⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-11 更新
Towards Controllable Speech Synthesis in the Era of Large Language Models: A Survey
Authors:Tianxin Xie, Yan Rong, Pengfei Zhang, Li Liu
Text-to-speech (TTS), also known as speech synthesis, is a prominent research area that aims to generate natural-sounding human speech from text. Recently, with the increasing industrial demand, TTS technologies have evolved beyond synthesizing human-like speech to enabling controllable speech generation. This includes fine-grained control over various attributes of synthesized speech such as emotion, prosody, timbre, and duration. Besides, advancements in deep learning, such as diffusion and large language models, have significantly enhanced controllable TTS over the past several years. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive survey of controllable TTS, covering approaches ranging from basic control techniques to methods utilizing natural language prompts, aiming to provide a clear understanding of the current state of research. We examine the general controllable TTS pipeline, challenges, model architectures, and control strategies, offering a comprehensive and clear taxonomy of existing methods. Additionally, we provide a detailed summary of datasets and evaluation metrics and shed some light on the applications and future directions of controllable TTS. To the best of our knowledge, this survey paper provides the first comprehensive review of emerging controllable TTS methods, which can serve as a beneficial resource for both academic researchers and industry practitioners.
文本转语音(TTS),也被称为语音合成,是一个显著的研究领域,旨在从文本生成听起来很自然的人类语音。最近,随着工业需求的增加,TTS技术已经发展超越了合成类似人类的语音,实现了可控的语音生成。这包括合成语音的各种属性的精细控制,如情感、语调、音色和持续时间。此外,深度学习中的扩散和大型语言模型等技术的进步,在过去的几年里极大地增强了可控TTS的性能。在本文中,我们对可控TTS进行了全面的调查,涵盖了从基本控制技术到利用自然语言提示的方法等多种方法,旨在为研究者提供一个清晰的研究现状理解。我们考察了可控TTS的一般流程、挑战、模型架构和控制策略,提供了现有方法的全面而清晰的分类。此外,我们还详细总结了数据集和评价指标,并对可控TTS的应用和未来发展方向进行了一些探讨。据我们所知,这篇综述论文首次全面回顾了新兴的可控TTS方法,对学术研究人员和行业从业者都具有参考价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF A comprehensive survey on controllable TTS, 23 pages, 6 tables, 4 figures, 280 references
Summary
文本转语音(TTS)是生成自然语音的重要研究领域。近年来,随着工业需求的增加,TTS技术已从单纯的模仿人类语音发展到了可实现可控的语音生成,能对语音的各种属性进行精细控制,如情感、语调、音质和时长等。深度学习的进步,如扩散模型和大型语言模型,为可控TTS带来了巨大的提升。本文全面回顾了可控TTS的研究现状,从基本控制技巧到利用自然语言提示的方法都有所涉及,旨在为学术界和工业界提供有益的参考。
Key Takeaways
- TTS (文本转语音) 是生成自然语音的重要研究领域。
- 近期TTS技术已经从单纯的模仿人类语音发展到实现可控的语音生成。
- 精细控制语音的各种属性已成为可能,如情感、语调、音质和时长等。
- 深度学习的进步,如扩散模型和大型语言模型,显著提升了可控TTS的性能。
- 本文对可控TTS进行了全面的综述,涵盖了各种方法,从基本控制技巧到自然语言提示方法。
- 文章提供了关于可控TTS的当前研究状态的清晰理解,包括通用管道、挑战、模型架构和控制策略等。
点此查看论文截图

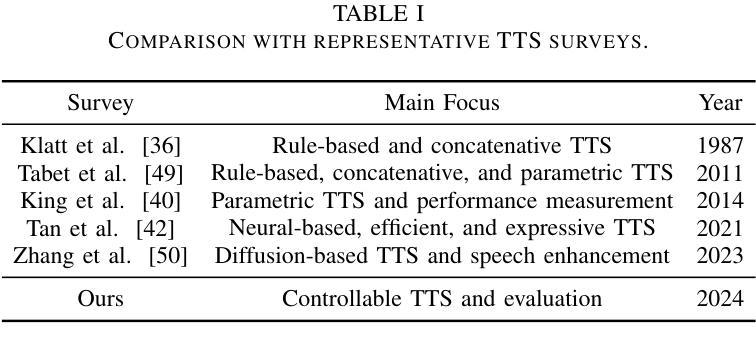
Not All Errors Are Equal: Investigation of Speech Recognition Errors in Alzheimer’s Disease Detection
Authors:Jiawen Kang, Junan Li, Jinchao Li, Xixin Wu, Helen Meng
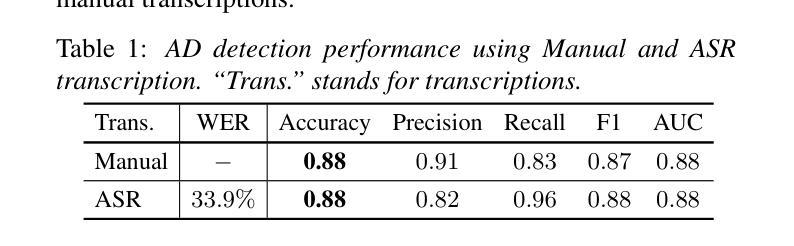
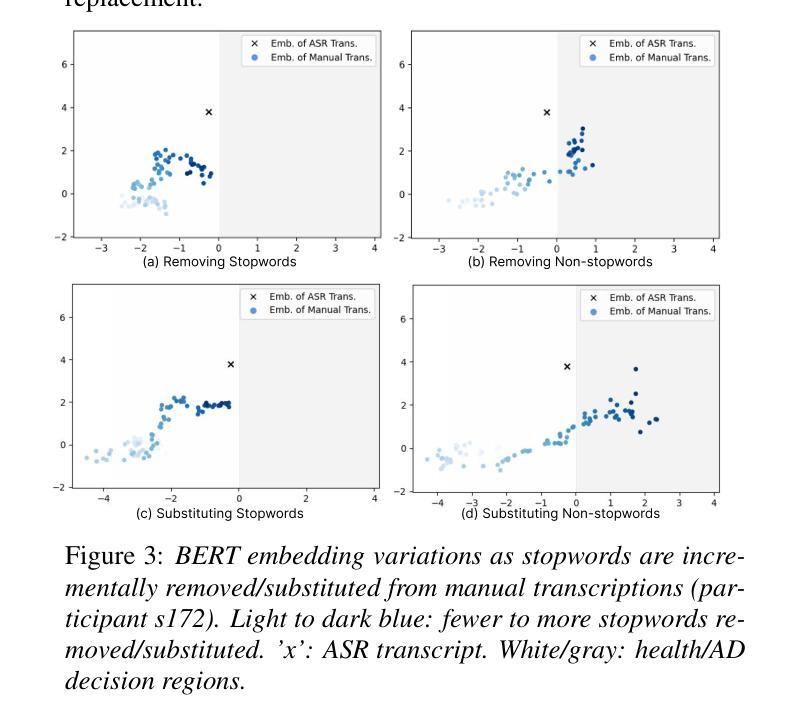
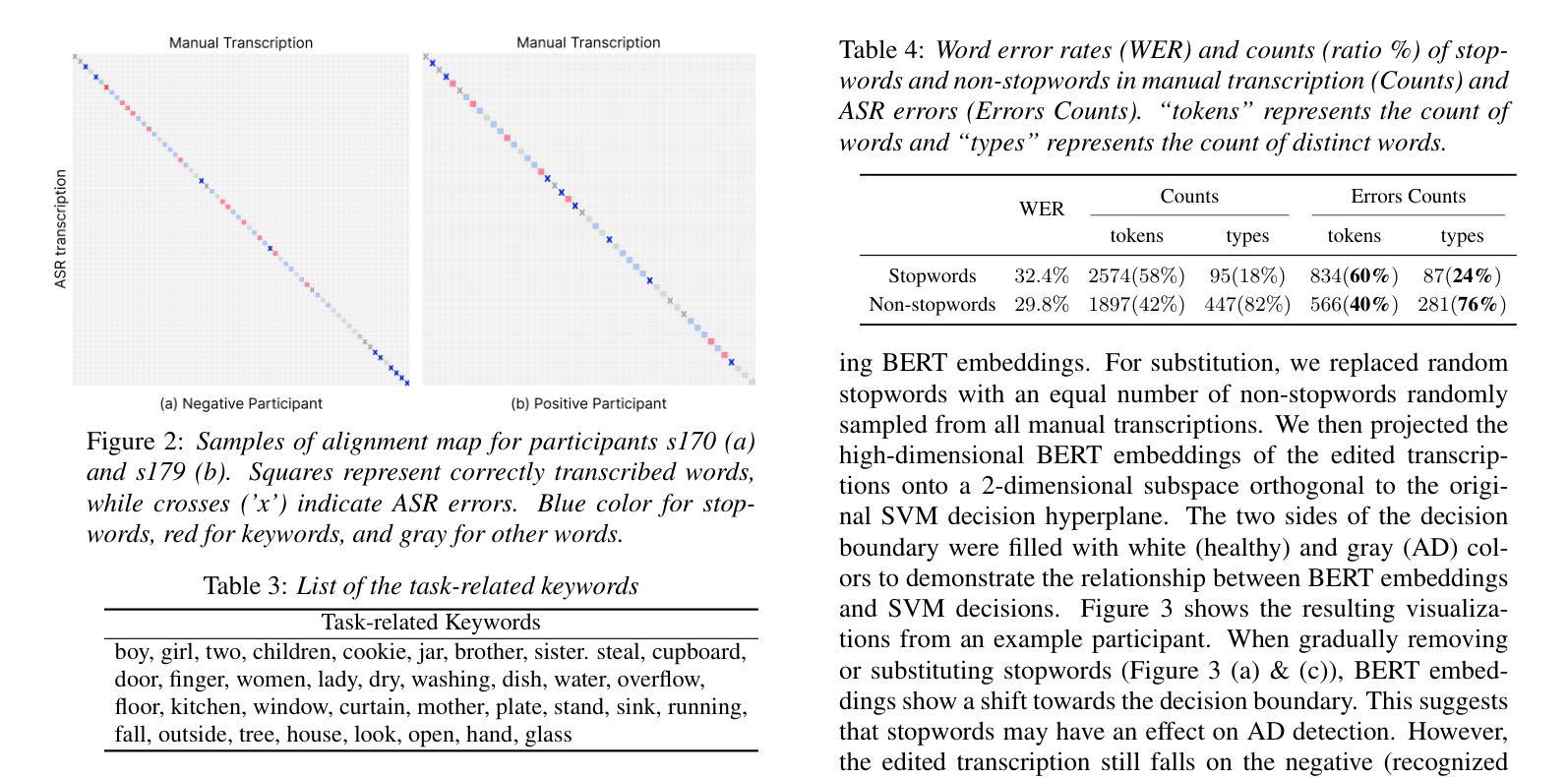
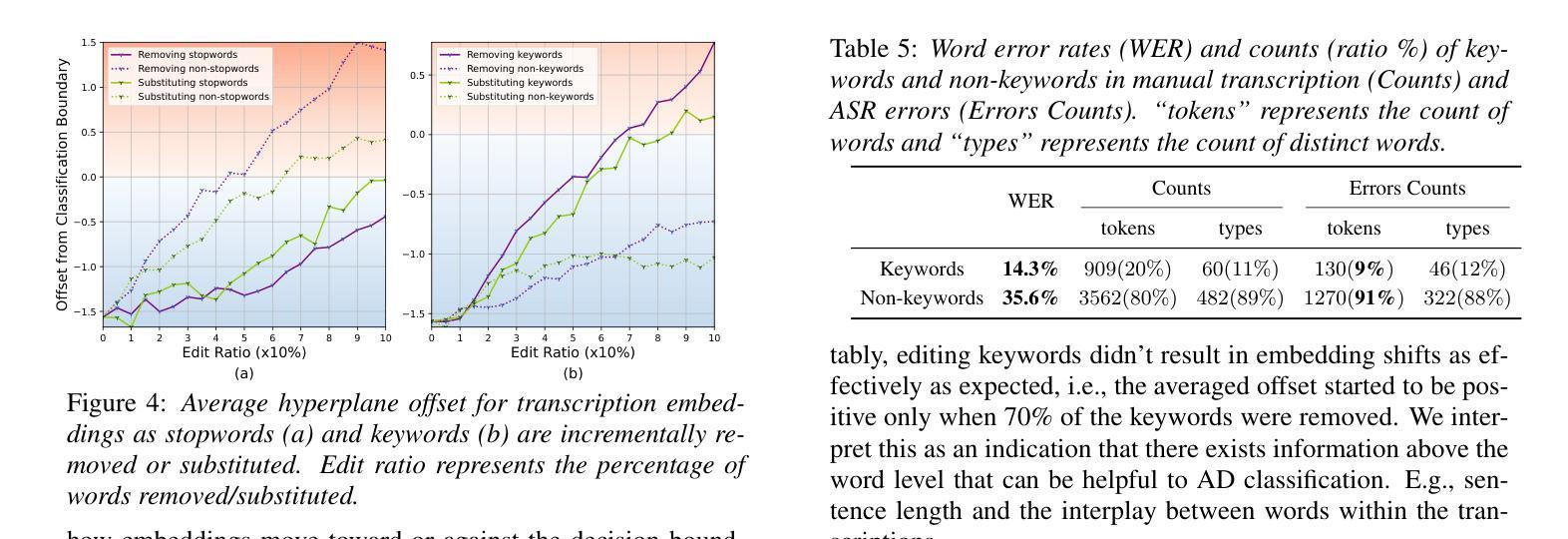
Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) plays an important role in speech-based automatic detection of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, recognition errors could propagate downstream, potentially impacting the detection decisions. Recent studies have revealed a non-linear relationship between word error rates (WER) and AD detection performance, where ASR transcriptions with notable errors could still yield AD detection accuracy equivalent to that based on manual transcriptions. This work presents a series of analyses to explore the effect of ASR transcription errors in BERT-based AD detection systems. Our investigation reveals that not all ASR errors contribute equally to detection performance. Certain words, such as stopwords, despite constituting a large proportion of errors, are shown to play a limited role in distinguishing AD. In contrast, the keywords related to diagnosis tasks exhibit significantly greater importance relative to other words. These findings provide insights into the interplay between ASR errors and the downstream detection model.
自动语音识别(ASR)在基于语音的阿尔茨海默病(AD)自动检测中扮演着重要角色。然而,识别错误可能会传播到下游,潜在地影响检测决策。最近的研究揭示了词错误率(WER)与AD检测性能之间的非线性关系,其中ASR转录的错误显著但仍然可以产生与手动转录相当的AD检测准确性。这项工作提供了一系列分析,以探索ASR转录错误在基于BERT的AD检测系统中的作用。我们的调查表明,并非所有的ASR错误对检测性能的影响都是均等的。某些词语,如停用词,虽然构成了错误的大部分,但在区分AD方面的作用有限。相比之下,与诊断任务相关的关键词相对于其他词语表现出极大的重要性。这些发现提供了ASR错误与下游检测模型之间相互作用的重要见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE ISCSLP 2024
Summary:语音识别技术在阿尔茨海默病(AD)的自动检测中扮演重要角色,但其识别错误可能影响下游检测决策。研究表明,词错误率(WER)与AD检测性能之间存在非线性关系,ASR转录中的错误仍可能获得与手动转录相当的AD检测准确性。本研究分析显示,并非所有ASR错误对检测性能的影响相同。某些词如停用词虽错误率高但对区分AD作用有限,而诊断任务相关的关键词则具有更大的重要性。这些发现揭示了ASR错误与下游检测模型之间的相互作用。
Key Takeaways:
- 自动语音识别(ASR)在阿尔茨海默病(AD)的自动检测中扮演重要角色。
- ASR的识别错误可能会影响下游的检测决策。
- 词错误率(WER)与AD检测性能之间存在非线性关系。
- ASR转录中的错误仍可能获得与手动转录相当的AD检测准确性。
- 在ASR错误中,停用词对区分AD的作用有限。
- 诊断任务相关的关键词在AD检测中具有更大的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

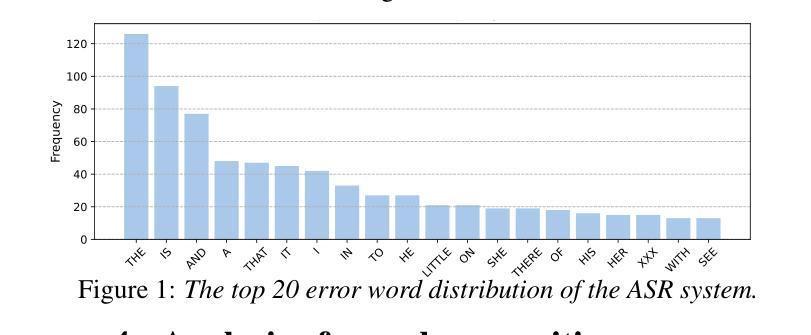
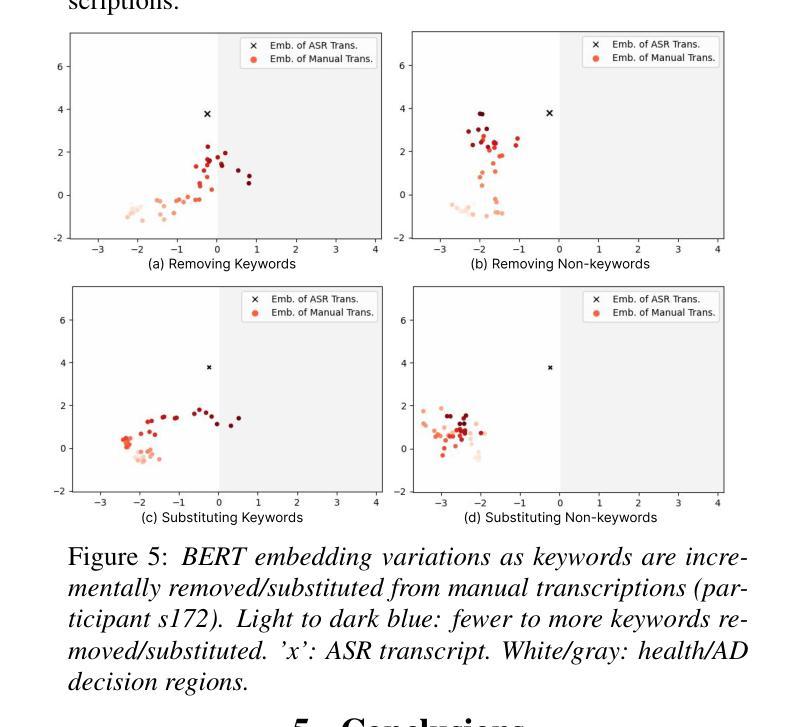
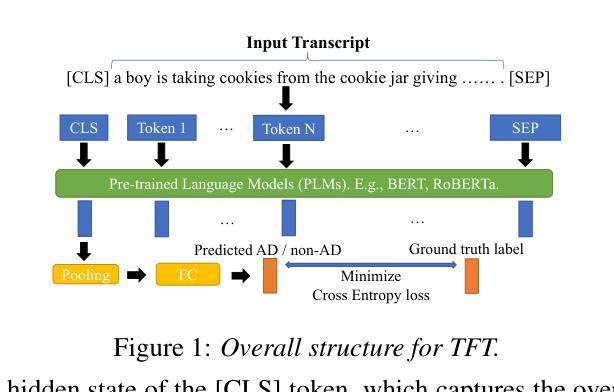
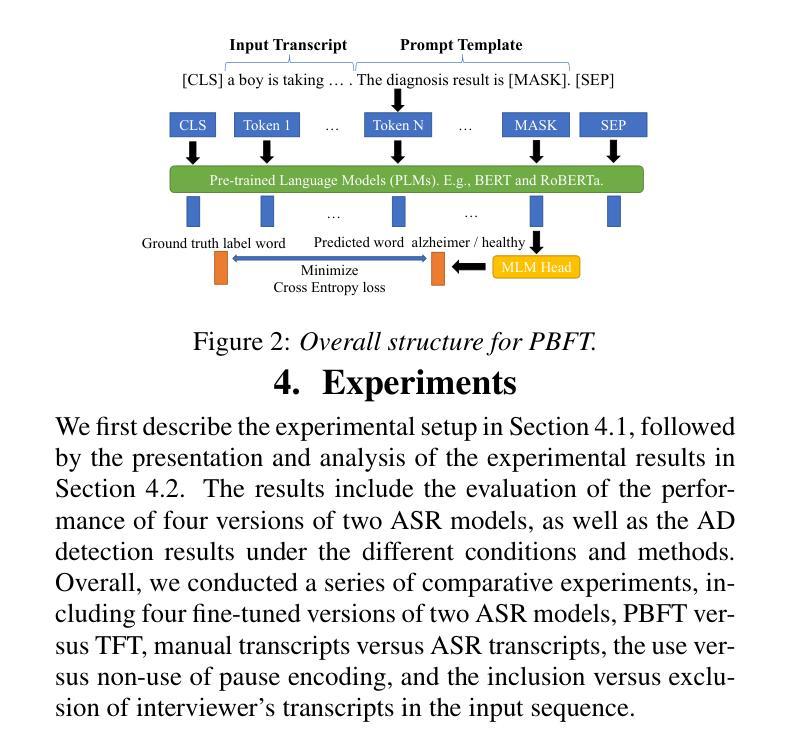
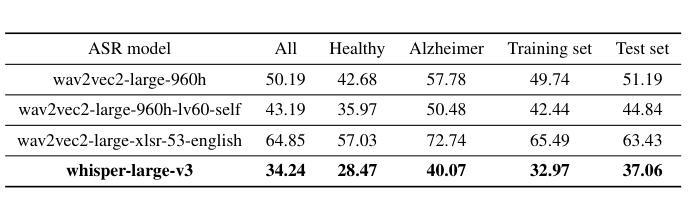
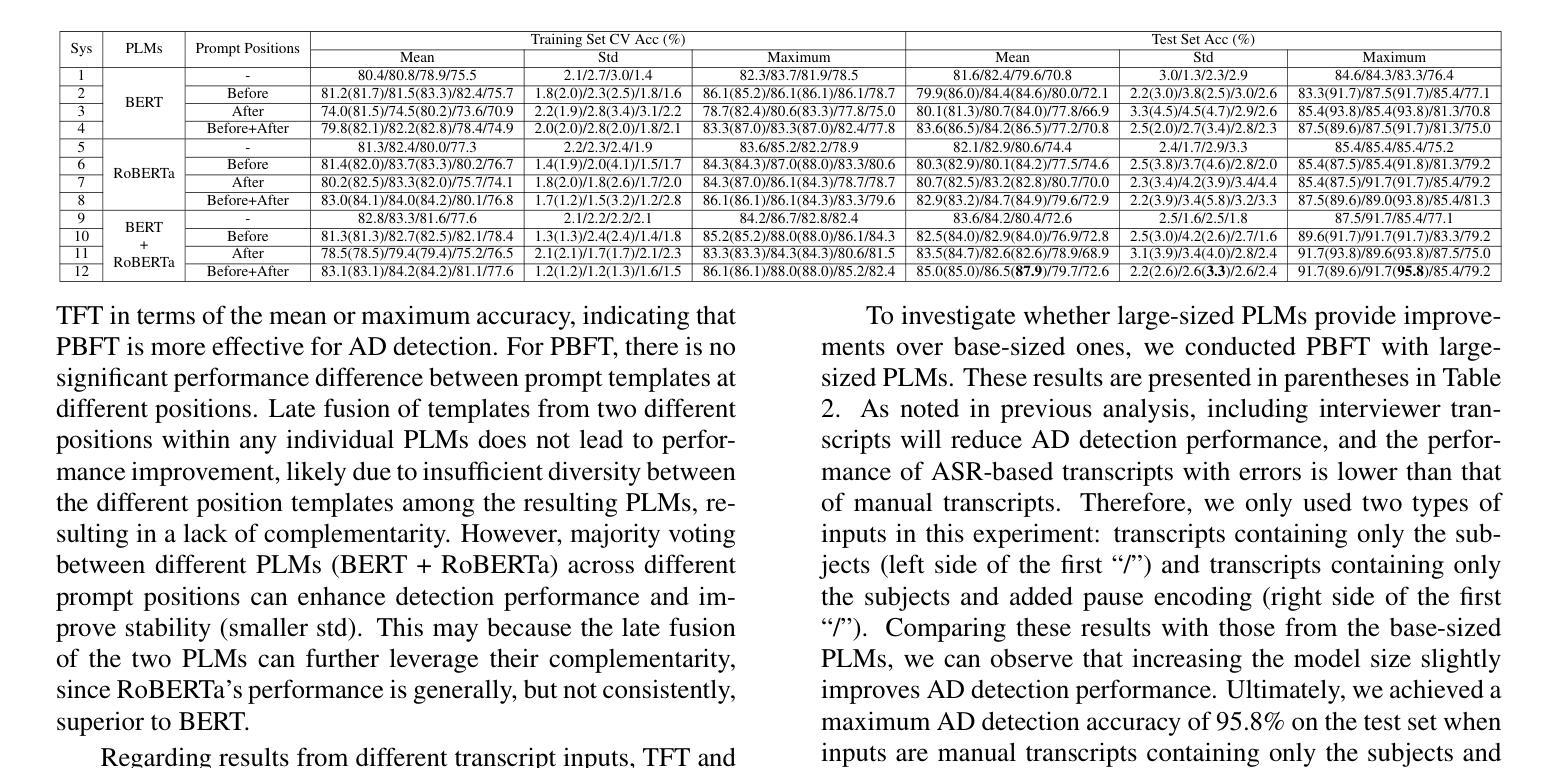
Leveraging Prompt Learning and Pause Encoding for Alzheimer’s Disease Detection
Authors:Yin-Long Liu, Rui Feng, Jia-Hong Yuan, Zhen-Hua Ling
Compared to other clinical screening techniques, speech-and-language-based automated Alzheimer’s disease (AD) detection methods are characterized by their non-invasiveness, cost-effectiveness, and convenience. Previous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of fine-tuning pre-trained language models (PLMs) for AD detection. However, the objective of this traditional fine-tuning method, which involves inputting only transcripts, is inconsistent with the masked language modeling (MLM) task used during the pre-training phase of PLMs. In this paper, we investigate prompt-based fine-tuning of PLMs, converting the classification task into a MLM task by inserting prompt templates into the transcript inputs. We also explore the impact of incorporating pause information from forced alignment into manual transcripts. Additionally, we compare the performance of various automatic speech recognition (ASR) models and select the Whisper model to generate ASR-based transcripts for comparison with manual transcripts. Furthermore, majority voting and ensemble techniques are applied across different PLMs (BERT and RoBERTa) using different random seeds. Ultimately, we obtain maximum detection accuracy of 95.8% (with mean 87.9%, std 3.3%) using manual transcripts, achieving state-of-the-art performance for AD detection using only transcripts on the ADReSS test set.
与其他临床筛查技术相比,基于语言和语音的自动化阿尔茨海默病(AD)检测方法具有非侵入性、成本效益和便捷性等特点。以往的研究已经证明了预训练语言模型(PLM)进行微调在AD检测中的有效性。然而,这种传统微调方法的目标仅涉及输入文本,这与预训练阶段中使用的语言模型的任务(即遮蔽语言建模)是不一致的。在本文中,我们研究了基于提示的PLM微调方法,通过在转录输入中插入提示模板,将分类任务转换为MLM任务。我们还探讨了将强制对齐中的停顿信息纳入手动转录的影响。此外,我们比较了不同自动语音识别(ASR)模型的性能,选择了Whisper模型生成基于ASR的转录本,以便与手动转录本进行比较。同时,我们还在不同的PLM(BERT和RoBERTa)上应用了多数投票和集成技术,使用不同的随机种子。最终,我们使用手动转录本获得了最高95.8%(平均值为87.9%,标准差为3.3%)的检测准确率,在ADReSS测试集上仅使用转录本实现了阿尔茨海默病检测的最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ISCSLP 2024
Summary
语音与语言基础的自动化阿尔茨海默病(AD)检测方法与其他临床筛查技术相比具有无创性、经济性和便利性。本研究探索了基于提示微调预训练语言模型的方法,将分类任务转化为掩码语言建模任务,并在输入转录中加入提示模板。同时,研究将停顿信息融入手动转录本中,对比多种自动语音识别模型并选择Whisper模型进行对比分析。最终通过集成不同预训练语言模型技术实现最高检测准确率95.8%(平均87.9%,标准差3.3%),在ADReSS测试集上取得了顶尖表现。
Key Takeaways
- 语音与语言基础的自动化阿尔茨海默病检测方法具有无创性、经济性和便利性,与传统临床筛查技术相比具有优势。
- 研究通过微调预训练语言模型,实现了有效阿尔茨海默病检测。
- 提示模板的引入提高了分类任务与预训练语言模型的掩码语言建模任务的一致性。
- 停顿信息融入手动转录本对阿尔茨海默病检测性能有积极影响。
- 对比多种自动语音识别模型后选择了Whisper模型进行性能对比。
- 集成不同预训练语言模型技术显著提高了阿尔茨海默病的检测准确率,达到最高95.8%。
点此查看论文截图

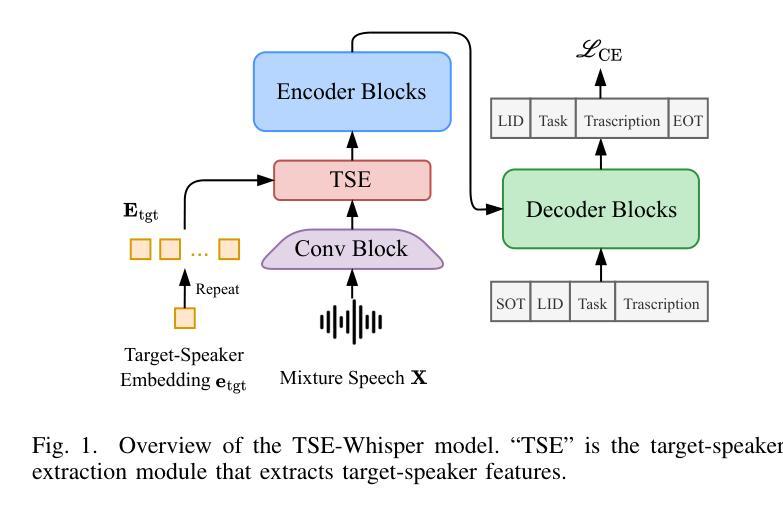
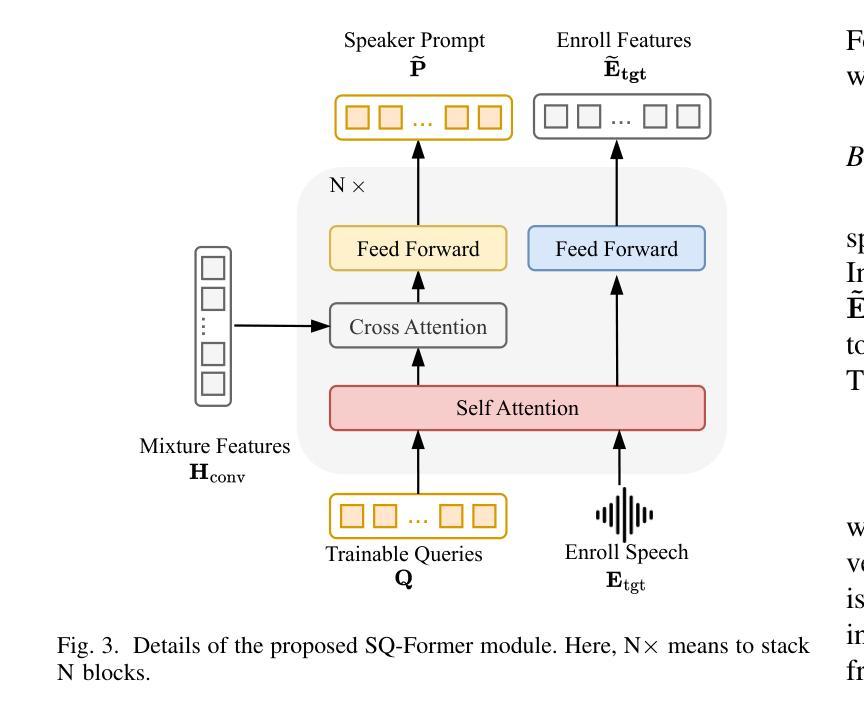
SQ-Whisper: Speaker-Querying based Whisper Model for Target-Speaker ASR
Authors:Pengcheng Guo, Xuankai Chang, Hang Lv, Shinji Watanabe, Lei Xie
Benefiting from massive and diverse data sources, speech foundation models exhibit strong generalization and knowledge transfer capabilities to a wide range of downstream tasks. However, a limitation arises from their exclusive handling of single-speaker speech input, making them ineffective in recognizing multi-speaker overlapped speech, a common occurrence in real-world scenarios. In this study, we delve into the adaptation of speech foundation models to eliminate interfering speakers from overlapping speech and perform target-speaker automatic speech recognition (TS-ASR). Initially, we utilize the Whisper model as the foundation for adaptation and conduct a thorough comparison of its integration with existing target-speaker adaptation techniques. We then propose an innovative model termed Speaker-Querying Whisper (SQ-Whisper), which employs a set number of trainable queries to capture speaker prompts from overlapping speech based on target-speaker enrollment. These prompts serve to steer the model in extracting speaker-specific features and accurately recognizing target-speaker transcriptions. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach effectively adapts the pre-trained speech foundation model to TS-ASR. Compared with the robust TS-HuBERT model, the proposed SQ-Whisper significantly improves performance, yielding up to 15% and 10% relative reductions in word error rates (WERs) on the Libri2Mix and WSJ0-2Mix datasets, respectively. With data augmentation, we establish new state-of-the-art WERs of 14.6% on the Libri2Mix Test set and 4.4% on the WSJ0-2Mix Test set. Furthermore, we evaluate our model on the real-world AMI meeting dataset, which shows consistent improvement over other adaptation methods.
得益于大规模和多样化的数据来源,语音基础模型在广泛的下游任务中展现出强大的泛化和知识迁移能力。然而,它们处理单说话人语音输入的局限性导致它们在识别多说话人重叠语音时效果不佳,而在现实世界中,这种情况经常发生。在这项研究中,我们深入探讨了语音基础模型对消除重叠语音中的干扰说话者的适应性,并进行了目标说话人自动语音识别(TS-ASR)。首先,我们以whisper模型为基础进行适应,并对其与现有目标说话人适应技术的集成进行了全面的比较。然后,我们提出了一种创新的模型——Speaker-Querying Whisper(SQ-Whisper),该模型通过使用一组可训练查询来捕获目标说话人的说话提示。这些提示基于目标说话人的注册信息,用于指导模型提取说话人特定特征并准确识别目标说话人的转录内容。实验结果表明,我们的方法有效地适应了预训练的语音基础模型进行TS-ASR。与强大的TS-HuBERT模型相比,提出的SQ-Whisper显著提高了性能,在Libri2Mix和WSJ0-2Mix数据集上相对减少了15%和10%的词错误率(WER)。通过数据增强,我们在Libri2Mix测试集上建立了最新的最佳WER为14.6%,在WSJ0-2Mix测试集上为4.4%。此外,我们在真实世界的AMI会议数据集上评估了我们的模型,与其他适应方法相比,表现出持续的可改进之处。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE/ACM TASLP
摘要
受益于大规模和多样化的数据源,语音基础模型展现出强大的泛化和知识迁移能力,能广泛应用于多种下游任务。然而,处理单讲者语音输入的局限性使得它们无法有效识别多讲者重叠语音,这在现实场景中很常见。本研究致力于适应语音基础模型,以消除重叠语音中的干扰讲者,并执行目标讲者自动语音识别(TS-ASR)。首先,我们使用whisper模型作为基础进行适应,并与其与现有的目标讲者适应技术进行了全面比较。接着,我们提出了一种创新的模型——Speaker-Querying Whisper(SQ-Whisper),它利用一系列可训练的查询来捕捉目标讲者的提示,基于这些提示从重叠语音中提取讲者特定的特征,并准确识别目标讲者的转录。实验结果表明,我们的方法有效地适应了预训练的语音基础模型进行TS-ASR。与强大的TS-HuBERT模型相比,提出的SQ-Whisper显著提高了性能,在Libri2Mix和WSJ0-2Mix数据集上分别降低了15%和10%的相对词错误率(WERs)。通过数据增强,我们在Libri2Mix测试集上建立了新的最佳WERs为14.6%,在WSJ0-2Mix测试集上为4.4%。此外,在真实世界的AMI会议数据集上,我们的模型也表现出比其他适应方法更持续的改进。
要点
- 语音基础模型受益于大规模和多样化数据源,具有强大的泛化和知识迁移能力。
- 现有模型在处理多讲者重叠语音时存在局限性。
- 本研究旨在通过适应语音基础模型来识别重叠语音中的目标讲者。
- 使用whisper模型作为基础进行适应,并与其现有的目标讲者适应技术进行比较。
- 提出创新的SQ-Whisper模型,利用可训练查询捕捉目标讲者提示,以识别目标讲者的语音。
- SQ-Whisper在多个数据集上显著提高了性能,包括Libri2Mix、WSJ0-2Mix和AMI会议数据集。
- 通过数据增强,建立了新的最佳WERs记录。
点此查看论文截图

WavFusion: Towards wav2vec 2.0 Multimodal Speech Emotion Recognition
Authors:Feng Li, Jiusong Luo, Wanjun Xia
Speech emotion recognition (SER) remains a challenging yet crucial task due to the inherent complexity and diversity of human emotions. To address this problem, researchers attempt to fuse information from other modalities via multimodal learning. However, existing multimodal fusion techniques often overlook the intricacies of cross-modal interactions, resulting in suboptimal feature representations. In this paper, we propose WavFusion, a multimodal speech emotion recognition framework that addresses critical research problems in effective multimodal fusion, heterogeneity among modalities, and discriminative representation learning. By leveraging a gated cross-modal attention mechanism and multimodal homogeneous feature discrepancy learning, WavFusion demonstrates improved performance over existing state-of-the-art methods on benchmark datasets. Our work highlights the importance of capturing nuanced cross-modal interactions and learning discriminative representations for accurate multimodal SER. Experimental results on two benchmark datasets (IEMOCAP and MELD) demonstrate that WavFusion succeeds over the state-of-the-art strategies on emotion recognition.
语音情感识别(SER)仍然是一项具有挑战但至关重要的任务,这是由于人类情绪的固有复杂性和多样性。为了解决这个问题,研究人员试图通过多模态学习融合其他模态的信息。然而,现有的多模态融合技术往往忽视了跨模态交互的复杂性,导致特征表示不佳。在本文中,我们提出了WavFusion,这是一个多模态语音情感识别框架,解决了有效多模态融合、模态之间的异质性和判别表示学习的关键研究问题。通过利用门控跨模态注意力机制和跨模态均匀特征差异学习,WavFusion在基准数据集上实现了对现有先进方法的性能提升。我们的工作强调了捕捉微妙的跨模态交互和学习判别性表示对于准确的多模态SER的重要性。在IEMOCAP和MELD两个基准数据集上的实验结果证明,WavFusion在情感识别方面超过了最新的策略。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by 31st International Conference on MultiMedia Modeling (MMM2025)
Summary
本文提出了一种名为WavFusion的多模态语音情感识别框架,解决了有效多模态融合、模态间异质性和判别表示学习等关键研究问题。通过利用门控跨模态注意力机制和模态内同质特征差异学习,WavFusion在基准数据集上的性能优于现有最先进的情绪识别方法。摘要总结了该文的主要贡献和实践结果。
Key Takeaways
- 语音情感识别(SER)是一个具有挑战性和重要性的问题,涉及人类情绪的复杂性和多样性。
- 多模态融合是解决SER问题的一种方法,但现有技术常常忽略跨模态交互的细节,导致特征表示不佳。
- WavFusion框架通过利用门控跨模态注意力机制和模态内同质特征差异学习来解决这些问题。
- WavFusion在基准数据集上表现出优于现有最先进的情感识别方法的性能。
- 捕获微妙的跨模态交互和学习的判别表示对于准确的多模态SER至关重要。
- 实验结果表明,WavFusion在情绪识别方面超过了现有策略。
点此查看论文截图

Adaptive Dropout for Pruning Conformers
Authors:Yotaro Kubo, Xingyu Cai, Michiel Bacchiani
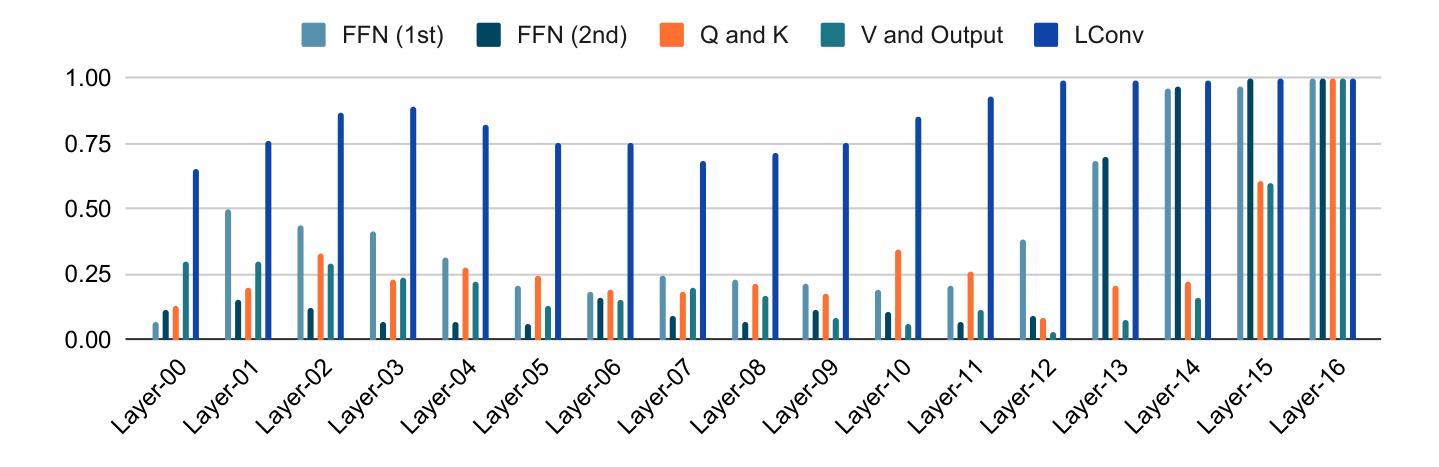
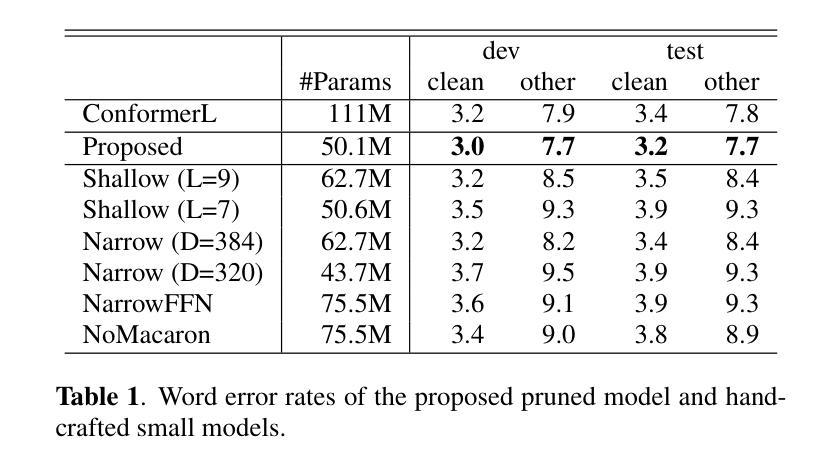
This paper proposes a method to effectively perform joint training-and-pruning based on adaptive dropout layers with unit-wise retention probabilities. The proposed method is based on the estimation of a unit-wise retention probability in a dropout layer. A unit that is estimated to have a small retention probability can be considered to be prunable. The retention probability of the unit is estimated using back-propagation and the Gumbel-Softmax technique. This pruning method is applied at several application points in Conformers such that the effective number of parameters can be significantly reduced. Specifically, adaptive dropout layers are introduced in three locations in each Conformer block: (a) the hidden layer of the feed-forward-net component, (b) the query vectors and the value vectors of the self-attention component, and (c) the input vectors of the LConv component. The proposed method is evaluated by conducting a speech recognition experiment on the LibriSpeech task. It was shown that this approach could simultaneously achieve a parameter reduction and accuracy improvement. The word error rates improved by approx 1% while reducing the number of parameters by 54%.
本文提出了一种基于自适应dropout层进行联合训练与剪枝的有效方法,该方法基于单位保留概率的估计。所提出的方法基于dropout层中单位保留概率的估计。估计保留概率较小的单位可以被视为可剪枝的。该单位的保留概率通过使用反向传播和Gumbel-Softmax技术进行估计。这种剪枝方法被应用于Conformers的几个应用点,从而可以显著减少有效参数的数量。具体来说,自适应dropout层在每个Conformer块的三个位置引入:(a)前馈网络组件的隐藏层,(b)自注意力组件的查询向量和值向量,以及(c)LConv组件的输入向量。该方法通过在LibriSpeech任务上进行语音识别实验进行评估。结果表明,该方法可以同时实现参数减少和准确性提高。词错误率提高了约1%,同时减少了54%的参数数量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于自适应dropout层进行联合训练与剪枝的方法,使用单元级别的保持概率来估计剪枝决策。这种方法用于降低模型参数数量,应用于语音任务如语音识别,实现参数减少与准确率提升的双重效果。在LibriSpeech任务上的实验表明,该方法减少了约54%的参数数量,同时提高了约1%的单词错误率。
Key Takeaways
- 该方法通过结合自适应dropout层和剪枝策略来实现模型的联合训练与参数优化。
- 利用单元级别的保持概率估计进行剪枝决策,预计剪枝单元较小的保持概率可进行删除操作。
- 采用后向传播和Gumbel-Softmax技术来估计单元保持概率。
- 该方法应用于Conformers中的多个点,包括前馈网络组件的隐藏层、自注意力组件的查询向量和价值向量以及LConv组件的输入向量。
点此查看论文截图

Integrated Minimum Mean Squared Error Algorithms for Combined Acoustic Echo Cancellation and Noise Reduction
Authors:Arnout Roebben, Toon van Waterschoot, Jan Wouters, Marc Moonen
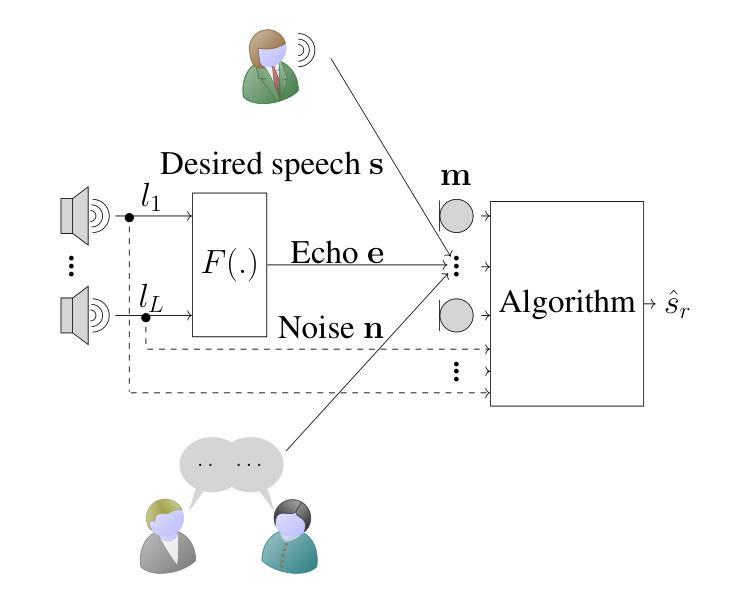
In many speech recording applications, noise and acoustic echo corrupt the desired speech. Consequently, combined noise reduction (NR) and acoustic echo cancellation (AEC) is required. Generally, a cascade approach is followed, i.e., the AEC and NR are designed in isolation by selecting a separate signal model, formulating a separate cost function, and using a separate solution strategy. The AEC and NR are then cascaded one after the other, not accounting for their interaction. In this paper, however, an integrated approach is proposed to consider this interaction in a general multi-microphone/multi-loudspeaker setup. Therefore, a single signal model of either the microphone signal vector or the extended signal vector, obtained by stacking microphone and loudspeaker signals, is selected, a single mean squared error cost function is formulated, and a common solution strategy is used. Using this microphone signal model, a multi channel Wiener filter (MWF) is derived. Using the extended signal model, an extended MWF (MWFext) is derived, and several equivalent expressions are found, which nevertheless are interpretable as cascade algorithms. Specifically, the MWFext is shown to be equivalent to algorithms where the AEC precedes the NR (AEC NR), the NR precedes the AEC (NR-AEC), and the extended NR (NRext) precedes the AEC and post-filter (PF) (NRext-AECPF). Under rank-deficiency conditions the MWFext is non-unique, such that this equivalence amounts to the expressions being specific, not necessarily minimum-norm solutions for this MWFext. The practical performances nonetheless differ due to non-stationarities and imperfect correlation matrix estimation, resulting in the AEC-NR and NRext-AEC-PF attaining best overall performance.
在许多语音记录应用中,噪声和声音回声会干扰所需的语音。因此,需要联合降噪(NR)和声音回声消除(AEC)。通常采用的是级联方法,即独立设计AEC和NR,通过选择单独的信号模型、制定单独的代价函数和使用单独的解决方案策略来实现。然后将AEC和NR一个接一个地进行级联,没有考虑到它们之间的相互作用。然而,本文提出一种综合考虑方法,在一般的多个麦克风/多个扬声器的设置中来考虑这种相互作用。因此,选择单个信号模型,该模型可以是麦克风信号向量也可以是通过对麦克风和扬声器信号进行堆叠而获得的扩展信号向量。制定一个单一的均方误差代价函数并使用一个通用的解决方案策略。基于这种麦克风信号模型,推导出了多通道维纳滤波器(MWF)。基于扩展的信号模型,推导出了扩展的MWF(MWFext),并找到了几个等效的表达式,这些表达式可以解释为级联算法。具体来说,MWFext相当于AEC先于NR(AEC NR)、NR先于AEC(NR-AEC)以及扩展NR(NRext)先于AEC和后置滤波器(PF)(NRext-AECPF)的算法。在秩不足的情况下,MWFext是非唯一的,因此这种等效表现为表达式特定,不一定是这个MWFext的最小范数解。但由于非平稳性和不完美的相关矩阵估计,实际性能仍然有所不同,使得AEC-NR和NRext-AEC-PF获得最佳的整体性能。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
在语音录制应用中,噪声和回声会影响所需的语音质量,因此需要结合降噪(NR)和声回消除(AEC)。通常采用级联方法,即独立设计AEC和NR,选择单独的信号模型、制定单独的成本函数和使用单独的解决方案策略。然后依次进行AEC和NR处理,而不考虑它们的相互作用。然而,本文提出了一种综合考虑这种相互作用的一般的多麦克风/多扬声器设置中的集成方法。因此,选择了麦克风信号向量或通过将麦克风和扬声器信号叠加得到的扩展信号向量的单一信号模型,制定了单一均方误差成本函数,并使用通用解决方案策略。基于这种麦克风信号模型,推导出了多通道维纳滤波器(MWF)。基于扩展信号模型,推导出了扩展MWF(MWFext),并找到了几个等效表达式,它们可以解释为级联算法。特别是,MWFext与AEC先于NR(AEC NR)、NR先于AEC(NR-AEC)以及扩展NR(NRext)先于AEC和后滤波器(PF)(NRext-AECPF)的算法等效。在秩不足的情况下,MWFext是非唯一的,这意味着这种等效性表现为表达式的特定性,不一定是MWFext的最小范数解。然而,由于非平稳性和相关矩阵估计的不完美性,它们的实际性能有所不同,使得AEC-NR和NRext-AEC-PF获得最佳的整体性能。
关键见解
- 论文提出了一种集成方法,考虑噪声消除和声回消除之间的相互作用。
- 论文介绍了基于麦克风信号模型的MWF和多通道维纳滤波器扩展版本(MWFext)。
- MWFext与不同的级联算法表现出等效性,包括AEC NR、NR-AEC、以及NRext-AECPF。
- 在秩不足的情况下,MWFext的非唯一性使得等效表达式的适用性受限。
- 实际性能差异源于非平稳性和相关矩阵估计的不完美性。
- AEC-NR和NRext-AEC-PF在处理噪声和回声时表现出最佳的整体性能。
- 该论文提供了一种有效的方法来考虑噪声消除和声回消除的相互作用,从而提高了语音录制的质量。
点此查看论文截图

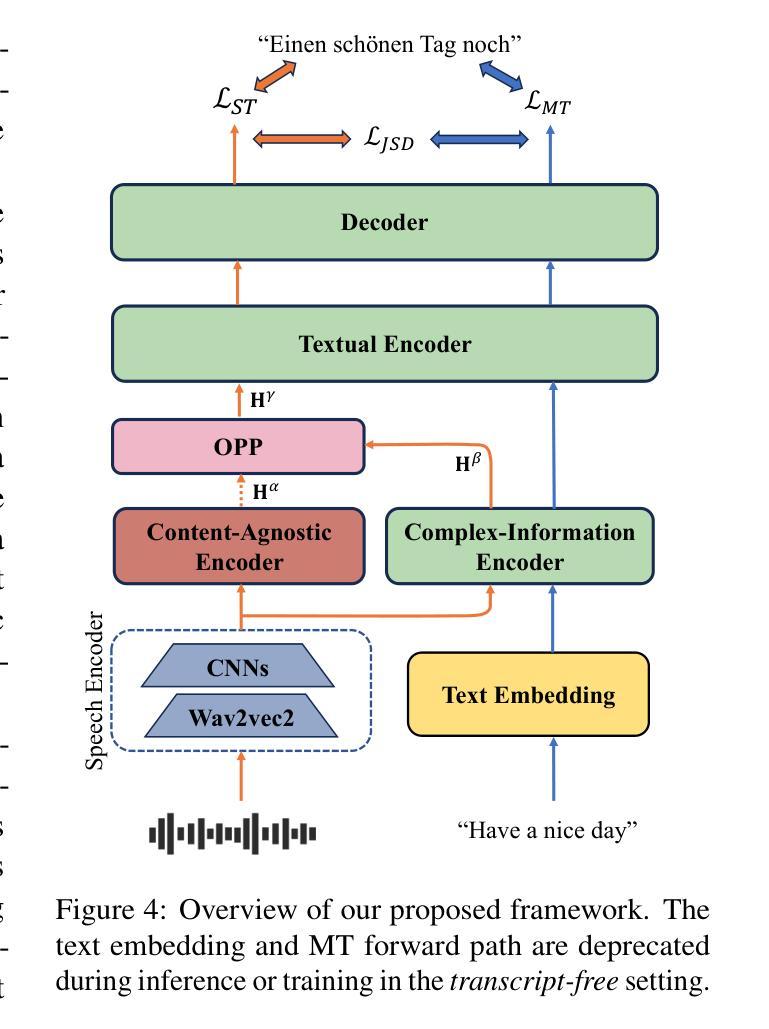
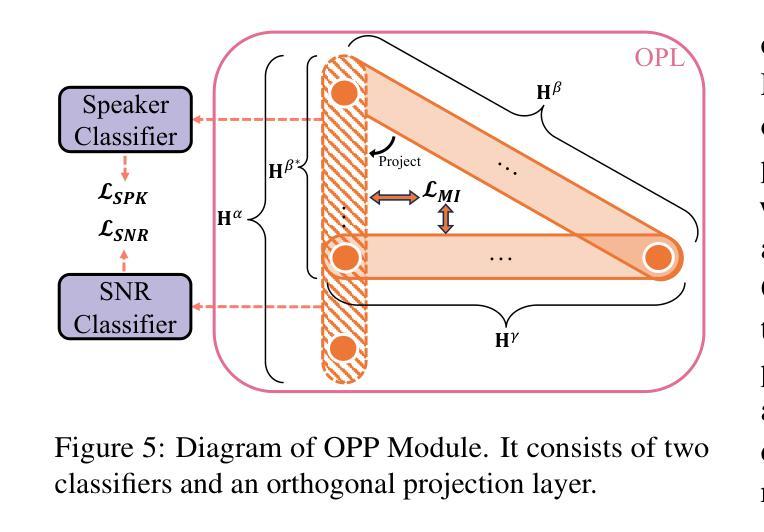
Representation Purification for End-to-End Speech Translation
Authors:Chengwei Zhang, Yue Zhou, Rui Zhao, Yidong Chen, Xiaodong Shi
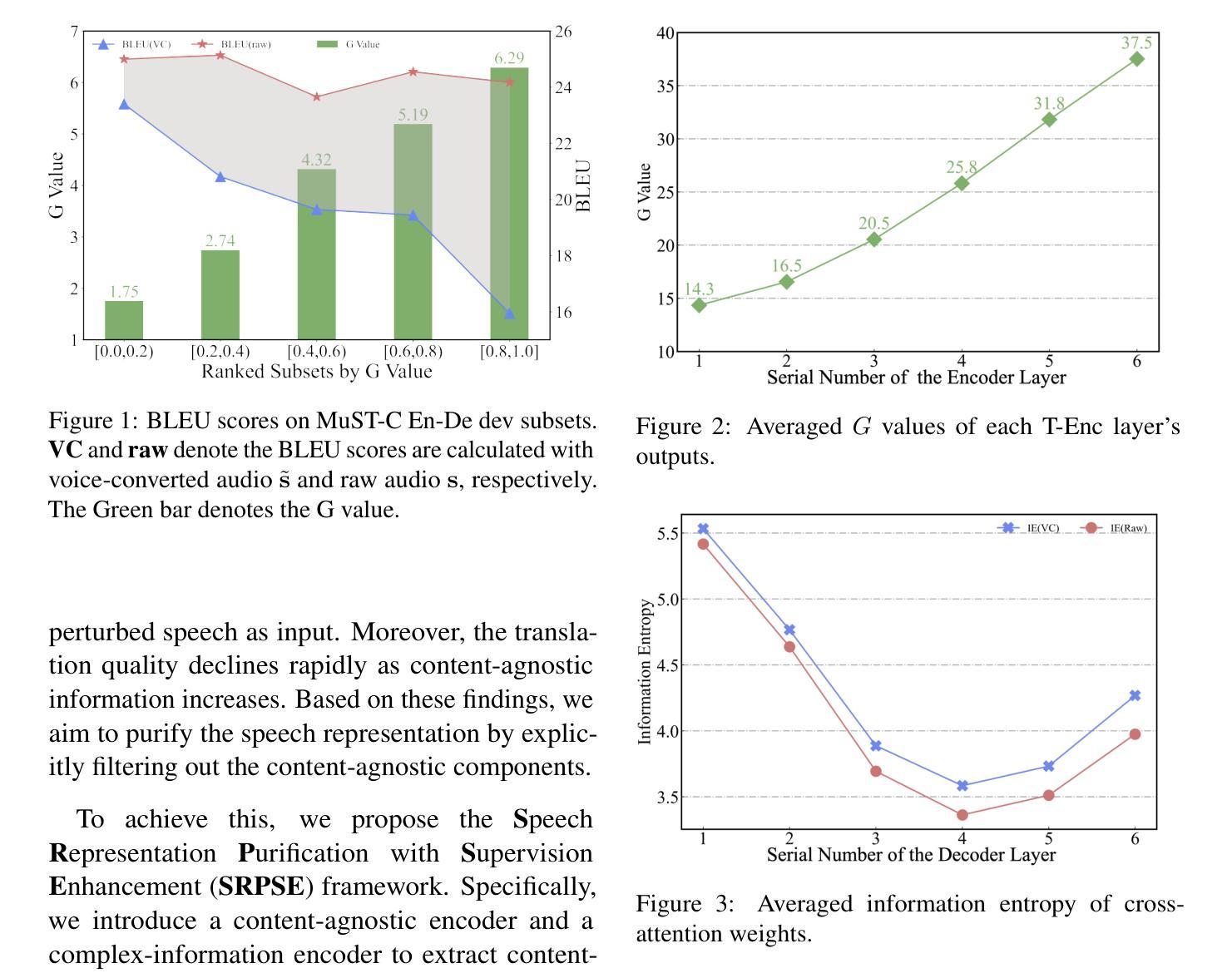
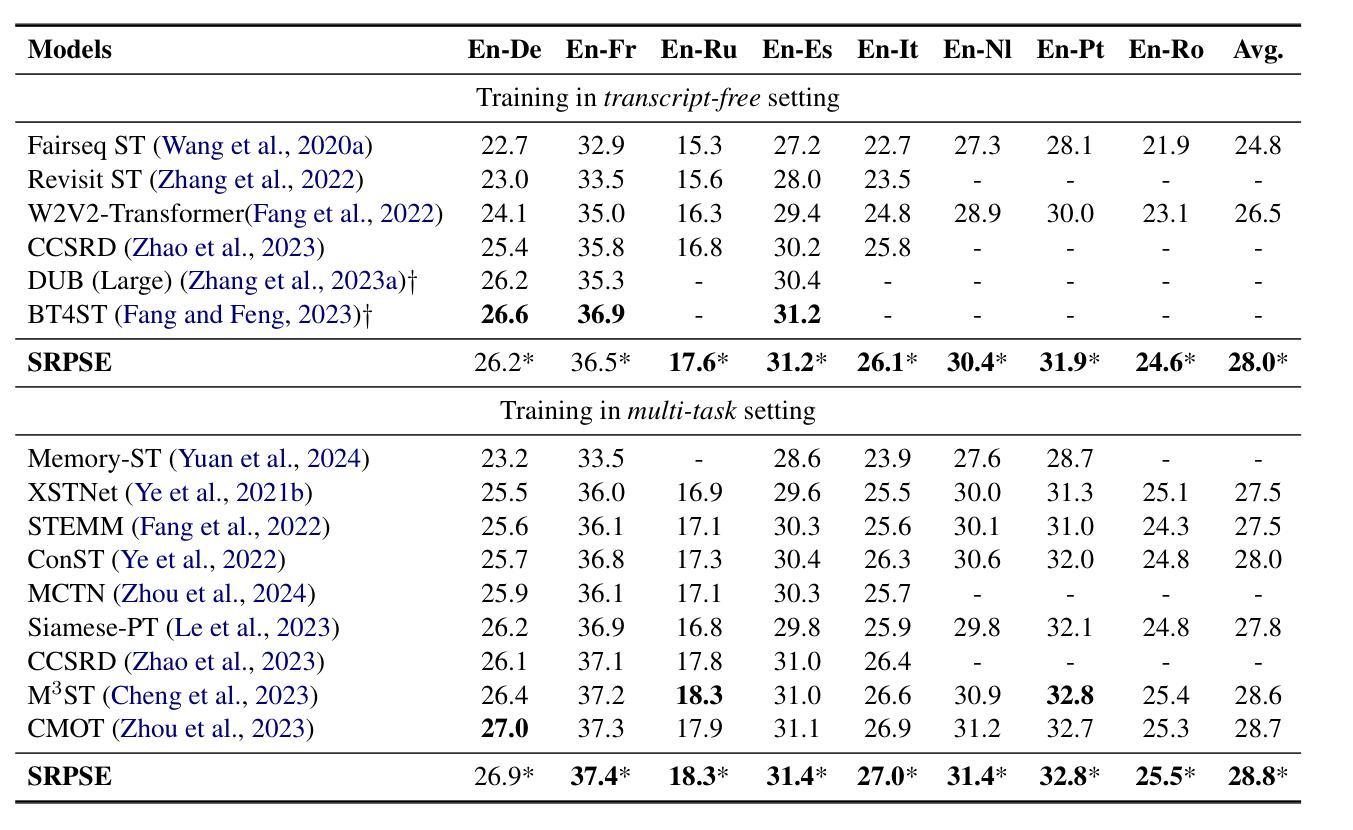
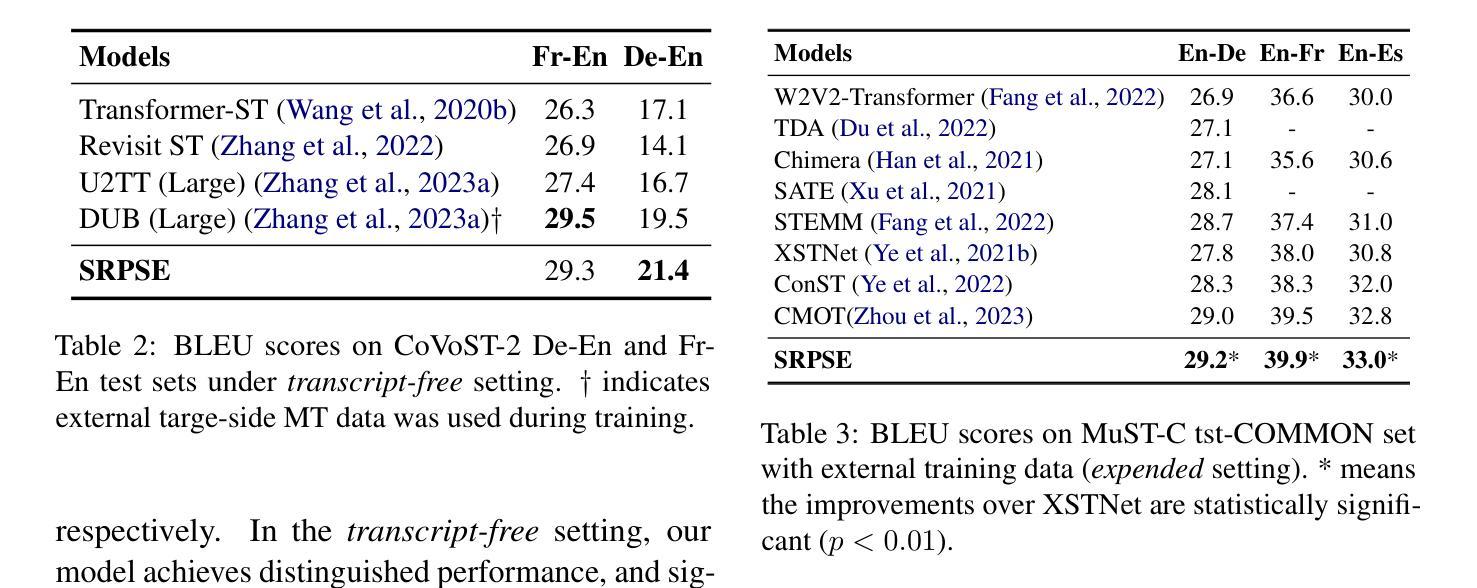
Speech-to-text translation (ST) is a cross-modal task that involves converting spoken language into text in a different language. Previous research primarily focused on enhancing speech translation by facilitating knowledge transfer from machine translation, exploring various methods to bridge the gap between speech and text modalities. Despite substantial progress made, factors in speech that are not relevant to translation content, such as timbre and rhythm, often limit the efficiency of knowledge transfer. In this paper, we conceptualize speech representation as a combination of content-agnostic and content-relevant factors. We examine the impact of content-agnostic factors on translation performance through preliminary experiments and observe a significant performance deterioration when content-agnostic perturbations are introduced to speech signals. To address this issue, we propose a \textbf{S}peech \textbf{R}epresentation \textbf{P}urification with \textbf{S}upervision \textbf{E}nhancement (SRPSE) framework, which excludes the content-agnostic components within speech representations to mitigate their negative impact on ST. Experiments on MuST-C and CoVoST-2 datasets demonstrate that SRPSE significantly improves translation performance across all translation directions in three settings and achieves preeminent performance under a \textit{transcript-free} setting.
语音到文本的翻译(ST)是一项涉及将口语转换为另一种语言的文本的多模式任务。以前的研究主要集中在通过促进机器翻译的知识转移来提高语音翻译的性能,探索各种方法来弥合语音和文本模式之间的差距。尽管取得了重大进展,但语音中与翻译内容不相关的因素,如音质和节奏,往往限制了知识转移的效率。在本文中,我们将语音表示概念化为与内容无关和与内容相关因素的结合。我们通过初步实验检查了与内容无关因素对翻译性能的影响,并观察到当向语音信号引入与内容无关的干扰时,性能会显著下降。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一个名为SRPSE(有监督增强的语音表示净化)的框架,该框架排除语音表示中的与内容无关的成分,以减轻它们对ST的负面影响。在MuST-C和CoVoST-2数据集上的实验表明,SRPSE在三种设置的各个翻译方向上显著提高了翻译性能,并在无字幕设置下取得了卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by COLING 2025
Summary
语音到文本的翻译(ST)是一个跨模态任务,涉及将口语转化为另一种语言的文本。尽管取得了实质性进展,但语音中那些与翻译内容无关的因素(如音色和节奏)经常限制知识转移的效率。本文概念化语音表示为与内容无关和与内容相关因素的组合,并通过初步实验发现内容无关的干扰对翻译性能有重大影响。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一个名为SRPSE的语音表示净化与监督增强框架,它通过排除语音表示中的与内容无关的成分,减轻其对ST的负面影响。实验表明,SRPSE在三种设置下的所有翻译方向上均显著提高翻译性能,并在无字幕设置下实现卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 语音到文本的翻译是跨模态任务,涉及将口语转化为另一种语言的文本。
- 语音中与内容无关的因素(如音色和节奏)对翻译性能有重要影响。
- 初步实验表明,内容无关的干扰会导致翻译性能显著下降。
- 为解决此问题,提出了SRPSE框架,旨在排除语音表示中的与内容无关的成分。
- SRPSE框架在多个数据集上的实验表明,它在各种翻译设置下显著提高翻译性能。
- SRPSE框架在无字幕设置下实现卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

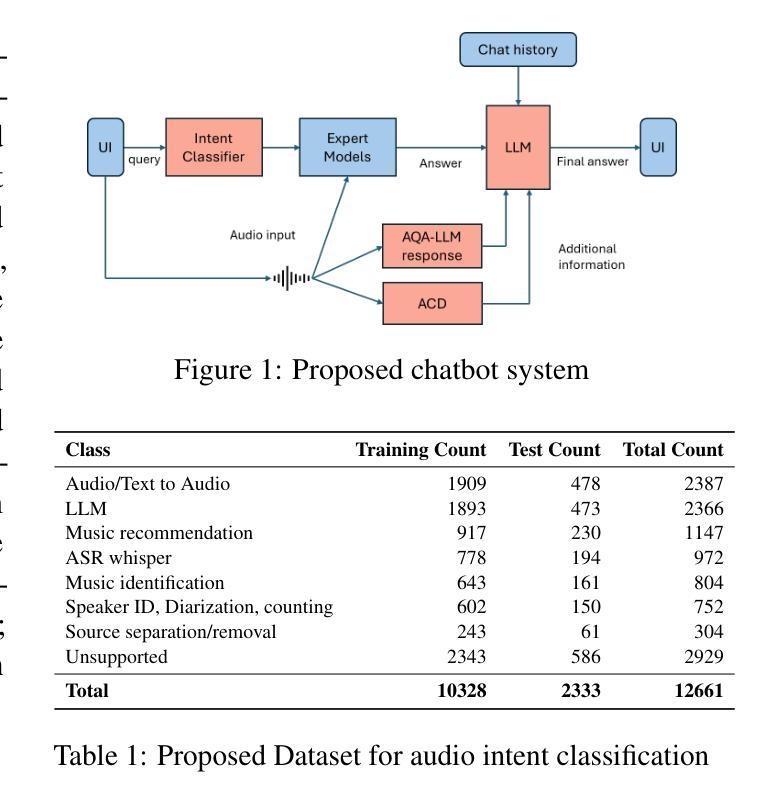
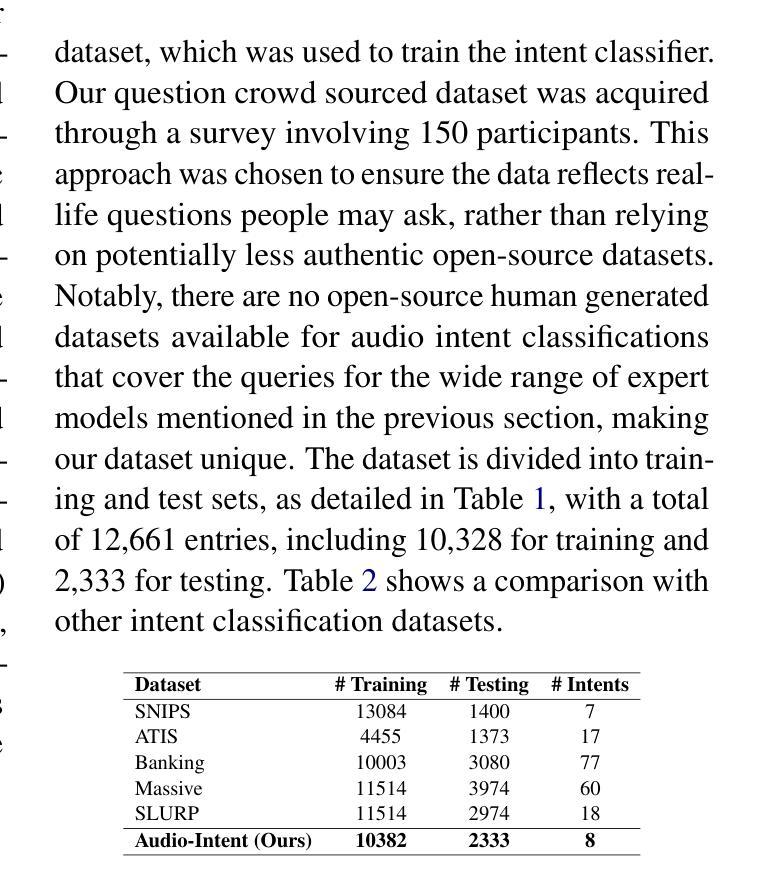
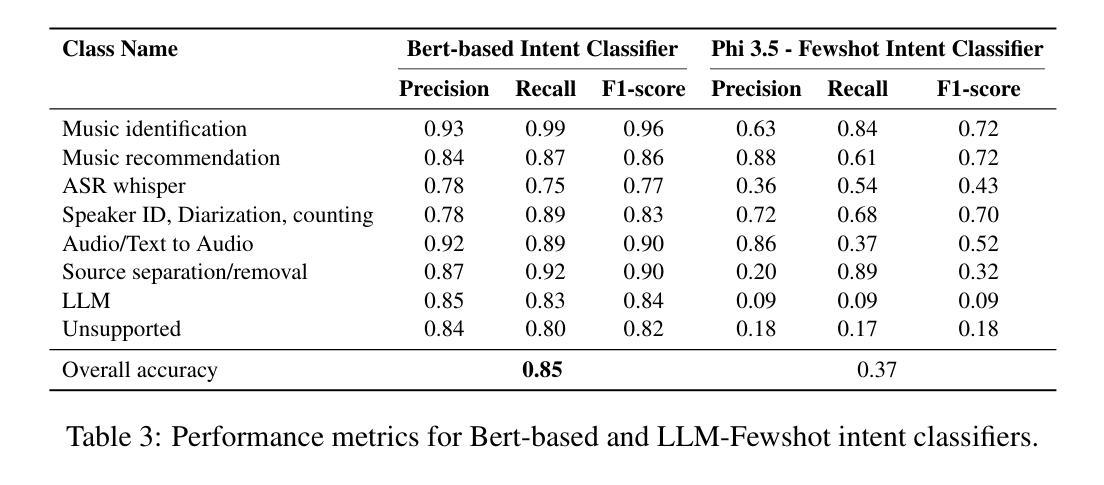
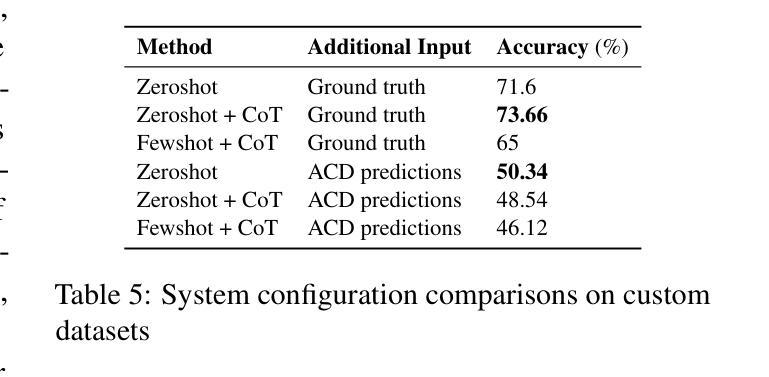
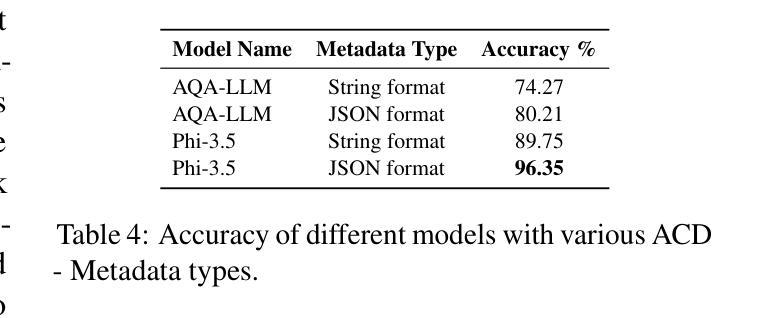
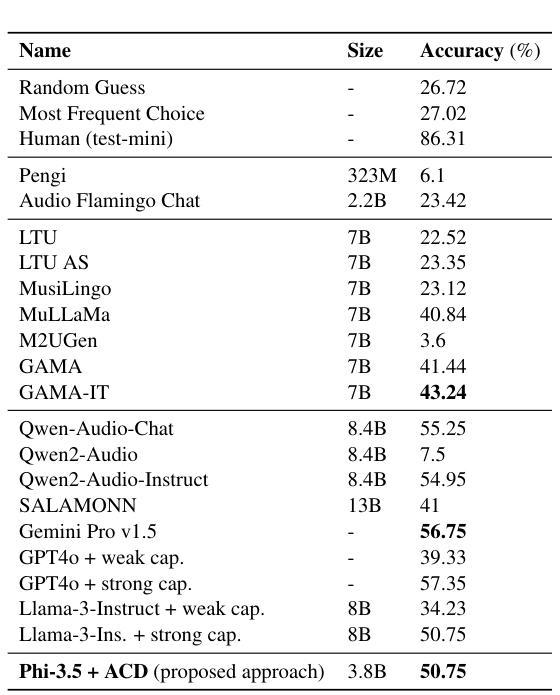
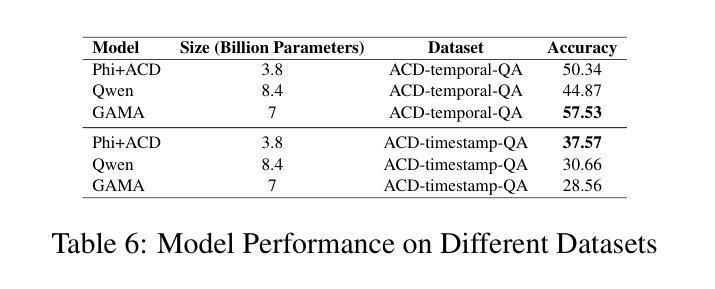
Comprehensive Audio Query Handling System with Integrated Expert Models and Contextual Understanding
Authors:Vakada Naveen, Arvind Krishna Sridhar, Yinyi Guo, Erik Visser
This paper presents a comprehensive chatbot system designed to handle a wide range of audio-related queries by integrating multiple specialized audio processing models. The proposed system uses an intent classifier, trained on a diverse audio query dataset, to route queries about audio content to expert models such as Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Speaker Diarization, Music Identification, and Text-to-Audio generation. A 3.8 B LLM model then takes inputs from an Audio Context Detection (ACD) module extracting audio event information from the audio and post processes text domain outputs from the expert models to compute the final response to the user. We evaluated the system on custom audio tasks and MMAU sound set benchmarks. The custom datasets were motivated by target use cases not covered in industry benchmarks and included ACD-timestamp-QA (Question Answering) as well as ACD-temporal-QA datasets to evaluate timestamp and temporal reasoning questions, respectively. First we determined that a BERT based Intent Classifier outperforms LLM-fewshot intent classifier in routing queries. Experiments further show that our approach significantly improves accuracy on some custom tasks compared to state-of-the-art Large Audio Language Models and outperforms models in the 7B parameter size range on the sound testset of the MMAU benchmark, thereby offering an attractive option for on device deployment.
本文介绍了一个综合聊天机器人系统,该系统通过集成多个专业音频处理模型,能够处理各种音频相关查询。所提出的系统使用意图分类器(基于多样化的音频查询数据集进行训练),将关于音频内容的查询路由到专家模型,如自动语音识别(ASR)、说话人身份识别、音乐识别和文本到音频生成等。然后,一个3.8 BLLM模型从音频上下文检测(ACD)模块接收输入,该模块从音频中提取音频事件信息,并对专家模型的文本领域输出进行后处理,以计算最终的用户响应。我们在自定义的音频任务和MMAU声音集基准测试上对系统进行了评估。自定义数据集的目标用例是行业基准测试未涵盖的领域,包括ACD时间戳问答(问题回答)以及ACD时间推理问答数据集,以评估时间戳和时间推理问题。首先,我们确定基于BERT的意图分类器在路由查询方面优于LLM少量意图分类器。实验进一步表明,与最新的大型音频语言模型相比,我们的方法在一些自定义任务上的准确性有了显著提高,并且在MMAU基准测试的声音测试集上优于参数大小为7 B的模型,因此成为了设备部署的吸引力选择。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个综合聊天机器人系统,该系统通过集成多个专业音频处理模型,能够处理广泛的音频查询。该系统使用训练于多样化音频查询数据集的意图分类器,将关于音频内容的查询路由到专家模型,如语音识别、说话人划序、音乐识别和文本到音频生成等。利用大型语言模型处理音频上下文检测模块提取的音频事件信息,对专家模型的文本领域输出进行后处理,计算最终的用户响应。在自定义音频任务和MMAU声音集基准测试上对该系统进行了评估,证明了其在某些自定义任务上的准确性显著提高,且在MMAU基准测试的声音测试集上优于其他大型音频语言模型。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文介绍了一个聊天机器人系统,能处理广泛的音频查询。
- 系统通过集成多个专业音频处理模型来实现其功能。
- 意图分类器用于将音频查询路由到相应的专家模型。
- 大型语言模型用于处理音频上下文信息并计算最终响应。
- 在自定义音频任务和MMAU基准测试上进行了系统评估。
- BERT基础的意图分类器在路由查询方面优于LLM少样本意图分类器。
点此查看论文截图

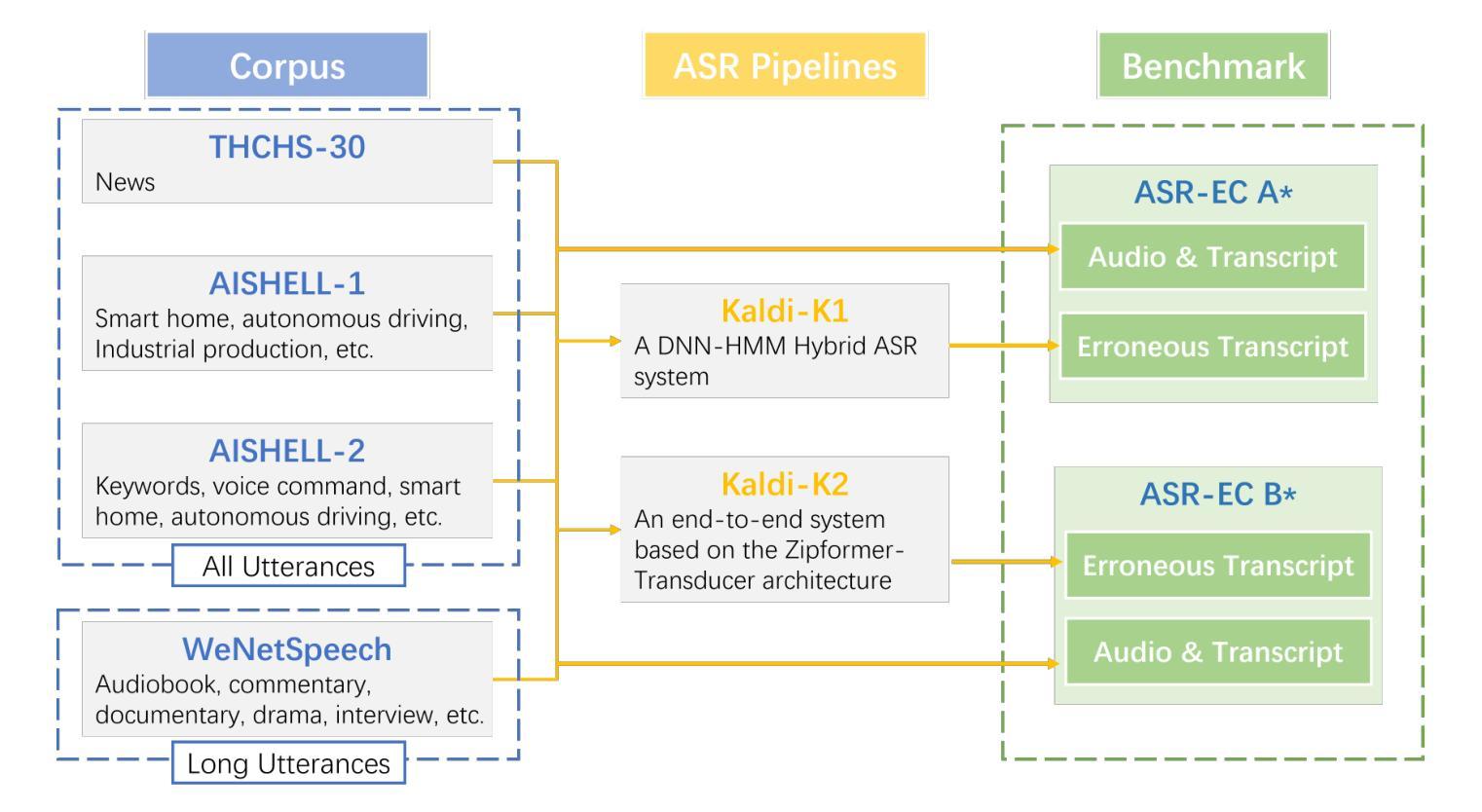
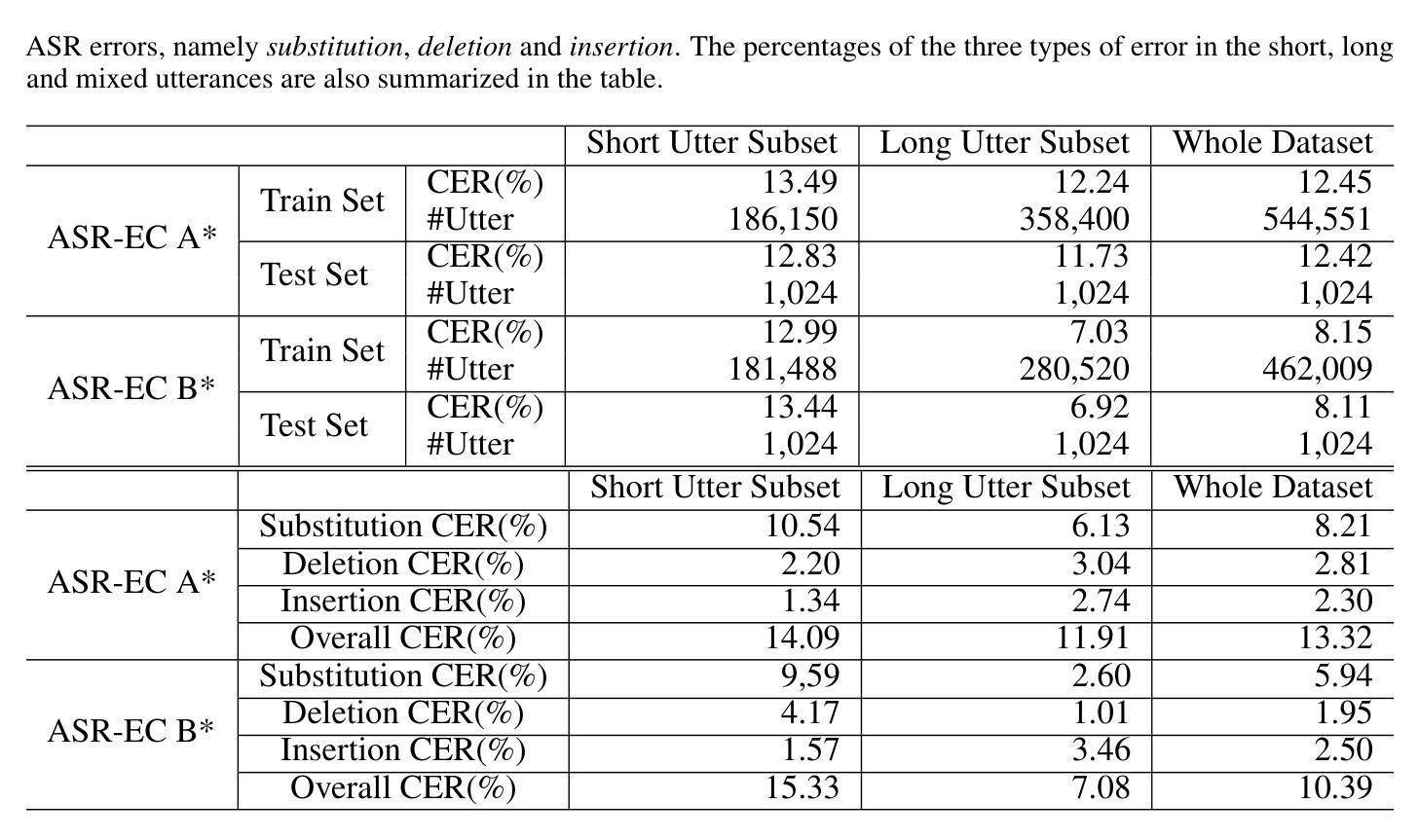
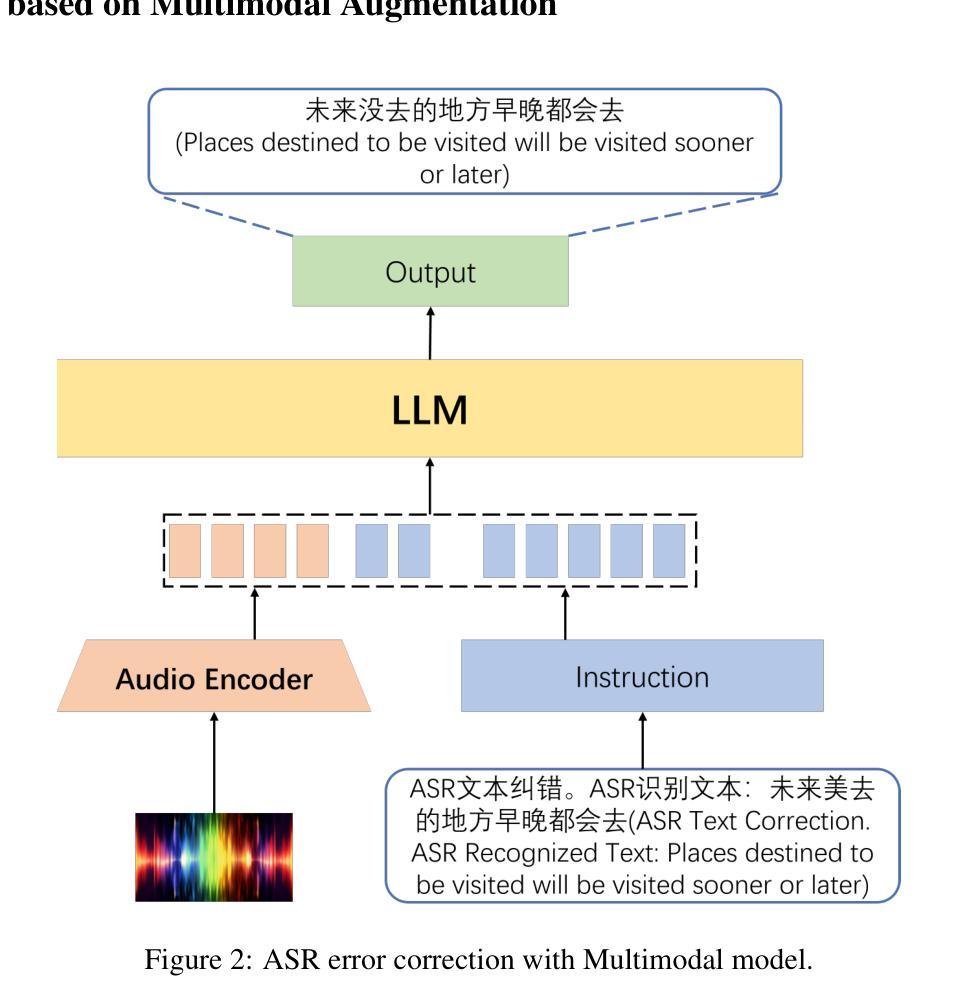
ASR-EC Benchmark: Evaluating Large Language Models on Chinese ASR Error Correction
Authors:Victor Junqiu Wei, Weicheng Wang, Di Jiang, Yuanfeng Song, Lu Wang
Automatic speech Recognition (ASR) is a fundamental and important task in the field of speech and natural language processing. It is an inherent building block in many applications such as voice assistant, speech translation, etc. Despite the advancement of ASR technologies in recent years, it is still inevitable for modern ASR systems to have a substantial number of erroneous recognition due to environmental noise, ambiguity, etc. Therefore, the error correction in ASR is crucial. Motivated by this, this paper studies ASR error correction in the Chinese language, which is one of the most popular languages and enjoys a large number of users in the world. We first create a benchmark dataset named \emph{ASR-EC} that contains a wide spectrum of ASR errors generated by industry-grade ASR systems. To the best of our knowledge, it is the first Chinese ASR error correction benchmark. Then, inspired by the recent advances in \emph{large language models (LLMs)}, we investigate how to harness the power of LLMs to correct ASR errors. We apply LLMs to ASR error correction in three paradigms. The first paradigm is prompting, which is further categorized as zero-shot, few-shot, and multi-step. The second paradigm is finetuning, which finetunes LLMs with ASR error correction data. The third paradigm is multi-modal augmentation, which collectively utilizes the audio and ASR transcripts for error correction. Extensive experiments reveal that prompting is not effective for ASR error correction. Finetuning is effective only for a portion of LLMs. Multi-modal augmentation is the most effective method for error correction and achieves state-of-the-art performance.
自动语音识别(ASR)是语音和自然语言处理领域的一项基本且重要的任务。它是许多应用程序(如语音助手、语音识别等)中的固有组成部分。尽管近年来ASR技术取得了进展,但由于环境噪声、歧义等因素,现代ASR系统仍然存在大量错误识别。因此,ASR中的错误校正至关重要。本文受到此启发,研究中文ASR错误校正。中文是世界上最流行、用户数量最多的语言之一。首先,我们创建了一个名为ASR-EC的基准数据集,其中包含由工业级ASR系统生成的广泛ASR错误。据我们所知,这是第一个中文ASR错误校正基准。然后,受到大型语言模型(LLM)的最新进展的启发,我们研究如何利用LLM的力量来纠正ASR错误。我们将LLM应用于ASR错误校正的三种范式中。第一种范式是提示,它进一步分为零样本、少样本和多步提示。第二种范式是微调,它使用ASR错误校正数据对LLM进行微调。第三种范式是多模态增强,它结合音频和ASR转录进行错误校正。大量实验表明,提示对于ASR错误校正并不有效。微调只对部分LLM有效。多模态增强是最有效的错误校正方法,并达到了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要研究了基于大规模语言模型(LLMs)的中文语音识别(ASR)错误校正问题。创建了首个中文ASR错误校正基准数据集ASR-EC,并探索了三种利用LLMs进行ASR错误校正的方法:提示法、微调法和多模态增强法。实验表明,多模态增强法是最有效的错误校正方法,并达到了目前最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 本文研究了中文语音识别(ASR)错误校正问题,创建了首个相关基准数据集ASR-EC。
- 利用大规模语言模型(LLMs)进行ASR错误校正的方法被探索。
- 提出了三种利用LLMs进行ASR错误校正的方法:提示法、微调法和多模态增强法。
- 提示法对于ASR错误校正并不有效。
- 微调法仅对部分LLMs有效。
- 多模态增强法是最有效的ASR错误校正方法。
点此查看论文截图

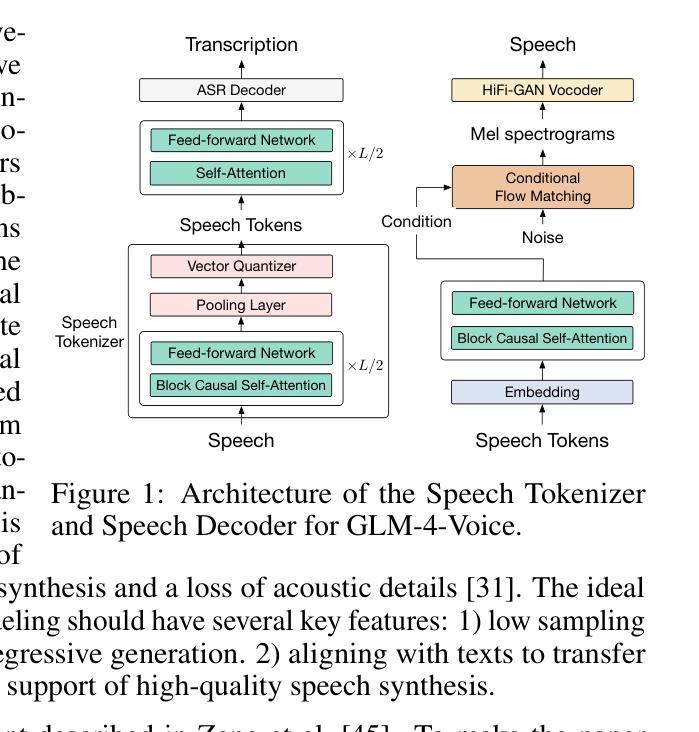
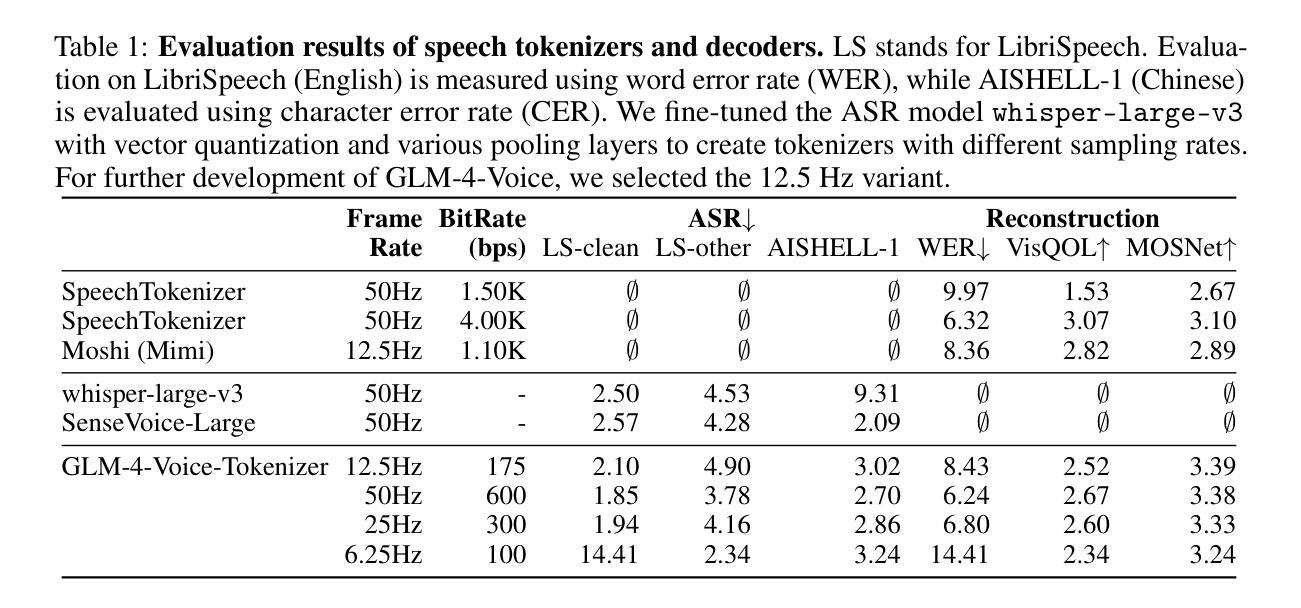
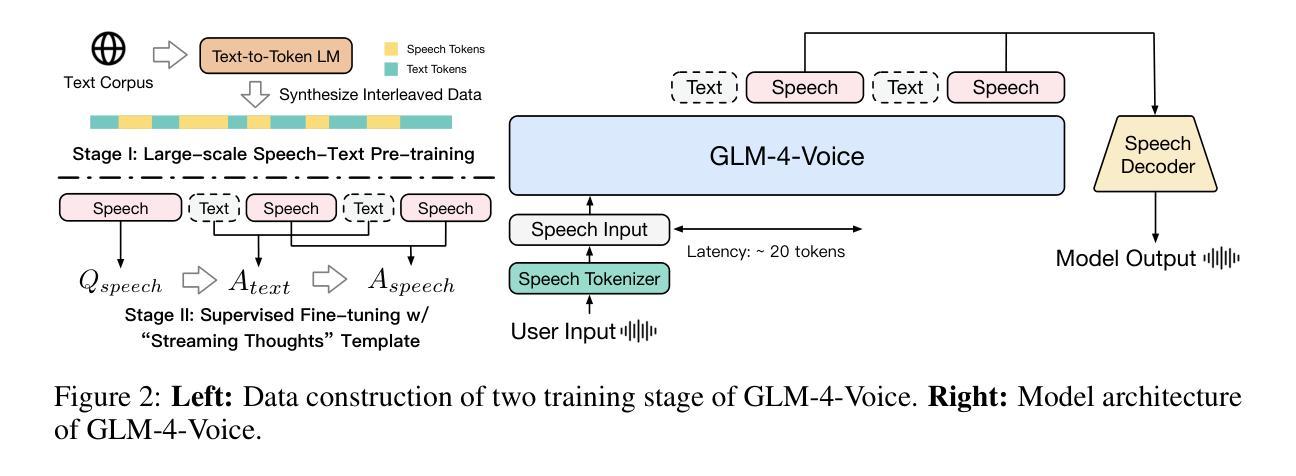
GLM-4-Voice: Towards Intelligent and Human-Like End-to-End Spoken Chatbot
Authors:Aohan Zeng, Zhengxiao Du, Mingdao Liu, Kedong Wang, Shengmin Jiang, Lei Zhao, Yuxiao Dong, Jie Tang
We introduce GLM-4-Voice, an intelligent and human-like end-to-end spoken chatbot. It supports both Chinese and English, engages in real-time voice conversations, and varies vocal nuances such as emotion, intonation, speech rate, and dialect according to user instructions. GLM-4-Voice uses an ultra-low bitrate (175bps), single-codebook speech tokenizer with 12.5Hz frame rate derived from an automatic speech recognition (ASR) model by incorporating a vector-quantized bottleneck into the encoder. To efficiently transfer knowledge from text to speech modalities, we synthesize speech-text interleaved data from existing text pre-training corpora using a text-to-token model. We continue pre-training from the pre-trained text language model GLM-4-9B with a combination of unsupervised speech data, interleaved speech-text data, and supervised speech-text data, scaling up to 1 trillion tokens, achieving state-of-the-art performance in both speech language modeling and spoken question answering. We then fine-tune the pre-trained model with high-quality conversational speech data, achieving superior performance compared to existing baselines in both conversational ability and speech quality. The open models can be accessed through https://github.com/THUDM/GLM-4-Voice and https://huggingface.co/THUDM/glm-4-voice-9b.
我们介绍了GLM-4-Voice,这是一个智能且人性化的端到端语音聊天机器人。它支持中文和英语,能进行实时语音对话,并根据用户指令变化情绪、语调、语速和方言等语音细微差别。GLM-4-Voice使用超低比特率(175bps)的单码本语音标记器,以12.5Hz的帧率从自动语音识别(ASR)模型中衍生出来,通过在编码器中加入向量量化瓶颈。为了有效地将知识从文本转移到语音模式,我们利用文本到令牌模型,通过现有文本预训练语料库合成语音文本交织数据。我们继续使用预训练的文本语言模型GLM-4-9B进行预训练,结合无监督语音数据、交织语音文本数据和监督语音文本数据,扩展到1万亿个令牌,在语音语言建模和语音问答方面都达到了最先进的性能。然后,我们使用高质量的对话语音数据对预训练模型进行微调,在对话能力和语音质量方面都达到了优于现有基准测试的性能。开放模型可通过https://github.com/THUDM/GLM-4-Voice和https://huggingface.co/THUDM/glm-4-voice-9b访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
GLM-4-Voice是一款智能、人性化的端到端语音聊天机器人,支持中英文实时语音对话,可根据用户指令调整语音情感、语调、语速和方言。它采用超低比特率(175bps)和12.5Hz帧率的单编码本语音标记器,结合自动语音识别(ASR)模型,融入向量量化瓶颈到编码器。通过合成语音文本交织数据,从现有文本预训练语料库中高效转换知识。预训练模型结合无监督语音数据、交织语音文本数据和监督语音文本数据,扩展到1万亿个令牌,在语音语言建模和语音问答方面达到最新技术水平。通过高质量对话语音数据进行微调,达到对话能力和语音质量方面的卓越性能。公开模型可通过https://github.com/THUDM/GLM-4-Voice和https://huggingface.co/THUDM/glm-4-voice-9b访问。
Key Takeaways
- GLM-4-Voice是一个智能、人性化的端到端语音聊天机器人,支持中英文实时对话。
- GLM-4-Voice能根据用户指令调整语音情感、语调、语速和方言。
- 它采用超低比特率和帧率的单编码本语音标记器技术结合ASR模型。
- 通过合成语音文本交织数据实现从文本到语音的高效知识转换。
- 预训练模型结合了多种数据,包括无监督、交织和监督的语音文本数据。
- GLM-4-Voice在语音语言建模和语音问答方面达到了最新技术水平。
点此查看论文截图


It Takes Two: Real-time Co-Speech Two-person’s Interaction Generation via Reactive Auto-regressive Diffusion Model
Authors:Mingyi Shi, Dafei Qin, Leo Ho, Zhouyingcheng Liao, Yinghao Huang, Junichi Yamagishi, Taku Komura
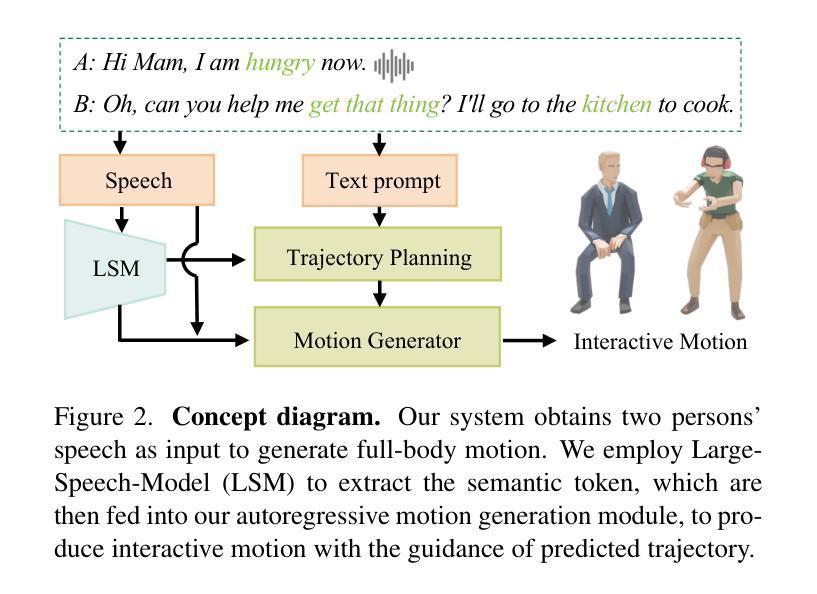
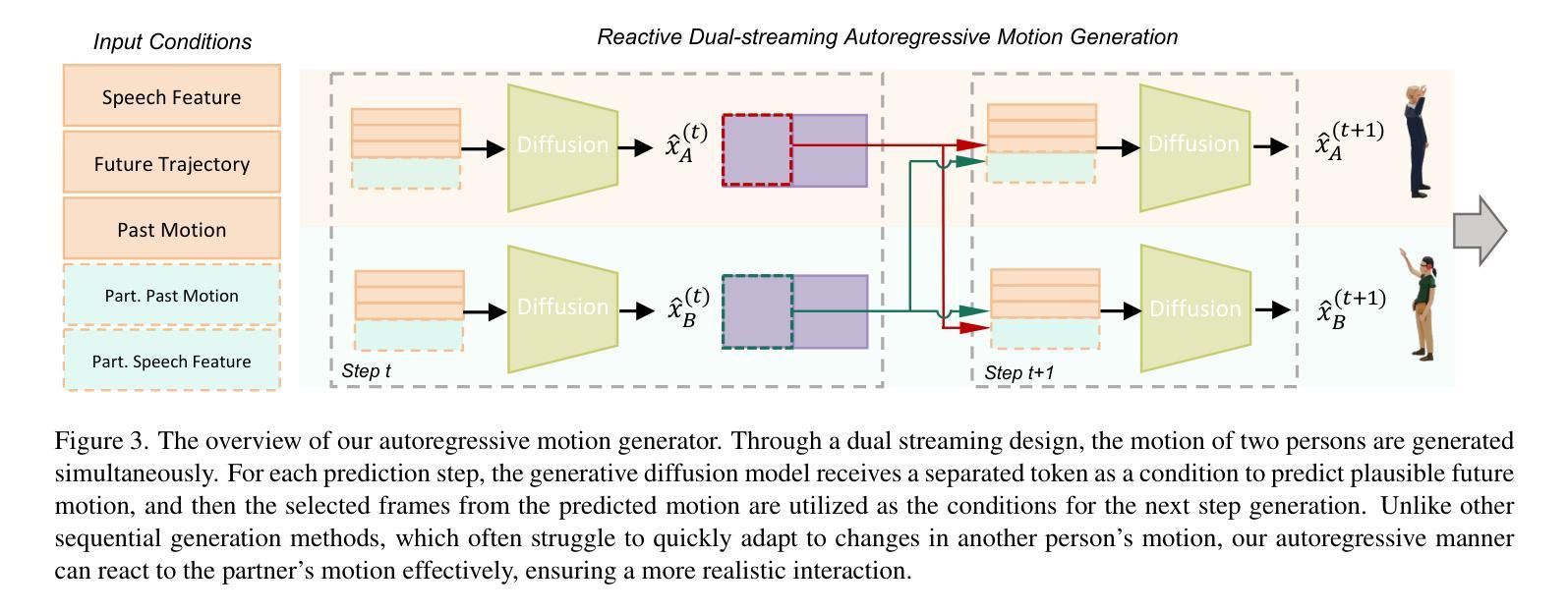
Conversational scenarios are very common in real-world settings, yet existing co-speech motion synthesis approaches often fall short in these contexts, where one person’s audio and gestures will influence the other’s responses. Additionally, most existing methods rely on offline sequence-to-sequence frameworks, which are unsuitable for online applications. In this work, we introduce an audio-driven, auto-regressive system designed to synthesize dynamic movements for two characters during a conversation. At the core of our approach is a diffusion-based full-body motion synthesis model, which is conditioned on the past states of both characters, speech audio, and a task-oriented motion trajectory input, allowing for flexible spatial control. To enhance the model’s ability to learn diverse interactions, we have enriched existing two-person conversational motion datasets with more dynamic and interactive motions. We evaluate our system through multiple experiments to show it outperforms across a variety of tasks, including single and two-person co-speech motion generation, as well as interactive motion generation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first system capable of generating interactive full-body motions for two characters from speech in an online manner.
对话场景在真实世界环境中非常常见。然而,现有的协同语音运动合成方法在这种情况下往往表现不足,一个人的音频和手势会影响另一个人的反应。此外,大多数现有方法依赖于离线序列到序列框架,这不适用于在线应用。在这项工作中,我们引入了一个音频驱动的自动回归系统,旨在合成对话期间两个角色的动态动作。我们的方法的核心是一个基于扩散的全身运动合成模型,该模型受两个角色过去状态、语音音频和面向任务的运动轨迹输入的制约,可实现灵活的空间控制。为了提高模型学习各种交互的能力,我们丰富了现有的两人对话运动数据集,加入了更多动态和交互性的动作。我们通过多次实验评估了我们的系统,结果表明它在各种任务上的表现都优于其他系统,包括单人及两人协同语音运动生成以及交互运动生成。据我们所知,这是第一个能够以在线方式从语音为两个角色生成交互全身动作的系统。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于音频的、自回归系统,用于合成对话场景中的两个角色的动态动作。该系统采用扩散模型为基础的全身动作合成模型,根据对话双方过去的状态、语音音频和任务导向的动作轨迹输入进行条件控制,实现灵活的空间控制。通过丰富两人对话动作数据集,提高了模型学习各种互动的能力。实验表明,该系统在单人及双人共语动作生成、互动动作生成等任务上的表现均优于其他方法。这是首个能够在线生成基于语音的两人互动全身动作的系统。
Key Takeaways
- 该系统是一种基于音频的、自回归的在线对话动作合成方法。
- 系统采用扩散模型为基础的全身动作合成模型。
- 系统根据对话双方过去的状态、语音音频和任务导向的动作轨迹进行条件控制。
- 系统可实现灵活的空间控制,适用于对话场景的动作合成。
- 通过丰富两人对话动作数据集,提高模型学习各种互动的能力。
- 实验表明,该系统在多种任务上的表现均优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

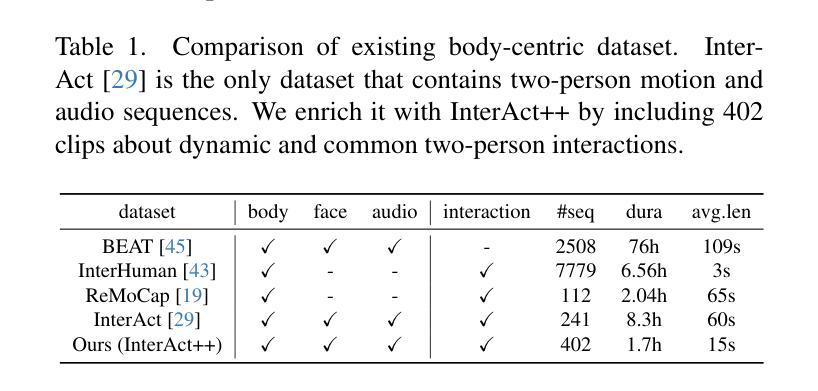
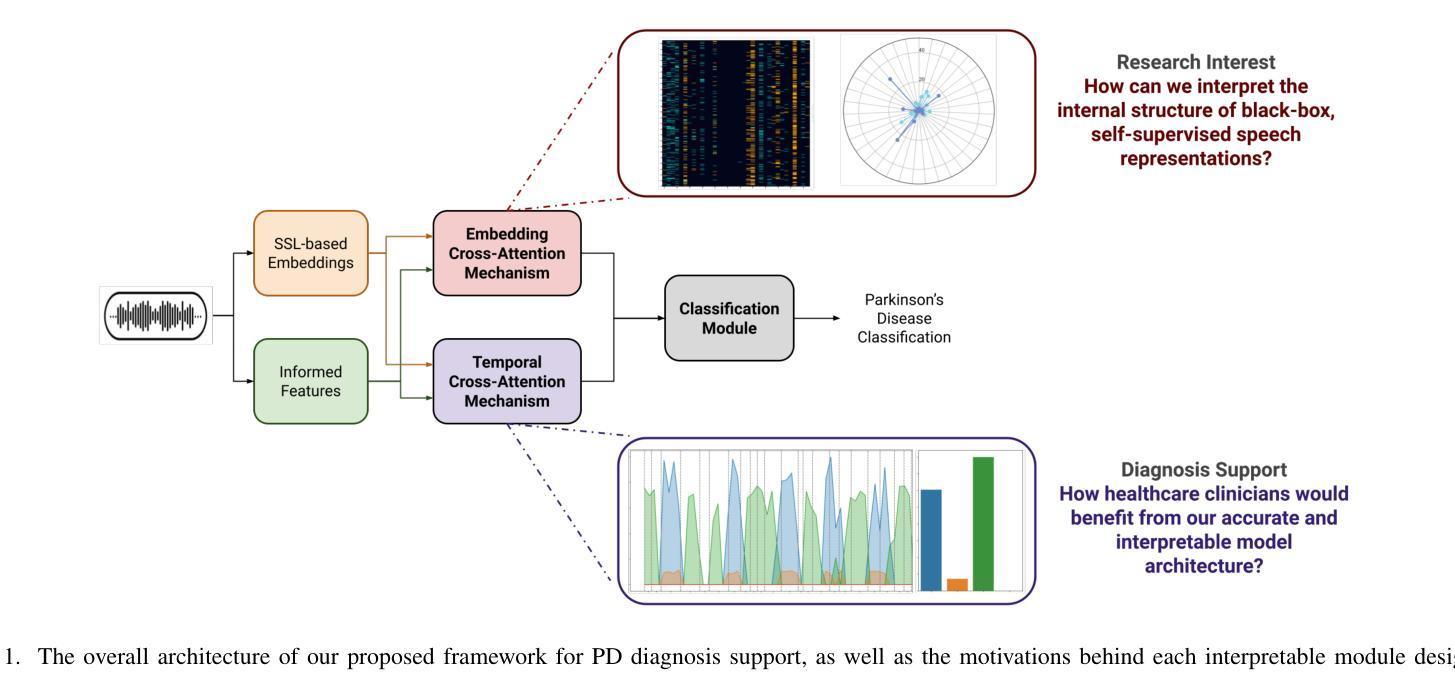
Unveiling Interpretability in Self-Supervised Speech Representations for Parkinson’s Diagnosis
Authors:David Gimeno-Gómez, Catarina Botelho, Anna Pompili, Alberto Abad, Carlos-D. Martínez-Hinarejos
Recent works in pathological speech analysis have increasingly relied on powerful self-supervised speech representations, leading to promising results. However, the complex, black-box nature of these embeddings and the limited research on their interpretability significantly restrict their adoption for clinical diagnosis. To address this gap, we propose a novel, interpretable framework specifically designed to support Parkinson’s Disease (PD) diagnosis. Through the design of simple yet effective cross-attention mechanisms for both embedding- and temporal-level analysis, the proposed framework offers interpretability from two distinct but complementary perspectives. Experimental findings across five well-established speech benchmarks for PD detection demonstrate the framework’s capability to identify meaningful speech patterns within self-supervised representations for a wide range of assessment tasks. Fine-grained temporal analyses further underscore its potential to enhance the interpretability of deep-learning pathological speech models, paving the way for the development of more transparent, trustworthy, and clinically applicable computer-assisted diagnosis systems in this domain. Moreover, in terms of classification accuracy, our method achieves results competitive with state-of-the-art approaches, while also demonstrating robustness in cross-lingual scenarios when applied to spontaneous speech production.
近期病理语音分析的研究越来越依赖于强大的自监督语音表征,这带来了充满希望的结果。然而,这些嵌入的复杂性和黑箱性质以及对其解释性的研究有限,显著限制了它们在临床诊断中的应用。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了一种新型的可解释框架,专门设计用于支持帕金森氏症(PD)的诊断。通过设计简单而有效的跨注意机制,用于嵌入级和时间级的分析,所提出的框架从两个独特但互补的角度提供了可解释性。在五个成熟的帕金森氏症检测语音基准测试上的实验结果表明,该框架能够在自监督表征中识别各种评估任务内的重要语音模式。精细的时间分析进一步强调了其在提高病理语音深度模型的解释潜力,为开发该领域更透明、更可靠的临床适用计算机辅助诊断系统铺平了道路。此外,在分类准确度方面,我们的方法实现了与国家前沿方法相竞争的结果,并且在应用于自然语音生产时表现出跨语言的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to the Special Issue on “Modelling and Processing Language and Speech in Neurodegenerative Disorders” published by Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing (JSTSP)
Summary
帕金森病的病理语音分析新工作提出一种新型可解释的框架,旨在支持帕金森病诊断。该框架设计简单有效的跨注意力机制,从嵌入和时序两个角度进行分析,提高自监督语音表示的模型解释性。实验结果表明,该框架能够在多个公认的帕金森病语音基准测试中识别有意义的语音模式,且时序分析增强了深度学习的语音模型的解释性。同时,该方法分类准确度高,且在跨语言场景下表现出稳健性。
Key Takeaways
- 近年来的病理语音分析工作越来越依赖强大的自监督语音表示,取得了令人鼓舞的结果。
- 当前方法存在解释性不足的问题,限制了其在临床诊断中的应用。
- 提出了一种新型可解释的框架,旨在支持帕金森病诊断。
- 通过嵌入和时序两个角度的跨注意力机制分析,提高模型的解释性。
- 实验结果表明该框架在多个帕金森语音基准测试中表现优异。
- 时序分析增强了深度学习的语音模型的解释性。
点此查看论文截图

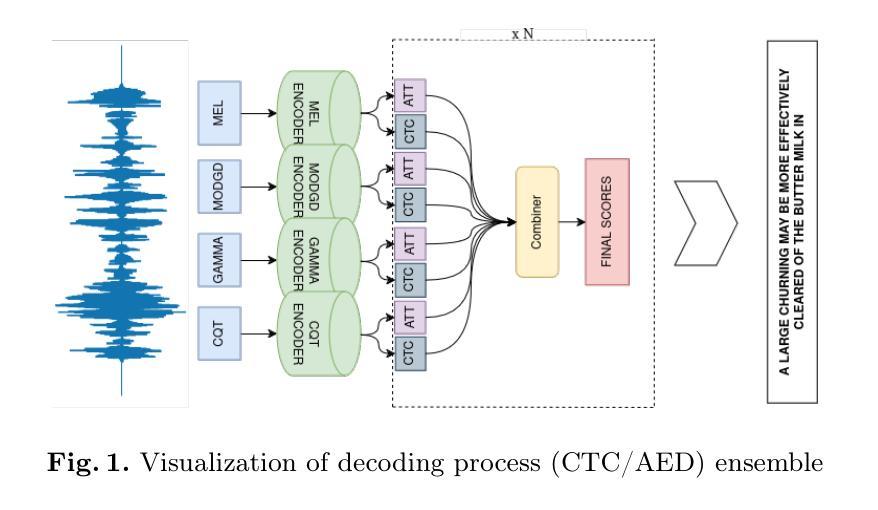
Late fusion ensembles for speech recognition on diverse input audio representations
Authors:Marin Jezidžić, Matej Mihelčić
We explore diverse representations of speech audio, and their effect on a performance of late fusion ensemble of E-Branchformer models, applied to Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) task. Although it is generally known that ensemble methods often improve the performance of the system even for speech recognition, it is very interesting to explore how ensembles of complex state-of-the-art models, such as medium-sized and large E-Branchformers, cope in this setting when their base models are trained on diverse representations of the input speech audio. The results are evaluated on four widely-used benchmark datasets: \textit{Librispeech, Aishell, Gigaspeech}, \textit{TEDLIUMv2} and show that improvements of $1% - 14%$ can still be achieved over the state-of-the-art models trained using comparable techniques on these datasets. A noteworthy observation is that such ensemble offers improvements even with the use of language models, although the gap is closing.
我们探索了语音音频的多种表示形式,以及它们对E-Branchformer模型晚期融合集成在自动语音识别(ASR)任务性能的影响。虽然集成方法通常会提高系统的性能,即使在语音识别方面也是如此,但探索复杂的最先进模型的集成方法非常有趣,例如在中型和大型E-Branchformers中,当它们的基准模型在输入语音音频的多种表示上进行训练时,它们如何应对这种情况。在四个广泛使用的基准数据集:Librispeech、Aishell、Gigaspeech和TEDLIUMv2上的评估结果表明,与在这些数据集上使用类似技术训练的最先进模型相比,仍可实现1%~14%的改进。值得注意的是,即使使用语言模型,这种集成也能提供改进,尽管差距正在缩小。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文主要探讨了语音音频的多样化表示形式,以及它们对E-Branchformer模型的后期融合组合在自动语音识别(ASR)任务中的影响。虽然已知集合方法通常会提高系统的性能,但对于在复杂先进的模型(如中等规模和大型E-Branchformers)中如何应对训练有语音音频多样化表示的基准模型时,仍然非常有趣。在四个广泛使用的基准数据集上的评估结果表明,与在这些数据集上使用类似技术训练的最新模型相比,改进幅度可达1%-14%。值得注意的是,即使使用语言模型,这种组合也能实现改进,尽管差距正在缩小。
关键见解
- 探讨了语音音频的多样化表示形式对自动语音识别任务的影响。
- 研究了E-Branchformer模型的后期融合组合的效果。
- 集合方法可以提高系统的性能,特别是在复杂先进的模型中。
- 在四个广泛使用的基准数据集上进行了评估,包括Librispeech、Aishell、Gigaspeech和TEDLIUMv2。
- 与现有技术相比,改进范围可达1%-14%。
- 集合方法即使在使用语言模型的情况下也能提供改进。
点此查看论文截图

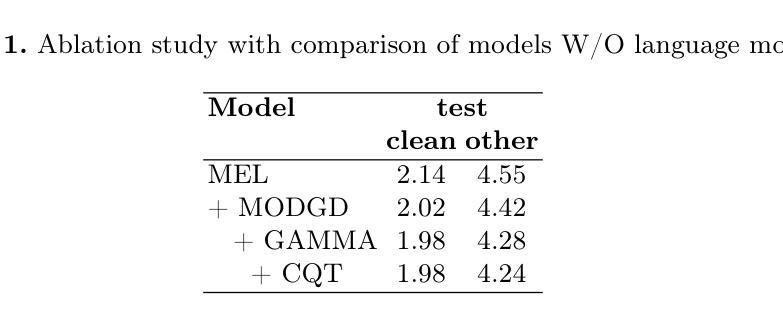
Advancing Speech Language Models by Scaling Supervised Fine-Tuning with Over 60,000 Hours of Synthetic Speech Dialogue Data
Authors:Shuaijiang Zhao, Tingwei Guo, Bajian Xiang, Tongtang Wan, Qiang Niu, Wei Zou, Xiangang Li
The GPT-4o represents a significant milestone in enabling real-time interaction with large language models (LLMs) through speech, its remarkable low latency and high fluency not only capture attention but also stimulate research interest in the field. This real-time speech interaction is particularly valuable in scenarios requiring rapid feedback and immediate responses, dramatically enhancing user experience. However, there is a notable lack of research focused on real-time large speech language models, particularly for Chinese. In this work, we present KE-Omni, a seamless large speech language model built upon Ke-SpeechChat, a large-scale high-quality synthetic speech interaction dataset consisting of 7 million Chinese and English conversations, featuring 42,002 speakers, and totaling over 60,000 hours, This contributes significantly to the advancement of research and development in this field. The demos can be accessed at \url{https://huggingface.co/spaces/KE-Team/KE-Omni}.
GPT-4o代表了通过语音与大型语言模型(LLM)进行实时交互的一个重要里程碑。其显著的低延迟和高流利性不仅引起了关注,还刺激了该领域的研究兴趣。这种实时语音交互在需要快速反馈和即时响应的场景中尤其有价值,能极大地提升用户体验。然而,关于实时大型语音语言模型的研究相对较少,尤其是针对中文的研究。在这项工作中,我们推出了KE-Omni,这是一款无缝大型语音语言模型,基于Ke-SpeechChat构建。Ke-SpeechChat是一个大规模高质量合成语音交互数据集,包含700万中文和英文对话,涉及42,002名发言者,总计超过6万小时,为该领域的研究和发展做出了重大贡献。演示网址为:[https://huggingface.co/spaces/KE-Team/KE-Omni]。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF KE-Omni, Ke-SpeechChat
Summary
GPT-4o实现了通过语音与大型语言模型(LLM)的实时交互,其低延迟和高流畅度引人注目,并刺激了相关领域的研究兴趣。特别是在需要快速反馈和即时响应的场景中,实时语音交互能大幅提升用户体验。本研究推出KE-Omni大型语音语言模型,基于包含7百万中英文对话的Ke-SpeechChat数据集,包含42,002位发言者的超过6万小时语音,为相关领域的研究和发展做出了重要贡献。演示可通过链接访问:[链接地址]。
Key Takeaways
- GPT-4o实现了实时语音与大型语言模型的交互。
- GPT-4o具有显著的低延迟和高流畅度。
- 实时语音交互在需要快速反馈和响应的场景中价值显著。
- KE-Omni模型是基于Ke-SpeechChat数据集的的大型语音语言模型。
- Ke-SpeechChat数据集包含7百万中英文对话,超过6万小时语音。
- KE-Omni对相关领域的研究和发展做出了重要贡献。
点此查看论文截图

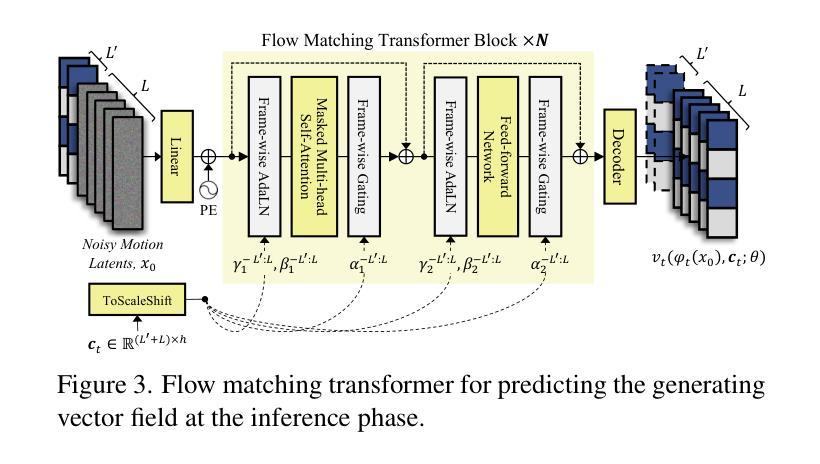
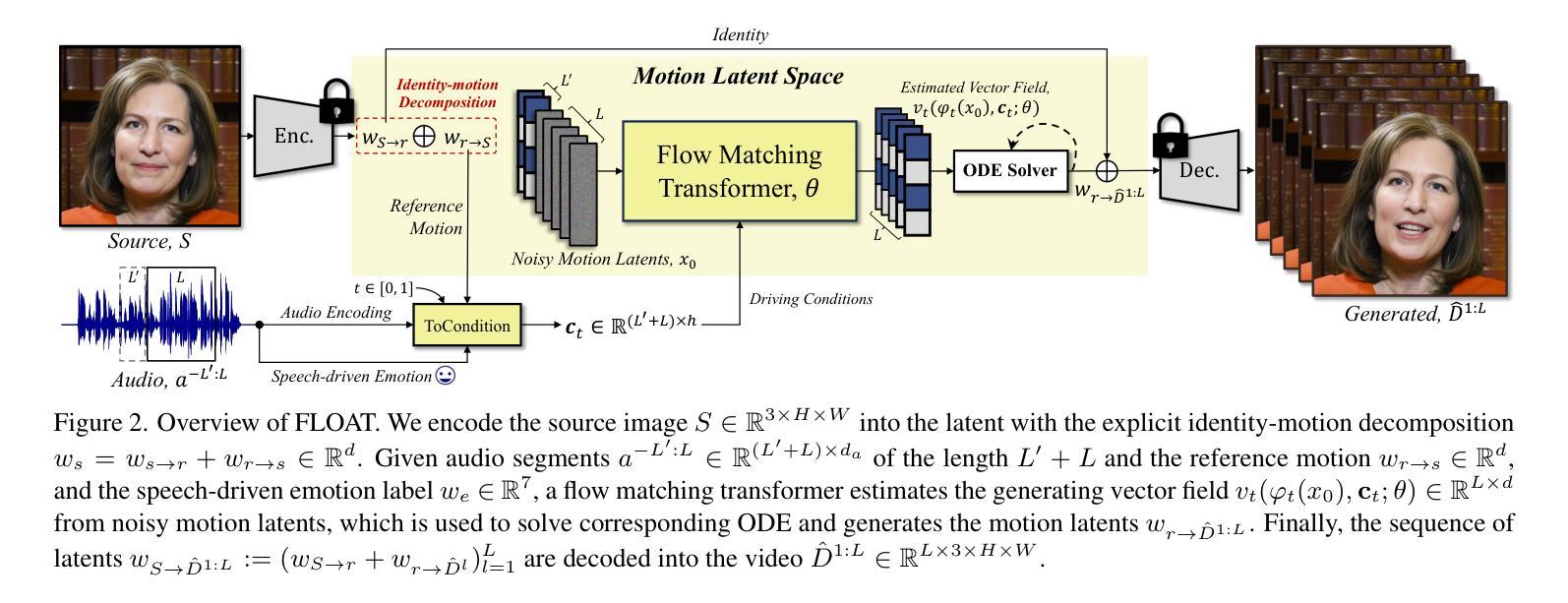
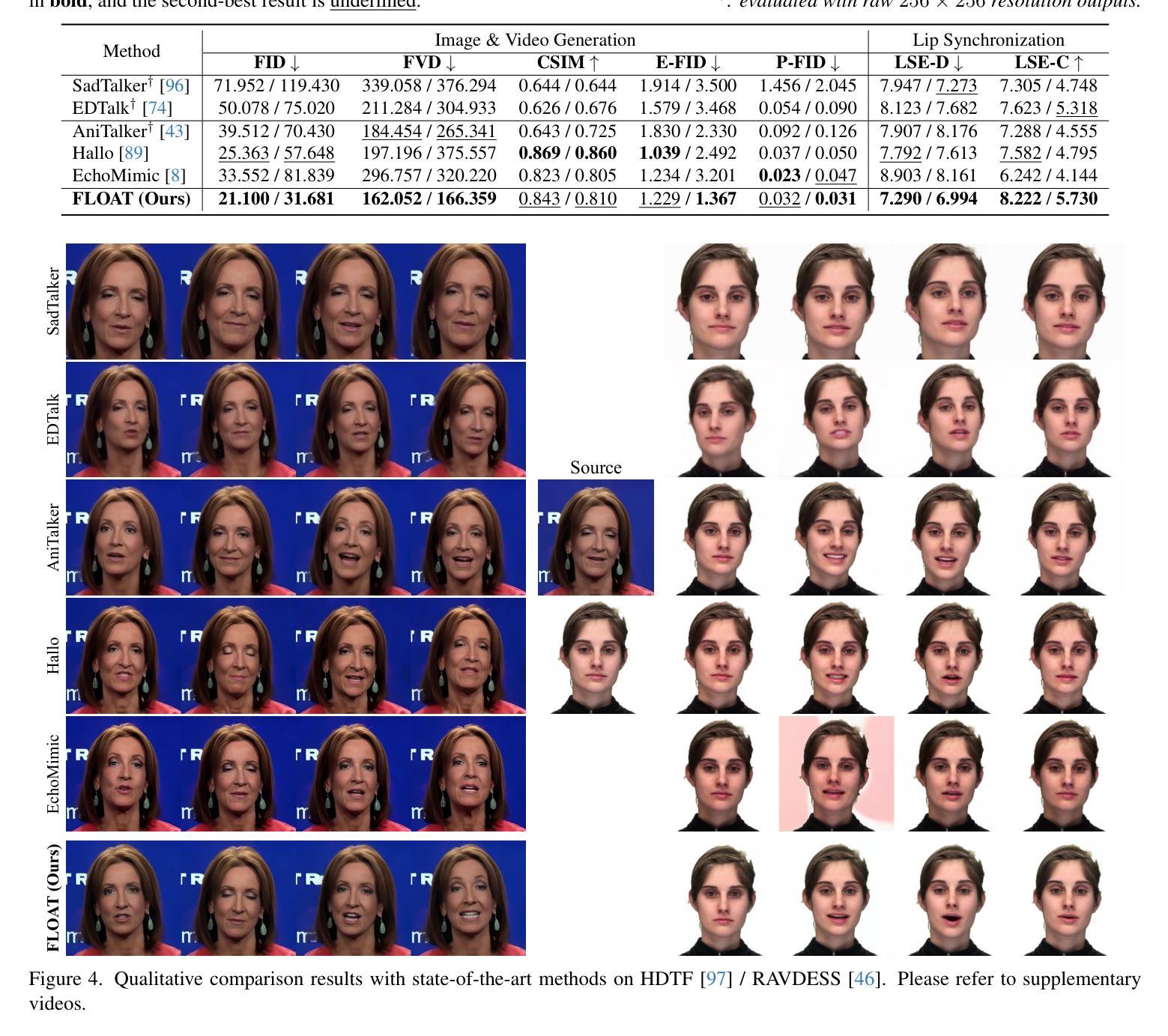
FLOAT: Generative Motion Latent Flow Matching for Audio-driven Talking Portrait
Authors:Taekyung Ki, Dongchan Min, Gyeongsu Chae
With the rapid advancement of diffusion-based generative models, portrait image animation has achieved remarkable results. However, it still faces challenges in temporally consistent video generation and fast sampling due to its iterative sampling nature. This paper presents FLOAT, an audio-driven talking portrait video generation method based on flow matching generative model. We shift the generative modeling from the pixel-based latent space to a learned motion latent space, enabling efficient design of temporally consistent motion. To achieve this, we introduce a transformer-based vector field predictor with a simple yet effective frame-wise conditioning mechanism. Additionally, our method supports speech-driven emotion enhancement, enabling a natural incorporation of expressive motions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art audio-driven talking portrait methods in terms of visual quality, motion fidelity, and efficiency.
随着基于扩散的生成模型的快速发展,肖像动画图像已经取得了显著的研究成果。然而,由于它的迭代采样特性,它在时序一致的视频生成和快速采样方面仍然面临挑战。本文提出了FLOAT,一种基于流匹配生成模型的音频驱动谈话肖像视频生成方法。我们将生成模型从基于像素的潜在空间转移到学习的运动潜在空间,实现了时序一致运动的有效设计。为此,我们引入了一个基于变压器的矢量场预测器,并设计了一个简单有效的帧条件机制。此外,我们的方法支持语音驱动的情绪增强,能够实现表达性运动的自然融合。大量实验表明,我们的方法在视觉质量、运动保真度和效率方面超越了最先进的音频驱动谈话肖像方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://deepbrainai-research.github.io/float/
Summary
随着扩散生成模型的快速发展,肖像图像动画已取得了显著成果,但仍面临视频生成的时序一致性和快速采样方面的挑战。本文提出了基于流匹配生成模型的音频驱动肖像视频生成方法FLOAT。该方法将生成建模从像素级的潜在空间转移到学习到的运动潜在空间,实现了时序一致运动的有效设计。为此,引入了一个基于变换器的向量场预测器,并采用了简单有效的帧条件机制。此外,该方法还支持语音驱动的情感增强,能够自然地融入表达性动作。实验证明,该方法在视觉质量、运动保真度和效率方面优于现有音频驱动的肖像动画方法。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散生成模型的快速发展推动了肖像图像动画的显著进步。
- 肖像图像动画仍面临视频生成的时序一致性和快速采样挑战。
- FLOAT方法是一种基于流匹配生成模型的音频驱动肖像视频生成方法。
- FLOAT通过将生成建模转移到学习到的运动潜在空间,实现了时序一致运动的有效设计。
- 该方法使用基于变换器的向量场预测器,并引入帧条件机制以提高性能。
- FLOAT支持语音驱动的情感增强,使动作表达更自然。
点此查看论文截图

Automating Feedback Analysis in Surgical Training: Detection, Categorization, and Assessment
Authors:Firdavs Nasriddinov, Rafal Kocielnik, Arushi Gupta, Cherine Yang, Elyssa Wong, Anima Anandkumar, Andrew Hung
This work introduces the first framework for reconstructing surgical dialogue from unstructured real-world recordings, which is crucial for characterizing teaching tasks. In surgical training, the formative verbal feedback that trainers provide to trainees during live surgeries is crucial for ensuring safety, correcting behavior immediately, and facilitating long-term skill acquisition. However, analyzing and quantifying this feedback is challenging due to its unstructured and specialized nature. Automated systems are essential to manage these complexities at scale, allowing for the creation of structured datasets that enhance feedback analysis and improve surgical education. Our framework integrates voice activity detection, speaker diarization, and automated speech recaognition, with a novel enhancement that 1) removes hallucinations (non-existent utterances generated during speech recognition fueled by noise in the operating room) and 2) separates speech from trainers and trainees using few-shot voice samples. These aspects are vital for reconstructing accurate surgical dialogues and understanding the roles of operating room participants. Using data from 33 real-world surgeries, we demonstrated the system’s capability to reconstruct surgical teaching dialogues and detect feedback instances effectively (F1 score of 0.79+/-0.07). Moreover, our hallucination removal step improves feedback detection performance by ~14%. Evaluation on downstream clinically relevant tasks of predicting Behavioral Adjustment of trainees and classifying Technical feedback, showed performances comparable to manual annotations with F1 scores of 0.82+/0.03 and 0.81+/0.03 respectively. These results highlight the effectiveness of our framework in supporting clinically relevant tasks and improving over manual methods.
本文介绍了一个从非结构化的现实世界录音中重建手术对话的首个框架,这对于描述教学任务至关重要。在手术训练中,培训人员在现场手术中向受训人员提供的形成性口头反馈对于确保安全、立即纠正行为和促进长期技能获取至关重要。然而,由于其非结构化和专业化的特点,分析和量化这种反馈具有挑战性。自动系统在大规模管理这些复杂性方面至关重要,能够创建增强反馈分析和改善手术教育的结构化数据集。我们的框架集成了语音活动检测、说话人识别和自动语音识别,以及一种新颖的提升方法,即1)消除幻听(在手术室噪音驱动的语音识别过程中产生的不存在的讲话)和2)使用少量的语音样本将培训师和受训人员的语音分开。这些方面对于重建准确的手术对话和理解手术室参与者的角色至关重要。我们使用来自33场真实手术的数据,证明了该系统在重建手术教学对话和有效检测反馈实例方面的能力(F1分数为0.79+/-0.07)。此外,我们的幻觉消除步骤提高了约14%的反馈检测性能。在对预测受训者行为调整的下游临床相关任务以及对技术反馈的分类评估中,与手动注释相比,F1分数分别为0.82+/0.03和0.81+/0.03。这些结果凸显了我们的框架在支持临床相关任务和改进手动方法方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted as a proceedings paper at Machine Learning for Health 2024
Summary
该文介绍了首个从现实世界的非结构化录音中重建手术对话的框架,这对于刻画教学任务至关重要。在手术培训中,培训师在现场手术中向受训人员提供的形成性口头反馈对于确保安全、立即纠正行为和促进长期技能获取至关重要。然而,由于反馈的非结构化和专业化特性,分析和量化这些反馈具有挑战性。自动化系统是大规模管理这些复杂性的关键,可以创建增强反馈分析和改善手术教育的结构化数据集。该框架集成了语音活动检测、说话人识别和自动语音识别,并有一种新颖的提升,即消除幻听(由手术室噪音引起的在语音识别过程中产生的非存在性发言)以及使用少数语音样本分离训练师和受训人员的语音。这些方面对于重建准确的手术对话和理解手术室参与者的角色至关重要。使用来自33场真实手术的数据,我们展示了该系统重建手术教学对话和检测反馈实例的能力(F1分数为0.79+/-0.07)。此外,我们的幻听消除步骤提高了反馈检测性能约14%。对预测受训者行为调整和分类技术反馈等临床相关任务的评估显示,其性能与手动注释相当,F1分数分别为0.82+/0.03和0.81+/0.03。这些结果突显了我们的框架在支持临床相关任务和改善手动方法方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 论文介绍了首个针对教学任务的手术对话重建框架。
- 自动化系统是处理复杂的手术环境的关键,有助于分析和量化反馈。
- 该框架集成了多项技术,包括语音活动检测、说话人识别和自动语音识别。
- 系统具备消除幻听的能力,即在语音识别过程中由于手术室噪音产生的非存在性发言。
- 通过使用少数语音样本,能够分离训练师和受训人员的语音。
- 使用真实手术数据测试了系统的性能,在反馈实例检测方面表现出较高的准确性(F1分数为0.79+/-0.07)。
点此查看论文截图


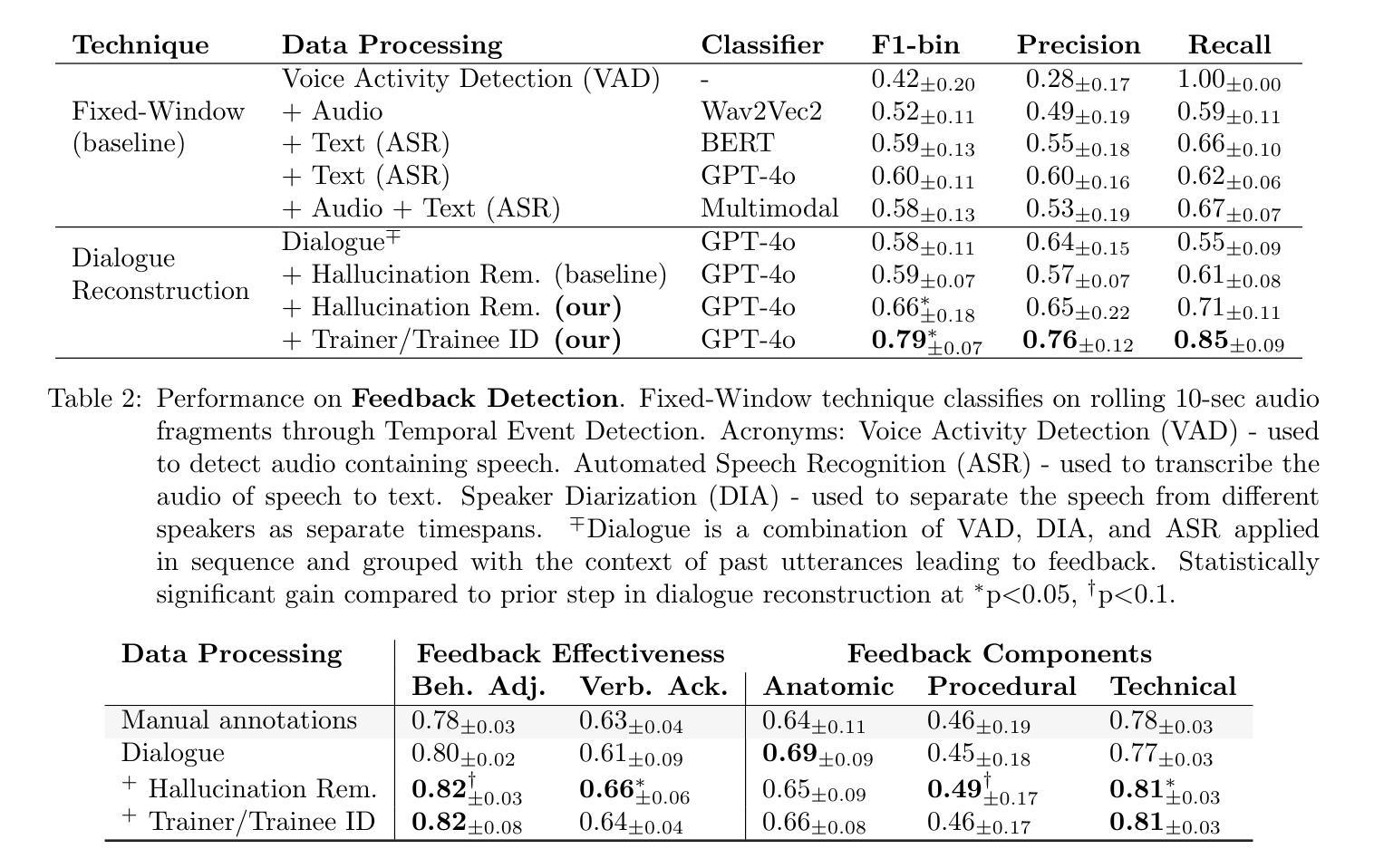
A Comparative Study of LLM-based ASR and Whisper in Low Resource and Code Switching Scenario
Authors:Zheshu Song, Ziyang Ma, Yifan Yang, Jianheng Zhuo, Xie Chen
Large Language Models (LLMs) have showcased exceptional performance across diverse NLP tasks, and their integration with speech encoder is rapidly emerging as a dominant trend in the Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) field. Previous works mainly concentrated on leveraging LLMs for speech recognition in English and Chinese. However, their potential for addressing speech recognition challenges in low resource settings remains underexplored. Hence, in this work, we aim to explore the capability of LLMs in low resource ASR and Mandarin-English code switching ASR. We also evaluate and compare the recognition performance of LLM-based ASR systems against Whisper model. Extensive experiments demonstrate that LLM-based ASR yields a relative gain of 12.8% over the Whisper model in low resource ASR while Whisper performs better in Mandarin-English code switching ASR. We hope that this study could shed light on ASR for low resource scenarios.
大型语言模型(LLMs)在多种NLP任务中表现出卓越的性能,它们与语音编码器的集成正在迅速成为自动语音识别(ASR)领域的主流趋势。之前的工作主要集中在利用LLMs进行英语和中文的语音识别。然而,它们在解决低资源设置中的语音识别挑战方面的潜力尚未得到充分探索。因此,在这项工作中,我们旨在探索LLMs在低资源ASR以及普通话-英语切换ASR中的能力。我们还评估和比较了基于LLM的ASR系统与Whisper模型的识别性能。大量实验表明,在低资源ASR中,基于LLM的ASR系统相对于Whisper模型有12.8%的相对增益,而在普通话-英语切换ASR中,Whisper的表现更好。我们希望这项研究能为低资源场景的ASR提供一些启示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work hasn’t been finished yet
总结
大型语言模型(LLMs)在多种自然语言处理任务中表现出卓越性能,其与语音编码器的集成正在迅速成为自动语音识别(ASR)领域的主流趋势。尽管之前的研究主要集中在利用LLMs进行英语和中文的语音识别,但它们在低资源环境下的语音识别挑战的潜力尚未得到充分探索。本研究旨在探索LLMs在低资源ASR和普通话-英语代码切换ASR中的能力,并评估其与Whisper模型的识别性能。实验表明,基于LLMs的ASR系统在低资源ASR上相对于Whisper模型有12.8%的相对增益,而在普通话-英语代码切换ASR中,Whisper表现更好。
要点
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在自动语音识别(ASR)领域具有显著优势,特别是在低资源环境中。
- LLMs与语音编码器的集成是ASR领域的新兴趋势。
- 之前的研究主要集中在英语和中文的语音识别,但对低资源环境下的语音识别挑战的研究仍然不足。
- 基于LLMs的ASR系统在低资源环境中的性能相较于Whisper模型有显著提升。
- 在普通话-英语代码切换的ASR场景下,Whisper模型的性能表现较好。
- 本研究为低资源环境下的ASR提供了新的见解和研究方向。
点此查看论文截图

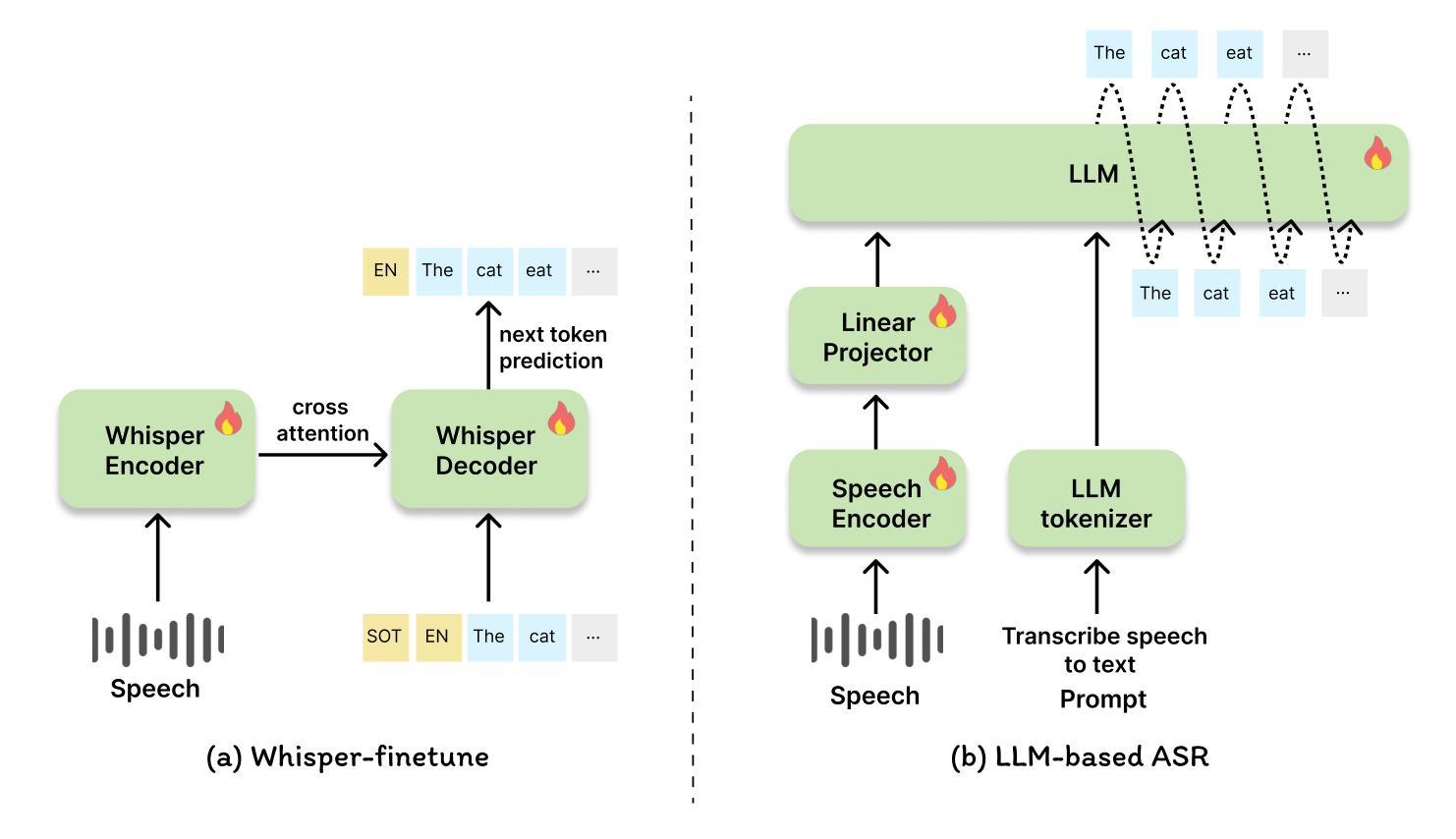
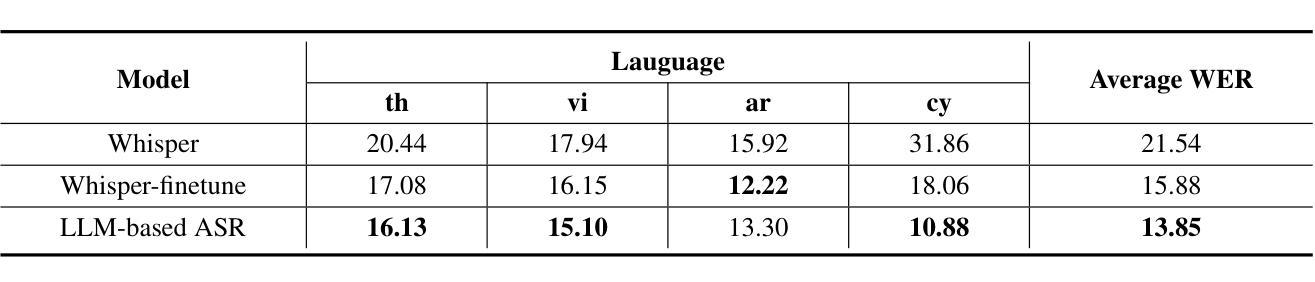
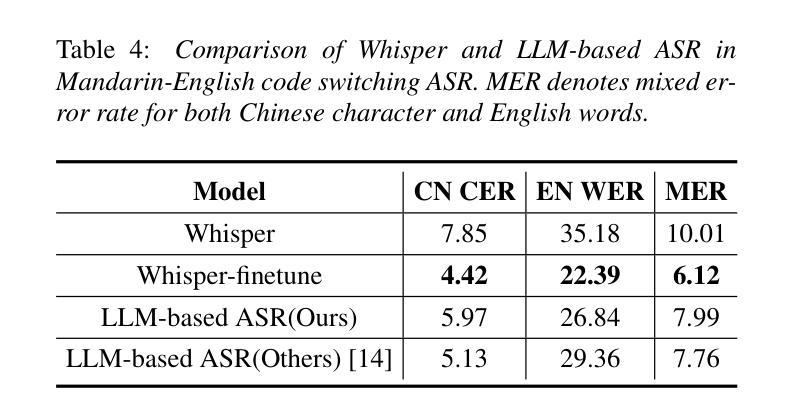
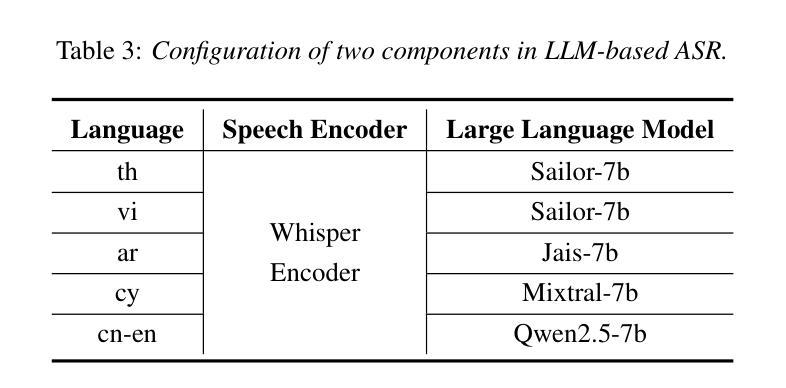
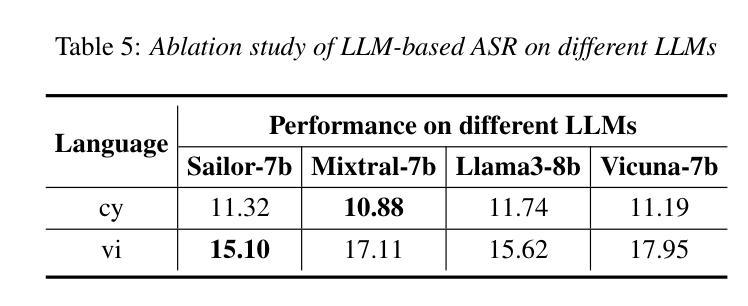
Empowering the Deaf and Hard of Hearing Community: Enhancing Video Captions Using Large Language Models
Authors:Nadeen Fathallah, Monika Bhole, Steffen Staab
In today’s digital age, video content is prevalent, serving as a primary source of information, education, and entertainment. However, the Deaf and Hard of Hearing (DHH) community often faces significant challenges in accessing video content due to the inadequacy of automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems in providing accurate and reliable captions. This paper addresses the urgent need to improve video caption quality by leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs). We present a comprehensive study that explores the integration of LLMs to enhance the accuracy and context-awareness of captions generated by ASR systems. Our methodology involves a novel pipeline that corrects ASR-generated captions using advanced LLMs. It explicitly focuses on models like GPT-3.5 and Llama2-13B due to their robust performance in language comprehension and generation tasks. We introduce a dataset representative of real-world challenges the DHH community faces to evaluate our proposed pipeline. Our results indicate that LLM-enhanced captions significantly improve accuracy, as evidenced by a notably lower Word Error Rate (WER) achieved by ChatGPT-3.5 (WER: 9.75%) compared to the original ASR captions (WER: 23.07%), ChatGPT-3.5 shows an approximate 57.72% improvement in WER compared to the original ASR captions.
在如今的数字化时代,视频内容普遍存在,成为信息、教育和娱乐的主要来源。然而,聋哑人群体在获取视频内容时常常面临重大挑战,这是因为自动语音识别(ASR)系统在提供准确可靠的字幕方面存在不足。本文针对利用大型语言模型(LLM)提高视频字幕质量的紧迫需求。我们进行了全面的研究,探索了将LLM集成到ASR系统中以提高生成字幕的准确性和上下文感知能力的方法。我们的方法包括使用先进的大型语言模型来校正ASR生成的字幕,重点关注GPT-3.5和Llama2-13B等模型,这些模型在理解和生成任务中表现出强大的性能。为了评估我们提出的管道,我们引入了一个代表真实世界挑战的数据集,该数据集反映了聋哑群体所面临的挑战。结果表明,大型语言模型增强的字幕显著提高准确性,以ChatGPT-3.5为例,其词错误率(WER)显著低于原始ASR字幕(WER:9.75%),相较于原始ASR字幕,ChatGPT-3.5的词错误率降低了约57.72%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在数字时代,视频内容广泛存在,作为信息、教育和娱乐的主要来源。然而,聋哑人群在获取视频内容时常常面临挑战,因为自动语音识别(ASR)系统在提供准确可靠的字幕方面存在不足。本文着重解决提高视频字幕质量的紧迫需求,通过利用大型语言模型(LLMs)。本文呈现了一项综合性研究,探讨了整合LLMs以提高ASR系统生成字幕的准确性和上下文意识。我们的方法涉及使用先进的LLMs来修正ASR生成的字幕,重点介绍了GPT-3.5和Llama2-13B等模型,它们在语言理解和生成任务中表现出强大的性能。我们引入了一个反映聋听群体面临现实挑战的数据集来评估我们提出的管道。结果表明,LLM增强的字幕显著提高了准确性,ChatGPT-3.5的单词错误率(WER)从原来的ASR字幕的23.07%降低到9.75%,显示出大约57.72%的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 视频内容在数字时代的重要性及其对聋哑人群的特别意义。
- 现有自动语音识别(ASR)系统在为聋哑人群提供准确可靠字幕方面的不足。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在提高视频字幕质量方面的潜力。
- 利用先进LLMs如GPT-3.5和Llama2-13B来增强ASR系统生成的字幕的准确性。
- 通过引入反映聋听群体现实挑战的数据集来评估新的字幕生成方法。
- LLM增强的字幕显示出显著提高的准确性,特别是ChatGPT-3.5在单词错误率(WER)方面的显著改进。
点此查看论文截图

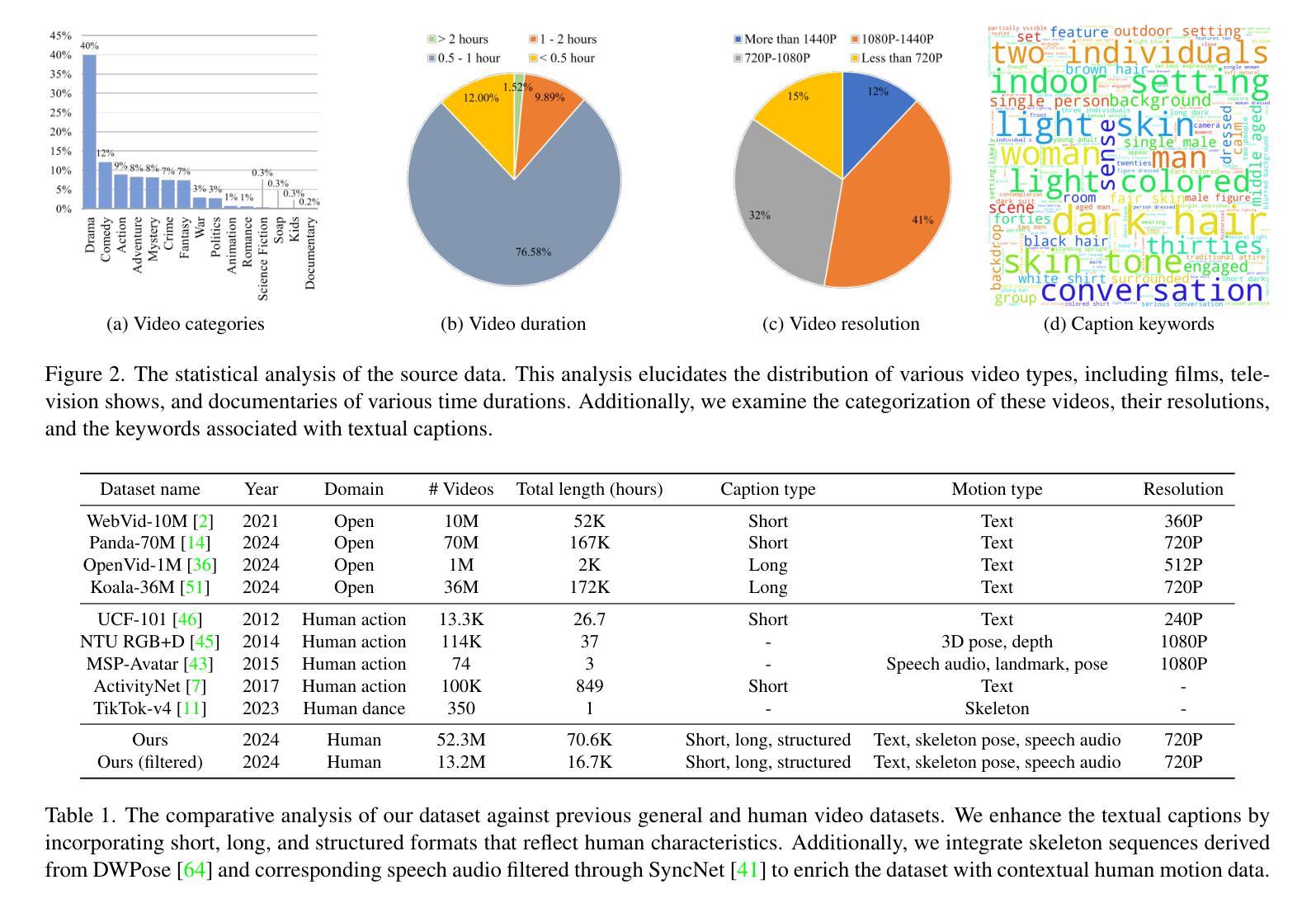
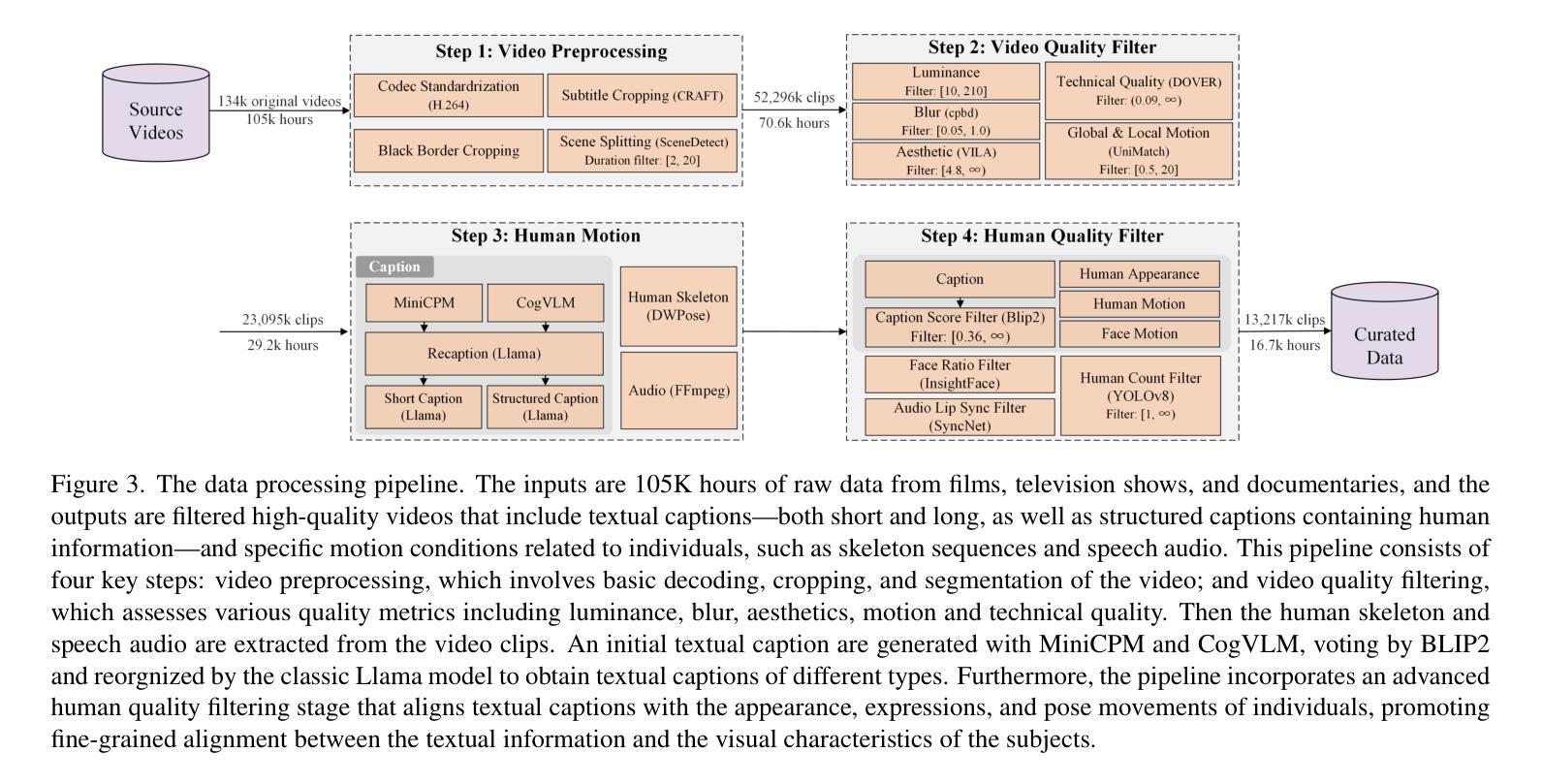
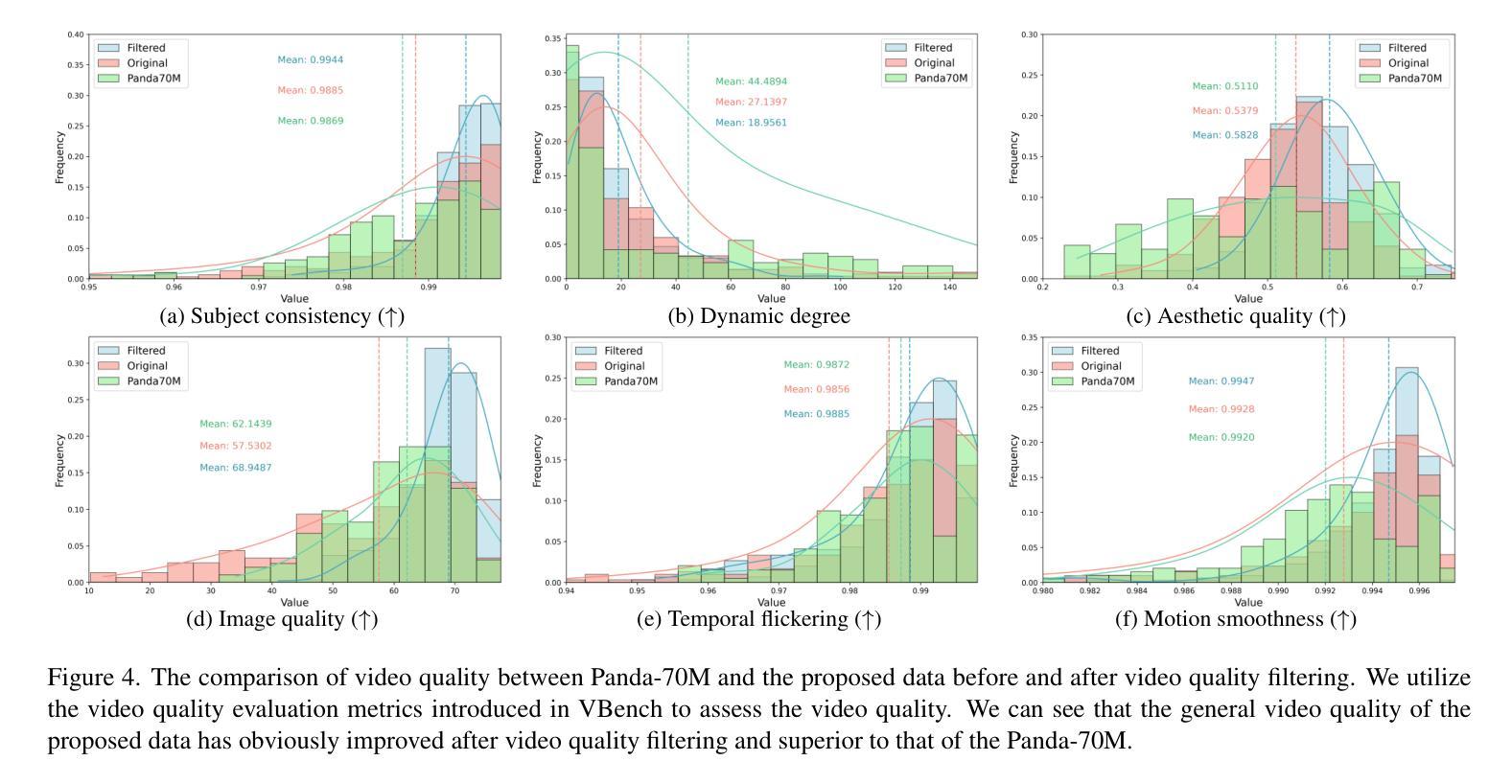
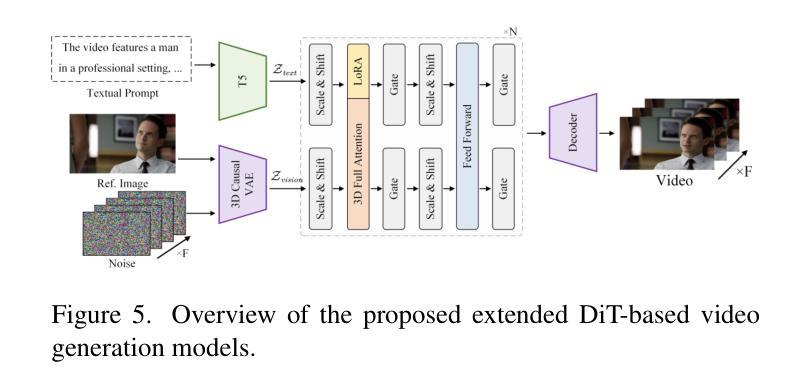
OpenHumanVid: A Large-Scale High-Quality Dataset for Enhancing Human-Centric Video Generation
Authors:Hui Li, Mingwang Xu, Yun Zhan, Shan Mu, Jiaye Li, Kaihui Cheng, Yuxuan Chen, Tan Chen, Mao Ye, Jingdong Wang, Siyu Zhu
Recent advancements in visual generation technologies have markedly increased the scale and availability of video datasets, which are crucial for training effective video generation models. However, a significant lack of high-quality, human-centric video datasets presents a challenge to progress in this field. To bridge this gap, we introduce OpenHumanVid, a large-scale and high-quality human-centric video dataset characterized by precise and detailed captions that encompass both human appearance and motion states, along with supplementary human motion conditions, including skeleton sequences and speech audio. To validate the efficacy of this dataset and the associated training strategies, we propose an extension of existing classical diffusion transformer architectures and conduct further pretraining of our models on the proposed dataset. Our findings yield two critical insights: First, the incorporation of a large-scale, high-quality dataset substantially enhances evaluation metrics for generated human videos while preserving performance in general video generation tasks. Second, the effective alignment of text with human appearance, human motion, and facial motion is essential for producing high-quality video outputs. Based on these insights and corresponding methodologies, the straightforward extended network trained on the proposed dataset demonstrates an obvious improvement in the generation of human-centric videos. Project page https://fudan-generative-vision.github.io/OpenHumanVid
随着视觉生成技术的最新进展,视频数据集的数量和可用性显著增加,这对于训练有效的视频生成模型至关重要。然而,高质量、以人为中心的视频数据集的缺乏为该领域的进步带来了挑战。为了弥补这一差距,我们推出了OpenHumanVid,这是一个大规模、高质量、以人为中心的视频数据集,其特点是具有精确和详细的字幕,涵盖了人类外观和运动状态,还包括额外的人类运动条件,如骨骼序列和语音音频。为了验证该数据集和相关训练策略的有效性,我们对现有的经典扩散变压器架构进行了扩展,并在所提出的数据集上对我们的模型进行了进一步的预训练。我们的研究发现两个关键见解:首先,使用大规模、高质量的数据集可以显著提高生成的人类视频的评价指标,同时保留了一般视频生成任务的性能。其次,文本与人类外观、人类运动和面部运动的有效对齐对于生成高质量视频输出至关重要。基于这些见解和相应的方法论,在所提出的数据集上训练的简单扩展网络在生成以人为中心的视频方面显示出明显的改进。项目页面https://fudan-generative-vision.github.io/OpenHumanVid。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 8 figures, 5 tables
Summary
OpenHumanVid是一个大规模、高质量的人机互动视频数据集,包含了精确详细的描述、人类动作状态以及额外的运动条件,如骨架序列和语音音频。利用该数据集进行预训练可以有效提升生成人类视频的评价指标,并保留了一般视频生成任务中的性能。该项目实现了基于深度学习的视频生成技术的重大突破。
Key Takeaways
- OpenHumanVid是一个大规模、高质量的人机互动视频数据集,提供了详细的描述、人类动作状态以及额外的运动条件。
- 利用OpenHumanVid数据集进行预训练能有效提高生成人类视频的评价指标。
- 保留了一般视频生成任务中的性能。
- 经典扩散变压器架构的扩展和模型在OpenHumanVid数据集上的预训练对于生成高质量视频至关重要。
- 将文本与人类外观、动作和面部动作有效对齐是生成高质量视频的关键。
- 通过使用OpenHumanVid数据集进行训练,能够显著提高以人类为中心的视频生成能力。
点此查看论文截图



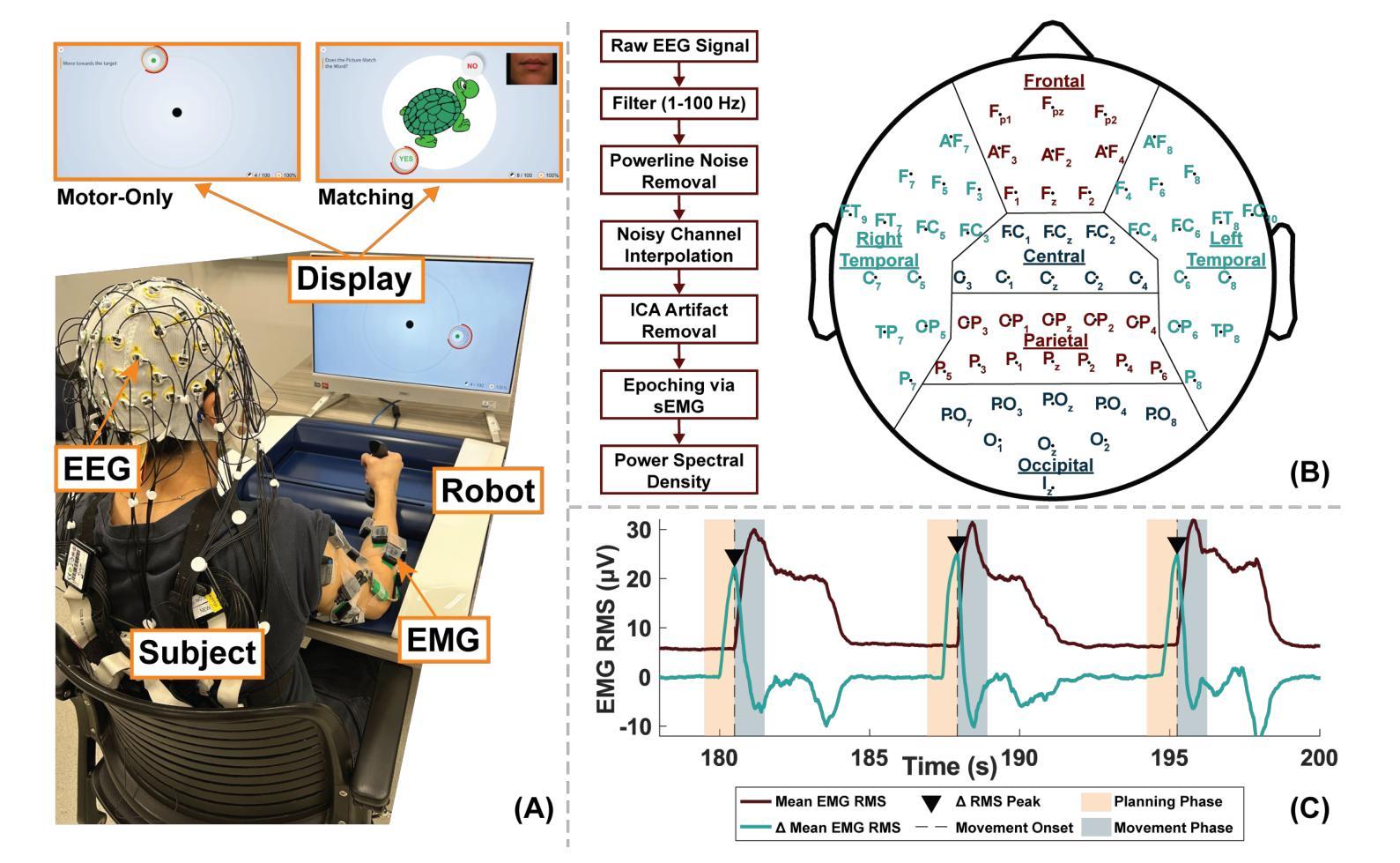
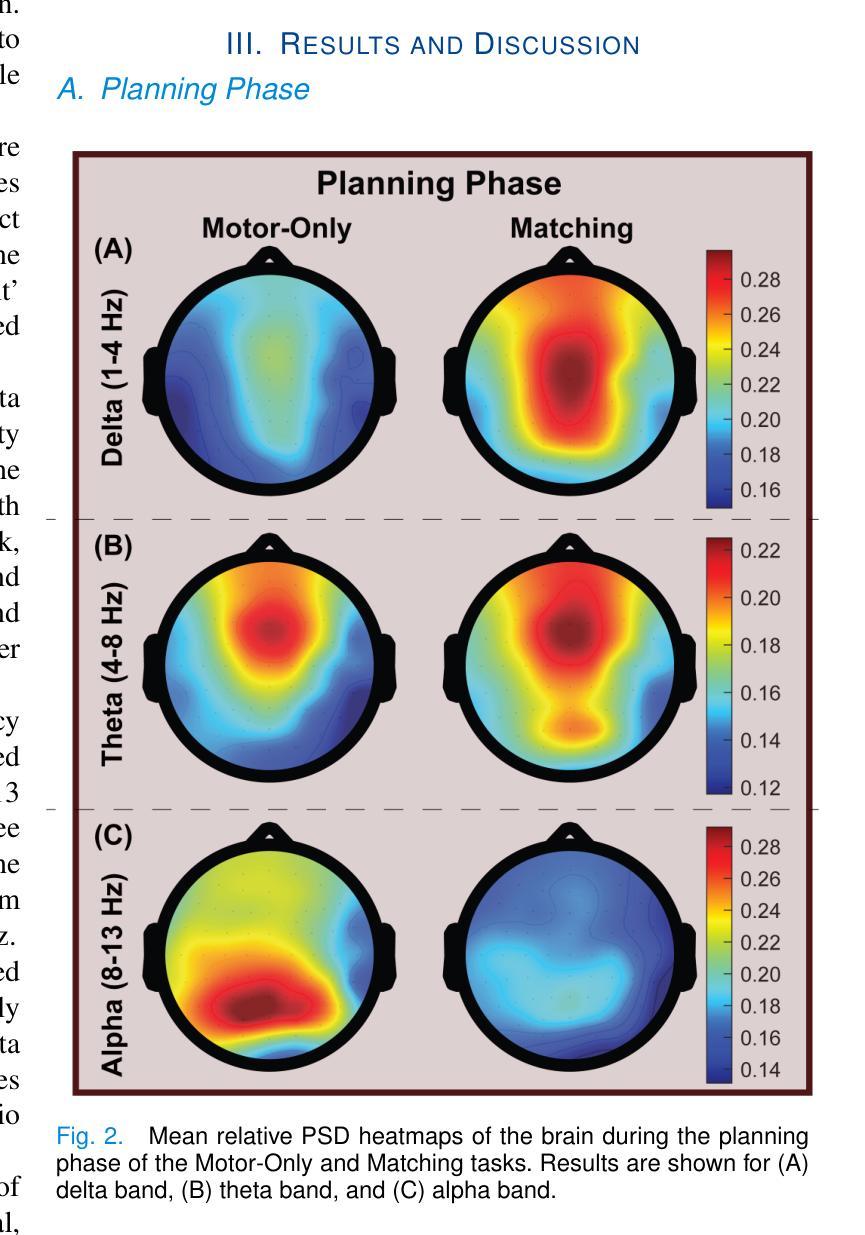
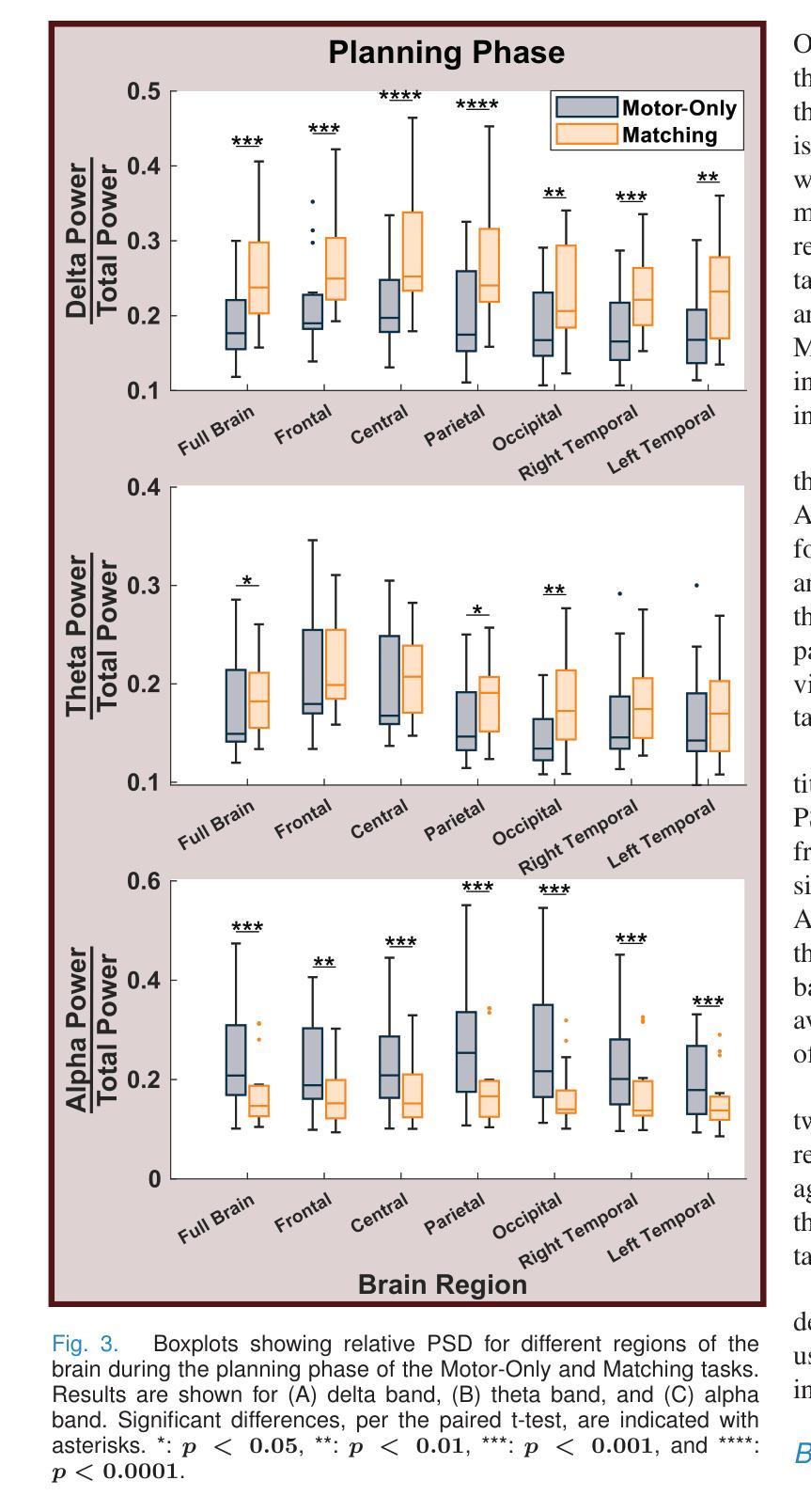
EEG-Based Analysis of Brain Responses in Multi-Modal Human-Robot Interaction: Modulating Engagement
Authors:Suzanne Oliver, Tomoko Kitago, Adam Buchwald, S. Farokh Atashzar
User engagement, cognitive participation, and motivation during task execution in physical human-robot interaction are crucial for motor learning. These factors are especially important in contexts like robotic rehabilitation, where neuroplasticity is targeted. However, traditional robotic rehabilitation systems often face challenges in maintaining user engagement, leading to unpredictable therapeutic outcomes. To address this issue, various techniques, such as assist-as-needed controllers, have been developed to prevent user slacking and encourage active participation. In this paper, we introduce a new direction through a novel multi-modal robotic interaction designed to enhance user engagement by synergistically integrating visual, motor, cognitive, and auditory (speech recognition) tasks into a single, comprehensive activity. To assess engagement quantitatively, we compared multiple electroencephalography (EEG) biomarkers between this multi-modal protocol and a traditional motor-only protocol. Fifteen healthy adult participants completed 100 trials of each task type. Our findings revealed that EEG biomarkers, particularly relative alpha power, showed statistically significant improvements in engagement during the multi-modal task compared to the motor-only task. Moreover, while engagement decreased over time in the motor-only task, the multi-modal protocol maintained consistent engagement, suggesting that users could remain engaged for longer therapy sessions. Our observations on neural responses during interaction indicate that the proposed multi-modal approach can effectively enhance user engagement, which is critical for improving outcomes. This is the first time that objective neural response highlights the benefit of a comprehensive robotic intervention combining motor, cognitive, and auditory functions in healthy subjects.
在物理人机交互中的任务执行过程中,用户参与度、认知参与度和动机对于运动学习至关重要。在针对神经可塑性目标的领域(如机器人康复)中,这些因素尤为重要。然而,传统的机器人康复系统常常面临维持用户参与度方面的挑战,从而导致不可预测的治疗结果。为了解决这一问题,已经开发出了各种技术,如按需辅助控制器,以防止用户懈怠并鼓励积极参与。在这篇论文中,我们通过一种新型的多模式机器人交互介绍了一个新方向,该交互通过协同整合视觉、运动、认知和听觉(语音识别)任务到一个单一的综合活动中,从而增强用户参与度。为了定量评估参与度,我们比较了这种多模式协议和传统仅运动模式的协议之间的多个脑电图(EEG)生物标志物。十五名健康成年参与者完成了每种任务类型的一百次试验。我们的研究结果表明,与仅运动任务相比,脑电图生物标志物(尤其是相对阿尔法功率)在多模式任务期间的参与度有显著改善。此外,尽管参与度在仅运动任务中随时间下降,但多模式协议保持了持续的参与度,这表明用户可以在更长的治疗过程中保持参与。我们对交互过程中神经反应的观察表明,所提出的多模式方法可以有效地提高用户参与度,这对于提高治疗效果至关重要。这是第一次客观神经反应突显出在健康受试者中结合运动、认知和听觉功能的综合机器人干预的益处。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 7 figures. Submitted to IEEE TNSRE
摘要
物理人机交互中的用户参与度、认知参与度和任务执行时的动机对于运动学习至关重要,特别是在机器人康复等针对神经可塑性目标的情境中。然而,传统的机器人康复系统往往面临维持用户参与度的挑战,从而导致治疗效果难以预测。为解决这一问题,研究者开发了按需辅助控制器等技术以防止用户懈怠并鼓励积极参与。本文介绍了一种通过新型多模式机器人交互增强用户参与度的方法,该方法通过协同整合视觉、运动、认知和听觉(语音识别)任务,将多种模式融入单一的全面活动中。为定量评估参与度,我们比较了多模态协议和传统运动协议下的脑电图(EEG)生物标志物,涉及15名健康成年参与者共完成每种任务类型各100次试验。结果显示,脑电图生物标志物即相对阿尔法功率在多模态任务中的改善具有统计学显著差异。此外,尽管参与者在仅进行运动任务的情景下随着时间推移其参与度下降,多模态协议则维持了一致的参与度水平,暗示用户在长时间治疗场景下也能保持高度参与。本研究观察到的神经反应表明,所提出的多模态方法可有效提升用户参与度,这对于改善治疗效果至关重要。这是首次在健康受试者中客观记录神经反应表明结合运动、认知和听觉功能的全面机器人干预的优势。
关键见解
- 用户参与度、认知参与度和动机在物理人机交互中的任务执行对运动学习非常重要,尤其在机器人康复领域。
- 传统机器人康复系统在维持用户参与度方面面临挑战,影响治疗效果的预测。
- 多模式机器人交互方法通过结合多种感官刺激(如视觉、运动、认知和听觉)来提高用户参与度。
- 研究比较了多模态任务与传统运动任务的脑电图生物标志物来衡量参与度。
- 相对阿尔法功率等EEG生物标志物在多模态任务中的改善显著,表明多模态方法能提高用户参与度。
- 多模态协议能维持稳定的参与度,即使随着时间推移,这在长期治疗中是关键。
点此查看论文截图
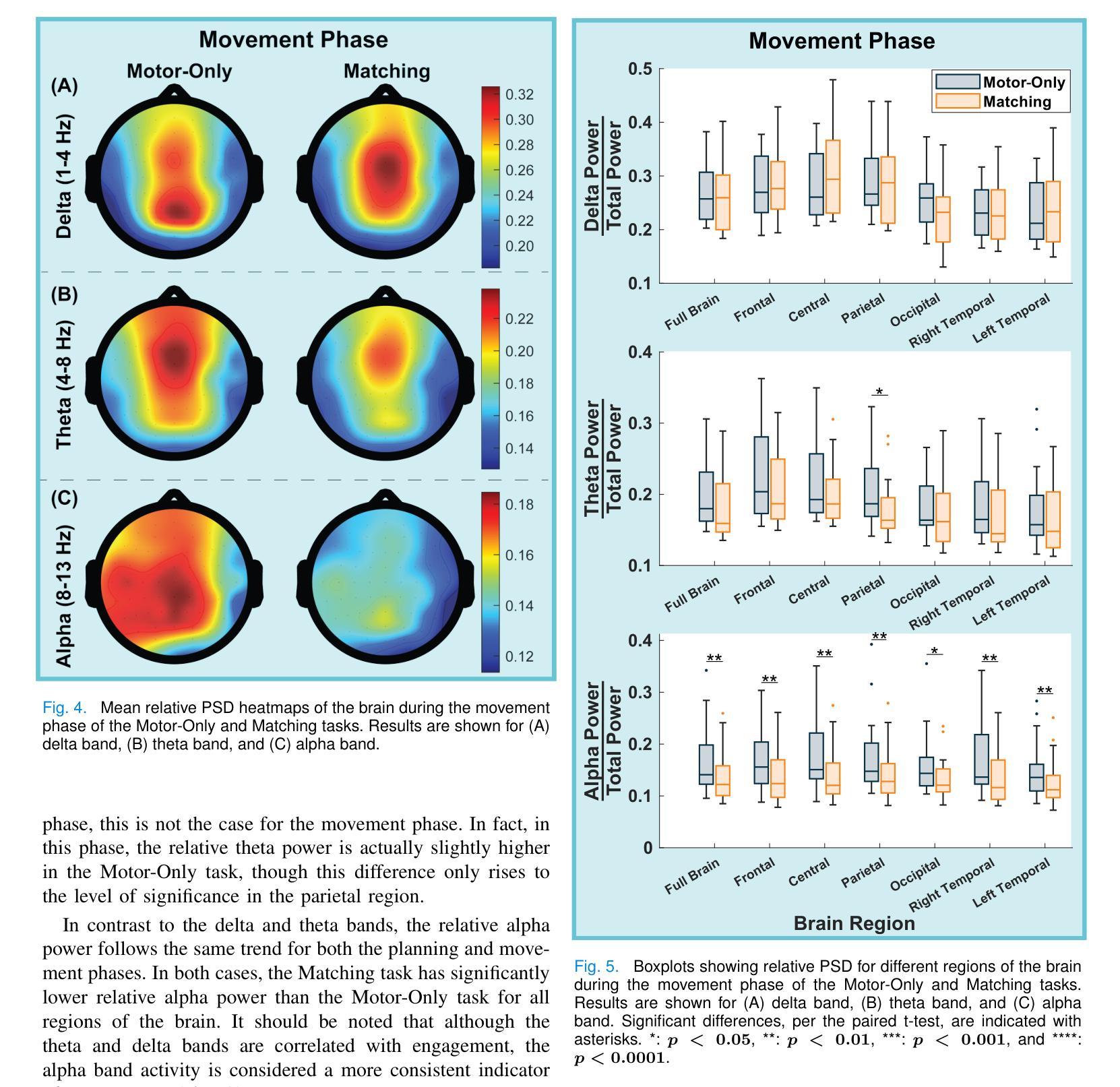
Multiple Choice Learning for Efficient Speech Separation with Many Speakers
Authors:David Perera, François Derrida, Théo Mariotte, Gaël Richard, Slim Essid
Training speech separation models in the supervised setting raises a permutation problem: finding the best assignation between the model predictions and the ground truth separated signals. This inherently ambiguous task is customarily solved using Permutation Invariant Training (PIT). In this article, we instead consider using the Multiple Choice Learning (MCL) framework, which was originally introduced to tackle ambiguous tasks. We demonstrate experimentally on the popular WSJ0-mix and LibriMix benchmarks that MCL matches the performances of PIT, while being computationally advantageous. This opens the door to a promising research direction, as MCL can be naturally extended to handle a variable number of speakers, or to tackle speech separation in the unsupervised setting.
在监督环境下训练语音分离模型会引发排列问题:即如何为模型预测和真实分离信号找到最佳的分配方案。这个本质上是模糊的任务通常通过使用排列不变训练(PIT)来解决。在本文中,我们考虑使用最初为解决模糊任务而引入的多选学习(MCL)框架。我们在流行的WSJ0-mix和LibriMix基准测试上进行了实验,证明了MCL的性能与PIT相匹配,同时计算上更有优势。这为研究方向打开了大门,因为MCL可以自然地扩展到处理可变数量的发言人,或解决非监督环境下的语音分离问题。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了语音分离模型的训练问题,特别是在有监督的环境下。由于模型预测和真实分离信号之间的分配存在排列问题,通常使用排列不变训练(PIT)来解决此固有的模糊任务。本文考虑采用原始用于解决模糊任务的多项选择学习(MCL)框架。实验表明,在流行的WSJ0-mix和LibriMix基准测试中,MCL的性能与PIT相匹配,同时计算上更有优势。这为MCL在可变说话人数或多通道语音分离等方向的研究开辟了新的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 语音分离模型的训练面临排列问题,即模型预测与真实分离信号之间的最佳分配问题。
- 排列不变训练(PIT)是常规解决此模糊任务的方法。
- 本文引入多项选择学习(MCL)框架作为替代方案。
- 在WSJ0-mix和LibriMix基准测试中,MCL性能与PIT相当。
- MCL具有计算优势,为处理可变说话人数或监督环境下的语音分离提供了研究潜力。
- MCL可自然扩展到处理不同场景,如多通道语音分离等。
点此查看论文截图

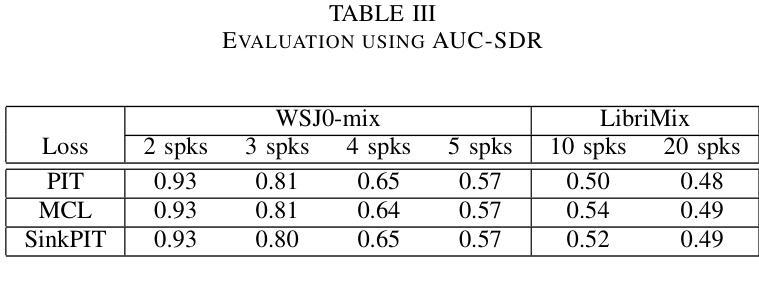
AMPS: ASR with Multimodal Paraphrase Supervision
Authors:Amruta Parulekar, Abhishek Gupta, Sameep Chattopadhyay, Preethi Jyothi
Spontaneous or conversational multilingual speech presents many challenges for state-of-the-art automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems. In this work, we present a new technique AMPS that augments a multilingual multimodal ASR system with paraphrase-based supervision for improved conversational ASR in multiple languages, including Hindi, Marathi, Malayalam, Kannada, and Nyanja. We use paraphrases of the reference transcriptions as additional supervision while training the multimodal ASR model and selectively invoke this paraphrase objective for utterances with poor ASR performance. Using AMPS with a state-of-the-art multimodal model SeamlessM4T, we obtain significant relative reductions in word error rates (WERs) of up to 5%. We present detailed analyses of our system using both objective and human evaluation metrics.
多语种自然口语为最先进的自动语音识别(ASR)系统带来了诸多挑战。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种新技术AMPS,该技术增强了一种多语种多媒体ASR系统,通过基于释义的监督改进了多种语言的对话ASR表现,包括印地语、马拉地语、马拉雅拉姆语、坎纳达语和尼扬贾语。我们在训练多媒体ASR模型时,会使用参考译文的释义作为额外的监督方式,并针对表现不佳的ASR表现选择性地启动这种释义目标。通过使用AMPS和最先进的多媒体模型无缝M4T的结合,我们实现了显著的相对减少,词错误率降低了高达5%。我们通过客观和人类评估指标两种方法对系统进行了详细分析。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自动语音识别(ASR)系统在处理自发性或多语种对话语音时面临诸多挑战。本研究提出了一种新技术AMPS,该技术通过基于同义短语监督的方式增强多语种多媒体ASR系统,以提高对包括印地语、马拉地语、马拉雅拉姆语、坎纳达语和尼亚贾语在内的多种语言的对话语音识别。在训练多媒体ASR模型时,我们使用参考转录的同义短语作为额外的监督,并选择性地对表现不佳的ASR性能片段使用同义短语目标。通过将AMPS与先进的SeamlessM4T多媒体模型结合使用,我们获得了显著的相对词错误率(WER)降低,最高达5%。本研究通过客观和人类评估指标对系统进行了详细分析。
Key Takeaways
- AMPS技术通过结合同义短语监督增强了多语种对话语音识别的性能。
- AMPS能够应用于多种语言,包括印地语、马拉地语、马拉雅拉姆语、坎纳达语和尼亚贾语。
- 在训练多媒体ASR模型时,使用了参考转录的同义短语作为额外的监督信息。
- 对于ASR性能不佳的部分,会选择性使用同义短语目标进行优化。
- 结合AMPS技术和先进的SeamlessM4T多媒体模型,显著降低了词错误率(WER)。
- 该研究通过客观评估指标和人类评估指标对系统进行了详细分析。
点此查看论文截图

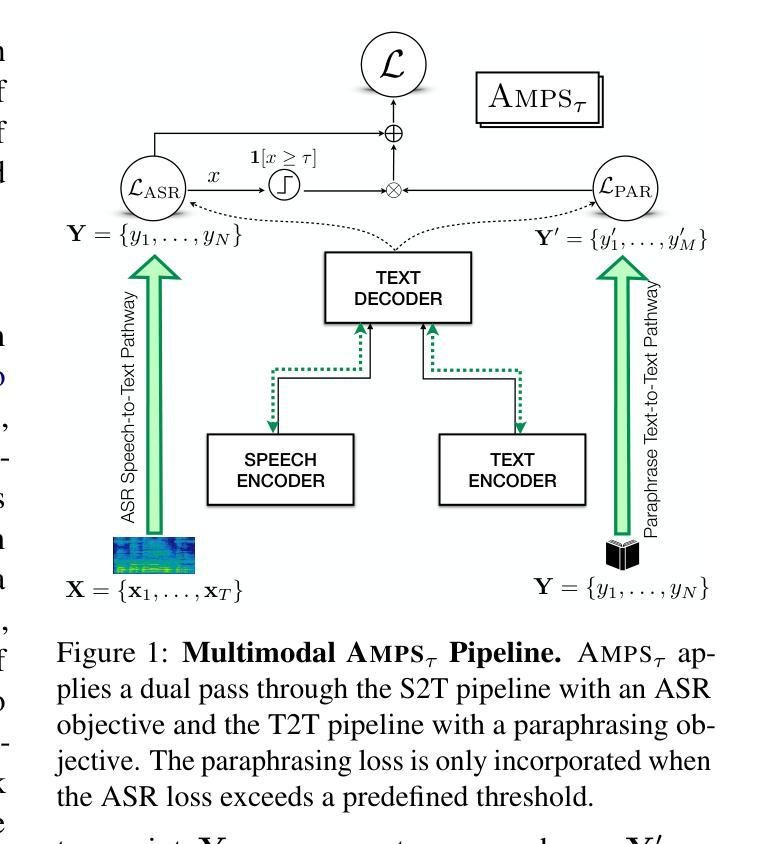
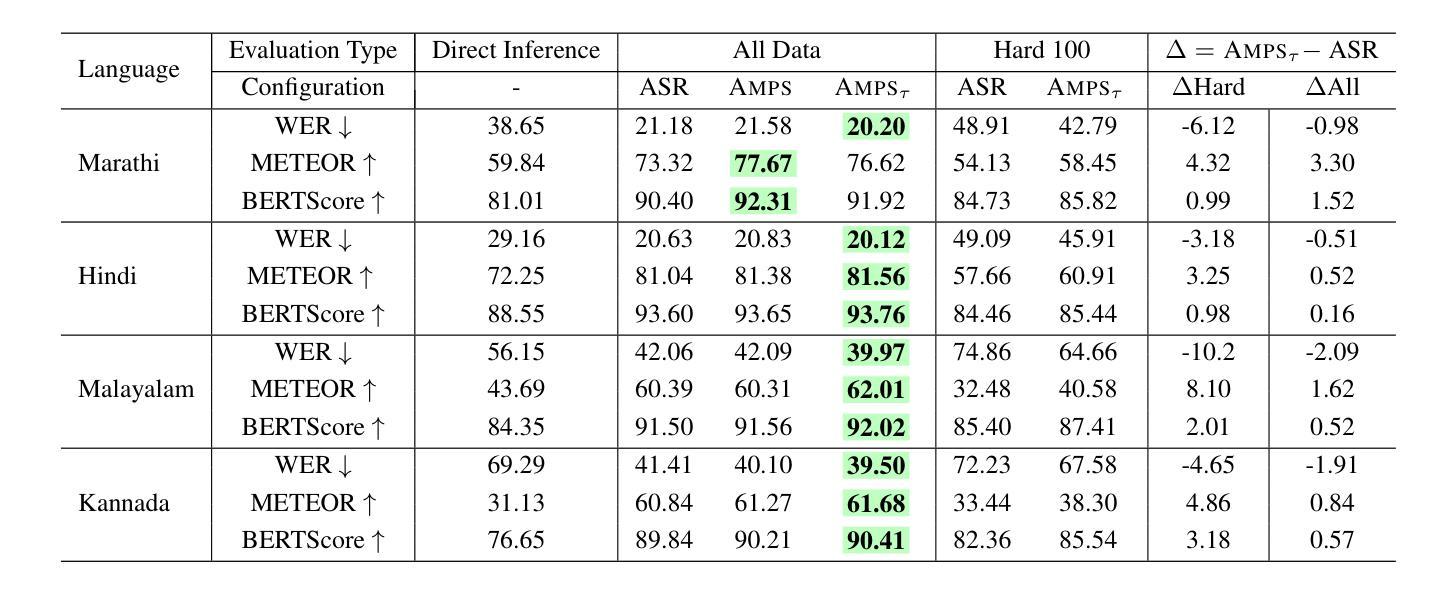
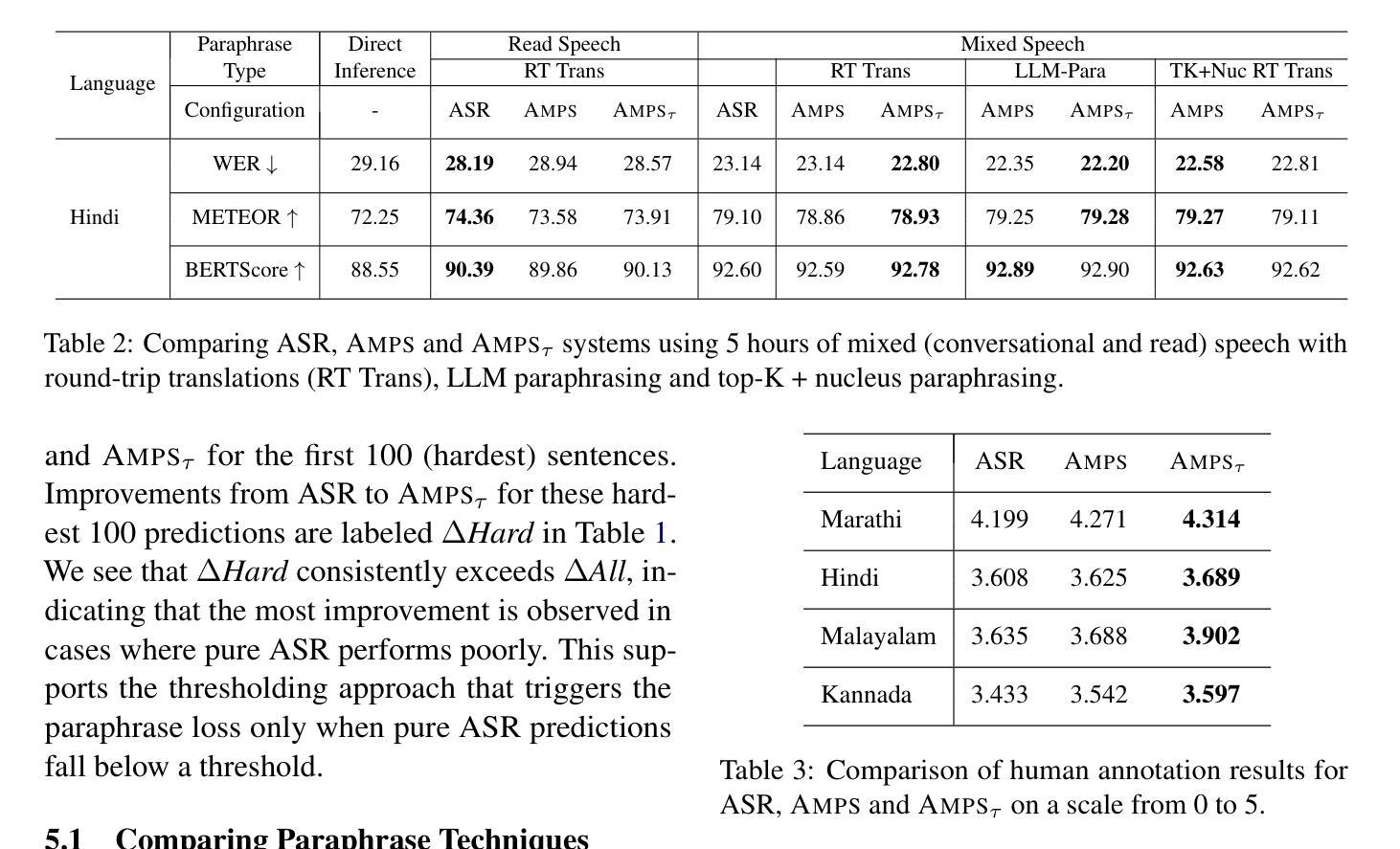
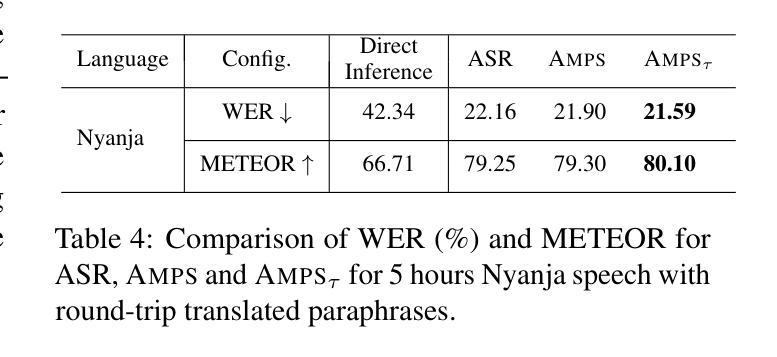
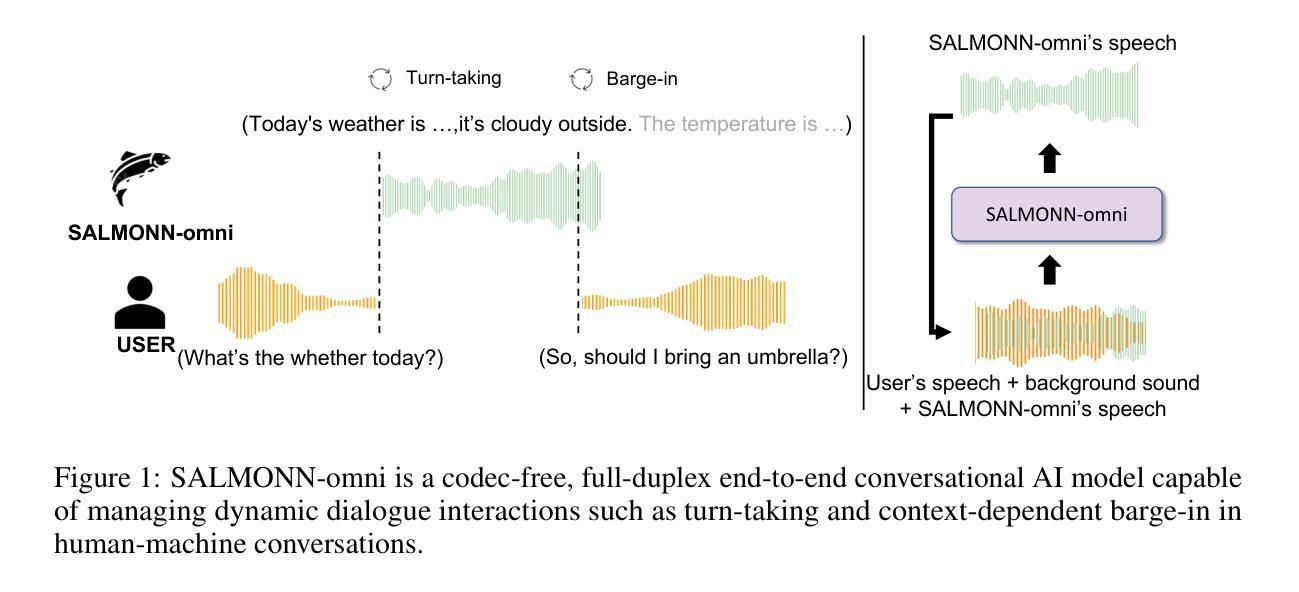
SALMONN-omni: A Codec-free LLM for Full-duplex Speech Understanding and Generation
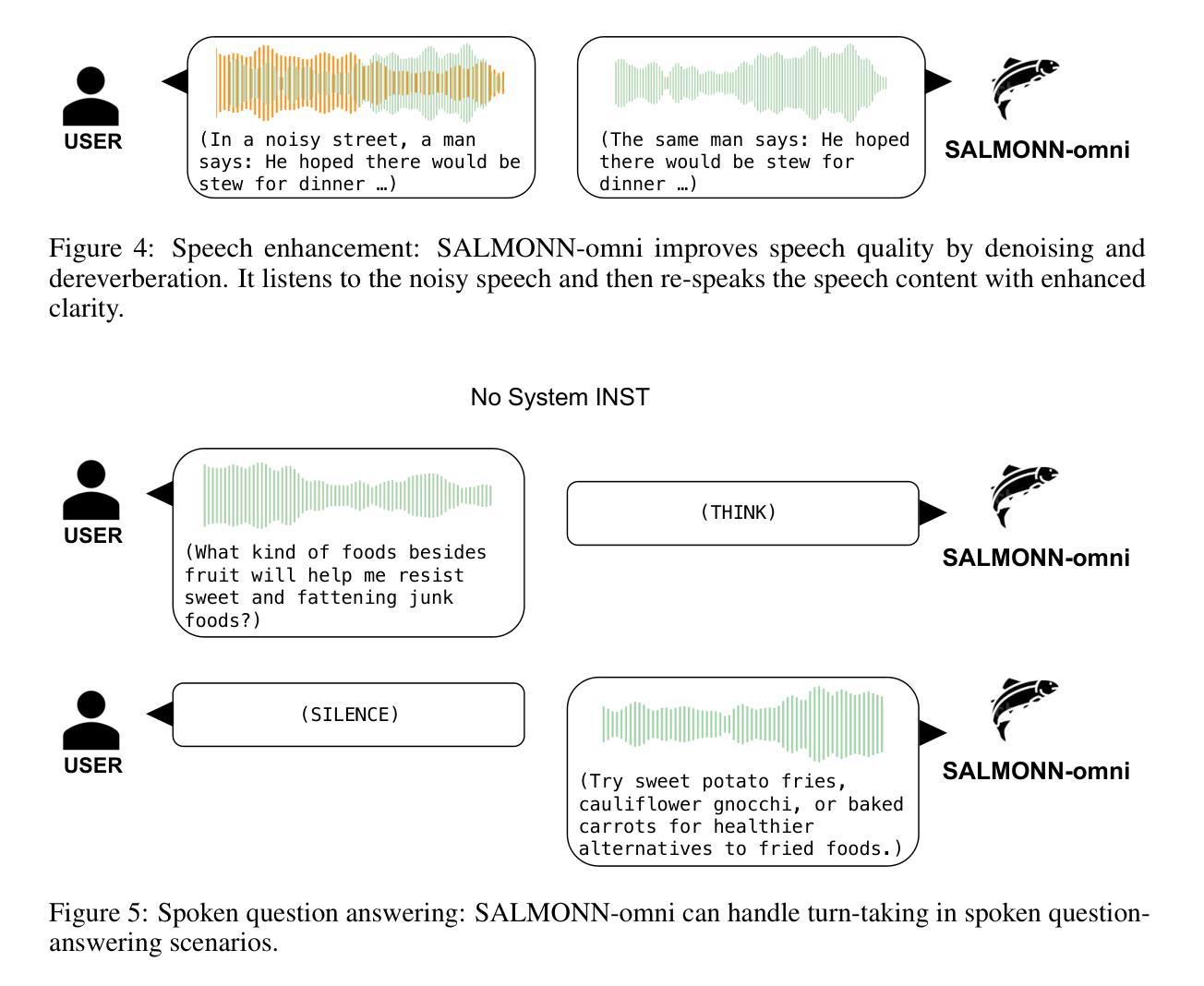
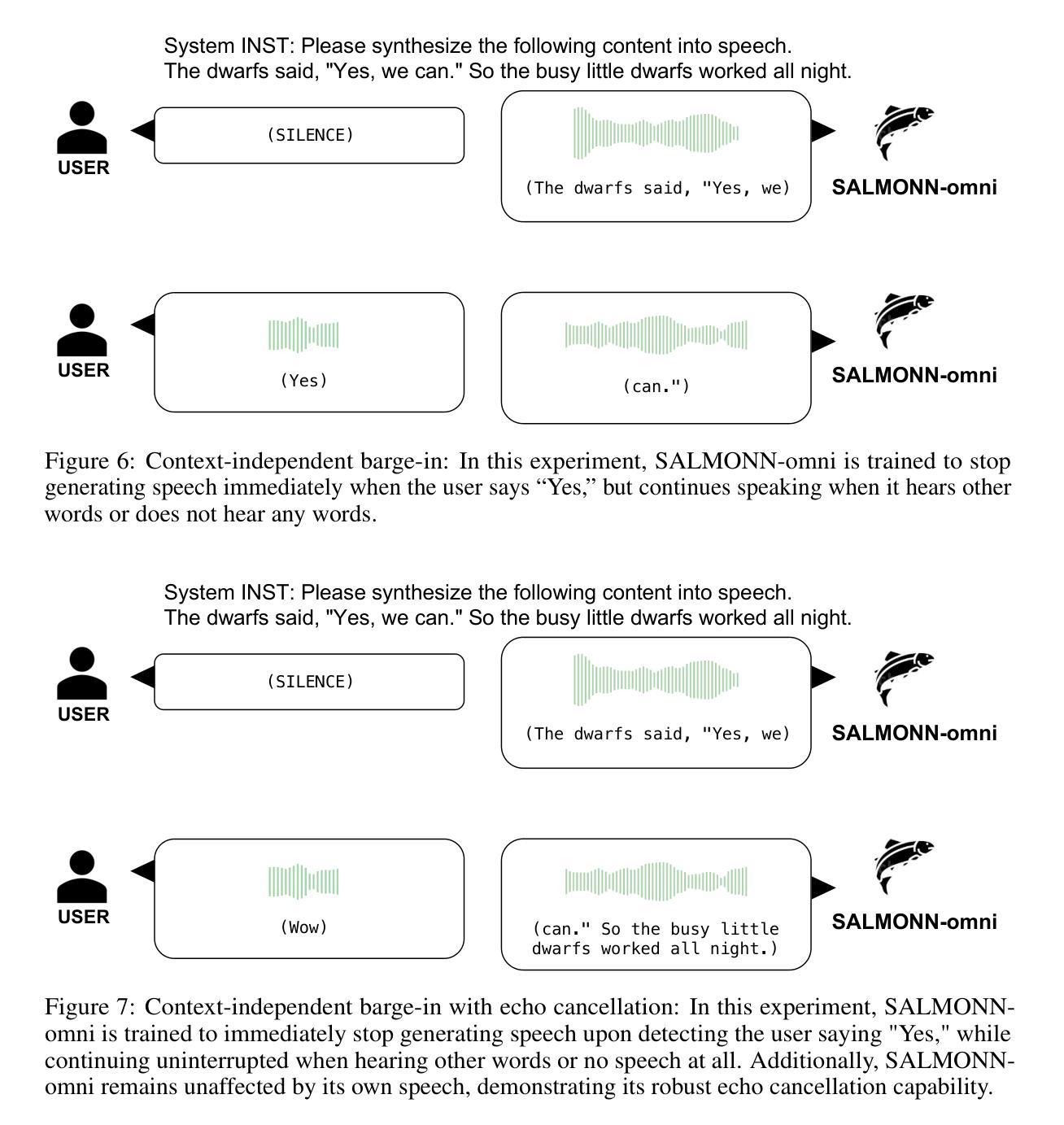
Authors:Wenyi Yu, Siyin Wang, Xiaoyu Yang, Xianzhao Chen, Xiaohai Tian, Jun Zhang, Guangzhi Sun, Lu Lu, Yuxuan Wang, Chao Zhang
Full-duplex multimodal large language models (LLMs) provide a unified framework for addressing diverse speech understanding and generation tasks, enabling more natural and seamless human-machine conversations. Unlike traditional modularised conversational AI systems, which separate speech recognition, understanding, and text-to-speech generation into distinct components, multimodal LLMs operate as single end-to-end models. This streamlined design eliminates error propagation across components and fully leverages the rich non-verbal information embedded in input speech signals. We introduce SALMONN-omni, a codec-free, full-duplex speech understanding and generation model capable of simultaneously listening to its own generated speech and background sounds while speaking. To support this capability, we propose a novel duplex spoken dialogue framework incorporating a ``thinking’’ mechanism that facilitates asynchronous text and speech generation relying on embeddings instead of codecs (quantized speech and audio tokens). Experimental results demonstrate SALMONN-omni’s versatility across a broad range of streaming speech tasks, including speech recognition, speech enhancement, and spoken question answering. Additionally, SALMONN-omni excels at managing turn-taking, barge-in, and echo cancellation scenarios, establishing its potential as a robust prototype for full-duplex conversational AI systems. To the best of our knowledge, SALMONN-omni is the first codec-free model of its kind. A full technical report along with model checkpoints will be released soon.
全双工多模态大型语言模型(LLM)为处理多样化的语音理解和生成任务提供了一个统一的框架,使人类与机器之间的对话更加自然和无缝。与传统的模块化对话AI系统不同,后者将语音识别、理解和文本到语音的生成过程划分为独立的不同组件,多模态LLM则以单一端到端的模型进行工作。这种流程化的设计消除了组件间错误传递,并充分利用输入语音信号中丰富的非语言信息。我们介绍了SALMONN-omni,这是一种无编解码器、全双工语音理解和生成模型,它能够在说话时同时监听自己的生成的语音和背景声音。为了支持这种能力,我们提出了一个新颖的双工对话框架,融入了一种“思考”机制,该机制依赖于嵌入而非编解码器(量化语音和音频令牌)来实现异步文本和语音生成。实验结果表明,SALMONN-omni在广泛的流式语音任务中表现出很强的通用性,包括语音识别、语音增强和语音问答。此外,SALMONN-omni在轮替发言、插话和回声消除等场景中表现出色,证明其作为全双工对话AI系统的稳健原型的潜力。据我们所知,SALMONN-omni是首个无编解码器的此类模型。我们将很快发布完整的技术报告和模型检查点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical report
Summary
基于全双工多模态大型语言模型(LLMs)的框架,可以统一解决多种语音理解和生成任务,促进更自然和无缝的人机对话。全双工模型SALMONN-omni无需编解码器,即可实现同时听取自身生成的语音和背景声音的同时进行语音输出。实验结果表明,SALMONN-omni在各种流式语音任务中表现优异,如语音识别、语音增强和语音问答等。其能妥善管理轮流发言、中断发言和回声消除等场景,为全双工对话式AI系统提供了稳健的原型。它是首个无需编解码器的模型。
Key Takeaways
- 全双工多模态大型语言模型(LLMs)提供了统一的框架来解决多种语音理解和生成任务。
- LLMs促进了更自然和无缝的人机对话。
- SALMONN-omni模型无需编解码器即可实现全双工语音理解和生成。
- SALMONN-omni在各种流式语音任务中表现优异,包括语音识别、语音增强和语音问答等。
- SALMONN-omni能妥善管理轮流发言、中断发言和回声消除等场景。
- SALMONN-omni为全双工对话式AI系统提供了稳健的原型。
点此查看论文截图

Speech Separation using Neural Audio Codecs with Embedding Loss
Authors:Jia Qi Yip, Chin Yuen Kwok, Bin Ma, Eng Siong Chng
Neural audio codecs have revolutionized audio processing by enabling speech tasks to be performed on highly compressed representations. Recent work has shown that speech separation can be achieved within these compressed domains, offering faster training and reduced inference costs. However, current approaches still rely on waveform-based loss functions, necessitating unnecessary decoding steps during training. We propose a novel embedding loss for neural audio codec-based speech separation that operates directly on compressed audio representations, eliminating the need for decoding during training. To validate our approach, we conduct comprehensive evaluations using both objective metrics and perceptual assessment techniques, including intrusive and non-intrusive methods. Our results demonstrate that embedding loss can be used to train codec-based speech separation models with a 2x improvement in training speed and computational cost while achieving better DNSMOS and STOI performance on the WSJ0-2mix dataset across 3 different pre-trained codecs.
神经网络音频编解码器通过允许在高度压缩的表示上执行语音任务,从而革新了音频处理。最近的研究表明,可以在这些压缩域内实现语音分离,从而提供更快的训练和推理成本。然而,当前的方法仍然依赖于基于波形的损失函数,在训练过程中需要进行不必要的解码步骤。我们提出了一种用于基于神经网络音频编解码器的语音分离的新型嵌入损失,它直接在压缩的音频表示上运行,从而在训练过程中消除了对解码的需求。为了验证我们的方法,我们使用客观指标和感知评估技术,包括侵入性和非侵入性方法,进行了全面的评估。结果表明,嵌入损失可用于训练基于编解码器的语音分离模型,在训练速度和计算成本方面实现2倍的提升,同时在WSJ0-2mix数据集上实现更好的DNSMOS和STOI性能,跨越3种不同的预训练编解码器。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by APSIPA ASC 2024
Summary
神经网络音频编码器的出现,为音频处理带来了革命性的变革,它能够在高度压缩的表示上执行语音任务。最新研究表明,可在这些压缩域内实现语音分离,降低了训练和推理成本。然而,当前方法仍依赖于基于波形的损失函数,训练过程中需要进行不必要的解码步骤。我们提出了一种新颖的嵌入损失,用于基于神经网络音频编码器的语音分离,可直接在压缩的音频表示上操作,从而消除训练过程中的解码需求。通过客观指标和感知评估技术,包括侵入性和非侵入性方法,我们验证了该方法的有效性。结果表明,嵌入损失可用于训练基于编码器的语音分离模型,在WSJ0-2mix数据集上实现了DNSMOS和STOI性能的改善,同时训练速度和计算成本提高了两倍。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络音频编码器实现了在高度压缩的表示上进行语音任务的能力。
- 最新研究证明了在压缩域内进行语音分离的可行性。
- 当前方法仍依赖于波形损失函数,导致训练过程中需要额外的解码步骤。
- 提出了一种新颖的嵌入损失函数,可直接在压缩的音频表示上进行语音分离训练,无需解码步骤。
- 嵌入损失函数能够提高训练速度和计算效率。
- 通过客观指标和感知评估技术验证了新方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

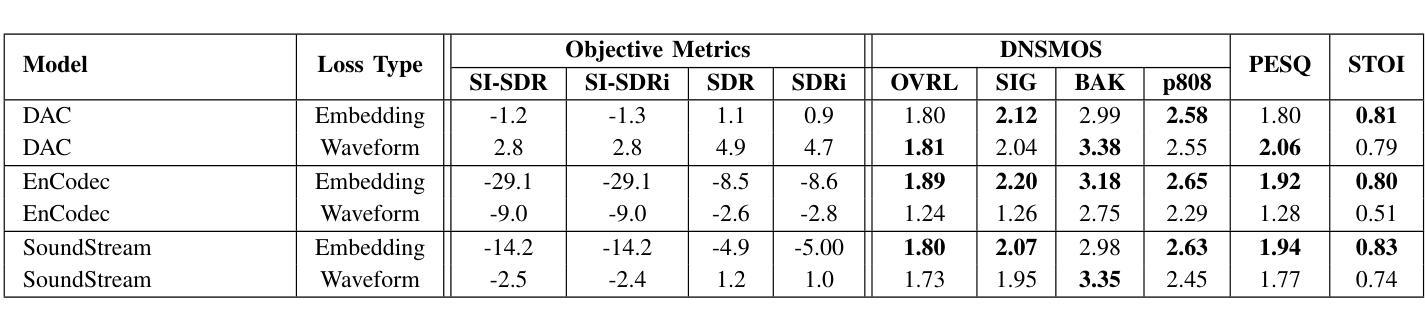
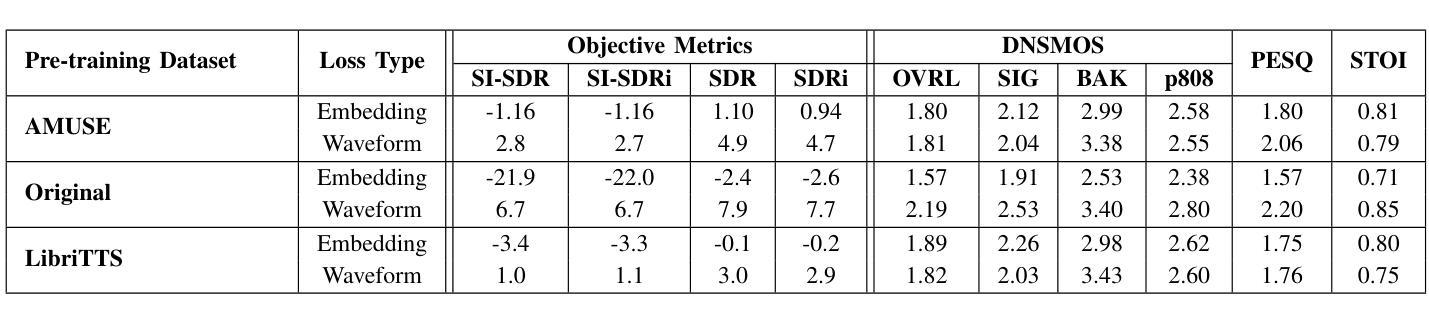
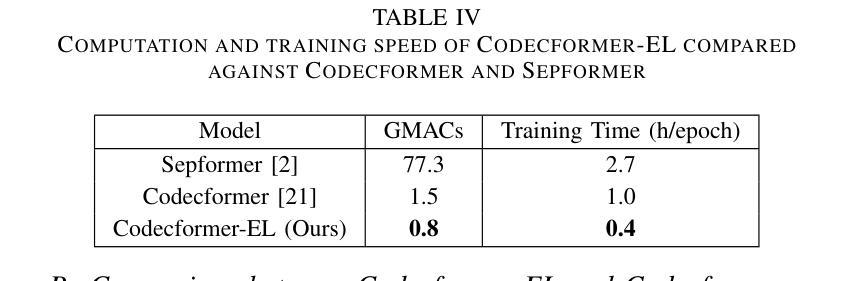
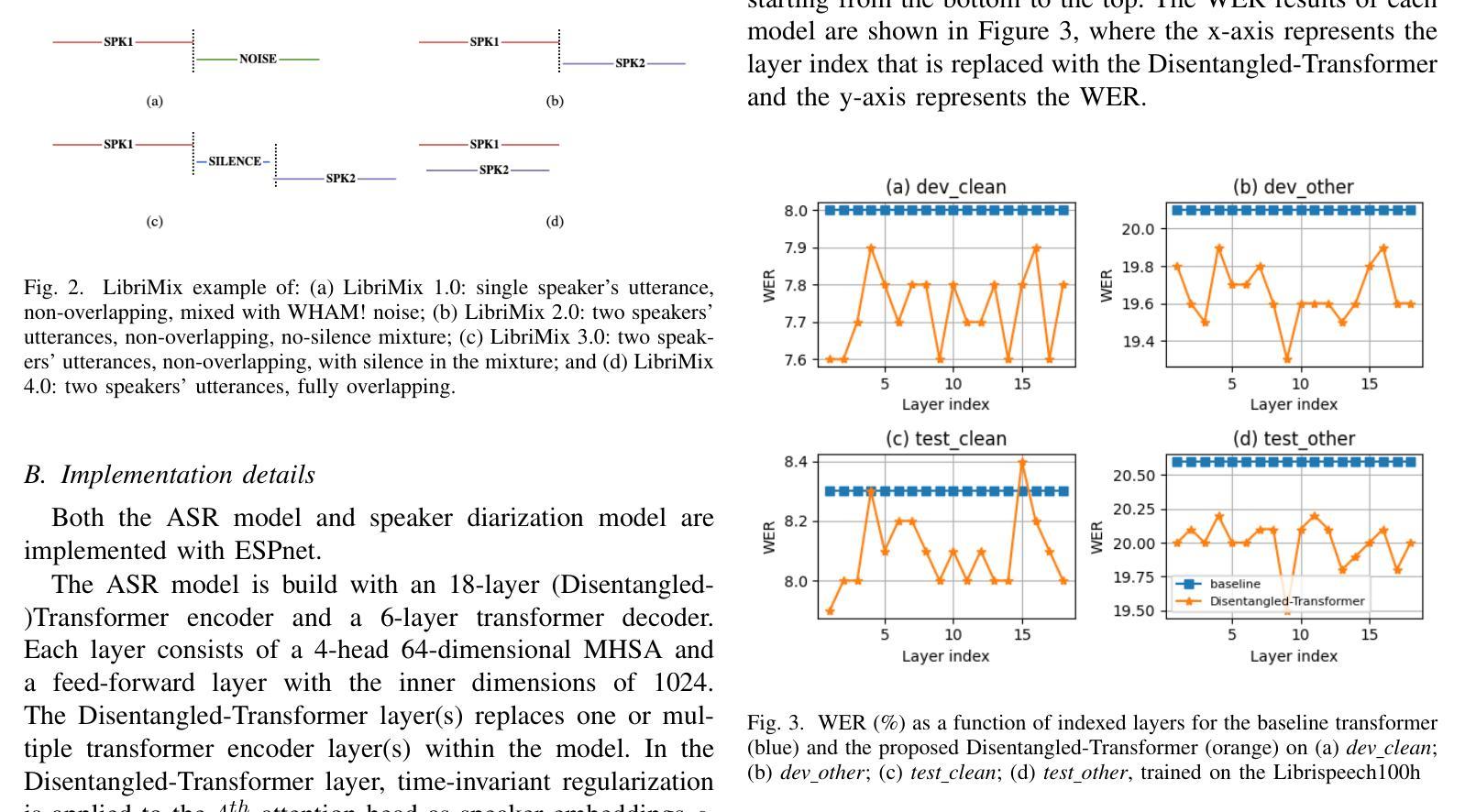
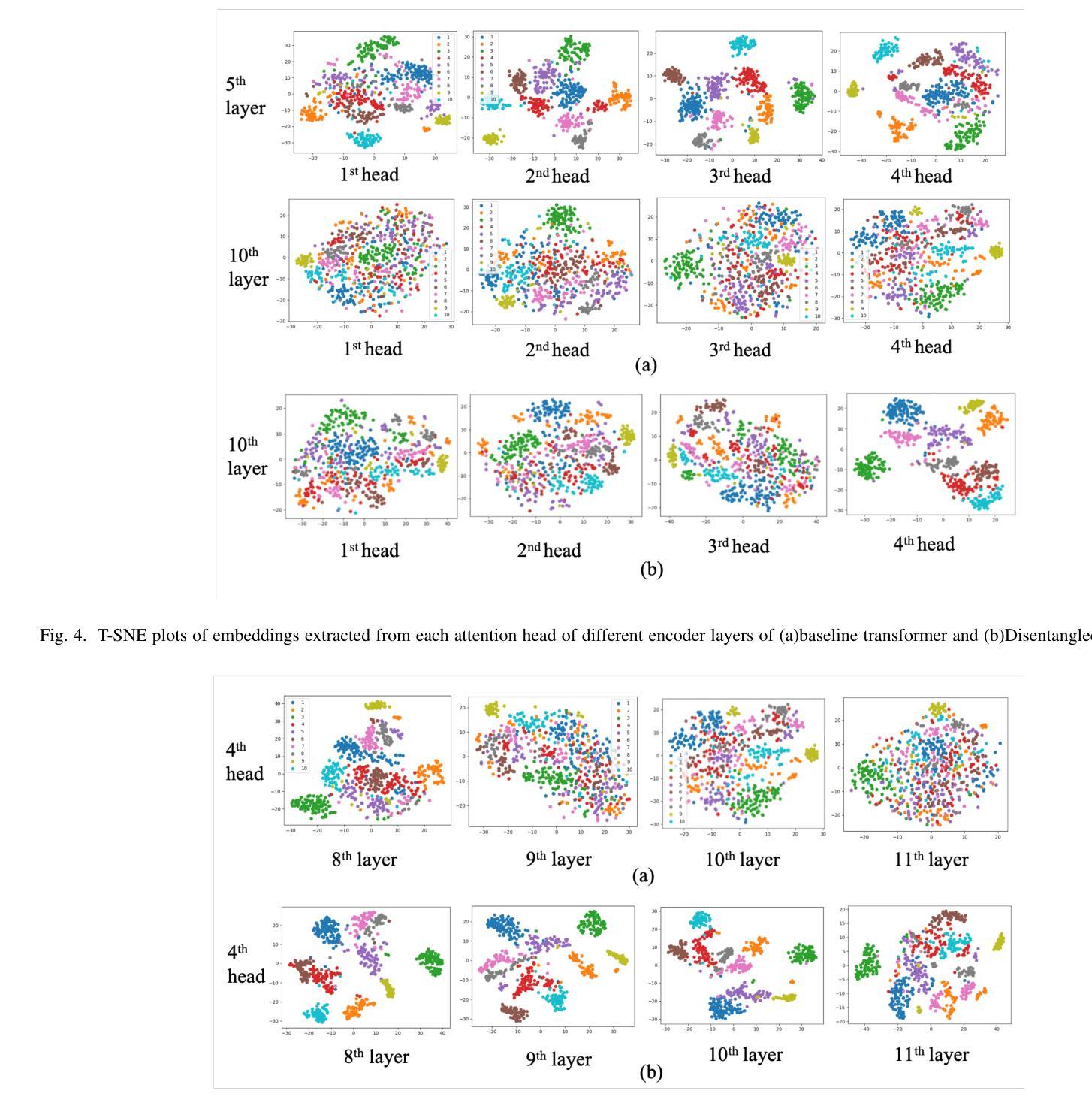
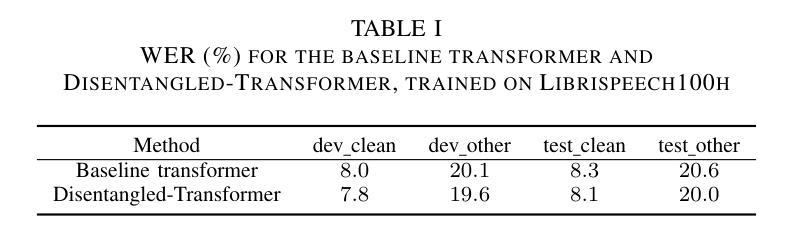
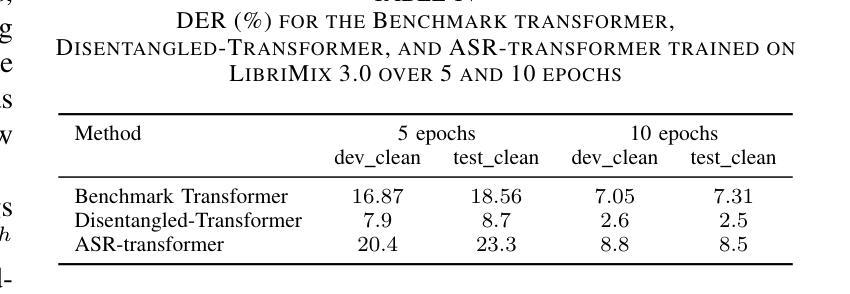
Disentangled-Transformer: An Explainable End-to-End Automatic Speech Recognition Model with Speech Content-Context Separation
Authors:Pu Wang, Hugo Van hamme
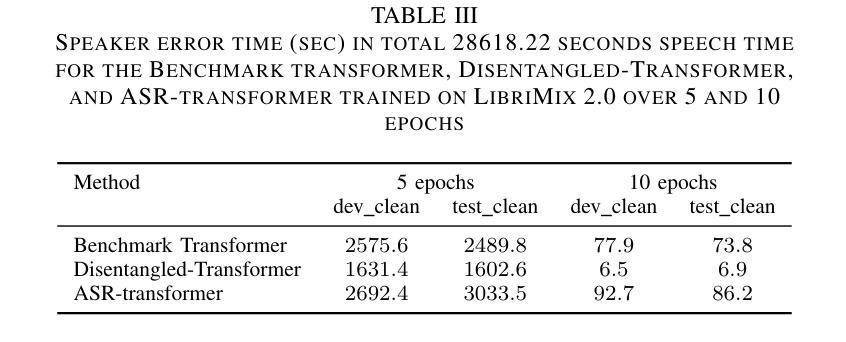
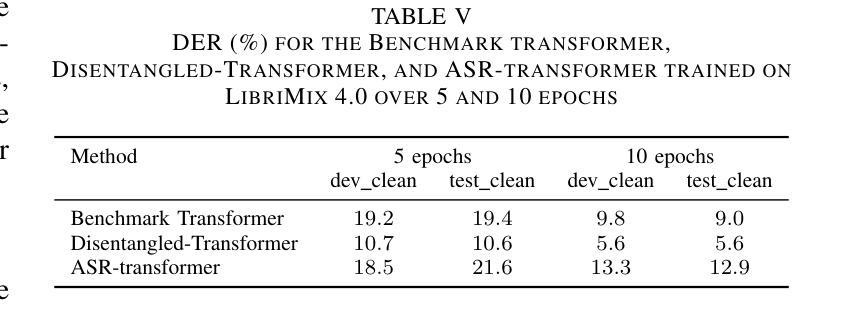
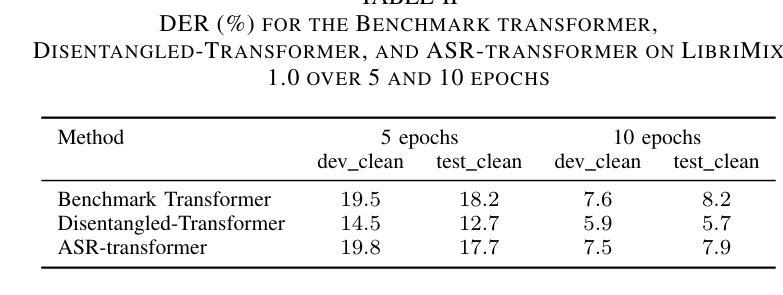
End-to-end transformer-based automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems often capture multiple speech traits in their learned representations that are highly entangled, leading to a lack of interpretability. In this study, we propose the explainable Disentangled-Transformer, which disentangles the internal representations into sub-embeddings with explicit content and speaker traits based on varying temporal resolutions. Experimental results show that the proposed Disentangled-Transformer produces a clear speaker identity, separated from the speech content, for speaker diarization while improving ASR performance.
基于端到端的转换器自动语音识别(ASR)系统在其学习到的表示中通常会捕获多个高度纠缠的语音特征,导致缺乏可解释性。本研究提出了可解释的解纠缠转换器(Disentangled-Transformer),该转换器将内部表示解纠缠为具有明确内容和说话者特征的子嵌入,基于不同的时间分辨率。实验结果表明,所提出的解纠缠转换器在说话人身份辨析中能够清晰地产生与语音内容分离的说话人身份,同时提高ASR性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the 6th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing Applications and Systems
Summary:本研究提出了可解释的解纠缠转换器(Disentangled-Transformer),该转换器可将端到端的基于转换器的自动语音识别(ASR)系统的内部表示形式解纠缠为具有明确内容和说话者特征的子嵌入,基于不同的时间分辨率。实验结果表明,所提出的解纠缠转换器在说话人身份清晰分离的情况下,提高了语音内容的识别性能,并可用于说话人摘要化。
Key Takeaways:
- 端到端的基于转换器的ASR系统存在多个语音特征高度纠缠的问题,导致缺乏可解释性。
- 研究提出了可解释的解纠缠转换器(Disentangled-Transformer)来解决这一问题。
- 解纠缠转换器能够将内部表示形式转化为子嵌入,这些子嵌入具有明确的内容和说话者特征。
- 基于不同的时间分辨率,解纠缠转换器实现了这一转化。
- 实验证明,解纠缠转换器能够清晰地分离说话人的身份和语音内容。
- 解纠缠转换器在说话人身份清晰分离的情况下,提高了语音内容的识别性能。
点此查看论文截图

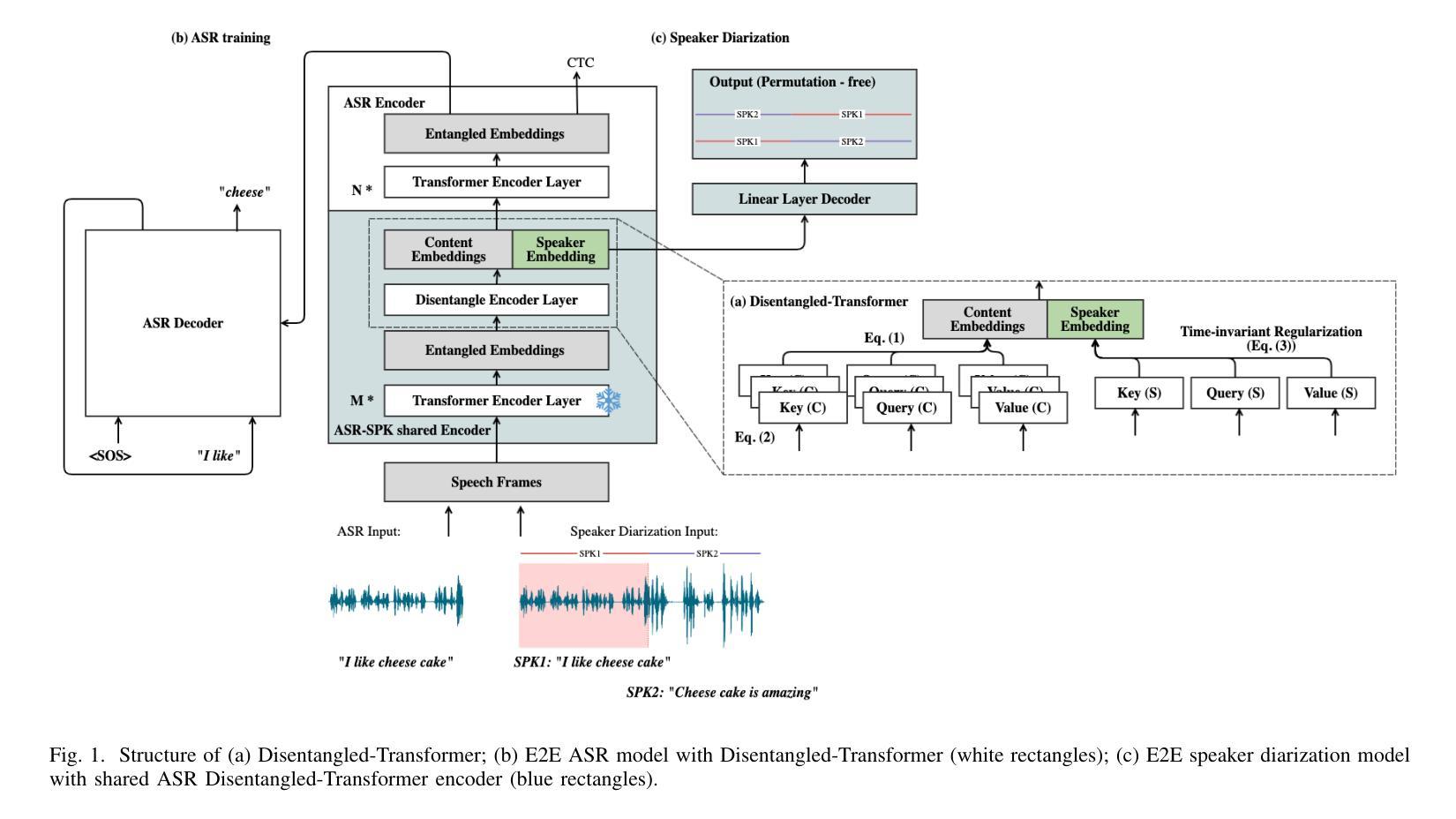
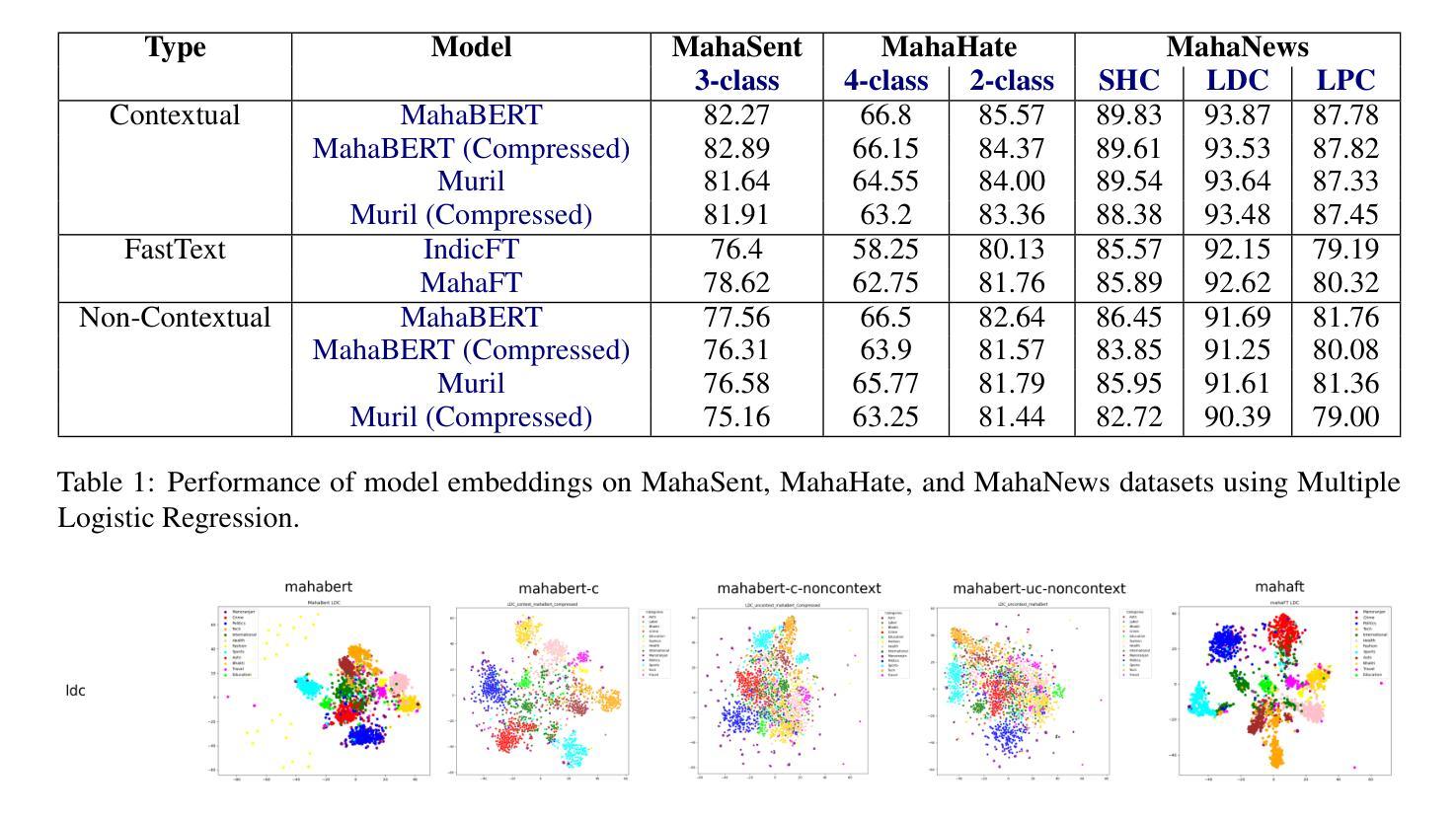
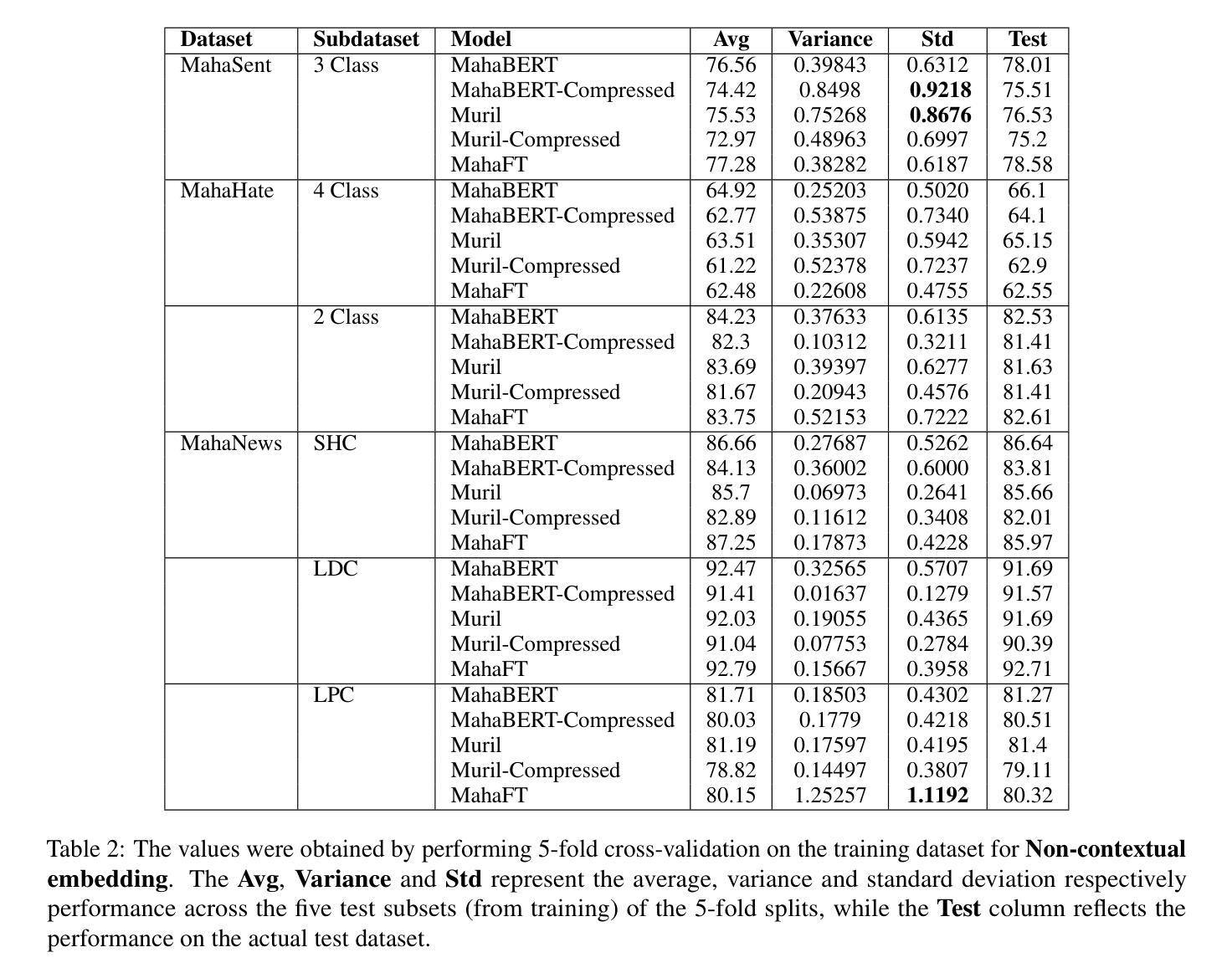
BERT or FastText? A Comparative Analysis of Contextual as well as Non-Contextual Embeddings
Authors:Abhay Shanbhag, Suramya Jadhav, Amogh Thakurdesai, Ridhima Sinare, Raviraj Joshi
Natural Language Processing (NLP) for low-resource languages presents significant challenges, particularly due to the scarcity of high-quality annotated data and linguistic resources. The choice of embeddings plays a critical role in enhancing the performance of NLP tasks, such as news classification, sentiment analysis, and hate speech detection, especially for low-resource languages like Marathi. In this study, we investigate the impact of various embedding techniques- Contextual BERT-based, Non-Contextual BERT-based, and FastText-based on NLP classification tasks specific to the Marathi language. Our research includes a thorough evaluation of both compressed and uncompressed embeddings, providing a comprehensive overview of how these embeddings perform across different scenarios. Specifically, we compare two BERT model embeddings, Muril and MahaBERT, as well as two FastText model embeddings, IndicFT and MahaFT. Our evaluation includes applying embeddings to a Multiple Logistic Regression (MLR) classifier for task performance assessment, as well as TSNE visualizations to observe the spatial distribution of these embeddings. The results demonstrate that contextual embeddings outperform non-contextual embeddings. Furthermore, BERT-based non-contextual embeddings extracted from the first BERT embedding layer yield better results than FastText-based embeddings, suggesting a potential alternative to FastText embeddings.
自然语言处理(NLP)对于低资源语言来说存在重大挑战,尤其是因为高质量标注数据和语言资源的稀缺。嵌入层的选择在提高NLP任务性能中起着关键作用,例如新闻分类、情感分析和仇恨言论检测,特别是对于像马拉地语这样的低资源语言。在这项研究中,我们调查了多种嵌入技术的影响,包括基于上下文的BERT、非基于上下文的BERT和基于FastText的技术,这些技术对马拉地语特定的NLP分类任务具有重要影响。我们的研究包括对压缩和非压缩嵌入的彻底评估,全面概述了这些嵌入在不同场景中的表现。具体来说,我们比较了两种BERT模型嵌入(Muril和MahaBERT),以及两种FastText模型嵌入(IndicFT和MahaFT)。我们的评估包括将这些嵌入应用于多重逻辑回归(MLR)分类器进行任务性能评估,并使用TSNE可视化观察这些嵌入的空间分布。结果表明,上下文嵌入优于非上下文嵌入。此外,从BERT嵌入的第一层提取的基于BERT的非上下文嵌入比基于FastText的嵌入产生更好的结果,这可能成为FastText嵌入的一种潜在替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了自然语言处理(NLP)在低资源语言面临的挑战,特别是高质量标注数据和语言资源的稀缺性。文章聚焦于嵌入技术对提升NLP任务性能的重要性,如新闻分类、情感分析和仇恨言论检测,特别是针对低资源语言如马拉地语。本研究评估了多种嵌入技术的影响,包括基于上下文的BERT、非上下文的BERT和基于FastText的嵌入技术,在马拉地语NLP分类任务中的表现。文章全面评价了压缩和非压缩嵌入,并通过实例展示其在不同场景中的应用效果。结果表明,上下文嵌入技术优于非上下文嵌入技术,基于BERT的非上下文嵌入表现优于基于FastText的嵌入,成为潜在的替代方案。
Key Takeaways
- 低资源语言NLP面临的主要挑战是高质量标注数据和语言资源的稀缺性。
- 嵌入技术对于提升NLP任务性能至关重要,特别是在低资源语言环境下。
- 研究评估了基于上下文的BERT、非上下文的BERT和基于FastText的嵌入技术在马拉地语NLP分类任务中的应用。
- 上下文嵌入技术表现优于非上下文嵌入技术。
- 基于BERT的非上下文嵌入在新闻分类、情感分析和仇恨言论检测等任务中表现优异。
- 相比基于FastText的嵌入技术,BERT非上下文嵌入提供了一种潜在替代方案。
点此查看论文截图

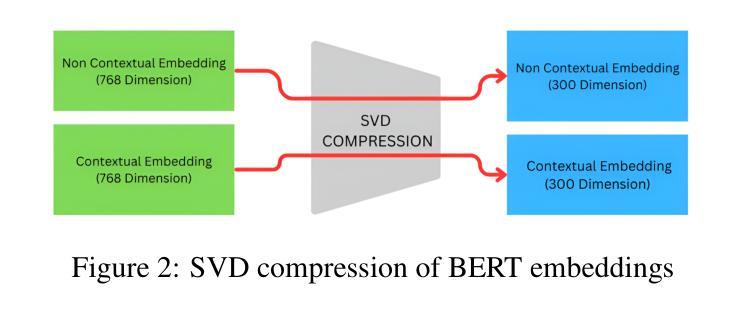
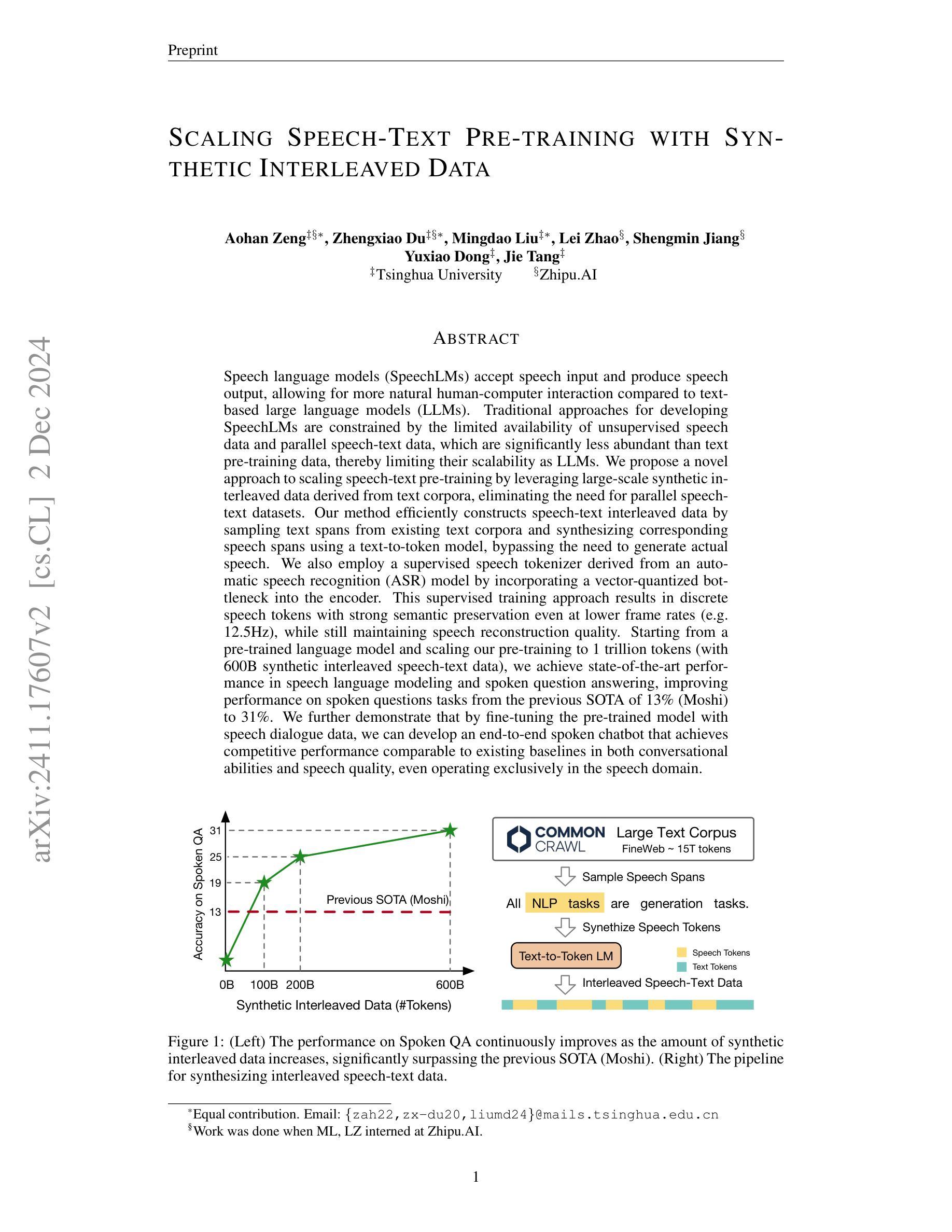
Scaling Speech-Text Pre-training with Synthetic Interleaved Data
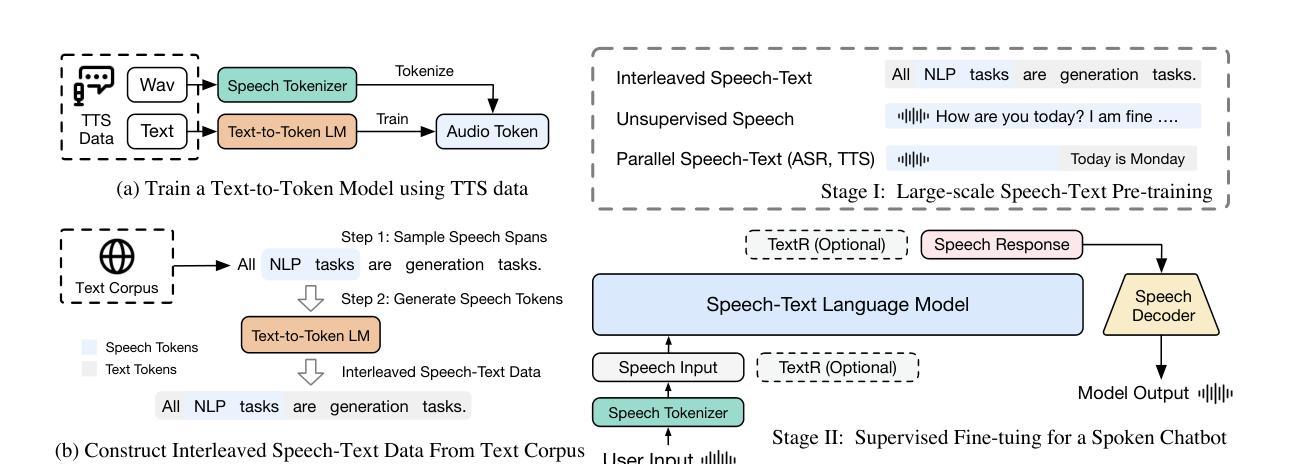
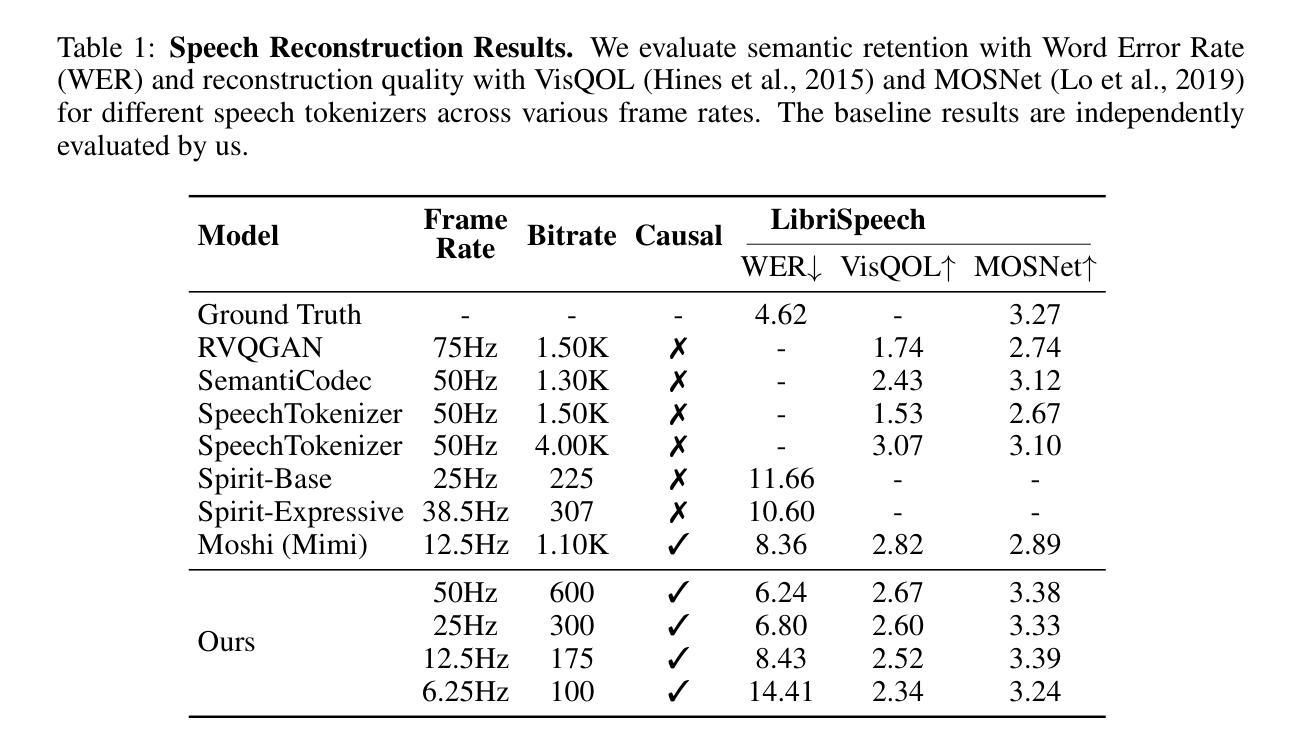
Authors:Aohan Zeng, Zhengxiao Du, Mingdao Liu, Lei Zhang, Shengmin Jiang, Yuxiao Dong, Jie Tang
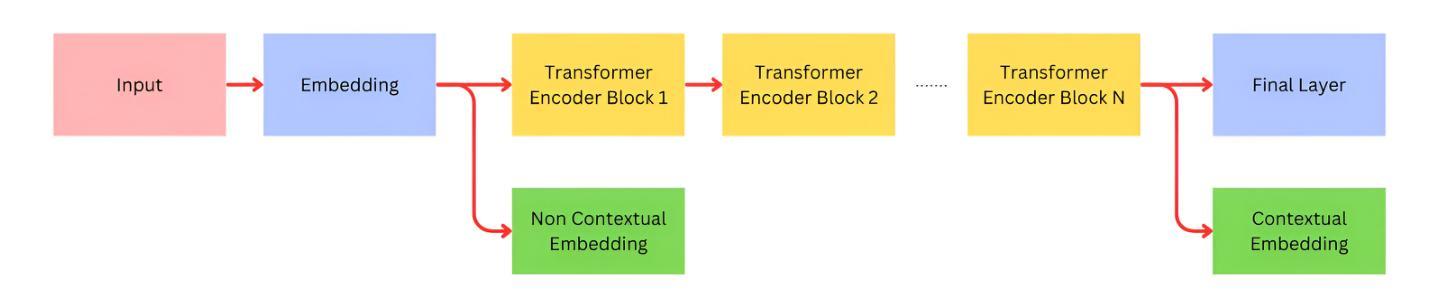
Speech language models (SpeechLMs) accept speech input and produce speech output, allowing for more natural human-computer interaction compared to text-based large language models (LLMs). Traditional approaches for developing SpeechLMs are constrained by the limited availability of unsupervised speech data and parallel speech-text data, which are significantly less abundant than text pre-training data, thereby limiting their scalability as LLMs. We propose a novel approach to scaling speech-text pre-training by leveraging large-scale synthetic interleaved data derived from text corpora, eliminating the need for parallel speech-text datasets. Our method efficiently constructs speech-text interleaved data by sampling text spans from existing text corpora and synthesizing corresponding speech spans using a text-to-token model, bypassing the need to generate actual speech. We also employ a supervised speech tokenizer derived from an automatic speech recognition (ASR) model by incorporating a vector-quantized bottleneck into the encoder. This supervised training approach results in discrete speech tokens with strong semantic preservation even at lower frame rates (e.g. 12.5Hz), while still maintaining speech reconstruction quality. Starting from a pre-trained language model and scaling our pre-training to 1 trillion tokens (with 600B synthetic interleaved speech-text data), we achieve state-of-the-art performance in speech language modeling and spoken question answering, improving performance on spoken questions tasks from the previous SOTA of 13% (Moshi) to 31%. We further demonstrate that by fine-tuning the pre-trained model with speech dialogue data, we can develop an end-to-end spoken chatbot that achieves competitive performance comparable to existing baselines in both conversational abilities and speech quality, even operating exclusively in the speech domain.
语音语言模型(SpeechLMs)接受语音输入并产生语音输出,与基于文本的大型语言模型(LLMs)相比,实现了更自然的人机交互。传统开发SpeechLMs的方法受限于监督语音数据的有限可用性,以及与文本预训练数据相比,并行语音-文本数据明显不足,从而限制了其可扩展性。我们提出了一种利用从文本语料库衍生的大规模合成交织数据来扩展语音-文本预训练的新方法,从而消除了对并行语音-文本数据集的需求。我们的方法通过从现有文本语料库中采样文本片段并使用文本到标记模型合成相应的语音片段,有效地构建了语音-文本交织数据,从而无需生成实际语音。我们还通过使用自动语音识别(ASR)模型并融入向量量化瓶颈到编码器中来建立监督语音标记器。这种监督训练方法即使在较低帧率(例如12.5Hz)下也能产生具有强烈语义保留的离散语音标记,同时仍保持语音重建质量。从一个预训练的语言模型开始,我们将预训练扩展到1万亿个标记(使用600B合成交织语音-文本数据),在语音语言建模和口语问答方面达到最新技术水平,口语问答任务的性能从之前的最佳水平13%(莫希)提高到31%。我们进一步证明,通过对预训练模型使用语音对话数据进行微调,我们可以开发一种端到端的口语聊天机器人,即使在语音领域,其在对话能力和语音质量方面的表现也可与现有基线相媲美。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了基于文本的语音语言模型的构建方法,该模型使用大规模合成交错数据对预训练模型进行扩展。使用这种方法可以避免对传统并行语音文本的依赖,更有效地构造语音文本交错数据,并提高性能表现。通过在端到端的语音聊天机器人中进行微调,该模型在对话能力和语音质量方面取得了显著的进展。
Key Takeaways
- 语音语言模型(SpeechLMs)接受语音输入并产生语音输出,与传统基于文本的大型语言模型相比,更加自然和人性化。
- 传统语音语言模型的发展受限于缺乏监督的语音数据和并行语音文本数据。提出了一个新型预训练方法,即通过大规模合成交错数据来解决这个问题。无需实际语音数据的生成过程也能高效构建模型。
- 提出一种有效的数据构建方式,通过从现有文本语料库中采样文本片段并使用文本到标记模型合成相应的语音片段来合成语音数据。这种方法避免了生成实际语音数据的复杂性。
- 利用来自自动语音识别模型的矢量量化瓶颈信息创建有监督的语音分词器。此训练方法可以实现较低频率(如每秒仅产生一次)的离散语音标记,同时保持语义保留和语音重建质量。
- 通过扩展到大量预训练数据(如高达一千亿个标记),这种新型预训练方法提高了语音语言建模和口语问答的性能表现,达到业界领先水平。
- 通过微调预训练模型与语音对话数据,成功开发出具有竞争力的端到端口语聊天机器人,其对话能力和语音质量均表现良好。该机器人在口语任务上的表现优于现有基准测试水平。
点此查看论文截图
X-CrossNet: A complex spectral mapping approach to target speaker extraction with cross attention speaker embedding fusion
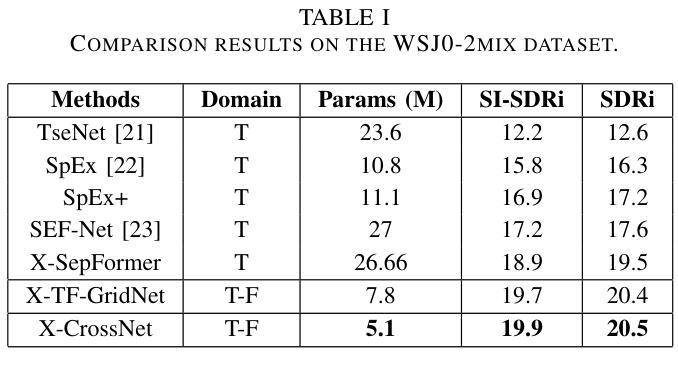
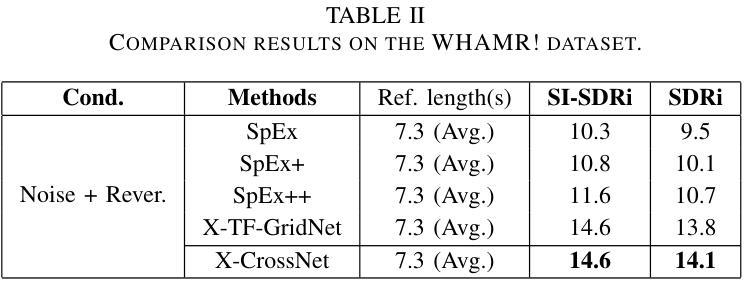
Authors:Chang Sun, Bo Qin
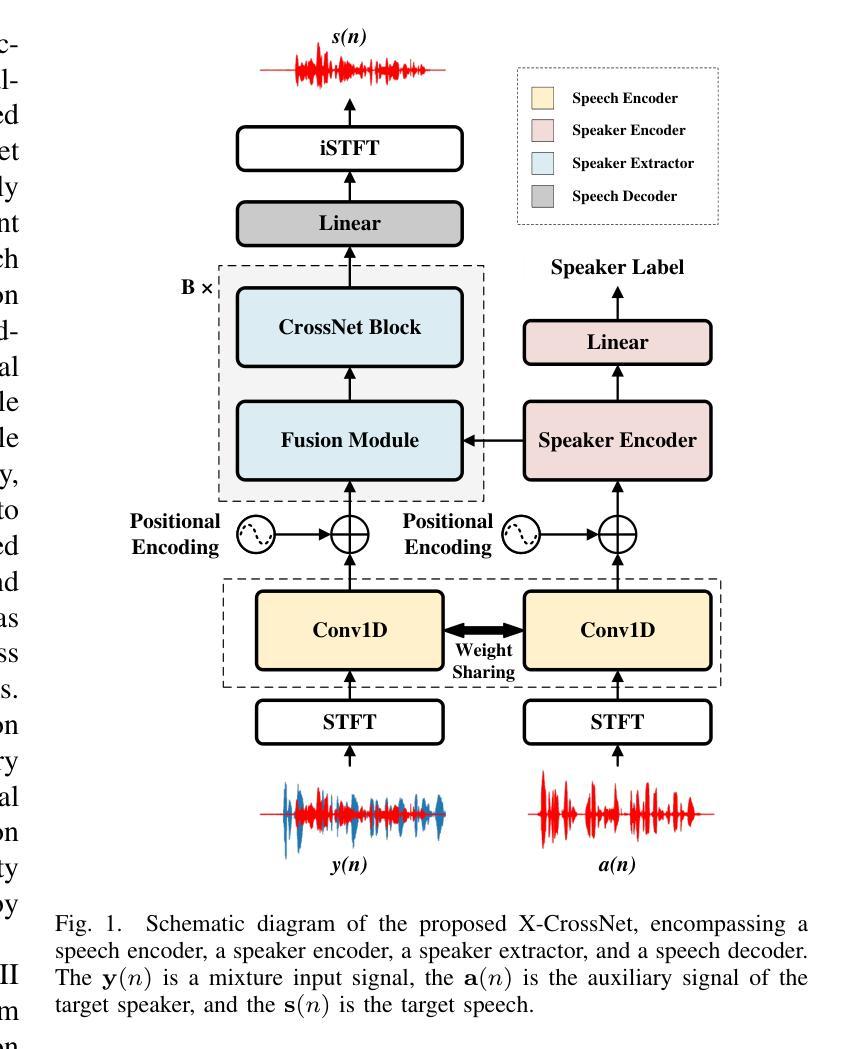
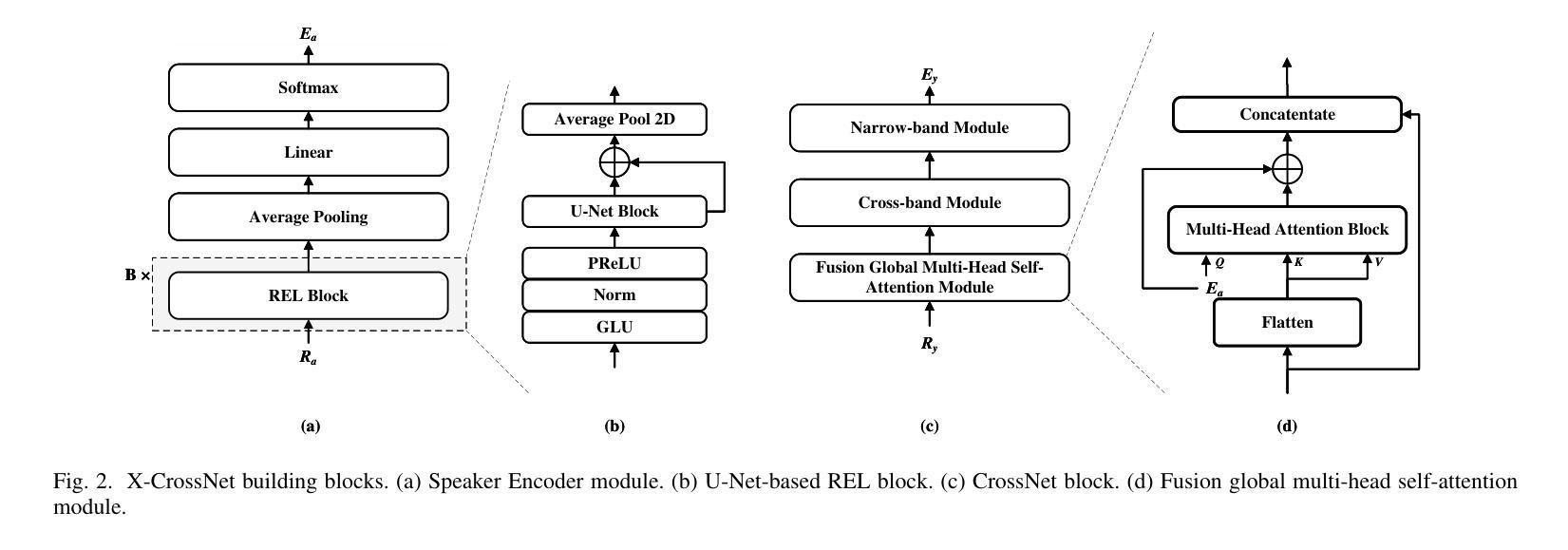
Target speaker extraction (TSE) is a technique for isolating a target speaker’s voice from mixed speech using auxiliary features associated with the target speaker. It is another attempt at addressing the cocktail party problem and is generally considered to have more practical application prospects than traditional speech separation methods. Although academic research in this area has achieved high performance and evaluation scores on public datasets, most models exhibit significantly reduced performance in real-world noisy or reverberant conditions. To address this limitation, we propose a novel TSE model, X-CrossNet, which leverages CrossNet as its backbone. CrossNet is a speech separation network specifically optimized for challenging noisy and reverberant environments, achieving state-of-the-art performance in tasks such as speaker separation under these conditions. Additionally, to enhance the network’s ability to capture and utilize auxiliary features of the target speaker, we integrate a Cross-Attention mechanism into the global multi-head self-attention (GMHSA) module within each CrossNet block. This facilitates more effective integration of target speaker features with mixed speech features. Experimental results show that our method performs superior separation on the WSJ0-2mix and WHAMR! datasets, demonstrating strong robustness and stability.
目标说话人提取(TSE)是一种利用与目标说话人相关的辅助特征从混合语音中分离出目标说话人声音的技术。它是解决鸡尾酒会问题的另一种尝试,并且通常被认为比传统的语音分离方法具有更实际的应用前景。尽管该领域的学术研究在公共数据集上取得了高性能和评估分数,但大多数模型在现实世界中噪声大或混响条件下性能显著下降。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种新型的TSE模型X-CrossNet,它以CrossNet作为骨干网。CrossNet是一种针对噪声大和混响等挑战环境的语音分离网络,在这些条件下,它在说话人分离等任务上实现了最先进的性能。此外,为了提高网络捕获和利用目标说话人的辅助特征的能力,我们将交叉注意机制集成到每个CrossNet块内的全局多头自注意(GMHSA)模块中。这有助于更有效地将目标说话人的特征与混合语音特征结合起来。实验结果表明,我们的方法在WSJ0-2mix和WHAMR!数据集上实现了出色的分离效果,显示出强大的鲁棒性和稳定性。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
目标说话人提取(TSE)技术通过利用目标说话人的辅助特征来从混合语音中分离出目标说话人的声音。尽管在公共数据集上的学术研究取得了高性能和评价分数,但在现实世界的嘈杂或混响环境中,大多数模型的性能会显著降低。为解决这一局限,我们提出一种新型TSE模型X-CrossNet,以CrossNet作为骨干。CrossNet是针对嘈杂和混响环境优化的语音分离网络,在这些条件下实现了最先进的性能。此外,为提高网络捕捉和利用目标说话人的辅助特征的能力,我们在每个CrossNet块的全球多头自注意力(GMHSA)模块中集成了交叉注意力机制。这有助于更有效地整合目标说话人的特征与混合语音特征。实验结果表明,我们的方法在WSJ0-2mix和WHAMR!数据集上实现了出色的分离性能,显示出强大的稳健性和稳定性。
关键见解
- 目标说话人提取(TSE)旨在从混合语音中隔离目标说话人的声音,使用与目标说话人相关的辅助特征。
- 现有模型在嘈杂或混响的现实中环境中性能降低。
- 提出的X-CrossNet模型以CrossNet为骨干,针对挑战性的嘈杂和混响环境进行了优化。
- 在每个CrossNet块的GMHSA模块中集成了交叉注意力机制,以更有效地整合目标说话人的特征与混合语音特征。
- X-CrossNet在WSJ0-2mix和WHAMR!数据集上实现了出色的分离性能。
- 该方法具有强大的稳健性和稳定性。
点此查看论文截图

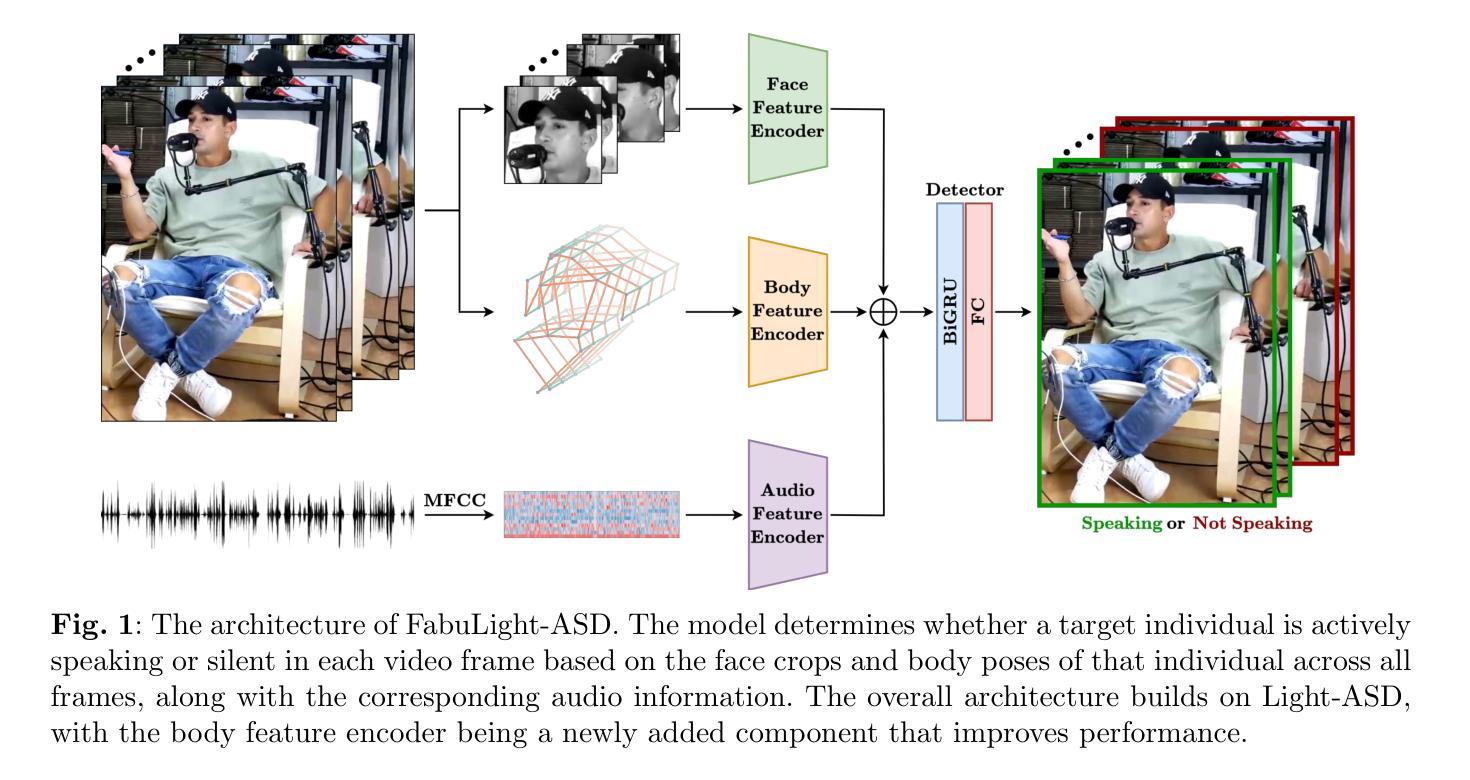
FabuLight-ASD: Unveiling Speech Activity via Body Language
Authors:Hugo Carneiro, Stefan Wermter
Active speaker detection (ASD) in multimodal environments is crucial for various applications, from video conferencing to human-robot interaction. This paper introduces FabuLight-ASD, an advanced ASD model that integrates facial, audio, and body pose information to enhance detection accuracy and robustness. Our model builds upon the existing Light-ASD framework by incorporating human pose data, represented through skeleton graphs, which minimises computational overhead. Using the Wilder Active Speaker Detection (WASD) dataset, renowned for reliable face and body bounding box annotations, we demonstrate FabuLight-ASD’s effectiveness in real-world scenarios. Achieving an overall mean average precision (mAP) of 94.3%, FabuLight-ASD outperforms Light-ASD, which has an overall mAP of 93.7% across various challenging scenarios. The incorporation of body pose information shows a particularly advantageous impact, with notable improvements in mAP observed in scenarios with speech impairment, face occlusion, and human voice background noise. Furthermore, efficiency analysis indicates only a modest increase in parameter count (27.3%) and multiply-accumulate operations (up to 2.4%), underscoring the model’s efficiency and feasibility. These findings validate the efficacy of FabuLight-ASD in enhancing ASD performance through the integration of body pose data. FabuLight-ASD’s code and model weights are available at https://github.com/knowledgetechnologyuhh/FabuLight-ASD.
在多媒体环境中,主动说话者检测(ASD)对于从视频会议到人机交互的各种应用都至关重要。本文介绍了FabuLight-ASD,这是一种先进的ASD模型,它集成了面部、音频和身体姿势信息,以提高检测准确性和稳健性。我们的模型基于现有的Light-ASD框架,通过融入通过骨骼图表示的人体姿势数据,以最小化计算开销。我们使用以可靠的脸部和身体边界框注释而闻名的Wilder Active Speaker Detection(WASD)数据集,展示了FabuLight-ASD在真实场景中的有效性。FabuLight-ASD的总体平均精度(mAP)达到94.3%,优于Light-ASD的93.7%,在各种具有挑战性的场景中表现更佳。融入身体姿势信息产生了特别有利的影响,在言语障碍、面部遮挡和背景人声噪音等场景中,mAP的改进尤为显著。此外,效率分析显示,参数计数仅增加了27.3%,乘法累加运算增加了高达2.4%,这突显了模型的效率和可行性。这些发现验证了FabuLight-ASD通过整合身体姿势数据提高ASD性能的有效性。FabuLight-ASD的代码和模型权重可在https://github.com/knowledgetechnologyuhh/FabuLight-ASD获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 23 pages, 8 figures, 3 tables, accepted for publication in Neural Computing and Applications
摘要
基于人脸、音频和身体姿态的多模态主动说话人检测。
要点掌握
- 主动说话者检测(ASD)在多模态环境中对于视频会议、人机交互等应用至关重要。
- FabuLight-ASD是一个先进的ASD模型,集成了面部、音频和身体姿态信息,提高了检测准确性和稳健性。
- 该模型基于Light-ASD框架,通过引入人体姿态数据(通过骨骼图表示)来优化计算开销。
- 使用著名的Wilder Active Speaker Detection(WASD)数据集进行验证,该数据集具有可靠的人脸和人体边界框注释。
- FabuLight-ASD在多种具有挑战性的场景中实现了平均精度(mAP)为94.3%,优于Light-ASD的93.7%。
- 引入身体姿态信息在多种场景中显著提高了mAP,如在有语音障碍、面部遮挡和背景噪音的情况下。
点此查看论文截图