⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-11 更新
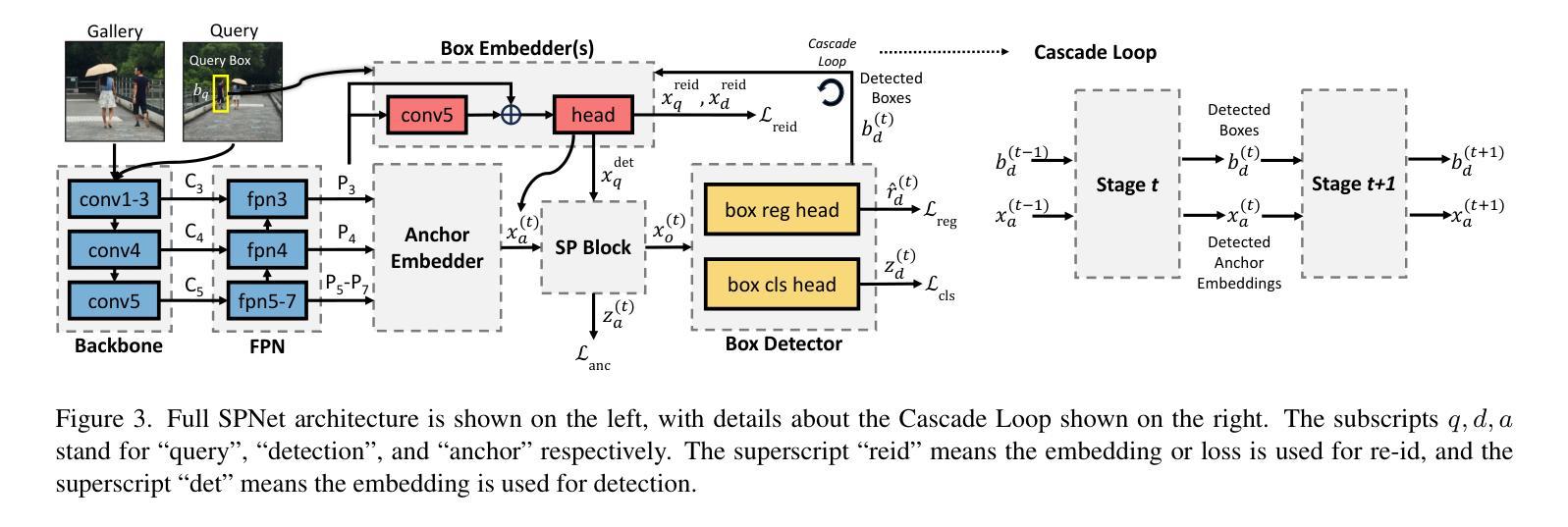
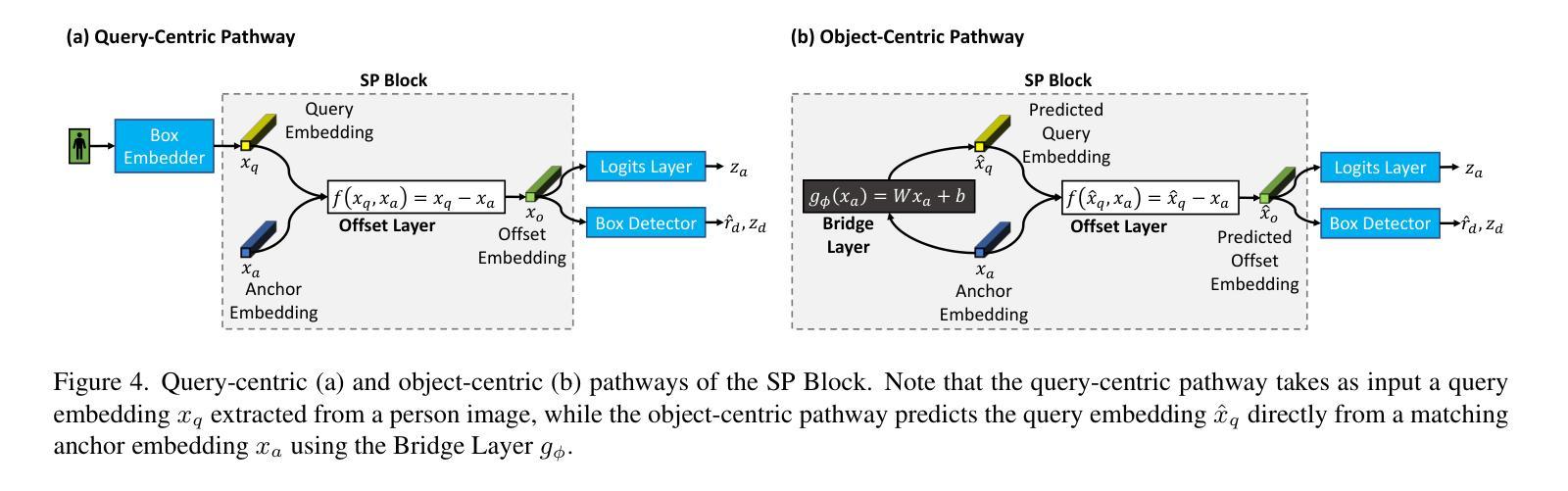
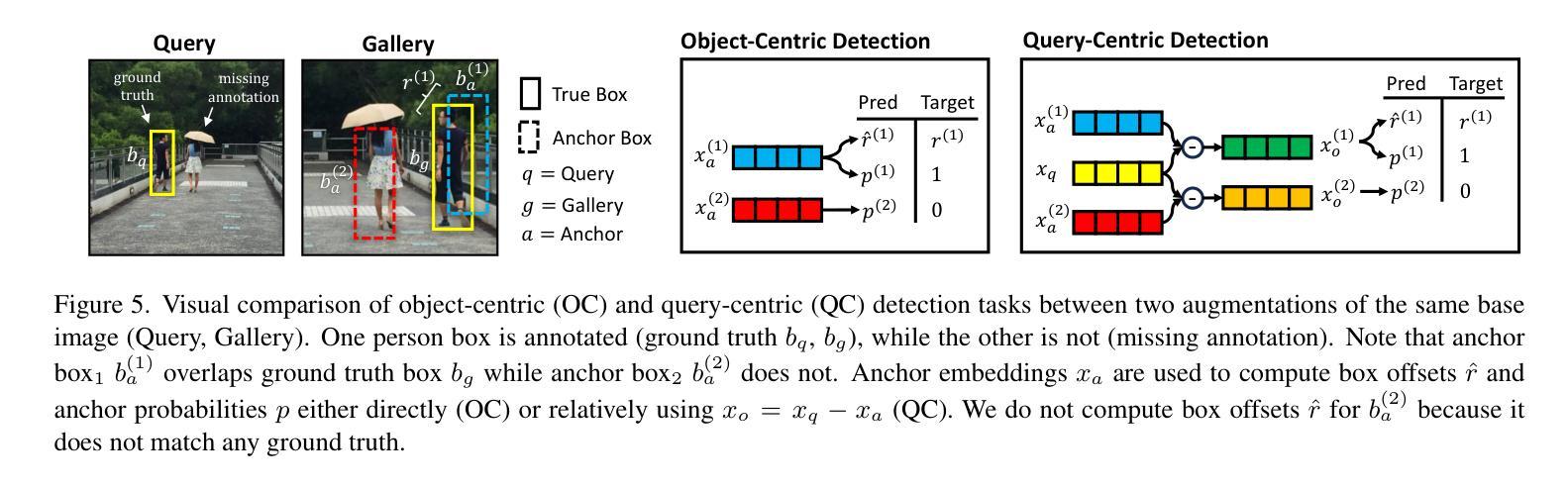
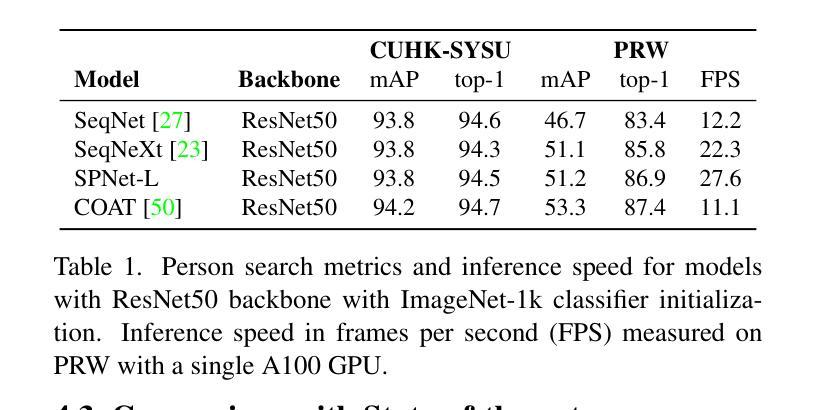
Swap Path Network for Robust Person Search Pre-training
Authors:Lucas Jaffe, Avideh Zakhor
In person search, we detect and rank matches to a query person image within a set of gallery scenes. Most person search models make use of a feature extraction backbone, followed by separate heads for detection and re-identification. While pre-training methods for vision backbones are well-established, pre-training additional modules for the person search task has not been previously examined. In this work, we present the first framework for end-to-end person search pre-training. Our framework splits person search into object-centric and query-centric methodologies, and we show that the query-centric framing is robust to label noise, and trainable using only weakly-labeled person bounding boxes. Further, we provide a novel model dubbed Swap Path Net (SPNet) which implements both query-centric and object-centric training objectives, and can swap between the two while using the same weights. Using SPNet, we show that query-centric pre-training, followed by object-centric fine-tuning, achieves state-of-the-art results on the standard PRW and CUHK-SYSU person search benchmarks, with 96.4% mAP on CUHK-SYSU and 61.2% mAP on PRW. In addition, we show that our method is more effective, efficient, and robust for person search pre-training than recent backbone-only pre-training alternatives.
在人物搜索中,我们在一系列画廊场景中对查询人物图像进行检测和匹配排名。大多数人物搜索模型都会使用特征提取主干网,然后分别用于检测和重新识别。虽然视觉主干的预训练方法已经确立,但针对人物搜索任务预训练附加模块尚未被研究。在这项工作中,我们提出了端到端人物搜索预训练的首个框架。我们的框架将人物搜索分为以物体为中心和以查询为中心的方法,并证明以查询为中心的方法对标签噪声具有鲁棒性,并且仅使用弱标签的人物边界框即可进行训练。此外,我们提供了一个名为Swap Path Net(SPNet)的新模型,实现了以查询为中心和以物体为中心的训练目标,并且在使用相同权重时可以互换。使用SPNet,我们证明了以查询为中心的预训练,随后以物体为中心的微调,可以在标准的PRW和CUHK-SYSU人物搜索基准测试上达到最佳结果,其中CUHK-SYSU的mAP为96.4%,PRW的mAP为61.2%。此外,我们还证明了我们的方法在人物搜索预训练方面比最近的仅使用主干的预训练替代方法更有效、更高效、更稳健。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF WACV 2025; Code: https://github.com/LLNL/spnet
Summary
本文介绍了针对人物搜索任务的首个端到端预训练框架。该框架将人物搜索分为对象中心方法和查询中心方法,并提出了一种新的模型Swap Path Net(SPNet),该模型实现了这两种训练目标,并可以在使用相同权重的同时进行切换。实验结果表明,使用SPNet进行查询中心预训练,然后进行对象中心微调,在PRW和CUHK-SYSU人物搜索标准数据集上取得了最佳结果。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了针对人物搜索任务的首个端到端预训练框架。
- 框架将人物搜索分为对象中心方法和查询中心方法。
- 查询中心框架能够应对标签噪声,并仅使用弱标签人物边界框进行训练。
- 提出了Swap Path Net (SPNet) 模型,实现了查询中心和对象中心训练目标的切换。
- SPNet在CUHK-SYSU和PRW数据集上取得了最佳结果,CUHK-SYSU上的mAP达到96.4%,PRW上的mAP达到61.2%。
- 相比最近的仅针对骨干网的预训练方法,该方法在人物搜索预训练方面更有效、更高效、更稳健。
点此查看论文截图

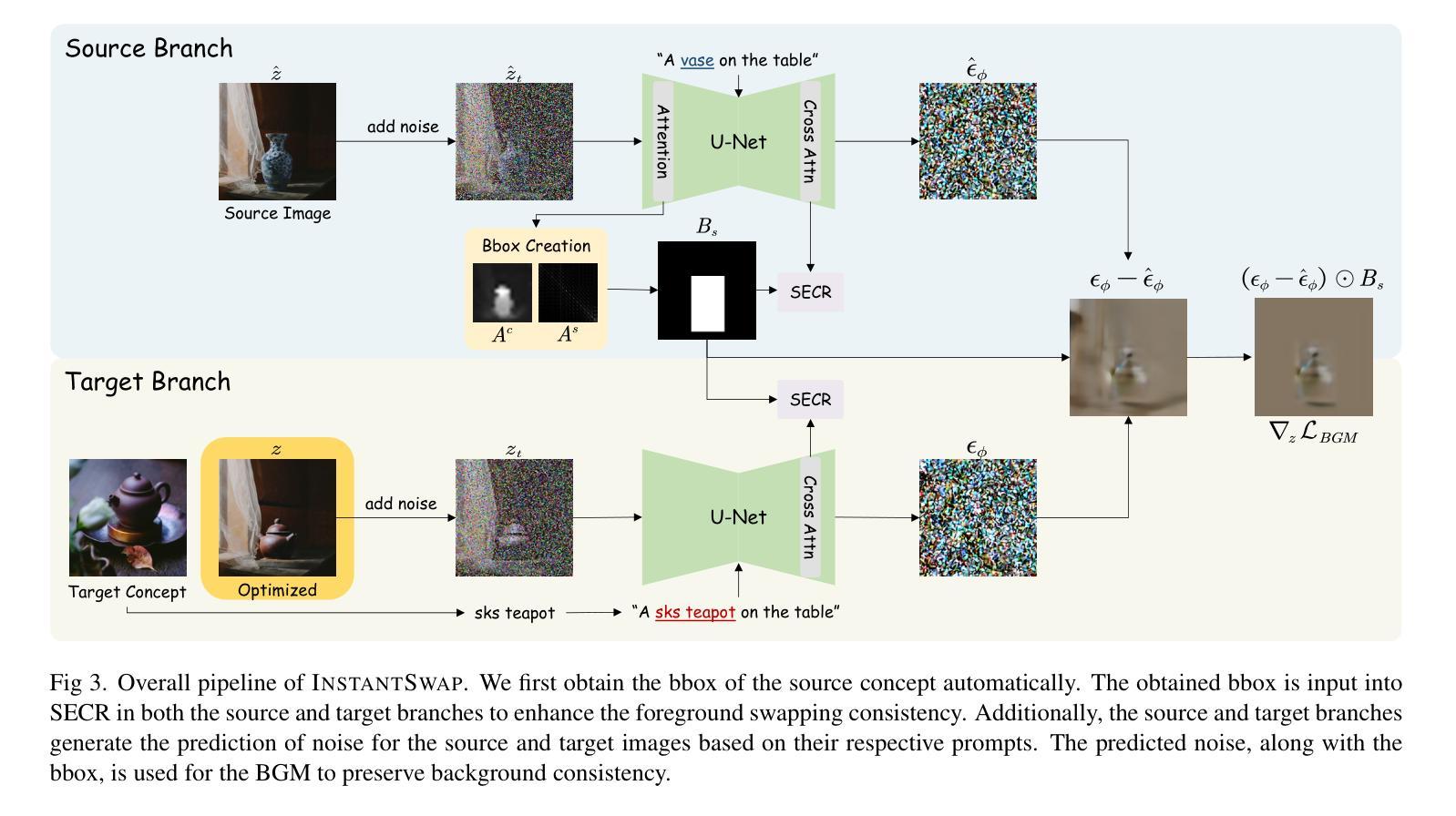
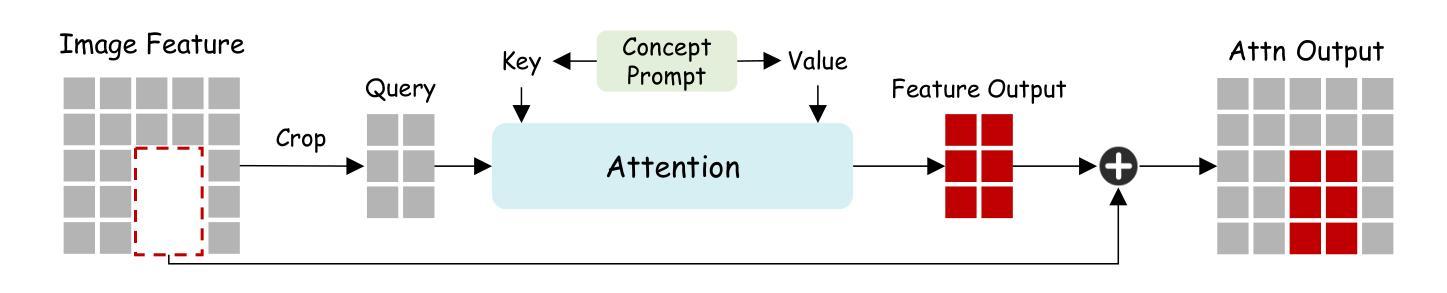
InstantSwap: Fast Customized Concept Swapping across Sharp Shape Differences
Authors:Chenyang Zhu, Kai Li, Yue Ma, Longxiang Tang, Chengyu Fang, Chubin Chen, Qifeng Chen, Xiu Li
Recent advances in Customized Concept Swapping (CCS) enable a text-to-image model to swap a concept in the source image with a customized target concept. However, the existing methods still face the challenges of inconsistency and inefficiency. They struggle to maintain consistency in both the foreground and background during concept swapping, especially when the shape difference is large between objects. Additionally, they either require time-consuming training processes or involve redundant calculations during inference. To tackle these issues, we introduce InstantSwap, a new CCS method that aims to handle sharp shape disparity at speed. Specifically, we first extract the bbox of the object in the source image automatically based on attention map analysis and leverage the bbox to achieve both foreground and background consistency. For background consistency, we remove the gradient outside the bbox during the swapping process so that the background is free from being modified. For foreground consistency, we employ a cross-attention mechanism to inject semantic information into both source and target concepts inside the box. This helps learn semantic-enhanced representations that encourage the swapping process to focus on the foreground objects. To improve swapping speed, we avoid computing gradients at each timestep but instead calculate them periodically to reduce the number of forward passes, which improves efficiency a lot with a little sacrifice on performance. Finally, we establish a benchmark dataset to facilitate comprehensive evaluation. Extensive evaluations demonstrate the superiority and versatility of InstantSwap. Project Page: https://instantswap.github.io/
最近,定制概念交换(CCS)的进展使得文本到图像模型能够用定制的目标概念替换源图像中的概念。然而,现有方法仍然面临一致性和效率方面的挑战。它们在概念交换时,特别是在前景和背景中都很难保持一致,尤其是物体形状差异较大时。此外,它们要么需要耗时的训练过程,要么在推理过程中涉及冗余的计算。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了InstantSwap,这是一种新的CCS方法,旨在快速处理明显的形状差异。具体来说,我们首先基于注意力图分析自动提取源图像中物体的bbox,并利用bbox来实现前景和背景的一致性。对于背景一致性,我们在交换过程中移除bbox外的梯度,使背景不受修改。对于前景一致性,我们采用跨注意力机制,将语义信息注入框内源和目标概念中。这有助于学习语义增强的表示,鼓励交换过程专注于前景对象。为了提高交换速度,我们避免在每个时间步计算梯度,而是定期计算梯度,以减少前向传递的次数,这在性能上稍有牺牲的情况下大大提高了效率。最后,我们建立了一个基准数据集,以促进全面评估。广泛评估证明了InstantSwap的优越性和通用性。项目页面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://instantswap.github.io/. Github Page: https://github.com/chenyangzhu1/InstantSwap
Summary
本文介绍了InstantSwap方法,这是一种新的定制概念交换(CCS)技术,旨在解决现有方法在概念交换时面临的形状差异大、前后景不一致及效率不高的问题。该方法基于注意力图分析自动提取目标对象的bbox,实现前景和背景的一致性。为提高交换速度,避免计算每个时间步的梯度,而是定期计算梯度以减少前向传递次数。最终建立了基准数据集进行综合评价,证明了InstantSwap的优越性和通用性。
Key Takeaways
- InstantSwap是一种新的定制概念交换(CCS)方法,旨在解决形状差异大、前后景不一致及效率不高的问题。
- InstantSwap通过注意力图分析自动提取目标对象的bbox,实现前景和背景一致性。
- 对于背景一致性,InstantSwap在交换过程中去除bbox外的梯度,避免背景被修改。
- 对于前景一致性,InstantSwap采用跨注意力机制,将语义信息注入源和目标概念中,学习语义增强的表示。
- InstantSwap通过定期计算梯度提高交换速度,减少前向传递次数,提高效率。
- InstantSwap建立了基准数据集,便于进行综合评价。
点此查看论文截图



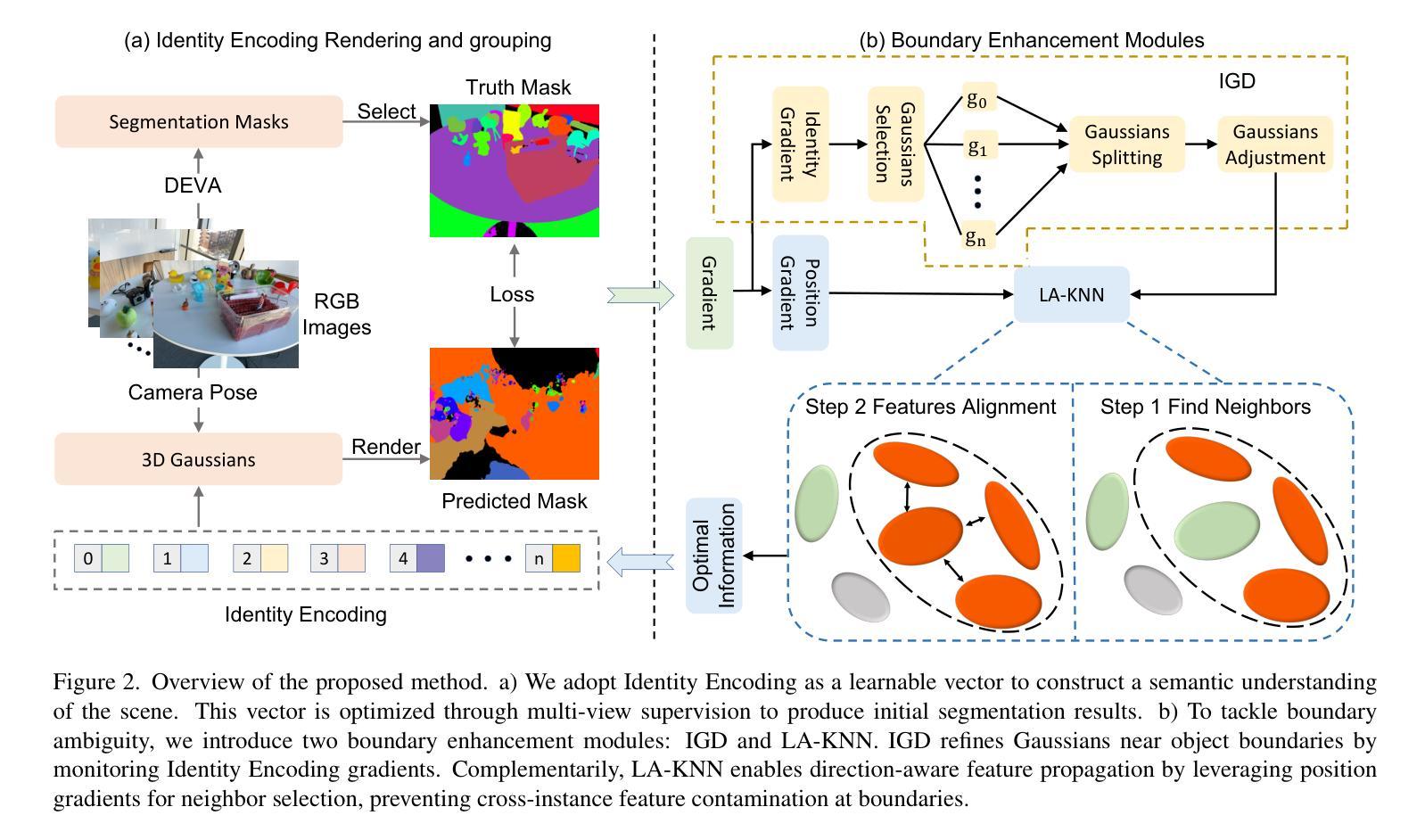
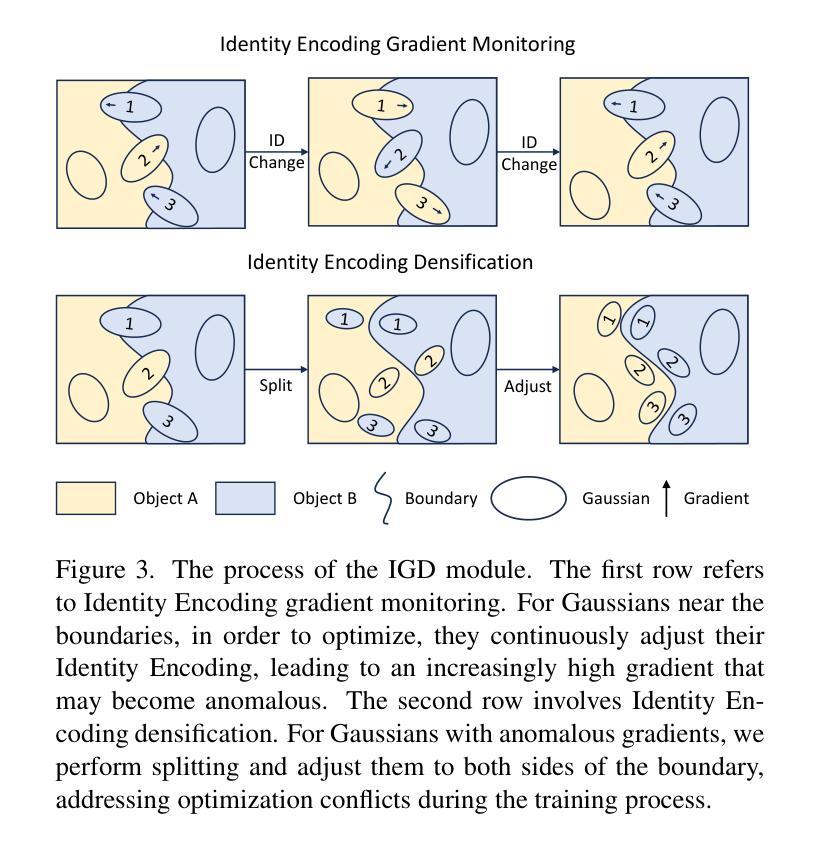
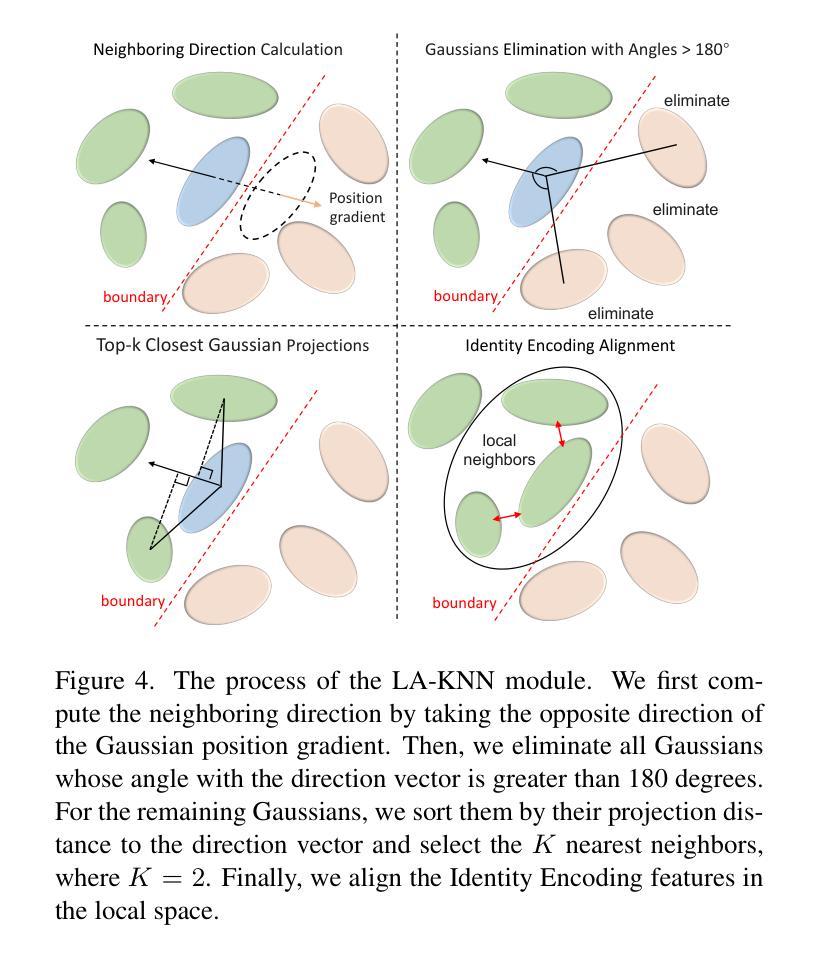
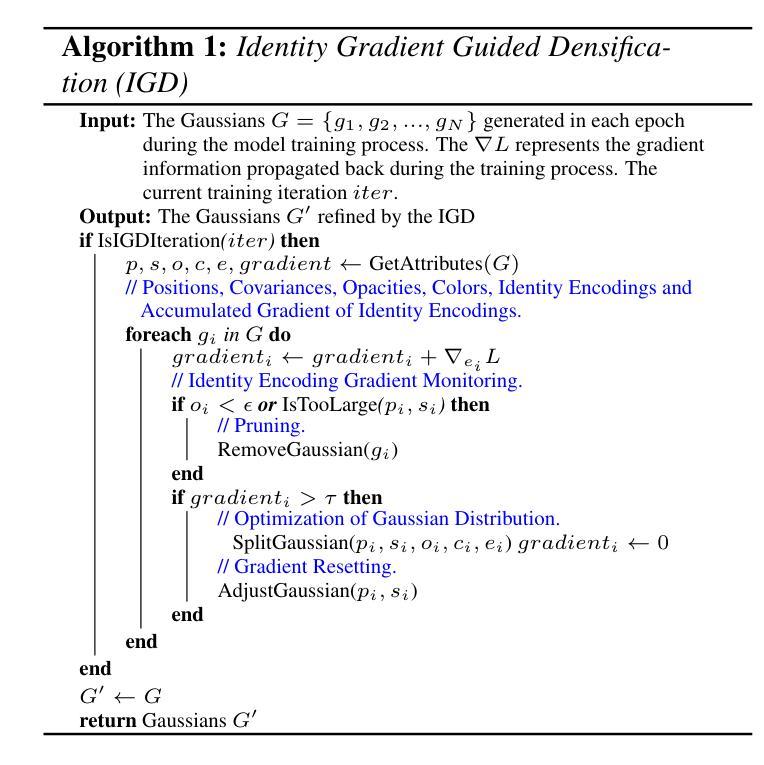
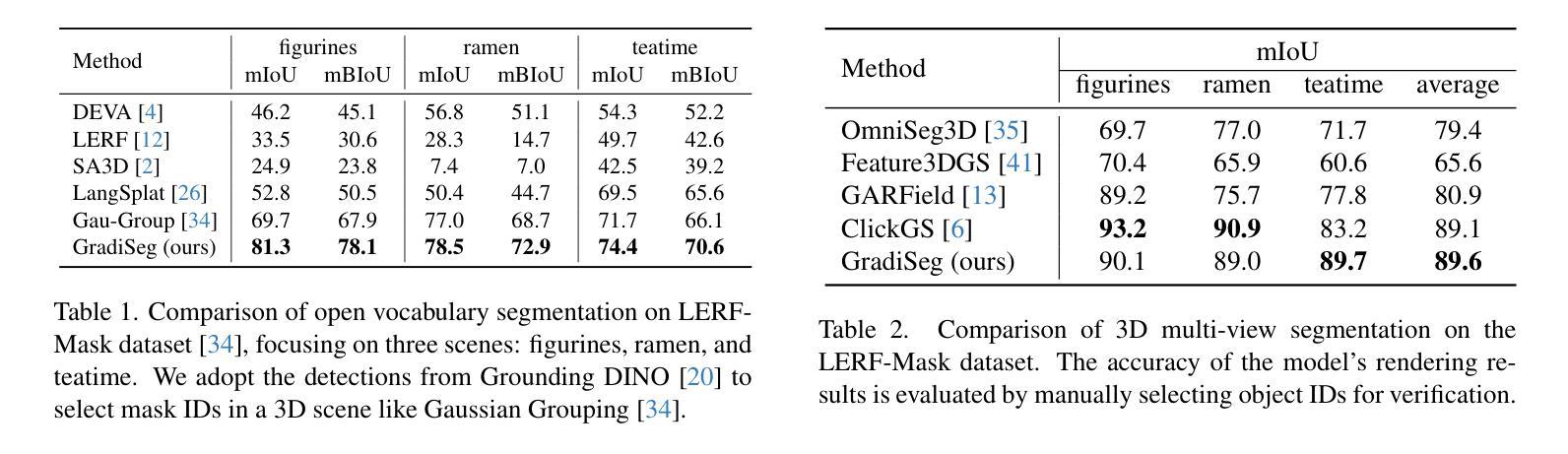
GradiSeg: Gradient-Guided Gaussian Segmentation with Enhanced 3D Boundary Precision
Authors:Zehao Li, Wenwei Han, Yujun Cai, Hao Jiang, Baolong Bi, Shuqin Gao, Honglong Zhao, Zhaoqi Wang
While 3D Gaussian Splatting enables high-quality real-time rendering, existing Gaussian-based frameworks for 3D semantic segmentation still face significant challenges in boundary recognition accuracy. To address this, we propose a novel 3DGS-based framework named GradiSeg, incorporating Identity Encoding to construct a deeper semantic understanding of scenes. Our approach introduces two key modules: Identity Gradient Guided Densification (IGD) and Local Adaptive K-Nearest Neighbors (LA-KNN). The IGD module supervises gradients of Identity Encoding to refine Gaussian distributions along object boundaries, aligning them closely with boundary contours. Meanwhile, the LA-KNN module employs position gradients to adaptively establish locality-aware propagation of Identity Encodings, preventing irregular Gaussian spreads near boundaries. We validate the effectiveness of our method through comprehensive experiments. Results show that GradiSeg effectively addresses boundary-related issues, significantly improving segmentation accuracy without compromising scene reconstruction quality. Furthermore, our method’s robust segmentation capability and decoupled Identity Encoding representation make it highly suitable for various downstream scene editing tasks, including 3D object removal, swapping and so on.
虽然3D高斯喷绘技术能够实现高质量实时渲染,但现有的基于高斯方法的3D语义分割框架在边界识别精度方面仍面临巨大挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新型的基于3DGS的框架,名为GradiSeg,它结合了身份编码来构建对场景的深层次语义理解。我们的方法引入了两个关键模块:身份梯度引导密集化(IGD)和局部自适应K近邻(LA-KNN)。IGD模块通过监督身份编码的梯度来优化对象边界的高斯分布,使其紧密对齐边界轮廓。同时,LA-KNN模块利用位置梯度自适应地建立身份编码的局部感知传播,防止边界附近的高斯分布出现不规则扩散。我们通过全面的实验验证了我们的方法的有效性。结果表明,GradiSeg有效地解决了边界相关的问题,在不影响场景重建质量的情况下显著提高分割精度。此外,我们方法的稳健分割能力和解耦的身份编码表示使其成为各种下游场景编辑任务的高度合适选择,包括3D对象移除、替换等。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于3DGS的新型框架GradiSeg,通过引入身份编码(Identity Encoding)技术,增强对场景语义的深层次理解。该框架包含两个关键模块:身份梯度引导密集化(IGD)和局部自适应K近邻(LA-KNN)。IGD模块通过监督身份编码的梯度来细化对象边界的高斯分布,使其与边界轮廓紧密对齐;而LA-KNN模块则利用位置梯度自适应地建立身份编码的局部传播,防止边界附近的高斯分布不规则扩散。实验证明,GradiSeg能有效解决边界相关问题,显著提高分割精度,同时不损害场景重建质量。
Key Takeaways
- 提出的GradiSeg框架基于3DGS,融入Identity Encoding技术,深化了对场景语义的理解。
- 框架包含两个核心模块:IGD和LA-KNN,分别处理高斯分布的细化和边界附近的不规则扩散问题。
- IGD模块通过监督身份编码的梯度来细化对象边界的高斯分布。
- LA-KNN模块利用位置梯度建立身份编码的局部传播,提高分割精度。
- GradiSeg在解决边界问题的同时,不损害场景重建质量。
- GradiSeg具有强大的分割能力和解耦的身份编码表示,适用于多种下游场景编辑任务,如3D对象移除、替换等。
点此查看论文截图

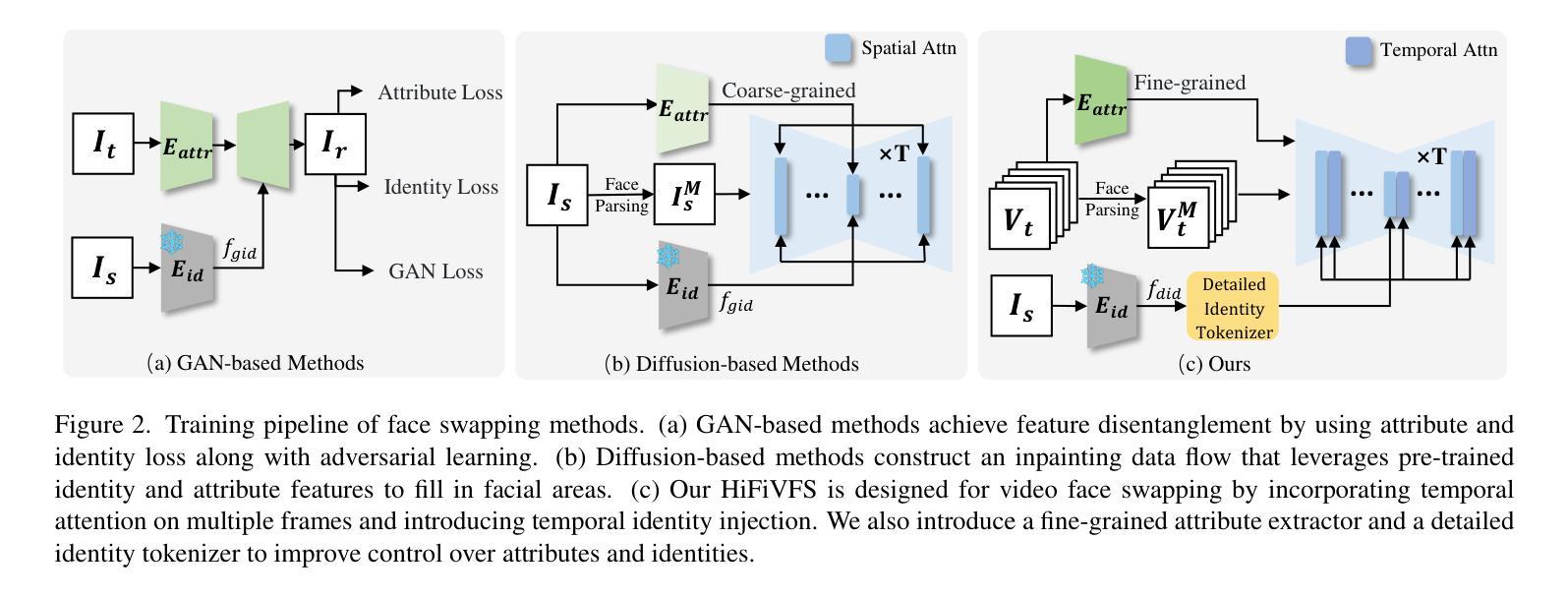
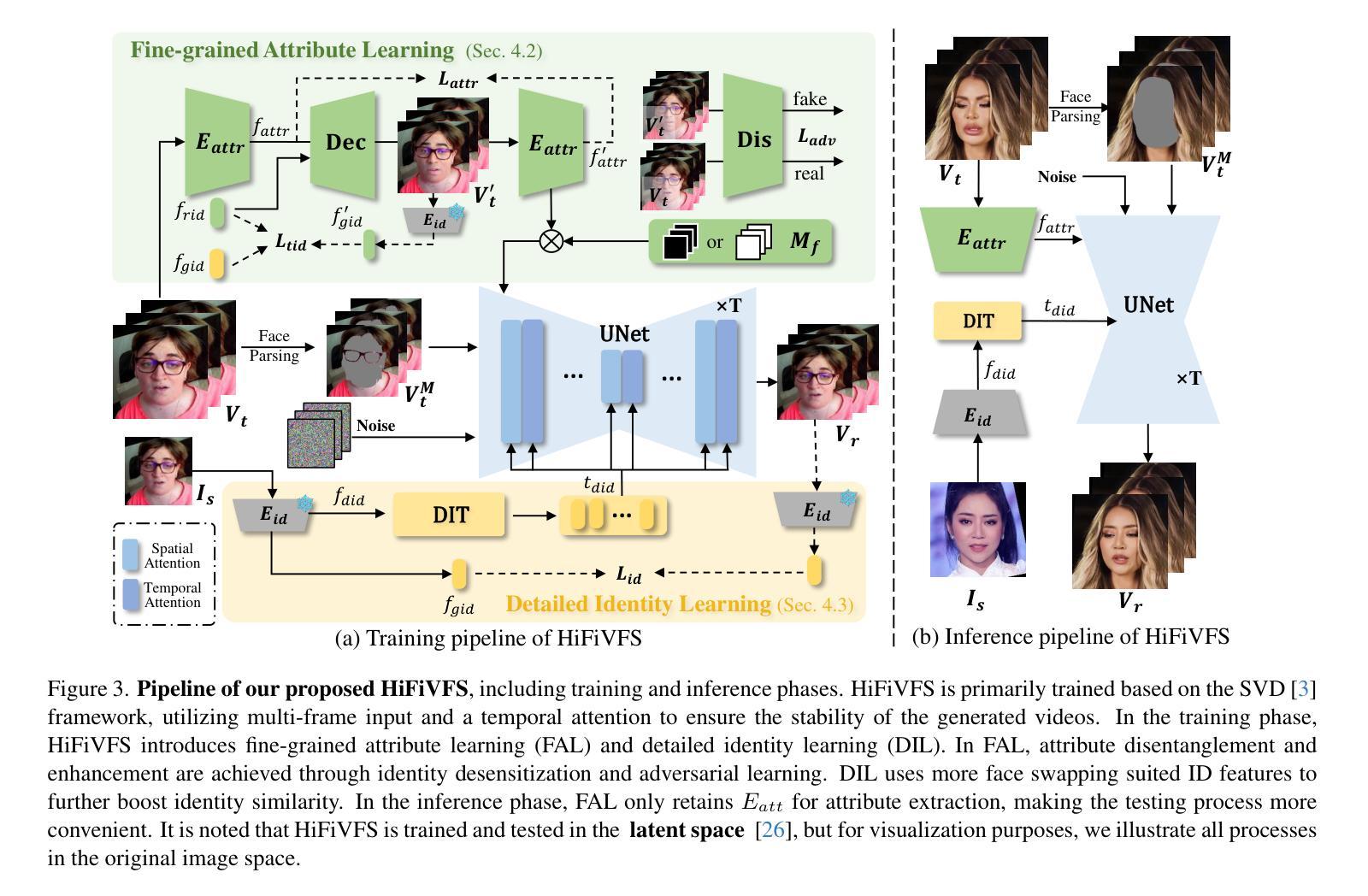
HiFiVFS: High Fidelity Video Face Swapping
Authors:Xu Chen, Keke He, Junwei Zhu, Yanhao Ge, Wei Li, Chengjie Wang
Face swapping aims to generate results that combine the identity from the source with attributes from the target. Existing methods primarily focus on image-based face swapping. When processing videos, each frame is handled independently, making it difficult to ensure temporal stability. From a model perspective, face swapping is gradually shifting from generative adversarial networks (GANs) to diffusion models (DMs), as DMs have been shown to possess stronger generative capabilities. Current diffusion-based approaches often employ inpainting techniques, which struggle to preserve fine-grained attributes like lighting and makeup. To address these challenges, we propose a high fidelity video face swapping (HiFiVFS) framework, which leverages the strong generative capability and temporal prior of Stable Video Diffusion (SVD). We build a fine-grained attribute module to extract identity-disentangled and fine-grained attribute features through identity desensitization and adversarial learning. Additionally, We introduce detailed identity injection to further enhance identity similarity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) in video face swapping, both qualitatively and quantitatively.
面部替换旨在生成结合源身份和目标属性的结果。现有方法主要集中在基于图像的面部替换上。在处理视频时,每一帧都是独立处理的,这很难保证时间稳定性。从模型的角度来看,面部替换正在逐渐从生成对抗网络(GANs)转向扩散模型(DMs),因为DMs已显示出具有更强的生成能力。当前的基于扩散的方法经常采用修复技术,这很难保留照明和妆容等精细属性。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了高保真视频面部替换(HiFiVFS)框架,该框架利用稳定视频扩散(SVD)的强大生成能力和时间先验。我们建立了一个精细属性模块,通过身份脱敏和对抗性学习提取身份分散和精细属性特征。此外,我们引入了详细的身份注入,以进一步增强身份相似性。大量实验表明,我们的方法在视频面部替换中无论是定性还是定量评估都达到了最先进的水平。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
该技术提出一种高保真视频人脸替换(HiFiVFS)框架,旨在解决视频人脸替换中的时间稳定性和精细属性保留问题。它结合了稳定视频扩散(SVD)的强大生成能力和时间先验知识,建立了一个精细属性模块,通过身份脱敏和对抗性学习提取身份分离和精细属性特征。此外,引入详细身份注入技术进一步增强身份相似性。实验证明,该方法在视频人脸替换方面达到了先进性能。
关键见解
- 视频人脸替换面临时间稳定性和精细属性保留的挑战。
- 现有方法主要关注图像人脸替换,处理视频时独立处理每一帧,难以确保时间稳定性。
- 人脸替换模型逐渐从生成对抗网络(GANs)转向扩散模型(DMs),因为DMs展现出更强大的生成能力。
- 当前扩散模型采用基于修复的技术,难以保留光照和妆容等精细属性。
- 提出的HiFiVFS框架结合了稳定视频扩散(SVD)的生成能力和时间先验知识。
- 建立了一个精细属性模块,通过身份脱敏和对抗性学习提取身份分离和精细属性特征。
- 引入详细身份注入技术增强身份相似性,达到先进性能。
点此查看论文截图

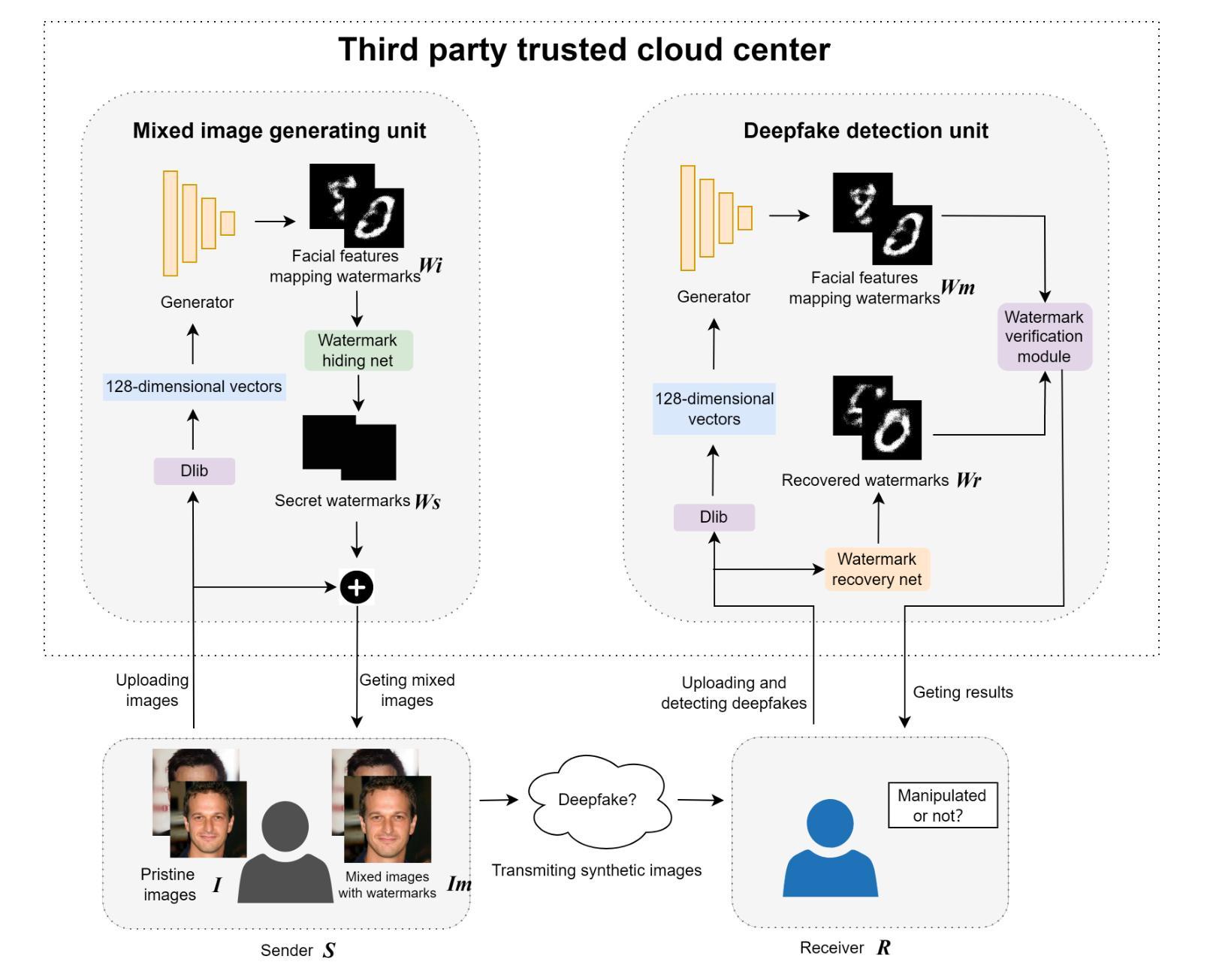
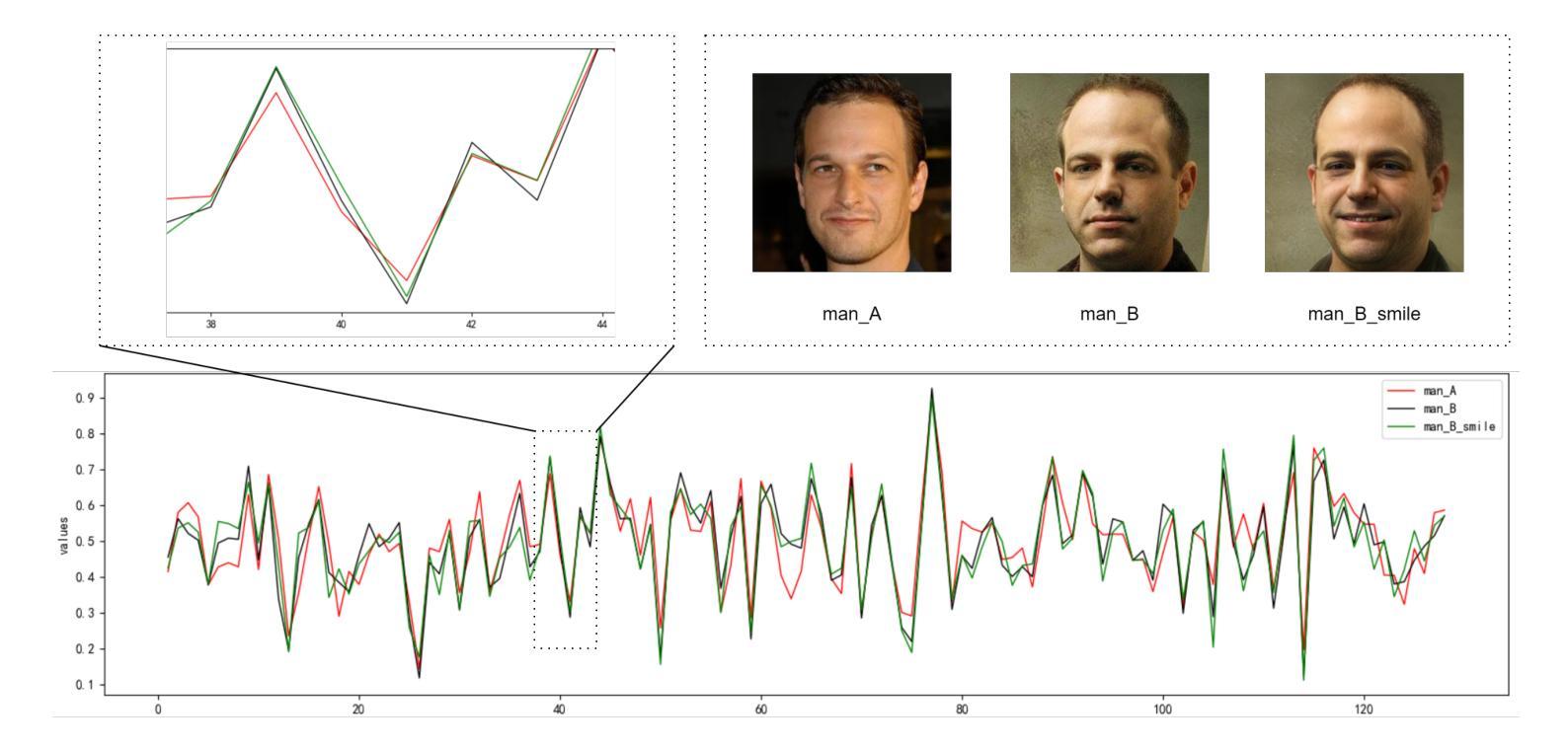
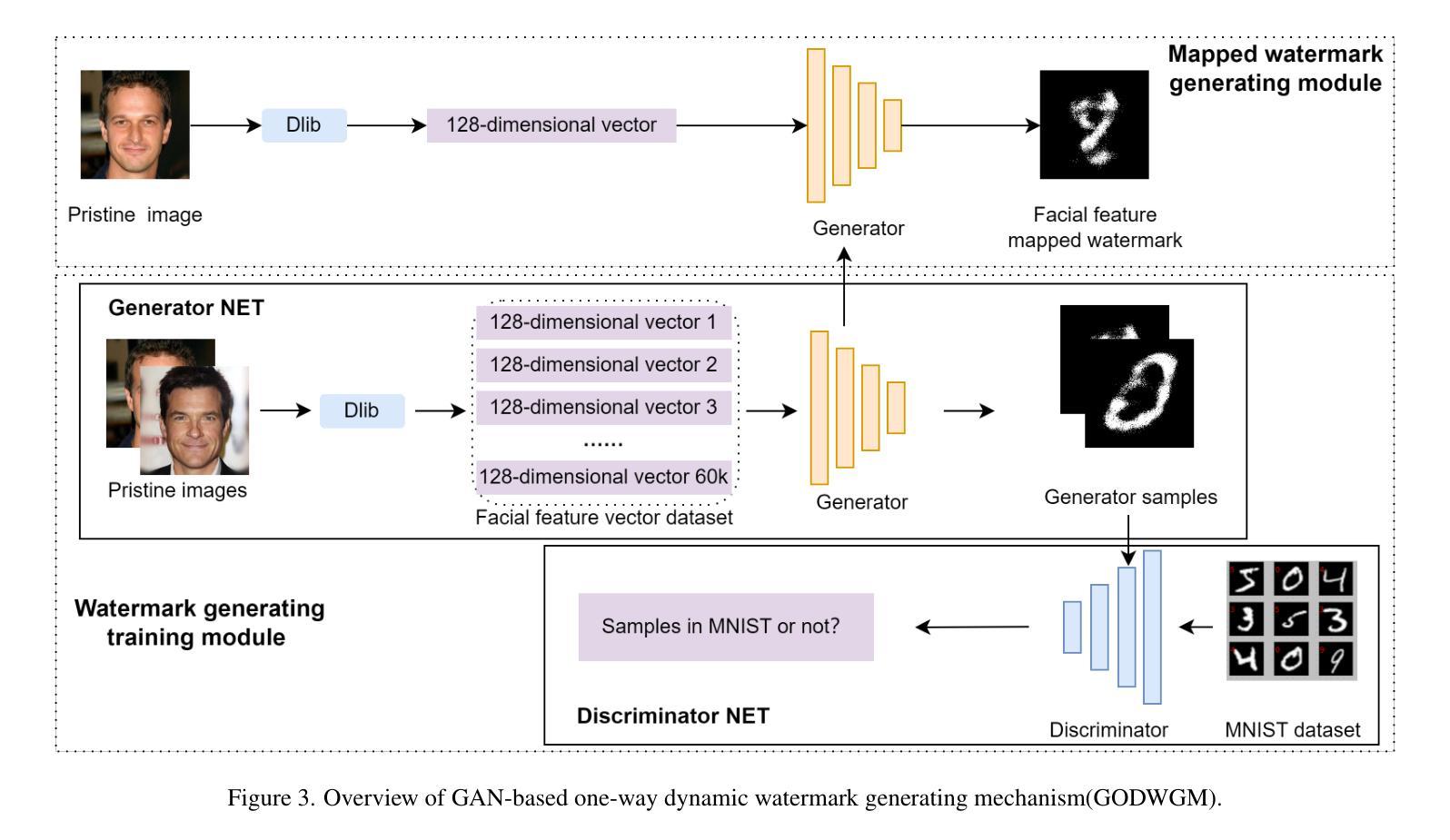
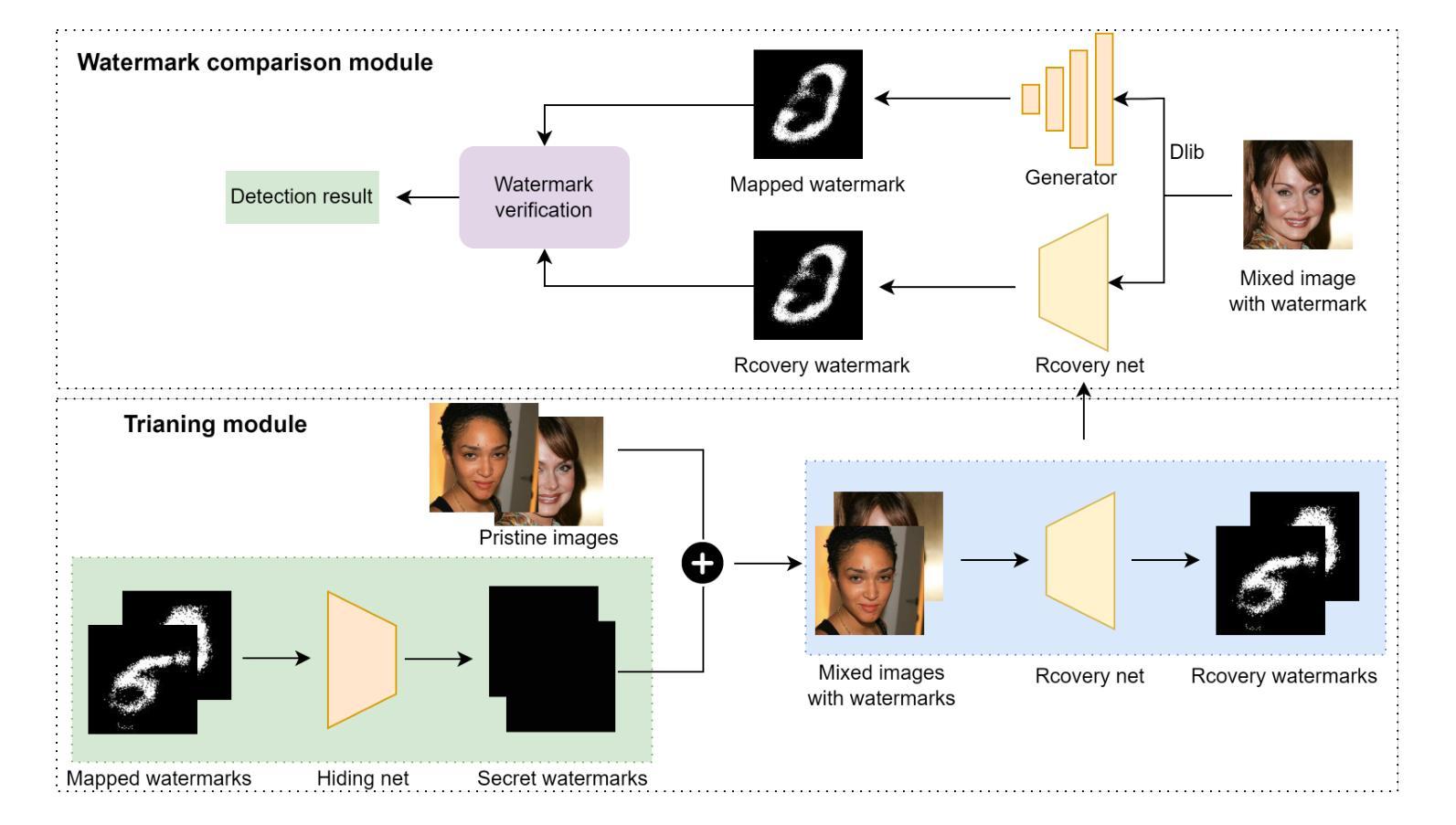
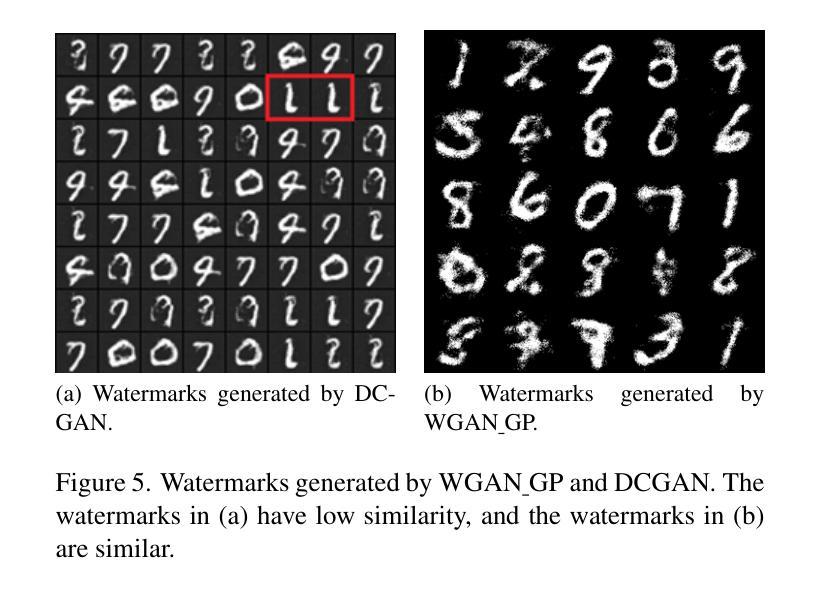
Facial Features Matter: a Dynamic Watermark based Proactive Deepfake Detection Approach
Authors:Shulin Lan, Kanlin Liu, Yazhou Zhao, Chen Yang, Yingchao Wang, Xingshan Yao, Liehuang Zhu
Current passive deepfake face-swapping detection methods encounter significance bottlenecks in model generalization capabilities. Meanwhile, proactive detection methods often use fixed watermarks which lack a close relationship with the content they protect and are vulnerable to security risks. Dynamic watermarks based on facial features offer a promising solution, as these features provide unique identifiers. Therefore, this paper proposes a Facial Feature-based Proactive deepfake detection method (FaceProtect), which utilizes changes in facial characteristics during deepfake manipulation as a novel detection mechanism. We introduce a GAN-based One-way Dynamic Watermark Generating Mechanism (GODWGM) that uses 128-dimensional facial feature vectors as inputs. This method creates irreversible mappings from facial features to watermarks, enhancing protection against various reverse inference attacks. Additionally, we propose a Watermark-based Verification Strategy (WVS) that combines steganography with GODWGM, allowing simultaneous transmission of the benchmark watermark representing facial features within the image. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed method maintains exceptional detection performance and exhibits high practicality on images altered by various deepfake techniques.
当前被动式的深度伪造面部替换检测技术在模型泛化能力方面遇到重大瓶颈。同时,主动检测方法通常使用固定水印,这些水印与其保护的内容缺乏密切联系,并存在安全风险。基于面部特征的动态水印提供了一种有前途的解决方案,因为这些特征提供了独特的标识符。因此,本文提出了一种基于面部特征的主动深度伪造检测方法(FaceProtect),该方法利用深度伪造操作期间面部特征的变化作为新型检测机制。我们引入了基于GAN的单向动态水印生成机制(GODWGM),该机制使用128维面部特征向量作为输入。这种方法创建了从面部特征到水印的不可逆映射,增强了对抗各种反向推理攻击的保护能力。此外,我们提出了基于水印的验证策略(WVS),它将隐写术与GODWGM相结合,允许在图像中同时传输代表面部特征的基准水印。实验结果表明,我们提出的方法在由各种深度伪造技术修改的图像上保持了出色的检测性能,并表现出高度的实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于面部特征的动态水印对Deepfake人脸替换技术中的图像伪造行为进行积极检测提供了可行性解决方案。本文通过结合GAN技术的单向动态水印生成机制,以利用面部特征变化作为伪造行为的检测依据。此机制可以抵抗逆向推理攻击并强化水印的保护能力。同时,通过结合隐写术和生成机制的水印验证策略可以在图像内部同步传输面部特征的水印标记,实现高效检测。实验证明,此方法在多种Deepfake技术处理过的图像上仍能保持出色的检测性能。
关键见解
- 当前被动式Deepfake检测技术存在模型泛化能力的瓶颈问题。
- 传统主动检测技术采用固定水印,与保护内容关联度低且存在安全风险。
- 基于面部特征的动态水印提供了一种新颖解决方案,利用面部特征作为独特标识符。
- 引入的FaceProtect方法利用Deepfake操作过程中的面部特征变化作为检测机制。
- GAN技术用于创建不可逆的映射关系,增强水印保护能力对抗逆向推理攻击。
- 结合隐写术和水印生成机制的验证策略实现高效验证,允许水印标记在图像内部同步传输。
点此查看论文截图

Saliency-Based diversity and fairness Metric and FaceKeepOriginalAugment: A Novel Approach for Enhancing Fairness and Diversity
Authors:Teerath Kumar, Alessandra Mileo, Malika Bendechache
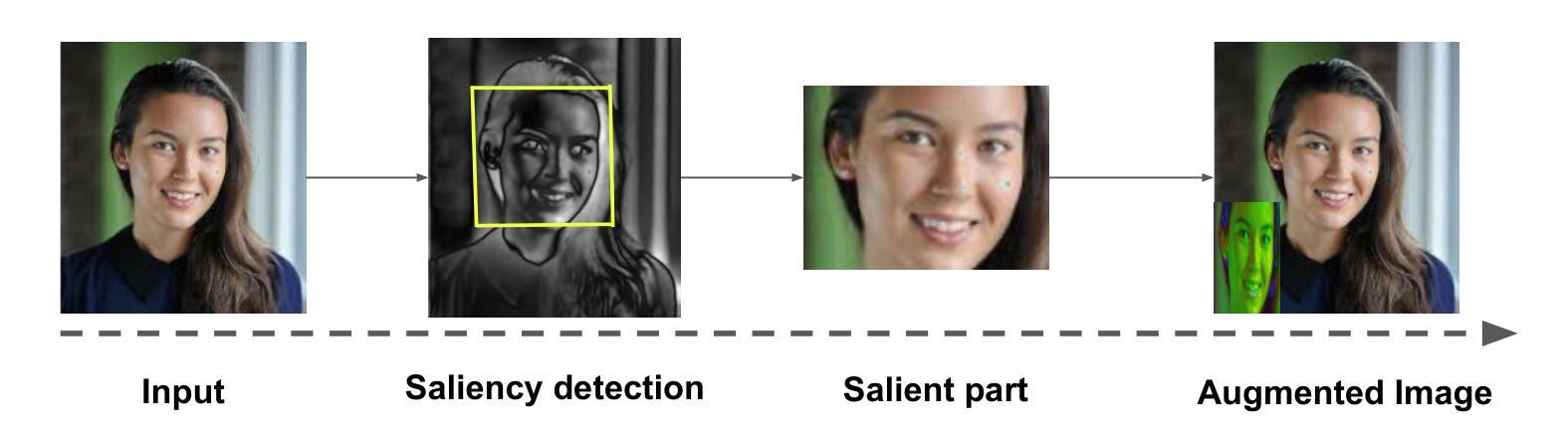
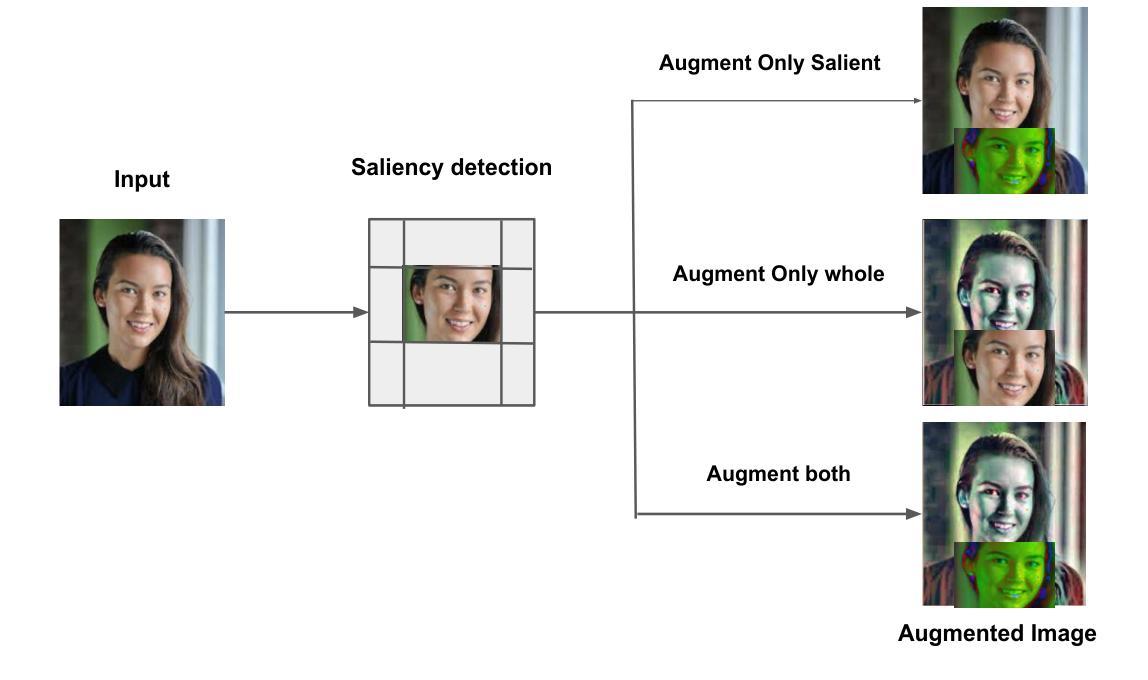
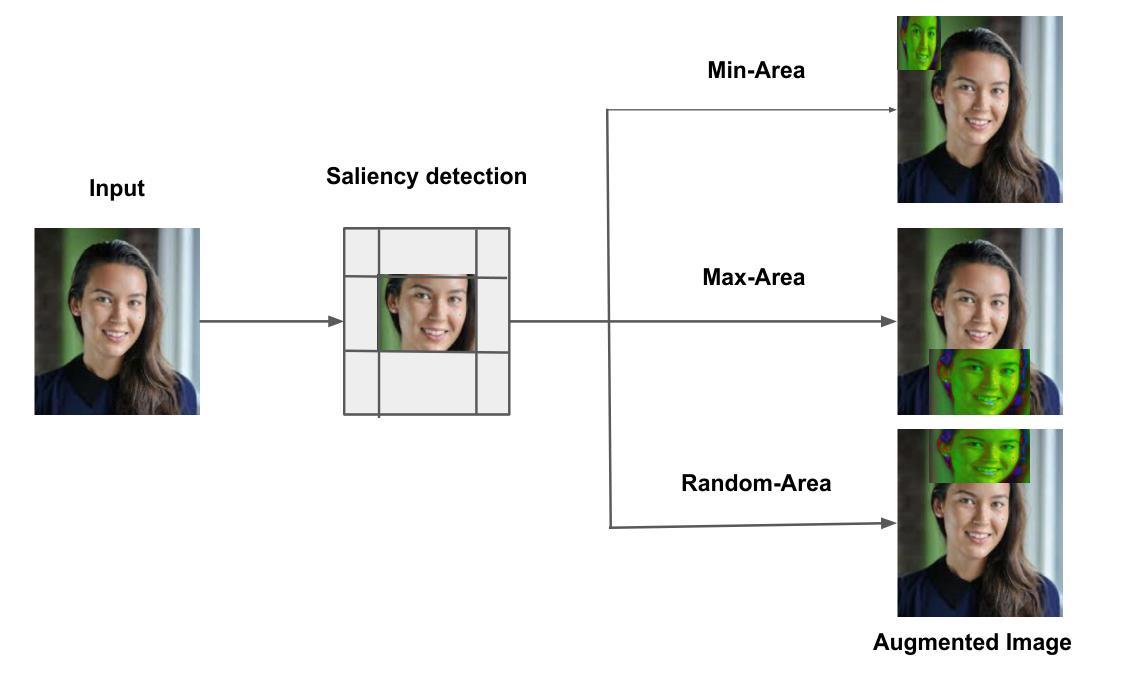
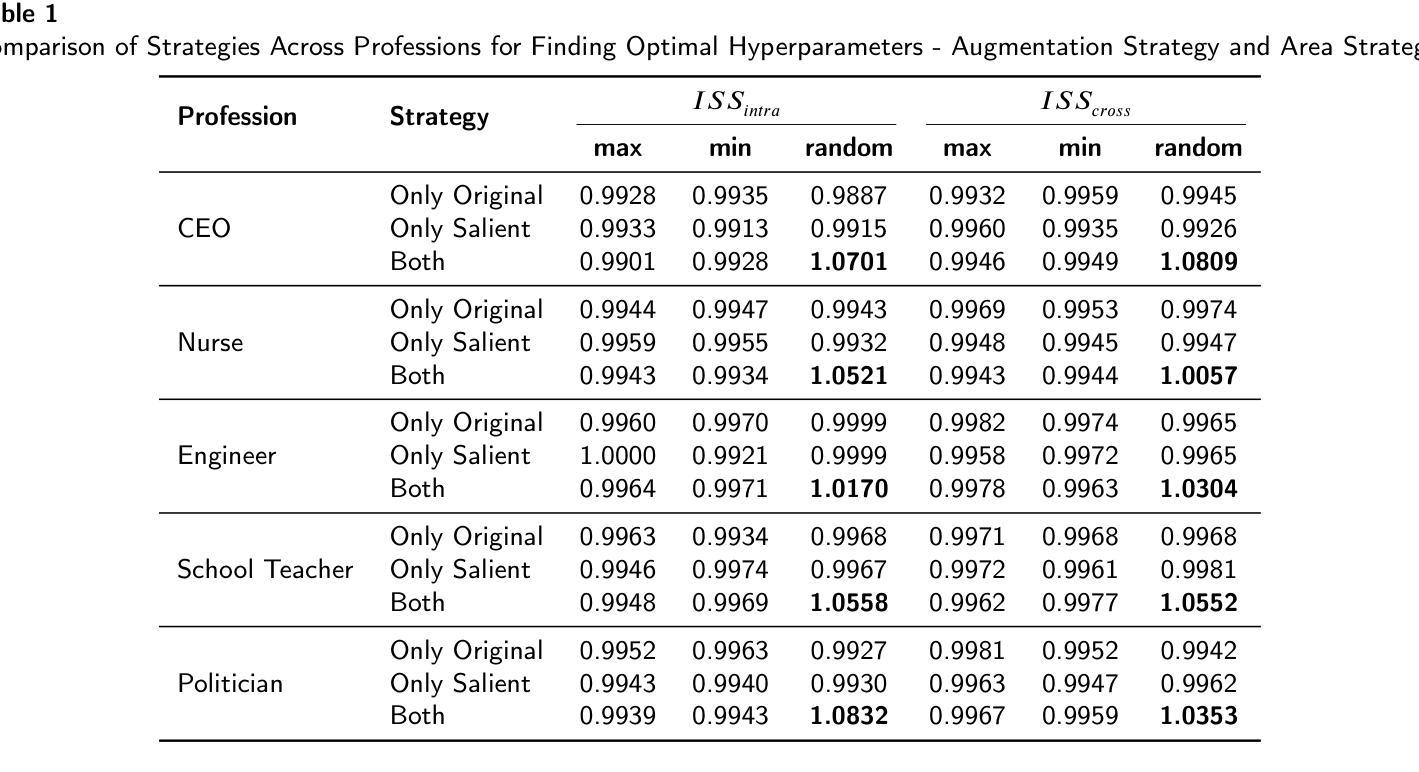
Data augmentation has become a pivotal tool in enhancing the performance of computer vision tasks, with the KeepOriginalAugment method emerging as a standout technique for its intelligent incorporation of salient regions within less prominent areas, enabling augmentation in both regions. Despite its success in image classification, its potential in addressing biases remains unexplored. In this study, we introduce an extension of the KeepOriginalAugment method, termed FaceKeepOriginalAugment, which explores various debiasing aspects-geographical, gender, and stereotypical biases-in computer vision models. By maintaining a delicate balance between data diversity and information preservation, our approach empowers models to exploit both diverse salient and non-salient regions, thereby fostering increased diversity and debiasing effects. We investigate multiple strategies for determining the placement of the salient region and swapping perspectives to decide which part undergoes augmentation. Leveraging the Image Similarity Score (ISS), we quantify dataset diversity across a range of datasets, including Flickr Faces HQ (FFHQ), WIKI, IMDB, Labelled Faces in the Wild (LFW), UTK Faces, and Diverse Dataset. We evaluate the effectiveness of FaceKeepOriginalAugment in mitigating gender bias across CEO, Engineer, Nurse, and School Teacher datasets, utilizing the Image-Image Association Score (IIAS) in convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs). Our findings shows the efficacy of FaceKeepOriginalAugment in promoting fairness and inclusivity within computer vision models, demonstrated by reduced gender bias and enhanced overall fairness. Additionally, we introduce a novel metric, Saliency-Based Diversity and Fairness Metric, which quantifies both diversity and fairness while handling data imbalance across various datasets.
数据增强已成为提高计算机视觉任务性能的关键工具,其中KeepOriginalAugment方法因其智能地将显著区域融入不太突出的区域而脱颖而出,能够在两个区域中进行增强。尽管它在图像分类方面的表现很出色,但其解决偏见问题的潜力尚未得到探索。在这项研究中,我们介绍了KeepOriginalAugment方法的扩展版本,称为FaceKeepOriginalAugment,它探索了计算机视觉模型中的各种去偏方面,包括地理、性别和刻板印象偏见。我们的方法能够在数据多样性和信息保留之间保持微妙的平衡,使模型能够利用多样化和非多样化的显著区域,从而促进增加多样性和去偏见效果。我们研究多种策略来确定显著区域的位置并改变视角,以确定哪些部分需要进行增强。我们利用图像相似度得分(ISS)来量化多个数据集(包括Flickr Faces HQ(FFHQ)、WIKI、IMDB、野外人脸(LFW)、UTK人脸和多样化数据集)的数据集多样性。我们评估了FaceKeepOriginalAugment在减轻CEO、工程师、护士和教师数据集中的性别偏见方面的有效性,并利用卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT)中的图像关联得分(IIAS)进行了评估。我们的研究结果表明,FaceKeepOriginalAugment在促进计算机视觉模型的公平性和包容性方面非常有效,表现为减少了性别偏见并提高了整体公平性。此外,我们还引入了一个新的度量标准——基于显著性的多样性和公平性度量,该度量标准可以量化多样性和公平性,同时处理各种数据集中的数据不平衡问题。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Paper is underReview in Image and Vision Computing Journal special issue: Advancing Transparency and Privacy: Explainable AI and Synthetic Data in Biometrics and Computer Vision
摘要
本段文字详细介绍了Data augmentation在计算机视觉任务中的关键作用以及新兴技术KeepOriginalAugment的应用效果。然而其应对偏见的问题仍待探索。针对这一问题,研究人员提出一种KeepOriginalAugment的扩展方法FaceKeepOriginalAugment,其探讨计算机视觉模型中的地理、性别和刻板印象等方面的偏见问题。该方法通过平衡数据多样性和信息保留来增强模型的性能,并采用图像相似度评分来量化数据集多样性。此外,该研究评估了FaceKeepOriginalAugment在缓解性别偏见方面的效果,同时介绍了一种新型评价指标来量化多样性和公平性。研究表明FaceKeepOriginalAugment可有效促进计算机视觉模型的公平性和包容性,有助于减少性别偏见并提高整体公平性。
关键收获点
- 数据增强已成为提高计算机视觉任务性能的重要工具,而KeepOriginalAugment方法通过智能融合显著区域和非显著区域实现了增强效果。
- 尽管在图像分类中取得了成功,但KeepOriginalAugment在解决偏见问题方面的潜力尚未被探索。
- 研究人员提出了FaceKeepOriginalAugment方法,这是KeepOriginalAugment的一个扩展,专注于解决计算机视觉模型中的地理、性别和刻板印象偏见。
- FaceKeepOriginalAugment通过平衡数据多样性和信息保留来增强模型性能,并采用图像相似度评分来量化数据集多样性。
- 研究评估了FaceKeepOriginalAugment在减少性别偏见方面的效果,并引入了一种新的评价指标来同时量化多样性和公平性。
点此查看论文截图

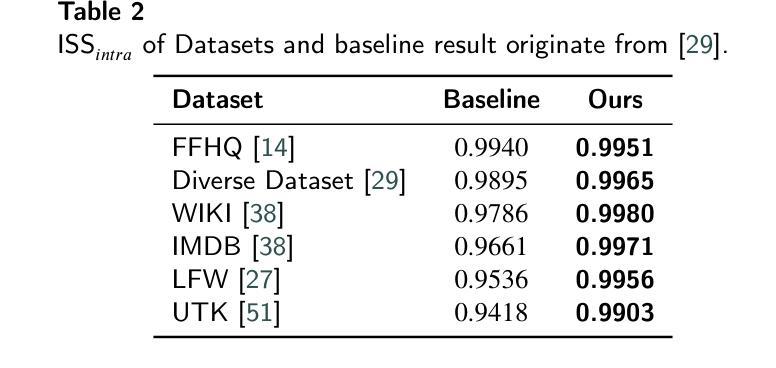
Face Anonymization Made Simple
Authors:Han-Wei Kung, Tuomas Varanka, Sanjay Saha, Terence Sim, Nicu Sebe
Current face anonymization techniques often depend on identity loss calculated by face recognition models, which can be inaccurate and unreliable. Additionally, many methods require supplementary data such as facial landmarks and masks to guide the synthesis process. In contrast, our approach uses diffusion models with only a reconstruction loss, eliminating the need for facial landmarks or masks while still producing images with intricate, fine-grained details. We validated our results on two public benchmarks through both quantitative and qualitative evaluations. Our model achieves state-of-the-art performance in three key areas: identity anonymization, facial attribute preservation, and image quality. Beyond its primary function of anonymization, our model can also perform face swapping tasks by incorporating an additional facial image as input, demonstrating its versatility and potential for diverse applications. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/hanweikung/face_anon_simple .
当前的面部匿名化技术通常依赖于面部识别模型计算的身份丢失,这可能会不准确且不可靠。此外,许多方法需要额外的数据(例如面部标记和面具)来指导合成过程。相比之下,我们的方法仅使用扩散模型与重建损失,无需面部标记或面具,同时仍能产生具有精细细节的图像。我们通过定量和定性评估在两个公共基准测试集上验证了我们的结果。我们的模型在身份匿名化、面部特征保留和图像质量三个关键领域达到了最先进的性能。除了匿名化的主要功能外,我们的模型还可以通过将额外的面部图像作为输入来执行面部替换任务,展示了其多样性和多种应用的潜力。我们的代码和模型可在https://github.com/hanweikung/face_anon_simple找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了当前面部匿名化技术的问题,如依赖不准确和不可靠的身份损失计算方式,以及需要额外的面部标志和掩膜来指导合成过程。相比之下,新方法采用扩散模型与重建损失相结合,无需面部标志或掩膜,生成图像仍具有精细的细节。在公共基准测试上的定量和定性评估验证了其有效性,并在身份匿名化、面部特征保留和图像质量方面达到领先水平。此外,该模型还具有面部替换功能,可通过引入额外的面部图像进行输入,展示其多样性和潜在应用潜力。代码和模型可在https://github.com/hanweikung/face_anon_simple上获取。
Key Takeaways
- 当前面部匿名化技术依赖不准确和不可靠的身份损失计算方式。
- 扩散模型结合重建损失成为新方法的核心。
- 该方法无需面部标志和掩膜数据,生成图像质量精细。
- 模型在身份匿名化、面部特征保留和图像质量方面表现领先。
- 模型具备面部替换功能,具有广泛的应用潜力。
- 模型已在两个公共基准测试上通过定量和定性评估验证。
点此查看论文截图
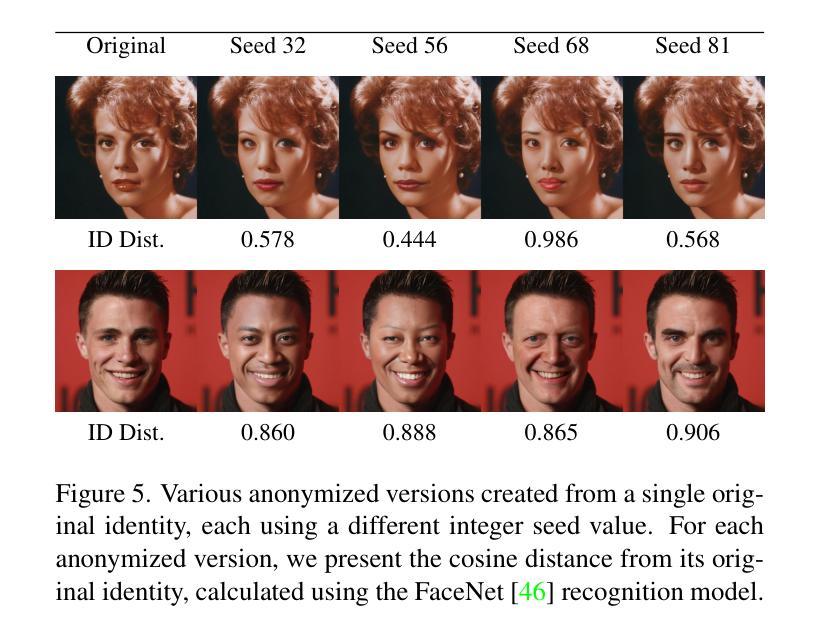

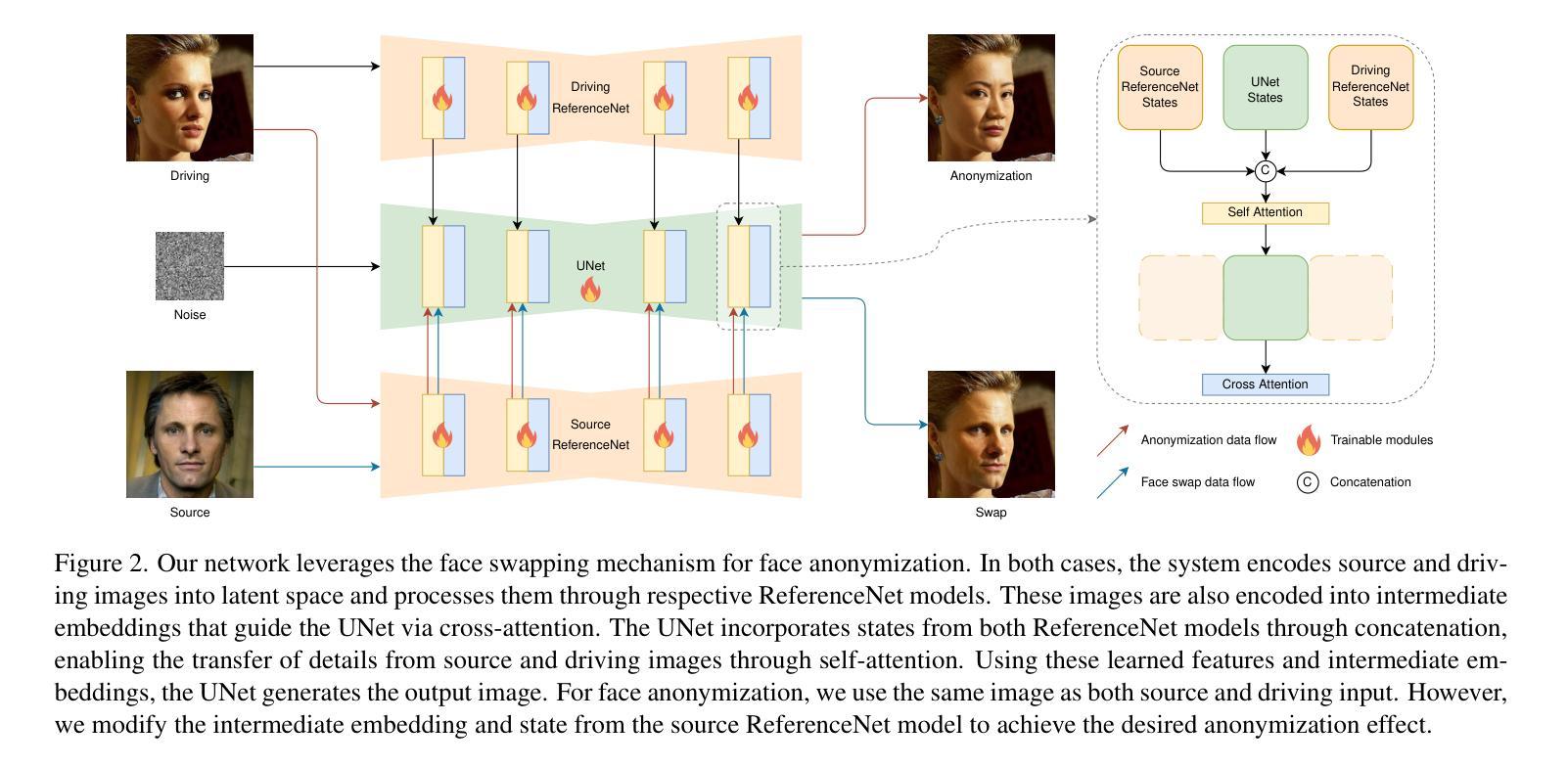
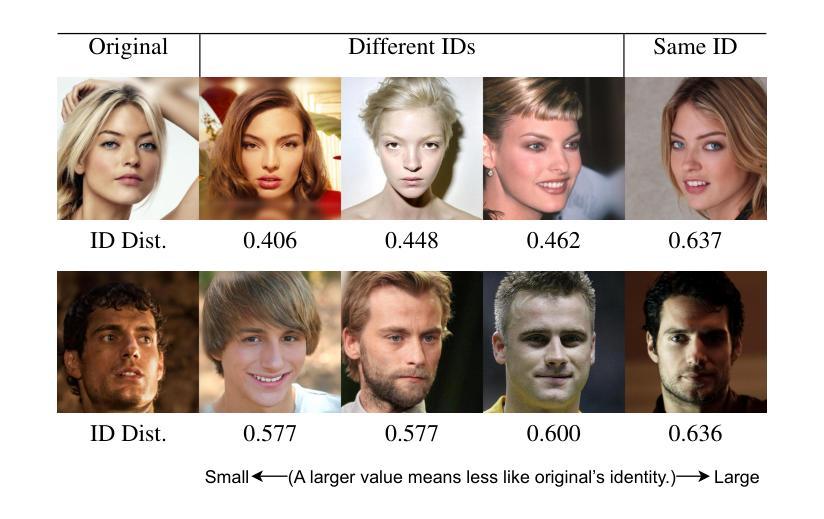

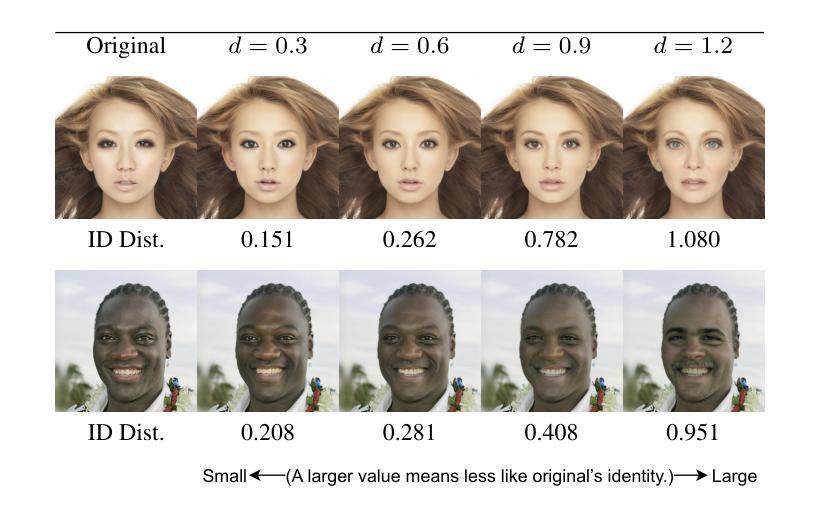
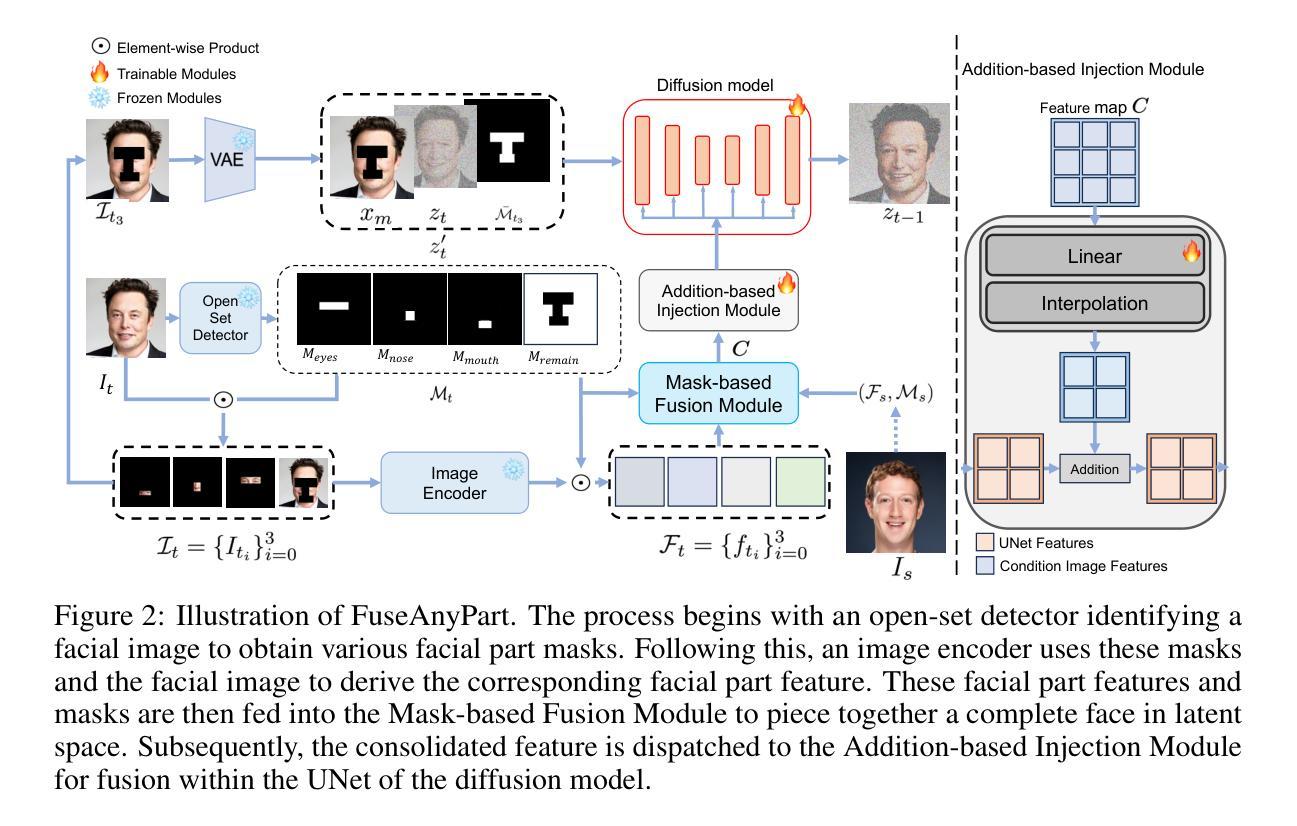
FuseAnyPart: Diffusion-Driven Facial Parts Swapping via Multiple Reference Images
Authors:Zheng Yu, Yaohua Wang, Siying Cui, Aixi Zhang, Wei-Long Zheng, Senzhang Wang
Facial parts swapping aims to selectively transfer regions of interest from the source image onto the target image while maintaining the rest of the target image unchanged. Most studies on face swapping designed specifically for full-face swapping, are either unable or significantly limited when it comes to swapping individual facial parts, which hinders fine-grained and customized character designs. However, designing such an approach specifically for facial parts swapping is challenged by a reasonable multiple reference feature fusion, which needs to be both efficient and effective. To overcome this challenge, FuseAnyPart is proposed to facilitate the seamless “fuse-any-part” customization of the face. In FuseAnyPart, facial parts from different people are assembled into a complete face in latent space within the Mask-based Fusion Module. Subsequently, the consolidated feature is dispatched to the Addition-based Injection Module for fusion within the UNet of the diffusion model to create novel characters. Extensive experiments qualitatively and quantitatively validate the superiority and robustness of FuseAnyPart. Source codes are available at https://github.com/Thomas-wyh/FuseAnyPart.
面部部件替换旨在选择性地将源图像的感兴趣区域转移到目标图像上,同时保持目标图像的其他部分不变。大多数专门设计用于全脸替换的面部替换研究,在替换单个面部部件时要么无法实现,要么受到很大限制,这阻碍了精细和定制的角色设计。然而,为面部部件替换设计专门的方法面临合理的多参考特征融合的挑战,这需要既高效又有效。为了克服这一挑战,提出了FuseAnyPart方法,以实现面部无缝“融合任何部分”的定制。在FuseAnyPart中,来自不同人的面部部件在基于掩膜的融合模块中在潜在空间内组合成一张完整的脸。随后,合并的特征被派发到基于添加的注入模块中,在扩散模型的UNet内进行融合,以创建新角色。大量的定性和定量实验验证了FuseAnyPart的优越性和稳健性。源代码可在https://github.com/Thomas-wyh/FuseAnyPart找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the NeurIPS 2024 (Spotlight). Homepage: https://thomas-wyh.github.io/
摘要
面部零件交换旨在从源图像中选择性转移感兴趣的区域到目标图像上,同时保持目标图像的其他部分不变。大多数专门设计用于全脸交换的研究,在进行面部零件交换时能力有限或无法实现,这阻碍了精细粒度和定制化的角色设计。然而,为面部零件交换设计这样的方法面临着合理的多参考特征融合的难题,这需要既高效又有效。为了克服这一挑战,提出了FuseAnyPart方法,以实现面部无缝融合任意部分的定制。在FuseAnyPart中,来自不同人的面部零件在基于掩膜的融合模块中组合成一个完整的面部潜在空间。然后,合并的特征被派发到基于添加的注入模块中,在扩散模型的UNet中进行融合以创建新角色。大量的实验定性和定量验证了FuseAnyPart的优越性和稳健性。相关源码已公开:https://github.com/Thomas-wyh/FuseAnyPart。
关键见解
- 面部零件交换旨在选择性地将源图像的特定区域转移到目标图像上,同时保持目标图像的其他部分不变。
- 当前面部交换研究多专注于全脸交换,难以进行精细的面部零件交换。
- 设计用于面部零件交换的方法面临多参考特征融合的难题,需要既高效又有效。
- FuseAnyPart方法能够在潜在空间中组合来自不同人的面部零件以创建新的完整面部。
- FuseAnyPart包含基于掩膜的融合模块和基于添加的注入模块。
- 通过大量实验验证,FuseAnyPart具有优越性和稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

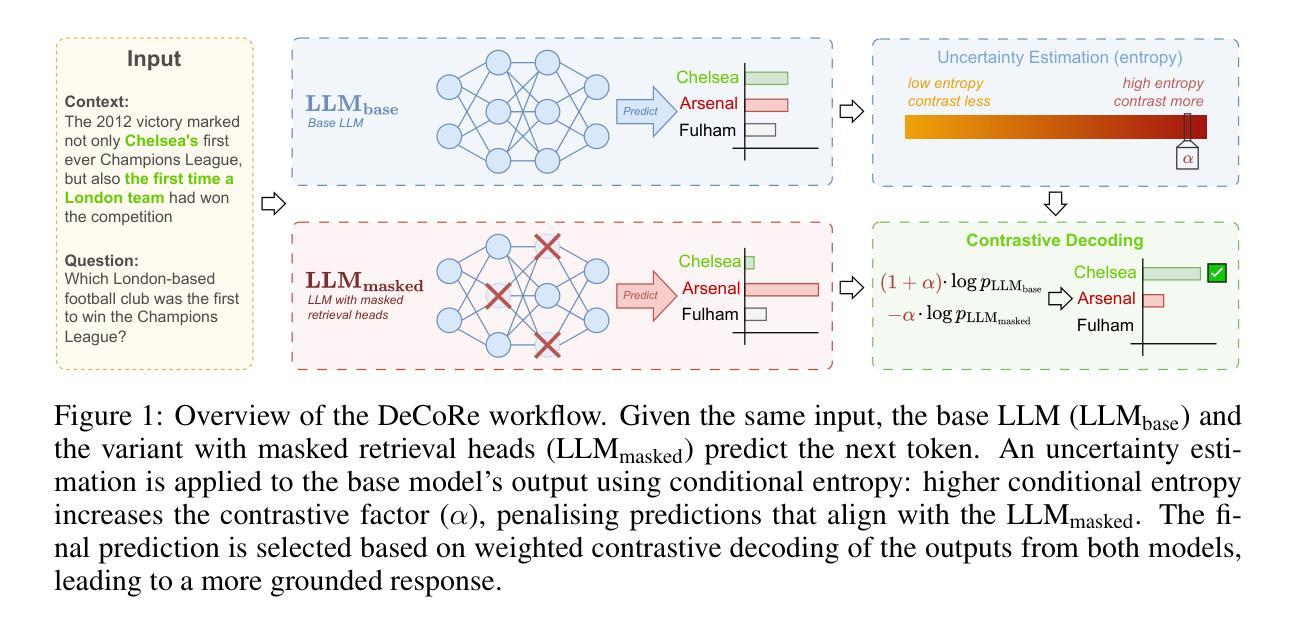
DeCoRe: Decoding by Contrasting Retrieval Heads to Mitigate Hallucinations
Authors:Aryo Pradipta Gema, Chen Jin, Ahmed Abdulaal, Tom Diethe, Philip Teare, Beatrice Alex, Pasquale Minervini, Amrutha Saseendran
Large Language Models (LLMs) often hallucinate, producing unfaithful or factually incorrect outputs by misrepresenting the provided context or incorrectly recalling internal knowledge. Recent studies have identified specific attention heads within the Transformer architecture, known as retrieval heads, responsible for extracting relevant contextual information. We hypothesise that masking these retrieval heads can induce hallucinations and that contrasting the outputs of the base LLM and the masked LLM can reduce hallucinations. To this end, we propose Decoding by Contrasting Retrieval Heads (DeCoRe), a novel training-free decoding strategy that amplifies information found in the context and model parameters. DeCoRe mitigates potentially hallucinated responses by dynamically contrasting the outputs of the base LLM and the masked LLM, using conditional entropy as a guide. Our extensive experiments confirm that DeCoRe significantly improves performance on tasks requiring high contextual faithfulness, such as summarisation (XSum by 18.6%), instruction following (MemoTrap by 10.9%), and open-book question answering (NQ-Open by 2.4% and NQ-Swap by 5.5%).
大型语言模型(LLM)常常出现幻觉,通过误代表提供的上下文或错误回忆内部知识,产生不真实或事实错误的输出。最近的研究已经识别出Transformer架构中的特定注意力头,称为检索头,负责提取相关的上下文信息。我们假设掩盖这些检索头会导致幻觉,并且对比基础LLM和掩盖LLM的输出可以减少幻觉。为此,我们提出了无需训练的解码策略——通过对比检索头进行解码(DeCoRe),这是一种放大上下文和模型参数中信息的方法。DeCoRe通过动态对比基础LLM和掩盖LLM的输出,使用条件熵作为指导,缓解可能产生的幻觉响应。我们的大量实验证实,DeCoRe在需要高上下文真实性的任务上表现显著改进,如在摘要(XSum提升18.6%)、执行指令(MemoTrap提升10.9%)和开放书籍问答(NQ-Open提升2.4%和NQ-Swap提升5.5%)等任务。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在生成输出时会出现幻觉,产生不真实或事实错误的输出,这可能是由于误解上下文或错误回忆内部知识所致。研究认为Transformer架构中的特定注意力头(称为检索头)负责提取相关上下文信息,而屏蔽这些检索头可能导致幻觉。本研究提出一种名为DeCoRe的新型解码策略,通过对比基础LLM和屏蔽LLM的输出,强化上下文和模型参数中的信息,以减少幻觉。实验证明,DeCoRe在需要高上下文忠实度的任务上表现显著,如摘要(XSum提升18.6%)、指令遵循(MemoTrap提升10.9%)和开放问答(NQ-Open提升2.4%,NQ-Swap提升5.5%)。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)有时会产生幻觉输出,这可能与误解上下文或错误回忆内部知识有关。
- 检索头是Transformer架构中负责提取相关上下文信息的特定注意力头。
- 屏蔽检索头可能导致幻觉输出。
- DeCoRe是一种新型解码策略,通过对比基础LLM和屏蔽LLM的输出,减少幻觉。
- DeCoRe通过强化上下文和模型参数中的信息来工作。
- DeCoRe在需要高上下文忠实度的任务上表现显著,如摘要、指令遵循和开放问答。
点此查看论文截图


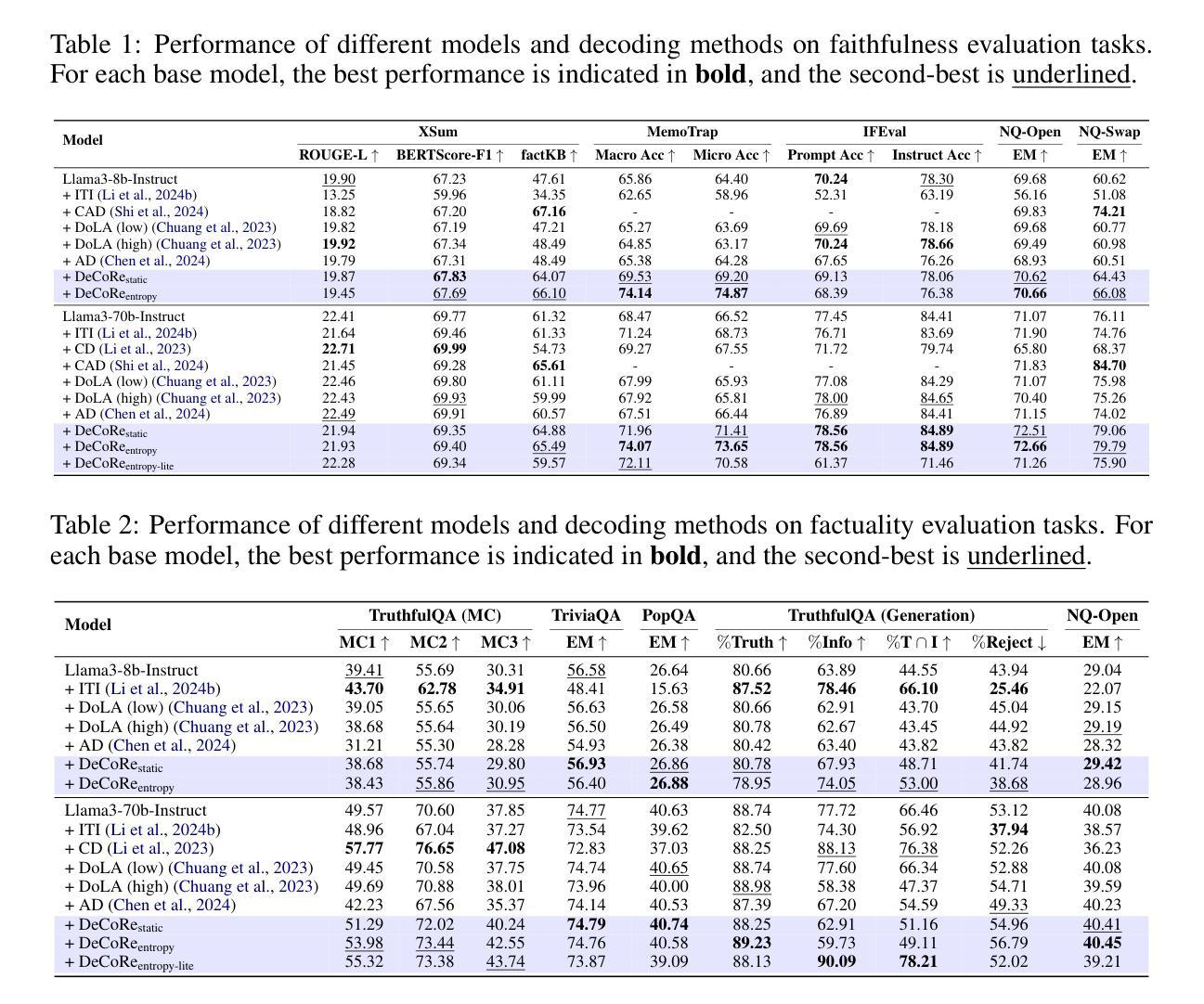
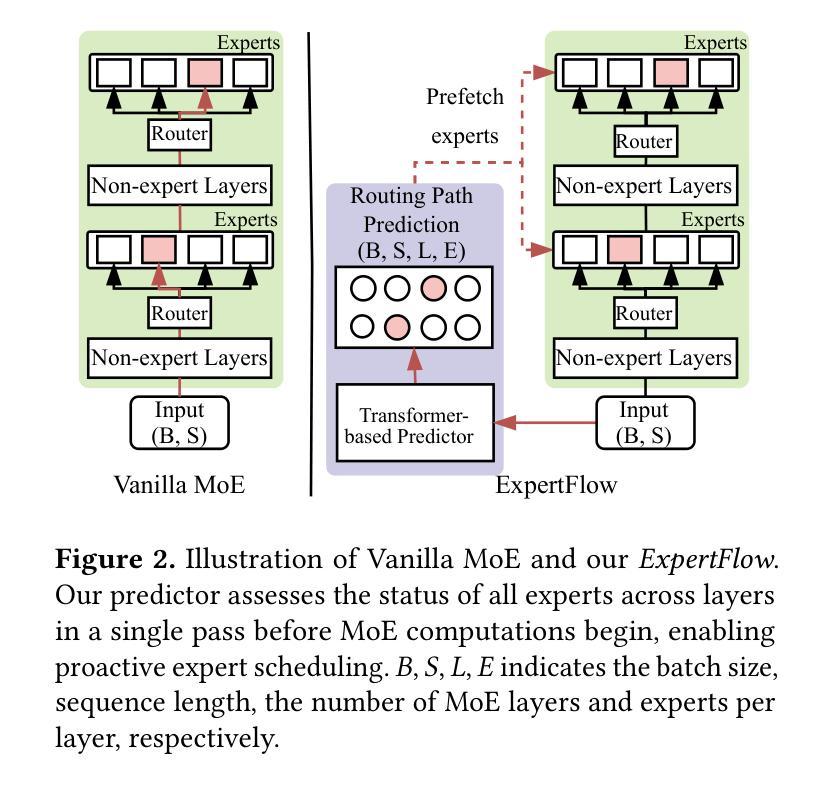
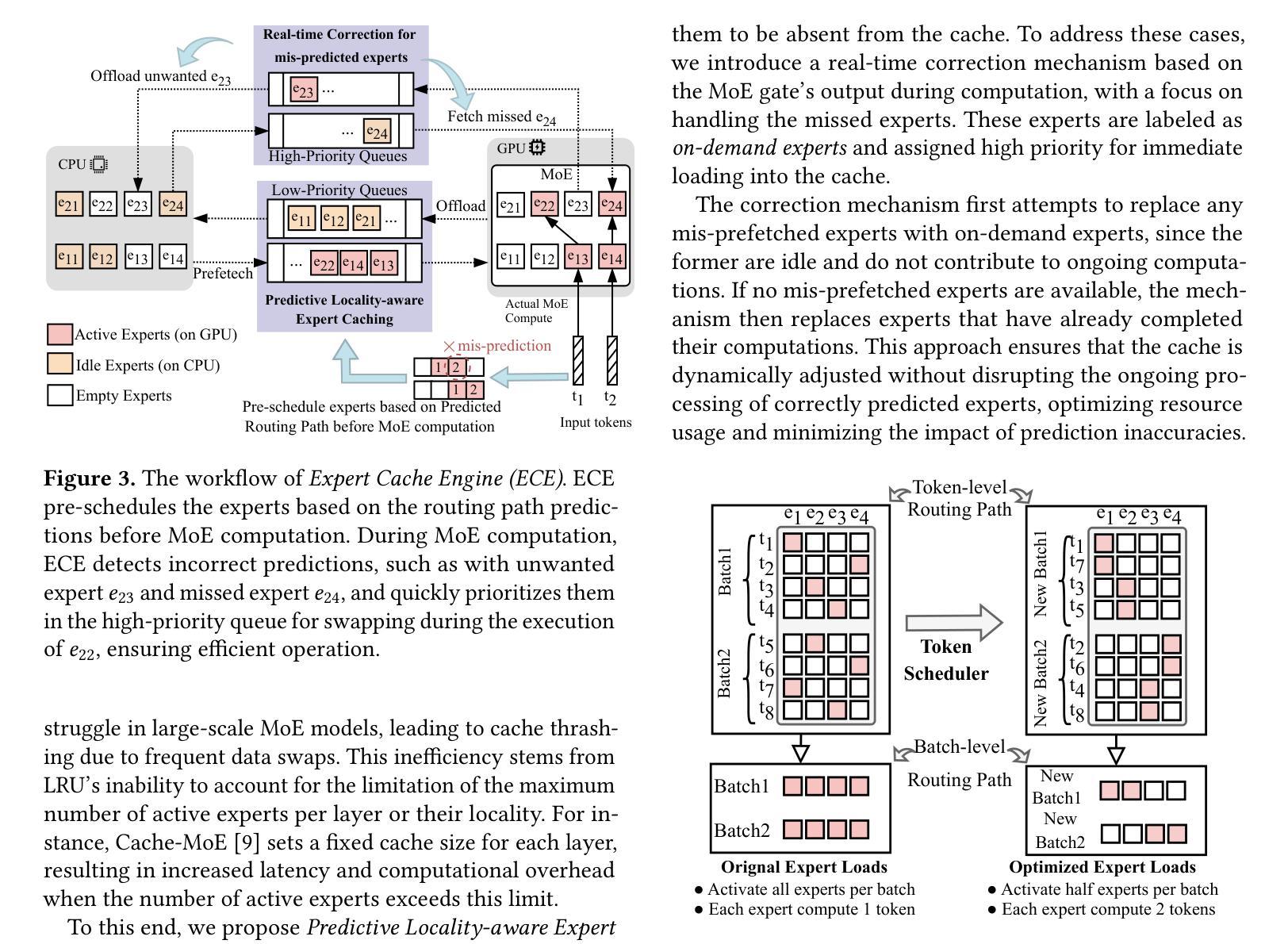
ExpertFlow: Optimized Expert Activation and Token Allocation for Efficient Mixture-of-Experts Inference
Authors:Xin He, Shunkang Zhang, Yuxin Wang, Haiyan Yin, Zihao Zeng, Shaohuai Shi, Zhenheng Tang, Xiaowen Chu, Ivor Tsang, Ong Yew Soon
Sparse Mixture of Experts (MoE) models, while outperforming dense Large Language Models (LLMs) in terms of performance, face significant deployment challenges during inference due to their high memory demands. Existing offloading techniques, which involve swapping activated and idle experts between the GPU and CPU, often suffer from rigid expert caching mechanisms. These mechanisms fail to adapt to dynamic routing, leading to inefficient cache utilization, or incur prohibitive costs for prediction training. To tackle these inference-specific challenges, we introduce ExpertFlow, a comprehensive system specifically designed to enhance inference efficiency by accommodating flexible routing and enabling efficient expert scheduling between CPU and GPU. This reduces overhead and boosts system performance. Central to our approach is a predictive routing path-based offloading mechanism that utilizes a lightweight predictor to accurately forecast routing paths before computation begins. This proactive strategy allows for real-time error correction in expert caching, significantly increasing cache hit ratios and reducing the frequency of expert transfers, thereby minimizing I/O overhead. Additionally, we implement a dynamic token scheduling strategy that optimizes MoE inference by rearranging input tokens across different batches. This method not only reduces the number of activated experts per batch but also improves computational efficiency. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that ExpertFlow achieves up to 93.72% GPU memory savings and enhances inference speed by 2 to 10 times compared to baseline methods, highlighting its effectiveness and utility as a robust solution for resource-constrained inference scenarios.
稀疏混合专家(MoE)模型虽然在性能方面超越了密集的大型语言模型(LLM),但在推理过程中面临着部署的巨大挑战,因为它们对内存的需求很高。现有的卸载技术,涉及在GPU和CPU之间交换激活和空闲的专家,通常受到僵化专家缓存机制的影响。这些机制无法适应动态路由,导致缓存利用率低,或者为预测训练造成高昂的成本。为了应对这些推理特定的挑战,我们引入了ExpertFlow,这是一个专门设计的综合系统,通过灵活的路由和CPU与GPU之间的高效专家调度,提高推理效率。这降低了开销并提高了系统性能。我们的方法的核心是基于预测路由路径的卸载机制,利用轻量级预测器在计算开始之前准确预测路由路径。这种主动策略允许实时纠正专家缓存中的错误,显著提高缓存命中率,减少专家转移的频率,从而最小化I/O开销。此外,我们实现了动态令牌调度策略,通过重新安排不同批次的输入令牌来优化MoE推理。这种方法不仅减少了每批激活的专家数量,而且提高了计算效率。我们的大量实验表明,与基准方法相比,ExpertFlow实现了高达93.72%的GPU内存节省,推理速度提高了2到10倍,突显了其在资源受限推理场景中的稳健性和实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Mixture-of-Experts, Inference, Offloading
Summary
基于Sparse Mixture of Experts模型的优化方案ExpertFlow能有效提高推理效率。它利用灵活的路由机制在CPU和GPU间实现高效专家调度,降低开销并提升系统性能。其通过预测路由路径进行任务卸载,并利用动态令牌调度策略优化MoE推理过程。实验证明,ExpertFlow可实现高达93.72%的GPU内存节省,并较基线方法提高推理速度2至10倍。
Key Takeaways
- ExpertFlow旨在解决Sparse Mixture of Experts模型在推理过程中面临的内存需求高的问题。
- 它通过灵活的路由机制实现CPU和GPU间的专家调度,以提高推理效率。
- ExpertFlow采用预测路由路径的卸载机制,利用轻量级预测器在计算开始前准确预测路由路径。
- 动态令牌调度策略用于优化MoE推理过程,减少每批次激活的专家数量并提高计算效率。
- ExpertFlow通过实时错误校正的专家缓存机制,显著提高缓存命中率并减少专家转移频率,从而最小化I/O开销。
- 实验结果表明,ExpertFlow在GPU内存节省和推理速度提升方面表现出显著效果。
点此查看论文截图

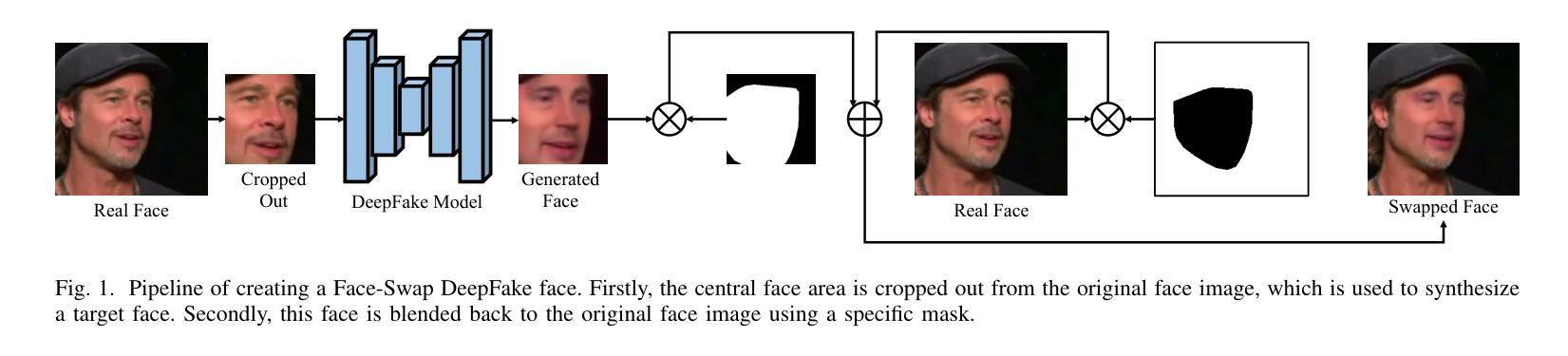
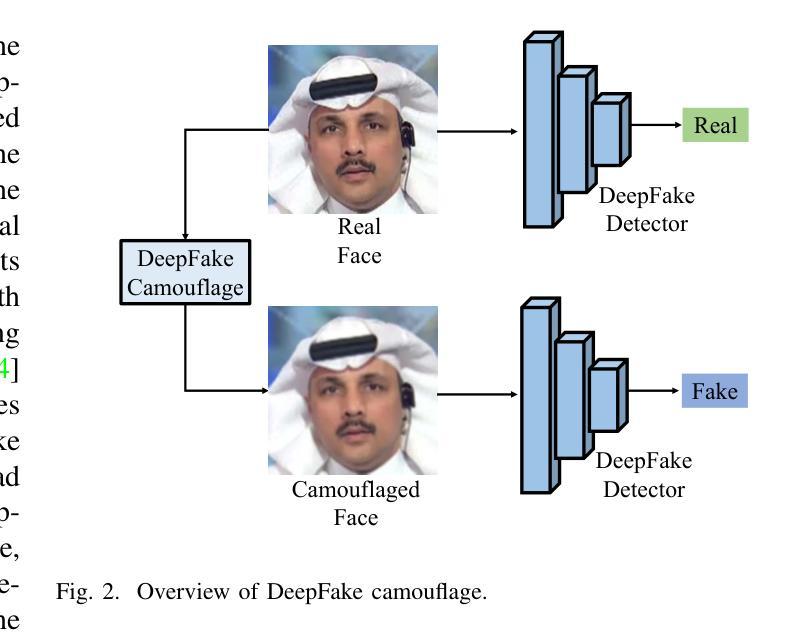
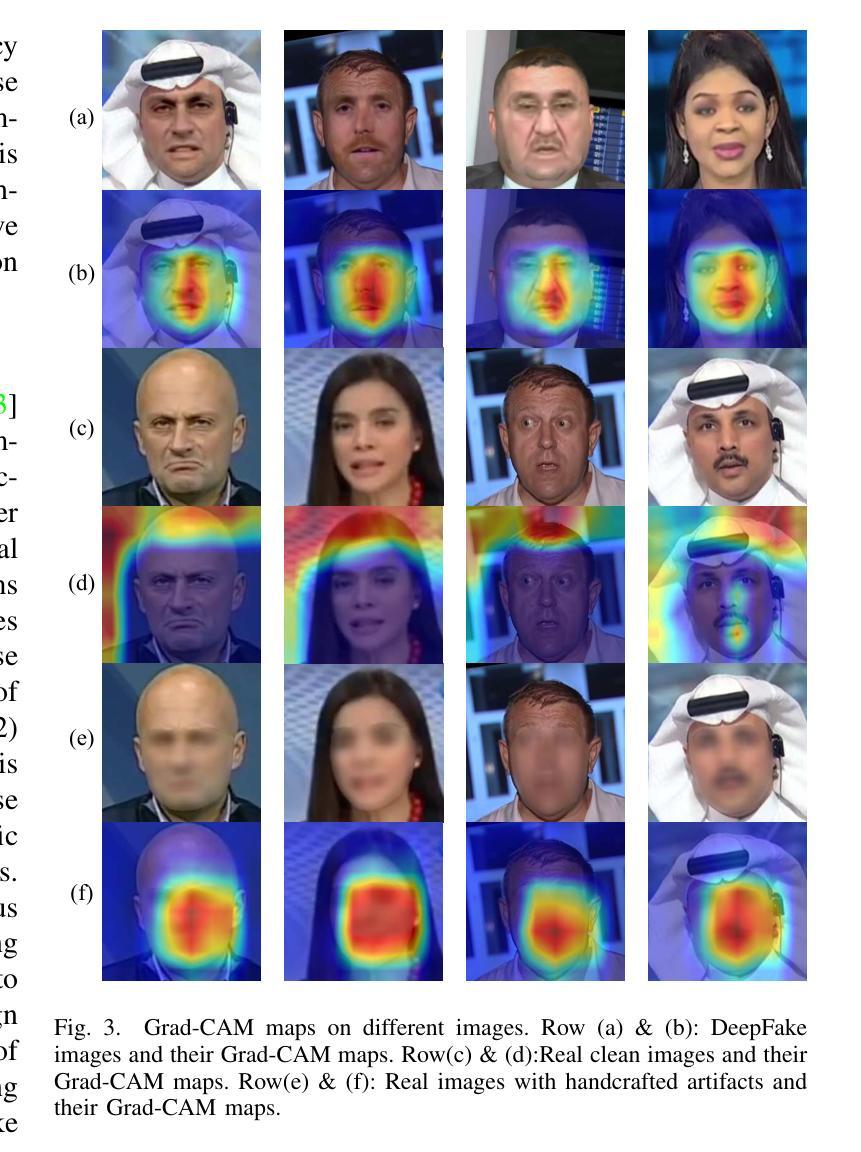
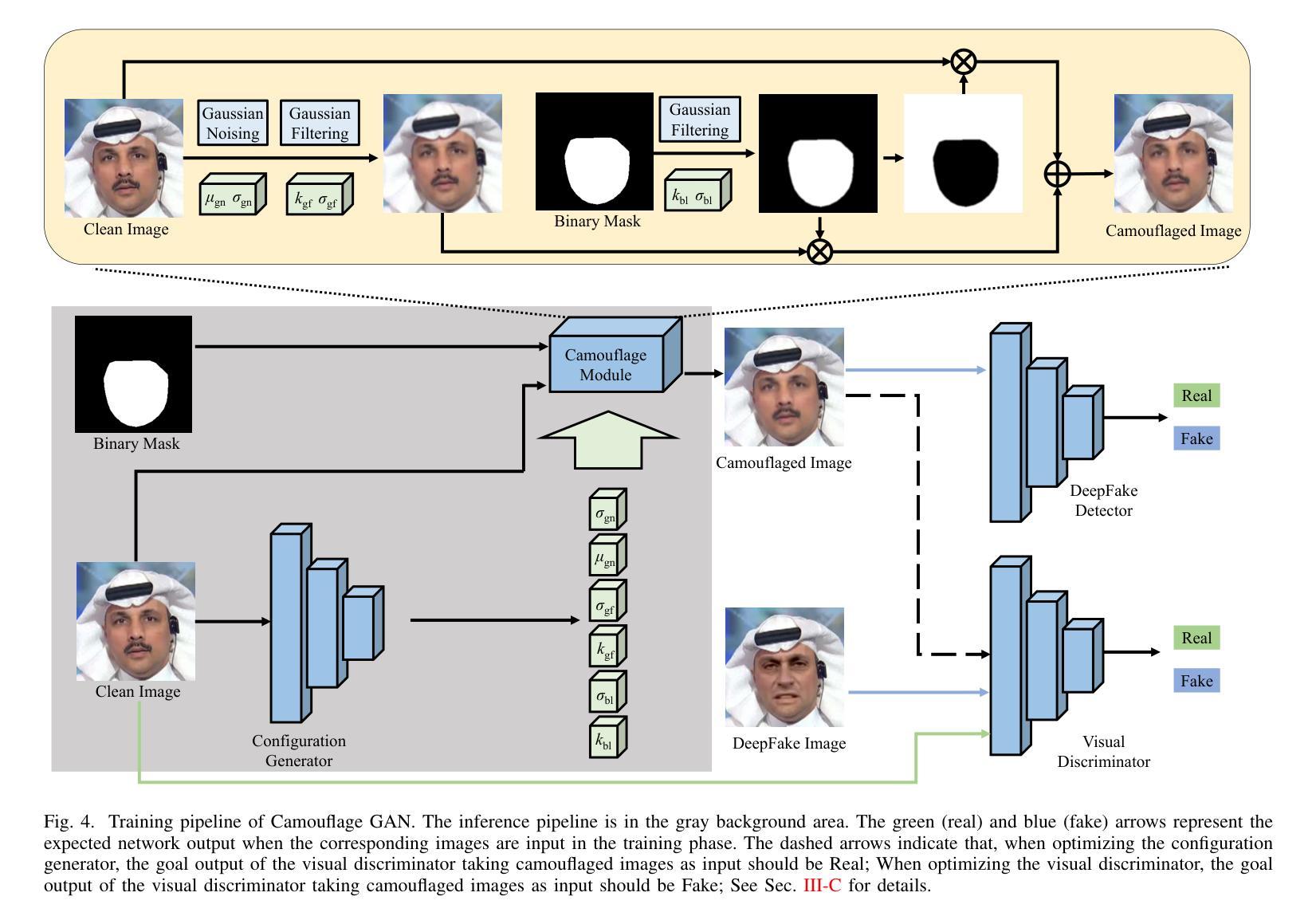
Active Fake: DeepFake Camouflage
Authors:Pu Sun, Honggang Qi, Yuezun Li
DeepFake technology has gained significant attention due to its ability to manipulate facial attributes with high realism, raising serious societal concerns. Face-Swap DeepFake is the most harmful among these techniques, which fabricates behaviors by swapping original faces with synthesized ones. Existing forensic methods, primarily based on Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), effectively expose these manipulations and have become important authenticity indicators. However, these methods mainly concentrate on capturing the blending inconsistency in DeepFake faces, raising a new security issue, termed Active Fake, emerges when individuals intentionally create blending inconsistency in their authentic videos to evade responsibility. This tactic is called DeepFake Camouflage. To achieve this, we introduce a new framework for creating DeepFake camouflage that generates blending inconsistencies while ensuring imperceptibility, effectiveness, and transferability. This framework, optimized via an adversarial learning strategy, crafts imperceptible yet effective inconsistencies to mislead forensic detectors. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of our method, highlighting the need for further research in active fake detection.
深度伪造技术因其能够高度逼真地操纵面部特征而受到广泛关注,这引发了社会的严重担忧。面部交换深度伪造是这些技术中最具危害性的,它通过交换原始面孔并合成新的面孔来伪造行为。现有的取证方法主要基于深度神经网络(DNN),能够有效地暴露这些操纵行为,并成为重要的真实性指标。然而,这些方法主要集中在捕捉深度伪造面孔的融合不一致性上,当个人故意在其真实视频中制造融合不一致性以逃避责任时,出现了一个新的安全问题,称为活动伪装(Active Fake)。这种策略被称为深度伪造伪装。为了实现这一点,我们引入了一个新的创建深度伪造伪装框架,该框架在生成融合不一致性的同时确保了不可感知性、有效性和可转移性。该框架通过对抗学习策略进行优化,能够制造出不可察觉但有效的不一致性来误导取证检测器。大量实验证明了我们方法的有效性和稳健性,强调了活动假检测研究的必要性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
深度伪造技术因其能够高度逼真地操纵面部特征而受到广泛关注,引发了社会的严重关切。其中,Face-Swap DeepFake技术通过替换原始面部为合成面部来制造行为假象,其危害最大。现有的基于深度神经网络(DNN)的取证方法能有效揭露这些操纵行为,成为重要的真实性指标。然而,这些方法主要集中在捕捉深度伪造面部融合的不一致性,从而引发了一个新的安全问题——主动伪装,即个人有意在其真实视频上制造融合的不一致性以逃避责任的行为,称为深度伪造伪装。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了新的深度伪造伪装框架,通过生成难以察觉的融合不一致性来实现伪装效果,确保隐蔽性、有效性和可迁移性。采用对抗性学习策略优化的该框架能生成难以觉察的不一致性以欺骗鉴定检测器。大量实验证明了我们方法的有效性和鲁棒性,同时也强调了主动伪装检测研究的必要性。
要点解析
- 深度伪造技术因其高度逼真地操纵面部特征的能力而受到广泛关注,引发了社会关注。
- Face-Swap DeepFake技术通过替换面部制造假象,成为深度伪造中最危险的技术之一。
- 基于深度神经网络的取证方法能有效揭露深度伪造行为。
- 现有方法主要关注捕捉深度伪造面部融合的不一致性,导致出现新的安全问题——主动伪装(Active Fake)。
- 主动伪装是指个人有意在真实视频上制造融合不一致性以逃避责任的行为。
- 为了应对这一问题,引入了新的深度伪造伪装框架,该框架能够生成难以觉察的融合不一致性,确保隐蔽性、有效性和可迁移性。
点此查看论文截图

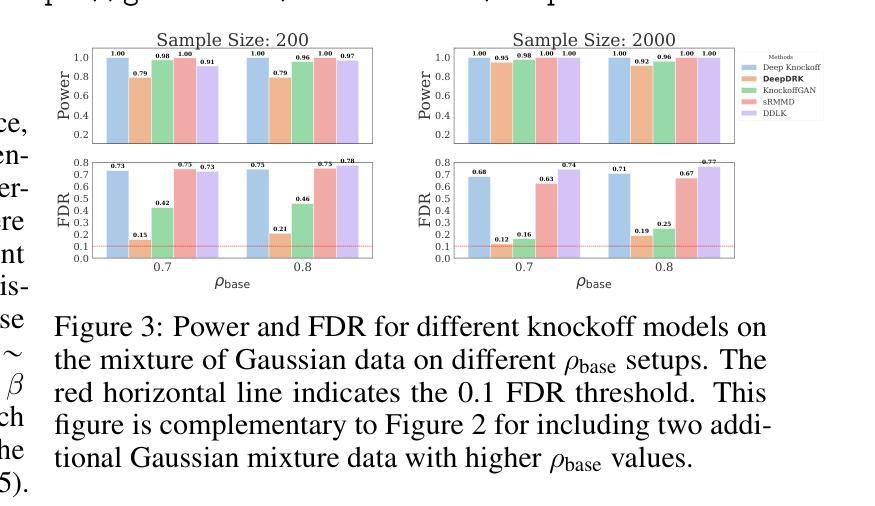
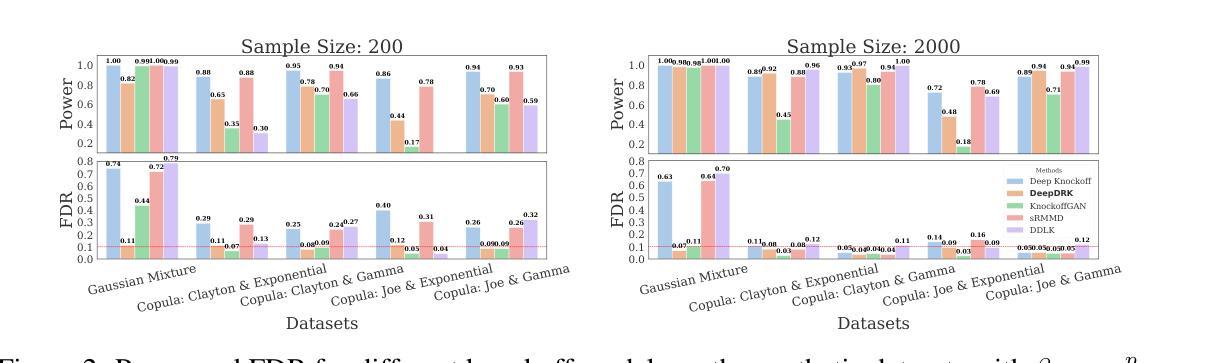
DeepDRK: Deep Dependency Regularized Knockoff for Feature Selection
Authors:Hongyu Shen, Yici Yan, Zhizhen Zhao
Model-X knockoff has garnered significant attention among various feature selection methods due to its guarantees for controlling the false discovery rate (FDR). Since its introduction in parametric design, knockoff techniques have evolved to handle arbitrary data distributions using deep learning-based generative models. However, we have observed limitations in the current implementations of the deep Model-X knockoff framework. Notably, the “swap property” that knockoffs require often faces challenges at the sample level, resulting in diminished selection power. To address these issues, we develop “Deep Dependency Regularized Knockoff (DeepDRK),” a distribution-free deep learning method that effectively balances FDR and power. In DeepDRK, we introduce a novel formulation of the knockoff model as a learning problem under multi-source adversarial attacks. By employing an innovative perturbation technique, we achieve lower FDR and higher power. Our model outperforms existing benchmarks across synthetic, semi-synthetic, and real-world datasets, particularly when sample sizes are small and data distributions are non-Gaussian.
模型X的假冒样本在各种特征选择方法中受到了广泛关注,因为它能保证控制误发现率(FDR)。自从参数化设计引入以来,假冒技术已经发展使用基于深度学习的生成模型来处理任意数据分布。然而,我们观察到当前深度模型X假冒框架的实现存在局限性。值得注意的是,假冒样本所需的“替换属性”在样本层面经常面临挑战,导致选择能力下降。为了解决这些问题,我们开发了“深度依赖正则化假冒(DeepDRK)”,这是一种无需分布的深度学习方法,可以有效地平衡FDR和功率。在DeepDRK中,我们将假冒模型作为一个多源对抗攻击下的学习问题进行了新颖的表达。通过采用创新的扰动技术,我们实现了较低的FDR和较高的功率。我们的模型在合成、半合成和真实世界的数据集上超越了现有的基准测试,特别是在样本量小且数据分布非高斯的情况下。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 33 pages, 15 figures, 9 tables
摘要
Model-X仿冒特征选择方法因其控制误发现率(FDR)的保证而受到广泛关注。自从在参数化设计中引入仿冒技术以来,该技术已演变为使用基于深度学习的生成模型处理任意数据分布。然而,我们在现有的深度Model-X仿冒框架实现中观察到局限性。特别是仿冒所需的“替换属性”在样本层面经常面临挑战,导致选择能力下降。为了解决这些问题,我们开发了“深度依赖正则化仿冒(DeepDRK)”,这是一种有效的平衡FDR和功率的深度学习方法,无需考虑数据分布。在DeepDRK中,我们将仿冒模型作为一个在多重来源对抗性攻击下的学习问题创新性地提出。通过采用新颖的扰动技术,我们实现了更低的FDR和更高的功率。我们的模型在合成、半合成和真实世界的数据集上均优于现有基准测试,特别是在样本量小且数据分布非高斯的情况下。
关键见解
- Model-X仿冒特征选择方法关注控制误发现率(FDR)。
- 当前的深度Model-X仿冒框架在样本层面存在局限性,特别是在实现“替换属性”时。
- 为了解决这些问题,提出了深度依赖正则化仿冒(DeepDRK)方法。
- DeepDRK是一种有效的平衡FDR和功率的深度学习方法,可处理任意数据分布。
- DeepDRK将仿冒模型创新地表述为一个在多重来源对抗性攻击下的学习问题。
- 通过新颖的扰动技术,DeepDRK实现了更低的FDR和更高的功率。
- 在合成、半合成和真实世界的数据集上,DeepDRK模型表现优于现有方法,特别是在样本量小且数据分布非高斯的情况下。
点此查看论文截图

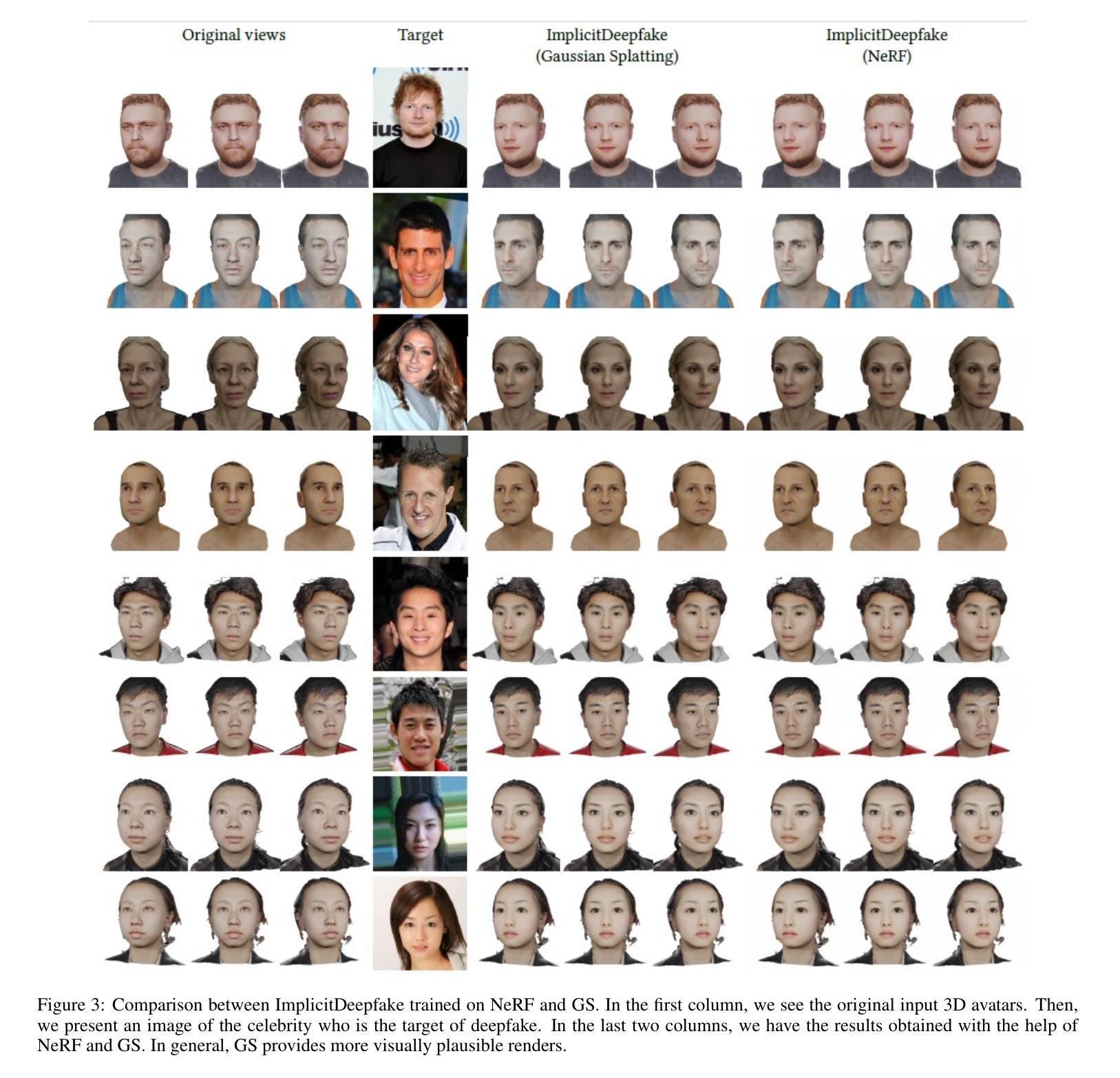
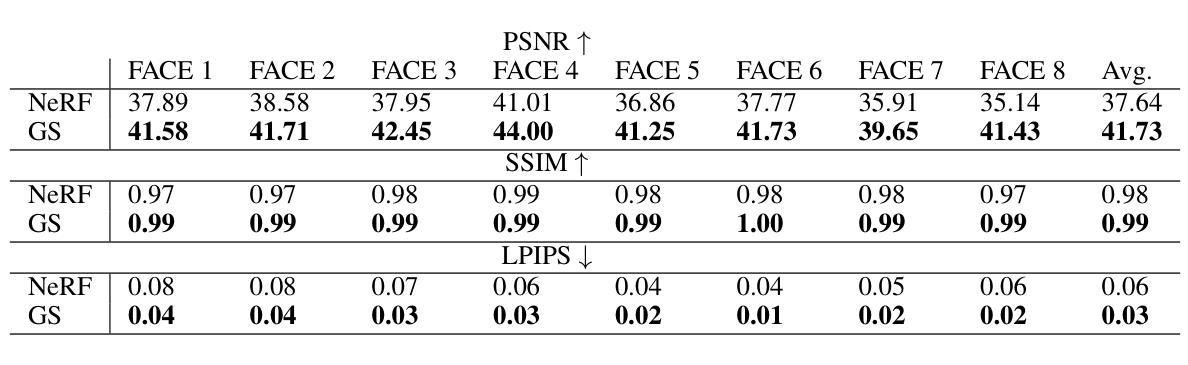
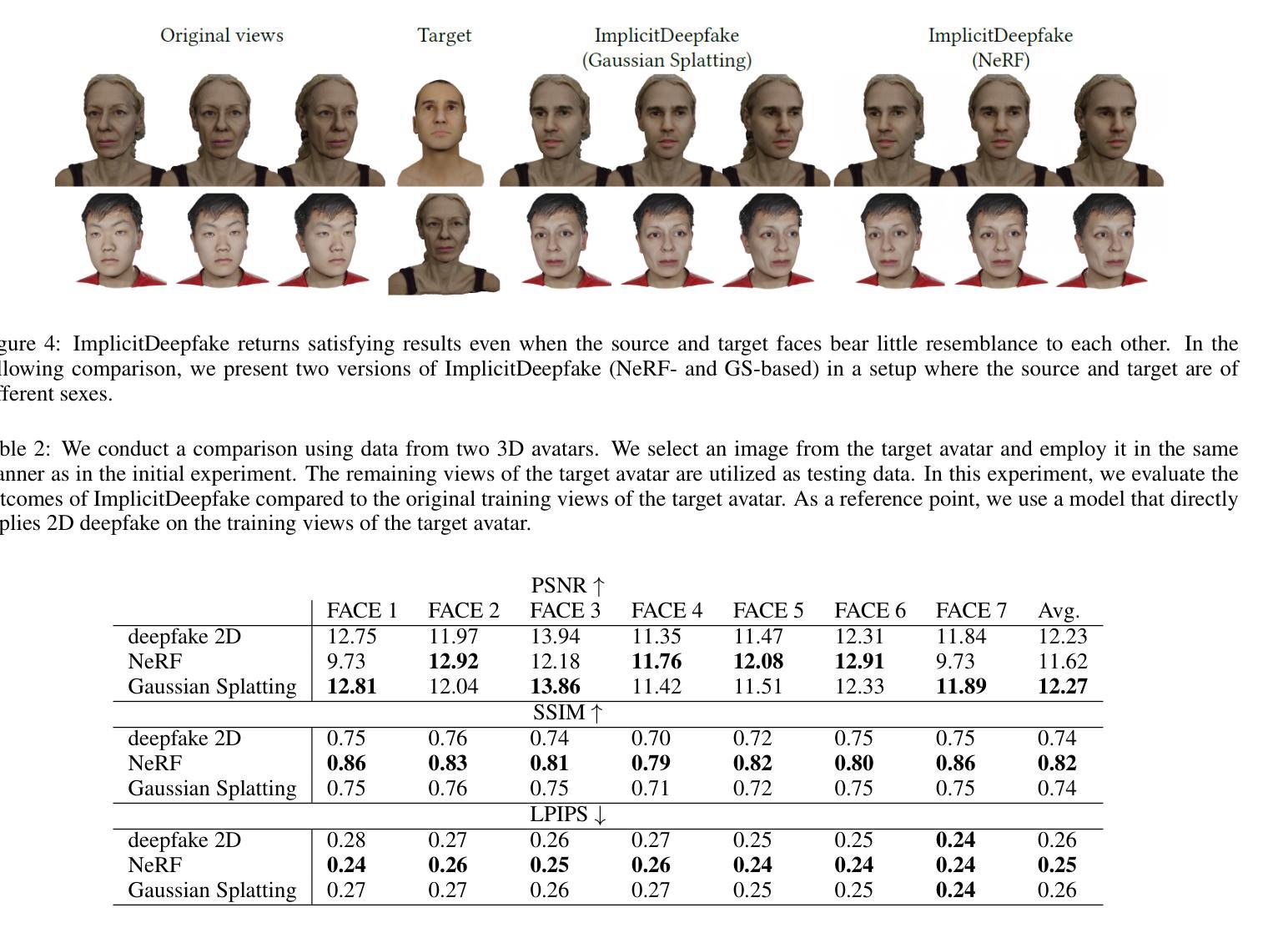
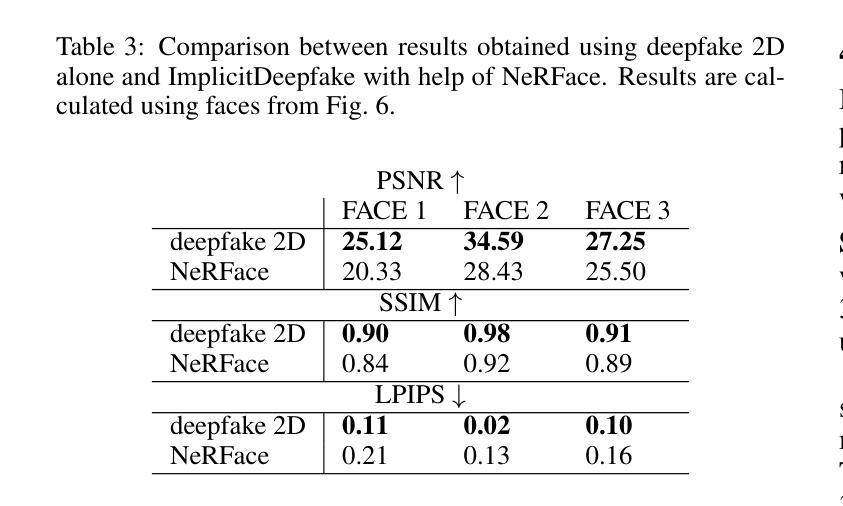
Deepfake for the Good: Generating Avatars through Face-Swapping with Implicit Deepfake Generation
Authors:Georgii Stanishevskii, Jakub Steczkiewicz, Tomasz Szczepanik, Sławomir Tadeja, Jacek Tabor, Przemysław Spurek
Numerous emerging deep-learning techniques have had a substantial impact on computer graphics. Among the most promising breakthroughs are the rise of Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) and Gaussian Splatting (GS). NeRFs encode the object’s shape and color in neural network weights using a handful of images with known camera positions to generate novel views. In contrast, GS provides accelerated training and inference without a decrease in rendering quality by encoding the object’s characteristics in a collection of Gaussian distributions. These two techniques have found many use cases in spatial computing and other domains. On the other hand, the emergence of deepfake methods has sparked considerable controversy. Deepfakes refers to artificial intelligence-generated videos that closely mimic authentic footage. Using generative models, they can modify facial features, enabling the creation of altered identities or expressions that exhibit a remarkably realistic appearance to a real person. Despite these controversies, deepfake can offer a next-generation solution for avatar creation and gaming when of desirable quality. To that end, we show how to combine all these emerging technologies to obtain a more plausible outcome. Our ImplicitDeepfake uses the classical deepfake algorithm to modify all training images separately and then train NeRF and GS on modified faces. Such simple strategies can produce plausible 3D deepfake-based avatars.
新兴的深度学习方法对计算机图形学产生了重大影响。其中最有前途的突破之一是神经辐射场(NeRF)和高斯拼贴(GS)的兴起。NeRF使用神经网络权重编码对象的形状和颜色,使用少量已知相机位置的图片来生成新型视图。相比之下,GS通过在一组高斯分布中编码对象特征,提供了加速训练和推理,而不会降低渲染质量。这两种技术在空间计算和其他领域找到了许多用例。另一方面,深度伪造方法的出现引起了很大的争议。深度伪造是指使用人工智能生成的视频,这些视频紧密模仿真实镜头。使用生成模型,它们可以修改面部特征,能够创建出改变身份或表情的虚假视频,其外观惊人地逼真于真人。尽管存在争议,但高质量的深度伪造可以为化身创建和游戏提供下一代解决方案。为此,我们展示了如何结合所有这些新兴技术来获得更合理的结果。我们的ImplicitDeepfake使用经典的深度伪造算法分别修改所有训练图像,然后在修改后的面部上训练NeRF和GS。这种简单的策略可以产生合理的基于深度伪造的3D化身。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习技术如神经网络辐射场(NeRF)和高斯平铺(GS)在计算机图形学中产生了重大影响。NeRF使用已知相机位置的几张图像来生成新型视角,将物体的形状和颜色编码在神经网络权重中。相比之下,GS通过编码物体特征在一系列高斯分布中实现了训练和推理的加速,同时不降低渲染质量。这两种技术广泛应用于空间计算等领域。另一方面,深度伪造方法的出现引发了巨大争议。深度伪造指使用人工智能生成的视频,能够模仿真实画面。通过生成模型,它们可以修改面部特征,创造出具有极高真实感的身份或表情变化。将新兴技术结合起来的隐性深度伪造技术可以实现更逼真的结果。本研究采用传统深度伪造算法单独修改所有训练图像,然后对修改后的面部进行NeRF和GS训练。这种简单策略可以产生基于深度伪造的逼真三维角色模型。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习技术如NeRF和GS在计算机图形学中产生了重大影响,特别是在空间计算等领域的应用。
- 深度伪造方法引发了争议,但其具有潜力为下一代游戏和虚拟角色创建提供解决方案。
- 隐性深度伪造结合了新兴技术以实现更逼真的结果。
- 传统深度伪造算法用于单独修改训练图像,进而在修改后的面部上进行NeRF和GS训练。
- 这种策略可以产生基于深度伪造的逼真三维角色模型。
- 结合NeRF和GS技术的深度伪造方法具有潜力在虚拟角色创建和渲染中实现更高级别的真实感和自然度。
点此查看论文截图
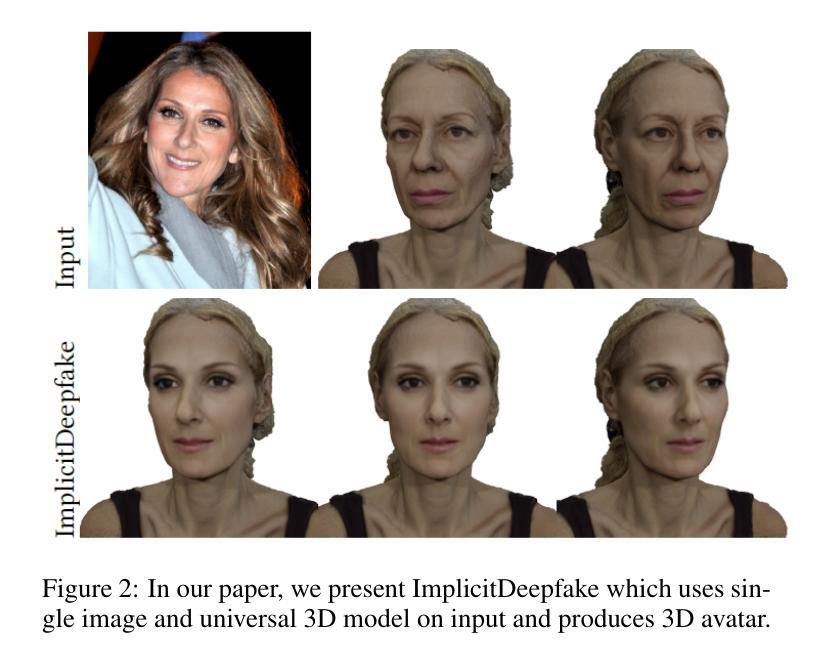


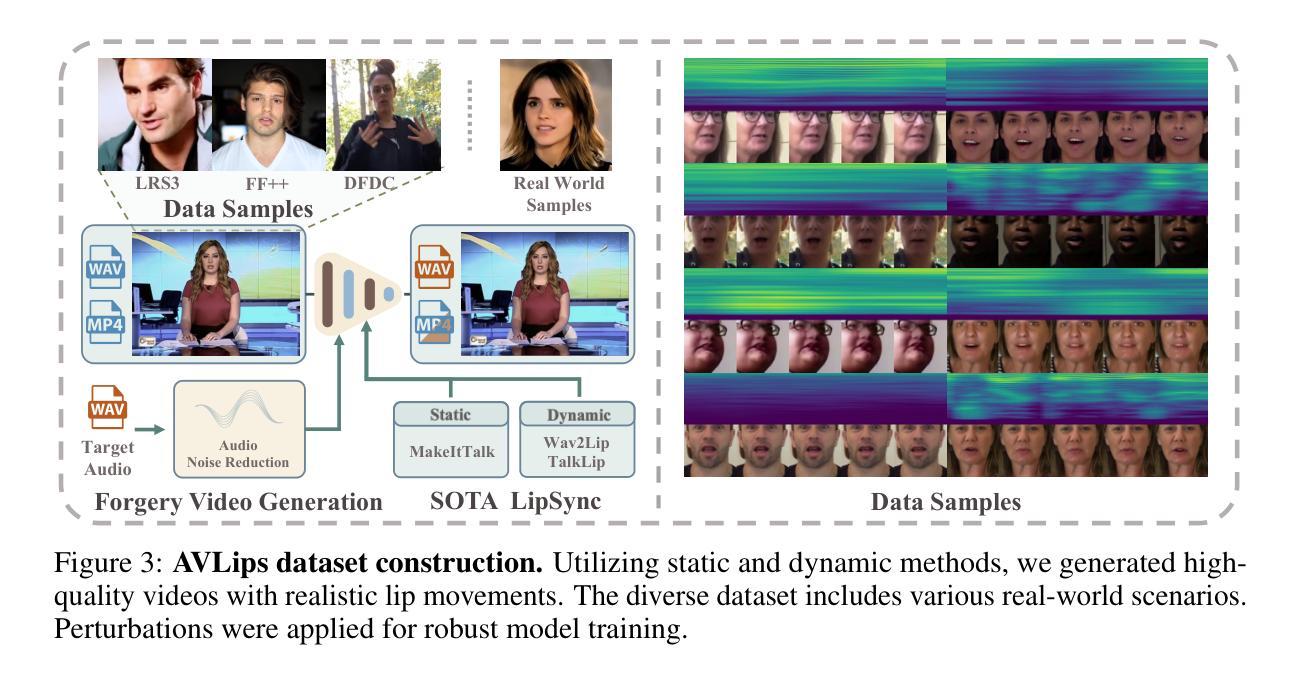
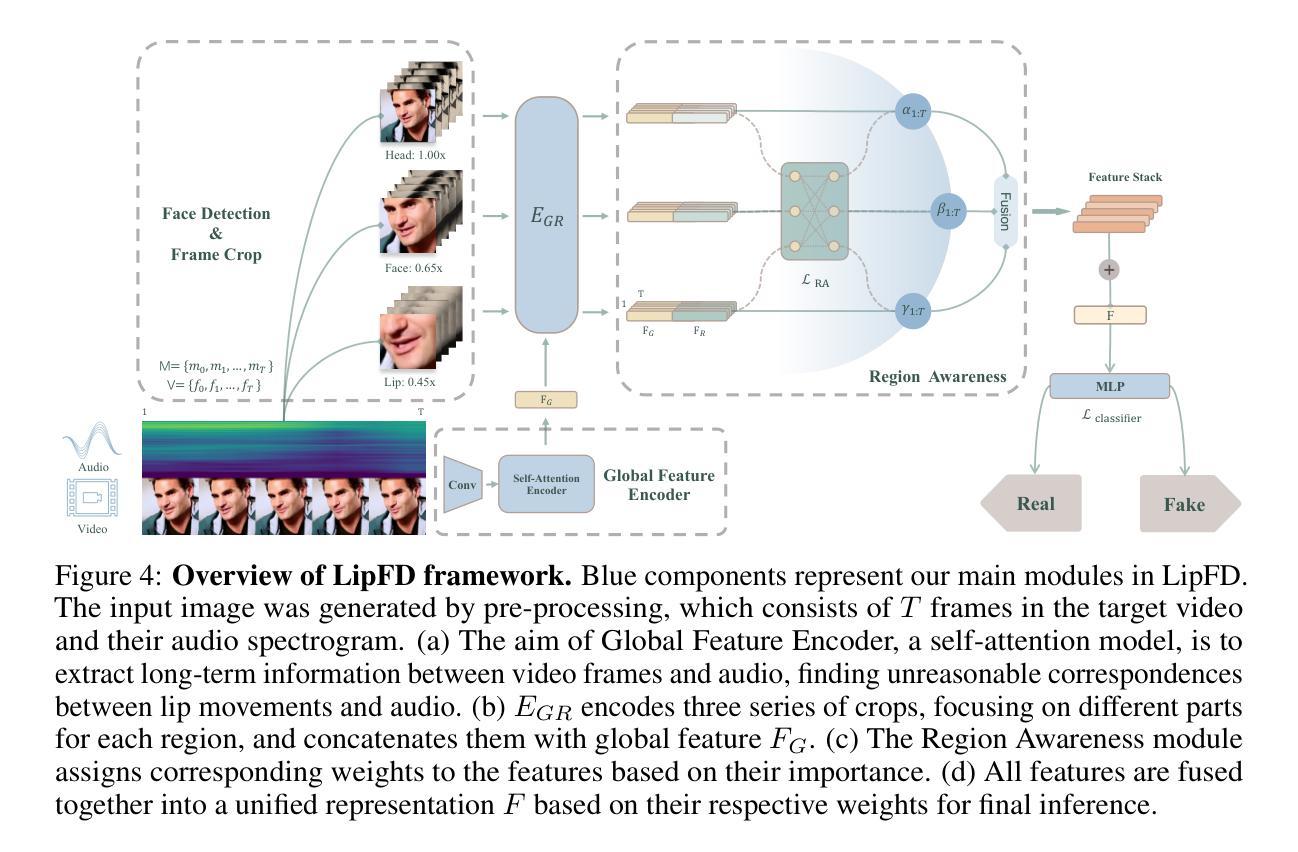
Lips Are Lying: Spotting the Temporal Inconsistency between Audio and Visual in Lip-Syncing DeepFakes
Authors:Weifeng Liu, Tianyi She, Jiawei Liu, Boheng Li, Dongyu Yao, Ziyou Liang, Run Wang
In recent years, DeepFake technology has achieved unprecedented success in high-quality video synthesis, but these methods also pose potential and severe security threats to humanity. DeepFake can be bifurcated into entertainment applications like face swapping and illicit uses such as lip-syncing fraud. However, lip-forgery videos, which neither change identity nor have discernible visual artifacts, present a formidable challenge to existing DeepFake detection methods. Our preliminary experiments have shown that the effectiveness of the existing methods often drastically decrease or even fail when tackling lip-syncing videos. In this paper, for the first time, we propose a novel approach dedicated to lip-forgery identification that exploits the inconsistency between lip movements and audio signals. We also mimic human natural cognition by capturing subtle biological links between lips and head regions to boost accuracy. To better illustrate the effectiveness and advances of our proposed method, we create a high-quality LipSync dataset, AVLips, by employing the state-of-the-art lip generators. We hope this high-quality and diverse dataset could be well served the further research on this challenging and interesting field. Experimental results show that our approach gives an average accuracy of more than 95.3% in spotting lip-syncing videos, significantly outperforming the baselines. Extensive experiments demonstrate the capability to tackle deepfakes and the robustness in surviving diverse input transformations. Our method achieves an accuracy of up to 90.2% in real-world scenarios (e.g., WeChat video call) and shows its powerful capabilities in real scenario deployment. To facilitate the progress of this research community, we release all resources at https://github.com/AaronComo/LipFD.
近年来,DeepFake技术在高质量视频合成方面取得了前所未有的成功,但这些方法也给人类带来了潜在且严重的安全威胁。DeepFake可以二分娱乐应用如换脸和非法用途如唇同步欺诈。然而,既不改变身份也没有明显视觉伪造的唇伪造视频,给现有的DeepFake检测方法带来了巨大挑战。我们的初步实验表明,现有方法在应对唇同步视频时,其有效性往往会大幅下降甚至失效。在本文中,我们首次提出了一种专门用于唇伪造识别的唇识别技术新方法。此方法利用唇部运动与音频信号之间的不一致性进行检测。通过捕捉唇部与头部区域之间的微妙生物学联系来模仿人类的自然认知过程以提高准确性。为了更好地说明我们提出的方法的有效性和先进性,我们使用最先进的唇生成器创建了高质量、多样化的AVLips LipSync数据集。我们希望这个高质量和多样化的数据集能够服务于这一充满挑战和有趣的领域的研究工作。实验结果表明,我们的方法在识别唇同步视频方面平均准确率超过95.3%,明显优于基线方法。大量实验证明了我们方法处理深度伪造的能力和应对各种输入转换的稳健性。我们的方法在真实场景(例如微信视频通话)中的准确率高达90.2%,展示了其在现实场景部署的强大能力。为了促进该领域研究的进步,我们在https://github.com/AaronComo/LipFD上发布了所有资源。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于深度伪造技术近年来的快速发展及其在视频合成领域的巨大成功,它所带来的潜在安全威胁也逐渐凸显。本文针对唇同步伪造视频识别难题,提出了一种利用唇动与音频信号不一致性的新型识别方法,并模仿人类自然认知,捕捉唇部和头部区域之间的微妙生物联系以提高准确性。为更好地验证方法的有效性,研究团队创建了一个高质量、多样化的LipSync数据集AVLips。实验结果显示,该方法平均准确率达95.3%以上,且在真实场景部署中展现强大能力,最高准确率可达90.2%。为促进该领域的研究进展,相关资源已公开发布。
关键见解
- 深度伪造技术在视频合成领域取得巨大成功,但带来了潜在的安全威胁。
- 唇同步伪造视频识别面临挑战,现有方法效果常显著下降或失效。
- 提出了一种新型识别方法,利用唇动与音频信号的不一致性。
- 模仿人类自然认知,捕捉唇部与头部区域的联系提升准确性。
- 创建了高质量、多样化的LipSync数据集AVLips以推动研究。
- 方法平均准确率超过95.3%,真实场景部署中最高准确率可达90.2%。
- 为促进研究进展,相关资源已公开发布。
点此查看论文截图


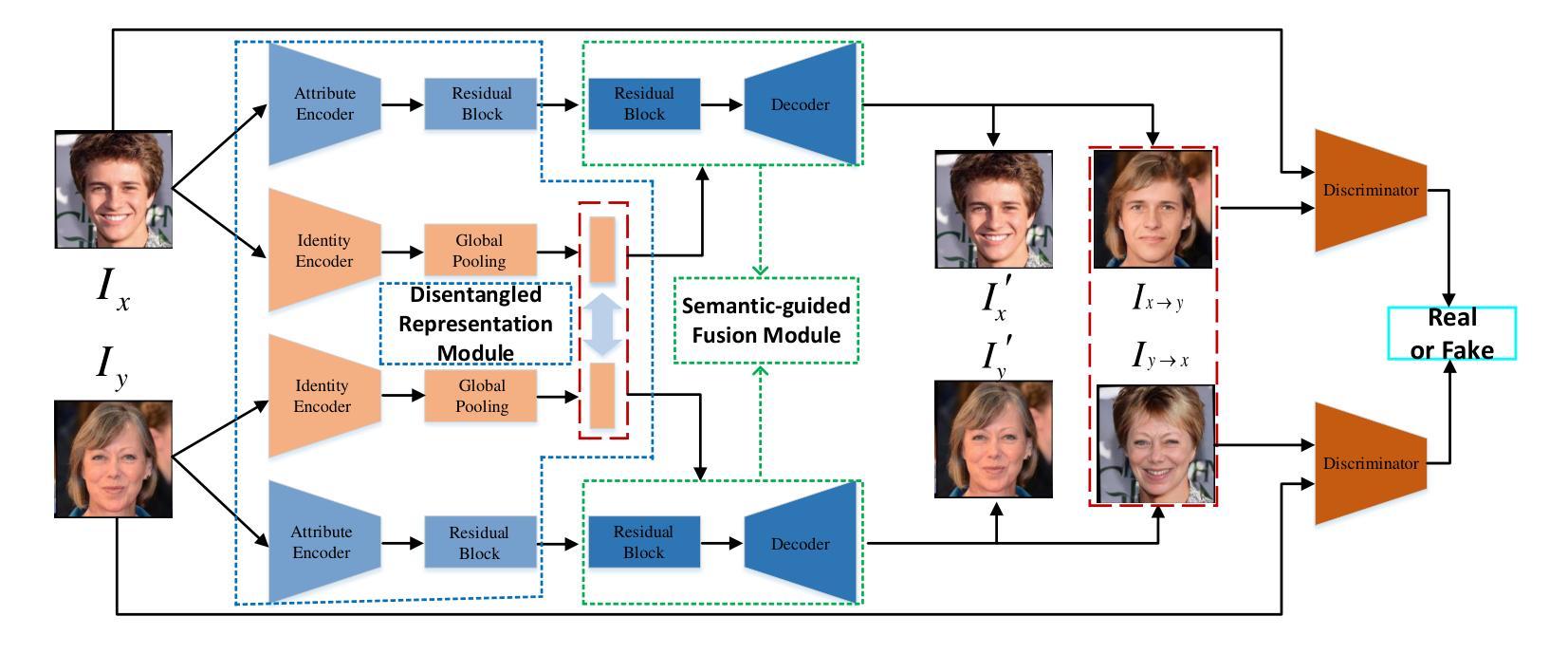
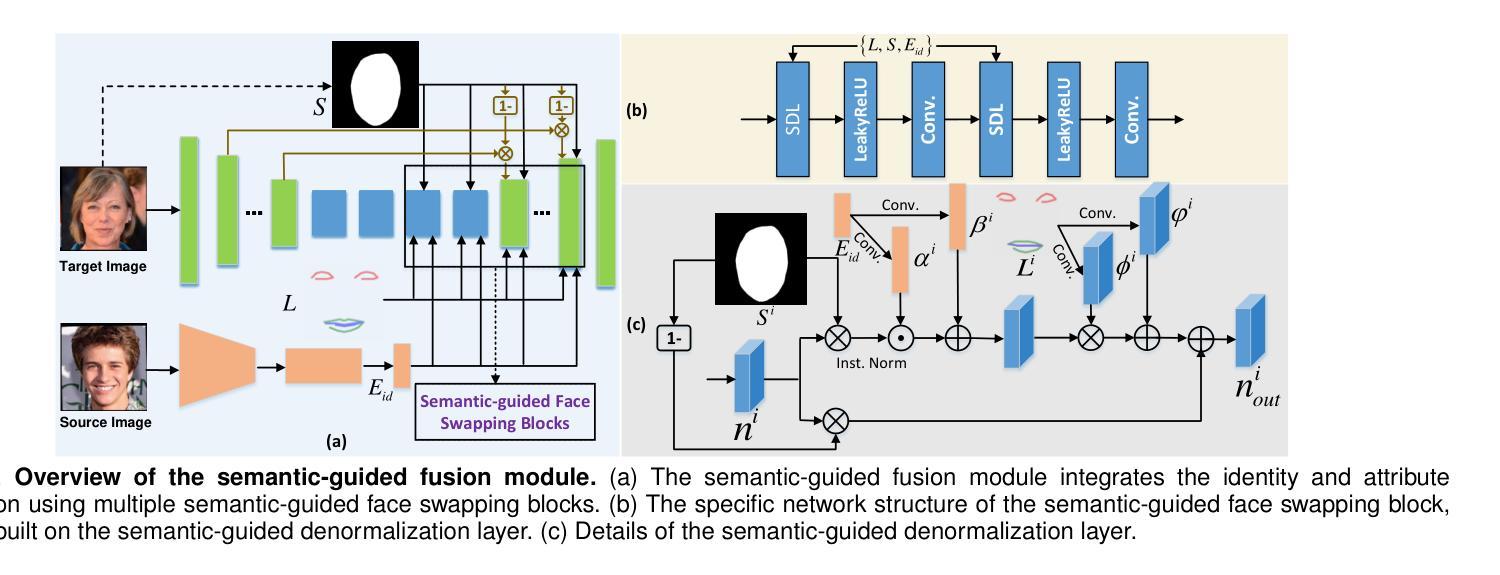
Learning Disentangled Representation for One-shot Progressive Face Swapping
Authors:Qi Li, Weining Wang, Chengzhong Xu, Zhenan Sun, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Although face swapping has attracted much attention in recent years, it remains a challenging problem. Existing methods leverage a large number of data samples to explore the intrinsic properties of face swapping without considering the semantic information of face images. Moreover, the representation of the identity information tends to be fixed, leading to suboptimal face swapping. In this paper, we present a simple yet efficient method named FaceSwapper, for one-shot face swapping based on Generative Adversarial Networks. Our method consists of a disentangled representation module and a semantic-guided fusion module. The disentangled representation module comprises an attribute encoder and an identity encoder, which aims to achieve the disentanglement of the identity and attribute information. The identity encoder is more flexible, and the attribute encoder contains more attribute details than its competitors. Benefiting from the disentangled representation, FaceSwapper can swap face images progressively. In addition, semantic information is introduced into the semantic-guided fusion module to control the swapped region and model the pose and expression more accurately. Experimental results show that our method achieves state-of-the-art results on benchmark datasets with fewer training samples. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/liqi-casia/FaceSwapper.
尽管人脸替换近年来引起了广泛关注,但它仍然是一个具有挑战性的问题。现有方法利用大量数据样本探索人脸替换的内在属性,而没有考虑人脸图像的语义信息。此外,身份信息的表示往往固定,导致人脸替换效果不佳。在本文中,我们提出了一种简单而高效的方法,名为FaceSwapper,基于生成对抗网络进行一次人脸替换。我们的方法包括一个分解表示模块和一个语义引导融合模块。分解表示模块包括一个属性编码器和一个身份编码器,旨在实现身份和属性信息的分解。身份编码器更灵活,而属性编码器包含比其竞争对手更多的属性细节。得益于分解表示,FaceSwapper可以逐步替换人脸图像。此外,语义信息被引入到语义引导融合模块中,以控制交换区域并更准确地模拟姿势和表情。实验结果表明,我们的方法在基准数据集上实现了卓越的结果,并且使用了较少的训练样本。我们的代码公开在https://github.com/liqi-casia/FaceSwapper。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的名为FaceSwapper的一键式人脸替换方法。该方法包括一个解纠缠表示模块和一个语义引导融合模块,旨在实现身份和属性信息的解纠缠表示,并引入语义信息以更准确地控制替换区域和模拟姿态表情。FaceSwapper具有高效性能,可以在基准数据集上实现卓越的结果,并且训练样本需求较少。相关代码已公开提供。
Key Takeaways
- Face swapping依然是一个具有挑战性的课题,尽管近年来得到了广泛关注。
- 现有方法往往忽略人脸图像的语义信息,使用大量数据样本探索人脸替换的内在属性。
- FaceSwapper方法基于生成对抗网络(GAN),实现了一键式人脸替换。
- FaceSwapper包括一个解纠缠表示模块,旨在实现身份和属性信息的解纠缠。
- FaceSwapper具有更灵活的身份编码器和包含更多属性细节的属性编码器。
- 通过引入语义信息,FaceSwapper可以更准确地控制替换区域和模拟姿态表情。
点此查看论文截图