⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-10 更新
MAVias: Mitigate any Visual Bias
Authors:Ioannis Sarridis, Christos Koutlis, Symeon Papadopoulos, Christos Diou
Mitigating biases in computer vision models is an essential step towards the trustworthiness of artificial intelligence models. Existing bias mitigation methods focus on a small set of predefined biases, limiting their applicability in visual datasets where multiple, possibly unknown biases exist. To address this limitation, we introduce MAVias, an open-set bias mitigation approach leveraging foundation models to discover spurious associations between visual attributes and target classes. MAVias first captures a wide variety of visual features in natural language via a foundation image tagging model, and then leverages a large language model to select those visual features defining the target class, resulting in a set of language-coded potential visual biases. We then translate this set of potential biases into vision-language embeddings and introduce an in-processing bias mitigation approach to prevent the model from encoding information related to them. Our experiments on diverse datasets, including CelebA, Waterbirds, ImageNet, and UrbanCars, show that MAVias effectively detects and mitigates a wide range of biases in visual recognition tasks outperforming current state-of-the-art.
减轻计算机视觉模型中的偏见是建立人工智能模型可信度的重要步骤。现有的偏见缓解方法主要关注一组预定义的偏见,这在存在多个可能未知的偏见的视觉数据集中限制了其适用性。为了解决这一局限性,我们引入了 MAVias,这是一种利用基础模型发现视觉属性与目标类别之间偶然关联的开集偏见缓解方法。MAVias 首先通过基础图像标记模型在自然语言中捕获各种视觉特征,然后利用大型语言模型选择定义目标类别的视觉特征,形成一组语言编码的潜在视觉偏见。然后,我们将这组潜在的偏见转化为视觉语言嵌入,并引入一种处理过程中的偏见缓解方法,以防止模型对与偏见相关的信息编码。我们在包括CelebA、Waterbirds、ImageNet和UrbanCars等多个数据集上的实验表明,MAVias有效地检测和缓解了视觉识别任务中的广泛偏见,性能优于当前最新技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了针对计算机视觉模型中偏见问题的新方法——MAVias。该方法利用基础模型发现并消除视觉属性与目标类别之间的潜在关联,从而减轻偏见问题。通过图像标注模型捕获丰富的视觉特征,并结合大型语言模型筛选与目标类别相关的特征,进而形成一系列的语言编码潜在偏见。随后将这些潜在偏见转化为视觉语言嵌入,并提出一种过程性偏见缓解方法来阻止模型对其进行编码。实验结果表明,在多个数据集上,MAVias能够有效检测并缓解视觉识别任务的偏见问题,并优于当前的主流方法。
Key Takeaways
- MAVias是一种用于缓解计算机视觉模型中偏见问题的新方法。
- MAVias利用基础模型发现潜在偏见,适用于存在多种未知偏见的情况。
- 通过图像标注模型结合大型语言模型来识别视觉属性与目标类别之间的潜在关联。
- MAVias将潜在偏见转化为视觉语言嵌入,便于后续处理。
- 提出了一种过程性偏见缓解方法,防止模型对潜在偏见进行编码。
- 实验结果表明,MAVias在多个数据集上有效检测并缓解偏见问题,表现优于当前主流方法。
点此查看论文截图

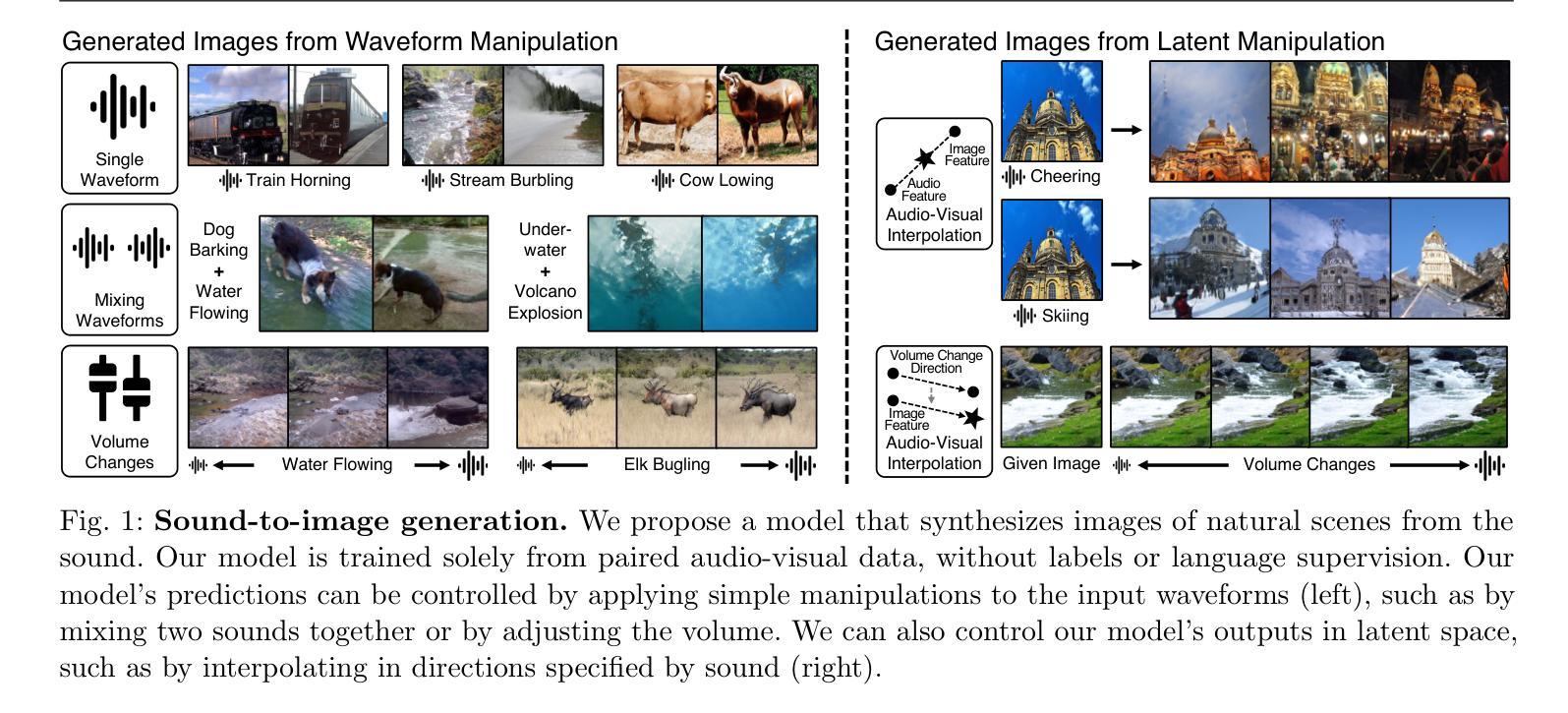
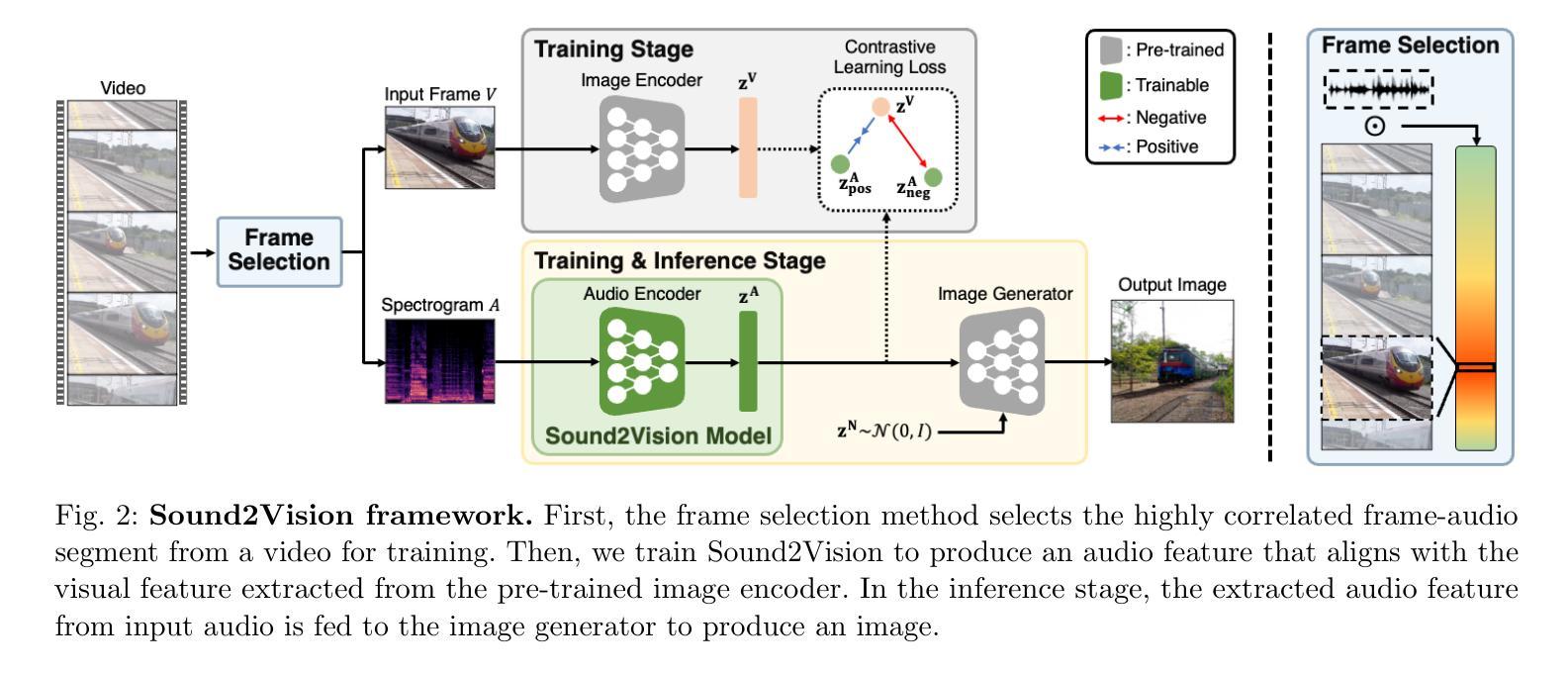
Sound2Vision: Generating Diverse Visuals from Audio through Cross-Modal Latent Alignment
Authors:Kim Sung-Bin, Arda Senocak, Hyunwoo Ha, Tae-Hyun Oh
How does audio describe the world around us? In this work, we propose a method for generating images of visual scenes from diverse in-the-wild sounds. This cross-modal generation task is challenging due to the significant information gap between auditory and visual signals. We address this challenge by designing a model that aligns audio-visual modalities by enriching audio features with visual information and translating them into the visual latent space. These features are then fed into the pre-trained image generator to produce images. To enhance image quality, we use sound source localization to select audio-visual pairs with strong cross-modal correlations. Our method achieves substantially better results on the VEGAS and VGGSound datasets compared to previous work and demonstrates control over the generation process through simple manipulations to the input waveform or latent space. Furthermore, we analyze the geometric properties of the learned embedding space and demonstrate that our learning approach effectively aligns audio-visual signals for cross-modal generation. Based on this analysis, we show that our method is agnostic to specific design choices, showing its generalizability by integrating various model architectures and different types of audio-visual data.
音频是如何描述我们周围的世界的?在这项工作中,我们提出了一种从多样化的野外声音生成视觉场景图像的方法。由于听觉和视觉信号之间存在巨大的信息差距,因此这种跨模态生成任务具有挑战性。我们通过设计一个将音频视觉模态对齐的模型来解决这一挑战,该模型通过丰富音频特征并添加视觉信息,然后将其转换为视觉潜在空间。这些特征随后被输入到预训练图像生成器中以生成图像。为了提高图像质量,我们使用声源定位来选择具有强跨模态关联的视听配对。我们的方法在VEGAS和VGGSound数据集上取得了比以前的工作更好的结果,通过简单操作输入波形或潜在空间实现对生成过程的控制。此外,我们分析了学习嵌入空间的几何属性,并证明我们的学习有效地对齐了音频视觉信号以实现跨模态生成。基于这些分析,我们展示了该方法对特定设计选择的无关性,通过集成各种模型架构和不同类型的视听数据来证明其普遍性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under-review
Summary
音频如何描述我们周围的世界?在这项工作中,我们提出了一种从各种自然声音生成视觉场景图像的方法。由于听觉和视觉信号之间存在巨大的信息差距,这一跨模态生成任务具有挑战性。我们通过设计一种模型来解决这一挑战,该模型通过丰富音频特征并对其进行视觉信息处理,将其翻译到视觉潜在空间来对齐音频-视觉模态。然后,这些特性被输入到预训练图像生成器中以产生图像。为提高图像质量,我们使用声源定位来选择具有强跨模态关联的音频-视觉对。我们的方法在VEGAS和VGGSound数据集上取得了比以往工作更好的结果,并通过简单操作输入波形或潜在空间来证明对生成过程的控制力。此外,我们分析了学习嵌入空间的几何属性,并证明我们的学习方法有效地对齐音频-视觉信号进行跨模态生成。基于此分析,我们证明了该方法对特定设计选择的无视性,并通过集成各种模型架构和不同类型的音频-视觉数据来展示其通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究提出了一种从自然声音生成视觉场景图像的方法。
- 该方法通过设计一种模型来解决跨模态生成挑战,该模型能够丰富音频特征并对其进行视觉信息处理。
- 通过声源定位技术提高图像质量,选择具有强跨模态关联的音频-视觉对。
- 在VEGAS和VGGSound数据集上取得了显著成果,表明该方法的有效性。
- 该方法能够实现简单的操作控制生成过程,证明其对输入波形或潜在空间的控制力。
- 分析表明,该方法对齐音频-视觉信号的能力较强。
点此查看论文截图



Annotations for Exploring Food Tweets From Multiple Aspects
Authors:Matīss Rikters, Edison Marrese-Taylor, Rinalds Vīksna
This research builds upon the Latvian Twitter Eater Corpus (LTEC), which is focused on the narrow domain of tweets related to food, drinks, eating and drinking. LTEC has been collected for more than 12 years and reaching almost 3 million tweets with the basic information as well as extended automatically and manually annotated metadata. In this paper we supplement the LTEC with manually annotated subsets of evaluation data for machine translation, named entity recognition, timeline-balanced sentiment analysis, and text-image relation classification. We experiment with each of the data sets using baseline models and highlight future challenges for various modelling approaches.
这篇研究基于拉脱维亚推特饮食语料库(LTEC),该语料库专注于与食物、饮料、饮食和饮水相关的狭窄领域的推文。LTEC已经收集了超过12年的时间,几乎包含了300万条推文的基本信息,以及扩展的自动和手动注释的元数据。在这篇论文中,我们以机器翻译、命名实体识别、时间平衡情感分析和文本图像关系分类的手动评估数据子集来补充LTEC。我们利用基准模型对每个数据集进行实验,并突出各种建模方法未来的挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文基于拉脱维亚Twitter食评语料库(LTEC),对涉及食品和饮料相关的推特内容进行深入研究。LTEC已收集超过12年,包含近3百万条推特,提供基本信息和扩展的手动及自动标注元数据。本文补充了LTEC的手动标注子集,包括机器翻译、命名实体识别、时间平衡情感分析和文本图像关系分类的评估数据。通过基线模型实验,展望了未来各种建模方法的挑战。
Key Takeaways:
- 研究基于拉脱维亚Twitter食评语料库(LTEC),专注于食品、饮料相关的推特内容。
- LTEC已收集超过12年,包含近3百万条推特,提供基本和扩展的标注元数据。
- 研究补充了LTEC的手动标注子集用于机器翻译、命名实体识别、时间平衡情感分析和文本图像关系分类的评估数据。
- 通过基线模型实验,验证了数据集的实用性。
- 研究展望了未来各种建模方法面临的挑战。
- LTEC数据集的长期积累为食品、饮料领域的推特分析提供了丰富资源。
点此查看论文截图


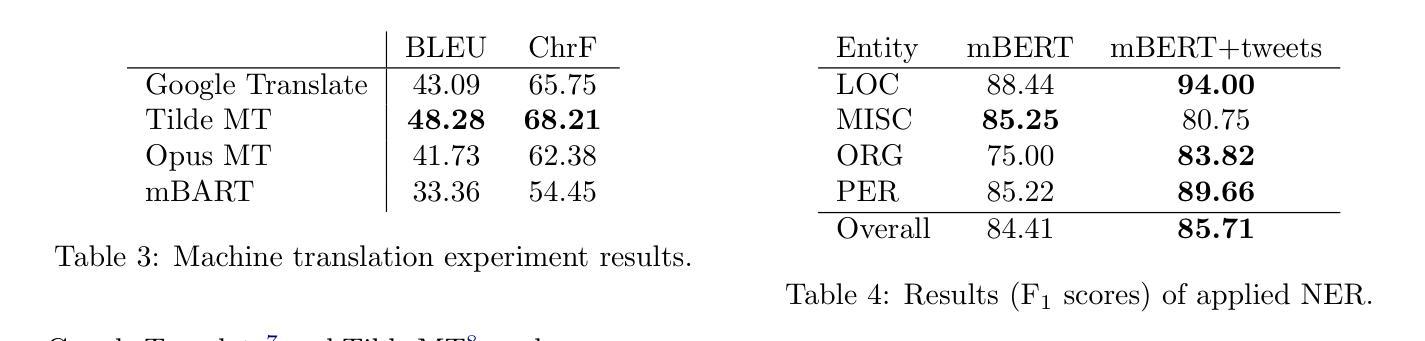
Language-Guided Image Tokenization for Generation
Authors:Kaiwen Zha, Lijun Yu, Alireza Fathi, David A. Ross, Cordelia Schmid, Dina Katabi, Xiuye Gu
Image tokenization, the process of transforming raw image pixels into a compact low-dimensional latent representation, has proven crucial for scalable and efficient image generation. However, mainstream image tokenization methods generally have limited compression rates, making high-resolution image generation computationally expensive. To address this challenge, we propose to leverage language for efficient image tokenization, and we call our method Text-Conditioned Image Tokenization (TexTok). TexTok is a simple yet effective tokenization framework that leverages language to provide high-level semantics. By conditioning the tokenization process on descriptive text captions, TexTok allows the tokenization process to focus on encoding fine-grained visual details into latent tokens, leading to enhanced reconstruction quality and higher compression rates. Compared to the conventional tokenizer without text conditioning, TexTok achieves average reconstruction FID improvements of 29.2% and 48.1% on ImageNet-256 and -512 benchmarks respectively, across varying numbers of tokens. These tokenization improvements consistently translate to 16.3% and 34.3% average improvements in generation FID. By simply replacing the tokenizer in Diffusion Transformer (DiT) with TexTok, our system can achieve a 93.5x inference speedup while still outperforming the original DiT using only 32 tokens on ImageNet-512. TexTok with a vanilla DiT generator achieves state-of-the-art FID scores of 1.46 and 1.62 on ImageNet-256 and -512 respectively. Furthermore, we demonstrate TexTok’s superiority on the text-to-image generation task, effectively utilizing the off-the-shelf text captions in tokenization.
图像标记化是将原始图像像素转换为紧凑的低维潜在表示的过程,已被证明对于可扩展和高效的图像生成至关重要。然而,主流的图像标记化方法通常压缩率有限,使得高分辨率图像生成的计算成本高昂。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出利用语言进行高效的图像标记化,并将我们的方法称为文本条件图像标记化(TexTok)。TexTok是一个简单而有效的标记化框架,它利用语言提供高级语义。通过以描述性文本字幕为标记化过程提供条件,TexTok允许标记化过程专注于将细微的视觉细节编码为潜在标记,从而提高重建质量和压缩率。与没有文本条件的传统标记器相比,TexTok在ImageNet-256和-512基准测试上的平均重建FID分别提高了29.2%和48.1%,跨越不同数量的标记。这些标记化改进始终转化为生成FID的16.3%和34.3%的平均改进。通过简单地用TexTok替换扩散变压器(DiT)中的标记器,我们的系统在使用只有32个标记的ImageNet-512上仍然优于原始DiT,同时实现了93.5倍的推理速度提升。TexTok与普通的DiT生成器在ImageNet-256和-512上分别达到了最先进的FID分数1.46和1.62。此外,我们在文本到图像生成任务上展示了TexTok的优越性,有效地利用了现成的文本字幕进行标记化。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
利用语言进行图像高效令牌化备受关注。新方法Text-Conditioned Image Tokenization(TexTok)结合文本描述,改善了图像令牌化过程,实现更高重建质量和压缩率。通过替换Diffusion Transformer中的令牌化器,TexTok加速推理并达到最先进的FID分数。
Key Takeaways
- TexTok是一个结合语言的简单有效的图像令牌化框架,利用语言提供高级语义信息。
- TexTok通过文本描述条件化令牌化过程,使令牌化专注于将细微的视觉细节编码为潜在令牌。
- 与没有文本条件的常规令牌化器相比,TexTok在ImageNet基准测试中实现了重建FID的显著改善。
- TexTok能提高生成质量,实现更高的压缩率和更快的推理速度。
- TexTok在与DiT生成器的结合下达到先进的FID分数。
- TexTok在文本到图像生成任务上表现出卓越性能,有效利用了现成的文本描述进行令牌化。
点此查看论文截图
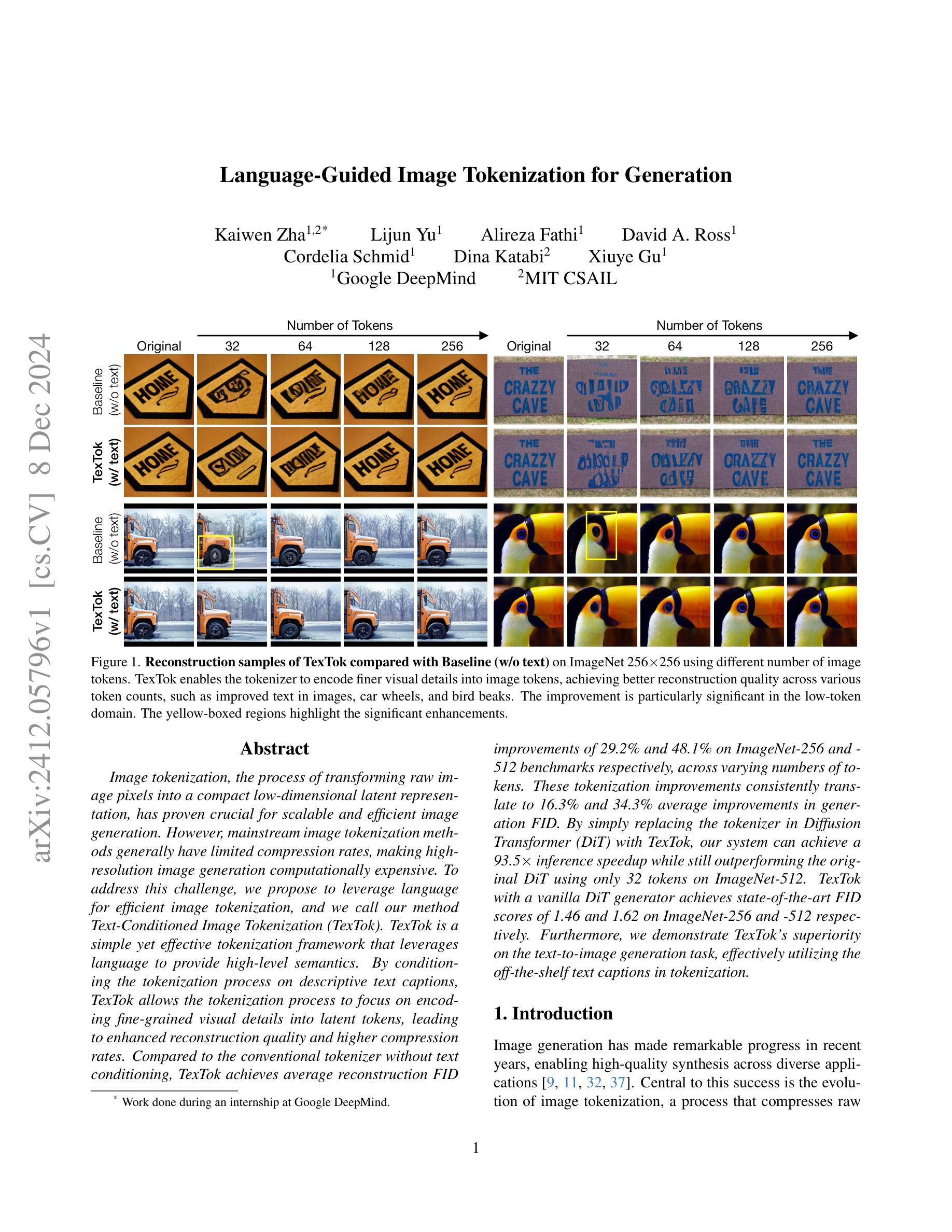
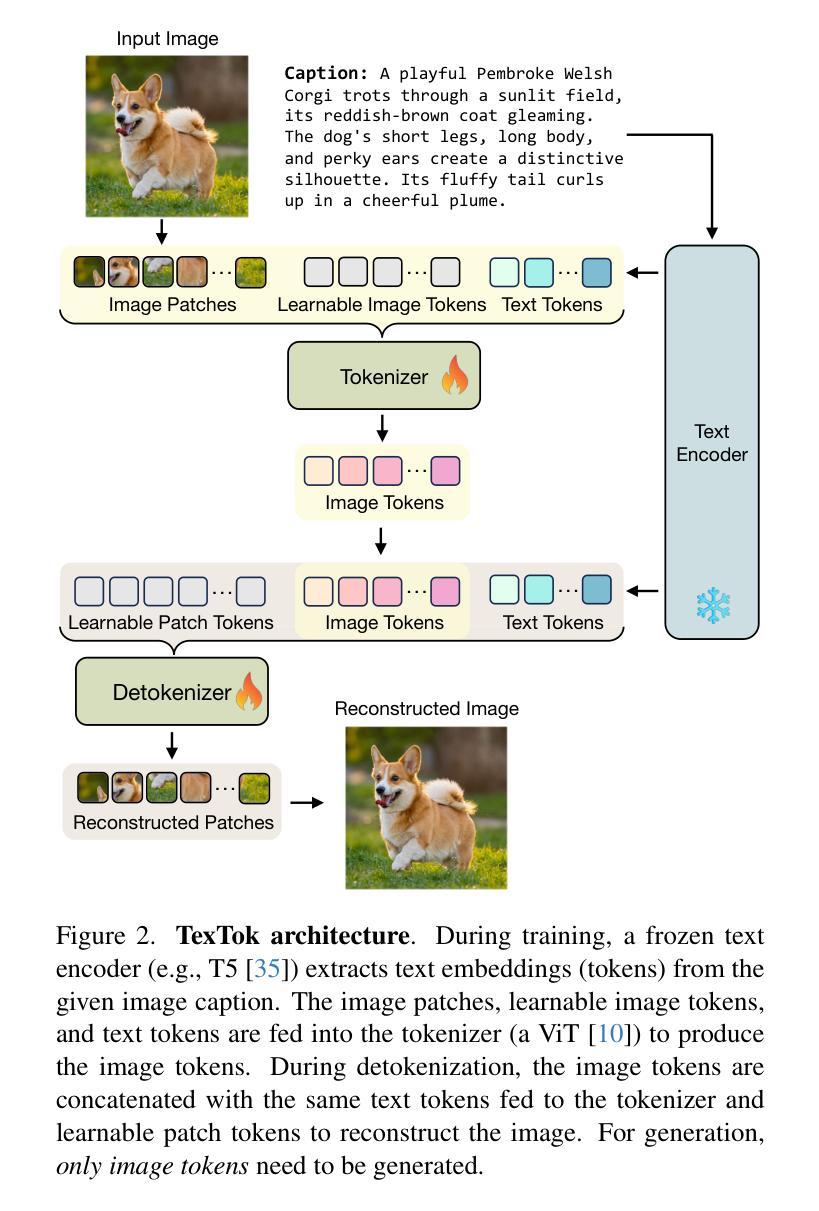
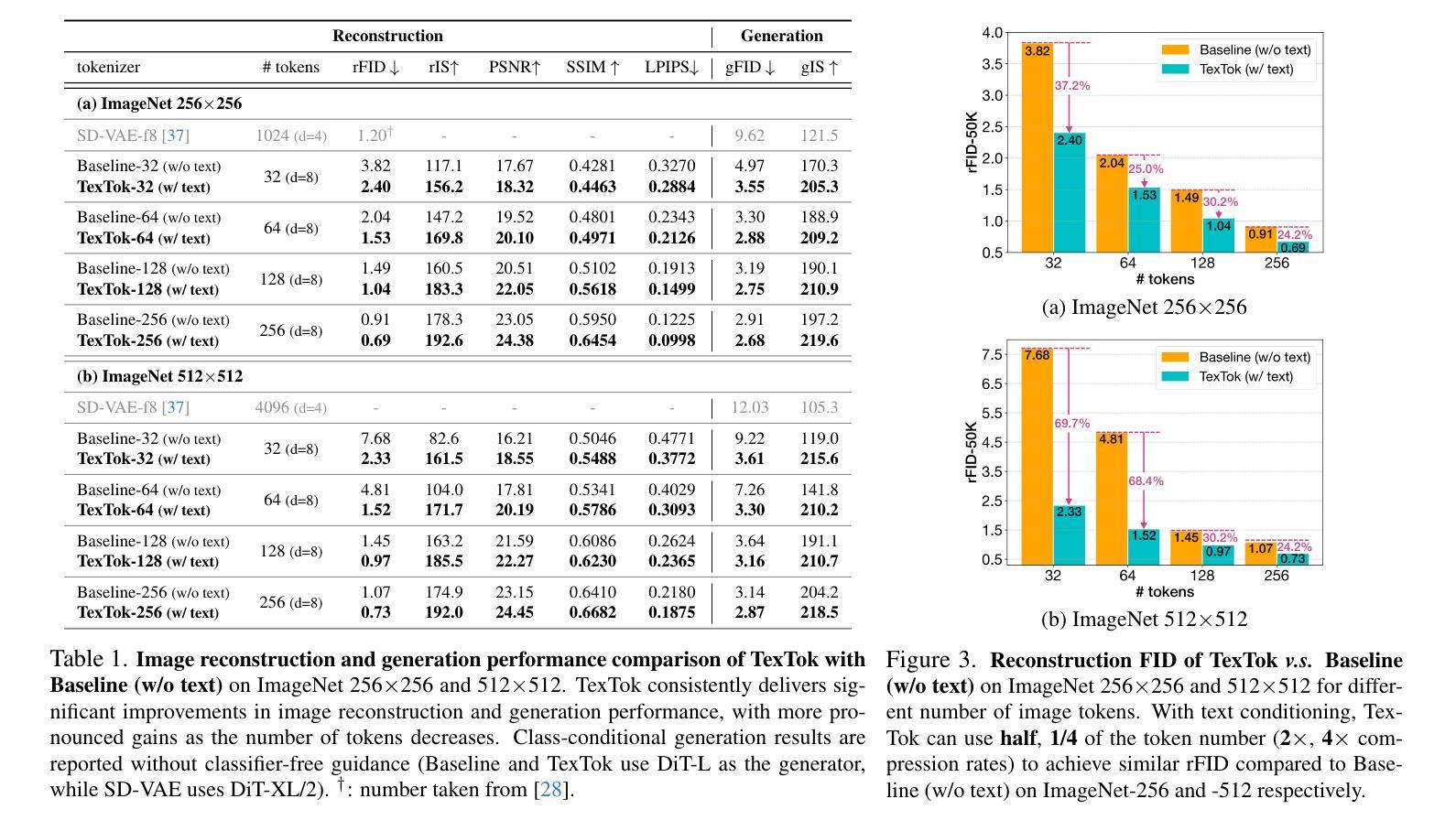
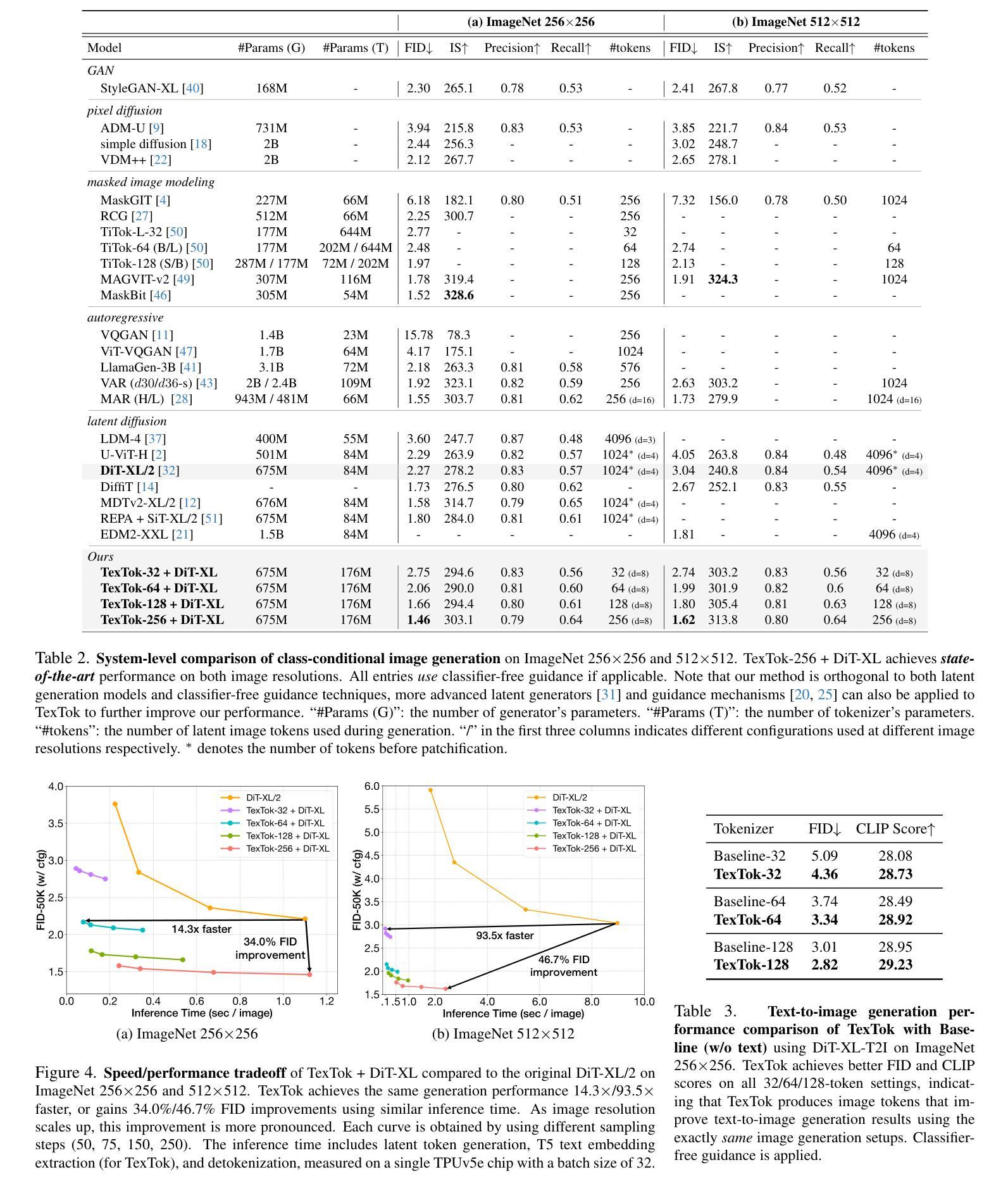
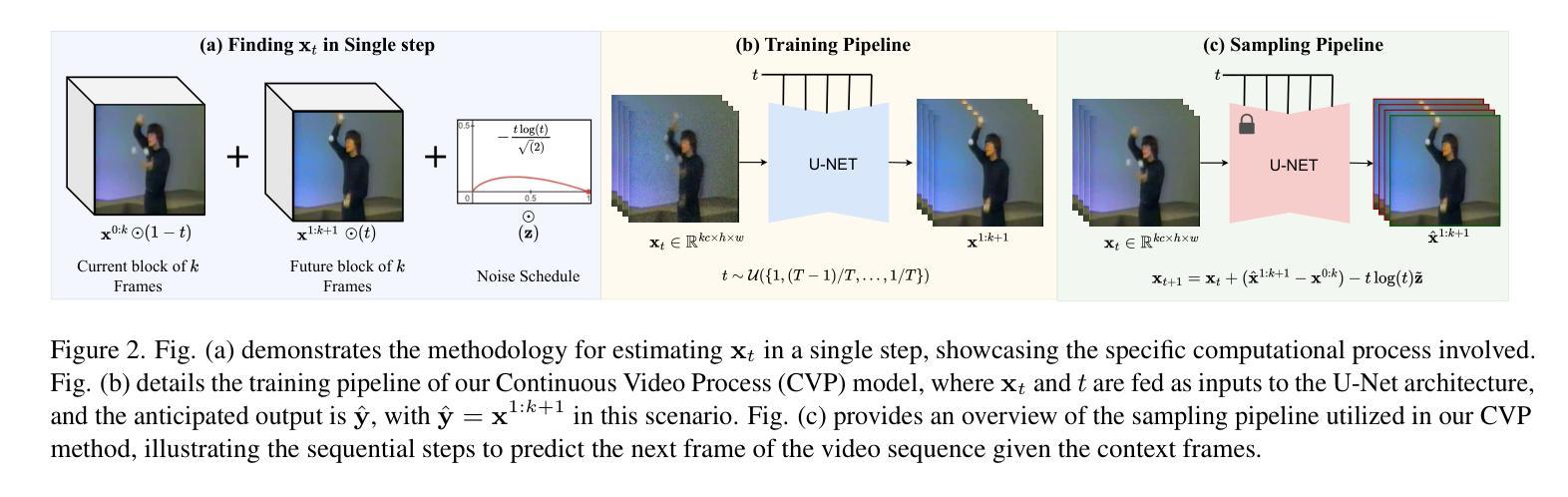
Continuous Video Process: Modeling Videos as Continuous Multi-Dimensional Processes for Video Prediction
Authors:Gaurav Shrivastava, Abhinav Shrivastava
Diffusion models have made significant strides in image generation, mastering tasks such as unconditional image synthesis, text-image translation, and image-to-image conversions. However, their capability falls short in the realm of video prediction, mainly because they treat videos as a collection of independent images, relying on external constraints such as temporal attention mechanisms to enforce temporal coherence. In our paper, we introduce a novel model class, that treats video as a continuous multi-dimensional process rather than a series of discrete frames. We also report a reduction of 75% sampling steps required to sample a new frame thus making our framework more efficient during the inference time. Through extensive experimentation, we establish state-of-the-art performance in video prediction, validated on benchmark datasets including KTH, BAIR, Human3.6M, and UCF101. Navigate to the project page https://www.cs.umd.edu/~gauravsh/cvp/supp/website.html for video results.
扩散模型在图像生成方面取得了重大进展,掌握了无条件图像合成、图文翻译和图像转换等任务。然而,它们在视频预测方面的能力还存在不足,主要是因为它们将视频视为独立图像的集合,依赖诸如时间注意力机制等外部约束来强制执行时间连贯性。在我们的论文中,我们介绍了一种新的模型类别,该模型将视频视为一个连续的多维过程,而不是一系列离散帧。我们还报告了采样新帧所需的采样步骤减少了75%,从而使我们的框架在推理时间更加高效。通过广泛的实验,我们在视频预测方面达到了最新技术水平,并在包括KTH、BAIR、Human3.6M和UCF101等多个基准数据集上进行了验证。有关视频结果,请访问项目页面:https://www.cs.umd.edu/~gauravsh/cvp/supp/website.html。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Navigate to the project page https://www.cs.umd.edu/~gauravsh/cvp/supp/website.html for video results. Extended version of published CVPR paper
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型在图像生成方面的最新进展,尤其是在无条件图像合成、文本图像翻译和图像到图像的转换任务中的卓越表现。然而,在视频预测方面,现有模型的能力仍有不足。为此,本文引入了一种新的模型类别,该模型将视频视为连续的多维过程而非一系列独立的帧,并减少了75%的采样步骤,提高了推理效率。通过广泛的实验验证,该模型在视频预测方面达到了先进水平,并在KTH、BAIR、Human3.6M和UCF101等基准数据集上表现出卓越性能。更多视频结果请访问项目页面:链接地址。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成领域取得显著进展,尤其在无条件图像合成等任务上表现优秀。
- 现有模型在处理视频预测时存在局限性,主要因为将视频视为独立图像集合。
- 本文引入的新型模型将视频视为连续的多维过程,提高了视频预测的效果。
- 新模型减少了75%的采样步骤,提高了推理效率。
- 该模型在多个基准数据集上实现了先进的视频预测性能。
- 项目页面提供了更多关于模型性能的视频结果。
点此查看论文截图

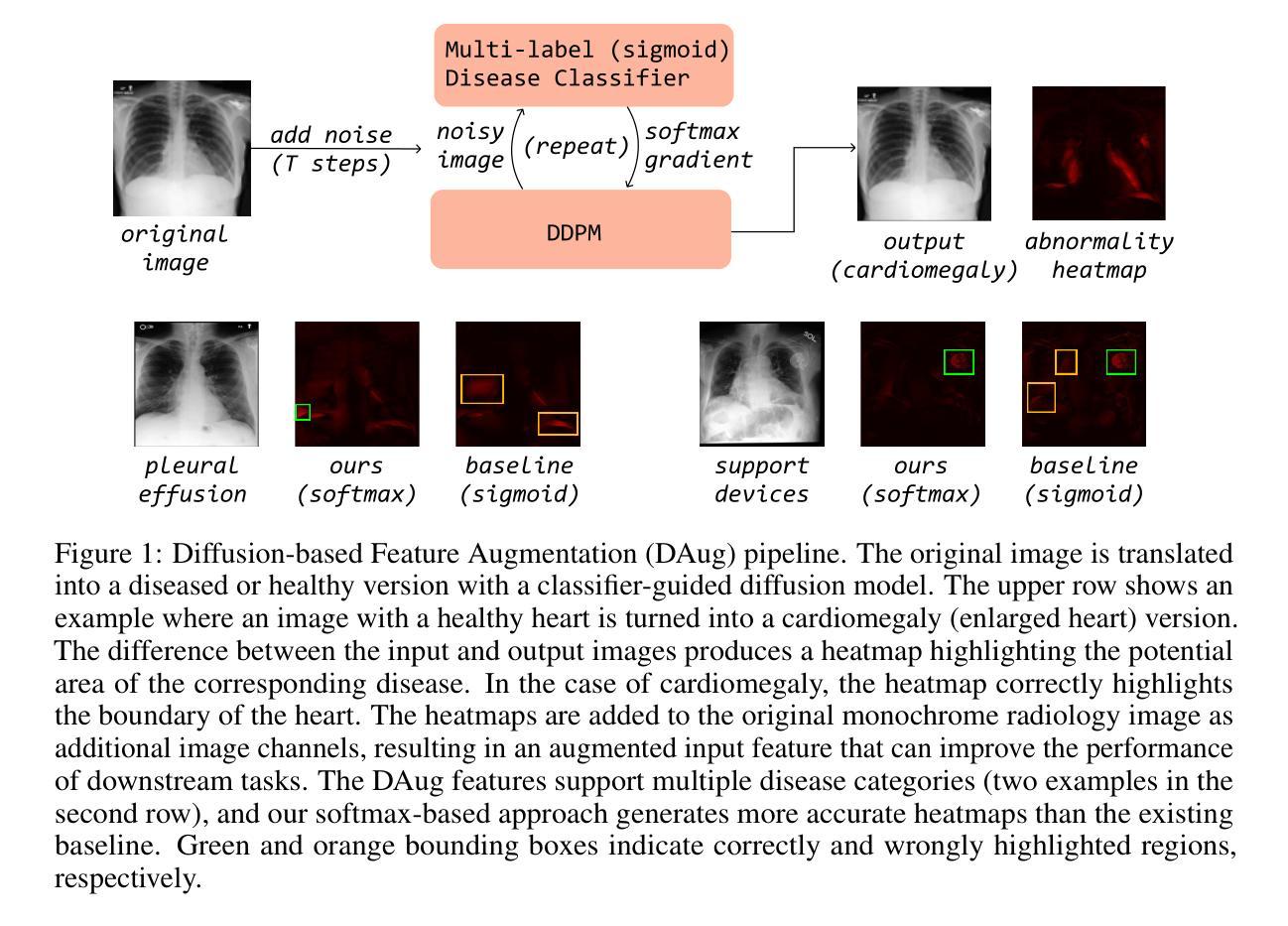
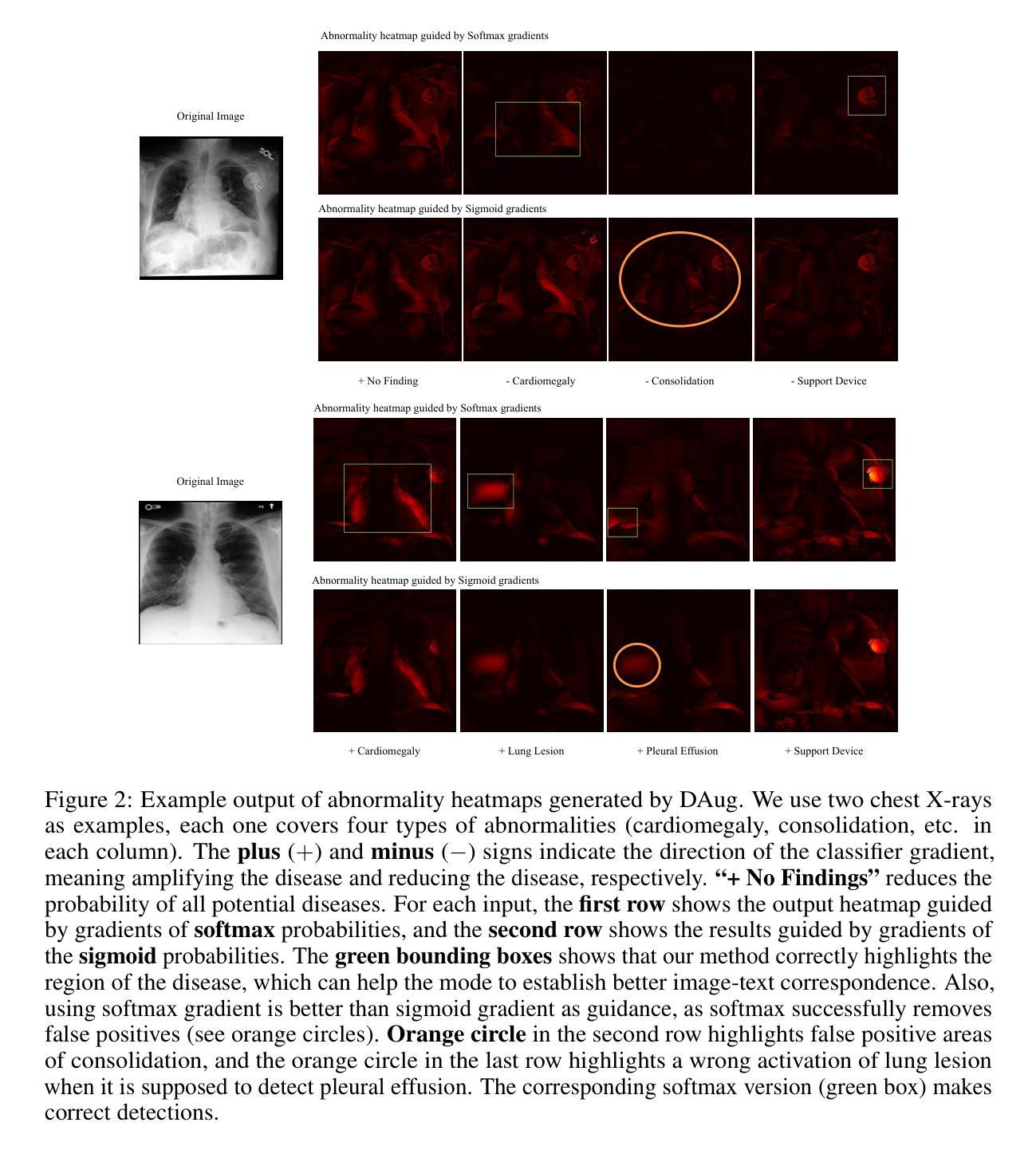
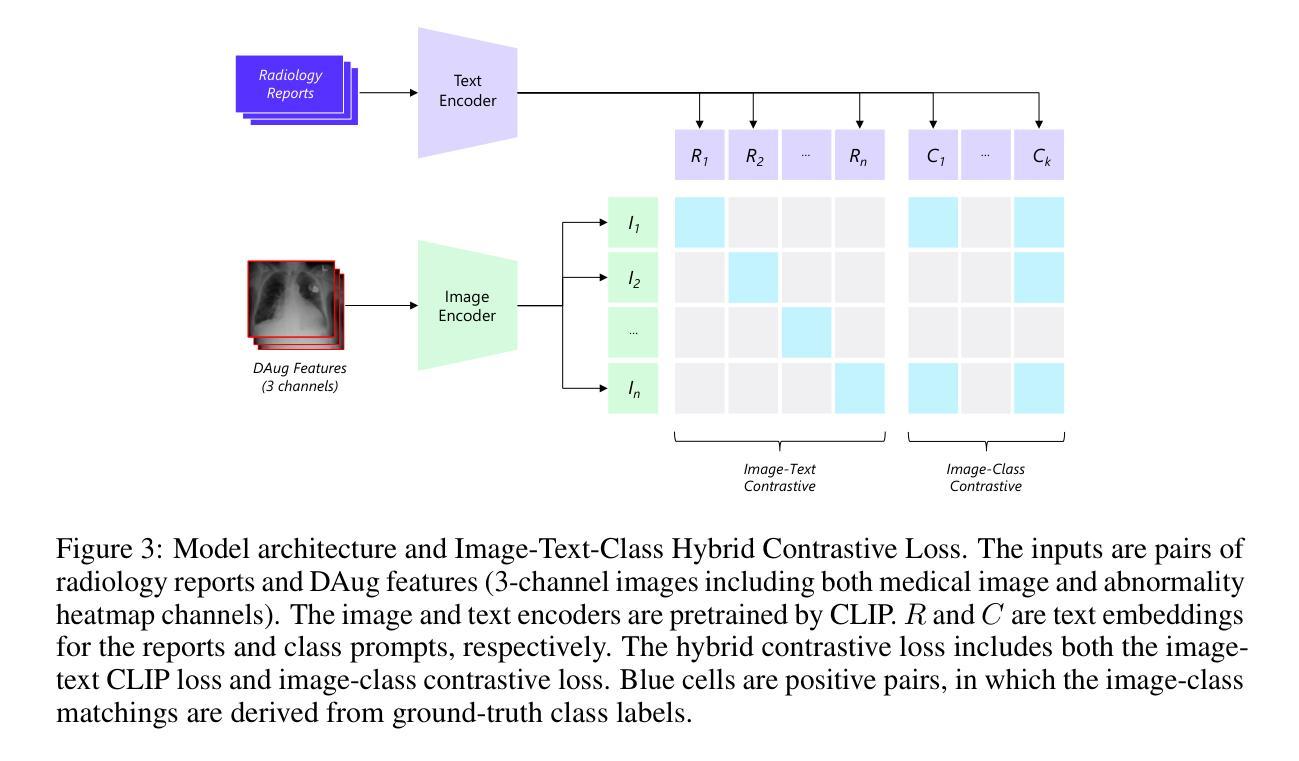
DAug: Diffusion-based Channel Augmentation for Radiology Image Retrieval and Classification
Authors:Ying Jin, Zhuoran Zhou, Haoquan Fang, Jenq-Neng Hwang
Medical image understanding requires meticulous examination of fine visual details, with particular regions requiring additional attention. While radiologists build such expertise over years of experience, it is challenging for AI models to learn where to look with limited amounts of training data. This limitation results in unsatisfying robustness in medical image understanding. To address this issue, we propose Diffusion-based Feature Augmentation (DAug), a portable method that improves a perception model’s performance with a generative model’s output. Specifically, we extend a radiology image to multiple channels, with the additional channels being the heatmaps of regions where diseases tend to develop. A diffusion-based image-to-image translation model was used to generate such heatmaps conditioned on selected disease classes. Our method is motivated by the fact that generative models learn the distribution of normal and abnormal images, and such knowledge is complementary to image understanding tasks. In addition, we propose the Image-Text-Class Hybrid Contrastive learning to utilize both text and class labels. With two novel approaches combined, our method surpasses baseline models without changing the model architecture, and achieves state-of-the-art performance on both medical image retrieval and classification tasks.
医学影像理解需要对细微的视觉细节进行细致的检查,特定区域需要特别注意。虽然放射科医生经过多年的经验积累获得了这样的专业知识,但对于人工智能模型来说,在有限的训练数据下学习应该关注的位置却是一个挑战。这种局限性导致医学影像理解的稳健性令人不满意。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了基于扩散的特征增强(DAug)方法,这是一种便携的方法,利用生成模型的输出来提高感知模型的性能。具体来说,我们将放射学图像扩展到多个通道,额外的通道是疾病倾向发展区域的热图。我们使用基于扩散的图像到图像翻译模型来生成这种热图,该热图是基于选择的疾病类别进行条件生成的。我们的方法受到以下事实的启发:生成模型学习正常和异常图像的分部,这种知识与图像理解任务是互补的。此外,我们提出了图像文本类混合对比学习,以利用文本和类别标签。通过结合这两种新方法,我们的方法在不需要更改模型架构的情况下超越了基线模型,并在医学图像检索和分类任务上达到了最新性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于扩散的特征增强(DAug)方法,通过结合生成模型的输出,提高感知模型在医学图像理解上的性能。为提高模型对关键区域的关注,生成疾病易发区域的热图并将其添加到医学图像中,以增强特征信息。通过扩散模型将图像转换为带有选定疾病类别条件的热图。结合图像文本分类混合对比学习,利用文本和类别标签提高模型性能。此方法在不改变模型架构的前提下超越基线模型,并在医学图像检索和分类任务上实现最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像理解需要精细的视觉分析,特定区域需要重点关注。
- AI模型在医学图像理解方面因训练数据有限面临挑战。
- 提出的扩散特征增强(DAug)方法通过生成模型输出提高感知模型性能。
- 通过生成疾病易发区域热图并将其添加到医学图像中,以增强特征信息。
- 采用扩散模型将图像转换为热图,此过程考虑选定的疾病类别条件。
- 结合图像文本分类混合对比学习,利用文本和类别标签提高模型性能。
点此查看论文截图

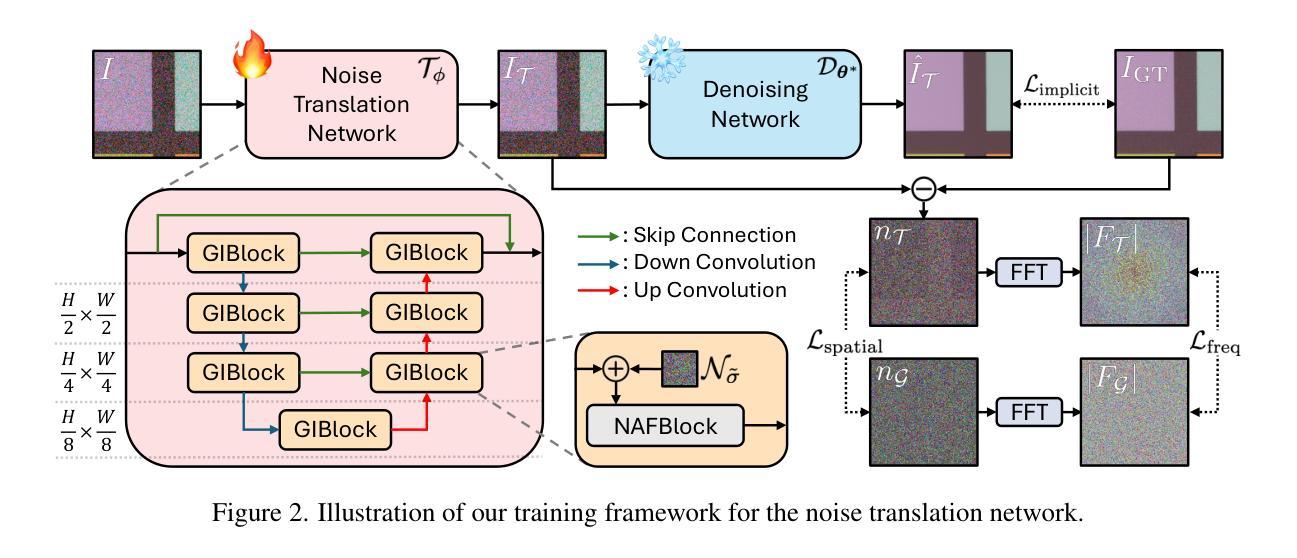
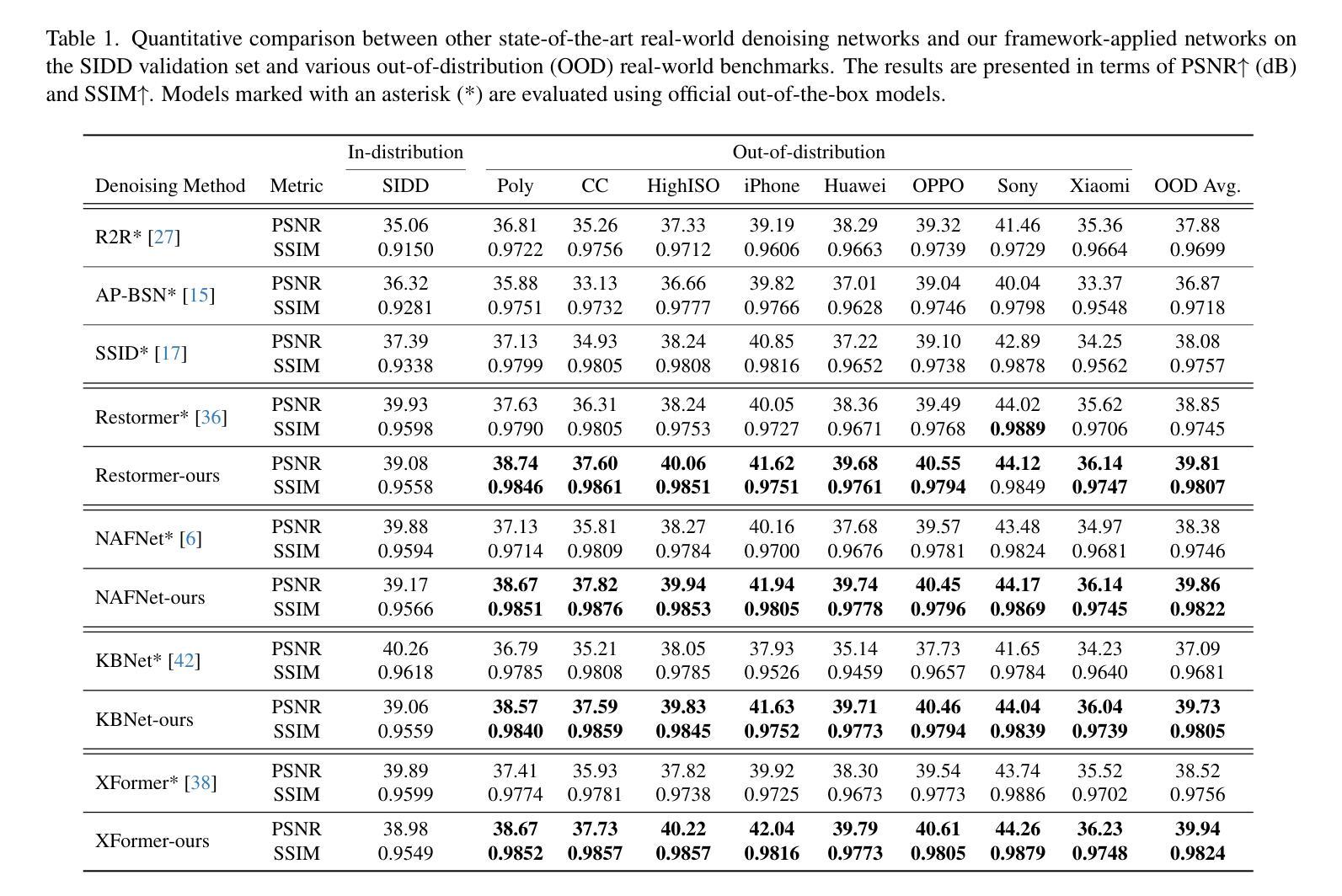
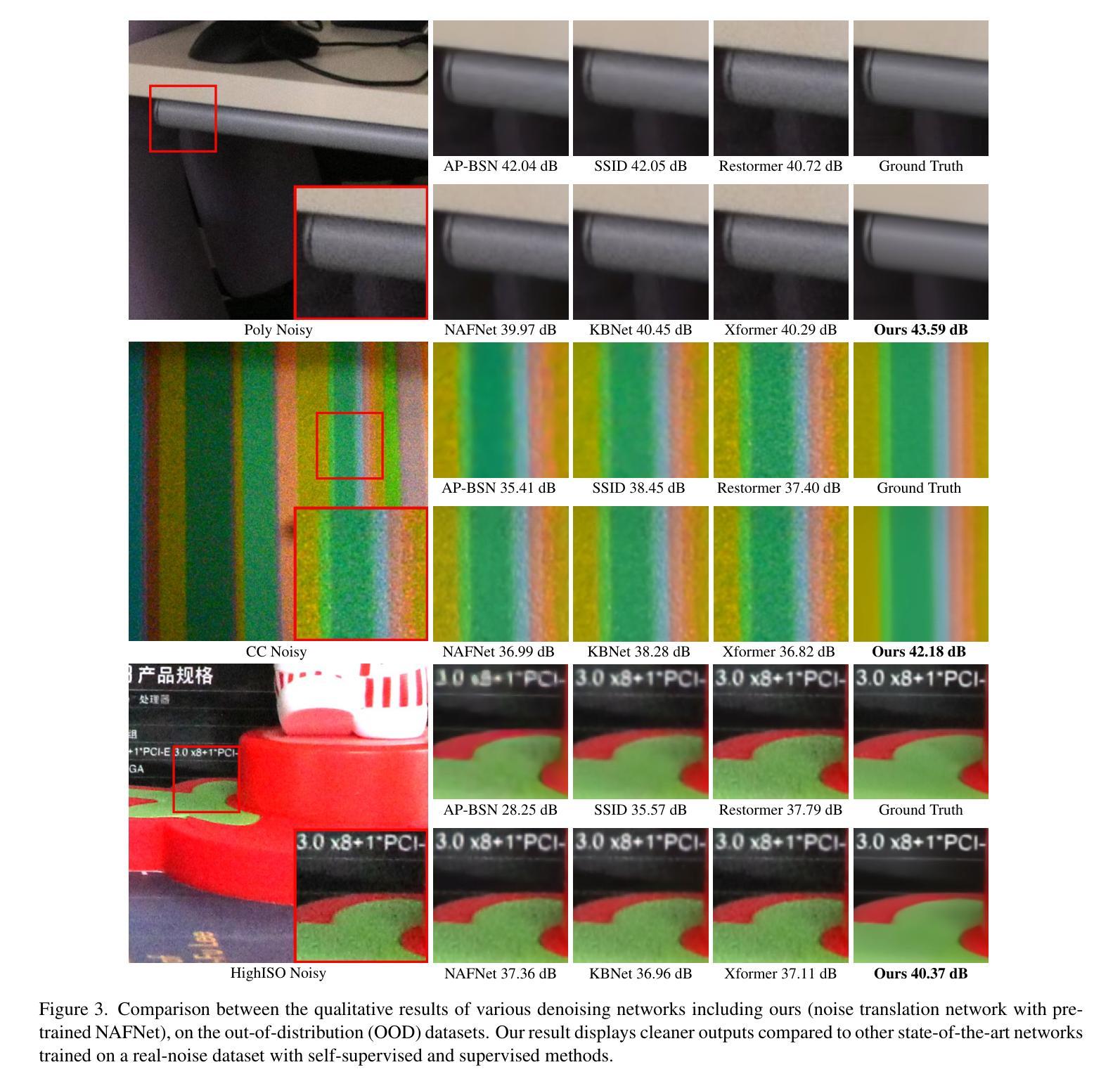
Learning to Translate Noise for Robust Image Denoising
Authors:Inju Ha, Donghun Ryou, Seonguk Seo, Bohyung Han
Deep learning-based image denoising techniques often struggle with poor generalization performance to out-of-distribution real-world noise. To tackle this challenge, we propose a novel noise translation framework that performs denoising on an image with translated noise rather than directly denoising an original noisy image. Specifically, our approach translates complex, unknown real-world noise into Gaussian noise, which is spatially uncorrelated and independent of image content, through a noise translation network. The translated noisy images are then processed by an image denoising network pretrained to effectively remove Gaussian noise, enabling robust and consistent denoising performance. We also design well-motivated loss functions and architectures for the noise translation network by leveraging the mathematical properties of Gaussian noise. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method substantially improves robustness and generalizability, outperforming state-of-the-art methods across diverse benchmarks. Visualized denoising results and the source code are available on our project page.
基于深度学习的图像去噪技术通常对于分布外的真实世界噪声的泛化性能较差。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了一种新的噪声翻译框架,该框架对经过翻译后的噪声图像进行去噪,而不是直接对原始含噪图像进行去噪。具体来说,我们的方法通过一个噪声翻译网络,将复杂的、未知的真实世界噪声翻译成空间上不相关且独立于图像内容的高斯噪声。翻译后的含噪图像然后被送到一个预先训练好的图像去噪网络中进行处理,该网络可以有效地去除高斯噪声,从而实现稳健和一致的去噪性能。我们还通过利用高斯噪声的数学属性,为噪声翻译网络设计了动机充分的损失函数和架构。实验结果表明,该方法大大提高了稳健性和泛化能力,在多种基准测试中优于最先进的方法。可视化去噪结果和项目源代码可在我们的项目页面查看。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The project page is available at https://hij1112.github.io/learning-to-translate-noise/
Summary
本文提出了一种新的噪声翻译框架,用于对图像进行去噪处理。该框架通过噪声翻译网络将复杂的、未知的现实世界噪声转换为高斯噪声,然后利用预先训练好的图像去噪网络对翻译后的噪声图像进行处理,从而实现稳健和一致的去噪性能。该方法提高了模型的鲁棒性和泛化能力,在多个基准测试中优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的噪声翻译框架,将复杂的现实世界噪声转换为高斯噪声。
- 通过噪声翻译网络实现这一转换,该网络利用数学高斯噪声属性设计损失函数和架构。
- 翻译后的噪声图像通过预训练的去噪网络进行处理,以提高去噪的稳健性和一致性。
- 该方法显著提高了模型的泛化性能,在多种基准测试中表现优于现有技术。
- 提供了可视化去噪结果和源代码。
- 噪声翻译网络的设计基于高斯噪声的数学属性,增强了去噪网络的性能。
点此查看论文截图


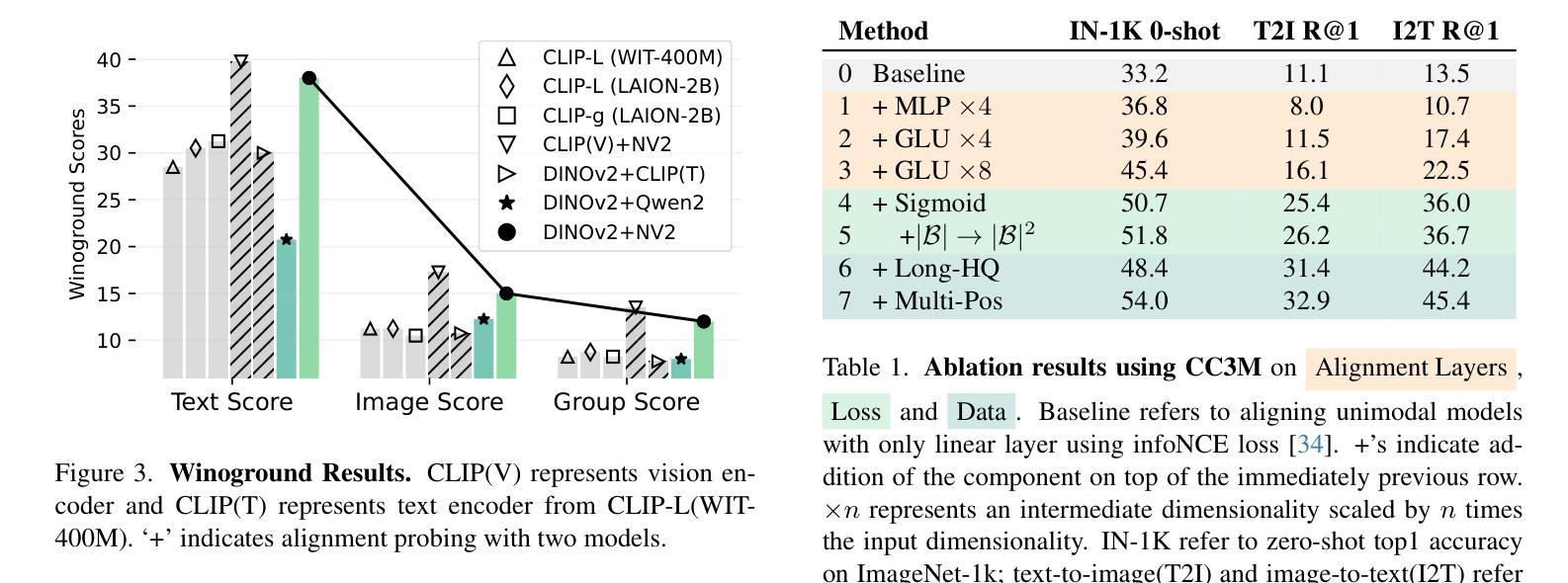
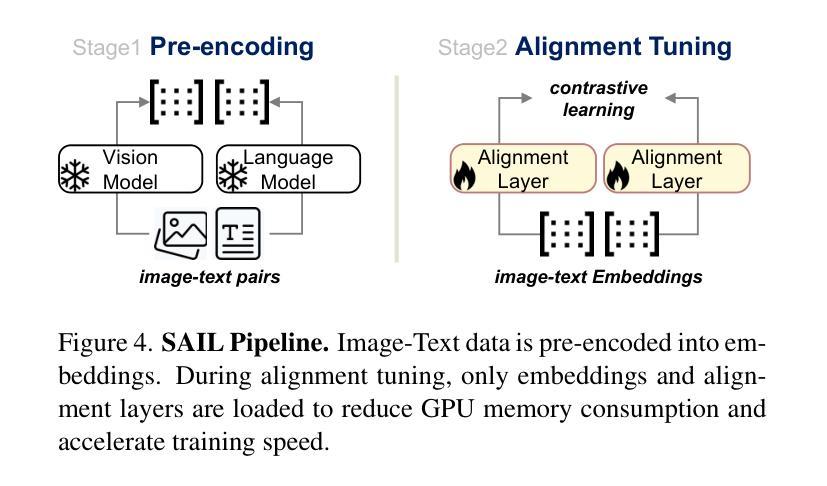
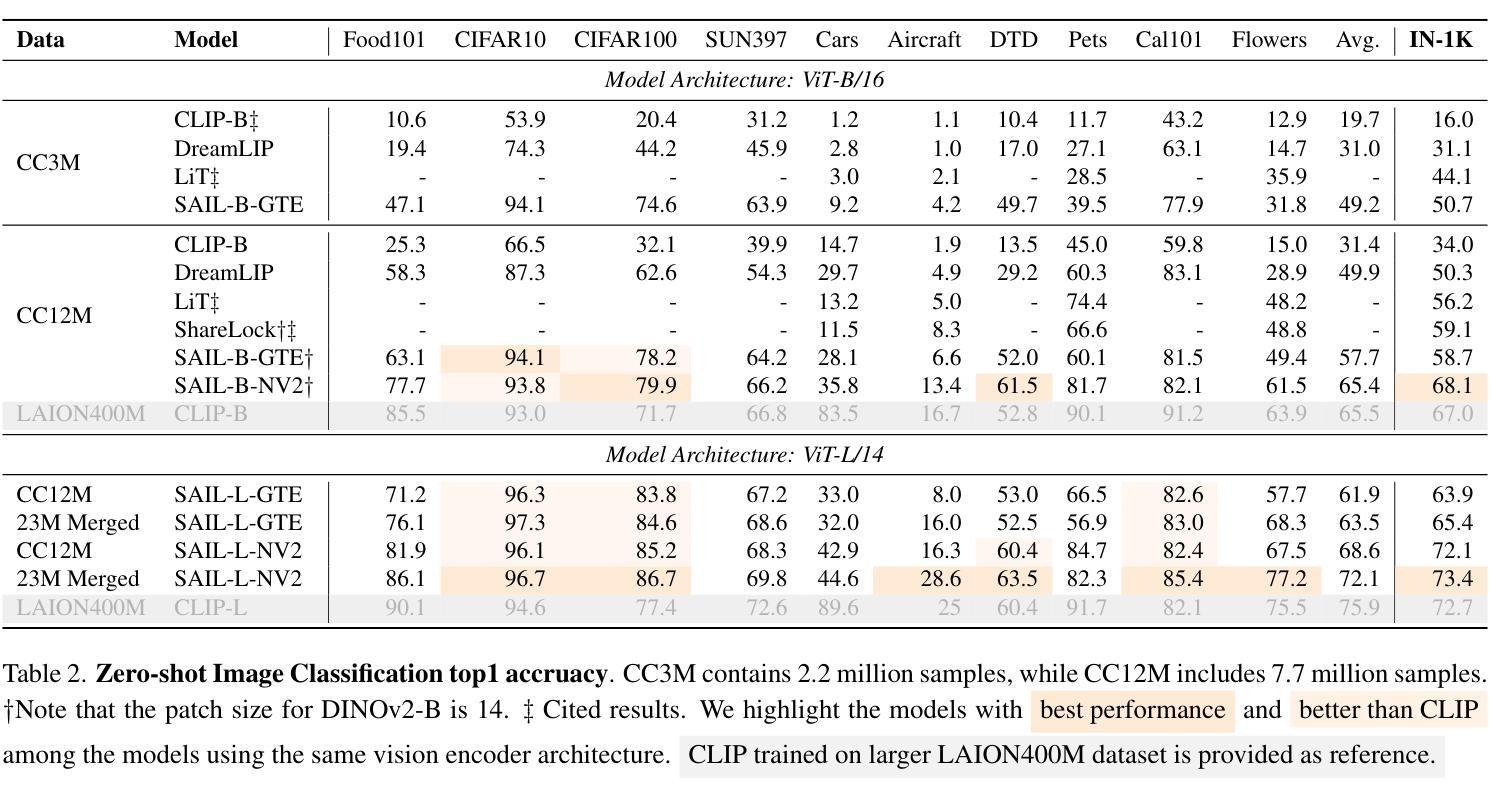
Assessing and Learning Alignment of Unimodal Vision and Language Models
Authors:Le Zhang, Qian Yang, Aishwarya Agrawal
How well are unimodal vision and language models aligned? Although prior work have approached answering this question, their assessment methods do not directly translate to how these models are used in practical vision-language tasks. In this paper, we propose a direct assessment method, inspired by linear probing, to assess vision-language alignment. We identify that the degree of alignment of the SSL vision models depends on their SSL training objective, and we find that the clustering quality of SSL representations has a stronger impact on alignment performance than their linear separability. Next, we introduce Swift Alignment of Image and Language (SAIL), a efficient transfer learning framework that aligns pretrained unimodal vision and language models for downstream vision-language tasks. Since SAIL leverages the strengths of pretrained unimodal models, it requires significantly fewer (6%) paired image-text data for the multimodal alignment compared to models like CLIP which are trained from scratch. SAIL training only requires a single A100 GPU, 5 hours of training and can accommodate a batch size up to 32,768. SAIL achieves 73.4% zero-shot accuracy on ImageNet (vs. CLIP’s 72.7%) and excels in zero-shot retrieval, complex reasoning, and semantic segmentation. Additionally, SAIL improves the language-compatibility of vision encoders that in turn enhance the performance of multimodal large language models. The entire codebase and model weights are open-source: https://lezhang7.github.io/sail.github.io/
单模态视觉和语言模型的对齐程度如何?尽管先前的工作已经尝试回答这个问题,但他们的评估方法并不能直接转化为这些模型在实际视觉语言任务中的使用方式。在本文中,我们提出了一种受线性探测启发的直接评估方法,以评估视觉语言对齐程度。我们发现SSL视觉模型的对齐程度取决于其SSL训练目标,并且我们发现SSL表示的聚类质量对对齐性能的影响强于其线性可分性。接下来,我们介绍了Swift图像和语言对齐(SAIL),这是一个高效的迁移学习框架,用于对齐预训练的单模态视觉和语言模型,以便进行下游视觉语言任务。由于SAIL利用了预训练单模态模型的优势,因此与从头开始训练的模型(例如CLIP)相比,它进行多模态对齐所需的配对图像文本数据大大减少(减少6%)。SAIL训练仅需单个A100 GPU,训练时间为5小时,并且可以容纳高达32,768的批次大小。SAIL在ImageNet上的零样本准确率达到了73.4%(相较于CLIP的72.7%),并在零样本检索、复杂推理和语义分割方面表现出色。此外,SAIL还提高了视觉编码器的语言兼容性,进而提高了多模态大型语言模型的性能。所有代码和模型权重均为开源:https://lezhang7.github.io/sail.github.io/
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本论文关注于评估视觉和语言模型的跨模态对齐效果。文章提出了利用线性探测的评估方法,深入研究了预训练模型中的视觉与语言对齐机制,并提出了高效迁移学习框架Swift Alignment of Image and Language(SAIL)。SAIL利用预训练的单模态模型优势,在跨模态对齐时减少了配对图像文本数据的需求,训练效率极高。SAIL在多个任务上表现优秀,提高了视觉编码器的语言兼容性并提升了多模态大模型的性能。其源代码和模型权重均已开源共享。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究提出使用线性探测来直接评估视觉与语言模型的跨模态对齐效果。
- 预训练模型的视觉与语言对齐程度受到自监督学习训练目标的影响。
- SSL表示的聚类质量比对齐性能的影响强于其线性可分性。
- 引入了一种高效迁移学习框架SAIL,用于对齐预训练的单模态视觉和语言模型。
- SAIL相较于从头开始训练的模型如CLIP,在对齐时减少了配对图像文本数据的需求。
- SAIL在多个任务上表现优秀,如ImageNet的零样本准确率提升,以及在零样本检索、复杂推理和语义分割上的优势。
点此查看论文截图
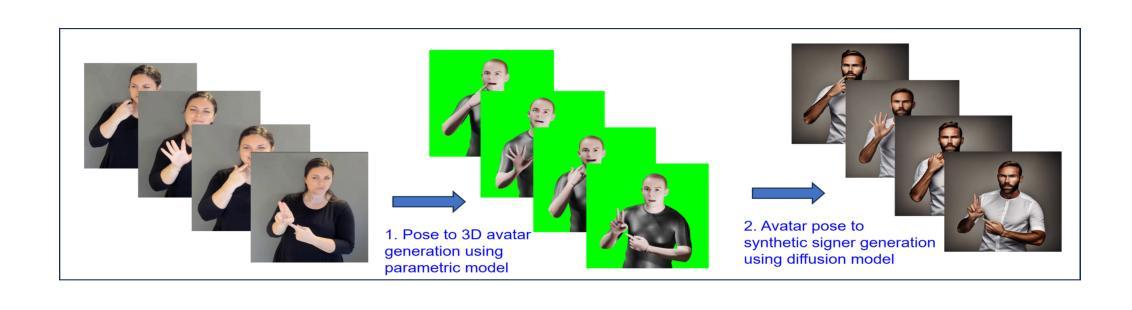
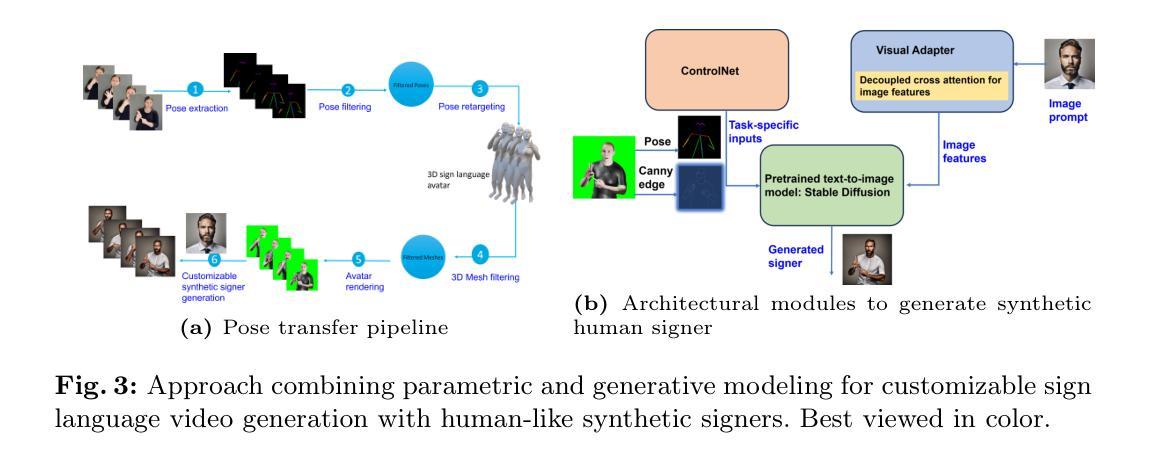
DiffSign: AI-Assisted Generation of Customizable Sign Language Videos With Enhanced Realism
Authors:Sudha Krishnamurthy, Vimal Bhat, Abhinav Jain
The proliferation of several streaming services in recent years has now made it possible for a diverse audience across the world to view the same media content, such as movies or TV shows. While translation and dubbing services are being added to make content accessible to the local audience, the support for making content accessible to people with different abilities, such as the Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHH) community, is still lagging. Our goal is to make media content more accessible to the DHH community by generating sign language videos with synthetic signers that are realistic and expressive. Using the same signer for a given media content that is viewed globally may have limited appeal. Hence, our approach combines parametric modeling and generative modeling to generate realistic-looking synthetic signers and customize their appearance based on user preferences. We first retarget human sign language poses to 3D sign language avatars by optimizing a parametric model. The high-fidelity poses from the rendered avatars are then used to condition the poses of synthetic signers generated using a diffusion-based generative model. The appearance of the synthetic signer is controlled by an image prompt supplied through a visual adapter. Our results show that the sign language videos generated using our approach have better temporal consistency and realism than signing videos generated by a diffusion model conditioned only on text prompts. We also support multimodal prompts to allow users to further customize the appearance of the signer to accommodate diversity (e.g. skin tone, gender). Our approach is also useful for signer anonymization.
近年来,多种流媒体服务的普及使得世界各地的观众都能观看相同的媒体内容,如电影或电视剧。虽然增加了翻译和配音服务,使内容能够面向当地观众,但对于不同能力人群(如聋哑和听力受损社区)的内容可访问性的支持仍然滞后。我们的目标是通过生成具有现实感和表现力的手语视频来使媒体内容更易于聋哑和听力受损社区访问。对于全球范围内观看的给定媒体内容使用同一手语者可能吸引力有限。因此,我们的方法结合了参数建模和生成建模,以生成看似逼真的合成手语者,并根据用户偏好定制其外观。我们首先将人手语姿势目标设定为三维手语动画角色,通过优化参数模型来实现。从渲染的动画角色中得到的高保真姿势然后用于确定使用基于扩散的生成模型生成的手语者的姿势。合成手语者的外观由通过视觉适配器提供的图像提示进行控制。我们的结果表明,使用我们的方法生成的手语视频比仅通过文本提示进行条件处理的手语视频具有更好的时间连贯性和逼真性。我们还支持多模式提示,以允许用户进一步定制手语者的外观以适应多样性(例如肤色、性别)。我们的方法对于手语者的匿名化也很有用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in Proceedings of ECCV, Workshop on Assistive Computer Vision and Robotics, 2024
Summary
内容摘要:近年来流媒体服务的增多使得全球观众能够观看相同的媒体内容,如电影或电视剧。尽管翻译和配音服务正在增加,使得内容对当地观众更具吸引力,但对于聋哑和听力受损群体的内容无障碍支持仍然不足。本文旨在通过生成具有现实感和表现力的手语视频合成签名者,使媒体内容更易于聋哑群体访问。我们的方法结合了参数建模和生成建模,以生成逼真的合成签名者并根据用户偏好定制外观。首先,我们通过优化参数模型将人类手语姿势转移到3D手语虚拟角色上。然后,使用基于扩散的生成模型模拟这些姿势,从渲染的虚拟角色获得的高精度姿势被用来模拟合成签名者的姿势。合成签名者的外观由视觉适配器提供的图像提示控制。实验结果表明,使用我们的方法生成的手语视频在时序一致性和逼真度方面优于仅由文本提示控制的扩散模型生成的手语视频。我们还支持多模式提示,允许用户进一步定制签名者的外观以适应多样性(如肤色、性别)。我们的方法还有助于实现签名者的匿名化。
Key Takeaways
- 多种流媒体服务的发展使得全球观众能够观看相同的媒体内容,如电影和电视剧。
- 当前虽然翻译和配音服务在增加,但对聋哑和听力受损群体的内容无障碍支持仍然不足。
- 本文的目标是使媒体内容更易于聋哑群体访问,通过生成具有现实感和表现力的手语视频合成签名者。
- 结合参数建模和生成建模的方法用于生成合成签名者,保证了视频的逼真度和多样性。
- 用户可以通过图像提示定制合成签名者的外观,包括肤色、性别等特征。
- 实验证明该方法生成的手语视频比传统方法更加逼真且具有更好的时序一致性。
点此查看论文截图


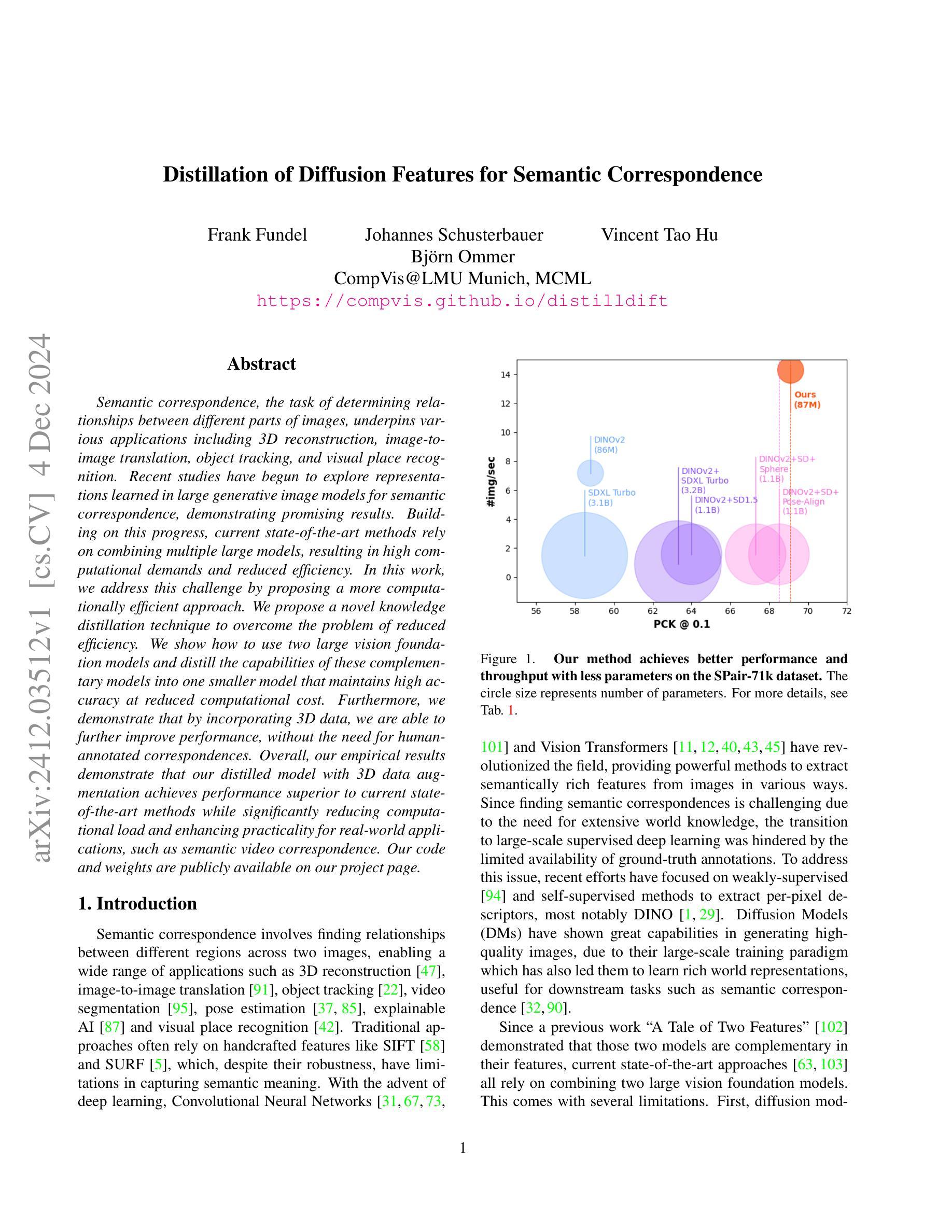
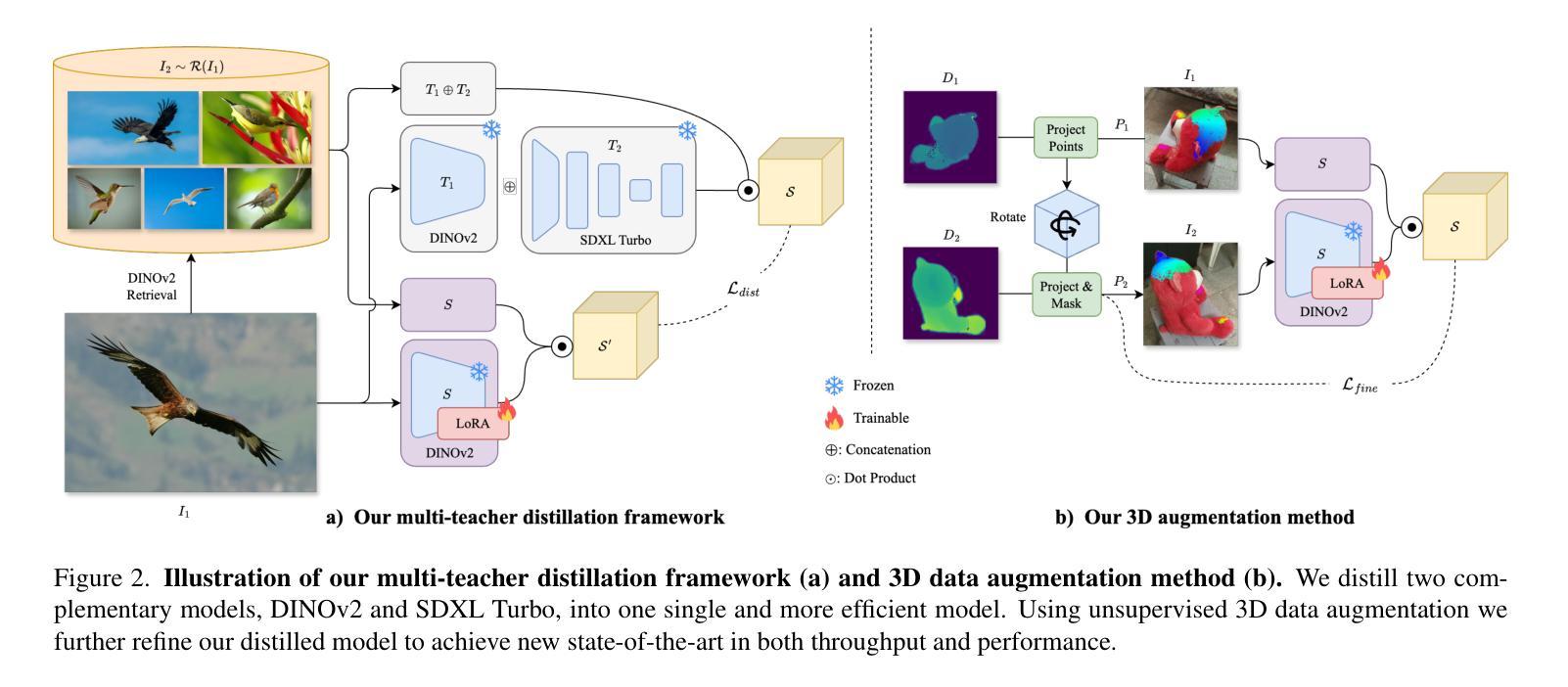
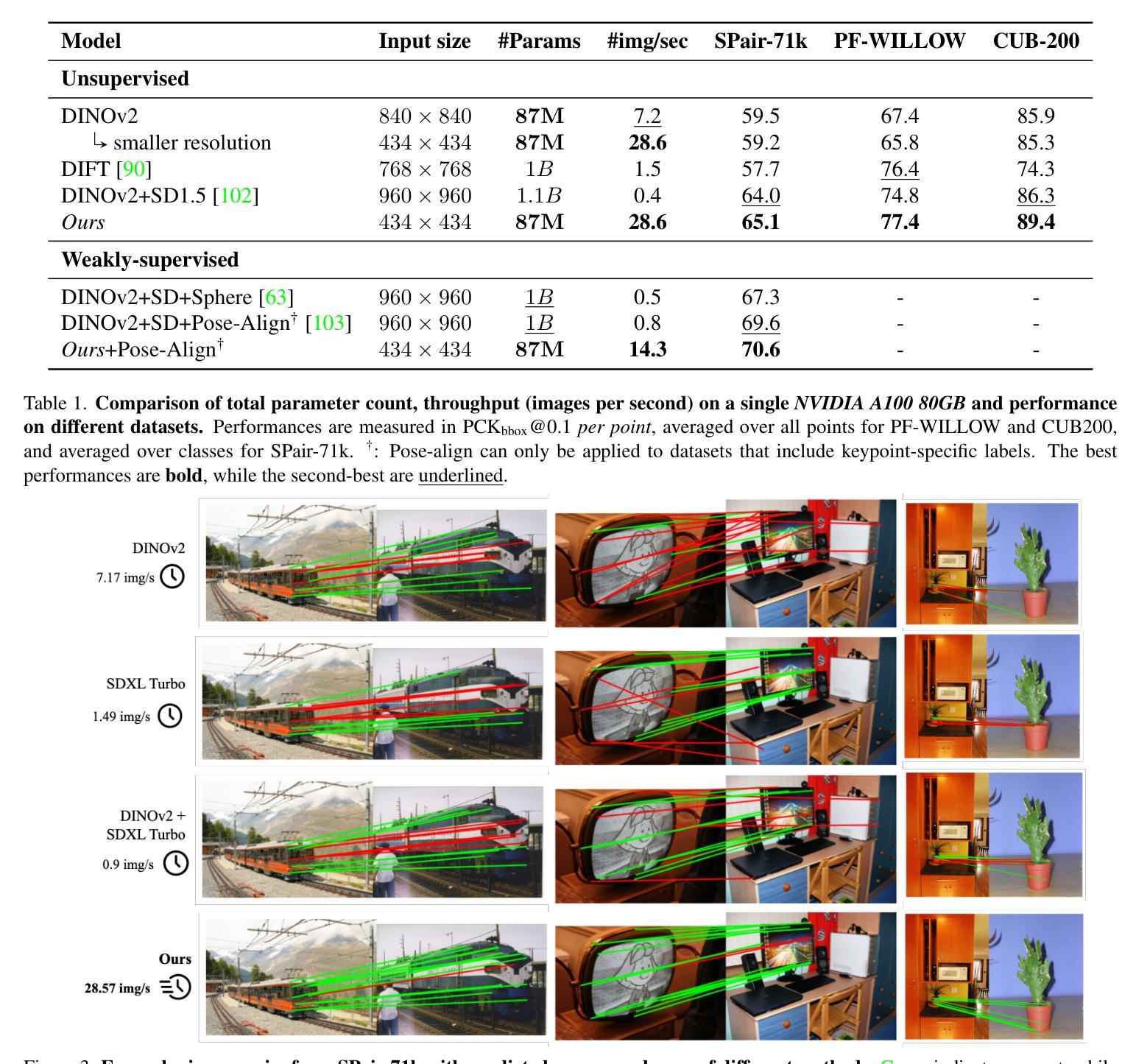
Distillation of Diffusion Features for Semantic Correspondence
Authors:Frank Fundel, Johannes Schusterbauer, Vincent Tao Hu, Björn Ommer
Semantic correspondence, the task of determining relationships between different parts of images, underpins various applications including 3D reconstruction, image-to-image translation, object tracking, and visual place recognition. Recent studies have begun to explore representations learned in large generative image models for semantic correspondence, demonstrating promising results. Building on this progress, current state-of-the-art methods rely on combining multiple large models, resulting in high computational demands and reduced efficiency. In this work, we address this challenge by proposing a more computationally efficient approach. We propose a novel knowledge distillation technique to overcome the problem of reduced efficiency. We show how to use two large vision foundation models and distill the capabilities of these complementary models into one smaller model that maintains high accuracy at reduced computational cost. Furthermore, we demonstrate that by incorporating 3D data, we are able to further improve performance, without the need for human-annotated correspondences. Overall, our empirical results demonstrate that our distilled model with 3D data augmentation achieves performance superior to current state-of-the-art methods while significantly reducing computational load and enhancing practicality for real-world applications, such as semantic video correspondence. Our code and weights are publicly available on our project page.
语义对应是确定图像不同部分之间关系的任务,它是各种应用的基础,包括3D重建、图像到图像的翻译、对象跟踪和视觉场所识别。最近的研究开始探索在大型生成图像模型中学习的表示用于语义对应,并显示出有希望的结果。在此基础上,当前最先进的方法依赖于结合多个大型模型,导致计算需求高、效率低。在这项工作中,我们通过提出一种更高效的计算方法来解决这一挑战。我们提出了一种新颖的知识蒸馏技术来解决效率降低的问题。我们展示了如何使用两个大型视觉基础模型,并将这些互补模型的能力提炼到一个较小的模型中,该模型可以在降低计算成本的同时保持高准确性。此外,我们证明,通过结合3D数据,我们能够进一步提高性能,而无需人工注释的对应关系。总的来说,我们的经验结果表明,使用3D数据增强的蒸馏模型实现了优于当前最先进方法的性能,同时显著降低了计算负载,提高了实际应用的实用性,如语义视频对应。我们的代码和权重已在项目页面上公开提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF WACV 2025, Page: https://compvis.github.io/distilldift
Summary
本文提出一种基于知识蒸馏技术的高效语义对应方法,通过结合两个大型视觉基础模型的能力,将其蒸馏到一个较小的模型中,实现高准确性与低计算成本。同时,结合3D数据增强,无需人工标注对应物,性能进一步提升。实验结果表明,该蒸馏模型在性能上优于当前先进方法,显著降低计算负载,增强现实应用中的实用性。
Key Takeaways
- 语义对应是确定图像不同部分之间关系的基础任务,广泛应用于多个领域。
- 当前先进方法依赖多个大型模型组合,导致高计算需求和低效率。
- 提出一种基于知识蒸馏的技术来克服效率降低的问题,将两个大型视觉基础模型的能力蒸馏到一个较小的模型中。
- 结合3D数据增强进一步提高性能,无需人工标注对应物。
- 蒸馏模型在性能上优于当前先进方法,显著降低计算负载。
- 提出的模型具有实用性,可应用于现实世界的语义视频对应等应用。
点此查看论文截图
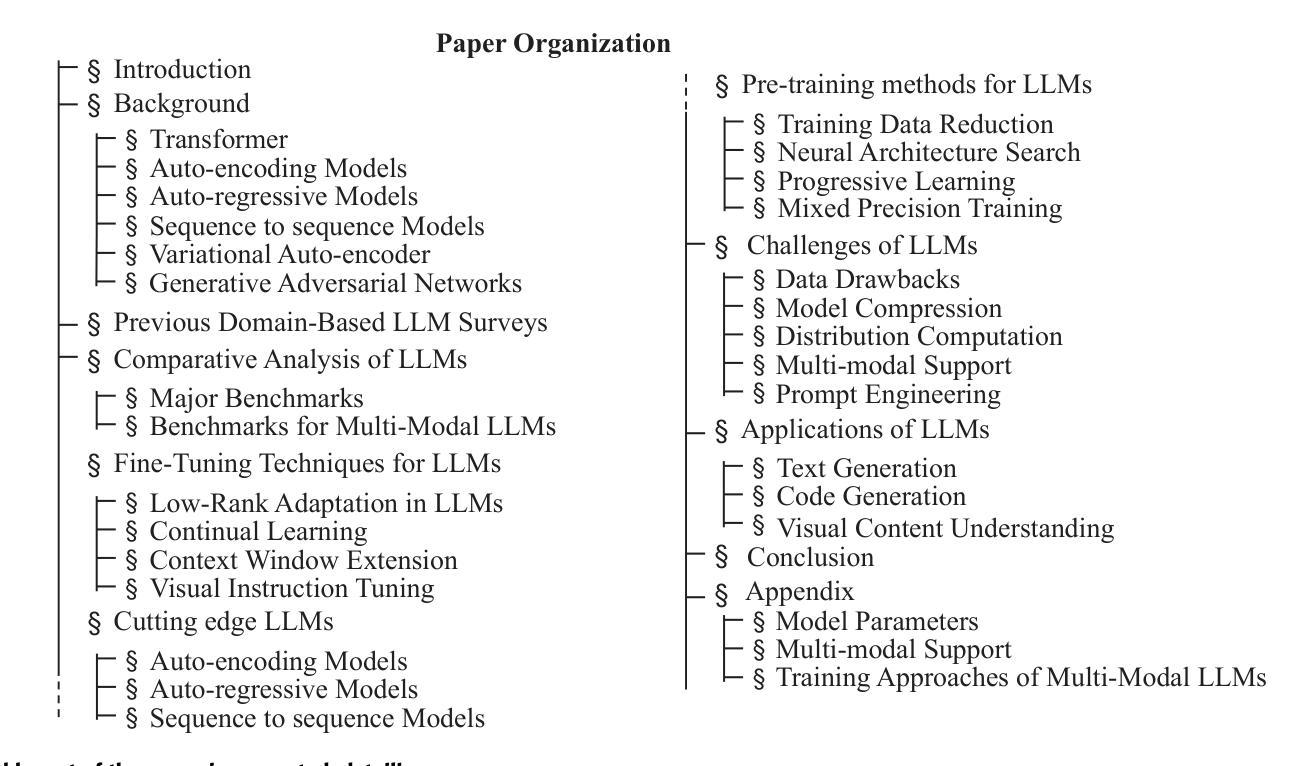
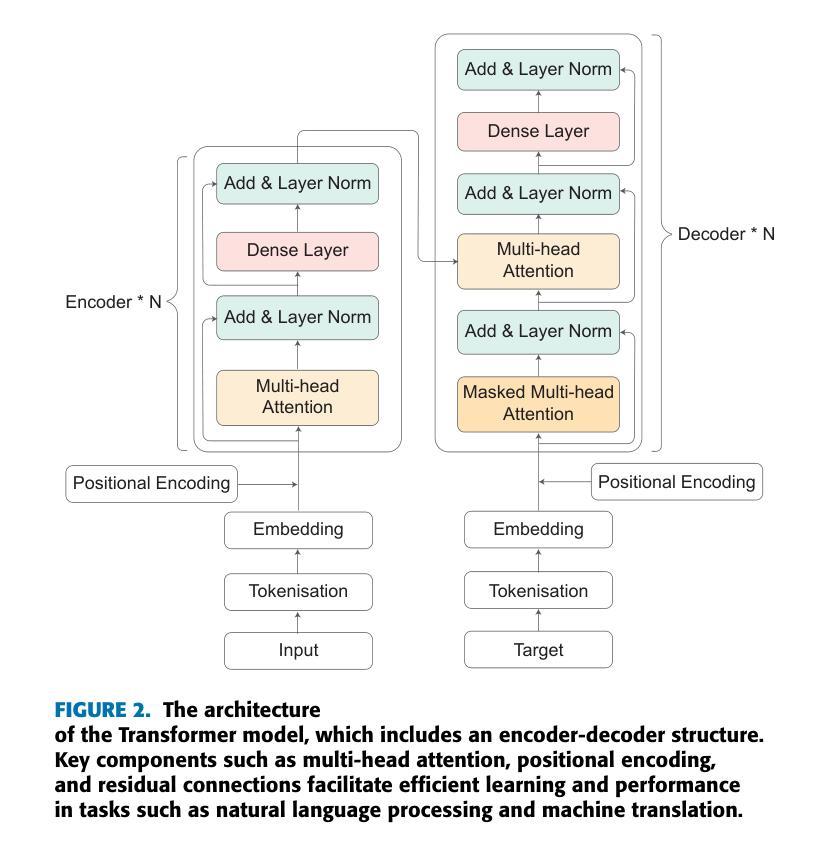
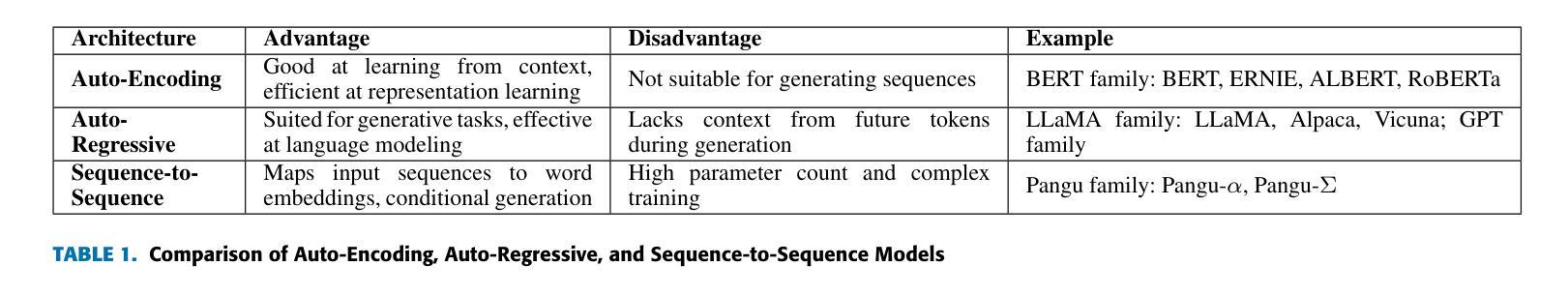
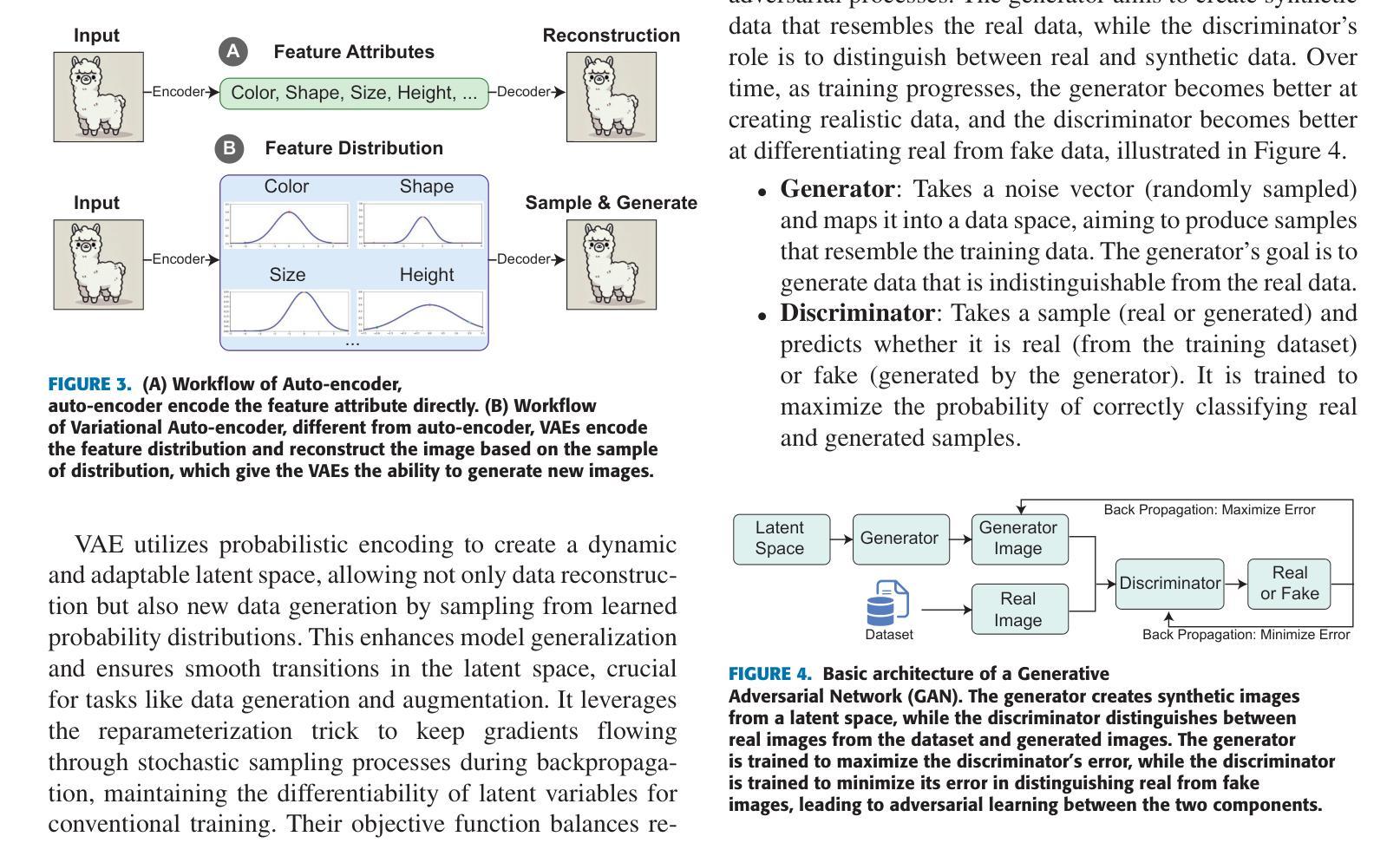
Survey of different Large Language Model Architectures: Trends, Benchmarks, and Challenges
Authors:Minghao Shao, Abdul Basit, Ramesh Karri, Muhammad Shafique
Large Language Models (LLMs) represent a class of deep learning models adept at understanding natural language and generating coherent responses to various prompts or queries. These models far exceed the complexity of conventional neural networks, often encompassing dozens of neural network layers and containing billions to trillions of parameters. They are typically trained on vast datasets, utilizing architectures based on transformer blocks. Present-day LLMs are multi-functional, capable of performing a range of tasks from text generation and language translation to question answering, as well as code generation and analysis. An advanced subset of these models, known as Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), extends LLM capabilities to process and interpret multiple data modalities, including images, audio, and video. This enhancement empowers MLLMs with capabilities like video editing, image comprehension, and captioning for visual content. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of the recent advancements in LLMs. We begin by tracing the evolution of LLMs and subsequently delve into the advent and nuances of MLLMs. We analyze emerging state-of-the-art MLLMs, exploring their technical features, strengths, and limitations. Additionally, we present a comparative analysis of these models and discuss their challenges, potential limitations, and prospects for future development.
大规模语言模型(LLM)代表了一类深度神经网络模型,它们擅长理解自然语言并为各种提示或查询生成连贯的响应。这些模型的复杂性远远超过了传统的神经网络,通常包含数十个神经网络层,参数从数十亿到数万亿不等。它们通常会在庞大的数据集上进行训练,采用基于transformer块的架构。现代的大型语言模型具有多功能性,能够执行一系列任务,如文本生成、语言翻译、问答以及代码生成和分析等。这些模型的一个高级子集被称为多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),它将大型语言模型的能力扩展到处理和解译多种数据模式,包括图像、音频和视频。这种增强功能赋予了多模态大型语言模型视频编辑、图像理解和为视觉内容添加字幕的能力。这篇综述全面概述了大型语言模型的最新进展。首先,我们追溯了大型语言模型的演变,然后深入探讨了多模态大型语言模型的兴起和细微之处。我们分析了新兴的最先进的多模态大型语言模型,探讨了它们的技术特点、优点和局限性。此外,我们还对这些模型进行了比较分析,并讨论了它们所面临的挑战、潜在局限性和未来发展的前景。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)是一类深度神经网络模型,能够理解自然语言并生成连贯的响应。它们通常包含数十层神经网络,参数规模达到数十亿至数十万亿,训练在庞大的数据集上,基于变压器块架构。LLMs具有多种功能,能够执行文本生成、语言翻译、问答以及代码生成和分析等任务。多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)是LLMs的一个高级子集,能够处理并解释多种数据模态,包括图像、音频和视频。它们具有视频编辑、图像理解和为视觉内容添加字幕等功能。本文提供了对LLMs的最新进展的全面概述,追溯了LLMs的演变,深入探讨了MLLMs的出现和特点,分析了最新先进的MLLMs的技术特点、优势和局限。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)是一类深度神经网络模型,能够理解自然语言。
- LLMs包含多层神经网络,参数规模庞大,通常在庞大的数据集上进行训练。
- LLMs具有多种功能,包括文本生成、语言翻译、问答和代码生成等。
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)是LLMs的一个子集,能够处理多种数据模态,如图像、音频和视频。
- MLLMs具有视频编辑、图像理解和为视觉内容添加字幕等高级功能。
- 文中概述了LLMs的最新进展,包括其演变、MLLMs的出现和特点。
点此查看论文截图

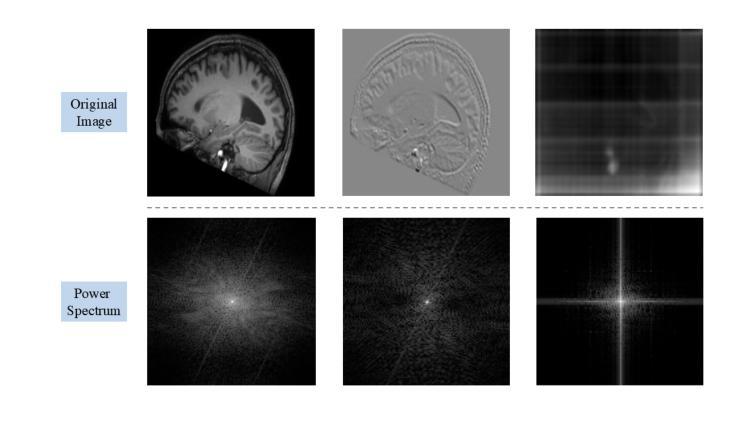
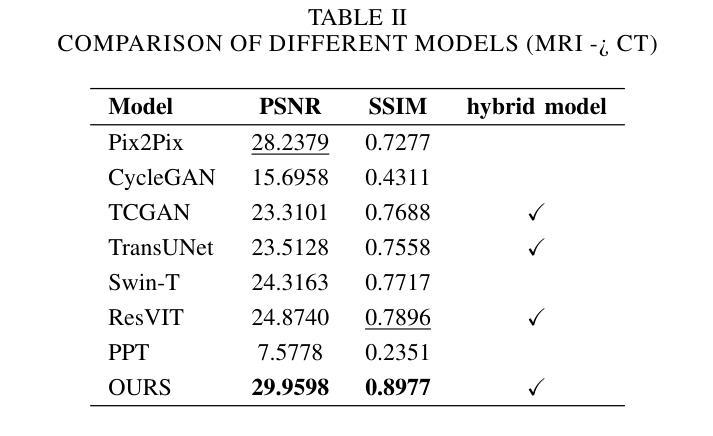
MRNet: Multifaceted Resilient Networks for Medical Image-to-Image Translation
Authors:Hyojeong Lee, Youngwan Jo, Inpyo Hong, Sanghyun Park
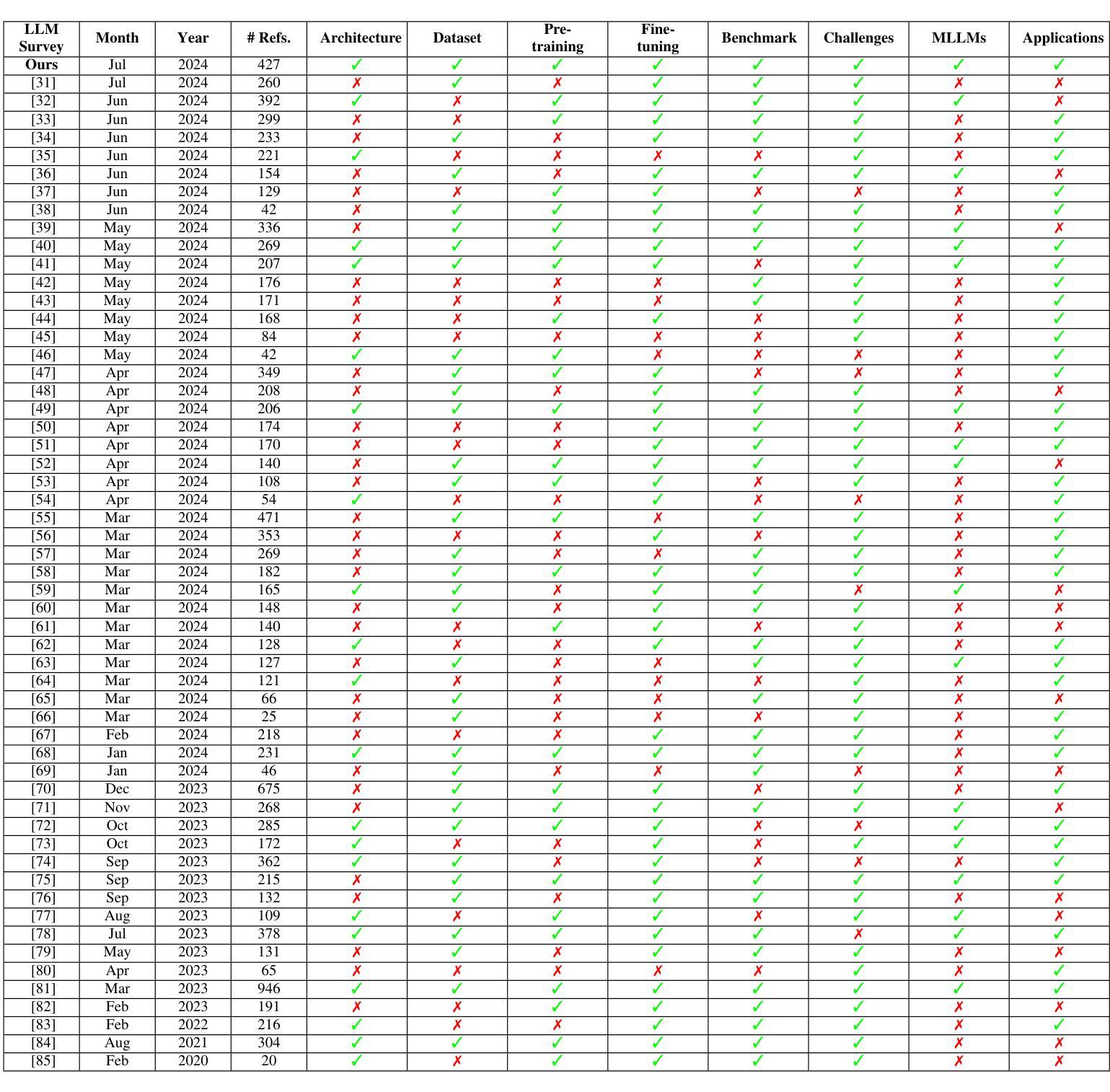
We propose a Multifaceted Resilient Network(MRNet), a novel architecture developed for medical image-to-image translation that outperforms state-of-the-art methods in MRI-to-CT and MRI-to-MRI conversion. MRNet leverages the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to exploit frequency-based features to build a powerful method for advanced medical image transformation. The architecture extracts comprehensive multiscale features from diverse datasets using a powerful SAM image encoder and performs resolution-aware feature fusion that consistently integrates U-Net encoder outputs with SAM-derived features. This fusion optimizes the traditional U-Net skip connection while leveraging transformer-based contextual analysis. The translation is complemented by an innovative dual-mask configuration incorporating dynamic attention patterns and a specialized loss function designed to address regional mapping mismatches, preserving both the gross anatomy and tissue details. Extensive validation studies have shown that MRNet outperforms state-of-the-art architectures, particularly in maintaining anatomical fidelity and minimizing translation artifacts.
我们提出了一种多面弹性网络(MRNet)这一新型架构,专为医学图像到图像的转换设计,其在MRI到CT和MRI到MRI的转换中表现出优于最新方法的效果。MRNet利用分段任何模型(SAM)来开发基于频率的特征,以构建一种先进的医学图像转换方法。该架构使用强大的SAM图像编码器从各种数据集中提取全面的多尺度特征,并执行具有分辨率感知的特征融合,该融合始终将U-Net编码器的输出与SAM派生的特征集成在一起。这种融合优化了传统的U-Net跳过连接,同时利用基于变压器的上下文分析。翻译通过创新的双掩码配置来完成,该配置结合了动态注意力模式,并设计了一种专门的损失函数,以解决区域映射不匹配的问题,同时保留整体解剖结构和组织细节。广泛的研究验证表明,MRNet优于最新的架构,特别是在保持解剖学的保真度和最小化翻译伪影方面。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
MRNet是一种用于医学图像到图像转换的新型架构,具有多面恢复能力。它利用Segment Anything Model(SAM)进行基于频率的特征提取,在MRI到CT和MRI到MRI转换中表现出卓越性能。通过强大的SAM图像编码器和多尺度特征提取,结合U-Net编码器的输出和SAM衍生的特征进行分辨率感知的特征融合。此外,它还采用创新的双掩膜配置和特殊设计的损失函数,以优化区域映射不匹配问题,同时保留大体解剖和组织细节。MRNet在保持解剖保真度和减少翻译伪影方面表现出优于其他先进架构的性能。
Key Takeaways
- MRNet是一种针对医学图像到图像转换的新型架构。
- MRNet利用Segment Anything Model(SAM)进行频率特征提取。
- MRNet在MRI到CT和MRI到MRI转换任务中表现出卓越性能。
- MRNet通过强大的SAM图像编码器进行多尺度特征提取。
- MRNet结合U-Net编码器的输出和SAM的特征进行分辨率感知的特征融合。
- MRNet采用创新的双掩膜配置和特殊设计的损失函数来优化区域映射不匹配问题。
- MRNet在保持解剖结构保真度和减少翻译伪影方面具有优势。
点此查看论文截图
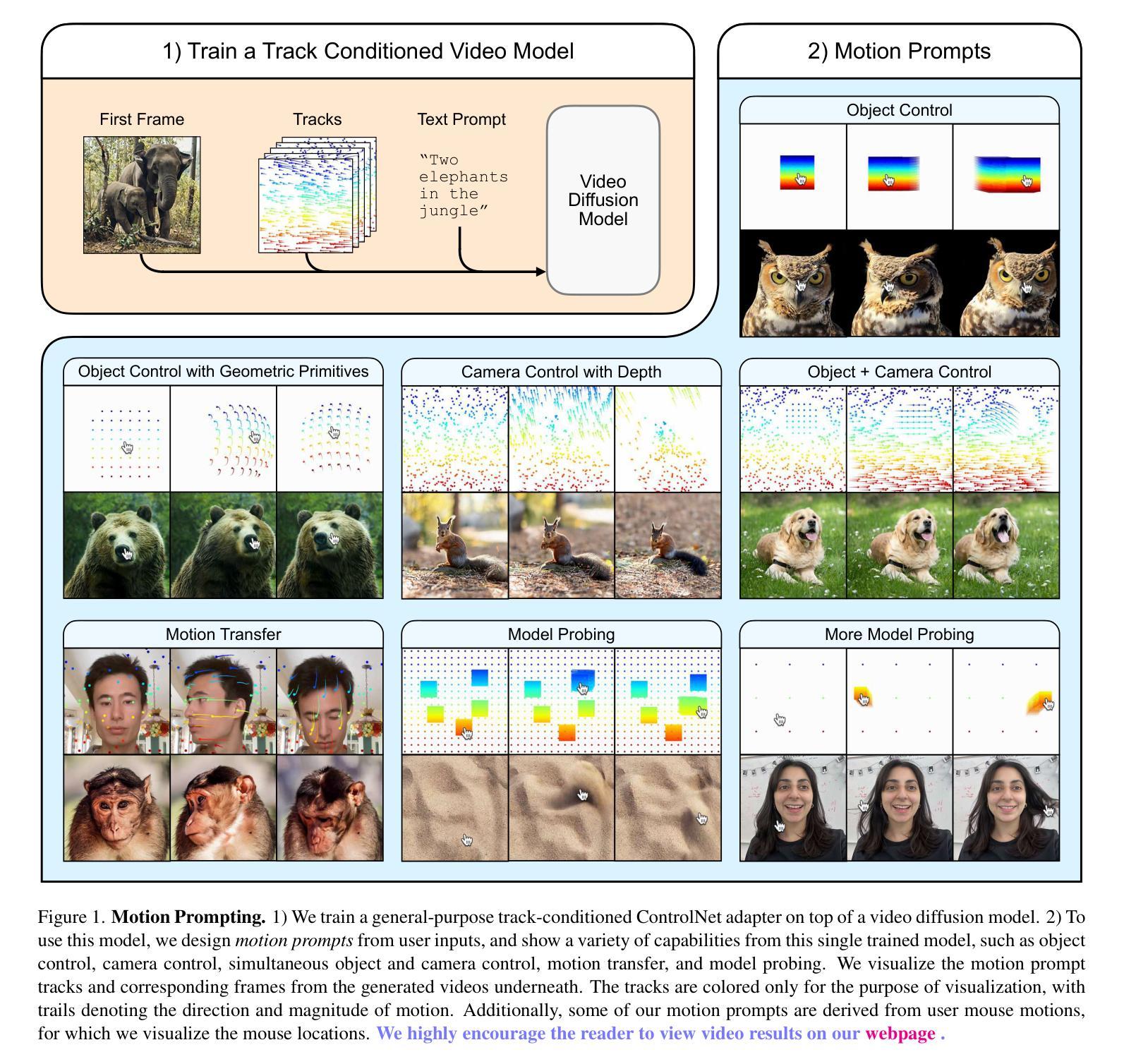
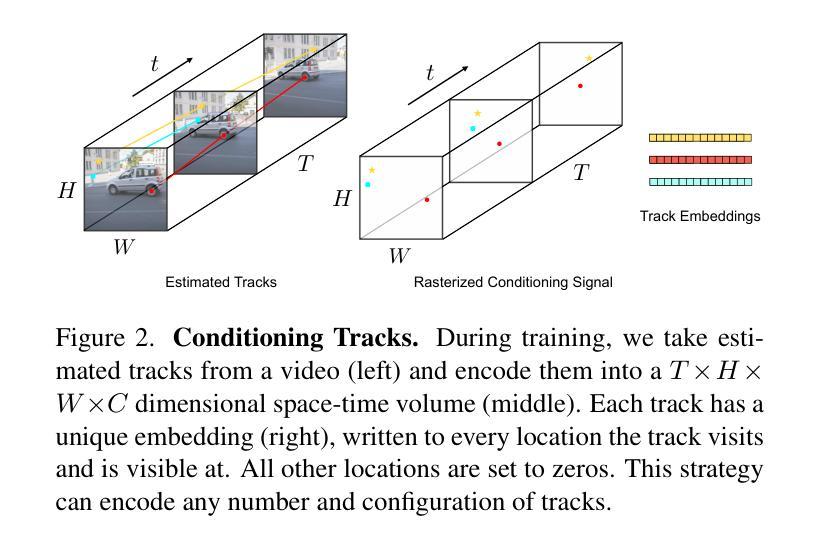
Motion Prompting: Controlling Video Generation with Motion Trajectories
Authors:Daniel Geng, Charles Herrmann, Junhwa Hur, Forrester Cole, Serena Zhang, Tobias Pfaff, Tatiana Lopez-Guevara, Carl Doersch, Yusuf Aytar, Michael Rubinstein, Chen Sun, Oliver Wang, Andrew Owens, Deqing Sun
Motion control is crucial for generating expressive and compelling video content; however, most existing video generation models rely mainly on text prompts for control, which struggle to capture the nuances of dynamic actions and temporal compositions. To this end, we train a video generation model conditioned on spatio-temporally sparse or dense motion trajectories. In contrast to prior motion conditioning work, this flexible representation can encode any number of trajectories, object-specific or global scene motion, and temporally sparse motion; due to its flexibility we refer to this conditioning as motion prompts. While users may directly specify sparse trajectories, we also show how to translate high-level user requests into detailed, semi-dense motion prompts, a process we term motion prompt expansion. We demonstrate the versatility of our approach through various applications, including camera and object motion control, “interacting” with an image, motion transfer, and image editing. Our results showcase emergent behaviors, such as realistic physics, suggesting the potential of motion prompts for probing video models and interacting with future generative world models. Finally, we evaluate quantitatively, conduct a human study, and demonstrate strong performance. Video results are available on our webpage: https://motion-prompting.github.io/
动作控制在生成富有表现力和引人注目的视频内容方面起着至关重要的作用。然而,现有的大多数视频生成模型主要依赖于文本提示进行动作控制,这在捕捉动态行为和时序组合细微差别上有所困难。为此,我们训练了一种基于时空稀疏或密集运动轨迹的视频生成模型。与之前的工作相比,这种灵活的表示可以编码任意数量的轨迹、特定对象的运动或全局场景的运动以及时序稀疏运动;由于其灵活性,我们将这种条件称为动作提示。用户可以直接指定稀疏轨迹,我们还展示了如何将高级用户请求转化为详细、半密集的动作提示,这一过程我们称之为动作提示扩展。我们通过各种应用展示了我们的方法的通用性,包括相机和对象运动控制、“与图像互动”、动作转移和图像编辑等。我们的结果展示了新兴行为,如逼真的物理效果,这表明动作提示在探索视频模型和与未来生成世界模型互动方面的潜力。最后,我们进行了定量评估、人类研究,并展示了出色的性能。视频结果可在我们的网页上查看:[网页链接](https://motion-prompting.github.io/)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://motion-prompting.github.io/
Summary
视频内容生成中,动作控制至关重要。现有模型主要依赖文本提示进行动作控制,难以捕捉动态行为和时序组合的细节。我们训练了一种基于时空稀疏或密集运动轨迹的视频生成模型,其灵活表示可编码任意数量的轨迹、特定对象或全局场景运动以及时序稀疏运动。我们称之为动作提示。用户可直接指定稀疏轨迹,我们也展示了如何将高级用户请求转化为详细的半密集动作提示,称为动作提示扩展。我们的方法在各种应用中表现出灵活性,包括相机和对象运动控制、与图像的“交互”、运动转移和图像编辑等。我们的结果展示了新兴行为,如真实物理,暗示了动作提示在探索视频模型和与未来生成世界模型交互中的潜力。我们的工作通过了定量评估、人类研究,并展示了强大的性能。视频结果请访问我们的网页链接:https://motion-prompting.github.io/。
Key Takeaways
- 动作控制在视频内容生成中起到关键作用,能生成表达性强且吸引人的视频内容。
- 现有视频生成模型主要依赖文本提示,难以捕捉动态行为和时序组合的细微差别。
- 提出了一种基于时空稀疏或密集运动轨迹的视频生成模型,具有灵活表示能力。
- 模型可编码任意数量的轨迹、特定对象或全局场景运动以及时序稀疏运动,称为动作提示。
- 用户可以直接指定稀疏轨迹,也能将高级用户请求转化为详细的半密集动作提示。
- 方法在多种应用中表现出灵活性,如相机和对象运动控制、与图像的交互、运动转移和图像编辑等。
点此查看论文截图



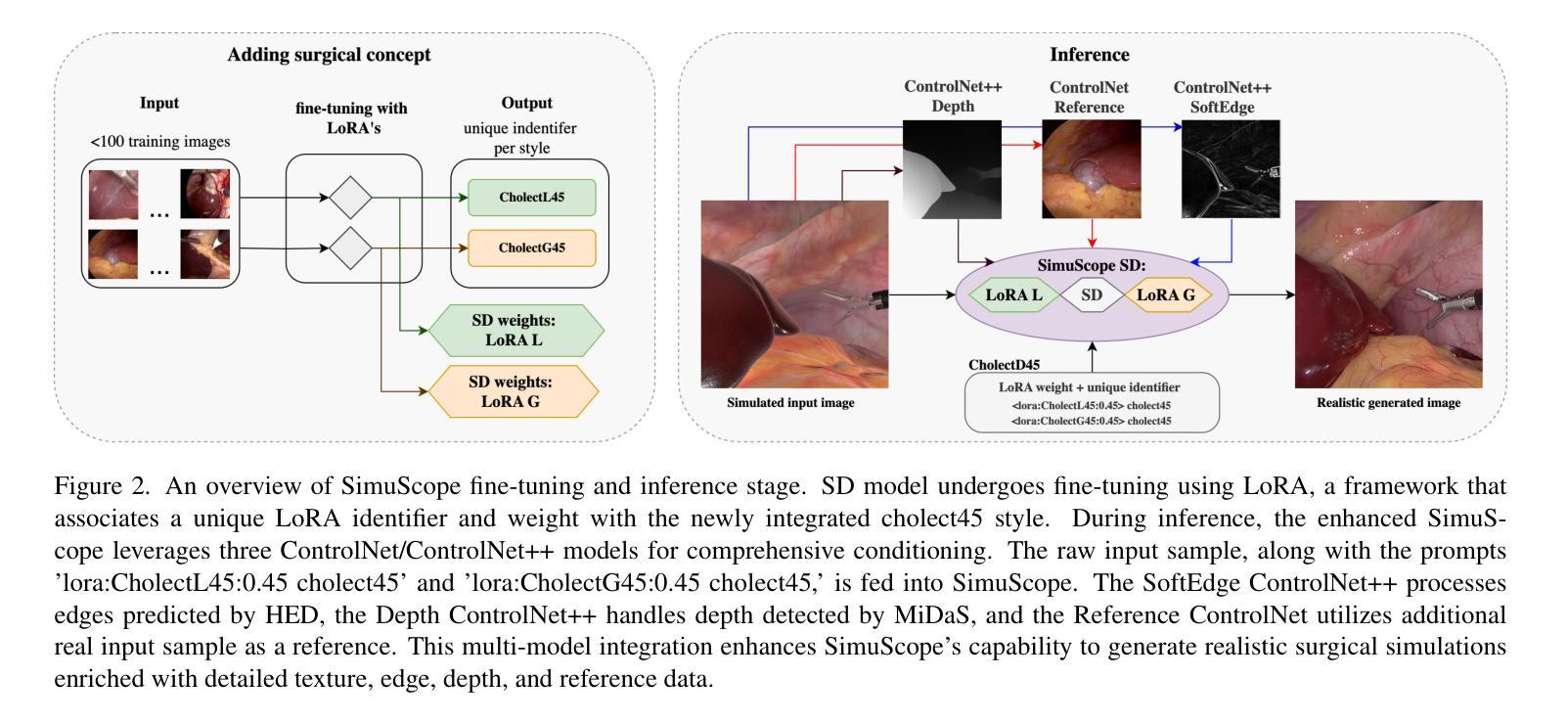
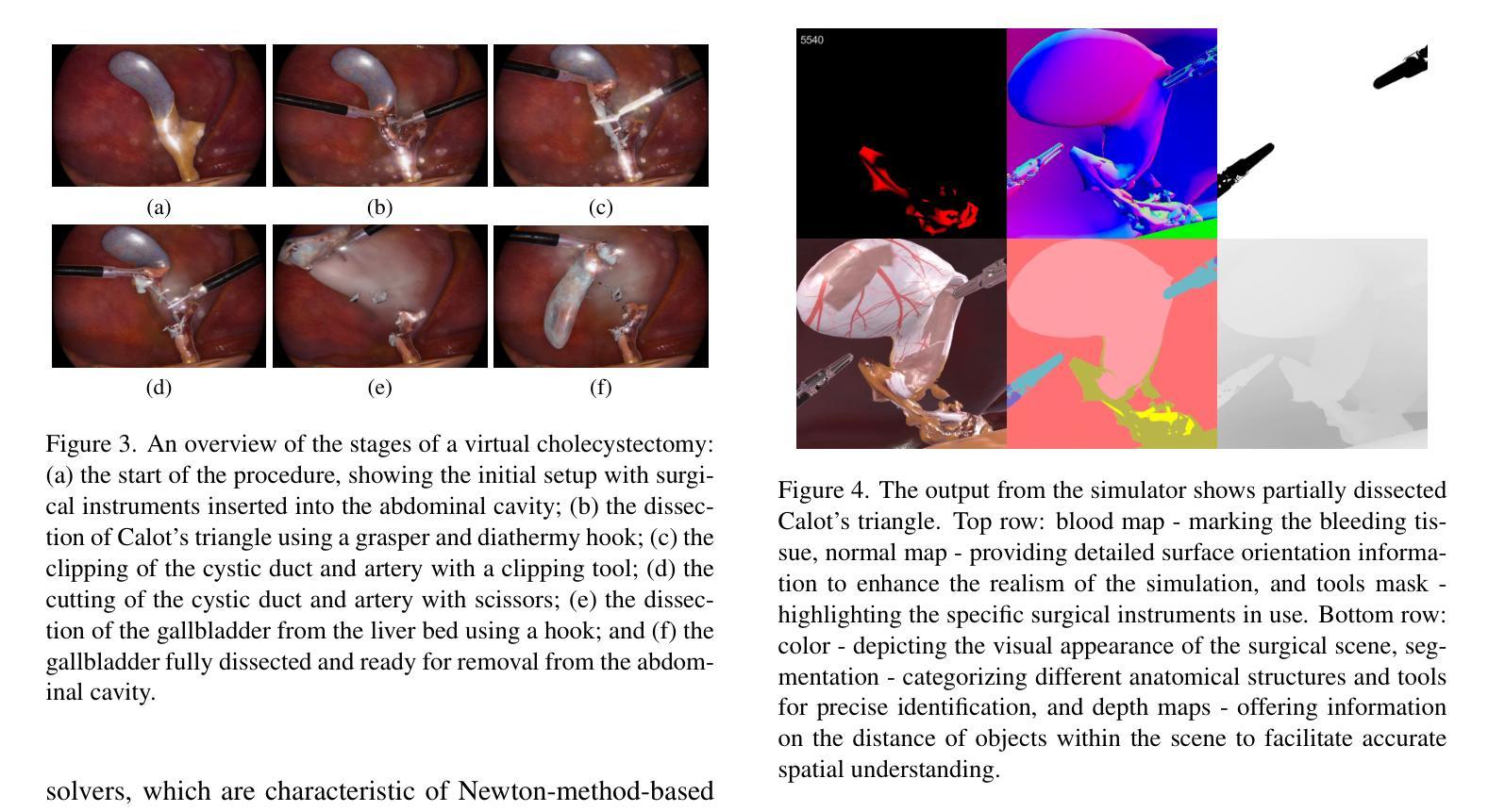
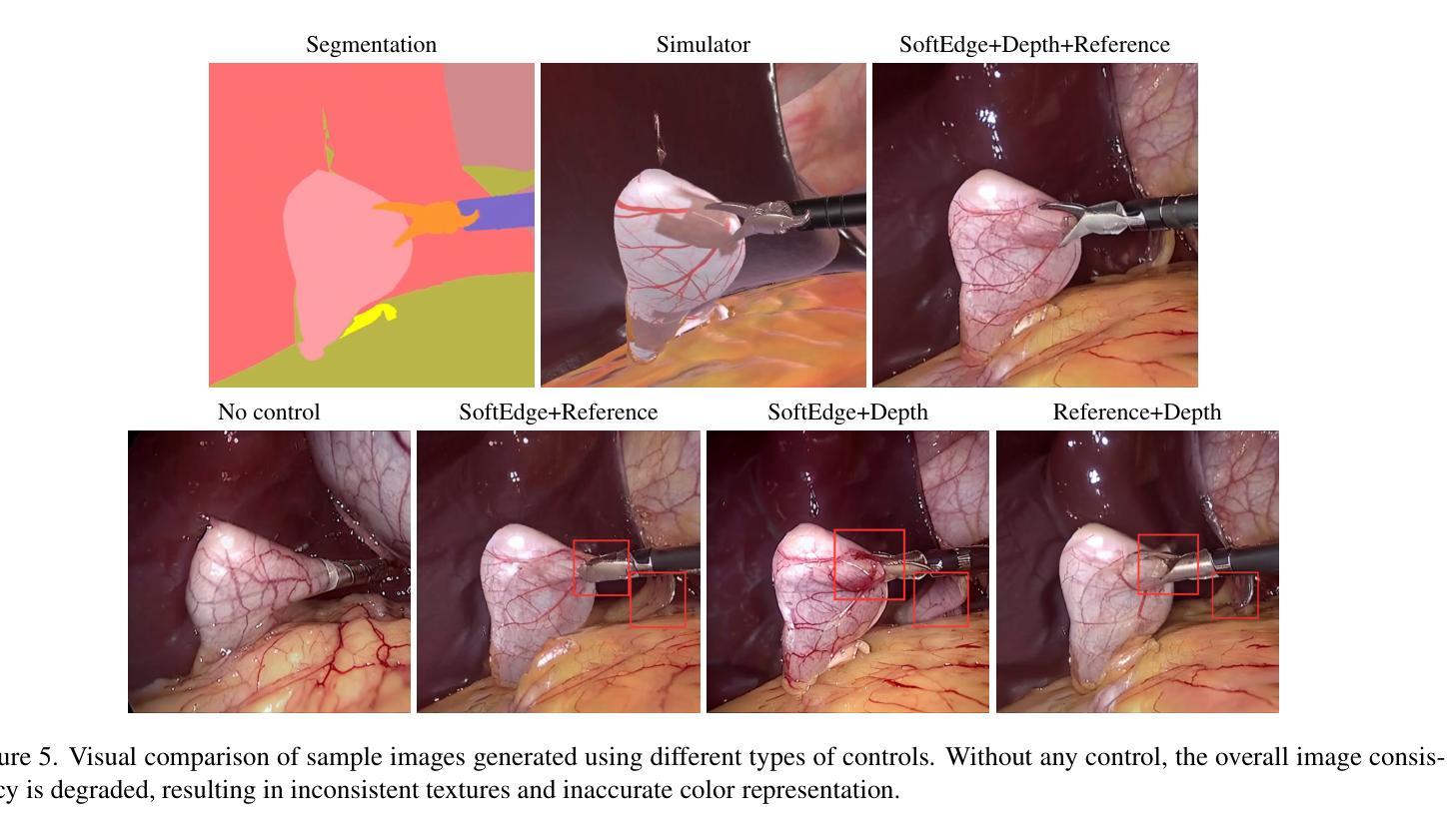
SimuScope: Realistic Endoscopic Synthetic Dataset Generation through Surgical Simulation and Diffusion Models
Authors:Sabina Martyniak, Joanna Kaleta, Diego Dall’Alba, Michał Naskręt, Szymon Płotka, Przemysław Korzeniowski
Computer-assisted surgical (CAS) systems enhance surgical execution and outcomes by providing advanced support to surgeons. These systems often rely on deep learning models trained on complex, challenging-to-annotate data. While synthetic data generation can address these challenges, enhancing the realism of such data is crucial. This work introduces a multi-stage pipeline for generating realistic synthetic data, featuring a fully-fledged surgical simulator that automatically produces all necessary annotations for modern CAS systems. This simulator generates a wide set of annotations that surpass those available in public synthetic datasets. Additionally, it offers a more complex and realistic simulation of surgical interactions, including the dynamics between surgical instruments and deformable anatomical environments, outperforming existing approaches. To further bridge the visual gap between synthetic and real data, we propose a lightweight and flexible image-to-image translation method based on Stable Diffusion (SD) and Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA). This method leverages a limited amount of annotated data, enables efficient training, and maintains the integrity of annotations generated by our simulator. The proposed pipeline is experimentally validated and can translate synthetic images into images with real-world characteristics, which can generalize to real-world context, thereby improving both training and CAS guidance. The code and the dataset are available at https://github.com/SanoScience/SimuScope.
计算机辅助手术(CAS)系统通过为外科医生提供高级支持,增强了手术执行和结果。这些系统通常依赖于在复杂、难以标注的数据上训练的深度学习模型。虽然合成数据生成可以应对这些挑战,但提高这些数据的真实性至关重要。
本研究引入了一个多阶段管道,用于生成逼真的合成数据,并配备了一个完善的手术模拟器,该模拟器可自动为现代CAS系统生成所有必要的注释。该模拟器生成的注释集广泛,超过了公共合成数据集中可用的注释。此外,它提供了更复杂和逼真的手术交互模拟,包括手术器械与可变形解剖环境之间的动态关系,优于现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种多阶段管道,用于生成具有真实感的合成数据。通过成熟的手术模拟器自动为现代计算机辅助手术系统生成所有必要的注释,解决了数据标注难的问题。该模拟器产生的注释集超过公共合成数据集,对手术器械与可变形解剖环境之间的动态关系提供了更复杂、更真实的模拟。为缩小合成数据与真实数据之间的视觉差距,提出了一种基于Stable Diffusion和Low-Rank Adaptation的轻量级、灵活的图像到图像的翻译方法。该方法利用有限的标注数据,实现了高效训练,并保持了模拟器生成的注释的完整性。所提管道经过实验验证,可将合成图像翻译成具有真实世界特征的图像,可推广至真实场景,提高训练和计算机辅助手术的指导效果。
Key Takeaways
- 计算机辅助手术系统通过提供高级支持来提升手术执行和结果。
- 深度学习模型在复杂、难以标注的数据上训练对于CAS系统至关重要。
- 合成数据生成是解决数据标注难的有效方法,但增强数据的真实性至关重要。
- 引入了一个多阶段管道,包括一个全面的手术模拟器,能自动生成所有必要的注释。
- 模拟器产生的注释集超过公共合成数据集,提供更为复杂和真实的手术模拟。
- 提出了一个基于Stable Diffusion和Low-Rank Adaptation的图像到图像的翻译方法,缩小了合成与真实数据间的视觉差距。
- 所提管道经过实验验证,能提高训练和计算机辅助手术的指导效果,相关代码和数据集已公开。
点此查看论文截图

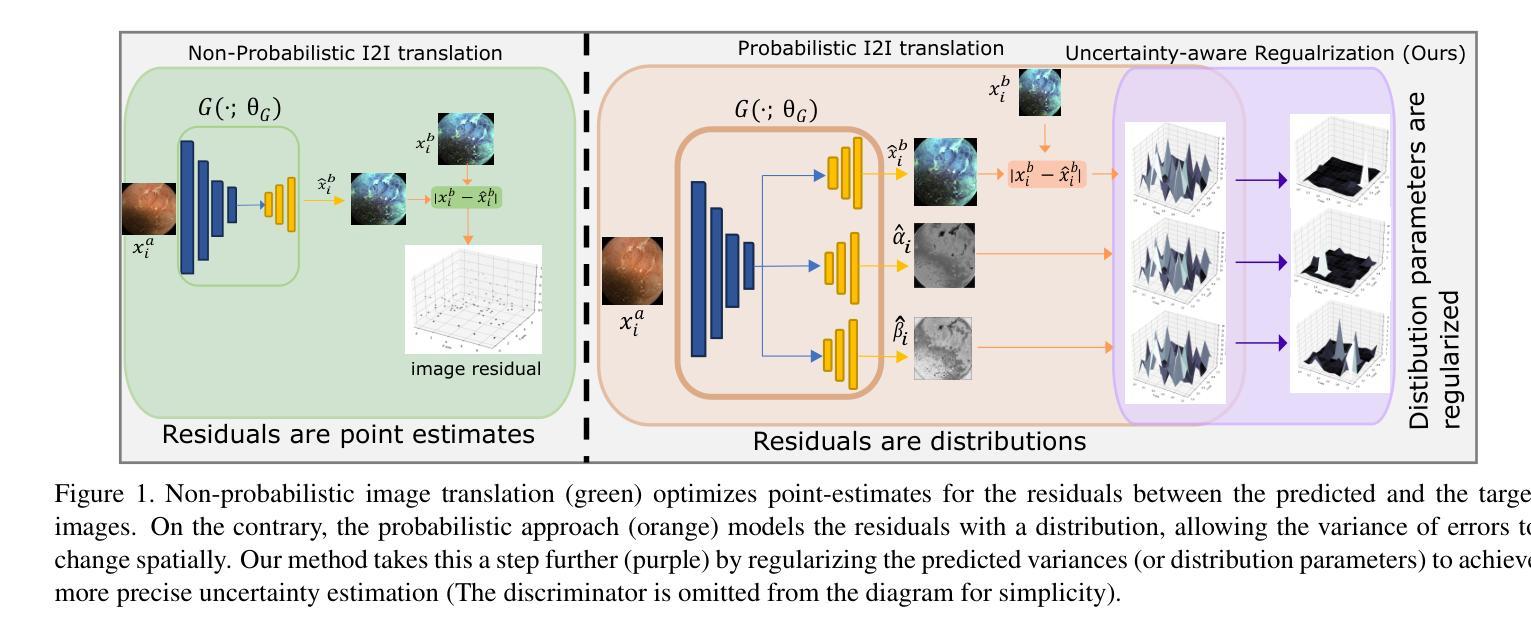
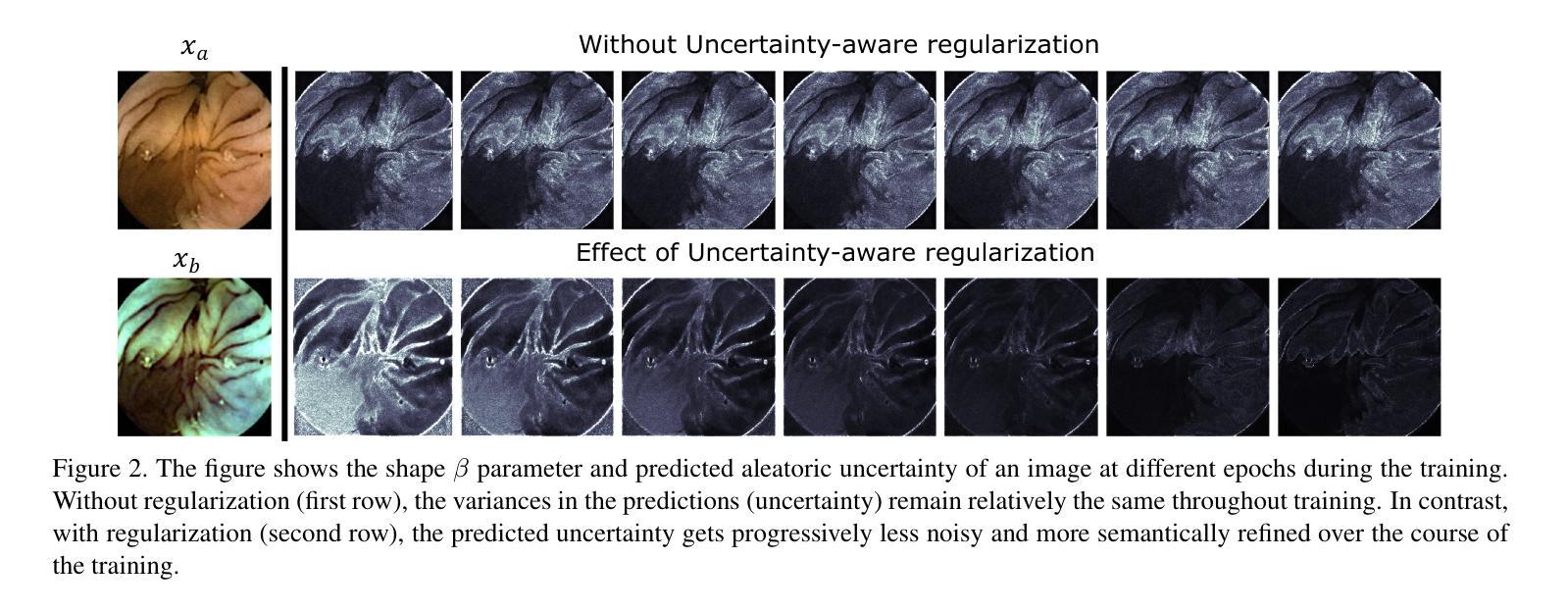
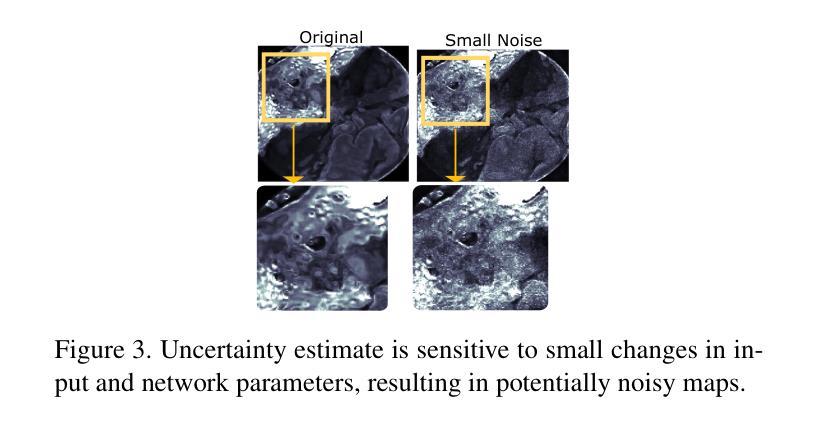
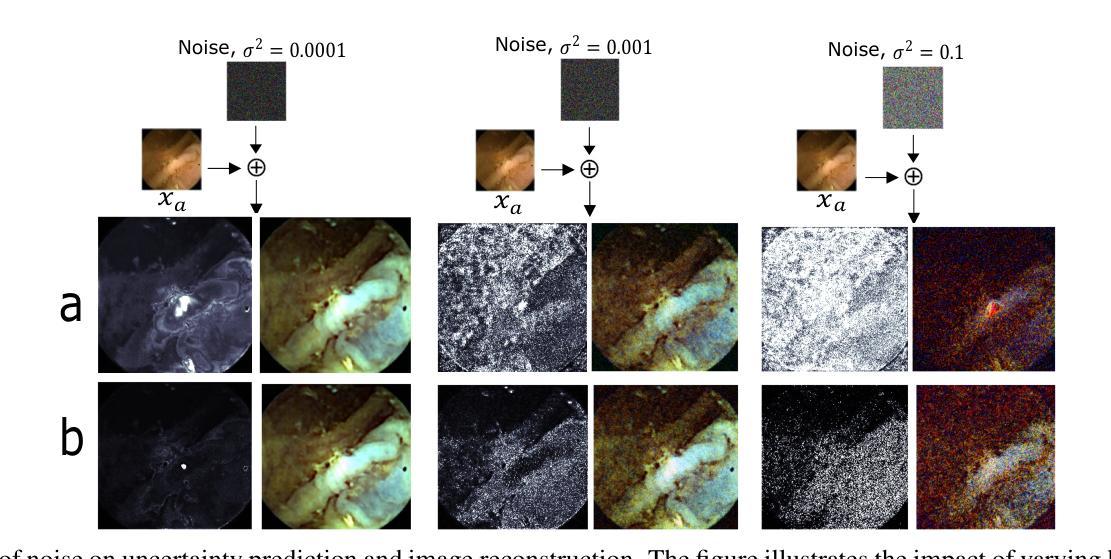
Uncertainty-Aware Regularization for Image-to-Image Translation
Authors:Anuja Vats, Ivar Farup, Marius Pedersen, Kiran Raja
The importance of quantifying uncertainty in deep networks has become paramount for reliable real-world applications. In this paper, we propose a method to improve uncertainty estimation in medical Image-to-Image (I2I) translation. Our model integrates aleatoric uncertainty and employs Uncertainty-Aware Regularization (UAR) inspired by simple priors to refine uncertainty estimates and enhance reconstruction quality. We show that by leveraging simple priors on parameters, our approach captures more robust uncertainty maps, effectively refining them to indicate precisely where the network encounters difficulties, while being less affected by noise. Our experiments demonstrate that UAR not only improves translation performance, but also provides better uncertainty estimations, particularly in the presence of noise and artifacts. We validate our approach using two medical imaging datasets, showcasing its effectiveness in maintaining high confidence in familiar regions while accurately identifying areas of uncertainty in novel/ambiguous scenarios.
在深度网络中将不确定性的量化应用于可靠的现实世界应用已变得至关重要。本文提出了一种改进医学图像对图像(I2I)转换中不确定性估计的方法。我们的模型结合了偶然性不确定性,并采用受简单先验启发的意识不确定性正则化(UAR)来优化不确定性估计并提高重建质量。我们表明,通过利用参数的简单先验,我们的方法捕获了更稳健的不确定性映射,有效地对其进行细化,以精确指示网络遇到困难的区域,同时受到噪声的影响较小。我们的实验表明,UAR不仅提高了翻译性能,而且提供了更好的不确定性估计,特别是在存在噪声和伪影的情况下。我们使用两个医学影像数据集验证了我们的方法,展示了其在熟悉区域保持高置信度以及在新型/模糊场景中准确识别不确定区域的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted WACV 2025
Summary
论文提出一种改进深度网络中不确定性估计的方法,特别是在医学图像到图像的转换中。通过整合偶然不确定性并采用受简单先验启发的不确定性感知正则化(UAR),该模型能更稳健地捕捉不确定性映射,提高重建质量,并有效指示网络遇到困难的区域。实验证明,UAR不仅提高了翻译性能,而且提供了更好的不确定性估计,特别是在存在噪声和伪影的情况下。
Key Takeaways
- 量化不确定性在深网中的可靠性对于真实世界应用至关重要。
- 论文提出一种改进不确定性估计的方法,应用于医学图像到图像的转换。
- 模型整合了偶然不确定性和受简单先验启发的不确定性感知正则化(UAR)。
- UAR能更稳健地捕捉不确定性映射,提高重建质量。
- UAR能指示网络遇到困难的区域。
- 实验证明,UAR提高了翻译性能,并提供了更好的不确定性估计。
点此查看论文截图

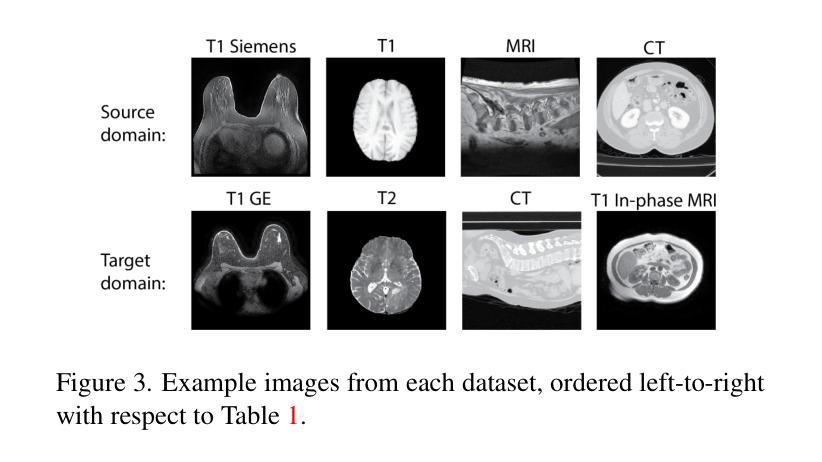
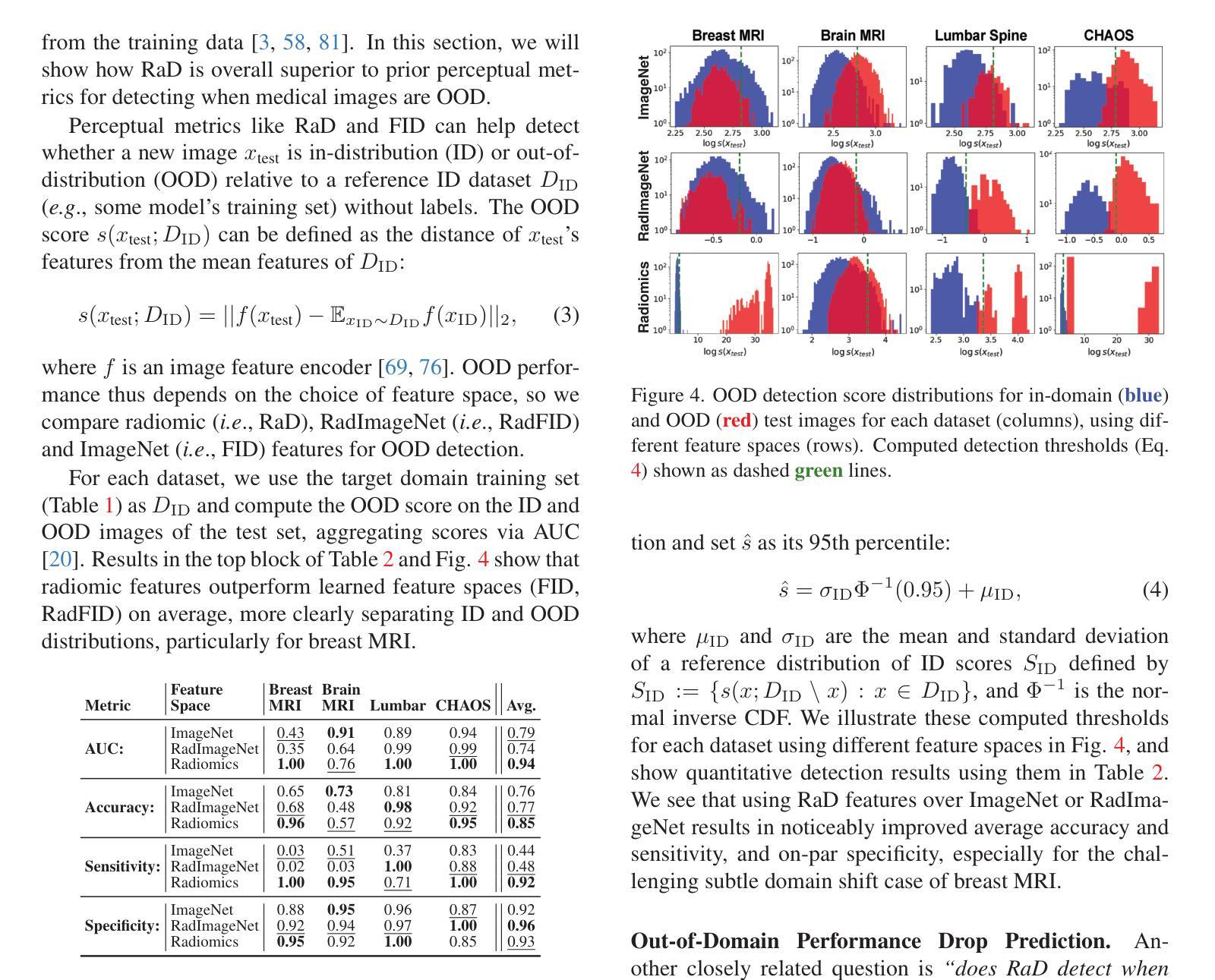
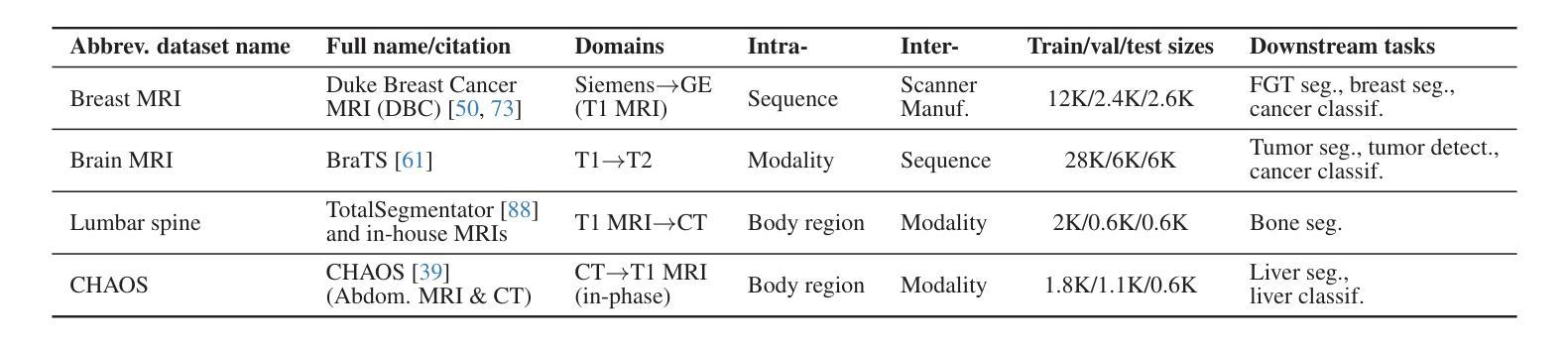
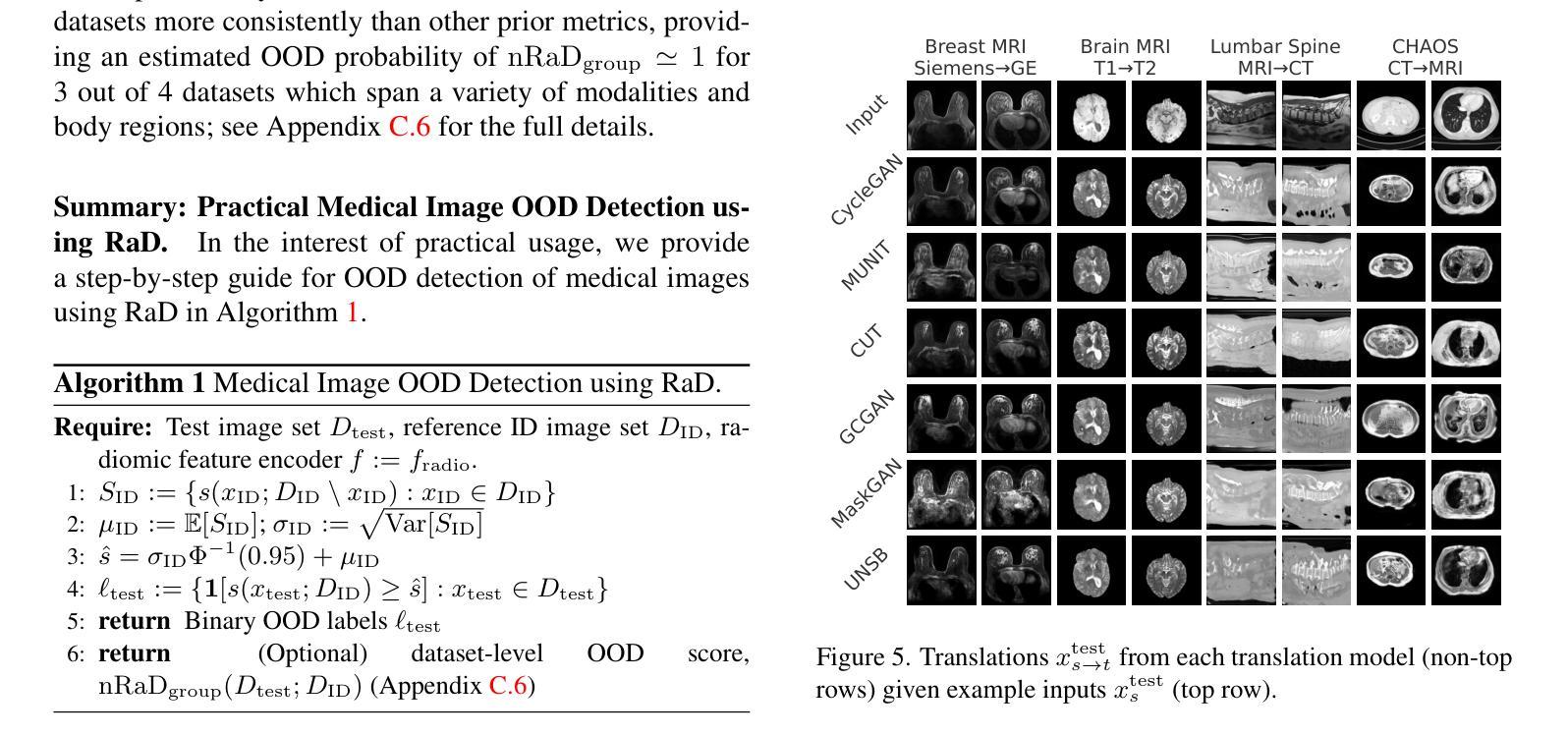
RaD: A Metric for Medical Image Distribution Comparison in Out-of-Domain Detection and Other Applications
Authors:Nicholas Konz, Yuwen Chen, Hanxue Gu, Haoyu Dong, Yaqian Chen, Maciej A. Mazurowski
Determining whether two sets of images belong to the same or different domain is a crucial task in modern medical image analysis and deep learning, where domain shift is a common problem that commonly results in decreased model performance. This determination is also important to evaluate the output quality of generative models, e.g., image-to-image translation models used to mitigate domain shift. Current metrics for this either rely on the (potentially biased) choice of some downstream task such as segmentation, or adopt task-independent perceptual metrics (e.g., FID) from natural imaging which insufficiently capture anatomical consistency and realism in medical images. We introduce a new perceptual metric tailored for medical images: Radiomic Feature Distance (RaD), which utilizes standardized, clinically meaningful and interpretable image features. We show that RaD is superior to other metrics for out-of-domain (OOD) detection in a variety of experiments. Furthermore, RaD outperforms previous perceptual metrics (FID, KID, etc.) for image-to-image translation by correlating more strongly with downstream task performance as well as anatomical consistency and realism, and shows similar utility for evaluating unconditional image generation. RaD also offers additional benefits such as interpretability, as well as stability and computational efficiency at low sample sizes. Our results are supported by broad experiments spanning four multi-domain medical image datasets, nine downstream tasks, six image translation models, and other factors, highlighting the broad potential of RaD for medical image analysis.
确定两组图像是否属于同一领域或不同领域,在现代医学图像分析和深度学习中是至关重要的任务。领域偏移是一个常见的问题,通常会导致模型性能下降。这一判断对于评估生成模型的输出质量也很重要,例如用于减轻领域偏移的图像到图像的翻译模型。目前的指标要么依赖于某些下游任务(如分割)的选择(这种选择可能存在偏见),要么采用自然成像中的任务独立感知指标(如FID),而这些指标不足以捕捉医学图像中的解剖一致性和真实性。我们针对医学图像引入了一种新的感知指标:放射学特征距离(RaD),它利用标准化、临床意义重大且可解释的图像特征。我们显示,在各种实验中,RaD在其他指标中表现出色,更擅长检测非领域(OOD)。此外,RaD在下游任务性能以及解剖一致性和真实性方面与之前的感知指标(如FID、KID等)相比表现出更强的相关性,并且在评估无条件图像生成时显示出类似的实用性。RaD还提供了可解释性、稳定性以及小样本计算效率等额外优势。我们的结果得到了广泛实验的支持,这些实验涉及四个多领域医学图像数据集、九个下游任务、六个图像翻译模型以及其他因素,突出了RaD在医学图像分析中的广阔潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对医学图像的新型感知度量方法——放射学特征距离(RaD),用于判断图像是否属于同一领域。该方法利用标准化、具有临床意义且可解释的图像特征,在多种实验中表现出优于其他度量的性能,尤其在检测域外数据和应用图像转换任务中表现突出。RaD具有可解释性、稳定性和计算效率等优点。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分析中,判断图像是否属于同一领域是重要任务,关系到模型性能及生成模型输出质量评估。
- 当前度量方法存在缺陷,依赖于下游任务选择或采用自然成像的感知度量,不足以捕捉医学图像的解剖一致性和真实性。
- 引入新型感知度量方法——放射学特征距离(RaD),适用于医学图像。
- RaD利用标准化、具有临床意义且可解释的图像特征,在域外检测实验中表现优越。
- RaD在其他感知度量上表现更优,与下游任务性能、解剖一致性和真实性有更强相关性,适用于图像转换任务。
- RaD在无条件图像生成评估中同样具有应用价值。
- RaD具有可解释性、稳定性和计算效率等额外优点。
点此查看论文截图

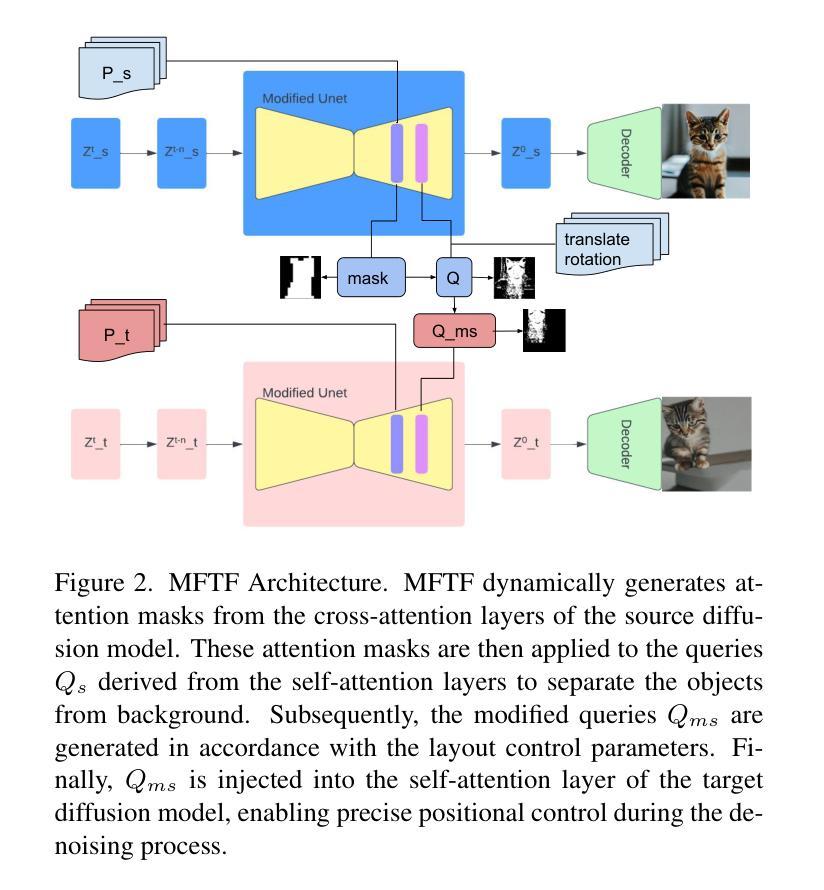
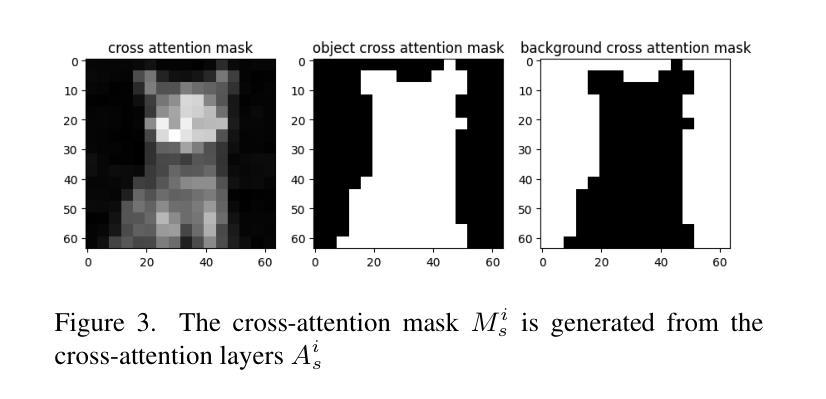
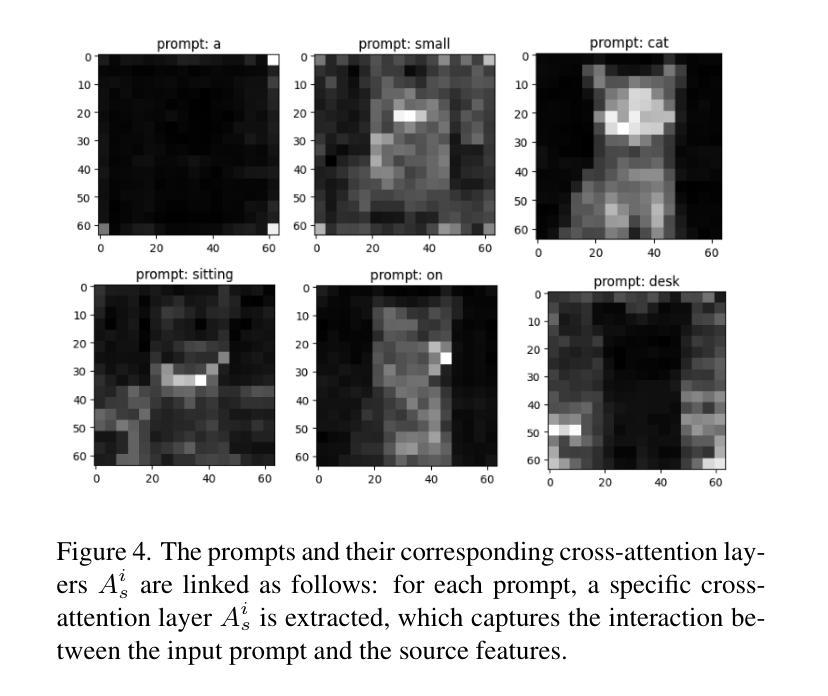
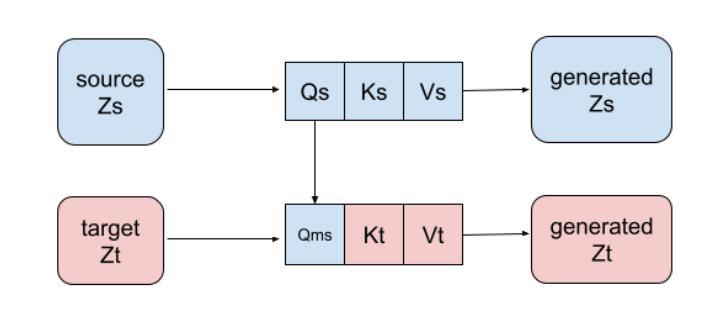
MFTF: Mask-free Training-free Object Level Layout Control Diffusion Model
Authors:Shan Yang
Text-to-image generation models have become transformative tools. However, diffusion-based vision language models still lack the ability to precisely control the shape, appearance, and positional placement of objects in generated images using text guidance alone. Global image editing models typically achieve global layout control by relying on additional masks or images as guidance, which often require model training. Although local object-editing models enable modification of object shapes, they do not provide control over the positional placement of these objects. To address these limitations, we propose the MFTF model, which enables precise control over object positioning without requiring additional masks or images. The MFTF model supports both single-object and multi-object positional control (such as translation, rotation, etc.) and allows for concurrent layout control and object semantic editing. This is achieved by controlling the denoising process of the diffusion model through parallel denoising. Attention masks are dynamically generated from the cross-attention layers of the source diffusion model and applied to queries from the self-attention layers to isolate objects. These queries are then modified according to layout control parameters and injected back into the self-attention layers of the target diffusion model to enable precise positional control.
文本转图像生成模型已成为变革性工具。然而,基于扩散的视语言模型仍然缺乏仅通过文本指导精确控制生成图像中物体的形状、外观和位置放置的能力。全局图像编辑模型通常通过依赖额外的蒙版或图像作为指导来实现全局布局控制,这通常需要模型训练。虽然局部对象编辑模型能够实现对象形状的修改,但它并不提供对象位置放置的控制。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了MFTF模型,该模型能够在不需要额外蒙版或图像的情况下,实现对物体位置的精确控制。MFTF模型支持单物体和多物体的位置控制(如平移、旋转等),并允许同时进行布局控制和物体语义编辑。这是通过控制扩散模型的去噪过程实现的,具体通过并行去噪来实现。注意力蒙版是根据源扩散模型的交叉注意力层动态生成的,并应用于来自自注意力层的查询以隔离物体。然后,这些查询根据布局控制参数进行修改,并注入到目标扩散模型的自注意力层,以实现精确的位置控制。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 12 figures
Summary
文本到图像生成模型成为变革性工具,但基于扩散的视觉语言模型在仅使用文本指导时,缺乏精确控制生成图像中物体的形状、外观和位置放置的能力。为解决这一问题,提出MFTF模型,该模型无需额外的蒙版或图像,就能实现对物体位置的精确控制,并支持单物体和多物体的位置控制(如平移、旋转等),并允许同时进行布局控制和物体语义编辑。这是通过控制扩散模型的去噪过程实现的并行去噪。动态生成注意力蒙版并应用于查询,根据布局控制参数修改查询,然后注入目标扩散模型的自注意力层以实现精确的位置控制。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像生成模型已成为重要的工具,但扩散模型在使用文本指导时存在对物体形状、外观和位置控制的局限。
- MFTF模型解决了这个问题,允许对物体的位置进行精确控制,无需额外的蒙版或图像。
- MFTF模型支持单物体和多物体的位置控制,如平移和旋转。
- MFTF模型可以同时进行布局控制和物体语义编辑。
- MFTF模型通过控制扩散模型的去噪过程实现精确位置控制,采用并行去噪技术。
- 注意力蒙版从源扩散模型的交叉注意力层动态生成,并应用于自我注意力层的查询到以实现位置控制。
点此查看论文截图


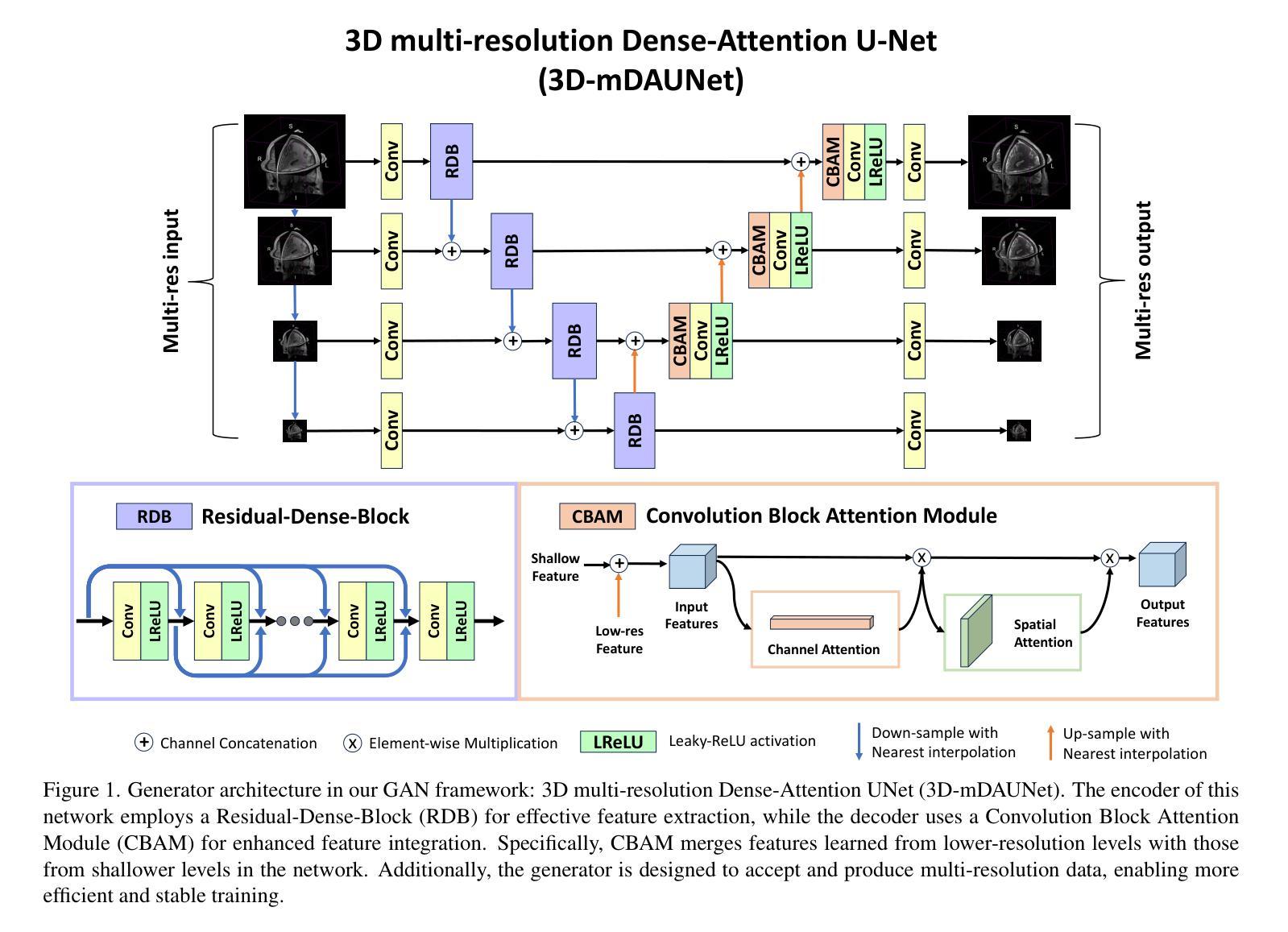
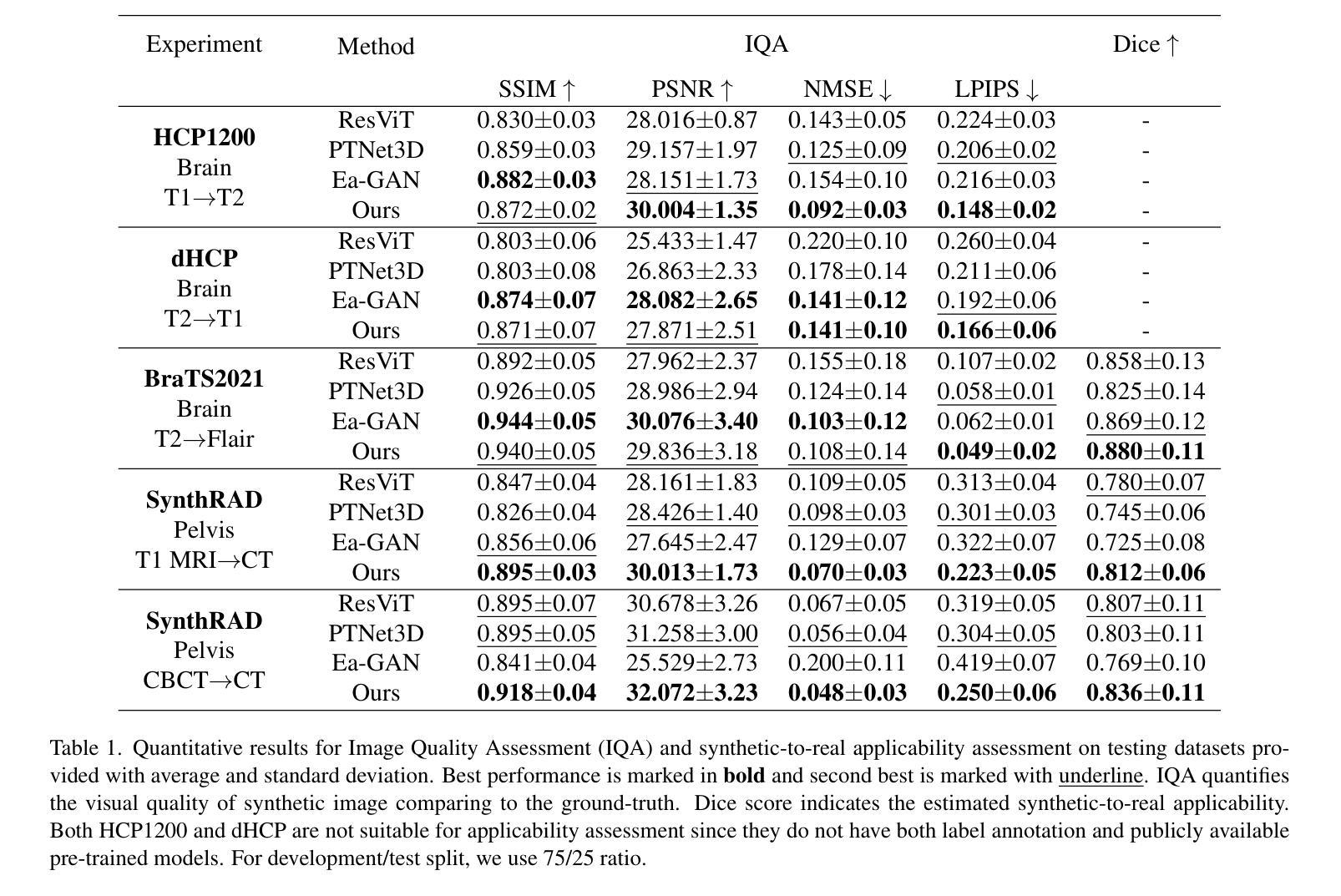
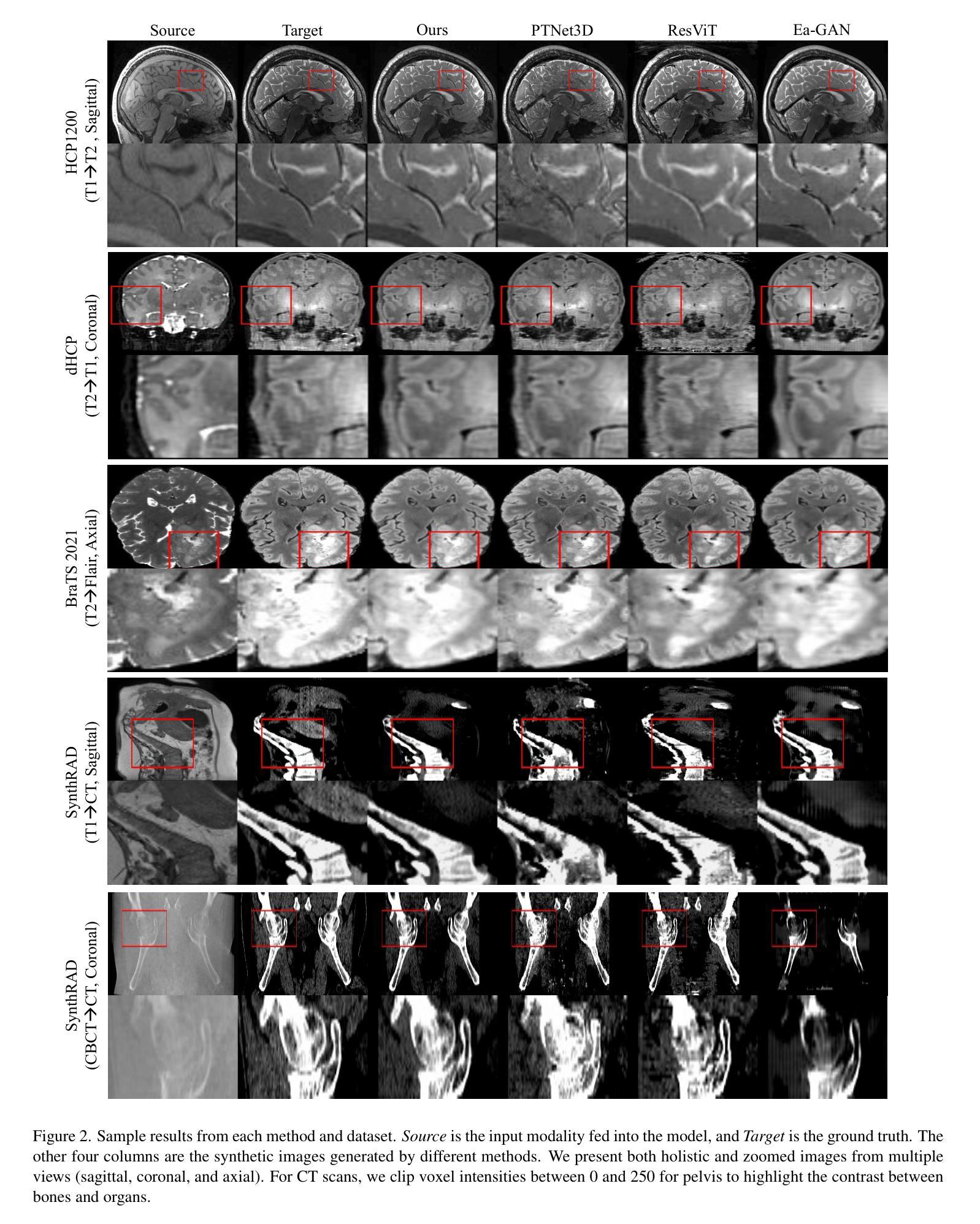
Multi-resolution Guided 3D GANs for Medical Image Translation
Authors:Juhyung Ha, Jong Sung Park, David Crandall, Eleftherios Garyfallidis, Xuhong Zhang
Medical image translation is the process of converting from one imaging modality to another, in order to reduce the need for multiple image acquisitions from the same patient. This can enhance the efficiency of treatment by reducing the time, equipment, and labor needed. In this paper, we introduce a multi-resolution guided Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)-based framework for 3D medical image translation. Our framework uses a 3D multi-resolution Dense-Attention UNet (3D-mDAUNet) as the generator and a 3D multi-resolution UNet as the discriminator, optimized with a unique combination of loss functions including voxel-wise GAN loss and 2.5D perception loss. Our approach yields promising results in volumetric image quality assessment (IQA) across a variety of imaging modalities, body regions, and age groups, demonstrating its robustness. Furthermore, we propose a synthetic-to-real applicability assessment as an additional evaluation to assess the effectiveness of synthetic data in downstream applications such as segmentation. This comprehensive evaluation shows that our method produces synthetic medical images not only of high-quality but also potentially useful in clinical applications. Our code is available at github.com/juhha/3D-mADUNet.
医学影像转换是将一种成像模式转换为另一种成像模式的过程,以减少对同一患者多次采集图像的需求。这可以通过减少所需的时间、设备和劳动力来提高治疗效率。在本文中,我们介绍了一种基于多分辨率引导生成对抗网络(GAN)的3D医学影像转换框架。我们的框架使用3D多分辨率密集注意力UNet(3D-mDAUNet)作为生成器,使用3D多分辨率UNet作为判别器,并通过包括像素级GAN损失和2.5D感知损失的独特组合损失函数进行优化。我们的方法在跨多种成像模式、身体部位和年龄组的体积图像质量评估(IQA)中取得了有前景的结果,证明了其稳健性。此外,我们提出了一种合成到现实的适用性评估作为额外的评估,以评估合成数据在分割等下游应用中的有效性。全面的评估表明,我们的方法生成的合成医学影像不仅质量高,而且在临床应用中也具有潜在用处。我们的代码可访问于:链接。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于多分辨率引导生成对抗网络(GAN)的3D医学图像转换框架,使用3D多分辨率Dense-Attention UNet作为生成器,3D多分辨率UNet作为判别器,通过结合多种损失函数进行优化,包括体素级的GAN损失和2.5D感知损失。该框架在多种成像模态、身体区域和年龄组的体积图像质量评估中表现出良好的结果,证明了其稳健性。此外,还提出了从合成到实际应用的适用性评估,以评估合成数据在分割等下游应用中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像翻译是通过一种成像方式转换为另一种成像方式的过程,以减少对同一病人进行多次图像采集的需要,提高治疗效率。
- 论文引入了一种基于多分辨率引导生成对抗网络(GAN)的3D医学图像转换框架。
- 该框架使用3D多分辨率Dense-Attention UNet作为生成器,以及一个优化的3D多分辨率UNet作为判别器。
- 框架结合了多种损失函数,包括体素级的GAN损失和2.5D感知损失。
- 该方法在多种成像模态、身体区域和年龄组的体积图像质量评估中表现出良好的结果,证明了其稳健性。
- 除了图像质量评估,还进行了合成到实际应用的适用性评估,以评估合成数据在下游应用中的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

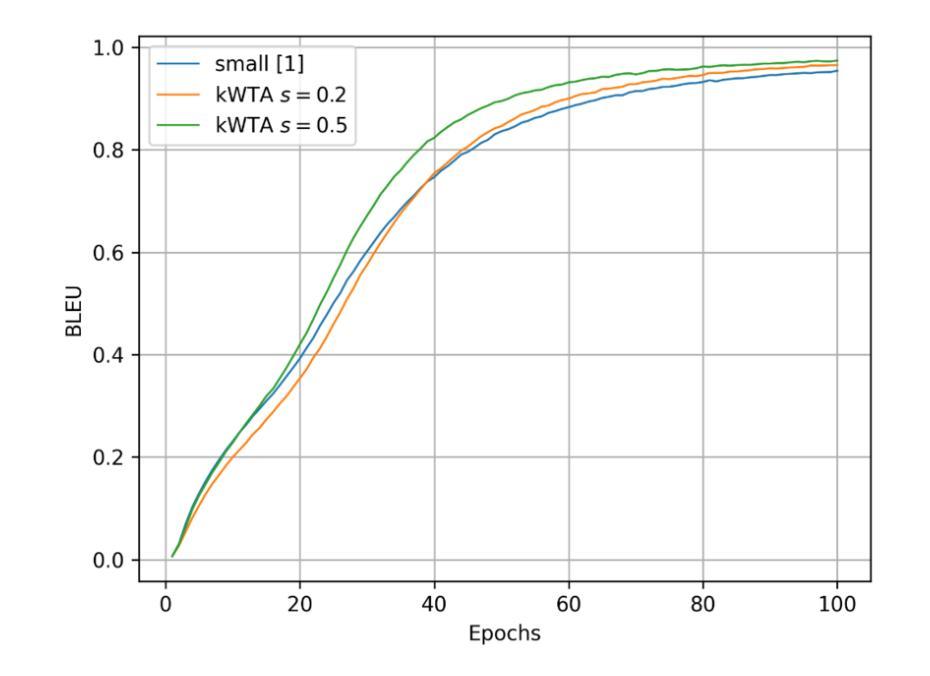
Homeostasis and Sparsity in Transformer
Authors:Leonid Kotyuzanskiy, Artem Klimov
The transformer architecture has become an integral part of the field of modern neural networks, playing a crucial role in a variety of tasks, such as text generation, machine translation, image and audio processing, among others. There is also an alternative approach to building intelligent systems, proposed by Jeff Hawkins and inspired by the processes occurring in the neocortex. In our article we want to combine some of these ideas and to propose the use of homeostasis mechanisms, such as RFB-kWTA and “Smart” Inhibition, in the attention mechanism of the transformer and at the output of the transformer block, as well as conducting an experiment involving the introduction of sparse distributed representations of the transformer at various points. RFB-kWTA utilizes statistics of layer activations across time to adjust the entire layer, enhancing the values of rare activations while reducing those of frequent ones. “Smart” Inhibition also uses activation statistics to sample sparsity masks, with rarer activation times are more likely to be activated. Our proposed mechanisms significantly outperform the classical transformer 0.2768 BLEU and a model that only makes use of dropout in the attention mechanism and output of the transformer block 0.3007 BLEU, achieving a score of 0.3062 on the Multi30K dataset.
Transformer架构已成为现代神经网络领域不可或缺的一部分,在文本生成、机器翻译、图像和音频处理等各种任务中发挥着关键作用。Jeff Hawkins提出了一种建立智能系统的替代方法,该方法受到大脑新皮层中发生过程的启发。在本文中,我们想结合这些思想,并提出在Transformer的注意机制和Transformer块输出中使用稳态机制,如RFB-kWTA和“智能”抑制,并进行一项实验,在Transformer的各个点引入稀疏分布式表示。RFB-kWTA利用跨时间的层激活统计信息来调整整个层,增强稀有激活的值,同时减少频繁出现的激活。“智能”抑制还使用激活统计信息来采样稀疏掩码,较少激活的时间更有可能被激活。我们提出的机制在Multi30K数据集上的表现显著优于经典Transformer(BLEU得分为0.2768)和仅使用dropout的模型(在Transformer的注意机制和输出块中的BLEU得分为0.3007),取得了0.3062的得分。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了结合智能系统构建新思路的变革者架构方法,利用内稳态机制,如RFB-kWTA和“智能”抑制,改进了变革者的注意力机制和输出块。实验证明,新方法在Multi30K数据集上的表现优于传统变革者和仅使用注意力机制和输出块dropout的模型。
Key Takeaways
- 变革者架构在现代神经网络领域扮演重要角色,用于多种任务,如文本生成、机器翻译、图像和音频处理等。
- 介绍了结合Jeff Hawkins的智能系统构建思路的方法。
- 提出在变革者的注意力机制和输出块中使用内稳态机制,如RFB-kWTA和“智能”抑制。
- RFB-kWTA通过统计层激活的时间变化来调整整个层,增强稀有激活值并减少频繁出现的激活值。
- “智能”抑制利用激活统计来采样稀疏掩码,稀有激活时间更有可能被激活。
- 实验证明,所提机制在Multi30K数据集上的表现优于传统变革者和仅使用dropout的模型。
点此查看论文截图

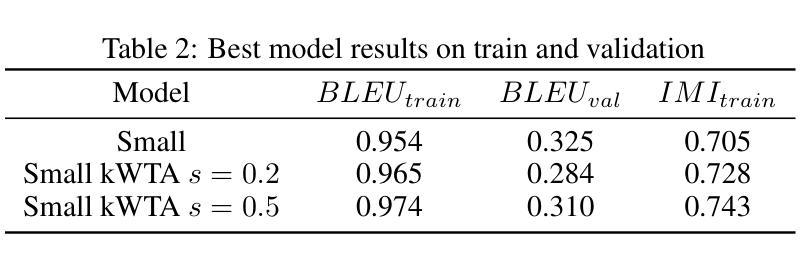
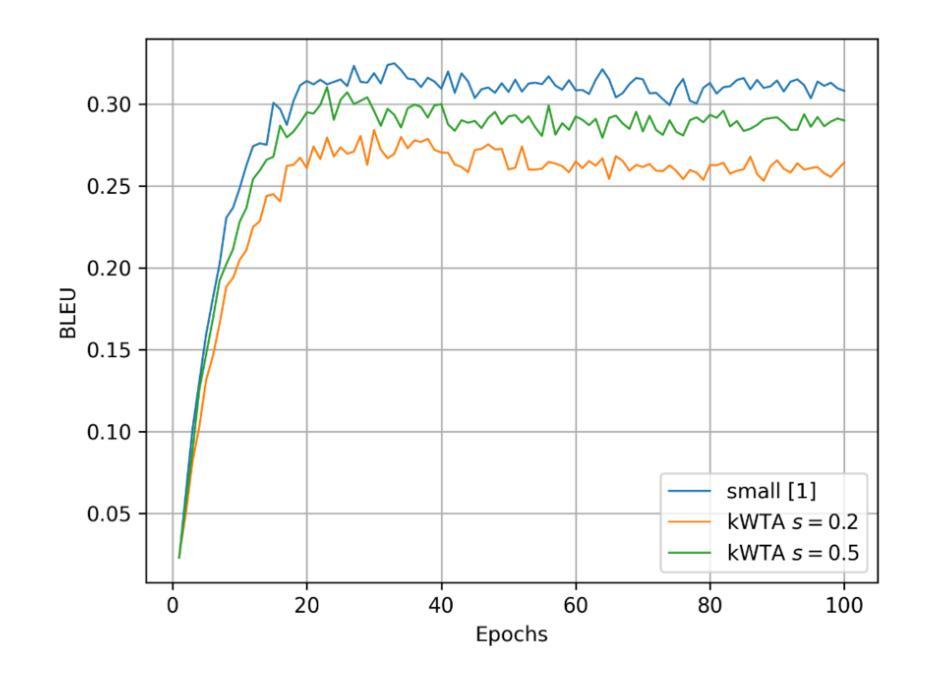
T2Vid: Translating Long Text into Multi-Image is the Catalyst for Video-LLMs
Authors:Shukang Yin, Chaoyou Fu, Sirui Zhao, Yunhang Shen, Chunjiang Ge, Yan Yang, Zuwei Long, Yuhan Dai, Tong Xu, Xing Sun, Ran He, Caifeng Shan, Enhong Chen
The success of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in the image domain has garnered wide attention from the research community. Drawing on previous successful experiences, researchers have recently explored extending the success to the video understanding realms. Apart from training from scratch, an efficient way is to utilize the pre-trained image-LLMs, leading to two mainstream approaches, i.e. zero-shot inference and further fine-tuning with video data. In this work, our study of these approaches harvests an effective data augmentation method. We first make a deeper inspection of the zero-shot inference way and identify two limitations, i.e. limited generalization and lack of temporal understanding capabilities. Thus, we further investigate the fine-tuning approach and find a low learning efficiency when simply using all the video data samples, which can be attributed to a lack of instruction diversity. Aiming at this issue, we develop a method called T2Vid to synthesize video-like samples to enrich the instruction diversity in the training corpus. Integrating these data enables a simple and efficient training scheme, which achieves performance comparable to or even superior to using full video datasets by training with just 15% the sample size. Meanwhile, we find that the proposed scheme can boost the performance of long video understanding without training with long video samples. We hope our study will spark more thinking about using MLLMs for video understanding and curation of high-quality data. The code is released at https://github.com/xjtupanda/T2Vid.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在图像领域的成功引起了研究界的广泛关注。基于之前的成功经验,研究人员最近开始探索将其成功扩展到视频理解领域。除了从头开始训练之外,一种有效的方法是利用预先训练好的图像LLM,从而产生了两种主流方法,即零样本推断和进一步使用视频数据进行微调。在这项工作中,我们对这些方法的研究收获了一种有效的数据增强方法。我们首先对零样本推断方法进行了深入研究,并发现了两个局限性,即有限的泛化能力和缺乏时间理解能力。因此,我们进一步研究了微调方法,并发现仅使用所有视频数据样本时存在学习效率低的问题,这可以归因于指令多样性的缺乏。针对这一问题,我们开发了一种名为T2Vid的方法来合成类似视频样本,以丰富训练语料库中的指令多样性。整合这些数据实现了一种简单高效的训练方案,仅使用15%的样本量就可以达到或超过使用完整视频数据集的性能。同时,我们发现所提出的方案可以在不使用长视频样本的情况下提高长视频理解性能。我们希望我们的研究能够激发更多关于使用MLLM进行视频理解和高质量数据筛选的思考。代码已发布在https://github.com/xjtupanda/T2Vid。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://github.com/xjtupanda/T2Vid
Summary
多模态大型语言模型在图像领域的成功引起了研究界的广泛关注。最近,研究者们尝试将这种成功扩展到视频理解领域。本文研究了两种主流方法,即零样本推理和通过视频数据进行微调的方法,并据此提出了一种有效的数据增强方法。针对零样本推理方法的局限性,本文提出了一种名为T2Vid的方法,通过合成类似视频样本来丰富训练语料库中的指令多样性。此方法能够在仅使用15%样本量的情况下实现与全视频数据集训练相当甚至更优的性能。同时,该研究发现在对长视频理解任务中,即使不使用长视频样本进行训练,此方法也能提升性能。本研究希望激发更多关于利用多模态大型语言模型进行视频理解和高质量数据收集的思考。相关代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在图像领域的成功吸引了研究者的注意,目前正在探索将其应用于视频理解领域。
- 研究人员主要尝试两种方法:零样本推理和微调方法,后者采用预训练的图像LLMs进行应用拓展。
- 研究指出了零样本推理方法的局限性,包括有限的泛化能力和缺乏时间理解能力。
- 针对这些局限性,提出了一种名为T2Vid的有效数据增强方法,通过合成类似视频样本丰富训练语料库中的指令多样性。
- T2Vid方法在减少样本使用的同时,能达到与使用全视频数据集相当的训练效果,展现了其在提升效率和提高性能方面的潜力。
- 该研究还表明,T2Vid对于提高长视频理解的性能有明显帮助,甚至在未使用长视频样本进行训练的情况下也能实现性能提升。
点此查看论文截图


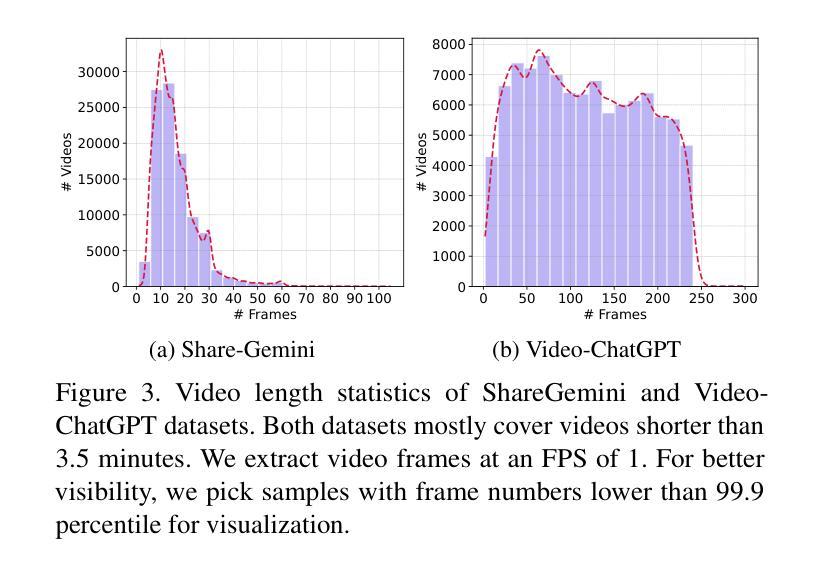
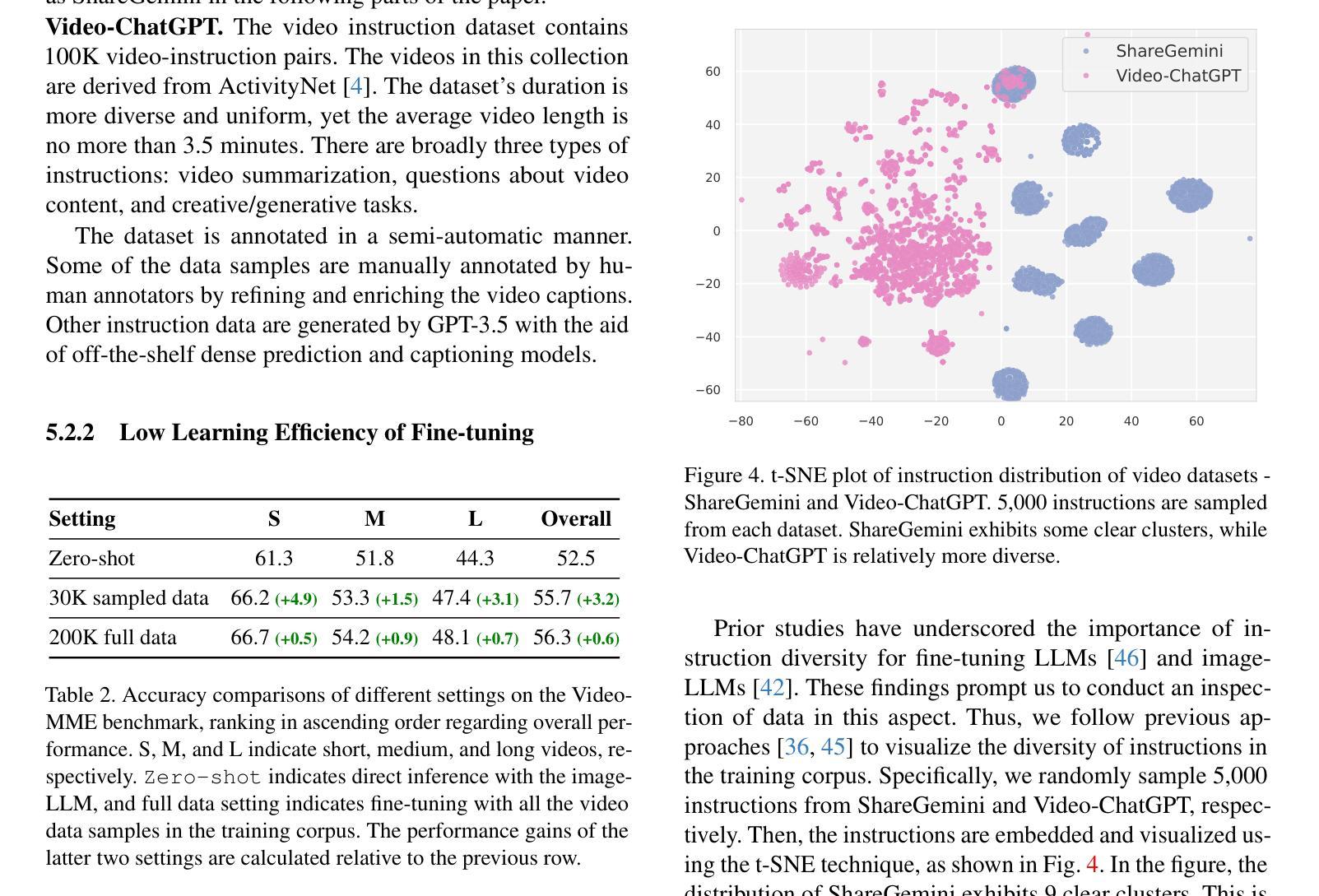
Latent Schrodinger Bridge: Prompting Latent Diffusion for Fast Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation
Authors:Jeongsol Kim, Beomsu Kim, Jong Chul Ye
Diffusion models (DMs), which enable both image generation from noise and inversion from data, have inspired powerful unpaired image-to-image (I2I) translation algorithms. However, they often require a larger number of neural function evaluations (NFEs), limiting their practical applicability. In this paper, we tackle this problem with Schrodinger Bridges (SBs), which are stochastic differential equations (SDEs) between distributions with minimal transport cost. We analyze the probability flow ordinary differential equation (ODE) formulation of SBs, and observe that we can decompose its vector field into a linear combination of source predictor, target predictor, and noise predictor. Inspired by this observation, we propose Latent Schrodinger Bridges (LSBs) that approximate the SB ODE via pre-trained Stable Diffusion, and develop appropriate prompt optimization and change of variables formula to match the training and inference between distributions. We demonstrate that our algorithm successfully conduct competitive I2I translation in unsupervised setting with only a fraction of computation cost required by previous DM-based I2I methods.
扩散模型(DMs)既能够生成图像,又能够实现对数据的反转,为强大的无配对图像到图像(I2I)转换算法提供了灵感。然而,它们通常需要大量的神经网络功能评估(NFEs),从而限制了其实际应用的可行性。针对这一问题,本文采用薛定谔桥(SBs)来解决,它是分布之间的随机微分方程(SDEs),具有最小的传输成本。我们分析了SBs的概率流常微分方程(ODE)公式,并观察到可以将其向量场分解为源预测器、目标预测器和噪声预测器的线性组合。受此观察启发,我们提出了潜在薛定谔桥(LSBs),通过预训练的稳定扩散来近似SB的ODE,并开发适当的提示优化和变量变换公式,以匹配分布之间的训练和推理。我们证明,我们的算法在无监督设置下成功实现了有竞争力的I2I转换,且计算成本仅为先前基于DM的I2I方法所需的一小部分。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型(DMs)在图像生成和反转任务中的应用,并指出其需要更多的神经网络功能评估(NFEs)限制了实际应用。为解决此问题,文章引入Schrodinger Bridges(SBs)通过最小传输成本的分布间随机微分方程(SDEs)。通过分析SBs的概率流常微分方程(ODE)公式,文章提出了Latent Schrodinger Bridges(LSBs),它通过预训练的Stable Diffusion近似SB ODE,并通过适当的提示优化和变量变换公式匹配分布之间的训练和推理。实验证明,该方法在无监督设置下的I2I翻译任务表现优异,且计算成本仅为之前DM-based I2I方法的一小部分。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型(DMs)可用于图像生成和反转任务,但在实际应用中需要更多的神经网络功能评估(NFEs)。
- Schrodinger Bridges(SBs)通过最小传输成本的分布间随机微分方程(SDEs)解决了这个问题。
- 文章分析了SBs的概率流常微分方程(ODE)公式,并将其向量场分解为源预测器、目标预测器和噪声预测器的线性组合。
- 基于这一观察,提出了Latent Schrodinger Bridges(LSBs),通过预训练的Stable Diffusion近似SB ODE。
- LSBs通过适当的提示优化和变量变换公式匹配分布之间的训练和推理。
- 实验证明,该方法在无监督设置下的图像到图像(I2I)翻译任务上具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

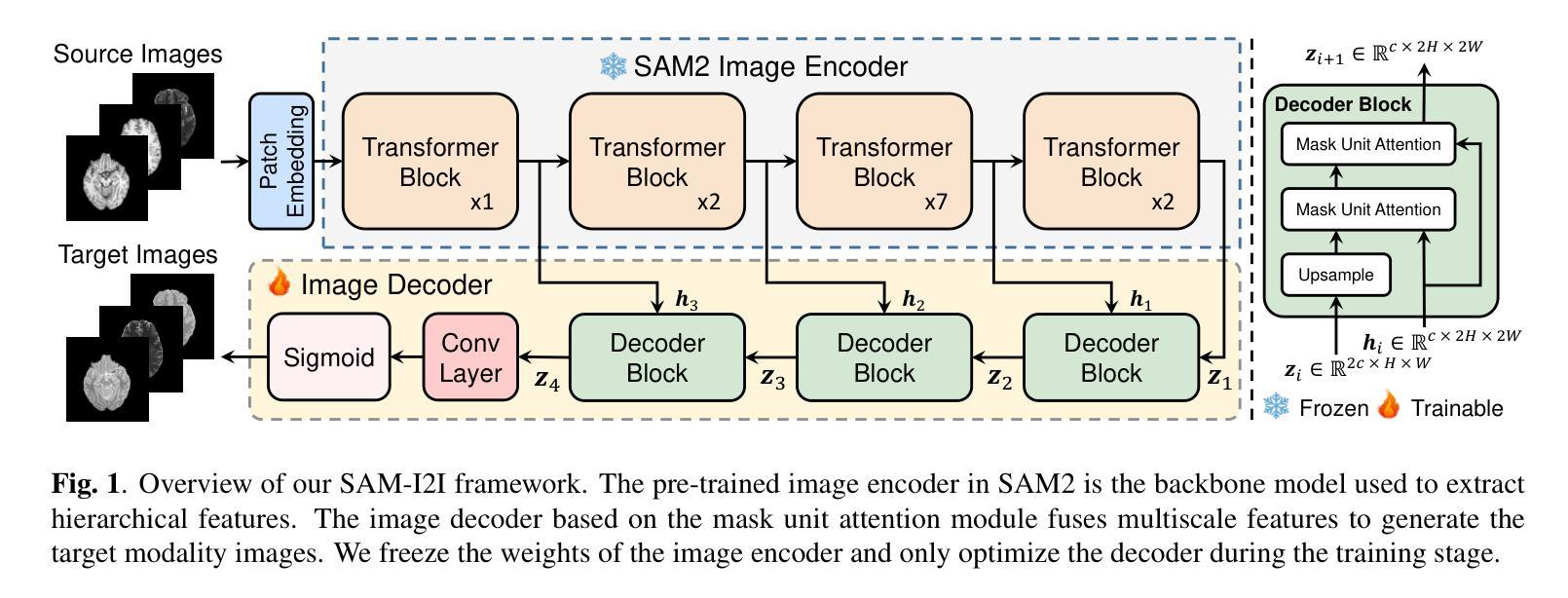
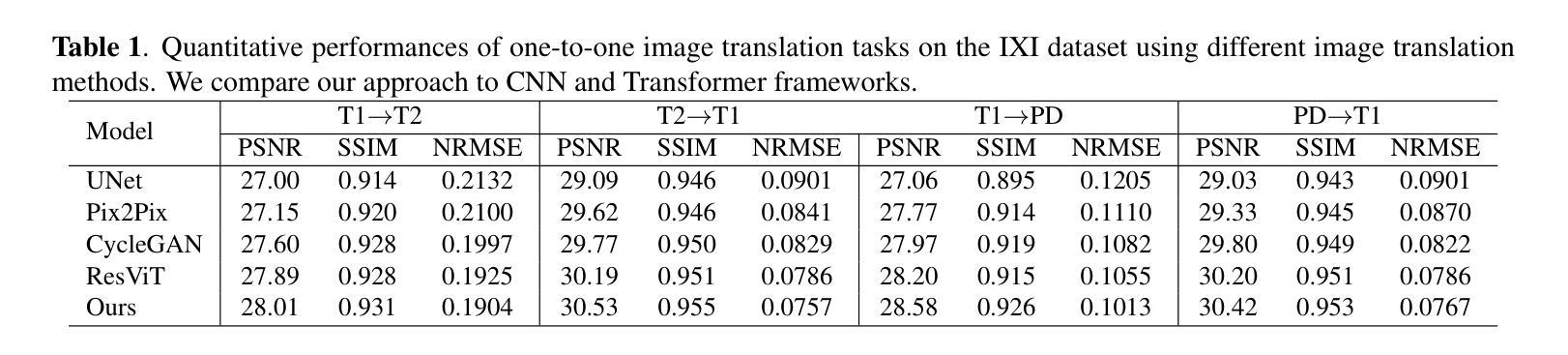
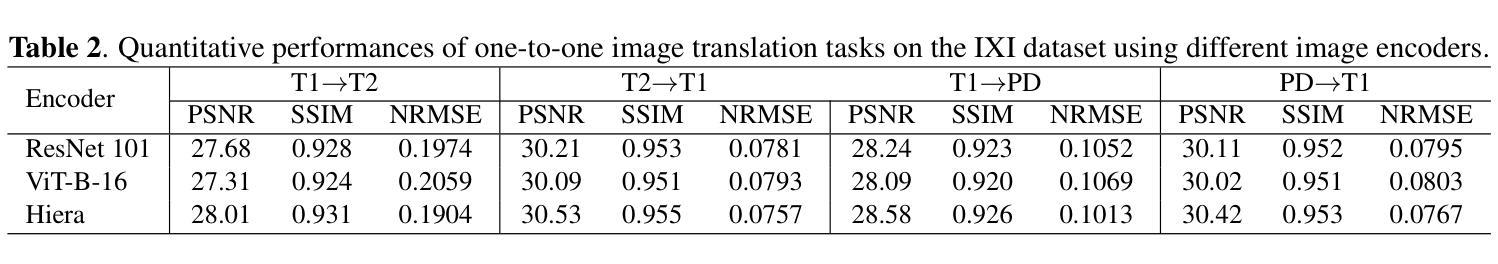
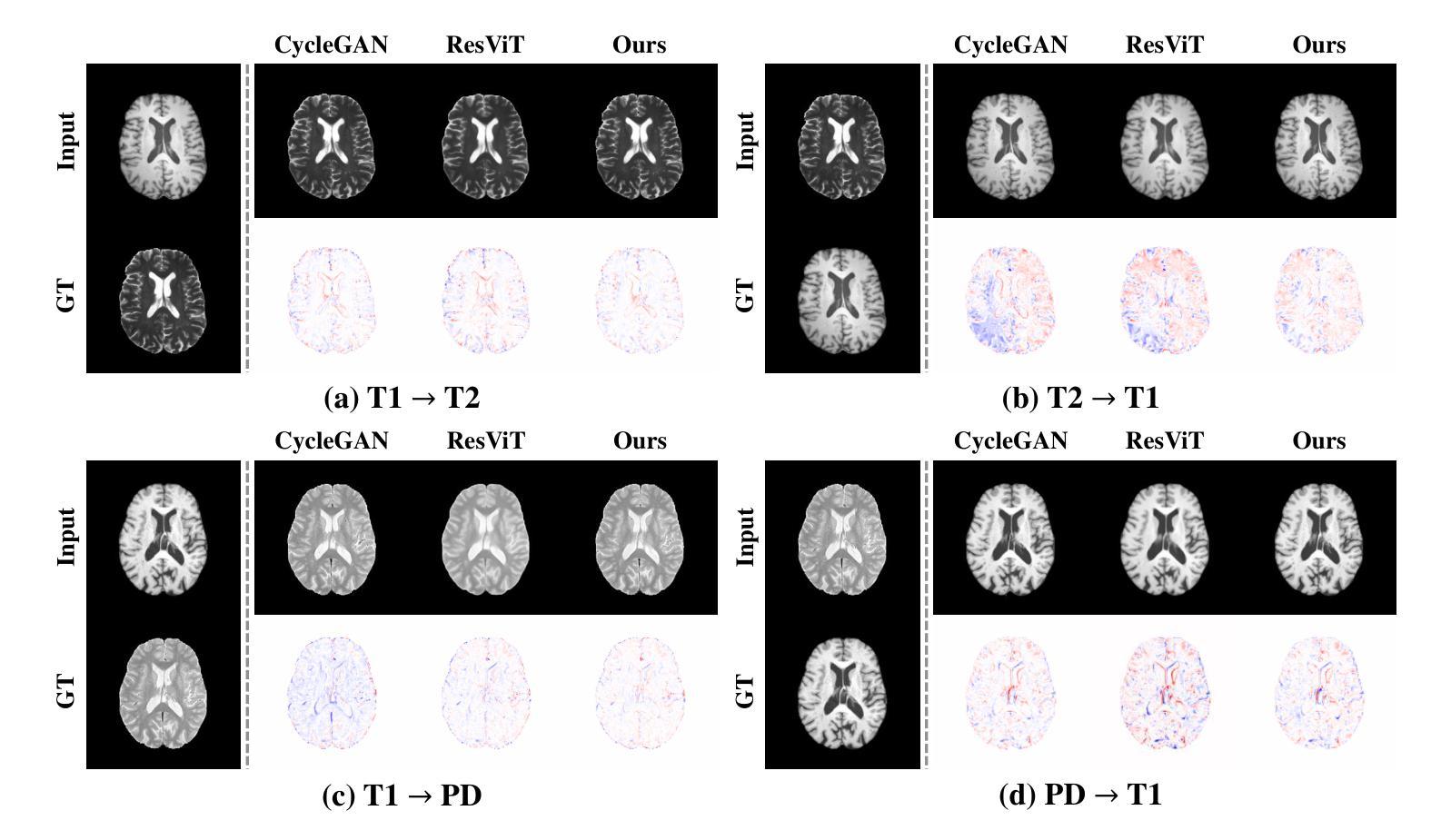
SAM-I2I: Unleash the Power of Segment Anything Model for Medical Image Translation
Authors:Jiayu Huo, Sebastien Ourselin, Rachel Sparks
Medical image translation is crucial for reducing the need for redundant and expensive multi-modal imaging in clinical field. However, current approaches based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Transformers often fail to capture fine-grain semantic features, resulting in suboptimal image quality. To address this challenge, we propose SAM-I2I, a novel image-to-image translation framework based on the Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2). SAM-I2I utilizes a pre-trained image encoder to extract multiscale semantic features from the source image and a decoder, based on the mask unit attention module, to synthesize target modality images. Our experiments on multi-contrast MRI datasets demonstrate that SAM-I2I outperforms state-of-the-art methods, offering more efficient and accurate medical image translation.
医学影像转换对于减少临床领域中冗余且昂贵的多模态成像需求至关重要。然而,目前基于卷积神经网络(CNNs)和Transformer的方法往往无法捕捉精细的语义特征,导致图像质量不佳。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了SAM-I2I,这是一种基于Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)的新型图像到图像转换框架。SAM-I2I利用预训练图像编码器从源图像中提取多尺度语义特征,并基于掩膜单元注意力模块采用解码器来合成目标模态图像。我们在多对比度MRI数据集上的实验表明,SAM-I2I优于最先进的方法,提供了更高效和准确的医学影像转换。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)的医学图像翻译框架SAM-I2I,用于减少临床领域冗余昂贵的多模态成像需求。通过采用预训练图像编码器提取源图像的多尺度语义特征,并结合基于掩膜单元注意力模块的解码器,合成目标模态图像。在对比MRI数据集上的实验表明,SAM-I2I较现有方法表现更优,能够实现更高效和准确的医学图像翻译。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像翻译有助于减少临床中冗余和昂贵的多模态成像需求。
- 当前基于卷积神经网络(CNNs)和Transformer的方法在捕捉精细语义特征方面存在不足,导致图像质量不佳。
- SAM-I2I是一种新型的图像到图像翻译框架,基于Segment Anything Model 2(SAM2)。
- SAM-I2I使用预训练的图像编码器从源图像中提取多尺度语义特征。
- SAM-I2I的解码器基于掩膜单元注意力模块,可以合成目标模态图像。
- 在对比MRI数据集上的实验表明,SAM-I2I较现有方法表现更优。
点此查看论文截图

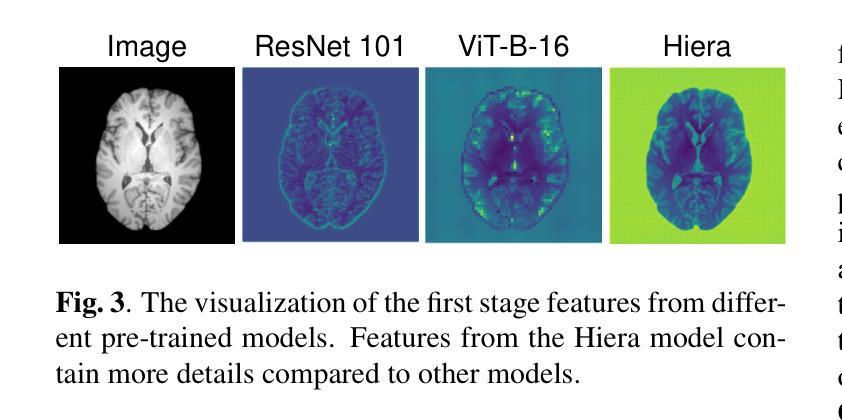
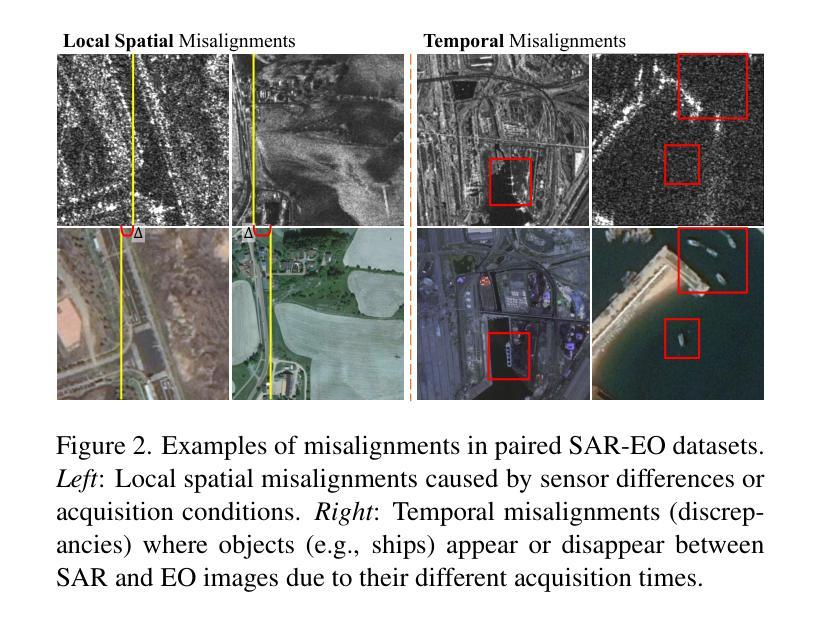
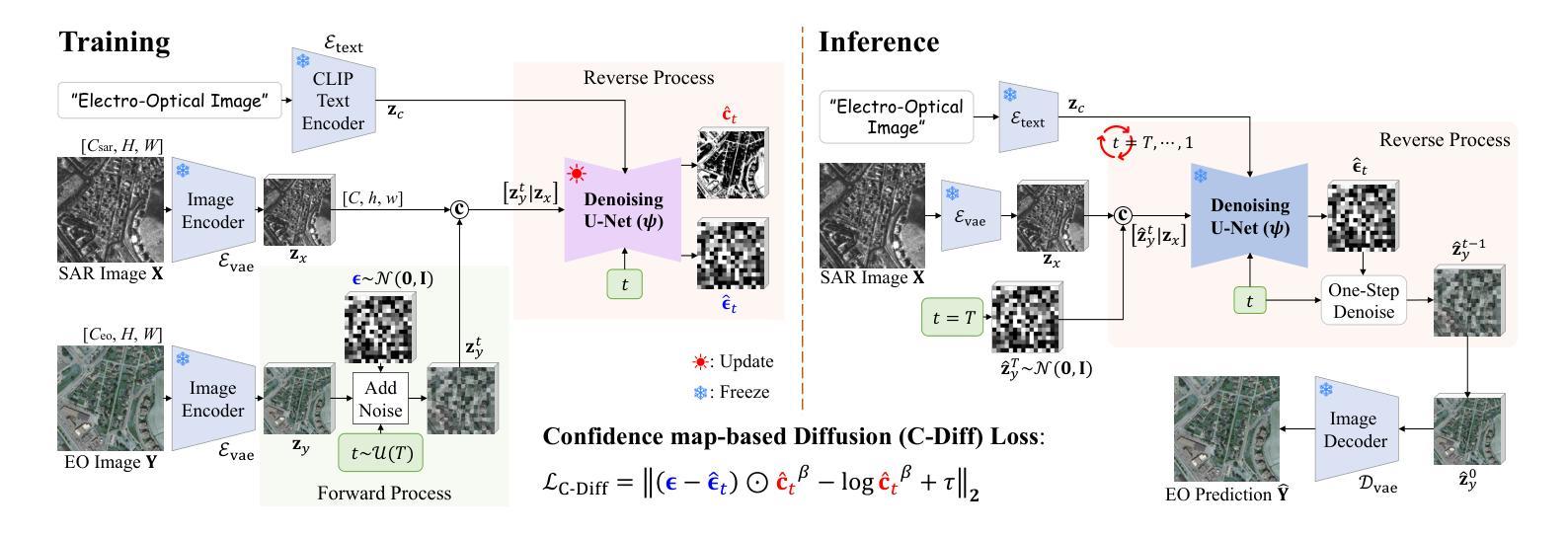
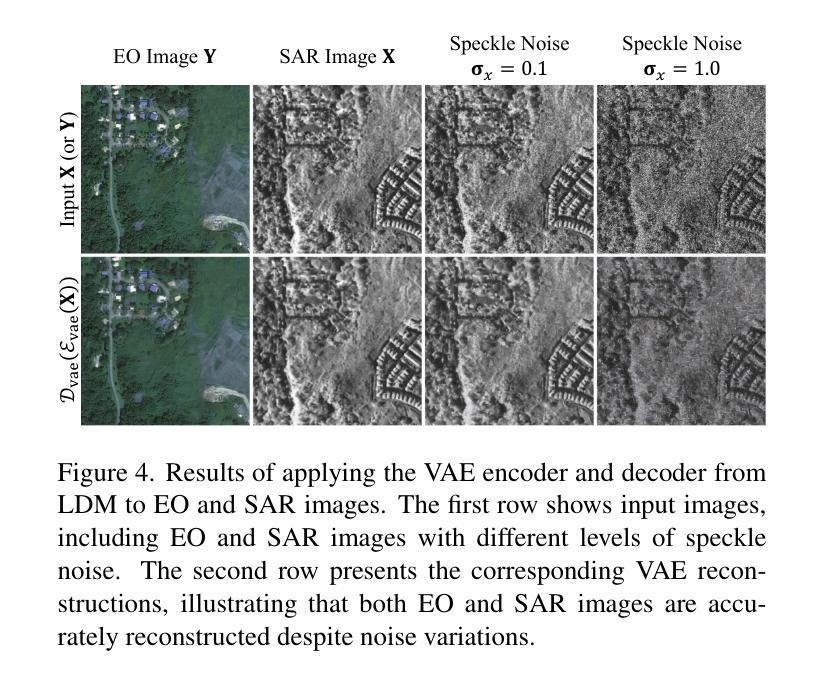
C-DiffSET: Leveraging Latent Diffusion for SAR-to-EO Image Translation with Confidence-Guided Reliable Object Generation
Authors:Jeonghyeok Do, Jaehyup Lee, Munchurl Kim
Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) imagery provides robust environmental and temporal coverage (e.g., during clouds, seasons, day-night cycles), yet its noise and unique structural patterns pose interpretation challenges, especially for non-experts. SAR-to-EO (Electro-Optical) image translation (SET) has emerged to make SAR images more perceptually interpretable. However, traditional approaches trained from scratch on limited SAR-EO datasets are prone to overfitting. To address these challenges, we introduce Confidence Diffusion for SAR-to-EO Translation, called C-DiffSET, a framework leveraging pretrained Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) extensively trained on natural images, thus enabling effective adaptation to the EO domain. Remarkably, we find that the pretrained VAE encoder aligns SAR and EO images in the same latent space, even with varying noise levels in SAR inputs. To further improve pixel-wise fidelity for SET, we propose a confidence-guided diffusion (C-Diff) loss that mitigates artifacts from temporal discrepancies, such as appearing or disappearing objects, thereby enhancing structural accuracy. C-DiffSET achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on multiple datasets, significantly outperforming the very recent image-to-image translation methods and SET methods with large margins.
雷达合成孔径(SAR)成像提供了稳健的环境和时间覆盖(例如在云、季节、昼夜循环期间),但其噪声和独特的结构模式给解释带来了挑战,尤其是对于非专家来说。SAR到EO(光电)图像翻译(SET)的出现使得SAR图像更加易于感知和理解。然而,从头开始以有限的SAR-EO数据集进行训练的传统方法容易出现过度拟合的情况。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了SAR到EO翻译的置信扩散,称为C-DiffSET。它利用在大量自然图像上训练的潜在扩散模型(LDM),从而有效地适应EO域。值得注意的是,我们发现预训练的VAE编码器即使在SAR输入中存在不同噪声水平的情况下,也能将SAR和EO图像对齐到同一潜在空间。为了进一步提高SET的像素级保真度,我们提出了置信引导扩散(C-Diff)损失,该损失减轻了由于时间差异造成的伪影,如出现的物体或消失的物体,从而提高了结构准确性。C-DiffSET在多数据集上取得了最先进的成果,显著超越了最新的图像到图像翻译方法和SET方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Please visit our project page https://kaist-viclab.github.io/C-DiffSET_site/
Summary
SAR影像具备稳健的环境和时序覆盖能力,但其噪声和独特结构模式给解读带来挑战,特别是对于非专家而言。为此,出现了SAR-to-EO(光电)图像翻译(SET)技术。然而,传统方法在小规模SAR-EO数据集上进行从头训练容易过拟合。为应对这些挑战,我们提出了基于预训练潜在扩散模型的SAR-to-EO翻译置信扩散框架(C-DiffSET)。此框架借助广泛训练于自然图像上的潜在扩散模型(LDM),有效适应光电领域。研究发现,预训练的VAE编码器可在不同噪声水平的SAR和EO影像之间建立同一潜在空间。为进一步提高SET的像素级保真度,我们提出了置信引导扩散(C-Diff)损失,该损失减轻了因时间差异造成的伪影,如物体的出现或消失,从而提高结构准确性。C-DiffSET在多个数据集上实现最佳结果,大幅超越最新的图像到图像翻译方法和SET方法。
Key Takeaways
- SAR影像提供稳健的环境和时序覆盖能力,但解读存在挑战。
- SAR-to-EO图像翻译(SET)技术旨在提高SAR影像的感知解读性。
- 传统SET方法在小规模数据集上容易过拟合。
- 引入基于预训练潜在扩散模型的C-DiffSET框架,有效适应光电领域。
- 预训练的VAE编码器可在不同噪声水平的SAR和EO影像之间建立同一潜在空间。
- 提出置信引导扩散(C-Diff)损失,以提高SET的像素级保真度和结构准确性。
- C-DiffSET在多个数据集上实现最佳结果,显著超越其他图像翻译方法。
点此查看论文截图

Mechanisms of Generative Image-to-Image Translation Networks
Authors:Guangzong Chen, Mingui Sun, Zhi-Hong Mao, Kangni Liu, Wenyan Jia
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are a class of neural networks that have been widely used in the field of image-to-image translation. In this paper, we propose a streamlined image-to-image translation network with a simpler architecture compared to existing models. We investigate the relationship between GANs and autoencoders and provide an explanation for the efficacy of employing only the GAN component for tasks involving image translation. We show that adversarial for GAN models yields results comparable to those of existing methods without additional complex loss penalties. Subsequently, we elucidate the rationale behind this phenomenon. We also incorporate experimental results to demonstrate the validity of our findings.
生成对抗网络(GANs)是一类在图像到图像翻译领域得到广泛应用的神经网络。在本文中,我们提出了一种简化的图像到图像翻译网络,其架构比现有模型更简单。我们研究了GANs和自编码器之间的关系,并解释了仅使用GAN组件进行图像翻译任务的有效性。我们表明,对抗性对于GAN模型可以在没有额外的复杂损失惩罚的情况下产生与现有方法相当的结果。随后,我们阐述了这种现象背后的原理。我们还结合了实验结果来证明我们的发现的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了生成对抗网络(GANs)在图像翻译领域的应用。提出了一种简化的图像翻译网络,其架构较现有模型更为简洁。文章探讨了GANs与自编码器的关系,并解释了仅使用GAN组件进行图像翻译任务的有效性。实验结果表明,对抗性GAN模型的结果与现有方法相当,无需额外的复杂损失惩罚。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种简化的图像翻译网络架构。
- 探讨了生成对抗网络(GANs)与自编码器的关系。
- 阐释了仅使用GAN组件进行图像翻译任务的有效性。
- 对抗性GAN模型结果堪比现有方法,无需复杂损失惩罚。
- 文中给出了实验验证结果的详细解释。
- 研究对图像翻译领域的贡献和启示。
点此查看论文截图
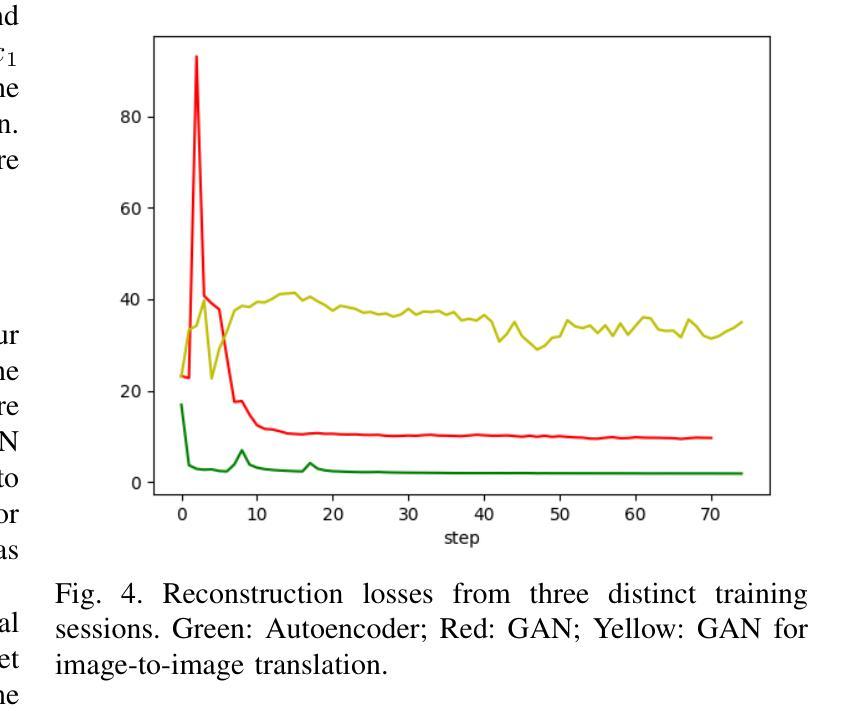
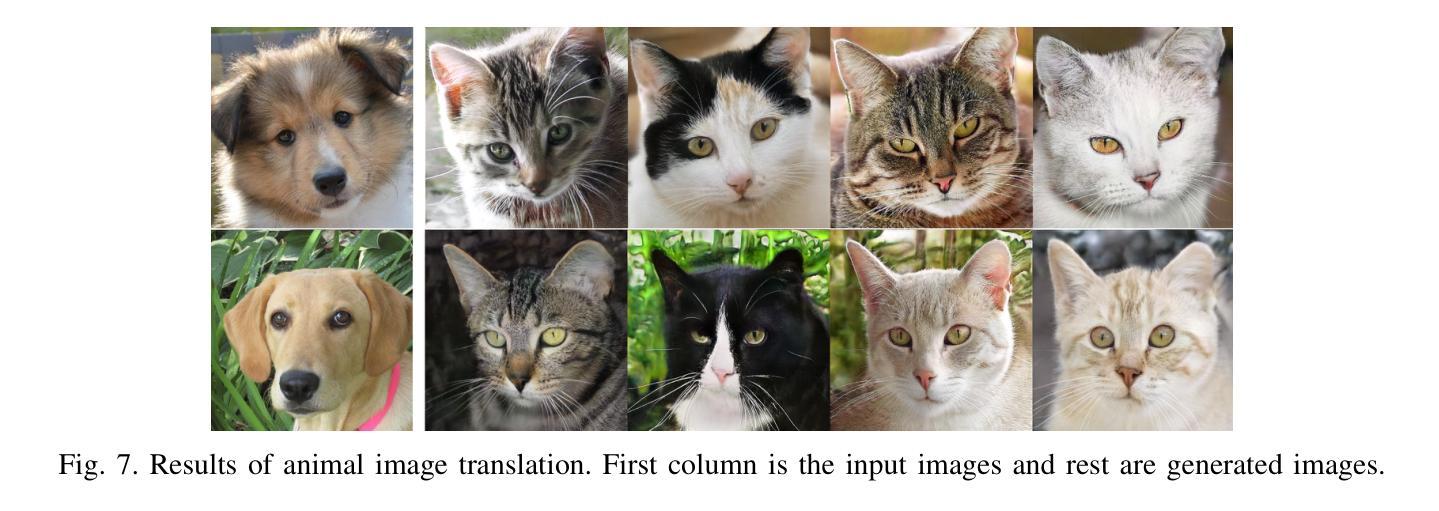

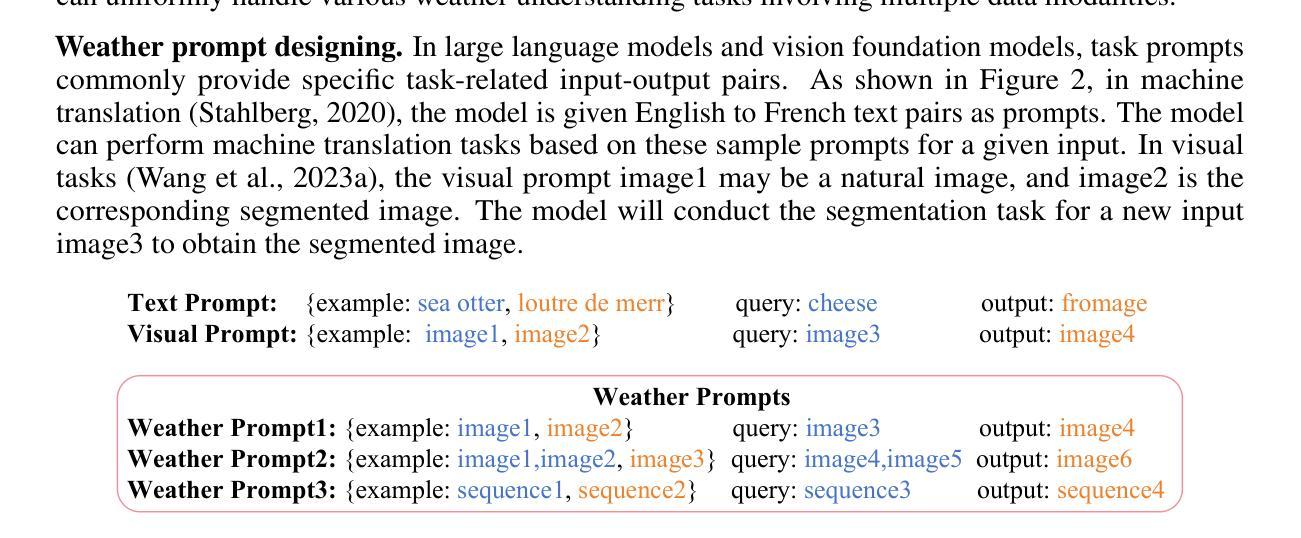
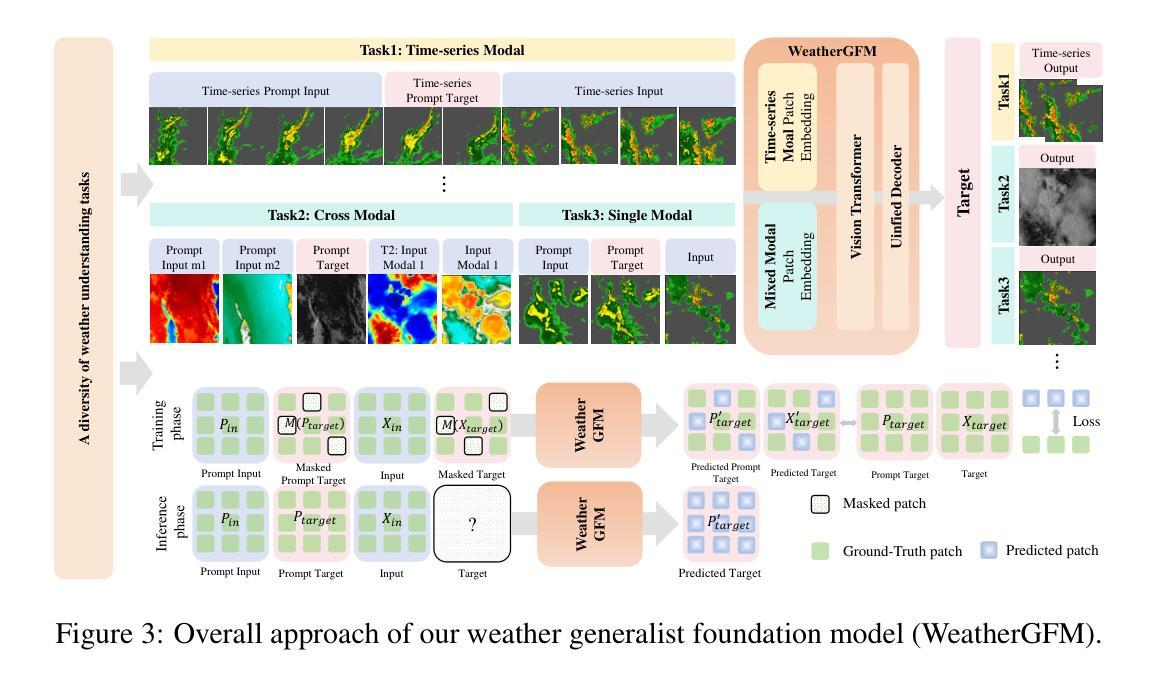
WeatherGFM: Learning A Weather Generalist Foundation Model via In-context Learning
Authors:Xiangyu Zhao, Zhiwang Zhou, Wenlong Zhang, Yihao Liu, Xiangyu Chen, Junchao Gong, Hao Chen, Ben Fei, Shiqi Chen, Wanli Ouyang, Xiao-Ming Wu, Lei Bai
The Earth’s weather system encompasses intricate weather data modalities and diverse weather understanding tasks, which hold significant value to human life. Existing data-driven models focus on single weather understanding tasks (e.g., weather forecasting). Although these models have achieved promising results, they fail to tackle various complex tasks within a single and unified model. Moreover, the paradigm that relies on limited real observations for a single scenario hinders the model’s performance upper bound. In response to these limitations, we draw inspiration from the in-context learning paradigm employed in state-of-the-art visual foundation models and large language models. In this paper, we introduce the first generalist weather foundation model (WeatherGFM), designed to address a wide spectrum of weather understanding tasks in a unified manner. More specifically, we initially unify the representation and definition of the diverse weather understanding tasks. Subsequently, we devised weather prompt formats to manage different weather data modalities, namely single, multiple, and temporal modalities. Finally, we adopt a visual prompting question-answering paradigm for the training of unified weather understanding tasks. Extensive experiments indicate that our WeatherGFM can effectively handle up to ten weather understanding tasks, including weather forecasting, super-resolution, weather image translation, and post-processing. Our method also showcases generalization ability on unseen tasks.
地球天气系统包含了复杂的天气数据模式和多样的天气理解任务,对人类生活具有重要意义。现有的数据驱动模型主要关注单个天气理解任务(例如天气预报)。虽然这些模型取得了有前景的结果,但它们无法在一个单一统一的模型中解决各种复杂任务。此外,依赖于单一场景的有限真实观测结果的范式阻碍了模型性能的上限。针对这些局限性,我们从最先进视觉基础模型和大语言模型中采用的上下文学习范式中汲取灵感。在本文中,我们介绍了第一个通用天气基础模型(WeatherGFM),旨在以统一的方式解决广泛的气候理解任务。更具体地说,我们最初统一了多种天气理解任务的表示和定义。随后,我们设计了天气提示格式来管理不同的天气数据模式,即单模态、多模态和时间模态。最后,我们采用视觉提示问答范式进行统一天气理解任务的训练。大量实验表明,我们的WeatherGFM可以有效处理多达十种天气理解任务,包括天气预报、超分辨率、天气图像翻译和后期处理。我们的方法还展示了在未见任务上的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出首个通用天气基础模型(WeatherGFM),旨在以统一的方式解决多种天气理解任务。该模型通过统一不同天气理解任务的表示和定义,采用天气提示格式管理不同的天气数据模态,并采用视觉提示问答模式进行训练。实验表明,WeatherGFM能处理多达十种天气理解任务,并在未见任务上展现出泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 天气系统对人类生活具有重要意义,现有数据驱动模型主要关注单一天气理解任务,如天气预报。
- 单一场景依赖有限真实观察的范式限制了模型性能的上限。
- 借鉴视觉基础模型和大语言模型的上下文学习范式,提出首个通用天气基础模型(WeatherGFM)。
- WeatherGFM统一表示和定义各种天气理解任务,并设计天气提示格式来管理不同的天气数据模态。
- 采用视觉提示问答模式进行训练,使WeatherGFM能处理多种天气理解任务。
- 实验显示,WeatherGFM能有效处理包括天气预报、超分辨率、天气图像翻译和后期处理在内的十种天气理解任务。
点此查看论文截图

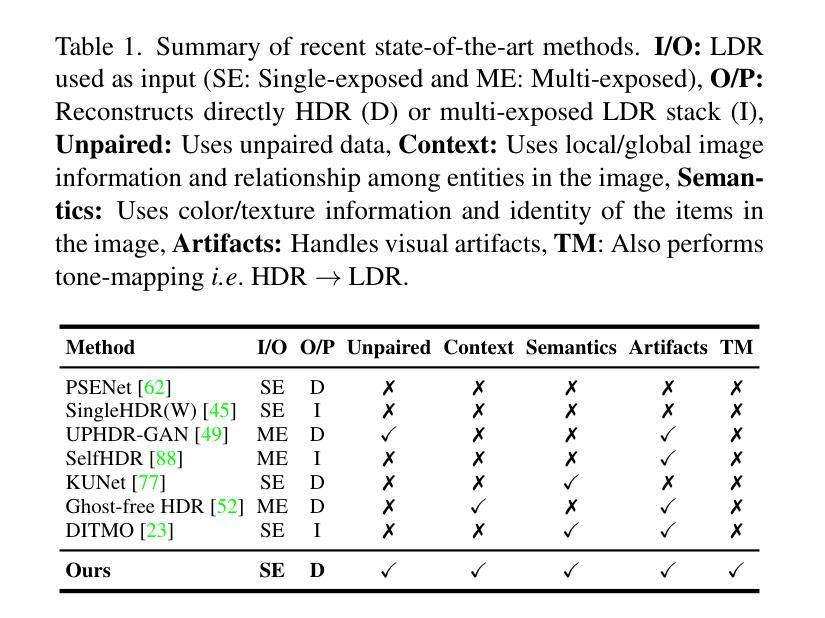
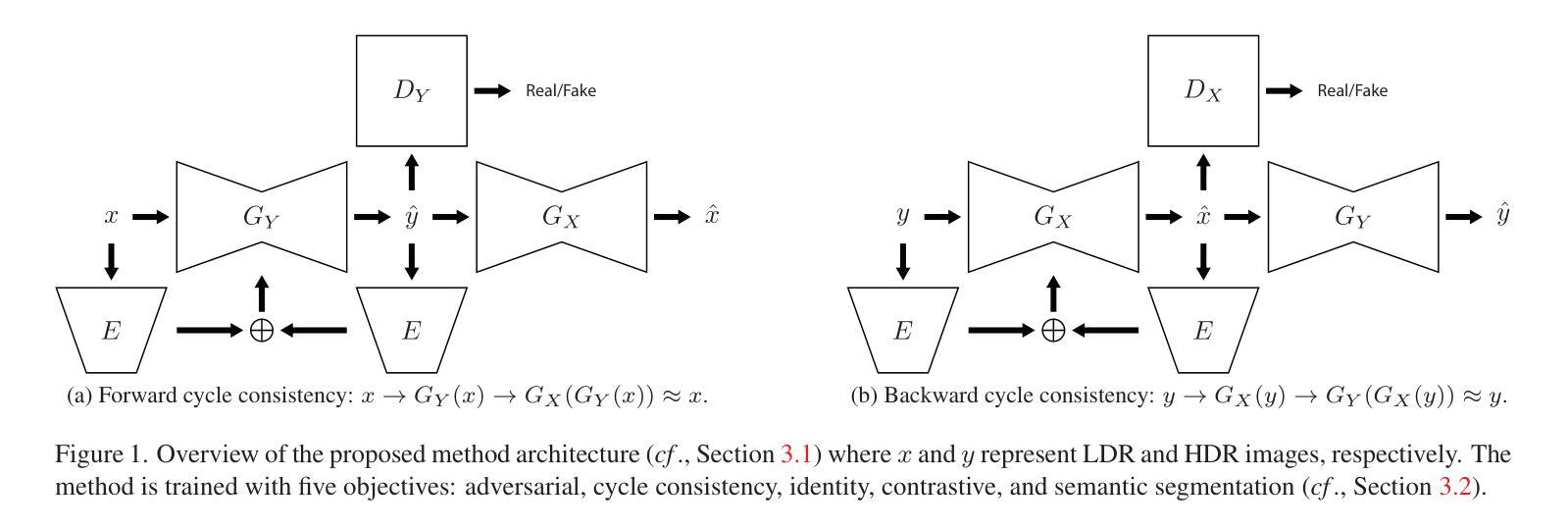
A Cycle Ride to HDR: Semantics Aware Self-Supervised Framework for Unpaired LDR-to-HDR Image Translation
Authors:Hrishav Bakul Barua, Stefanov Kalin, Lemuel Lai En Che, Dhall Abhinav, Wong KokSheik, Krishnasamy Ganesh
Low Dynamic Range (LDR) to High Dynamic Range (HDR) image translation is an important computer vision problem. There is a significant amount of research utilizing both conventional non-learning methods and modern data-driven approaches, focusing on using both single-exposed and multi-exposed LDR for HDR image reconstruction. However, most current state-of-the-art methods require high-quality paired {LDR,HDR} datasets for model training. In addition, there is limited literature on using unpaired datasets for this task where the model learns a mapping between domains, i.e., LDR to HDR. To address limitations of current methods, such as the paired data constraint , as well as unwanted blurring and visual artifacts in the reconstructed HDR, we propose a method that uses a modified cycle-consistent adversarial architecture and utilizes unpaired {LDR,HDR} datasets for training. The method introduces novel generators to address visual artifact removal and an encoder and loss to address semantic consistency, another under-explored topic. The method achieves state-of-the-art results across several benchmark datasets and reconstructs high-quality HDR images.
从低动态范围(LDR)到高动态范围(HDR)的图像转换是计算机视觉领域的一个重要问题。有大量研究采用传统的非学习方法和现代的数据驱动方法,重点关注使用单曝光和多曝光LDR进行HDR图像重建。然而,目前大多数最先进的方法都需要高质量配对{LDR,HDR}数据集进行模型训练。此外,关于使用非配对数据集进行此任务的研究很少,模型在此任务中学习域之间的映射,即LDR到HDR。为了解决当前方法的局限性,例如配对数据的约束以及重建HDR中的不需要的模糊和视觉伪影,我们提出了一种使用修改后的循环一致性对抗架构的方法,并利用非配对{LDR,HDR}数据集进行训练。该方法引入新型生成器来解决视觉伪影去除问题,以及解决语义一致性这一尚未深入研究的主题引入编码器和损失函数。该方法在多个基准数据集上达到了最新结果,并重建了高质量HDR图像。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to IEEE
Summary:
本文介绍了从低动态范围(LDR)图像到高动态范围(HDR)图像的翻译是计算机视觉领域的一个重要问题。尽管存在使用传统非学习方法和现代数据驱动方法的许多研究,但大多数最先进的方法都需要高质量配对的LDR和HDR数据集进行模型训练。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种使用修改后的循环一致性对抗架构的方法,该方法利用未配对的LDR和HDR数据集进行训练,并引入了新的生成器来解决视觉伪影的去除以及语义一致性的不足。该方法在多个基准数据集上实现了最佳结果,并能重建高质量的HDR图像。
Key Takeaways:
- LDR到HDR的图像翻译是计算机视觉领域的重要问题。
- 当前的研究方法大多需要高质量配对的LDR和HDR数据集进行模型训练。
- 存在一些使用未配对数据集的研究,模型学习域之间的映射,即LDR到HDR。
- 本文提出了一种使用修改后的循环一致性对抗架构的方法来解决上述问题。
- 该方法引入了新的生成器解决视觉伪影去除的问题。
- 方法中还使用了编码器和损失函数来处理语义一致性,这是一个尚未被充分研究的话题。
点此查看论文截图

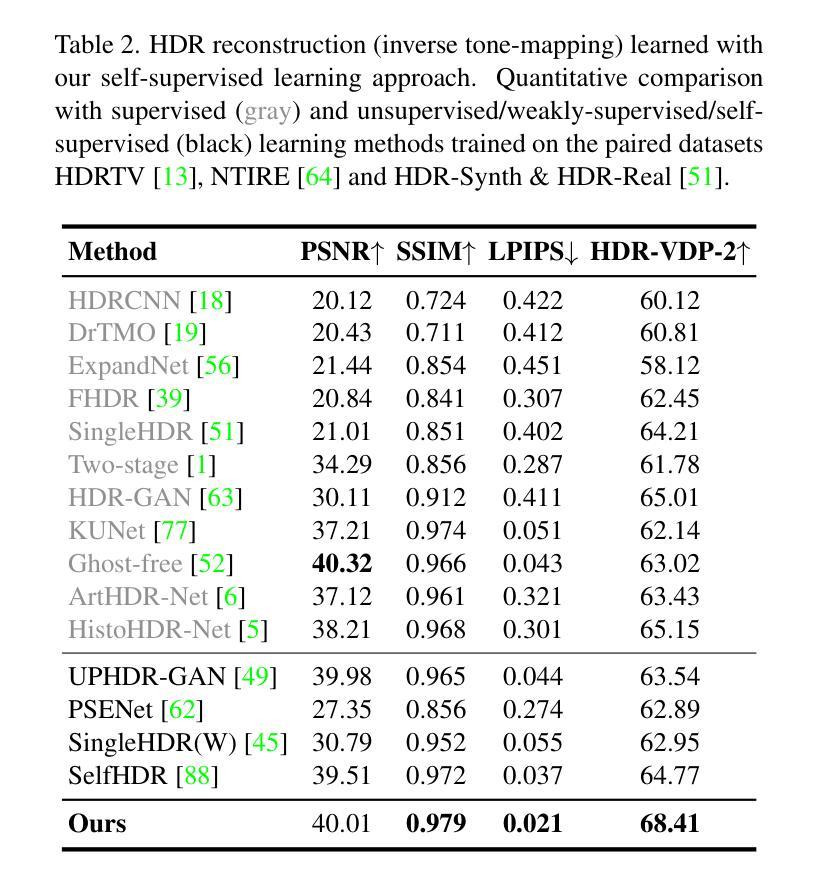
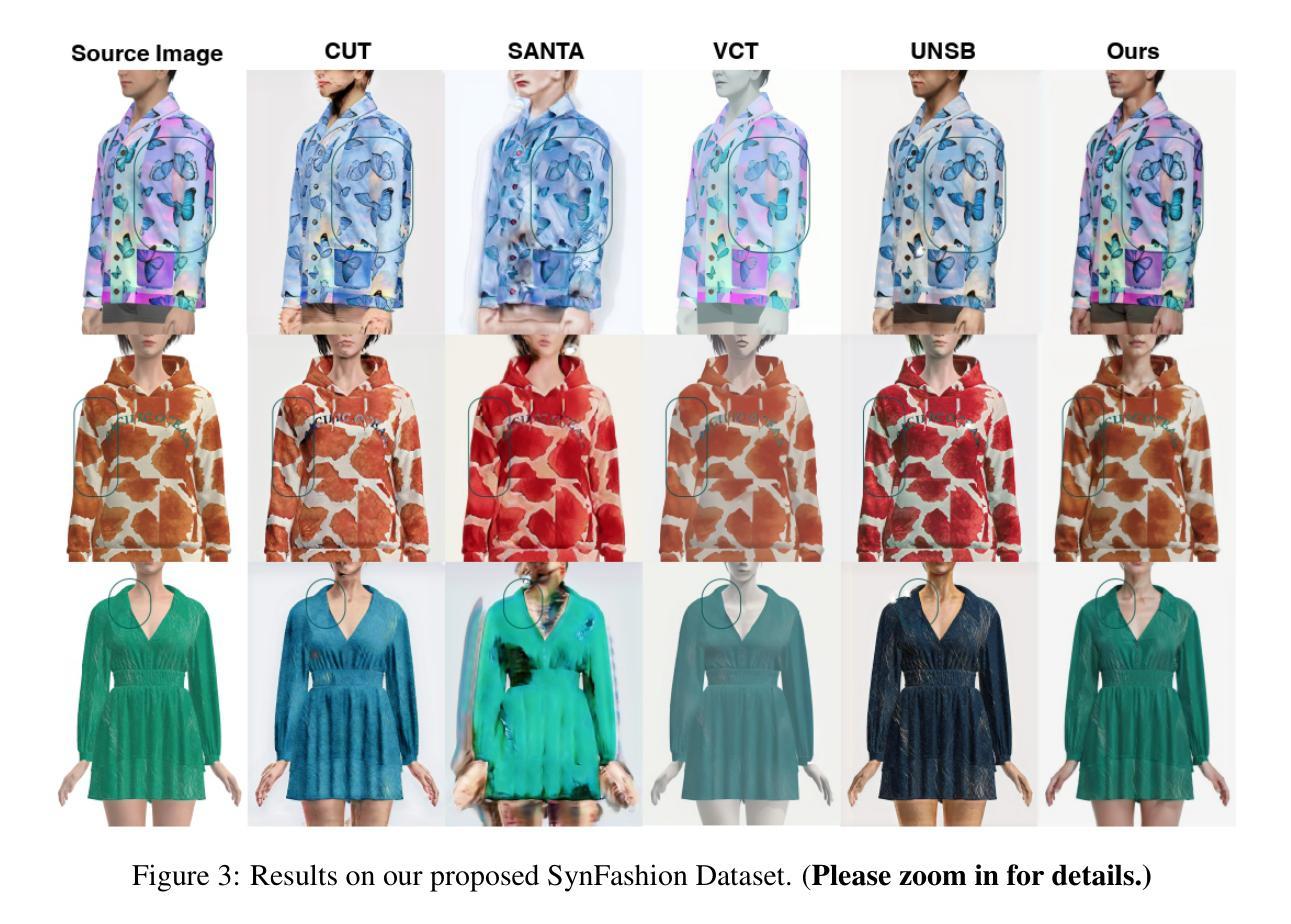
FashionR2R: Texture-preserving Rendered-to-Real Image Translation with Diffusion Models
Authors:Rui Hu, Qian He, Gaofeng He, Jiedong Zhuang, Huang Chen, Huafeng Liu, Huamin Wang
Modeling and producing lifelike clothed human images has attracted researchers’ attention from different areas for decades, with the complexity from highly articulated and structured content. Rendering algorithms decompose and simulate the imaging process of a camera, while are limited by the accuracy of modeled variables and the efficiency of computation. Generative models can produce impressively vivid human images, however still lacking in controllability and editability. This paper studies photorealism enhancement of rendered images, leveraging generative power from diffusion models on the controlled basis of rendering. We introduce a novel framework to translate rendered images into their realistic counterparts, which consists of two stages: Domain Knowledge Injection (DKI) and Realistic Image Generation (RIG). In DKI, we adopt positive (real) domain finetuning and negative (rendered) domain embedding to inject knowledge into a pretrained Text-to-image (T2I) diffusion model. In RIG, we generate the realistic image corresponding to the input rendered image, with a Texture-preserving Attention Control (TAC) to preserve fine-grained clothing textures, exploiting the decoupled features encoded in the UNet structure. Additionally, we introduce SynFashion dataset, featuring high-quality digital clothing images with diverse textures. Extensive experimental results demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of our method in rendered-to-real image translation.
建模和生成逼真的穿衣人体图像几十年来吸引了不同领域研究人员的关注,这涉及到高度复杂和结构化内容。渲染算法分解并模拟相机的成像过程,但受限于建模变量的准确性和计算效率。生成模型可以产生令人印象深刻的生动人体图像,但在可控性和可编辑性方面仍然不足。本文研究了渲染图像的光照现实主义增强技术,利用扩散模型的生成能力并在渲染的基础上进行控制。我们介绍了一个将渲染图像翻译成逼真图像的新型框架,该框架包括两个阶段:领域知识注入(DKI)和逼真图像生成(RIG)。在DKI阶段,我们通过正(真实)领域微调与负(渲染)领域嵌入将知识注入到预训练的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型中。在RIG阶段,我们根据输入的渲染图像生成逼真的图像,利用纹理保留注意力控制(TAC)来保留精细的衣物纹理,并利用UNet结构编码的解耦特征。此外,我们还介绍了SynFashion数据集,该数据集以高质量的数字服装图像为特色,具有多样的纹理。大量的实验结果证明了我们的方法在渲染到现实图像翻译中的优越性和有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文研究了利用扩散模型提升渲染图像的真实感。文章提出了一种新型框架,分为两个阶段:领域知识注入(DKI)和真实图像生成(RIG)。DKI通过正向(真实)领域微调与反向(渲染)领域嵌入来将知识注入预训练的文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型。在RIG阶段,生成与输入渲染图像对应的真实图像,利用纹理保留注意力控制(TAC)来保留精细的衣物纹理,并利用UNet结构编码的解耦特征。此外,文章还介绍了SynFashion数据集,包含高质量的数字服装图像,具有多样化的纹理。实验结果证明了该方法在渲染到真实图像翻译中的优越性和有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 本文关注于将渲染图像转化为更真实的图像,研究利用扩散模型提升渲染图像的真实感。
- 提出了一种新型框架,包括领域知识注入(DKI)和真实图像生成(RIG)两个阶段。
- DKI阶段通过正向和反向领域嵌入来增强预训练模型的性能。
- RIG阶段利用纹理保留注意力控制(TAC)生成具有精细衣物纹理的真实图像。
- 引入了SynFashion数据集,包含高质量、多样化纹理的数字服装图像。
- 实验结果证明了该方法在渲染到真实图像翻译领域的优越性和有效性。
点此查看论文截图

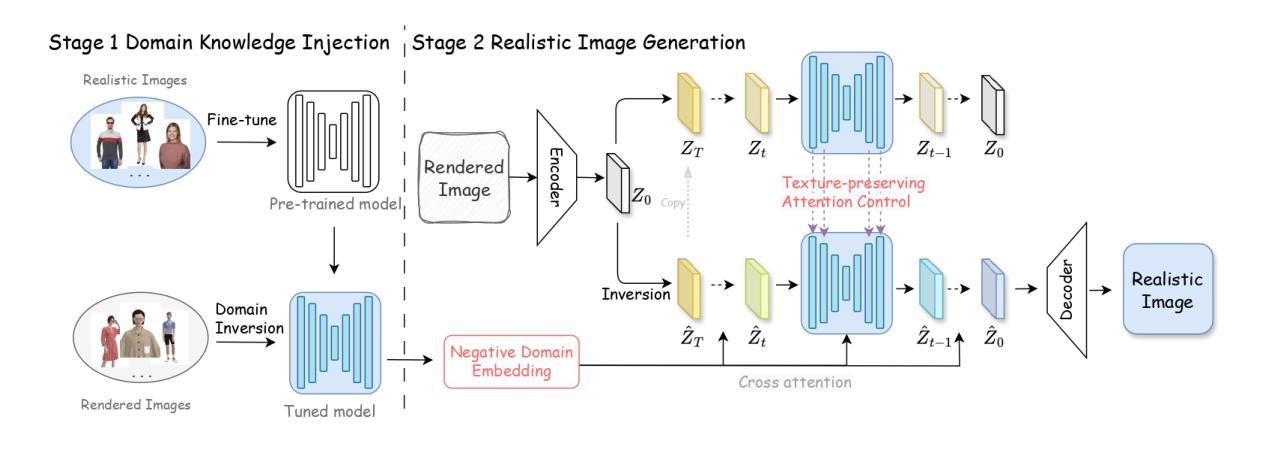

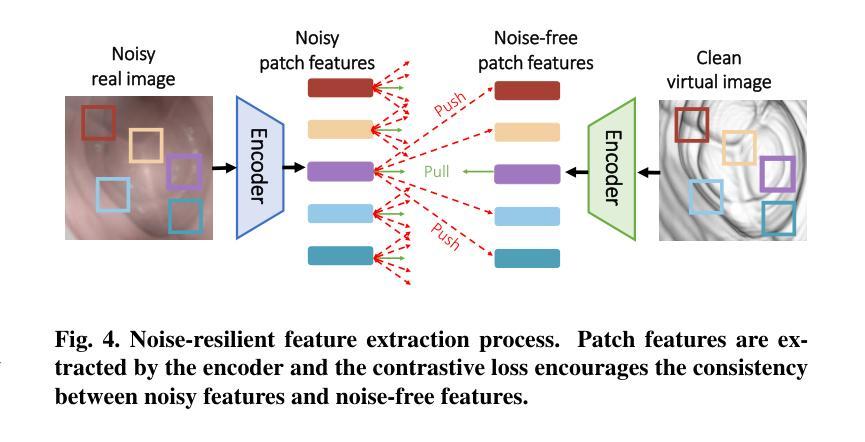
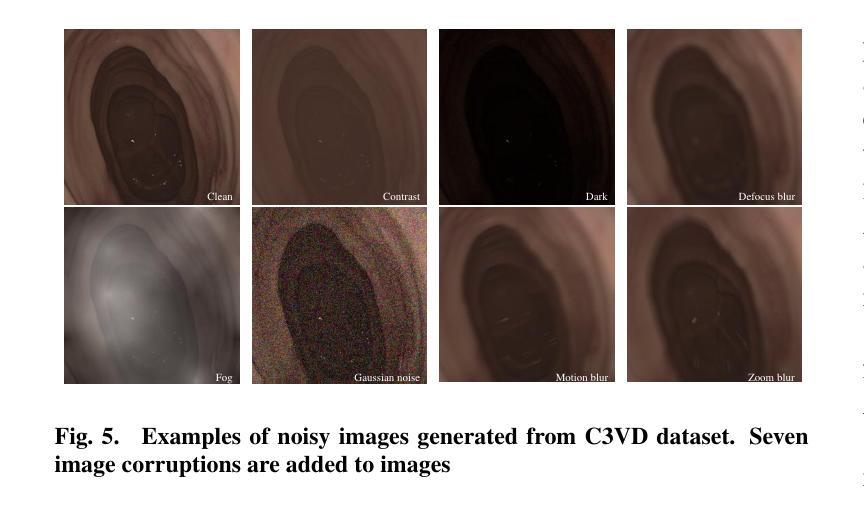
From Real Artifacts to Virtual Reference: A Robust Framework for Translating Endoscopic Images
Authors:Junyang Wu, Fangfang Xie, Jiayuan Sun, Yun Gu, Guang-Zhong Yang
Domain adaptation, which bridges the distributions across different modalities, plays a crucial role in multimodal medical image analysis. In endoscopic imaging, combining pre-operative data with intra-operative imaging is important for surgical planning and navigation. However, existing domain adaptation methods are hampered by distribution shift caused by in vivo artifacts, necessitating robust techniques for aligning noisy and artifact abundant patient endoscopic videos with clean virtual images reconstructed from pre-operative tomographic data for pose estimation during intraoperative guidance. This paper presents an artifact-resilient image translation method and an associated benchmark for this purpose. The method incorporates a novel ``local-global’’ translation framework and a noise-resilient feature extraction strategy. For the former, it decouples the image translation process into a local step for feature denoising, and a global step for global style transfer. For feature extraction, a new contrastive learning strategy is proposed, which can extract noise-resilient features for establishing robust correspondence across domains. Detailed validation on both public and in-house clinical datasets has been conducted, demonstrating significantly improved performance compared to the current state-of-the-art.
领域适应(domain adaptation)在多模态医疗图像分析中扮演着至关重要的角色,它架起了不同分布之间的桥梁。在内窥成像中,将术前数据与术中成像相结合对于手术规划和导航至关重要。然而,现有的领域适应方法受到体内伪影引起的分布变化的影响。因此,需要强大的技术来对齐充满噪声和伪影的患者内窥镜视频与通过术前断层扫描数据重建的干净虚拟图像,以用于术中指导的姿势估计。本文提出了一种用于此目的的抗伪影图像翻译方法和相关基准测试。该方法结合了一种新型的“局部-全局”翻译框架和抗噪声特征提取策略。对于前者,它将图像翻译过程分解为局部特征去噪和全局风格转换两个步骤。对于特征提取,提出了一种新的对比学习策略,可以提取出稳健的特征,以在各个领域之间建立稳健的对应关系。在公共和内部临床数据集上的详细验证显示,与当前先进技术相比,该方法性能显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
多模态医学图像分析中,域适应技术对于弥不同模态间的数据分布差异至关重要。在内窥成像领域,结合术前数据与术中影像对手术规划与导航具有重要意义。现有域适应方法受到体内伪影导致的分布偏移的制约,需要稳健技术来对含噪声和丰富伪影的患者内窥视频与从术前断层扫描数据中重建的干净虚拟图像进行对齐,以实现术中指导的姿态估计。本文提出了一种耐伪影的图像翻译方法和相关基准测试。该方法结合了一种新颖的“局部-全局”翻译框架和一种耐噪声的特征提取策略。前者将图像翻译过程分解为局部特征去噪和全局风格转换两个步骤。对于特征提取,提出了一种新的对比学习策略,可以提取跨域建立稳健对应的噪声鲁棒特征。在公共和院内临床数据集上的详细验证显示,与当前最新技术相比,该方法性能显著提高。
Key Takeaways
- 域适应在多模态医学图像分析中起到关键作用,尤其在连接不同模态数据分布方面。
- 内窥成像中结合术前与术中影像对手术规划和导航很重要。
- 现有域适应方法受到体内伪影导致的分布偏移的制约。
- 需要稳健的技术来对齐含噪声和伪影的内窥视频与虚拟图像。
- 提出的图像翻译方法结合“局部-全局”翻译框架和噪声鲁棒特征提取策略。
- 对比学习策略用于提取跨域的噪声鲁棒特征。
点此查看论文截图

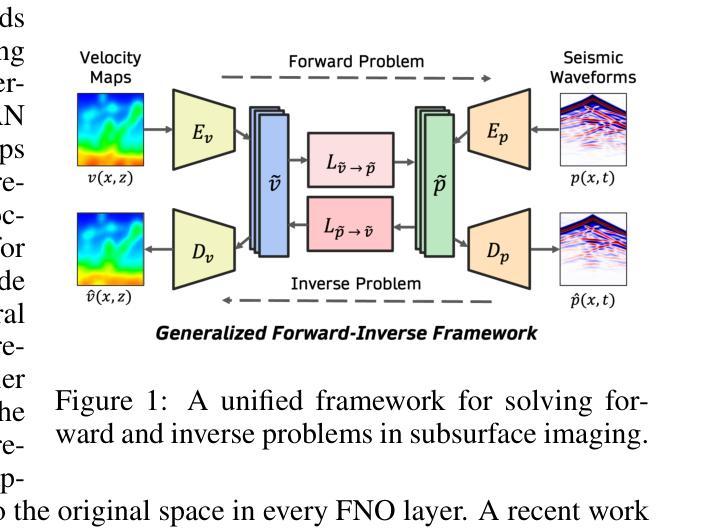
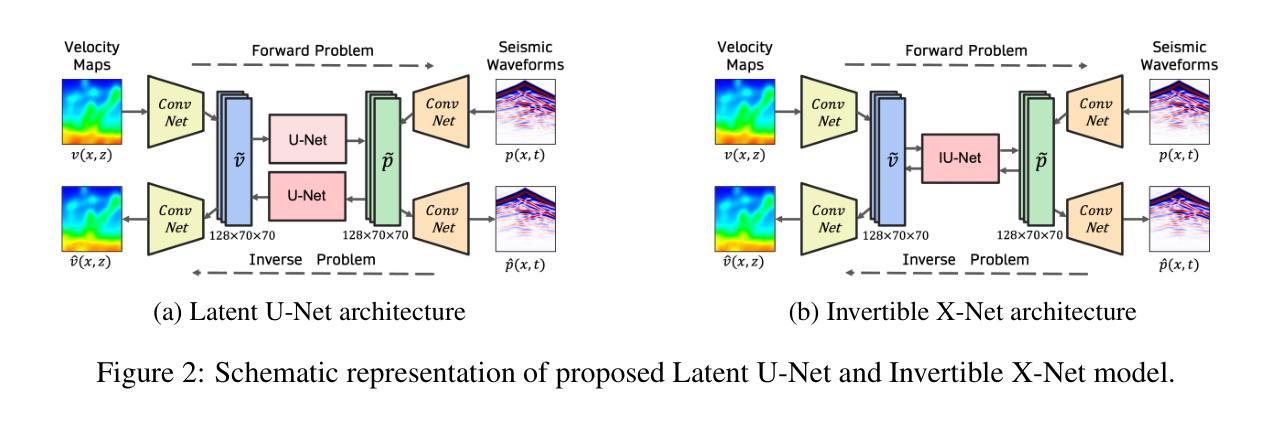
A Unified Framework for Forward and Inverse Problems in Subsurface Imaging using Latent Space Translations
Authors:Naveen Gupta, Medha Sawhney, Arka Daw, Youzuo Lin, Anuj Karpatne
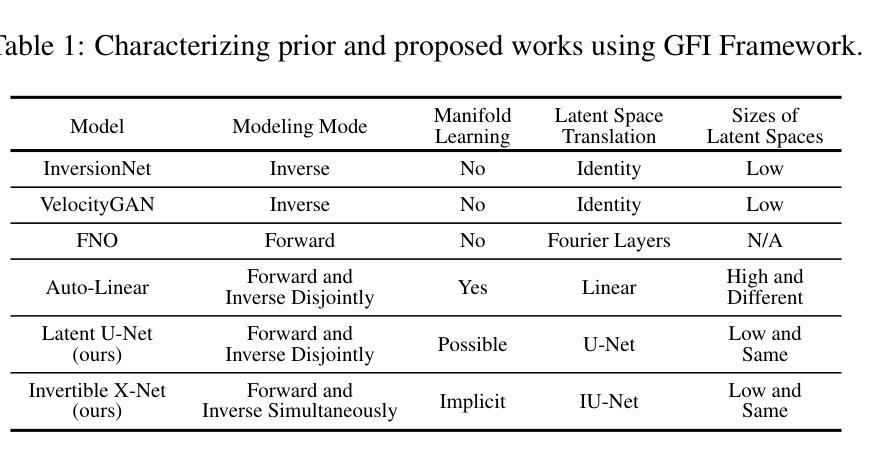
In subsurface imaging, learning the mapping from velocity maps to seismic waveforms (forward problem) and waveforms to velocity (inverse problem) is important for several applications. While traditional techniques for solving forward and inverse problems are computationally prohibitive, there is a growing interest in leveraging recent advances in deep learning to learn the mapping between velocity maps and seismic waveform images directly from data. Despite the variety of architectures explored in previous works, several open questions still remain unanswered such as the effect of latent space sizes, the importance of manifold learning, the complexity of translation models, and the value of jointly solving forward and inverse problems. We propose a unified framework to systematically characterize prior research in this area termed the Generalized Forward-Inverse (GFI) framework, building on the assumption of manifolds and latent space translations. We show that GFI encompasses previous works in deep learning for subsurface imaging, which can be viewed as specific instantiations of GFI. We also propose two new model architectures within the framework of GFI: Latent U-Net and Invertible X-Net, leveraging the power of U-Nets for domain translation and the ability of IU-Nets to simultaneously learn forward and inverse translations, respectively. We show that our proposed models achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance for forward and inverse problems on a wide range of synthetic datasets, and also investigate their zero-shot effectiveness on two real-world-like datasets.
在地下成像中,学习从速度图到地震波形的映射(正问题)以及从波形到速度(反问题)对于多种应用至关重要。虽然传统的解决正问题和反问题的技术在计算上受到很大限制,但人们越来越有兴趣利用深度学习的最新进展直接从数据中学习速度图与地震波形图像之间的映射。尽管之前的研究工作探索了各种架构,但仍有许多开放问题尚未解决,例如潜在空间大小的影响、流形学习的重要性、翻译模型的复杂性以及联合解决正问题和反问题的价值。我们提出了一个统一的框架来系统地刻画这一领域的先前研究,称为广义正逆(GFI)框架,该框架建立在流形和潜在空间翻译假设的基础上。我们展示了GFI涵盖了地下成像深度学习领域的先前研究,这些研究可以被视为GFI的特定实例。在GFI框架内,我们还提出了两种新型模型架构:潜在U-Net和可逆X-Net,它们利用U-Net在领域翻译方面的优势以及IU-Net同时学习正向和逆向翻译的能力。我们展示了我们提出的模型在多种合成数据集上的正向和反向问题上实现了最新技术水平(SOTA),并调查了它们在两个现实世界类似数据集的零样本有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了利用深度学习技术解决地下成像中的正问题和反问题的重要性及方法。针对现有技术计算量大、模型复杂等问题,提出了广义正逆(GFI)框架,并对潜空间大小、流形学习的重要性等开放性问题进行了系统探讨。同时,文章提出了两种新模型架构——Latent U-Net和Invertible X-Net,并通过实验证明了这些模型在合成数据集上的优异性能以及对两个真实世界数据集的零样本有效性。
Key Takeaways:
- 地下成像中,正问题和反问题的研究对于多种应用至关重要。传统技术计算量大,而深度学习在解决这些问题方面具有潜力。
- 广义正逆(GFI)框架用于系统地描述和研究该领域的先前研究。
- GFI框架包含潜空间大小和流形学习等关键要素的研究。
- Latent U-Net和Invertible X-Net模型在合成数据集上表现优异。
- 新模型架构利用U-Net进行领域转换,并能同时学习正逆转换。
- 文章探讨了新模型在真实世界数据集上的零样本有效性。
点此查看论文截图

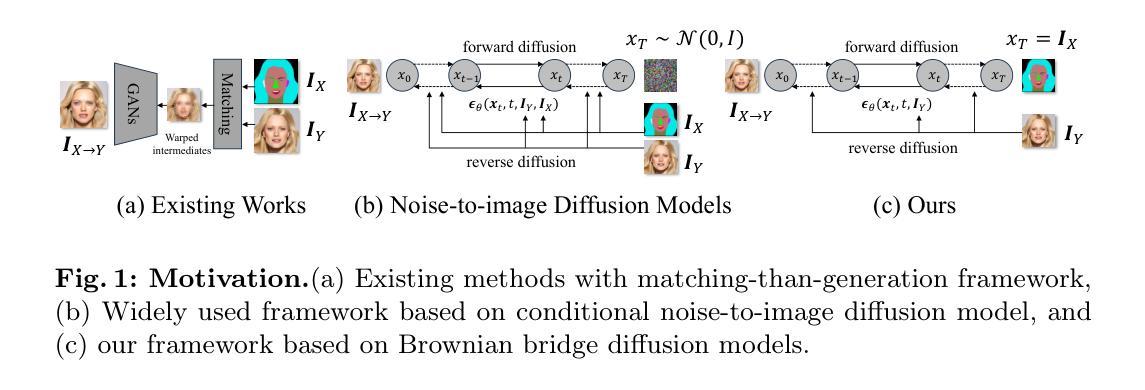
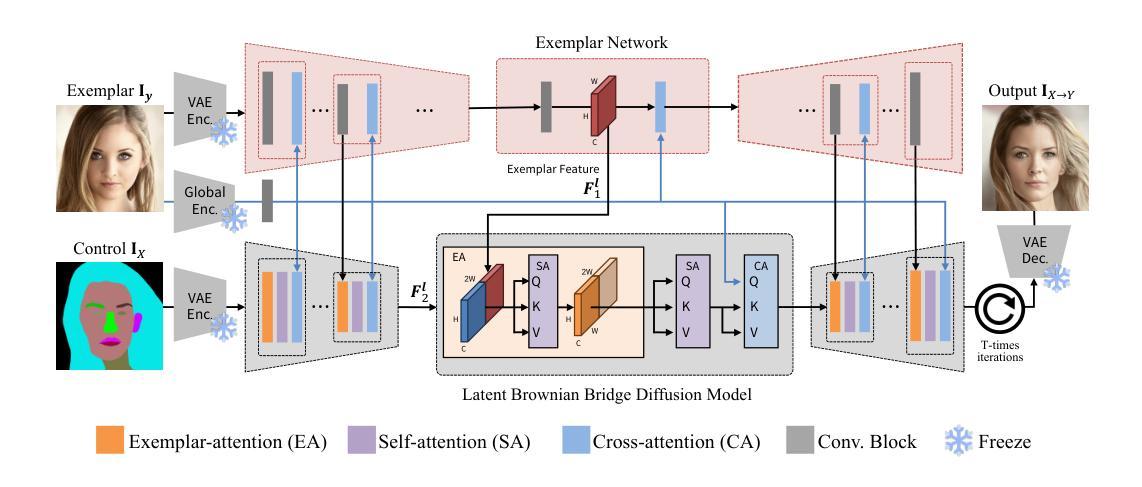
EBDM: Exemplar-guided Image Translation with Brownian-bridge Diffusion Models
Authors:Eungbean Lee, Somi Jeong, Kwanghoon Sohn
Exemplar-guided image translation, synthesizing photo-realistic images that conform to both structural control and style exemplars, is attracting attention due to its ability to enhance user control over style manipulation. Previous methodologies have predominantly depended on establishing dense correspondences across cross-domain inputs. Despite these efforts, they incur quadratic memory and computational costs for establishing dense correspondence, resulting in limited versatility and performance degradation. In this paper, we propose a novel approach termed Exemplar-guided Image Translation with Brownian-Bridge Diffusion Models (EBDM). Our method formulates the task as a stochastic Brownian bridge process, a diffusion process with a fixed initial point as structure control and translates into the corresponding photo-realistic image while being conditioned solely on the given exemplar image. To efficiently guide the diffusion process toward the style of exemplar, we delineate three pivotal components: the Global Encoder, the Exemplar Network, and the Exemplar Attention Module to incorporate global and detailed texture information from exemplar images. Leveraging Bridge diffusion, the network can translate images from structure control while exclusively conditioned on the exemplar style, leading to more robust training and inference processes. We illustrate the superiority of our method over competing approaches through comprehensive benchmark evaluations and visual results.
范例引导的图像翻译技术正在吸引人们的关注,因为它能够合成既符合结构控制又符合样式范例的光栅图像。之前的方法主要依赖于建立跨域输入的密集对应关系。尽管付出了这些努力,但由于建立密集对应关系需要二次内存和计算成本,导致灵活性有限和性能下降。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的方法,称为基于布朗桥扩散模型的范例引导图像翻译(EBDM)。我们的方法将任务表述为随机布朗桥过程,这是一个以固定初始点为结构控制的扩散过程,并仅根据给定的范例图像翻译成相应的光栅图像。为了有效地将扩散过程引向范例的风格,我们划定了三个关键组成部分:全局编码器、范例网络和范例注意力模块,以融入范例图像中的全局和详细纹理信息。借助桥梁扩散,网络可以在仅受范例风格制约的同时,从结构控制翻译图像,从而实现更稳健的训练和推理过程。我们通过综合基准评估和产品视觉结果,说明了我们的方法优于其他方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ECCV 2024
Summary:
图像翻译技术在结构和风格典范指导下合成逼真的图像方面引起了关注。虽然现有的方法主要通过建立跨域输入的密集对应关系来实现,但它们需要二次内存和计算成本,限制了灵活性和性能。本文提出了一种新的方法,称为基于布朗桥扩散模型的范例引导图像翻译(EBDM),它将任务形式化为一个随机布朗桥过程,仅依赖于给定的范例图像进行翻译。通过全球编码器、范例网络和范例注意力模块三个关键组件有效地引导扩散过程向范例风格发展。利用桥梁扩散网络可以在遵循结构控制的同时,仅根据范例风格进行图像翻译,实现更稳健的训练和推理过程。
Key Takeaways:
- 图像翻译技术在合成逼真图像方面受到关注,特别是在结构和风格典范的指导下。
- 现有方法主要依赖建立跨域输入的密集对应关系,但存在内存和计算成本高的缺点。
- 提出了一种新的图像翻译方法EBDM,将任务形式化为随机布朗桥过程。
- EBDM方法仅依赖于给定的范例图像进行翻译,提高了灵活性和性能。
- 通过全球编码器、范例网络和范例注意力模块三个关键组件引导扩散过程向范例风格发展。
- 利用桥梁扩散网络可以在遵循结构控制的同时,仅根据范例风格进行图像翻译。
点此查看论文截图