⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-11 更新
Towards Controllable Speech Synthesis in the Era of Large Language Models: A Survey
Authors:Tianxin Xie, Yan Rong, Pengfei Zhang, Li Liu
Text-to-speech (TTS), also known as speech synthesis, is a prominent research area that aims to generate natural-sounding human speech from text. Recently, with the increasing industrial demand, TTS technologies have evolved beyond synthesizing human-like speech to enabling controllable speech generation. This includes fine-grained control over various attributes of synthesized speech such as emotion, prosody, timbre, and duration. Besides, advancements in deep learning, such as diffusion and large language models, have significantly enhanced controllable TTS over the past several years. In this paper, we conduct a comprehensive survey of controllable TTS, covering approaches ranging from basic control techniques to methods utilizing natural language prompts, aiming to provide a clear understanding of the current state of research. We examine the general controllable TTS pipeline, challenges, model architectures, and control strategies, offering a comprehensive and clear taxonomy of existing methods. Additionally, we provide a detailed summary of datasets and evaluation metrics and shed some light on the applications and future directions of controllable TTS. To the best of our knowledge, this survey paper provides the first comprehensive review of emerging controllable TTS methods, which can serve as a beneficial resource for both academic researchers and industry practitioners.
文本转语音(TTS),也称为语音合成,是一个旨在从文本生成听起来很自然的人类语音的重要研究领域。最近,随着工业需求的增加,TTS技术已经超越了合成人类语音的范围,实现了可控的语音生成。这包括合成语音的各种属性的精细控制,如情绪、语调、音质和持续时间。此外,深度学习领域的进步,如扩散和大型语言模型,在过去的几年里显著增强了可控TTS的性能。在本文中,我们对可控TTS进行了全面的调查,涵盖了从基本控制技术到利用自然语言提示的方法等多种方法,旨在提供对研究现状的清晰理解。我们研究了可控TTS的一般流程、挑战、模型架构和控制策略,提供了现有方法的全面而清晰的分类。此外,我们还详细总结了数据集和评估指标,并指出了可控TTS的应用和未来发展方向。据我们所知,这篇综述论文对新兴的可控TTS方法进行了首次全面的回顾,对学术研究人员和工业从业者都大有裨益。
论文及项目相关链接
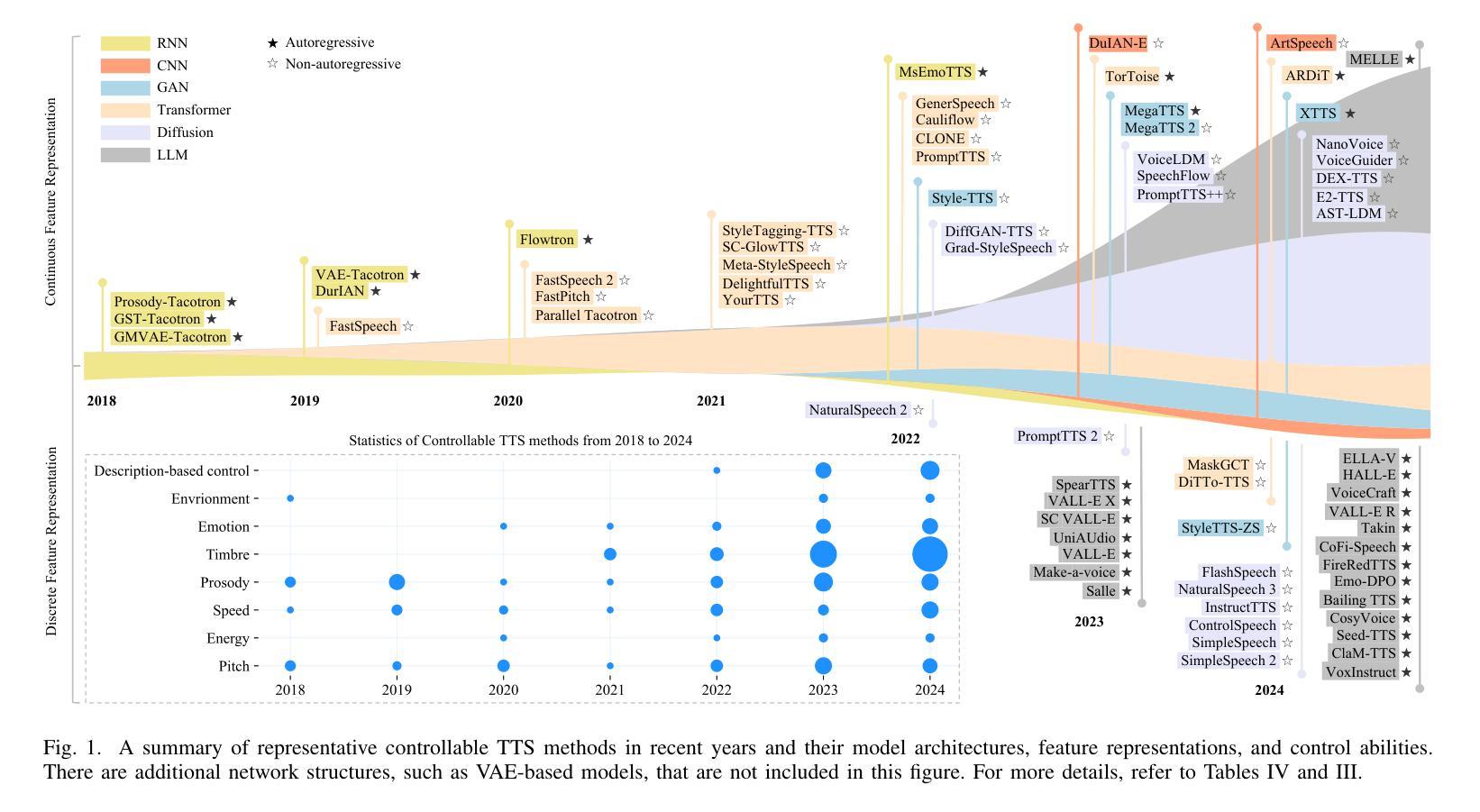
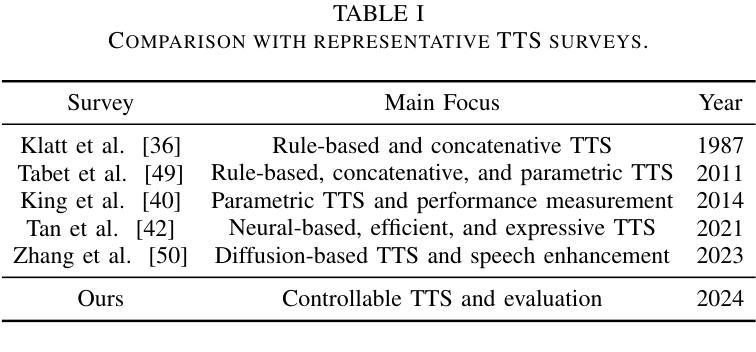
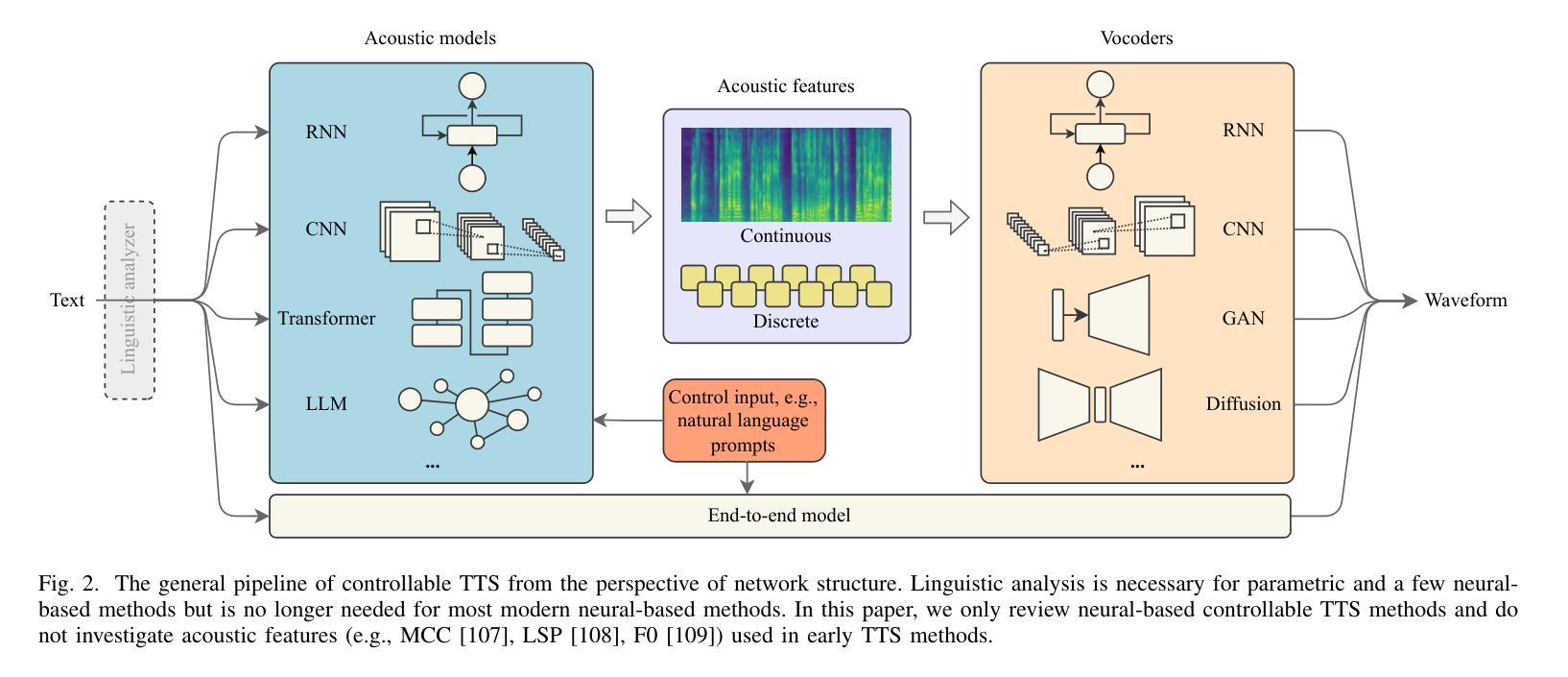
PDF A comprehensive survey on controllable TTS, 23 pages, 6 tables, 4 figures, 280 references
Summary
文本转语音(TTS)也称为语音合成,是一个旨在从文本生成自然声音的人类语音的研究领域。随着工业需求的增长,TTS技术已经超越了合成类似人类语音的阶段,实现了可控的语音生成。这包括对合成语音的各种属性进行精细控制,如情感、语调、音质和持续时间。此外,深度学习的进步,如扩散模型和大型语言模型,显著增强了可控TTS的性能。本文对可控TTS进行了全面调查,涵盖了从基本控制技术到利用自然语言提示的方法,旨在提供对当前研究状态的清晰理解。本文详细探讨了可控TTS的通用管道、挑战、模型架构和控制策略,为现有方法提供了清晰的分类。此外,本文还总结了数据集和评估指标,并对可控TTS的应用和未来方向进行了阐述。本文是对新兴的可控TTS方法的首次全面综述,对学术研究人员和行业从业者都具有参考价值。
Key Takeaways
- TTS技术已经从单纯的模仿人类语音进化到可控的语音生成阶段。
- TTS能够实现精细控制合成语音的各种属性,如情感、语调、音质和持续时间。
- 深度学习的进步如扩散模型和大型语言模型显著提升了可控TTS的性能。
- 论文对可控TTS进行了全面的调查,涵盖了各种方法并提供了清晰的分类。
- 论文详细探讨了可控TTS的通用管道、挑战和模型架构。
- 论文总结了现有的数据集和评估指标,为研究者提供了重要的参考信息。
点此查看论文截图

Text Is Not All You Need: Multimodal Prompting Helps LLMs Understand Humor
Authors:Ashwin Baluja
While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive natural language understanding capabilities across various text-based tasks, understanding humor has remained a persistent challenge. Humor is frequently multimodal, relying on phonetic ambiguity, rhythm and timing to convey meaning. In this study, we explore a simple multimodal prompting approach to humor understanding and explanation. We present an LLM with both the text and the spoken form of a joke, generated using an off-the-shelf text-to-speech (TTS) system. Using multimodal cues improves the explanations of humor compared to textual prompts across all tested datasets.
虽然大型语言模型(LLM)在各种文本任务中表现出了令人印象深刻的自然语言理解能力,但理解幽默仍然是一个持久的挑战。幽默通常是多模式的,依赖于语音的模糊性、节奏和时机来传达意义。在这项研究中,我们探索了一种简单的多模式提示方法来理解并解释幽默。我们向LLM展示了一个笑话的文本和语音形式,该语音形式使用现成的文本到语音(TTS)系统生成。使用多模式线索与仅使用文本提示相比,在所有测试数据集上都能更好地解释幽默。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本研究了大型语言模型(LLM)在理解幽默方面的挑战,并提出了一种简单的多模态提示方法。通过向LLM提供笑话的文本和语音形式,使用多模态线索可以提高幽默解释的效果。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在理解幽默方面存在挑战。
- 幽默是多模态的,依赖于语音的韵律、节奏和时机来传达意义。
- 研究提出了一种简单的多模态提示方法,将文本和语音形式的笑话呈现给LLM。
- 使用多模态线索提高了在所有测试数据集上的幽默解释效果。
- 该方法利用了文本到语音(TTS)系统的生成语音形式。
- 通过结合文本和语音信息,LLM能够更好地理解和解释幽默。
点此查看论文截图

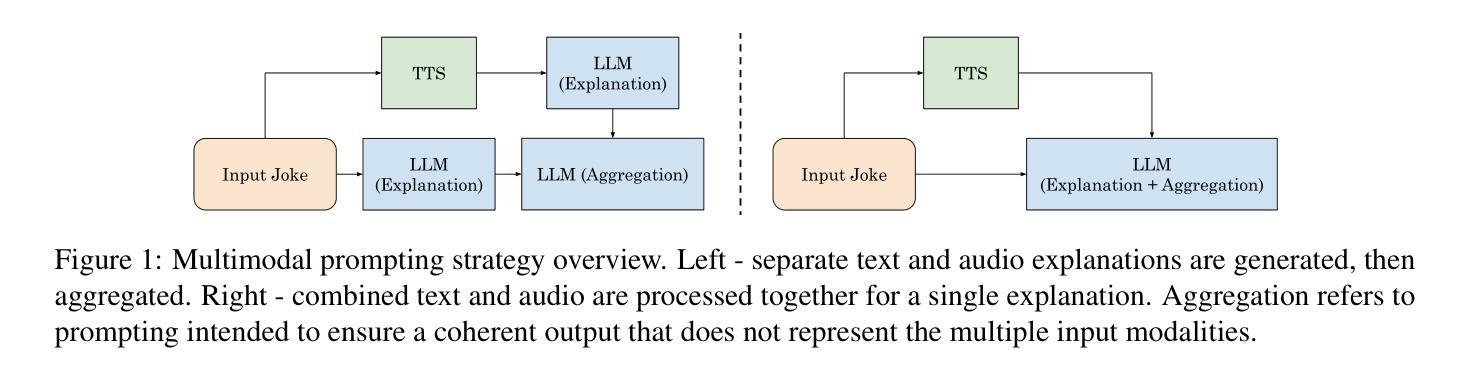
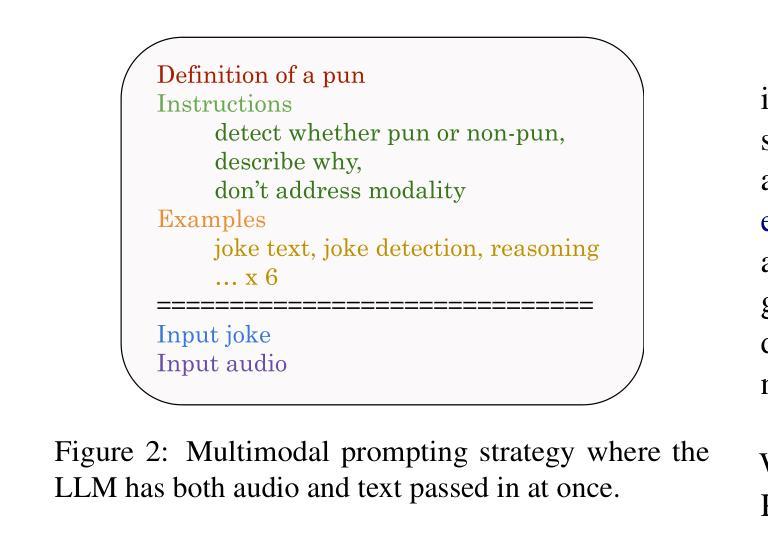
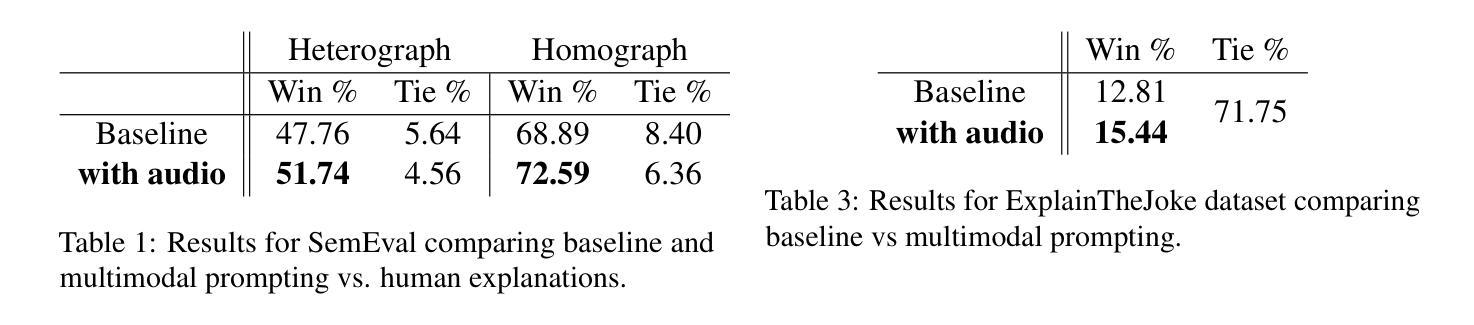
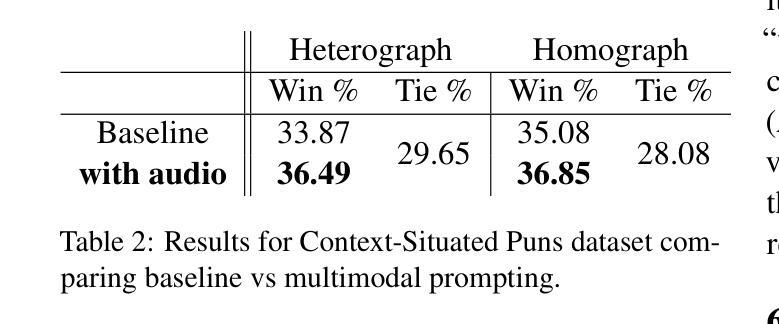
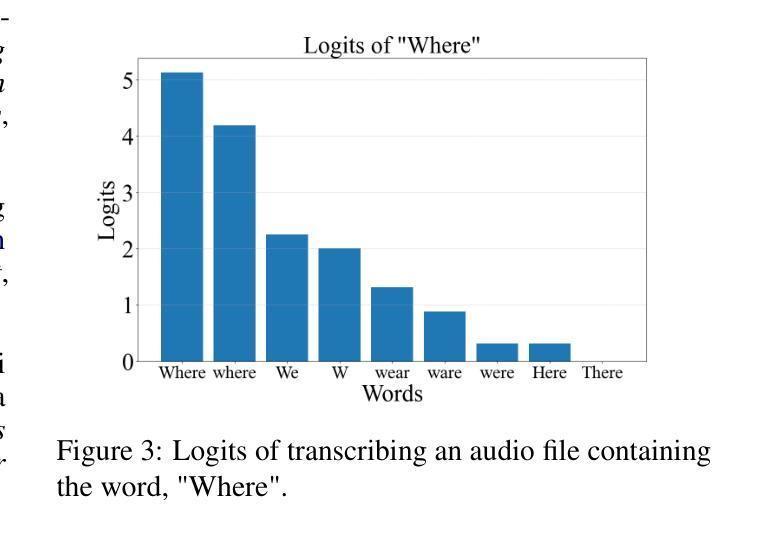
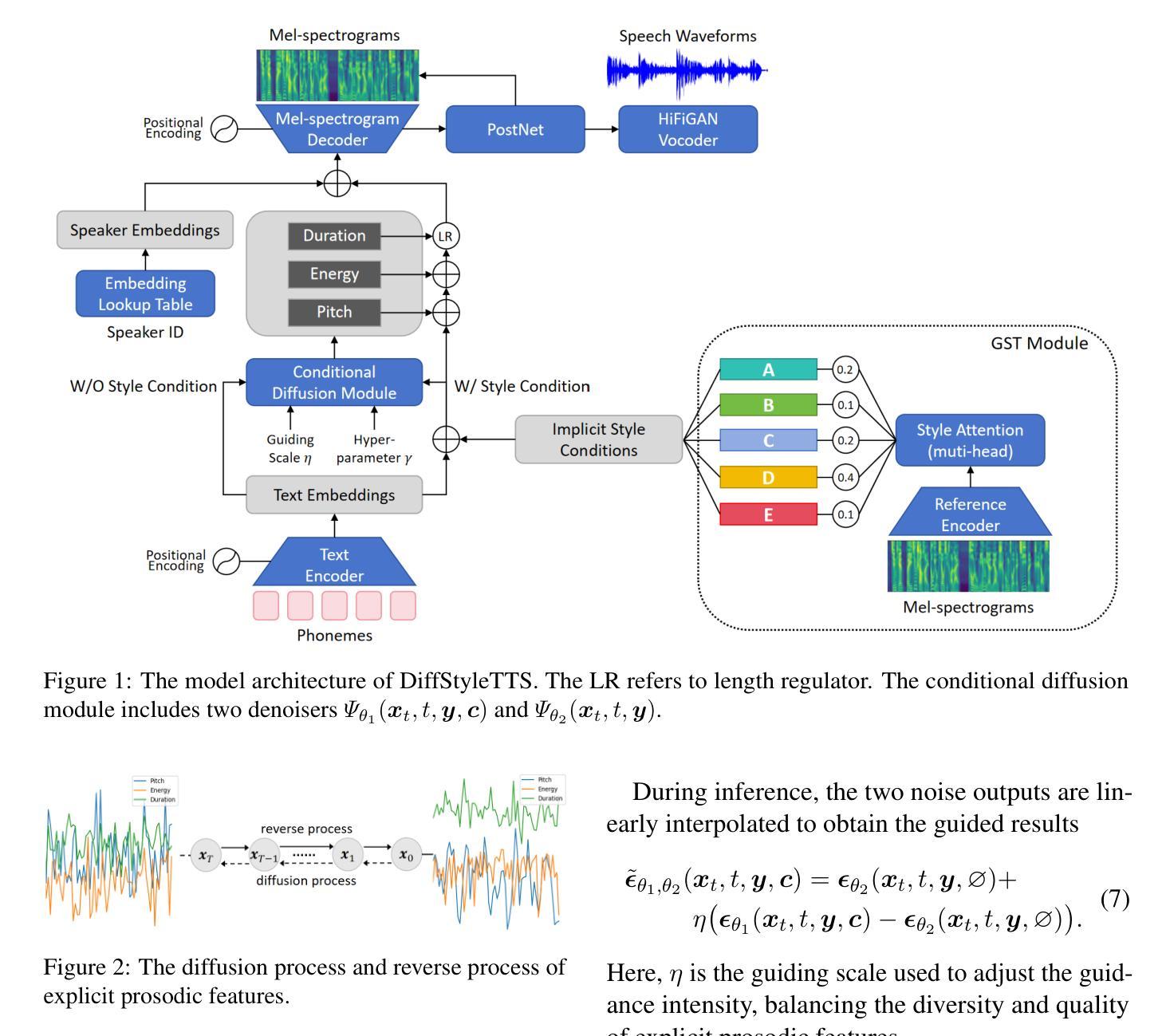
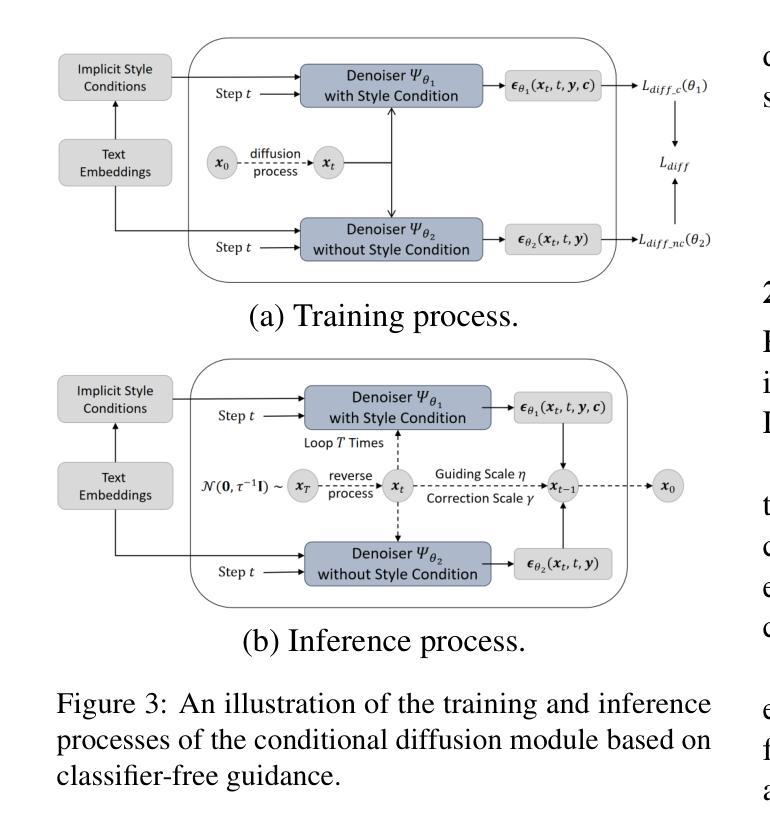
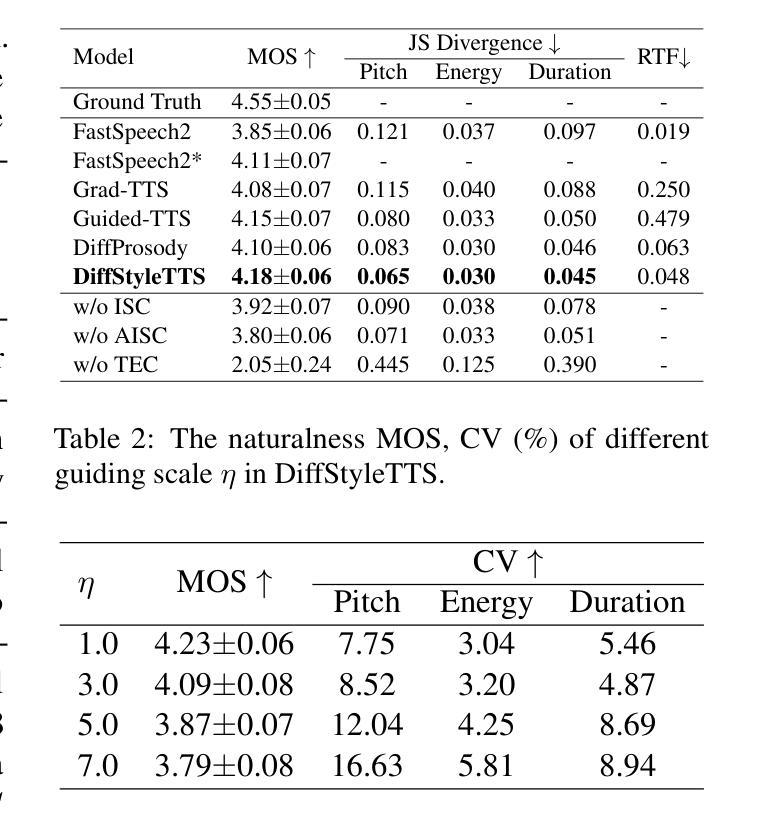
DiffStyleTTS: Diffusion-based Hierarchical Prosody Modeling for Text-to-Speech with Diverse and Controllable Styles
Authors:Jiaxuan Liu, Zhaoci Liu, Yajun Hu, Yingying Gao, Shilei Zhang, Zhenhua Ling
Human speech exhibits rich and flexible prosodic variations. To address the one-to-many mapping problem from text to prosody in a reasonable and flexible manner, we propose DiffStyleTTS, a multi-speaker acoustic model based on a conditional diffusion module and an improved classifier-free guidance, which hierarchically models speech prosodic features, and controls different prosodic styles to guide prosody prediction. Experiments show that our method outperforms all baselines in naturalness and achieves superior synthesis speed compared to three diffusion-based baselines. Additionally, by adjusting the guiding scale, DiffStyleTTS effectively controls the guidance intensity of the synthetic prosody.
人类语音展现出丰富灵活的韵律变化。为了解决文本到韵律的一对多映射问题,并实现合理灵活的方式,我们提出了DiffStyleTTS,这是一种基于条件扩散模块和改进的无分类器引导的多人声音学模型。该模型分层建模语音韵律特征,并通过控制不同的韵律风格来引导韵律预测。实验表明,我们的方法在自然度方面超越了所有基线方法,与三种基于扩散的基线方法相比,合成速度更优越。此外,通过调整引导尺度,DiffStyleTTS可以有效地控制合成韵律的引导强度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF COLING 2025
Summary
文本中提出了DiffStyleTTS,这是一种基于条件扩散模块和改进的无分类器引导的多说话者声学模型。它通过分层建模语音韵律特征和控制不同的韵律风格来指导韵律预测,解决了文本到语音的灵活多变问题。实验表明,该方法在自然性方面优于所有基线方法,并在合成速度方面超过了三个基于扩散的方法。此外,通过调整引导尺度,DiffStyleTTS可以有效地控制合成韵律的引导强度。
Key Takeaways
- DiffStyleTTS是一种多说话者声学模型,基于条件扩散模块和改进的无分类器引导技术。
- 该模型通过分层建模语音韵律特征,解决文本到语音的灵活多变问题。
- DiffStyleTTS能控制不同的韵律风格,以指导韵律预测。
- 实验结果显示,DiffStyleTTS在自然性方面优于其他方法,合成速度也更快。
- 通过调整引导尺度,可以有效地控制合成韵律的引导强度。
- 该模型的应用场景可能包括语音合成、智能语音助手、语音交互等。
点此查看论文截图

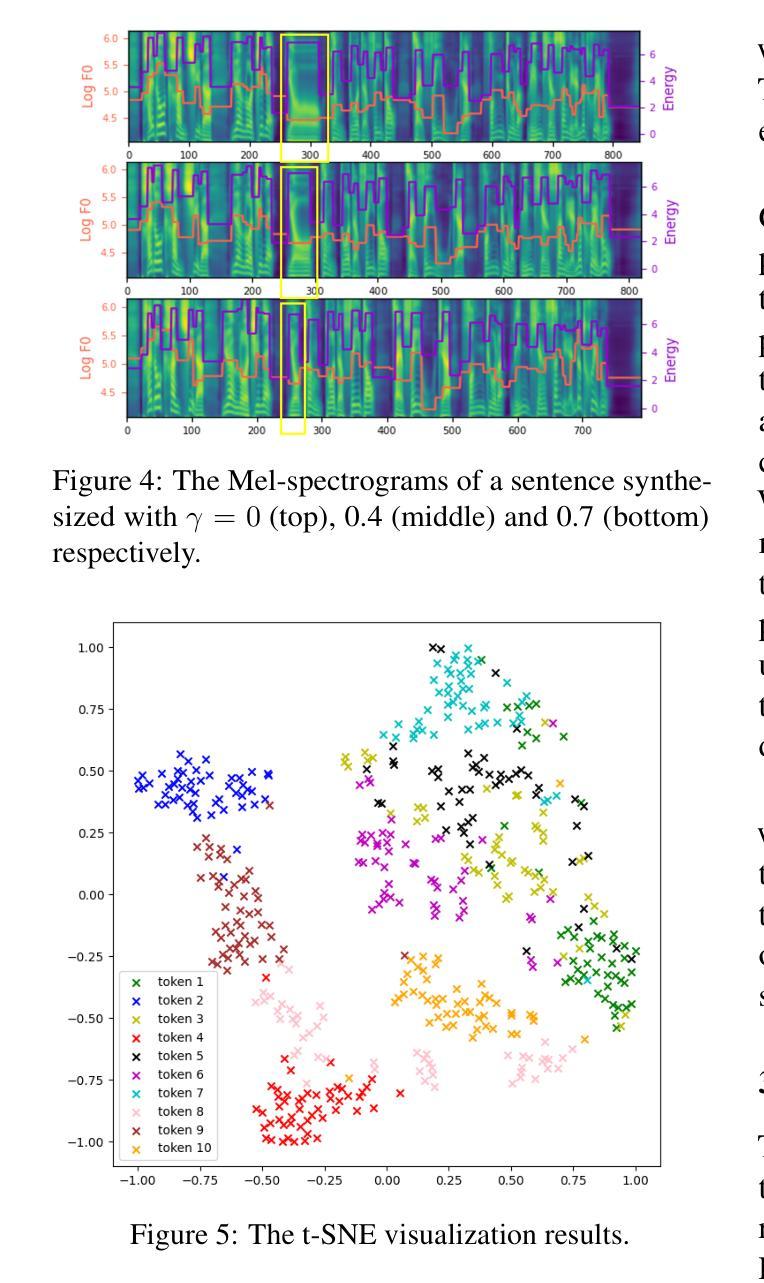
Analytic Study of Text-Free Speech Synthesis for Raw Audio using a Self-Supervised Learning Model
Authors:Joonyong Park, Daisuke Saito, Nobuaki Minematsu
We examine the text-free speech representations of raw audio obtained from a self-supervised learning (SSL) model by analyzing the synthesized speech using the SSL representations instead of conventional text representations. Since raw audio does not have paired speech representations as transcribed texts do, obtaining speech representations from unpaired speech is crucial for augmenting available datasets for speech synthesis. Specifically, the proposed speech synthesis is conducted using discrete symbol representations from the SSL model in comparison with text representations, and analytical examinations of the synthesized speech have been carried out. The results empirically show that using text representations is advantageous for preserving semantic information, while using discrete symbol representations is superior for preserving acoustic content, including prosodic and intonational information.
我们通过分析使用SSL表示法合成的语音,而不是传统的文本表示法,来检查从自监督学习(SSL)模型中获得的原始音频的非文本语音表示。由于原始音频没有像转录文本那样的配对语音表示,因此从非配对语音中获得语音表示对于增强现有语音合成数据集至关重要。具体而言,与文本表示相比,所提出的语音合成是使用SSL模型的离散符号表示来完成的,并对合成的语音进行了分析检查。实证结果表明,使用文本表示法有利于保留语义信息,而使用离散符号表示法则在保留声学内容(包括韵律和语调信息)方面更为优越。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF APSIPA ASC 2024
Summary
本文探讨了使用自监督学习模型从原始音频中获取非文本语音表示的方法,并通过合成语音进行分析。由于原始音频没有像转录文本那样的配对语音表示,因此从非配对语音中获得语音表示对于增强现有语音合成数据集至关重要。本文采用SSL模型的离散符号表示与文本表示进行对比,并对合成语音进行了分析。实证结果表明,使用文本表示有助于保留语义信息,而使用离散符号表示则更擅长保留声音内容,包括韵律和语调信息。
Key Takeaways
- 自监督学习模型可从原始音频获取非文本语音表示。
- 合成语音分析是用于评估这种表示方法的关键手段。
- 由于原始音频没有配套的文本表示,因此需要利用非配对语音来获取语音表示。
- 使用SSL模型的离散符号表示与文本表示在语音合成中各有优势。
- 文本表示有助于保留语义信息。
- 离散符号表示更擅长保留声音内容,如韵律和语调信息。
点此查看论文截图

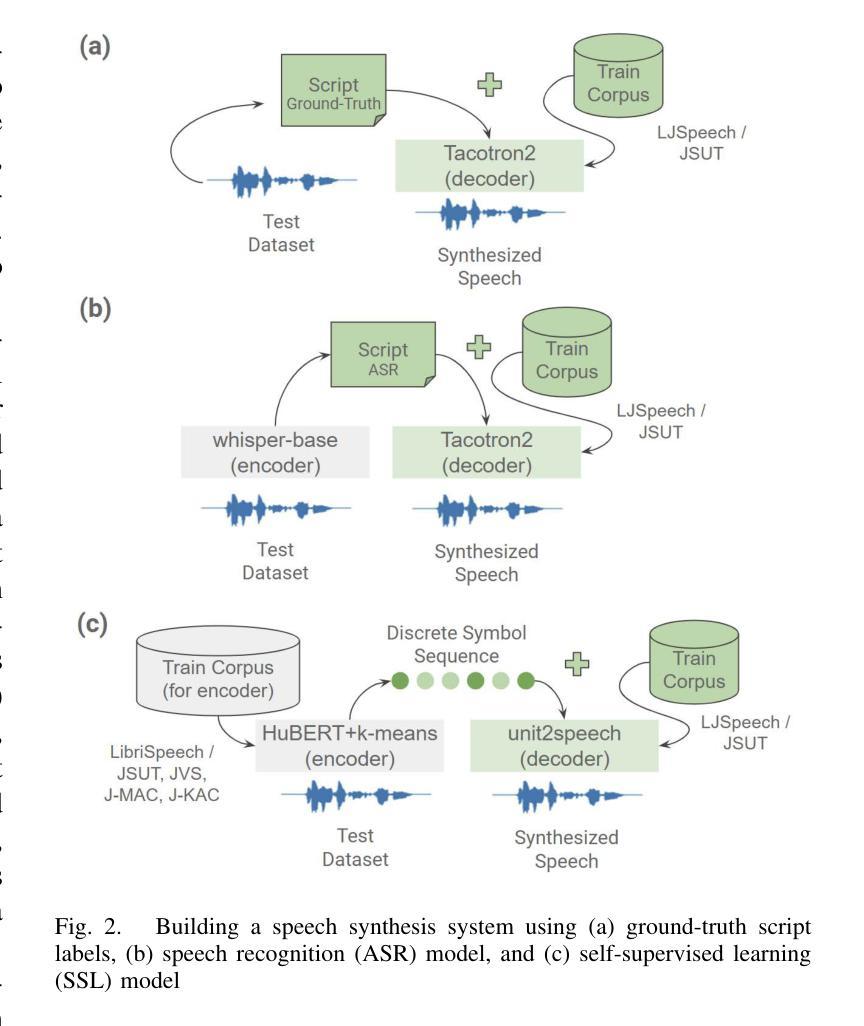
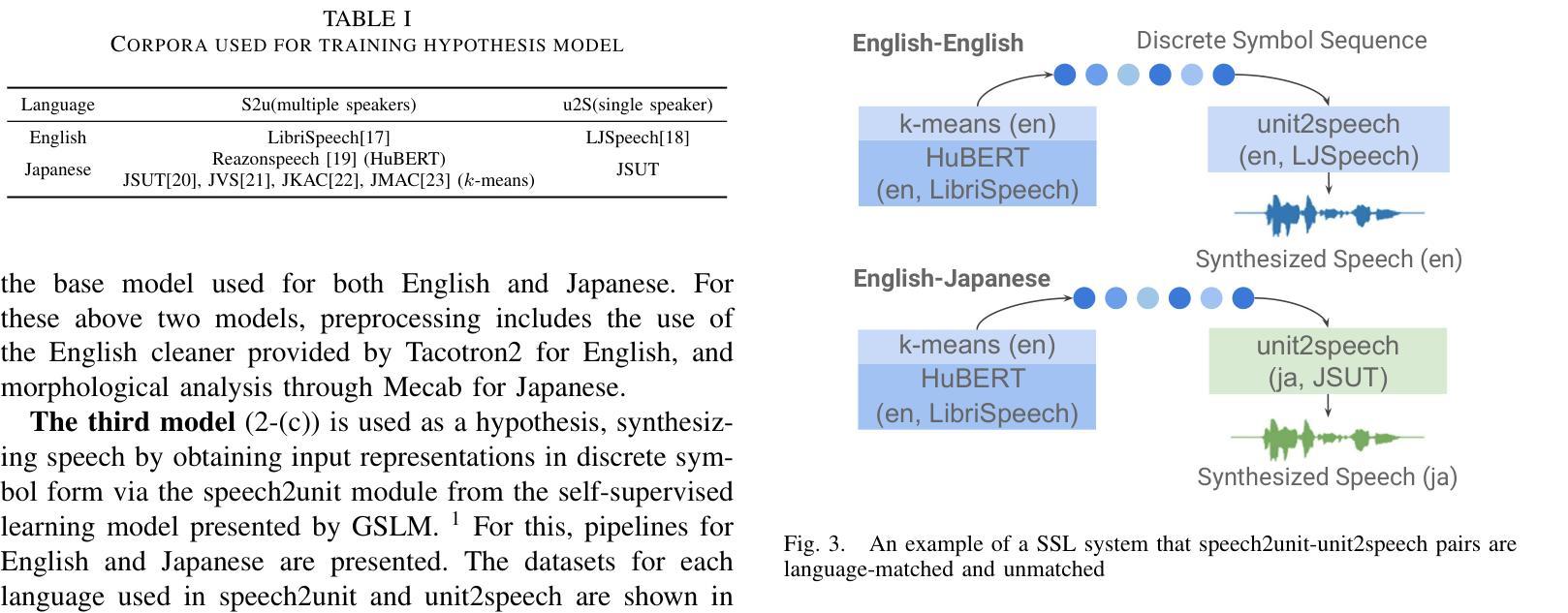
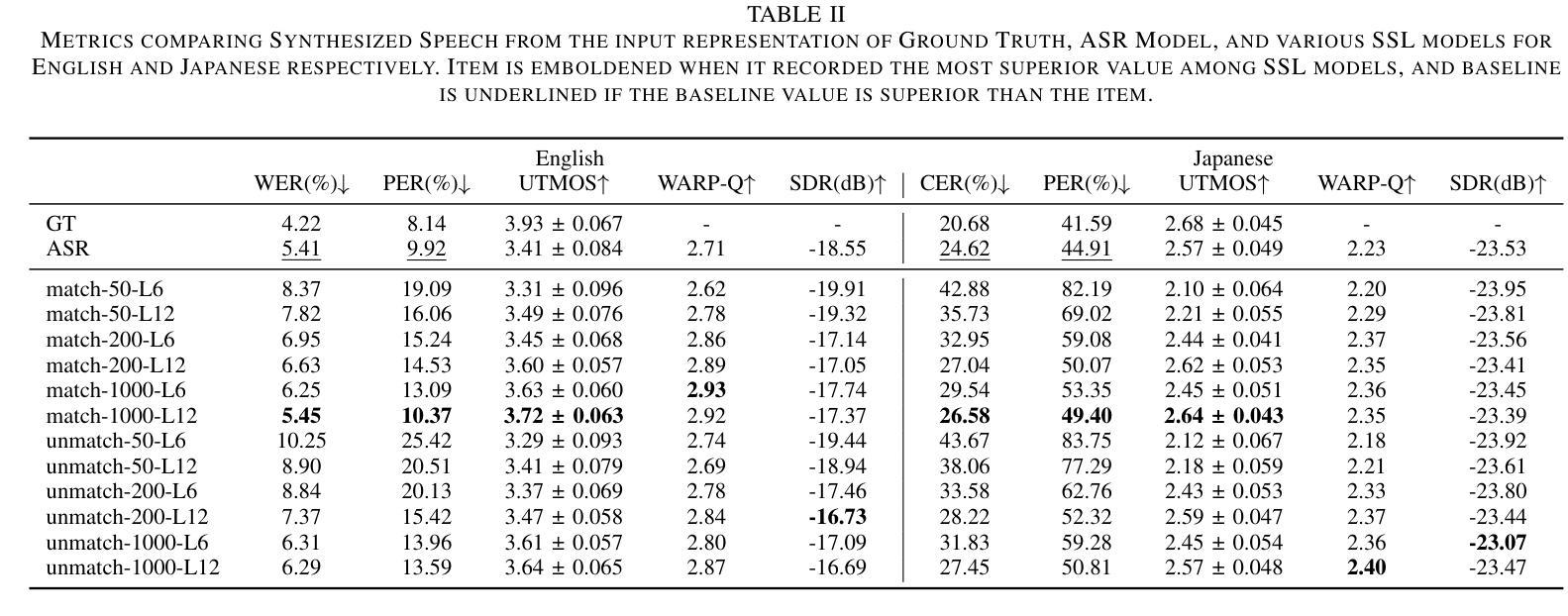
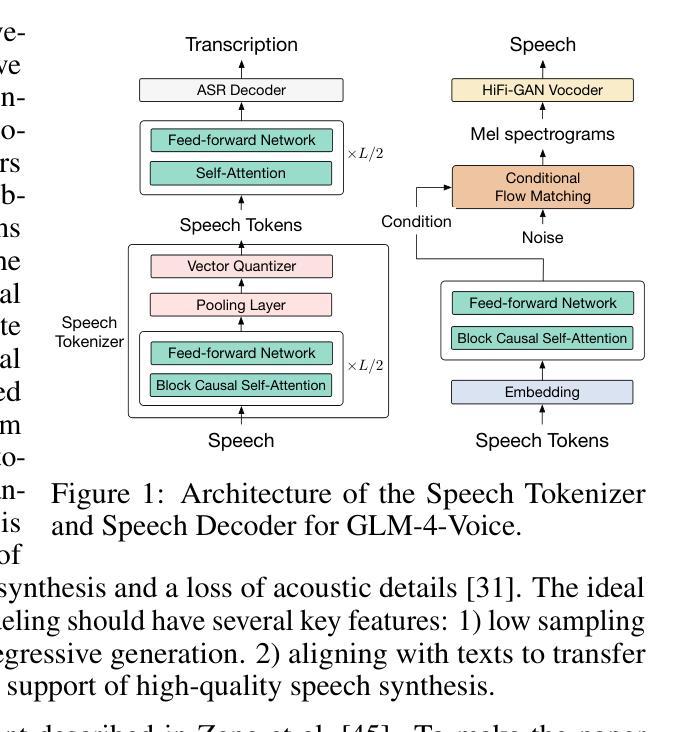
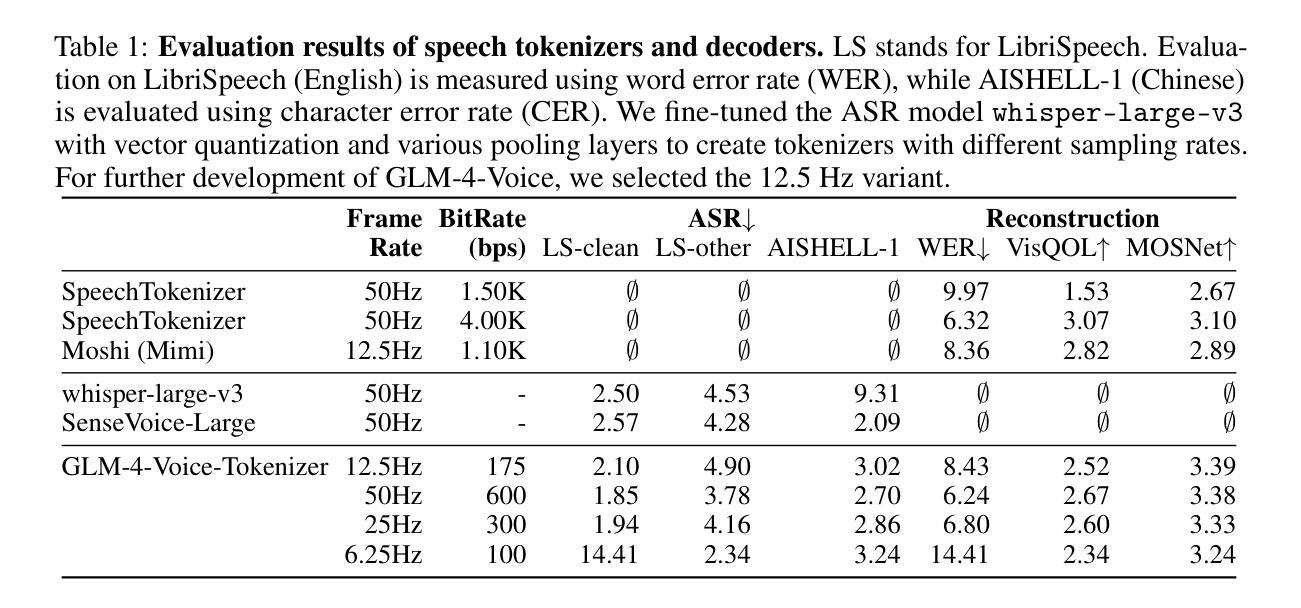
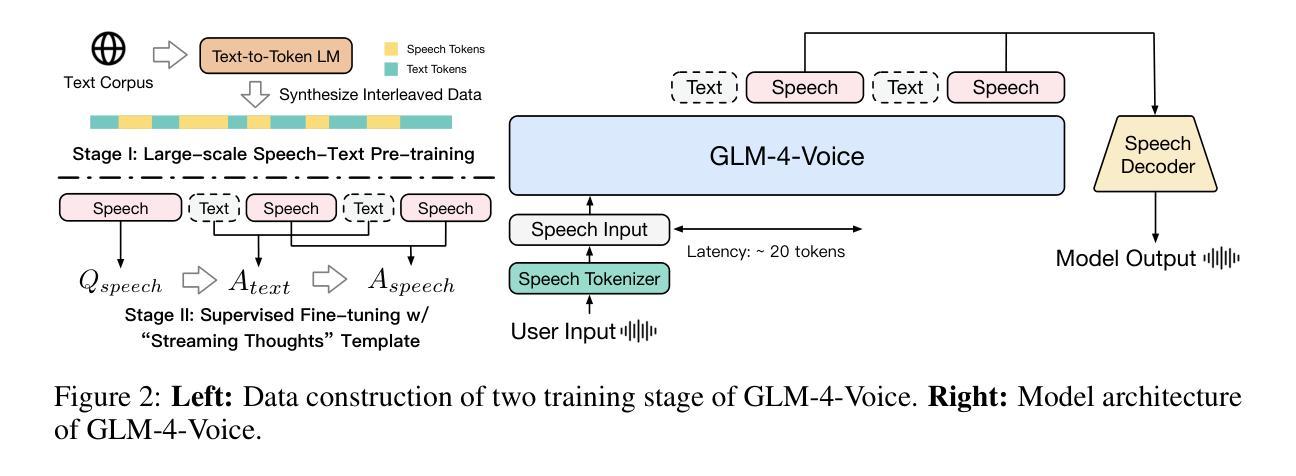
GLM-4-Voice: Towards Intelligent and Human-Like End-to-End Spoken Chatbot
Authors:Aohan Zeng, Zhengxiao Du, Mingdao Liu, Kedong Wang, Shengmin Jiang, Lei Zhao, Yuxiao Dong, Jie Tang
We introduce GLM-4-Voice, an intelligent and human-like end-to-end spoken chatbot. It supports both Chinese and English, engages in real-time voice conversations, and varies vocal nuances such as emotion, intonation, speech rate, and dialect according to user instructions. GLM-4-Voice uses an ultra-low bitrate (175bps), single-codebook speech tokenizer with 12.5Hz frame rate derived from an automatic speech recognition (ASR) model by incorporating a vector-quantized bottleneck into the encoder. To efficiently transfer knowledge from text to speech modalities, we synthesize speech-text interleaved data from existing text pre-training corpora using a text-to-token model. We continue pre-training from the pre-trained text language model GLM-4-9B with a combination of unsupervised speech data, interleaved speech-text data, and supervised speech-text data, scaling up to 1 trillion tokens, achieving state-of-the-art performance in both speech language modeling and spoken question answering. We then fine-tune the pre-trained model with high-quality conversational speech data, achieving superior performance compared to existing baselines in both conversational ability and speech quality. The open models can be accessed through https://github.com/THUDM/GLM-4-Voice and https://huggingface.co/THUDM/glm-4-voice-9b.
我们推出GLM-4-Voice,这是一款智能且人性化的端到端语音聊天机器人。它支持中文和英语,能进行实时语音对话,并根据用户指令调整语音的语调、语调、语速和方言等。GLM-4-Voice采用超低比特率(175bps)的单编码本语音标记器,帧率为12.5Hz,源于融入向量量化瓶颈的自动语音识别(ASR)模型。为了有效地将知识从文本转移到语音模式,我们利用文本到令牌模型,以合成来自现有文本预训练语料库的语音文本交织数据。我们继续利用预训练的文本语言模型GLM-4-9B进行预训练,结合无监督语音数据、交织语音文本数据和监督语音文本数据,扩展至高达1万亿令牌,在语音语言建模和语音问答方面达到了最新的技术性能。然后,我们使用高质量的对话语音数据对预训练模型进行微调,在对话能力和语音质量方面均达到了优于现有基准的性能。开放模型可通过https://github.com/THUDM/GLM-4-Voice和https://huggingface.co/THUDM/glm-4-voice-9b访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
GLM-4-Voice是一款智能、人性化的端到端语音聊天机器人,支持中英文实时语音对话,可根据用户指令调整语音的情感、语调、语速和方言。它采用超低比特率(175bps)和12.5Hz帧率的单编码本语音标记器,并结合自动语音识别(ASR)模型中的向量量化瓶颈编码器实现高效语音转文本。通过合成现有文本预训练语料库中的语音文本交织数据,实现文本到语音模态的知识高效转移。通过预训练文本语言模型GLM-4-9B,结合无监督语音数据、交织语音文本数据和监督语音文本数据,扩展至1万亿个令牌,实现语音语言和口语问答的最先进性能。使用高质量对话语音数据进行微调,达到对话能力和语音质量的最佳性能。公开模型可通过https://github.com/THUDM/GLM-4-Voice和https://huggingface.co/THUDM/glm-4-voice-9b访问。
Key Takeaways
- GLM-4-Voice是一个智能、人性化的端到端语音聊天机器人,支持中英文实时对话。
- 它能够根据用户指令调整语音的情感、语调、语速和方言。
- GLM-4-Voice采用了先进的语音处理技术,包括超低比特率编码和自动语音识别模型。
- 通过合成语音文本交织数据,实现了文本到语音模态的知识高效转移。
- 该模型在预训练的基础上结合了多种数据,包括无监督、交织和监督语音文本数据。
- GLM-4-Voice在语音语言和口语问答方面达到了最先进性能。
点此查看论文截图


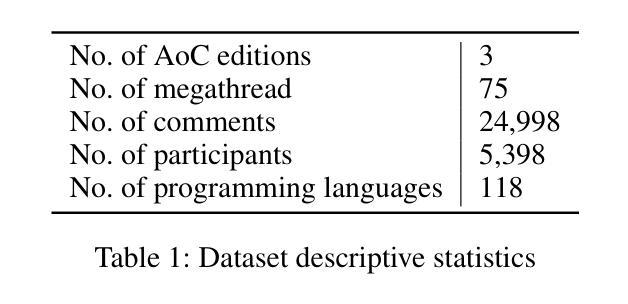
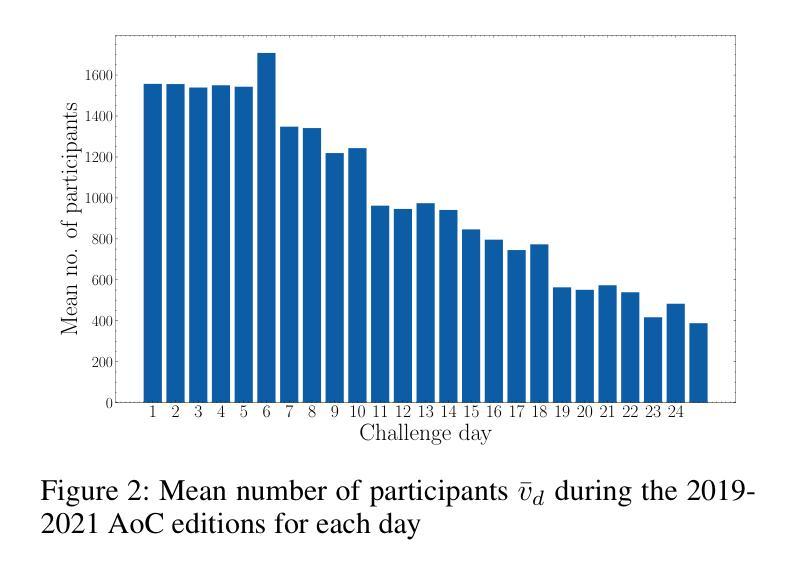
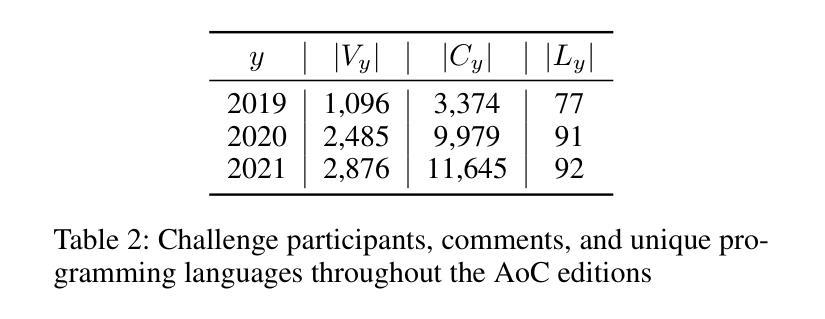
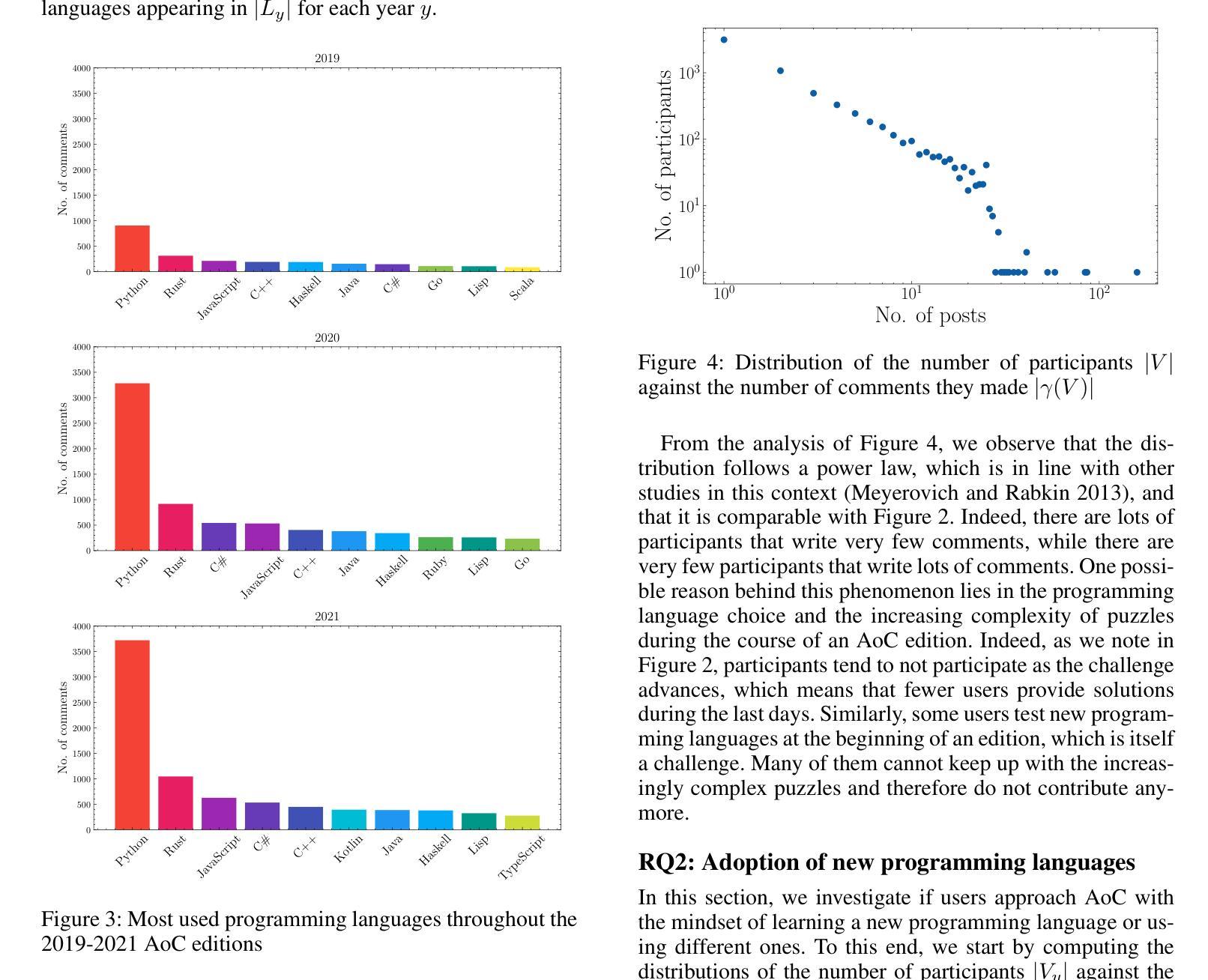
Characterizing Information Shared by Participants to Coding Challenges: The Case of Advent of Code
Authors:Francesco Cauteruccio, Enrico Corradini, Luca Virgili
Advent of Code (AoC from now on) is a popular coding challenge requiring to solve programming puzzles for a variety of skill sets and levels. AoC follows the advent calendar, therefore it is an annual challenge that lasts for 25 days. AoC participants usually post their solutions on social networks and discuss them online. These challenges are interesting to study since they could highlight the adoption of new tools, the evolution of the developer community, or the technological requirements of well-known companies. For these reasons, we first create a dataset of the 2019-2021 AoC editions containing the discussion threads made on the subreddit {\tt /r/adventofcode}. Then, we propose a model based on stream graphs to best study this context, where we represent its most important actors through time: participants, comments, and programming languages. Thanks to our model, we investigate user participation, adoption of new programming languages during a challenge and between two of them, and resiliency of programming languages based on a Stack Overflow survey. We find that the top-used programming languages are almost the same in the three years, pointing out their importance. Moreover, participants tend to keep the same programming language for the whole challenge, while the ones attending two AoCs usually change it in the next one. Finally, we observe interesting results about the programming languages that are Popular'' or Loved’’ according to the Stack Overflow survey. Firstly, these are the ones adopted for the longest time in an AoC edition, thanks to which users have a high chance of reaching the end of the challenge. Secondly, they are the most chosen when a participant decides to change programming language during the same challenge.
“Advent of Code”(简称AoC)是一项广受欢迎的编码挑战,要求针对不同技能和水平的参与者解决编程谜题。AoC遵循历法,因此是一项为期25天的年度挑战。AoC参与者通常会在社交网络上发布自己的解决方案,并在线进行讨论。这些挑战很有趣,因为它们可能反映出新工具的使用情况、开发者社区的演变,或知名公司的技术需求。为此,我们首先创建了一个包含2019-2021年AoC版本讨论帖的数据集,这些讨论帖来自Reddit上的{/r/adventofcode}社区。然后,我们提出了一个基于流图的模型来更好地研究这一环境,通过时间展现最重要的参与者:参与者、评论和编程语言。借助我们的模型,我们研究了用户参与度、新编程语言的采用情况以及在两次挑战之间的采用情况,以及基于Stack Overflow调查的编程语言的韧性。我们发现,在三年内使用的最流行的编程语言几乎相同,凸显了它们的重要性。此外,参与者往往在整个挑战中坚持使用同一种编程语言,而参加两次AoC的参与者通常会在下一次挑战中更换语言。最后,关于Stack Overflow调查中标记为“流行”或“受喜爱”的编程语言,我们观察到了一些有趣的结果。首先,这些语言是AoC版本中采用时间最长的语言,借助这些语言,用户有很大机会完成整个挑战。其次,当参与者决定在同一挑战中更换编程语言时,它们是最受欢迎的选择。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文研究了Advent of Code(AoC)的挑战。该挑战持续长达25天,每年举行一次,参与者会在线上分享和讨论解决方案。研究团队利用流图模型,通过对社区参与者、评论和编程语言的分析,研究了用户参与度、新编程语言的采纳情况以及编程语言的持久性。研究发现,虽然编程语言的流行趋势略有变化,但过去三年中最受欢迎的编程语言几乎没有变化。同时,参与者更倾向于在整个挑战期间使用同一种编程语言,而连续参加两次挑战的参与者往往会更换编程语言。此外,根据Stack Overflow调查的结果,最受欢迎或最受喜爱的编程语言更有可能帮助用户完成挑战并持续较长时间。总的来说,这项研究揭示了AoC挑战中编程语言和社区的动态变化。
Key Takeaways
以下是七个关键见解:
- Advent of Code是一项年度挑战,持续25天,参与者会在社交媒体上分享和讨论解决方案。
- 利用流图模型对社区参与者、评论和编程语言进行综合分析,可以更全面地研究用户参与度和技术趋势。
- 研究发现,在过去三年中,主流的编程语言变化不大。说明存在一些常用的语言能够在不同时期都被广泛应用。这可能揭示这些语言具有稳定性和可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

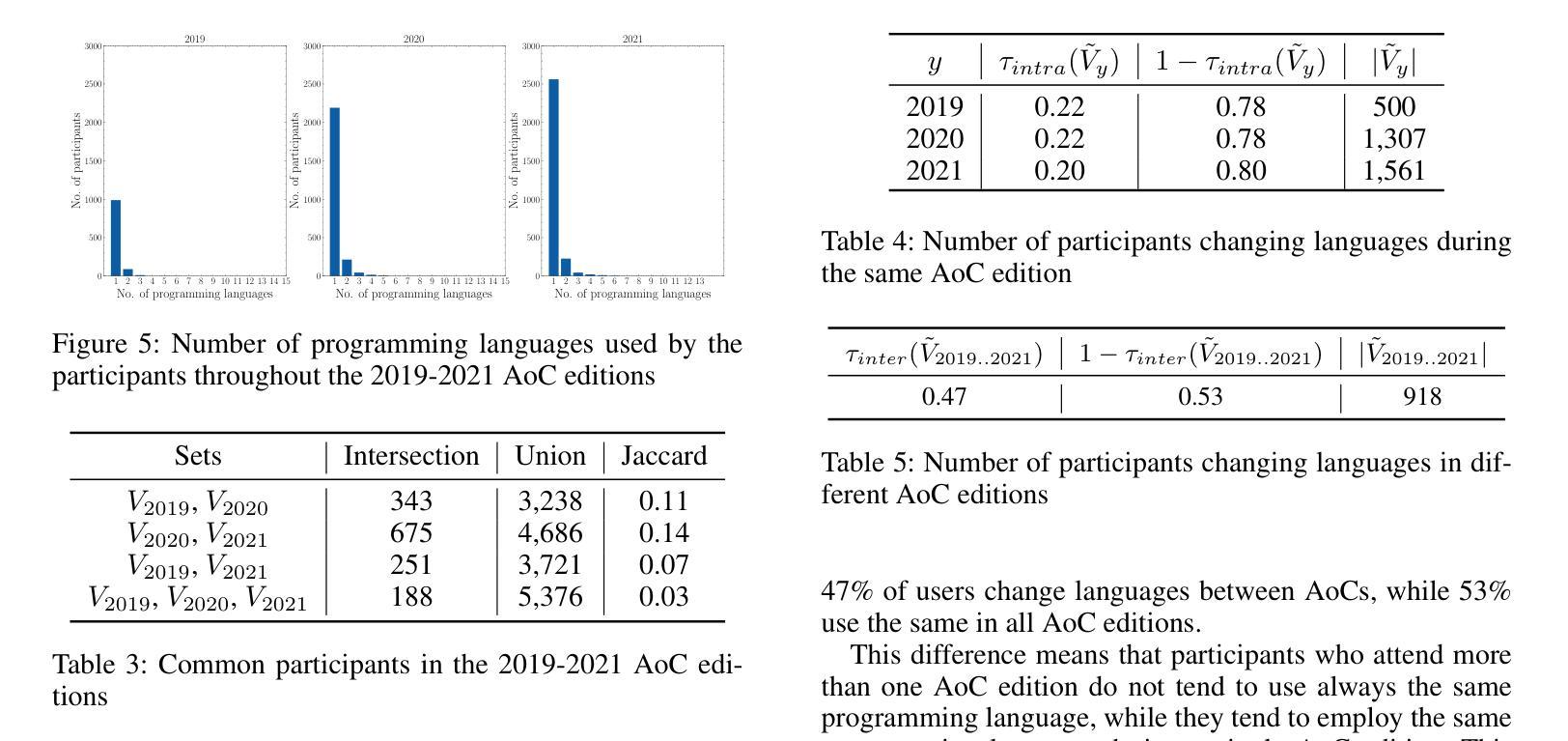
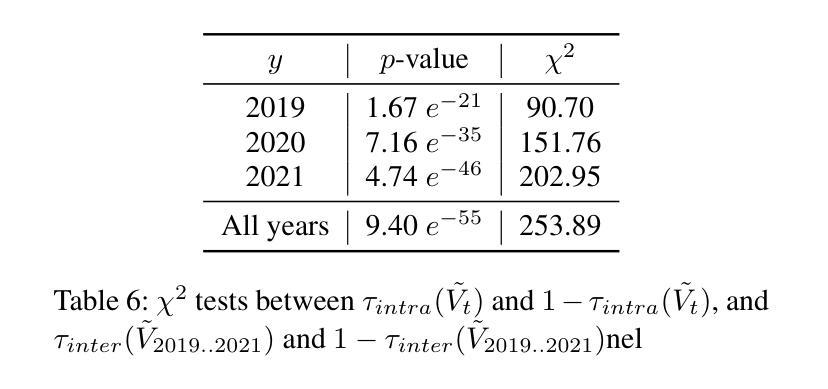
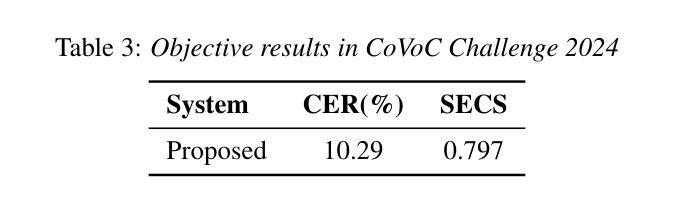
The Codec Language Model-based Zero-Shot Spontaneous Style TTS System for CoVoC Challenge 2024
Authors:Shuoyi Zhou, Yixuan Zhou, Weiqing Li, Jun Chen, Runchuan Ye, Weihao Wu, Zijian Lin, Shun Lei, Zhiyong Wu
This paper describes the zero-shot spontaneous style TTS system for the ISCSLP 2024 Conversational Voice Clone Challenge (CoVoC). We propose a LLaMA-based codec language model with a delay pattern to achieve spontaneous style voice cloning. To improve speech intelligibility, we introduce the Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG) strategy in the language model to strengthen conditional guidance on token prediction. To generate high-quality utterances, we adopt effective data preprocessing operations and fine-tune our model with selected high-quality spontaneous speech data. The official evaluations in the CoVoC constrained track show that our system achieves the best speech naturalness MOS of 3.80 and obtains considerable speech quality and speaker similarity results.
本文介绍了针对ISCSLP 2024对话式语音克隆挑战赛(CoVoC)的零样本自发风格TTS系统。我们提出了一种基于LLaMA的编解码语言模型,采用延迟模式来实现自发风格的声音克隆。为了提高语音清晰度,我们在语言模型中引入了无分类器引导(CFG)策略,以加强令牌预测的条件引导。为了生成高质量的短语,我们采用了有效的数据预处理操作,并使用精选的高质量自发语音数据对模型进行微调。在CoVoC约束轨道的官方评估中,我们的系统达到了最佳语音自然度MOS 3.80,并获得了相当不错的语音质量和说话人相似性结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ISCSLP 2024
Summary
本文介绍了针对ISCSLP 2024对话式语音克隆挑战(CoVoC)的零样本自发式语音TTS系统。该研究提出基于LLaMA编码语言模型的自发式语音克隆方法,并结合延迟模式和分类器自由指导策略改善语音清晰度。通过有效数据预处理和精细模型调优,使用高质量自发语音数据生成高质量的话语。官方评价显示,该系统在CoVoC约束赛道中获得了最佳语音自然度MOS 3.80分,并在语音质量和说话人相似性方面取得了显著成果。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了针对ISCSLP 2024对话式语音克隆挑战的零样本自发式TTS系统。
- 采用基于LLaMA编码的语言模型实现自发式语音克隆,并引入延迟模式以增强语音的自然度。
- 使用分类器自由指导策略改善语音清晰度,提高语音的辨识度。
- 通过有效数据预处理和精细模型调优,使用高质量自发语音数据来生成高质量的话语。
- 系统在官方评价中表现出最佳语音自然度。
- 系统获得了较高的语音质量和说话人相似性结果。
点此查看论文截图


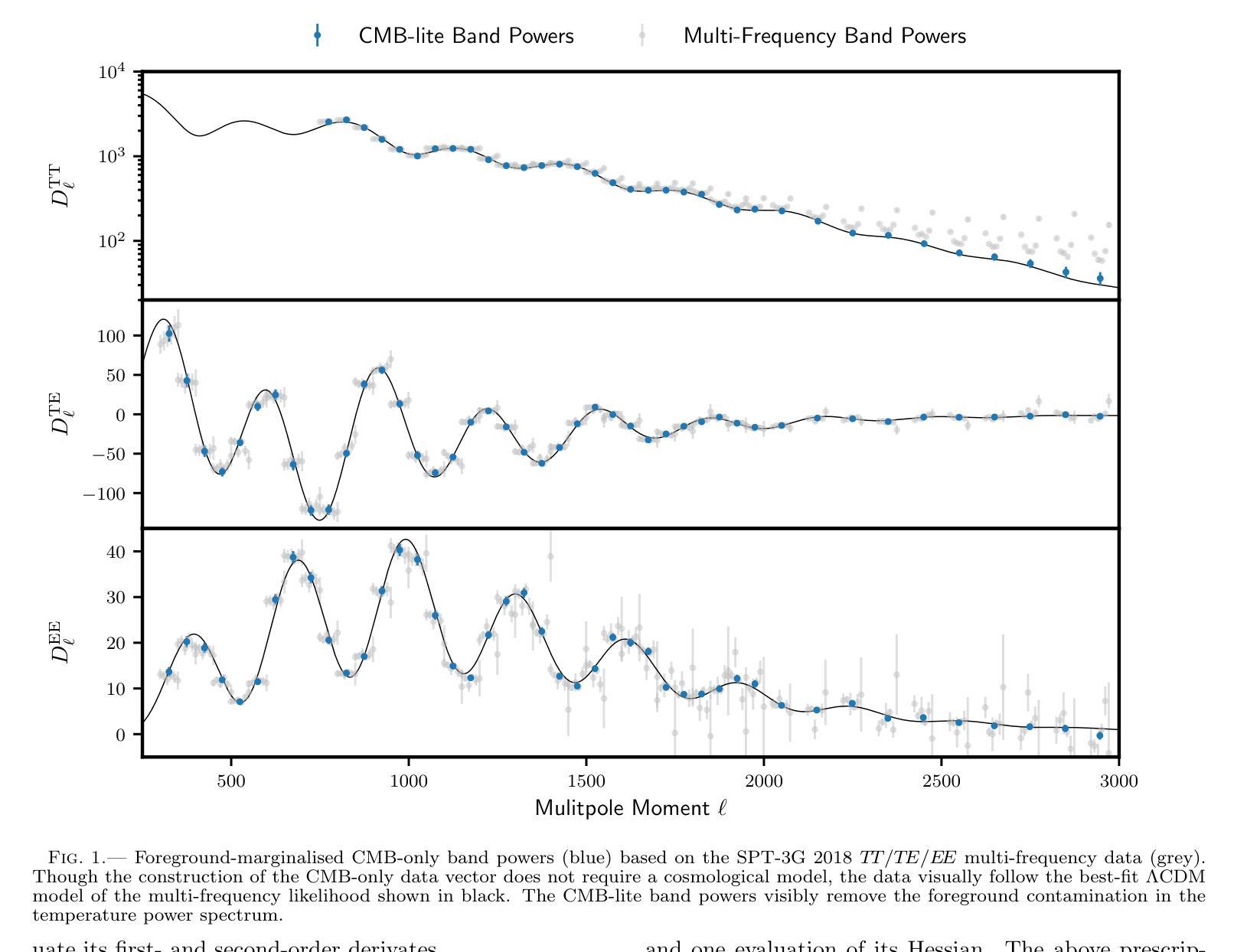
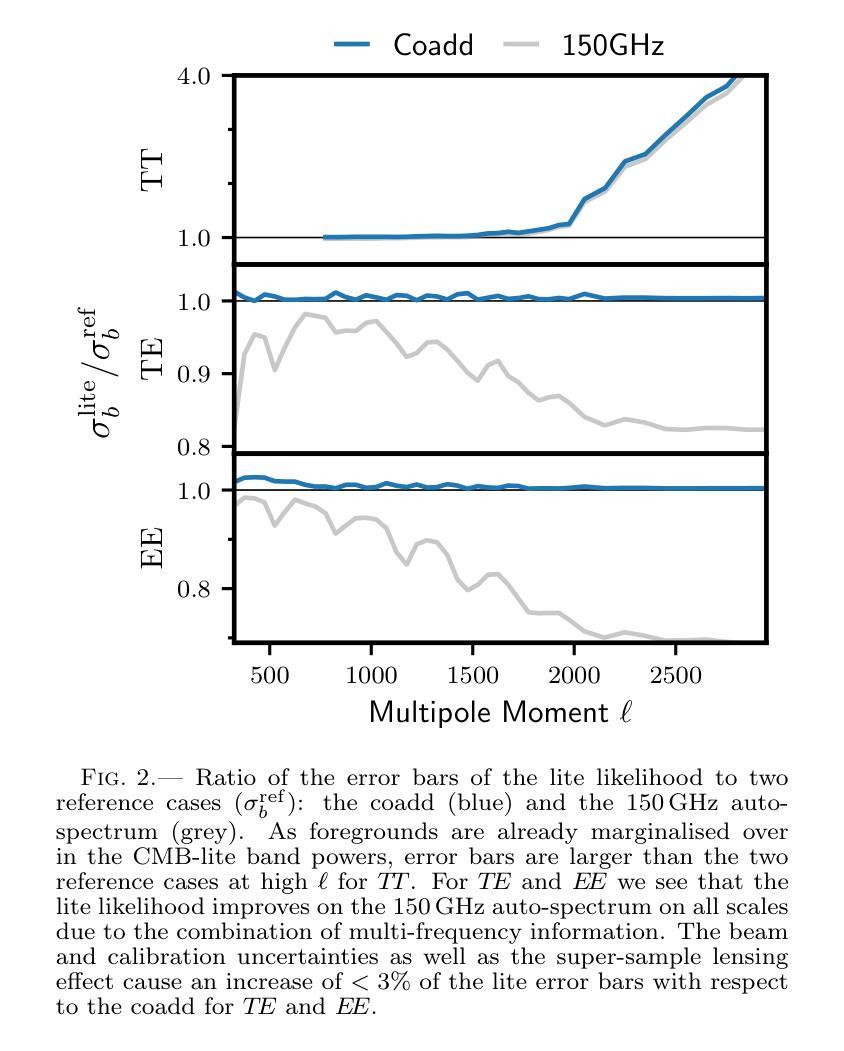
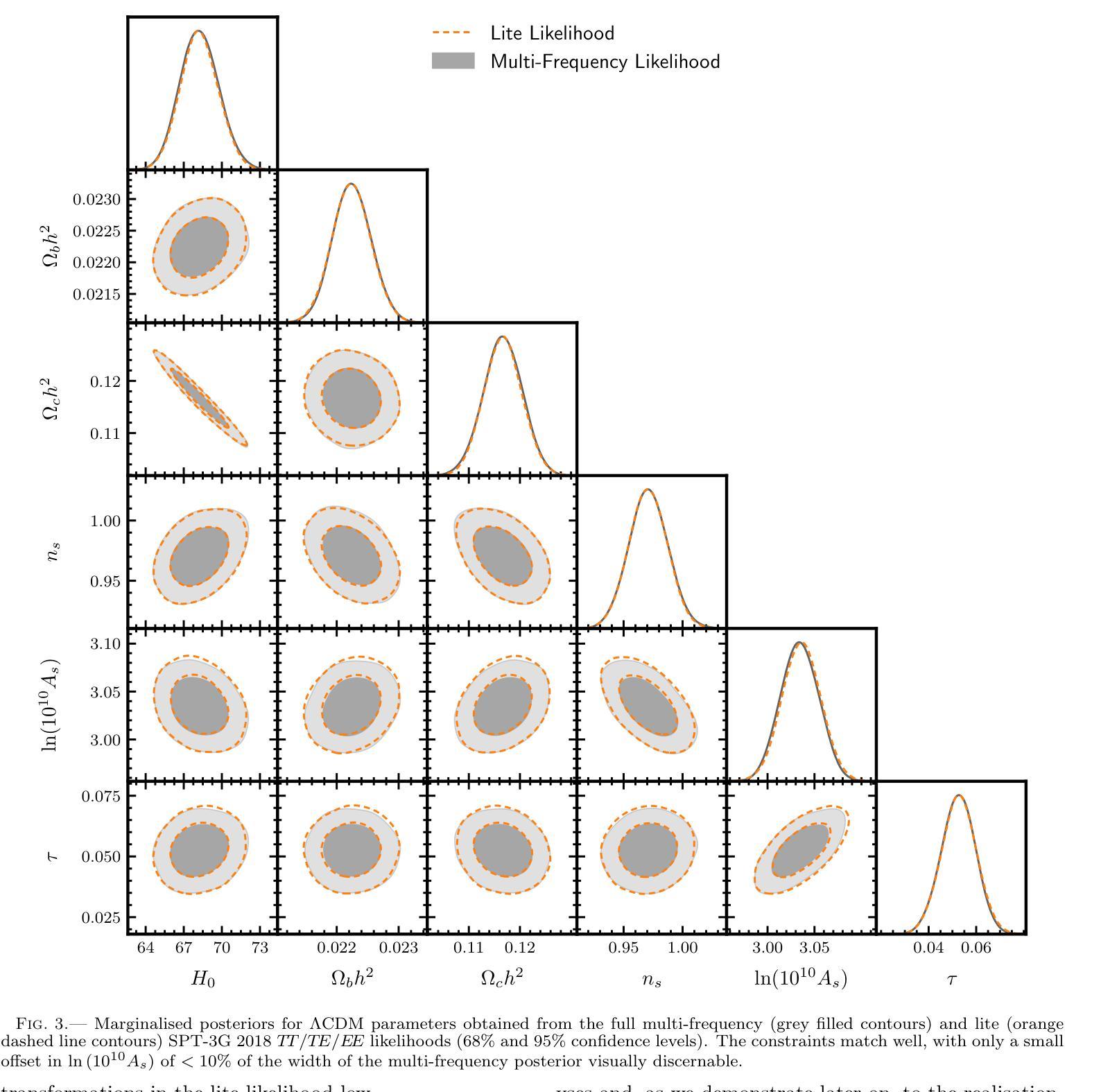
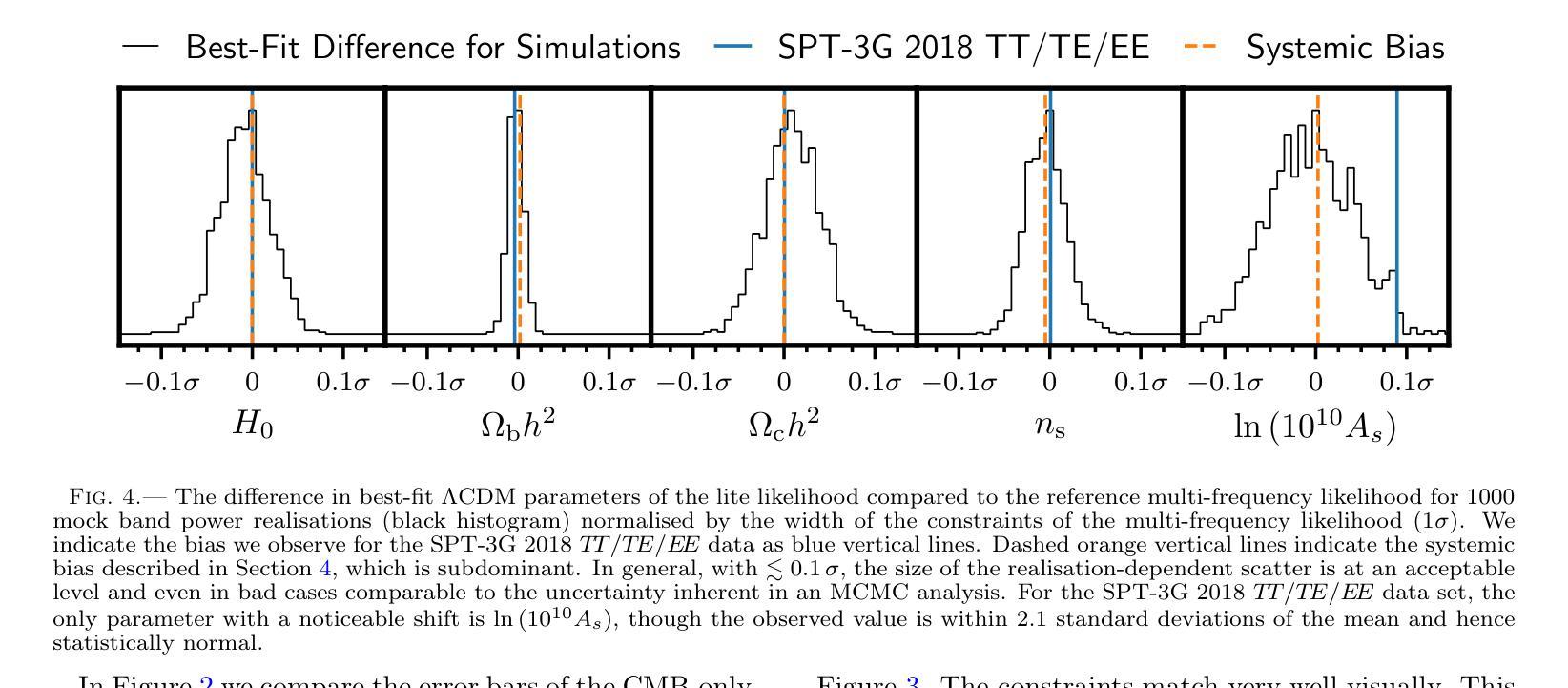
Compressed ‘CMB-lite’ Likelihoods Using Automatic Differentiation
Authors:L. Balkenhol
The compression of multi-frequency cosmic microwave background (CMB) power spectrum measurements into a series of foreground-marginalised CMB-only band powers allows for the construction of faster and more easily interpretable ‘lite’ likelihoods. However, obtaining the compressed data vector is computationally expensive and yields a covariance matrix with sampling noise. In this work, we present an implementation of the CMB-lite framework relying on automatic differentiation. The technique presented reduces the computational cost of the lite likelihood construction to one minimisation and one Hessian evaluation, which run on a personal computer in about a minute. We demonstrate the efficiency and accuracy of this procedure by applying it to the differentiable SPT-3G 2018 TT/TE/EE likelihood from the candl library. We find good agreement between the marginalised posteriors of cosmological parameters yielded by the resulting lite likelihood and the reference multi-frequency version for all cosmological models tested; the best-fit values shift by $<0.1,\sigma$, where $\sigma$ is the width of the multi-frequency posterior, and the inferred parameter error bars match to within $<10%$. We publicly release the SPT-3G 2018 TT/TE/EE lite likelihood and a python notebook showing its construction at https://github.com/Lbalkenhol/candl .
将多频宇宙微波背景(CMB)功率谱测量值压缩成一系列前景边缘化的仅包含CMB的波段功率,从而可以构建更快、更易解读的“轻量级”似然函数。然而,获取压缩数据向量在计算上非常昂贵,并且产生的协方差矩阵具有采样噪声。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种依赖自动微分技术的CMB-lite框架的实现。所提出的技术将轻量级似然函数构建的计算成本降低到一次最小化和一次Hessian评估,可在个人计算机上大约一分钟内运行。我们通过将其应用于可微分的SPT-3G 2018 TT/TE/EE似然函数(来自candl库)来展示该程序的效率和准确性。我们发现,对于测试的所有宇宙学模型,由所得轻量级似然函数产生的边缘化宇宙学参数后验与参考多频版本具有良好的一致性;最佳拟合值在$<0.1\sigma$内移动,其中$\sigma$是多频后验的宽度,推断的参数误差范围匹配度在$<10%$以内。我们在https://github.com/Lbalkenhol/candl公开发布了SPT-3G 2018 TT/TE/EE轻量级似然函数以及展示其构建的Python笔记本。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 4 figures, 1 table, prepared for OJA submission
Summary
本文介绍了如何将多频宇宙微波背景(CMB)功率谱的测量值压缩成一系列仅包含CMB信号的轻量级谱带功率,以构建更快、更易解读的轻量级概率分布。尽管压缩数据向量存在计算成本高和采样噪声的问题,但本文提出了一种依赖自动微分技术的CMB轻量级框架实现方案。该技术将轻量级概率分布的计算成本降低到仅一次最小化和一次Hessian评估,可在个人计算机上大约一分钟内运行。通过应用该技术到可微分的SPT-3G 2018 TT/TE/EE概率分布库,验证了其效率和准确性。发现对于所有测试的宇宙学模型,由此产生的轻量级概率分布产生的边际后验宇宙学参数与多频版本的后验参数具有良好的一致性,最佳拟合值在$< 0.1σ$以内变化,其中σ为多频后验的宽度,推断的参数误差范围匹配度在$< 10%$以内。
Key Takeaways
- CMB功率谱测量值可压缩成一系列仅包含CMB信号的轻量级谱带功率,构建更快、更易解读的轻量级概率分布。
- 计算压缩数据向量存在计算成本高和采样噪声的问题。
- 提出依赖自动微分技术的CMB轻量级框架实现方案,降低计算成本。
- 应用技术到SPT-3G 2018 TT/TE/EE概率分布库验证其效率和准确性。
- 轻量级概率分布产生的边际后验宇宙学参数与多频版本的后验参数具有良好一致性。
- 最佳拟合值在$< 0.1σ$以内变化,其中σ为多频后验的宽度。
点此查看论文截图

A Context-Based Numerical Format Prediction for a Text-To-Speech System
Authors:Yaser Darwesh, Lit Wei Wern, Mumtaz Begum Mustafa
Many of the existing TTS systems cannot accurately synthesize text containing a variety of numerical formats, resulting in reduced intelligibility of the synthesized speech. This research aims to develop a numerical format classifier that can classify six types of numeric contexts. Experiments were carried out using the proposed context-based feature extraction technique, which is focused on extracting keywords, punctuation marks, and symbols as the features of the numbers. Support Vector Machine, K-Nearest Neighbors Linear Discriminant Analysis, and Decision Tree were used as classifiers. We have used the 10-fold cross-validation technique to determine the classification accuracy in terms of recall and precision. It can be found that the proposed solution is better than the existing feature extraction technique with improvement to the classification accuracy by 30% to 37%. The use of the number format classification can increase the intelligibility of the TTS systems.
现有的许多TTS系统无法准确合成包含多种数字格式的文本,导致合成语音的清晰度降低。本研究旨在开发一种数字格式分类器,该分类器能够分类六种数字上下文类型。实验采用了基于上下文的特征提取技术,该技术侧重于提取关键词、标点符号和符号作为数字的特征。支持向量机、K近邻线性判别分析和决策树被用作分类器。我们采用了10倍交叉验证技术来确定召回率和精确率方面的分类精度。可以发现,所提出的解决方案优于现有的特征提取技术,分类精度提高了30%至37%。使用数字格式分类可以提高TTS系统的清晰度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 6 tables, 1 figure
Summary
本研究旨在开发一种数值格式分类器,能够分类六种数值上下文。采用基于上下文的特征提取技术,关注数字的特征提取,如关键词、标点符号和符号。使用支持向量机、K近邻线性判别分析和决策树作为分类器。使用10倍交叉验证技术确定召回率和精确度的分类精度。结果表明,所提出的解决方案优于现有的特征提取技术,分类精度提高了30%至37%。数值格式分类的使用可以提高TTS系统的清晰度。
Key Takeaways
- 研究目标是开发一种能够分类六种数值上下文的数值格式分类器。
- 采用基于上下文的特征提取技术,关注数字的特征,如关键词、标点符号和符号。
- 使用支持向量机、K近邻线性判别分析和决策树作为分类器。
- 使用10倍交叉验证技术评估分类器的性能。
- 与现有技术相比,新方法的分类精度提高了30%至37%。
- 数值格式分类的应用可以增加TTS系统的清晰度。
- 该研究对于提高TTS系统在处理包含多种数值格式的文本时的准确性具有潜在意义。
点此查看论文截图

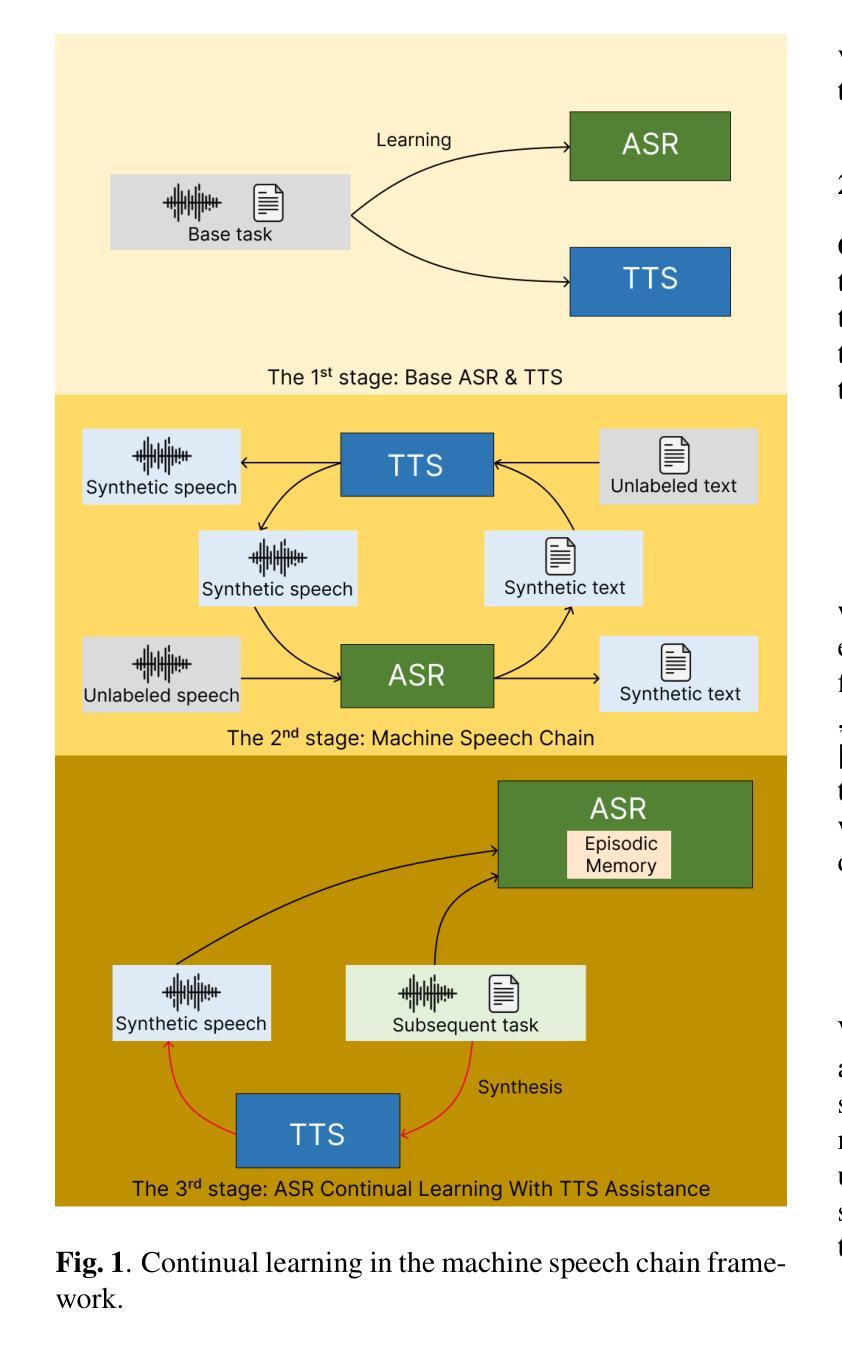
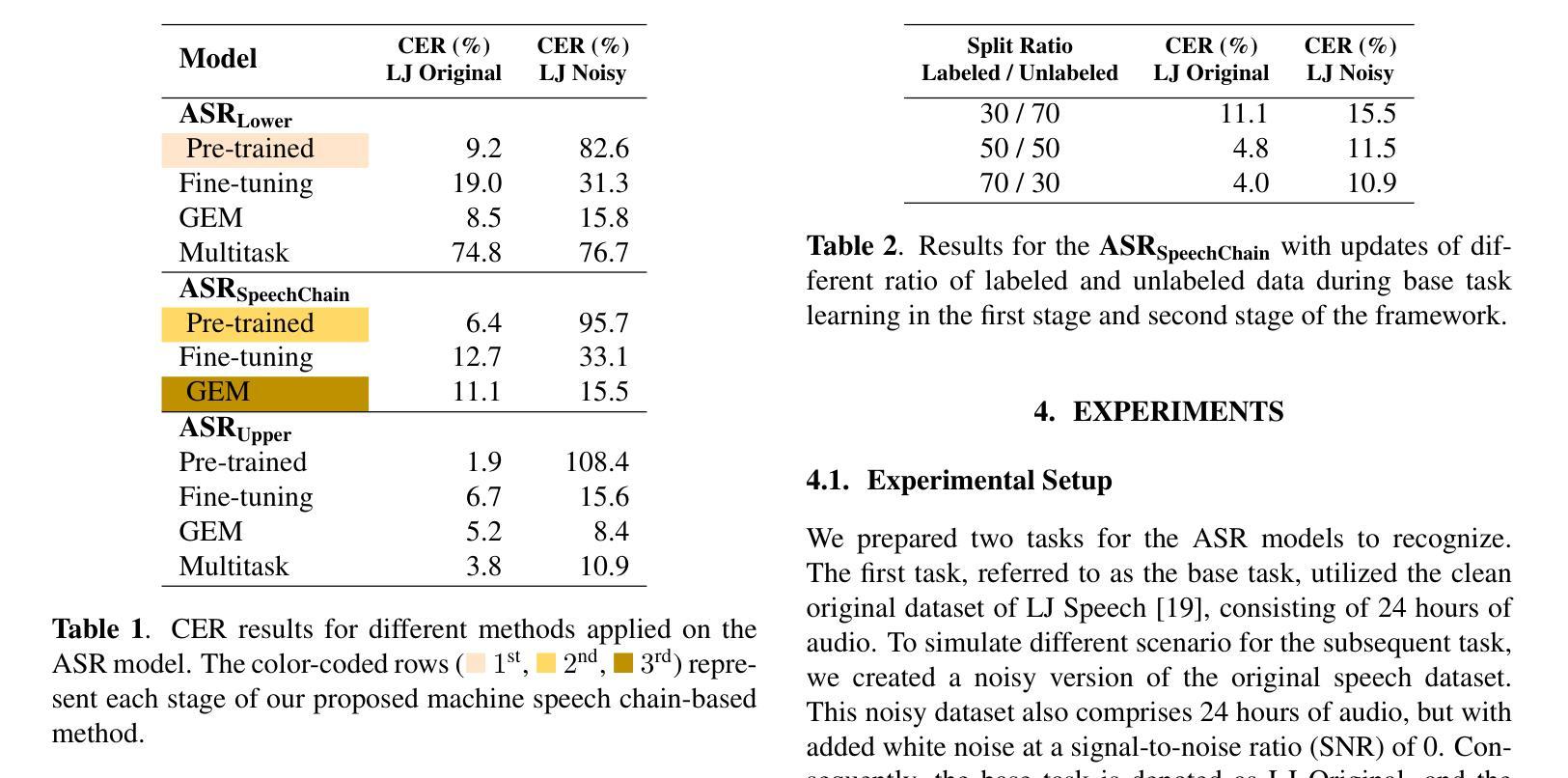
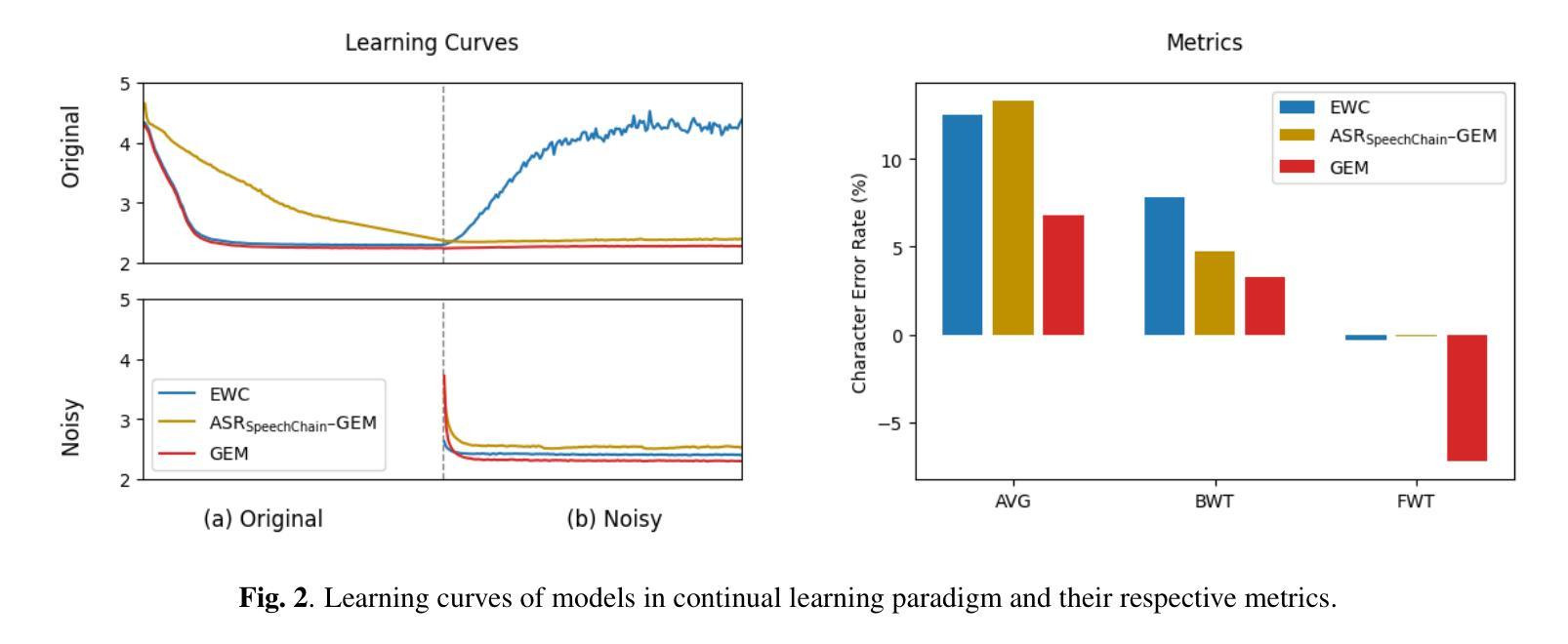
Continual Learning in Machine Speech Chain Using Gradient Episodic Memory
Authors:Geoffrey Tyndall, Kurniawati Azizah, Dipta Tanaya, Ayu Purwarianti, Dessi Puji Lestari, Sakriani Sakti
Continual learning for automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems poses a challenge, especially with the need to avoid catastrophic forgetting while maintaining performance on previously learned tasks. This paper introduces a novel approach leveraging the machine speech chain framework to enable continual learning in ASR using gradient episodic memory (GEM). By incorporating a text-to-speech (TTS) component within the machine speech chain, we support the replay mechanism essential for GEM, allowing the ASR model to learn new tasks sequentially without significant performance degradation on earlier tasks. Our experiments, conducted on the LJ Speech dataset, demonstrate that our method outperforms traditional fine-tuning and multitask learning approaches, achieving a substantial error rate reduction while maintaining high performance across varying noise conditions. We showed the potential of our semi-supervised machine speech chain approach for effective and efficient continual learning in speech recognition.
自动语音识别(ASR)系统的持续学习是一个挑战,尤其是在需要避免灾难性遗忘的同时,还要保持对先前学习任务的性能。本文引入了一种利用机器语音链框架实现ASR中持续学习的新方法,采用梯度片段记忆(GEM)。通过在机器语音链中融入文本到语音(TTS)组件,我们支持对GEM至关重要的回放机制,使ASR模型能够按顺序学习新任务,而不会显著降低早期任务的性能。我们在LJ Speech数据集上进行的实验表明,我们的方法优于传统的微调和多任务学习方法,在大幅降低错误率的同时,在不同噪声条件下保持高性能。我们展示了半监督机器语音链方法在语音识别中的有效和高效持续学习的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published as a conference paper at O-COCOSDA 2024. 6 pages; 2 figures
Summary
这篇论文提出了一种基于机器语音链框架的利用梯度经验记忆(GEM)实现自动语音识别(ASR)系统的持续学习的新方法。通过引入文本转语音(TTS)组件,支持GEM所需的回放机制,使ASR模型能够顺序学习新任务,而不会显著影响早期任务的性能。在LJ Speech数据集上的实验表明,该方法优于传统的微调和多任务学习方法,实现了错误率的大幅降低,并在各种噪声条件下保持了高性能。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了一个基于机器语音链框架的新方法,实现ASR系统的持续学习。
- 通过引入TTS组件,支持了回放机制,这是GEM的关键部分。
- 该方法能够在不影响早期任务性能的情况下,使ASR模型顺序学习新任务。
- 在LJ Speech数据集上的实验验证了该方法的优越性。
- 该方法实现了错误率的大幅降低。
- 该方法在各种噪声条件下保持了高性能。
点此查看论文截图

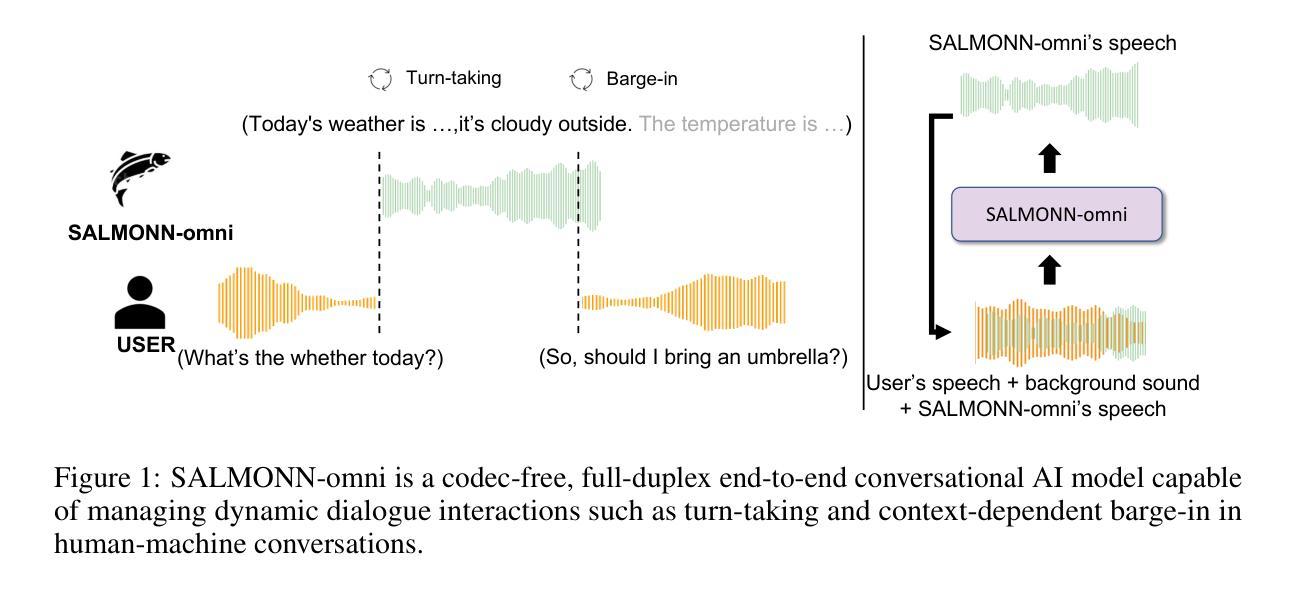
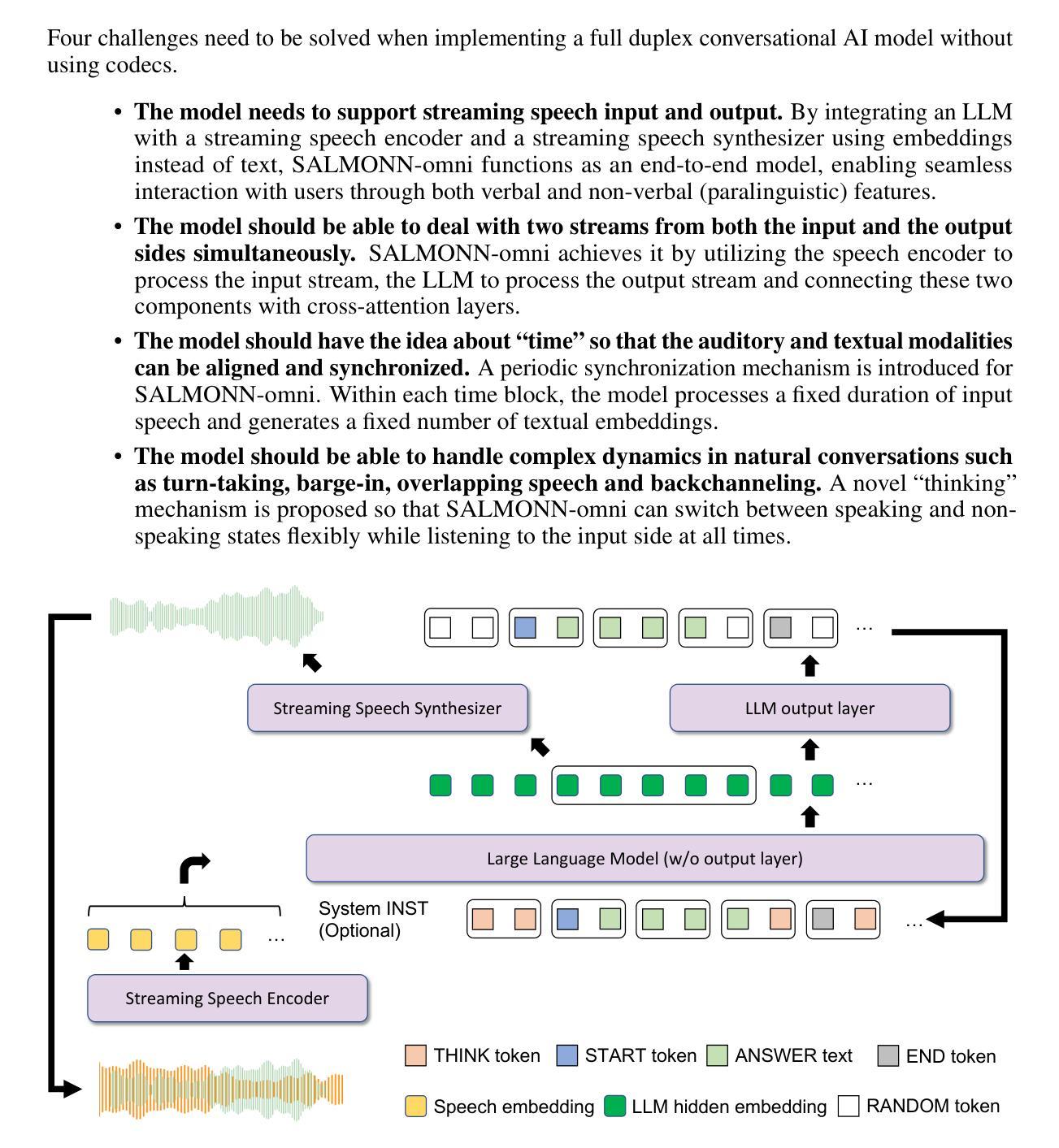
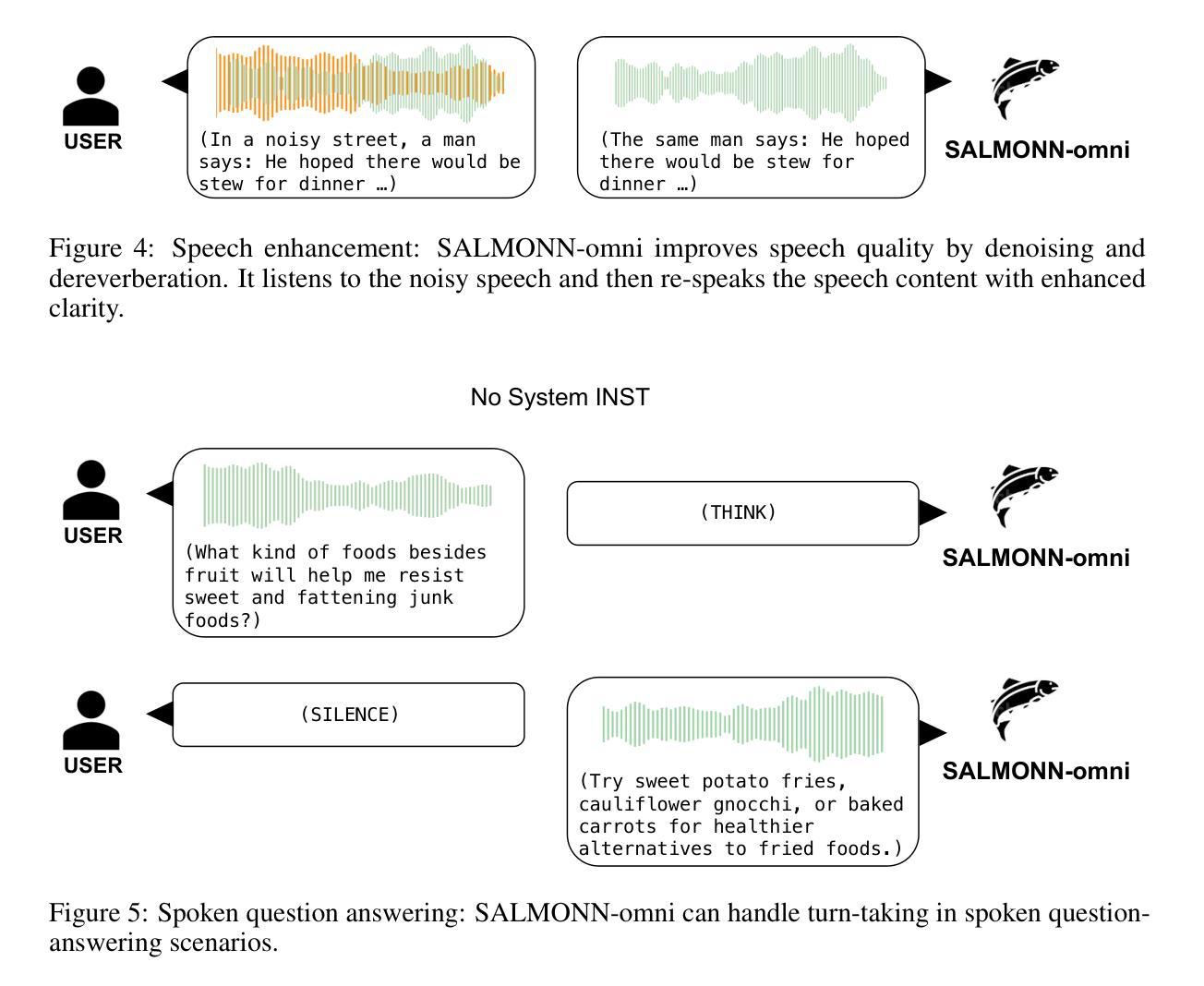
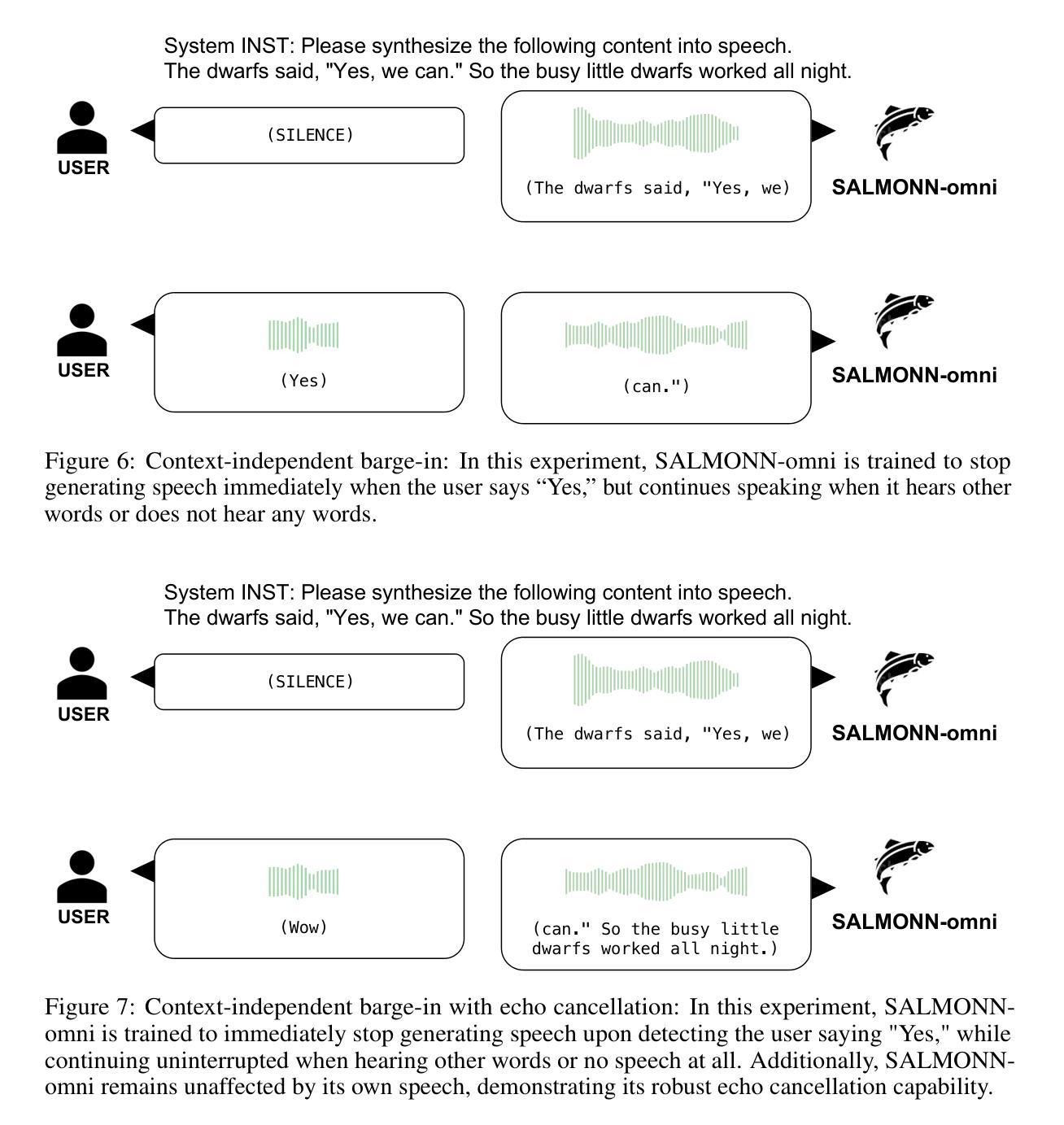
SALMONN-omni: A Codec-free LLM for Full-duplex Speech Understanding and Generation
Authors:Wenyi Yu, Siyin Wang, Xiaoyu Yang, Xianzhao Chen, Xiaohai Tian, Jun Zhang, Guangzhi Sun, Lu Lu, Yuxuan Wang, Chao Zhang
Full-duplex multimodal large language models (LLMs) provide a unified framework for addressing diverse speech understanding and generation tasks, enabling more natural and seamless human-machine conversations. Unlike traditional modularised conversational AI systems, which separate speech recognition, understanding, and text-to-speech generation into distinct components, multimodal LLMs operate as single end-to-end models. This streamlined design eliminates error propagation across components and fully leverages the rich non-verbal information embedded in input speech signals. We introduce SALMONN-omni, a codec-free, full-duplex speech understanding and generation model capable of simultaneously listening to its own generated speech and background sounds while speaking. To support this capability, we propose a novel duplex spoken dialogue framework incorporating a ``thinking’’ mechanism that facilitates asynchronous text and speech generation relying on embeddings instead of codecs (quantized speech and audio tokens). Experimental results demonstrate SALMONN-omni’s versatility across a broad range of streaming speech tasks, including speech recognition, speech enhancement, and spoken question answering. Additionally, SALMONN-omni excels at managing turn-taking, barge-in, and echo cancellation scenarios, establishing its potential as a robust prototype for full-duplex conversational AI systems. To the best of our knowledge, SALMONN-omni is the first codec-free model of its kind. A full technical report along with model checkpoints will be released soon.
全双工多模态大型语言模型(LLM)为处理各种语音理解和生成任务提供了一个统一的框架,使人与机器之间的对话更加自然和无缝。与传统的模块化对话AI系统不同,后者将语音识别、理解和文本到语音生成划分为不同的组件,多模态LLM则作为单个端到端的模型进行操作。这种简化的设计消除了组件间错误传播,并充分利用了输入语音信号中嵌入的丰富的非语音信息。我们介绍了SALMONN-omni,这是一种无编解码器的全双工语音理解和生成模型,能够在说话的同时聆听自己生成的语音和背景声音。为了支持这一功能,我们提出了一个新的双工口语对话框架,该框架包含一种“思考”机制,能够依赖嵌入而不是编解码器实现异步文本和语音生成(量化语音和音频标记)。实验结果表明,SALMONN-omni在广泛的流式语音任务中表现出强大的通用性,包括语音识别、语音增强和口语问答。此外,SALMONN-omni在轮流发言、抢话和回声消除等场景中表现出色,证明了其作为全双工对话AI系统的稳健原型的潜力。据我们所知,SALMONN-omni是首个无编解码器的此类模型。我们将很快发布完整的技术报告和模型检查点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical report
Summary
基于全双工模态的大型语言模型(LLMs)提供了一个统一的框架,用于处理多样的语音理解和生成任务,实现了更自然、无缝的人机对话。SALMONN-omni是一个无编解码器、全双工语音理解和生成模型,可以同时聆听其自身生成的语音和背景声音,并可在说话的同时进行思考。该模型引入了新型的双工对话框架,借助嵌入技术实现异步文本和语音生成,无需编解码器。实验结果表明,SALMONN-omni在多种流式语音任务中表现出卓越的性能,如语音识别、语音增强和语音问答等。此外,该模型在处理对话中的轮替发言、即时介入和回声消除等场景方面具有显著优势,成为了全双工对话AI系统的稳健原型。据我们所知,SALMONN-omni是首个无需编解码器的此类模型。
Key Takeaways
- 全双工模态大型语言模型(LLMs)提供了一个统一的框架用于多样的语音理解和生成任务。
- SALMONN-omni模型可以无编解码器地进行语音生成和理解,实现全双工对话。
- SALMONN-omni可以同时聆听自身生成的语音和背景声音,提升语音识别的准确性。
- 模型引入了新型的双工对话框架,借助嵌入技术实现异步文本和语音生成。
- 实验证明,SALMONN-omni在多种流式语音任务中表现出卓越性能。
- SALMONN-omni在处理对话中的轮替发言、即时介入和回声消除等场景具有显著优势。
点此查看论文截图

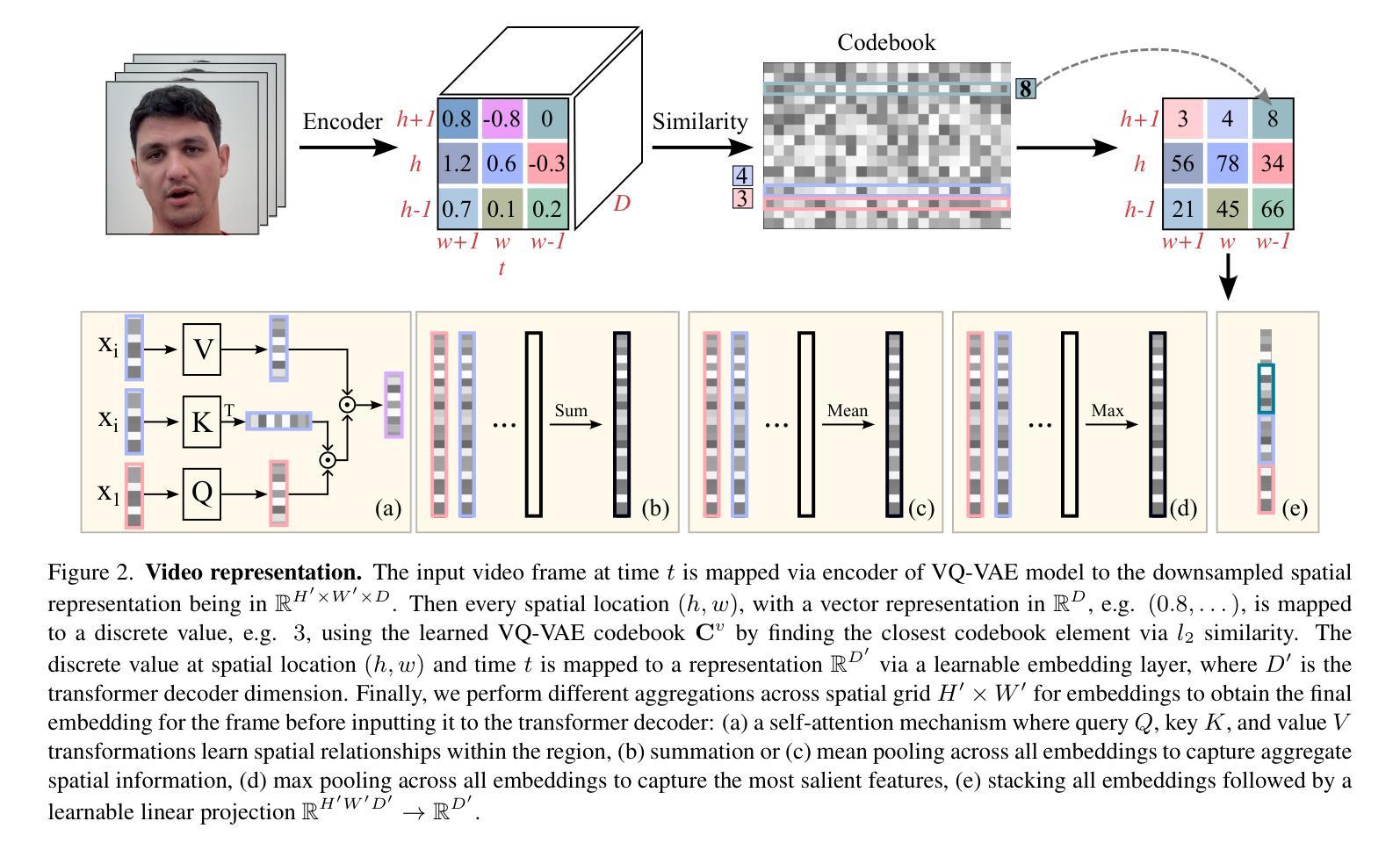
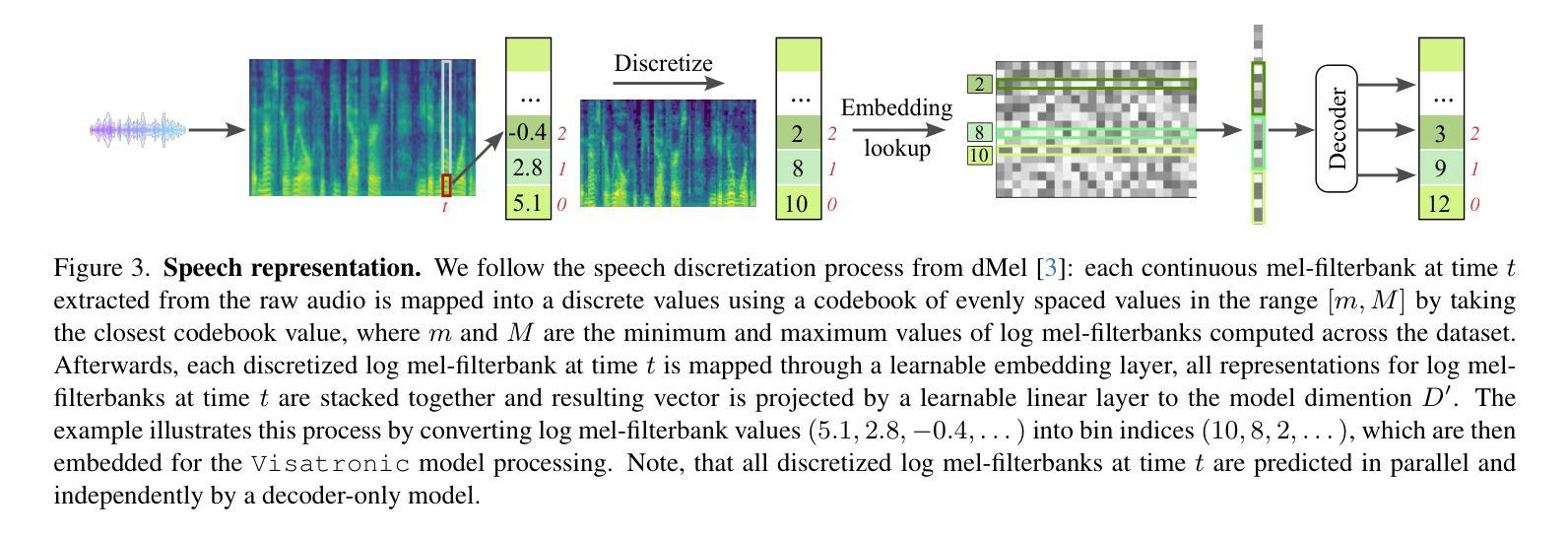
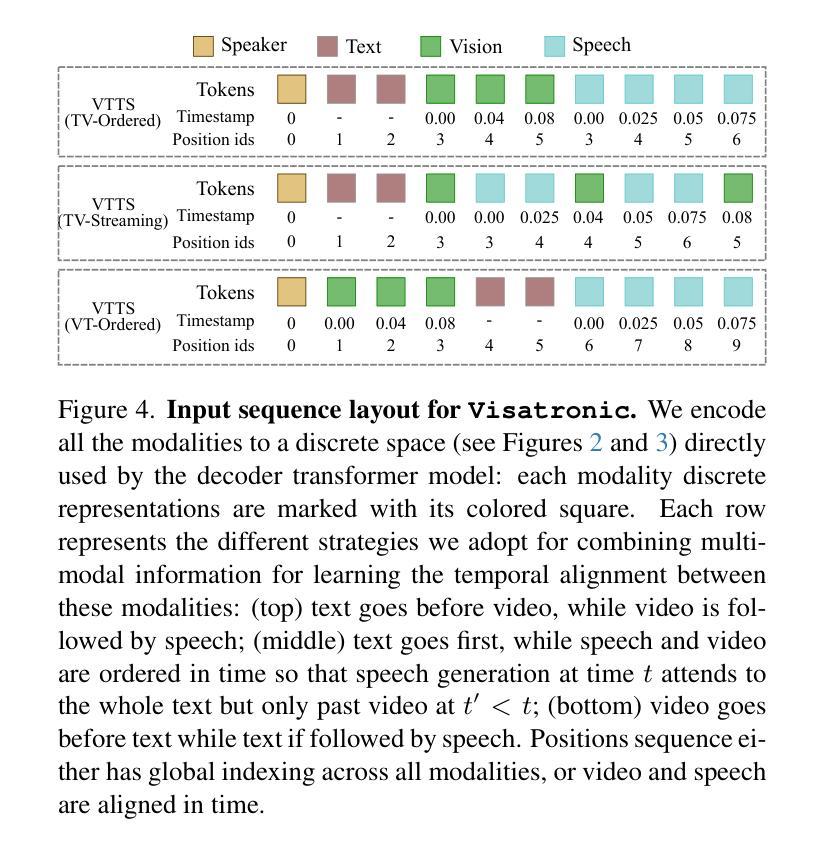
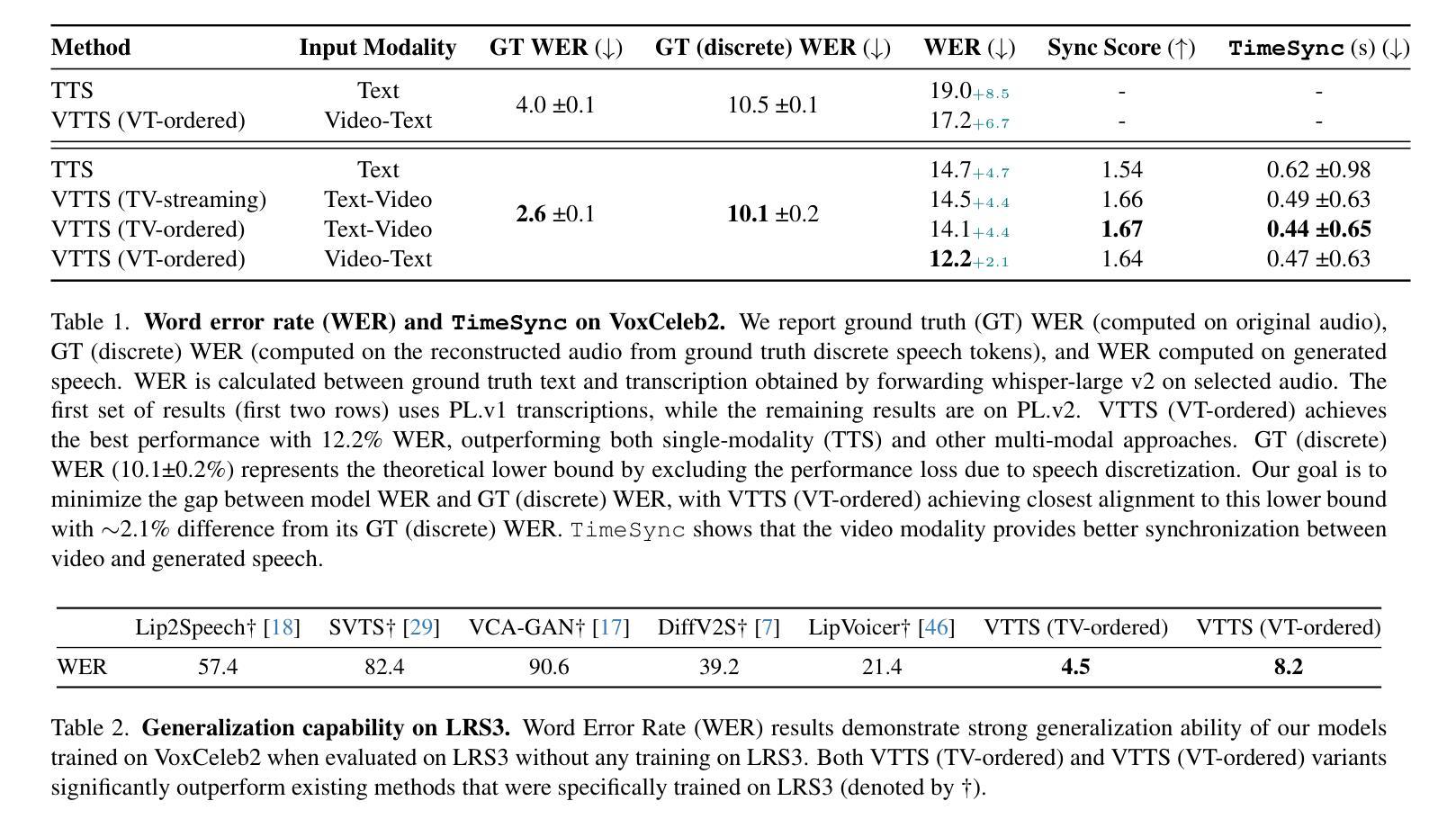
Visatronic: A Multimodal Decoder-Only Model for Speech Synthesis
Authors:Akshita Gupta, Tatiana Likhomanenko, Karren Dai Yang, Richard He Bai, Zakaria Aldeneh, Navdeep Jaitly
In this paper, we propose a new task – generating speech from videos of people and their transcripts (VTTS) – to motivate new techniques for multimodal speech generation. This task generalizes the task of generating speech from cropped lip videos, and is also more complicated than the task of generating generic audio clips (e.g., dog barking) from videos and text. Multilingual versions of the task could lead to new techniques for cross-lingual dubbing. We also present a decoder-only multimodal model for this task, which we call Visatronic. This model embeds vision, text and speech directly into the common subspace of a transformer model and uses an autoregressive loss to learn a generative model of discretized mel-spectrograms conditioned on speaker videos and transcripts of their speech. By embedding all modalities into a common subspace, Visatronic can achieve improved results over models that use only text or video as input. Further, it presents a much simpler approach for multimodal speech generation compared to prevailing approaches which rely on lip-detectors and complicated architectures to fuse modalities while producing better results. Since the model is flexible enough to accommodate different ways of ordering inputs as a sequence, we carefully explore different strategies to better understand the best way to propagate information to the generative steps. To facilitate further research on VTTS, we will release (i) our code, (ii) clean transcriptions for the large-scale VoxCeleb2 dataset, and (iii) a standardized evaluation protocol for VTTS incorporating both objective and subjective metrics.
本文提出了一个新的任务——从人物视频及其字幕生成语音(Video-based Text-to-Speech,VTTS),以激励多模态语音生成的新技术。这个任务泛化了从裁剪的唇语视频中生成语音的任务,并且比从视频和文本中生成通用音频片段(例如狗叫)的任务更加复杂。该任务的多语言版本可能会导致跨语言配音的新技术。我们还为此任务提出了一种仅解码器多模态模型,我们称之为Visatronic。此模型将视觉、文本和语音直接嵌入到变压器的公共子空间中,并使用自回归损失来学习基于说话人视频和他们的语音字幕的离散梅尔频谱图的生成模型。通过将所有模态嵌入公共子空间中,Visatronic可以实现在仅使用文本或视频作为输入的模型上获得更好的结果。此外,与传统的依赖于唇语检测器和复杂的架构来融合模态的方法相比,它提供了更简单的方法来实现多模态语音生成同时产生更好的结果。由于该模型足够灵活,可以容纳不同的输入序列顺序方式,因此我们仔细探索了不同的策略,以更好地了解如何将信息传播到生成步骤的最佳方式。为了促进对VTTS的进一步研究,我们将发布(i)我们的代码,(ii)大规模VoxCeleb2数据集的干净转录,(iii)包含客观和主观指标的VTTS标准化评估协议。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本提出了一种新的任务——从人的视频和他们的文字脚本生成语音(VTTS),以激发多模态语音生成的新技术。此任务不仅涵盖了从裁剪的唇部视频生成语音的任务,而且相较于从视频和文字生成通用音频剪辑(例如狗叫)的任务更为复杂。多语言版本的任务可能会导致跨语言配音的新技术。此外,文中还介绍了一种针对该任务的仅解码器多模态模型Visatronic。它将视觉、文本和语音直接嵌入到transformer模型的公共子空间中,并使用自回归损失来学习以发言人视频和他们的语音文本为条件的离散梅尔频谱图的生成模型。通过将所有模态嵌入公共子空间,Visatronic可以在仅使用文本或视频作为输入的模型上实现更好的结果。此外,相较于依赖唇检测器和复杂架构来融合模态的主流方法,它为多模态语音生成提供了一种更为简单的方法。最后,为便于进一步进行VTTS研究,将公开代码、大规模VoxCeleb2数据集的标准转录以及VTTS的标准评估协议,该协议包括客观和主观指标。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的任务——从人的视频和他们的文字脚本生成语音(VTTS),旨在推动多模态语音生成技术的发展。
- 介绍了一种名为Visatronic的仅解码器多模态模型,该模型将视觉、文本和语音嵌入到公共子空间中,并基于发言人视频和语音文本进行生成学习。
- Visatronic在融合多种输入模态时取得了良好效果,优于仅使用文本或视频的模型。
- Visatronic为多模态语音生成提供了一种相对简单的方法,与主流方法相比,无需依赖复杂的唇检测器和架构。
- 模型具有灵活性,能够适应不同的输入序列顺序策略,可以更好地理解如何传播信息到生成步骤。
- 为了推动VTTS的进一步研究,公开了代码、大规模VoxCeleb2数据集的标准转录以及VTTS的标准评估协议。
点此查看论文截图

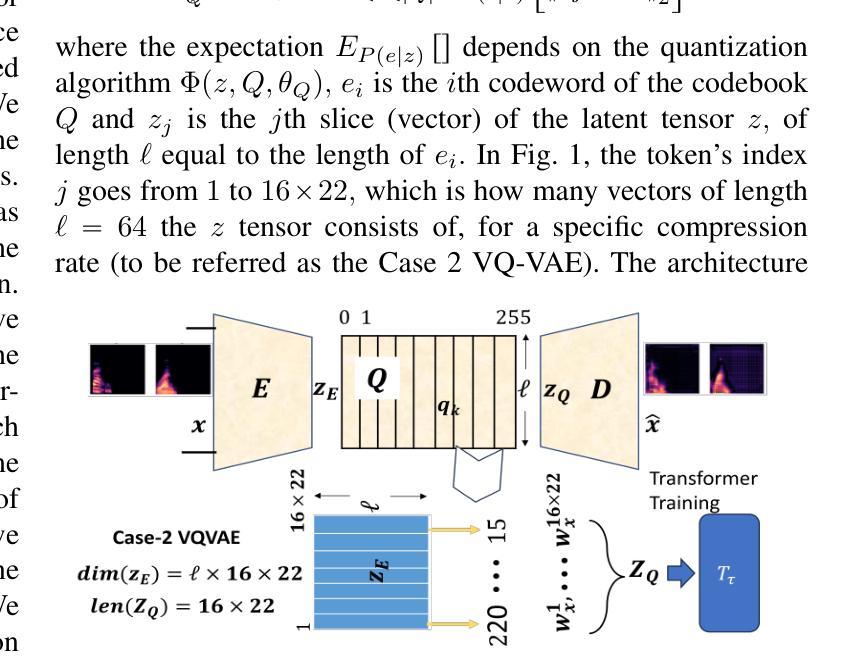
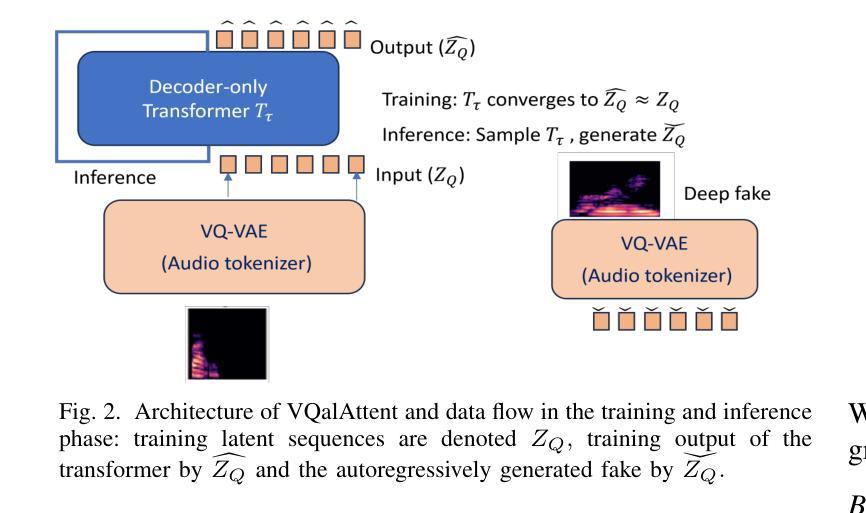
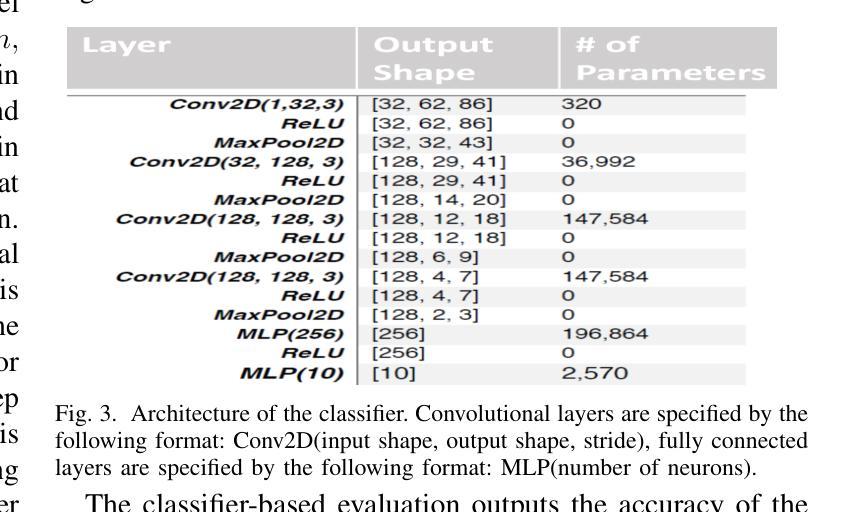
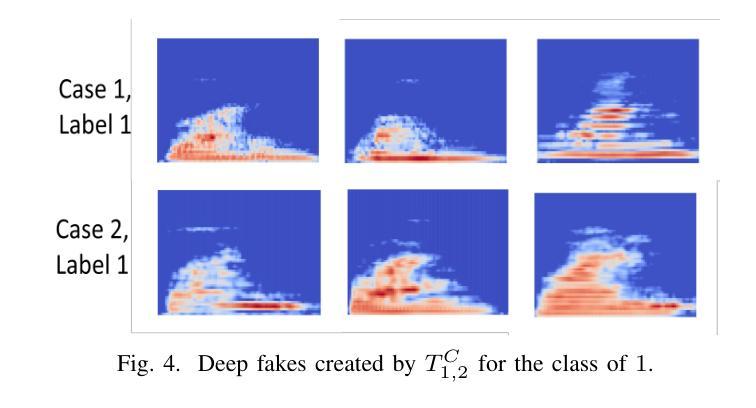
VQalAttent: a Transparent Speech Generation Pipeline based on Transformer-learned VQ-VAE Latent Space
Authors:Armani Rodriguez, Silvija Kokalj-Filipovic
Generating high-quality speech efficiently remains a key challenge for generative models in speech synthesis. This paper introduces VQalAttent, a lightweight model designed to generate fake speech with tunable performance and interpretability. Leveraging the AudioMNIST dataset, consisting of human utterances of decimal digits (0-9), our method employs a two-step architecture: first, a scalable vector quantized autoencoder (VQ-VAE) that compresses audio spectrograms into discrete latent representations, and second, a decoder-only transformer that learns the probability model of these latents. Trained transformer generates similar latent sequences, convertible to audio spectrograms by the VQ-VAE decoder, from which we generate fake utterances. Interpreting statistical and perceptual quality of the fakes, depending on the dimension and the extrinsic information of the latent space, enables guided improvements in larger, commercial generative models. As a valuable tool for understanding and refining audio synthesis, our results demonstrate VQalAttent’s capacity to generate intelligible speech samples with limited computational resources, while the modularity and transparency of the training pipeline helps easily correlate the analytics with modular modifications, hence providing insights for the more complex models.
生成高质量语音的效率仍然是语音合成中生成模型的关键挑战。本文介绍了VQalAttent,这是一个轻量级的模型,旨在以可调的性能和可解释性生成虚假的语音。我们利用由人手发音的十进制数字(0-9)组成的AudioMNIST数据集,采用两步架构:首先,一个可扩展的向量量化自编码器(VQ-VAE),它将音频谱图压缩成离潜在表示;其次,仅解码器端的变压器,学习这些潜在概率模型。训练过的变压器生成类似的潜在序列,可以通过VQ-VAE解码器转换为音频谱图,从而生成虚假的语音。根据潜在空间的维度和外在信息来解释虚假语音的统计和感知质量,能够在更大的商业生成模型中实现有针对性的改进。作为理解和改进音频合成的有价值的工具,我们的结果证明了VQalAttent在有限计算资源的情况下生成可理解的语音样本的能力,而培训管道模块化和透明度的特点有助于轻松地将分析与模块化修改相关联,从而为更复杂的模型提供见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了一种名为VQalAttent的轻量级模型,用于生成高质量语音。该模型利用AudioMNIST数据集,采用两步架构:首先使用可伸缩向量量化自动编码器(VQ-VAE)将音频光谱图压缩成离散潜在表示,然后通过仅解码器转换器学习这些潜在概率模型。通过训练,生成类似潜在序列的假发声,可通过VQ-VAE解码器转换为音频光谱图。模型的可解释性和效率使其成为大型商业生成模型的有价值的工具,可生成具有有限计算资源的可理解语音样本。其模块化训练管道有助于轻松关联分析并模块化改进,为更复杂的模型提供见解。
Key Takeaways
- VQalAttent模型旨在解决语音合成中生成高质量语音的效率问题。
- 模型利用AudioMNIST数据集并采用两步架构:VQ-VAE压缩音频光谱图到离散潜在表示,然后使用解码器转换器进行概率建模。
- 模型生成类似潜在序列的假发声,再转换成音频光谱图生成假发声。
- VQalAttent具有良好的可解释性,有助于理解并改进音频合成过程。
- 模型具有有限的计算资源生成可理解语音样本的能力。
- VQalAttent的模块化训练管道有助于与模块化修改轻松关联分析,为复杂模型提供有价值的见解。
点此查看论文截图



WavChat: A Survey of Spoken Dialogue Models
Authors:Shengpeng Ji, Yifu Chen, Minghui Fang, Jialong Zuo, Jingyu Lu, Hanting Wang, Ziyue Jiang, Long Zhou, Shujie Liu, Xize Cheng, Xiaoda Yang, Zehan Wang, Qian Yang, Jian Li, Yidi Jiang, Jingzhen He, Yunfei Chu, Jin Xu, Zhou Zhao
Recent advancements in spoken dialogue models, exemplified by systems like GPT-4o, have captured significant attention in the speech domain. Compared to traditional three-tier cascaded spoken dialogue models that comprise speech recognition (ASR), large language models (LLMs), and text-to-speech (TTS), modern spoken dialogue models exhibit greater intelligence. These advanced spoken dialogue models not only comprehend audio, music, and other speech-related features, but also capture stylistic and timbral characteristics in speech. Moreover, they generate high-quality, multi-turn speech responses with low latency, enabling real-time interaction through simultaneous listening and speaking capability. Despite the progress in spoken dialogue systems, there is a lack of comprehensive surveys that systematically organize and analyze these systems and the underlying technologies. To address this, we have first compiled existing spoken dialogue systems in the chronological order and categorized them into the cascaded and end-to-end paradigms. We then provide an in-depth overview of the core technologies in spoken dialogue models, covering aspects such as speech representation, training paradigm, streaming, duplex, and interaction capabilities. Each section discusses the limitations of these technologies and outlines considerations for future research. Additionally, we present a thorough review of relevant datasets, evaluation metrics, and benchmarks from the perspectives of training and evaluating spoken dialogue systems. We hope this survey will contribute to advancing both academic research and industrial applications in the field of spoken dialogue systems. The related material is available at https://github.com/jishengpeng/WavChat.
最近,以GPT-4o等系统为代表,口语对话模型的发展在语音领域引起了极大的关注。与传统的三级级联口语对话模型相比,现代口语对话模型展现出更高的智能水平,这些模型包括语音识别(ASR)、大型语言模型(LLM)和文本到语音(TTS)。先进的口语对话模型不仅能够理解音频、音乐和其他语音相关特征,还能捕捉语音中的风格和音色特征。此外,它们能够生成高质量的多轮语音响应,具有低延迟性,通过同时的听和说能力实现实时交互。尽管口语对话系统的进展显著,但缺乏系统组织和分析这些系统和底层技术的全面综述。为了解决这个问题,我们首先按时间顺序整理了现有的口语对话系统,并将其分为级联和端到端范式。然后,我们深入概述了口语对话模型的核心技术,涵盖了语音表示、训练范式、流媒体、双向对话和交互能力等方面。每个部分都讨论了这些技术的局限性,并概述了未来研究的考虑因素。此外,我们还从训练和评估口语对话系统的角度,对相关数据集、评估指标和基准测试进行了全面的回顾。我们希望这份综述能为口语对话系统的学术研究和工业应用做出贡献。相关资料可在https://github.com/jishengpeng/WavChat找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 60 papes, working in progress
Summary
近期,如GPT-4o等先进对话模型在语音领域引起广泛关注。与传统三级级联对话模型相比,现代对话模型展现出更高智能,不仅能理解音频、音乐等语音相关特征,还能捕捉语音的风格和音色特点。它们能生成高质量、多轮次的语音回应,实现实时互动。然而,缺乏系统分析和总结这些系统和底层技术的综述文章。本文首先按时间顺序整理现有对话系统,将其分为级联和端到端范式。接着深入概述对话模型的核心技术,如语音表示、训练范式、流式处理、双向对话和交互能力等。同时,讨论各技术的局限性和未来研究方向,并从训练和评估对话系统的角度全面回顾相关数据集、评估指标和基准测试。本文旨在为学术界和工业界推进对话系统的发展做出贡献。
Key Takeaways
- 现代对话模型如GPT-4o展现出高智能,能理解多种语音相关特征并捕捉语音风格及音色。
2.与传统模型相比,先进对话模型能生成高质量、多轮次的语音回应,实现实时互动。 - 当前缺乏系统分析和总结现代对话系统和底层技术的综述文章。
- 本文按时间顺序整理对话系统,并深入讨论其核心技术的局限性和未来研究方向。
- 文章概述了语音表示、训练范式、流式处理等方面的技术细节。
- 从训练和评估角度全面回顾相关数据集、评估指标和基准测试。
点此查看论文截图

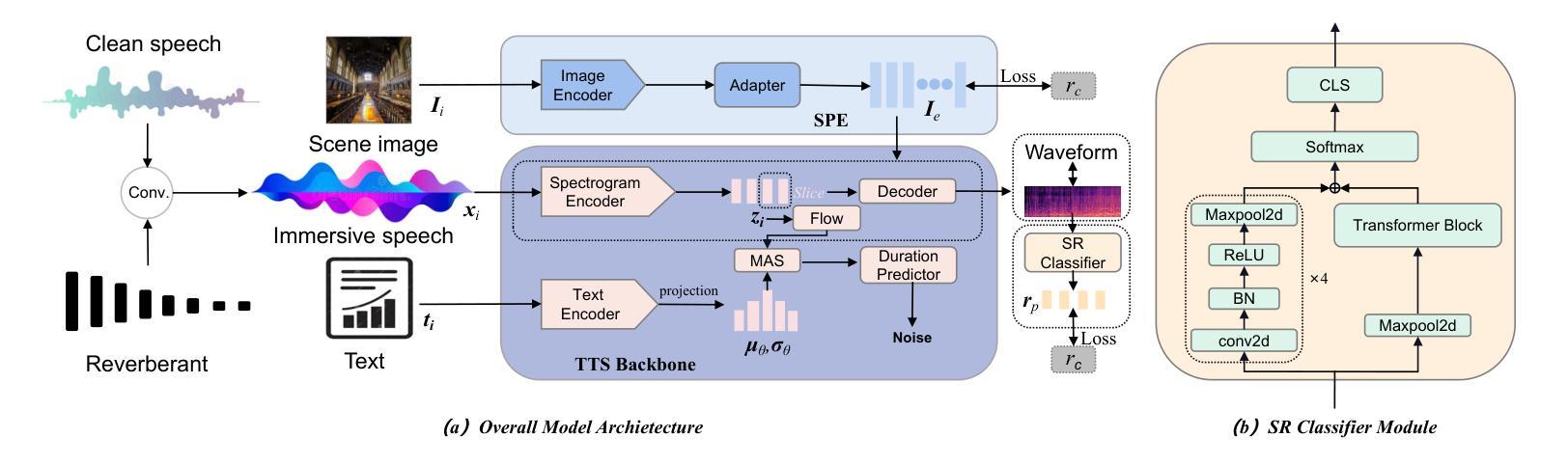
I2TTS: Image-indicated Immersive Text-to-speech Synthesis with Spatial Perception
Authors:Jiawei Zhang, Tian-Hao Zhang, Jun Wang, Jiaran Gao, Xinyuan Qian, Xu-Cheng Yin
Controlling the style and characteristics of speech synthesis is crucial for adapting the output to specific contexts and user requirements. Previous Text-to-speech (TTS) works have focused primarily on the technical aspects of producing natural-sounding speech, such as intonation, rhythm, and clarity. However, they overlook the fact that there is a growing emphasis on spatial perception of synthesized speech, which may provide immersive experience in gaming and virtual reality. To solve this issue, in this paper, we present a novel multi-modal TTS approach, namely Image-indicated Immersive Text-to-speech Synthesis (I2TTS). Specifically, we introduce a scene prompt encoder that integrates visual scene prompts directly into the synthesis pipeline to control the speech generation process. Additionally, we propose a reverberation classification and refinement technique that adjusts the synthesized mel-spectrogram to enhance the immersive experience, ensuring that the involved reverberation condition matches the scene accurately. Experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves high-quality scene and spatial matching without compromising speech naturalness, marking a significant advancement in the field of context-aware speech synthesis. Project demo page: https://spatialTTS.github.io/ Index Terms-Speech synthesis, scene prompt, spatial perception
控制语音合成的风格和特性对于适应特定的上下文和用户要求至关重要。之前的文本到语音(TTS)工作主要集中在产生自然语音的技术方面,如语调、节奏和清晰度。然而,他们忽略了一个事实,那就是对于合成语音的空间感知的重视程度正在增长,这可能在游戏和虚拟现实提供沉浸式体验。为了解决这一问题,本文提出了一种新型的多模式TTS方法,即图像指示沉浸式文本到语音合成(I2TTS)。具体来说,我们引入了一个场景提示编码器,它将视觉场景提示直接集成到合成管道中,以控制语音生成过程。此外,我们提出了一种混响分类和细化技术,该技术可以调节合成的梅尔频谱图以增强沉浸式体验,确保所涉及的混响条件与场景准确匹配。实验结果表明,我们的模型在不影响语音自然性的情况下实现了高质量的场景和空间匹配,标志着上下文感知语音合成领域的一项重大进展。项目演示页面:https://spatialTTS.github.io/ 索引术语-语音合成、场景提示、空间感知。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The paper is missing some information
Summary
文本介绍了一种名为I2TTS的新型多模态TTS方法,它通过引入场景提示编码器将视觉场景提示直接集成到合成管道中,控制语音生成过程。同时提出一种混响分类和细化技术,调整合成mel频谱图以增强沉浸式体验,确保涉及的混响条件与场景准确匹配。该方法实现了高质量场景和空间匹配,不损失语音自然性。
Key Takeaways
- 控制语音合成的风格和特点是适应特定上下文和用户需求的关键。
- 传统的TTS技术主要关注自然语音的技术方面,如语调、节奏和清晰度。
- 目前对合成语音的空间感知有越来越强的关注,这在游戏和虚拟现实等领域提供沉浸式体验方面非常重要。
- 论文提出了一种新型的多模态TTS方法I2TTS,引入场景提示编码器,将视觉场景提示直接集成到语音合成过程中。
- I2TTS能提高合成语音的沉浸式体验,通过调整mel频谱图实现高质量场景和空间匹配,同时保持语音的自然性。
- 论文还介绍了混响分类和细化技术,确保涉及的混响条件与场景准确匹配。
点此查看论文截图

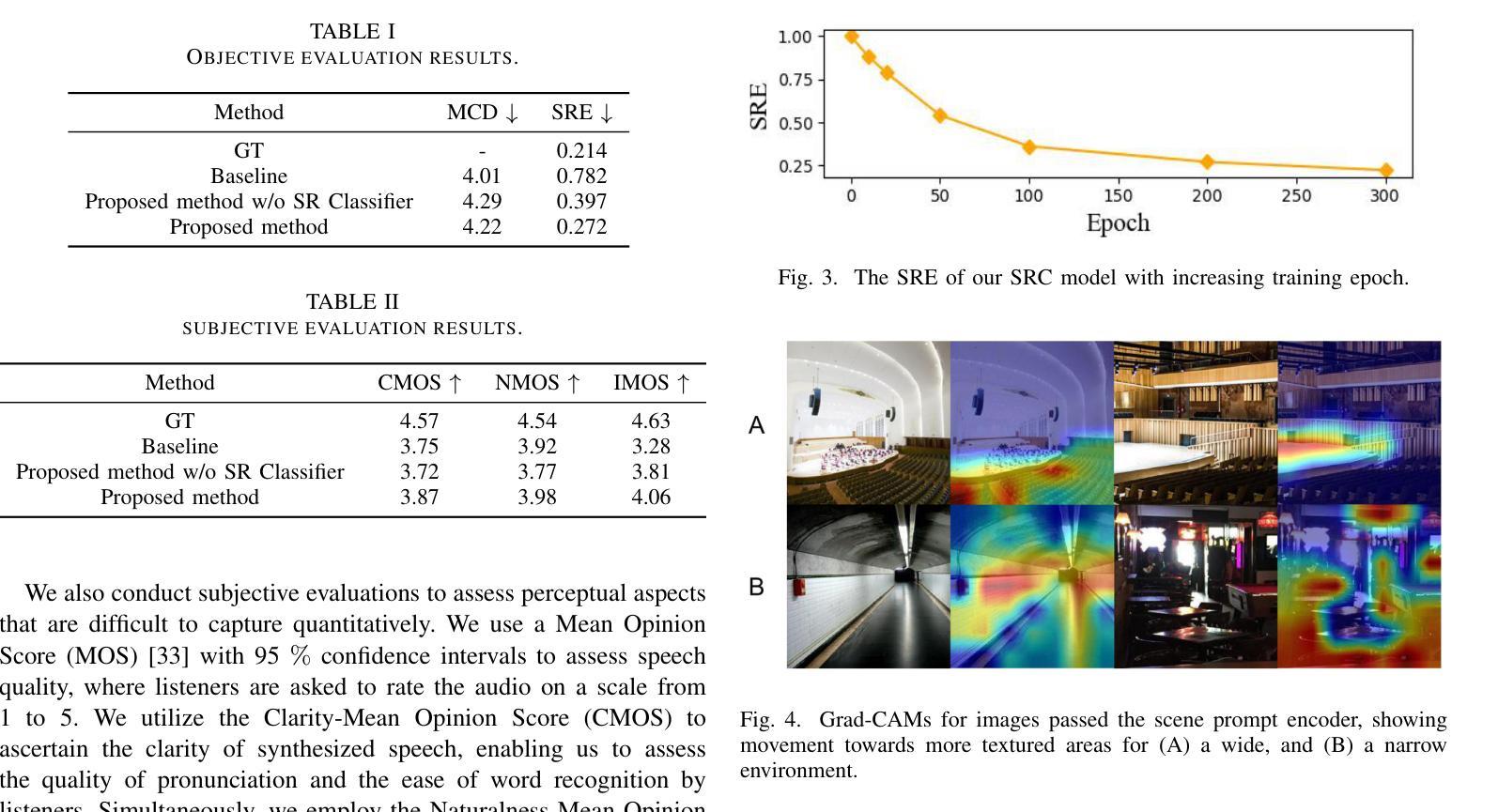
Hard-Synth: Synthesizing Diverse Hard Samples for ASR using Zero-Shot TTS and LLM
Authors:Jiawei Yu, Yuang Li, Xiaosong Qiao, Huan Zhao, Xiaofeng Zhao, Wei Tang, Min Zhang, Hao Yang, Jinsong Su
Text-to-speech (TTS) models have been widely adopted to enhance automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems using text-only corpora, thereby reducing the cost of labeling real speech data. Existing research primarily utilizes additional text data and predefined speech styles supported by TTS models. In this paper, we propose Hard-Synth, a novel ASR data augmentation method that leverages large language models (LLMs) and advanced zero-shot TTS. Our approach employs LLMs to generate diverse in-domain text through rewriting, without relying on additional text data. Rather than using predefined speech styles, we introduce a hard prompt selection method with zero-shot TTS to clone speech styles that the ASR model finds challenging to recognize. Experiments demonstrate that Hard-Synth significantly enhances the Conformer model, achieving relative word error rate (WER) reductions of 6.5%/4.4% on LibriSpeech dev/test-other subsets. Additionally, we show that Hard-Synth is data-efficient and capable of reducing bias in ASR.
文本转语音(TTS)模型已被广泛应用于仅使用文本语料库增强自动语音识别(ASR)系统,从而降低标记真实语音数据的成本。现有研究主要利用额外的文本数据和TTS模型支持的预定义语音风格。在本文中,我们提出了Hard-Synth,这是一种新型的ASR数据增强方法,它利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和先进的零样本TTS。我们的方法通过重写的方式,采用LLMs生成多样化的领域内文本,而不依赖额外的文本数据。我们摒弃使用预定义的语音风格,而采用硬性提示选择方法和零样本TTS来复制ASR模型发现难以识别的语音风格。实验表明,Hard-Synth可以显著增强Conformer模型的性能,在LibriSpeech的dev/test-other子集上相对字词错误率(WER)降低了6.5%/4.4%。此外,我们还证明了Hard-Synth数据效率较高且能降低ASR的偏见。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种利用大型语言模型(LLMs)和零样本TTS进行ASR数据增强的新方法——Hard-Synth。该方法通过LLMs改写生成多样化和特定领域的文本,无需额外文本数据,并采用硬提示选择方法,利用零样本TTS复制ASR模型难以识别的语音风格。实验表明,Hard-Synth可显著提高Conformer模型的性能,在LibriSpeech的dev/test-other子集上相对字词错误率(WER)分别降低6.5%\textbackslash和4.4%。此外,Hard-Synth具有数据高效性和减少ASR偏见的能力。
Key Takeaways
- Hard-Synth是一种新型的ASR数据增强方法,结合了LLMs和零样本TTS技术。
- 该方法通过LLMs生成多样化和特定领域的文本,无需额外文本数据。
- 采用硬提示选择方法,利用零样本TTS复制ASR模型难以识别的语音风格。
- 实验结果显示,Hard-Synth能显著提高Conformer模型的性能,降低字词错误率。
- Hard-Synth方法具有数据高效性,能够有效利用有限的数据资源。
- 该方法能够减少ASR模型的偏见,提高模型的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图



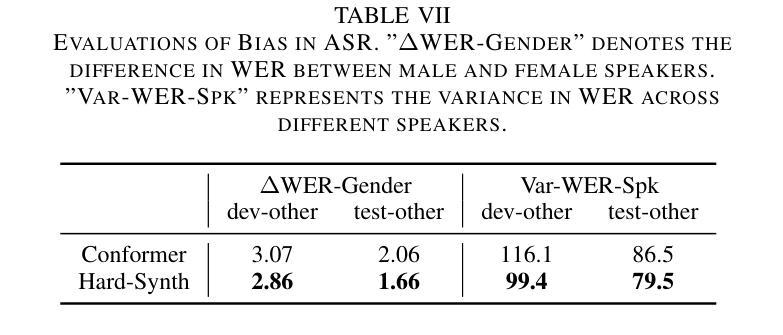
Rethinking MUSHRA: Addressing Modern Challenges in Text-to-Speech Evaluation
Authors:Praveen Srinivasa Varadhan, Amogh Gulati, Ashwin Sankar, Srija Anand, Anirudh Gupta, Anirudh Mukherjee, Shiva Kumar Marepally, Ankur Bhatia, Saloni Jaju, Suvrat Bhooshan, Mitesh M. Khapra
Despite rapid advancements in TTS models, a consistent and robust human evaluation framework is still lacking. For example, MOS tests fail to differentiate between similar models, and CMOS’s pairwise comparisons are time-intensive. The MUSHRA test is a promising alternative for evaluating multiple TTS systems simultaneously, but in this work we show that its reliance on matching human reference speech unduly penalises the scores of modern TTS systems that can exceed human speech quality. More specifically, we conduct a comprehensive assessment of the MUSHRA test, focusing on its sensitivity to factors such as rater variability, listener fatigue, and reference bias. Based on our extensive evaluation involving 471 human listeners across Hindi and Tamil we identify two primary shortcomings: (i) reference-matching bias, where raters are unduly influenced by the human reference, and (ii) judgement ambiguity, arising from a lack of clear fine-grained guidelines. To address these issues, we propose two refined variants of the MUSHRA test. The first variant enables fairer ratings for synthesized samples that surpass human reference quality. The second variant reduces ambiguity, as indicated by the relatively lower variance across raters. By combining these approaches, we achieve both more reliable and more fine-grained assessments. We also release MANGO, a massive dataset of 47,100 human ratings, the first-of-its-kind collection for Indian languages, aiding in analyzing human preferences and developing automatic metrics for evaluating TTS systems.
尽管TTS模型迅速进步,但仍缺乏一致且稳健的人类评估框架。例如,MOS测试无法区分相似的模型,CMOS的配对比较则非常耗时。MUSHRA测试是评估多个TTS系统的有前途的替代方法,但在这项工作中我们表明,其对匹配人类参考语音的依赖会过度惩罚那些已经超过人类语音质量的现代TTS系统的分数。更具体地说,我们对MUSHRA测试进行了全面评估,重点关注其对评分者变异性、听者疲劳和参考偏见等因素的敏感性。基于我们涉及印地语和泰米尔语471名人类听者的广泛评估,我们确定了两个主要缺点:(i)参考匹配偏见,即评分者受到不必要的人类参考影响;(ii)由于缺乏明确的精细指南而产生的判断模糊性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了MUSHRA测试的两种改进变体。第一种变体使合成样本的评分更加公平,即使其质量超过人类参考质量。第二种变体减少了模糊性,如评分者之间的方差相对较低所示。通过结合这些方法,我们实现了更可靠和更精细的评估。我们还发布了MANGO数据集,这是一个人类评分的巨大数据集,包含47,100项评分,是印度语言的首个此类集合,有助于分析人类偏好并开发用于评估TTS系统的自动度量标准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 12 Figures
Summary
本文探讨了TTS模型评估中存在的问题,指出尽管TTS技术快速发展,但仍缺乏一致且稳健的人评框架。作者重点对MUSHRA测试进行了全面评估,发现其存在的两个主要问题:一是受参考匹配偏见影响,二是判断模糊。为解决这些问题,作者提出了两种改进的MUSHRA测试方法,并发布了针对印度语言的大规模数据集MANGO,有助于分析人类偏好并开发自动评估指标。
Key Takeaways
- TTS领域缺乏统一稳健的人评框架,现有测试方法如MOS和CMOS存在局限性。
- MUSHRA测试是一个有前景的TTS评估方法,但存在参考匹配偏见和判断模糊的问题。
- 作者提出了两种改进的MUSHRA测试方法,以公平评价超过人类参考质量的合成样本并减少判断模糊。
- 通过结合这两种方法,可以实现更可靠和更精细的评估。
- 发布了针对印度语言的大规模数据集MANGO,有助于分析人类偏好和开发自动评估指标。
- 研究涉及了471名人类听众的广泛评估,包括印度语言(如印地语和泰米尔语)。
点此查看论文截图

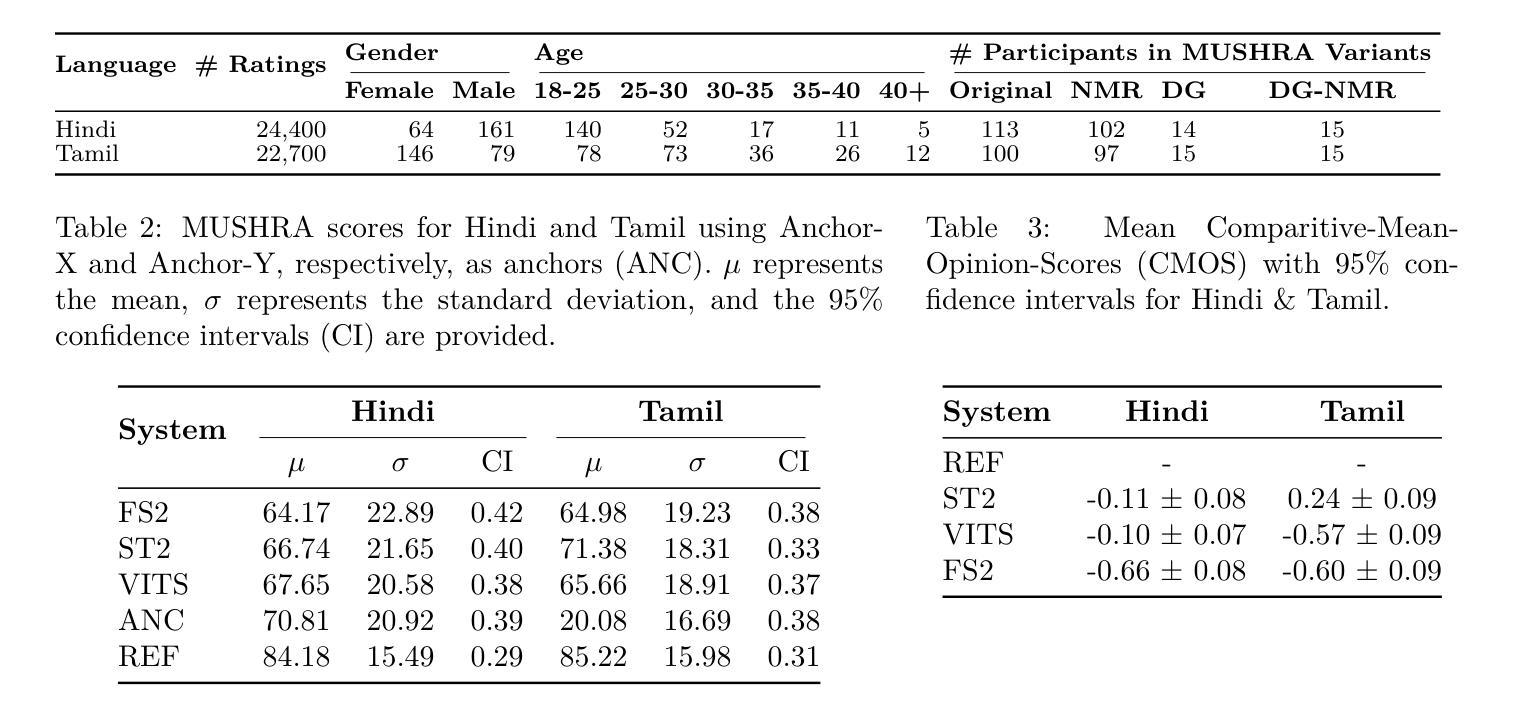
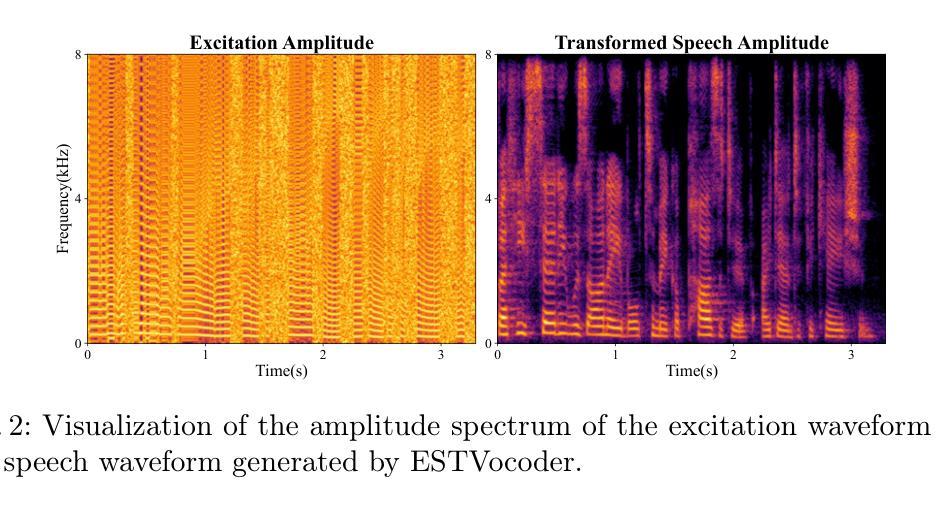
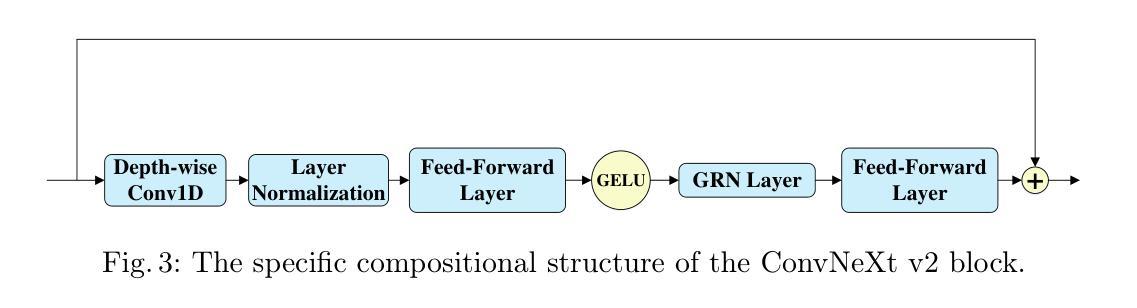
ESTVocoder: An Excitation-Spectral-Transformed Neural Vocoder Conditioned on Mel Spectrogram
Authors:Xiao-Hang Jiang, Hui-Peng Du, Yang Ai, Ye-Xin Lu, Zhen-Hua Ling
This paper proposes ESTVocoder, a novel excitation-spectral-transformed neural vocoder within the framework of source-filter theory. The ESTVocoder transforms the amplitude and phase spectra of the excitation into the corresponding speech amplitude and phase spectra using a neural filter whose backbone is ConvNeXt v2 blocks. Finally, the speech waveform is reconstructed through the inverse short-time Fourier transform (ISTFT). The excitation is constructed based on the F0: for voiced segments, it contains full harmonic information, while for unvoiced segments, it is represented by noise. The excitation provides the filter with prior knowledge of the amplitude and phase patterns, expecting to reduce the modeling difficulty compared to conventional neural vocoders. To ensure the fidelity of the synthesized speech, an adversarial training strategy is applied to ESTVocoder with multi-scale and multi-resolution discriminators. Analysis-synthesis and text-to-speech experiments both confirm that our proposed ESTVocoder outperforms or is comparable to other baseline neural vocoders, e.g., HiFi-GAN, SiFi-GAN, and Vocos, in terms of synthesized speech quality, with a reasonable model complexity and generation speed. Additional analysis experiments also demonstrate that the introduced excitation effectively accelerates the model’s convergence process, thanks to the speech spectral prior information contained in the excitation.
本文提出了ESTVocoder,这是一种在源滤波器理论框架下,采用激励谱变换技术的新型神经vocoder。ESTVocoder使用神经滤波器将激励的幅度和相位谱转换为相应的语音幅度和相位谱,该滤波器的骨干是ConvNeXt v2块。最后,通过逆短时傅里叶变换(ISTFT)重建语音波形。激励的构造基于F0:对于有声段,它包含完整的谐波信息,而对于无声段,则用噪声表示。激励为滤波器提供幅度和相位模式的先验知识,以期与常规神经vocoder相比降低建模难度。为了保证合成语音的保真度,ESTVocoder采用了对抗性训练策略,并配备了多尺度、多分辨率鉴别器。分析和文本转语音实验均证实,与其他基线神经vocoder(如HiFi-GAN、SiFi-GAN和Vocos)相比,我们提出的ESTVocoder在合成语音质量方面表现优异或相当,具有合理的模型复杂度和生成速度。另外的分析实验还表明,引入的激励有效地加速了模型的收敛过程,这得益于激励中所包含的语音谱先验信息。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NCMMSC2024
Summary
本文提出一种名为ESTVocoder的新型激励-频谱转换神经网络编码器,该编码器在源滤波器理论框架下运行。它利用神经网络过滤器将激励的幅度和相位谱转换为相应的语音幅度和相位谱,并通过逆短时傅里叶变换(ISTFT)重建语音波形。激励基于F0构建,对于发音段,包含全部谐波信息,而对于非发音段,则通过噪声表示。此外,采用对抗训练策略确保合成语音的保真度,并利用多尺度、多分辨率鉴别器对ESTVocoder进行鉴别。实验证实,ESTVocoder在合成语音质量方面优于或与其他基线神经网络编码器相当,如HiFi-GAN、SiFi-GAN和Vocos等,同时模型复杂度合理,生成速度快。
Key Takeaways
- ESTVocoder是一种基于源滤波器理论的激励-频谱转换神经网络编码器。
- 通过神经网络过滤器将激励的幅度和相位谱转换为语音幅度和相位谱。
- 采用逆短时傅里叶变换(ISTFT)重建语音波形。
- 激励由F0构建,包含发音段的全部谐波信息和非发音段的噪声表示。
- 对抗训练策略用于确保合成语音的保真度。
- ESTVocoder在合成语音质量方面表现出优异的性能,与其他基线神经网络编码器相比具有竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

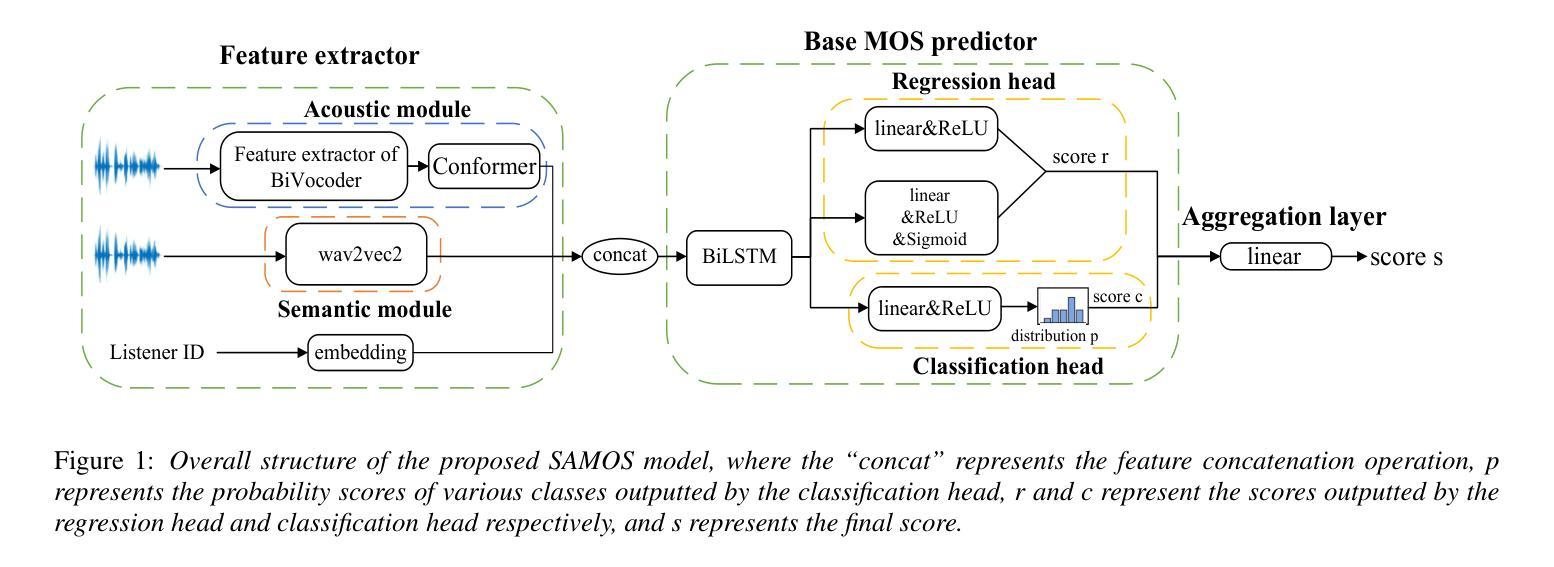
SAMOS: A Neural MOS Prediction Model Leveraging Semantic Representations and Acoustic Features
Authors:Yu-Fei Shi, Yang Ai, Ye-Xin Lu, Hui-Peng Du, Zhen-Hua Ling
Assessing the naturalness of speech using mean opinion score (MOS) prediction models has positive implications for the automatic evaluation of speech synthesis systems. Early MOS prediction models took the raw waveform or amplitude spectrum of speech as input, whereas more advanced methods employed self-supervised-learning (SSL) based models to extract semantic representations from speech for MOS prediction. These methods utilized limited aspects of speech information for MOS prediction, resulting in restricted prediction accuracy. Therefore, in this paper, we propose SAMOS, a MOS prediction model that leverages both Semantic and Acoustic information of speech to be assessed. Specifically, the proposed SAMOS leverages a pretrained wav2vec2 to extract semantic representations and uses the feature extractor of a pretrained BiVocoder to extract acoustic features. These two types of features are then fed into the prediction network, which includes multi-task heads and an aggregation layer, to obtain the final MOS score. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed SAMOS outperforms current state-of-the-art MOS prediction models on the BVCC dataset and performs comparable performance on the BC2019 dataset, according to the results of system-level evaluation metrics.
使用平均意见得分(MOS)预测模型评估语音的自然度,对于自动评估语音合成系统具有积极的影响。早期的MOS预测模型以语音的原始波形或幅度谱作为输入,而更先进的方法则使用基于自监督学习(SSL)的模型来从语音中提取语义表示以进行MOS预测。这些方法仅利用语音的有限方面来进行MOS预测,导致预测精度受到限制。因此,本文提出了一种名为SAMOS的MOS预测模型,该模型利用语音的语义和声音信息进行评估。具体来说,提出的SAMOS利用预训练的wav2vec2提取语义表示,并使用预训练的BiVocoder的特征提取器提取声音特征。然后,这两种类型的特征被输入到预测网络中,该网络包括多任务头和聚合层,以获得最终的MOS得分。实验结果表明,在BVCC数据集上,所提出的SAMOS在性能上优于当前最先进的MOS预测模型,并在BC2019数据集上的系统级评估指标中表现出相当的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于文本中的信息,使用平均意见得分(MOS)预测模型评估语音的自然度对自动评估语音合成系统具有积极影响。早期的MOS预测模型采用语音的原始波形或幅度谱作为输入,而更先进的方法使用基于自监督学习(SSL)的模型从语音中提取语义表示以进行MOS预测。然而,这些方法仅使用有限的语音信息来进行MOS预测,导致预测准确性受限。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种新的MOS预测模型SAMOS,该模型结合了语音的语义和声音信息进行评估。实验结果表明,SAMOS在BVCC数据集上的性能优于当前最先进的MOS预测模型,在BC2019数据集上的性能与之相当。系统级评估指标显示其卓越表现。
Key Takeaways
- 使用平均意见得分(MOS)预测模型评估语音自然度对自动评估语音合成系统有积极影响。
- 早期的MOS预测模型主要基于原始波形或幅度谱进行预测。
- 更先进的MOS预测方法采用自监督学习模型从语音中提取语义表示。
- 现有方法仅使用有限的语音信息,导致预测准确性受限。
- SAMOS模型结合了语义和声音信息来进行更准确的MOS预测。
- SAMOS在BVCC数据集上的性能优于其他先进模型。
点此查看论文截图

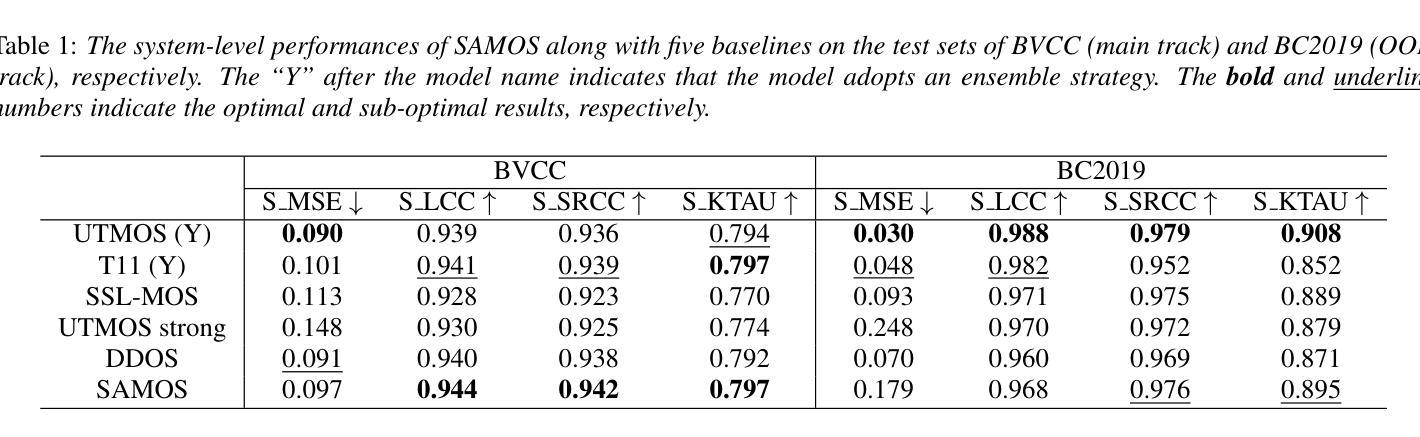
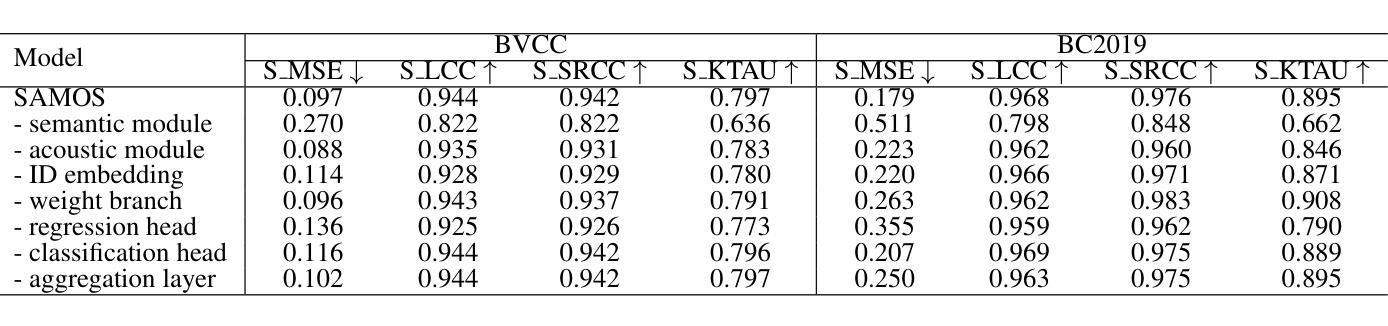
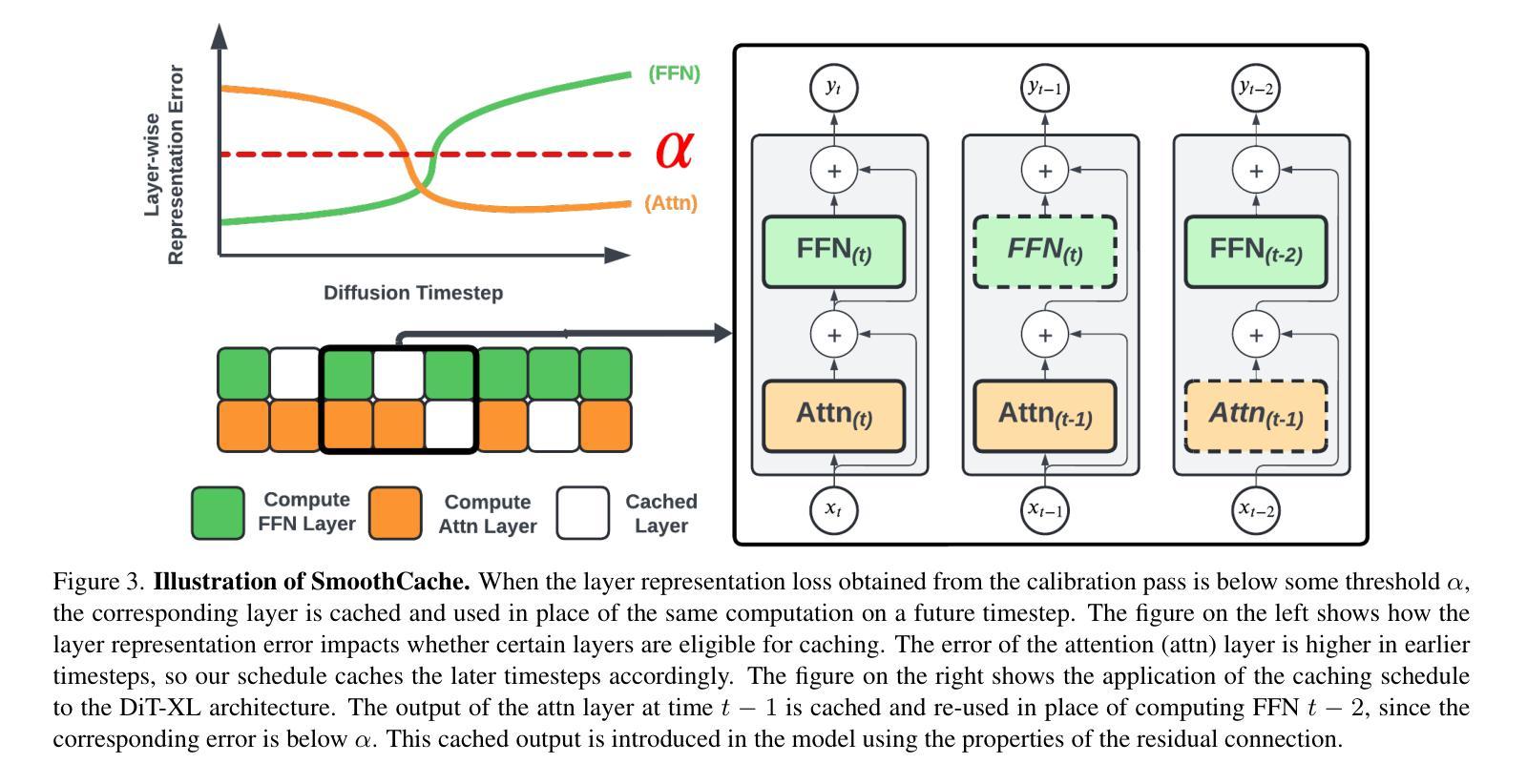
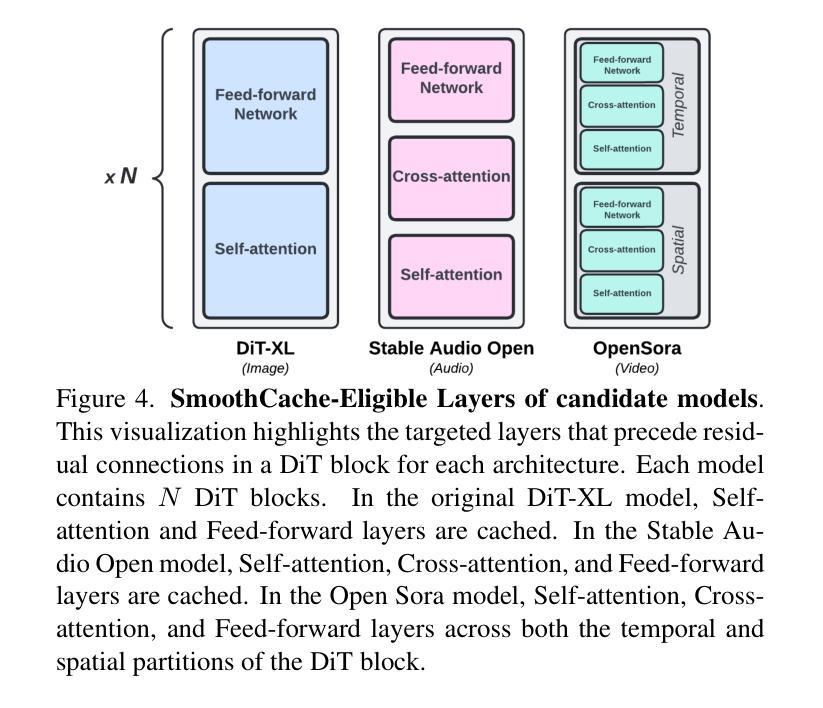
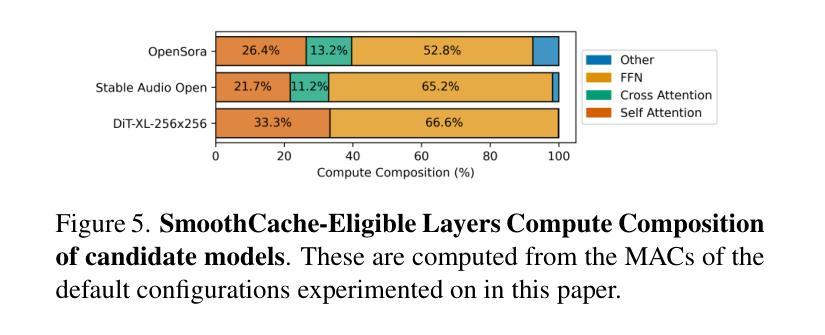
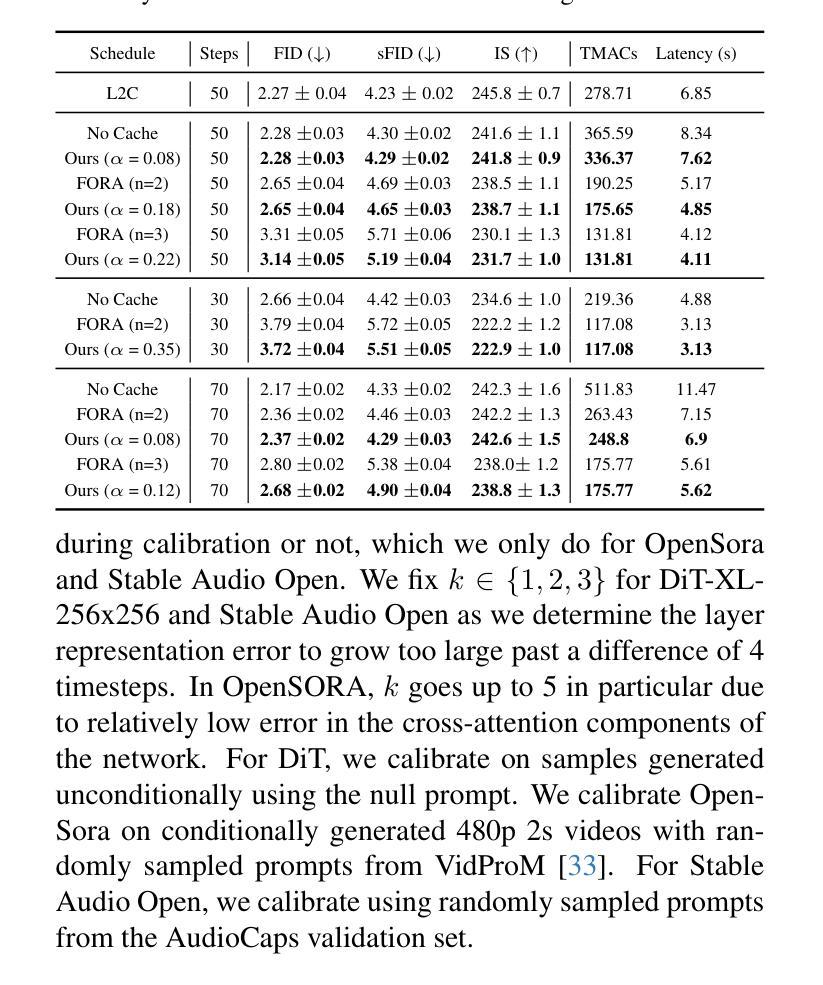
SmoothCache: A Universal Inference Acceleration Technique for Diffusion Transformers
Authors:Joseph Liu, Joshua Geddes, Ziyu Guo, Haomiao Jiang, Mahesh Kumar Nandwana
Diffusion Transformers (DiT) have emerged as powerful generative models for various tasks, including image, video, and speech synthesis. However, their inference process remains computationally expensive due to the repeated evaluation of resource-intensive attention and feed-forward modules. To address this, we introduce SmoothCache, a model-agnostic inference acceleration technique for DiT architectures. SmoothCache leverages the observed high similarity between layer outputs across adjacent diffusion timesteps. By analyzing layer-wise representation errors from a small calibration set, SmoothCache adaptively caches and reuses key features during inference. Our experiments demonstrate that SmoothCache achieves 8% to 71% speed up while maintaining or even improving generation quality across diverse modalities. We showcase its effectiveness on DiT-XL for image generation, Open-Sora for text-to-video, and Stable Audio Open for text-to-audio, highlighting its potential to enable real-time applications and broaden the accessibility of powerful DiT models.
扩散Transformer(DiT)已经成为包括图像、视频和语音合成在内的各种任务的强大生成模型。然而,由于需要重复评估资源密集型的注意力和前馈模块,它们的推理过程计算成本仍然很高。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了SmoothCache,这是一种适用于DiT架构的模型无关推理加速技术。SmoothCache利用相邻扩散时间步长之间层输出的高相似性。通过分析来自小型校准集的层表示误差,SmoothCache在推理过程中自适应地缓存和重用关键特征。我们的实验表明,SmoothCache在保持或甚至提高生成质量的同时,实现了8%至71%的加速。我们在图像生成的DiT-XL、文本到视频的Open-Sora以及文本到音频的Stable Audio Open上展示了其有效性,突出了其实现实时应用和扩大强大DiT模型可及性的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code can be found at https://github.com/Roblox/SmoothCache
Summary
扩散Transformer(DiT)已成为图像、视频和语音合成等任务的强大生成模型,但其推理过程计算成本高昂。为解决这一问题,本文提出了SmoothCache,这是一种适用于DiT架构的模型无关推理加速技术。SmoothCache利用相邻扩散时序步骤间层输出之间的高相似性,通过分析校准集上的层表示误差来自适应缓存和重用关键特征,从而加速推理过程。实验表明,SmoothCache在保持或提高生成质量的同时,实现了8%至71%的提速,在图像生成、文本到视频以及文本到音频等多个模态中均展现出其有效性,具有实现实时应用和扩大强大DiT模型访问潜力的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散Transformer(DiT)是图像、视频和语音合成等任务的强大生成模型。
- DiT的推理过程计算成本高昂,需要加速。
- SmoothCache是一种适用于DiT架构的模型无关推理加速技术。
- SmoothCache利用相邻扩散时序步骤间层输出的高相似性来加速推理。
- SmoothCache通过自适应缓存和重用关键特征来实现加速。
- 实验表明,SmoothCache实现了8%至71%的提速,同时保持或提高了生成质量。
点此查看论文截图
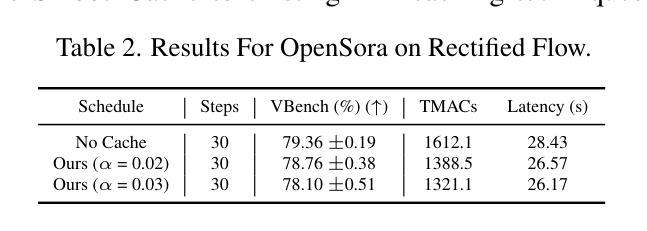
Improving Grapheme-to-Phoneme Conversion through In-Context Knowledge Retrieval with Large Language Models
Authors:Dongrui Han, Mingyu Cui, Jiawen Kang, Xixin Wu, Xunying Liu, Helen Meng
Grapheme-to-phoneme (G2P) conversion is a crucial step in Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems, responsible for mapping grapheme to corresponding phonetic representations. However, it faces ambiguities problems where the same grapheme can represent multiple phonemes depending on contexts, posing a challenge for G2P conversion. Inspired by the remarkable success of Large Language Models (LLMs) in handling context-aware scenarios, contextual G2P conversion systems with LLMs’ in-context knowledge retrieval (ICKR) capabilities are proposed to promote disambiguation capability. The efficacy of incorporating ICKR into G2P conversion systems is demonstrated thoroughly on the Librig2p dataset. In particular, the best contextual G2P conversion system using ICKR outperforms the baseline with weighted average phoneme error rate (PER) reductions of 2.0% absolute (28.9% relative). Using GPT-4 in the ICKR system can increase of 3.5% absolute (3.8% relative) on the Librig2p dataset.
字形到音素(G2P)转换是文本到语音(TTS)系统中的关键步骤,负责将字形映射到相应的语音表示。然而,它面临着歧义问题,即同一个字形可以根据上下文代表多个音素,这给G2P转换带来了挑战。受大型语言模型(LLM)在处理上下文感知场景时取得显著成功的启发,提出了具有LLM上下文知识检索(ICKR)能力的上下文G2P转换系统,以提高解歧义能力。将ICKR纳入G2P转换系统的有效性在Librig2p数据集上得到了充分证明。特别是,使用ICKR的最佳上下文G2P转换系统比基线系统的平均音素错误率(PER)绝对降低了2.0%(相对降低了28.9%)。在ICKR系统中使用GPT-4可以在Librig2p数据集上绝对提高3.5%(相对提高3.8%)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by ISCSLP 2024
Summary
文本提到,在文本转语音(TTS)系统中,字母音转换(G2P)是关键步骤之一,负责将字母映射到相应的语音表示。然而,由于同一字母在不同的上下文中可能代表不同的音素,因此存在歧义问题。为了解决这个问题,研究人员提出了利用大型语言模型(LLM)的上下文知识检索(ICKR)能力构建上下文感知的G2P转换系统。在Librig2p数据集上的实验表明,加入ICKR的G2P转换系统的有效性得到了验证。特别是使用GPT-4的ICKR系统,在Librig2p数据集上的表现最佳,绝对平均音素错误率降低了2.0%(相对降低28.9%),进一步融入GPT-4能额外降低平均音素错误率3.5%(相对降低仅增加了额外的效率),展示出良好应用前景。
Key Takeaways
以下是从文本中提取的关键见解:
- G2P转换在TTS系统中具有重要性,它将字母映射到对应的语音表示形式。但在处理不同上下文时存在歧义问题。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在解决上下文感知的字母音转换(G2P)中展现出潜力。
- 使用LLM的ICKR能力有助于提高G2P转换系统的性能。
- 在Librig2p数据集上的实验表明,最佳上下文感知的G2P转换系统相比基线模型绝对平均音素错误率降低了2.0%(相对降低了28.9%)。 融入GPT-4进一步提升效果显著效果良好表现,表现出巨大的应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

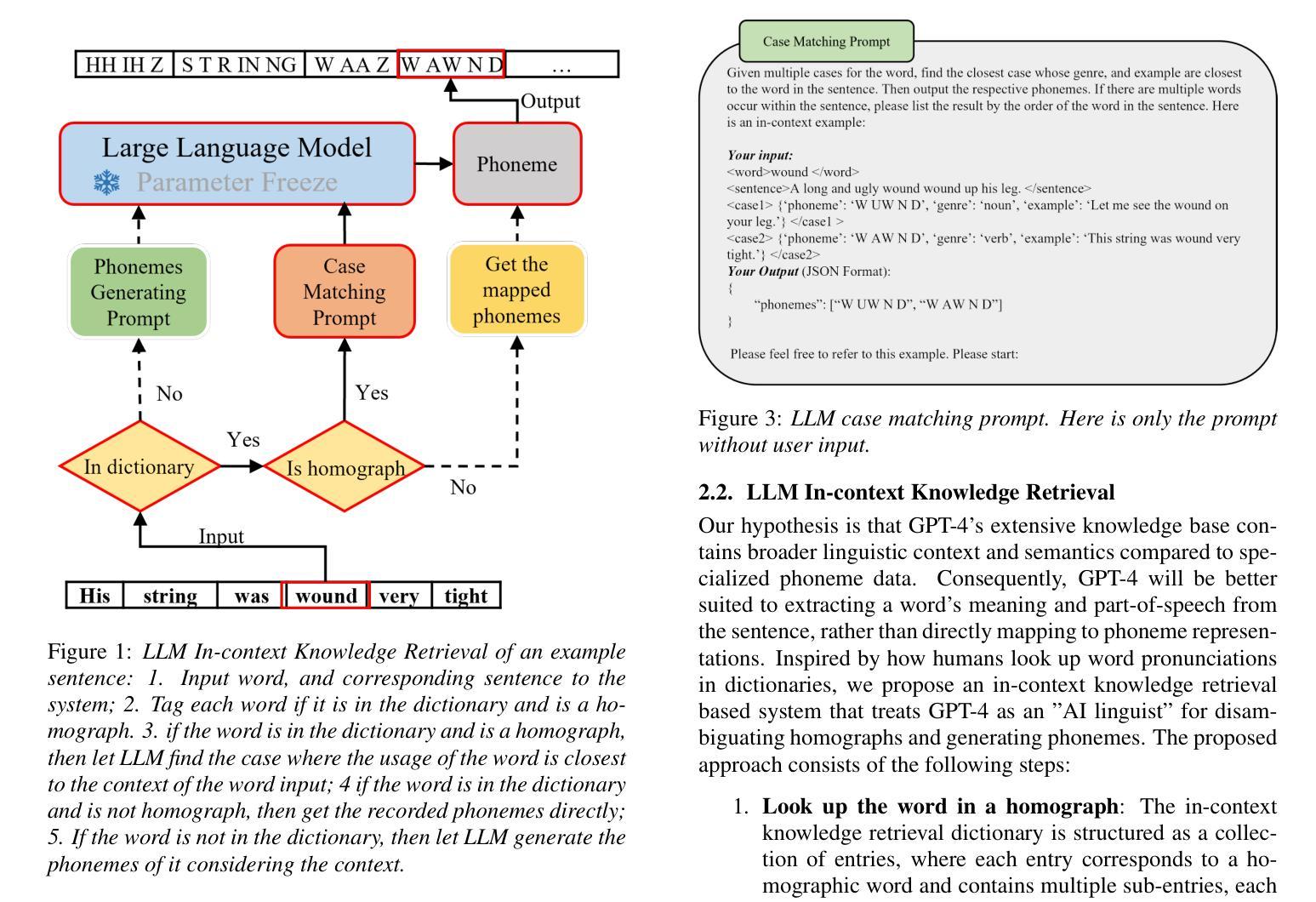
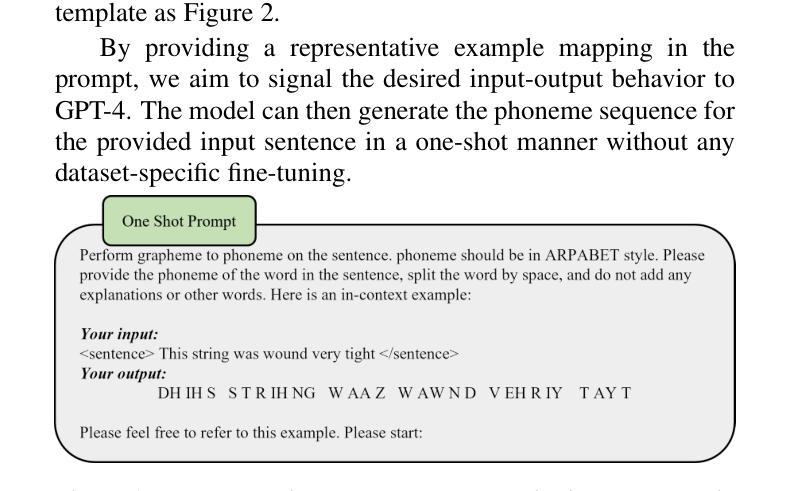


Debatts: Zero-Shot Debating Text-to-Speech Synthesis
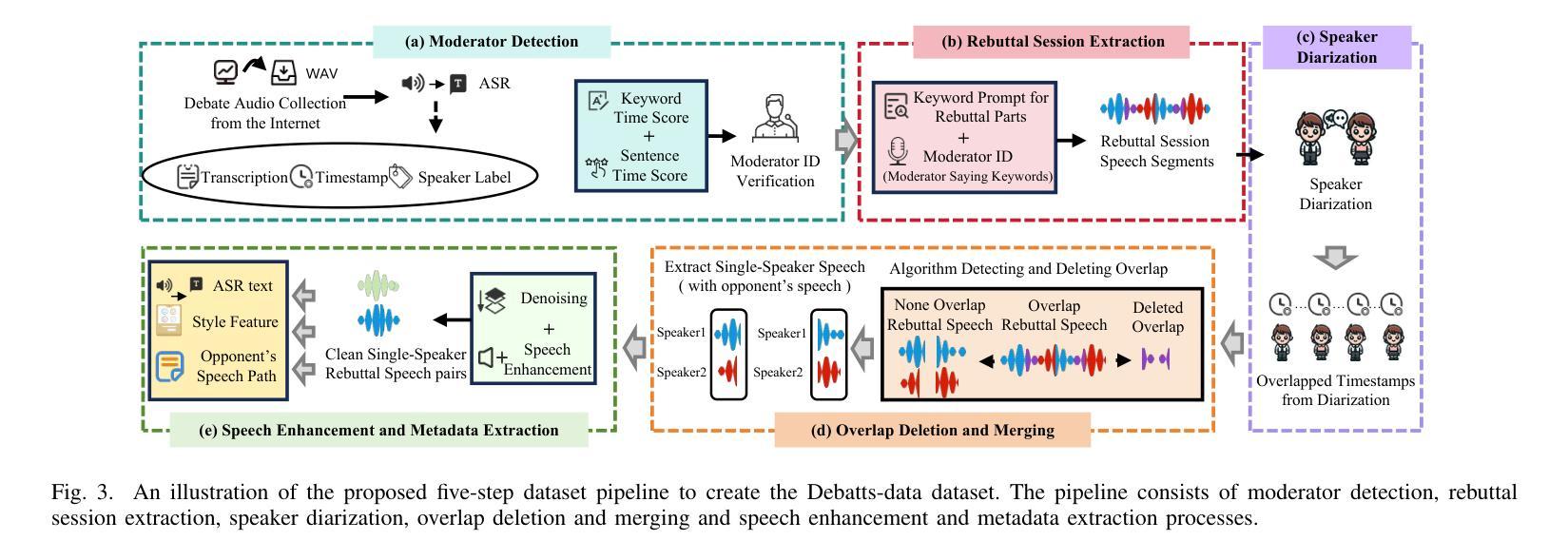
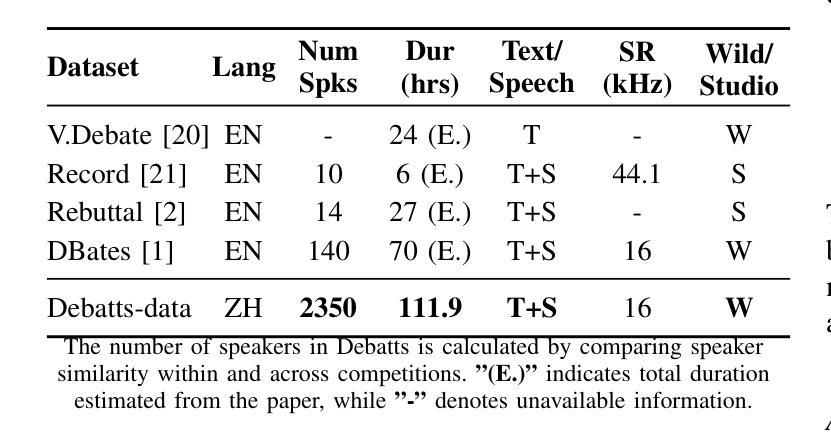
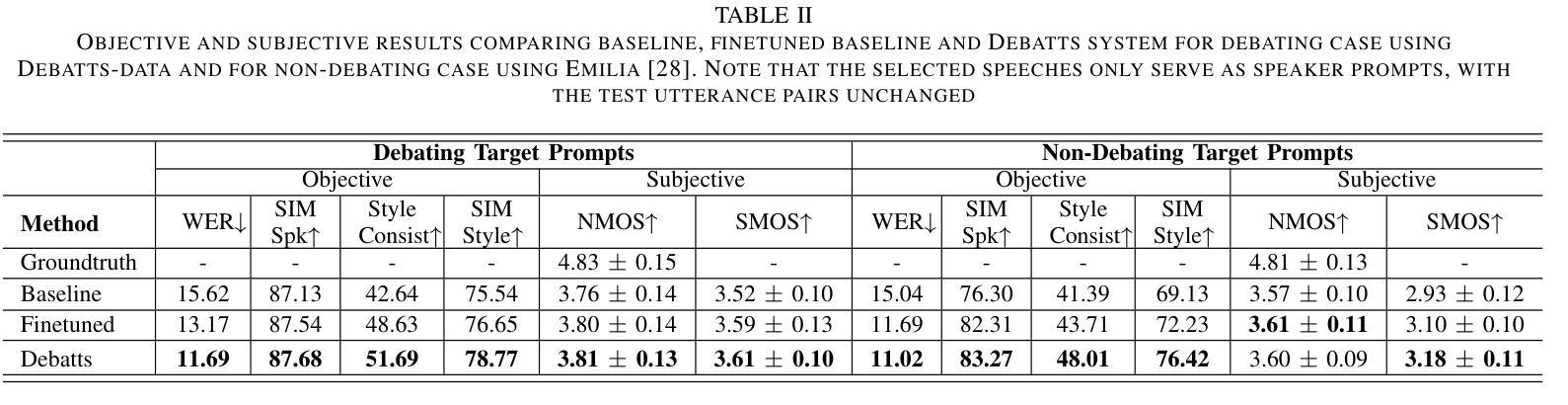
Authors:Yiqiao Huang, Yuancheng Wang, Jiaqi Li, Haotian Guo, Haorui He, Shunsi Zhang, Zhizheng Wu
In debating, rebuttal is one of the most critical stages, where a speaker addresses the arguments presented by the opposing side. During this process, the speaker synthesizes their own persuasive articulation given the context from the opposing side. This work proposes a novel zero-shot text-to-speech synthesis system for rebuttal, namely Debatts. Debatts takes two speech prompts, one from the opposing side (i.e. opponent) and one from the speaker. The prompt from the opponent is supposed to provide debating style prosody, and the prompt from the speaker provides identity information. In particular, we pretrain the Debatts system from in-the-wild dataset, and integrate an additional reference encoder to take debating prompt for style. In addition, we also create a debating dataset to develop Debatts. In this setting, Debatts can generate a debating-style speech in rebuttal for any voices. Experimental results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed system in comparison with the classic zero-shot TTS systems.
在辩论中,反驳是最关键的阶段之一,辩手需要针对对方提出的观点进行回应。在此过程中,辩手需要基于对方的语境,结合自身的论点进行有说服力的表述。本文提出了一种新型的零样本文本到语音合成系统,用于进行反驳,称为Debatts。Debatts接受两个语音提示,一个来自对方(即对手),另一个来自辩手自身。对手的提示旨在提供辩论风格的韵律,而辩手自身的提示则提供身份信息。特别地,我们从野生数据集对Debatts系统进行预训练,并集成一个额外的参考编码器来提取辩论提示的风格。此外,我们还创建了一个辩论数据集来开发Debatts。在此设定下,Debatts可以生成任何声音的辩论式反驳语音。实验结果证实,与经典的零样本TTS系统相比,所提出的系统具有有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
辩论中的反驳环节至关重要,发言者需针对对方观点进行回应。本文提出一种新型零样本文本到语音合成系统,名为Debatts,用于反驳环节。该系统采用两个语音提示,一个来自对方,一个来自发言者。对方提示提供辩论风格,发言者提示提供身份信息。Debatts通过野外数据集进行预训练,并集成参考编码器以获取辩论提示风格。此外,还创建了辩论数据集来开发Debatts,可生成具有反驳性的辩论语音,适用于任何声音。实验结果表明,与经典零样本TTS系统相比,Debatts系统更有效。
Key Takeaways
- 反驳在辩论中是关键阶段,需要发言者针对对方观点进行回应。
- 本文提出了一种新型零样本文本到语音合成系统Debatts,专门用于生成辩论中的反驳环节。
- Debatts采用两个语音提示,分别来自对方和发言者,以提供辩论风格和身份信息。
- 系统通过野外数据集进行预训练,并集成参考编码器以获取辩论提示风格。
- 创建了专门的辩论数据集以开发Debatts系统。
- Debatts可以生成具有反驳性的辩论语音,适用于任何声音。
点此查看论文截图

CUIfy the XR: An Open-Source Package to Embed LLM-powered Conversational Agents in XR
Authors:Kadir Burak Buldu, Süleyman Özdel, Ka Hei Carrie Lau, Mengdi Wang, Daniel Saad, Sofie Schönborn, Auxane Boch, Enkelejda Kasneci, Efe Bozkir
Recent developments in computer graphics, machine learning, and sensor technologies enable numerous opportunities for extended reality (XR) setups for everyday life, from skills training to entertainment. With large corporations offering consumer-grade head-mounted displays (HMDs) in an affordable way, it is likely that XR will become pervasive, and HMDs will develop as personal devices like smartphones and tablets. However, having intelligent spaces and naturalistic interactions in XR is as important as technological advances so that users grow their engagement in virtual and augmented spaces. To this end, large language model (LLM)–powered non-player characters (NPCs) with speech-to-text (STT) and text-to-speech (TTS) models bring significant advantages over conventional or pre-scripted NPCs for facilitating more natural conversational user interfaces (CUIs) in XR. In this paper, we provide the community with an open-source, customizable, extensible, and privacy-aware Unity package, CUIfy, that facilitates speech-based NPC-user interaction with various LLMs, STT, and TTS models. Our package also supports multiple LLM-powered NPCs per environment and minimizes the latency between different computational models through streaming to achieve usable interactions between users and NPCs. We publish our source code in the following repository: https://gitlab.lrz.de/hctl/cuify
最近的计算机图形学、机器学习和传感器技术的发展为扩展现实(XR)在日常生活中的设置提供了众多机会,从技能培训到娱乐。随着大型公司以负担得起的方式提供面向消费者的头戴式显示器(HMD),XR很可能变得普及,HMD将像智能手机和平板电脑一样发展成为个人设备。然而,拥有智能空间和自然交互同样重要,这样用户才能增加他们在虚拟和增强空间中的参与度。为此,大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的非玩家角色(NPC)使用语音转文本(STT)和文本转语音(TTS)模型,相较于传统的或预先设定的NPC,为XR中促进更自然的对话式用户界面(CUI)带来了巨大优势。在这篇论文中,我们为社区提供了一个开源的、可定制的、可扩展的、具有隐私意识的Unity包,名为CUIfy,它促进了基于语音的NPC-用户与各种LLM、STT和TTS模型的交互。我们的包还支持每个环境多个LLM驱动的NPC,并通过流技术最小化不同计算模型之间的延迟,以实现用户和NPC之间的可用交互。我们在以下仓库中发布源代码:https://gitlab.lrz.de/hctl/cuify
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
近期计算机图形学、机器学习和传感器技术的发展为扩展现实(XR)技术在生活中的应用提供了机会,如技能培训和娱乐等。随着大型企业提供负担得起的头戴式显示器(HMDs),XR可能变得无处不在,并成为像智能手机和平板电脑一样的个人设备。为了增加用户对虚拟和增强空间的参与度,智能空间和自然交互变得与技术进步同样重要。为此,使用大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的非玩家角色(NPCs)结合语音识别(STT)和文本合成(TTS)模型,相较于传统或预设的NPCs,可为XR中构建更自然的对话用户界面(CUI)带来显著优势。本文介绍了一个开源、可定制、可扩展且注重隐私的Unity包“CUIfy”,它促进了基于语音的NPC-用户互动,支持多种LLM、STT和TTS模型。我们的软件包还支持每个环境多个LLM驱动NPCs,并通过流技术最小化不同计算模型之间的延迟,以实现用户和NPCs之间的可用交互。
Key Takeaways
- 科技进步使得扩展现实(XR)在日常生活中的运用日益广泛,尤其是技能培训和娱乐领域。
- 头戴式显示器(HMDs)可能变得像智能手机和平板电脑一样普及。
- 自然交互和智能空间对于提高用户在虚拟和增强空间的参与度至关重要。
- 大型语言模型(LLM)驱动的非玩家角色(NPCs)结合语音识别(STT)和文本合成(TTS)模型能构建更自然的对话用户界面(CUI)。
- “CUIfy”是一款开源的Unity包,支持基于语音的NPC-用户互动,并采用多种LLM、STT和TTS模型。
- 该软件包支持多个LLM驱动的NPCs在同一环境中,并实现与用户的可用交互。
点此查看论文截图

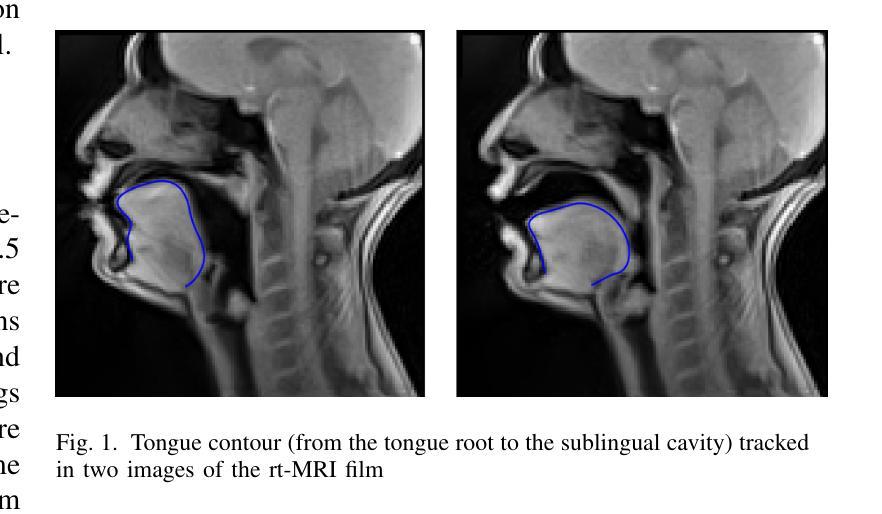
Complete reconstruction of the tongue contour through acoustic to articulatory inversion using real-time MRI data
Authors:Sofiane Azzouz, Pierre-André Vuissoz, Yves Laprie
Acoustic articulatory inversion is a major processing challenge, with a wide range of applications from speech synthesis to feedback systems for language learning and rehabilitation. In recent years, deep learning methods have been applied to the inversion of less than a dozen geometrical positions corresponding to sensors glued to easily accessible articulators. It is therefore impossible to know the shape of the whole tongue from root to tip. In this work, we use high-quality real-time MRI data to track the contour of the tongue. The data used to drive the inversion are therefore the unstructured speech signal and the tongue contours. Several architectures relying on a Bi-MSTM including or not an autoencoder to reduce the dimensionality of the latent space, using or not the phonetic segmentation have been explored. The results show that the tongue contour can be recovered with a median accuracy of 2.21 mm (or 1.37 pixel) taking a context of 1 MFCC frame (static, delta and double-delta cepstral features).
声学发音倒置是一个主要的处理挑战,其应用范围广泛,从语音合成到语言学习和康复的反馈系统。近年来,深度学习的方法被应用于倒置的几何位置少于十几个,这些位置对应于粘贴在容易接触的发音器官上的传感器。因此,无法知道整个舌头的形状,从根部到尖端。在这项工作中,我们使用高质量的实时MRI数据来跟踪舌头的轮廓。用于驱动倒置的数据因此是无结构化的语音信号和舌头轮廓。我们探索了几种依赖于双向记忆增强网络(Bi-MSTM)的架构,包括使用自动编码器进行降维和不使用自动编码器的情况,以及是否使用语音分段。结果表明,舌轮廓的恢复精度中位数为2.21毫米(或1.37像素),在1个MFCC帧(静态、delta和双delta倒谱特征)的上下文中。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本介绍了声学发音反转技术面临的挑战以及最新进展。采用深度学习方法对舌体轮廓进行实时追踪,以真实MRI数据为驱动,提高声学发音反转的准确性。结果证明使用MFCC框架能有效提高预测精度,采用自适应编码器可以减少潜在空间的维度,减少语境变化的误差影响。研究成果将影响多个领域,如语音合成、语言学习和康复等。
Key Takeaways
- 声学发音反转是语音合成等领域的重要处理挑战。近年来采用深度学习技术解决了一些特定问题,但难以全面预测整个舌头的形状。
- 本研究利用高质量的实时MRI数据追踪舌体轮廓,使得对舌体轮廓的预测更为准确。数据驱动方法采用非结构化语音信号和舌轮廓信息。
- 研究探索了多种架构,包括使用双向多模态状态机(Bi-MSTM)和自适应编码器等技术来提高预测精度和降低维度空间。同时探索了使用语音分割技术的影响。
- 研究结果表明,采用MFCC框架能提高预测精度,通过自适应编码器减少潜在空间的维度,进一步提高了预测准确性。同时指出,采用MFCC框架需要考虑静态、delta和双delta频谱特征等因素。
点此查看论文截图

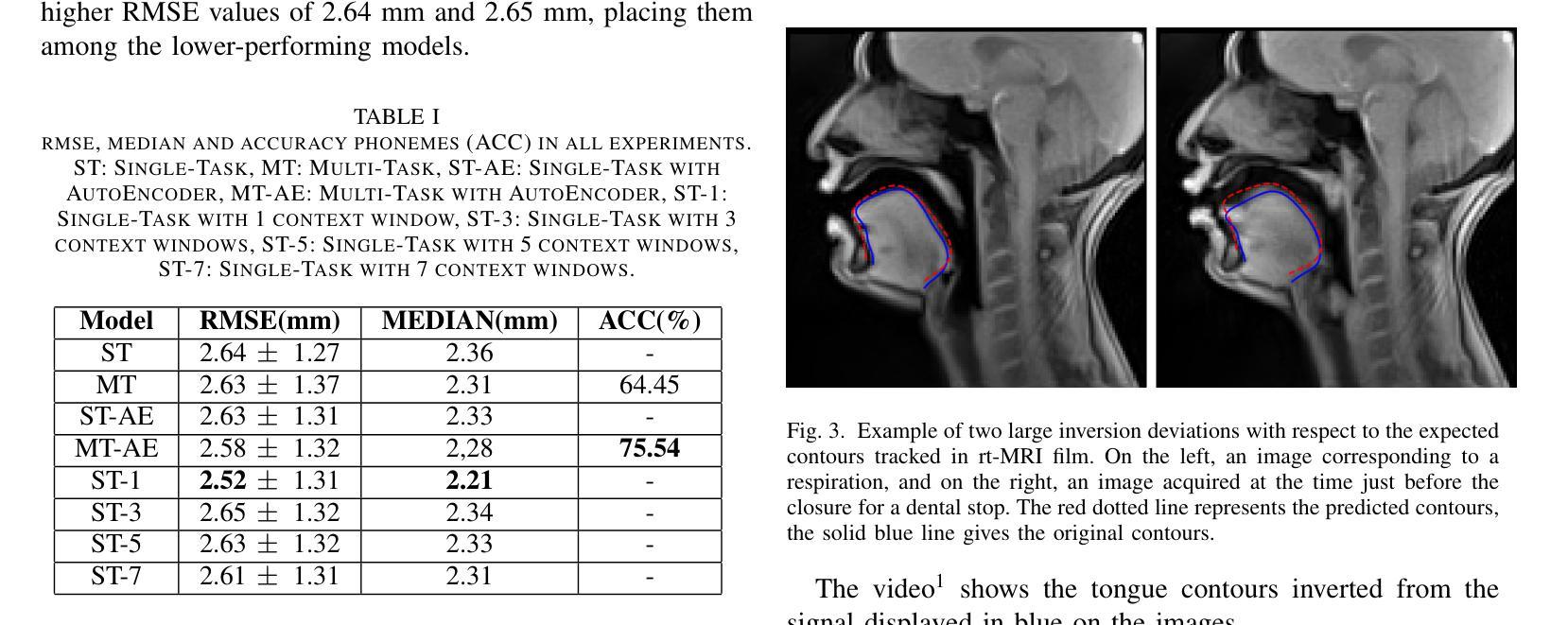
Fish-Speech: Leveraging Large Language Models for Advanced Multilingual Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Authors:Shijia Liao, Yuxuan Wang, Tianyu Li, Yifan Cheng, Ruoyi Zhang, Rongzhi Zhou, Yijin Xing
Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems face ongoing challenges in processing complex linguistic features, handling polyphonic expressions, and producing natural-sounding multilingual speech - capabilities that are crucial for future AI applications. In this paper, we present Fish-Speech, a novel framework that implements a serial fast-slow Dual Autoregressive (Dual-AR) architecture to enhance the stability of Grouped Finite Scalar Vector Quantization (GFSQ) in sequence generation tasks. This architecture improves codebook processing efficiency while maintaining high-fidelity outputs, making it particularly effective for AI interactions and voice cloning. Fish-Speech leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) for linguistic feature extraction, eliminating the need for traditional grapheme-to-phoneme (G2P) conversion and thereby streamlining the synthesis pipeline and enhancing multilingual support. Additionally, we developed FF-GAN through GFSQ to achieve superior compression ratios and near 100% codebook utilization. Our approach addresses key limitations of current TTS systems while providing a foundation for more sophisticated, context-aware speech synthesis. Experimental results show that Fish-Speech significantly outperforms baseline models in handling complex linguistic scenarios and voice cloning tasks, demonstrating its potential to advance TTS technology in AI applications. The implementation is open source at \href{https://github.com/fishaudio/fish-speech}{https://github.com/fishaudio/fish-speech}.
文本转语音(TTS)系统在处理复杂的语言特性、处理多音表达和产生自然的多语言语音方面持续面临挑战——这些能力是未来人工智能应用的关键。在本文中,我们提出了Fish-Speech,这是一个新型框架,它实现了串行快速慢速双自回归(Dual-AR)架构,以提高分组有限标量矢量量化(GFSQ)在序列生成任务中的稳定性。该架构提高了代码本处理效率,同时保持高保真输出,使其成为人工智能交互和语音克隆的特别有效工具。
Fish-Speech利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行语言特性提取,消除了传统字母到音节(G2P)转换的需要,从而简化了合成管道并增强了多语言支持。此外,我们通过GFSQ开发了FF-GAN,实现了较高的压缩率和近100%的代码本利用率。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了一种名为Fish-Speech的新型框架,它采用串行快速慢速双自回归架构,提高分组有限标量矢量量化在序列生成任务中的稳定性,增强代码本处理效率并保持高保真输出。Fish-Speech利用大型语言模型进行语言特征提取,无需传统的字母到音素转换,从而简化了合成管道并增强了多语言支持。此外,通过分组有限标量矢量量化开发FF-GAN实现较高的压缩率和近百分之百的代码本利用率。实验结果表明,Fish-Speech在处理复杂语言场景和语音克隆任务方面显著优于基准模型,为AI应用的文本转语音技术提供了发展潜力。该框架已开源。
关键见解
- Fish-Speech是一种新型框架,采用双自回归架构增强稳定性,适用于复杂的语音合成任务。
- 该框架提高了代码本处理效率并保持高保真输出,特别适用于AI交互和语音克隆。
- Fish-Speech利用大型语言模型进行语言特征提取,无需传统的字母到音素转换,简化了合成流程并增强了多语言支持。
- 通过分组有限标量矢量量化开发FF-GAN技术实现高效压缩和代码本利用率。
- 实验结果显示Fish-Speech在处理复杂语言场景和语音克隆任务方面表现出卓越性能。
- Fish-Speech框架具有开放性源代码,有助于推动文本转语音技术的发展。
点此查看论文截图

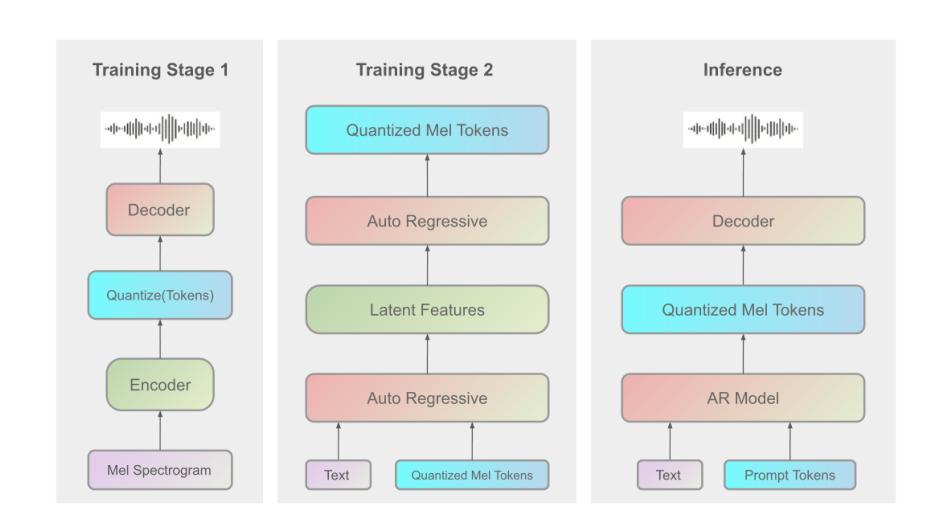
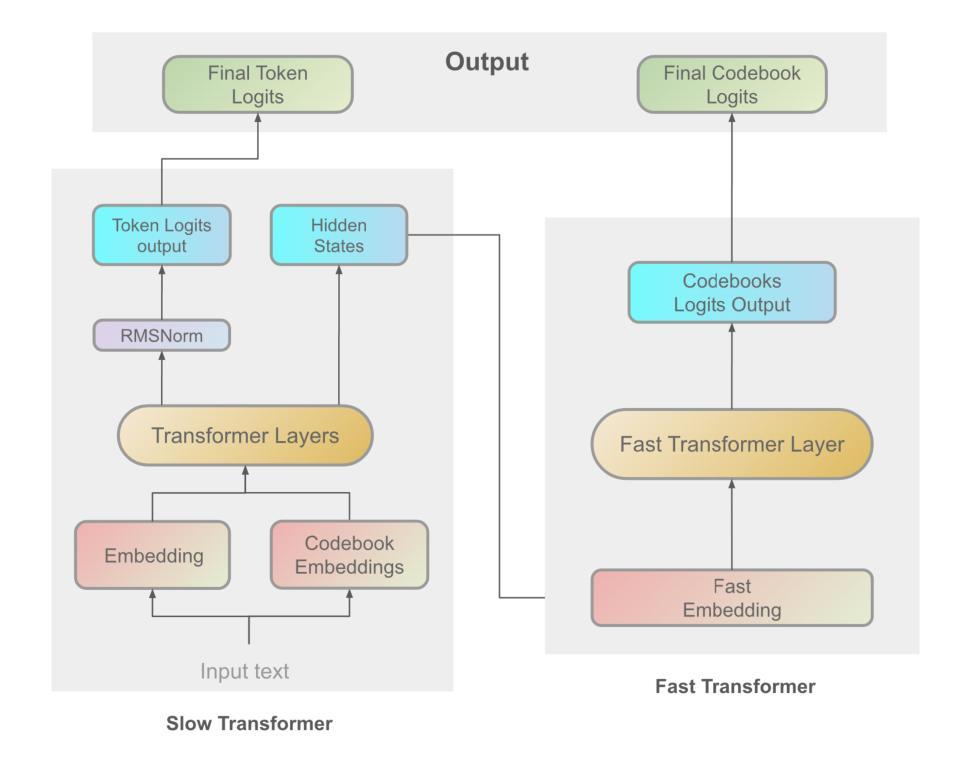
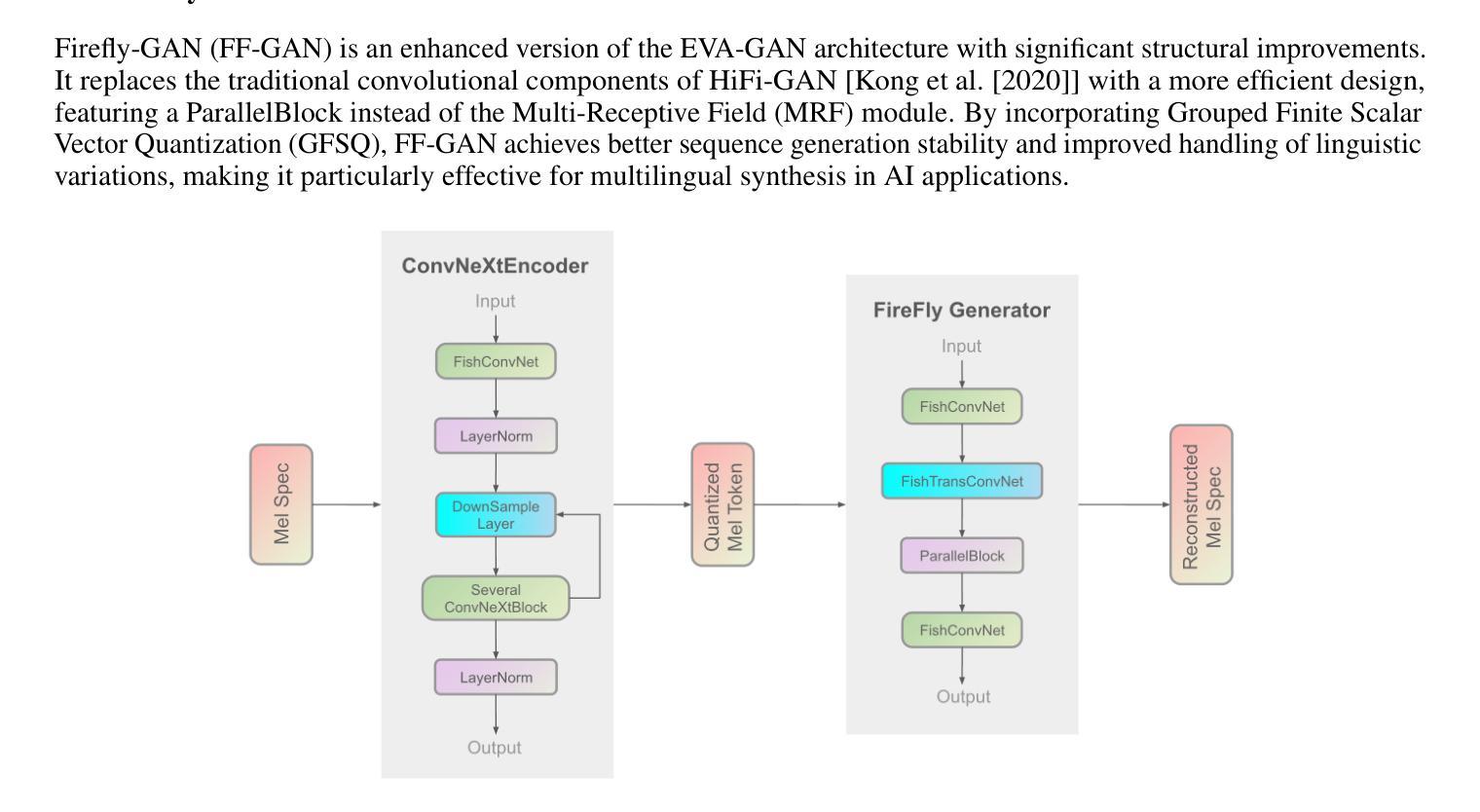
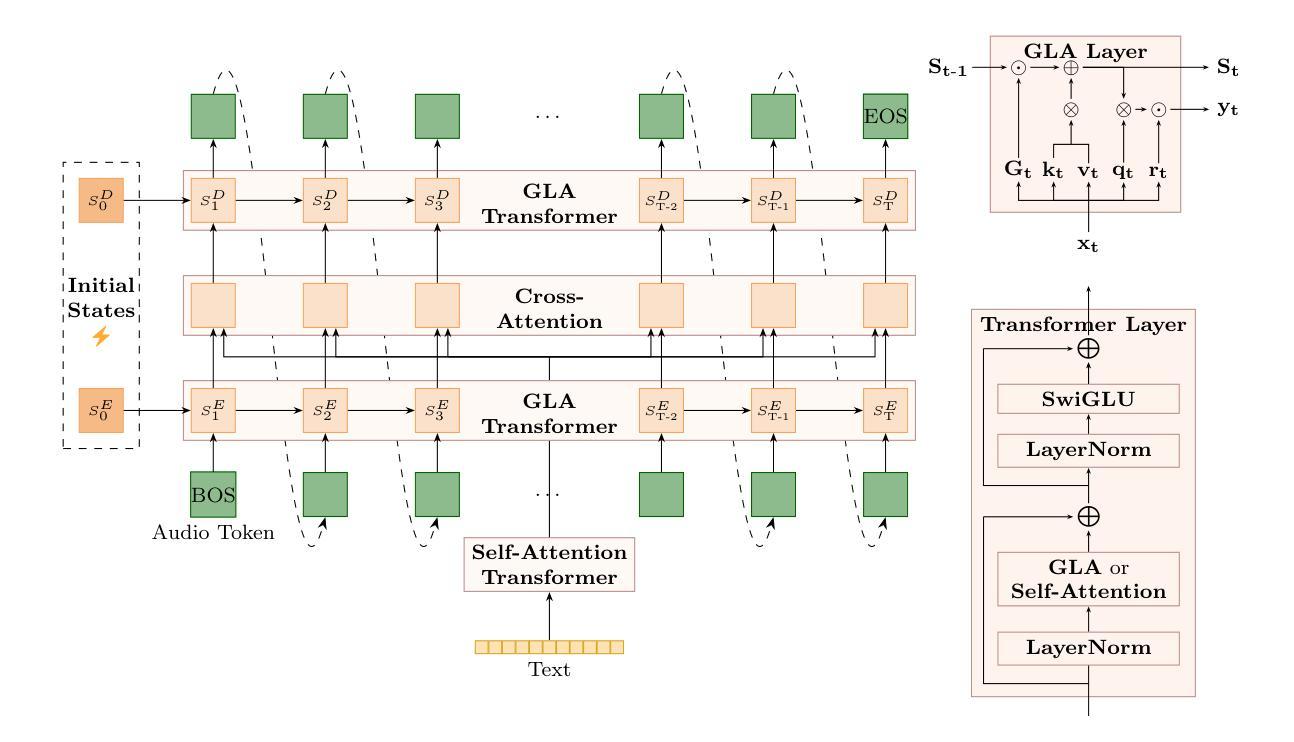
Lina-Speech: Gated Linear Attention is a Fast and Parameter-Efficient Learner for text-to-speech synthesis
Authors:Théodor Lemerle, Harrison Vanderbyl, Vaibhav Srivastav, Nicolas Obin, Axel Roebel
Neural codec language models have achieved state-of-the-art performance in text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis, leveraging scalable architectures like autoregressive transformers and large-scale speech datasets. By framing voice cloning as a prompt continuation task, these models excel at cloning voices from short audio samples. However, this approach is limited in its ability to handle numerous or lengthy speech excerpts, since the concatenation of source and target speech must fall within the maximum context length which is determined during training. In this work, we introduce Lina-Speech, a model that replaces traditional self-attention mechanisms with emerging recurrent architectures like Gated Linear Attention (GLA). Building on the success of initial-state tuning on RWKV, we extend this technique to voice cloning, enabling the use of multiple speech samples and full utilization of the context window in synthesis. This approach is fast, easy to deploy, and achieves performance comparable to fine-tuned baselines when the dataset size ranges from 3 to 15 minutes. Notably, Lina-Speech matches or outperforms state-of-the-art baseline models, including some with a parameter count up to four times higher or trained in an end-to-end style. We release our code and checkpoints. Audio samples are available at https://theodorblackbird.github.io/blog/demo_lina/.
神经网络编解码器语言模型在文本到语音(TTS)合成方面取得了最先进的性能,它利用可扩展的架构(如自回归变压器)和大规模的语音数据集。通过将以声音克隆作为提示延续任务,这些模型在克隆短音频样本的声音方面表现出色。然而,这种方法在处理大量或冗长的语音片段时存在局限性,因为源语音和目标语音的拼接必须在训练期间确定的最大上下文长度之内。在这项工作中,我们引入了Lina-Speech模型,它用新兴的循环架构(如门控线性注意力)取代了传统的自注意力机制。我们在RWKV初始状态调整的成功基础上,将其技术扩展到声音克隆,能够使用多个语音样本并在合成中充分利用上下文窗口。这种方法快速且易于部署,当数据集大小在3到15分钟之间时,其性能可与微调基线相当。值得注意的是,Lina-Speech与最先进的基线模型相匹配或表现更好,包括一些参数计数高达四倍或采用端到端风格训练的模型。我们发布了我们的代码和检查点。音频样本可在https://theodorblackbird.github.io/blog/demo_lina/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint
Summary
神经网络编解码器语言模型在文本转语音(TTS)合成中取得了最新性能,使用自回归变压器等可扩展架构和大规模语音数据集。通过将被声音克隆视作提示延续任务,这些模型在克隆短音频样本的声音方面表现出色。然而,由于合成中源语音和目标语音的拼接必须在训练期间确定的最大上下文长度内,这种方法在处理大量或冗长的语音片段时存在局限性。在此研究中,我们推出了Lina-Speech模型,它采用新兴循环架构(如门控线性注意力)替代传统自注意力机制。在RWKV初始状态调整成功的基础上,我们将该技术扩展到声音克隆,可使用多个语音样本并充分利用合成中的上下文窗口。该方法快速且易于部署,当数据集大小在3至15分钟之间时,其性能与精细调整的基线相当。值得注意的是,Lina-Speech与包括一些参数计数高达四倍或采用端到端训练的先进基线模型相比具有同等或更好的表现。我们公开了代码和检查点。音频样本链接。
Key Takeaways
- 神经网络编解码器语言模型在TTS领域表现卓越,利用自回归变压器等可扩展架构和大规模语音数据集。
- 通过将被声音克隆视作提示延续任务,这些模型在克隆短音频样本方面表现出色。
- 传统自注意力机制在处理长语音片段时存在局限性,需要拼接源和目标语音且需在训练的最大上下文长度内。
- Lina-Speech模型采用新兴循环架构(如GLA)替代传统自注意力机制,提高处理效率。
- Lina-Speech扩展到声音克隆,能使用多个语音样本并充分利用合成中的上下文窗口。
- Lina-Speech性能与精细调整的基线相当,尤其在数据集大小适中的情况下。
点此查看论文截图

Augmenting Polish Automatic Speech Recognition System With Synthetic Data
Authors:Łukasz Bondaruk, Jakub Kubiak, Mateusz Czyżnikiewicz
This paper presents a system developed for submission to Poleval 2024, Task 3: Polish Automatic Speech Recognition Challenge. We describe Voicebox-based speech synthesis pipeline and utilize it to augment Conformer and Whisper speech recognition models with synthetic data. We show that addition of synthetic speech to training improves achieved results significantly. We also present final results achieved by our models in the competition.
本文介绍了一个为Poleval 2024的Task 3:Polish自动语音识别挑战赛而开发的系统。我们描述了基于Voicebox的语音合成流程,并将其用于增强Conformer和Whisper语音识别模型的合成数据。我们证明了在训练中加入合成语音可以显著提高效果。此外,我们还展示了我们的模型在比赛中的最终成绩。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一个为Poleval 2024的Task 3:Polish Automatic Speech Recognition Challenge而开发的系统。文中描述了基于Voicebox的语音合成流程,并将其用于增强Conformer和Whisper语音识别模型的训练数据,加入合成语音能显著提高模型的性能。同时,本文还介绍了在比赛中的最终成绩。
Key Takeaways
- 论文为Poleval 2024的Task 3挑战开发了一个系统。
- 论文描述了基于Voicebox的语音合成流程。
- 合成语音数据被用于增强Conformer和Whisper语音识别模型的训练。
- 加入合成语音能显著提高语音识别模型的性能。
- 论文展示了在比赛中的最终成绩。
- 该系统利用合成数据增强了模型的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

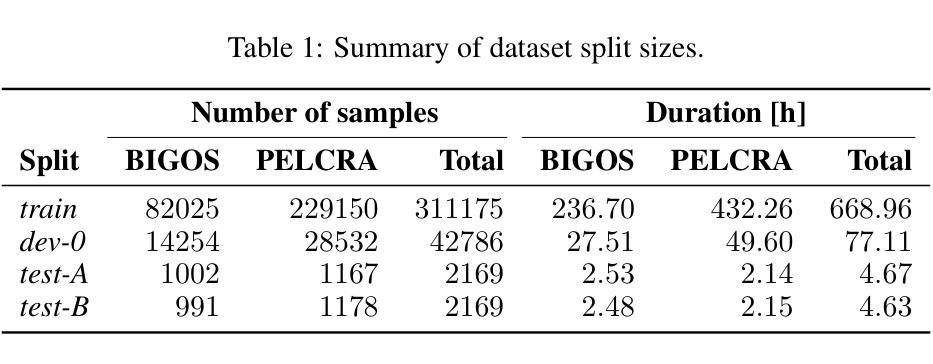

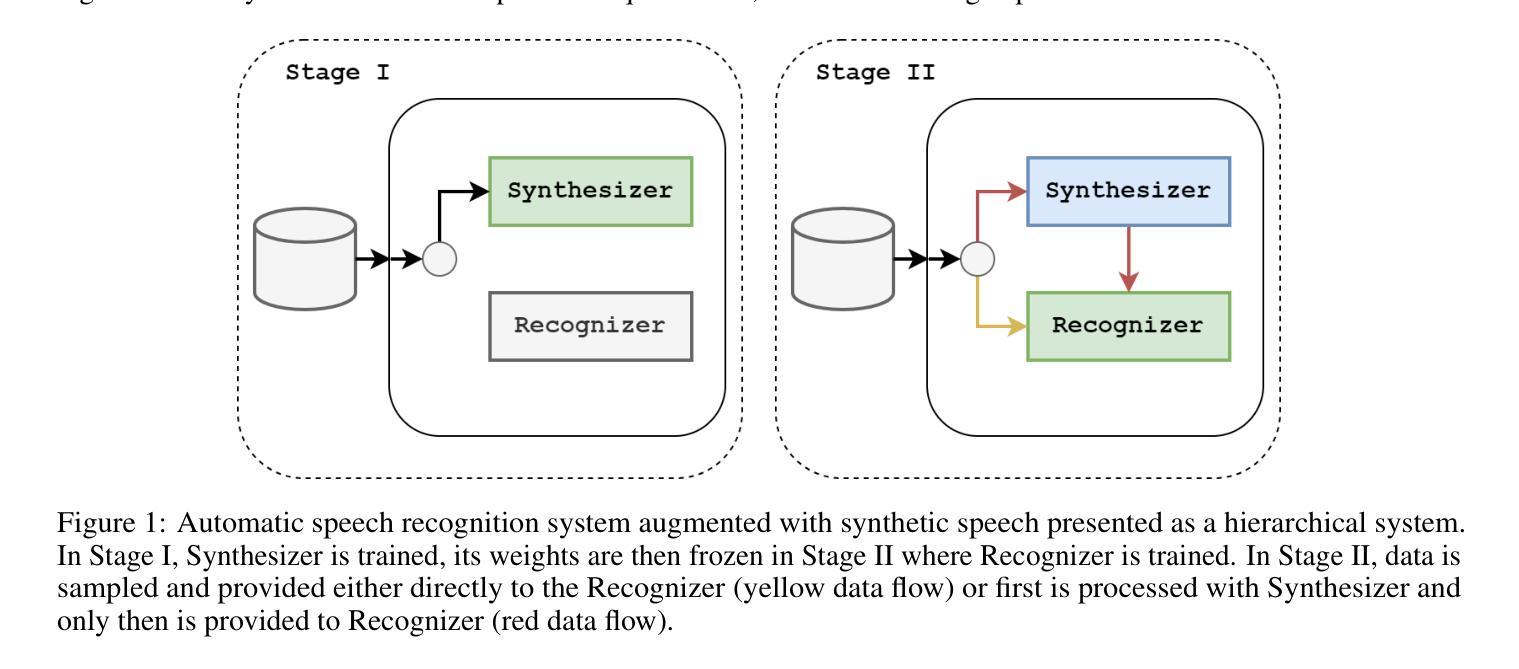
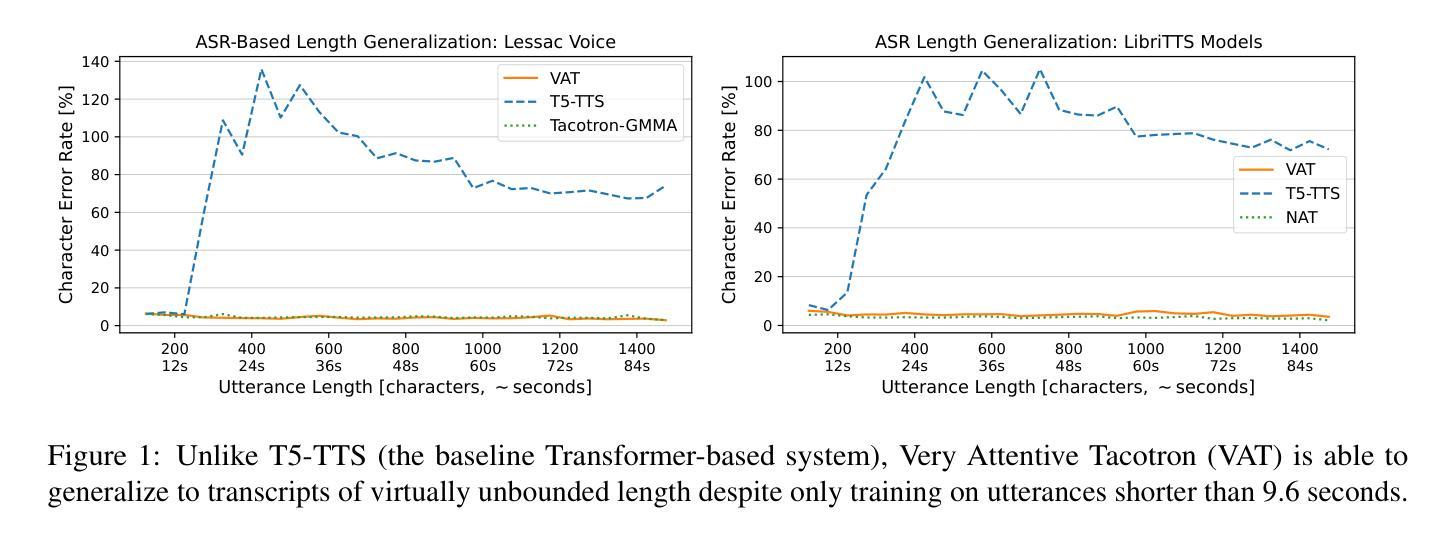
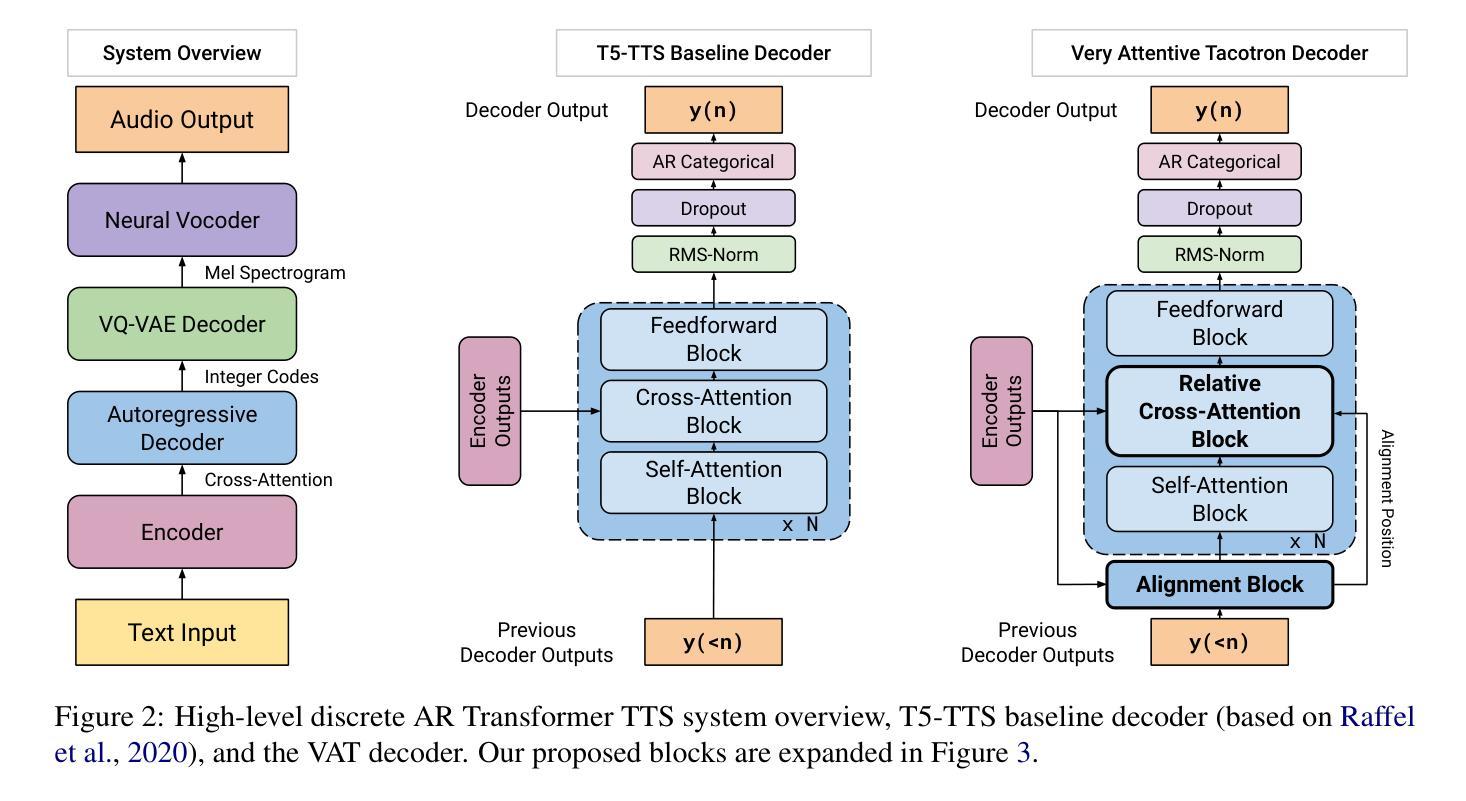
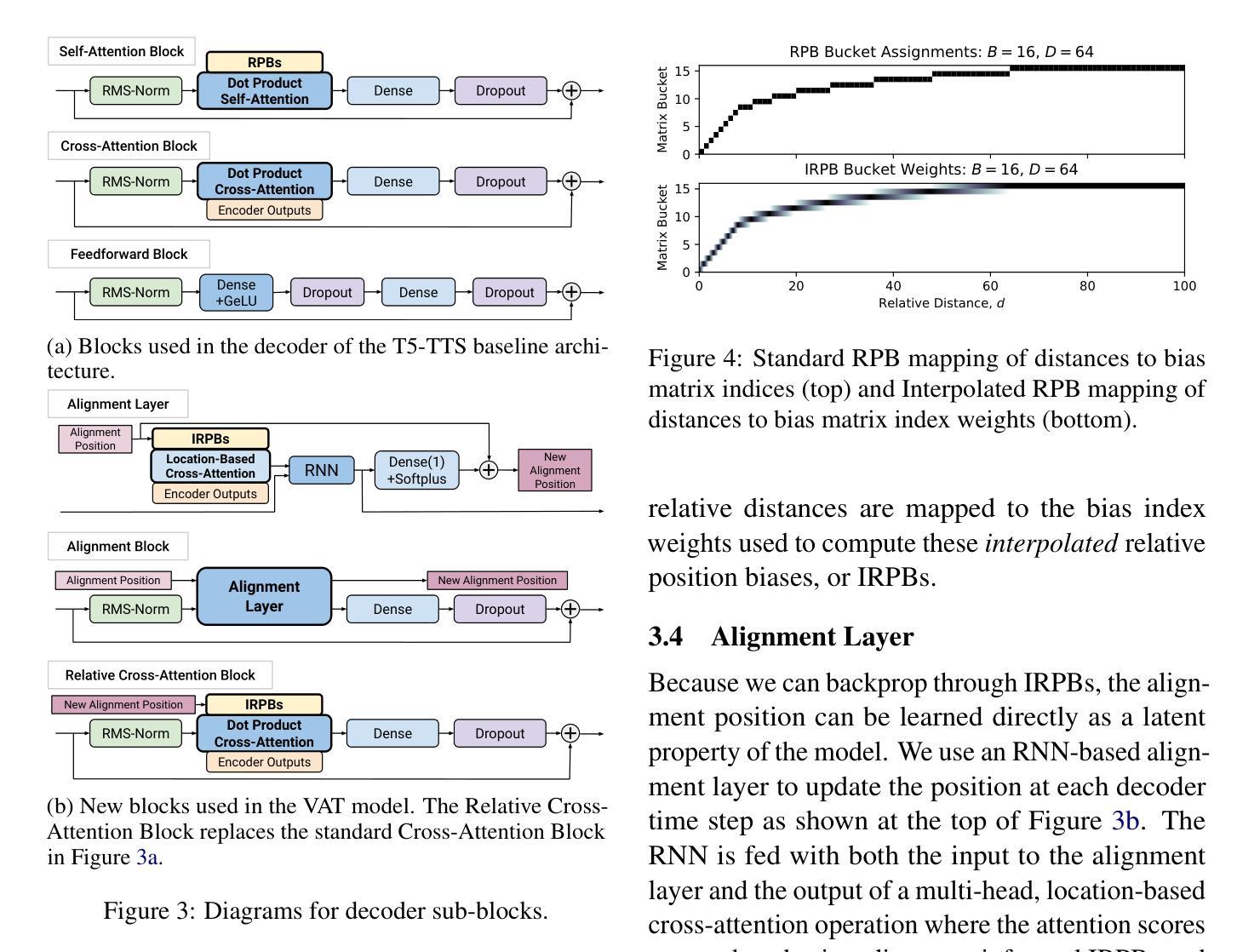
Very Attentive Tacotron: Robust and Unbounded Length Generalization in Autoregressive Transformer-Based Text-to-Speech
Authors:Eric Battenberg, RJ Skerry-Ryan, Daisy Stanton, Soroosh Mariooryad, Matt Shannon, Julian Salazar, David Kao
Autoregressive (AR) Transformer-based sequence models are known to have difficulty generalizing to sequences longer than those seen during training. When applied to text-to-speech (TTS), these models tend to drop or repeat words or produce erratic output, especially for longer utterances. In this paper, we introduce enhancements aimed at AR Transformer-based encoder-decoder TTS systems that address these robustness and length generalization issues. Our approach uses an alignment mechanism to provide cross-attention operations with relative location information. The associated alignment position is learned as a latent property of the model via backprop and requires no external alignment information during training. While the approach is tailored to the monotonic nature of TTS input-output alignment, it is still able to benefit from the flexible modeling power of interleaved multi-head self- and cross-attention operations. A system incorporating these improvements, which we call Very Attentive Tacotron, matches the naturalness and expressiveness of a baseline T5-based TTS system, while eliminating problems with repeated or dropped words and enabling generalization to any practical utterance length.
基于自回归(AR)的Transformer序列模型在推广到训练过程中未见的长序列时,存在普遍化困难的问题。当应用于文本到语音(TTS)时,这些模型往往会出现遗漏或重复单词的情况,或者产生不规则的输出,特别是在较长的连续发言中。在本文中,我们介绍了针对基于AR Transformer的编码器-解码器TTS系统的改进方案,以解决这些鲁棒性和长度泛化问题。我们的方法使用对齐机制来提供带有相对位置信息的交叉注意操作。相关的对齐位置是通过反向传播作为模型的潜在属性来学习的,在训练过程中不需要外部的对齐信息。虽然该方法针对TTS输入输出对齐的单调性质进行了定制,但它仍然能够从交替的多头自注意力和交叉注意操作中获得灵活的建模能力。结合了这些改进的系统,我们称之为非常专注的Tacotron,它与基于T5的基线TTS系统的自然度和表达力相匹配,同时解决了重复或遗漏单词的问题,并实现了对任何实际发言长度的泛化。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to NAACL
总结
基于自回归(AR)Transformer的序列模型在应用于文本到语音(TTS)转换时,对于训练期间未接触到的较长序列,其泛化能力存在问题。这类模型在长语句转换中容易出现遗漏、重复词汇或产生不稳定的输出。本文介绍了一种针对基于AR Transformer的编码器-解码器TTS系统的增强方案,旨在解决这些问题并改善其在长度上的泛化能力。通过引入对齐机制,该方案为交叉注意力操作提供相对位置信息。相关的对齐位置是作为模型的潜在属性通过反向传播学习的,训练过程中无需外部对齐信息。尽管这一方案是针对TTS输入输出对齐的单调性质的,但它仍能从交织的多头自我和交叉注意力操作中获益,提供灵活的建模能力。集成了这些改进的系统,我们称之为“非常专注的Tacotron”,它与基于T5的TTS系统的自然度和表现力相匹配,同时解决了词汇重复或遗漏的问题,并实现了对任何实际语句长度的泛化。
关键见解
- 基于自回归(AR)Transformer的序列模型在TTS中面临泛化问题,特别是在处理长语句时。
- 引入对齐机制来改善AR Transformer模型的性能,为交叉注意力操作提供相对位置信息。
- 对齐位置是模型的潜在属性,通过反向传播学习,无需外部对齐信息。
- 增强方案适用于TTS的输入输出对齐的单调性质,同时保留多头自我和交叉注意力操作的灵活建模能力。
- “非常专注的Tacotron”系统匹配了T5-based TTS系统的自然度和表现力。
- 该系统解决了词汇重复或遗漏的问题。
- 系统实现了对任何实际语句长度的泛化。
点此查看论文截图

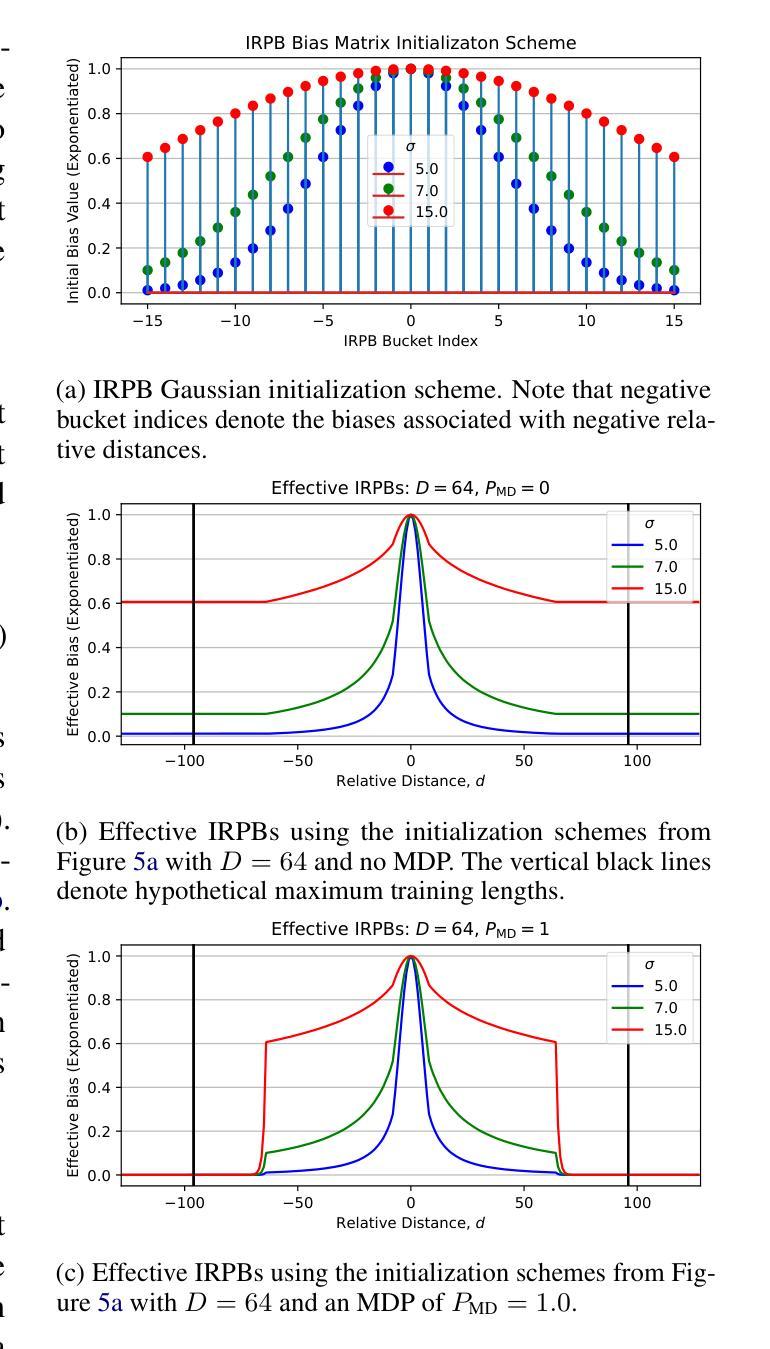
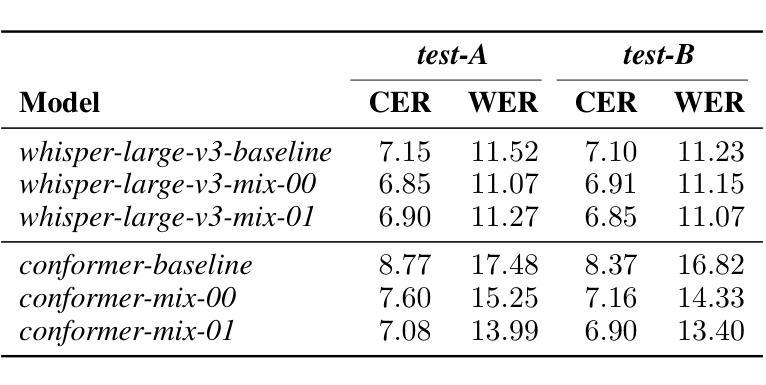
Fast and High-Quality Auto-Regressive Speech Synthesis via Speculative Decoding
Authors:Bohan Li, Hankun Wang, Situo Zhang, Yiwei Guo, Kai Yu
The auto-regressive architecture, like GPTs, is widely used in modern Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems. However, it incurs substantial inference time, particularly due to the challenges in the next-token prediction posed by lengthy sequences of speech tokens. In this work, we introduce VADUSA, one of the first approaches to accelerate auto-regressive TTS through speculative decoding. Our results show that VADUSA not only significantly improves inference speed but also enhances performance by incorporating draft heads to predict future speech content auto-regressively. Furthermore, the inclusion of a tolerance mechanism during sampling accelerates inference without compromising quality. Our approach demonstrates strong generalization across large datasets and various types of speech tokens.
自回归架构,如GPT,在现代文本到语音(TTS)系统中有着广泛应用。然而,它产生了大量的推理时间,特别是由于语音令牌序列长度所带来的下一个令牌预测挑战。在这项工作中,我们引入了VADUSA,这是通过预测解码加速自回归TTS的第一种方法。我们的结果表明,VADUSA不仅显著提高了推理速度,而且通过融入草稿头以自回归方式预测未来语音内容,提高了性能。此外,采样过程中容错机制的加入在不影响质量的情况下加速了推理。我们的方法在大规模数据集和各种语音令牌类型上表现出强大的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 3 figures, 3 tables. Submitted to ICASSP 2025
Summary
本文介绍了在文本转语音(TTS)系统中广泛使用的自回归架构(如GPT)存在的推理时间较长的问题。为解决这一问题,本文提出了VADUSA方法,这是一种通过预测未来语音内容来加速自回归TTS的推测解码方法。VADUSA不仅显著提高了推理速度,还通过引入草案头来提高性能。此外,采样过程中的容忍机制可以加速推理而不影响质量。该方法在大规模数据集和各种语音标记类型上具有良好的通用性。
Key Takeaways
- 自回归架构(如GPT)在TTS系统中广泛应用,但存在推理时间长的问题。
- VADUSA是首个通过推测解码来加速自回归TTS的方法。
- VADUSA通过引入草案头预测未来语音内容,提高推理速度和性能。
- 采样过程中的容忍机制可以加速推理,同时不损害质量。
- VADUSA方法对大规模数据集和各种语音标记类型具有良好的通用性。
- VADUSA的引入是对现有TTS系统性能提升的重要突破。
点此查看论文截图

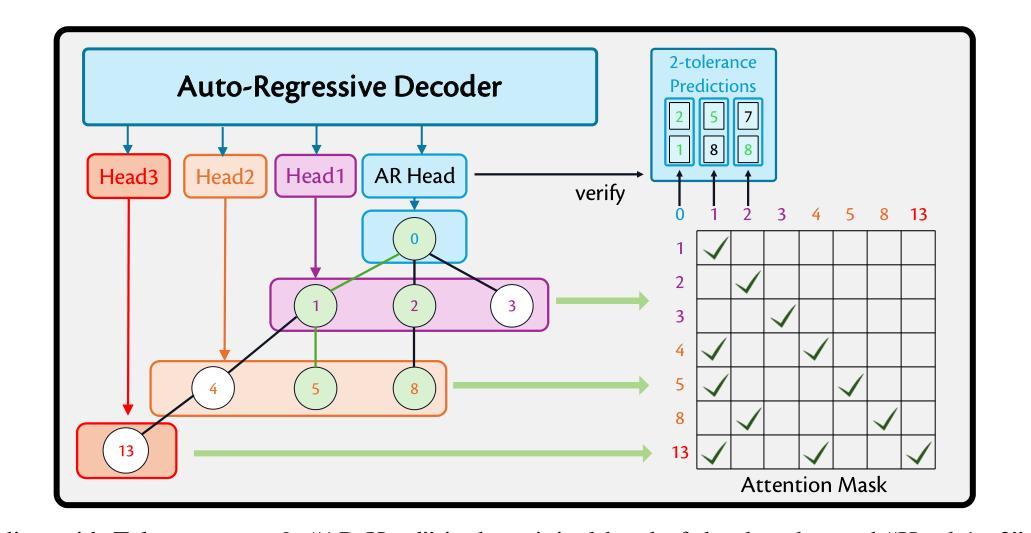
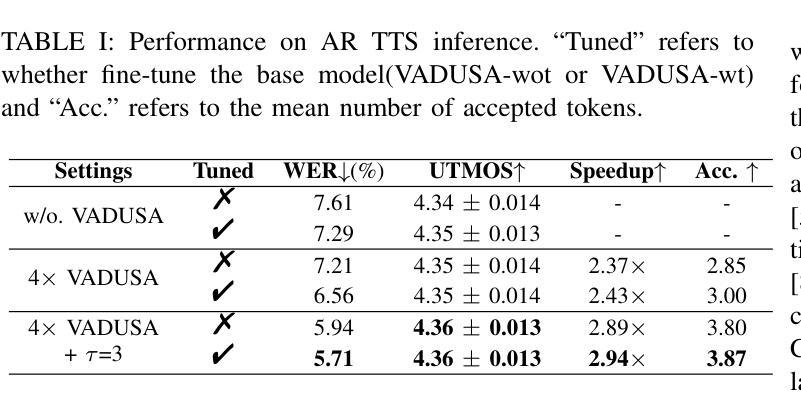
Enhancing TTS Stability in Hebrew using Discrete Semantic Units
Authors:Ella Zeldes, Or Tal, Yossi Adi
This study introduces a refined approach to Text-to-Speech (TTS) generation that significantly enhances sampling stability across languages, with a particular focus on Hebrew. By leveraging discrete semantic units with higher phonetic correlation obtained from a self-supervised model, our method addresses the inherent instability often encountered in TTS systems, especially those dealing with non-diacriticized scripts like Hebrew. Utilizing HuBERT codes, our model generates discrete representations that are optimized for TTS tasks, thereby reducing the dependency on diacritic-based text processing. This advancement not only simplifies the language modeling process but also improves the robustness and shows controllability of the speech output due to disentenglement properties of the semantic units. The inclusion of a speaker embedding in the vocoder further aids in capturing the unique vocal characteristics of the speaker, contributing to the naturalness of the synthesized speech. Our experimental results demonstrate that this approach not only maintains high performance in Hebrew but also shows adaptability to English, underscoring its effectiveness in enhancing stability in TTS systems universally. Our method, named LOTHM (Language of The Hebrew Man), outperforms existing methods in terms of stability while achieving naturalness and speaker similarity on par with previous methods, making it a compelling choice for future speech synthesis applications. Samples can be found in our page pages.cs.huji.ac.il/adiyoss-lab/LoTHM .
本研究介绍了一种精细的文本转语音(TTS)生成方法,该方法显著提高了跨语言的采样稳定性,特别专注于希伯来语。通过利用从自监督模型中获得的高语音相关离散语义单元,我们的方法解决了TTS系统中经常遇到的固有不稳定问题,尤其是处理希伯来语等非变音符号脚本时。利用HuBERT代码,我们的模型生成针对TTS任务优化的离散表示,从而减少了基于变音符号的文本处理的依赖性。这一进展不仅简化了语言建模过程,而且通过语义单元的解纠缠属性提高了鲁棒性,并显示出语音输出的可控性。在vocoder中加入说话人嵌入还有助于捕捉说话人的独特语音特征,为合成语音的自然度做出贡献。我们的实验结果表明,这一方法不仅在希伯来语中保持高性能,而且显示出对英语的适应性,强调了其在普遍提高TTS系统稳定性方面的有效性。我们的方法名为LOTHM(希伯来人的语言),在稳定性方面优于现有方法,同时在自然度和说话人相似性方面与以前的方法相当,因此它是未来语音合成应用的有力选择。样本可在我们的页面找到pages.cs.huji.ac.il/adiyoss-lab/LoTHM。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究提出了一种改进的文生语音(TTS)生成方法,该方法通过利用自监督模型获得的更高语音相关性的离散语义单元,显著提高了跨语言的采样稳定性,特别是在希伯来语等非变音脚本的处理上。借助HuBERT代码,该方法生成了针对TTS任务优化的离散表示形式,减少了基于变音的文本处理的依赖性。该研究不仅简化了语言建模过程,还提高了语音输出的稳健性和可控性。此外,将说话人嵌入到vocoder中还有助于捕捉说话人的独特语音特征,为合成语音的自然度做出贡献。实验结果表明,该方法不仅在希伯来语中表现优异,而且适应于英语,凸显其在提高TTS系统稳定性方面的普遍有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了一种新的TTS生成方法,提高了跨语言的采样稳定性。
- 方法重点关注希伯来语等非变音脚本的处理,解决了TTS系统常见的内在不稳定问题。
- 利用自监督模型的离散语义单元,通过HuBERT代码优化TTS任务。
- 方法简化了语言建模过程,提高了语音输出的稳健性和可控性。
- Vocoder中嵌入的说话人特征有助于捕捉说话人的独特语音特征,增强了合成语音的自然度。
- 该方法不仅适用于希伯来语,也适应于英语,具有普遍有效性。
点此查看论文截图
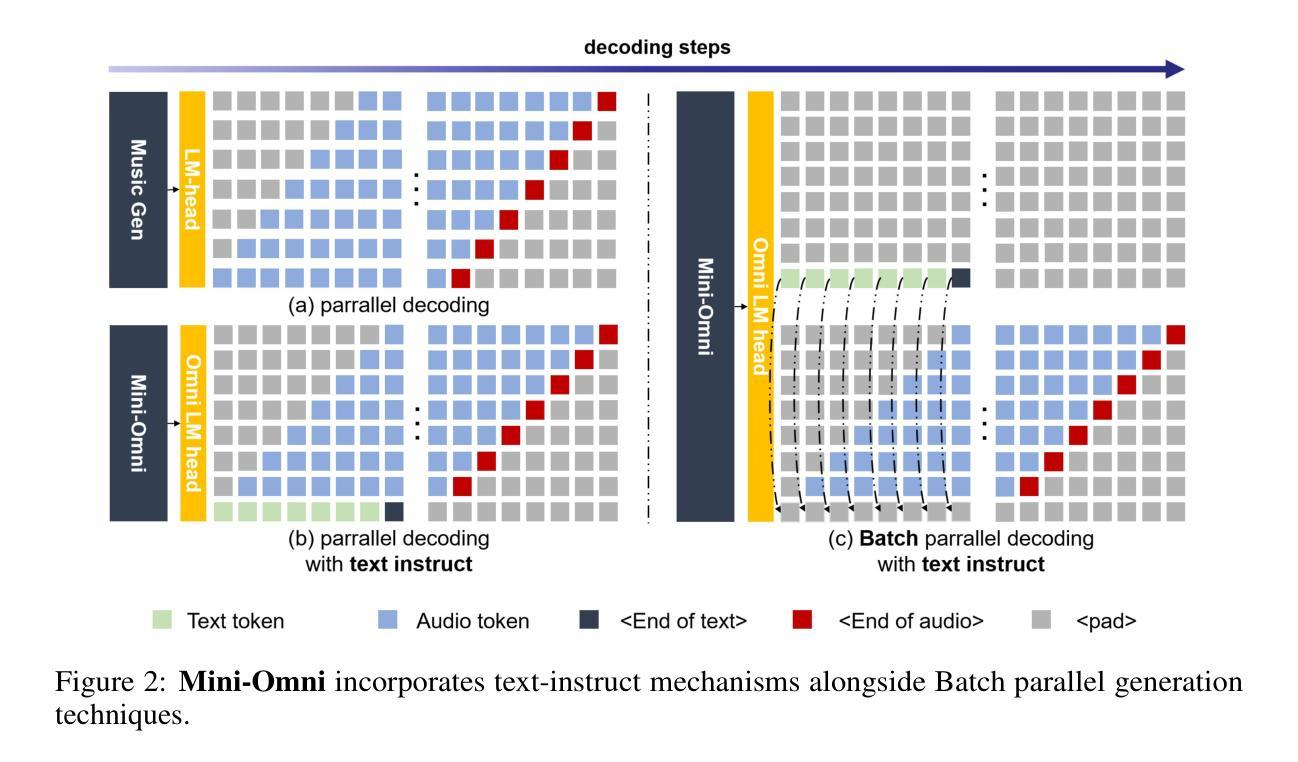
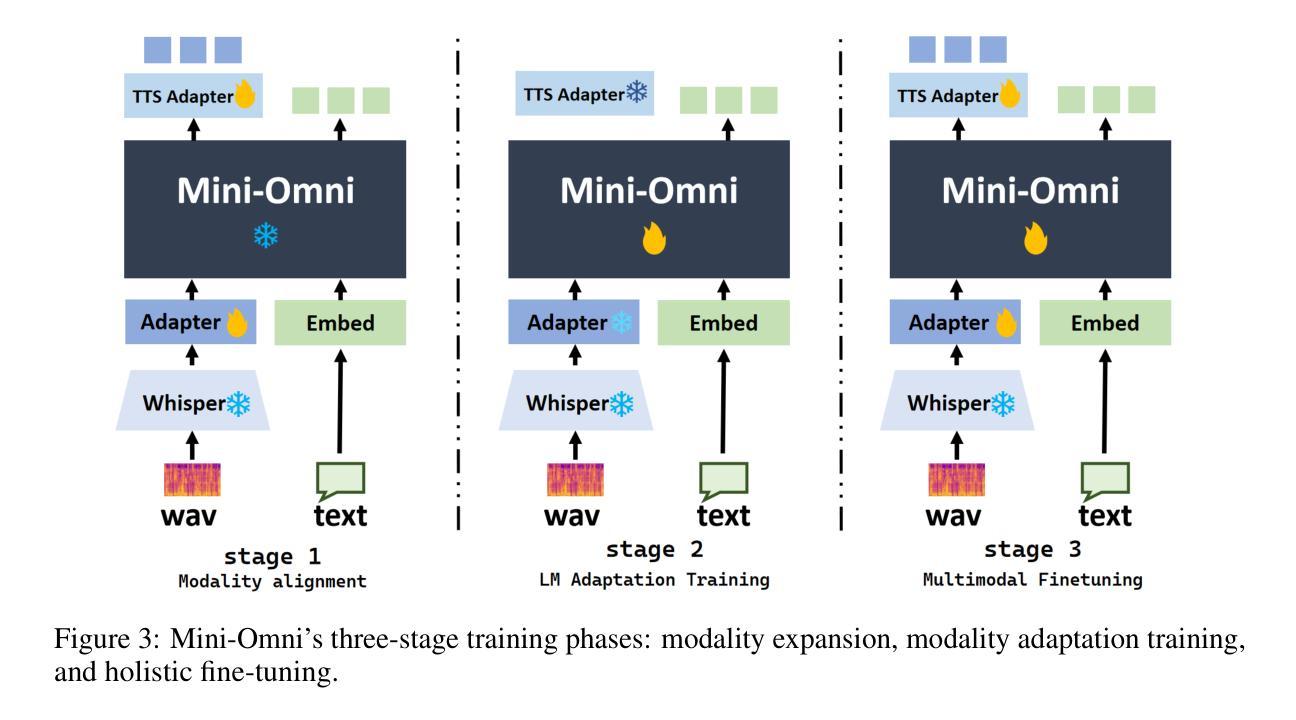
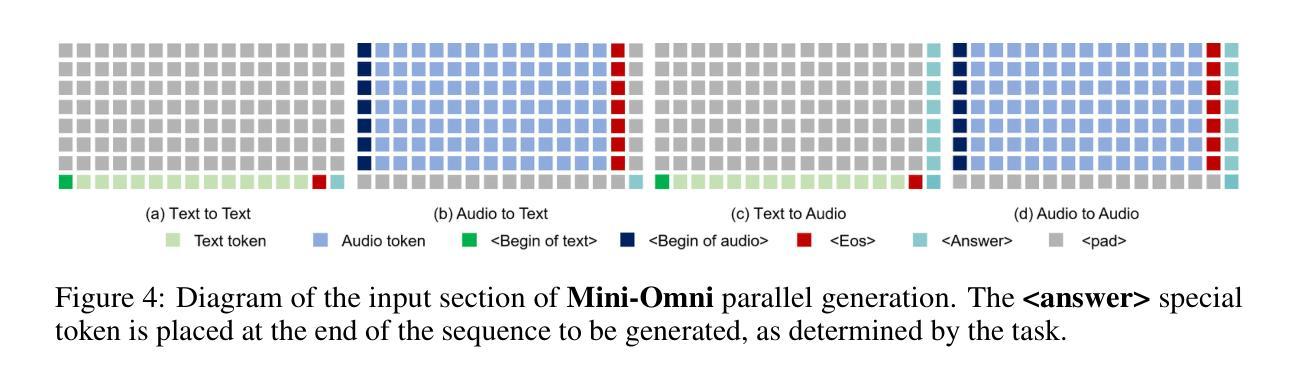
Mini-Omni: Language Models Can Hear, Talk While Thinking in Streaming
Authors:Zhifei Xie, Changqiao Wu
Recent advances in language models have achieved significant progress. GPT-4o, as a new milestone, has enabled real-time conversations with humans, demonstrating near-human natural fluency. Such human-computer interaction necessitates models with the capability to perform reasoning directly with the audio modality and generate output in streaming. However, this remains beyond the reach of current academic models, as they typically depend on extra TTS systems for speech synthesis, resulting in undesirable latency. This paper introduces the Mini-Omni, an audio-based end-to-end conversational model, capable of real-time speech interaction. To achieve this capability, we propose a text-instructed speech generation method, along with batch-parallel strategies during inference to further boost the performance. Our method also helps to retain the original model’s language capabilities with minimal degradation, enabling other works to establish real-time interaction capabilities. We call this training method “Any Model Can Talk”. We also introduce the VoiceAssistant-400K dataset to fine-tune models optimized for speech output. To our best knowledge, Mini-Omni is the first fully end-to-end, open-source model for real-time speech interaction, offering valuable potential for future research.
近期语言模型领域的进展取得了显著成就。GPT-4o作为一个新里程碑,实现了与人类实时对话的能力,展现出近似人类的自然流畅度。这种人机交互需要模型具备直接以音频模式进行推理并流式生成输出的能力。然而,当前学术模型尚无法实现这一功能,因为它们通常依赖于额外的文本转语音(TTS)系统进行语音合成,导致不理想的延迟。本文介绍了Mini-Omni,一个基于音频的端到端对话模型,能够实现实时语音交互。为实现此功能,我们提出了一种文本指导的语音生成方法,并在推理过程中采用批量并行策略进一步提升性能。我们的方法还有助于保持原始模型的语言能力轻微退化,使其他工作能够建立实时交互能力。我们将这种训练方法称为“任何模型都能说话”。我们还介绍了VoiceAssistant-400K数据集,用于对优化语音输出的模型进行微调。据我们所知,Mini-Omni是首个完全端到端、开源的实时语音交互模型,为未来研究提供了宝贵的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical report, work in progress. Demo and code: https://github.com/gpt-omni/mini-omni
Summary
最新语言模型进展显著,GPT-4o实现了实时对话。当前模型需借助额外文本转语音(TTS)系统进行语音合成,导致延迟。本文介绍了一种音频端到端的对话模型Mini-Omni,可实现实时语音交互。采用文本指导的语音生成方法和批量并行推理策略提升性能,保持原有语言功能,引入VoiceAssistant-400K数据集优化语音输出模型。Mini-Omni是首个全端、开源的实时语音交互模型,具有潜在的研究价值。
Key Takeaways
- GPT-4o实现了实时对话,展现了近乎人类自然流畅度。
- 当前模型依赖于额外的TTS系统进行语音合成,造成延迟问题。
- Mini-Omni是一种音频端到端的对话模型,旨在实现实时语音交互。
- Mini-Omni采用文本指导的语音生成方法。
- 批量并行策略被用于进一步提升Mini-Omni的性能。
- Mini-Omni保持原有语言功能的同时实现了实时交互能力的提升。
点此查看论文截图

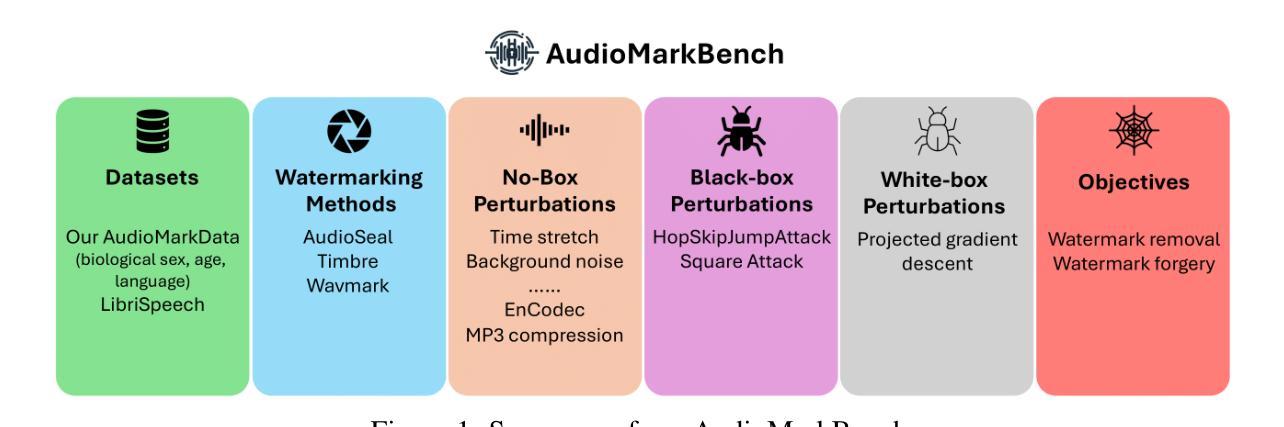
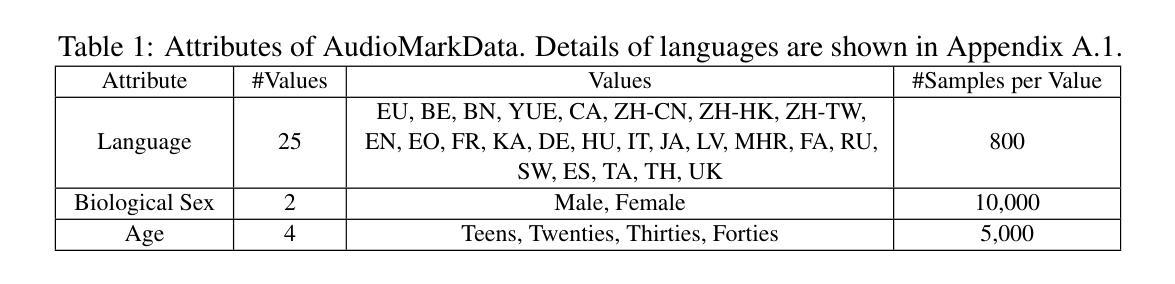
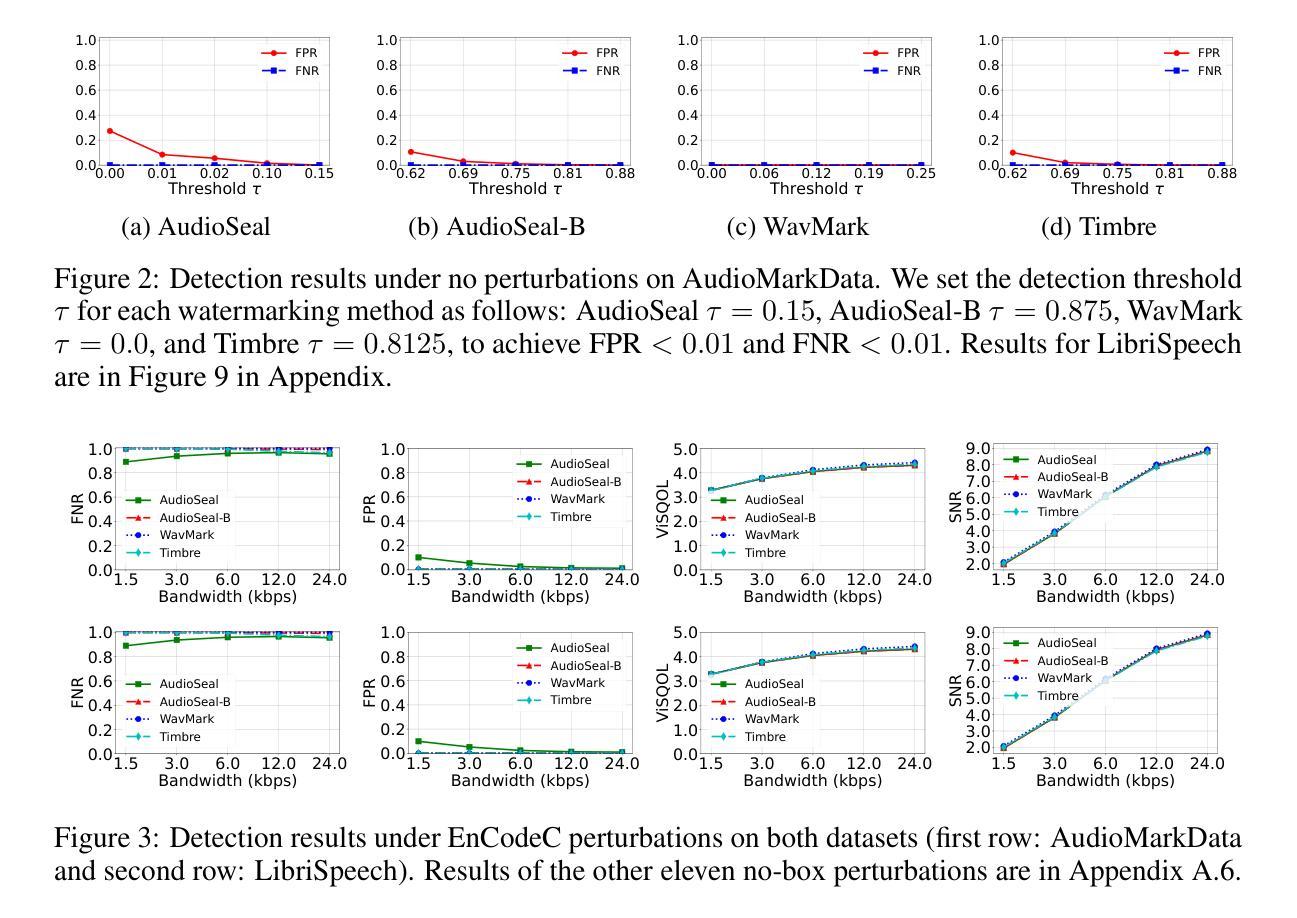
AudioMarkBench: Benchmarking Robustness of Audio Watermarking
Authors:Hongbin Liu, Moyang Guo, Zhengyuan Jiang, Lun Wang, Neil Zhenqiang Gong
The increasing realism of synthetic speech, driven by advancements in text-to-speech models, raises ethical concerns regarding impersonation and disinformation. Audio watermarking offers a promising solution via embedding human-imperceptible watermarks into AI-generated audios. However, the robustness of audio watermarking against common/adversarial perturbations remains understudied. We present AudioMarkBench, the first systematic benchmark for evaluating the robustness of audio watermarking against watermark removal and watermark forgery. AudioMarkBench includes a new dataset created from Common-Voice across languages, biological sexes, and ages, 3 state-of-the-art watermarking methods, and 15 types of perturbations. We benchmark the robustness of these methods against the perturbations in no-box, black-box, and white-box settings. Our findings highlight the vulnerabilities of current watermarking techniques and emphasize the need for more robust and fair audio watermarking solutions. Our dataset and code are publicly available at https://github.com/moyangkuo/AudioMarkBench.
随着文本到语音模型的进步,合成语音的逼真度越来越高,这引发了关于冒充和虚假信息的道德担忧。音频水印技术通过在人工智能生成的音频中嵌入人类无法察觉的水印,提供了一个很有前途的解决方案。然而,音频水印对常见/对抗性扰动的稳健性尚未得到充分研究。我们推出了AudioMarkBench,这是第一个系统基准测试,用于评估音频水印对水印移除和伪造操作的稳健性。AudioMarkBench包括使用Common-Voice创建的新数据集,涵盖多种语言、生物性别和年龄,包含三种最先进的水印方法,以及1 5种扰动类型。我们对这些方法在无框、黑箱和白箱设置下的扰动稳健性进行了基准测试。我们的研究结果突出了当前水印技术的漏洞,并强调了需要更稳健和公平的音频水印解决方案。我们的数据集和代码可在https://github.com/moyangkuo/AudioMarkBench公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear in NeurIPS Datasets and Benchmarks, 2024
Summary
随着文本转语音模型的进步,合成语音的逼真度不断提高,引发了关于身份伪装和虚假信息的伦理问题。音频水印技术为在AI生成的音频中嵌入人类无法察觉的水印提供了解决方案。然而,音频水印对常见/对抗性扰动的稳健性尚待研究。我们推出了AudioMarkBench,这是第一个用于评估音频水印稳健性的系统基准测试,它对抗水印移除和水印伪造进行了测试。AudioMarkBench包括使用Common-Voice创建的新数据集,涵盖多种语言、生物性别和年龄,还有三种最先进的水印方法和十五种扰动类型。我们对这些方法在无盒、黑盒和白盒设置中的扰动进行了基准测试。我们的研究突出了当前水印技术的漏洞,并强调了需要更稳健和公平的音频水印解决方案。我们的数据集和代码可在https://github.com/moyangkuo/AudioMarkBench获取。
Key Takeaways
- 合成语音逼真度的提高引发了关于身份伪装和虚假信息的伦理问题。
- 音频水印技术为AI生成的音频提供了嵌入不可察觉水印的解决方案。
- 音频水印对常见和对抗性的扰动的稳健性尚未得到充分研究。
- 推出了AudioMarkBench基准测试,用于评估音频水印的稳健性。
- AudioMarkBench包含多语言、性别和年龄的新数据集。
- 当前水印技术存在漏洞,需要更稳健和公平的音频水印解决方案。
点此查看论文截图