⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-11 更新
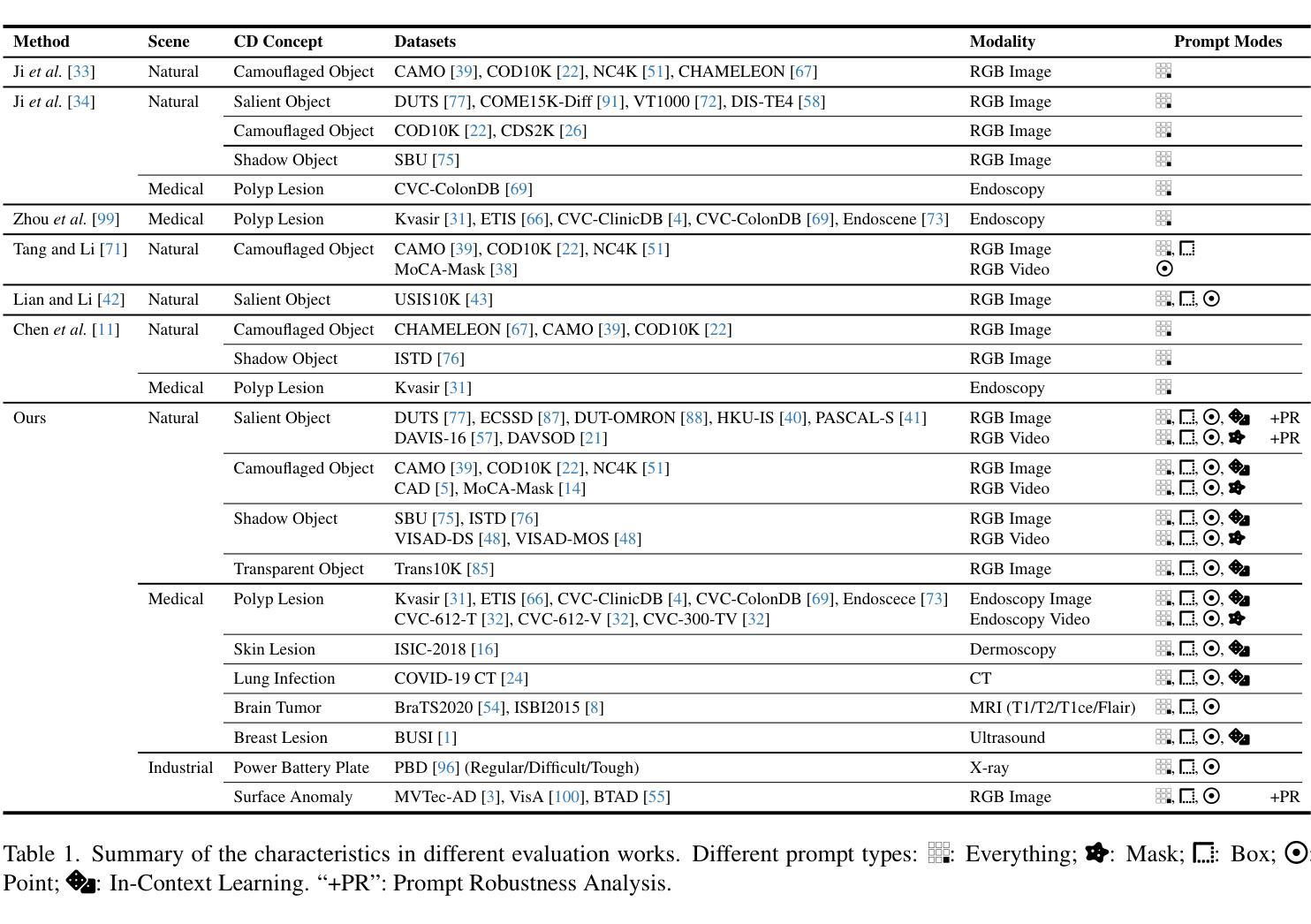
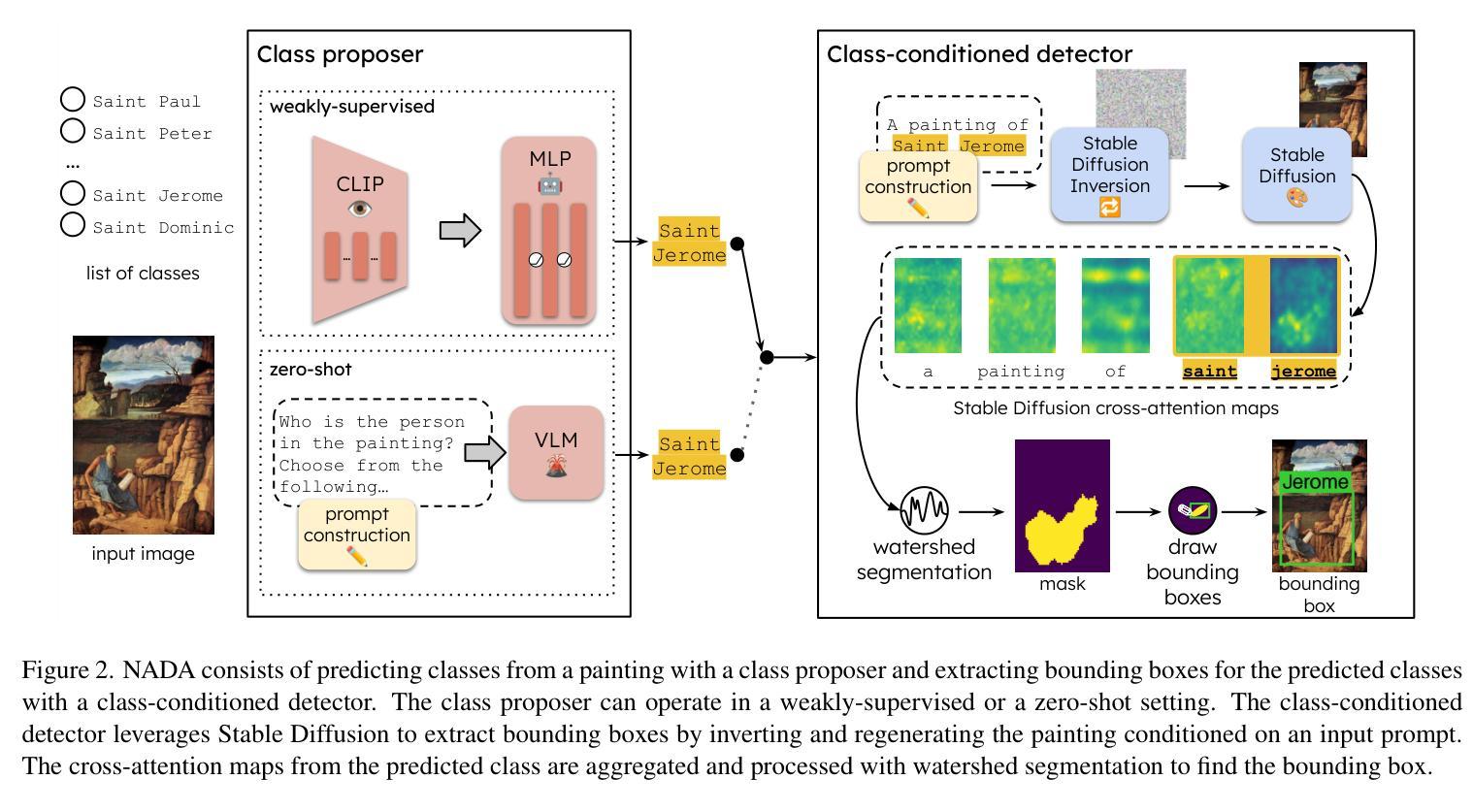
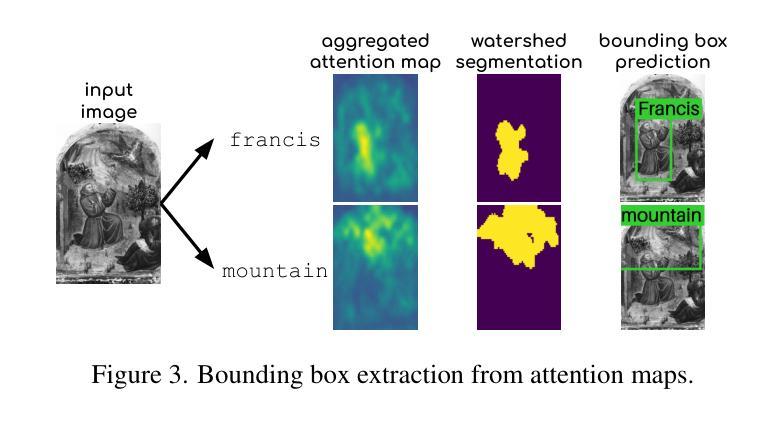
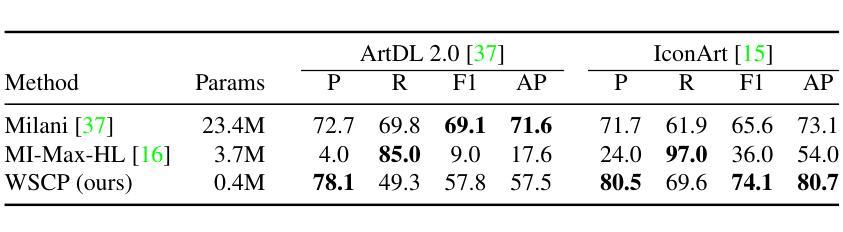
No Annotations for Object Detection in Art through Stable Diffusion
Authors:Patrick Ramos, Nicolas Gonthier, Selina Khan, Yuta Nakashima, Noa Garcia
Object detection in art is a valuable tool for the digital humanities, as it allows for faster identification of objects in artistic and historical images compared to humans. However, annotating such images poses significant challenges due to the need for specialized domain expertise. We present NADA (no annotations for detection in art), a pipeline that leverages diffusion models’ art-related knowledge for object detection in paintings without the need for full bounding box supervision. Our method, which supports both weakly-supervised and zero-shot scenarios and does not require any fine-tuning of its pretrained components, consists of a class proposer based on large vision-language models and a class-conditioned detector based on Stable Diffusion. NADA is evaluated on two artwork datasets, ArtDL 2.0 and IconArt, outperforming prior work in weakly-supervised detection, while being the first work for zero-shot object detection in art. Code is available at https://github.com/patrick-john-ramos/nada
艺术中的目标检测对于数字人文来说是一个有价值的工具,因为它与人类相比,可以更快地识别艺术和历史图像中的目标。然而,对这些图像进行标注却面临着巨大的挑战,因为需要专业的领域知识。我们提出了NADA(艺术中无需注释的检测),这是一种管道,它利用扩散模型的与艺术相关的知识,在绘画中进行目标检测,无需完整的边界框监督。我们的方法支持弱监督和无源场景,并且不需要对其预训练组件进行任何微调,它由基于大型视觉语言模型的类提出者和基于Stable Diffusion的类条件检测器组成。NADA在ArtDL 2.0和IconArt两个艺术品数据集上进行了评估,在弱监督检测方面优于先前的工作,并且是艺术中无源目标检测的第一项工作。代码可在https://github.com/patrick-john-ramos/nada找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures, to be published in WACV 2025
Summary
基于艺术领域的扩散模型技术,NADA模型可实现无标注对象检测,可广泛应用于画作中,无需精细标注框。该方法采用大型视觉语言模型和稳定扩散技术,支持弱监督和无源检测场景,预训练组件无需微调。NADA模型在ArtDL 2.0和IconArt两个艺术品数据集上的表现优于现有弱监督检测工作,并且是艺术品零样本目标检测的首次工作。
Key Takeaways
- NADA模型利用扩散模型的艺术相关知识进行画作中的对象检测。
- 该方法无需完整的边界框标注,降低了标注难度。
- NADA模型基于大型视觉语言模型和稳定扩散技术构建。
- NADA模型支持弱监督和无源检测场景应用。
- 预训练组件无需微调即可应用于艺术品数据集。
- NADA模型在ArtDL 2.0和IconArt数据集上的表现优于其他弱监督检测方法。
点此查看论文截图

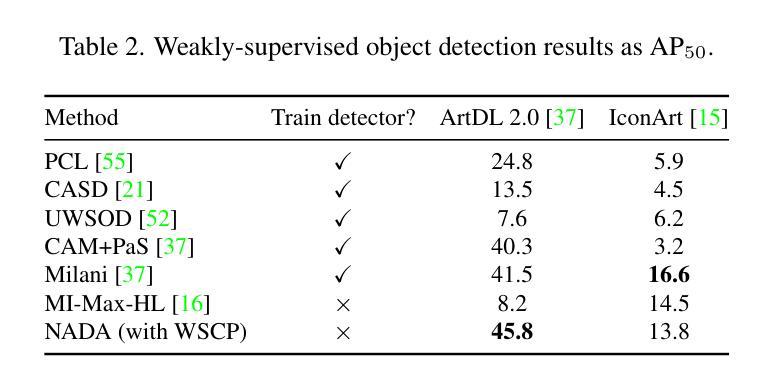
A Real-Time Defense Against Object Vanishing Adversarial Patch Attacks for Object Detection in Autonomous Vehicles
Authors:Jaden Mu
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) increasingly use DNN-based object detection models in vision-based perception. Correct detection and classification of obstacles is critical to ensure safe, trustworthy driving decisions. Adversarial patches aim to fool a DNN with intentionally generated patterns concentrated in a localized region of an image. In particular, object vanishing patch attacks can cause object detection models to fail to detect most or all objects in a scene, posing a significant practical threat to AVs. This work proposes ADAV (Adversarial Defense for Autonomous Vehicles), a novel defense methodology against object vanishing patch attacks specifically designed for autonomous vehicles. Unlike existing defense methods which have high latency or are designed for static images, ADAV runs in real-time and leverages contextual information from prior frames in an AV’s video feed. ADAV checks if the object detector’s output for the target frame is temporally consistent with the output from a previous reference frame to detect the presence of a patch. If the presence of a patch is detected, ADAV uses gradient-based attribution to localize adversarial pixels that break temporal consistency. This two stage procedure allows ADAV to efficiently process clean inputs, and both stages are optimized to be low latency. ADAV is evaluated using real-world driving data from the Berkeley Deep Drive BDD100K dataset, and demonstrates high adversarial and clean performance.
自动驾驶车辆(AVs)越来越多地采用基于深度神经网络(DNN)的对象检测模型进行视觉感知。正确检测和分类障碍物对于确保安全可靠的驾驶决策至关重要。对抗性补丁旨在用有意生成的图案欺骗DNN,这些图案集中在图像的局部区域。特别是,对象消失补丁攻击可能导致对象检测模型无法检测到场景中的大多数或所有对象,对自动驾驶汽车构成重大实际威胁。
本研究提出了ADAV(针对自动驾驶汽车的对抗性防御),这是一种专门用于对抗自动驾驶汽车所面临的对象消失补丁攻击的新型防御方法。与具有高音延迟或专为静态图像设计的现有防御方法不同,ADAV具有实时运行能力,并利用自动驾驶汽车视频馈送中先前帧的上下文信息。ADAV检查目标帧的对象检测器的输出是否与先前参考帧的输出在时间上一致,以检测补丁的存在。如果检测到补丁的存在,ADAV会使用基于梯度的归属来定位破坏时间一致性的对抗性像素。这个两阶段的过程允许ADAV有效地处理干净输入,两个阶段都经过优化以实现低延迟。使用Berkeley Deep Drive BDD100K数据集的现实世界驾驶数据对ADAV进行了评估,显示出其良好的对抗性和清洁性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度神经网络(DNN)的自动驾驶车辆(AV)对象检测模型在实际驾驶环境中面临攻击风险。ADAV防御策略是一种针对对象消失补丁攻击的新型实时防御方法,它通过利用视频流的上下文信息来提高防御效率。ADAV检测补丁存在与否,并通过梯度归因定位破坏时间一致性的像素点。该方法在Berkeley Deep Drive BDD100K数据集上的真实驾驶数据评估中表现出高对抗性和清洁性能。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶车辆越来越多地采用基于深度神经网络的对象检测模型,用于视觉感知。
- 对抗补丁可能使DNN对象检测模型无法正确识别障碍物,造成安全威胁。
- ADAV是一种针对自动驾驶车辆的实时防御策略,旨在抵御对象消失补丁攻击。
- ADAV利用视频流的上下文信息来提高防御效率,运行速度快且具有低延迟特性。
- ADAV通过检查目标帧的对象检测器输出是否与先前参考帧的输出在时间上一致来检测补丁的存在。
- ADAV采用梯度归因技术来定位破坏时间一致性的像素点,即对抗性像素。
点此查看论文截图


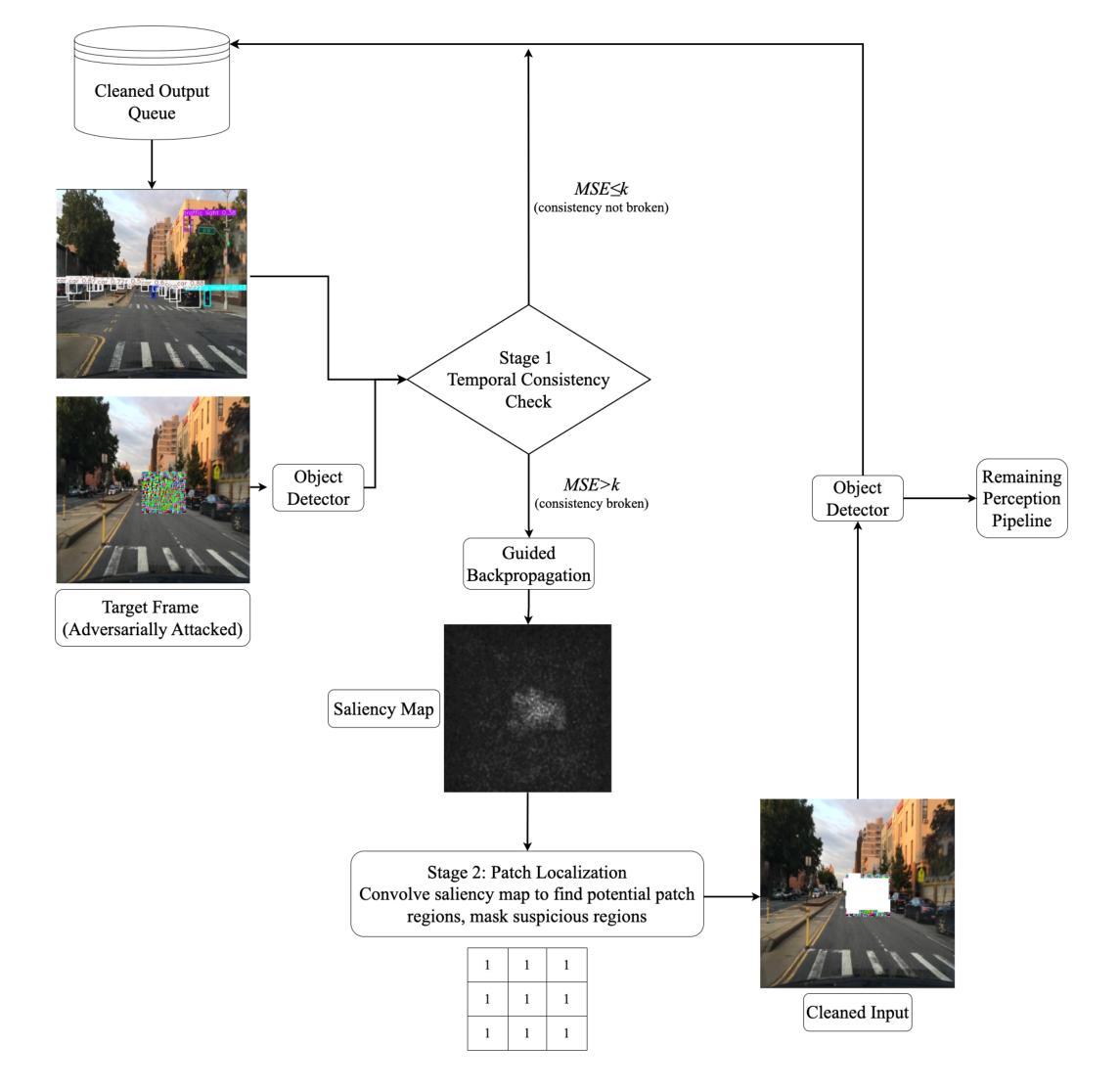
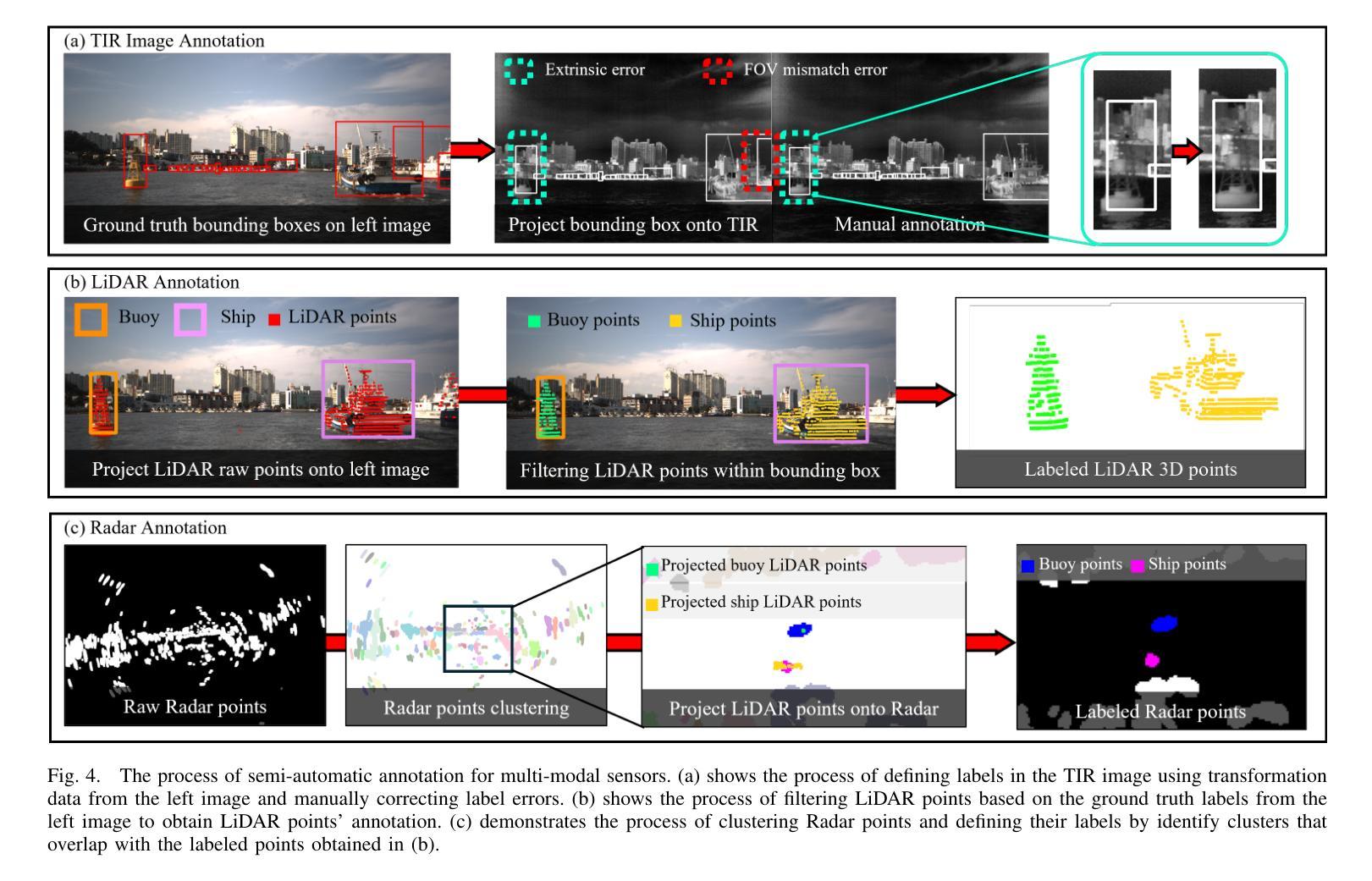
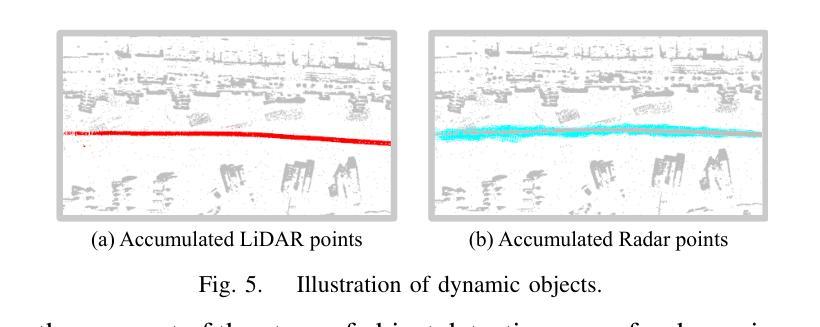
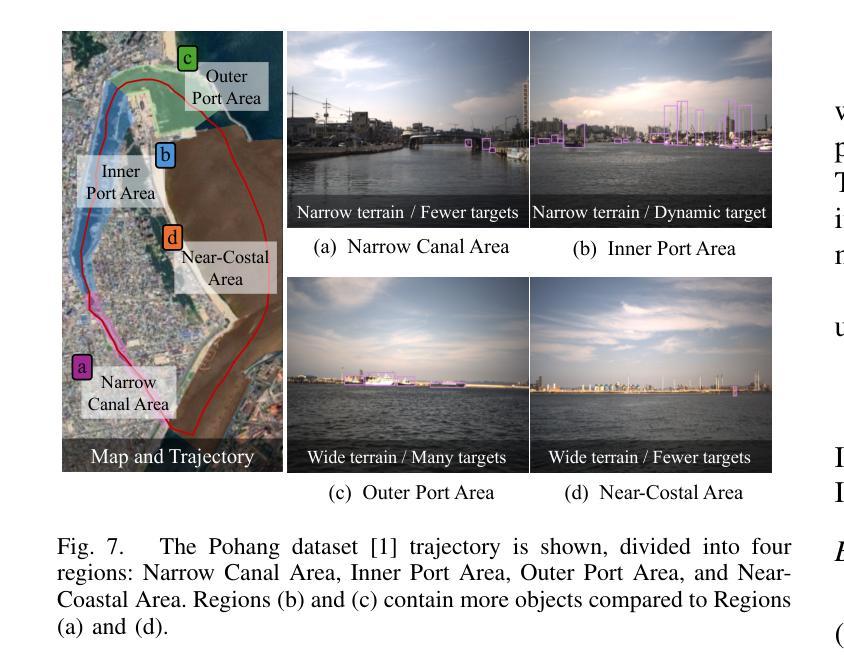
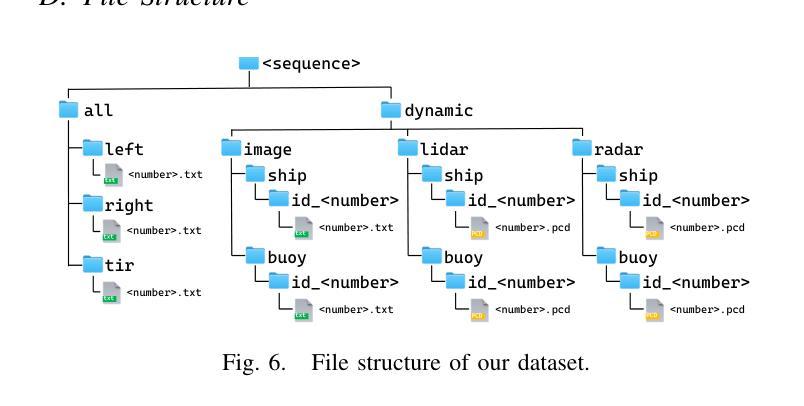
PoLaRIS Dataset: A Maritime Object Detection and Tracking Dataset in Pohang Canal
Authors:Jiwon Choi, Dongjin Cho, Gihyeon Lee, Hogyun Kim, Geonmo Yang, Joowan Kim, Younggun Cho
Maritime environments often present hazardous situations due to factors such as moving ships or buoys, which become obstacles under the influence of waves. In such challenging conditions, the ability to detect and track potentially hazardous objects is critical for the safe navigation of marine robots. To address the scarcity of comprehensive datasets capturing these dynamic scenarios, we introduce a new multi-modal dataset that includes image and point-wise annotations of maritime hazards. Our dataset provides detailed ground truth for obstacle detection and tracking, including objects as small as 10$\times$10 pixels, which are crucial for maritime safety. To validate the dataset’s effectiveness as a reliable benchmark, we conducted evaluations using various methodologies, including \ac{SOTA} techniques for object detection and tracking. These evaluations are expected to contribute to performance improvements, particularly in the complex maritime environment. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first dataset offering multi-modal annotations specifically tailored to maritime environments. Our dataset is available at https://sites.google.com/view/polaris-dataset.
海洋环境常常由于船只或浮标的移动等因素而面临危险情况,这些物体在波浪的影响下成为障碍。在这样具有挑战性的条件下,检测和跟踪潜在危险物体的能力对于海洋机器人的安全导航至关重要。为了解决缺乏捕捉这些动态场景的全面数据集的问题,我们引入了一个新的多模式数据集,包括海洋危险的海浪图像和点注释。我们的数据集为障碍检测和跟踪提供了详细的真实地面信息,包括小到10x10像素的物体,这对于海上安全至关重要。为了验证数据集作为可靠基准的有效性,我们采用了各种方法进行了评估,包括当前最先进的技术用于目标检测和跟踪。这些评估有望对性能提升做出贡献,尤其是在复杂的海洋环境中。据我们所知,这是第一个专门为海洋环境量身定制的多模式注释数据集。我们的数据集可在https://sites.google.com/view/polaris-dataset找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新的多模态海事危险物体检测与跟踪数据集,包含图像和点标注信息,旨在解决海事环境中复杂场景的缺失问题。该数据集详细提供了障碍物检测的地面真实情况,包含小至10x10像素的对象标注信息,能有效促进海事环境中的目标检测与跟踪技术的发展。目前,该数据集已经被验证为一个可靠的基准测试集,评估了各种先进的目标检测与跟踪技术。该数据集填补了现有研究的空白,首次专门针对海事环境提供了多模态标注,目前已公开可用。
Key Takeaways
- 新数据集专注于海事环境中复杂场景的障碍检测和跟踪任务。
- 数据集包含了多模态信息,如图像和点标注数据。
- 数据集注重小型障碍物的标注,其大小甚至可以小到10x10像素。
- 数据集被验证为一个可靠的基准测试集,用于评估目标检测与跟踪技术的性能。
- 该数据集填补了现有的研究空白,是首个专门为海事环境设计的多模态标注数据集。
- 数据集提供了详细的地面真实情况信息,有助于推动海事环境中的障碍检测和跟踪技术的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

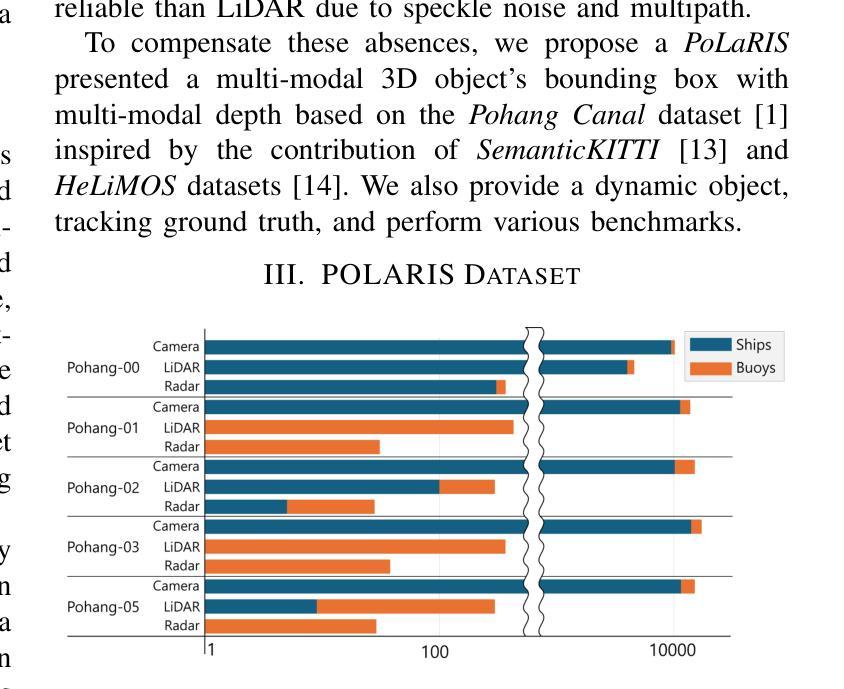
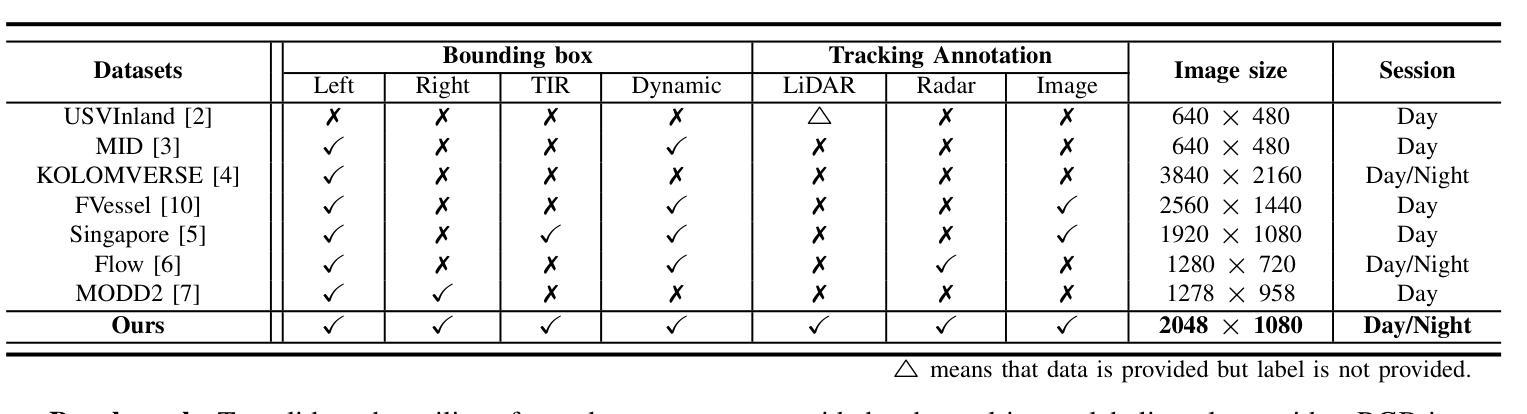

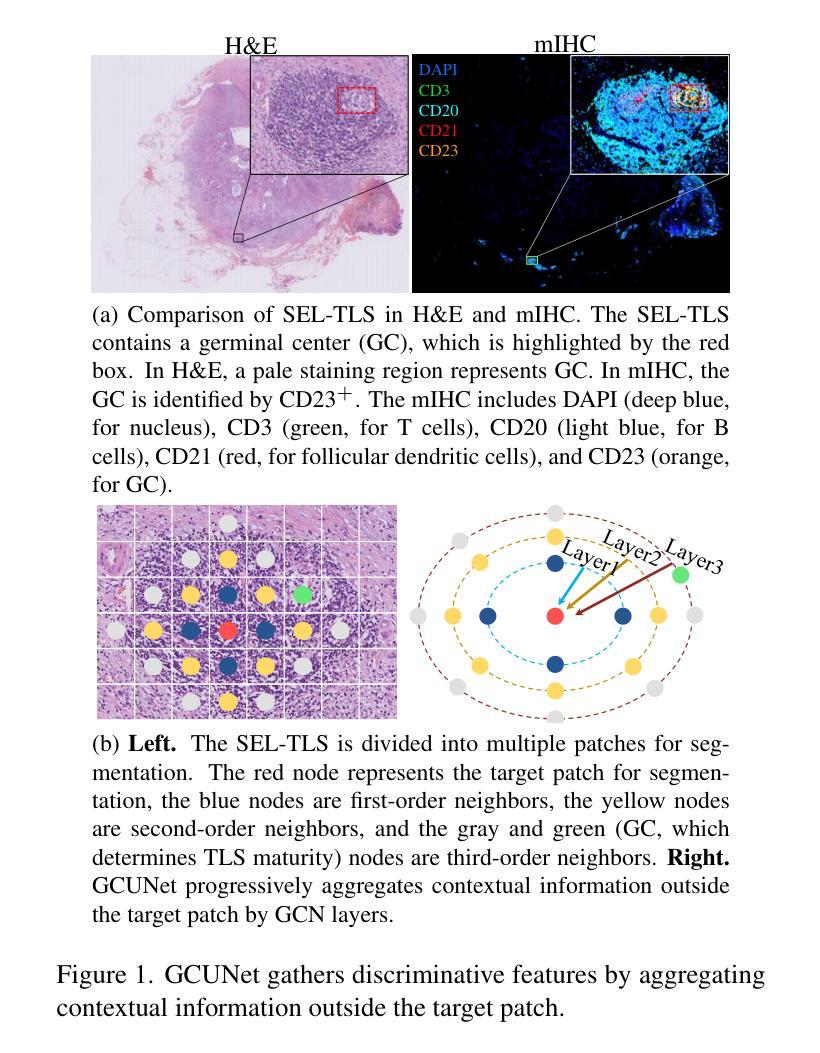
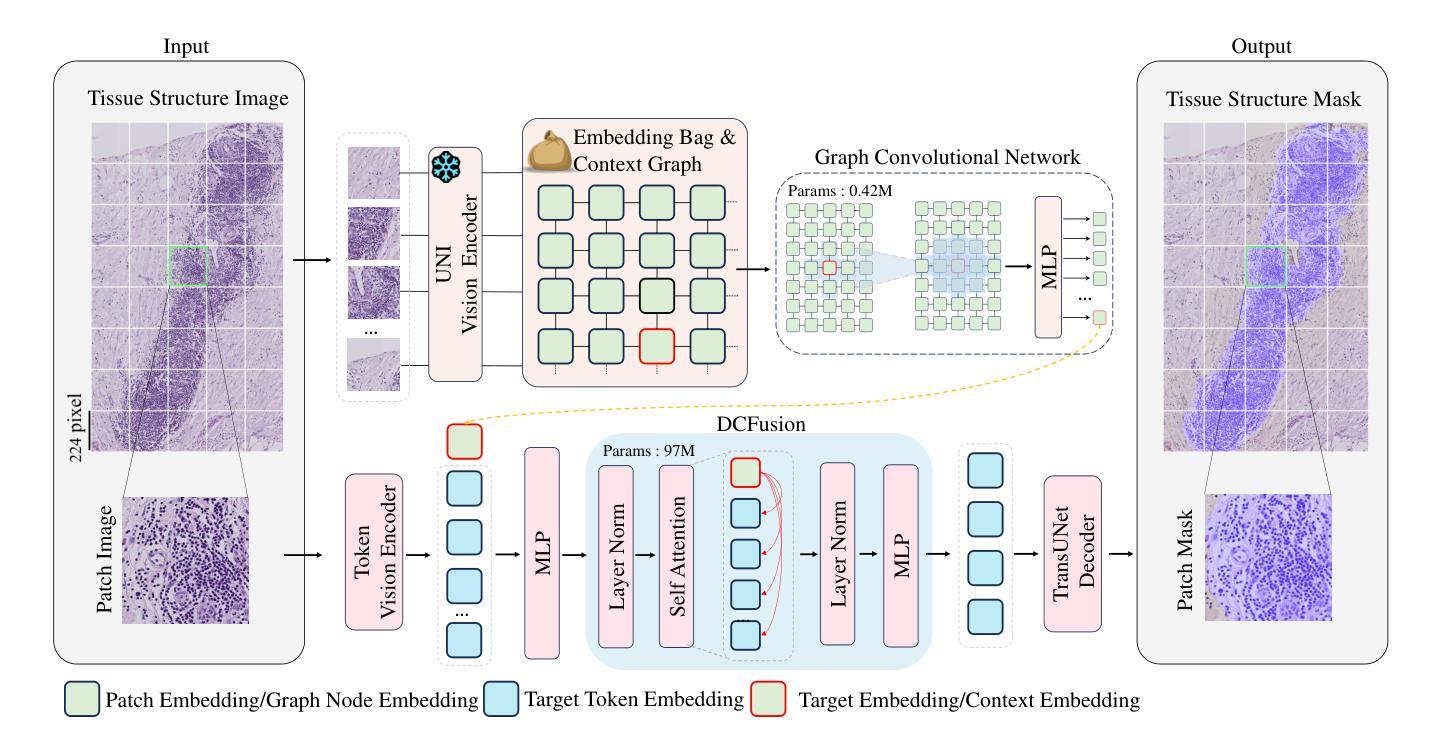
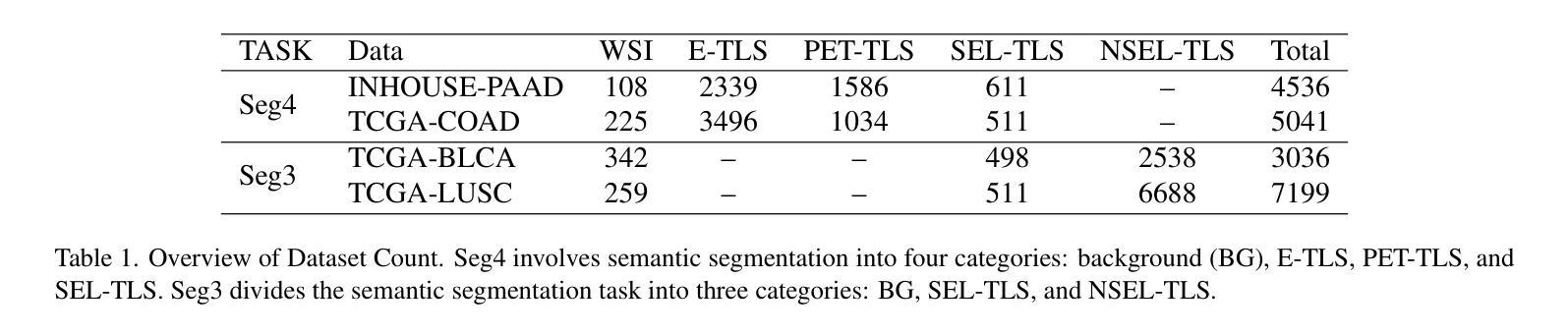
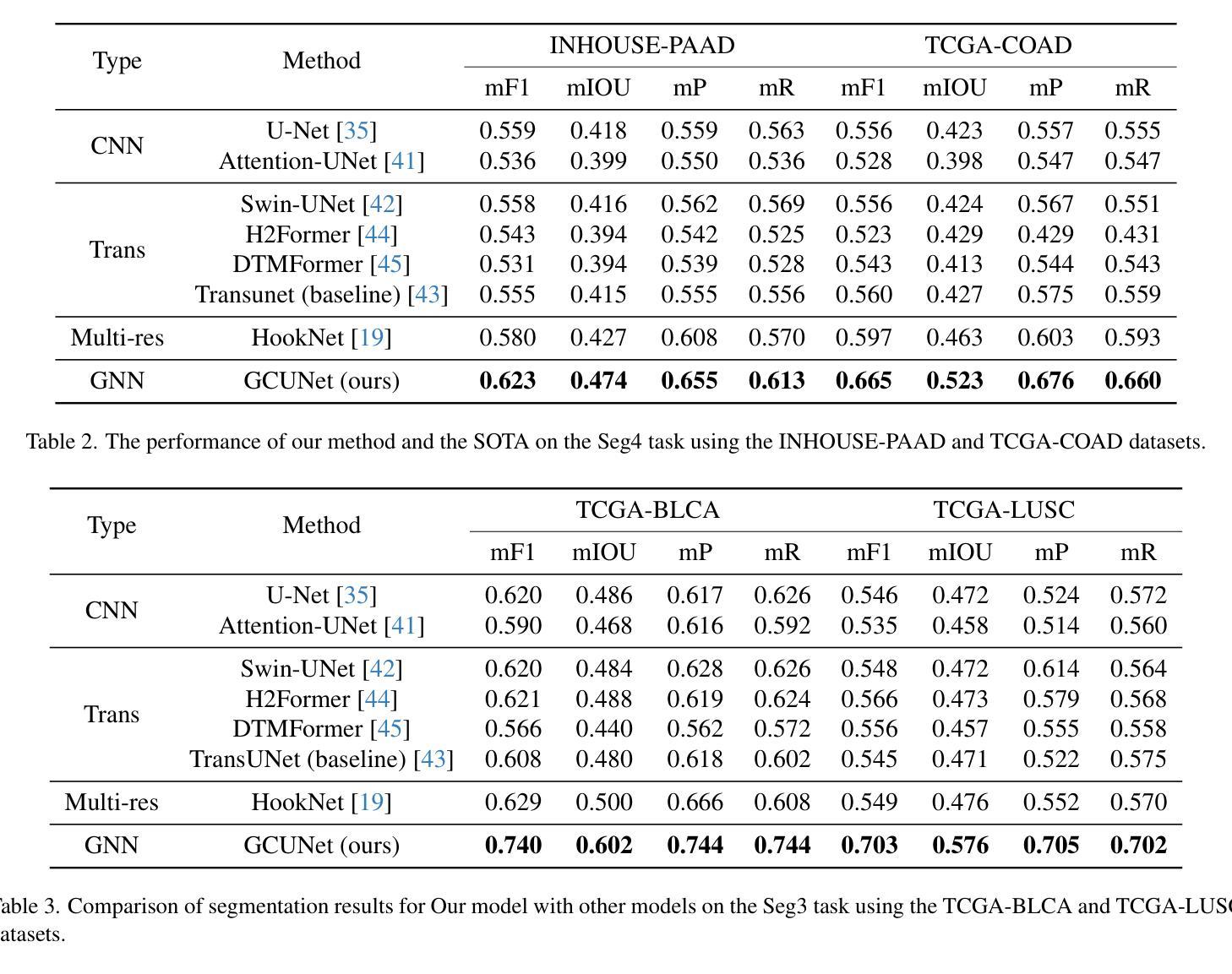
GCUNet: A GNN-Based Contextual Learning Network for Tertiary Lymphoid Structure Semantic Segmentation in Whole Slide Image
Authors:Lei Su, Yang Du
We focus on tertiary lymphoid structure (TLS) semantic segmentation in whole slide image (WSI). Unlike TLS binary segmentation, TLS semantic segmentation identifies boundaries and maturity, which requires integrating contextual information to discover discriminative features. Due to the extensive scale of WSI (e.g., 100,000 \times 100,000 pixels), the segmentation of TLS is usually carried out through a patch-based strategy. However, this prevents the model from accessing information outside of the patches, limiting the performance. To address this issue, we propose GCUNet, a GNN-based contextual learning network for TLS semantic segmentation. Given an image patch (target) to be segmented, GCUNet first progressively aggregates long-range and fine-grained context outside the target. Then, a Detail and Context Fusion block (DCFusion) is designed to integrate the context and detail of the target to predict the segmentation mask. We build four TLS semantic segmentation datasets, called TCGA-COAD, TCGA-LUSC, TCGA-BLCA and INHOUSE-PAAD, and make the former three datasets (comprising 826 WSIs and 15,276 TLSs) publicly available to promote the TLS semantic segmentation. Experiments on these datasets demonstrate the superiority of GCUNet, achieving at least 7.41% improvement in mF1 compared with SOTA.
本文关注全切片图像(WSI)中的三级淋巴结构(TLS)语义分割。不同于TLS二元分割,TLS语义分割需要识别边界和成熟度,这需要整合上下文信息以发现判别特征。鉴于WSI的大规模范围(例如,100,000 x 100,000像素),TLS的分割通常采用基于补丁的策略进行。然而,这会阻止模型访问补丁之外的信息,限制了性能。为解决这一问题,我们提出了GCUNet,这是一个基于图神经网络(GNN)的上下文学习网络,用于TLS语义分割。对于要分割的图像补丁(目标),GCUNet首先逐步聚合目标外部的长程和精细上下文。然后,设计了一个细节和上下文融合块(DCFusion),以整合目标和上下文的细节来预测分割掩膜。我们建立了四个TLS语义分割数据集,分别是TCGA-COAD、TCGA-LUSC、TCGA-BLCA和INHOUSE-PAAD,并将前三个数据集(包含826张WSI和15,276个TLS)公开,以促进TLS语义分割的发展。在这些数据集上的实验表明,GCUNet具有优越性,与最先进的方法相比,mF1提高了至少7.41%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:该研究聚焦于全视野显微图像中的三级淋巴结构语义分割问题。针对该问题,提出了一种基于图神经网络(GNN)的上下文学习网络GCUNet。GCUNet通过渐进式聚合目标外部的长程和精细上下文信息,解决了传统基于补丁策略的TLS分割方法无法获取上下文信息的局限性。此外,该研究还构建了四个TLS语义分割数据集并公开了部分数据集以促进研究。实验结果表明,GCUNet相较于现有技术有显著改善,mF1得分提高了至少7.41%。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究重点为全视野显微图像中的三级淋巴结构(TLS)语义分割。
- TLS语义分割需要识别边界和成熟度,需整合上下文信息来发现判别特征。
- 由于全视野图像规模庞大,通常采用基于补丁的策略进行TLS分割,但这限制了模型的性能。
- 提出GCUNet,一个基于图神经网络(GNN)的上下文学习网络,以解决上述问题。
- GCUNet通过渐进式聚合目标外部的长程和精细上下文信息,提高TLS分割的准确性。
- 研究构建了四个TLS语义分割数据集,并公开部分数据集以促进研究。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Semantic Splatting for Remote Sensing Multi-view Segmentation
Authors:Zipeng Qi, Hao Chen, Haotian Zhang, Zhengxia Zou, Zhenwei Shi
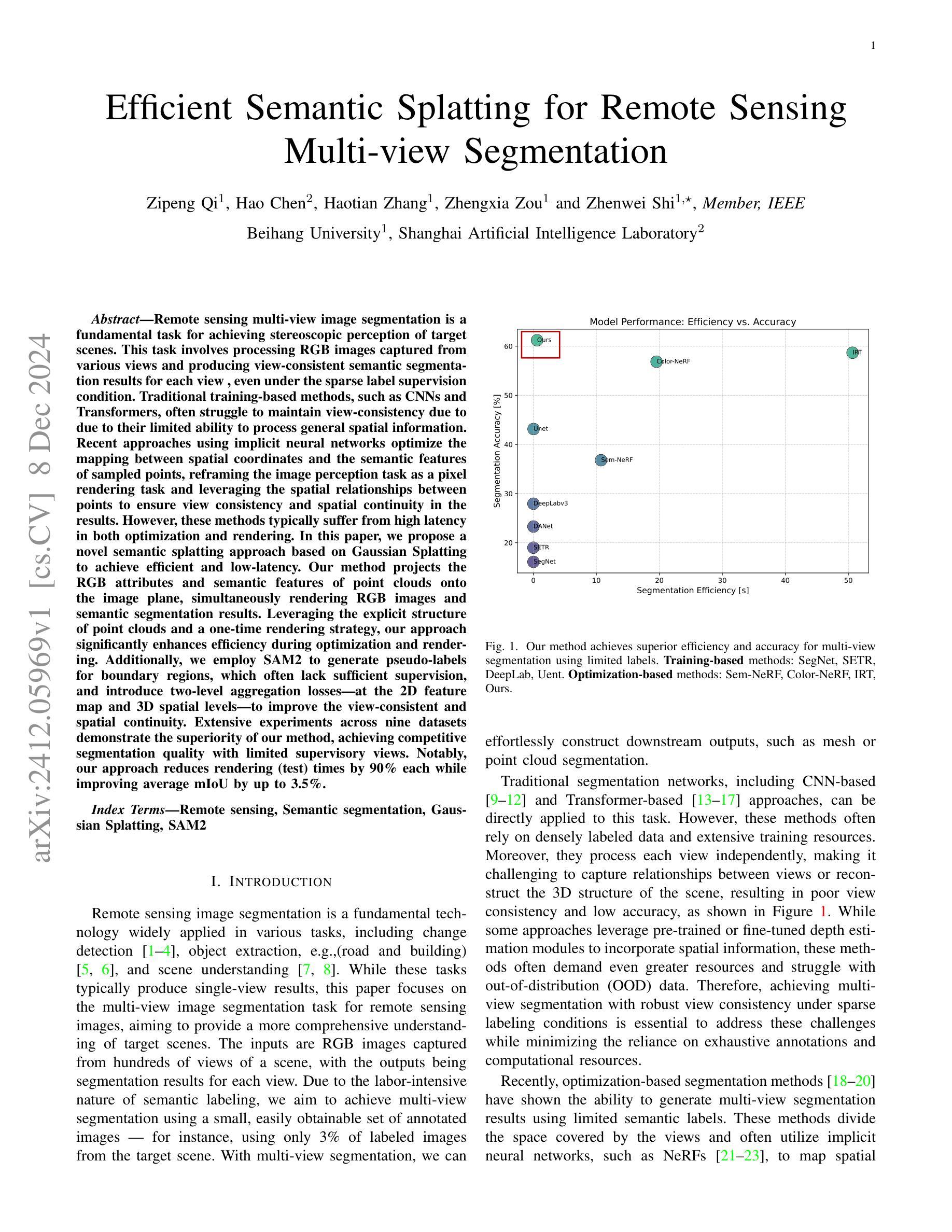
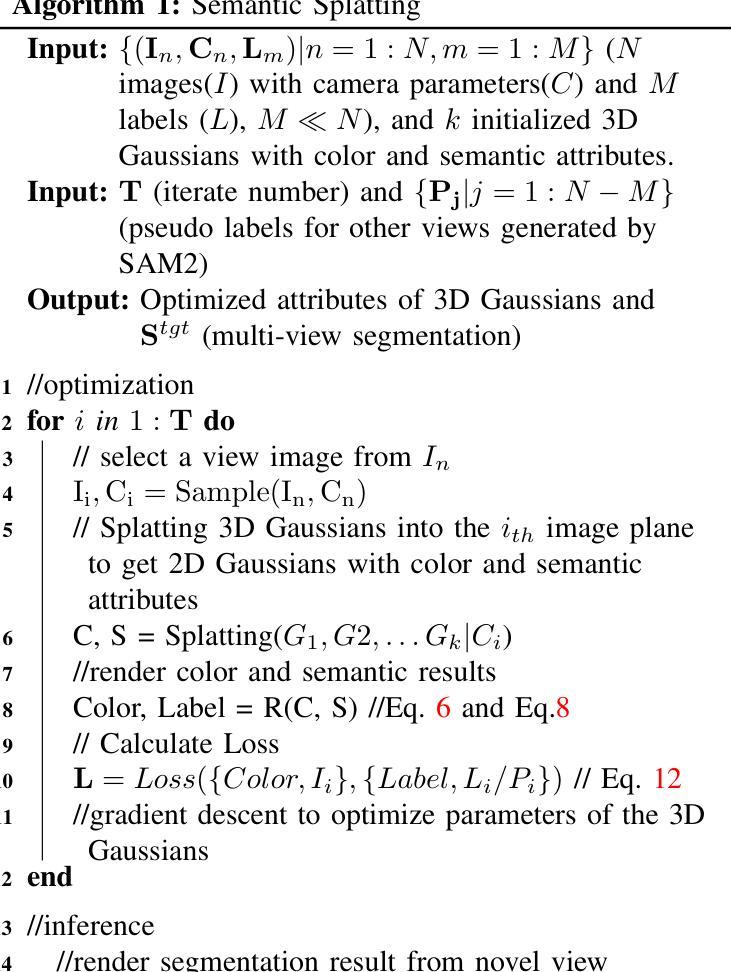
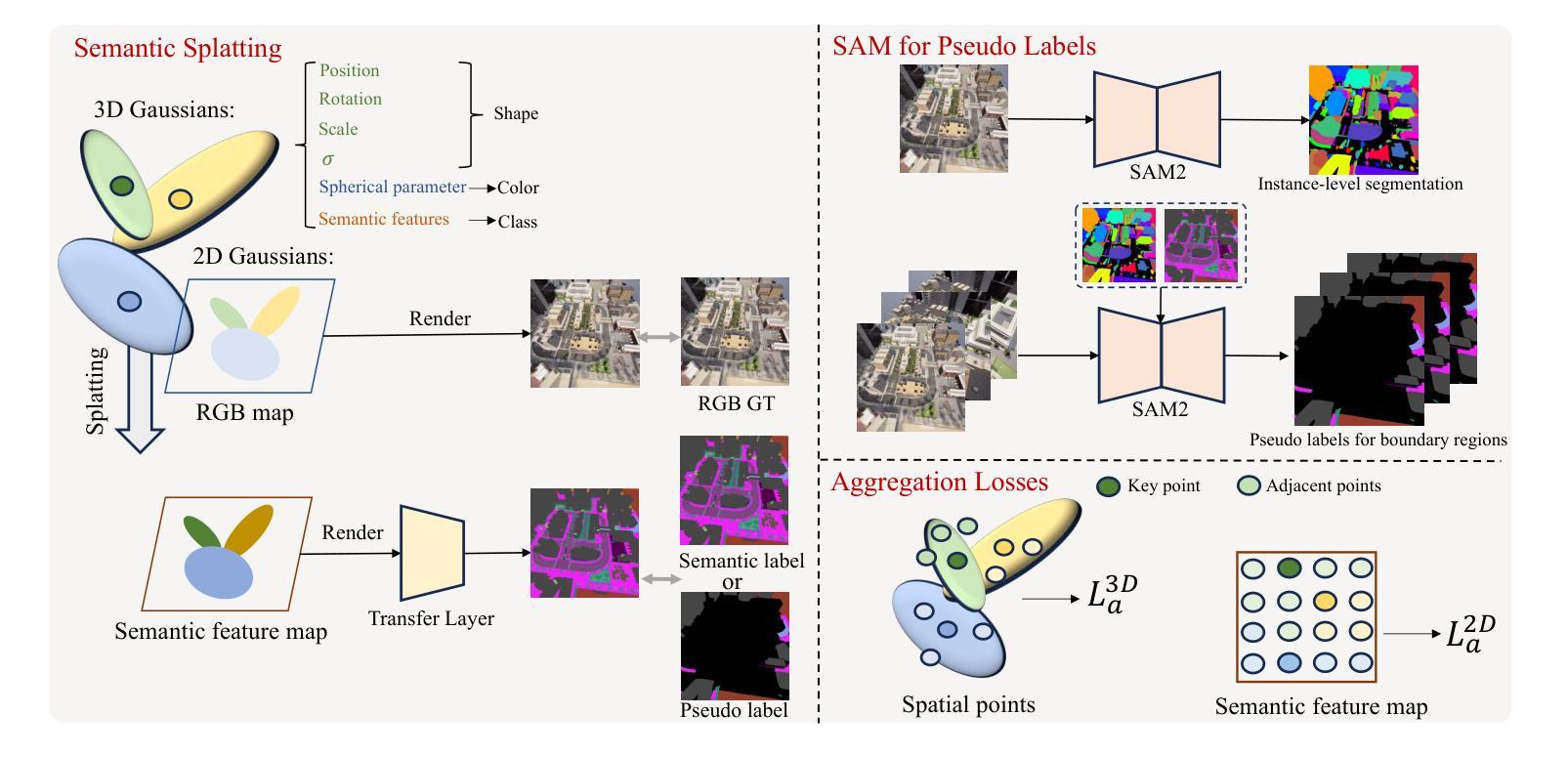
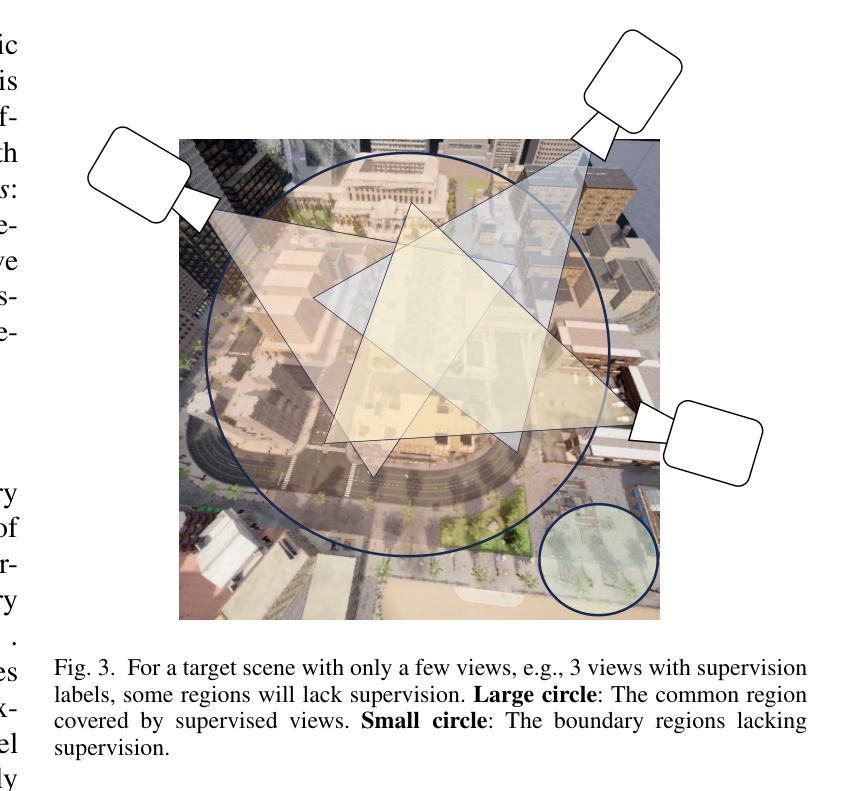
In this paper, we propose a novel semantic splatting approach based on Gaussian Splatting to achieve efficient and low-latency. Our method projects the RGB attributes and semantic features of point clouds onto the image plane, simultaneously rendering RGB images and semantic segmentation results. Leveraging the explicit structure of point clouds and a one-time rendering strategy, our approach significantly enhances efficiency during optimization and rendering. Additionally, we employ SAM2 to generate pseudo-labels for boundary regions, which often lack sufficient supervision, and introduce two-level aggregation losses at the 2D feature map and 3D spatial levels to improve the view-consistent and spatial continuity.
在这篇论文中,我们提出了一种基于高斯splat的新颖语义splat方法,以实现高效和低延迟。我们的方法将点云的RGB属性和语义特征投影到图像平面上,同时呈现RGB图像和语义分割结果。通过利用点云的明确结构和一次性渲染策略,我们的方法在优化和渲染过程中大大提高了效率。此外,我们采用SAM2为边界区域生成伪标签,这些区域通常缺乏足够的监督信息,并在二维特征图和三维空间级别引入两级聚合损失,以提高视图一致性和空间连续性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于高斯映射法,本文提出了一种新颖的语义涂抹方法,实现了高效且低延迟的点云RGB属性和语义特征投影至图像平面的渲染过程。通过利用点云的显式结构和一次渲染策略,该方法显著提高了优化和渲染阶段的效率。同时,使用SAM2为边界区域生成伪标签,并引入二维特征图和三维空间的两级聚合损失,以提高视图一致性和空间连续性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于高斯涂抹的语义涂抹方法,实现高效低延迟的点云渲染。
- 将点云的RGB属性和语义特征投影至图像平面,同时生成RGB图像和语义分割结果。
- 利用点云的显式结构和一次渲染策略提高优化和渲染效率。
- 使用SAM2生成边界区域的伪标签,解决监督不足的问题。
- 引入二维特征图和三维空间的两级聚合损失,提高视图一致性和空间连续性。
点此查看论文截图
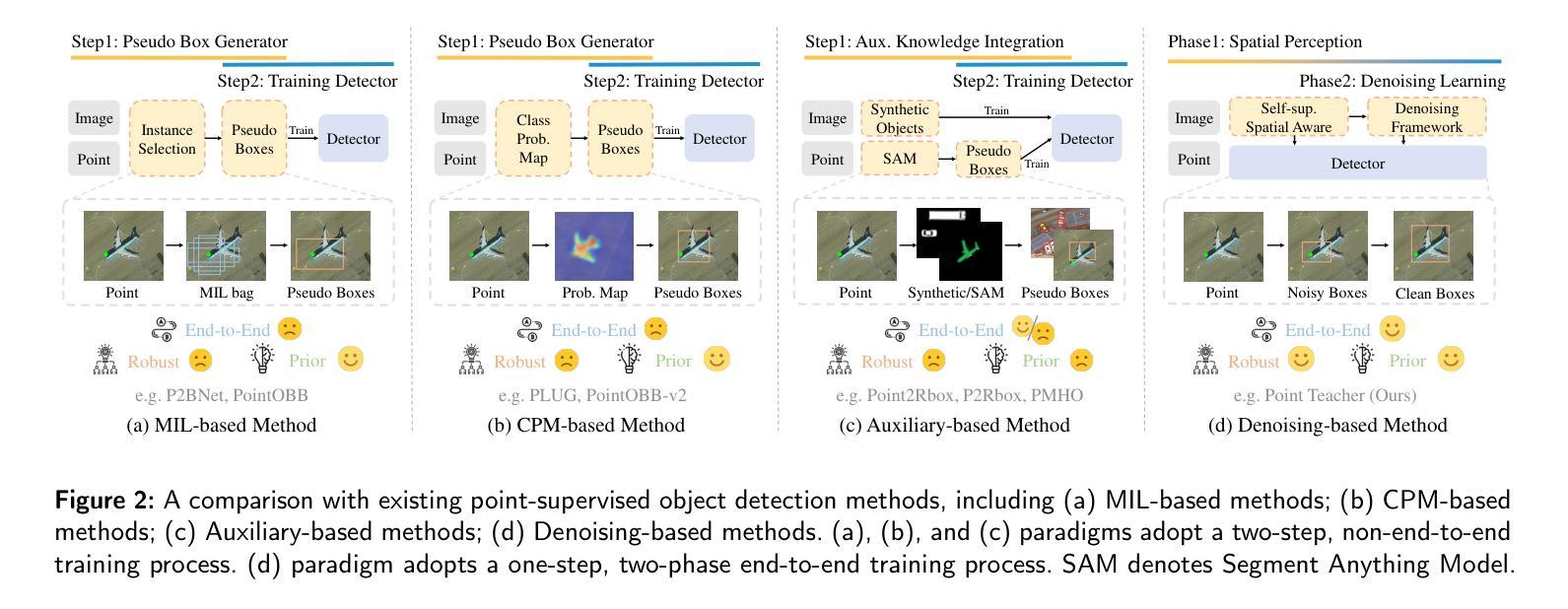
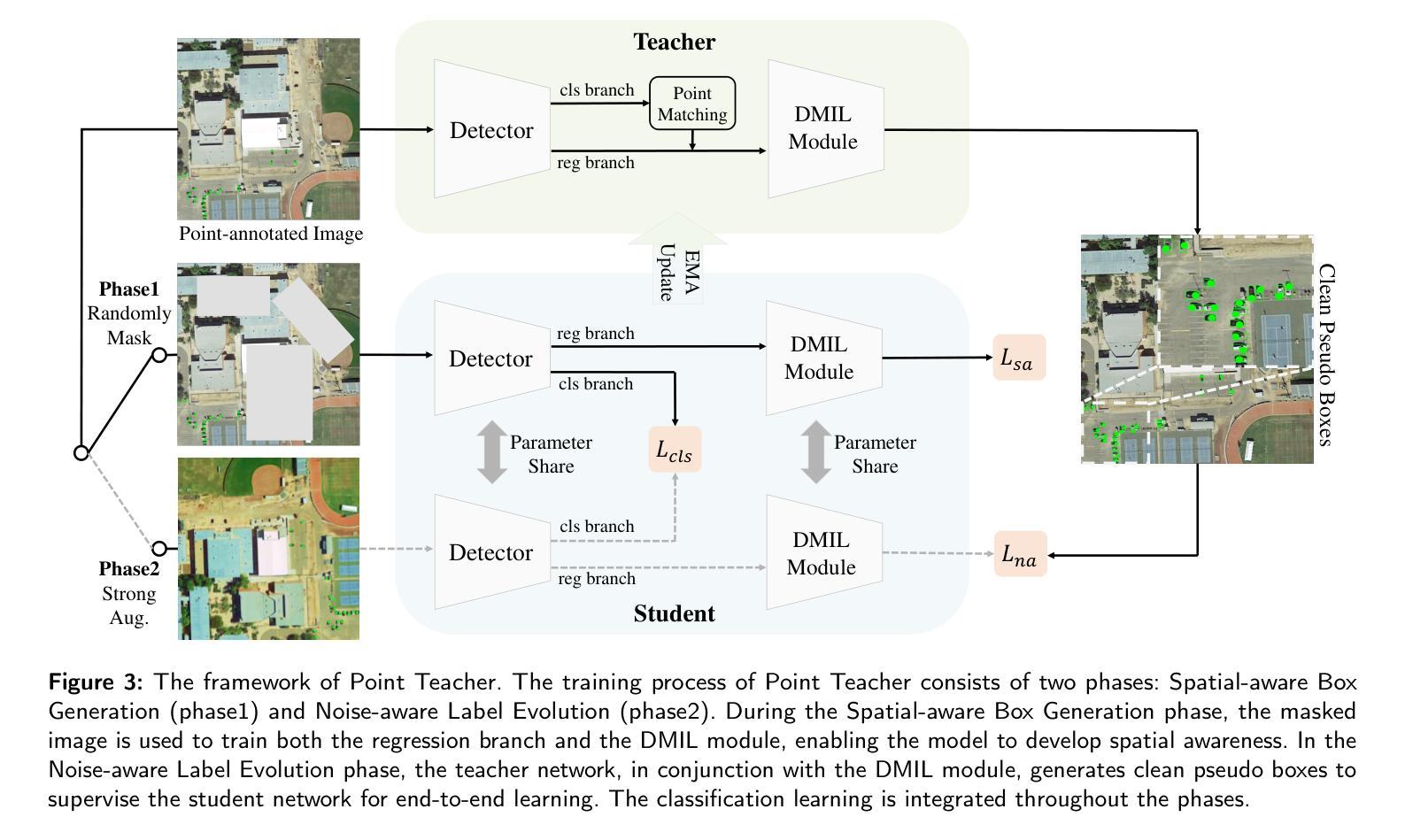
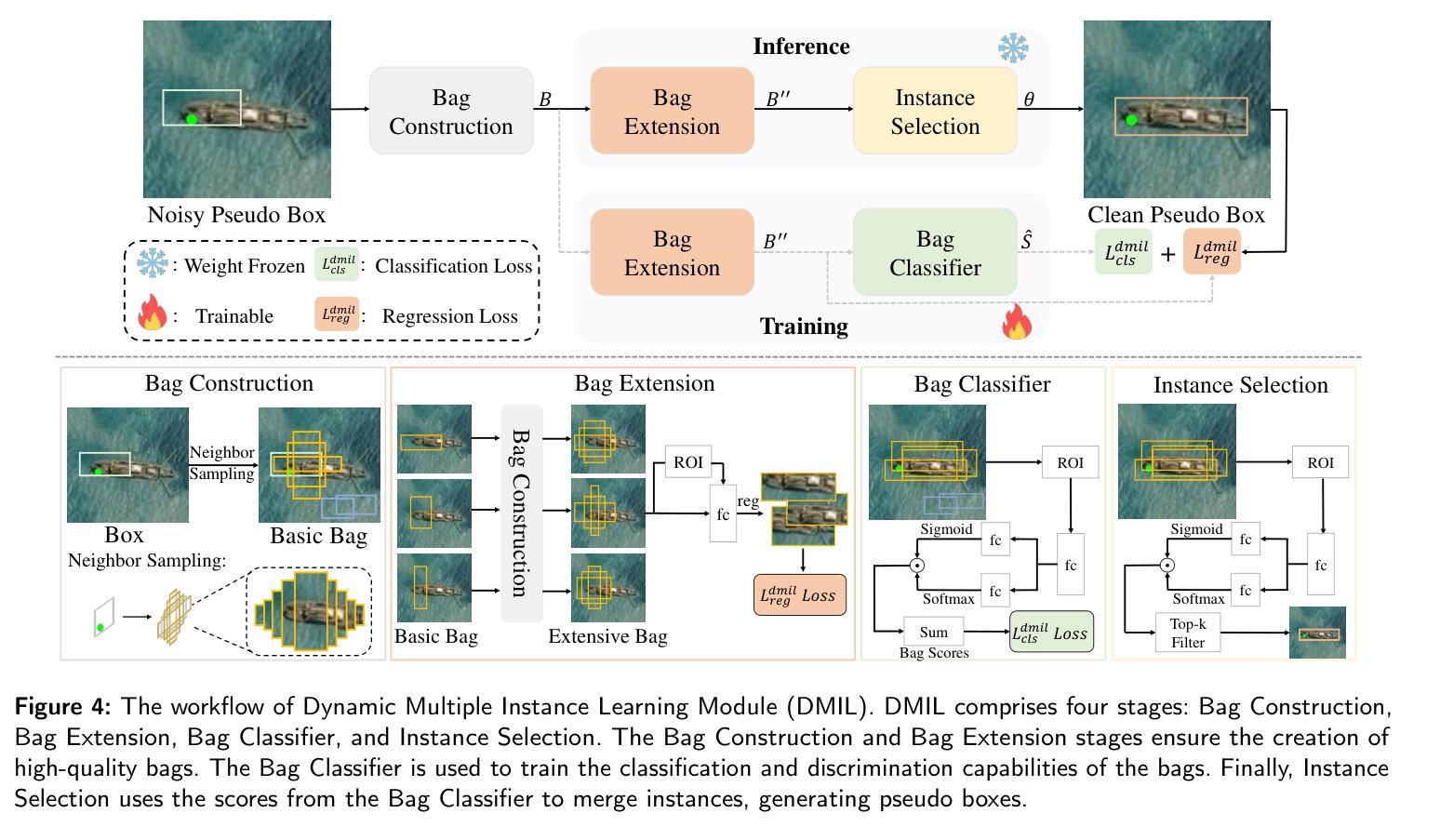
Tiny Object Detection with Single Point Supervision
Authors:Haoran Zhu, Chang Xu, Ruixiang Zhang, Fang Xu, Wen Yang, Haijian Zhang, Gui-Song Xia
Tiny objects, with their limited spatial resolution, often resemble point-like distributions. As a result, bounding box prediction using point-level supervision emerges as a natural and cost-effective alternative to traditional box-level supervision. However, the small scale and lack of distinctive features of tiny objects make point annotations prone to noise, posing significant hurdles for model robustness. To tackle these challenges, we propose Point Teacher–the first end-to-end point-supervised method for robust tiny object detection in aerial images. To handle label noise from scale ambiguity and location shifts in point annotations, Point Teacher employs the teacher-student architecture and decouples the learning into a two-phase denoising process. In this framework, the teacher network progressively denoises the pseudo boxes derived from noisy point annotations, guiding the student network’s learning. Specifically, in the first phase, random masking of image regions facilitates regression learning, enabling the teacher to transform noisy point annotations into coarse pseudo boxes. In the second phase, these coarse pseudo boxes are refined using dynamic multiple instance learning, which adaptively selects the most reliable instance from dynamically constructed proposal bags around the coarse pseudo boxes. Extensive experiments on three tiny object datasets (i.e., AI-TOD-v2, SODA-A, and TinyPerson) validate the proposed method’s effectiveness and robustness against point location shifts. Notably, relying solely on point supervision, our Point Teacher already shows comparable performance with box-supervised learning methods. Codes and models will be made publicly available.
对于具有有限空间分辨率的微小物体来说,由于其外形类似点状分布的特点,因此采用点状监督(point-level supervision)的边界框预测方法成为了传统框级监督的一种自然且经济的替代方案。然而,微小物体体积小、特征缺乏辨别力的特点使得点标注容易引入噪声,为模型稳健性带来显著挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了Point Teacher——这是首个端到端的点监督方法,主要用于鲁棒的航空图像微小目标检测。为处理点标注中因尺度模糊和位置偏移导致的标签噪声问题,Point Teacher采用师生架构并将学习过程分解为两阶段的降噪过程。在这一框架中,教师网络对由噪声点标注生成的伪盒子进行渐进降噪处理,引导学生网络的学习。具体来说,在第一阶段,通过随机屏蔽图像区域来促进回归学习,使教师能够从噪声点标注生成粗略的伪盒子。在第二阶段,使用动态多实例学习来精炼这些粗略的伪盒子,该方法自适应地从围绕粗略伪盒构建的动态提案包中选择最可靠的实例。在三个微小目标数据集(即AI-TOD-v2、SODA-A和TinyPerson)上的大量实验验证了所提方法的抗干扰能力和稳健性。值得注意的是,仅依赖点监督的Point Teacher已经显示出与框监督学习方法相当的性能。相关代码和模型将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为Point Teacher的点监督方法,用于稳健地检测航空图像中的微小物体。该方法采用教师-学生架构,通过两阶段去噪过程处理点注释中的标签噪声。教师网络将噪声点注释转化为粗略的伪盒子,并在第二阶段进行精炼。实验证明,该方法在微小物体数据集上表现出有效性和鲁棒性。仅依赖点监督,Point Teacher的性能已接近盒监督学习方法。
Key Takeaways
- Point-level supervision作为一种自然且经济实惠的替代方案,用于解决微小物体检测中的空间分辨率有限问题。
- 微小物体的尺度和缺乏显著特征使得点注释容易受到噪声影响。
- Point Teacher是首个端到端的点监督方法,用于稳健地检测航空图像中的微小物体。
- 教师-学生架构用于处理标签噪声,通过两阶段去噪过程来优化点注释的伪盒子。
- 第一阶段通过随机掩蔽图像区域促进回归学习,将噪声点注释转化为粗略伪盒子。
- 第二阶段使用动态多重实例学习精炼伪盒子,自适应选择最可靠的实例。
- 在三个微小物体数据集上的实验验证了Point Teacher的有效性和鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图

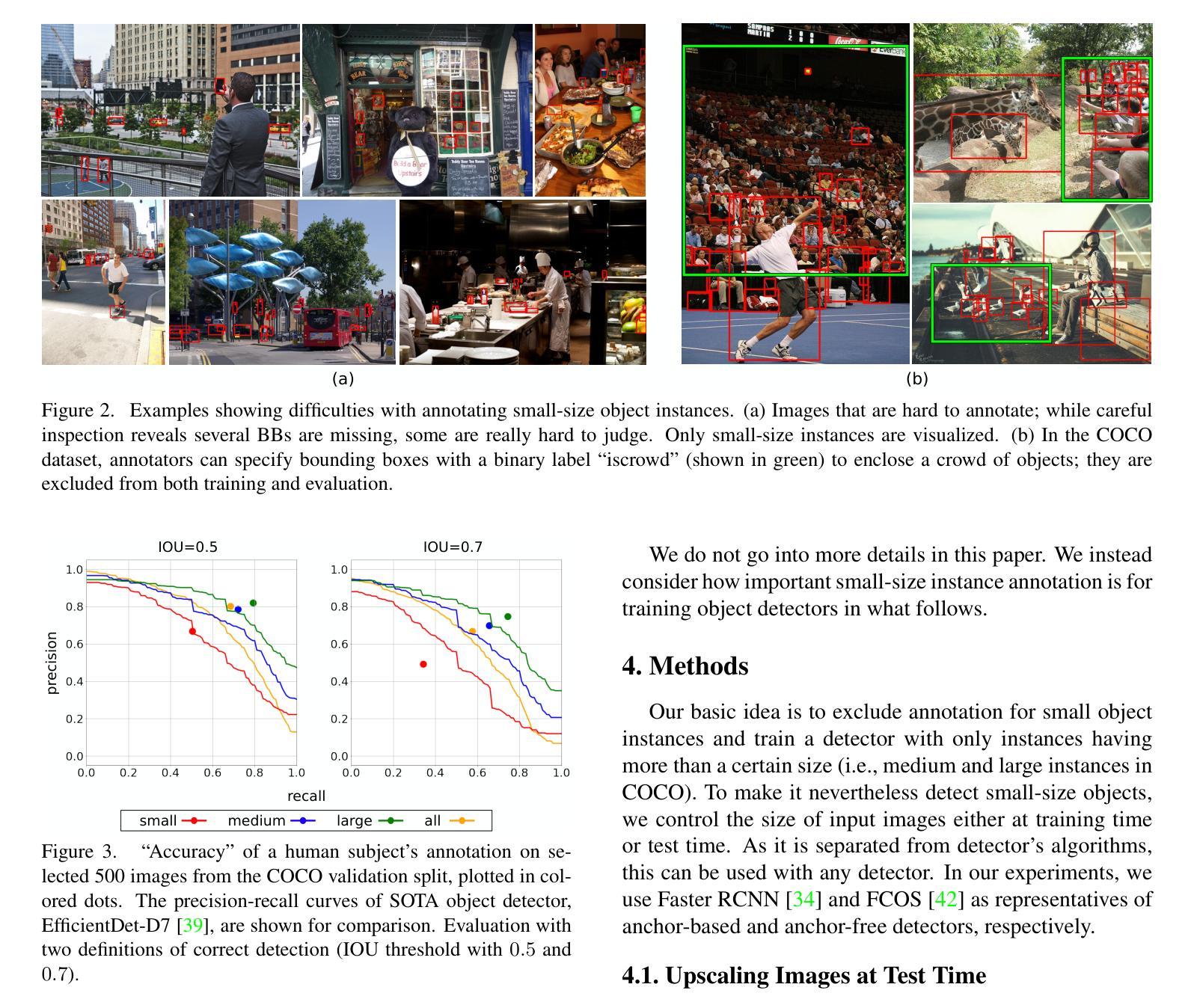
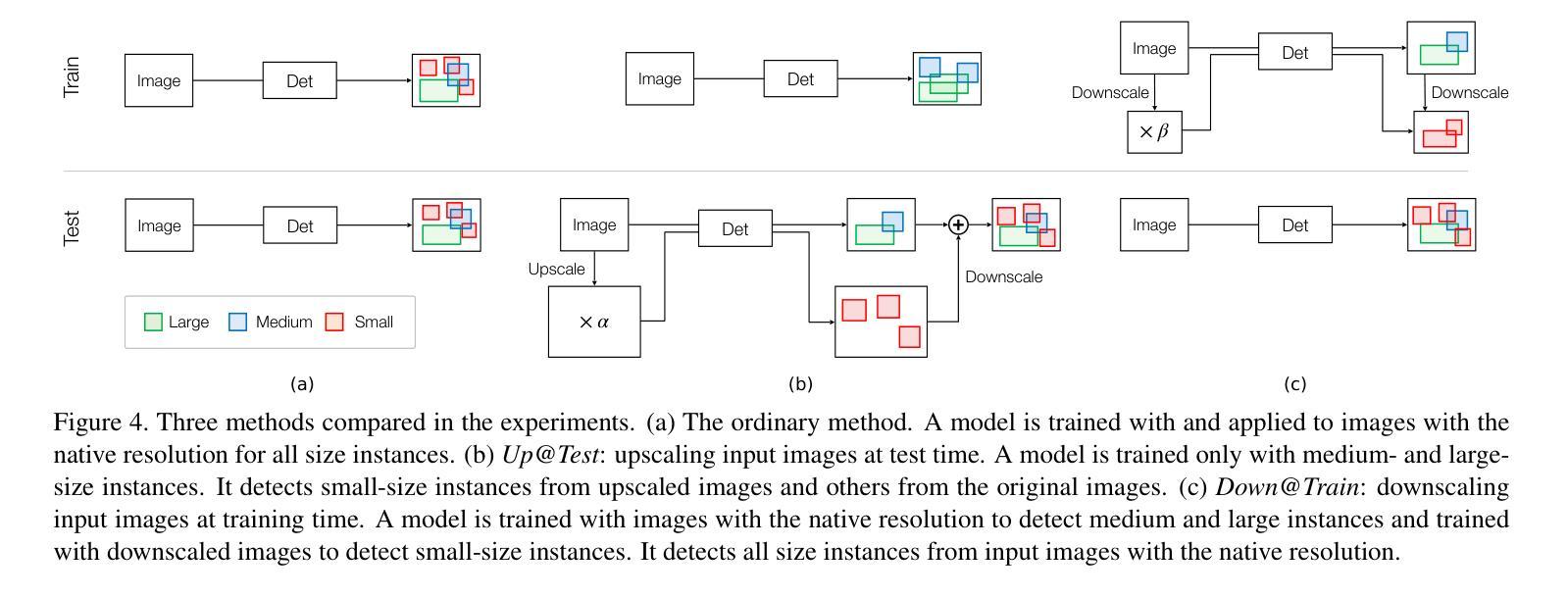
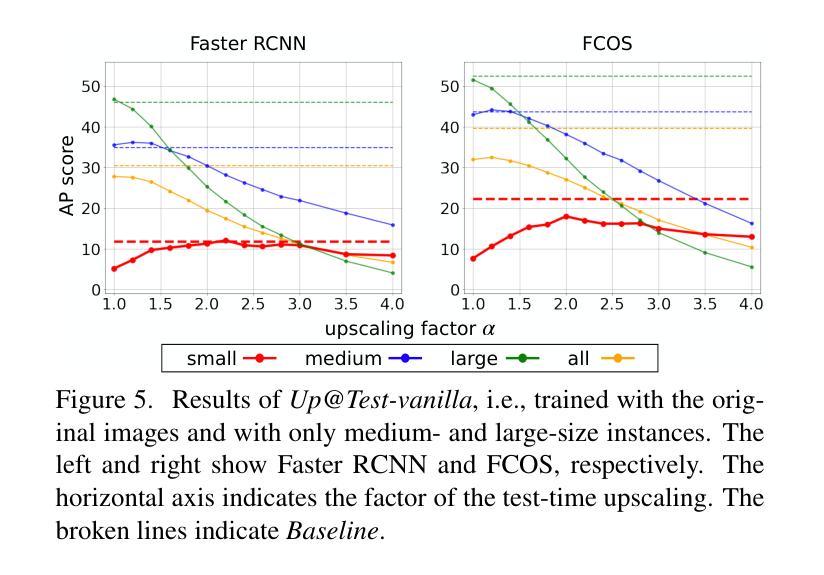
Rethinking Annotation for Object Detection: Is Annotating Small-size Instances Worth Its Cost?
Authors:Yusuke Hosoya, Masanori Suganuma, Takayuki Okatani
Detecting objects occupying only small areas in an image is difficult, even for humans. Therefore, annotating small-size object instances is hard and thus costly. This study questions common sense by asking the following: is annotating small-size instances worth its cost? We restate it as the following verifiable question: can we detect small-size instances with a detector trained using training data free of small-size instances? We evaluate a method that upscales input images at test time and a method that downscales images at training time. The experiments conducted using the COCO dataset show the following. The first method, together with a remedy to narrow the domain gap between training and test inputs, achieves at least comparable performance to the baseline detector trained using complete training data. Although the method needs to apply the same detector twice to an input image with different scaling, we show that its distillation yields a single-path detector that performs equally well to the same baseline detector. These results point to the necessity of rethinking the annotation of training data for object detection.
检测图像中只占很小面积的目标物体是很困难的,即使是对于人类来说也是如此。因此,对小型目标实例进行标注是很困难且成本很高的。本研究通过以下问题质疑常识:标注小型实例值得其成本吗?我们将其重新表述为以下可验证的问题:我们能否使用未包含小型实例的训练数据进行训练,从而检测小型实例?我们评估了一种在测试时对输入图像进行放大的方法,以及一种在训练时对图像进行缩小的方法。使用COCO数据集进行的实验表明:第一种方法配合缩小训练与测试输入之间领域差距的补救措施,至少可与使用完整训练数据进行训练的基线检测器实现相当的性能。尽管该方法需要对输入图像两次应用相同的检测器并进行不同的缩放,但我们表明其提炼产生了单路径检测器,其性能与相同的基线检测器同样出色。这些结果指向了重新思考目标检测训练数据标注的必要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 9 figures
Summary
本研究探讨了检测图像中小尺寸物体的问题,提出标注小尺寸实例是否值得其成本的问题。通过评估一种测试时放大输入图像的方法以及训练时缩小图像的方法,发现训练时采用完全的数据集和训练数据免费的小尺寸实例的探测器之间的性能至少相当。实验结果表明需要重新思考训练数据标注的问题。
Key Takeaways
- 检测图像中小尺寸物体是困难的,标注小尺寸实例成本高且困难。
- 研究质疑了是否需要标注小尺寸实例来训练检测器。
- 提出了一种测试时放大输入图像的方法来提高小尺寸物体的检测性能。
- 采用了一种缩小训练时图像大小的方法进行评估。
- 实验使用COCO数据集进行验证,结果表明使用完全数据集训练的检测器性能相当或更好。
- 尽管需要两次应用同一检测器于输入图像的不同缩放级别,但可以通过蒸馏方法获得具有相同性能的单路径检测器。
点此查看论文截图

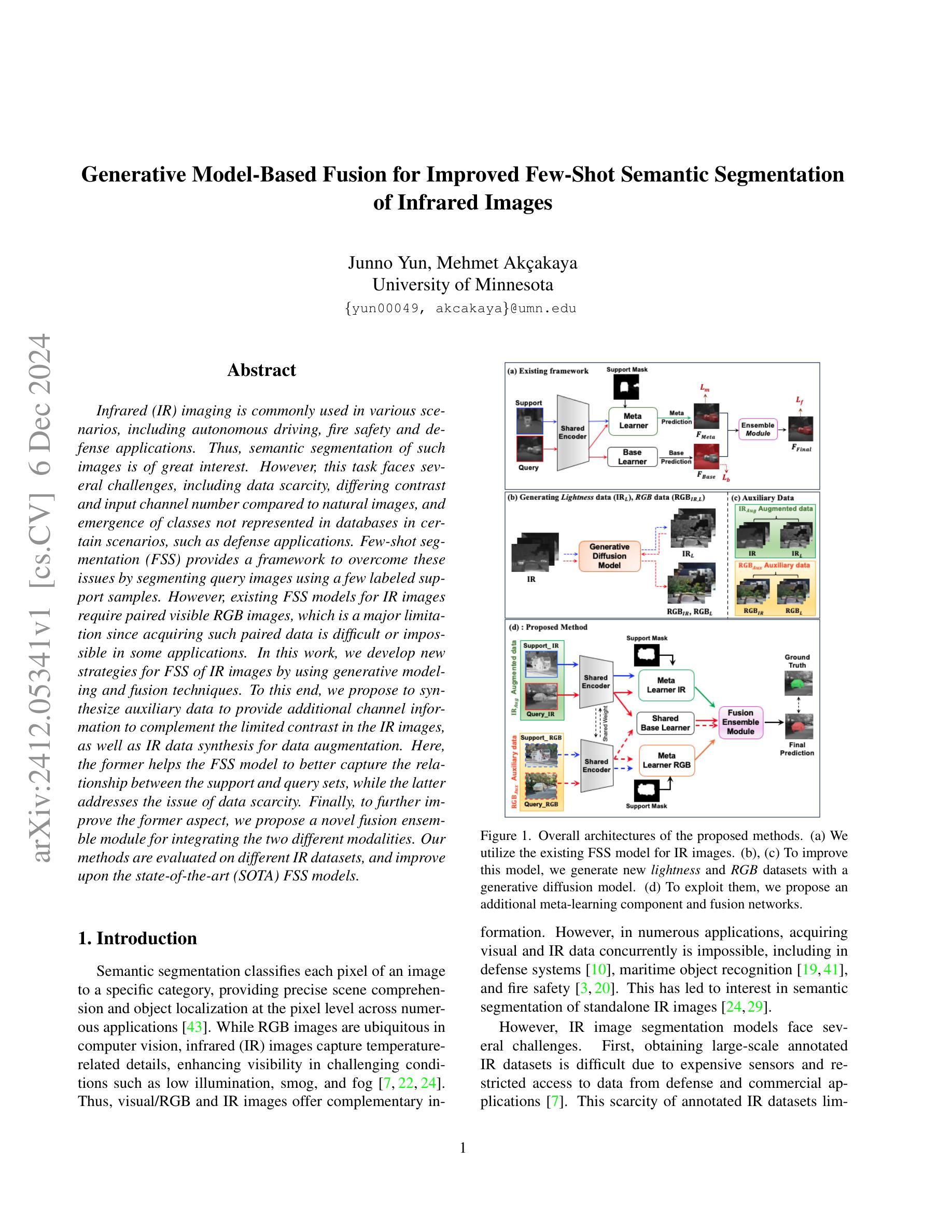
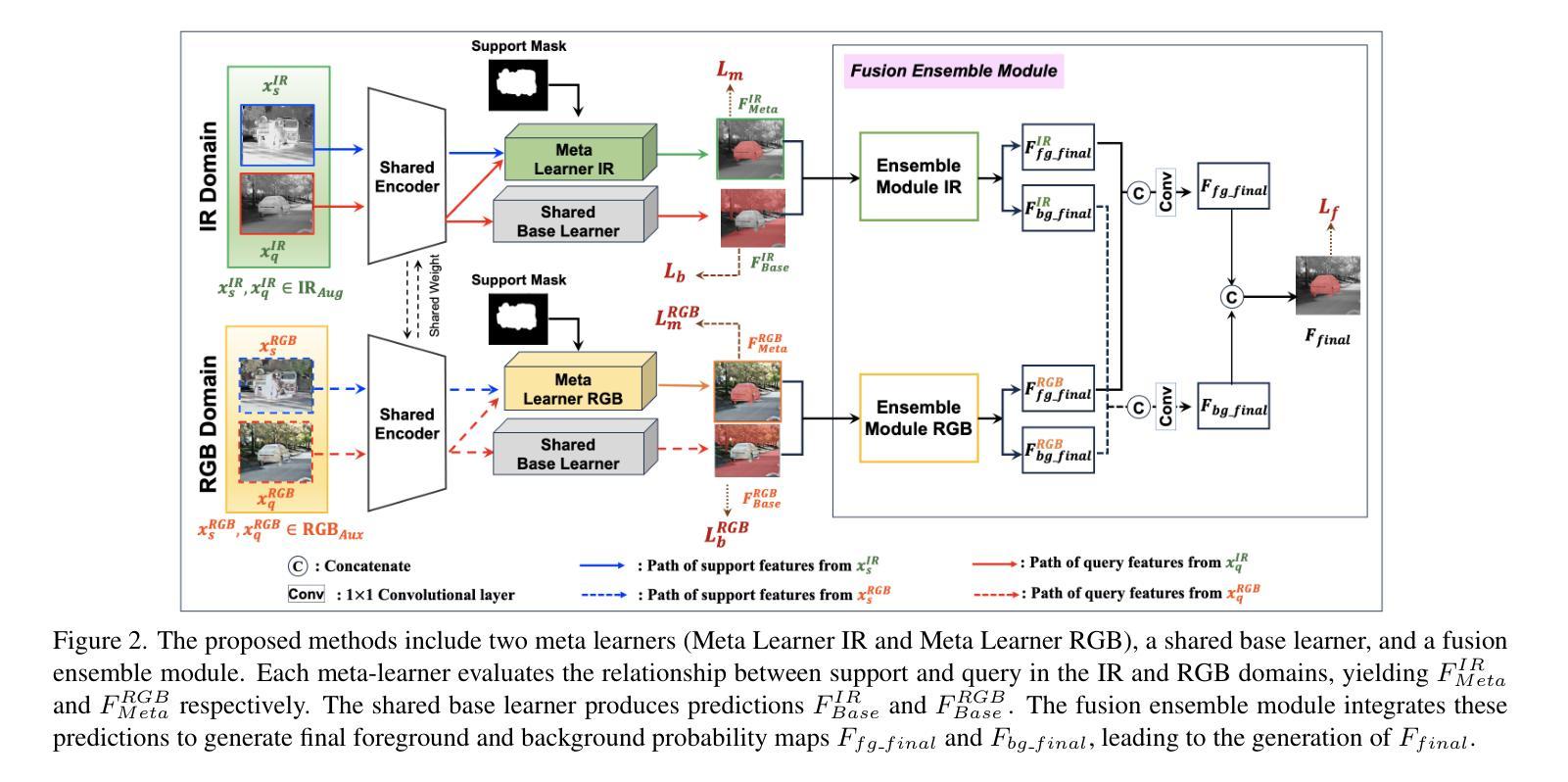
Generative Model-Based Fusion for Improved Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation of Infrared Images
Authors:Junno Yun, Mehmet Akçakaya
Infrared (IR) imaging is commonly used in various scenarios, including autonomous driving, fire safety and defense applications. Thus, semantic segmentation of such images is of great interest. However, this task faces several challenges, including data scarcity, differing contrast and input channel number compared to natural images, and emergence of classes not represented in databases in certain scenarios, such as defense applications. Few-shot segmentation (FSS) provides a framework to overcome these issues by segmenting query images using a few labeled support samples. However, existing FSS models for IR images require paired visible RGB images, which is a major limitation since acquiring such paired data is difficult or impossible in some applications. In this work, we develop new strategies for FSS of IR images by using generative modeling and fusion techniques. To this end, we propose to synthesize auxiliary data to provide additional channel information to complement the limited contrast in the IR images, as well as IR data synthesis for data augmentation. Here, the former helps the FSS model to better capture the relationship between the support and query sets, while the latter addresses the issue of data scarcity. Finally, to further improve the former aspect, we propose a novel fusion ensemble module for integrating the two different modalities. Our methods are evaluated on different IR datasets, and improve upon the state-of-the-art (SOTA) FSS models.
红外(IR)成像在自动驾驶、消防安全及国防应用等多种场景中都有广泛应用。因此,这类图像的语义分割引起了极大的兴趣。然而,此任务面临诸多挑战,包括数据稀缺、对比度差异以及与自然图像相比输入通道数量的不同,以及在某些特定场景(如国防应用)中数据库中未出现的新兴类别等问题。少样本分割(FSS)提供了一种通过利用少量标记样本对查询图像进行分割来克服这些问题的框架。然而,现有的红外图像FSS模型需要配对可见RGB图像,这在某些应用中获取此类配对数据是困难甚至不可能的,这是一个主要局限。在这项工作中,我们开发新的策略来对红外图像进行FSS,采用生成建模和融合技术。为此,我们提出合成辅助数据以提供额外的通道信息来补充红外图像中有限的对比度,以及红外数据合成用于数据增强。其中,前者有助于FSS模型更好地捕获支持与查询集之间的关系,而后者解决了数据稀缺的问题。最后,为了进一步提升前者方面的效果,我们提出了一种新颖的融合集成模块来整合两种不同的模式。我们的方法在多个红外数据集上进行了评估,并改进了当前最先进的FSS模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), 2025
Summary
本文介绍红外图像语义分割的重要性和面临的挑战,提出基于生成模型和融合技术的策略解决少数样本红外图像分割问题。通过合成辅助数据提供额外的通道信息,以解决红外图像对比度有限的问题,并采用红外数据合成进行数据增强。同时,引入融合集成模块整合两种不同模态的数据,提高模型性能。在多个红外数据集上的评估结果显示,该方法优于现有少数样本分割模型。
Key Takeaways
- 红外图像语义分割在自动驾驶、消防安全、国防应用等领域有广泛应用价值。
- 红外图像语义分割面临数据稀缺、对比度差异、输入通道数量有限等挑战。
- 少数样本分割(FSS)为解决这些问题提供了框架,但现有模型需要配对可见RGB图像,这在某些应用中难以实现。
- 本文提出通过生成模型和融合技术解决红外图像的FSS问题。
- 合成辅助数据提供额外的通道信息,以解决红外图像对比度有限的问题。
- 引入红外数据合成进行数据增强,解决数据稀缺问题。
点此查看论文截图
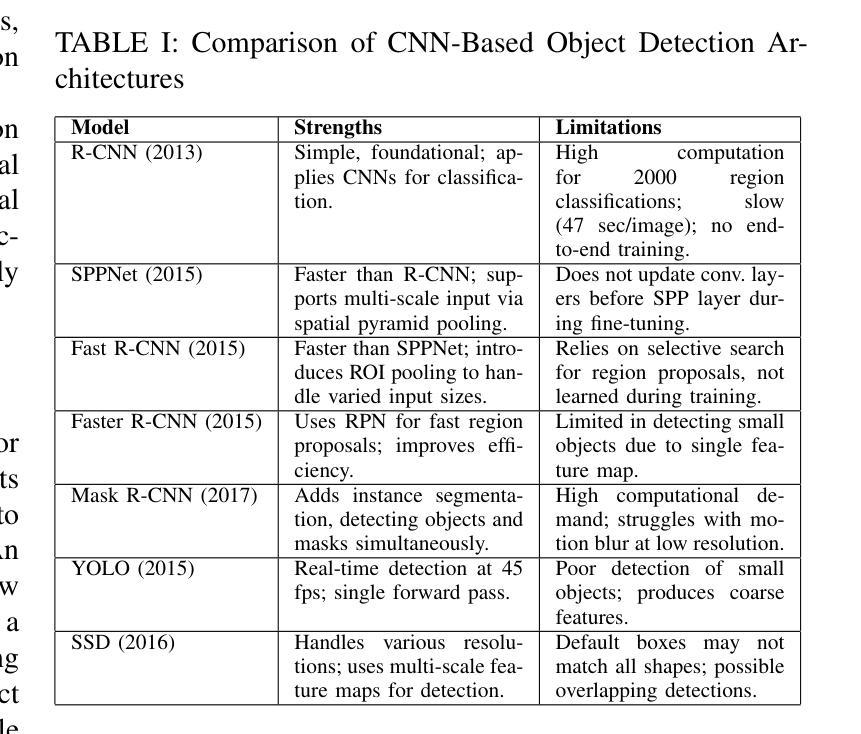
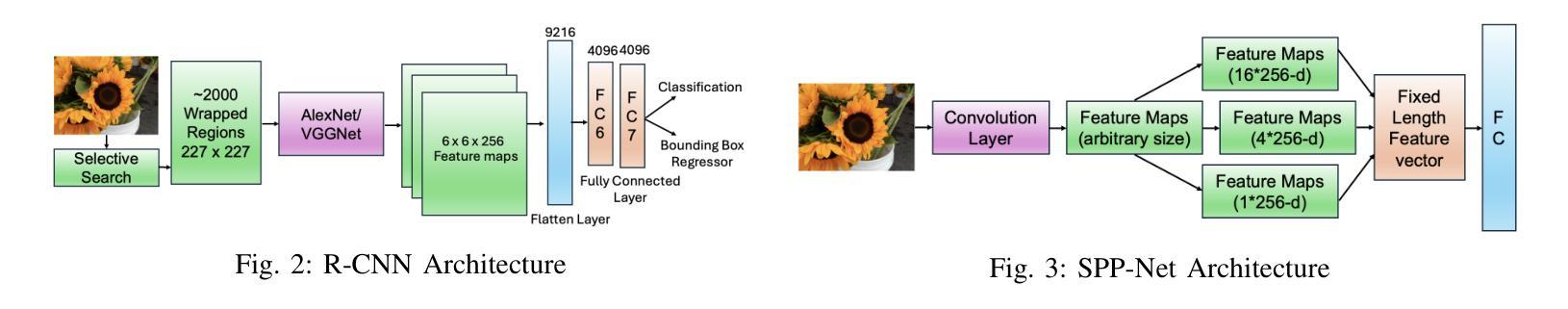
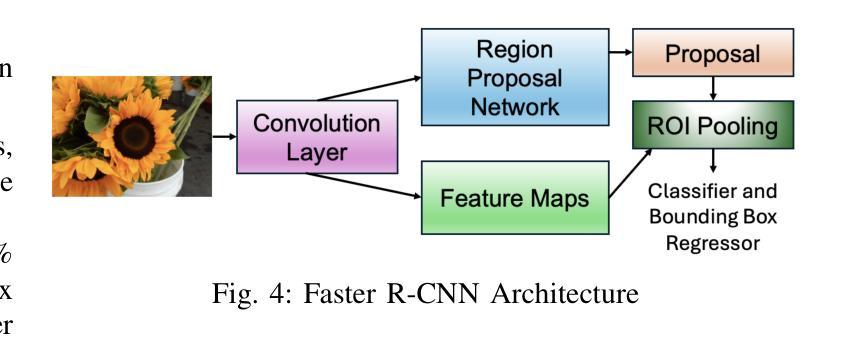
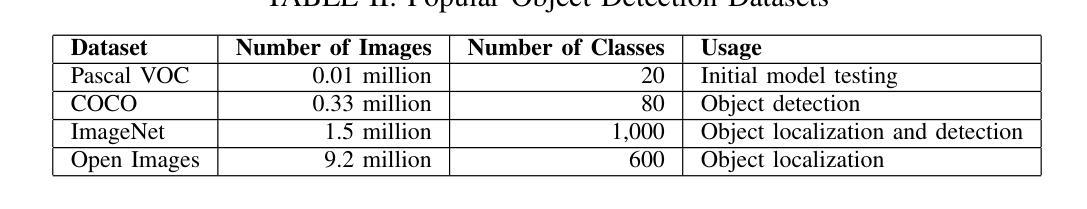
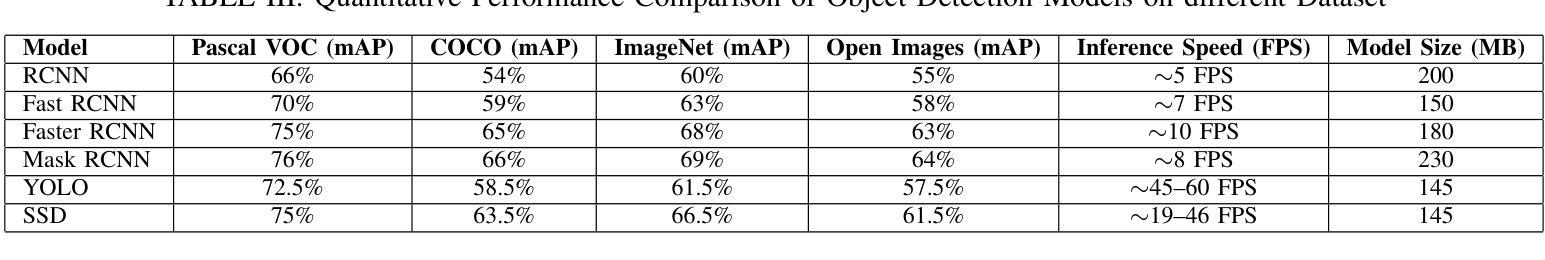
From classical techniques to convolution-based models: A review of object detection algorithms
Authors:Fnu Neha, Deepshikha Bhati, Deepak Kumar Shukla, Md Amiruzzaman
Object detection is a fundamental task in computer vision and image understanding, with the goal of identifying and localizing objects of interest within an image while assigning them corresponding class labels. Traditional methods, which relied on handcrafted features and shallow models, struggled with complex visual data and showed limited performance. These methods combined low-level features with contextual information and lacked the ability to capture high-level semantics. Deep learning, especially Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), addressed these limitations by automatically learning rich, hierarchical features directly from data. These features include both semantic and high-level representations essential for accurate object detection. This paper reviews object detection frameworks, starting with classical computer vision methods. We categorize object detection approaches into two groups: (1) classical computer vision techniques and (2) CNN-based detectors. We compare major CNN models, discussing their strengths and limitations. In conclusion, this review highlights the significant advancements in object detection through deep learning and identifies key areas for further research to improve performance.
目标检测是计算机视觉和图像理解中的一项基本任务,其目标是在图像中识别和定位感兴趣的目标,同时为它们分配相应的类别标签。传统的方法依赖于手工特征和浅层模型,难以处理复杂的视觉数据,表现有限。这些方法将低级特征与上下文信息相结合,缺乏捕获高级语义的能力。深度学习,尤其是卷积神经网络(CNN),通过直接从数据中学习丰富、分层的特点,解决了这些问题。这些特征包括语义和高级表示,对于准确的目标检测至关重要。本文回顾了目标检测框架,从经典计算机视觉方法开始。我们将目标检测方法分为两类:(1)经典计算机视觉技术和(2)基于CNN的检测器。我们比较了主要的CNN模型,讨论了它们的优点和局限性。总之,这篇综述强调了深度学习在目标检测方面的显著进展,并指出了进一步提高性能的关键研究领域。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了目标检测的基本概念及其在计算机视觉和图像理解领域的重要性。传统方法面临复杂视觉数据的挑战,表现有限,而深度学习,尤其是卷积神经网络(CNN)解决了这些问题。本文回顾了目标检测框架,包括经典计算机视觉方法和CNN检测器,并对主要CNN模型进行了比较,强调了深度学习在目标检测方面的显著进展,并指出了进一步提高性能的关键研究领域。
Key Takeaways
- 目标检测是计算机视觉和图像理解领域的基本任务,旨在识别和定位图像中的感兴趣对象,并分配相应的类别标签。
- 传统方法依赖手工特征和浅层模型,难以处理复杂视觉数据,性能有限。
- 深度学习,特别是卷积神经网络(CNN),通过自动学习丰富的层次特征来解决这些问题,这些特征对于准确的目标检测至关重要。
- 目标检测方法可分为两类:经典计算机视觉技术和CNN检测器。
- 本文比较了主要的CNN模型,讨论了它们的优点和局限性。
- 深度学习在目标检测方面取得了显著进展。
点此查看论文截图

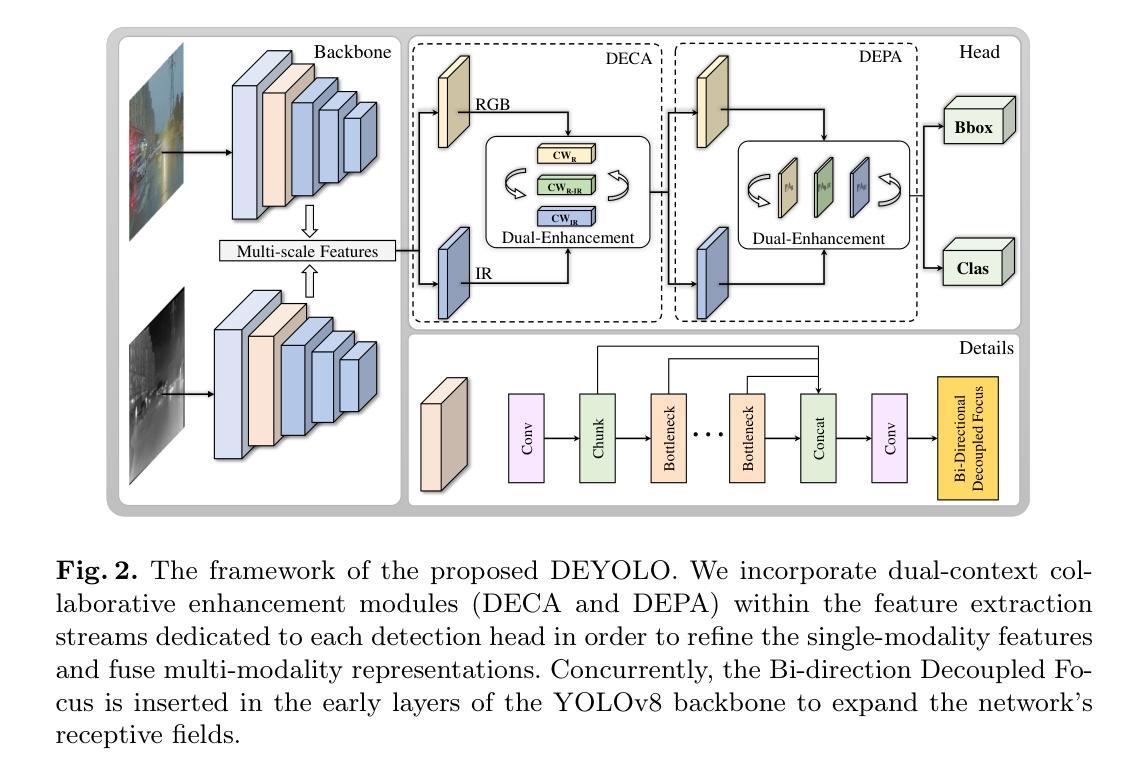
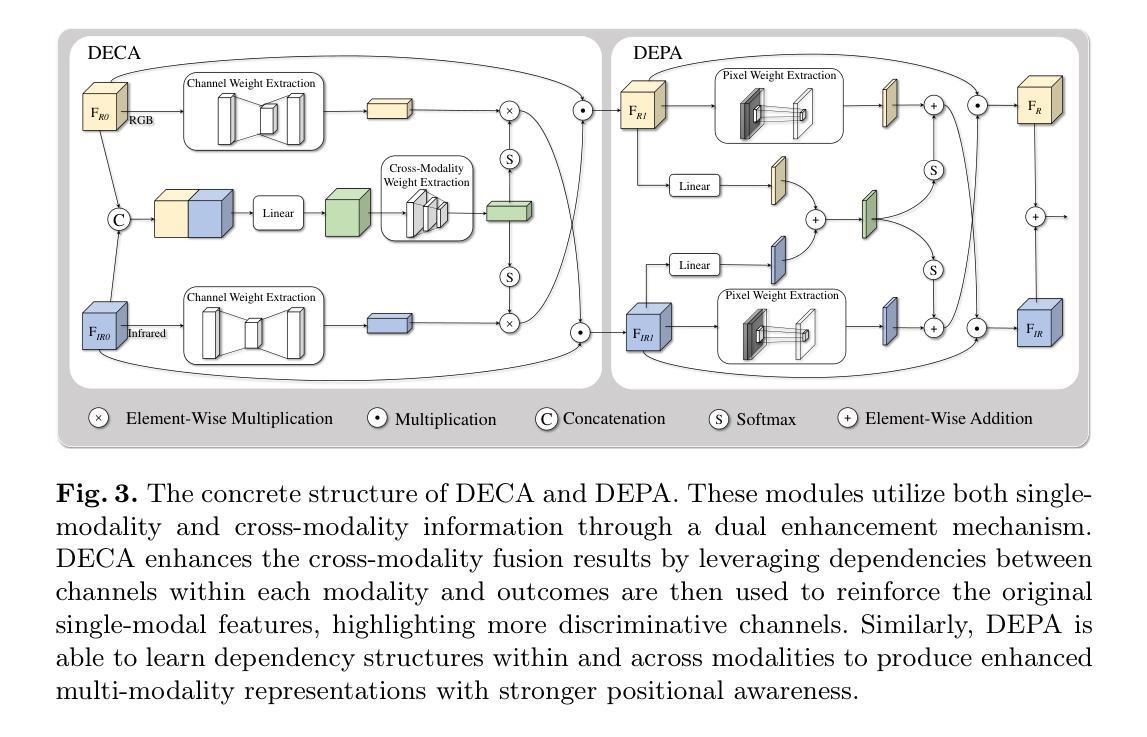
DEYOLO: Dual-Feature-Enhancement YOLO for Cross-Modality Object Detection
Authors:Yishuo Chen, Boran Wang, Xinyu Guo, Wenbin Zhu, Jiasheng He, Xiaobin Liu, Jing Yuan
Object detection in poor-illumination environments is a challenging task as objects are usually not clearly visible in RGB images. As infrared images provide additional clear edge information that complements RGB images, fusing RGB and infrared images has potential to enhance the detection ability in poor-illumination environments. However, existing works involving both visible and infrared images only focus on image fusion, instead of object detection. Moreover, they directly fuse the two kinds of image modalities, which ignores the mutual interference between them. To fuse the two modalities to maximize the advantages of cross-modality, we design a dual-enhancement-based cross-modality object detection network DEYOLO, in which semantic-spatial cross modality and novel bi-directional decoupled focus modules are designed to achieve the detection-centered mutual enhancement of RGB-infrared (RGB-IR). Specifically, a dual semantic enhancing channel weight assignment module (DECA) and a dual spatial enhancing pixel weight assignment module (DEPA) are firstly proposed to aggregate cross-modality information in the feature space to improve the feature representation ability, such that feature fusion can aim at the object detection task. Meanwhile, a dual-enhancement mechanism, including enhancements for two-modality fusion and single modality, is designed in both DECAand DEPAto reduce interference between the two kinds of image modalities. Then, a novel bi-directional decoupled focus is developed to enlarge the receptive field of the backbone network in different directions, which improves the representation quality of DEYOLO. Extensive experiments on M3FD and LLVIP show that our approach outperforms SOTA object detection algorithms by a clear margin. Our code is available at https://github.com/chips96/DEYOLO.
在低光照环境下进行目标检测是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为在RGB图像中目标通常不清晰。由于红外图像提供了额外的清晰边缘信息,可以与RGB图像互补,因此融合RGB和红外图像有可能提高在低光照环境中的检测能力。然而,现有的涉及可见光和红外图像的工作只关注图像融合,而不是目标检测。此外,它们直接融合这两种图像模式,忽略了它们之间的相互干扰。为了融合这两种模式,以最大化跨模式的优势,我们设计了一种基于双增强的跨模式目标检测网络DEYOLO,其中设计了语义空间跨模式和新型双向解耦焦点模块,以实现以检测为中心RGB-红外(RGB-IR)的相互增强。具体来说,首先提出了双语义增强通道权重分配模块(DECA)和双空间增强像素权重分配模块(DEPA),以在特征空间中聚合跨模式信息,提高特征表示能力,使特征融合能够针对目标检测任务。同时,在DECA和DEPA中都设计了包括两种模式融合和单一模式的增强在内的双重增强机制,以减少两种图像模式之间的干扰。然后,开发了一种新的双向解耦焦点,以不同方向扩大主干网络的感受野,提高了DEYOLO的表示质量。在M3FD和LLVIP上的大量实验表明,我们的方法明显优于最新目标检测算法。我们的代码可在https://github.com/chips96/DEYOLO中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
在光照不足环境下,对象检测是一项具有挑战性的任务。红外图像可以提供清晰的边缘信息,与RGB图像相结合可提高检测能力。然而,现有工作仅关注图像融合而非对象检测,且直接融合两种图像模式,忽略了它们之间的相互影响。为了最大化跨模态的优势,我们设计了一种基于双增强的跨模态对象检测网络DEYOLO,其中包含语义空间跨模态和新型双向解耦焦点模块,以实现RGB-红外(RGB-IR)的检测中心相互增强。
Key Takeaways:
- 对象检测在光照不足环境下是一大挑战。
- 红外图像提供了清晰的边缘信息,与RGB图像融合能提高检测能力。
- 现有方法主要关注图像融合而非对象检测。
- 直接融合两种图像模式忽略了它们之间的相互影响。
- DEYOLO网络通过设计双增强机制实现跨模态融合,提高特征表示能力。
- DEYOLO包含语义空间跨模态和新型双向解耦焦点模块,旨在提高RGB-IR的检测中心相互增强。
点此查看论文截图


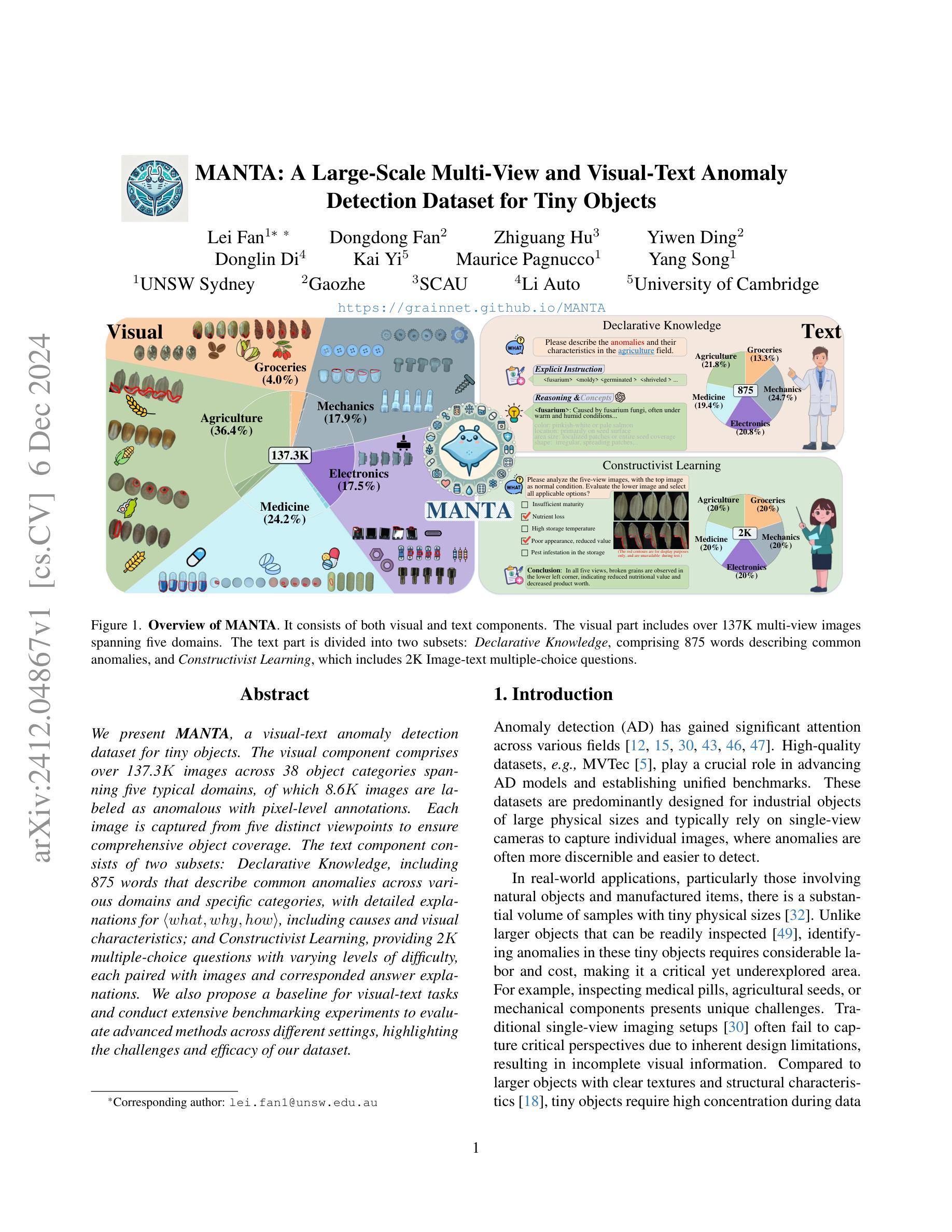
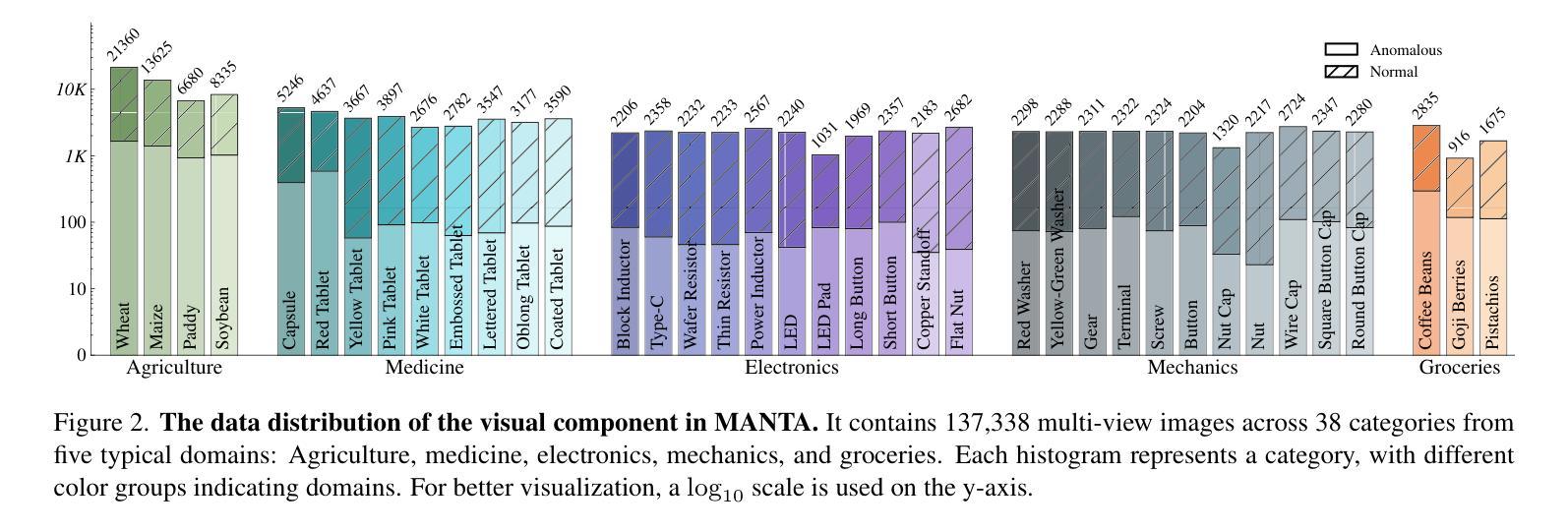
MANTA: A Large-Scale Multi-View and Visual-Text Anomaly Detection Dataset for Tiny Objects
Authors:Lei Fan, Dongdong Fan, Zhiguang Hu, Yiwen Ding, Donglin Di, Kai Yi, Maurice Pagnucco, Yang Song
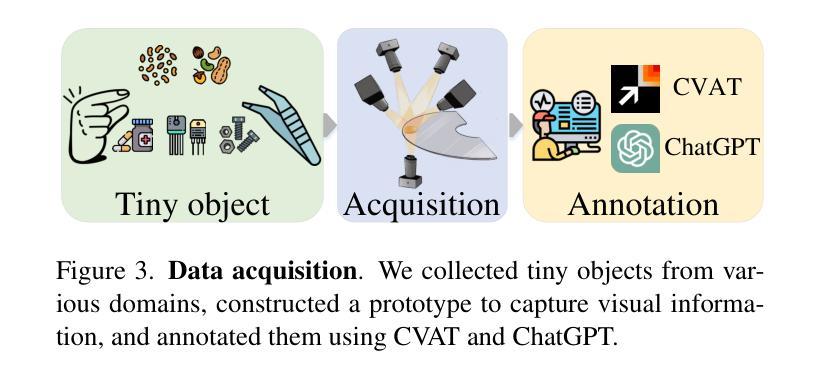
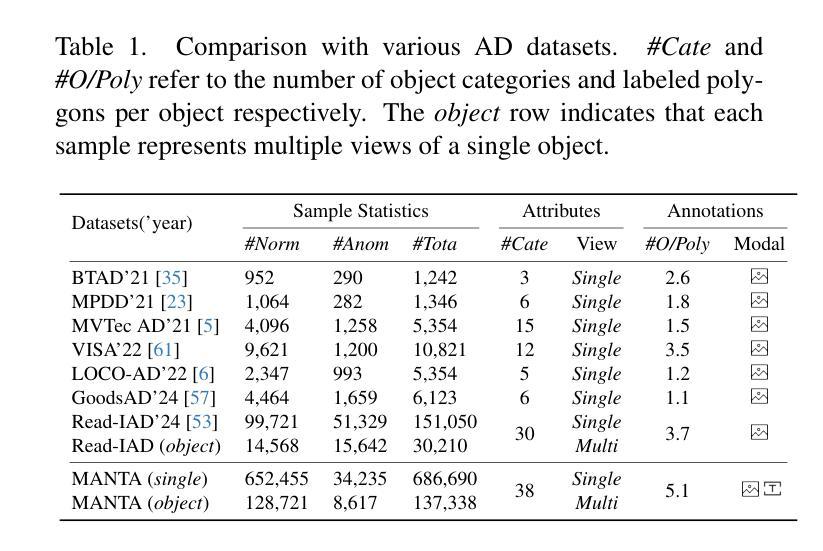
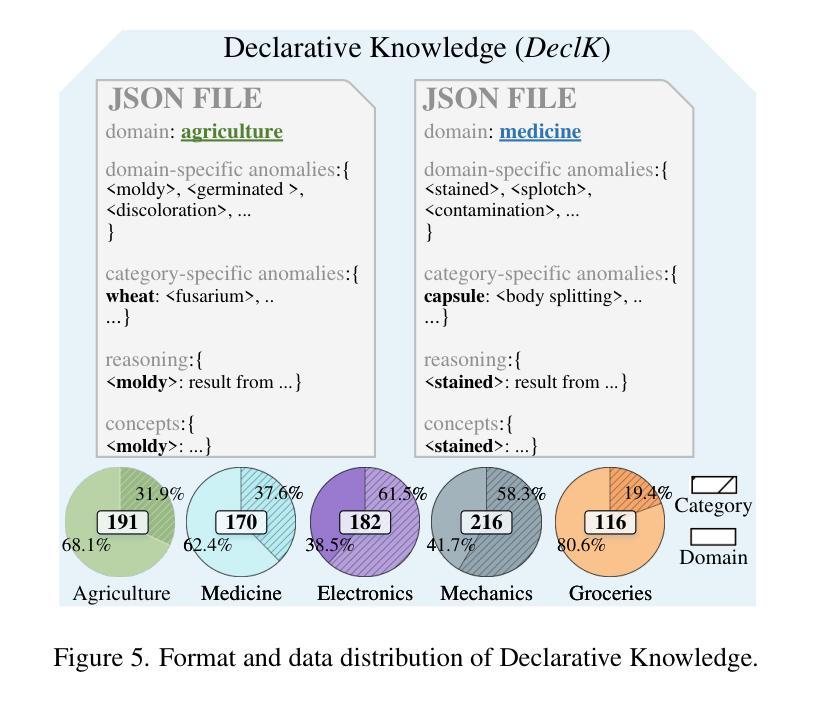
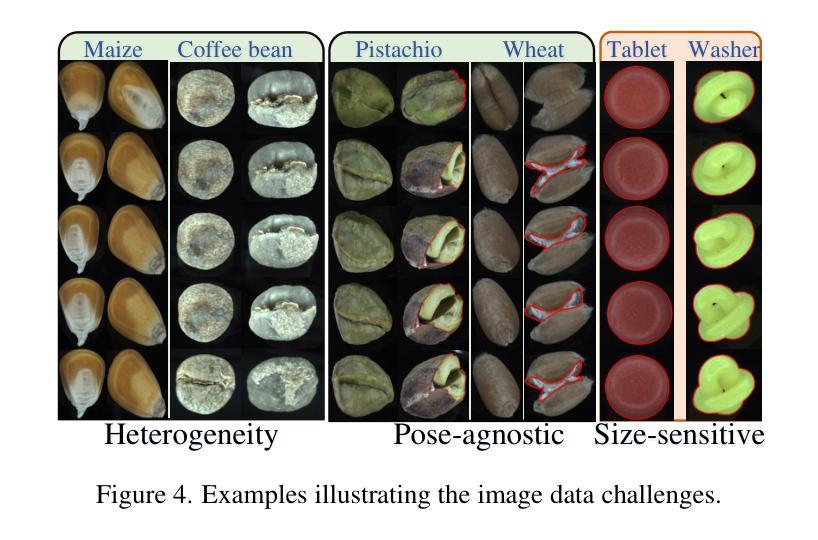
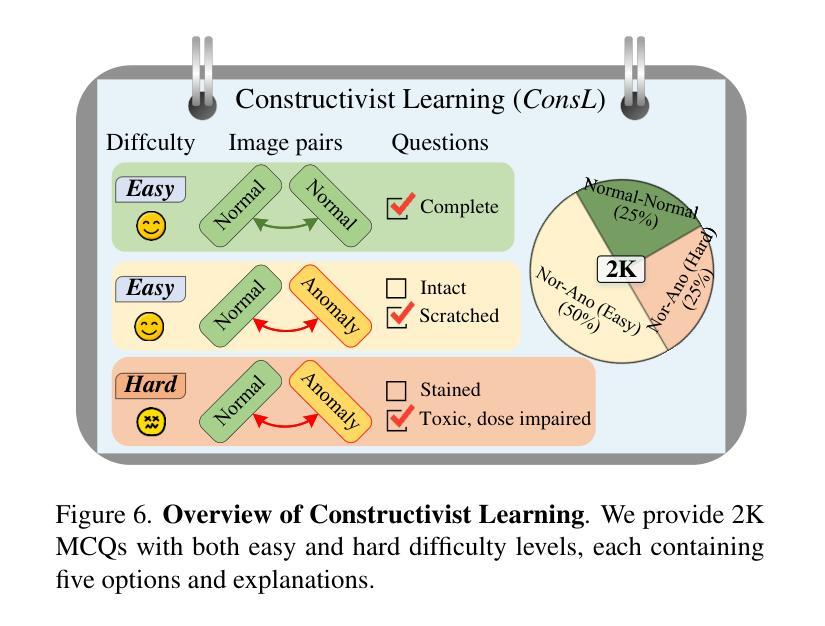
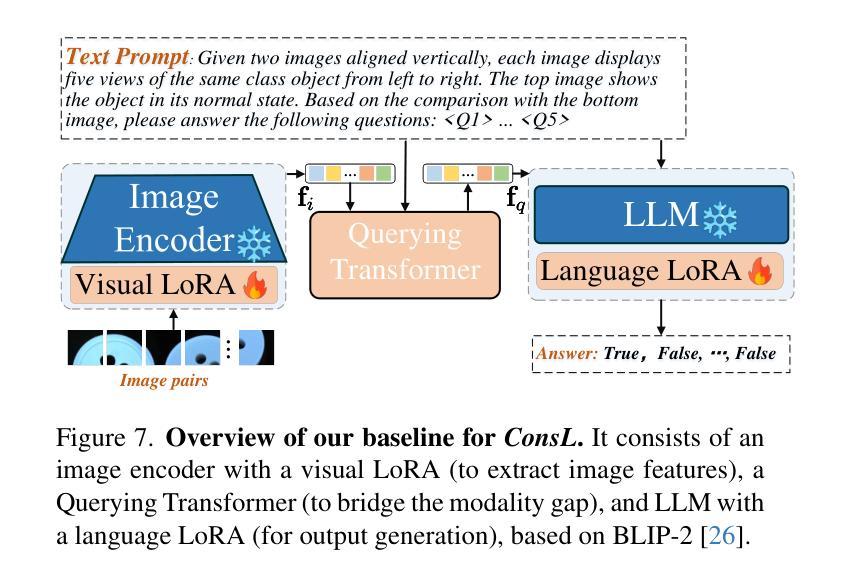
We present MANTA, a visual-text anomaly detection dataset for tiny objects. The visual component comprises over 137.3K images across 38 object categories spanning five typical domains, of which 8.6K images are labeled as anomalous with pixel-level annotations. Each image is captured from five distinct viewpoints to ensure comprehensive object coverage. The text component consists of two subsets: Declarative Knowledge, including 875 words that describe common anomalies across various domains and specific categories, with detailed explanations for < what, why, how>, including causes and visual characteristics; and Constructivist Learning, providing 2K multiple-choice questions with varying levels of difficulty, each paired with images and corresponded answer explanations. We also propose a baseline for visual-text tasks and conduct extensive benchmarking experiments to evaluate advanced methods across different settings, highlighting the challenges and efficacy of our dataset.
我们推出了MANTA数据集,这是一个用于微小物体视觉文本异常检测的数据集。视觉部分包含超过38个对象类别的超过13万张图像,跨越五个典型领域,其中标注为异常的图像有8千张,并带有像素级别的注释。每个图像都是从五个不同的视角捕获的,以确保对物体的全面覆盖。文本部分包含两个子集:描述性知识集包括描述跨不同领域和特定类别的常见异常的875个单词,包括“是什么”、“为什么”、“怎么办”的详细解释,包括原因和视觉特征;以及构建主义学习集,提供难度各异的2千道选择题,每个题目都配有图像和相应的答案解释。我们还为视觉文本任务提供了基准线,并进行了广泛的基准测试实验来评估不同设置下的高级方法,突出我们数据集面临的挑战和有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF https://grainnet.github.io/MANTA
Summary
MANTA数据集是一个用于微小物体视觉文本异常检测的数据集。它包含视觉和文本两部分,视觉部分涵盖38个对象类别,共有超过137.3K张图像,其中8.6K张图像被标注为异常,并提供像素级注释。文本部分包括描述跨域和特定类别的通用异常的Declarative Knowledge,以及提供带图像和答案解释的2K道选择题以辅助学习的Constructivist Learning。同时,提出基线方法并进行基准测试实验评估不同环境下的先进方法,突出数据集的挑战性和有效性。
Key Takeaways
- MANTA数据集是一个用于微小物体视觉文本异常检测的大型数据集。
- 数据集包含视觉和文本两部分,涵盖广泛的物体类别和领域。
- 数据集中有详细的像素级异常标注。
- 文本部分包含描述异常的Declarative Knowledge和用于辅助学习的Constructivist Learning。
- 数据集提供多种视角的图像捕捉,确保全面的物体覆盖。
- 数据集提供了基线方法和基准测试实验,以评估不同环境下的方法性能。
点此查看论文截图
Reflective Teacher: Semi-Supervised Multimodal 3D Object Detection in Bird’s-Eye-View via Uncertainty Measure
Authors:Saheli Hazra, Sudip Das, Rohit Choudhary, Arindam Das, Ganesh Sistu, Ciaran Eising, Ujjwal Bhattacharya
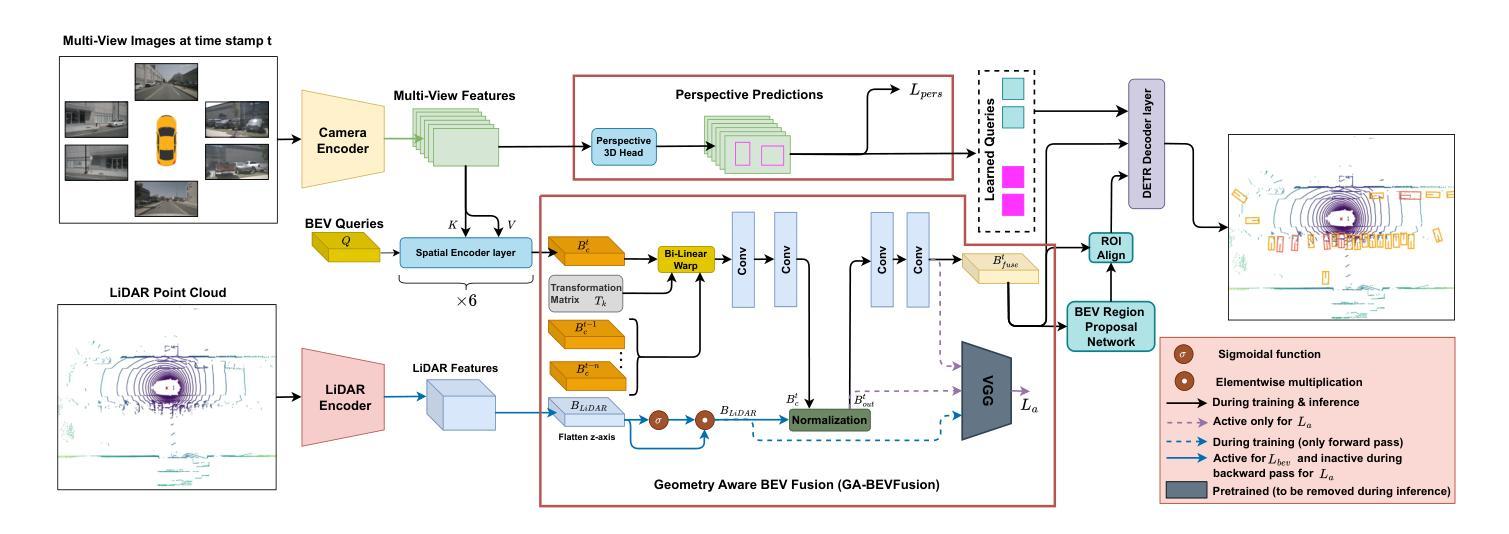
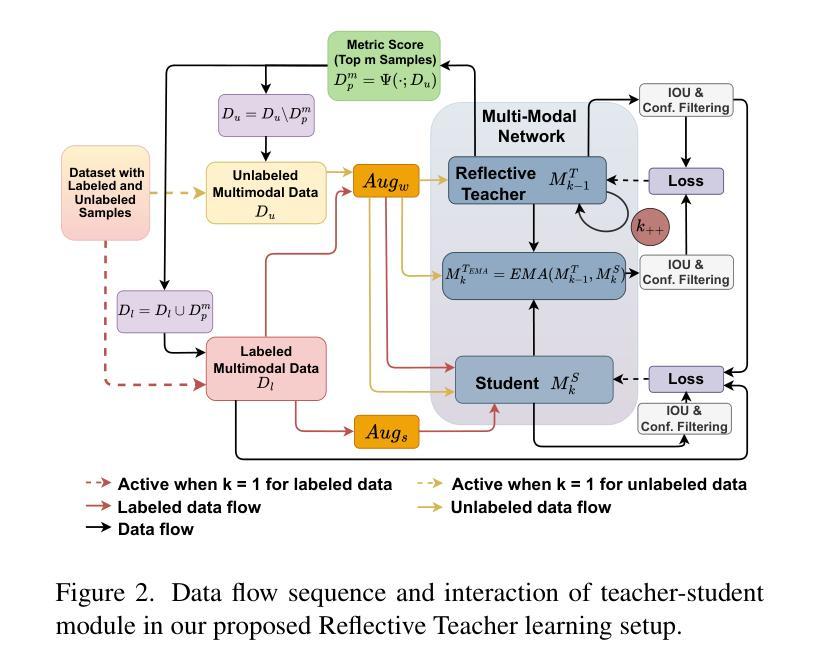
Applying pseudo labeling techniques has been found to be advantageous in semi-supervised 3D object detection (SSOD) in Bird’s-Eye-View (BEV) for autonomous driving, particularly where labeled data is limited. In the literature, Exponential Moving Average (EMA) has been used for adjustments of the weights of teacher network by the student network. However, the same induces catastrophic forgetting in the teacher network. In this work, we address this issue by introducing a novel concept of Reflective Teacher where the student is trained by both labeled and pseudo labeled data while its knowledge is progressively passed to the teacher through a regularizer to ensure retention of previous knowledge. Additionally, we propose Geometry Aware BEV Fusion (GA-BEVFusion) for efficient alignment of multi-modal BEV features, thus reducing the disparity between the modalities - camera and LiDAR. This helps to map the precise geometric information embedded among LiDAR points reliably with the spatial priors for extraction of semantic information from camera images. Our experiments on the nuScenes and Waymo datasets demonstrate: 1) improved performance over state-of-the-art methods in both fully supervised and semi-supervised settings; 2) Reflective Teacher achieves equivalent performance with only 25% and 22% of labeled data for nuScenes and Waymo datasets respectively, in contrast to other fully supervised methods that utilize the full labeled dataset.
在自动驾驶的鸟瞰图(BEV)半监督三维目标检测(SSOD)中,应用伪标签技术已被证明是有利的,特别是在标签数据有限的情况下。文献中,指数移动平均(EMA)已被用于学生网络调整教师网络的权重。然而,这会导致教师网络中的灾难性遗忘。在这项工作中,我们通过引入反射教师(Reflective Teacher)的新概念来解决这个问题,学生在有标签和伪标签数据的训练下,通过正则化器逐渐将知识传递给教师,以确保保留以前的知识。此外,我们提出了几何感知BEV融合(GA-BEVFusion),用于有效地对齐多模式BEV特征,从而减少相机和激光雷达之间的模式差异。这有助于可靠地将嵌入激光雷达点中的精确几何信息与空间先验信息相结合,从相机图像中提取语义信息。我们在nuScenes和Waymo数据集上的实验表明:1)在全监督和半监督设置下,相较于最先进的方法,我们的方法性能有所提升;2)反射教师仅使用nuScenes和Waymo数据集的25%和22%的标签数据即可实现相当的性能,而其他全监督方法则需要使用完整的标签数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
伪标签技术在半监督三维物体检测领域中的鸟瞳图视角(BEV)对自动驾驶技术具有优势,特别是在标签数据有限的情况下。然而,现有文献中的指数移动平均(EMA)用于调整教师网络的权重,这会导致教师网络遗忘原有知识的问题。本研究通过引入“反射教师”概念来解决这一问题,学生网络通过标签和伪标签数据进行训练,同时通过正则化器逐渐获取知识来确保原有知识的保留。此外,提出了几何感知的BEV融合(GA-BEVFusion),实现多模态BEV特征的有效对齐,从而减少摄像头和激光雷达之间的模式差异。实验结果表明,该方法在nuScenes和Waymo数据集上的性能优于现有方法,尤其在标签数据减少时,反射教师的性能更是优于全监督方法。总体而言,该技术将为自动化驾驶的半监督物体检测提供新的视角和方法。
Key Takeaways
- 伪标签技术在半监督三维物体检测中对自动驾驶有益,特别是在有限标签数据的情况下。
- 指数移动平均(EMA)在调整教师网络权重时可能导致原有知识的遗忘。
- 提出“反射教师”概念,通过学生网络结合标签和伪标签数据进行训练,同时通过正则化器传递知识给教师网络以确保原有知识的保留。
- 提出几何感知的BEV融合(GA-BEVFusion),实现多模态BEV特征的有效对齐。
- 实验结果显示该方法在nuScenes和Waymo数据集上的性能优于现有方法。
- 在减少标签数据时,反射教师的性能与全监督方法相当甚至更优。
点此查看论文截图

Frequency-Adaptive Low-Latency Object Detection Using Events and Frames
Authors:Haitian Zhang, Xiangyuan Wang, Chang Xu, Xinya Wang, Fang Xu, Huai Yu, Lei Yu, Wen Yang
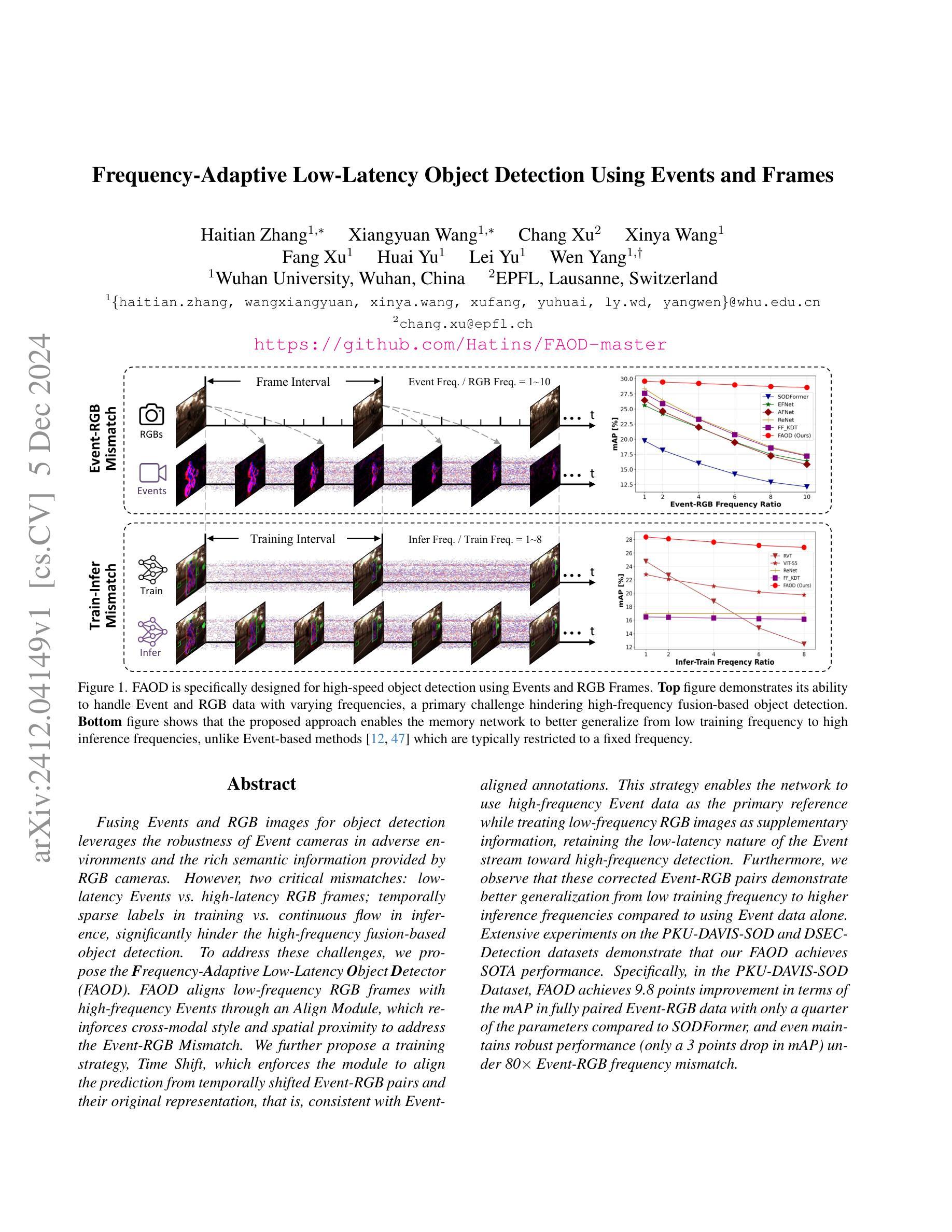
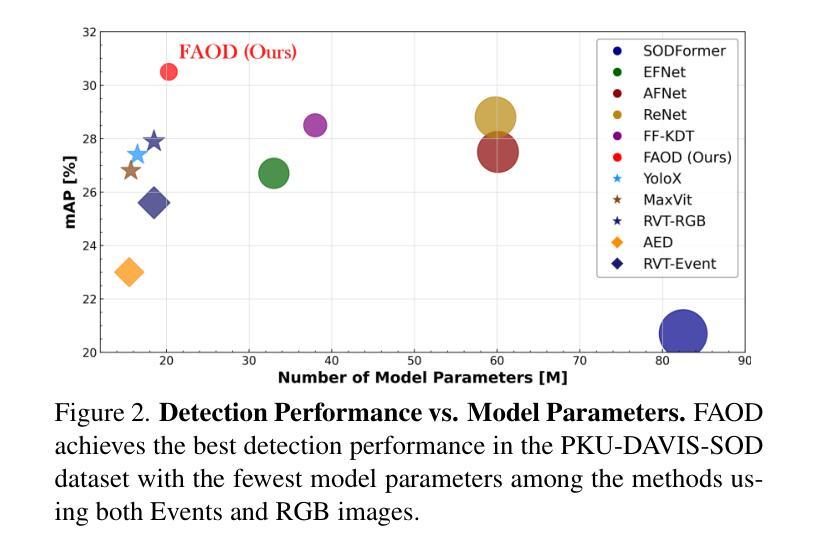
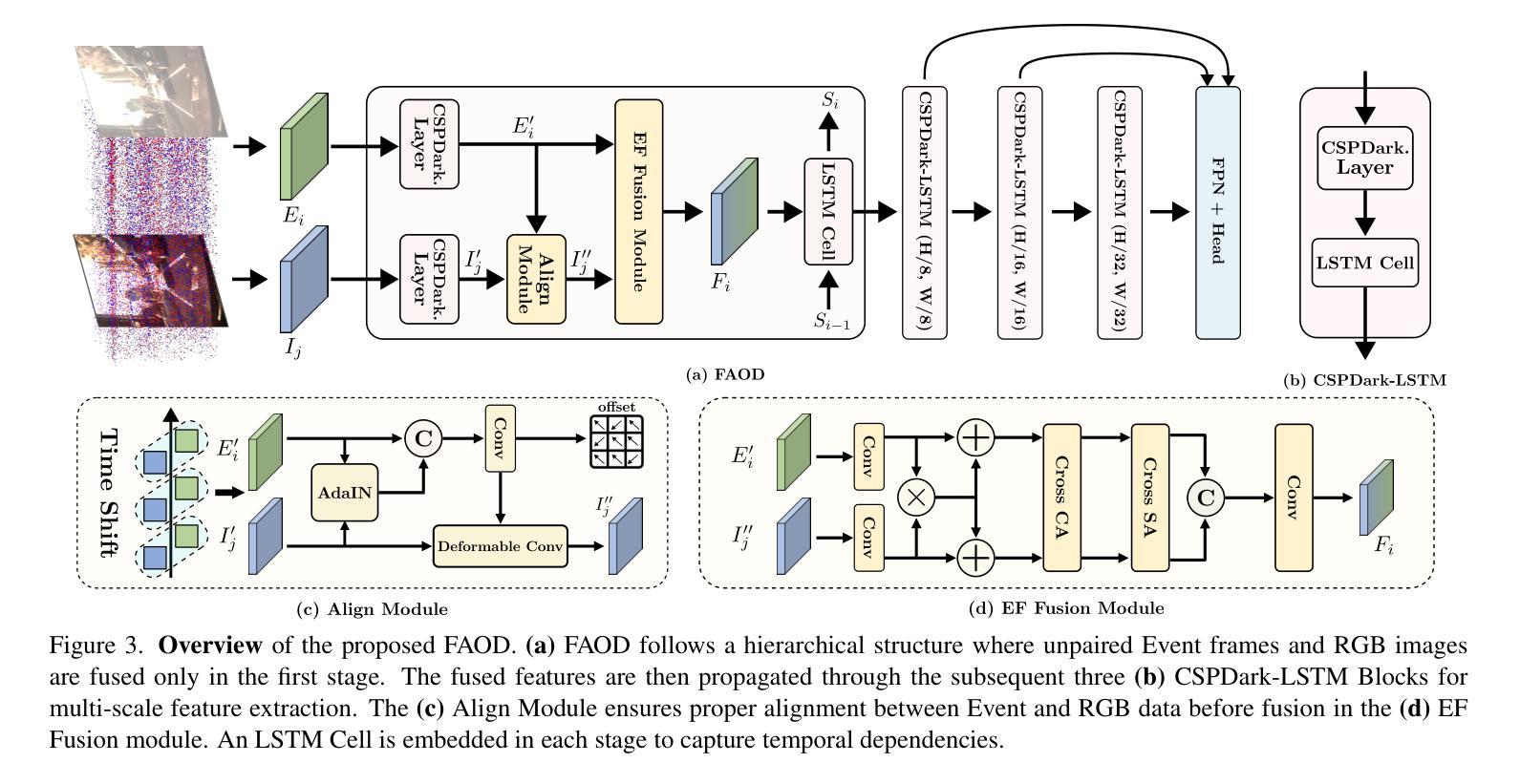
Fusing Events and RGB images for object detection leverages the robustness of Event cameras in adverse environments and the rich semantic information provided by RGB cameras. However, two critical mismatches: low-latency Events \textit{vs.}high-latency RGB frames; temporally sparse labels in training \textit{vs.}continuous flow in inference, significantly hinder the high-frequency fusion-based object detection. To address these challenges, we propose the \textbf{F}requency-\textbf{A}daptive Low-Latency \textbf{O}bject \textbf{D}etector (FAOD). FAOD aligns low-frequency RGB frames with high-frequency Events through an Align Module, which reinforces cross-modal style and spatial proximity to address the Event-RGB Mismatch. We further propose a training strategy, Time Shift, which enforces the module to align the prediction from temporally shifted Event-RGB pairs and their original representation, that is, consistent with Event-aligned annotations. This strategy enables the network to use high-frequency Event data as the primary reference while treating low-frequency RGB images as supplementary information, retaining the low-latency nature of the Event stream toward high-frequency detection. Furthermore, we observe that these corrected Event-RGB pairs demonstrate better generalization from low training frequency to higher inference frequencies compared to using Event data alone. Extensive experiments on the PKU-DAVIS-SOD and DSEC-Detection datasets demonstrate that our FAOD achieves SOTA performance. Specifically, in the PKU-DAVIS-SOD Dataset, FAOD achieves 9.8 points improvement in terms of the mAP in fully paired Event-RGB data with only a quarter of the parameters compared to SODFormer, and even maintains robust performance (only a 3 points drop in mAP) under 80$\times$ Event-RGB frequency mismatch.
融合事件和RGB图像进行目标检测,利用事件相机在恶劣环境中的稳健性和RGB相机提供的丰富语义信息。然而,两个关键不匹配问题:低延迟事件与高延迟RGB帧之间的不匹配;训练中的时间稀疏标签与推理中的连续流之间的不匹配,显著阻碍了基于高频融合的目标检测。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了频率自适应低延迟目标检测器(FAOD)。FAOD通过一个对齐模块,将低频的RGB帧与高频的事件进行对齐,该模块加强了跨模态风格和空间邻近性,以解决事件-RGB不匹配问题。我们还提出了一种训练策略,即时间偏移策略,该策略强制模块对齐时间偏移的事件-RGB对与其原始表示(即与事件对齐的注释一致)。该策略使网络能够使用高频事件数据作为主要参考,而将低频RGB图像视为辅助信息,保持事件流的低延迟特性以实现高频检测。此外,我们观察到,这些校正后的事件-RGB对在低训练频率到较高推理频率之间表现出更好的泛化能力,与仅使用事件数据相比。在PKU-DAVIS-SOD和DSEC-Detection数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的FAOD达到了最先进的表现。具体而言,在PKU-DAVIS-SOD数据集上,FAOD在全配对事件-RGB数据中的mAP提高了9.8点,而且与SODFormer相比,参数只有四分之一,即使在事件-RGB频率不匹配达到80倍的情况下,mAP也只下降了3点,仍保持了稳健的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了融合事件和RGB图像进行物体检测的技术。针对事件相机在恶劣环境下的稳健性和RGB相机提供的丰富语义信息,提出一种频率自适应低延迟物体检测器(FAOD)。FAOD通过对低频RGB帧与高频事件进行对齐,解决了事件与RGB帧之间的不匹配问题。同时,采用时间偏移训练策略,使网络能够利用高频事件数据作为主要参考,将低频率的RGB图像作为补充信息。实验表明,校正后的事件-RGB对在低训练频率到高推理频率的情况下具有更好的泛化性能。在PKU-DAVIS-SOD和DSEC-Detection数据集上的实验表明,FAOD达到最新技术水平。特别是在PKU-DAVIS-SOD数据集上,与SODFormer相比,FAOD在全配对事件RGB数据上的mAP提高了9.8点,即使在80倍的事件RGB频率不匹配的情况下,mAP也只下降了3点。
Key Takeaways
- 事件相机在恶劣环境下的稳健性和RGB相机的丰富语义信息融合,有助于提高物体检测的准确性。
- 低延迟事件与高频RGB帧之间存在不匹配问题,需要通过FAOD解决。
- FAOD通过Align Module对齐低频RGB帧与高频事件,强化跨模态风格和空间邻近性。
- 提出时间偏移训练策略,使网络能够利用高频事件数据作为主要参考。
- 校正后的事件-RGB对在低训练频率到高推理频率的情况下具有更好的泛化性能。
- 在PKU-DAVIS-SOD和DSEC-Detection数据集上,FAOD达到最新技术水平,表现优异。
- 在PKU-DAVIS-SOD数据集上,FAOD与现有技术相比具有显著优势。
点此查看论文截图
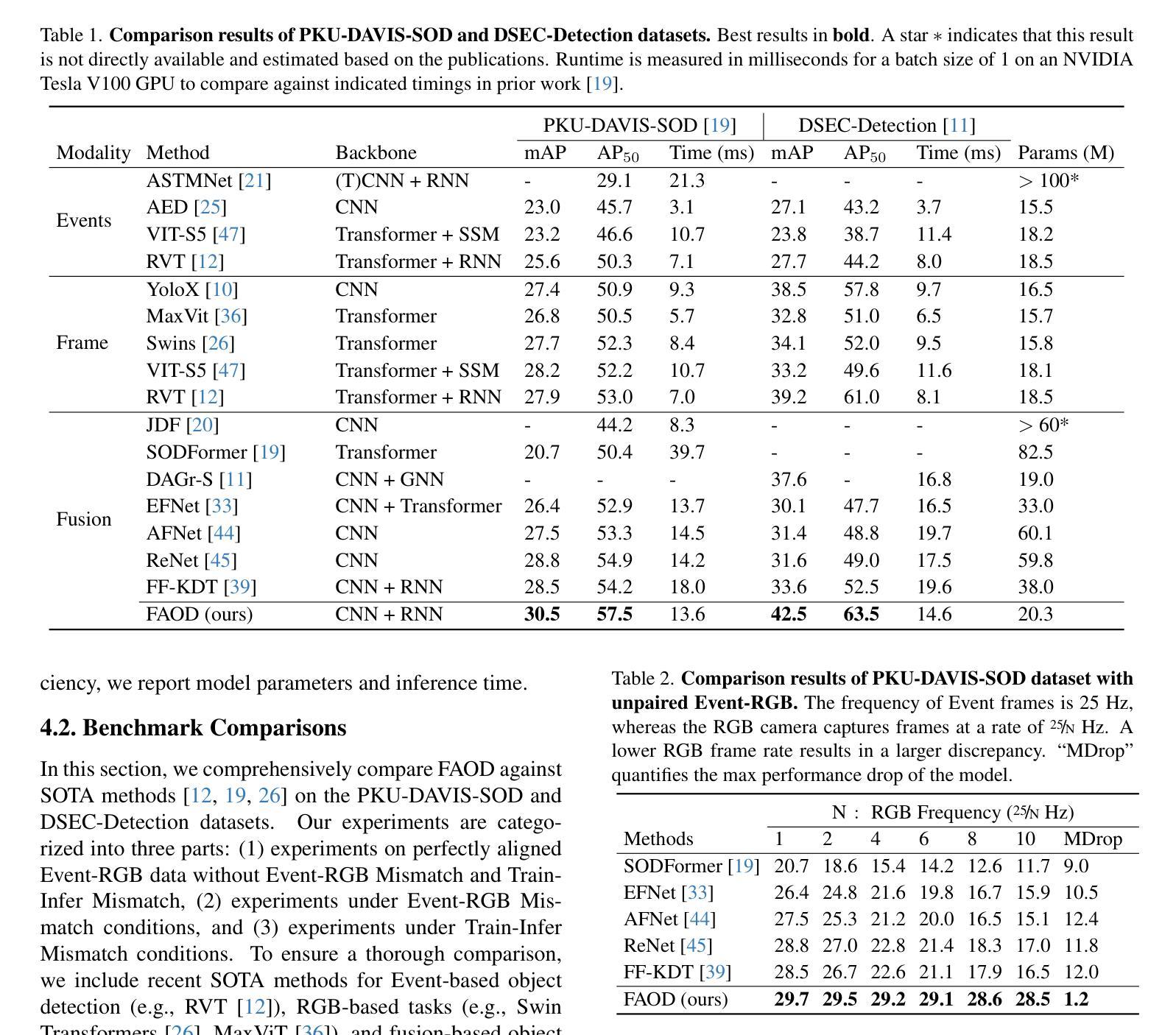
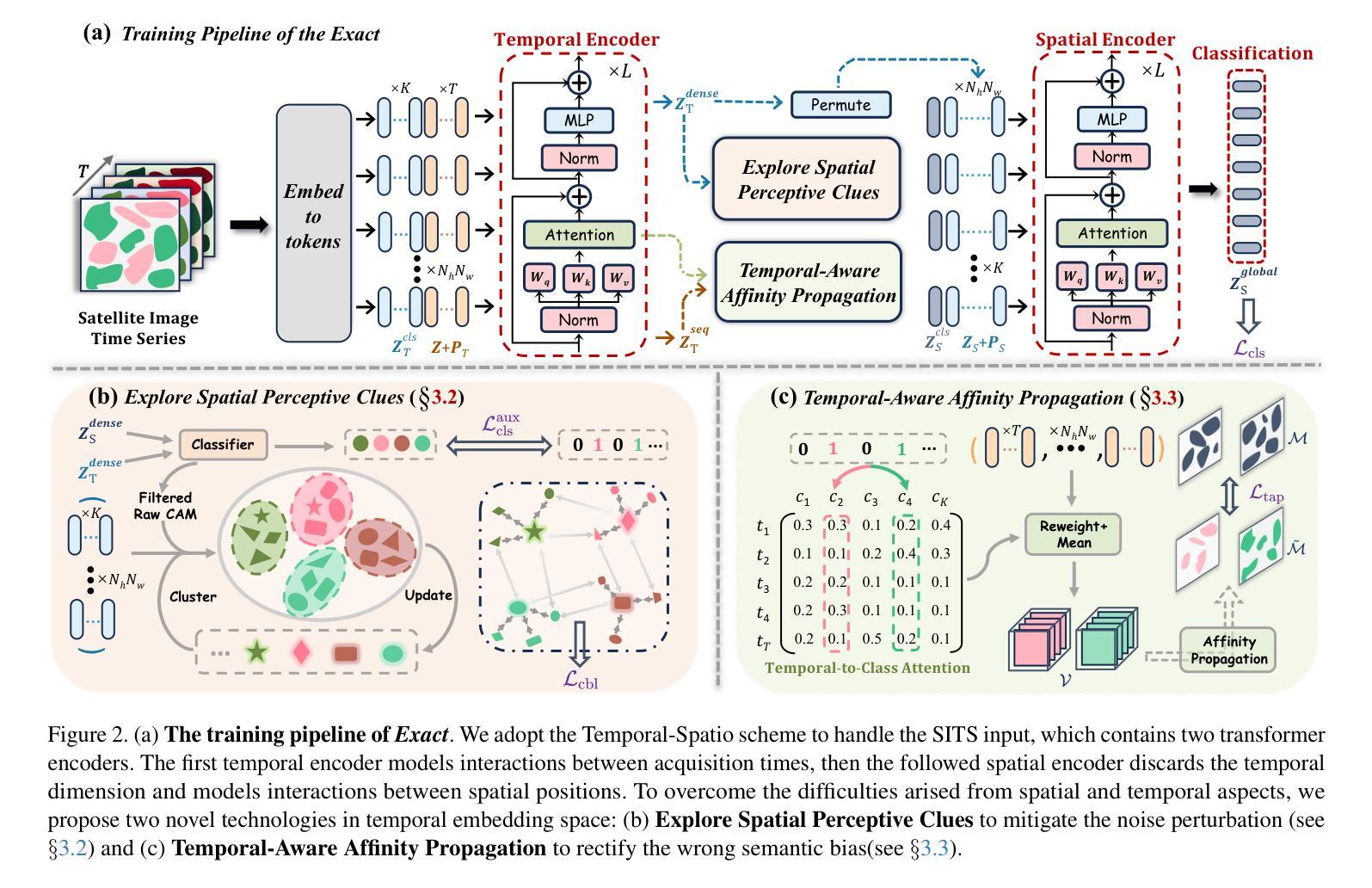
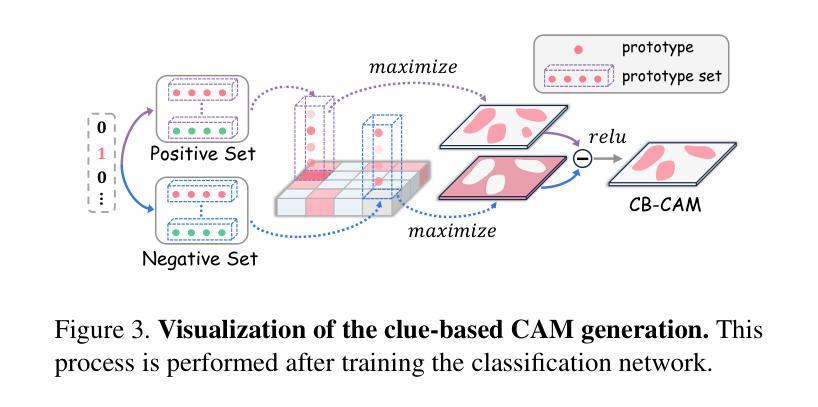
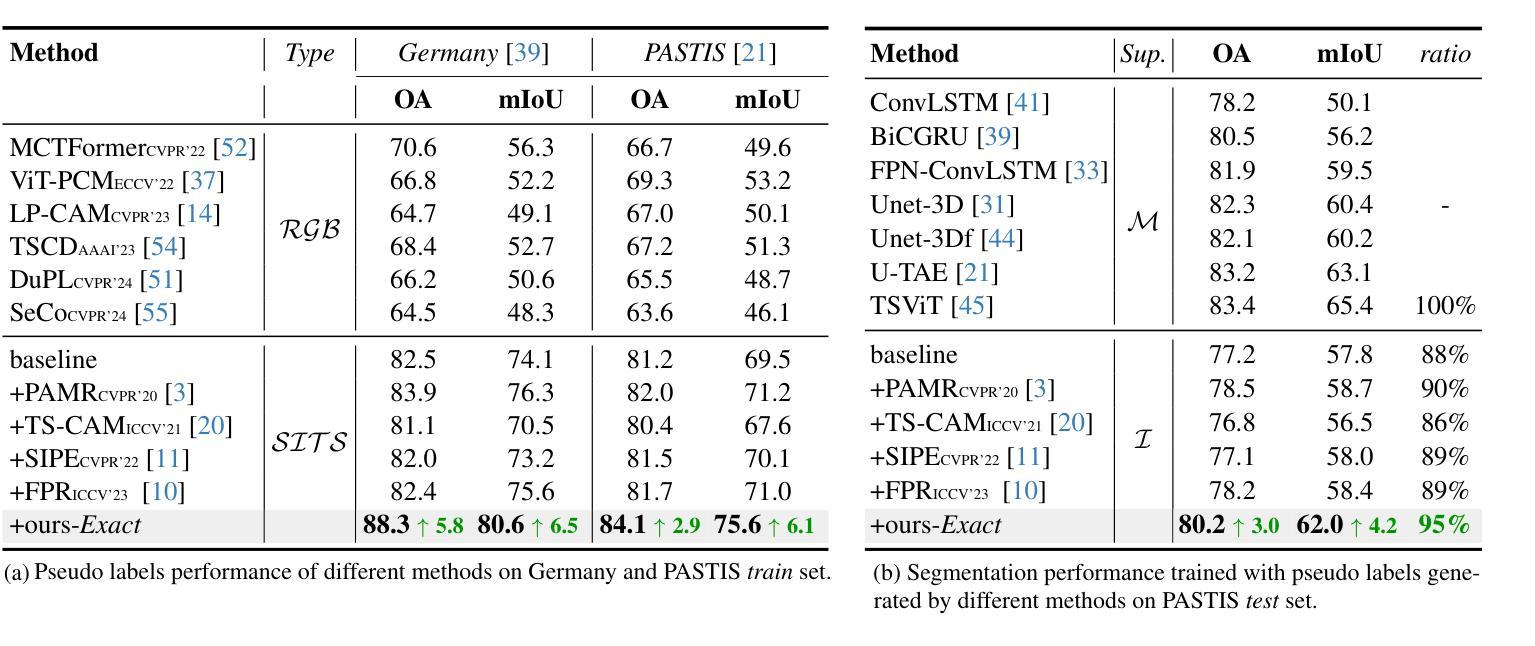
Exact: Exploring Space-Time Perceptive Clues for Weakly Supervised Satellite Image Time Series Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Hao Zhu, Yan Zhu, Jiayu Xiao, Tianxiang Xiao, Yike Ma, Yucheng Zhang, Feng Dai
Automated crop mapping through Satellite Image Time Series (SITS) has emerged as a crucial avenue for agricultural monitoring and management. However, due to the low resolution and unclear parcel boundaries, annotating pixel-level masks is exceptionally complex and time-consuming in SITS. This paper embraces the weakly supervised paradigm (i.e., only image-level categories available) to liberate the crop mapping task from the exhaustive annotation burden. The unique characteristics of SITS give rise to several challenges in weakly supervised learning: (1) noise perturbation from spatially neighboring regions, and (2) erroneous semantic bias from anomalous temporal periods. To address the above difficulties, we propose a novel method, termed exploring space-time perceptive clues (Exact). First, we introduce a set of spatial clues to explicitly capture the representative patterns of different crops from the most class-relative regions. Besides, we leverage the temporal-to-class interaction of the model to emphasize the contributions of pivotal clips, thereby enhancing the model perception for crop regions. Build upon the space-time perceptive clues, we derive the clue-based CAMs to effectively supervise the SITS segmentation network. Our method demonstrates impressive performance on various SITS benchmarks. Remarkably, the segmentation network trained on Exact-generated masks achieves 95% of its fully supervised performance, showing the bright promise of weakly supervised paradigm in crop mapping scenario. Our code will be publicly available.
通过卫星图像时间序列(SITS)进行自动作物地图绘制已成为农业监测和管理的重要途径。然而,由于分辨率较低和地块边界不清晰,在SITS中进行像素级掩模标注极为复杂且耗时。本文针对只有图像级类别可用的弱监督模式,将作物地图绘制任务从详尽的标注负担中解放出来。SITS的独特特性给弱监督学习带来了几个挑战:(1)来自空间邻近区域的噪声干扰;(2)来自异常时间段的错误语义偏差。为了应对上述困难,我们提出了一种新方法,称为探索时空感知线索(Exact)。首先,我们引入了一组空间线索,以显式捕获不同作物的代表性模式,这些模式来自最相关的区域。此外,我们利用模型的时空类别交互作用来强调关键片段的贡献,从而提高模型对作物区域的感知能力。基于时空感知线索,我们得出基于线索的CAMs,以有效监督SITS分割网络。我们的方法在多种SITS基准测试上表现出令人印象深刻的效果。值得注意的是,在Exact生成的掩模上训练的分割网络达到了全监督性能的95%,显示出弱监督模式在作物地图绘制场景中的光明前景。我们的代码将公开可用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review. Code will be available at https://github.com/MiSsU-HH/Exact
Summary
本论文针对卫星图像时间序列(SITS)的自动作物映射问题,提出了利用弱监督学习的方法来解决标注繁琐的问题。通过引入空间线索和时空感知线索(Exact),该方法能有效应对噪声干扰和语义偏差等挑战,提升了模型对作物区域的感知能力。实验结果在多个SITS基准测试集上表现优异,基于Exact生成的掩膜训练的分割网络性能达到全监督性能的95%,展现出弱监督学习在作物映射领域的广阔前景。
Key Takeaways
- 卫星图像时间序列(SITS)在农业监测和管理中扮演重要角色,但标注繁琐限制了其发展。
- 低分辨率和模糊的地块边界使得像素级掩膜的标注在SITS中极为复杂和耗时。
- 本研究采用弱监督学习方法,仅利用图像级别的类别信息,减轻了标注负担。
- 面对SITS中的噪声干扰和语义偏差挑战,引入了空间线索和时空感知线索(Exact)。
- 通过空间线索捕捉不同作物的代表性模式,并强调关键时段的重要性,增强了模型对作物区域的感知。
- 基于时空感知线索,生成了线索引导的CAMs,有效监督了SITS分割网络。
点此查看论文截图

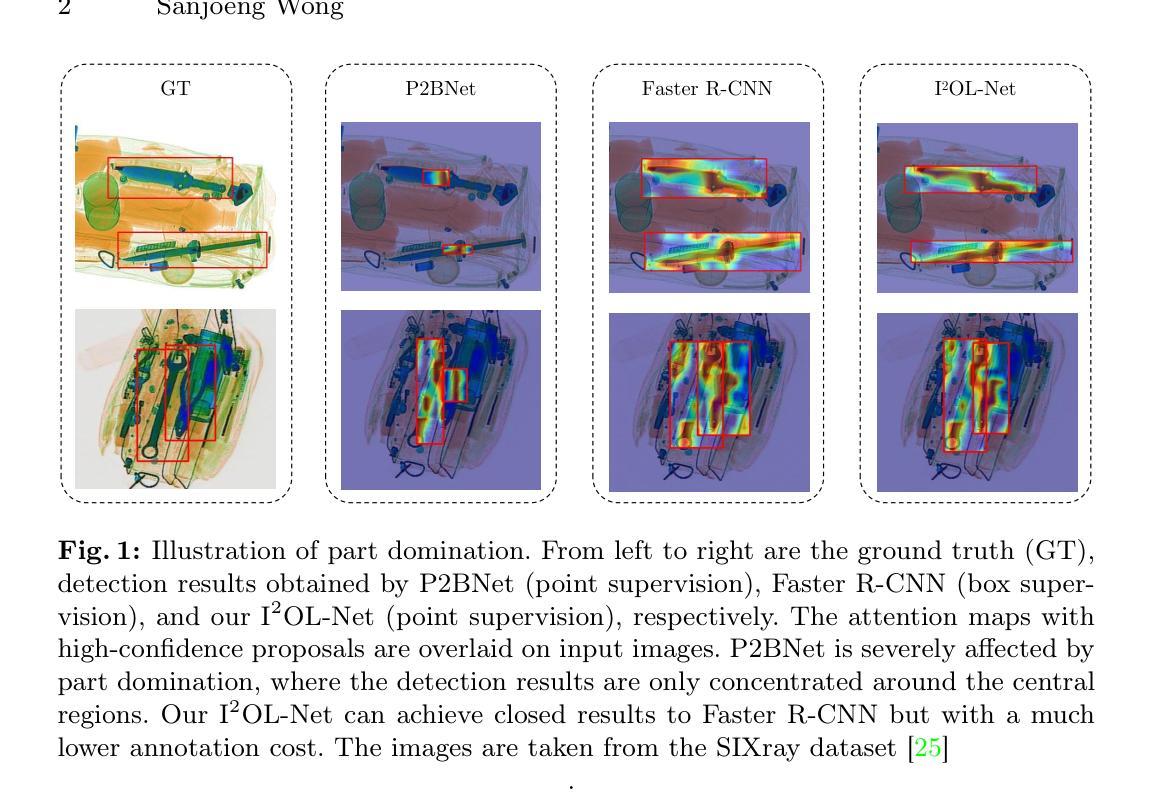
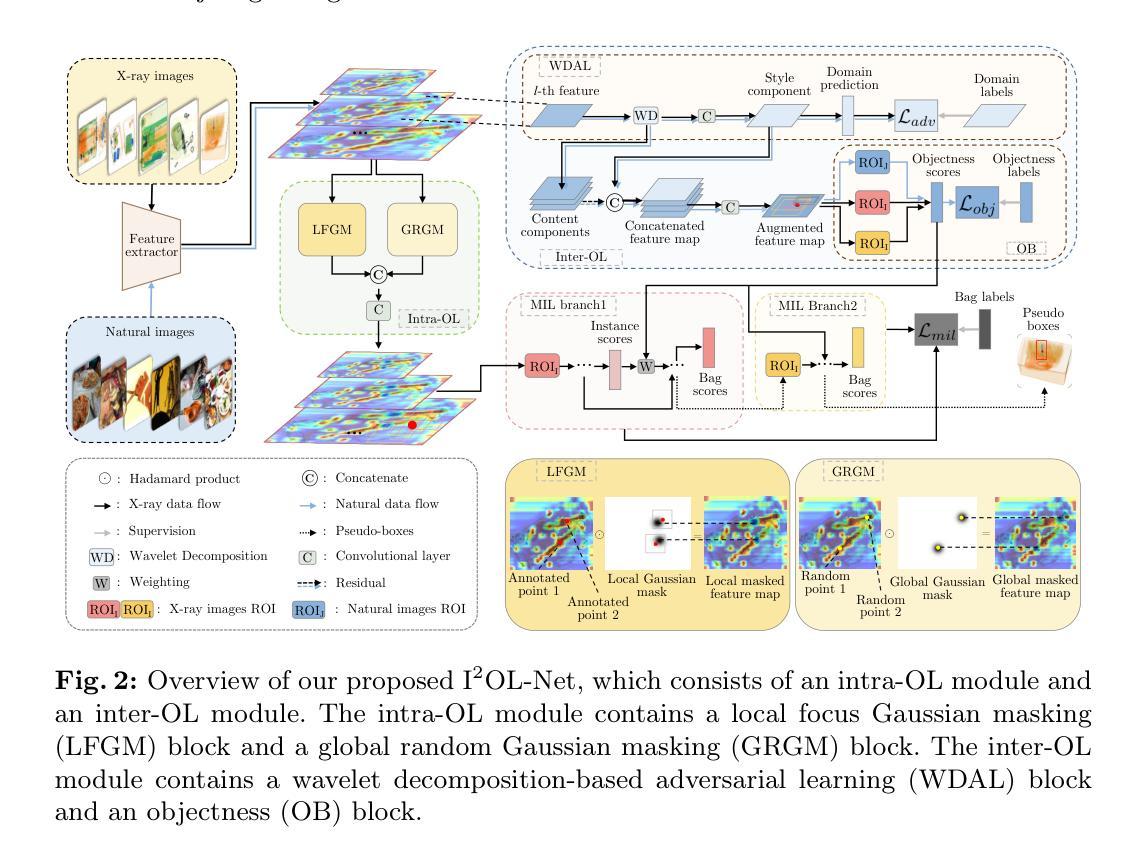
I$^2$OL-Net: Intra-Inter Objectness Learning Network for Point-Supervised X-Ray Prohibited Item Detection
Authors:Sanjoeng Wong, Yan Yan
Automatic detection of prohibited items in X-ray images plays a crucial role in public security. However, existing methods rely heavily on labor-intensive box annotations. To address this, we investigate X-ray prohibited item detection under labor-efficient point supervision and develop an intra-inter objectness learning network (I$^2$OL-Net). I$^2$OL-Net consists of two key modules: an intra-modality objectness learning (intra-OL) module and an inter-modality objectness learning (inter-OL) module. The intra-OL module designs a local focus Gaussian masking block and a global random Gaussian masking block to collaboratively learn the objectness in X-ray images. Meanwhile, the inter-OL module introduces the wavelet decomposition-based adversarial learning block and the objectness block, effectively reducing the modality discrepancy and transferring the objectness knowledge learned from natural images with box annotations to X-ray images. Based on the above, I$^2$OL-Net greatly alleviates the problem of part domination caused by severe intra-class variations in X-ray images. Experimental results on four X-ray datasets show that I$^2$OL-Net can achieve superior performance with a significant reduction of annotation cost, thus enhancing its accessibility and practicality.
在X光图像中自动检测违禁物品对公共安全至关重要。然而,现有方法严重依赖于劳动密集型的框注释。为了解决这一问题,我们在劳动力效率高的点监督下研究了X光违禁物品检测,并开发了一种内外对象性学习网络(I$^2$OL-Net)。I$^2$OL-Net由两个关键模块组成:同模态对象性学习(intra-OL)模块和跨模态对象性学习(inter-OL)模块。Intra-OL模块设计了一个局部焦点高斯掩膜块和一个全局随机高斯掩膜块,以协同学习X光图像中的对象性。同时,inter-OL模块引入了基于小波分解的对抗性学习块和对象性块,有效地减少了模态差异,并将从带有框注释的自然图像中学习到的对象性知识转移到X光图像上。基于以上内容,I$^2$OL-Net大大缓解了由X光图像中严重的类内变化引起的部分主导问题。在四个X光数据集上的实验结果表明,I$^2$OL-Net在显著降低标注成本的同时,可以取得卓越的性能,从而提高了其可访问性和实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文研究了X光图像中的违禁物品自动检测问题,提出一种劳动效率高的点监督方式下的违禁物品检测网络I$^2$OL-Net。该网络由两个关键模块组成:intra-OL模块和inter-OL模块。前者通过局部聚焦高斯掩膜块和全局随机高斯掩膜块协同学习X光图像中的对象性;后者引入基于小波分解的对抗学习块和对象性块,有效减少模态差异,将从自然图像中学习到的对象性知识转移到X光图像上。实验结果表明,I$^2$OL-Net在四个X光数据集上的性能优越,且标注成本大幅降低,提高了其可用性和实用性。
Key Takeaways
- X光图像中的违禁物品自动检测对公共安全至关重要。
- 现有方法过于依赖劳动密集型的框标注,提出了一种新的解决方案。
- I$^2$OL-Net网络由intra-OL和inter-OL两个关键模块组成。
- intra-OL模块通过局部和全局高斯掩膜块学习X光图像中的对象性。
- inter-OL模块利用小波分解的对抗学习块和对象性块,减少模态差异,并将自然图像中的对象性知识转移到X光图像上。
- I$^2$OL-Net在四个X光数据集上的性能优越,降低了标注成本,增强了其实际应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

Evaluating Single Event Upsets in Deep Neural Networks for Semantic Segmentation: an embedded system perspective
Authors:Jon Gutiérrez-Zaballa, Koldo Basterretxea, Javier Echanobe
As the deployment of artifical intelligence (AI) algorithms at edge devices becomes increasingly prevalent, enhancing the robustness and reliability of autonomous AI-based perception and decision systems is becoming as relevant as precision and performance, especially in applications areas considered safety-critical such as autonomous driving and aerospace. This paper delves into the robustness assessment in embedded Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), particularly focusing on the impact of parameter perturbations produced by single event upsets (SEUs) on convolutional neural networks (CNN) for image semantic segmentation. By scrutinizing the layer-by-layer and bit-by-bit sensitivity of various encoder-decoder models to soft errors, this study thoroughly investigates the vulnerability of segmentation DNNs to SEUs and evaluates the consequences of techniques like model pruning and parameter quantization on the robustness of compressed models aimed at embedded implementations. The findings offer valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying SEU-induced failures that allow for evaluating the robustness of DNNs once trained in advance. Moreover, based on the collected data, we propose a set of practical lightweight error mitigation techniques with no memory or computational cost suitable for resource-constrained deployments. The code used to perform the fault injection (FI) campaign is available at https://github.com/jonGuti13/TensorFI2 , while the code to implement proposed techniques is available at https://github.com/jonGuti13/parameterProtection .
随着人工智能(AI)算法在边缘设备的部署越来越普遍,提高基于AI的自主感知和决策系统的稳健性和可靠性变得与精度和性能同样重要,特别是在安全关键领域,如自动驾驶和航空航天等应用中。本文深入探讨了嵌入式深度神经网络(DNN)的稳健性评估,特别是关注由单事件扰动(SEU)产生的参数扰动对图像语义分割卷积神经网络(CNN)的影响。通过对各种编码器-解码器模型的逐层和逐位敏感性进行仔细审查,本研究全面研究了分割DNN对SEU的脆弱性,并评估了模型修剪和参数量化等技术对面向嵌入式实现的压缩模型的稳健性的影响。研究结果提供了深入了解SEU诱导故障机制的有价值见解,这些见解可以评估预先训练的DNN的稳健性。此外,基于收集的数据,我们提出了一套实用的轻量级错误缓解技术,适用于资源受限的部署,并且不产生任何内存或计算成本。用于执行故障注入(FI)运动的代码可在https://github.com/jonGuti13/TensorFI2上找到,而实现所提出技术的代码可在https://github.com/jonGuti13/parameterProtection上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了在嵌入式深度神经网络(DNNs)中进行鲁棒性评估的问题,特别是针对单事件扰动(SEUs)引起的参数扰动对图像语义分割卷积神经网络(CNN)的影响。文章深入探讨了分割DNN对SEUs的脆弱性,并评估了模型修剪和参数量化等技术对嵌入式实现中压缩模型的鲁棒性的影响。此外,文章还提出了一系列实用的轻量级错误缓解技术,可在资源受限的部署环境中使用,而无需增加内存或计算成本。
Key Takeaways
- 人工智能(AI)算法在边缘设备的部署越来越普遍,提高自主AI感知和决策系统的稳健性和可靠性变得至关重要。特别是在安全关键领域如自动驾驶和航空航天领域尤为重要。
- 本文重点关注嵌入式深度神经网络(DNNs)中的鲁棒性评估问题,特别是参数扰动对卷积神经网络(CNN)图像语义分割的影响。
- 文章通过逐层和逐位敏感性分析,深入探讨了分割DNN对单事件扰动(SEUs)的脆弱性。评估了模型修剪和参数量化技术对压缩模型鲁棒性的影响。这对于嵌入式实现具有实际意义。
- 文章提供了有关SEU引起故障机制的宝贵见解,有助于评估预先训练的DNN的鲁棒性。这些见解对于理解AI系统的稳定性和可靠性至关重要。
- 基于收集的数据,文章提出了一系列实用的轻量级错误缓解技术,适用于资源受限的部署环境,并且不会增加内存或计算成本。这对于在边缘设备上部署AI算法具有重要意义。
- 文章公开了用于执行故障注入活动的代码,并提供了实施所提议技术的代码。这对于研究人员和开发人员来说是一个宝贵的资源,有助于进一步研究和改进AI系统的鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图


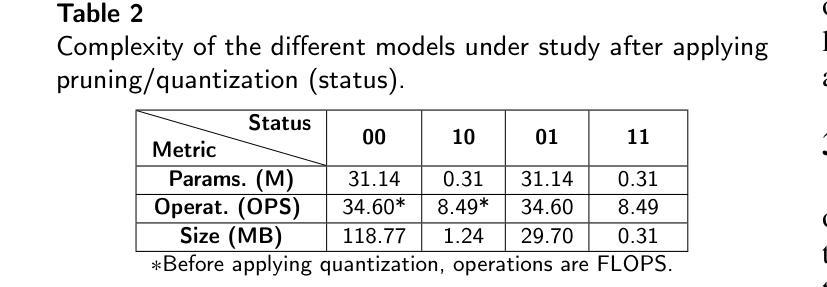
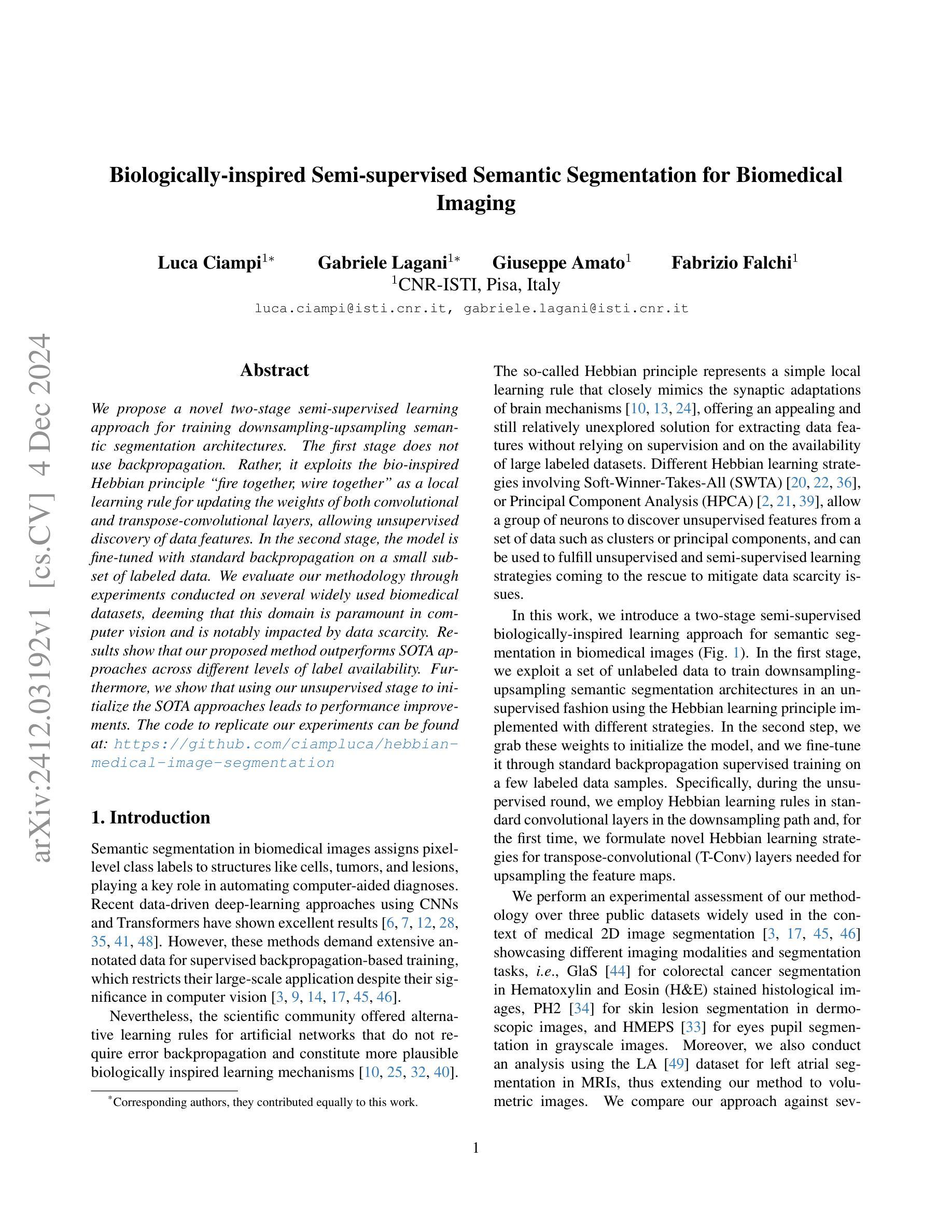
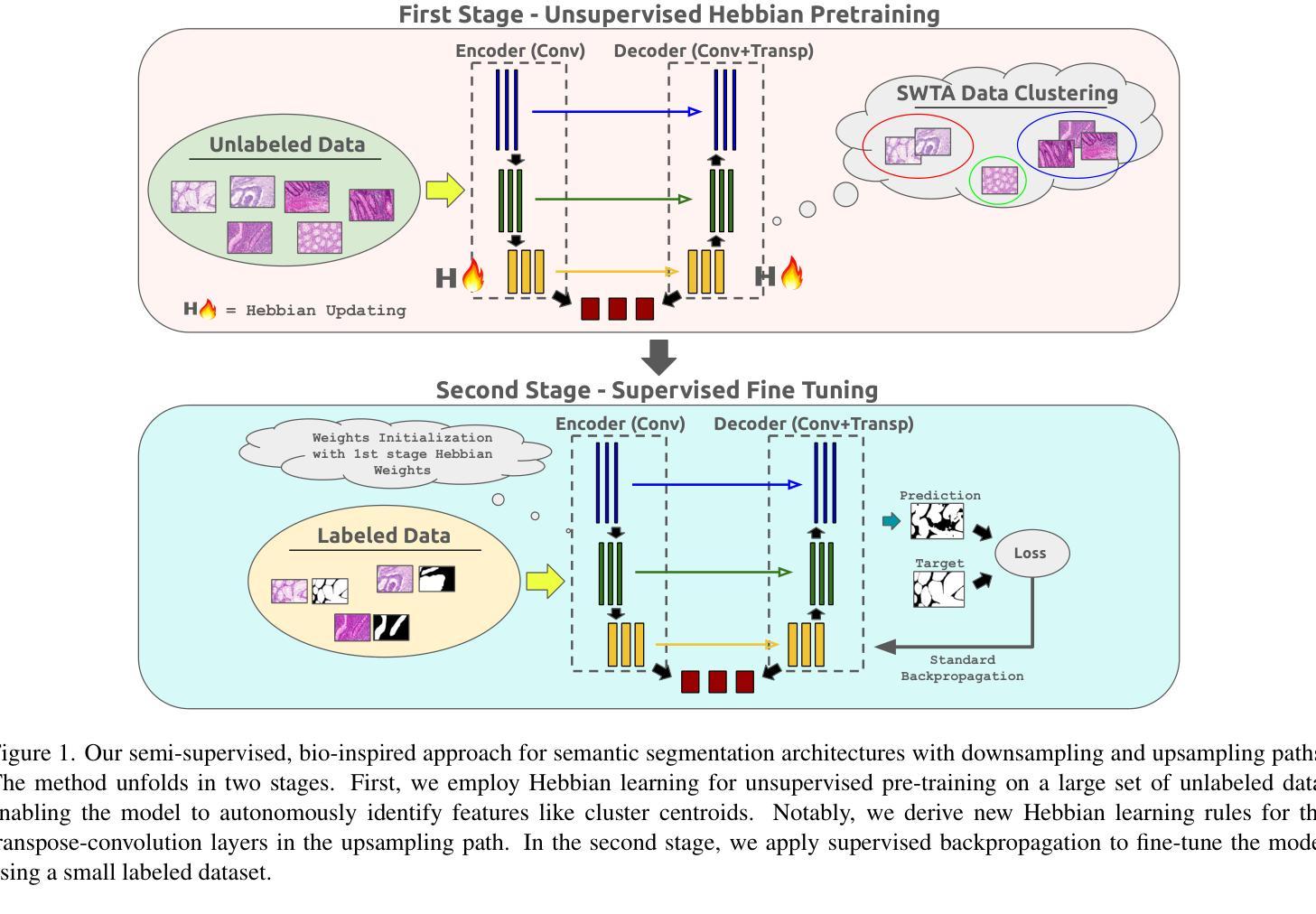
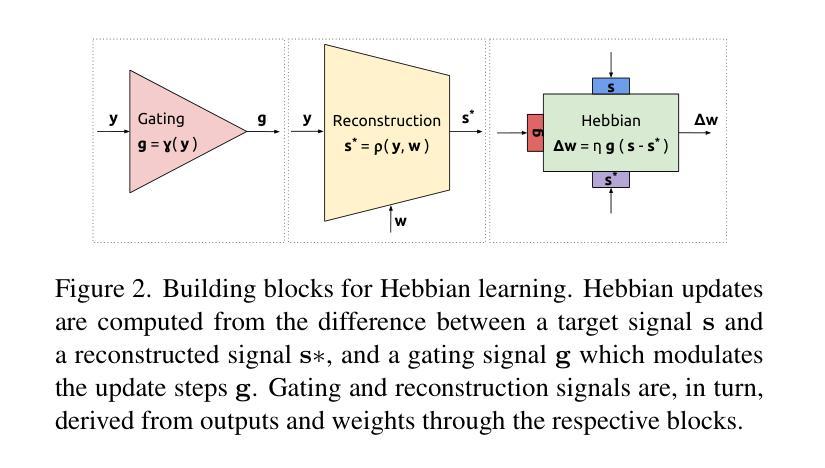
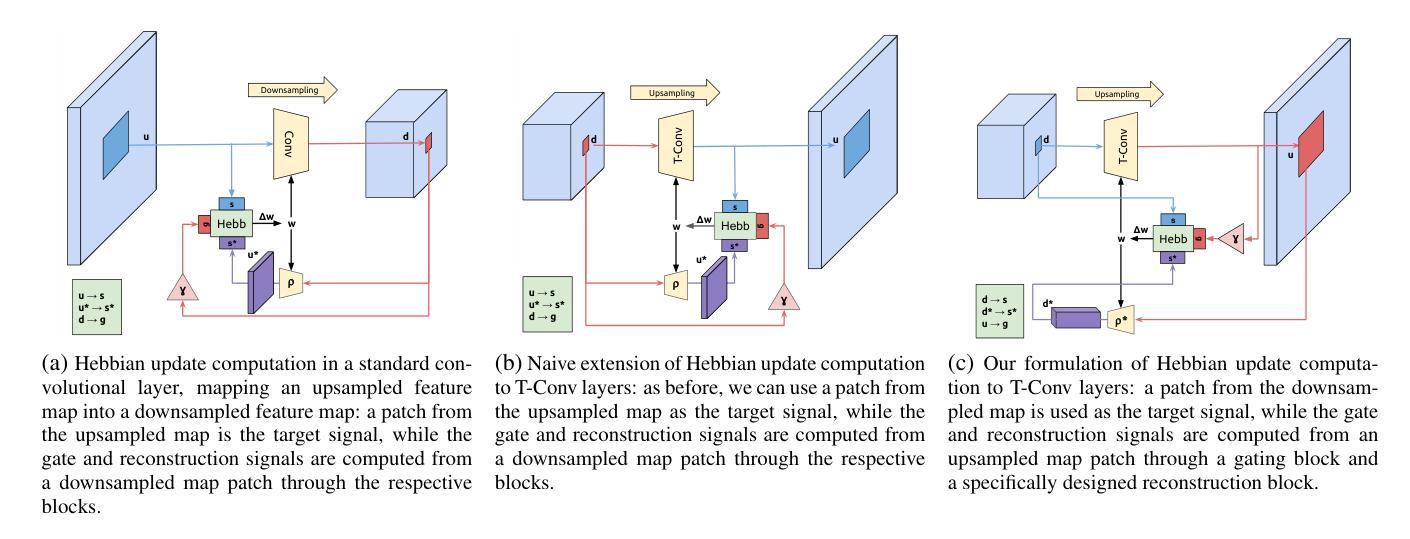
Biologically-inspired Semi-supervised Semantic Segmentation for Biomedical Imaging
Authors:Luca Ciampi, Gabriele Lagani, Giuseppe Amato, Fabrizio Falchi
We propose a novel two-stage semi-supervised learning approach for training downsampling-upsampling semantic segmentation architectures. The first stage does not use backpropagation. Rather, it exploits the bio-inspired Hebbian principle “fire together, wire together” as a local learning rule for updating the weights of both convolutional and transpose-convolutional layers, allowing unsupervised discovery of data features. In the second stage, the model is fine-tuned with standard backpropagation on a small subset of labeled data. We evaluate our methodology through experiments conducted on several widely used biomedical datasets, deeming that this domain is paramount in computer vision and is notably impacted by data scarcity. Results show that our proposed method outperforms SOTA approaches across different levels of label availability. Furthermore, we show that using our unsupervised stage to initialize the SOTA approaches leads to performance improvements. The code to replicate our experiments can be found at: https://github.com/ciampluca/hebbian-medical-image-segmentation
我们提出了一种新颖的两阶段半监督学习方法,用于训练下采样-上采样语义分割架构。第一阶段不使用反向传播。相反,它利用生物启发的赫布原则“一起放电,一起连接”作为局部学习规则,以更新卷积层和转置卷积层的权重,从而实现数据特征的无监督发现。在第二阶段,模型使用一小部分标记数据的标准反向传播进行微调。我们通过在一系列广泛使用的生物医学数据集上进行的实验评估了我们的方法,认为计算机视觉领域是这一方法的关键应用领域,并且该方法显著地受到了数据稀缺的影响。结果表明,在标签可用性的不同级别上,我们的方法均优于最新技术方法。此外,我们还展示了使用我们的无监督阶段来初始化最新技术方法可以提高性能。复制我们实验的代码可以在以下网址找到:https://github.com/ciampluca/hebbian-medical-image-segmentation
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
提出一种新型的两阶段半监督学习方法,用于训练下采样-上采样语义分割架构。第一阶段不采用反向传播,而是利用生物启发的海布原理(fire together,wire together)作为局部学习规则,更新卷积和转置卷积层的权重,实现数据特征的无监督发现。第二阶段则采用标准反向传播对小量标记数据进行微调。在多个广泛使用的生物医学数据集上进行的实验表明,该方法在数据稀缺的计算机视觉领域优于现有技术,并在不同标签可用性水平上表现突出。初始化现有技术时采用无监督阶段可提高性能。相关实验代码可在GitHub上找到:https://github.com/ciampluca/hebbian-medical-image-segmentation 。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种两阶段半监督学习方法用于训练语义分割架构。
- 第一阶段利用海布原理进行无监督学习,更新卷积和转置卷积层的权重。
- 第二阶段采用标准反向传播在少量标记数据上进行微调。
- 在生物医学数据集上的实验表明该方法优于现有技术。
- 不同标签可用性水平上表现突出。
- 采用无监督阶段初始化现有技术可提高性能。
点此查看论文截图
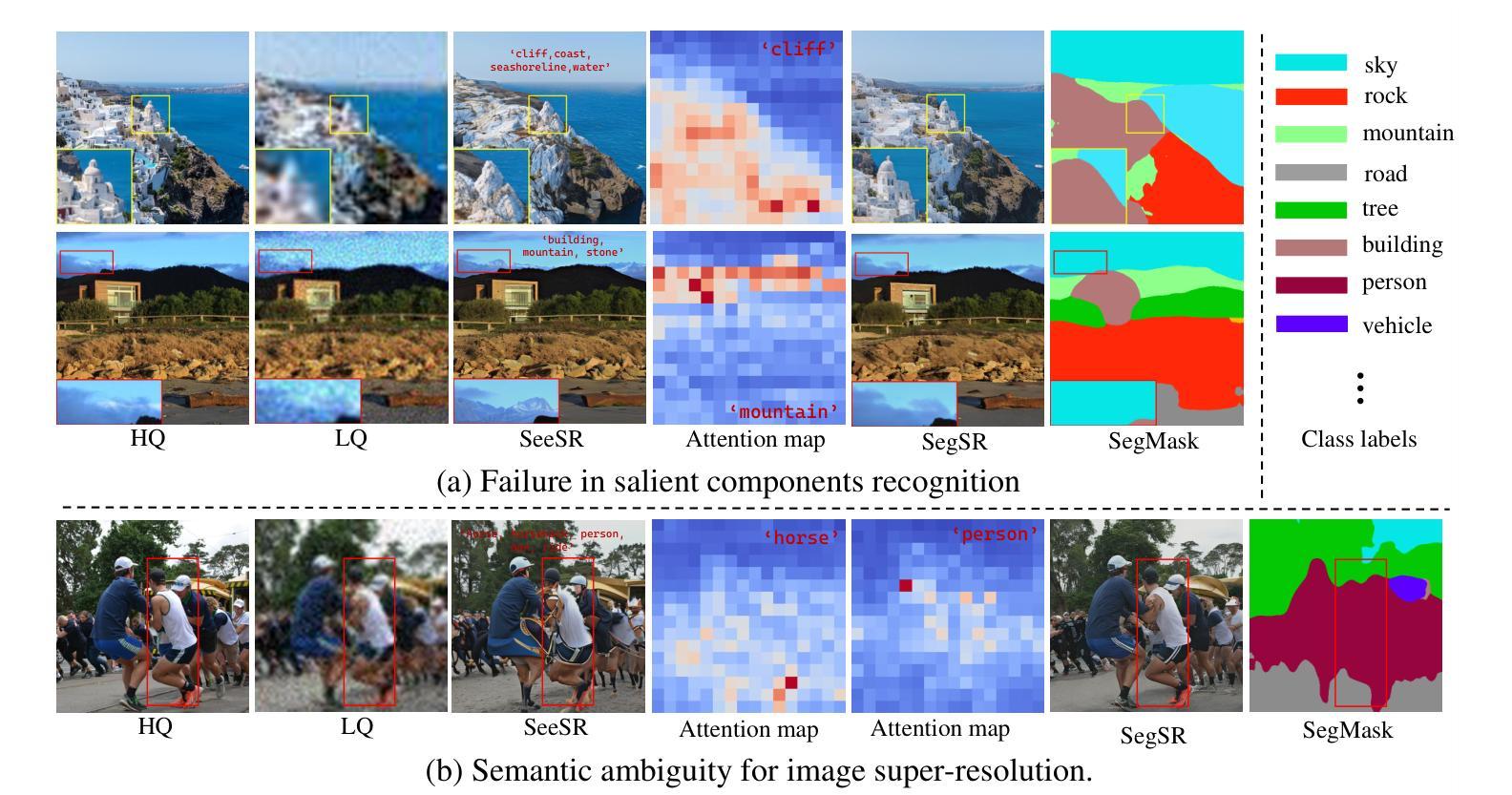
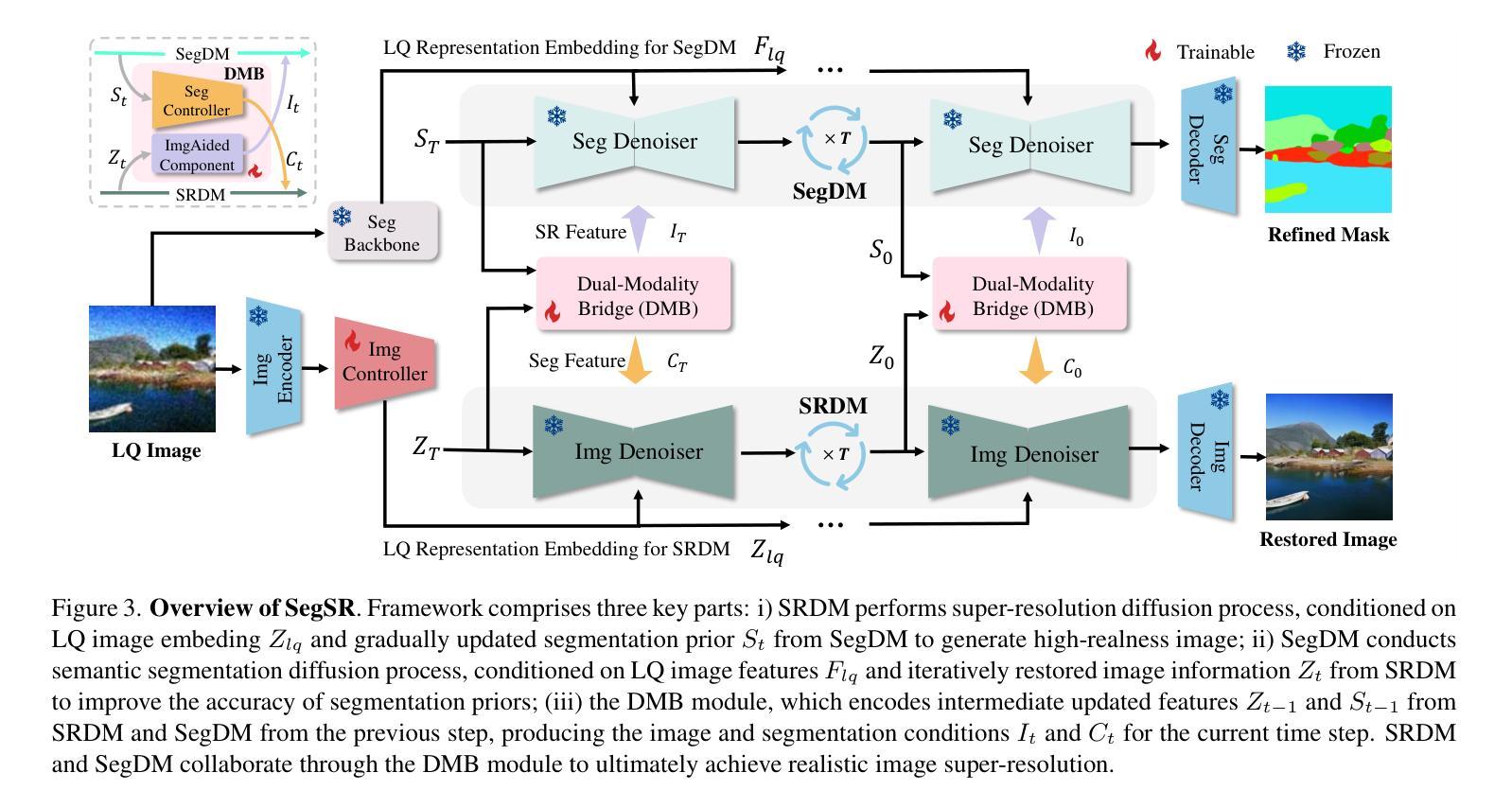
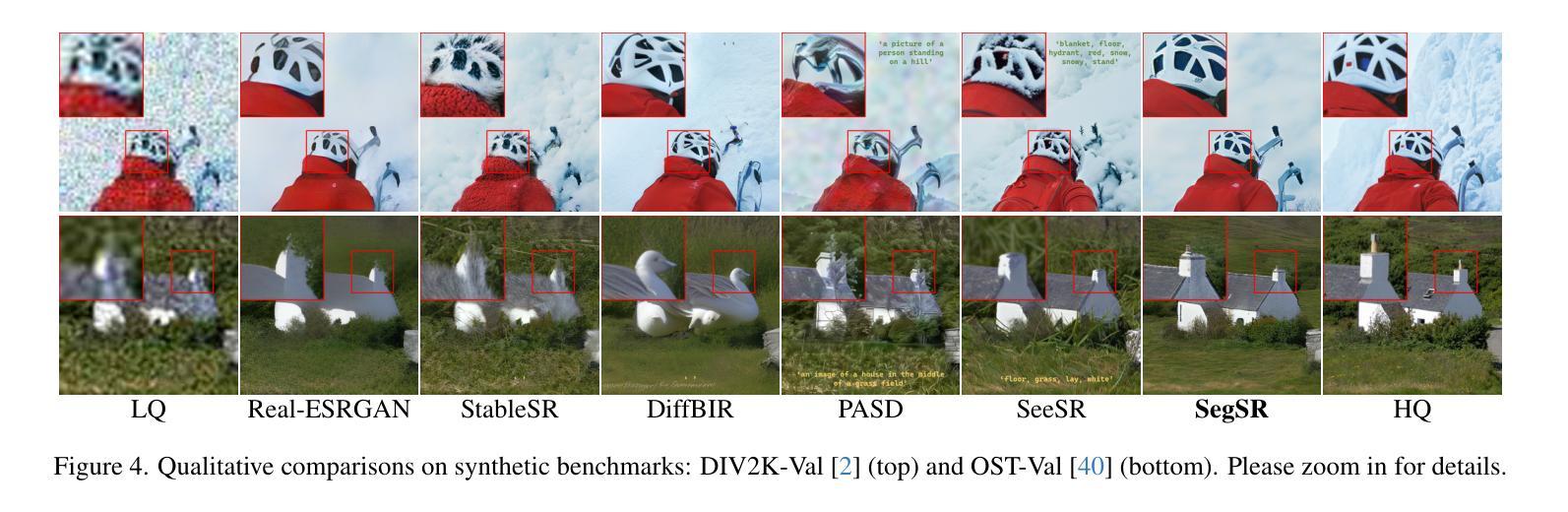
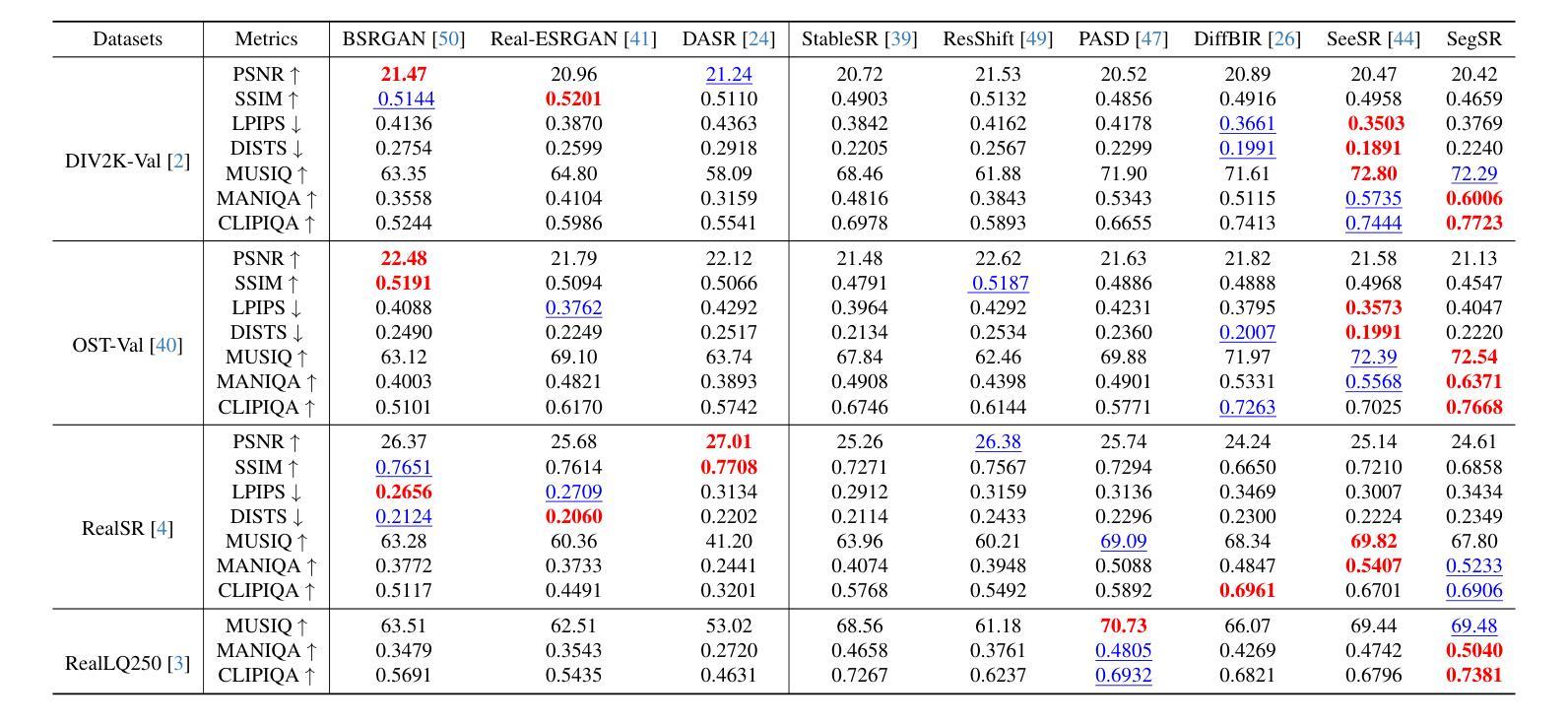
Semantic Segmentation Prior for Diffusion-Based Real-World Super-Resolution
Authors:Jiahua Xiao, Jiawei Zhang, Dongqing Zou, Xiaodan Zhang, Jimmy Ren, Xing Wei
Real-world image super-resolution (Real-ISR) has achieved a remarkable leap by leveraging large-scale text-to-image models, enabling realistic image restoration from given recognition textual prompts. However, these methods sometimes fail to recognize some salient objects, resulting in inaccurate semantic restoration in these regions. Additionally, the same region may have a strong response to more than one prompt and it will lead to semantic ambiguity for image super-resolution. To alleviate the above two issues, in this paper, we propose to consider semantic segmentation as an additional control condition into diffusion-based image super-resolution. Compared to textual prompt conditions, semantic segmentation enables a more comprehensive perception of salient objects within an image by assigning class labels to each pixel. It also mitigates the risks of semantic ambiguities by explicitly allocating objects to their respective spatial regions. In practice, inspired by the fact that image super-resolution and segmentation can benefit each other, we propose SegSR which introduces a dual-diffusion framework to facilitate interaction between the image super-resolution and segmentation diffusion models. Specifically, we develop a Dual-Modality Bridge module to enable updated information flow between these two diffusion models, achieving mutual benefit during the reverse diffusion process. Extensive experiments show that SegSR can generate realistic images while preserving semantic structures more effectively.
现实世界图像超分辨率(Real-ISR)借助大规模文本到图像模型实现了显著飞跃,能够从给定的识别文本提示中恢复现实图像。然而,这些方法有时无法识别出一些显著物体,导致这些区域的语义恢复不准确。此外,同一区域可能对多个提示有强烈的反应,这将导致图像超分辨率的语义模糊。为了解决上述两个问题,本文提出将语义分割作为扩散式图像超分辨率的附加控制条件。与文本提示条件相比,语义分割通过为每个像素分配类别标签,使图像内的显著物体得到更全面的感知。它还通过显式地将物体分配给其各自的空间区域,减轻了语义模糊的风险。在实践中,受到图像超分辨率和分割可以相互受益的启发,我们提出了SegSR,它引入了双扩散框架,以促进图像超分辨率和分割扩散模型之间的交互。具体来说,我们开发了一个双模态桥接模块,以实现这两个扩散模型之间的更新信息流动,在反向扩散过程中实现相互受益。大量实验表明,SegSR能够生成逼真的图像,同时更有效地保留语义结构。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:借助大规模文本图像模型,真实世界图像超分辨率技术取得了显著进展,能够根据实际文本提示进行逼真的图像恢复。但此方法有时无法识别显著物体,导致语义恢复不准确。为解决这些问题,本文提出将语义分割作为扩散图像超分辨率的附加控制条件,通过为每个像素分配类别标签,更全面地感知图像中的显著物体,并显式地将物体分配给其相应的空间区域以降低语义模糊的风险。受图像超分辨率和分割可相互受益的启发,本文提出SegSR方法,采用双扩散框架促进图像超分辨率和分割扩散模型间的交互。通过开发双模态桥模块,实现两者在反向扩散过程中的信息流通和相互受益。实验表明,SegSR能够生成更真实且有效保留语义结构的图像。
Key Takeaways:
- 大型文本图像模型在真实世界图像超分辨率技术中发挥了重要作用,能够实现基于文本提示的图像恢复。
- 当前方法在某些情况下无法准确识别显著物体,导致语义恢复不准确。
- 语义分割作为附加控制条件被引入到扩散图像超分辨率中,以更全面地感知图像中的显著物体并降低语义模糊风险。
- 语义分割通过为每个像素分配类别标签,显式地将物体分配给其相应的空间区域。
- SegSR方法采用双扩散框架,通过双模态桥模块实现图像超分辨率和分割扩散模型间的交互。
- SegSR能够在生成真实图像的同时更有效地保留语义结构。
点此查看论文截图

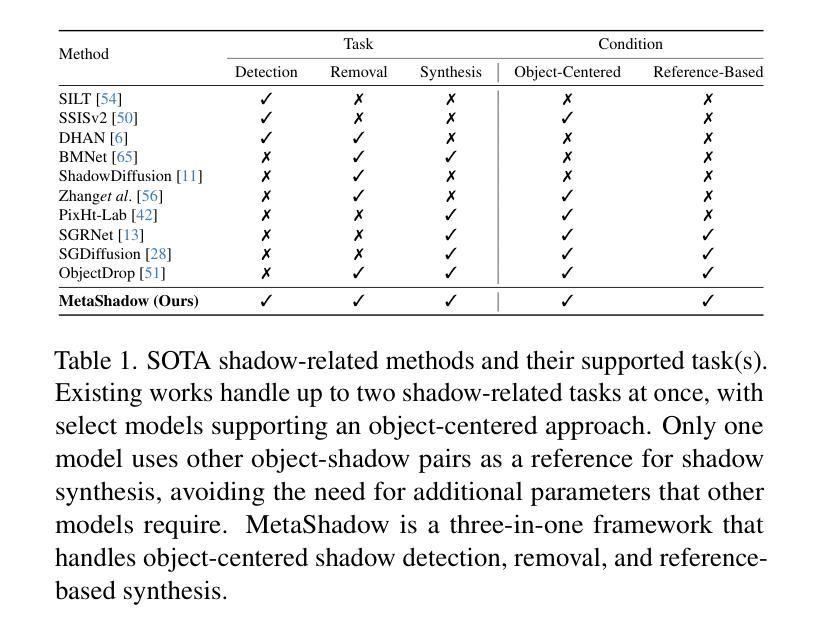
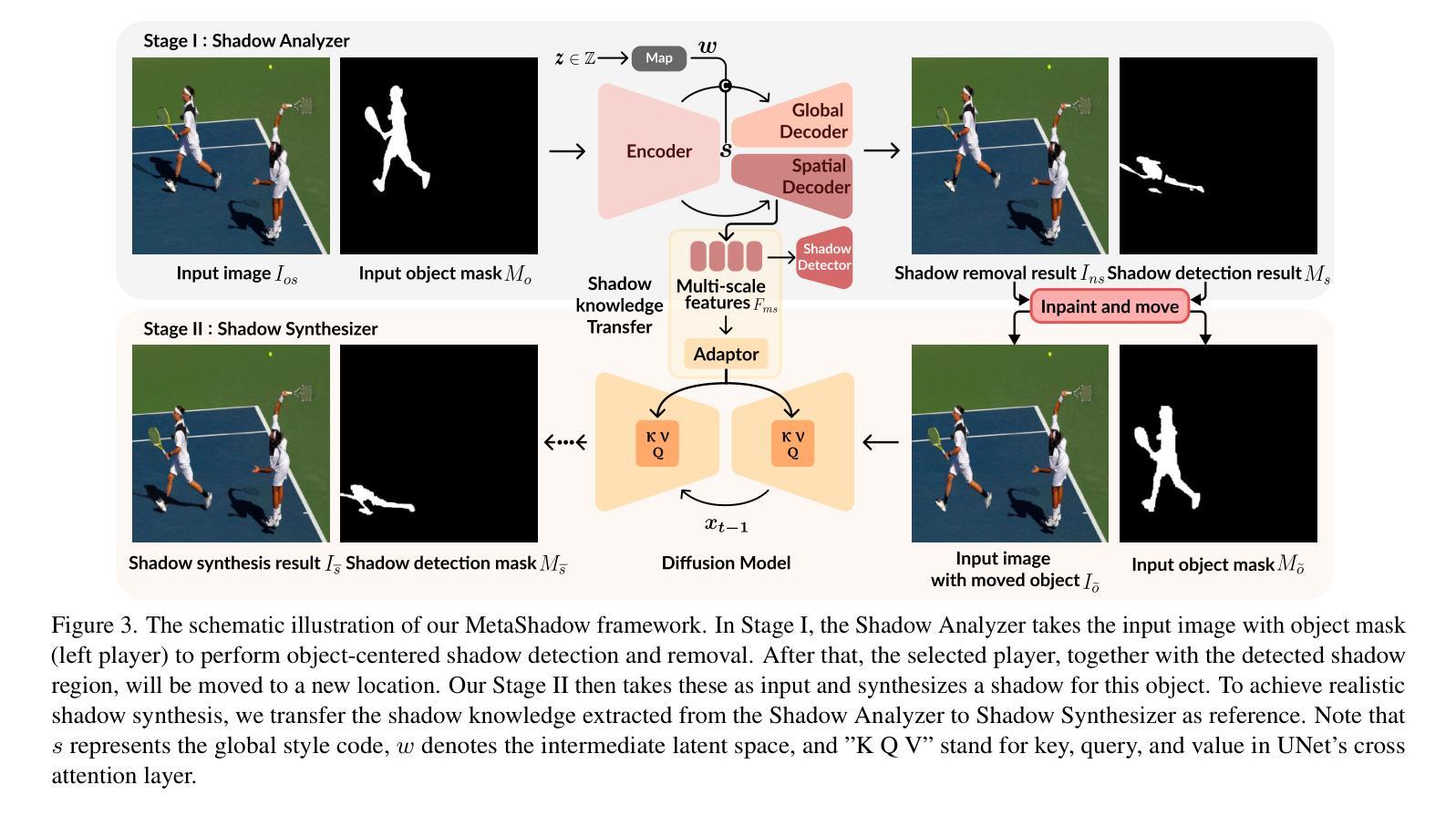
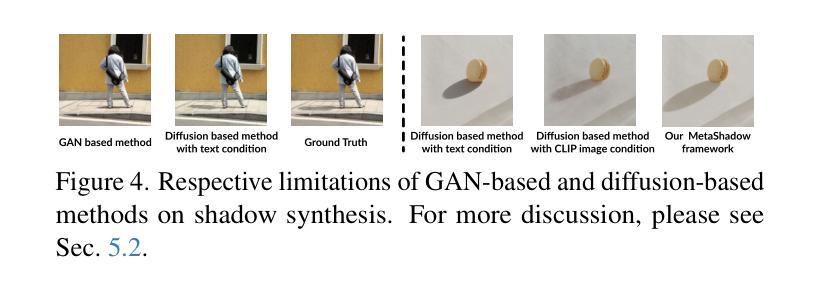
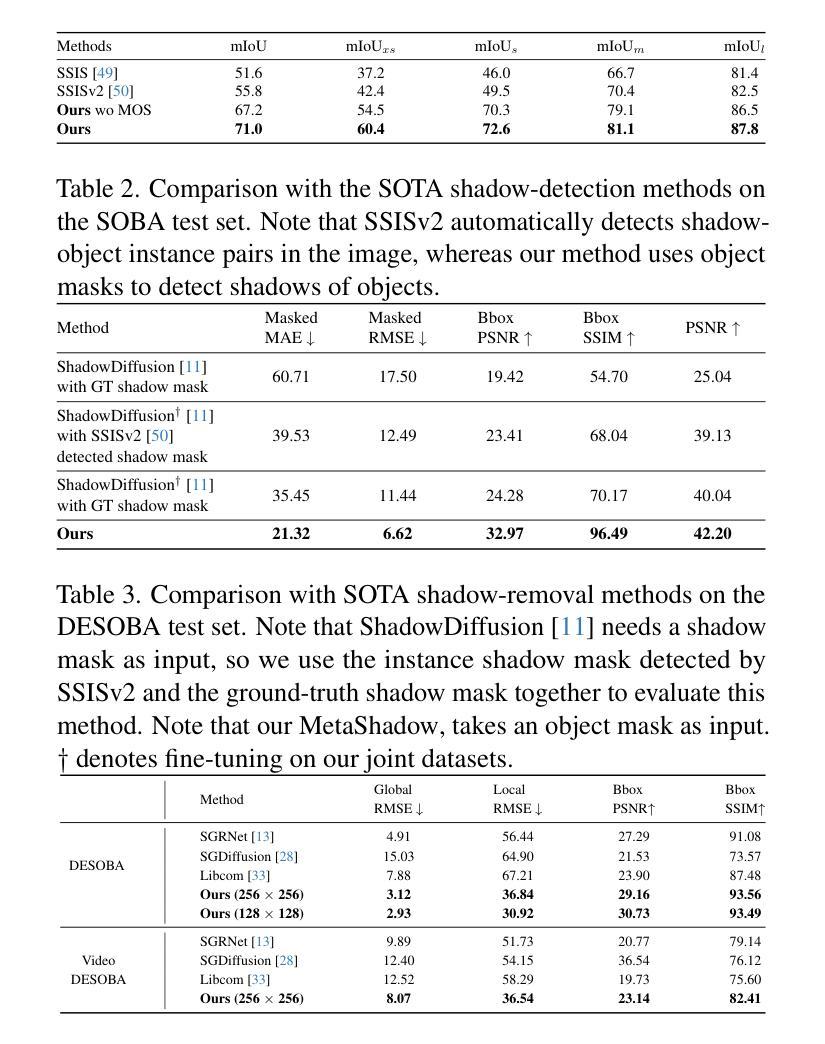
MetaShadow: Object-Centered Shadow Detection, Removal, and Synthesis
Authors:Tianyu Wang, Jianming Zhang, Haitian Zheng, Zhihong Ding, Scott Cohen, Zhe Lin, Wei Xiong, Chi-Wing Fu, Luis Figueroa, Soo Ye Kim
Shadows are often under-considered or even ignored in image editing applications, limiting the realism of the edited results. In this paper, we introduce MetaShadow, a three-in-one versatile framework that enables detection, removal, and controllable synthesis of shadows in natural images in an object-centered fashion. MetaShadow combines the strengths of two cooperative components: Shadow Analyzer, for object-centered shadow detection and removal, and Shadow Synthesizer, for reference-based controllable shadow synthesis. Notably, we optimize the learning of the intermediate features from Shadow Analyzer to guide Shadow Synthesizer to generate more realistic shadows that blend seamlessly with the scene. Extensive evaluations on multiple shadow benchmark datasets show significant improvements of MetaShadow over the existing state-of-the-art methods on object-centered shadow detection, removal, and synthesis. MetaShadow excels in image-editing tasks such as object removal, relocation, and insertion, pushing the boundaries of object-centered image editing.
在图像编辑应用中,阴影往往被忽视或忽略,这限制了编辑结果的逼真性。在本文中,我们介绍了MetaShadow,这是一个三合一的通用框架,以对象为中心的方式,实现对自然图像中的阴影进行检测、去除和可控合成。MetaShadow结合了阴影分析器和阴影合成器两个协作组件的优势:阴影分析器用于以对象为中心的阴影检测和去除,而阴影合成器则用于基于参考的阴影可控合成。值得注意的是,我们优化了阴影分析器中间特征的学习,以指导阴影合成器生成更逼真的阴影,使其无缝融入场景中。在多个阴影基准数据集上的广泛评估表明,MetaShadow在面向对象的阴影检测、去除和合成方面均优于现有最先进的算法。MetaShadow在图像编辑任务(如对象移除、重新定位和插入)方面表现出色,突破了面向对象的图像编辑的界限。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了MetaShadow,一个集检测、移除和可控合成为一体的多功能框架,用于以对象为中心的自然图像阴影处理。该框架通过Shadow Analyzer进行对象为中心的阴影检测和移除,通过Shadow Synthesizer进行参考可控的阴影合成。优化中间特征的学习,使合成的阴影更真实、场景融合度更高。在多个阴影基准数据集上的广泛评估表明,MetaShadow在面向对象的阴影检测、移除和合成方面均优于现有最先进的方法,尤其在图像编辑任务如对象移除、重新定位和插入方面表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways:
- MetaShadow是一个集检测、移除和可控合成为一体的多功能框架,专注于自然图像的阴影处理。
- 该框架包含两个合作组件:Shadow Analyzer用于对象为中心的阴影检测和移除,而Shadow Synthesizer用于参考可控的阴影合成。
- 通过优化Shadow Analyzer的中间特征学习,指导Shadow Synthesizer生成更真实、场景融合度更高的阴影。
- MetaShadow在面向对象的阴影检测、移除和合成方面均表现出显著改进。
- 该框架在图像编辑任务如对象移除、重新定位和插入方面有很强的应用能力。
- MetaShadow能够提升图像编辑的真实感和质量。
点此查看论文截图


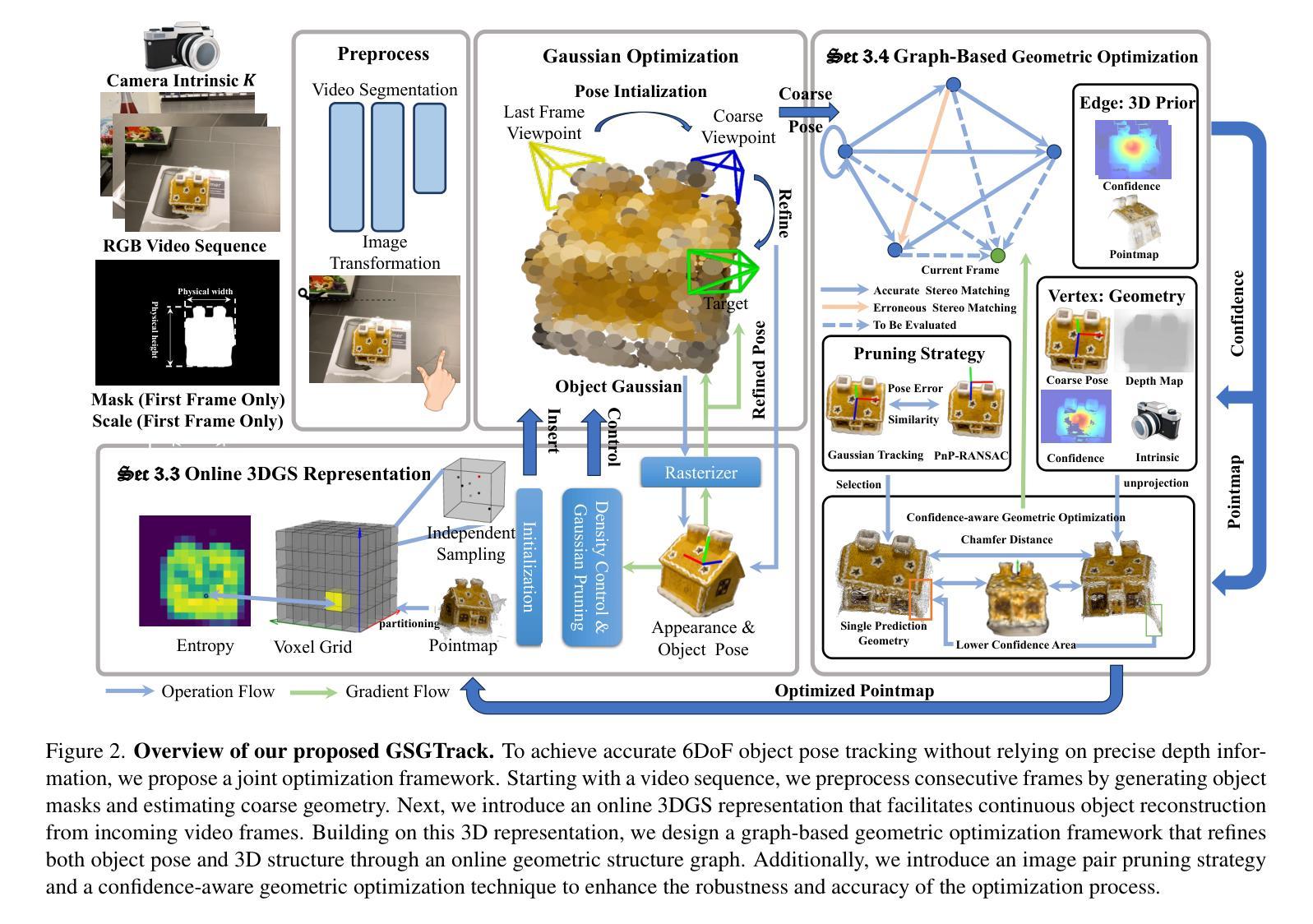
GSGTrack: Gaussian Splatting-Guided Object Pose Tracking from RGB Videos
Authors:Zhiyuan Chen, Fan Lu, Guo Yu, Bin Li, Sanqing Qu, Yuan Huang, Changhong Fu, Guang Chen
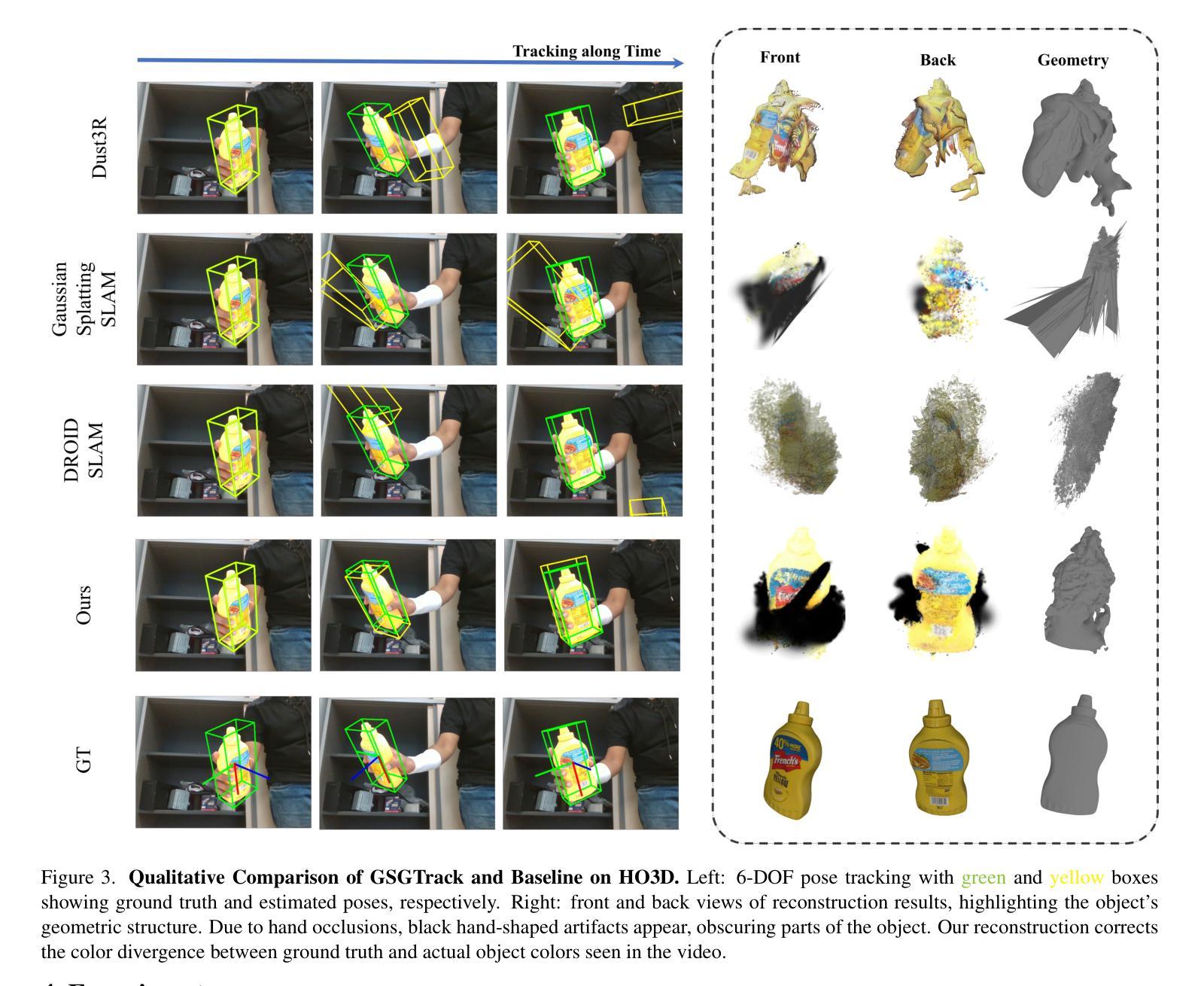
Tracking the 6DoF pose of unknown objects in monocular RGB video sequences is crucial for robotic manipulation. However, existing approaches typically rely on accurate depth information, which is non-trivial to obtain in real-world scenarios. Although depth estimation algorithms can be employed, geometric inaccuracy can lead to failures in RGBD-based pose tracking methods. To address this challenge, we introduce GSGTrack, a novel RGB-based pose tracking framework that jointly optimizes geometry and pose. Specifically, we adopt 3D Gaussian Splatting to create an optimizable 3D representation, which is learned simultaneously with a graph-based geometry optimization to capture the object’s appearance features and refine its geometry. However, the joint optimization process is susceptible to perturbations from noisy pose and geometry data. Thus, we propose an object silhouette loss to address the issue of pixel-wise loss being overly sensitive to pose noise during tracking. To mitigate the geometric ambiguities caused by inaccurate depth information, we propose a geometry-consistent image pair selection strategy, which filters out low-confidence pairs and ensures robust geometric optimization. Extensive experiments on the OnePose and HO3D datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of GSGTrack in both 6DoF pose tracking and object reconstruction.
针对单目RGB视频序列中的未知对象进行6DoF姿态跟踪对于机器人操作至关重要。然而,现有方法通常依赖于精确的深度信息,这在现实场景中获取并不容易。虽然可以使用深度估计算法,但几何不准确性会导致基于RGBD的姿态跟踪方法失败。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了GSGTrack,这是一种新颖的基于RGB的姿态跟踪框架,它联合优化几何和姿态。具体来说,我们采用3D高斯展布技术来创建一个可优化的3D表示,这是通过与基于图的几何优化同时学习来捕捉对象的外观特征并细化其几何形状。然而,联合优化过程容易受到噪声姿态和几何数据引起的扰动影响。因此,我们提出了一种对象轮廓损失来解决跟踪过程中像素级损失对姿态噪声过于敏感的问题。为了减轻由不准确的深度信息引起的几何模糊性,我们提出了一种几何一致性图像对选择策略,该策略可以过滤掉低置信度的对,并确保稳健的几何优化。在OnePose和HO3D数据集上的大量实验表明,GSGTrack在6DoF姿态跟踪和对象重建方面都非常有效。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了GSGTrack这一新型的基于RGB的视频序列中物体姿态跟踪方法的重要性,尤其是在无法获得准确的深度信息时面临的挑战。为了解决该问题,该研究通过采用联合优化的方式融合了物体几何信息与姿态数据。研究提出利用基于图论的几何优化方法与三维高斯贴图技术,共同构建可优化的三维表示模型。同时,引入对象轮廓损失来应对噪声数据带来的干扰问题,并通过几何一致性图像配对策略提升几何优化的稳健性。在OnePose和HO3D数据集上的实验证明,GSGTrack对于六自由度(6DoF)的物体姿态跟踪和重建效果卓越。
Key Takeaways
以下是基于文本的关键见解要点:
- GSGTrack解决了在缺乏准确深度信息情况下,RGB视频序列中物体姿态跟踪的难题。
- 该方法采用联合优化策略,融合物体的几何信息与姿态数据。
- 利用三维高斯贴图技术创建可优化的三维表示模型。
- 图论几何优化方法用于捕捉物体的外观特征并精细调整其几何形态。
- 通过引入对象轮廓损失来解决因噪声引起的敏感问题。
- 几何一致性图像配对策略可提高几何优化的稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

GSOT3D: Towards Generic 3D Single Object Tracking in the Wild
Authors:Yifan Jiao, Yunhao Li, Junhua Ding, Qing Yang, Song Fu, Heng Fan, Libo Zhang
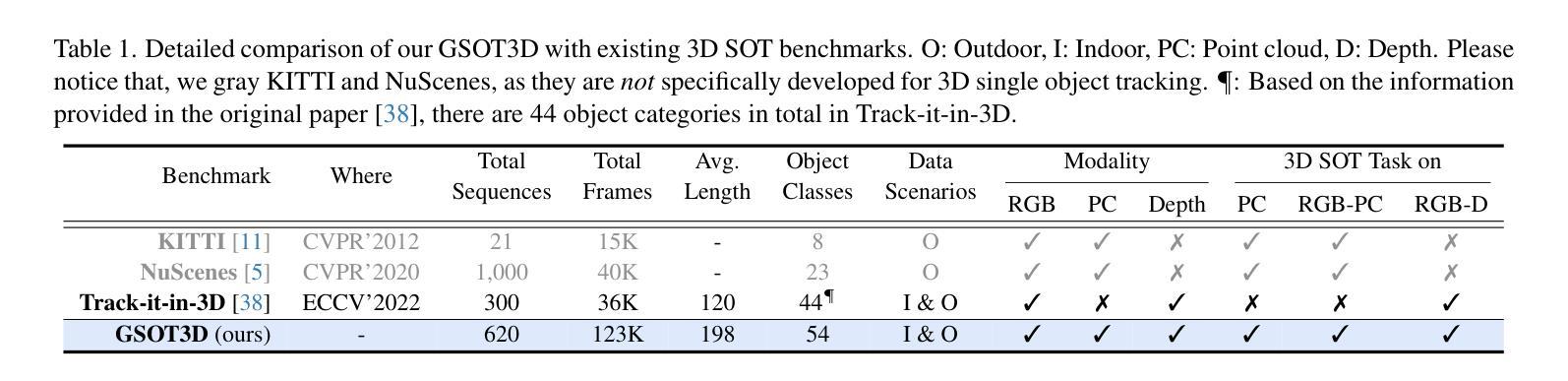
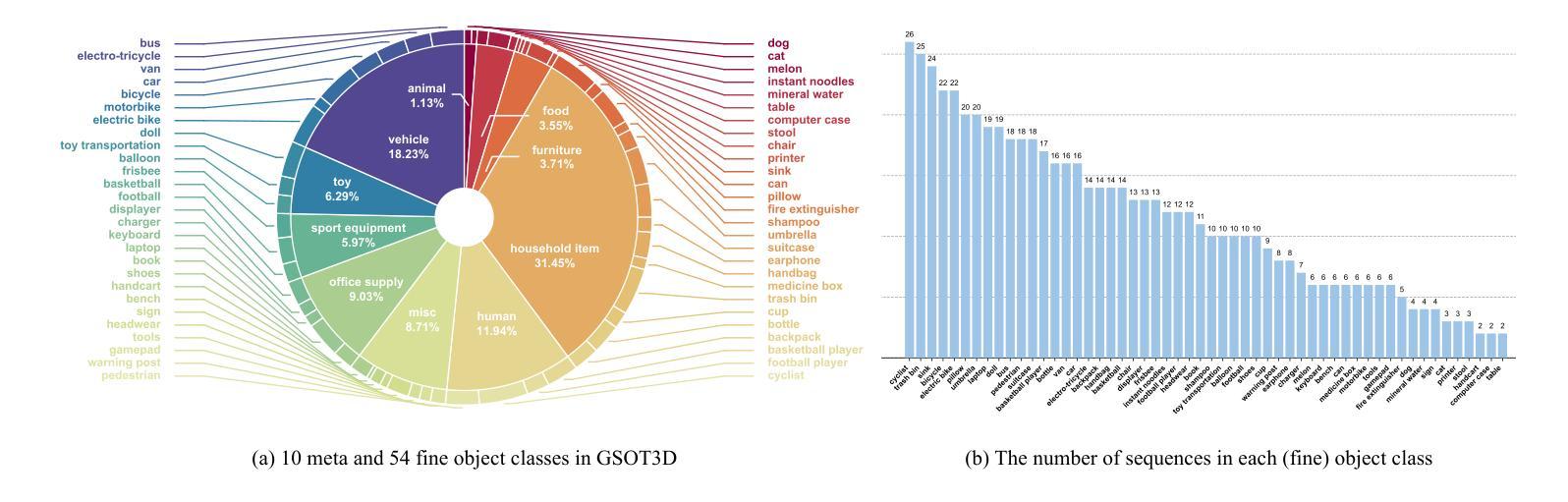
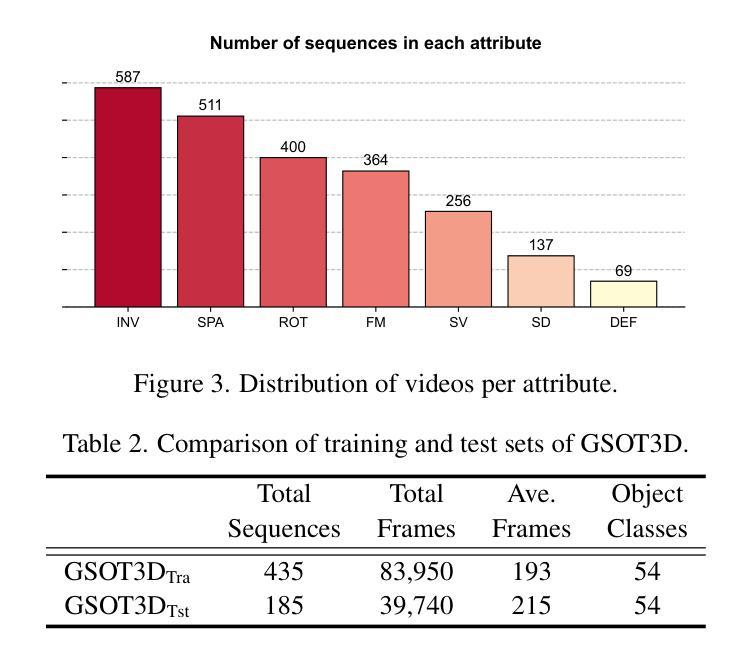
In this paper, we present a novel benchmark, GSOT3D, that aims at facilitating development of generic 3D single object tracking (SOT) in the wild. Specifically, GSOT3D offers 620 sequences with 123K frames, and covers a wide selection of 54 object categories. Each sequence is offered with multiple modalities, including the point cloud (PC), RGB image, and depth. This allows GSOT3D to support various 3D tracking tasks, such as single-modal 3D SOT on PC and multi-modal 3D SOT on RGB-PC or RGB-D, and thus greatly broadens research directions for 3D object tracking. To provide highquality per-frame 3D annotations, all sequences are labeled manually with multiple rounds of meticulous inspection and refinement. To our best knowledge, GSOT3D is the largest benchmark dedicated to various generic 3D object tracking tasks. To understand how existing 3D trackers perform and to provide comparisons for future research on GSOT3D, we assess eight representative point cloud-based tracking models. Our evaluation results exhibit that these models heavily degrade on GSOT3D, and more efforts are required for robust and generic 3D object tracking. Besides, to encourage future research, we present a simple yet effective generic 3D tracker, named PROT3D, that localizes the target object via a progressive spatial-temporal network and outperforms all current solutions by a large margin. By releasing GSOT3D, we expect to advance further 3D tracking in future research and applications. Our benchmark and model as well as the evaluation results will be publicly released at our webpage https://github.com/ailovejinx/GSOT3D.
本文介绍了一个新型基准测试GSOT3D,旨在推动野生环境中通用三维单目标跟踪(SOT)的发展。具体来说,GSOT3D提供了620个序列,包含12.3万个框架,并涵盖了54个对象类别。每个序列都提供多种模式,包括点云(PC)、RGB图像和深度。这使得GSOT3D能够支持各种三维跟踪任务,如PC上的单模态三维SOT和RGB-PC或RGB-D上的多模态三维SOT,从而大大拓宽了三维目标跟踪的研究方向。为了提供高质量的逐帧三维注释,所有序列都是经过多轮精细检查和精细处理的手工标注。据我们所知,GSOT3D是专门用于各种通用三维目标跟踪任务的最大基准测试。为了了解现有三维跟踪器的性能,并为GSOT3D上的未来研究提供比较,我们对八个具有代表性的点云跟踪模型进行了评估。我们的评估结果表明,这些模型在GSOT3D上严重退化,需要更多的努力来实现稳健和通用的三维目标跟踪。此外,为了鼓励未来的研究,我们提出了一种简单有效的通用三维跟踪器PROT3D,它通过渐进时空网络定位目标对象,并大幅度超越当前所有解决方案。通过发布GSOT3D,我们希望在未来的研究和应用中进一步推动三维跟踪的发展。我们的基准测试、模型和评估结果将在我们的网页https://github.com/ailovejinx/GSOT3D上公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 12 figures
Summary
GSOT3D是一个针对通用三维单目标跟踪(SOT)的新基准数据集,包含多种模态数据,如点云、RGB图像和深度信息。它包含大量手动标注的三维数据序列,并支持多种三维跟踪任务。当前跟踪模型在该数据集上的表现有待提高,论文中提出了一种新的通用三维跟踪器PROT3D,其在该数据集上表现优于现有解决方案。数据集及评估结果均已公开发布在GitHub页面上。
Key Takeaways
- GSOT3D是一个新的基准数据集,用于推动通用三维单目标跟踪(SOT)的发展。
- 数据集包含多种模态数据,如点云、RGB图像和深度信息,覆盖多种三维跟踪任务。
- 当前跟踪模型在GSOT3D上的性能不足,需要更多努力进行改进。
- PROT3D是一种新的通用三维跟踪器,通过渐进时空网络定位目标物体,性能优于现有解决方案。
点此查看论文截图


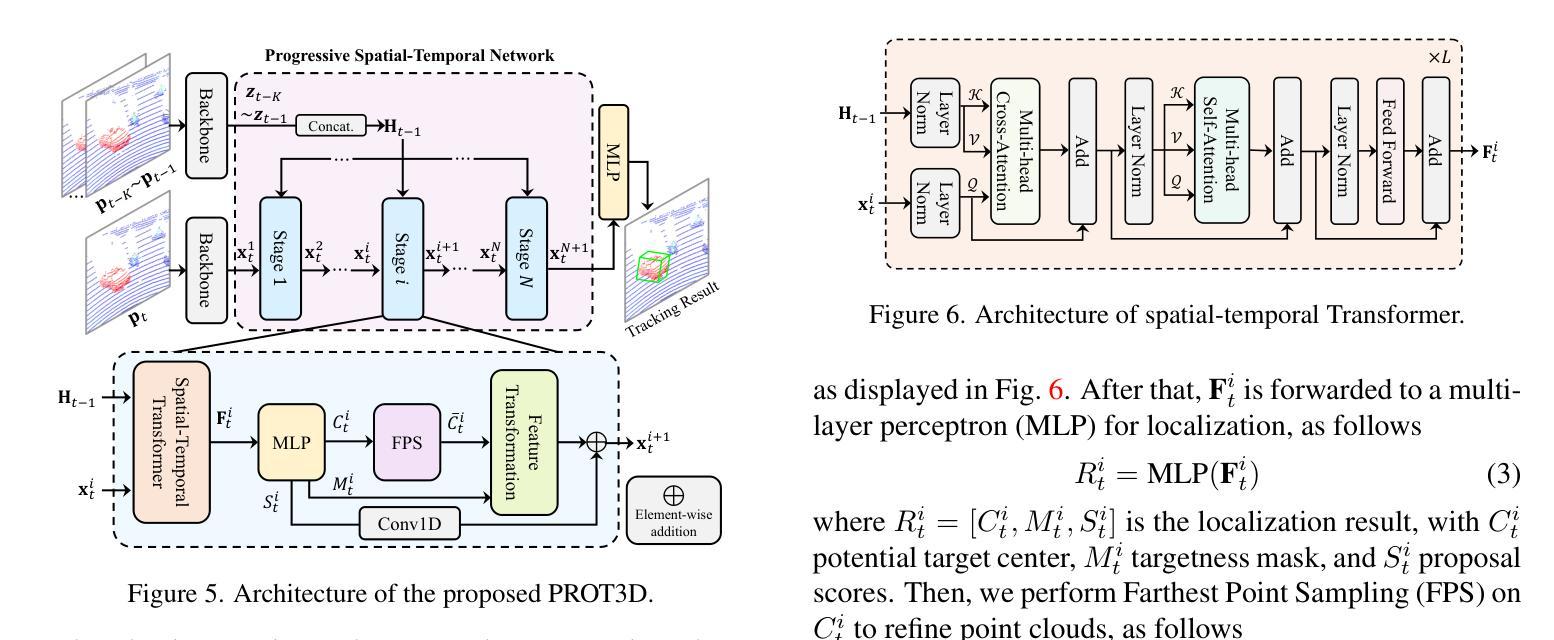
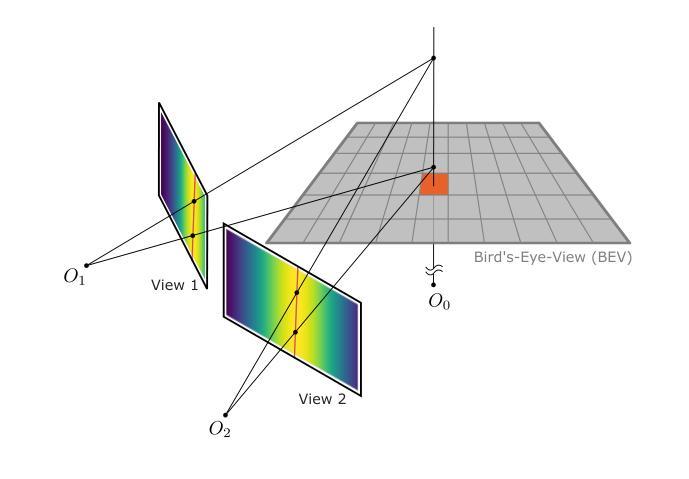
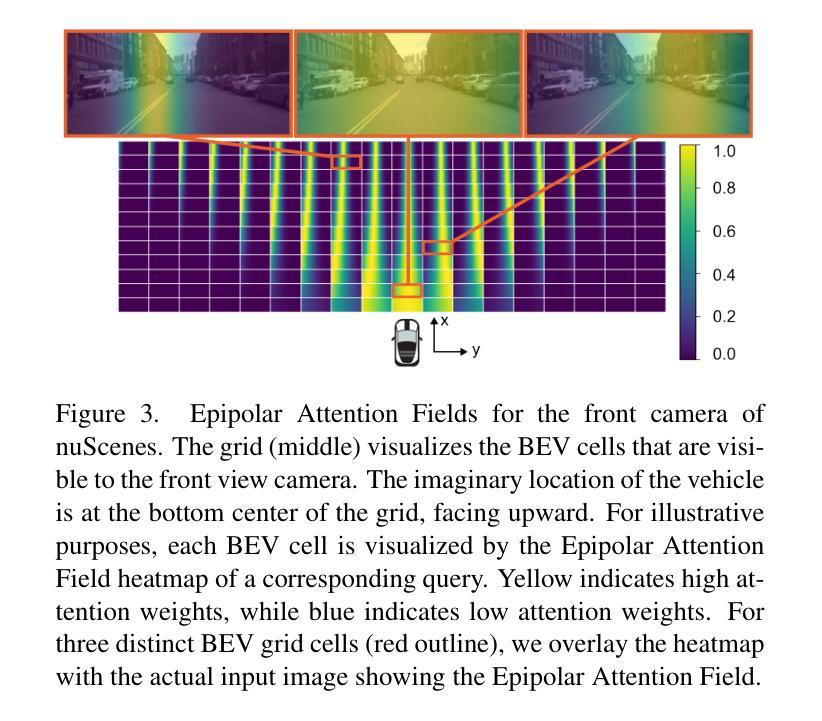
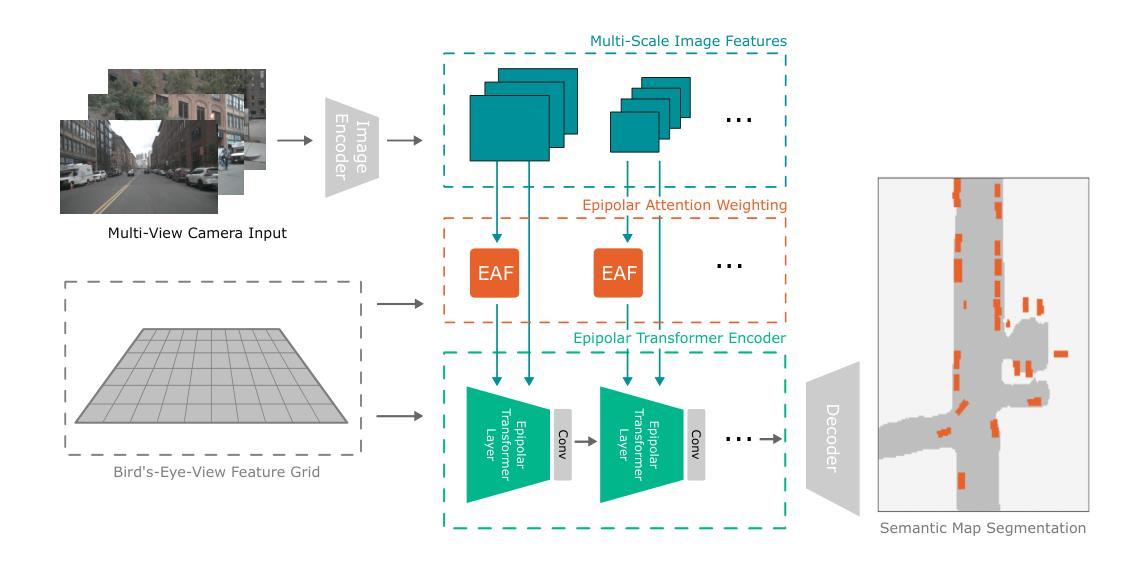
Epipolar Attention Field Transformers for Bird’s Eye View Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Christian Witte, Jens Behley, Cyrill Stachniss, Marvin Raaijmakers
Spatial understanding of the semantics of the surroundings is a key capability needed by autonomous cars to enable safe driving decisions. Recently, purely vision-based solutions have gained increasing research interest. In particular, approaches extracting a bird’s eye view (BEV) from multiple cameras have demonstrated great performance for spatial understanding. This paper addresses the dependency on learned positional encodings to correlate image and BEV feature map elements for transformer-based methods. We propose leveraging epipolar geometric constraints to model the relationship between cameras and the BEV by Epipolar Attention Fields. They are incorporated into the attention mechanism as a novel attribution term, serving as an alternative to learned positional encodings. Experiments show that our method EAFormer outperforms previous BEV approaches by 2% mIoU for map semantic segmentation and exhibits superior generalization capabilities compared to implicitly learning the camera configuration.
周围环境的语义空间理解是自动驾驶汽车做出安全驾驶决策所需的关键能力。最近,纯视觉解决方案已经引起了越来越多的研究兴趣。特别是,从多个摄像头提取鸟瞰图(BEV)的方法在空间理解方面表现出了卓越的性能。本文解决了基于变压器的方法将图像和BEV特征映射元素相关联所依赖的学习位置编码的问题。我们提出利用极几何约束来模拟摄像头和BEV之间的关系,即采用极注意力领域(Epipolar Attention Fields)。它们被融入注意力机制作为一个新的属性项,作为对学习位置编码的替代。实验表明,我们的EAFormer方法在地图语义分割上的mIoU性能优于之前的BEV方法,并且相较于隐式学习相机配置展现出更好的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at WACV 2025
Summary
本文探讨了自主驾驶汽车的空间语义理解能力,特别是通过多相机提取鸟瞰图(BEV)的方法。文章针对基于变换器的方法对位置编码的依赖问题,提出了利用极几何约束建立相机与鸟瞰图之间的关系的方法。实验结果证明了该方法的性能优于先前的方法,实现了地图语义分割的更高准确度。文章的重点是开发出了一种称为“EAformer”的方法,它可以作为现有方案的改进升级选项。文章关注纯粹的视觉解决方案来提高自动驾驶技术中的空间理解能力,尤其关注了基于极几何约束建立摄像机与鸟瞰视图之间的新方法关系,而不是依赖学习位置编码。实验结果展示了新方法在提高地图语义分割上的性能优势,并具有出色的泛化能力。该研究的成果有望为自主驾驶汽车提供更强大的空间理解能力,从而提高驾驶安全性。
Key Takeaways
以下是该文本的关键见解:
- 自主驾驶汽车需要空间语义理解能力以确保安全驾驶决策。
- 基于视觉的解决方案,特别是从多个相机中提取鸟瞰图(BEV)的方法,对于空间理解表现出良好的性能。
点此查看论文截图

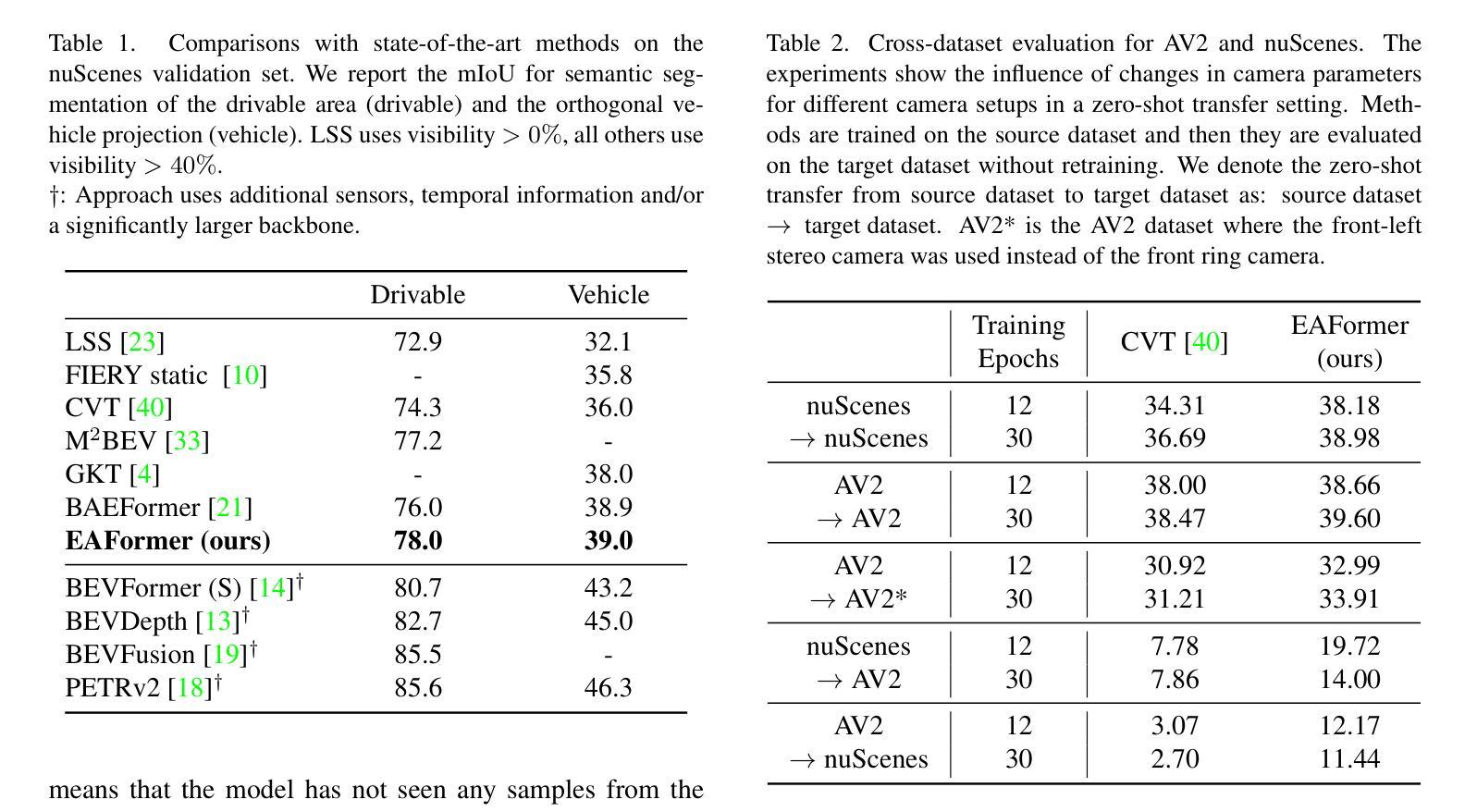
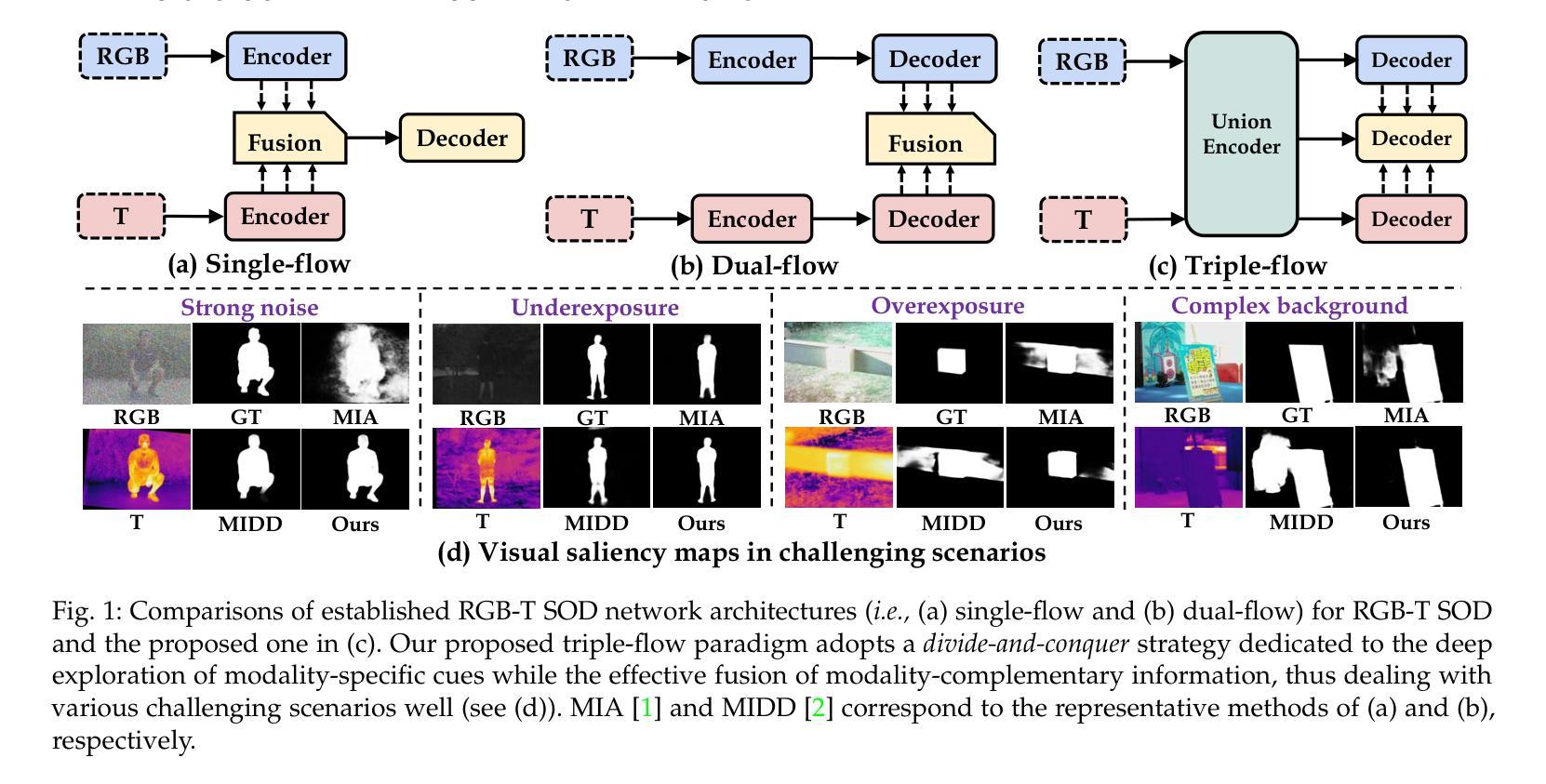
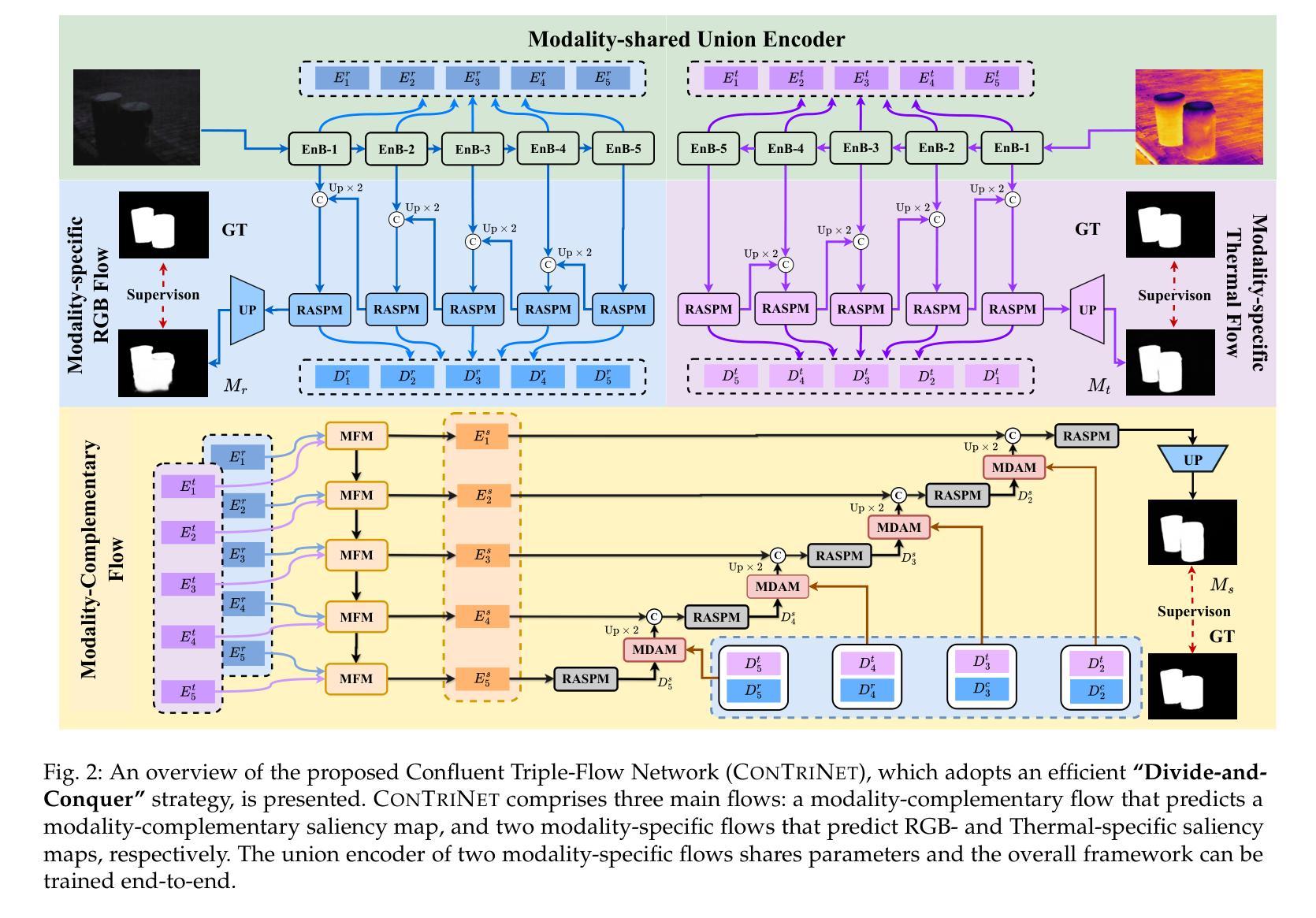
Divide-and-Conquer: Confluent Triple-Flow Network for RGB-T Salient Object Detection
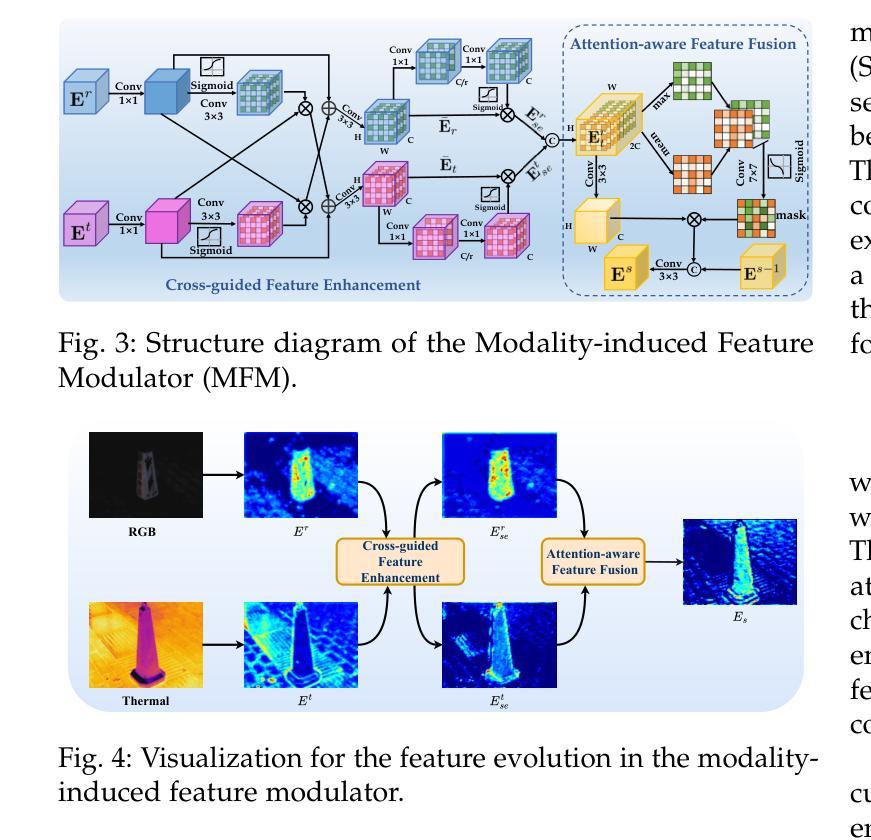
Authors:Hao Tang, Zechao Li, Dong Zhang, Shengfeng He, Jinhui Tang
RGB-Thermal Salient Object Detection aims to pinpoint prominent objects within aligned pairs of visible and thermal infrared images. Traditional encoder-decoder architectures, while designed for cross-modality feature interactions, may not have adequately considered the robustness against noise originating from defective modalities. Inspired by hierarchical human visual systems, we propose the ConTriNet, a robust Confluent Triple-Flow Network employing a Divide-and-Conquer strategy. Specifically, ConTriNet comprises three flows: two modality-specific flows explore cues from RGB and Thermal modalities, and a third modality-complementary flow integrates cues from both modalities. ConTriNet presents several notable advantages. It incorporates a Modality-induced Feature Modulator in the modality-shared union encoder to minimize inter-modality discrepancies and mitigate the impact of defective samples. Additionally, a foundational Residual Atrous Spatial Pyramid Module in the separated flows enlarges the receptive field, allowing for the capture of multi-scale contextual information. Furthermore, a Modality-aware Dynamic Aggregation Module in the modality-complementary flow dynamically aggregates saliency-related cues from both modality-specific flows. Leveraging the proposed parallel triple-flow framework, we further refine saliency maps derived from different flows through a flow-cooperative fusion strategy, yielding a high-quality, full-resolution saliency map for the final prediction. To evaluate the robustness and stability of our approach, we collect a comprehensive RGB-T SOD benchmark, VT-IMAG, covering various real-world challenging scenarios. Extensive experiments on public benchmarks and our VT-IMAG dataset demonstrate that ConTriNet consistently outperforms state-of-the-art competitors in both common and challenging scenarios.
RGB-热显著目标检测旨在确定可见和红外热图像配对中的突出目标。传统的编码器-解码器架构虽然旨在实现跨模态特征交互,但可能未能充分考虑到来自缺陷模态的噪声的鲁棒性。受分层人类视觉系统的启发,我们提出了ConTriNet,这是一个稳健的汇聚三流网络,采用分而治之的策略。具体来说,ConTriNet包含三个流:两个模态特定流探索RGB和热模态的线索,第三个模态互补流整合两种模态的线索。ConTriNet具有几个显著的优势。它在模态共享联合编码器中引入了模态诱导特征调制器,以最小化模态之间的差异并减轻缺陷样本的影响。此外,分离流中的基础残差空洞空间金字塔模块扩大了感受野,能够捕获多尺度上下文信息。此外,模态互补流中的模态感知动态聚合模块动态聚合来自特定模态流的显著性相关线索。利用所提出的并行三流框架,我们通过协同流融合策略进一步细化从不同流派导出的显著性图,从而产生高质量、全分辨率显著性图用于最终预测。为了评估我们方法的鲁棒性和稳定性,我们收集了一个全面的RGB-T SOD基准,VT-IMAG,涵盖了各种现实世界的挑战场景。在公共基准和我们自己的VT-IMAG数据集上的大量实验表明,ConTriNet在普通和具有挑战的场景中均优于最新竞争对手。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE TPAMI. Project page: https://cser-tang-hao.github.io/contrinet.html
Summary:
RGB-T显著目标检测旨在识别可见光与热红外图像对齐后的突出物体。针对传统编码解码架构在处理跨模态特征交互时未充分考虑到噪声干扰的问题,我们提出了基于层次人类视觉系统的ConTriNet模型。该模型采用分而治之的策略,包含三个分支:两个模态特定分支分别探索RGB和热模态的线索,第三个模态互补分支整合两个模态的线索。ConTriNet具备多优势:在共享联合编码器中加入模态诱导特征调制器,减少模态间差异并减轻缺陷样本的影响;分离的流中的基础残差空洞金字塔模块扩大了感受野,捕获多尺度上下文信息;模态感知动态聚合模块在模态互补流中动态聚合来自两个模态特定流的显著性相关线索。通过并行三流框架,我们进一步通过流协同融合策略优化来自不同流的显著性图,从而得到高质量的全分辨率显著性图用于最终预测。我们收集了全面的RGB-T显著性目标检测基准数据集VT-IMAG,涵盖各种现实挑战场景。在公共基准数据集和我们的VT-IMAG数据集上的实验表明,ConTriNet在常规和具有挑战性的场景中均表现优于最新竞争对手。
Key Takeaways:
- RGB-Thermal Salient Object Detection (RGB-TSOD)旨在识别可见光和热红外图像中的突出物体。
- 提出ConTriNet模型,采用分而治之策略,包含三个流:两个模态特定流和一个模态互补流。
- ConTriNet利用模态诱导特征调制器减少模态间差异,并减轻缺陷样本的影响。
- ConTriNet通过扩大的感受野捕获多尺度上下文信息。
- 模态感知动态聚合模块动态聚合来自两个模态的显著性线索。
- 通过并行三流框架和流协同融合策略优化显著性图。
点此查看论文截图
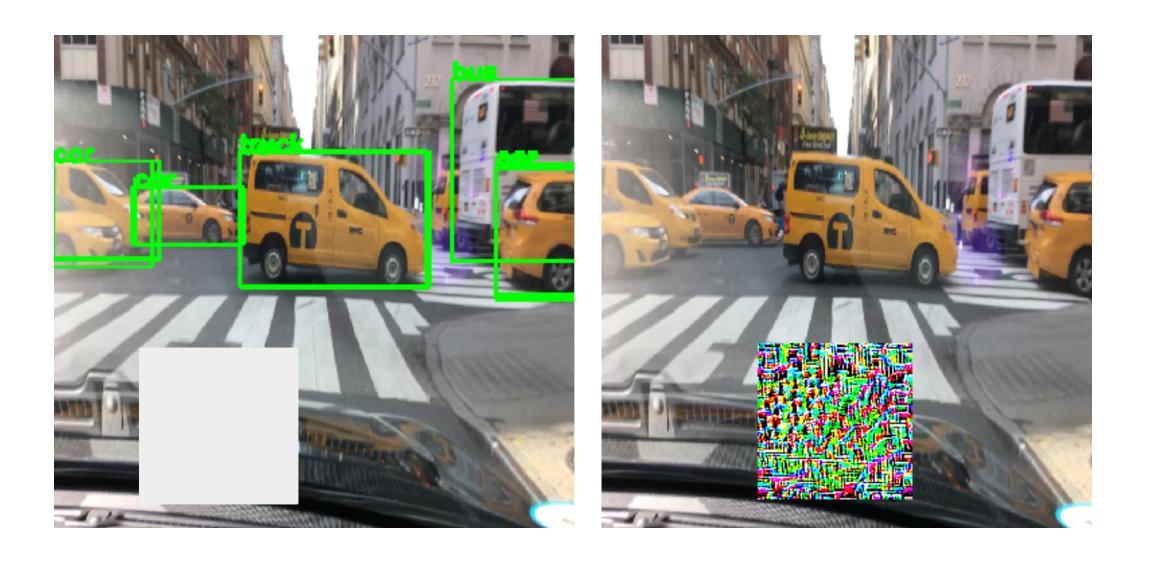
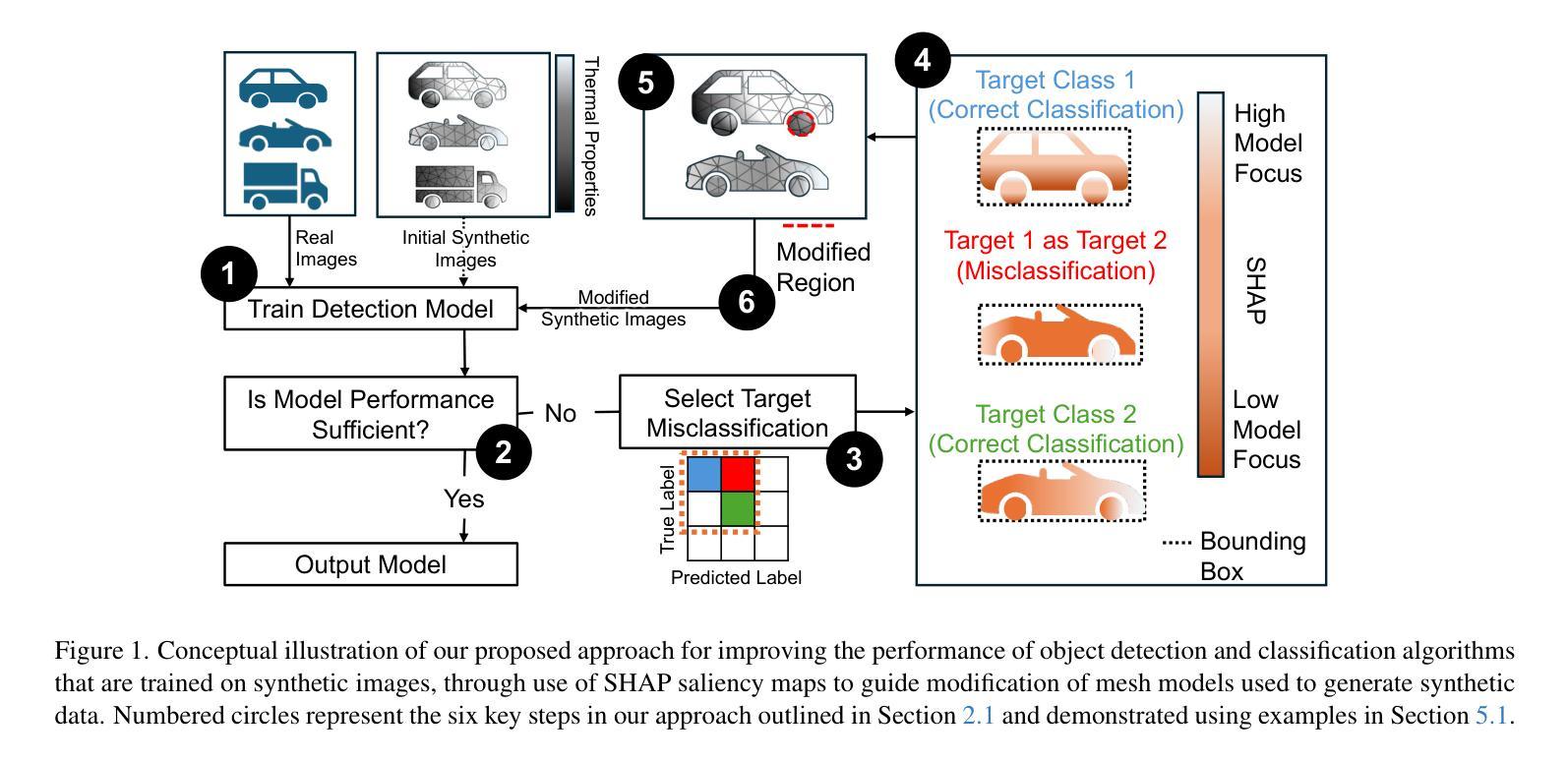
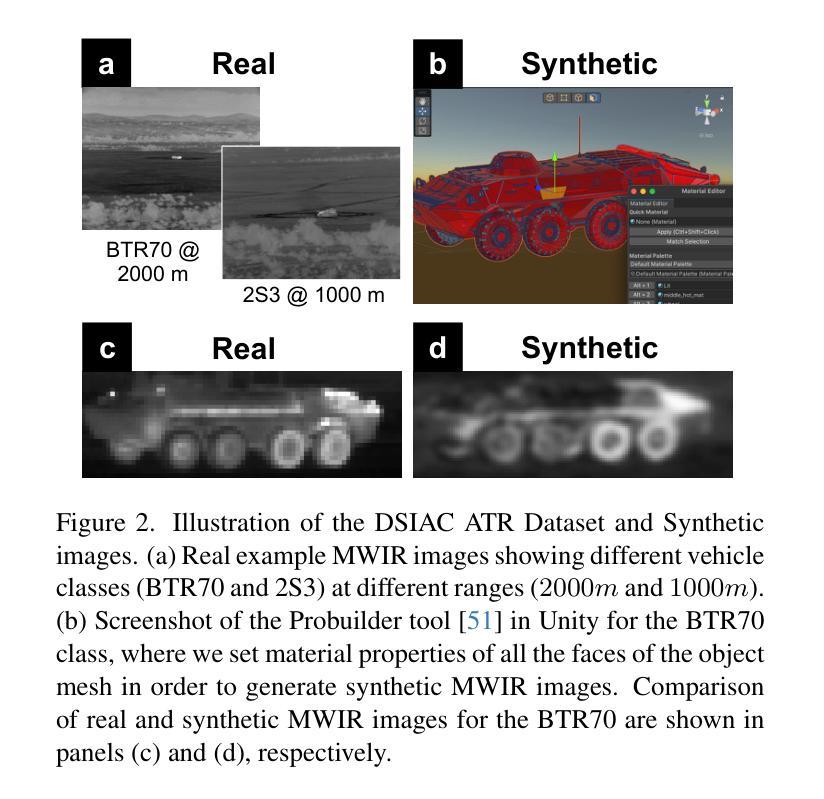
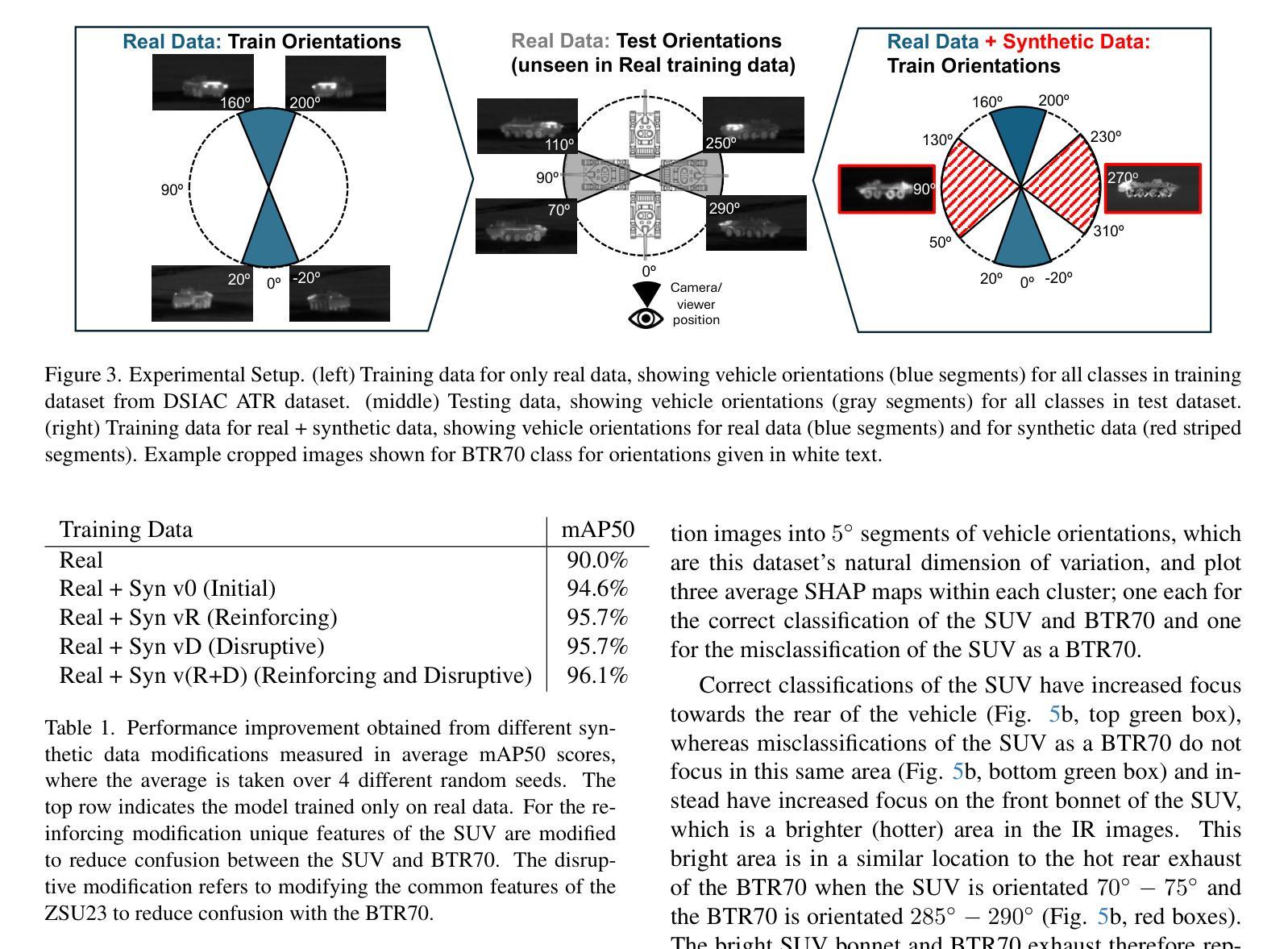
Improving Object Detection by Modifying Synthetic Data with Explainable AI
Authors:Nitish Mital, Simon Malzard, Richard Walters, Celso M. De Melo, Raghuveer Rao, Victoria Nockles
In many computer vision domains the collection of sufficient real-world data is challenging and can severely impact model performance, particularly when running inference on samples that are unseen or underrepresented in training. Synthetically generated images provide a promising solution, but it remains unclear how to design synthetic data to optimally improve model performance, for example whether to introduce more realism or more abstraction in such datasets. Here we propose a novel conceptual approach to improve the performance of computer vision models trained on synthetic images, by using robust Explainable AI (XAI) techniques to guide the modification of 3D models used to generate these images. Importantly, this framework allows both modifications that increase and decrease realism in synthetic data, which can both improve model performance. We illustrate this concept using a real-world example where data are sparse; the detection of vehicles in infrared imagery. We fine-tune an initial YOLOv8 model on the ATR DSIAC infrared dataset and synthetic images generated from 3D mesh models in the Unity gaming engine, and then use XAI saliency maps to guide modification of our Unity models. We show that synthetic data can improve detection of vehicles in orientations unseen in training by 4.6% (to mAP50 scores of 94.6%). We further improve performance by an additional 1.5% (to 96.1%) through our new XAI-guided approach, which reduces misclassifications through both increasing and decreasing the realism of different parts of the synthetic data. These proof-of-concept results pave the way for fine, XAI-controlled curation of synthetic datasets through detailed feature modifications, tailored to improve object detection performance.
在许多计算机视觉领域,收集足够的真实世界数据是一个挑战,并可能严重影响模型性能,特别是在对训练过程中未见或代表性不足的样本进行推理时。合成图像提供了一种很有前途的解决方案,但如何设计合成数据以最优方式提高模型性能仍不清楚,例如,是在这些数据集中引入更多的现实主义还是更多的抽象。在这里,我们提出了一种基于计算机视觉模型训练的新型概念方法,利用稳健的可解释性人工智能(XAI)技术来指导生成这些图像所使用的3D模型的修改。重要的是,该框架允许增加或减少合成数据中的逼真度,这都可以提高模型性能。我们使用现实世界数据稀疏的例子——红外图像中的车辆检测来阐释这一概念。我们对初始的YOLOv8模型进行微调,使其适应ATR DSIAC红外数据集和由Unity游戏引擎中的3D网格模型生成的合成图像,然后使用XAI显著性图来指导我们的Unity模型的修改。我们表明,合成数据可以提高训练过程中未见方向的车辆检测性能,提高4.6%(达到mAP50分数为94.6%)。通过我们的新型XAI引导方法,我们进一步提高了性能,再提高1.5%(达到96.1%),该方法通过增加和减少合成数据不同部分的逼真度来减少误分类。这些概念验证结果开辟了通过详细特征修改精细控制XAI合成数据集的道路,以改善目标检测性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了一种利用可解释的AI(XAI)技术改进计算机视觉模型性能的新方法,特别是在合成图像数据集上。通过XAI技术引导对用于生成图像的3D模型的修改,该框架允许增加或减少合成数据的逼真度,以提高模型性能。在车辆红外图像检测的实际例子中,展示了合成数据和使用XAI指导的修改能够提高模型在未训练方向上的车辆检测性能。
Key Takeaways
- 合成图像为解决计算机视觉领域数据收集难题提供了解决方案。
- 仅靠增加逼真度并不能保证模型性能的最优提升。
- 利用Explainable AI(XAI)技术可以指导合成数据的改进。
- 通过调整合成数据的逼真度,可以提高模型在未训练方向上的性能。
- 在车辆红外图像检测的实际应用中,合成数据和XAI指导的修改提高了模型性能。
- XAI引导的精细调整能够减少误分类,进一步优化模型性能。
点此查看论文截图

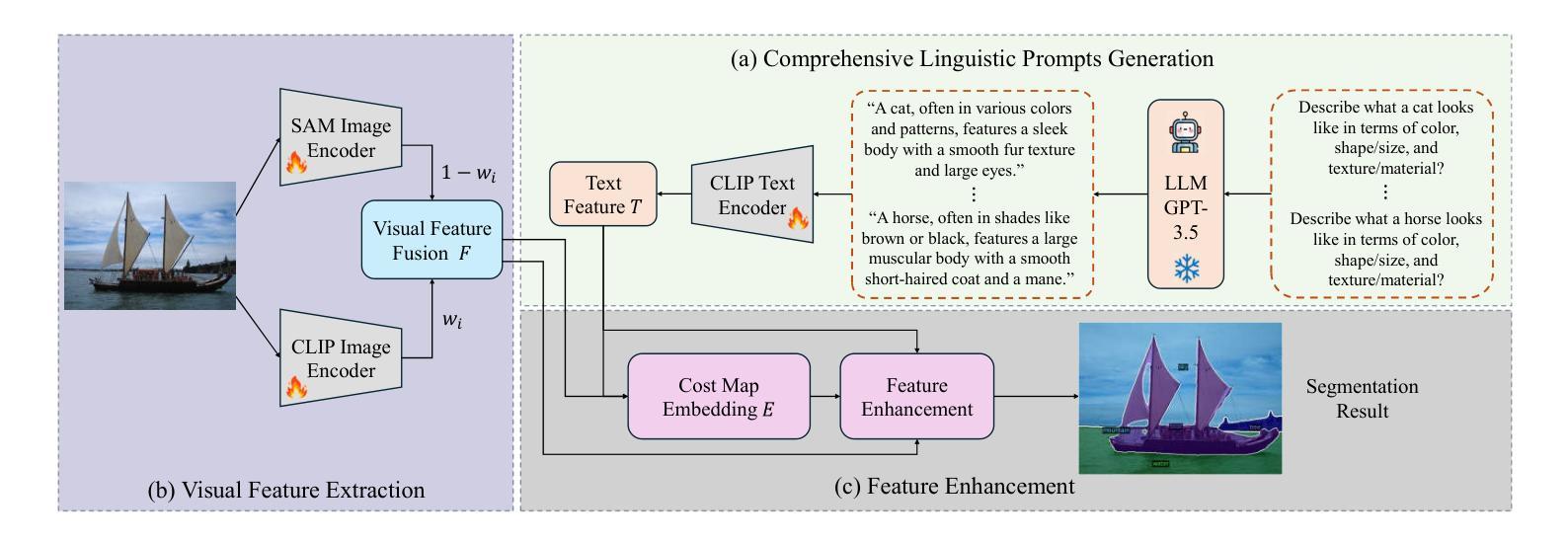
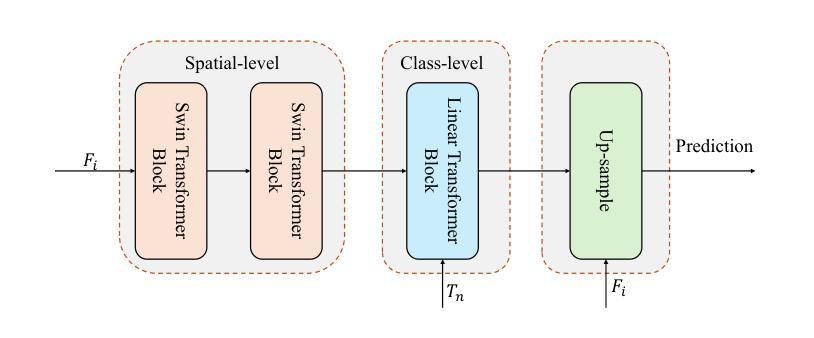
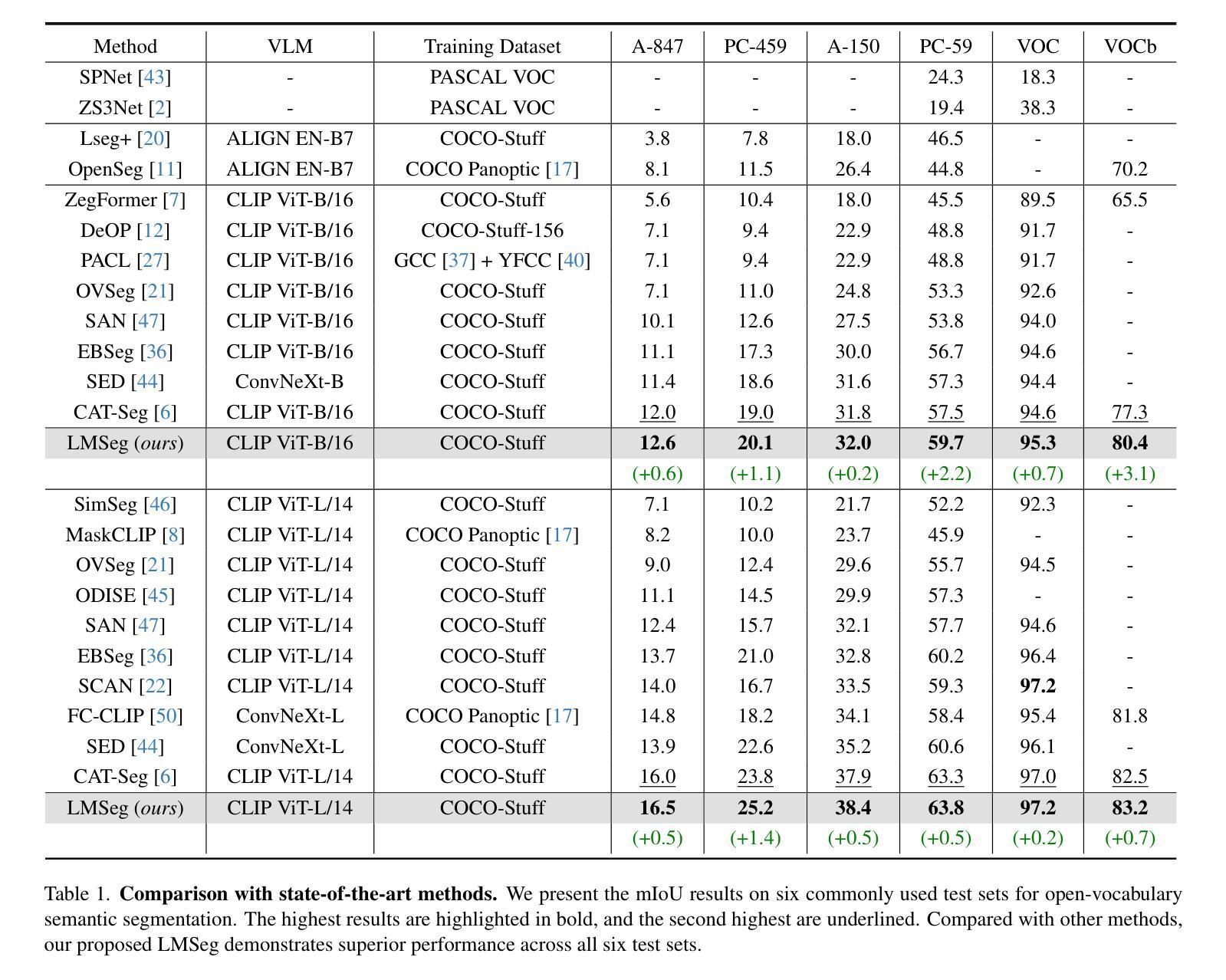
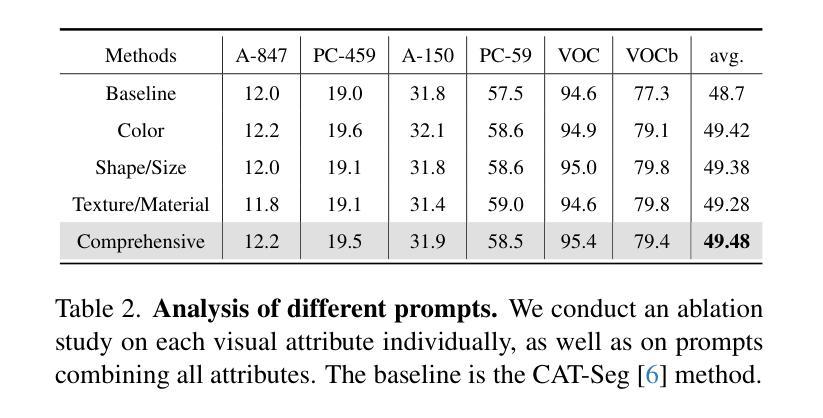
LMSeg: Unleashing the Power of Large-Scale Models for Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Huadong Tang, Youpeng Zhao, Yan Huang, Min Xu, Jun Wang, Qiang Wu
It is widely agreed that open-vocabulary-based approaches outperform classical closed-set training solutions for recognizing unseen objects in images for semantic segmentation. Existing open-vocabulary approaches leverage vision-language models, such as CLIP, to align visual features with rich semantic features acquired through pre-training on large-scale vision-language datasets. However, the text prompts employed in these methods are short phrases based on fixed templates, failing to capture comprehensive object attributes. Moreover, while the CLIP model excels at exploiting image-level features, it is less effective at pixel-level representation, which is crucial for semantic segmentation tasks. In this work, we propose to alleviate the above-mentioned issues by leveraging multiple large-scale models to enhance the alignment between fine-grained visual features and enriched linguistic features. Specifically, our method employs large language models (LLMs) to generate enriched language prompts with diverse visual attributes for each category, including color, shape/size, and texture/material. Additionally, for enhanced visual feature extraction, the SAM model is adopted as a supplement to the CLIP visual encoder through a proposed learnable weighted fusion strategy. Built upon these techniques, our method, termed LMSeg, achieves state-of-the-art performance across all major open-vocabulary segmentation benchmarks. The code will be made available soon.
普遍认为,基于开放词汇的方法在语义分割中识别未见物体时,其性能优于经典的封闭集训练解决方案。现有的开放词汇方法利用视觉语言模型(如CLIP)对齐视觉特征与通过大规模视觉语言数据集预训练获得的丰富语义特征。然而,这些方法中所使用的文本提示是基于固定模板的短语,无法捕捉全面的对象属性。此外,虽然CLIP模型在利用图像级特征方面表现出色,但在像素级表示方面效果较差,这对于语义分割任务至关重要。在这项工作中,我们提出通过利用多个大规模模型来缓解上述问题,以增强精细视觉特征与丰富语言特征之间的对齐。具体来说,我们的方法采用大型语言模型(LLM)为每个类别生成具有各种视觉属性的丰富语言提示,包括颜色、形状/大小、纹理/材质。此外,为了增强视觉特征提取,我们采用SAM模型作为对CLIP视觉编码器的补充,通过提出的可学习加权融合策略。基于这些技术,我们的方法——LMSeg,在所有主要的开放词汇分割基准测试中均实现了最先进的性能。代码将很快公布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出利用多大型模型增强精细视觉特征与丰富语言特征的对齐,解决现有开放词汇表方法在语义分割中识别未见物体的问题。通过大型语言模型生成包含多种视觉属性的丰富语言提示,并结合SAM模型增强CLIP视觉编码器的特征提取能力,实现先进性能。
Key Takeaways
- 开放词汇表方法普遍优于经典封闭集训练解决方案,用于识别图像中未见物体的语义分割。
- 现有开放词汇表方法利用视觉语言模型(如CLIP)对齐视觉特征和通过预训练获得丰富语义特征。
- 现有方法的文本提示基于固定模板的短语,无法捕捉全面的对象属性。
- CLIP模型在图像级特征利用上表现优异,但在像素级表示上效果较差,对语义分割任务至关重要。
- 提出利用多大型模型增强精细视觉特征与丰富语言特征的对齐。
- 使用大型语言模型(LLMs)生成包含各种视觉属性的丰富语言提示,如颜色、形状/大小、纹理/材质。
点此查看论文截图

SpaRC: Sparse Radar-Camera Fusion for 3D Object Detection
Authors:Philipp Wolters, Johannes Gilg, Torben Teepe, Fabian Herzog, Felix Fent, Gerhard Rigoll
In this work, we present SpaRC, a novel Sparse fusion transformer for 3D perception that integrates multi-view image semantics with Radar and Camera point features. The fusion of radar and camera modalities has emerged as an efficient perception paradigm for autonomous driving systems. While conventional approaches utilize dense Bird’s Eye View (BEV)-based architectures for depth estimation, contemporary query-based transformers excel in camera-only detection through object-centric methodology. However, these query-based approaches exhibit limitations in false positive detections and localization precision due to implicit depth modeling. We address these challenges through three key contributions: (1) sparse frustum fusion (SFF) for cross-modal feature alignment, (2) range-adaptive radar aggregation (RAR) for precise object localization, and (3) local self-attention (LSA) for focused query aggregation. In contrast to existing methods requiring computationally intensive BEV-grid rendering, SpaRC operates directly on encoded point features, yielding substantial improvements in efficiency and accuracy. Empirical evaluations on the nuScenes and TruckScenes benchmarks demonstrate that SpaRC significantly outperforms existing dense BEV-based and sparse query-based detectors. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance metrics of 67.1 NDS and 63.1 AMOTA. The code and pretrained models are available at https://github.com/phi-wol/sparc.
在这项工作中,我们提出了SpaRC,这是一种用于3D感知的新型稀疏融合变压器,它融合了多视图图像语义与雷达和摄像头点特征。雷达和摄像头的融合已成为自动驾驶系统的高效感知范式。虽然传统方法使用密集的鸟瞰图(BEV)基架构进行深度估计,但当代基于查询的变压器通过以对象为中心的方法在仅使用相机进行检测方面表现出色。然而,这些基于查询的方法由于隐式深度建模而在误报检测和定位精度方面存在局限性。我们通过三个主要贡献来解决这些挑战:(1)用于跨模态特征对齐的稀疏棱镜融合(SFF),(2)用于精确对象定位的雷达范围自适应聚合(RAR),以及(3)用于有重点查询聚合的局部自注意力(LSA)。与现有方法不同,这些方法需要计算密集型的BEV网格渲染,SpaRC直接在编码的点特征上运行,在效率和准确性方面取得了显著改进。在nuScenes和TruckScenes基准测试上的实证评估表明,SpaRC显著优于现有的密集BEV基和稀疏查询基检测器。我们的方法达到了最先进的性能指标,NDS为67.1,AMOTA为63.1。代码和预先训练的模型可在https://github.com/phi-wol/sparc上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
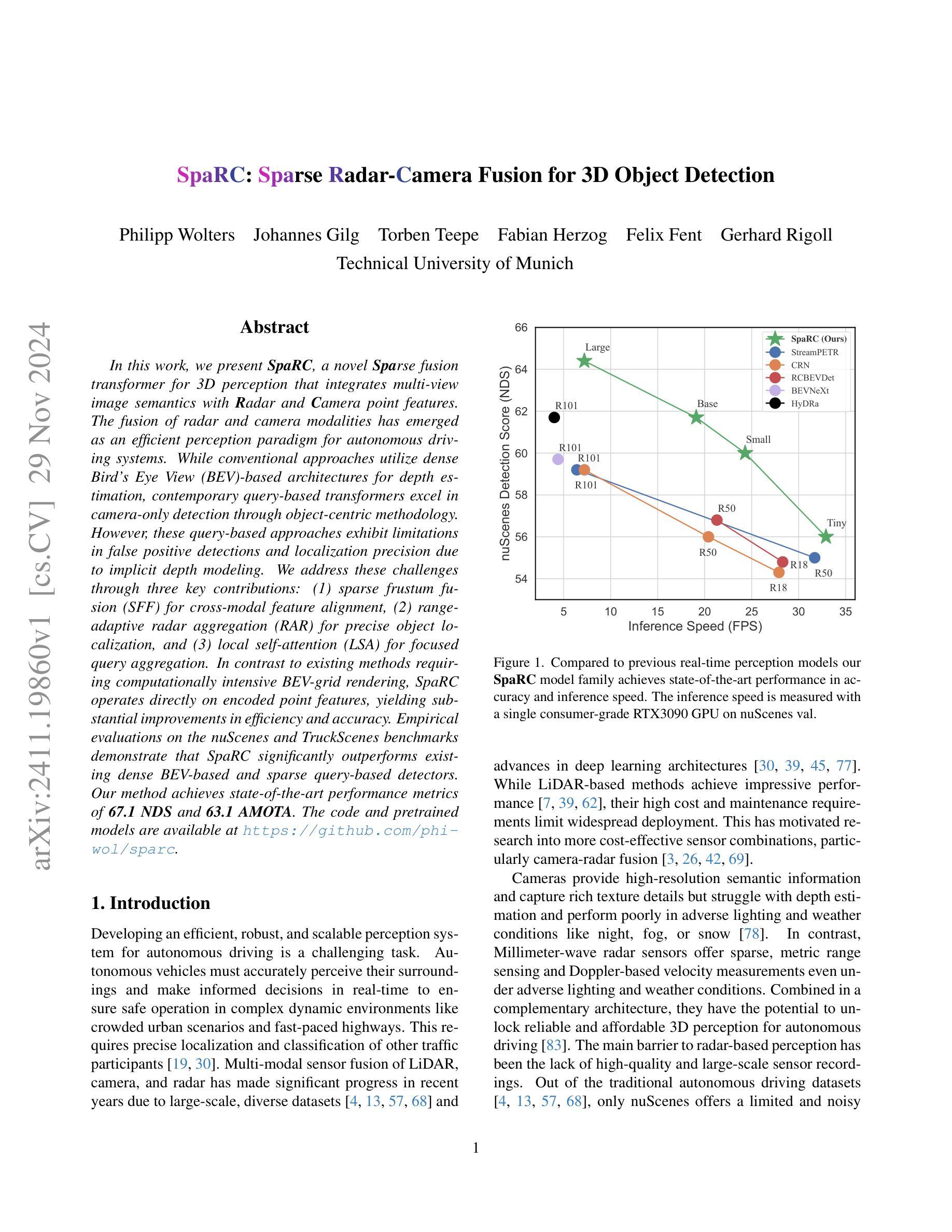
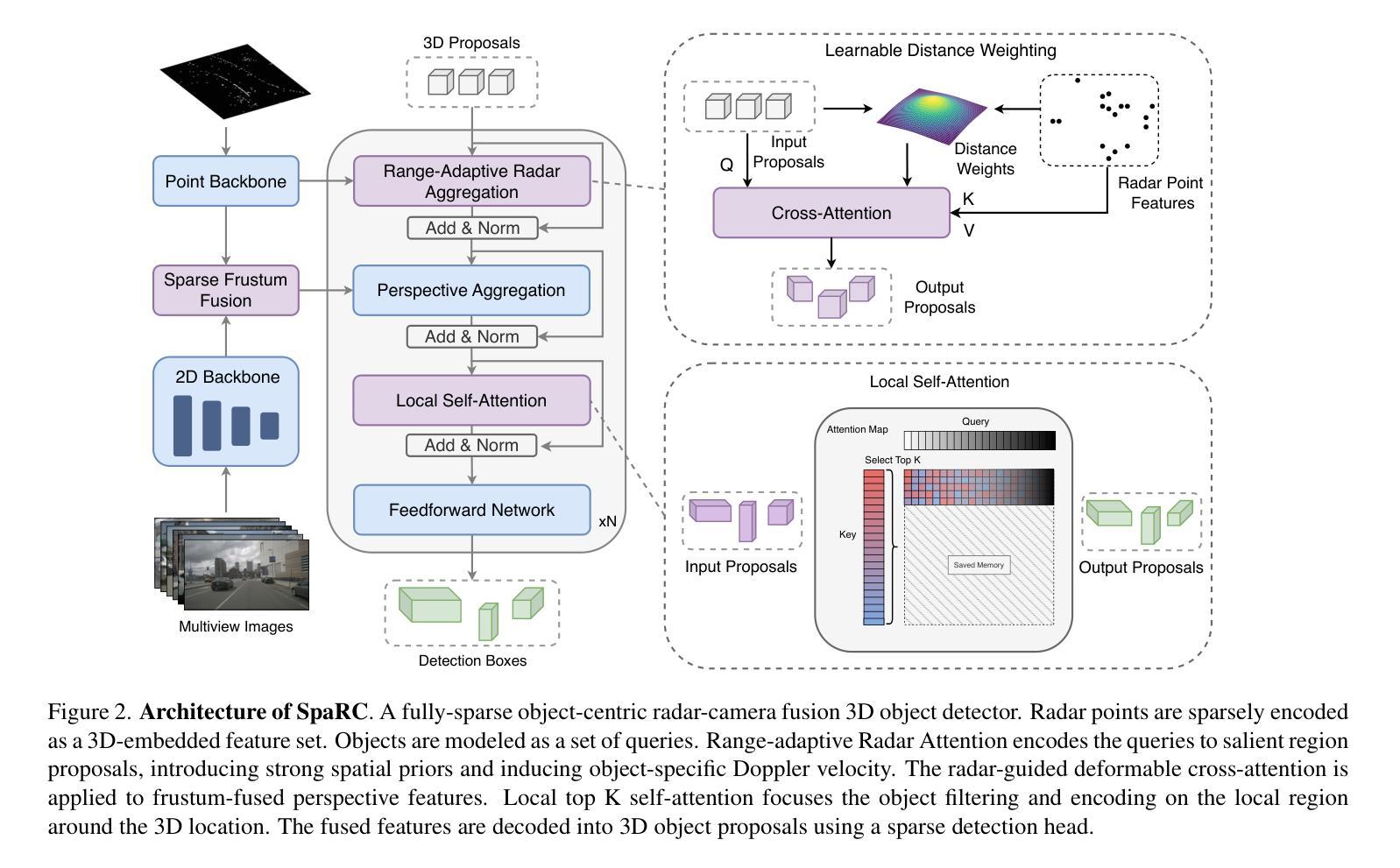
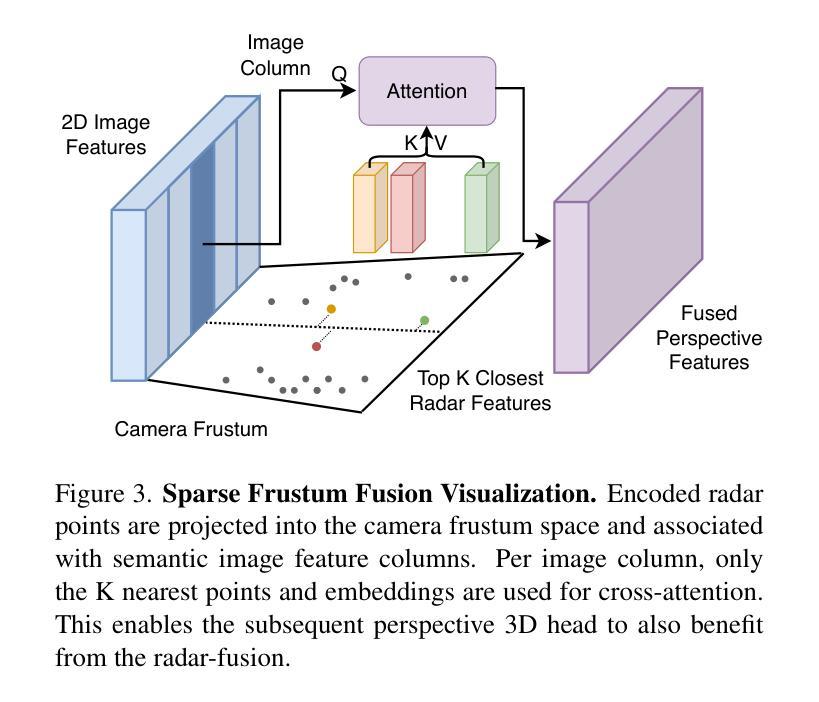
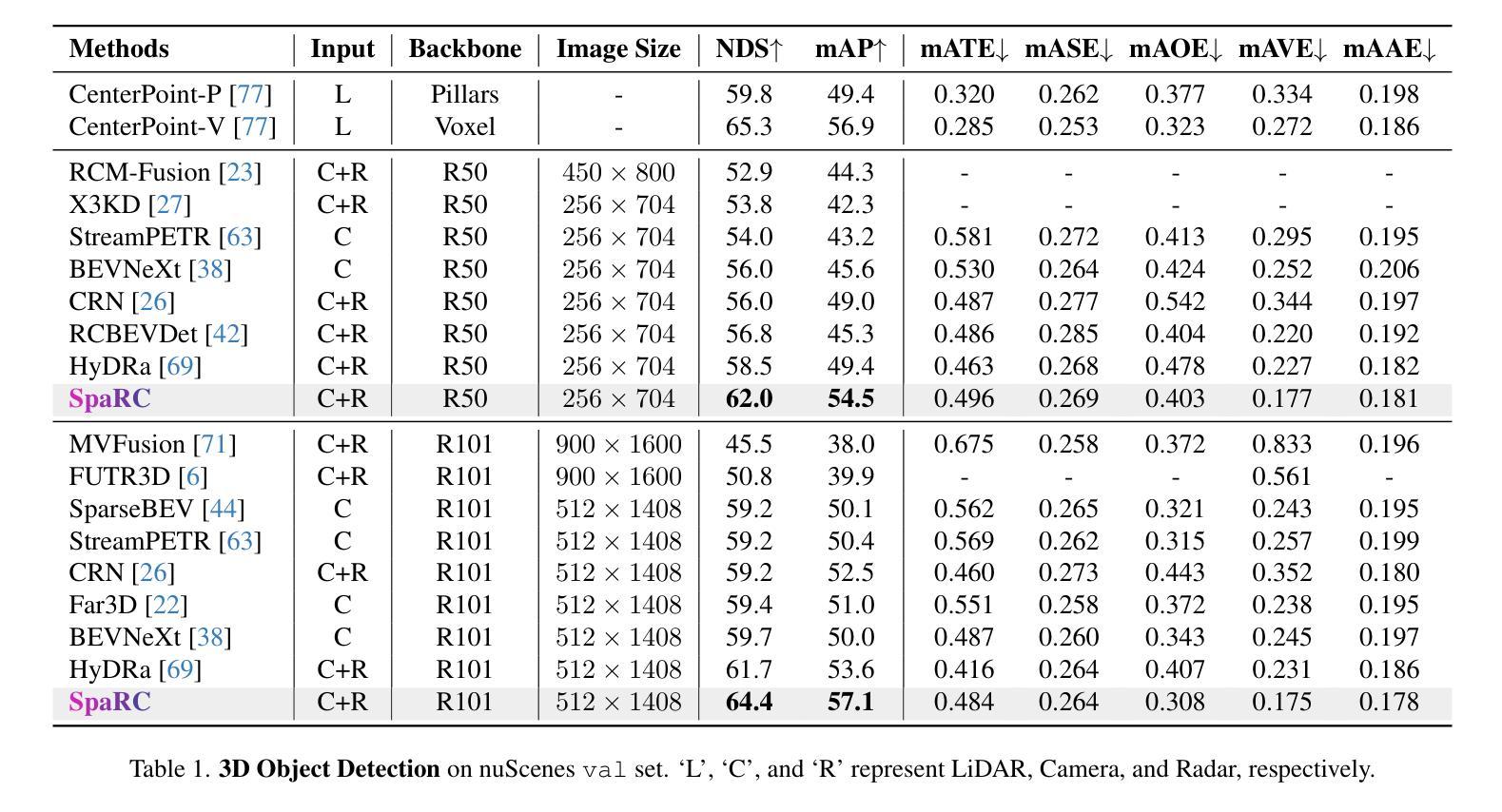
PDF 18 pages, 11 figures
Summary
在研究中,我们提出了名为SpaRC的新型稀疏融合转换器,用于三维感知,它将雷达和摄像头的点特征与多视图图像语义融合。我们针对现有方法的不足,提出了三项关键贡献:稀疏棱镜融合(SFF)用于跨模态特征对齐,范围自适应雷达聚合(RAR)用于精确目标定位,以及局部自注意力(LSA)用于集中查询聚合。SpaRC直接在编码的点特征上运行,与现有的需要大量计算资源的BEV网格渲染方法形成对比,提高了效率和准确性。在nuScenes和TruckScenes基准测试上的评估表明,SpaRC显著优于现有的密集BEV基和稀疏查询基检测器。我们的方法实现了最高性能:67.1NDS和63.1AMOTA。代码和预训练模型可在GitHub上找到。
Key Takeaways
- SpaRC是一个新型稀疏融合转换器,旨在实现多视图图像语义与雷达和摄像头的点特征融合。它直接操作点特征而非复杂的图像视图模型,极大提升了计算效率与准确性。
- 三项核心技术的提出有效解决了雷达和摄像头融合所面临的难题,包括跨模态特征对齐(通过稀疏棱镜融合)、精确目标定位(通过范围自适应雷达聚合)以及查询聚合的集中化(通过局部自注意力机制)。
- SpaRC相比传统方法有着明显的性能优势,例如在nuScenes和TruckScenes测试中实现显著超越的业绩指标(例如高达67.1NDS和63.1AMOTA)。这显示了SpaRC在复杂环境下的强大感知能力。
点此查看论文截图
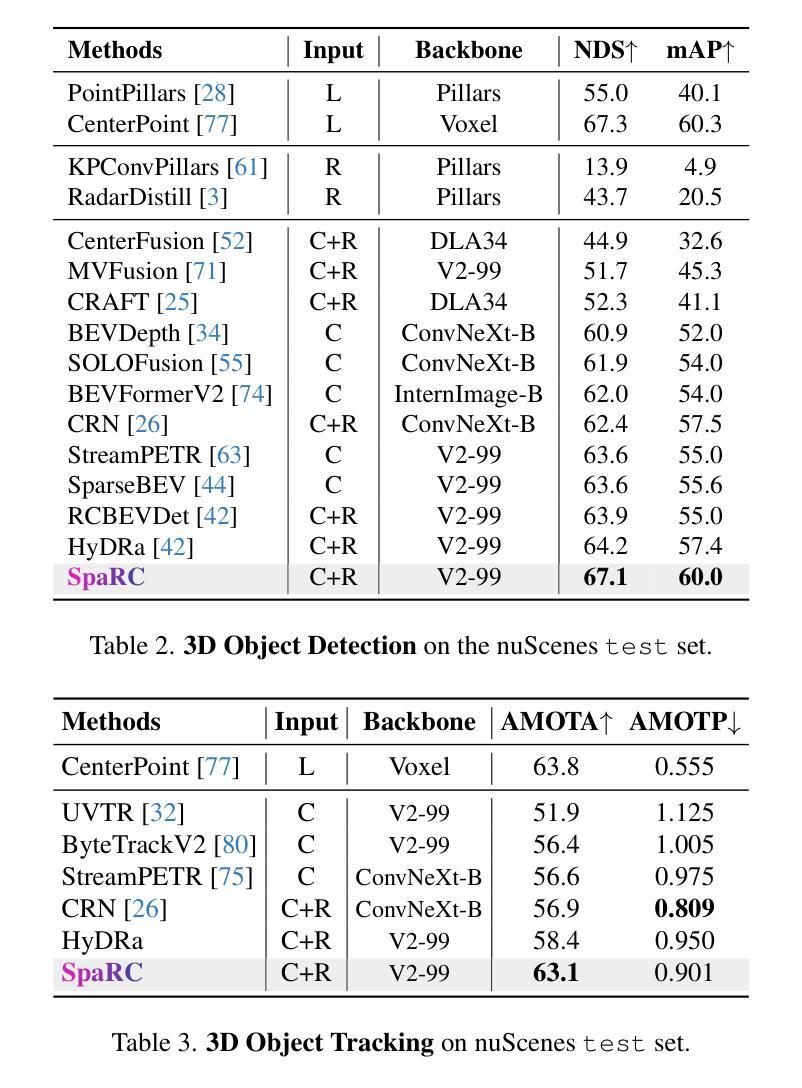
Feedback-driven object detection and iterative model improvement
Authors:Sönke Tenckhoff, Mario Koddenbrock, Erik Rodner
Automated object detection has become increasingly valuable across diverse applications, yet efficient, high-quality annotation remains a persistent challenge. In this paper, we present the development and evaluation of a platform designed to interactively improve object detection models. The platform allows uploading and annotating images as well as fine-tuning object detection models. Users can then manually review and refine annotations, further creating improved snapshots that are used for automatic object detection on subsequent image uploads - a process we refer to as semi-automatic annotation resulting in a significant gain in annotation efficiency. Whereas iterative refinement of model results to speed up annotation has become common practice, we are the first to quantitatively evaluate its benefits with respect to time, effort, and interaction savings. Our experimental results show clear evidence for a significant time reduction of up to 53% for semi-automatic compared to manual annotation. Importantly, these efficiency gains did not compromise annotation quality, while matching or occasionally even exceeding the accuracy of manual annotations. These findings demonstrate the potential of our lightweight annotation platform for creating high-quality object detection datasets and provide best practices to guide future development of annotation platforms. The platform is open-source, with the frontend and backend repositories available on GitHub.
自动化目标检测在许多应用中变得越来越有价值,然而高效、高质量的标注仍然是一个持续存在的挑战。在本文中,我们介绍了一个交互式改进目标检测模型的平台的开发评估工作。该平台允许上传和标注图像,并微调目标检测模型。用户随后可以手动审查和修改标注,进一步创建改进的快照,这些快照用于后续图像上传的自动目标检测——我们称之为半自动标注,该过程在标注效率上获得了显著的提升。虽然通过迭代优化模型结果以加快标注速度已成为常见做法,但我们是首次在时间上、努力程度上和交互节省方面定量评估其好处。我们的实验结果表明,与手动标注相比,半自动标注的时间减少了高达53%。重要的是,这些效率的提升并没有损害标注质量,同时达到了或偶尔甚至超过了手动标注的准确性。这些发现证明了我们轻量级标注平台在创建高质量目标检测数据集方面的潜力,并为未来标注平台的发展提供了最佳实践指导。该平台是开源的,前端和后端仓库均可在GitHub上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AI4EA24 preprint
Summary
本文介绍了一个交互式平台,旨在提高物体检测模型的性能。该平台支持图像上传、标注和模型微调。用户可手动审查和修正标注,创建改进的快照用于后续图像上传的自动物体检测。该平台采用半自动标注方式,显著提高了标注效率。实验结果表明,半自动标注与手动标注相比,时间减少了高达53%。重要的是,效率的提升并没有损害标注质量,甚至在某些情况下超过了手动标注的准确性。这为创建高质量物体检测数据集提供了潜力,并为未来开发标注平台提供了最佳实践指南。
Key Takeaways
- 该平台旨在提高物体检测模型的性能,支持图像上传、标注和模型微调。
- 用户可以手动审查和修正标注,创建改进的快照用于自动物体检测。
- 平台采用半自动标注方式,显著提高了标注效率。
- 实验结果表明,半自动标注与手动标注相比,时间减少了高达53%。
- 效率的提升并没有损害标注质量,甚至在某些情况下超过了手动标注的准确性。
- 该平台是开源的,前端和后端代码已在GitHub上发布。
点此查看论文截图


Automatic Prompt Generation and Grounding Object Detection for Zero-Shot Image Anomaly Detection
Authors:Tsun-Hin Cheung, Ka-Chun Fung, Songjiang Lai, Kwan-Ho Lin, Vincent Ng, Kin-Man Lam
Identifying defects and anomalies in industrial products is a critical quality control task. Traditional manual inspection methods are slow, subjective, and error-prone. In this work, we propose a novel zero-shot training-free approach for automated industrial image anomaly detection using a multimodal machine learning pipeline, consisting of three foundation models. Our method first uses a large language model, i.e., GPT-3. generate text prompts describing the expected appearances of normal and abnormal products. We then use a grounding object detection model, called Grounding DINO, to locate the product in the image. Finally, we compare the cropped product image patches to the generated prompts using a zero-shot image-text matching model, called CLIP, to identify any anomalies. Our experiments on two datasets of industrial product images, namely MVTec-AD and VisA, demonstrate the effectiveness of this method, achieving high accuracy in detecting various types of defects and anomalies without the need for model training. Our proposed model enables efficient, scalable, and objective quality control in industrial manufacturing settings.
识别工业产品中的缺陷和异常是质量控制的关键任务。传统的手动检查方法速度慢、主观、易出错。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种全新的零样本无需训练的自适应工业图像异常检测方案,该方案采用多模态机器学习管道,由三个基础模型组成。我们的方法首先使用大型语言模型,即GPT-3,生成描述正常和异常产品预期外观的文本提示。然后,我们使用名为Grounding DINO的定位目标检测模型来定位图像中的产品。最后,我们使用零样本图像文本匹配模型CLIP,将裁剪后的产品图像块与生成的提示进行比较,以检测任何异常。我们在工业产品图像数据集MVTec-AD和VisA上的实验证明了该方法的有效性,在无需模型训练的情况下实现了高准确度的各种缺陷和异常的检测。我们提出的模型能够在工业制造环境中实现高效、可扩展和客观的质量控制。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to APSIPA ASC 2024
Summary
基于工业产品图像,本文提出了一种无需训练的零样本异常检测新方法。该方法利用大型语言模型生成文本提示,结合定位模型和图像文本匹配模型,实现对产品图像中缺陷和异常的自动检测。实验证明,该方法在MVTec-AD和VisA数据集上实现了高准确率,无需训练模型即可有效检测多种类型的缺陷和异常,为工业制造环境中的质量控制提供了高效、可扩展和客观的方案。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究提出了基于工业产品图像的零样本异常检测新方法。
- 方法结合了大型语言模型、定位模型和图像文本匹配模型。
- 语言模型用于生成描述正常和异常产品外观的文本提示。
- 定位模型用于在图像中定位产品。
- 图像文本匹配模型用于将裁剪后的产品图像与生成的文本提示进行比较,以检测异常。
- 实验在MVTec-AD和VisA数据集上验证了方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

HOT3D: Hand and Object Tracking in 3D from Egocentric Multi-View Videos
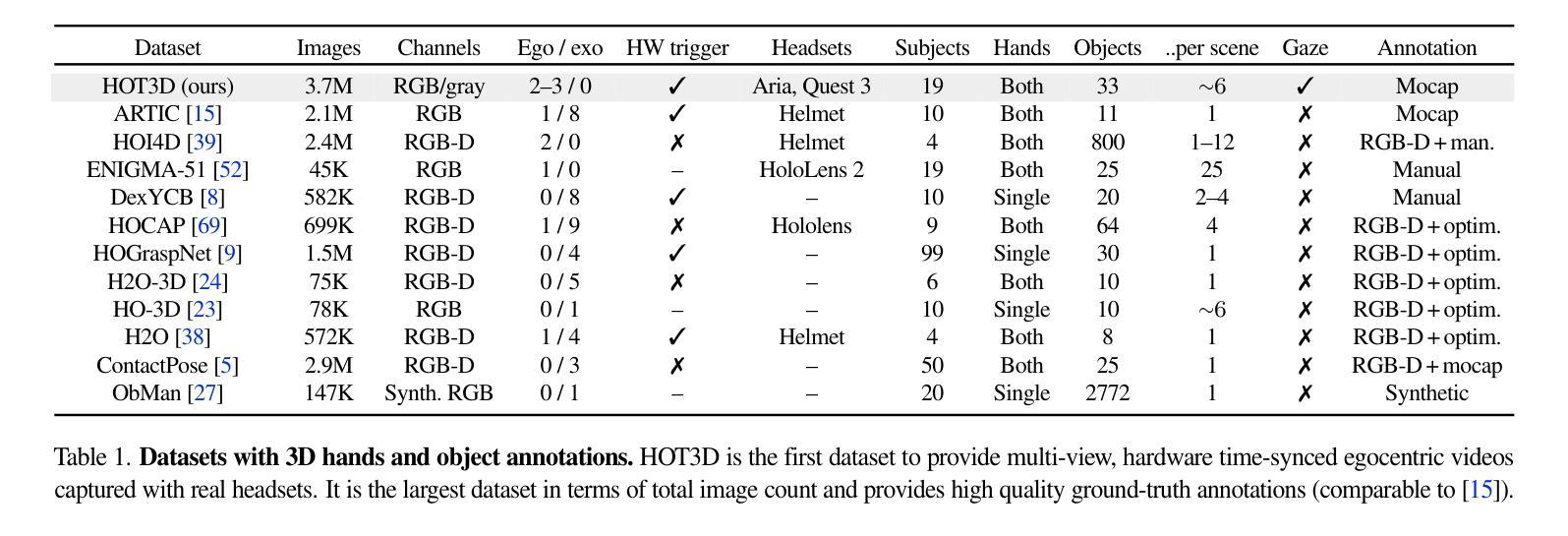
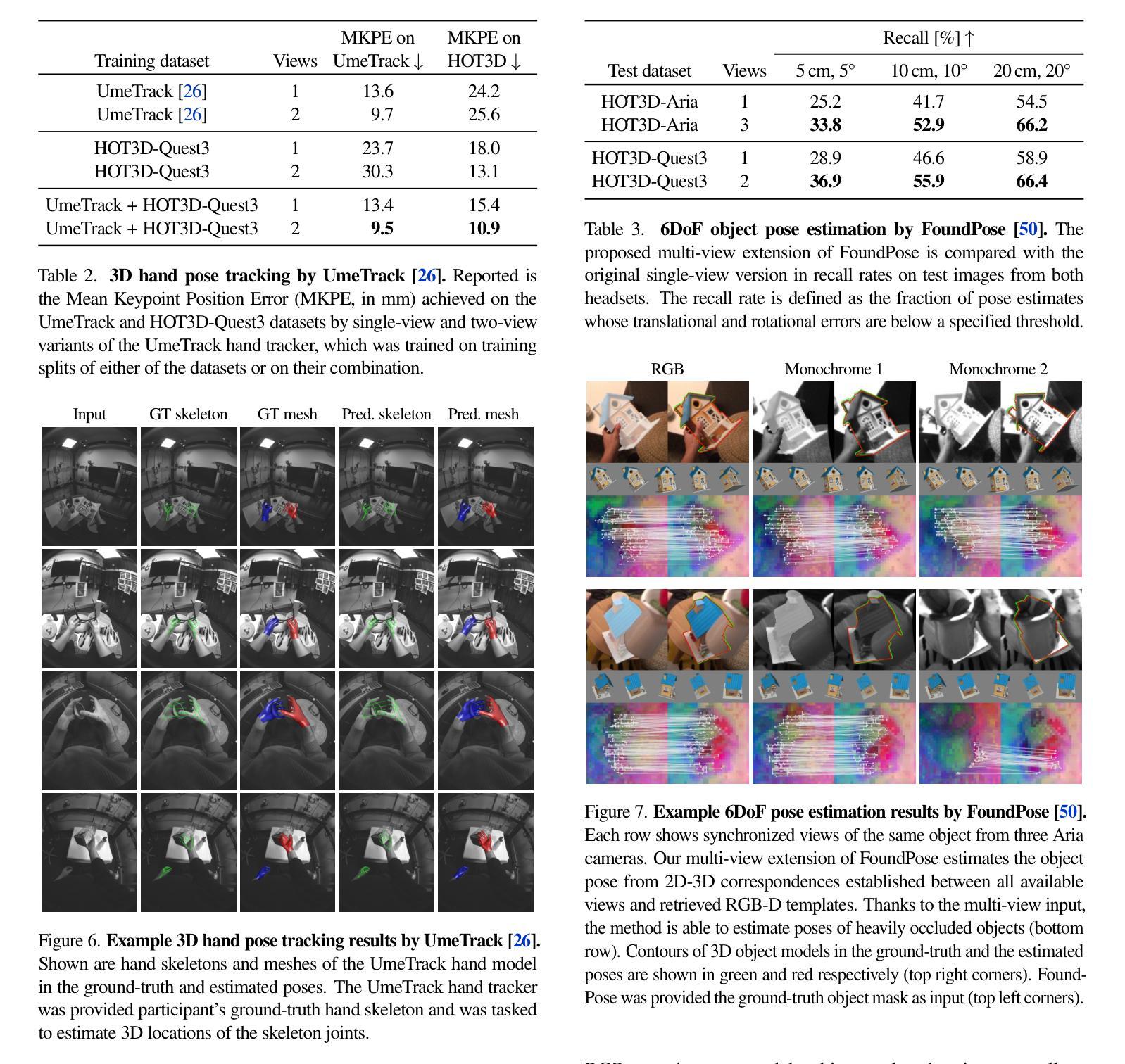
Authors:Prithviraj Banerjee, Sindi Shkodrani, Pierre Moulon, Shreyas Hampali, Shangchen Han, Fan Zhang, Linguang Zhang, Jade Fountain, Edward Miller, Selen Basol, Richard Newcombe, Robert Wang, Jakob Julian Engel, Tomas Hodan
We introduce HOT3D, a publicly available dataset for egocentric hand and object tracking in 3D. The dataset offers over 833 minutes (more than 3.7M images) of multi-view RGB/monochrome image streams showing 19 subjects interacting with 33 diverse rigid objects, multi-modal signals such as eye gaze or scene point clouds, as well as comprehensive ground-truth annotations including 3D poses of objects, hands, and cameras, and 3D models of hands and objects. In addition to simple pick-up/observe/put-down actions, HOT3D contains scenarios resembling typical actions in a kitchen, office, and living room environment. The dataset is recorded by two head-mounted devices from Meta: Project Aria, a research prototype of light-weight AR/AI glasses, and Quest 3, a production VR headset sold in millions of units. Ground-truth poses were obtained by a professional motion-capture system using small optical markers attached to hands and objects. Hand annotations are provided in the UmeTrack and MANO formats and objects are represented by 3D meshes with PBR materials obtained by an in-house scanner. In our experiments, we demonstrate the effectiveness of multi-view egocentric data for three popular tasks: 3D hand tracking, 6DoF object pose estimation, and 3D lifting of unknown in-hand objects. The evaluated multi-view methods, whose benchmarking is uniquely enabled by HOT3D, significantly outperform their single-view counterparts.
我们推出HOT3D数据集,这是一个用于以自我为中心的手和对象在三维空间中的跟踪的公开数据集。该数据集提供了超过833分钟(超过370万张图像)的多视角RGB/单色图像流,展示了19个主体与33种不同的刚性对象的互动,还包括多种模式的信号,如眼动追踪或场景点云。此外,还包括全面的真实标注信息,如物体、手和相机的三维姿态,以及手和对象的三维模型。除了简单的拿起/观察/放下的动作外,HOT3D还包括在厨房、办公室和客厅环境中典型的动作场景。该数据集是通过Meta的两款头戴设备记录的:Project Aria是轻便的AR/AI眼镜的研究原型,而Quest 3则是销量达数百万的生产级虚拟现实耳机。通过附着在手和物体上的小型光学标记,采用专业运动捕捉系统获得真实姿态。手的注释以UmeTrack和MANO格式提供,物体则由内部扫描仪获得的物理基础渲染(PBR)材料表示的三维网格模型表示。在我们的实验中,我们展示了多视角自我中心数据对于三个流行任务的实用性:三维手跟踪、六自由度对象姿态估计和三维手中未知物体的提升。经过评估的多视角方法明显超过了单一视角的对应方法,而这一切的独特基准测试都是由HOT3D实现的。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF arXiv admin note: substantial text overlap with arXiv:2406.09598
摘要
HOT3D是一个公开的、用于以自我为中心的手和对象在三维空间中的跟踪的数据集。它包含超过833分钟(超过370万张图像)的多视角RGB/单色图像流,展示19个主体与33个不同刚性对象的互动,包括多模态信号如眼睛注视或场景点云等。此外,还有全面的地面真实注释,包括对象、手和相机的三维姿势,以及手和对象的三维模型。该数据集记录了典型的厨房、办公室和客厅环境场景中的动作。通过两个头戴式设备Meta Project Aria(轻量级AR/AI眼镜的研究原型)和Quest 3(销量达数百万的生产级虚拟现实耳机)进行记录。地面真实姿势通过专业运动捕捉系统获得,该系统使用附着在手和对象上的小型光学标记。手注释以UmeTrack和MANO格式提供,对象则由内部扫描仪获得的具有PBR材质的三维网格表示。我们的实验表明,多视角自我中心数据对于三个流行任务的有效性:三维手跟踪、六自由度对象姿态估计和三维手部未知对象的升降。通过HOT3D唯一启用的多视角评估方法显著优于其单视角对应物。
关键见解
- HOT3D是一个用于以自我为中心的手和对象在三维空间跟踪的公开数据集。
- 数据集包含多视角RGB/单色图像流、多模态信号、全面的地面真实注释等。
- 数据集涵盖日常活动场景,包括厨房、办公室和客厅环境。
- 使用了两个头戴设备来记录数据:Meta Project Aria和Quest 3。
- 地面真实姿势是通过专业运动捕捉系统和小型光学标记获得的。
- 实验证明了多视角数据对于三个任务的有效性:三维手跟踪、六自由度对象姿态估计和手部未知对象的升降。
点此查看论文截图




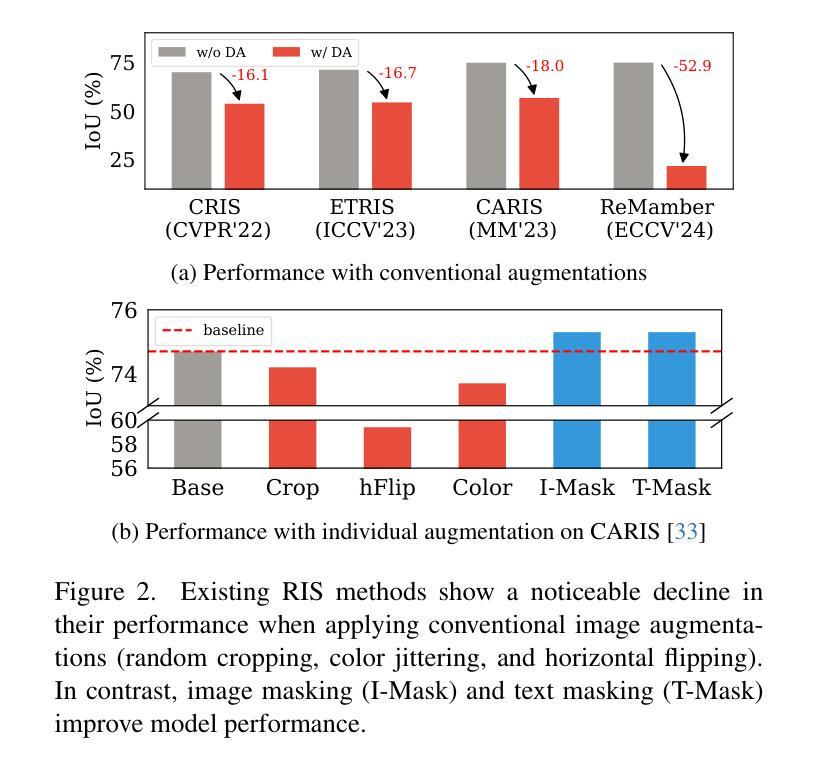
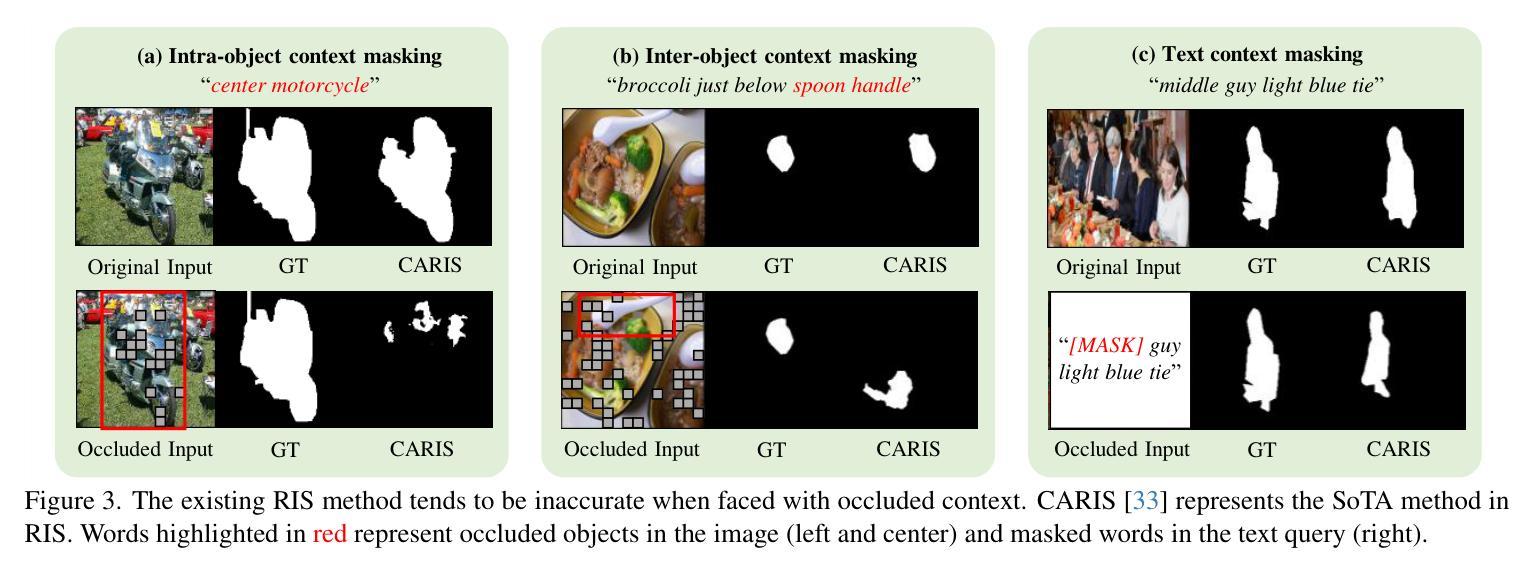
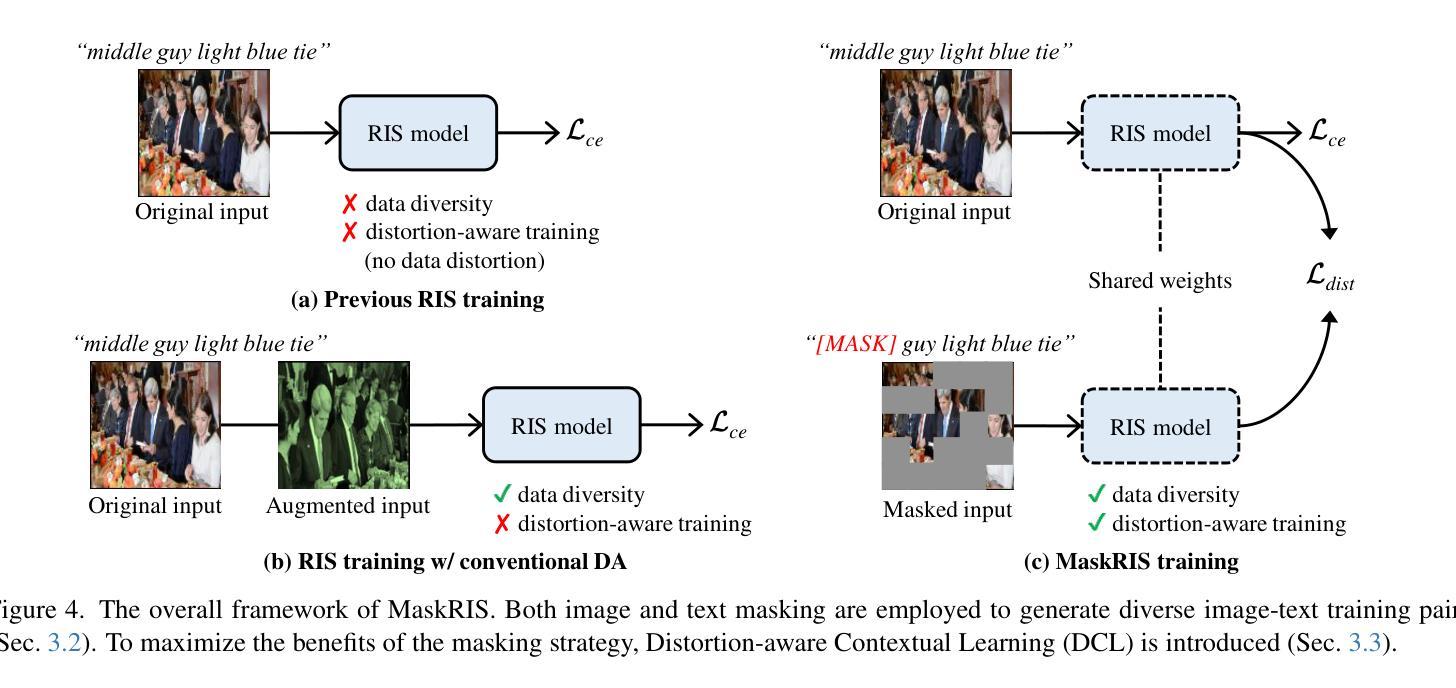
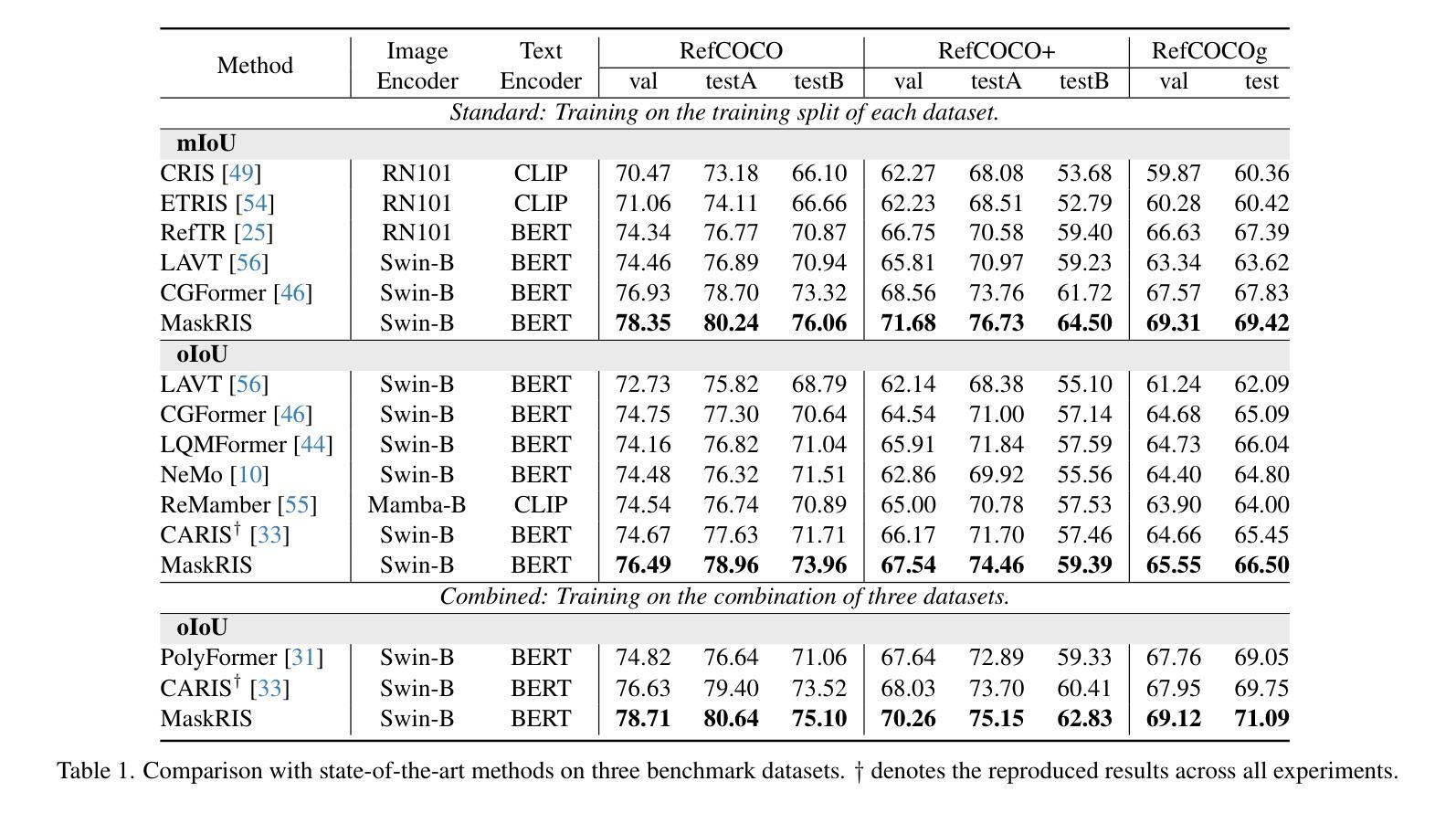
MaskRIS: Semantic Distortion-aware Data Augmentation for Referring Image Segmentation
Authors:Minhyun Lee, Seungho Lee, Song Park, Dongyoon Han, Byeongho Heo, Hyunjung Shim
Referring Image Segmentation (RIS) is an advanced vision-language task that involves identifying and segmenting objects within an image as described by free-form text descriptions. While previous studies focused on aligning visual and language features, exploring training techniques, such as data augmentation, remains underexplored. In this work, we explore effective data augmentation for RIS and propose a novel training framework called Masked Referring Image Segmentation (MaskRIS). We observe that the conventional image augmentations fall short of RIS, leading to performance degradation, while simple random masking significantly enhances the performance of RIS. MaskRIS uses both image and text masking, followed by Distortion-aware Contextual Learning (DCL) to fully exploit the benefits of the masking strategy. This approach can improve the model’s robustness to occlusions, incomplete information, and various linguistic complexities, resulting in a significant performance improvement. Experiments demonstrate that MaskRIS can easily be applied to various RIS models, outperforming existing methods in both fully supervised and weakly supervised settings. Finally, MaskRIS achieves new state-of-the-art performance on RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, and RefCOCOg datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/naver-ai/maskris.
指代图像分割(RIS)是一项先进的视觉语言任务,它涉及根据自由形式的文本描述来识别和分割图像中的对象。虽然以前的研究主要集中在视觉和语言特征的对齐上,但探索训练技术,如数据增强,仍然被低估。在这项工作中,我们探索了RIS的有效数据增强方法,并提出了一种名为Masked Referring Image Segmentation(MaskRIS)的新型训练框架。我们发现传统的图像增强方法对于RIS来说效果不足,导致性能下降,而简单的随机遮挡可以显着提高RIS的性能。MaskRIS同时使用图像和文本遮挡,然后进行Distortion-aware Contextual Learning(DCL)以充分利用遮挡策略的优势。这种方法可以提高模型对遮挡、不完整信息和各种语言复杂性的鲁棒性,从而大大提高性能。实验表明,MaskRIS可以轻松应用于各种RIS模型,在全监督和弱监督设置中都优于现有方法。最后,MaskRIS在RefCOCO、RefCOCO+和RefCOCOg数据集上达到了最新的最先进的性能。代码可通过https://github.com/naver-ai/maskris获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF First two authors contributed equally
Summary
本研究探讨了用于图像描述分割(RIS)的有效数据增强方法,并提出了一种新的训练框架——MaskRIS。研究发现,常规图像增强方法不适用于RIS,而简单的随机掩码可以显著提高RIS性能。MaskRIS结合了图像和文本掩码,并通过扭曲感知上下文学习(DCL)充分利用掩码策略的优势。该方法提高了模型对遮挡、信息不完整和各种语言复杂性的鲁棒性,显著提高了性能。实验表明,MaskRIS可轻松应用于各种RIS模型,在全监督和弱监督设置中都优于现有方法。MaskRIS在RefCOCO、RefCOCO+和RefCOCOg数据集上取得了最新技术成果。
Key Takeaways
- Masked Referring Image Segmentation (MaskRIS)是一种新的训练框架,用于改进图像描述分割(RIS)的性能。
- 传统图像增强方法在RIS上效果不佳,简单随机掩码能显著提高性能。
- MaskRIS结合图像和文本掩码策略以增强模型处理遮挡和不完整信息的能力。
- MaskRIS通过扭曲感知上下文学习(DCL)充分利用掩码策略的优势。
- MaskRIS方法能够提高模型对各种语言复杂性的鲁棒性。
- 实验结果显示MaskRIS在全监督和弱监督环境下均优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图