⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-11 更新
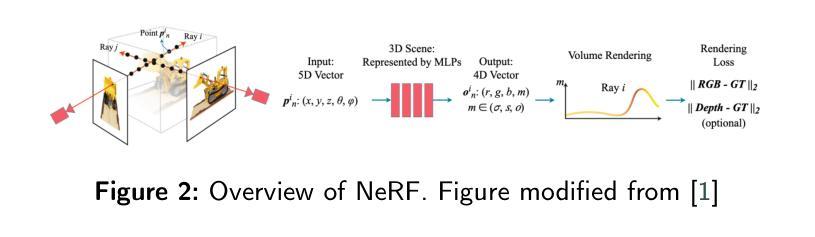
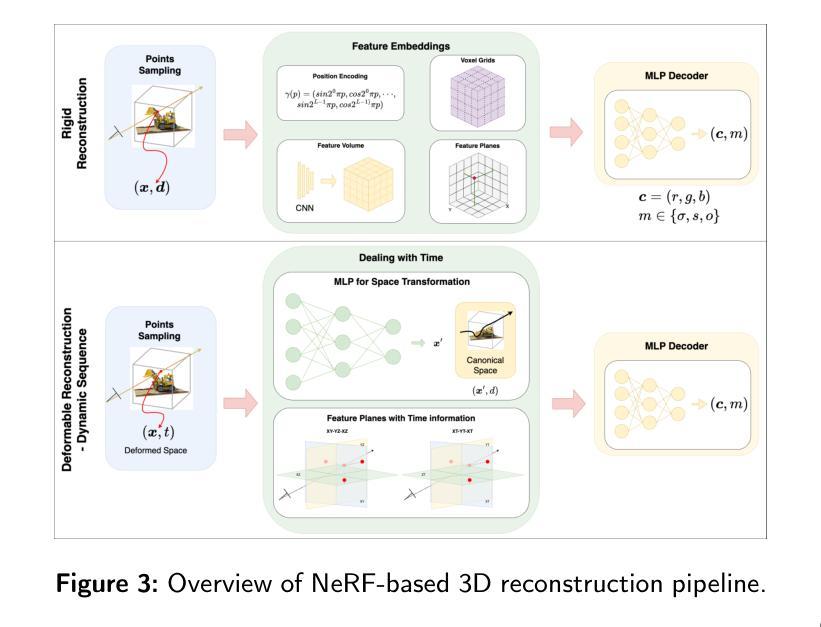
Dynamic EventNeRF: Reconstructing General Dynamic Scenes from Multi-view Event Cameras
Authors:Viktor Rudnev, Gereon Fox, Mohamed Elgharib, Christian Theobalt, Vladislav Golyanik
Volumetric reconstruction of dynamic scenes is an important problem in computer vision. It is especially challenging in poor lighting and with fast motion. It is partly due to the limitations of RGB cameras: To capture fast motion without much blur, the framerate must be increased, which in turn requires more lighting. In contrast, event cameras, which record changes in pixel brightness asynchronously, are much less dependent on lighting, making them more suitable for recording fast motion. We hence propose the first method to spatiotemporally reconstruct a scene from sparse multi-view event streams and sparse RGB frames. We train a sequence of cross-faded time-conditioned NeRF models, one per short recording segment. The individual segments are supervised with a set of event- and RGB-based losses and sparse-view regularisation. We assemble a real-world multi-view camera rig with six static event cameras around the object and record a benchmark multi-view event stream dataset of challenging motions. Our work outperforms RGB-based baselines, producing state-of-the-art results, and opens up the topic of multi-view event-based reconstruction as a new path for fast scene capture beyond RGB cameras. The code and the data will be released soon at https://4dqv.mpi-inf.mpg.de/DynEventNeRF/
动态场景的体积重建是计算机视觉领域的一个重要问题。在光线不足和快速运动的情况下,这一任务更具挑战性。这在一定程度上是由于RGB相机的局限性所致:为了在不模糊的情况下捕捉快速运动,必须增加帧率,这反过来又需要更多的光线。相比之下,事件相机能够异步记录像素亮度的变化,对光线的依赖性较小,因此更适合记录快速运动。因此,我们提出了第一种从稀疏的多视角事件流和稀疏RGB帧中重建场景时空信息的方法。我们训练了一系列跨淡入淡出时间条件的NeRF模型序列,每个短期记录片段一个。各个片段受到事件和RGB基损失以及稀疏视图正则化的监督。我们使用六个静态事件相机围绕对象构建了一个真实世界的多视角相机装置,并记录了具有挑战性运动的基准多视角事件流数据集。我们的工作优于基于RGB的基线,取得了最新结果,并开启了基于多视角事件重建的主题作为超越RGB相机进行快速场景捕获的新途径。代码和数据将很快在https://4dqv.mpi-inf.mpg.de/DynEventNeRF/发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 11 figures, 6 tables
Summary
本文提出一种基于事件流和RGB帧的时空场景重建方法,采用跨淡入的时间条件NeRF模型序列,以应对动态场景在弱光条件下的重建挑战。通过结合事件相机记录的像素亮度变化,该方法在记录快速运动场景时具有较低的光线依赖性。实验表明,该方法优于基于RGB的基线方法,实现了前沿的重建效果,为事件流的多视角重建开启了新的研究路径。
Key Takeaways
- 动态场景的体积重建是计算机视觉中的重要问题,特别是在弱光和快速运动条件下更具挑战性。
- 事件相机能够记录像素亮度的异步变化,适合录制快速运动场景,相较于RGB相机具有较低的光线依赖性。
- 提出了首个基于稀疏多视角事件流和RGB帧的时空场景重建方法。
- 采用跨淡入的时间条件NeRF模型序列进行建模,对个别段落进行基于事件和RGB的损失以及稀疏视图正则化的监督。
- 建立了一个真实世界的多视角相机系统,包含六个静态事件相机,并录制了一个具有挑战性运动的多视角事件流数据集。
- 该方法优于基于RGB的基线方法,实现了先进的重建结果。
点此查看论文截图


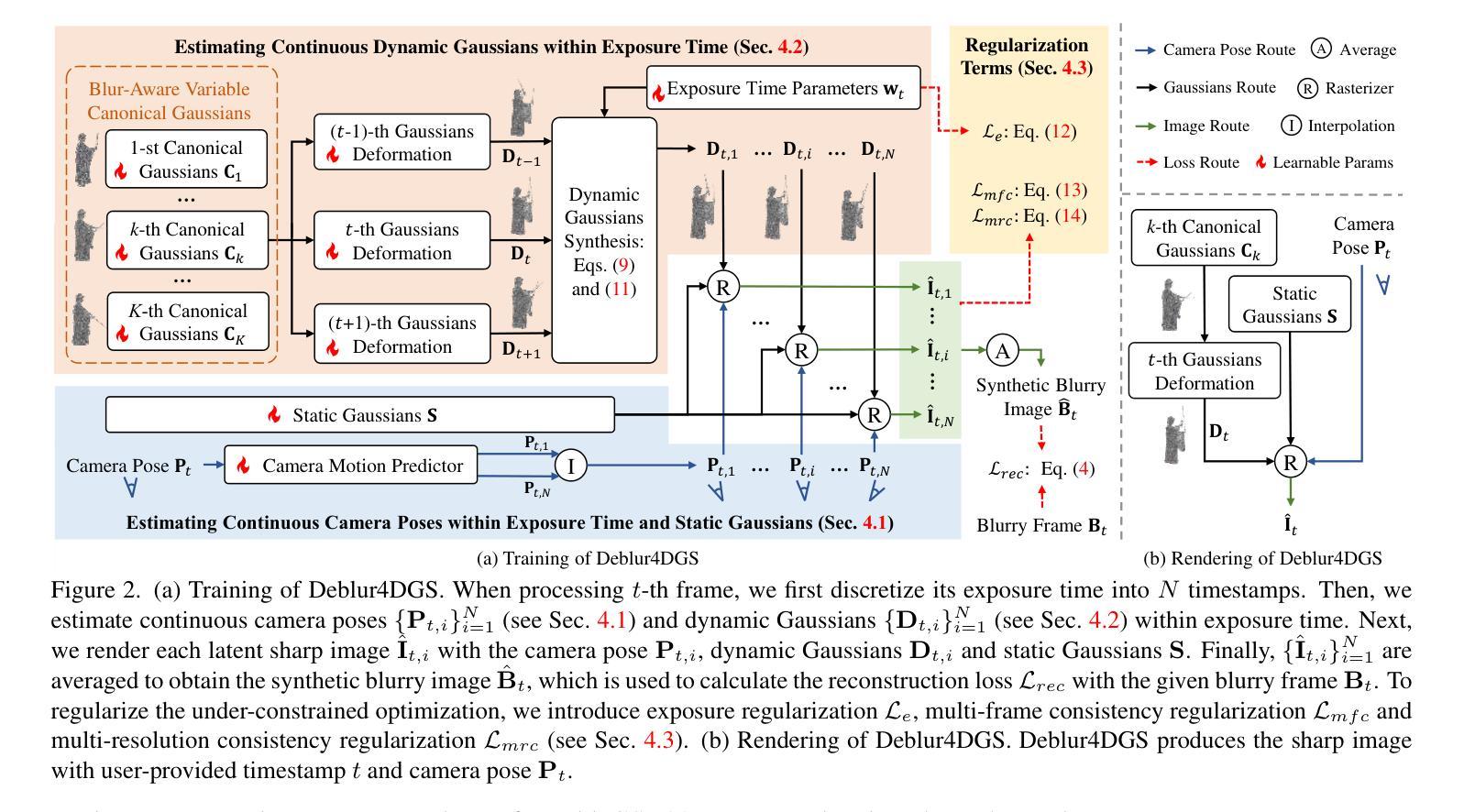
Deblur4DGS: 4D Gaussian Splatting from Blurry Monocular Video
Authors:Renlong Wu, Zhilu Zhang, Mingyang Chen, Xiaopeng Fan, Zifei Yan, Wangmeng Zuo
Recent 4D reconstruction methods have yielded impressive results but rely on sharp videos as supervision. However, motion blur often occurs in videos due to camera shake and object movement, while existing methods render blurry results when using such videos for reconstructing 4D models. Although a few NeRF-based approaches attempted to address the problem, they struggled to produce high-quality results, due to the inaccuracy in estimating continuous dynamic representations within the exposure time. Encouraged by recent works in 3D motion trajectory modeling using 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), we suggest taking 3DGS as the scene representation manner, and propose the first 4D Gaussian Splatting framework to reconstruct a high-quality 4D model from blurry monocular video, named Deblur4DGS. Specifically, we transform continuous dynamic representations estimation within an exposure time into the exposure time estimation. Moreover, we introduce exposure regularization to avoid trivial solutions, as well as multi-frame and multi-resolution consistency ones to alleviate artifacts. Furthermore, to better represent objects with large motion, we suggest blur-aware variable canonical Gaussians. Beyond novel-view synthesis, Deblur4DGS can be applied to improve blurry video from multiple perspectives, including deblurring, frame interpolation, and video stabilization. Extensive experiments on the above four tasks show that Deblur4DGS outperforms state-of-the-art 4D reconstruction methods. The codes are available at https://github.com/ZcsrenlongZ/Deblur4DGS.
近期的4D重建方法已经取得了令人印象深刻的结果,但它们依赖于清晰视频作为监督。然而,由于相机抖动和物体移动,视频中的运动模糊经常发生,而当使用此类视频进行4D模型重建时,现有方法会产生模糊的结果。尽管有几种基于NeRF的方法试图解决这个问题,但由于在曝光时间内估计连续动态表示的不准确性,它们很难产生高质量的结果。受到近期使用3D高斯涂抹(3DGS)进行3D运动轨迹建模的工作的启发,我们建议将3DGS作为场景表示方式,并提出第一个4D高斯涂抹框架,可以从模糊的单目视频中重建高质量的4D模型,名为Deblur4DGS。具体来说,我们将曝光时间内连续动态表示的估计转化为曝光时间估计。此外,我们引入了曝光正则化以避免平凡解,以及多帧和多分辨率一致性来解决伪影问题。此外,为了更好地表示具有大运动的物体,我们建议使用模糊感知可变规范高斯。除了新型视图合成外,Deblur4DGS还可以应用于从多个角度提高模糊视频的质量,包括去模糊、帧内插值和视频稳定。在以上四个任务上的大量实验表明,Deblur4DGS优于最新的4D重建方法。代码可用在https://github.com/ZcsrenlongZ/Deblur4DGS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages
Summary
本文提出一种名为Deblur4DGS的4D高斯喷绘框架,能够从模糊的单目视频中重建高质量的4D模型。通过采用3D高斯喷绘作为场景表现方式,解决了现有方法在模糊视频下重建4D模型时产生的问题。通过估计曝光时间来解决连续动态表示的估计问题,引入曝光正则化以及多帧和多分辨率一致性来减少伪影。此外,对于大动作物体有更好的表现能力。除了新型视图合成外,Deblur4DGS还可应用于去模糊、帧插值和视频稳定等多个方面。实验表明,Deblur4DGS在四项任务上的表现均优于现有最佳4D重建方法。
Key Takeaways
- Deblur4DGS是首个能够从模糊的单目视频中重建高质量4D模型的框架。
- 采用3D高斯喷绘作为场景表现方式,解决了现有方法在模糊视频下的挑战。
- 通过估计曝光时间解决连续动态表示的问题。
- 引入曝光正则化、多帧和多分辨率一致性来减少伪影。
- 适用于大动作物体的表现能力更强。
- 除了新型视图合成,Deblur4DGS还可应用于去模糊、帧插值和视频稳定等任务。
点此查看论文截图



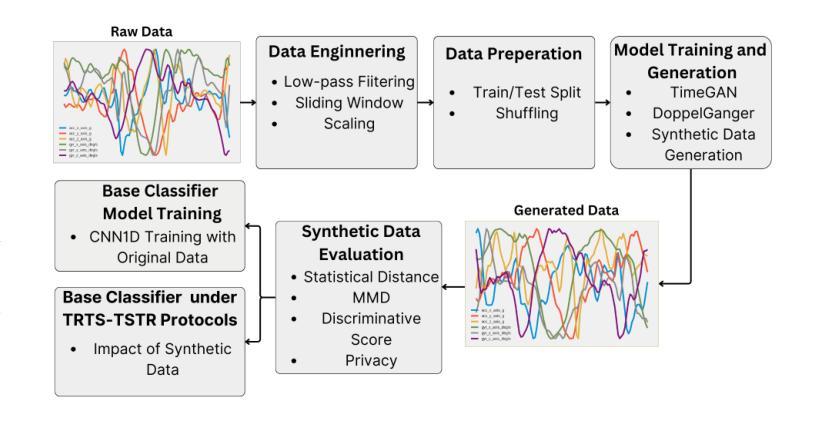
Exploring the Impact of Synthetic Data on Human Gesture Recognition Tasks Using GANs
Authors:George Kontogiannis, Pantelis Tzamalis, Sotiris Nikoletseas
In the evolving domain of Human Activity Recognition (HAR) using Internet of Things (IoT) devices, there is an emerging interest in employing Deep Generative Models (DGMs) to address data scarcity, enhance data quality, and improve classification metrics scores. Among these types of models, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have arisen as a powerful tool for generating synthetic data that mimic real-world scenarios with high fidelity. However, Human Gesture Recognition (HGR), a subset of HAR, particularly in healthcare applications, using time series data such as allergic gestures, remains highly unexplored. In this paper, we examine and evaluate the performance of two GANs in the generation of synthetic gesture motion data that compose a part of an open-source benchmark dataset. The data is related to the disease identification domain and healthcare, specifically to allergic rhinitis. We also focus on these AI models’ performance in terms of fidelity, diversity, and privacy. Furthermore, we examine the scenario if the synthetic data can substitute real data, in training scenarios and how well models trained on synthetic data can be generalized for the allergic rhinitis gestures. In our work, these gestures are related to 6-axes accelerometer and gyroscope data, serving as multi-variate time series instances, and retrieved from smart wearable devices. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to explore the feasibility of synthesizing motion gestures for allergic rhinitis from wearable IoT device data using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and testing their impact on the generalization of gesture recognition systems. It is worth noting that, even if our method has been applied to a specific category of gestures, it is designed to be generalized and can be deployed also to other motion data in the HGR domain.
在人类活动识别(HAR)不断进化的领域中,利用物联网(IoT)设备,人们越来越有兴趣采用深度生成模型(DGMs)来解决数据稀缺问题,提高数据质量,并改善分类指标得分。在这些类型的模型中,生成对抗网络(GANs)已成为生成合成数据的强大工具,这些合成数据以高保真度模拟真实场景。然而,特别是在医疗保健应用中,使用时间序列数据如过敏性手势进行的人类手势识别(HGR)仍是HAR的一个子集,尚未得到充分探索。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures, 20th International Conference on Distributed Computing in Smart Systems and the Internet of Things (DCOSS-IoT), 2024
Summary
本文探讨了使用物联网设备在人体活动识别领域中的新兴技术,特别是深度生成模型在处理手势识别中的应用。特别是针对过敏性鼻炎等疾病的姿态识别,研究利用生成对抗网络生成合成姿态运动数据,评估其性能。研究发现合成数据可以替代真实数据进行训练,并有望提高模型在过敏性鼻手势识别方面的泛化能力。该研究首次探索了利用生成对抗网络合成过敏性鼻手势数据的可行性并测试了对手势识别系统的影响。这项技术的设计目的不仅是应用于特定的疾病类型,也适用于其他领域的运动姿态识别。本文的分析集中于数据质量、隐私保护和模型的性能评估等方面。该方法的优势在于提高了数据质量和模型泛化能力,有助于解决实际应用中的数据稀缺问题。研究为该领域的发展提供了重要的见解和启示。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注物联网设备在人体活动识别领域的应用,特别是手势识别。
- 采用深度生成模型中的生成对抗网络来生成合成姿态运动数据。
- 研究集中在过敏性鼻手势识别方面,但该技术适用于其他运动姿态识别领域。
- 研究评估了合成数据的性能,包括真实数据替代训练的可行性及模型泛化能力。
- 研究首次探索了利用生成对抗网络合成过敏性鼻手势数据的可行性。
点此查看论文截图

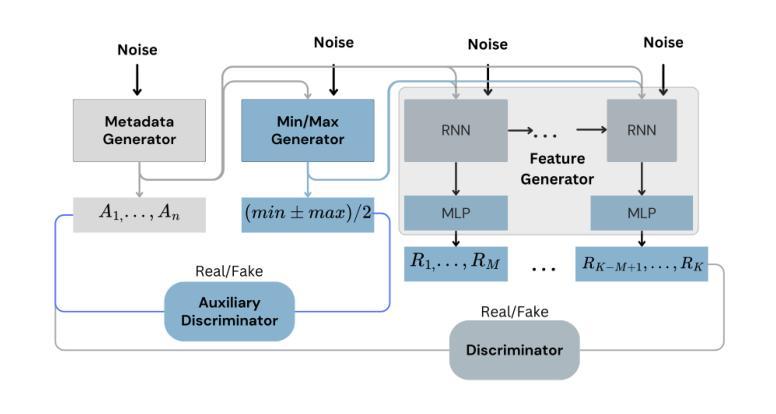
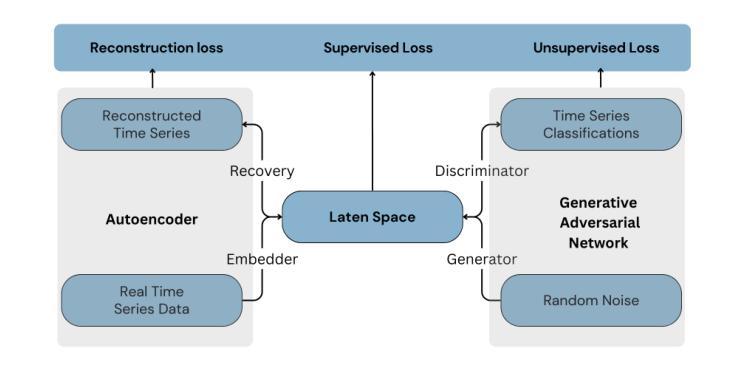
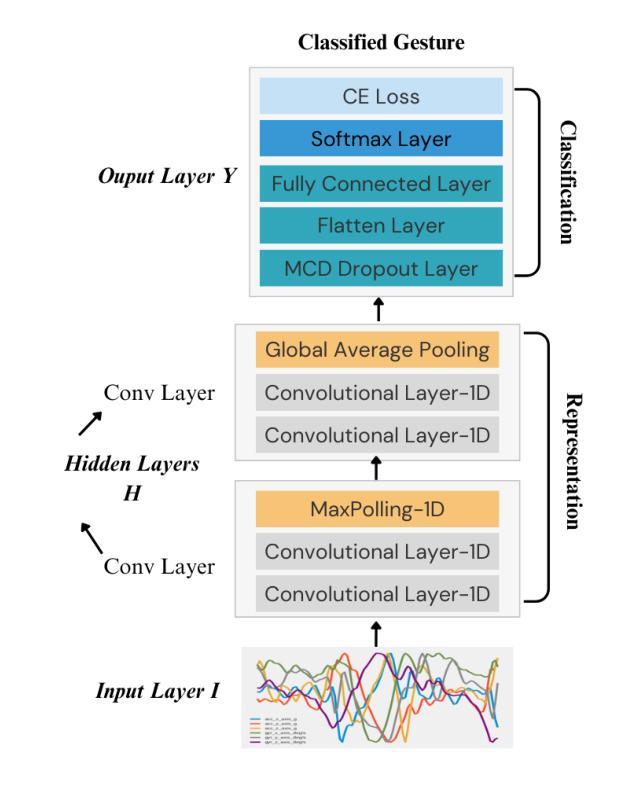
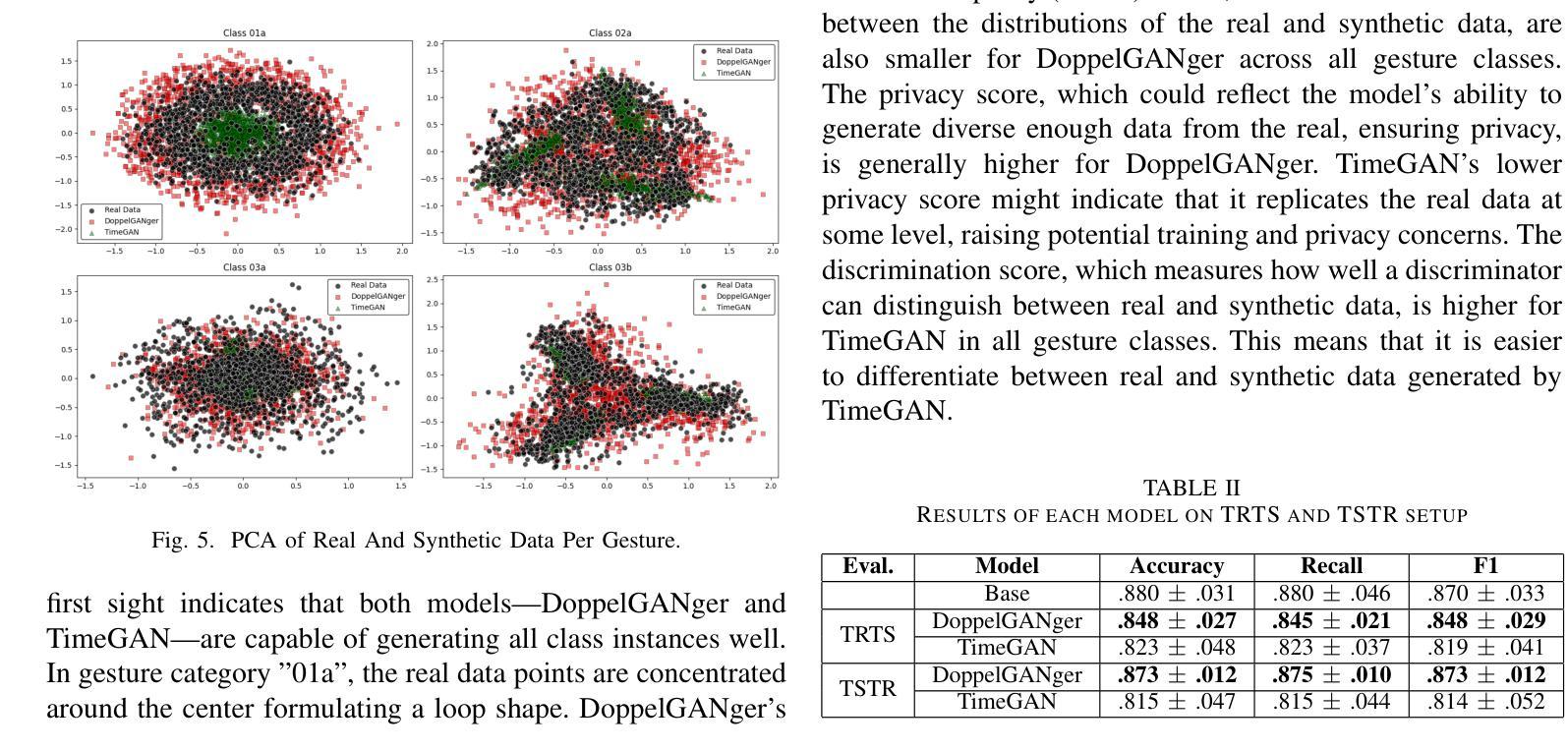
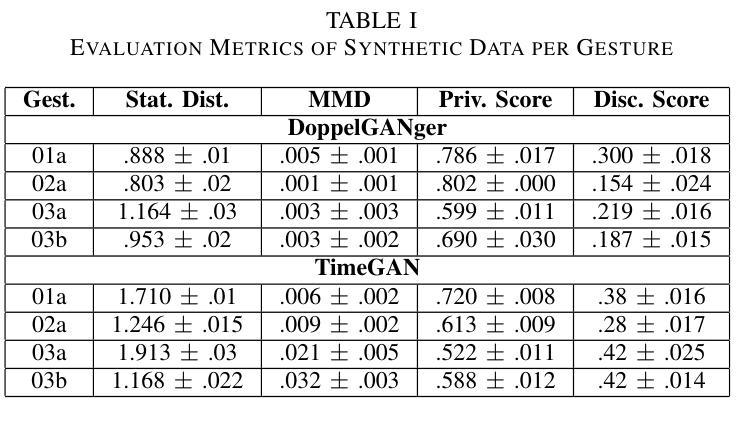
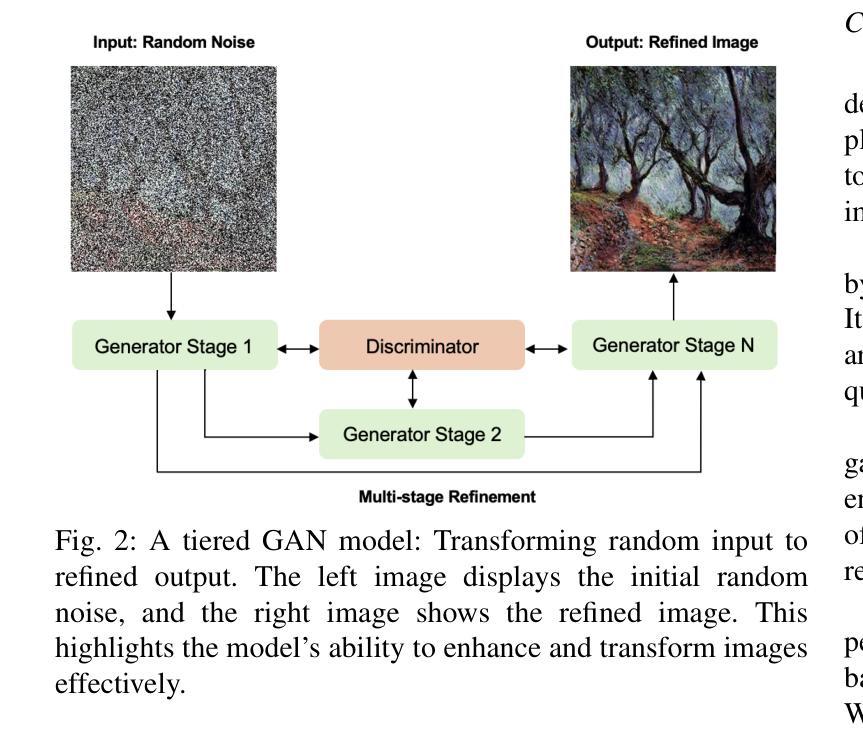
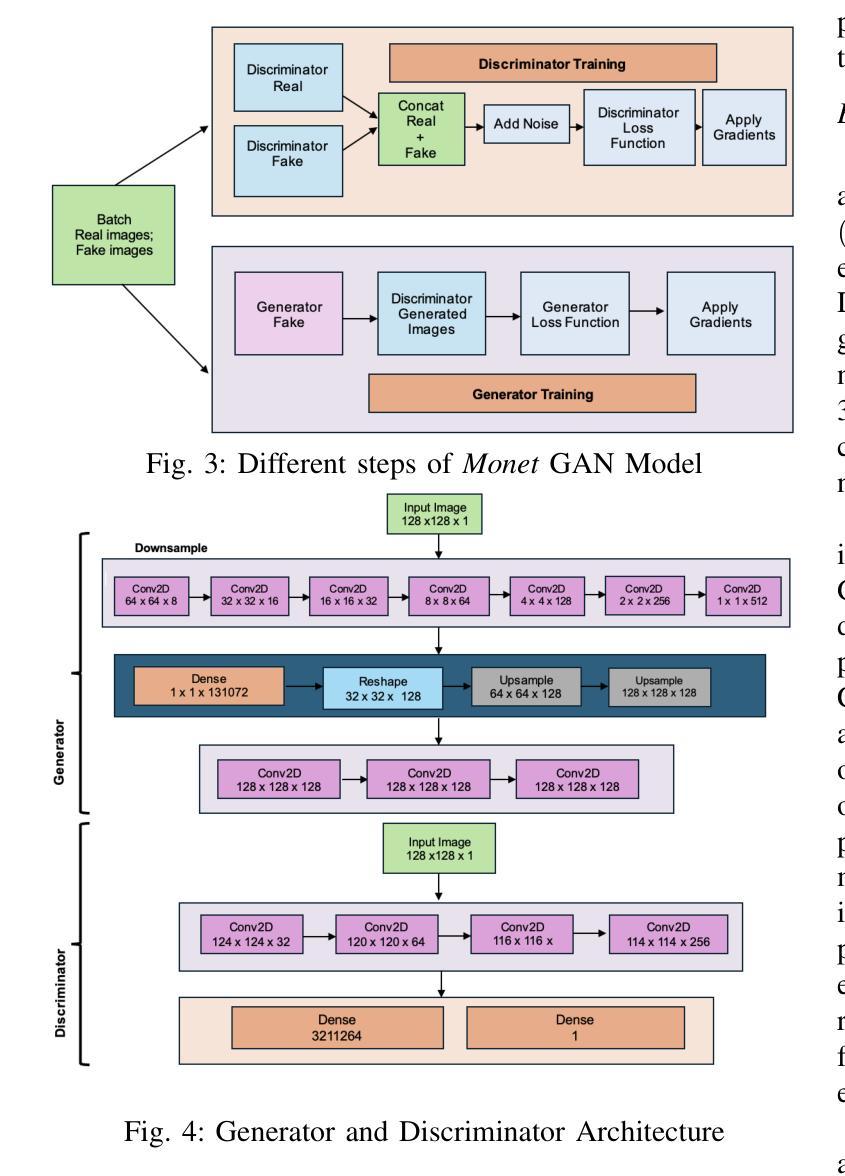
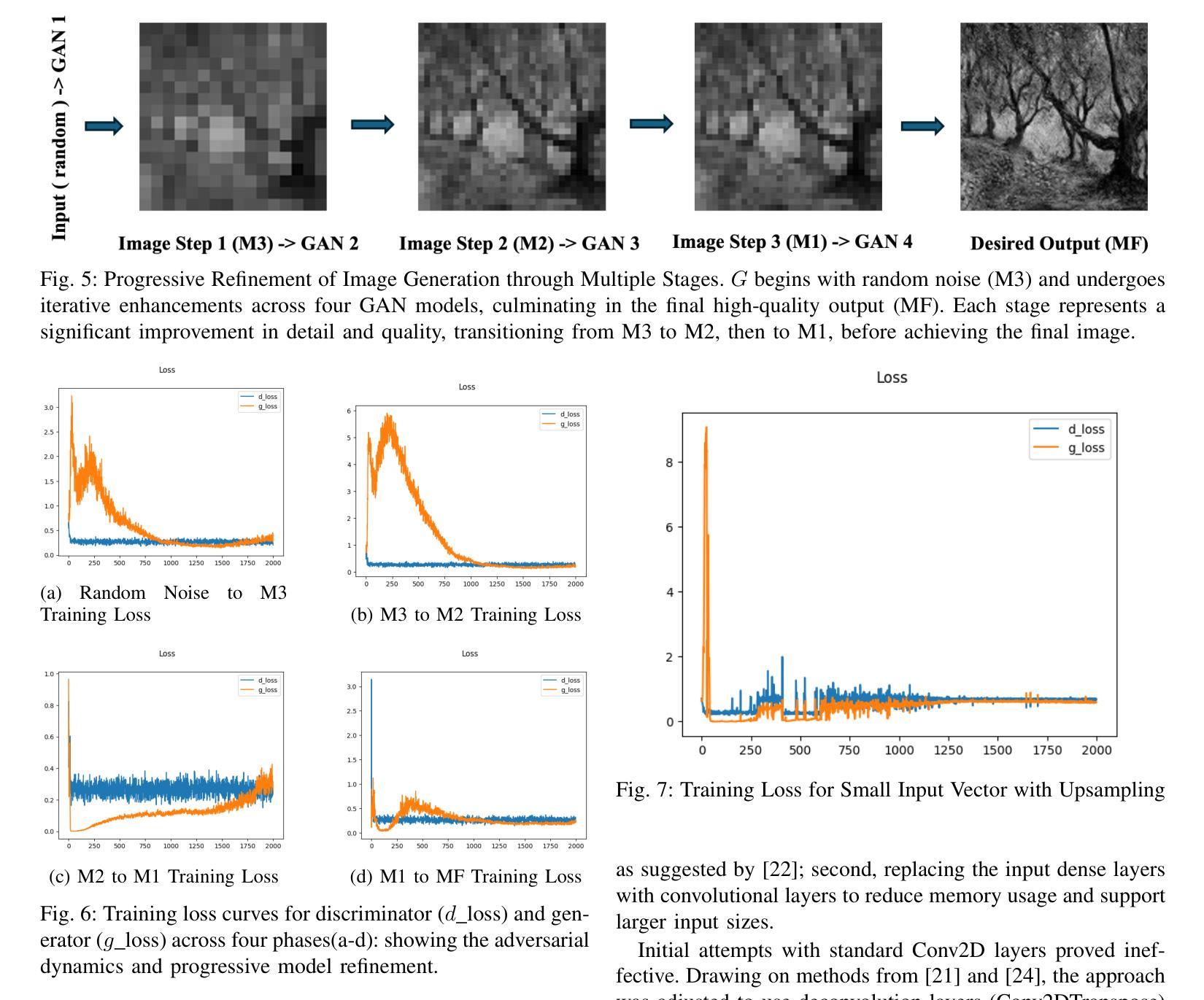
A Tiered GAN Approach for Monet-Style Image Generation
Authors:FNU Neha, Deepshikha Bhati, Deepak Kumar Shukla, Md Amiruzzaman
Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have proven to be a powerful tool in generating artistic images, capable of mimicking the styles of renowned painters, such as Claude Monet. This paper introduces a tiered GAN model to progressively refine image quality through a multi-stage process, enhancing the generated images at each step. The model transforms random noise into detailed artistic representations, addressing common challenges such as instability in training, mode collapse, and output quality. This approach combines downsampling and convolutional techniques, enabling the generation of high-quality Monet-style artwork while optimizing computational efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate the architecture’s ability to produce foundational artistic structures, though further refinements are necessary for achieving higher levels of realism and fidelity to Monet’s style. Future work focuses on improving training methodologies and model complexity to bridge the gap between generated and true artistic images. Additionally, the limitations of traditional GANs in artistic generation are analyzed, and strategies to overcome these shortcomings are proposed.
生成对抗网络(GANs)已被证明是生成艺术图像的强大工具,能够模仿著名画家(如克劳德·莫奈)的风格。本文介绍了一种分层GAN模型,通过多阶段过程逐步改进图像质量,每一步都增强生成的图像。该模型将随机噪声转换为详细的艺术表示形式,解决了训练不稳定、模式崩溃和输出质量等常见挑战。该方法结合了降采样和卷积技术,能够生成高质量的莫奈风格的艺术作品,同时优化计算效率。实验结果证明了该架构生成基础艺术结构的能力,但要实现更高程度的逼真度和对莫奈风格的忠实度,还需要进一步的改进。未来的工作重点是通过改进训练方法和模型复杂性来缩小生成的艺术图像和真正的艺术图像之间的差距。此外,还分析了传统GAN在艺术创作中的局限性,并提出了克服这些不足的对策。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文提出了一种层次化生成对抗网络模型,通过多阶段过程逐步优化图像质量。模型能够将随机噪声转化为详细的艺术表示形式,解决训练不稳定、模式崩溃和输出质量差等常见问题。通过结合下采样和卷积技术,该模型能够生成高质量的莫奈风格艺术作品,同时优化计算效率。实验结果表明,该架构能够生成基础艺术结构,但仍需进一步改进以实现更高水平的真实感和莫奈风格的忠实度。
Key Takeaways
- 论文介绍了一种基于生成对抗网络(GANs)的分层模型,用于逐步优化图像质量。
- 该模型能够将随机噪声转化为详细的艺术表示,解决训练中的不稳定性和模式崩溃问题。
- 通过结合下采样和卷积技术,模型能够生成高质量的莫奈风格艺术作品。
- 实验结果表明该架构具备生成基础艺术结构的能力,但仍需进一步改进以提高真实感和忠实度。
- 未来工作方向包括改进训练方法和模型复杂性,以缩小生成图像和真实艺术作品之间的差距。
- 论文分析了传统GANs在艺术创作方面的局限性,并提出了克服这些不足的策略。
点此查看论文截图

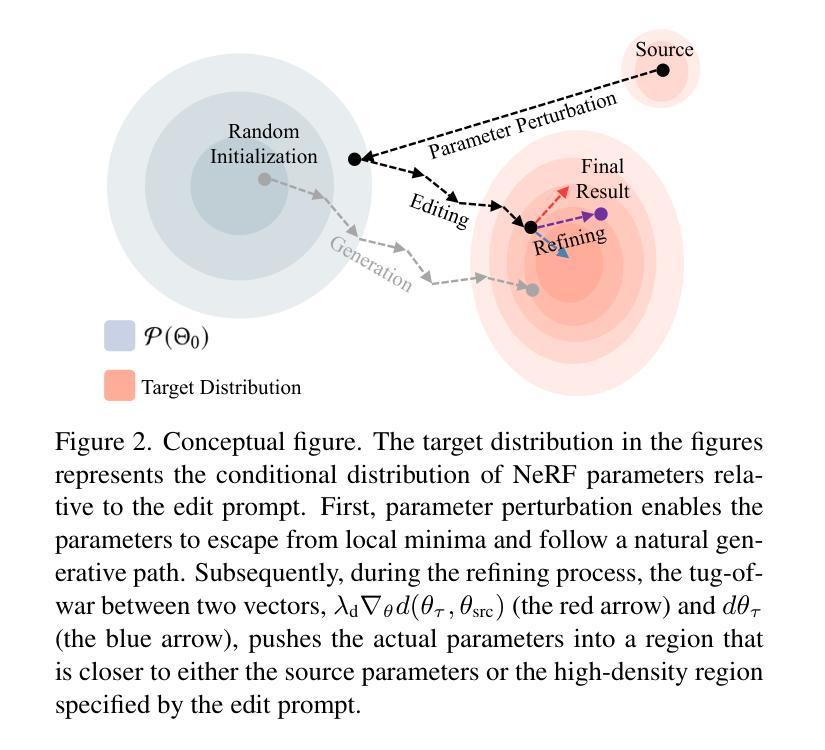
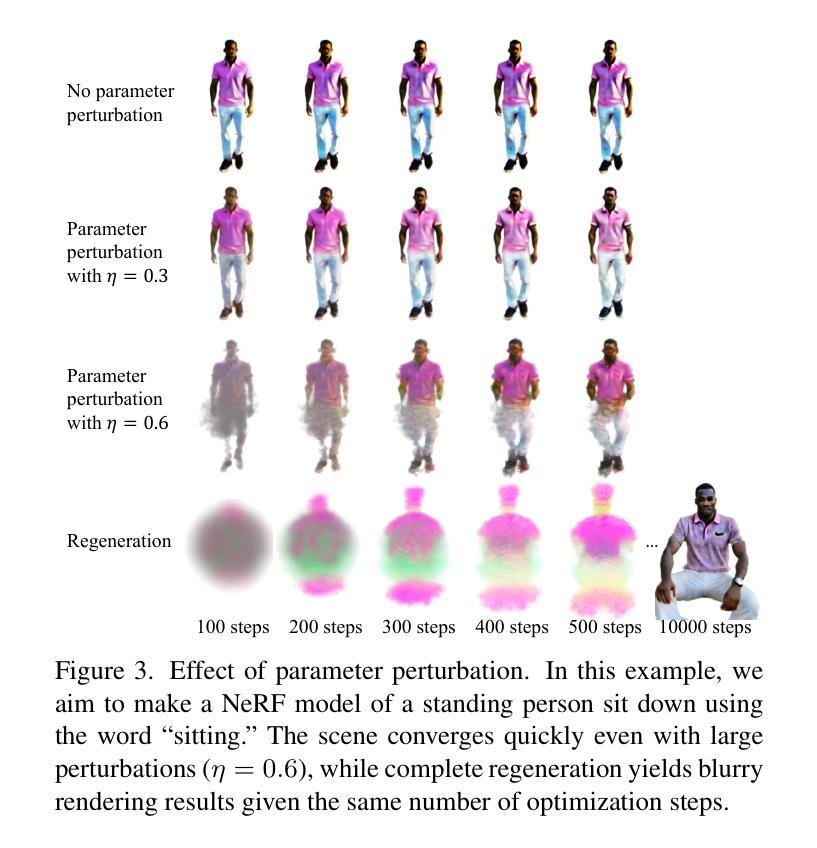
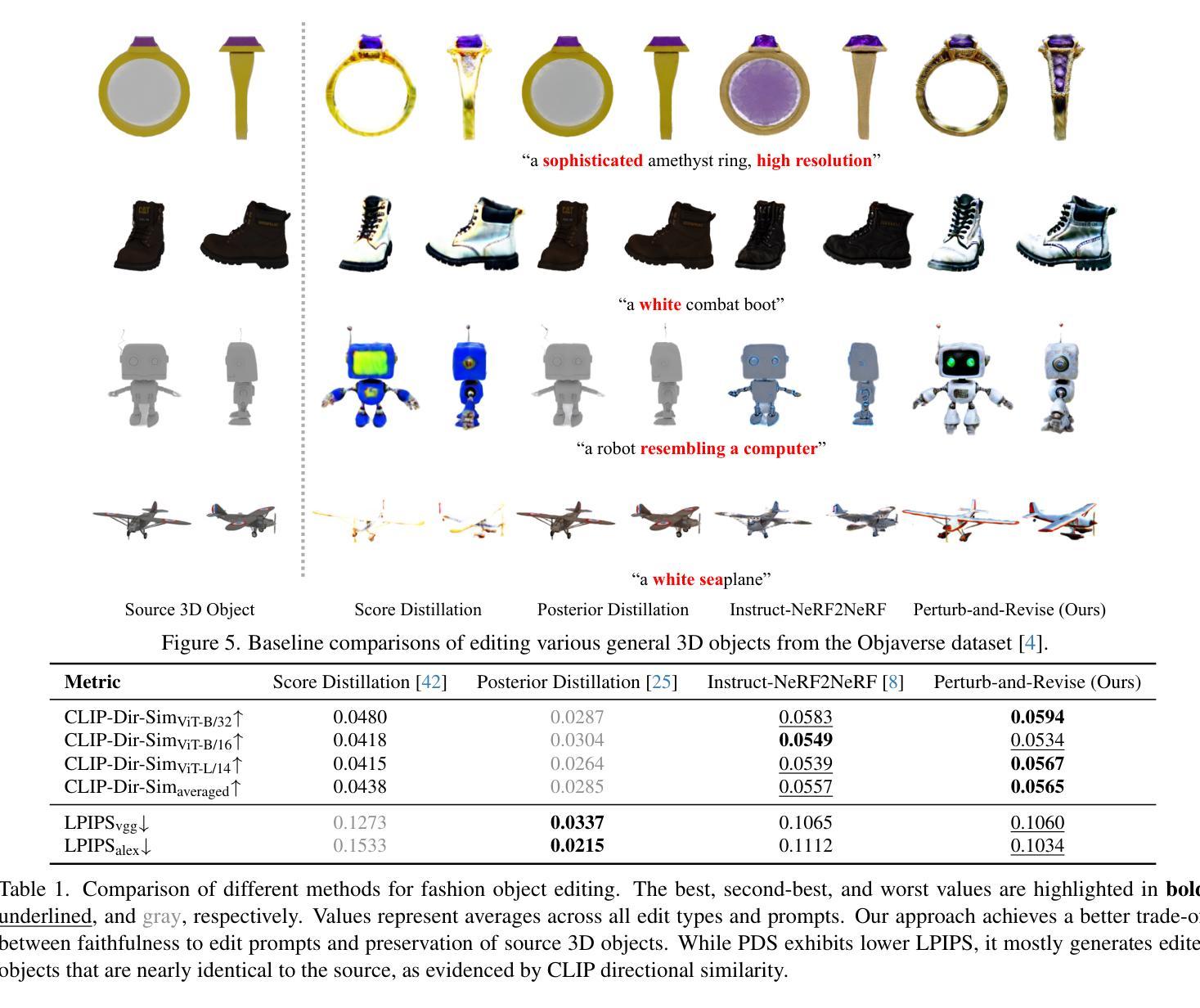
Perturb-and-Revise: Flexible 3D Editing with Generative Trajectories
Authors:Susung Hong, Johanna Karras, Ricardo Martin-Brualla, Ira Kemelmacher-Shlizerman
The fields of 3D reconstruction and text-based 3D editing have advanced significantly with the evolution of text-based diffusion models. While existing 3D editing methods excel at modifying color, texture, and style, they struggle with extensive geometric or appearance changes, thus limiting their applications. We propose Perturb-and-Revise, which makes possible a variety of NeRF editing. First, we perturb the NeRF parameters with random initializations to create a versatile initialization. We automatically determine the perturbation magnitude through analysis of the local loss landscape. Then, we revise the edited NeRF via generative trajectories. Combined with the generative process, we impose identity-preserving gradients to refine the edited NeRF. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Perturb-and-Revise facilitates flexible, effective, and consistent editing of color, appearance, and geometry in 3D. For 360{\deg} results, please visit our project page: https://susunghong.github.io/Perturb-and-Revise.
随着基于文本的扩散模型的演变,3D重建和基于文本的3D编辑领域已经取得了显著进展。虽然现有的3D编辑方法在修改颜色、纹理和风格方面表现出色,但在进行大规模的几何或外观更改时却遇到了困难,从而限制了其应用。我们提出了Perturb-and-Revise方法,使各种NeRF编辑成为可能。首先,我们通过随机初始化扰动NeRF参数来创建一个通用的初始化方案。我们通过分析局部损失景观自动确定扰动幅度。然后,我们通过生成轨迹来修订编辑后的NeRF。结合生成过程,我们施加保持身份不变的梯度来优化编辑后的NeRF。大量实验表明,Perturb-and-Revise能够实现灵活、有效且一致的3D彩色、外观和几何编辑。有关360°的结果,请访问我们的项目页面:https://susunghong.github.io/Perturb-and-Revise。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://susunghong.github.io/Perturb-and-Revise
Summary
本文介绍了基于文本扩散模型的3D重建和文本为基础的3D编辑领域的最新进展。针对现有3D编辑方法在几何或外观变化方面的局限,提出一种名为Perturb-and-Revise的新方法。该方法通过扰动NeRF参数并自动确定扰动幅度,实现了灵活的3D编辑,可以修改颜色、外观和几何形状。
Key Takeaways
- 文本扩散模型的演进推动了3D重建和文本基础的3D编辑领域的发展。
- 现有3D编辑方法在几何或外观变化方面存在局限性。
- Perturb-and-Revise方法通过扰动NeRF参数,实现了多样化的3D编辑。
- 该方法通过自动确定扰动幅度,提高了编辑的灵活性、效果和一致性。
- Perturb-and-Revise方法可以修改颜色、外观和几何形状。
- 该方法结合了生成过程,通过施加身份保留梯度来优化编辑的NeRF。
点此查看论文截图


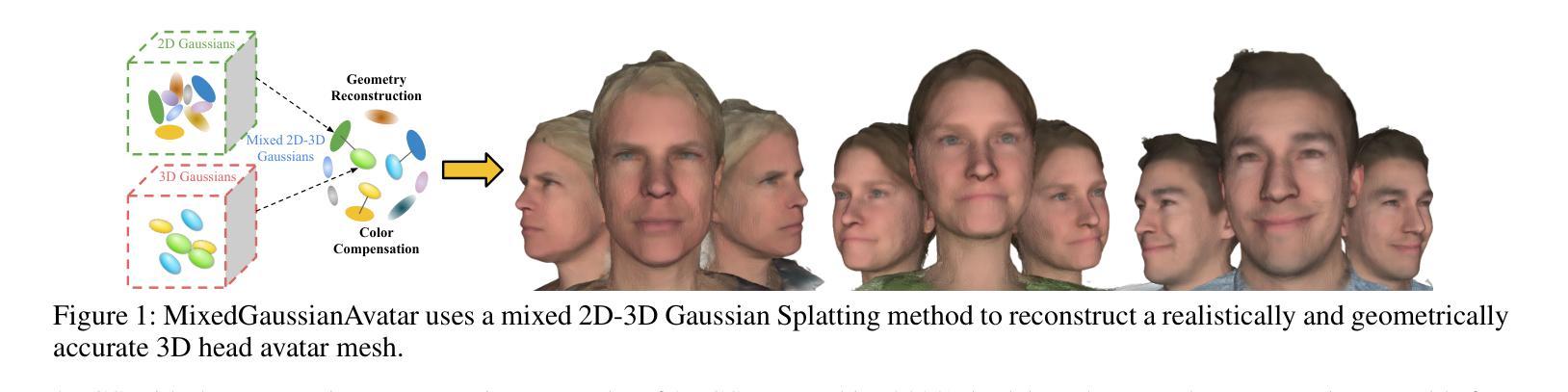
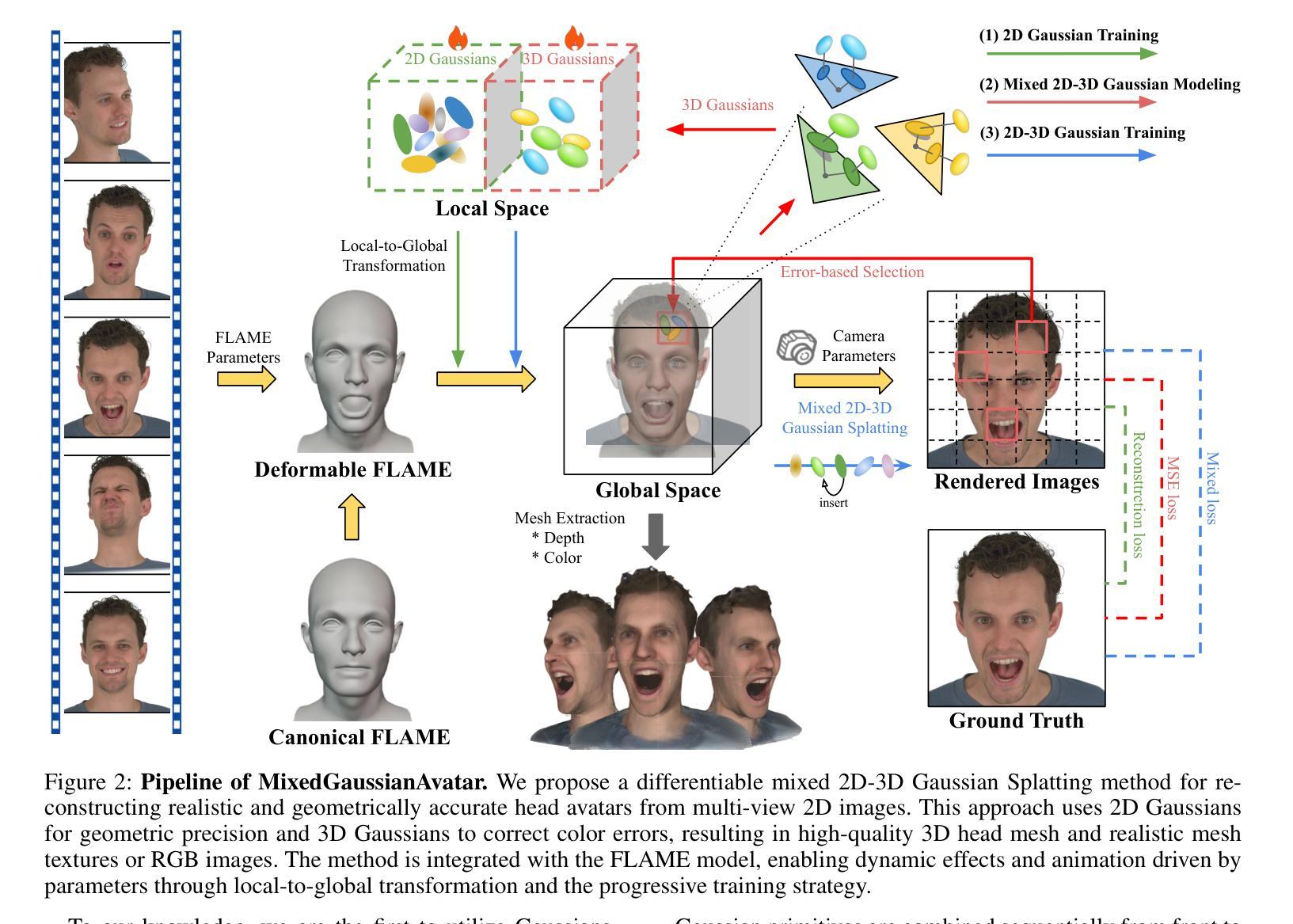
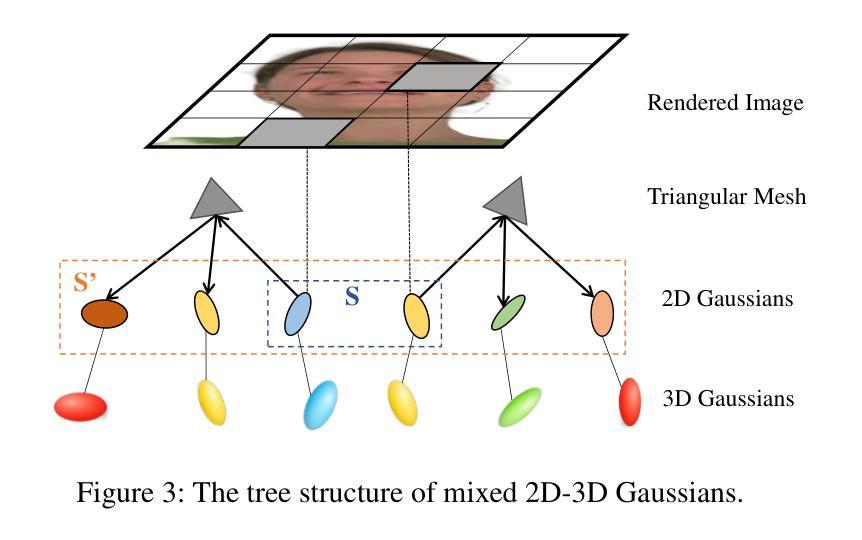
MixedGaussianAvatar: Realistically and Geometrically Accurate Head Avatar via Mixed 2D-3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Peng Chen, Xiaobao Wei, Qingpo Wuwu, Xinyi Wang, Xingyu Xiao, Ming Lu
Reconstructing high-fidelity 3D head avatars is crucial in various applications such as virtual reality. The pioneering methods reconstruct realistic head avatars with Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), which have been limited by training and rendering speed. Recent methods based on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) significantly improve the efficiency of training and rendering. However, the surface inconsistency of 3DGS results in subpar geometric accuracy; later, 2DGS uses 2D surfels to enhance geometric accuracy at the expense of rendering fidelity. To leverage the benefits of both 2DGS and 3DGS, we propose a novel method named MixedGaussianAvatar for realistically and geometrically accurate head avatar reconstruction. Our main idea is to utilize 2D Gaussians to reconstruct the surface of the 3D head, ensuring geometric accuracy. We attach the 2D Gaussians to the triangular mesh of the FLAME model and connect additional 3D Gaussians to those 2D Gaussians where the rendering quality of 2DGS is inadequate, creating a mixed 2D-3D Gaussian representation. These 2D-3D Gaussians can then be animated using FLAME parameters. We further introduce a progressive training strategy that first trains the 2D Gaussians and then fine-tunes the mixed 2D-3D Gaussians. We demonstrate the superiority of MixedGaussianAvatar through comprehensive experiments. The code will be released at: https://github.com/ChenVoid/MGA/.
重建高保真3D头像对于虚拟现实等各种应用至关重要。开创性的方法使用神经辐射场(NeRF)重建逼真的头像,但受限于训练和渲染速度。基于3D高斯喷涂(3DGS)的最近的方法显著提高了训练和渲染的效率。然而,3DGS的表面不一致导致几何精度不佳;后来的2DGS使用2D表面提高了几何精度,但牺牲了渲染保真度。为了结合2DGS和3DGS的优点,我们提出了一种名为MixedGaussianAvatar的新方法,用于真实且几何精确的头像重建。我们的主要想法是利用2D高斯重建3D头像的表面,以确保几何精度。我们将2D高斯附加到FLAME模型的三角网格上,并在2DGS渲染质量不足的地方连接到额外的3D高斯,创建混合的2D-3D高斯表示。这些2D-3D高斯可以使用FLAME参数进行动画处理。我们还引入了一种渐进的训练策略,首先训练2D高斯,然后对混合的2D-3D高斯进行微调。我们通过全面的实验展示了MixedGaussianAvatar的优越性。代码将在https://github.com/ChenVoid/MGA/发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project: https://chenvoid.github.io/MGA/
Summary
该研究提出了一种名为MixedGaussianAvatar的新方法,结合了3D高斯平铺(3DGS)和二维高斯平铺(2DGS)的优点,旨在重建具有真实感和几何精度的头部虚拟形象。MixedGaussianAvatar利用二维高斯重建头部三维表面的几何精度,并通过附加到FLAME模型的三角网格和连接额外的三维高斯来提高渲染质量。此外,该研究还采用了一种渐进的训练策略,先训练二维高斯,再微调混合的二维-三维高斯。该方法在实验中表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了MixedGaussianAvatar方法,结合了二维高斯平铺和三维高斯平铺的优势,旨在重建真实且几何精确的头部虚拟形象。
- 该方法利用二维高斯重建头部三维表面的几何精度,通过附加到FLAME模型的三角网格实现。
- 为了提高渲染质量,在需要的地方连接了额外的三维高斯。
- MixedGaussianAvatar方法采用了渐进的训练策略,先训练二维高斯,再微调混合的二维-三维高斯。
- 该方法在实验中的表现卓越,能够重建出高质量的头部虚拟形象。
- 研究成果将在GitHub上发布。
点此查看论文截图

Few-Shot Learning with Adaptive Weight Masking in Conditional GANs
Authors:Jiacheng Hu, Zhen Qi, Jianjun Wei, Jiajing Chen, Runyuan Bao, Xinyu Qiu
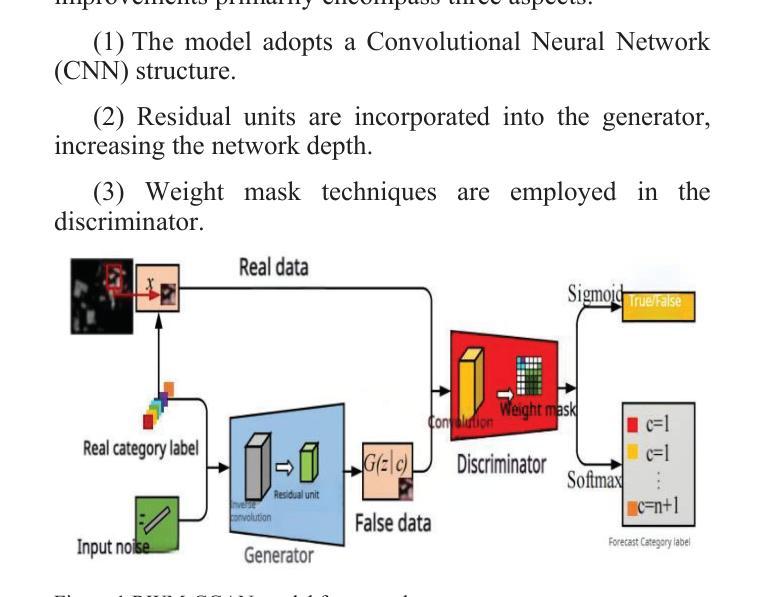
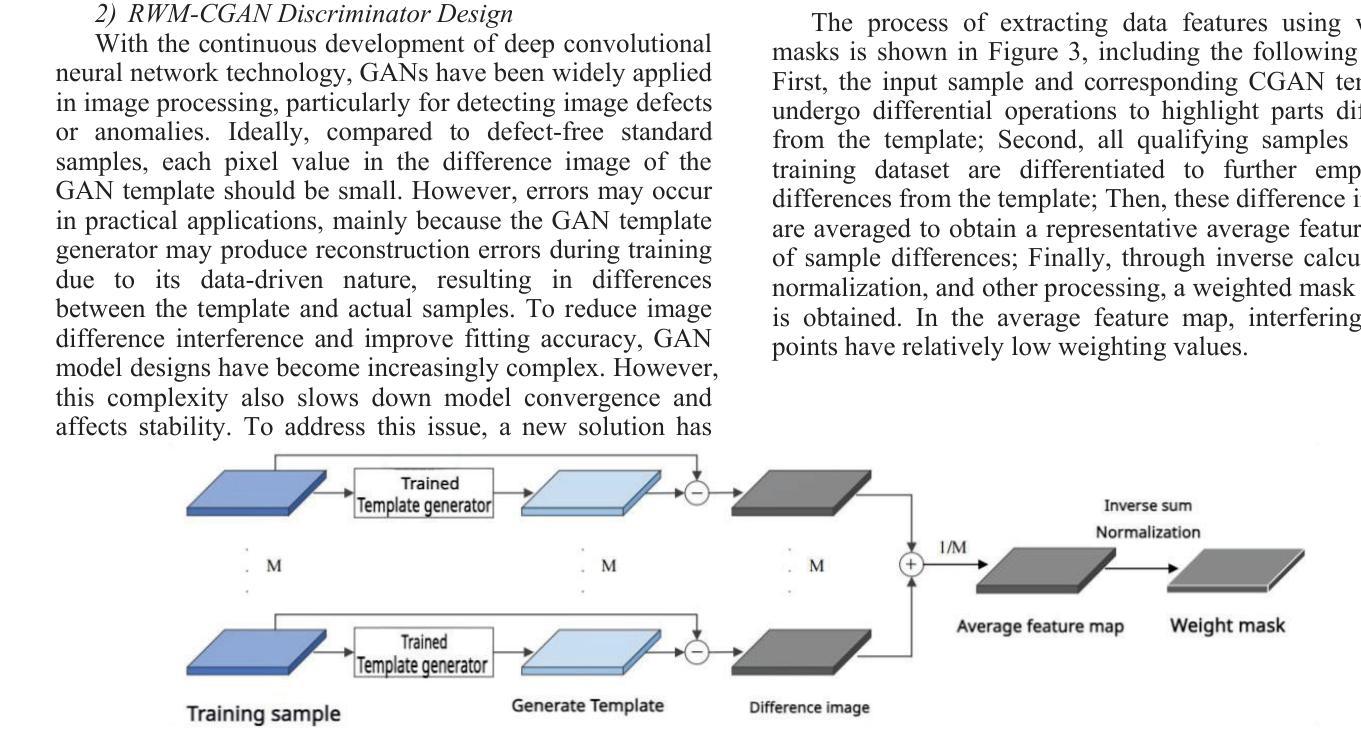
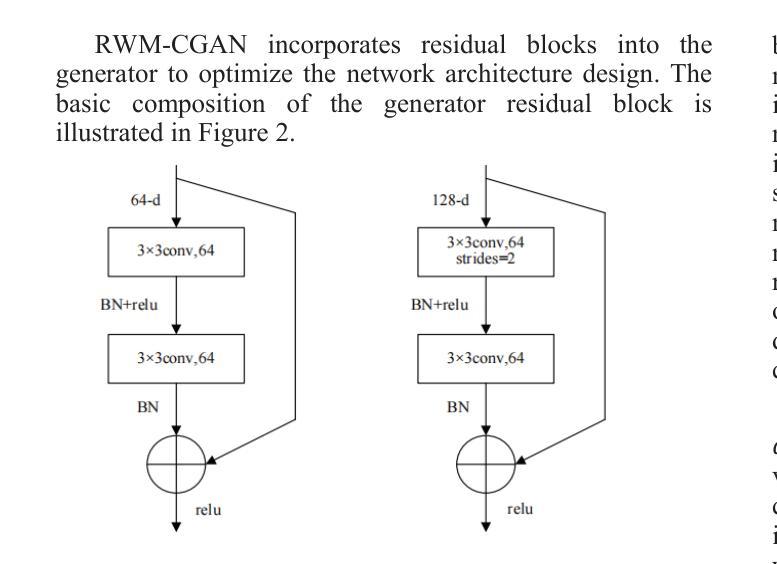
Deep learning has revolutionized various fields, yet its efficacy is hindered by overfitting and the requirement of extensive annotated data, particularly in few-shot learning scenarios where limited samples are available. This paper introduces a novel approach to few-shot learning by employing a Residual Weight Masking Conditional Generative Adversarial Network (RWM-CGAN) for data augmentation. The proposed model integrates residual units within the generator to enhance network depth and sample quality, coupled with a weight mask regularization technique in the discriminator to improve feature learning from small-sample categories. This method addresses the core issues of robustness and generalization in few-shot learning by providing a controlled and clear augmentation of the sample space. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RWM-CGAN not only expands the sample space effectively but also enriches the diversity and quality of generated samples, leading to significant improvements in detection and classification accuracy on public datasets. The paper contributes to the advancement of few-shot learning by offering a practical solution to the challenges posed by data scarcity and the need for rapid generalization to new tasks or categories.
深度学习已经革新了多个领域,但其效果受到了过拟合和需要大量标注数据的影响,特别是在样本数量有限的场景下的学习更少的情况下。本文引入了一种利用剩余权重掩码条件生成对抗网络(RWM-CGAN)进行数据增强的新型少样本学习方法。所提出的模型在生成器中集成残差单元,以提高网络深度和样本质量,同时在鉴别器中采用权重掩码正则化技术,以提高小样本类别的特征学习能力。该方法通过提供可控且清晰的样本空间扩展来解决少样本学习的核心问题和泛化问题。大量实验表明,RWM-CGAN不仅有效地扩展了样本空间,而且丰富了生成样本的多样性和质量,显著提高了公共数据集上的检测和分类准确性。该论文为解决数据稀缺和快速泛化到新任务或类别所面临的挑战提供了实际解决方案,为少样本学习领域的发展做出了贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
深度学习虽在多领域引起革命性变革,但在小样本学习场景下,其效果受限于过拟合及需要大量标注数据的要求。本文引入了一种采用残差权重掩膜条件生成对抗网络(RWM-CGAN)进行数据增强的新型小样本学习方法。该方法通过生成器中的残差单元增强网络深度和样本质量,结合判别器中的权重掩膜正则化技术,提高小样本类别的特征学习能力。此方法通过提供可控且清晰的样本空间扩展,解决了小样本学习中鲁棒性和泛化能力方面的核心问题。大量实验表明,RWM-CGAN不仅有效地扩展了样本空间,还提高了生成样本的多样性和质量,在公开数据集上显著提高了检测和分类的准确性。本文为解决数据稀缺和快速泛化到新任务或类别所带来的挑战提供了实用解决方案,推动了小样本学习的进步。
要点速览
- 深度学习在小样本学习场景下受限于过拟合和标注数据需求。
- 本文采用RWM-CGAN进行数据增强,解决小样本学习中的鲁棒性和泛化问题。
- RWM-CGAN通过生成器中的残差单元增强网络性能。
- 判别器中的权重掩膜正则化技术提高小样本类别的特征学习能力。
- RWM-CGAN有效扩展样本空间,提高生成样本的多样性和质量。
- 在公开数据集上,RWM-CGAN显著提高检测和分类的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

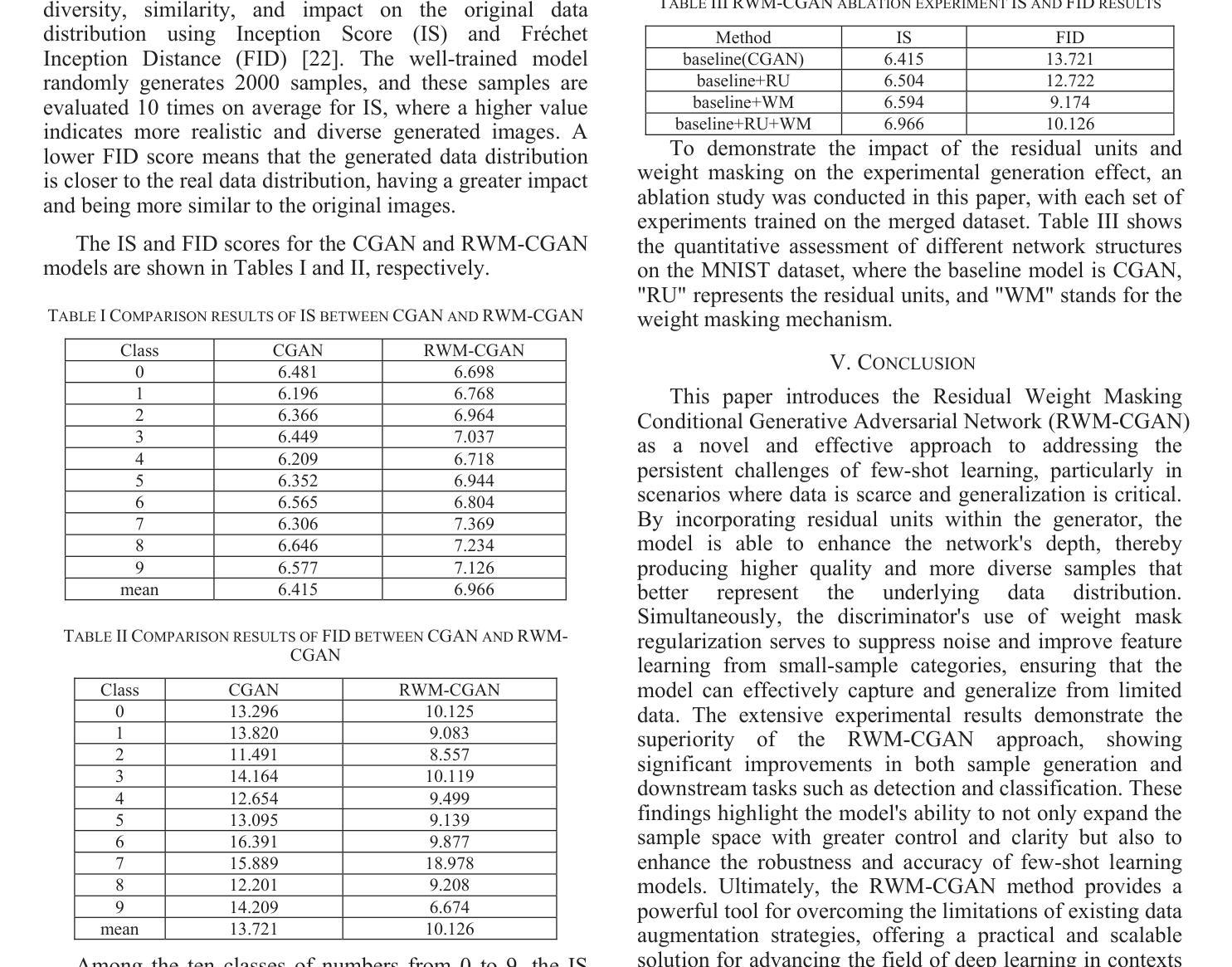
dc-GAN: Dual-Conditioned GAN for Face Demorphing From a Single Morph
Authors:Nitish Shukla, Arun Ross
A facial morph is an image created by combining two face images pertaining to two distinct identities. Face demorphing inverts the process and tries to recover the original images constituting a facial morph. While morph attack detection (MAD) techniques can be used to flag morph images, they do not divulge any visual information about the faces used to create them. Demorphing helps address this problem. Existing demorphing techniques are either very restrictive (assume identities during testing) or produce feeble outputs (both outputs look very similar). In this paper, we overcome these issues by proposing dc-GAN, a novel GAN-based demorphing method conditioned on the morph images. Our method overcomes morph-replication and produces high quality reconstructions of the bonafide images used to create the morphs. Moreover, our method is highly generalizable across demorphing paradigms (differential/reference-free). We conduct experiments on AMSL, FRLL-Morphs and MorDiff datasets to showcase the efficacy of our method.
面部形态图像是通过结合两张属于不同身份的人脸图像而产生的。面部去形态化则逆转这一过程,试图恢复构成面部形态图像的原始图像。虽然形态攻击检测(MAD)技术可用于标记形态图像,但它们不会泄露用于创建形态图像的任何面部视觉信息。去形态化有助于解决这一问题。现有的去形态化技术在操作上要么存在限制(假设测试时的身份信息),要么输出效果不佳(两个输出非常相似)。针对这些问题,我们在本文中提出了一种新型的基于GAN的去形态化方法dc-GAN,该方法以形态图像为条件。我们的方法克服了形态复制问题,并成功重建了用于创建形态图像的真实图像的优质版本。此外,我们的方法高度通用化各种去形态化模式(差分/无参考)。我们在AMSL、FRLL-Morphs和MorDiff数据集上进行实验,以展示我们方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于GAN技术的面部图像复原技术dc-GAN。该技术能克服现有的面部复原技术的缺陷,通过对形态图像的条件约束,实现对原始面部图像的复原,提高图像质量,并且具有良好的泛化能力。通过在不同数据集上的实验,展示了dc-GAN方法的优良效果。
Key Takeaways
- dc-GAN是基于GAN技术的面部图像复原方法。
- 该技术能克服现有面部复原技术的缺陷,如假设身份或输出质量不高的问题。
- dc-GAN通过对形态图像的条件约束,实现高质量的原始面部图像复原。
- 该方法具有良好的泛化能力,可以应用于不同的复原模式。
点此查看论文截图



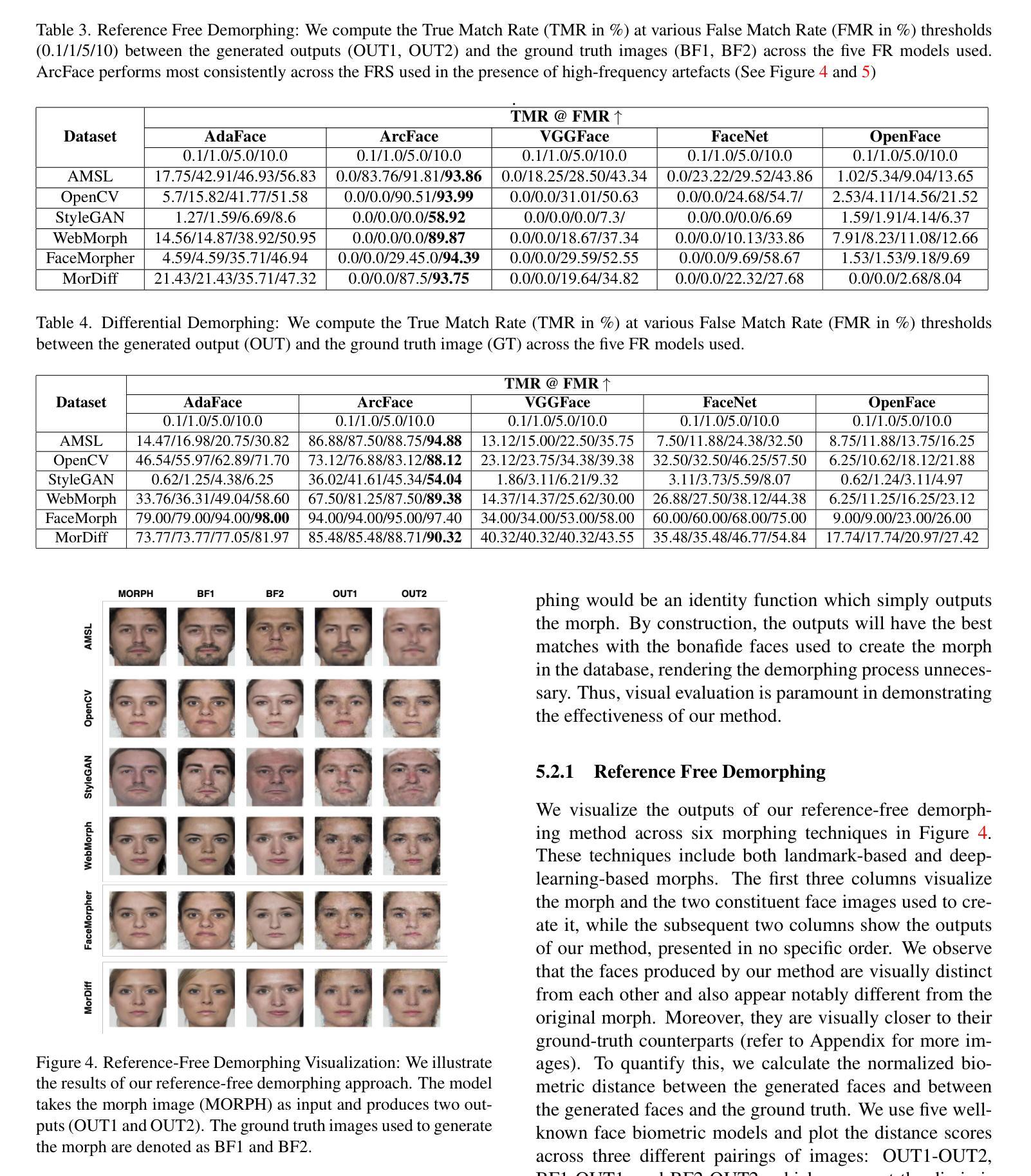
RNG: Relightable Neural Gaussians
Authors:Jiahui Fan, Fujun Luan, Jian Yang, Miloš Hašan, Beibei Wang
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has shown impressive results for the novel view synthesis task, where lighting is assumed to be fixed. However, creating relightable 3D assets, especially for objects with ill-defined shapes (fur, fabric, etc.), remains a challenging task. The decomposition between light, geometry, and material is ambiguous, especially if either smooth surface assumptions or surfacebased analytical shading models do not apply. We propose Relightable Neural Gaussians (RNG), a novel 3DGS-based framework that enables the relighting of objects with both hard surfaces or soft boundaries, while avoiding assumptions on the shading model. We condition the radiance at each point on both view and light directions. We also introduce a shadow cue, as well as a depth refinement network to improve shadow accuracy. Finally, we propose a hybrid forward-deferred fitting strategy to balance geometry and appearance quality. Our method achieves significantly faster training (1.3 hours) and rendering (60 frames per second) compared to a prior method based on neural radiance fields and produces higher-quality shadows than a concurrent 3DGS-based method.
3D高斯模糊(3DGS)在新视角合成任务中取得了令人印象深刻的结果,该任务假设光照是固定的。然而,创建可重新照明的3D资产,尤其是对于形状不明确(如毛发、织物等)的对象,仍然是一项具有挑战性的任务。光线、几何形状和材料之间的分解是模糊的,尤其是当光滑表面假设或基于表面的分析着色模型不适用时。我们提出了可重新照明的神经高斯(RNG),这是一种新型的基于3DGS的框架,能够实现具有硬表面或软边界的对象的重新照明,同时避免了对着色模型的假设。我们将每个点的辐射度与视图和光线的方向联系起来。我们还引入了一个阴影线索和一个深度细化网络来提高阴影的准确性。最后,我们提出了一种混合的前向延迟拟合策略来平衡几何形状和外观质量。我们的方法实现了与前一种基于神经辐射场的方法相比显著更快的训练和渲染(训练时间为1.3小时,渲染帧率为每秒60帧),并且相对于当前的基于3DGS的方法产生了更高质量的阴影。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submission version
Summary
本文提出了一种基于Relightable Neural Gaussians(RNG)的3DGS框架,实现了对具有硬表面或软边界对象的重新照明功能,无需对阴影模型进行假设。该方法结合了视点和光线方向的辐射条件,引入了阴影线索和深度优化网络以提高阴影精度,并采用混合的前向延迟拟合策略来平衡几何和外观质量。相较于基于神经辐射场的前方法,RNG方法训练更快(仅1.3小时),渲染速度更高(每秒60帧),且生成的阴影质量更高。
Key Takeaways
- RNG基于3DGS框架实现了物体的重新照明功能,适用于硬表面和软边界对象。
- RNG无需对阴影模型进行假设,提高了辐射条件的准确性。
- 引入阴影线索和深度优化网络,提高了阴影精度。
- 采用混合的前向延迟拟合策略,平衡几何和外观质量。
- RNG方法训练速度快,仅需要1.3小时,渲染速度高,每秒可达60帧。
- RNG生成的阴影质量高于同期基于3DGS的方法。
点此查看论文截图

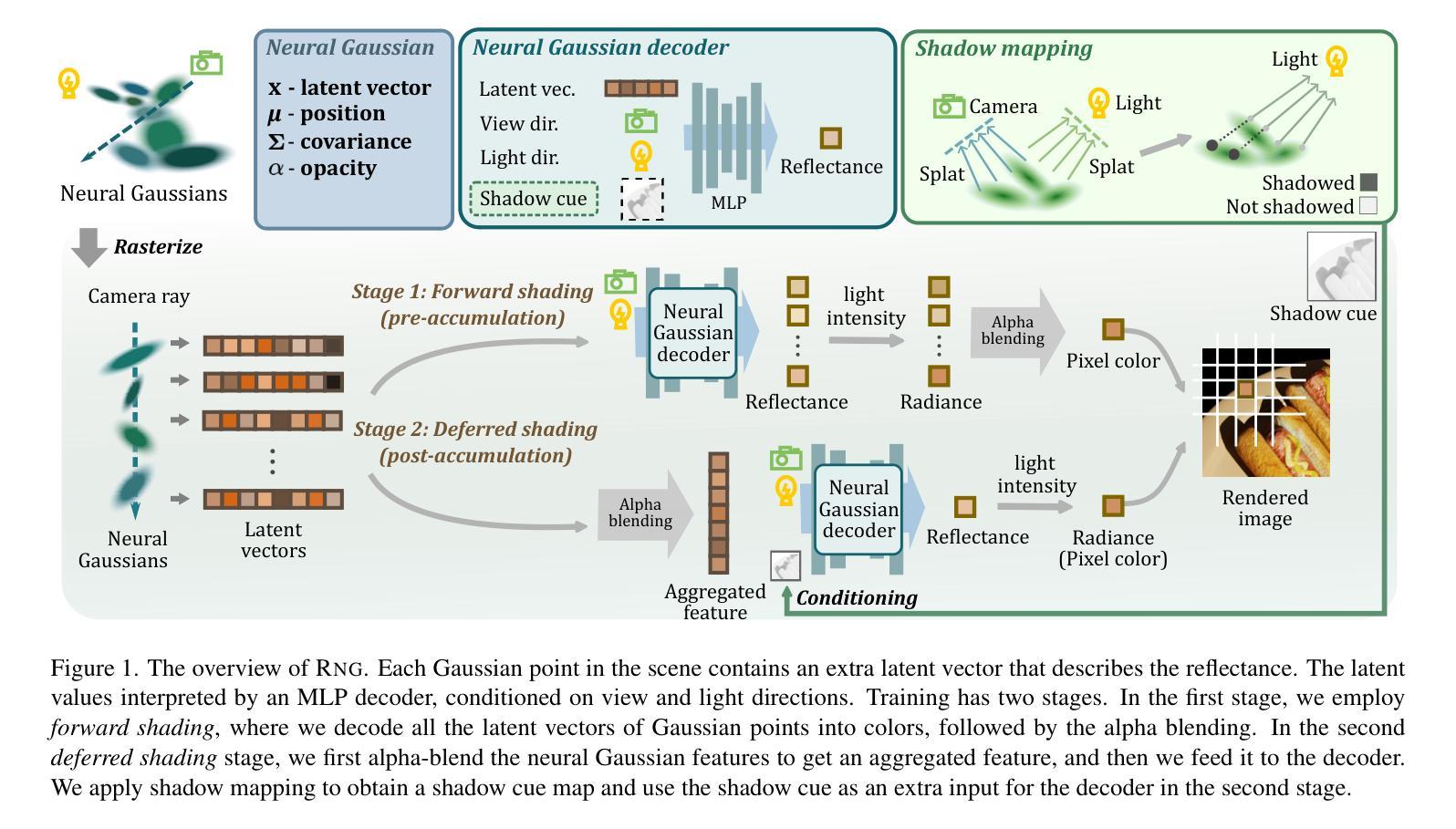
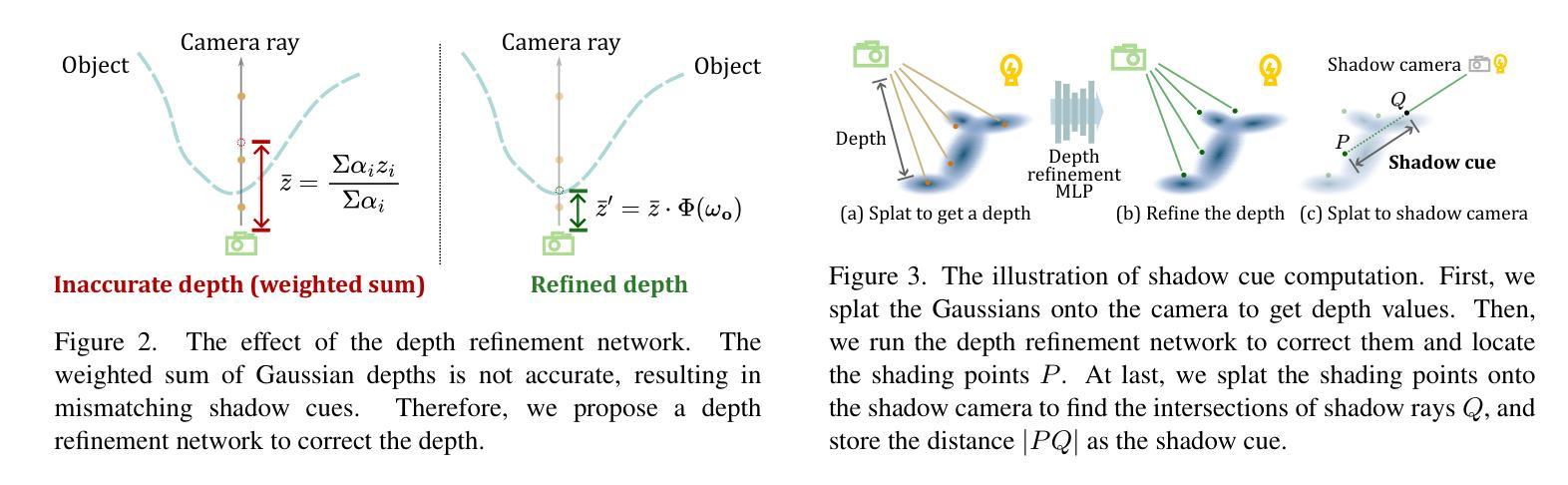
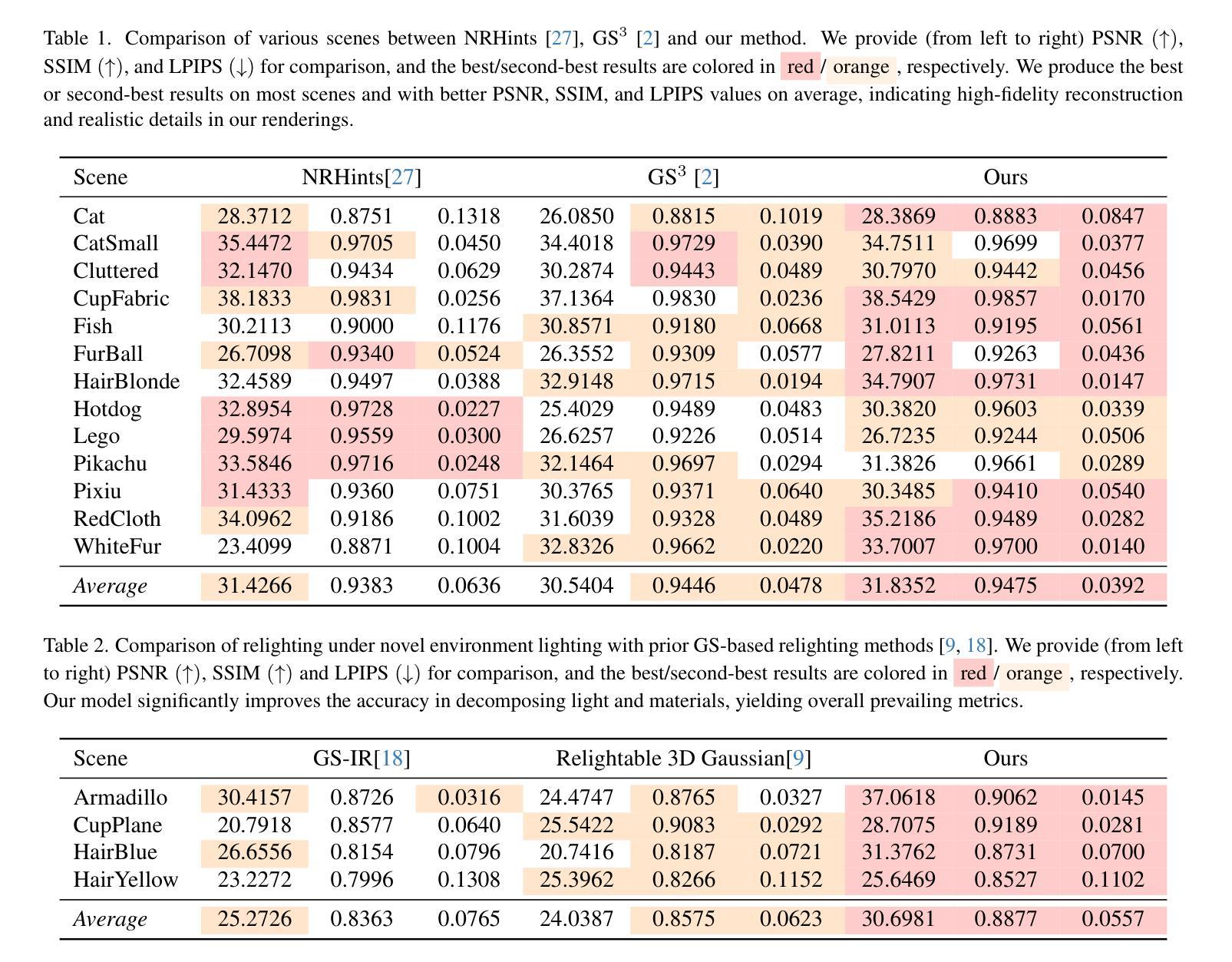
TFS-NeRF: Template-Free NeRF for Semantic 3D Reconstruction of Dynamic Scene
Authors:Sandika Biswas, Qianyi Wu, Biplab Banerjee, Hamid Rezatofighi
Despite advancements in Neural Implicit models for 3D surface reconstruction, handling dynamic environments with interactions between arbitrary rigid, non-rigid, or deformable entities remains challenging. The generic reconstruction methods adaptable to such dynamic scenes often require additional inputs like depth or optical flow or rely on pre-trained image features for reasonable outcomes. These methods typically use latent codes to capture frame-by-frame deformations. Another set of dynamic scene reconstruction methods, are entity-specific, mostly focusing on humans, and relies on template models. In contrast, some template-free methods bypass these requirements and adopt traditional LBS (Linear Blend Skinning) weights for a detailed representation of deformable object motions, although they involve complex optimizations leading to lengthy training times. To this end, as a remedy, this paper introduces TFS-NeRF, a template-free 3D semantic NeRF for dynamic scenes captured from sparse or single-view RGB videos, featuring interactions among two entities and more time-efficient than other LBS-based approaches. Our framework uses an Invertible Neural Network (INN) for LBS prediction, simplifying the training process. By disentangling the motions of interacting entities and optimizing per-entity skinning weights, our method efficiently generates accurate, semantically separable geometries. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach produces high-quality reconstructions of both deformable and non-deformable objects in complex interactions, with improved training efficiency compared to existing methods.
尽管三维表面重建的神经隐式模型取得了进展,但处理动态环境以及任意刚性、非刚性或可变形实体之间的交互仍然具有挑战性。能够适应这种动态场景的通用重建方法通常需要额外的输入,如深度或光流,或依赖于预训练的图像特征来获得合理的结果。这些方法通常使用潜在代码来捕捉帧到帧的变形。另一组动态场景重建方法是针对特定实体的,主要关注人类,并依赖于模板模型。相比之下,一些无模板的方法绕过了这些要求,并采用传统的LBS(线性混合蒙皮)权重来详细表示可变形物体的运动,尽管它们涉及复杂的优化,导致训练时间较长。鉴于此,本文介绍了TFS-NeRF,这是一种无模板的3D语义NeRF,用于从稀疏或单视图RGB视频中捕捉动态场景,具有两个实体之间的交互并且比其他基于LBS的方法更高效。我们的框架使用可逆神经网络(INN)进行LBS预测,简化了训练过程。通过分离交互实体的运动并优化每个实体的蒙皮权重,我们的方法可以高效生成准确且语义上可分离的形状。大量实验表明,我们的方法在复杂交互中对可变形和非可变形物体的重建质量很高,与现有方法相比,训练效率也更高。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in NeurIPS 2024 https://github.com/sbsws88/TFS-NeRF
摘要
本文主要探讨动态环境场景下NeRF神经网络模型的问题。现有的NeRF重建方法难以处理复杂交互中的动态实体,包括刚性和非刚性实体之间的交互。某些方法依赖额外的输入或预先训练的图像特征进行重建,并主要通过隐代码捕捉帧间变形。本文提出了一种无模板的3D语义NeRF模型—— TFS-NeRF,用于从稀疏或单视角RGB视频中捕获动态场景和交互,其比基于LBS的方法更加高效。使用可逆神经网络(INN)进行LBS预测并优化实体皮骨化权重。实验结果证明了该方法在复杂交互场景下对可变形和非可变形物体的高质量重建能力,并提高了训练效率。
关键见解
- 动态环境场景下的NeRF重建仍存在挑战,特别是在处理包含多种实体的复杂交互时。
- 当前方法通常需要额外的输入或依赖预训练图像特征进行重建。
- TFS-NeRF是一种无模板的3D语义NeRF模型,适用于从稀疏或单视角RGB视频捕获动态场景和交互。
- TFS-NeRF使用可逆神经网络(INN)简化LBS预测的训练过程。
- 该方法可以精确地生成语义上可分离的形状,并优化实体间的交互运动。
- 实验结果证明了该方法在复杂交互场景下的高质量重建能力。
点此查看论文截图


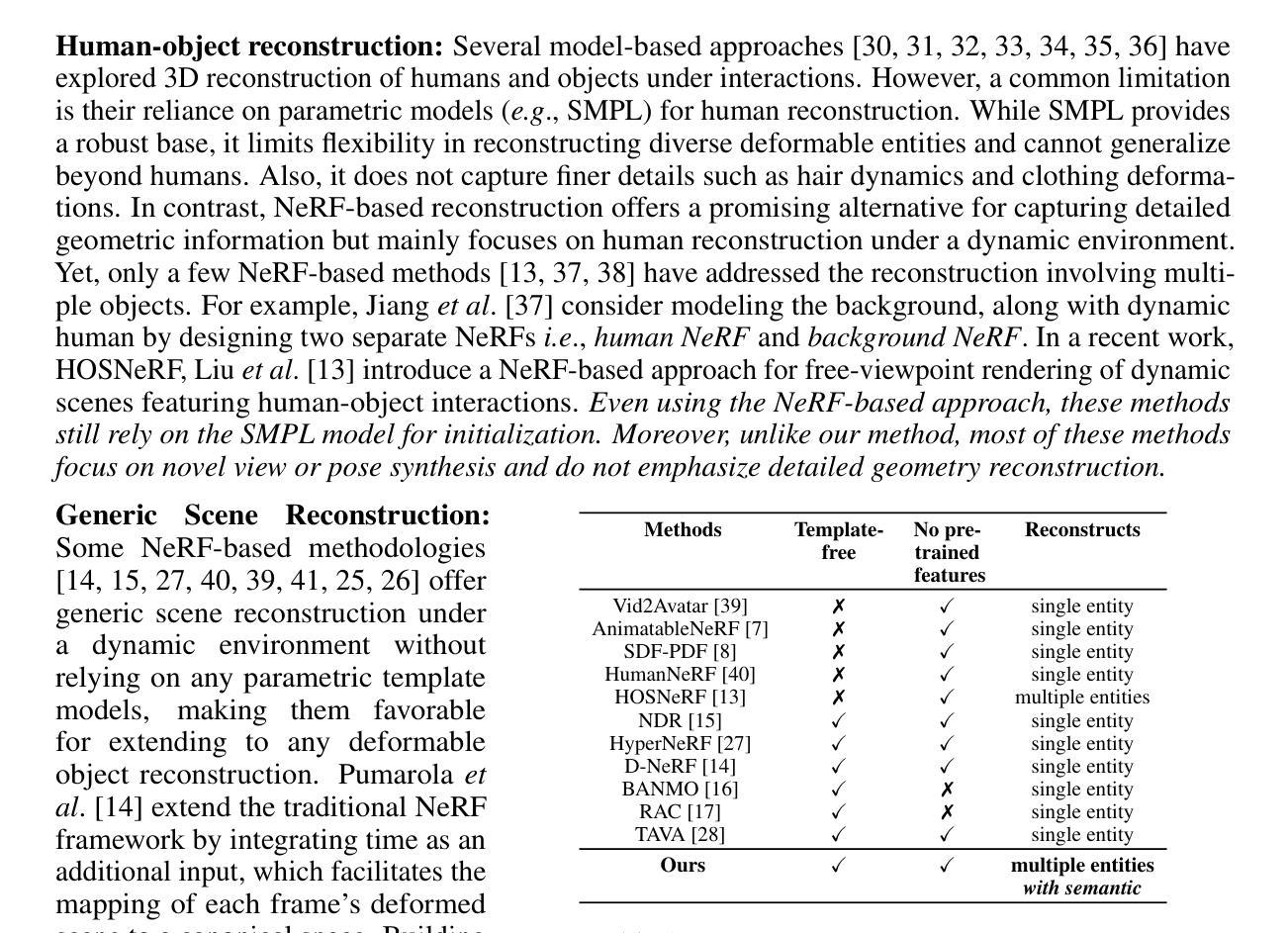
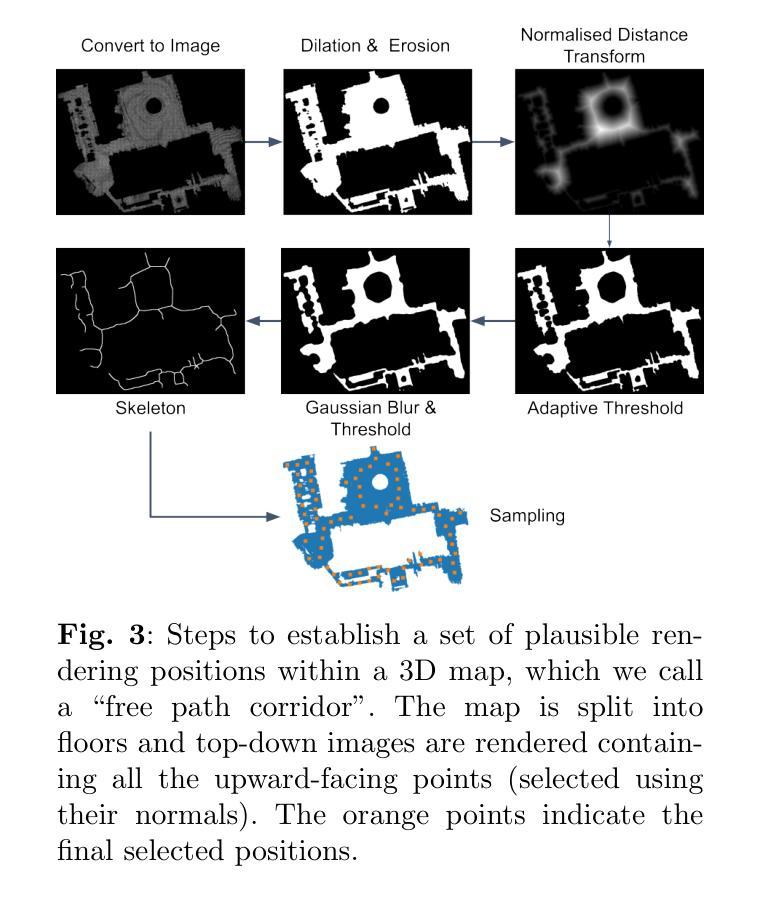
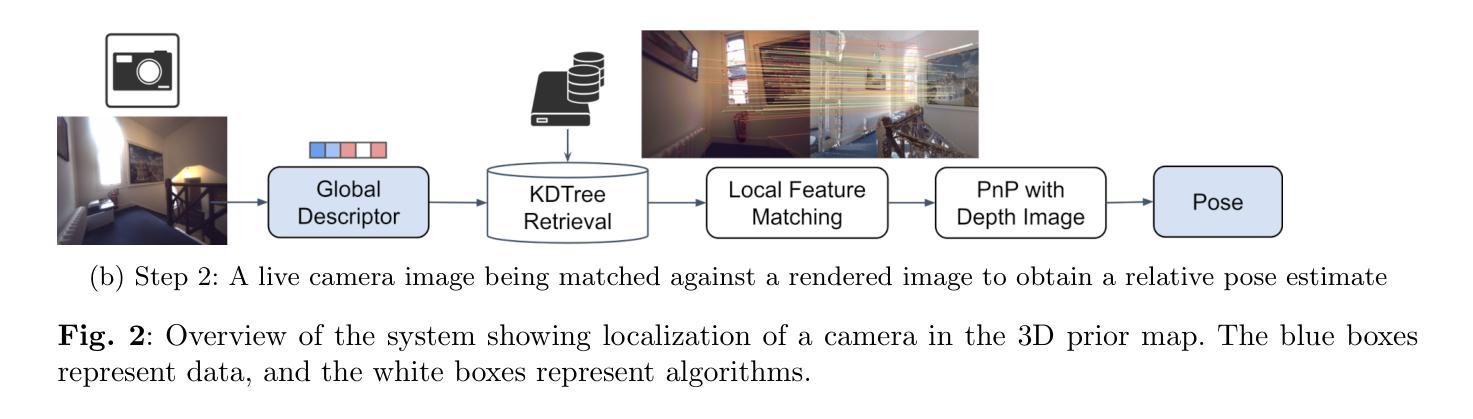
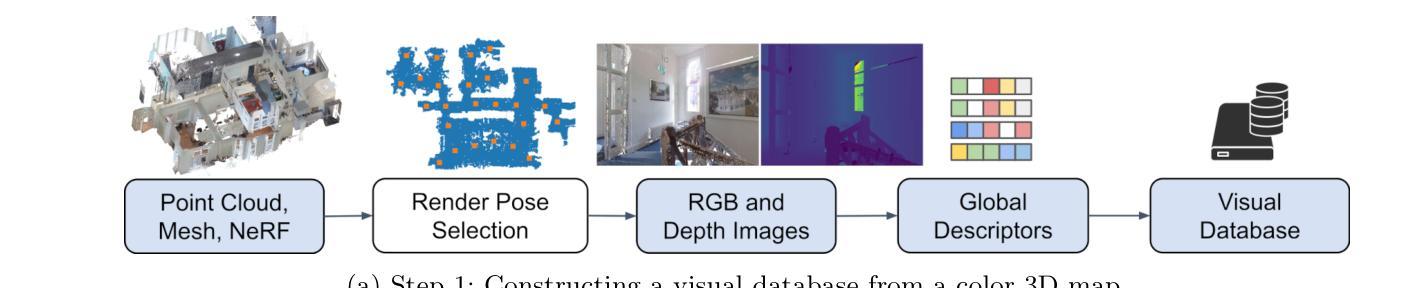
Visual Localization in 3D Maps: Comparing Point Cloud, Mesh, and NeRF Representations
Authors:Lintong Zhang, Yifu Tao, Jiarong Lin, Fu Zhang, Maurice Fallon
Recent advances in mapping techniques have enabled the creation of highly accurate dense 3D maps during robotic missions, such as point clouds, meshes, or NeRF-based representations. These developments present new opportunities for reusing these maps for localization. However, there remains a lack of a unified approach that can operate seamlessly across different map representations. This paper presents and evaluates a global visual localization system capable of localizing a single camera image across various 3D map representations built using both visual and lidar sensing. Our system generates a database by synthesizing novel views of the scene, creating RGB and depth image pairs. Leveraging the precise 3D geometric map, our method automatically defines rendering poses, reducing the number of database images while preserving retrieval performance. To bridge the domain gap between real query camera images and synthetic database images, our approach utilizes learning-based descriptors and feature detectors. We evaluate the system’s performance through extensive real-world experiments conducted in both indoor and outdoor settings, assessing the effectiveness of each map representation and demonstrating its advantages over traditional structure-from-motion (SfM) localization approaches. The results show that all three map representations can achieve consistent localization success rates of 55% and higher across various environments. NeRF synthesized images show superior performance, localizing query images at an average success rate of 72%. Furthermore, we demonstrate an advantage over SfM-based approaches that our synthesized database enables localization in the reverse travel direction which is unseen during the mapping process. Our system, operating in real-time on a mobile laptop equipped with a GPU, achieves a processing rate of 1Hz.
在测绘技术方面的最新进展使得在机器人任务期间能够创建高度精确的三维密集地图,例如点云、网格或基于NeRF的表示。这些发展对于利用这些地图进行定位提供了新的机会。然而,仍然存在缺乏一种可以在不同地图表示之间无缝操作的统一方法。本文介绍并评估了一种全球视觉定位系统,该系统能够使用视觉和激光雷达传感器对各种三维地图表示中的单张相机图像进行定位。我们的系统通过合成场景的新视角来生成数据库,创建RGB和深度图像对。利用精确的3D几何地图,我们的方法可以自动定义渲染姿态,减少数据库图像的数量,同时保留检索性能。为了弥真实查询相机图像和合成数据库图像之间的领域差距,我们的方法采用基于学习的描述符和特征检测器。我们通过室内和室外环境中的大量真实世界实验对系统的性能进行了评估,评估了各种地图表示的有效性,并证明了其与传统的结构从运动(SfM)定位方法的优势。结果表明,所有三种地图表示都能在各种环境中实现一致的定位成功率达到或超过55%。NeRF合成的图像显示出卓越的性能,查询图像的平均定位成功率达到72%。此外,我们证明了与基于SfM的方法相比的优势,即我们的合成数据库能够在逆向旅行方向上进行定位,这在映射过程中是看不见的。我们的系统在配备GPU的移动笔记本电脑上实时运行,处理速度达到每秒一帧(1Hz)。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文针对机器人任务中的高密度三维地图创建技术,提出了一种全局视觉定位系统。该系统可在多种三维地图表示中进行定位,并利用视觉和激光雷达传感器生成数据库。通过合成场景的新视角,创建RGB和深度图像对,自动定义渲染姿态,减少数据库图像数量同时保留检索性能。论文还评估了不同地图表示的有效性,并在室内和室外环境中进行了大量实验,展示其在各种环境中的稳定性能和对传统结构从运动(SfM)定位方法的优势。利用NeRF合成图像的平均成功率达到72%,并在反向旅行方向上的定位具有优势。该系统在配备GPU的移动笔记本上实现实时处理,处理速率达到1Hz。
Key Takeaways
- 先进的映射技术能够创建高度准确的三维地图,如点云、网格或基于NeRF的表示。
- 缺乏能在不同地图表示之间无缝操作的统一方法。
- 该论文提出了一种全局视觉定位系统,可定位在由视觉和激光雷达感知生成的各种三维地图表示中的单一相机图像。
- 系统通过合成场景的新视角生成数据库,自动定义渲染姿态,减少数据库图像数量同时保留检索性能。
- 论文评估了不同地图表示的有效性,并展示了在各种环境中的稳定性能和对传统SfM定位方法的优势。
- 利用NeRF合成图像的定位成功率较高,平均达到72%。
点此查看论文截图

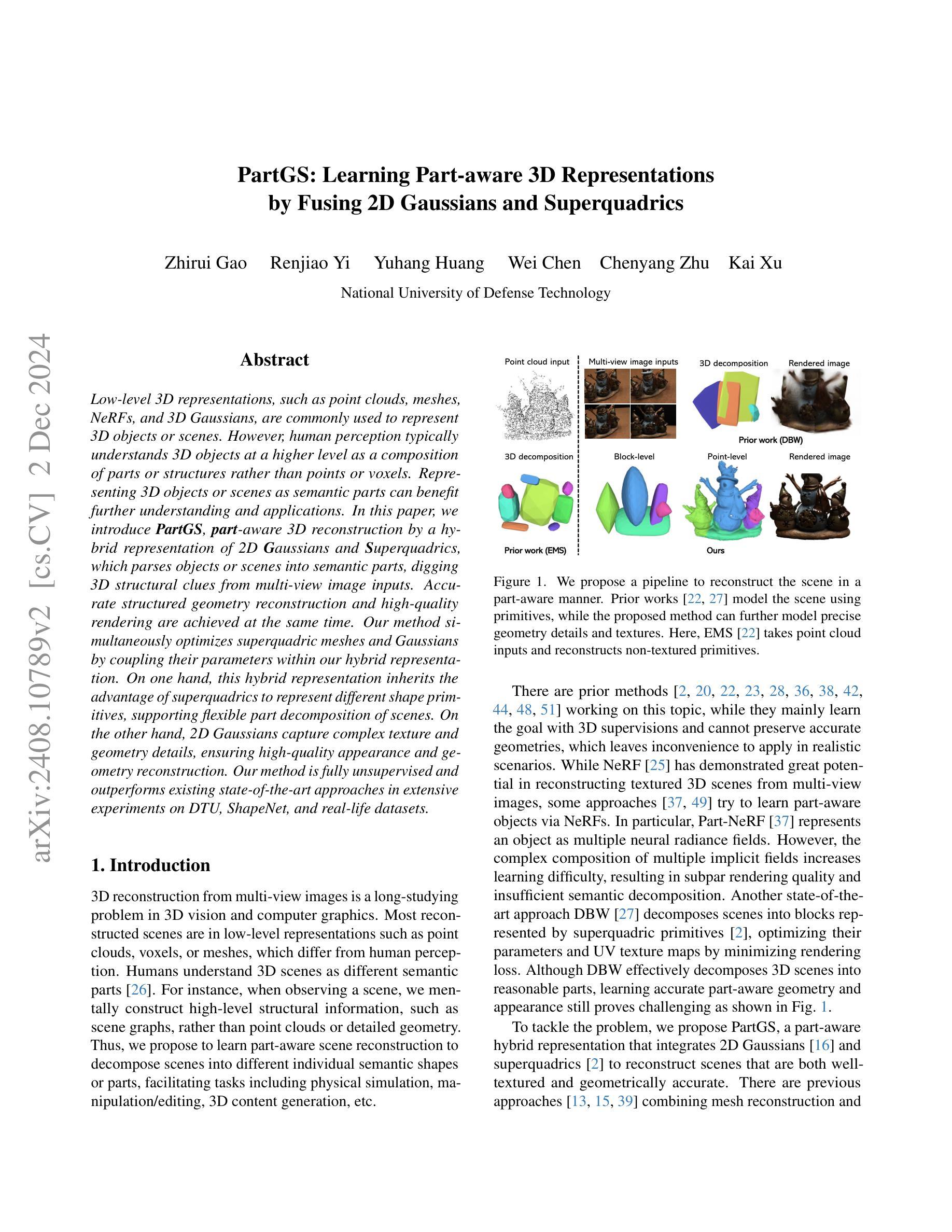
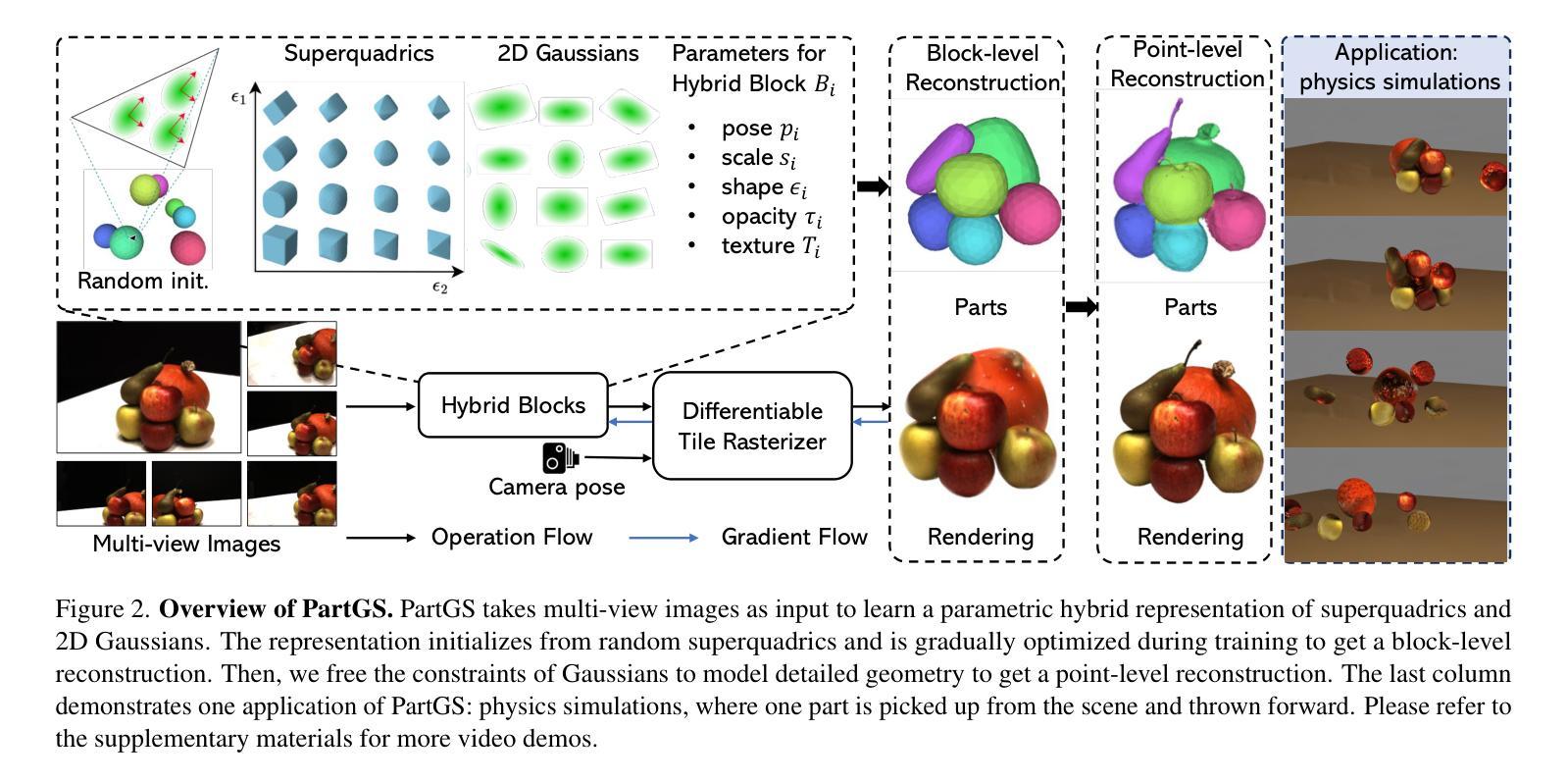
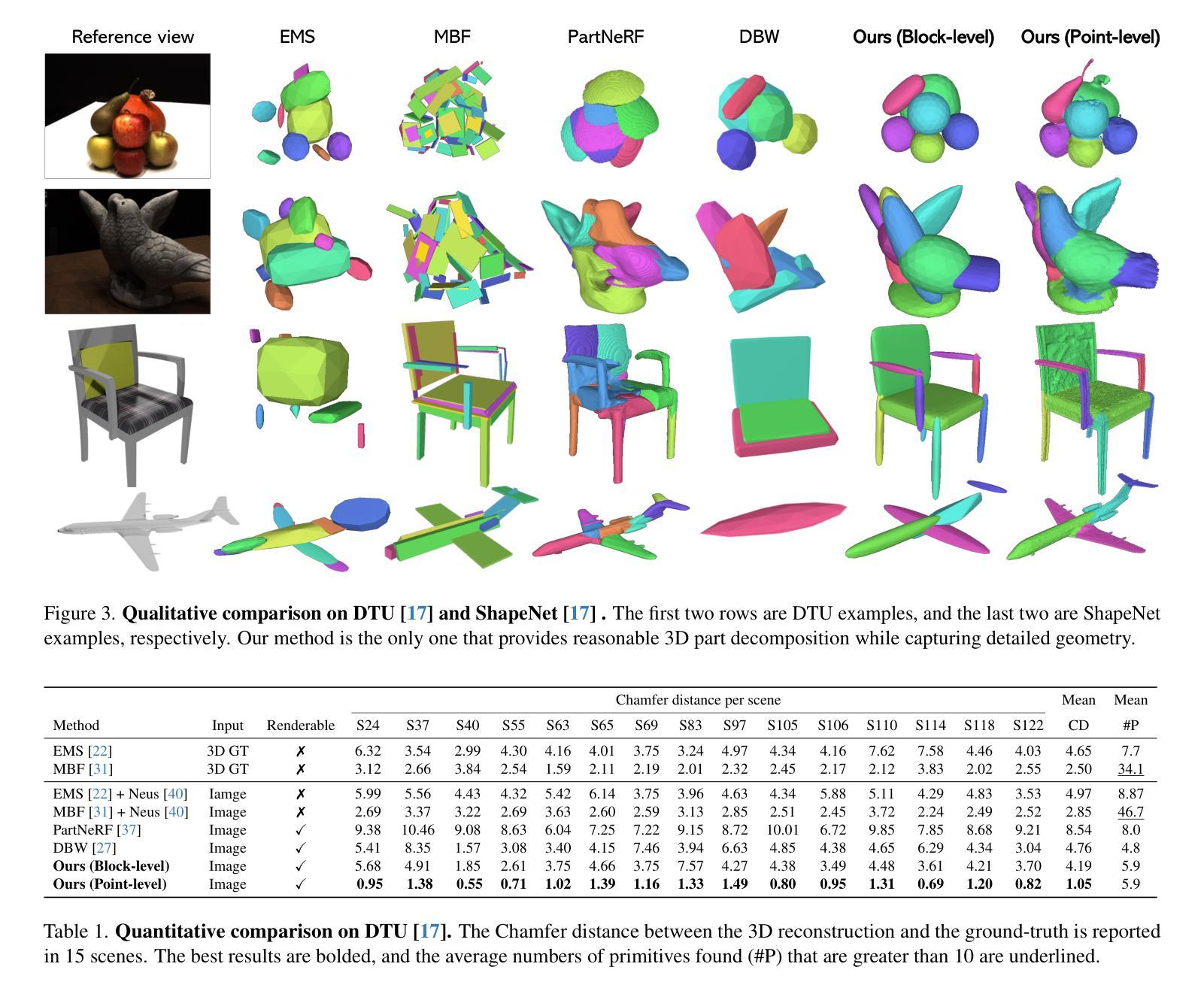
PartGS:Learning Part-aware 3D Representations by Fusing 2D Gaussians and Superquadrics
Authors:Zhirui Gao, Renjiao Yi, Yuhang Huang, Wei Chen, Chenyang Zhu, Kai Xu
Low-level 3D representations, such as point clouds, meshes, NeRFs, and 3D Gaussians, are commonly used to represent 3D objects or scenes. However, human perception typically understands 3D objects at a higher level as a composition of parts or structures rather than points or voxels. Representing 3D objects or scenes as semantic parts can benefit further understanding and applications. In this paper, we introduce $\textbf{PartGS}$, $\textbf{part}$-aware 3D reconstruction by a hybrid representation of 2D $\textbf{G}$aussians and $\textbf{S}$uperquadrics, which parses objects or scenes into semantic parts, digging 3D structural clues from multi-view image inputs. Accurate structured geometry reconstruction and high-quality rendering are achieved at the same time. Our method simultaneously optimizes superquadric meshes and Gaussians by coupling their parameters within our hybrid representation. On one hand, this hybrid representation inherits the advantage of superquadrics to represent different shape primitives, supporting flexible part decomposition of scenes. On the other hand, 2D Gaussians capture complex texture and geometry details, ensuring high-quality appearance and geometry reconstruction. Our method is fully unsupervised and outperforms existing state-of-the-art approaches in extensive experiments on DTU, ShapeNet, and real-life datasets.
低级别的三维表示,如点云、网格、NeRF和高斯分布等,通常用于表示三维物体或场景。然而,人类的感知通常是在更高层次上理解三维物体,将其视为部件或结构的组合,而非点或体素。将三维物体或场景表示为语义部件可以进一步促进理解和应用。在本文中,我们引入了PartGS,这是一种通过二维高斯和超级二次元的混合表示来进行部件感知的三维重建。它能够将物体或场景解析为语义部件,从多视角图像输入中挖掘三维结构线索。同时实现了精确的几何结构重建和高质量渲染。我们的方法通过混合表示中的参数耦合来同时优化超级二次元网格和高斯分布。一方面,这种混合表示继承了超级二次元表示不同形状原始部件的优势,支持场景灵活的部分分解。另一方面,二维高斯分布捕捉复杂的纹理和几何细节,确保高质量的外貌和几何重建。我们的方法完全无监督,在DTU、ShapeNet和真实数据集上的大量实验中表现优于现有先进技术方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个名为PartGS的3D重建方法,它采用混合表示方式,结合了二维高斯和超级曲面(superquadrics),将对象或场景解析为语义部分。该方法能够从多视角图像输入中挖掘出3D结构线索,实现精确的结构几何重建和高质量渲染。PartGS同时优化超级曲面网格和高斯分布,通过混合表示中的参数耦合来实现。该方法既继承了超级曲面表示不同形状原语的优势,支持场景灵活的部分分解,又通过二维高斯捕捉复杂的纹理和几何细节,确保高质量的外观和几何重建。该方法完全无监督,在DTU、ShapeNet和真实数据集上的实验表现均优于现有先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- PartGS采用混合表示方法,结合了二维高斯和超级曲面(superquadrics),以解析3D对象或场景的语义部分。
- 该方法能够从多视角图像中挖掘出3D结构线索,实现精确的结构几何重建和高质量渲染。
- PartGS可以同时优化超级曲面网格和高斯分布,通过参数耦合来实现这一功能。
- 超级曲面能够表示不同的形状原语,支持场景灵活的部分分解。
- 二维高斯可以捕捉复杂的纹理和几何细节,确保高质量的外观和几何重建。
- PartGS方法完全无监督,适用于多种数据集。
点此查看论文截图
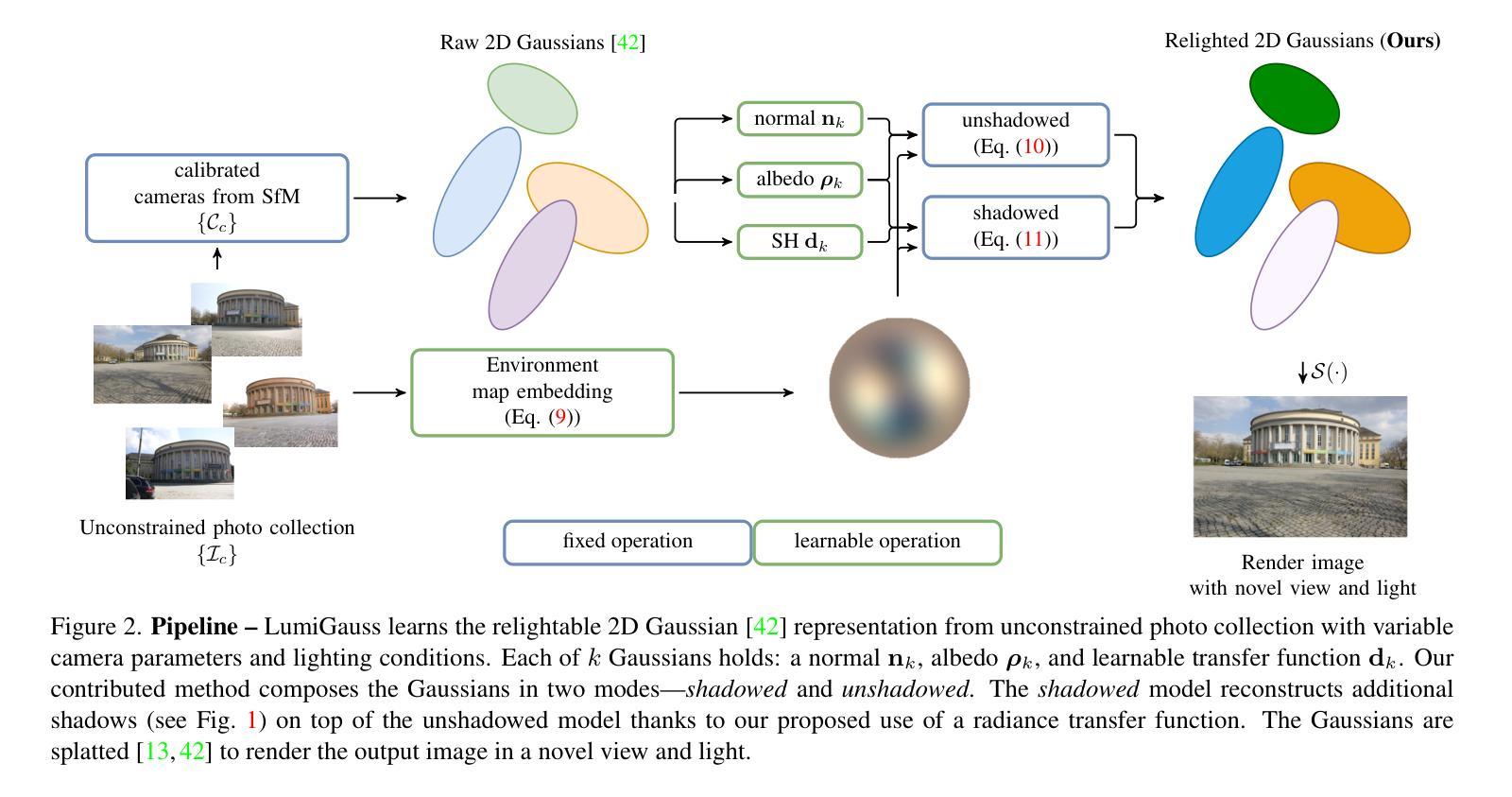
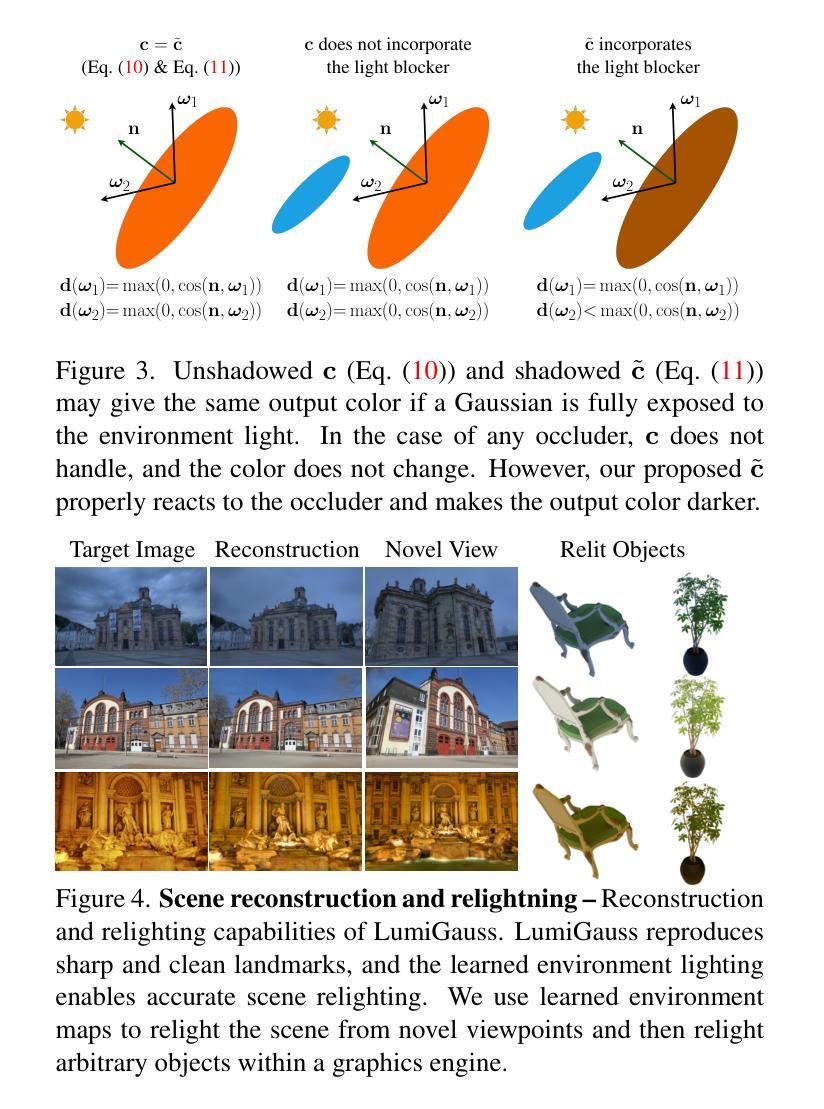
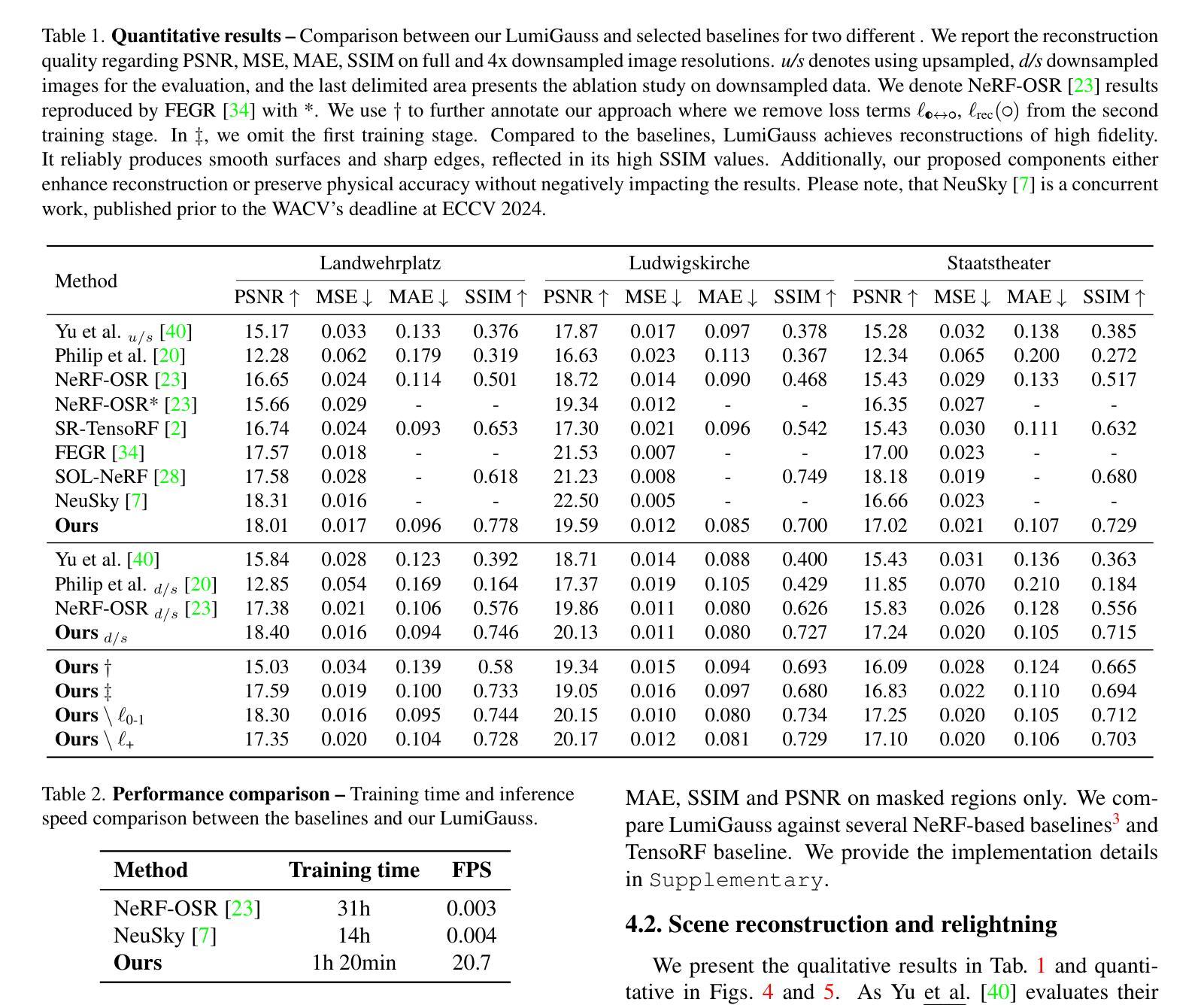
LumiGauss: Relightable Gaussian Splatting in the Wild
Authors:Joanna Kaleta, Kacper Kania, Tomasz Trzcinski, Marek Kowalski
Decoupling lighting from geometry using unconstrained photo collections is notoriously challenging. Solving it would benefit many users as creating complex 3D assets takes days of manual labor. Many previous works have attempted to address this issue, often at the expense of output fidelity, which questions the practicality of such methods. We introduce LumiGauss - a technique that tackles 3D reconstruction of scenes and environmental lighting through 2D Gaussian Splatting. Our approach yields high-quality scene reconstructions and enables realistic lighting synthesis under novel environment maps. We also propose a method for enhancing the quality of shadows, common in outdoor scenes, by exploiting spherical harmonics properties. Our approach facilitates seamless integration with game engines and enables the use of fast precomputed radiance transfer. We validate our method on the NeRF-OSR dataset, demonstrating superior performance over baseline methods. Moreover, LumiGauss can synthesize realistic images for unseen environment maps. Our code: https://github.com/joaxkal/lumigauss.
使用无约束照片集将照明与几何分离是众所周知的挑战。解决这一问题将使许多用户受益,因为创建复杂的3D资产需要数天的人工劳动。许多早期作品试图解决这一问题,通常以牺牲输出保真度为代价,这引发了对此类方法实用性的质疑。我们引入了LumiGauss技术,该技术通过二维高斯贴图解决场景的三维重建和环境照明问题。我们的方法产生了高质量的场景重建,并在新的环境贴图下实现了逼真的照明合成。我们还提出了一种利用球面谐波属性来提高室外场景中常见阴影质量的方法。我们的方法与游戏引擎无缝集成,并利用快速预计算辐射传输。我们在NeRF-OSR数据集上验证了我们的方法,证明了其在基线方法上的优越性。此外,LumiGauss还可以为未见的环境地图合成逼真的图像。我们的代码:https://github.com/joaxkal/lumigauss。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at WACV2025
Summary
基于未约束照片集,实现光照与几何的解耦具有挑战性。为解决此问题,我们提出了LumiGauss技术,该技术采用二维高斯splat方法重建三维场景并合成环境光照。该方法可实现高质量场景重建,并在新型环境贴图下生成逼真的光照效果。同时,通过利用球面谐波属性改进户外场景中常见的阴影质量。我们的方法与游戏引擎无缝集成,并采用快速预计算辐射传输。在NeRF-OSR数据集上的实验验证表明,我们的方法优于基线方法,并且可以合成针对未见环境映射的逼真图像。
Key Takeaways
- LumiGauss技术解决了在解耦光照和几何时的挑战。
- 该技术使用二维高斯splat方法进行三维场景的重建和环境光照的合成。
- LumiGauss能实现高质量的场景重建,并生成逼真的光照效果。
- 通过利用球面谐波属性,改进了户外场景中的阴影质量。
- 该方法与游戏引擎无缝集成,并采用快速预计算辐射传输。
- 在NeRF-OSR数据集上的实验验证了LumiGauss方法的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

Evaluating Modern Approaches in 3D Scene Reconstruction: NeRF vs Gaussian-Based Methods
Authors:Yiming Zhou, Zixuan Zeng, Andi Chen, Xiaofan Zhou, Haowei Ni, Shiyao Zhang, Panfeng Li, Liangxi Liu, Mengyao Zheng, Xupeng Chen
Exploring the capabilities of Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) and Gaussian-based methods in the context of 3D scene reconstruction, this study contrasts these modern approaches with traditional Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) systems. Utilizing datasets such as Replica and ScanNet, we assess performance based on tracking accuracy, mapping fidelity, and view synthesis. Findings reveal that NeRF excels in view synthesis, offering unique capabilities in generating new perspectives from existing data, albeit at slower processing speeds. Conversely, Gaussian-based methods provide rapid processing and significant expressiveness but lack comprehensive scene completion. Enhanced by global optimization and loop closure techniques, newer methods like NICE-SLAM and SplaTAM not only surpass older frameworks such as ORB-SLAM2 in terms of robustness but also demonstrate superior performance in dynamic and complex environments. This comparative analysis bridges theoretical research with practical implications, shedding light on future developments in robust 3D scene reconstruction across various real-world applications.
本文探讨了Neural Radiance Fields(NeRF)和高斯基方法在3D场景重建方面的能力,并将这些现代方法与传统的Simultaneous Localization and Mapping(SLAM)系统进行了对比。我们利用Replica和ScanNet等数据集,根据跟踪精度、映射保真度和视图合成来评估性能。研究结果表明,NeRF在视图合成方面表现出色,能够从现有数据中生成新的视角,尽管处理速度较慢。相反,高斯基方法处理速度快,表达力强,但场景完成度不够全面。通过全局优化和闭环技术增强,NICE-SLAM和SplaTAM等新方法不仅提高了鲁棒性,超越了早期的ORB-SLAM2框架,而且在动态和复杂环境中也表现出卓越的性能。这一比较分析将理论研究与实际应用相结合,为各种现实应用中的稳健3D场景重建的未来发展提供了启示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by 2024 6th International Conference on Data-driven Optimization of Complex Systems
Summary
NeRF与基于高斯的方法在3D场景重建中的性能研究,与传统SLAM系统相比,探讨了NeRF的优势和局限性。研究通过Replica和ScanNet数据集评估了跟踪精度、地图精度和视角合成的性能。NeRF在视角合成方面表现出卓越的能力,但处理速度较慢。基于高斯的方法处理速度快且表现力强,但场景完整性方面有所欠缺。新型方法如NICE-SLAM和SplaTAM不仅提高了稳健性,而且在动态和复杂环境中表现出卓越性能。该研究为理论研究和实际应用之间的桥梁,为未来的稳健3D场景重建的未来发展提供了启示。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF在视角合成方面具有卓越性能,能够生成新的视角数据。
- 基于高斯的方法处理速度快,但可能在场景完整性方面有所不足。
- NeRF处理速度较慢,需要优化以提高效率。
- 新方法如NICE-SLAM和SplaTAM在复杂和动态环境中表现出更好的稳健性。
- 对比分析有助于理解不同方法在3D场景重建中的优势和局限性。
- 研究结果对3D场景重建的未来发展具有启示作用。
点此查看论文截图

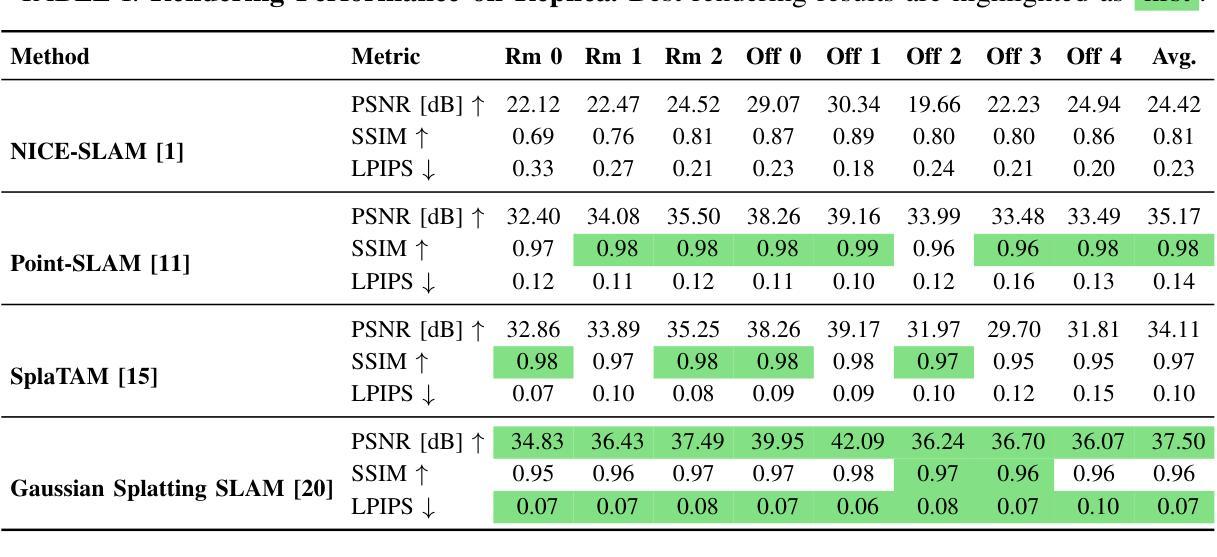
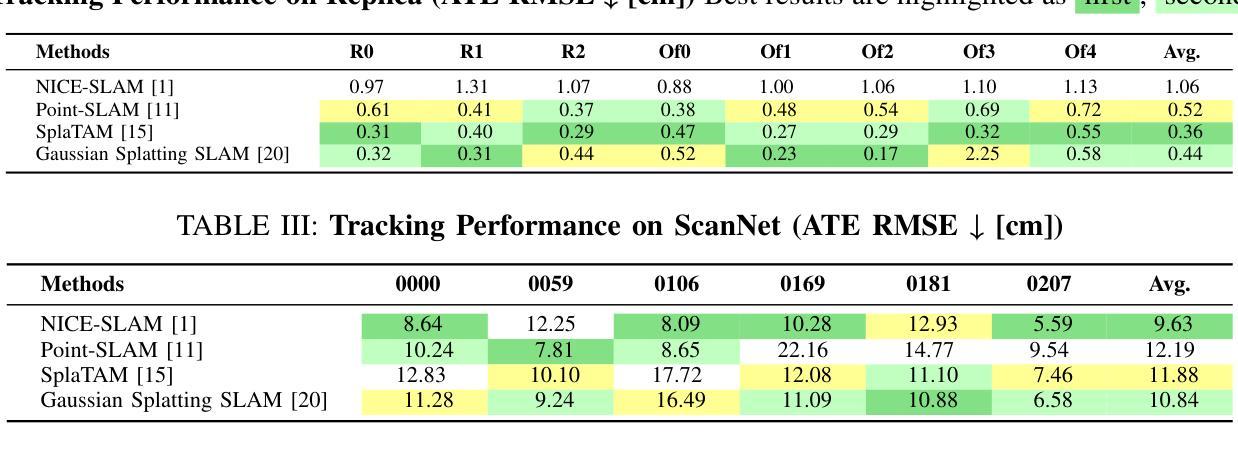

IE-NeRF: Inpainting Enhanced Neural Radiance Fields in the Wild
Authors:Shuaixian Wang, Haoran Xu, Yaokun Li, Jiwei Chen, Guang Tan
We present a novel approach for synthesizing realistic novel views using Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) with uncontrolled photos in the wild. While NeRF has shown impressive results in controlled settings, it struggles with transient objects commonly found in dynamic and time-varying scenes. Our framework called \textit{Inpainting Enhanced NeRF}, or \ours, enhances the conventional NeRF by drawing inspiration from the technique of image inpainting. Specifically, our approach extends the Multi-Layer Perceptrons (MLP) of NeRF, enabling it to simultaneously generate intrinsic properties (static color, density) and extrinsic transient masks. We introduce an inpainting module that leverages the transient masks to effectively exclude occlusions, resulting in improved volume rendering quality. Additionally, we propose a new training strategy with frequency regularization to address the sparsity issue of low-frequency transient components. We evaluate our approach on internet photo collections of landmarks, demonstrating its ability to generate high-quality novel views and achieve state-of-the-art performance.
我们提出了一种利用神经辐射场(NeRF)合成逼真的新视角的新方法,适用于不受控制的野外照片。虽然NeRF在受控环境中表现出了令人印象深刻的结果,但在动态和时变场景中常见的瞬态对象上却遇到了困难。我们的框架称为“修复增强NeRF”,或简称为“我们的方法”,它通过借鉴图像修复技术来增强传统的NeRF。具体来说,我们的方法扩展了NeRF的多层感知器(MLP),使其能够同时生成内在属性(静态颜色、密度)和外在瞬态掩膜。我们引入了一个修复模块,该模块利用瞬态掩膜有效地排除遮挡,从而提高体积渲染质量。此外,我们提出了一种新的带有频率正则化的训练策略,以解决瞬态组件低频的稀疏性问题。我们在地标互联网照片集上评估了我们的方法,证明了其生成高质量新视角的能力,并达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于神经网络辐射场(NeRF)技术,我们提出了一种合成真实视角的新方法,采用野生环境中的非控制照片。我们提出名为“增强NeRF修复”的框架,旨在提高传统NeRF技术,灵感来源于图像修复技术。它扩展了NeRF的多层感知器(MLP),能够同时生成固有属性(静态颜色、密度)和外置瞬态掩膜。通过引入修复模块并利用瞬态掩膜有效排除遮挡物,提高了体积渲染质量。此外,我们还提出了一种新的带有频率正则化的训练策略,以解决瞬态组件的低频稀疏性问题。我们在互联网地标照片集上评估了我们的方法,证明其能够生成高质量的新视角并达到最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于神经网络辐射场(NeRF)技术的合成真实视角新方法。
- 利用野生环境中的非控制照片进行NeRF合成。
- 提出名为“增强NeRF修复”的框架,结合图像修复技术,增强NeRF表现。
- 通过扩展多层感知器(MLP),可同时生成固有属性和外置瞬态掩膜。
- 利用瞬态掩膜修复模块排除遮挡物,提高体积渲染质量。
- 提出带有频率正则化的新训练策略,解决瞬态组件的低频稀疏性问题。
点此查看论文截图

Radiance Fields from Photons
Authors:Sacha Jungerman, Aryan Garg, Mohit Gupta
Neural radiance fields, or NeRFs, have become the de facto approach for high-quality view synthesis from a collection of images captured from multiple viewpoints. However, many issues remain when capturing images in-the-wild under challenging conditions, such as low light, high dynamic range, or rapid motion leading to smeared reconstructions with noticeable artifacts. In this work, we introduce quanta radiance fields, a novel class of neural radiance fields that are trained at the granularity of individual photons using single-photon cameras (SPCs). We develop theory and practical computational techniques for building radiance fields and estimating dense camera poses from unconventional, stochastic, and high-speed binary frame sequences captured by SPCs. We demonstrate, both via simulations and a SPC hardware prototype, high-fidelity reconstructions under high-speed motion, in low light, and for extreme dynamic range settings.
神经辐射场(NeRF)已经成为从多个视角捕获的图像集中进行高质量视图合成的一种实际方法。然而,在具有挑战性的条件下(如低光照、高动态范围或快速运动等)进行野外图像捕获时仍存在许多问题,这会导致重建模糊并出现明显的伪影。在这项工作中,我们引入了量子辐射场(Quanta Radiance Fields),这是一种新型神经辐射场,它使用单光子相机(SPC)以单个光子为单位进行训练。我们为构建辐射场和估计由SPC捕获的非传统、随机和高速二进制帧序列的密集相机姿态,发展理论和实用计算技术。我们通过模拟和SPC硬件原型证明,在高速运动、低光照和极端动态范围设置下,可以实现高保真重建。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经网络辐射场(NeRF)已经成为从多个视角捕获的图像进行高质量视图合成的主流方法。然而,在野外拍摄时,由于低光、高动态范围或快速运动等挑战条件,仍存在许多难题,导致重建模糊并出现明显的伪影。本研究引入量子辐射场(quanta radiance fields),这是一种新型神经网络辐射场,以单个光子相机(SPC)为单位进行训练。我们构建了辐射场的理论及实用计算技术,并估算了来自SPC捕获的非传统、随机和高速二进制帧序列的密集相机姿态。我们通过模拟和SPC硬件原型演示了在高速运动、低光和高动态范围设置下的高保真重建。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF已成为高质量视图合成的标准方法,但在挑战条件下的野外拍摄仍存在诸多问题。
- 研究提出了量子辐射场(quanta radiance fields)——新型神经网络辐射场方法,适用于单个光子相机(SPC)。
- 该方法通过理论及实用计算技术构建辐射场,并估算密集相机姿态。
- 量子辐射场可以在高速运动、低光和高动态范围设置下进行高保真重建。
- 通过模拟和SPC硬件原型验证了该方法的有效性。
- 该技术有助于改进在复杂环境下的图像捕获和重建。
点此查看论文截图
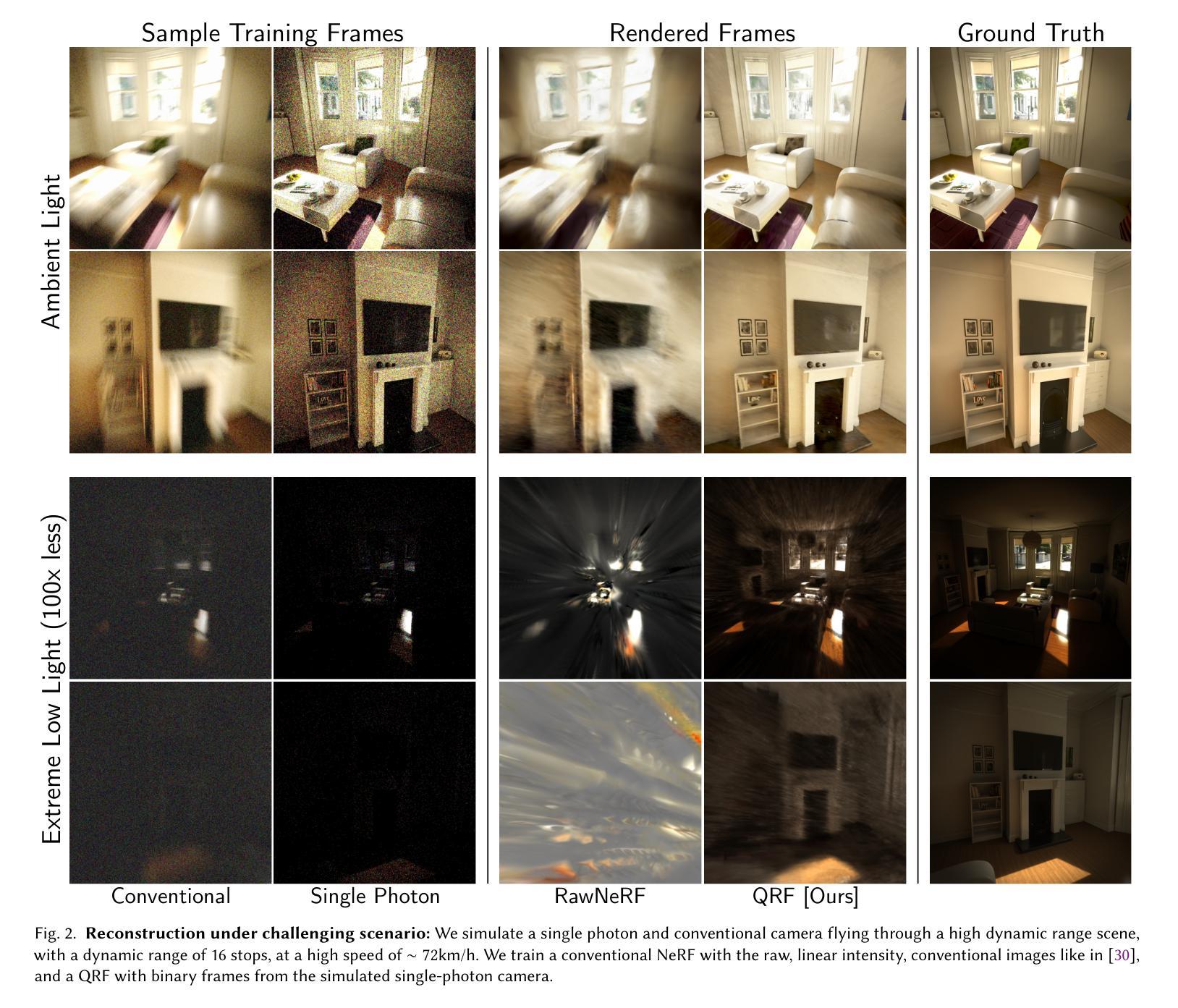



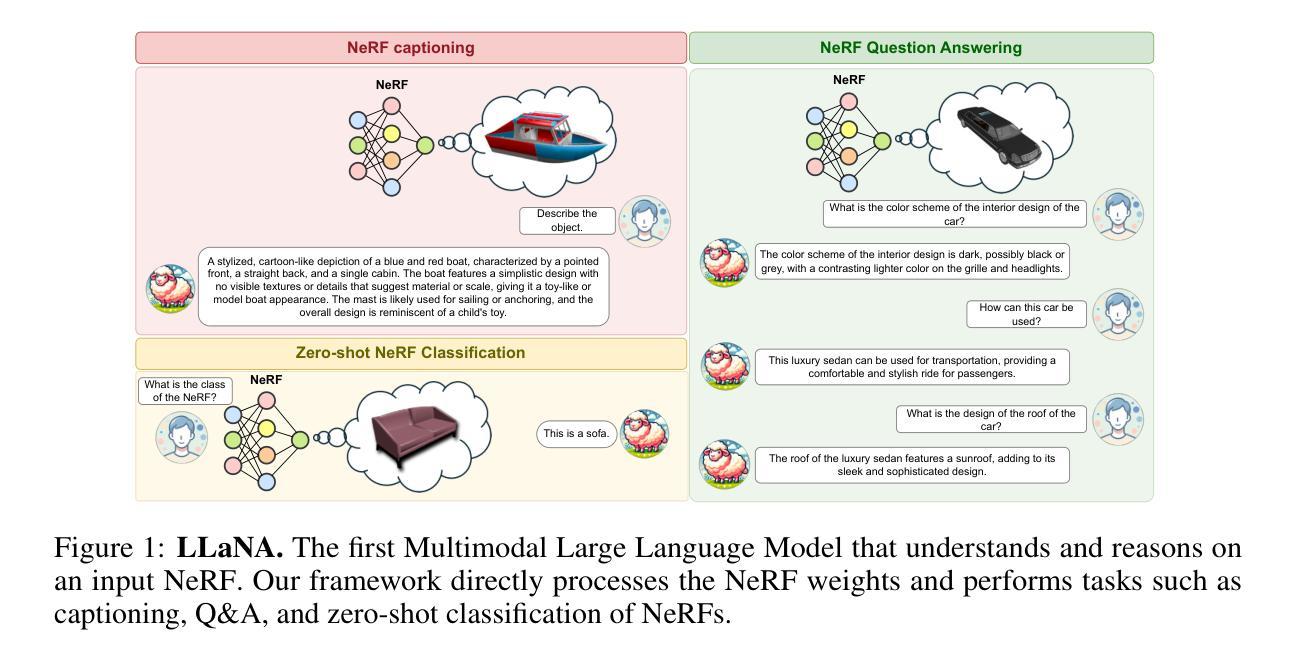
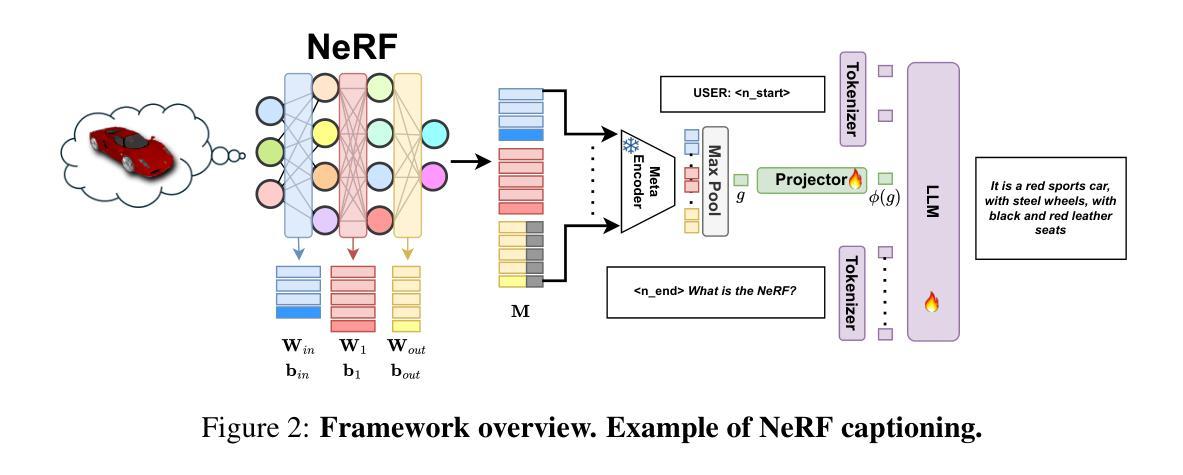
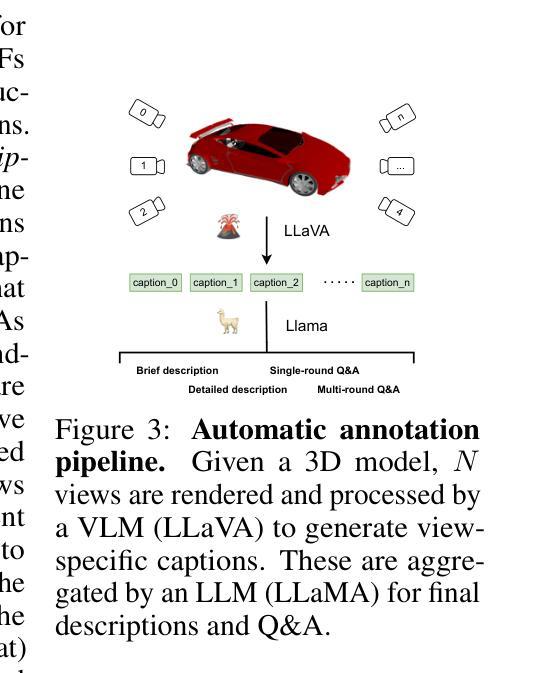
LLaNA: Large Language and NeRF Assistant
Authors:Andrea Amaduzzi, Pierluigi Zama Ramirez, Giuseppe Lisanti, Samuele Salti, Luigi Di Stefano
Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated an excellent understanding of images and 3D data. However, both modalities have shortcomings in holistically capturing the appearance and geometry of objects. Meanwhile, Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs), which encode information within the weights of a simple Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP), have emerged as an increasingly widespread modality that simultaneously encodes the geometry and photorealistic appearance of objects. This paper investigates the feasibility and effectiveness of ingesting NeRF into MLLM. We create LLaNA, the first general-purpose NeRF-language assistant capable of performing new tasks such as NeRF captioning and Q&A. Notably, our method directly processes the weights of the NeRF’s MLP to extract information about the represented objects without the need to render images or materialize 3D data structures. Moreover, we build a dataset of NeRFs with text annotations for various NeRF-language tasks with no human intervention. Based on this dataset, we develop a benchmark to evaluate the NeRF understanding capability of our method. Results show that processing NeRF weights performs favourably against extracting 2D or 3D representations from NeRFs.
多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)已经展现出对图像和3D数据的出色理解。然而,两种模式在全面捕捉物体的外观和几何特征方面都存在不足。同时,神经辐射场(NeRF)作为一种日益普及的模式,它通过简单的多层感知器(MLP)的权重编码信息,能够同时编码物体的几何和逼真的外观。本文研究了将NeRF纳入MLLM的可行性和有效性。我们创建了LLaNA,这是第一个通用的NeRF语言助手,能够执行新的任务,如NeRF描述和问答。值得注意的是,我们的方法直接处理NeRF的MLP权重来提取有关所表示对象的信息,无需呈现图像或形成三维数据结构。此外,我们建立了一个带有各种NeRF语言任务的文本注释的NeRF数据集,无需人工干预。基于该数据集,我们开发了一个基准测试来评估我们方法的NeRF理解能力。结果表明,处理NeRF权重比从NeRF中提取二维或三维表示更为有利。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review. Project page: https://andreamaduzzi.github.io/llana/
Summary
本文介绍了将Neural Radiance Fields(NeRF)技术引入多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)的研究。通过创建名为LLaNA的首个通用NeRF语言助理,该论文展示了将NeRF与语言处理结合的能力,实现了NeRF描述和问答等新型任务。该研究直接处理NeRF的MLP权重以提取对象信息,无需渲染图像或实现3D数据结构。此外,论文建立了一个带有文本注释的NeRF数据集,用于各种NeRF语言任务,并基于此数据集开发了一个评估方法。结果显示,处理NeRF权重的方法优于从NeRF中提取2D或3D表示的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLM)在理解和处理图像和3D数据上表现出色,但仍存在对物体外观和几何结构整体捕捉的不足。
- Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF)技术能同时编码物体的几何和逼真的外观信息。
- LLaNA是首个通用NeRF语言助理,能执行NeRF描述和问答等新型任务。
- 该研究直接处理NeRF的MLP权重提取信息,无需通过图像渲染或实现3D数据结构。
- 建立了一个带有文本注释的NeRF数据集,用于各种NeRF语言任务,且该数据集无需人工干预。
- 基于该数据集开发了一个评估方法,以评估对NeRF的理解能力。
点此查看论文截图

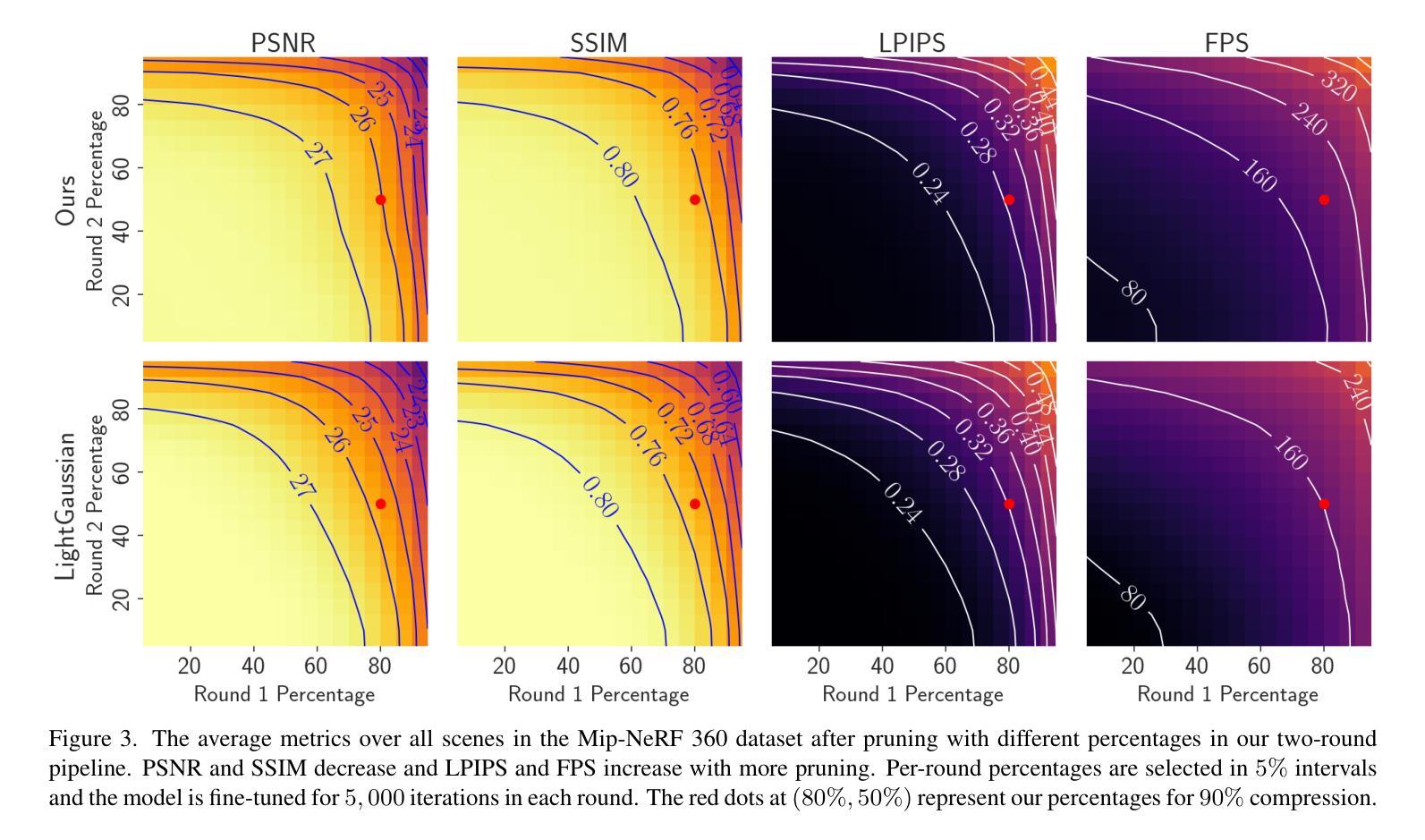
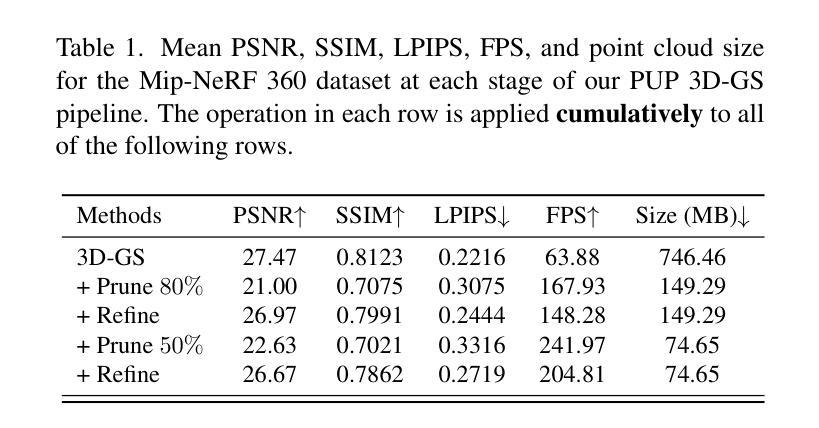
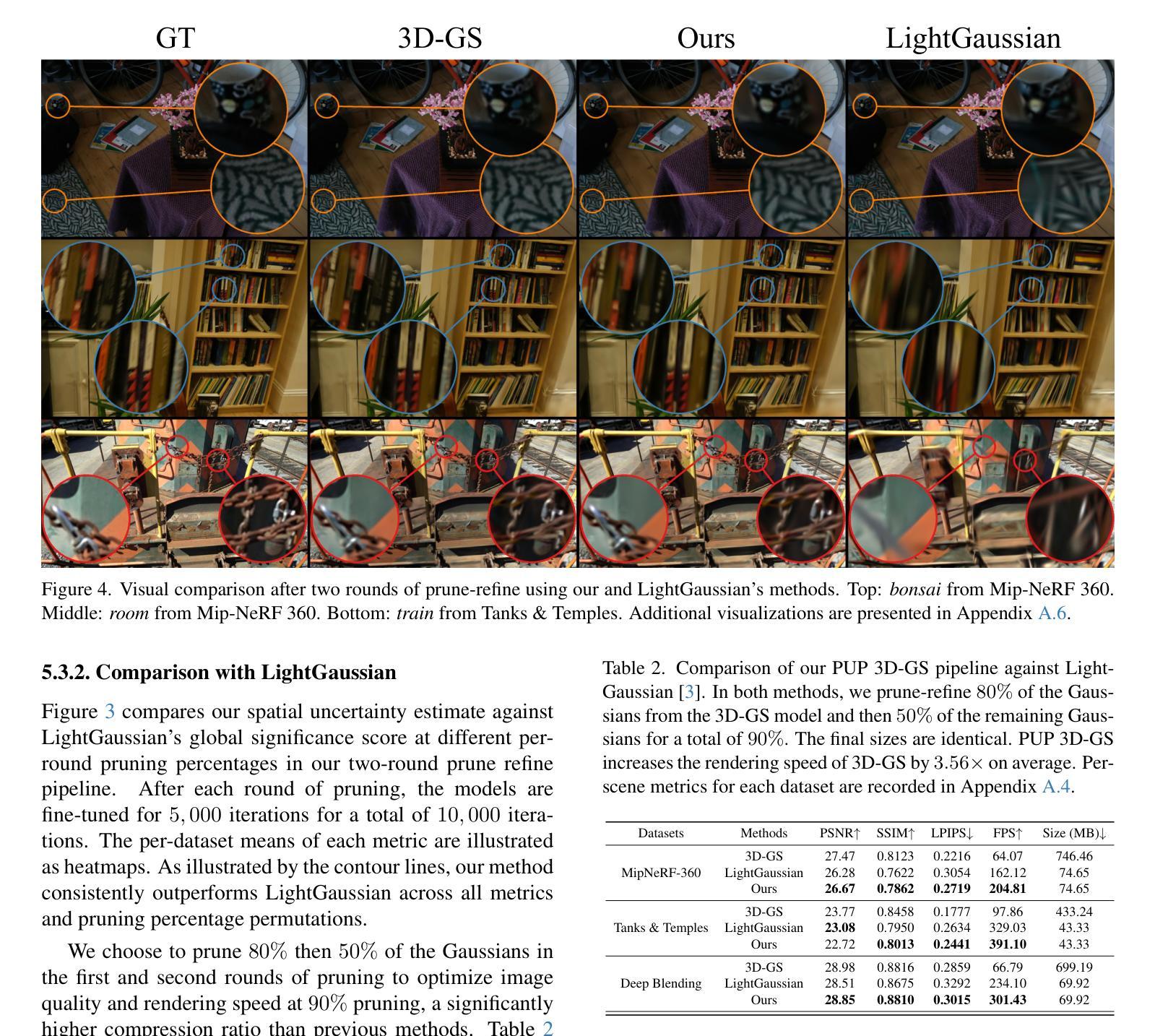
PUP 3D-GS: Principled Uncertainty Pruning for 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Alex Hanson, Allen Tu, Vasu Singla, Mayuka Jayawardhana, Matthias Zwicker, Tom Goldstein
Recent advances in novel view synthesis have enabled real-time rendering speeds with high reconstruction accuracy. 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS), a foundational point-based parametric 3D scene representation, models scenes as large sets of 3D Gaussians. However, complex scenes can consist of millions of Gaussians, resulting in high storage and memory requirements that limit the viability of 3D-GS on devices with limited resources. Current techniques for compressing these pretrained models by pruning Gaussians rely on combining heuristics to determine which Gaussians to remove. At high compression ratios, these pruned scenes suffer from heavy degradation of visual fidelity and loss of foreground details. In this paper, we propose a principled sensitivity pruning score that preserves visual fidelity and foreground details at significantly higher compression ratios than existing approaches. It is computed as a second-order approximation of the reconstruction error on the training views with respect to the spatial parameters of each Gaussian. Additionally, we propose a multi-round prune-refine pipeline that can be applied to any pretrained 3D-GS model without changing its training pipeline. After pruning 90% of Gaussians, a substantially higher percentage than previous methods, our PUP 3D-GS pipeline increases average rendering speed by 3.56$\times$ while retaining more salient foreground information and achieving higher image quality metrics than existing techniques on scenes from the Mip-NeRF 360, Tanks & Temples, and Deep Blending datasets.
最新的视点合成技术进展已经实现了高重建精度的实时渲染速度。三维高斯定位技术(3D-GS)是一种基于点的参数化三维场景表示方法,将场景建模为大量三维高斯数据集。然而,复杂场景可能包含数百万个高斯数据,导致存储和内存需求很高,限制了资源有限的设备上使用三维高斯定位技术的可行性。当前通过修剪高斯值来压缩这些预训练模型的技术依赖于结合启发式方法来确定要删除哪些高斯值。在高压缩率下,这些修剪后的场景在视觉保真度上遭受严重损失,前景细节丢失。在本文中,我们提出了一种有原则的敏感性修剪评分,能够在比现有方法更高的压缩率下保持视觉保真度和前景细节。它是通过计算训练视图上相对于每个高斯的空间参数的重建误差的二阶近似来计算的。此外,我们提出了一种多轮修剪和精炼管道,可以应用于任何预训练的三维高斯定位模型,而无需更改其训练管道。修剪90%的高斯后,我们的PUP 3D-GS管道在保持更突出的前景信息和实现比现有技术在Mip-NeRF 360、坦克与寺庙以及深度混合数据集上的更高图像质量指标的同时,提高了平均渲染速度高达3.56倍。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本研究提出一种基于敏感度评估的裁剪策略,用于压缩三维高斯平铺(3D-GS)模型,能在高压缩率下保持视觉保真度和前景细节。该策略通过计算重建误差的二阶近似值来确定每个高斯的重要性,并提出多轮裁剪-优化流程,可应用于任何预训练的3D-GS模型,无需改变其训练流程。研究在Mip-NeRF 360、Tanks & Temples和Deep Blending数据集上的实验表明,该方法在裁剪90%的高斯后,平均渲染速度提高3.56倍,同时保留更多显著的前景信息,达到更高的图像质量指标。
要点
- 利用敏感度评估的裁剪策略压缩三维高斯场景表示模型,实现高压缩率下的视觉保真度保持。
- 提出一种基于重建误差二阶近似值的敏感度评分机制,确定每个高斯的重要性。
- 引入多轮裁剪-优化流程,适用于任何预训练的3D-GS模型,无需改变其训练流程。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,该方法在大幅提高渲染速度的同时,保留了显著的前景信息,达到了更高的图像质量指标。
- 与现有技术相比,能够在更高的压缩率下工作,且性能表现更优。
- 该方法对于资源受限的设备上的实时渲染应用具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

Benchmarking Neural Radiance Fields for Autonomous Robots: An Overview
Authors:Yuhang Ming, Xingrui Yang, Weihan Wang, Zheng Chen, Jinglun Feng, Yifan Xing, Guofeng Zhang
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have emerged as a powerful paradigm for 3D scene representation, offering high-fidelity renderings and reconstructions from a set of sparse and unstructured sensor data. In the context of autonomous robotics, where perception and understanding of the environment are pivotal, NeRF holds immense promise for improving performance. In this paper, we present a comprehensive survey and analysis of the state-of-the-art techniques for utilizing NeRF to enhance the capabilities of autonomous robots. We especially focus on the perception, localization and navigation, and decision-making modules of autonomous robots and delve into tasks crucial for autonomous operation, including 3D reconstruction, segmentation, pose estimation, simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM), navigation and planning, and interaction. Our survey meticulously benchmarks existing NeRF-based methods, providing insights into their strengths and limitations. Moreover, we explore promising avenues for future research and development in this domain. Notably, we discuss the integration of advanced techniques such as 3D Gaussian splatting (3DGS), large language models (LLM), and generative AIs, envisioning enhanced reconstruction efficiency, scene understanding, decision-making capabilities. This survey serves as a roadmap for researchers seeking to leverage NeRFs to empower autonomous robots, paving the way for innovative solutions that can navigate and interact seamlessly in complex environments.
神经辐射场(NeRF)已经成为一种强大的3D场景表示范式,能够从稀疏的非结构化传感器数据中生成高保真渲染和重建。在自主机器人领域,环境的感知和理解至关重要,NeRF在提升机器人性能方面具有巨大潜力。本文全面回顾和分析了利用NeRF增强自主机器人能力的最新技术。我们特别关注自主机器人的感知、定位和导航以及决策模块,并深入探讨了自主操作的关键任务,包括3D重建、分割、姿态估计、同时定位与地图构建(SLAM)、导航和规划以及交互。我们的调查仔细评估了现有的基于NeRF的方法,深入了解其优点和局限性。此外,我们还探讨了未来该领域研究和发展的有前途的方向。值得注意的是,我们讨论了集成先进技术,如3D高斯喷涂(3DGS)、大型语言模型(LLM)和生成式人工智能,设想提高重建效率、场景理解和决策能力。本综述为希望利用NeRF赋能自主机器人的研究者提供了路线图,为在复杂环境中无缝导航和交互的创新解决方案铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 32 pages, 5 figures, 8 tables
Summary
NeRF技术为自主机器人提供了强大的三维场景表示方法,能提高感知、定位、导航和决策等关键模块的性能。本文全面综述了利用NeRF技术增强自主机器人能力的最新进展,探讨了其在三维重建、分割、姿态估计、SLAM、导航规划以及交互等任务中的应用,并探讨了未来研究方向,如集成3DGS、LLM和生成式AI等技术。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF技术成为自主机器人领域强大的三维场景表示方法。
- NeRF能提高自主机器人的感知、定位、导航和决策等关键模块性能。
- 综述了利用NeRF技术增强自主机器人的最新进展。
- 探讨了NeRF在三维重建、分割、姿态估计等任务中的应用。
- 介绍了NeRF与SLAM、导航规划以及交互等任务的结合。
- 探讨了未来研究方向,包括集成3DGS、LLM和生成式AI等技术。
点此查看论文截图

DGE: Direct Gaussian 3D Editing by Consistent Multi-view Editing
Authors:Minghao Chen, Iro Laina, Andrea Vedaldi
We consider the problem of editing 3D objects and scenes based on open-ended language instructions. A common approach to this problem is to use a 2D image generator or editor to guide the 3D editing process, obviating the need for 3D data. However, this process is often inefficient due to the need for iterative updates of costly 3D representations, such as neural radiance fields, either through individual view edits or score distillation sampling. A major disadvantage of this approach is the slow convergence caused by aggregating inconsistent information across views, as the guidance from 2D models is not multi-view consistent. We thus introduce the Direct Gaussian Editor (DGE), a method that addresses these issues in two stages. First, we modify a given high-quality image editor like InstructPix2Pix to be multi-view consistent. To do so, we propose a training-free approach that integrates cues from the 3D geometry of the underlying scene. Second, given a multi-view consistent edited sequence of images, we directly and efficiently optimize the 3D representation, which is based on 3D Gaussian Splatting. Because it avoids incremental and iterative edits, DGE is significantly more accurate and efficient than existing approaches and offers additional benefits, such as enabling selective editing of parts of the scene.
我们考虑了基于开放语言指令编辑3D对象和场景的问题。解决这个问题的常见方法是使用2D图像生成器或编辑器来指导3D编辑过程,从而无需3D数据。然而,由于需要迭代更新昂贵的3D表示(如神经辐射场),这一过程通常效率不高,无论是通过单独的视图编辑还是分数蒸馏采样。这种方法的主要缺点是由跨视图的不一致信息聚合导致的收敛缓慢,因为来自2D模型的指导并非多视图一致。因此,我们引入了Direct Gaussian Editor(DGE)方法,分两个阶段解决这些问题。首先,我们修改给定的高质量图像编辑器(如InstructPix2Pix),使其具有多视图一致性。为此,我们提出了一种无需训练的方法,该方法结合了底层场景3D几何的线索。其次,给定一个具有多视图一致性的图像编辑序列,我们直接有效地优化基于3D高斯拼贴的3D表示。由于避免了增量和迭代编辑,DGE比现有方法更准确、更高效,并提供了额外的优势,例如能够选择性地编辑场景的部分。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ECCV 2024. Project Page: https://silent-chen.github.io/DGE/
Summary
本文解决基于开放语言指令编辑3D物体和场景的问题。传统方法使用2D图像生成器或编辑器指导3D编辑过程,无需3D数据,但效率低下,且需迭代更新昂贵的3D表示。为解决这些问题,本文引入Direct Gaussian Editor(DGE)方法,分为两个阶段:首先,改造现有高质量图像编辑器如InstructPix2Pix,实现多视角一致性;其次,给定多视角一致性的编辑图像序列,直接高效优化基于3D高斯映射的3D表示。DGE显著提高了准确性和效率,并提供了额外的好处,如能够选择性地编辑场景的某些部分。
Key Takeaways
- 使用传统方法编辑基于开放语言指令的3D物体和场景效率低下,且需要迭代更新昂贵的3D表示。
- Direct Gaussian Editor (DGE) 方法引入两个阶段来解决这一问题。
- 第一阶段改造高质量图像编辑器以实现多视角一致性,通过结合场景底层3D几何的线索实现无需训练的方法。
- 第二阶段基于多视角一致性的编辑图像序列,直接优化基于3D高斯映射的3D表示,提高了效率和准确性。
- DGE避免了增量和迭代编辑,显著优于现有方法。
- DGE提供了额外好处,如能够选择性地编辑场景的某些部分。
点此查看论文截图

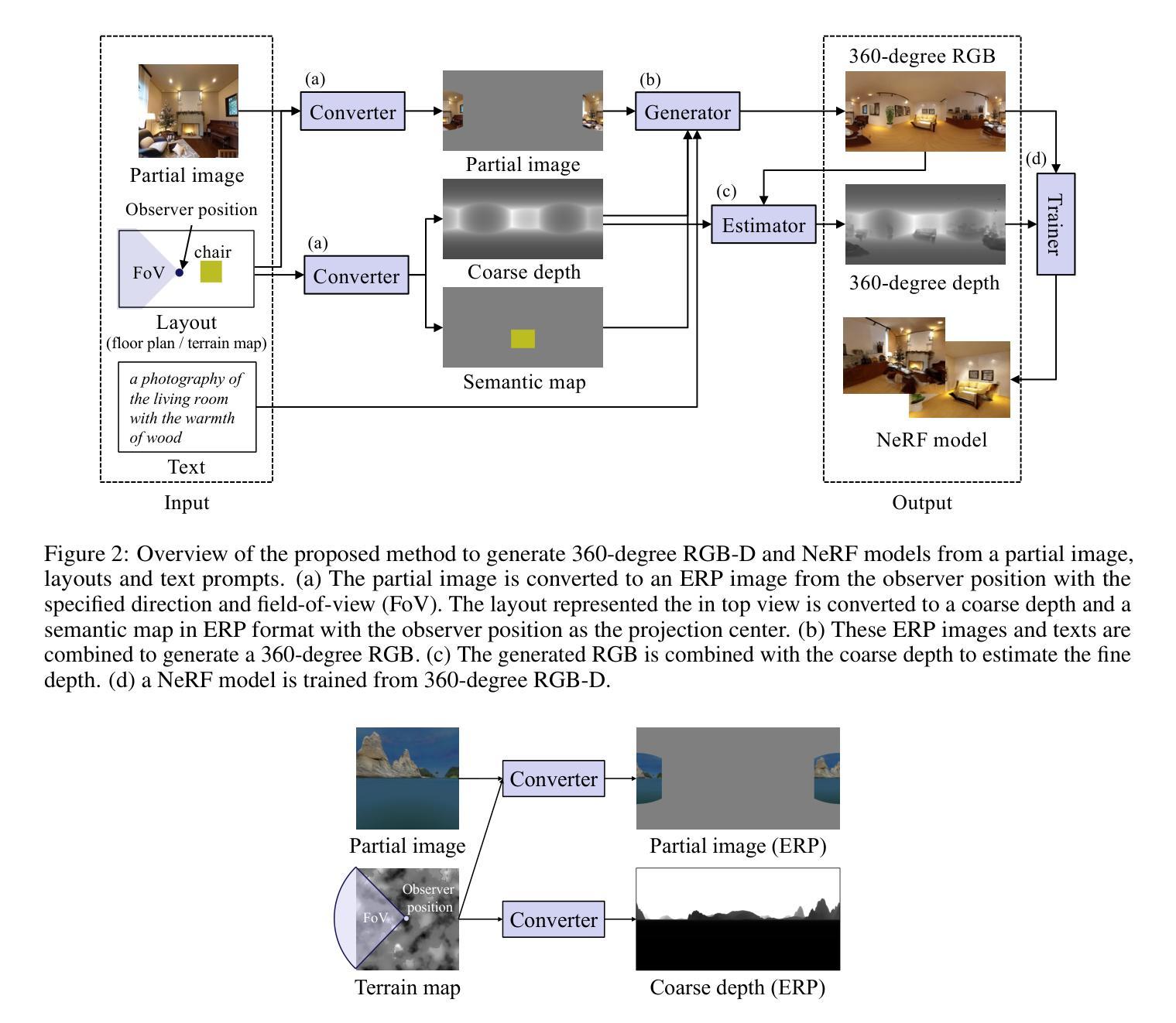
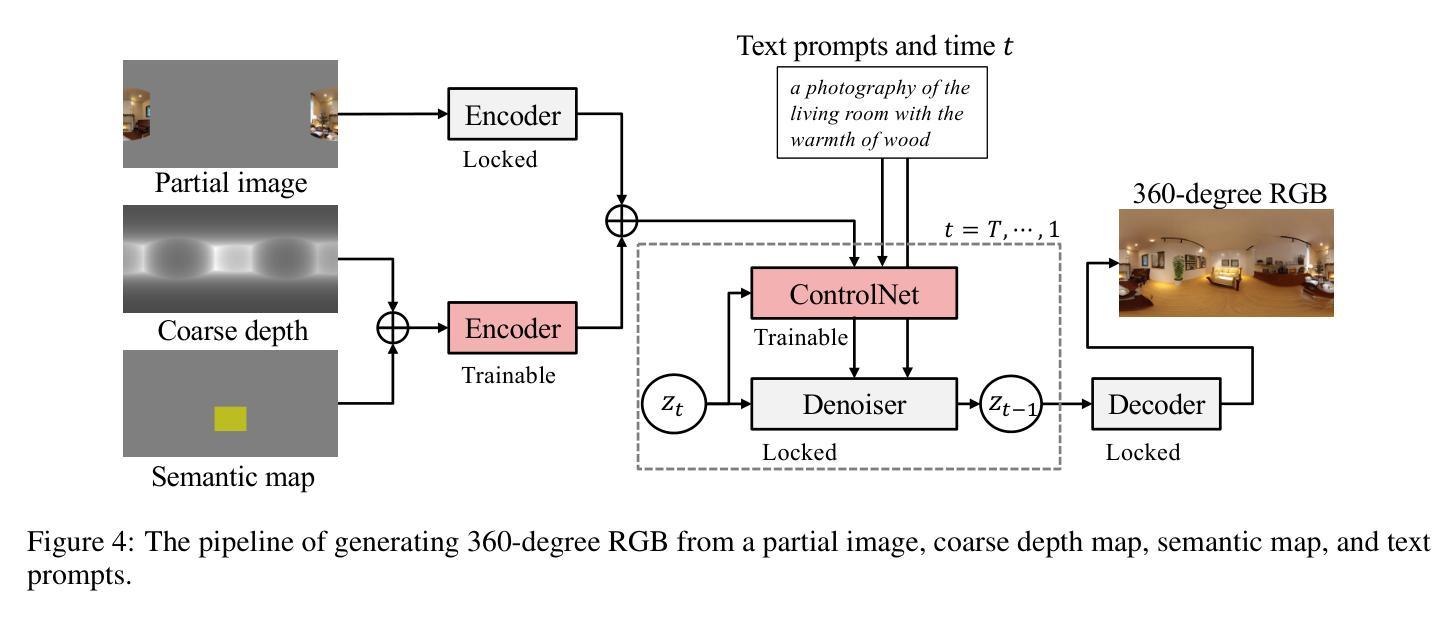
MaGRITTe: Manipulative and Generative 3D Realization from Image, Topview and Text
Authors:Takayuki Hara, Tatsuya Harada
The generation of 3D scenes from user-specified conditions offers a promising avenue for alleviating the production burden in 3D applications. Previous studies required significant effort to realize the desired scene, owing to limited control conditions. We propose a method for controlling and generating 3D scenes under multimodal conditions using partial images, layout information represented in the top view, and text prompts. Combining these conditions to generate a 3D scene involves the following significant difficulties: (1) the creation of large datasets, (2) reflection on the interaction of multimodal conditions, and (3) domain dependence of the layout conditions. We decompose the process of 3D scene generation into 2D image generation from the given conditions and 3D scene generation from 2D images. 2D image generation is achieved by fine-tuning a pretrained text-to-image model with a small artificial dataset of partial images and layouts, and 3D scene generation is achieved by layout-conditioned depth estimation and neural radiance fields (NeRF), thereby avoiding the creation of large datasets. The use of a common representation of spatial information using 360-degree images allows for the consideration of multimodal condition interactions and reduces the domain dependence of the layout control. The experimental results qualitatively and quantitatively demonstrated that the proposed method can generate 3D scenes in diverse domains, from indoor to outdoor, according to multimodal conditions.
从用户指定的条件生成3D场景,为缓解3D应用中的生产负担提供了有前景的途径。由于控制条件的限制,先前的研究需要大量的努力才能实现所需的场景。我们提出了一种在多模态条件下利用部分图像、俯视图中的布局信息和文本提示进行控制和生成3D场景的方法。结合这些条件生成3D场景涉及以下重大挑战:(1)创建大规模数据集;(2)对多模态条件交互的反思;(3)布局条件的领域依赖性。我们将3D场景的生成过程分解为基于给定条件的二维图像生成和基于二维图像的3D场景生成。通过微调预训练的文本到图像模型与部分图像和布局的小型人工数据集来实现二维图像生成,通过布局调节的深度估计和神经辐射场(NeRF)来实现三维场景的生成,从而避免了创建大规模数据集的需要。使用基于全景图的常见空间信息表示允许考虑多模态条件的交互,并降低了布局控制的领域依赖性。实验定性和定量结果表明,该方法可以根据多模态条件生成不同领域的室内和室外三维场景。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://hara012.github.io/MaGRITTe-project
Summary
本文提出一种利用部分图像、俯视图中的布局信息和文本提示,在多模态条件下控制和生成3D场景的方法。该方法将3D场景生成过程分解为基于给定条件的2D图像生成和从2D图像生成3D场景。通过微调预训练的文本到图像模型和小规模的人工数据集,实现2D图像生成;利用布局条件深度估计和神经辐射场(NeRF)实现3D场景生成,避免了大规模数据集的创建。使用360度图像的共同空间信息表示,考虑多模态条件交互,降低布局控制的领域依赖性。实验结果表明,该方法可根据多模态条件生成从室内到室外不同领域的3D场景。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种利用部分图像、俯视图中的布局信息和文本提示,结合多模态条件生成3D场景的方法。
- 将3D场景生成过程分解为基于给定条件的2D图像生成和从2D图像到3D场景的转换。
- 通过微调预训练的文本到图像模型实现2D图像生成。
- 利用布局条件深度估计和NeRF实现3D场景生成,避免创建大规模数据集。
- 使用360度图像的共同空间信息表示,考虑多模态条件交互。
- 方法可生成从室内到室外不同领域的3D场景。
点此查看论文截图

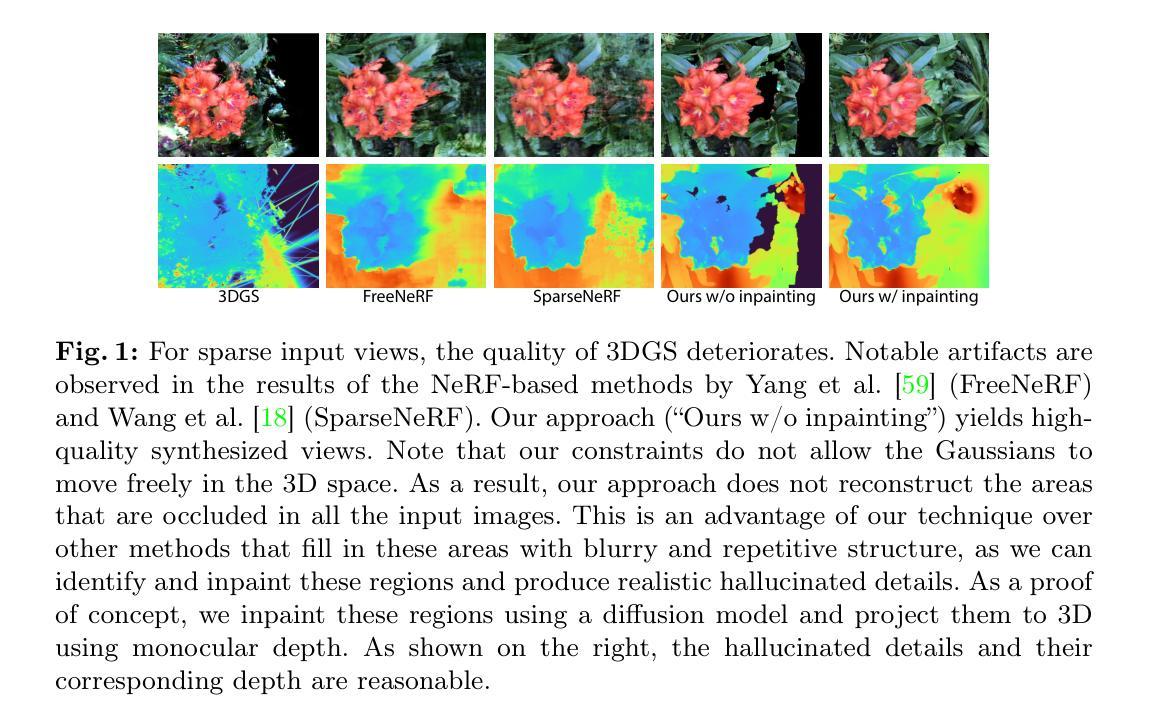
CoherentGS: Sparse Novel View Synthesis with Coherent 3D Gaussians
Authors:Avinash Paliwal, Wei Ye, Jinhui Xiong, Dmytro Kotovenko, Rakesh Ranjan, Vikas Chandra, Nima Khademi Kalantari
The field of 3D reconstruction from images has rapidly evolved in the past few years, first with the introduction of Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) and more recently with 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS). The latter provides a significant edge over NeRF in terms of the training and inference speed, as well as the reconstruction quality. Although 3DGS works well for dense input images, the unstructured point-cloud like representation quickly overfits to the more challenging setup of extremely sparse input images (e.g., 3 images), creating a representation that appears as a jumble of needles from novel views. To address this issue, we propose regularized optimization and depth-based initialization. Our key idea is to introduce a structured Gaussian representation that can be controlled in 2D image space. We then constraint the Gaussians, in particular their position, and prevent them from moving independently during optimization. Specifically, we introduce single and multiview constraints through an implicit convolutional decoder and a total variation loss, respectively. With the coherency introduced to the Gaussians, we further constrain the optimization through a flow-based loss function. To support our regularized optimization, we propose an approach to initialize the Gaussians using monocular depth estimates at each input view. We demonstrate significant improvements compared to the state-of-the-art sparse-view NeRF-based approaches on a variety of scenes.
基于图像的3D重建领域在过去几年中发展迅速,先是引入了神经辐射场(NeRF),最近又引入了3D高斯喷涂(3DGS)。后者在训练和推理速度以及重建质量方面都比NeRF有明显优势。虽然3DGS对于密集输入图像效果很好,但对于极稀疏输入图像(例如3张图像)的更具挑战性的设置,其非结构化的点云式表示很快就会过度拟合,从而产生从新视角看去的看似杂乱无章的针状表示。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了正则化优化和基于深度的初始化。我们的核心思想是在二维图像空间中引入结构化高斯表示。然后我们对高斯体(特别是其位置)施加约束,防止它们在优化过程中独立移动。具体来说,我们通过隐式卷积解码器和全变差损失分别引入单视图和多视图约束。由于高斯体的连贯性,我们通过基于流的损失函数进一步约束优化。为了支持我们的正则化优化,我们提出了一种使用每个输入视图的单目深度估计来初始化高斯体的方法。我们在各种场景上展示了与最先进的稀疏视图NeRF方法相比的显著改进。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ECCV2024, Project page: https://people.engr.tamu.edu/nimak/Papers/CoherentGS, Code: https://github.com/avinashpaliwal/CoherentGS
Summary
基于提供的文本,研究者研究了使用NeRF进行图像的三维重建问题。提出了一种具有结构化高斯表示的方法,以解决在稀疏输入图像情况下,重建质量不佳的问题。该方法结合了正则化优化和基于深度的初始化,并通过引入单视图和多视图约束以及流损失函数来进一步约束优化过程。相较于现有的稀疏视图NeRF方法,该方法在各种场景下的表现显著改善。
Key Takeaways
以下是基于文本的关键见解,用精简和清晰的列表呈现:
- 该文本讨论了在从图像进行三维重建领域中的最新发展,重点关注Neural Radiance Field(NeRF)和3D Gaussian Splatting(3DGS)的优劣。
- 相较于NeRF,3DGS在训练和推理速度以及重建质量上具有优势。但对于稀疏输入图像,其表现有待提高。
- 针对稀疏输入图像的问题,研究者提出了正则化优化和基于深度的初始化方法。
- 引入结构化高斯表示,并通过在二维图像空间中的控制来实现。
- 通过引入单视图和多视图约束以及总变异损失函数,对优化过程进行进一步约束。
- 为了支持正则化优化,研究者还提出了一种使用单目深度估计在每个输入视图进行高斯初始化的方法。
点此查看论文截图

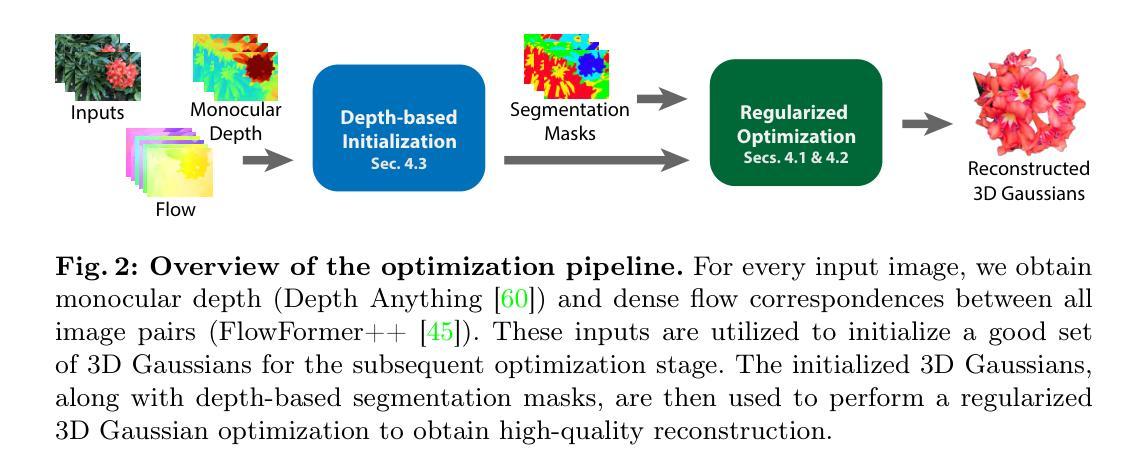
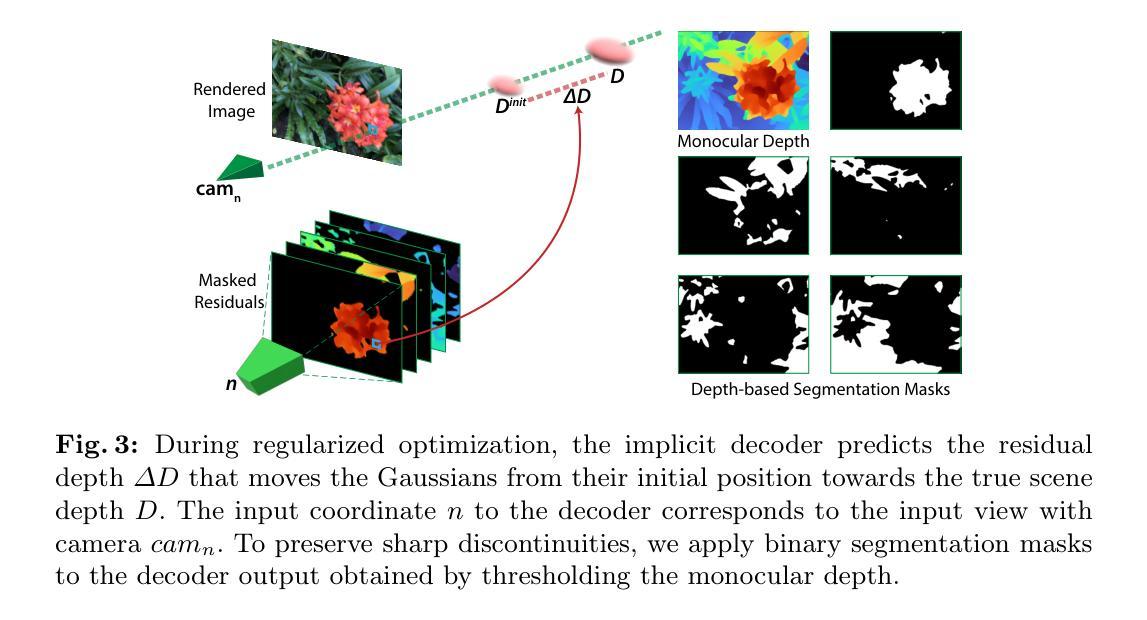
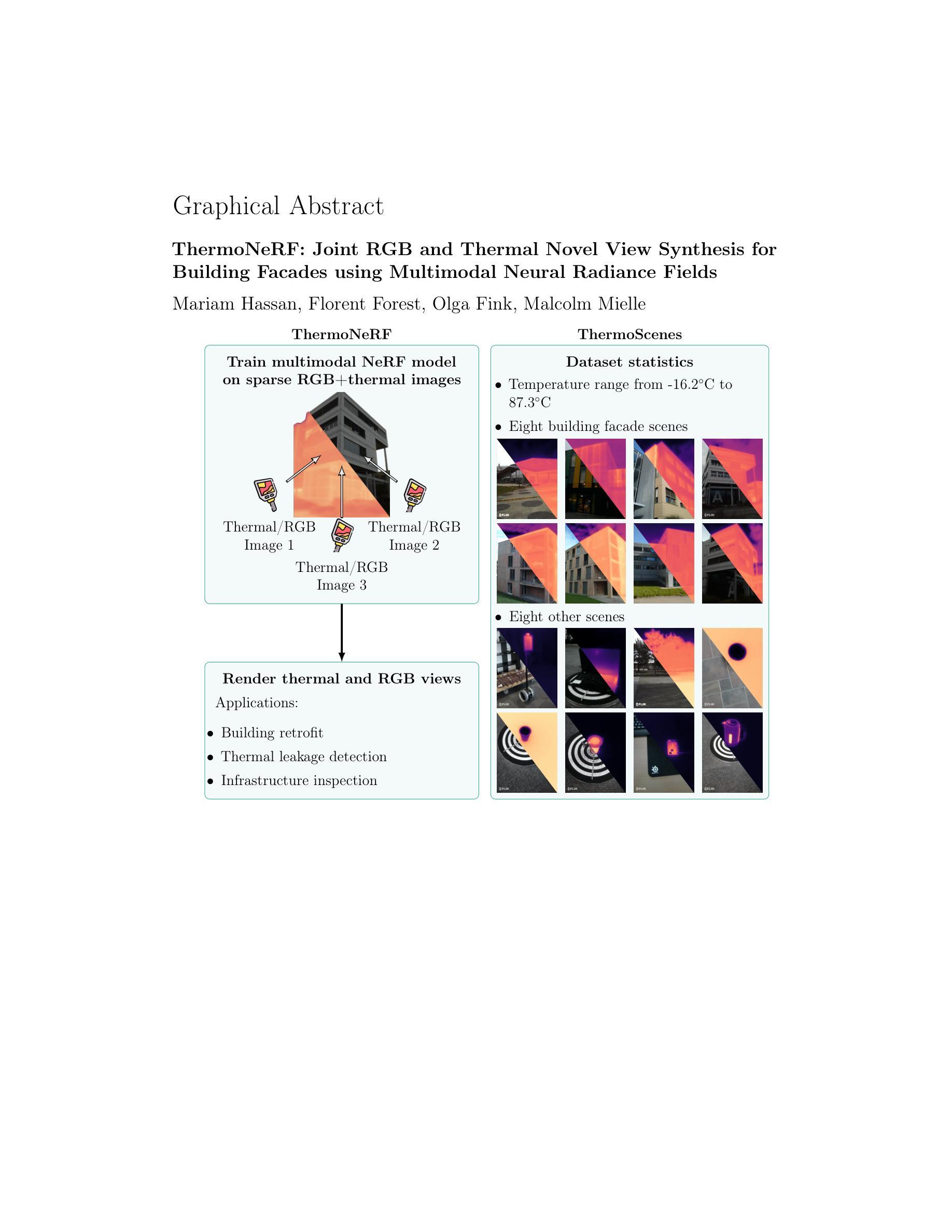
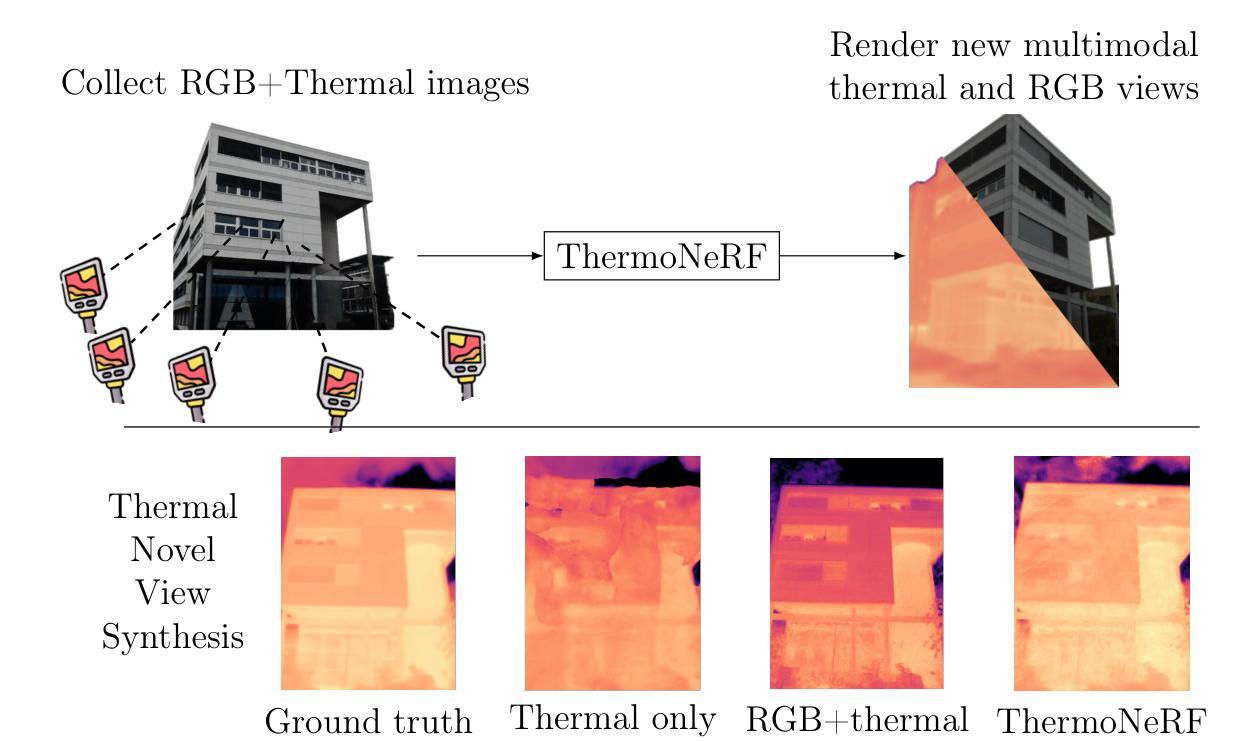
ThermoNeRF: Joint RGB and Thermal Novel View Synthesis for Building Facades using Multimodal Neural Radiance Fields
Authors:Mariam Hassan, Florent Forest, Olga Fink, Malcolm Mielle
Thermal scene reconstruction holds great potential for various applications, such as analyzing building energy consumption and performing non-destructive infrastructure testing. However, existing methods typically require dense scene measurements and often rely on RGB images for 3D geometry reconstruction, projecting thermal information post-reconstruction. This can lead to inconsistencies between the reconstructed geometry and temperature data and their actual values. To address this challenge, we propose ThermoNeRF, a novel multimodal approach based on Neural Radiance Fields that jointly renders new RGB and thermal views of a scene, and ThermoScenes, a dataset of paired RGB+thermal images comprising 8 scenes of building facades and 8 scenes of everyday objects. To address the lack of texture in thermal images, ThermoNeRF uses paired RGB and thermal images to learn scene density, while separate networks estimate color and temperature data. Unlike comparable studies, our focus is on temperature reconstruction and experimental results demonstrate that ThermoNeRF achieves an average mean absolute error of 1.13C and 0.41C for temperature estimation in buildings and other scenes, respectively, representing an improvement of over 50% compared to using concatenated RGB+thermal data as input to a standard NeRF. Code and dataset are available online.
热场景重建在多种应用中具有巨大潜力,例如分析建筑能耗和执行非破坏性基础设施测试。然而,现有方法通常需要密集的场景测量,并且经常依赖于RGB图像进行三维几何重建,在重建后投射热信息。这可能导致重建的几何形状与温度数据及其实际值之间存在不一致。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了ThermoNeRF,这是一种基于神经辐射场的新型多模式方法,可共同呈现场景的RGB和热力视图,以及ThermoScenes数据集,包含由建筑外观和日常对象组成的配对RGB+热力图像。为了应对热力图像缺乏纹理的问题,ThermoNeRF使用配对RGB和热力图像来学习场景密度,而单独的网络估计颜色和温度数据。与类似的研究不同,我们的重点是温度重建,实验结果表明,ThermoNeRF在建筑物和其他场景的温差估计中平均绝对误差达到1.13摄氏度和0.41摄氏度,与使用标准NeRF将拼接的RGB+热力数据作为输入相比,提高了超过50%。代码和数据集可在网上获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了ThermoNeRF这一基于神经辐射场的多模态方法,可联合渲染场景的RGB和红外图像,并解决了现有场景重建方法在处理热信息时的不足。通过引入ThermoScenes数据集,实现了对建筑物外观和日常物体的RGB与热图像的配对。ThermoNeRF通过采用配对的RGB和热图像来学习场景密度,同时单独的网络估计颜色和温度数据。该方法专注于温度重建,实验结果显示,与传统的NeRF相比,ThermoNeRF在建筑物和其他场景的温度估计方面实现了平均绝对误差的显著降低。
Key Takeaways
- ThermoNeRF是一种基于神经辐射场的多模态方法,能够联合渲染场景的RGB和红外图像。
- 现有场景重建方法在处理热信息时存在不足,而ThermoNeRF解决了这一问题。
- ThermoScenes数据集包含配对的RGB和热图像,用于训练和测试ThermoNeRF。
- ThermoNeRF通过采用配对的RGB和热图像来学习场景密度。
- ThermoNeRF采用单独的网络估计颜色和温度数据,以解决热图像中纹理缺失的问题。
- ThermoNeRF专注于温度重建,并在建筑物和其他场景的温度估计方面表现出较高的准确性。
点此查看论文截图
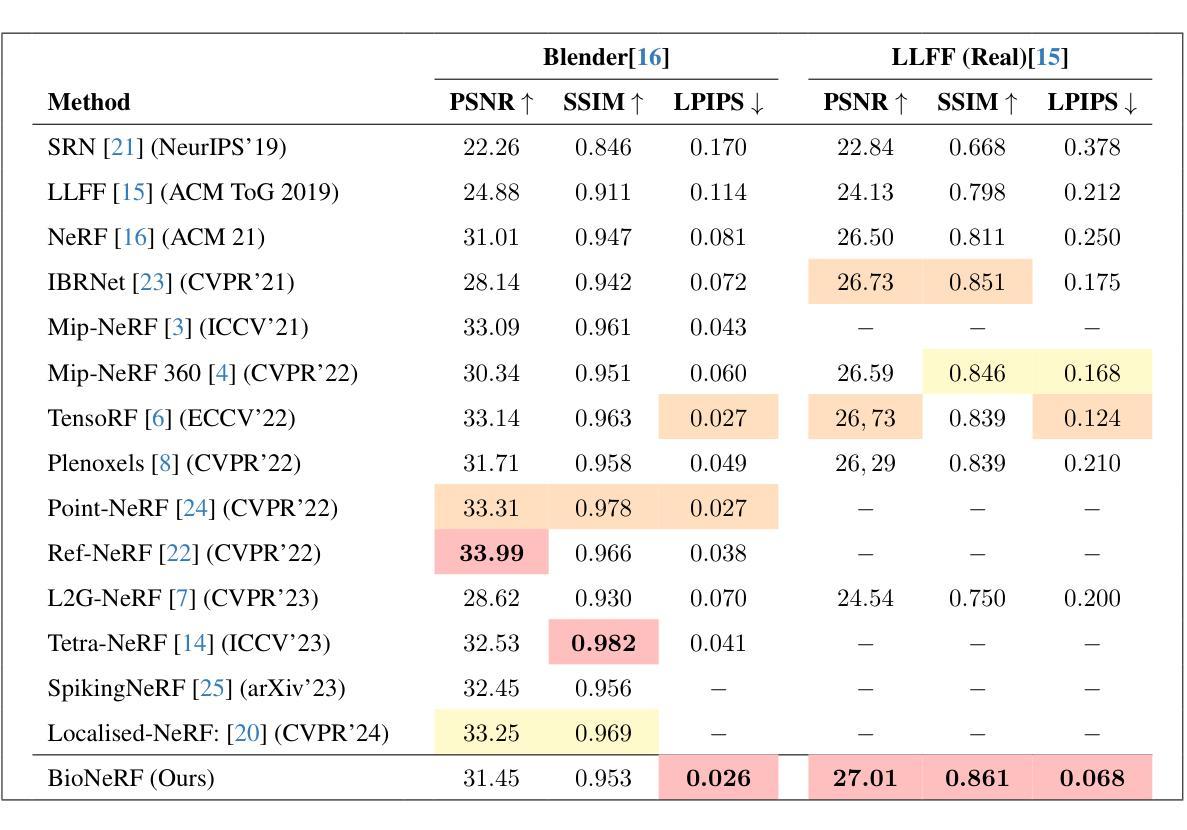
BioNeRF: Biologically Plausible Neural Radiance Fields for View Synthesis
Authors:Leandro A. Passos, Douglas Rodrigues, Danilo Jodas, Kelton A. P. Costa, Ahsan Adeel, João Paulo Papa
This paper presents BioNeRF, a biologically plausible architecture that models scenes in a 3D representation and synthesizes new views through radiance fields. Since NeRF relies on the network weights to store the scene’s 3-dimensional representation, BioNeRF implements a cognitive-inspired mechanism that fuses inputs from multiple sources into a memory-like structure, improving the storing capacity and extracting more intrinsic and correlated information. BioNeRF also mimics a behavior observed in pyramidal cells concerning contextual information, in which the memory is provided as the context and combined with the inputs of two subsequent neural models, one responsible for producing the volumetric densities and the other the colors used to render the scene. Experimental results show that BioNeRF outperforms state-of-the-art results concerning a quality measure that encodes human perception in two datasets: real-world images and synthetic data.
本文介绍了BioNeRF,这是一种生物学上合理的架构,它采用三维表示对场景进行建模,并通过辐射场合成新的视图。由于NeRF依赖于网络权重来存储场景的三维表示,BioNeRF实现了一种受认知启发的机制,该机制将来自多个源的输入融合到一个类似记忆的结构中,提高了存储能力,并提取了更多内在和相关的信息。BioNeRF还模仿了锥体细胞在上下文信息方面的行为,其中记忆作为上下文与两个后续神经模型的输入相结合,一个负责生成体积密度,另一个负责生成用于渲染场景的颜色。实验结果表明,BioNeRF在两项数据集上的表现优于最新技术成果的质量衡量标准,这两项数据集包括真实世界图像和合成数据,并编码了人类感知。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了BioNeRF,这是一种具有生物学可行性的架构,用于以三维形式呈现场景,并通过辐射场合成新视图。BioNeRF通过认知启发机制将多个来源的输入融合到一个记忆结构中,以提高存储能力并提取更多内在关联信息。同时,它模仿金字塔细胞的行为来处理上下文信息,将记忆作为上下文与两个后续神经网络模型的输入相结合,一个负责生成体积密度,另一个负责生成渲染场景的颜色。实验结果表明,在真实图像和合成数据上,BioNeRF在编码人类感知的质量度量上优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- BioNeRF是一个结合了生物学原理的NeRF架构。
- 它通过认知启发机制融合多源输入到一个记忆结构中。
- BioNeRF提高了存储能力并提取更多内在和关联信息。
- 该架构模仿金字塔细胞处理上下文信息的方式。
- BioNeRF使用记忆作为上下文,与两个神经网络模型结合,分别负责生成体积密度和颜色。
- 实验表明,BioNeRF在真实和合成数据上优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

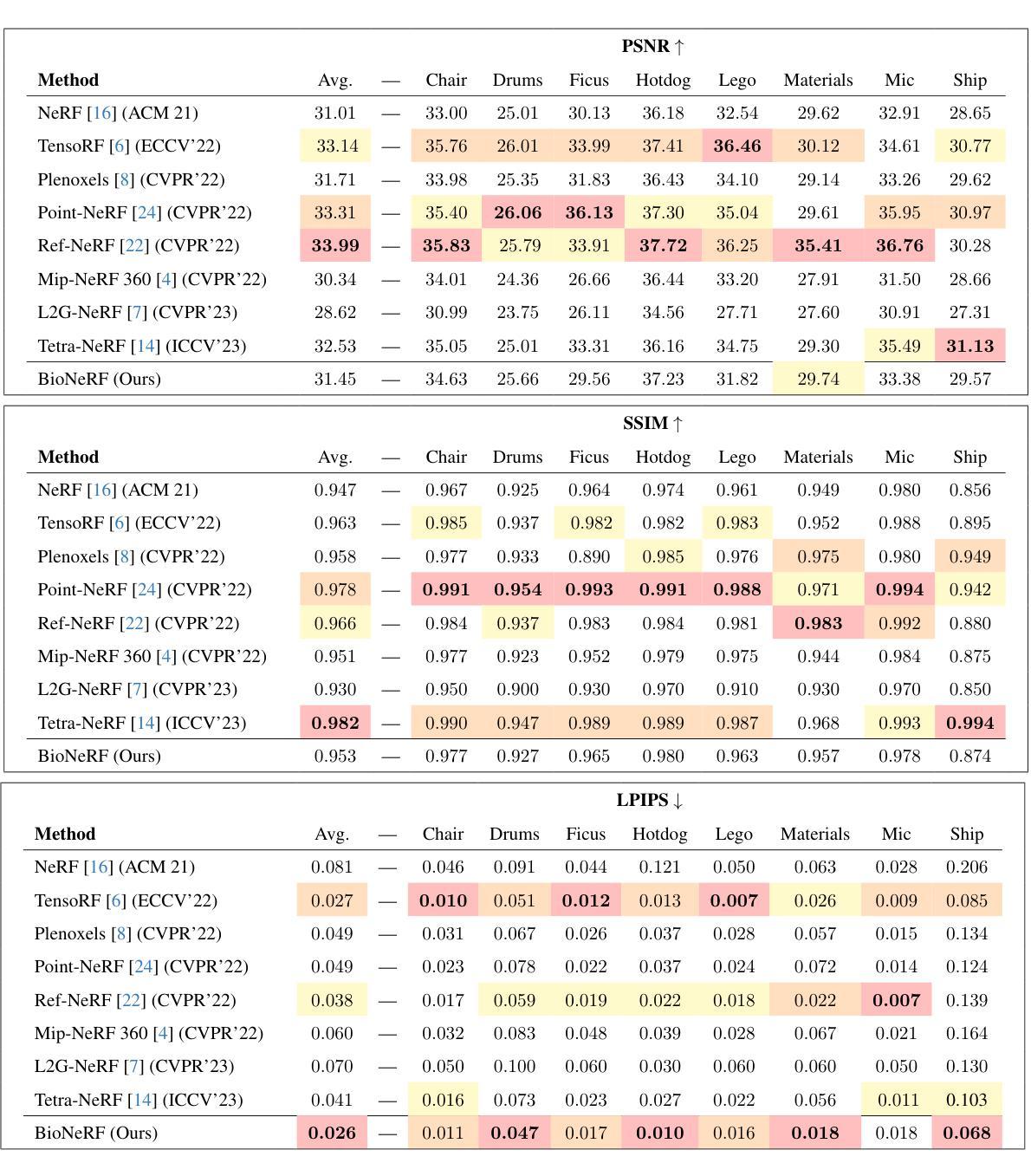
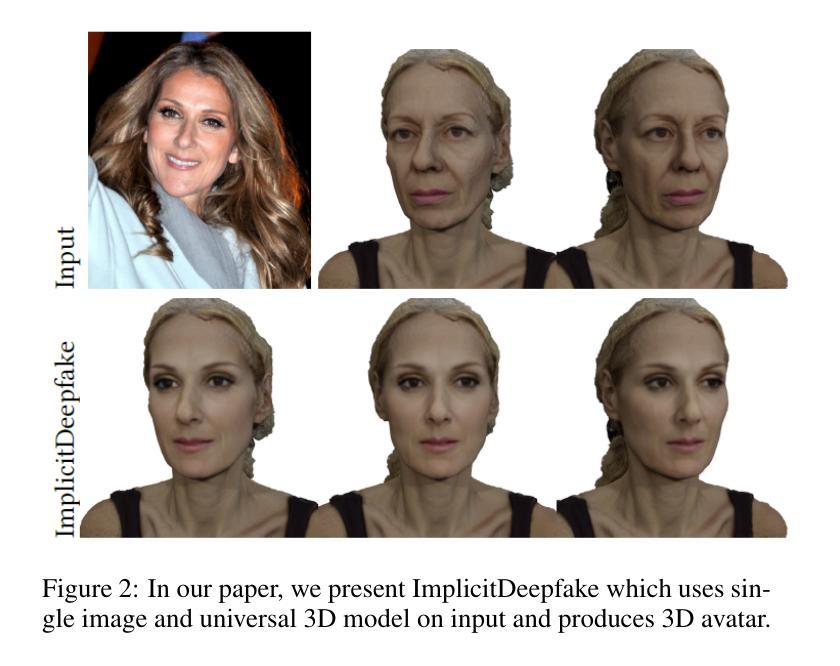
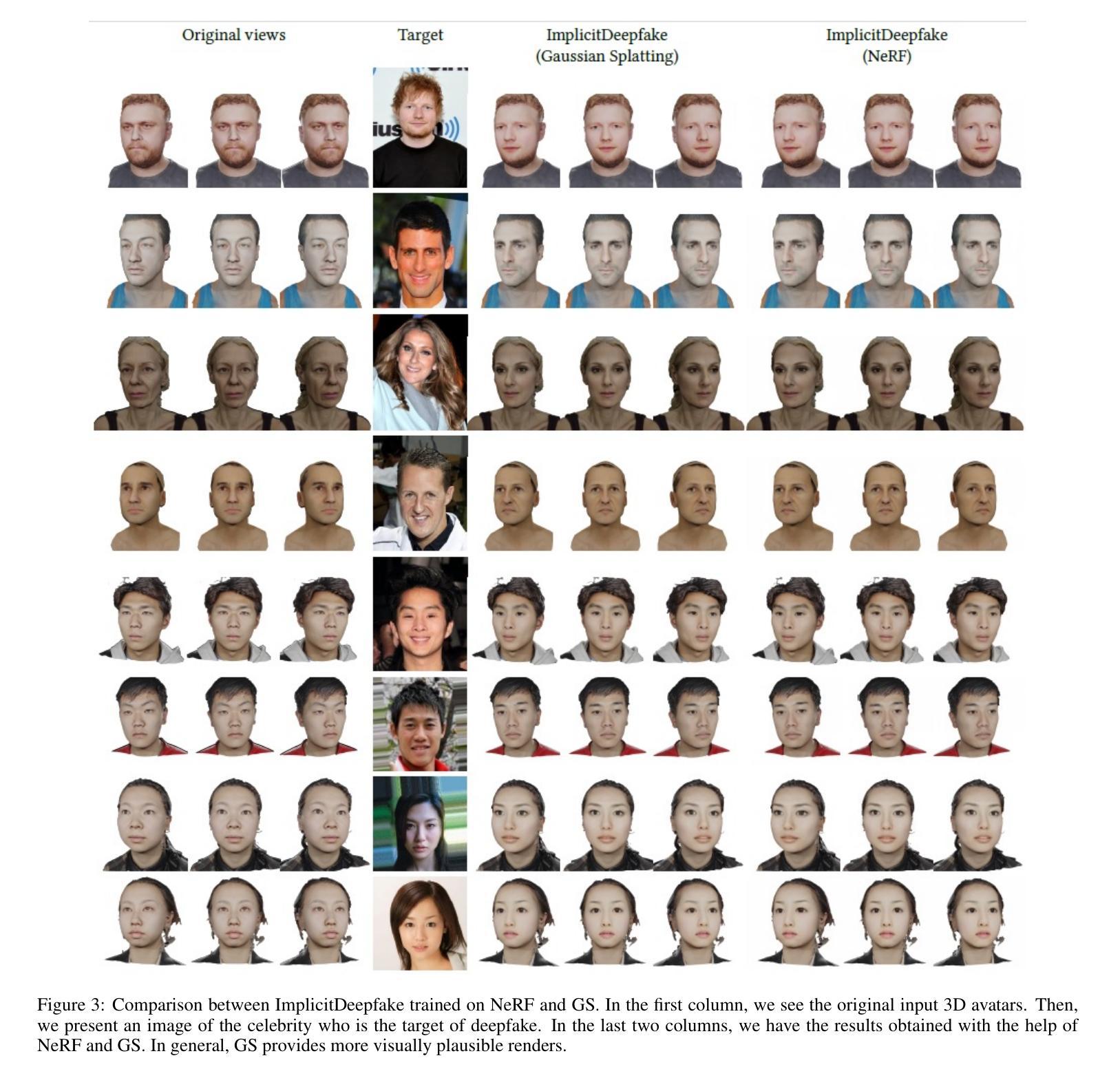
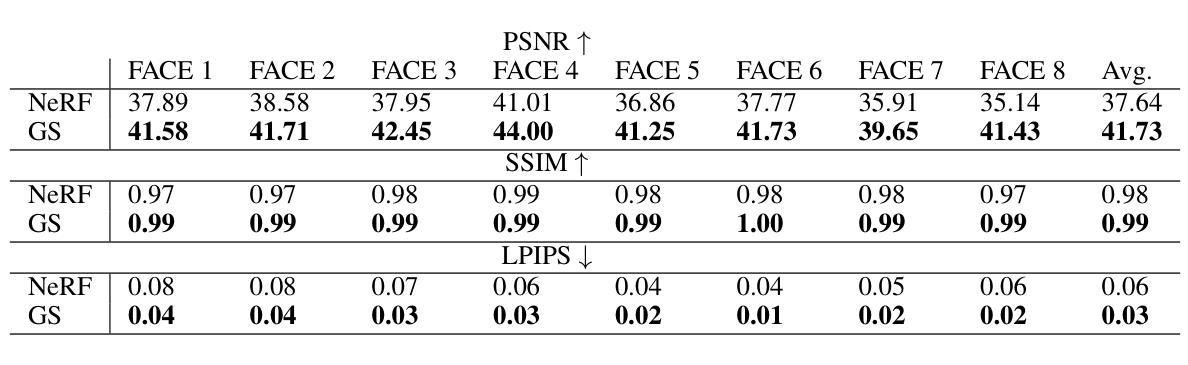
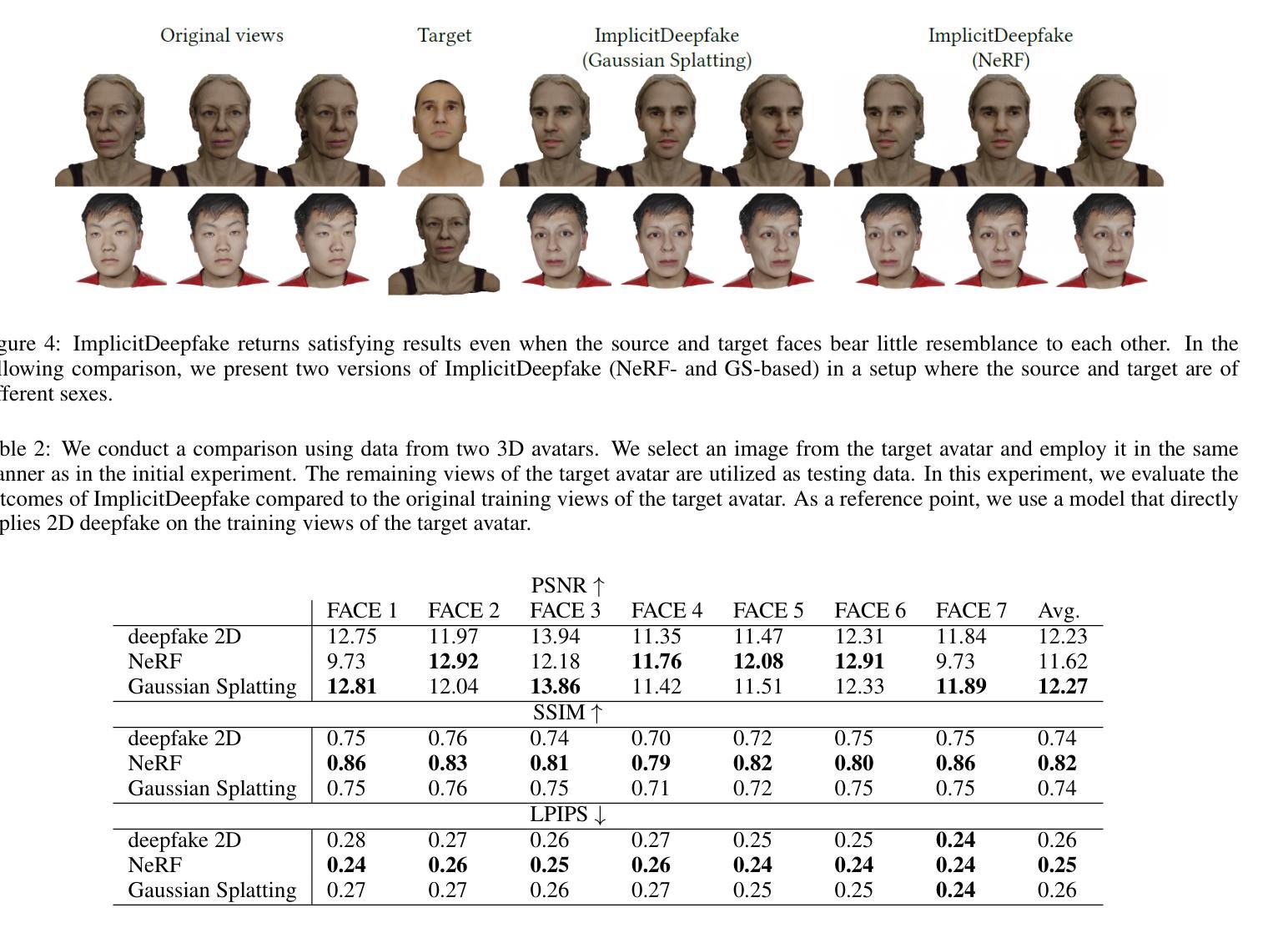
Deepfake for the Good: Generating Avatars through Face-Swapping with Implicit Deepfake Generation
Authors:Georgii Stanishevskii, Jakub Steczkiewicz, Tomasz Szczepanik, Sławomir Tadeja, Jacek Tabor, Przemysław Spurek
Numerous emerging deep-learning techniques have had a substantial impact on computer graphics. Among the most promising breakthroughs are the rise of Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) and Gaussian Splatting (GS). NeRFs encode the object’s shape and color in neural network weights using a handful of images with known camera positions to generate novel views. In contrast, GS provides accelerated training and inference without a decrease in rendering quality by encoding the object’s characteristics in a collection of Gaussian distributions. These two techniques have found many use cases in spatial computing and other domains. On the other hand, the emergence of deepfake methods has sparked considerable controversy. Deepfakes refers to artificial intelligence-generated videos that closely mimic authentic footage. Using generative models, they can modify facial features, enabling the creation of altered identities or expressions that exhibit a remarkably realistic appearance to a real person. Despite these controversies, deepfake can offer a next-generation solution for avatar creation and gaming when of desirable quality. To that end, we show how to combine all these emerging technologies to obtain a more plausible outcome. Our ImplicitDeepfake uses the classical deepfake algorithm to modify all training images separately and then train NeRF and GS on modified faces. Such simple strategies can produce plausible 3D deepfake-based avatars.
众多新兴的深度学习方法对计算机图形学产生了重大影响。其中最有前途的突破之一是神经辐射场(NeRF)和高斯拼贴(GS)的兴起。NeRF使用少量已知相机位置的图片将物体的形状和颜色编码到神经网络权重中,从而生成新的视角。相比之下,GS通过在一组高斯分布中编码物体特性,实现了训练和推理的加速,同时不降低渲染质量。这两种技术在空间计算和其他领域找到了许多用例。另一方面,深度伪造方法的出现引起了很大的争议。深度伪造是指使用人工智能生成的视频,这些视频密切模仿真实镜头。使用生成模型,它们可以修改面部特征,能够创建出身份或表情改变的形象,对真人表现出惊人的真实感。尽管存在争议,但高质量的深度伪造可以提供下一代解决方案,用于化身创建和游戏。为此,我们展示了如何结合所有这些新兴技术来获得更合理的结果。我们的ImplicitDeepfake使用经典的深度伪造算法分别修改所有训练图像,然后在修改后的面部上训练NeRF和GS。这种简单的策略可以产生合理的基于深度伪造的3D化身。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经网络辐射场(NeRF)和高斯涂斑技术(GS)等深度学习技术对计算机图形学产生了重大影响。NeRF使用已知相机位置的少量图像在神经网络权重中编码对象的形状和颜色,以生成新视图。GS通过在一组高斯分布中编码对象特性,实现了训练和推理的加速,同时不降低渲染质量。这两种技术都在空间计算等领域找到了许多用例。另一方面,深度伪造方法的出现引起了很大的争议。深度伪造指的是使用人工智能生成的视频,这些视频模仿真实的画面非常逼真。本文展示了如何结合所有这些新兴技术来获得更可信的结果。我们的ImplicitDeepfake使用经典深度伪造算法分别修改所有训练图像,然后在修改后的面部上训练NeRF和GS。这种简单的策略可以产生基于深度伪造的3D逼真头像。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习技术如NeRF和高斯涂斑(GS)对计算机图形学产生了重大影响。
- NeRF通过编码对象在神经网络权重中的形状和颜色,生成新视图。
- GS能加速训练和推理过程,同时保持渲染质量。
- 深度伪造方法引发了关于真实性和道德使用的争议。
- 深度伪造可以用于生成逼真的人工智能视频,可以修改面部特征,创建改变的身份或表情。
- 深度伪造在avatar创建和游戏中具有潜力,当质量足够好时。
点此查看论文截图


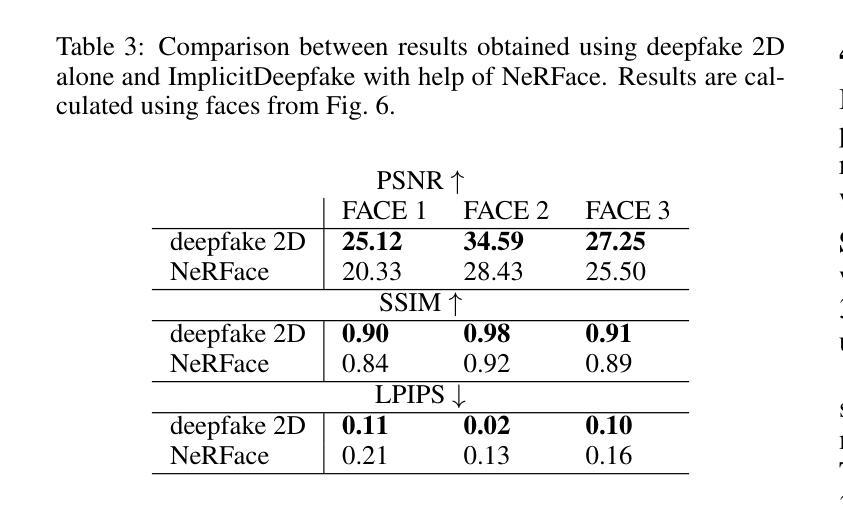
Efficient Dynamic-NeRF Based Volumetric Video Coding with Rate Distortion Optimization
Authors:Zhiyu Zhang, Guo Lu, Huanxiong Liang, Anni Tang, Qiang Hu, Li Song
Volumetric videos, benefiting from immersive 3D realism and interactivity, hold vast potential for various applications, while the tremendous data volume poses significant challenges for compression. Recently, NeRF has demonstrated remarkable potential in volumetric video compression thanks to its simple representation and powerful 3D modeling capabilities, where a notable work is ReRF. However, ReRF separates the modeling from compression process, resulting in suboptimal compression efficiency. In contrast, in this paper, we propose a volumetric video compression method based on dynamic NeRF in a more compact manner. Specifically, we decompose the NeRF representation into the coefficient fields and the basis fields, incrementally updating the basis fields in the temporal domain to achieve dynamic modeling. Additionally, we perform end-to-end joint optimization on the modeling and compression process to further improve the compression efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves higher compression efficiency compared to ReRF on various datasets.
体积视频受益于沉浸式3D现实和交互性,在多种应用上具有巨大潜力,而庞大的数据量给压缩带来了巨大挑战。最近,NeRF由于其简单的表示形式和强大的3D建模能力,在体积视频压缩方面表现出显著潜力,其中一项重要工作是ReRF。然而,ReRF将建模与压缩过程分开,导致压缩效率不佳。相比之下,本文提出了一种基于动态NeRF的更紧凑的体积视频压缩方法。具体来说,我们将NeRF表示分解为系数场和基场,在时序域中增量更新基场以实现动态建模。此外,我们对建模和压缩过程进行端到端的联合优化,以进一步提高压缩效率。大量实验表明,我们的方法在多个数据集上相对于ReRF实现了更高的压缩效率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE ICME 2024
摘要
NeRF技术因其在体积视频压缩中的显著潜力而受到关注,得益于其简单的表现和强大的3D建模能力。当前,尽管已有诸如ReRF等方法进行体积视频压缩,但其在建模与压缩过程中存在分离现象,导致压缩效率较低。本文提出了一种基于动态NeRF的体积视频压缩方法,将NeRF表示分解为系数场和基场,在时序域中增量更新基场以实现动态建模。同时,对建模和压缩过程进行端到端的联合优化,进一步提高压缩效率。实验证明,该方法在多个数据集上的压缩效率高于ReRF。
关键见解
- NeRF技术在体积视频压缩中具有显著潜力,得益于其简单的表现和强大的3D建模能力。
- 当前方法如ReRF在建模与压缩过程中存在分离,导致压缩效率较低。
- 本文提出一种基于动态NeRF的体积视频压缩方法,将NeRF分解为系数场和基场。
- 增量更新基场在时序域中实现动态建模。
- 端到端的联合优化提高了压缩效率。
- 实验证明,该方法在多个数据集上的压缩效率高于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

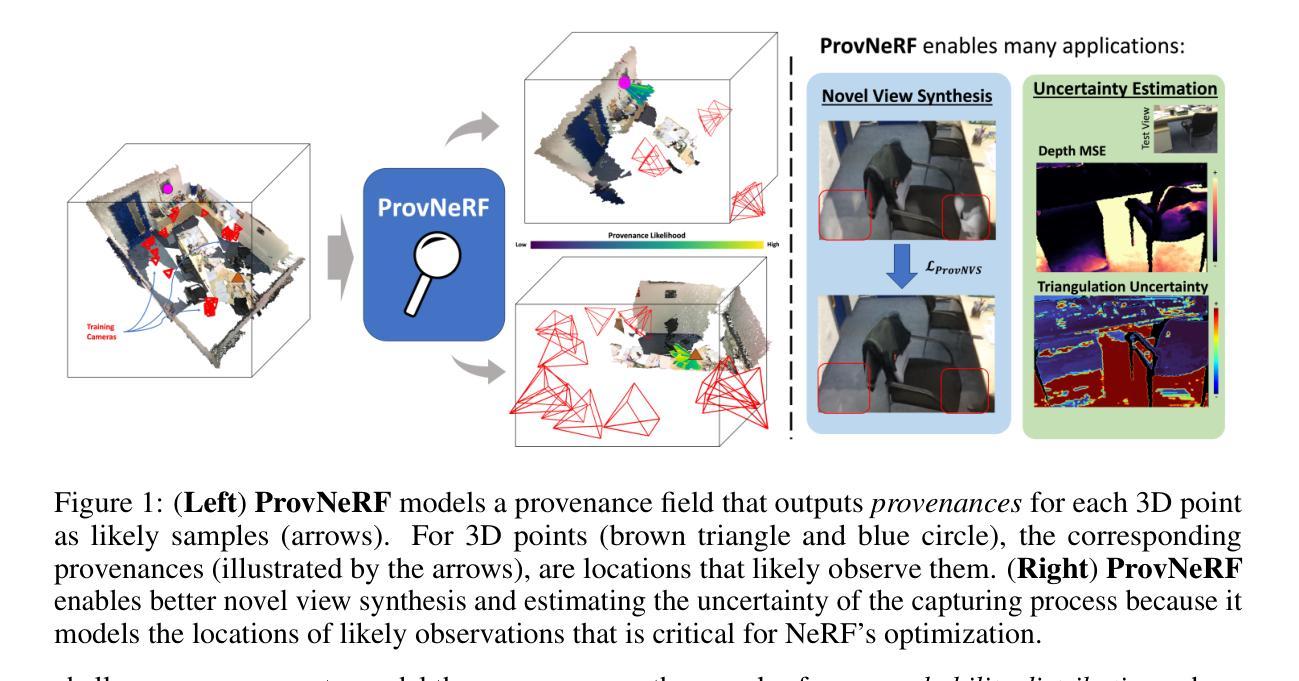
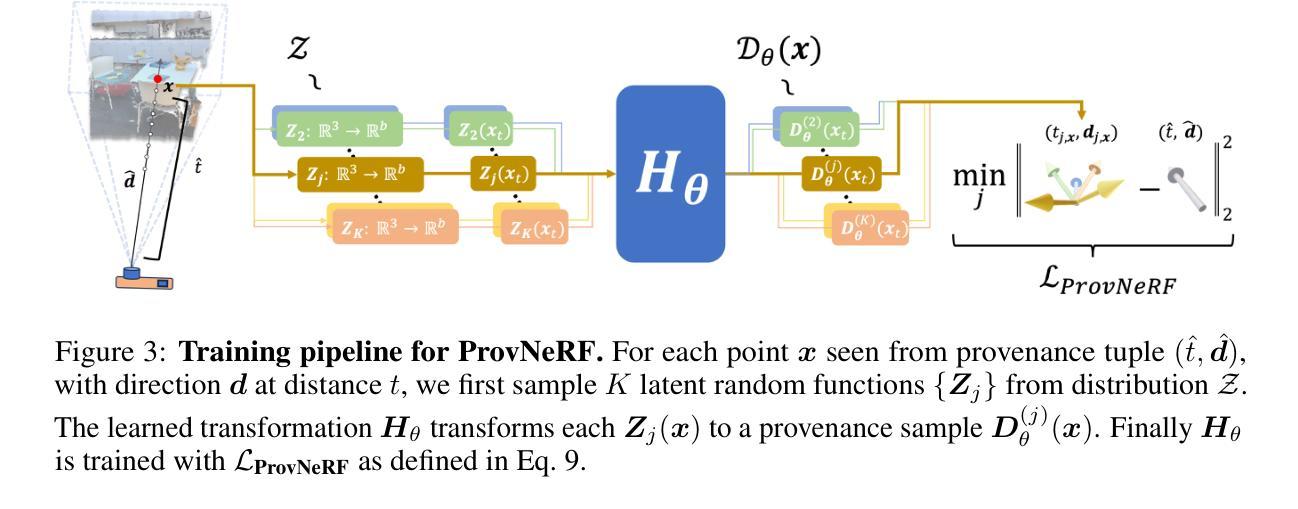
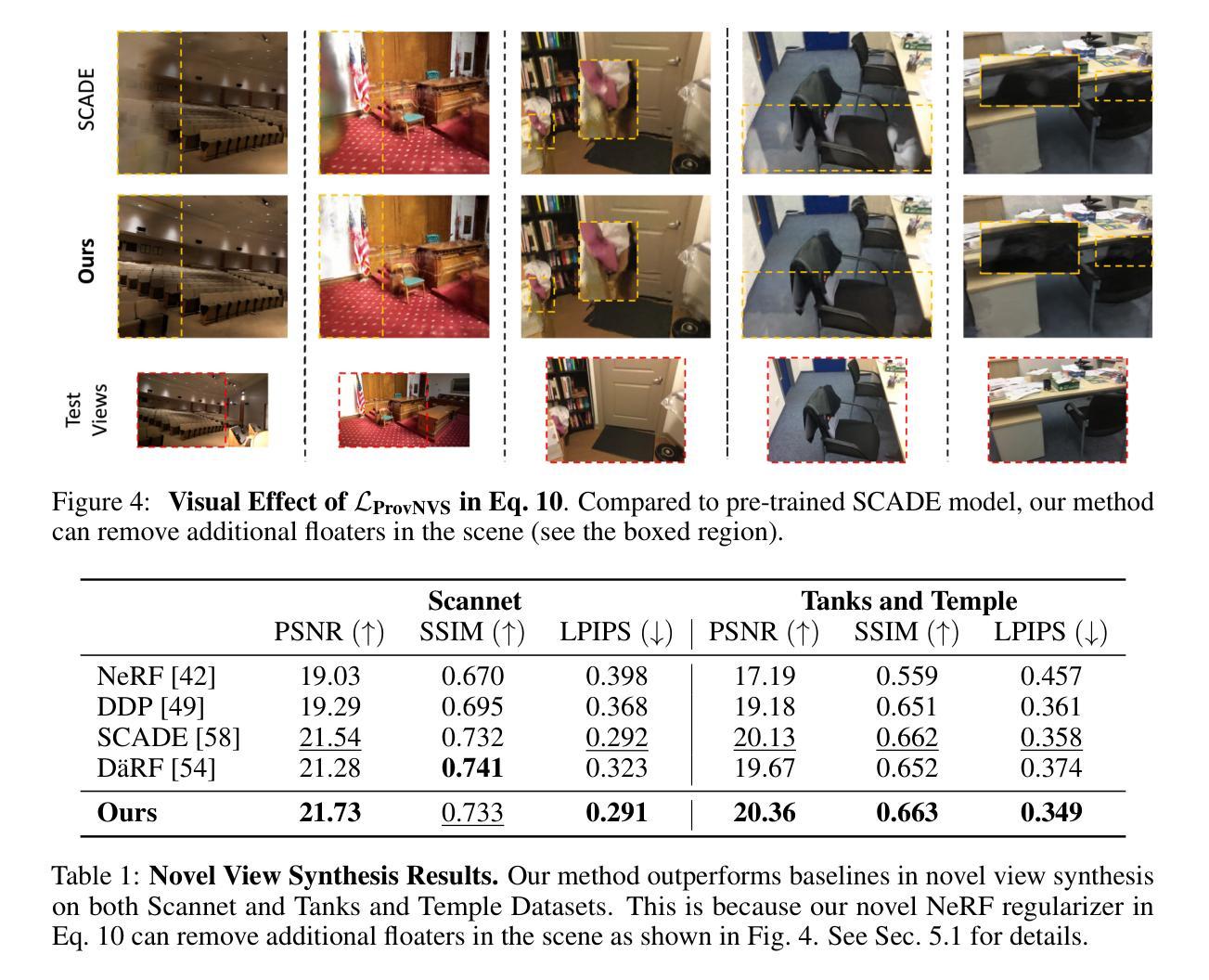
ProvNeRF: Modeling per Point Provenance in NeRFs as a Stochastic Field
Authors:Kiyohiro Nakayama, Mikaela Angelina Uy, Yang You, Ke Li, Leonidas J. Guibas
Neural radiance fields (NeRFs) have gained popularity with multiple works showing promising results across various applications. However, to the best of our knowledge, existing works do not explicitly model the distribution of training camera poses, or consequently the triangulation quality, a key factor affecting reconstruction quality dating back to classical vision literature. We close this gap with ProvNeRF, an approach that models the \textbf{provenance} for each point – i.e., the locations where it is likely visible – of NeRFs as a stochastic field. We achieve this by extending implicit maximum likelihood estimation (IMLE) to functional space with an optimizable objective. We show that modeling per-point provenance during the NeRF optimization enriches the model with information on triangulation leading to improvements in novel view synthesis and uncertainty estimation under the challenging sparse, unconstrained view setting against competitive baselines.
神经辐射场(NeRF)在多份工作中受到广泛关注,并在各种应用中显示出令人鼓舞的结果。然而,据我们了解,现有工作并没有显式地模拟训练相机姿态的分布,也没有模拟由此产生的三角测量质量,这是从经典视觉文献开始就影响重建质量的关键因素。我们借助ProvNeRF方法填补这一空白,该方法为NeRF的每个点——即可能可见的位置——建立一个随机场模型。我们通过将隐最大似然估计(IMLE)扩展到功能空间,并使用可优化的目标来实现这一点。我们表明,在NeRF优化过程中为每个点建模来源信息,增加了关于三角测量的信息,进而改进了在具有挑战性的稀疏、无约束视图设置下的新型视图合成和不确定性估计,相较于竞争性基线有明显提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 38th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2024)
Summary
本文介绍了Neural Radiance Fields(NeRF)的新应用,提出了一种名为ProvNeRF的方法,该方法通过建模每个点的来源信息来填充现有研究的空白,以提高重建质量。这种方法利用随机场模拟NeRF每个点的可见区域。此外,通过将隐式最大似然估计扩展到功能空间并优化目标函数,建模每个点的来源信息可以丰富模型中的三角信息,从而改善新的视图合成和不确定性估计在挑战稀疏约束视角下的基准竞争情况。此方法不仅可以丰富模型的三角化信息,还可以提高重建质量。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF技术在多个应用中展现出潜力,但现有研究未明确建模训练相机姿态分布和三角化质量这一关键因素。
- ProvNeRF方法填补了这一空白,通过建模每个点的来源信息(即可能可见的位置)作为随机场。
- ProvNeRF扩展了隐式最大似然估计到功能空间,实现了优化的目标函数。
点此查看论文截图


GauFRe: Gaussian Deformation Fields for Real-time Dynamic Novel View Synthesis
Authors:Yiqing Liang, Numair Khan, Zhengqin Li, Thu Nguyen-Phuoc, Douglas Lanman, James Tompkin, Lei Xiao
We propose a method that achieves state-of-the-art rendering quality and efficiency on monocular dynamic scene reconstruction using deformable 3D Gaussians. Implicit deformable representations commonly model motion with a canonical space and time-dependent backward-warping deformation field. Our method, GauFRe, uses a forward-warping deformation to explicitly model non-rigid transformations of scene geometry. Specifically, we propose a template set of 3D Gaussians residing in a canonical space, and a time-dependent forward-warping deformation field to model dynamic objects. Additionally, we tailor a 3D Gaussian-specific static component supported by an inductive bias-aware initialization approach which allows the deformation field to focus on moving scene regions, improving the rendering of complex real-world motion. The differentiable pipeline is optimized end-to-end with a self-supervised rendering loss. Experiments show our method achieves competitive results and higher efficiency than both previous state-of-the-art NeRF and Gaussian-based methods. For real-world scenes, GauFRe can train in ~20 mins and offer 96 FPS real-time rendering on an RTX 3090 GPU. Project website: https://lynl7130.github.io/gaufre/index.html
我们提出了一种方法,使用可变形三维高斯分布实现了单目动态场景重建的最新渲染质量和效率。隐式可变形表示通常通过规范空间和与时间相关的向后扭曲变形场对运动进行建模。我们的方法GauFRe使用正向扭曲变形显式地模拟场景几何的非刚性变换。具体来说,我们提出了一套位于规范空间中的三维高斯分布模板,以及一个与时间相关的正向扭曲变形场来模拟动态物体。此外,我们针对三维高斯分布的静态组件进行定制,采用归纳偏见感知初始化方法,使变形场专注于移动场景区域,提高了复杂现实世界运动的渲染效果。可微管道通过自我监督的渲染损失进行端到端优化。实验表明,我们的方法与之前的先进NeRF和高斯方法相比,取得了有竞争力的结果和更高的效率。对于现实世界场景,GauFRe可以在大约20分钟内进行训练,并在RTX 3090 GPU上提供96 FPS的实时渲染。项目网站:https://lynl7130.github.io/gaufre/index.html
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 8 figures, 5 tables
Summary
基于可变形3D高斯模型的单目动态场景重建方法GauFRe实现了出色的渲染质量和效率。它采用正向变形技术显式建模场景几何的非刚性变换,并结合模板集和静态组件优化端到端的可微管道,实现了实时渲染。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于可变形3D高斯模型的方法GauFRe,用于单目动态场景重建。
- 采用正向变形技术,显式建模场景几何的非刚性变换。
- 通过模板集和静态组件优化端到端的可微管道。
- 方法实现了高效的实时渲染,训练时间短,渲染速度快。
- 与现有方法相比,GauFRe在渲染质量和效率方面表现出竞争力。
- 支持自我监督渲染损失,以进一步提高渲染质量。
点此查看论文截图
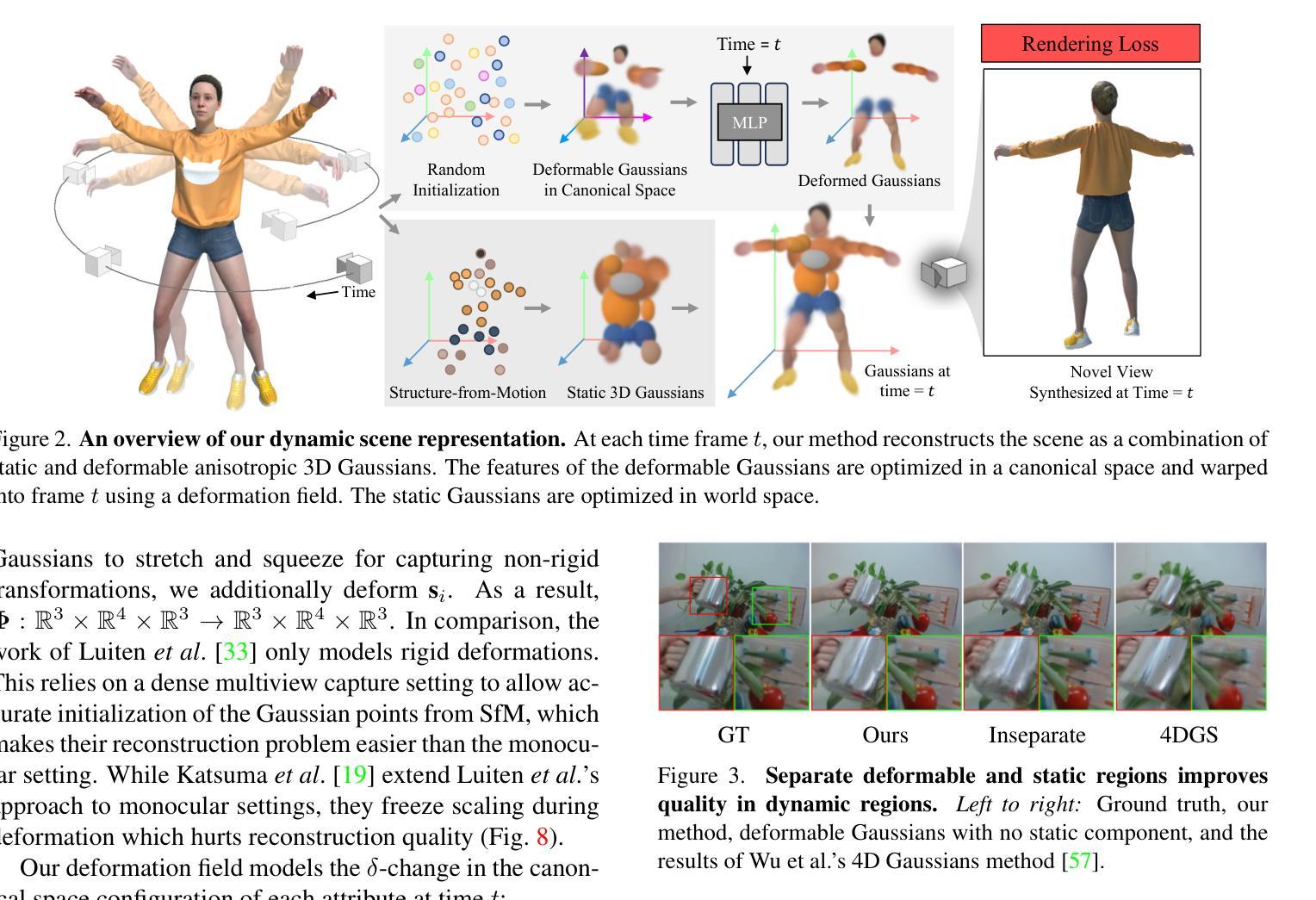


EvaSurf: Efficient View-Aware Implicit Textured Surface Reconstruction
Authors:Jingnan Gao, Zhuo Chen, Yichao Yan, Bowen Pan, Zhe Wang, Jiangjing Lyu, Xiaokang Yang
Reconstructing real-world 3D objects has numerous applications in computer vision, such as virtual reality, video games, and animations. Ideally, 3D reconstruction methods should generate high-fidelity results with 3D consistency in real-time. Traditional methods match pixels between images using photo-consistency constraints or learned features, while differentiable rendering methods like Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) use differentiable volume rendering or surface-based representation to generate high-fidelity scenes. However, these methods require excessive runtime for rendering, making them impractical for daily applications. To address these challenges, we present $\textbf{EvaSurf}$, an $\textbf{E}$fficient $\textbf{V}$iew-$\textbf{A}$ware implicit textured $\textbf{Surf}$ace reconstruction method. In our method, we first employ an efficient surface-based model with a multi-view supervision module to ensure accurate mesh reconstruction. To enable high-fidelity rendering, we learn an implicit texture embedded with view-aware encoding to capture view-dependent information. Furthermore, with the explicit geometry and the implicit texture, we can employ a lightweight neural shader to reduce the expense of computation and further support real-time rendering on common mobile devices. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method can reconstruct high-quality appearance and accurate mesh on both synthetic and real-world datasets. Moreover, our method can be trained in just 1-2 hours using a single GPU and run on mobile devices at over 40 FPS (Frames Per Second), with a final package required for rendering taking up only 40-50 MB.
重建真实世界的3D物体在计算机视觉领域具有许多应用,例如虚拟现实、视频游戏和动画。理想的3D重建方法应该能够实时生成具有3D一致性的高保真结果。传统方法通过照片一致性约束或学习特征来匹配图像之间的像素,而像神经辐射场(NeRF)这样的可微分渲染方法则使用可微分体积渲染或基于表面的表示来生成高保真场景。然而,这些方法渲染所需的运行时间过长,不适合日常应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TVCG2024. Project Page: http://g-1nonly.github.io/EvaSurf-Website/
摘要
该文本介绍了一种高效的三维重建方法EvaSurf,适用于计算机视觉领域中的虚拟世界、视频游戏和动画等应用。EvaSurf采用基于表面的模型和多视角监督模块确保准确的三维网格重建。同时,为了进行高保真渲染,该方法学习了具有视角感知编码的隐含纹理,捕捉视角相关的信息。结合明确的几何形状和隐含纹理,采用轻量级神经网络着色器,减少计算成本,支持在普通移动设备上进行实时渲染。实验表明,该方法在合成和真实数据集上都能重建出高质量外观和精确网格。此外,该方法可在单个GPU上训练仅需1-2小时,在移动设备上以超过每秒40帧的速度运行,最终渲染所需的软件包大小仅为40-50MB。
关键见解
- EvaSurf是一种高效的三维重建方法,适用于多种应用。
- EvaSurf采用基于表面的模型和多视角监督模块确保准确的三维网格重建。
- EvaSurf结合隐含纹理和明确几何形状进行高保真渲染。
- 隐含纹理具有视角感知编码,能捕捉视角相关的信息。
- EvaSurf采用轻量级神经网络着色器,减少计算成本,支持实时渲染。
- EvaSurf可在合成和真实数据集上重建出高质量外观和精确网格。
点此查看论文截图

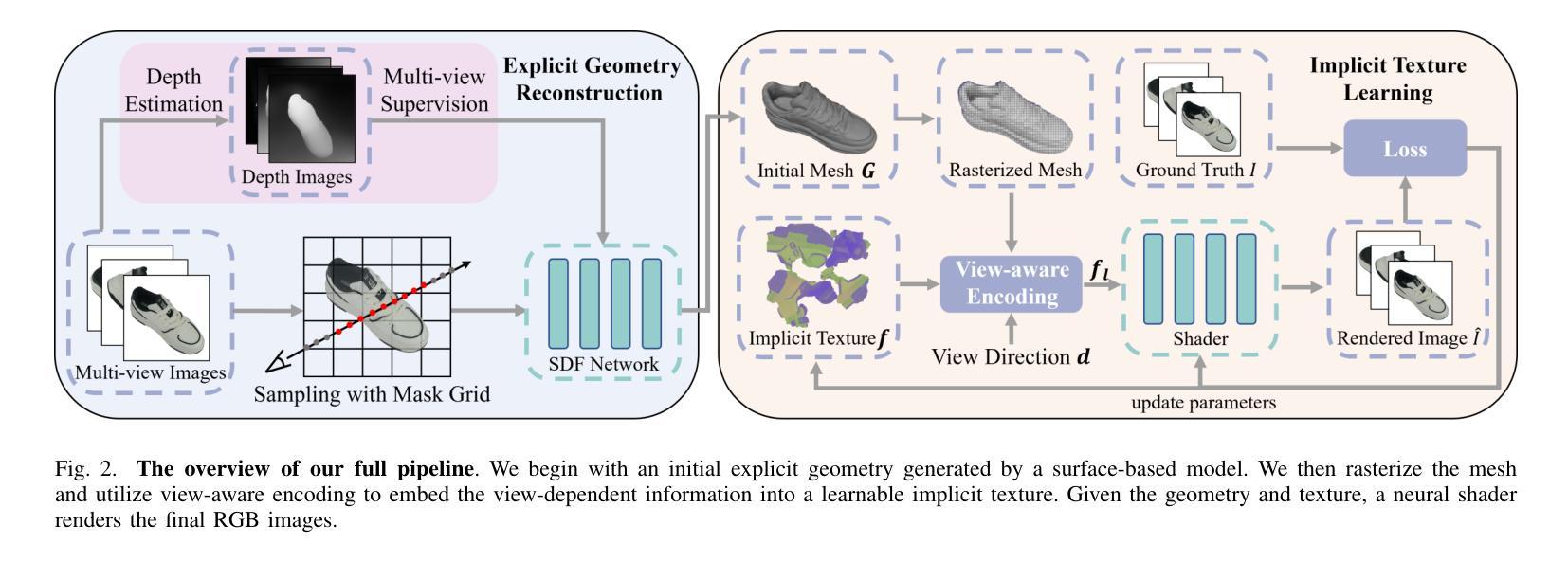
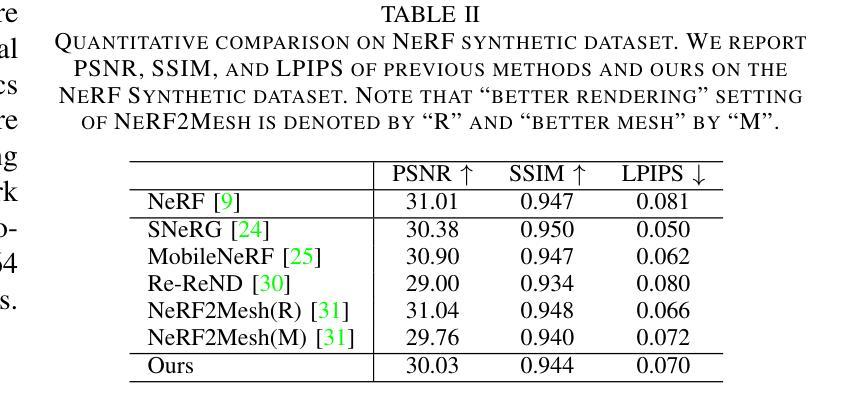
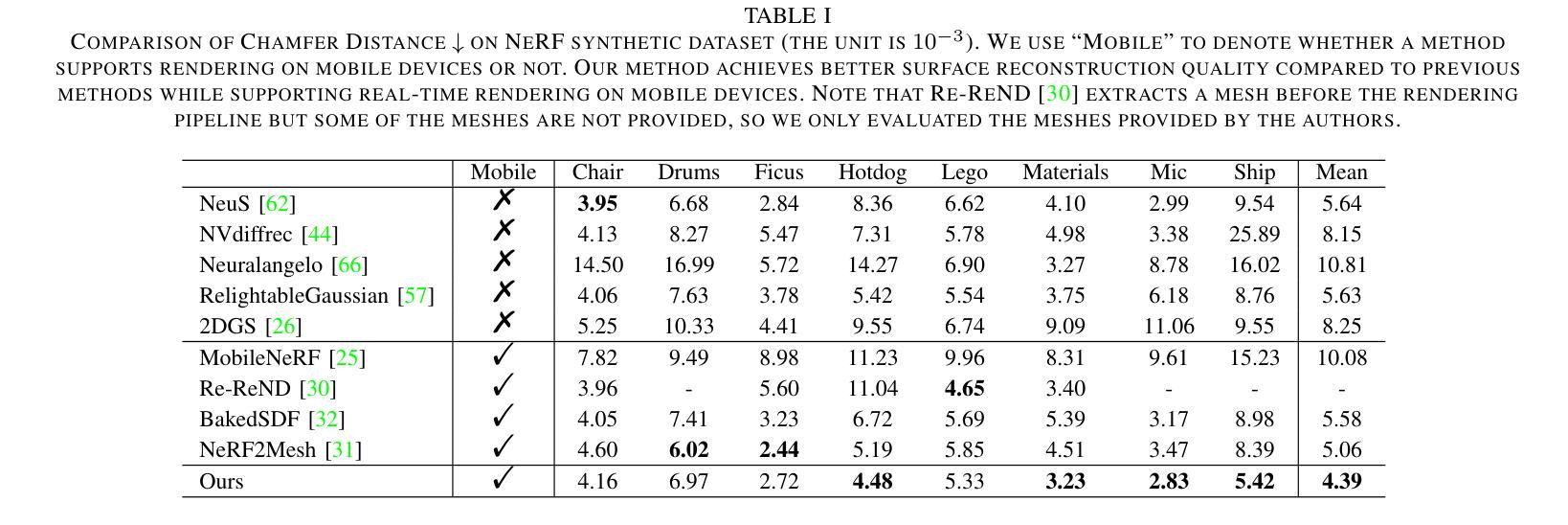
VoxNeRF: Bridging Voxel Representation and Neural Radiance Fields for Enhanced Indoor View Synthesis
Authors:Sen Wang, Qing Cheng, Stefano Gasperini, Wei Zhang, Shun-Cheng Wu, Niclas Zeller, Daniel Cremers, Nassir Navab
The generation of high-fidelity view synthesis is essential for robotic navigation and interaction but remains challenging, particularly in indoor environments and real-time scenarios. Existing techniques often require significant computational resources for both training and rendering, and they frequently result in suboptimal 3D representations due to insufficient geometric structuring. To address these limitations, we introduce VoxNeRF, a novel approach that utilizes easy-to-obtain geometry priors to enhance both the quality and efficiency of neural indoor reconstruction and novel view synthesis. We propose an efficient voxel-guided sampling technique that allocates computational resources selectively to the most relevant segments of rays based on a voxel-encoded geometry prior, significantly reducing training and rendering time. Additionally, we incorporate a robust depth loss to improve reconstruction and rendering quality in sparse view settings. Our approach is validated with extensive experiments on ScanNet and ScanNet++ where VoxNeRF outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods and establishes a new benchmark for indoor immersive interpolation and extrapolation settings.
高保真视图合成的生成对于机器人的导航和交互至关重要,但仍然存在挑战,特别是在室内环境和实时场景中。现有技术通常需要大量的计算资源进行训练和渲染,并且由于几何结构不足,它们常常产生不理想的3D表示。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了VoxNeRF,这是一种利用易于获得的几何先验知识来提高神经室内重建和新颖视图合成的质量和效率的新方法。我们提出了一种高效的体素引导采样技术,该技术根据体素编码的几何先验知识,有选择地为最相关的射线段分配计算资源,从而大大减少了训练和渲染时间。此外,我们引入了一种稳健的深度损失,以提高稀疏视图设置中的重建和渲染质量。我们的方法在ScanNet和ScanNet++上的大量实验验证了VoxNeRF的优越性,它超越了现有的最先进方法,为室内沉浸式插值和外推设置建立了新的基准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 4 figures
Summary
本文介绍了VoxNeRF,这是一种利用易于获得的几何先验信息来提高室内重建和新颖视图合成质量和效率的新方法。它通过有效的体素引导采样技术,根据体素编码的几何先验信息,有选择地为最重要的射线段分配计算资源,从而显著减少训练和渲染时间。此外,还引入了一种稳健的深度损失,以提高稀疏视图设置下的重建和渲染质量。在ScanNet和ScanNet++上的实验验证了VoxNeRF的优越性,它超越了现有的最新方法,为室内沉浸式插值和插补设置建立了新的基准。
Key Takeaways
- VoxNeRF解决了室内环境中高保真视图合成的问题,对于机器人导航和交互至关重要。
- 现有技术存在计算资源需求大、训练及渲染效率不高以及3D表示质量欠佳的问题。
- VoxNeRF引入了一种利用几何先验信息的创新方法,以提高神经室内重建和新颖视图合成的质量。
- 采用高效的体素引导采样技术,基于体素编码的几何先验信息选择性地分配计算资源。
- 通过引入稳健的深度损失,提高了稀疏视图设置下的重建和渲染质量。
- 在ScanNet和ScanNet++上的实验表明,VoxNeRF的性能超越了现有技术,为室内环境插值和插补设置树立了新的基准。
点此查看论文截图

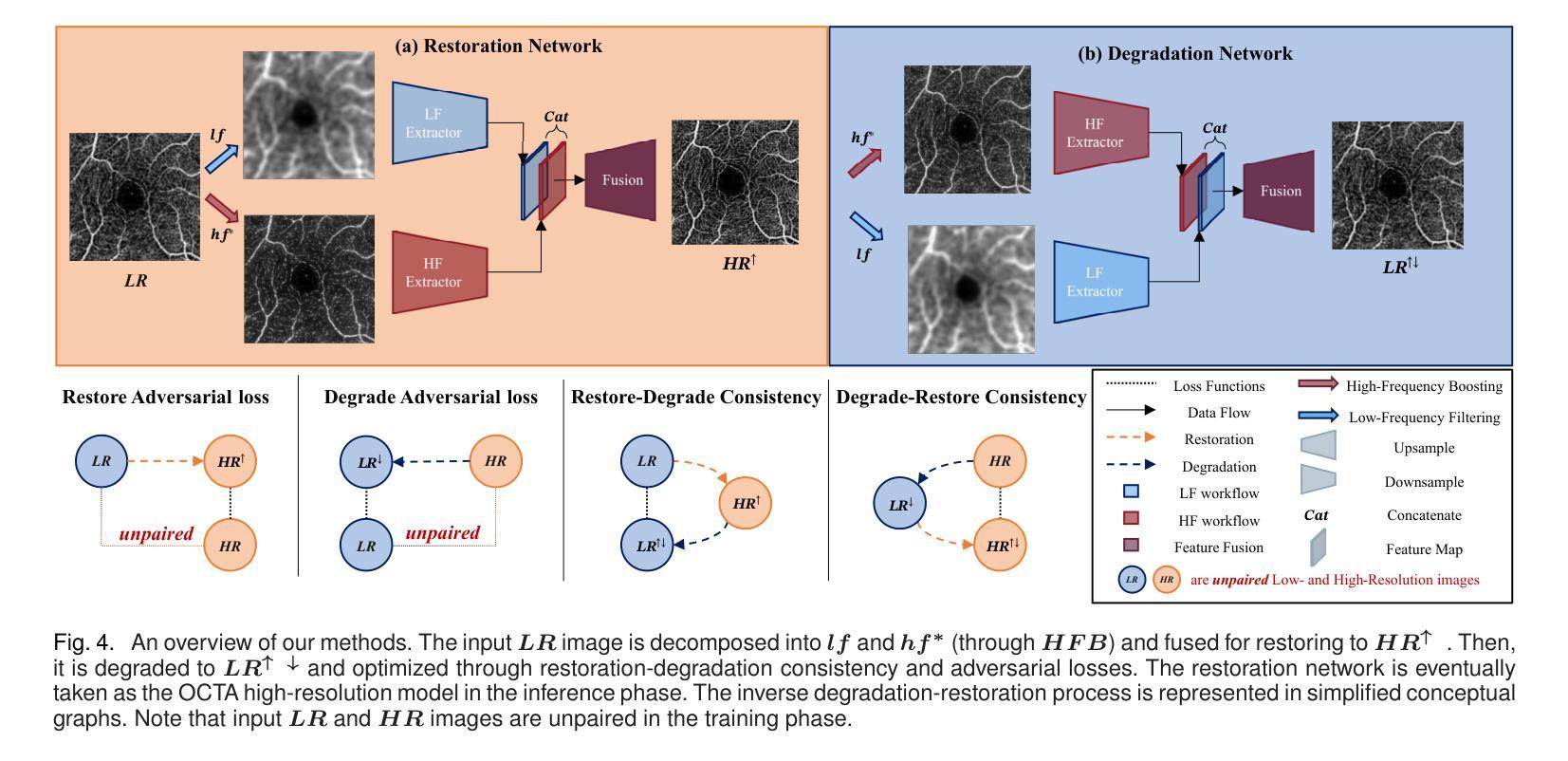
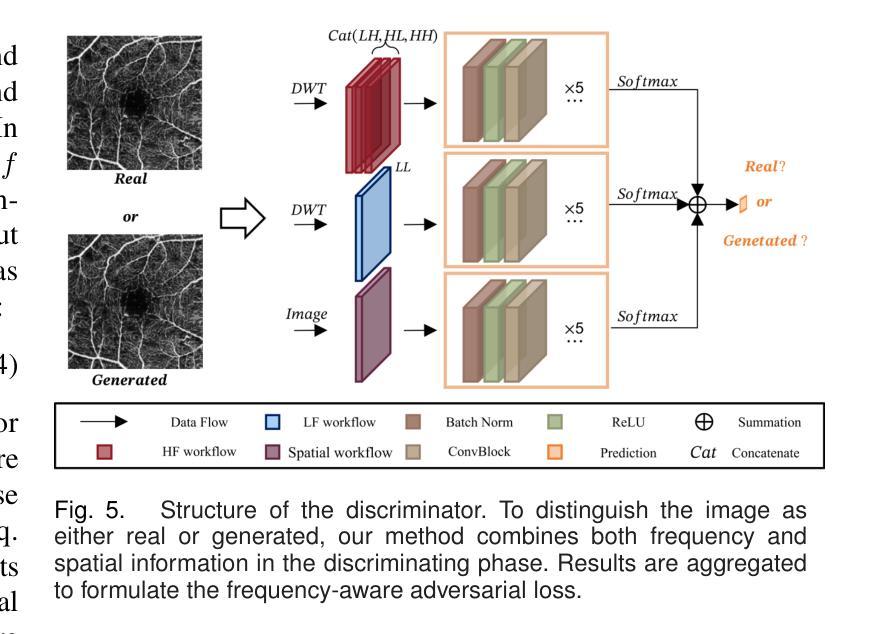
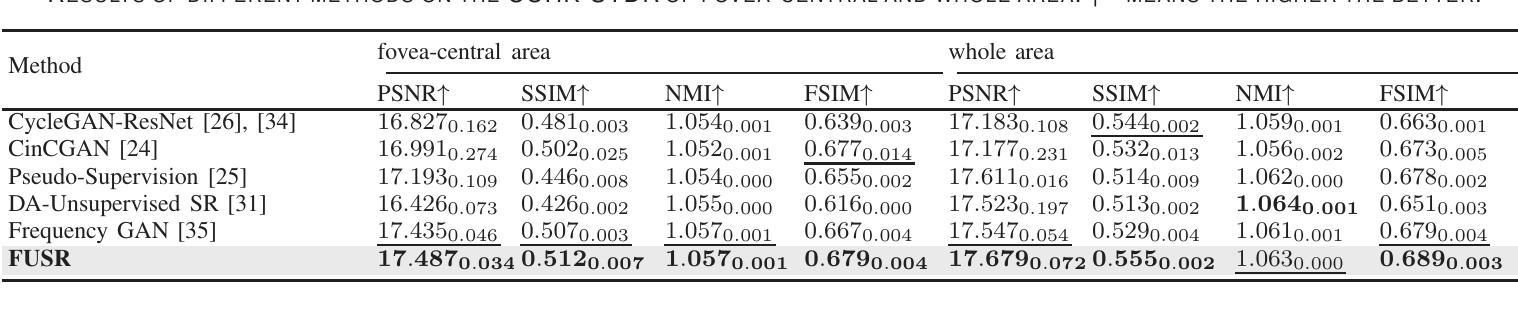
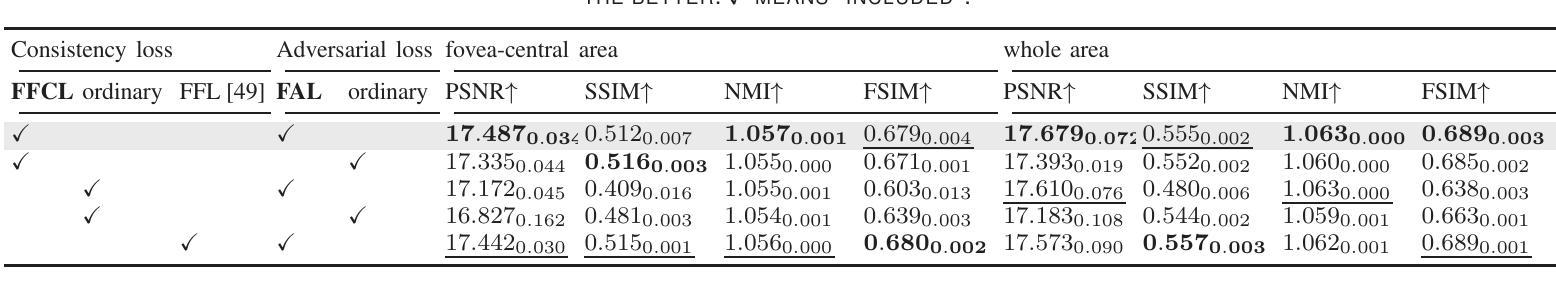
Unpaired Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Image Super-Resolution via Frequency-Aware Inverse-Consistency GAN
Authors:Weiwen Zhang, Dawei Yang, Haoxuan Che, An Ran Ran, Carol Y. Cheung, Hao Chen
For optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) images, a limited scanning rate leads to a trade-off between field-of-view (FOV) and imaging resolution. Although larger FOV images may reveal more parafoveal vascular lesions, their application is greatly hampered due to lower resolution. To increase the resolution, previous works only achieved satisfactory performance by using paired data for training, but real-world applications are limited by the challenge of collecting large-scale paired images. Thus, an unpaired approach is highly demanded. Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) has been commonly used in the unpaired setting, but it may struggle to accurately preserve fine-grained capillary details, which are critical biomarkers for OCTA. In this paper, our approach aspires to preserve these details by leveraging the frequency information, which represents details as high-frequencies ($\textbf{hf}$) and coarse-grained backgrounds as low-frequencies ($\textbf{lf}$). In general, we propose a GAN-based unpaired super-resolution method for OCTA images and exceptionally emphasize $\textbf{hf}$ fine capillaries through a dual-path generator. To facilitate a precise spectrum of the reconstructed image, we also propose a frequency-aware adversarial loss for the discriminator and introduce a frequency-aware focal consistency loss for end-to-end optimization. Experiments show that our method outperforms other state-of-the-art unpaired methods both quantitatively and visually.
对于光学相干层析血管造影(OCTA)图像,有限的扫描速率导致视野(FOV)与成像分辨率之间的权衡。虽然更大的视野图像可能会揭示更多的旁视网膜血管病变,但由于分辨率较低,其应用受到了很大的阻碍。为了增加分辨率,以前的工作只有通过使用配对数据进行训练才能达到令人满意的效果,但现实世界的应用受到收集大规模配对图像的挑战的限制。因此,对未配对方法的需求非常高。生成对抗网络(GAN)已在未配对设置中广泛使用,但它可能难以准确保留毛细血管的细微细节,这对于OCTA来说是非常重要的生物标志物。本文的方法旨在通过利用频率信息来保留这些细节,将毛细血管细节视为高频(hf),将粗粒背景视为低频(lf)。总的来说,我们提出了一种基于GAN的未配对超分辨率方法用于OCTA图像,并通过双路径生成器特别强调了高频毛细血管。为了促进重建图像的精确频谱,我们还为鉴别器提出了频率感知对抗损失,并为端到端优化引入了频率感知焦点一致性损失。实验表明,我们的方法在定量和视觉上均优于其他最先进的未配对方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 10 figures, in IEEE J-BHI, 2024
Summary
本文提出了一种基于GAN的无配对超分辨率方法,用于处理OCTA图像。该方法利用频率信息,通过双路径生成器突出高频细节和低频背景,实现高保真度。此外,本文还提出了频率感知对抗损失和频率感知焦点一致性损失,以提高图像重建的精确度。实验证明,该方法在定量和视觉上都优于其他先进的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 对于OCTA图像,扫描率的限制导致视野与成像分辨率之间的权衡问题。虽然较大的视野可能揭示更多的眼周围血管病变,但其应用受到分辨率低的限制。
- 之前的研究通过使用配对数据进行训练来获得令人满意的性能,但现实世界的应用受到收集大规模配对图像的挑战限制。因此,无配对方法的需求迫切。
- 生成对抗网络(GAN)在无配对设置中已被广泛使用,但可能难以准确保留重要的毛细血管细节。这些毛细血管细节对于OCTA是关键的生物标志物。
- 本文利用频率信息,通过双路径生成器提出一种基于GAN的无配对超分辨率方法。高频代表细节,低频代表粗颗粒背景。这种方法旨在保留毛细血管细节。
- 为了实现精确重建的图像频谱,本文还提出了频率感知对抗损失和频率感知焦点一致性损失。这些损失有助于端到端的优化。
点此查看论文截图