⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-11 更新
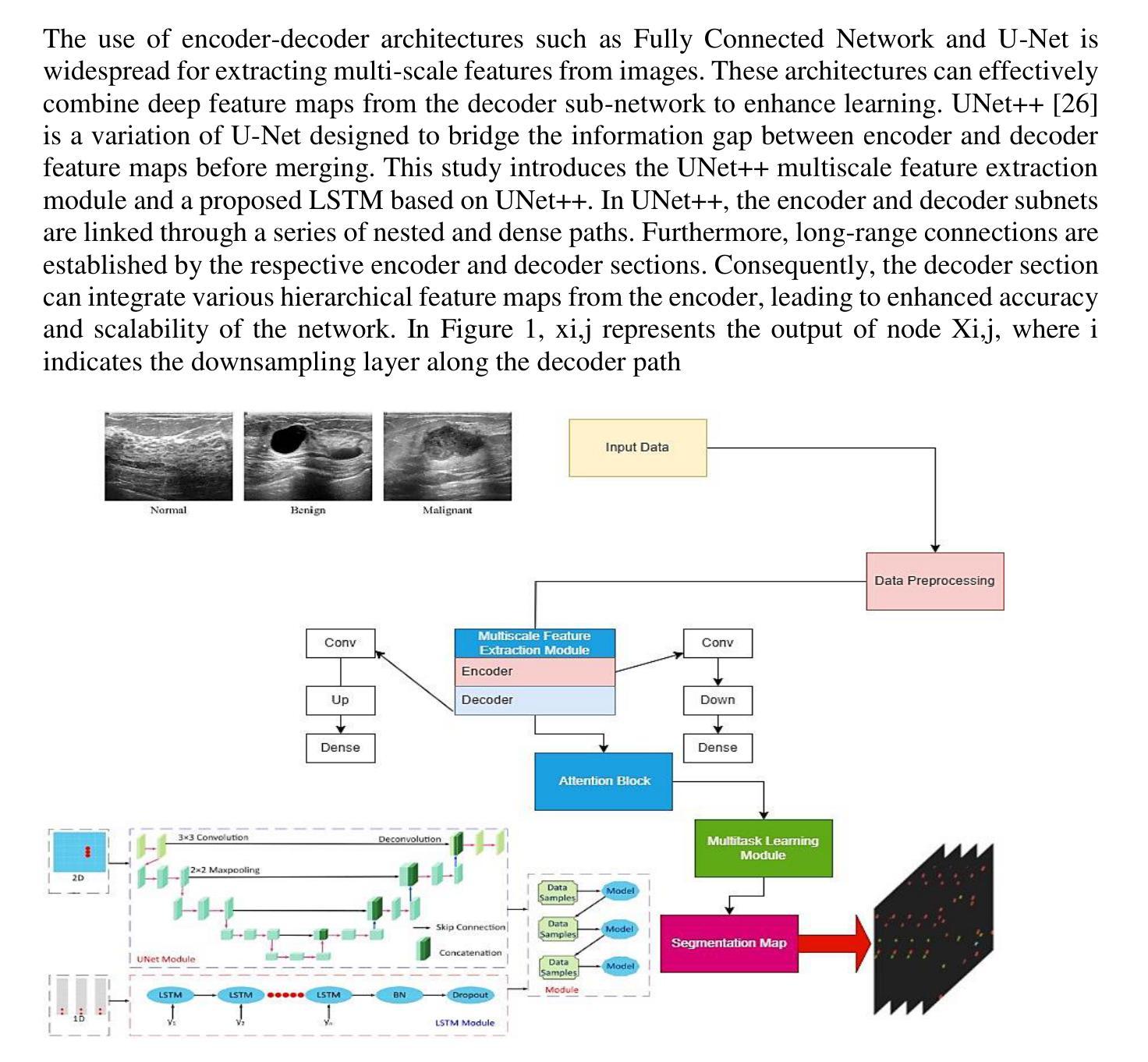
UNet++ and LSTM combined approach for Breast Ultrasound Image Segmentation
Authors:Saba Hesaraki, Morteza Akbari, Ramin Mousa
Breast cancer stands as a prevalent cause of fatality among females on a global scale, with prompt detection playing a pivotal role in diminishing mortality rates. The utilization of ultrasound scans in the BUSI dataset for medical imagery pertaining to breast cancer has exhibited commendable segmentation outcomes through the application of UNet and UNet++ networks. Nevertheless, a notable drawback of these models resides in their inattention towards the temporal aspects embedded within the images. This research endeavors to enrich the UNet++ architecture by integrating LSTM layers and self-attention mechanisms to exploit temporal characteristics for segmentation purposes. Furthermore, the incorporation of a Multiscale Feature Extraction Module aims to grasp varied scale features within the UNet++. Through the amalgamation of our proposed methodology with data augmentation on the BUSI with GT dataset, an accuracy rate of 98.88%, specificity of 99.53%, precision of 95.34%, sensitivity of 91.20%, F1-score of 93.74, and Dice coefficient of 92.74% are achieved. These findings demonstrate competitiveness with cutting-edge techniques outlined in existing literature.
乳腺癌是全球女性常见的致命疾病原因之一,及时检测在降低死亡率方面起着至关重要的作用。在乳腺癌医学图像方面的BUSI数据集利用超声扫描,通过应用UNet和UNet++网络展现了令人称赞的分割效果。然而,这些模型的一个显著缺点是对图像中嵌入的暂时方面的忽视。本研究致力于通过集成LSTM层和自注意力机制来丰富UNet++架构,以利用暂时特征进行分割。此外,多尺度特征提取模块的引入旨在捕获UNet++中的不同尺度特征。通过将本研究提出的方法与BUSI数据集上GT数据集的数据扩充相结合,获得了98.88%的准确率、99.53%的特异性、95.34%的精确度、91.20%的灵敏度、93.74%的F1分数和92.74%的Dice系数。这些发现与现有文献中概述的最先进技术相比具有竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
乳腺癌是全球女性常见的致命疾病,及时检测对降低死亡率至关重要。超声扫描在BUSI数据集上的医学图像分割表现良好,通过应用UNet和UNet++网络取得显著成果。然而,这些模型忽视了图像中的时间特性。本研究旨在通过集成LSTM层和自注意力机制来丰富UNet++架构,以利用时间特性进行分割。此外,多尺度特征提取模块的引入旨在捕获UNet++中的不同尺度特征。通过将本研究方法与BUSI with GT数据集的数据增强相结合,实现了高准确率。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌是全球女性常见的致命疾病,及时检测对降低死亡率有重要作用。
- 超声扫描在BUSI数据集的医学图像分割中表现良好。
- UNet和UNet++网络在图像分割方面取得了显著成果。
- 现有模型忽略了图像中的时间特性。
- 本研究通过集成LSTM层和自注意力机制来丰富UNet++架构,以利用时间特性进行分割。
- 引入多尺度特征提取模块以捕获不同尺度的特征。
点此查看论文截图

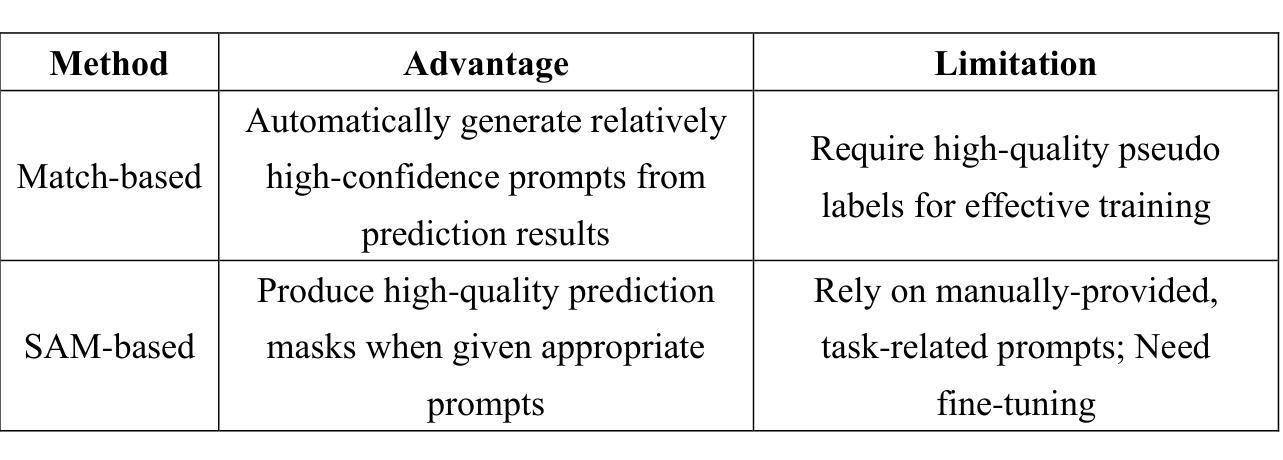
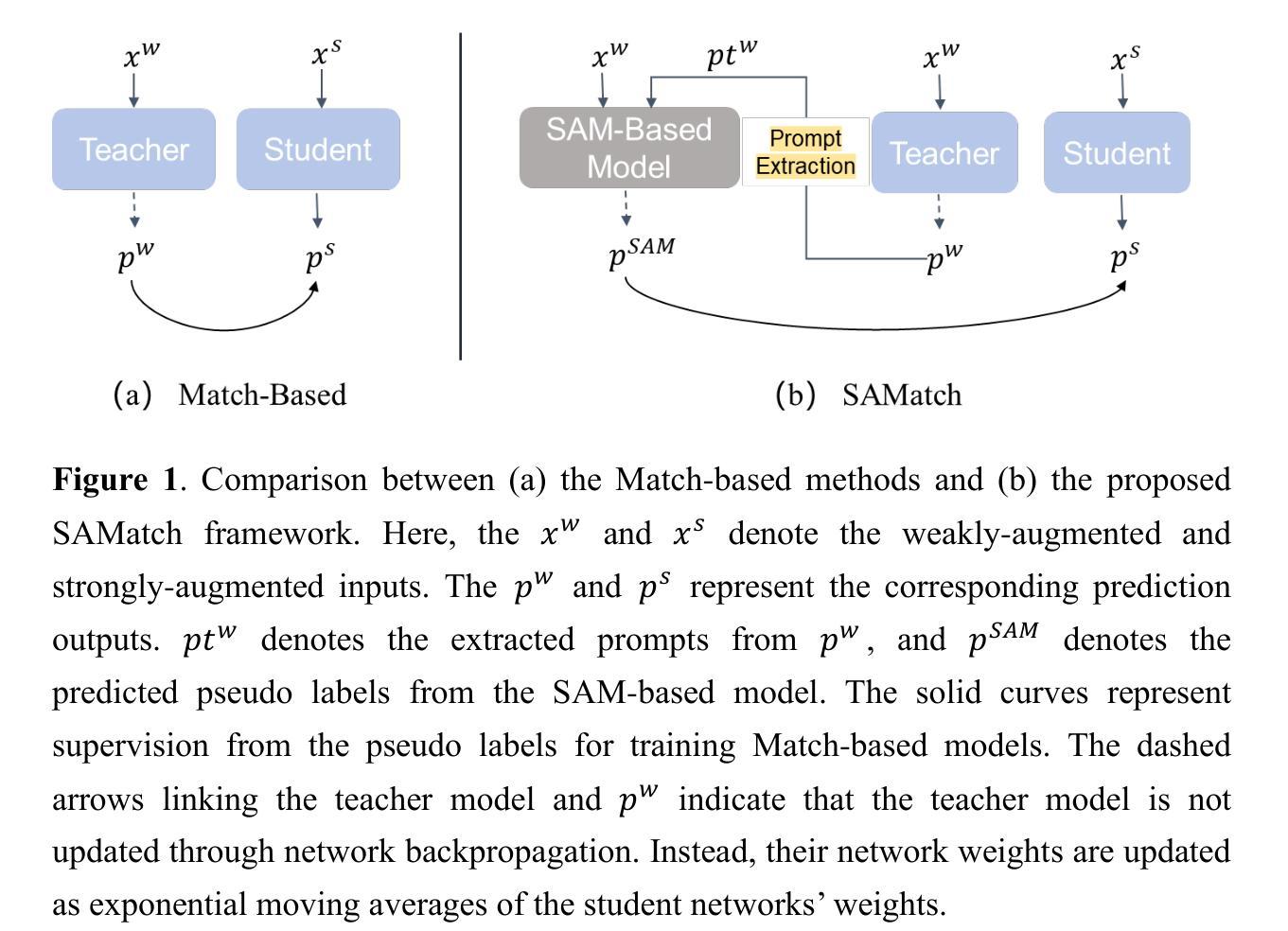
A SAM-guided and Match-based Semi-Supervised Segmentation Framework for Medical Imaging
Authors:Guoping Xu, Xiaoxue Qian, Hua Chieh Shao, Jax Luo, Weiguo Lu, You Zhang
This study introduces SAMatch, a SAM-guided Match-based framework for semi-supervised medical image segmentation, aimed at improving pseudo label quality in data-scarce scenarios. While Match-based frameworks are effective, they struggle with low-quality pseudo labels due to the absence of ground truth. SAM, pre-trained on a large dataset, generalizes well across diverse tasks and assists in generating high-confidence prompts, which are then used to refine pseudo labels via fine-tuned SAM. SAMatch is trained end-to-end, allowing for dynamic interaction between the models. Experiments on the ACDC cardiac MRI, BUSI breast ultrasound, and MRLiver datasets show SAMatch achieving state-of-the-art results, with Dice scores of 89.36%, 77.76%, and 80.04%, respectively, using minimal labeled data. SAMatch effectively addresses challenges in semi-supervised segmentation, offering a powerful tool for segmentation in data-limited environments. Code and data are available at https://github.com/apple1986/SAMatch.
本研究介绍了SAMatch,这是一种基于SAM引导的基于匹配的半监督医学图像分割框架,旨在在数据稀缺的情况下提高伪标签质量。虽然基于匹配的框架很有效,但由于缺少真实标签,它们难以处理低质量的伪标签。SAM在大规模数据集上进行预训练,在不同的任务中具有良好的通用性,并有助于生成高置信度的提示,然后这些提示被用于通过微调SAM来优化伪标签。SAMatch是端到端进行训练的,允许模型之间的动态交互。在ACDC心脏MRI、BUSI乳腺超声和MRLiver数据集上的实验表明,SAMatch取得了最先进的成果,Dice得分分别为89.36%、77.76%和80.04%,使用的是少量有标签数据。SAMatch有效地解决了半监督分割中的挑战,为数据有限环境中的分割提供了强大的工具。相关代码和数据可通过https://github.com/apple1986/SAMatch获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
SAMatch框架介绍,这是一种基于SAM引导的半监督医学图像分割匹配框架,旨在数据稀缺的场景中提高伪标签质量。它通过预训练的大型数据集进行训练,能够很好地泛化不同的任务并生成高置信度的提示,进而通过微调SAM来优化伪标签。SAMatch框架采用端到端训练,允许模型之间的动态交互。实验结果表明,在ACDC心脏MRI、BUSI乳腺超声和MRLiver数据集上,SAMatch取得了最先进的成果,Dice得分分别为89.36%、77.76%、和80.04%,并且仅使用少量标记数据。该框架解决了半监督分割中的挑战,为数据有限的环境中的分割提供了强大的工具。代码和数据可在GitHub上找到。
Key Takeaways
- SAMatch是一个基于SAM引导的半监督医学图像分割匹配框架,适用于数据稀缺场景。
- SAMatch利用预训练的大型数据集进行训练,能很好地泛化不同任务。
- SAMatch通过生成高置信度的提示来优化伪标签质量。
- SAMatch采用端到端训练,允许模型间的动态交互。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,SAMatch取得了最先进的成果。
- SAMatch的Dice得分在ACDC心脏MRI、BUSI乳腺超声和MRLiver数据集上分别为89.36%、77.76%、和80.04%。
点此查看论文截图


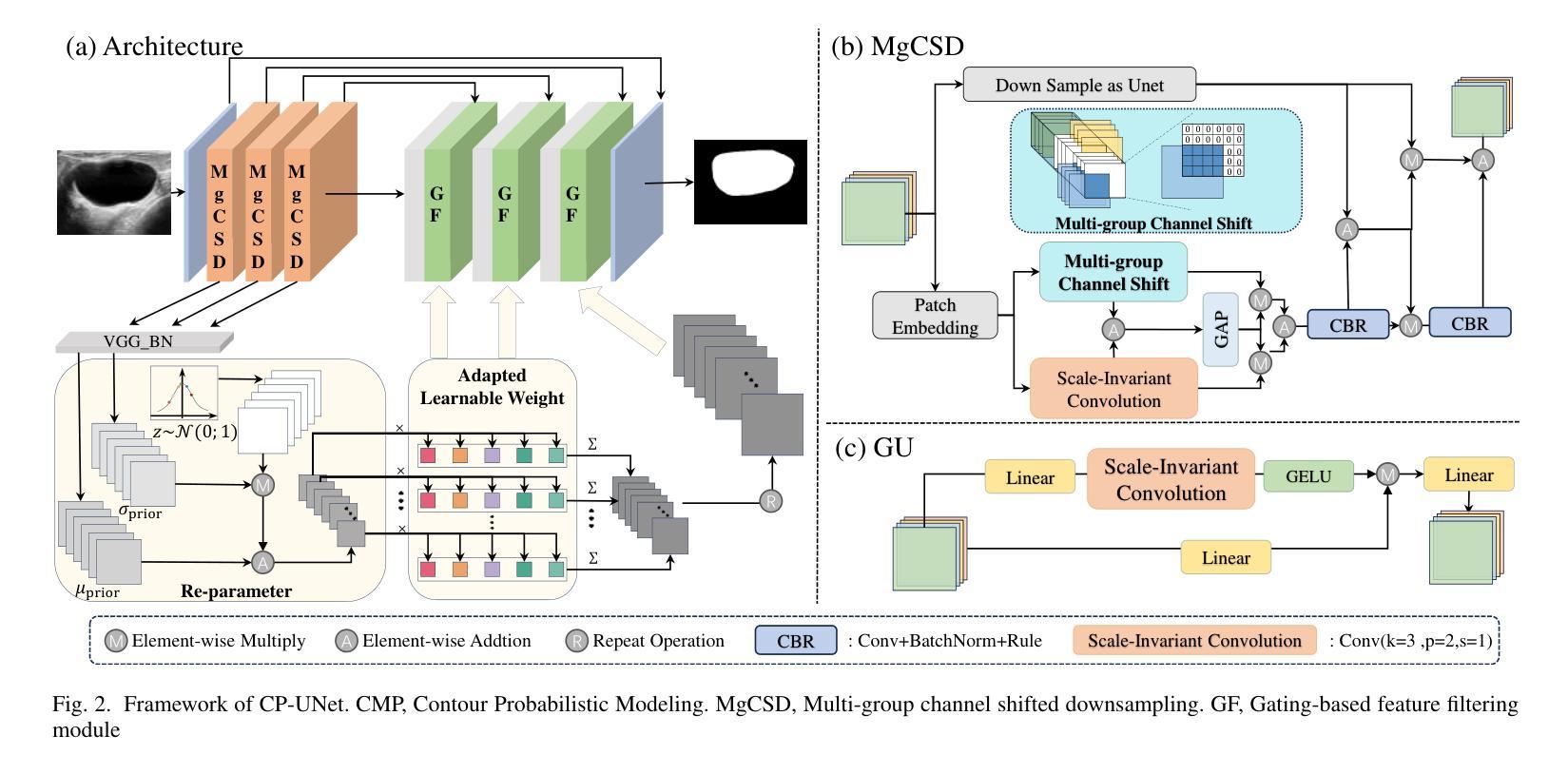
CP-UNet: Contour-based Probabilistic Model for Medical Ultrasound Images Segmentation
Authors:Ruiguo Yu, Yiyang Zhang, Yuan Tian, Zhiqiang Liu, Xuewei Li, Jie Gao
Deep learning-based segmentation methods are widely utilized for detecting lesions in ultrasound images. Throughout the imaging procedure, the attenuation and scattering of ultrasound waves cause contour blurring and the formation of artifacts, limiting the clarity of the acquired ultrasound images. To overcome this challenge, we propose a contour-based probabilistic segmentation model CP-UNet, which guides the segmentation network to enhance its focus on contour during decoding. We design a novel down-sampling module to enable the contour probability distribution modeling and encoding stages to acquire global-local features. Furthermore, the Gaussian Mixture Model utilizes optimized features to model the contour distribution, capturing the uncertainty of lesion boundaries. Extensive experiments with several state-of-the-art deep learning segmentation methods on three ultrasound image datasets show that our method performs better on breast and thyroid lesions segmentation.
基于深度学习的分割方法广泛应用于超声图像中的病灶检测。在成像过程中,超声波的衰减和散射会导致轮廓模糊和伪影的形成,降低了获取的超声图像的清晰度。为了克服这一挑战,我们提出了一种基于轮廓的概率分割模型CP-UNet,它引导分割网络在解码过程中重点关注轮廓。我们设计了一个新型的下采样模块,以实现在轮廓概率分布建模和编码阶段获取全局-局部特征。此外,高斯混合模型利用优化后的特征对轮廓分布进行建模,捕捉病灶边界的不确定性。在三个超声图像数据集上与几种最先进的深度学习分割方法进行的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在乳腺和甲状腺病灶分割方面表现更好。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 4 figures, 2 tables;For icassp2025
Summary
深度学习在超声图像分割中的应用已广泛应用于病灶检测。由于超声波的衰减和散射导致的轮廓模糊和伪影形成,影响了超声图像的清晰度。为此,我们提出了一种基于轮廓的概率分割模型CP-UNet,引导分割网络在解码过程中重点关注轮廓。设计了一种新型的下采样模块,用于实现轮廓概率分布建模和编码阶段的全局局部特征获取。此外,高斯混合模型利用优化后的特征对轮廓分布进行建模,捕捉病灶边界的不确定性。在三个超声图像数据集上与先进的深度学习分割方法进行的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在乳腺和甲状腺病灶分割方面具有更好的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在超声图像分割中广泛应用,主要用于病灶检测。
- 超声波图像的轮廓模糊和伪影形成是主要的挑战。
- 提出了一种基于轮廓的概率分割模型CP-UNet,关注轮廓的解码过程。
- 设计了下采样模块,实现轮廓概率分布建模和全局局部特征的获取。
- 利用高斯混合模型捕捉病灶边界的不确定性。
- 在多个超声图像数据集上进行了广泛的实验验证。
点此查看论文截图

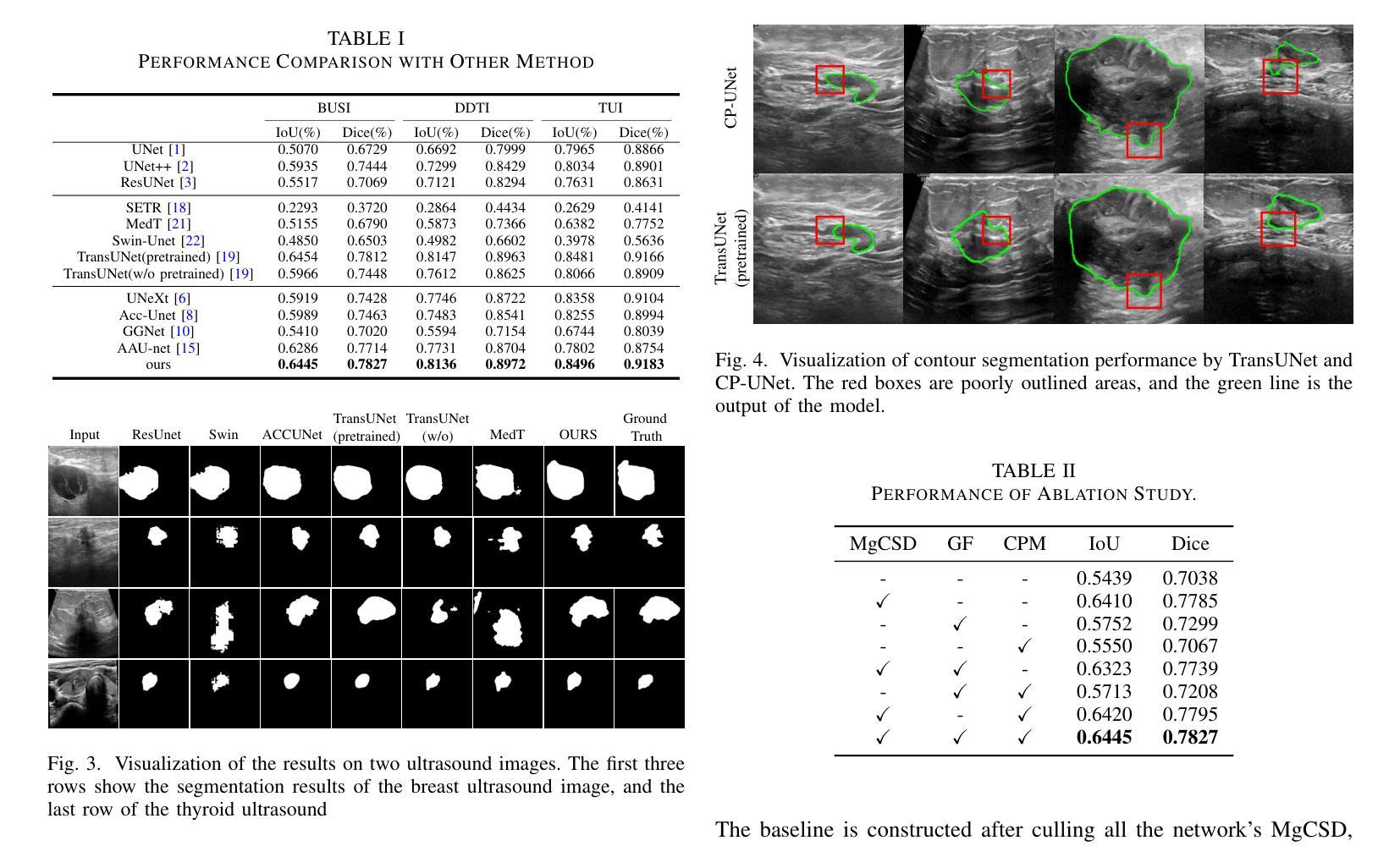
DBF-Net: A Dual-Branch Network with Feature Fusion for Ultrasound Image Segmentation
Authors:Guoping Xu, Ximing Wu, Wentao Liao, Xinglong Wu, Qing Huang, Chang Li
Accurately segmenting lesions in ultrasound images is challenging due to the difficulty in distinguishing boundaries between lesions and surrounding tissues. While deep learning has improved segmentation accuracy, there is limited focus on boundary quality and its relationship with body structures. To address this, we introduce UBBS-Net, a dual-branch deep neural network that learns the relationship between body and boundary for improved segmentation. We also propose a feature fusion module to integrate body and boundary information. Evaluated on three public datasets, UBBS-Net outperforms existing methods, achieving Dice Similarity Coefficients of 81.05% for breast cancer, 76.41% for brachial plexus nerves, and 87.75% for infantile hemangioma segmentation. Our results demonstrate the effectiveness of UBBS-Net for ultrasound image segmentation. The code is available at https://github.com/apple1986/DBF-Net.
在超声图像中精确地分割病变组织是一个挑战,因为很难区分病变组织和周围组织的边界。虽然深度学习已经提高了分割的准确性,但对于边界质量和其与身体结构的关系的关注有限。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了UBBS-Net,这是一个双分支深度神经网络,它学习身体与边界之间的关系以改进分割。我们还提出了一个特征融合模块,以整合身体和边界信息。在三个公共数据集上进行了评估,UBBS-Net的性能优于现有方法,在乳腺癌、臂丛神经和婴儿血管瘤的分割上实现了迪斯科相似系数(Dice Similarity Coefficient)分别为81.05%、76.4 %和87.75%。我们的结果证明了UBBS-Net在超声图像分割中的有效性。代码可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/apple1986/DBF-Net。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
UBBS-Net是一种针对超声图像分割的双分支深度神经网络。它通过学习与身体结构的关联来改善边界分割质量。该网络引入特征融合模块,以整合身体和边界信息。在三个公共数据集上的评估显示,UBBS-Net的狄氏相似系数(Dice Similarity Coefficients)分别为乳腺癌81.05%、臂丛神经76.41%、婴儿血管瘤87.75%,优于现有方法。结果证明了UBBS-Net在超声图像分割中的有效性。代码可在https://github.com/apple1986/DBF-Net获取。
要点
- UBBS-Net是一种双分支深度神经网络,用于超声图像分割,旨在提高分割准确性。
- 网络引入了特征融合模块,以整合身体和边界信息,从而提高边界分割质量。
- UBBS-Net在三个公共数据集上的表现优于现有方法,特别是在乳腺癌、臂丛神经和婴儿血管瘤的分割方面。
- 狄氏相似系数是评估超声图像分割效果的重要指标,UBBS-Net的狄氏相似系数达到了较高的水平。
- UBBS-Net通过学习与身体结构的关联来改善边界分割质量,这是其与其他分割方法的重要区别。
- 代码已公开发布,可供其他研究人员使用和改进。
点此查看论文截图

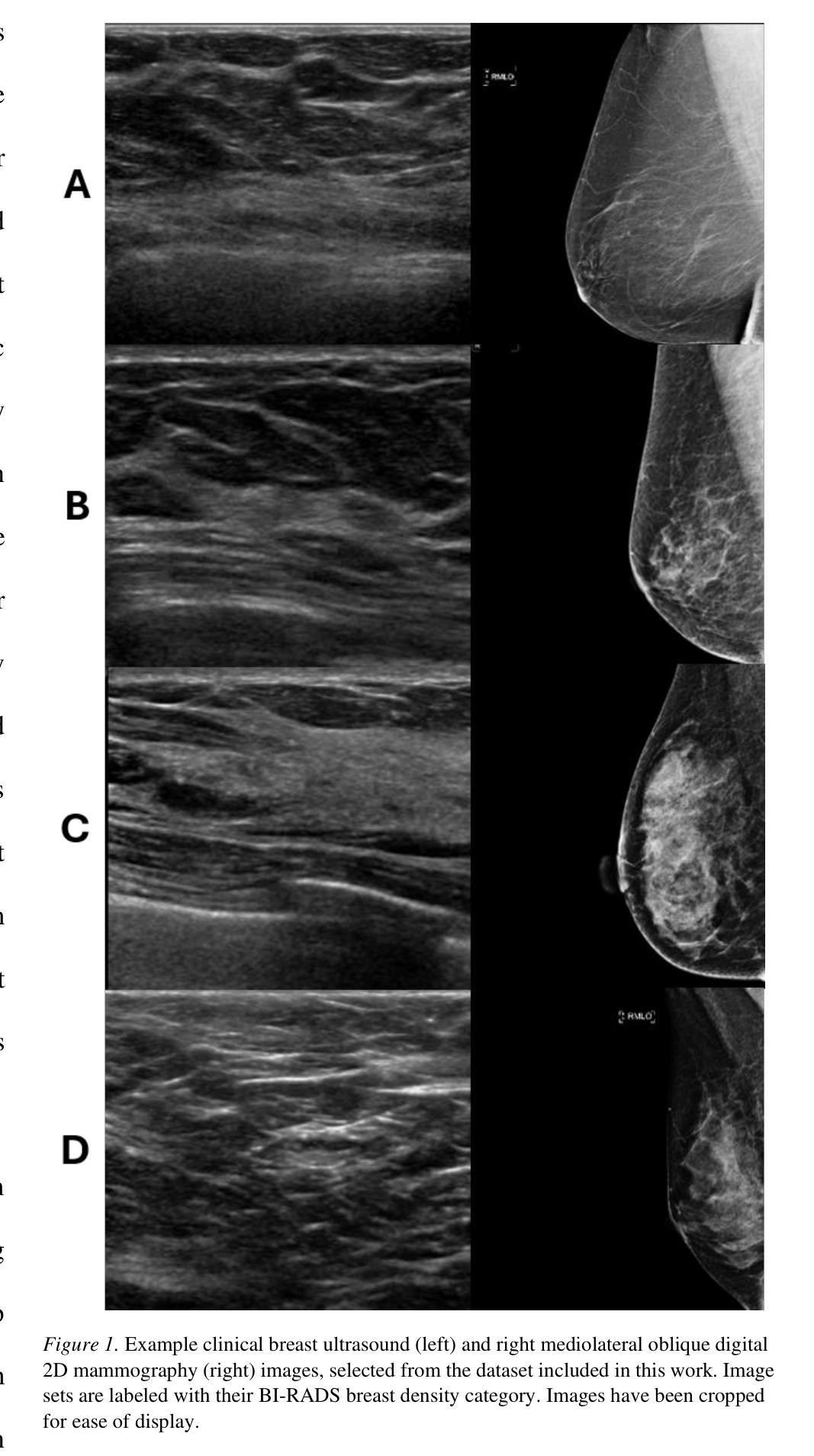
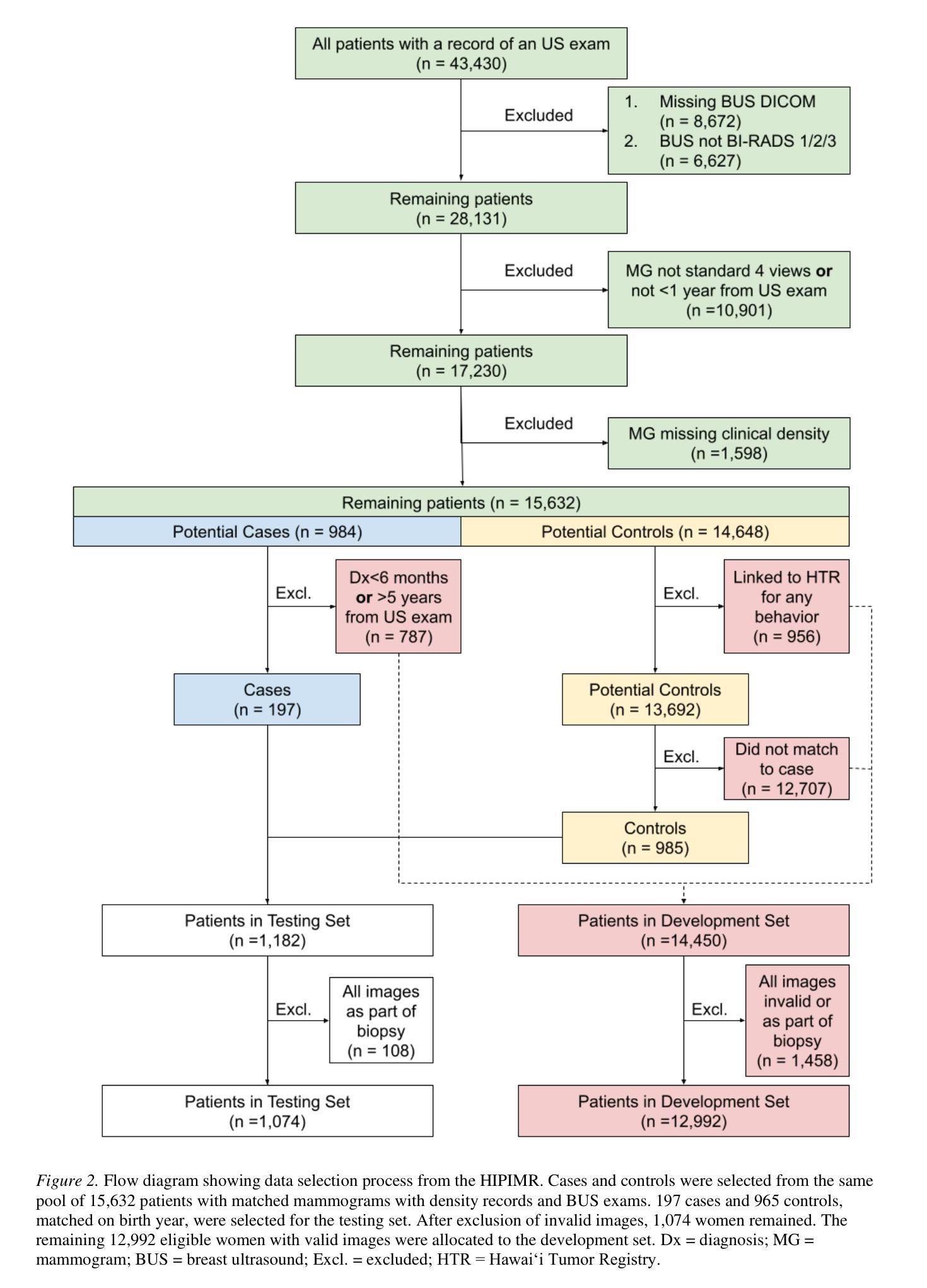
Deep Learning Predicts Mammographic Breast Density in Clinical Breast Ultrasound Images
Authors:Arianna Bunnell, Dustin Valdez, Thomas K. Wolfgruber, Brandon Quon, Kailee Hung, Brenda Y. Hernandez, Todd B. Seto, Jeffrey Killeen, Marshall Miyoshi, Peter Sadowski, John A. Shepherd
Background: Breast density, as derived from mammographic images and defined by the American College of Radiology’s Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS), is one of the strongest risk factors for breast cancer. Breast ultrasound (BUS) is an alternative breast cancer screening modality, particularly useful for early detection in low-resource, rural contexts. The purpose of this study was to explore an artificial intelligence (AI) model to predict BI-RADS mammographic breast density category from clinical, handheld BUS imaging. Methods: All data are sourced from the Hawaii and Pacific Islands Mammography Registry. We compared deep learning methods from BUS imaging, as well as machine learning models from image statistics alone. The use of AI-derived BUS density as a risk factor for breast cancer was then compared to clinical BI-RADS breast density while adjusting for age. The BUS data were split by individual into 70/20/10% groups for training, validation, and testing. Results: 405,120 clinical BUS images from 14.066 women were selected for inclusion in this study, resulting in 9.846 women for training (302,574 images), 2,813 for validation (11,223 images), and 1,406 for testing (4,042 images). On the held-out testing set, the strongest AI model achieves AUROC 0.854 predicting BI-RADS mammographic breast density from BUS imaging and outperforms all shallow machine learning methods based on image statistics. In cancer risk prediction, age-adjusted AI BUS breast density predicted 5-year breast cancer risk with 0.633 AUROC, as compared to 0.637 AUROC from age-adjusted clinical breast density. Conclusions: BI-RADS mammographic breast density can be estimated from BUS imaging with high accuracy using a deep learning model. Furthermore, we demonstrate that AI-derived BUS breast density is predictive of 5-year breast cancer risk in our population.
背景:乳腺密度是从乳腺X光图像中衍生出来的,由美国放射学院的乳腺影像报告和数据系统(BI-RADS)定义,是乳腺癌的最强风险因素之一。乳腺超声(BUS)是一种替代的乳腺癌筛查方法,特别是在资源匮乏的农村环境中对早期检测非常有用。本研究旨在探索一种人工智能(AI)模型,根据临床手持式BUS图像预测BI-RADS乳腺X光乳腺密度类别。方法:所有数据均来自夏威夷和太平洋岛屿乳腺X光登记处。我们比较了来自BUS成像的深度学习方法和仅基于图像统计的机器学习模型。然后,将AI衍生的BUS密度作为乳腺癌的风险因素与临床BI-RADS乳腺密度进行比较,同时考虑年龄因素。BUS数据按个人分为70/20/10%的组别,用于训练、验证和测试。结果:本研究入选了来自14,066名妇女的405,120张临床BUS图像,其中9,846名妇女用于训练(302,574张图像),2,813名用于验证(11,223张图像),1,406名用于测试(4,042张图像)。在独立测试集上,表现最佳的AI模型的曲线下面积(AUROC)为0.854,能够从BUS图像预测BI-RADS乳腺X光乳腺密度,并且基于图像统计的浅层机器学习方法的性能更佳。在癌症风险预测方面,与年龄调整后的临床乳腺密度相比,年龄调整的AI BUS乳腺密度预测的5年乳腺癌风险的曲线下面积为0.633 AUROC。结论:使用深度学习模型,可以从BUS图像准确估计BI-RADS乳腺X光乳腺密度。此外,我们证明AI衍生的BUS乳腺密度可以预测我们人群中的5年乳腺癌风险。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:本研究旨在利用人工智能模型,根据临床手持式乳腺超声检查图像预测BI-RADS乳腺密度分类。研究采用深度学习方法和仅基于图像统计的机器学习模型,并比较了AI预测的乳腺超声密度与临床BI-RADS乳腺密度作为乳腺癌风险因素的预测效果。结果表明,AI模型可以从乳腺超声检查图像中准确估计BI-RADS乳腺密度分类,并且对五年乳腺癌风险的预测表现良好。
Key Takeaways:
- 本研究旨在利用AI模型从手持式乳腺超声检查图像预测BI-RADS乳腺密度分类。
- 研究数据来自夏威夷和太平洋岛屿的乳腺摄影注册处。
- 研究采用了深度学习和仅基于图像统计的机器学习模型。
- AI模型可以准确估计BI-RADS乳腺密度分类。
- AI预测的乳腺超声密度与临床BI-RADS乳腺密度相比,在预测五年乳腺癌风险方面表现良好。
- AI模型预测BI-RADS乳腺密度的最佳表现是AUROC 0.854。
点此查看论文截图

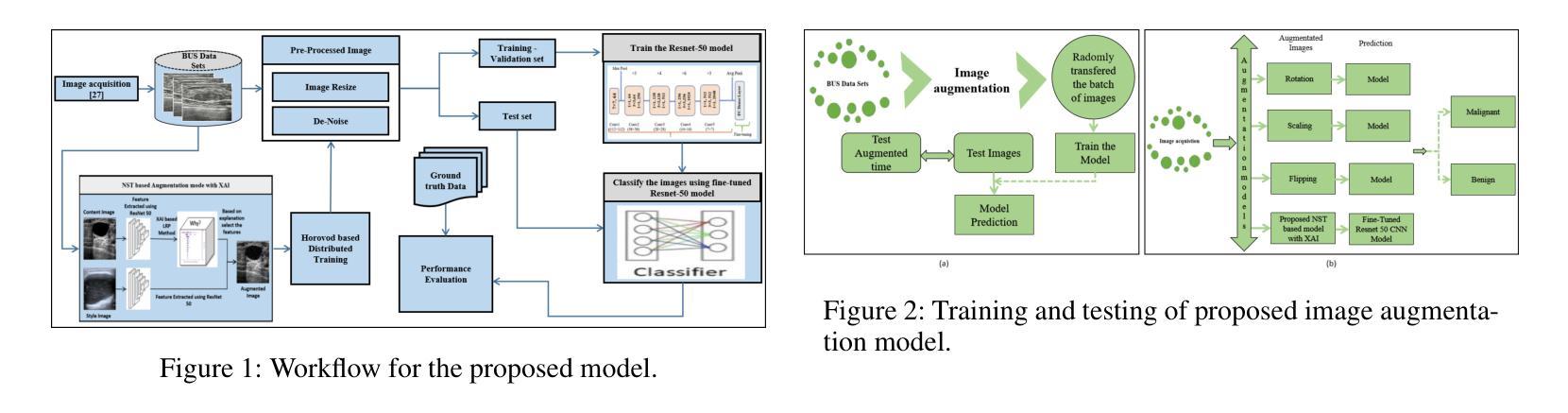
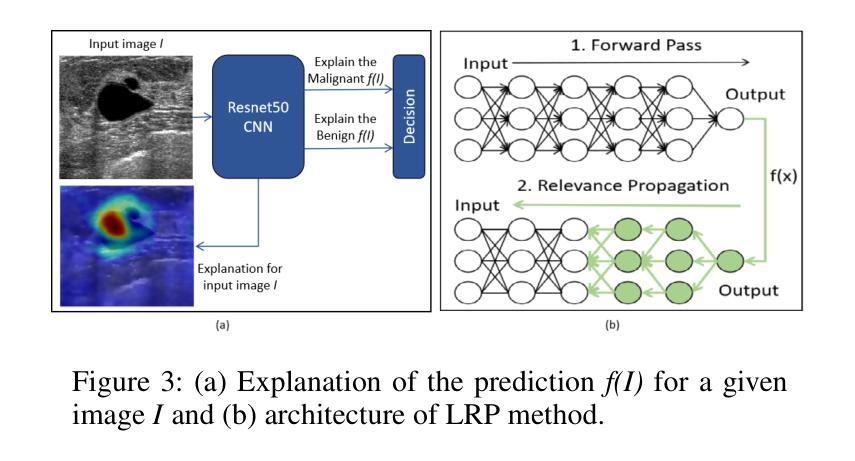
A Novel Breast Ultrasound Image Augmentation Method Using Advanced Neural Style Transfer: An Efficient and Explainable Approach
Authors:Lipismita Panigrahi, Prianka Rani Saha, Jurdana Masuma Iqrah, Sushil Prasad
Clinical diagnosis of breast malignancy (BM) is a challenging problem in the recent era. In particular, Deep learning (DL) models have continued to offer important solutions for early BM diagnosis but their performance experiences overfitting due to the limited volume of breast ultrasound (BUS) image data. Further, large BUS datasets are difficult to manage due to privacy and legal concerns. Hence, image augmentation is a necessary and challenging step to improve the performance of the DL models. However, the current DL-based augmentation models are inadequate and operate as a black box resulting lack of information and justifications about their suitability and efficacy. Additionally, pre and post-augmentation need high-performance computational resources and time to produce the augmented image and evaluate the model performance. Thus, this study aims to develop a novel efficient augmentation approach for BUS images with advanced neural style transfer (NST) and Explainable AI (XAI) harnessing GPU-based parallel infrastructure. We scale and distribute the training of the augmentation model across 8 GPUs using the Horovod framework on a DGX cluster, achieving a 5.09 speedup while maintaining the model’s accuracy. The proposed model is evaluated on 800 (348 benign and 452 malignant) BUS images and its performance is analyzed with other progressive techniques, using different quantitative analyses. The result indicates that the proposed approach can successfully augment the BUS images with 92.47% accuracy.
乳腺癌(BM)的临床诊断是当代的一个难题。尤其是深度学习(DL)模型在早期诊断乳腺癌方面提供了重要的解决方案,但由于乳腺超声(BUS)图像数据的数量有限,其性能会出现过拟合现象。此外,由于隐私和法规的担忧,管理大型的BUS数据集是一项艰巨的任务。因此,图像增强是改进深度学习模型性能的必要且具有挑战性的步骤。然而,当前的基于深度学习的增强模型存在不足,它们像黑箱一样运作,缺乏关于其适用性和有效性的信息和理由。此外,增强前后需要高性能的计算资源和时间来生成增强图像并评估模型性能。因此,本研究旨在利用基于GPU的并行基础设施开发一种新型的、高效的乳腺超声图像增强方法,该方法结合了先进的神经样式转移(NST)和可解释的AI(XAI)。我们使用DGX集群上的Horovod框架,在8个GPU上分布和扩展增强模型的训练,实现了5.09的加速,同时保持了模型的准确性。所提出的模型在800张(348张良性,452张恶性)BUS图像上进行评估,与其他先进技术进行性能分析,使用不同的定量分析方法。结果表明,所提出的方法可以成功地将BUS图像的准确率提高到92.47%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
这篇文本介绍了使用深度学习和图像增强技术对乳腺超声图像进行诊断的挑战。文中提到由于数据量限制,深度学习模型存在过拟合问题,因此提出了利用先进的神经网络风格转移和可解释人工智能的新的高效图像增强方法。该研究旨在实现在分布式GPU环境中提高模型训练效率,同时保持模型准确性。实验结果表明,该方法的图像增强准确率可达92.47%。
要点速览
- 临床乳腺恶性肿瘤诊断面临挑战,深度学习为解决该问题提供了解决方案,但仍存在数据限制问题。
- 乳腺超声(BUS)数据量有限导致深度学习模型过拟合问题。
- 图像增强技术能提高深度学习模型的性能,但现有的方法缺乏透明度和解释性。
- 提出一种新型高效的图像增强方法,结合了神经网络风格转移和可解释人工智能。
- 研究采用GPU并行基础设施和Horovod框架进行分布式训练,实现了模型的加速并保持了准确性。
点此查看论文截图


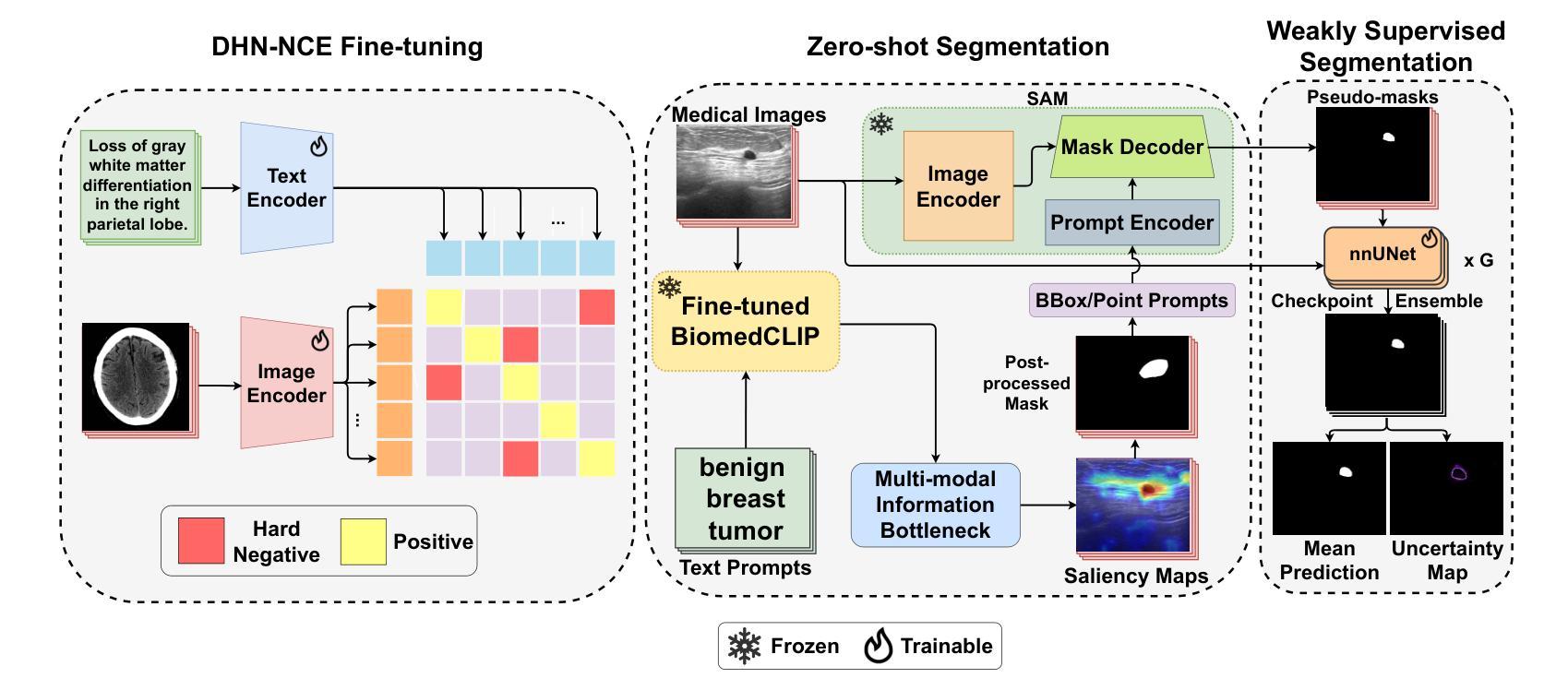
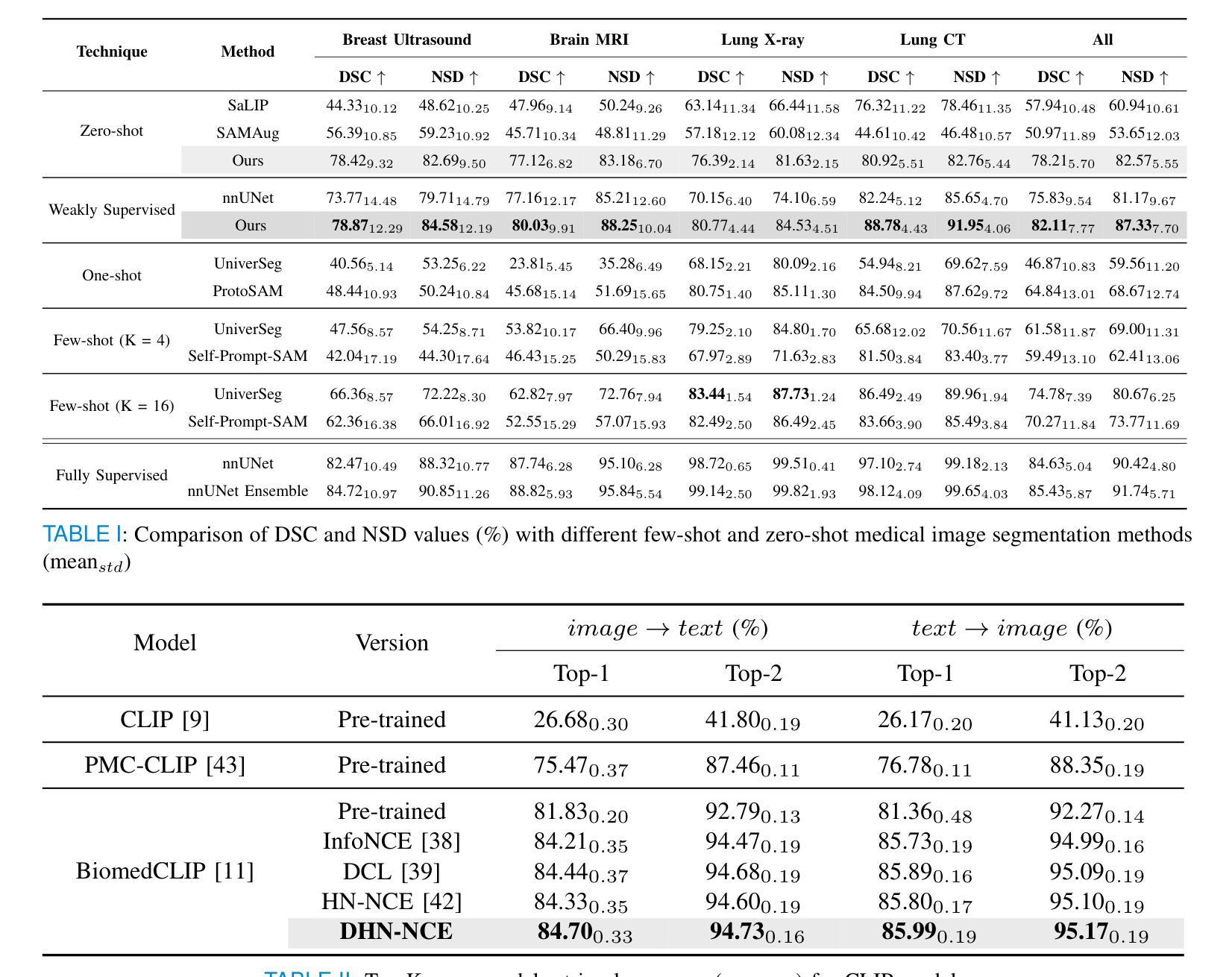
MedCLIP-SAMv2: Towards Universal Text-Driven Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Taha Koleilat, Hojat Asgariandehkordi, Hassan Rivaz, Yiming Xiao
Segmentation of anatomical structures and pathological regions in medical images is essential for modern clinical diagnosis, disease research, and treatment planning. While significant advancements have been made in deep learning-based segmentation techniques, many of these methods still suffer from limitations in data efficiency, generalizability, and interactivity. As a result, developing precise segmentation methods that require fewer labeled datasets remains a critical challenge in medical image analysis. Recently, the introduction of foundation models like CLIP and Segment-Anything-Model (SAM), with robust cross-domain representations, has paved the way for interactive and universal image segmentation. However, further exploration of these models for data-efficient segmentation in medical imaging is still needed and highly relevant. In this paper, we introduce MedCLIP-SAMv2, a novel framework that integrates the CLIP and SAM models to perform segmentation on clinical scans using text prompts, in both zero-shot and weakly supervised settings. Our approach includes fine-tuning the BiomedCLIP model with a new Decoupled Hard Negative Noise Contrastive Estimation (DHN-NCE) loss, and leveraging the Multi-modal Information Bottleneck (M2IB) to create visual prompts for generating segmentation masks from SAM in the zero-shot setting. We also investigate using zero-shot segmentation labels within a weakly supervised paradigm to enhance segmentation quality further. Extensive testing across four diverse segmentation tasks and medical imaging modalities (breast tumor ultrasound, brain tumor MRI, lung X-ray, and lung CT) demonstrates the high accuracy of our proposed framework. Our code is available at https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/MedCLIP-SAMv2.
医学影像中的解剖结构和病理区域分割对于现代临床诊断、疾病研究和治疗计划制定至关重要。虽然基于深度学习的分割技术已经取得了重大进展,但许多这些方法在数据效率、通用性和交互性方面仍存在局限性。因此,开发需要较少标注数据集的精确分割方法仍然是医学图像分析中的一项关键挑战。最近,引入具有稳健跨域表示能力的CLIP和Segment-Anything-Model(SAM)等基础模型,为交互式和通用图像分割铺平了道路。然而,需要进一步探索这些模型在医学成像中的数据高效分割,这仍然是非常相关和必要的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 2 figures, 6 tables
Summary
论文提出MedCLIP-SAMv2框架,结合CLIP和SAM模型,利用文本提示进行临床扫描的分割,涉及零样本和弱监督设置。通过fine-tuning BiomedCLIP模型并使用DHN-NCE损失和M2IB创建视觉提示,实现在医疗影像中的高效数据分割。经过四项不同分割任务和医学影像模态的广泛测试,证明框架的高准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像中的解剖结构和病理区域分割对于现代临床诊断、疾病研究和治疗计划至关重要。
- 虽然深度学习在医学图像分割上取得了显著进展,但仍存在数据效率、通用性和交互性方面的挑战。
- MedCLIP-SAMv2框架结合了CLIP和SAM模型,实现了在零样本和弱监督设置下的医学图像分割。
- 通过fine-tuning BiomedCLIP模型并使用DHN-NCE损失提高分割性能。
- 利用M2IB创建视觉提示,生成SAM的分割掩膜。
- 论文在多种医学影像模态(如乳腺肿瘤超声、脑肿瘤MRI、肺部X光和CT)进行了广泛测试,证明了框架的高准确性。
- 论文代码已公开,可供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图

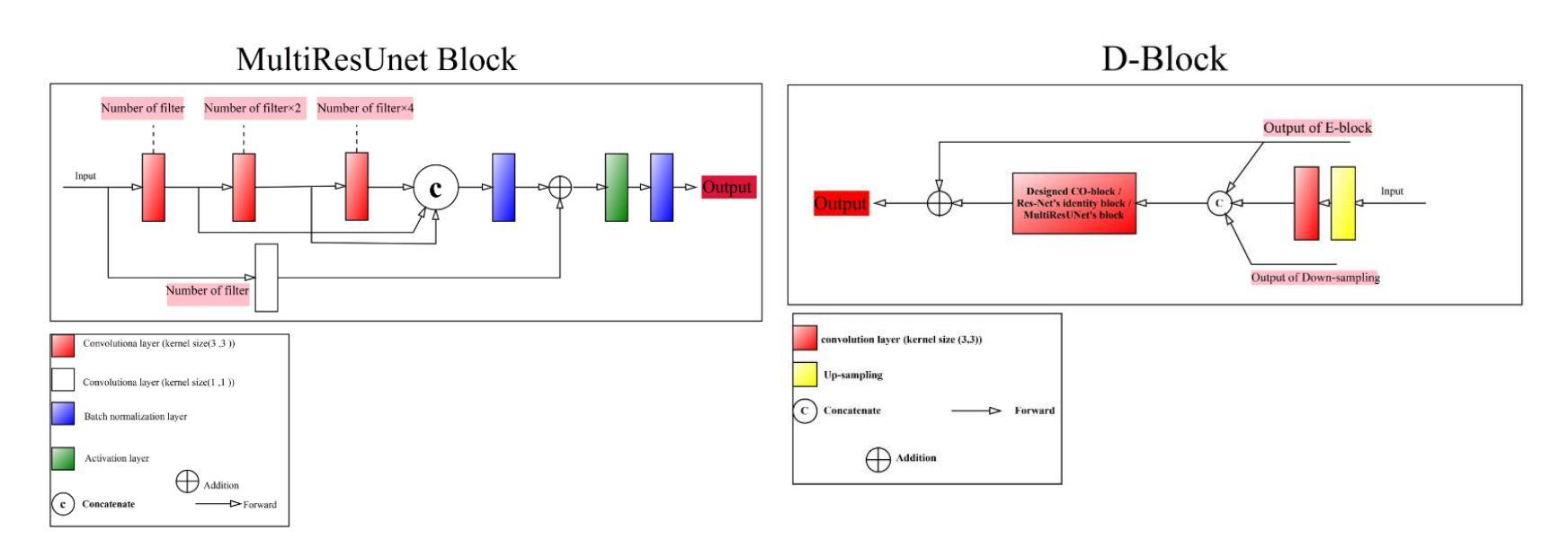
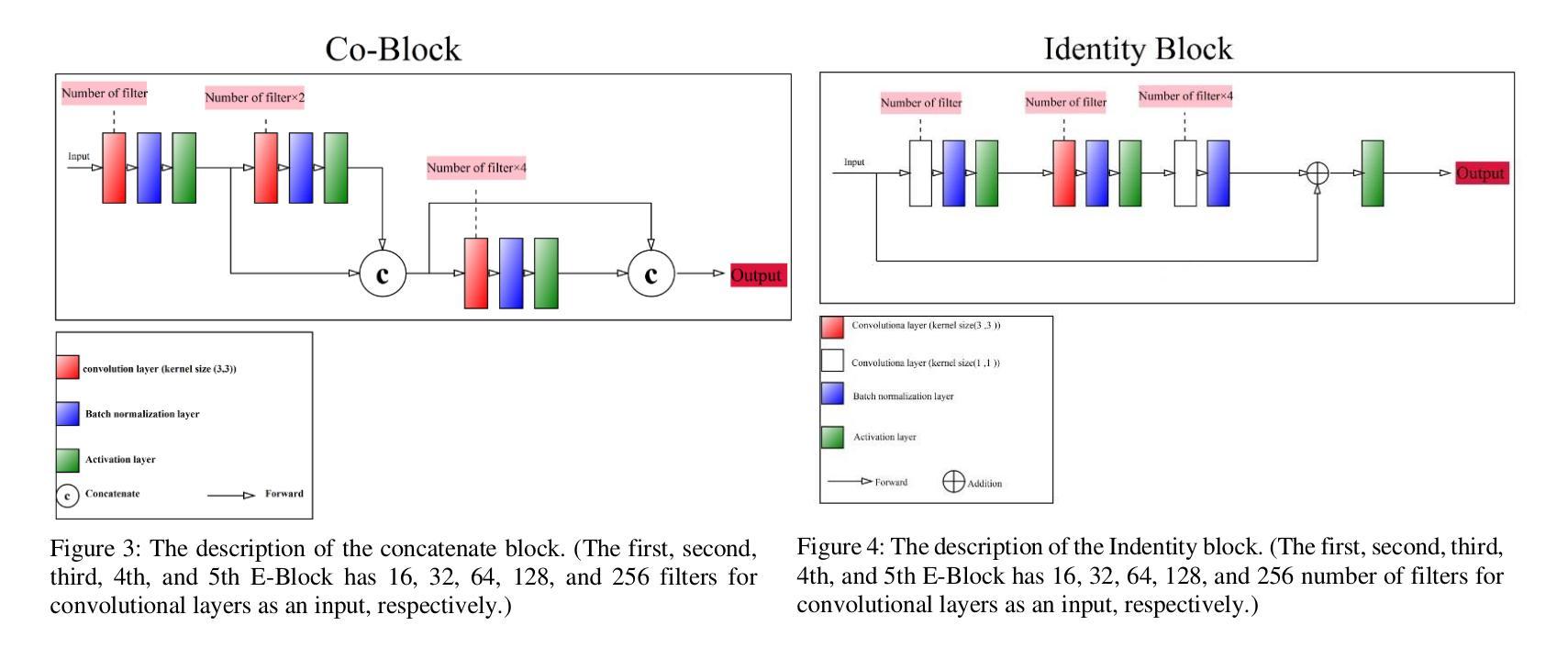
Modifying the U-Net’s Encoder-Decoder Architecture for Segmentation of Tumors in Breast Ultrasound Images
Authors:Sina Derakhshandeh, Ali Mahloojifar
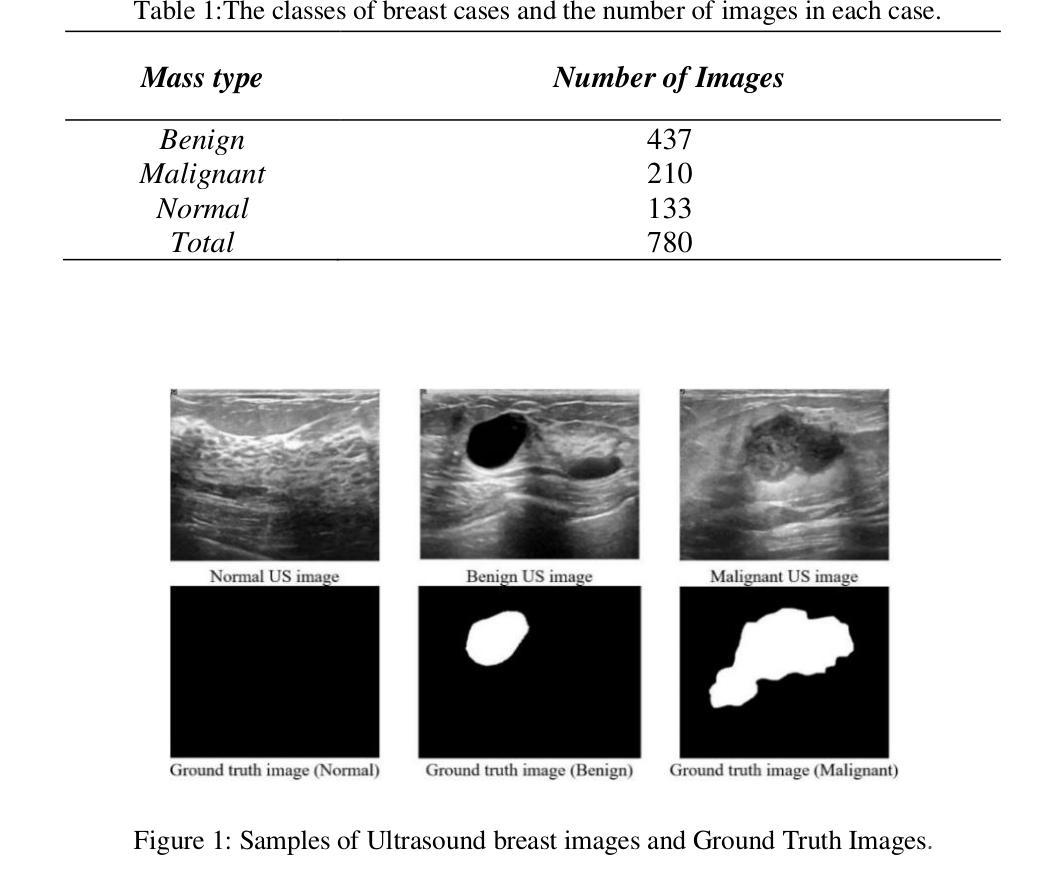
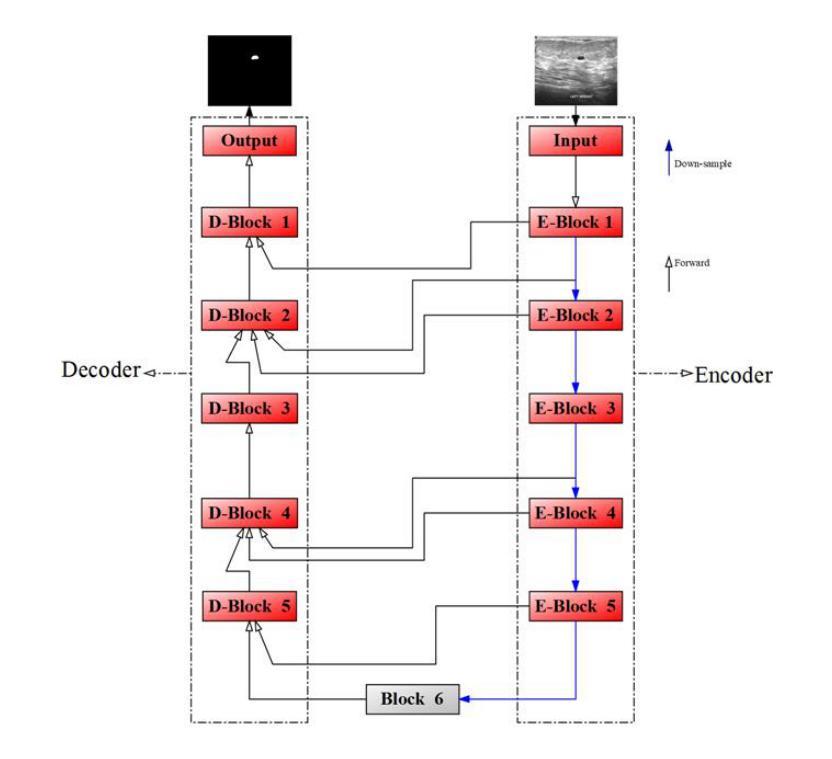
Segmentation is one of the most significant steps in image processing. Segmenting an image is a technique that makes it possible to separate a digital image into various areas based on the different characteristics of pixels in the image. In particular, segmentation of breast ultrasound images is widely used for cancer identification. As a result of image segmentation, it is possible to make early diagnoses of a diseases via medical images in a very effective way. Due to various ultrasound artifacts and noises, including speckle noise, low signal-to-noise ratio, and intensity heterogeneity, the process of accurately segmenting medical images, such as ultrasound images, is still a challenging task. In this paper, we present a new method to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of breast ultrasound image segmentation. More precisely, we propose a Neural Network (NN) based on U-Net and an encoder-decoder architecture. By taking U-Net as the basis, both encoder and decoder parts are developed by combining U-Net with other Deep Neural Networks (Res-Net and MultiResUNet) and introducing a new approach and block (Co-Block), which preserve as much as possible the low-level and the high-level features. Designed network is evaluated using the Breast Ultrasound Images (BUSI) Dataset. It consists of 780 images and the images are categorized into three classes, which are normal, benign, and malignant. According to our extensive evaluations on a public breast ultrasound dataset, designed network segments the breast lesions more accurately than other state-of-the-art deep learning methods. With only 8.88M parameters, our network (CResU-Net) obtained 82.88%, 77.5%, 90.3%, and 98.4% in terms of Dice similarity coefficients (DSC), Intersection over Union (IoU), Area under curve (AUC), and global accuracy (ACC), respectively, on BUSI dataset.
分割是图像处理中最关键的步骤之一。图像分割是一种技术,能够将数字图像基于图像中像素的不同特征划分为不同的区域。特别是,乳房超声波图像的分割被广泛用于癌症的识别。通过图像分割,可以有效地通过医学图像进行早期疾病诊断。由于各种超声波伪影和噪声,包括斑点噪声、低信噪比和强度异质性,准确分割医学图像(如超声波图像)仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。在本文中,我们提出了一种提高乳房超声波图像分割准确性和效率的新方法。更具体地说,我们提出了一种基于U-Net的神经网络(NN),并结合了编码器-解码器架构。我们以U-Net为基础,结合U-Net与其他深度神经网络(Res-Net和MultiResUNet)进行开发,并引入了一种新的方法和块(Co-Block),尽可能地保留低级和高级特征。所设计的网络使用乳房超声图像(BUSI)数据集进行评估。该数据集包含780张图像,这些图像分为三类:正常、良性及恶性。根据我们在公共乳房超声数据集上的全面评估,所设计的网络比其他最先进的深度学习方法更准确地分割了乳腺病变。我们的网络(CResU-Net)仅有880万个参数,在BUSI数据集上获得了82.88%、77.5%、90.3%和98.4%的Dice相似系数(DSC)、交并比(IoU)、曲线下面积(AUC)和全局准确率(ACC)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于U-Net和编码器-解码器架构的神经网络,用于提高乳腺超声图像分割的准确性和效率。通过结合U-Net与其他深度神经网络(如Res-Net和MultiResUNet),并引入新的方法和块(Co-Block),提出网络CResU-Net能够在公共乳腺超声数据集上更准确地分割乳腺病变。
Key Takeaways
- 图像处理中,分割是最重要的步骤之一,特别是在乳腺超声图像中,用于癌症识别。
- 超声图像分割面临多种超声伪像和噪声的挑战,包括斑点噪声、低信噪比和强度异质性。
- 本文提出了一种基于U-Net和编码器-解码器架构的神经网络,以提高乳腺超声图像分割的精度和效率。
- 该网络结合了U-Net与其他深度神经网络(如Res-Net和MultiResUNet),并引入了Co-Block,以尽可能保留低级别和高级别的特征。
- 在公共乳腺超声数据集上进行的广泛评估表明,该网络(CResU-Net)能够更准确地分割乳腺病变,相较于其他先进深度学习方法的性能更佳。
- CResU-Net网络参数仅有8.88M,在BUSI数据集上取得了较高的表现,其Dice相似性系数(DSC)、交并比(IoU)、曲线下面积(AUC)和全局准确率(ACC)分别为82.88%、77.5%、90.3%和98.4%。
点此查看论文截图

BUSClean: Open-source software for breast ultrasound image pre-processing and knowledge extraction for medical AI
Authors:Arianna Bunnell, Kailee Hung, John A. Shepherd, Peter Sadowski
Development of artificial intelligence (AI) for medical imaging demands curation and cleaning of large-scale clinical datasets comprising hundreds of thousands of images. Some modalities, such as mammography, contain highly standardized imaging. In contrast, breast ultrasound imaging (BUS) can contain many irregularities not indicated by scan metadata, such as enhanced scan modes, sonographer annotations, or additional views. We present an open-source software solution for automatically processing clinical BUS datasets. The algorithm performs BUS scan filtering (flagging of invalid and non-B-mode scans), cleaning (dual-view scan detection, scan area cropping, and caliper detection), and knowledge extraction (BI-RADS Labeling and Measurement fields) from sonographer annotations. Its modular design enables users to adapt it to new settings. Experiments on an internal testing dataset of 430 clinical BUS images achieve >95% sensitivity and >98% specificity in detecting every type of text annotation, >98% sensitivity and specificity in detecting scans with blood flow highlighting, alternative scan modes, or invalid scans. A case study on a completely external, public dataset of BUS scans found that BUSClean identified text annotations and scans with blood flow highlighting with 88.6% and 90.9% sensitivity and 98.3% and 99.9% specificity, respectively. Adaptation of the lesion caliper detection method to account for a type of caliper specific to the case study demonstrates the intended use of BUSClean in new data distributions and improved performance in lesion caliper detection from 43.3% and 93.3% out-of-the-box to 92.1% and 92.3% sensitivity and specificity, respectively. Source code, example notebooks, and sample data are available at https://github.com/hawaii-ai/bus-cleaning.
针对医学影像领域的人工智能(AI)开发,需要整理大规模的临床数据集,这些数据集包含数十万张图像。某些模态(如乳腺摄影)的成像非常标准化。相比之下,乳腺超声成像(BUS)可能包含许多由扫描元数据未指示的不规则性,例如增强的扫描模式、超声医师的注释或额外的视图。我们提出了一种用于自动处理临床BUS数据集的开源软件解决方案。该算法执行BUS扫描过滤(标记无效和非B模式扫描)、清洁处理(双视图扫描检测、扫描区域裁剪和夹具检测)和知识提取(从超声医师注释中提取BI-RADS标签和测量字段)。其模块化设计使用户能够将其适应新环境。在包含430张临床BUS图像的内部测试数据集上进行的实验表明,检测每种类型的文本注释的灵敏度和特异度均大于95%和98%,检测带有血流突出显示、替代扫描模式或无效扫描的灵敏度及特异度均大于98%。另一项关于完全外部的公开BUS扫描数据集的研究发现,BUSClean对文本注释和带有血流突出显示的扫描的识别敏感度分别为88.6%和90.9%,特异度分别为98.3%和99.9%。为适应案例研究中特定类型的夹具而进行病变夹具检测方法的调整,证明了BUSClean在新数据分布中的预期用途以及病变夹具检测性能的改进,从初始的灵敏度和特异度为43.3%和93.3%,提升到使用BUSClean后的92.1%和92.3%。源代码、示例笔记本和样本数据可通过https://github.com/hawaii-ai/bus-cleaning获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一项针对乳腺超声影像的开源软件解决方案,用于自动处理临床数据集。该软件能够进行乳腺超声扫描的过滤、清洁和知识提取,包括文本标注检测、血流高亮扫描检测、替代扫描模式及无效扫描检测等。软件模块化的设计使其能够适应不同的环境。经过对内部测试数据集的实验验证,其敏感性大于95%,特异性大于98%。此外,该解决方案还展示了在公共数据集上的良好性能,并提供了源代码、示例笔记本和样本数据以供下载和使用。
Key Takeaways
- 该软件解决方案专为乳腺超声影像临床数据集设计,用于自动处理大规模数据。
- 软件能够进行乳腺超声扫描的过滤、清洁和知识提取,包括多种检测功能。
- 软件采用模块化设计,能够适应不同的环境和需求。
- 在内部测试数据集上的实验结果显示其高敏感性和特异性。
- 该解决方案在公共数据集上也表现出良好的性能。
点此查看论文截图


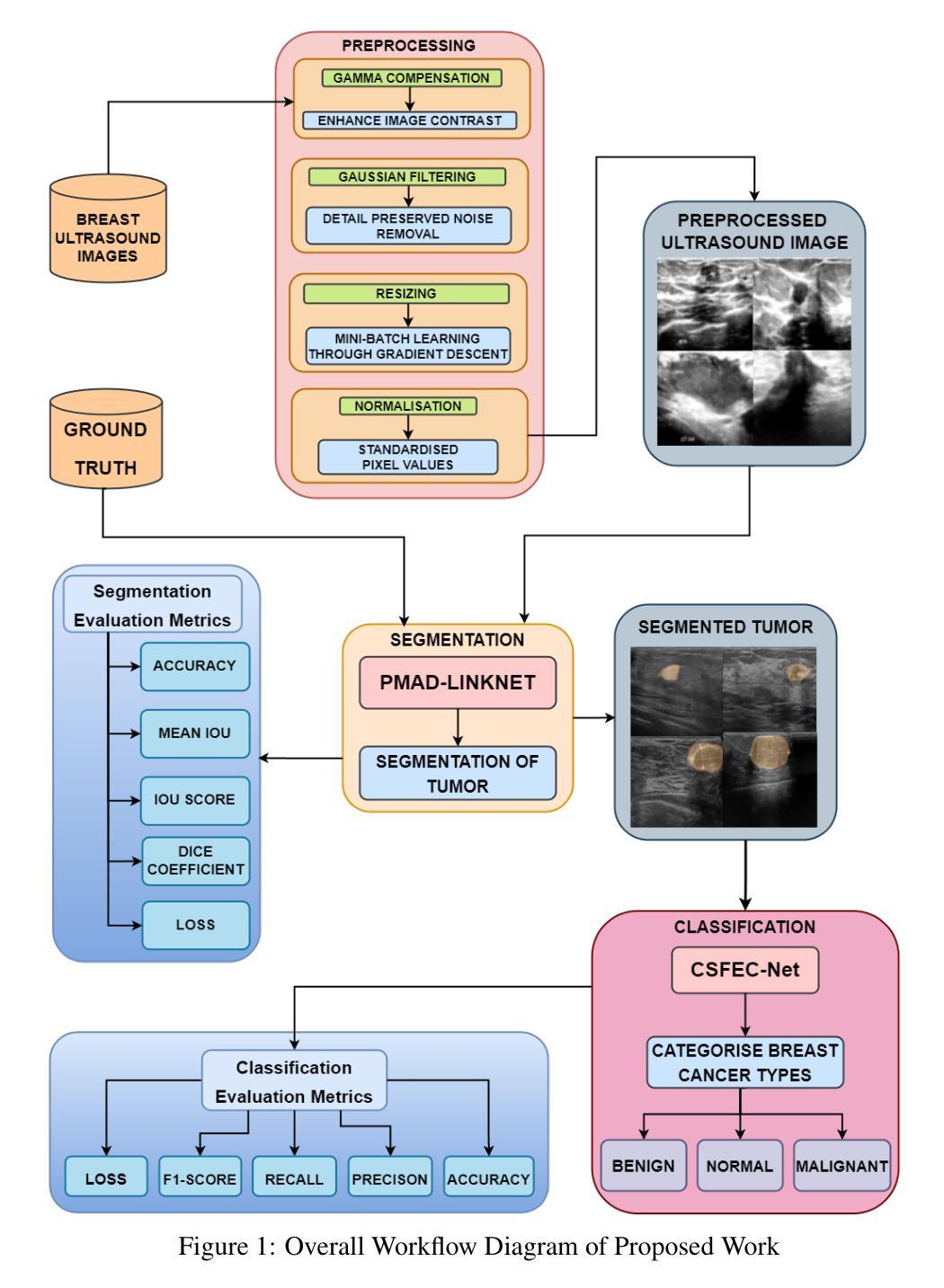
Exploiting Precision Mapping and Component-Specific Feature Enhancement for Breast Cancer Segmentation and Identification
Authors:Pandiyaraju V, Shravan Venkatraman, Pavan Kumar S, Santhosh Malarvannan, Kannan A
Breast cancer is one of the leading causes of death globally, and thus there is an urgent need for early and accurate diagnostic techniques. Although ultrasound imaging is a widely used technique for breast cancer screening, it faces challenges such as poor boundary delineation caused by variations in tumor morphology and reduced diagnostic accuracy due to inconsistent image quality. To address these challenges, we propose novel Deep Learning (DL) frameworks for breast lesion segmentation and classification. We introduce a precision mapping mechanism (PMM) for a precision mapping and attention-driven LinkNet (PMAD-LinkNet) segmentation framework that dynamically adapts spatial mappings through morphological variation analysis, enabling precise pixel-level refinement of tumor boundaries. Subsequently, we introduce a component-specific feature enhancement module (CSFEM) for a component-specific feature-enhanced classifier (CSFEC-Net). Through a multi-level attention approach, the CSFEM magnifies distinguishing features of benign, malignant, and normal tissues. The proposed frameworks are evaluated against existing literature and a diverse set of state-of-the-art Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) architectures. The obtained results show that our segmentation model achieves an accuracy of 98.1%, an IoU of 96.9%, and a Dice Coefficient of 97.2%. For the classification model, an accuracy of 99.2% is achieved with F1-score, precision, and recall values of 99.1%, 99.3%, and 99.1%, respectively.
乳腺癌是全球导致死亡的主要原因之一,因此急需早期且准确的诊断技术。虽然超声成像广泛用于乳腺癌筛查,但它仍面临着由于肿瘤形态变化导致的边界划分不清以及图像质量不一致导致的诊断准确性降低等挑战。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了用于乳腺病灶分割和分类的新型深度学习(DL)框架。我们为精确映射和注意力驱动LinkNet(PMAD-LinkNet)分割框架引入了一种精度映射机制(PMM),通过形态变化分析动态适应空间映射,实现对肿瘤边界的精确像素级细化。接着,我们为组件特定特征增强分类器(CSFEC-Net)引入了一个组件特定特征增强模块(CSFEM)。通过多级注意力方法,CSFEM放大了良性、恶性和正常组织的区分特征。所提出的框架与现有文献和一系列先进的卷积神经网络(CNN)架构进行了评估比较。获得的结果显示,我们的分割模型达到了98.1%的准确率,96.9%的IoU,以及97.2%的Dice系数。分类模型方面,使用F1分数、精确度、召回率分别达到了99.2%、99.1%、99.3%、和99.1%。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 27 pages, 18 figures, 6 tables
Summary
乳腺癌是全球主要的致死原因之一,因此早期准确诊断技术至关重要。针对超声成像在乳腺癌筛查中面临的挑战,如肿瘤形态变化导致的边界不清和图像质量不一致影响诊断准确度,我们提出了新型的深度学习框架进行乳腺病灶分割和分类。提出精准映射机制(PMM)和注意力驱动LinkNet(PMAD-LinkNet)分割框架,对肿瘤边界进行精确像素级优化。同时,引入组件特定特征增强模块(CSFEM)和组件特定特征增强分类器(CSFEC-Net),通过多层次注意力方法强化良、恶性和正常组织的辨识特征。评估结果显示,分割模型准确度达98.1%,IoU和Dice系数分别为96.9%和97.2%;分类模型准确度为99.2%,F1分数、精确度和召回率分别为99.1%、99.3%和99.1%。
Key Takeaways
- 乳腺癌是全球主要的健康问题,需要早期和准确的诊断技术。
- 超声成像在乳腺癌筛查中面临挑战,包括肿瘤形态变化和图像质量不一致。
- 引入新型深度学习框架进行乳腺病灶分割和分类。
- 精准映射机制(PMM)和注意力驱动LinkNet(PMAD-LinkNet)用于精确像素级优化肿瘤边界。
- 组件特定特征增强模块(CSFEM)强化良、恶性和正常组织的辨识特征。
- 分割模型评估结果:准确度98.1%,IoU 96.9%,Dice系数97.2%。
点此查看论文截图