⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-11 更新
Take Fake as Real: Realistic-like Robust Black-box Adversarial Attack to Evade AIGC Detection
Authors:Caiyun Xie, Dengpan Ye, Yunming Zhang, Long Tang, Yunna Lv, Jiacheng Deng, Jiawei Song
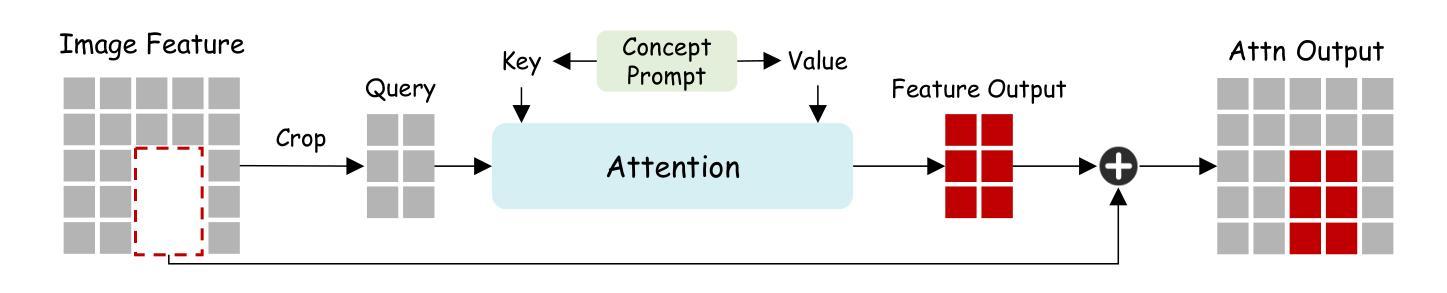
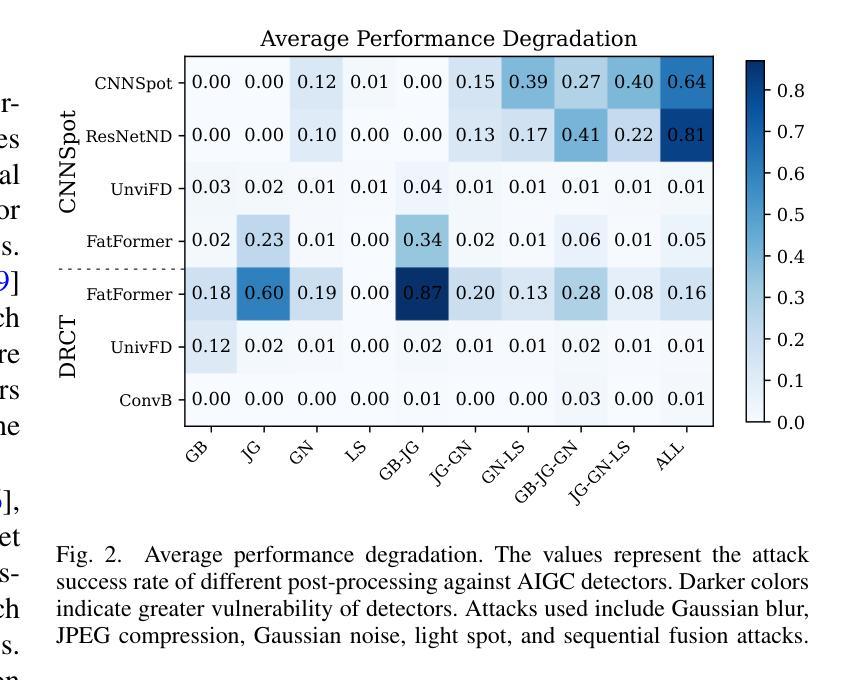
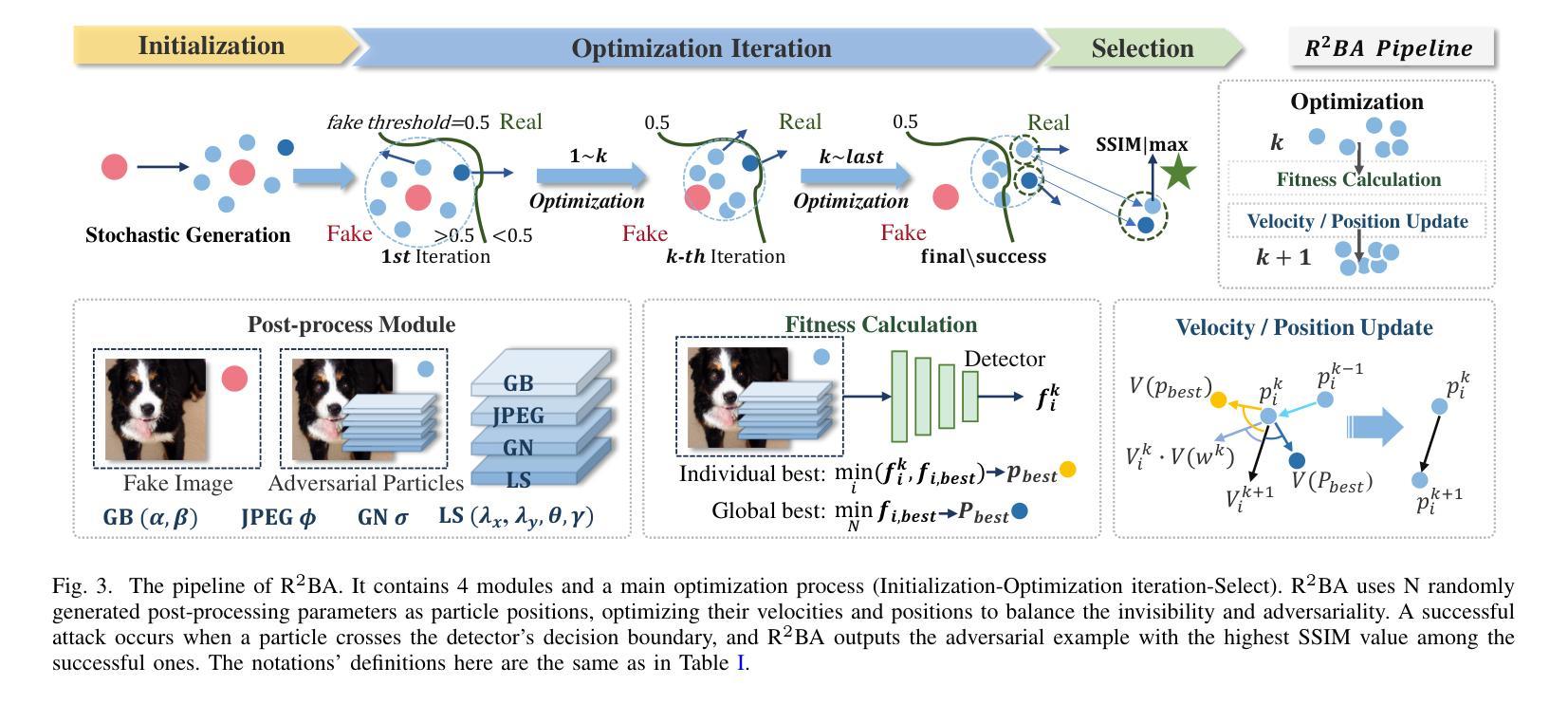
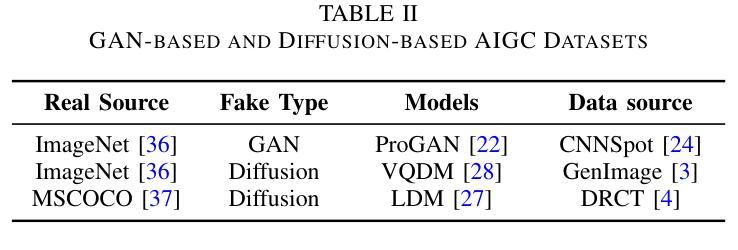
The security of AI-generated content (AIGC) detection based on GANs and diffusion models is closely related to the credibility of multimedia content. Malicious adversarial attacks can evade these developing AIGC detection. However, most existing adversarial attacks focus only on GAN-generated facial images detection, struggle to be effective on multi-class natural images and diffusion-based detectors, and exhibit poor invisibility. To fill this gap, we first conduct an in-depth analysis of the vulnerability of AIGC detectors and discover the feature that detectors vary in vulnerability to different post-processing. Then, considering the uncertainty of detectors in real-world scenarios, and based on the discovery, we propose a Realistic-like Robust Black-box Adversarial attack (R$^2$BA) with post-processing fusion optimization. Unlike typical perturbations, R$^2$BA uses real-world post-processing, i.e., Gaussian blur, JPEG compression, Gaussian noise and light spot to generate adversarial examples. Specifically, we use a stochastic particle swarm algorithm with inertia decay to optimize post-processing fusion intensity and explore the detector’s decision boundary. Guided by the detector’s fake probability, R$^2$BA enhances/weakens the detector-vulnerable/detector-robust post-processing intensity to strike a balance between adversariality and invisibility. Extensive experiments on popular/commercial AIGC detectors and datasets demonstrate that R$^2$BA exhibits impressive anti-detection performance, excellent invisibility, and strong robustness in GAN-based and diffusion-based cases. Compared to state-of-the-art white-box and black-box attacks, R$^2$BA shows significant improvements of 15% and 21% in anti-detection performance under the original and robust scenario respectively, offering valuable insights for the security of AIGC detection in real-world applications.
基于生成对抗网络(GANs)和扩散模型的AI生成内容(AIGC)检测的安全性,与多媒体内容的可信度密切相关。恶意的对抗性攻击可以躲避正在发展的AIGC检测。然而,现有的大多数对抗性攻击仅专注于GAN生成的面部图像检测,对于多类自然图像和基于扩散的检测器效果不佳,隐身性较差。为了填补这一空白,我们首先对AIGC检测器的脆弱性进行了深入分析,并发现了检测器在不同后处理中的脆弱性特征存在差异。然后,考虑到真实场景中检测器的不确定性,基于这一发现,我们提出了一种具有后处理融合优化的类似现实的稳健黑盒对抗性攻击(R$^2$BA)。不同于典型的扰动,R$^2$BA采用现实世界后处理,例如高斯模糊、JPEG压缩、高斯噪声和光斑来生成对抗样本。具体来说,我们使用具有惯性衰减的随机粒子群算法来优化后处理融合强度,并探索检测器的决策边界。在检测器的虚假概率引导下,R$^2$BA增强/减弱了检测器脆弱/检测器稳健的后处理强度,在对抗性和隐身性之间达到了平衡。在流行/商业AIGC检测器和数据集上的大量实验表明,R$^2$BA具有令人印象深刻的抗检测性能、出色的隐身性和强大的稳健性,在基于GAN和基于扩散的情况下都表现良好。与最先进的白盒和黑盒攻击相比,R$^2$BA在原始和稳健场景下的抗检测性能分别提高了15%和21%,为AIGC在现实世界应用中的检测安全提供了有价值的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于GAN和扩散模型的AI生成内容(AIGC)检测的安全性与多媒体内容的可信度密切相关。存在恶意对抗攻击可以躲避发展中的AIGC检测。针对现有对抗攻击在GAN生成的面部图像检测上的局限性,本文深入分析了AIGC检测器的脆弱性,并提出了一种现实性强的稳健黑盒对抗攻击(R^2BA)方法,结合后处理融合优化策略。R^2BA利用真实世界的后处理,如高斯模糊、JPEG压缩、高斯噪声和光斑,生成对抗样本。实验证明,R^2BA在流行的AIGC检测器和数据集上表现出强大的抗检测性能和稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- AI生成内容(AIGC)检测的安全性与多媒体可信度紧密相关。
- 存在恶意对抗攻击可以绕过发展中的AIGC检测技术。
- 当前对抗攻击主要关注GAN生成的面部图像检测,但在多类别自然图像和扩散模型检测器上的效果有限。
- 深入研究AIGC检测器的脆弱性,发现不同后处理导致的检测器差异。
- 提出一种新型黑盒对抗攻击方法R^2BA,结合后处理融合优化策略。
- R^2BA利用真实世界的后处理生成对抗样本,以增强检测器的平衡对抗性和隐蔽性。
点此查看论文截图


Rendering-Refined Stable Diffusion for Privacy Compliant Synthetic Data
Authors:Kartik Patwari, David Schneider, Xiaoxiao Sun, Chen-Nee Chuah, Lingjuan Lyu, Vivek Sharma
Growing privacy concerns and regulations like GDPR and CCPA necessitate pseudonymization techniques that protect identity in image datasets. However, retaining utility is also essential. Traditional methods like masking and blurring degrade quality and obscure critical context, especially in human-centric images. We introduce Rendering-Refined Stable Diffusion (RefSD), a pipeline that combines 3D-rendering with Stable Diffusion, enabling prompt-based control over human attributes while preserving posture. Unlike standard diffusion models that fail to retain posture or GANs that lack realism and flexible attribute control, RefSD balances posture preservation, realism, and customization. We also propose HumanGenAI, a framework for human perception and utility evaluation. Human perception assessments reveal attribute-specific strengths and weaknesses of RefSD. Our utility experiments show that models trained on RefSD pseudonymized data outperform those trained on real data in detection tasks, with further performance gains when combining RefSD with real data. For classification tasks, we consistently observe performance improvements when using RefSD data with real data, confirming the utility of our pseudonymized data.
随着隐私问题的日益突出以及GDPR和CCPA等法规的出台,保护图像数据集中的身份隐私成为必需,这催生了匿名化技术。然而,保持数据实用性也同样关键。像掩蔽和模糊处理这样的传统方法会降低质量并掩盖关键上下文信息,特别是在以人类为中心的图像中更是如此。我们推出了经过渲染优化的稳定扩散(RefSD)流程,它结合了3D渲染和稳定扩散技术,能够实现基于提示控制人类属性同时保持姿态。不同于无法保持姿态的标准扩散模型或缺乏真实感和灵活属性控制的生成对抗网络(GANs),RefSD在姿态保留、真实性和定制化之间取得了平衡。我们还推出了HumanGenAI框架,用于人类感知和效用评估。人类感知评估揭示了RefSD在特定属性方面的优势和劣势。我们的效用实验表明,在检测任务中,基于RefSD匿名化数据训练的模型表现优于基于真实数据训练的模型,并且当将RefSD与真实数据结合时,性能会得到进一步提升。在分类任务中,使用RefSD数据与真实数据相结合时,我们观察到性能持续改善,证实了匿名化数据的实用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
图像数据集隐私保护需求日益增长,GDPR和CCPA等法规促使对伪名化技术的需求上升。本研究推出一种名为Rendering-Refined Stable Diffusion(RefSD)的管道,结合3D渲染与Stable Diffusion技术,能够在保持姿态的同时实现基于提示的人类属性控制,并具备真实感和可定制性。此外,本研究还提出了HumanGenAI框架用于人类感知和实用性评估。结果显示,RefSD技术在属性感知上具有优点与不足,且在检测任务上表现优越。同时,使用RefSD数据的模型在分类任务上也表现优异,证明了其伪名化数据的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 图像数据集的隐私保护需求日益增长,促使伪名化技术的发展。
- Rendering-Refined Stable Diffusion(RefSD)结合3D渲染与Stable Diffusion技术,保持姿态的同时实现基于提示的人类属性控制。
- RefSD技术实现了真实感和可定制性的平衡。
- HumanGenAI框架用于评估图像数据的人类感知和实用性。
- RefSD技术在属性感知方面具有一定的优点和局限。
- 使用RefSD技术的模型在检测任务上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图


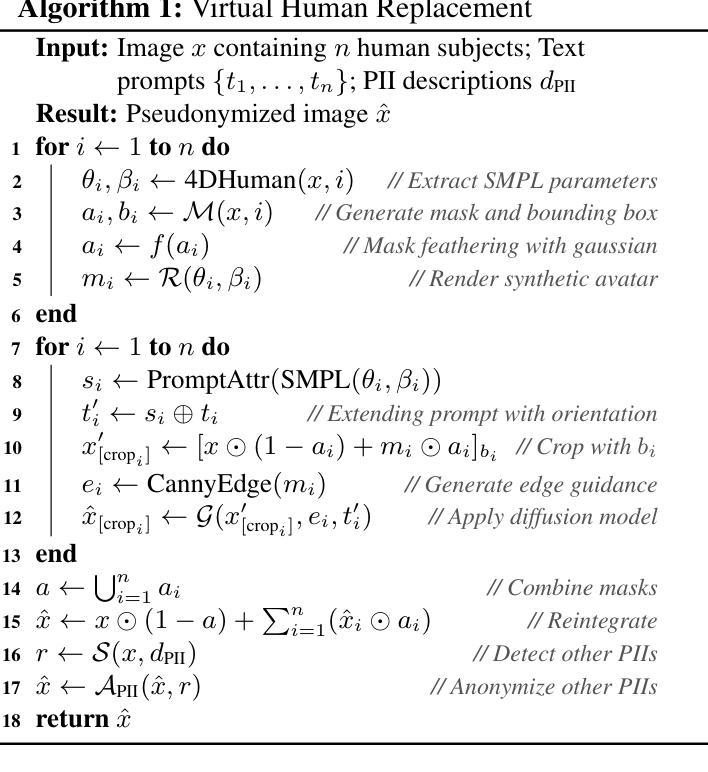
Accelerating Video Diffusion Models via Distribution Matching
Authors:Yuanzhi Zhu, Hanshu Yan, Huan Yang, Kai Zhang, Junnan Li
Generative models, particularly diffusion models, have made significant success in data synthesis across various modalities, including images, videos, and 3D assets. However, current diffusion models are computationally intensive, often requiring numerous sampling steps that limit their practical application, especially in video generation. This work introduces a novel framework for diffusion distillation and distribution matching that dramatically reduces the number of inference steps while maintaining-and potentially improving-generation quality. Our approach focuses on distilling pre-trained diffusion models into a more efficient few-step generator, specifically targeting video generation. By leveraging a combination of video GAN loss and a novel 2D score distribution matching loss, we demonstrate the potential to generate high-quality video frames with substantially fewer sampling steps. To be specific, the proposed method incorporates a denoising GAN discriminator to distil from the real data and a pre-trained image diffusion model to enhance the frame quality and the prompt-following capabilities. Experimental results using AnimateDiff as the teacher model showcase the method’s effectiveness, achieving superior performance in just four sampling steps compared to existing techniques.
生成模型,特别是扩散模型,在各种模态的数据合成中都取得了显著的成功,包括图像、视频和3D资产。然而,当前的扩散模型计算量大,通常需要大量的采样步骤,限制了其实际应用,尤其是在视频生成方面。这项工作介绍了一种新的扩散蒸馏和分布匹配框架,该框架在维持甚至可能提高生成质量的同时,大幅减少了推理步骤的数量。我们的方法侧重于将预训练的扩散模型蒸馏到一个更有效率的多步生成器中,特别针对视频生成。通过结合视频GAN损失和一种新的2D分数分布匹配损失,我们展示了用更少的采样步骤生成高质量视频帧的潜力。具体来说,所提出的方法采用一个去噪GAN鉴别器从真实数据和预训练的图像扩散模型中提炼精华,以提升帧质量和遵循提示的能力。使用AnimateDiff作为教师模型进行的实验结果展示了该方法的有效性,在仅四个采样步骤内便实现了对现有技术的超越。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型,特别是在图像、视频和3D资产等多个领域的数据合成方面取得了显著的成功。然而,当前扩散模型计算量大,需要大量采样步骤,限制了其实际应用,特别是在视频生成方面。本文介绍了一种新的扩散蒸馏和分布匹配框架,通过蒸馏预训练的扩散模型,能显著减少推理步骤,同时保持甚至提高生成质量。该方法专注于针对视频生成的更高效的几步生成器。通过结合视频GAN损失和新的二维分数分布匹配损失,我们展示了在减少采样步骤的同时生成高质量视频帧的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型已在多领域数据合成上取得显著成功,但计算量大和采样步骤多限制了其实际应用。
- 本文提出了一个新的扩散蒸馏和分布匹配框架,旨在提高扩散模型的效率。
- 新方法通过蒸馏预训练的扩散模型,能显著减少推理步骤。
- 方法专注于针对视频生成的更高效生成器设计。
- 结合视频GAN损失和二维分数分布匹配损失,生成高质量视频帧。
- 使用AnimateDiff作为教师模型进行实验,展示新方法在四个采样步骤内即可实现优越性能。
点此查看论文截图


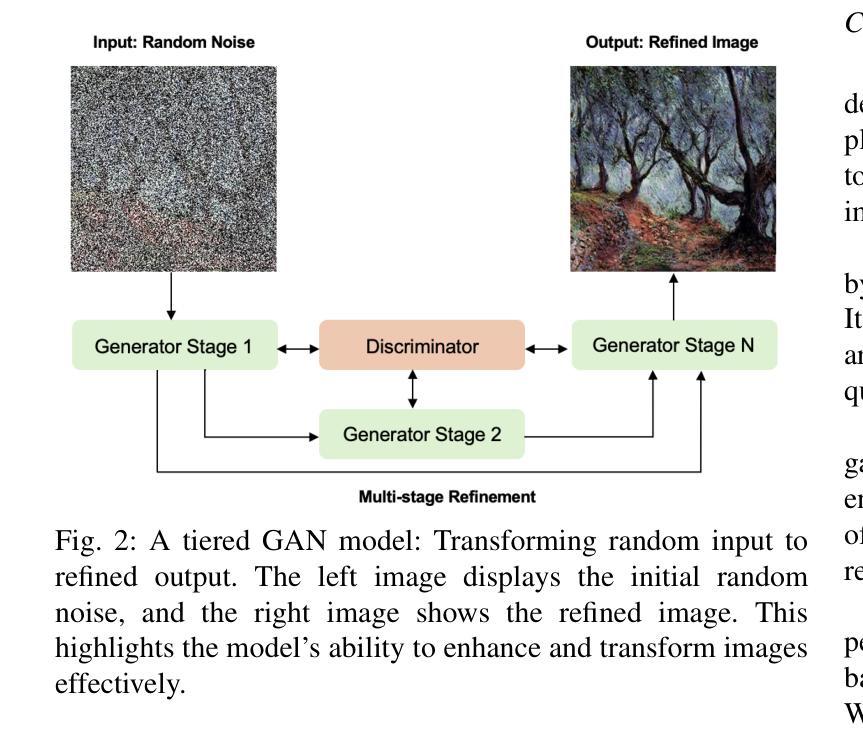
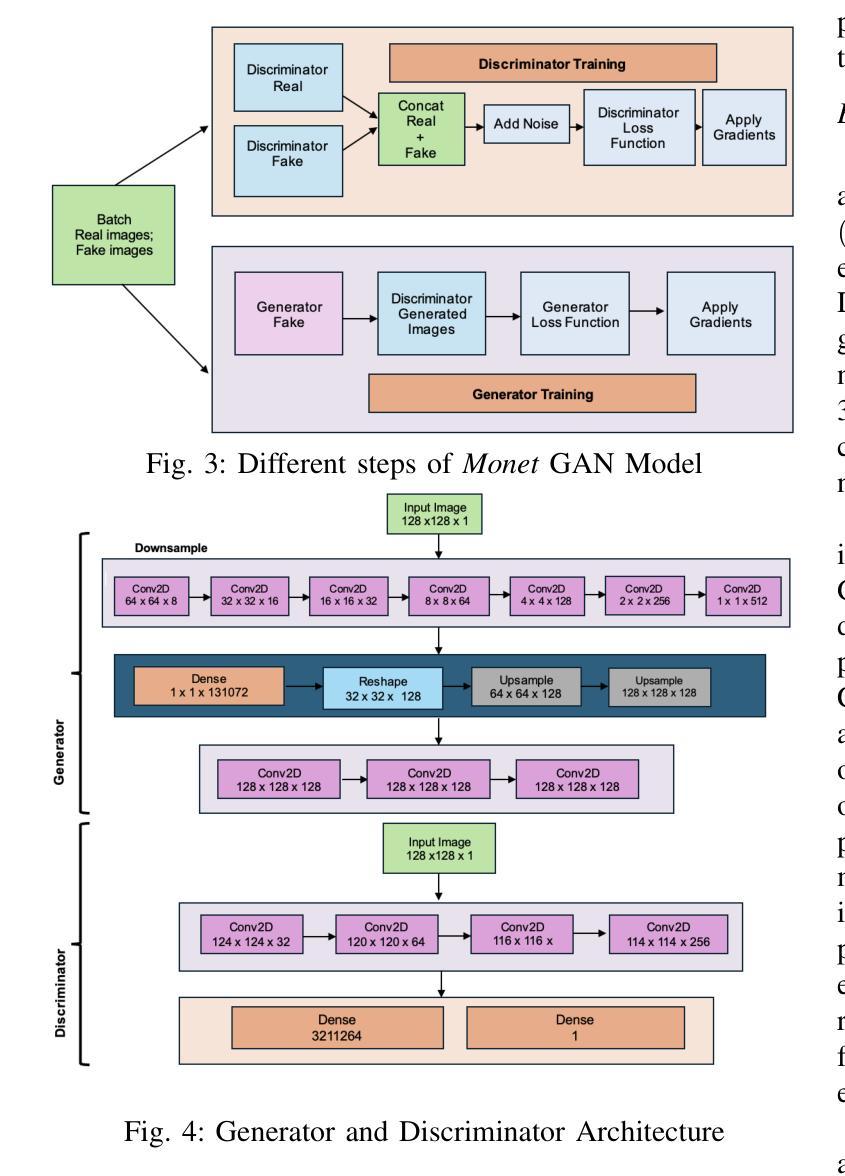
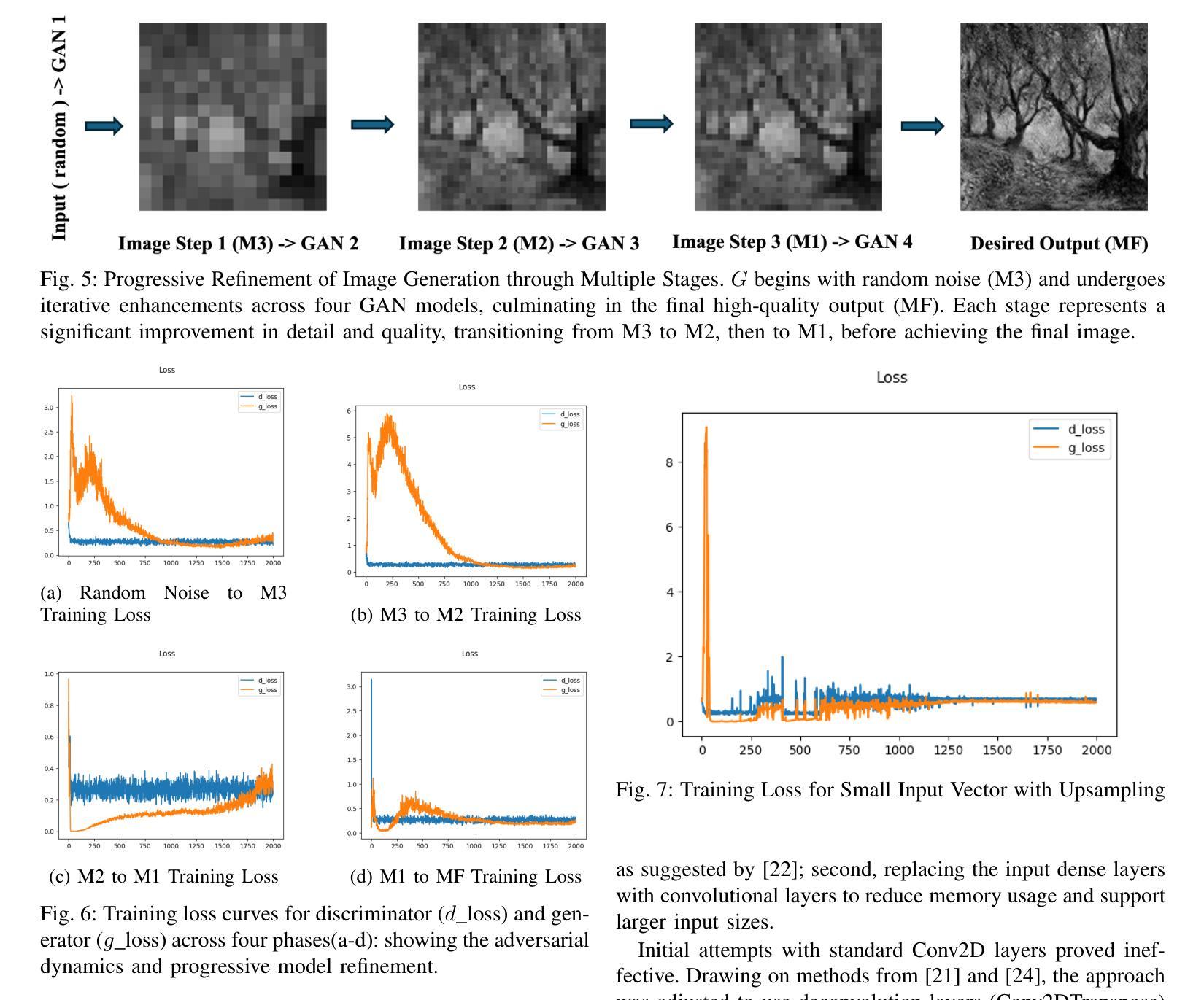
A Tiered GAN Approach for Monet-Style Image Generation
Authors:FNU Neha, Deepshikha Bhati, Deepak Kumar Shukla, Md Amiruzzaman
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have proven to be a powerful tool in generating artistic images, capable of mimicking the styles of renowned painters, such as Claude Monet. This paper introduces a tiered GAN model to progressively refine image quality through a multi-stage process, enhancing the generated images at each step. The model transforms random noise into detailed artistic representations, addressing common challenges such as instability in training, mode collapse, and output quality. This approach combines downsampling and convolutional techniques, enabling the generation of high-quality Monet-style artwork while optimizing computational efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate the architecture’s ability to produce foundational artistic structures, though further refinements are necessary for achieving higher levels of realism and fidelity to Monet’s style. Future work focuses on improving training methodologies and model complexity to bridge the gap between generated and true artistic images. Additionally, the limitations of traditional GANs in artistic generation are analyzed, and strategies to overcome these shortcomings are proposed.
生成对抗网络(GANs)已被证明是生成艺术图像的强大工具,能够模仿著名画家如克劳德·莫奈的风格。本文介绍了一种分层GAN模型,通过多阶段过程逐步改进图像质量,每一步都增强生成的图像。该模型将随机噪声转换为详细的艺术表示,解决了训练不稳定、模式崩溃和输出质量等常见挑战。这种方法结合了降采样和卷积技术,能够在优化计算效率的同时生成高质量的莫奈风格艺术作品。实验结果证明了该架构产生基础艺术结构的能力,但为了实现更高水平的现实主义和对莫奈风格的忠实度,还需要进一步的改进。未来的工作重点将放在改进训练方法和模型复杂性上,以缩小生成图像和真实艺术图像之间的差距。此外,还分析了传统GAN在艺术创作中的局限性,并提出了克服这些不足的策略。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文介绍了一种分层GAN模型,通过多阶段过程逐步改进图像质量。模型能够将随机噪声转换为详细的艺术表示形式,解决了训练不稳定、模式崩溃和输出质量等问题。结合下采样和卷积技术,能够生成高质量的艺术作品,如模仿克劳德·莫奈的风格。实验结果表明,该架构能够生成基础艺术结构,但仍需进一步改进以实现更高的真实感和对莫奈风格的忠实度。未来工作重点将放在改进训练方法和模型复杂性上,以缩小生成图像和真实艺术作品之间的差距。
Key Takeaways
- 分层GAN模型通过多阶段过程逐步改进图像质量。
- 模型能够模仿著名画家的风格,如克劳德·莫奈。
- 通过结合下采样和卷积技术,生成高质量的艺术作品。
- 模型解决了传统GAN在图像生成中常见的挑战,如训练不稳定和模式崩溃。
- 实验结果表明该架构在生成基础艺术结构方面表现出能力,但仍需改进以达成更高的真实性和对特定风格的忠实度。
- 未来工作方向包括改进训练方法和模型复杂性,以缩小生成图像和真实艺术作品之间的差距。
点此查看论文截图

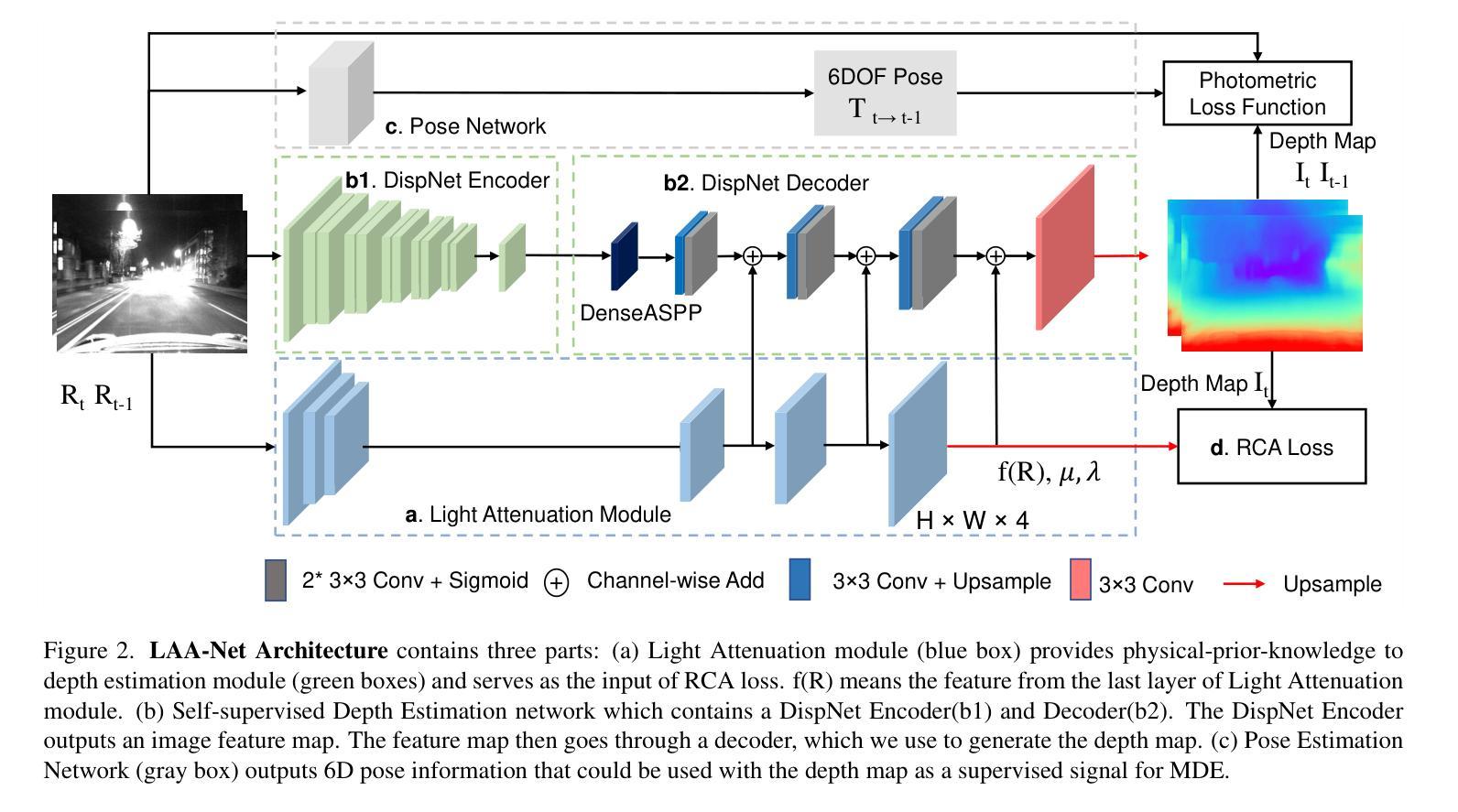
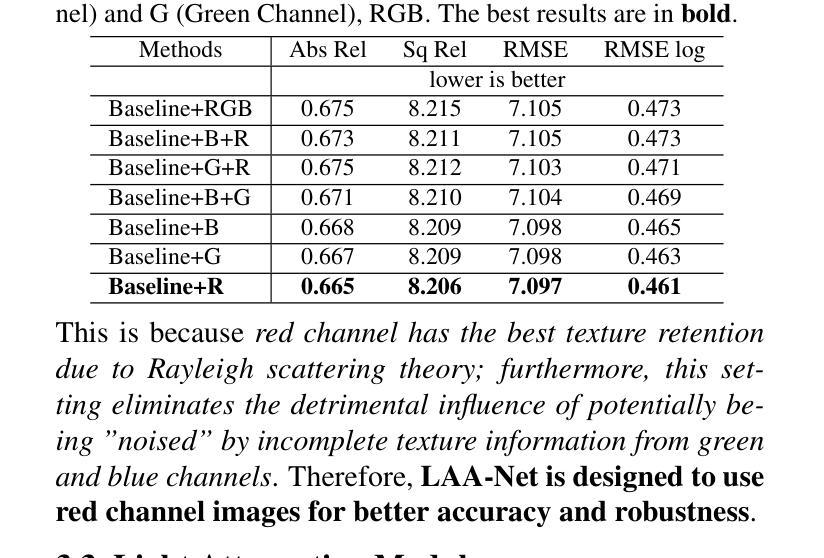
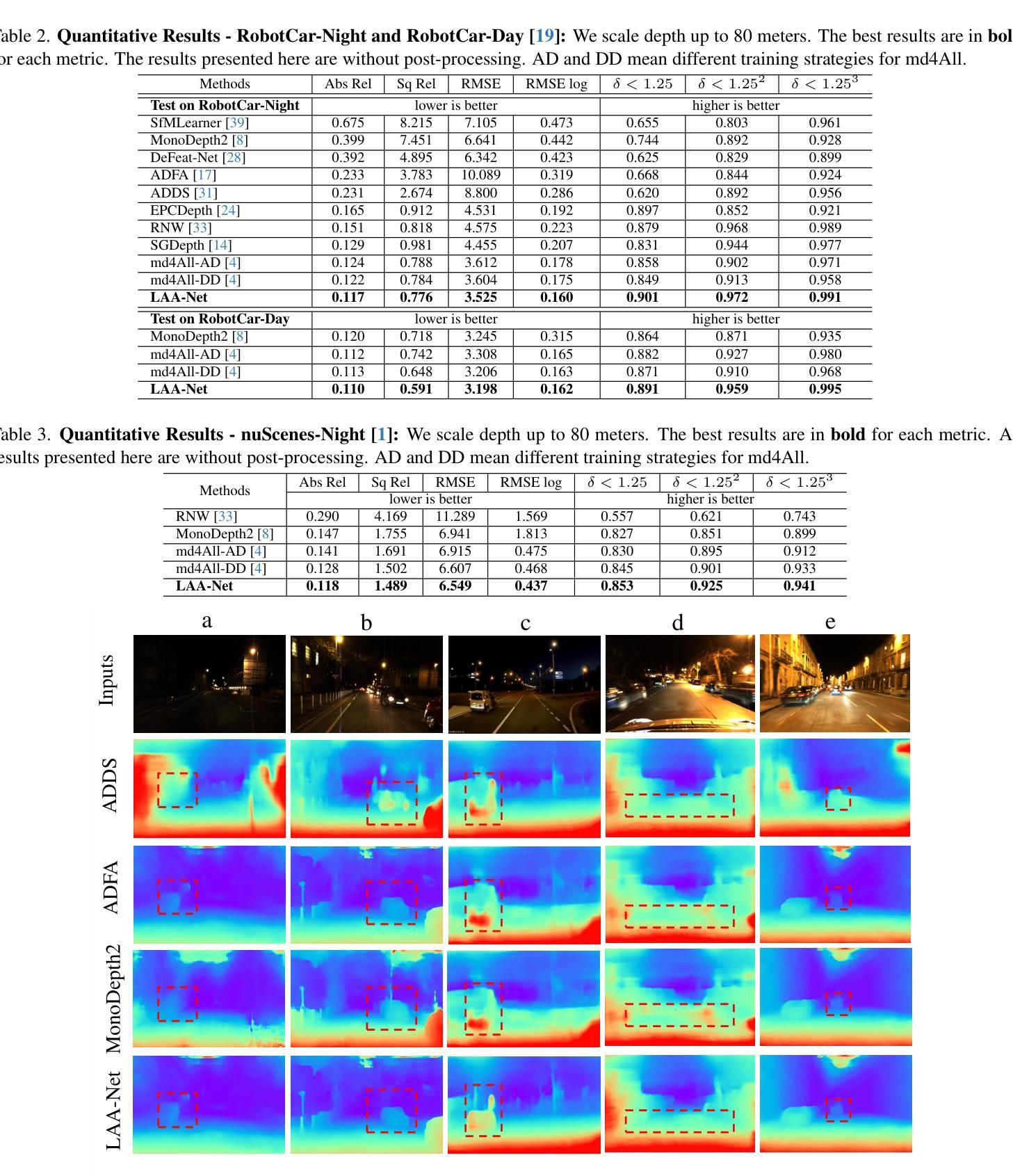
LAA-Net: A Physical-prior-knowledge Based Network for Robust Nighttime Depth Estimation
Authors:Kebin Peng, Haotang Li, Zhenyu Qi, Huashan Chen, Zi Wang, Wei Zhang, Sen He
Existing self-supervised monocular depth estimation (MDE) models attempt to improve nighttime performance by using GANs to transfer nighttime images into their daytime versions. However, this can introduce inconsistencies due to the complexities of real-world daytime lighting variations, which may finally lead to inaccurate estimation results. To address this issue, we leverage physical-prior-knowledge about light wavelength and light attenuation during nighttime. Specifically, our model, Light-Attenuation-Aware Network (LAA-Net), incorporates physical insights from Rayleigh scattering theory for robust nighttime depth estimation: LAA-Net is trained based on red channel values because red light preserves more information under nighttime scenarios due to its longer wavelength. Additionally, based on Beer-Lambert law, we introduce Red Channel Attenuation (RCA) loss to guide LAA-Net’s training. Experiments on the RobotCar-Night, nuScenes-Night, RobotCar-Day, and KITTI datasets demonstrate that our model outperforms SOTA models.
现有的自监督单眼深度估计(MDE)模型尝试使用GAN将夜间图像转换为日间版本,以提高夜间性能。然而,由于现实世界白天光照变化的复杂性,这可能会引入不一致性,最终导致估计结果不准确。为了解决这一问题,我们利用关于夜间光线波长和光线衰减的物理先验知识。具体来说,我们的模型——Light-Attenuation-Aware Network(LAA-Net)结合了瑞利散射理论的物理洞察,以实现稳健的夜间深度估计:LAA-Net基于红色通道值进行训练,因为由于红色光的波长较长,其在夜间场景中可以保留更多信息。此外,基于比尔-朗伯定律,我们引入了Red Channel Attenuation(RCA)损失来指导LAA-Net的训练。在RobotCar-Night、nuScenes-Night、RobotCar-Day和KITTI数据集上的实验表明,我们的模型优于最新模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
基于物理特性的夜间场景深度估算网络LAA-Net利用光的波长和夜间衰减特性,通过引入Rayleigh散射理论的物理洞察,并结合Red Channel Attenuation(RCA)损失,提高了夜间深度估算的准确性,并且在多个数据集上的实验表明其优于现有模型。
Key Takeaways:
- 利用GANs对夜间图像进行转译,现有模型存在日间光照变化引入的不一致性,导致深度估计结果不准确的问题。
- 提出一种结合物理特性的夜间深度估算模型LAA-Net,利用光的波长和夜间衰减特性进行改进。
- LAA-Net基于夜间场景中红色通道信息的重要性进行训练,因为红色光波长较长,在夜间场景下能保留更多信息。
- 引入基于Beer-Lambert定律的Red Channel Attenuation(RCA)损失,用于指导LAA-Net的训练。
- 实验结果表明,LAA-Net在夜间场景深度估算上优于现有模型。
- LAA-Net在不同数据集上的实验验证证明了其普适性和性能优势。
点此查看论文截图

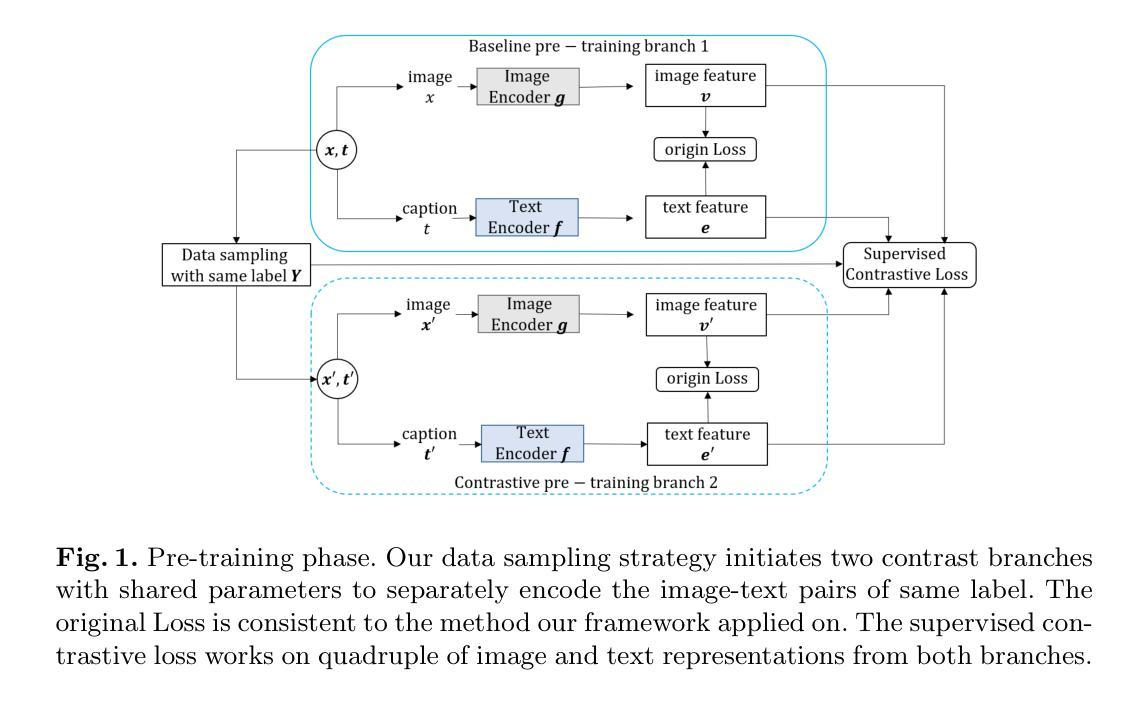
A Framework For Image Synthesis Using Supervised Contrastive Learning
Authors:Yibin Liu, Jianyu Zhang, Li Zhang, Shijian Li, Gang Pan
Text-to-image (T2I) generation aims at producing realistic images corresponding to text descriptions. Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) has proven to be successful in this task. Typical T2I GANs are 2 phase methods that first pretrain an inter-modal representation from aligned image-text pairs and then use GAN to train image generator on that basis. However, such representation ignores the inner-modal semantic correspondence, e.g. the images with same label. The semantic label in priory describes the inherent distribution pattern with underlying cross-image relationships, which is supplement to the text description for understanding the full characteristics of image. In this paper, we propose a framework leveraging both inter- and inner-modal correspondence by label guided supervised contrastive learning. We extend the T2I GANs to two parameter-sharing contrast branches in both pretraining and generation phases. This integration effectively clusters the semantically similar image-text pair representations, thereby fostering the generation of higher-quality images. We demonstrate our framework on four novel T2I GANs by both single-object dataset CUB and multi-object dataset COCO, achieving significant improvements in the Inception Score (IS) and Frechet Inception Distance (FID) metrics of imagegeneration evaluation. Notably, on more complex multi-object COCO, our framework improves FID by 30.1%, 27.3%, 16.2% and 17.1% for AttnGAN, DM-GAN, SSA-GAN and GALIP, respectively. We also validate our superiority by comparing with other label guided T2I GANs. The results affirm the effectiveness and competitiveness of our approach in advancing the state-of-the-art GAN for T2I generation
文本到图像(T2I)生成旨在根据文本描述生成逼真的图像。生成对抗网络(GAN)在此任务中已被证明是成功的。典型的T2I GANs是分为两阶段的方法,首先使用对齐的图像文本对预训练一个跨模态表示,然后在此基础上使用GAN训练图像生成器。然而,这种表示忽略了内模态语义对应关系,例如具有相同标签的图像。先验中的语义标签描述了图像之间关系的内在分布模式,这是对文本描述的理解图像的完整特征的补充。在本文中,我们提出了一个利用跨模态和内模态对应关系的框架,通过标签引导的监督对比学习来实现。我们将T2I GANs扩展到预训练和生成阶段的两个参数共享对比分支。这种集成有效地聚类了语义上相似的图像文本对表示,从而促进了更高质量图像的生成。我们在单目标数据集CUB和多目标数据集COCO上的四种新型T2I GANs上展示了我们的框架,在图像生成的评估指标Inception Score(IS)和Frechet Inception Distance(FID)方面取得了显著的改进。特别是在更复杂的多目标COCO上,我们的框架改进了FID指标,分别为AttnGAN、DM-GAN、SSA-GAN和GALIP提高了30.1%、27.3%、16.2%和17.1%。我们还通过与其他标签引导的T2I GANs进行比较来验证我们的优越性。结果证实了我们方法在推进T2I生成的最新GAN技术中的有效性和竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到图像(T2I)生成的目标是生成与文本描述对应的真实图像。生成对抗网络(GAN)在此任务中取得了成功。典型的T2I GANs是分为两个阶段的方法,首先使用对齐的图像文本对预训练跨模态表示,然后使用GAN在此基础上训练图像生成器。然而,这种表示忽略了内模态语义对应关系,例如具有相同标签的图像。本文提出一个框架,利用跨模态和内模态对应关系,通过标签引导的监督对比学习。在预训练和生成阶段,本文将T2I GANs扩展到两个参数共享对比分支。这种集成有效地聚类了语义上相似的图像文本对表示,从而促进生成更高质量的图像。在单目标数据集CUB和多目标数据集COCO上,本文的方法在四种新型的T2I GANs上实现了显著的改进,在图像生成的Inception Score(IS)和Frechet Inception Distance(FID)指标上都有显著提升。特别是在更复杂的COCO数据集上,我们的框架改进了FID分数超过其他四种方法。通过与其他标签引导的T2I GANs的比较,验证了本文方法的先进性和竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- T2I生成的目标为根据文本描述生成真实图像,GAN在此任务中表现优异。
- 典型T2I GANs采用两阶段方法,先预训练跨模态表示,再使用GAN进行图像生成。
- 现有方法忽略了内模态语义对应,本文方法通过标签引导的监督对比学习来利用跨模态和内模态对应关系。
- 本文方法在预训练和生成阶段扩展了T2I GANs至两个参数共享对比分支。
- 该方法有效聚类了语义相似的图像文本对表示,提高了图像生成质量。
- 在多种数据集上的实验结果表明,本文方法显著改进了图像生成的FID指标。
点此查看论文截图

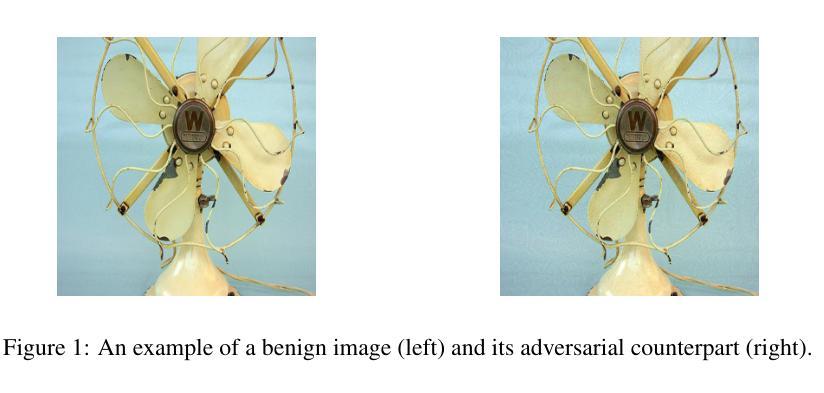
NODE-AdvGAN: Improving the transferability and perceptual similarity of adversarial examples by dynamic-system-driven adversarial generative model
Authors:Xinheng Xie, Yue Wu, Cuiyu He
Understanding adversarial examples is crucial for improving the model’s robustness, as they introduce imperceptible perturbations that deceive models. Effective adversarial examples, therefore, offer the potential to train more robust models by removing their singularities. We propose NODE-AdvGAN, a novel approach that treats adversarial generation as a continuous process and employs a Neural Ordinary Differential Equation (NODE) for simulating the dynamics of the generator. By mimicking the iterative nature of traditional gradient-based methods, NODE-AdvGAN generates smoother and more precise perturbations that preserve high perceptual similarity when added to benign images. We also propose a new training strategy, NODE-AdvGAN-T, which enhances transferability in black-box attacks by effectively tuning noise parameters during training. Experiments demonstrate that NODE-AdvGAN and NODE-AdvGAN-T generate more effective adversarial examples that achieve higher attack success rates while preserving better perceptual quality than traditional GAN-based methods.
理解对抗样本对于提高模型的鲁棒性至关重要,因为它们引入了难以察觉的扰动来欺骗模型。因此,有效的对抗样本可以通过消除其奇异性来训练更稳健的模型。我们提出了NODE-AdvGAN,这是一种将对抗生成视为连续过程的新方法,采用神经常微分方程(NODE)来模拟生成器的动态。通过模仿传统的基于梯度的方法的迭代性质,NODE-AdvGAN生成更平滑、更精确的扰动,在添加到良性图像时保持高度感知相似性。我们还提出了一种新的训练策略NODE-AdvGAN-T,它通过有效调整训练过程中的噪声参数,提高了在黑盒攻击中的可迁移性。实验表明,NODE-AdvGAN和NODE-AdvGAN-T生成更有效的对抗样本,在保持比传统基于GAN的方法更好的感知质量的同时,实现了更高的攻击成功率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
对抗性样本的理解对于提高模型的稳健性至关重要,因为它们引入了难以察觉的扰动来欺骗模型。我们提出一种新型的对抗生成方法NODE-AdvGAN,将对抗生成视为一个连续过程,并使用神经常微分方程(NODE)来模拟生成器的动态。通过模仿传统的基于梯度的方法的迭代性质,NODE-AdvGAN生成更平滑、更精确的扰动,在添加到良性图像时保持高度感知相似性。我们还提出了一种新的训练策略NODE-AdvGAN-T,通过有效调整训练过程中的噪声参数,提高了在黑盒攻击中的迁移性。实验表明,NODE-AdvGAN和NODE-AdvGAN-T生成的对抗样本攻击成功率更高,同时保持了比传统基于GAN的方法更好的感知质量。
Key Takeaways
- 对抗性样本对模型稳健性至关重要,能揭示模型漏洞。
- NODE-AdvGAN使用神经常微分方程(NODE)模拟生成器的动态,将对抗生成视为连续过程。
- NODE-AdvGAN生成的扰动更平滑、精确,保持高度感知相似性。
- 提出了新的训练策略NODE-AdvGAN-T,提高在黑盒攻击中的迁移性。
- 通过有效调整噪声参数,增强模型的攻击效果。
- 实验证明,NODE-AdvGAN和NODE-AdvGAN-T生成的对抗样本攻击成功率更高。
点此查看论文截图

Scaling Image Tokenizers with Grouped Spherical Quantization
Authors:Jiangtao Wang, Zhen Qin, Yifan Zhang, Vincent Tao Hu, Björn Ommer, Rania Briq, Stefan Kesselheim
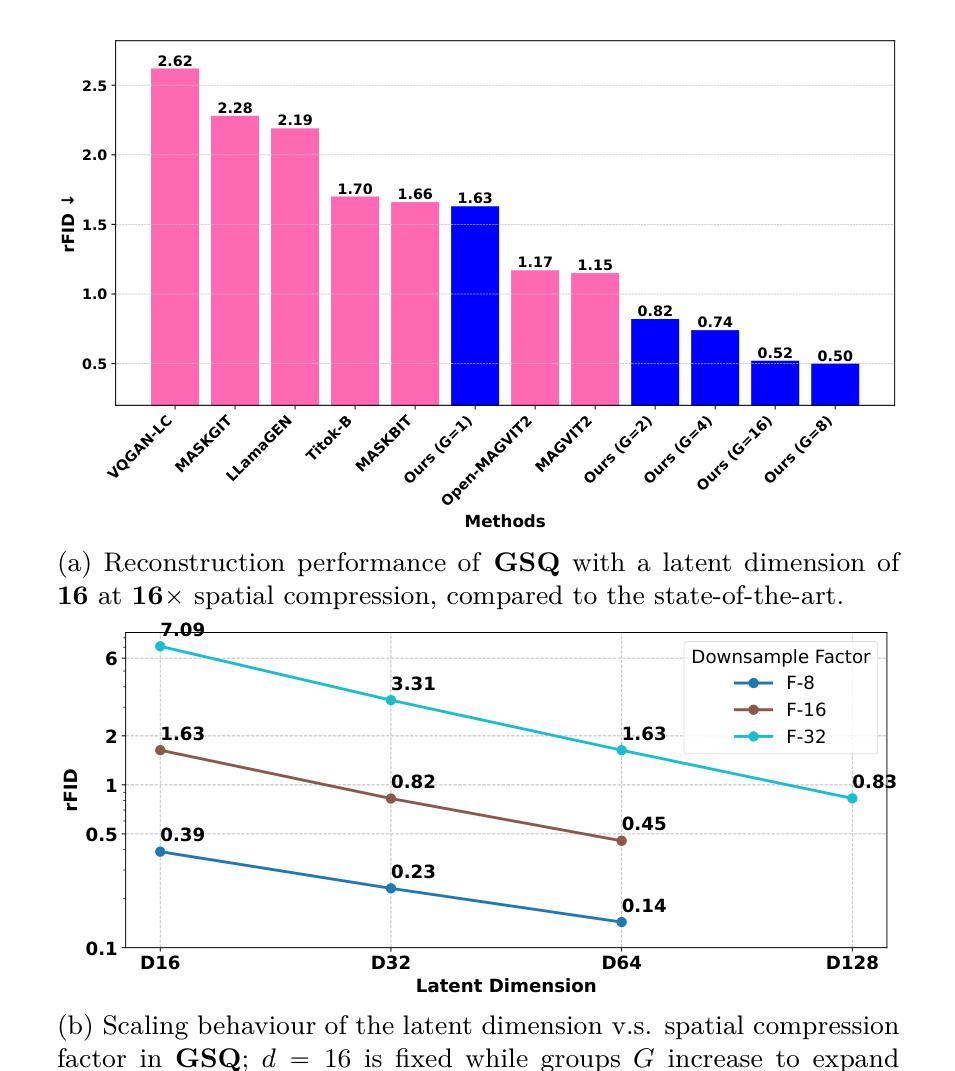
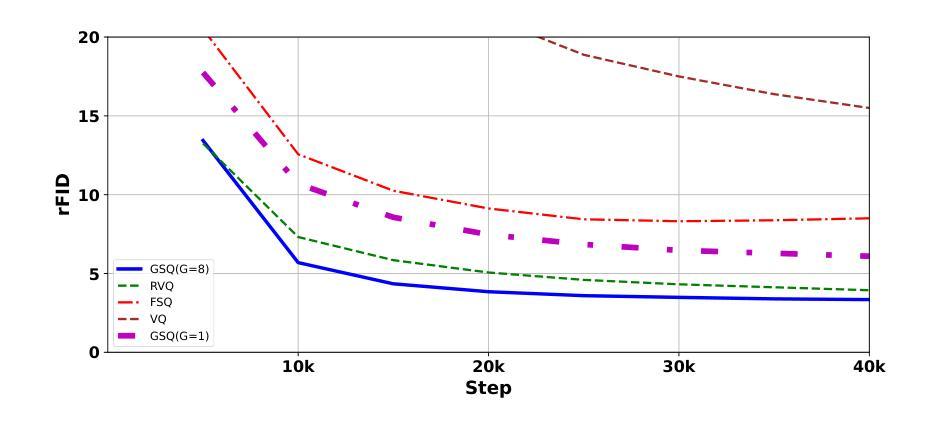
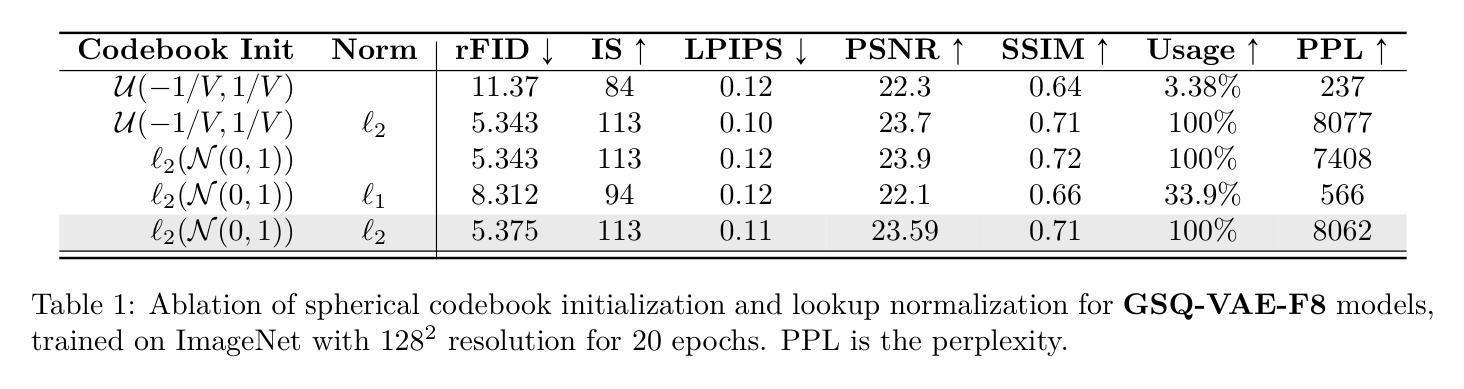
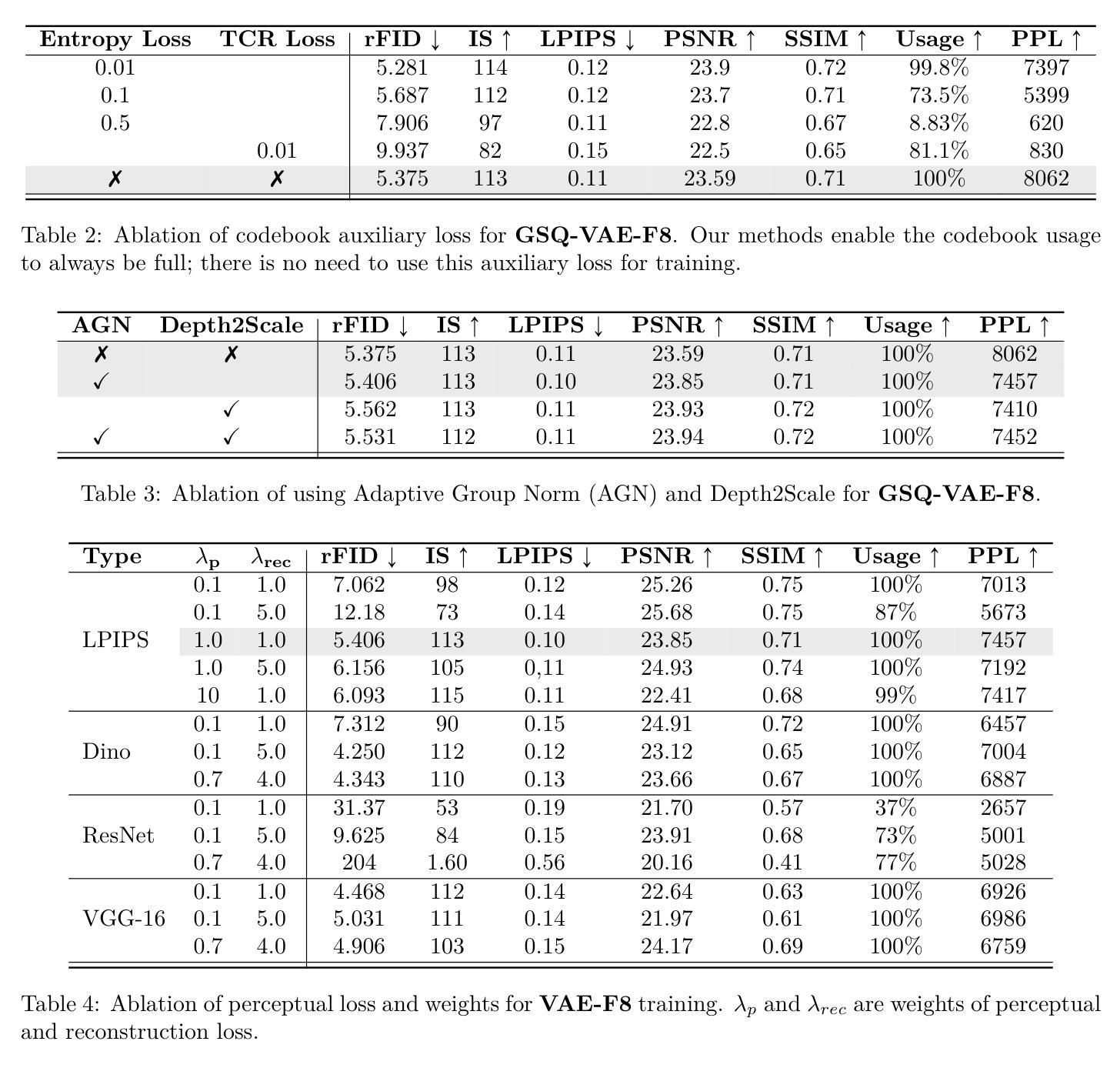
Vision tokenizers have gained a lot of attraction due to their scalability and compactness; previous works depend on old-school GAN-based hyperparameters, biased comparisons, and a lack of comprehensive analysis of the scaling behaviours. To tackle those issues, we introduce Grouped Spherical Quantization (GSQ), featuring spherical codebook initialization and lookup regularization to constrain codebook latent to a spherical surface. Our empirical analysis of image tokenizer training strategies demonstrates that GSQ-GAN achieves superior reconstruction quality over state-of-the-art methods with fewer training iterations, providing a solid foundation for scaling studies. Building on this, we systematically examine the scaling behaviours of GSQ, specifically in latent dimensionality, codebook size, and compression ratios, and their impact on model performance. Our findings reveal distinct behaviours at high and low spatial compression levels, underscoring challenges in representing high-dimensional latent spaces. We show that GSQ can restructure high-dimensional latent into compact, low-dimensional spaces, thus enabling efficient scaling with improved quality. As a result, GSQ-GAN achieves a 16x down-sampling with a reconstruction FID (rFID) of 0.50.
由于视觉令牌化器的可扩展性和紧凑性,它们已经吸引了大量关注。之前的研究依赖于旧式的基于GAN的超参数、有偏比较,以及对缩放行为缺乏综合分析。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了分组球面量化(GSQ),它采用球面代码本初始化并查找正则化来约束代码本潜在空间到球面。我们对图像令牌化器训练策略的实证分析表明,GSQ-GAN在较少的训练迭代次数内实现了优于最新技术的重建质量,为缩放研究提供了坚实的基础。在此基础上,我们系统地研究了GSQ的缩放行为,特别是在潜在维度、代码本大小和压缩率方面及其对模型性能的影响。我们的研究发现,在高、低空间压缩级别下表现出不同的行为,强调了在高维潜在空间表示方面的挑战。我们表明,GSQ可以重新组织高维潜在空间到紧凑、低维空间,从而实现高效缩放并提高了质量。因此,GSQ-GAN实现了16倍下采样,重建FID(rFID)为0.50。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了Grouped Spherical Quantization(GSQ)技术,该技术采用球形编码本初始化和查找正则化来约束编码本潜在空间为球形表面。实证分析表明,GSQ-GAN在图像令牌化训练策略上实现了较高的重建质量,具有较少的训练迭代次数。在此基础上,系统研究了GSQ在潜在维度、编码本大小和压缩率方面的扩展行为及其对模型性能的影响。结果表明,GSQ能够重组高维潜在空间为紧凑的低维空间,从而实现高效扩展并改善质量。
Key Takeaways
- GSQ技术引入球形编码本初始化和查找正则化,有效约束编码本潜在空间。
- GSQ-GAN在图像令牌化训练策略上实现高质量重建,减少训练迭代次数。
- 系统研究了GSQ在潜在维度、编码本大小和压缩率方面的扩展行为。
- 高、低空间压缩级别下表现出不同行为,挑战高维潜在空间的表示。
- GSQ能够重组高维潜在空间为低维空间,实现高效扩展。
- GSQ-GAN实现16倍下采样,重建FID(rFID)为0.50。
点此查看论文截图

Continual Learning of Personalized Generative Face Models with Experience Replay
Authors:Annie N. Wang, Luchao Qi, Roni Sengupta
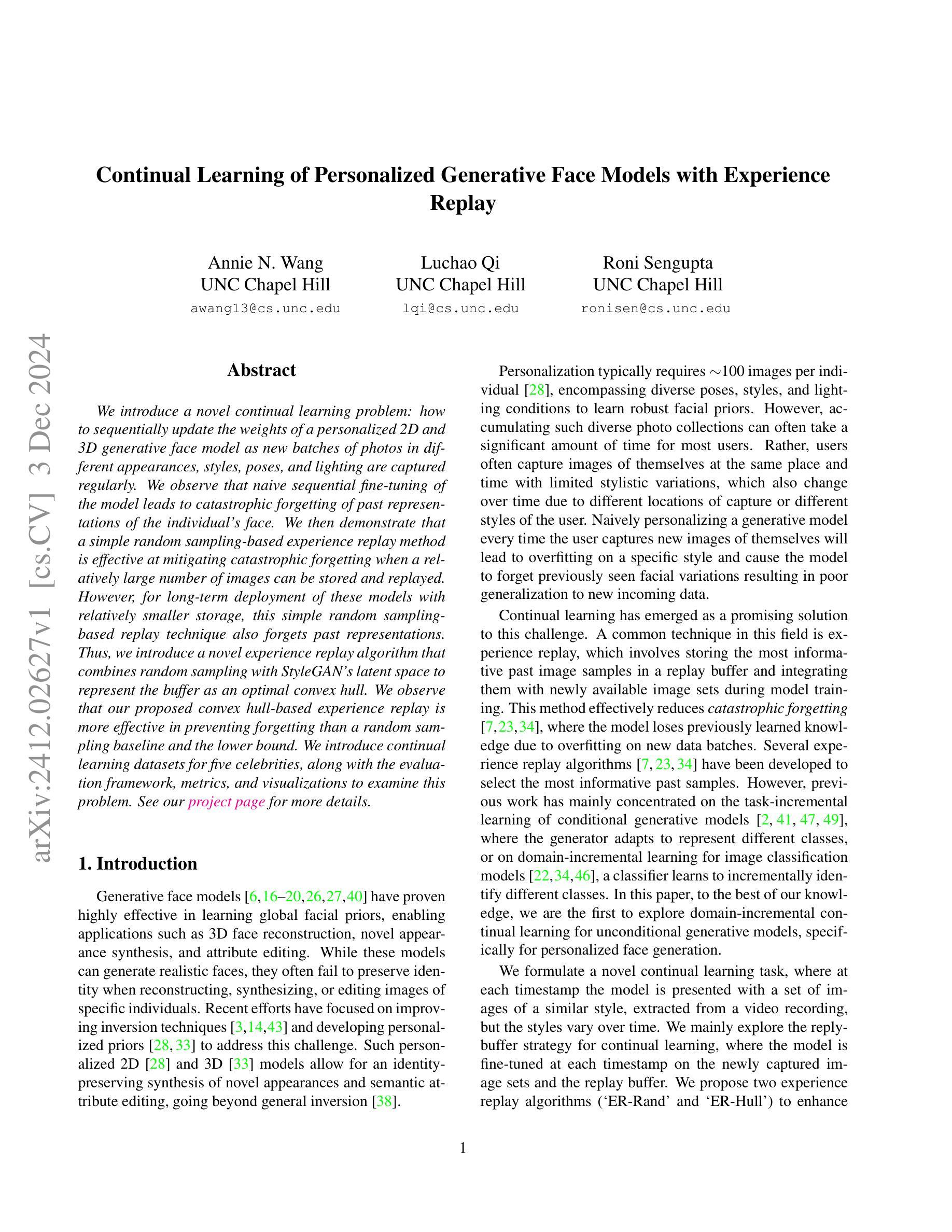
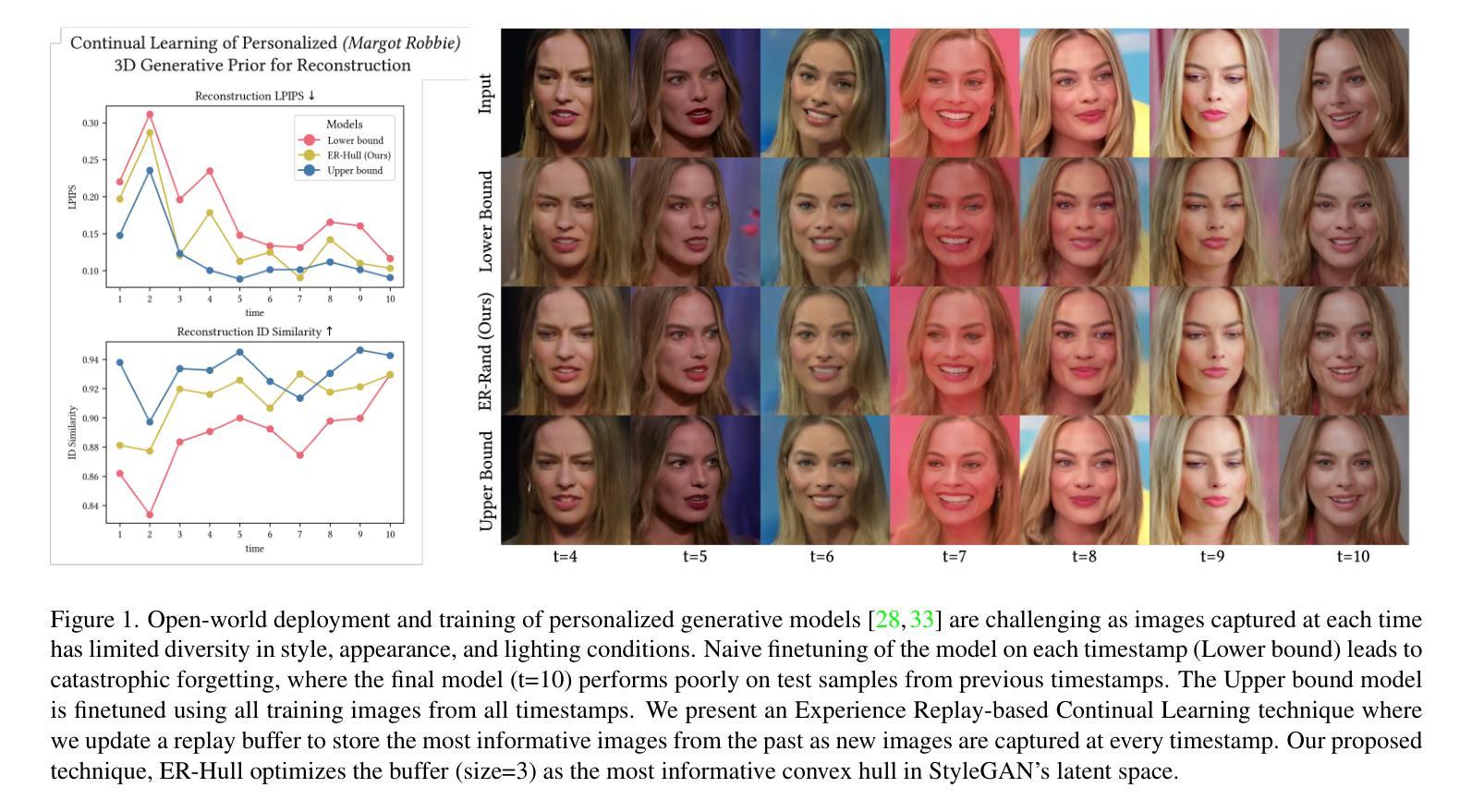
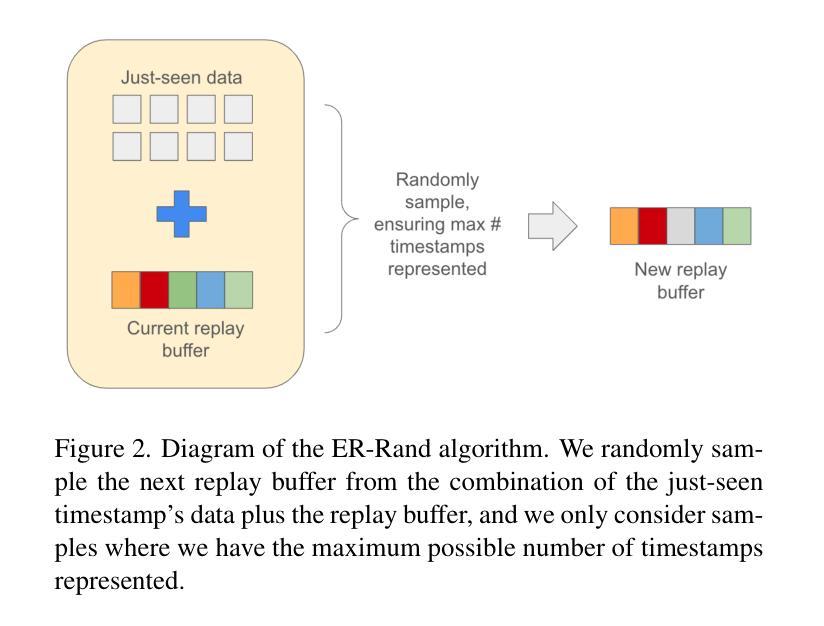
We introduce a novel continual learning problem: how to sequentially update the weights of a personalized 2D and 3D generative face model as new batches of photos in different appearances, styles, poses, and lighting are captured regularly. We observe that naive sequential fine-tuning of the model leads to catastrophic forgetting of past representations of the individual’s face. We then demonstrate that a simple random sampling-based experience replay method is effective at mitigating catastrophic forgetting when a relatively large number of images can be stored and replayed. However, for long-term deployment of these models with relatively smaller storage, this simple random sampling-based replay technique also forgets past representations. Thus, we introduce a novel experience replay algorithm that combines random sampling with StyleGAN’s latent space to represent the buffer as an optimal convex hull. We observe that our proposed convex hull-based experience replay is more effective in preventing forgetting than a random sampling baseline and the lower bound.
我们引入了一个新型的持续学习问题:如何按顺序更新个性化2D和3D生成面部模型的权重,以适应定期捕获的不同外观、风格、姿势和光照条件的新批次照片。我们发现,模型简单的顺序微调会导致个人面部过去表征的灾难性遗忘。然后,我们证明了一种基于简单随机采样的经验回放方法能够在相对较大的图像存储和重播时有效减轻灾难性遗忘。但对于相对较小的存储长期部署这些模型时,这种简单的基于随机采样的回放技术也会忘记过去的表征。因此,我们提出了一种新型的经验回放算法,它将随机采样与StyleGAN的潜在空间相结合,将缓冲区表示为最优凸包。我们发现,基于凸包的经验回放比随机采样基线更能有效地防止遗忘。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to WACV 2025. Project page (incl. supplementary materials): https://anniedde.github.io/personalizedcontinuallearning.github.io/
Summary
本文探讨了一个新型持续学习问题:如何按顺序更新个性化2D和3D生成面部模型的权重,以应对不断捕捉到的面部新照片批次的不同外观、风格、姿势和光照条件。本文观察到简单的模型顺序微调会导致对个体面部过去表示的灾难性遗忘。通过展示一个简单的基于随机采样的经验回放方法,可以有效缓解灾难性遗忘问题,前提是能够存储和回放大量的图像。但对于需要长期部署的模型来说,存储相对有限,因此这种简单的随机采样回放技术也会遗忘过去的表示。因此,本文提出了一种新型的经验回放算法,结合了随机采样与StyleGAN的潜在空间,将缓冲区表示为最优凸包。实验表明,基于凸包的经验回放方法比随机采样基线有更好的防止遗忘效果。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种新型持续学习问题:如何更新个性化生成面部模型的权重以应对新照片的不同条件。
- 观察到简单模型顺序微调会导致个体面部表示的灾难性遗忘。
- 提出了一个基于随机采样的经验回放方法,在存储充足时能有效缓解灾难性遗忘问题。
- 对于存储有限的长期部署场景,简单的随机采样回放技术会遗忘过去的表示。
- 提出了一种新型经验回放算法,结合了随机采样与StyleGAN的潜在空间,将缓冲区表示为最优凸包。
- 基于凸包的经验回放方法比随机采样基线更有效地防止遗忘。
点此查看论文截图
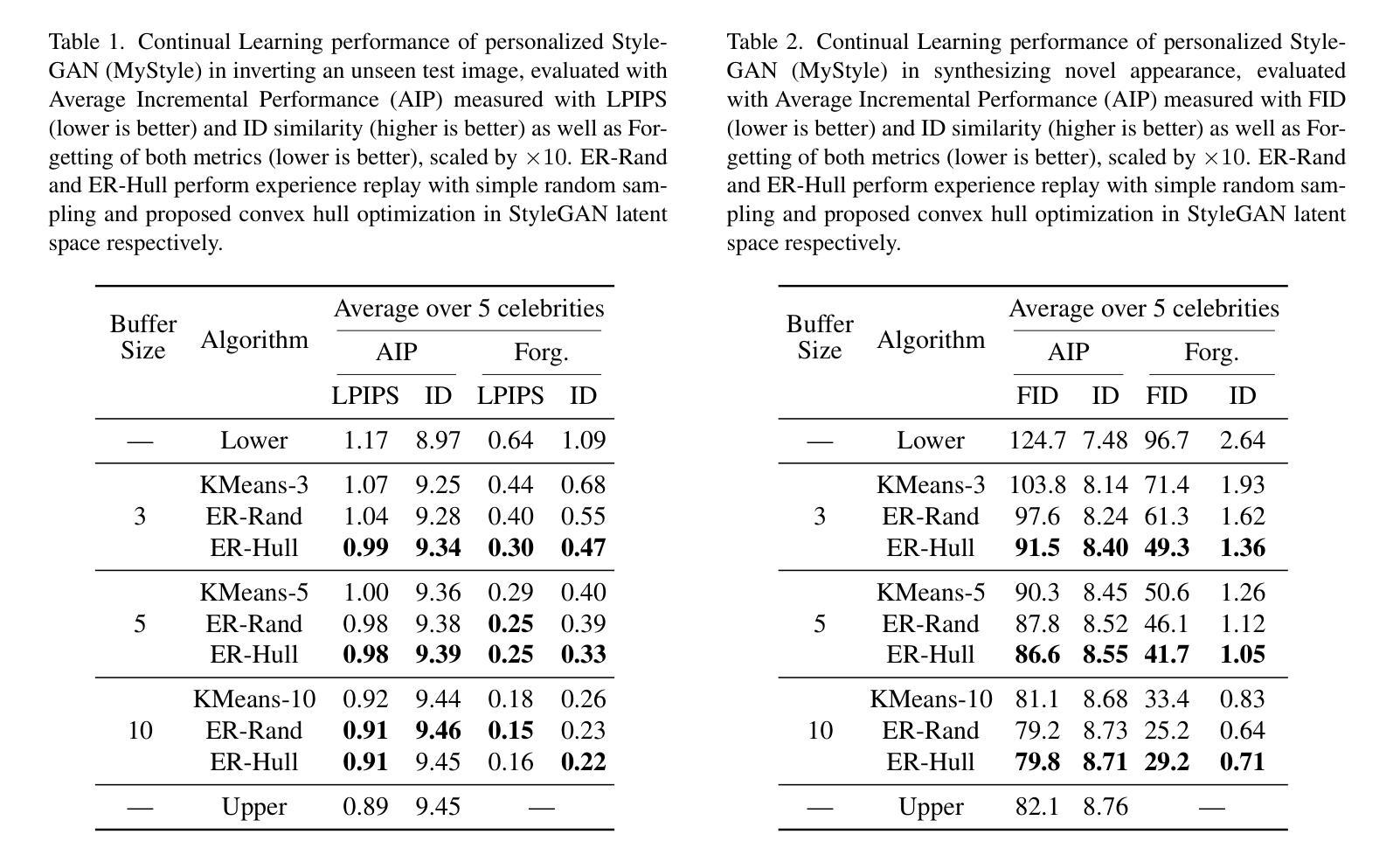
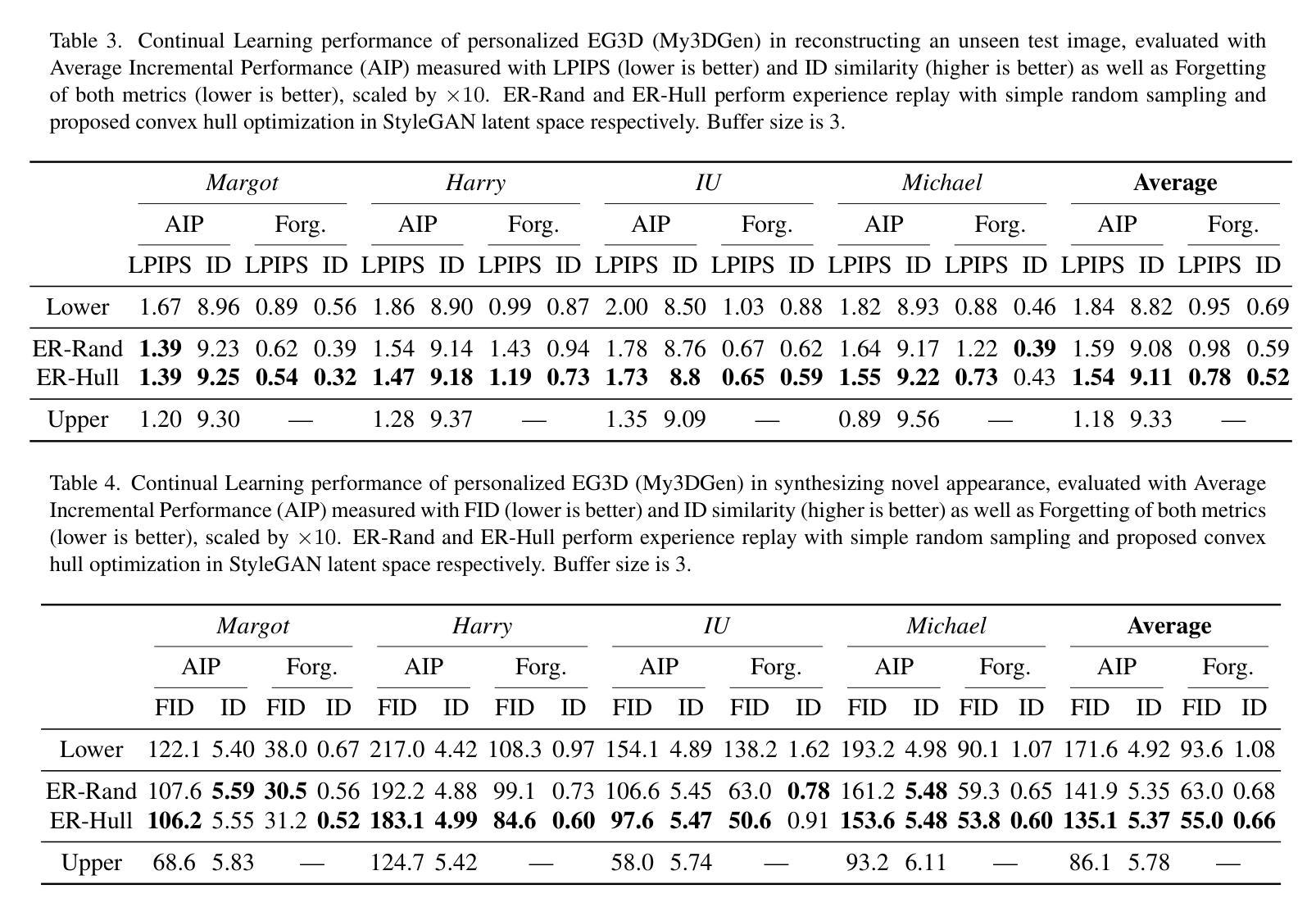
WEM-GAN: Wavelet transform based facial expression manipulation
Authors:Dongya Sun, Yunfei Hu, Xianzhe Zhang, Yingsong Hu
Facial expression manipulation aims to change human facial expressions without affecting face recognition. In order to transform the facial expressions to target expressions, previous methods relied on expression labels to guide the manipulation process. However, these methods failed to preserve the details of facial features, which causes the weakening or the loss of identity information in the output image. In our work, we propose WEM-GAN, in short for wavelet-based expression manipulation GAN, which puts more efforts on preserving the details of the original image in the editing process. Firstly, we take advantage of the wavelet transform technique and combine it with our generator with a U-net autoencoder backbone, in order to improve the generator’s ability to preserve more details of facial features. Secondly, we also implement the high-frequency component discriminator, and use high-frequency domain adversarial loss to further constrain the optimization of our model, providing the generated face image with more abundant details. Additionally, in order to narrow the gap between generated facial expressions and target expressions, we use residual connections between encoder and decoder, while also using relative action units (AUs) several times. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments have demonstrated that our model performs better in preserving identity features, editing capability, and image generation quality on the AffectNet dataset. It also shows superior performance in metrics such as Average Content Distance (ACD) and Expression Distance (ED).
面部表情操纵旨在改变人类面部表情而不影响面部识别。为了将面部表情转变为目标表情,之前的方法依赖于表情标签来指导操纵过程。然而,这些方法未能保留面部特征的细节,导致输出图像中的身份信息减弱或丢失。在我们的工作中,我们提出了WEM-GAN,即基于小波的表情操纵GAN的简称,它在编辑过程中更加注重保留原始图像的细节。首先,我们利用小波变换技术与我们的生成器相结合,生成器采用U-net自编码器骨干网,以提高生成器保留面部特征细节的能力。其次,我们还实现了高频分量鉴别器,并使用高频域对抗损失来进一步约束我们模型的优化,为生成的面部图像提供更丰富的细节。此外,为了缩小生成面部表情与目标表情之间的差距,我们在编码器和解码器之间使用残差连接,同时使用相对动作单元(AU)多次。大量的定性和定量实验表明,我们的模型在身份特征保留、编辑能力和图像生成质量方面,在AffectNet数据集上的表现更好。它在平均内容距离(ACD)和表情距离(ED)等指标上也表现出优异的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
面部表情操纵旨在改变人类面部表情而不影响面部识别。以往的方法依赖于表情标签来指导操纵过程,但未能保留面部特征的细节,导致输出图像中的身份信息减弱或丢失。我们提出基于小波的面部表情操纵GAN(WEM-GAN),注重在编辑过程中保留原始图像的细节。借助小波变换技术与带有U-net自编码器骨架的生成器相结合,提高生成器保留面部特征细节的能力。此外,我们还实现了高频分量鉴别器并使用高频域对抗损失进一步约束模型的优化,为生成的面部图像提供更丰富的细节。实验证明,我们的模型在身份特征保留、编辑能力和图像生成质量方面表现更好。
Key Takeaways
- 面部表情操纵旨在不改变面部识别的情况下调整人类面部表情。
- 早期方法依赖表情标签引导操纵过程,但会丢失面部特征的细节,影响身份信息的保留。
- WEM-GAN基于小波变换技术,旨在保留原始图像细节,提高生成器性能。
- 高频分量鉴别器和高频域对抗损失用于丰富生成的面部图像细节。
- 通过残差连接和相对动作单元(AUs)的多次使用,缩小生成面部表情与目标表情之间的差距。
- 在AffectNet数据集上进行的实验证明,WEM-GAN在保留身份特征、编辑能力和图像生成质量方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图
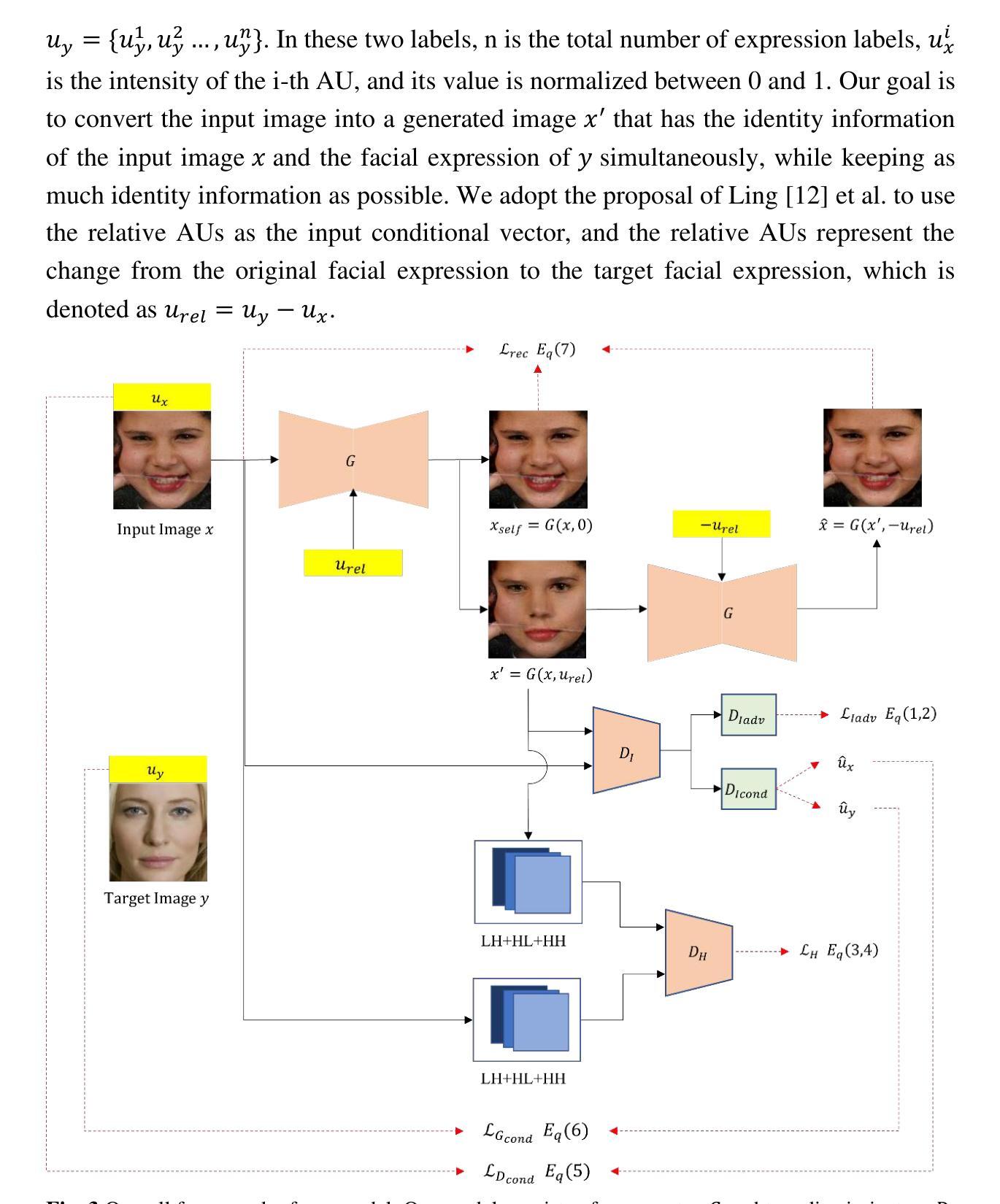
CLERF: Contrastive LEaRning for Full Range Head Pose Estimation
Authors:Ting-Ruen Wei, Haowei Liu, Huei-Chung Hu, Xuyang Wu, Yi Fang, Hsin-Tai Wu
We introduce a novel framework for representation learning in head pose estimation (HPE). Previously such a scheme was difficult due to head pose data sparsity, making triplet sampling infeasible. Recent progress in 3D generative adversarial networks (3D-aware GAN) has opened the door for easily sampling triplets (anchor, positive, negative). We perform contrastive learning on extensively augmented data including geometric transformations and demonstrate that contrastive learning allows networks to learn genuine features that contribute to accurate HPE. On the other hand, we observe that existing HPE works struggle to predict head poses as accurately when test image rotation matrices are slightly out of the training dataset distribution. Experiments show that our methodology performs on par with state-of-the-art models on standard test datasets and outperforms them when images are slightly rotated/ flipped or full range head pose. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to deliver a true full range HPE model capable of accurately predicting any head pose including upside-down pose. Furthermore, we compared with other existing full-yaw range models and demonstrated superior results.
我们引入了一种新的头部姿态估计(HPE)表示学习框架。之前由于头部姿态数据稀疏,使得三元组采样变得不可行,因此这样的方案很难实现。最近,在三维生成对抗网络(具有三维感知能力的GAN)方面的进展为轻松采样三元组(锚点、正样本、负样本)打开了大门。我们对大量扩充的数据执行对比学习,包括几何变换,并证明对比学习可以使网络学习有助于准确HPE的真实特征。另一方面,我们观察到现有的HPE工作在测试图像旋转矩阵略超出训练数据集分布时,难以准确预测头部姿态。实验表明,我们的方法在标准测试数据集上的表现与最先进的模型相当,在图像稍微旋转、翻转或全范围头部姿态的情况下表现优于它们。据我们所知,我们是第一个提供能够准确预测包括倒立姿势在内的任何头部姿态的真正全范围HPE模型的团队。此外,我们还与其他现有的全偏航范围模型进行了比较,并取得了更好的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种用于头部姿态估计(HPE)的新型表示学习框架。借助最近3D生成对抗网络(3D-aware GAN)的进步,实现了轻松采样三元组(锚点、正面、负面),并利用对比学习在广泛扩充的数据上进行训练,包括几何变换。对比学习使网络能够学习真实特征,有助于实现准确的HPE。此外,该方法能够在超出训练数据集分布范围的图像旋转矩阵上准确预测头部姿态,是目前首个能够准确预测包括倒立姿态在内的任何头部姿态的全范围HPE模型。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了一种新型头部姿态估计(HPE)的表示学习框架。
- 利用对比学习在扩充的数据集上进行训练,有助于提高模型的准确性。
- 利用3D生成对抗网络(3D-aware GAN)实现轻松采样三元组。
- 模型能够在图像轻微旋转、翻转或全范围头部姿态的情况下进行准确预测。
- 模型是首个能够准确预测任何头部姿态的全范围HPE模型,包括倒立姿态。
- 与其他全偏航范围模型相比,该模型表现出优越的结果。
点此查看论文截图

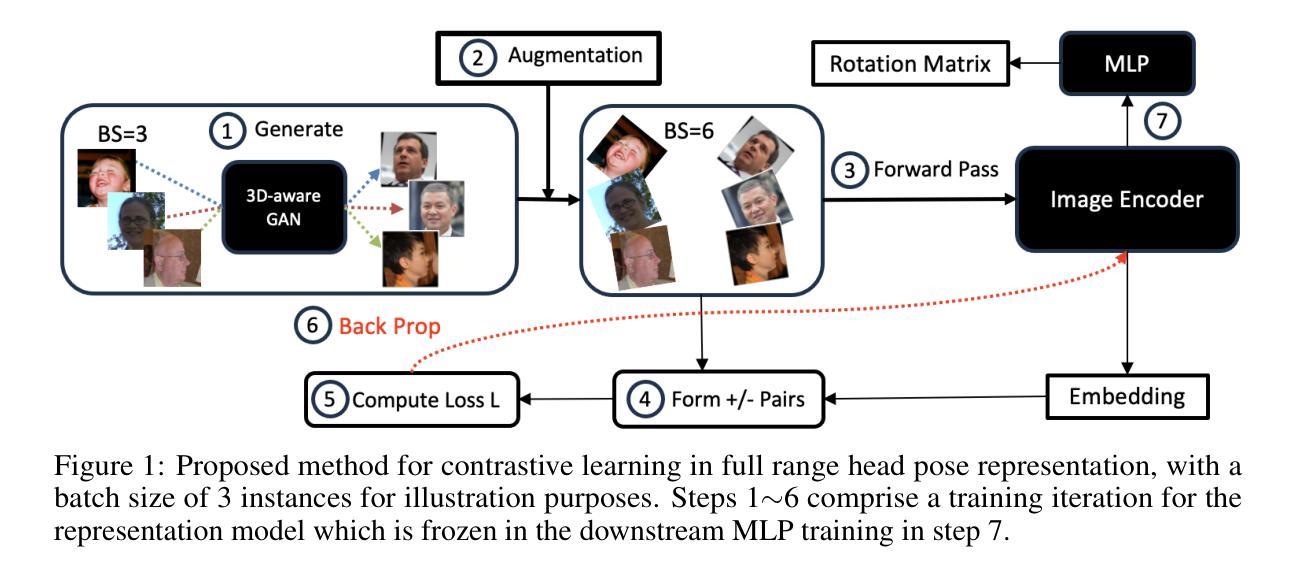
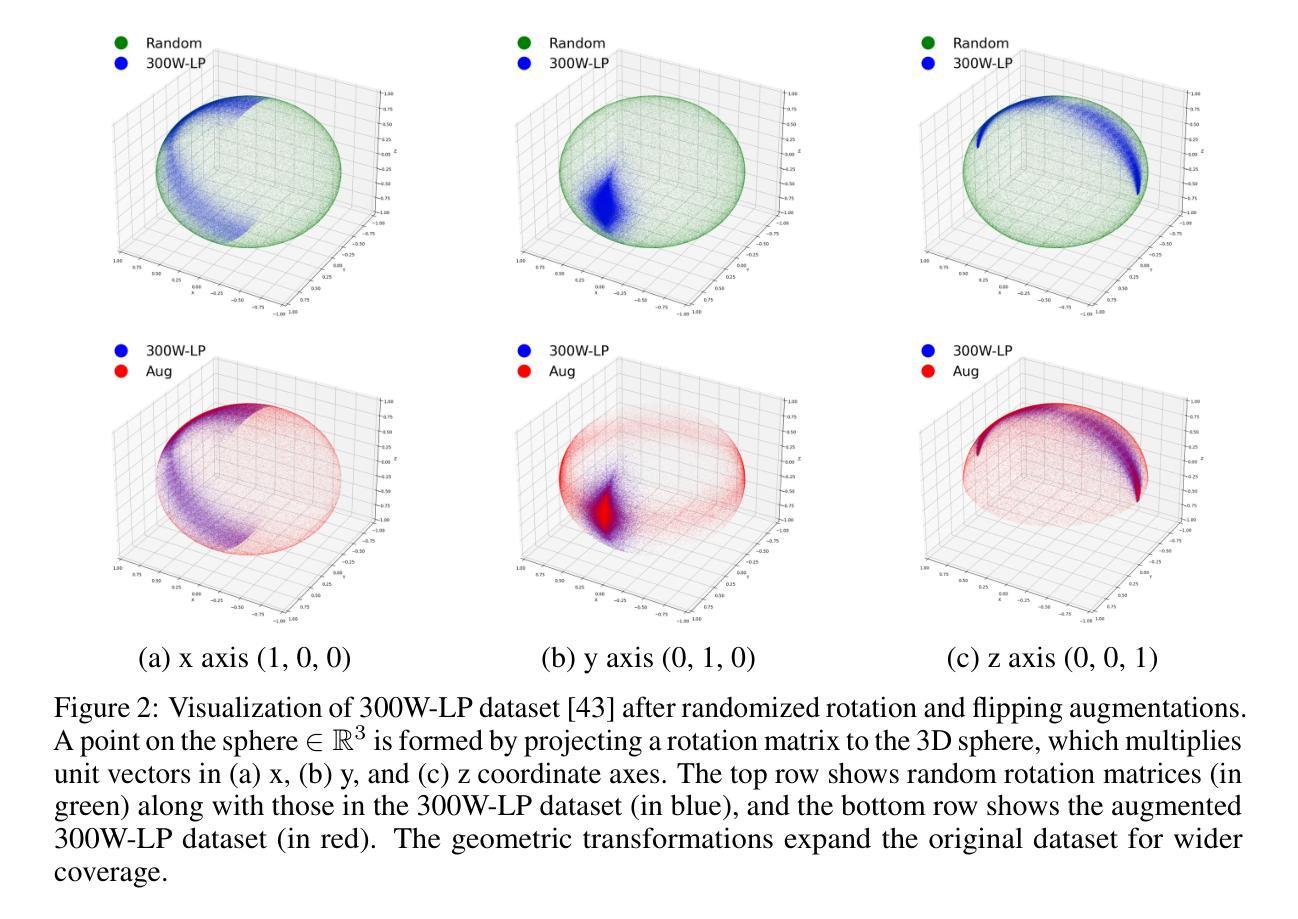

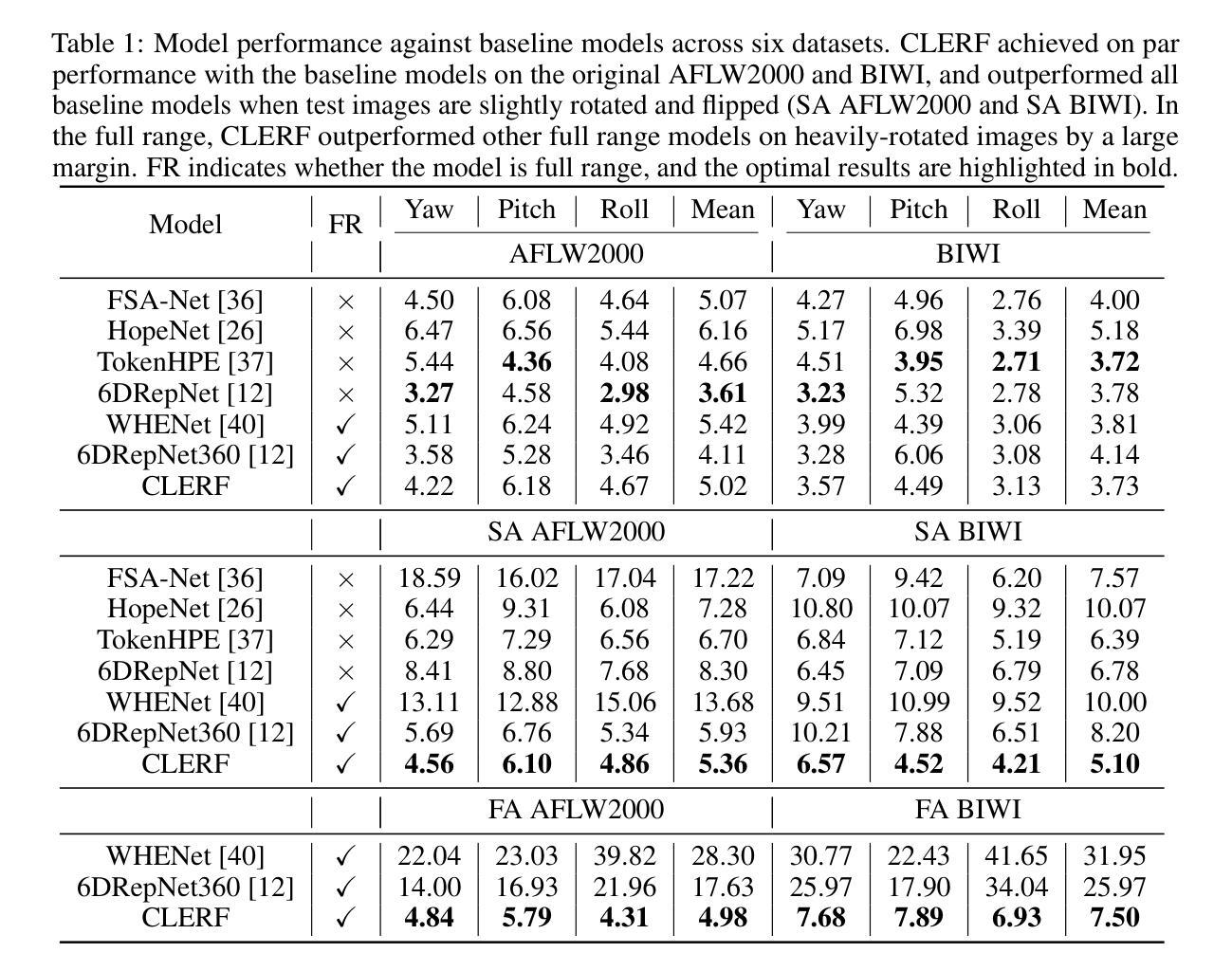
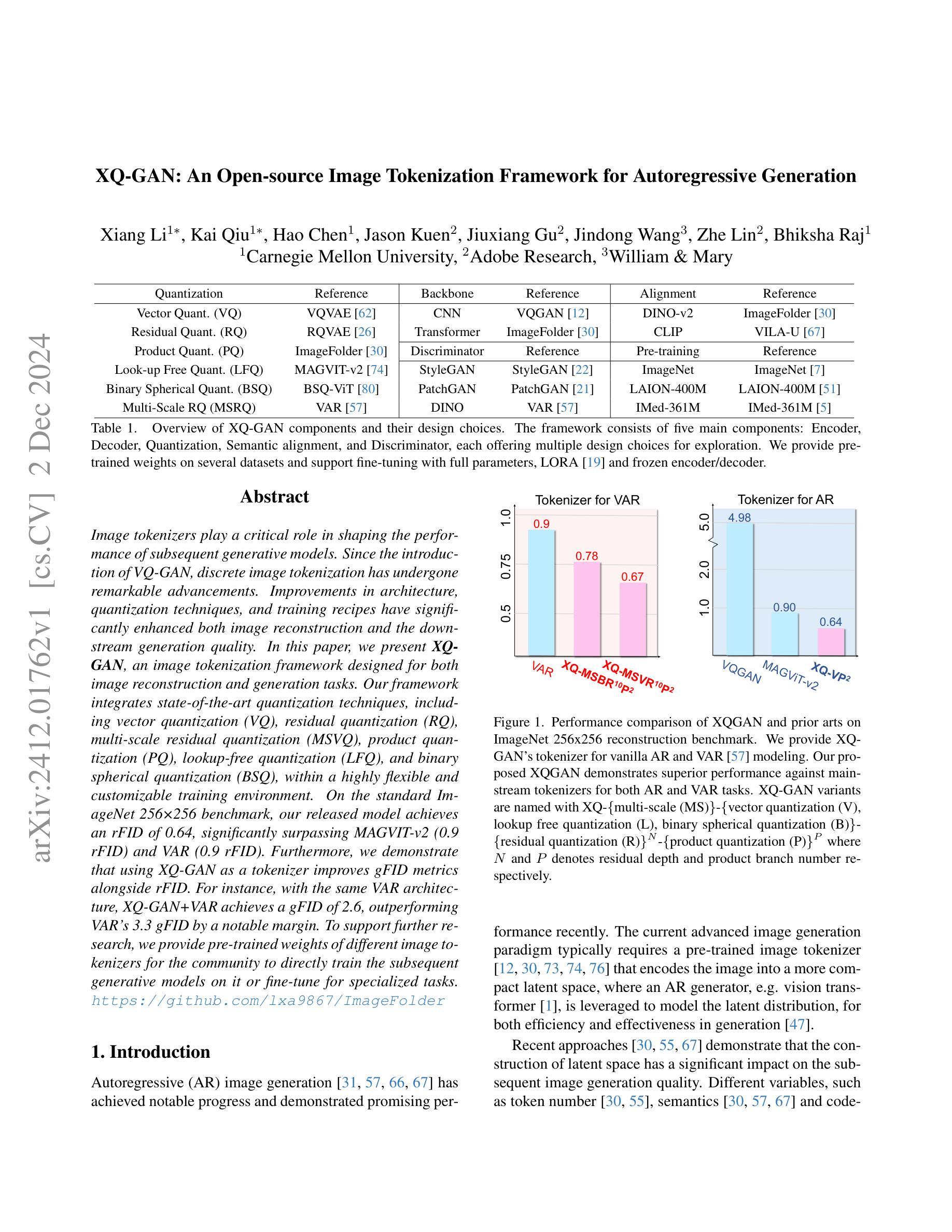
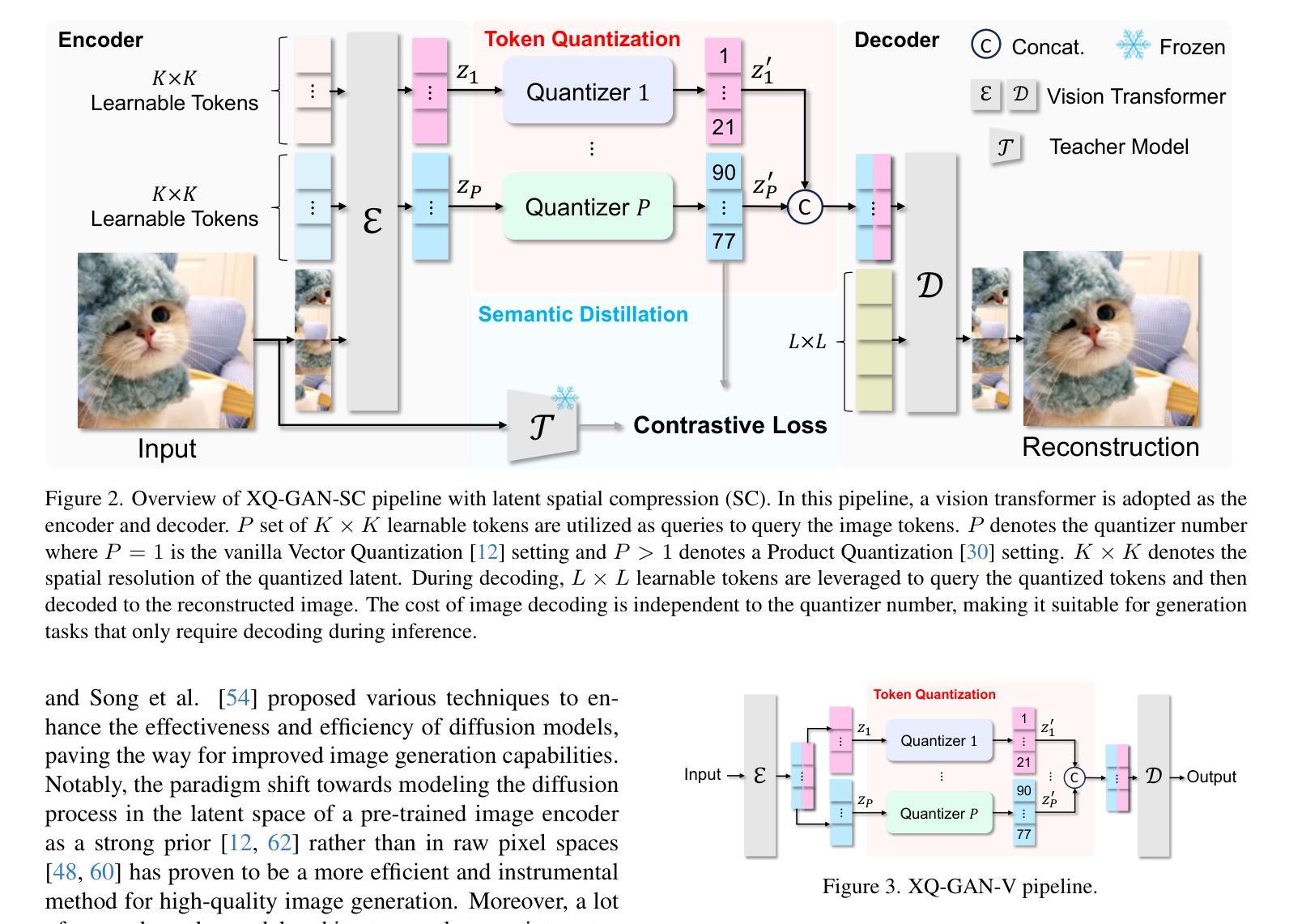
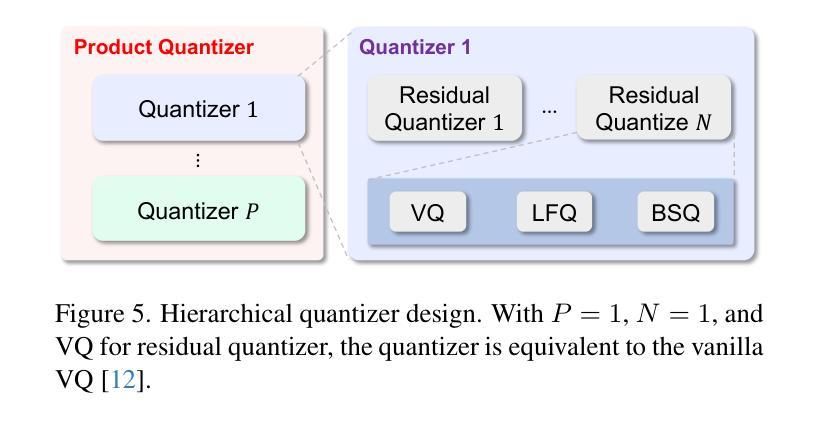
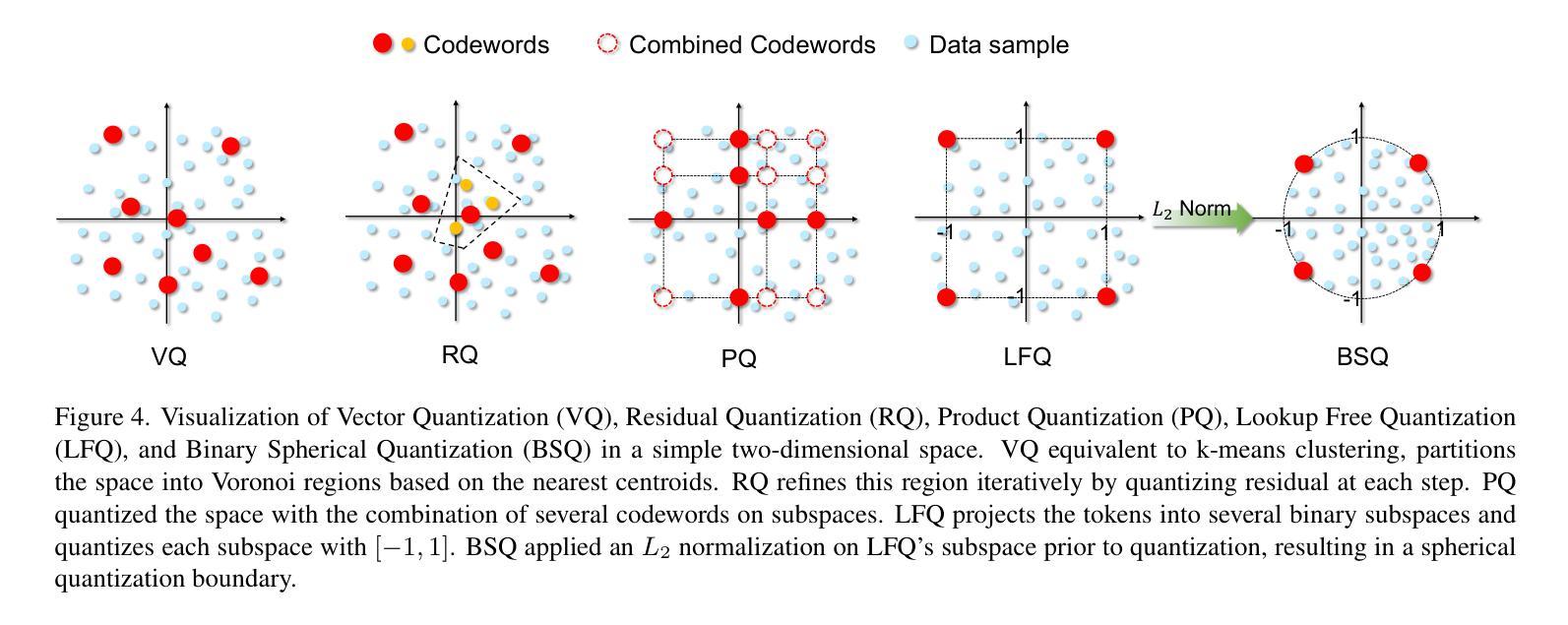
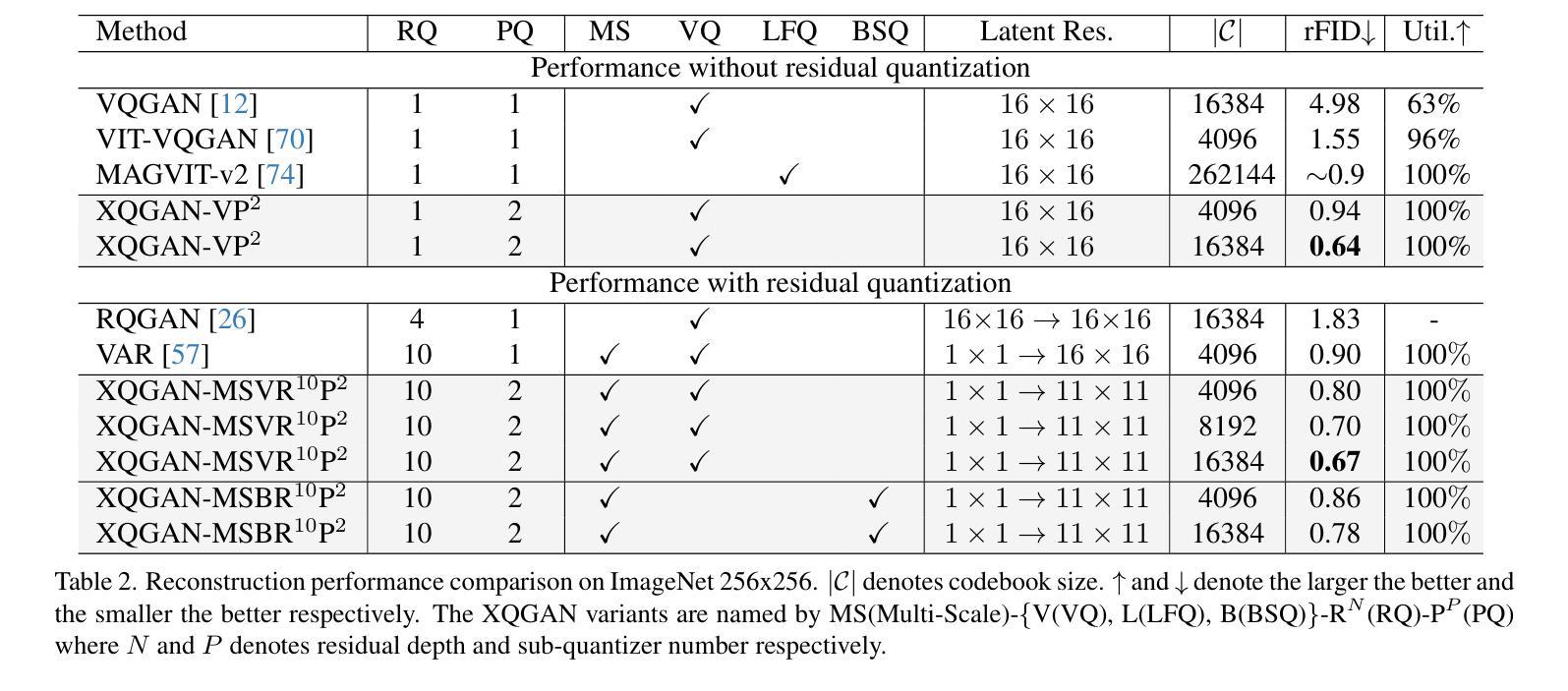
XQ-GAN: An Open-source Image Tokenization Framework for Autoregressive Generation
Authors:Xiang Li, Kai Qiu, Hao Chen, Jason Kuen, Jiuxiang Gu, Jindong Wang, Zhe Lin, Bhiksha Raj
Image tokenizers play a critical role in shaping the performance of subsequent generative models. Since the introduction of VQ-GAN, discrete image tokenization has undergone remarkable advancements. Improvements in architecture, quantization techniques, and training recipes have significantly enhanced both image reconstruction and the downstream generation quality. In this paper, we present XQ-GAN, an image tokenization framework designed for both image reconstruction and generation tasks. Our framework integrates state-of-the-art quantization techniques, including vector quantization (VQ), residual quantization (RQ), multi-scale residual quantization (MSVQ), product quantization (PQ), lookup-free quantization (LFQ), and binary spherical quantization (BSQ), within a highly flexible and customizable training environment. On the standard ImageNet 256x256 benchmark, our released model achieves an rFID of 0.64, significantly surpassing MAGVIT-v2 (0.9 rFID) and VAR (0.9 rFID). Furthermore, we demonstrate that using XQ-GAN as a tokenizer improves gFID metrics alongside rFID. For instance, with the same VAR architecture, XQ-GAN+VAR achieves a gFID of 2.6, outperforming VAR’s 3.3 gFID by a notable margin. To support further research, we provide pre-trained weights of different image tokenizers for the community to directly train the subsequent generative models on it or fine-tune for specialized tasks.
图像令牌化器在塑造后续生成模型的性能中起着关键作用。自从引入VQ-GAN以来,离散图像令牌化已经取得了显著的进步。架构、量化技术和训练配方的改进显著提高了图像重建和下游生成质量。在本文中,我们提出了XQ-GAN,这是一个为图像重建和生成任务而设计的图像令牌化框架。我们的框架整合了最先进的量化技术,包括矢量量化(VQ)、残差量化(RQ)、多尺度残差量化(MSVQ)、产品量化(PQ)、无查找量化(LFQ)和二进位球面量化(BSQ),在一个高度灵活和可定制的训练环境中。在标准的ImageNet 256x256基准测试中,我们发布的模型实现了0.64的rFID,显著超越了MAGVIT-v2(0.9 rFID)和VAR(0.9 rFID)。此外,我们证明使用XQ-GAN作为令牌化器可以提高rFID以外的gFID指标。例如,使用相同的VAR架构,XQ-GAN+VAR实现了2.6的gFID,显著超越了VAR的3.3 gFID。为了支持进一步的研究,我们为社区提供了不同图像令牌器的预训练权重,可以直接在其上训练后续的生成模型,或进行微调以适应特定任务。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/lxa9867/ImageFolder
Summary
本文介绍了XQ-GAN图像令牌化框架,该框架集成了先进的量化技术,包括向量量化、残差量化等,用于图像重建和生成任务。在ImageNet 256x256标准上,XQ-GAN模型实现了rFID 0.64的高性能,超越了MAGVIT-v2和VAR等模型。此外,使用XQ-GAN作为令牌化器可以改善gFID指标。还提供预训练图像令牌化器权重,供社区直接使用或微调特定任务。
Key Takeaways
- XQ-GAN是一个图像令牌化框架,用于图像重建和生成任务。
- 该框架集成了多种先进的量化技术,如向量量化、残差量化等。
- 在ImageNet 256x256标准上,XQ-GAN实现了rFID 0.64的高性能。
- XQ-GAN显著超越了MAGVIT-v2和VAR等模型。
- 使用XQ-GAN作为令牌化器可以改善gFID指标。
- XQ-GAN+VAR组合实现了优于VAR的gFID性能。
点此查看论文截图
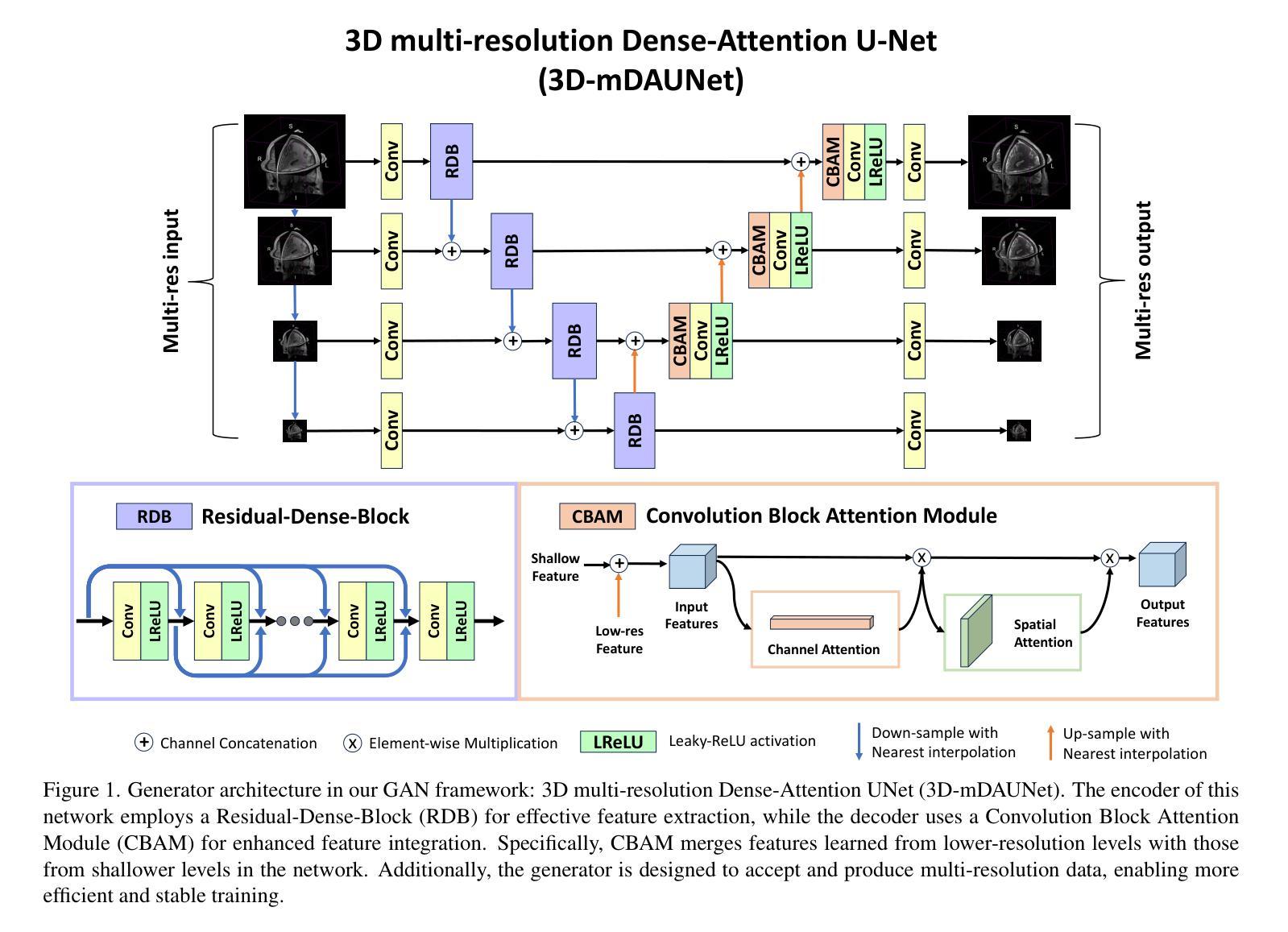
Multi-resolution Guided 3D GANs for Medical Image Translation
Authors:Juhyung Ha, Jong Sung Park, David Crandall, Eleftherios Garyfallidis, Xuhong Zhang
Medical image translation is the process of converting from one imaging modality to another, in order to reduce the need for multiple image acquisitions from the same patient. This can enhance the efficiency of treatment by reducing the time, equipment, and labor needed. In this paper, we introduce a multi-resolution guided Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based framework for 3D medical image translation. Our framework uses a 3D multi-resolution Dense-Attention UNet (3D-mDAUNet) as the generator and a 3D multi-resolution UNet as the discriminator, optimized with a unique combination of loss functions including voxel-wise GAN loss and 2.5D perception loss. Our approach yields promising results in volumetric image quality assessment (IQA) across a variety of imaging modalities, body regions, and age groups, demonstrating its robustness. Furthermore, we propose a synthetic-to-real applicability assessment as an additional evaluation to assess the effectiveness of synthetic data in downstream applications such as segmentation. This comprehensive evaluation shows that our method produces synthetic medical images not only of high-quality but also potentially useful in clinical applications. Our code is available at github.com/juhha/3D-mADUNet.
医学图像翻译是将一种成像模式转换为另一种成像模式的过程,以减少对同一患者多次采集图像的需求。这可以通过减少所需的时间、设备和劳动力来提高治疗效率。在本文中,我们介绍了一种基于多分辨率引导生成对抗网络(GAN)的3D医学图像翻译框架。我们的框架使用3D多分辨率Dense-Attention UNet(3D-mDAUNet)作为生成器,使用3D多分辨率UNet作为判别器,通过包括体素级GAN损失和2.5D感知损失的独特组合的损失函数进行优化。我们的方法在多种成像模式、身体区域和年龄组的体积图像质量评估(IQA)中产生了有前景的结果,证明了其稳健性。此外,我们提出了一种合成到现实的适用性评估,作为一种额外的评估,以评估合成数据在如下流应用(例如分割)中的有效性。全面的评估表明,我们的方法生成的合成医学图像不仅质量高,而且在临床应用中也具有潜在的有用性。我们的代码可在github.com/juhha/3D-mADUNet找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于多分辨率引导生成对抗网络(GAN)的3D医学图像转换框架,利用3D多分辨率Dense-Attention UNet作为生成器,3D多分辨率UNet作为判别器,通过结合多种损失函数进行优化,包括体素级的GAN损失和2.5D感知损失。该方法在多种成像模态、不同部位和年龄段都有较好的体积图像质量评估表现,且提出合成到现实的适用性评估,证明合成数据在后续应用中的有效性。此框架可提高医学图像处理的效率和治疗质量。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像转换旨在将一种成像模态转换为另一种,以减少多次图像采集的需求,提高治疗效率。
- 提出了一种基于多分辨率引导生成对抗网络(GAN)的3D医学图像转换框架。
- 框架中使用了创新的结合方法,包括一个使用注意力机制的生成器和一个用于判别真伪的判别器。
- 结合了多种损失函数,包括体素级的GAN损失和感知损失来优化模型性能。
- 该方法在多种成像模态、不同部位和年龄段具有稳健的评估表现。
- 通过合成到现实的适用性评估验证了合成数据在后续任务(如分割)中的有效性。这意味着所生成的合成图像可为实际应用提供支持。
- 该研究的代码已公开发布在GitHub上供其他研究人员使用和学习。
点此查看论文截图

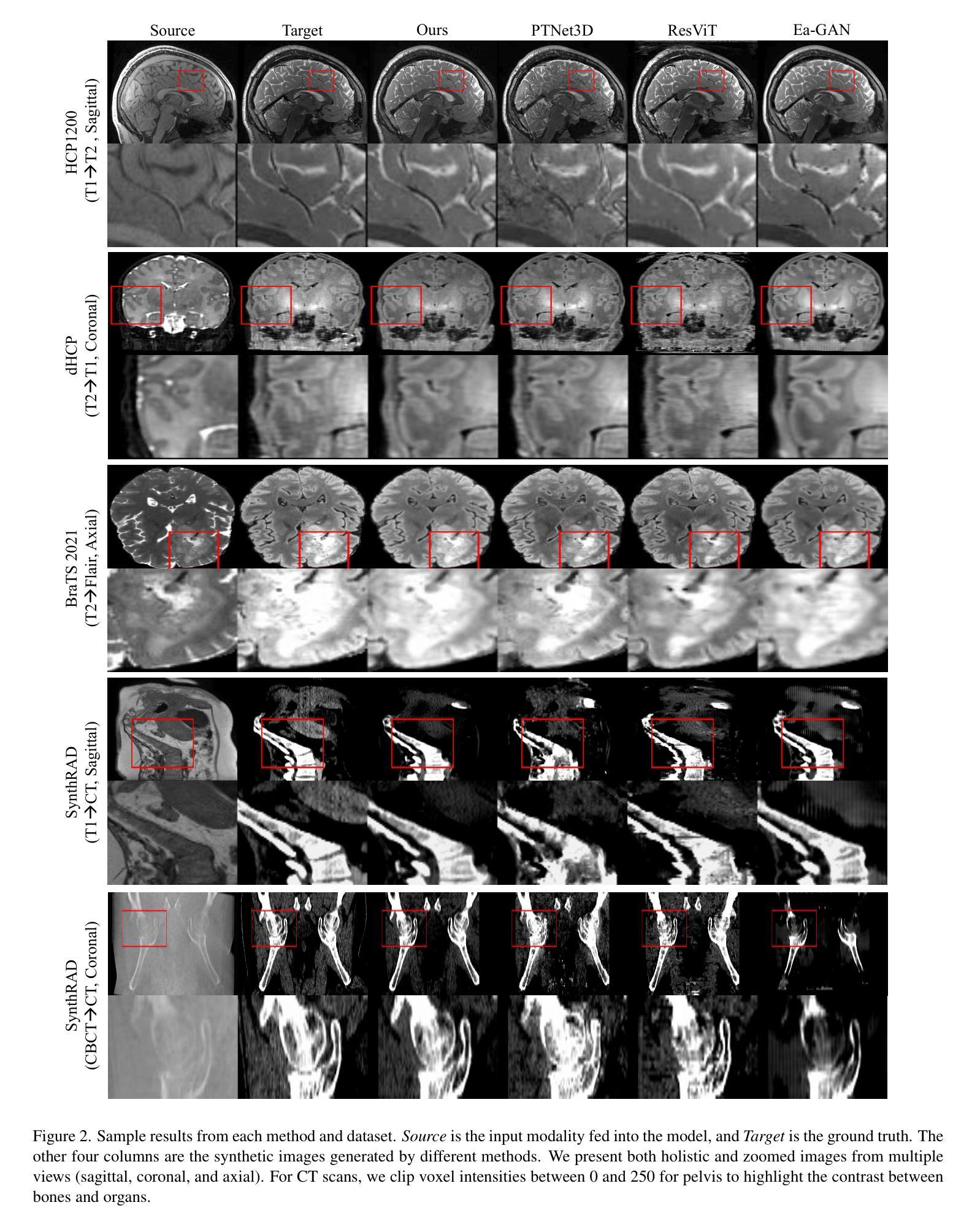
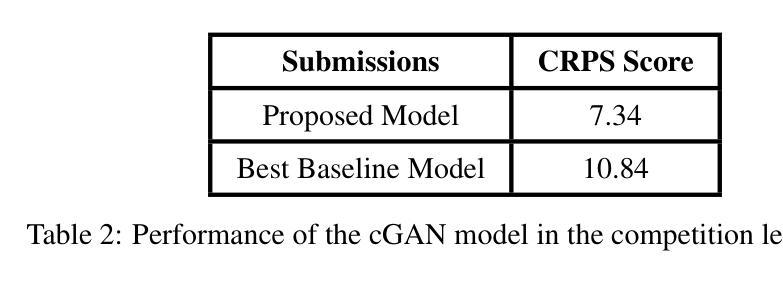
A conditional Generative Adversarial network model for the Weather4Cast 2024 Challenge
Authors:Atharva Deshpande, Kaushik Gopalan, Jeet Shah, Hrishikesh Simu
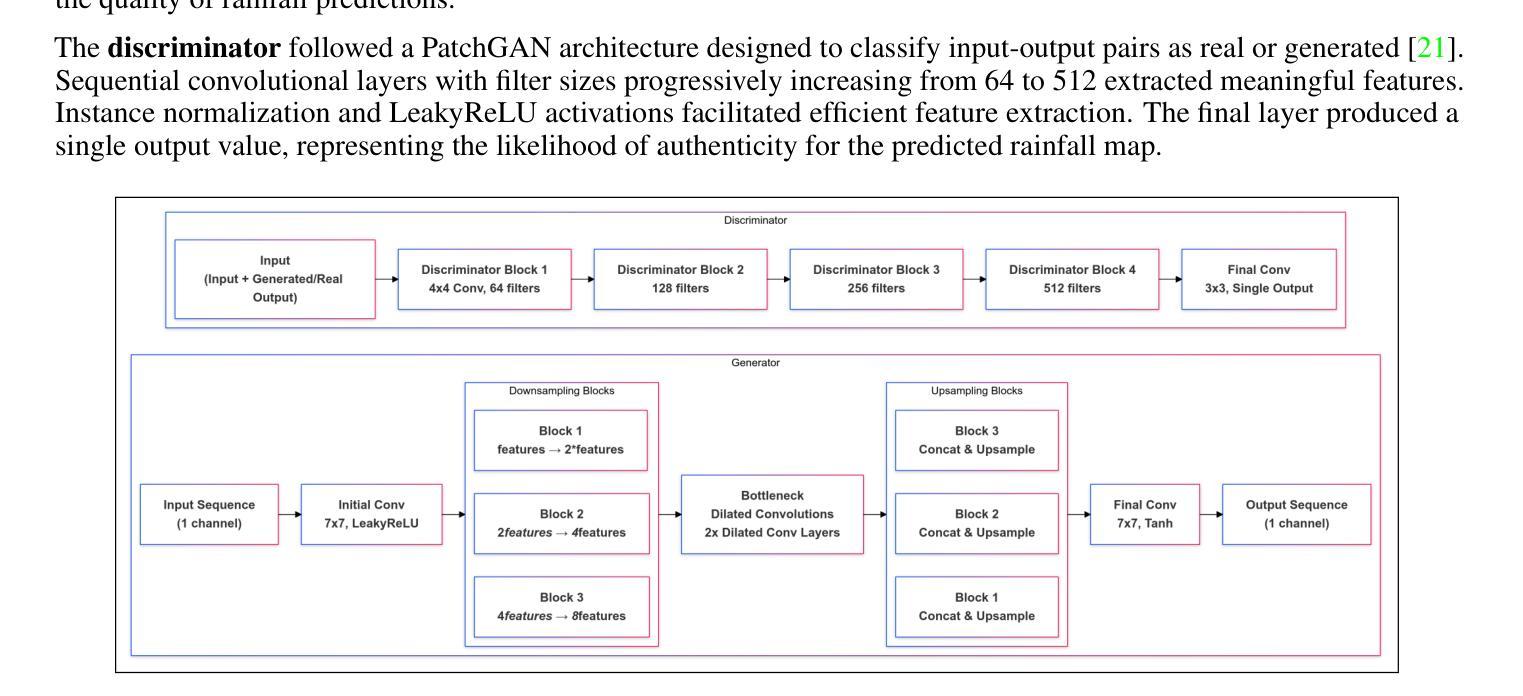
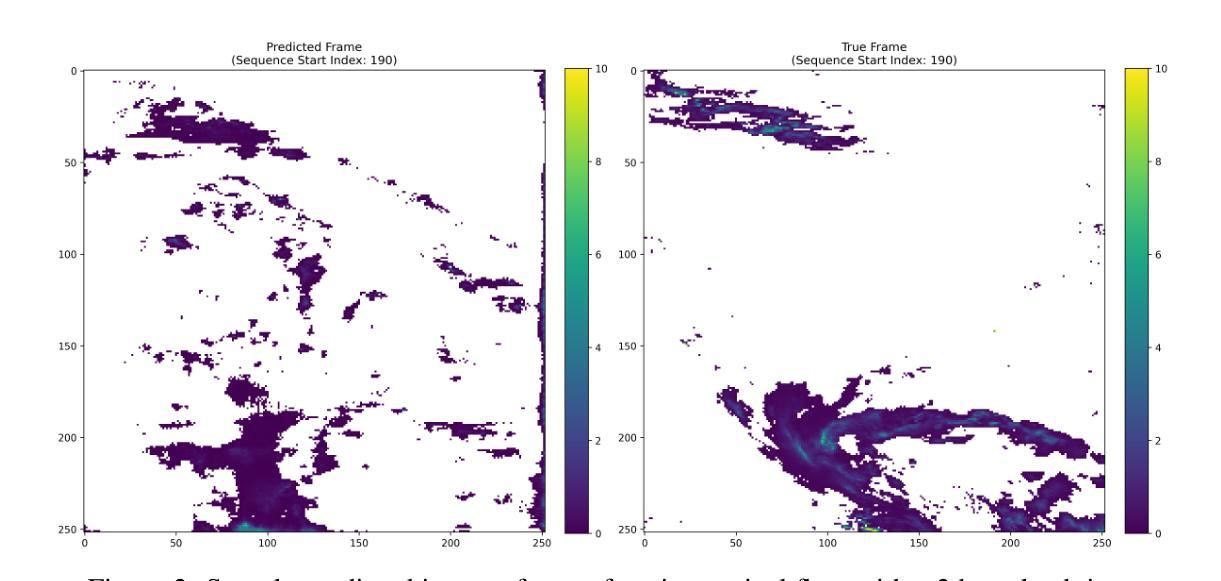
This study explores the application of deep learning for rainfall prediction, leveraging the Spinning Enhanced Visible and Infrared Imager (SEVIRI) High rate information transmission (HRIT) data as input and the Operational Program on the Exchange of weather RAdar information (OPERA) ground-radar reflectivity data as ground truth. We use the mean of 4 InfraRed frequency channels as the input. The radiance images are forecasted up to 4 hours into the future using a dense optical flow algorithm. A conditional generative adversarial network (GAN) model is employed to transform the predicted radiance images into rainfall images which are aggregated over the 4 hour forecast period to generate cumulative rainfall values. This model scored a value of approximately 7.5 as the Continuous Ranked Probability Score (CRPS) in the Weather4Cast 2024 competition and placed 1st on the core challenge leaderboard.
本研究探讨了深度学习在降水预测中的应用,利用SEVIRI(增强可见光和红外成像仪)的高速率信息传输(HRIT)数据作为输入,以及用于气象雷达信息交换的操作程序(OPERA)地面雷达反射数据作为真实参照。我们使用红外频道的平均值作为输入。使用密集的光流算法预测未来长达4小时的辐射图像。采用条件生成对抗网络(GAN)模型将预测的辐射图像转换为降水图像,这些图像汇集在为期4小时的预测期内,生成累计降水量值。在Weather4Cast 2024竞赛中,该模型的连续排名概率得分(CRPS)约为7.5分,并在核心挑战排行榜上排名第一。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究利用深度学习进行降雨预测,使用SEVIRI高传输速率数据和OPERA地面雷达反射数据作为参考真实数据。以红外频道的均值作为输入,利用密集光流算法预测未来四小时的辐射图像。采用条件生成对抗网络(GAN)模型将预测的辐射图像转化为降雨图像,并基于预测期内4小时的降雨图像生成累计降雨量值。在Weather4Cast 2024竞赛中,该模型连续排名概率得分约为7.5,核心挑战排行榜排名第一。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究探讨了深度学习在降雨预测中的应用。
- 研究使用了SEVIRI HRIT数据和OPERA地面雷达反射数据作为输入和参考真实数据。
- 研究采用红外频道均值作为输入,并预测未来四小时的辐射图像。
- 采用密集光流算法进行预测。
- 研究采用了条件生成对抗网络(GAN)模型,将预测的辐射图像转化为降雨图像。
- 模型能够在四小时的预测期内生成累计降雨量值。
点此查看论文截图

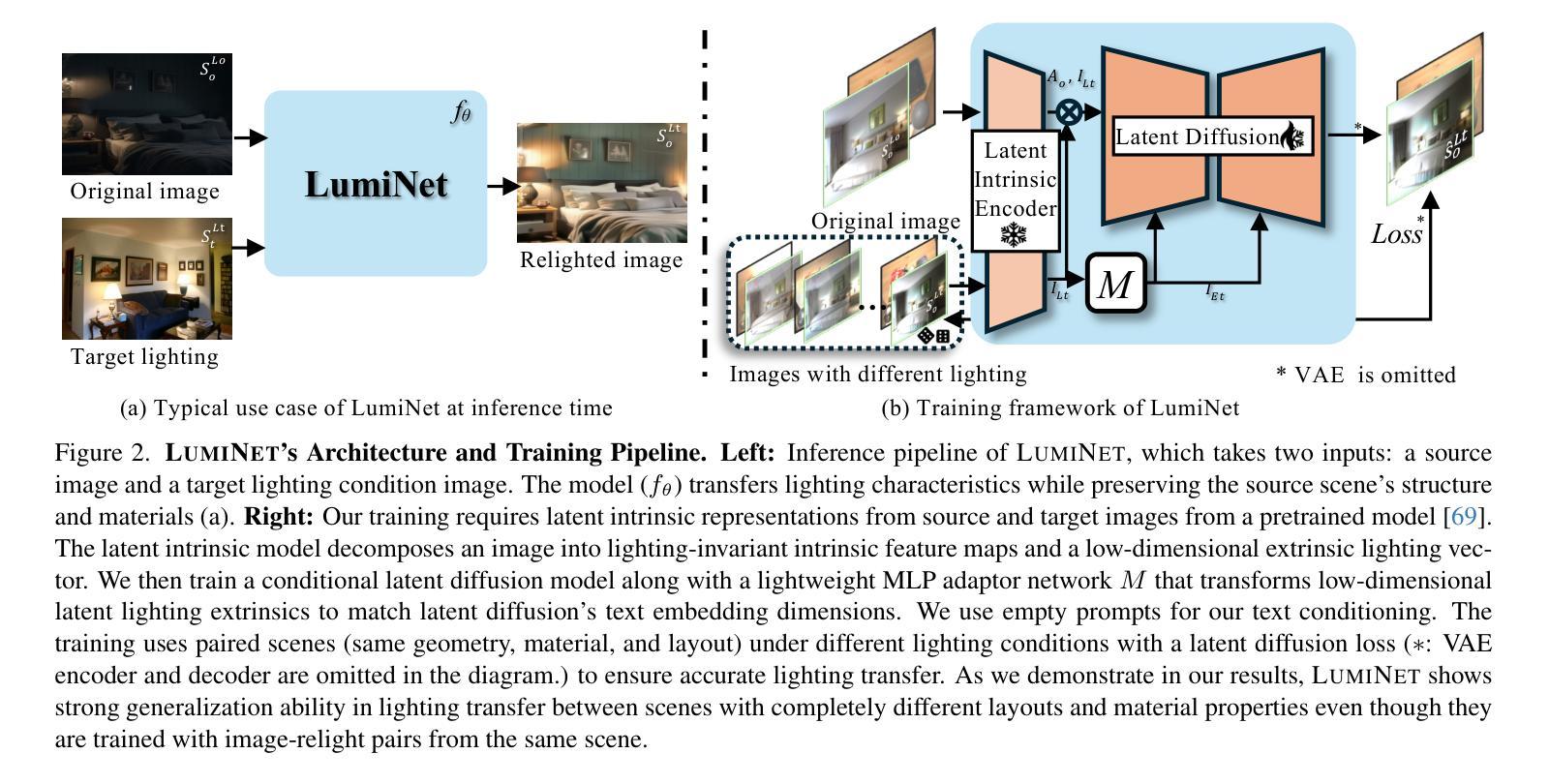
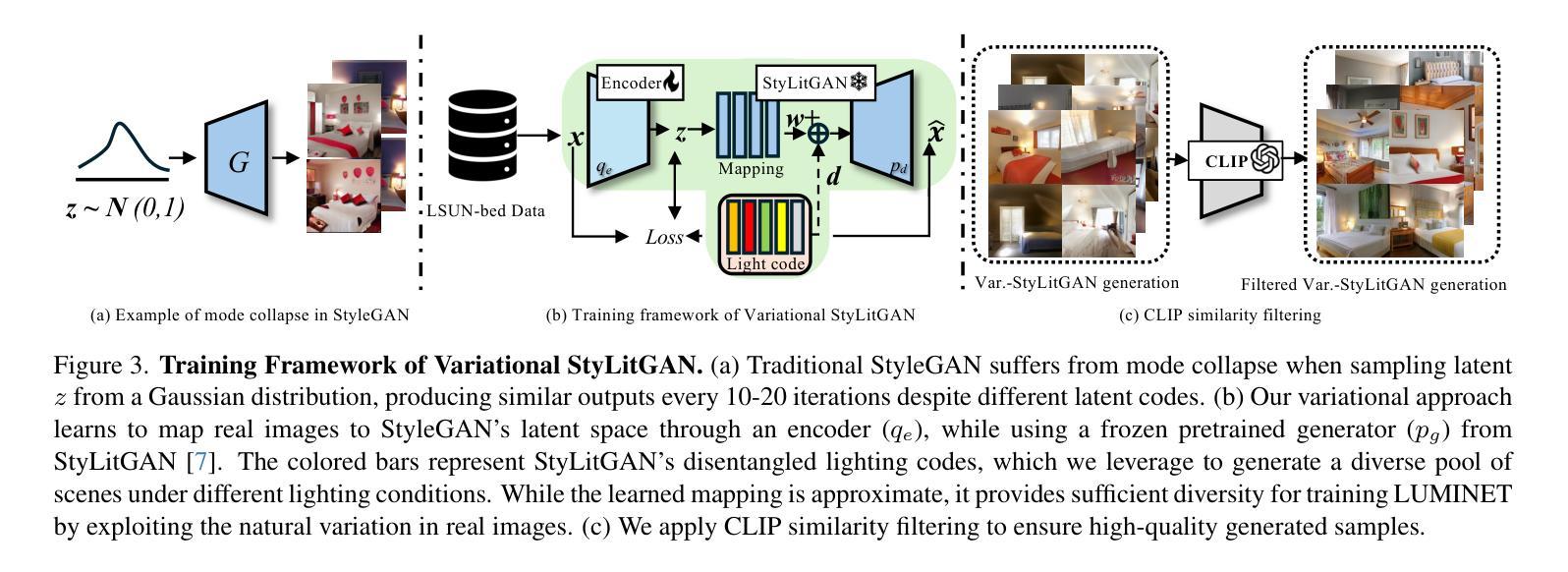
LumiNet: Latent Intrinsics Meets Diffusion Models for Indoor Scene Relighting
Authors:Xiaoyan Xing, Konrad Groh, Sezer Karaoglu, Theo Gevers, Anand Bhattad
We introduce LumiNet, a novel architecture that leverages generative models and latent intrinsic representations for effective lighting transfer. Given a source image and a target lighting image, LumiNet synthesizes a relit version of the source scene that captures the target’s lighting. Our approach makes two key contributions: a data curation strategy from the StyleGAN-based relighting model for our training, and a modified diffusion-based ControlNet that processes both latent intrinsic properties from the source image and latent extrinsic properties from the target image. We further improve lighting transfer through a learned adaptor (MLP) that injects the target’s latent extrinsic properties via cross-attention and fine-tuning. Unlike traditional ControlNet, which generates images with conditional maps from a single scene, LumiNet processes latent representations from two different images - preserving geometry and albedo from the source while transferring lighting characteristics from the target. Experiments demonstrate that our method successfully transfers complex lighting phenomena including specular highlights and indirect illumination across scenes with varying spatial layouts and materials, outperforming existing approaches on challenging indoor scenes using only images as input.
我们介绍了LumiNet,这是一种新型架构,它利用生成模型和潜在内在表示来进行有效的光照转移。给定源图像和目标光照图像,LumiNet合成源场景的重照版本,该版本捕捉目标的光照。我们的方法做出了两个主要贡献:一是基于StyleGAN的重照模型的数据整理策略,用于我们的训练;二是对基于扩散的ControlNet进行了修改,该网络处理来自源图像的潜在内在属性和来自目标图像潜在外在属性。我们进一步通过学习的适配器(MLP)改进光照转移,该适配器通过交叉注意力和微调注入目标潜在外在属性。与传统的ControlNet不同,后者根据单个场景生成带有条件映射的图像,LumiNet处理来自两个不同图像的潜在表示——保留源场景的几何形状和反射率,同时转移目标场景的光照特性。实验表明,我们的方法在跨越具有不同空间布局和材料的不同场景时,成功地转移了包括高光和间接照明等复杂光照现象,仅在输入图像的情况下就可在具有挑战性的室内场景上优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://luminet-relight.github.io
Summary
LumiNet是一种新型架构,利用生成模型和潜在内在表征进行高效的光照转移。给定源图像和目标光照图像,LumiNet可以合成重新照明的源场景,捕捉目标的光照。其方法包括数据整理策略、基于StyleGAN的照明模型训练,以及处理源图像潜在内在属性与目标图像潜在外在属性的改进型扩散控制网络(ControlNet)。此外,通过利用目标潜在外在属性的学习适配器(MLP)进行跨注意力和微调,进一步改善了光照转移。不同于传统ControlNet只处理单一场景的图像生成,LumiNet能够处理来自两个不同图像的潜在表征,既保留源场景的几何形状和反射率,又转移目标场景的光照特性。实验表明,该方法在场景空间布局和材料各异的情况下,成功转移复杂的光照现象,包括高光和间接照明,且在仅使用图像作为输入的情况下,优于现有方法在室内场景的应用。
Key Takeaways
- LumiNet是一种基于生成模型和潜在表征的新型架构,用于实现有效的光照转移。
- 该方法通过数据整理策略训练模型,并采用StyleGAN进行光照模型训练。
- LumiNet使用改进型ControlNet处理源图像的潜在内在属性与目标图像的潜在外在属性。
- 通过学习适配器(MLP)进行跨注意力和微调来改进光照转移。
- LumiNet能处理来自两个不同图像的潜在表征,同时保留几何形状和反射率并转移光照特性。
- 实验表明,该方法在光照转移方面表现出色,尤其是在复杂光照现象和多种场景方面。
点此查看论文截图


A Novel Approach to Image Steganography Using Generative Adversarial Networks
Authors:Waheed Rehman
The field of steganography has long been focused on developing methods to securely embed information within various digital media while ensuring imperceptibility and robustness. However, the growing sophistication of detection tools and the demand for increased data hiding capacity have revealed limitations in traditional techniques. In this paper, we propose a novel approach to image steganography that leverages the power of generative adversarial networks (GANs) to address these challenges. By employing a carefully designed GAN architecture, our method ensures the creation of stego-images that are visually indistinguishable from their original counterparts, effectively thwarting detection by advanced steganalysis tools. Additionally, the adversarial training paradigm optimizes the balance between embedding capacity, imperceptibility, and robustness, enabling more efficient and secure data hiding. We evaluate our proposed method through a series of experiments on benchmark datasets and compare its performance against baseline techniques, including least significant bit (LSB) substitution and discrete cosine transform (DCT)-based methods. Our results demonstrate significant improvements in metrics such as Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM), and robustness against detection. This work not only contributes to the advancement of image steganography but also provides a foundation for exploring GAN-based approaches for secure digital communication.
隐写术领域长期以来一直致力于开发能够在各种数字媒体中安全嵌入信息的方法,同时确保不可察觉性和稳健性。然而,检测工具的日益成熟和对增加数据隐藏容量的需求已经显示出传统技术的局限性。在本文中,我们提出了一种利用生成对抗网络(GANs)解决这些挑战的图像隐写新方法。通过采用精心设计的GAN架构,我们的方法可确保生成的隐写图像在视觉上无法与原始图像区分开,从而有效阻止高级隐写分析工具的检测。此外,对抗训练范式优化了嵌入容量、不可察觉性和稳健性之间的平衡,使数据隐藏更加高效和安全。我们通过一系列基准数据集上的实验评估了所提出的方法,并将其性能与包括最低有效位(LSB)替换和基于离散余弦变换(DCT)的方法在内的基线技术进行了比较。我们的结果在峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)以及对抗检测的稳健性等方面均表现出显著改进。这项工作不仅推动了图像隐写技术的发展,而且为基于GAN的安全数字通信方法的研究提供了基础。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本研究提出一种基于生成对抗网络(GANs)的图像隐写分析新方法,旨在解决传统技术面临的挑战,如检测工具的日益成熟和对更大隐藏容量的需求。该方法利用精心设计的GAN架构创建隐写图像,这些图像在视觉上几乎与原始图像无法区分,有效抵抗先进的隐写分析工具。此外,对抗性训练范式优化了嵌入容量、不可察觉性和稳健性之间的平衡,提高了数据隐藏的效率和安全性。
Key Takeaways:
- 本研究利用GANs解决图像隐写分析中的挑战。
- GAN架构被用于创建与原始图像视觉上不可区分的隐写图像。
- 对抗性训练范式提高了嵌入容量、不可察觉性和稳健性的平衡。
- 该方法有效抵抗先进的隐写分析工具。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在峰值信噪比(PSNR)、结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)和抗检测方面的性能有显著改善。
- 此研究不仅推动了图像隐写分析的发展,还为基于GANs的安全数字通信提供了基础。
点此查看论文截图

Addressing Vulnerabilities in AI-Image Detection: Challenges and Proposed Solutions
Authors:Justin Jiang
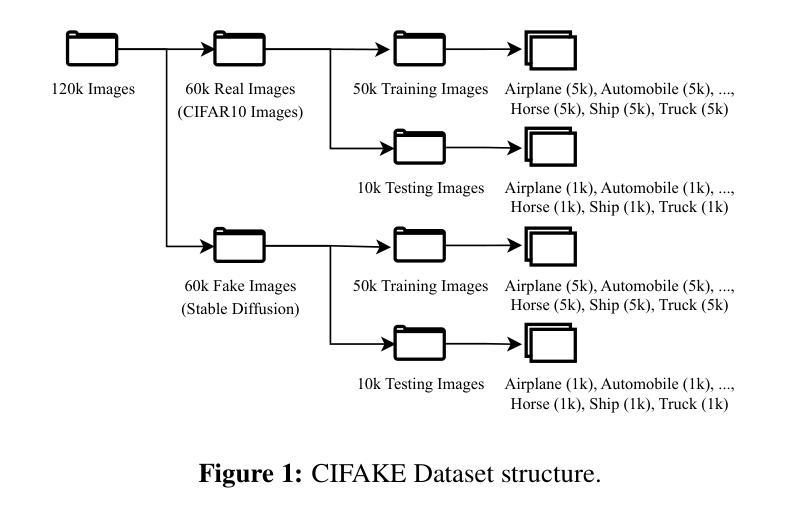
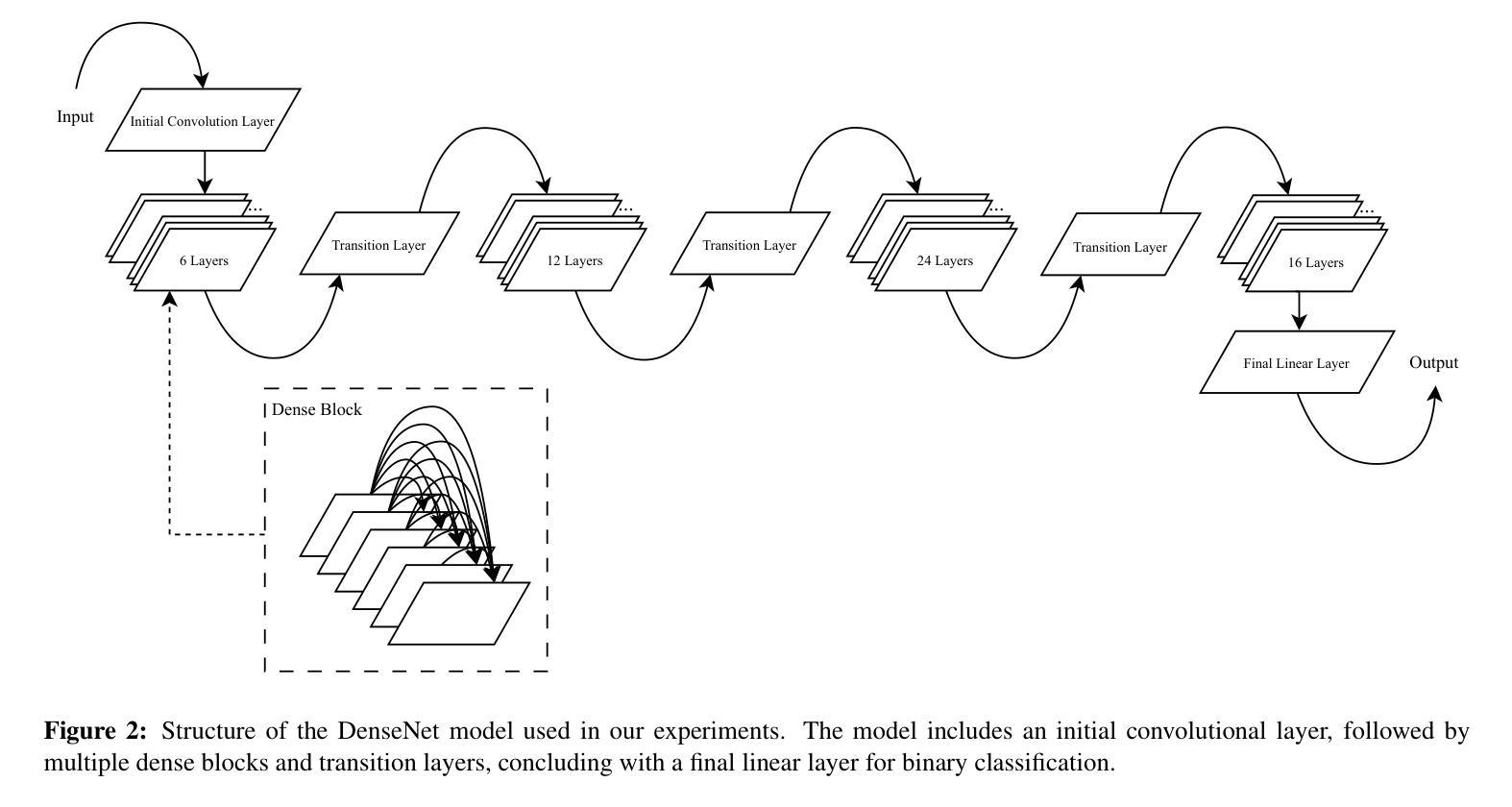
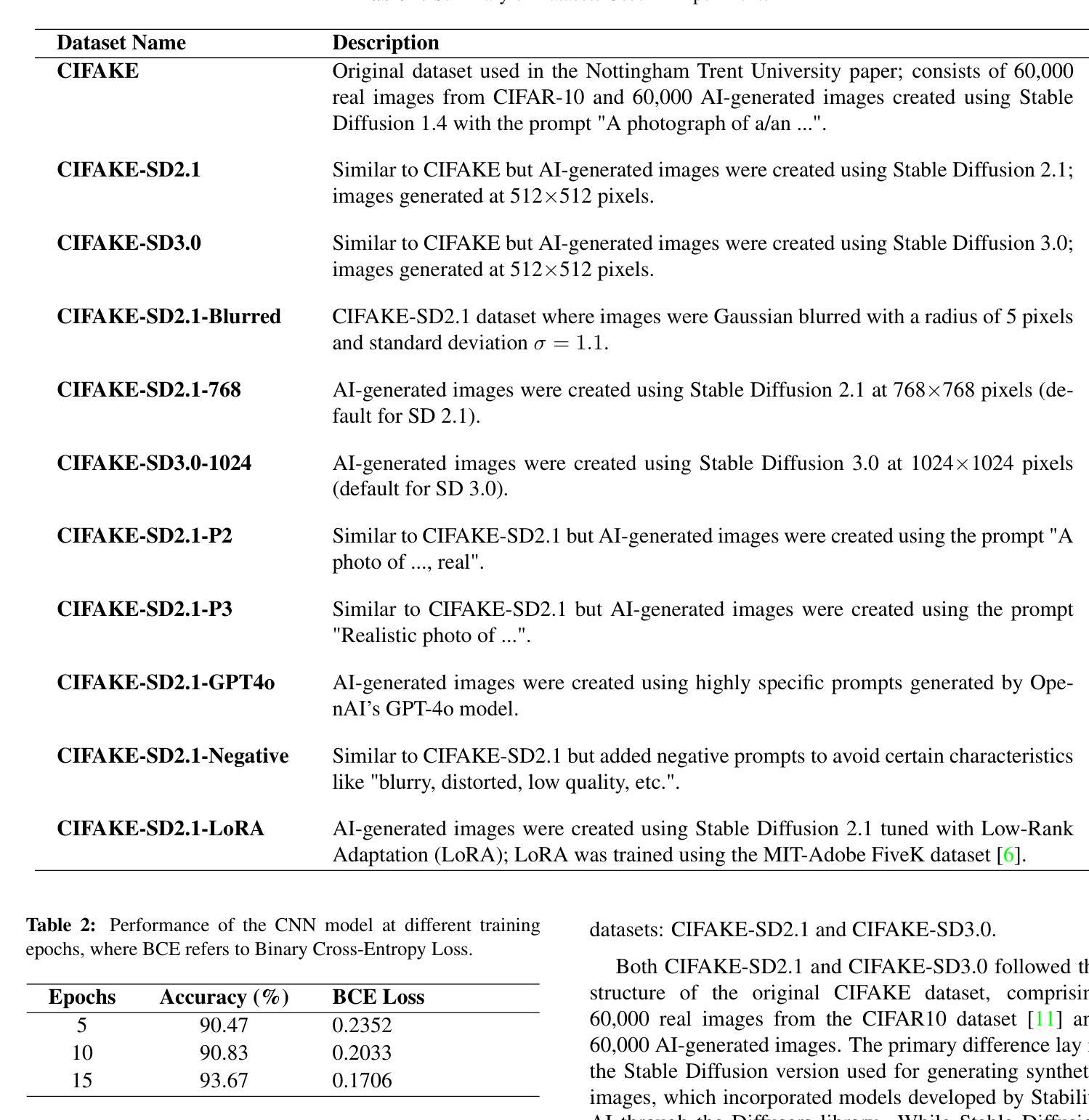
The rise of advanced AI models like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and diffusion models such as Stable Diffusion has made the creation of highly realistic images accessible, posing risks of misuse in misinformation and manipulation. This study evaluates the effectiveness of convolutional neural networks (CNNs), as well as DenseNet architectures, for detecting AI-generated images. Using variations of the CIFAKE dataset, including images generated by different versions of Stable Diffusion, we analyze the impact of updates and modifications such as Gaussian blurring, prompt text changes, and Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) on detection accuracy. The findings highlight vulnerabilities in current detection methods and propose strategies to enhance the robustness and reliability of AI-image detection systems.
随着生成对抗网络(GANs)等高级AI模型和Stable Diffusion等扩散模型的兴起,创建高度逼真的图像变得更加容易,这带来了误用和误导信息的风险。本研究旨在评估卷积神经网络(CNN)和DenseNet架构在检测AI生成的图像方面的有效性。我们使用了CIFAR的变体数据集,包括由不同版本的Stable Diffusion生成的图像,分析了高斯模糊处理、提示文本更改和低秩适应(LoRA)等更新和修改对检测准确率的影响。研究指出了当前检测方法的漏洞并提出了增强AI图像检测系统稳健性和可靠性的策略。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
先进AI模型如生成对抗网络(GANs)和稳定扩散等扩散模型的出现,使得生成高度逼真的图像成为可能,但也存在被误用导致误导和操纵的风险。本研究评估了卷积神经网络(CNN)和DenseNet架构在检测AI生成图像方面的有效性。通过使用包括不同版本的稳定扩散生成的图像在内的CIFAKE数据集变种,分析了更新和修改如高斯模糊、提示文本变化和Low-Rank Adaptation(LoRA)对检测精度的影响。研究突出了当前检测方法的漏洞,并提出了增强AI图像检测系统稳健性和可靠性的策略。
Key Takeaways
- AI模型如GANs和稳定扩散能生成高度逼真的图像,存在被误用导致误导和操纵的风险。
- 研究评估了CNN和DenseNet架构在检测AI生成图像方面的有效性。
- 使用CIFAKE数据集变种来分析不同因素,包括图像生成方法的更新和修改,对检测精度的影响。
- 当前检测方法存在漏洞,需要增强AI图像检测系统的稳健性和可靠性。
- 高斯模糊、提示文本变化和LoRA等修改可能影响AI生成图像的检测精度。
- 研究强调了更新和改进现有AI图像检测系统的必要性。
点此查看论文截图


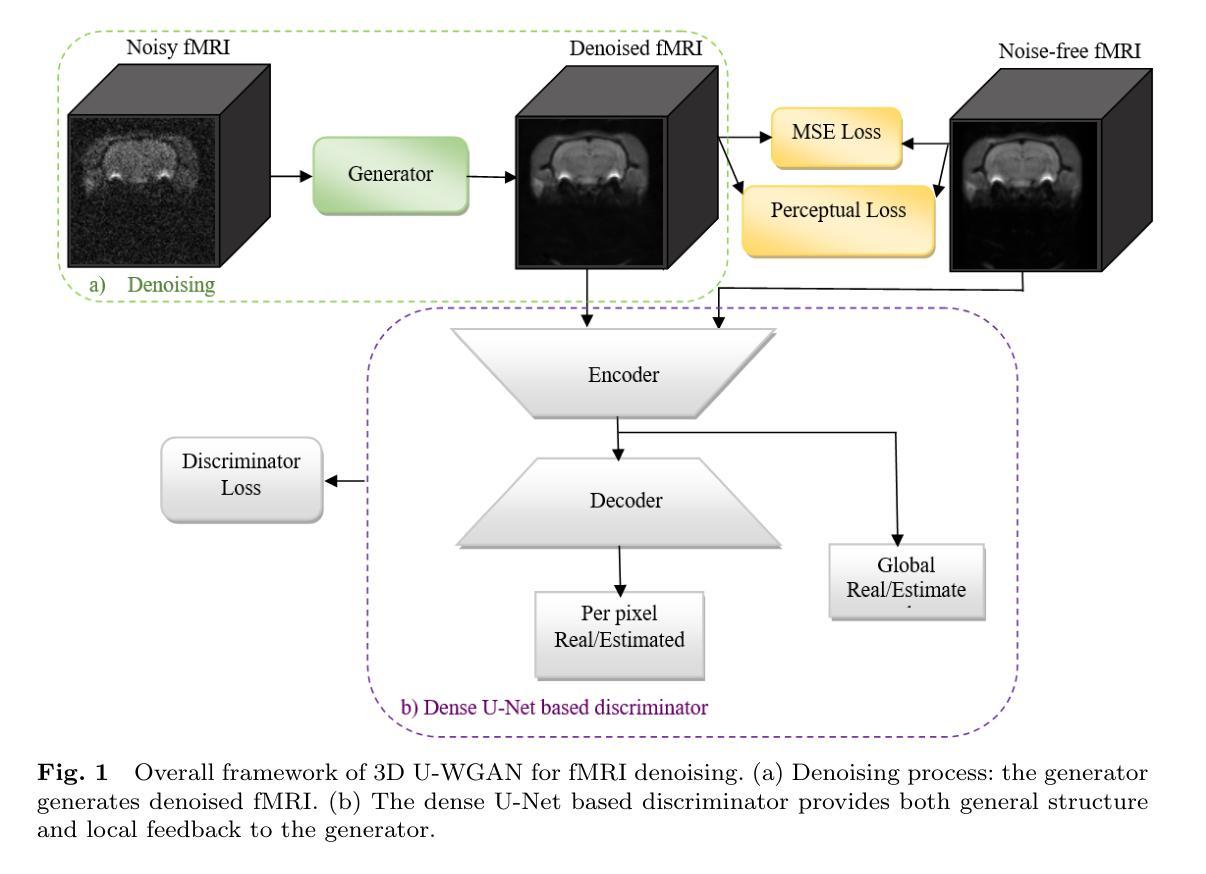
3D Wasserstein generative adversarial network with dense U-Net based discriminator for preclinical fMRI denoising
Authors:Sima Soltanpour, Arnold Chang, Dan Madularu, Praveen Kulkarni, Craig Ferris, Chris Joslin
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) is extensively used in clinical and preclinical settings to study brain function, however, fMRI data is inherently noisy due to physiological processes, hardware, and external noise. Denoising is one of the main preprocessing steps in any fMRI analysis pipeline. This process is challenging in preclinical data in comparison to clinical data due to variations in brain geometry, image resolution, and low signal-to-noise ratios. In this paper, we propose a structure-preserved algorithm based on a 3D Wasserstein generative adversarial network with a 3D dense U-net based discriminator called, 3D U-WGAN. We apply a 4D data configuration to effectively denoise temporal and spatial information in analyzing preclinical fMRI data. GAN-based denoising methods often utilize a discriminator to identify significant differences between denoised and noise-free images, focusing on global or local features. To refine the fMRI denoising model, our method employs a 3D dense U-Net discriminator to learn both global and local distinctions. To tackle potential over-smoothing, we introduce an adversarial loss and enhance perceptual similarity by measuring feature space distances. Experiments illustrate that 3D U-WGAN significantly improves image quality in resting-state and task preclinical fMRI data, enhancing signal-to-noise ratio without introducing excessive structural changes in existing methods. The proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art methods when applied to simulated and real data in a fMRI analysis pipeline.
功能磁共振成像(fMRI)在临床和临床前环境中广泛应用于研究脑功能。然而,由于生理过程、硬件和外部噪声,fMRI数据本质上存在噪声。去噪是任何fMRI分析管道中的主要预处理步骤之一。与临床数据相比,去噪在临床前数据中更具挑战性,因为存在大脑几何结构、图像分辨率和信噪比低的差异。在本文中,我们提出了一种基于3D Wasserstein生成对抗网络的结构保留算法,该算法具有一个名为3D U-WGAN的基于3D密集U-net的鉴别器。我们采用4D数据配置,以有效地对临床前fMRI数据进行去噪处理并分析时空信息。基于GAN的去噪方法通常使用鉴别器来识别去噪图像和无噪声图像之间的显著差异,侧重于全局或局部特征。为了改进fMRI去噪模型,我们的方法采用了一个三维密集U-Net鉴别器来学习全局和局部的区别。为了解决可能的过度平滑问题,我们引入了对抗损失并通过测量特征空间距离来提高感知相似性。实验表明,三维U-WGAN显著提高了静息状态和任务态临床前fMRI的图像质量,提高了信噪比,同时在现有方法中不会引起过度的结构变化。当应用于模拟数据和真实数据时,该方法在fMRI分析管道中的表现优于现有先进技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于三维Wasserstein生成对抗网络(3D U-WGAN)的结构保留算法,用于对临床前的功能磁共振成像(fMRI)数据进行去噪处理。该算法采用四维数据配置,有效去除了时空噪声,提高了图像质量。通过引入对抗损失和特征空间距离的度量,解决了过度平滑的问题,增强了感知相似性。实验结果表明,该算法在静息态和任务态的fMRI数据中表现优异,提高了信噪比,且在现有方法中未引入过多的结构变化。与现有先进方法相比,该算法在模拟和真实数据上的表现更优秀。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了一种基于三维Wasserstein生成对抗网络(3D U-WGAN)的算法,用于对临床前的功能磁共振成像(fMRI)数据进行预处理去噪。
- 该算法采用四维数据配置,旨在有效去除fMRI数据中的时空噪声。
- 论文使用了一个3D密集U-Net判别器来同时学习全局和局部特征,以优化去噪模型。
- 为了解决过度平滑的问题,引入了对抗损失,并通过测量特征空间距离增强了感知相似性。
- 实验结果表明,该算法在静息态和任务态的fMRI数据中表现优异,能够显著提高图像质量并增强信噪比。
- 与现有方法相比,该算法在模拟和真实数据上表现出更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图

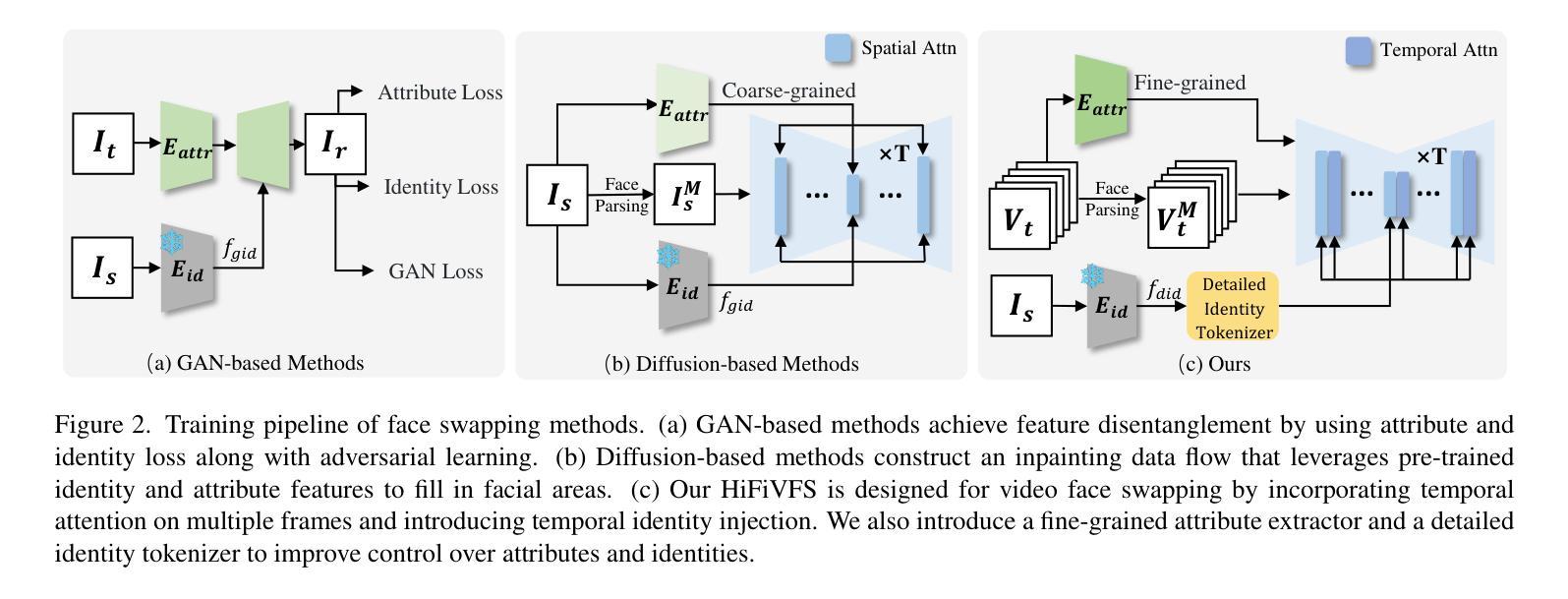
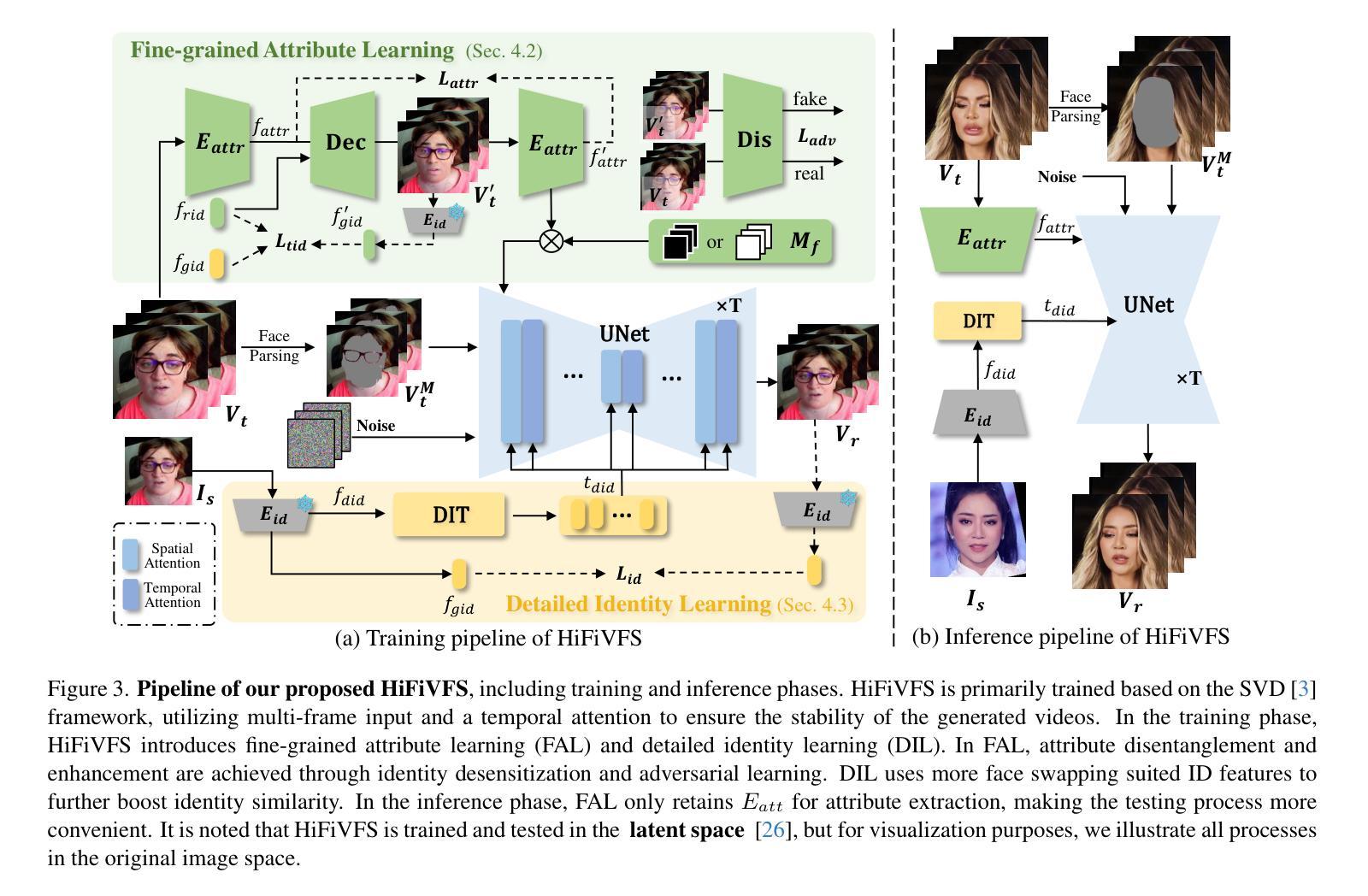
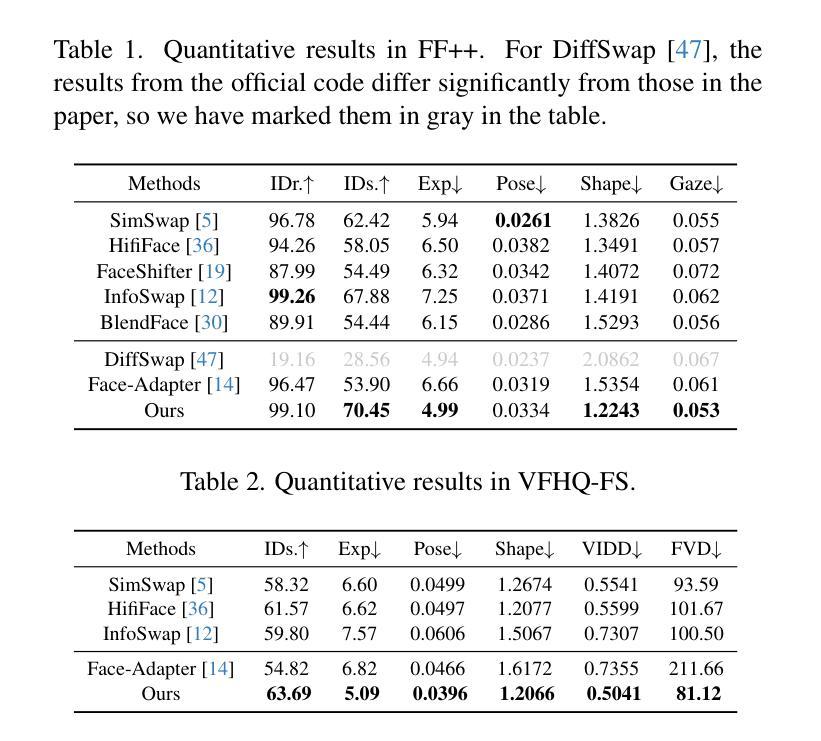
HiFiVFS: High Fidelity Video Face Swapping
Authors:Xu Chen, Keke He, Junwei Zhu, Yanhao Ge, Wei Li, Chengjie Wang
Face swapping aims to generate results that combine the identity from the source with attributes from the target. Existing methods primarily focus on image-based face swapping. When processing videos, each frame is handled independently, making it difficult to ensure temporal stability. From a model perspective, face swapping is gradually shifting from generative adversarial networks (GANs) to diffusion models (DMs), as DMs have been shown to possess stronger generative capabilities. Current diffusion-based approaches often employ inpainting techniques, which struggle to preserve fine-grained attributes like lighting and makeup. To address these challenges, we propose a high fidelity video face swapping (HiFiVFS) framework, which leverages the strong generative capability and temporal prior of Stable Video Diffusion (SVD). We build a fine-grained attribute module to extract identity-disentangled and fine-grained attribute features through identity desensitization and adversarial learning. Additionally, We introduce detailed identity injection to further enhance identity similarity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) in video face swapping, both qualitatively and quantitatively.
面部替换旨在生成结合源身份和目标属性的结果。现有方法主要集中在基于图像的面部替换上。在处理视频时,每一帧都是独立处理的,很难保证时间稳定性。从模型的角度来看,面部替换正逐渐从生成对抗网络(GANs)转向扩散模型(DMs),因为DMs已显示出具有更强的生成能力。当前的基于扩散的方法通常采用图像修复技术,这在保留光照和妆容等精细属性方面存在困难。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了高保真视频面部替换(HiFiVFS)框架,它利用稳定视频扩散(SVD)的强大生成能力和时间先验。我们建立了一个精细属性模块,通过身份脱敏和对抗性学习提取身份分离和精细属性特征。此外,我们还引入了详细的身份注入,以进一步增强身份相似性。大量实验表明,我们的方法在视频面部替换中实现了定性和定量上的最先进水平(SOTA)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种高保真视频人脸替换(HiFiVFS)框架,利用稳定视频扩散(SVD)的强生成能力和时间先验,解决现有视频人脸替换技术在时间稳定性和细节属性保存方面的问题。通过身份脱敏和对抗学习,构建细粒度属性模块以提取身份分离和细粒度属性特征。引入详细身份注入,进一步提高身份相似性。实验证明,该方法在视频人脸替换方面达到最新水平。
Key Takeaways
- 视频人脸替换面临时间稳定性和细节属性保存的挑战。
- 现有方法主要关注图像人脸替换,处理视频时独立处理每一帧,难以确保时间稳定性。
- 人脸替换技术逐渐从生成对抗网络(GANs)转向扩散模型(DMs),因为DMs展现出更强的生成能力。
- 当前扩散模型方法常采用补全技术,难以保存光照和妆容等细粒度属性。
- 提出的高保真视频人脸替换(HiFiVFS)框架利用稳定视频扩散(SVD)的生成能力和时间先验。
- 构建细粒度属性模块,通过身份脱敏和对抗学习提取身份分离和细粒度属性特征。
点此查看论文截图

Towards Lensless Image Deblurring with Prior-Embedded Implicit Neural Representations in the Low-Data Regime
Authors:Abeer Banerjee, Sanjay Singh
The field of computational imaging has witnessed a promising paradigm shift with the emergence of untrained neural networks, offering novel solutions to inverse computational imaging problems. While existing techniques have demonstrated impressive results, they often operate either in the high-data regime, leveraging Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) as image priors, or through untrained iterative reconstruction in a data-agnostic manner. This paper delves into lensless image reconstruction, a subset of computational imaging that replaces traditional lenses with computation, enabling the development of ultra-thin and lightweight imaging systems. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to leverage implicit neural representations for lensless image deblurring, achieving reconstructions without the requirement of prior training. We perform prior-embedded untrained iterative optimization to enhance reconstruction performance and speed up convergence, effectively bridging the gap between the no-data and high-data regimes. Through a thorough comparative analysis encompassing various untrained and low-shot methods, including under-parameterized non-convolutional methods and domain-restricted low-shot methods, we showcase the superior performance of our approach by a significant margin.
计算成像领域见证了未训练神经网络的出现所带来的充满希望的模式转变,为解决反计算成像问题提供了新的解决方案。虽然现有技术已经取得了令人印象深刻的结果,但它们通常在高数据状态下运行,利用生成对抗网络(GANs)作为图像先验,或者以数据无关的方式通过未训练的迭代重建。本文深入探讨了无透镜图像重建,这是计算成像的一个子集,用计算代替传统透镜,为实现超薄和轻便的成像系统的发展创造了条件。据我们所知,我们是首次利用隐式神经表征进行无透镜图像去模糊处理,实现无需预先训练的重建。我们执行嵌入先验的未训练迭代优化,以提高重建性能并加快收敛速度,有效地缩小了无数据和高数据状态之间的鸿沟。通过对各种未训练和少量拍摄的方法进行全面比较分析,包括参数不足的卷积方法以及受域限制的低射击方法,我们展示了我们的方法在这些方法中表现优越。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
计算成像领域出现了未训练神经网络,为逆计算成像问题提供了新的解决方案。本文专注于无透镜图像重建,利用隐式神经表征进行无透镜图像去模糊,无需预先训练即可实现重建。通过嵌入先验的未训练迭代优化,提高了重建性能和收敛速度,缩小了无数据和高数据之间的鸿沟。对比分析了各种未训练和低样本方法,本文方法表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 未训练神经网络在计算成像领域展现出新的解决方案潜力。
- 无透镜图像重建作为计算成像的一个子集,替换了传统透镜,有助于开发超薄和轻型的成像系统。
- 首次尝试利用隐式神经表征进行无透镜图像去模糊。
- 嵌入先验的未训练迭代优化提高了重建性能和收敛速度。
- 缩小了无数据和高数据之间的鸿沟,实现了更广泛的适用性和灵活性。
- 与其他未训练和低样本方法相比,包括参数不足的非卷积方法和受域限制的低样本方法,本文提出的方法表现出显著优势。
点此查看论文截图

OSDFace: One-Step Diffusion Model for Face Restoration
Authors:Jingkai Wang, Jue Gong, Lin Zhang, Zheng Chen, Xing Liu, Hong Gu, Yutong Liu, Yulun Zhang, Xiaokang Yang
Diffusion models have demonstrated impressive performance in face restoration. Yet, their multi-step inference process remains computationally intensive, limiting their applicability in real-world scenarios. Moreover, existing methods often struggle to generate face images that are harmonious, realistic, and consistent with the subject’s identity. In this work, we propose OSDFace, a novel one-step diffusion model for face restoration. Specifically, we propose a visual representation embedder (VRE) to better capture prior information and understand the input face. In VRE, low-quality faces are processed by a visual tokenizer and subsequently embedded with a vector-quantized dictionary to generate visual prompts. Additionally, we incorporate a facial identity loss derived from face recognition to further ensure identity consistency. We further employ a generative adversarial network (GAN) as a guidance model to encourage distribution alignment between the restored face and the ground truth. Experimental results demonstrate that OSDFace surpasses current state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods in both visual quality and quantitative metrics, generating high-fidelity, natural face images with high identity consistency. The code and model will be released at https://github.com/jkwang28/OSDFace.
扩散模型在人脸修复方面表现出了令人印象深刻的性能。然而,其多步推理过程仍然计算密集,限制了其在现实场景中的应用。此外,现有方法往往难以生成和谐、逼真且与人脸身份一致的人脸图像。在这项工作中,我们提出了OSDFace,这是一种用于人脸修复的新型一步扩散模型。具体来说,我们提出了一种视觉表示嵌入器(VRE)来更好地捕获先验信息并理解输入的人脸。在VRE中,低质量的人脸通过视觉标记器进行处理,随后使用向量量化字典嵌入生成视觉提示。此外,我们结合人脸识别中得到的面部身份损失来进一步确保身份一致性。我们还采用生成对抗网络(GAN)作为指导模型,以鼓励修复的人脸与地面实况之间的分布对齐。实验结果表明,OSDFace在视觉质量和定量指标方面都超越了当前最先进的(SOTA)方法,生成了高保真、自然的人脸图像,具有很高的身份一致性。代码和模型将在https://github.com/jkwang28/OSDFace上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures. The code and model will be available at https://github.com/jkwang28/OSDFace
Summary
本文提出了一种名为OSDFace的新型一步扩散模型,用于面部修复。该模型通过视觉表示嵌入器(VRE)更好地捕捉先验信息并理解输入面部。模型还结合了面部身份损失以确保身份一致性,并采用生成对抗网络(GAN)作为引导模型来鼓励恢复面部与真实面部之间的分布对齐。实验结果表明,OSDFace在视觉质量和定量指标方面均超越了当前先进水平,能够生成高保真、自然的面部图像,具有高度的身份一致性。
Key Takeaways
- OSDFace是一个新型的一步扩散模型,用于面部修复,旨在解决多步推理计算量大和在现实场景应用有限的问题。
- 通过视觉表示嵌入器(VRE)捕捉先验信息并理解输入面部。
- 使用视觉令牌器和向量量化词典生成视觉提示来处理低质量面部图像。
- 结合面部身份损失以确保生成的面部图像与主体身份一致。
- 采用生成对抗网络(GAN)作为引导模型,使修复后的面部与真实面部之间的分布对齐。
- 实验结果表明,OSDFace在视觉质量和定量指标上超越了当前最先进的方法。
点此查看论文截图

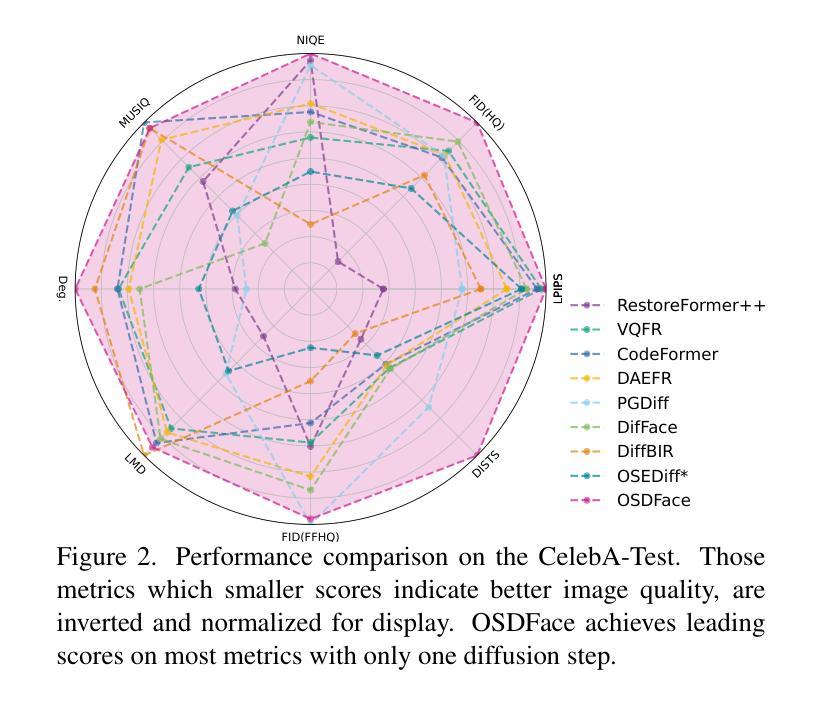
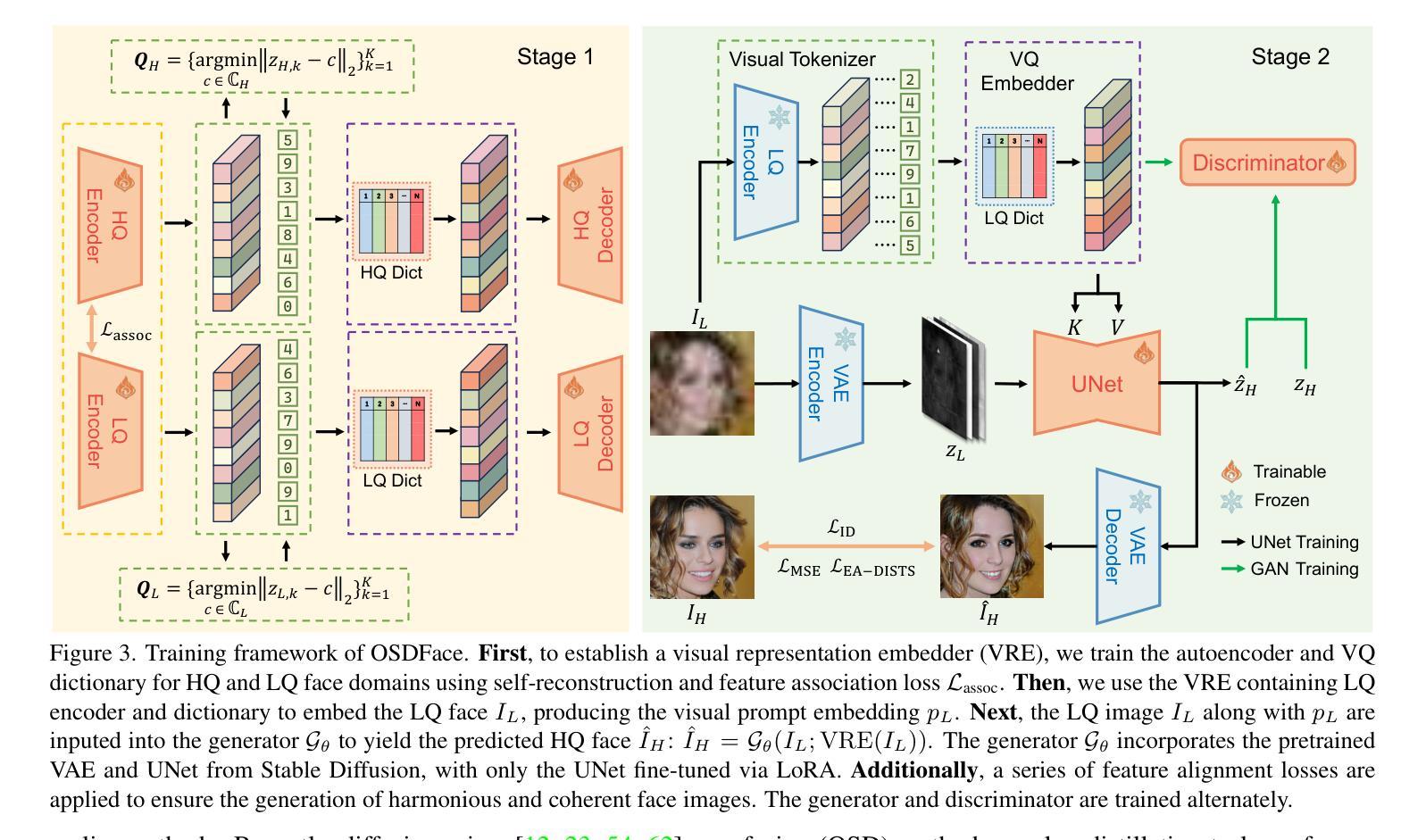

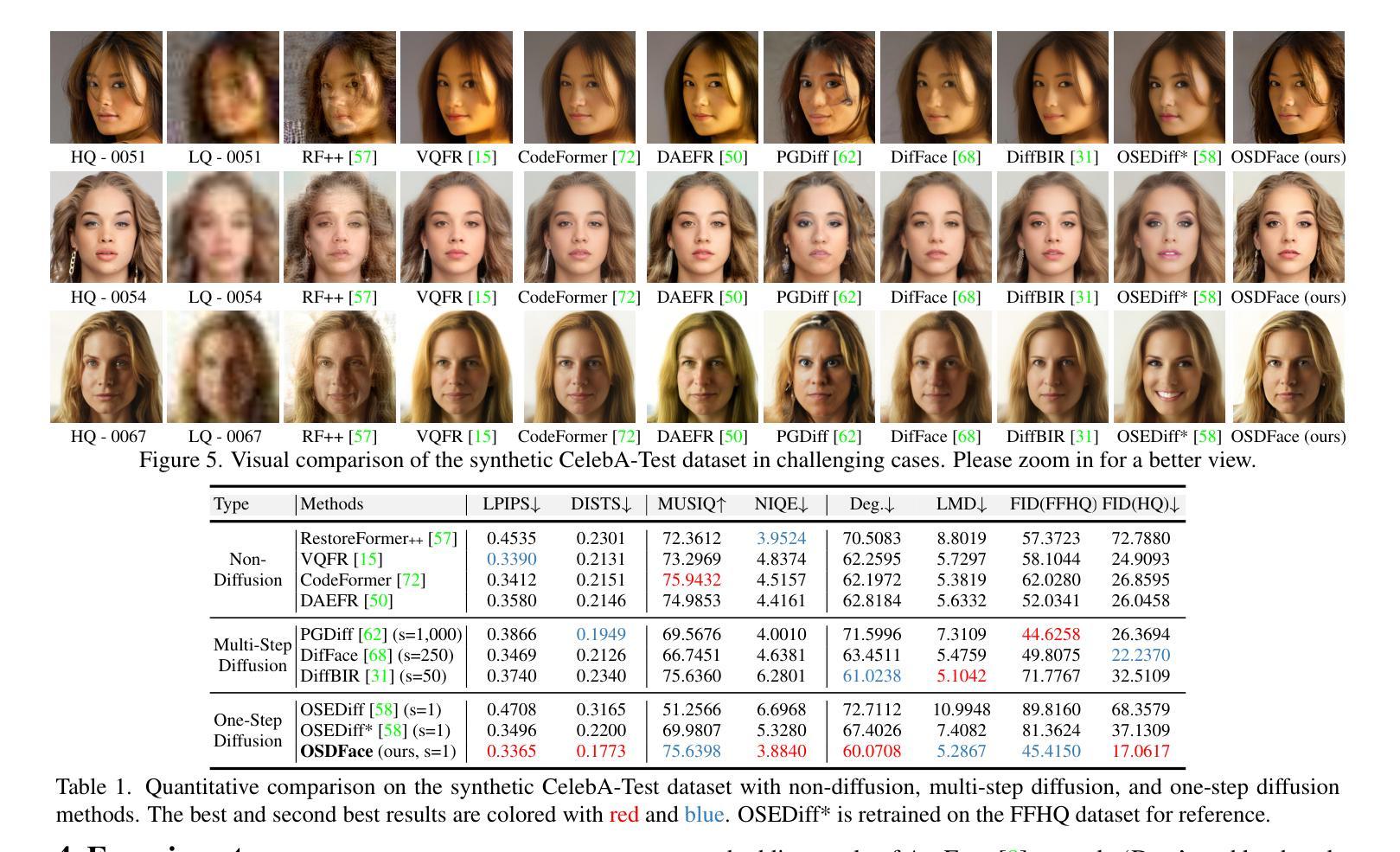
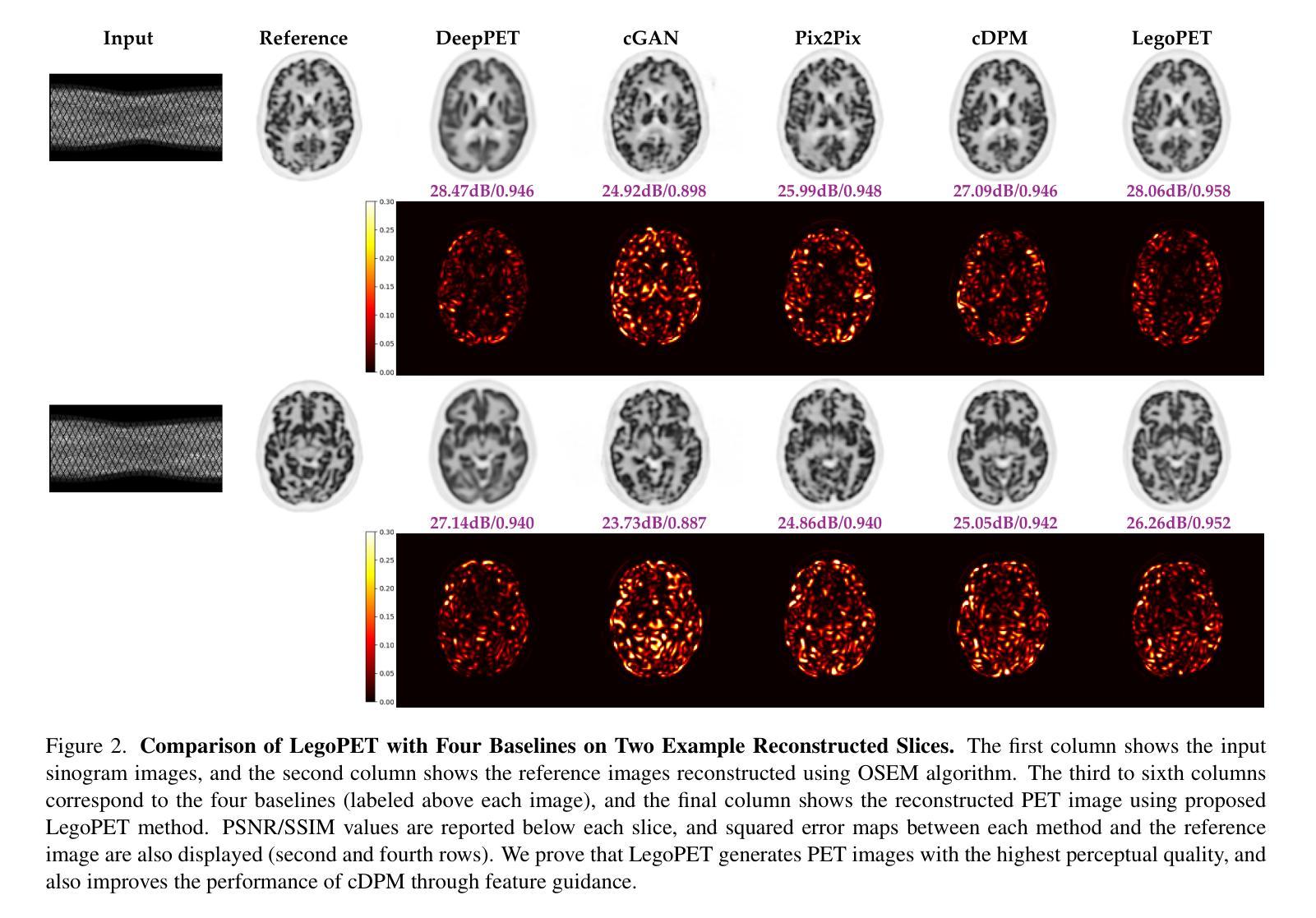
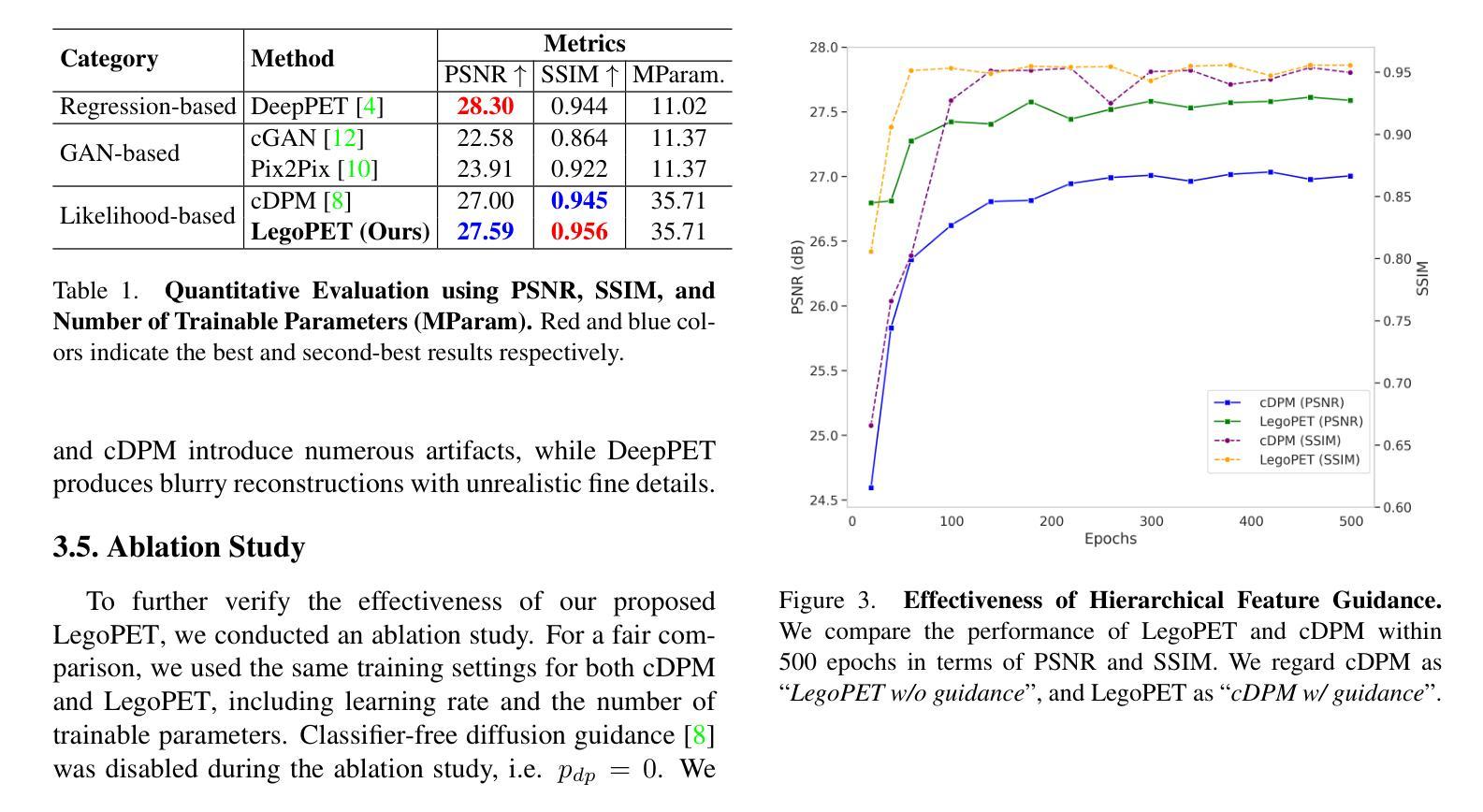
LegoPET: Hierarchical Feature Guided Conditional Diffusion for PET Image Reconstruction
Authors:Yiran Sun, Osama Mawlawi
Positron emission tomography (PET) is widely utilized for cancer detection due to its ability to visualize functional and biological processes in vivo. PET images are usually reconstructed from histogrammed raw data (sinograms) using traditional iterative techniques (e.g., OSEM, MLEM). Recently, deep learning (DL) methods have shown promise by directly mapping raw sinogram data to PET images. However, DL approaches that are regression-based or GAN-based often produce overly smoothed images or introduce various artifacts respectively. Image-conditioned diffusion probabilistic models (cDPMs) are another class of likelihood-based DL techniques capable of generating highly realistic and controllable images. While cDPMs have notable strengths, they still face challenges such as maintain correspondence and consistency between input and output images when they are from different domains (e.g., sinogram vs. image domain) as well as slow convergence rates. To address these limitations, we introduce LegoPET, a hierarchical feature guided conditional diffusion model for high-perceptual quality PET image reconstruction from sinograms. We conducted several experiments demonstrating that LegoPET not only improves the performance of cDPMs but also surpasses recent DL-based PET image reconstruction techniques in terms of visual quality and pixel-level PSNR/SSIM metrics. Our code is available at https://github.com/yransun/LegoPET.
正电子发射断层扫描(PET)由于其能够可视化体内功能和生物过程的能力,广泛用于癌症检测。PET图像通常从直方化原始数据(辛勒格)使用传统的迭代技术(例如OSEM、MLEM)重建。最近,深度学习(DL)方法通过直接映射原始辛勒格数据到PET图像显示出潜力。然而,基于回归或生成对抗网络(GAN)的DL方法通常会产生过于平滑的图像或分别引入各种伪影。图像条件扩散概率模型(cPMS)是另一类基于可能性的深度学习技术,能够生成高度逼真且可控的图像。虽然cPMS具有显著的优势,但它们仍然面临挑战,例如在输入和输出图像来自不同域(例如辛勒格与图像域)时保持对应性和一致性,以及收敛速度慢。为了解决这些限制,我们引入了LegoPET,这是一种分层特征引导的条件扩散模型,用于从辛勒格对PET图像进行高质量感知重建。我们进行了几项实验,结果表明LegoPET不仅提高了cPMS的性能,而且在视觉质量和像素级峰值信噪比(PSNR)/结构相似性度量(SSIM)指标方面超越了最近的基于DL的PET图像重建技术。我们的代码可在https://github.com/yransun/LegoPET找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 3 figures
Summary
PET图像重建技术在医学诊断中具有广泛应用。传统的迭代技术,如OSEM和MLEM,通常从直方化的原始数据(辛氏图)重建图像。最近,深度学习(DL)方法通过直接映射原始辛氏图数据到PET图像显示出潜力。然而,基于回归或生成对抗网络(GAN)的DL方法常常产生过于平滑的图像或引入各种伪影。针对这些问题,提出了LegoPET,一种分级特征引导的条件扩散模型,用于从辛氏图进行高质量的PET图像重建。实验表明,LegoPET不仅提升了基于特征金字塔的网络性能,还在视觉质量和像素级PSNR/SSIM指标上超越了最新的DL-based PET图像重建技术。
Key Takeaways
- PET广泛用于癌症检测,能够可视化体内功能和生物过程。
- 传统迭代技术如OSEM和MLEM通常用于从辛氏图重建PET图像。
- 深度学习(DL)方法可直接映射辛氏图数据到PET图像,具有潜力。
- 基于回归或GAN的DL方法可能产生过于平滑的图像或引入伪影。
- cDPMs是一种基于概率的DL技术,能够生成高度逼真且可控的图像。
- cDPMs面临跨域对应性和一致性的挑战(如辛氏图与图像域之间)。
点此查看论文截图

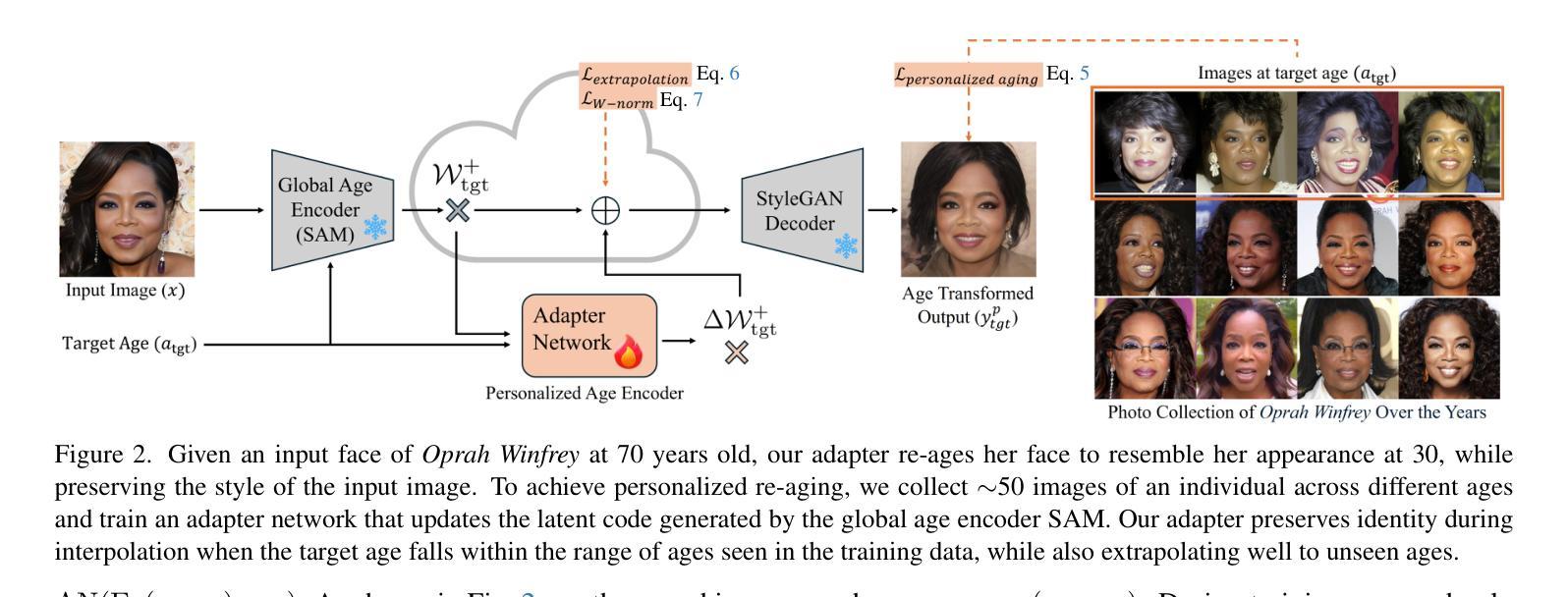
MyTimeMachine: Personalized Facial Age Transformation
Authors:Luchao Qi, Jiaye Wu, Bang Gong, Annie N. Wang, David W. Jacobs, Roni Sengupta
Facial aging is a complex process, highly dependent on multiple factors like gender, ethnicity, lifestyle, etc., making it extremely challenging to learn a global aging prior to predict aging for any individual accurately. Existing techniques often produce realistic and plausible aging results, but the re-aged images often do not resemble the person’s appearance at the target age and thus need personalization. In many practical applications of virtual aging, e.g. VFX in movies and TV shows, access to a personal photo collection of the user depicting aging in a small time interval (20$\sim$40 years) is often available. However, naive attempts to personalize global aging techniques on personal photo collections often fail. Thus, we propose MyTimeMachine (MyTM), which combines a global aging prior with a personal photo collection (using as few as 50 images) to learn a personalized age transformation. We introduce a novel Adapter Network that combines personalized aging features with global aging features and generates a re-aged image with StyleGAN2. We also introduce three loss functions to personalize the Adapter Network with personalized aging loss, extrapolation regularization, and adaptive w-norm regularization. Our approach can also be extended to videos, achieving high-quality, identity-preserving, and temporally consistent aging effects that resemble actual appearances at target ages, demonstrating its superiority over state-of-the-art approaches.
面部老化是一个复杂的过程,它高度依赖于性别、种族、生活方式等多种因素,因此,要想准确预测任何个体的老化情况并学习全局老化先验知识,是一项极具挑战性的任务。现有技术虽然能够产生真实且合理的老化结果,但重新老化的图像往往与目标年龄的人的外貌不相符,因此需要进行个性化设置。在虚拟老化的许多实际应用中,例如在电影和电视剧的VFX特效中,通常可以获取到用户在短时间内(20~40年)的个人照片集来展示老化过程。然而,简单尝试对个人照片集进行全局老化技术的个性化设置往往会失败。因此,我们提出了MyTimeMachine(MyTM),它将全局老化先验知识与个人照片集(仅使用50张图像)相结合,以学习个性化的年龄转变。我们引入了一种新型适配器网络,它将个性化老化特征与全局老化特征相结合,并使用StyleGAN2生成重新老化的图像。我们还引入了三种损失函数来个性化适配器网络,包括个性化老化损失、外推正则化和自适应w-norm正则化。我们的方法还可以扩展到视频,实现高质量、身份保留、时间一致的老化效果,与实际目标年龄的外貌相符,证明了其在最先进方法中的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://mytimemachine.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了面部衰老的复杂性,并指出现有技术虽然能生成逼真的衰老结果,但重新生成的图像往往不能反映目标年龄的外观特征,因此需要个性化。为此,文章提出了一种结合全局衰老先验和个人照片集(仅使用50张图像)学习个性化年龄转换的方法——MyTimeMachine(MyTM)。通过引入一个新的Adapter网络,结合个性化衰老特征和全局衰老特征,并利用StyleGAN2生成重新衰老的图像。此外,还引入了三种损失函数来个性化Adapter网络。该方法可扩展到视频,实现高质量、身份保留、时间一致的衰老效果,与实际目标年龄的外观相匹配,优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 面部衰老是一个复杂的过程,受到多种因素的影响,如性别、种族和生活方式等,因此准确预测个体的衰老具有挑战性。
- 现有技术虽然能产生逼真的衰老结果,但重新生成的图像往往无法反映目标年龄的个人外观特征。
- 文章提出了一种新方法MyTimeMachine(MyTM),结合全局衰老先验和个人照片集(使用极少的图像)来学习个性化的年龄转换。
- 引入了新的Adapter网络,结合了个性化衰老特征和全局衰老特征,生成了重新衰老的图像。
- 使用了三种损失函数来个性化Adapter网络,包括个性化衰老损失、外推正则化和自适应w-norm正则化。
- MyTimeMachine方法可以扩展到视频,产生高质量、身份保留、时间一致的衰老效果。
点此查看论文截图


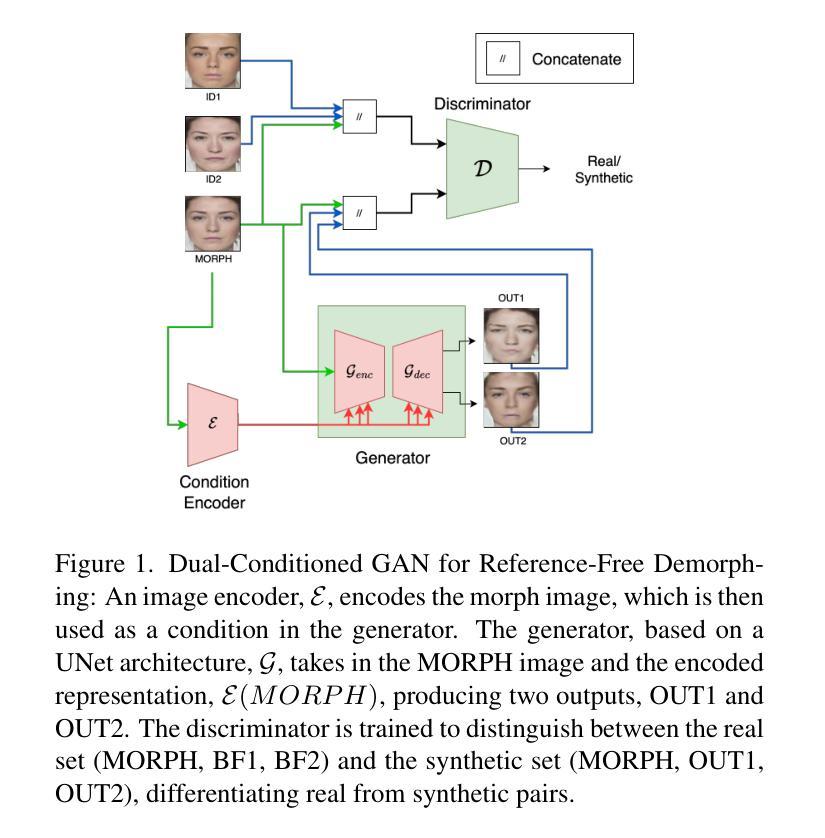
dc-GAN: Dual-Conditioned GAN for Face Demorphing From a Single Morph
Authors:Nitish Shukla, Arun Ross
A facial morph is an image created by combining two face images pertaining to two distinct identities. Face demorphing inverts the process and tries to recover the original images constituting a facial morph. While morph attack detection (MAD) techniques can be used to flag morph images, they do not divulge any visual information about the faces used to create them. Demorphing helps address this problem. Existing demorphing techniques are either very restrictive (assume identities during testing) or produce feeble outputs (both outputs look very similar). In this paper, we overcome these issues by proposing dc-GAN, a novel GAN-based demorphing method conditioned on the morph images. Our method overcomes morph-replication and produces high quality reconstructions of the bonafide images used to create the morphs. Moreover, our method is highly generalizable across demorphing paradigms (differential/reference-free). We conduct experiments on AMSL, FRLL-Morphs and MorDiff datasets to showcase the efficacy of our method.
面部形态学是一种通过融合两张属于不同身份的人脸图像而生成的新型图像。面部反形态学则是对这一过程进行反转,试图恢复构成面部形态的原始图像。虽然形态攻击检测(MAD)技术可以用于标记形态图像,但它们不会透露用于创建它们的任何面部视觉信息。反形态学有助于解决这个问题。现有的反形态学技术要么非常受限(在测试期间假定身份),要么产生的输出较弱(两个输出看起来非常相似)。在本文中,我们通过提出dc-GAN,一种基于新型GAN且根据形态图像进行条件设定的反形态学方法,克服了这些问题。我们的方法克服了形态复制问题,并生成了用于创建形态的高品质重建的诚信图像。此外,我们的方法具有很高的反形态学范式(差异/参考自由)的通用性。我们在AMSL、FRLL-Morphs和MorDiff数据集上进行实验,以展示我们的方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了一种基于GAN的面部去形态技术(dc-GAN)。该技术克服了现有面部去形态方法存在的限制和问题,能够基于形态图像进行条件化操作,解决了面部形态图像复原的问题。新方法不仅克服了形态复制问题,还能在跨去形态范式(差分/参考自由)的情况下实现高质量重建。实验结果表明,该方法在AMSL、FRLL-Morphs和MorDiff数据集上具有良好的效果。
关键见解
- 面部形态是一种由两个不同身份的面部图像结合而成的图像。
- 去形态技术试图恢复构成面部形态的原始图像。
- 形态攻击检测(MAD)技术可以标记形态图像,但不提供关于创建它们所使用的面部的视觉信息。
- 现有去形态技术存在限制或输出质量不高的问题。
- dc-GAN是一种基于GAN的新型去形态方法,可基于形态图像进行条件操作。
- dc-GAN克服了形态复制问题,并能高质量地重建用于创建形态的原始图像。
- dc-GAN具有高度泛化性,可应用于不同的去形态范式。
点此查看论文截图


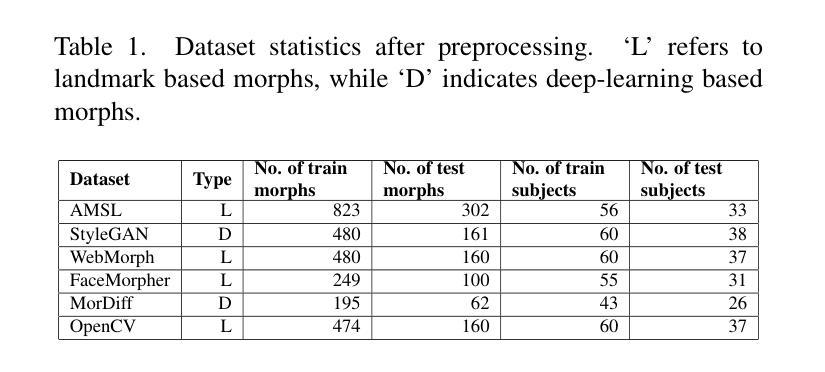
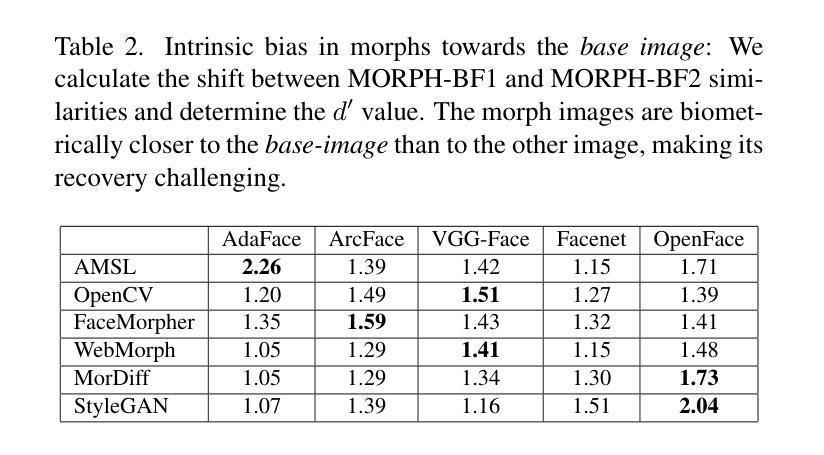

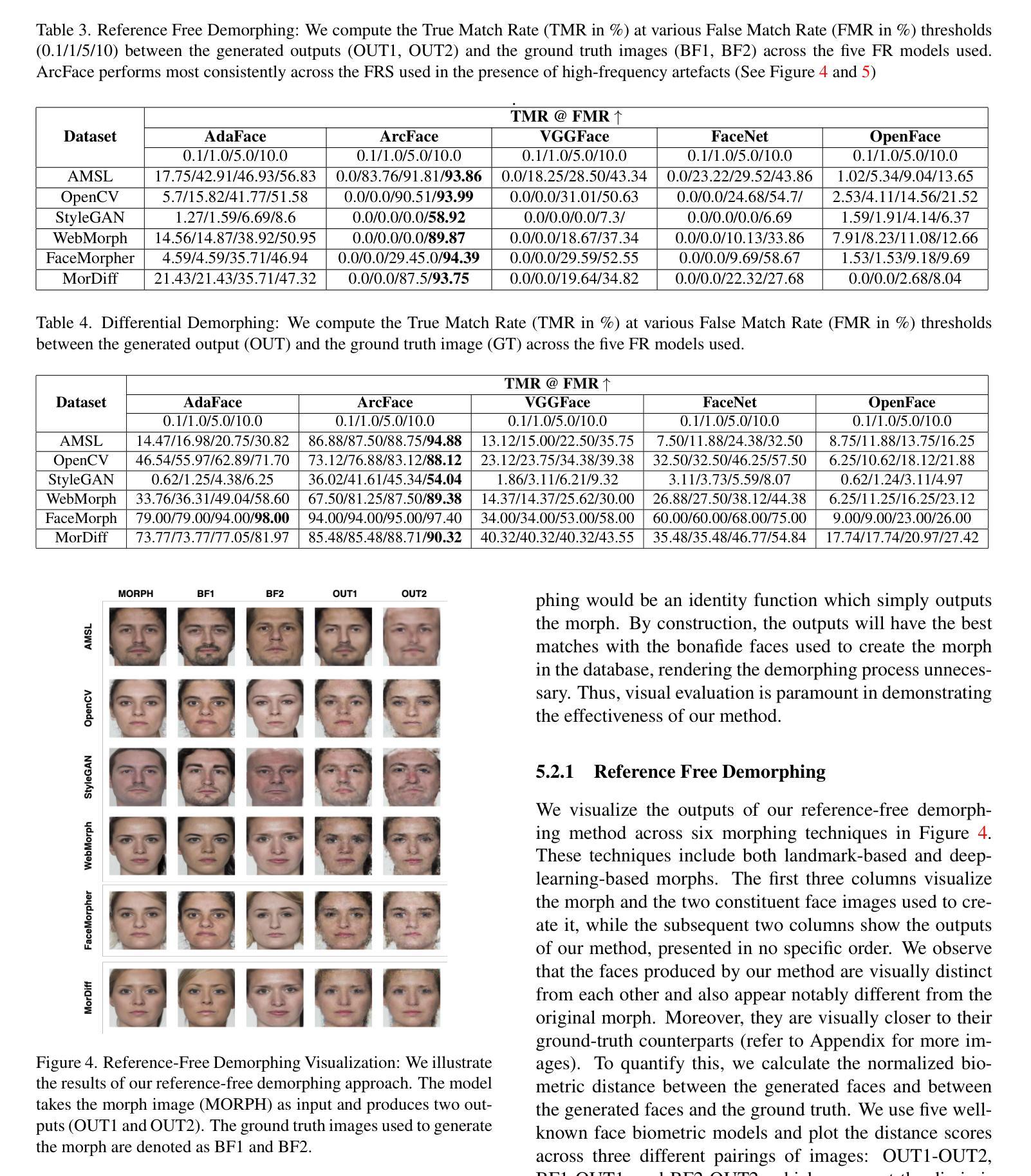
HyperGAN-CLIP: A Unified Framework for Domain Adaptation, Image Synthesis and Manipulation
Authors:Abdul Basit Anees, Ahmet Canberk Baykal, Muhammed Burak Kizil, Duygu Ceylan, Erkut Erdem, Aykut Erdem
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), particularly StyleGAN and its variants, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating highly realistic images. Despite their success, adapting these models to diverse tasks such as domain adaptation, reference-guided synthesis, and text-guided manipulation with limited training data remains challenging. Towards this end, in this study, we present a novel framework that significantly extends the capabilities of a pre-trained StyleGAN by integrating CLIP space via hypernetworks. This integration allows dynamic adaptation of StyleGAN to new domains defined by reference images or textual descriptions. Additionally, we introduce a CLIP-guided discriminator that enhances the alignment between generated images and target domains, ensuring superior image quality. Our approach demonstrates unprecedented flexibility, enabling text-guided image manipulation without the need for text-specific training data and facilitating seamless style transfer. Comprehensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations confirm the robustness and superior performance of our framework compared to existing methods.
生成对抗网络(GANs),特别是StyleGAN及其变体,在生成高度逼真的图像方面表现出了显著的能力。尽管它们取得了成功,但这些模型在有限的训练数据下适应各种任务,如域适应、参考引导合成和文本引导操作仍然具有挑战性。针对这一问题,本研究提出了一种新型框架,它通过超网络集成了CLIP空间,从而极大地扩展了预训练的StyleGAN的能力。这种集成允许根据参考图像或文本描述定义的新域动态地适应StyleGAN。此外,我们还引入了CLIP引导的鉴别器,增强了生成图像与目标域之间的对齐,确保图像质量上乘。我们的方法表现出前所未有的灵活性,能够实现无需特定文本训练数据的文本引导图像操作,并实现无缝风格转换。综合的定性和定量评估证实,与现有方法相比,我们的框架具有稳健性和卓越性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in SIGGRAPH Asia 2024. Project Website: https://cyberiada.github.io/HyperGAN-CLIP/
Summary
本文介绍了通过整合CLIP空间和超网络(hypernetworks)来扩展预训练StyleGAN的能力的新框架。该框架实现了动态适应由参考图像或文本描述定义的新领域,并引入CLIP导向判别器,提高生成图像与目标领域之间的对齐度,确保图像质量上乘。此新方法具有前所未有的灵活性,可实现无需特定文本训练数据的文本导向图像操作,并能实现无缝风格转换。该框架的稳健性和卓越性能得到了综合定性和定量评估的证实。
Key Takeaways
- 新框架成功整合CLIP空间和超网络,显著扩展了StyleGAN模型的能力。
- 该框架实现了动态适应参考图像或文本描述定义的新领域。
- 引入CLIP导向判别器,增强了生成图像与目标领域之间的对齐度。
- 该方法在保证图像质量的同时,具有很高的灵活性。
- 无需特定文本训练数据即可实现文本导向的图像操作。
- 新框架能实现无缝风格转换。
点此查看论文截图

Local Lesion Generation is Effective for Capsule Endoscopy Image Data Augmentation in a Limited Data Setting
Authors:Adrian B. Chłopowiec, Adam R. Chłopowiec, Krzysztof Galus, Wojciech Cebula, Martin Tabakov
Limited medical imaging datasets challenge deep learning models by increasing risks of overfitting and reduced generalization, particularly in Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), where discriminators may overfit, leading to training divergence. This constraint also impairs classification models trained on small datasets. Generative Data Augmentation (GDA) addresses this by expanding training datasets with synthetic data, although it requires training a generative model. We propose and evaluate two local lesion generation approaches to address the challenge of augmenting small medical image datasets. The first approach employs the Poisson Image Editing algorithm, a classical image processing technique, to create realistic image composites that outperform current state-of-the-art methods. The second approach introduces a novel generative method, leveraging a fine-tuned Image Inpainting GAN to synthesize realistic lesions within specified regions of real training images. A comprehensive comparison of the two proposed methods demonstrates that effective local lesion generation in a data-constrained setting allows for reaching new state-of-the-art results in capsule endoscopy lesion classification. Combination of our techniques achieves a macro F1-score of 33.07%, surpassing the previous best result by 7.84 percentage points (p.p.) on the highly imbalanced Kvasir Capsule Dataset, a benchmark for capsule endoscopy. To the best of our knowledge, this work is the first to apply a fine-tuned Image Inpainting GAN for GDA in medical imaging, demonstrating that an image-conditional GAN can be adapted effectively to limited datasets to generate high-quality examples, facilitating effective data augmentation. Additionally, we show that combining this GAN-based approach with classical image processing techniques further improves the results.
有限的医学成像数据集通过增加过拟合和降低泛化的风险来挑战深度学习模型,特别是在生成对抗网络(GANs)中,鉴别器可能会过拟合,从而导致训练发散。这一限制也影响了在小型数据集上训练的分类模型。生成数据增强(GDA)通过用合成数据扩充训练数据集来解决这个问题,尽管这需要训练一个生成模型。我们提出并评估了两种局部病变生成方法来应对小型医学图像数据集增强所面临的挑战。第一种方法采用Poisson图像编辑算法这一经典图像处理技术,创建逼真的图像组合,优于当前最先进的方法。第二种方法引入了一种新的生成方法,它利用经过精细调整的图像修复GAN在真实训练图像的指定区域内合成逼真的病变。对这两种方法的全面比较表明,在数据受限的环境中进行有效的局部病变生成,可以在胶囊内镜病变分类方面达到新的最先进的成果。结合我们的技术,在高度不平衡的Kvasir胶囊数据集上达到了33.07%的宏F1分数,超过了之前最好的结果7.84个百分点,这是一个胶囊内镜的基准测试集。据我们所知,这项工作首次将经过精细调整的图像修复GAN应用于医学成像的GDA,表明图像条件GAN可以有效地适应有限数据集,生成高质量样本,实现有效的数据增强。此外,我们还表明,将基于GAN的方法与经典图像处理技术相结合可以进一步提高结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 54 pages, 35 figures
Summary
针对医学成像数据集有限的问题,研究提出两种局部病变生成方法,以扩充小数据集并提升分类模型性能。第一种方法使用Poisson图像编辑算法生成合成图像;第二种方法则运用微调后的图像修复生成对抗网络(Image Inpainting GAN)在真实图像指定区域内合成真实病变。两种方法结合达到了新的先进结果,在胶囊内镜病变分类方面表现出优异性能。研究是首次将微调后的Image Inpainting GAN应用于医学成像的数据增强,并证明其适应有限数据集生成高质量样本的有效性。结合经典图像处理技术进一步提高了结果。
Key Takeaways
- 医学成像数据集有限的问题会增大深度学习模型,尤其是生成对抗网络(GANs)的过拟合风险,降低其泛化能力。
- 生成数据增强(GDA)通过生成合成数据来扩充训练数据集,但需要训练生成模型。
- 第一种提出的局部病变生成方法利用Poisson图像编辑算法生成真实图像复合体,其性能优于当前先进方法。
- 第二种方法使用微调后的Image Inpainting GAN在真实训练图像的指定区域合成真实病变。
- 结合两种提出的方法在数据受限的情况下实现了有效的局部病变生成,并在胶囊内镜病变分类上达到了新的先进结果。
- 在Kvasir胶囊数据集上的宏观F1分数达到了33.07%,较之前最佳结果提高了7.84个百分点。
点此查看论文截图

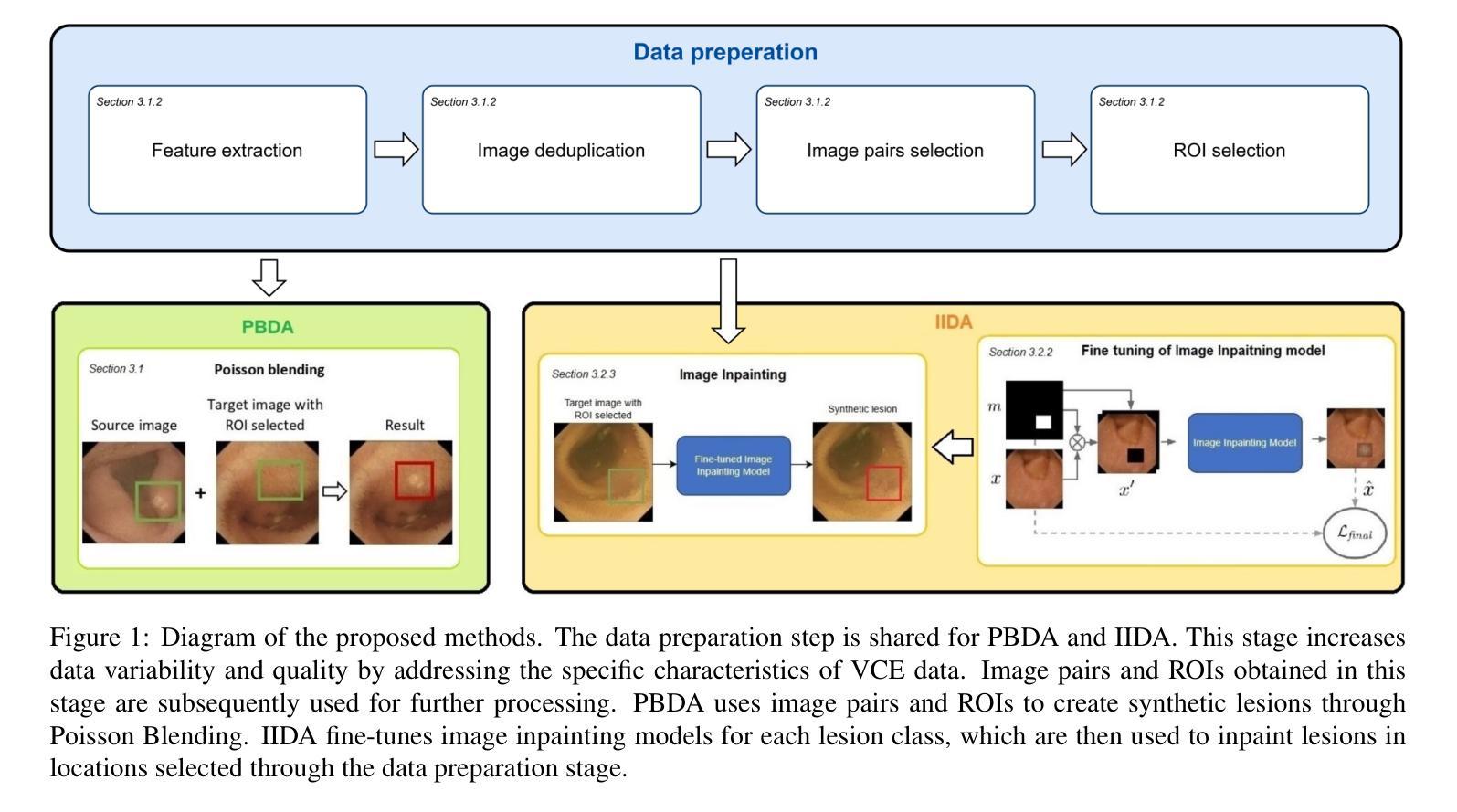
HairDiffusion: Vivid Multi-Colored Hair Editing via Latent Diffusion
Authors:Yu Zeng, Yang Zhang, Jiachen Liu, Linlin Shen, Kaijun Deng, Weizhao He, Jinbao Wang
Hair editing is a critical image synthesis task that aims to edit hair color and hairstyle using text descriptions or reference images, while preserving irrelevant attributes (e.g., identity, background, cloth). Many existing methods are based on StyleGAN to address this task. However, due to the limited spatial distribution of StyleGAN, it struggles with multiple hair color editing and facial preservation. Considering the advancements in diffusion models, we utilize Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) for hairstyle editing. Our approach introduces Multi-stage Hairstyle Blend (MHB), effectively separating control of hair color and hairstyle in diffusion latent space. Additionally, we train a warping module to align the hair color with the target region. To further enhance multi-color hairstyle editing, we fine-tuned a CLIP model using a multi-color hairstyle dataset. Our method not only tackles the complexity of multi-color hairstyles but also addresses the challenge of preserving original colors during diffusion editing. Extensive experiments showcase the superiority of our method in editing multi-color hairstyles while preserving facial attributes given textual descriptions and reference images.
头发编辑是一项关键的图像合成任务,旨在使用文本描述或参考图像来编辑发色和发型,同时保留无关属性(例如身份、背景、服装)。许多现有方法基于StyleGAN来解决此任务。然而,由于StyleGAN的空间分布有限,它在多色发色编辑和面部保留方面遇到了困难。考虑到扩散模型的进步,我们利用潜在扩散模型(LDMs)进行发型编辑。我们的方法引入了多阶段发型混合(MHB),有效地在扩散潜在空间中分离了发色和发型控制。此外,我们训练了一个变形模块,以将发色与目标区域对齐。为了进一步增强多色发型编辑,我们使用多色发型数据集对CLIP模型进行了微调。我们的方法不仅解决了多色发型编辑的复杂性,还解决了在扩散编辑过程中保留原始颜色的挑战。大量实验表明,我们的方法在给定文本描述和参考图像的情况下,在编辑多色发型的同时保留面部属性方面具有优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于文本描述或参考图像进行头发编辑是一项重要的图像合成任务,旨在改变发色和发型,同时保留其他无关属性。尽管许多现有方法基于StyleGAN,但其有限的空间分布导致在多重发色编辑和面部保留方面存在挑战。本研究利用扩散模型(Latent Diffusion Models,LDMs)进行发型编辑,提出多阶段发型融合(MHB)方法,有效分离发色和发型在扩散潜在空间中的控制。此外,训练了颜色对齐模块,使发色与目标区域相匹配。通过微调CLIP模型和多色发型数据集,不仅解决了多色发型的复杂性,还解决了扩散编辑过程中保持原始颜色的挑战。实验表明,该方法在编辑多色发型时具有优越性,能够根据文本描述和参考图像保留面部特征。
Key Takeaways
- 头发编辑是图像合成中的关键任务,旨在通过文本描述或参考图像编辑头发颜色和发型,同时保留其他属性。
- StyleGAN由于空间分布限制,在多重发色编辑和面部保留方面存在挑战。
- 本研究采用Latent Diffusion Models(LDMs)进行发型编辑,提出多阶段发型融合(MHB)方法以改善发色和发型控制。
- 通过训练颜色对齐模块,使修改后的发色与目标区域相匹配。
- 利用多色发型数据集微调CLIP模型,增强多色发型的编辑能力。
- 方法能在保持面部特征的同时进行多色发型的编辑。
- 实验结果显示该方法在编辑多色发型方面具有优越性。
点此查看论文截图

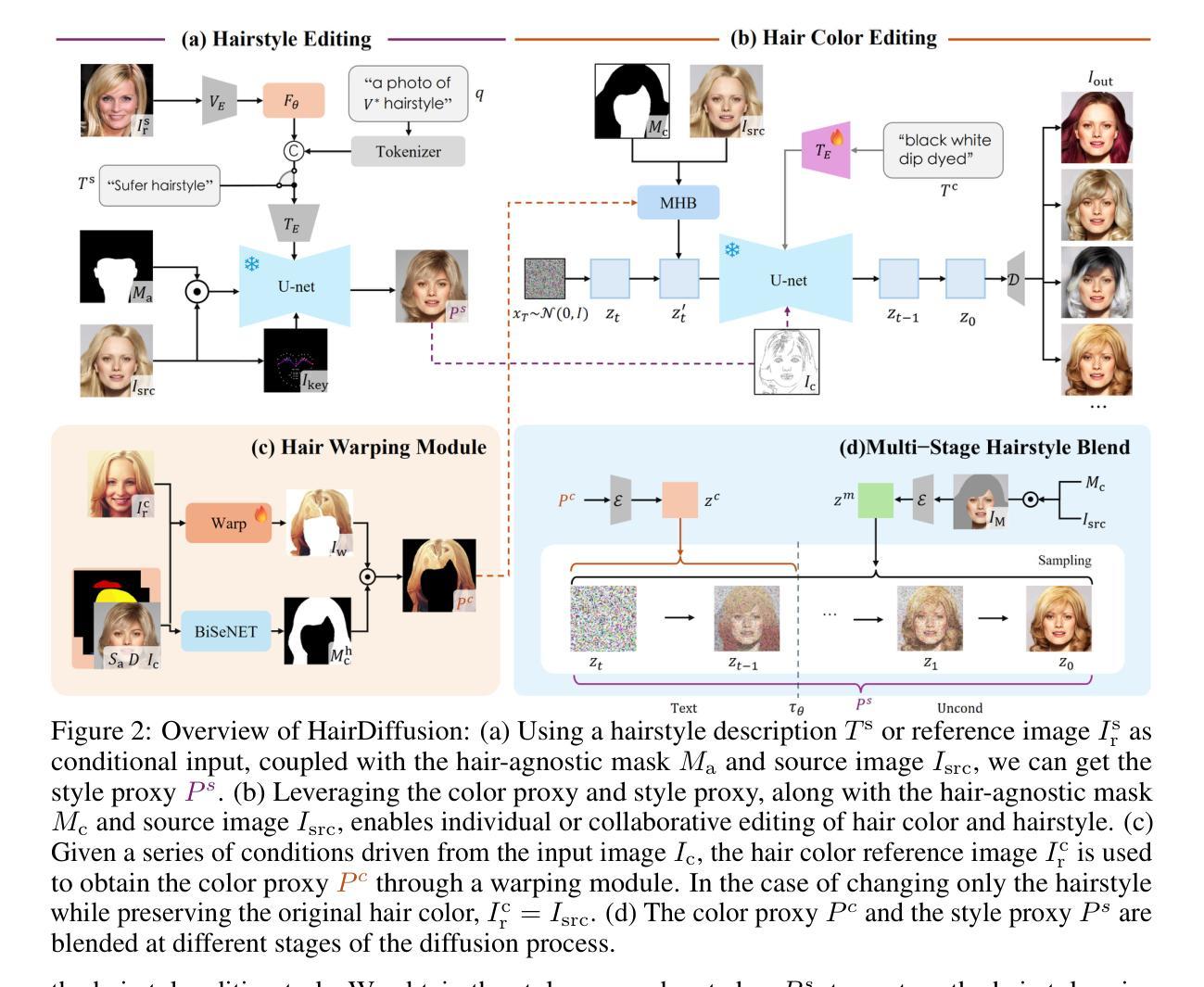
Unsupervised Panoptic Interpretation of Latent Spaces in GANs Using Space-Filling Vector Quantization
Authors:Mohammad Hassan Vali, Tom Bäckström
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) learn a latent space whose samples can be mapped to real-world images. Such latent spaces are difficult to interpret. Some earlier supervised methods aim to create an interpretable latent space or discover interpretable directions that require exploiting data labels or annotated synthesized samples for training. However, we propose using a modification of vector quantization called space-filling vector quantization (SFVQ), which quantizes the data on a piece-wise linear curve. SFVQ can capture the underlying morphological structure of the latent space and thus make it interpretable. We apply this technique to model the latent space of pretrained StyleGAN2 and BigGAN networks on various datasets. Our experiments show that the SFVQ curve yields a general interpretable model of the latent space that determines which part of the latent space corresponds to what specific generative factors. Furthermore, we demonstrate that each line of SFVQ’s curve can potentially refer to an interpretable direction for applying intelligible image transformations. We also showed that the points located on an SFVQ line can be used for controllable data augmentation.
生成对抗网络(GANs)学习一个潜在空间,该空间的样本可以映射到现实世界图像。这样的潜在空间很难解释。一些早期的监督方法旨在创建一个可解释的潜在空间或发现可解释的方向,这需要利用数据标签或注释的合成样本进行训练。然而,我们提出了一种称为空间填充向量量化(SFVQ)的向量量化修改方法,它在分段线性曲线上对数据进行量化。SFVQ可以捕获潜在空间的基本形态结构,从而使其具有可解释性。我们将此技术应用于各种数据集上预训练的StyleGAN2和BigGAN网络的潜在空间建模。我们的实验表明,SFVQ曲线提供了一个通用的潜在空间可解释模型,该模型确定了潜在空间的哪一部分对应于哪些特定的生成因素。此外,我们证明SFVQ曲线的每一行都可能是一个可解释的方向,用于应用可理解的图像转换。我们还表明,位于SFVQ线上的点可用于可控的数据增强。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
生成对抗网络(GANs)学习一个潜在空间,该空间的样本可以映射到真实图像。本文提出一种名为空间填充矢量量化(SFVQ)的方法,可以在无需数据标签或合成样本标注的情况下,使潜在空间具有可解释性。通过应用SFVQ技术于预训练的StyleGAN2和BigGAN网络的不同数据集上,实验表明SFVQ曲线提供了一个通用的潜在空间解释模型,可以确定潜在空间的哪一部分对应于哪些特定的生成因素。此外,我们还展示了SFVQ曲线的每一行都可能指代一个可解释的方向,用于应用可理解的图像转换。同时,位于SFVQ线上的点也可用于可控的数据增强。
Key Takeaways
- 生成对抗网络(GANs)学习潜在空间,将其样本映射到真实图像。
- 潜在空间很难解释,早期监督方法旨在创建可解释的空间或发现可解释的方向,但需要数据标签或合成样本标注。
- 提出一种名为空间填充矢量量化(SFVQ)的技术,可以在无需标注的情况下使潜在空间具有可解释性。
- SFVQ通过量化数据在分段线性曲线上,能够捕捉潜在空间的基本形态结构。
- 应用SFVQ到预训练网络(如StyleGAN2和BigGAN)的不同数据集上,实验证实SFVQ曲线提供了一个解释潜在空间的通用模型。
- SFVQ曲线的每一行都可能代表一个可解释的方向,可进行可控的图像转换。
点此查看论文截图

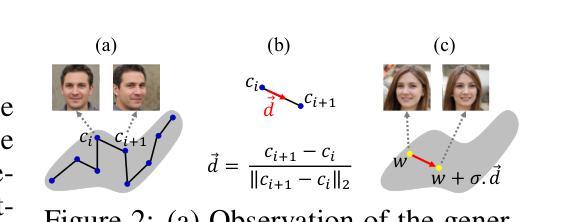


Medical Imaging Complexity and its Effects on GAN Performance
Authors:William Cagas, Chan Ko, Blake Hsiao, Shryuk Grandhi, Rishi Bhattacharya, Kevin Zhu, Michael Lam
The proliferation of machine learning models in diverse clinical applications has led to a growing need for high-fidelity, medical image training data. Such data is often scarce due to cost constraints and privacy concerns. Alleviating this burden, medical image synthesis via generative adversarial networks (GANs) emerged as a powerful method for synthetically generating photo-realistic images based on existing sets of real medical images. However, the exact image set size required to efficiently train such a GAN is unclear. In this work, we experimentally establish benchmarks that measure the relationship between a sample dataset size and the fidelity of the generated images, given the dataset’s distribution of image complexities. We analyze statistical metrics based on delentropy, an image complexity measure rooted in Shannon’s entropy in information theory. For our pipeline, we conduct experiments with two state-of-the-art GANs, StyleGAN 3 and SPADE-GAN, trained on multiple medical imaging datasets with variable sample sizes. Across both GANs, general performance improved with increasing training set size but suffered with increasing complexity.
在多种临床应用中,机器学习模型的普及导致了对于高保真医疗图像训练数据日益增长的需求。由于成本约束和隐私担忧,此类数据通常很稀缺。为了缓解这一负担,通过生成对抗网络(GANs)进行医学图像合成出现为一种强大的方法,可以基于现有的真实医学图像集合成生成逼真的图像。然而,为了有效地训练这样的GAN所需要的精确图像集大小尚不清楚。在这项工作中,我们通过实验建立了基准测试,该测试衡量样本数据集大小与生成图像的保真度之间的关系,考虑到数据集图像复杂性的分布。我们分析了基于信息熵的delentropy的统计指标,这是一种基于信息论中的香农熵的图像复杂性度量。在我们的管道中,我们使用两个最先进的GAN(StyleGAN 3和SPADE-GAN)进行了实验,它们在多个医疗图像数据集上进行训练,样本大小可变。在这两种GAN中,随着训练集大小的增加,总体性能有所提高,但随着复杂性的增加,性能有所下降。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACCV, Workshop on Generative AI for Synthetic Medical Data
Summary
本研究探讨利用生成对抗网络(GANs)合成医学图像的方法,以解决因成本限制和隐私担忧导致的医学图像训练数据稀缺问题。实验建立了数据集样本量与生成图像保真度之间的基准关系,分析基于信息论中的香农熵延伸出的图像复杂度度量方法——德尔塔熵。实验采用两种先进的GANs(StyleGAN 3和SPADE-GAN),在多个医学图像数据集上进行训练,发现随着训练集样本量的增加,总体性能提升,但在复杂度增加的情况下性能有所下降。
Key Takeaways
- 机器学习任务对高保真医学图像训练数据的需求日益增强。
- GANs能有效合成逼真的医学图像。
- 训练集样本量与生成图像的质量存在直接关系。
- 使用了基于德尔塔熵的统计指标衡量图像复杂度对训练过程的影响。
- 随着训练集样本量增加,总体性能有所提升。
点此查看论文截图

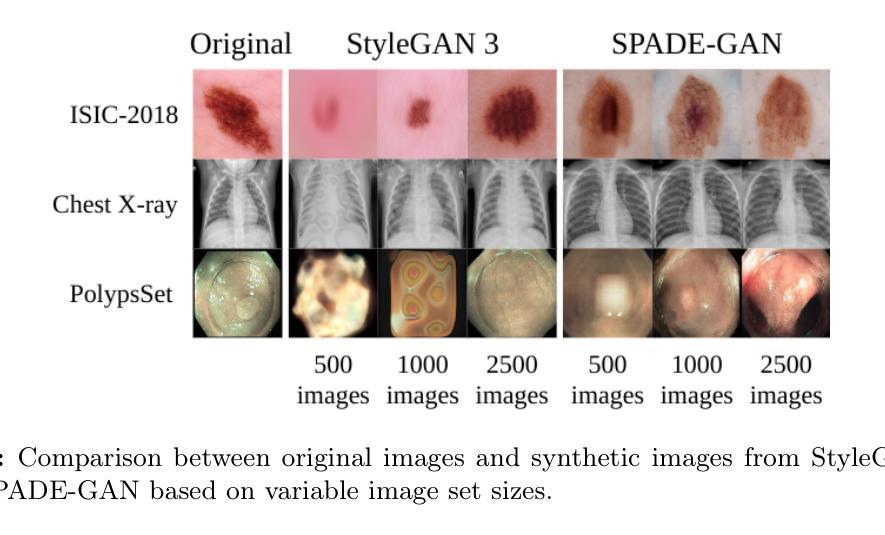
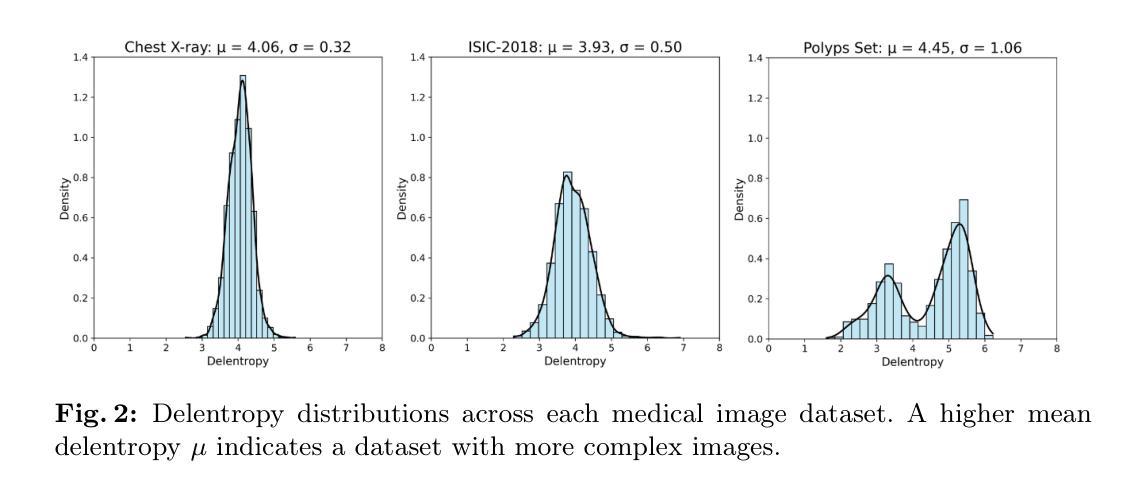
3D-GANTex: 3D Face Reconstruction with StyleGAN3-based Multi-View Images and 3DDFA based Mesh Generation
Authors:Rohit Das, Tzung-Han Lin, Ko-Chih Wang
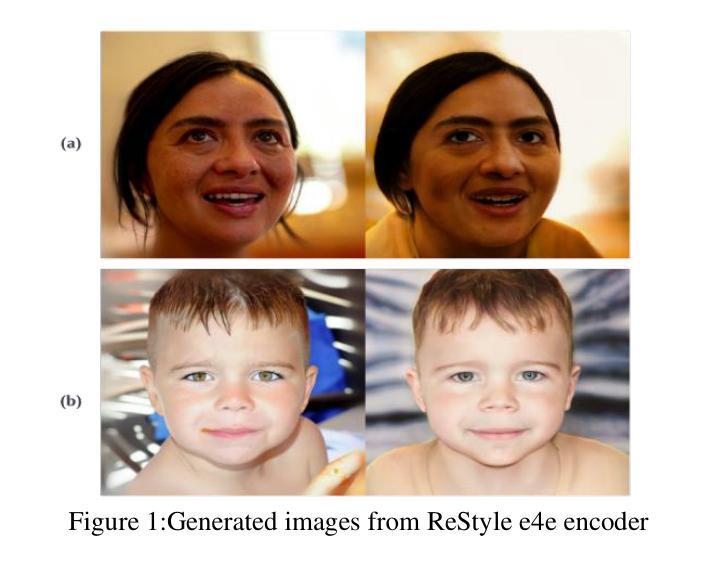
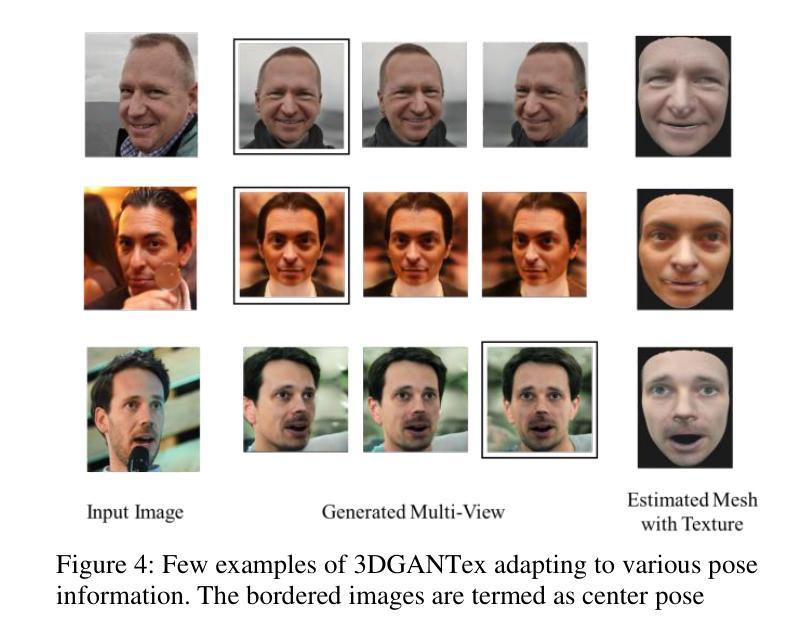
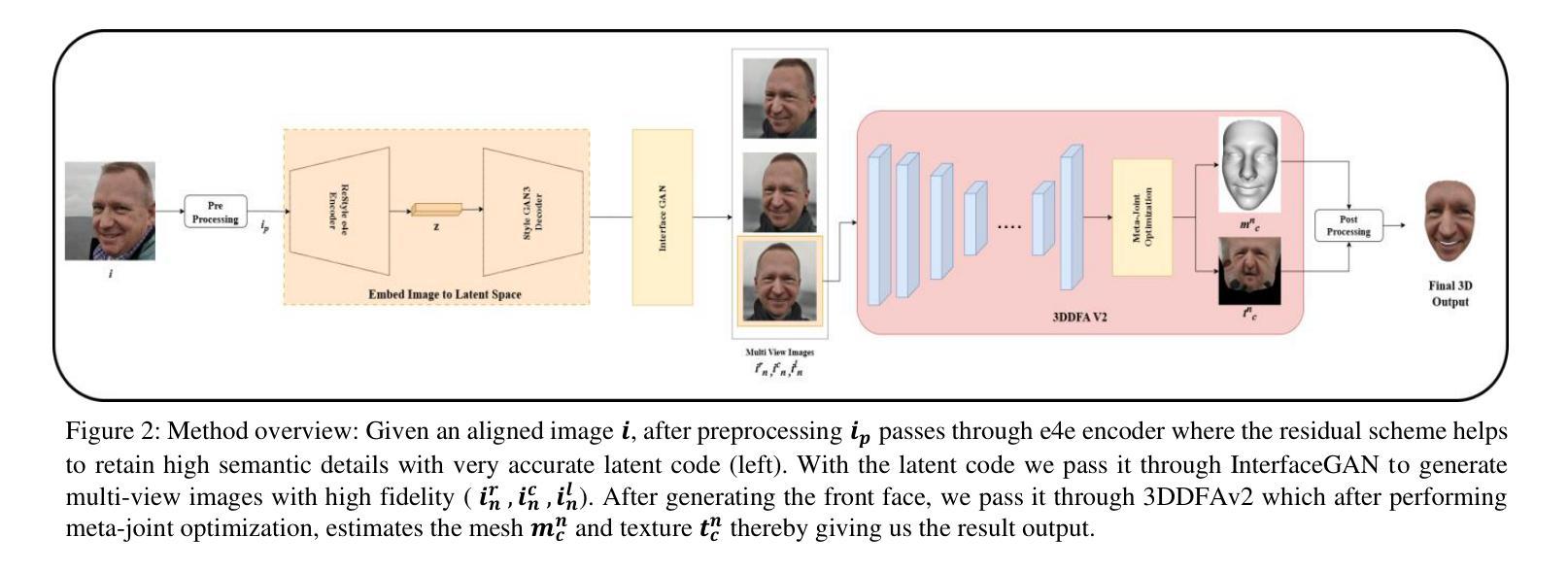
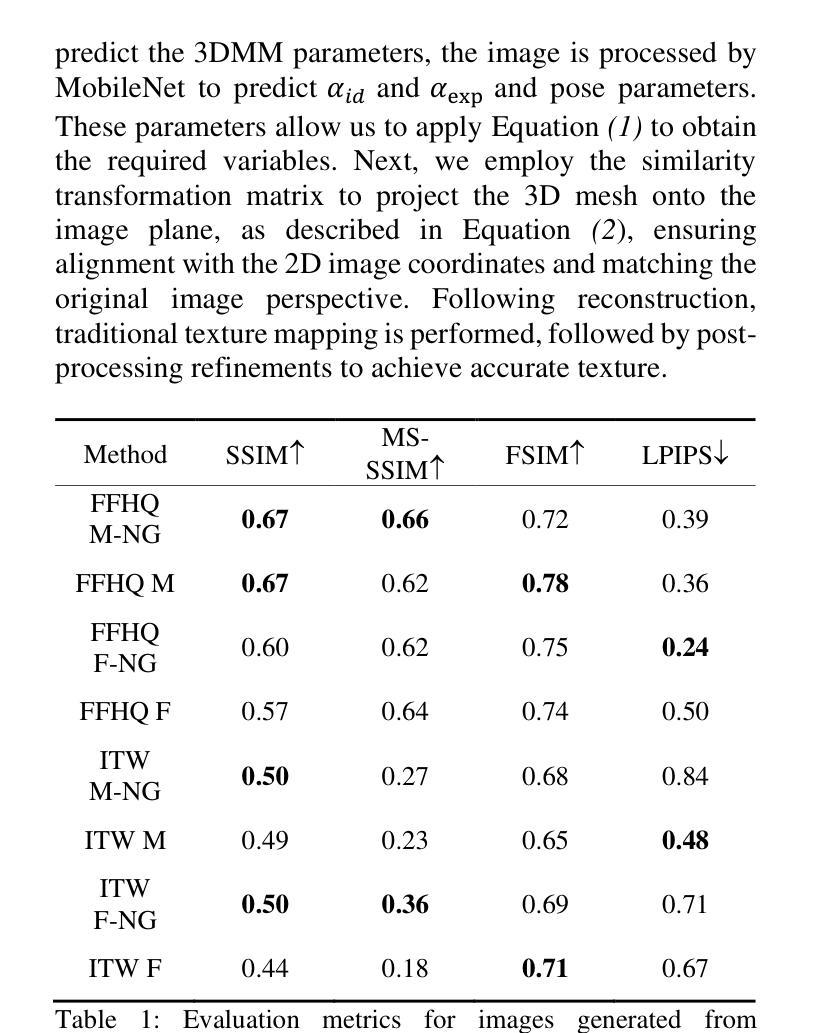
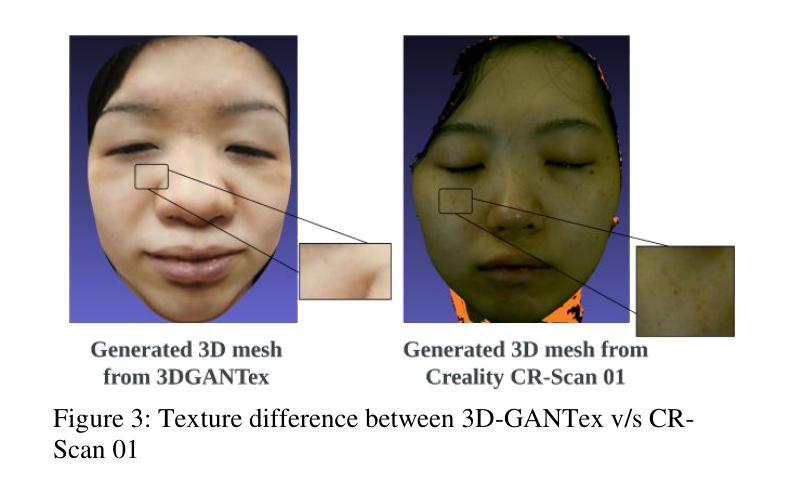
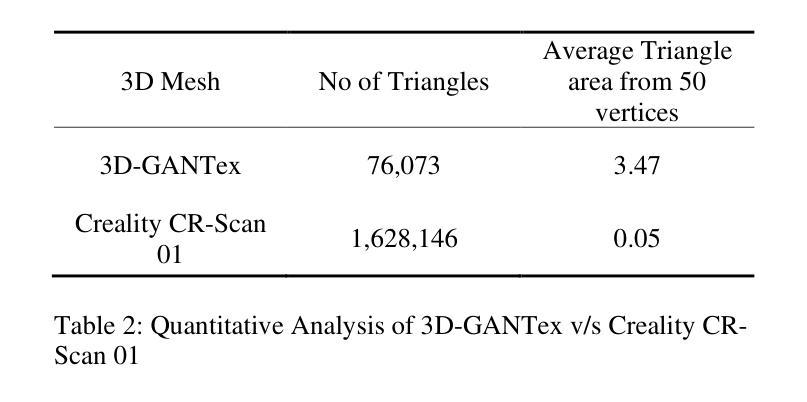
Geometry and texture estimation from a single face image is an ill-posed problem since there is very little information to work with. The problem further escalates when the face is rotated at a different angle. This paper tries to tackle this problem by introducing a novel method for texture estimation from a single image by first using StyleGAN and 3D Morphable Models. The method begins by generating multi-view faces using the latent space of GAN. Then 3DDFA trained on 3DMM estimates a 3D face mesh as well as a high-resolution texture map that is consistent with the estimated face shape. The result shows that the generated mesh is of high quality with near to accurate texture representation.
从单张人脸图像中估计几何和纹理是一个不适定问题,因为可用信息非常少。当人脸以不同角度旋转时,这个问题会进一步加剧。本文试图通过引入一种从单张图像进行纹理估计的新方法来解决这个问题。该方法首先使用StyleGAN和3D可变形模型。通过利用GAN的潜在空间生成多角度人脸,然后使用基于3DMM训练的3DDFA估计一个与估计的人脸形状一致的高分辨率纹理贴图以及3D人脸网格。结果表明,生成的网格具有高质量的近似准确纹理表示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 7 pages, 4 figures, 2 tables, pre-print version
Summary
本文提出一种基于StyleGAN和3D可变形模型(3DMM)的单图像纹理估计新方法。该方法通过利用GAN的潜在空间生成多角度人脸,并结合3DDFA进行3D人脸网格和纹理图的估算,从而解决单人脸图像几何和纹理估计的不适定问题。研究结果表明,生成的网格具有高质量且纹理表示准确。
Key Takeaways
- 单人脸图像几何和纹理估计是一个不适定问题,缺乏足够的信息进行准确分析。
- 本文利用StyleGAN生成多角度人脸图像,解决了单一视角信息不足的问题。
- 引入3D可变形模型(3DMM)以辅助估算3D人脸网格。
- 3DDFA被用于基于3DMM的估计,生成与估计的人脸形状一致的高分辨率纹理图。
- 生成的网格具有高质量,纹理表示准确。
- 该方法提供了一种有效的解决方案,用于从单一图像中估计人脸的几何和纹理信息。
点此查看论文截图