊断技术。超声成像虽然是乳腺癌筛查中广泛使用的一种技术,但它面临着因肿瘤形态变化导致的边界划分不良以及图像质量不一致导致的诊断准确性降低等挑战。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了用于乳腺病灶分割和分类的新型深度学习(DL)框架。我们为精确映射和注意力驱动的LinkNet(PMAD-LinkNet)分割框架引入了一种精确映射机制(PMM),该机制通过形态变化分析动态适应空间映射,实现对肿瘤边界的精确像素级细化。接着,我们为组件特定特征增强分类器(CSFEC-Net)引入了一个组件特定特征增强模块(CSFEM)。通过多级注意力方法,CSFEM放大了良性、恶性和正常组织的区分特征。所提出的框架与现有文献和一系列先进的卷积神经网络(CNN)架构进行了评估比较。获得的结果显示,我们的分割模型达到了98.1%的准确率,96.9%的IoU和97.2%的Dice系数。分类模型则实现了99.2%的准确率,F1分数、精确度和召回率分别为99.1%、99.3%和99.1%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 18 figures, 6 tables
Summary
本研究针对乳腺癌超声成像中存在的边界模糊和图像质量不一导致的诊断准确性问题,提出了基于深度学习的乳腺病灶分割和分类新框架。通过精确映射机制和组件特定特征增强模块,实现对肿瘤边界的精确像素级细化和良、恶性及正常组织的特征增强分类。评估结果显示,分割模型准确率为98.1%,IoU和Dice系数分别为96.9%和97.2%;分类模型准确率为99.2%,F1分数、精确度和召回率分别为99.1%、99.3%和99.1%。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌是全球主要的死亡原因之一,需要早期和准确的诊断技术。
- 超声成像在乳腺癌筛查中广泛应用,但存在边界模糊和图像质量不一的挑战。
- 引入深度学习方法解决这些挑战,包括精确映射机制和组件特定特征增强模块。
- 精确映射机制能够实现动态适应空间映射,进行肿瘤边界的精确像素级细化。
- 组件特定特征增强模块通过多级别注意力方法放大良、恶性及正常组织之间的特征差异。
- 分割模型评估结果显示高准确率、IoU和Dice系数。
点此查看论文截图

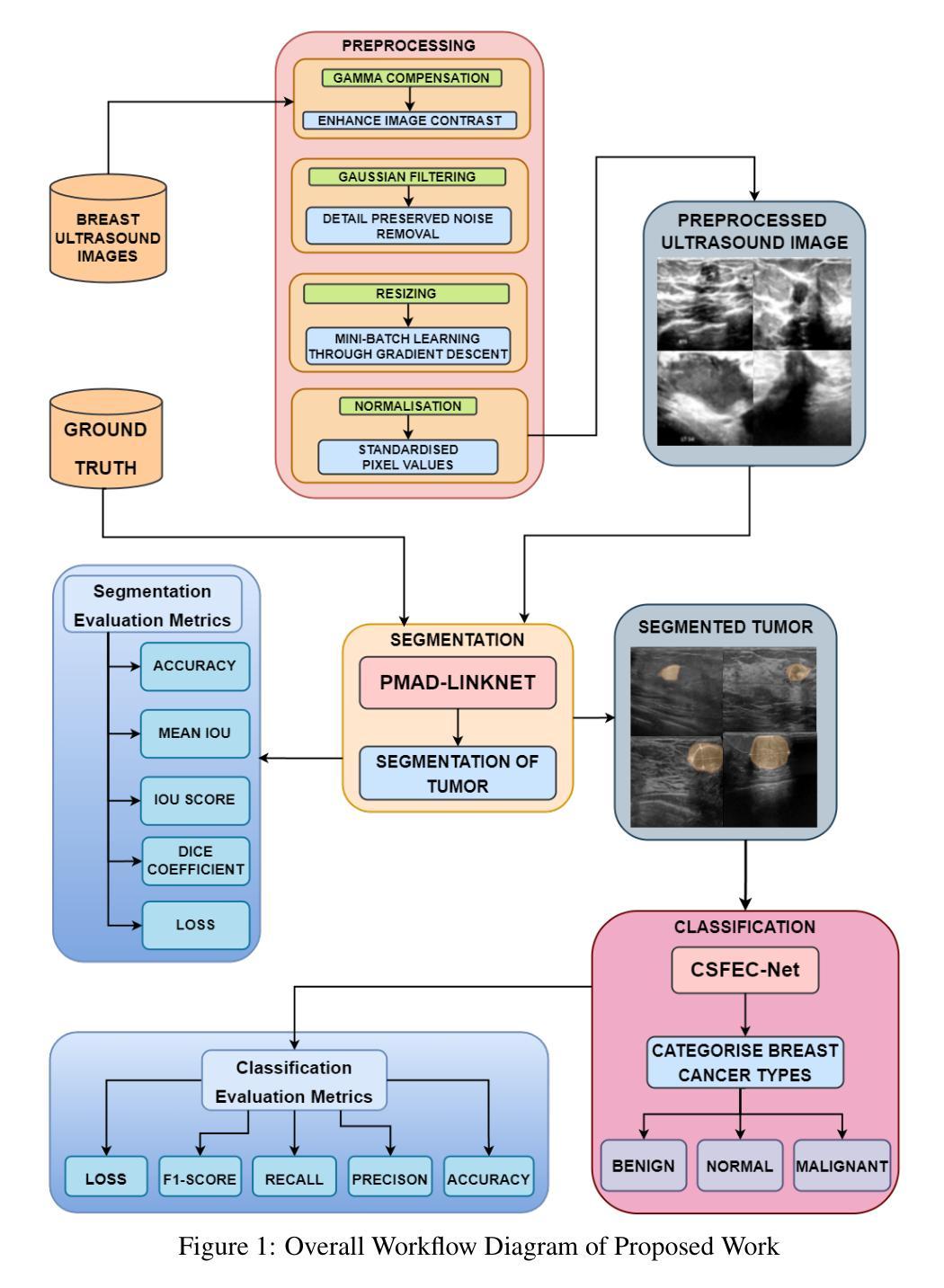
DDGS-CT: Direction-Disentangled Gaussian Splatting for Realistic Volume Rendering
Authors:Zhongpai Gao, Benjamin Planche, Meng Zheng, Xiao Chen, Terrence Chen, Ziyan Wu
Digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) are simulated 2D X-ray images generated from 3D CT volumes, widely used in preoperative settings but limited in intraoperative applications due to computational bottlenecks, especially for accurate but heavy physics-based Monte Carlo methods. While analytical DRR renderers offer greater efficiency, they overlook anisotropic X-ray image formation phenomena, such as Compton scattering. We present a novel approach that marries realistic physics-inspired X-ray simulation with efficient, differentiable DRR generation using 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS). Our direction-disentangled 3DGS (DDGS) method separates the radiosity contribution into isotropic and direction-dependent components, approximating complex anisotropic interactions without intricate runtime simulations. Additionally, we adapt the 3DGS initialization to account for tomography data properties, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art techniques in image accuracy. Furthermore, our DDGS shows promise for intraoperative applications and inverse problems such as pose registration, delivering superior registration accuracy and runtime performance compared to analytical DRR methods.
数字重建放射图像(DRRs)是从三维CT体积中生成的模拟二维X射线图像,广泛应用于术前环境,但由于计算瓶颈,特别是在精确但基于物理的蒙特卡洛方法方面,其在术中应用受到限制。虽然分析型DRR渲染器提供了更高的效率,但它们忽略了各向异性的X射线图像形成现象,如康普顿散射。我们提出了一种新颖的方法,它将基于现实物理的X射线模拟与高效、可微分的DRR生成相结合,使用三维高斯溅射(3DGS)。我们的方向分离的三维高斯溅射(DDGS)方法将辐射度贡献分为各向同性和方向依赖性成分,在不需要复杂运行时模拟的情况下近似复杂的各向异性相互作用。此外,我们适应了3DGS初始化以考虑层析数据属性,提高了准确性和效率。我们的方法在图像准确性方面优于最新技术。此外,我们的DDGS对于术中和逆向问题(如姿势注册)显示出潜力,与解析DRR方法相比,提供了更高的注册准确性和运行时性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NeurIPS2024
Summary
基于三维CT体积数据的数字化重建放射图像(DRRs)是模拟的二维X射线图像,广泛应用于术前设置。然而,由于计算瓶颈,特别是在准确的物理蒙特卡洛方法方面,其在术中应用受限。本文提出了一种结合真实物理驱动的X射线模拟与高效可微分的DRR生成新方法,使用三维高斯溅射(3DGS)。我们的方向分离的三维高斯溅射(DDGS)方法将辐射贡献分为各向同性和方向依赖性成分,近似复杂的各向异性相互作用,无需复杂的运行时模拟。该方法在图像准确性方面优于现有技术,并且在术中应用和反向问题如姿态注册中显示出潜力,与解析DRR方法相比,具有更高的注册准确性和运行性能。
Key Takeaways
- DRRs是从三维CT体积数据生成的模拟二维X射线图像,广泛应用于术前设置。
- 现有DRR方法在术中应用受限,主要由于计算瓶颈和复杂的物理模拟。
- 本文提出了一种结合真实物理驱动的X射线模拟与高效可微分的DRR生成新方法——三维高斯溅射(DDGS)。
- DDGS通过将辐射贡献分为各向同性和方向依赖性成分,来近似复杂的各向异性相互作用。
- DDGS方法在不需复杂运行时模拟的情况下,提高了图像生成的准确性和效率。
- DDGS在图像准确性和术中应用方面优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图