⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-11 更新
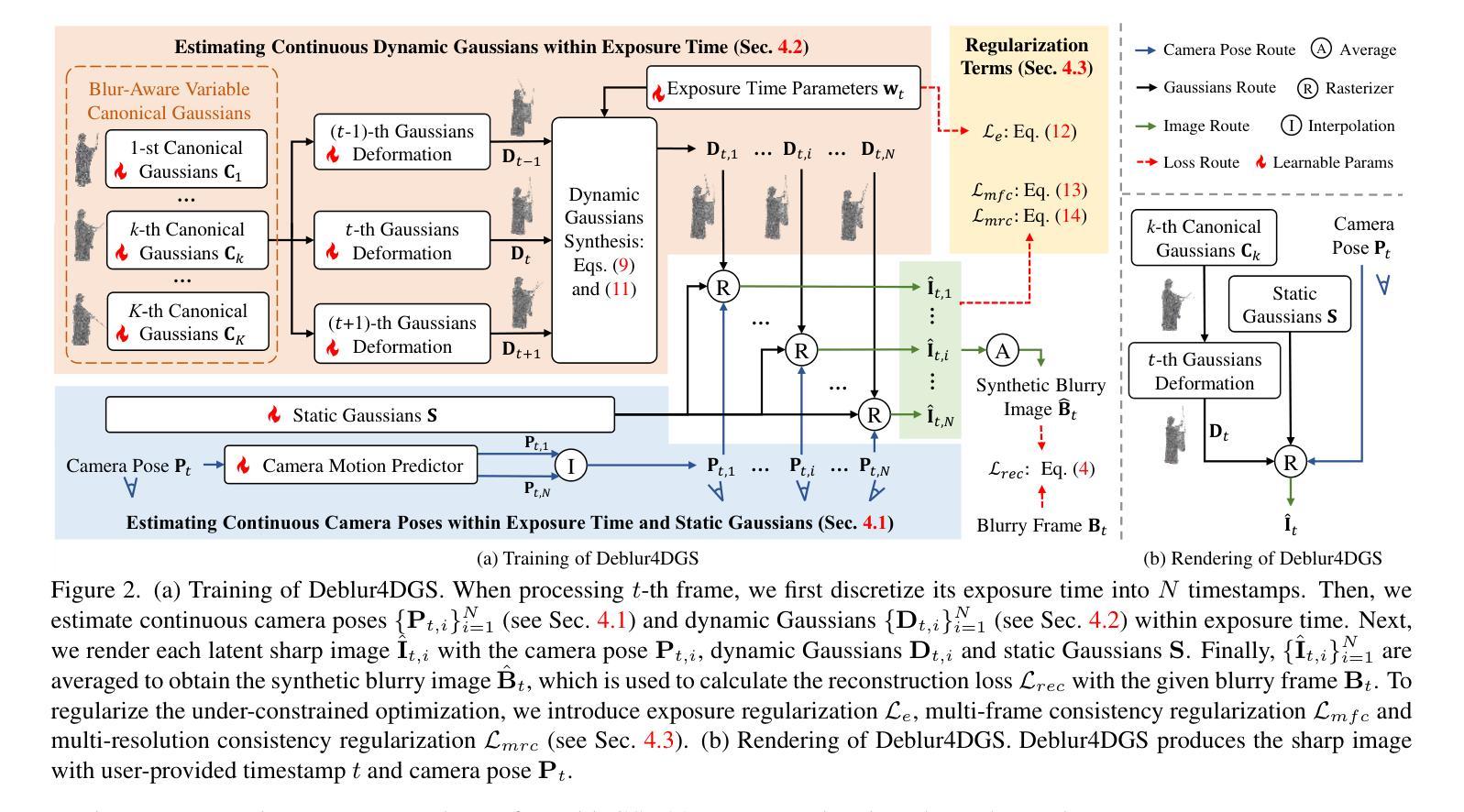
Deblur4DGS: 4D Gaussian Splatting from Blurry Monocular Video
Authors:Renlong Wu, Zhilu Zhang, Mingyang Chen, Xiaopeng Fan, Zifei Yan, Wangmeng Zuo
Recent 4D reconstruction methods have yielded impressive results but rely on sharp videos as supervision. However, motion blur often occurs in videos due to camera shake and object movement, while existing methods render blurry results when using such videos for reconstructing 4D models. Although a few NeRF-based approaches attempted to address the problem, they struggled to produce high-quality results, due to the inaccuracy in estimating continuous dynamic representations within the exposure time. Encouraged by recent works in 3D motion trajectory modeling using 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), we suggest taking 3DGS as the scene representation manner, and propose the first 4D Gaussian Splatting framework to reconstruct a high-quality 4D model from blurry monocular video, named Deblur4DGS. Specifically, we transform continuous dynamic representations estimation within an exposure time into the exposure time estimation. Moreover, we introduce exposure regularization to avoid trivial solutions, as well as multi-frame and multi-resolution consistency ones to alleviate artifacts. Furthermore, to better represent objects with large motion, we suggest blur-aware variable canonical Gaussians. Beyond novel-view synthesis, Deblur4DGS can be applied to improve blurry video from multiple perspectives, including deblurring, frame interpolation, and video stabilization. Extensive experiments on the above four tasks show that Deblur4DGS outperforms state-of-the-art 4D reconstruction methods. The codes are available at https://github.com/ZcsrenlongZ/Deblur4DGS.
最近的4D重建方法取得了令人印象深刻的结果,但它们依赖于清晰视频作为监督。然而,由于相机抖动和物体移动,视频中的运动模糊经常发生,而当使用此类视频进行4D模型重建时,现有方法会产生模糊的结果。尽管有一些基于NeRF的方法试图解决这个问题,但由于在曝光时间内估计连续动态表示的不准确性,它们很难产生高质量的结果。受到使用3D高斯贴图(3DGS)进行3D运动轨迹建模的近期工作的启发,我们建议将3DGS作为场景表示方式,并提出第一个4D高斯贴图框架,从模糊的单目视频中重建高质量4D模型,命名为Deblur4DGS。具体来说,我们将连续动态表示估计转化为曝光时间估计。此外,我们引入了曝光正则化以避免平凡解,以及多帧和多分辨率一致性方法来减轻伪影。此外,为了更好地表示具有大运动的物体,我们建议使用模糊感知可变规范高斯。除了新型视图合成外,Deblur4DGS还可以应用于从多个角度提高模糊视频的质量,包括去模糊、帧内插和视频稳定。在上述四个任务上进行的大量实验表明,Deblur4DGS优于最新的4D重建方法。代码可在https://github.com/ZcsrenlongZ/Deblur4DGS获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages
Summary
本文介绍了基于3D高斯描画(3DGS)的4D高斯描画框架,用于从模糊的单目视频中重建高质量的四维模型。通过转换曝光时间内的连续动态表示估计为曝光时间估计,引入曝光正则化以及多帧和多分辨率一致性,以减轻模糊和伪影。此外,为了更好地表示具有大运动的物体,建议使用模糊感知的可变规范高斯。除了新颖视图合成外,Deblur4DGS还可应用于从多个角度改进模糊视频,包括去模糊、帧插值、视频稳定等任务。实验结果证明Deblur4DGS优于现有的最先进的4D重建方法。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究解决了使用模糊视频重建四维模型的问题,提出了首个基于3D高斯描画(3DGS)的4D高斯描画框架——Deblur4DGS。
- Deblur4DGS通过转换连续动态表示估计到曝光时间估计来处理运动模糊。
- 引入曝光正则化以及多帧和多分辨率一致性来减轻伪影和模糊。
- 为了更好地表示大运动物体,提出了模糊感知的可变规范高斯。
- 除了新颖视图合成,Deblur4DGS还能应用于去模糊、帧插值、视频稳定等任务。
- 实验结果表明,Deblur4DGS在多个任务上优于现有最先进的4D重建方法。
点此查看论文截图



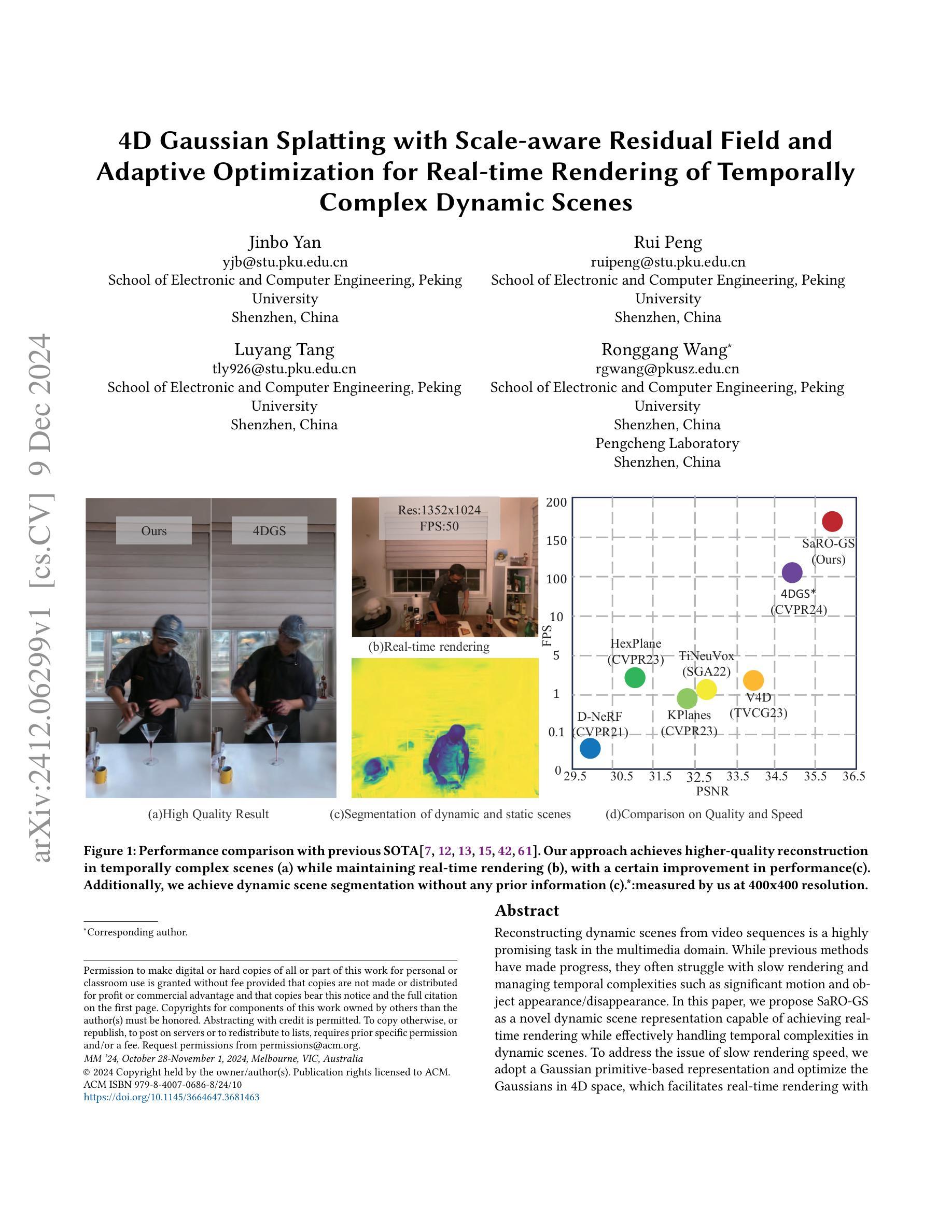
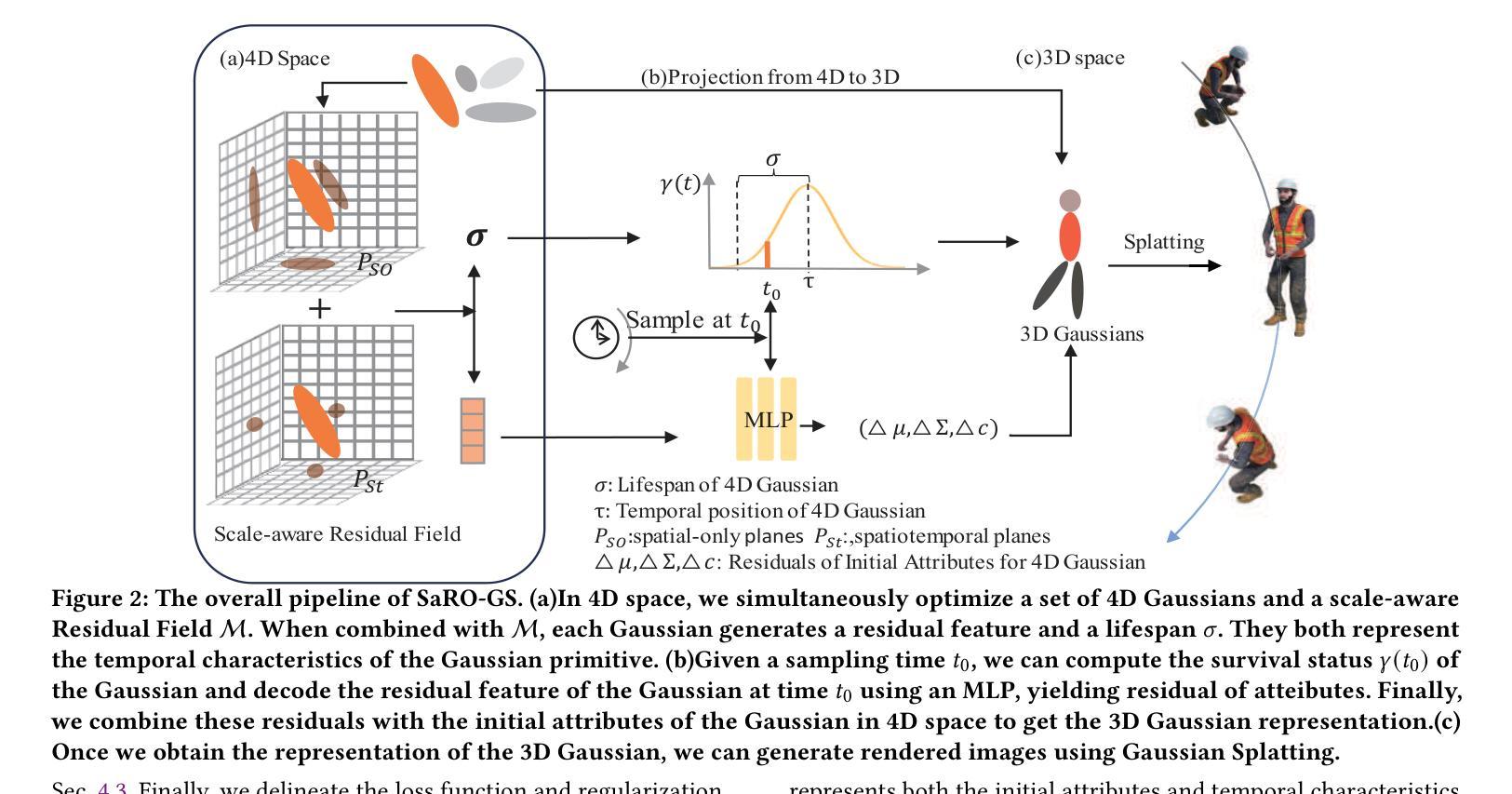
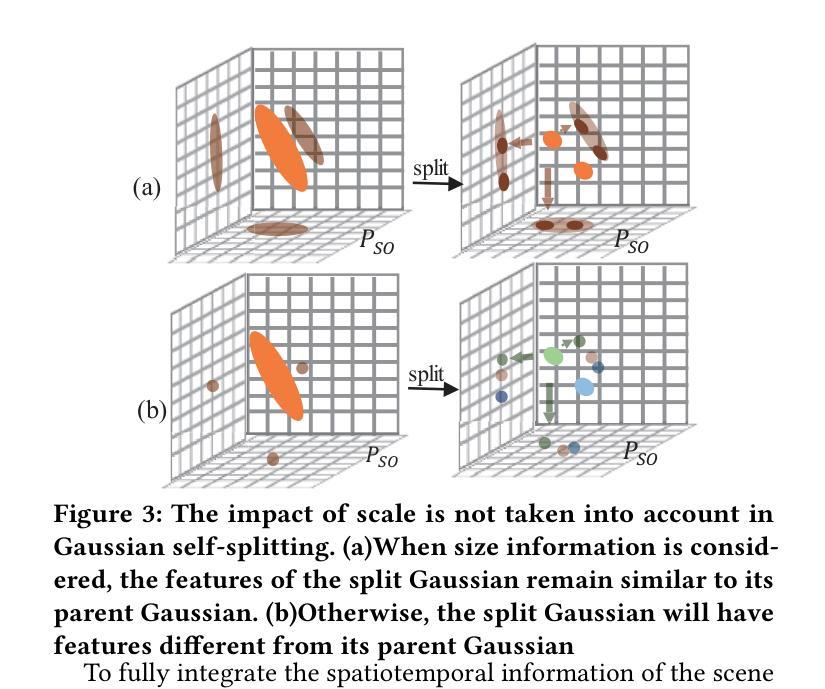
4D Gaussian Splatting with Scale-aware Residual Field and Adaptive Optimization for Real-time Rendering of Temporally Complex Dynamic Scenes
Authors:Jinbo Yan, Rui Peng, Luyang Tang, Ronggang Wang
Reconstructing dynamic scenes from video sequences is a highly promising task in the multimedia domain. While previous methods have made progress, they often struggle with slow rendering and managing temporal complexities such as significant motion and object appearance/disappearance. In this paper, we propose SaRO-GS as a novel dynamic scene representation capable of achieving real-time rendering while effectively handling temporal complexities in dynamic scenes. To address the issue of slow rendering speed, we adopt a Gaussian primitive-based representation and optimize the Gaussians in 4D space, which facilitates real-time rendering with the assistance of 3D Gaussian Splatting. Additionally, to handle temporally complex dynamic scenes, we introduce a Scale-aware Residual Field. This field considers the size information of each Gaussian primitive while encoding its residual feature and aligns with the self-splitting behavior of Gaussian primitives. Furthermore, we propose an Adaptive Optimization Schedule, which assigns different optimization strategies to Gaussian primitives based on their distinct temporal properties, thereby expediting the reconstruction of dynamic regions. Through evaluations on monocular and multi-view datasets, our method has demonstrated state-of-the-art performance. Please see our project page at https://yjb6.github.io/SaRO-GS.github.io.
从视频序列重建动态场景是多媒体领域一个非常有前景的任务。尽管之前的方法已经取得了一些进展,但它们在处理显著的动态场景和物体出现与消失等复杂的时空动态方面仍存在渲染缓慢的问题。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的动态场景表示方法SaRO-GS,它能够实时渲染并有效处理动态场景的时空复杂性。为解决渲染速度较慢的问题,我们采用基于高斯原语表示的方法,在四维空间中对高斯进行优化,借助三维高斯平展技术实现实时渲染。此外,为了处理复杂的动态场景,我们引入了尺度感知残差场。该场在编码每个高斯原语的残差特征时考虑了其大小信息,并与高斯原语的自分裂行为相一致。此外,我们提出了一种自适应优化调度策略,根据高斯原语的不同时间特性为其分配不同的优化策略,从而加快动态区域的重建速度。在单目和多视角数据集上的评估表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的性能。请访问我们的项目页面了解更多信息:https://yjb6.github.io/SaRO-GS.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种名为SaRO-GS的新型动态场景表示方法,能够实现实时渲染,并有效处理动态场景中的时间复杂性。通过采用基于高斯原始表示的4D空间优化和3D高斯Splatting技术,解决了渲染速度慢的问题。同时,引入了尺度感知残差场和自适应优化调度策略,以提高对复杂动态场景的处理能力和优化动态区域的重建速度。在单目和多视角数据集上的评估结果表明,该方法达到了先进水平。
Key Takeaways
- SaRO-GS是一种新型动态场景表示方法,能实时渲染并处理动态场景中的时间复杂性。
- 采用高斯原始表示的4D空间优化和3D高斯Splatting技术解决渲染速度慢的问题。
- 引入尺度感知残差场,考虑高斯原始的大小信息,编码其残差特征,并与高斯原始的自分裂行为对齐。
- 提出自适应优化调度策略,根据高斯原始的不同时间属性分配不同的优化策略,加快动态区域的重建速度。
- 方法在单目和多视角数据集上表现出卓越性能。
- 项目页面提供了更多详细信息和资源链接([链接地址需实际链接地址替换])。
点此查看论文截图
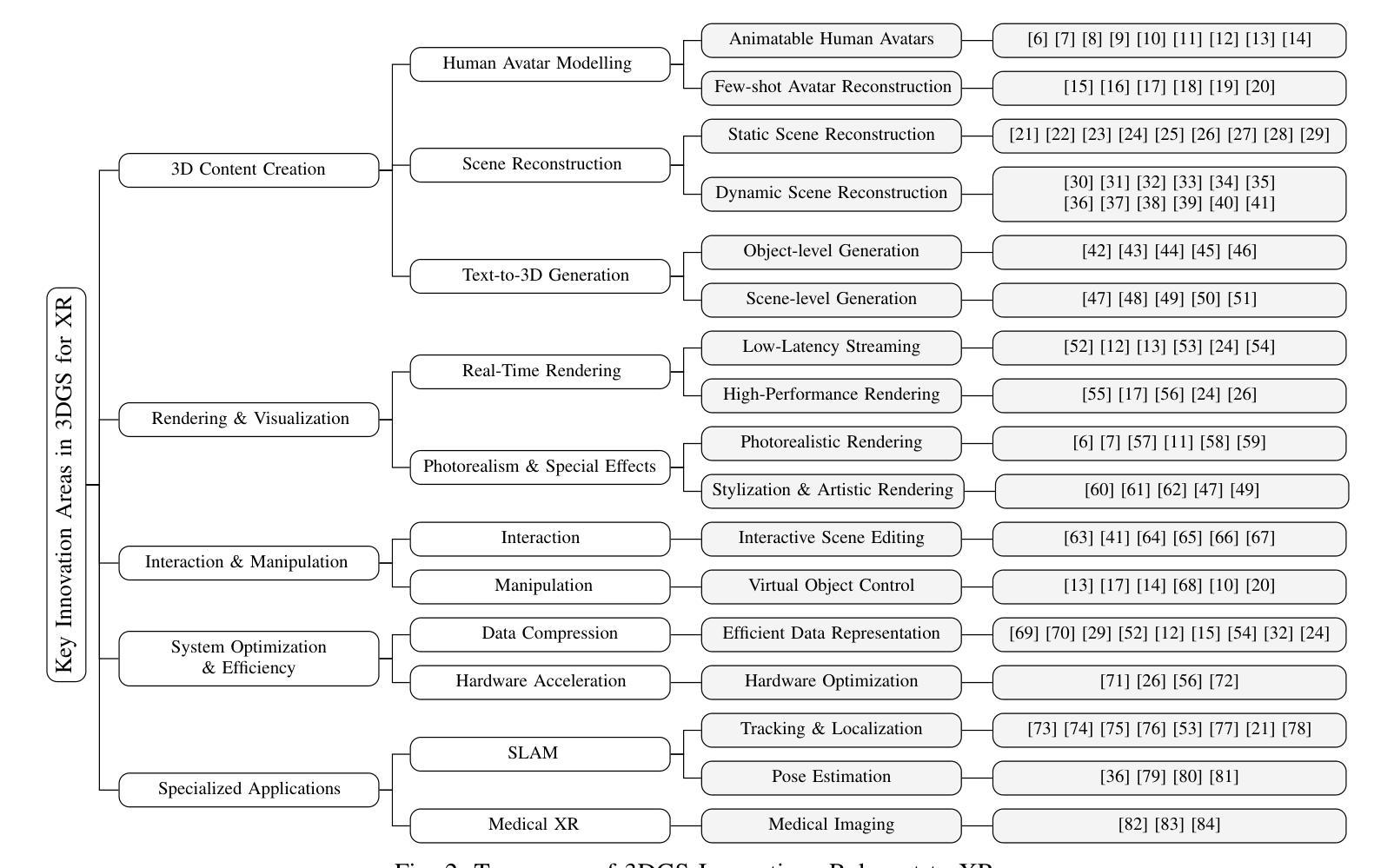
Advancing Extended Reality with 3D Gaussian Splatting: Innovations and Prospects
Authors:Shi Qiu, Binzhu Xie, Qixuan Liu, Pheng-Ann Heng
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has attracted significant attention for its potential to revolutionize 3D representation, rendering, and interaction. Despite the rapid growth of 3DGS research, its direct application to Extended Reality (XR) remains underexplored. Although many studies recognize the potential of 3DGS for XR, few have explicitly focused on or demonstrated its effectiveness within XR environments. In this paper, we aim to synthesize innovations in 3DGS that show specific potential for advancing XR research and development. We conduct a comprehensive review of publicly available 3DGS papers, with a focus on those referencing XR-related concepts. Additionally, we perform an in-depth analysis of innovations explicitly relevant to XR and propose a taxonomy to highlight their significance. Building on these insights, we propose several prospective XR research areas where 3DGS can make promising contributions, yet remain rarely touched. By investigating the intersection of 3DGS and XR, this paper provides a roadmap to push the boundaries of XR using cutting-edge 3DGS techniques.
3D高斯摊铺(3DGS)因其改变3D表示、渲染和交互的潜力而备受关注。尽管3DGS研究发展迅速,但其在扩展现实(XR)中的直接应用仍然被忽视。尽管许多研究认识到了3DGS在XR领域的潜力,但很少有研究明确关注或证明其在XR环境中的有效性。在本文中,我们旨在合成在推动XR研发方面具有特定潜力的创新型3DGS技术。我们对公开的关于研究现状进行了全面综述分析论文重点聚焦于涉及XR相关概念的文献。此外,我们还深入分析了与XR明确相关的创新技术并提出了分类,以突出其重要性。基于这些见解,我们提出了几个具有前景的XR研究领域,在这些领域中,使用前沿的3DGS技术有望做出有前景的贡献,但目前这些领域的研究很少触及。本文通过探讨3DGS与XR的交集,为使用前沿的3DGS技术推动XR的边界提供了一条路线图。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE AIxVR 2025
Summary
3DGS技术对于扩展现实(XR)领域具有巨大潜力,尽管已有研究认识到了这一点,但其在XR环境中的实际应用仍被较少探索。本文对公开的3DGS文献进行全面回顾,重点关注与XR相关的研究内容,同时深入分析对XR有明确意义的技术创新,并提出分类方案。基于这些见解,本文提出了几个有望由3DGS技术做出重要贡献的XR研究领域,并给出了使用前沿的3DGS技术推动XR边界的研究路线图。
Key Takeaways
- 3D高斯卷展(3DGS)具有革新3D表示、渲染和交互的潜力。
- 尽管已有研究认识到了其在扩展现实(XR)中的潜力,但在XR环境中的实际应用仍较少探索。
- 本文对涉及XR相关的概念和技术创新的文献进行了全面回顾和分析。
- 通过深入分析对XR有明确意义的技术创新,提出了一个分类方案来突出其重要性。
- 基于这些见解,本文指出了几个有望由3DGS技术做出重要贡献的XR研究领域。
点此查看论文截图

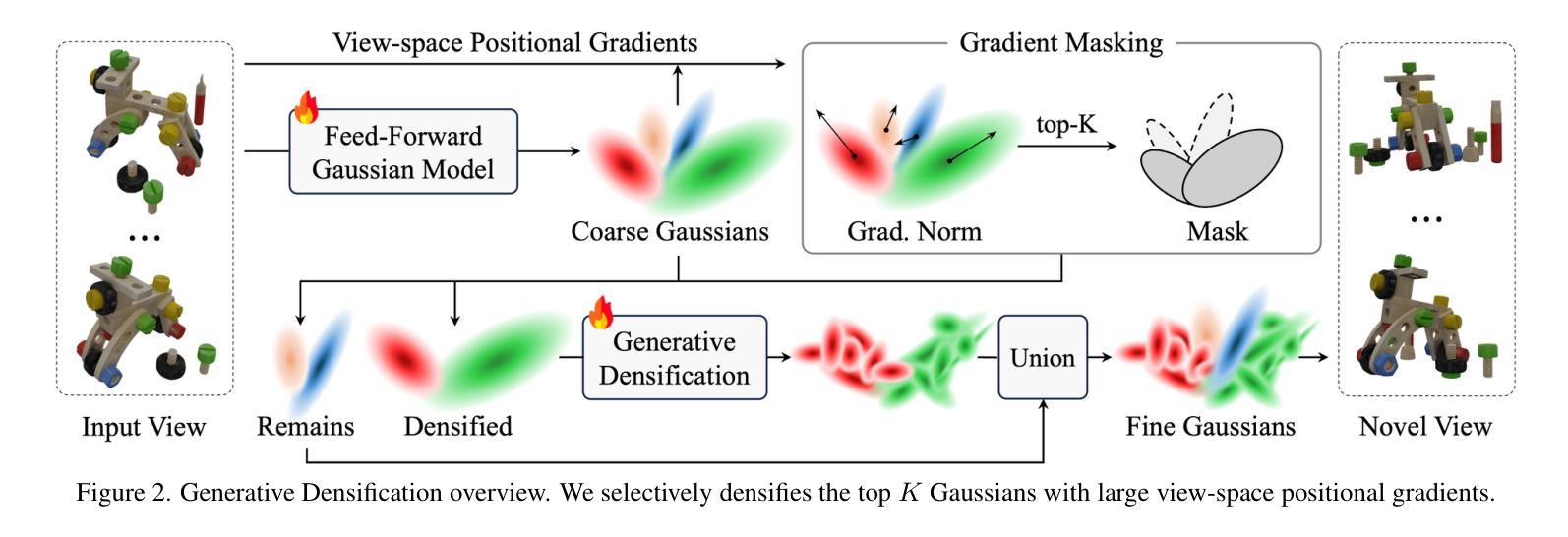
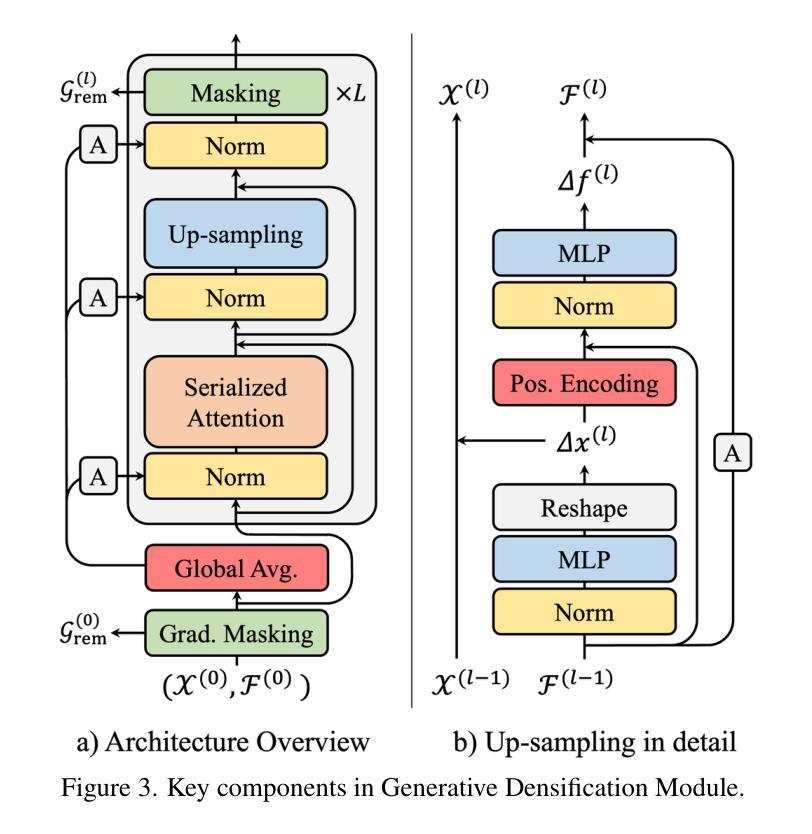
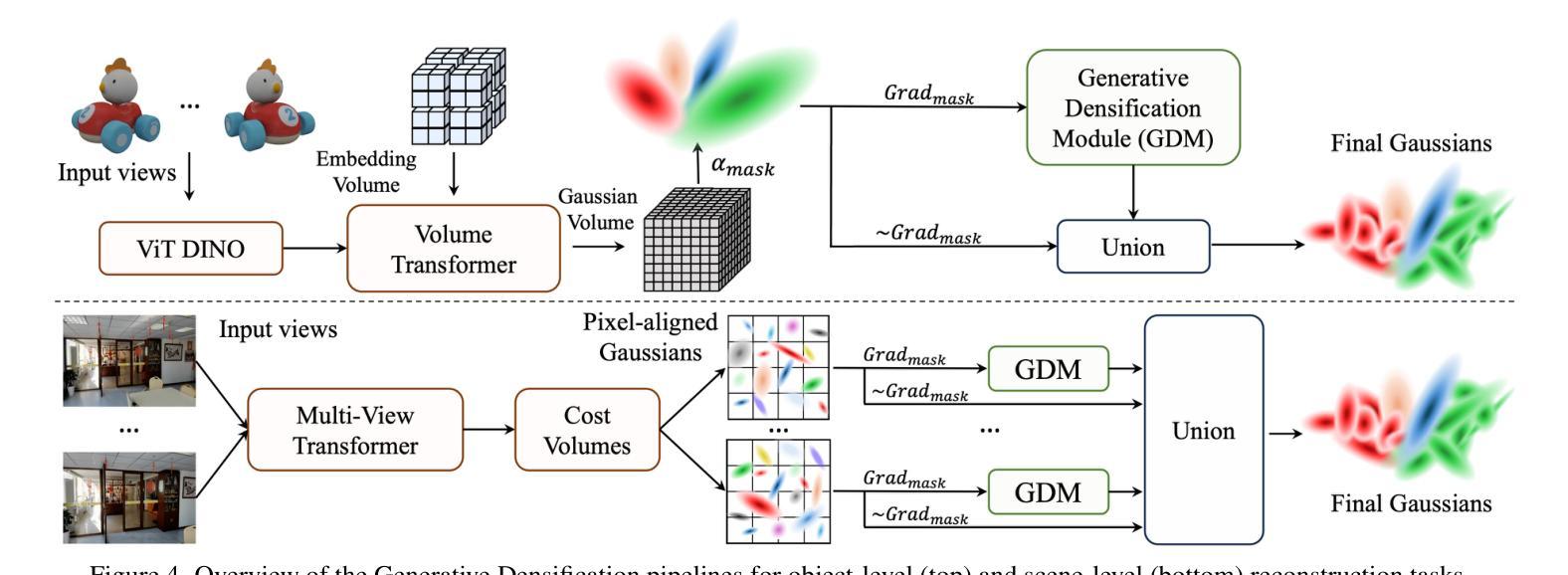
Generative Densification: Learning to Densify Gaussians for High-Fidelity Generalizable 3D Reconstruction
Authors:Seungtae Nam, Xiangyu Sun, Gyeongjin Kang, Younggeun Lee, Seungjun Oh, Eunbyung Park
Generalized feed-forward Gaussian models have achieved significant progress in sparse-view 3D reconstruction by leveraging prior knowledge from large multi-view datasets. However, these models often struggle to represent high-frequency details due to the limited number of Gaussians. While the densification strategy used in per-scene 3D Gaussian splatting (3D-GS) optimization can be adapted to the feed-forward models, it may not be ideally suited for generalized scenarios. In this paper, we propose Generative Densification, an efficient and generalizable method to densify Gaussians generated by feed-forward models. Unlike the 3D-GS densification strategy, which iteratively splits and clones raw Gaussian parameters, our method up-samples feature representations from the feed-forward models and generates their corresponding fine Gaussians in a single forward pass, leveraging the embedded prior knowledge for enhanced generalization. Experimental results on both object-level and scene-level reconstruction tasks demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches with comparable or smaller model sizes, achieving notable improvements in representing fine details.
广义前馈高斯模型通过利用大型多视角数据集中的先验知识,在稀疏视角3D重建方面取得了显著进展。然而,由于高斯数量的限制,这些模型往往难以表示高频细节。虽然场景3D高斯拼贴(3D-GS)优化中使用的密集化策略可以适应前馈模型,但可能并不适合通用场景。在本文中,我们提出了生成密集化(Generative Densification),这是一种有效且通用的方法来密集化前馈模型产生的高斯。与3D-GS密集化策略不同,我们的方法不是在迭代中分裂和克隆原始高斯参数,而是对前馈模型的特性表示进行上采样,并在单次前向传递中生成其对应的精细高斯,利用嵌入的先验知识来提高泛化能力。在对象级和场景级的重建任务上的实验结果表明,我们的方法在具有相当或更小模型大小的最先进方法中表现更好,在表示细节方面取得了显著的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种针对广义稀疏视图3D重建的高效可泛化方法——生成型稠化法。通过在前馈模型生成的样本上进行稠化,提升了模型对高频细节的表达能力。与传统的逐场景三维高斯模糊(3D-GS)优化不同,生成型稠化法在前向传播过程中即可生成精细的高斯数据,实现了更佳的泛化性能。实验结果表明,该方法在物体级别和场景级别的重建任务中均优于现有技术,且在模型大小相当的情况下表现尤为出色。
Key Takeaways
- 广义前馈高斯模型在稀疏视图3D重建中取得了显著进展,但受限于高斯数量的高频细节表示能力较弱。
- 传统的高斯稠化策略(如3D-GS)可能不适用于前馈模型的泛化场景。
- 提出了一种新的生成型稠化法,该方法在前馈模型生成的样本上进行稠化,提高了模型的泛化能力和高频细节表达能力。
- 生成型稠化法在前向传播过程中生成精细的高斯数据,不同于传统的迭代分裂和克隆原始高斯参数的方法。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在物体级别和场景级别的重建任务中均优于现有技术。
- 该方法在模型大小相当的情况下表现出更佳的性能。
点此查看论文截图

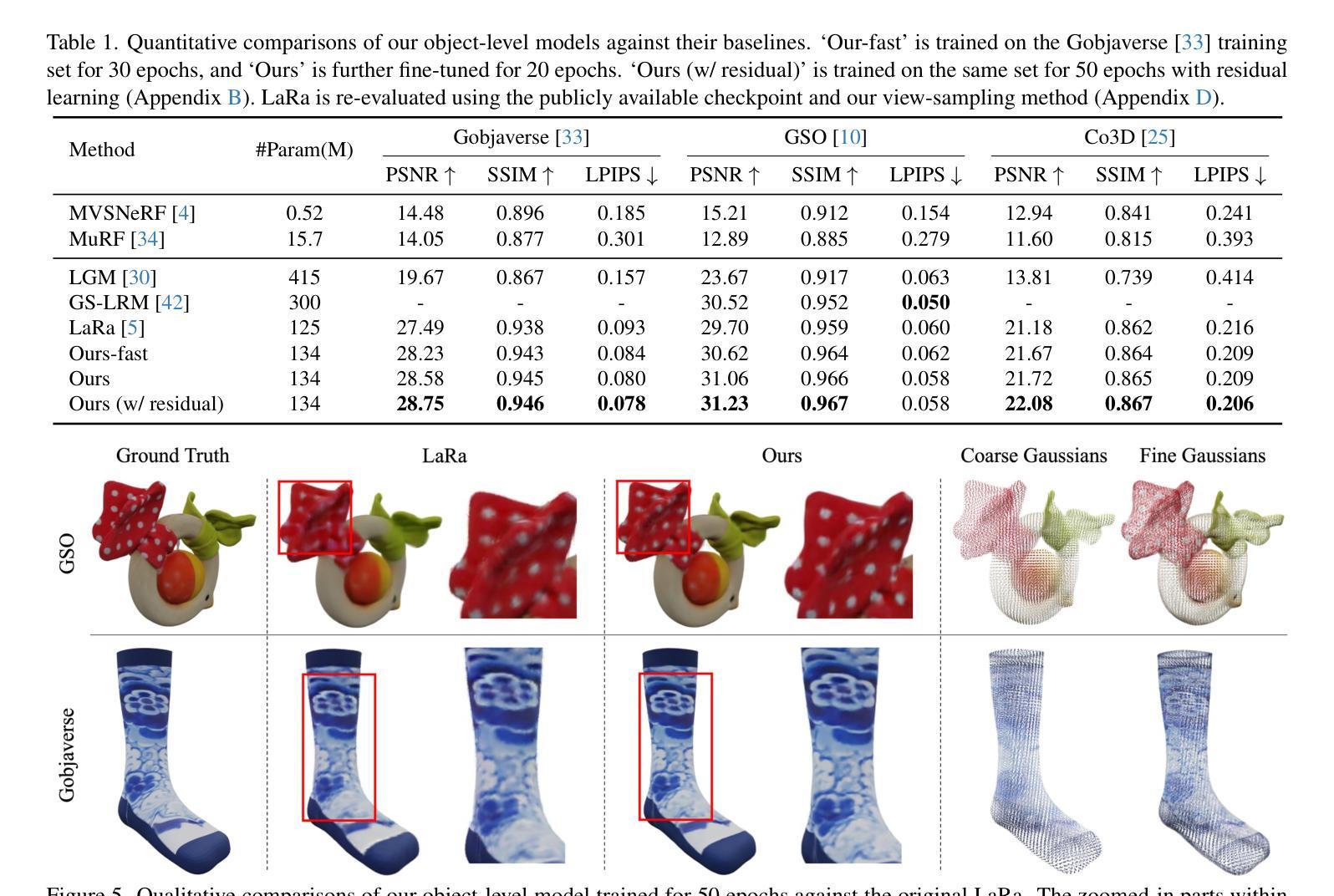
Efficient Semantic Splatting for Remote Sensing Multi-view Segmentation
Authors:Zipeng Qi, Hao Chen, Haotian Zhang, Zhengxia Zou, Zhenwei Shi
In this paper, we propose a novel semantic splatting approach based on Gaussian Splatting to achieve efficient and low-latency. Our method projects the RGB attributes and semantic features of point clouds onto the image plane, simultaneously rendering RGB images and semantic segmentation results. Leveraging the explicit structure of point clouds and a one-time rendering strategy, our approach significantly enhances efficiency during optimization and rendering. Additionally, we employ SAM2 to generate pseudo-labels for boundary regions, which often lack sufficient supervision, and introduce two-level aggregation losses at the 2D feature map and 3D spatial levels to improve the view-consistent and spatial continuity.
本文提出了一种基于高斯Splatting的新型语义Splatting方法,以实现高效和低延迟。我们的方法将点云的RGB属性和语义特征投影到图像平面上,同时呈现RGB图像和语义分割结果。我们利用点云的明确结构和一次性渲染策略,在优化和渲染过程中显著提高效率。此外,我们还采用SAM2为缺乏足够监督的边界区域生成伪标签,并在二维特征图和三维空间层次上引入两级聚合损失,以提高视图一致性和空间连续性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
该论文提出了一种基于高斯投影的语义点云映射技术,实现了高效和低延迟的渲染效果。该方法将点云的RGB属性和语义特征投影到图像平面上,同时生成RGB图像和语义分割结果。通过利用点云的明确结构和一次渲染策略,提高了优化和渲染过程的效率。此外,还使用SAM2技术为边界区域生成伪标签,解决了监督不足的问题,并引入二维特征图和三维空间两个级别的聚合损失,提高了视图一致性和空间连续性。
关键见解
- 该论文提出了一种新的基于高斯投影的语义点云映射方法,实现了高效和低延迟的渲染。
- 方法将点云的RGB属性和语义特征投影到图像平面上,同时生成RGB图像和语义分割结果。
- 利用点云的明确结构和一次渲染策略,提高了优化和渲染的效率。
- 使用SAM2技术为边界区域生成伪标签,解决监督不足的问题。
- 引入二维特征图和三维空间两个级别的聚合损失,提高了视图一致性和空间连续性。
- 该方法具有广泛的应用前景,可应用于虚拟现实、增强现实等需要高效渲染的领域。
点此查看论文截图
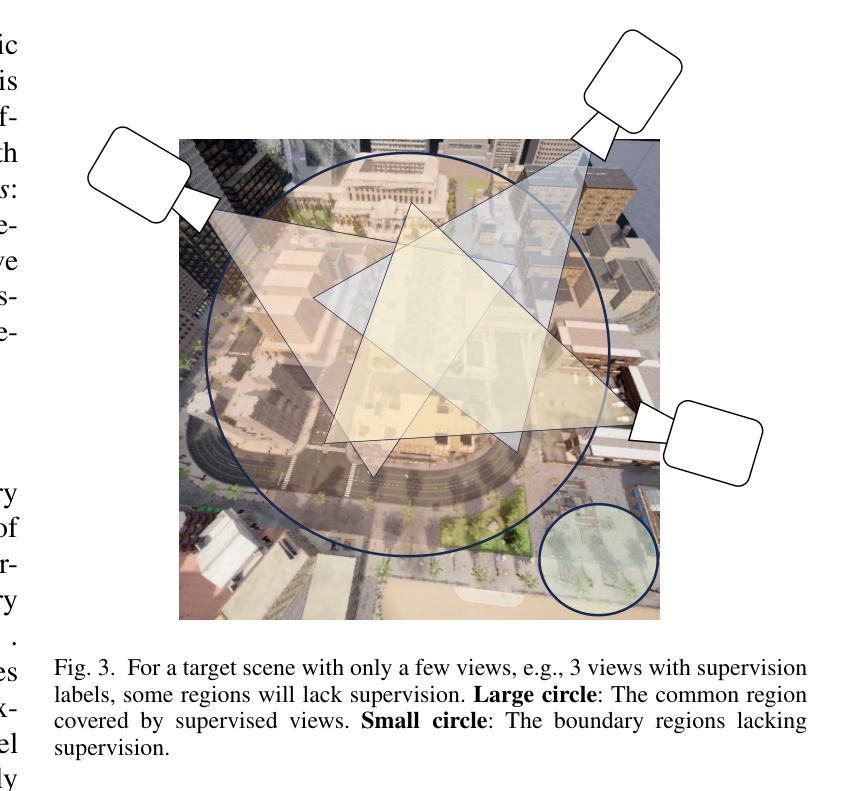
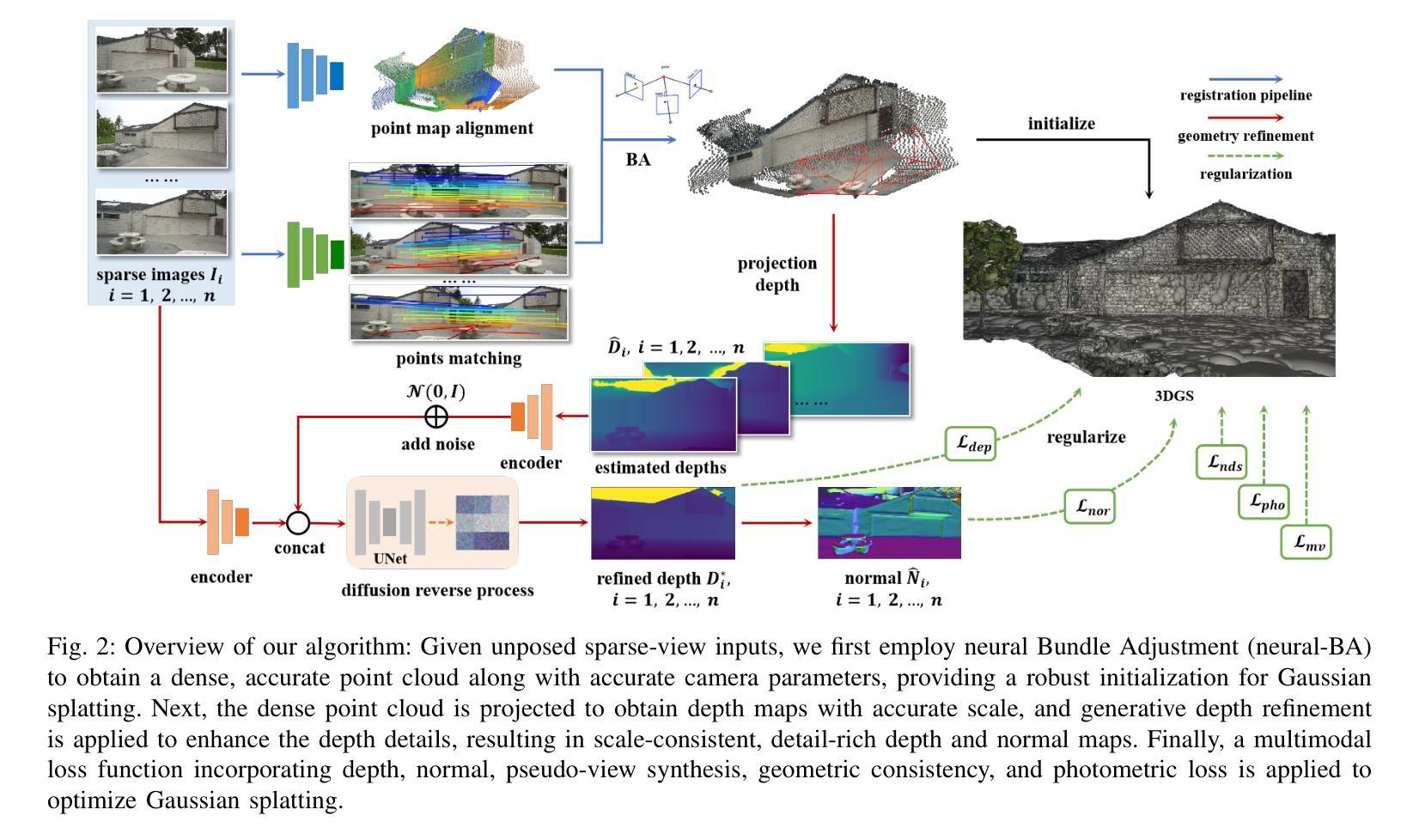
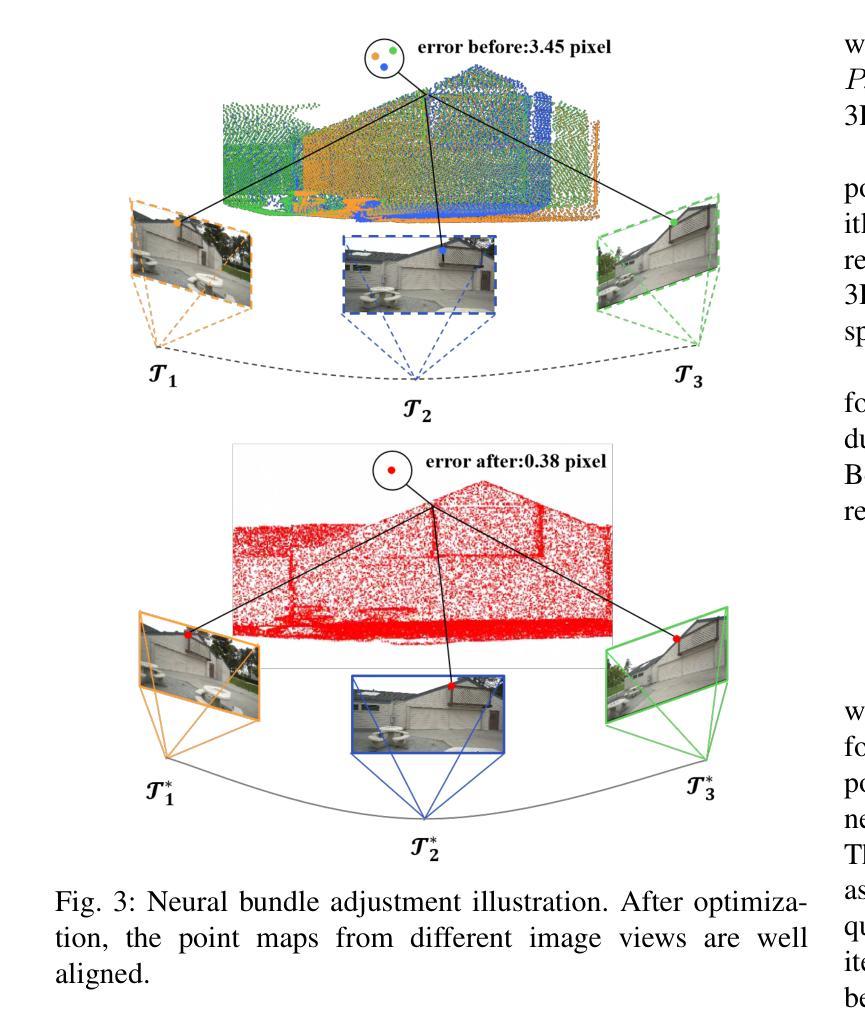
GBR: Generative Bundle Refinement for High-fidelity Gaussian Splatting and Meshing
Authors:Jianing Zhang, Yuchao Zheng, Ziwei Li, Qionghai Dai, Xiaoyun Yuan
Gaussian splatting has gained attention for its efficient representation and rendering of 3D scenes using continuous Gaussian primitives. However, it struggles with sparse-view inputs due to limited geometric and photometric information, causing ambiguities in depth, shape, and texture. we propose GBR: Generative Bundle Refinement, a method for high-fidelity Gaussian splatting and meshing using only 4-6 input views. GBR integrates a neural bundle adjustment module to enhance geometry accuracy and a generative depth refinement module to improve geometry fidelity. More specifically, the neural bundle adjustment module integrates a foundation network to produce initial 3D point maps and point matches from unposed images, followed by bundle adjustment optimization to improve multiview consistency and point cloud accuracy. The generative depth refinement module employs a diffusion-based strategy to enhance geometric details and fidelity while preserving the scale. Finally, for Gaussian splatting optimization, we propose a multimodal loss function incorporating depth and normal consistency, geometric regularization, and pseudo-view supervision, providing robust guidance under sparse-view conditions. Experiments on widely used datasets show that GBR significantly outperforms existing methods under sparse-view inputs. Additionally, GBR demonstrates the ability to reconstruct and render large-scale real-world scenes, such as the Pavilion of Prince Teng and the Great Wall, with remarkable details using only 6 views.
高斯点云技术因其使用连续的高斯基元对3D场景进行高效表示和渲染而受到关注。然而,由于几何和光度信息有限,它在稀疏视图输入方面表现挣扎,导致深度、形状和纹理的模糊性。我们提出GBR:生成束调整法(Generative Bundle Refinement),这是一种仅使用4-6个输入视图进行高保真高斯点云和网格化的方法。GBR集成了一个神经束调整模块,以提高几何精度和一个生成深度细化模块,以提高几何保真度。更具体地说,神经束调整模块集成了一个基础网络,用于从非定位图像生成初始的3D点图和点匹配,然后进行束调整优化,以提高多视图的一致性和点云精度。生成深度细化模块采用基于扩散的策略,以增强几何细节和保真度,同时保持尺度。最后,针对高斯点云优化,我们提出了一个多模态损失函数,融合了深度和法向量一致性、几何正则化和伪视图监督,在稀疏视图条件下提供稳健的引导。在常用数据集上的实验表明,GBR在稀疏视图输入下显著优于现有方法。此外,GBR还展示了仅使用6个视图就能重建和渲染大规模真实场景,如太子亭和大长城,具有令人瞩目的细节。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了基于高斯原语的连续高斯蒙皮方法及其在稀疏视角输入下的高效表示和渲染。针对此问题,提出了GBR(生成束优化法),通过神经网络束调整模块提高几何精度,通过生成深度细化模块提高几何保真度。GBR在仅使用4-6个输入视角的情况下,实现了高保真度的高斯蒙皮和网格生成。实验证明,在稀疏视角输入下,GBR显著优于现有方法,并能重建和渲染大规模真实场景,如滕公殿和长城等。
Key Takeaways
- 高斯蒙皮方法使用连续高斯原语进行三维场景的表示和渲染,但其在稀疏视角输入下存在深度、形状和纹理的歧义性问题。
- GBR通过神经网络束调整模块和生成深度细化模块解决上述问题,提高几何精度和几何保真度。
- GBR仅使用4-6个视角的输入,即可实现高保真度的高斯蒙皮和网格生成。
- GBR使用多模态损失函数进行优化,该函数在稀疏视角条件下提供稳健的引导。
- 实验证明,GBR在稀疏视角输入下的性能显著优于现有方法。
- GBR能够重建和渲染大规模真实场景,如滕公殿和长城等,并展现出精细的细节。
点此查看论文截图

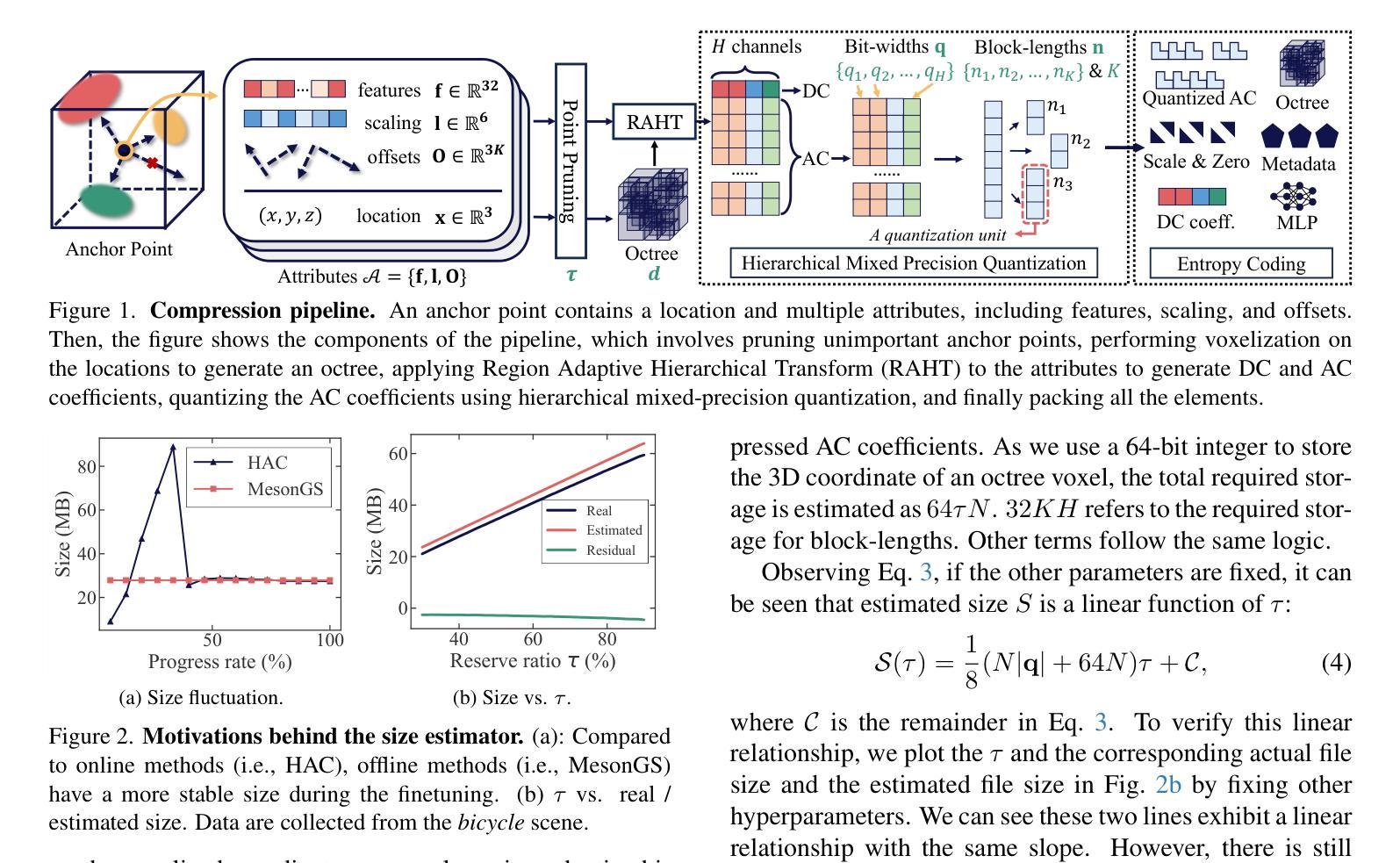
SizeGS: Size-aware Compression of 3D Gaussians with Hierarchical Mixed Precision Quantization
Authors:Shuzhao Xie, Jiahang Liu, Weixiang Zhang, Shijia Ge, Sicheng Pan, Chen Tang, Yunpeng Bai, Zhi Wang
Effective compression technology is crucial for 3DGS to adapt to varying storage and transmission conditions. However, existing methods fail to address size constraints while maintaining optimal quality. In this paper, we introduce SizeGS, a framework that compresses 3DGS within a specified size budget while optimizing visual quality. We start with a size estimator to establish a clear relationship between file size and hyperparameters. Leveraging this estimator, we incorporate mixed precision quantization (MPQ) into 3DGS attributes, structuring MPQ in two hierarchical level – inter-attribute and intra-attribute – to optimize visual quality under the size constraint. At the inter-attribute level, we assign bit-widths to each attribute channel by formulating the combinatorial optimization as a 0-1 integer linear program, which can be efficiently solved. At the intra-attribute level, we divide each attribute channel into blocks of vectors, quantizing each vector based on the optimal bit-width derived at the inter-attribute level. Dynamic programming determines block lengths. Using the size estimator and MPQ, we develop a calibrated algorithm to identify optimal hyperparameters in just 10 minutes, achieving a 1.69$\times$ efficiency increase with quality comparable to state-of-the-art methods.
有效的压缩技术对于3DGS适应不同的存储和传输条件至关重要。然而,现有方法无法在保持最优质量的同时解决大小约束问题。在本文中,我们介绍了SizeGS框架,它能够在指定的大小预算内压缩3DGS,同时优化视觉质量。我们首先使用大小估计器来建立文件大小与超参数之间的明确关系。利用这个估计器,我们将混合精度量化(MPQ)融入到3DGS属性中,将MPQ构建为两个层次——跨属性内和属性内,以在大小约束下优化视觉质量。在跨属性层面,我们通过将组合优化制定为0-1整数线性规划来为每个属性通道分配位宽,这可以高效求解。在属性内部层面,我们将每个属性通道分为向量块,基于跨属性层面得出的最优位宽对每个向量进行量化。动态规划确定块长度。通过使用大小估计器和MPQ,我们开发了一种校准算法,只需10分钟即可确定最佳超参数,实现了1.69倍的效率提升,同时质量可与最先进的方法相媲美。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Automatically compressing 3DGS into the desired file size while maximizing the visual quality
Summary
本文提出SizeGS框架,针对3DGS进行压缩,在限定文件大小的同时优化视觉质量。通过尺寸估计器建立文件大小与超参数之间的关系,结合混合精度量化(MPQ)技术,分两级优化视觉质量。在属性间级别,通过组合优化公式分配各属性通道的位宽,以0-1整数线性规划求解;在属性内级别,将每个属性通道分为向量块进行量化。使用尺寸估计器和MPQ,开发出高效校准的算法,可在短时间内确定最佳超参数,提高效率1.69倍,同时保持与现有技术相当的质量。
Key Takeaways
- SizeGS框架用于3DGS压缩,可在限定文件大小的同时优化视觉质量。
- 引入尺寸估计器来建立文件大小与超参数之间的关系。
- 结合混合精度量化(MPQ)技术,实现两级优化视觉质量:属性间和属性内。
- 在属性间级别,通过0-1整数线性规划分配各属性通道的位宽。
- 在属性内级别,将属性通道分为向量块进行量化。
- 使用尺寸估计器和MPQ开发出高效校准的算法,短时间内确定最佳超参数。
点此查看论文截图

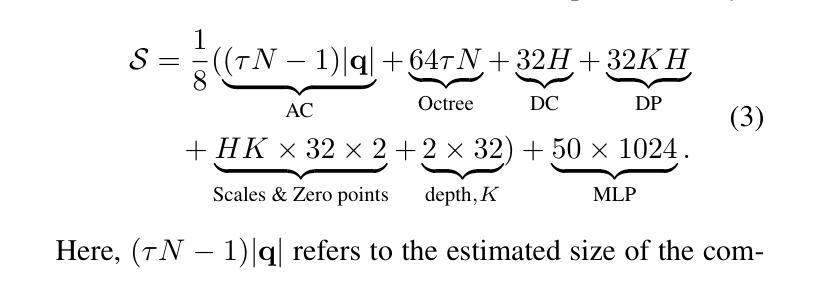

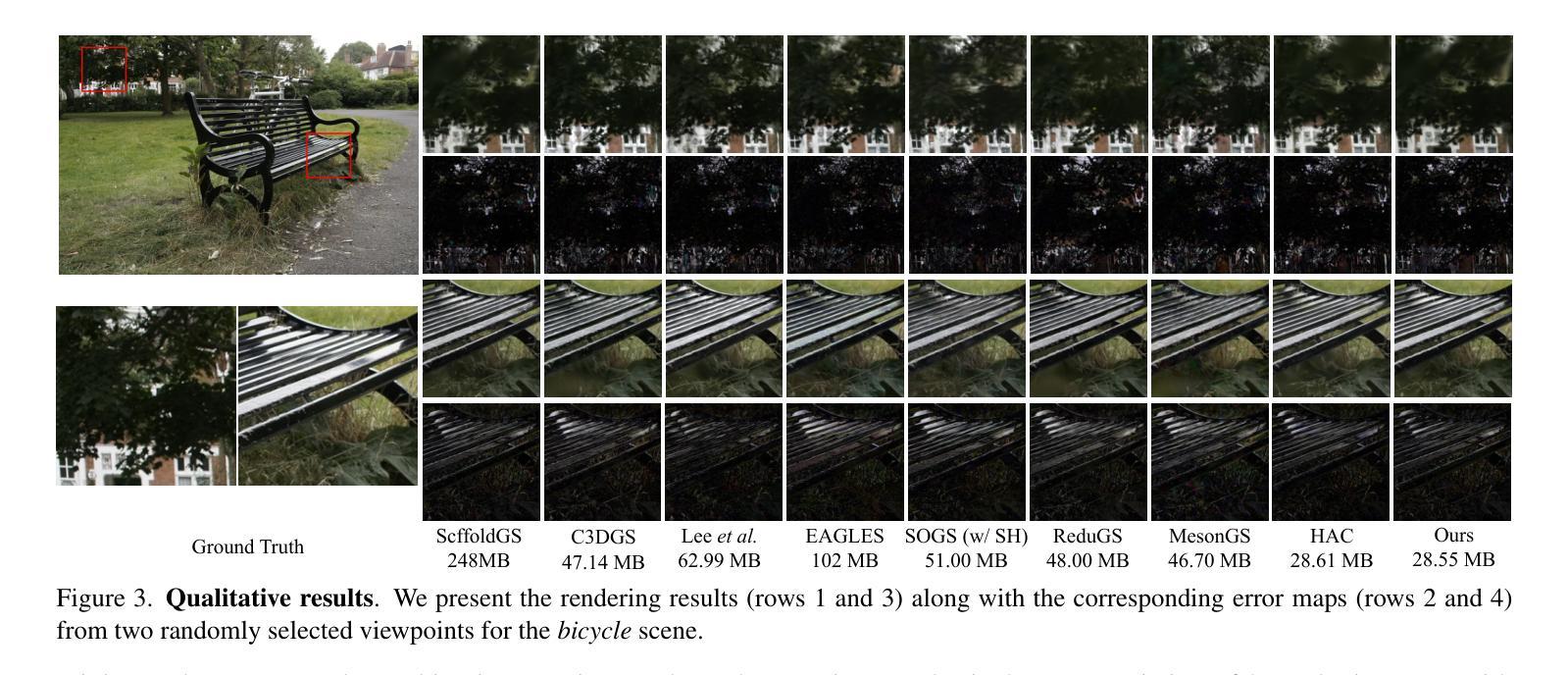
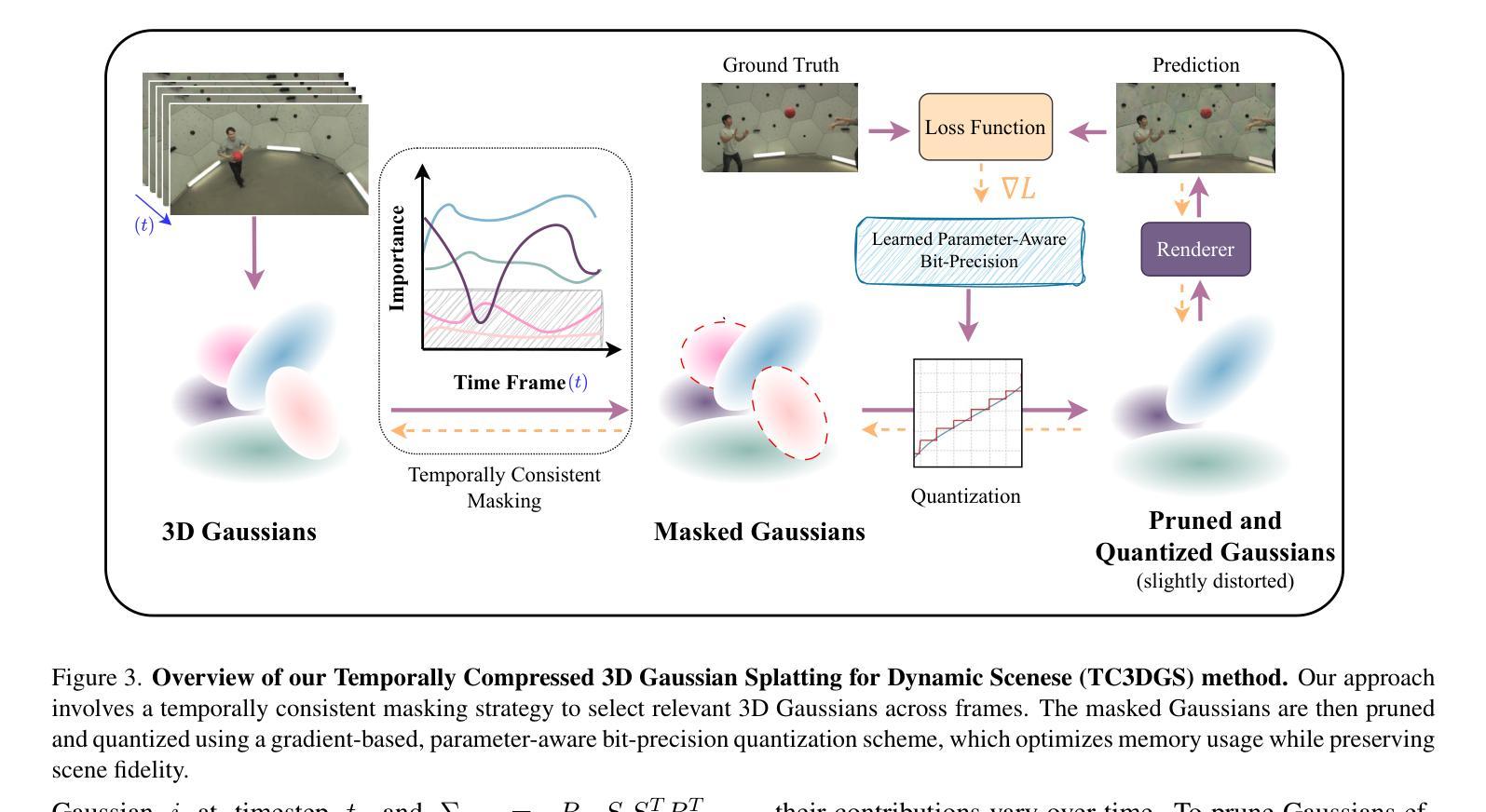
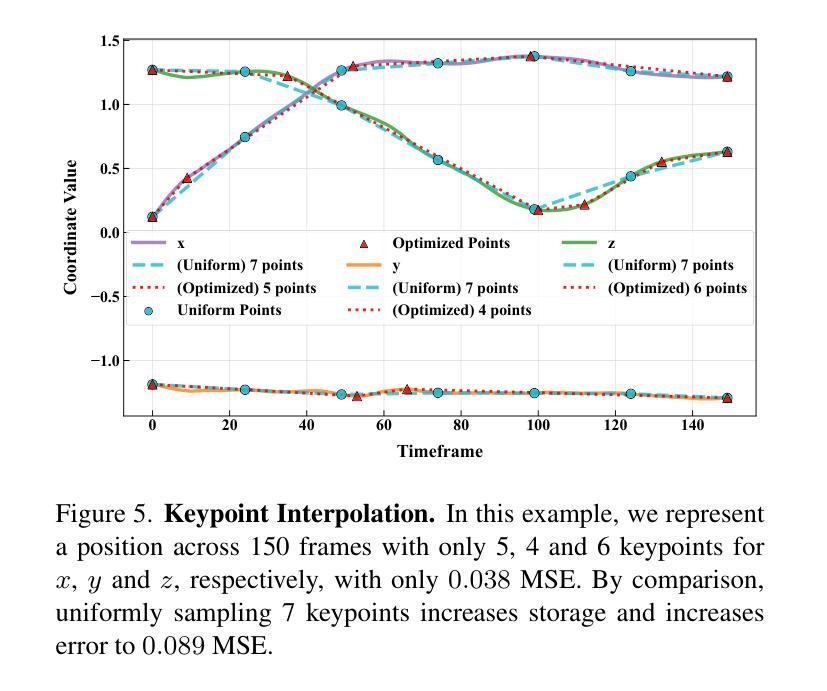
Temporally Compressed 3D Gaussian Splatting for Dynamic Scenes
Authors:Saqib Javed, Ahmad Jarrar Khan, Corentin Dumery, Chen Zhao, Mathieu Salzmann
Recent advancements in high-fidelity dynamic scene reconstruction have leveraged dynamic 3D Gaussians and 4D Gaussian Splatting for realistic scene representation. However, to make these methods viable for real-time applications such as AR/VR, gaming, and rendering on low-power devices, substantial reductions in memory usage and improvements in rendering efficiency are required. While many state-of-the-art methods prioritize lightweight implementations, they struggle in handling scenes with complex motions or long sequences. In this work, we introduce Temporally Compressed 3D Gaussian Splatting (TC3DGS), a novel technique designed specifically to effectively compress dynamic 3D Gaussian representations. TC3DGS selectively prunes Gaussians based on their temporal relevance and employs gradient-aware mixed-precision quantization to dynamically compress Gaussian parameters. It additionally relies on a variation of the Ramer-Douglas-Peucker algorithm in a post-processing step to further reduce storage by interpolating Gaussian trajectories across frames. Our experiments across multiple datasets demonstrate that TC3DGS achieves up to 67$\times$ compression with minimal or no degradation in visual quality.
近期高保真动态场景重建的最新进展利用动态三维高斯和四维高斯溅射进行真实场景表示。然而,为了使这些方法对于增强现实/虚拟现实、游戏和在低功耗设备上进行渲染等实时应用变得可行,需要大幅度减少内存使用并提高渲染效率。虽然许多最新方法都优先考虑轻便的实现,但它们在处理复杂运动场景或长序列时遇到困难。在这项工作中,我们引入了时间压缩三维高斯溅射(TC3DGS),这是一种专门设计用于有效压缩动态三维高斯表示的新技术。TC3DGS根据高斯的时间相关性选择性地删除高斯,并采用梯度感知混合精度量化来动态压缩高斯参数。此外,它还在后处理步骤中依赖Ramer-Douglas-Peucker算法的变体,通过跨帧插值高斯轨迹来进一步减少存储。我们在多个数据集上的实验表明,TC3DGS实现了高达67倍的压缩,视觉质量几乎没有或没有降级。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code will be released soon
Summary
最新高保真动态场景重建技术利用动态3D高斯和4D高斯泼溅进行真实场景表示。为使这些方法适用于AR/VR、游戏和低功耗设备的实时渲染,需要大幅减少内存使用并提高渲染效率。我们引入时间压缩3D高斯泼溅(TC3DGS)新技术,专门有效压缩动态3D高斯表示。TC3DGS基于时间相关性选择性删除高斯,并采用梯度感知混合精度量化进行动态压缩高斯参数。此外,它在后处理步骤中采用Ramer-Douglas-Peucker算法的变体,通过跨帧插值高斯轨迹进一步减少存储。实验证明,TC3DGS可实现高达67倍的压缩,视觉质量几乎无损失或几乎没有退化。
Key Takeaways
- 最新技术利用动态3D高斯和4D高斯泼溅进行高保真动态场景重建。
- 为实现实时应用,需要降低内存使用和提高渲染效率。
- 引入TC3DGS技术,专门压缩动态3D高斯表示。
- TC3DGS基于时间相关性选择性删除高斯。
- 采用梯度感知混合精度量化进行动态压缩高斯参数。
- 后处理步骤采用Ramer-Douglas-Peucker算法的变体进一步减少存储。
- 实验证明TC3DGS可实现高效压缩,且视觉质量无明显损失。
点此查看论文截图

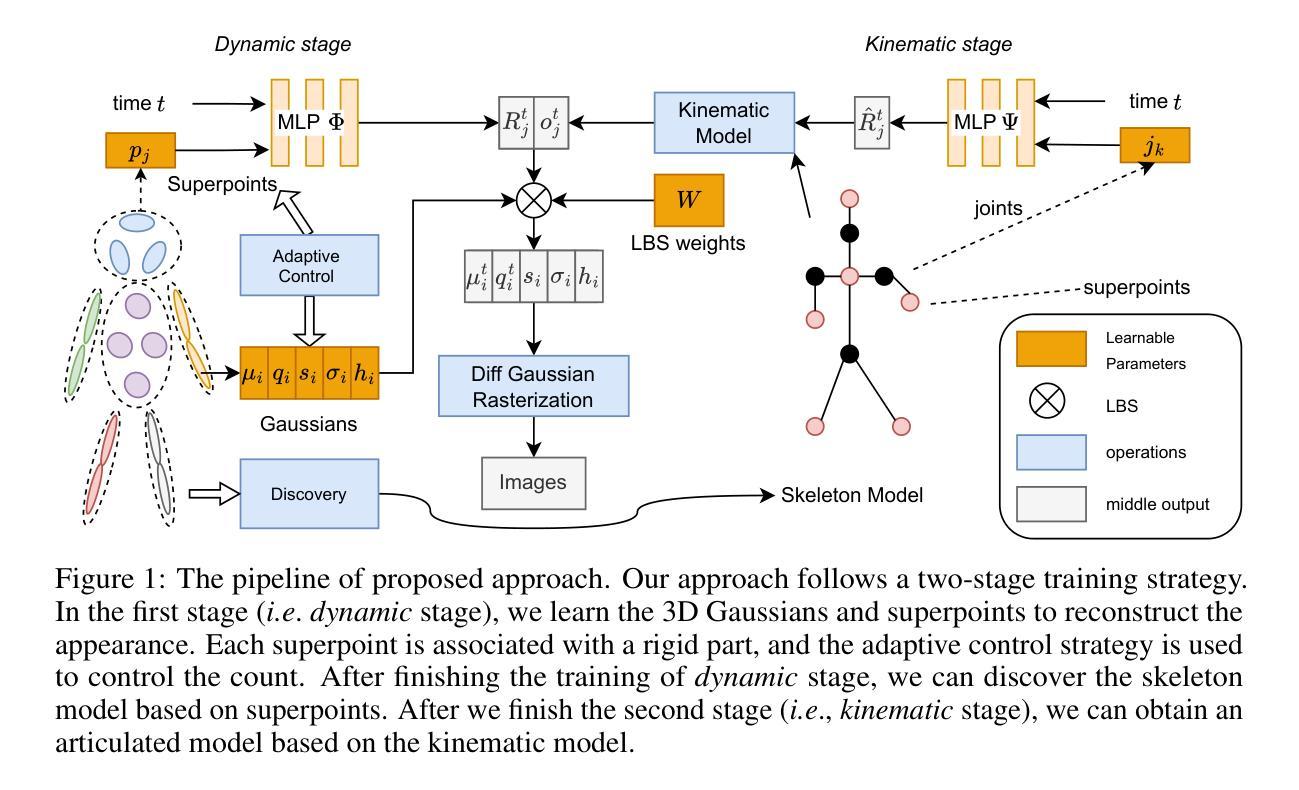
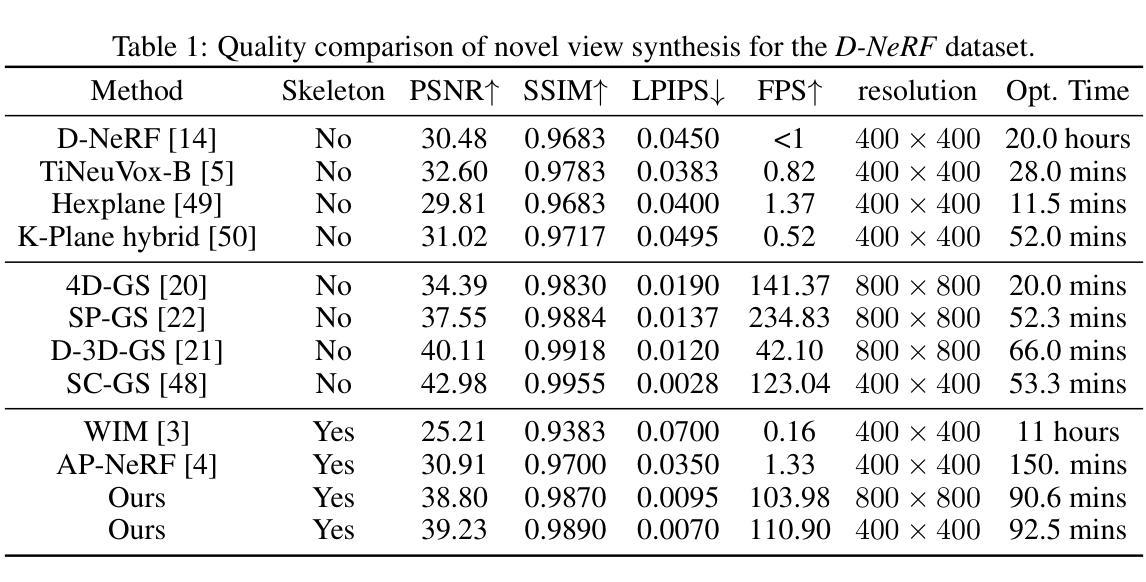
Template-free Articulated Gaussian Splatting for Real-time Reposable Dynamic View Synthesis
Authors:Diwen Wan, Yuxiang Wang, Ruijie Lu, Gang Zeng
While novel view synthesis for dynamic scenes has made significant progress, capturing skeleton models of objects and re-posing them remains a challenging task. To tackle this problem, in this paper, we propose a novel approach to automatically discover the associated skeleton model for dynamic objects from videos without the need for object-specific templates. Our approach utilizes 3D Gaussian Splatting and superpoints to reconstruct dynamic objects. Treating superpoints as rigid parts, we can discover the underlying skeleton model through intuitive cues and optimize it using the kinematic model. Besides, an adaptive control strategy is applied to avoid the emergence of redundant superpoints. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our method in obtaining re-posable 3D objects. Not only can our approach achieve excellent visual fidelity, but it also allows for the real-time rendering of high-resolution images.
关于动态场景的新视图合成虽然已经有了显著的进步,但捕捉物体的骨架模型并对其进行重新定位仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种新方法,无需特定对象的模板,即可自动从视频中发现动态对象的关联骨架模型。我们的方法利用3D高斯拼接和超级点来重建动态对象。通过将超级点视为刚性部分,我们可以通过直观线索发现潜在的骨架模型,并使用运动学模型对其进行优化。此外,还应用了自适应控制策略,以避免出现冗余的超级点。大量实验表明,我们的方法在获得可重新定位的三维物体方面既有效又高效。我们的方法不仅能达到优秀的视觉保真度,还能实现高分辨率图像的实时渲染。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文提出一种从视频中自动发现动态对象关联骨架模型的新方法,无需特定对象模板。该方法利用3D高斯喷绘和超点重建动态对象,通过直观线索发现底层骨架模型,并使用运动学模型进行优化。自适应控制策略避免了冗余超点的出现,实现了可重新定位的三维对象的高效获取。该方法不仅达到卓越的视觉保真度,还允许实时渲染高分辨率图像。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究提出了一种新的方法,能够从视频中自动发现动态对象的骨架模型,无需特定对象的模板。
- 方法结合了3D高斯喷绘和超点技术,用于重建动态对象。
- 通过直观线索发现底层骨架模型,并利用运动学模型进行优化。
- 自适应控制策略避免了冗余超点的产生。
- 该方法能够高效地获取可重新定位的三维对象。
- 方法的视觉保真度卓越。
点此查看论文截图

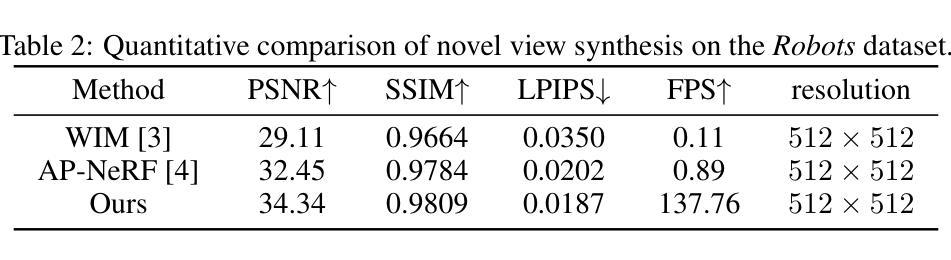
Text-to-3D Gaussian Splatting with Physics-Grounded Motion Generation
Authors:Wenqing Wang, Yun Fu
Text-to-3D generation is a valuable technology in virtual reality and digital content creation. While recent works have pushed the boundaries of text-to-3D generation, producing high-fidelity 3D objects with inefficient prompts and simulating their physics-grounded motion accurately still remain unsolved challenges. To address these challenges, we present an innovative framework that utilizes the Large Language Model (LLM)-refined prompts and diffusion priors-guided Gaussian Splatting (GS) for generating 3D models with accurate appearances and geometric structures. We also incorporate a continuum mechanics-based deformation map and color regularization to synthesize vivid physics-grounded motion for the generated 3D Gaussians, adhering to the conservation of mass and momentum. By integrating text-to-3D generation with physics-grounded motion synthesis, our framework renders photo-realistic 3D objects that exhibit physics-aware motion, accurately reflecting the behaviors of the objects under various forces and constraints across different materials. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves high-quality 3D generations with realistic physics-grounded motion.
文本到三维生成技术是虚拟现实的数字内容创建中的一项宝贵技术。尽管近期的研究已经推动了文本到三维生成的边界,但是仍存在未解决的挑战,例如使用不高效的提示来生成高保真度的三维物体,以及准确模拟基于物理的运动。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种创新的框架,利用大型语言模型(LLM)精炼提示和扩散先验引导的Gaussian Splatting(GS)来生成具有准确外观和几何结构的三维模型。我们还结合了基于连续力学的变形图和颜色正则化,以合成生动的基于物理的运动,用于生成的三维高斯分布,同时遵守质量和动量的守恒。通过将文本到三维生成与基于物理的运动合成相结合,我们的框架能够渲染出具有物理感知运动的光学逼真三维物体,准确反映不同材料下物体在各种力和约束下的行为。大量实验证明,我们的方法能够实现具有真实物理基础运动的高质量三维生成。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到三维生成技术是虚拟现实和数字内容创建中的一项重要技术。针对文本到三维生成中的挑战,提出一种利用大型语言模型优化提示和扩散先验引导的高斯涂布法生成三维模型,采用基于连续力学的变形图和颜色正则化合成生动逼真的物理运动。该框架实现了文本到三维生成与物理运动合成的结合,可生成具有物理感知运动的光照真实三维对象。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到三维生成技术是虚拟现实和数字内容创建的重要领域。
- 当前面临的挑战包括生成高保真三维对象和使用有效提示模拟其基于物理的运动。
- 提出一种新型框架,利用大型语言模型优化提示和扩散先验引导的高斯涂布法生成三维模型。
- 框架结合了文本到三维生成和物理运动合成,生成具有物理感知运动的光照真实三维对象。
- 采用基于连续力学的变形图和颜色正则化技术,确保生成的三维高斯符合物理规律。
- 通过广泛实验验证,该方法可实现高质量的三维生成,具有逼真的物理运动。
- 该技术有助于推进虚拟现实的真实感和数字内容创建的丰富性。
点此查看论文截图

Radiant: Large-scale 3D Gaussian Rendering based on Hierarchical Framework
Authors:Haosong Peng, Tianyu Qi, Yufeng Zhan, Hao Li, Yalun Dai, Yuanqing Xia
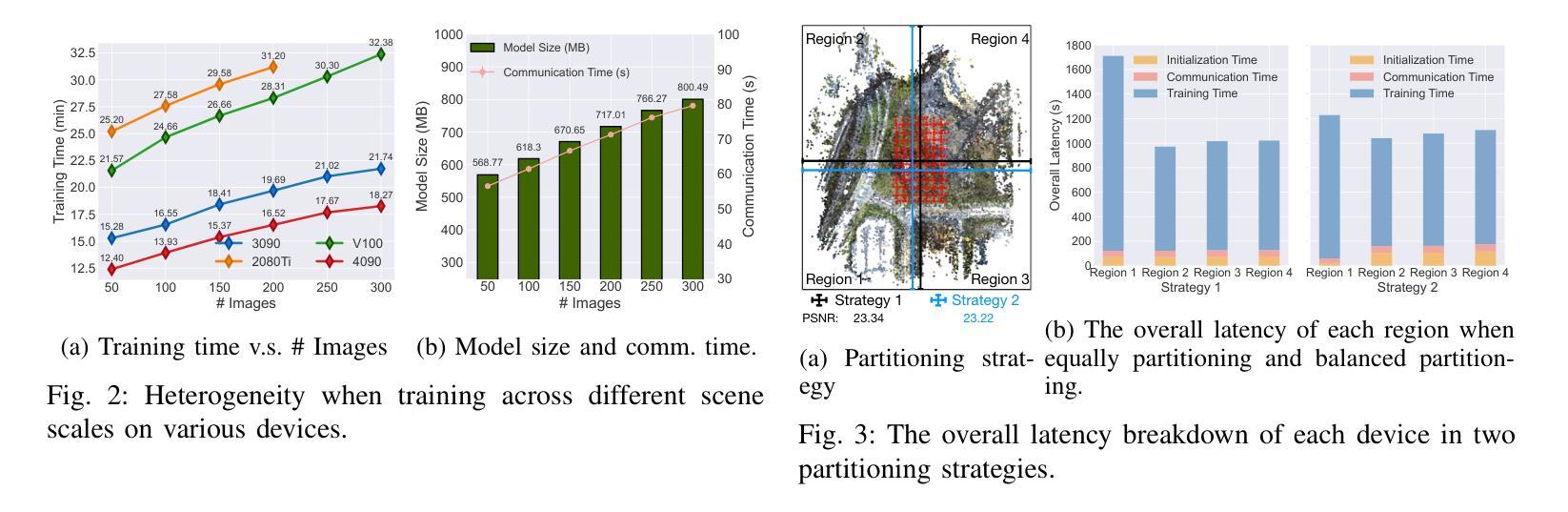
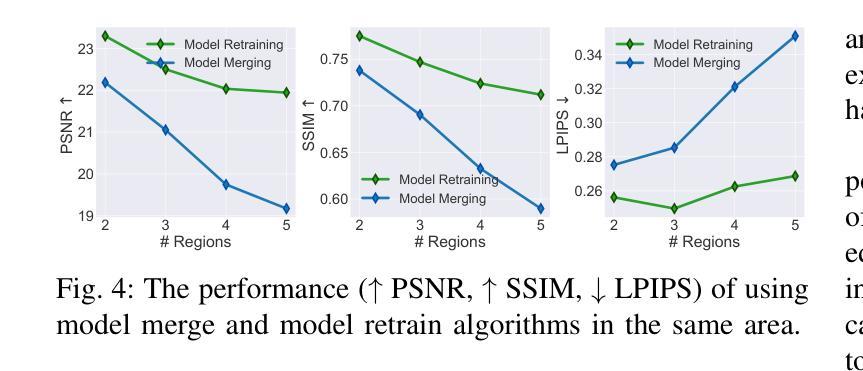
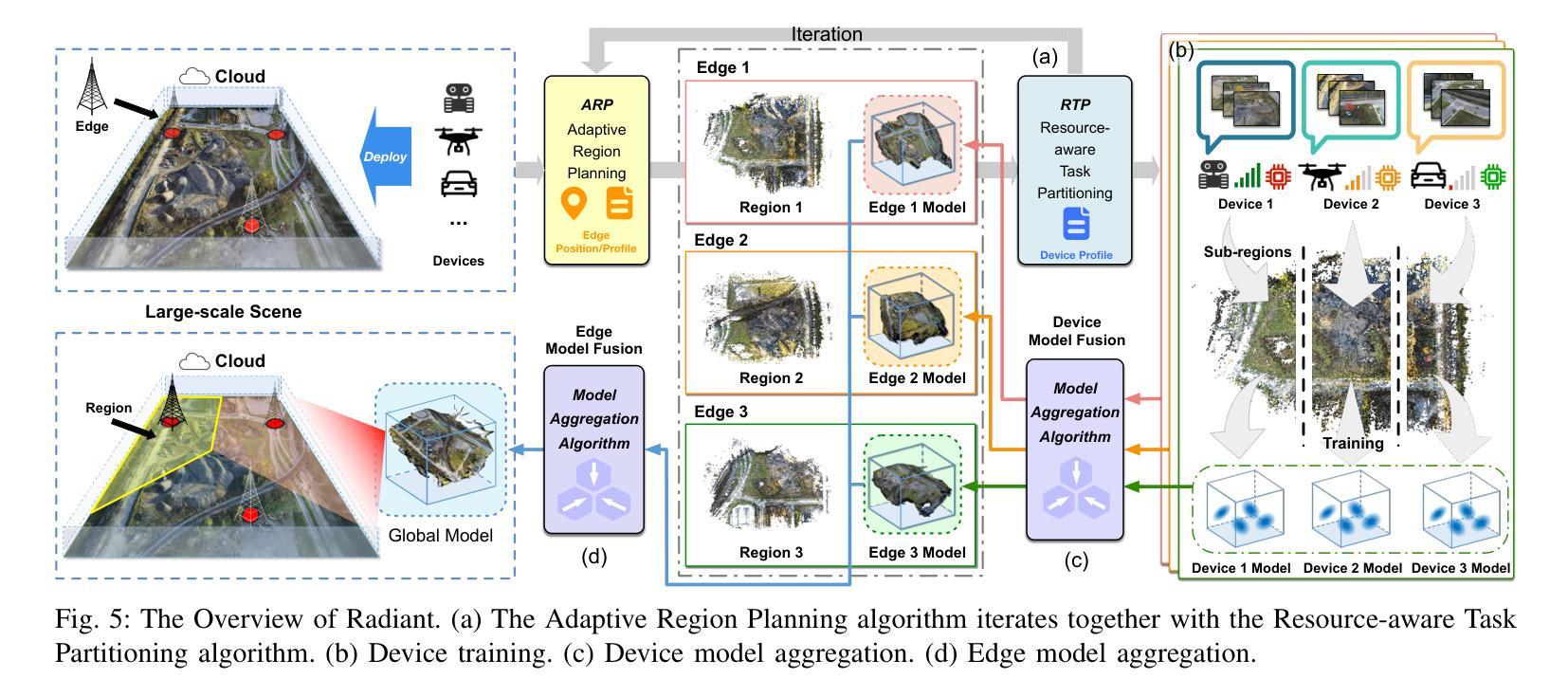
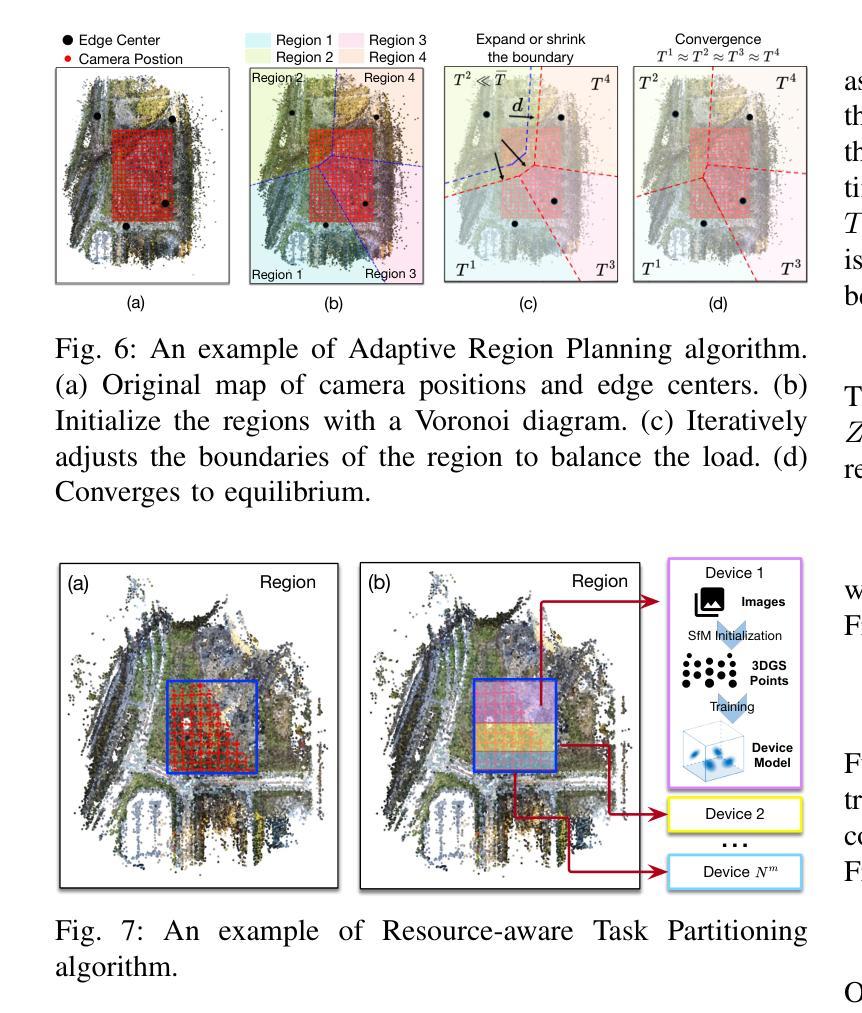
With the advancement of computer vision, the recently emerged 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has increasingly become a popular scene reconstruction algorithm due to its outstanding performance. Distributed 3DGS can efficiently utilize edge devices to directly train on the collected images, thereby offloading computational demands and enhancing efficiency. However, traditional distributed frameworks often overlook computational and communication challenges in real-world environments, hindering large-scale deployment and potentially posing privacy risks. In this paper, we propose Radiant, a hierarchical 3DGS algorithm designed for large-scale scene reconstruction that considers system heterogeneity, enhancing the model performance and training efficiency. Via extensive empirical study, we find that it is crucial to partition the regions for each edge appropriately and allocate varying camera positions to each device for image collection and training. The core of Radiant is partitioning regions based on heterogeneous environment information and allocating workloads to each device accordingly. Furthermore, we provide a 3DGS model aggregation algorithm that enhances the quality and ensures the continuity of models’ boundaries. Finally, we develop a testbed, and experiments demonstrate that Radiant improved reconstruction quality by up to 25.7% and reduced up to 79.6% end-to-end latency.
随着计算机视觉技术的进步,最近出现的3D高斯喷涂(3DGS)因其卓越性能而越来越成为流行的场景重建算法。分布式3DGS能够有效利用边缘设备对收集的图像进行直接训练,从而减轻计算负担,提高效率。然而,传统的分布式框架往往忽略了真实环境中的计算和通信挑战,阻碍了大规模部署,并可能带来隐私风险。在本文中,我们提出了一种用于大规模场景重建的分层3DGS算法——Radiant,该算法考虑了系统异质性,提高了模型性能和训练效率。通过广泛的实证研究,我们发现适当地为每个边缘划分区域,并为图像收集和训练分配不同的相机位置是至关重要的。Radiant的核心是根据异构环境信息划分区域,并相应地将工作量分配给每个设备。此外,我们提供了一种3DGS模型聚合算法,以提高模型质量并确保模型边界的连续性。最后,我们开发了一个测试平台,实验表明,Radiant提高了重建质量,最高达25.7%,并减少了高达79.6%的端到端延迟。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着计算机视觉技术的发展,3D高斯融合技术(3DGS)因出色的性能而逐渐成为场景重建的热门算法。然而,传统分布式框架在现实环境中忽略了计算和通信的挑战,阻碍了大规模部署并可能带来隐私风险。本文提出了一种针对大规模场景重建的分层3DGS算法Radiant,考虑系统异质性以提高模型性能和训练效率。通过对边缘区域的适当分区和不同的相机位置分配,Radiant能够在图像采集和训练方面更加高效。核心是通过环境信息的异质性进行区域划分,并相应分配工作负载。此外,还提供了一种提高模型质量并确保模型边界连续性的3DGS模型聚合算法。实验证明,Radiant提高了重建质量达25.7%,并减少了高达79.6%的端到端延迟。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS算法已成为场景重建领域的热门选择,因其在性能上的出色表现。
- 传统分布式框架存在计算和通信挑战,影响大规模部署并可能引发隐私风险。
- Radiant算法是一种分层的3DGS方法,旨在解决大规模场景重建问题,并考虑系统异质性。
- 区域适当分区和相机位置分配对图像采集和训练效率至关重要。
- Radiant的核心是根据环境信息的异质性进行区域划分,并相应分配工作负载。
- 提供了一种新的3DGS模型聚合算法,以提高模型质量和确保边界连续性。
点此查看论文截图


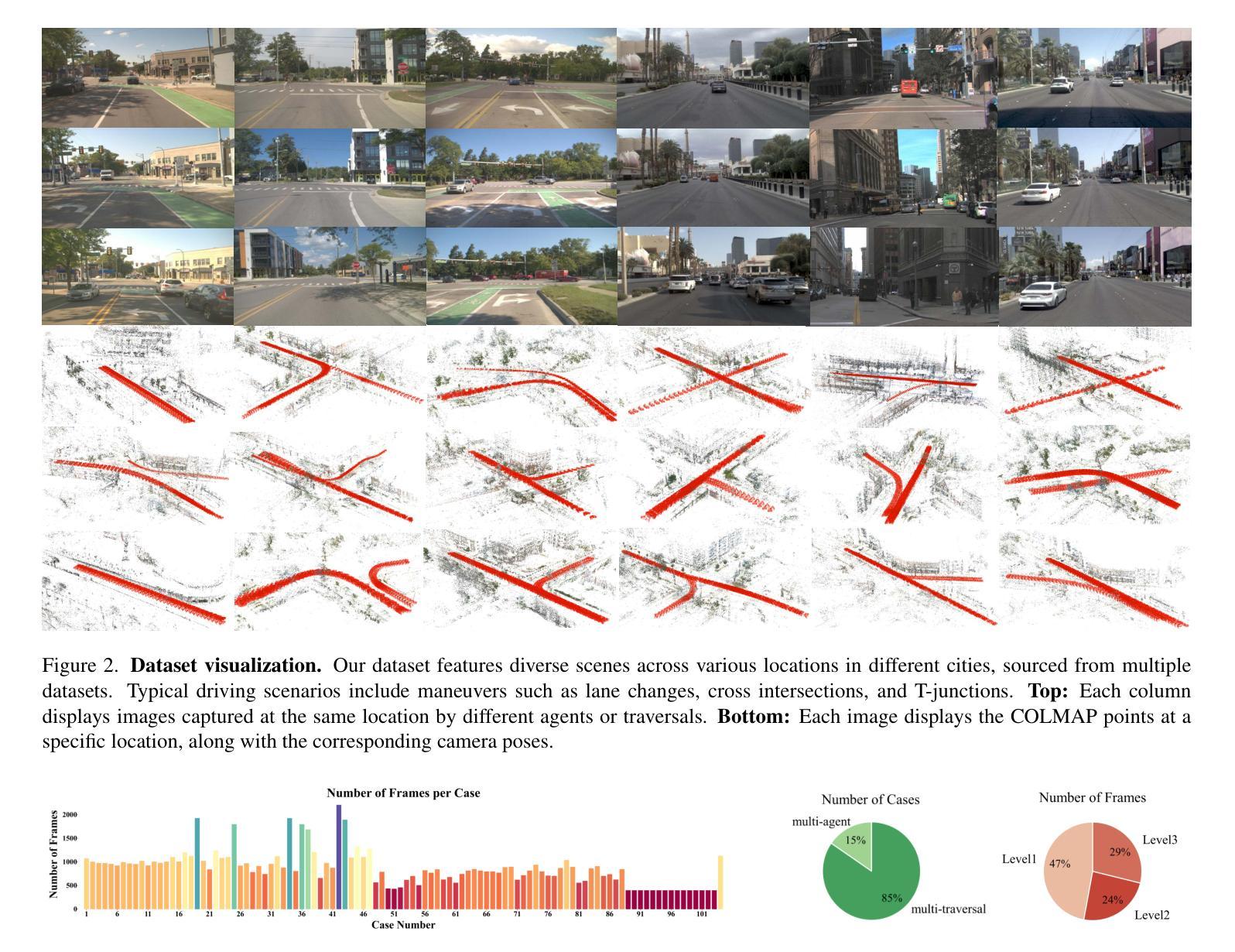
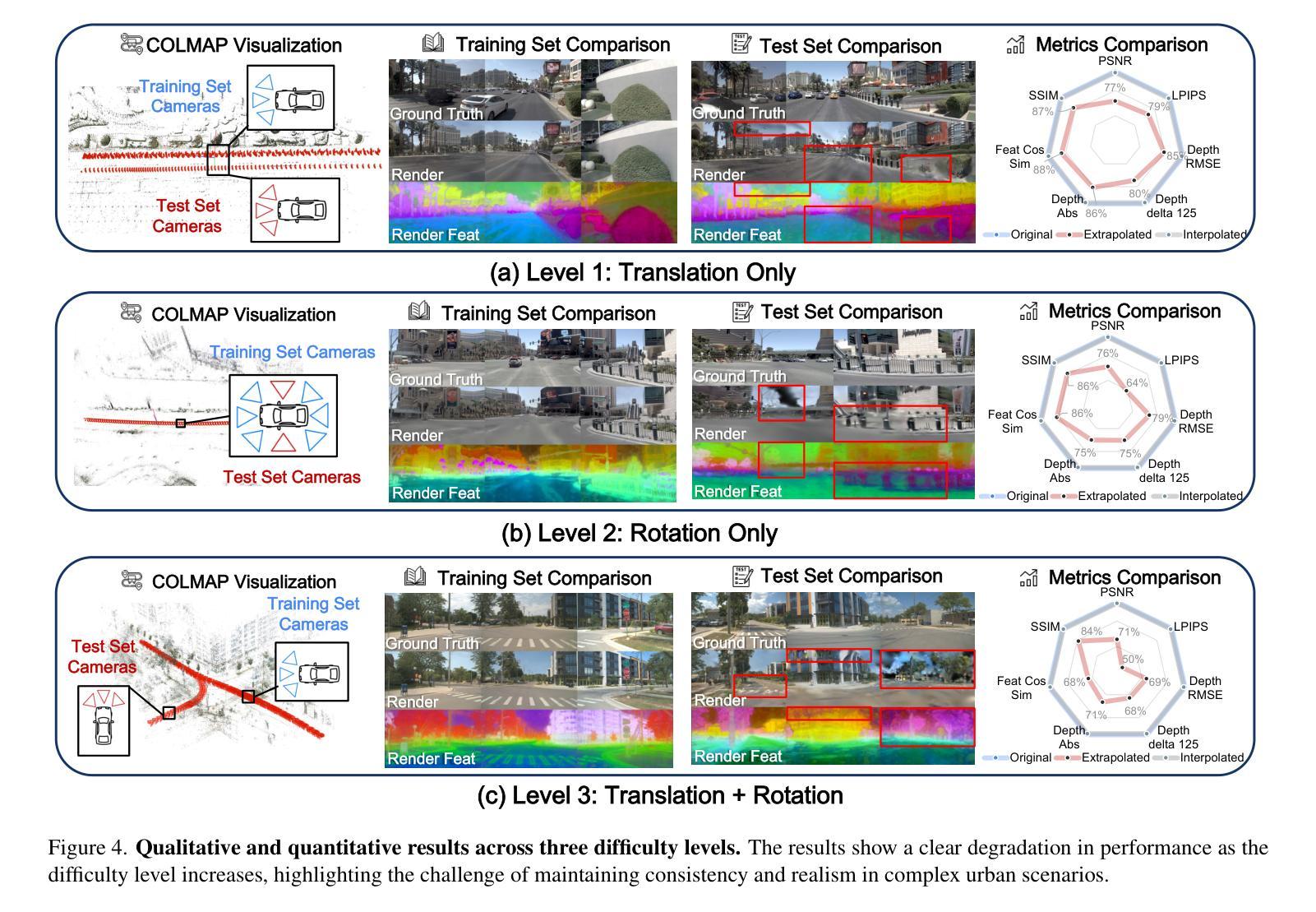
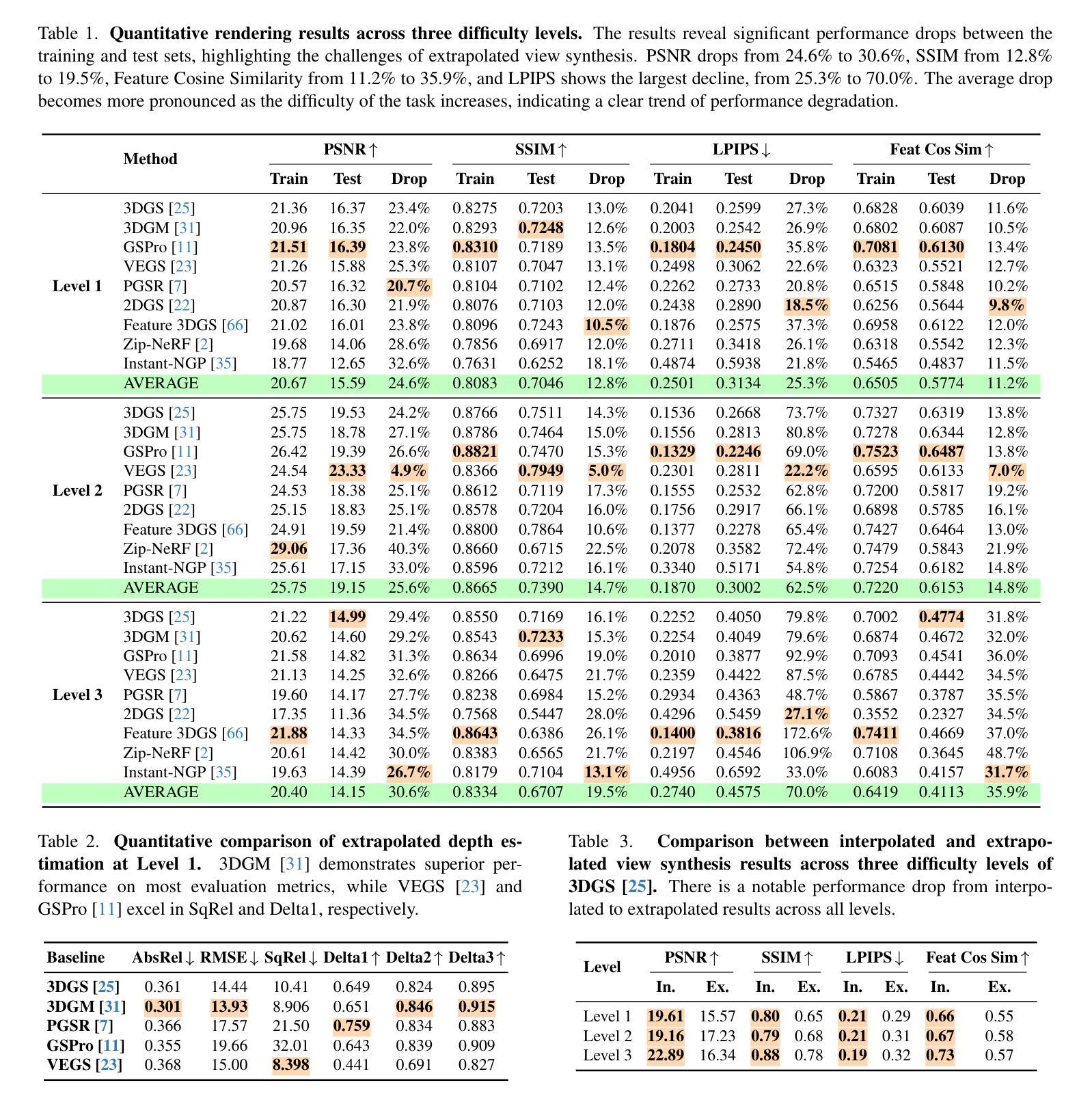
Extrapolated Urban View Synthesis Benchmark
Authors:Xiangyu Han, Zhen Jia, Boyi Li, Yan Wang, Boris Ivanovic, Yurong You, Lingjie Liu, Yue Wang, Marco Pavone, Chen Feng, Yiming Li
Photorealistic simulators are essential for the training and evaluation of vision-centric autonomous vehicles (AVs). At their core is Novel View Synthesis (NVS), a crucial capability that generates diverse unseen viewpoints to accommodate the broad and continuous pose distribution of AVs. Recent advances in radiance fields, such as 3D Gaussian Splatting, achieve photorealistic rendering at real-time speeds and have been widely used in modeling large-scale driving scenes. However, their performance is commonly evaluated using an interpolated setup with highly correlated training and test views. In contrast, extrapolation, where test views largely deviate from training views, remains underexplored, limiting progress in generalizable simulation technology. To address this gap, we leverage publicly available AV datasets with multiple traversals, multiple vehicles, and multiple cameras to build the first Extrapolated Urban View Synthesis (EUVS) benchmark. Meanwhile, we conduct quantitative and qualitative evaluations of state-of-the-art Gaussian Splatting methods across different difficulty levels. Our results show that Gaussian Splatting is prone to overfitting to training views. Besides, incorporating diffusion priors and improving geometry cannot fundamentally improve NVS under large view changes, highlighting the need for more robust approaches and large-scale training. We have released our data to help advance self-driving and urban robotics simulation technology.
真实感模拟器对于以视觉为中心的自动驾驶汽车的训练和评估至关重要。其核心是新型视图合成(NVS),这是一种能够生成多种未见观点以适应自动驾驶汽车广泛和连续姿态分布的关键能力。最近,辐射场取得了进展,例如3D高斯拼贴技术,能够以实时速度实现真实感渲染,并已广泛应用于模拟大规模驾驶场景。然而,它们的性能通常使用插值设置进行评估,其中训练和测试观点高度相关。相比之下,外推(即测试观点与训练观点存在较大偏差)的情况仍被较少探索,这限制了通用仿真技术的进步。为了弥补这一空白,我们利用公开可用的自动驾驶数据集(包含多次遍历、多辆车和多相机)来建立第一个外推城市视图合成(EUVS)基准测试。同时,我们对不同难度级别的最新高斯拼贴方法进行了定量和定性评估。结果表明,高斯拼贴容易对训练观点产生过度拟合。此外,融入扩散先验知识和改进几何结构并不能在较大视角变化下从根本上改善NVS,这凸显了需要更稳健的方法和大规模训练。我们已经发布数据,以帮助推动自动驾驶和城市机器人仿真技术的进步。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://ai4ce.github.io/EUVS-Benchmark/
Summary
本文强调了真实感模拟器对于以视觉为中心的自动驾驶汽车(AVs)训练和评估的重要性。文章介绍了关键技术——Novel View Synthesis(NVS),它能生成多样化的未见视角以适应AVs广泛的连续姿态分布。虽然近期辐射场技术如3D高斯拼贴达到了实时渲染逼真度并在大规模驾驶场景建模中广泛应用,但其性能评估通常采用插值设置,测试视角与训练视角高度相关。针对这种情况,文章建立了首个Extrapolated Urban View Synthesis(EUVS)基准测试平台,该平台使用公开可用的包含多轨迹、多车辆和多相机的AV数据集进行构建,同时对最新高斯拼贴方法进行了定量和定性评估。研究结果表明,高斯拼贴易对训练视角产生过拟合现象,而引入扩散先验和改进几何结构并不能从根本上改善大视角变化下的NVS性能,这凸显了需要更稳健的方法和大规模训练数据。
Key Takeaways
- 真实感模拟器对于自动驾驶汽车的训练和评估至关重要。
- Novel View Synthesis(NVS)是生成多样化未见视角的核心技术,适应了自动驾驶汽车的广泛姿态分布。
- 现有技术如3D高斯拼贴在辐射场技术中实现了实时渲染,但在处理测试视角与训练视角高度相关时存在局限性。
- 建立了首个Extrapolated Urban View Synthesis(EUVS)基准测试平台来推动研究进步。
- 高斯拼贴方法存在过拟合现象,需要更稳健的方法和大规模训练数据来改善性能。
- 引入扩散先验和改进几何结构在大视角变化下对NVS性能的提升有限。
点此查看论文截图

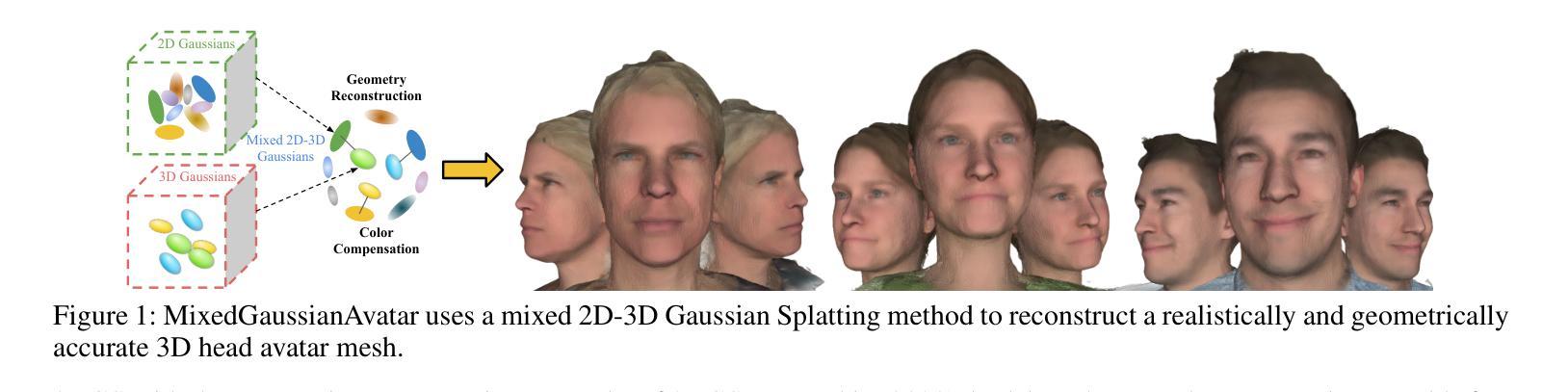
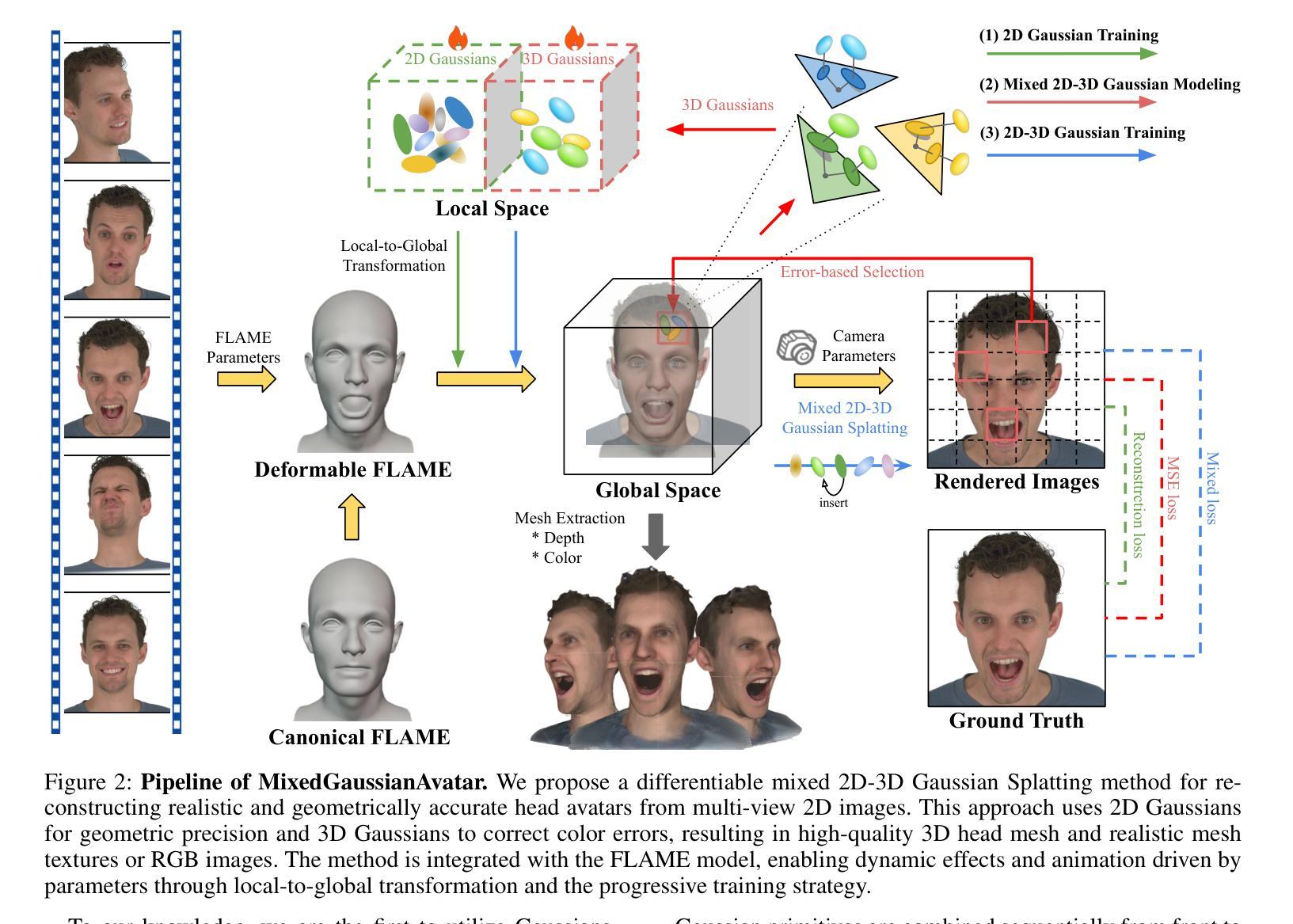
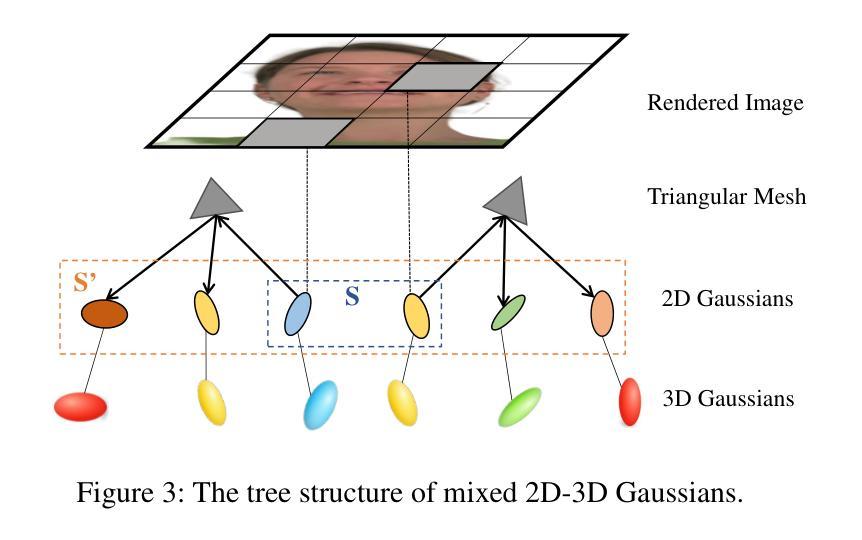
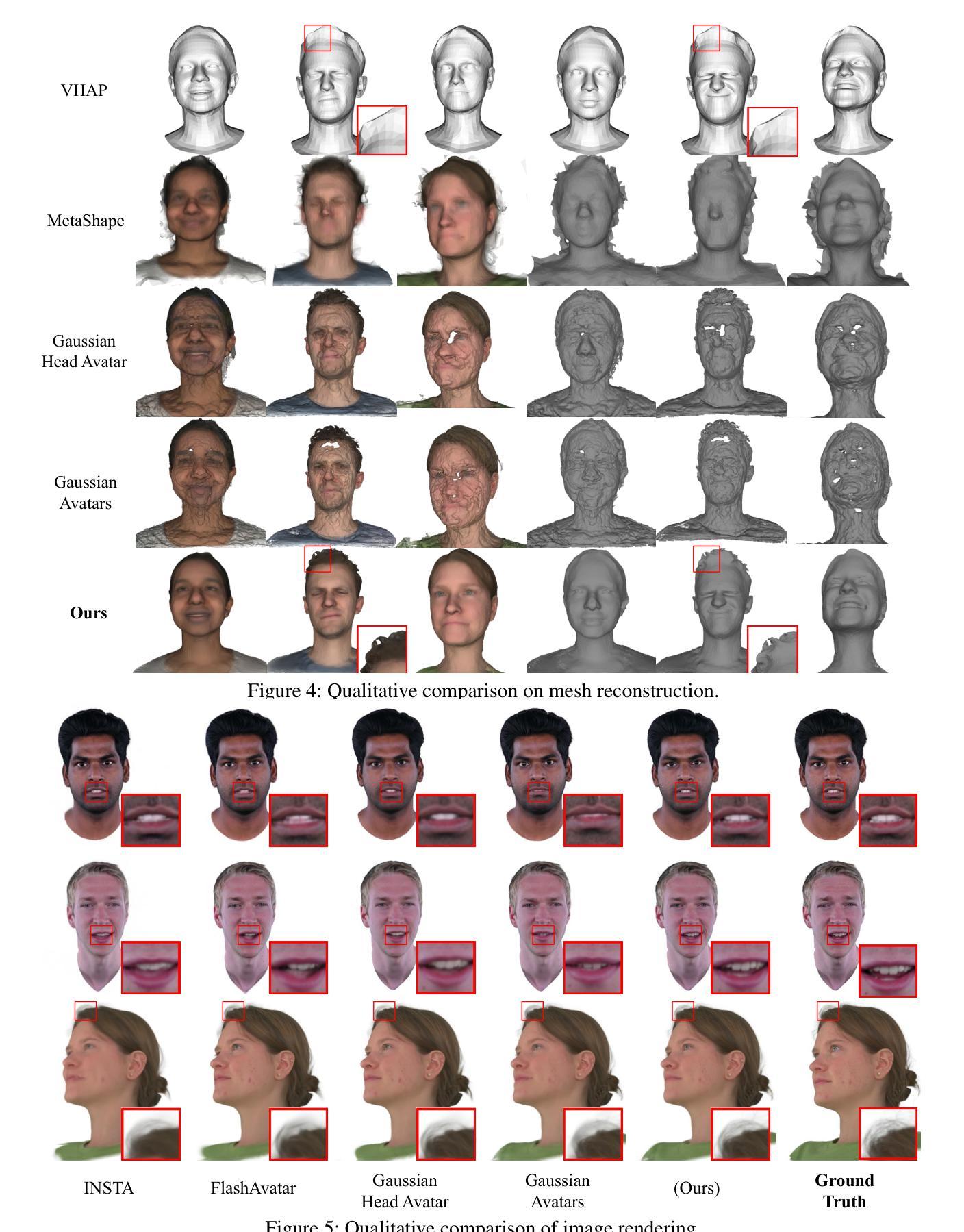
MixedGaussianAvatar: Realistically and Geometrically Accurate Head Avatar via Mixed 2D-3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Peng Chen, Xiaobao Wei, Qingpo Wuwu, Xinyi Wang, Xingyu Xiao, Ming Lu
Reconstructing high-fidelity 3D head avatars is crucial in various applications such as virtual reality. The pioneering methods reconstruct realistic head avatars with Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), which have been limited by training and rendering speed. Recent methods based on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) significantly improve the efficiency of training and rendering. However, the surface inconsistency of 3DGS results in subpar geometric accuracy; later, 2DGS uses 2D surfels to enhance geometric accuracy at the expense of rendering fidelity. To leverage the benefits of both 2DGS and 3DGS, we propose a novel method named MixedGaussianAvatar for realistically and geometrically accurate head avatar reconstruction. Our main idea is to utilize 2D Gaussians to reconstruct the surface of the 3D head, ensuring geometric accuracy. We attach the 2D Gaussians to the triangular mesh of the FLAME model and connect additional 3D Gaussians to those 2D Gaussians where the rendering quality of 2DGS is inadequate, creating a mixed 2D-3D Gaussian representation. These 2D-3D Gaussians can then be animated using FLAME parameters. We further introduce a progressive training strategy that first trains the 2D Gaussians and then fine-tunes the mixed 2D-3D Gaussians. We demonstrate the superiority of MixedGaussianAvatar through comprehensive experiments. The code will be released at: https://github.com/ChenVoid/MGA/.
重建高保真3D头像对于虚拟现实等应用至关重要。前沿的方法使用神经辐射场(NeRF)重建逼真的头像,但受限于训练和渲染速度。基于3D高斯贴图(3DGS)的最新方法显著提高了训练和渲染的效率。然而,3DGS的表面不一致导致几何精度不佳;后来的2DGS使用2D表面元素以提高几何精度,但牺牲了渲染保真度。为了结合2DGS和3DGS的优点,我们提出了一种名为MixedGaussianAvatar的新方法,用于真实且几何精确的头像重建。我们的主要思想是利用2D高斯重建3D头像的表面,以确保几何精度。我们将2D高斯附加到FLAME模型的三角网格上,并在2DGS的渲染质量不足的地方连接到额外的3D高斯,创建混合的2D-3D高斯表示。这些2D-3D高斯可以使用FLAME参数进行动画设置。我们还引入了一种渐进的训练策略,首先训练2D高斯,然后对混合的2D-3D高斯进行微调。我们通过全面的实验证明了MixedGaussianAvatar的优越性。代码将在https://github.com/ChenVoid/MGA/发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project: https://chenvoid.github.io/MGA/
Summary
在虚拟现实中重建高保真三维头部化身非常关键。最近采用基于三维高斯拼接技术的方法提高了训练和渲染效率,但其表面一致性不足导致几何精度较差。针对此问题,研究者提出了一种混合二维高斯与三维高斯技术的全新方法,即MixedGaussianAvatar。它通过二维高斯重建三维头部表面确保几何精度,在必要时采用三维高斯进行补充。这种方法可实现动画化,并引入渐进式训练策略,即先训练二维高斯再微调混合二维-三维高斯技术。MixedGaussianAvatar的优势通过实验得到验证。相关代码将在GitHub上发布。
Key Takeaways
- 三维头部化身重建在虚拟现实中具有重要意义。
- 最近的三维高斯拼接技术方法虽然提高了训练和渲染效率,但存在几何精度问题。
- MixedGaussianAvatar方法结合二维高斯和三维高斯技术,旨在解决几何精度问题。
- 该方法利用二维高斯重建三维头部表面,并在必要时使用三维高斯补充。
- MixedGaussianAvatar可以实现动画化,并采用了渐进式训练策略来提高效率。
点此查看论文截图

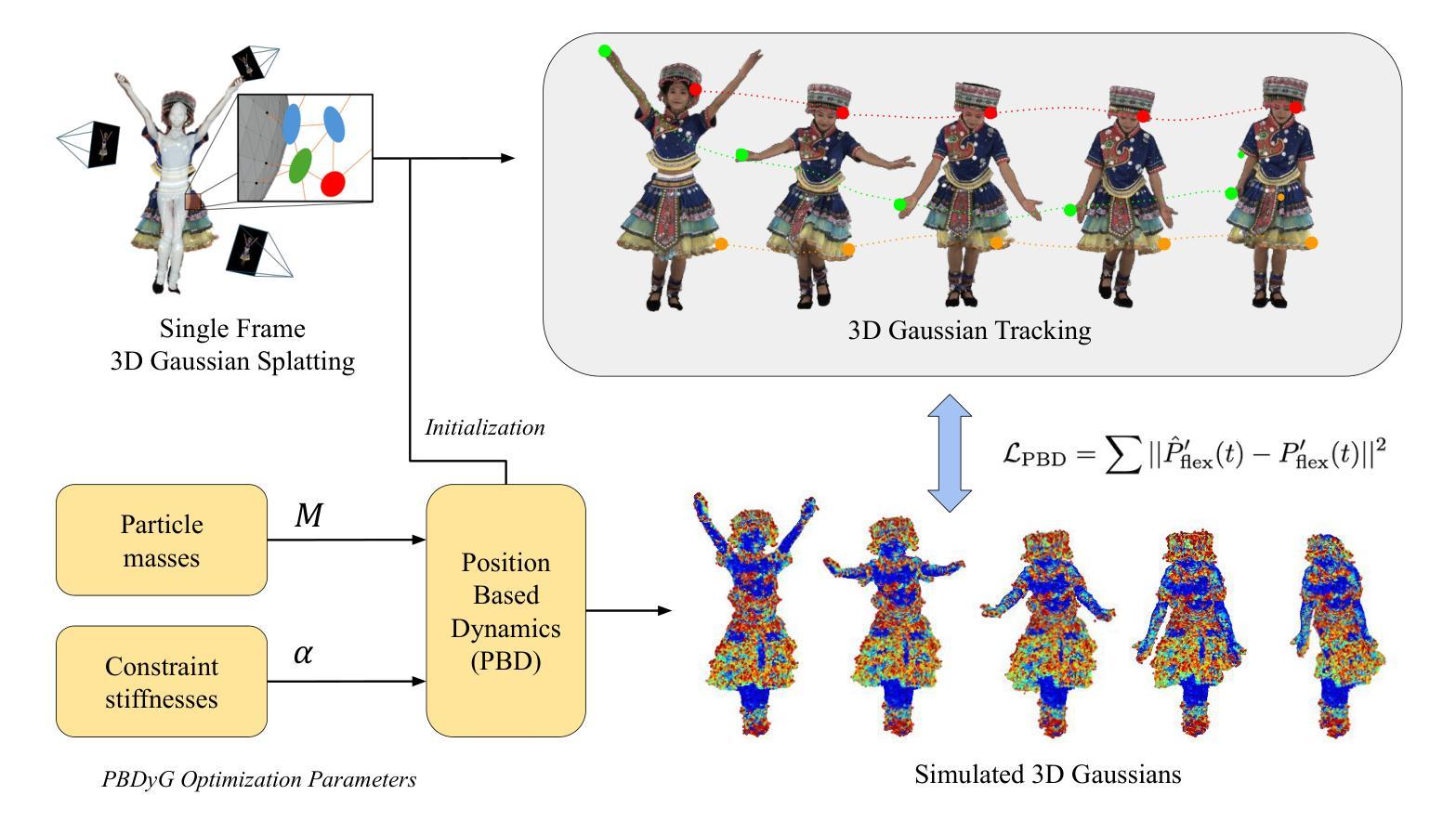
PBDyG: Position Based Dynamic Gaussians for Motion-Aware Clothed Human Avatars
Authors:Shota Sasaki, Jane Wu, Ko Nishino
This paper introduces a novel clothed human model that can be learned from multiview RGB videos, with a particular emphasis on recovering physically accurate body and cloth movements. Our method, Position Based Dynamic Gaussians (PBDyG), realizes movement-dependent'' cloth deformation via physical simulation, rather than merely relying on pose-dependent’’ rigid transformations. We model the clothed human holistically but with two distinct physical entities in contact: clothing modeled as 3D Gaussians, which are attached to a skinned SMPL body that follows the movement of the person in the input videos. The articulation of the SMPL body also drives physically-based simulation of the clothes’ Gaussians to transform the avatar to novel poses. In order to run position based dynamics simulation, physical properties including mass and material stiffness are estimated from the RGB videos through Dynamic 3D Gaussian Splatting. Experiments demonstrate that our method not only accurately reproduces appearance but also enables the reconstruction of avatars wearing highly deformable garments, such as skirts or coats, which have been challenging to reconstruct using existing methods.
本文介绍了一种可以从多角度RGB视频中学习的新型着装人体模型,特别侧重于恢复物理上准确的身体和衣物运动。我们的方法,基于位置的动力学高斯(PBDyG),通过物理模拟实现“运动相关”的布料变形,而不是仅仅依赖“姿态相关”的刚性变换。我们对穿衣的人体进行整体建模,但将其接触为两个独立的物理实体:将衣物建模为三维高斯,附着在跟随输入视频人物运动的皮肤化SMPL身体上。SMPL身体的关节活动也驱动衣物的基于物理的高斯模拟,将角色转变为新的姿态。为了运行基于位置的动力学模拟,我们通过动态三维高斯喷涂从RGB视频中估计质量、材料刚度等物理属性。实验表明,我们的方法不仅准确地再现了外观,还能重建穿着高度可变形服装的角色,如裙子或外套,这在以前使用现有方法重建时具有挑战性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了一种从多视角RGB视频中学习人体着装模型的新方法,特别注重恢复物理准确的身体和衣物运动。该方法通过物理模拟实现“运动相关”的衣物变形,而不是仅依赖“姿态相关”的刚性变换。建模人体着装为一个整体,但接触面由两个独立的物理实体组成:衣物被模拟为3D高斯分布,附着在跟随输入视频人物运动的皮肤化SMPL身体上。SMPL身体的关节活动也驱动衣物的高斯物理模拟,以生成新颖姿态的虚拟形象。通过动态三维高斯碎点技术从RGB视频中估算质量、材料刚度等物理属性。实验表明,该方法不仅准确再现外观,还能重建穿着高度可变形衣物的虚拟形象,如裙子或外套,这是现有方法难以重建的。
要点
- 本文介绍了一种新的从多视角RGB视频学习人体着装模型的方法。
- 重点在于恢复物理准确的身体和衣物运动。
- 通过物理模拟实现运动相关的衣物变形。
- 人体着装被建模为一个整体,接触面由两个物理实体(衣物和皮肤化SMPL身体)组成。
- SMPL身体的关节活动驱动衣物的物理模拟。
- 利用动态三维高斯碎点技术从RGB视频中估算物理属性。
点此查看论文截图


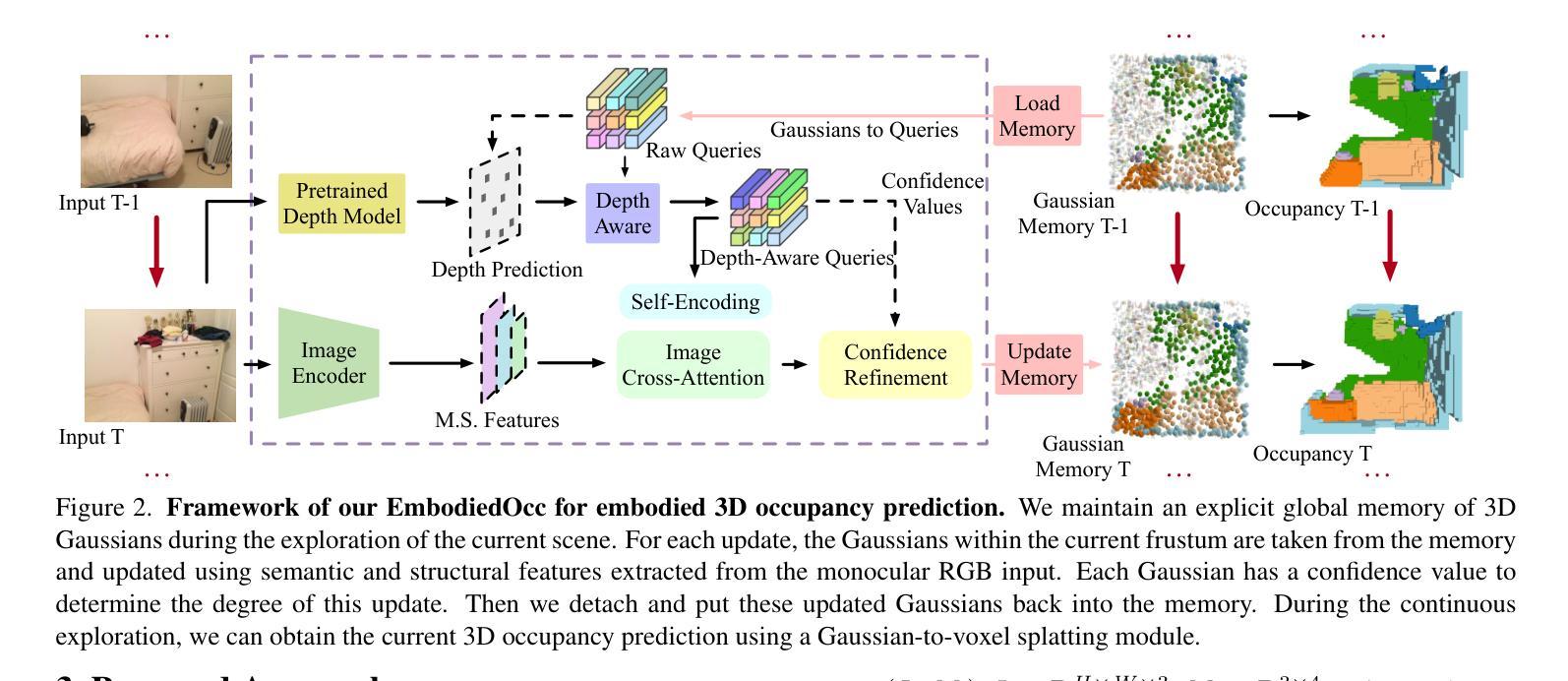
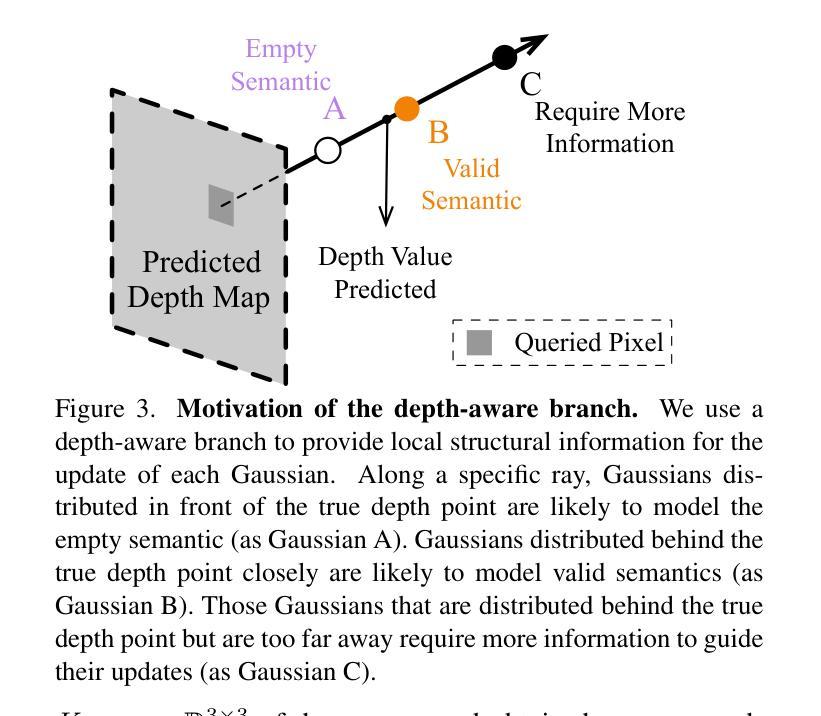
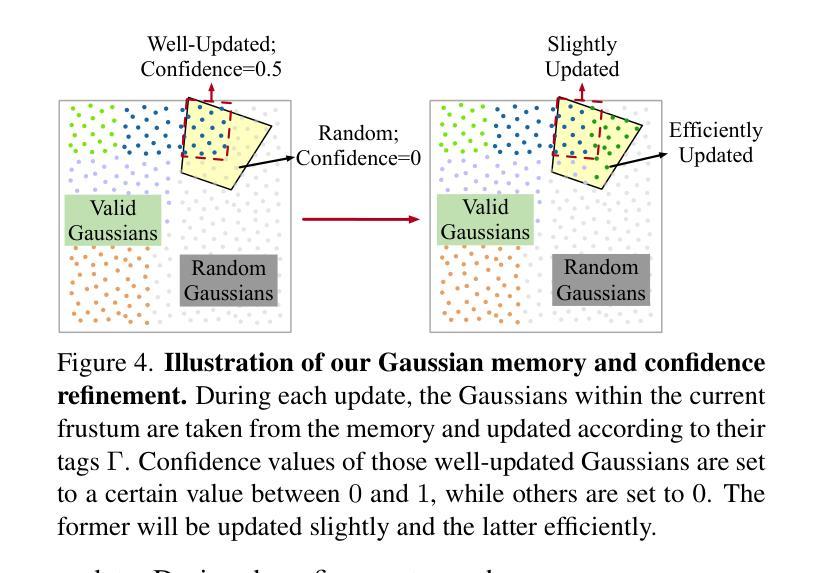
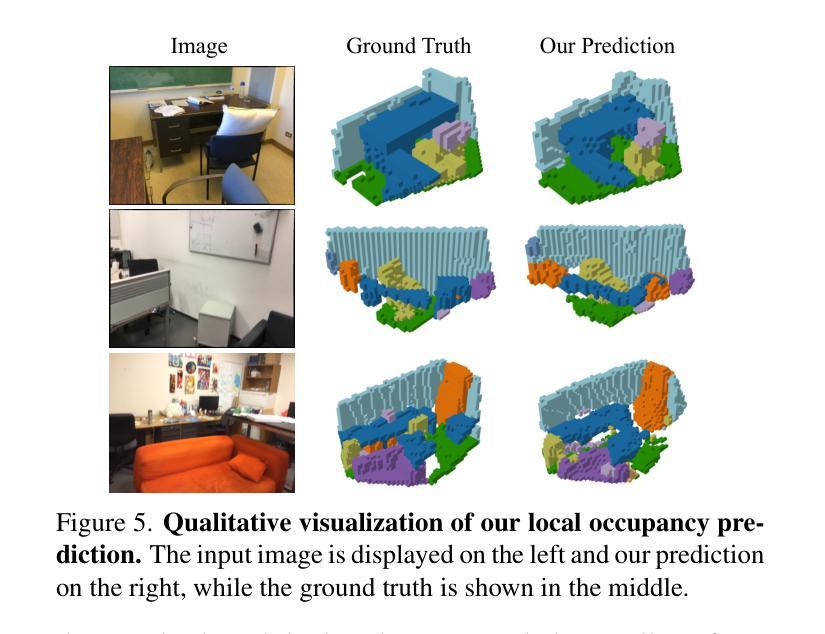
EmbodiedOcc: Embodied 3D Occupancy Prediction for Vision-based Online Scene Understanding
Authors:Yuqi Wu, Wenzhao Zheng, Sicheng Zuo, Yuanhui Huang, Jie Zhou, Jiwen Lu
3D occupancy prediction provides a comprehensive description of the surrounding scenes and has become an essential task for 3D perception. Most existing methods focus on offline perception from one or a few views and cannot be applied to embodied agents which demands to gradually perceive the scene through progressive embodied exploration. In this paper, we formulate an embodied 3D occupancy prediction task to target this practical scenario and propose a Gaussian-based EmbodiedOcc framework to accomplish it. We initialize the global scene with uniform 3D semantic Gaussians and progressively update local regions observed by the embodied agent. For each update, we extract semantic and structural features from the observed image and efficiently incorporate them via deformable cross-attention to refine the regional Gaussians. Finally, we employ Gaussian-to-voxel splatting to obtain the global 3D occupancy from the updated 3D Gaussians. Our EmbodiedOcc assumes an unknown (i.e., uniformly distributed) environment and maintains an explicit global memory of it with 3D Gaussians. It gradually gains knowledge through the local refinement of regional Gaussians, which is consistent with how humans understand new scenes through embodied exploration. We reorganize an EmbodiedOcc-ScanNet benchmark based on local annotations to facilitate the evaluation of the embodied 3D occupancy prediction task. Experiments demonstrate that our EmbodiedOcc outperforms existing local prediction methods and accomplishes the embodied occupancy prediction with high accuracy and strong expandability. Code: https://github.com/YkiWu/EmbodiedOcc.
3D占用预测为周围场景提供了全面的描述,已成为3D感知的重要任务。大多数现有方法侧重于从一个或少数几个视角进行的离线感知,无法应用于需要通过逐步的身体探索来感知场景的主体代理。本文针对这一实际场景制定了主体3D占用预测任务,并提出了基于高斯函数的EmbodiedOcc框架来完成。我们利用统一的3D语义高斯图初始化全局场景,并逐步更新主体代理观察到的局部区域。对于每次更新,我们从观察到的图像中提取语义和结构特征,并通过可变形交叉注意力有效地结合它们,以优化区域高斯图。最后,我们使用高斯到体素的摊开来获得全局3D占用图,这些图是从更新的3D高斯图中获取的。我们的EmbodiedOcc假设环境未知(即均匀分布),并利用明确的全球内存使用三维高斯对其进行维护。它通过区域高斯图的局部优化逐步获取知识,这与人类通过身体探索理解新场景的方式是一致的。我们根据局部注释重新组织了EmbodiedOcc-ScanNet基准测试,以便对主体3D占用预测任务进行评估。实验表明,我们的EmbodiedOcc优于现有的局部预测方法,并能以高度的准确性和强大的可扩展性完成主体占用预测。代码地址:https://github.com/YkiWu/EmbodiedOcc。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/YkiWu/EmbodiedOcc
Summary
本文提出了一个基于高斯分布的EmbodiedOcc框架,用于实现场景中的三维占用预测。通过逐步更新由智能体观察到的局部区域,该框架能够逐步感知场景,适用于智能体在现实环境中的实际应用。实验表明,EmbodiedOcc在本地预测方法上具有优势,能够实现高度准确和可扩展的三维占用预测。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一个全新的EmbodiedOcc框架用于三维占用预测。
- 该框架适用于智能体通过渐进式探索感知场景的实际应用场景。
- EmbodiedOcc采用基于高斯分布的方法,通过更新局部区域来逐步感知场景。
- 框架通过提取图像中的语义和结构特征,并结合可变形交叉注意力机制来优化局部高斯分布。
- 采用高斯到体素扩散技术,从更新的三维高斯分布中获取全局三维占用信息。
- EmbodiedOcc假设环境未知,并使用全局内存中的三维高斯分布来维护场景的明确表示。
点此查看论文截图

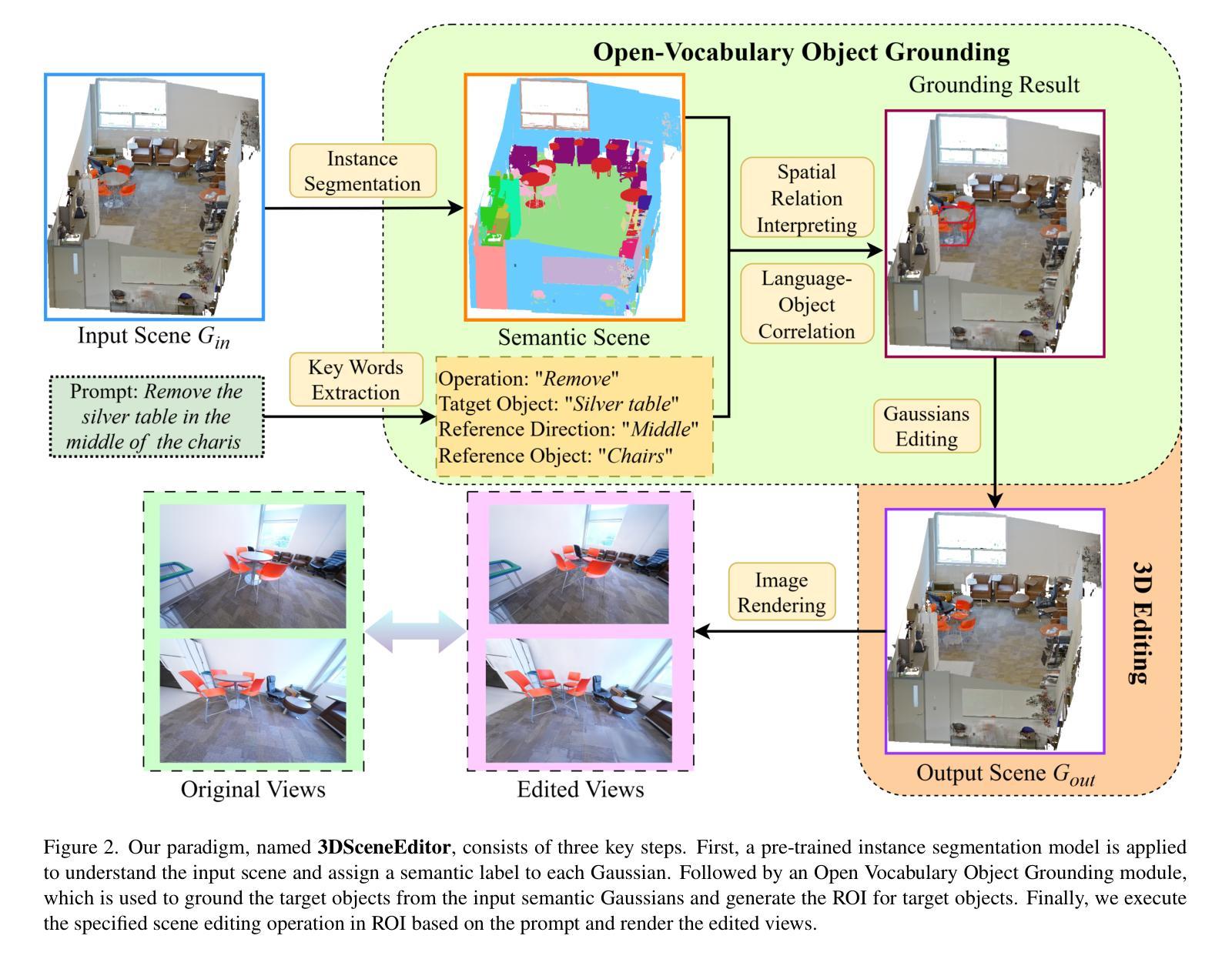
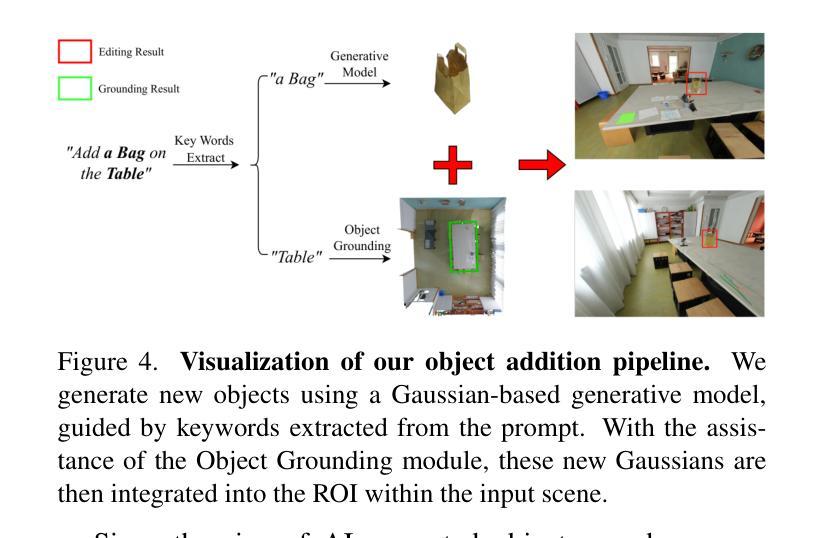
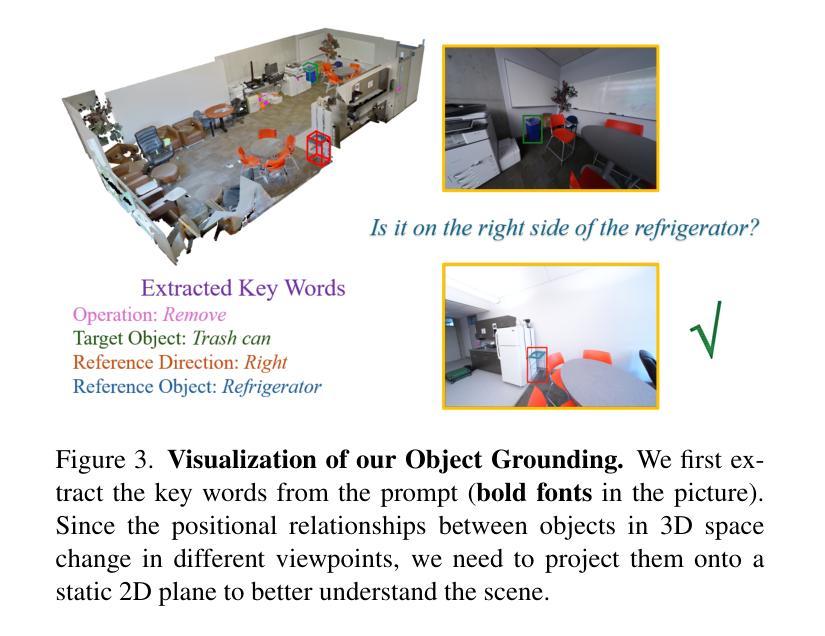
3DSceneEditor: Controllable 3D Scene Editing with Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Ziyang Yan, Lei Li, Yihua Shao, Siyu Chen, Zongkai Wu, Jenq-Neng Hwang, Hao Zhao, Fabio Remondino
The creation of 3D scenes has traditionally been both labor-intensive and costly, requiring designers to meticulously configure 3D assets and environments. Recent advancements in generative AI, including text-to-3D and image-to-3D methods, have dramatically reduced the complexity and cost of this process. However, current techniques for editing complex 3D scenes continue to rely on generally interactive multi-step, 2D-to-3D projection methods and diffusion-based techniques, which often lack precision in control and hamper real-time performance. In this work, we propose 3DSceneEditor, a fully 3D-based paradigm for real-time, precise editing of intricate 3D scenes using Gaussian Splatting. Unlike conventional methods, 3DSceneEditor operates through a streamlined 3D pipeline, enabling direct manipulation of Gaussians for efficient, high-quality edits based on input prompts.The proposed framework (i) integrates a pre-trained instance segmentation model for semantic labeling; (ii) employs a zero-shot grounding approach with CLIP to align target objects with user prompts; and (iii) applies scene modifications, such as object addition, repositioning, recoloring, replacing, and deletion directly on Gaussians. Extensive experimental results show that 3DSceneEditor achieves superior editing precision and speed with respect to current SOTA 3D scene editing approaches, establishing a new benchmark for efficient and interactive 3D scene customization.
传统上创建三维场景既耗费劳力又成本高昂,需要设计师精心配置三维资源和环境。近期生成式人工智能的进步,包括文本转三维和图像转三维的方法,已经大大降低了这一过程的复杂性和成本。然而,当前编辑复杂三维场景的技术仍然依赖于一般交互式的多步骤二维转三维投影方法和扩散技术,这些方法往往缺乏控制精度并影响实时性能。在这项工作中,我们提出了基于全三维的实时精确编辑复杂三维场景的范式——三维场景编辑器(SceneEditor)。它通过高斯渲染技术(Gaussian Splatting)进行直接操作。与传统的编辑方法不同,三维场景编辑器通过简化的三维流程进行操作,能够实现基于输入提示的高效高质量编辑。所提出的框架(一)集成了预训练的实例分割模型进行语义标注;(二)采用CLIP进行零样本定位法来匹配目标对象与用户提示;(三)直接在高斯渲染上对场景进行修改,如添加对象、重新定位、更改颜色、替换和删除对象等。大量的实验结果表明,相较于当前先进的三维场景编辑方法,三维场景编辑器在编辑精度和速度上更胜一筹,为高效交互式三维场景定制树立了新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://ziyangyan.github.io/3DSceneEditor
Summary
本文介绍了传统创建3D场景既耗时又昂贵的问题,并指出近年来生成式AI的进步显著降低了这一过程的复杂性和成本。然而,现有的复杂3D场景编辑技术仍依赖于互动多步骤的2D-to-3D投影方法和扩散技术,缺乏精确控制和实时性能。因此,本文提出了一个全新的全3D场景编辑框架——3DSceneEditor,它采用高斯描画技术,能够实现实时精确编辑复杂的3D场景。该框架集成了预训练的实例分割模型进行语义标注,并采用零样本定位法与用户提示对齐目标对象,实现场景修改,如添加、重新定位、改变颜色、替换和删除对象等。实验结果表明,相较于当前最先进的3D场景编辑方法,3DSceneEditor在编辑精度和速度上更胜一筹,为高效、交互式的3D场景定制树立了新标杆。
Key Takeaways
- 传统创建3D场景过程既耗时又昂贵。
- 生成式AI的进步降低了创建过程的复杂性和成本。
- 当前复杂3D场景编辑技术缺乏精确控制和实时性能。
- 提出了全新的全3D场景编辑框架——3DSceneEditor。
- 3DSceneEditor采用高斯描画技术实现实时精确编辑。
- 3DSceneEditor集成了预训练的实例分割模型和零样本定位法。
点此查看论文截图


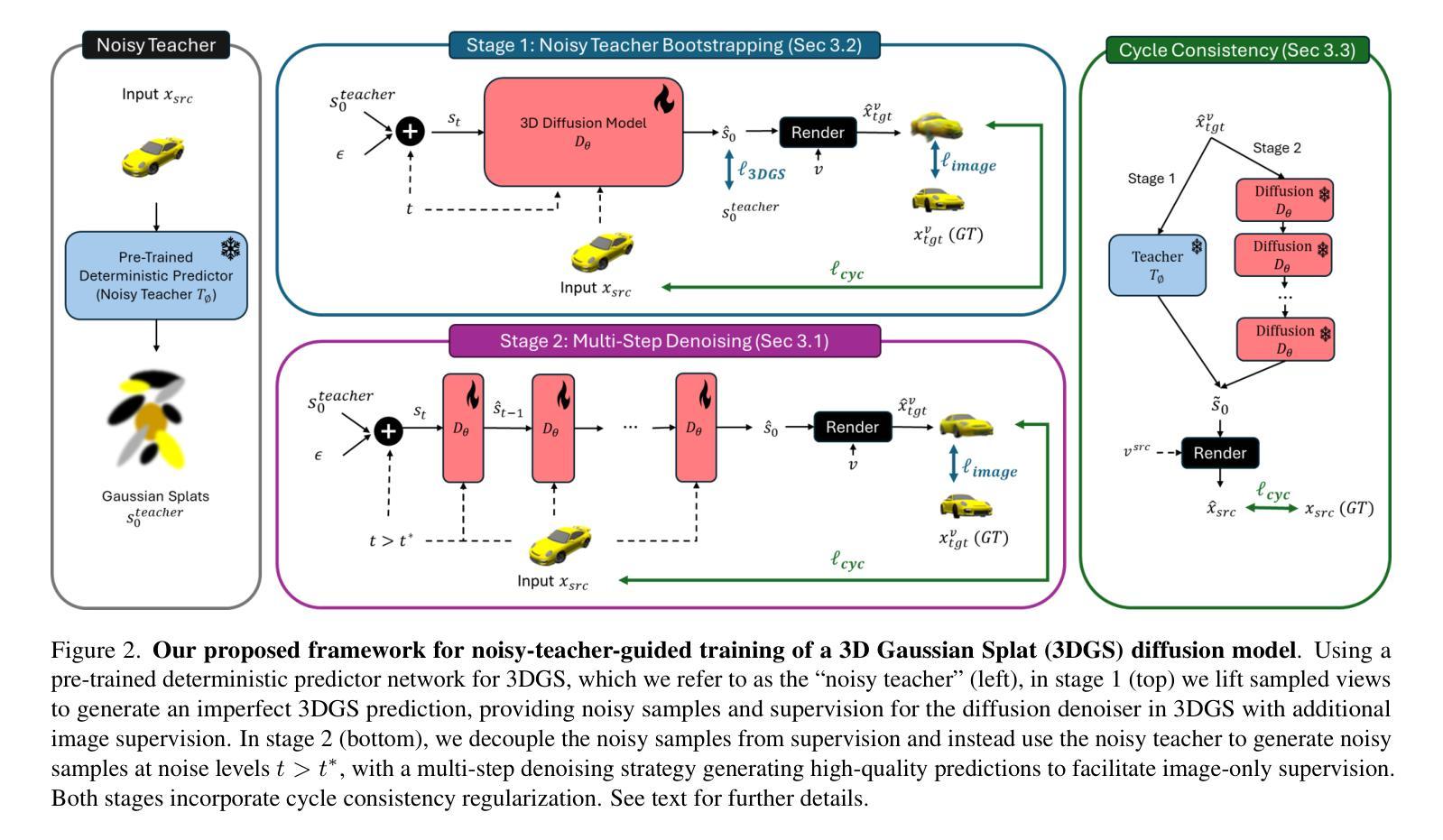
A Lesson in Splats: Teacher-Guided Diffusion for 3D Gaussian Splats Generation with 2D Supervision
Authors:Chensheng Peng, Ido Sobol, Masayoshi Tomizuka, Kurt Keutzer, Chenfeng Xu, Or Litany
We introduce a diffusion model for Gaussian Splats, SplatDiffusion, to enable generation of three-dimensional structures from single images, addressing the ill-posed nature of lifting 2D inputs to 3D. Existing methods rely on deterministic, feed-forward predictions, which limit their ability to handle the inherent ambiguity of 3D inference from 2D data. Diffusion models have recently shown promise as powerful generative models for 3D data, including Gaussian splats; however, standard diffusion frameworks typically require the target signal and denoised signal to be in the same modality, which is challenging given the scarcity of 3D data. To overcome this, we propose a novel training strategy that decouples the denoised modality from the supervision modality. By using a deterministic model as a noisy teacher to create the noised signal and transitioning from single-step to multi-step denoising supervised by an image rendering loss, our approach significantly enhances performance compared to the deterministic teacher. Additionally, our method is flexible, as it can learn from various 3D Gaussian Splat (3DGS) teachers with minimal adaptation; we demonstrate this by surpassing the performance of two different deterministic models as teachers, highlighting the potential generalizability of our framework. Our approach further incorporates a guidance mechanism to aggregate information from multiple views, enhancing reconstruction quality when more than one view is available. Experimental results on object-level and scene-level datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework.
我们引入了一种高斯Splats的扩散模型,称为SplatDiffusion,用于从单张图像生成三维结构,解决将二维输入提升到三维的不适定性问题。现有方法依赖于确定性前馈预测,这限制了它们处理从二维数据到三维推断的内在模糊性的能力。扩散模型最近在三维数据的强大生成模型方面显示出潜力,包括高斯splats;然而,标准的扩散框架通常需要目标信号和去噪信号处于同一模态,这在三维数据稀缺的情况下具有挑战性。为了克服这一问题,我们提出了一种新的训练策略,将去噪模态与监督模态解耦。通过使用确定性模型作为噪声教师来创建噪声信号,并从单步过渡到由图像渲染损失监督的多步去噪,我们的方法在性能上显著优于确定性教师。此外,我们的方法很灵活,可以很容易地从各种三维高斯Splat(3DGS)教师那里学习,并且几乎不需要适应;我们通过超越两个不同确定性模型教师的性能来证明这一点,突出了我们框架的潜在通用性。我们的方法还采用了一种指导机制来整合多个视角的信息,在可用多个视角时提高重建质量。在对象级和场景级数据集上的实验结果证明了我们的框架的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究介绍了一种用于从单一图像生成三维结构的扩散模型——SplatDiffusion。该模型解决了将二维输入提升到三维的适定性问题。现有方法依赖于确定性前馈预测,这限制了它们处理从二维数据推断三维信息的固有模糊性的能力。本研究采用扩散模型,提出一种新型训练策略,将去噪模态与监督模态解耦,使用确定性模型作为噪声教师创建噪声信号,从单步过渡到多步去噪,由图像渲染损失进行监督。该方法显著提高了性能,并具备灵活性,能够从不同3D高斯平板教师模型中学习,通过超越两个不同确定性教师的性能来展示框架的潜在通用性。此外,该方法还融入了一种指导机制,能够聚合多视角的信息,提高重建质量。
Key Takeaways
- 研究引入了SplatDiffusion模型,这是一种用于从单一图像生成三维结构的扩散模型。
- 该模型解决了将二维输入提升到三维的适定性问题。
- 现有方法主要依赖确定性前馈预测,存在处理3D推断的固有模糊性的限制。
- 研究采用扩散模型并提出新型训练策略,将去噪模态与监督模态解耦。
- 使用确定性模型作为噪声教师,从单步去噪过渡到多步去噪,通过图像渲染损失进行监督,提高性能。
- 模型具备灵活性,能够轻松适应不同的3D高斯平板教师模型。
点此查看论文截图

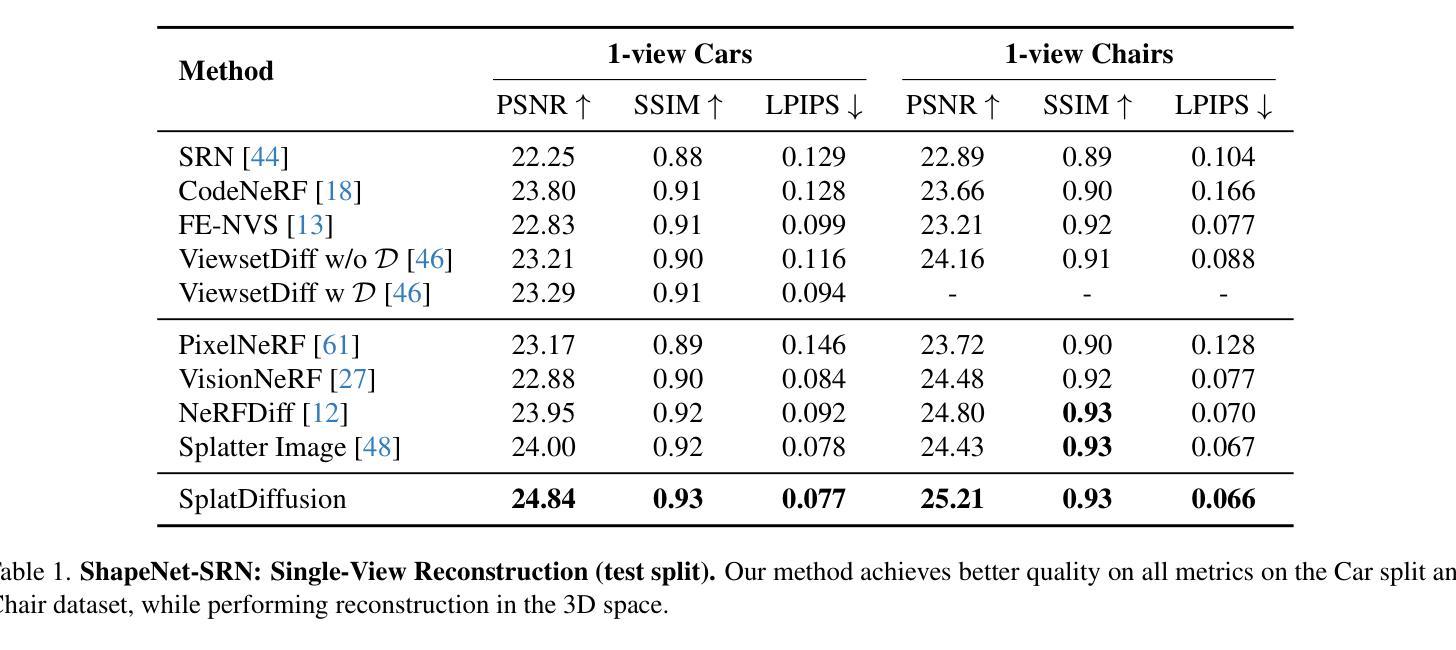
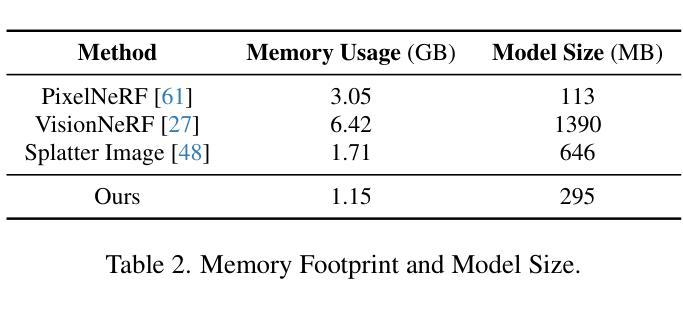
Make-It-Animatable: An Efficient Framework for Authoring Animation-Ready 3D Characters
Authors:Zhiyang Guo, Jinxu Xiang, Kai Ma, Wengang Zhou, Houqiang Li, Ran Zhang
3D characters are essential to modern creative industries, but making them animatable often demands extensive manual work in tasks like rigging and skinning. Existing automatic rigging tools face several limitations, including the necessity for manual annotations, rigid skeleton topologies, and limited generalization across diverse shapes and poses. An alternative approach is to generate animatable avatars pre-bound to a rigged template mesh. However, this method often lacks flexibility and is typically limited to realistic human shapes. To address these issues, we present Make-It-Animatable, a novel data-driven method to make any 3D humanoid model ready for character animation in less than one second, regardless of its shapes and poses. Our unified framework generates high-quality blend weights, bones, and pose transformations. By incorporating a particle-based shape autoencoder, our approach supports various 3D representations, including meshes and 3D Gaussian splats. Additionally, we employ a coarse-to-fine representation and a structure-aware modeling strategy to ensure both accuracy and robustness, even for characters with non-standard skeleton structures. We conducted extensive experiments to validate our framework’s effectiveness. Compared to existing methods, our approach demonstrates significant improvements in both quality and speed.
三维角色在现代创意产业中至关重要,但使其可动画化通常需要大量手动工作,如装配和蒙皮等任务。现有的自动装配工具面临多种限制,包括需要手动注释、刚性的骨骼拓扑结构以及在各种形状和姿势上的通用性有限。另一种方法是生成预先绑定到装配模板网格的可动画化身。然而,这种方法通常缺乏灵活性,并且通常仅限于逼真的人形。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Make-It-Animatable这一新型数据驱动方法,可在不到一秒的时间内使任何三维人形模型为角色动画做好准备,无论其形状和姿势如何。我们的统一框架生成高质量的混合权重、骨骼和姿势转换。通过采用基于粒子的形状自编码器,我们的方法支持各种三维表示,包括网格和三维高斯斑块。此外,我们还采用了从粗到细的代表和结构感知建模策略,以确保即使在具有非标准骨骼结构的角色身上也能实现准确性和稳健性。我们进行了大量实验来验证我们框架的有效性。与现有方法相比,我们的方法在质量和速度方面都显示出显着改进。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://jasongzy.github.io/Make-It-Animatable/
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Make-It-Animatable的新型数据驱动方法,该方法可在不到一秒的时间内使任何3D人类模型为角色动画做好准备,不受形状和姿势的限制。该方法通过生成高质量混合权重、骨骼和姿势转换,支持多种3D表示形式,包括网格和3D高斯斑块。该方法采用由粗到细的表现形式和结构感知建模策略,确保准确性和稳健性,即使对于具有非标准骨骼结构的角色也是如此。
Key Takeaways
- 3D角色在现代创意产业中的重要性以及自动使其可动画化的挑战。
- 现有自动矫形工具存在的局限性,包括需要手动注释、骨骼拓扑结构僵硬以及难以在多种形状和姿势之间实现通用性。
- Make-It-Animatable方法的核心特点:在不到一秒的时间内使任何3D人类模型为角色动画做好准备,不受形状和姿势限制。
- 该方法通过生成高质量混合权重、骨骼和姿势转换来支持多种3D表示形式,包括网格和3D高斯斑块。
- 方法的两个关键组成部分:粒子基础的形状自编码器和从粗到细的表现方式及结构感知建模策略。
- 该方法在质量和速度方面与现有方法的显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

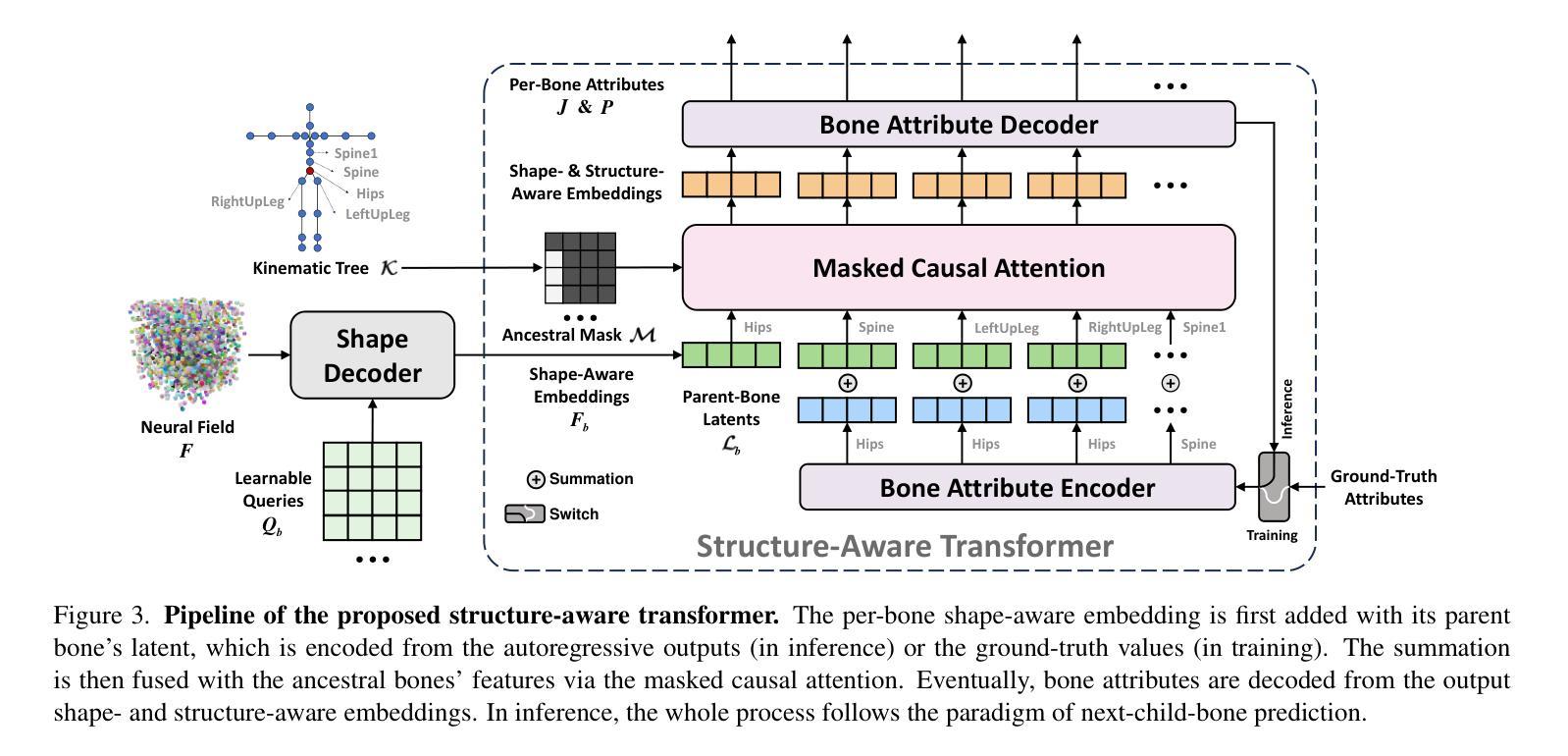
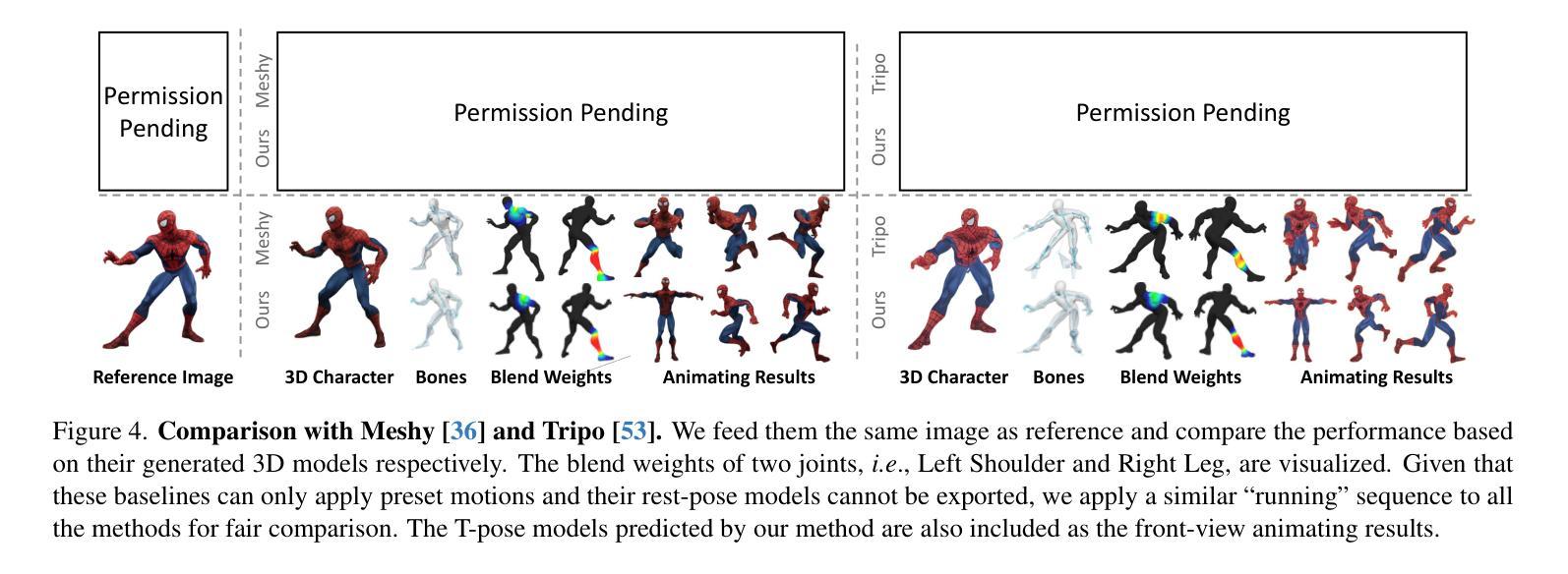
SpectroMotion: Dynamic 3D Reconstruction of Specular Scenes
Authors:Cheng-De Fan, Chen-Wei Chang, Yi-Ruei Liu, Jie-Ying Lee, Jiun-Long Huang, Yu-Chee Tseng, Yu-Lun Liu
We present SpectroMotion, a novel approach that combines 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) with physically-based rendering (PBR) and deformation fields to reconstruct dynamic specular scenes. Previous methods extending 3DGS to model dynamic scenes have struggled to represent specular surfaces accurately. Our method addresses this limitation by introducing a residual correction technique for accurate surface normal computation during deformation, complemented by a deformable environment map that adapts to time-varying lighting conditions. We implement a coarse-to-fine training strategy that significantly enhances scene geometry and specular color prediction. It is the only existing 3DGS method capable of synthesizing photorealistic real-world dynamic specular scenes, outperforming state-of-the-art methods in rendering complex, dynamic, and specular scenes. See our project page for video results at https://cdfan0627.github.io/spectromotion/.
我们提出了SpectroMotion,这是一种结合3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)、基于物理的渲染(PBR)和变形场来重建动态镜面场景的新方法。之前将3DGS扩展到动态场景建模的方法在准确表示镜面表面方面遇到了困难。我们的方法通过引入残差校正技术来解决这一限制,以在变形过程中进行准确的表面法线计算,辅以可适应时间变化光照条件的可变形环境贴图。我们实现了从粗到细的训练策略,显著提高了场景几何和镜面颜色预测。它是目前唯一一种能够合成逼真动态镜面场景的3DGS方法,在渲染复杂、动态和镜面场景方面优于最先进的方法。视频结果请参见我们的项目页面:https://cdfan0627.github.io/spectromotion/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://cdfan0627.github.io/spectromotion/
Summary
光谱运动是一种结合3D高斯喷溅技术(3DGS)、物理渲染(PBR)和变形场来重建动态镜面场景的新方法。该方法解决了之前将3DGS扩展到动态场景建模中难以准确表示镜面表面的问题,并可通过残余校正技术和可变形环境映射技术来适应随时间变化的光照条件。实施了一种由粗到细的训练策略,可显著提高场景几何和镜面颜色的预测能力,成为唯一能够合成逼真现实动态镜面场景的3DGS方法,优于当前在渲染复杂、动态和镜面场景方面的其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- SpectroMotion结合了3DGS、PBR和变形场技术来重建动态镜面场景。
- 引入残余校正技术,解决了之前方法难以准确表示镜面表面的问题。
- 通过可变形环境映射技术,适应了随时间变化的光照条件。
- 采用了由粗到细的训练策略,提高了场景几何和镜面颜色预测的精确度。
- 成为唯一能够合成逼真现实动态镜面场景的3DGS方法。
- 该方法在渲染复杂、动态和镜面场景方面优于当前的其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

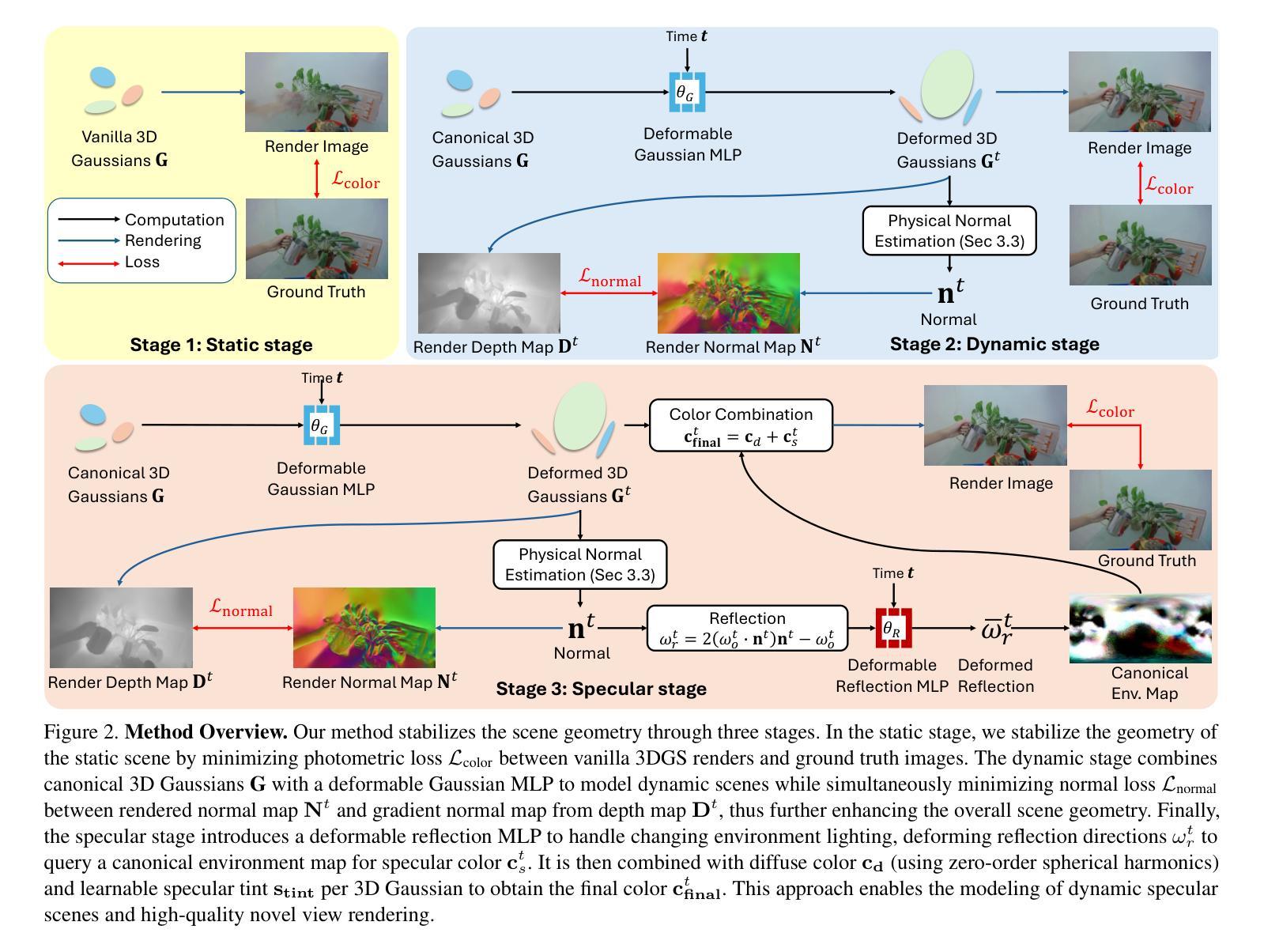
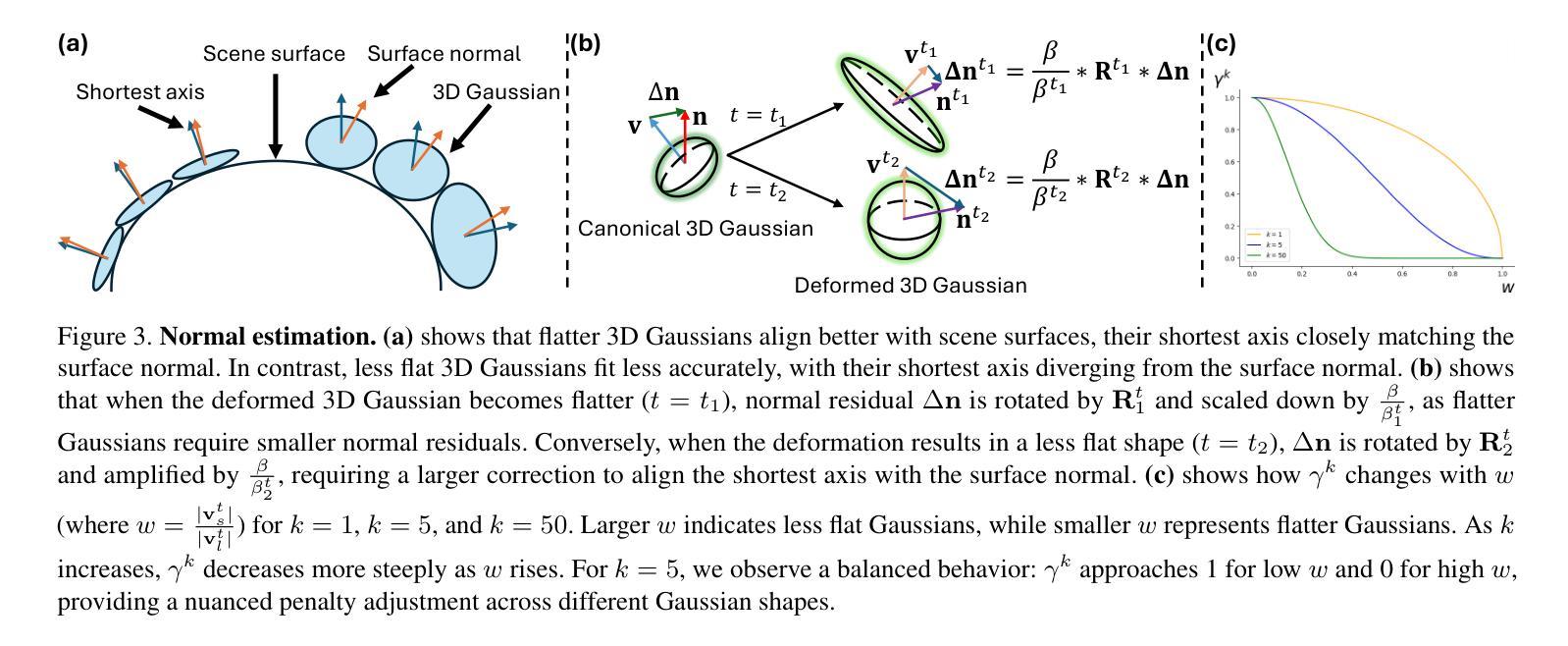
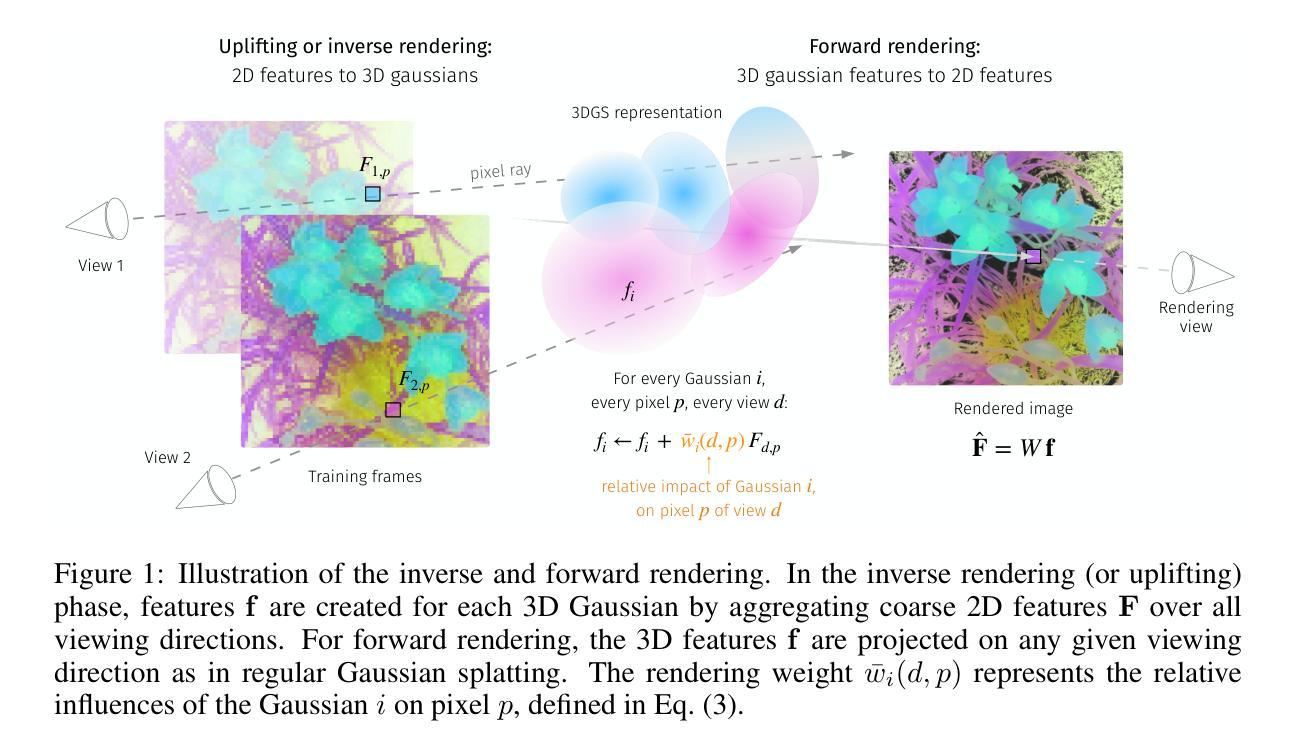
LUDVIG: Learning-free Uplifting of 2D Visual features to Gaussian Splatting scenes
Authors:Juliette Marrie, Romain Menegaux, Michael Arbel, Diane Larlus, Julien Mairal
We address the problem of extending the capabilities of vision foundation models such as DINO, SAM, and CLIP, to 3D tasks. Specifically, we introduce a novel method to uplift 2D image features into 3D Gaussian Splatting scenes. Unlike traditional approaches that rely on minimizing a reconstruction loss, our method employs a simpler and more efficient feature aggregation technique, augmented by a graph diffusion mechanism. Graph diffusion enriches features from a given model, such as CLIP, by leveraging 3D geometry and pairwise similarities induced by another strong model such as DINOv2. Our approach achieves performance comparable to the state of the art on multiple downstream tasks while delivering significant speed-ups. Notably, we obtain competitive segmentation results using generic DINOv2 features, despite DINOv2 not being trained on millions of annotated segmentation masks like SAM. When applied to CLIP features, our method demonstrates strong performance in open-vocabulary object detection tasks, highlighting the versatility of our approach.
我们致力于扩展如DINO、SAM和CLIP等视觉基础模型在3D任务上的能力。具体来说,我们提出了一种将2D图像特征提升到3D高斯贴图场景的新方法。不同于传统方法依赖最小化重建损失,我们的方法采用更简单高效的特征聚合技术,辅以图扩散机制。图扩散通过利用3D几何和由另一个强大模型(如DINOv2)引起的配对相似性,丰富了给定模型(如CLIP)的特征。我们的方法在多个下游任务上实现了与最新技术相当的性能,同时提供了显著的速度提升。值得注意的是,即使DINOv2没有像SAM那样在数百万个标注的分割掩膜上进行训练,我们仍然获得了具有竞争力的分割结果。当应用于CLIP特性时,我们的方法在开放词汇表对象检测任务中表现出强大的性能,凸显了我们方法的通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨如何将视觉基础模型(如DINO、SAM和CLIP)的能力扩展到3D任务。提出了一种新颖的方法,将2D图像特征提升为3D高斯混合场景。与传统方法不同,该方法采用更简单高效的特征聚合技术,辅以图扩散机制。图扩散丰富了给定模型(如CLIP)的特征,利用3D几何和由另一强大模型(如DINOv2)引起的成对相似性。该方法在多个下游任务上的性能与最新技术相当,同时提供了显著的速度提升。在通用DINOv2特征上获得具有竞争力的分割结果,即使在SAM未进行数百万标注分割掩膜训练的情况下也是如此。当应用于CLIP特性时,该方法在开放词汇表目标检测任务中表现出强大的性能,体现了该方法的通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 本文扩展了视觉基础模型(如DINO、SAM和CLIP)在3D任务中的应用能力。
- 提出了一种新的方法,通过3D高斯混合场景将2D图像特征转化为3D。
- 与传统方法相比,新方法采用特征聚合技术和图扩散机制,更高效、更简单。
- 图扩散机制丰富了模型的特征,结合了3D几何和成对相似性。
- 该方法在多个下游任务上的性能与最新技术相当,并且具有显著的速度优势。
- 使用通用的DINOv2特征获得有竞争力的分割结果,即使在没有专门的训练数据的情况下也是如此。
点此查看论文截图

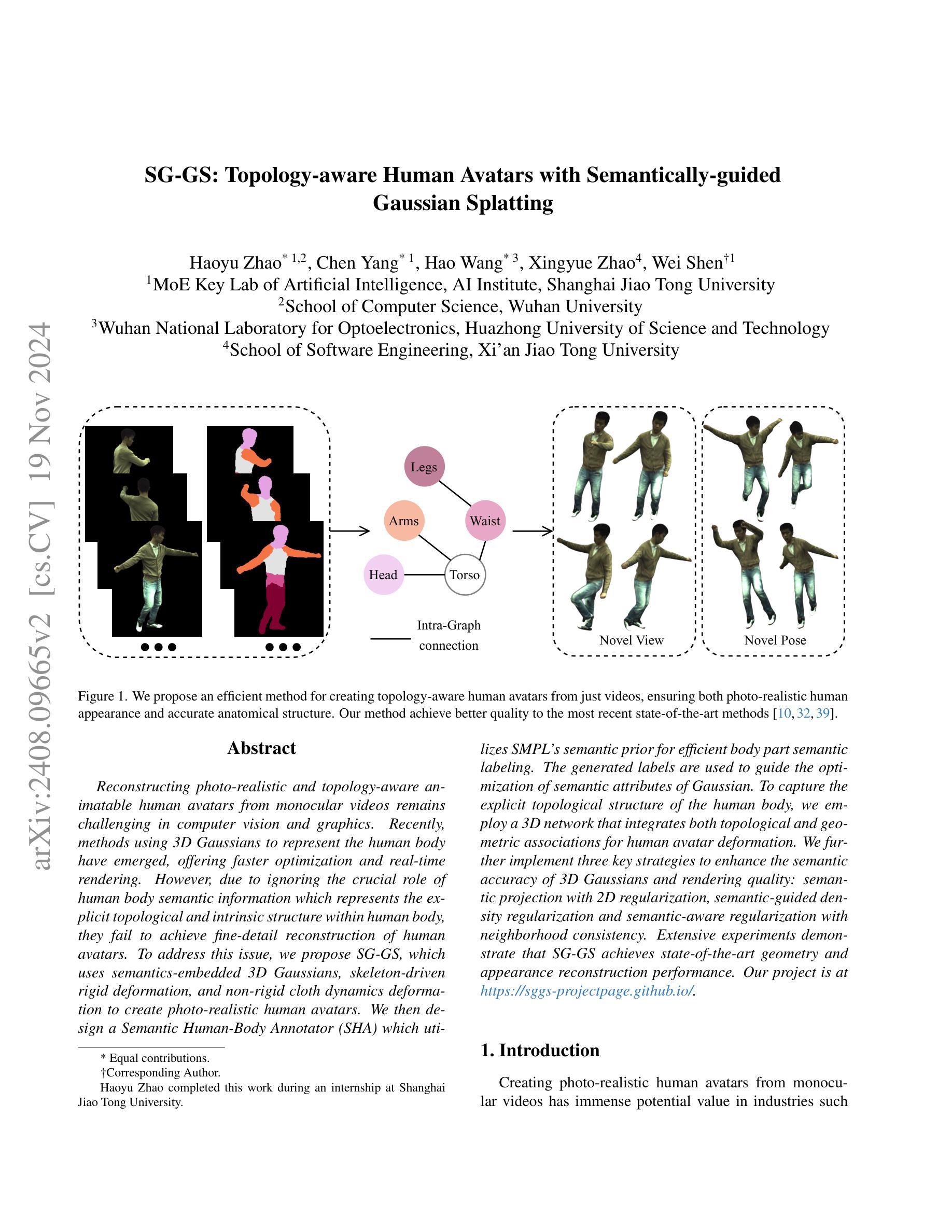
Topology-aware Human Avatars with Semantically-guided Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Haoyu Zhao, Chen Yang, Hao Wang, Xingyue Zhao, Wei Shen
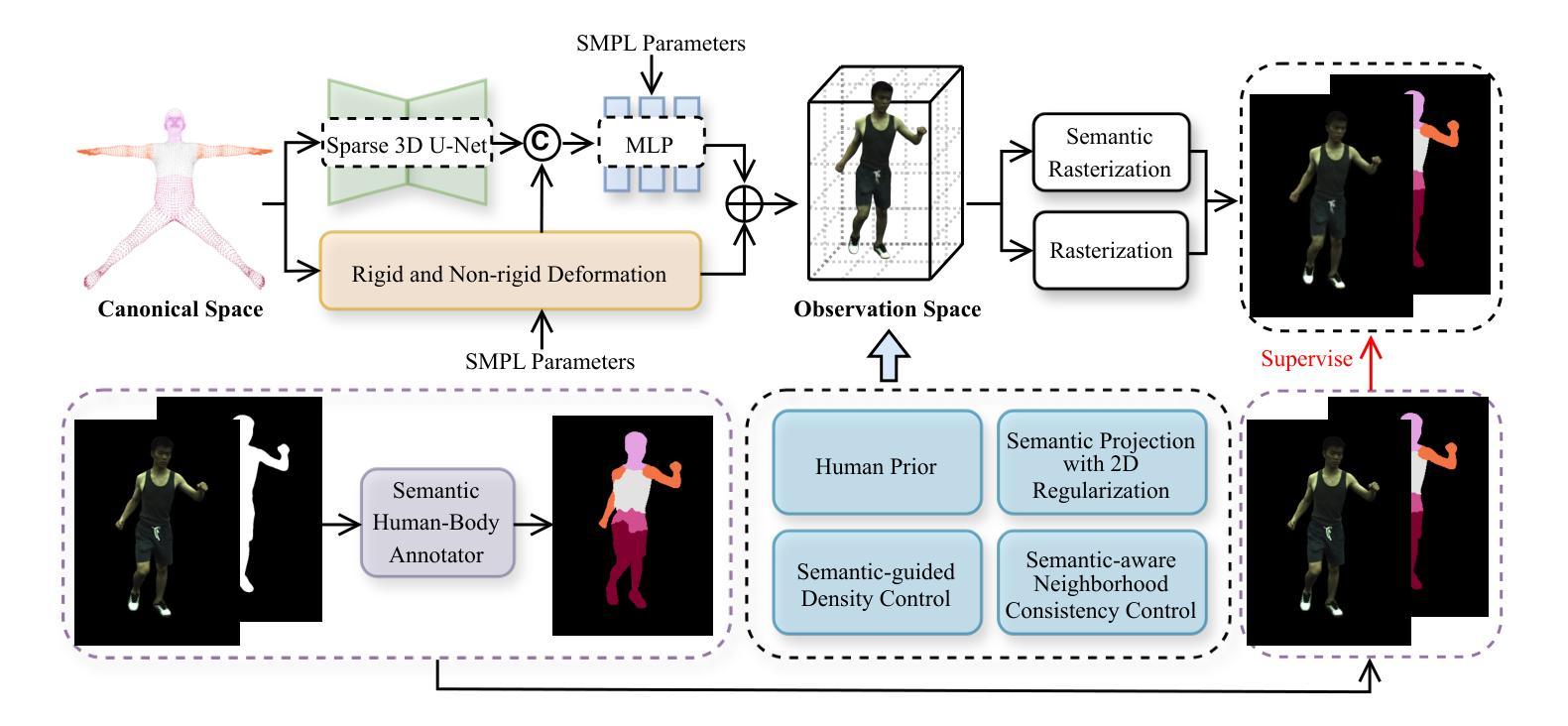
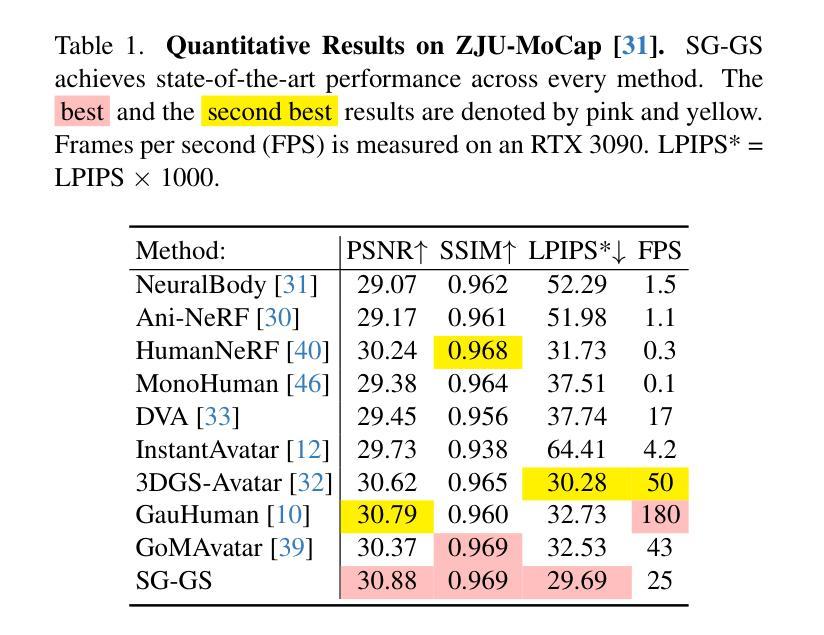
Reconstructing photo-realistic and topology-aware animatable human avatars from monocular videos remains challenging in computer vision and graphics. Recently, methods using 3D Gaussians to represent the human body have emerged, offering faster optimization and real-time rendering. However, due to ignoring the crucial role of human body semantic information which represents the explicit topological and intrinsic structure within human body, they fail to achieve fine-detail reconstruction of human avatars. To address this issue, we propose SG-GS, which uses semantics-embedded 3D Gaussians, skeleton-driven rigid deformation, and non-rigid cloth dynamics deformation to create photo-realistic human avatars. We then design a Semantic Human-Body Annotator (SHA) which utilizes SMPL’s semantic prior for efficient body part semantic labeling. The generated labels are used to guide the optimization of semantic attributes of Gaussian. To capture the explicit topological structure of the human body, we employ a 3D network that integrates both topological and geometric associations for human avatar deformation. We further implement three key strategies to enhance the semantic accuracy of 3D Gaussians and rendering quality: semantic projection with 2D regularization, semantic-guided density regularization and semantic-aware regularization with neighborhood consistency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SG-GS achieves state-of-the-art geometry and appearance reconstruction performance.
重建单眼视频中的照片级真实和拓扑感知动画人形,在计算机视觉和图形学中仍然是一个挑战。近期,使用三维高斯表示人体的方法已经出现,提供了更快的优化和实时渲染。然而,由于忽略了人体语义信息的重要角色,这些语义信息代表人体内部的明确拓扑结构和内在结构,因此它们无法实现对人形的精细细节重建。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了SG-GS,它使用嵌入语义的三维高斯、骨架驱动的刚性变形和非刚性布料动态变形来创建照片级真实的人形。然后,我们设计了一个语义人体注释器(SHA),它利用SMPL的语义先验来进行有效的身体部位语义标记。生成的标签被用来指导高斯语义属性的优化。为了捕捉人体的明确拓扑结构,我们采用了一个三维网络,该网络结合了拓扑和几何关联来进行人形变形。我们还实施了三个关键策略,以提高三维高斯的语义准确性和渲染质量:二维正则化的语义投影、语义引导的密度正则化和具有邻域一致性的语义感知正则化。大量实验表明,SG-GS达到了最先进的几何和外观重建性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于单目视频重建具有真实感和拓扑感知的动态人体avatar仍具有挑战性。最近出现使用3D高斯表示人体的方法,但忽略了人体语义信息的重要性,无法实现精细的人体重建。为解决此问题,我们提出SG-GS方法,结合语义嵌入的3D高斯、骨架驱动的刚性变形和非刚性布料动态变形技术,创建真实感的人体avatar。我们设计了一个语义人体标注器(SHA),利用SMPL的语义先验进行高效的部位语义标注。通过实施三个关键策略提高3D高斯的语义准确性和渲染质量:二维正则化的语义投影、语义引导的密度正则化和具有邻域一致性的语义感知正则化。实验证明SG-GS达到领先的几何和外观重建性能。
Key Takeaways
- 重建真实和拓扑感知的动态人体avatar在单目视频中仍面临挑战。
- 目前方法使用3D高斯表示人体,但忽略了语义信息的重要性,影响精细重建。
- 提出SG-GS方法结合语义嵌入的3D高斯和骨架驱动变形技术,实现真实感的人体avatar创建。
- 设计语义人体标注器(SHA)进行高效部位语义标注。
- 实施三个策略提高语义准确性和渲染质量:语义投影、密度正则化和语义感知正则化。
点此查看论文截图

3D-Consistent Human Avatars with Sparse Inputs via Gaussian Splatting and Contrastive Learning
Authors:Haoyu Zhao, Hao Wang, Chen Yang, Wei Shen
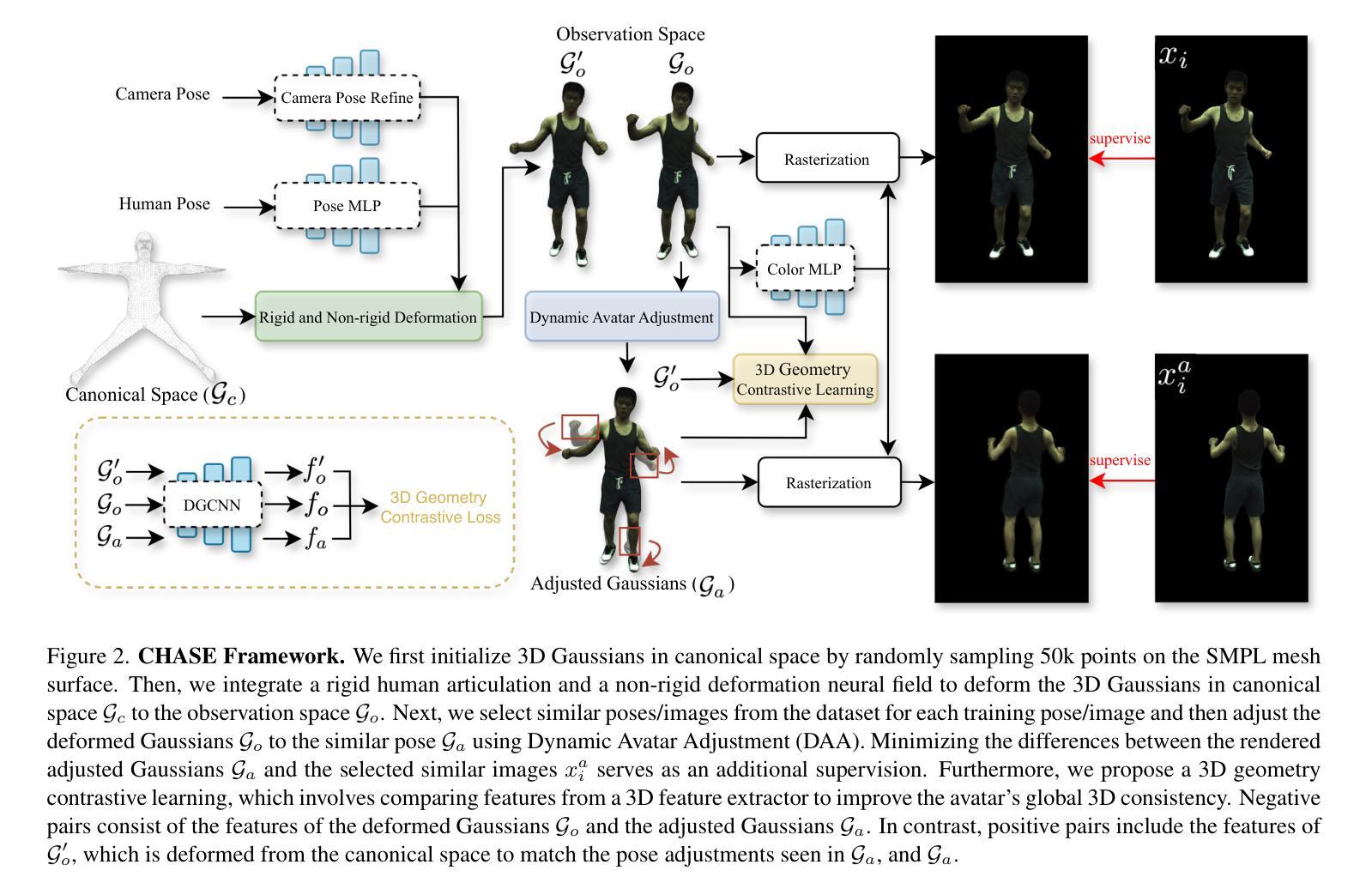
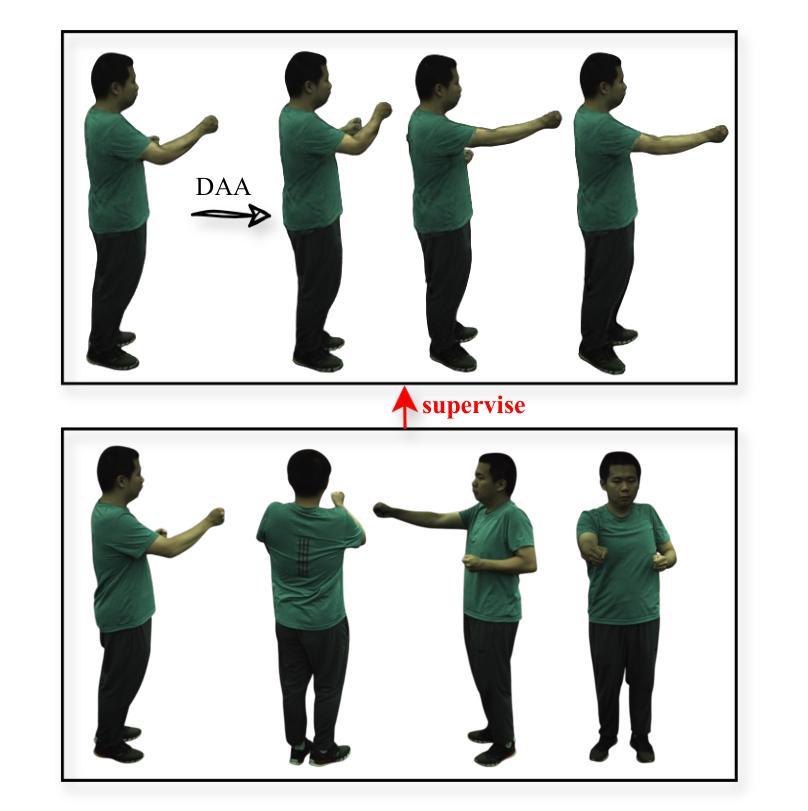
Existing approaches for human avatar generation–both NeRF-based and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) based–struggle with maintaining 3D consistency and exhibit degraded detail reconstruction, particularly when training with sparse inputs. To address this challenge, we propose CHASE, a novel framework that achieves dense-input-level performance using only sparse inputs through two key innovations: cross-pose intrinsic 3D consistency supervision and 3D geometry contrastive learning. Building upon prior skeleton-driven approaches that combine rigid deformation with non-rigid cloth dynamics, we first establish baseline avatars with fundamental 3D consistency. To enhance 3D consistency under sparse inputs, we introduce a Dynamic Avatar Adjustment (DAA) module, which refines deformed Gaussians by leveraging similar poses from the training set. By minimizing the rendering discrepancy between adjusted Gaussians and reference poses, DAA provides additional supervision for avatar reconstruction. We further maintain global 3D consistency through a novel geometry-aware contrastive learning strategy. While designed for sparse inputs, CHASE surpasses state-of-the-art methods across both full and sparse settings on ZJU-MoCap and H36M datasets, demonstrating that our enhanced 3D consistency leads to superior rendering quality.
现有的人形化身生成方法,无论是基于NeRF的还是基于3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)的,在保持3D一致性方面都存在困难,并且在细节重建方面表现出退化,特别是在使用稀疏输入进行训练时更是如此。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了CHASE,这是一个新型框架,它仅通过两项关键创新——跨姿势内在3D一致性监督和3D几何对比学习,使用稀疏输入实现密集输入级别的性能。我们建立在先前结合刚性变形与非刚性布料动力学的骨架驱动方法之上,首先建立具有基本3D一致性的基准化身。为了提高稀疏输入下的3D一致性,我们引入了动态化身调整(DAA)模块,该模块通过利用训练集中的相似姿势来优化变形的高斯。通过最小化调整后的高斯与参考姿势之间的渲染差异,DAA为化身重建提供了额外的监督。我们还通过一种新型几何感知对比学习策略来保持全局3D一致性。虽然是为稀疏输入而设计的,但CHASE在ZJU-MoCap和H36M数据集上的全面和稀疏设置方面都超越了最新方法,表明我们增强的3D一致性导致了更高的渲染质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于现有的人类角色生成方法面临的挑战,本文提出了一种名为CHASE的新型框架,该框架在稀疏输入下实现了密集输入级别的性能表现。通过引入跨姿态内在三维一致性监督和三维几何对比学习两大创新点,该框架优化了三维一致性并保持了对稀疏输入的细节重建。此外,本文还引入动态角色调整模块来优化现有角色,以及几何感知对比学习策略来维持全局三维一致性。通过实验证明,无论是在全数据还是稀疏数据环境下,CHASE框架在ZJU-MoCap和H36M数据集上的表现均超越了现有方法,展现了其卓越的三维一致性和渲染质量。
Key Takeaways
- CHASE框架解决了现有方法在保持三维一致性和重建细节方面的挑战。
- CHASE框架引入两大创新点:跨姿态内在三维一致性监督和三维几何对比学习。
- 动态角色调整模块用于优化现有角色,通过最小化调整后的高斯和参考姿态之间的渲染差异来实现对角色重建的额外监督。
- 几何感知对比学习策略用于维持全局三维一致性。
- CHASE框架在ZJU-MoCap和H36M数据集上的表现超越了现有方法。
- CHASE框架适用于不同的输入环境,包括稀疏输入和全数据环境。
点此查看论文截图


LumiGauss: Relightable Gaussian Splatting in the Wild
Authors:Joanna Kaleta, Kacper Kania, Tomasz Trzcinski, Marek Kowalski
Decoupling lighting from geometry using unconstrained photo collections is notoriously challenging. Solving it would benefit many users as creating complex 3D assets takes days of manual labor. Many previous works have attempted to address this issue, often at the expense of output fidelity, which questions the practicality of such methods. We introduce LumiGauss - a technique that tackles 3D reconstruction of scenes and environmental lighting through 2D Gaussian Splatting. Our approach yields high-quality scene reconstructions and enables realistic lighting synthesis under novel environment maps. We also propose a method for enhancing the quality of shadows, common in outdoor scenes, by exploiting spherical harmonics properties. Our approach facilitates seamless integration with game engines and enables the use of fast precomputed radiance transfer. We validate our method on the NeRF-OSR dataset, demonstrating superior performance over baseline methods. Moreover, LumiGauss can synthesize realistic images for unseen environment maps. Our code: https://github.com/joaxkal/lumigauss.
使用无约束照片集将照明与几何分离是出了名的具有挑战性。解决这一问题将使许多用户受益,因为创建复杂的3D资产需要数天的人工劳动。许多以前的工作试图解决这一问题,通常以输出保真度的损失为代价,这引发了对此类方法实用性的质疑。我们介绍了LumiGauss——一种通过二维高斯Splatting解决场景三维重建和环境照明问题的技术。我们的方法能产生高质量的场景重建,并在新的环境贴图下实现逼真的照明合成。我们还提出了一种利用球面谐波属性改善户外场景中常见阴影质量的方法。我们的方法与游戏引擎无缝集成,并利用快速预计算辐射传输。我们在NeRF-OSR数据集上验证了我们的方法,表现出优于基准方法的性能。此外,LumiGauss还可以为未见过的环境地图合成逼真的图像。我们的代码:https://github.com/joaxkal/lumigauss。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at WACV2025
Summary
光照与几何的解耦是一项挑战性任务,涉及大量复杂的3D建模工作。现有的解决方案常会影响输出的真实感,影响了实际应用效果。本研究推出LumiGauss技术,借助二维高斯细分解决三维场景的重建和照明问题。不仅能重构高质量场景,还能在全新环境下生成真实照明环境地图。同时,该技术还能优化户外场景中的阴影质量,利用球面谐波属性提升效果。该技术易于与游戏引擎集成,支持快速预计算辐射度转移。在NeRF-OSR数据集上的验证显示其性能优于基准方法,还能合成未见环境地图的真实图像。
Key Takeaways
- LumiGauss技术能够实现光照与几何解耦的三维场景重建和照明合成。
- 通过二维高斯细分实现高质量场景重构及真实感照明合成。
- 利用球面谐波属性优化户外场景的阴影质量。
- 技术易于与游戏引擎集成,支持快速预计算辐射度转移。
- 在NeRF-OSR数据集上的验证证明了其性能优越性。
- LumiGauss能合成未见环境地图的真实图像。
- 该技术对于简化复杂3D资产创建过程具有潜在应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

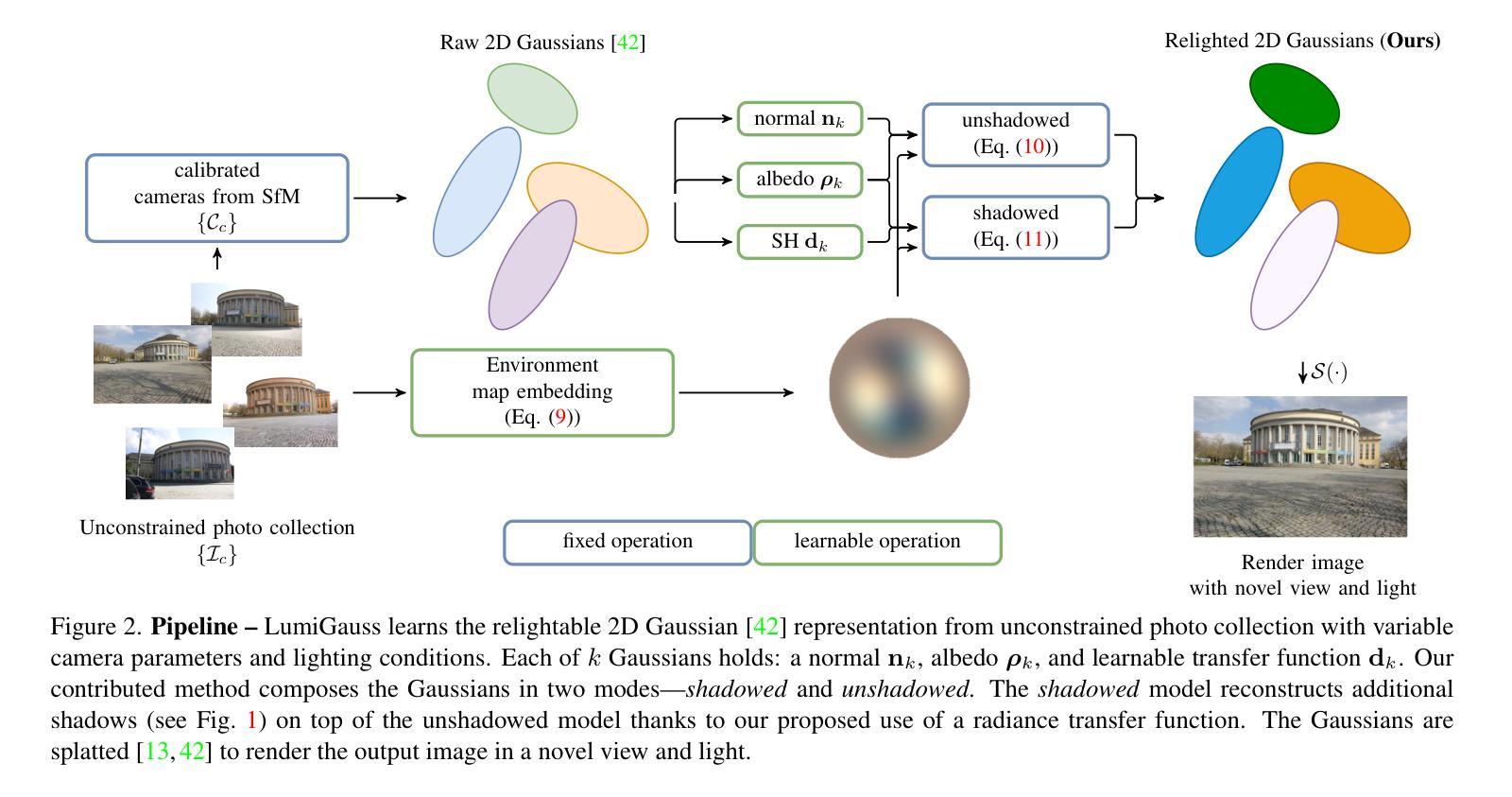
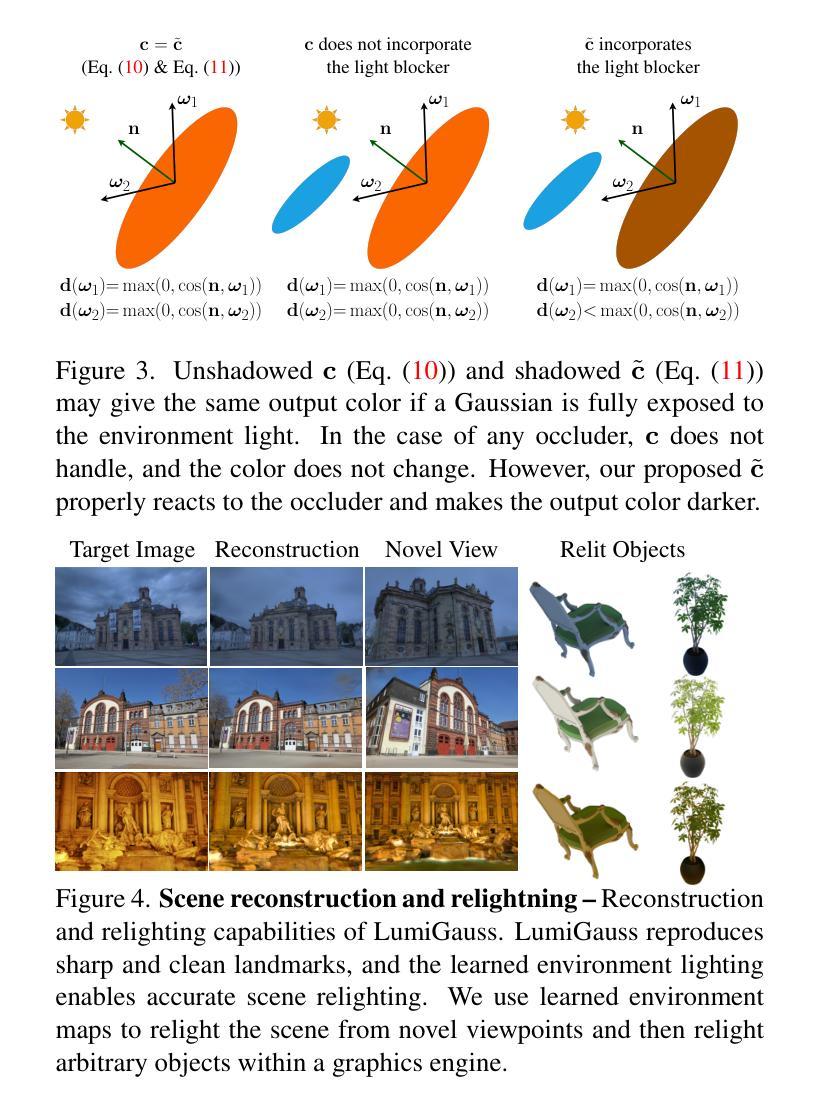
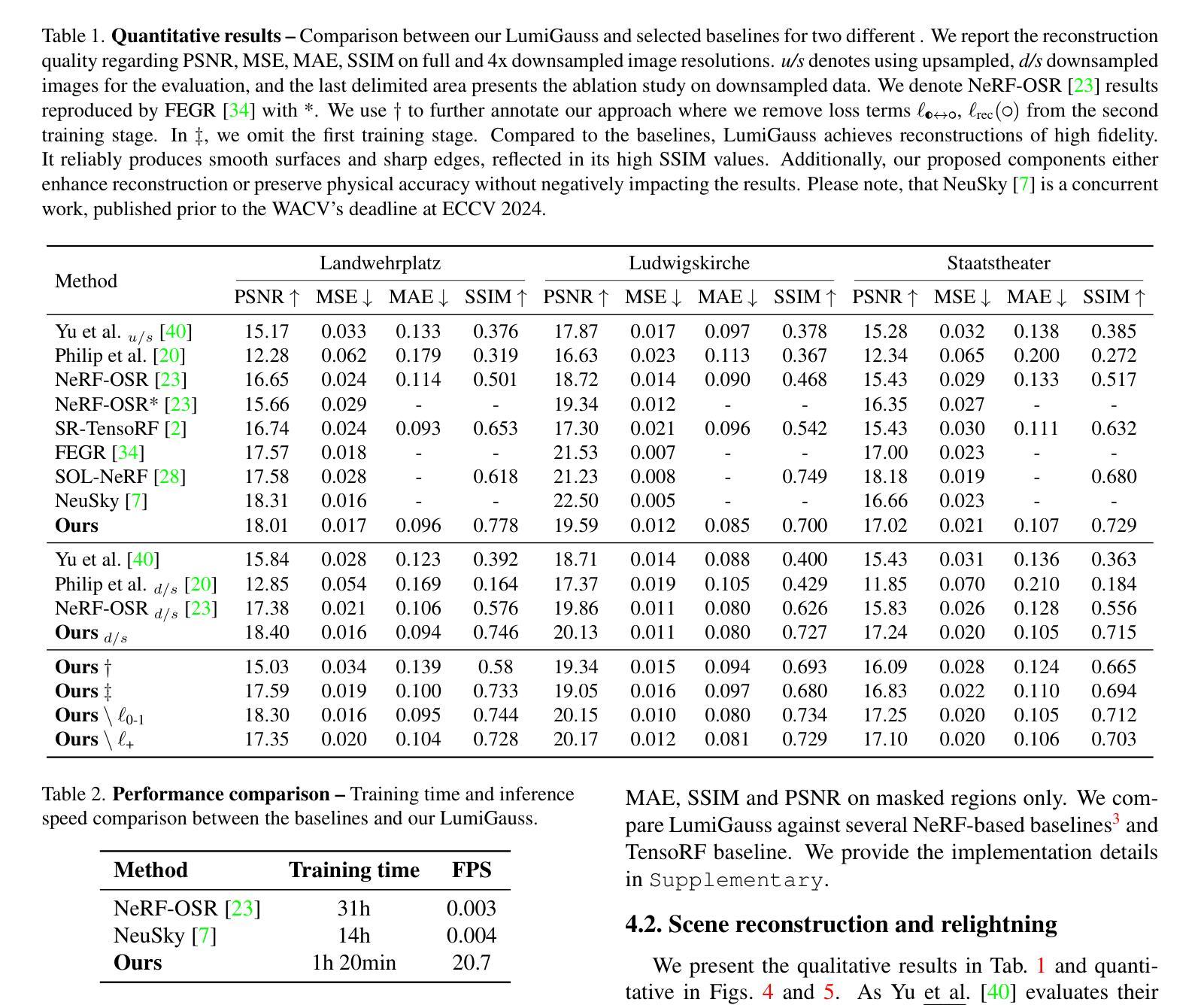
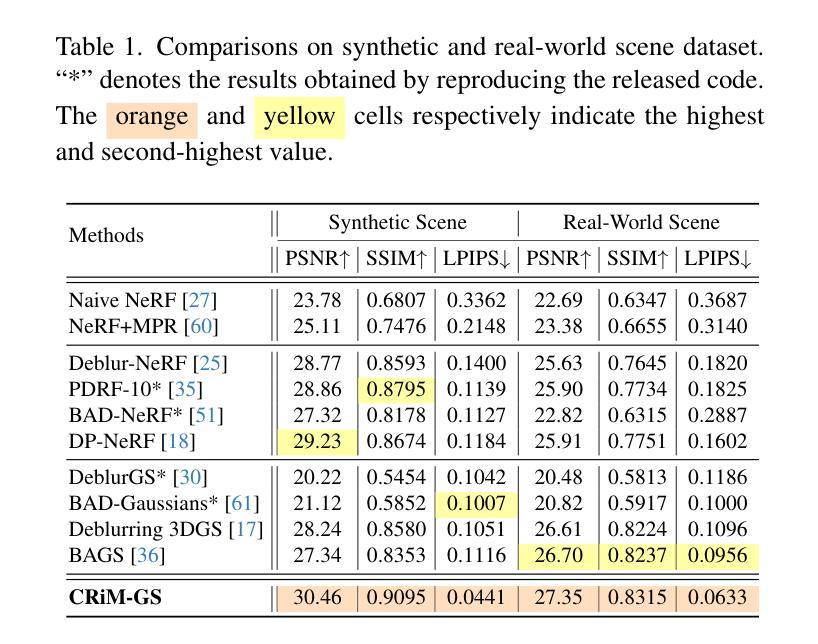
CRiM-GS: Continuous Rigid Motion-Aware Gaussian Splatting from Motion-Blurred Images
Authors:Jungho Lee, Donghyeong Kim, Dogyoon Lee, Suhwan Cho, Minhyeok Lee, Sangyoun Lee
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has gained significant attention for their high-quality novel view rendering, motivating research to address real-world challenges. A critical issue is the camera motion blur caused by movement during exposure, which hinders accurate 3D scene reconstruction. In this study, we propose CRiM-GS, a \textbf{C}ontinuous \textbf{Ri}gid \textbf{M}otion-aware \textbf{G}aussian \textbf{S}platting that reconstructs precise 3D scenes from motion-blurred images while maintaining real-time rendering speed. Considering the complex motion patterns inherent in real-world camera movements, we predict continuous camera trajectories using neural ordinary differential equations (ODE). To ensure accurate modeling, we employ rigid body transformations with proper regularization, preserving object shape and size. Additionally, we introduce an adaptive distortion-aware transformation to compensate for potential nonlinear distortions, such as rolling shutter effects, and unpredictable camera movements. By revisiting fundamental camera theory and leveraging advanced neural training techniques, we achieve precise modeling of continuous camera trajectories. Extensive experiments demonstrate state-of-the-art performance both quantitatively and qualitatively on benchmark datasets.
三维高斯混刷技术(3DGS)因其高质量的新视角渲染而受到广泛关注,这激发了解决现实世界挑战的研究动力。一个关键问题是曝光过程中运动引起的相机运动模糊,这阻碍了准确的3D场景重建。本研究提出了CRiM-GS,一种连续刚体运动感知高斯混刷技术(Gaussian Splatting),能够从运动模糊图像重建精确的3D场景,同时保持实时渲染速度。考虑到真实世界相机运动所固有的复杂运动模式,我们使用神经常微分方程(ODE)预测连续的相机轨迹。为了确保准确建模,我们采用刚体变换和适当的正则化,保持物体形状和大小。此外,我们引入自适应畸变感知变换,以补偿潜在的非线性畸变,如滚降效应和不可预测的相机运动。通过重温基本相机理论并利用先进的神经训练技术,我们实现了对连续相机轨迹的精确建模。大量实验表明,在基准数据集上,无论在数量上还是质量上,我们的性能均达到了领先水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page : https://jho-yonsei.github.io/CRiM-Gaussian/
Summary
本文主要研究了基于三维高斯描画(3DGS)技术的运动模糊图像下的三维场景重建方法。针对相机运动模糊问题,提出一种连续刚性运动感知的高斯描画方法(CRiM-GS),能在保持实时渲染速度的同时,从运动模糊图像中精确重建三维场景。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS在新型视图渲染方面表现出显著优势,引发了对现实挑战的研究。
- 相机运动模糊是阻碍准确三维场景重建的关键因素。
- 提出了一种新的方法CRiM-GS,能够从运动模糊的图像中重建精确的三维场景,同时保持实时渲染速度。
- 利用神经常微分方程预测连续的相机轨迹,以应对现实世界中的复杂运动模式。
- 采用刚体变换和适当的正则化,确保精确建模,同时保持物体形状和大小。
- 引入自适应畸变感知变换,以补偿潜在的非线性畸变,如滚动快门效应和不可预测的相机运动。
点此查看论文截图

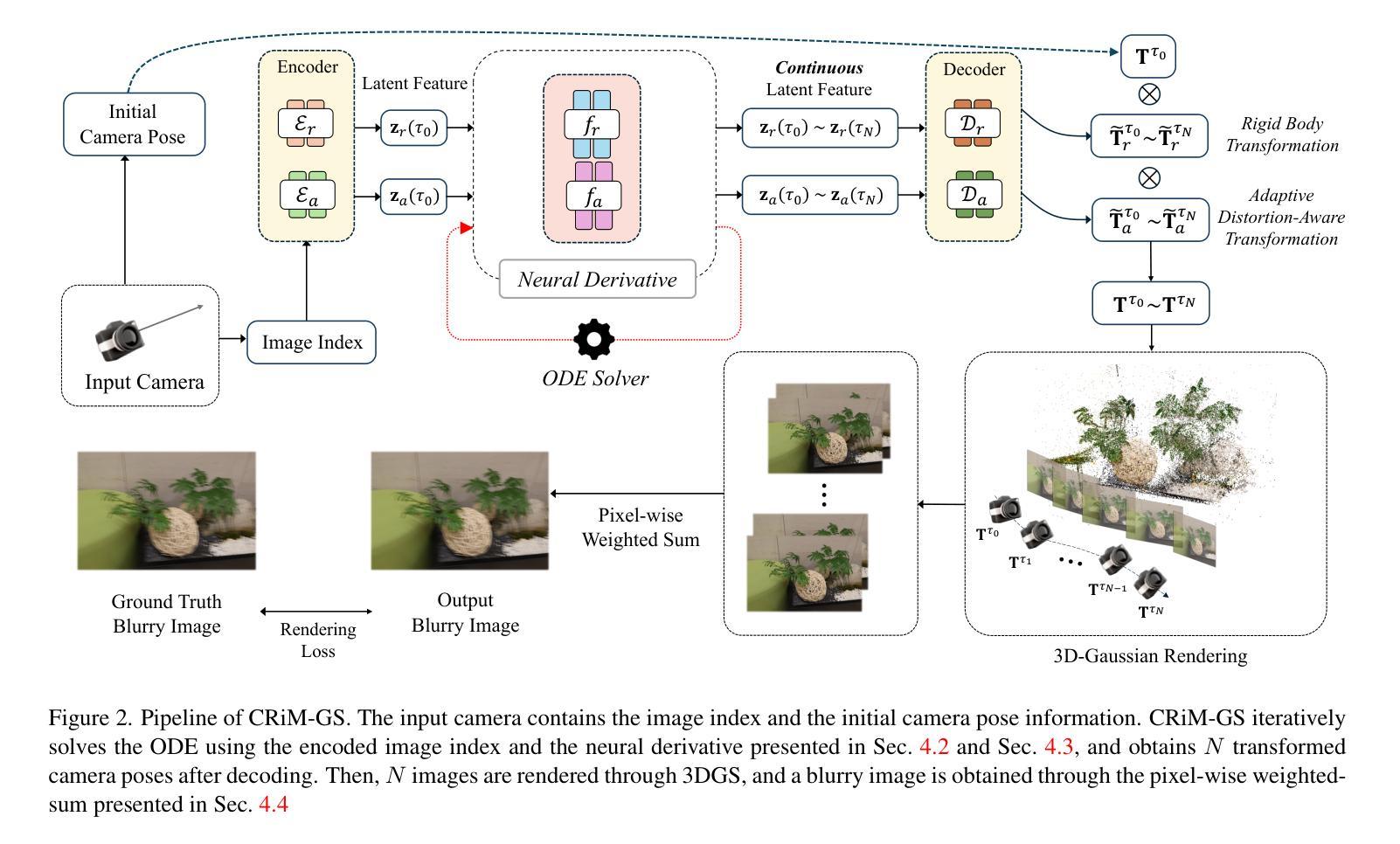
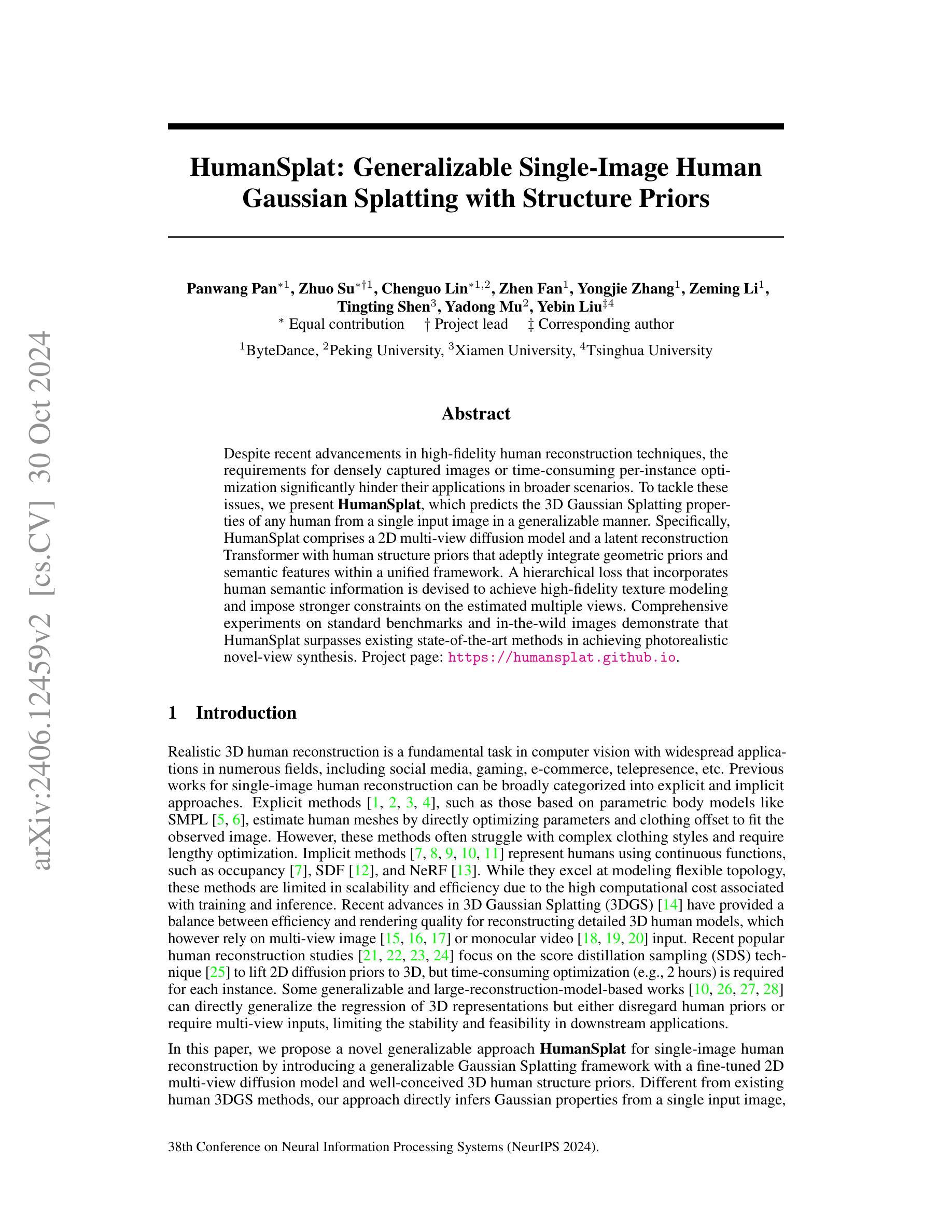
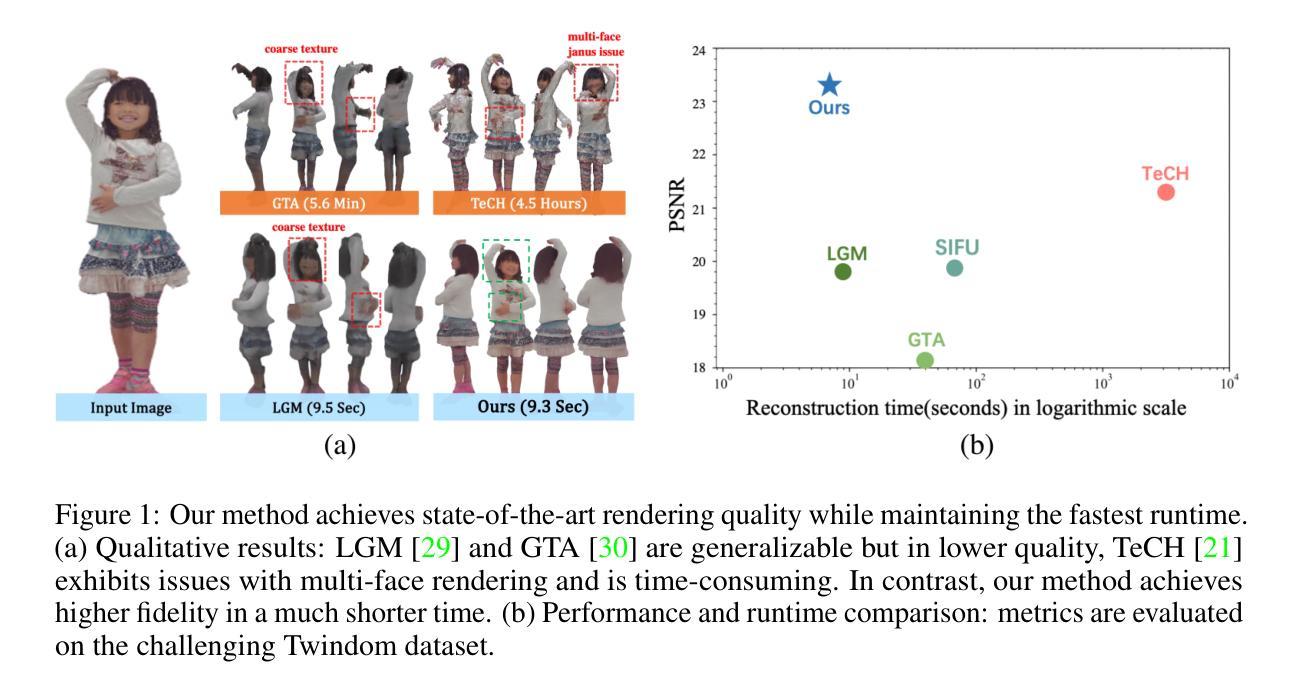
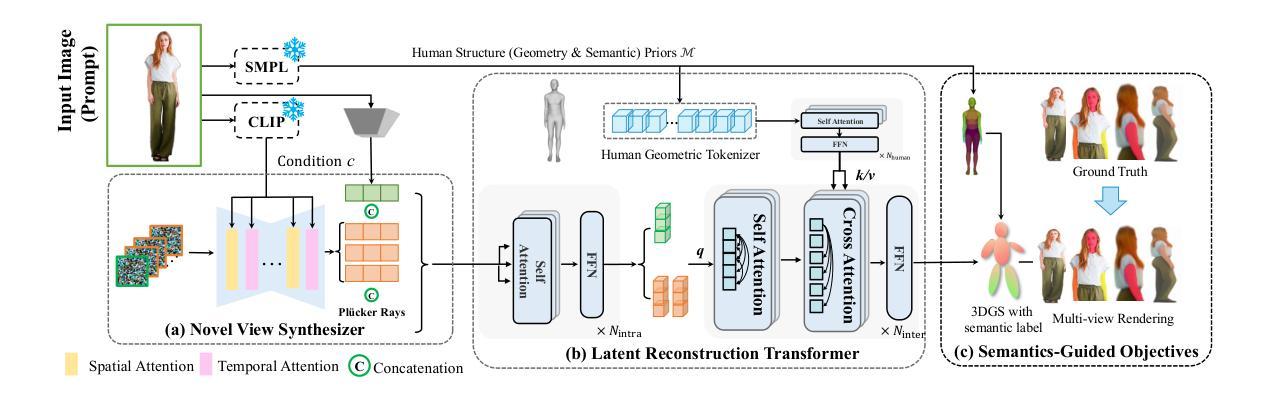
HumanSplat: Generalizable Single-Image Human Gaussian Splatting with Structure Priors
Authors:Panwang Pan, Zhuo Su, Chenguo Lin, Zhen Fan, Yongjie Zhang, Zeming Li, Tingting Shen, Yadong Mu, Yebin Liu
Despite recent advancements in high-fidelity human reconstruction techniques, the requirements for densely captured images or time-consuming per-instance optimization significantly hinder their applications in broader scenarios. To tackle these issues, we present HumanSplat which predicts the 3D Gaussian Splatting properties of any human from a single input image in a generalizable manner. In particular, HumanSplat comprises a 2D multi-view diffusion model and a latent reconstruction transformer with human structure priors that adeptly integrate geometric priors and semantic features within a unified framework. A hierarchical loss that incorporates human semantic information is further designed to achieve high-fidelity texture modeling and better constrain the estimated multiple views. Comprehensive experiments on standard benchmarks and in-the-wild images demonstrate that HumanSplat surpasses existing state-of-the-art methods in achieving photorealistic novel-view synthesis.
尽管最近高保真人类重建技术有所进展,但对密集捕获图像或耗时的逐实例优化的要求仍然极大地阻碍了它们在更广泛场景中的应用。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了HumanSplat,它以通用方式预测任何人类的3D高斯展开属性,仅从单张输入图像进行预测。特别的是,HumanSplat包括一个2D多视角扩散模型和一个具有人体结构先验的潜在重建转换器,该转换器巧妙地在一个统一框架内整合几何先验和语义特征。为了进一步实现高保真纹理建模并更好地约束估计的多视角,设计了包含人体语义信息的分层损失。在标准基准测试和野生图像上的综合实验表明,HumanSplat在达到高度逼真的新视角合成方面超越了现有的最先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为HumanSplat的方法,可以从单一输入图像预测任何人的3D高斯喷溅属性,并以通用方式实现。该方法结合了二维多视角扩散模型和具有人类结构先验的潜在重建转换器,在一个统一框架内巧妙地融合了几何先验和语义特征。设计了一种分层损失函数,以结合人类语义信息,实现高保真纹理建模,并更好地约束估计的多视角。在标准基准测试和真实世界图像上的综合实验表明,HumanSplat在达到逼真的新视角合成方面超越了现有最先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- HumanSplat解决了高保真人类重建技术面临的挑战,包括需要密集采集的图像或耗时的逐实例优化,使其能够在更广泛的应用场景中使用。
- HumanSplat从单一输入图像预测3D高斯喷溅属性并实现了一般化。
- 方法结合了二维多视角扩散模型和具有人类结构先验的潜在重建转换器。
- HumanSplat巧妙地在一个统一框架内融合几何先验和语义特征。
- 设计了一种结合人类语义信息的分层损失函数,以实现高保真纹理建模和更好的多视角估计约束。
- 在标准基准测试和真实世界图像上的综合实验验证了HumanSplat的有效性。
点此查看论文截图
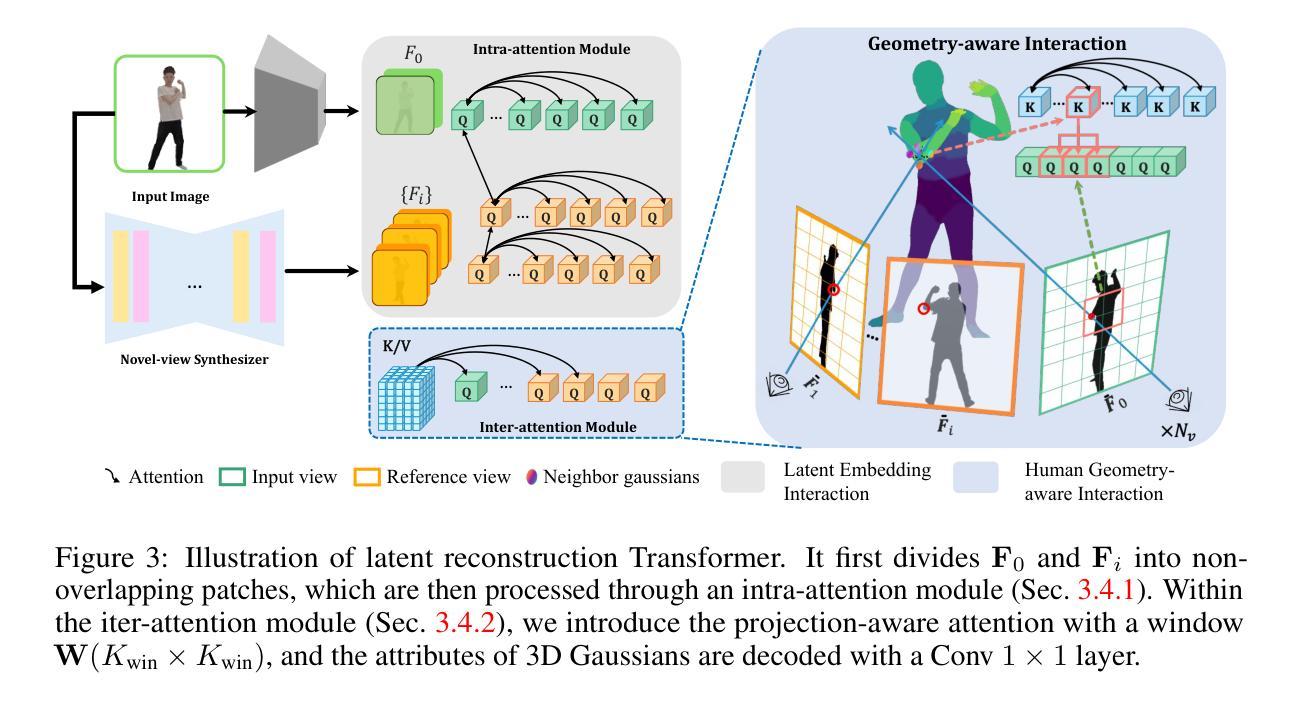
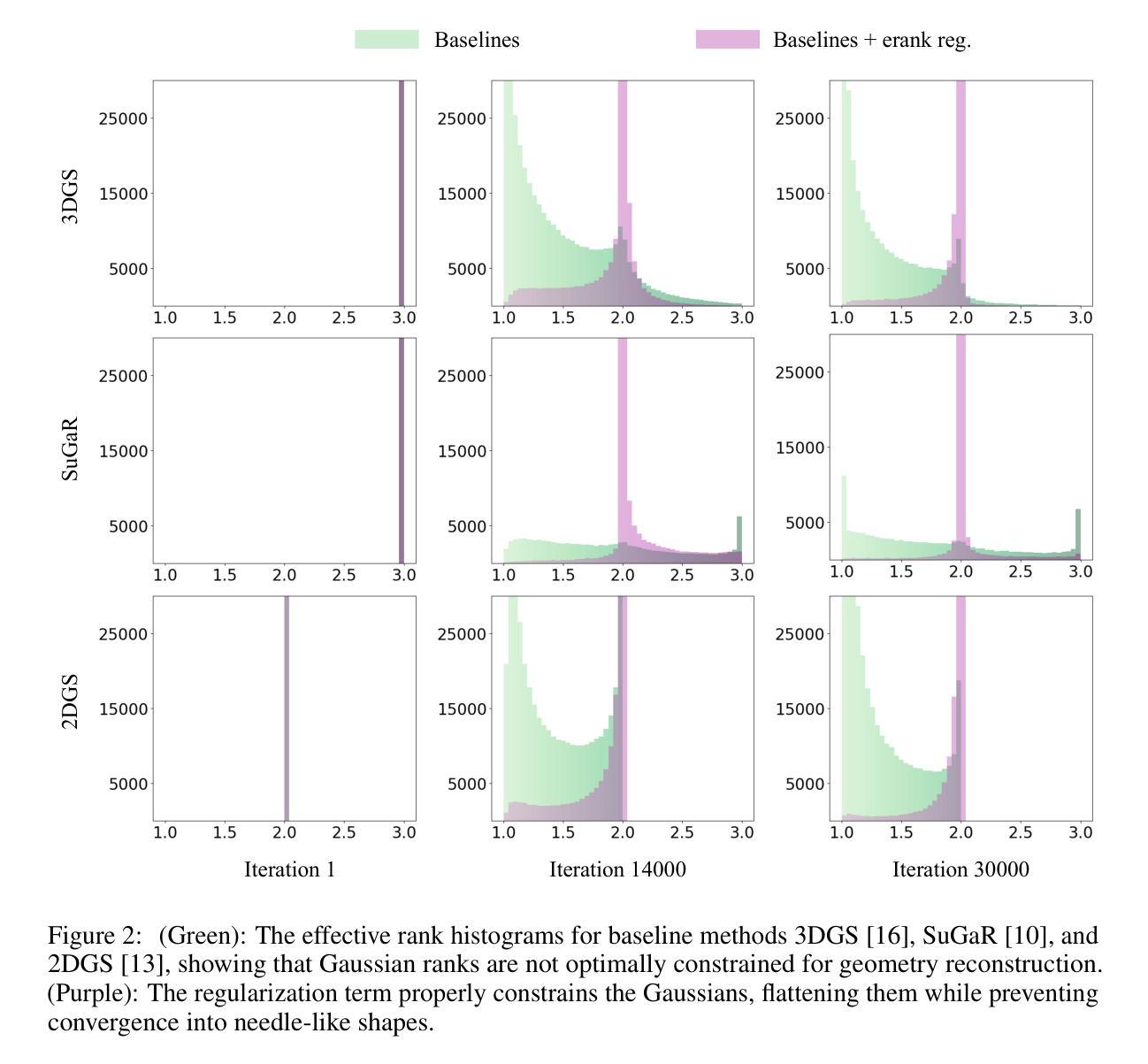
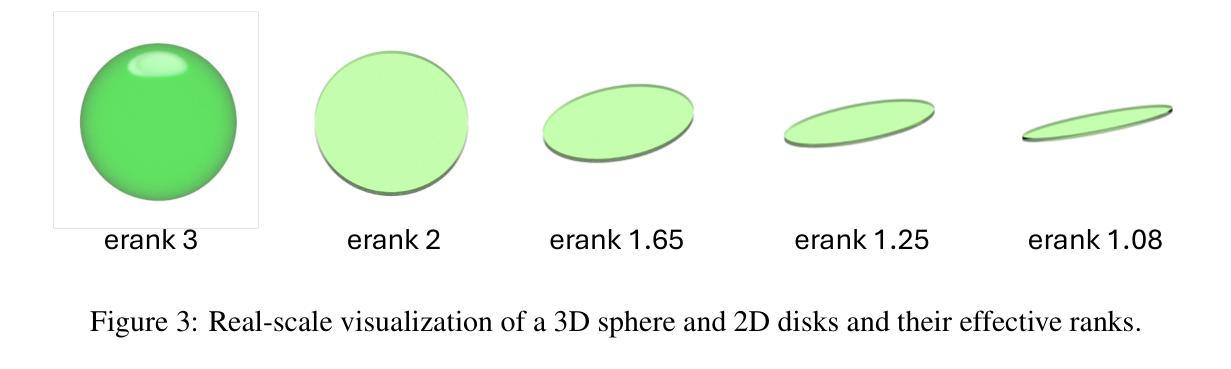
Effective Rank Analysis and Regularization for Enhanced 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Junha Hyung, Susung Hong, Sungwon Hwang, Jaeseong Lee, Jaegul Choo, Jin-Hwa Kim
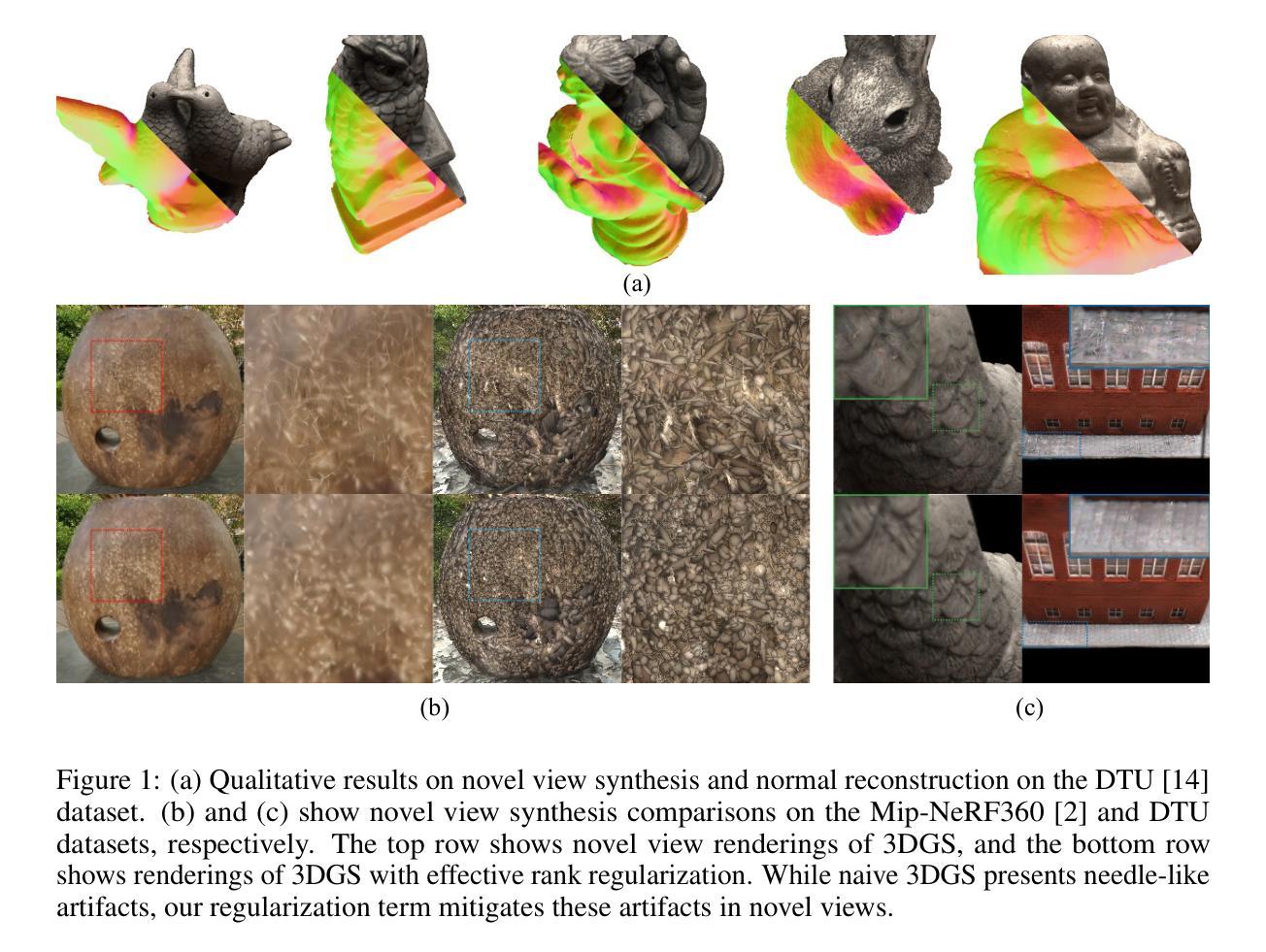
3D reconstruction from multi-view images is one of the fundamental challenges in computer vision and graphics. Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a promising technique capable of real-time rendering with high-quality 3D reconstruction. This method utilizes 3D Gaussian representation and tile-based splatting techniques, bypassing the expensive neural field querying. Despite its potential, 3DGS encounters challenges such as needle-like artifacts, suboptimal geometries, and inaccurate normals caused by the Gaussians converging into anisotropic shapes with one dominant variance. We propose using the effective rank analysis to examine the shape statistics of 3D Gaussian primitives, and identify the Gaussians indeed converge into needle-like shapes with the effective rank 1. To address this, we introduce the effective rank as a regularization, which constrains the structure of the Gaussians. Our new regularization method enhances normal and geometry reconstruction while reducing needle-like artifacts. The approach can be integrated as an add-on module to other 3DGS variants, improving their quality without compromising visual fidelity. The project page is available at https://junhahyung.github.io/erankgs.github.io.
从多视角图像进行3D重建是计算机视觉和图形学中的基本挑战之一。近期,3D高斯展铺(3DGS)作为一种具有实时渲染能力的潜力技术备受关注,并可实现高质量的3D重建。该方法利用3D高斯表示和基于瓦片的展铺技术,避免了昂贵的神经网络查询。尽管潜力巨大,但3DGS面临一些挑战,如针状伪影、几何形状不佳以及由于高斯收敛为具有一个主导方差各向异性形状所导致的法线不准确等问题。我们提出使用有效秩分析来检查3D高斯原始形状统计数据,并发现高斯确实会收敛成具有有效秩1的针状形状。为解决这一问题,我们将有效秩作为正则化方法加以介绍,约束高斯结构。我们的新正则化方法提高了法线和几何重建效果,同时减少了针状伪影。该方法可以作为其他3DGS变体的附加模块进行集成,在提高质量的同时不会损害视觉保真度。项目页面位于https://junhahyung.github.io/erankgs.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF project page: https://junhahyung.github.io/erankgs.github.io
Summary
本文介绍了基于多视角图像的实时高质量三维重建技术中的一项新兴技术——三维高斯喷绘技术(3DGS)。通过采用三维高斯表示和基于瓦片的喷绘技术,避免了昂贵的神经网络查询过程。本文分析了三维高斯基本体的形状统计问题,提出利用有效秩分析来解决高斯几何在重构时可能出现的尖锐状形状问题。针对这些问题,引入有效秩作为正则化约束,以提高几何和法线重建质量,同时减少尖锐状伪影。此方法可作为其他三维重建技术的附加模块集成,以提高质量而不损失视觉保真度。项目页面已发布在相关网站上。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS是一种新兴的三维重建技术,可实现实时高质量渲染。
- 该技术利用三维高斯表示和瓦片喷绘技术。
- 3DGS面临的挑战包括针状伪影、几何形状不佳和法线不准确等问题。
- 有效秩分析用于研究三维高斯基本体的形状统计问题。
- 高斯几何在重构时呈现尖锐状形状的问题可通过引入有效秩正则化解决。
- 有效秩正则化能提高几何和法线重建质量,同时减少尖锐状伪影的出现。
点此查看论文截图


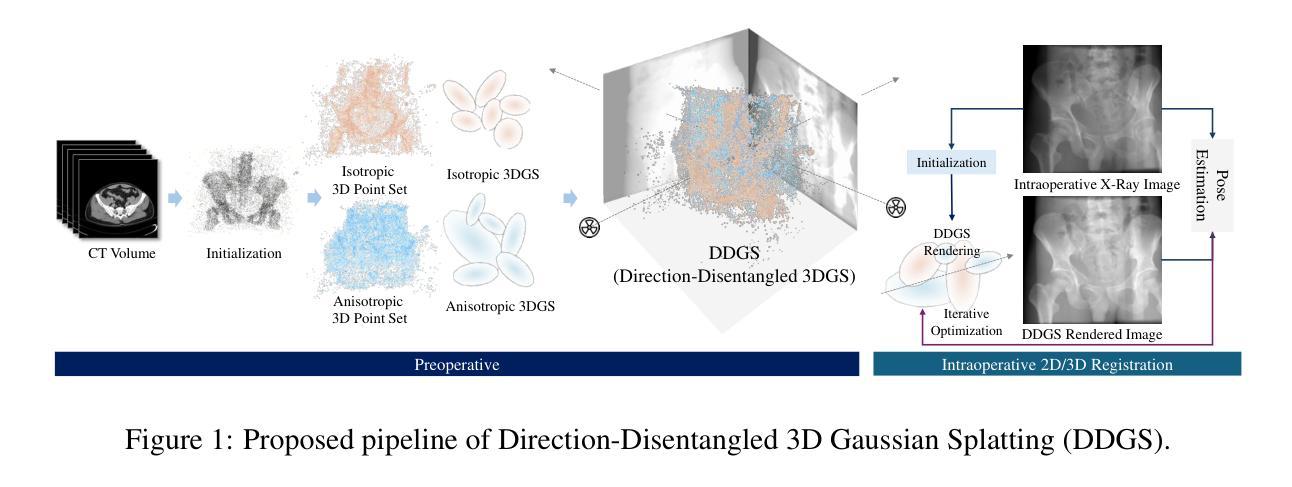
DDGS-CT: Direction-Disentangled Gaussian Splatting for Realistic Volume Rendering
Authors:Zhongpai Gao, Benjamin Planche, Meng Zheng, Xiao Chen, Terrence Chen, Ziyan Wu
Digitally reconstructed radiographs (DRRs) are simulated 2D X-ray images generated from 3D CT volumes, widely used in preoperative settings but limited in intraoperative applications due to computational bottlenecks, especially for accurate but heavy physics-based Monte Carlo methods. While analytical DRR renderers offer greater efficiency, they overlook anisotropic X-ray image formation phenomena, such as Compton scattering. We present a novel approach that marries realistic physics-inspired X-ray simulation with efficient, differentiable DRR generation using 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS). Our direction-disentangled 3DGS (DDGS) method separates the radiosity contribution into isotropic and direction-dependent components, approximating complex anisotropic interactions without intricate runtime simulations. Additionally, we adapt the 3DGS initialization to account for tomography data properties, enhancing accuracy and efficiency. Our method outperforms state-of-the-art techniques in image accuracy. Furthermore, our DDGS shows promise for intraoperative applications and inverse problems such as pose registration, delivering superior registration accuracy and runtime performance compared to analytical DRR methods.
数字重建放射影像(DRRs)是从三维CT体积生成的模拟二维X射线影像,广泛应用于术前环境,但由于计算瓶颈,特别是在精确但复杂的基于物理的蒙特卡罗方法方面,在术中应用有限。虽然分析型DRR渲染器提供了更高的效率,但它们忽略了各向异性的X射线图像形成现象,如康普顿散射。我们提出了一种新方法,它将逼真的受物理启发的X射线仿真与高效、可区分的DRR生成相结合,使用三维高斯涂抹技术(3DGS)。我们的方向分离三维高斯涂抹技术(DDGS)方法将放射贡献分为各向同性和方向依赖成分,在不需要复杂运行时仿真情况下近似复杂的各向异性交互。此外,我们根据断层扫描数据特性调整3DGS初始化,以提高准确性和效率。我们的方法在图像准确性方面优于最新技术。此外,我们的DDGS在术中应用和反向问题(如姿势注册)方面显示出巨大潜力,与解析型DRR方法相比,可提供更高的注册准确性和运行性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NeurIPS2024
Summary
基于数字重建放射影像(DRRs)技术的创新应用,研究者提出一种结合物理原理与高效可微分的DRR生成技术的新方法,使用三维高斯映射技术(3DGS)。此方法通过将放射线贡献分为同向和定向相关的成分,简化了复杂的异构交互过程,并且适应断层扫描数据特性,提高精准度和效率。此技术相对于现有的图像处理方法表现出更高的图像准确度,在术中应用和反向问题(如姿态注册)中具有良好前景。
Key Takeaways
- DRRs是从三维CT体积生成的模拟二维X射线图像,广泛应用于术前设置。
- 现有技术面临计算瓶颈,特别是在术中应用和物理基础蒙特卡洛方法中的高精度计算。
- 传统的DRR渲染器忽视了X射线图像的异构现象,如康普顿散射。
- 新的方法结合了物理原理的X射线模拟和高效的、可微分的DRR生成技术。
- 使用三维高斯映射技术(3DGS),将放射线贡献分为同向和定向相关的成分,简化了复杂的计算过程。
- 适应断层扫描数据特性,提高精准度和效率。
点此查看论文截图

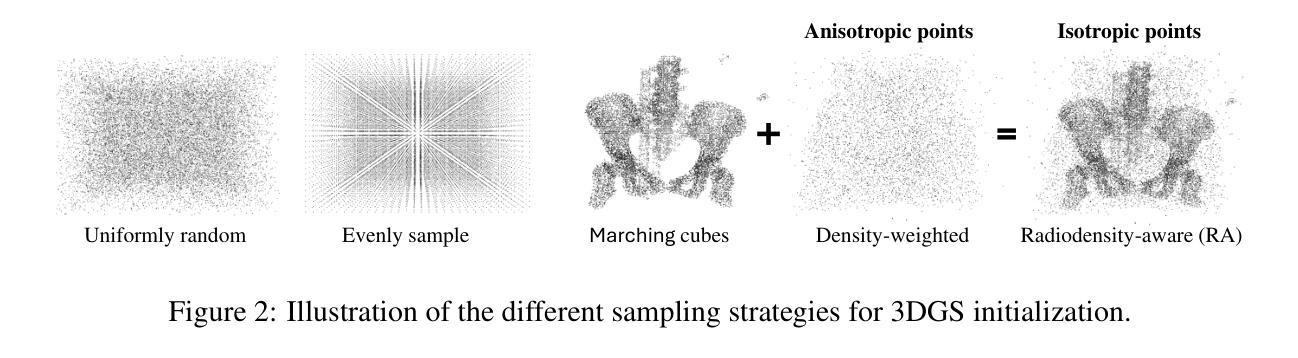
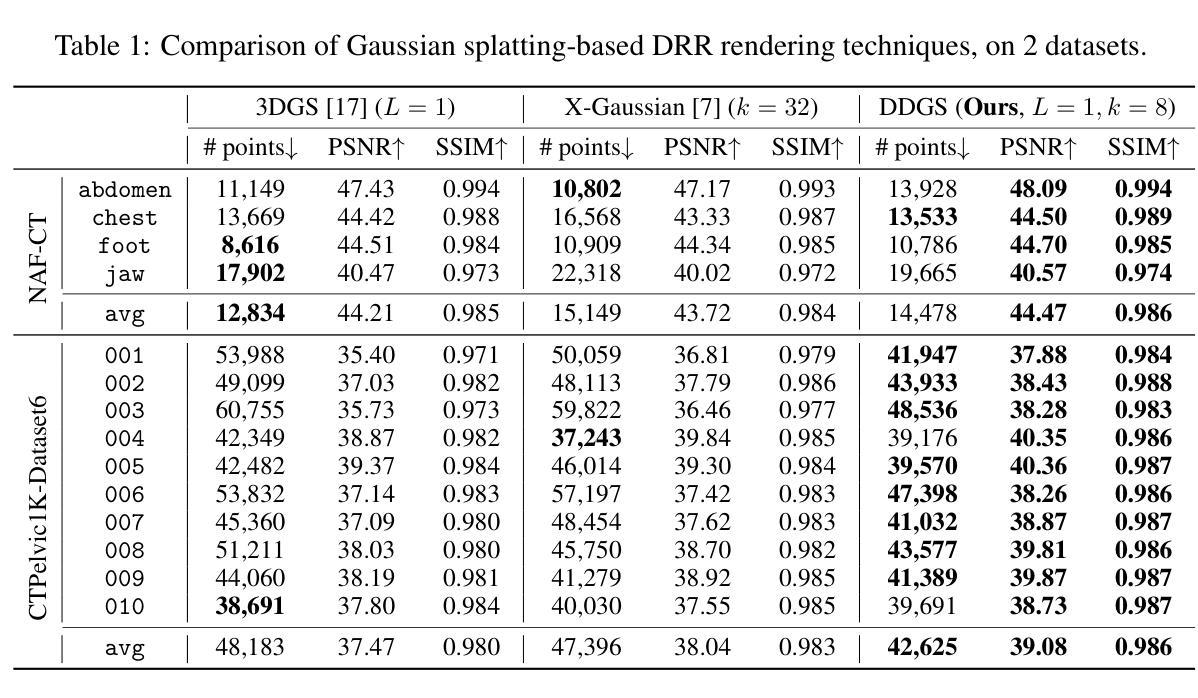
OpenGaussian: Towards Point-Level 3D Gaussian-based Open Vocabulary Understanding
Authors:Yanmin Wu, Jiarui Meng, Haijie Li, Chenming Wu, Yahao Shi, Xinhua Cheng, Chen Zhao, Haocheng Feng, Errui Ding, Jingdong Wang, Jian Zhang
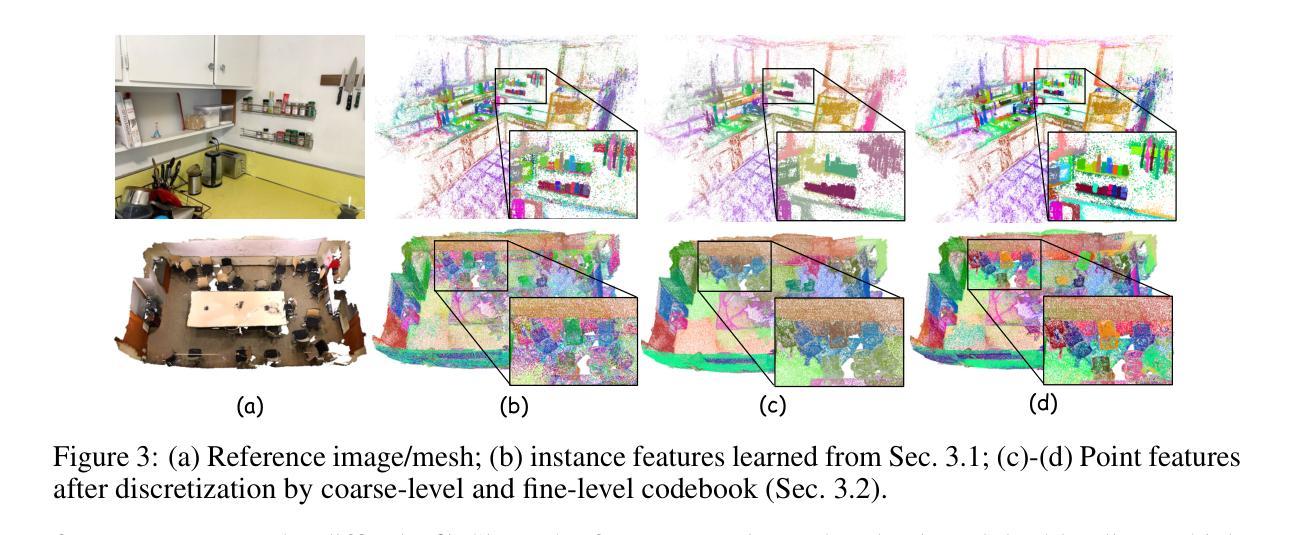
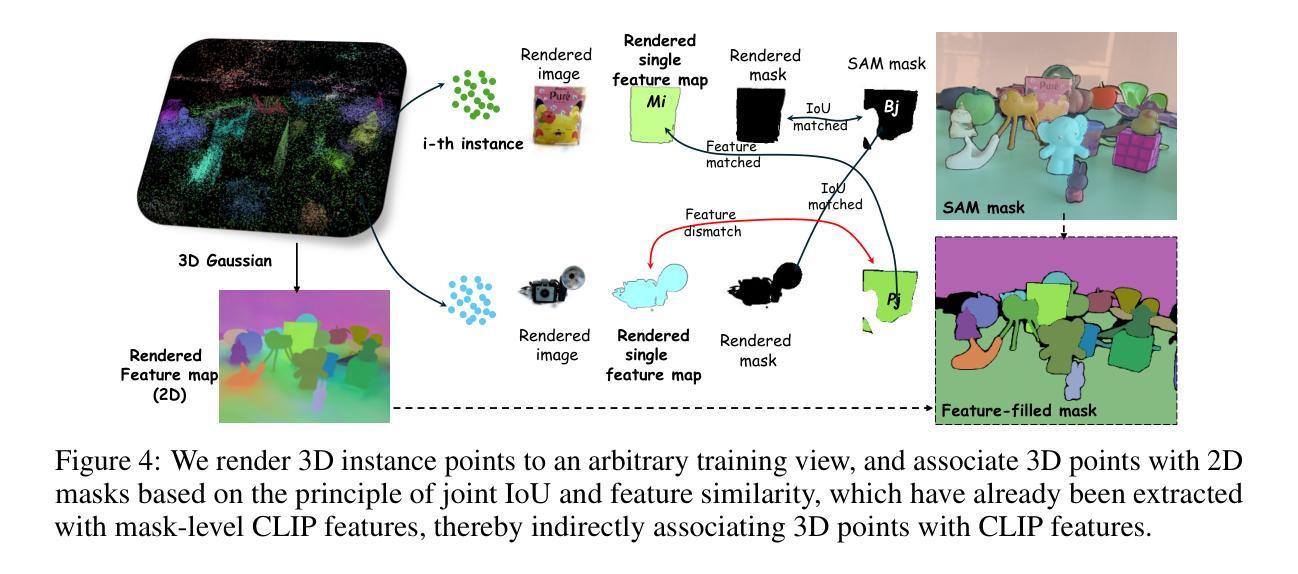
This paper introduces OpenGaussian, a method based on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) capable of 3D point-level open vocabulary understanding. Our primary motivation stems from observing that existing 3DGS-based open vocabulary methods mainly focus on 2D pixel-level parsing. These methods struggle with 3D point-level tasks due to weak feature expressiveness and inaccurate 2D-3D feature associations. To ensure robust feature presentation and 3D point-level understanding, we first employ SAM masks without cross-frame associations to train instance features with 3D consistency. These features exhibit both intra-object consistency and inter-object distinction. Then, we propose a two-stage codebook to discretize these features from coarse to fine levels. At the coarse level, we consider the positional information of 3D points to achieve location-based clustering, which is then refined at the fine level. Finally, we introduce an instance-level 3D-2D feature association method that links 3D points to 2D masks, which are further associated with 2D CLIP features. Extensive experiments, including open vocabulary-based 3D object selection, 3D point cloud understanding, click-based 3D object selection, and ablation studies, demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method. The source code is available at our project page: https://3d-aigc.github.io/OpenGaussian
本文介绍了OpenGaussian方法,这是一种基于3D高斯贴图(3DGS)的方法,能够实现3D点级别的开放词汇理解。我们的主要动机源于观察到现有的基于3DGS的开放词汇方法主要集中在2D像素级别的解析上。这些方法在3D点级别任务上表现不佳,原因在于特征表达较弱以及2D-3D特征关联不准确。为了确保稳健的特征表达和3D点级别理解,我们首先采用SAM掩膜进行训练,无需跨帧关联,以生成具有3D一致性的实例特征。这些特征在内部对象之间表现出一致性,并在不同对象之间有所区分。然后,我们提出了一个两级编码簿,从粗略到精细层次离散化这些特征。在粗略层次上,我们考虑3D点的位置信息来实现基于位置的聚类,然后在精细层次上进行细化。最后,我们引入了一种实例级别的3D-2D特征关联方法,将3D点与2D掩膜相关联,并进一步与2D CLIP特征相关联。大量实验包括基于开放词汇表的3D对象选择、3D点云理解、基于点击的3D对象选择以及消融研究,证明了我们的方法的有效性。项目源代码可在我们的项目页面获取:https://3d-aigc.github.io/OpenGaussian 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS2024
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于3D高斯插值(3DGS)的OpenGaussian方法,可实现3D点级的开放词汇理解。该方法旨在解决现有3DGS开放词汇方法主要专注于2D像素级解析的问题,面临3D点级任务时特征表达较弱以及2D-3D特征关联不准确的问题。通过采用SAM掩膜训练实例特征,实现3D一致性,提出两阶段代码簿对特征进行离散化,并在粗到细级别上实现位置信息驱动聚类。最后引入实例级的3D-2D特征关联方法,将3D点与2D掩膜以及CLIP特征关联起来。实验证明该方法在开放词汇的3D对象选择、3D点云理解、点击式3D对象选择等任务上效果显著。
Key Takeaways
- OpenGaussian是一种基于3DGS的开放词汇理解方法。
- 现有基于3DGS的开放词汇方法主要关注于2D像素级解析,难以处理复杂的3D点级任务。
- OpenGaussian通过SAM掩膜训练实例特征以实现稳健的特征表达和3D点级理解。
- 提出两阶段代码簿对特征进行离散化,从粗到细级别进行位置信息驱动聚类。
- 引入实例级的3D-2D特征关联方法,实现跨维度的信息整合。
- 实验结果证明OpenGaussian在多种任务上的表现均优于传统方法。
点此查看论文截图

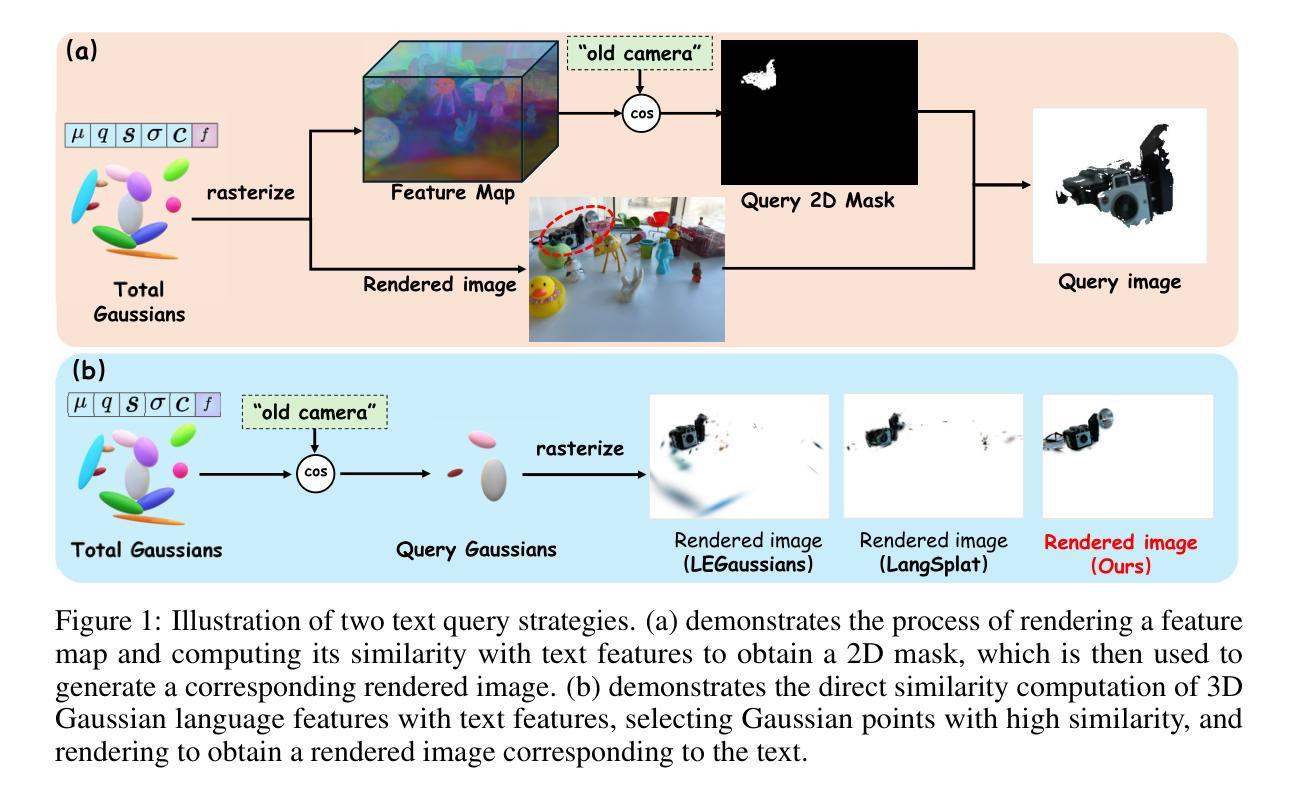
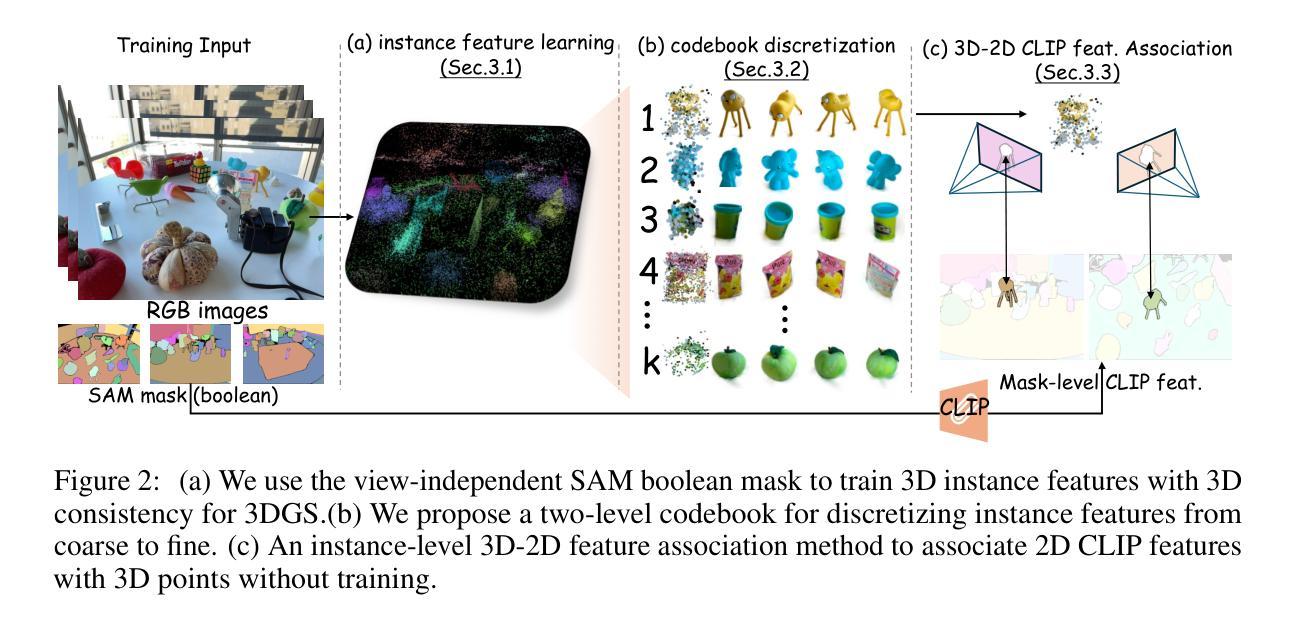
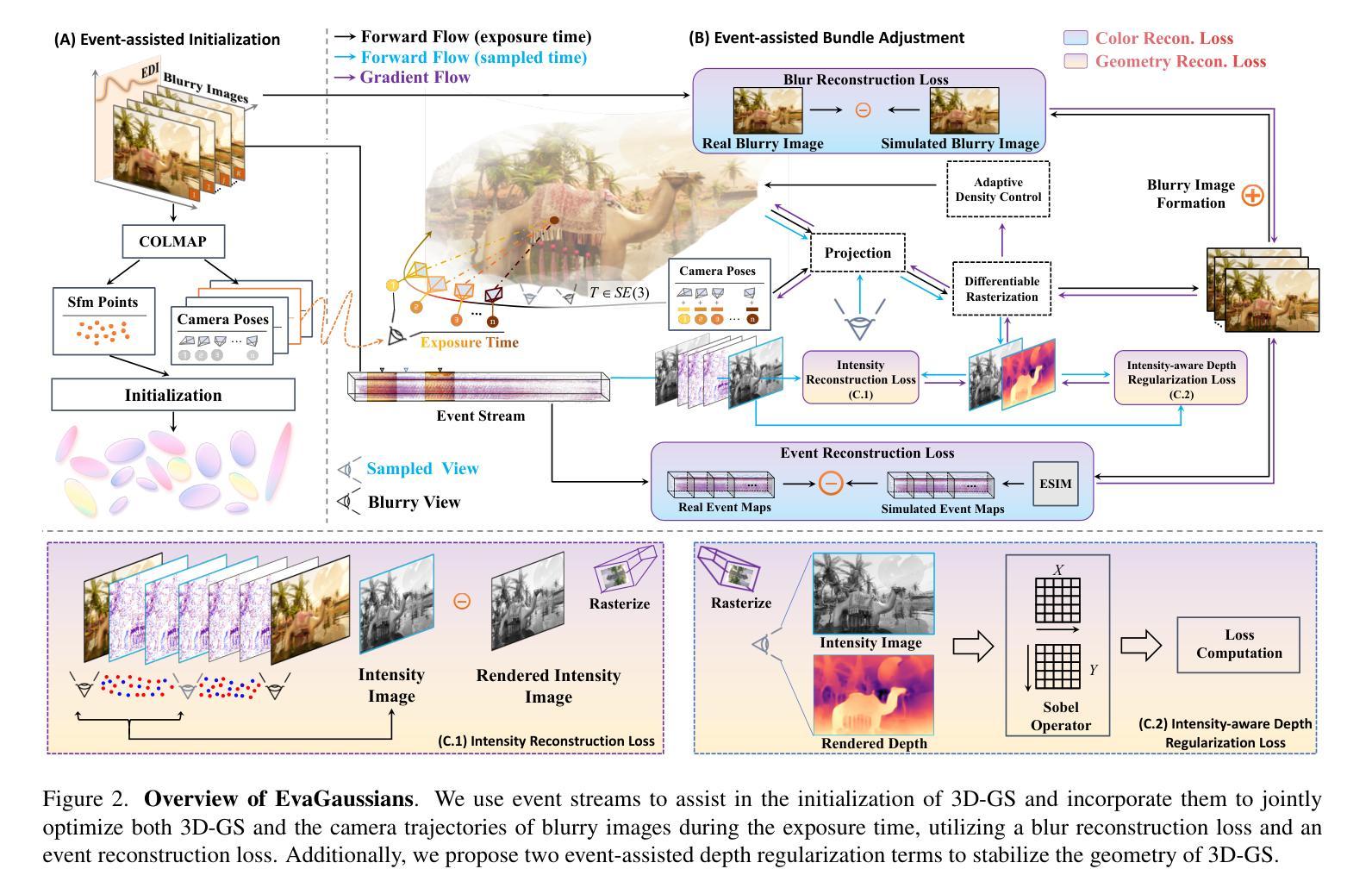
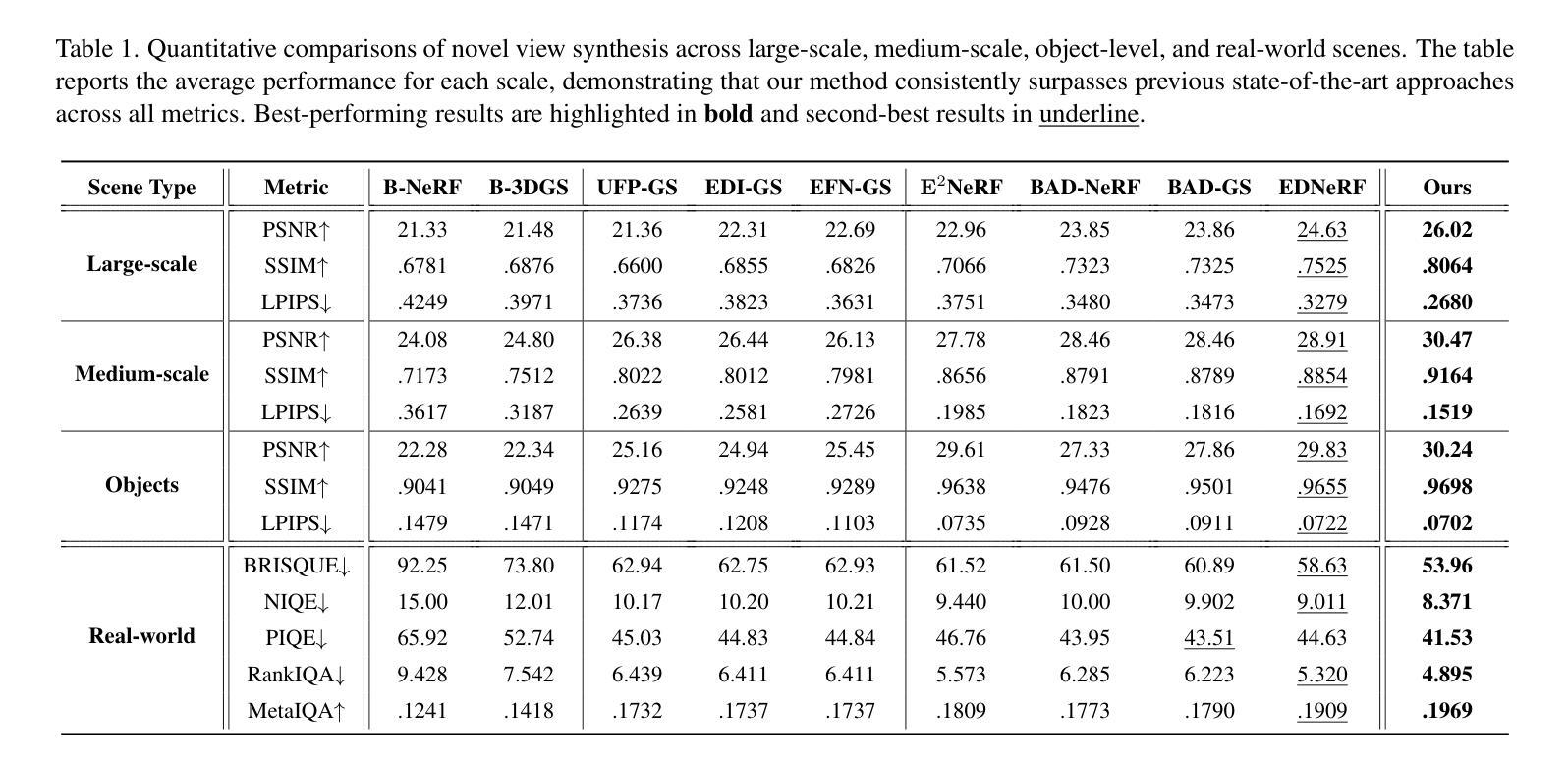
EvaGaussians: Event Stream Assisted Gaussian Splatting from Blurry Images
Authors:Wangbo Yu, Chaoran Feng, Jiye Tang, Jiashu Yang, Zhenyu Tang, Xu Jia, Yuchao Yang, Li Yuan, Yonghong Tian
3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) has demonstrated exceptional capabilities in 3D scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis. However, its training heavily depends on high-quality, sharp images and accurate camera poses. Fulfilling these requirements can be challenging in non-ideal real-world scenarios, where motion-blurred images are commonly encountered in high-speed moving cameras or low-light environments that require long exposure times. To address these challenges, we introduce Event Stream Assisted Gaussian Splatting (EvaGaussians), a novel approach that integrates event streams captured by an event camera to assist in reconstructing high-quality 3D-GS from blurry images. Capitalizing on the high temporal resolution and dynamic range offered by the event camera, we leverage the event streams to explicitly model the formation process of motion-blurred images and guide the deblurring reconstruction of 3D-GS. By jointly optimizing the 3D-GS parameters and recovering camera motion trajectories during the exposure time, our method can robustly facilitate the acquisition of high-fidelity novel views with intricate texture details. We comprehensively evaluated our method and compared it with previous state-of-the-art deblurring rendering methods. Both qualitative and quantitative comparisons demonstrate that our method surpasses existing techniques in restoring fine details from blurry images and producing high-fidelity novel views.
3D高斯Splatting(3D-GS)在3D场景重建和新颖视角合成方面表现出卓越的能力。然而,其训练严重依赖于高质量、清晰的图像和准确的相机姿态。在非理想的真实世界场景中,满足这些要求可能具有挑战性,因为在高速运动相机或低光照环境中经常会遇到运动模糊图像,这些环境需要长时间曝光。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了事件流辅助高斯Splatting(EvaGaussians)方法,这是一种将事件相机捕获的事件流集成到重建高质量3D-GS中的新方法,以从模糊图像中协助重建。利用事件相机提供的高时间分辨率和动态范围,我们借助事件流显式建模运动模糊图像的形成过程,并引导3D-GS的去模糊重建。通过联合优化3D-GS参数并在曝光时间内恢复相机运动轨迹,我们的方法可以稳健地获取具有精细纹理细节的高保真新颖视角。我们全面评估了我们的方法,并与之前的最新去模糊渲染方法进行了比较。定性和定量比较均表明,我们的方法在恢复模糊图像中的细节以及生成高保真新颖视角方面超越了现有技术。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://www.falcary.com/EvaGaussians/
摘要
事件流辅助高斯贴图技术(EvaGaussians)结合了事件相机捕捉的事件流,用于从模糊图像重建高质量的三维高斯贴图(3D-GS),解决了在高速相机或低光照环境下运动模糊图像的问题。借助事件相机提供的高时间分辨率和动态范围,该技术显式建模运动模糊图像的形成过程,引导3D-GS去模糊重建。通过联合优化3D-GS参数和曝光时间内相机运动轨迹的恢复,该方法可稳健地获取具有精细纹理细节的高保真新视角。综合评估表明,相较于最新的去模糊渲染技术,该方法在恢复模糊图像细节和生成高保真新视角方面更胜一筹。
要点
- Event Stream Assisted Gaussian Splatting (EvaGaussians) 结合了事件相机捕捉的事件流,用于解决非理想现实场景中的运动模糊和低光照问题。
- EvaGaussians 利用事件相机的高时间分辨率和动态范围,显式建模运动模糊图像的形成过程。
- EvaGaussians 能够指导去模糊重建3D-GS,通过联合优化3D-GS参数和曝光时间内相机运动轨迹的恢复。
- 该方法能稳健地获取高保真新视角,具有精细纹理细节。
- EvaGaussians 在恢复模糊图像细节方面表现优异,超越了现有的去模糊渲染技术。
- 综合评估证明EvaGaussians在生成高保真图像方面的优势。
- EvaGaussians 的应用将促进3D场景重建和新颖视角合成的质量提升。
点此查看论文截图

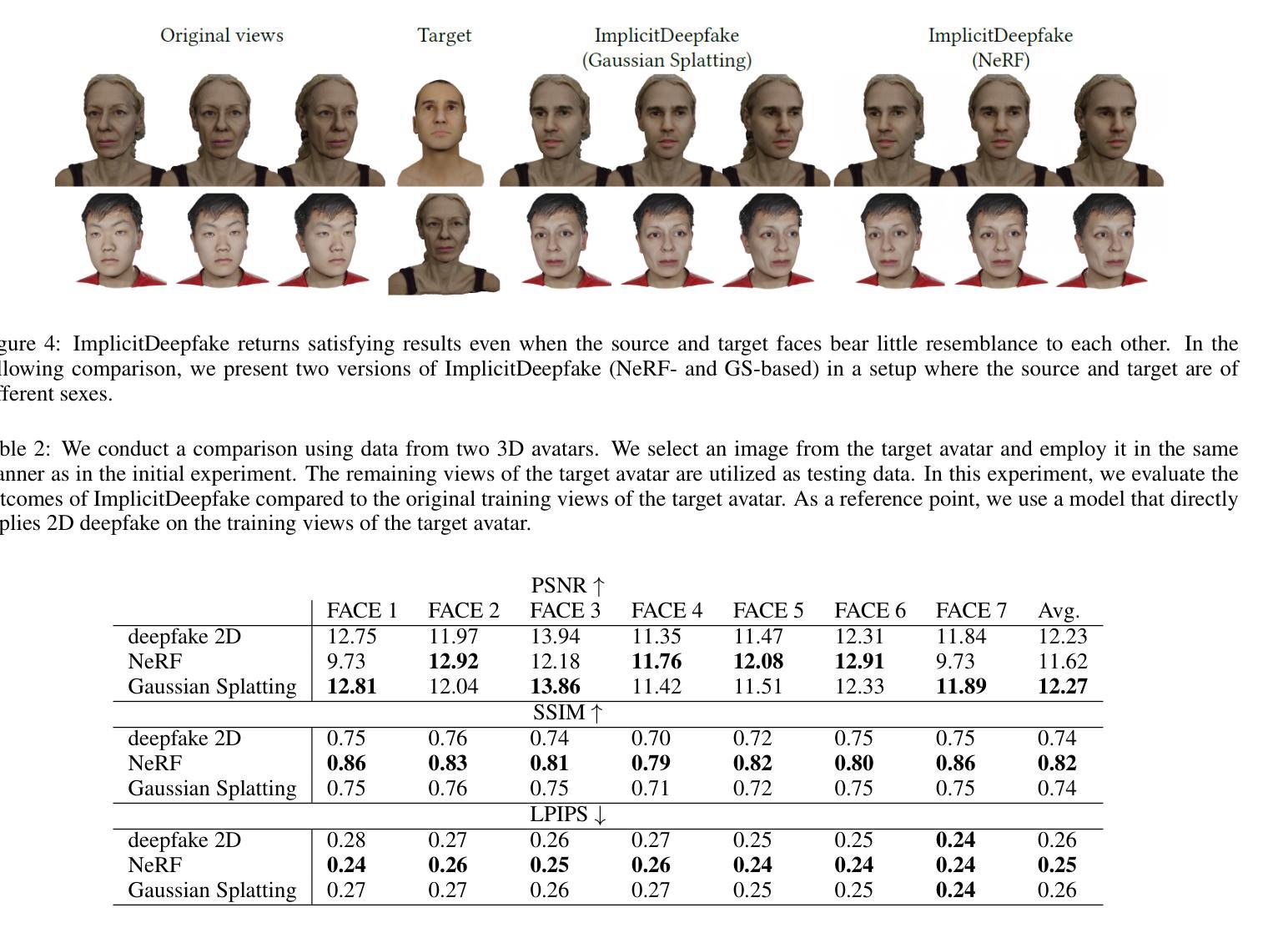
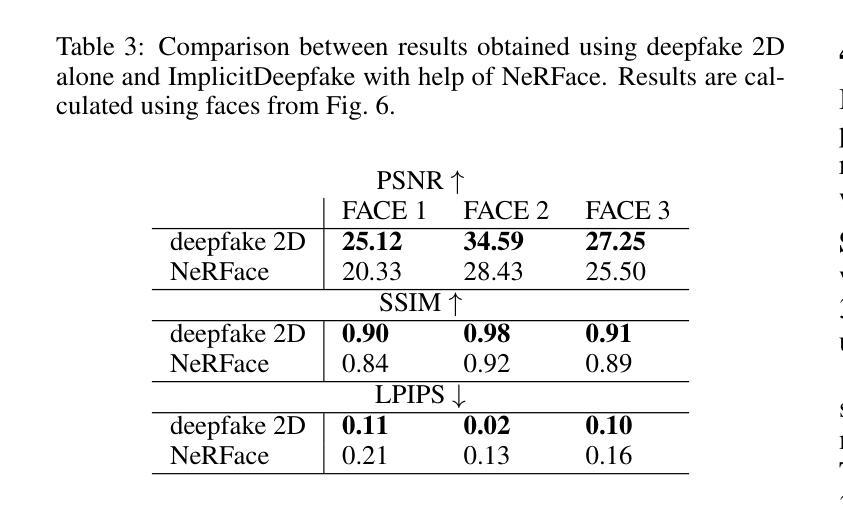
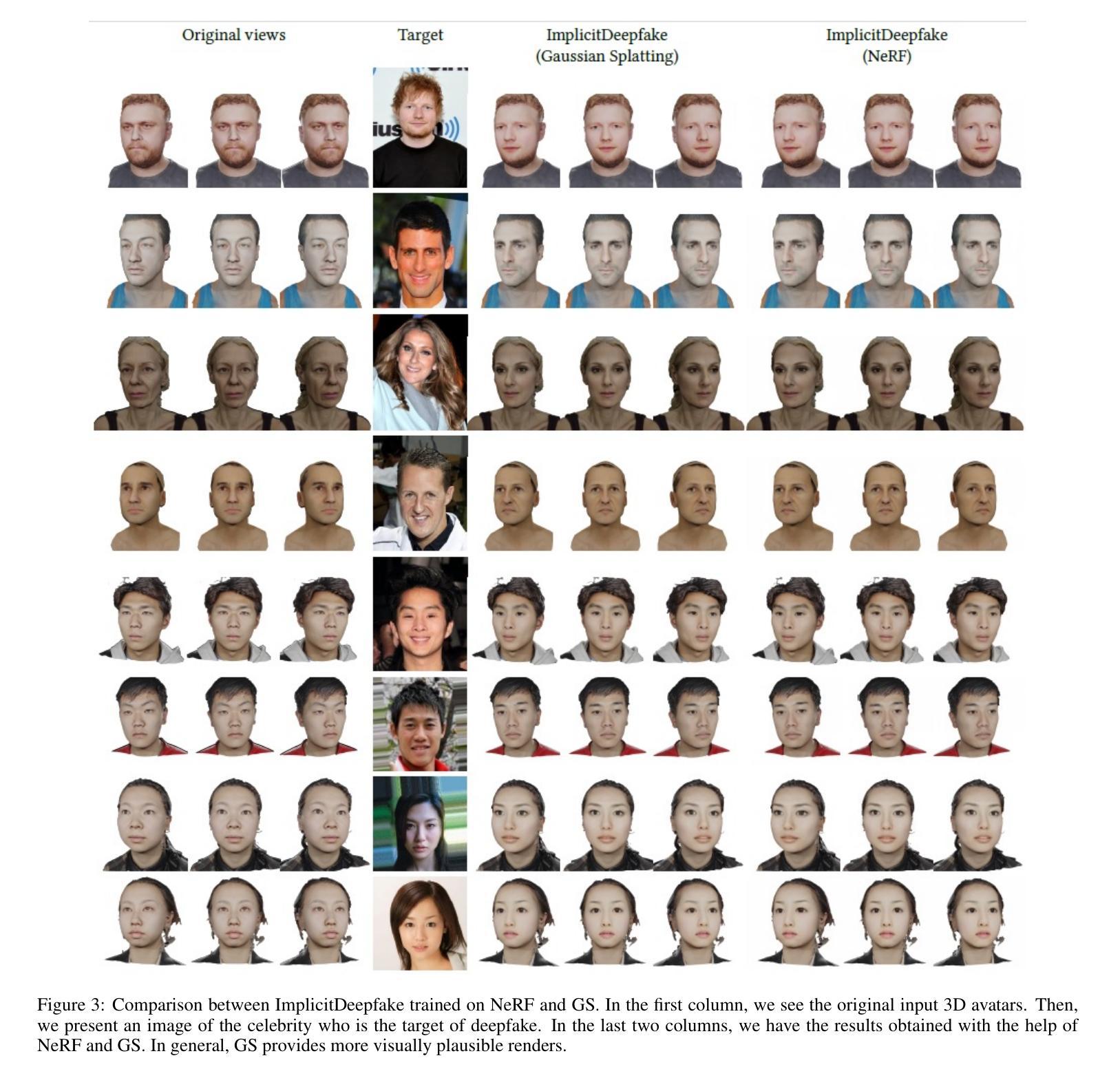
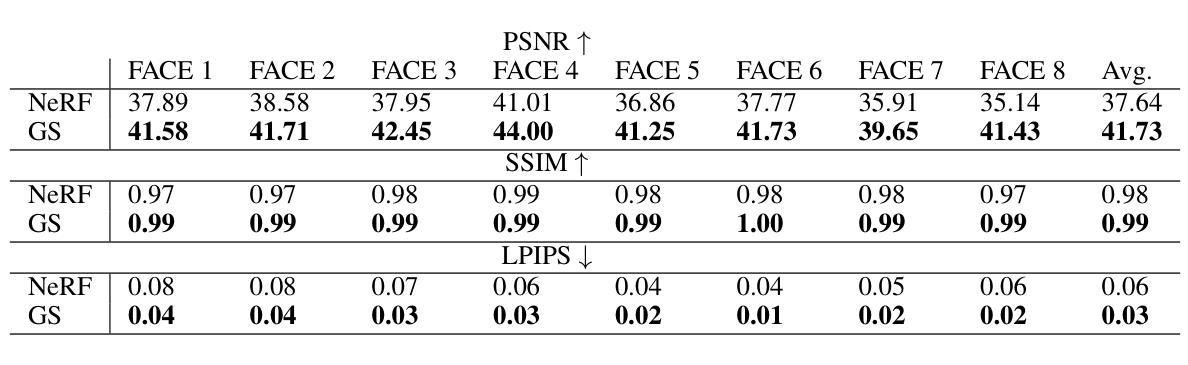
Deepfake for the Good: Generating Avatars through Face-Swapping with Implicit Deepfake Generation
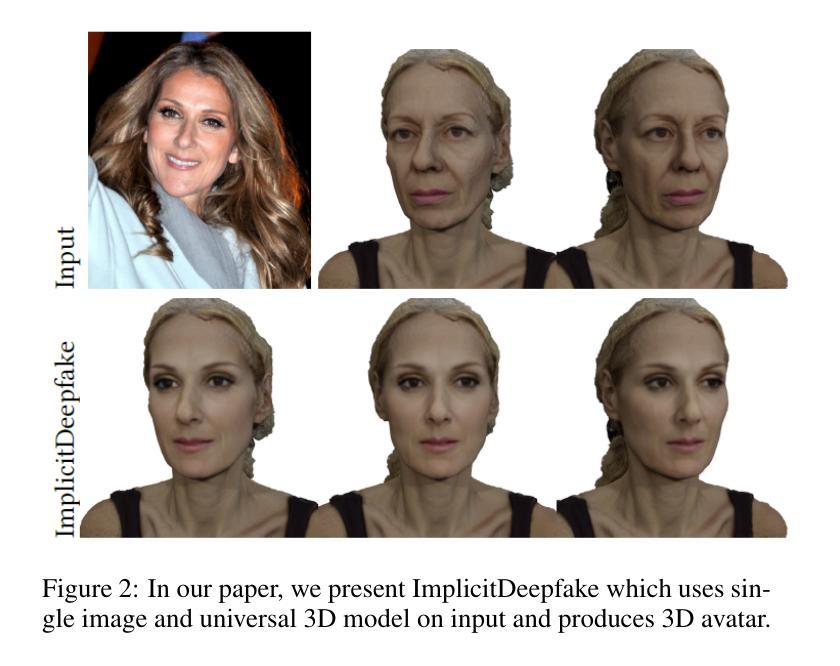
Authors:Georgii Stanishevskii, Jakub Steczkiewicz, Tomasz Szczepanik, Sławomir Tadeja, Jacek Tabor, Przemysław Spurek
Numerous emerging deep-learning techniques have had a substantial impact on computer graphics. Among the most promising breakthroughs are the rise of Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) and Gaussian Splatting (GS). NeRFs encode the object’s shape and color in neural network weights using a handful of images with known camera positions to generate novel views. In contrast, GS provides accelerated training and inference without a decrease in rendering quality by encoding the object’s characteristics in a collection of Gaussian distributions. These two techniques have found many use cases in spatial computing and other domains. On the other hand, the emergence of deepfake methods has sparked considerable controversy. Deepfakes refers to artificial intelligence-generated videos that closely mimic authentic footage. Using generative models, they can modify facial features, enabling the creation of altered identities or expressions that exhibit a remarkably realistic appearance to a real person. Despite these controversies, deepfake can offer a next-generation solution for avatar creation and gaming when of desirable quality. To that end, we show how to combine all these emerging technologies to obtain a more plausible outcome. Our ImplicitDeepfake uses the classical deepfake algorithm to modify all training images separately and then train NeRF and GS on modified faces. Such simple strategies can produce plausible 3D deepfake-based avatars.
众多新兴的深度学习技术已对计算机图形产生巨大影响。其中最有前途的突破之一是神经辐射场(NeRF)和高斯喷涂(GS)的兴起。NeRF使用神经网络权重编码对象的形状和颜色,利用少量已知相机位置的图片来生成新视角。相比之下,GS通过在一组高斯分布中编码对象特性,提供了加速训练和推理,同时不降低渲染质量。这两种技术在空间计算和其他领域找到了许多用例。另一方面,深度伪造方法的出现引起了相当大的争议。深度伪造是指使用人工智能生成的视频,这些视频密切模仿真实镜头。使用生成模型,它们可以修改面部特征,能够创建出具有惊人真实外观的更改身份或表情,与真实人物非常相似。尽管存在这些争议,但深度伪造技术可以在质量达标的情况下为化身创建和游戏提供下一代解决方案。为此,我们展示了如何结合所有这些新兴技术来获得更合理的结果。我们的ImplicitDeepfake使用经典的深度伪造算法分别修改所有训练图像,然后在修改后的面部上训练NeRF和GS。这种简单的策略可以产生基于深度伪造的合理3D化身。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新兴深度学习技术对计算机图形产生了重大影响,神经辐射场(NeRF)和高斯涂布(GS)等突破技术为空间计算等领域带来了许多用例。同时,深度伪造方法的出现引起了广泛争议。深度伪造指的是使用人工智能生成的视频,能够模仿真实画面。结合各种新兴技术,我们可以获得更逼真的结果。本研究结合深度伪造算法修改所有训练图像,然后对修改后的面部进行NeRF和GS训练,产生可信的3D深度伪造虚拟形象。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习技术对计算机图形产生重大影响,出现多种新兴技术如神经辐射场(NeRF)和高斯涂布(GS)。
- NeRF通过编码对象的形状和颜色在神经网络权重中,使用已知相机位置的图片生成新视角。
- GS通过高斯分布编码对象特性,提供加速训练和推理,同时不降低渲染质量。
- 深度伪造方法引起广泛争议,但可为化身创建和游戏提供下一代解决方案。
- 结合深度伪造算法修改训练图像,然后使用NeRF和GS训练,可以产生更逼真的3D深度伪造虚拟形象。
- 深度伪造技术需要进一步提高质量,以实现更广泛的应用。
点此查看论文截图


 q
q