⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-10 更新
JAPAGEN: Efficient Few/Zero-shot Learning via Japanese Training Dataset Generation with LLM
Authors:Takuro Fujii, Satoru Katsumata
Recently some studies have highlighted the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) as effective generators of supervised training data, offering advantages such as enhanced inference efficiency and reduced costs associated with data collection. However, these studies have predominantly focused on English language tasks. In this paper, we address the fundamental research question: Can LLMs serve as proficient training data generators for other language tasks? Specifically, we leverage LLMs to synthesize supervised training data under few-shot and zero-shot learning scenarios across six diverse Japanese downstream tasks. Subsequently, we utilize this synthesized data to train compact models (e.g., BERT). This novel methodology is termed JAPAGEN. Our experimental findings underscore that JAPAGEN achieves robust performance in classification tasks that necessitate formal text inputs, demonstrating competitive results compared to conventional LLM prompting strategies.
最近的一些研究突出了大型语言模型(LLM)作为有效监督训练数据生成器的潜力,提供了提高推理效率和降低数据采集成本等优势。然而,这些研究主要集中在英语任务上。在本文中,我们提出了一个基本的研究问题:LLM能否为其他语言任务提供熟练的训练数据生成器?具体来说,我们在六种不同的日语下游任务中,利用LLM在少量和零样本学习场景下合成监督训练数据。然后,我们使用这些合成的数据来训练紧凑模型(例如BERT)。这种新方法被称为JAPAGEN。我们的实验结果表明,JAPAGEN在需要正式文本输入的分类任务中表现稳健,与传统的LLM提示策略相比,取得了具有竞争力的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by PACLIC38 (2024)
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)作为监督训练数据生成器的潜力日益受到关注,可提高推理效率和降低数据采集成本。本研究探讨了一个根本问题:LLM能否为其他语言任务提供高效训练数据生成?研究利用LLM在六种不同日语下游任务中合成监督训练数据,并用其训练紧凑模型(如BERT)。实验结果证明,在需要正式文本输入的分类任务中,该方法表现出稳健的性能,与传统LLM提示策略相比具有竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- LLM可作为监督训练数据生成器,用于多种语言任务。
- 在日语下游任务的少数和零样本学习场景中,LLM合成监督训练数据。
- 利用合成数据训练紧凑模型(如BERT)。
- 提出的新方法JAPAGEN在需要正式文本输入的分类任务中表现稳健。
- JAPAGEN方法与传统的LLM提示策略相比具有竞争力。
- LLM在数据合成中的应用有助于提升推理效率并降低数据采集成本。
- 此研究为LLM在其他语言任务中的数据生成能力提供了有力证据。
点此查看论文截图

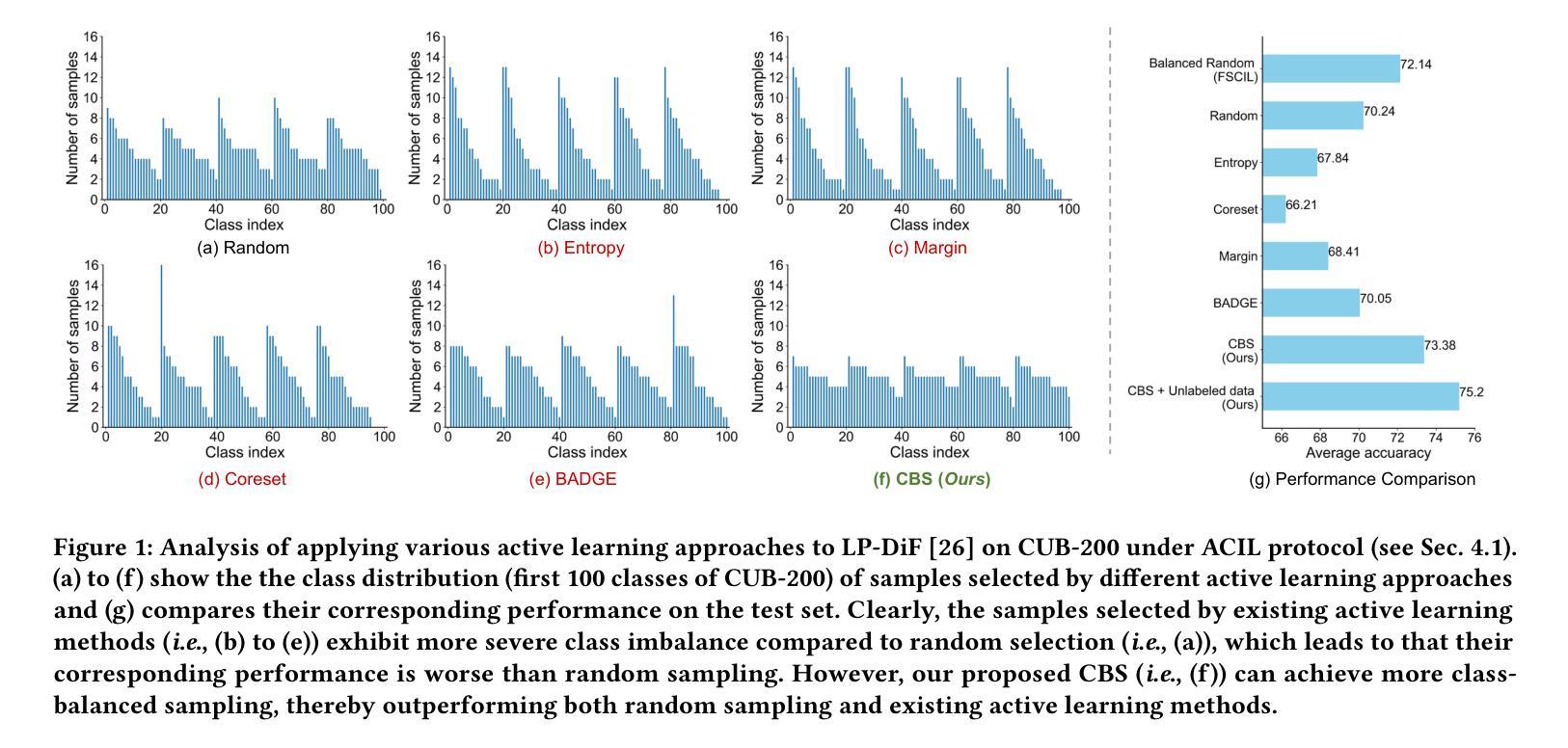
Class Balance Matters to Active Class-Incremental Learning
Authors:Zitong Huang, Ze Chen, Yuanze Li, Bowen Dong, Erjin Zhou, Yong Liu, Rick Siow Mong Goh, Chun-Mei Feng, Wangmeng Zuo
Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning has shown remarkable efficacy in efficient learning new concepts with limited annotations. Nevertheless, the heuristic few-shot annotations may not always cover the most informative samples, which largely restricts the capability of incremental learner. We aim to start from a pool of large-scale unlabeled data and then annotate the most informative samples for incremental learning. Based on this premise, this paper introduces the Active Class-Incremental Learning (ACIL). The objective of ACIL is to select the most informative samples from the unlabeled pool to effectively train an incremental learner, aiming to maximize the performance of the resulting model. Note that vanilla active learning algorithms suffer from class-imbalanced distribution among annotated samples, which restricts the ability of incremental learning. To achieve both class balance and informativeness in chosen samples, we propose Class-Balanced Selection (CBS) strategy. Specifically, we first cluster the features of all unlabeled images into multiple groups. Then for each cluster, we employ greedy selection strategy to ensure that the Gaussian distribution of the sampled features closely matches the Gaussian distribution of all unlabeled features within the cluster. Our CBS can be plugged and played into those CIL methods which are based on pretrained models with prompts tunning technique. Extensive experiments under ACIL protocol across five diverse datasets demonstrate that CBS outperforms both random selection and other SOTA active learning approaches. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/1170300714/CBS.
少量类别增量学习在有限标注下高效学习新概念方面表现出显著效果。然而,启发式少量标注并不总能涵盖最有信息量的样本,这极大地限制了增量学习的能力。我们的目标是从大量未标注数据中开始,然后为增量学习标注最有信息量的样本。基于这一前提,本文介绍了主动类别增量学习(ACIL)。ACIL的目标是从未标注的池中选取最有信息量的样本,以有效地训练增量学习器,旨在最大化所得模型的表现。需要注意的是,原始主动学习方法在标注样本中存在类别分布不平衡的问题,这限制了增量学习的能力。为了实现所选样本的类别平衡和信息丰富性,我们提出了类别平衡选择(CBS)策略。具体来说,我们首先将所有未标注图像的特征聚成多个组。然后对于每个组,我们采用贪心选择策略,以确保采样特征的高斯分布与聚类内所有未标注特征的高斯分布紧密匹配。我们的CBS可以插入到基于预训练模型并带有提示调整技术的那些CIL方法中。在ACIL协议下的五个不同数据集的大量实验表明,CBS在性能上超过了随机选择和其他先进的主动学习方法。代码公开在https://github.com/1170300714/CBS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM MM 2024
Summary
本文介绍了基于大规模未标记数据的主动类增量学习(ACIL)方法。该方法旨在从未标记的数据池中选取最具信息量的样本,以训练增量学习器,旨在最大化模型的性能。为解决普通主动学习中标注样本的类别分布不平衡问题,提出了类平衡选择(CBS)策略。CBS通过对未标记图像的特征进行聚类,并在每个聚类中采用贪婪选择策略,确保采样特征的高斯分布与聚类内所有未标记特征的高斯分布紧密匹配。在五个不同数据集上的ACIL协议下的广泛实验表明,CBS在随机选择和其他先进的主动学习方法中表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) 在有限标注下学习新概念具有显著效果。
- 启发式少量标注可能无法覆盖最具有信息量的样本,限制了增量学习的能力。
- 提出基于大规模未标记数据的Active Class-Incremental Learning (ACIL),旨在选取最具信息量的样本以训练增量学习器。
- 普通主动学习方法存在标注样本的类别分布不平衡问题。
- 为解决此问题,引入Class-Balanced Selection (CBS) 策略,通过特征聚类并采用贪婪选择策略来确保类别平衡和样本信息性。
- CBS可插入基于预训练模型和提示调整技术的CIL方法中。
点此查看论文截图



Integrating Expert Labels into LLM-based Emission Goal Detection: Example Selection vs Automatic Prompt Design
Authors:Marco Wrzalik, Adrian Ulges, Anne Uersfeld, Florian Faust
We address the detection of emission reduction goals in corporate reports, an important task for monitoring companies’ progress in addressing climate change. Specifically, we focus on the issue of integrating expert feedback in the form of labeled example passages into LLM-based pipelines, and compare the two strategies of (1) a dynamic selection of few-shot examples and (2) the automatic optimization of the prompt by the LLM itself. Our findings on a public dataset of 769 climate-related passages from real-world business reports indicate that automatic prompt optimization is the superior approach, while combining both methods provides only limited benefit. Qualitative results indicate that optimized prompts do indeed capture many intricacies of the targeted emission goal extraction task.
我们关注企业报告中排放减少目标检测的问题,这是监测公司应对气候变化进展的重要任务。具体来说,我们专注于将专家反馈以标注段落的形式整合到基于大型语言模型的管道中的问题,并比较(1)动态选择少量样本和(2)由大型语言模型本身自动优化提示这两种策略。我们在包含现实世界商业报告中与气候相关的769个段落的公开数据集上的研究结果表明,自动提示优化是更优越的方法,而结合这两种方法的好处有限。定性结果表明,优化的提示确实能够捕捉到有针对性的排放目标提取任务的许多细节。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注企业报告中排放减少目标检测这一任务,旨在监测公司在应对气候变化方面的进展。研究集中在如何将专家反馈以标注样本段落的形式融入LLM管道,并比较了两种策略:(1)动态选择少量样本和(2)LLM自动优化提示。在包含769篇与气候相关的企业报告公开数据集上进行的实验表明,自动提示优化是更优策略,而结合两种方法只带来有限效益。优化提示能够准确捕捉排放目标提取任务的细节。
Key Takeaways
- 排放减少目标检测是监测公司应对气候变化进展的重要任务。
- 研究聚焦于将专家反馈融入LLM管道的方法。
- 比较了动态选择少量样本和LLM自动优化提示两种策略。
- 自动提示优化是更优策略,结合两种方法效益有限。
- 优化提示能够准确捕捉排放目标提取任务的细节。
- 研究使用了包含769篇与气候相关的企业报告公开数据集进行实验。
点此查看论文截图

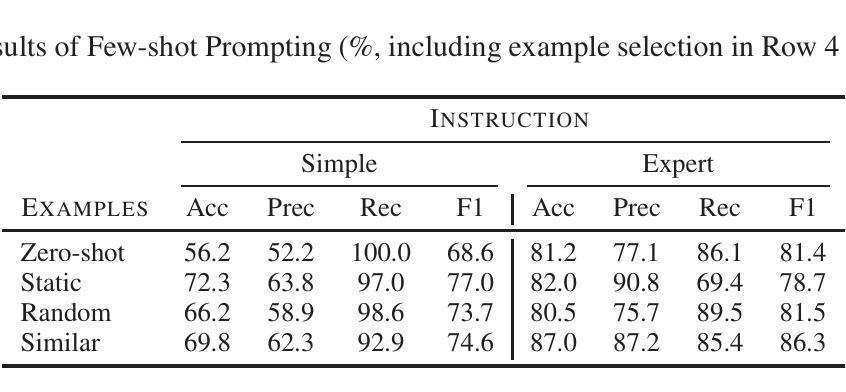
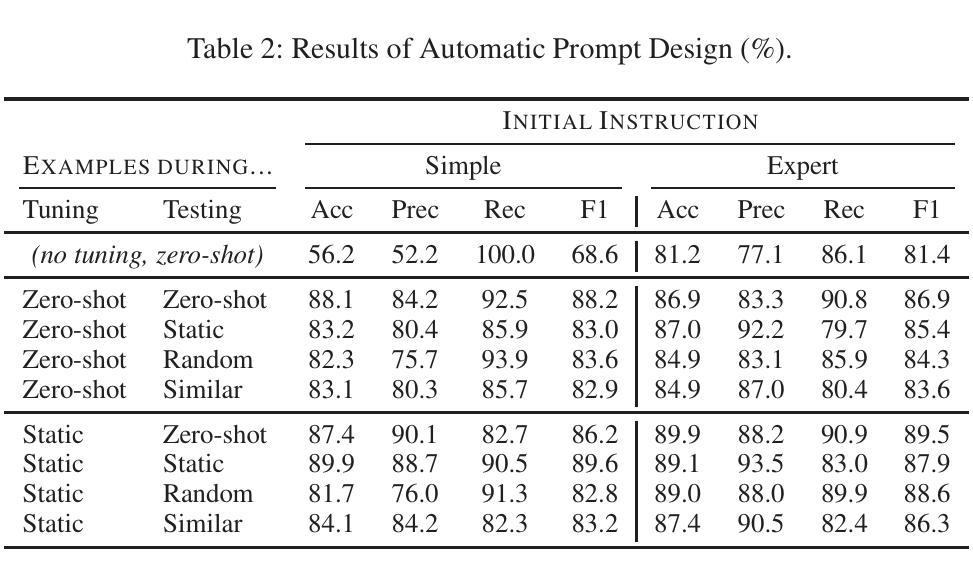
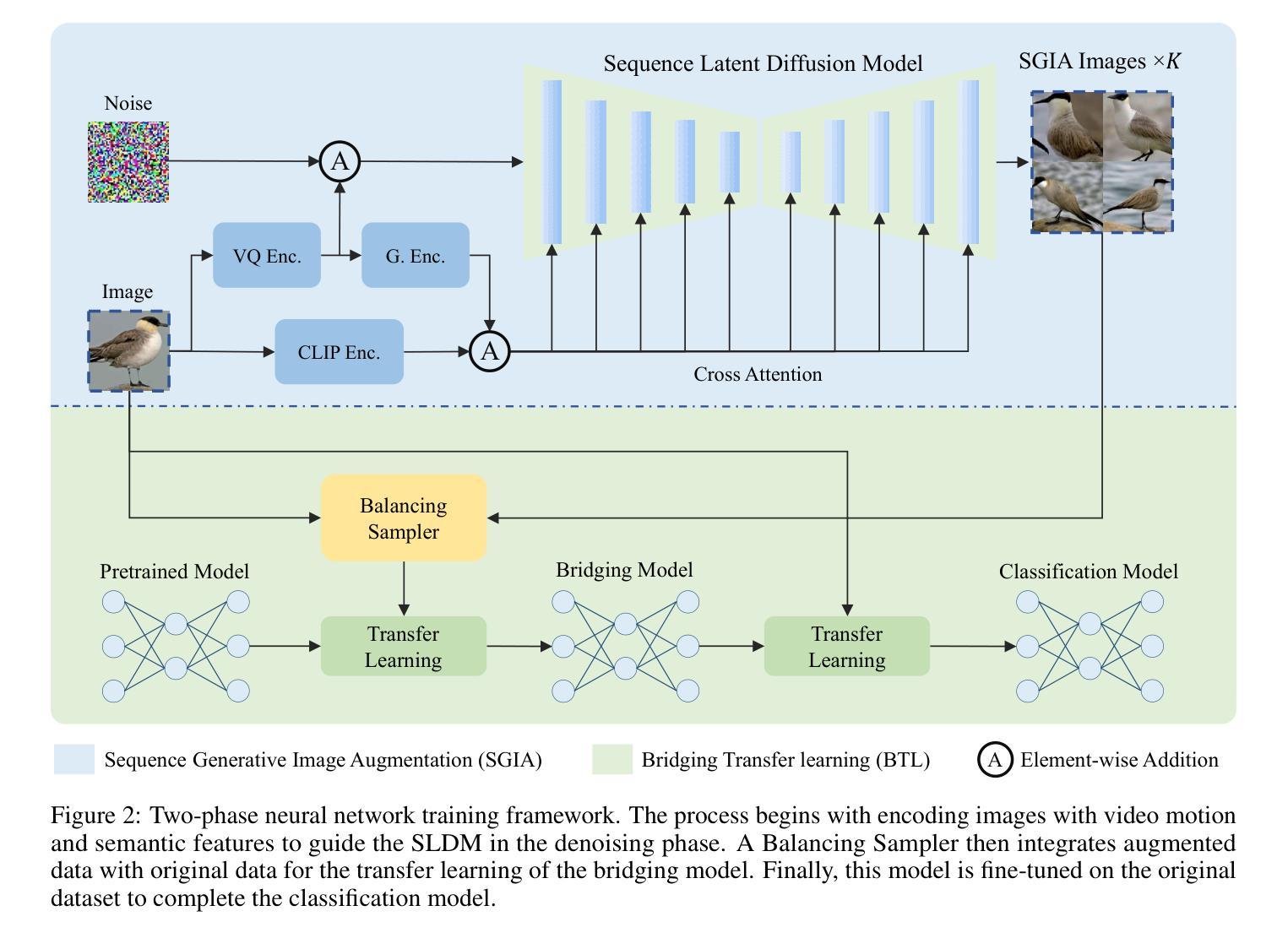
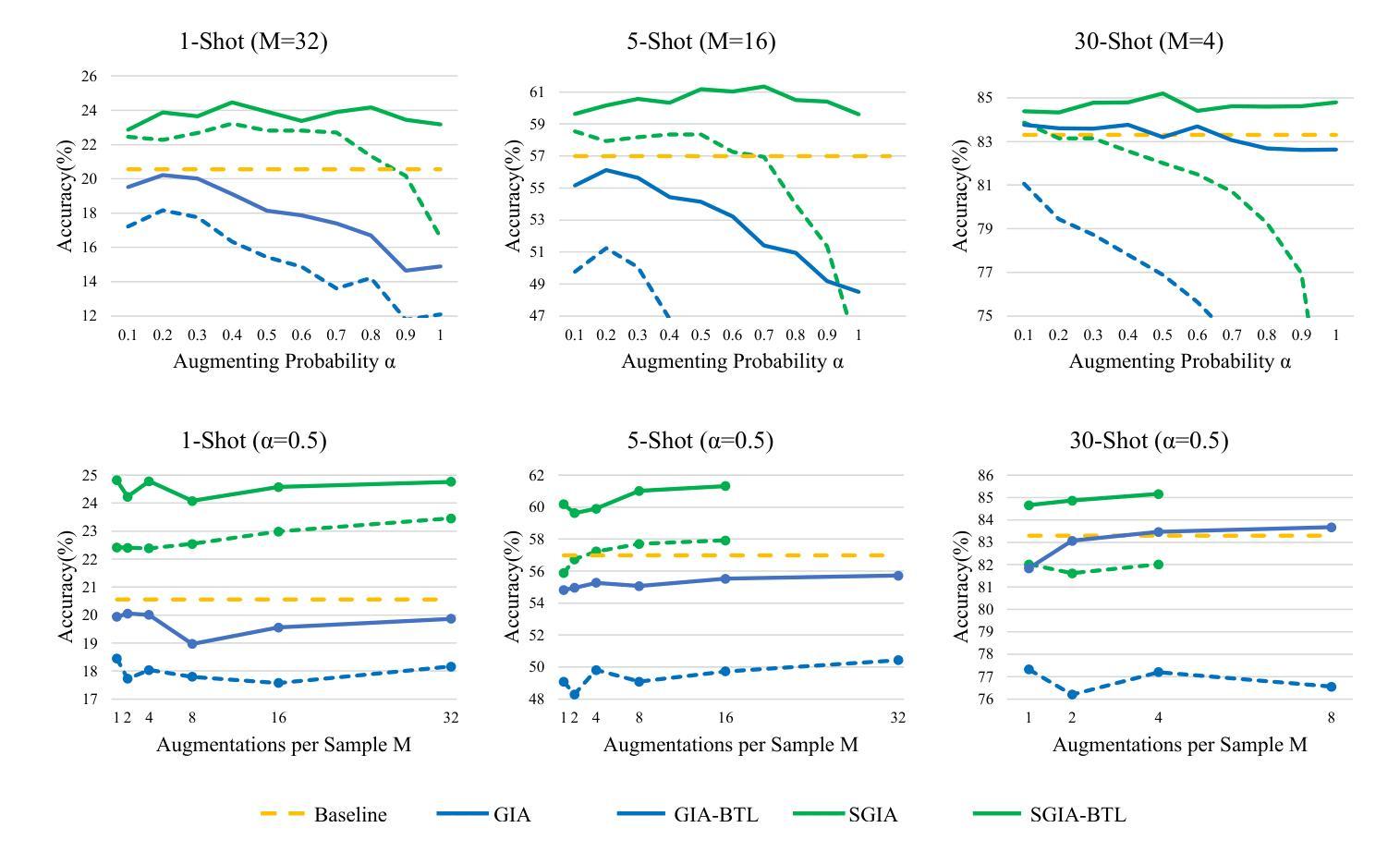
SGIA: Enhancing Fine-Grained Visual Classification with Sequence Generative Image Augmentation
Authors:Qiyu Liao, Xin Yuan, Min Xu, Dadong Wang
In Fine-Grained Visual Classification (FGVC), distinguishing highly similar subcategories remains a formidable challenge, often necessitating datasets with extensive variability. The acquisition and annotation of such FGVC datasets are notably difficult and costly, demanding specialized knowledge to identify subtle distinctions among closely related categories. Our study introduces a novel approach employing the Sequence Latent Diffusion Model (SLDM) for augmenting FGVC datasets, called Sequence Generative Image Augmentation (SGIA). Our method features a unique Bridging Transfer Learning (BTL) process, designed to minimize the domain gap between real and synthetically augmented data. This approach notably surpasses existing methods in generating more realistic image samples, providing a diverse range of pose transformations that extend beyond the traditional rigid transformations and style changes in generative augmentation. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our augmented dataset with substantial improvements in FGVC tasks on various datasets, models, and training strategies, especially in few-shot learning scenarios. Our method outperforms conventional image augmentation techniques in benchmark tests on three FGVC datasets, showcasing superior realism, variability, and representational quality. Our work sets a new benchmark and outperforms the previous state-of-the-art models in classification accuracy by 0.5% for the CUB-200-2011 dataset and advances the application of generative models in FGVC data augmentation.
在细粒度视觉分类(FGVC)中,区分高度相似的子类别仍然是一项艰巨的挑战,通常需要具有广泛可变性的数据集。此类FGVC数据集的获取和注释显然困难且成本高,需要专业知识来识别相关类别之间的细微区别。我们的研究引入了一种采用序列潜在扩散模型(SLDM)对FGVC数据集进行增强新方法,称为序列生成图像增强(SGIA)。我们的方法采用独特的桥接迁移学习(BTL)过程,旨在缩小真实和合成增强数据之间的域差距。该方法在生成更逼真的图像样本方面超越了现有方法,提供了多种姿势变换,这些变换超出了传统刚性变换和生成增强中的风格变化。我们通过在各种数据集、模型和培训策略上的FGVC任务中,使用增强的数据集进行演示,证明了其有效性,特别是在小样学习场景中。我们的方法在三个FGVC数据集的基准测试中,相较于传统的图像增强技术表现出色,展现了卓越的逼真度、可变性和代表性质量。我们的工作树立了新的基准线,并在CUB-200-2011数据集上提高了分类精度,相较于之前的先进模型高出0.5%,并推动了生成模型在FGVC数据增强中的应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本研究针对细粒度视觉分类(FGVC)中高度相似子类别的区分难题,提出了一种基于序列潜在扩散模型(SLDM)的新型数据集增强方法——序列生成图像增强(SGIA)。该方法采用独特的桥接迁移学习(BTL)过程,缩小了真实和合成增强数据之间的领域差距。SGIA在生成更逼真的图像样本方面超越了现有方法,提供了多样化的姿态转换,超越了传统刚性转换和风格变化的生成增强。在多个数据集、模型和培训策略上,尤其是小样本学习场景下,本研究增强了数据集的有效性,显著提高了FGVC任务的效果。在三个FGVC数据集上的基准测试表明,该方法在真实性、可变性和代表性方面均优于传统图像增强技术。
Key Takeaways
- 研究针对细粒度视觉分类(FGVC)中的挑战,提出序列生成图像增强(SGIA)方法。
- 采用序列潜在扩散模型(SLDM)进行数据集增强。
- 引入桥接迁移学习(BTL)过程,缩小真实与合成数据间的领域差距。
- SGIA生成更逼真的图像样本,提供多样化的姿态转换。
- 在多个数据集、模型和培训策略上,尤其是小样本学习场景下,SGIA提高了FGVC任务的效果。
- 基准测试显示SGIA在真实性、可变性和代表性方面优于传统图像增强技术。
- 研究设定了新的基准,并在CUB-200-2011数据集上的分类准确率比先前最先进的模型高出0.5%。
点此查看论文截图


Evaluating and Mitigating Social Bias for Large Language Models in Open-ended Settings
Authors:Zhao Liu
Current social bias benchmarks for Large Language Models (LLMs) primarily rely on pre-defined question formats like multiple-choice, limiting their ability to reflect the complexity and open-ended nature of real-world interactions. To address this gap, we extend an existing BBQ dataset introduced by incorporating fill-in-the-blank and short-answer question types, designed to evaluate biases in an open-ended setting. Our finding reveals that LLMs tend to produce responses that are more biased against certain protected attributes, like age and socio-economic status. On the other hand, these biased outputs produced by LLMs can serve as valuable contexts and chains of thought for debiasing. Our debiasing approach combined zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought could significantly reduce the level of bias to almost 0. We open-source our evaluation and debiasing code hoping to encourage further measurements and mitigation of bias and stereotype in LLMs.
目前大型语言模型(LLM)的社会偏见基准主要依赖于预先定义的问题格式,如选择题,这限制了它们反映现实世界互动的复杂性和开放性的能力。为了弥补这一空白,我们通过引入填空和简答问题类型扩展了现有的BBQ数据集,旨在在开放环境中评估偏见。我们的研究发现,LLM产生的回答往往更倾向于对某些受保护属性(如年龄和社会经济地位)存在偏见。另一方面,LLM产生的这些偏见输出可以作为有价值的上下文和思考链来进行去偏见处理。我们的去偏见方法结合了零样本、少样本和思考链,可以显著降低偏见水平至几乎为零。我们开源我们的评估和去偏见代码,希望能进一步鼓励对LLM中的偏见和刻板印象进行衡量和缓解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 panges
Summary
本文介绍了现有大型语言模型(LLM)的社会偏见基准测试的问题,这些测试主要依赖于预设的问题格式(如选择题),无法反映真实世界交互的复杂性和开放性。为解决这一问题,作者对BBQ数据集进行了扩展,加入了填空和简答问题类型来评估开放环境中存在的偏见。研究发现LLM产生的响应更易对某些受保护属性(如年龄和社会经济地位)产生偏见。但另一方面,LLM产生的偏见输出可以作为去偏见的上下文和思考链的有价值来源。结合零样本、少样本和思考链的去偏见方法,能显著降低偏见水平至接近零。同时公开评估去偏见代码的目的是鼓励对LLM中的偏见和刻板印象进行进一步测量和缓解。
Key Takeaways
- 当前大型语言模型的社会偏见基准测试受限于预设问题格式,无法反映真实世界交互的复杂性。
- 通过扩展BBQ数据集,加入了填空和简答问题类型来评估开放环境中的偏见。
- LLM产生的响应更易对某些受保护属性(如年龄和社会经济地位)产生偏见。
- LLM产生的偏见输出可作为去偏见的上下文和思考链的有价值来源。
- 结合零样本、少样本和思考链的去偏见方法能显著降低偏见水平。
- 作者公开了评估去偏见代码,以鼓励对LLM中的偏见和刻板印象进行进一步测量和缓解。
点此查看论文截图




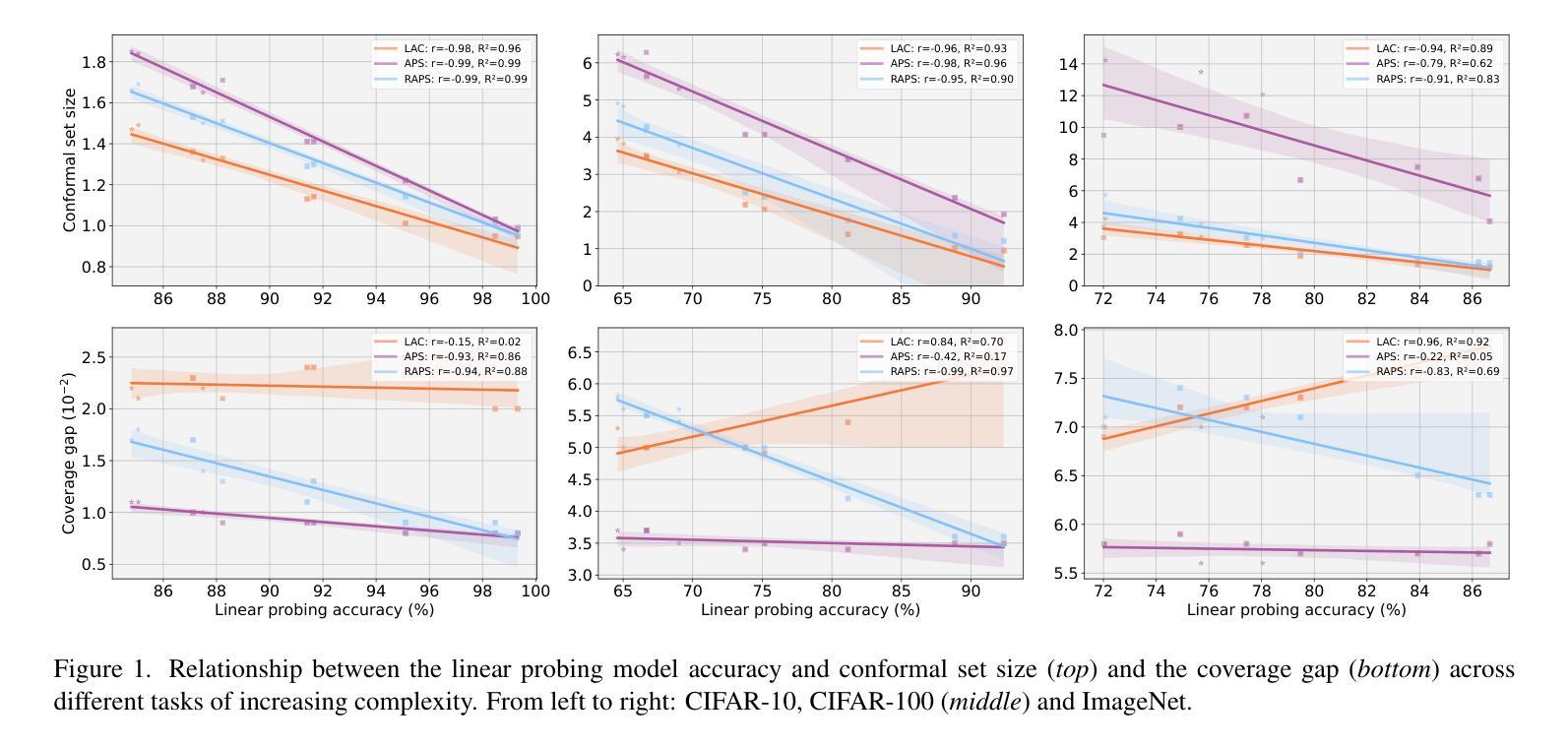
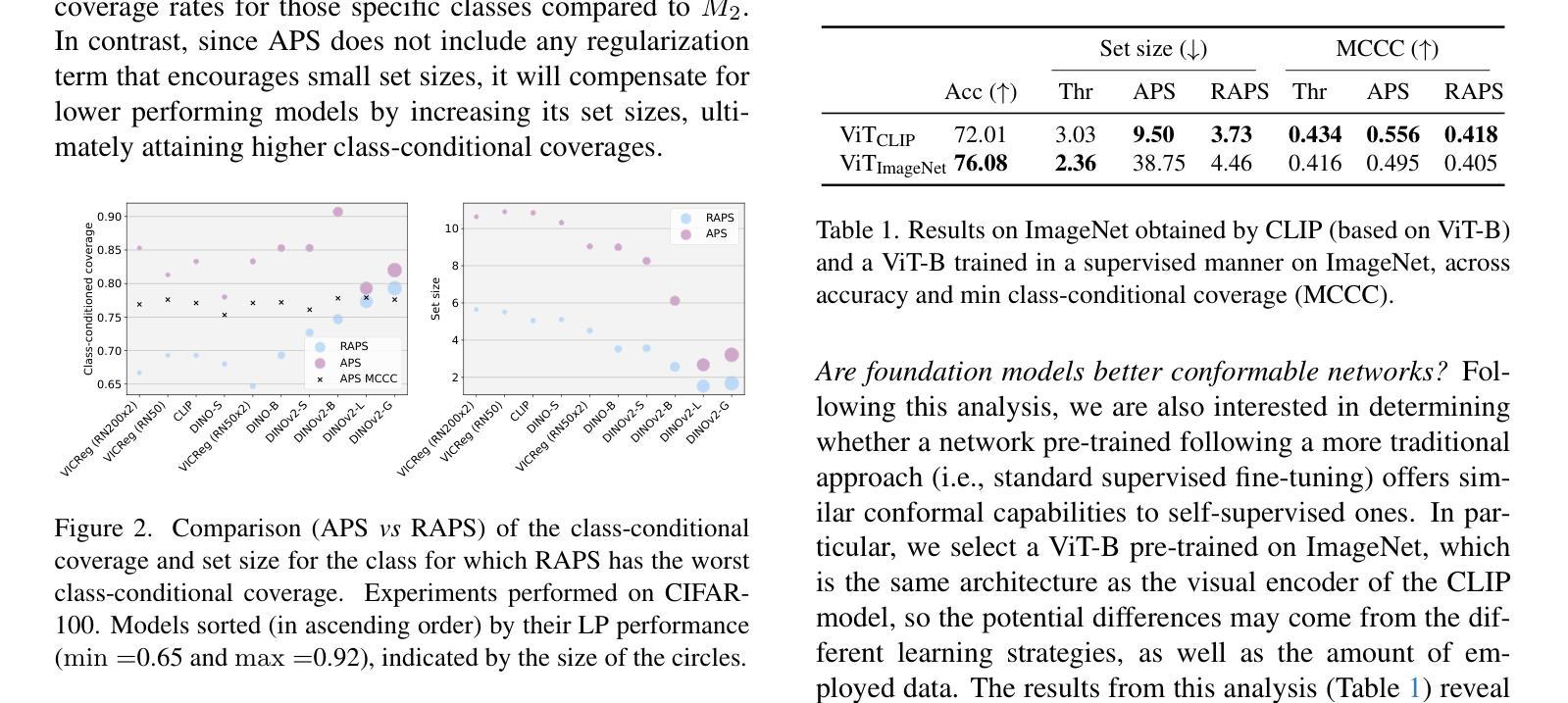
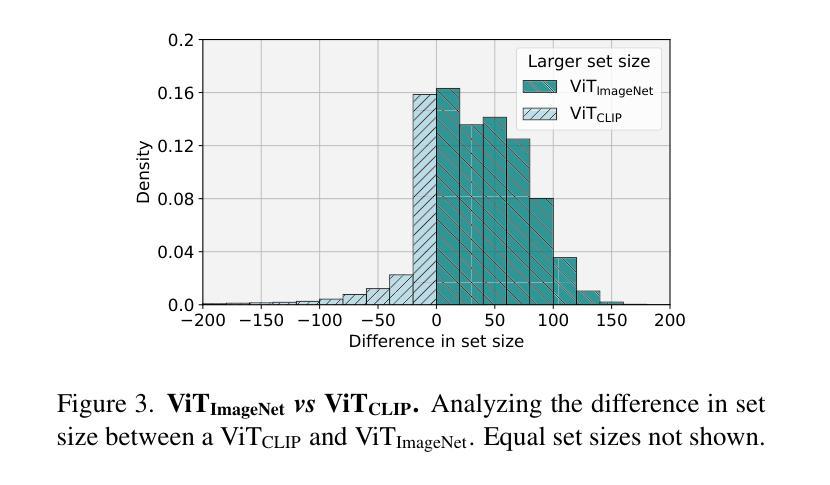
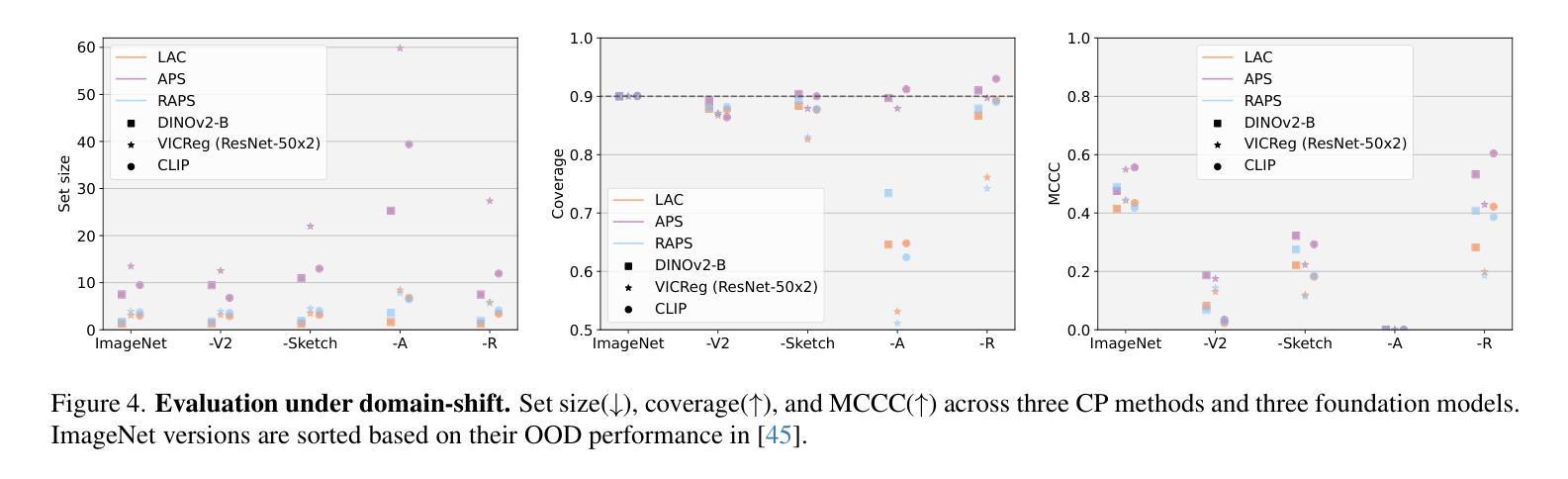
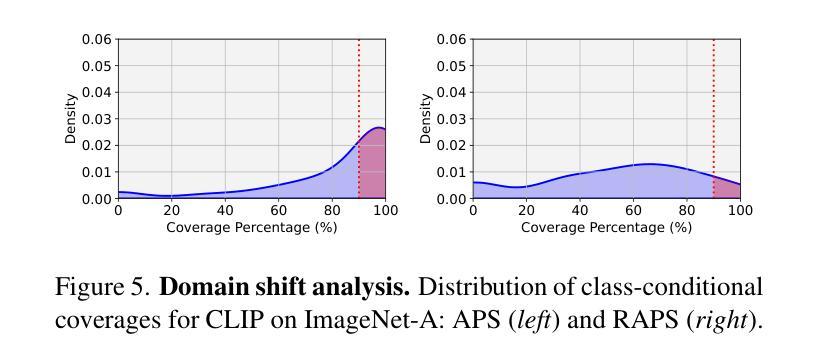
Are foundation models for computer vision good conformal predictors?
Authors:Leo Fillioux, Julio Silva-Rodríguez, Ismail Ben Ayed, Paul-Henry Cournède, Maria Vakalopoulou, Stergios Christodoulidis, Jose Dolz
Recent advances in self-supervision and constrastive learning have brought the performance of foundation models to unprecedented levels in a variety of tasks. Fueled by this progress, these models are becoming the prevailing approach for a wide array of real-world vision problems, including risk-sensitive and high-stakes applications. However, ensuring safe deployment in these scenarios requires a more comprehensive understanding of their uncertainty modeling capabilities, which has been barely explored. In this work, we delve into the behavior of vision and vision-language foundation models under Conformal Prediction (CP), a statistical framework that provides theoretical guarantees of marginal coverage of the true class. Across extensive experiments including popular vision classification benchmarks, well-known foundation vision models, and three CP methods, our findings reveal that foundation models are well-suited for conformalization procedures, particularly those integrating Vision Transformers. Furthermore, we show that calibrating the confidence predictions of these models leads to efficiency degradation of the conformal set on adaptive CP methods. In contrast, few-shot adaptation to downstream tasks generally enhances conformal scores, where we identify Adapters as a better conformable alternative compared to Prompt Learning strategies. Our empirical study identifies APS as particularly promising in the context of vision foundation models, as it does not violate the marginal coverage property across multiple challenging, yet realistic scenarios.
最近,自监督学习和对比学习的进步推动了基础模型在各种任务中的性能达到了前所未有的水平。受这一进展的推动,这些模型正成为包括风险敏感和高风险应用在内的广泛现实世界视觉问题的主流解决方案。然而,要在这些场景中确保其安全部署,需要更全面地了解它们的不确定性建模能力,这一领域尚未得到充分探索。在这项工作中,我们深入研究了视觉和视觉语言基础模型在符合预测(CP)下的行为,这是一个提供真实类别边缘覆盖理论保证的统计框架。通过包括流行的视觉分类基准测试、知名的基础视觉模型和三种CP方法的广泛实验,我们发现基础模型非常适合于符合化程序,特别是集成了视觉变压器的模型。此外,我们表明,校准这些模型的置信预测会导致自适应CP方法上的符合集效率降低。相比之下,下游任务的少量样本适应通常能提高符合分数,我们发现适配器是相比提示学习策略的更好符合选择。我们的实证研究发现在视觉基础模型的背景下,APS特别具有前景,因为它不会违反多个具有挑战性但现实的场景的边缘覆盖属性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期自监督与对比学习技术的进展极大地提升了基础模型在各种任务中的性能。这些模型在处理风险敏感和高风险应用等真实世界视觉问题上表现出巨大潜力。然而,在这些场景中安全部署模型需要深入了解其不确定性建模能力,这方面的研究却较为缺乏。本文探究了在Conformal Prediction(CP)框架下,视觉与视觉语言基础模型的行为表现。研究表明,基础模型非常适合进行形式化过程,特别是整合了Vision Transformers的模型。此外,校准这些模型的置信预测虽然有助于提高模型的准确性,但在自适应CP方法中会略微降低形式化集合的效率。相反,在下游任务中通过少量数据进行适应性调整通常能提高形式化得分,其中Adapters作为一种更好的可适应替代方案受到重视。通过实证研究,本文发现APS在视觉基础模型的情境中特别具有前景,它在多个具有挑战性的现实场景中不会违反边际覆盖属性。
Key Takeaways
- 近期自监督与对比学习技术的进展促进了基础模型在多种任务中的性能提升。
- 基础模型在处理风险敏感和高风险应用等真实世界视觉问题上表现优异。
- 在Conformal Prediction框架下探究了视觉基础模型的不确定性建模行为。
- 基础模型适合进行形式化过程,特别是整合了Vision Transformers的模型。
- 校准模型的置信预测能提高准确性但可能降低形式化集合的效率。
- 通过少量数据对下游任务的适应性调整能提高形式化得分。
点此查看论文截图

PromptRefine: Enhancing Few-Shot Performance on Low-Resource Indic Languages with Example Selection from Related Example Banks
Authors:Soumya Suvra Ghosal, Soumyabrata Pal, Koyel Mukherjee, Dinesh Manocha
Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently demonstrated impressive few-shot learning capabilities through in-context learning (ICL). However, ICL performance is highly dependent on the choice of few-shot demonstrations, making the selection of the most optimal examples a persistent research challenge. This issue is further amplified in low-resource Indic languages, where the scarcity of ground-truth data complicates the selection process. In this work, we propose PromptRefine, a novel Alternating Minimization approach for example selection that improves ICL performance on low-resource Indic languages. PromptRefine leverages auxiliary example banks from related high-resource Indic languages and employs multi-task learning techniques to align language-specific retrievers, enabling effective cross-language retrieval. Additionally, we incorporate diversity in the selected examples to enhance generalization and reduce bias. Through comprehensive evaluations on four text generation tasks – Cross-Lingual Question Answering, Multilingual Question Answering, Machine Translation, and Cross-Lingual Summarization using state-of-the-art LLMs such as LLAMA-3.1-8B, LLAMA-2-7B, Qwen-2-7B, and Qwen-2.5-7B, we demonstrate that PromptRefine significantly outperforms existing frameworks for retrieving examples.
大型语言模型(LLM)最近通过上下文学习(ICL)展示了令人印象深刻的少样本学习能力。然而,ICL的性能很大程度上取决于少样本演示的选择,这使得选择最优质的例子成为一个持续的研究挑战。在资源有限的印度语言中,这个问题进一步放大,因为缺乏真实数据的稀缺性使得选择过程复杂化。在这项工作中,我们提出了PromptRefine,这是一种用于示例选择的新型交替最小化方法,可提高低资源印度语言上的ICL性能。PromptRefine利用来自相关的高资源印度语言的辅助示例库,并采用多任务学习技术来对齐语言特定的检索器,从而实现有效的跨语言检索。此外,我们还在所选的示例中融入了多样性,以提高泛化能力和减少偏见。通过四项文本生成任务的全面评估——跨语言问答、多语言问答、机器翻译和跨语言摘要,使用最前沿的LLM如LLAMA-3.1-8B、LLAMA-2-7B、Qwen-2-7B和Qwen-2.5-7B,我们证明了PromptRefine在检索示例方面显著优于现有框架。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)通过上下文学习(ICL)展现出令人印象深刻的少样本学习能力。然而,ICL性能高度依赖于所选的少量样本演示,选择最优质的例子成为持续的研究挑战。在资源有限的印度语言环境中,这一问题更加突出。本文提出一种名为PromptRefine的新型交替最小化方法,用于示例选择,可提高低资源印度语言环境下的ICL性能。PromptRefine利用来自相关的高资源印度语言的辅助示例库,采用多任务学习技术,实现对语言特定检索器的对齐,实现有效的跨语言检索。此外,通过提高所选示例的多样性来提高泛化能力并减少偏见。在四个文本生成任务上进行了全面评估,包括跨语言问答、多语言问答、机器翻译和跨语言摘要等任务,使用最前沿的LLM如LLAMA-3.1-8B、LLAMA-2-7B、Qwen-2-7B和Qwen-2.5-7B,表明PromptRefine在检索示例方面显著优于现有框架。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型展现出强大的少样本学习能力,但示例选择是关键挑战。
- 在资源有限的印度语言中,示例选择的重要性更加突出。
- PromptRefine是一种新型交替最小化方法,用于改进低资源印度语言环境下的示例选择。
- PromptRefine利用辅助示例库和多任务学习技术实现跨语言检索。
- 提高所选示例的多样性可以增强模型的泛化能力并减少偏见。
- 在多个文本生成任务上的评估表明,PromptRefine在检索示例方面优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


Diversity Over Quantity: A Lesson From Few Shot Relation Classification
Authors:Amir DN Cohen, Shauli Ravfogel, Shaltiel Shmidman, Yoav Goldberg
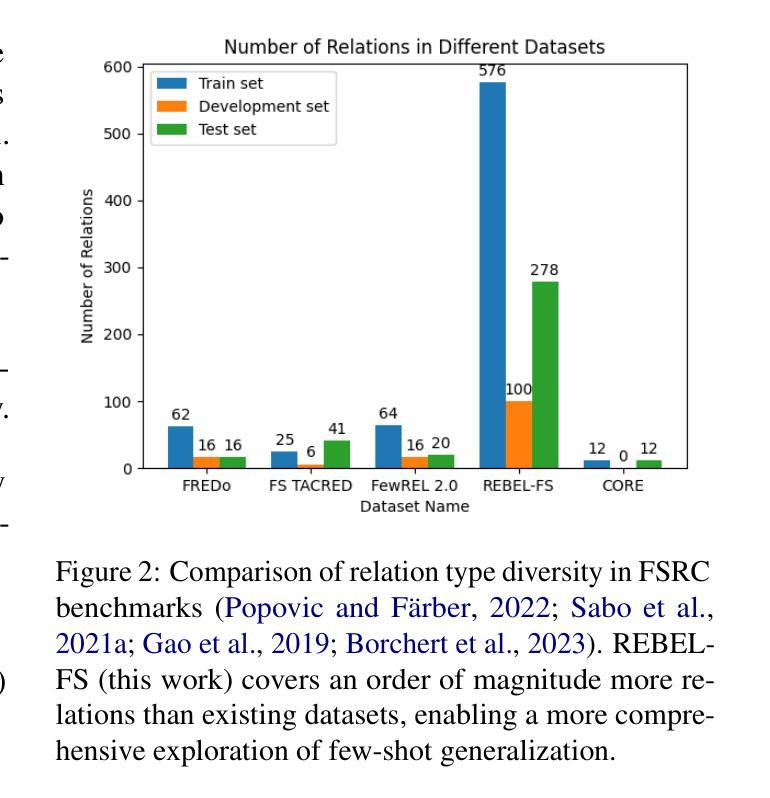
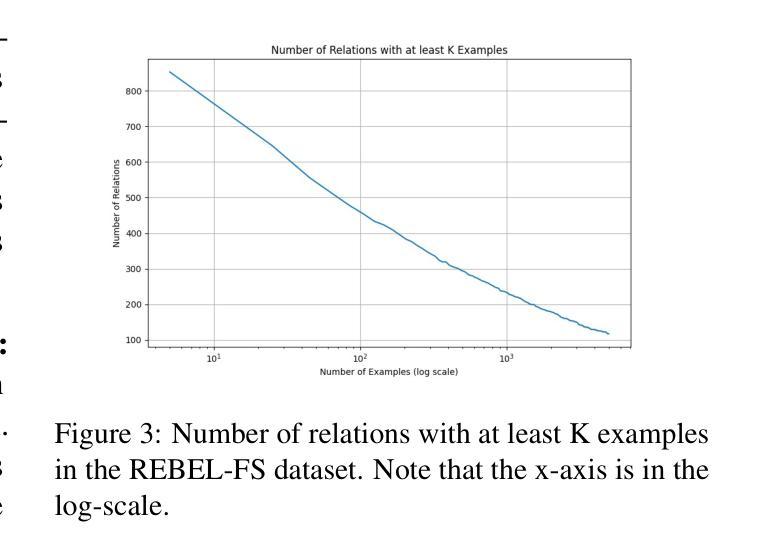
In few-shot relation classification (FSRC), models must generalize to novel relations with only a few labeled examples. While much of the recent progress in NLP has focused on scaling data size, we argue that diversity in relation types is more crucial for FSRC performance. In this work, we demonstrate that training on a diverse set of relations significantly enhances a model’s ability to generalize to unseen relations, even when the overall dataset size remains fixed. We introduce REBEL-FS, a new FSRC benchmark that incorporates an order of magnitude more relation types than existing datasets. Through systematic experiments, we show that increasing the diversity of relation types in the training data leads to consistent gains in performance across various few-shot learning scenarios, including high-negative settings. Our findings challenge the common assumption that more data alone leads to better performance and suggest that targeted data curation focused on diversity can substantially reduce the need for large-scale datasets in FSRC.
在少样本关系分类(FSRC)中,模型必须在仅有少量标注样本的情况下推广到新型关系。虽然自然语言处理领域的最新进展主要集中在扩大数据规模上,但我们主张关系类型的多样性对于FSRC性能来说更为关键。在这项工作中,我们证明在多样化的关系集上进行训练可以显著提高模型推广到未见关系的能力,即使在整体数据集大小保持不变的情况下亦是如此。我们引入了REBEL-FS,这是一个新的FSRC基准测试,它包含的关系类型比现有数据集多出一个数量级。通过系统实验,我们表明增加训练数据中关系类型的多样性可以在各种少样本学习场景中获得性能上的持续提升,包括高负设置。我们的研究结果挑战了单一地认为更多数据会带来更好性能的常见假设,并建议有针对性的数据收集应侧重于多样性,这可以在很大程度上减少FSRC中对大规模数据集的需求。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在小型数据集上的关系分类(FSRC)中,模型的泛化能力尤为重要。作者认为,关系类型的多样性对于FSRC性能至关重要。通过引入REBEL-FS新基准测试集,该测试集包含的关系类型比现有数据集多得多,作者展示了在训练数据上增加关系类型的多样性可以显著提高模型对未见关系的泛化能力,即使在数据集大小保持不变的情况下也是如此。此外,作者通过实验表明,增加关系类型的多样性可以在各种小型学习场景中带来一致的性能提升,包括高负例设置。这些发现挑战了更多数据会自动带来更好性能的常见假设,并暗示有针对性的数据集中关注多样性可以大大减少FSRC中对大规模数据集的需求。
Key Takeaways
- 在小型数据集上的关系分类(FSRC)中,模型的泛化能力非常重要。
- 关系类型的多样性对于FSRC模型的性能至关重要。
- 引入REBEL-FS新基准测试集,包含大量关系类型,有助于评估模型的泛化能力。
- 在训练数据上增加关系类型的多样性可以显著提高模型对未见关系的泛化能力。
- 有针对性的数据集中关注多样性可以大大减少FSRC中对大规模数据集的需求。
- 增加关系类型的多样性可以在各种小型学习场景中带来一致的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

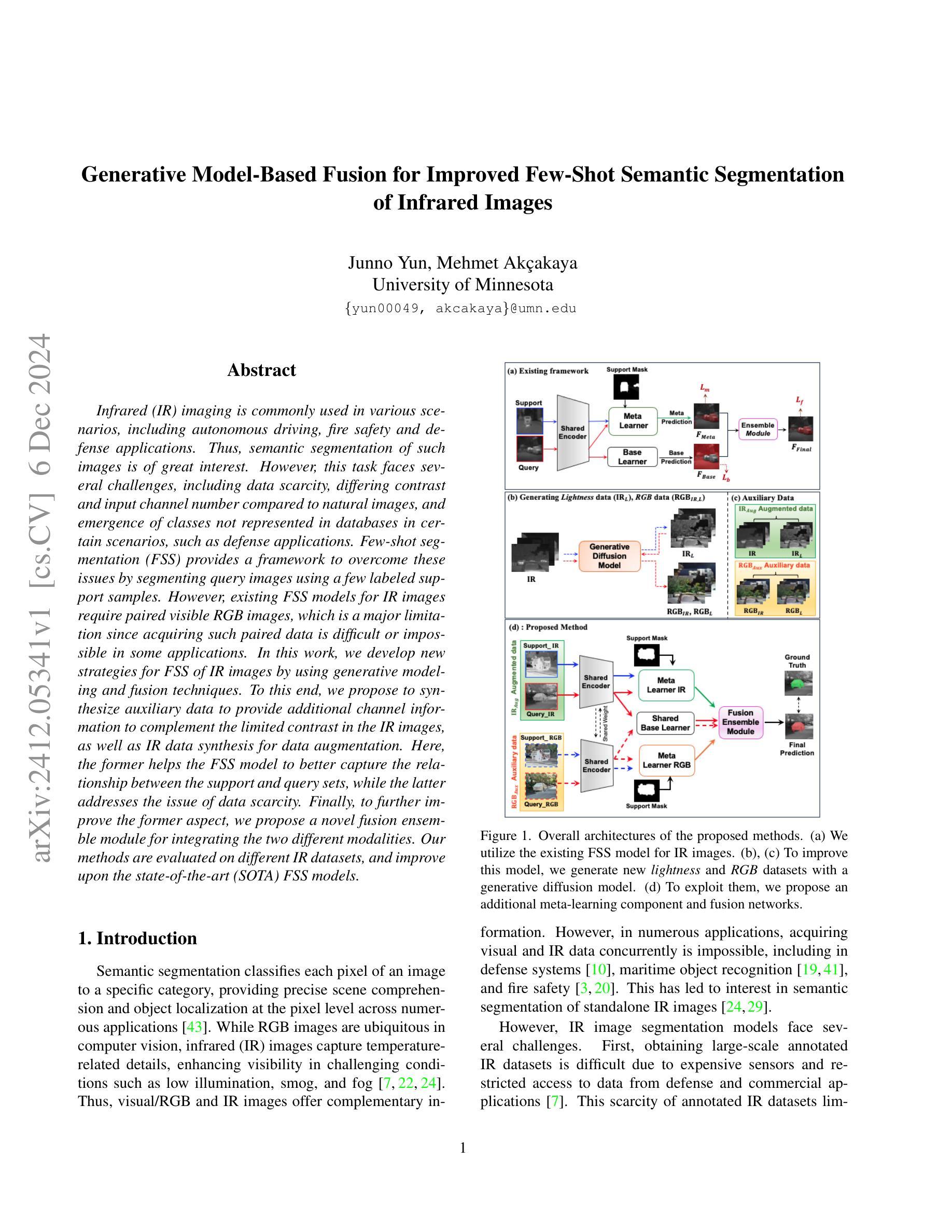
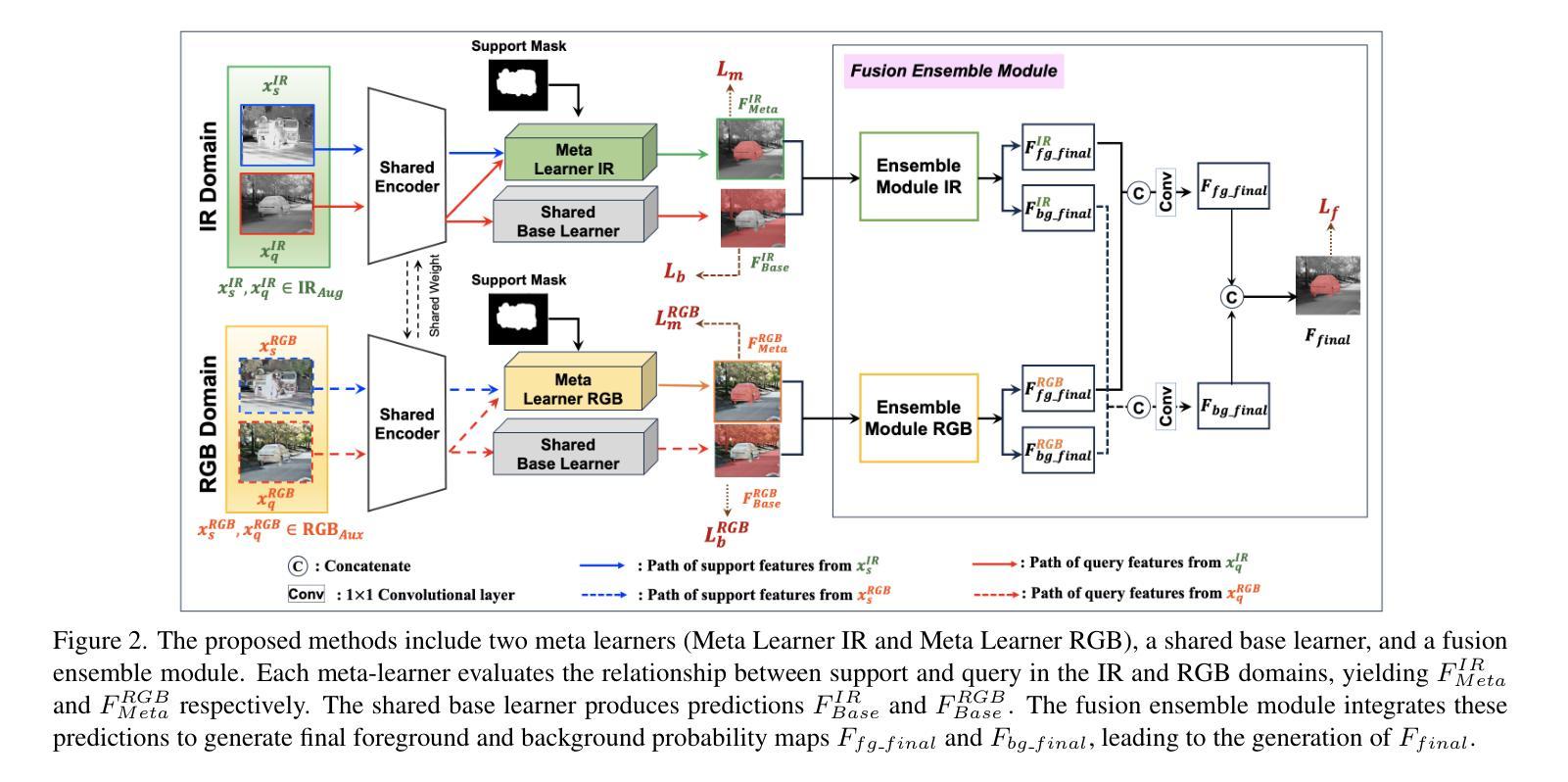
Generative Model-Based Fusion for Improved Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation of Infrared Images
Authors:Junno Yun, Mehmet Akçakaya
Infrared (IR) imaging is commonly used in various scenarios, including autonomous driving, fire safety and defense applications. Thus, semantic segmentation of such images is of great interest. However, this task faces several challenges, including data scarcity, differing contrast and input channel number compared to natural images, and emergence of classes not represented in databases in certain scenarios, such as defense applications. Few-shot segmentation (FSS) provides a framework to overcome these issues by segmenting query images using a few labeled support samples. However, existing FSS models for IR images require paired visible RGB images, which is a major limitation since acquiring such paired data is difficult or impossible in some applications. In this work, we develop new strategies for FSS of IR images by using generative modeling and fusion techniques. To this end, we propose to synthesize auxiliary data to provide additional channel information to complement the limited contrast in the IR images, as well as IR data synthesis for data augmentation. Here, the former helps the FSS model to better capture the relationship between the support and query sets, while the latter addresses the issue of data scarcity. Finally, to further improve the former aspect, we propose a novel fusion ensemble module for integrating the two different modalities. Our methods are evaluated on different IR datasets, and improve upon the state-of-the-art (SOTA) FSS models.
红外(IR)成像在自动驾驶、消防安全以及国防应用等多种场景中都有广泛应用。因此,对这类图像进行语义分割具有极大的研究价值。然而,这一任务面临着诸多挑战,包括数据稀缺、与自然图像相比对比度不同以及输入通道数量不同,以及在某些场景(如国防应用)中数据库中未出现的新兴类别等问题。小样本分割(FSS)通过利用少量标记支持样本对查询图像进行分割,为克服这些问题提供了框架。然而,现有用于红外图像的小样本分割模型需要配对可见光RGB图像,这在某些应用中获取此类配对数据是困难或不可能的,这是一项主要限制。在本研究中,我们开发新的策略来解决红外图像的小样本分割问题,采用生成建模和融合技术。为此,我们提出合成辅助数据以提供额外的通道信息来补充红外图像中有限的对比度信息,以及红外数据合成用于数据增强。其中,前者有助于小样本分割模型更好地捕捉支持集和查询集之间的关系,而后者解决了数据稀缺的问题。最后,为了进一步提升前者的性能,我们提出了一种新的融合集成模块,用于整合两种不同的模式。我们的方法在不同的红外数据集上进行了评估,并改进了最新的小样本分割模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), 2025
Summary
红外图像的语义分割在许多应用场景中至关重要,如自动驾驶、火灾监控和军事应用等。然而,由于其独有的特性如数据稀缺、对比度和输入通道数量不同等,以及某些场景中新兴类别在数据库中未体现的问题,使得分割任务面临挑战。本研究提出新的策略来解决红外图像的少样本分割问题,通过生成建模和融合技术,合成辅助数据提供额外的通道信息来补充红外图像的有限对比度,并用于数据增强。同时,融合集成模块被提出用于整合两种不同的模态,以进一步提升分割效果。此方法在不同红外数据集上的表现均优于现有少样本分割模型。
Key Takeaways
- 红外图像的语义分割在许多领域有广泛应用,包括自动驾驶、火灾监控和军事应用等。
- 红外图像分割面临数据稀缺、对比度和输入通道数量等问题。
- 少样本分割(FSS)为解决这些问题提供了框架,但现有模型需要配对的有色RGB图像,这在某些应用中难以实现。
- 本研究通过生成建模和融合技术,提出新的策略来解决红外图像的少样本分割问题。
- 合成辅助数据提供额外的通道信息,以补充红外图像的有限对比度,并用于数据增强。
- 融合集成模块用于整合两种不同模态,进一步提升分割效果。
点此查看论文截图
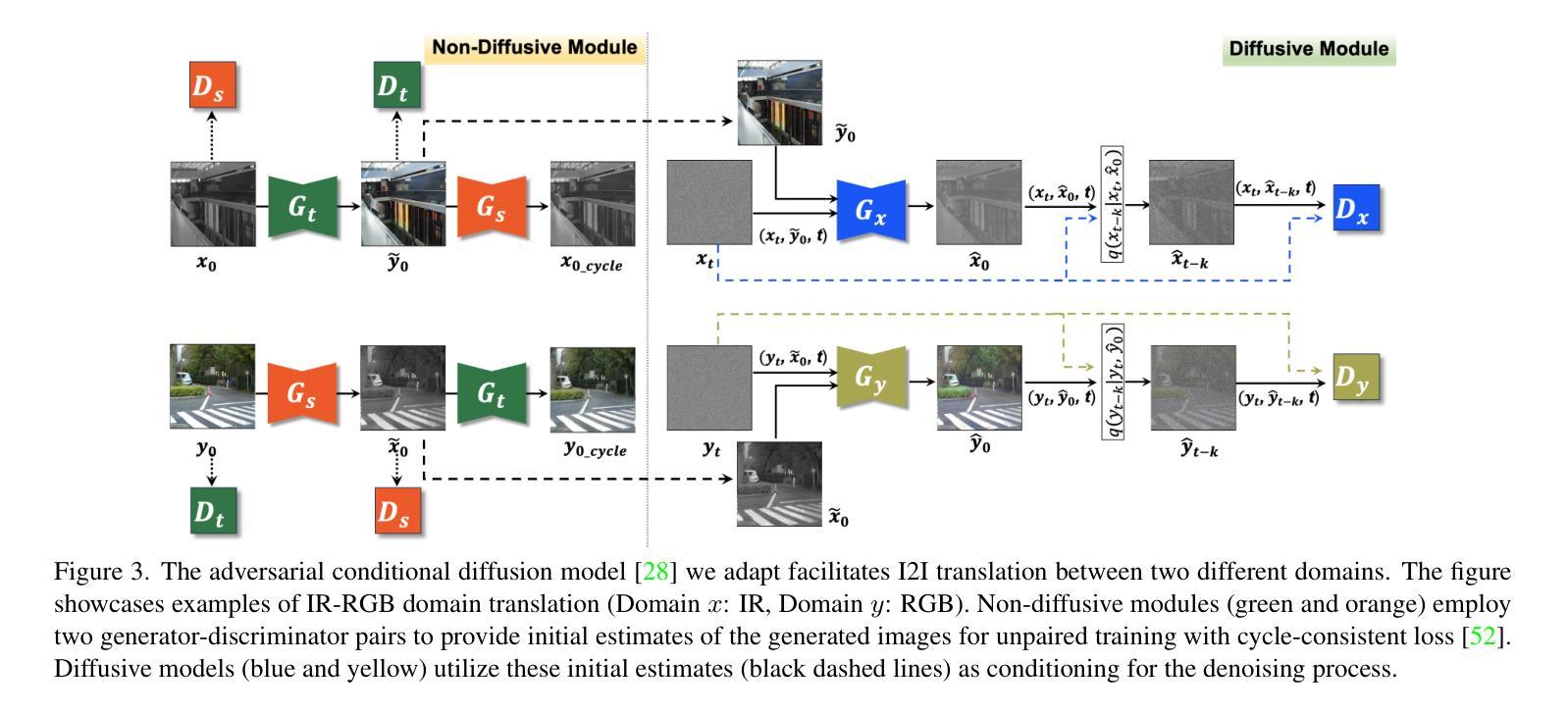
The Prompt Canvas: A Literature-Based Practitioner Guide for Creating Effective Prompts in Large Language Models
Authors:Michael Hewing, Vincent Leinhos
The rise of large language models (LLMs) has highlighted the importance of prompt engineering as a crucial technique for optimizing model outputs. While experimentation with various prompting methods, such as Few-shot, Chain-of-Thought, and role-based techniques, has yielded promising results, these advancements remain fragmented across academic papers, blog posts and anecdotal experimentation. The lack of a single, unified resource to consolidate the field’s knowledge impedes the progress of both research and practical application. This paper argues for the creation of an overarching framework that synthesizes existing methodologies into a cohesive overview for practitioners. Using a design-based research approach, we present the Prompt Canvas, a structured framework resulting from an extensive literature review on prompt engineering that captures current knowledge and expertise. By combining the conceptual foundations and practical strategies identified in prompt engineering, the Prompt Canvas provides a practical approach for leveraging the potential of Large Language Models. It is primarily designed as a learning resource for pupils, students and employees, offering a structured introduction to prompt engineering. This work aims to contribute to the growing discourse on prompt engineering by establishing a unified methodology for researchers and providing guidance for practitioners.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)的兴起,提示工程作为优化模型输出的关键技术,其重要性日益凸显。虽然通过少样本、思维链和基于角色的技术等提示方法的实验已经取得了令人鼓舞的结果,但这些进展仍然分散在学术论文、博客文章和经验实验之中。缺乏一个统一整合该领域知识的单一资源,阻碍了研究和实际应用的发展。本文主张创建一个全面的框架,将现有方法进行综合概述,为从业者提供实用的指南。本研究采用基于设计的研究方法,提出了提示画布(Prompt Canvas),这是通过对提示工程进行广泛的文献综述而得出的结构化框架,能够捕捉当前的知识和专业知识。提示画布结合了提示工程中的概念基础和实用策略,为利用大型语言模型的潜力提供了一种实用方法。它主要为学习者、学生和雇员设计,提供了一个结构化介绍提示工程的资源。本工作的目标是通过对提示工程建立统一方法论,为研究人员提供指导,并为从业者做出贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)的兴起凸显了提示工程作为优化模型输出的重要技术。本文通过设计研究法提出Prompt Canvas框架,该框架通过广泛文献综述整合了现有的提示工程方法和策略,为从业者提供了一个系统的知识概览。其目的是为研究者建立统一的方法论,为从业者提供指导,并作为学习资源供学生和其他人员学习提示工程。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的兴起突出了提示工程在优化模型输出中的重要性。
- 目前存在多种提示方法,如Few-shot、Chain-of-Thought和基于角色的技术,已经产生了有前景的结果。
- 当前缺乏一个统一的资源来整合该领域的知识,这阻碍了研究和实际应用的发展。
- 本文提出了Prompt Canvas框架,这是一个基于文献综述的结构化框架,旨在整合现有的提示工程方法和策略。
- Prompt Canvas结合了概念基础和实用策略,为利用大型语言模型的潜力提供了实用方法。
- 该框架主要作为针对学员、学生和员工的学习资源,为他们提供结构化的提示工程介绍。
点此查看论文截图
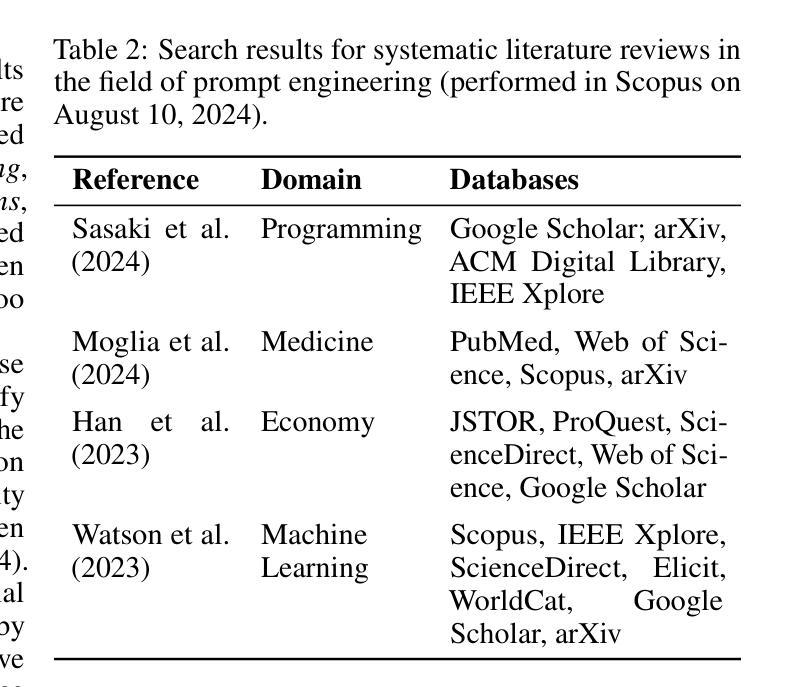
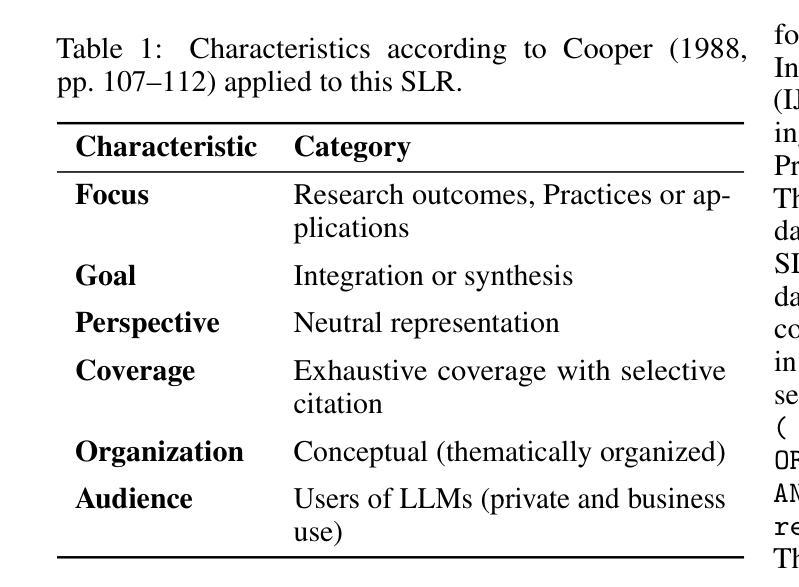
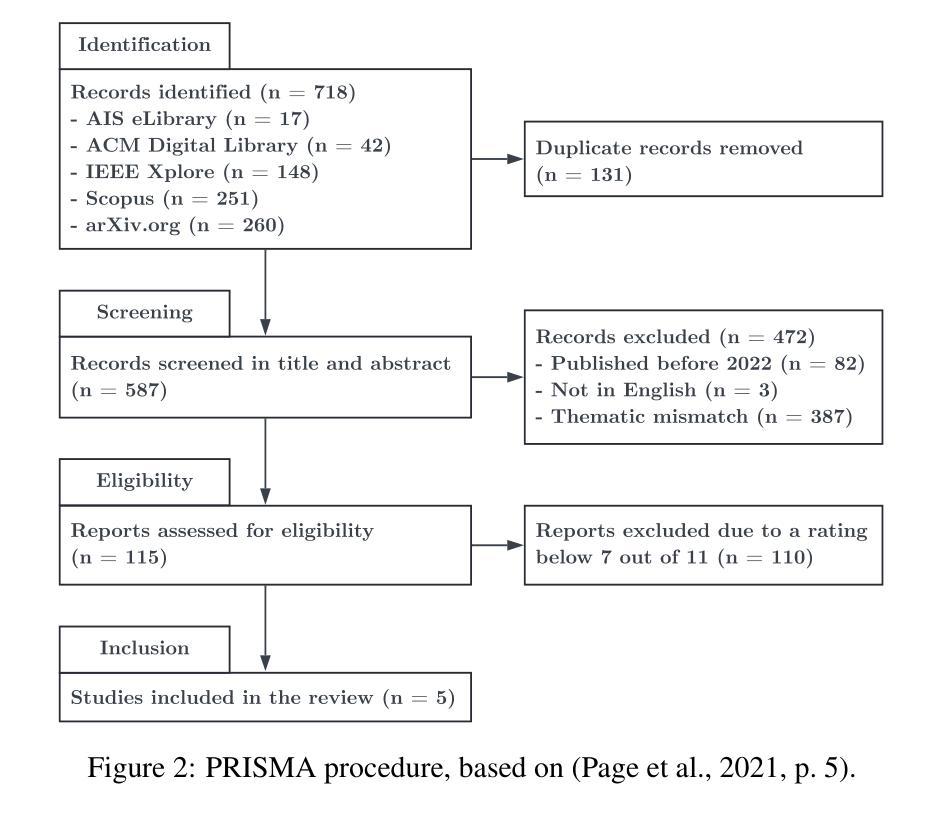

Steps are all you need: Rethinking STEM Education with Prompt Engineering
Authors:Krishnasai Addala, Kabir Dev Paul Baghel, Chhavi Kirtani, Avinash Anand, Rajiv Ratn Shah
Few shot and Chain-of-Thought prompting have shown promise when applied to Physics Question Answering Tasks, but are limited by the lack of mathematical ability inherent to LLMs, and are prone to hallucination. By utilizing a Mixture of Experts (MoE) Model, along with analogical prompting, we are able to show improved model performance when compared to the baseline on standard LLMs. We also survey the limits of these prompting techniques and the effects they have on model performance. Additionally, we propose Analogical CoT prompting, a prompting technique designed to allow smaller, open source models to leverage Analogical prompting, something they have struggled with, possibly due to a lack of specialist training data.
在物理问答任务中应用少量提示和思维链提示已显示出其潜力,但由于大型语言模型固有的数学能力缺失,这些技术仍受到一定限制,并且容易出现幻觉。通过利用混合专家模型(MoE)和类比提示,与基准的大型语言模型相比,我们能够在标准模型上展示改进后的模型性能。我们还调查了这些提示技术的局限性及其对模型性能的影响。此外,我们提出了类比思维链提示(Analogical CoT prompting)这一提示技术,旨在让较小的开源模型能够利用类比提示,这在很大程度上一直困扰着它们,可能是因为缺乏专业训练数据。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
少样本技术与链式思维提示对于物理问答任务有应用前景,但仍受限于大型语言模型内在的数学能力与易于产生幻觉的问题。利用混合专家模型与类比提示,可以改善模型在标准大型语言模型基线之上的表现。此外,我们还探讨了这些提示技术的局限性及其对模型性能的影响,并首次提出了类比思维链提示技术,旨在使小型开源模型也能利用类比提示,这之前由于缺少专业训练数据而受到阻碍。
Key Takeaways
- 少样本与链式思维提示在物理问答任务中有应用前景。
- 大型语言模型在数学能力上仍有局限,易产生幻觉。
- 混合专家模型与类比提示能改善模型表现。
- 提示技术存在局限性,对模型性能有影响。
- 首次提出类比思维链提示技术。
- 该技术使小型开源模型也能利用类比提示。
点此查看论文截图

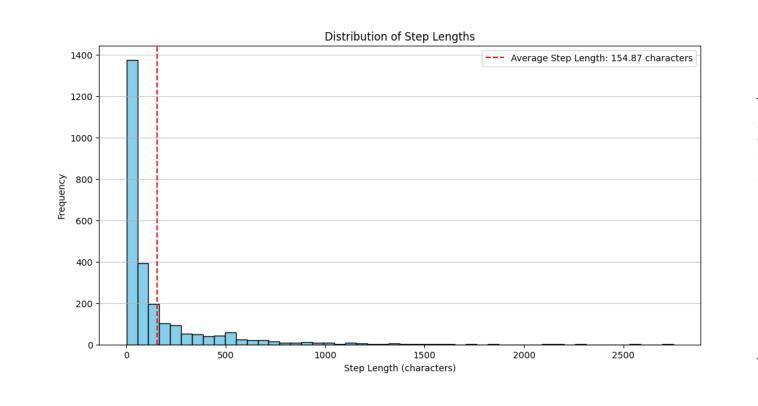
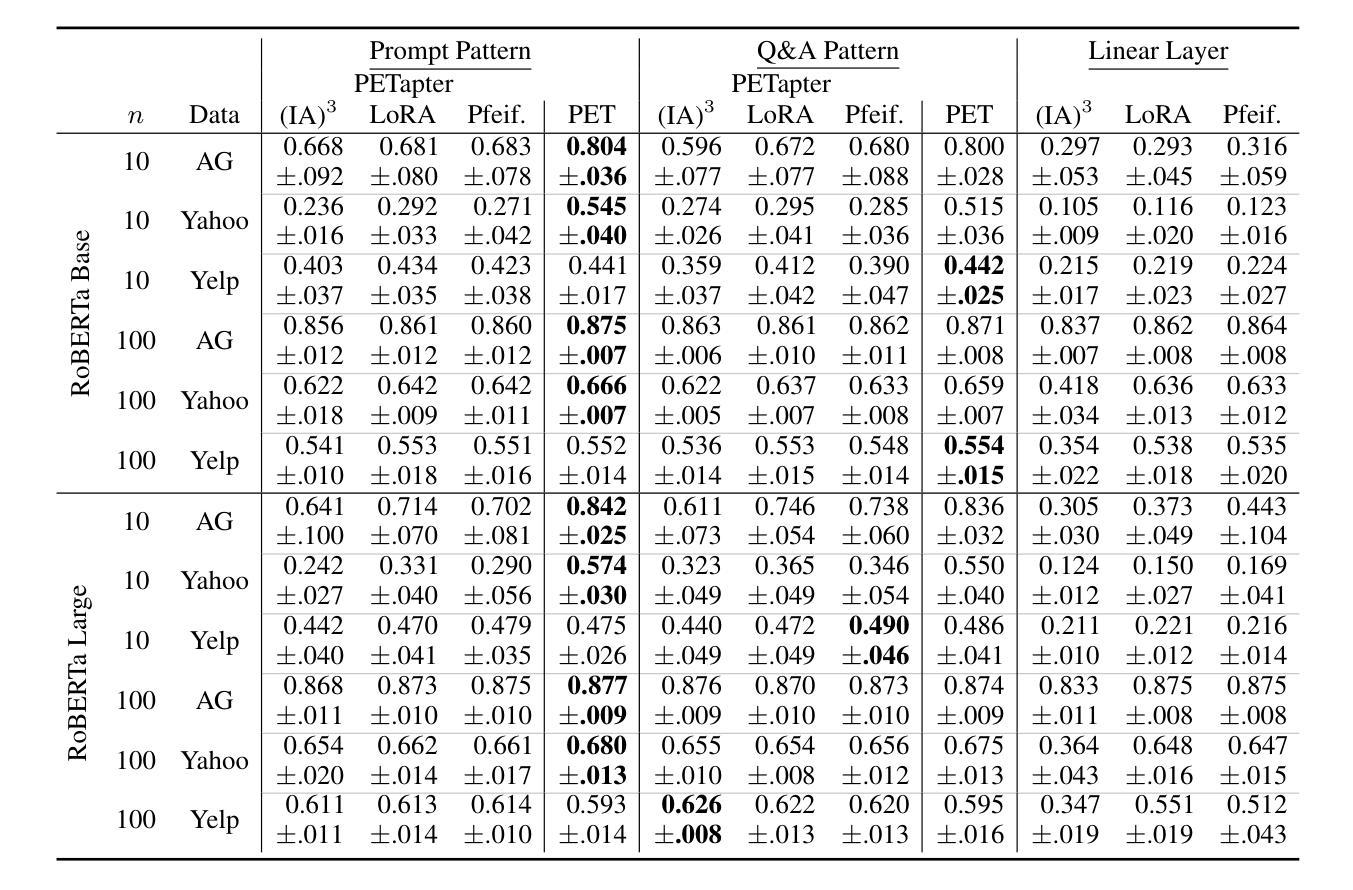
PETapter: Leveraging PET-style classification heads for modular few-shot parameter-efficient fine-tuning
Authors:Jonas Rieger, Mattes Ruckdeschel, Gregor Wiedemann
Few-shot learning and parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) are crucial to overcome the challenges of data scarcity and ever growing language model sizes. This applies in particular to specialized scientific domains, where researchers might lack expertise and resources to fine-tune high-performing language models to nuanced tasks. We propose PETapter, a novel method that effectively combines PEFT methods with PET-style classification heads to boost few-shot learning capabilities without the significant computational overhead typically associated with full model training. We validate our approach on three established NLP benchmark datasets and one real-world dataset from communication research. We show that PETapter not only achieves comparable performance to full few-shot fine-tuning using pattern-exploiting training (PET), but also provides greater reliability and higher parameter efficiency while enabling higher modularity and easy sharing of the trained modules, which enables more researchers to utilize high-performing NLP-methods in their research.
少量学习(few-shot learning)和参数高效微调(PEFT)对于克服数据稀缺和不断增长的语言模型规模所带来的挑战至关重要。这在特定的科学领域尤其适用,在这些领域中,研究人员可能缺乏专业知识和资源来微调高性能语言模型以执行微妙的任务。我们提出了一种新的方法PETapter,它有效地结合了PEFT方法与PET风格的分类头,可以在不引入与全模型训练相关的重大计算开销的情况下,提升少量学习的能力。我们在三个成熟的NLP基准数据集和一个通信研究领域的真实世界数据集上验证了我们的方法。我们证明了PETapter不仅实现了与利用模式训练(PET)进行的全少量精细调整相当的性能,而且提供了更高的可靠性和参数效率,同时增强了模块的更高可重用性和易共享性,从而使得更多的研究人员能够在其研究中利用高性能的NLP方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了PEFT(参数高效微调)与few-shot学习相结合的新方法——PETapter。该方法适用于专业科学领域,解决数据稀缺和不断增长的语言模型规模带来的挑战。PETapter结合了PEFT方法和PET风格分类头,提高了少样本学习能力,同时降低了全模型训练的巨大计算开销。在多个NLP基准数据集和通信研究领域的真实数据集上验证了该方法的有效性。结果表明,PETapter不仅实现了与全少样本微调相近的性能,还提供了更高的可靠性和参数效率,同时实现了更高的模块化和易于分享的已训练模块,使得更多研究者能够在其研究中利用高性能的NLP方法。
Key Takeaways
- PETapter结合了参数高效微调(PEFT)和few-shot学习,旨在解决数据稀缺和大型语言模型微调挑战。
- 方法特别适用于专业科学领域,其中研究者可能缺乏专业知识和资源来微调高性能语言模型以执行细微任务。
- PETapter通过使用PEFT方法和PET风格分类头,在提高少样本学习能力的同时,降低了通常与全模型训练相关的巨大计算开销。
- 在多个NLP基准数据集和通信研究领域的真实数据集上验证了PETapter的有效性。
- PETapter实现了与全少样本微调相近的性能。
- PETapter提供了更高的可靠性和参数效率。
点此查看论文截图

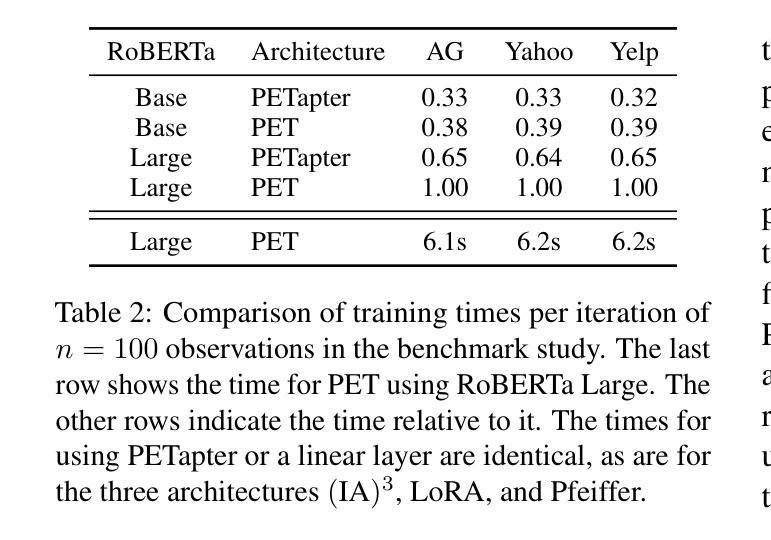
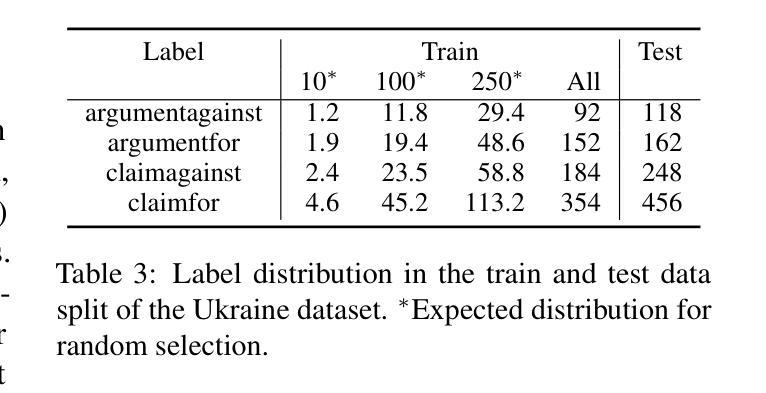
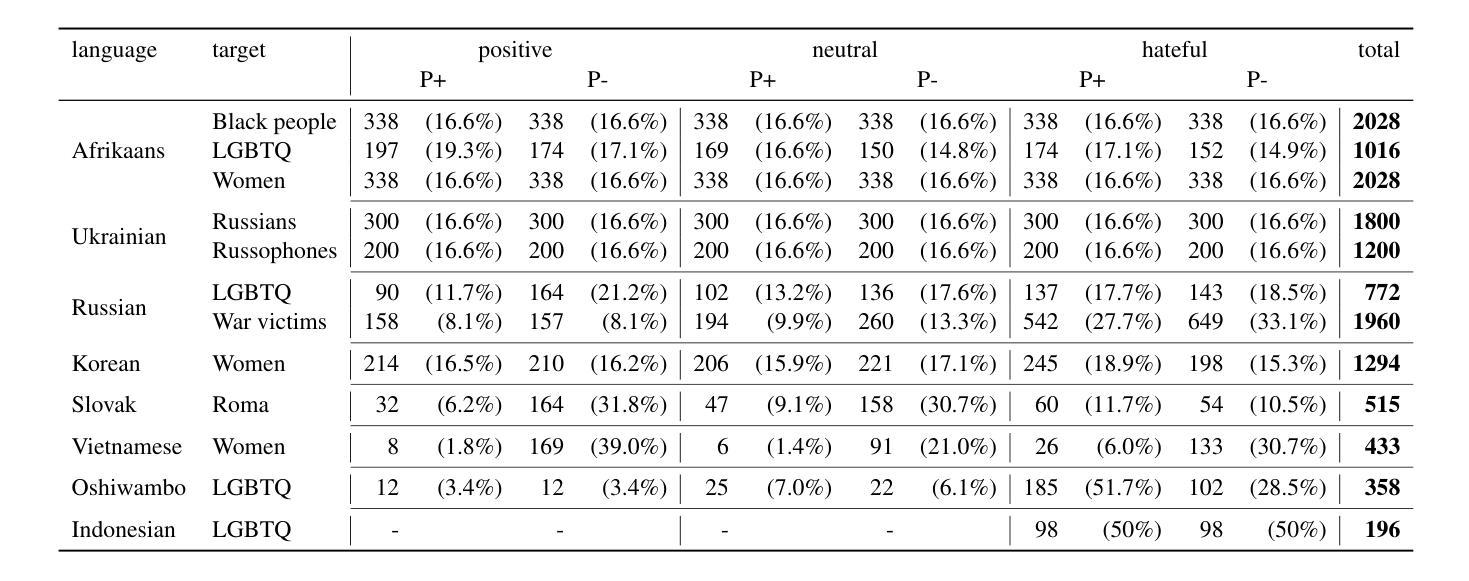
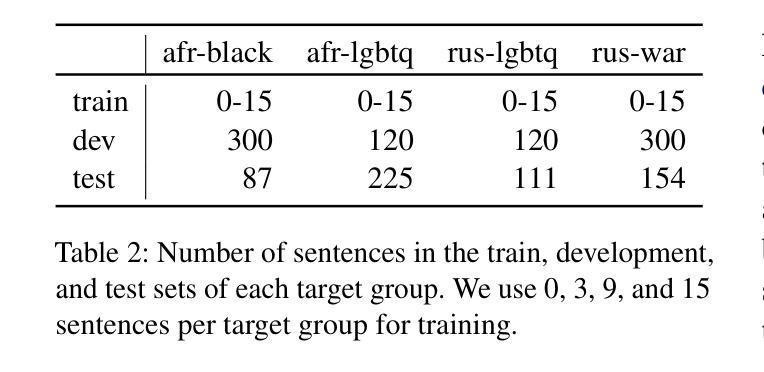
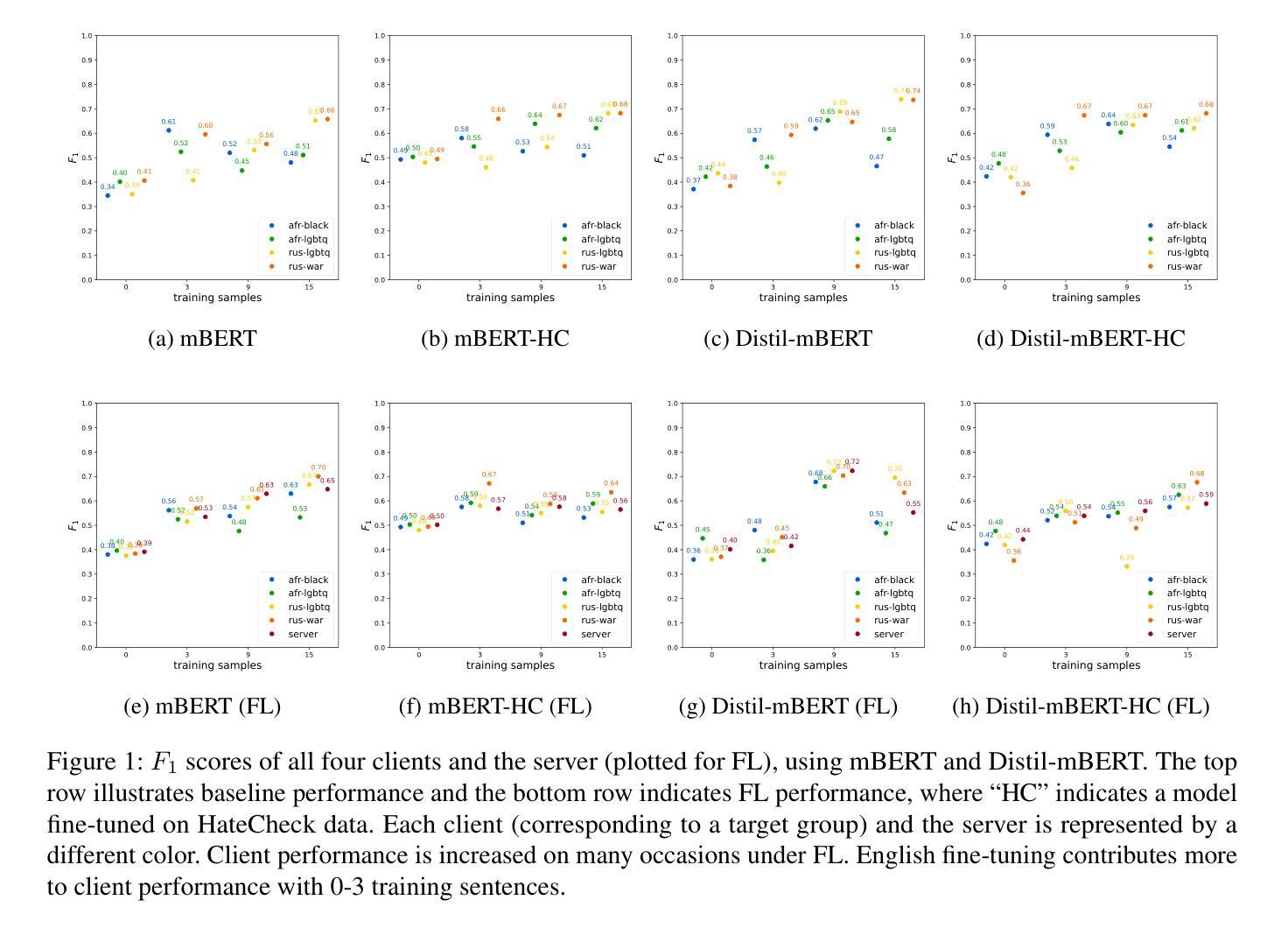
A Federated Approach to Few-Shot Hate Speech Detection for Marginalized Communities
Authors:Haotian Ye, Axel Wisiorek, Antonis Maronikolakis, Özge Alaçam, Hinrich Schütze
Hate speech online remains an understudied issue for marginalized communities, and has seen rising relevance, especially in the Global South, which includes developing societies with increasing internet penetration. In this paper, we aim to provide marginalized communities living in societies where the dominant language is low-resource with a privacy-preserving tool to protect themselves from hate speech on the internet by filtering offensive content in their native languages. Our contribution in this paper is twofold: 1) we release REACT (REsponsive hate speech datasets Across ConTexts), a collection of high-quality, culture-specific hate speech detection datasets comprising seven distinct target groups in eight low-resource languages, curated by experienced data collectors; 2) we propose a solution to few-shot hate speech detection utilizing federated learning (FL), a privacy-preserving and collaborative learning approach, to continuously improve a central model that exhibits robustness when tackling different target groups and languages. By keeping the training local to the users’ devices, we ensure the privacy of the users’ data while benefitting from the efficiency of federated learning. Furthermore, we personalize client models to target-specific training data and evaluate their performance. Our results indicate the effectiveness of FL across different target groups, whereas the benefits of personalization on few-shot learning are not clear.
网络上的仇恨言论仍然是一个针对边缘化群体的问题,并且其重要性日益增加,特别是在全球南方,包括互联网普及率不断增加的发展中国家。在本文中,我们的目标是向生活在主导语言为资源稀缺的社会的边缘化群体提供一个保护隐私的工具,以过滤其母语中的冒犯内容,从而保护他们免受网络上的仇恨言论的伤害。本文我们的贡献有两方面:首先,我们发布了REACT(跨语境响应仇恨言论数据集),这是一组高质量、具有文化特异性的仇恨言论检测数据集,包含七个不同的目标群体和八种资源稀缺的语言,由经验丰富的数据收集者编制;其次,我们提出了一种利用联邦学习(FL)解决小样本仇恨言论检测问题的解决方案。联邦学习是一种保护隐私的协作学习方法,能够不断改进中心模型,在处理不同目标群体和语言时表现出稳健性。通过将训练保持在用户设备上,我们确保了用户数据的隐私性,同时享受了联邦学习的效率优势。此外,我们对客户模型进行了针对特定目标数据的训练,并评估了它们的性能。我们的结果表明,联邦学习在不同目标群体中的有效性,而个性化在小样本学习上的优势尚不清楚。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文旨在为低资源语言环境中的边缘化社区提供一种保护个人隐私的工具,对抗网络上仇恨言论的威胁。研究发布了REACT数据集,包括七个目标群体和八种低资源语言的仇恨言论检测数据集。此外,提出了利用联邦学习解决少数样本仇恨言论检测问题的方法,这种方法在保护用户隐私的同时,提高了模型的鲁棒性,能够适应不同的目标群体和语言。虽然个性化训练在少数样本学习上的优势尚不明显,但研究结果表明联邦学习在不同目标群体中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 仇恨言论在线对边缘化社区的影响日益严重,特别是在全球南方国家。
- 研究发布了REACT数据集,包含七个目标群体和八种低资源语言的仇恨言论检测数据集。
- 联邦学习被用来解决少数样本仇恨言论检测问题,这是一种保护用户隐私的协作学习方式。
- 联邦学习模型展现出对不同目标群体和语言的鲁棒性。
- 用户数据训练保持本地化,确保用户隐私。
- 尝试个性化客户端模型以针对特定目标数据进行训练,但个性化在少数样本学习上的优势尚不明显。
点此查看论文截图

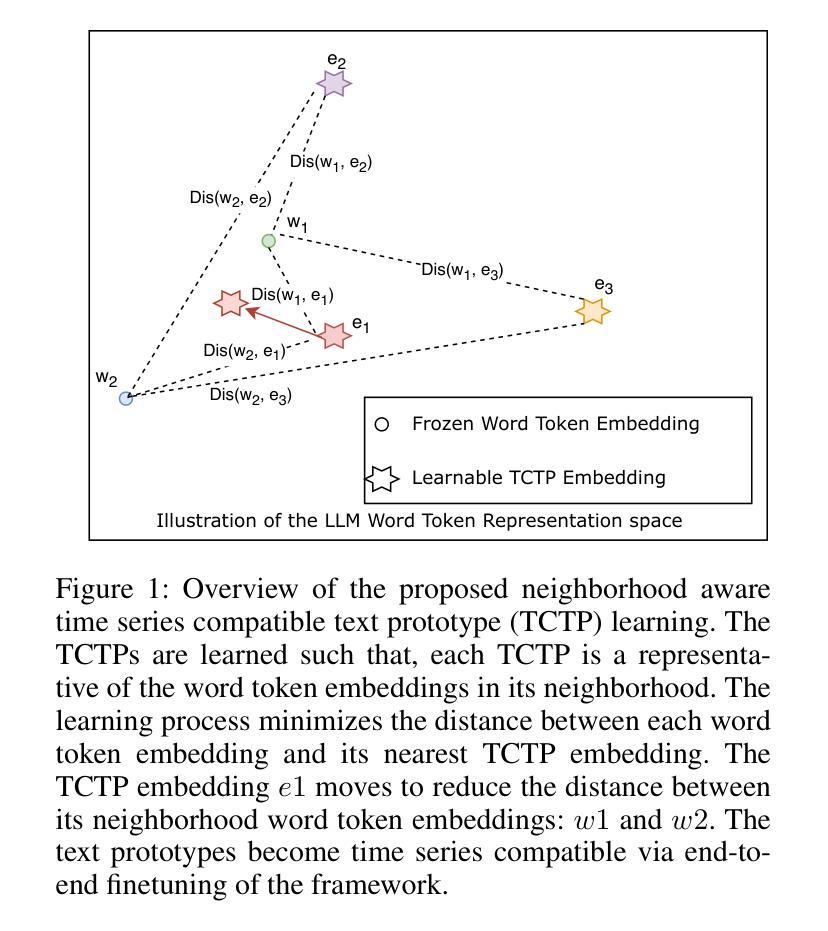
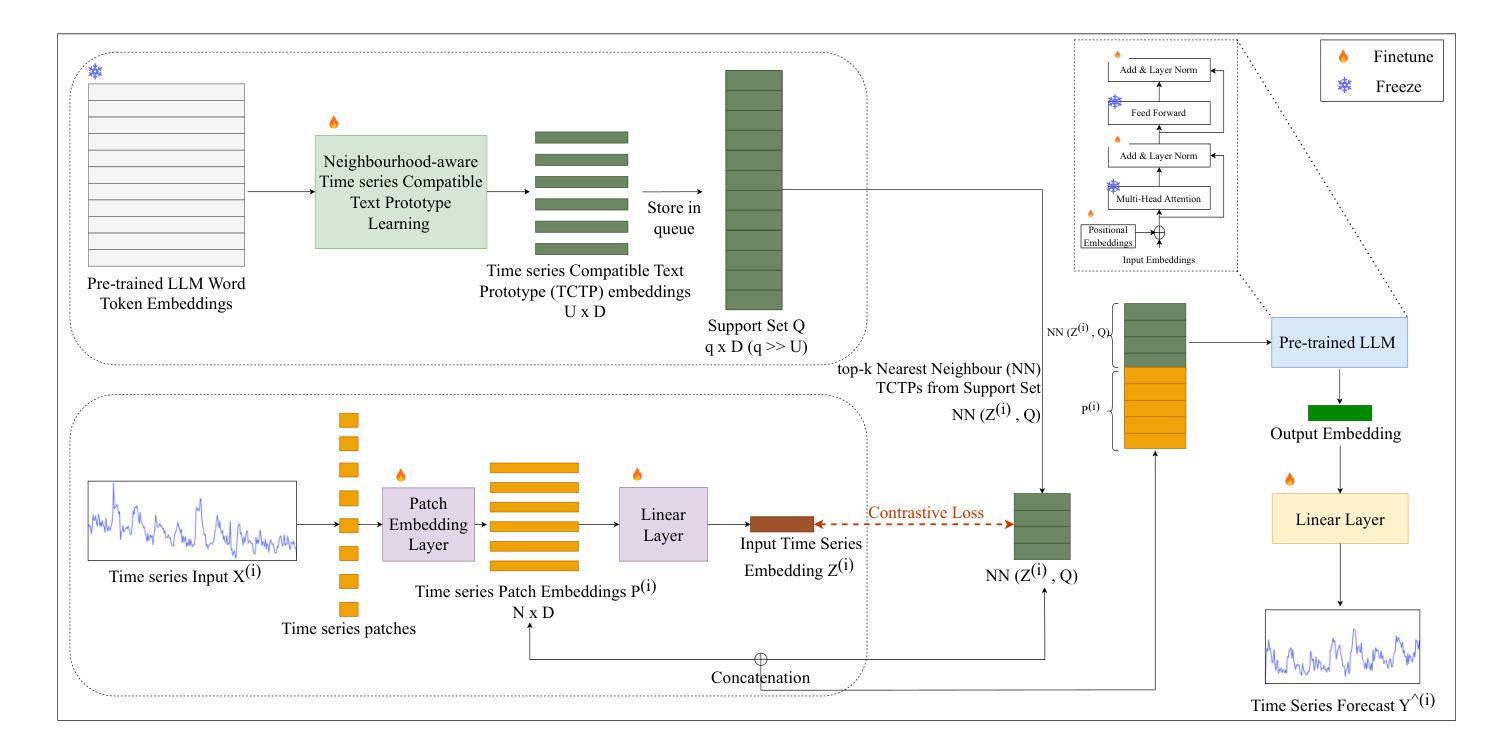
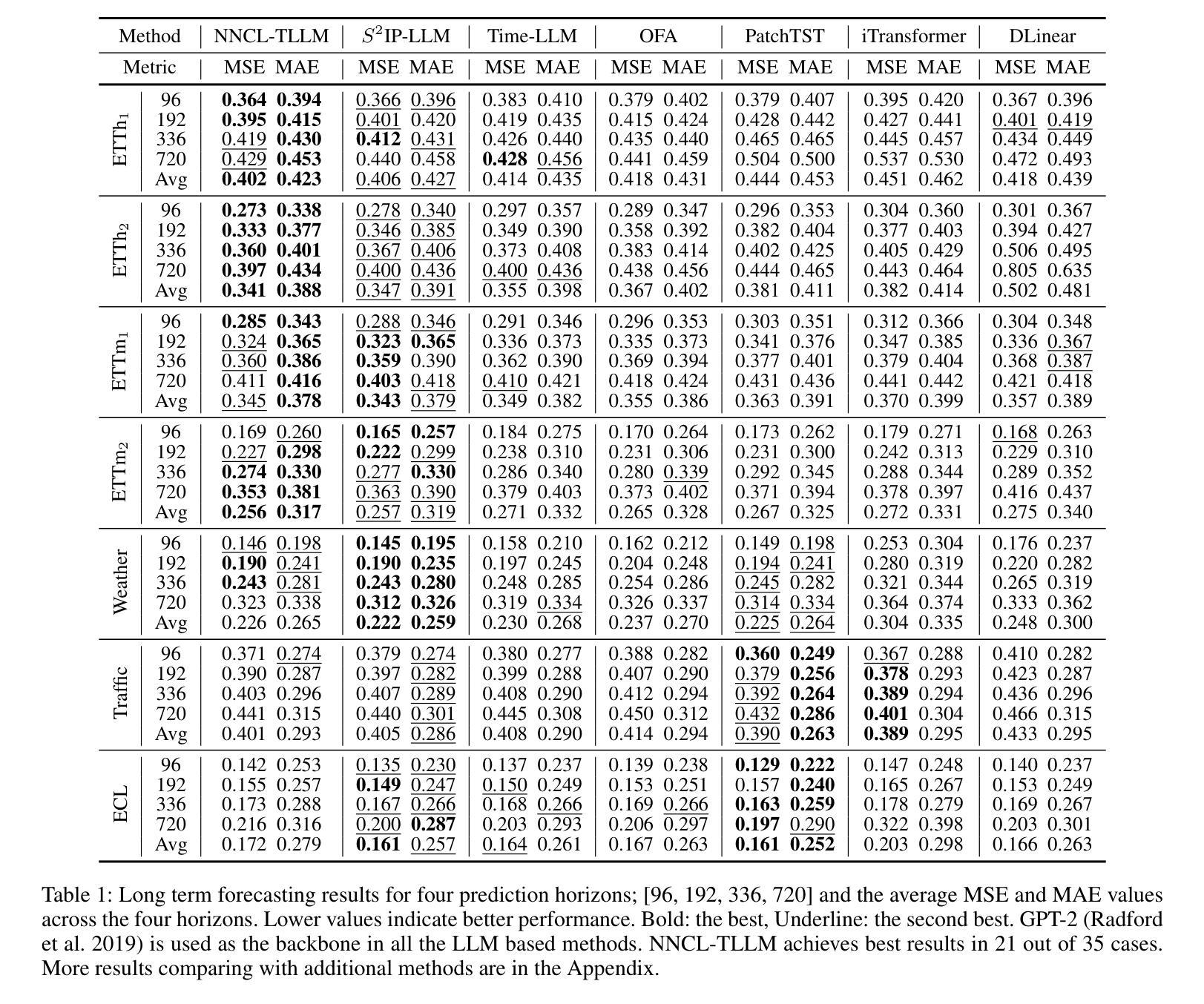
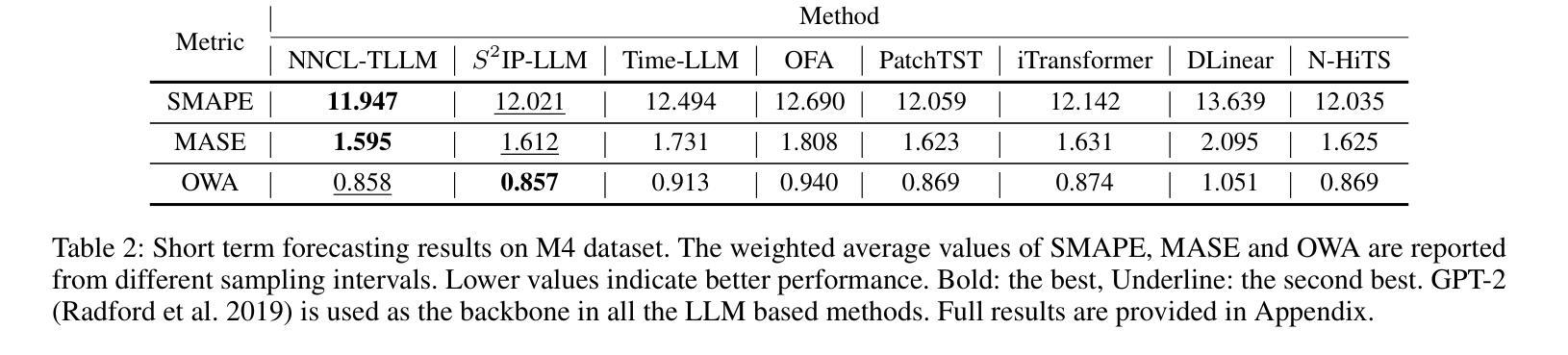
Rethinking Time Series Forecasting with LLMs via Nearest Neighbor Contrastive Learning
Authors:Jayanie Bogahawatte, Sachith Seneviratne, Maneesha Perera, Saman Halgamuge
Adapting Large Language Models (LLMs) that are extensively trained on abundant text data, and customizing the input prompt to enable time series forecasting has received considerable attention. While recent work has shown great potential for adapting the learned prior of LLMs, the formulation of the prompt to finetune LLMs remains challenging as prompt should be aligned with time series data. Additionally, current approaches do not effectively leverage word token embeddings which embody the rich representation space learned by LLMs. This emphasizes the need for a robust approach to formulate the prompt which utilizes the word token embeddings while effectively representing the characteristics of the time series. To address these challenges, we propose NNCL-TLLM: Nearest Neighbor Contrastive Learning for Time series forecasting via LLMs. First, we generate time series compatible text prototypes such that each text prototype represents both word token embeddings in its neighborhood and time series characteristics via end-to-end finetuning. Next, we draw inspiration from Nearest Neighbor Contrastive Learning to formulate the prompt while obtaining the top-$k$ nearest neighbor time series compatible text prototypes. We then fine-tune the layer normalization and positional embeddings of the LLM, keeping the other layers intact, reducing the trainable parameters and decreasing the computational cost. Our comprehensive experiments demonstrate that NNCL-TLLM outperforms in few-shot forecasting while achieving competitive or superior performance over the state-of-the-art methods in long-term and short-term forecasting tasks.
适应在大量文本数据上经过广泛训练的大型语言模型(LLM),并通过定制输入提示来实现时间序列预测已经引起了相当大的关注。虽然最近的工作显示适应LLM的先验知识具有巨大潜力,但调整LLM的提示的公式仍然具有挑战性,因为提示应该与时间序列数据对齐。此外,当前的方法并没有有效利用LLM所学习到的丰富的单词标记嵌入空间。这强调了需要一种稳健的方法来制定提示,该方法利用单词标记嵌入同时有效地表示时间序列的特征。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了NNCL-TLLM:基于LLM的时间序列预测最近邻对比学习。首先,我们生成与时间序列兼容的文本原型,使每个文本原型都能代表其邻域中的单词标记嵌入和通过端到端微调体现时间序列的特征。接下来,我们从最近邻对比学习中汲取灵感,制定提示并获取前k个最接近的时间序列兼容文本原型。然后我们对LLM的层归一化和位置嵌入进行微调,保持其他层不变,从而减少可训练参数和计算成本。我们的综合实验表明,NNCL-TLLM在少样本预测方面表现出卓越性能,同时在长期和短期预测任务中实现了与最新技术竞争或更优越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的时间序列预测技术受到广泛关注。尽管LLM的先验知识适应展现出巨大潜力,但调整提示以与时间序列数据对齐仍然具有挑战性。本文提出NNCL-TLLM方法,通过最近邻对比学习,生成与时间序列兼容的文本原型,并利用LLM进行时间序列预测。实验表明,NNCL-TLLM在少样本预测中表现优异,并在长期和短期预测任务中达到或超过现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在时间序列预测中展现出巨大潜力。
- 调整提示以与时间序列数据对齐是当前的挑战之一。
- NNCL-TLLM方法通过生成与时间序列兼容的文本原型来解决这一挑战。
- NNCL-TLLM利用最近邻对比学习技术,结合LLM进行时间序列预测。
- NNCL-TLLM在少样本预测中表现优异。
- NNCL-TLLM在长期和短期预测任务中达到或超过现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

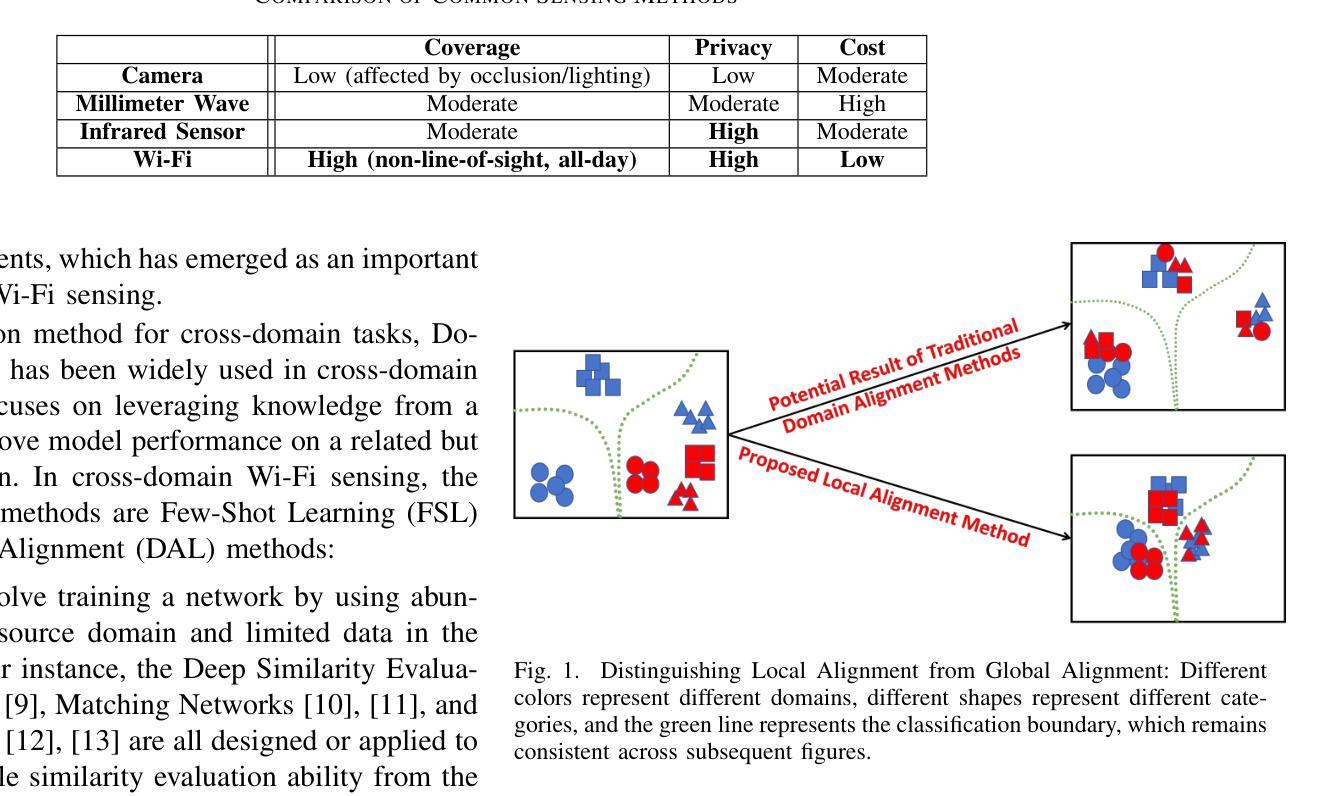
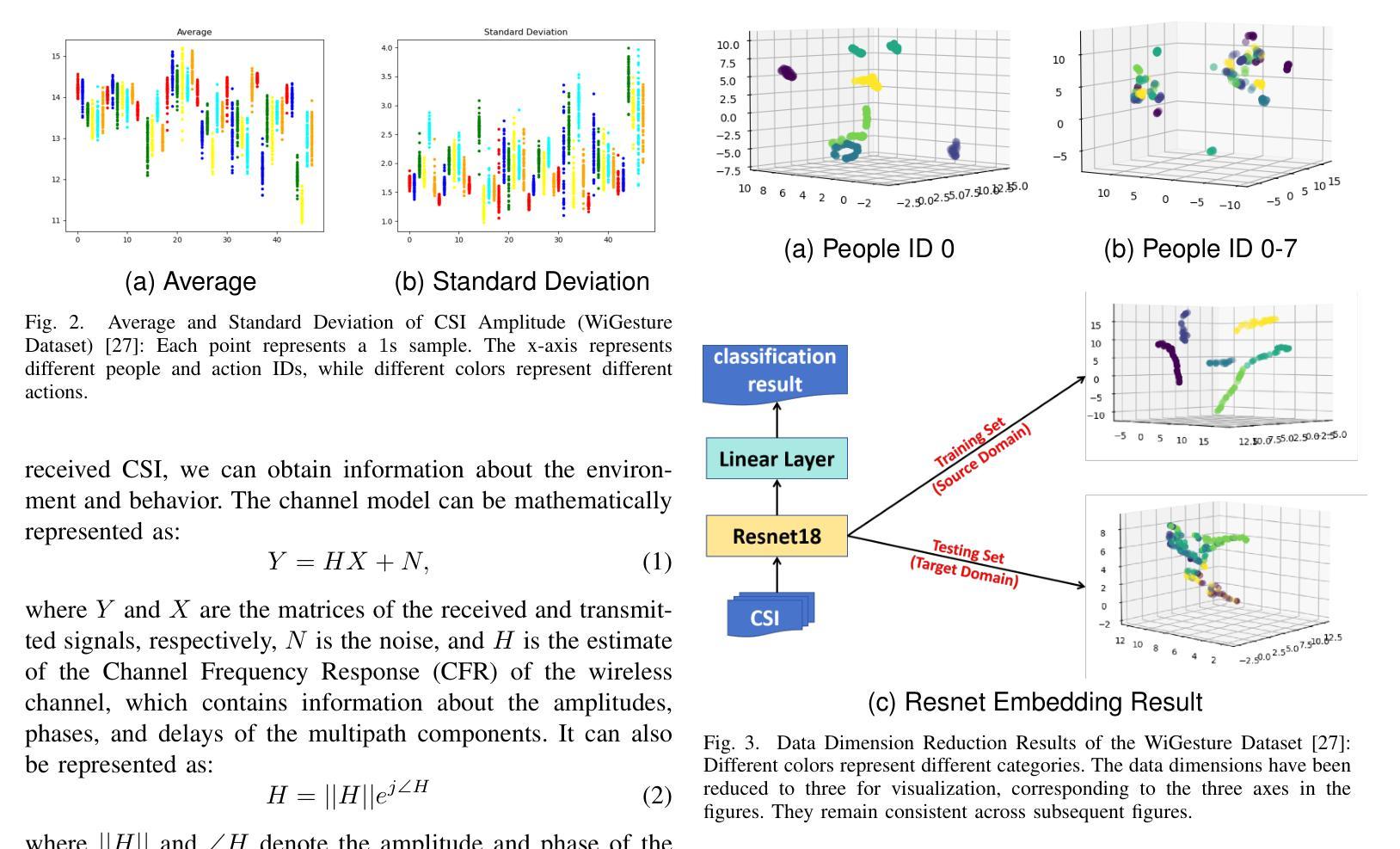
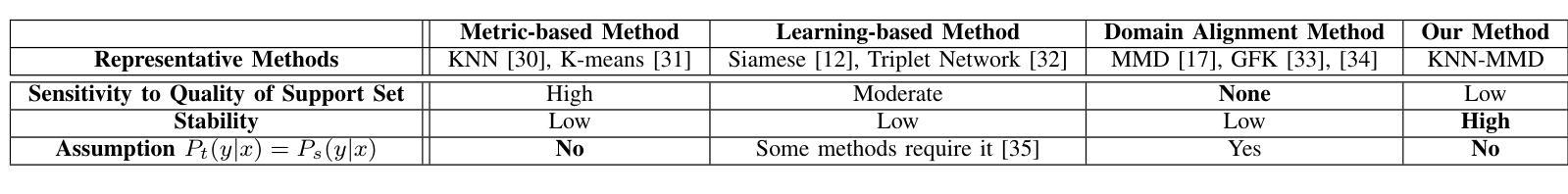
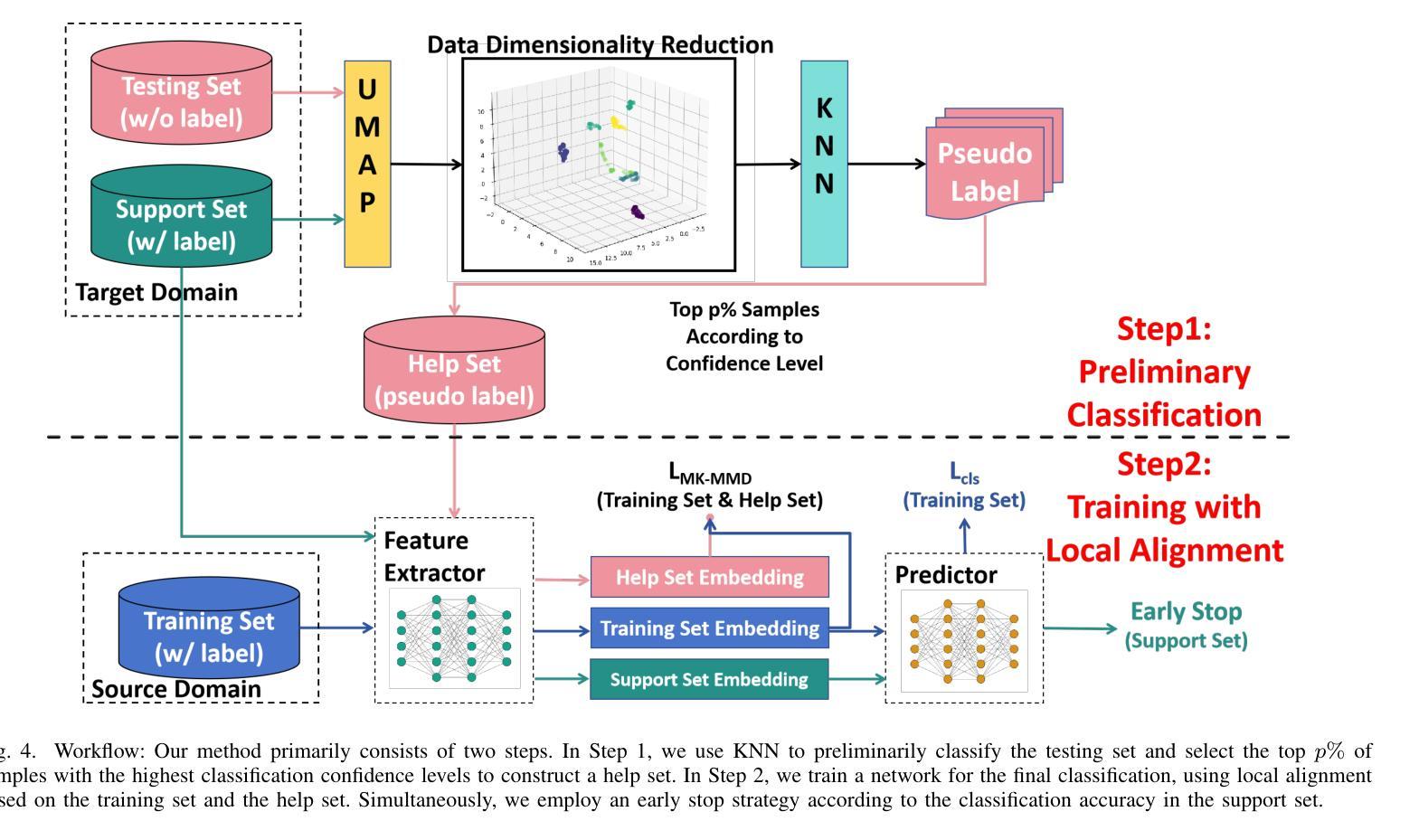
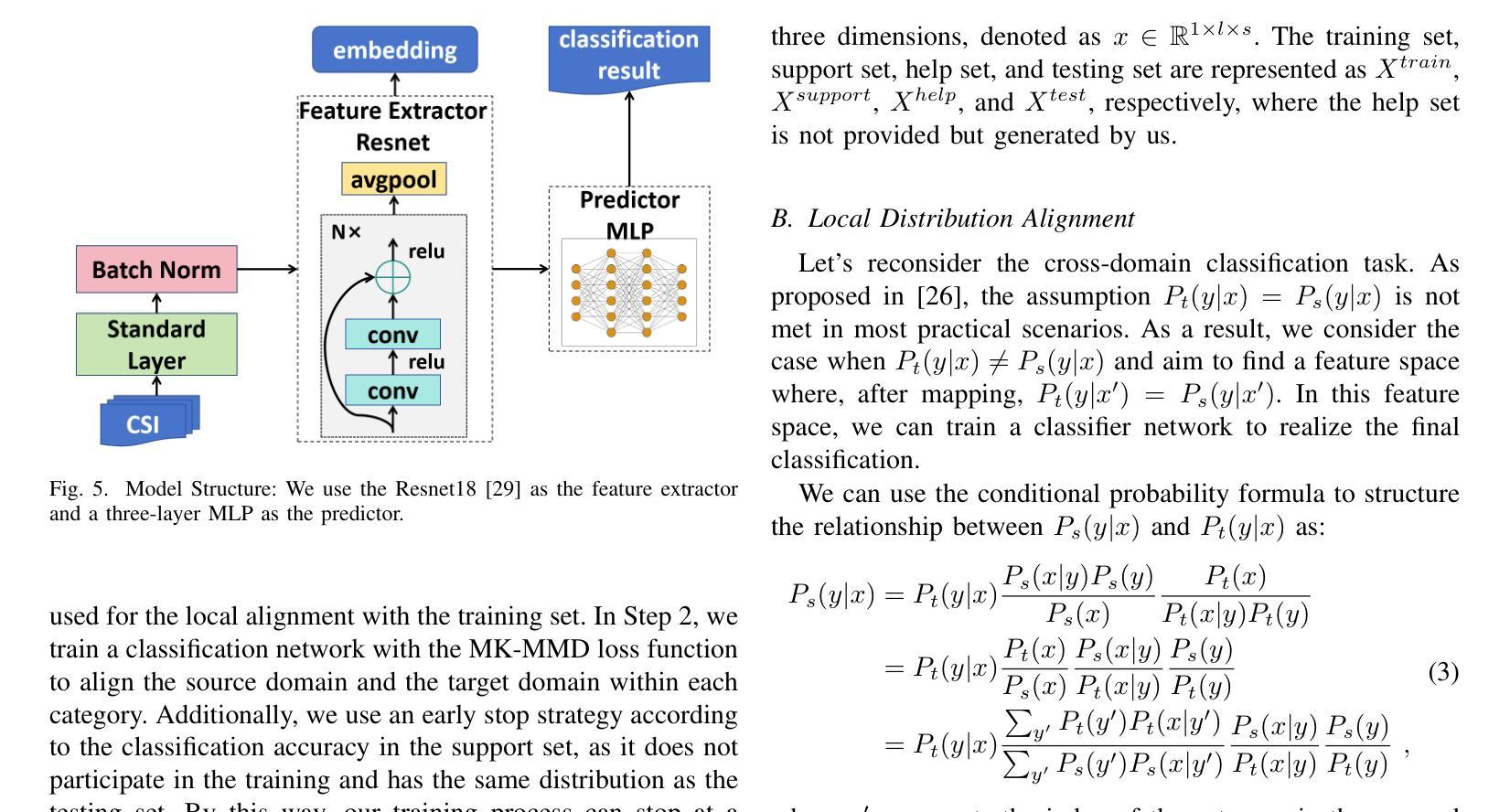
KNN-MMD: Cross Domain Wi-Fi Sensing Based on Local Distribution Alignment
Authors:Zijian Zhao, Zhijie Cai, Tingwei Chen, Xiaoyang Li, Hang Li, Guangxu Zhu
As a key technology in Integrated Sensing and Communications (ISAC), Wi-Fi sensing has gained widespread application in various settings such as homes, offices, and public spaces. By analyzing the patterns of Channel State Information (CSI), we can obtain information about people’s actions for tasks like person identification, gesture recognition, and fall detection. However, the CSI is heavily influenced by the environment, such that even minor environmental changes can significantly alter the CSI patterns. This will cause the performance deterioration and even failure when applying the Wi-Fi sensing model trained in one environment to another. To address this problem, we introduce a K-Nearest Neighbors Maximum Mean Discrepancy (KNN-MMD) model, a few-shot method for cross-domain Wi-Fi sensing. We propose a local distribution alignment method within each category, which outperforms traditional Domain Adaptation (DA) methods based on global alignment. Besides, our method can determine when to stop training, which cannot be realized by most DA methods. As a result, our method is more stable and can be better used in practice. The effectiveness of our method are evaluated in several cross-domain Wi-Fi sensing tasks, including gesture recognition, person identification, fall detection, and action recognition, using both a public dataset and a self-collected dataset. In one-shot scenario, our method achieves accuracy of 93.26%, 81.84%, 77.62%, and 75.30% in the four tasks respectively. To facilitate future research, we will make our code and dataset publicly available upon publication.
作为集成感知和通信(ISAC)的关键技术,Wi-Fi感知在家庭、办公室和公共场所等各种场景中得到了广泛应用。通过分析信道状态信息(CSI)的模式,我们可以获取人们的行为信息,用于人员识别、手势识别和跌倒检测等任务。然而,CSI受到环境的高度重视影响,即使微小的环境变化也可能显著改变CSI模式。这将导致将在一种环境中训练的Wi-Fi感知模型应用到另一种环境时性能下降甚至失败。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了基于K近邻最大均值差异(KNN-MMD)的模型,这是一种用于跨域Wi-Fi感知的少量样本方法。我们提出了一种基于局部分布对齐的方法,在各类内部进行对齐,这优于基于全局对齐的传统域自适应(DA)方法。此外,我们的方法可以决定何时停止训练,而大多数DA方法无法实现这一点。因此,我们的方法更加稳定,并能更好地用于实践。我们的方法在多个跨域Wi-Fi感知任务中的有效性得到了评估,包括手势识别、人员识别、跌倒检测和动作识别等任务,使用了公共数据集和自我收集的数据集。在单样本场景中,我们的方法在四项任务中的准确率分别达到93.26%、81.84%、77.62%和75.30%。为了便于未来的研究,我们会在发布论文的同时公开代码和数据集。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Wi-Fi感知作为关键技术在集成感知和通信(ISAC)领域的应用,通过解析信道状态信息(CSI)的模式,可以实现人物识别、动作识别等功能。然而,由于环境对CSI模式的影响较大,跨环境应用Wi-Fi感知模型会出现性能下降甚至失效的问题。针对这一问题,本文提出了基于K最近邻最大均值差异(KNN-MMD)模型的跨域Wi-Fi感知方法。该方法采用局部分布对齐策略,在各类别内部进行对齐,相较于传统的全局对齐方法表现更优。此外,该方法还能确定训练何时停止,这是大多数领域自适应方法无法实现的。实验结果表明,该方法在跨域Wi-Fi感知任务中的准确率较高。
Key Takeaways
- Wi-Fi感知技术通过分析信道状态信息(CSI)的模式,可应用于人物识别、动作识别等任务。
- 环境因素对CSI模式影响显著,导致Wi-Fi感知模型跨环境应用时性能下降。
- 引入KNN-MMD模型作为跨域Wi-Fi感知的解决策略。
- KNN-MMD模型采用局部分布对齐策略,表现优于传统全局对齐方法。
- KNN-MMD模型能自动确定训练何时停止,这是大多数领域自适应方法无法实现的。
- 在多个跨域Wi-Fi感知任务中,包括手势识别、人物识别等,KNN-MMD模型表现出较高的准确率。
点此查看论文截图

Improving LLM Group Fairness on Tabular Data via In-Context Learning
Authors:Valeriia Cherepanova, Chia-Jung Lee, Nil-Jana Akpinar, Riccardo Fogliato, Martin Andres Bertran, Michael Kearns, James Zou
Large language models (LLMs) have been shown to be effective on tabular prediction tasks in the low-data regime, leveraging their internal knowledge and ability to learn from instructions and examples. However, LLMs can fail to generate predictions that satisfy group fairness, that is, produce equitable outcomes across groups. Critically, conventional debiasing approaches for natural language tasks do not directly translate to mitigating group unfairness in tabular settings. In this work, we systematically investigate four empirical approaches to improve group fairness of LLM predictions on tabular datasets, including fair prompt optimization, soft prompt tuning, strategic selection of few-shot examples, and self-refining predictions via chain-of-thought reasoning. Through experiments on four tabular datasets using both open-source and proprietary LLMs, we show the effectiveness of these methods in enhancing demographic parity while maintaining high overall performance. Our analysis provides actionable insights for practitioners in selecting the most suitable approach based on their specific requirements and constraints.
大型语言模型(LLM)在低数据状态下已被证明在表格预测任务上非常有效,它们利用内部知识和从指令和示例中学习的能力。然而,LLM可能会生成不满足群体公平性的预测结果,即在群体间产生不公平的结果。重要的是,用于自然语言任务的传统去偏方法并不能直接转化为减轻表格设置中群体不公平的方法。在这项工作中,我们系统地研究了四种实证方法,以提高LLM在表格数据集上的预测结果的群体公平性,包括公平提示优化、软提示调整、少数案例的战略选择以及通过链式思维推理进行预测的自我修正。我们在四个表格数据集上进行了实验,采用了开源和专用的LLM模型,实验结果表明这些方法在提高人口统计学平衡性的同时保持了较高的整体性能。我们的分析可为从业者在选择最适合他们特定需求和约束的方法时提供实际的操作建议。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在低数据情况下对表格预测任务有效,但可能无法满足群体公平性。本文系统探讨了四种提高LLM在表格数据集上预测群体公平性的方法,包括公平提示优化、软提示调整、战略选择少量示例和通过思维链推理自我修正预测。实验表明,这些方法在提高人口统计学公平性的同时,保持了较高的整体性能。
Key Takeaways
- LLMs在表格预测任务中展现有效性,尤其在低数据情况下。
- LLMs可能无法满足群体公平性要求,在表格数据集中产生不公平的预测结果。
- 公平提示优化、软提示调整、战略选择少量示例和思维链推理是提高LLM群体公平性的四种实证方法。
- 这些方法在增强人口统计学公平性的同时,保持了较高的整体预测性能。
- 针对不同需求和约束,从业者可根据实际情况选择合适的方法。
- 本文的实验结果基于四个表格数据集和开源及专有LLMs。
点此查看论文截图

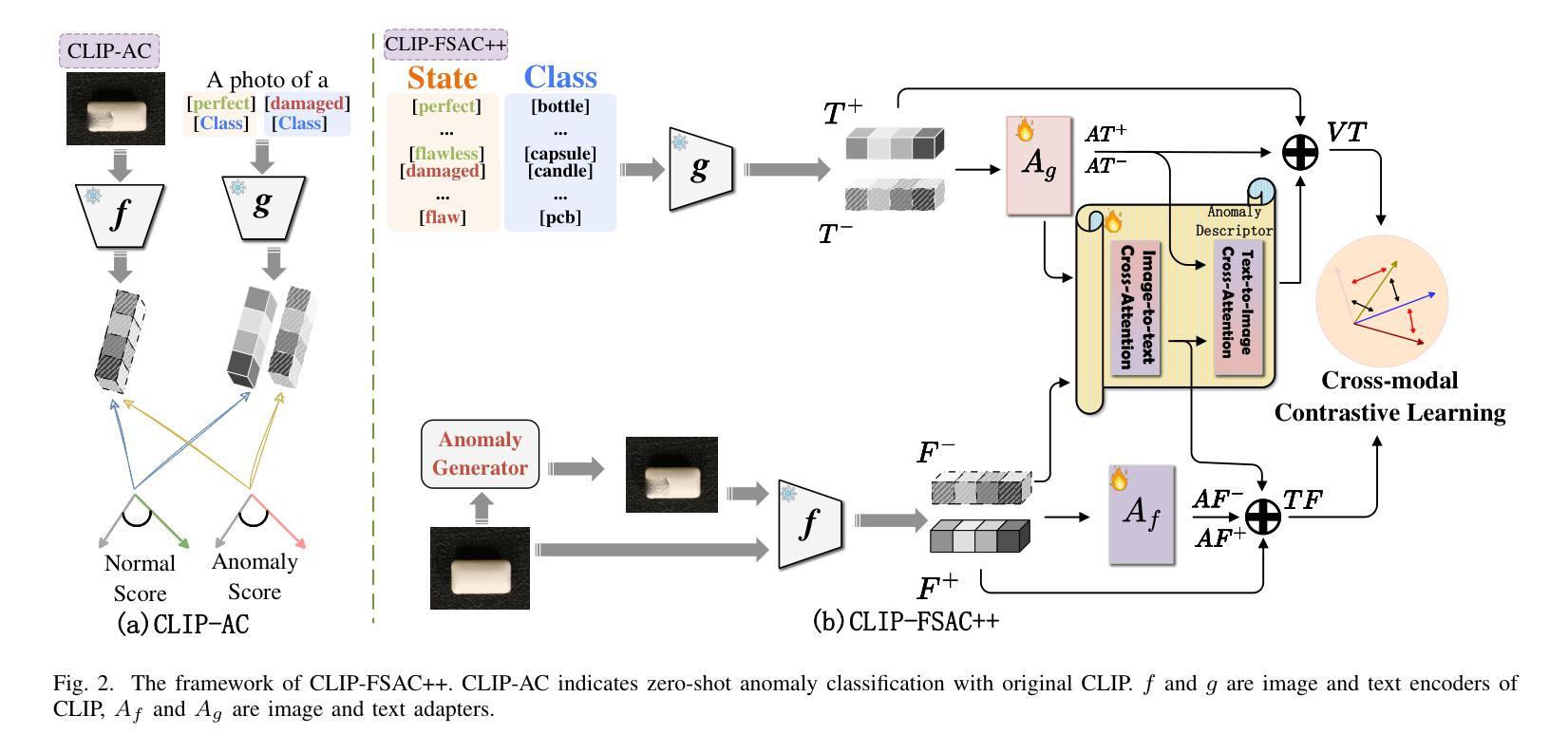
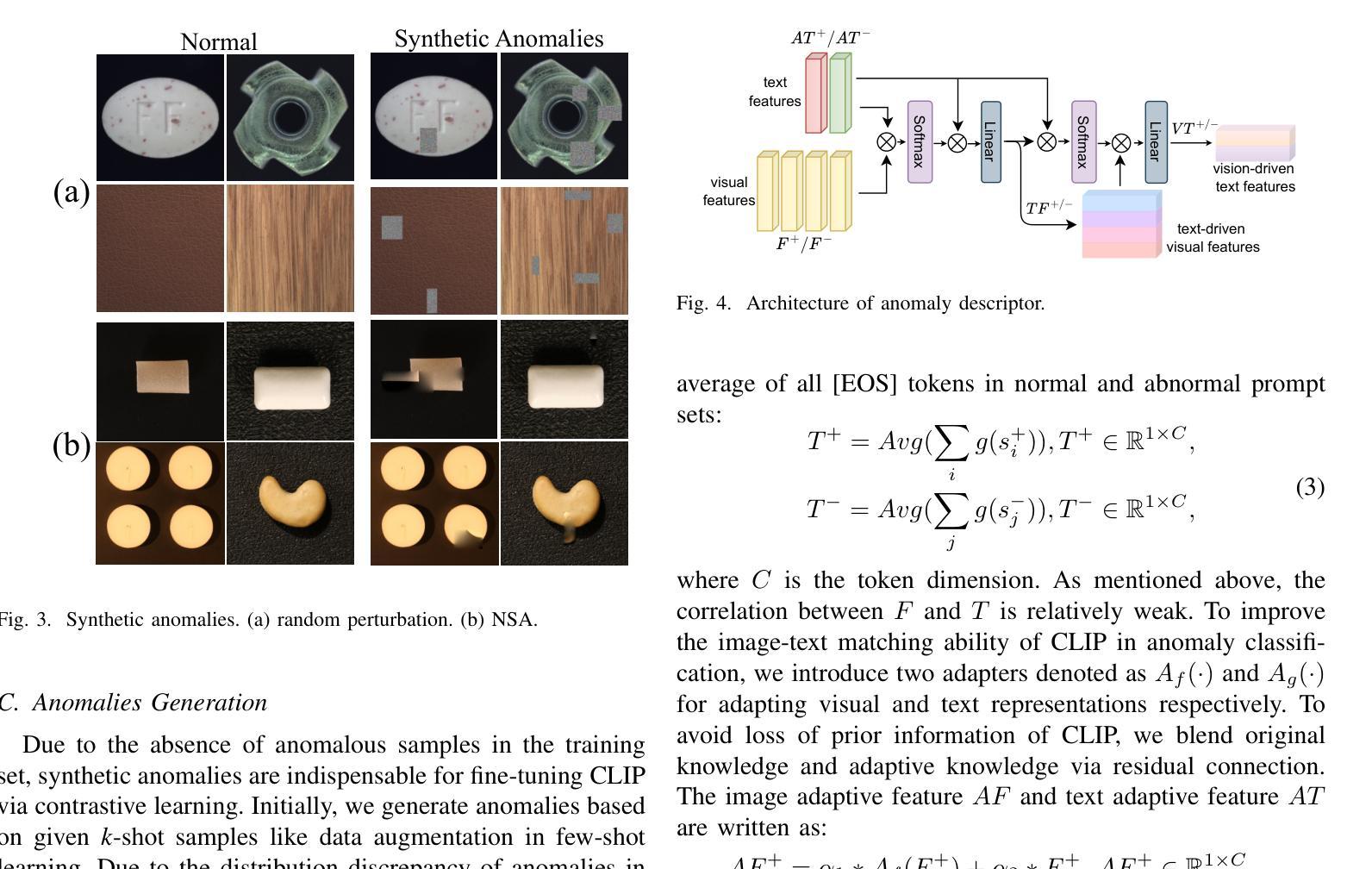
CLIP-FSAC++: Few-Shot Anomaly Classification with Anomaly Descriptor Based on CLIP
Authors:Zuo Zuo, Jiahao Dong, Yao Wu, Yanyun Qu, Zongze Wu
Industrial anomaly classification (AC) is an indispensable task in industrial manufacturing, which guarantees quality and safety of various product. To address the scarcity of data in industrial scenarios, lots of few-shot anomaly detection methods emerge recently. In this paper, we propose an effective few-shot anomaly classification (FSAC) framework with one-stage training, dubbed CLIP-FSAC++. Specifically, we introduce a cross-modality interaction module named Anomaly Descriptor following image and text encoders, which enhances the correlation of visual and text embeddings and adapts the representations of CLIP from pre-trained data to target data. In anomaly descriptor, image-to-text cross-attention module is used to obtain image-specific text embeddings and text-to-image cross-attention module is used to obtain text-specific visual embeddings. Then these modality-specific embeddings are used to enhance original representations of CLIP for better matching ability. Comprehensive experiment results are provided for evaluating our method in few-normal shot anomaly classification on VisA and MVTEC-AD for 1, 2, 4 and 8-shot settings. The source codes are at https://github.com/Jay-zzcoder/clip-fsac-pp
工业异常分类(AC)是工业制造中不可或缺的任务,它保证了各种产品的质量与安全。为了解决工业场景中数据稀缺的问题,最近出现了许多小样本异常检测方法。本文提出了一种有效的小样本异常分类(FSAC)框架,该框架采用一阶段训练,被称为CLIP-FSAC++。具体来说,我们在图像和文本编码器之后引入了一个名为Anomaly Descriptor的跨模态交互模块,该模块增强了视觉和文本嵌入的相关性,并将CLIP的预训练数据表示适应于目标数据。在异常描述符中,使用图像到文本的跨注意力模块来获得图像特定的文本嵌入,以及使用文本到图像的跨注意力模块来获得文本特定的视觉嵌入。然后,这些模态特定的嵌入被用来增强CLIP的原始表示,以提高匹配能力。我们提供了全面的实验结果,以评估我们在VisA和MVTEC-AD上进行的小样本正常异常分类方法,包括1、2、4和8种设置。源代码位于https://github.com/Jay-zzcoder/clip-fsac-pp。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF under review
Summary
这篇论文提出了一种有效的基于CLIP模型的一阶段训练少样本异常分类(FSAC)框架,名为CLIP-FSAC++。该框架引入了跨模态交互模块Anomaly Descriptor,通过图像和文本编码器增强视觉和文本嵌入的相关性,并将CLIP的预训练数据表示适应于目标数据。该框架通过图像到文本的跨注意力模块和文本到图像的跨注意力模块获取模态特定嵌入,以增强CLIP的原始表示,提高匹配能力。实验结果显示,该方法在少样本异常分类任务上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了一种基于CLIP模型的少样本异常分类(FSAC)框架。
- 框架中引入了Anomaly Descriptor这一跨模态交互模块。
- Anomaly Descriptor通过图像和文本编码器增强视觉和文本嵌入的相关性。
- 框架使用图像到文本的跨注意力模块和文本到图像的跨注意力模块获取模态特定嵌入。
- CLIP的预训练数据表示被适应于目标数据。
- 在VisA和MVTEC-AD数据集上进行了实验验证,表现优异。
点此查看论文截图
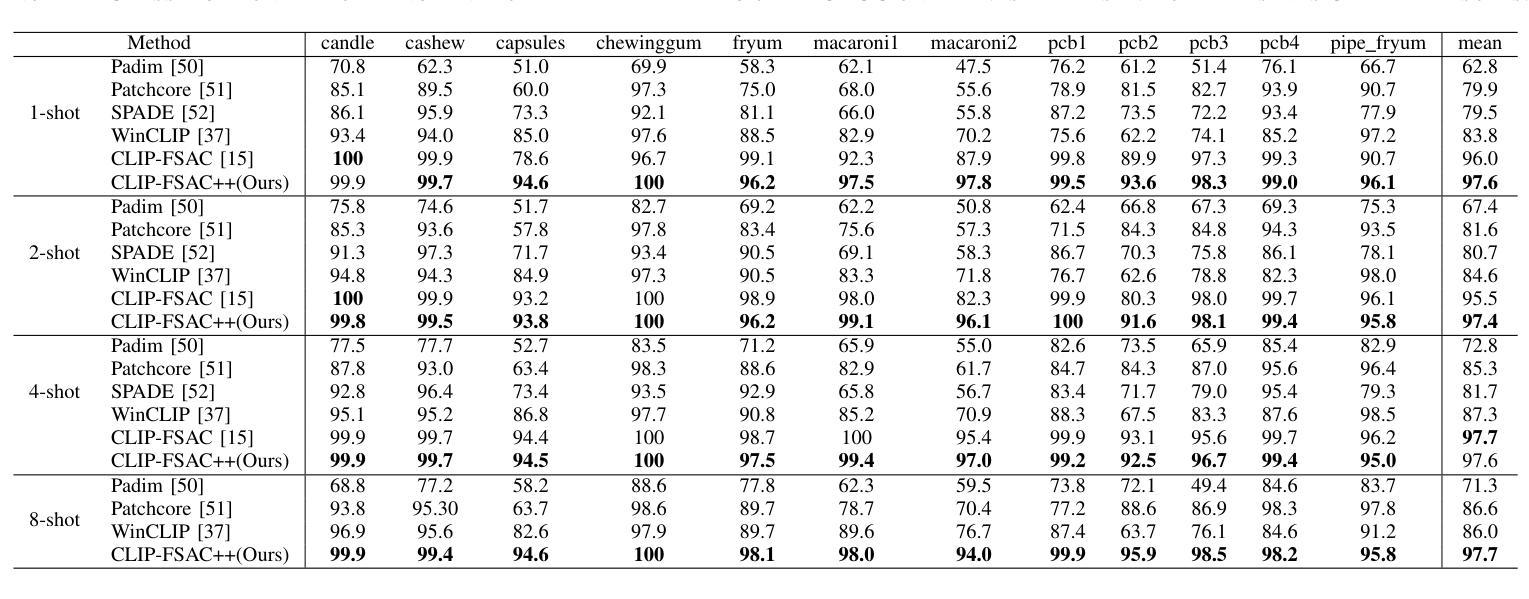
The broader spectrum of in-context learning
Authors:Andrew Kyle Lampinen, Stephanie C. Y. Chan, Aaditya K. Singh, Murray Shanahan
The ability of language models to learn a task from a few examples in context has generated substantial interest. Here, we provide a perspective that situates this type of supervised few-shot learning within a much broader spectrum of meta-learned in-context learning. Indeed, we suggest that any distribution of sequences in which context non-trivially decreases loss on subsequent predictions can be interpreted as eliciting a kind of in-context learning. We suggest that this perspective helps to unify the broad set of in-context abilities that language models exhibit $\unicode{x2014}$ such as adapting to tasks from instructions or role play, or extrapolating time series. This perspective also sheds light on potential roots of in-context learning in lower-level processing of linguistic dependencies (e.g. coreference or parallel structures). Finally, taking this perspective highlights the importance of generalization, which we suggest can be studied along several dimensions: not only the ability to learn something novel, but also flexibility in learning from different presentations, and in applying what is learned. We discuss broader connections to past literature in meta-learning and goal-conditioned agents, and other perspectives on learning and adaptation. We close by suggesting that research on in-context learning should consider this broader spectrum of in-context capabilities and types of generalization.
语言模型从少数几个上下文示例中学习任务的能力已经引起了广泛关注。在这里,我们提供了一个视角,将这类监督型小样本学习置于更广泛的元语境学习范围内。实际上,我们提出,任何分布序列,其中上下文对后续预测的损失有非平凡减少,都可以解释为激发了一种语境学习。我们认为,这个视角有助于统一语言模型所表现出的广泛语境能力,如根据指令或角色扮演适应任务,或外推时间序列等。这个视角还揭示了语境学习的潜在根源在于语言依赖性的低级处理(例如核心引用或并行结构)。最后,从这个角度来看,强调了泛化的重要性,我们认为泛化可以从多个维度进行研究:不仅是学习新事物的能力,还包括从不同表现中学习以及应用所学内容的灵活性。我们讨论了与元学习和目标条件代理的过去文献的更广泛联系,以及学习和适应的其他视角。最后,我们建议对语境学习的研究应考虑更广泛的语境能力和泛化类型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了语言模型从少数几个例子中学习任务的潜力,并将其置于更广泛的元学习语境中。文章指出,任何通过上下文减少后续预测损失的序列分布都可以被解释为一种语境学习。这种视角有助于统一语言模型展现的各种语境能力,如从指令或角色扮演中适应任务,或外推时间序列等。同时,该视角也揭示了语境学习的潜在根源在于语言依赖性的低级处理,并强调了泛化的重要性,包括学习新事物的能力、从不同呈现方式中学习的灵活性以及应用所学内容的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 语言模型能够从少数几个例子中学习任务的潜力引发了广泛关注。
- 语境学习可以看作是元学习的一种形式,适用于广泛的序列分布。
- 语境学习的视角有助于理解语言模型的各种能力,如适应任务、外推时间序列等。
- 语境学习的潜在根源可能在于语言依赖性的低级处理。
- 泛化在语言学习中非常重要,包括学习新事物、不同呈现方式的灵活性以及应用所学内容的能力。
- 文章讨论了与元学习和目标条件代理相关的过去文献的广泛联系。
点此查看论文截图

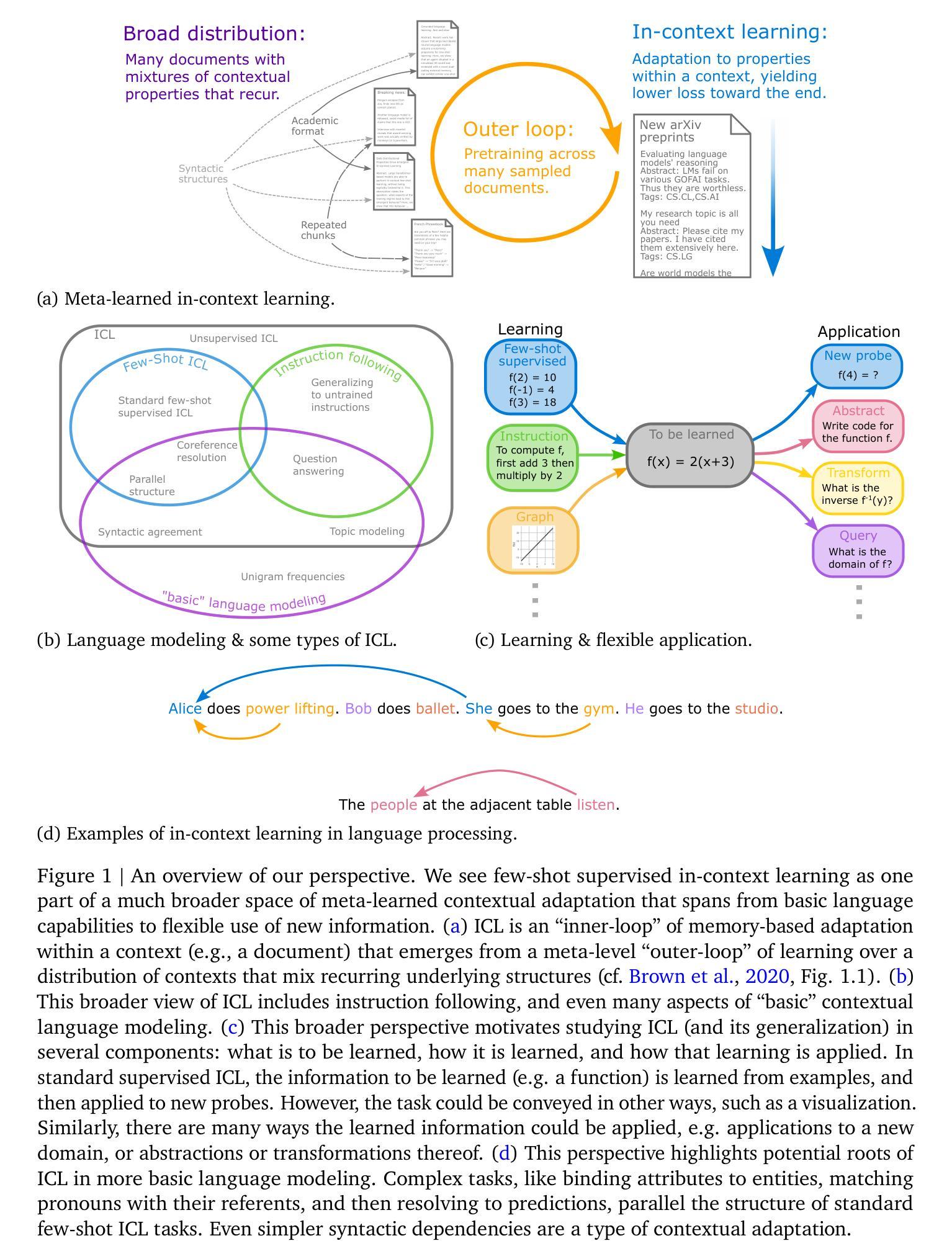
UniVAD: A Training-free Unified Model for Few-shot Visual Anomaly Detection
Authors:Zhaopeng Gu, Bingke Zhu, Guibo Zhu, Yingying Chen, Ming Tang, Jinqiao Wang
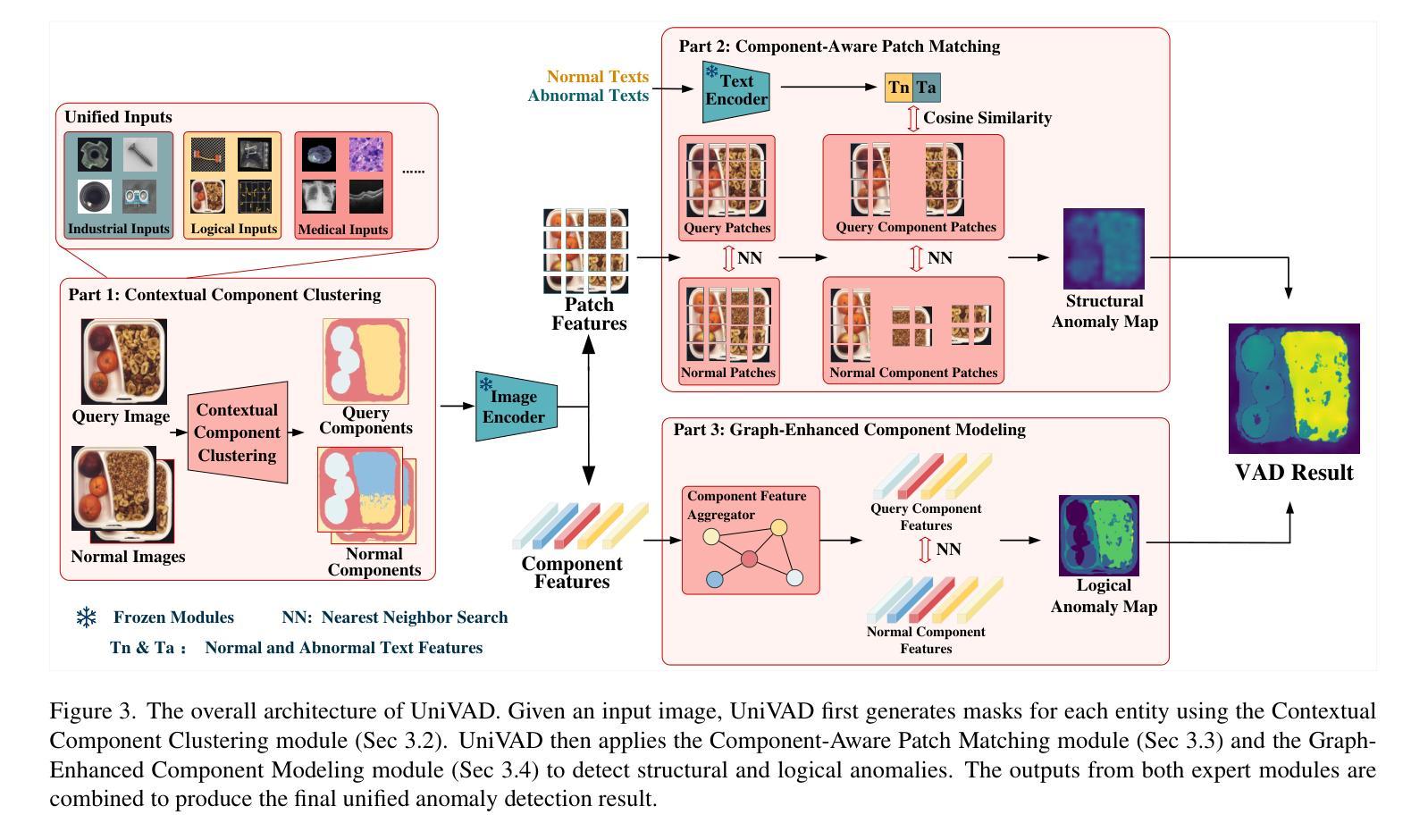
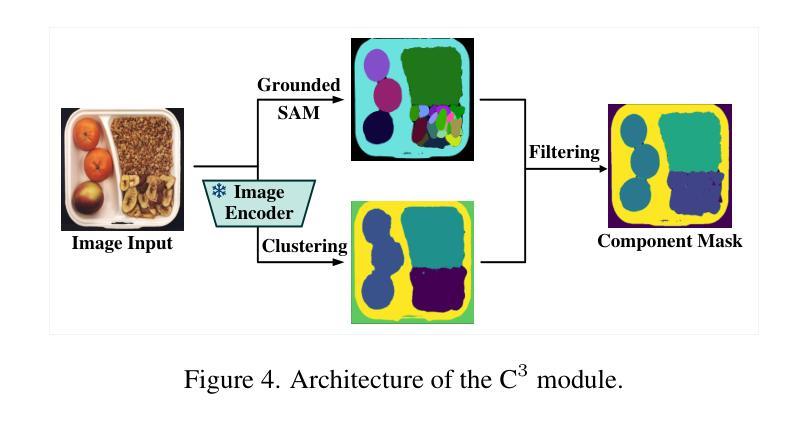
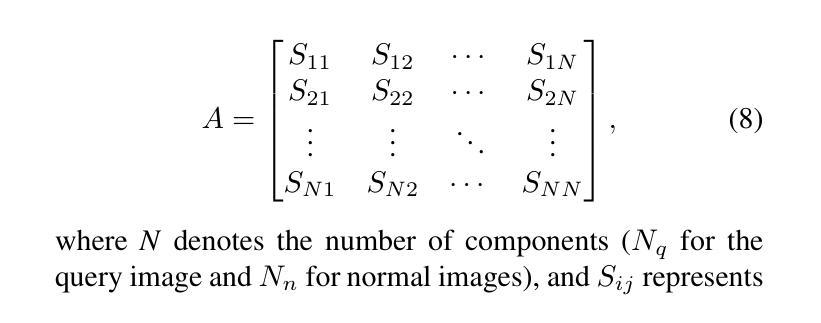
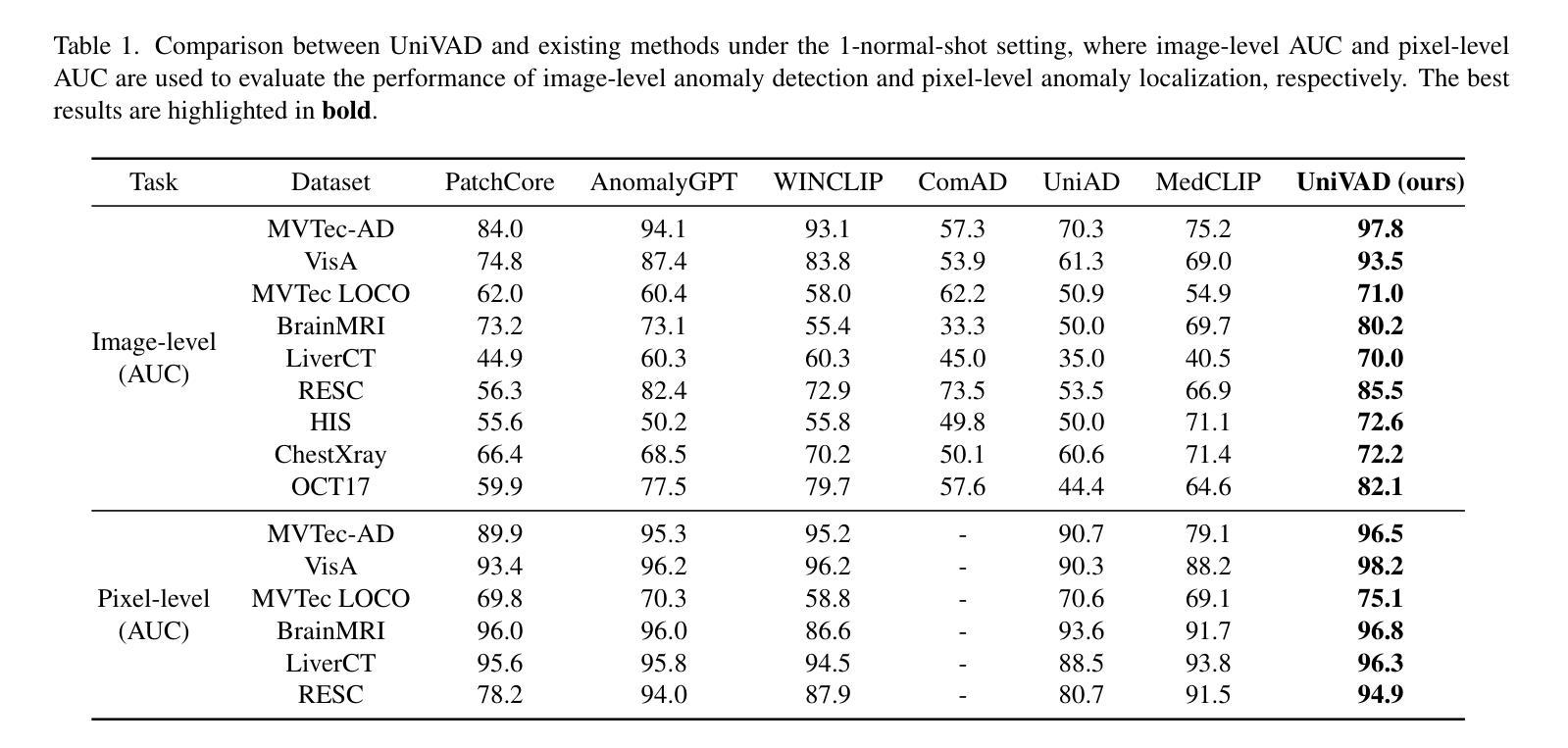
Visual Anomaly Detection (VAD) aims to identify abnormal samples in images that deviate from normal patterns, covering multiple domains, including industrial, logical, and medical fields. Due to the domain gaps between these fields, existing VAD methods are typically tailored to each domain, with specialized detection techniques and model architectures that are difficult to generalize across different domains. Moreover, even within the same domain, current VAD approaches often follow a “one-category-one-model” paradigm, requiring large amounts of normal samples to train class-specific models, resulting in poor generalizability and hindering unified evaluation across domains. To address this issue, we propose a generalized few-shot VAD method, UniVAD, capable of detecting anomalies across various domains, such as industrial, logical, and medical anomalies, with a training-free unified model. UniVAD only needs few normal samples as references during testing to detect anomalies in previously unseen objects, without training on the specific domain. Specifically, UniVAD employs a Contextual Component Clustering ($C^3$) module based on clustering and vision foundation models to segment components within the image accurately, and leverages Component-Aware Patch Matching (CAPM) and Graph-Enhanced Component Modeling (GECM) modules to detect anomalies at different semantic levels, which are aggregated to produce the final detection result. We conduct experiments on nine datasets spanning industrial, logical, and medical fields, and the results demonstrate that UniVAD achieves state-of-the-art performance in few-shot anomaly detection tasks across multiple domains, outperforming domain-specific anomaly detection models. The code will be made publicly available.
视觉异常检测(VAD)旨在识别图像中的异常样本,这些样本偏离了正常模式,涉及多个领域,包括工业、逻辑和医疗领域。由于这些领域之间存在领域差距,现有的VAD方法通常针对每个领域进行定制,具有专门化的检测技术和模型架构,难以在不同领域中推广。此外,即使在同一领域内,当前的VAD方法通常遵循“一类一模型”的模式,需要大量正常样本来训练特定类别的模型,导致泛化能力较差,阻碍了跨领域的统一评估。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种通用的少样本VAD方法UniVAD,能够检测各种领域的异常,如工业、逻辑和医疗异常,采用无需训练的统一模型。UniVAD在测试时只需要少数正常样本作为参考,即可检测以前未见过的对象中的异常,而无需在特定领域上进行训练。具体来说,UniVAD采用基于聚类和视觉基础模型的上下文组件聚类(C^3)模块,精确分割图像内的组件,并利用组件感知补丁匹配(CAPM)和图增强组件建模(GECM)模块在不同的语义级别检测异常,这些异常被聚合以产生最终的检测结果。我们在九个数据集上进行了实验,这些数据集涵盖了工业、逻辑和医疗领域,结果表明UniVAD在跨多个领域的少样本异常检测任务中实现了最先进的性能,优于领域特定的异常检测模型。代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF project page: https://uni-vad.github.io/
Summary
基于上下文组件聚类(C³模块)的UniVAD方法能够实现跨领域的视觉异常检测。它只需少量的正常样本作为参考,即可检测未知对象中的异常,无需针对特定领域进行训练。通过组件感知补丁匹配(CAPM)和图增强组件建模(GECM)模块,UniVAD能够在不同的语义级别上检测异常,并聚合结果以产生最终的检测结果。在跨越工业、逻辑和医疗领域的九个数据集上的实验结果表明,UniVAD在跨领域的少样本异常检测任务中实现了最先进的性能,优于特定领域的异常检测模型。
Key Takeaways
- UniVAD方法旨在解决视觉异常检测中的跨领域问题,覆盖工业、逻辑和医疗等多个领域。
- 现有VAD方法通常针对每个领域进行定制,而UniVAD则提出一种通用的少样本解决方案。
- UniVAD利用C³模块进行上下文组件聚类,能够准确分割图像内的组件。
- 通过CAPM和GECM模块,UniVAD能够在不同语义级别上检测异常。
- UniVAD仅需少量正常样本作为参考,即可检测未知对象中的异常。
- 实验结果表明,UniVAD在多个领域的数据集上实现了跨领域的少样本异常检测任务的最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图
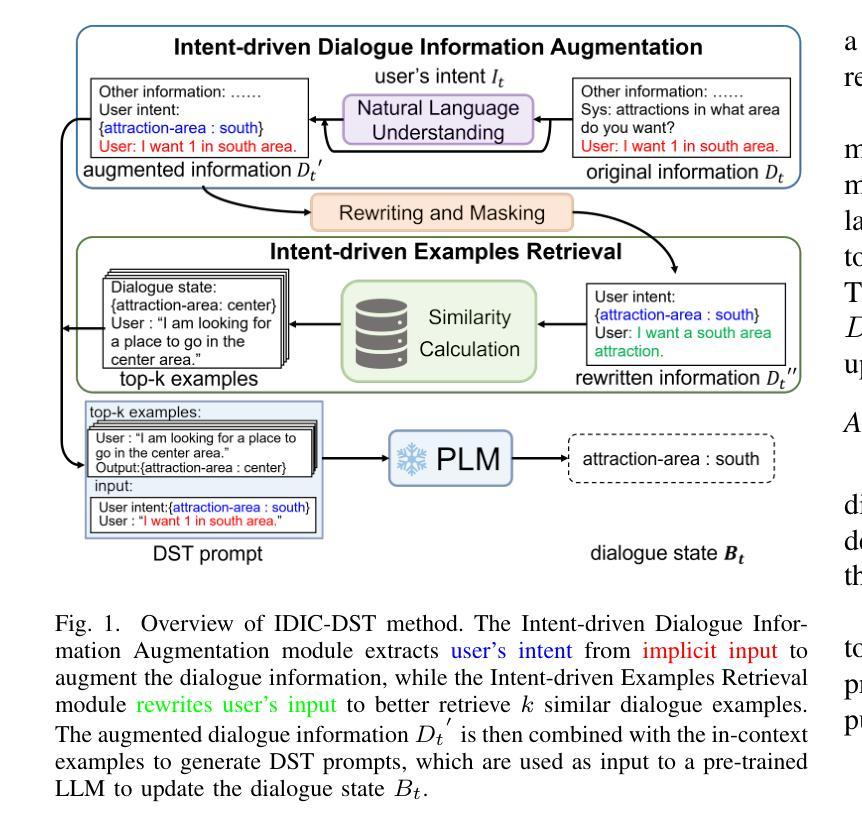
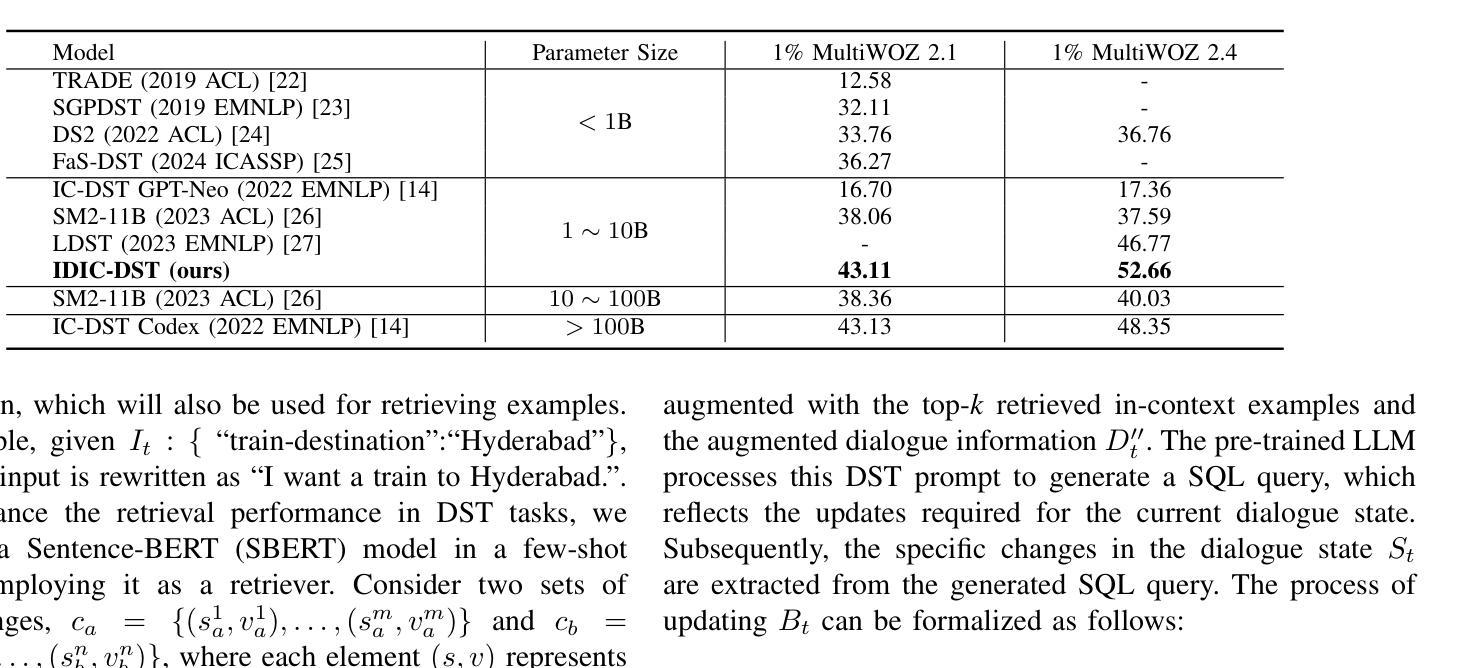
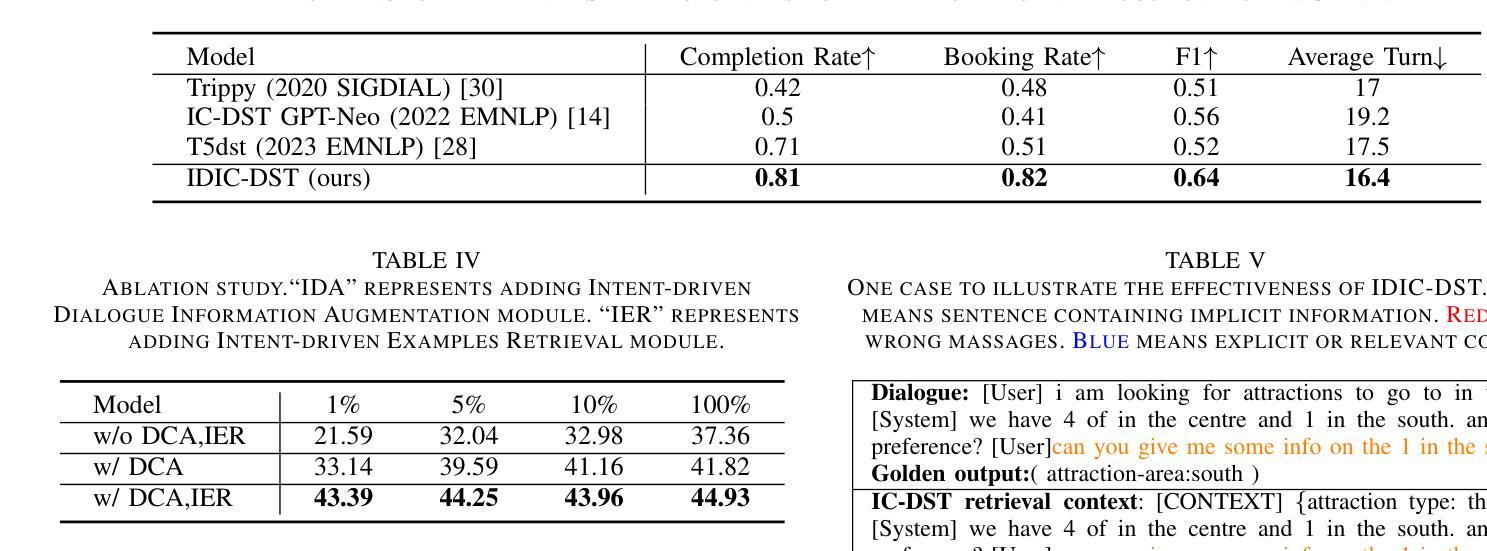
Intent-driven In-context Learning for Few-shot Dialogue State Tracking
Authors:Zihao Yi, Zhe Xu, Ying Shen
Dialogue state tracking (DST) plays an essential role in task-oriented dialogue systems. However, user’s input may contain implicit information, posing significant challenges for DST tasks. Additionally, DST data includes complex information, which not only contains a large amount of noise unrelated to the current turn, but also makes constructing DST datasets expensive. To address these challenges, we introduce Intent-driven In-context Learning for Few-shot DST (IDIC-DST). By extracting user’s intent, we propose an Intent-driven Dialogue Information Augmentation module to augment the dialogue information, which can track dialogue states more effectively. Moreover, we mask noisy information from DST data and rewrite user’s input in the Intent-driven Examples Retrieval module, where we retrieve similar examples. We then utilize a pre-trained large language model to update the dialogue state using the augmented dialogue information and examples. Experimental results demonstrate that IDIC-DST achieves state-of-the-art performance in few-shot settings on MultiWOZ 2.1 and MultiWOZ 2.4 datasets.
对话状态跟踪(DST)在面向任务的对话系统中扮演着至关重要的角色。然而,用户的输入可能包含隐含信息,给DST任务带来了重大挑战。此外,DST数据包含复杂信息,不仅包含大量与当前回合无关的噪声,而且构建DST数据集的成本也很高。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了用于少量DST的意图驱动上下文学习(IDIC-DST)。通过提取用户的意图,我们提出了一个意图驱动对话信息增强模块,以增强对话信息,从而更有效地跟踪对话状态。此外,我们从DST数据中屏蔽了嘈杂的信息,并在意图驱动的例子检索模块中重写了用户的输入,我们检索了类似的例子。然后,我们利用预训练的的大型语言模型,使用增强的对话信息和例子来更新对话状态。实验结果表明,IDIC-DST在MultiWOZ 2.1和MultiWOZ 2.4数据集上的少量设置达到了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了对话状态追踪(DST)在任务导向型对话系统中的重要角色,并指出了用户输入中隐含信息和数据复杂性对DST任务带来的挑战。针对这些挑战,本文提出了基于意图驱动的内语境学习(IDIC-DST)方法。该方法通过提取用户意图,构建了一个意图驱动对话信息增强模块,以更有效地追踪对话状态。同时,该方法还通过掩噪处理和重写用户输入的方式优化了数据集。实验结果表明,IDIC-DST在MultiWOZ 2.1和MultiWOZ 2.4数据集上的小样本设置上取得了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 对话状态追踪(DST)在任务导向型对话系统中至关重要。
- 用户输入中的隐含信息和数据复杂性对DST任务带来挑战。
- IDIC-DST方法通过意图驱动的内语境学习来解决这些挑战。
- 意图驱动对话信息增强模块能更有效地追踪对话状态。
- IDIC-DST通过掩噪处理和重写用户输入的方式优化了数据集。
- 实验结果表明,IDIC-DST在MultiWOZ数据集上的小样本设置上取得了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

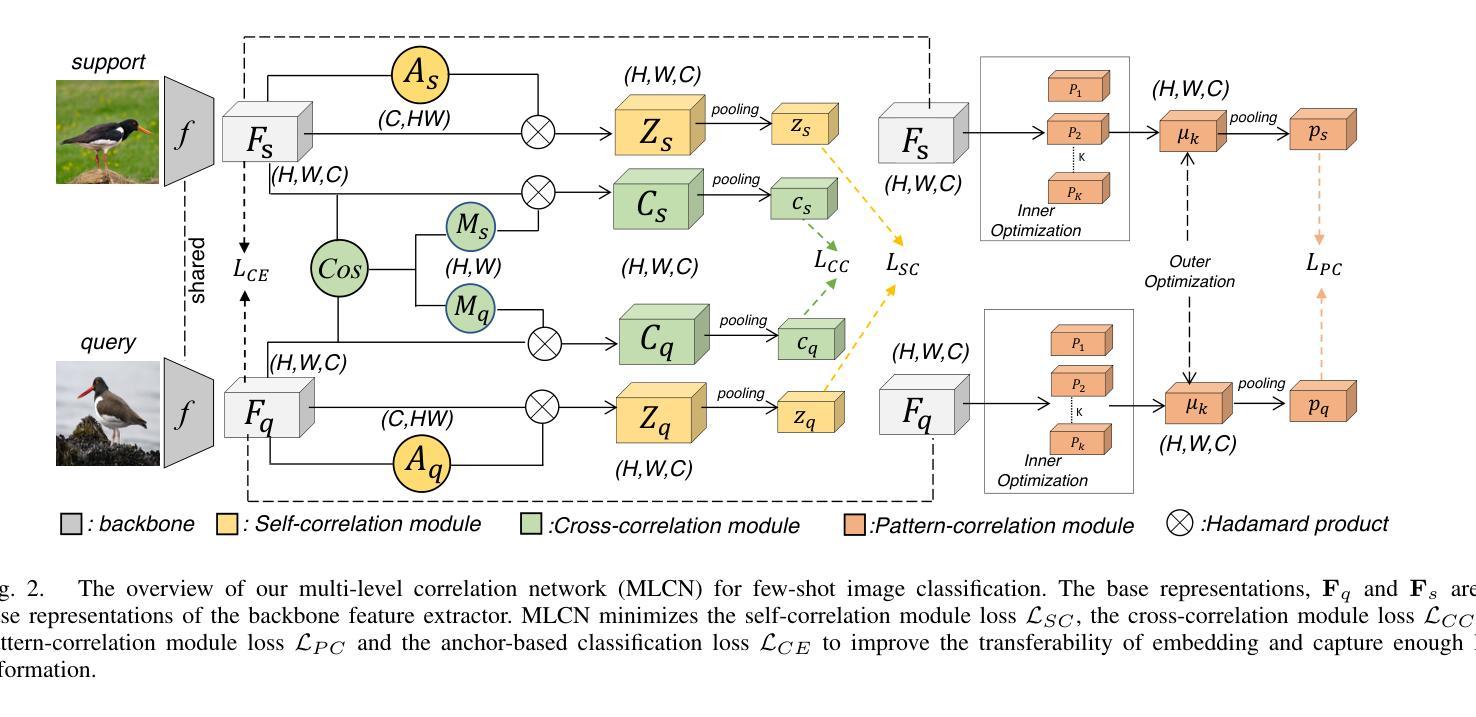
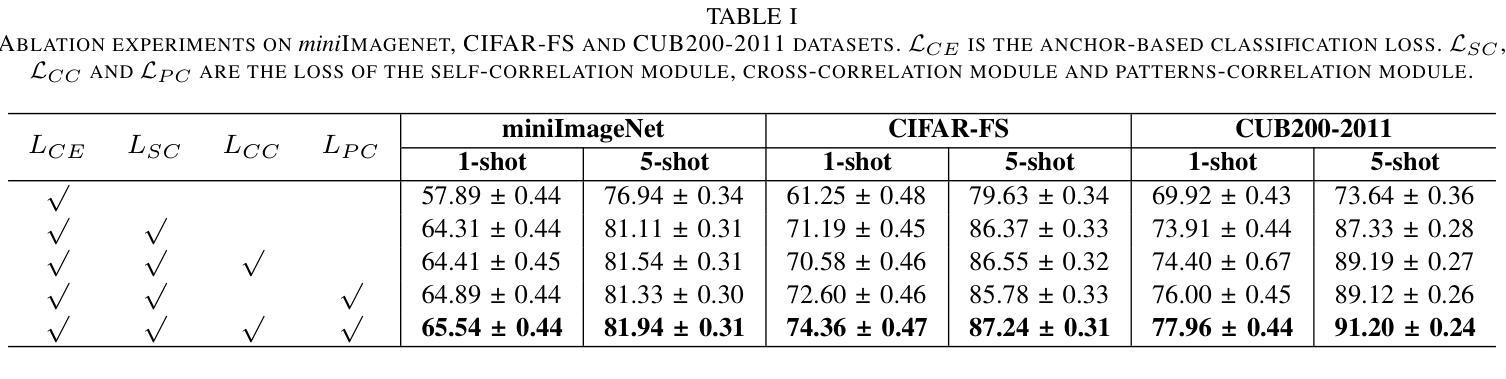
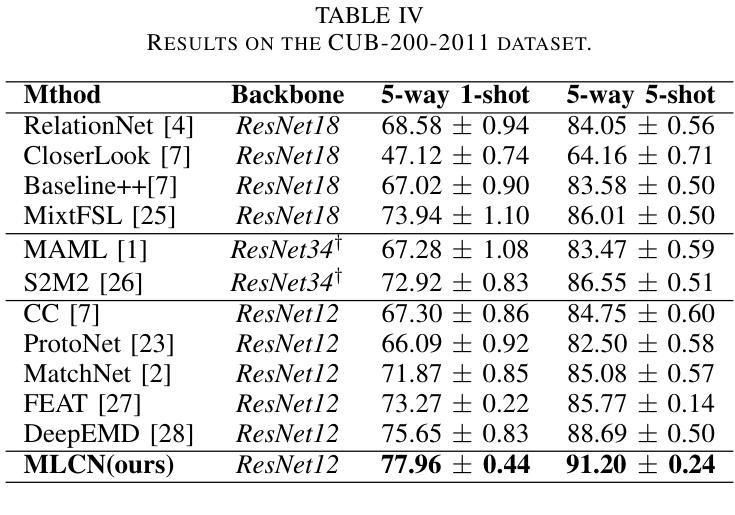
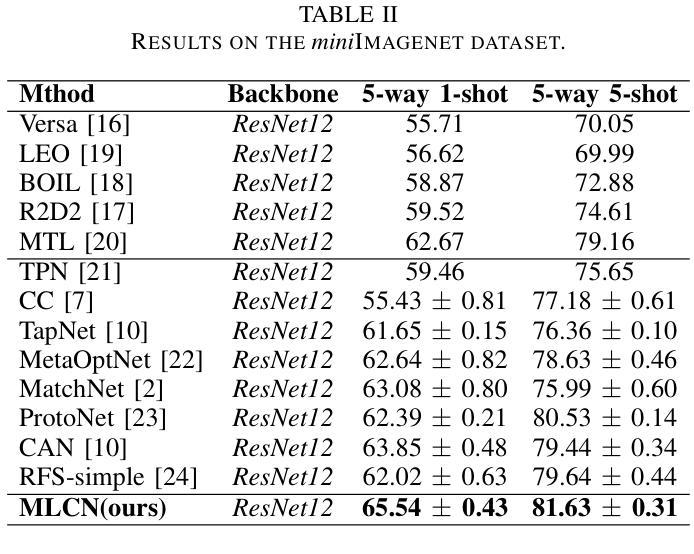
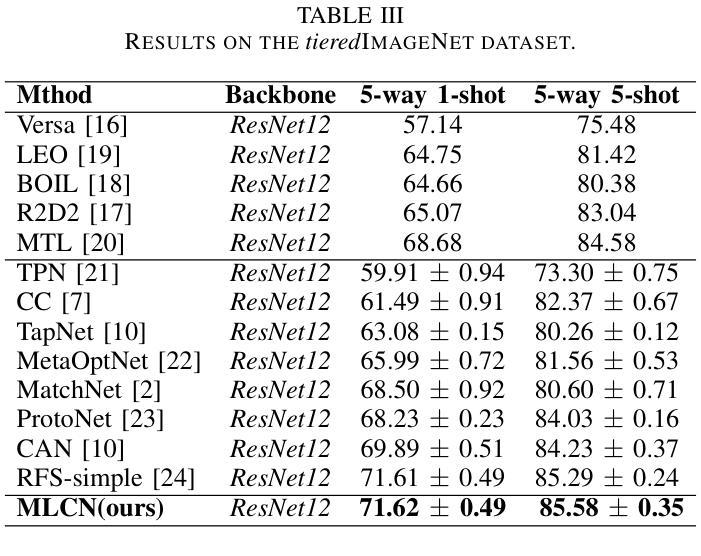
Multi-Level Correlation Network For Few-Shot Image Classification
Authors:Yunkai Dang, Min Zhang, Zhengyu Chen, Xinliang Zhang, Zheng Wang, Meijun Sun, Donglin Wang
Few-shot image classification(FSIC) aims to recognize novel classes given few labeled images from base classes. Recent works have achieved promising classification performance, especially for metric-learning methods, where a measure at only image feature level is usually used. In this paper, we argue that measure at such a level may not be effective enough to generalize from base to novel classes when using only a few images. Instead, a multi-level descriptor of an image is taken for consideration in this paper. We propose a multi-level correlation network (MLCN) for FSIC to tackle this problem by effectively capturing local information. Concretely, we present the self-correlation module and cross-correlation module to learn the semantic correspondence relation of local information based on learned representations. Moreover, we propose a pattern-correlation module to capture the pattern of fine-grained images and find relevant structural patterns between base classes and novel classes. Extensive experiments and analysis show the effectiveness of our proposed method on four widely-used FSIC benchmarks. The code for our approach is available at: https://github.com/Yunkai696/MLCN.
小样图像分类(FSIC)的目标是识别新的类别,同时仅基于基础类别的少量标记图像。近期的研究工作已经取得了有前景的分类性能,特别是度量学习方法,通常只使用图像特征层面的度量。在本文中,我们认为仅使用少量图像时,仅在如此层面上的度量可能不足以从基础类别推广到新类别。相反,本文考虑了一张图像的多层次描述符。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了用于FSIC的多层次关联网络(MLCN),以有效地捕获局部信息。具体来说,我们介绍了自关联模块和交叉关联模块,基于学习到的表示来学习局部信息的语义对应关系。此外,我们提出了模式关联模块,以捕获细粒度图像的模式,并在基础类别和新类别之间找到相关的结构模式。广泛的实验和分析表明,我们的方法在四个广泛使用的FSIC基准测试上都验证了方法的有效性。我们的方法的代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/Yunkai696/MLCN。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
少样本图像分类(FSIC)旨在通过基础类别的少量标记图像来识别新型类别。本文提出一种多层次关联网络(MLCN)来解决该问题,通过捕捉局部信息来实现有效的特征提取。论文引入了自关联模块和跨关联模块来学习基于学习表示的局部信息的语义对应关系,并提出模式关联模块来捕捉细粒度图像的模式,找到基础类别和新型类别之间的相关结构模式。实验证明该方法在四个广泛使用的FSIC基准测试集上有效。
Key Takeaways
- 少样本图像分类(FSIC)旨在利用基础类别的少量标记图像识别新型类别。
- 现有方法在度量学习方面取得较好成绩,但仅通过图像特征级别的度量可能不够有效。
- 论文提出了一种多层次关联网络(MLCN)来解决该问题,关注图像的多层次描述信息。
- 引入自关联模块和跨关联模块来学习局部信息的语义对应关系。
- 提出模式关联模块来捕捉细粒度图像的模式,并找到基础类别和新型类别之间的结构模式关联。
- 在四个广泛使用的FSIC基准测试集上进行了大量实验,证明了方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图
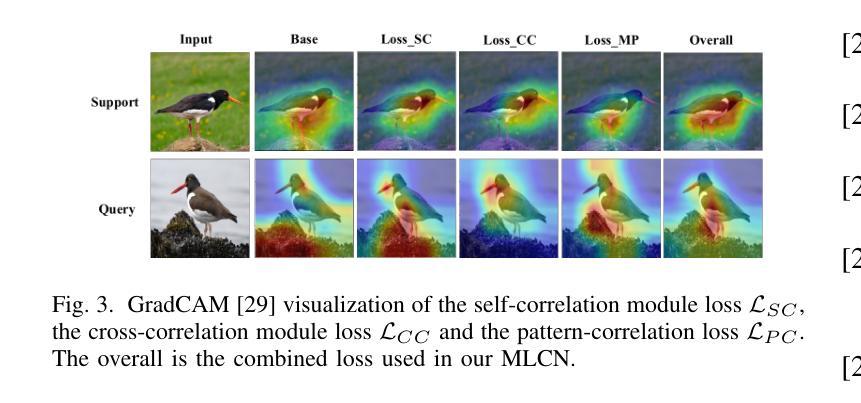


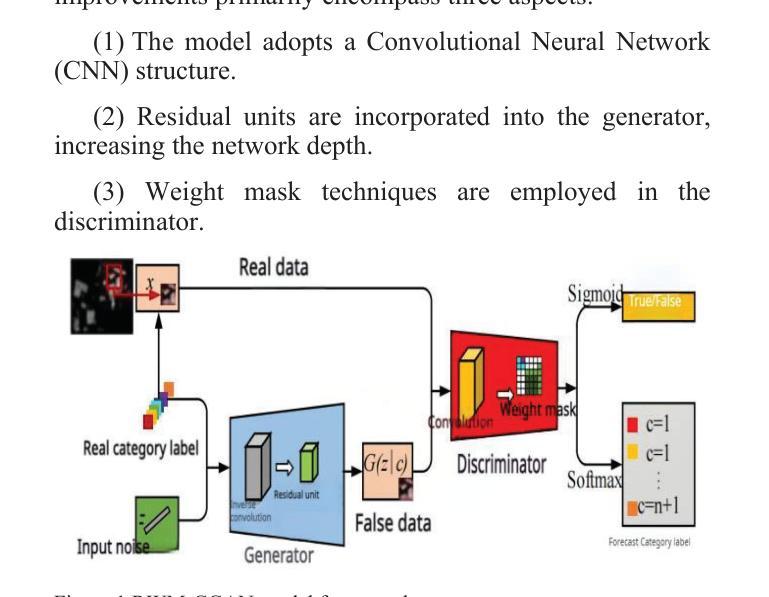
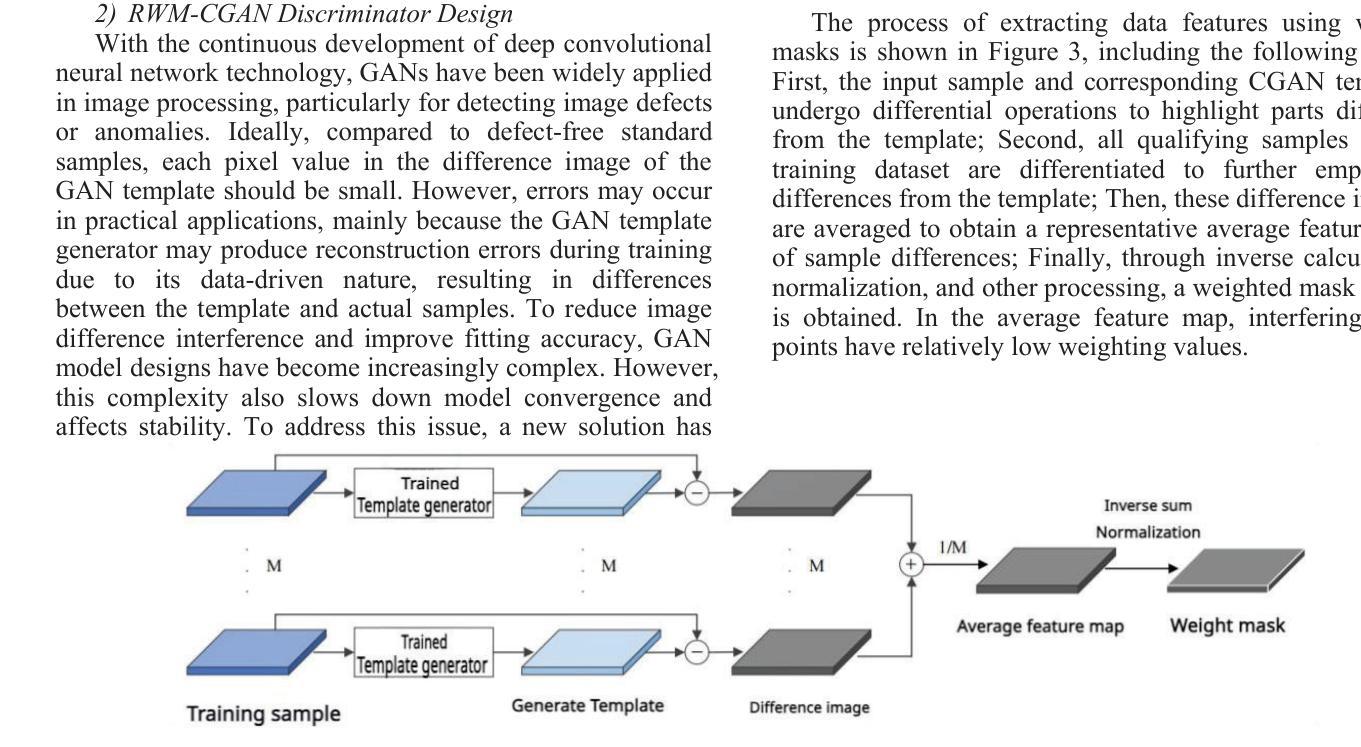
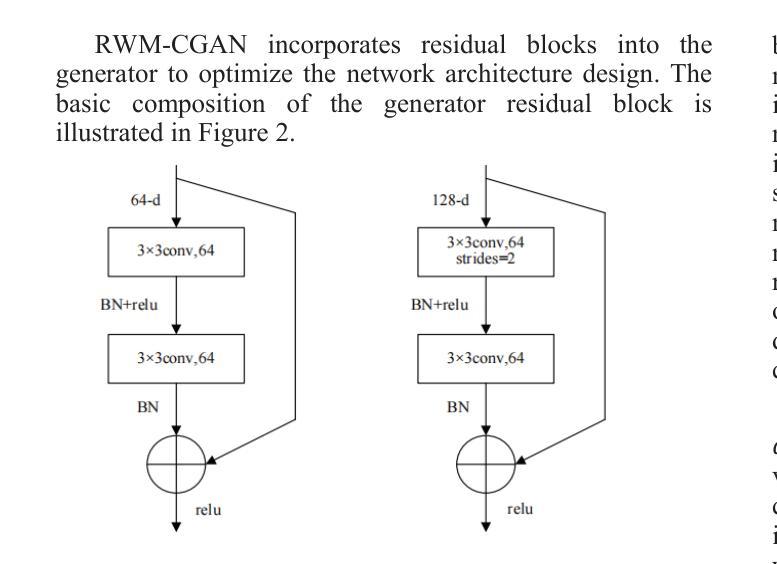
Few-Shot Learning with Adaptive Weight Masking in Conditional GANs
Authors:Jiacheng Hu, Zhen Qi, Jianjun Wei, Jiajing Chen, Runyuan Bao, Xinyu Qiu
Deep learning has revolutionized various fields, yet its efficacy is hindered by overfitting and the requirement of extensive annotated data, particularly in few-shot learning scenarios where limited samples are available. This paper introduces a novel approach to few-shot learning by employing a Residual Weight Masking Conditional Generative Adversarial Network (RWM-CGAN) for data augmentation. The proposed model integrates residual units within the generator to enhance network depth and sample quality, coupled with a weight mask regularization technique in the discriminator to improve feature learning from small-sample categories. This method addresses the core issues of robustness and generalization in few-shot learning by providing a controlled and clear augmentation of the sample space. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RWM-CGAN not only expands the sample space effectively but also enriches the diversity and quality of generated samples, leading to significant improvements in detection and classification accuracy on public datasets. The paper contributes to the advancement of few-shot learning by offering a practical solution to the challenges posed by data scarcity and the need for rapid generalization to new tasks or categories.
深度学习已经对各领域产生了革命性的影响,但在小样学习场景中,其有效性受到过拟合和需要大量标注数据的限制。本文介绍了一种采用残差权重掩蔽条件生成对抗网络(RWM-CGAN)进行数据增强的少样本学习新方法。所提模型在生成器中集成残差单元,以提高网络深度和样本质量,同时在鉴别器中采用权重掩蔽正则化技术,以提高小样本类别的特征学习能力。该方法通过提供可控且清晰的样本空间扩充,解决了小样学习中的鲁棒性和泛化性问题核心。大量实验表明,RWM-CGAN不仅有效地扩大了样本空间,还丰富了生成样本的多样性和质量,在公开数据集上显著提高了检测和分类的准确性。本文为解决数据稀缺和快速推广到新任务或类别等挑战提供了实际解决方案,推动了小样学习的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习已广泛应用于多个领域,但在小样例学习场景下存在过拟合和需要大量标注数据的问题。本文提出了一种采用残差权重掩膜条件生成对抗网络(RWM-CGAN)进行小样例学习的新方法。该方法通过生成器中的残差单元增强网络深度和样本质量,通过判别器中的权重掩膜正则化技术改进小样本类别的特征学习。该方法解决了小样例学习中鲁棒性和泛化性的核心问题,通过控制清晰的样本空间扩充来实现。实验表明,RWM-CGAN不仅有效地扩充了样本空间,还提高了生成样本的多样性和质量,在公开数据集上的检测和分类精度显著提高。本文为解决数据稀缺和快速泛化到新任务或类别所带来的挑战提供了实际解决方案,为小样例学习领域的发展做出了贡献。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习在多个领域有广泛应用,但在小样例学习场景中面临过拟合和标注数据需求的问题。
- 本文提出了一种基于RWM-CGAN的新方法,通过残差单元和权重掩膜正则化技术来解决小样例学习中的问题。
- RWM-CGAN能够有效地扩充样本空间,提高生成样本的多样性和质量。
- 该方法在公开数据集上的检测和分类精度显著提高。
- 该方法为解决数据稀缺和快速泛化到新任务或类别所带来的挑战提供了实际解决方案。
- 本文对小样例学习领域的发展做出了贡献。
点此查看论文截图

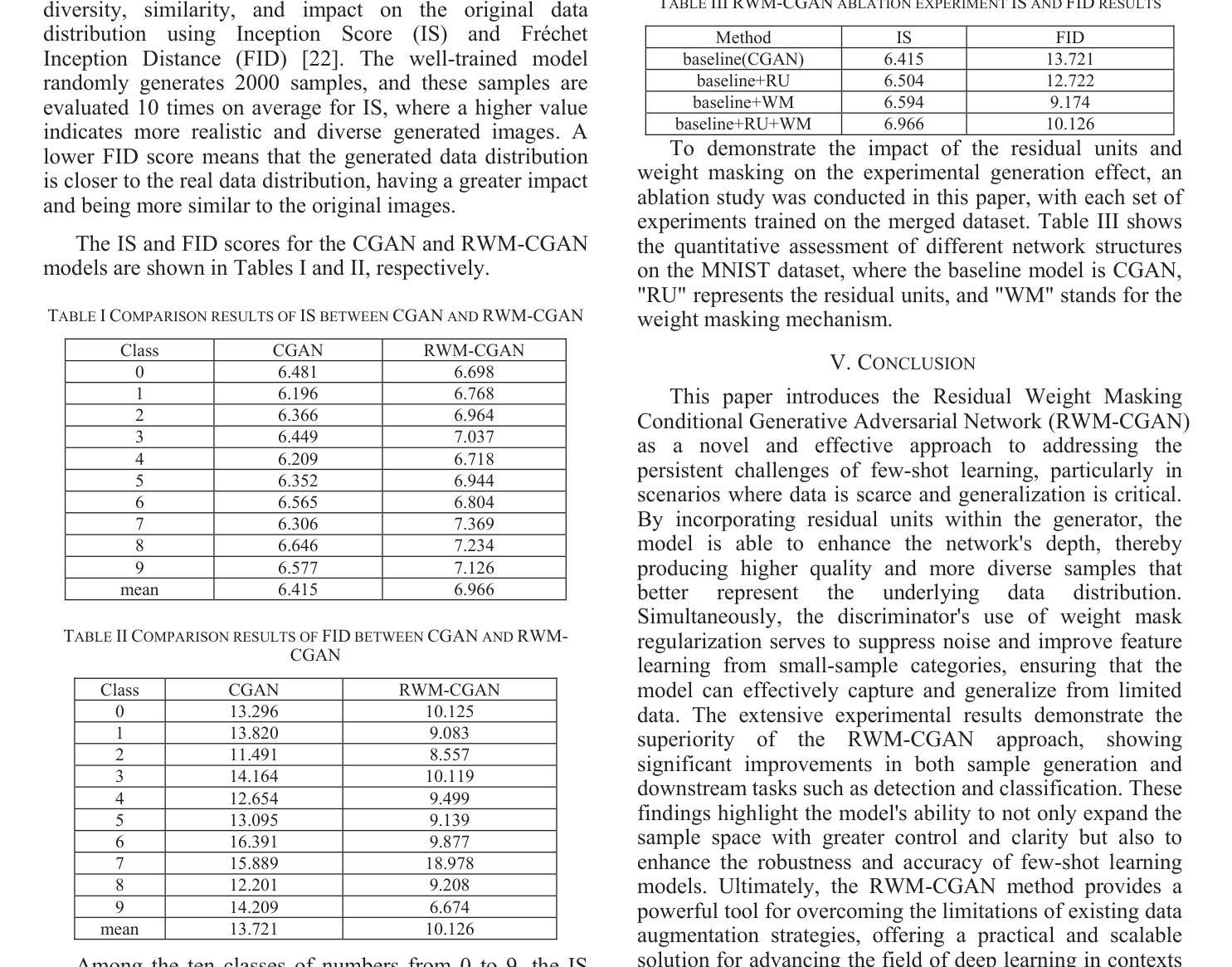
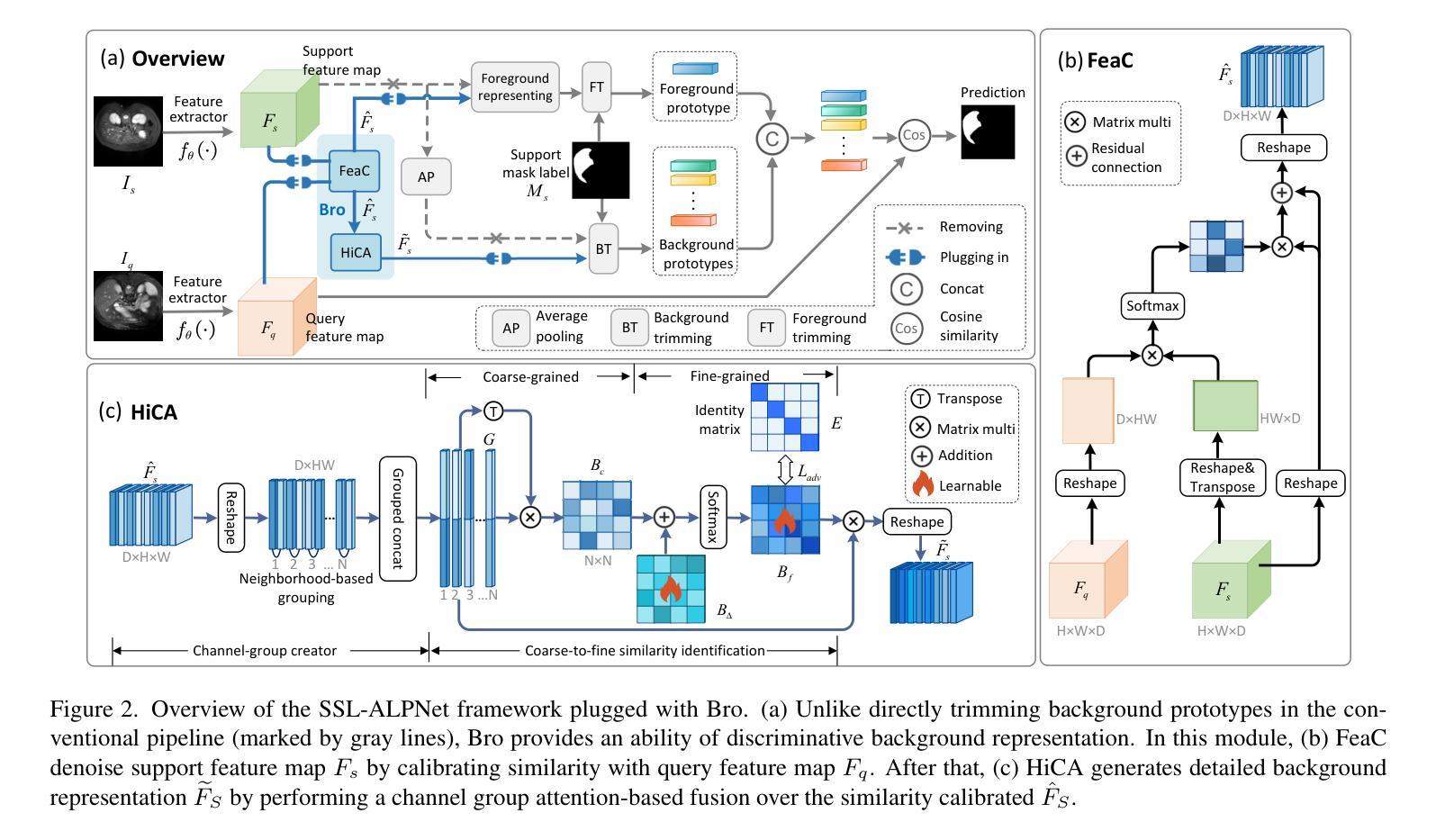
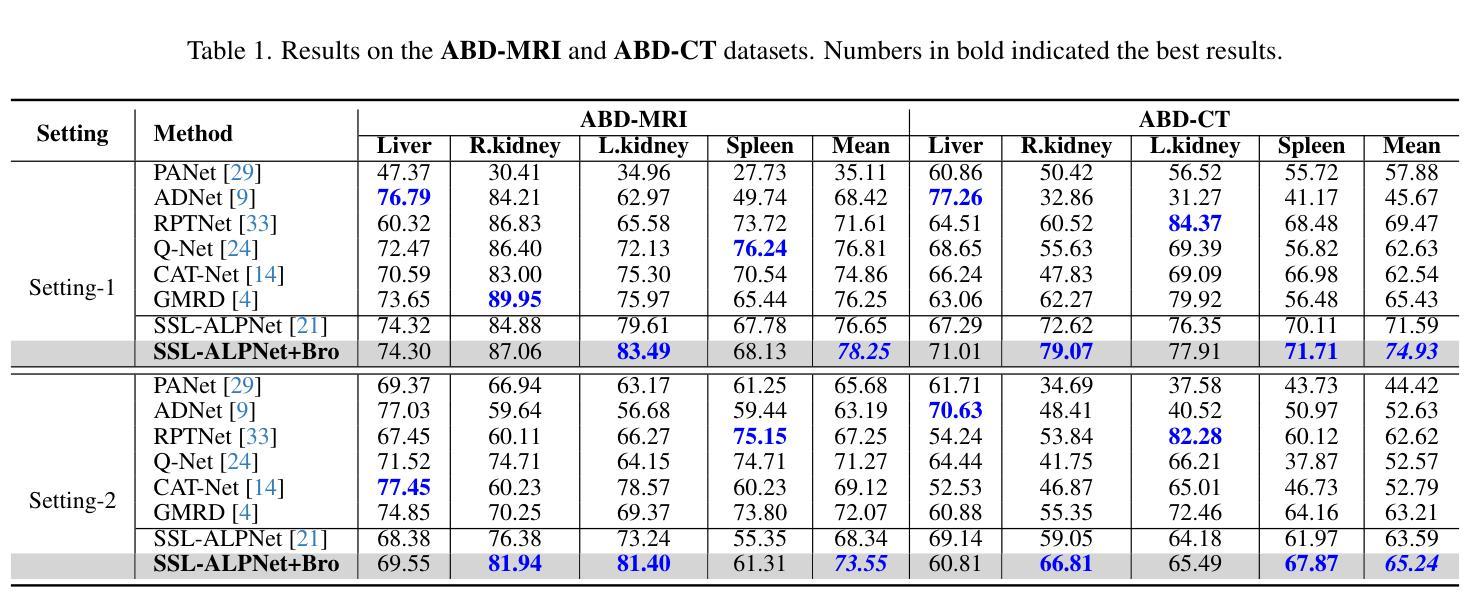
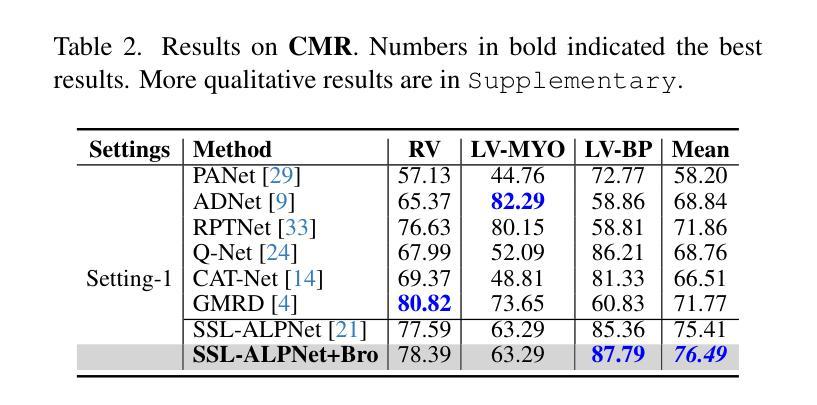
Is Foreground Prototype Sufficient? Few-Shot Medical Image Segmentation with Background-Fused Prototype
Authors:Song Tang, Chunxiao Zu, Wenxin Su, Yuan Dong, Mao Ye, Yan Gan, Xiatian Zhu
Few-shot Semantic Segmentation(FSS)aim to adapt a pre-trained model to new classes with as few as a single labeled training sample per class. The existing prototypical work used in natural image scenarios biasedly focus on capturing foreground’s discrimination while employing a simplistic representation for background, grounded on the inherent observation separation between foreground and background. However, this paradigm is not applicable to medical images where the foreground and background share numerous visual features, necessitating a more detailed description for background. In this paper, we present a new pluggable Background-fused prototype(Bro)approach for FSS in medical images. Instead of finding a commonality of background subjects in support image, Bro incorporates this background with two pivot designs. Specifically, Feature Similarity Calibration(FeaC)initially reduces noise in the support image by employing feature cross-attention with the query image. Subsequently, Hierarchical Channel Adversarial Attention(HiCA)merges the background into comprehensive prototypes. We achieve this by a channel groups-based attention mechanism, where an adversarial Mean-Offset structure encourages a coarse-to-fine fusion. Extensive experiments show that previous state-of-the-art methods, when paired with Bro, experience significant performance improvements. This demonstrates a more integrated way to represent backgrounds specifically for medical image.
少量样本语义分割(FSS)旨在将预训练模型适应新类别,每类只需一个标记的训练样本。目前自然图像场景中使用的原型工作偏向于捕捉前景的辨别力,同时采用简单的背景表示,基于前景和背景之间的固有观察分离。然而,这种模式不适用于医学图像,因为前景和背景共享许多视觉特征,需要对背景进行更详细的描述。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的可插入式背景融合原型(Bro)方法,用于医学图像的FSS。Bro方法并没有在支持图像中寻找背景主题的共性,而是结合了背景和两个关键设计。具体来说,特征相似性校准(FeaC)首先通过采用与查询图像的特征交叉注意力来减少支持图像中的噪声。随后,层次化通道对抗性注意力(HiCA)将背景合并到综合原型中。我们通过基于通道组的注意力机制实现这一点,其中对抗性Mean-Offset结构鼓励从粗略到精细的融合。大量实验表明,与之前最先进的方法相比,当与Bro相结合时,它们的性能有了显著提高。这表明了一种更集成的方式来表示医学图像中的背景。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文提出了一种针对医学图像的新型的可插入背景融合模型(Bro)。此模型改善了现有的模型对背景处理不够细致的问题,通过使用特征相似性校准(FeaC)减少支持图像中的噪声,再通过层次化通道对抗注意力(HiCA)将背景融合到全面的原型中。实验结果证明,结合了Bro的方法可以显著提高性能,为医学图像背景表示提供了更一体化的方式。
Key Takeaways
- FSS旨在使用少量标记样本进行语义分割任务,医学图像领域中尤为需要细化背景的表述方法。
- 传统模型在处理自然图像时更关注前景识别而忽视背景。但医学图像中的前景和背景有很多共同特征,所以需要更为详尽地描述背景。
- 背景融合模型(Bro)是一个新的解决方案,适用于医学图像的FSS任务。
点此查看论文截图

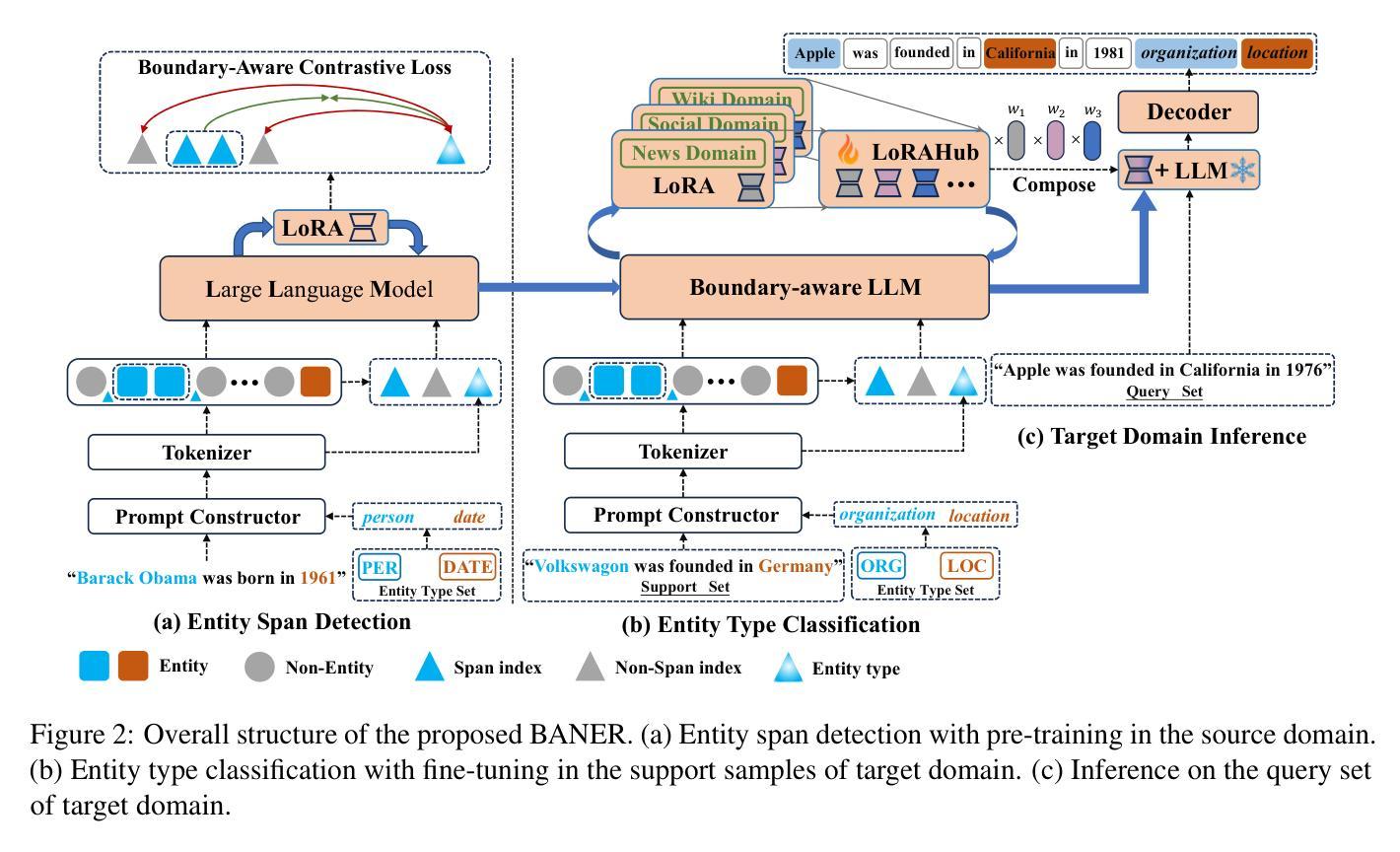
BANER: Boundary-Aware LLMs for Few-Shot Named Entity Recognition
Authors:Quanjiang Guo, Yihong Dong, Ling Tian, Zhao Kang, Yu Zhang, Sijie Wang
Despite the recent success of two-stage prototypical networks in few-shot named entity recognition (NER), challenges such as over/under-detected false spans in the span detection stage and unaligned entity prototypes in the type classification stage persist. Additionally, LLMs have not proven to be effective few-shot information extractors in general. In this paper, we propose an approach called Boundary-Aware LLMs for Few-Shot Named Entity Recognition to address these issues. We introduce a boundary-aware contrastive learning strategy to enhance the LLM’s ability to perceive entity boundaries for generalized entity spans. Additionally, we utilize LoRAHub to align information from the target domain to the source domain, thereby enhancing adaptive cross-domain classification capabilities. Extensive experiments across various benchmarks demonstrate that our framework outperforms prior methods, validating its effectiveness. In particular, the proposed strategies demonstrate effectiveness across a range of LLM architectures. The code and data are released on https://github.com/UESTC-GQJ/BANER.
尽管两阶段原型网络在少样本命名实体识别(NER)方面取得了最新成功,但仍然存在一些挑战,如在跨度检测阶段的过度或未检测到的错误跨度以及在类型分类阶段的不对齐实体原型。此外,大型语言模型(LLMs)尚未证明在一般少样本信息提取方面有效。针对这些问题,本文提出了一种名为边界感知大型语言模型(Boundary-Aware LLMs)的Few-Shot命名实体识别方法。我们引入了一种边界感知对比学习策略,以提高大型语言模型对广义实体跨度的实体边界感知能力。此外,我们还利用LoRAHub将目标域的信息与源域对齐,从而提高了自适应跨域分类能力。在不同基准测试上的大量实验表明,我们的框架优于先前的方法,验证了其有效性。特别是,所提出策略在各种大型语言模型架构中都表现出良好的效果。相关代码和数据已在https://github.com/UESTC-GQJ/BANER上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Appear on COLING 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为Boundary-Aware LLMs的方法,用于解决小样本的命名实体识别问题。通过引入边界感知对比学习策略,提高LLM对实体边界的感知能力,并采用LoRAHub进行源域和目标域的信息对齐,增强了跨域分类的适应性。实验证明,该方法在多个基准测试上表现优异,有效提高了实体识别的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 提出Boundary-Aware LLMs方法解决小样本的命名实体识别挑战。
- 引入边界感知对比学习策略,提高LLM对实体边界的感知能力。
- 采用LoRAHub进行源域和目标域的信息对齐。
- 方法在多个基准测试上表现优异,提高了实体识别的准确性。
- 方法适用于多种LLM架构。
- 公开了代码和数据,可供进一步研究使用。
点此查看论文截图

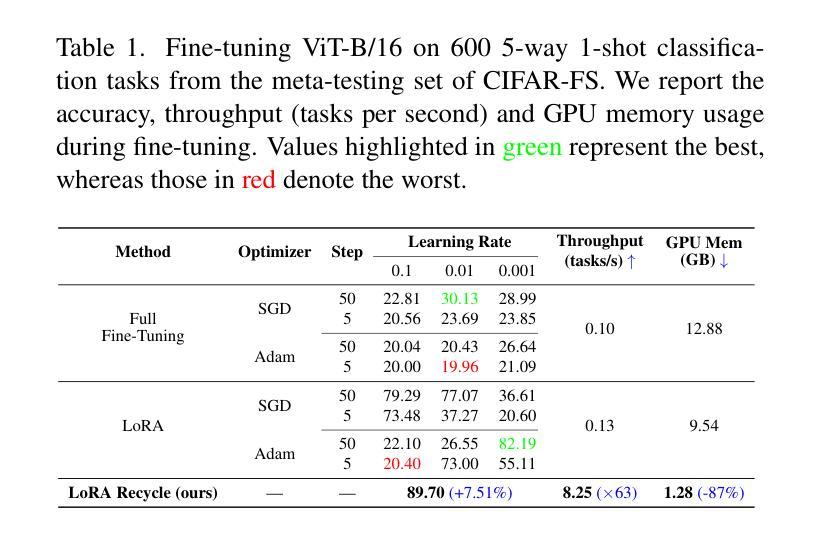
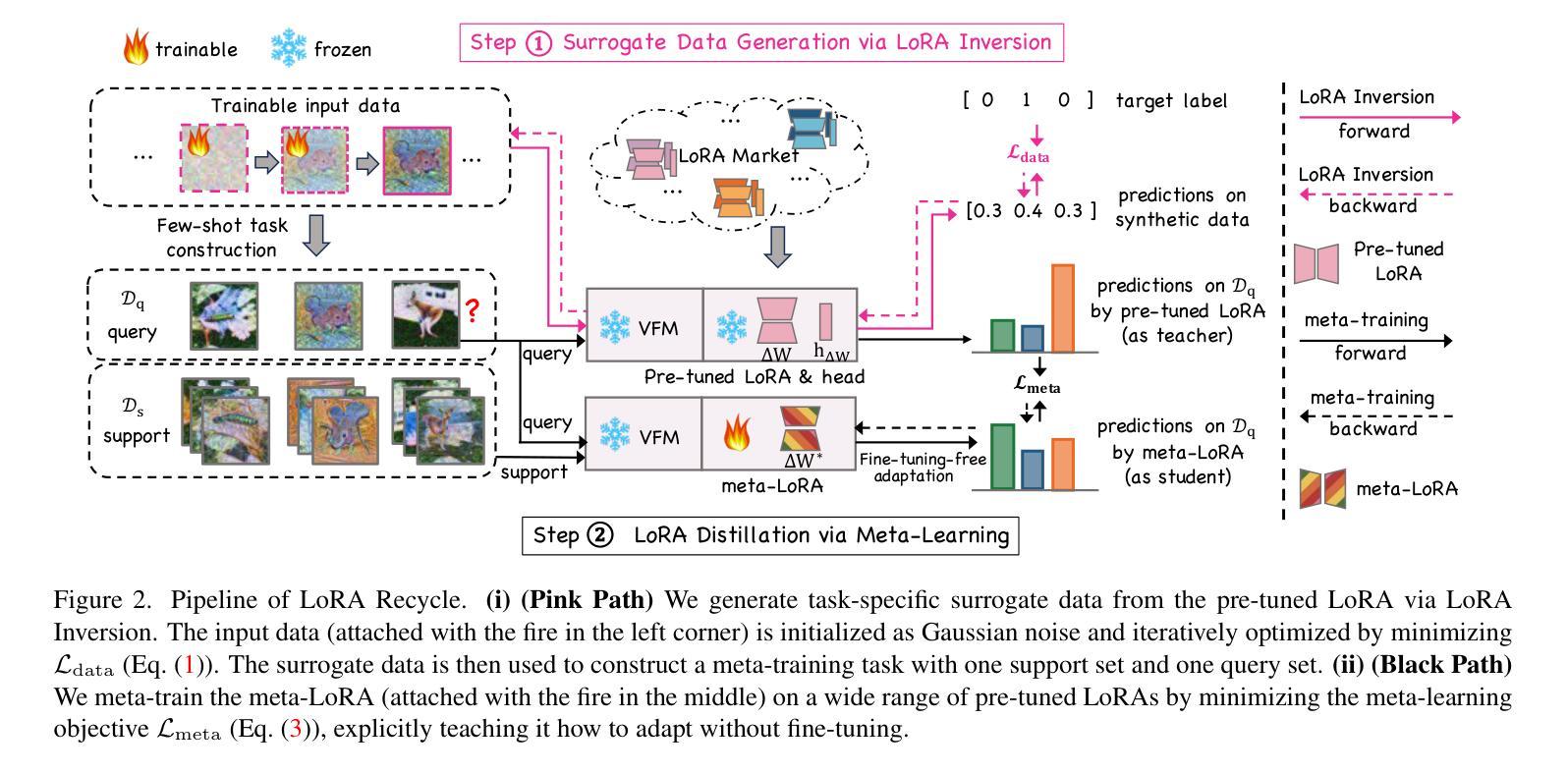
Unlocking Tuning-Free Few-Shot Adaptability in Visual Foundation Models by Recycling Pre-Tuned LoRAs
Authors:Zixuan Hu, Yongxian Wei, Li Shen, Chun Yuan, Dacheng Tao
Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT demonstrate strong few-shot adaptability without requiring fine-tuning, positioning them ideal for data-limited and real-time applications. However, this adaptability has not yet been replicated in current Visual Foundation Models (VFMs), which require explicit fine-tuning with sufficient tuning data. Besides, the pretraining-finetuning paradigm has led to the surge of numerous task-specific modular components, such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA). For the first time, we explore the potential of reusing diverse pre-tuned LoRAs without accessing their original training data, to achieve tuning-free few-shot adaptation in VFMs. Our framework, LoRA Recycle, distills a meta-LoRA from diverse pre-tuned LoRAs with a meta-learning objective, using surrogate data generated inversely from pre-tuned LoRAs themselves. The VFM, once equipped with the meta-LoRA, is empowered to solve new few-shot tasks in a single forward pass, akin to the in-context learning of LLMs. Additionally, we incorporate a double-efficient mechanism tailored to our framework, significantly accelerating the meta-training process while maintaining or even improving performance. Extensive experiments across various few-shot classification benchmarks across both in- and cross-domain scenarios demonstrate the superiority of our framework.
大型语言模型(LLMs)如ChatGPT展现出强大的少样本适应能力,无需微调即可适应新任务,使其成为数据有限和实时应用的理想选择。然而,这种适应能力在现有的视觉基础模型(VFMs)中尚未实现,后者需要大量的微调数据和明确的微调过程。此外,预训练-微调范式导致了大量针对特定任务的模块化组件的涌现,如低秩适配(LoRA)。我们首次探索了复用多种预训练LoRA的潜力,而无需访问其原始训练数据,以实现VFMs中的无微调少样本适应。我们的框架LoRA Recycle通过元学习目标和反向生成的代理数据从多种预训练LoRA中提炼出元LoRA。一旦装备上该元LoRA,视觉基础模型就能像LLMs那样通过上下文学习一次性解决新的少样本任务。此外,我们还结合了针对我们框架设计的双重高效机制,显著加速了元训练过程,同时保持了甚至提高了性能。在不同领域的少样本分类基准测试的大量实验证明了我们框架的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)如ChatGPT展现出强大的少样本适应能力,无需微调即可适应新任务。相比之下,当前视觉基础模型(VFMs)缺乏这种能力,需要显式微调及充足数据。研究探索了利用预训练LoRA(低秩适配)实现VFMs无微调少样本适配的潜力。通过构建一个名为LoRA Recycle的框架,利用元学习目标从多个预训练LoRA中提取元LoRA,并利用反向生成的代理数据进行训练。装备元LoRA的VFM能像LLMs那样,在一次前向传递中解决新的少样本任务。此外,研究还提出了一个高效的双重机制,以加速元训练过程并保持或提升性能。实验证明,该框架在多种少样本分类基准测试中表现卓越。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)如ChatGPT可在无需微调的情况下适应新任务,适用于数据有限和实时应用。
- 当前视觉基础模型(VFMs)缺乏这种少样本适应性,需要显式微调及数据。
- 研究首次探索利用预训练的LoRA(低秩适配)实现VFMs的无微调少样本适配潜力。
- LoRA Recycle框架通过元学习目标和代理数据提取元LoRA。
- 装备元LoRA的VFM能像LLMs一样,快速适应新任务。
- 研究提出一个高效的双重机制,以加速元训练过程并保持性能。
点此查看论文截图

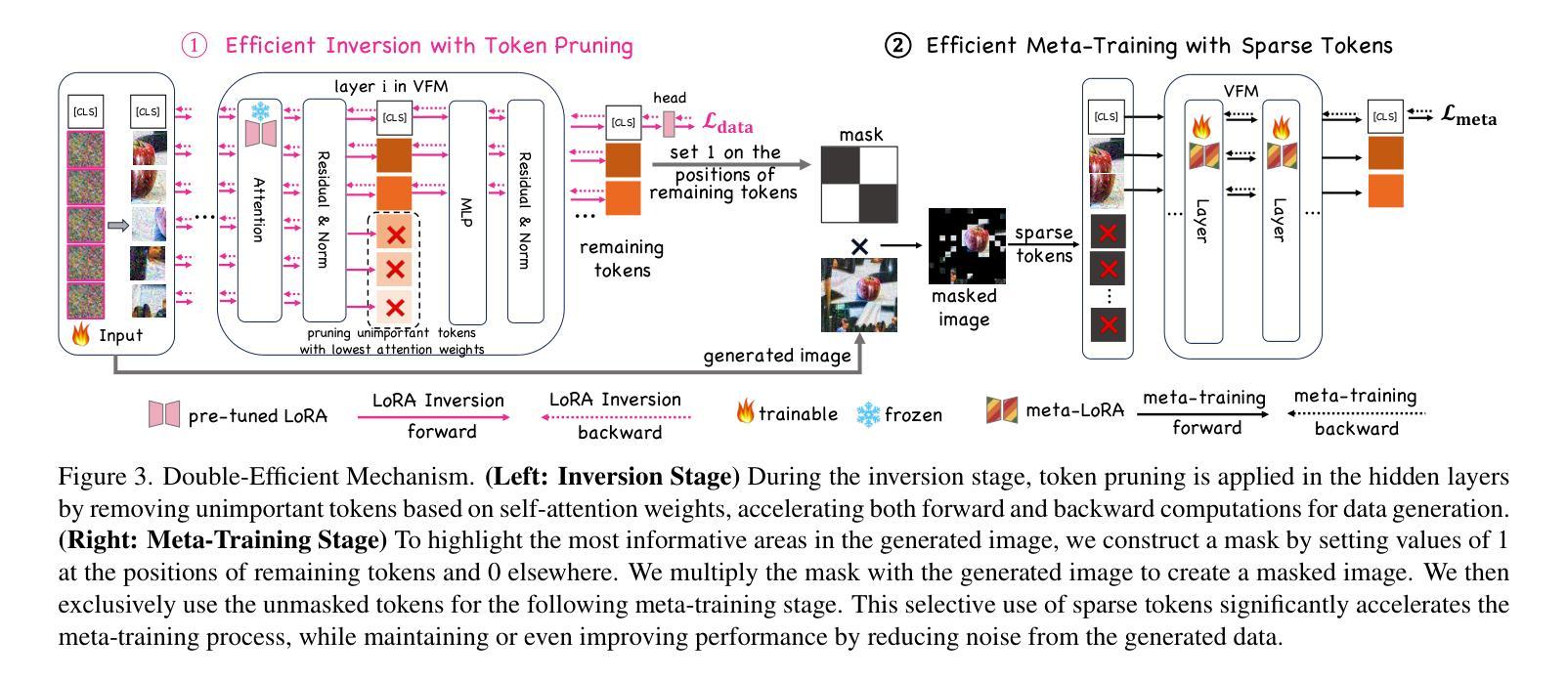
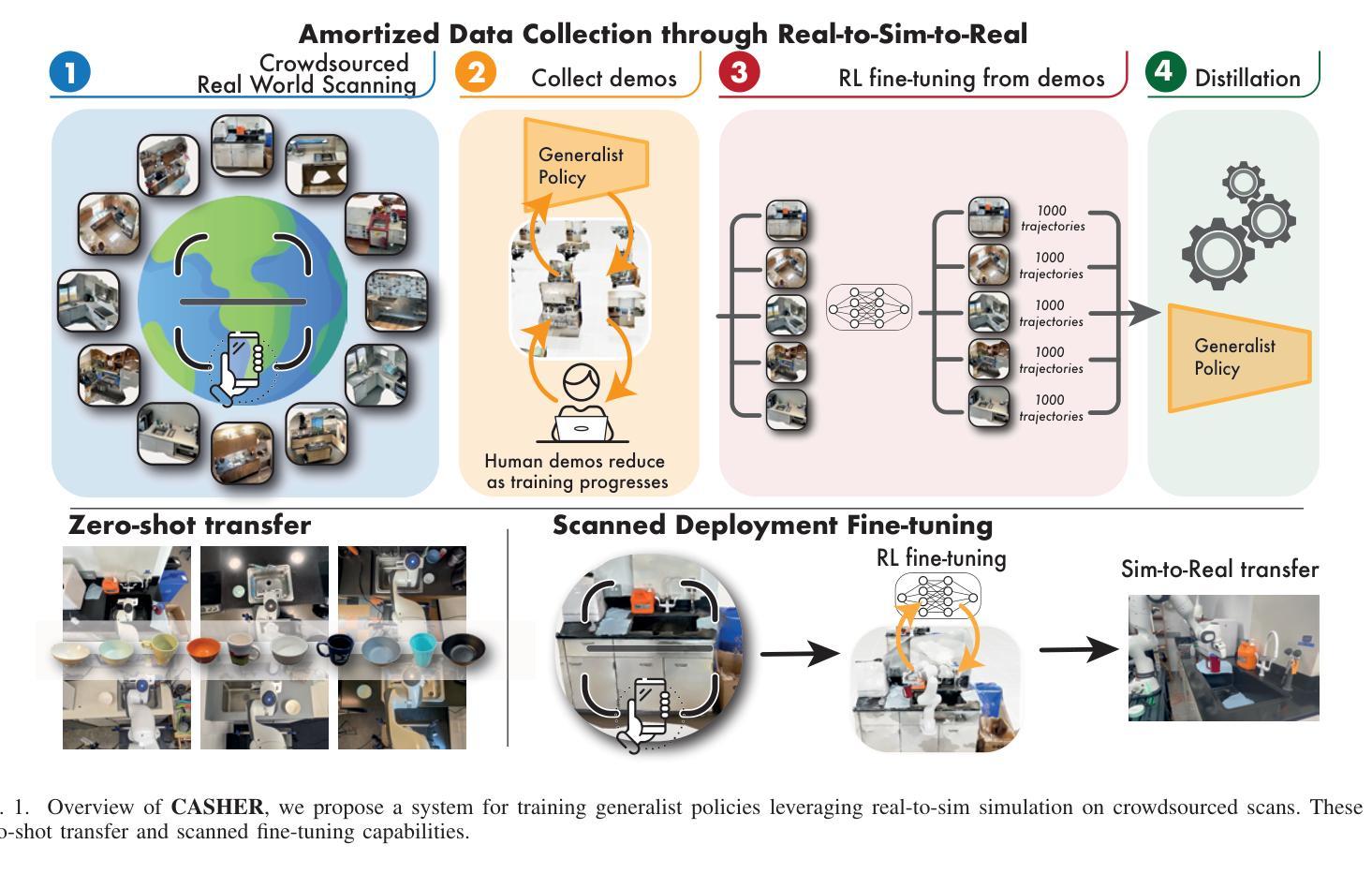
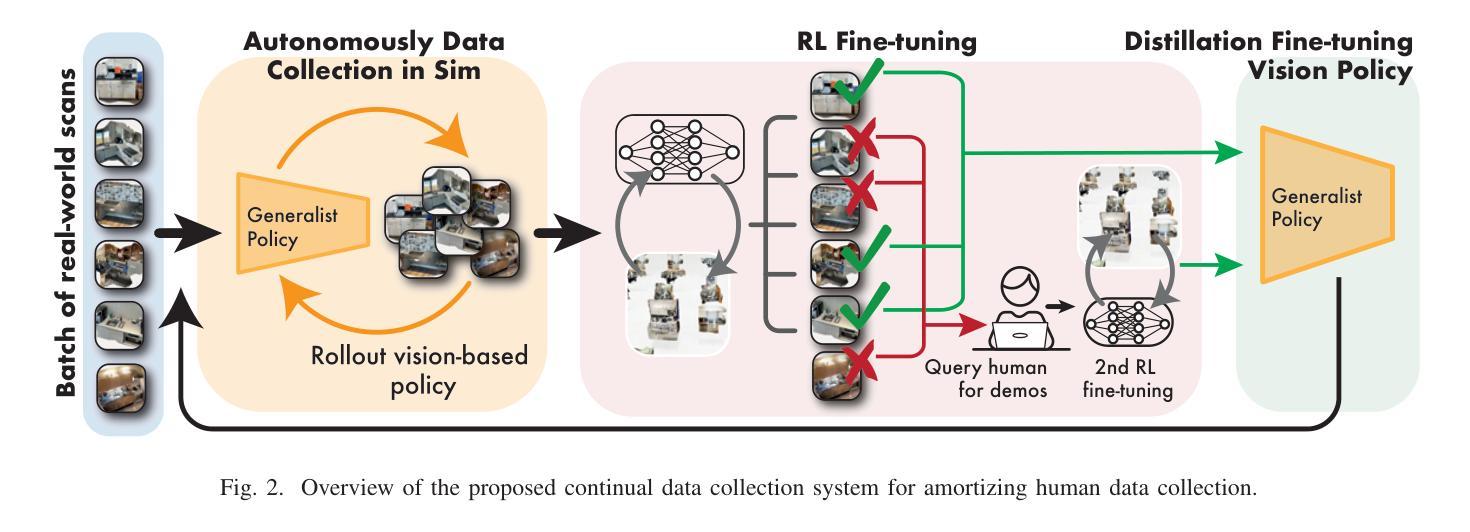
Robot Learning with Super-Linear Scaling
Authors:Marcel Torne, Arhan Jain, Jiayi Yuan, Vidaaranya Macha, Lars Ankile, Anthony Simeonov, Pulkit Agrawal, Abhishek Gupta
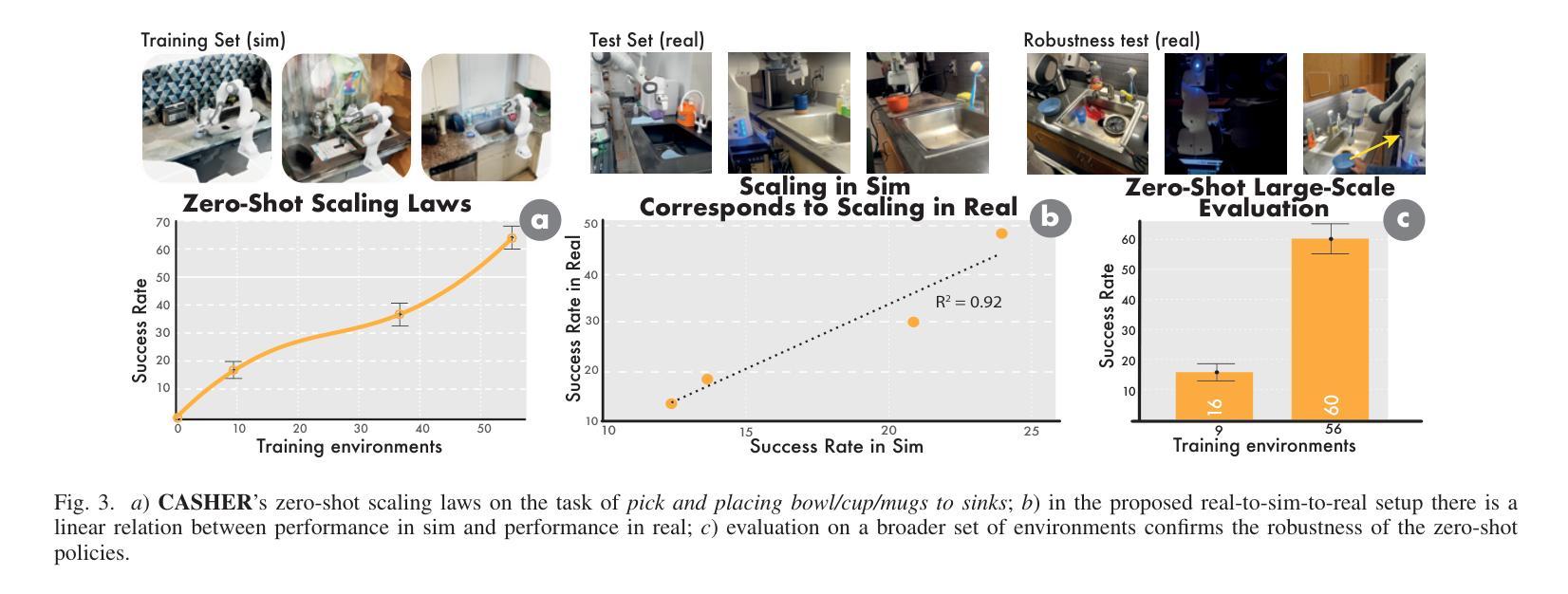
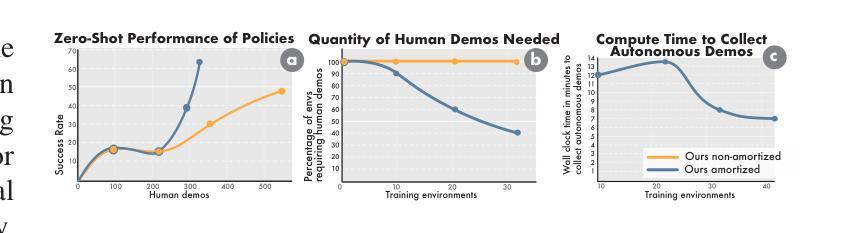
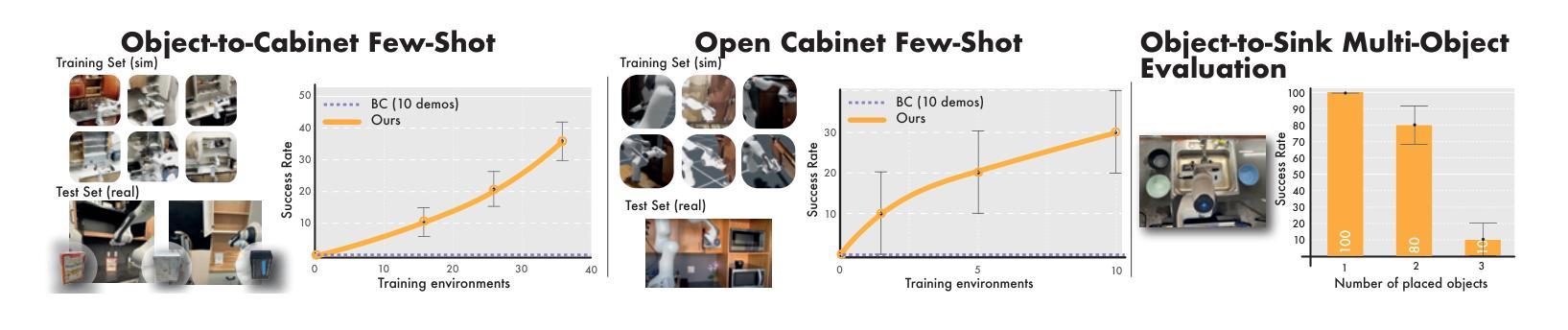
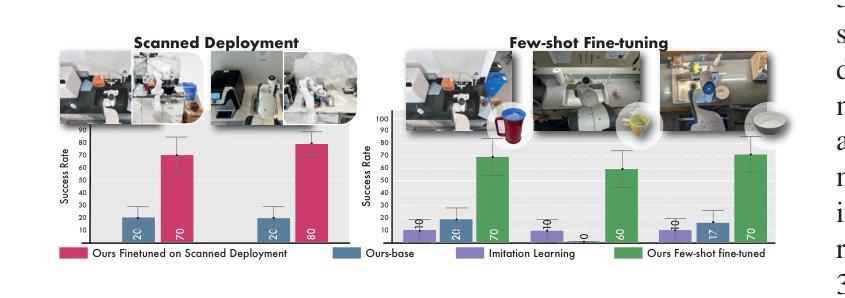
Scaling robot learning requires data collection pipelines that scale favorably with human effort. In this work, we propose Crowdsourcing and Amortizing Human Effort for Real-to-Sim-to-Real(CASHER), a pipeline for scaling up data collection and learning in simulation where the performance scales superlinearly with human effort. The key idea is to crowdsource digital twins of real-world scenes using 3D reconstruction and collect large-scale data in simulation, rather than the real-world. Data collection in simulation is initially driven by RL, bootstrapped with human demonstrations. As the training of a generalist policy progresses across environments, its generalization capabilities can be used to replace human effort with model generated demonstrations. This results in a pipeline where behavioral data is collected in simulation with continually reducing human effort. We show that CASHER demonstrates zero-shot and few-shot scaling laws on three real-world tasks across diverse scenarios. We show that CASHER enables fine-tuning of pre-trained policies to a target scenario using a video scan without any additional human effort. See our project website: https://casher-robot-learning.github.io/CASHER/
在扩大机器人学习规模时,我们需要有利于人类投入的数据采集流程。在这项工作中,我们提出了针对模拟环境下数据采集与学习的“群源化与消解人力投入的实时仿真采集(CASHER)”流程,该流程实现了超越人力投入的线性增长规模化效应。其主要思想是利用三维重建技术众包现实场景的数字双胞胎,并在模拟环境中而非真实环境中收集大规模数据。模拟环境中的数据采集最初由强化学习驱动,辅以人类示范。随着通用策略在不同环境中的训练进展,其通用能力可用来替换模拟生成的演示代替人力投入。这导致了一种模拟行为数据采集的流程,并随着训练过程持续减少人力投入。我们在三个真实任务的不同场景中展示了CASHER的无预设和少预设扩展定律。我们还展示了CASHER能够通过视频扫描对预训练策略进行微调以适应目标场景,无需任何额外的人力投入。更多详情,请访问我们的项目网站:CASHER项目网站链接。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为CASHER的数据收集流水线,旨在通过模拟环境实现机器人学习的规模化。CASHER利用3D重建技术众包数字双胞胎场景,在模拟环境中收集大规模数据,并通过强化学习和人类演示驱动数据收集过程。随着通用策略的训练进展,利用其在不同环境中的泛化能力逐步减少人力参与,转而使用模型生成演示数据。最终实现在模拟环境中收集行为数据的同时,持续减少人力投入。在三个真实任务中,CASHER展现出零样本和少样本扩展定律的优势,并能通过视频扫描对预训练策略进行微调,无需额外人力投入。
Key Takeaways
- CASHER是一种用于机器人学习的数据收集流水线,旨在通过模拟环境实现规模化数据收集和学习。
- 利用3D重建技术众包数字双胞胎场景,以收集模拟环境中的大规模数据。
- 通过强化学习和人类演示相结合,驱动数据收集过程。
- 随着通用策略的训练进展,利用其在不同环境中的泛化能力逐步减少人力参与。
- CASHER实现了在模拟环境中收集行为数据的同时,持续减少人力投入。
- 在三个真实任务中,CASHER展现出零样本和少样本扩展定律的优势。
点此查看论文截图

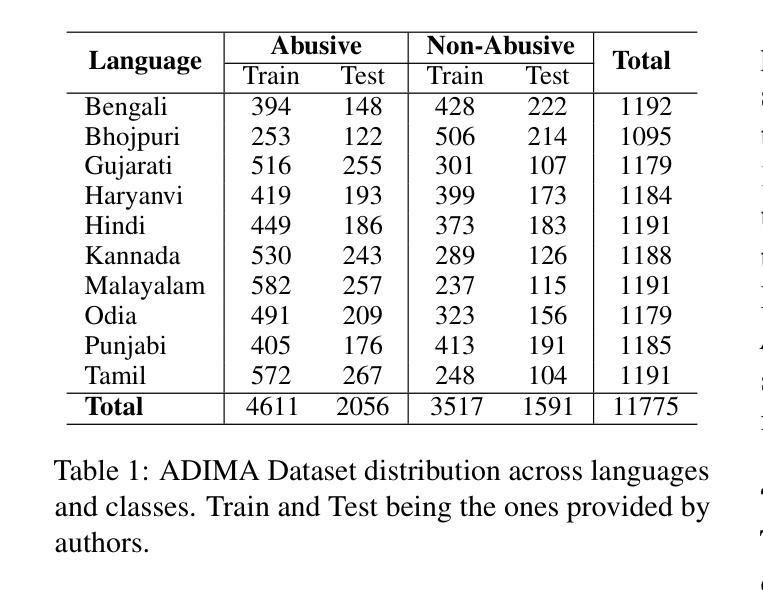
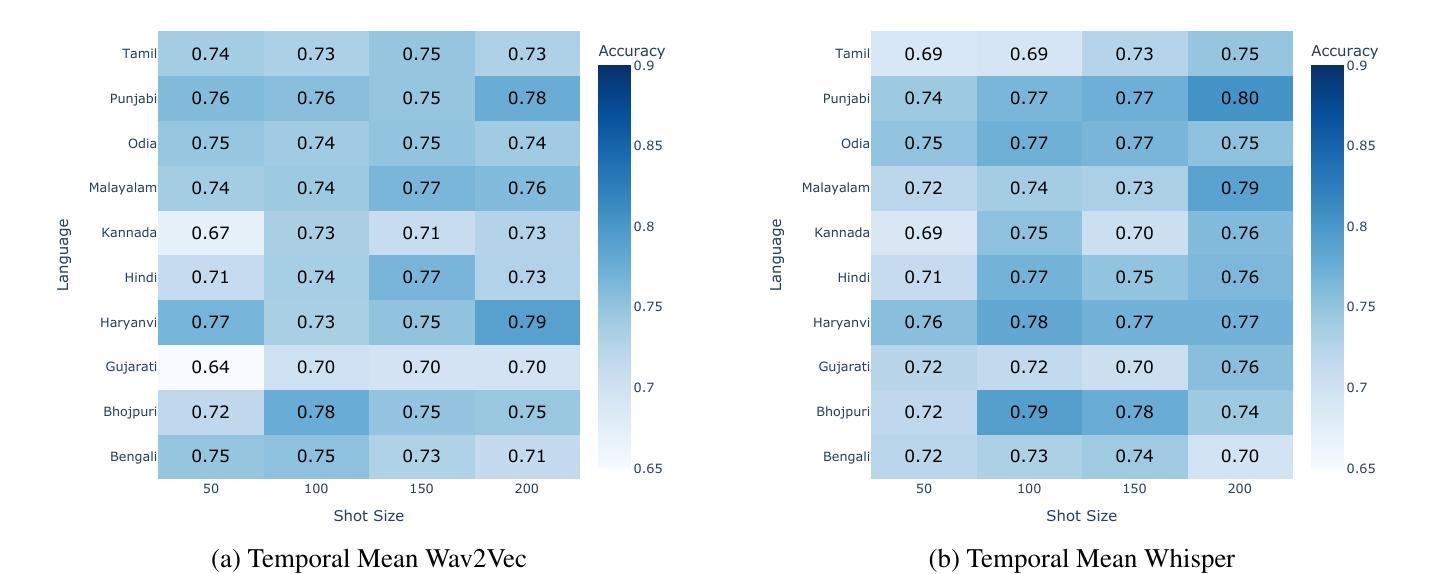
Towards Cross-Lingual Audio Abuse Detection in Low-Resource Settings with Few-Shot Learning
Authors:Aditya Narayan Sankaran, Reza Farahbakhsh, Noel Crespi
Online abusive content detection, particularly in low-resource settings and within the audio modality, remains underexplored. We investigate the potential of pre-trained audio representations for detecting abusive language in low-resource languages, in this case, in Indian languages using Few Shot Learning (FSL). Leveraging powerful representations from models such as Wav2Vec and Whisper, we explore cross-lingual abuse detection using the ADIMA dataset with FSL. Our approach integrates these representations within the Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML) framework to classify abusive language in 10 languages. We experiment with various shot sizes (50-200) evaluating the impact of limited data on performance. Additionally, a feature visualization study was conducted to better understand model behaviour. This study highlights the generalization ability of pre-trained models in low-resource scenarios and offers valuable insights into detecting abusive language in multilingual contexts.
网络滥用内容检测,特别是在资源匮乏的环境和音频模式下,仍然研究不足。我们调查了预训练音频表示在检测低资源语言中的攻击性语言的潜力,本例中为使用小样本学习(FSL)的印度语言。我们利用Wav2Vec和Whisper等模型的强大表示能力,使用ADIMA数据集进行跨语言滥用检测FSL。我们的方法将这些表示形式纳入模型无关元学习(MAML)框架,以在10种语言中分类攻击性语言。我们试验了各种射击规模(50-200),评估有限数据对性能的影响。此外,还进行了特征可视化研究,以更好地了解模型的行为。这项研究突出了预训练模型在资源匮乏场景中的泛化能力,并为在多语种环境中检测攻击性语言提供了有价值的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as part of the proceedings of COLING 2025
Summary
本研究探索了预训练音频表示在低资源语言环境中检测滥用语言的潜力,特别是针对印度语言。研究利用Wav2Vec和Whisper等模型的强大表示能力,结合Few Shot Learning(FSL)方法,使用ADIMA数据集进行跨语言滥用检测。该研究将预训练模型集成到Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning(MAML)框架中,以在有限的训练数据下分类滥用语言,涉及多种语言。此外,还进行了特征可视化研究,以更好地理解模型行为。研究突显了预训练模型在低资源场景中的泛化能力,并为多语言环境检测滥用语言提供了有价值的见解。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究探讨了在线滥用内容检测的音频模态方面的问题,特别是在低资源环境中。
- 研究关注在印度语言中利用预训练音频表示进行滥用检测。
- 研究采用Few Shot Learning (FSL)方法进行跨语言滥用检测。
- 使用Wav2Vec和Whisper等模型进行强大的表示,集成到Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning (MAML)框架中分类滥用语言。
- 实验涉及多种语言和不同的训练数据量(从50到200个样本)。
- 特征可视化研究有助于更好地理解模型行为。
- 研究发现预训练模型在低资源场景下具有良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

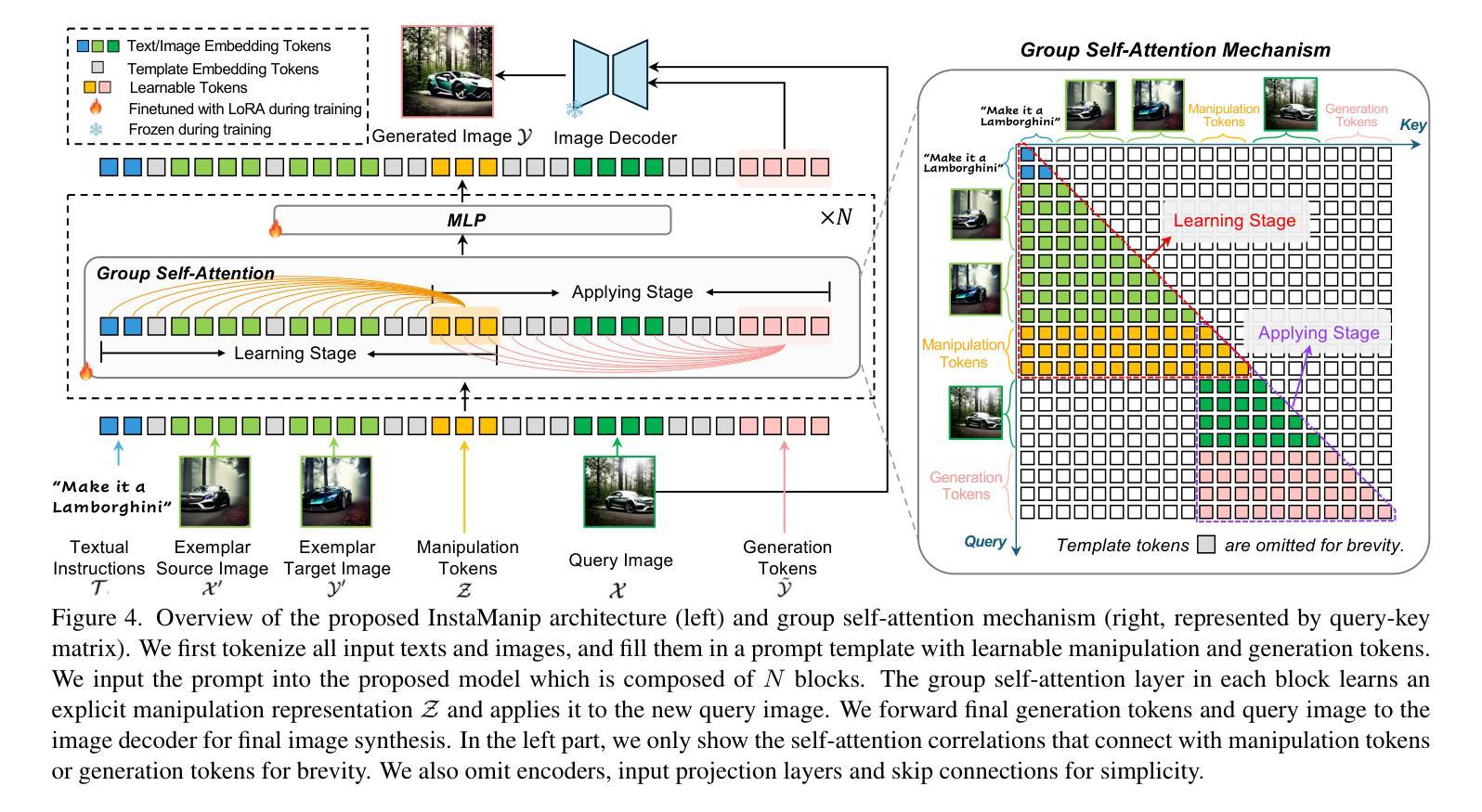
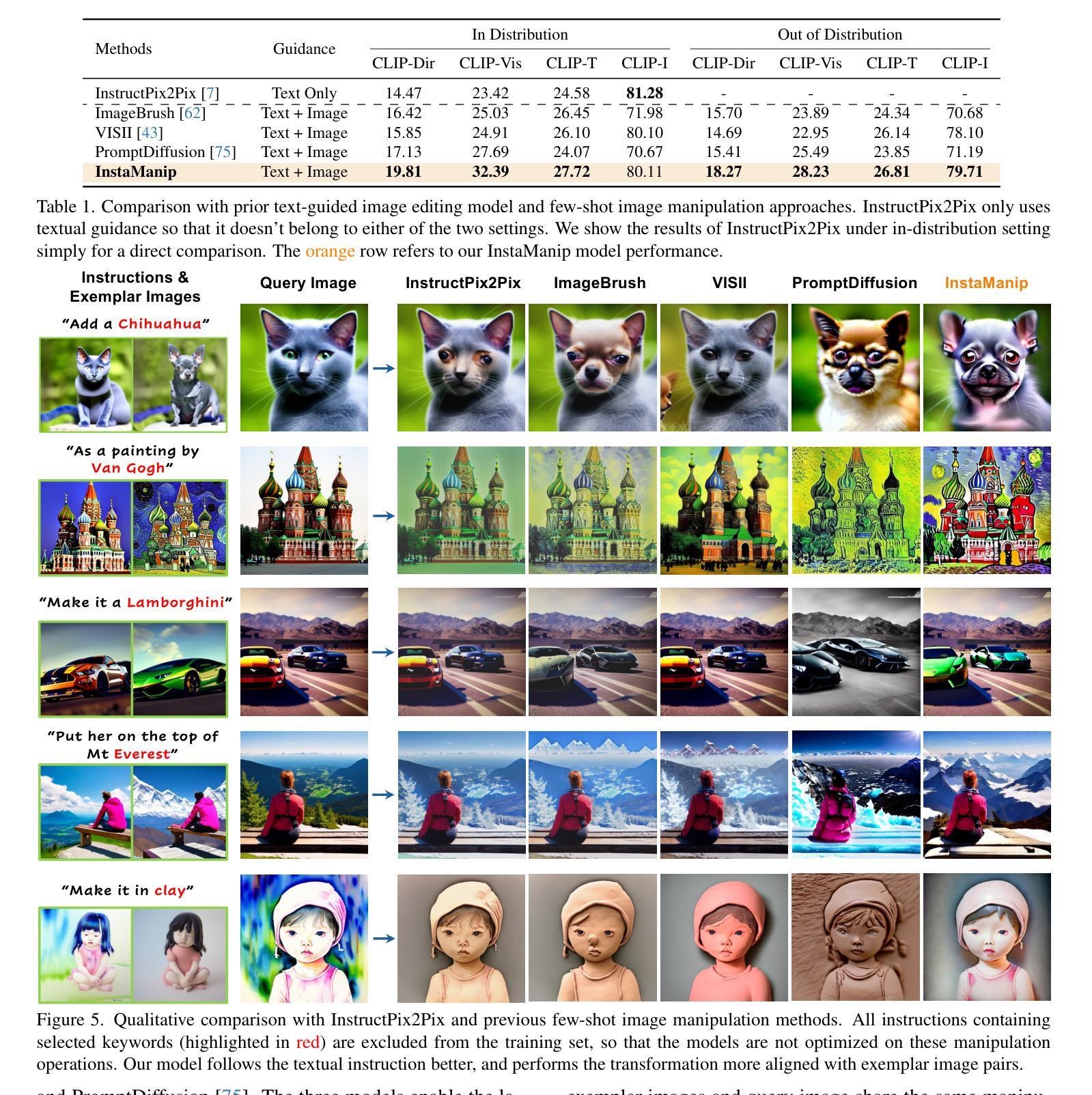
Unleashing In-context Learning of Autoregressive Models for Few-shot Image Manipulation
Authors:Bolin Lai, Felix Juefei-Xu, Miao Liu, Xiaoliang Dai, Nikhil Mehta, Chenguang Zhu, Zeyi Huang, James M. Rehg, Sangmin Lee, Ning Zhang, Tong Xiao
Text-guided image manipulation has experienced notable advancement in recent years. In order to mitigate linguistic ambiguity, few-shot learning with visual examples has been applied for instructions that are underrepresented in the training set, or difficult to describe purely in language. However, learning from visual prompts requires strong reasoning capability, which diffusion models are struggling with. To address this issue, we introduce a novel multi-modal autoregressive model, dubbed $\textbf{InstaManip}$, that can $\textbf{insta}$ntly learn a new image $\textbf{manip}$ulation operation from textual and visual guidance via in-context learning, and apply it to new query images. Specifically, we propose an innovative group self-attention mechanism to break down the in-context learning process into two separate stages – learning and applying, which simplifies the complex problem into two easier tasks. We also introduce a relation regularization method to further disentangle image transformation features from irrelevant contents in exemplar images. Extensive experiments suggest that our method surpasses previous few-shot image manipulation models by a notable margin ($\geq$19% in human evaluation). We also find our model can be further boosted by increasing the number or diversity of exemplar images.
文本引导的图像操作近年来取得了显著的进展。为了减轻语言模糊性,使用视觉示例进行的小样本学习被应用于训练集中表示不足或仅凭语言难以描述的指令。然而,从视觉提示中学习需要强大的推理能力,这正是扩散模型所面临的挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了一种新型的多模式自回归模型,名为InstaManip,该模型能够即刻从文本和视觉指导中学习新的图像操作,并通过上下文学习应用于新的查询图像。具体来说,我们提出了一种创新性的分组自注意力机制,将上下文学习过程分解为两个单独的阶段——学习和应用,将复杂问题简化为两个更容易的任务。我们还引入了一种关系正则化方法,以进一步从示例图像中的无关内容中分离出图像转换特征。大量实验表明,我们的方法在少数图像操作模型中的表现超过了之前的模型,在人类评估中的优势显著(提高≥19%)。我们还发现,通过增加示例图像的数量或多样性,我们的模型可以进一步提高性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 16 figures, 5 tables
Summary
本文介绍了文本引导的图像操作技术的最新进展。为解决少数学习情况下视觉提示的语言模糊和推理能力不足的问题,提出了一种新型的多模态自回归模型——InstaManip。该模型能够即时从文本和视觉指导中学习新的图像操作,并应用于新的查询图像。模型通过分组自注意力机制将学习过程分为学习和应用两个阶段,并引入关系正则化方法来进一步分离图像转换特征。实验表明,该方法在少数图像操作任务上的表现优于先前的方法,并且可以通过增加示例图像的数量或多样性进一步提高性能。
Key Takeaways
- 文本引导的图像操作技术近年来取得显著进展。
- 为解决语言模糊和推理能力不足的问题,引入了多模态自回归模型InstaManip。
- InstaManip能够从文本和视觉指导中学习新的图像操作并即时应用。
- 模型通过分组自注意力机制将学习过程分为学习和应用两个阶段。
- 引入关系正则化方法来分离图像转换特征。
- 实验表明,InstaManip在少数图像操作任务上的表现优于先前的方法。
点此查看论文截图



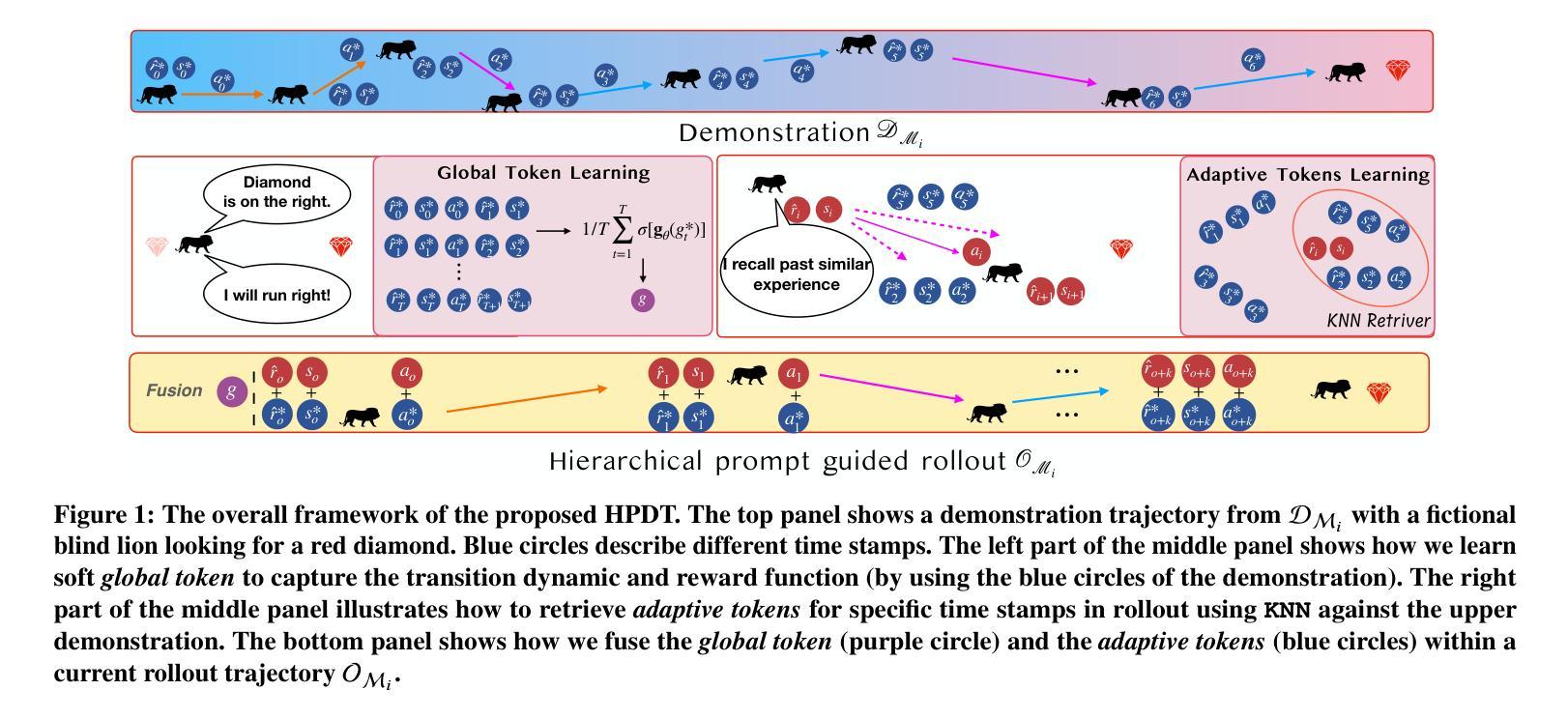
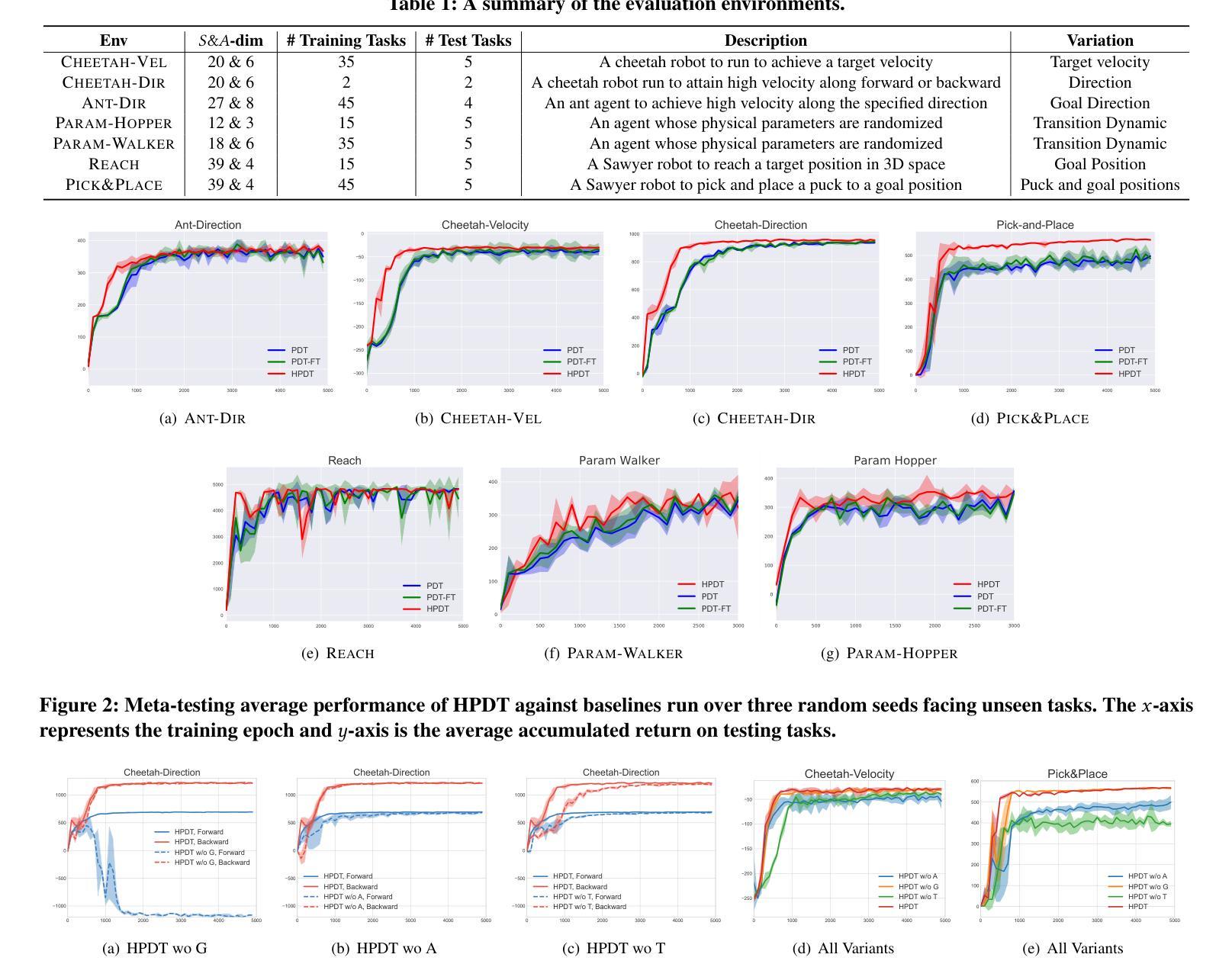
Hierarchical Prompt Decision Transformer: Improving Few-Shot Policy Generalization with Global and Adaptive
Authors:Zhe Wang, Haozhu Wang, Yanjun Qi
Decision transformers recast reinforcement learning as a conditional sequence generation problem, offering a simple but effective alternative to traditional value or policy-based methods. A recent key development in this area is the integration of prompting in decision transformers to facilitate few-shot policy generalization. However, current methods mainly use static prompt segments to guide rollouts, limiting their ability to provide context-specific guidance. Addressing this, we introduce a hierarchical prompting approach enabled by retrieval augmentation. Our method learns two layers of soft tokens as guiding prompts: (1) global tokens encapsulating task-level information about trajectories, and (2) adaptive tokens that deliver focused, timestep-specific instructions. The adaptive tokens are dynamically retrieved from a curated set of demonstration segments, ensuring context-aware guidance. Experiments across seven benchmark tasks in the MuJoCo and MetaWorld environments demonstrate the proposed approach consistently outperforms all baseline methods, suggesting that hierarchical prompting for decision transformers is an effective strategy to enable few-shot policy generalization.
决策变压器将强化学习重新构建为条件序列生成问题,为传统的基于价值或政策的方法提供了一种简单而有效的替代方案。该领域的最新关键进展是在决策变压器中融入提示,以促进少量策略泛化。然而,当前的方法主要使用静态提示段来指导滚动过程,这限制了它们提供特定上下文指导的能力。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了通过检索增强功能实现分层提示方法。我们的方法学习了两层软令牌作为指导提示:(1)全局令牌,封装轨迹的任务级别信息,(2)自适应令牌,传递聚焦的、时间步长特定的指令。自适应令牌是从精选的演示段集中动态检索的,确保上下文感知的指导。在MuJoCo和MetaWorld环境中的七个基准任务的实验表明,所提出的方法始终优于所有基线方法,这表明为决策变压器进行分层提示是一种有效的策略,可实现少量策略泛化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
决策变压器通过将强化学习重新构建为条件序列生成问题,提供了一种简单有效的替代传统价值或策略基础方法的方式。最新的关键进展是决策变压器中提示的集成,以促进少量策略泛化。然而,当前的方法主要使用静态提示段来指导演练,这限制了它们提供特定上下文指导的能力。为解决此问题,我们引入了通过检索增强实现分层提示的方法。我们的方法学习了两层软令牌作为引导提示:1)全局令牌,封装轨迹的任务级信息;2)自适应令牌,提供专注的、时间步长特定的指令。自适应令牌是从精选的演示段集中动态检索的,以确保上下文感知的指导。在MuJoCo和MetaWorld环境中的七个基准任务上的实验表明,所提出的方法始终优于所有基线方法,这表明为决策变压器进行分层提示是一种有效的策略,可实现少量策略泛化。
Key Takeaways
- 决策变压器将强化学习重新定位为条件序列生成问题,提供了对传统价值或策略基础的替代方法。
- 当前方法主要通过静态提示段引导决策变压器,限制了上下文特定的指导能力。
- 提出了一种通过检索增强实现分层提示的方法,包括全局令牌和自适应令牌。
- 全局令牌封装任务级别的轨迹信息。
- 自适应令牌从演示段集中动态检索,提供针对性的时间步长特定指令。
- 在多个环境中的实验表明,所提出的方法在少量策略泛化方面优于所有基线方法。
- 分层提示对于提高决策变压器的性能是有效的。
点此查看论文截图

Prompt as Free Lunch: Enhancing Diversity in Source-Free Cross-domain Few-shot Learning through Semantic-Guided Prompting
Authors:Linhai Zhuo, Zheng Wang, Yuqian Fu, Tianwen Qian
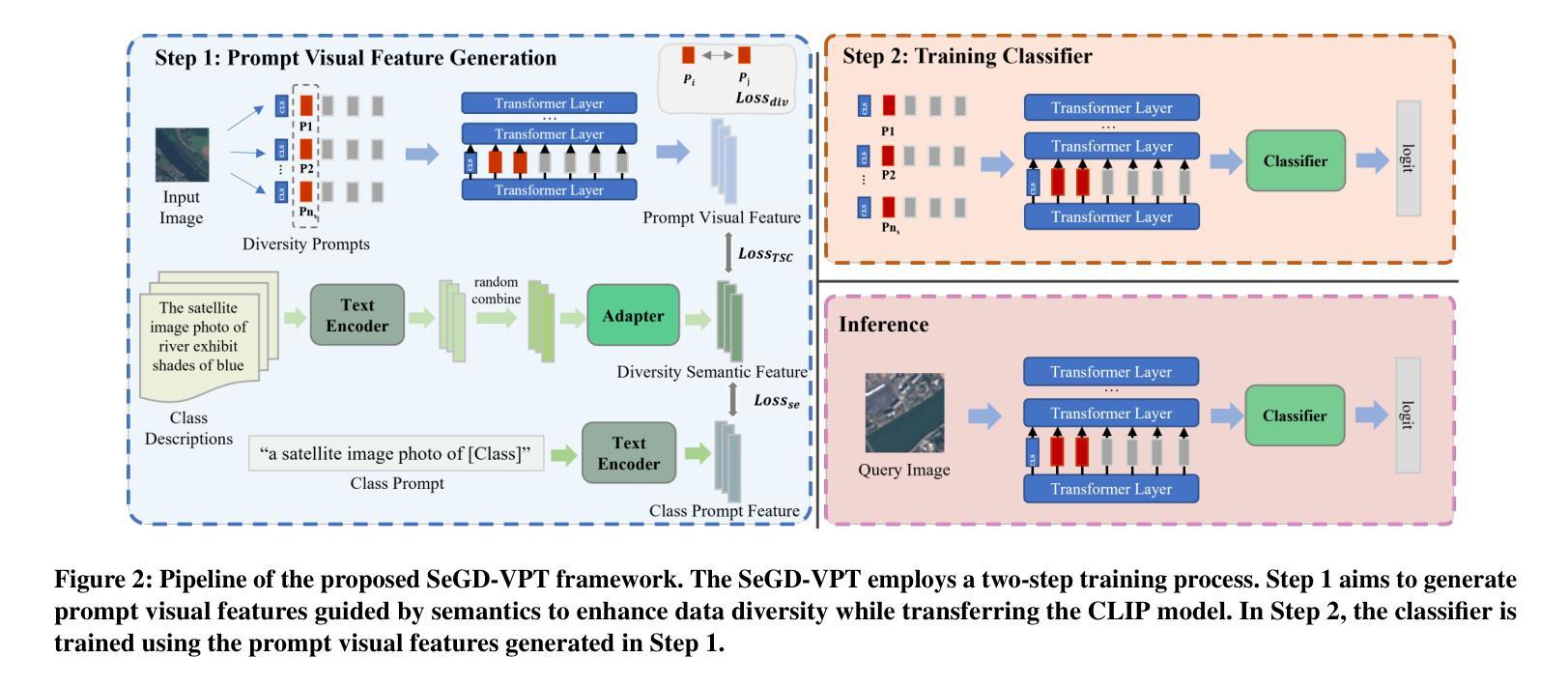
The source-free cross-domain few-shot learning (CD-FSL) task aims to transfer pretrained models to target domains utilizing minimal samples, eliminating the need for source domain data. Addressing this issue requires models to have robust generalization abilities and strong feature representation, aligning with the characteristics of large-scale pretrained models. However, large-scale models tend to lose representational ability in cross-domain scenarios due to limited sample diversity. \zlh{Given the abundant diversity provided by semantic modality, this paper leverages textual modality to enhance training sample diversity with CLP model}, meanwhile improving model transfer efficiency. Specifically, we propose the SeGD-VPT framework, which is divided into two phases. The first step aims to increase feature diversity by adding diversity prompts to each support sample, thereby generating varying input and enhancing sample diversity. Furthermore, we use diversity descriptions of classes to guide semantically meaningful learning of diversity prompts, proposing random combinations and selections of texts to increase textual diversity. Additionally, deep prompt tuning is introduced to enhance the model’s transfer capability. After training of the first step, support samples with different diversity prompts are input into the CLIP backbone to generate enhanced features. After generation, the second phase trains classifiers using the generated features. Extensive experimental results across several benchmarks verify our method is comparable to SOTA source-utilized models and attain the best performance under the source-free CD-FSL setting.
无源跨域小样本学习(CD-FSL)任务旨在利用少量样本将预训练模型迁移到目标域,从而消除对源域数据的需求。解决此问题需要模型具备强大的泛化能力和特征表示能力,这与大规模预训练模型的特征相吻合。然而,大规模模型在跨域场景中往往会因样本多样性有限而失去表示能力。鉴于语义模态提供的丰富多样性,本文利用文本模态通过CLP模型增强训练样本的多样性,同时提高模型的迁移效率。具体来说,我们提出了SeGD-VPT框架,该框架分为两个阶段。第一步旨在通过为每个支持样本添加多样性提示来增加特征多样性,从而产生不同的输入并增强样本多样性。此外,我们使用类的多样性描述来指导多样性提示的语义有意义学习,提出文本的随机组合和选择来增加文本多样性。另外,还引入了深度提示调整来增强模型的迁移能力。完成第一步的训练后,带有不同多样性提示的支持样本被输入到CLIP主干网中生成增强特征。特征生成后,第二阶段使用生成的特性训练分类器。在多个基准测试上的广泛实验结果验证了我们的方法与源利用模型的最佳性能相当,并在无源CD-FSL设置下取得了最佳性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了无源跨域小样本学习(CD-FSL)任务,旨在利用预训练模型在目标域中使用少量样本进行迁移,无需源域数据。文章提出了SeGD-VPT框架,通过增加特征多样性来提高模型在跨域场景中的表现,利用文本模态增强训练样本的多样性,同时提高模型的迁移效率。通过两个阶段的训练,生成增强特征并训练分类器。实验结果表明,该方法与最先进的源利用模型相当,并在无源CD-FSL设置中达到最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 源自由跨域小样本学习(CD-FSL)任务旨在利用预训练模型在目标域中使用少量样本进行迁移,无需源域数据。
- 模型需要强大的泛化能力和特征表示能力以应对CD-FSL的挑战。
- 大规模预训练模型在跨域场景中可能会失去代表性能力。
- 文本模态被用来增强训练样本的多样性,提高模型迁移效率。
- 提出了SeGD-VPT框架,通过增加特征多样性和利用文本模态来提高模型性能。
- SeGD-VPT框架分为两个阶段:第一阶段增加特征多样性,第二阶段使用增强特征训练分类器。
点此查看论文截图