⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-11 更新
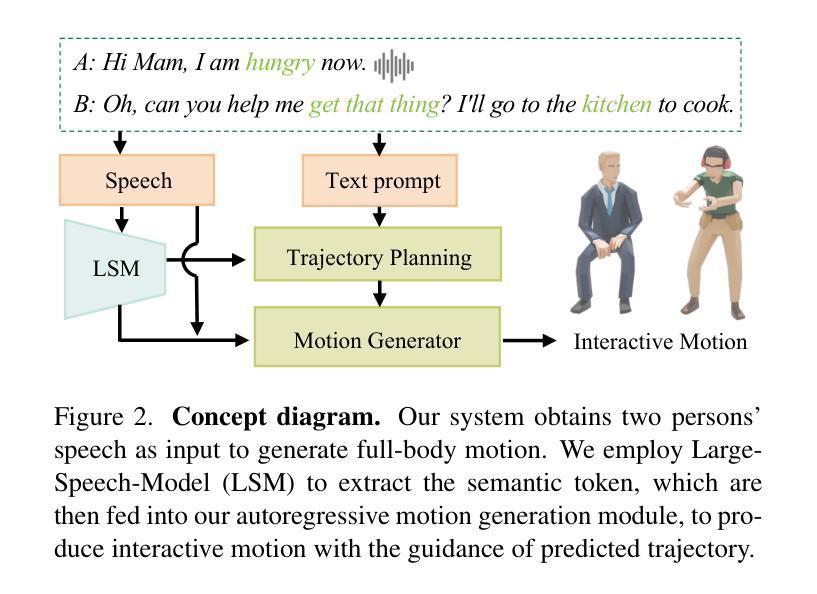
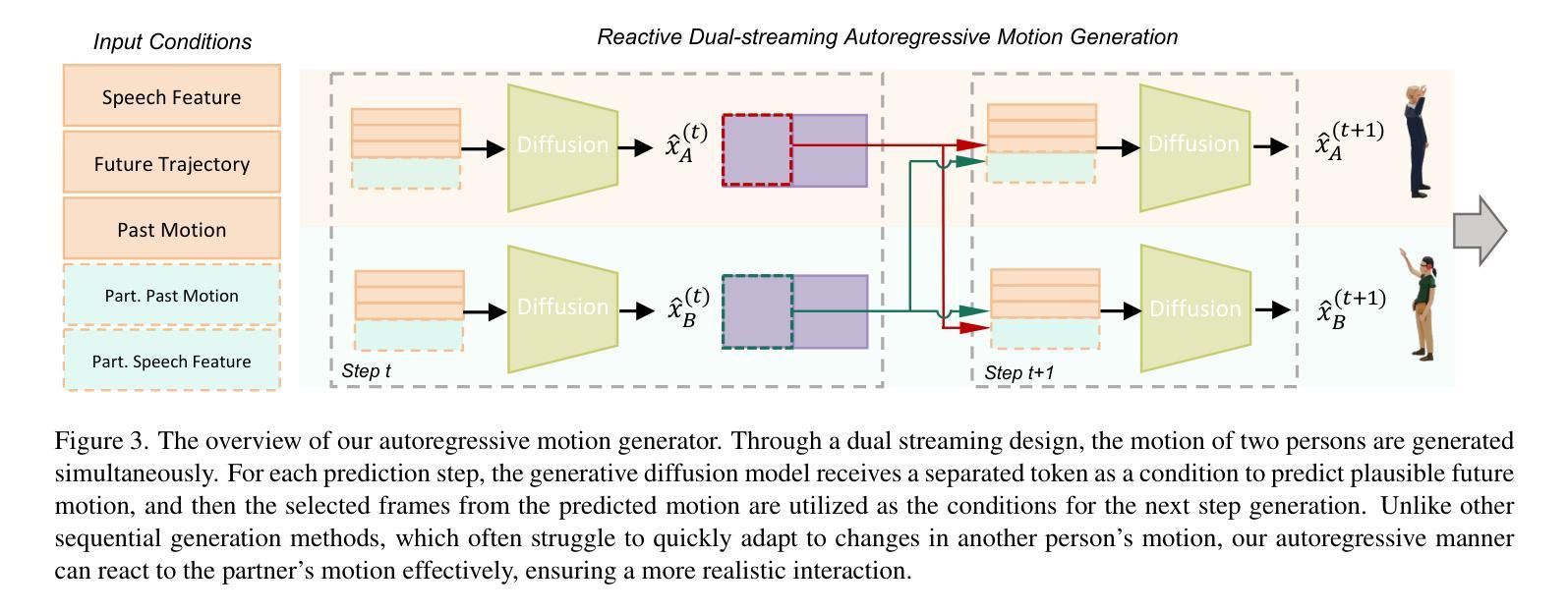
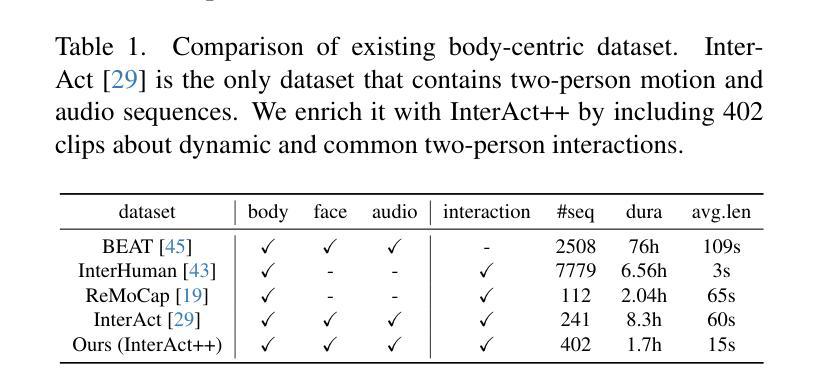
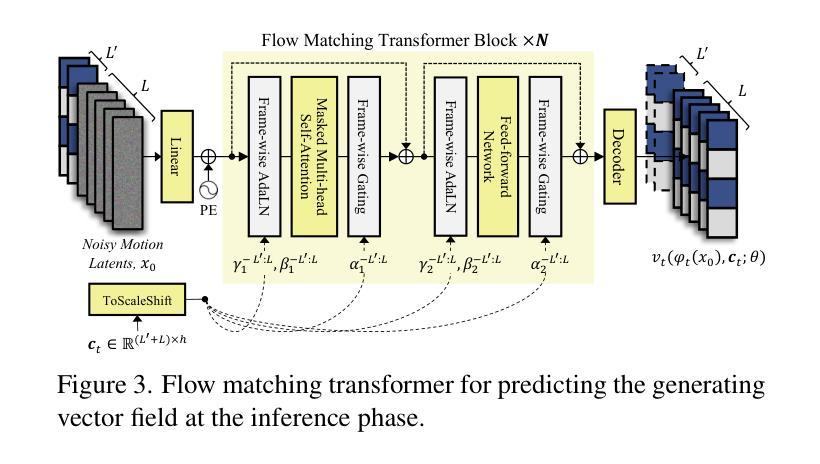
It Takes Two: Real-time Co-Speech Two-person’s Interaction Generation via Reactive Auto-regressive Diffusion Model
Authors:Mingyi Shi, Dafei Qin, Leo Ho, Zhouyingcheng Liao, Yinghao Huang, Junichi Yamagishi, Taku Komura
Conversational scenarios are very common in real-world settings, yet existing co-speech motion synthesis approaches often fall short in these contexts, where one person’s audio and gestures will influence the other’s responses. Additionally, most existing methods rely on offline sequence-to-sequence frameworks, which are unsuitable for online applications. In this work, we introduce an audio-driven, auto-regressive system designed to synthesize dynamic movements for two characters during a conversation. At the core of our approach is a diffusion-based full-body motion synthesis model, which is conditioned on the past states of both characters, speech audio, and a task-oriented motion trajectory input, allowing for flexible spatial control. To enhance the model’s ability to learn diverse interactions, we have enriched existing two-person conversational motion datasets with more dynamic and interactive motions. We evaluate our system through multiple experiments to show it outperforms across a variety of tasks, including single and two-person co-speech motion generation, as well as interactive motion generation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first system capable of generating interactive full-body motions for two characters from speech in an online manner.
在真实世界环境中,对话场景非常常见。然而,现有的协同语音运动合成方法在这些场景中往往表现不足,一个人的音频和手势会影响另一方的反应。此外,大多数现有方法依赖于离线序列到序列框架,这不适用于在线应用。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种音频驱动的、自回归系统,旨在合成对话过程中两个角色的动态动作。我们的方法核心是基于扩散的全身运动合成模型,该模型受两个角色过去状态、语音音频和面向任务的运动轨迹输入的制约,可实现灵活的空间控制。为了提高模型学习各种交互的能力,我们丰富了现有的两人对话运动数据集,加入了更多动态和交互动作。我们通过多次实验评估了我们的系统,表明它在各种任务上的表现都优于其他系统,包括单人及两人协同语音运动生成以及交互运动生成。据我们所知,这是第一个能够以在线方式从语音中生成两个角色的交互式全身动作的体系。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于音频的、自回归的系统,用于合成对话中两个角色的动态动作。系统采用基于扩散算法的全身动作合成模型,根据两个角色的过去状态、语音音频和任务导向的动作轨迹输入进行条件化,实现灵活的空间控制。通过丰富两人对话动作数据集,模型能够学习更多样化的交互动作。实验表明,该系统在单人及双人对话动作生成、交互动作生成等多项任务上表现优异,是首个能够在线生成两个角色互动全身动作的语音驱动系统。
Key Takeaways
- 该系统是基于音频的自回归系统,用于合成对话中两个角色的动态动作。
- 系统采用扩散算法模型,该模型可基于两个角色的过去状态、语音音频和任务导向的动作轨迹进行条件化。
- 系统可实现灵活的空间控制,即根据对话场景中的互动调整角色的动作。
- 通过丰富数据集,模型能够学习更多样化的交互动作,提高生成动作的真实感和自然度。
- 实验表明,该系统在多种任务上表现优异,包括单人及双人对话动作生成、交互动作生成等。
- 该系统是首个能够在线生成两个角色互动全身动作的语音驱动系统。
点此查看论文截图

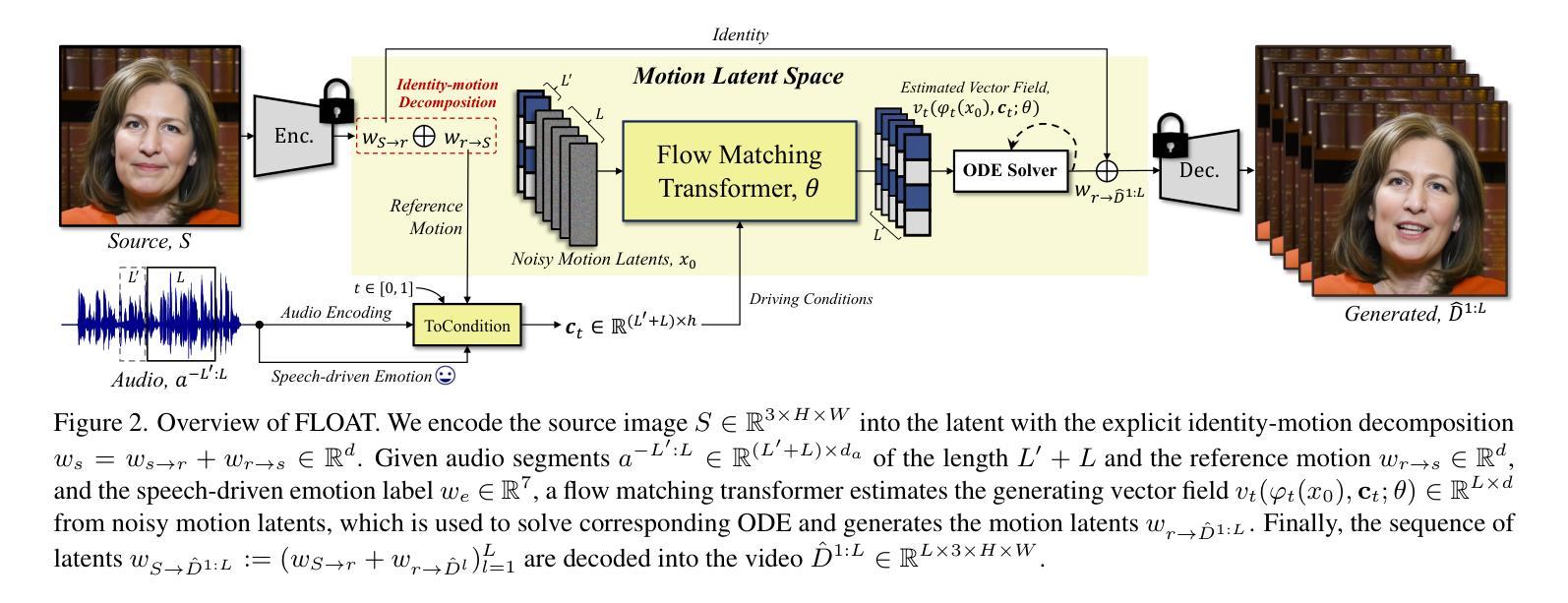
FLOAT: Generative Motion Latent Flow Matching for Audio-driven Talking Portrait
Authors:Taekyung Ki, Dongchan Min, Gyeongsu Chae
With the rapid advancement of diffusion-based generative models, portrait image animation has achieved remarkable results. However, it still faces challenges in temporally consistent video generation and fast sampling due to its iterative sampling nature. This paper presents FLOAT, an audio-driven talking portrait video generation method based on flow matching generative model. We shift the generative modeling from the pixel-based latent space to a learned motion latent space, enabling efficient design of temporally consistent motion. To achieve this, we introduce a transformer-based vector field predictor with a simple yet effective frame-wise conditioning mechanism. Additionally, our method supports speech-driven emotion enhancement, enabling a natural incorporation of expressive motions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art audio-driven talking portrait methods in terms of visual quality, motion fidelity, and efficiency.
随着基于扩散的生成模型的快速发展,肖像图像动画已经取得了显著成果。然而,由于它的迭代采样特性,它在时间一致的视频生成和快速采样方面仍然面临挑战。本文提出了FLOAT,一种基于流匹配生成模型的音频驱动肖像视频生成方法。我们将生成建模从基于像素的潜在空间转移到学习的运动潜在空间,实现了时间一致运动的有效设计。为此,我们引入了一个基于变压器的向量场预测器,配备了一个简单有效的帧级条件机制。此外,我们的方法支持语音驱动的情绪增强,能够实现表达性运动的自然融合。大量实验表明,我们的方法在视觉质量、运动保真度和效率方面优于最新的音频驱动肖像方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://deepbrainai-research.github.io/float/
Summary
本文介绍了基于流匹配生成模型的音频驱动肖像视频生成方法FLOAT。该方法将生成建模从像素级的潜在空间转移到学习的运动潜在空间,实现了高效设计的时序一致运动。通过引入基于变压器的向量场预测器,以及简单有效的帧条件机制,该方法支持语音驱动的情感增强,能够自然融入表达性动作。实验表明,该方法在视觉质量、运动保真度和效率方面优于现有音频驱动的肖像方法。
Key Takeaways
- FLOAT是一种基于流匹配生成模型的音频驱动肖像视频生成方法。
- 该方法将生成建模从像素级潜在空间转移到运动潜在空间,以实现高效设计的时序一致运动。
- 通过引入基于变压器的向量场预测器,实现了对运动的精确预测和控制。
- 该方法采用了简单有效的帧条件机制,使模型能够自然融入表达性动作。
- FLOAT支持语音驱动的情感增强,能够根据音频信息调整角色的表情和动作。
- 实验表明,该方法在视觉质量、运动保真度和效率方面优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

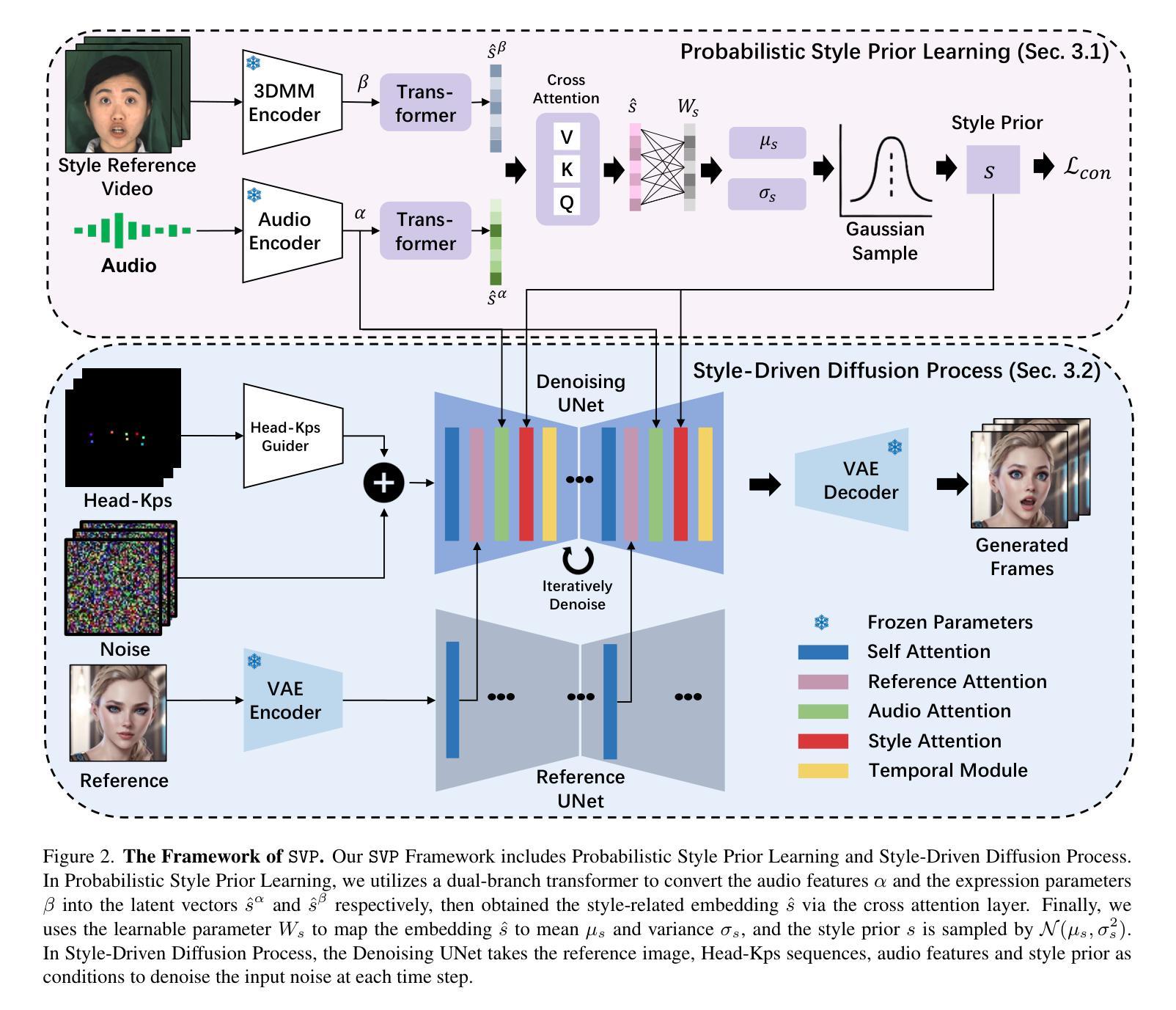
SVP: Style-Enhanced Vivid Portrait Talking Head Diffusion Model
Authors:Weipeng Tan, Chuming Lin, Chengming Xu, Xiaozhong Ji, Junwei Zhu, Chengjie Wang, Yunsheng Wu, Yanwei Fu
Talking Head Generation (THG), typically driven by audio, is an important and challenging task with broad application prospects in various fields such as digital humans, film production, and virtual reality. While diffusion model-based THG methods present high quality and stable content generation, they often overlook the intrinsic style which encompasses personalized features such as speaking habits and facial expressions of a video. As consequence, the generated video content lacks diversity and vividness, thus being limited in real life scenarios. To address these issues, we propose a novel framework named Style-Enhanced Vivid Portrait (SVP) which fully leverages style-related information in THG. Specifically, we first introduce the novel probabilistic style prior learning to model the intrinsic style as a Gaussian distribution using facial expressions and audio embedding. The distribution is learned through the ‘bespoked’ contrastive objective, effectively capturing the dynamic style information in each video. Then we finetune a pretrained Stable Diffusion (SD) model to inject the learned intrinsic style as a controlling signal via cross attention. Experiments show that our model generates diverse, vivid, and high-quality videos with flexible control over intrinsic styles, outperforming existing state-of-the-art methods.
基于音频的Talking Head Generation(THG)是一项重要且具有挑战性的任务,在数字人类、电影制作和虚拟现实等领域具有广阔的应用前景。虽然基于扩散模型的THG方法呈现出高质量且内容稳定生成,但它们常常忽略了内在风格,包括说话习惯和视频的面部表情等个性化特征。因此,生成的视频内容缺乏多样性和生动性,在现实场景中的应用受到限制。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种名为Style-Enhanced Vivid Portrait(SVP)的新型框架,充分利用THG中的风格相关信息。具体来说,我们首先引入新颖的概率风格先验学习,使用面部表情和音频嵌入来模拟内在风格的高斯分布。该分布是通过“定制”对比目标学习得到的,有效捕捉每个视频中的动态风格信息。然后,我们对预训练的Stable Diffusion(SD)模型进行微调,通过交叉注意力将学习到的内在风格作为控制信号注入。实验表明,我们的模型能够生成多样、生动、高质量的视频,对内在风格具有灵活的控制力,超越了现有的最先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在音频驱动的“说话人生成”(Talking Head Generation,THG)任务中,新的框架Style-Enhanced Vivid Portrait(SVP)充分利用了与风格相关的信息,解决了现有扩散模型方法忽略内在风格(如说话习惯和面部表情)的问题。SVP通过引入概率性风格先验学习,将内在风格建模为高斯分布,并通过对比目标有效捕捉视频中的动态风格信息。此外,SVP还微调了预训练的Stable Diffusion模型,通过交叉注意力注入学到的内在风格作为控制信号。实验表明,SVP能够生成多样化、生动、高质量的视频,对内在风格具有灵活的控制,超越了现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- Talking Head Generation (THG)是一个在数字人类、电影制作和虚拟现实等领域有广泛应用前景的重要任务。
- 现有基于扩散模型的方法在THG中往往忽略内在风格,导致生成内容缺乏多样性和生动性。
- Style-Enhanced Vivid Portrait (SVP)框架被提出以解决这一问题,它充分利用与风格相关的信息。
- SVP通过概率性风格先验学习建模内在风格为高斯分布,并引入“bespoked”对比目标来捕捉视频中的动态风格信息。
- SVP通过微调预训练的Stable Diffusion模型,注入学到的内在风格作为控制信号。
- 实验表明,SVP能够生成高质量、多样化、生动的视频,对内在风格具有灵活控制。
点此查看论文截图

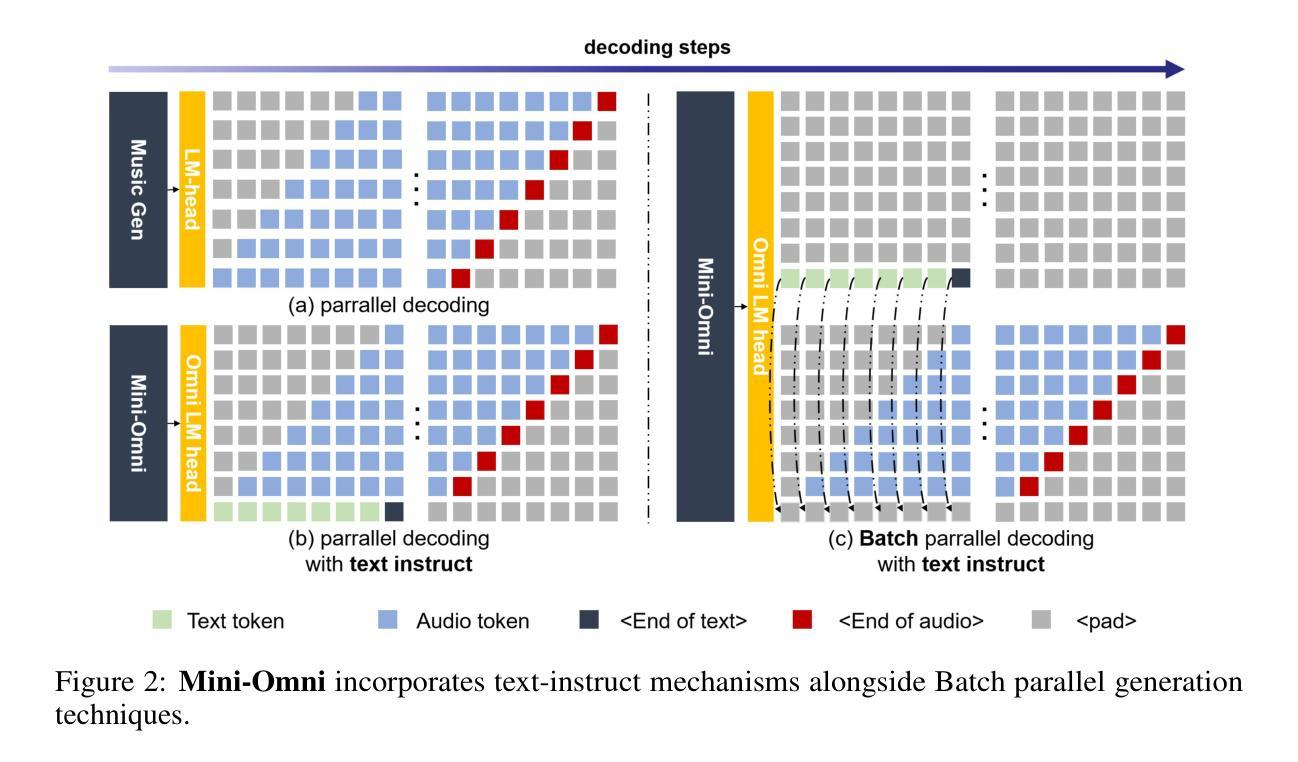
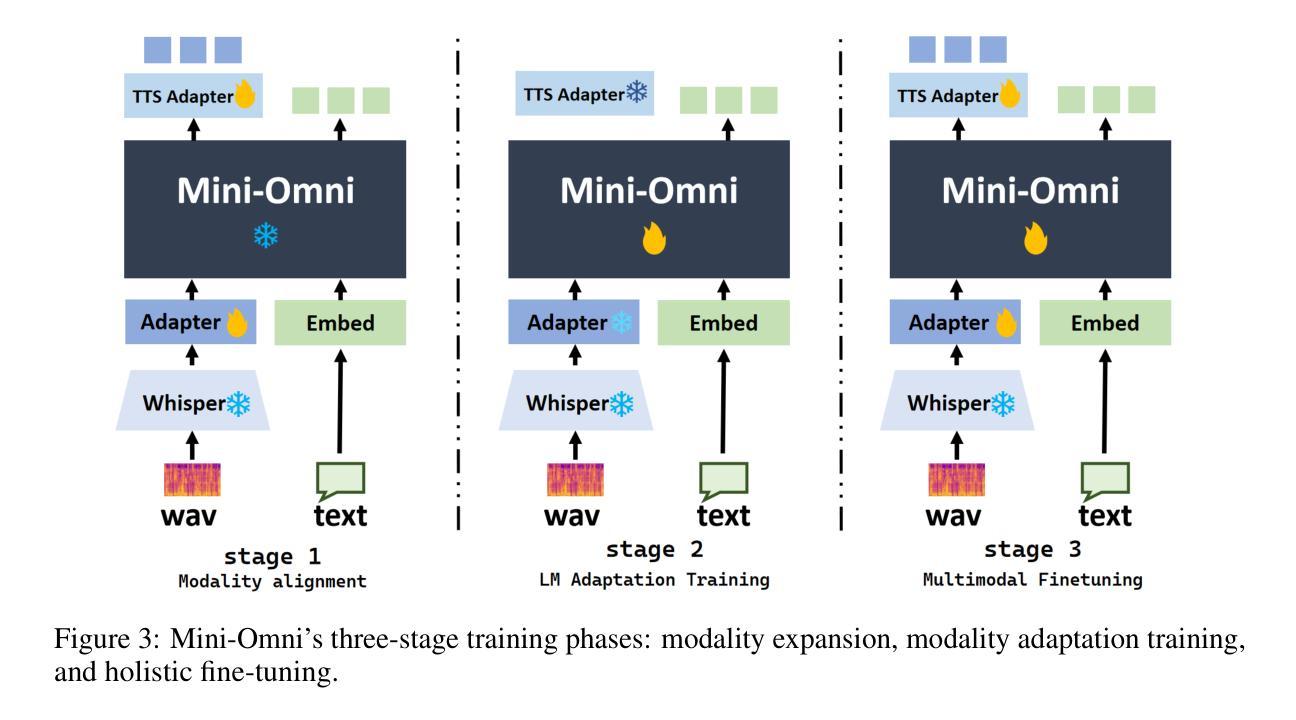
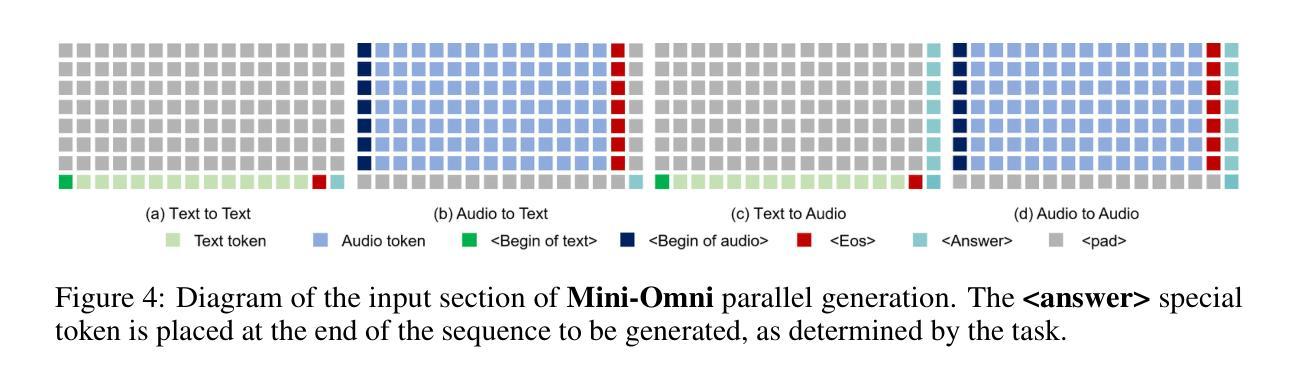
Mini-Omni: Language Models Can Hear, Talk While Thinking in Streaming
Authors:Zhifei Xie, Changqiao Wu
Recent advances in language models have achieved significant progress. GPT-4o, as a new milestone, has enabled real-time conversations with humans, demonstrating near-human natural fluency. Such human-computer interaction necessitates models with the capability to perform reasoning directly with the audio modality and generate output in streaming. However, this remains beyond the reach of current academic models, as they typically depend on extra TTS systems for speech synthesis, resulting in undesirable latency. This paper introduces the Mini-Omni, an audio-based end-to-end conversational model, capable of real-time speech interaction. To achieve this capability, we propose a text-instructed speech generation method, along with batch-parallel strategies during inference to further boost the performance. Our method also helps to retain the original model’s language capabilities with minimal degradation, enabling other works to establish real-time interaction capabilities. We call this training method “Any Model Can Talk”. We also introduce the VoiceAssistant-400K dataset to fine-tune models optimized for speech output. To our best knowledge, Mini-Omni is the first fully end-to-end, open-source model for real-time speech interaction, offering valuable potential for future research.
最近的自然语言模型进展显著。GPT-4o作为一个新里程碑,已经能够实现与人类实时对话,展现出近乎人类自然的流畅度。这样的人机交互需要模型能够直接对音频模式进行推理并以流式方式生成输出。然而,这仍然是当前学术模型无法企及的能力,因为它们通常依赖于额外的文本转语音系统来进行语音合成,导致不可取的延迟。本文介绍了Mini-Omni,一个基于音频的端到端对话模型,能够进行实时语音交互。为了实现这一功能,我们提出了一种文本指导的语音生成方法,并在推理过程中采用批量并行策略来进一步提升性能。我们的方法还有助于在最小退化的情况下保留原始模型的语言能力,使其他工作能够建立实时交互能力。我们将这种训练方法称为“任何模型都能说话”。我们还引入了VoiceAssistant-400K数据集,对优化语音输出的模型进行微调。据我们所知,Mini-Omni是第一个完全端到端、开源的实时语音交互模型,为未来研究提供了宝贵的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical report, work in progress. Demo and code: https://github.com/gpt-omni/mini-omni
Summary
GPT-4o展现了与人类近乎自然流畅的实时对话能力。当前学术模型仍无法直接处理音频模态进行推理和生成输出,依赖于TTS系统进行语音合成带来不便。本研究提出了Mini-Omni,首个基于音频端到端的会话模型实现实时语音交互。采用文本指令语音生成方法和批并行推断策略提升性能,且能保留原始模型语言能力,有助于其他工作建立实时交互功能。同时介绍VoiceAssistant-400K数据集用于优化语音输出模型,为未来的研究提供了有价值潜力。
Key Takeaways
- GPT-4o展现了与人类自然的实时对话能力。
- 当前学术模型在处理音频模态进行推理方面存在局限性,依赖TTS系统造成不便。
- Mini-Omni是一个基于音频端到端的会话模型,实现实时语音交互。
- Mini-Omni采用文本指令语音生成方法。
- 批并行推断策略用于提升Mini-Omni的性能。
- Mini-Omni能保留原始模型的语言能力,有助于其他工作建立实时交互功能。
点此查看论文截图

Talking the Talk Does Not Entail Walking the Walk: On the Limits of Large Language Models in Lexical Entailment Recognition
Authors:Candida M. Greco, Lucio La Cava, Andrea Tagarelli
Verbs form the backbone of language, providing the structure and meaning to sentences. Yet, their intricate semantic nuances pose a longstanding challenge. Understanding verb relations through the concept of lexical entailment is crucial for comprehending sentence meanings and grasping verb dynamics. This work investigates the capabilities of eight Large Language Models in recognizing lexical entailment relations among verbs through differently devised prompting strategies and zero-/few-shot settings over verb pairs from two lexical databases, namely WordNet and HyperLex. Our findings unveil that the models can tackle the lexical entailment recognition task with moderately good performance, although at varying degree of effectiveness and under different conditions. Also, utilizing few-shot prompting can enhance the models’ performance. However, perfectly solving the task arises as an unmet challenge for all examined LLMs, which raises an emergence for further research developments on this topic.
动词是语言的主干,为句子提供结构和意义。然而,它们复杂的语义细微差别构成了一个长期存在的挑战。通过词汇蕴涵的概念理解动词关系对于理解句子意义和把握动词动态至关重要。本研究通过两种不同的提示策略和零/少镜头设置,调查了八个大型语言模型在识别来自WordNet和HyperLex两个词汇数据库的动词之间的词汇蕴涵关系的能力。我们的研究结果表明,这些模型能够较好地处理词汇蕴涵识别任务,尽管在有效性和条件上存在差异。此外,利用少镜头提示可以提高模型的性能。然而,对于所有被检测的大型语言模型来说,完美完成任务仍然是一个未解决的挑战,这为该话题的进一步研究发展提出了要求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication at The 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-2024) - Findings
Summary
本研究探讨了八大语言模型在识别动词之间的词汇蕴涵关系方面的能力。通过不同的提示策略和零/少样本设置,研究涉及了从WordNet和HyperLex两个词汇数据库中选取的动词对。研究发现,这些模型能够较好地完成词汇蕴涵识别任务,但不同条件下的有效性存在差异。利用少样本提示可以增强模型的性能,但完美解决此任务对于所有检查的语言模型来说仍是未实现的挑战,因此有必要对此进行进一步的研究与发展。
Key Takeaways
- 语言中的动词为句子提供了结构和意义。
- 词汇蕴涵在理解句子含义和把握动词动态方面至关重要。
- 八种大型语言模型在识别动词间的词汇蕴涵关系方面表现出一定的能力。
- 不同提示策略和零/少样本设置会影响语言模型的性能。
- 模型在解决词汇蕴涵识别任务时仍存在挑战,需要进一步提高。
- 利用少样本提示可以增强模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

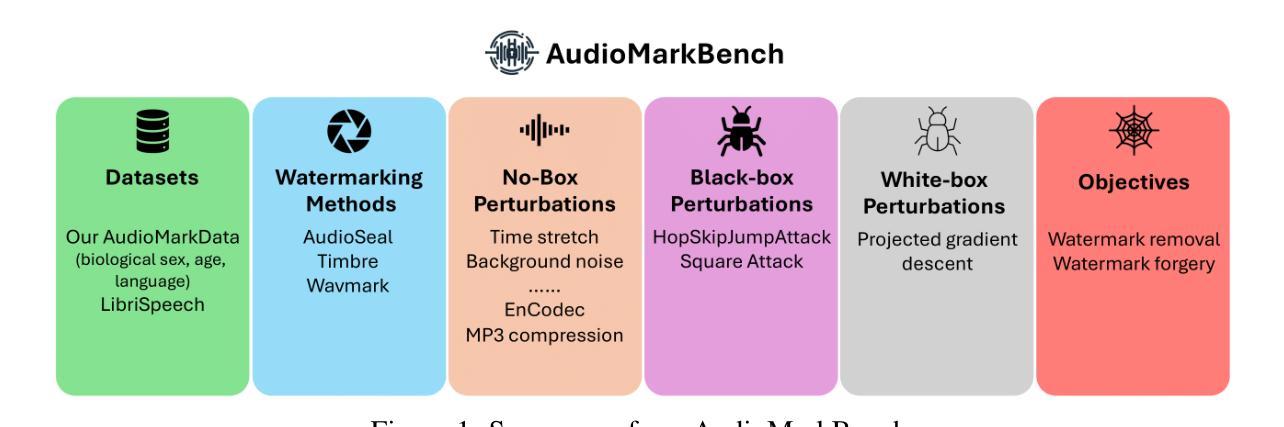
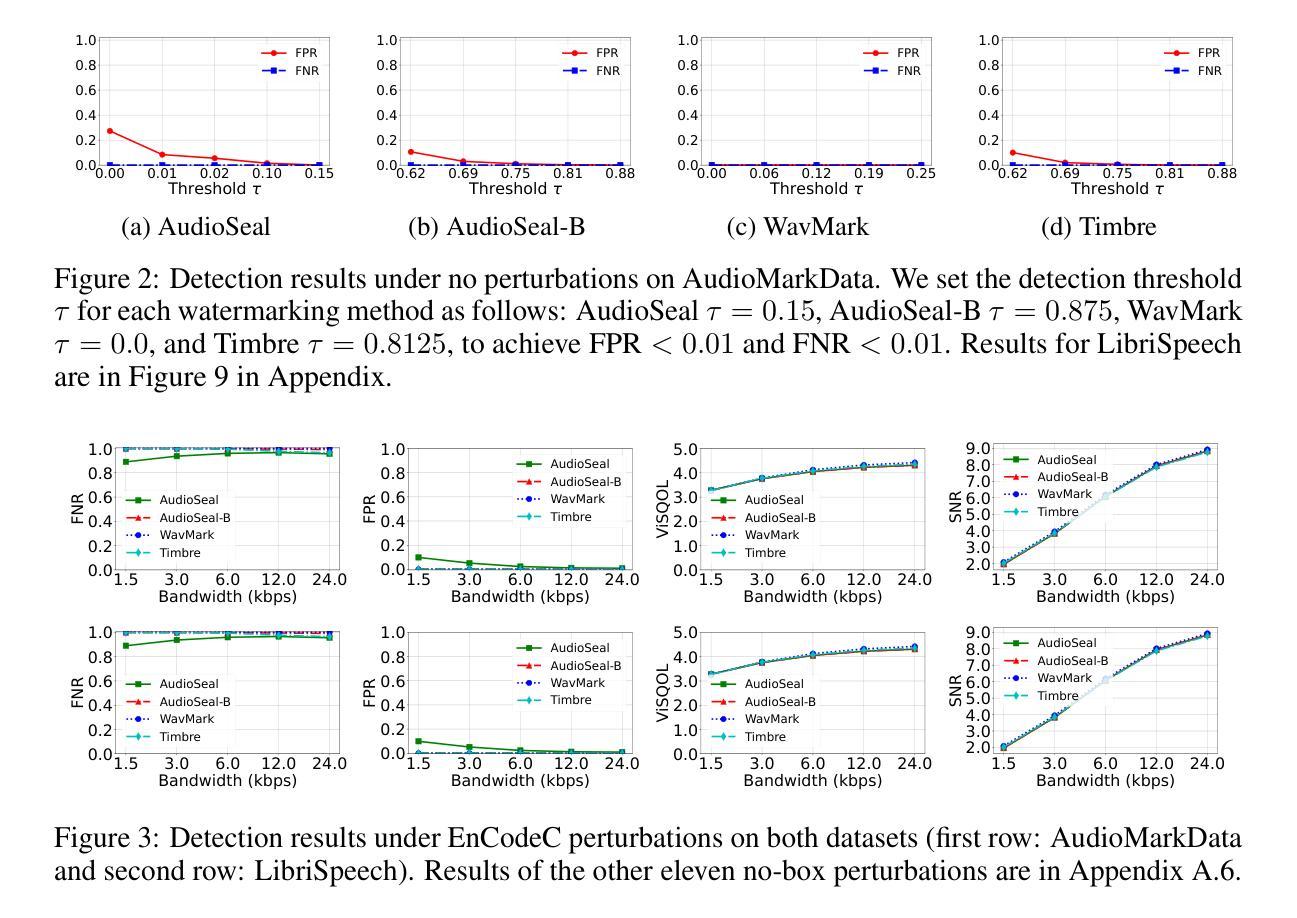
AudioMarkBench: Benchmarking Robustness of Audio Watermarking
Authors:Hongbin Liu, Moyang Guo, Zhengyuan Jiang, Lun Wang, Neil Zhenqiang Gong
The increasing realism of synthetic speech, driven by advancements in text-to-speech models, raises ethical concerns regarding impersonation and disinformation. Audio watermarking offers a promising solution via embedding human-imperceptible watermarks into AI-generated audios. However, the robustness of audio watermarking against common/adversarial perturbations remains understudied. We present AudioMarkBench, the first systematic benchmark for evaluating the robustness of audio watermarking against watermark removal and watermark forgery. AudioMarkBench includes a new dataset created from Common-Voice across languages, biological sexes, and ages, 3 state-of-the-art watermarking methods, and 15 types of perturbations. We benchmark the robustness of these methods against the perturbations in no-box, black-box, and white-box settings. Our findings highlight the vulnerabilities of current watermarking techniques and emphasize the need for more robust and fair audio watermarking solutions. Our dataset and code are publicly available at https://github.com/moyangkuo/AudioMarkBench.
随着文本到语音模型的进步,合成语音的逼真度不断提高,引发了关于冒充和虚假信息传播的伦理担忧。音频水印技术通过嵌入人类难以察觉的水印到人工智能生成的音频中,提供了一种有前景的解决方案。然而,音频水印对于常规/对抗性干扰的稳健性仍研究不足。我们推出了AudioMarkBench,这是第一个系统的基准测试,用于评估音频水印对水印移除和水印伪造干扰的稳健性。AudioMarkBench包括使用Common-Voice创建的新数据集,涵盖多种语言、生物性别和年龄,还包括3种最新水印方法以及1peirone5种扰动类型。我们对这些方法在无框、黑框和白框设置中对干扰的稳健性进行了基准测试。我们的研究结果突出了当前水印技术的漏洞,并强调了需要更稳健和公平的音频水印解决方案。我们的数据集和代码可在https://github.com/moyangkuo/AudioMarkBench公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To appear in NeurIPS Datasets and Benchmarks, 2024
Summary
随着文本转语音模型的进步,合成语音的逼真度不断提升,引发了关于身份冒充和虚假信息的伦理问题。音频水印技术为在AI生成的音频中嵌入人类无法察觉的水印提供了解决方案。然而,音频水印对常见/对抗性扰动的稳健性尚未得到充分研究。我们推出了AudioMarkBench,这是第一个系统评估音频水印稳健性的基准测试,针对水印移除和伪造。AudioMarkBench包括使用Common-Voice创建的新数据集,涵盖多种语言、性别和年龄,3种先进的水印方法,和15种扰动类型。我们评估这些方法在无盒、黑盒和白盒设置中对扰动的稳健性。研究发现当前水印技术的漏洞,强调需要更稳健和公平的音频水印解决方案。数据集和代码公开可访问于https://github.com/moyangkuo/AudioMarkBench。
Key Takeaways
- 合成语音逼真度的提升引发了关于身份冒充和虚假信息的伦理担忧。
- 音频水印技术为AI生成的音频中嵌入不可察觉的水印提供了解决方案。
- 音频水印对于各种扰动(包括常见和对抗性的)的稳健性尚待研究。
- AudioMarkBench是首个评估音频水印稳健性的基准测试,包括新数据集和三种先进的水印方法。
- 测试了水印方法在不同设置(无盒、黑盒、白盒)中对扰动的稳健性。
- 当前音频水印技术存在漏洞,需要更稳健和公平的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图

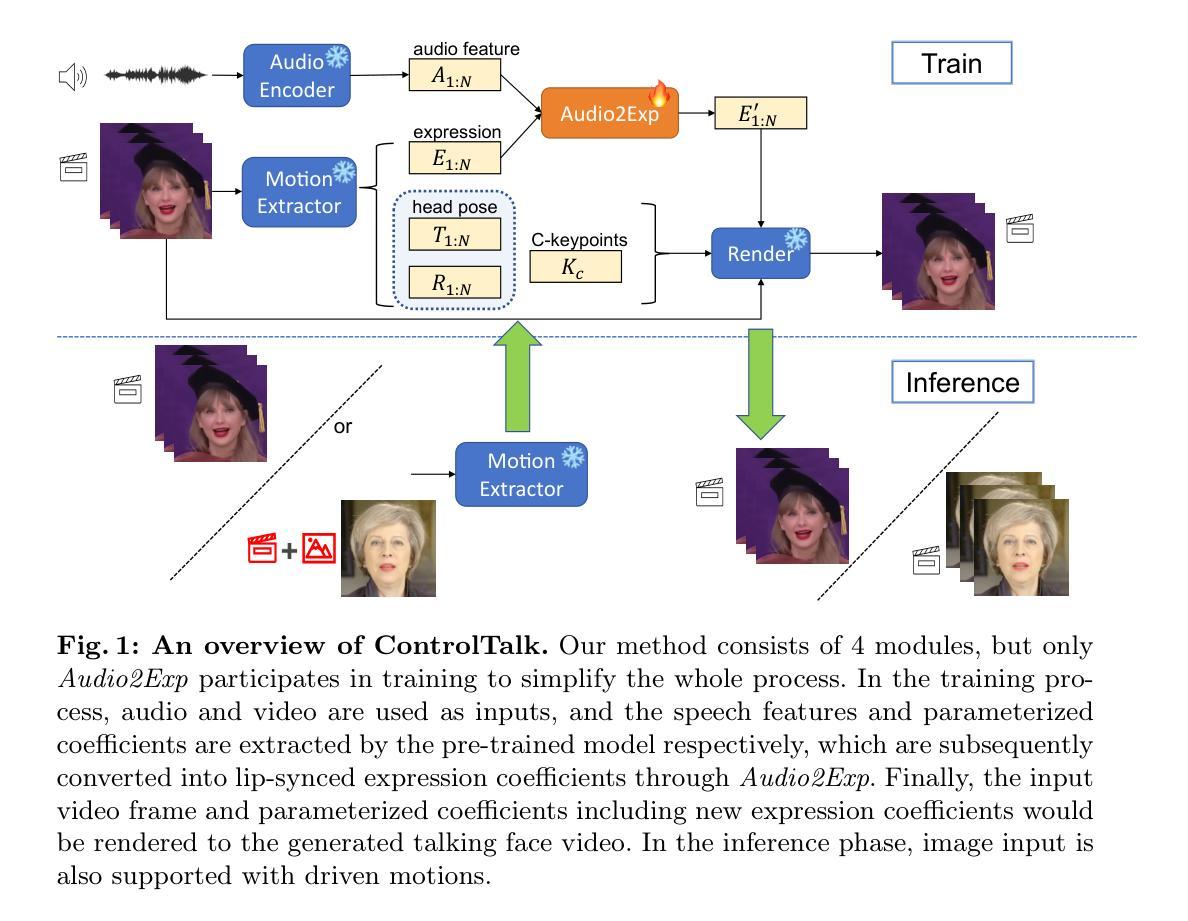
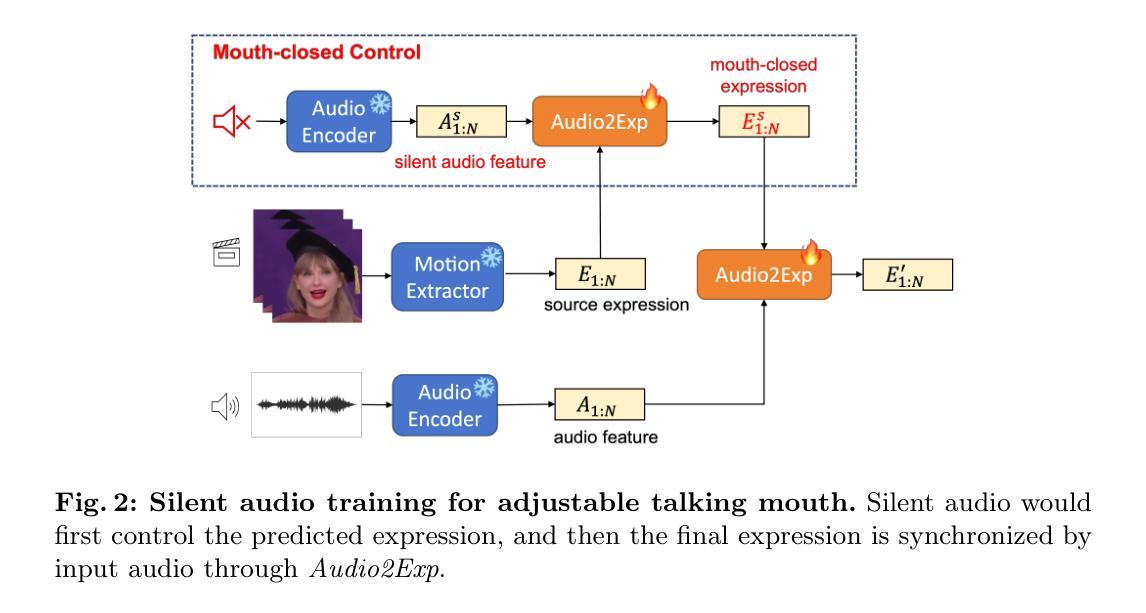
Controllable Talking Face Generation by Implicit Facial Keypoints Editing
Authors:Dong Zhao, Jiaying Shi, Wenjun Li, Shudong Wang, Shenghui Xu, Zhaoming Pan
Audio-driven talking face generation has garnered significant interest within the domain of digital human research. Existing methods are encumbered by intricate model architectures that are intricately dependent on each other, complicating the process of re-editing image or video inputs. In this work, we present ControlTalk, a talking face generation method to control face expression deformation based on driven audio, which can construct the head pose and facial expression including lip motion for both single image or sequential video inputs in a unified manner. By utilizing a pre-trained video synthesis renderer and proposing the lightweight adaptation, ControlTalk achieves precise and naturalistic lip synchronization while enabling quantitative control over mouth opening shape. Our experiments show that our method is superior to state-of-the-art performance on widely used benchmarks, including HDTF and MEAD. The parameterized adaptation demonstrates remarkable generalization capabilities, effectively handling expression deformation across same-ID and cross-ID scenarios, and extending its utility to out-of-domain portraits, regardless of languages. Code is available at https://github.com/NetEase-Media/ControlTalk.
音频驱动的说话人脸生成技术在数字人类研究领域引起了极大的兴趣。现有方法受到复杂模型架构的束缚,这些架构彼此之间有着错综复杂的依赖关系,从而加剧了重新编辑图像或视频输入的过程的难度。在这项工作中,我们提出了ControlTalk,这是一种基于驱动音频的控制面部表情变形的方法,可以统一地为单张图像或连续视频输入构建头部姿势和面部表情,包括嘴唇运动。通过利用预训练的视频合成渲染器并提出轻量级适配,ControlTalk实现了精确且自然的唇部同步,同时实现对嘴巴开口形状的定量控制。我们的实验表明,我们的方法在广泛使用的基准测试上优于最新技术,包括HDTF和MEAD。参数化适配表现出显著的泛化能力,有效处理同一身份和跨身份场景下的表情变形,并将其效用扩展到跨域肖像,不受语言限制。代码可通过https://github.com/NetEase-Media/ControlTalk获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
控制对话(ControlTalk)是一种基于音频驱动的面部表情控制方法,能够统一处理单张图片或连续视频输入的头部位姿和面部表情,包括唇动。该方法利用预训练的视频合成渲染器,并提出轻量级适配方案,实现了精准自然的唇同步,同时实现对开口形状的量化控制。实验表明,ControlTalk在HDTF和MEAD等常用基准测试上的表现优于当前技术水平,参数化适配展现出卓越泛化能力,能够处理同一身份和不同身份的面部表情变形,并扩展应用于跨领域肖像,不受语言限制。
Key Takeaways
- ControlTalk是一种基于音频驱动的面部表情控制方法,用于生成对话时的面部动画。
- 该方法可以处理单张图片或连续视频输入,统一进行头部姿态和面部表情的生成。
- 利用预训练的视频合成渲染器,实现精准自然的唇同步。
- 通过轻量级适配方案,ControlTalk实现了对开口形状的量化控制。
- 实验表明,ControlTalk在多个基准测试上的表现优于现有技术。
- 方法的参数化适配展现出强大的泛化能力,能够处理不同场景的面部表情变形。
点此查看论文截图

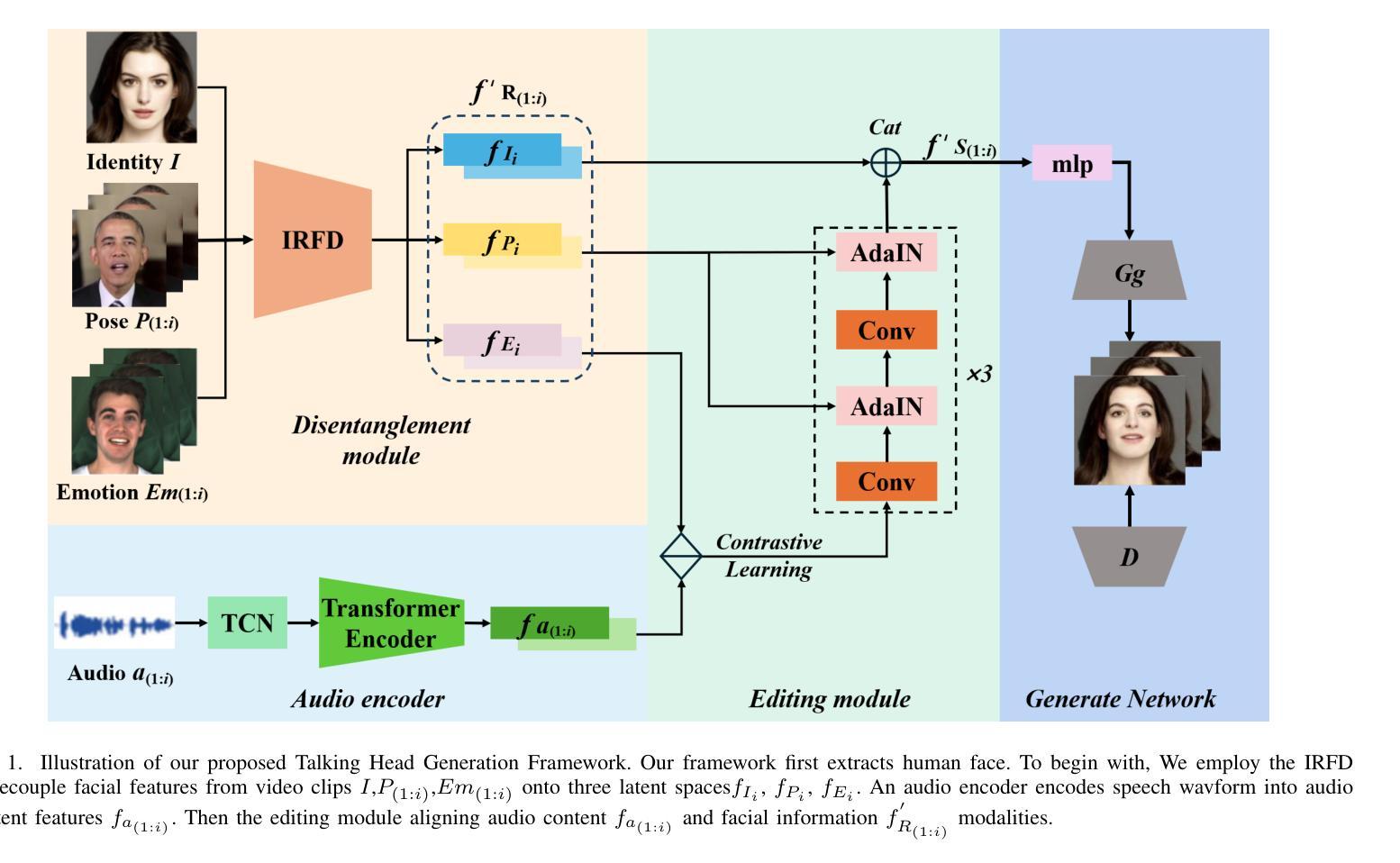
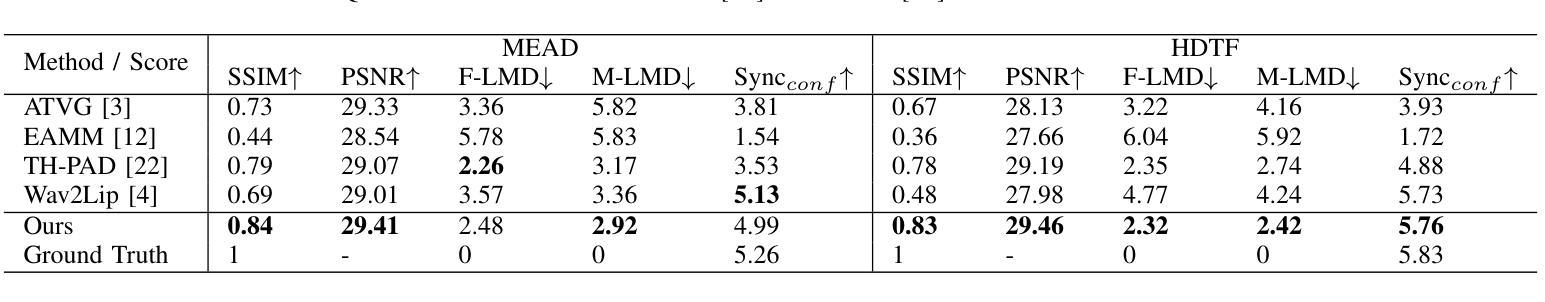
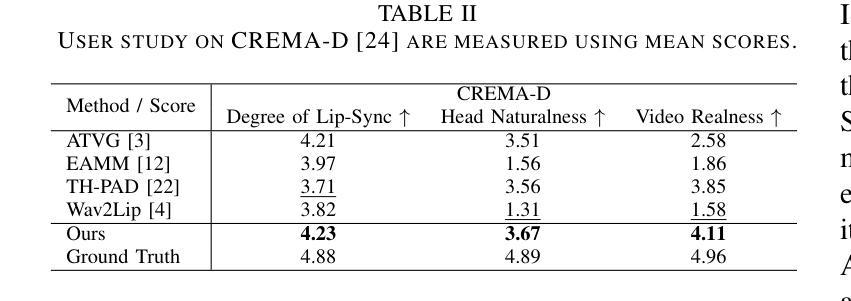
SPEAK: Speech-Driven Pose and Emotion-Adjustable Talking Head Generation
Authors:Changpeng Cai, Guinan Guo, Jiao Li, Junhao Su, Fei Shen, Chenghao He, Jing Xiao, Yuanxu Chen, Lei Dai, Feiyu Zhu
Most earlier researches on talking face generation have focused on the synchronization of lip motion and speech content. However, head pose and facial emotions are equally important characteristics of natural faces. While audio-driven talking face generation has seen notable advancements, existing methods either overlook facial emotions or are limited to specific individuals and cannot be applied to arbitrary subjects. In this paper, we propose a novel one-shot Talking Head Generation framework (SPEAK) that distinguishes itself from the general Talking Face Generation by enabling emotional and postural control. Specifically, we introduce Inter-Reconstructed Feature Disentanglement (IRFD) module to decouple facial features into three latent spaces. Then we design a face editing module that modifies speech content and facial latent codes into a single latent space. Subsequently, we present a novel generator that employs modified latent codes derived from the editing module to regulate emotional expression, head poses, and speech content in synthesizing facial animations. Extensive trials demonstrate that our method ensures lip synchronization with the audio while enabling decoupled control of facial features, it can generate realistic talking head with coordinated lip motions, authentic facial emotions, and smooth head movements. The demo video is available: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/SPEAK-8A22
早期关于说话人脸生成的研究大多聚焦于唇部运动与语音内容的同步。然而,头部姿态和面部情绪同样是自然人脸的重要特征。尽管音频驱动的说话人脸生成技术已经取得了显著的进步,但现有方法要么忽视面部情绪,要么仅限于特定个体,无法应用于任意主体。在本文中,我们提出了一种新型的一次性说话人头生成框架(SPEAK),它与一般的说话脸生成相区别,能够实现情绪与姿态控制。具体来说,我们引入了重建特征解耦(IRFD)模块,将面部特征解耦为三个潜在空间。然后,我们设计了一个面部编辑模块,该模块能够修改语音内容和面部潜在代码,将其合并为一个单一潜在空间。接着,我们提出了一种新型生成器,该生成器采用编辑模块生成的修改后的潜在代码,在合成面部动画时调控情绪表达、头部姿态和语音内容。大量试验表明,我们的方法能保证音频的唇部同步,同时实现面部特征的解耦控制,能够生成具有协调唇部运动、真实面部情绪和流畅头部动作的现实感说话人头。演示视频链接:https://anonymous.4open.science/r/SPEAK-8A22。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为SPEAK的新型一次谈话头生成框架,该框架通过引入IRFD模块将面部特征解耦为三个潜在空间,并设计了一个面部编辑模块来修改语音内容和面部潜在代码。通过采用修改后的潜在代码,该框架能够控制情感表达、头部姿势和语音内容,从而合成具有协调的唇部运动、真实的面部表情和流畅的头部动作的谈话头部动画。
Key Takeaways
- 早期谈话面部生成研究主要关注唇部运动和语音内容的同步。
- 头部姿势和面部情感是自然面部同样重要的特征。
- 当前音频驱动谈话面部生成方法要么忽略面部情感,要么仅限于特定个体,不能应用于任意主体。
- 本文提出了一种新型的一次谈话头生成框架(SPEAK),能够控制情感和姿势。
5.SPEAK框架通过IRFD模块将面部特征解耦为三个潜在空间,并设计了一个面部编辑模块来修改语音和面部潜在代码。 - 通过采用修改后的潜在代码,SPEAK框架可以合成具有协调的唇部运动、真实的面部表情和流畅的头部动作的谈话头部动画。
点此查看论文截图


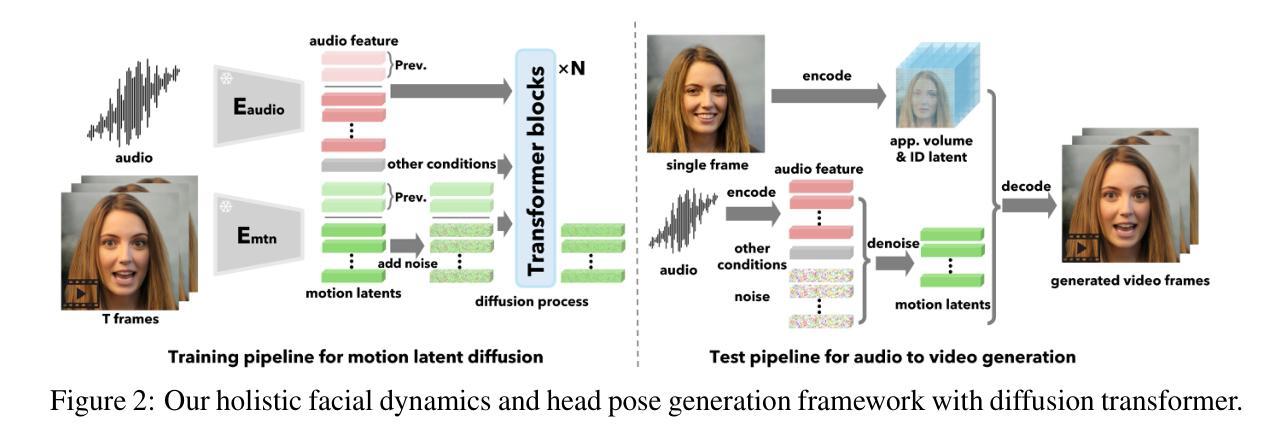
VASA-1: Lifelike Audio-Driven Talking Faces Generated in Real Time
Authors:Sicheng Xu, Guojun Chen, Yu-Xiao Guo, Jiaolong Yang, Chong Li, Zhenyu Zang, Yizhong Zhang, Xin Tong, Baining Guo
We introduce VASA, a framework for generating lifelike talking faces with appealing visual affective skills (VAS) given a single static image and a speech audio clip. Our premiere model, VASA-1, is capable of not only generating lip movements that are exquisitely synchronized with the audio, but also producing a large spectrum of facial nuances and natural head motions that contribute to the perception of authenticity and liveliness. The core innovations include a holistic facial dynamics and head movement generation model that works in a face latent space, and the development of such an expressive and disentangled face latent space using videos. Through extensive experiments including evaluation on a set of new metrics, we show that our method significantly outperforms previous methods along various dimensions comprehensively. Our method not only delivers high video quality with realistic facial and head dynamics but also supports the online generation of 512x512 videos at up to 40 FPS with negligible starting latency. It paves the way for real-time engagements with lifelike avatars that emulate human conversational behaviors.
我们介绍了VASA框架,该框架能够在给定的单张静态图像和语音音频片段上生成具有吸引力的视觉情感技能(VAS)的逼真谈话面孔。我们的旗舰型号VASA-1不仅能够生成与音频精细同步的嘴唇运动,还能产生一系列面部细微差别和自然头部运动,这些都有助于感知真实性和生动性。核心创新包括在面部潜在空间中工作的整体面部动态和头部运动生成模型,以及使用视频开发如此表达性和脱离的面部潜在空间。通过大量实验,包括在新指标集上的评估,我们证明我们的方法在各个方面都显著优于以前的方法。我们的方法不仅提供高质量的视频,具有逼真的面部和头部动态,还支持在线生成512x512分辨率的视频,帧率高达40 FPS,启动延迟可以忽略不计。这为与模拟人类对话行为的逼真化身进行实时交互铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024 (Oral) Camera ready. Project webpage: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/project/vasa-1/
摘要
VASA框架能够利用单张静态图像和语音音频片段生成具有逼真情感表达能力的说话面孔。其核心模型VASA-1不仅能够精准同步音频生成唇动,还能生成多种面部表情和自然的头部动作,增强真实感和生动性。主要创新包括面部动态和头部动作的整体生成模型,该模型在面部潜在空间内运作,以及通过视频开发如此表达和脱离的面部潜在空间。实验证明,沿多个维度全面超越现有方法。此方法不仅提供高质量的视频,具有逼真的面部和头部动态,还支持在线生成512x512分辨率的视频,帧率高达每秒40帧,几乎无初始延迟。这为实时与模拟人类对话行为的逼真化身互动开辟了道路。
关键见解
- VASA是一个能够生成逼真的说话头模型的框架,使用静态图像和语音音频片段生成具有吸引力的视觉情感技能(VAS)。
- VASA-1模型能精准同步音频生成唇动,生成多种面部表情和自然的头部动作,增强了真实感和生动性。
- 框架的主要创新包括整体面部动态和头部动作生成模型在面部潜在空间内的工作方式。
- 通过视频开发了一种表达和脱离的面部潜在空间。
- 实验证明,VASA方法在各种维度上显著优于以前的方法。
- 该方法不仅提供高质量的视频,具有逼真的面部和头部动态,还支持在线生成高分辨率视频,帧率高达每秒40帧,延迟小。
点此查看论文截图


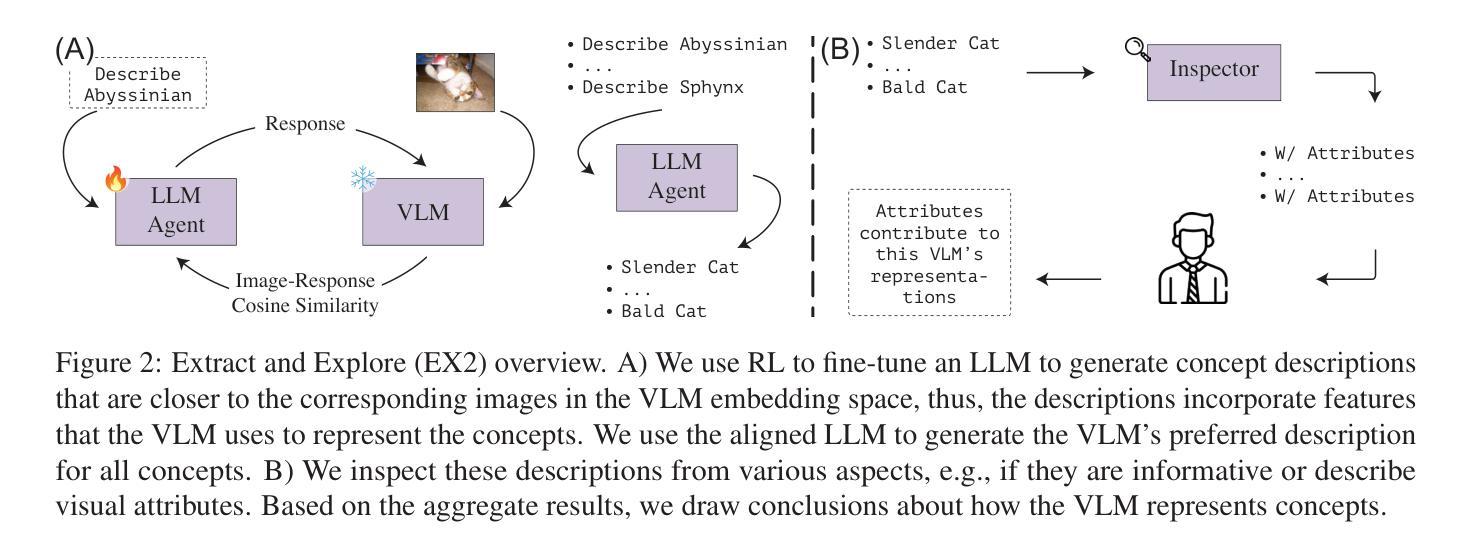
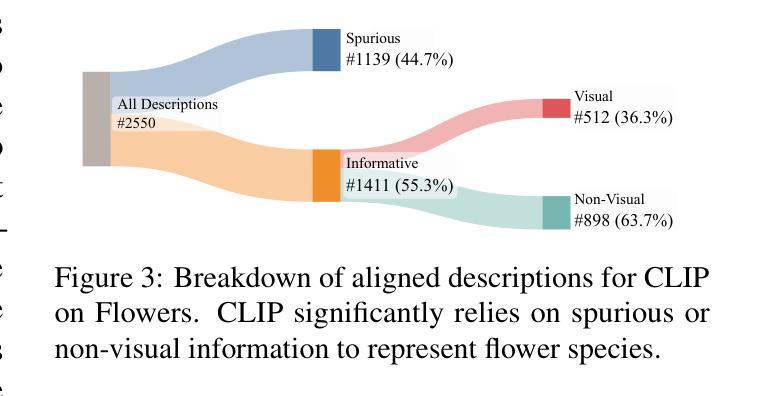
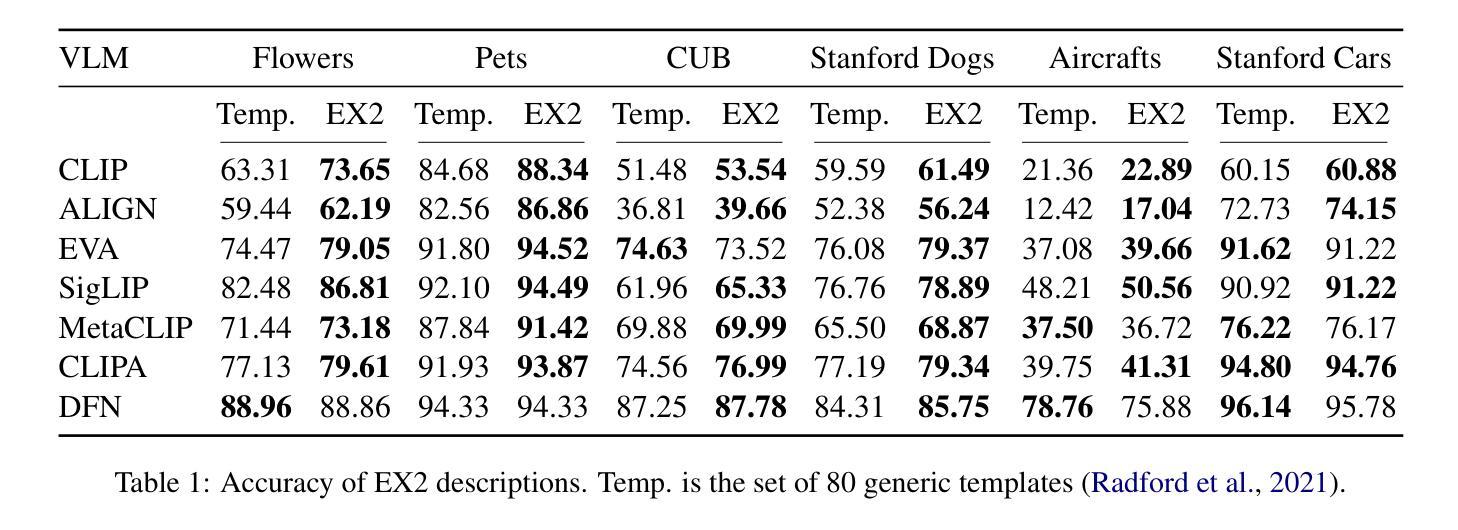
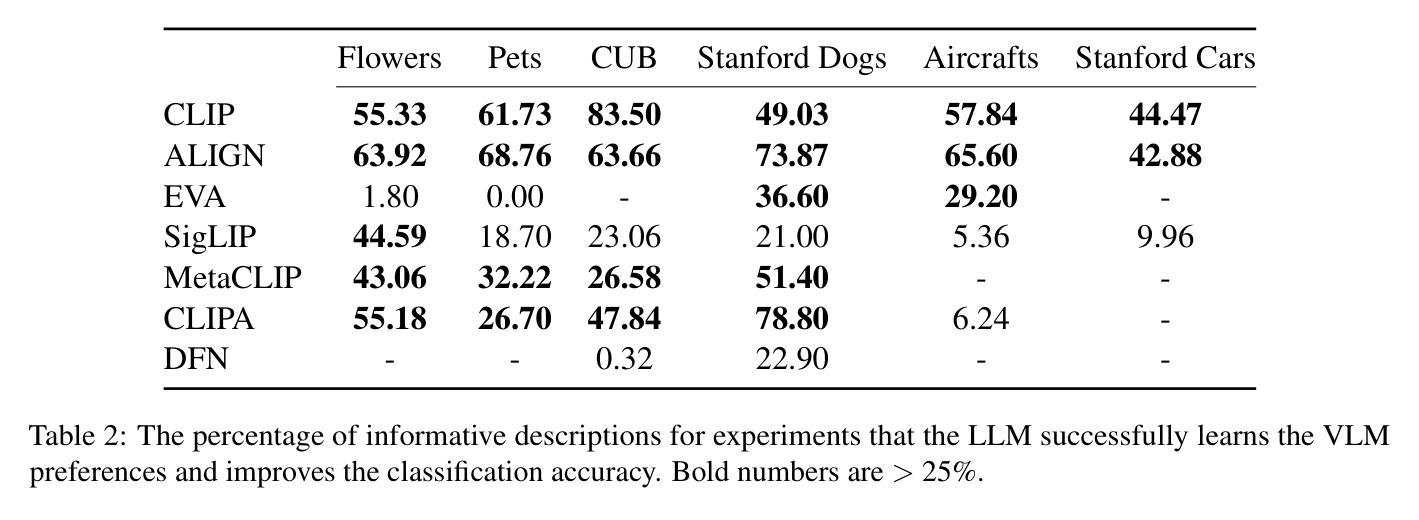
If CLIP Could Talk: Understanding Vision-Language Model Representations Through Their Preferred Concept Descriptions
Authors:Reza Esfandiarpoor, Cristina Menghini, Stephen H. Bach
Recent works often assume that Vision-Language Model (VLM) representations are based on visual attributes like shape. However, it is unclear to what extent VLMs prioritize this information to represent concepts. We propose Extract and Explore (EX2), a novel approach to characterize textual features that are important for VLMs. EX2 uses reinforcement learning to align a large language model with VLM preferences and generates descriptions that incorporate features that are important for the VLM. Then, we inspect the descriptions to identify features that contribute to VLM representations. Using EX2, we find that spurious descriptions have a major role in VLM representations despite providing no helpful information, e.g., Click to enlarge photo of CONCEPT. More importantly, among informative descriptions, VLMs rely significantly on non-visual attributes like habitat (e.g., North America) to represent visual concepts. Also, our analysis reveals that different VLMs prioritize different attributes in their representations. Overall, we show that VLMs do not simply match images to scene descriptions and that non-visual or even spurious descriptions significantly influence their representations.
最近的研究工作通常假设视觉语言模型(VLM)的表示是基于视觉属性,如形状。然而,尚不清楚VLM在多大程度上优先利用这些信息来代表概念。我们提出了一种新的方法来表征对VLM重要的文本特征,称为“提取与探索”(EX2)。EX2使用强化学习将大型语言模型与VLM偏好对齐,生成融入对VLM重要的特征的描述。然后,我们检查这些描述以识别对VLM表示有贡献的特征。使用EX2,我们发现尽管没有提供任何有用信息,但误导性描述在VLM表示中起到了重要作用,例如,“点击放大概念的照片”。更重要的是,在有信息的描述中,VLM在很大程度上依赖于非视觉属性(例如栖息地(如北美))来表示视觉概念。此外,我们的分析还发现不同的VLM在其表示中优先考虑不同的属性。总体而言,我们证明了VLM并不只是简单地将图像与场景描述相匹配,非视觉甚至误导性的描述对其表示产生了重大影响。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF EMNLP 2024
Summary
本文探讨了视觉语言模型(VLM)在表示概念时如何优先处理视觉属性。通过提出一种名为EX2的新方法,研究团队对VLM重视的文本特征进行了深入剖析。该方法结合了强化学习和语言模型技术,用于分析语言模型中VLM的偏好。分析结果显示,非视觉属性(如环境)在描述视觉概念方面起着重要作用,同时发现一些无关的描述也能影响VLM的解读。总之,本研究表明VLM不仅将图像与场景描述相对应,同时文本属性和概念也可能极大地影响其解释能力。简而言之,准确评估理解和分析使用复杂的自然语言辅助技术在多媒体分析中的应用非常关键。因为并非所有输入都包含直观相关的特征,有时VLM可能需要更复杂、非直接的推理才能形成精确的解释和表示。这一点提醒我们在实际应用中不能仅依赖简单的假设或未经验证的模式来理解或优化这些系统的行为。相反,我们需要通过更细致的研究和更全面的分析来确保这些系统的准确性。这将有助于开发更准确、更具鲁棒性的视觉语言模型,并为进一步改进人工智能技术在复杂场景中的感知和理解能力奠定基础。因此,我们需要更多地关注和研究自然语言在多媒体分析和视觉语言模型中的复杂性以及它在其中的作用机制。
Key Takeaways
点此查看论文截图

FT2TF: First-Person Statement Text-To-Talking Face Generation
Authors:Xingjian Diao, Ming Cheng, Wayner Barrios, SouYoung Jin
Talking face generation has gained immense popularity in the computer vision community, with various applications including AR, VR, teleconferencing, digital assistants, and avatars. Traditional methods are mainly audio-driven, which have to deal with the inevitable resource-intensive nature of audio storage and processing. To address such a challenge, we propose FT2TF - First-Person Statement Text-To-Talking Face Generation, a novel one-stage end-to-end pipeline for talking face generation driven by first-person statement text. Different from previous work, our model only leverages visual and textual information without any other sources (e.g., audio/landmark/pose) during inference. Extensive experiments are conducted on LRS2 and LRS3 datasets, and results on multi-dimensional evaluation metrics are reported. Both quantitative and qualitative results showcase that FT2TF outperforms existing relevant methods and reaches the state-of-the-art. This achievement highlights our model’s capability to bridge first-person statements and dynamic face generation, providing insightful guidance for future work.
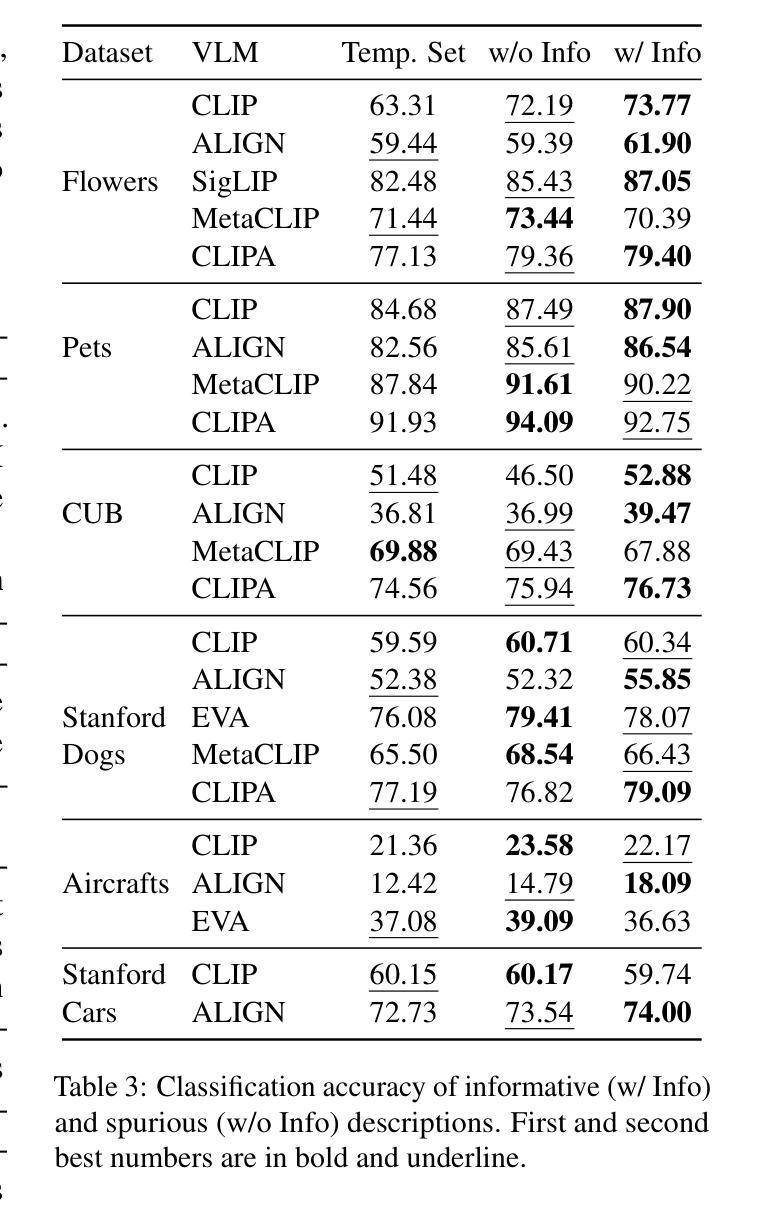
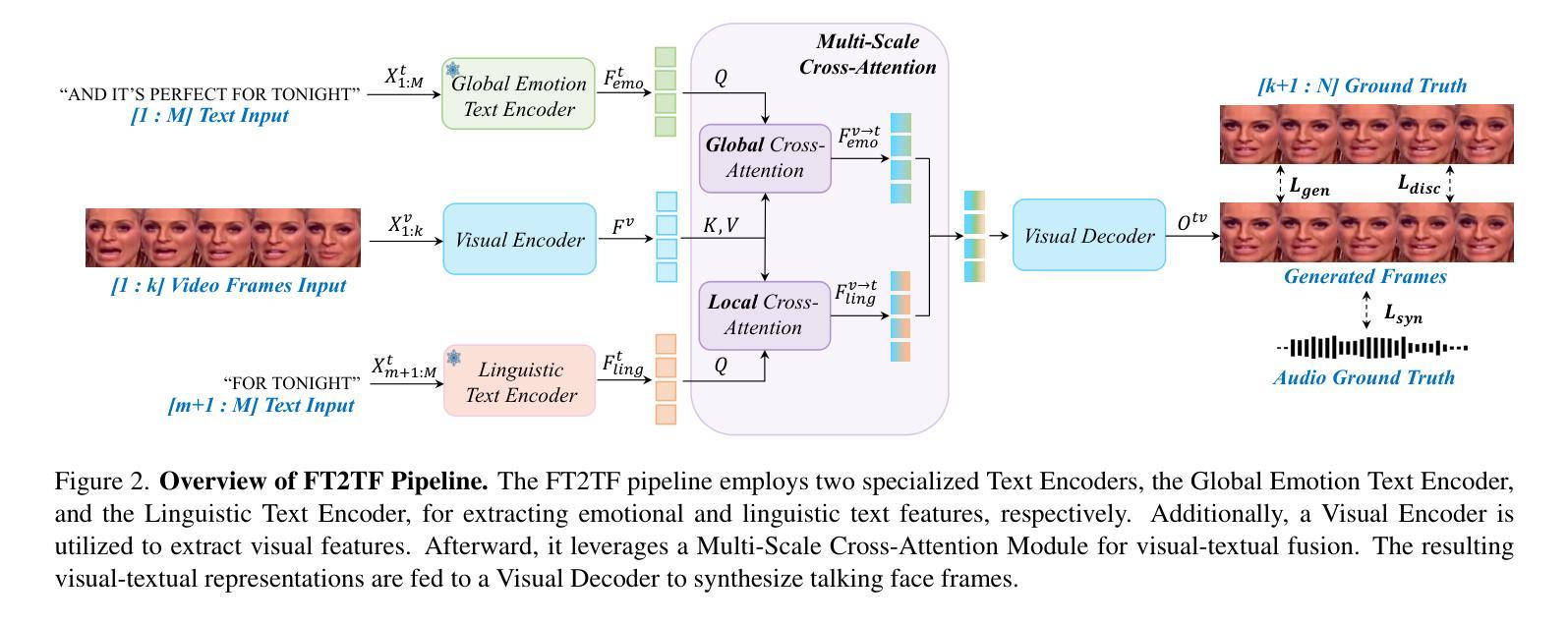
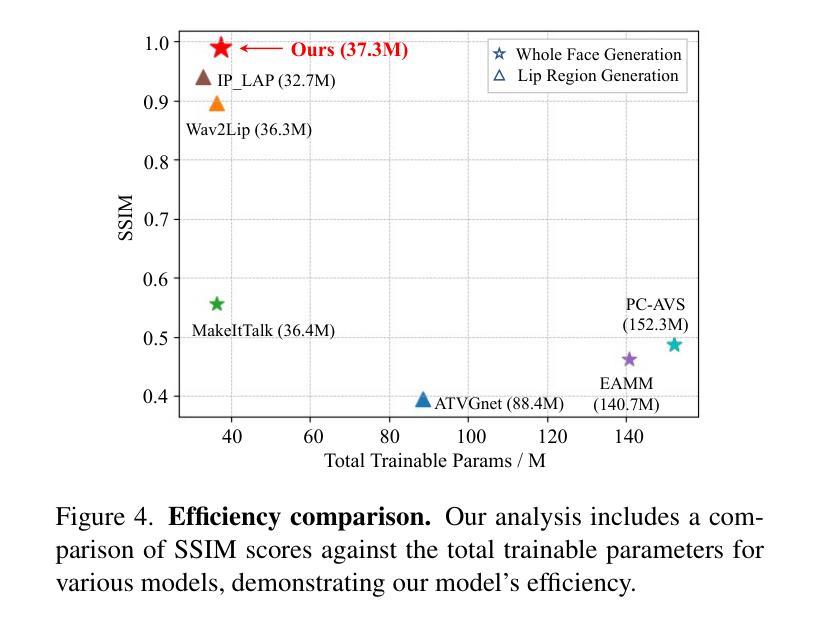
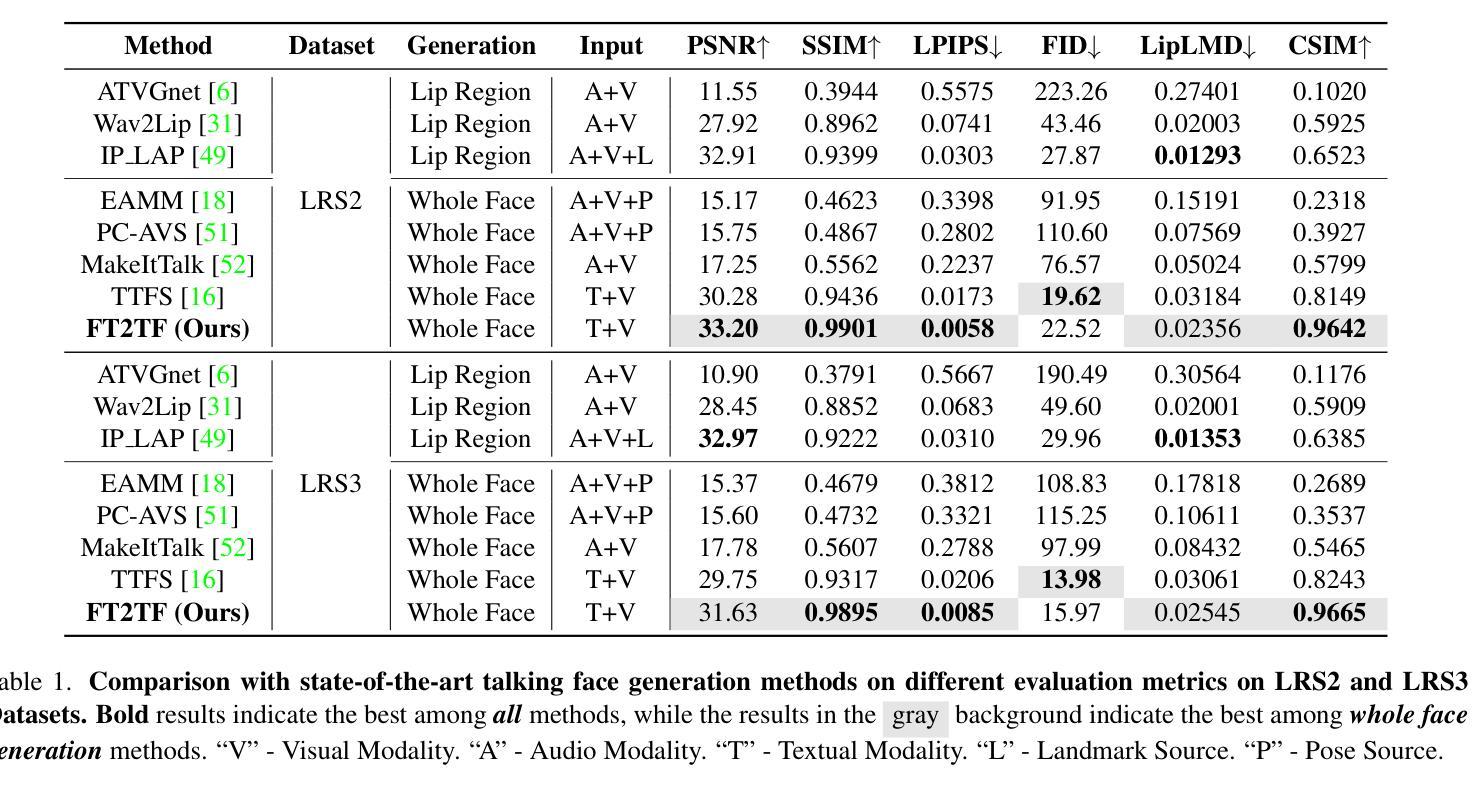
面部生成技术已在计算机视觉领域获得了极大的普及,并广泛应用于AR、VR、视频会议、数字助理和化身等各种应用场景。传统的方法主要是音频驱动的,必须应对音频存储和处理资源密集型的不可避免的性质。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了FT2TF——基于第一人称叙述文本的说话面部生成技术。这是一种新型的、端到端的一站式流程,用于根据第一人称叙述文本生成说话面部。不同于以前的工作,我们的模型在推理过程中仅利用视觉和文本信息,不依赖任何其他来源(如音频/地标/姿势)。我们在LRS2和LRS3数据集上进行了大量实验,并报告了多维评价指标的结果。定量和定性结果均表明,FT2TF优于现有的相关方法,达到了最新水平。这一成就凸显了我们的模型将第一人称叙述与动态面部生成相结合的能力,为未来工作提供了有益的指导。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at WACV 2025
Summary
基于文本的第一人称叙述进行说话人脸生成的技术在计算机视觉领域已广受欢迎,特别是在增强现实、虚拟现实、远程会议、数字助理和化身等应用中。传统方法主要依赖音频驱动,面临音频存储和处理的资源密集型挑战。为解决这一问题,我们提出了FT2TF——基于第一人称叙述文本到说话人脸生成的一站式端到端管道。不同于以前的工作,我们的模型在推理过程中仅利用视觉和文本信息,无需其他来源(如音频/地标/姿态)。在LRS2和LRS3数据集上进行了大量实验,并在多维评价指标上报告了结果。定量和定性结果均表明,FT2TF优于现有相关方法并达到了最新水平,这突显了我们模型将第一人称叙述与动态人脸生成相结合的能力,为未来工作提供了有益的指导。
Key Takeaways
- 说话人脸生成技术在计算机视觉领域受到广泛关注,并应用于AR、VR、远程会议等场景。
- 传统方法主要依赖音频驱动,存在资源密集型的挑战。
- FT2TF是一种新颖的一站式端到端管道,基于文本的第一人称叙述进行说话人脸生成。
- FT2TF模型在推理过程中仅利用视觉和文本信息。
- FT2TF在LRS2和LRS3数据集上进行了实验验证,表现出优异性能。
- FT2TF优于现有方法并达到最新水平,突显了模型的能力。
点此查看论文截图
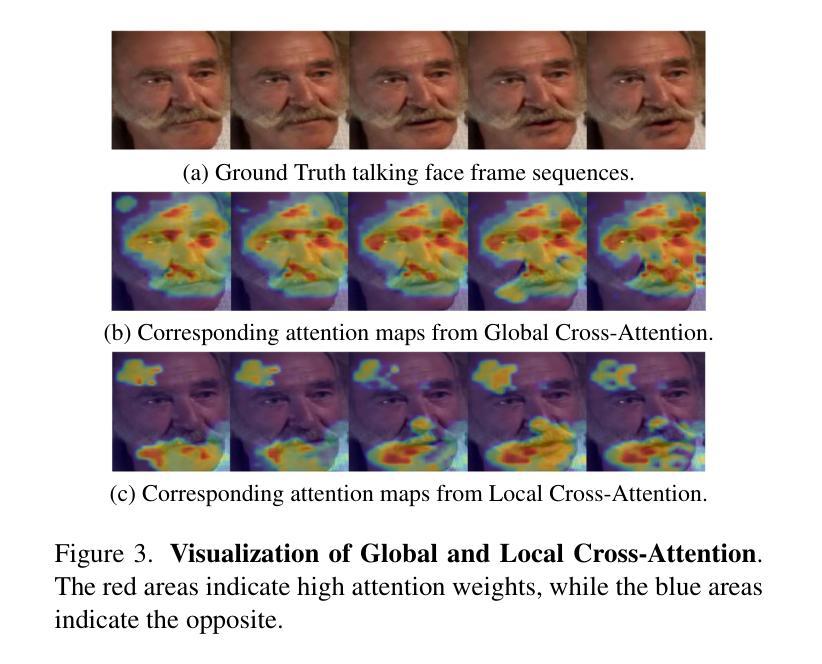


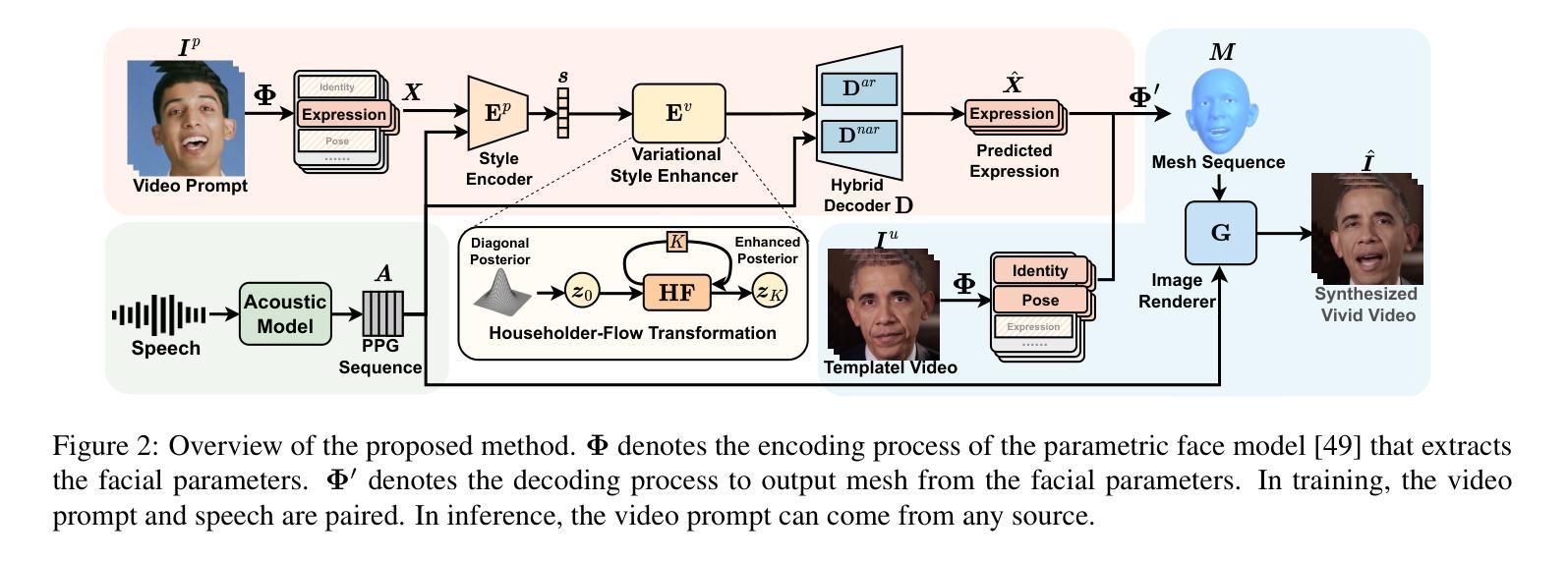
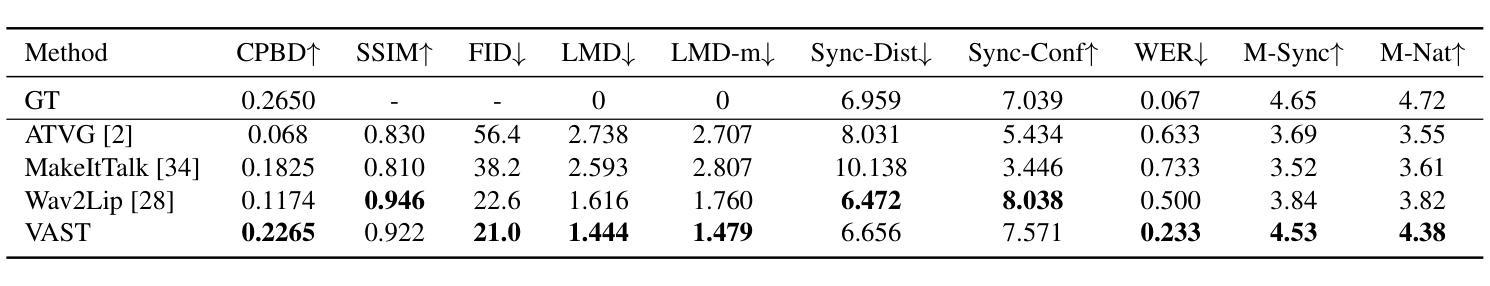
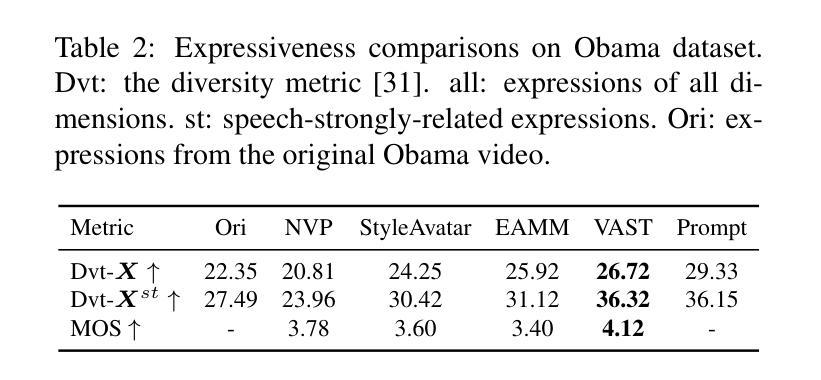
VAST: Vivify Your Talking Avatar via Zero-Shot Expressive Facial Style Transfer
Authors:Liyang Chen, Zhiyong Wu, Runnan Li, Weihong Bao, Jun Ling, Xu Tan, Sheng Zhao
Current talking face generation methods mainly focus on speech-lip synchronization. However, insufficient investigation on the facial talking style leads to a lifeless and monotonous avatar. Most previous works fail to imitate expressive styles from arbitrary video prompts and ensure the authenticity of the generated video. This paper proposes an unsupervised variational style transfer model (VAST) to vivify the neutral photo-realistic avatars. Our model consists of three key components: a style encoder that extracts facial style representations from the given video prompts; a hybrid facial expression decoder to model accurate speech-related movements; a variational style enhancer that enhances the style space to be highly expressive and meaningful. With our essential designs on facial style learning, our model is able to flexibly capture the expressive facial style from arbitrary video prompts and transfer it onto a personalized image renderer in a zero-shot manner. Experimental results demonstrate the proposed approach contributes to a more vivid talking avatar with higher authenticity and richer expressiveness.
当前的人脸说话生成方法主要关注语音与嘴唇的同步。然而,对面部说话风格的研究不足导致生成的虚拟角色缺乏生命力和单调。之前的大多数工作无法模仿来自任意视频提示的表达风格,也无法确保生成视频的真实性。本文提出了一种无监督的变风格转移模型(VAST),以赋予中性逼真的虚拟角色生命力。我们的模型由三个关键组件组成:一个风格编码器,用于从给定的视频提示中提取面部风格表示;一个混合面部表情解码器,以模拟准确的语音相关动作;一个变风格增强器,用于增强风格空间,使其具有高度表达力和意义。通过对面部风格学习的关键设计,我们的模型能够灵活地捕捉来自任意视频提示的表达性面部风格,并将其以零样本的方式转移到个性化图像渲染器上。实验结果表明,所提出的方法有助于创建一个更生动、更真实、更具表现力的说话虚拟角色。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICCV2023
Summary
:当前主流的面部生成技术主要关注语音与嘴唇的同步,但对面部说话风格的研究不足导致生成的虚拟形象缺乏生命力和多样性。本文提出了一种无监督的变风格转移模型(VAST),旨在使中性逼真的头像更加生动。该模型包括三个关键组件:从给定视频提示中提取面部风格表示的风格编码器;模拟精确语音相关动作的混合面部表情解码器;增强风格空间以实现高度表达和有意义的变风格增强器。通过对面部风格学习的关键设计,该模型能够灵活地捕捉任意视频提示中的表达性面部风格,并将其零样本方式转移到个性化图像渲染器上。实验结果表明,该方法有助于创建更生动、更真实、更具表现力的说话头像。
Key Takeaways
- 当前面部生成技术主要关注语音与嘴唇同步,忽视了面部说话风格的多样性。
- 提出的无监督变风格转移模型(VAST)旨在增强中性头像的生动性。
- 模型包括风格编码器、混合面部表情解码器和变风格增强器三个关键组件。
- 风格编码器从视频提示中提取面部风格表示。
- 混合面部表情解码器模拟语音相关的精确动作。
- 变风格增强器能够增强风格空间,使表达更加丰富多彩。
点此查看论文截图
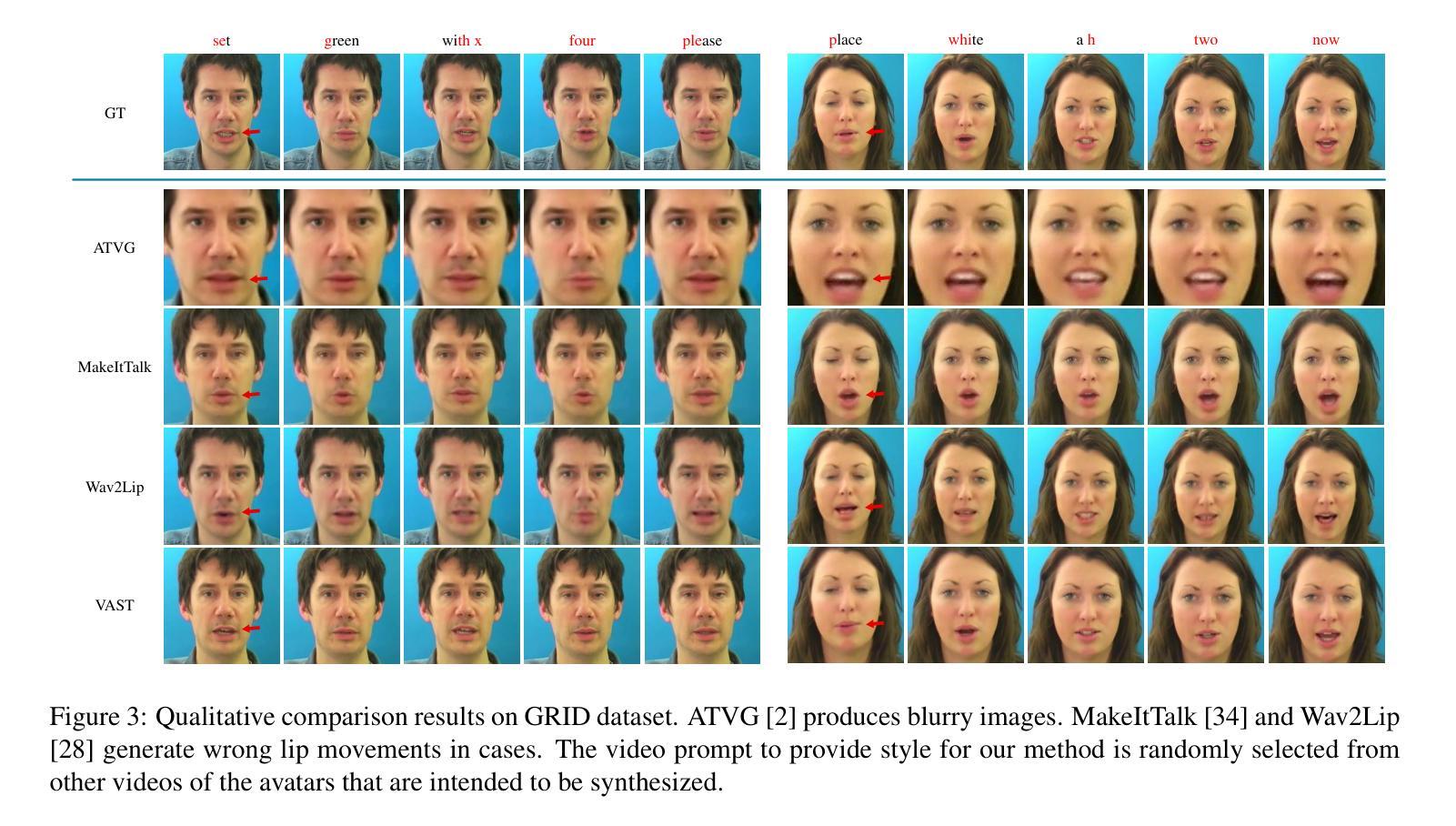
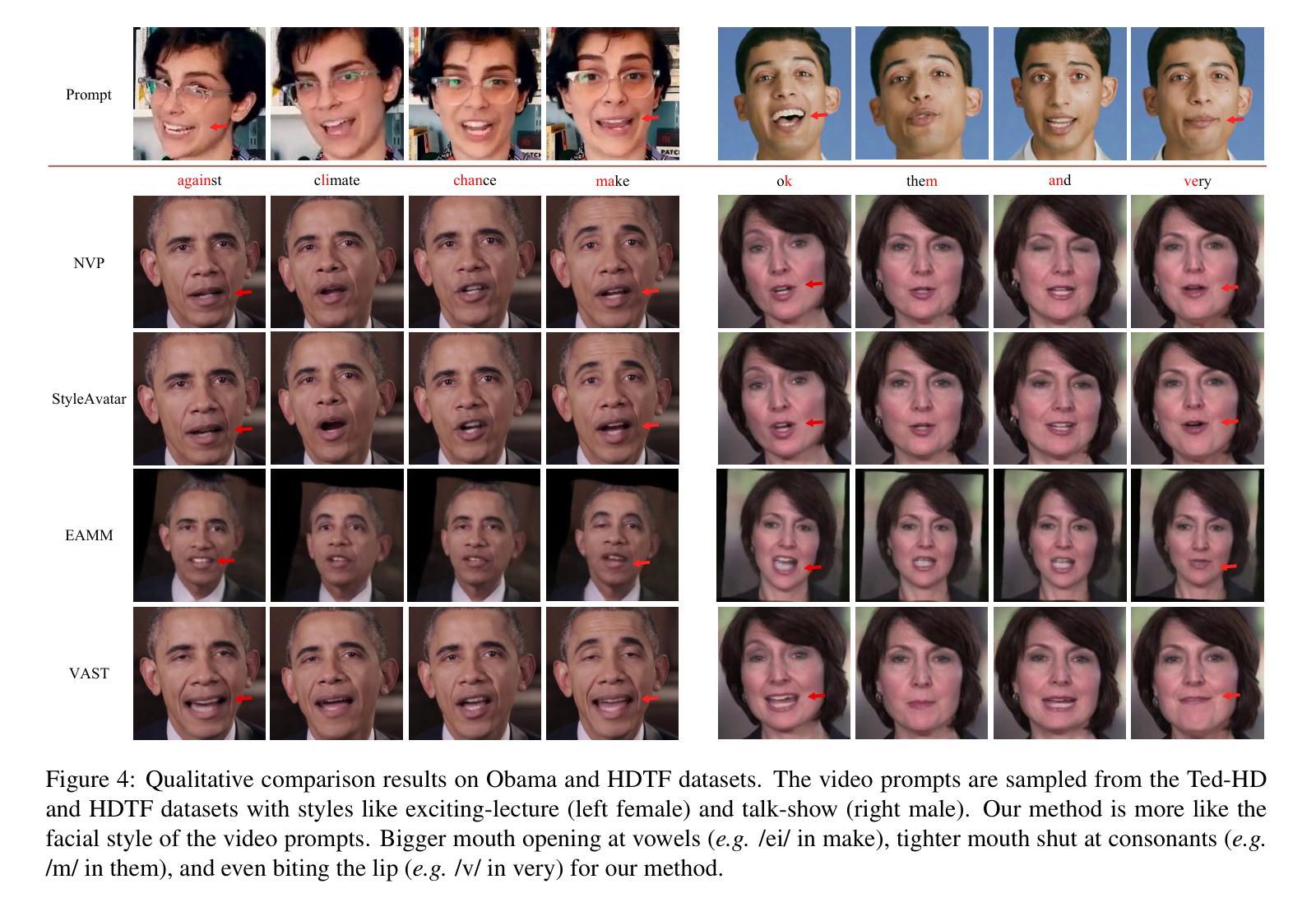



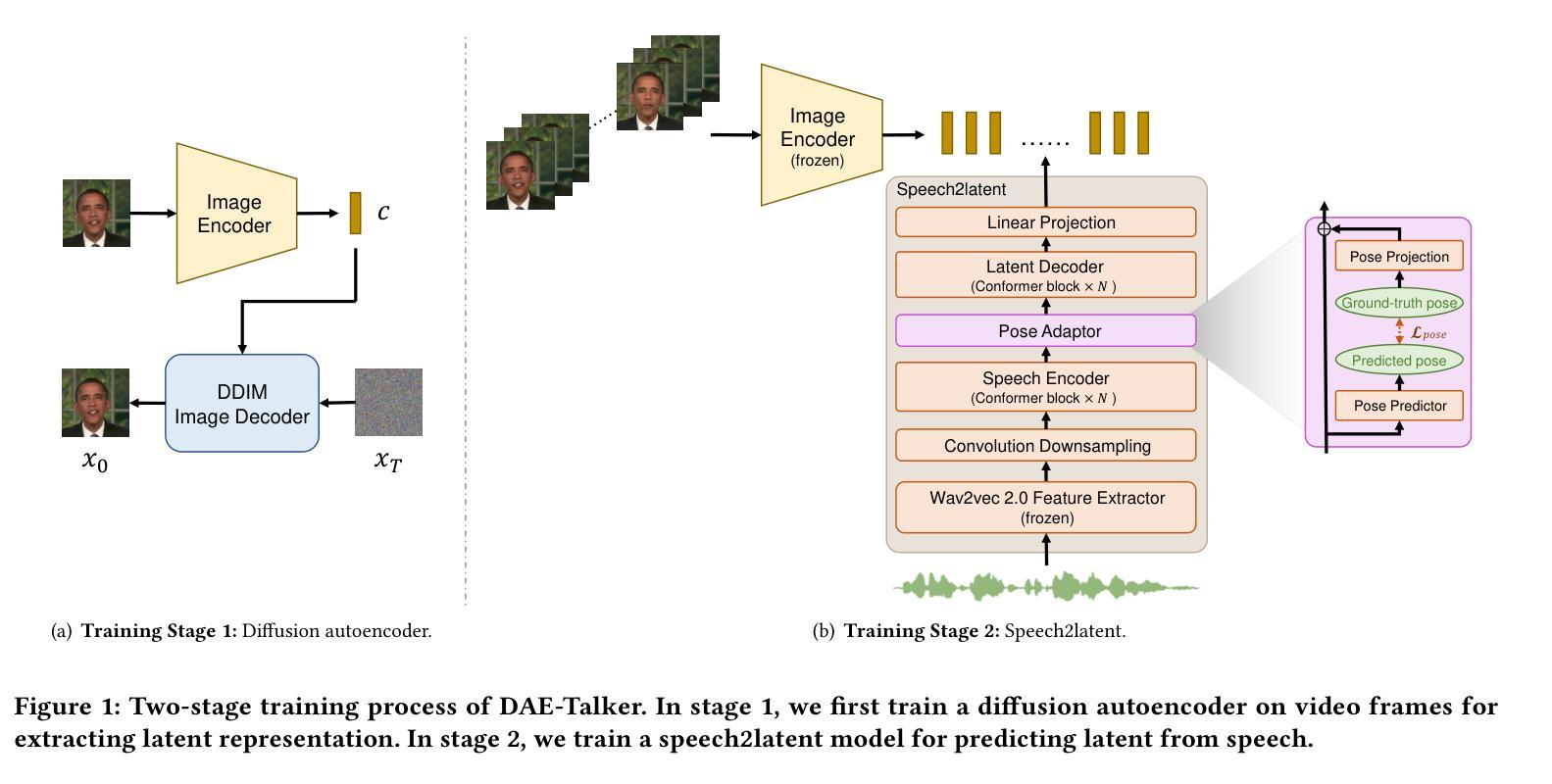
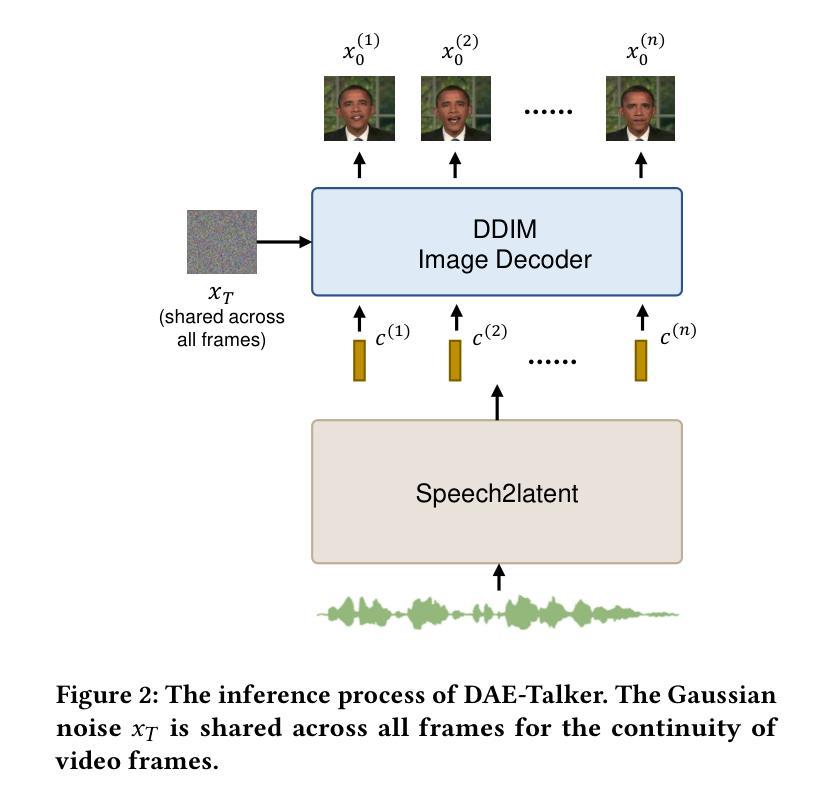
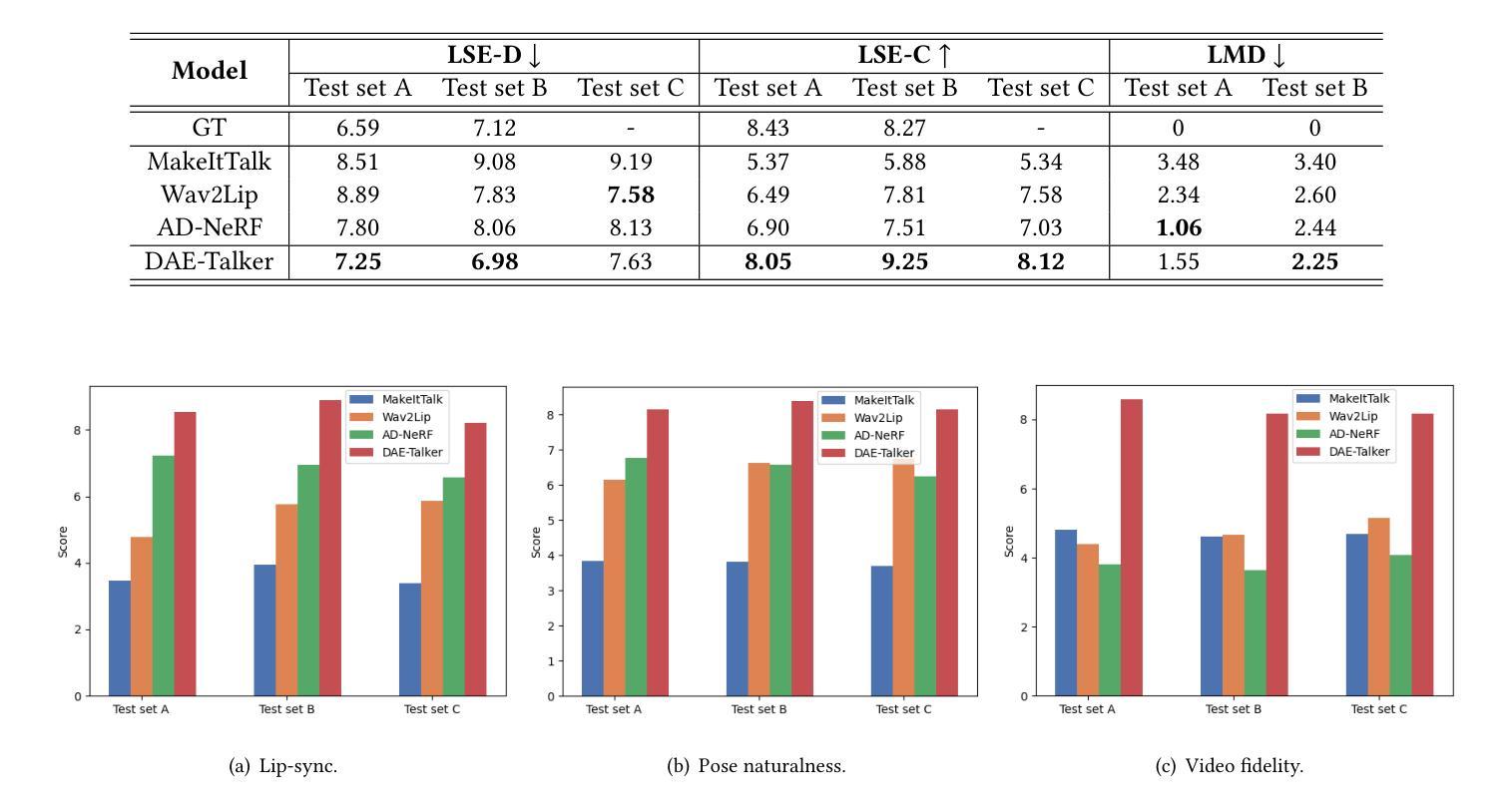
DAE-Talker: High Fidelity Speech-Driven Talking Face Generation with Diffusion Autoencoder
Authors:Chenpeng Du, Qi Chen, Tianyu He, Xu Tan, Xie Chen, Kai Yu, Sheng Zhao, Jiang Bian
While recent research has made significant progress in speech-driven talking face generation, the quality of the generated video still lags behind that of real recordings. One reason for this is the use of handcrafted intermediate representations like facial landmarks and 3DMM coefficients, which are designed based on human knowledge and are insufficient to precisely describe facial movements. Additionally, these methods require an external pretrained model for extracting these representations, whose performance sets an upper bound on talking face generation. To address these limitations, we propose a novel method called DAE-Talker that leverages data-driven latent representations obtained from a diffusion autoencoder (DAE). DAE contains an image encoder that encodes an image into a latent vector and a DDIM image decoder that reconstructs the image from it. We train our DAE on talking face video frames and then extract their latent representations as the training target for a Conformer-based speech2latent model. This allows DAE-Talker to synthesize full video frames and produce natural head movements that align with the content of speech, rather than relying on a predetermined head pose from a template video. We also introduce pose modelling in speech2latent for pose controllability. Additionally, we propose a novel method for generating continuous video frames with the DDIM image decoder trained on individual frames, eliminating the need for modelling the joint distribution of consecutive frames directly. Our experiments show that DAE-Talker outperforms existing popular methods in lip-sync, video fidelity, and pose naturalness. We also conduct ablation studies to analyze the effectiveness of the proposed techniques and demonstrate the pose controllability of DAE-Talker.
尽管最近的研究在语音驱动的头部分说生成方面取得了重大进展,但生成视频的质里仍然落后于真实录像。造成这一问题的其中一个原因是使用手工制作的中介表示,如面部标志和3DMM系数,这些表示是基于人类知识设计的,不足以精确描述面部动作。此外,这些方法需要外部预训练模型来提取这些表示,其性能为头部分说话生成设置了上限。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了一种名为DAE-Talker的新方法,它利用从扩散自编码器(DAE)获得的数据驱动潜在表示。DAE包含一个将图像编码为潜在向量的图像编码器和一个从该向量重建图像的DDIM图像解码器。我们在说话的面部视频帧上训练我们的DAE,然后提取其潜在表示作为基于Conformer的speech2latent模型的训练目标。这使得DAE-Talker能够合成完整的视频帧并产生与语音内容相符的自然头部动作,而不是依赖于模板视频的预设头部姿势。我们还为speech2latent引入了姿势建模以实现姿势可控性。此外,我们提出了一种用DDIM图像解码器对单独帧进行训练以生成连续视频帧的新方法,从而无需直接对连续帧的联合分布进行建模。我们的实验表明,在唇同步、视频保真度和姿势自然性方面,DAE-Talker优于现有的流行方法。我们还进行了剔除研究以分析所提出技术的有效性并展示DAE-Talker的姿势可控性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM Multimedia 2023
Summary
近期尽管在语音驱动谈话头生成方面取得显著进展,但生成视频的质量仍然落后于真实录音。为解决这个问题,提出了DAE-Talker方法,它利用扩散自编码器(DAE)获得数据驱动潜在表示,能合成完整视频帧并产生与语音内容对齐的自然头部运动。新方法提升了唇形同步、视频保真度和姿势自然度,并具备姿势控制能力。
Key Takeaways
- 语音驱动谈话头生成虽有所进展,但生成视频质量与真实录音相比仍有差距。
- 现有方法依赖手工设计的中间表示,如面部标志和3DMM系数,不足以精确描述面部运动。
- DAE-Talker使用扩散自编码器(DAE)获得潜在表示,改进了上述问题。
- DAE-Talker能合成完整视频帧,产生自然头部运动,与语音内容对齐。
- 引入姿势建模以增强语音生成视频的姿势控制能力。
- 新方法提升了唇形同步、视频保真度和姿势自然度,实验证明其性能优于现有流行方法。
点此查看论文截图
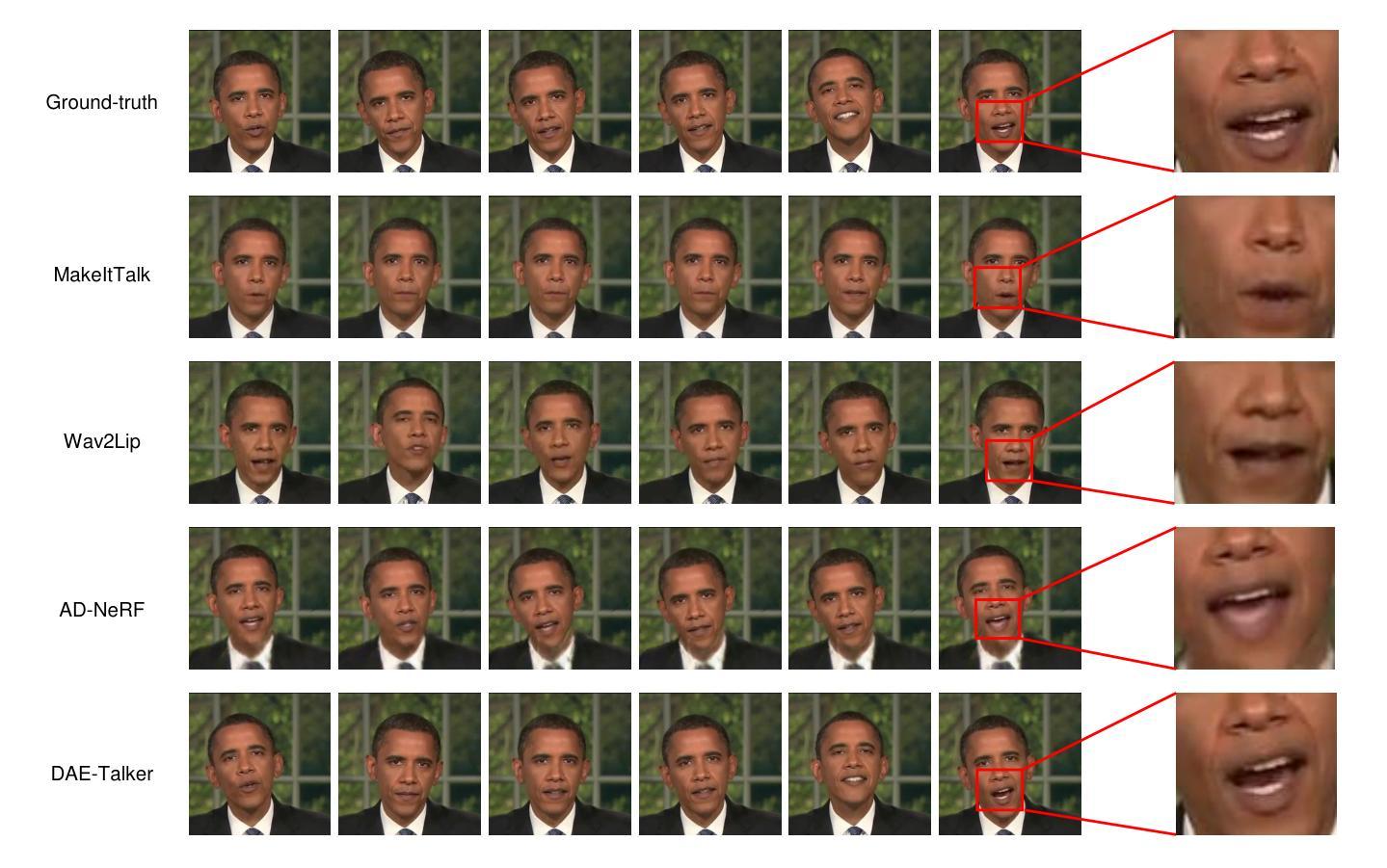


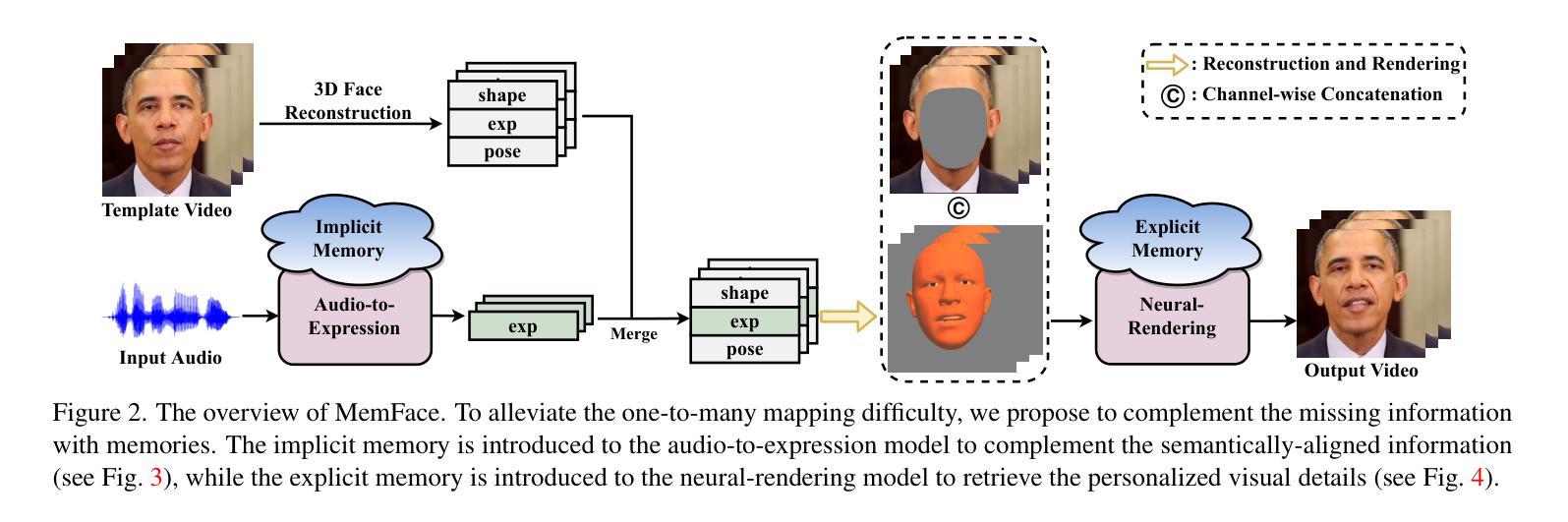
Memories are One-to-Many Mapping Alleviators in Talking Face Generation
Authors:Anni Tang, Tianyu He, Xu Tan, Jun Ling, Li Song
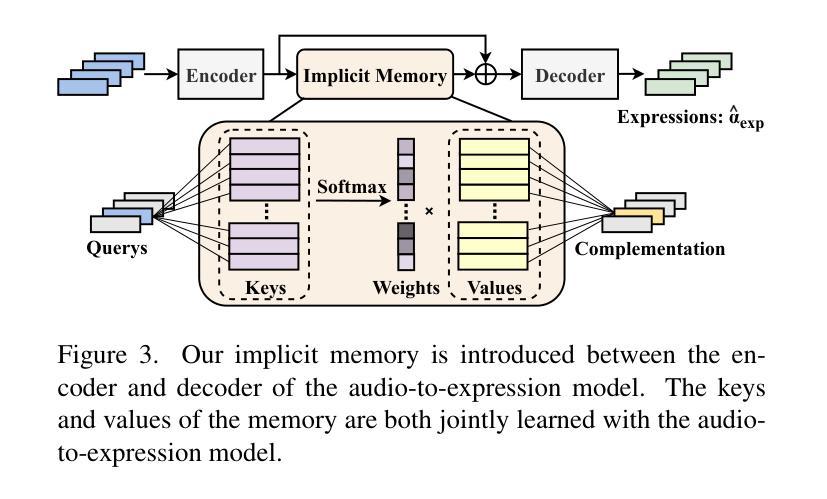
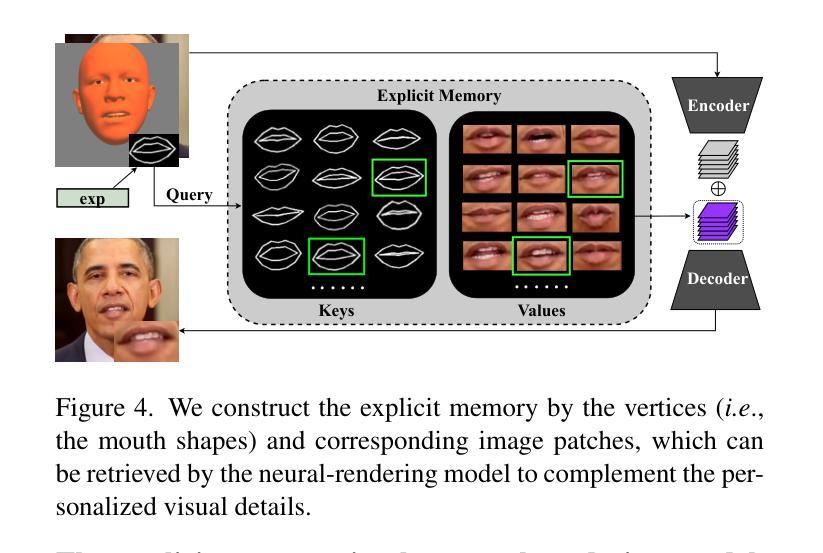
Talking face generation aims at generating photo-realistic video portraits of a target person driven by input audio. Due to its nature of one-to-many mapping from the input audio to the output video (e.g., one speech content may have multiple feasible visual appearances), learning a deterministic mapping like previous works brings ambiguity during training, and thus causes inferior visual results. Although this one-to-many mapping could be alleviated in part by a two-stage framework (i.e., an audio-to-expression model followed by a neural-rendering model), it is still insufficient since the prediction is produced without enough information (e.g., emotions, wrinkles, etc.). In this paper, we propose MemFace to complement the missing information with an implicit memory and an explicit memory that follow the sense of the two stages respectively. More specifically, the implicit memory is employed in the audio-to-expression model to capture high-level semantics in the audio-expression shared space, while the explicit memory is employed in the neural-rendering model to help synthesize pixel-level details. Our experimental results show that our proposed MemFace surpasses all the state-of-the-art results across multiple scenarios consistently and significantly.
面部谈话生成的目标是根据输入音频生成目标人物的照片级真实视频肖像。由于其从输入音频到输出视频的一对多映射特性(例如,一种语音内容可能具有多种可行的视觉外观),像之前的工作那样学习确定性映射会在训练过程中带来模糊性,从而导致视觉结果较差。虽然这种一对多映射可以通过两阶段框架部分缓解(即音频到表情模型,然后是神经渲染模型),但由于预测结果缺乏足够的信息(例如情绪、皱纹等),因此仍然不足。在本文中,我们提出MemFace,通过隐性记忆和显性记忆来补充缺失的信息,这两阶段分别遵循各自的意义。更具体地说,隐性记忆被应用于音频到表情模型,以捕获音频表情共享空间中的高级语义,而显性记忆则被应用于神经渲染模型,以帮助合成像素级细节。我们的实验结果表明,我们提出的MemFace在多场景下一贯且显著地超越了所有最新技术成果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (2024). Project page: see https://memoryface.github.io
Summary
本文介绍了面向目标人物的语音驱动的视频肖像生成技术。由于音频输入与视频输出之间的一到多映射关系,使得学习确定性映射存在训练过程中的歧义性,导致视觉结果质量不佳。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一种名为MemFace的两阶段框架,通过隐式记忆和显式记忆来补充缺失信息。隐式记忆用于捕捉音频与表情共享空间中的高级语义信息,显式记忆则用于合成像素级细节。实验结果表明,MemFace在多个场景下均超越现有技术,表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- 面向目标人物的语音驱动的视频肖像生成技术旨在生成真实感强的视频肖像。
- 音频输入与视频输出之间存在一到多映射关系,导致训练过程中的歧义性。
- MemFace采用两阶段框架来解决这一问题,包括音频到表情模型和神经渲染模型。
- 隐式记忆用于捕捉音频与表情共享空间中的高级语义信息。
- 显式记忆用于合成像素级细节,提高视频质量。
- MemFace在多个场景下均超越现有技术。
点此查看论文截图