⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-11 更新
Delve into Visual Contrastive Decoding for Hallucination Mitigation of Large Vision-Language Models
Authors:Yi-Lun Lee, Yi-Hsuan Tsai, Wei-Chen Chiu
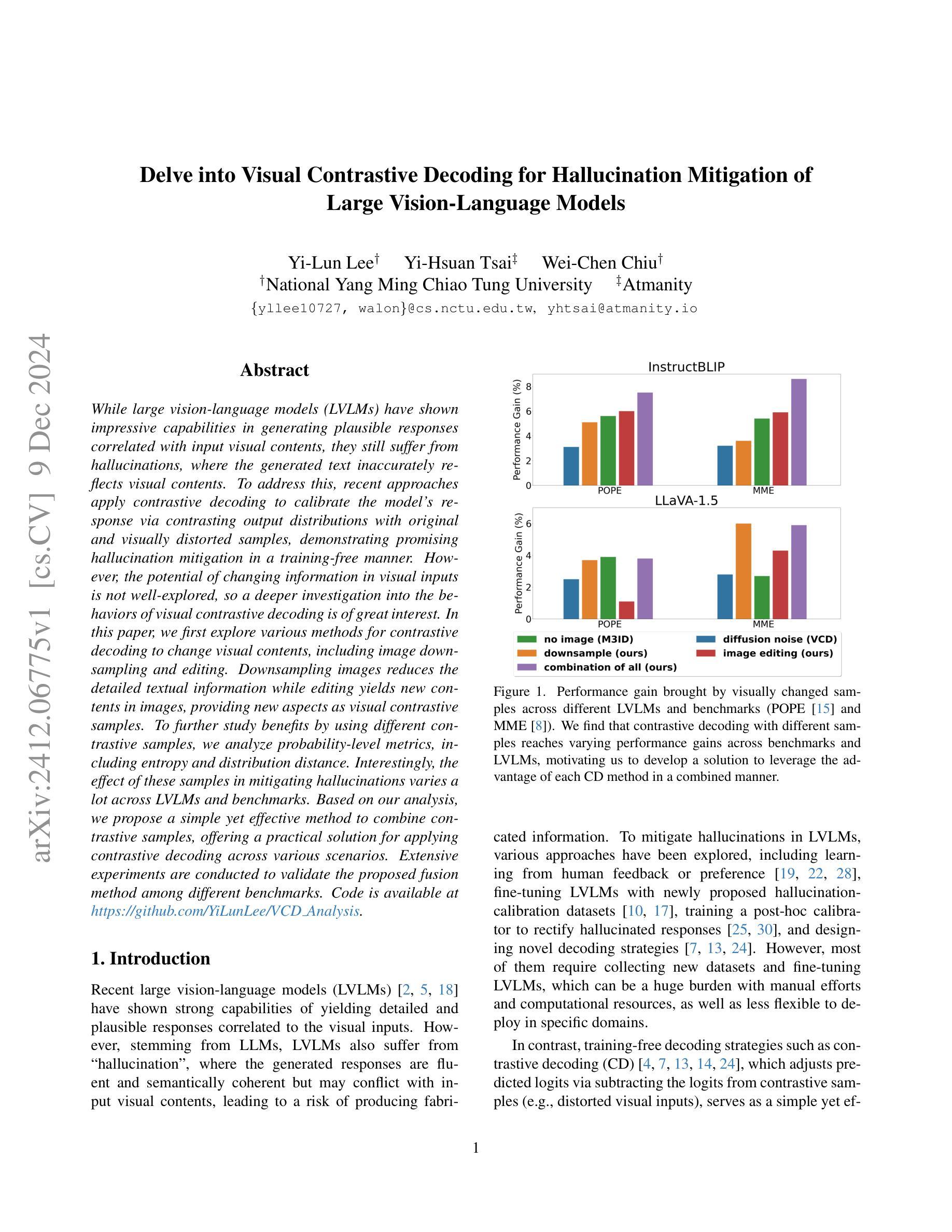
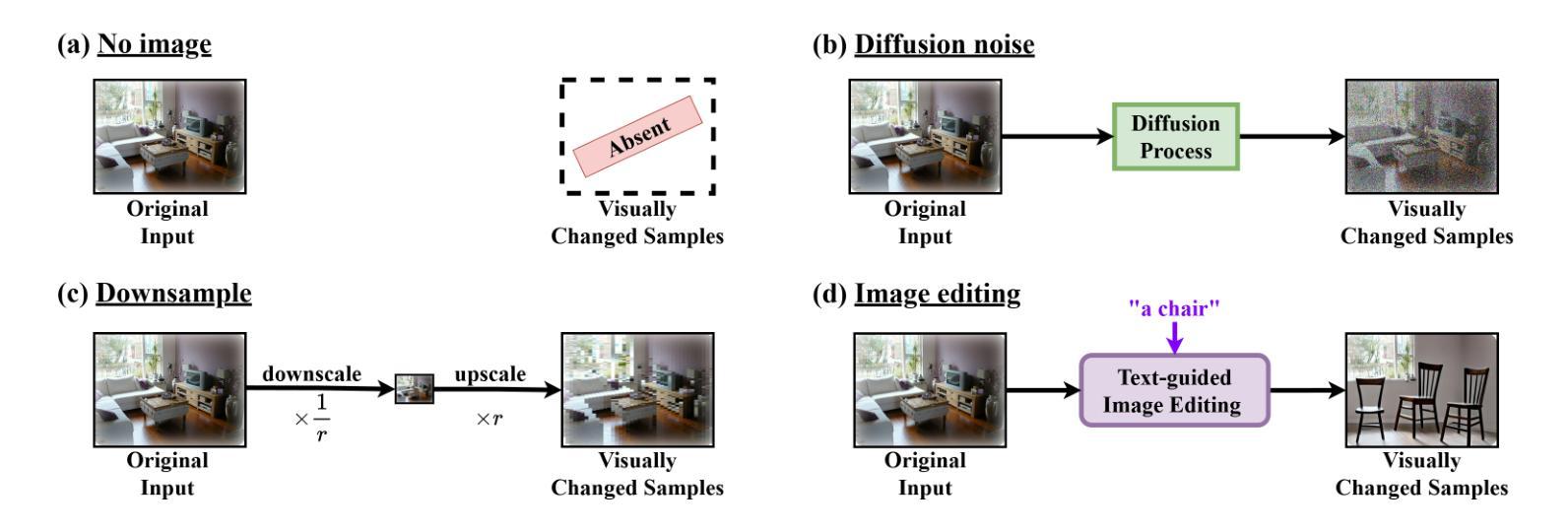
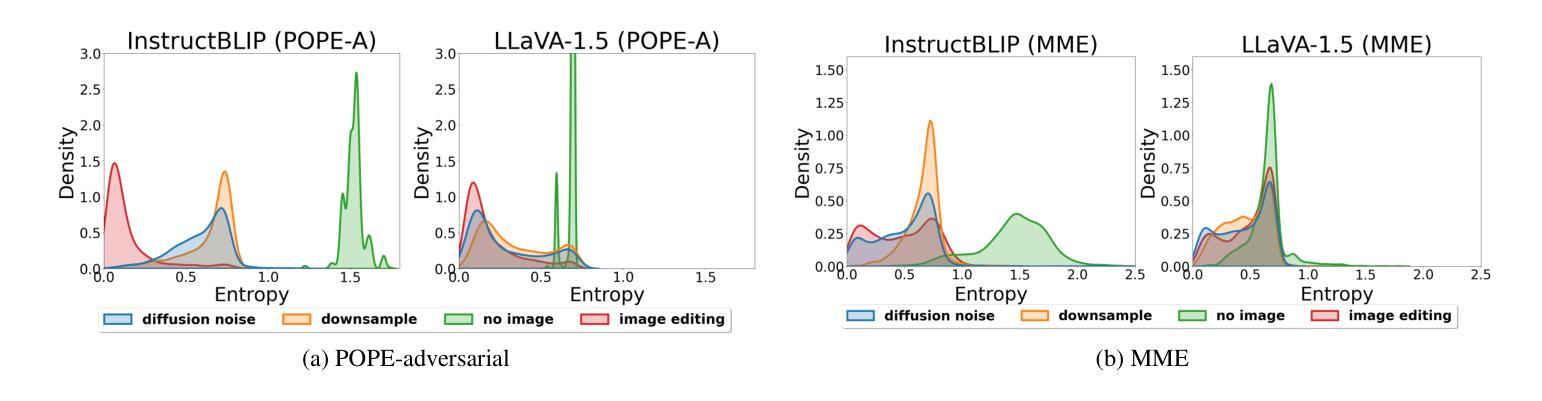
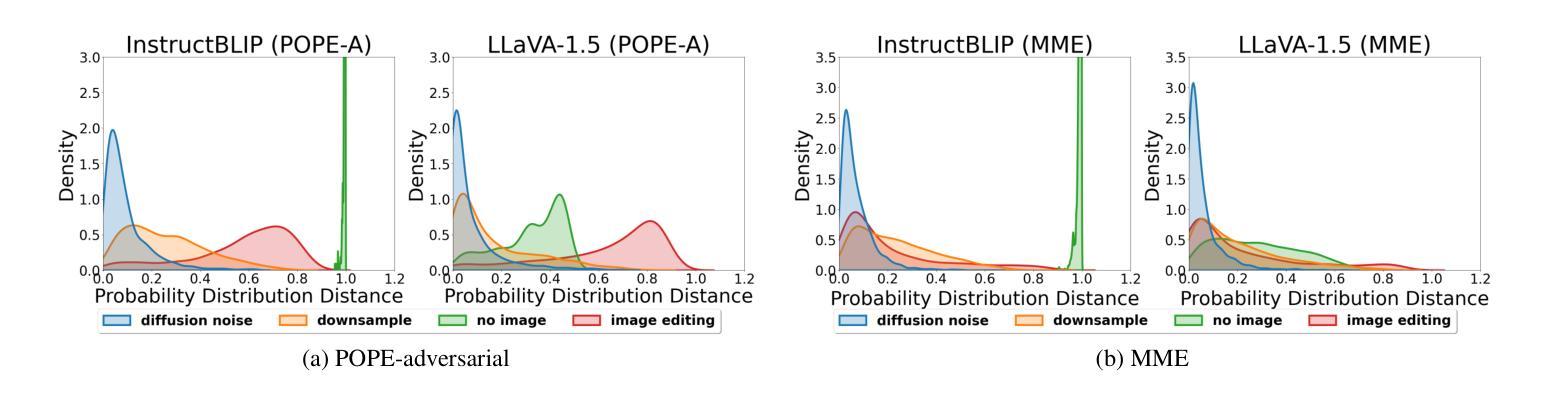
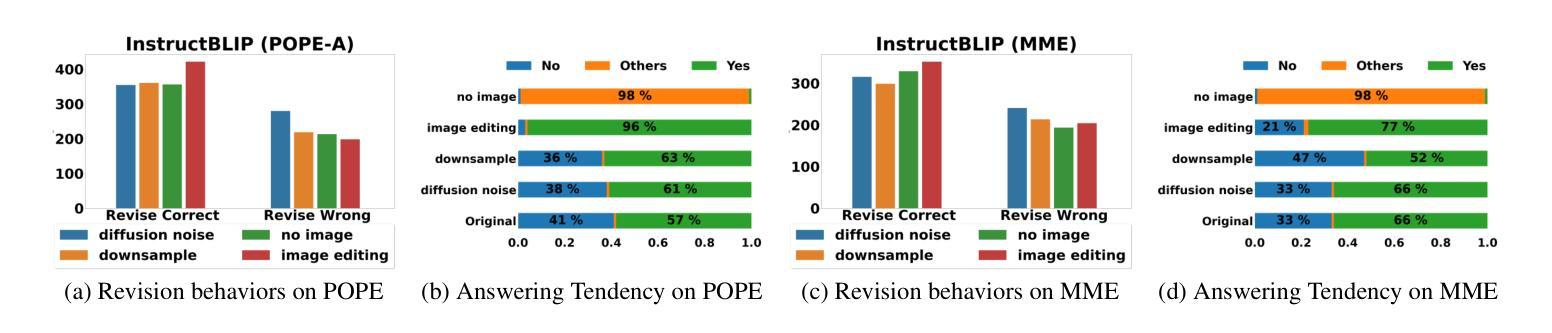
While large vision-language models (LVLMs) have shown impressive capabilities in generating plausible responses correlated with input visual contents, they still suffer from hallucinations, where the generated text inaccurately reflects visual contents. To address this, recent approaches apply contrastive decoding to calibrate the model’s response via contrasting output distributions with original and visually distorted samples, demonstrating promising hallucination mitigation in a training-free manner. However, the potential of changing information in visual inputs is not well-explored, so a deeper investigation into the behaviors of visual contrastive decoding is of great interest. In this paper, we first explore various methods for contrastive decoding to change visual contents, including image downsampling and editing. Downsampling images reduces the detailed textual information while editing yields new contents in images, providing new aspects as visual contrastive samples. To further study benefits by using different contrastive samples, we analyze probability-level metrics, including entropy and distribution distance. Interestingly, the effect of these samples in mitigating hallucinations varies a lot across LVLMs and benchmarks. Based on our analysis, we propose a simple yet effective method to combine contrastive samples, offering a practical solution for applying contrastive decoding across various scenarios. Extensive experiments are conducted to validate the proposed fusion method among different benchmarks.
大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在生成与输入视觉内容相关的合理响应方面展现出了令人印象深刻的能力,但它们仍然受到幻觉的影响,即生成的文本不能准确地反映视觉内容。为了解决这个问题,最近的方法采用对比解码,通过对比输出分布与原始和视觉失真样本,以无需训练的方式展示出了有前景的幻觉减轻效果。然而,视觉输入中改变信息的潜力尚未得到很好的探索,因此深入探讨视觉对比解码的行为具有重要意义。在本文中,我们首先探索了各种对比解码方法来改变视觉内容,包括图像下采样和编辑。下采样图像会减少详细的文本信息,而编辑则会在图像中产生新的内容,作为视觉对比样本提供了新的视角。为了进一步研究使用不同对比样本的好处,我们分析了概率级别的指标,包括熵和分布距离。有趣的是,这些样本在减轻幻觉方面的效果在LVLMs和基准测试中的表现差异很大。基于我们的分析,我们提出了一种简单有效的结合对比样本的方法,为在各种场景下应用对比解码提供了实用解决方案。进行了大量实验来验证在不同基准测试中提出的融合方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review. Project pages: https://github.com/YiLunLee/VCD_Analysis
Summary
本文探索了对比解码在视觉内容改变方面的应用,包括图像下采样和编辑。通过对比解码,使用原始和视觉扭曲的样本对比输出分布,以减轻视觉语言模型在大规模数据集上的生成文本的不准确性问题。研究深入分析了对比样本的不同表现形式及其影响,提出了一种简单有效的结合对比样本的方法,用于在各种场景中应用对比解码。实验验证了该方法在不同基准测试中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 对比解码用于通过对比输出分布与原始和视觉扭曲的样本来校准模型的响应,显示出有前景的无训练减轻幻觉的能力。
- 研究了改变视觉输入信息的潜力,探索了对比解码在视觉内容改变方面的不同方法,包括图像下采样和编辑。
- 图像下采样减少了文本细节信息,而编辑则产生新的图像内容,为对比解码提供了新视角的样本。
- 通过分析概率度量(如熵和分布距离),探讨了不同对比样本的利益。对比样本在减轻幻觉方面的效果在大型视觉语言模型和基准测试中差异很大。
- 提出了一种简单有效的结合对比样本的方法,适用于各种场景中的对比解码应用。
- 广泛的实验验证了所提融合方法在不同基准测试中的有效性。
点此查看论文截图
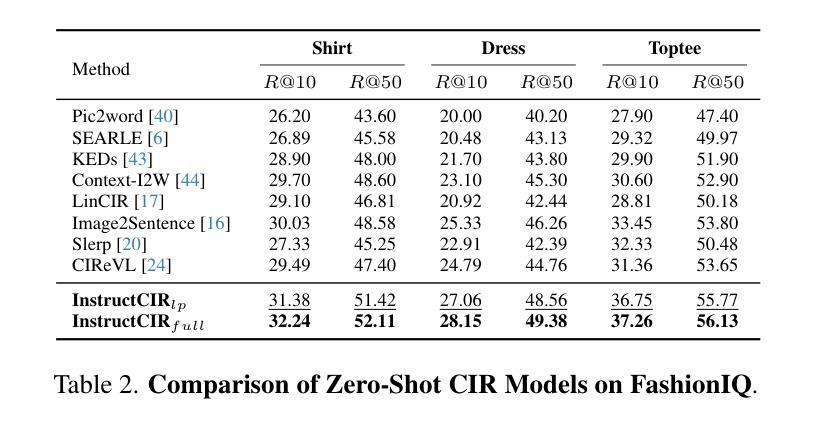
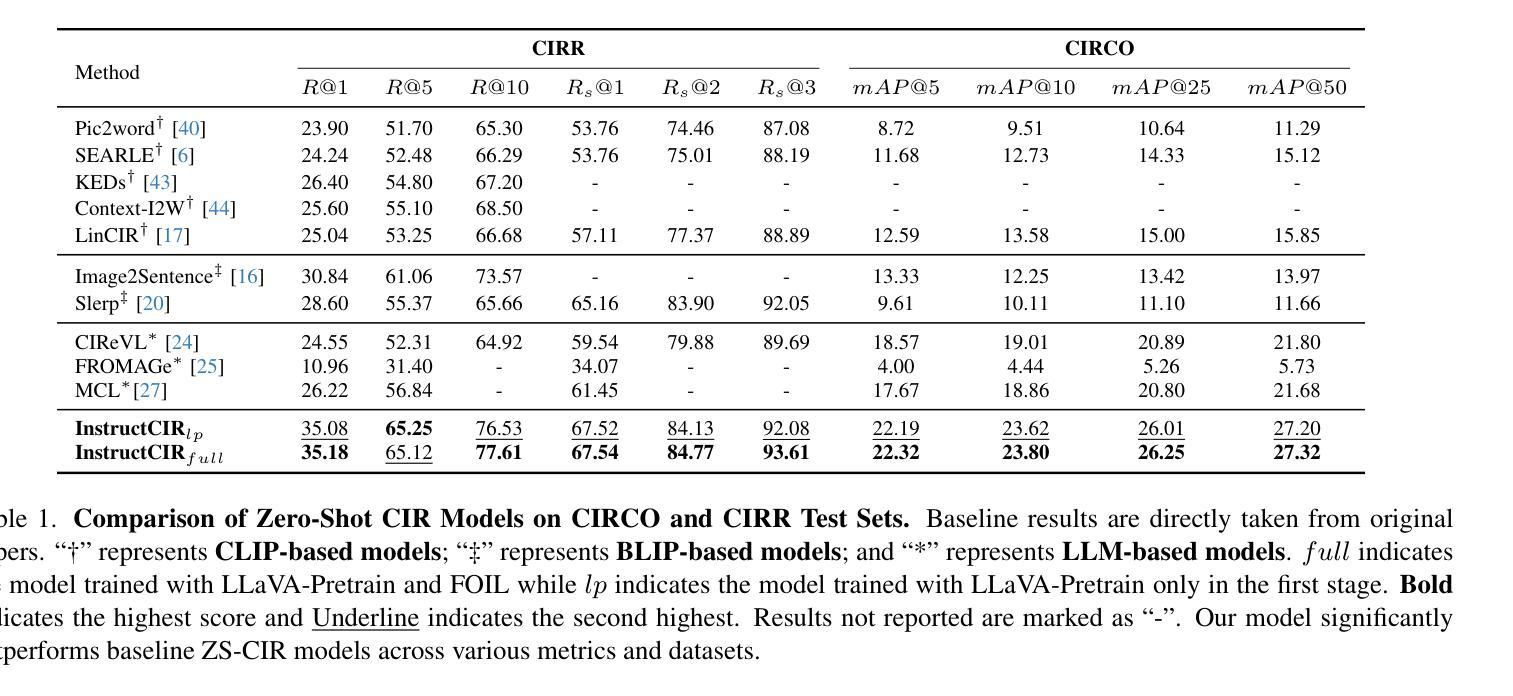
Compositional Image Retrieval via Instruction-Aware Contrastive Learning
Authors:Wenliang Zhong, Weizhi An, Feng Jiang, Hehuan Ma, Yuzhi Guo, Junzhou Huang
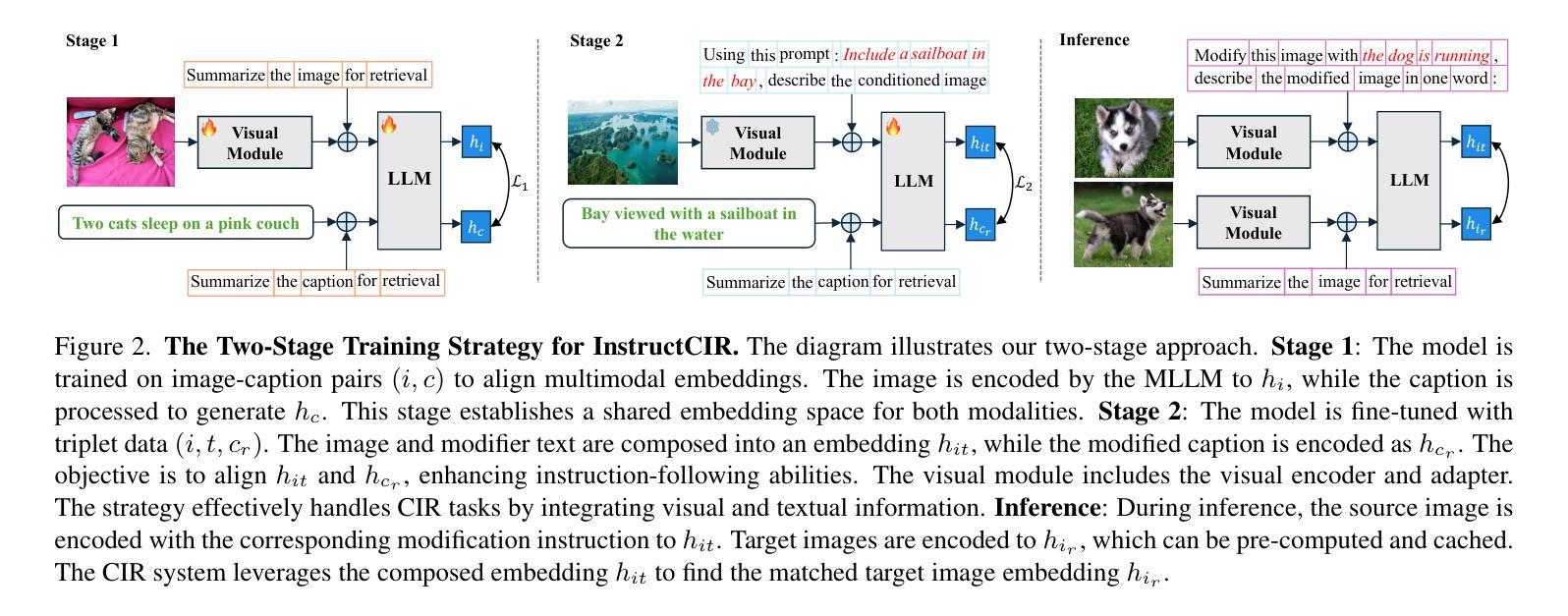
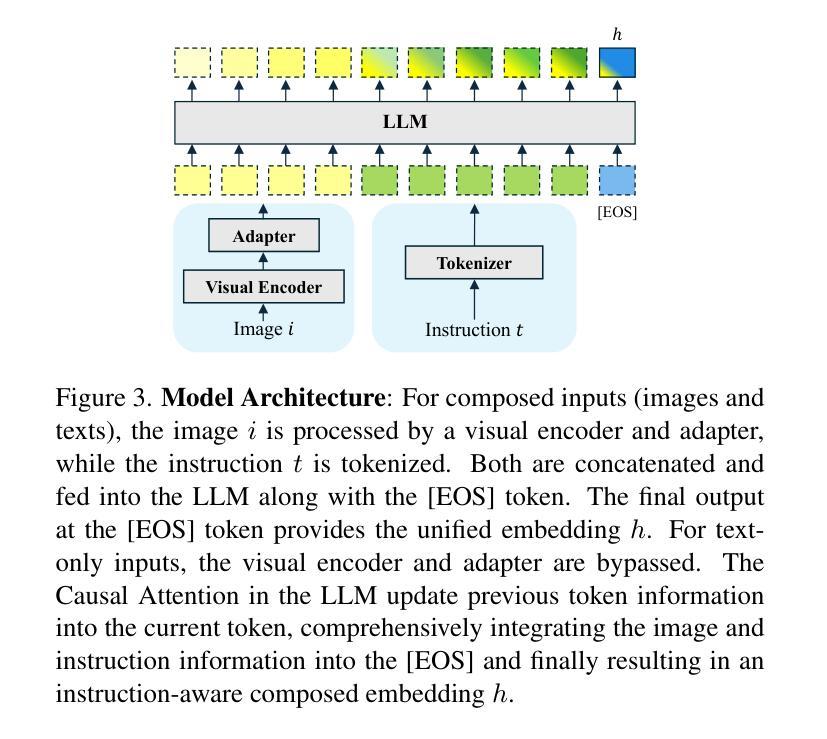
Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) involves retrieving a target image based on a composed query of an image paired with text that specifies modifications or changes to the visual reference. CIR is inherently an instruction-following task, as the model needs to interpret and apply modifications to the image. In practice, due to the scarcity of annotated data in downstream tasks, Zero-Shot CIR (ZS-CIR) is desirable. While existing ZS-CIR models based on CLIP have shown promising results, their capability in interpreting and following modification instructions remains limited. Some research attempts to address this by incorporating Large Language Models (LLMs). However, these approaches still face challenges in effectively integrating multimodal information and instruction understanding. To tackle above challenges, we propose a novel embedding method utilizing an instruction-tuned Multimodal LLM (MLLM) to generate composed representation, which significantly enhance the instruction following capability for a comprehensive integration between images and instructions. Nevertheless, directly applying MLLMs introduces a new challenge since MLLMs are primarily designed for text generation rather than embedding extraction as required in CIR. To address this, we introduce a two-stage training strategy to efficiently learn a joint multimodal embedding space and further refining the ability to follow modification instructions by tuning the model in a triplet dataset similar to the CIR format. Extensive experiments on four public datasets: FashionIQ, CIRR, GeneCIS, and CIRCO demonstrates the superior performance of our model, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines by a significant margin. Codes are available at the GitHub repository.
组成图像检索(CIR)是根据由图像和文本组成的查询来检索目标图像,该文本指定对视觉参考的修改或更改。CIR本质上是一个遵循指令的任务,因为模型需要解释并应用对图像的修改。在实践中,由于下游任务中标注数据的稀缺性,零样本组成图像检索(ZS-CIR)是理想的解决方案。虽然基于CLIP的现有ZS-CIR模型已经显示出有希望的结果,但它们在解释和遵循修改指令方面的能力仍然有限。一些研究试图通过融入大型语言模型(LLM)来解决这个问题。然而,这些方法在有效整合多模式信息和指令理解方面仍面临挑战。为了应对上述挑战,我们提出了一种新的嵌入方法,利用经过指令训练的多媒体LLM(MLLM)生成组成表示,这显著提高了遵循指令的能力,实现了图像和指令之间的全面集成。然而,直接应用MLLMs带来了新的挑战,因为MLLMs主要设计用于文本生成,而不是如CIR所需的嵌入提取。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了一种两阶段训练策略,以有效地学习联合多模式嵌入空间,并通过在类似CIR格式的三元组数据集上调整模型,进一步改善遵循修改指令的能力。在四个公共数据集FashionIQ、CIRR、GeneCIS和CIRCO上的广泛实验表明,我们的模型性能卓越,大大超越了最新基准模型。代码可在GitHub仓库中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文提出了利用指令微调的多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)生成组合表示的新嵌入方法,该方法能显著提升模型遵循指令的能力,实现了图像和指令之间的全面整合。为应对直接使用MLLM的挑战,采用两阶段训练策略,高效学习联合多模态嵌入空间,并通过在类似CIR格式的三元组数据集上进行微调,进一步提升遵循修改指令的能力。在四个公开数据集上的实验表明,该方法显著优于现有技术基线。
Key Takeaways
- Composed Image Retrieval (CIR)允许基于图像与指定修改或变化文本的配对组合查询来检索目标图像。
- CIR本质上是遵循指令的任务,需要模型解释并应用对图像的修改。
- 零样本CIR(ZS-CIR)因下游任务中标注数据的稀缺性而具有吸引力。
- 现有基于CLIP的ZS-CIR模型在解释和遵循修改指令方面的能力有限。
- 引入多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)来解决这一问题,但仍面临有效整合多模态信息和指令理解方面的挑战。
- 提出新型嵌入方法,利用指令调教的MLLM生成组合表示,显著增强模型遵循指令的能力。
点此查看论文截图

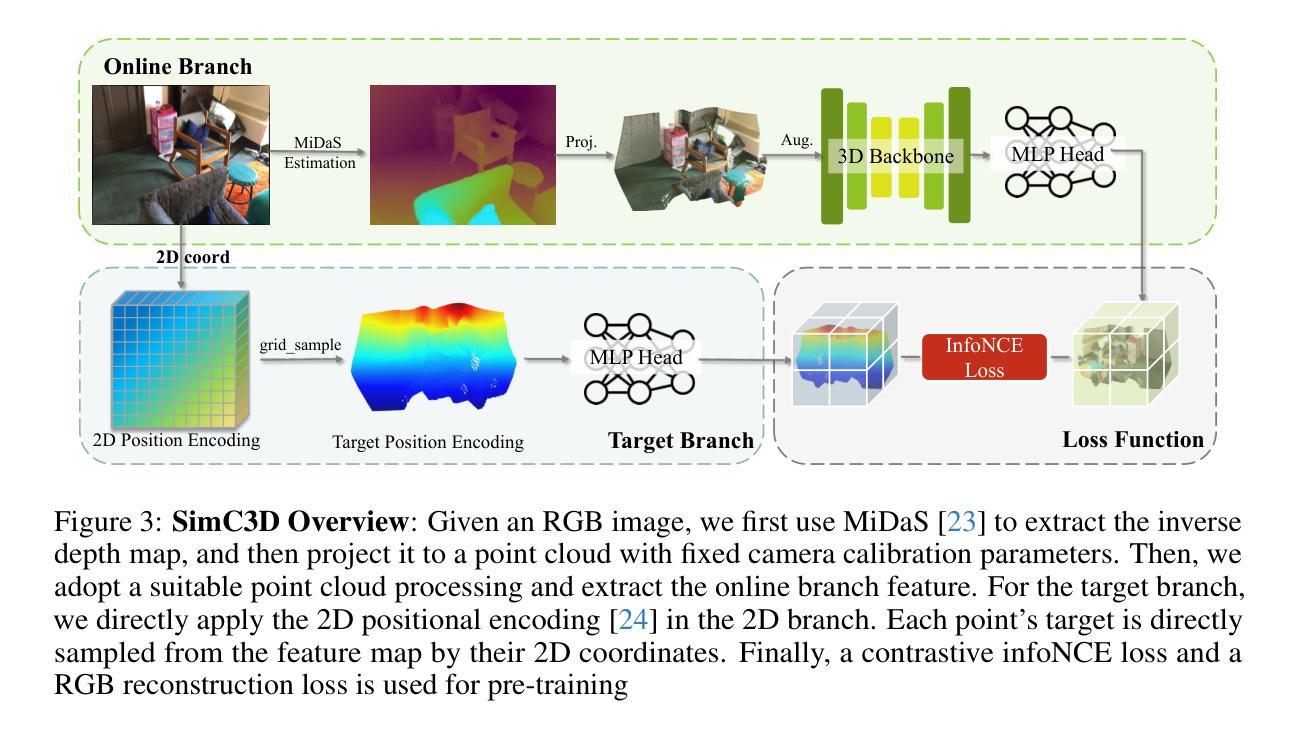
SimC3D: A Simple Contrastive 3D Pretraining Framework Using RGB Images
Authors:Jiahua Dong, Tong Wu, Rui Qian, Jiaqi Wang
The 3D contrastive learning paradigm has demonstrated remarkable performance in downstream tasks through pretraining on point cloud data. Recent advances involve additional 2D image priors associated with 3D point clouds for further improvement. Nonetheless, these existing frameworks are constrained by the restricted range of available point cloud datasets, primarily due to the high costs of obtaining point cloud data. To this end, we propose SimC3D, a simple but effective 3D contrastive learning framework, for the first time, pretraining 3D backbones from pure RGB image data. SimC3D performs contrastive 3D pretraining with three appealing properties. (1) Pure image data: SimC3D simplifies the dependency of costly 3D point clouds and pretrains 3D backbones using solely RBG images. By employing depth estimation and suitable data processing, the monocular synthesized point cloud shows great potential for 3D pretraining. (2) Simple framework: Traditional multi-modal frameworks facilitate 3D pretraining with 2D priors by utilizing an additional 2D backbone, thereby increasing computational expense. In this paper, we empirically demonstrate that the primary benefit of the 2D modality stems from the incorporation of locality information. Inspired by this insightful observation, SimC3D directly employs 2D positional embeddings as a stronger contrastive objective, eliminating the necessity for 2D backbones and leading to considerable performance improvements. (3) Strong performance: SimC3D outperforms previous approaches that leverage ground-truth point cloud data for pretraining in various downstream tasks. Furthermore, the performance of SimC3D can be further enhanced by combining multiple image datasets, showcasing its significant potential for scalability. The code will be available at https://github.com/Dongjiahua/SimC3D.
3D对比学习范式通过在点云数据上进行预训练,在下游任务中表现出了卓越的性能。最近的进展涉及与3D点云相关的额外2D图像先验,以进一步提高性能。然而,这些现有框架受到可用点云数据集范围有限的限制,主要是由于获取点云数据的成本很高。为此,我们提出了SimC3D,这是一个简单有效的3D对比学习框架,首次从纯RGB图像数据对3D主干网进行预训练。SimC3D进行3D对比预训练时具有三个吸引人的特点。(1)纯图像数据:SimC3D简化了对昂贵的3D点云的依赖,仅使用RGB图像对3D主干网进行预训练。通过深度估计和合适的数据处理,单目合成点云在3D预训练中具有很大潜力。(2)简单的框架:传统的多模态框架通过利用额外的2D先验知识来促进3D预训练,从而增加了计算成本。在本文中,我们通过实证研究证明,2D模态的主要优势来自于局部信息的融合。受这一见解的启发,SimC3D直接采用2D位置嵌入作为更强的对比目标,消除了对2D主干的依赖,并带来了显著的性能改进。(3)卓越性能:在各种下游任务中,SimC3D超越了以前那些利用真实点云数据进行预训练的方法。此外,通过结合多个图像数据集,SimC3D的性能可以得到进一步提升,展示了其可扩展性的显著潜力。代码将在https://github.com/Dongjiahua/SimC3D上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个名为SimC3D的简单的3D对比学习框架,它能够从纯粹的RGB图像数据中预训练3D骨架。该框架具有三个吸引人的特性:纯图像数据、简单的框架和强大的性能。SimC3D简化了对昂贵3D点云数据的依赖,利用深度估计和适当的数据处理,从单目合成点云中预训练3D骨架。此外,SimC3D直接采用2D位置嵌入作为更强的对比目标,不需要额外的2D骨架,实现了显著的性能提升。在多种下游任务中,SimC3D超越了利用真实点云数据进行预训练的前瞻方法。结合多个图像数据集,SimC3D的性能可以得到进一步提升。
Key Takeaways
- SimC3D是一个新的3D对比学习框架,可以从纯粹的RGB图像数据中预训练3D骨架。
- SimC3D简化了对高成本点云数据的依赖,通过深度估计和数据处理从单目合成点云进行预训练。
- SimC3D利用简单的框架设计直接采用2D位置嵌入作为对比目标,提高了性能且不需要额外的2D骨架。
- SimC3D在多种下游任务中表现出强大的性能,超越了使用真实点云数据进行预训练的方法。
- 结合多个图像数据集可以进一步提升SimC3D的性能,显示出其可扩展性的潜力。
- SimC3D的代码将在https://github.com/Dongjiahua/SimC3D上提供。这对于研究者和开发者进一步了解和使用该方法至关重要。
点此查看论文截图


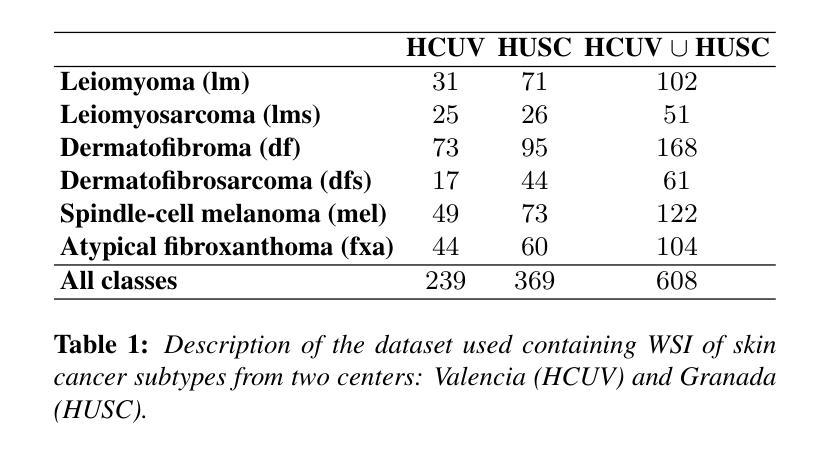
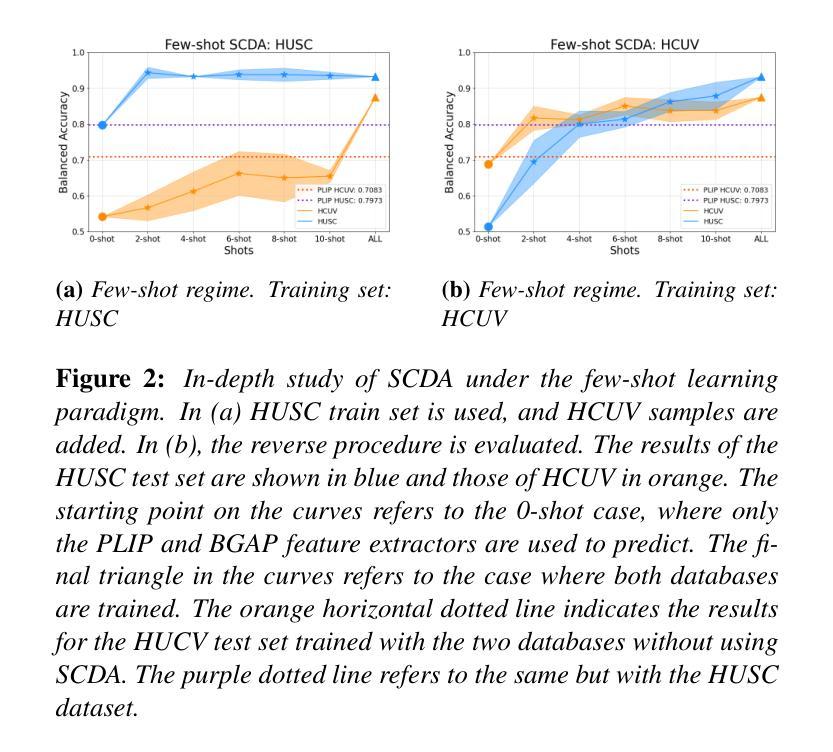
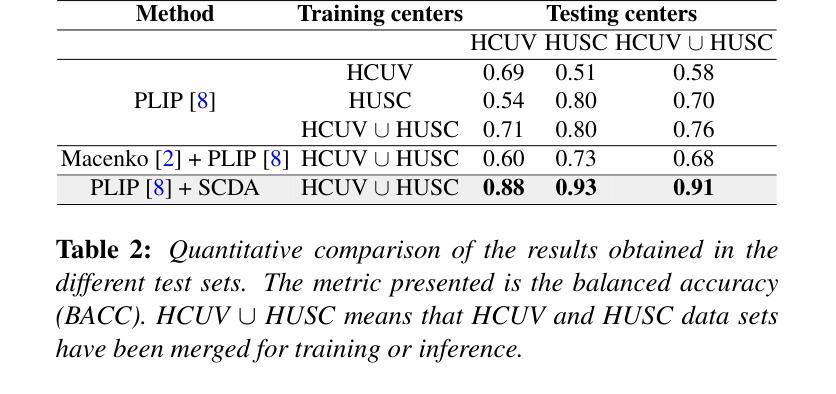
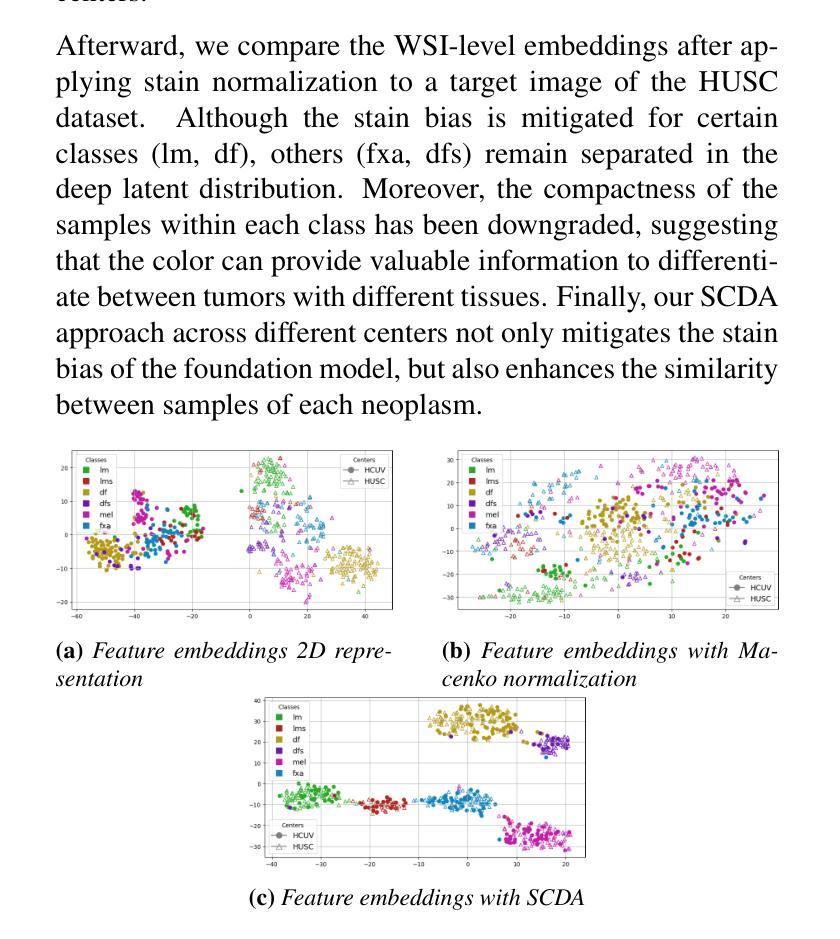
Enhancing Whole Slide Image Classification through Supervised Contrastive Domain Adaptation
Authors:Ilán Carretero, Pablo Meseguer, Rocío del Amor, Valery Naranjo
Domain shift in the field of histopathological imaging is a common phenomenon due to the intra- and inter-hospital variability of staining and digitization protocols. The implementation of robust models, capable of creating generalized domains, represents a need to be solved. In this work, a new domain adaptation method to deal with the variability between histopathological images from multiple centers is presented. In particular, our method adds a training constraint to the supervised contrastive learning approach to achieve domain adaptation and improve inter-class separability. Experiments performed on domain adaptation and classification of whole-slide images of six skin cancer subtypes from two centers demonstrate the method’s usefulness. The results reflect superior performance compared to not using domain adaptation after feature extraction or staining normalization.
病理成像领域中的域偏移现象很常见,这是由于各医院内部和之间的染色和数字化协议存在差异性。实施能够创建通用域的强大模型代表了一种需要解决的问题。在这项工作中,提出了一种新的域适应方法来处理来自多个中心的病理图像之间的差异。特别是,我们的方法为监督对比学习方法增加了训练约束,以实现域适应并改善类间可分性。对来自两个中心的六种皮肤癌亚型的全幻灯片图像进行的域适应和分类实验证明了该方法的有效性。结果表明,与在特征提取或染色归一化后不使用域适应相比,该方法具有卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in CASEIB 2024
Summary
本文介绍了针对多中心病理图像领域偏移问题的一种新的域适应方法。该方法通过添加训练约束到监督对比学习来实现域适应,提高类间可分性。实验证明该方法在跨中心皮肤癌全切片图像分类中的有效性,相较于特征提取后不使用域适应或仅进行染色标准化处理,该方法表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 病理图像领域存在由于不同医院染色和数字化协议导致的域偏移问题。
- 介绍了一种新的域适应方法,用于处理来自多个中心的病理图像间的差异。
- 方法基于监督对比学习,通过添加训练约束实现域适应和类间可分性的提高。
- 实验在跨中心皮肤癌全切片图像分类中验证了该方法的有效性。
- 与其他处理方法相比,该方法在性能上表现出优越性。
- 该方法有助于创建通用化的模型,能够适应不同来源的病理图像。
点此查看论文截图

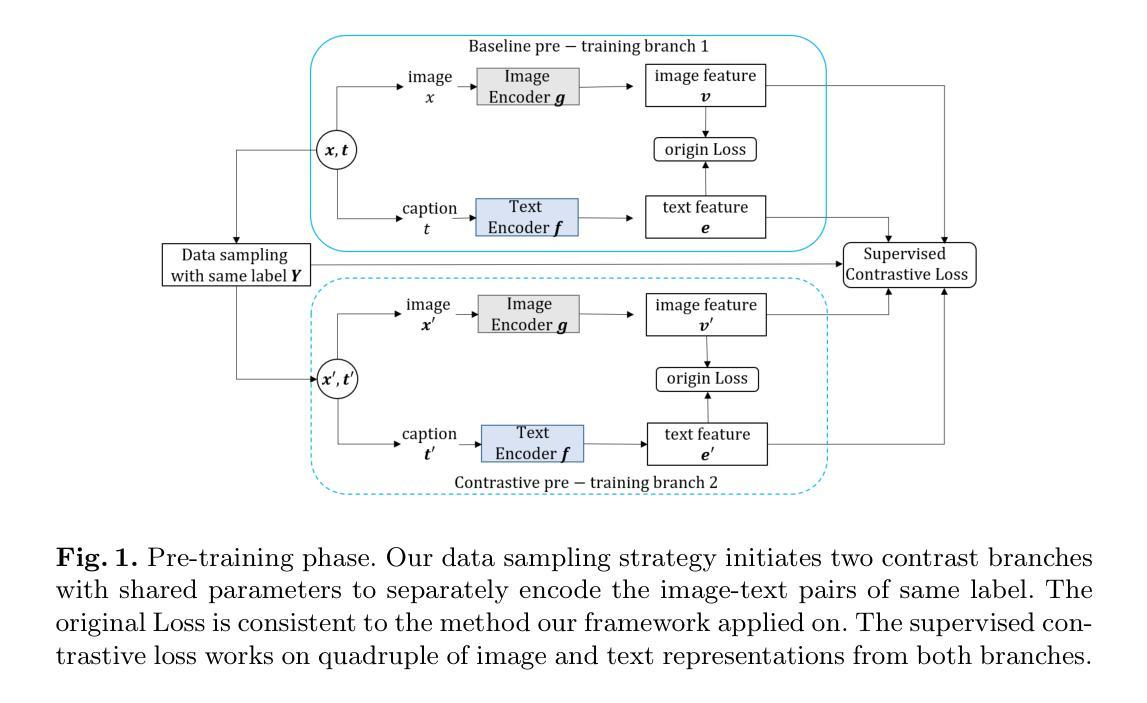
A Framework For Image Synthesis Using Supervised Contrastive Learning
Authors:Yibin Liu, Jianyu Zhang, Li Zhang, Shijian Li, Gang Pan
Text-to-image (T2I) generation aims at producing realistic images corresponding to text descriptions. Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) has proven to be successful in this task. Typical T2I GANs are 2 phase methods that first pretrain an inter-modal representation from aligned image-text pairs and then use GAN to train image generator on that basis. However, such representation ignores the inner-modal semantic correspondence, e.g. the images with same label. The semantic label in priory describes the inherent distribution pattern with underlying cross-image relationships, which is supplement to the text description for understanding the full characteristics of image. In this paper, we propose a framework leveraging both inter- and inner-modal correspondence by label guided supervised contrastive learning. We extend the T2I GANs to two parameter-sharing contrast branches in both pretraining and generation phases. This integration effectively clusters the semantically similar image-text pair representations, thereby fostering the generation of higher-quality images. We demonstrate our framework on four novel T2I GANs by both single-object dataset CUB and multi-object dataset COCO, achieving significant improvements in the Inception Score (IS) and Frechet Inception Distance (FID) metrics of imagegeneration evaluation. Notably, on more complex multi-object COCO, our framework improves FID by 30.1%, 27.3%, 16.2% and 17.1% for AttnGAN, DM-GAN, SSA-GAN and GALIP, respectively. We also validate our superiority by comparing with other label guided T2I GANs. The results affirm the effectiveness and competitiveness of our approach in advancing the state-of-the-art GAN for T2I generation
文本到图像(T2I)生成旨在根据文本描述生成逼真的图像。生成对抗网络(GAN)在此任务中已证明是成功的。典型的T2I GANs是两阶段的方法,首先根据对齐的图像-文本对预训练一个跨模态表示,然后在此基础上使用GAN训练图像生成器。然而,这种表示忽略了内模态语义对应关系,例如具有相同标签的图像。先验的语义标签描述了图像之间关系的内在分布模式,这是对文本描述理解图像完整特征的补充。在本文中,我们提出了一个利用跨模态和内模态对应关系的框架,通过标签引导的监督对比学习。我们将T2I GANs扩展到预训练和生成阶段的两个共享参数的对比分支。这种集成有效地聚类了语义相似的图像-文本对表示,从而促进了更高质量图像的生成。我们在单对象数据集CUB和多对象数据集COCO上的四个新型T2I GANs上展示了我们的框架,在图像生成的评估指标Inception Score(IS)和Frechet Inception Distance(FID)上取得了显著的改进。值得注意的是,在更复杂的多对象COCO上,我们的框架分别将AttnGAN、DM-GAN、SSA-GAN和GALIP的FID提高了30.1%、27.3%、16.2%和17.1%。我们还通过与其他标签引导的T2I GANs进行比较来验证我们的优越性。结果证实了我们方法在推进先进GAN进行T2I生成方面的有效性和竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本生成图像(T2I)旨在根据文本描述生成逼真的图像。生成对抗网络(GAN)在此任务中取得了成功。典型的T2I GANs是分为两个阶段的方法,首先根据对齐的图像文本对进行跨模态表示预训练,然后在该基础上使用GAN训练图像生成器。然而,这种表示方法忽略了同一模态内部语义的对应关系,例如具有相同标签的图像之间的对应关系。这种语义标签能够描述图像内在的分布模式以及潜在的跨图像关系,这对于理解图像的全貌是对文本描述的补充。本文提出了一个利用跨模态和模态内部对应关系的框架,通过标签引导的监督对比学习实现这一点。本文将T2I GANs扩展到预训练和生成阶段的两个共享参数对比分支。这种集成有效地聚类了语义上相似的图像文本对表示,从而促进生成更高质量的图像。在单目标数据集CUB和多目标数据集COCO上的四种新型T2I GANs上验证了我们的框架,在图像生成的Inception Score(IS)和Frechet Inception Distance(FID)指标上取得了显著改进。特别是在更复杂的多目标COCO数据集上,我们的框架在AttnGAN、DM-GAN、SSA-GAN和GALIP上的FID分别提高了30.1%、27.3%、16.2%和17.1%。我们也通过与其他的标签引导的T2I GANs进行比较验证了我们的优越性,证明了我们的方法在推进文本生成图像领域的GAN技术方面的有效性和竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 文本生成图像(T2I)任务旨在基于文本描述生成真实图像,生成对抗网络(GAN)在此领域表现卓越。
- 现有T2I GANs方法主要依赖跨模态表示,但忽略了同一模态内部语义的对应关系。
- 语义标签对于描述图像的内在分布模式和潜在跨图像关系很重要,是对文本描述的补充。
- 本文提出了一个结合跨模态和模态内部对应关系的框架,通过标签引导的监督对比学习提升T2I GANs的性能。
- 框架在多种T2I GANs上进行验证,并在Inception Score(IS)和Frechet Inception Distance(FID)指标上取得显著改进。
- 在更复杂的多目标数据集COCO上,框架表现出较强的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

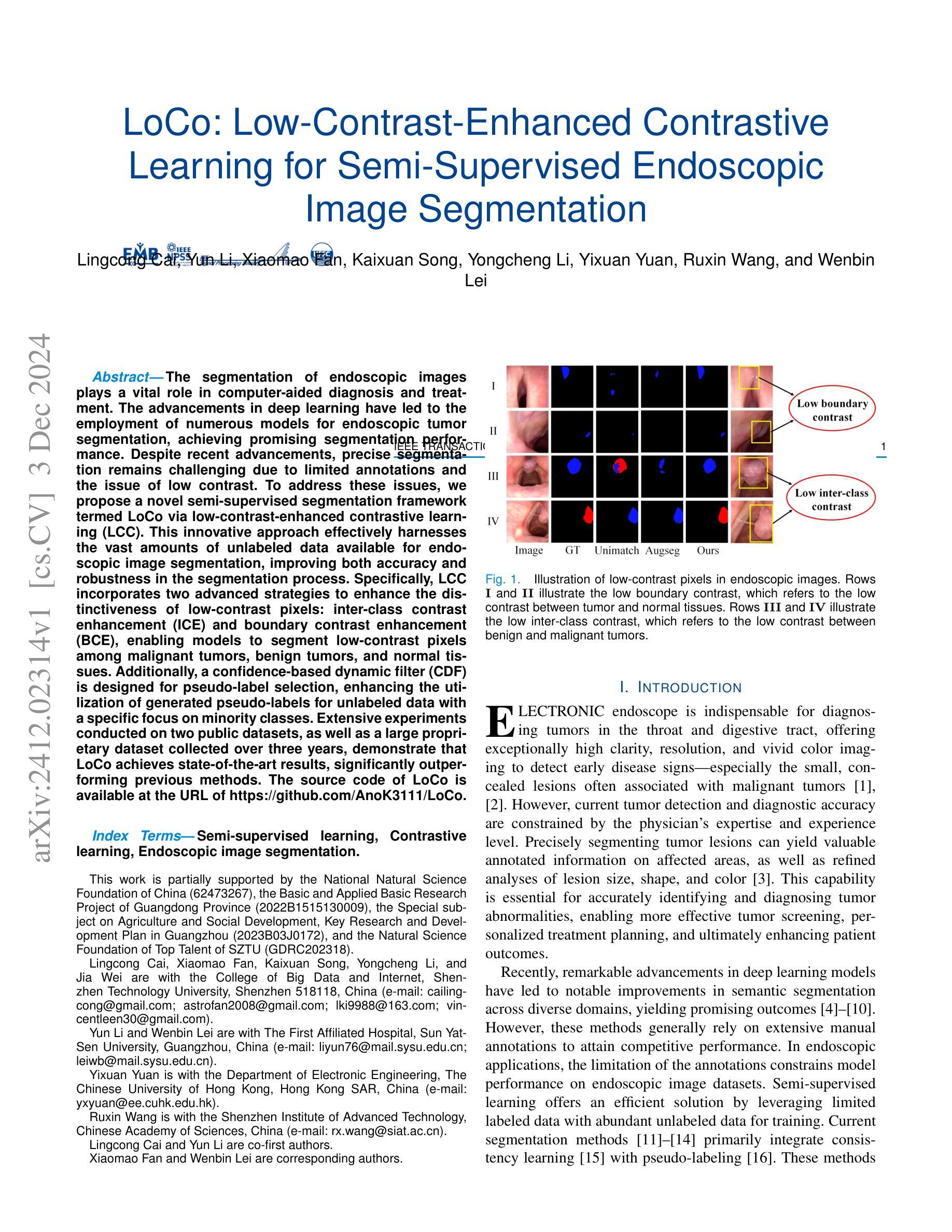
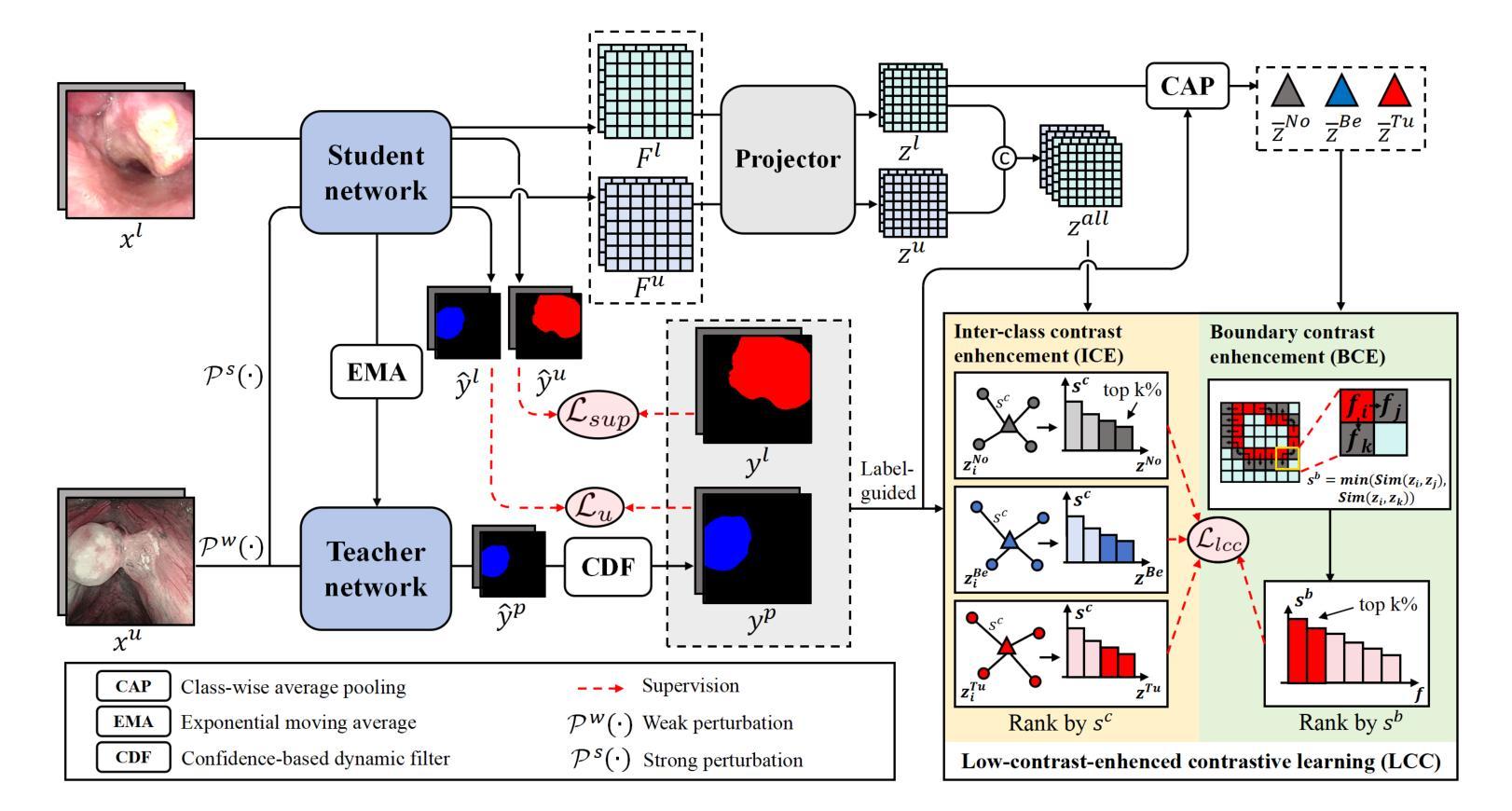
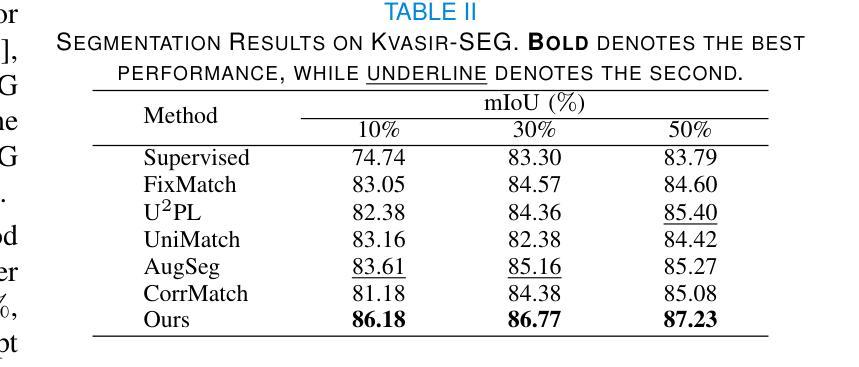
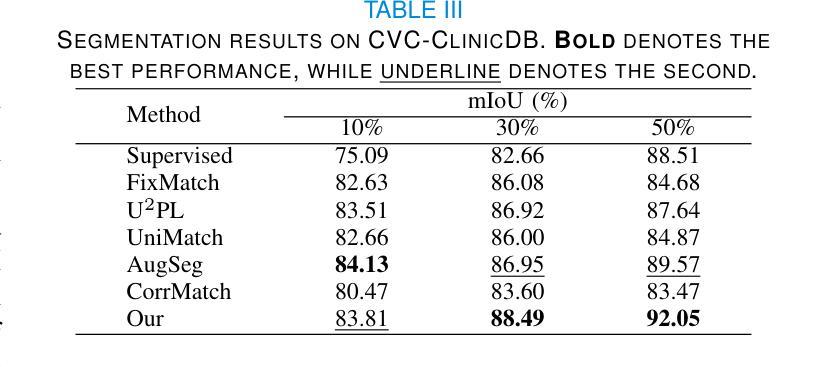
LoCo: Low-Contrast-Enhanced Contrastive Learning for Semi-Supervised Endoscopic Image Segmentation
Authors:Lingcong Cai, Yun Li, Xiaomao Fan, Kaixuan Song, Yongcheng Li, Yixuan Yuan, Ruxin Wang, Wenbin Lei
The segmentation of endoscopic images plays a vital role in computer-aided diagnosis and treatment. The advancements in deep learning have led to the employment of numerous models for endoscopic tumor segmentation, achieving promising segmentation performance. Despite recent advancements, precise segmentation remains challenging due to limited annotations and the issue of low contrast. To address these issues, we propose a novel semi-supervised segmentation framework termed LoCo via low-contrast-enhanced contrastive learning (LCC). This innovative approach effectively harnesses the vast amounts of unlabeled data available for endoscopic image segmentation, improving both accuracy and robustness in the segmentation process. Specifically, LCC incorporates two advanced strategies to enhance the distinctiveness of low-contrast pixels: inter-class contrast enhancement (ICE) and boundary contrast enhancement (BCE), enabling models to segment low-contrast pixels among malignant tumors, benign tumors, and normal tissues. Additionally, a confidence-based dynamic filter (CDF) is designed for pseudo-label selection, enhancing the utilization of generated pseudo-labels for unlabeled data with a specific focus on minority classes. Extensive experiments conducted on two public datasets, as well as a large proprietary dataset collected over three years, demonstrate that LoCo achieves state-of-the-art results, significantly outperforming previous methods. The source code of LoCo is available at the URL of https://github.com/AnoK3111/LoCo.
内镜图像的分割在计算机辅助诊断和治疗中起着至关重要的作用。深度学习的进步导致了多种内镜肿瘤分割模型的应用,并实现了有前景的分割性能。尽管最近有所进展,但由于标注有限和对比度低的问题,精确分割仍然具有挑战性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型半监督分割框架,名为LoCo,通过低对比度增强对比学习(LCC)实现。这种创新方法有效地利用了内镜图像分割中大量可用的未标记数据,提高了分割过程的准确性和稳健性。具体而言,LCC结合了两种先进策略,以提高低对比度像素的区分度:类间对比度增强(ICE)和边界对比度增强(BCE),使模型能够在恶性肿瘤、良性肿瘤和正常组织之间分割低对比度像素。此外,还设计了一种基于置信度的动态滤波器(CDF)进行伪标签选择,以提高生成的伪标签在未标记数据上的利用率,重点关注少数类。在两个公共数据集以及一个收集超过三年的专有数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,LoCo达到了最先进的性能,显著优于以前的方法。LoCo的源代码可在https://github.com/AnoK3111/LoCo获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为LoCo的半监督分割框架,该框架通过低对比增强对比学习(LCC)技术,有效地利用大量无标签数据进行内窥镜图像分割。LoCo采用两种策略增强低对比像素的辨别力,并实现高精度和稳健的分割。此外,设计了一种基于信心的动态过滤器(CDF)用于伪标签选择,提高生成的伪标签对未标记数据的利用率,特别是在少数类别上。在多个公共和专有数据集上的实验表明,LoCo取得了最先进的成果。
Key Takeaways
- LoCo是一个半监督分割框架,用于内窥镜图像分割。
- 利用低对比增强对比学习(LCC)技术,有效使用大量无标签数据。
- 采用两种策略:ICE和BCE,增强低对比像素的辨别力。
- 基于信心的动态过滤器(CDF)用于伪标签选择,提高未标记数据的利用率。
- LoCo在多个数据集上实现最先进的成果。
- LoCo源代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图
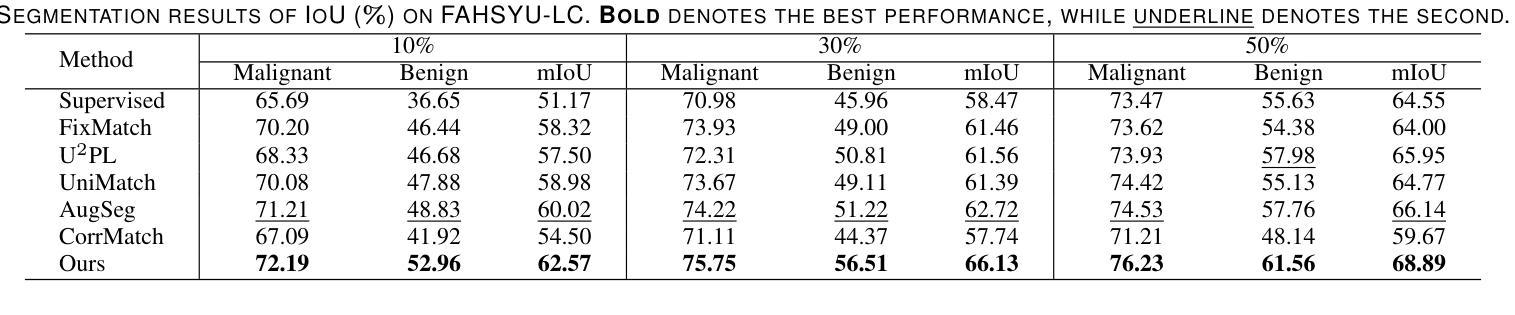
CLERF: Contrastive LEaRning for Full Range Head Pose Estimation
Authors:Ting-Ruen Wei, Haowei Liu, Huei-Chung Hu, Xuyang Wu, Yi Fang, Hsin-Tai Wu
We introduce a novel framework for representation learning in head pose estimation (HPE). Previously such a scheme was difficult due to head pose data sparsity, making triplet sampling infeasible. Recent progress in 3D generative adversarial networks (3D-aware GAN) has opened the door for easily sampling triplets (anchor, positive, negative). We perform contrastive learning on extensively augmented data including geometric transformations and demonstrate that contrastive learning allows networks to learn genuine features that contribute to accurate HPE. On the other hand, we observe that existing HPE works struggle to predict head poses as accurately when test image rotation matrices are slightly out of the training dataset distribution. Experiments show that our methodology performs on par with state-of-the-art models on standard test datasets and outperforms them when images are slightly rotated/ flipped or full range head pose. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to deliver a true full range HPE model capable of accurately predicting any head pose including upside-down pose. Furthermore, we compared with other existing full-yaw range models and demonstrated superior results.
我们引入了一种用于头部姿态估计(HPE)表示学习的新型框架。之前由于头部姿态数据稀疏,使得三元组采样变得不可行,因此难以实现这种方案。基于最近的三维生成对抗网络(3D感知GAN)的进步,可以轻松采样三元组(锚点、正样本、负样本)。我们对大量扩充的数据执行对比学习,包括几何变换,并证明对比学习可以使网络学习真实的特征,有助于实现准确的HPE。另一方面,我们观察到现有的HPE工作在测试图像旋转矩阵略超出训练数据集分布时,难以准确预测头部姿态。实验表明,我们的方法在标准测试数据集上的表现与最先进的模型相当,在图像稍微旋转、翻转或全范围头部姿态的情况下表现优于它们。据我们所知,我们是第一个提供能够准确预测包括倒立姿态在内的任何头部姿态的真正全范围HPE模型的团队。此外,我们还与其他现有的全偏航范围模型进行了比较,并展示了更优越的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于头部姿态估计(HPE)的表示学习新框架。该框架基于对比学习,能够在大量扩充的数据上进行几何变换,从而学习真实特征以实现准确的HPE。此外,该框架能够应对测试图像旋转矩阵略超出训练数据集分布的情况,并在标准测试数据集上表现优异,特别是在图像稍微旋转、翻转或全范围头部姿态预测时表现更出色。据我们所知,我们是第一个提供能够准确预测任何头部姿态(包括倒立姿态)的全范围HPE模型,并在与其他全偏航范围模型的比较中展现出卓越结果。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种新的头部姿态估计(HPE)表示学习框架,基于对比学习进行特征学习。
- 利用3D生成对抗网络(3D-aware GAN)轻松采样三元组(锚点、正例、负例),解决了之前因头部姿态数据稀疏导致的采样困难问题。
- 框架在大量扩充的数据上进行了几何变换,增强了网络的性能。
- 对比学习有助于网络学习真实特征,从而提高头部姿态估计的准确性。
- 该框架能够应对测试图像旋转矩阵略超出训练数据集分布的情况。
- 在标准测试数据集上表现优异,特别是在图像稍微旋转、翻转或全范围头部姿态预测时表现更出色。
点此查看论文截图


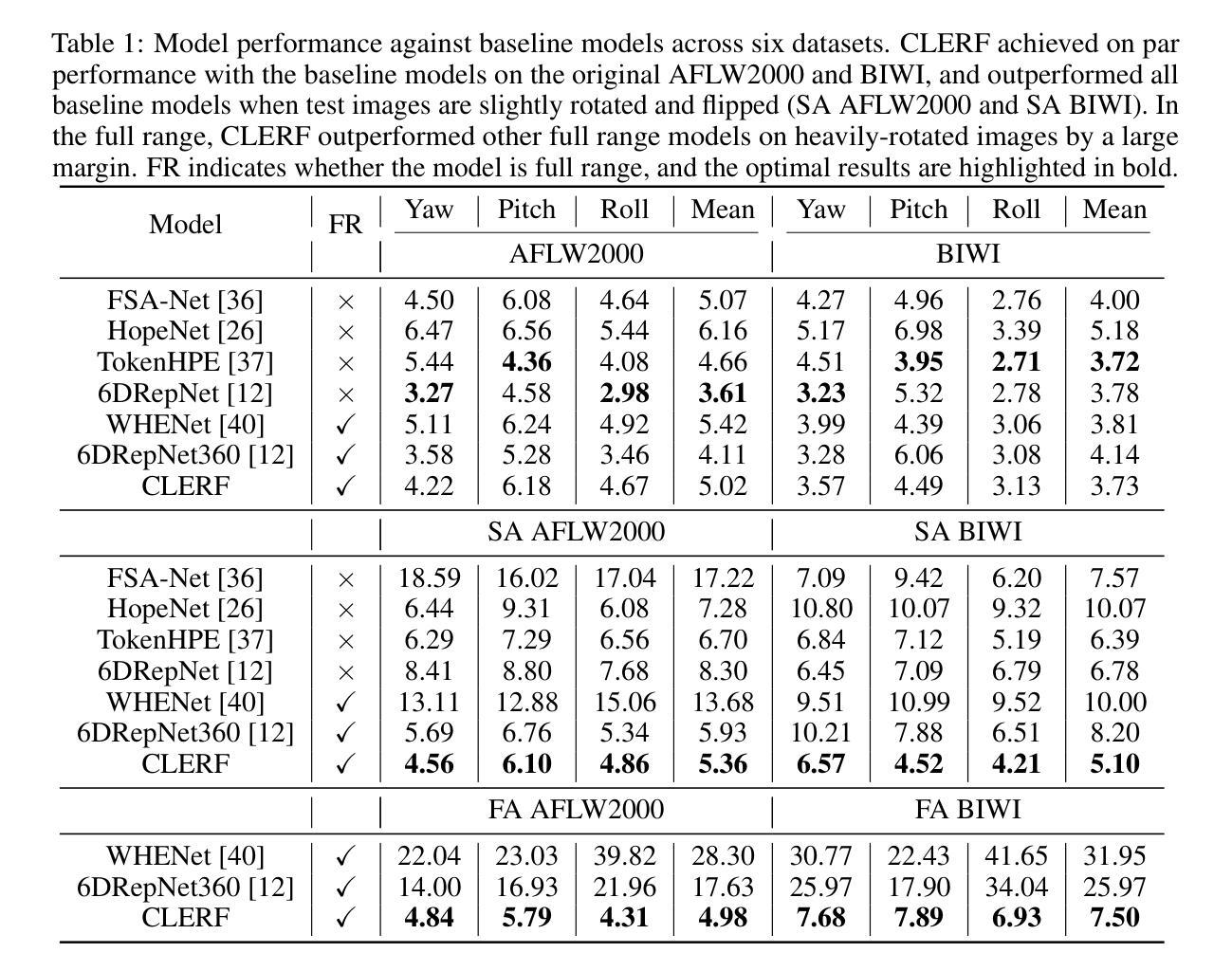
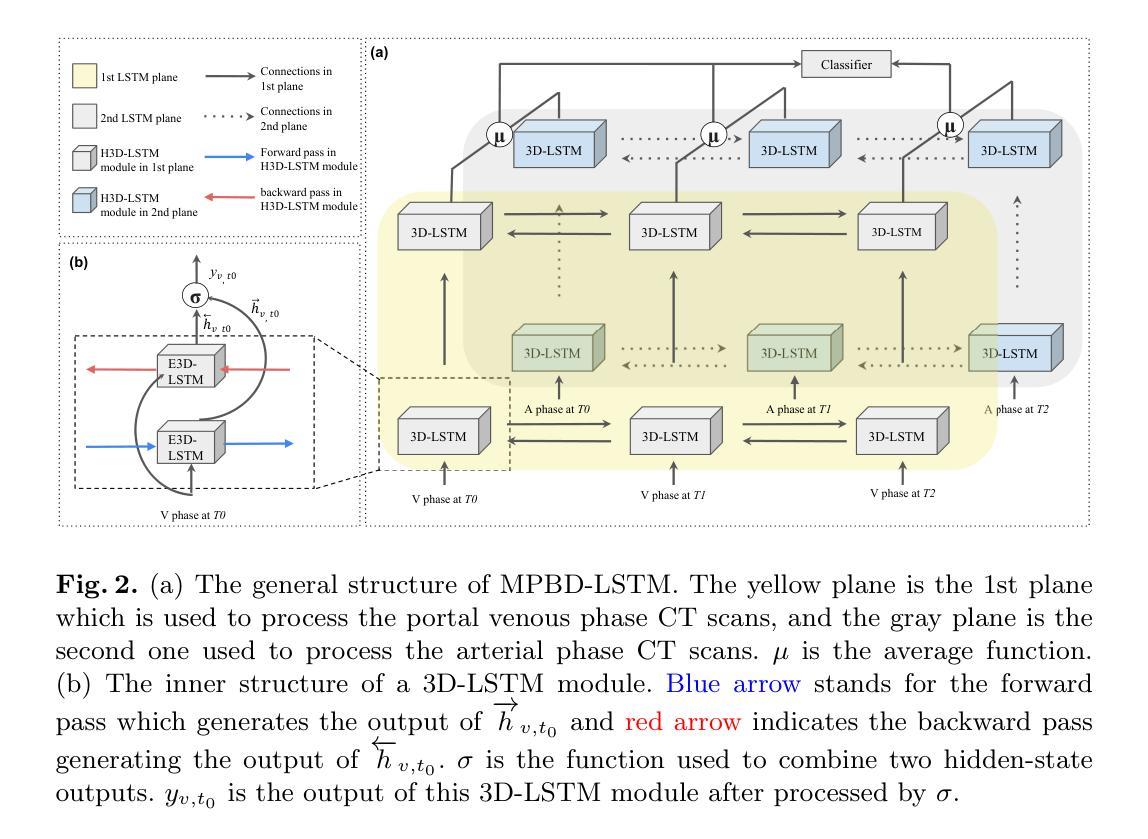
MPBD-LSTM: A Predictive Model for Colorectal Liver Metastases Using Time Series Multi-phase Contrast-Enhanced CT Scans
Authors:Xueyang Li, Han Xiao, Weixiang Weng, Xiaowei Xu, Yiyu Shi
Colorectal cancer is a prevalent form of cancer, and many patients develop colorectal cancer liver metastasis (CRLM) as a result. Early detection of CRLM is critical for improving survival rates. Radiologists usually rely on a series of multi-phase contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) scans done during follow-up visits to perform early detection of the potential CRLM. These scans form unique five-dimensional data (time, phase, and axial, sagittal, and coronal planes in 3D CT). Most of the existing deep learning models can readily handle four-dimensional data (e.g., time-series 3D CT images) and it is not clear how well they can be extended to handle the additional dimension of phase. In this paper, we build a dataset of time-series CECT scans to aid in the early diagnosis of CRLM, and build upon state-of-the-art deep learning techniques to evaluate how to best predict CRLM. Our experimental results show that a multi-plane architecture based on 3D bi-directional LSTM, which we call MPBD-LSTM, works best, achieving an area under curve (AUC) of 0.79. On the other hand, analysis of the results shows that there is still great room for further improvement.
结肠癌是一种常见的癌症,许多患者会发展为结肠癌肝转移(CRLM)。早期发现CRLM对于提高存活率至关重要。放射科医生通常依赖于一系列多期增强计算机断层扫描(CECT)检查来进行早期检测潜在的CRLM。这些扫描形成独特的五维数据(时间、阶段和轴向、矢状面和冠状面在三维CT中)。现有的大多数深度学习模型可以轻松处理四维数据(例如,时间序列三维CT图像),尚不清楚它们扩展到处理额外的阶段维度的好坏。在本文中,我们建立了一个时间序列CECT扫描数据集,以辅助CRLM的早期诊断,并基于最新深度学习技术评估如何最佳预测CRLM。我们的实验结果表明,基于三维双向LSTM的多平面架构表现最佳,我们称之为MPBD-LSTM,其曲线下面积(AUC)达到0.79。另一方面,对结果的分析表明,仍有很大的改进空间。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文研究结直肠癌肝转移(CRLM)的早期诊断,利用时间序列的对比增强计算机断层扫描(CECT)数据构建数据集,并基于先进的深度学习技术评估最佳的预测方法。实验结果表明,基于三维双向LSTM的多平面架构(MPBD-LSTM)表现最佳,曲线下面积(AUC)达到0.79,但仍存在改进空间。
Key Takeaways:
- 结直肠癌是一种常见的癌症,其中许多患者会发展为结直肠癌肝转移(CRLM)。
- 早期检测CRLM对于提高存活率至关重要。
- 放射科医生通常依赖于多阶段对比增强计算机断层扫描(CECT)进行早期检测。
- CECT扫描形成独特的数据维度,包括时间、阶段以及三维CT的三个平面。
- 目前大多数深度学习模型可以处理四维数据,但对于包含额外维度的数据(如阶段)的处理能力尚不清楚。
- 研究者构建了一个基于时间序列CECT扫描的数据集来辅助早期CRLM诊断,并采用基于三维双向LSTM的多平面架构(MPBD-LSTM)进行预测,取得了最佳效果。
点此查看论文截图


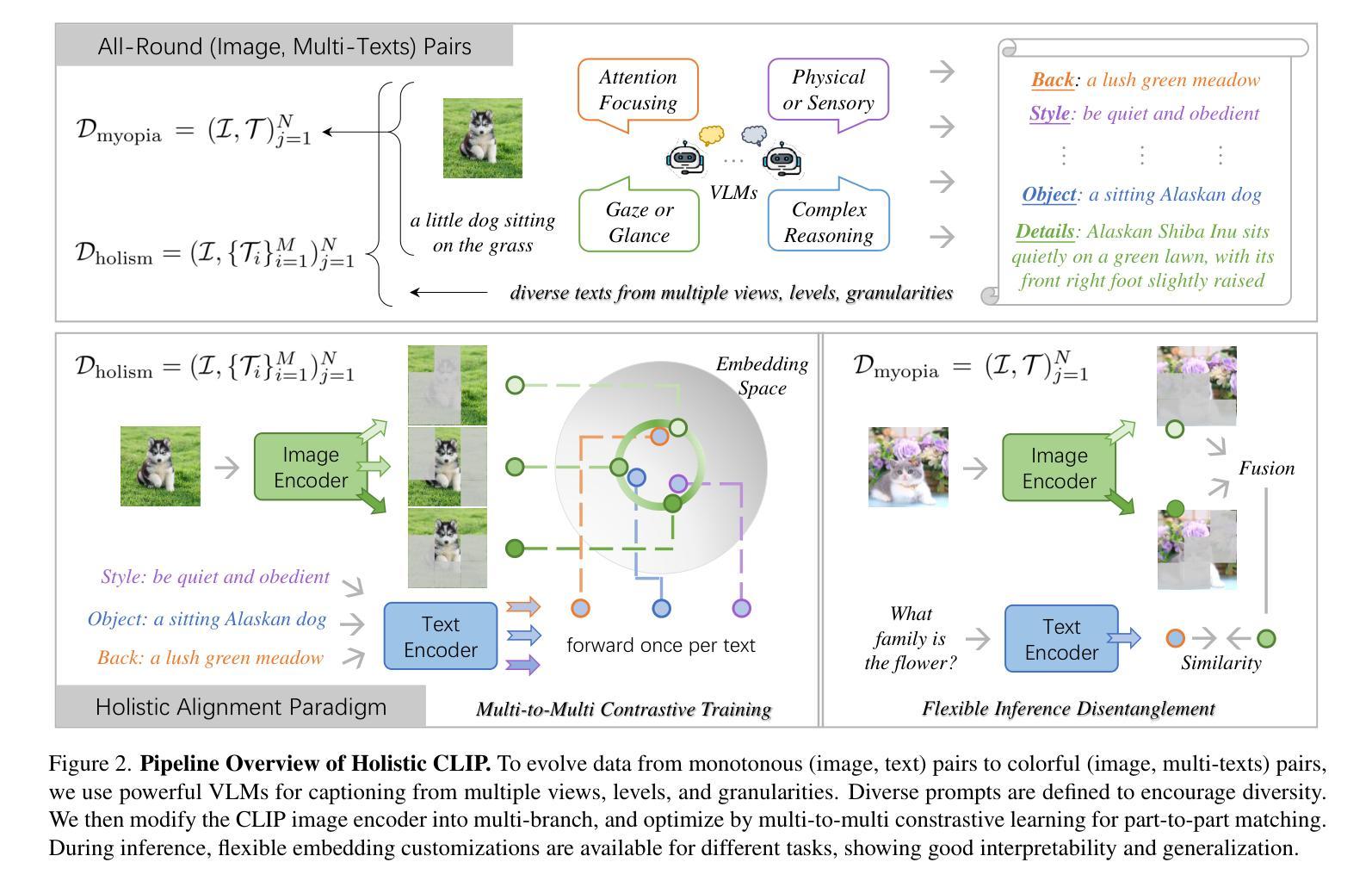
Advancing Myopia To Holism: Fully Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training
Authors:Haicheng Wang, Chen Ju, Weixiong Lin, Shuai Xiao, Mengting Chen, Yixuan Huang, Chang Liu, Mingshuai Yao, Jinsong Lan, Ying Chen, Qingwen Liu, Yanfeng Wang
In rapidly evolving field of vision-language models (VLMs), contrastive language-image pre-training (CLIP) has made significant strides, becoming foundation for various downstream tasks. However, relying on one-to-one (image, text) contrastive paradigm to learn alignment from large-scale messy web data, CLIP faces a serious myopic dilemma, resulting in biases towards monotonous short texts and shallow visual expressivity. To overcome these issues, this paper advances CLIP into one novel holistic paradigm, by updating both diverse data and alignment optimization. To obtain colorful data with low cost, we use image-to-text captioning to generate multi-texts for each image, from multiple perspectives, granularities, and hierarchies. Two gadgets are proposed to encourage textual diversity. To match such (image, multi-texts) pairs, we modify the CLIP image encoder into multi-branch, and propose multi-to-multi contrastive optimization for image-text part-to-part matching. As a result, diverse visual embeddings are learned for each image, bringing good interpretability and generalization. Extensive experiments and ablations across over ten benchmarks indicate that our holistic CLIP significantly outperforms existing myopic CLIP, including image-text retrieval, open-vocabulary classification, and dense visual tasks.
在快速发展的视觉语言模型(VLMs)领域,对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)取得了重大进展,成为各种下游任务的基础。然而,CLIP依赖于一对一(图像、文本)对比模式来学习大规模杂乱网络数据的对齐方式,面临着严重的近视困境,导致对单调短文本的偏见和视觉表达的肤浅。为了克服这些问题,本文通过将CLIP推进到一个新的整体模式,更新各种数据和对齐优化来解决这些问题。为了获得低成本的多彩数据,我们从多个角度、粒度和层次结构出发,利用图像到文本的标题生成来为每张图像生成多文本。提出了两种小工具来鼓励文本多样性。为了匹配这样的(图像、多文本)对,我们将CLIP图像编码器改为多分支,并提出多对多的对比优化来实现图像文本部分之间的匹配。因此,每张图像都学会了多样化的视觉嵌入,带来了良好的可解释性和泛化性。在超过十个基准测试上的大量实验和消融研究结果表明,我们的整体CLIP显著优于现有的近视CLIP,包括图像文本检索、开放词汇分类和密集视觉任务。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文针对视觉语言模型(VLMs)领域存在的问题,提出了将CLIP(对比语言图像预训练)升级为一种新型整体范式的方法。通过更新多样化的数据和优化对齐方式,解决了CLIP在面临大规模混杂网络数据时出现的短视困境。论文使用图像到文本的描述生成多角度、多层次和多粒度的多文本数据,并提出两种方法来鼓励文本多样性。通过修改CLIP图像编码器为多分支,并提出多对多的对比优化,实现了图像与文本的部分匹配。实验表明,这种整体方法显著提高了CLIP的性能,包括图像文本检索、开放词汇分类和密集视觉任务。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP在视觉语言模型领域取得了显著进展,成为各种下游任务的基础。
- CLIP面临依赖一对一(图像,文本)对比范式的困境,导致对单调短文本的偏见和视觉表达力浅。
- 为了解决这些问题,论文提出了一种新型的整体范式,通过更新多样化的数据和优化对齐方式。
- 使用图像到文本的描述生成多文本数据,从多个角度、粒度和层次对图像进行描述。
- 论文提出了两种方法来鼓励文本多样性,并修改CLIP图像编码器为多分支。
- 通过多对多的对比优化,实现了图像与文本的部分匹配,提高了模型的解释性和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

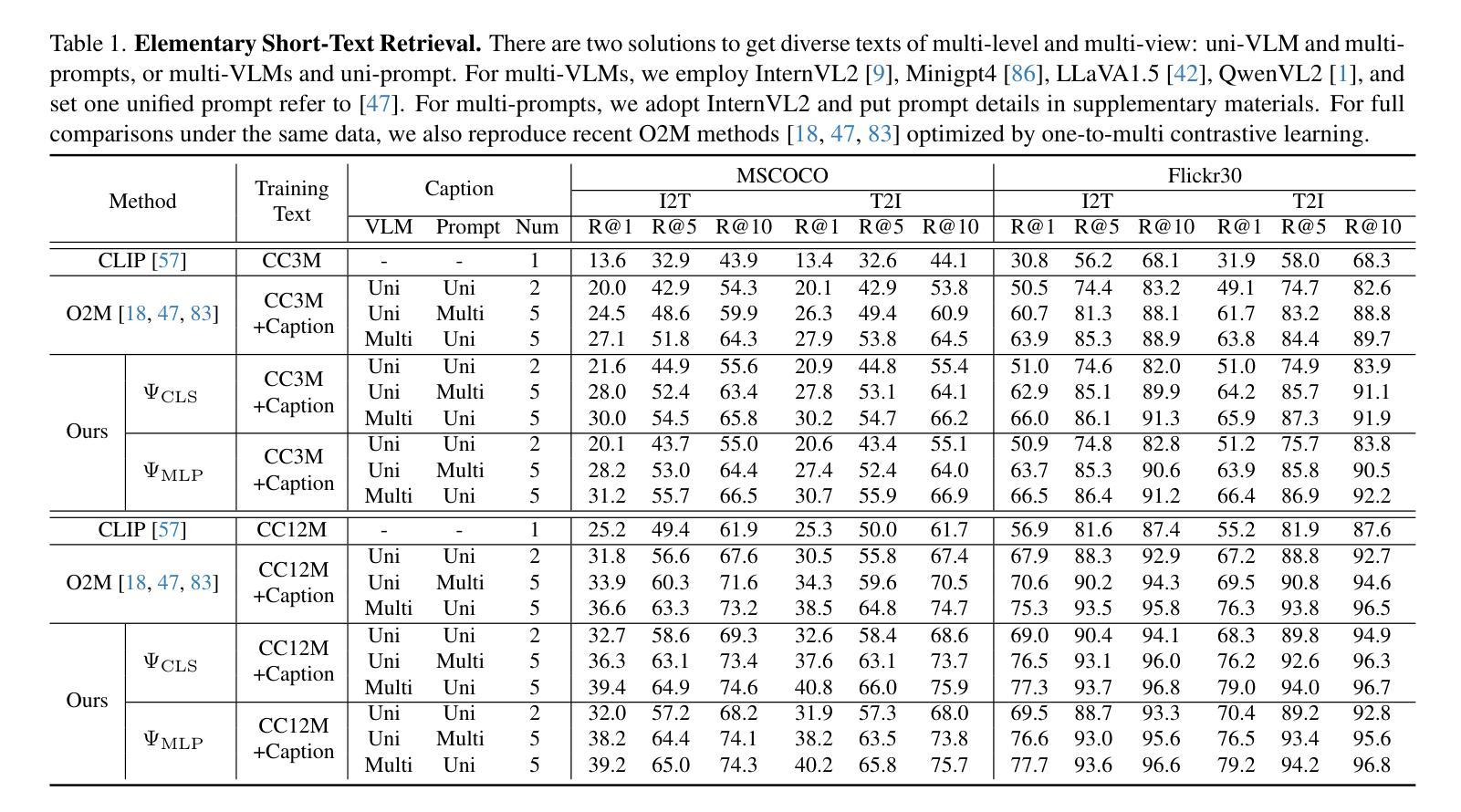
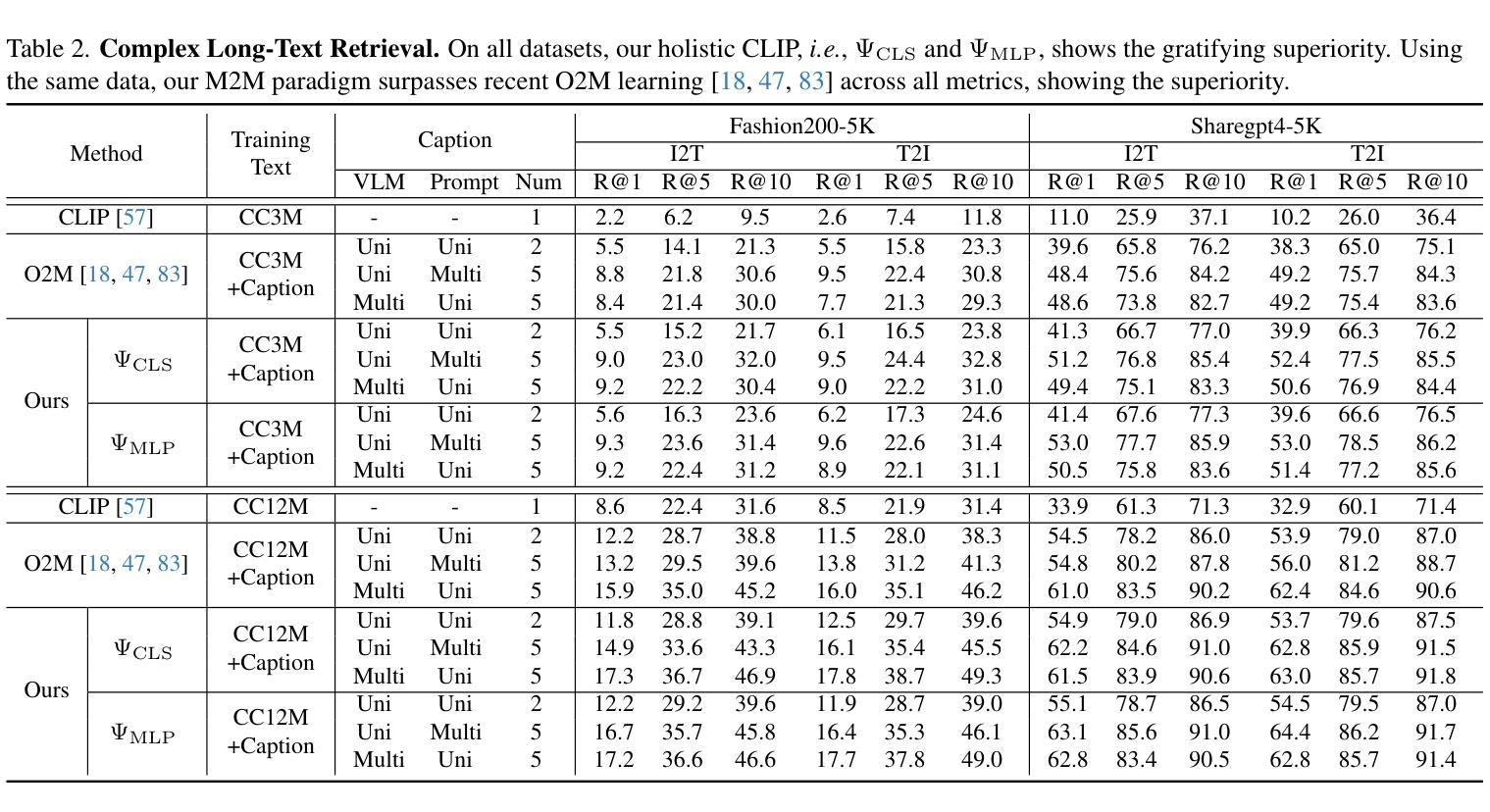
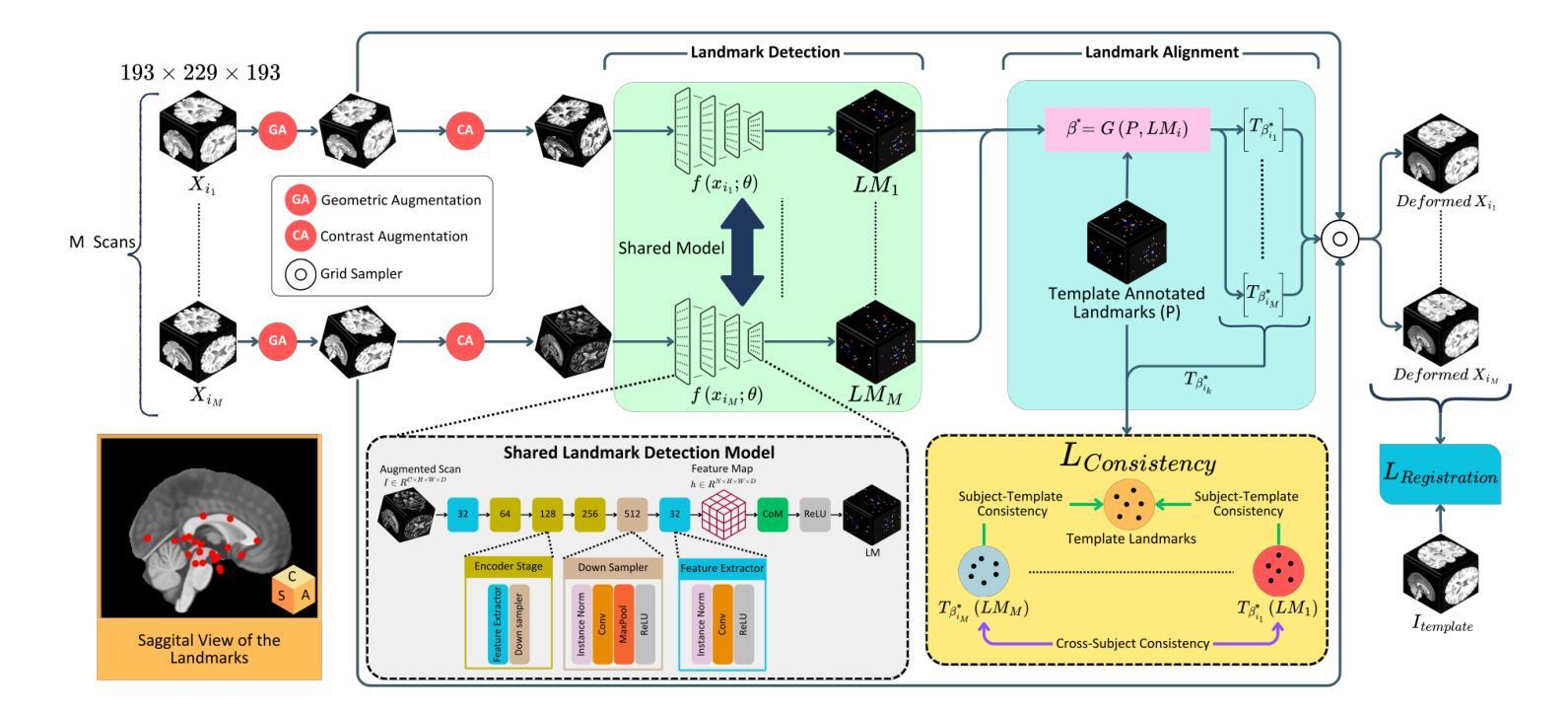
CAMLD: Contrast-Agnostic Medical Landmark Detection with Consistency-Based Regularization
Authors:Soorena Salari, Arash Harirpoush, Hassan Rivaz, Yiming Xiao
Anatomical landmark detection in medical images is essential for various clinical and research applications, including disease diagnosis and surgical planning. However, manual landmark annotation is time-consuming and requires significant expertise. Existing deep learning (DL) methods often require large amounts of well-annotated data, which are costly to acquire. In this paper, we introduce CAMLD, a novel self-supervised DL framework for anatomical landmark detection in unlabeled scans with varying contrasts by using only a single reference example. To achieve this, we employed an inter-subject landmark consistency loss with an image registration loss while introducing a 3D convolution-based contrast augmentation strategy to promote model generalization to new contrasts. Additionally, we utilize an adaptive mixed loss function to schedule the contributions of different sub-tasks for optimal outcomes. We demonstrate the proposed method with the intricate task of MRI-based 3D brain landmark detection. With comprehensive experiments on four diverse clinical and public datasets, including both T1w and T2w MRI scans at different MRI field strengths, we demonstrate that CAMLD outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of mean radial errors (MREs) and success detection rates (SDRs). Our framework provides a robust and accurate solution for anatomical landmark detection, reducing the need for extensively annotated datasets and generalizing well across different imaging contrasts. Our code will be publicly available at: https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/CAMLD.
医学图像中的解剖标志点检测对于各种临床和研究应用(包括疾病诊断和手术计划)至关重要。然而,手动标注标志点既耗时又需要丰富的专业知识。现有的深度学习(DL)方法通常需要大量标注良好的数据,而这些数据的获取成本高昂。在本文中,我们介绍了CAMLD,这是一种新型的自监督深度学习框架,它能够在具有不同对比度的未标记扫描中仅使用一个参考样本进行解剖标志点检测。为实现这一目标,我们采用了主体间标志点一致性损失和图像配准损失,同时引入了一种基于3D卷积的对比度增强策略,以促进模型对新对比度的泛化能力。此外,我们还采用自适应混合损失函数来调度不同子任务的贡献,以获取最佳结果。我们通过基于MRI的3D脑标志点检测这一复杂任务来展示所提出的方法。在四个多样化和公共的临床数据集上进行了全面的实验,包括不同MRI场强的T1w和T2w MRI扫描。我们证明CAMLD在平均径向误差(MRE)和成功检测率(SDR)方面优于最先进的方法。我们的框架为解剖标志点检测提供了稳健和准确的解决方案,减少了大量标注数据集的需求,并在不同的成像对比度上具有良好的泛化能力。我们的代码将在以下网址公开提供:https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/CAMLD 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 6 figures, 3 tables
Summary
本文提出了一种名为CAMLD的新型自监督深度学习框架,用于在无标签扫描中实现解剖学标记检测。该方法通过使用单一参考样本和不同数据集的混合损失函数,实现了在不同对比度下的解剖学标记检测。在MRI脑部标记检测任务上进行了验证,并在多个临床和公共数据集上表现出优异的性能,减少了大量标注数据集的需求,且能够在不同成像对比度之间良好地推广。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种新型的自监督深度学习框架CAMLD,用于在医学图像中进行解剖学标记检测。
- 通过使用单一参考样本,实现了对无标签扫描的解剖学标记检测。
- 采用了跨主体标记一致性损失和图像注册损失,提高了模型的准确性和鲁棒性。
- 通过采用基于3D卷积的对比增强策略,促进了模型对新对比度数据的泛化能力。
- 使用了自适应混合损失函数,以优化不同子任务的贡献。
- 在MRI脑部标记检测任务上进行了验证,并在多个数据集上表现出优异的性能,包括T1w和T2w MRI扫描和不同MRI场强。
点此查看论文截图
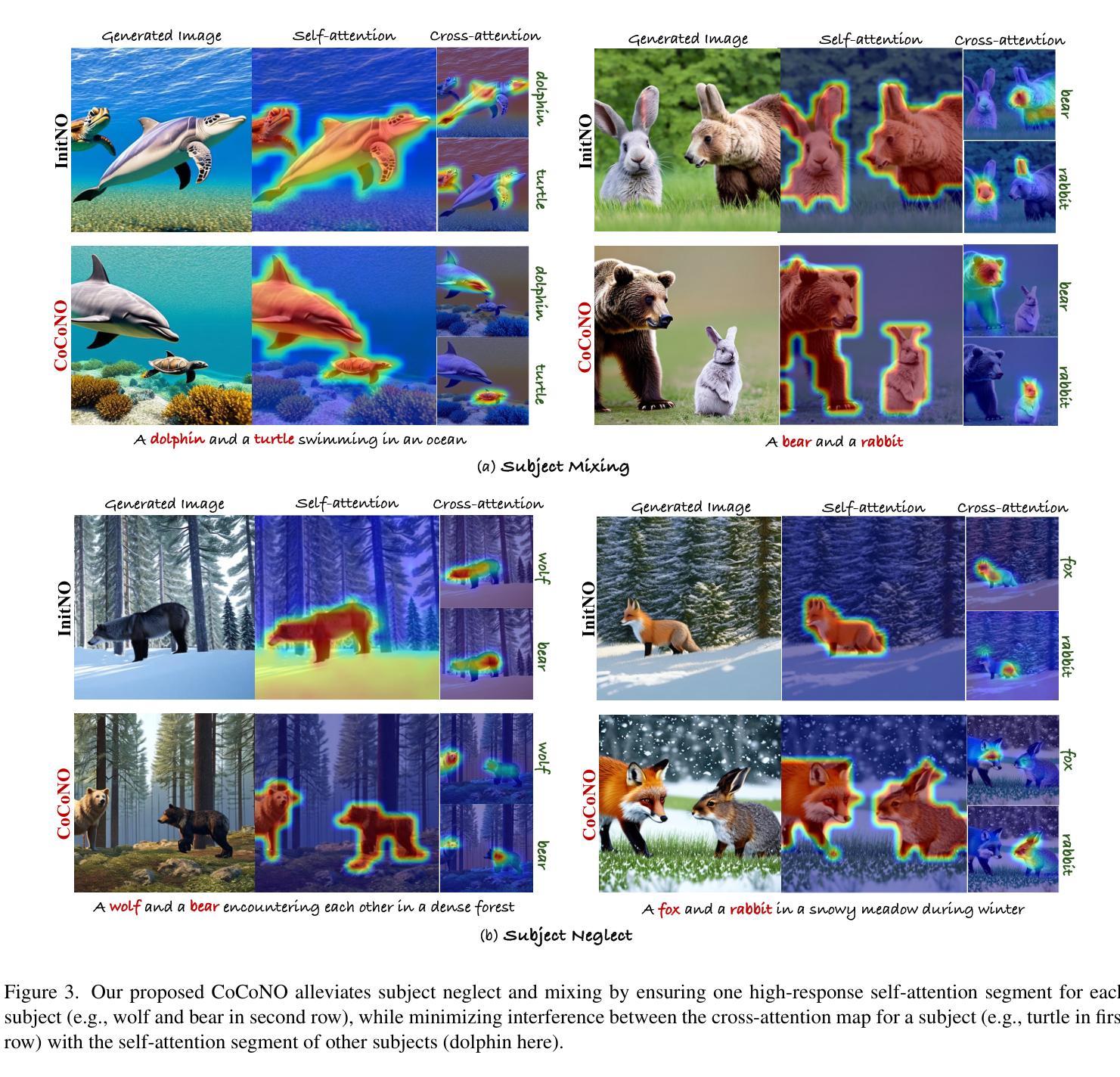
CoCoNO: Attention Contrast-and-Complete for Initial Noise Optimization in Text-to-Image Synthesis
Authors:Aravindan Sundaram, Ujjayan Pal, Abhimanyu Chauhan, Aishwarya Agarwal, Srikrishna Karanam
Despite recent advancements in text-to-image models, achieving semantically accurate images in text-to-image diffusion models is a persistent challenge. While existing initial latent optimization methods have demonstrated impressive performance, we identify two key limitations: (a) attention neglect, where the synthesized image omits certain subjects from the input prompt because they do not have a designated segment in the self-attention map despite despite having a high-response cross-attention, and (b) attention interference, where the generated image has mixed-up properties of multiple subjects because of a conflicting overlap between cross- and self-attention maps of different subjects. To address these limitations, we introduce CoCoNO, a new algorithm that optimizes the initial latent by leveraging the complementary information within self-attention and cross-attention maps. Our method introduces two new loss functions: the attention contrast loss, which minimizes undesirable overlap by ensuring each self-attention segment is exclusively linked to a specific subject’s cross attention map, and the attention complete loss, which maximizes the activation within these segments to guarantee that each subject is fully and distinctly represented. Our approach operates within a noise optimization framework, avoiding the need to retrain base models. Through extensive experiments on multiple benchmarks, we demonstrate that CoCoNO significantly improves text-image alignment and outperforms the current state of the art.
尽管文本到图像模型最近有所进展,但在文本到图像扩散模型中实现语义准确的图像仍然是一个持续存在的挑战。尽管现有的初始潜在优化方法已经取得了令人印象深刻的表现,但我们发现了两个关键局限:
(a)注意力忽视,即合成图像忽略了输入提示中的某些主题,因为它们在自注意力图中没有指定段落,尽管它们具有较高的响应交叉注意力;
(b)注意力干扰,即由于不同主题的交叉注意力和自注意力图之间的冲突重叠,生成图像混合了多个主题的性质。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 12 figures
Summary
本文探讨了文本到图像扩散模型中语义准确图像生成的问题,指出了现有初始潜在优化方法的两个关键局限性:注意力忽视和注意力干扰。为此,提出了CoCoNO算法,通过利用自注意力图和交叉注意力图中的互补信息来优化初始潜在状态。该方法引入了两个新的损失函数:注意力对比损失和注意力完整性损失,以最小化不必要的重叠并保证每个主题都得到完整且独特的表示。此方法在多个基准测试中显著提高了文本与图像的匹配度,并超越了当前的最佳水平。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像扩散模型在语义准确图像生成方面存在挑战。
- 现有初始潜在优化方法存在两个关键局限性:注意力忽视和注意力干扰。
- CoCoNO算法通过利用自注意力图和交叉注意力图中的互补信息来解决这些问题。
- CoCoNO引入了两个新的损失函数:注意力对比损失和注意力完整性损失。
- 注意力对比损失最小化不必要的重叠,确保每个自我注意段只与特定主题的交叉注意力图相关联。
- 注意力完整性损失确保每个主题在图像中得到完整且独特的表示。
点此查看论文截图



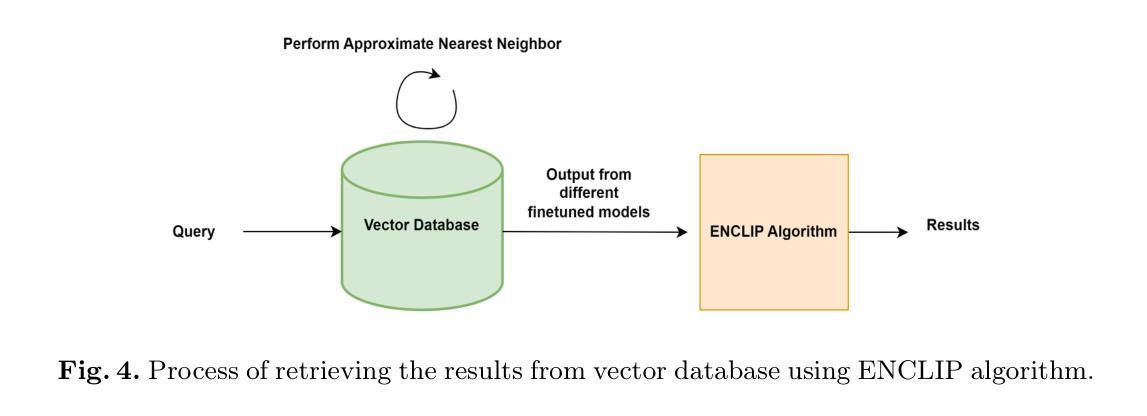
ENCLIP: Ensembling and Clustering-Based Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining for Fashion Multimodal Search with Limited Data and Low-Quality Images
Authors:Prithviraj Purushottam Naik, Rohit Agarwal
Multimodal search has revolutionized the fashion industry, providing a seamless and intuitive way for users to discover and explore fashion items. Based on their preferences, style, or specific attributes, users can search for products by combining text and image information. Text-to-image searches enable users to find visually similar items or describe products using natural language. This paper presents an innovative approach called ENCLIP, for enhancing the performance of the Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) model, specifically in Multimodal Search targeted towards the domain of fashion intelligence. This method focuses on addressing the challenges posed by limited data availability and low-quality images. This paper proposes an algorithm that involves training and ensembling multiple instances of the CLIP model, and leveraging clustering techniques to group similar images together. The experimental findings presented in this study provide evidence of the effectiveness of the methodology. This approach unlocks the potential of CLIP in the domain of fashion intelligence, where data scarcity and image quality issues are prevalent. Overall, the ENCLIP method represents a valuable contribution to the field of fashion intelligence and provides a practical solution for optimizing the CLIP model in scenarios with limited data and low-quality images.
多模态搜索已经彻底改变了时尚产业,为用户提供了一种无缝、直观的方式来发现和探索时尚产品。用户可以根据他们的偏好、风格或特定属性,结合文本和图像信息进行产品搜索。文本到图像的搜索使用户能够找到视觉上相似的项目或使用自然语言描述产品。本文提出了一种名为ENCLIP的创新方法,旨在提高对比语言图像预训练模型(CLIP模型)在面向时尚智能的多模态搜索中的性能。该方法侧重于解决数据有限和图像质量低下所带来的挑战。本文提出了一个算法,包括训练CLIP模型的多个实例并进行集成,以及利用聚类技术将相似的图像分组在一起。本研究提供的实验结果为该方法的有效性提供了证据。这种方法释放了CLIP在时尚智能领域的潜力,其中数据稀缺和图像质量问题普遍存在。总体而言,ENCLIP方法为时尚智能领域提供了宝贵的贡献,并为在数据有限和图像质量较低的情况下优化CLIP模型提供了实际解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态搜索已革新时尚产业,通过结合文本和图像信息,为用户提供无缝且直观的方式发现和探索时尚产品。本文提出一种增强Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP)模型性能的创新方法ENCLIP,特别针对时尚智能领域的多模态搜索。该方法解决数据有限和图像质量低的问题,通过训练和集成多个CLIP模型实例,并利用聚类技术将相似图像分组。实验结果表明该方法的有效性,释放CLIP在时尚智能领域的潜力,为在数据稀缺和图像质量问题普遍的情况下优化CLIP模型提供了实用解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态搜索在时尚产业中实现了无缝且直观的产品搜索方式,结合文本和图像信息满足用户偏好、风格和特定属性需求。
- ENCLIP方法旨在增强CLIP模型在时尚智能领域的多模态搜索性能,解决数据有限和图像质量低的问题。
- ENCLIP方法通过训练和集成多个CLIP模型实例,利用聚类技术分组相似图像。
- 实验结果证明了ENCLIP方法的有效性。
- ENCLIP在CLIP模型优化方面提供了实用解决方案,特别是在数据稀缺和图像质量问题常见的情况下。
- ENCLIP方法对时尚智能领域具有重大贡献。
点此查看论文截图

CLIC: Contrastive Learning Framework for Unsupervised Image Complexity Representation
Authors:Shipeng Liu, Liang Zhao, Dengfeng Chen
As an essential visual attribute, image complexity affects human image comprehension and directly influences the performance of computer vision tasks. However, accurately assessing and quantifying image complexity faces significant challenges. Previous works needed more generalization capabilities and well-labeled datasets to learn image complexity features. However, creating such datasets requires expensive manual labeling costs, and the models inevitably learn about human subjective biases. To address the above problems, we propose CLIC, an unsupervised framework based on contrastive learning, for learning image complexity representations. The method learns image complexity features on unlabeled data, avoiding the high labeling cost. Specifically, we propose a unique positive and negative sample selection strategy to reinforce the differences in complexity features. At the same time, we introduce an image prior-based Complexity-Aware Loss to constrain the learning process of the model. We conducted extensive experiments for verification, and the results show that CLIC can effectively learn the image complexity representation. CLIC obtained competitive results with supervised methods by fine-tuning on IC9600. In addition, CLIC applied to downstream tasks shows significant performance improvements, demonstrating the potential for application in various real-world scenarios. \href{https://github.com/xauat-liushipeng/CLIC}{code}
图像复杂度作为一个重要的视觉属性,影响人类图像理解,并直接关联计算机视觉任务的性能。然而,准确评估和量化图像复杂度面临重大挑战。以往的研究需要更强的泛化能力和标注好的数据集来学习图像复杂度特征。但是,创建这样的数据集需要昂贵的手动标注成本,而且模型不可避免地会学习到人类的主观偏见。为了解决上述问题,我们提出了基于对比学习的无监督框架CLIC,用于学习图像复杂度表示。该方法在无需标注的数据上学习图像复杂度特征,从而避免了高昂的标注成本。具体来说,我们提出了一种独特的正负样本选择策略,以强化复杂度特征的差异。同时,我们引入了一种基于图像先验的复杂度感知损失,以约束模型的学习过程。我们进行了大量的实验进行验证,结果表明CLIC可以有效地学习图像复杂度表示。CLIC在IC9600上进行微调后,其表现与监督方法相当。此外,CLIC应用于下游任务时显示出显著的性能提升,证明了其在各种实际场景中的应用潜力。代码
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图像复杂度是影响人类图像理解和计算机视觉任务性能的关键因素。为解决评估图像复杂度面临的挑战,如缺乏通用性和标注数据集,以及高昂的标注成本和模型学习的主观偏见问题,我们提出了基于对比学习的无监督框架CLIC,用于学习图像复杂度表征。CLIC能够在无标注数据上学习图像复杂度特征,避免了高昂的标注成本,并提出独特的正负样本选择策略来强化复杂度特征的差异。同时,我们引入了基于图像先验的复杂度感知损失来约束模型的学习过程。实验结果表明,CLIC能够有效学习图像复杂度表征,并在IC9600上进行微调后获得与监督方法相当的结果。此外,CLIC在下游任务中的应用显示出显著的性能提升,展现出在各种实际场景中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 图像复杂度对图像理解和计算机视觉任务性能至关重要。
- 准确评估和量化图像复杂度存在挑战,如缺乏通用性和标注数据集。
- 为解决上述问题,提出了基于对比学习的无监督框架CLIC。
- CLIC能够在无标注数据上学习图像复杂度特征,避免高昂的标注成本。
- CLIC采用独特的正负样本选择策略来强化复杂度特征的差异。
- 引入基于图像先验的复杂度感知损失以约束模型学习。
- CLIC在实验中表现出有效学习图像复杂度表征的能力,并在下游任务中展现出显著性能提升。
点此查看论文截图
Debias your Large Multi-Modal Model at Test-Time with Non-Contrastive Visual Attribute Steering
Authors:Neale Ratzlaff, Matthew Lyle Olson, Musashi Hinck, Estelle Aflalo, Shao-Yen Tseng, Vasudev Lal, Phillip Howard
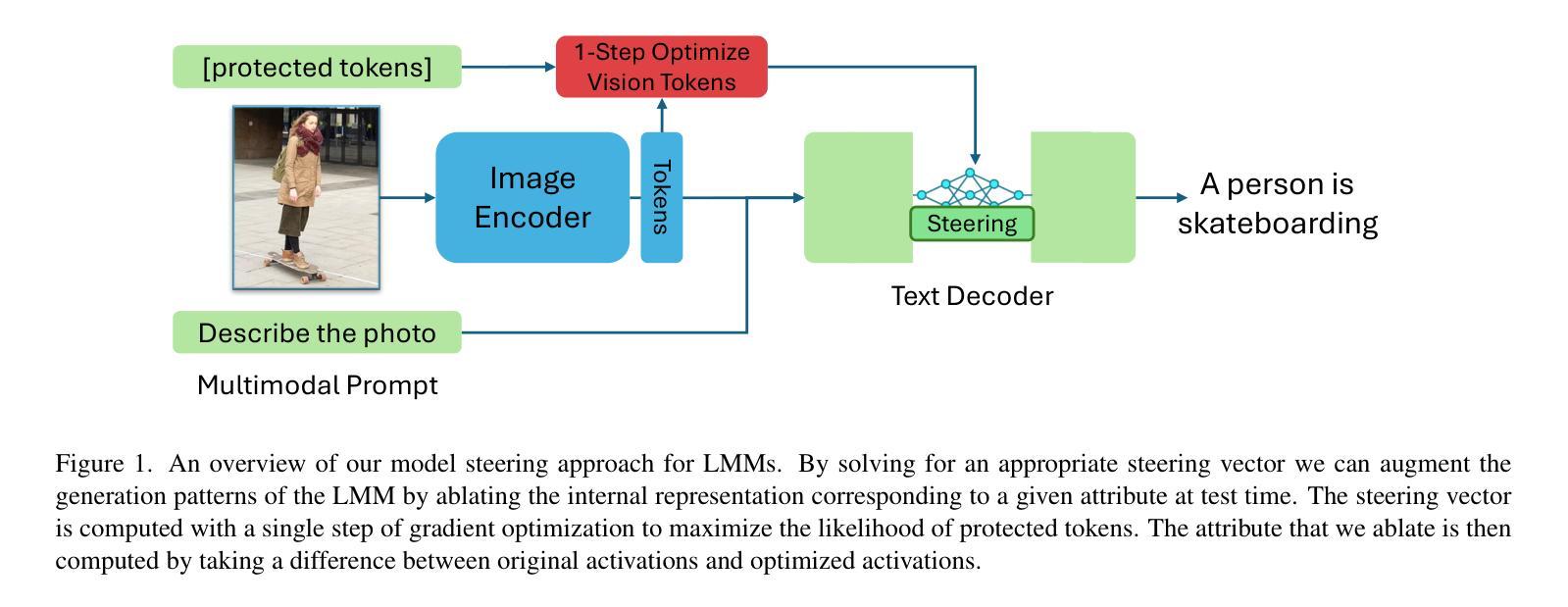
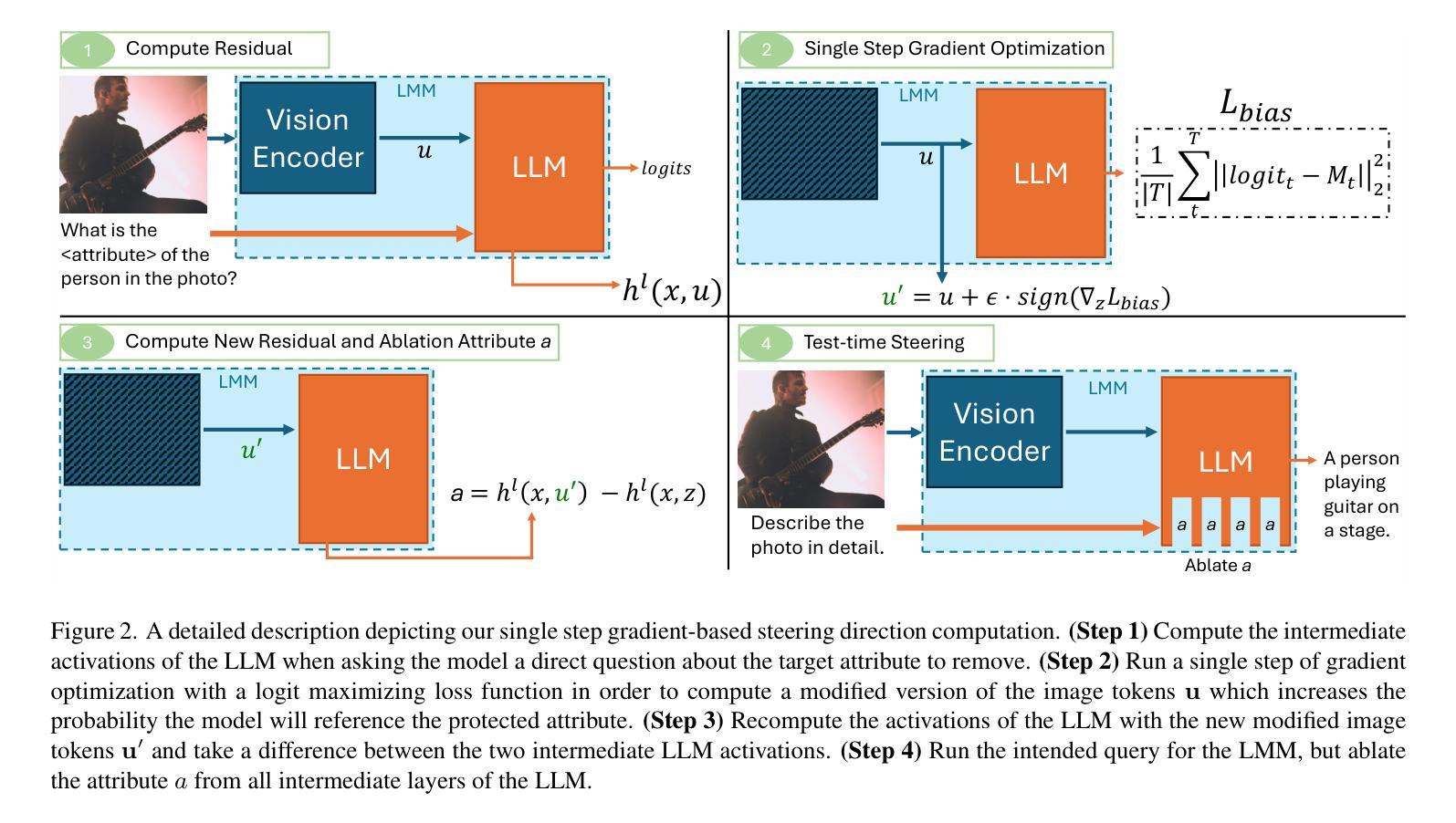
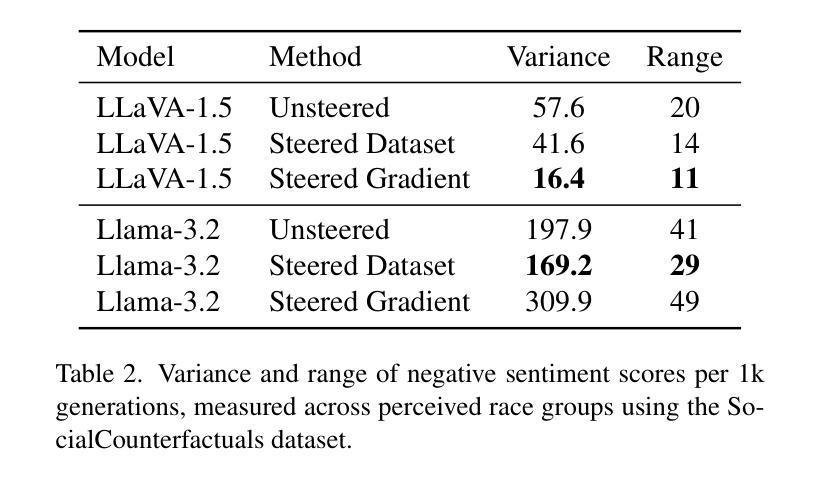
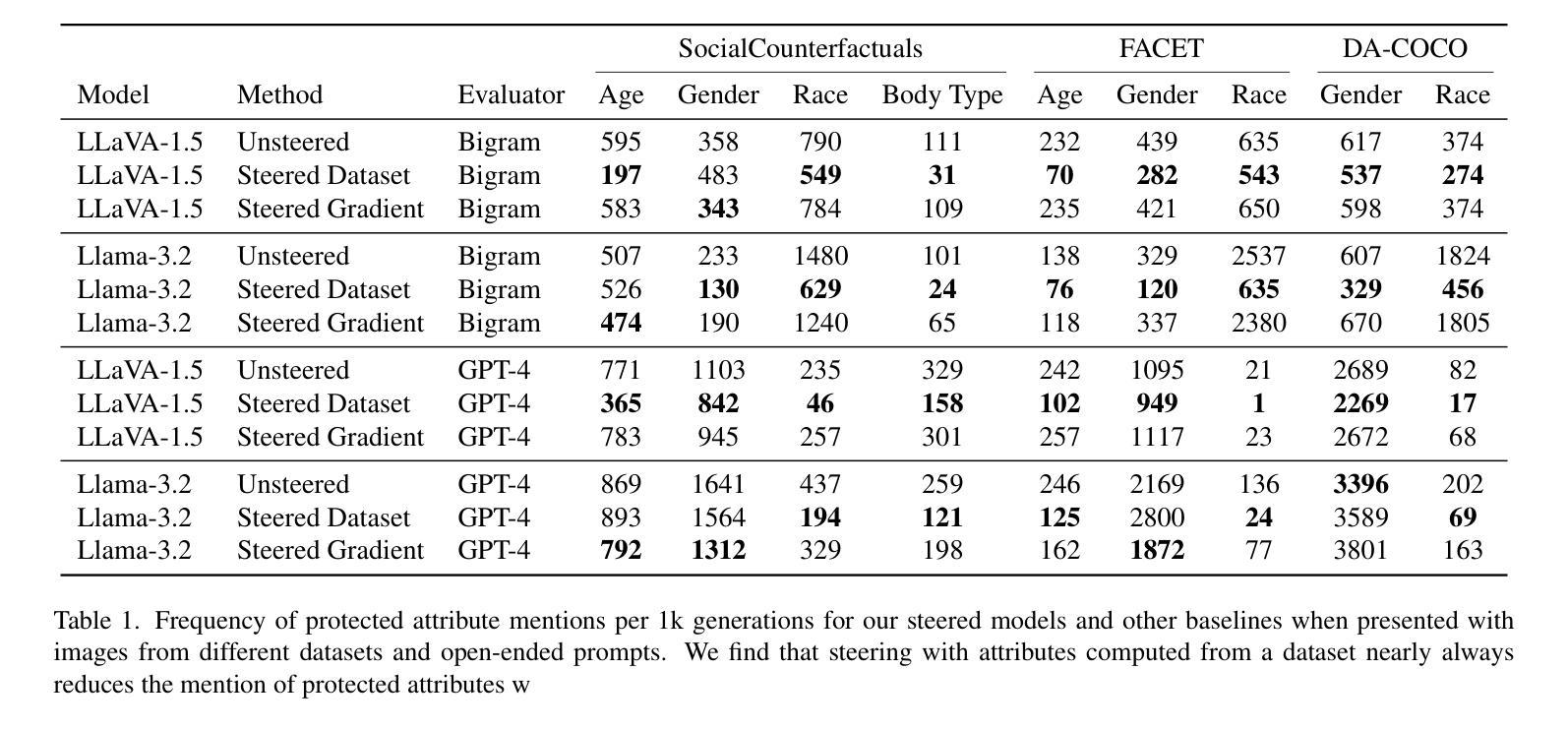
Large Multi-Modal Models (LMMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities as general-purpose chatbots that can engage in conversations about a provided input, such as an image. However, their responses are influenced by societal biases present in their training datasets, leading to undesirable differences in how the model responds when presented with images depicting people of different demographics. In this work, we propose a novel debiasing framework for LMMs that directly removes biased representations during text generation to decrease outputs related to protected attributes, or even representing them internally. Our proposed method is training-free; given a single image and a list of target attributes, we can ablate the corresponding representations with just one step of gradient descent on the image itself. Our experiments show that not only can we can minimize the propensity of LMMs to generate text related to protected attributes, but we can improve sentiment and even simply use synthetic data to inform the ablation while retaining language modeling capabilities on real data such as COCO or FACET. Furthermore, we find the resulting generations from a debiased LMM exhibit similar accuracy as a baseline biased model, showing that debiasing effects can be achieved without sacrificing model performance.
大型多模态模型(LMMs)在作为通用聊天机器人方面表现出了令人印象深刻的能力,它们可以进行关于所提供输入(如图像)的对话。然而,它们的回应受到其训练数据集中存在的社会偏见的影响,导致模型在面对描绘不同人口统计图像的输入时,回应方式存在不希望出现的差异。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种用于LMMs的新型去偏框架,该框架在文本生成过程中直接去除有偏表示,以减少与受保护属性相关的输出,甚至不内部表示它们。我们提出的方法是免培训的;给定一个图像和一系列目标属性,我们只需在图像本身上进行一步梯度下降,就可以消除相应的表示。我们的实验表明,我们不仅能够最小化LMMs生成与受保护属性相关文本的倾向,而且我们还可以改善情感,甚至只需使用合成数据来指导消除过程,同时保留在真实数据(如COCO或FACET)上的语言建模能力。此外,我们发现去偏LMM生成的成果与基线偏见模型的准确性相似,这表明可以在不牺牲模型性能的情况下实现去偏效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 3 Figures, 3 Tables. arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2410.13976
Summary
大型多模态模型(LMMs)在作为通用聊天机器人方面表现出强大的能力,但它们受训练数据集的社会偏见影响,导致对不同人口特征的图像的反应存在不必要的差异。本研究提出了一种针对LMMs的新型去偏框架,该框架在文本生成过程中直接消除偏见表示,减少与受保护属性相关的输出,甚至不内部表示它们。所提出的方法无需训练;只需给定单个图像和目标属性列表,我们就可以通过图像本身的梯度下降一步消除相应的表示。实验表明,我们不仅可以减少LMMs生成与受保护属性相关文本的趋势,还可以改善情感,甚至使用合成数据来指导消除过程,同时保留在真实数据(如COCO或FACET)上的语言建模能力。此外,我们发现去偏后的LMM生成的准确性类似于基线偏见模型,表明可以在不牺牲模型性能的情况下实现去偏效果。
Key Takeaways
- LMMs虽然作为聊天机器人表现出强大的能力,但受训练数据中的社会偏见影响,对不同人口特征的图像反应存在偏差。
- 提出一种新型去偏框架,可以在文本生成过程中消除偏见表示。
- 所提出的方法无需训练,只需给定图像和目标属性列表即可消除相关表示。
- 实验表明,该方法不仅可以减少与受保护属性相关的文本输出,还能改善语言模型的性能。
- 去偏后的LMM生成的准确性不逊色于基线偏见模型。
- 该方法可以利用合成数据来指导消除过程,同时保留在真实数据上的语言建模能力。
点此查看论文截图

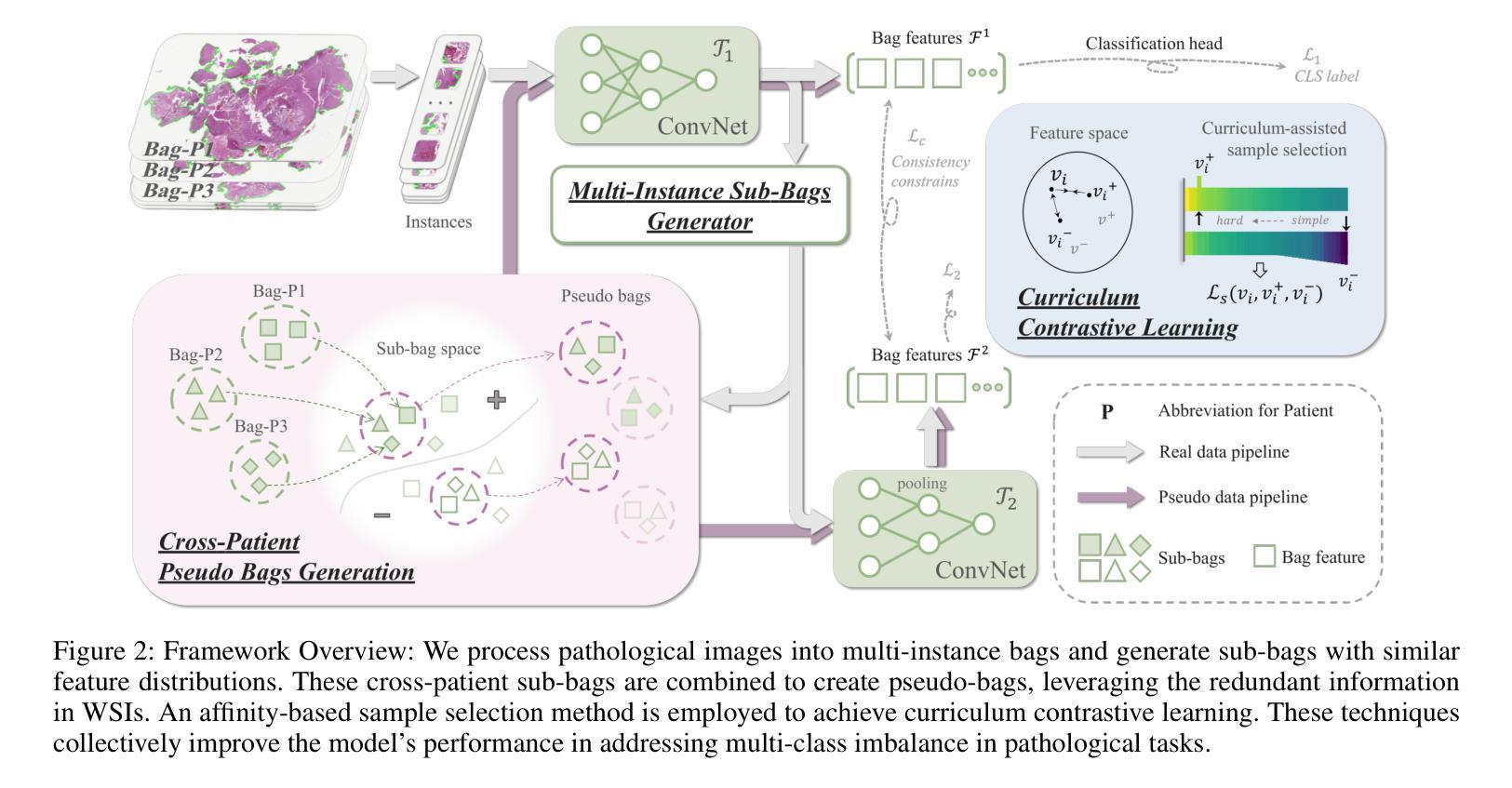
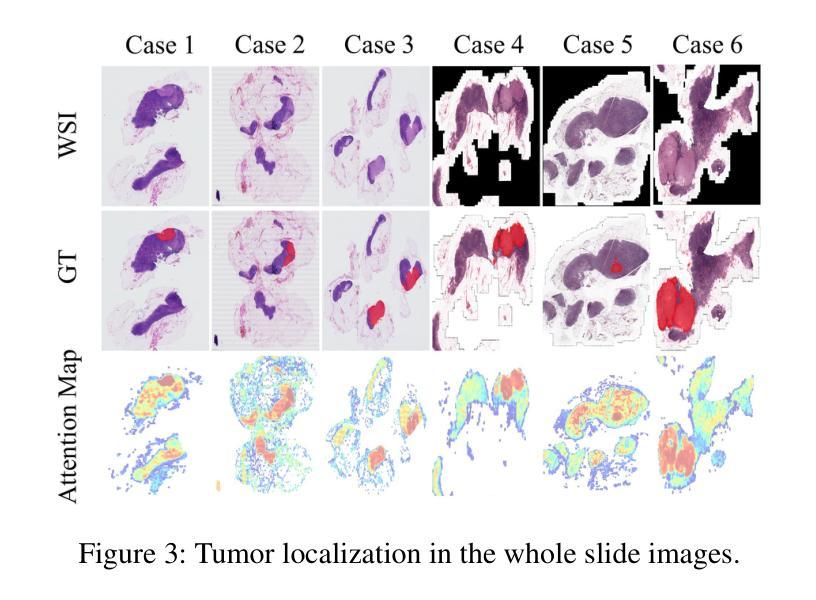
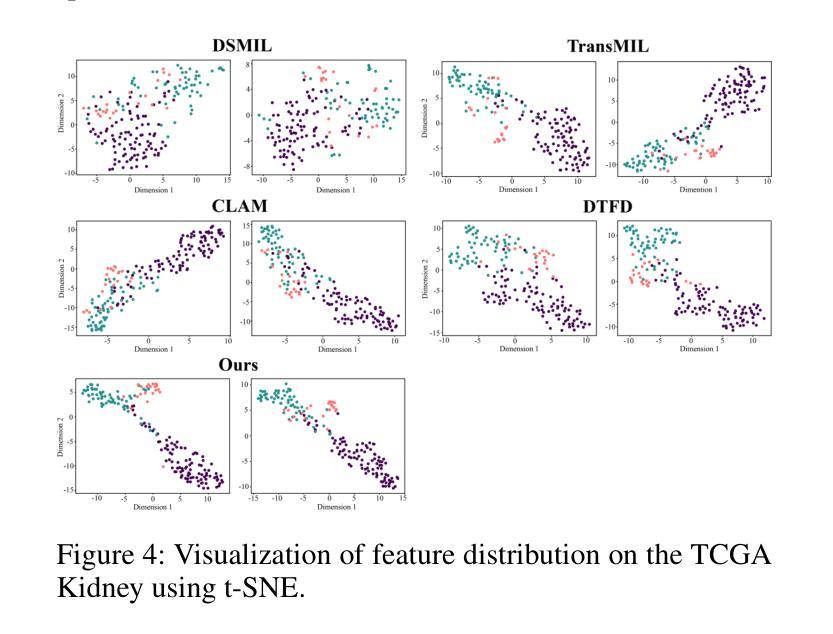
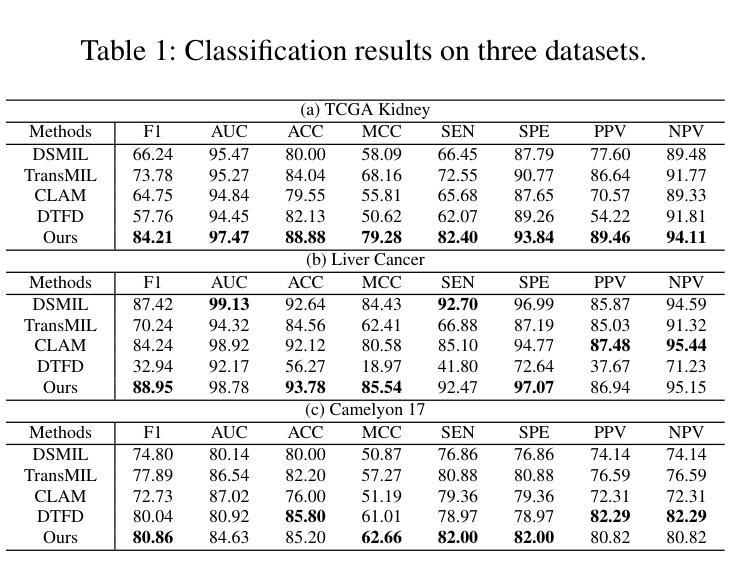
Cross-Patient Pseudo Bags Generation and Curriculum Contrastive Learning for Imbalanced Multiclassification of Whole Slide Image
Authors:Yonghuang Wu, Xuan Xie, Xinyuan Niu, Chengqian Zhao, Jinhua Yu
Pathology computing has dramatically improved pathologists’ workflow and diagnostic decision-making processes. Although computer-aided diagnostic systems have shown considerable value in whole slide image (WSI) analysis, the problem of multi-classification under sample imbalance remains an intractable challenge. To address this, we propose learning fine-grained information by generating sub-bags with feature distributions similar to the original WSIs. Additionally, we utilize a pseudo-bag generation algorithm to further leverage the abundant and redundant information in WSIs, allowing efficient training in unbalanced-sample multi-classification tasks. Furthermore, we introduce an affinity-based sample selection and curriculum contrastive learning strategy to enhance the stability of model representation learning. Unlike previous approaches, our framework transitions from learning bag-level representations to understanding and exploiting the feature distribution of multi-instance bags. Our method demonstrates significant performance improvements on three datasets, including tumor classification and lymph node metastasis. On average, it achieves a 4.39-point improvement in F1 score compared to the second-best method across the three tasks, underscoring its superior performance.
病理学计算显著改善了病理学家的工作流程和诊断决策过程。虽然计算机辅助诊断系统在全幻灯片图像(WSI)分析中显示出相当大的价值,但在样本不平衡下的多分类问题仍然是一个难以解决的问题。为了解决这一问题,我们提出通过生成具有与原始WSI相似的特征分布的子包来学习精细信息。此外,我们利用伪袋生成算法进一步利用WSI中丰富且多余的信息,实现在不平衡样本多分类任务中的高效训练。此外,我们引入基于亲和力的样本选择和课程对比学习策略,以提高模型表示学习的稳定性。与之前的方法不同,我们的框架从学习袋级表示过渡到理解和利用多实例袋的特征分布。我们的方法在三个数据集上实现了显著的性能改进,包括肿瘤分类和淋巴结转移。平均而言,与三项任务中第二好的方法相比,它在F1分数上提高了4.39分,突显了其卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 4 figures
Summary
针对病理图像分析中的样本不平衡多分类问题,本文提出通过生成具有与原始WSI相似特征分布的细粒度信息的子包进行学习。同时利用伪包生成算法,进一步挖掘WSI中的丰富冗余信息,实现在不平衡样本多分类任务中的高效训练。此外,引入基于亲和力的样本选择和课程对比学习策略,提高模型表示学习的稳定性。相较于以往方法,本文框架从学习包级表示转向理解和利用多实例包的特征分布,显著提高了肿瘤分类和淋巴结转移等三个数据集的性能,平均F1分数较第二好的方法提高了4.39个百分点。
Key Takeaways
- 病理学计算显著改进了病理学家的工作流程和诊断决策过程。
- 计算机辅助诊断系统在全切片图像(WSI)分析中展现出显著价值。
- 样本不平衡的多分类问题是WSI分析中的一大挑战。
- 本文通过生成具有与原始WSI相似特征分布的细粒度信息的子包来学习。
- 利用伪包生成算法挖掘WSIs中的丰富冗余信息,实现高效训练。
- 引入基于亲和力的样本选择和课程对比学习策略,提高模型稳定性。
点此查看论文截图


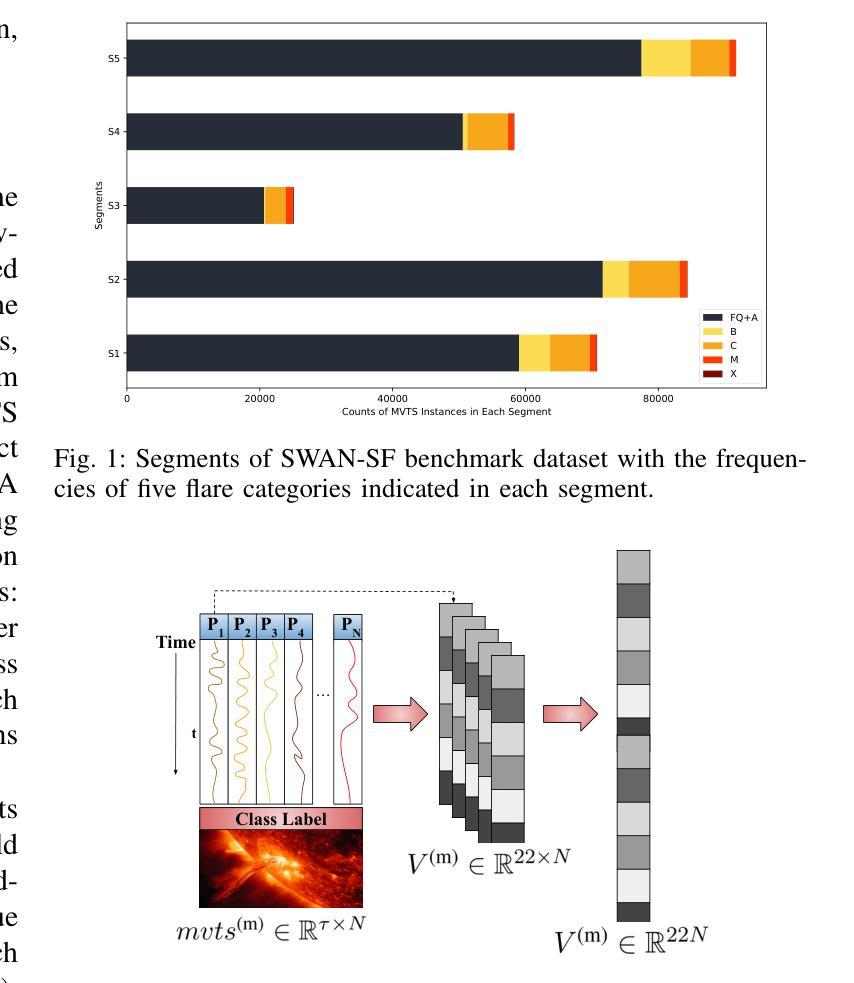
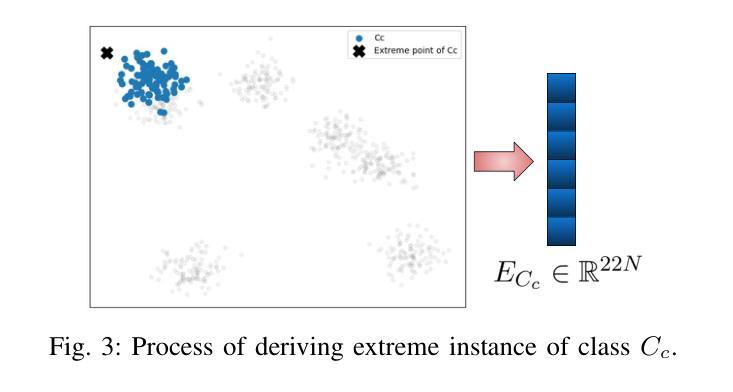
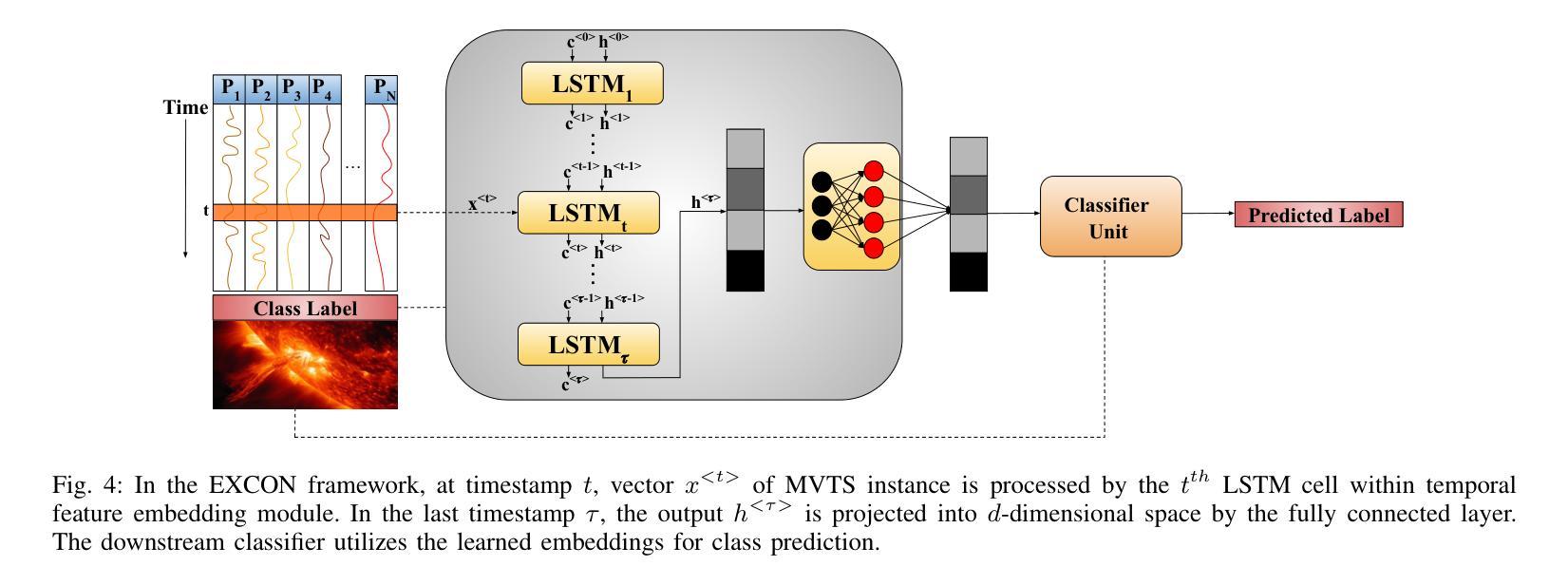
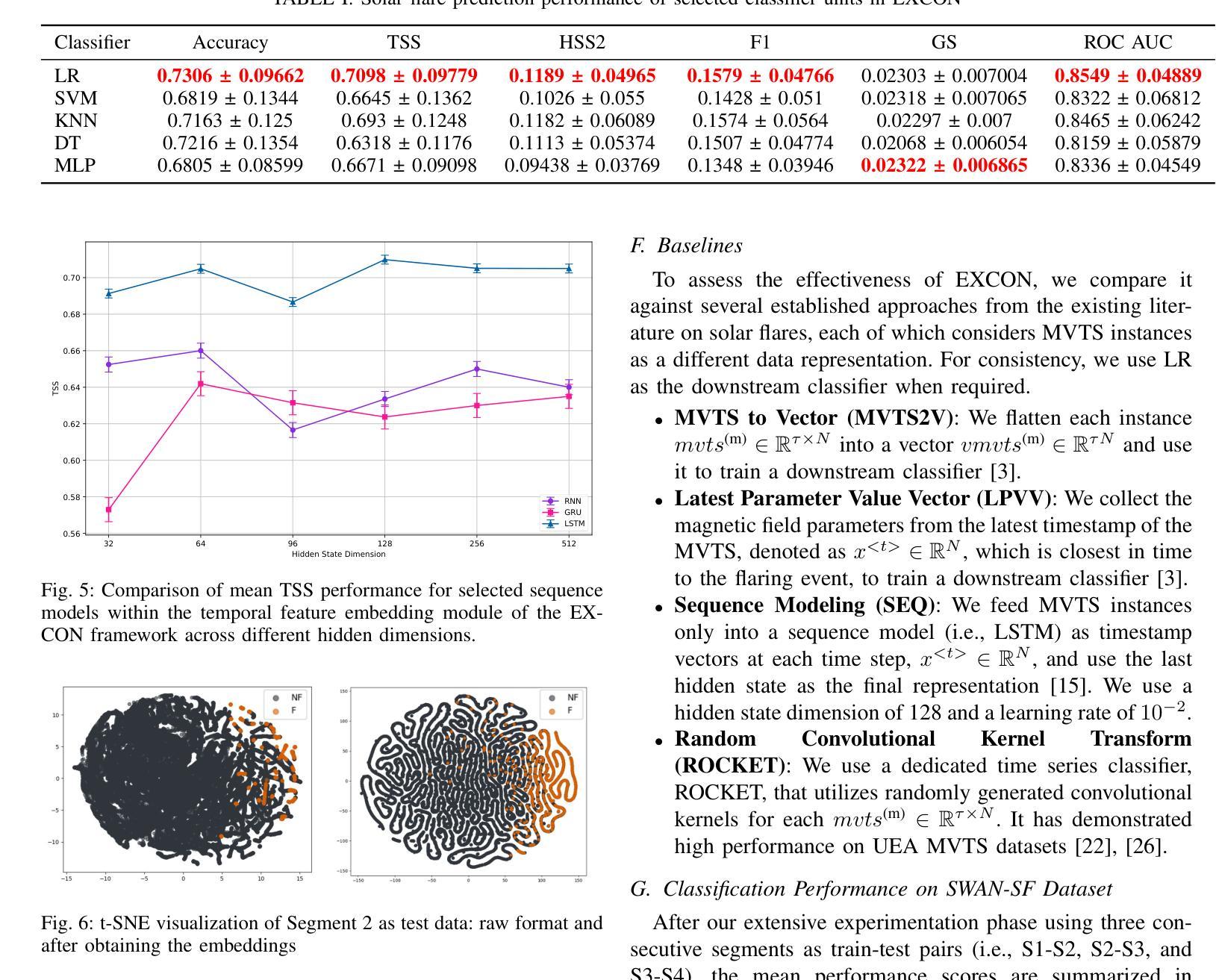
EXCON: Extreme Instance-based Contrastive Representation Learning of Severely Imbalanced Multivariate Time Series for Solar Flare Prediction
Authors:Onur Vural, Shah Muhammad Hamdi, Soukaina Filali Boubrahimi
In heliophysics research, predicting solar flares is crucial due to their potential to impact both space-based systems and Earth’s infrastructure substantially. Magnetic field data from solar active regions, recorded by solar imaging observatories, are transformed into multivariate time series to enable solar flare prediction using temporal window-based analysis. In the realm of multivariate time series-driven solar flare prediction, addressing severe class imbalance with effective strategies for multivariate time series representation learning is key to developing robust predictive models. Traditional methods often struggle with overfitting to the majority class in prediction tasks where major solar flares are infrequent. This work presents EXCON, a contrastive representation learning framework designed to enhance classification performance amidst such imbalances. EXCON operates through four stages: obtaining core features from multivariate time series data; selecting distinctive contrastive representations for each class to maximize inter-class separation; training a temporal feature embedding module with a custom extreme reconstruction loss to minimize intra-class variation; and applying a classifier to the learned embeddings for robust classification. The proposed method leverages contrastive learning principles to map similar instances closer in the feature space while distancing dissimilar ones, a strategy not extensively explored in solar flare prediction tasks. This approach not only addresses class imbalance but also offers a versatile solution applicable to univariate and multivariate time series across binary and multiclass classification problems. Experimental results, including evaluations on the benchmark solar flare dataset and multiple time series archive datasets with binary and multiclass labels, demonstrate EXCON’s efficacy in enhancing classification performance.
在日冕物理学研究中,预测太阳耀斑至关重要,因为它们可能对天基系统和地球基础设施产生重大影响。来自太阳活动区域的磁场数据,由太阳成像观测站记录,被转化为多元时间序列,以通过基于时间窗口的分析进行太阳耀斑预测。在多元时间序列驱动的太阳耀斑预测领域,采用有效策略解决严重类别不平衡问题对于开发稳健的预测模型至关重要。传统方法在预测任务中往往会对多数类过度拟合,而大型太阳耀斑的发生频率较低。这项工作提出了EXCON,一个对比表示学习框架,旨在在此类不平衡情况下提高分类性能。EXCON通过四个阶段进行操作:从多元时间序列数据中获取核心特征;为每个类别选择有特色的对比表示,以最大化类间分离;训练具有自定义极端重建损失的临时特征嵌入模块,以最小化类内变化;对学习的嵌入应用分类器以实现稳健分类。所提出的方法利用对比学习原理将相似的实例映射到特征空间中的较近距离,同时使不相似的实例远离,这一策略在太阳耀斑预测任务中尚未被广泛探索。这种方法不仅解决了类别不平衡问题,而且提供了一个通用解决方案,适用于二元和多元分类问题的单元和多元时间序列。实验结果包括在基准太阳耀斑数据集和具有二元和多元标签的多个时间序列归档数据集上的评估,证明了EXCON在提高分类性能方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been accepted at the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (IEEE BigData 2024) on October 27, 2024, as a main conference paper
Summary
针对太阳活动区域记录的磁场数据进行多元时间序列转换,用以预测太阳耀斑。为解决预测任务中的严重类别不平衡问题,提出EXCON对比学习框架,通过核心特征提取、对比表示学习、时间特征嵌入和分类器应用四个阶段,提高分类性能。该框架不仅解决了类别不平衡问题,还适用于单变量和多变量时间序列的二元和多类分类问题。实验结果表明,EXCON在增强分类性能方面效果显著。
Key Takeaways
- 预测太阳耀斑对空间系统和地球基础设施的影响至关重要。
- 多元时间序列数据在太阳耀斑预测中起到关键作用。
- 传统方法在预测任务中面临类别不平衡和过度拟合的问题。
- EXCON对比学习框架通过四个步骤提高分类性能:核心特征提取、对比表示学习、时间特征嵌入和分类器应用。
- EXCON利用对比学习原则,将相似实例映射到特征空间中的近距离,同时使不同实例相距较远。
- EXCON框架可应用于二元和多类分类问题的单变量和多变量时间序列。
点此查看论文截图

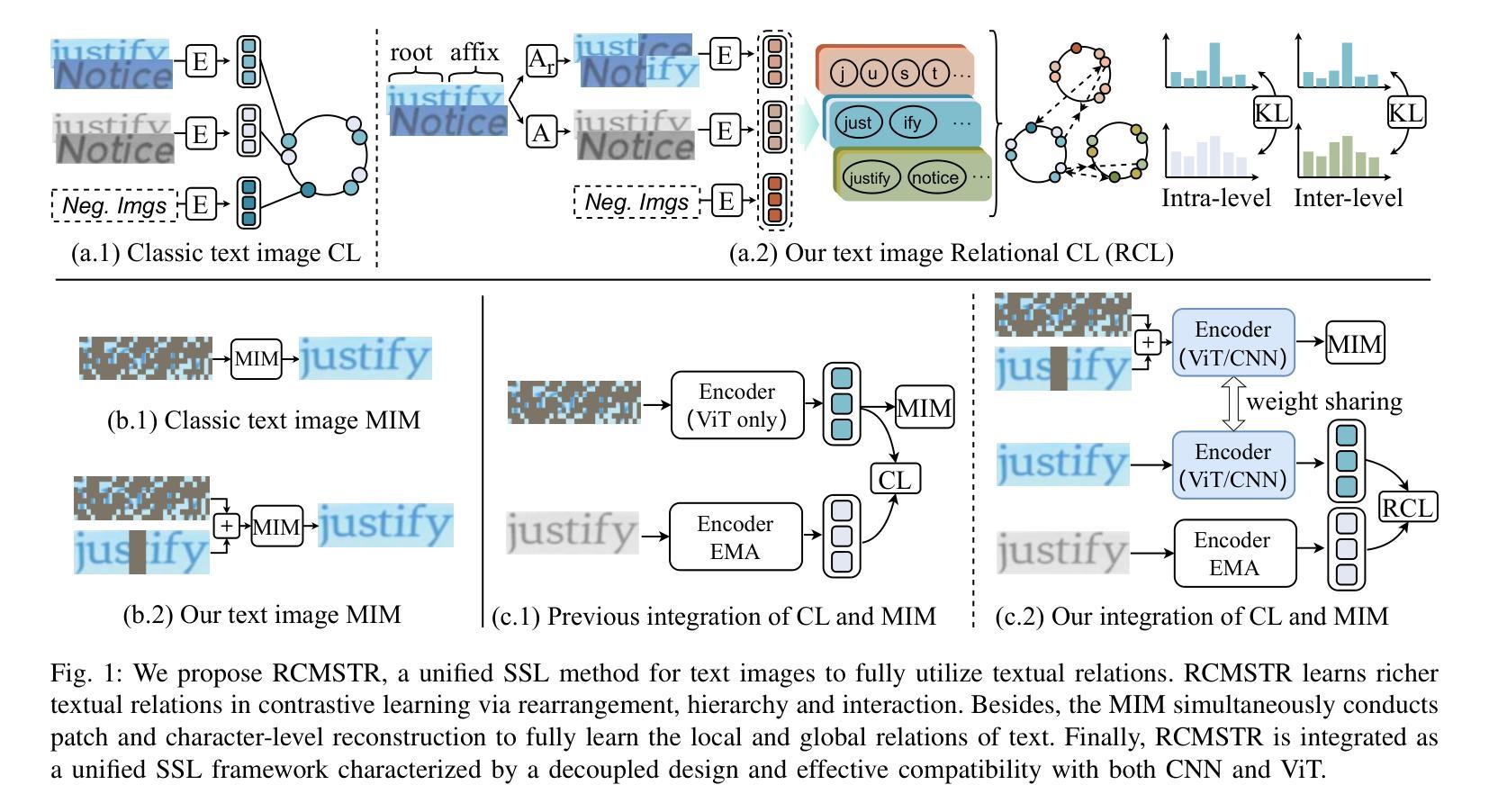
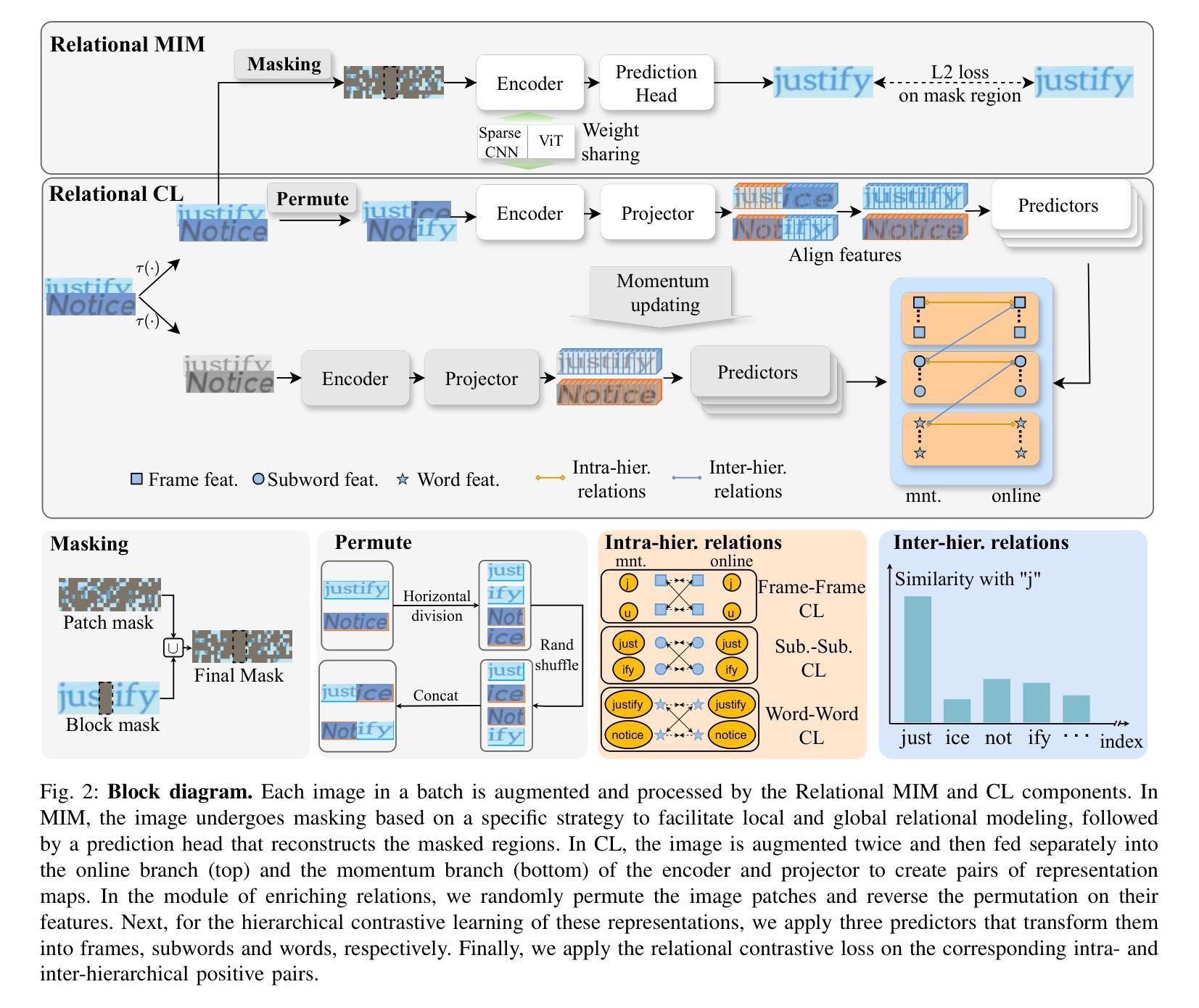
Relational Contrastive Learning and Masked Image Modeling for Scene Text Recognition
Authors:Tiancheng Lin, Jinglei Zhang, Yi Xu, Kai Chen, Rui Zhang, Chang-Wen Chen
Context-aware methods have achieved remarkable advancements in supervised scene text recognition by leveraging semantic priors from words. Considering the heterogeneity of text and background in STR, we propose that such contextual priors can be reinterpreted as the relations between textual elements, serving as effective self-supervised labels for representation learning. However, textual relations are restricted to the finite size of the dataset due to lexical dependencies, which causes over-fitting problem, thus compromising the representation quality. To address this, our work introduces a unified framework of Relational Contrastive Learning and Masked Image Modeling for STR (RCMSTR), which explicitly models the enriched textual relations. For the RCL branch, we first introduce the relational rearrangement module to cultivate new relations on the fly. Based on this, we further conduct relational contrastive learning to model the intra- and inter-hierarchical relations for frames, sub-words and words. On the other hand, MIM can naturally boost the context information via masking, where we find that the block masking strategy is more effective for STR. For the effective integration of RCL and MIM, we also introduce a novel decoupling design aimed at mitigating the impact of masked images on contrastive learning. Additionally, to enhance the compatibility of MIM with CNNs, we propose the adoption of sparse convolutions and directly sharing the weights with dense convolutions in training. The proposed RCMSTR demonstrates superior performance in various evaluation protocols for different STR-related downstream tasks, outperforming the existing state-of-the-art self-supervised STR techniques. Ablation studies and qualitative experimental results further validate the effectiveness of our method. The code and pre-trained models will be available at https://github.com/ThunderVVV/RCMSTR .
针对有监督的场景文本识别,结合词级的语义先验知识,上下文感知方法已经取得了显著的进步。考虑到场景文本(STR)中的文本和背景多样性,我们提出可以将此类上下文先验知识重新解释为文本元素之间的关系,作为表示学习的有效自监督标签。然而,由于词汇依赖关系,文本关系受限于数据集的大小,这会导致过拟合问题,从而影响表示质量。为了解决这一问题,我们的工作引入了针对STR的Relational Contrastive Learning和Masked Image Modeling的统一框架(RCMSTR),该框架对丰富的文本关系进行显式建模。在RCL分支中,我们首先引入关系重构模块来实时培养新关系。在此基础上,我们进一步进行关系对比学习,对帧、子词和词的内部和层次间关系进行建模。另一方面,MIM可以通过掩码自然地提升上下文信息,我们发现对于STR而言,块掩码策略更为有效。为了有效地整合RCL和MIM,我们还引入了一种新型解耦设计,旨在减轻遮挡图像对对比学习的影响。此外,为了提高MIM与卷积神经网络(CNN)的兼容性,我们提出了采用稀疏卷积的方法,并在训练中直接共享与密集卷积的权重。所提出的RCMSTR在各种评估协议下表现出卓越的性能,在多种与STR相关的下游任务中超越了现有的最先进的自监督STR技术。消融研究和定性实验结果进一步验证了我们的方法的有效性。代码和预训练模型将在https://github.com/ThunderVVV/RCMSTR上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2308.00508
Summary:
基于场景文本识别的语境意识方法,借助词汇语义先验信息取得了显著进展。为应对场景文本识别(STR)中文字和背景的异质性,提出将文本元素间的关系解释为上下文先验,作为表示学习的有效自监督标签。然而,由于词汇依赖,文本关系受限于数据集的大小,会导致过拟合问题,影响表示质量。为解决此问题,我们提出了结合关系对比学习和遮罩图像建模的统一框架(RCMSTR),用于显式建模丰富的文本关系。通过关系重组模块生成新关系,并在此基础上进行关系对比学习,以建模帧、子词和词之间的内部和层次间关系。遮罩图像建模自然提升了上下文信息,我们发现对于STR来说,块遮罩策略更为有效。为有效整合关系对比学习和遮罩图像建模,我们引入了缓解遮罩图像对对比学习影响的解耦设计。此外,为提高MIM与CNN的兼容性,我们提议采用稀疏卷积并在训练中直接共享权重。RCMSTR在各种评估协议下的不同STR相关下游任务中表现出卓越性能,超越了现有的自监督STR技术。
Key Takeaways:
- 文本元素间的关系可作为上下文先验,用于场景文本识别的表示学习。
- 文本关系受限于数据集大小,会导致过拟合问题。
- 引入关系对比学习(RCL)和遮罩图像建模(MIM)的统一框架RCMSTR。
- RCMSTR通过关系重组模块生成新关系,并进行关系对比学习。
- 遮罩图像建模能提升上下文信息,块遮罩策略对STR更有效。
- 引入解耦设计以缓解遮罩图像对对比学习的影响。
点此查看论文截图


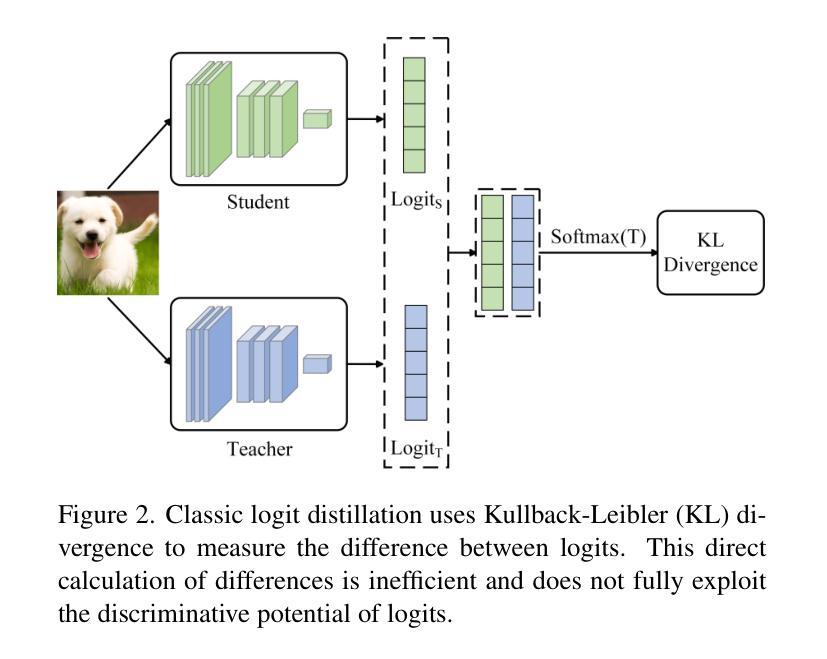
Multi-perspective Contrastive Logit Distillation
Authors:Qi Wang, Jinjia Zhou
We propose a novel and efficient logit distillation method, Multi-perspective Contrastive Logit Distillation (MCLD), which leverages contrastive learning to distill logits from multiple perspectives in knowledge distillation. Recent research on logit distillation has primarily focused on maximizing the information learned from the teacher model’s logits to enhance the performance of the student model. To this end, we propose MCLD, which consists of three key components: Instance-wise CLD, Sample-wise CLD, and Category-wise CLD. These components are designed to facilitate the transfer of more information from the teacher’s logits to the student model. Comprehensive evaluations on image classification tasks using CIFAR-100 and ImageNet, alongside representation transferability assessments on STL-10 and Tiny-ImageNet, highlight the significant advantages of our method. The knowledge distillation with our MCLD, surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods.
我们提出了一种新的高效logit蒸馏方法——多角度对比logit蒸馏(MCLD),该方法利用对比学习从多个角度进行知识蒸馏中的logit蒸馏。关于logit蒸馏的最新研究主要集中在最大化从教师模型的logit中学到的信息,以提高学生模型的性能。为此,我们提出了MCLD,它包括三个关键组件:实例级别的CLD、样本级别的CLD和类别级别的CLD。这些组件的设计旨在便于将更多信息从教师模型的logit转移到学生模型中。我们在CIFAR-100和ImageNet图像分类任务上进行了全面评估,并在STL-10和Tiny-ImageNet上进行了表示迁移性评估,凸显了我们方法的重要优势。使用我们的MCLD进行知识蒸馏超越了现有的最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 6 figures, 11 tabels, 9 formulas, including pseudo-code
Summary
提出一种新型高效的logit蒸馏方法——多角度对比logit蒸馏(MCLD),利用对比学习从多个角度对知识进行蒸馏。MCLD包括实例级、样本级和类别级的对比学习,旨在从教师模型的logit中向学生模型转移更多信息。在图像分类任务上的评估结果表明,使用MCLD的知识蒸馏超越了现有最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的logit蒸馏方法——多角度对比logit蒸馏(MCLD)。
- 利用对比学习,从多个角度进行知识蒸馏。
- MCLD包括实例级、样本级和类别级的对比学习组件。
- 该方法旨在从教师模型的logit中向学生模型转移更多信息。
- 在图像分类任务上的评估,包括CIFAR-100和ImageNet,显示了MCLD的优势。
- 在知识蒸馏方面的应用,MCLD超越了现有的最先进方法。
点此查看论文截图
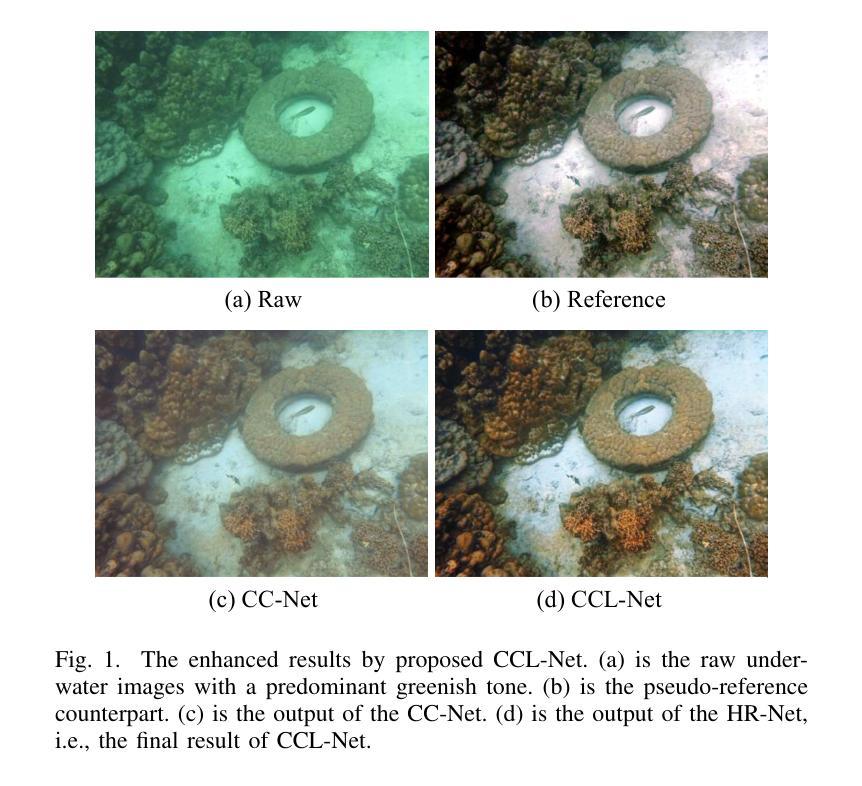
Underwater Image Enhancement with Cascaded Contrastive Learning
Authors:Yi Liu, Qiuping Jiang, Xinyi Wang, Ting Luo, Jingchun Zhou
Underwater image enhancement (UIE) is a highly challenging task due to the complexity of underwater environment and the diversity of underwater image degradation. Due to the application of deep learning, current UIE methods have made significant progress. Most of the existing deep learning-based UIE methods follow a single-stage network which cannot effectively address the diverse degradations simultaneously. In this paper, we propose to address this issue by designing a two-stage deep learning framework and taking advantage of cascaded contrastive learning to guide the network training of each stage. The proposed method is called CCL-Net in short. Specifically, the proposed CCL-Net involves two cascaded stages, i.e., a color correction stage tailored to the color deviation issue and a haze removal stage tailored to improve the visibility and contrast of underwater images. To guarantee the underwater image can be progressively enhanced, we also apply contrastive loss as an additional constraint to guide the training of each stage. In the first stage, the raw underwater images are used as negative samples for building the first contrastive loss, ensuring the enhanced results of the first color correction stage are better than the original inputs. While in the second stage, the enhanced results rather than the raw underwater images of the first color correction stage are used as the negative samples for building the second contrastive loss, thus ensuring the final enhanced results of the second haze removal stage are better than the intermediate color corrected results. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmark datasets demonstrate that our CCL-Net can achieve superior performance compared to many state-of-the-art methods. The source code of CCL-Net will be released at https://github.com/lewis081/CCL-Net.
水下图像增强(UIE)是一项极具挑战性的任务,因为水下环境的复杂性和水下图像退化的多样性。由于深度学习的应用,当前的UIE方法已经取得了显著的进步。大多数现有的基于深度学习的UIE方法遵循单阶段网络,无法同时有效地解决多种退化问题。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种两阶段深度学习框架,并利用级联对比学习来指导每个阶段的网络训练。所提方法简称为CCL-Net。具体来说,所提出的CCL-Net包括两个级联阶段,即针对色彩偏差问题的色彩校正阶段和旨在提高水下图像的可见度和对比度的除雾阶段。为了保证水下图像能够逐步增强,我们还采用对比损失作为额外的约束来指导每个阶段的训练。在第一阶段,将原始水下图像用作构建第一个对比损失的负样本,确保第一阶段色彩校正的增强结果优于原始输入。而在第二阶段,将第一阶段色彩校正的增强结果而非原始水下图像用作构建第二个对比损失的负样本,从而确保第二阶段除雾的最终增强结果优于中间色彩校正的结果。在多个基准数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的CCL-Net相较于许多最先进的方法可以实现卓越的性能。CCL-Net的源代码将在https://github.com/lewis030/CCL-Net上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE Transacitons on MultiMedia
总结
本文提出了一种基于深度学习的两阶段水下图像增强方法,名为CCL-Net。该方法通过颜色校正阶段和烟雾去除阶段来解决水下图像存在的多样化和复杂性问题。在每个阶段,使用级联对比学习作为网络训练的指导,以确保图像逐渐改进。通过广泛的基准测试集实验,证明了CCL-Net相比其他先进的方法具有卓越的性能。
关键见解
- 当前的水下图像增强方法面临多种挑战,包括水下环境的复杂性和水下图像退化的多样性。
- 大多数现有的基于深度学习的水下图像增强方法采用单阶段网络,无法同时解决多样化的退化问题。
- 本文提出了一个两阶段的深度学习方法框架,通过颜色校正阶段解决颜色偏差问题,并通过烟雾去除阶段提高水下图像的可见度和对比度。
- 对比损失被用作每个阶段的附加约束,以确保图像逐渐增强。在第一阶段中,原始水下图像被用作负样本构建对比损失。在第二阶段中,第一阶段的颜色校正结果用于构建第二个对比损失,确保最终的增强结果优于中间结果。
- 通过多个基准数据集的实验证明,本文提出的CCL-Net相较于其他前沿方法表现出卓越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

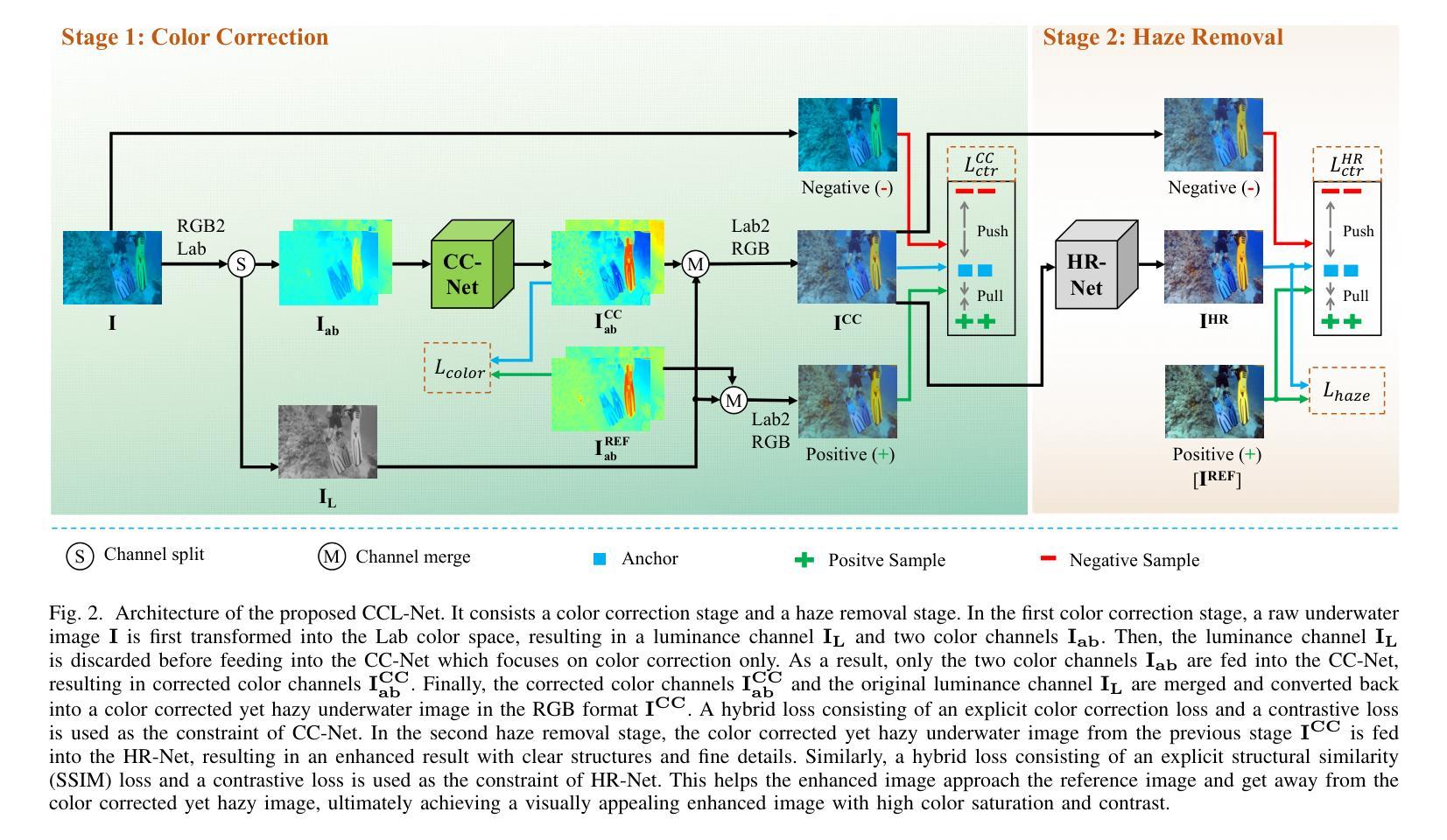

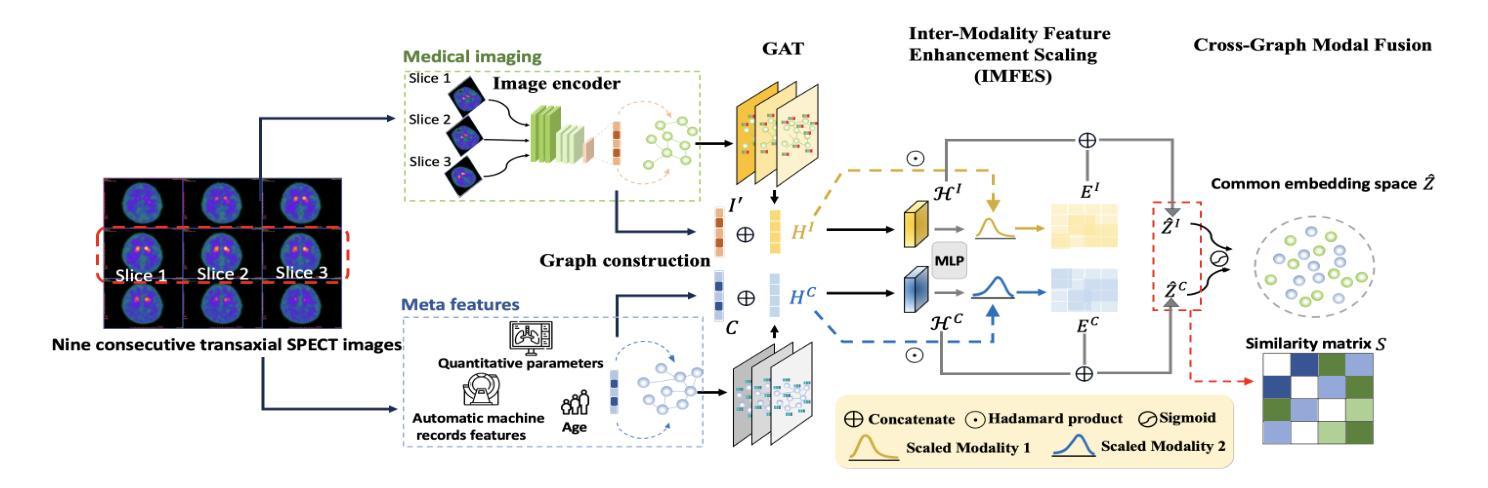
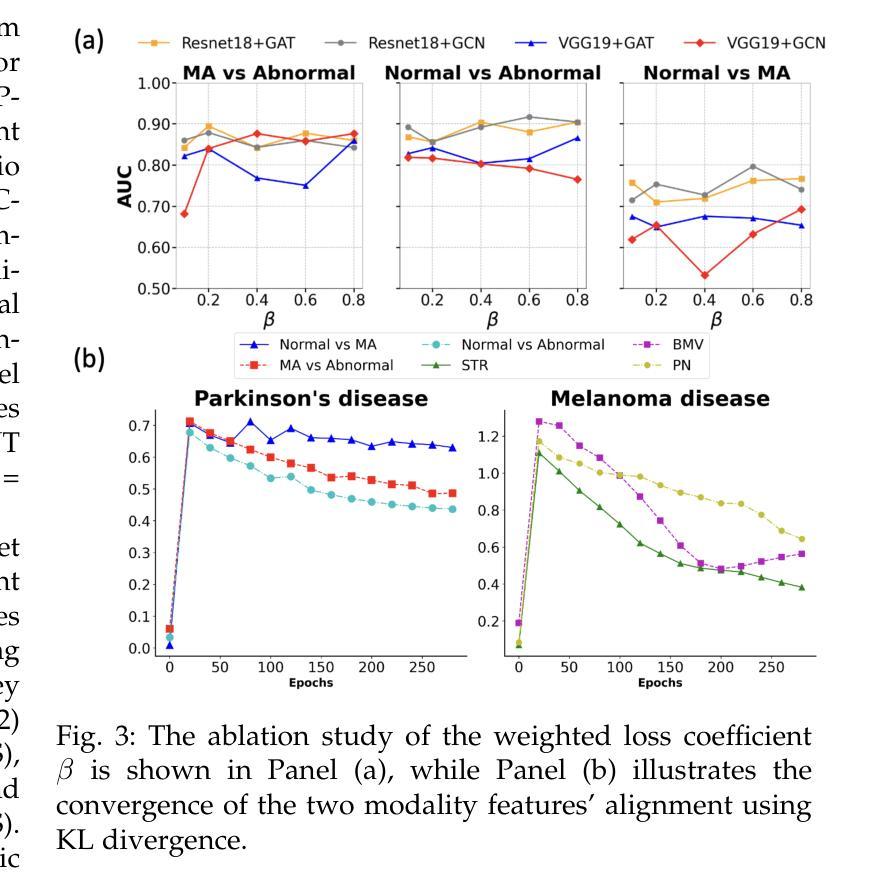
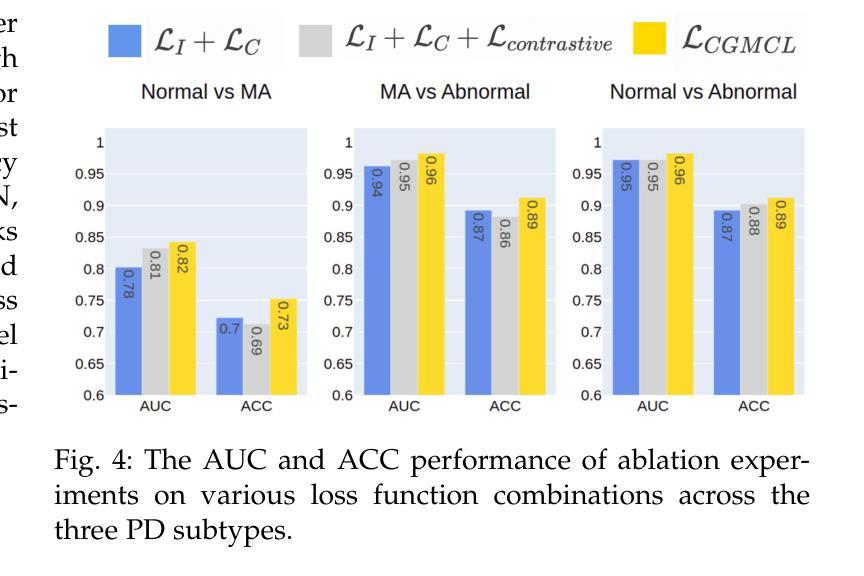
Enhancing Multimodal Medical Image Classification using Cross-Graph Modal Contrastive Learning
Authors:Jun-En Ding, Chien-Chin Hsu, Feng Liu
The classification of medical images is a pivotal aspect of disease diagnosis, often enhanced by deep learning techniques. However, traditional approaches typically focus on unimodal medical image data, neglecting the integration of diverse non-image patient data. This paper proposes a novel Cross-Graph Modal Contrastive Learning (CGMCL) framework for multimodal medical image classification. The model effectively integrates both image and non-image data by constructing cross-modality graphs and leveraging contrastive learning to align multimodal features in a shared latent space. An inter-modality feature scaling module further optimizes the representation learning process by reducing the gap between heterogeneous modalities. The proposed approach is evaluated on two datasets: a Parkinson’s disease (PD) dataset and a public melanoma dataset. Results demonstrate that CGMCL outperforms conventional unimodal methods in accuracy, interpretability, and early disease prediction. Additionally, the method shows superior performance in multi-class melanoma classification. The CGMCL framework provides valuable insights into medical image classification while offering improved disease interpretability and predictive capabilities.
医疗图像分类是疾病诊断的关键环节,往往可以通过深度学习技术得到增强。然而,传统方法通常专注于单模态医疗图像数据,忽略了不同非图像患者数据的整合。本文针对多模态医疗图像分类,提出了一种新型的跨图模态对比学习(CGMCL)框架。该模型通过构建跨模态图并利用对比学习来对齐多模态特征在共享潜在空间,从而有效地整合图像和非图像数据。跨模态特征缩放模块进一步优化了表示学习过程,缩小了不同模态之间的差距。所提出的方法在两个数据集上进行了评估:帕金森病(PD)数据集和公共黑色素瘤数据集。结果表明,在准确性、可解释性和早期疾病预测方面,CGMCL优于传统单模态方法。此外,该方法在多类黑色素瘤分类中表现出卓越的性能。CGMCL框架为医疗图像分类提供了有价值的见解,同时提高了疾病可解释性和预测能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于跨模态图对比学习(CGMCL)的多模态医学图像分类框架。该框架通过构建跨模态图并利用对比学习,有效地整合了图像和非图像数据。此外,还通过优化不同模态间特征的比例,减少不同模态之间的差异,进一步提高特征学习的表现。实验结果表明,在帕金森病和黑色素瘤数据集上,CGmcl框架的分类性能优于传统的单模态方法,在准确性和早期疾病预测方面表现出显著优势。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分类是疾病诊断的关键环节,但传统方法主要关注单模态医学图像数据,忽略了非图像数据的整合。
- 本文提出了一种新的跨模态图对比学习(CGmcl)框架,实现了多模态医学图像的有效分类。
- 该框架利用对比学习技术和构建跨模态图,成功融合了图像和非图像数据。
- 通过优化不同模态特征的比例,该框架减少了不同模态之间的差异,提高了特征学习的效果。
- 在帕金森病和黑色素瘤数据集上的实验结果表明,CGmcl框架在分类性能上优于传统方法。
- CGMCL框架在提高医学图像分类的准确性和早期疾病预测方面表现出显著优势。
点此查看论文截图
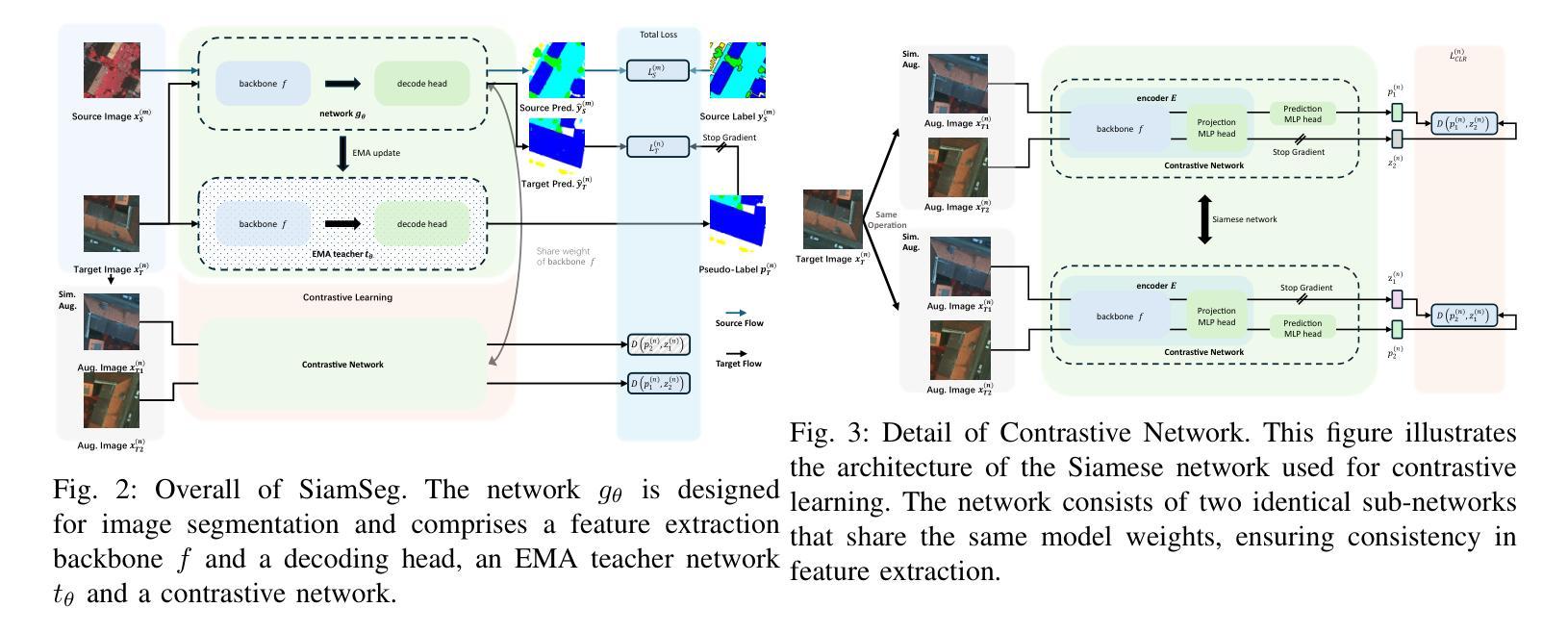
SiamSeg: Self-Training with Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation Semantic Segmentation in Remote Sensing
Authors:Bin Wang, Fei Deng, Shuang Wang, Wen Luo, Zhixuan Zhang, Peifan Jiang
Semantic segmentation of remote sensing (RS) images is a challenging yet essential task with broad applications. While deep learning, particularly supervised learning with large-scale labeled datasets, has significantly advanced this field, the acquisition of high-quality labeled data remains costly and time-intensive. Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) provides a promising alternative by enabling models to learn from unlabeled target domain data while leveraging labeled source domain data. Recent self-training (ST) approaches employing pseudo-label generation have shown potential in mitigating domain discrepancies. However, the application of ST to RS image segmentation remains underexplored. Factors such as variations in ground sampling distance, imaging equipment, and geographic diversity exacerbate domain shifts, limiting model performance across domains. In that case, existing ST methods, due to significant domain shifts in cross-domain RS images, often underperform. To address these challenges, we propose integrating contrastive learning into UDA, enhancing the model’s ability to capture semantic information in the target domain by maximizing the similarity between augmented views of the same image. This additional supervision improves the model’s representational capacity and segmentation performance in the target domain. Extensive experiments conducted on RS datasets, including Potsdam, Vaihingen, and LoveDA, demonstrate that our method, SimSeg, outperforms existing approaches, achieving state-of-the-art results. Visualization and quantitative analyses further validate SimSeg’s superior ability to learn from the target domain. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/woldier/SiamSeg.
遥感(RS)图像的语义分割是一项具有挑战性但至关重要的任务,广泛应用于各个领域。深度学习,特别是利用大规模标记数据集进行监督学习,已经大大推动了这一领域的发展,但是获取高质量标记数据仍然成本高昂且耗时。无监督域自适应(UDA)提供了一种有前途的替代方案,使模型能够从目标域的无标签数据中学习,同时利用源域的有标签数据。最近采用伪标签生成进行自我训练(ST)的方法在减少域差异方面显示出潜力。然而,将ST应用于RS图像分割仍然未被充分探索。地面采样距离、成像设备和地理多样性的变化等因素加剧了域偏移,限制了模型在不同域之间的性能。在这种情况下,由于跨域RS图像中的域偏移较大,现有的ST方法往往表现不佳。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出将对比学习整合到UDA中,通过最大化同一图像的增强视图之间的相似性,增强模型在目标域捕获语义信息的能力。这种额外的监督提高了模型在目标域中的表示能力和分割性能。在包括Potsdam、Vaihingen和LoveDA的RS数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的SimSeg方法优于现有方法,达到了最新技术水平。可视化及定量分析进一步验证了SimSeg从目标域学习的高级能力。代码已公开在https://github.com/woldier/SiamSeg。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
遥感图像语义分割是一项具有挑战性的重要任务,广泛应用于各个领域。深度学习,特别是使用大规模标记数据集进行监督学习,已在此领域取得了显著进展。然而,获取高质量标记数据成本高昂且耗时。无监督域自适应(UDA)提供了一种有前途的替代方案,使模型能够从无标签的目标域数据中学习,同时利用有标签的源域数据。最近采用伪标签生成的自训练(ST)方法显示出减少域差异潜力。然而,将ST应用于遥感图像分割仍被较少探索。由于地面采样距离、成像设备和地理多样性的变化导致的域偏移因素加剧了模型跨域的性差距。在这种情况下,由于遥感图像跨域的巨大域偏移,现有的ST方法往往表现不佳。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出将对比学习整合到UDA中,通过最大化同一图像增强视图之间的相似性,增强模型在目标域捕获语义信息的能力。这种额外的监督提高了模型的表征能力和目标域的分割性能。在包括Potsdam、Vaihingen和LoveDA在内的遥感数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的SimSeg方法优于现有方法,达到最先进的水平。可视化定量分析了SimSeg从目标域学习的高级能力。代码公开在:https://github.com/woldier/SiamSeg。
关键见解
- 遥感图像语义分割是一个具有挑战性和广泛应用的任务。
- 深度学习和监督学习在遥感图像分割中取得了进展,但标记数据获取成本高昂且耗时。
- 无监督域自适应(UDA)为从目标域无标签数据中学习提供了解决方案。
- 自训练(ST)方法通过伪标签生成显示出减少域差异潜力,但在遥感图像分割中应用有限。
- 域偏移因素如地面采样距离、成像设备和地理多样性加剧了跨域模型的性能差异。
- 对比学习被整合到UDA中,通过最大化同一图像的增强视图之间的相似性,增强了模型在目标域的语义捕获能力。
- SimSeg方法通过结合无监督学习和对比学习在遥感图像分割上取得了先进的结果。
点此查看论文截图

Bridging Text and Image for Artist Style Transfer via Contrastive Learning
Authors:Zhi-Song Liu, Li-Wen Wang, Jun Xiao, Vicky Kalogeiton
Image style transfer has attracted widespread attention in the past few years. Despite its remarkable results, it requires additional style images available as references, making it less flexible and inconvenient. Using text is the most natural way to describe the style. More importantly, text can describe implicit abstract styles, like styles of specific artists or art movements. In this paper, we propose a Contrastive Learning for Artistic Style Transfer (CLAST) that leverages advanced image-text encoders to control arbitrary style transfer. We introduce a supervised contrastive training strategy to effectively extract style descriptions from the image-text model (i.e., CLIP), which aligns stylization with the text description. To this end, we also propose a novel and efficient adaLN based state space models that explore style-content fusion. Finally, we achieve a text-driven image style transfer. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in artistic style transfer. More importantly, it does not require online fine-tuning and can render a 512x512 image in 0.03s.
图像风格转换在近几年内引起了广泛的关注。尽管其取得了显著的效果,但它需要额外的风格图像作为参考,这使得其灵活性较差,使用不便。使用文本是最自然地描述风格的方式。更重要的是,文本可以描述隐含的抽象风格,如特定艺术家的风格或艺术运动风格。在本文中,我们提出了一种用于艺术风格转换的对比学习(CLAST)方法,该方法利用先进的图像文本编码器来控制任意风格转换。我们引入了一种有监督的对比训练策略,以有效地从图像文本模型(例如CLIP)中提取风格描述,使风格化与文本描述保持一致。为此,我们还提出了一种基于adaLN的新型高效状态空间模型,探索风格内容的融合。最终,我们实现了文本驱动图像风格转换。大量实验表明,我们的方法在艺术风格转换方面优于现有先进技术。更重要的是,它不需要在线微调,可以在0.03秒内渲染一个512x512的图像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 8 figures. arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2202.13562
Summary
基于文本描述的艺术风格迁移对比学习。该研究利用先进的图像文本编码器进行任意风格迁移,采用监督对比训练策略从图像文本模型(如CLIP)中提取风格描述,并与文本描述对齐。提出高效的状态空间模型,实现文本驱动图像风格迁移,显著优于现有方法,且无需在线微调,可快速渲染图像。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究关注图像风格迁移领域,尤其是如何利用文本描述进行风格迁移。
- 提出一种基于对比学习的艺术风格迁移方法(CLAST),利用图像文本编码器进行控制。
- 采用监督对比训练策略,从图像文本模型(如CLIP)中提取风格描述,实现与文本描述的对齐。
- 引入一种新的高效状态空间模型(adaLN),探索风格与内容融合。
- 实现文本驱动的图像风格迁移,显著优于现有方法。
- 无需在线微调,可快速渲染高分辨率图像(如512x512像素)。
点此查看论文截图



Adaptive Patch Contrast for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Wangyu Wu, Tianhong Dai, Zhenhong Chen, Xiaowei Huang, Jimin Xiao, Fei Ma, Renrong Ouyang
Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) using only image-level labels has gained significant attention due to its cost-effectiveness. The typical framework involves using image-level labels as training data to generate pixel-level pseudo-labels with refinements. Recently, methods based on Vision Transformers (ViT) have demonstrated superior capabilities in generating reliable pseudo-labels, particularly in recognizing complete object regions, compared to CNN methods. However, current ViT-based approaches have some limitations in the use of patch embeddings, being prone to being dominated by certain abnormal patches, as well as many multi-stage methods being time-consuming and lengthy in training, thus lacking efficiency. Therefore, in this paper, we introduce a novel ViT-based WSSS method named \textit{Adaptive Patch Contrast} (APC) that significantly enhances patch embedding learning for improved segmentation effectiveness. APC utilizes an Adaptive-K Pooling (AKP) layer to address the limitations of previous max pooling selection methods. Additionally, we propose a Patch Contrastive Learning (PCL) to enhance patch embeddings, thereby further improving the final results. Furthermore, we improve upon the existing multi-stage training framework without CAM by transforming it into an end-to-end single-stage training approach, thereby enhancing training efficiency. The experimental results show that our approach is effective and efficient, outperforming other state-of-the-art WSSS methods on the PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 dataset within a shorter training duration.
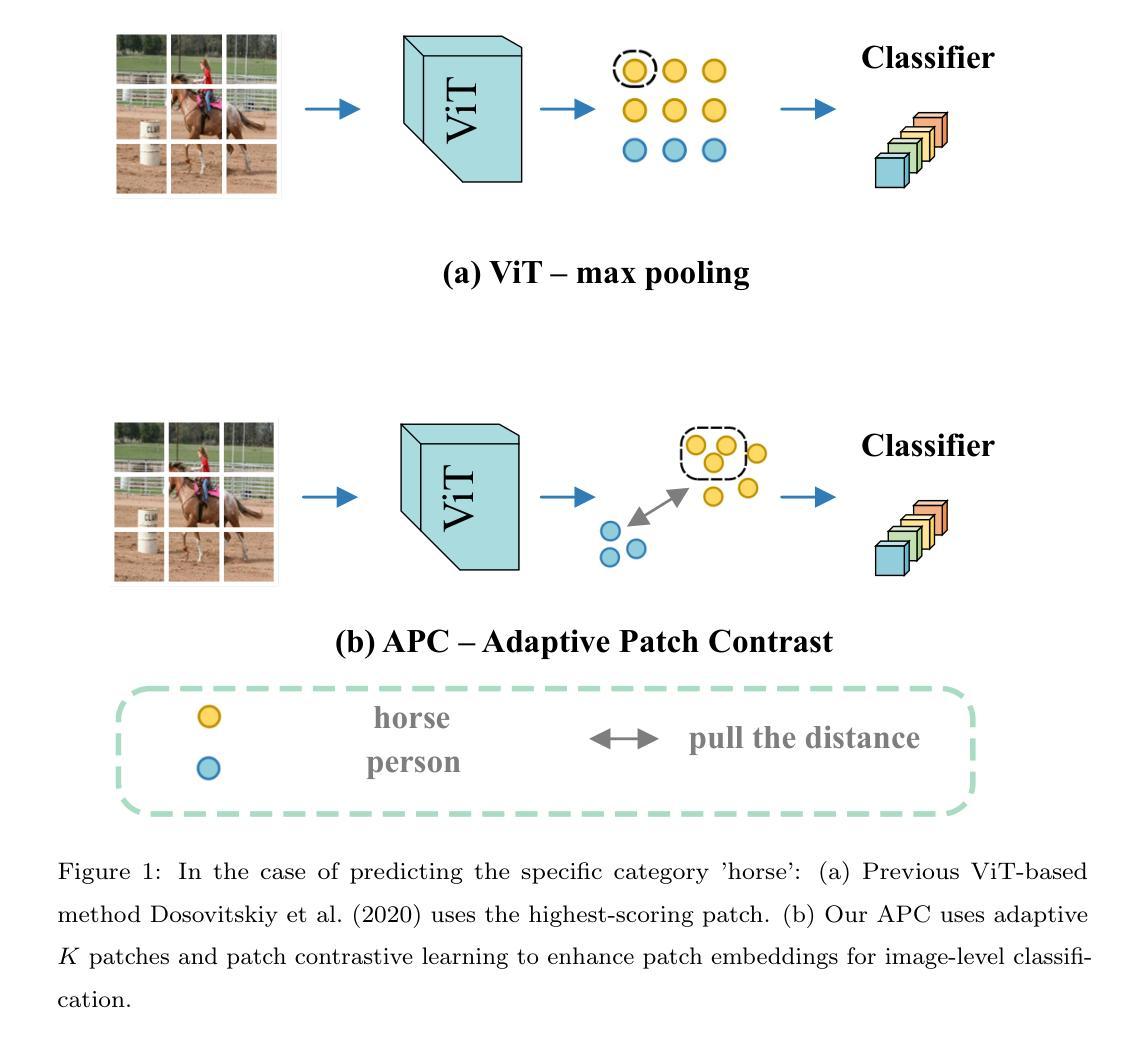
使用仅图像级标签的弱监督语义分割(WSSS)因其成本效益而备受关注。典型的框架是使用图像级标签作为训练数据,通过改进生成像素级伪标签。最近,基于视觉转换器(ViT)的方法在生成可靠的伪标签方面表现出了卓越的能力,特别是在识别完整的对象区域方面优于CNN方法。然而,当前的ViT方法在使用补丁嵌入时存在一些局限性,容易受到某些异常补丁的主导,而且许多多阶段方法训练耗时且冗长,因此缺乏效率。因此,本文介绍了一种新型的基于ViT的WSSS方法,名为自适应补丁对比(APC),它显著增强了补丁嵌入学习,提高了分割效果。APC利用自适应K池化(AKP)层解决了以前最大池化选择方法的局限性。此外,我们提出了补丁对比学习(PCL)来增强补丁嵌入,从而进一步提高最终结果。此外,我们改进了现有的多阶段训练框架,将其转变为端到端的单阶段训练方法,提高了训练效率。实验结果表明,我们的方法高效且有效,在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上的表现优于其他先进的WSSS方法,且训练时间更短。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the EAAI Journal
Summary
本文提出了一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的弱监督语义分割(WSSS)新方法——自适应补丁对比(APC),用于改进补丁嵌入学习以提高分割效果。APC通过自适应K池化层解决先前最大池化选择方法的局限性,并提出补丁对比学习(PCL)增强补丁嵌入,从而进一步提高最终结果。此外,我们将现有的多阶段训练框架改进为端到端的单阶段训练,提高了训练效率。实验结果表明,该方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上表现出色,训练时间短。
Key Takeaways
- WSSS利用图像级标签作为训练数据生成像素级伪标签,具有成本效益。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)在生成可靠的伪标签方面表现出卓越的能力,特别是在识别完整对象区域方面优于CNN方法。
- 当前ViT方法在使用补丁嵌入时存在局限性,容易受到异常补丁的主导。
- 本文提出了一种新的ViT-based WSSS方法——自适应补丁对比(APC),增强了补丁嵌入学习以提高分割效果。
- APC通过自适应K池化层和补丁对比学习(PCL)解决先前方法的局限性,进一步提高分割结果的准确性。
- 本文改进了现有的多阶段训练框架,将其转换为端到端的单阶段训练,提高了训练效率。
点此查看论文截图

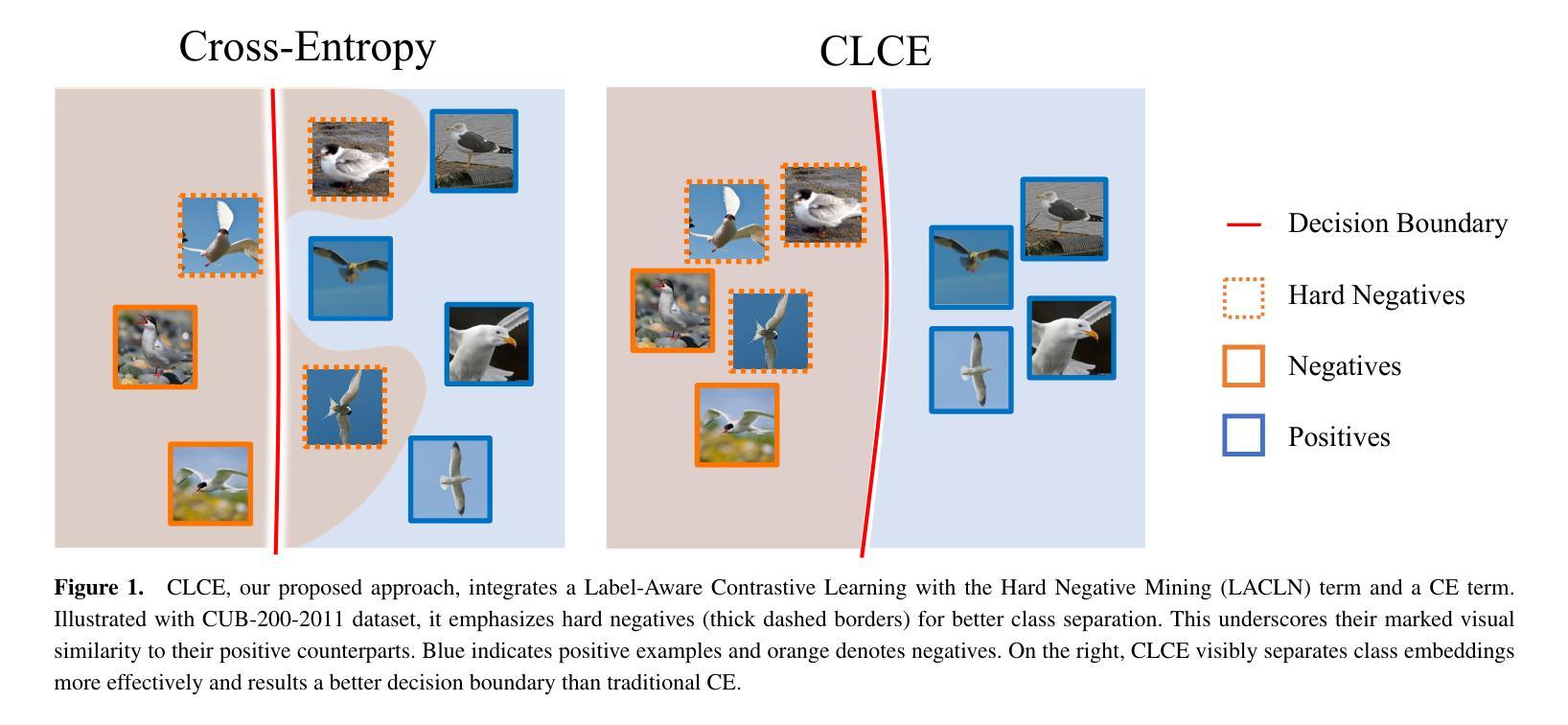
CLCE: An Approach to Refining Cross-Entropy and Contrastive Learning for Optimized Learning Fusion
Authors:Zijun Long, George Killick, Lipeng Zhuang, Gerardo Aragon-Camarasa, Zaiqiao Meng, Richard Mccreadie
State-of-the-art pre-trained image models predominantly adopt a two-stage approach: initial unsupervised pre-training on large-scale datasets followed by task-specific fine-tuning using Cross-Entropy loss~(CE). However, it has been demonstrated that CE can compromise model generalization and stability. While recent works employing contrastive learning address some of these limitations by enhancing the quality of embeddings and producing better decision boundaries, they often overlook the importance of hard negative mining and rely on resource intensive and slow training using large sample batches. To counter these issues, we introduce a novel approach named CLCE, which integrates Label-Aware Contrastive Learning with CE. Our approach not only maintains the strengths of both loss functions but also leverages hard negative mining in a synergistic way to enhance performance. Experimental results demonstrate that CLCE significantly outperforms CE in Top-1 accuracy across twelve benchmarks, achieving gains of up to 3.52% in few-shot learning scenarios and 3.41% in transfer learning settings with the BEiT-3 model. Importantly, our proposed CLCE approach effectively mitigates the dependency of contrastive learning on large batch sizes such as 4096 samples per batch, a limitation that has previously constrained the application of contrastive learning in budget-limited hardware environments.
当前先进的预训练图像模型主要采取两阶段方法:首先在大型数据集上进行初始的无监督预训练,然后使用交叉熵损失(CE)进行特定任务的微调。然而,已经证明CE可能损害模型的泛化和稳定性。虽然最近采用对比学习的方法通过提高嵌入质量和产生更好的决策边界来解决这些限制,但它们往往忽视了硬负样本挖掘的重要性,并依赖于资源密集型和缓慢的大样本批次训练。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种名为CLCE的新方法,它将标签感知对比学习与CE相结合。我们的方法不仅保持了两种损失函数的优点,而且以协同方式利用硬负样本挖掘来提高性能。实验结果表明,CLCE在十二个基准测试中显著优于CE,在少镜头学习场景中实现了高达3.52%的增益,在迁移学习设置中实现了3.41%的增益,使用BEiT-3模型。重要的是,我们提出的CLCE方法有效地缓解了对比学习对大量批次大小的依赖,例如每个批次4096个样本,这一限制以前在有预算限制硬件环境中限制了对比学习的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为CLCE的新方法,它将标签感知对比学习与交叉熵(CE)相结合,旨在解决当前图像模型使用CE损失带来的泛化能力和稳定性问题。CLCE不仅结合了两种损失函数的优势,还通过硬负样本挖掘提高了性能。实验结果表明,CLCE在十二个基准测试中显著优于CE,在少样本学习场景中提高了高达3.52%的Top-1准确率,在迁移学习设置中提高了3.41%。此外,CLCE还解决了对比学习对大批次大小的依赖问题,使其更适合预算有限的硬件环境。
Key Takeaways
- 当前图像模型主要采用的预训练方法是两阶段法:首先是基于大规模数据集的无监督预训练,然后是使用交叉熵(CE)损失的特定任务微调。
- 交叉熵损失可能损害模型的泛化和稳定性。
- 对比学习方法已用于增强嵌入质量和决策边界,但常常忽视硬负样本挖掘,且依赖于资源密集型的大样本批次训练。
- 提出的CLCE方法结合了标签感知对比学习与交叉熵的优势,并通过协同方式利用硬负样本挖掘来提高性能。
- CLCE在少样本学习和迁移学习场景下显著优于交叉熵,并在多个基准测试中实现性能提升。
- CLCE有效减轻了对比学习对大批次大小的依赖,使其更适用于硬件资源有限的环境。
点此查看论文截图

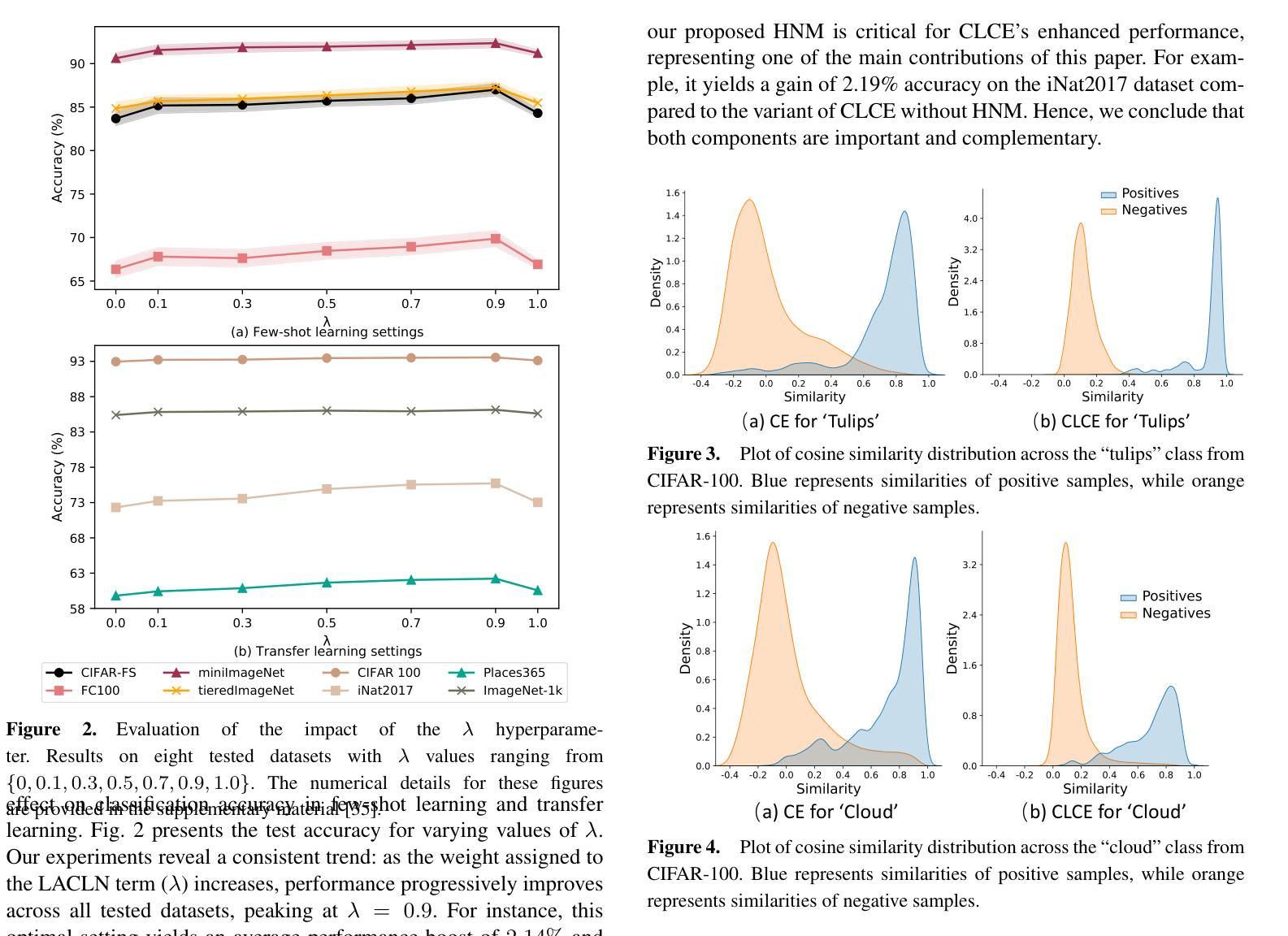
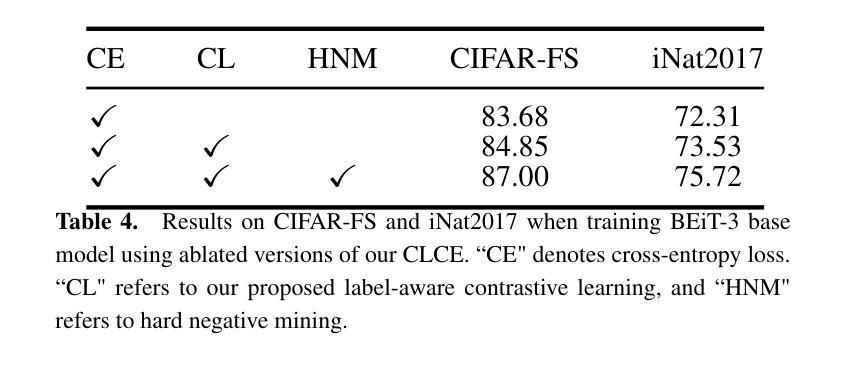
Emotion-Aligned Contrastive Learning Between Images and Music
Authors:Shanti Stewart, Kleanthis Avramidis, Tiantian Feng, Shrikanth Narayanan
Traditional music search engines rely on retrieval methods that match natural language queries with music metadata. There have been increasing efforts to expand retrieval methods to consider the audio characteristics of music itself, using queries of various modalities including text, video, and speech. While most approaches aim to match general music semantics to the input queries, only a few focus on affective qualities. In this work, we address the task of retrieving emotionally-relevant music from image queries by learning an affective alignment between images and music audio. Our approach focuses on learning an emotion-aligned joint embedding space between images and music. This embedding space is learned via emotion-supervised contrastive learning, using an adapted cross-modal version of the SupCon loss. We evaluate the joint embeddings through cross-modal retrieval tasks (image-to-music and music-to-image) based on emotion labels. Furthermore, we investigate the generalizability of the learned music embeddings via automatic music tagging. Our experiments show that the proposed approach successfully aligns images and music, and that the learned embedding space is effective for cross-modal retrieval applications.
传统音乐搜索引擎依赖于匹配自然语言查询和音乐元数据的方法来进行检索。目前,人们正越来越多地努力扩展检索方法,以考虑音乐本身的音频特征,并使用包括文本、视频和语音在内的各种模态查询。虽然大多数方法旨在将一般音乐语义与输入查询相匹配,但只有少数方法关注情感品质。在这项工作中,我们通过学习图像和音乐音频之间的情感对齐来解决从图像查询中检索情感相关音乐的任务。我们的方法侧重于在图像和音乐之间学习一个情感对齐的联合嵌入空间。这个嵌入空间是通过情感监督对比学习来学习的,使用适应的跨模态版本的SupCon损失。我们通过基于情感标签的跨模态检索任务(图像到音乐和音乐到图像)来评估联合嵌入。此外,我们还通过自动音乐标记来探讨学习到的音乐嵌入的泛化能力。我们的实验表明,所提出的方法成功地对齐了图像和音乐,并且学习到的嵌入空间对于跨模态检索应用是有效的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at ICASSP 2024. Code: https://github.com/shantistewart/Emo-CLIM
摘要
本文关注图像与音乐之间的情感对齐问题,提出了一种通过情绪监督对比学习的方法来实现图像和音乐之间的联合嵌入空间学习。该研究采用跨模态版本的SupCon损失进行适应调整,通过情感标签进行跨模态检索任务评估,并探究了音乐嵌入的可泛化性。实验表明,该方法成功实现了图像和音乐的对齐,并有效应用于跨模态检索应用。
关键见解
- 传统音乐搜索引擎主要依赖自然语言查询与音乐元数据匹配进行检索。
- 目前已有研究扩展检索方法,考虑音乐的音频特性及多种查询模式,如文本、视频和语音。
- 大多数方法旨在匹配一般音乐语义到输入查询,而只有少数关注情感特质。
- 本研究通过情感监督对比学习实现图像和音乐之间的情感对齐。
- 提出了一种情绪对齐的跨模态联合嵌入空间学习方法。
- 通过情感标签进行跨模态检索任务评估,证实所学嵌入空间的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

Cross-View-Prediction: Exploring Contrastive Feature for Hyperspectral Image Classification
Authors:Anyu Zhang, Haotian Wu, Zeyu Cao
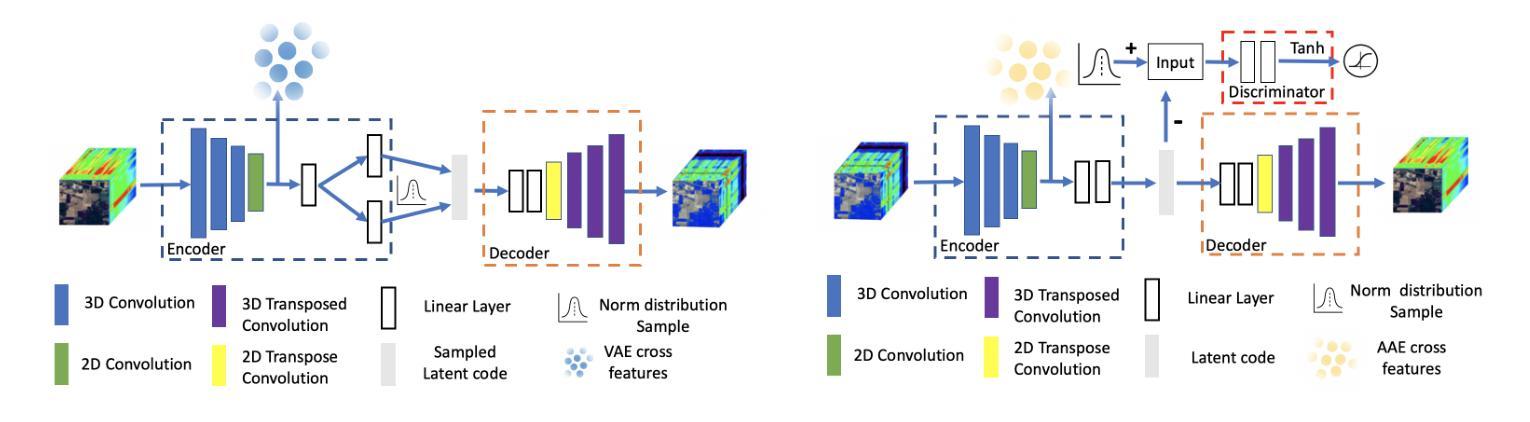
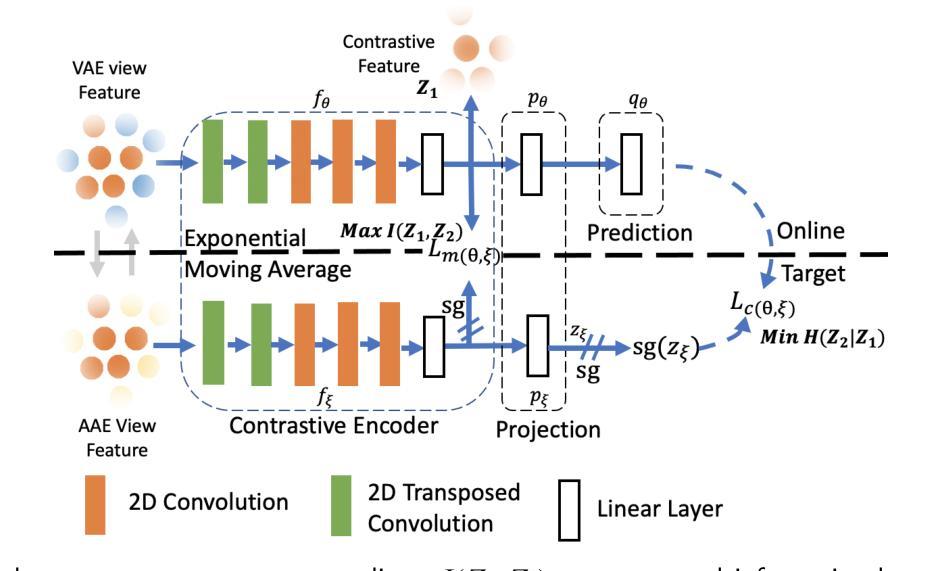
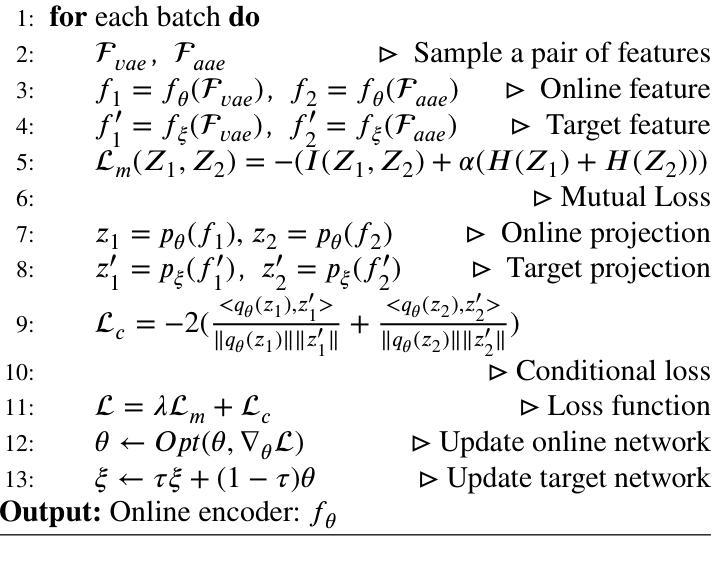
This paper presents a self-supervised feature learning method for hyperspectral image classification. Our method tries to construct two different views of the raw hyperspectral image through a cross-representation learning method. And then to learn semantically consistent representation over the created views by contrastive learning method. Specifically, four cross-channel-prediction based augmentation methods are naturally designed to utilize the high dimension characteristic of hyperspectral data for the view construction. And the better representative features are learned by maximizing mutual information and minimizing conditional entropy across different views from our contrastive network. This ‘Cross-View-Predicton’ style is straightforward and gets the state-of-the-art performance of unsupervised classification with a simple SVM classifier.
本文提出了一种用于高光谱图像分类的自监督特征学习方法。我们的方法试图通过跨表示学习方法构建高光谱原始图像的两个不同视图。然后,通过对比学习方法学习创建的视图上语义一致的表示。具体来说,基于四通道预测的增强方法自然地利用高光谱数据的高维特性来构建视图。通过最大化互信息和最小化来自对比网络不同视图之间的条件熵,学习更具代表性的特征。这种“跨视图预测”风格简单直接,使用简单的SVM分类器即可实现最先进的无监督分类性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文提出一种基于自监督特征学习的超光谱图像分类方法。通过跨表示学习方法构建超光谱图像的不同视图,然后采用对比学习方法学习语义一致的表示。设计四种基于跨通道预测的增强方法,利用超光谱数据的高维特性进行视图构建。通过最大化互信息和最小化条件熵,从对比网络中学习更具代表性的特征。这种“跨视图预测”风格简单直接,采用简单的SVM分类器便获得无监督分类的最新性能。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了一种自监督特征学习方法用于超光谱图像分类。
- 通过跨表示学习方法构建图像的不同视图。
- 采用对比学习方法学习语义一致的表示。
- 设计了四种基于跨通道预测的增强方法,利用超光谱数据的高维特性。
- 通过对比网络最大化互信息和最小化条件熵,学习更具代表性的特征。
- 该方法在无监督分类任务中表现出色,达到了最新性能水平。
点此查看论文截图