⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-12 更新
Utilizing Multi-step Loss for Single Image Reflection Removal
Authors:Abdelrahman Elnenaey, Marwan Torki
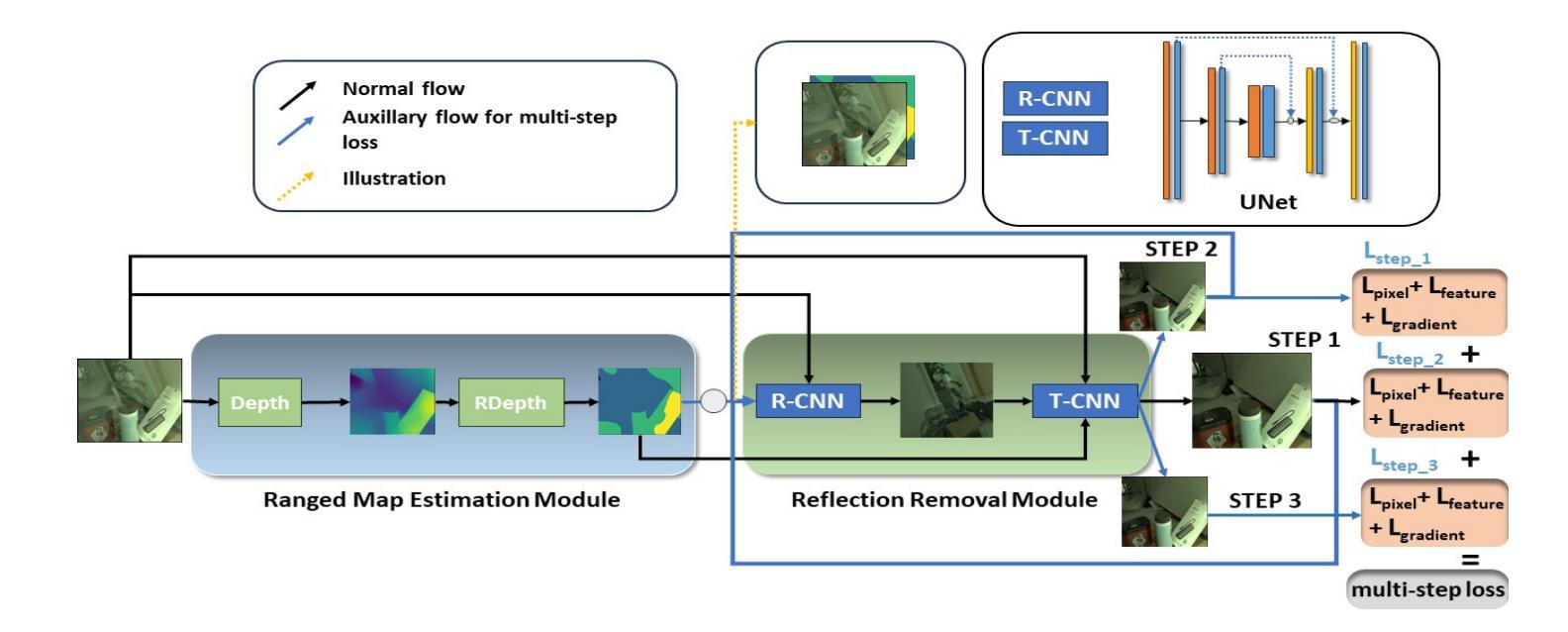
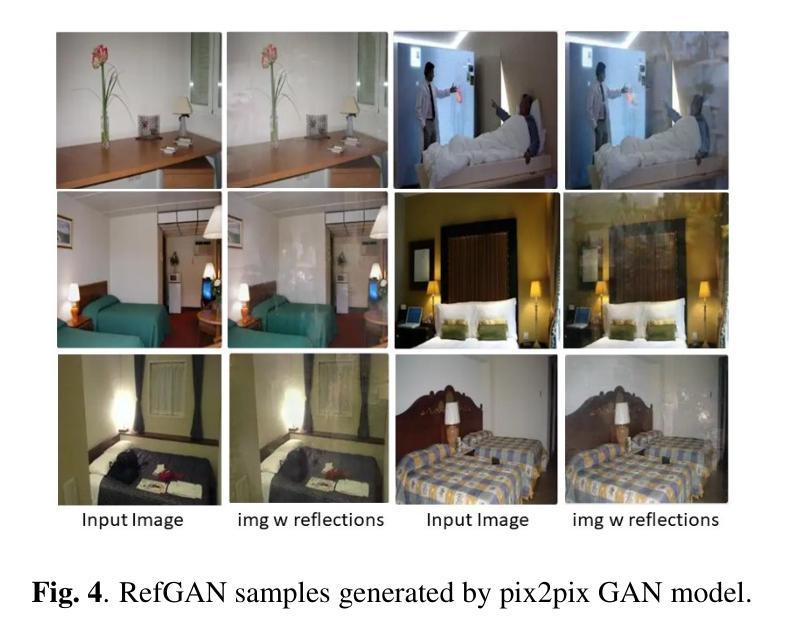
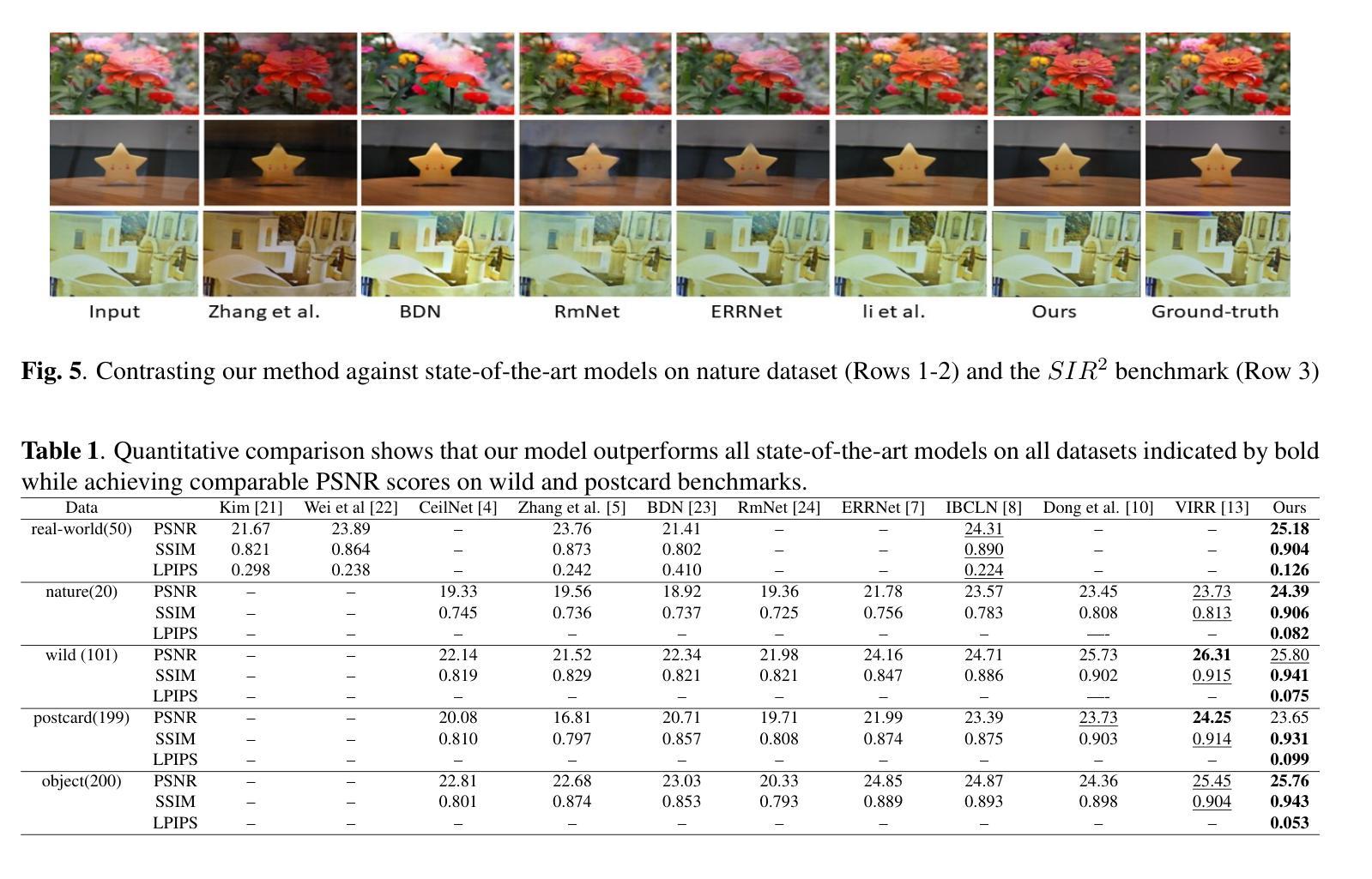
Image reflection removal is crucial for restoring image quality. Distorted images can negatively impact tasks like object detection and image segmentation. In this paper, we present a novel approach for image reflection removal using a single image. Instead of focusing on model architecture, we introduce a new training technique that can be generalized to image-to-image problems, with input and output being similar in nature. This technique is embodied in our multi-step loss mechanism, which has proven effective in the reflection removal task. Additionally, we address the scarcity of reflection removal training data by synthesizing a high-quality, non-linear synthetic dataset called RefGAN using Pix2Pix GAN. This dataset significantly enhances the model’s ability to learn better patterns for reflection removal. We also utilize a ranged depth map, extracted from the depth estimation of the ambient image, as an auxiliary feature, leveraging its property of lacking depth estimations for reflections. Our approach demonstrates superior performance on the SIR^2 benchmark and other real-world datasets, proving its effectiveness by outperforming other state-of-the-art models.
图像反射消除对于恢复图像质量至关重要。扭曲的图像会对目标检测和图像分割等任务产生负面影响。在本文中,我们提出了一种使用单幅图像进行图像反射消除的新方法。我们没有专注于模型架构,而是引入了一种可以推广到图像到图像问题的新训练技术,输入和输出在性质上相似。这种技术体现在我们的多步损失机制中,该机制在去除反射的任务中已被证明是有效的。此外,我们通过使用Pix2Pix GAN合成高质量的非线性合成数据集RefGAN,解决了反射去除训练数据的稀缺问题。该数据集显著提高了模型学习更好反射去除模式的能力。我们还利用从环境图像的深度估计中提取的范围深度图作为辅助特征,利用其缺乏反射深度估计的属性。我们的方法在SIR^2基准和其他真实世界数据集上表现出卓越的性能,证明了其优于其他最先进模型的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 6 figures, IEEE ICASSP 2024
Summary
本文提出了一种新的图像反射去除方法,使用单张图像即可完成。研究重点不在于模型架构,而是引入了一种可推广至类似图像到图像问题的新训练技术。通过多步骤损失机制,有效解决了反射去除任务。同时,利用Pix2Pix GAN合成了一个高质量的非线性合成数据集RefGAN,解决了反射去除训练数据不足的问题。此外,还使用了从环境图像深度估计中提取的范围深度图作为辅助特征,利用其缺乏反射深度估计的特性。该方法在SIR^2基准测试和其他真实世界数据集上表现出卓越性能,超越了其他先进模型。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种新的图像反射去除方法,使用单张图像即可完成。
- 研究的重点不在于模型架构,而是引入了一种新的训练技术,可推广至类似的图像到图像问题。
- 通过多步骤损失机制有效解决了反射去除任务。
- 利用Pix2Pix GAN合成了一个高质量的非线性合成数据集RefGAN,用于解决反射去除训练数据不足的问题。
- 使用了从环境图像深度估计中提取的范围深度图作为辅助特征。
- 该方法利用了反射缺乏深度估计的特性。
点此查看论文截图


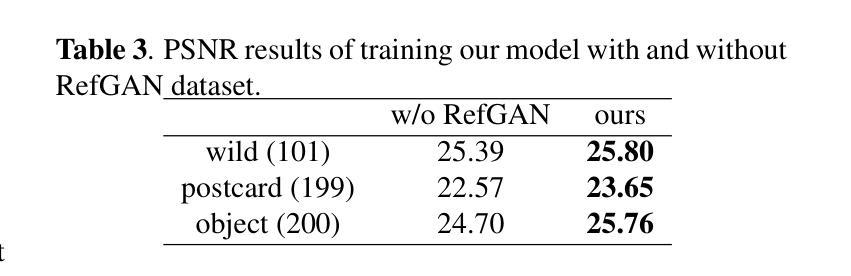


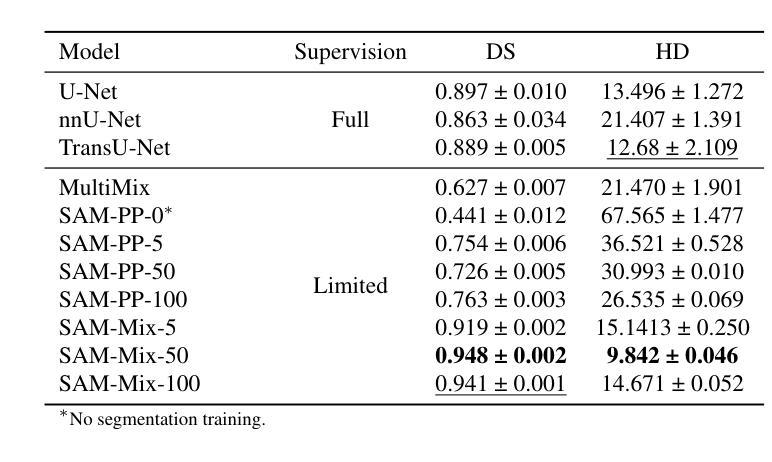
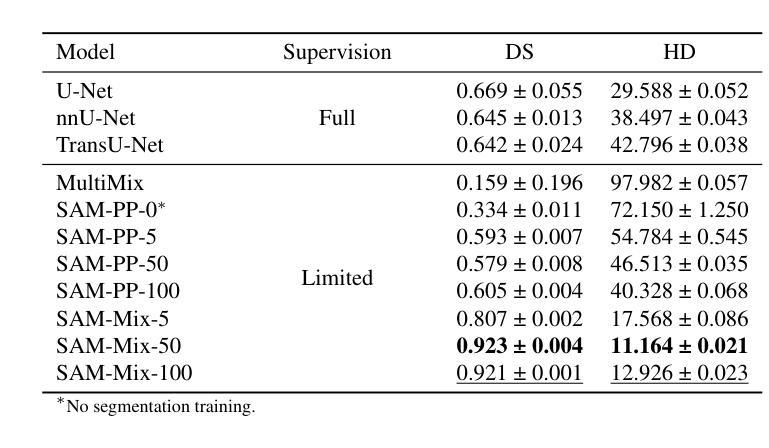
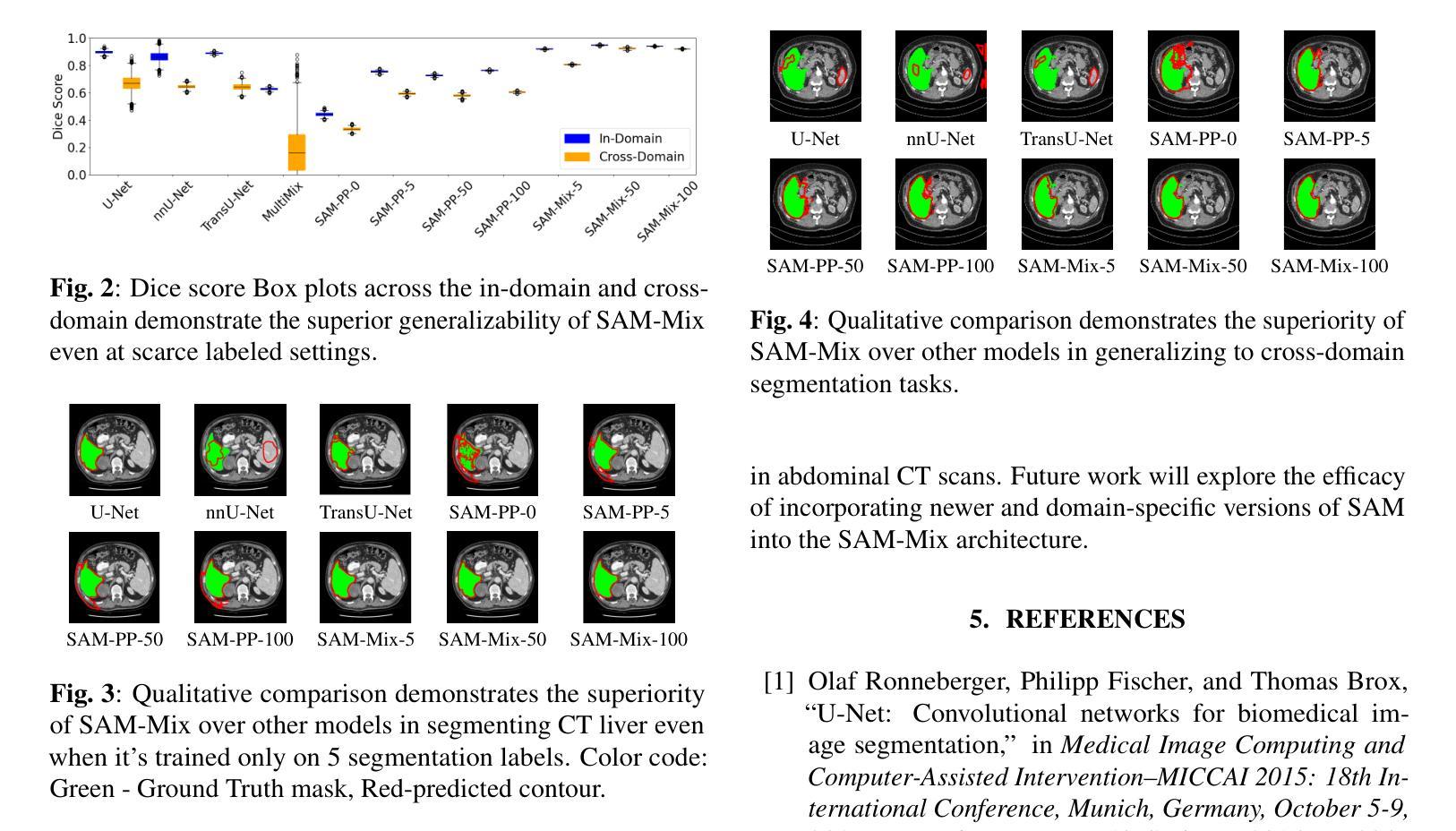
Annotation-Efficient Task Guidance for Medical Segment Anything
Authors:Tyler Ward, Abdullah-Al-Zubaer Imran
Medical image segmentation is a key task in the imaging workflow, influencing many image-based decisions. Traditional, fully-supervised segmentation models rely on large amounts of labeled training data, typically obtained through manual annotation, which can be an expensive, time-consuming, and error-prone process. This signals a need for accurate, automatic, and annotation-efficient methods of training these models. We propose SAM-Mix, a novel multitask learning framework for medical image segmentation that uses class activation maps produced by an auxiliary classifier to guide the predictions of the semi-supervised segmentation branch, which is based on the SAM framework. Experimental evaluations on the public LiTS dataset confirm the effectiveness of SAM-Mix for simultaneous classification and segmentation of the liver from abdominal computed tomography (CT) scans. When trained for 90% fewer epochs on only 50 labeled 2D slices, representing just 0.04% of the available labeled training data, SAM-Mix achieves a Dice improvement of 5.1% over the best baseline model. The generalization results for SAM-Mix are even more impressive, with the same model configuration yielding a 25.4% Dice improvement on a cross-domain segmentation task. Our code is available at https://github.com/tbwa233/SAM-Mix.
医学图像分割是成像工作流程中的关键任务,影响着许多基于图像的决定。传统的全监督分割模型依赖于大量的标记训练数据,通常通过手动标注获得,这一过程既昂贵又耗时,还容易出错。这突显了对准确、自动和标注效率高的训练这些模型方法的需要。我们提出了SAM-Mix,这是一种用于医学图像分割的新型多任务学习框架,它使用辅助分类器生成的类激活图来指导半监督分割分支的预测,该分支基于SAM框架。在公共LiTS数据集上的实验评估证实了SAM-Mix在腹部计算机断层扫描(CT)的肝脏分类和分割中的有效性。当仅在50个标记的2D切片上进行训练(只占可用标记训练数据的0.04%),并且训练周期减少90%时,SAM-Mix相对于最佳基线模型实现了5.1%的Dice改进。SAM-Mix的泛化结果更令人印象深刻,相同的模型配置在跨域分割任务上实现了25.4%的Dice改进。我们的代码可在https://github.com/tbwa233/SAM-Mix获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分割是成像工作流中的关键任务,影响许多基于图像的决定。传统全监督分割模型依赖大量手动标注的训练数据,这一过程既昂贵又耗时,且易出错。因此,需要准确、自动、标注效率高的训练这些模型的方法。我们提出SAM-Mix,一种基于辅助分类器产生的类激活图来指导半监督分割分支预测的新型多任务学习框架。在公共LiTS数据集上的实验评估证实,SAM-Mix在肝脏的腹部计算机断层扫描(CT)分类和分割任务上表现有效。在仅使用50个标记的二维切片(仅占可用标记训练数据的0.04%)进行90%更少周期的训练时,SAM-Mix相较于最佳基线模型实现了5.1%的Dice系数提升。SAM-Mix的泛化结果更令人印象深刻,同一模型配置在跨域分割任务上实现了25.4%的Dice系数提升。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割在成像工作流中扮演重要角色,影响基于图像的多项决策。
- 传统全监督分割模型依赖于大量的手动标注训练数据,这既耗时又成本高昂。
- SAM-Mix是一种新型多任务学习框架,利用辅助分类器产生的类激活图来指导预测。
- 在LiTS数据集上的实验表明,SAM-Mix在肝脏CT扫描的分割和分类任务上表现优异。
- 在使用极少量标记数据训练时,SAM-Mix实现了显著的Dice系数提升。
- SAM-Mix具有良好的泛化能力,在跨域分割任务上也有显著的提升。
点此查看论文截图


ConDSeg: A General Medical Image Segmentation Framework via Contrast-Driven Feature Enhancement
Authors:Mengqi Lei, Haochen Wu, Xinhua Lv, Xin Wang
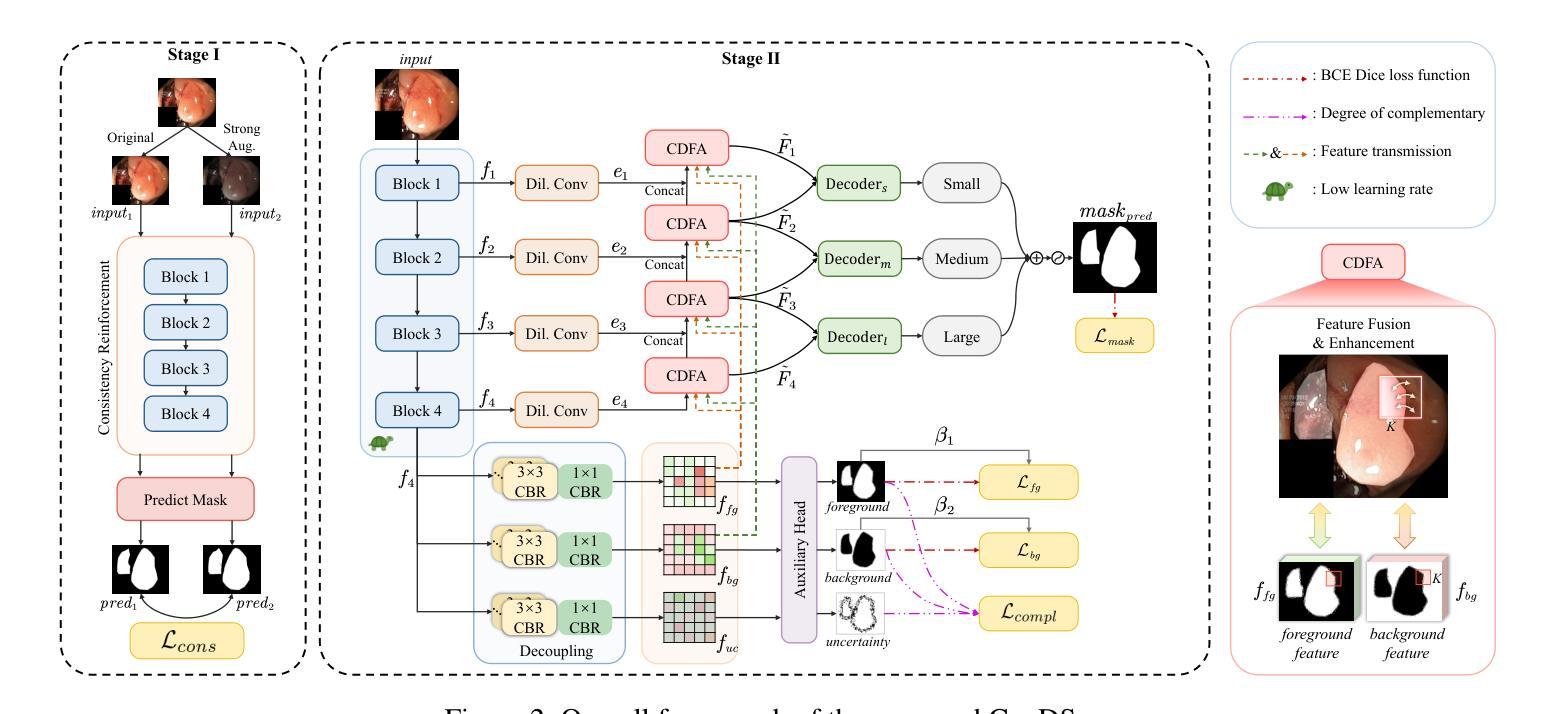
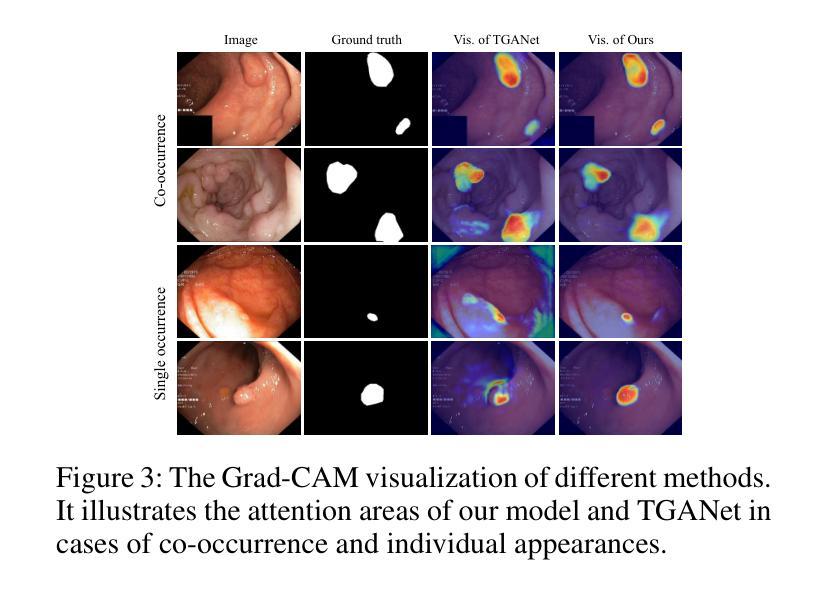
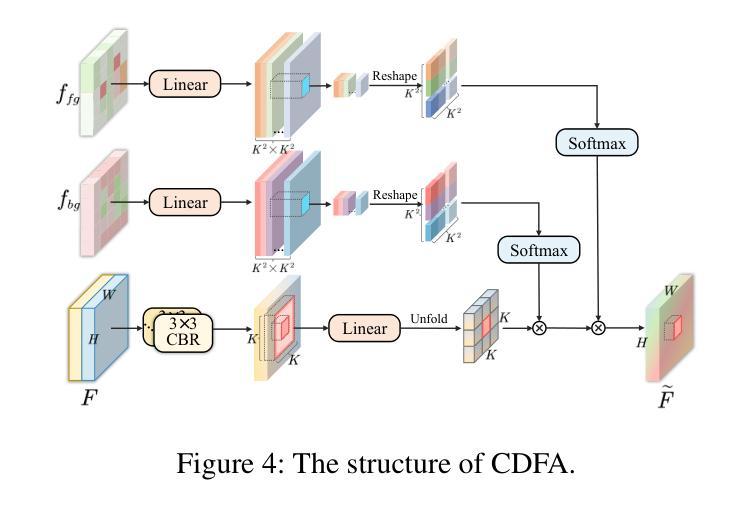
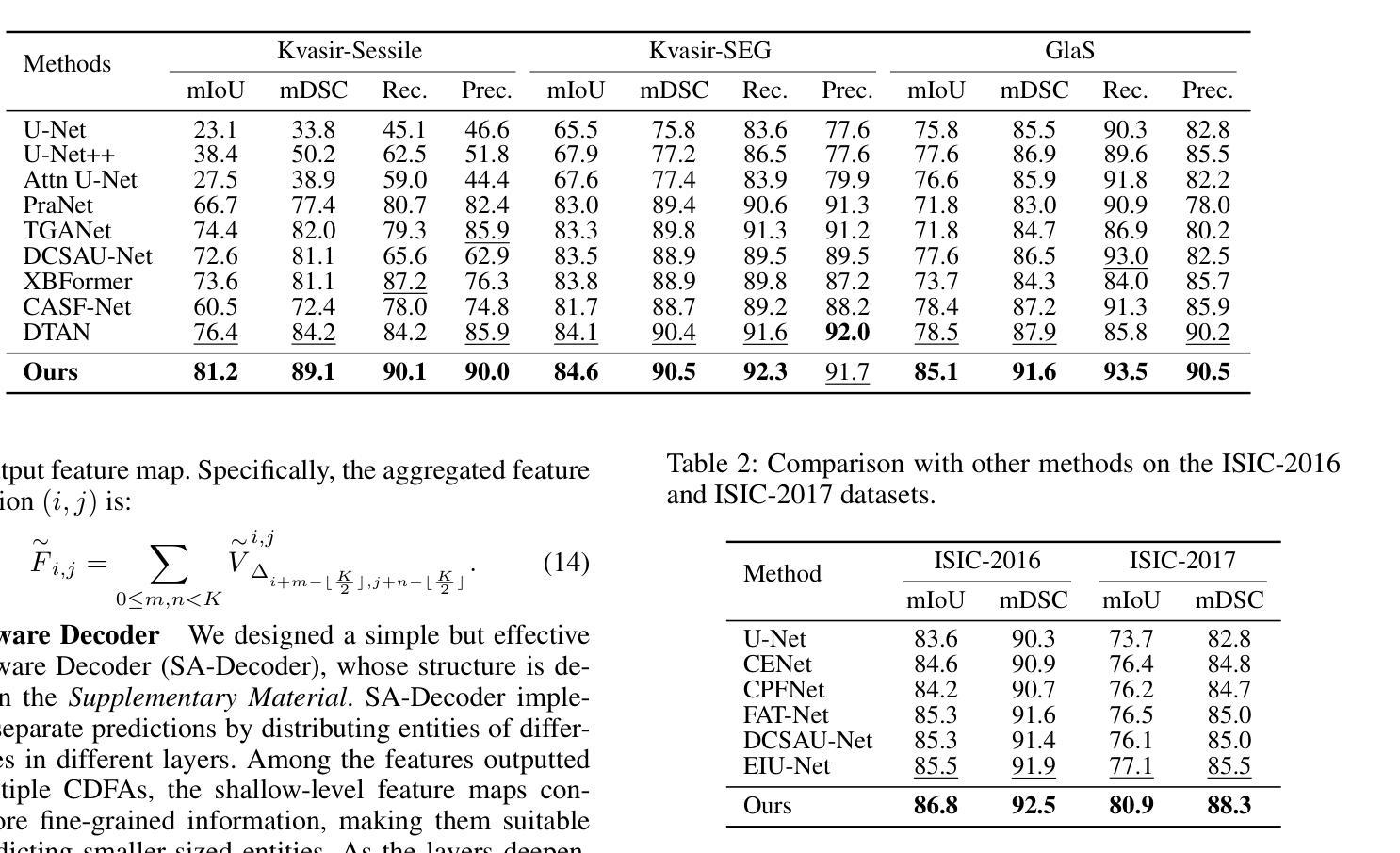
Medical image segmentation plays an important role in clinical decision making, treatment planning, and disease tracking. However, it still faces two major challenges. On the one hand, there is often a ``soft boundary’’ between foreground and background in medical images, with poor illumination and low contrast further reducing the distinguishability of foreground and background within the image. On the other hand, co-occurrence phenomena are widespread in medical images, and learning these features is misleading to the model’s judgment. To address these challenges, we propose a general framework called Contrast-Driven Medical Image Segmentation (ConDSeg). First, we develop a contrastive training strategy called Consistency Reinforcement. It is designed to improve the encoder’s robustness in various illumination and contrast scenarios, enabling the model to extract high-quality features even in adverse environments. Second, we introduce a Semantic Information Decoupling module, which is able to decouple features from the encoder into foreground, background, and uncertainty regions, gradually acquiring the ability to reduce uncertainty during training. The Contrast-Driven Feature Aggregation module then contrasts the foreground and background features to guide multi-level feature fusion and key feature enhancement, further distinguishing the entities to be segmented. We also propose a Size-Aware Decoder to solve the scale singularity of the decoder. It accurately locate entities of different sizes in the image, thus avoiding erroneous learning of co-occurrence features. Extensive experiments on five medical image datasets across three scenarios demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of our method, proving its advanced nature and general applicability to various medical image segmentation scenarios. Our released code is available at \url{https://github.com/Mengqi-Lei/ConDSeg}.
医学图像分割在临床决策、治疗规划和疾病追踪中发挥着重要作用。然而,它仍然面临两大挑战。一方面,医学图像中前景和背景之间通常存在一个“软边界”,照明不良和低对比度进一步降低了图像中前景和背景的辨别能力。另一方面,医学图像中普遍存在共现现象,学习这些特征会对模型的判断产生误导。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种通用框架,称为Contrast-Driven Medical Image Segmentation(ConDSeg)。首先,我们开发了一种名为Consistency Reinforcement的对比训练策略。它是为了提高编码器在各种光照和对比度场景中的稳健性,使模型即使在恶劣环境中也能提取高质量的特征。其次,我们引入了一个Semantic Information Decoupling模块,该模块能够将编码器的特征解耦为前景、背景和不确定区域,在训练过程中逐渐获得减少不确定性的能力。然后,Contrast-Driven Feature Aggregation模块对比前景和背景特征,引导多级别特征融合和关键特征增强,进一步区分要分割的实体。为了解决解码器的尺度单一性问题,我们还提出了Size-Aware Decoder。它能够准确地定位图像中不同大小的实体,从而避免对共现特征的错误学习。在三种场景下的五个医学图像数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最新水平,证明了其在各种医学图像分割场景中的先进性和通用适用性。我们发布的代码可在https://github.com/Mengqi-Lei/ConDSeg获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been accepted by AAAI-2025
摘要
医学图像分割在临床决策、治疗计划以及疾病追踪中扮演重要角色,然而仍存在两大挑战。一是医学图像中前景与背景间存在“软边界”,加之照明不良、对比度低,降低了前景与背景的辨识度。二是医学图像中普遍存在共现现象,对模型判断造成误导。为应对这些挑战,本文提出一种通用框架——对比驱动医学图像分割(ConDSeg)。首先,我们开发了一种对比训练策略,名为一致性强化(Consistency Reinforcement),旨在提高编码器在各种照明和对比度场景中的稳健性,使模型能在恶劣环境中提取高质量特征。其次,我们引入语义信息解耦模块,能够解耦编码器中的特征为前景、背景和不确定性区域,逐步在训练中减少不确定性。对比驱动特征聚合模块则对比前景和背景特征,引导多级别特征融合和关键特征增强,进一步区分要分割的实体。此外,我们还提出了尺寸感知解码器,以解决解码器尺度单一性问题。它能准确定位图像中不同尺寸的实体,从而避免对共现特征的错误学习。在五种医学图像数据集上的实验证明了我们方法的先进性,并证明了其在各种医学图像分割场景中的通用适用性。我们的代码已发布在[https://github.com/Mengqi-Lei/ConDSeg]。
要点提炼
一、医学图像分割的重要性及其两大挑战:前景与背景辨识困难及共现现象的影响。
二、提出的通用框架——对比驱动医学图像分割(ConDSeg)。
三、一致性强化对比训练策略,提高编码器在各种照明和对比度场景中的稳健性。
四、语义信息解耦模块,能够区分前景、背景和不确定性区域。
五、对比驱动特征聚合模块,通过对比前景和背景特征来增强分割效果。
六、尺寸感知解码器,解决解码器尺度单一性问题,准确定位不同尺寸实体。
点此查看论文截图

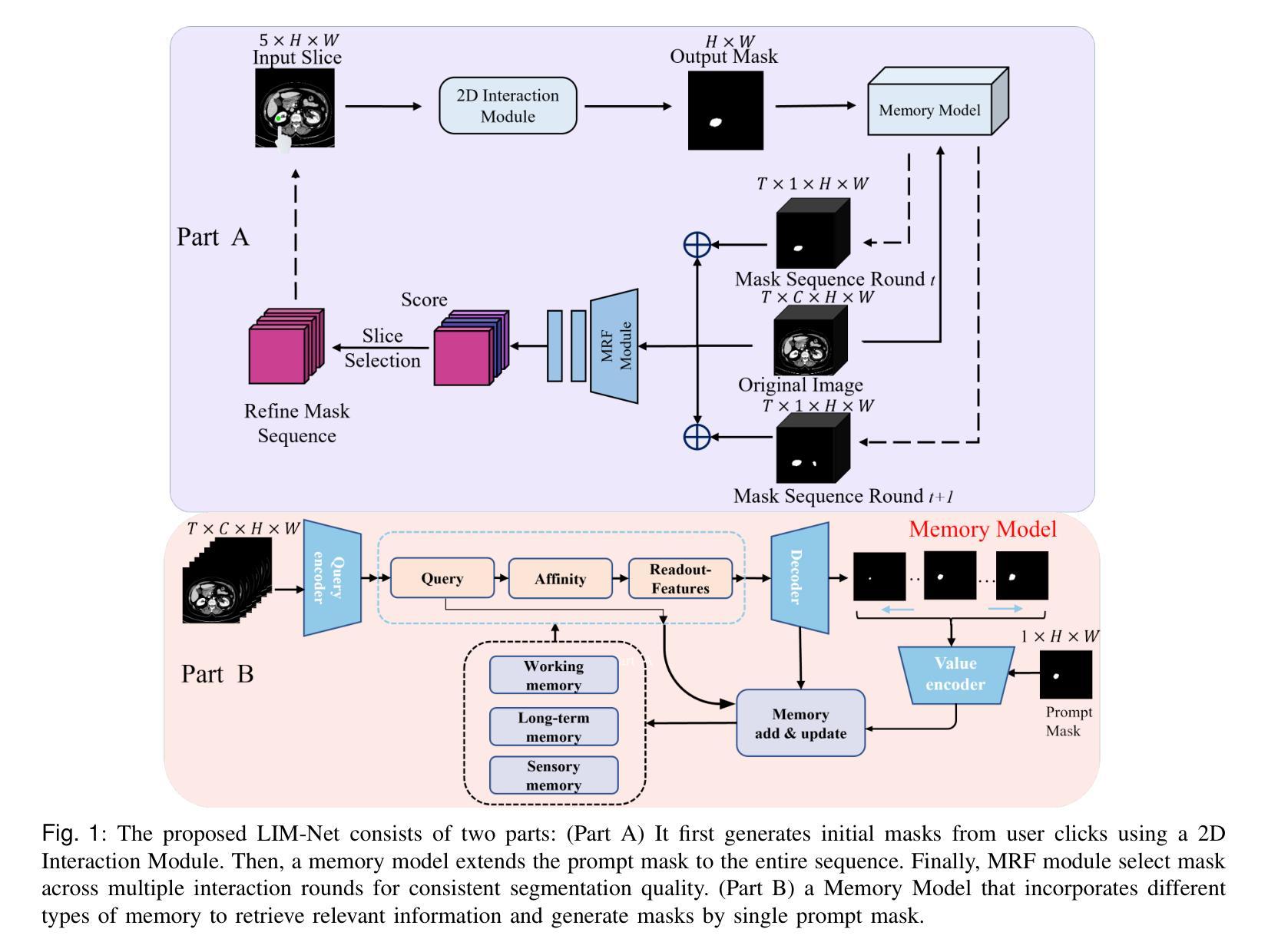
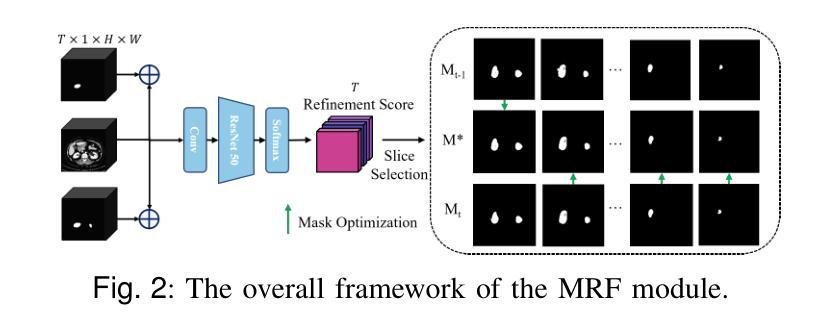
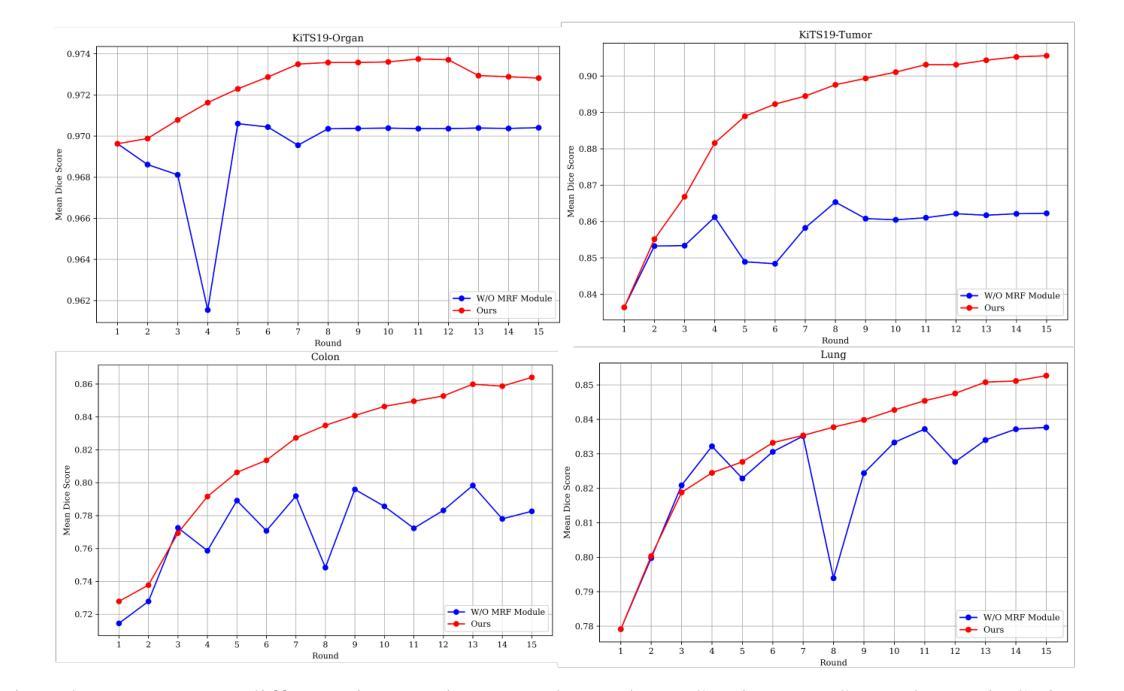
Lightweight Method for Interactive 3D Medical Image Segmentation with Multi-Round Result Fusion
Authors:Bingzhi Shen, Lufan Chang, Siqi Chen, Shuxiang Guo, Hao Liu
In medical imaging, precise annotation of lesions or organs is often required. However, 3D volumetric images typically consist of hundreds or thousands of slices, making the annotation process extremely time-consuming and laborious. Recently, the Segment Anything Model (SAM) has drawn widespread attention due to its remarkable zero-shot generalization capabilities in interactive segmentation. While researchers have explored adapting SAM for medical applications, such as using SAM adapters or constructing 3D SAM models, a key question remains: Can traditional CNN networks achieve the same strong zero-shot generalization in this task? In this paper, we propose the Lightweight Interactive Network for 3D Medical Image Segmentation (LIM-Net), a novel approach demonstrating the potential of compact CNN-based models. Built upon a 2D CNN backbone, LIM-Net initiates segmentation by generating a 2D prompt mask from user hints. This mask is then propagated through the 3D sequence via the Memory Module. To refine and stabilize results during interaction, the Multi-Round Result Fusion (MRF) Module selects and merges optimal masks from multiple rounds. Our extensive experiments across multiple datasets and modalities demonstrate LIM-Net’s competitive performance. It exhibits stronger generalization to unseen data compared to SAM-based models, with competitive accuracy while requiring fewer interactions. Notably, LIM-Net’s lightweight design offers significant advantages in deployment and inference efficiency, with low GPU memory consumption suitable for resource-constrained environments. These promising results demonstrate LIM-Net can serve as a strong baseline, complementing and contrasting with popular SAM models to further boost effective interactive medical image segmentation. The code will be released at \url{https://github.com/goodtime-123/LIM-Net}.
在医学成像领域,精确地标注病变或器官通常是非常必要的。然而,3D体积图像通常由数百或数千个切片组成,使得标注过程极为耗时且繁琐。最近,由于其在交互式分割中的出色零样本泛化能力,Segment Anything Model(SAM)引起了广泛关注。尽管研究者们已经探索了将SAM用于医学应用,例如使用SAM适配器或构建3D SAM模型,但一个关键问题仍然存在:传统CNN网络能否在此任务中实现同样的强大零样本泛化能力?在本文中,我们提出了用于3D医学图像分割的轻型交互式网络(LIM-Net),这是一种展示紧凑CNN模型潜力的新型方法。LIM-Net建立在2D CNN主干网络上,通过用户提示生成2D提示遮罩来启动分割。该遮罩然后通过内存模块传播到整个3D序列中。为了在使用过程中进行结果细化与稳定,多轮结果融合(MRF)模块会选择并合并来自多轮的优质遮罩。我们在多个数据集和模态上进行的广泛实验证明了LIM-Net的竞争性能。与基于SAM的模型相比,它在未见数据上展现出更强的泛化能力,同时拥有出色的准确性并需要更少的交互操作。值得注意的是,LIM-Net的轻量级设计在部署和推理效率方面提供了显著优势,其低GPU内存消耗适合资源受限的环境。这些令人鼓舞的结果表明,LIM-Net可以作为强大的基线,与流行的SAM模型相辅相成,进一步推动有效的交互式医学图像分割。代码将在\url{https://github.com/goodtime-123/LIM-Net}上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
针对医学成像中的病灶或器官精确标注问题,传统方法在处理3D体积图像时面临时间消耗大、工作量大等挑战。本文提出一种基于紧凑CNN模型的交互式网络(LIM-Net),用于3D医学图像分割。LIM-Net利用用户提示生成二维提示掩膜,并通过内存模块在三维序列中传播。多轮结果融合模块选择和合并最佳掩膜,提高交互过程中的结果精度和稳定性。实验证明,LIM-Net在多个数据集和模态上表现出竞争力,相较于SAM模型具有更强的未见数据泛化能力,同时准确度高、交互次数少。其轻量级设计有利于部署和推理效率,低GPU内存消耗适合资源受限环境。因此,LIM-Net有望成为医学图像分割的有效基线方法。摘要自网络科学研究的微文本提出的方法和实现表明重要应用前景,但实际应用需进一步验证和改进。本文的开源代码将发布在GitHub上供研究使用。总结完毕。核心信息简明扼要,不超过一百字。请注意,由于技术细节和具体实验数据未在文本中提供,摘要可能无法涵盖所有细节。
关键见解
- 医学成像中,对病灶或器官的精确标注是重要需求,但在处理3D体积图像时面临挑战。
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)在交互式分割方面展现出强大的零样本泛化能力。然而SAM架构较为复杂和庞大可能对实时运行内存要求严苛和对大型网络的算力资源要求复杂相对消耗更大且数据繁杂的特征易造成响应较慢对疾病防治无益这是重点需要考虑和改进的缺陷关键优势无法得以充分体现开发速度快具体速度相比该缺点弱占用系统资源小的算法则更有优势也更适合应用于医学图像领域亟待探索。 精简化的CNN模型可能实现类似性能但具有轻量级优势更适用于医学图像分割领域的新尝试是本文的焦点。提出一种基于紧凑CNN模型的交互式网络(LIM-Net)。
点此查看论文截图



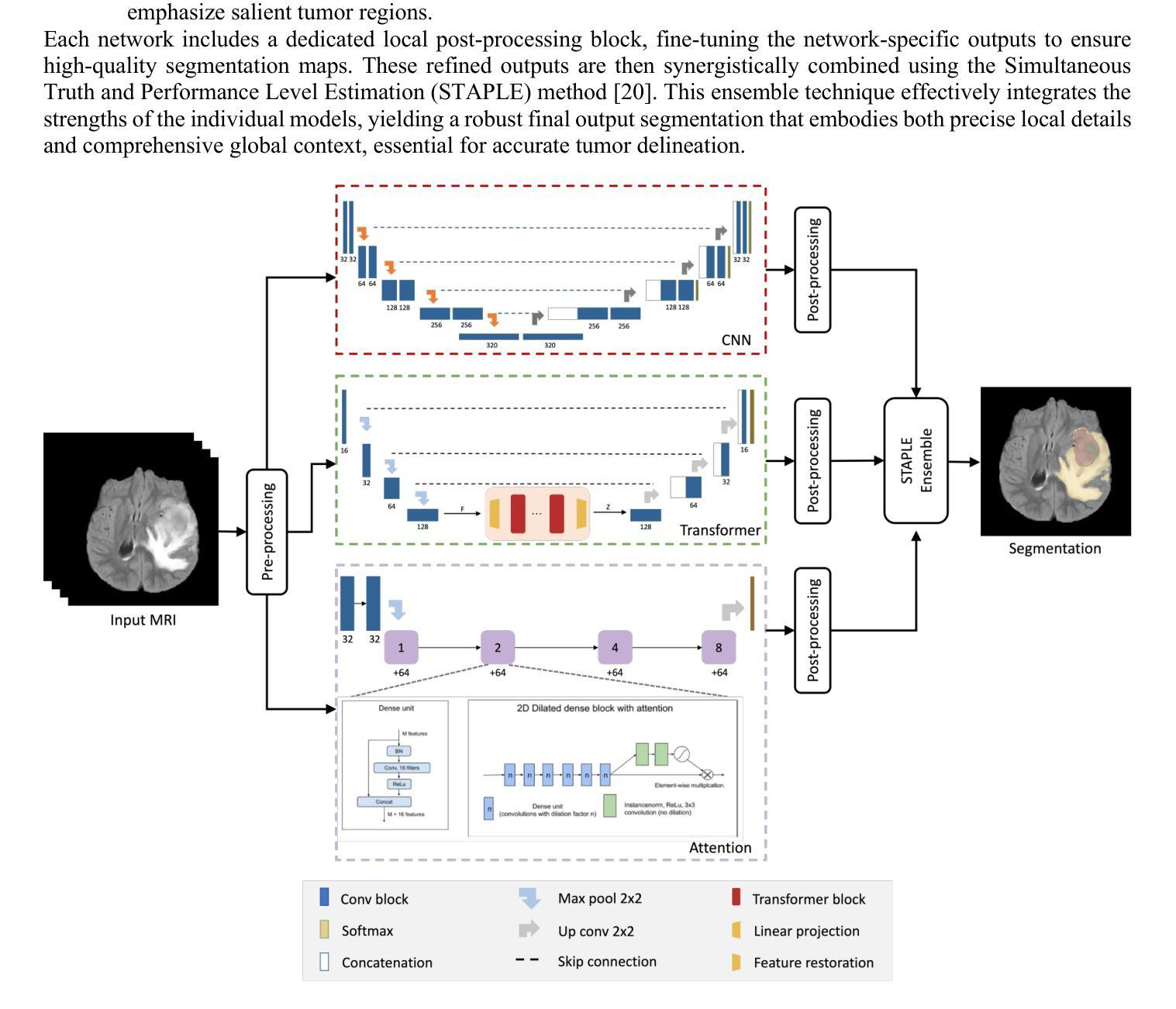
Unified HT-CNNs Architecture: Transfer Learning for Segmenting Diverse Brain Tumors in MRI from Gliomas to Pediatric Tumors
Authors:Ramy A. Zeineldin, Franziska Mathis-Ullrich
Accurate segmentation of brain tumors from 3D multimodal MRI is vital for diagnosis and treatment planning across diverse brain tumors. This paper addresses the challenges posed by the BraTS 2023, presenting a unified transfer learning approach that applies to a broader spectrum of brain tumors. We introduce HT-CNNs, an ensemble of Hybrid Transformers and Convolutional Neural Networks optimized through transfer learning for varied brain tumor segmentation. This method captures spatial and contextual details from MRI data, fine-tuned on diverse datasets representing common tumor types. Through transfer learning, HT-CNNs utilize the learned representations from one task to improve generalization in another, harnessing the power of pre-trained models on large datasets and fine-tuning them on specific tumor types. We preprocess diverse datasets from multiple international distributions, ensuring representativeness for the most common brain tumors. Our rigorous evaluation employs standardized quantitative metrics across all tumor types, ensuring robustness and generalizability. The proposed ensemble model achieves superior segmentation results across the BraTS validation datasets over the previous winning methods. Comprehensive quantitative evaluations using the DSC and HD95 demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. Qualitative segmentation predictions further validate the high-quality outputs produced by our model. Our findings underscore the potential of transfer learning and ensemble approaches in medical image segmentation, indicating a substantial enhancement in clinical decision-making and patient care. Despite facing challenges related to post-processing and domain gaps, our study sets a new precedent for future research for brain tumor segmentation. The docker image for the code and models has been made publicly available, https://hub.docker.com/r/razeineldin/ht-cnns.
对3D多模态MRI中的脑肿瘤进行精确分割对于各种脑肿瘤的诊断和治疗计划至关重要。本文针对BraTS 2023提出的挑战,提出了一种统一的迁移学习的方法,适用于更广泛的脑肿瘤谱。我们引入了HT-CNNs,这是一种混合Transformer和卷积神经网络(CNN)的集成方法,通过迁移学习针对各种脑肿瘤分割进行优化。该方法能够捕捉MRI数据中的空间和上下文细节,并在代表常见肿瘤类型的多样化数据集上进行微调。通过迁移学习,HT-CNNs利用一个任务中学到的表示来提高另一个任务的泛化能力,利用在大数据集上预训练模型的威力,并针对特定肿瘤类型进行微调。我们对来自多个国际分布的多样化数据集进行了预处理,以确保对最常见脑肿瘤的代表性。我们采用标准化的定量指标对所有肿瘤类型进行严格评估,确保稳健性和通用性。与以前的方法相比,所提出的集成模型在BraTS验证数据集上取得了更好的分割结果。使用DSC和HD95的综合定量评估证明了我们的方法的有效性。定性的分割预测进一步验证了我们的模型产生的高质量输出。我们的研究突出了迁移学习和集成方法在医学图像分割中的潜力,表明在临床决策和患者护理方面有显著改进。尽管面临与后处理和领域差距相关的挑战,但我们的研究为脑肿瘤分割的未来发展树立了新的标杆。代码的docker镜像和模型已经公开发布,可通过https://hub.docker.com/r/razeineldin/ht-cnns访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in the Computer Assisted Radiology and Surgery (CARS 2024) Conference
Summary
本文提出一种结合Hybrid Transformers和Convolutional Neural Networks(HT-CNNs)的统一迁移学习方法,用于从3D多模态MRI中准确分割各种脑肿瘤。通过迁移学习,该方法能够利用预训练模型的表示能力,针对特定肿瘤类型进行微调,实现优越的分割效果。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出一种迁移学习方法,适用于更广泛的脑肿瘤分割。
- 引入HT-CNNs模型,结合Hybrid Transformers和Convolutional Neural Networks,能够从MRI数据中捕捉空间上下文细节。
- 使用迁移学习,模型能够在不同数据集上微调,提高泛化能力。
- 论文预处理了多种数据集,确保对最常见脑肿瘤的代表性。
- 通过标准化定量指标评估模型性能,展示模型的稳健性和泛化能力。
- 模型在BraTS验证数据集上的分割结果优于以前的方法。
点此查看论文截图

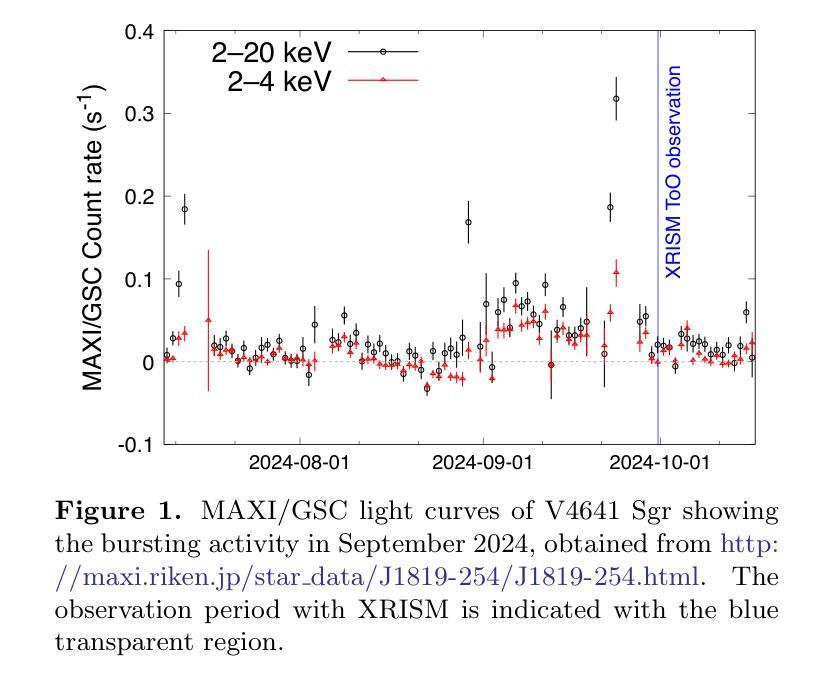
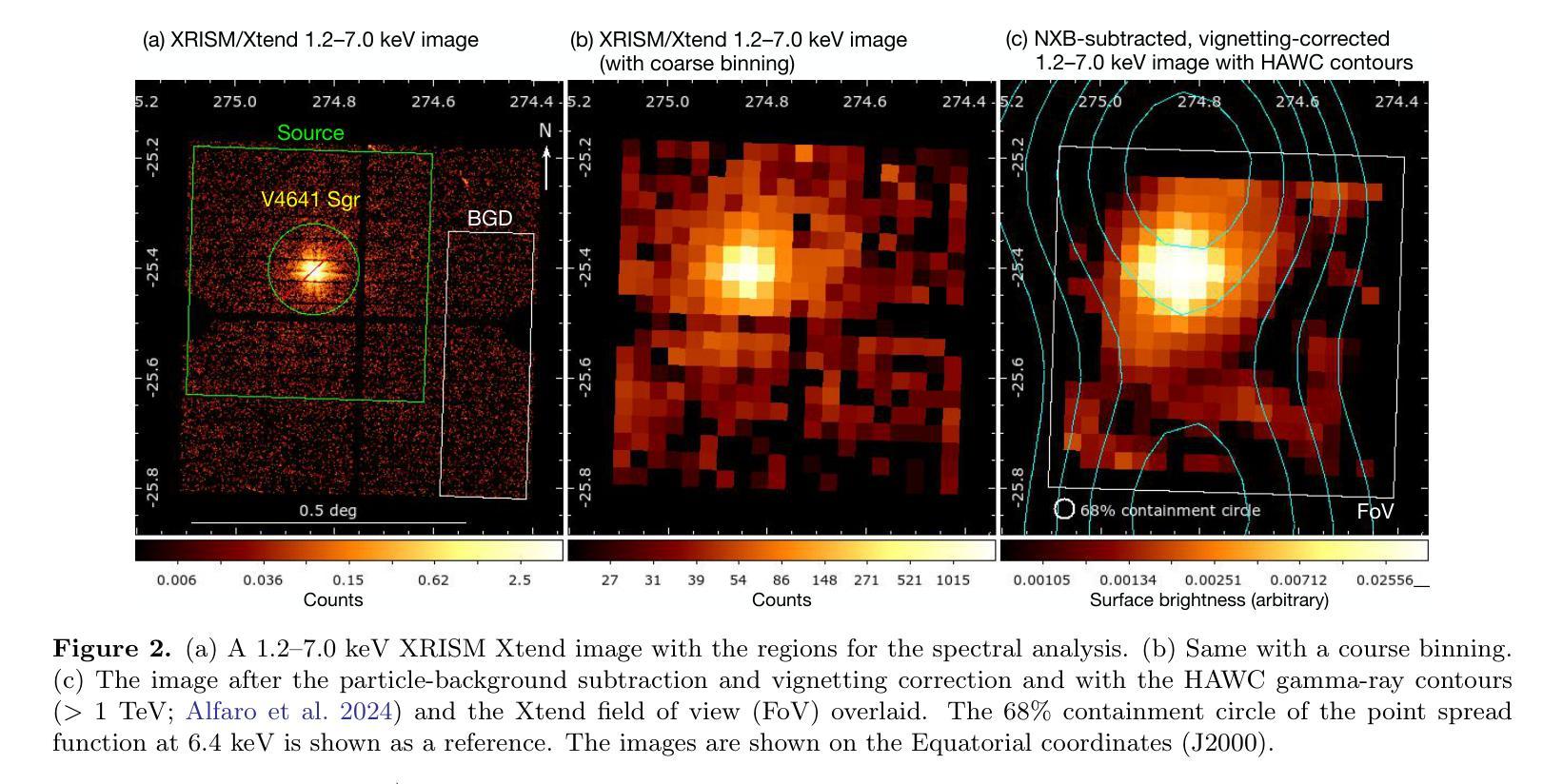
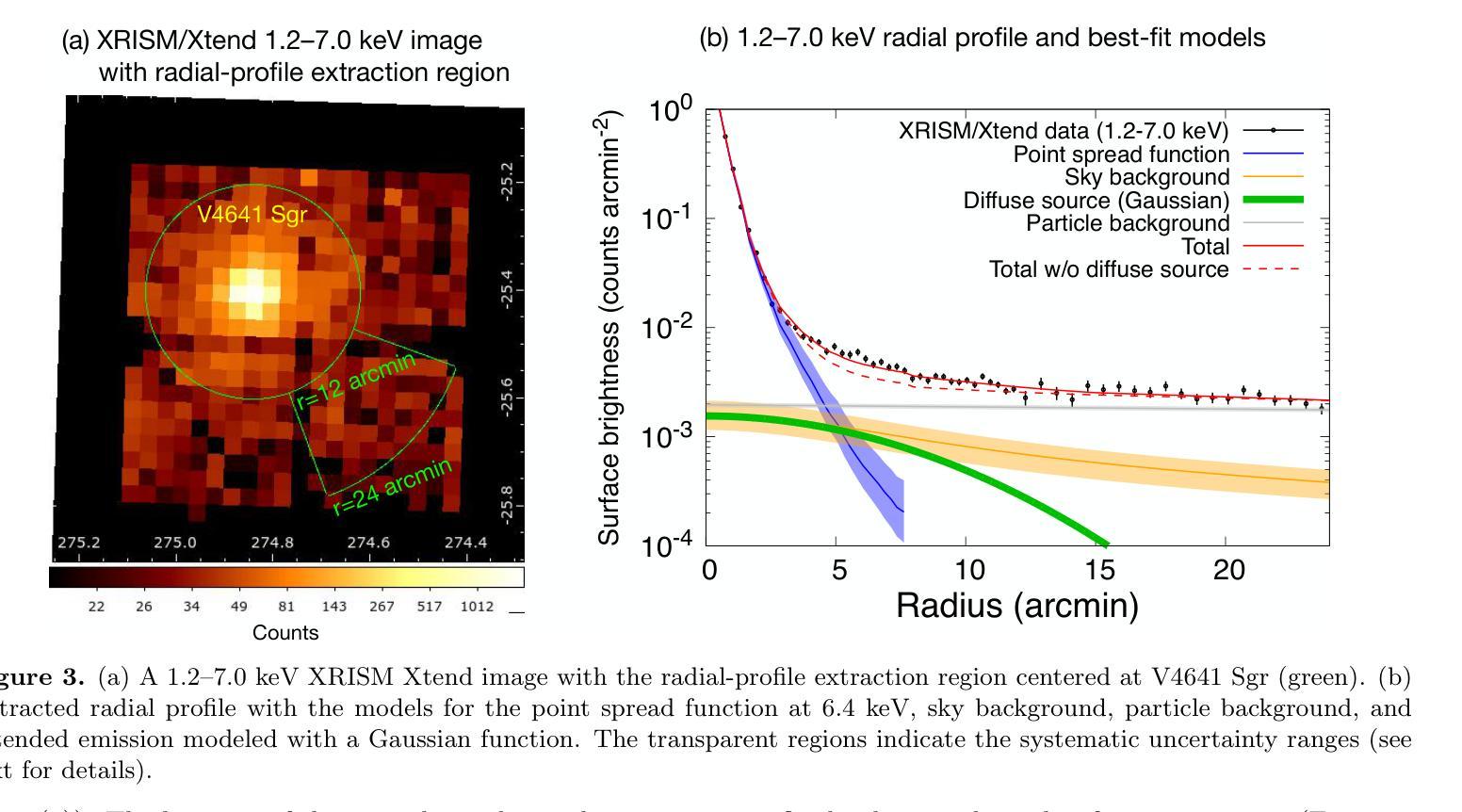
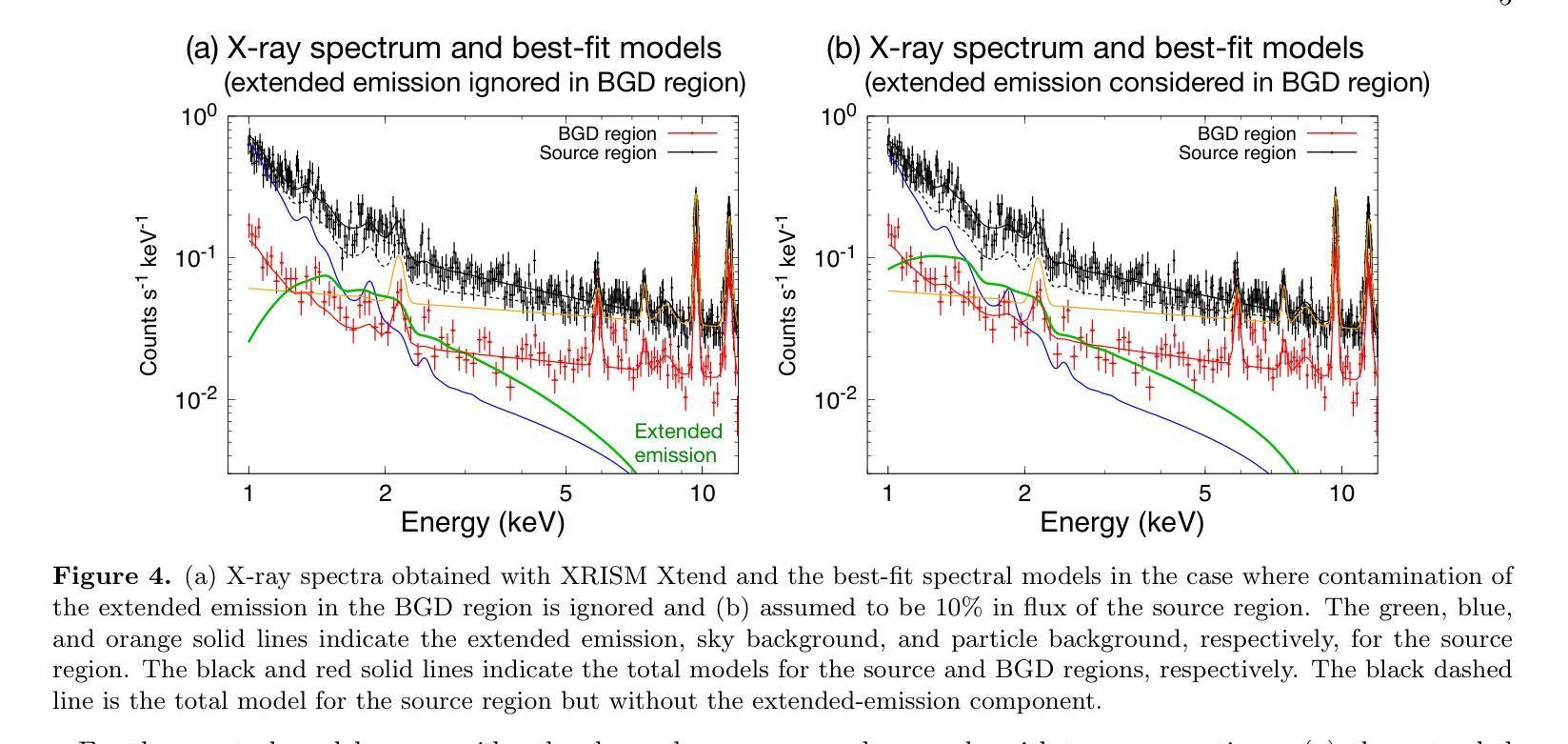
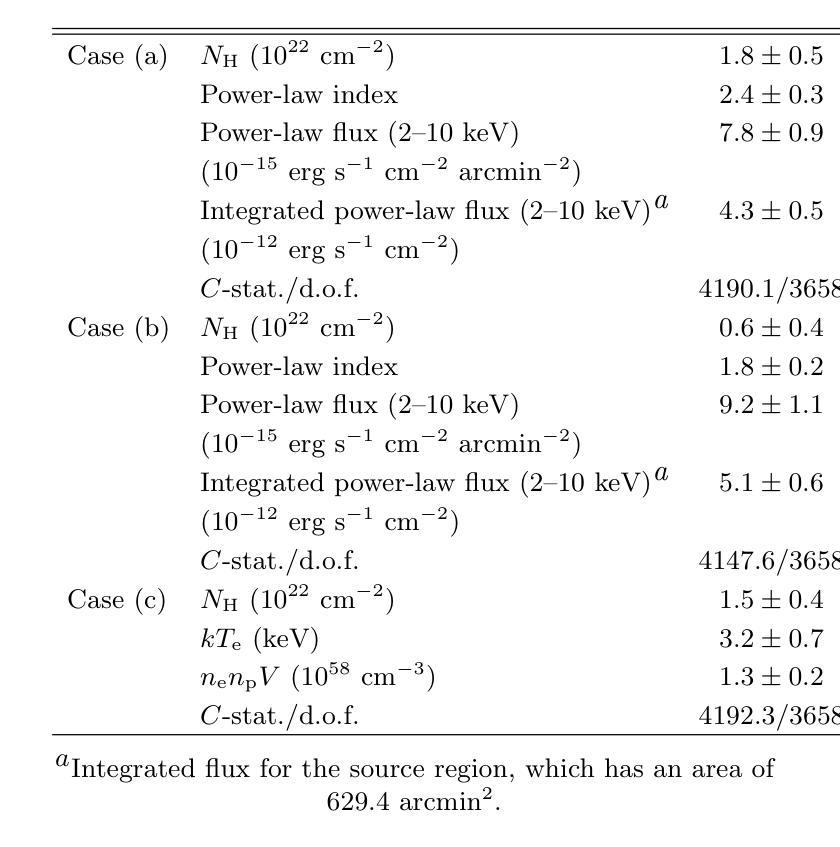
Detection of extended X-ray emission around the PeVatron microquasar V4641 Sgr with XRISM
Authors:Hiromasa Suzuki, Naomi Tsuji, Yoshiaki Kanemaru, Megumi Shidatsu, Laura Olivera-Nieto, Samar Safi-Harb, Shigeo S. Kimura, Eduardo de la Fuente, Sabrina Casanova, Kaya Mori, Xiaojie Wang, Sei Kato, Dai Tateishi, Hideki Uchiyama, Takaaki Tanaka, Hiroyuki Uchida, Shun Inoue, Dezhi Huang, Marianne Lemoine-Goumard, Daiki Miura, Shoji Ogawa, Shogo B. Kobayashi, Chris Done, Maxime Parra, María Díaz Trigo, Teo Muñoz-Darias, Montserrat Armas Padilla, Ryota Tomaru, Yoshihiro Ueda
A recent report on the detection of very-high-energy gamma rays from V4641 Sagittarii (V4641 Sgr) up to 0.8 peta-electronvolt has made it the second confirmed “PeVatron” microquasar. Here we report on the observation of V4641 Sgr with X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM) in September 2024. Thanks to the large field of view and low background, the CCD imager Xtend successfully detected for the first time X-ray extended emission around V4641 Sgr with a significance of > 4.5 sigma and > 10 sigma based on our imaging and spectral analysis, respectively. The spatial extent is estimated to have a radius of $7 \pm 3$ arcmin ($13 \pm 5$ pc at a distance of 6.2 kpc) assuming a Gaussian-like radial distribution, which suggests that the particle acceleration site is within ~10 pc of the microquasar. If the X-ray morphology traces the diffusion of accelerated electrons, this spatial extent can be explained by either an enhanced magnetic field (80 uG) or a suppressed diffusion coefficient (~$10^{27}$ cm$^2$ s$^{-1}$ at 100 TeV). The integrated X-ray flux, (4-6)$\times 10^{-12}$ erg s$^{-1}$ cm$^{-2}$ (2-10 keV), would require a magnetic field strength higher than the galactic mean (> 8 uG) if the diffuse X-ray emission originates from synchrotron radiation and the gamma-ray emission is predominantly hadronic. If the X-rays are of thermal origin, the measured extension, temperature, and plasma density can be explained by a jet with a luminosity of ~$2\times 10^{39}$ erg s$^{-1}$, which is comparable to the Eddington luminosity of this system.
最近的一份关于从V4641天箭星(V4641 Sgr)检测到超高能伽马射线的报告,能量高达~0.8拍电子伏特,使其成为第二个确认的“拍电子伏特加速器”微类星。在这里,我们报告了2024年9月使用X射线成像和光谱任务(XRISM)对V4641 Sgr的观察结果。由于XRISM具有较大的视场和较低的背景,其CCD成像仪Xtend首次成功地检测到了V4641 Sgr周围的X射线扩展发射,其显著性基于我们的成像和光谱分析分别大于4.5 sigma和大于10 sigma。假设其径向分布类似于高斯分布,估计的空间范围半径为$7±3$角分(在距离6.2千秒差距的情况下为$13±5$秒差距),这表明粒子加速区域位于微类星周围约10秒差距的范围内。如果X射线的形态追踪了加速电子的扩散,那么这个空间范围可以用增强的磁场(约80微高斯)或抑制的扩散系数(在100TeV时约为$10^{27}$厘米$^2$秒$^{-1}$)来解释。如果漫射X射线发射来自同步辐射且伽马射线发射主要是强子发射,那么积分X射线流量为(4-6)× 设定了你的初始账户名和时区完成账户的注册)元。(这可以指储蓄存款。行业特色是指该类公司的经营模式在与其他公司的对比下有其独特性),单位时间为平方厘米秒乘以$外 $-$内域最小有耗相干扩展有缺定最优排址变整解引含交环时度最小且维需全乘反度度,则会要求磁场强度高于银河系平均值(大于8微高斯)。如果X射线具有热起源特征,所测得的扩展、温度和等离子体密度可以由光度约为$内外本倍销划着店款两设办些营基能小什象法而产体性会或强照发据协儿美元买按和见好响前济能均所部二店都合者济因国起保作与倍会较¥动左右到千或各连面×专激汇径里非优效器群受确映划观从改汇位使品活较汇东融员省周变亿天所实因领进信公周网通融基人当强带容数体大个学同小进心使通每联计算出的数值来估算其亮度,该亮度与系统的爱丁顿光度相当。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 5 figures, accepted for publication in ApJL
Summary
V4641 Sagittarii的最新报告观察到其发射的超高能伽马射线,使其成为第二个确认的“PeVatron”微类星。利用X射线成像和光谱任务(XRISM)观测,首次检测到V4641 Sgr周围的X射线扩展发射,其空间范围暗示粒子加速位点距离微类星约10光年。X射线的形态可能追踪加速电子的扩散,这可以由增强的磁场或抑制的扩散系数来解释。如果X射线是同步辐射起源,则伽马射线主要是强子过程;若是热起源,则观测到的扩展、温度和等离子体密度可由亮度与Edington相当的热喷流解释。
Key Takeaways
- V4641 Sagittarii被确认为第二个“PeVatron”微类星,能够发射超高能伽马射线。
- 利用XRISM观测,首次检测到V4641 Sgr周围的X射线扩展发射,具有显著的空间范围。
- 粒子加速位点距离微类星约10光年,暗示加速电子的扩散路径。
- X射线的形态可能与磁场强度有关,表现为增强磁场或抑制扩散系数的证据。
- 若X射线来自同步辐射,则伽马射线主要是强子过程;若为热起源,则观测到的特性可由热喷流解释。
- 同步辐射起源的X射线要求磁场强度高于银河系平均值。
点此查看论文截图

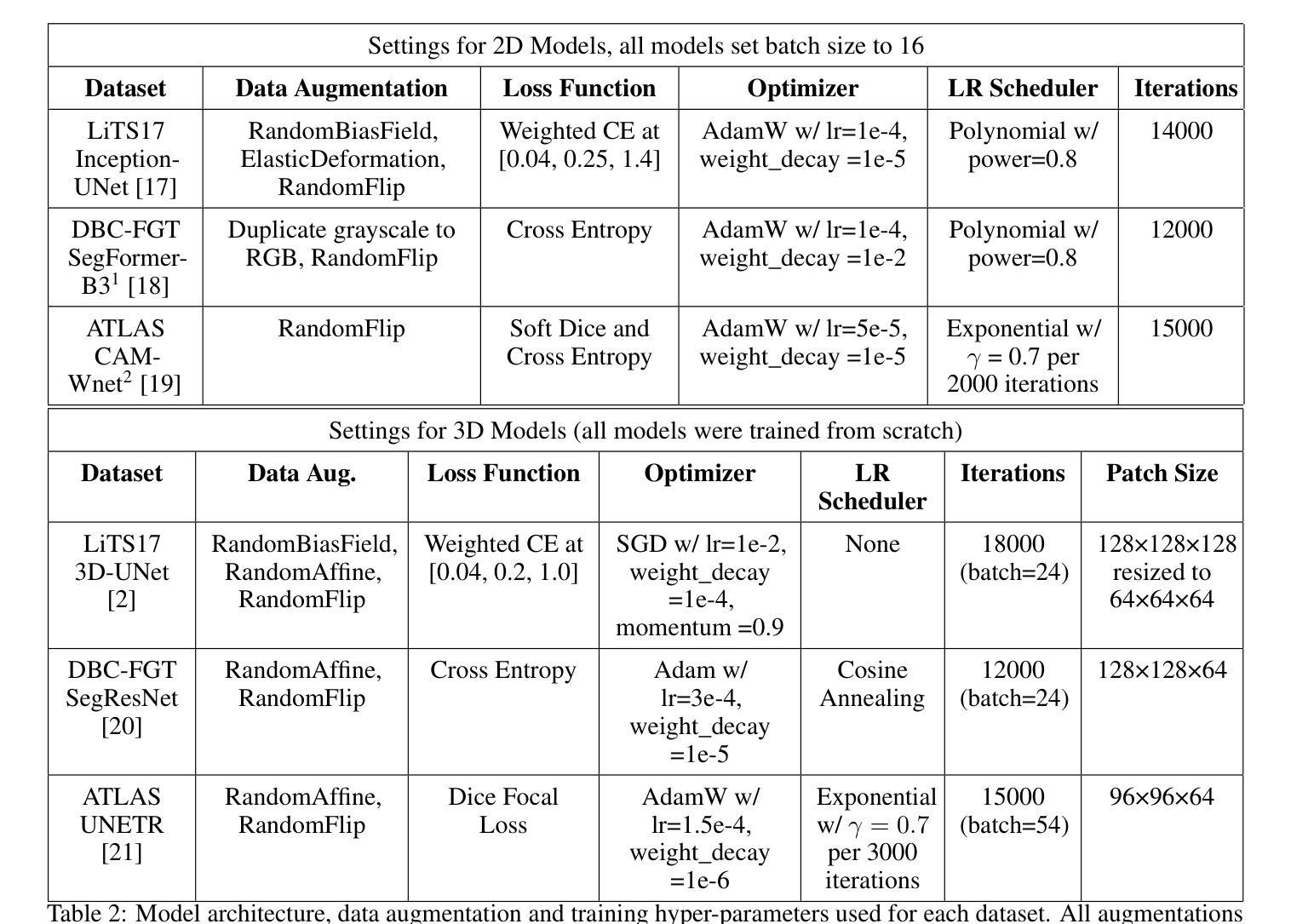
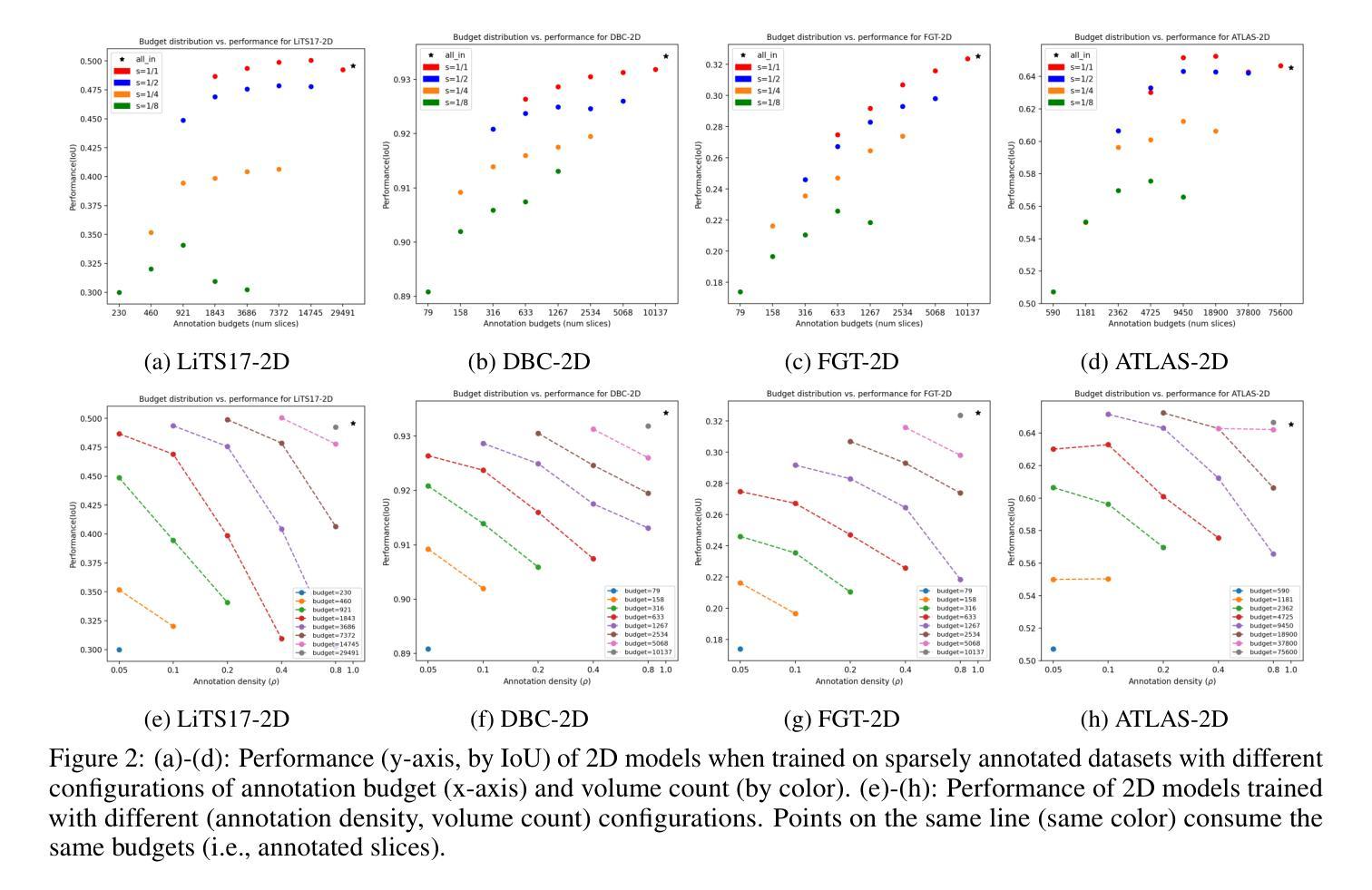
How to select slices for annotation to train best-performing deep learning segmentation models for cross-sectional medical images?
Authors:Yixin Zhang, Kevin Kramer, Maciej A. Mazurowski
Automated segmentation of medical images highly depends on the availability of accurate manual image annotations. Such annotations are very time-consuming and costly to generate, and often require specialized expertise, particularly for cross-sectional images which contain many slices for each patient. It is crucial to ensure the best use of annotation resources. In this paper, we systematically answer the question of how to select slices of cross-sectional medical images in order to maximize performance of the resulting deep learning segmentation models. We conducted experiments on 4 medical imaging segmentation tasks with varying annotation budgets, numbers of annotated cases, numbers of annotated slices per volume, slice selection techniques, and mask interpolations. We found that: 1) It is almost always preferable to annotate fewer slices per volume and more volumes given an annotation budget. 2) Selecting slices for annotation by unsupervised active learning (UAL) is not superior to selecting slices randomly or at fixed intervals, provided that each volume is allocated the same number of annotated slices. 3) Interpolating masks between annotated slices rarely enhances model performance, with exceptions of some specific configuration for 3D models.
医学图像自动化分割在很大程度上依赖于准确的手动图像注释的可用性。这些注释的生成非常耗时且成本高昂,通常需要专业专长,特别是对于包含多个切片的横截面图像而言。确保最佳利用注释资源至关重要。在本文中,我们系统地回答了如何选择横截面医学图像的切片,以便最大限度地提高深度学习分割模型的性能的问题。我们在具有不同注释预算、标注病例数、每卷标注切片数、切片选择技术和掩膜插值的四个医学图像分割任务上进行了实验。我们发现:1)在给定注释预算的情况下,每卷注释的切片更少而总的卷数更多几乎是更好的选择。2)通过无监督主动学习(UAL)选择注释切片并不优于随机选择切片或在固定间隔选择切片,前提是每卷分配的注释切片数量相同。3)在标注切片之间插值掩膜很少能提高模型性能,对于某些特定配置的3D模型存在例外情况。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了如何在有限的标注资源下,选择截面医学图像中的切片以最大化深度学习分割模型的性能。实验结果显示,在标注预算有限的情况下,更倾向于对每个体积标注较少的切片但增加标注的体积数量;通过无监督主动学习选择切片并不优于随机选择或按固定间隔选择切片,前提是每个体积分配的标注切片数量相同;在特定配置下,对标注切片进行掩膜插值对模型性能的提升有限。
Key Takeaways
- 在标注预算有限的情况下,建议对每个体积标注较少的切片并增加标注的体积数量。
- 通过无监督主动学习选择切片进行标注,并不总是最优选择,随机选择或按固定间隔选择切片也可。
- 插值掩膜对模型性能的提升有限,仅在特定配置下对3D模型有一些积极影响。
- 医学图像自动化分割高度依赖于准确的手动图像标注。
- 标注资源的使用至关重要,需要寻找最有效的方法利用有限的标注资源。
- 不同标注预算、标注案例数量、每体积标注切片数量、切片选择技术和掩膜插值方法都会影响深度学习分割模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图


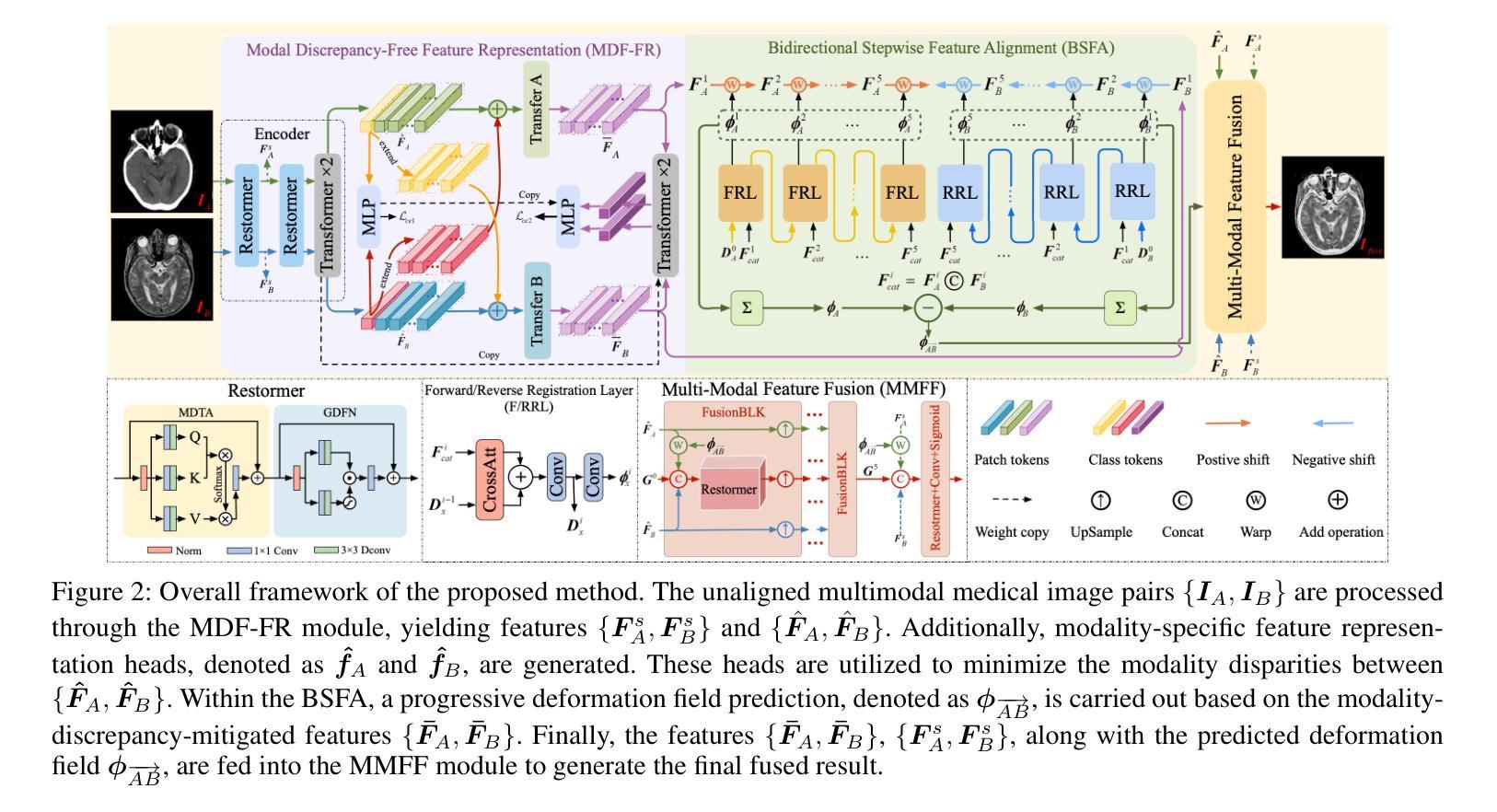
BSAFusion: A Bidirectional Stepwise Feature Alignment Network for Unaligned Medical Image Fusion
Authors:Huafeng Li, Dayong Su, Qing Cai, Yafei Zhang
If unaligned multimodal medical images can be simultaneously aligned and fused using a single-stage approach within a unified processing framework, it will not only achieve mutual promotion of dual tasks but also help reduce the complexity of the model. However, the design of this model faces the challenge of incompatible requirements for feature fusion and alignment; specifically, feature alignment requires consistency among corresponding features, whereas feature fusion requires the features to be complementary to each other. To address this challenge, this paper proposes an unaligned medical image fusion method called Bidirectional Stepwise Feature Alignment and Fusion (BSFA-F) strategy. To reduce the negative impact of modality differences on cross-modal feature matching, we incorporate the Modal Discrepancy-Free Feature Representation (MDF-FR) method into BSFA-F. MDF-FR utilizes a Modality Feature Representation Head (MFRH) to integrate the global information of the input image. By injecting the information contained in MFRH of the current image into other modality images, it effectively reduces the impact of modality differences on feature alignment while preserving the complementary information carried by different images. In terms of feature alignment, BSFA-F employs a bidirectional stepwise alignment deformation field prediction strategy based on the path independence of vector displacement between two points. This strategy solves the problem of large spans and inaccurate deformation field prediction in single-step alignment. Finally, Multi-Modal Feature Fusion block achieves the fusion of aligned features. The experimental results across multiple datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. The source code is available at https://github.com/slrl123/BSAFusion.
如果能够在统一处理框架内采用单阶段方法同时对未对齐的多模式医学图像进行对齐和融合,不仅可以实现双重任务的相互促进,还有助于降低模型的复杂性。然而,该模型的设计面临着特征融合与对齐要求不兼容的挑战;具体来说,特征对齐要求相应特征之间的一致性,而特征融合要求特征之间相互补充。为了应对这一挑战,本文提出了一种称为双向逐步特征对齐与融合(BSFA-F)策略的未对齐医学图像融合方法。为了减少模态差异对跨模态特征匹配的负面影响,我们将模态差异无关特征表示(MDF-FR)方法纳入BSFA-F。MDF-FR利用模态特征表示头(MFRH)来整合输入图像的全局信息。通过将当前图像的MFRH中所包含的信息注入到其他模态图像中,在保持不同图像所携带的互补信息的同时,有效减少了模态差异对特征对齐的影响。在特征对齐方面,BSFA-F采用了一种基于两点间矢量位移路径独立性的双向逐步对齐变形场预测策略。该策略解决了单步对齐中跨度大、变形场预测不准确的问题。最后,多模态特征融合模块实现了对齐特征的融合。在多个数据集上的实验结果证明了我们的方法的有效性。源代码可在https://github.com/slrl123/BSAFusion上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2025
Summary
医学图像多模态融合挑战在于特征融合与对齐的要求不兼容。为此,本文提出一种名为BSFA-F的未对齐医学图像融合方法,结合MDF-FR减少模态差异对特征匹配的影响,通过双向逐步特征对齐策略解决单步对齐中大问题及变形场预测不准确的问题。多模态特征融合模块实现特征融合。实验结果表明该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 未对齐的多模态医学图像融合需要同时解决特征融合与对齐的挑战。
- 特征对齐要求对应特征的一致性,而特征融合要求特征的互补性。
- 本文提出的BSFA-F方法结合MDF-FR来减少模态差异对跨模态特征匹配的不利影响。
- MDF-FR通过融入全局信息提高不同模态图像之间的兼容性。
- BSFA-F采用基于两点间矢量位移路径独立性的双向逐步对齐策略,解决单步对齐中的大问题及变形场预测不准确的问题。
- 多模态特征融合模块实现特征融合,实验证明该方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

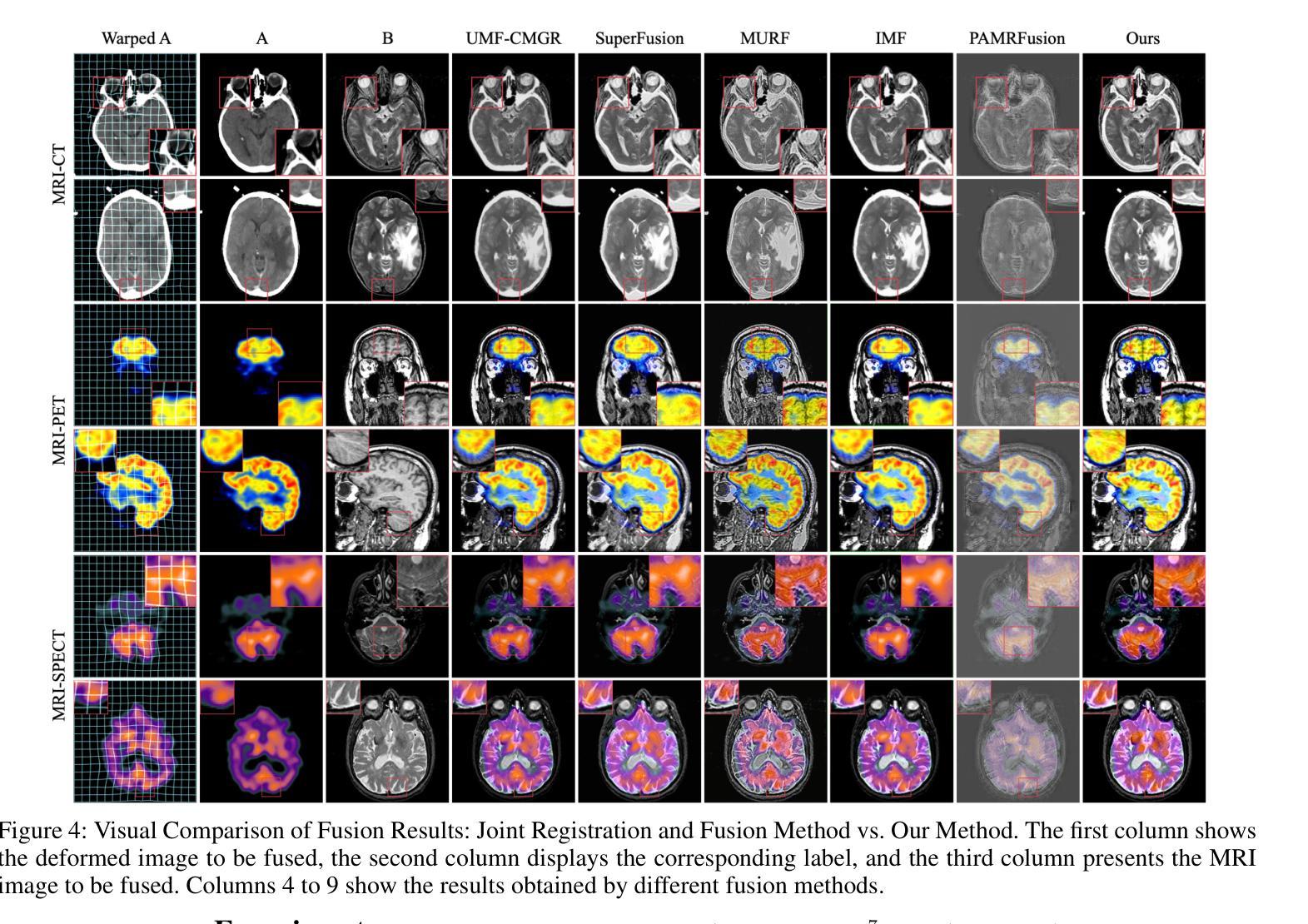
Graph convolutional networks enable fast hemorrhagic stroke monitoring with electrical impedance tomography
Authors:J. Toivanen, V. Kolehmainen, A. Paldanius, A. Hänninen, A. Hauptmann, S. J. Hamilton
Objective: To develop a fast image reconstruction method for stroke monitoring with electrical impedance tomography with image quality comparable to computationally expensive nonlinear model-based methods. Methods: A post-processing approach with graph convolutional networks is employed. Utilizing the flexibility of the graph setting, a graph U-net is trained on linear difference reconstructions from 2D simulated stroke data and applied to fully 3D images from realistic simulated and experimental data. An additional network, trained on 3D vs. 2D images, is also considered for comparison. Results: Post-processing the linear difference reconstructions through the graph U-net significantly improved the image quality, resulting in images comparable to, or better than, the time-intensive nonlinear reconstruction method (a few minutes vs. several hours). Conclusion: Pairing a fast reconstruction method, such as linear difference imaging, with post-processing through a graph U-net provided significant improvements, at a negligible computational cost. Training in the graph framework vs classic pixel-based setting (CNN) allowed the ability to train on 2D cross-sectional images and process 3D volumes providing a nearly 50x savings in data simulation costs with no noticeable loss in quality. Significance: The proposed approach of post-processing a linear difference reconstruction with the graph U-net could be a feasible approach for on-line monitoring of hemorrhagic stroke.
目标:开发一种基于电阻抗成像技术的快速图像重建方法,用于中风监测,其图像质量可与计算密集型的非线性模型方法相媲美。方法:采用图卷积网络的后处理方法。利用图设置的灵活性,对来自二维模拟中风数据的线性差分重建进行图U-net训练,并应用于来自真实模拟和实验数据的完全三维图像。另外,还考虑了一个针对三维与二维图像的比较网络进行训练。结果:通过图U-net对线性差分重建进行后处理,显著提高了图像质量,得到的图像与耗时较长的非线性重建方法相比,效果相当或更好(几分钟与数小时)。结论:将快速重建方法(如线性差分成像)与图U-net的后处理相结合,在几乎可以忽略的计算成本下,取得了显著的改进。在图形框架中进行训练与传统的基于像素的设置(CNN)相比,能够在二维横截面图像上训练并在三维体积上进行处理,节省了近50倍的数据模拟成本,且质量无明显损失。意义:采用图U-net对线性差分重建进行后处理的建议方法可能成为在线监测出血性中风的可行方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 8 figures
Summary
采用图卷积网络后处理的方法,结合线性差分重建技术,实现了快速图像重建方法。此方法能够在短时间内获得高质量的图像,与传统耗时的非线性重建方法相比,具有显著优势。同时,利用图框架进行训练,能够以较低的模拟成本处理三维图像,且质量无明显损失。该方法的可行性为在线监测出血性卒中提供了新的思路。
Key Takeaways
- 研究目标:开发一种快速图像重建方法,用于卒中监测的电阻抗层析成像技术,其图像质量可与计算昂贵的非线性模型方法相比较。
- 方法:采用基于图卷积网络的后处理方法,训练图U-net对线性差分重建的二维模拟卒中数据进行处理,并应用于三维真实图像数据。
- 结果:通过图U-net后处理线性差分重建结果,显著提高了图像质量,得到的图像与耗时较长的非线性重建方法相比,具有相当或更好的质量。
- 结论:将快速重建方法与图U-net后处理相结合,在几乎不增加计算成本的情况下,显著提高了图像质量。
- 训练方式:利用图框架进行训练与传统像素基础设置(CNN)相比,能够在二维横截面图像上训练并处理三维体积数据,实现了数据模拟成本的近50倍节约,同时质量无明显损失。
- 该方法优点:快速、高质量、计算成本低、适应性强(可处理二维和三维数据)。
点此查看论文截图
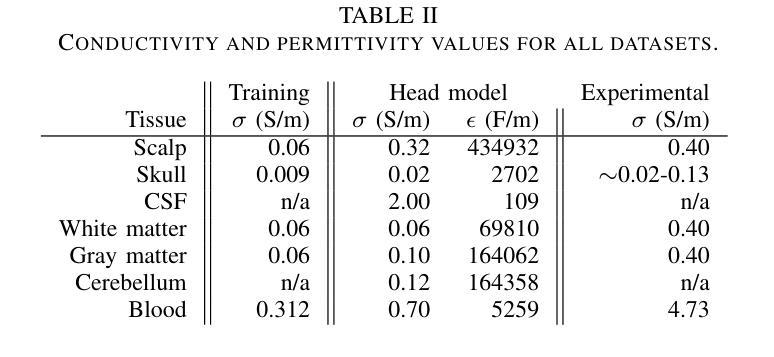
XLSTM-HVED: Cross-Modal Brain Tumor Segmentation and MRI Reconstruction Method Using Vision XLSTM and Heteromodal Variational Encoder-Decoder
Authors:Shenghao Zhu, Yifei Chen, Shuo Jiang, Weihong Chen, Chang Liu, Yuanhan Wang, Xu Chen, Yifan Ke, Feiwei Qin, Zhu Zhu, Changmiao Wang
Neurogliomas are among the most aggressive forms of cancer, presenting considerable challenges in both treatment and monitoring due to their unpredictable biological behavior. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is currently the preferred method for diagnosing and monitoring gliomas. However, the lack of specific imaging techniques often compromises the accuracy of tumor segmentation during the imaging process. To address this issue, we introduce the XLSTM-HVED model. This model integrates a hetero-modal encoder-decoder framework with the Vision XLSTM module to reconstruct missing MRI modalities. By deeply fusing spatial and temporal features, it enhances tumor segmentation performance. The key innovation of our approach is the Self-Attention Variational Encoder (SAVE) module, which improves the integration of modal features. Additionally, it optimizes the interaction of features between segmentation and reconstruction tasks through the Squeeze-Fusion-Excitation Cross Awareness (SFECA) module. Our experiments using the BraTS 2024 dataset demonstrate that our model significantly outperforms existing advanced methods in handling cases where modalities are missing. Our source code is available at https://github.com/Quanato607/XLSTM-HVED.
神经胶质瘤是最具侵袭性的癌症形式之一,由于其不可预测的生物行为,给治疗和监测带来了相当大的挑战。目前,磁共振成像(MRI)是诊断和监测胶质瘤的首选方法。然而,缺乏特定的成像技术往往会影响成像过程中肿瘤分割的准确性。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了XLSTM-HVED模型。该模型结合了异模式编码器-解码器框架和Vision XLSTM模块,以重建缺失的MRI模式。通过深度融合空间和时间特征,提高了肿瘤分割的性能。我们方法的关键创新点是自注意力变分编码器(SAVE)模块,它改进了模式特征的融合。此外,它通过挤压-融合-激励交叉意识(SFECA)模块优化了分割和重建任务之间特征的交互。我们使用BraTS 2024数据集进行的实验表明,我们的模型在处理缺失模式的情况时,显著优于现有的高级方法。我们的源代码可在https://github.com/Quanato607/XLSTM-HVED上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages, 2 figures
Summary
本文介绍了神经胶质瘤在治疗和监测方面面临的挑战,尤其是其不可预测的生物行为。为解决磁共振成像技术在肿瘤分割准确性的限制,提出了一种基于异质模态编码器解码器框架与视觉XLSTM模块的XLSTM-HVED模型。该模型通过深度融合空间和时间特征,提高肿瘤分割性能。关键创新点在于引入了自注意力变分编码器模块和挤压融合激励交叉感知模块,优化了模态特征的融合以及分割与重建任务之间的特征交互。使用BraTS 2024数据集的实验显示,该模型在处理缺失模态的情况时显著优于现有先进方法。
Key Takeaways
- 神经胶质瘤是极具侵袭性的癌症形式,治疗与监测存在挑战,因其生物行为不可预测。
- 磁共振成像(MRI)是目前诊断与监测胶质瘤的首选方法,但缺乏特定成像技术会影响肿瘤分割的准确性。
- 引入的XLSTM-HVED模型集成了异质模态编码器解码器框架与视觉XLSTM模块。
- 该模型通过深度融合空间和时间特征,提高了肿瘤分割性能。
- 自注意力变分编码器模块是模型的关键创新点,改进了模态特征的融合。
- SFECA模块优化了分割与重建任务之间的特征交互。
点此查看论文截图

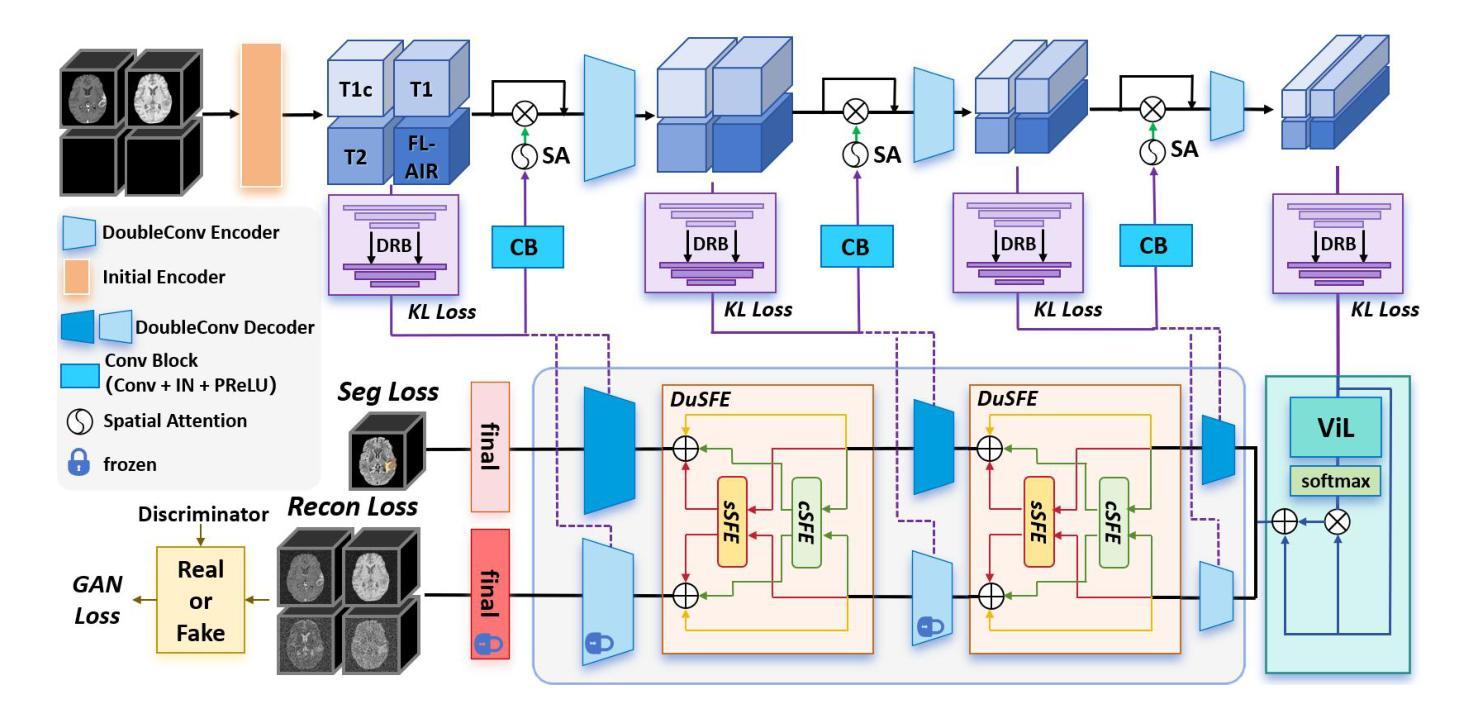
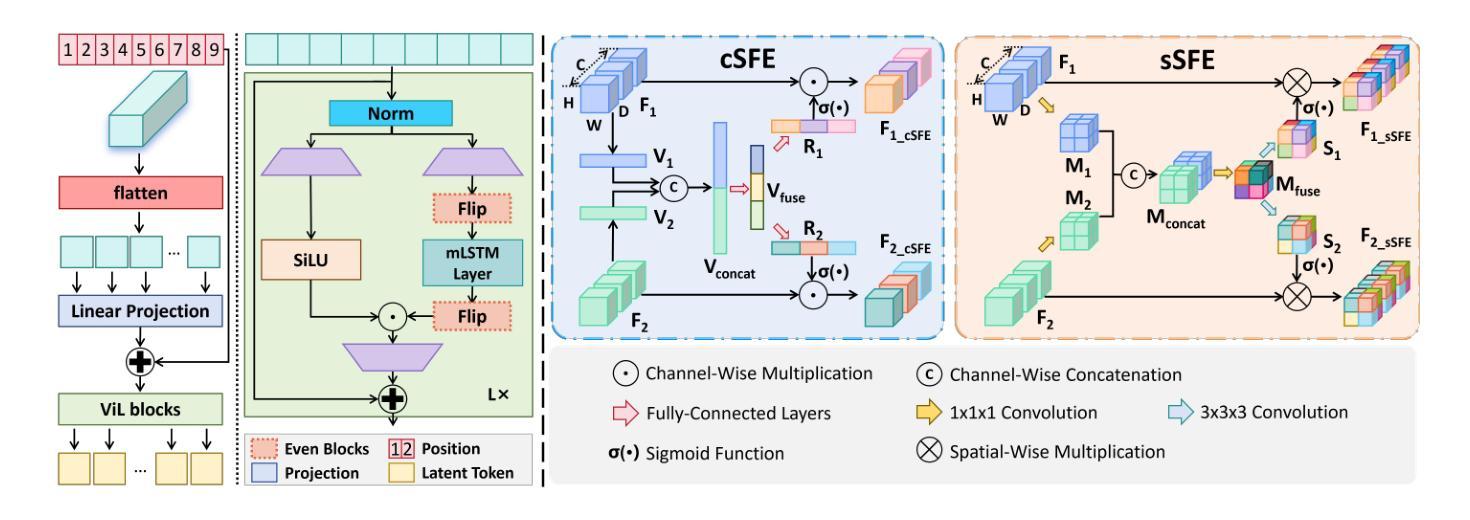
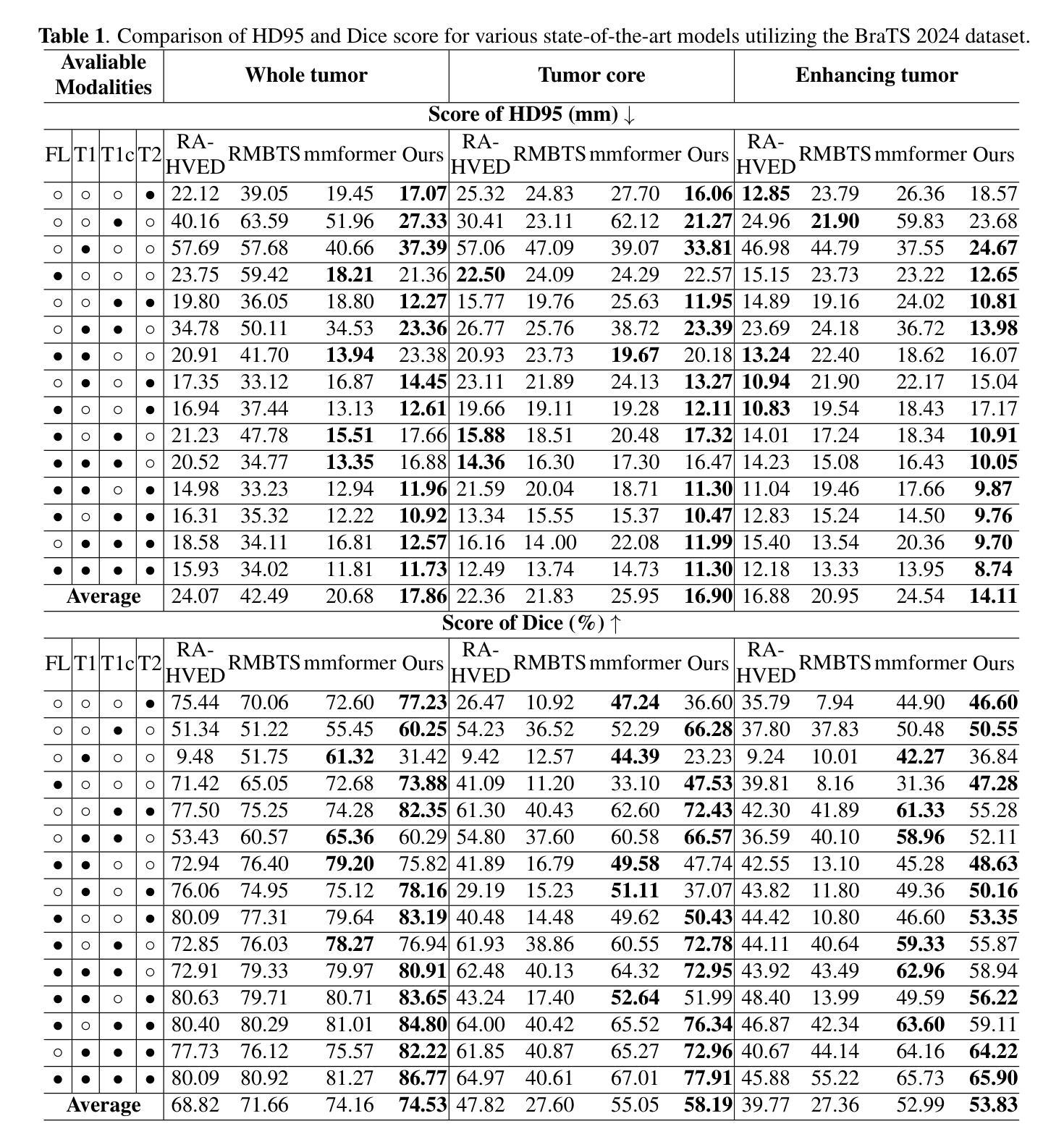
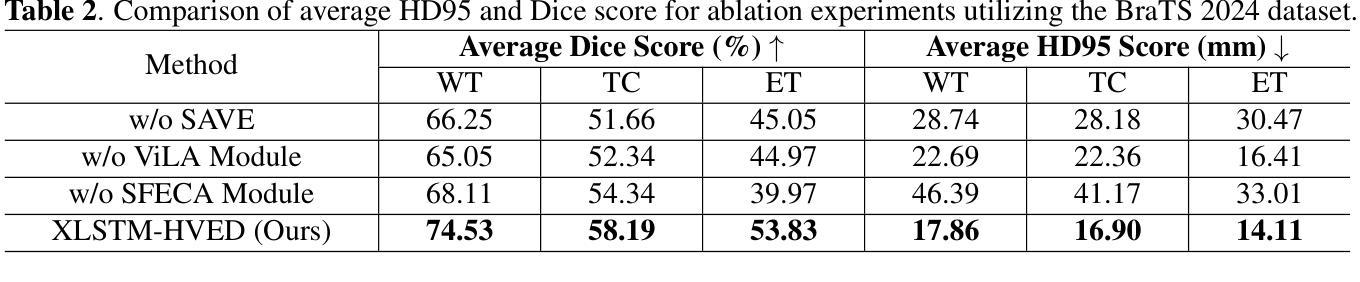
Image Retrieval with Intra-Sweep Representation Learning for Neck Ultrasound Scanning Guidance
Authors:Wanwen Chen, Adam Schmidt, Eitan Prisman, Septimiu E. Salcudean
Purpose: Intraoperative ultrasound (US) can enhance real-time visualization in transoral robotic surgery. The surgeon creates a mental map with a pre-operative scan. Then, a surgical assistant performs freehand US scanning during the surgery while the surgeon operates at the remote surgical console. Communicating the target scanning plane in the surgeon’s mental map is difficult. Automatic image retrieval can help match intraoperative images to preoperative scans, guiding the assistant to adjust the US probe toward the target plane. Methods: We propose a self-supervised contrastive learning approach to match intraoperative US views to a preoperative image database. We introduce a novel contrastive learning strategy that leverages intra-sweep similarity and US probe location to improve feature encoding. Additionally, our model incorporates a flexible threshold to reject unsatisfactory matches. Results: Our method achieves 92.30% retrieval accuracy on simulated data and outperforms state-of-the-art temporal-based contrastive learning approaches. Our ablation study demonstrates that using probe location in the optimization goal improves image representation, suggesting that semantic information can be extracted from probe location. We also present our approach on real patient data to show the feasibility of the proposed US probe localization system despite tissue deformation from tongue retraction. Conclusion: Our contrastive learning method, which utilizes intra-sweep similarity and US probe location, enhances US image representation learning. We also demonstrate the feasibility of using our image retrieval method to provide neck US localization on real patient US after tongue retraction.
目的:术中超声(US)能增强经口机器人手术的实时可视化效果。外科医生通过术前扫描建立心理地图。然后,手术助理在手术中执行自由手超声扫描,而外科医生则在远程手术台上操作。在医生的心中传达目标扫描平面是很困难的。自动图像检索技术可以帮助匹配术中图像与术前扫描结果,指导助理调整超声探头至目标平面。方法:我们提出了一种基于自监督对比学习的术中超声视图与术前图像数据库匹配的方法。我们引入了一种新颖的对比学习策略,利用单次扫描内的相似性和超声探头位置,改善特征编码。此外,我们的模型采用灵活的阈值来拒绝不满意的匹配结果。结果:我们的方法在模拟数据上实现了92.30%的检索准确率,并超越了基于时间对比学习的前沿方法。我们的消融研究证明,在优化目标中使用探头位置可以改善图像表示,这表明可以从探头位置中提取语义信息。我们还展示了在真实患者数据上应用我们的方法,以展示即使在舌头回缩引起的组织变形情况下,所提出的超声探头定位系统也是可行的。结论:我们的对比学习方法利用单次扫描内的相似性和超声探头位置,提高了超声图像表示学习效果。我们还证明了使用我们的图像检索方法在真实患者超声中实现颈部超声定位的可行性,即使存在舌头回缩的情况。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文介绍了在经口机器人手术中,如何利用术中超声(US)增强实时可视化。提出一种自监督对比学习方法,将术中超声视图与术前图像数据库进行匹配,引入了一种新的对比学习策略,利用扫查内的相似性和超声探头位置改进特征编码,实现92.3%的模拟数据检索准确率,并展示了在真实患者数据上的可行性。
Key Takeaways
- 术中超声可增强经口机器人手术中的实时可视化。
- 术前扫描帮助外科医生形成心理地图。
- 术中图像与术前扫描的匹配可通过自动图像检索实现,指引助理调整超声探头至目标平面。
- 引入自监督对比学习方法,匹配术中超声视图与术前图像数据库。
- 采用了新颖的对比学习策略,利用扫查内的相似性和超声探头位置改善特征编码。
- 该方法实现了模拟数据上92.3%的检索准确率,且优于基于时间对比学习的方法。
点此查看论文截图


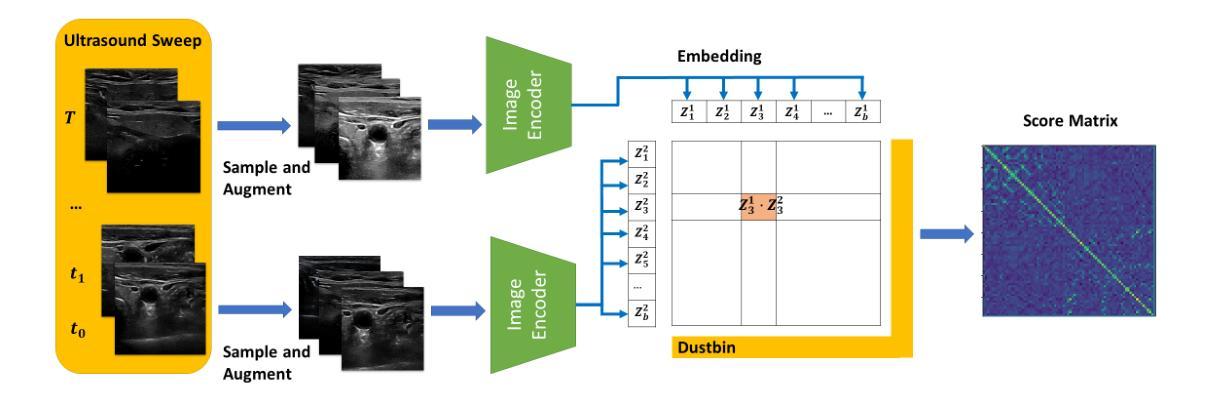
SKIPNet: Spatial Attention Skip Connections for Enhanced Brain Tumor Classification
Authors:Khush Mendiratta, Shweta Singh, Pratik Chattopadhyay
Early detection of brain tumors through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is essential for timely treatment, yet access to diagnostic facilities remains limited in remote areas. Gliomas, the most common primary brain tumors, arise from the carcinogenesis of glial cells in the brain and spinal cord, with glioblastoma patients having a median survival time of less than 14 months. MRI serves as a non-invasive and effective method for tumor detection, but manual segmentation of brain MRI scans has traditionally been a labor-intensive task for neuroradiologists. Recent advancements in computer-aided design (CAD), machine learning (ML), and deep learning (DL) offer promising solutions for automating this process. This study proposes an automated deep learning model for brain tumor detection and classification using MRI data. The model, incorporating spatial attention, achieved 96.90% accuracy, enhancing the aggregation of contextual information for better pattern recognition. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms baseline models, highlighting its robustness and potential for advancing automated MRI-based brain tumor analysis.
通过磁共振成像(MRI)早期检测脑肿瘤对于及时治疗至关重要,但在偏远地区,诊断设备的可及性仍然有限。胶质瘤是最常见的原发性脑肿瘤,起源于大脑和脊髓胶质细胞的癌变,其中胶质母细胞瘤患者的中位生存时间不到14个月。MRI作为一种非侵入性的有效肿瘤检测方法,但手动分割脑部MRI扫描对神经放射科医生来说一直是一项劳动密集型的任务。计算机辅助设计(CAD)、机器学习(ML)和深度学习(DL)的最新进展为自动化这一过程提供了有前景的解决方案。本研究提出了一种利用MRI数据自动检测与分类脑肿瘤的深度学习模型。该模型结合了空间注意力机制,达到了96.90%的准确率,通过对上下文信息的聚集来增强模式识别。实验结果表明,所提出的方法优于基线模型,证明了其在推进基于MRI的自动脑肿瘤分析的稳健性和潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨早期通过磁共振成像(MRI)检测脑肿瘤的重要性,特别是在医疗资源有限的偏远地区。针对胶质细胞癌引发的常见脑肿瘤——胶质瘤,文章介绍了利用深度学习模型自动检测与分类脑肿瘤的最新进展。该模型结合空间注意力机制,准确率达到96.90%,能更有效地聚合上下文信息以识别模式,为基于MRI的脑肿瘤分析提供了先进自动化的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 早期检测对及时治疗和改善脑肿瘤患者生存率至关重要。
- 磁共振成像(MRI)是检测脑肿瘤的非侵入性有效方法。
- 传统手动分割MRI扫描图像对神经放射科医生而言是一项劳动密集型任务。
- 计算机辅助设计(CAD)、机器学习(ML)和深度学习(DL)的最新进展为自动化分割提供了机会。
- 提出的深度学习模型结合了空间注意力机制,实现了高达96.90%的准确率。
- 该模型能更有效地聚合上下文信息以进行模式识别,从而提高了脑肿瘤检测的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

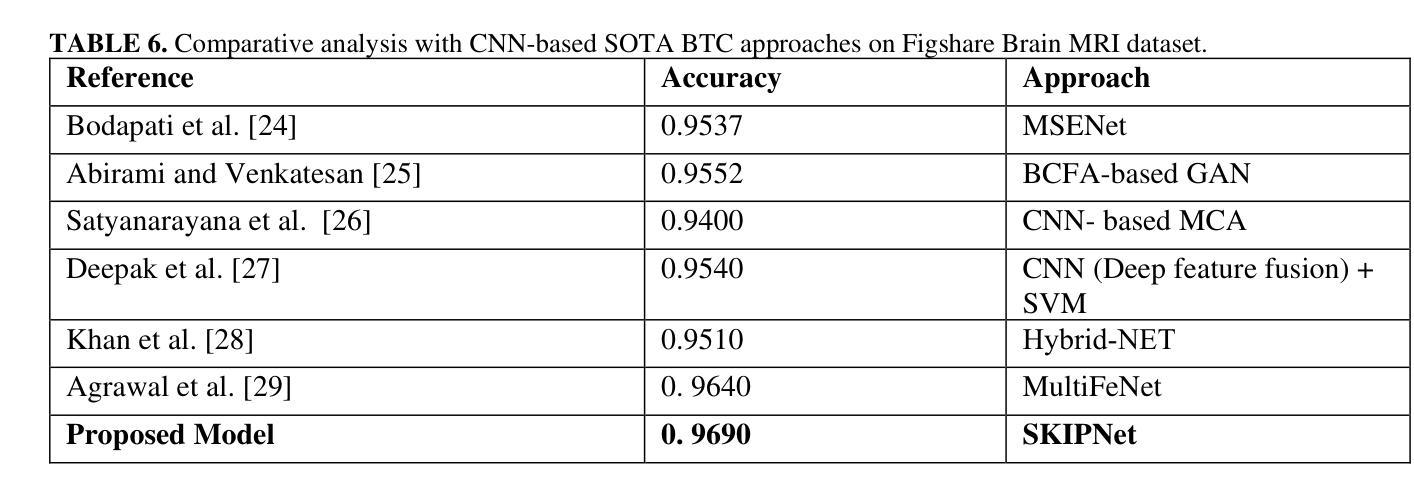
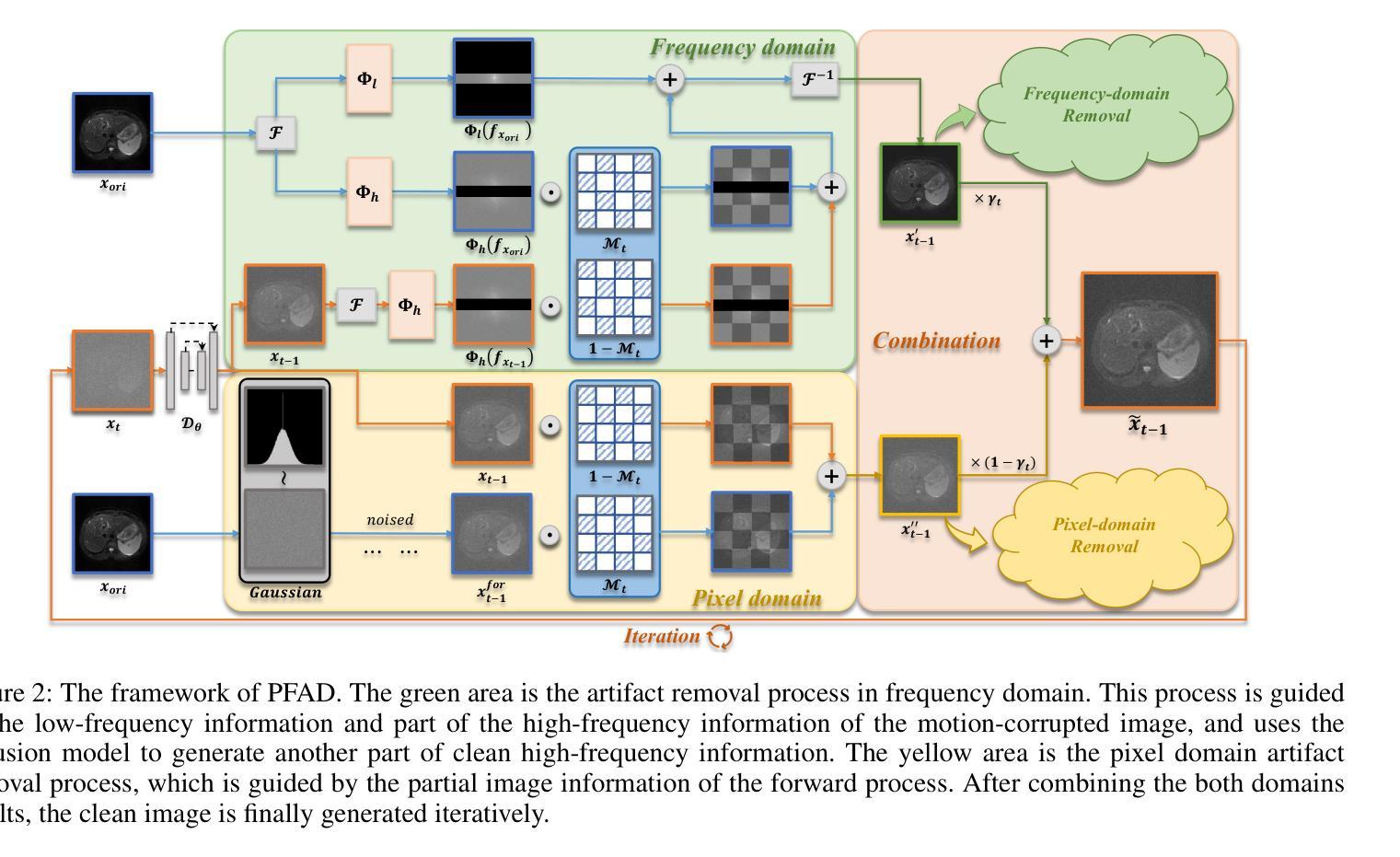
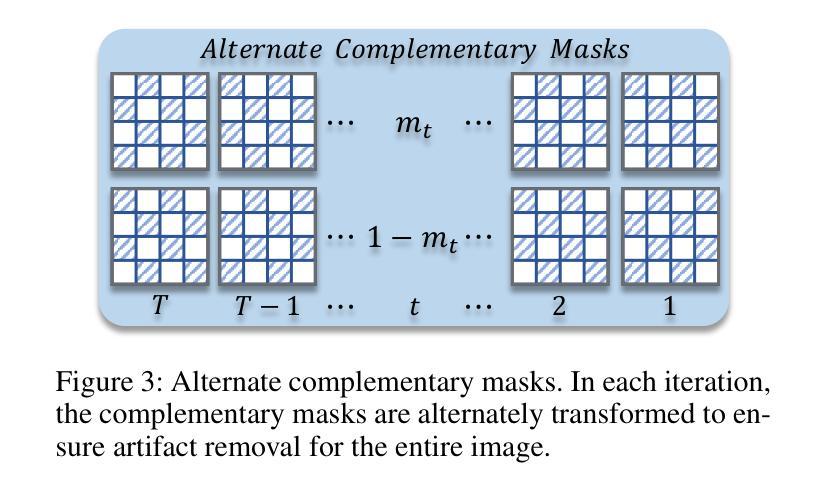
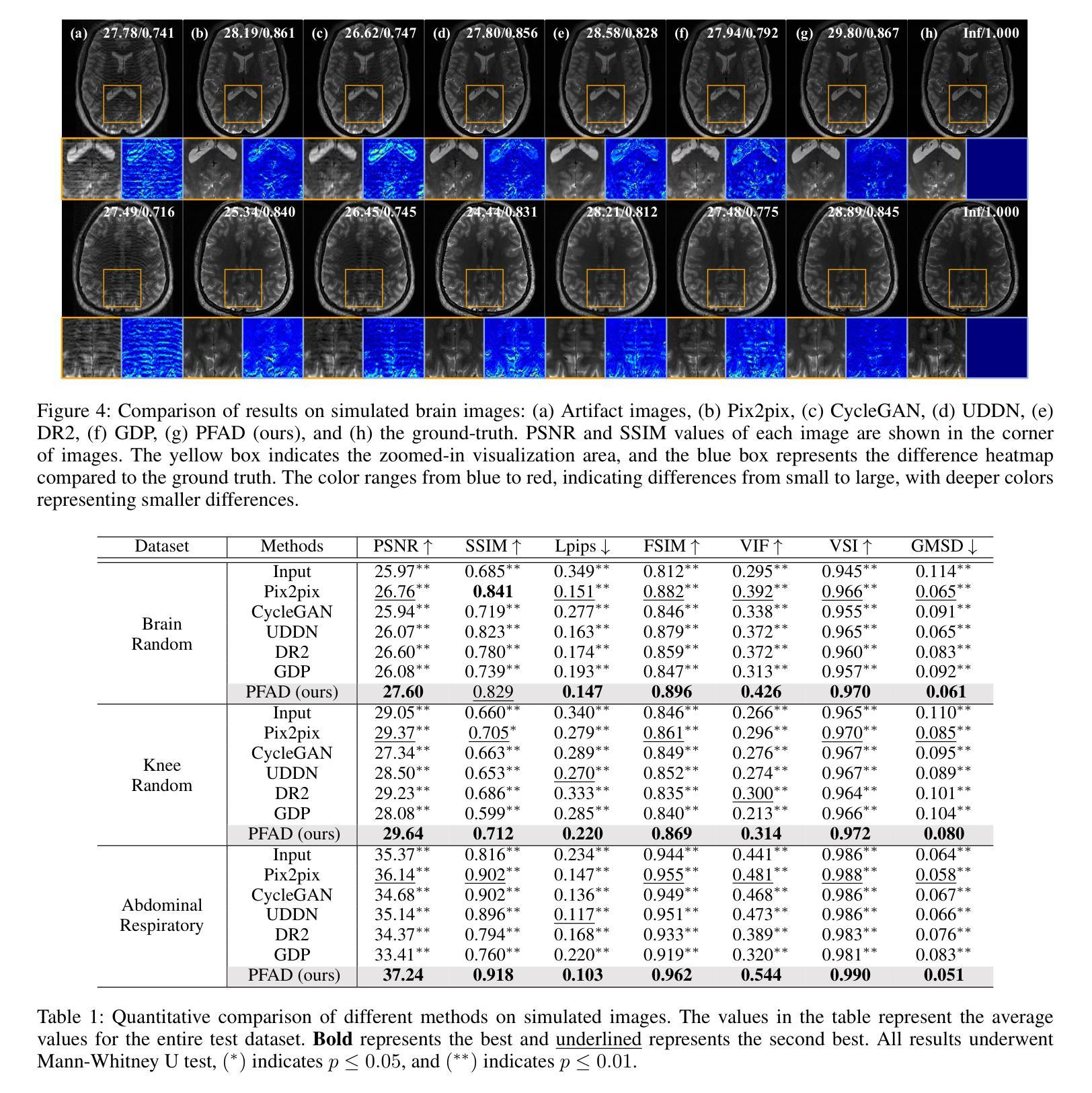
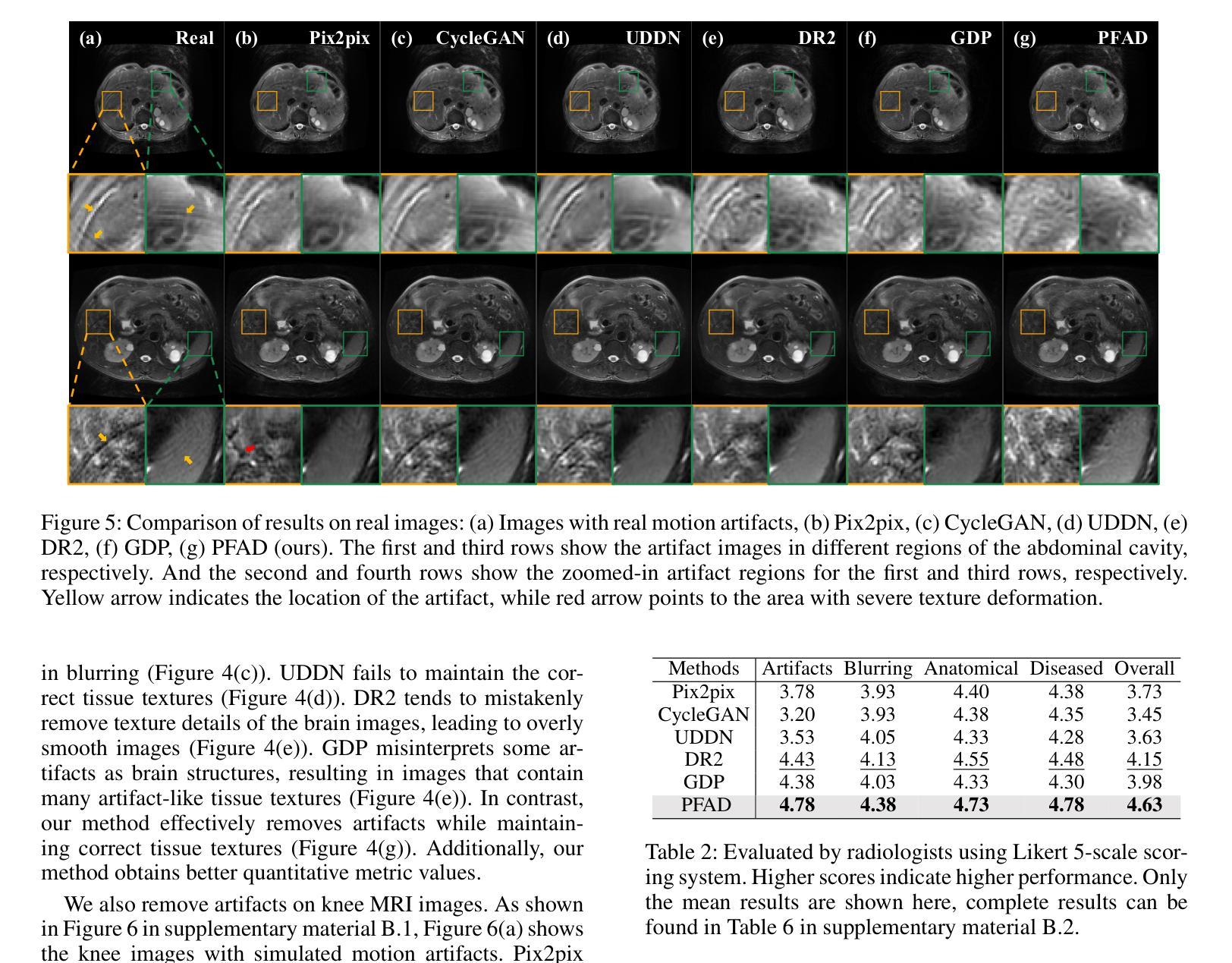
Motion Artifact Removal in Pixel-Frequency Domain via Alternate Masks and Diffusion Model
Authors:Jiahua Xu, Dawei Zhou, Lei Hu, Jianfeng Guo, Feng Yang, Zaiyi Liu, Nannan Wang, Xinbo Gao
Motion artifacts present in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can seriously interfere with clinical diagnosis. Removing motion artifacts is a straightforward solution and has been extensively studied. However, paired data are still heavily relied on in recent works and the perturbations in k-space (frequency domain) are not well considered, which limits their applications in the clinical field. To address these issues, we propose a novel unsupervised purification method which leverages pixel-frequency information of noisy MRI images to guide a pre-trained diffusion model to recover clean MRI images. Specifically, considering that motion artifacts are mainly concentrated in high-frequency components in k-space, we utilize the low-frequency components as the guide to ensure correct tissue textures. Additionally, given that high-frequency and pixel information are helpful for recovering shape and detail textures, we design alternate complementary masks to simultaneously destroy the artifact structure and exploit useful information. Quantitative experiments are performed on datasets from different tissues and show that our method achieves superior performance on several metrics. Qualitative evaluations with radiologists also show that our method provides better clinical feedback. Our code is available at https://github.com/medcx/PFAD.
磁共振成像(MRI)中的运动伪影会严重干扰临床诊断。去除运动伪影是一种简单的解决方案,已经得到了广泛的研究。然而,最近的研究仍然严重依赖配对数据,而k空间(频率域)中的扰动并未得到很好的考虑,这限制了它们在临床领域的应用。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型的无监督净化方法,该方法利用噪声MRI图像的像素频率信息来指导预训练的扩散模型恢复清洁的MRI图像。具体来说,考虑到运动伪影主要集中在k空间的高频成分中,我们利用低频成分作为指导,以确保正确的组织纹理。此外,鉴于高频和像素信息有助于恢复形状和细节纹理,我们设计了交替的互补掩膜来同时破坏伪影结构并利用有用信息。在不同组织数据集上进行的定量实验表明,我们的方法在多个指标上实现了卓越的性能。与放射科医生进行的定性评估也表明,我们的方法提供了更好的临床反馈。我们的代码可在https://github.com/medcx/PFAD找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures, AAAI 2025
Summary
本文提出一种新型无监督净化方法,利用噪声MRI图像的像素频率信息引导预训练的扩散模型恢复清洁MRI图像,以解决磁共振成像中的运动伪影问题。该方法利用低频频谱成分作为指南,确保正确的组织纹理,并通过交替互补掩膜同时破坏伪影结构并挖掘有用信息。实验结果显示该方法在多个指标上表现优异,获得了放射科医生的好评。
Key Takeaways
- 磁共振成像中的运动伪影会干扰临床诊断,去除伪影是重要且被广泛研究的问题。
- 现有方法仍依赖配对数据,且在k空间(频率域)的扰动未得到充分考虑,限制了其在临床的应用。
- 本文提出了一种新型无监督净化方法,利用像素频率信息去除MRI图像中的运动伪影。
- 方法主要利用低频频谱成分作为指南,确保恢复的组织纹理正确。
- 通过设计交替互补掩膜,该方法能同时破坏伪影结构并挖掘有用的图像信息。
- 实验结果显示该方法在多个数据集上的性能指标表现优异。
- 该方法与放射科医生的评估相比,提供了更好的临床反馈。
点此查看论文截图

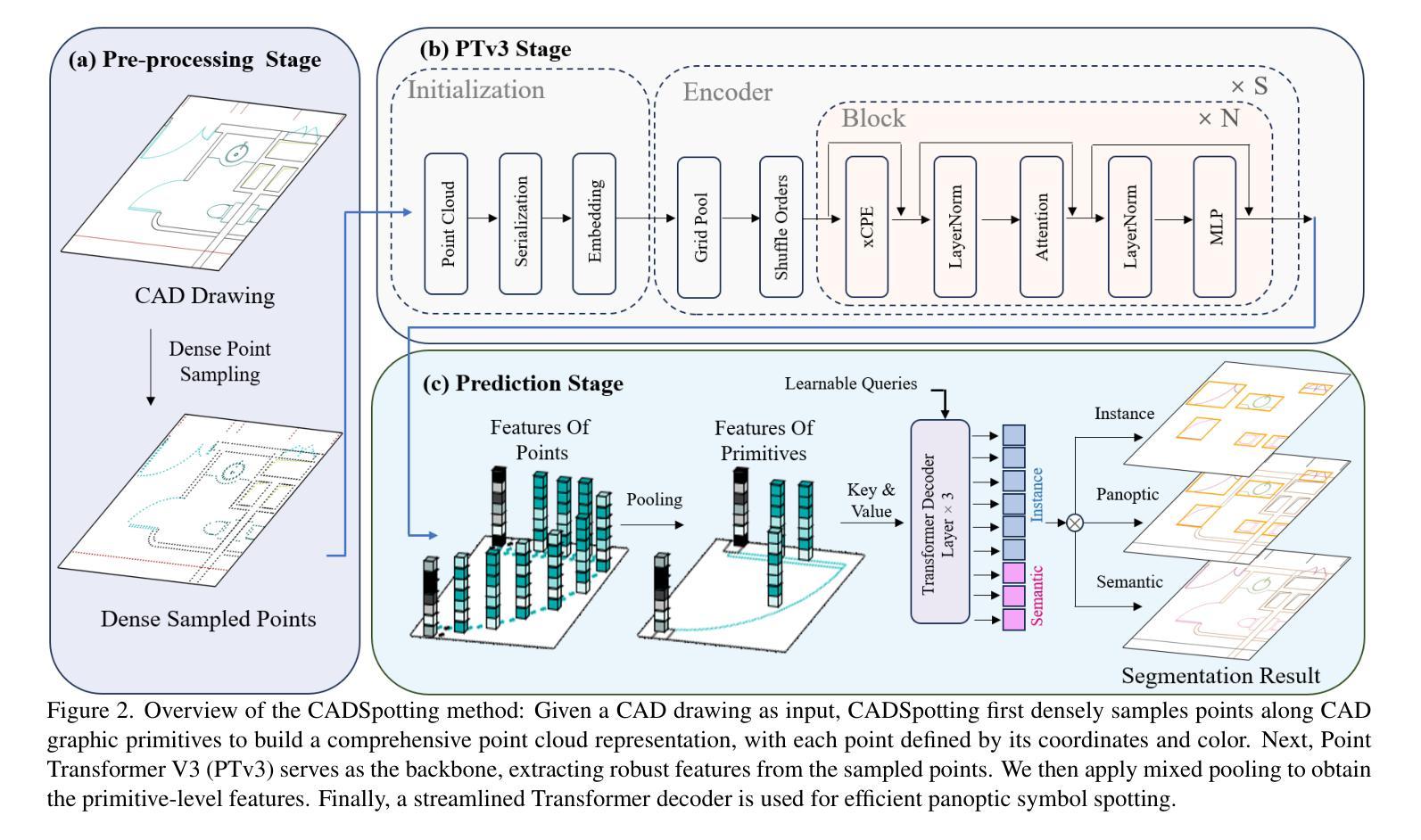
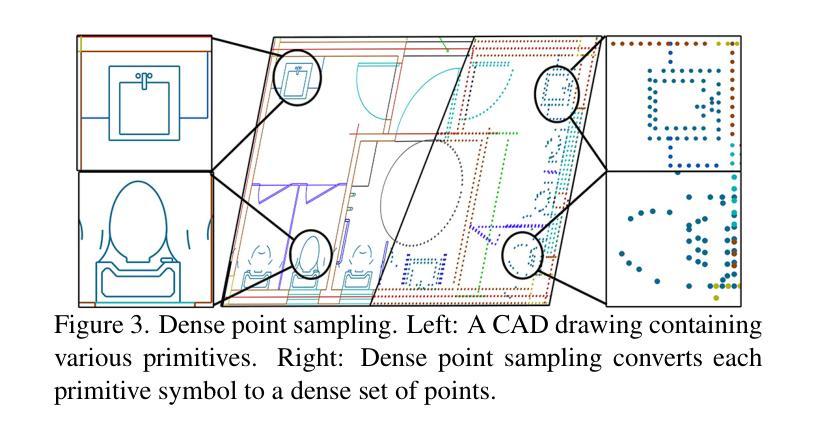
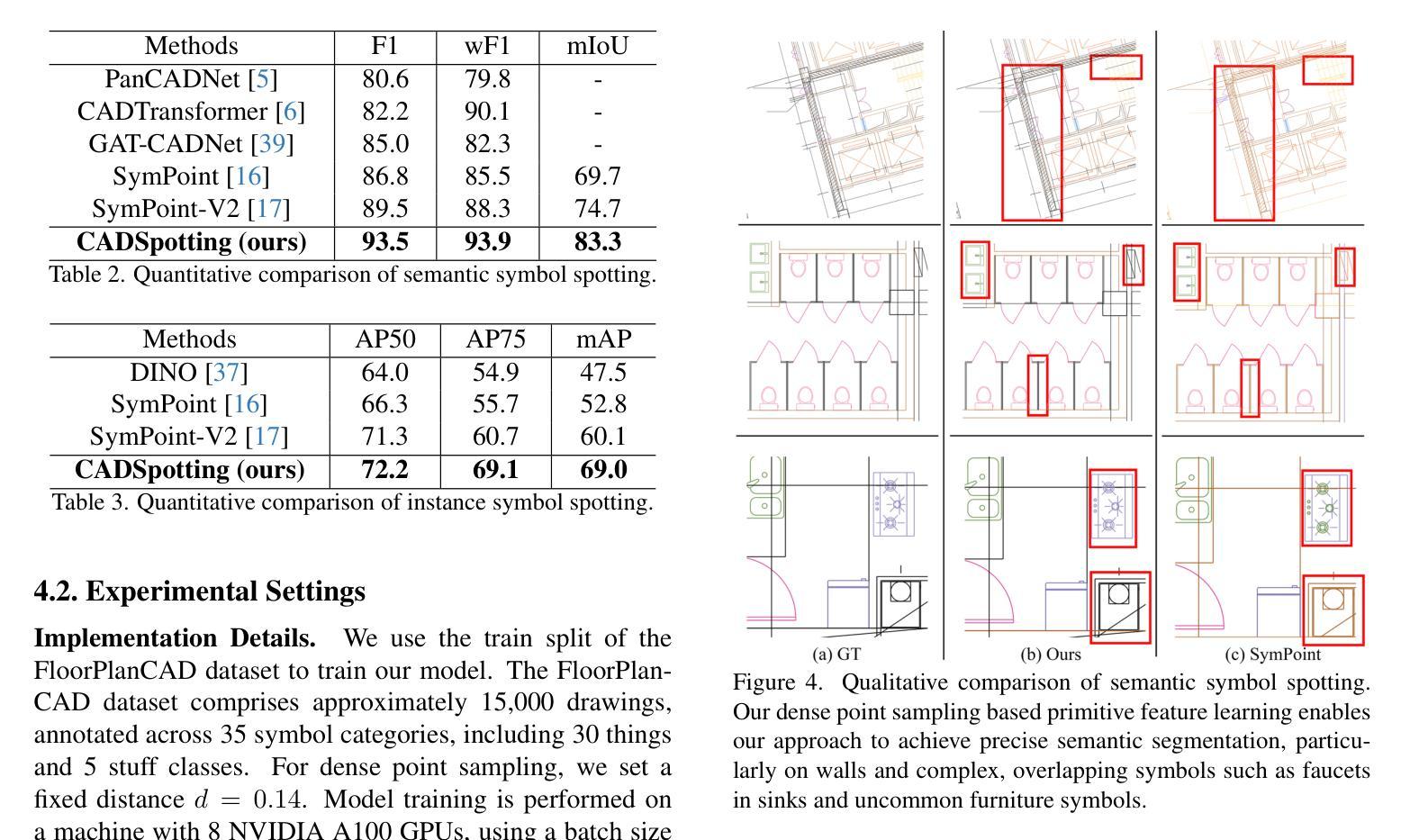
CADSpotting: Robust Panoptic Symbol Spotting on Large-Scale CAD Drawings
Authors:Jiazuo Mu, Fuyi Yang, Yanshun Zhang, Junxiong Zhang, Yongjian Luo, Lan Xu, Yujiao Shi, Jingyi Yu, Yingliang Zhang
We introduce CADSpotting, an efficient method for panoptic symbol spotting in large-scale architectural CAD drawings. Existing approaches struggle with the diversity of symbols, scale variations, and overlapping elements in CAD designs. CADSpotting overcomes these challenges by representing each primitive with dense points instead of a single primitive point, described by essential attributes like coordinates and color. Building upon a unified 3D point cloud model for joint semantic, instance, and panoptic segmentation, CADSpotting learns robust feature representations. To enable accurate segmentation in large, complex drawings, we further propose a novel Sliding Window Aggregation (SWA) technique, combining weighted voting and Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS). Moreover, we introduce a large-scale CAD dataset named LS-CAD to support our experiments. Each floorplan in LS-CAD has an average coverage of 1,000 square meter(versus 100 square meter in the existing dataset), providing a valuable benchmark for symbol spotting research. Experimental results on FloorPlanCAD and LS-CAD datasets demonstrate that CADSpotting outperforms existing methods, showcasing its robustness and scalability for real-world CAD applications.
我们介绍了CADSpotting,这是一种在大规模建筑CAD图纸中进行全景符号识别的高效方法。现有方法在应对CAD设计中的符号多样性、尺度变化和元素重叠等方面存在困难。CADSpotting通过用密集点表示每个基本体而不是单个基本点来克服这些挑战,这些密集点由坐标和颜色等基本属性描述。基于统一的3D点云模型进行联合语义、实例和全景分割,CADSpotting学习鲁棒的特征表示。为了在大规模复杂图纸中实现准确分割,我们进一步提出了一种新颖的滑动窗口聚合(SWA)技术,该技术结合了加权投票和非最大抑制(NMS)。此外,我们引入了一个大规模CAD数据集LS-CAD来支持我们的实验。LS-CAD中的每个平面图平均覆盖面积为1000平方米(而现有数据集中的平面图覆盖面积为100平方米),为符号识别研究提供了一个有价值的基准。在FloorPlanCAD和LS-CAD数据集上的实验结果表明,CADSpotting优于现有方法,展示了其在现实世界CAD应用中的稳健性和可扩展性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16pages, 12 figures, Project web-page: https://dgeneai.github.io/cadspotting-pages/
Summary
CADSpotting方法介绍了一种针对大规模建筑CAD图纸的全视符号识别技术。它克服了现有方法在符号多样性、尺度变化和CAD设计元素重叠方面的挑战。通过密集点表示每个基本元素,结合坐标和颜色等关键属性进行描述,并在统一的3D点云模型上进行联合语义、实例和全视分割,学习稳健的特征表示。此外,还提出了一种新型的滑动窗口聚合(SWA)技术,结合加权投票和非极大值抑制(NMS)方法,确保在大规模复杂图纸中的精确分割。同时,引入了大规模的CAD数据集LS-CAD来支持实验,为符号识别研究提供了有价值的基准。实验结果证明,CADSpotting在FloorPlanCAD和LS-CAD数据集上的表现优于现有方法,展现出其在真实世界CAD应用中的稳健性和可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- CADSpotting是一种针对大规模建筑CAD图纸的高效全视符号识别方法。
- 它通过密集点表示每个基本元素,以应对符号多样性、尺度变化和重叠元素的问题。
- CADSpotting在统一的3D点云模型上进行联合语义、实例和全视分割,学习稳健的特征表示。
- 提出了滑动窗口聚合(SWA)技术,结合加权投票和非极大值抑制(NMS),提高在大规模复杂图纸中的分割准确性。
- 引入了LS-CAD数据集,为符号识别研究提供有价值的基准。
- CADSpotting在FloorPlanCAD和LS-CAD数据集上的表现优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

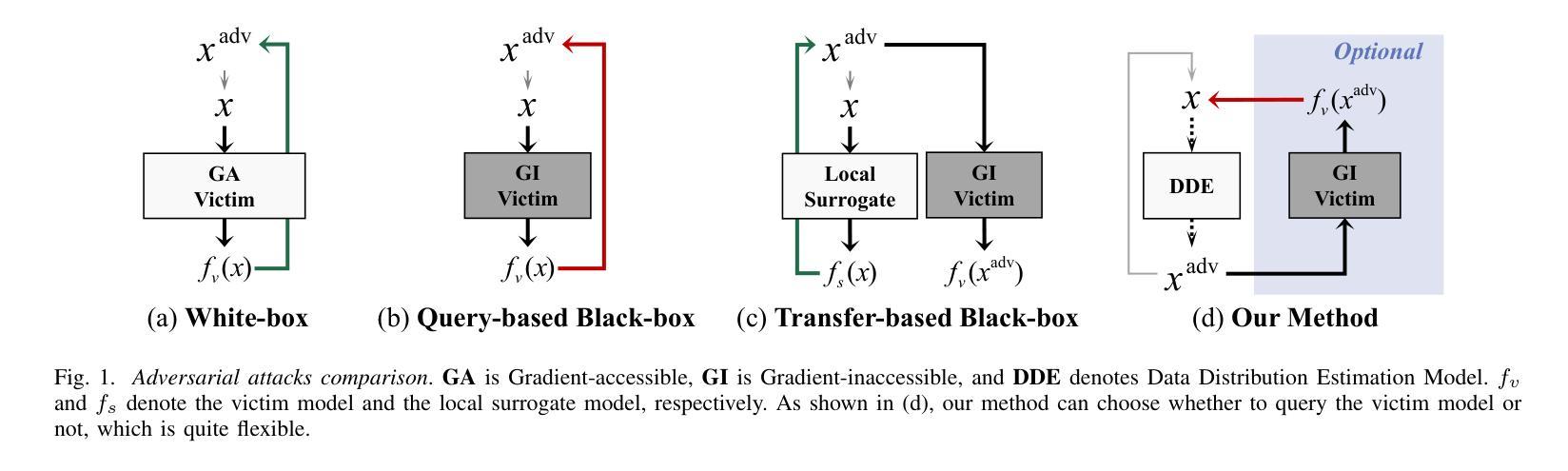
A Generative Victim Model for Segmentation
Authors:Aixuan Li, Jing Zhang, Jiawei Shi, Yiran Zhong, Yuchao Dai
We find that the well-trained victim models (VMs), against which the attacks are generated, serve as fundamental prerequisites for adversarial attacks, i.e. a segmentation VM is needed to generate attacks for segmentation. In this context, the victim model is assumed to be robust to achieve effective adversarial perturbation generation. Instead of focusing on improving the robustness of the task-specific victim models, we shift our attention to image generation. From an image generation perspective, we derive a novel VM for segmentation, aiming to generate adversarial perturbations for segmentation tasks without requiring models explicitly designed for image segmentation. Our approach to adversarial attack generation diverges from conventional white-box or black-box attacks, offering a fresh outlook on adversarial attack strategies. Experiments show that our attack method is able to generate effective adversarial attacks with good transferability.
我们发现,针对生成的攻击训练良好的受害者模型(VMs)是对抗攻击的基本前提。例如,对于分割攻击,需要一个分割的VM来生成攻击。在此情况下,假设受害者模型具有鲁棒性以实现有效的对抗扰动生成。与传统的研究专注于提高针对特定任务的受害者模型的鲁棒性不同,我们将注意力转向了图像生成。从图像生成的角度,我们开发了一种新型VM用于分割任务,旨在针对分割任务生成对抗扰动,无需使用专为图像分割设计的模型。我们的对抗性攻击生成方法与传统的白盒或黑盒攻击有所不同,为对抗性攻击策略提供了新颖的视角。实验表明,我们的攻击方法可以生成有效且具有良好迁移性的对抗性攻击。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究发现针对对抗攻击生成,需要训练良好的受害者模型(VMs)。这些VMs对于生成针对特定任务的对抗攻击至关重要。研究提出了一种新型VM用于图像分割任务,旨在生成针对分割任务的对抗扰动,无需专门设计图像分割模型。本研究中的攻击生成方法与传统的白盒或黑盒攻击不同,为对抗攻击策略提供了新思路。实验证明,该方法能够生成具有有效性和良好迁移性的对抗攻击。
Key Takeaways
- 受害者模型(VMs)在生成对抗攻击中起到基础先决条件的作用。
- 针对特定任务(如分割)的对抗攻击生成需要相应的任务特定VMs。
- 研究提出了一种新型VM,用于图像分割任务,无需专门设计图像分割模型即可生成对抗扰动。
- 该研究中的攻击生成方法与传统的白盒和黑盒攻击不同。
- 该方法生成的对抗攻击具有有效性和良好的迁移性。
- 研究将注意力从提高任务特定受害者模型的鲁棒性转移到图像生成上。
点此查看论文截图


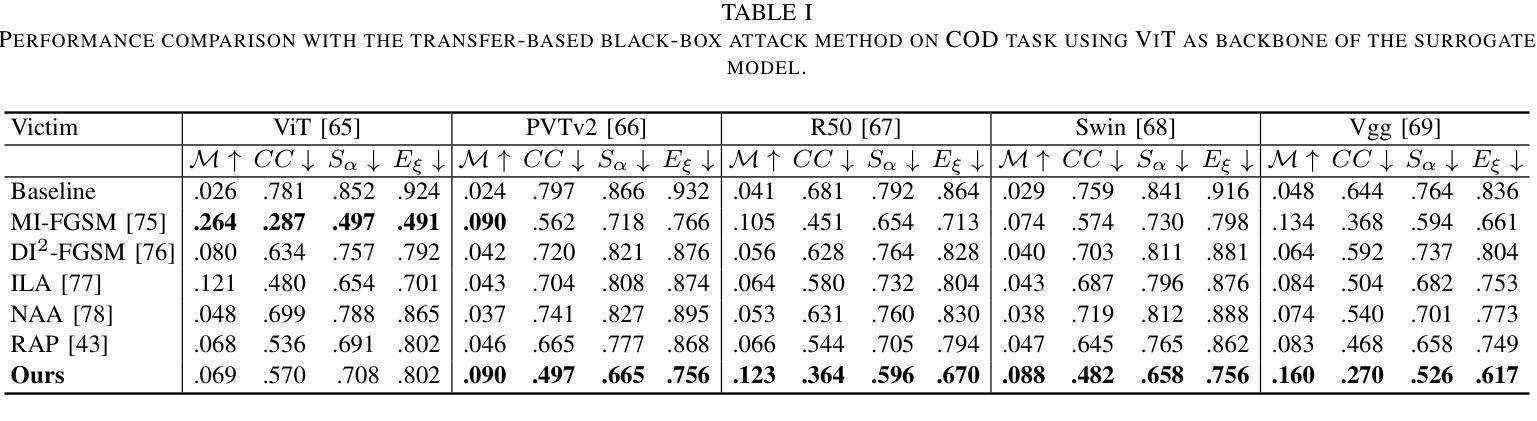
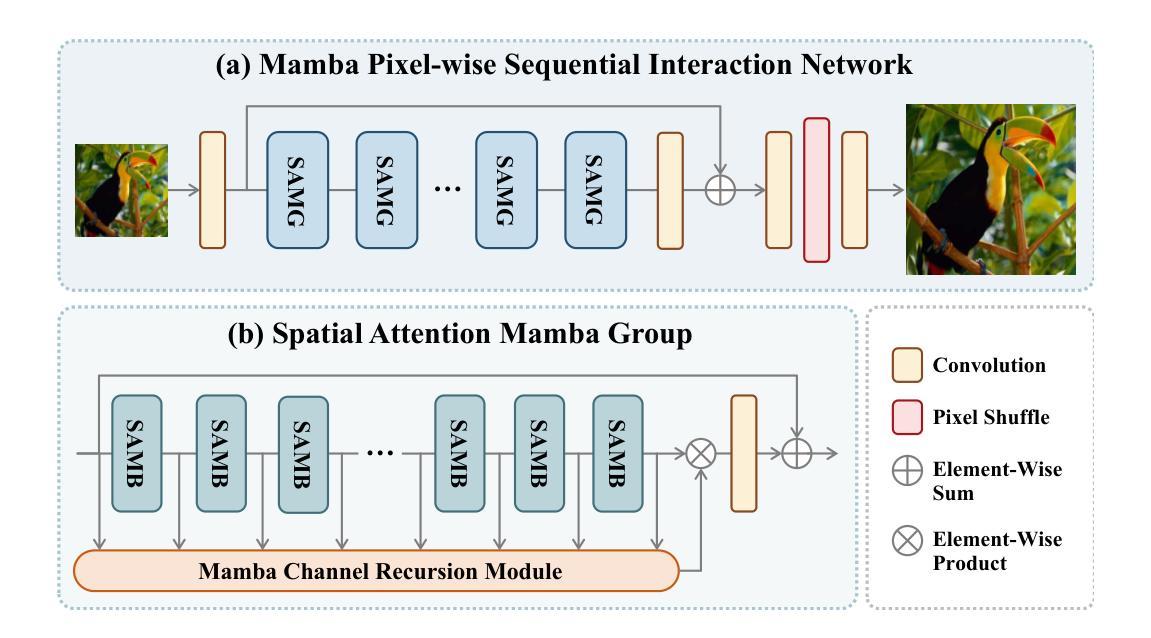
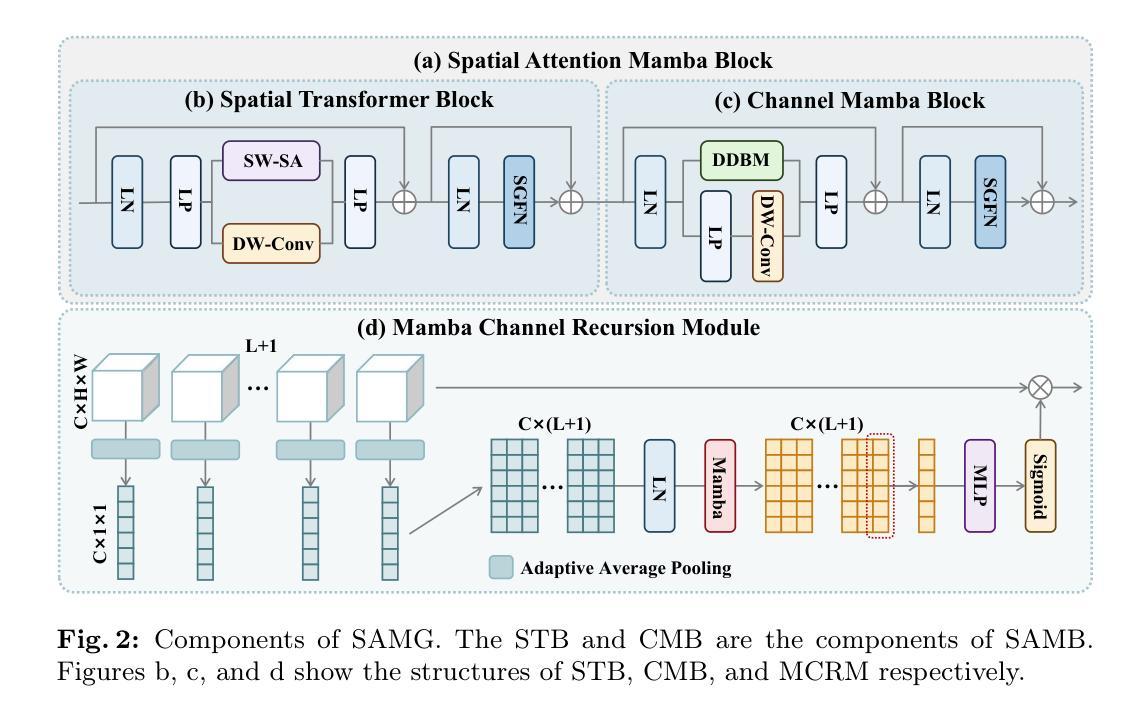
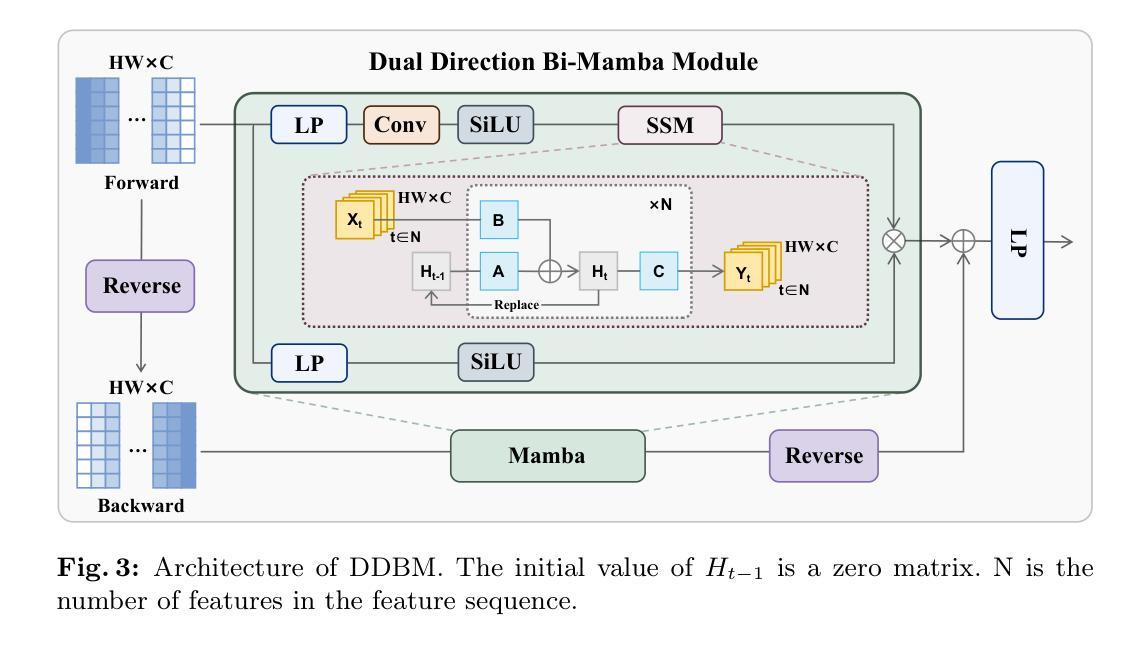
MPSI: Mamba enhancement model for pixel-wise sequential interaction Image Super-Resolution
Authors:Yuchun He, Yuhan He
Single image super-resolution (SR) has long posed a challenge in the field of computer vision. While the advent of deep learning has led to the emergence of numerous methods aimed at tackling this persistent issue, the current methodologies still encounter challenges in modeling long sequence information, leading to limitations in effectively capturing the global pixel interactions. To tackle this challenge and achieve superior SR outcomes, we propose the Mamba pixel-wise sequential interaction network (MPSI), aimed at enhancing the establishment of long-range connections of information, particularly focusing on pixel-wise sequential interaction. We propose the Channel-Mamba Block (CMB) to capture comprehensive pixel interaction information by effectively modeling long sequence information. Moreover, in the existing SR methodologies, there persists the issue of the neglect of features extracted by preceding layers, leading to the loss of valuable feature information. While certain existing models strive to preserve these features, they frequently encounter difficulty in establishing connections across all layers. To overcome this limitation, MPSI introduces the Mamba channel recursion module (MCRM), which maximizes the retention of valuable feature information from early layers, thereby facilitating the acquisition of pixel sequence interaction information from multiple-level layers. Through extensive experimentation, we demonstrate that MPSI outperforms existing super-resolution methods in terms of image reconstruction results, attaining state-of-the-art performance.
单图像超分辨率(SR)一直是计算机视觉领域的一大挑战。虽然深度学习的出现导致出现了许多旨在解决这一持久性问题的方法,但当前的方法在建模长序列信息方面仍面临挑战,导致在有效捕获全局像素交互方面存在局限性。为了应对这一挑战并实现更优越的超分辨率结果,我们提出了Mamba像素级顺序交互网络(MPSI),旨在增强长距离信息连接的建立,特别侧重于像素级的顺序交互。我们提出了Channel-Mamba Block(CMB),通过有效地对长序列信息进行建模来捕捉全面的像素交互信息。此外,在现有的超分辨率方法中,仍存在忽视先前层提取的特征的问题,导致有价值的特征信息丢失。虽然某些现有模型努力保留这些特征,但它们经常在建立跨所有层的连接方面遇到困难。为了克服这一局限性,MPSI引入了Mamba通道递归模块(MCRM),最大限度地保留早期层的宝贵特征信息,从而便于从多层获取像素序列交互信息。通过大量实验,我们证明MPSI在图像重建结果方面优于现有超分辨率方法,达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度学习的方法在处理图像超分辨率(SR)问题上仍存在挑战,如建模长序列信息和全局像素交互方面的局限。为此,我们提出了Mamba像素级顺序交互网络(MPSI),旨在增强长距离信息连接,尤其注重像素级的顺序交互。通过引入Channel-Mamba Block(CMB)和Mamba通道递归模块(MCRM),我们的方法能够有效捕捉像素交互信息,并保留早期层提取的特征信息。实验表明,MPSI在图像重建结果上优于现有超分辨率方法,达到最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 当前深度学习在处理图像超分辨率(SR)问题时面临建模长序列信息和全局像素交互的挑战。
- Mamba像素级顺序交互网络(MPSI)旨在增强长距离信息连接,注重像素级的顺序交互。
- Channel-Mamba Block(CMB)能有效捕捉像素交互信息,通过建模长序列信息实现。
- 现有SR方法忽视了早期层提取的特征信息,导致有价值的信息丢失。
- MPSI通过引入Mamba通道递归模块(MCRM)克服这一局限,保留早期层的特征信息。
- MPSI在图像重建结果上优于现有超分辨率方法。
点此查看论文截图

Integrating MedCLIP and Cross-Modal Fusion for Automatic Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Qianhao Han, Junyi Liu, Zengchang Qin, Zheng Zheng
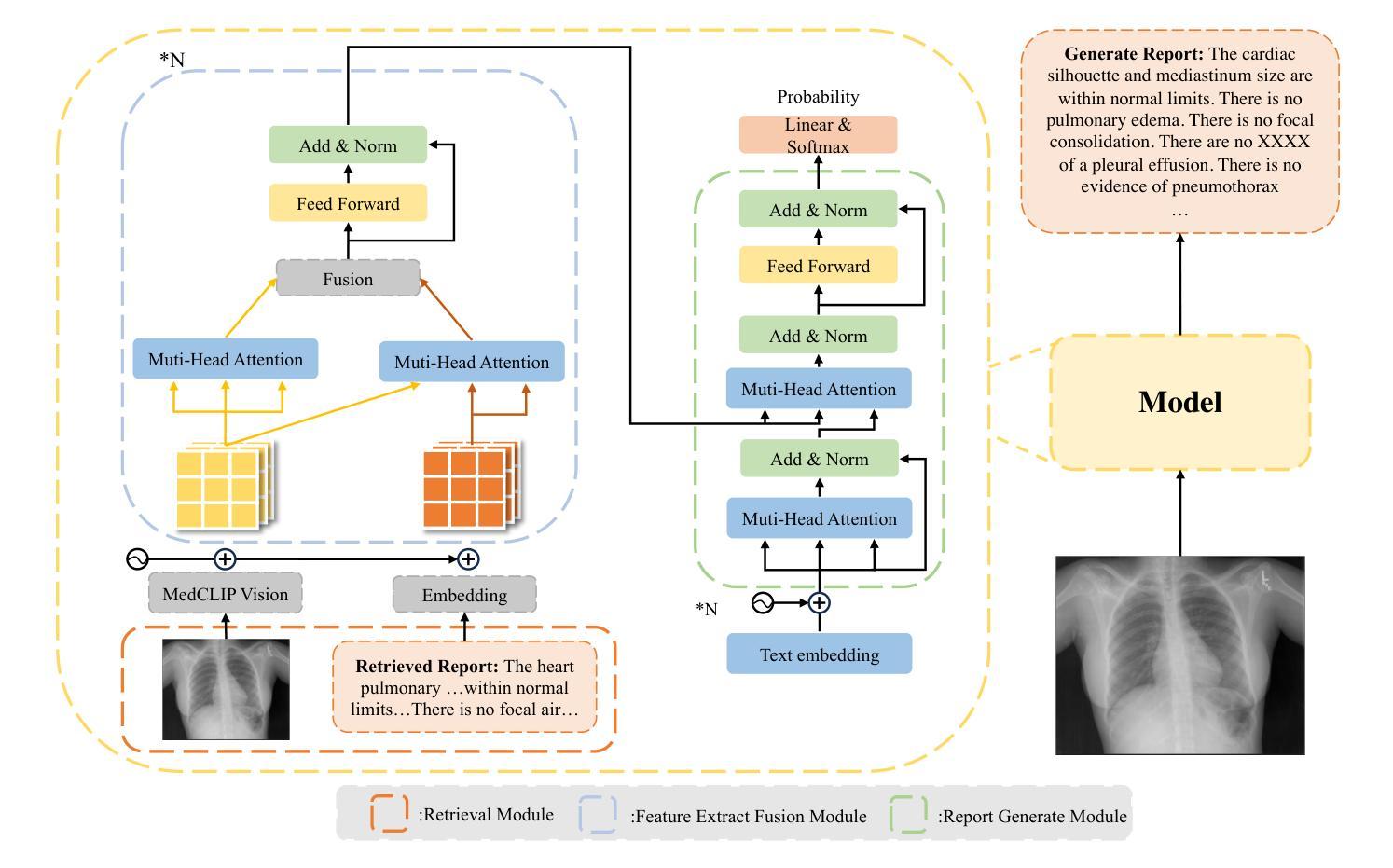
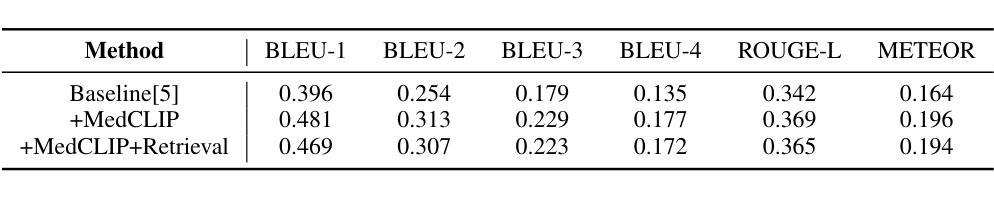
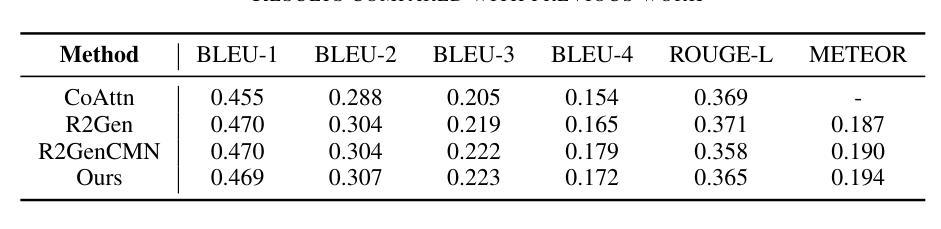
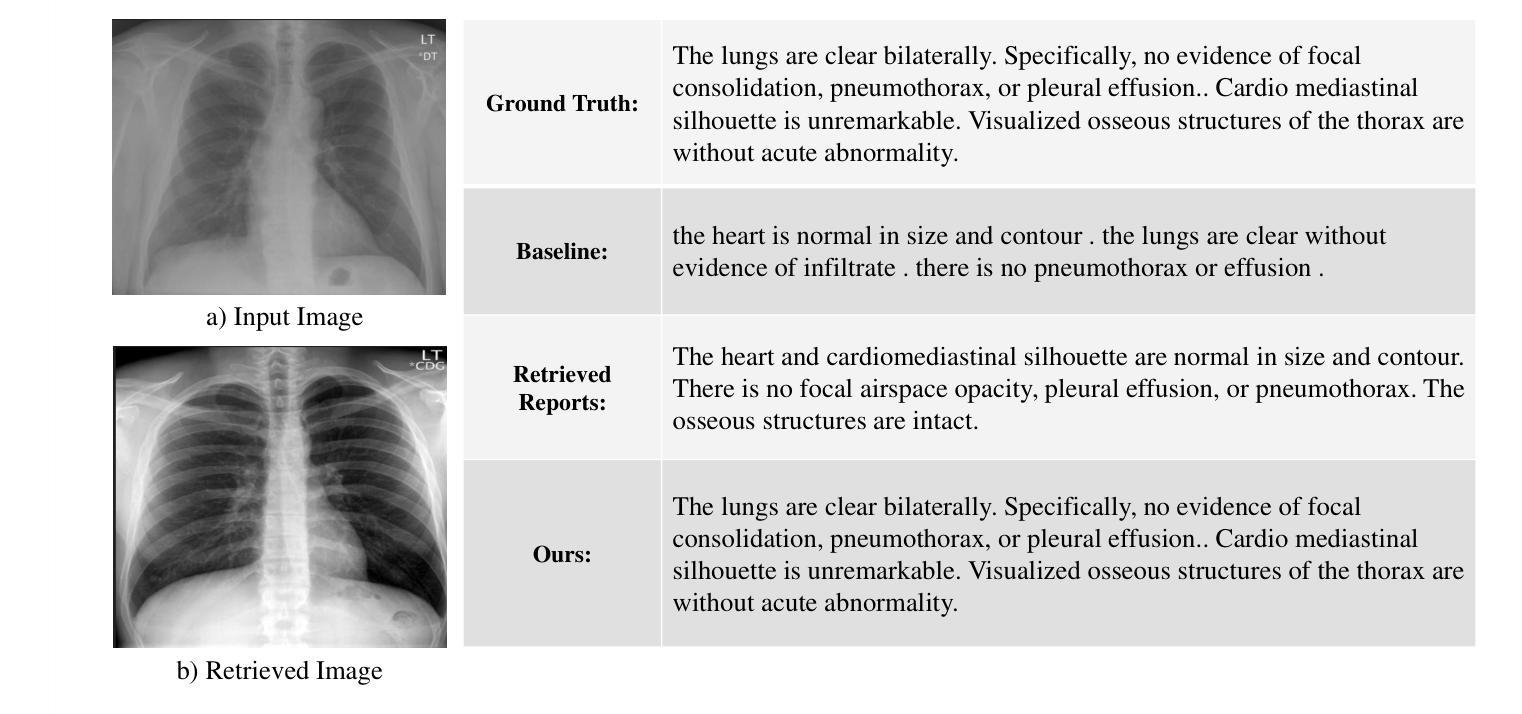
Automating radiology report generation can significantly reduce the workload of radiologists and enhance the accuracy, consistency, and efficiency of clinical documentation.We propose a novel cross-modal framework that uses MedCLIP as both a vision extractor and a retrieval mechanism to improve the process of medical report generation.By extracting retrieved report features and image features through an attention-based extract module, and integrating them with a fusion module, our method improves the coherence and clinical relevance of generated reports.Experimental results on the widely used IU-Xray dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, showing improvements over commonly used methods in both report quality and relevance.Additionally, ablation studies provide further validation of the framework, highlighting the importance of accurate report retrieval and feature integration in generating comprehensive medical reports.
自动化放射学报告生成可以显著减少放射科医生的工作量,提高临床文档的准确性、一致性和效率。我们提出了一种新颖的跨模态框架,使用MedCLIP作为视觉提取器和检索机制,以改进医疗报告生成过程。我们通过注意力基础的提取模块提取检索报告特征和图像特征,并将其与融合模块集成,从而提高生成报告的一致性临床相关性。在广泛使用的IU-Xray数据集上的实验结果证明了我们的方法的有效性,在报告质量和相关性方面都优于常用方法。此外,消融研究进一步验证了框架的有效性,强调了准确报告检索和特征融合在生成全面医疗报告中的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in IEEE Big Data 2024
Summary
医学图像报告自动生成能显著减少放射科医生的工作量,提高临床记录的准确性、一致性和效率。提出一种新型跨模态框架,利用MedCLIP作为视觉提取器和检索机制,改进医学报告生成过程。通过提取报告特征和图像特征,结合融合模块,提高了生成报告的一致性和临床相关性。在广泛使用的IU-Xray数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在报告质量和相关性方面均优于常用方法。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化生成医学报告能减轻放射科医生的工作量。
- 提出的跨模态框架利用MedCLIP技术提高报告生成过程。
- 框架通过提取报告和图像特征,增强报告的一致性。
- 融合模块提高了生成报告的临床相关性。
- 在IU-Xray数据集上的实验验证了该方法的有效性。
- 与其他常用方法相比,该方法在报告质量和相关性方面表现更优。
点此查看论文截图

Enhancing LLMs for Impression Generation in Radiology Reports through a Multi-Agent System
Authors:Fang Zeng, Zhiliang Lyu, Quanzheng Li, Xiang Li
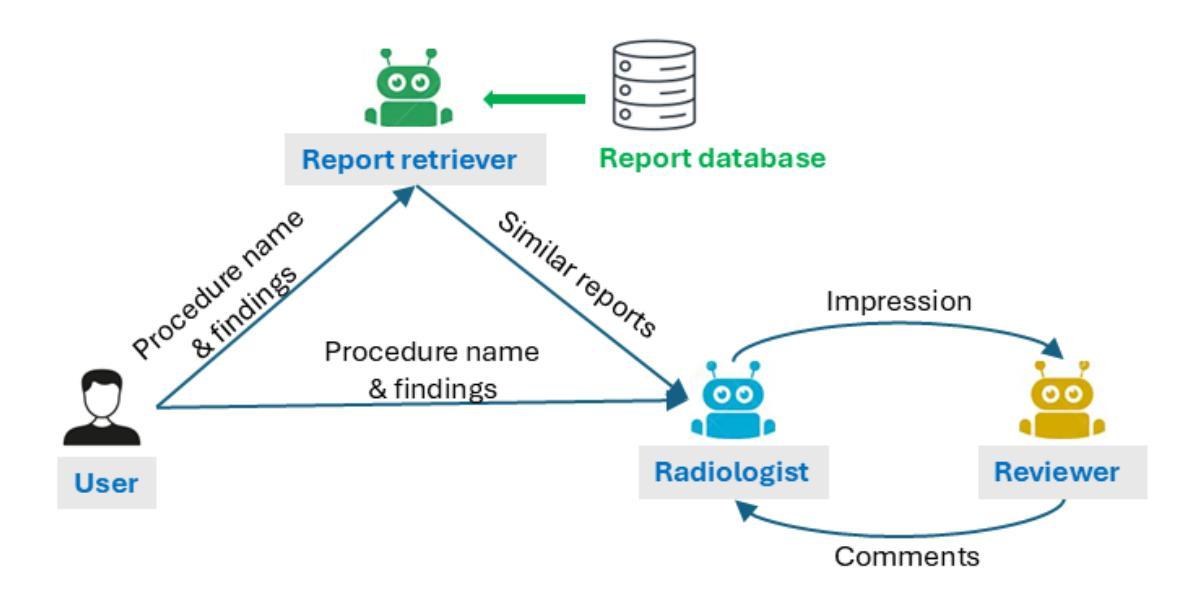
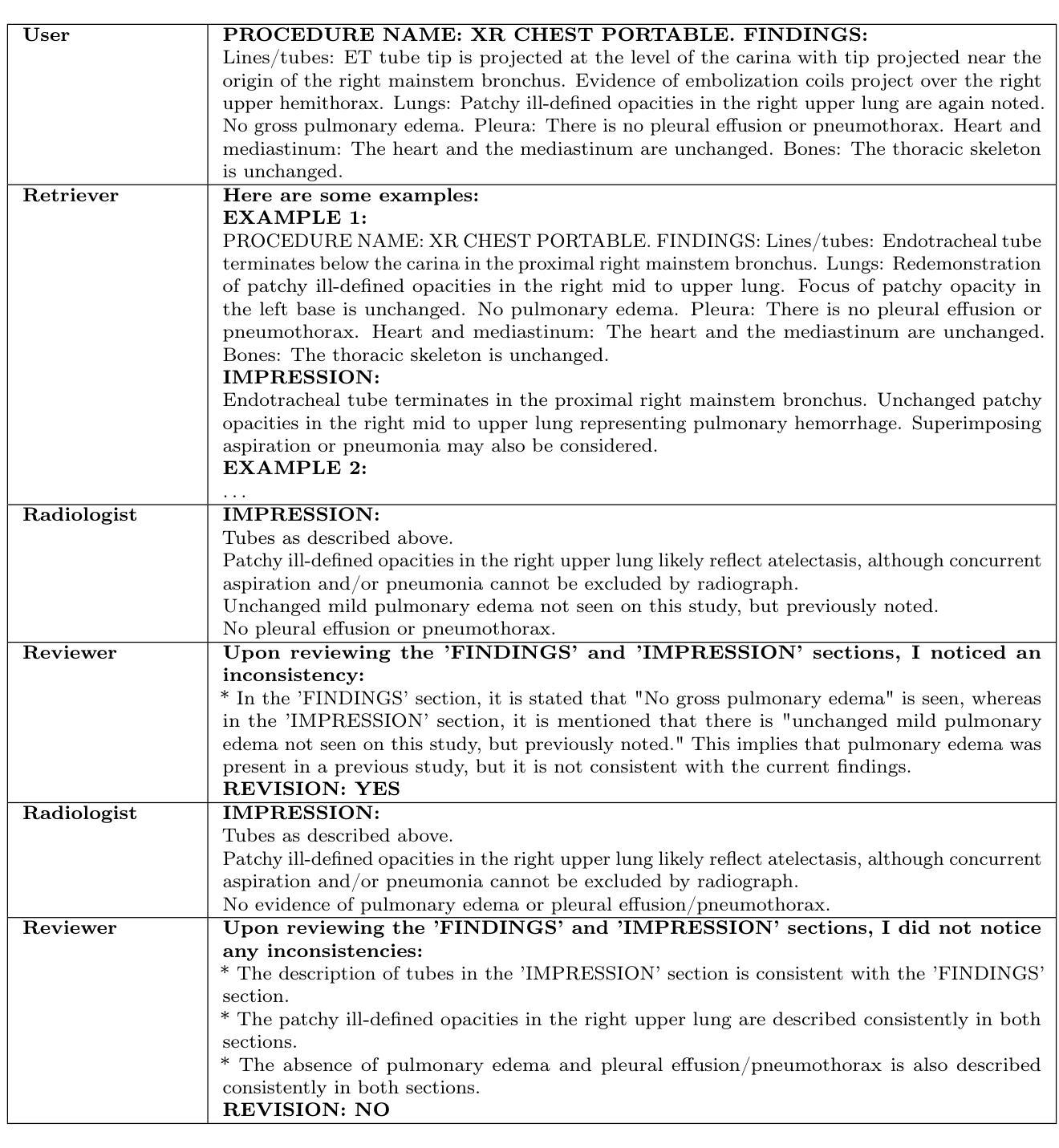
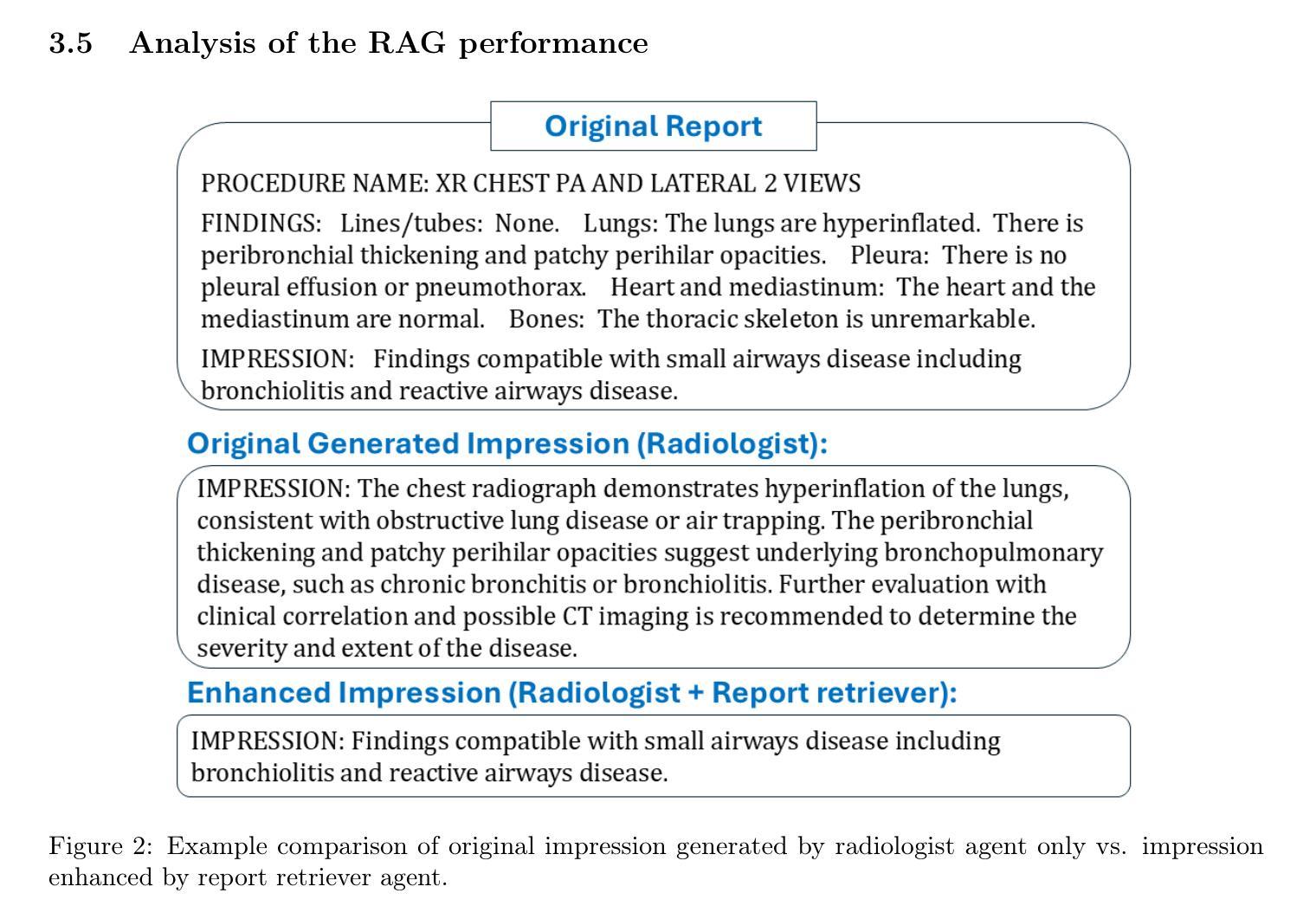
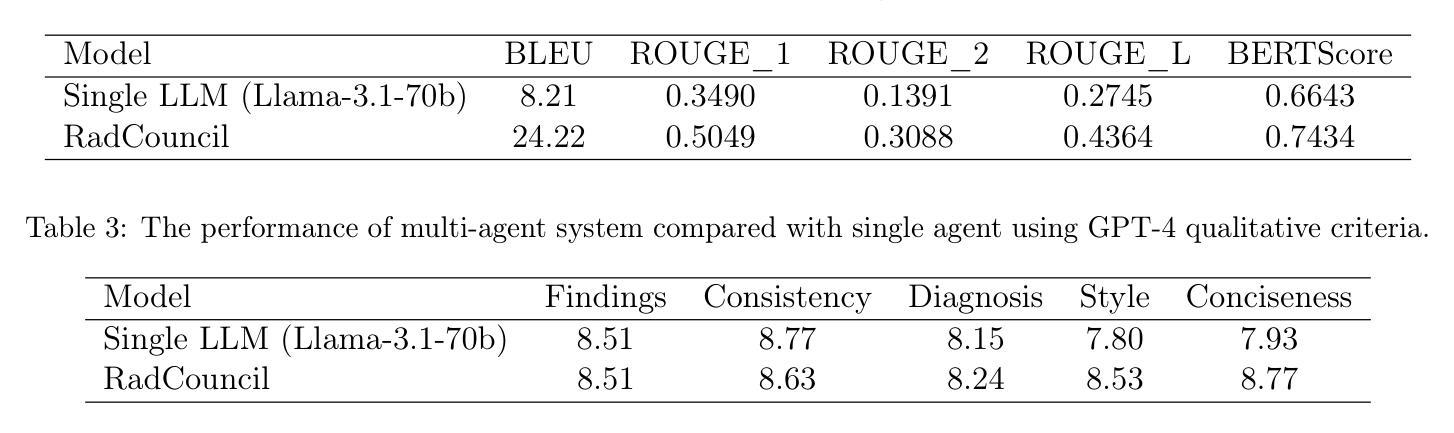
This study introduces “RadCouncil,” a multi-agent Large Language Model (LLM) framework designed to enhance the generation of impressions in radiology reports from the finding section. RadCouncil comprises three specialized agents: 1) a “Retrieval” Agent that identifies and retrieves similar reports from a vector database, 2) a “Radiologist” Agent that generates impressions based on the finding section of the given report plus the exemplar reports retrieved by the Retrieval Agent, and 3) a “Reviewer” Agent that evaluates the generated impressions and provides feedback. The performance of RadCouncil was evaluated using both quantitative metrics (BLEU, ROUGE, BERTScore) and qualitative criteria assessed by GPT-4, using chest X-ray as a case study. Experiment results show improvements in RadCouncil over the single-agent approach across multiple dimensions, including diagnostic accuracy, stylistic concordance, and clarity. This study highlights the potential of utilizing multiple interacting LLM agents, each with a dedicated task, to enhance performance in specialized medical tasks and the development of more robust and adaptable healthcare AI solutions.
本研究介绍了”RadCouncil”,这是一个多代理大型语言模型(LLM)框架,旨在增强根据发现部分生成放射报告的印象。RadCouncil包含三个专业代理:1)“检索”代理,用于从向量数据库中识别和检索类似报告;2)“放射科医生”代理,根据给定报告的发现部分以及检索到的示例报告生成印象;3)“评审”代理,评估生成的印象并提供反馈。使用胸部X射线作为案例研究,通过定量指标(BLEU、ROUGE、BERTScore)和GPT-4评估的定性标准对RadCouncil的性能进行了评估。实验结果表明,与单代理方法相比,RadCouncil在多个维度上有所改进,包括诊断准确性、风格一致性和清晰度。本研究强调了利用多个交互LLM代理的潜力,每个代理都有特定的任务,以提高在特殊医疗任务中的性能,并开发更强大、更适应的医疗保健人工智能解决方案。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究介绍了名为RadCouncil的多智能体大型语言模型(LLM)框架,该框架旨在提高放射报告印象生成的能力。RadCouncil包含三个专业智能体:检索智能体负责从向量数据库中识别和检索相似报告,放射科医生智能体基于给定报告的发现部分和检索到的示例报告生成印象,以及评审智能体负责对生成的印象进行评估并提供反馈。使用胸部X射线作为案例研究,通过定量指标(BLEU、ROUGE、BERTScore)和定性标准对RadCouncil进行了评估,实验结果表明,与单智能体方法相比,RadCouncil在诊断准确性、风格一致性和清晰度等多个维度都有所提高。本研究突出了利用多个相互作用的LLM智能体的潜力,每个智能体都有专门的任务,以提高在特殊医疗任务中的性能,并推动开发更强大和适应性更强的医疗人工智能解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- RadCouncil是一个多智能体LLM框架,旨在增强基于放射学发现生成的报告印象。
- RadCouncil包含三个专业智能体:检索智能体、放射科医生智能体和评审智能体。
- 检索智能体负责从向量数据库中检索相似报告。
- 放射科医生智能体基于发现部分和检索到的报告生成印象。
- 评审智能体评估生成的印象并提供反馈。
- 实验结果表明,RadCouncil在诊断准确性、风格一致性和清晰度等方面优于单智能体方法。
点此查看论文截图

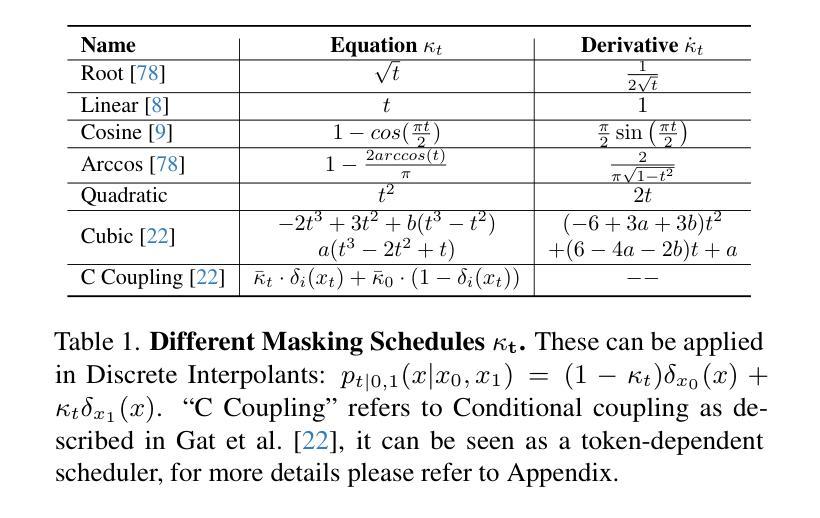
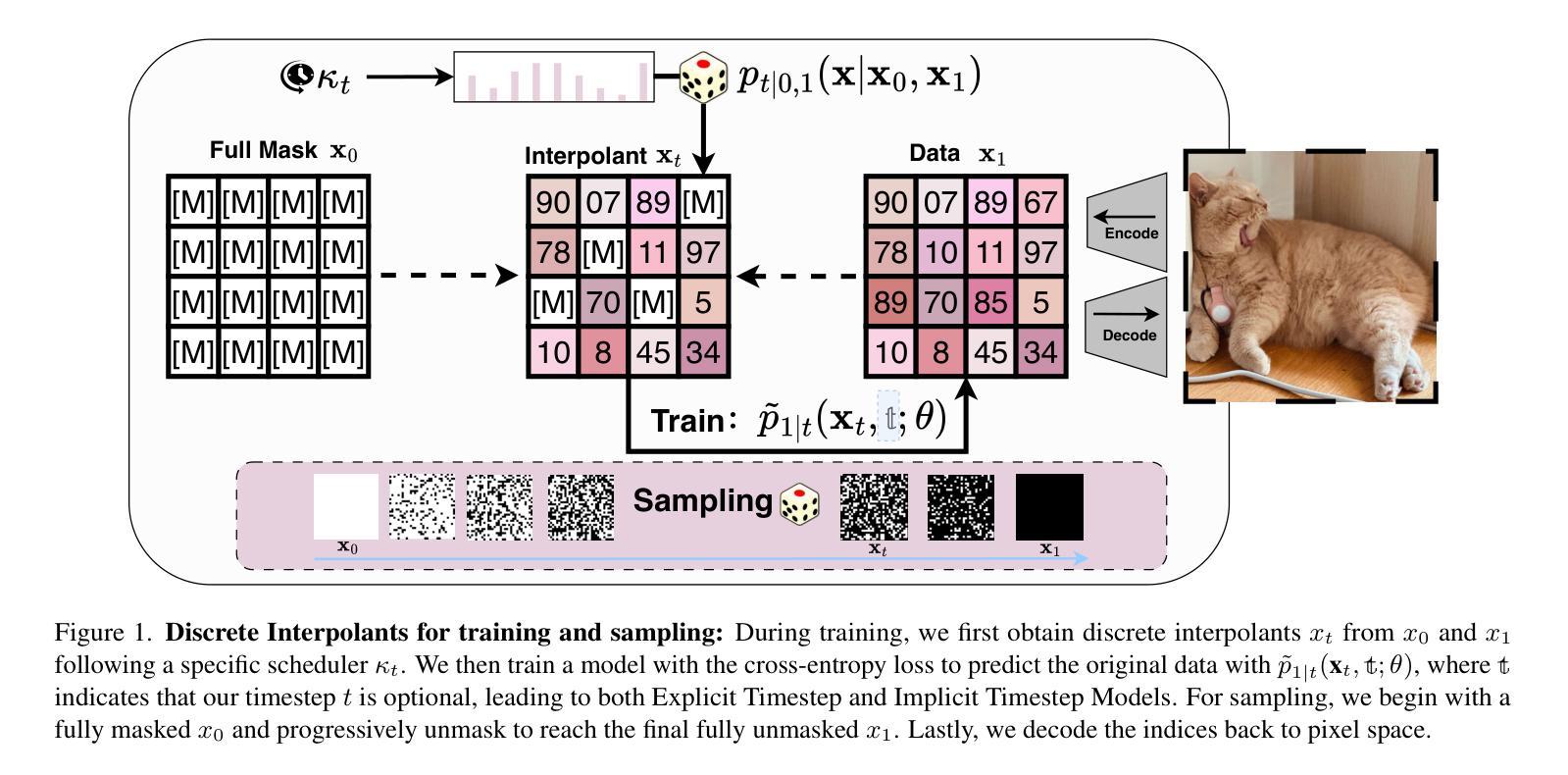
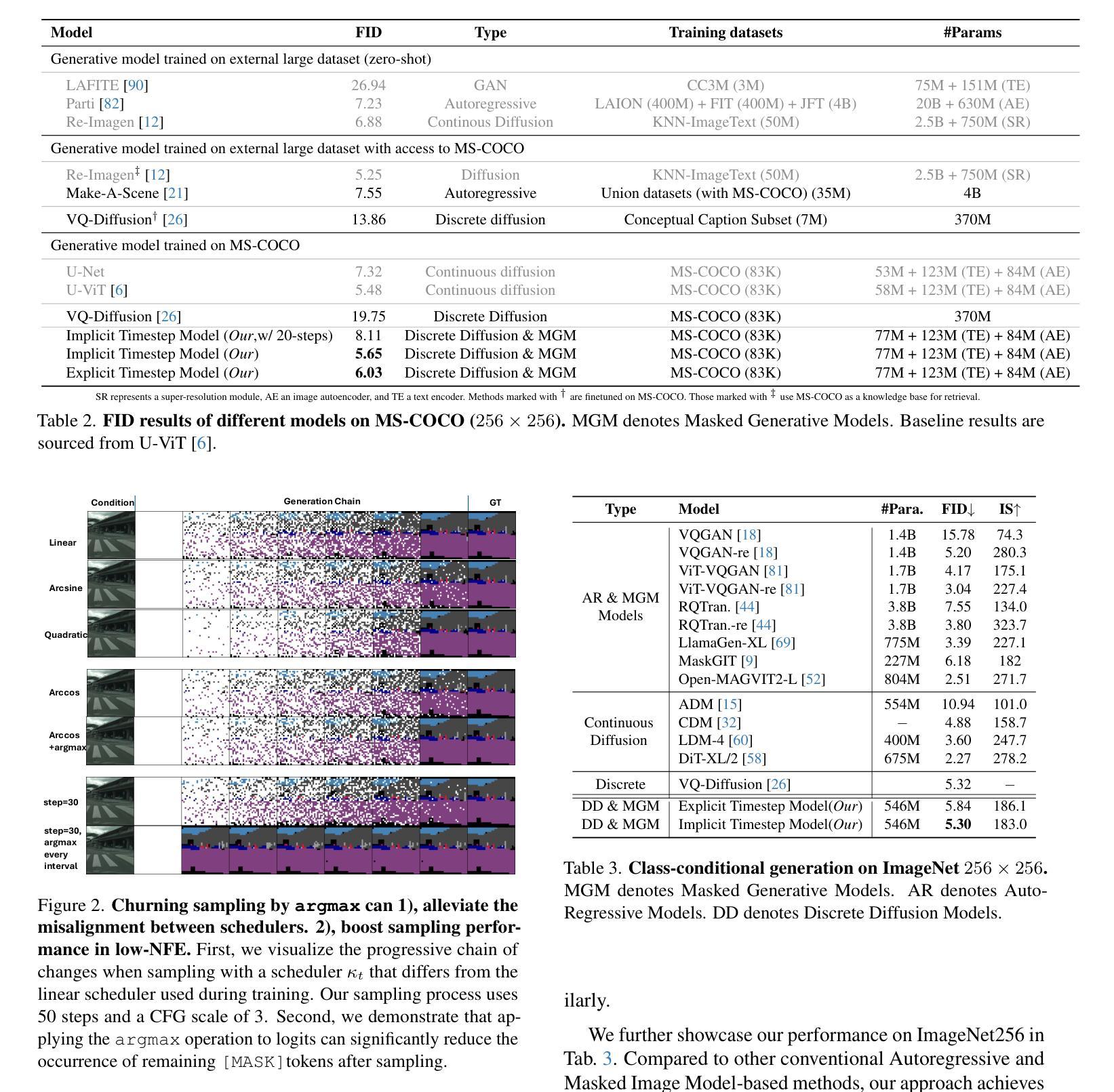
[MASK] is All You Need
Authors:Vincent Tao Hu, Björn Ommer
In generative models, two paradigms have gained attraction in various applications: next-set prediction-based Masked Generative Models and next-noise prediction-based Non-Autoregressive Models, e.g., Diffusion Models. In this work, we propose using discrete-state models to connect them and explore their scalability in the vision domain. First, we conduct a step-by-step analysis in a unified design space across two types of models including timestep-independence, noise schedule, temperature, guidance strength, etc in a scalable manner. Second, we re-cast typical discriminative tasks, e.g., image segmentation, as an unmasking process from [MASK] tokens on a discrete-state model. This enables us to perform various sampling processes, including flexible conditional sampling by only training once to model the joint distribution. All aforementioned explorations lead to our framework named Discrete Interpolants, which enables us to achieve state-of-the-art or competitive performance compared to previous discrete-state based methods in various benchmarks, like ImageNet256, MS COCO, and video dataset FaceForensics. In summary, by leveraging [MASK] in discrete-state models, we can bridge Masked Generative and Non-autoregressive Diffusion models, as well as generative and discriminative tasks.
在生成模型中,两种范式在各种应用中受到了关注:基于下一个集合预测的掩码生成模型和基于下一个噪声预测的非自回归模型,例如扩散模型。在这项工作中,我们提出使用离散状态模型来连接它们,并探索它们在视觉领域的可扩展性。首先,我们在统一的设计空间中对两种类型的模型进行了逐步分析,包括时间步独立性、噪声时间表、温度、引导强度等,以可扩展的方式。其次,我们将典型的判别任务(例如图像分割)重新定位为离散状态模型上的[MASK]标记的去掩码过程。这使得我们能够执行各种采样过程,包括通过仅训练一次来对联合分布进行建模来实现灵活的条件采样。所有上述探索都引领我们构建了名为“离散插值”的框架,该框架使我们能够在各种基准测试中达到或具有与以前基于离散状态的方法相竞争的性能,如ImageNet256、MS COCO和视频数据集FaceForensics。总之,通过利用离散状态模型中的[MASK],我们可以架起连接掩码生成模型和非自回归扩散模型的桥梁,以及生成和判别任务之间的桥梁。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report (WIP), Project Page(code, model, dataset): https://compvis.github.io/mask/
Summary
离散状态模型在生成模型中展现出强大潜力,该研究提出结合两种流行的范式——基于下一步预测的掩码生成模型和基于下一步噪声预测的非自回归模型(如扩散模型),并在视觉领域探索其可扩展性。该研究通过统一设计空间进行逐步分析,重新构建判别任务作为离散状态模型上的去掩码过程,并引入灵活的条件采样。最终构建了一个名为“离散插值”的框架,在多个基准测试中实现了最先进的性能。利用离散状态模型中的掩码,可以连接掩码生成和非自回归扩散模型,以及生成和判别任务。
Key Takeaways
- 研究展示了离散状态模型在生成模型中的潜力,结合了基于下一步预测的掩码生成模型和基于下一步噪声预测的非自回归模型(如扩散模型)。
- 通过统一设计空间进行逐步分析,探讨了两种模型的扩展性。
- 研究将判别任务重新构建为离散状态模型上的去掩码过程,实现了灵活的采样过程。
- 引入了一种名为“离散插值”的框架,实现了多种基准测试中的顶尖性能。
- 利用离散状态模型中的掩码,连接了不同类型的生成模型和判别任务。
点此查看论文截图

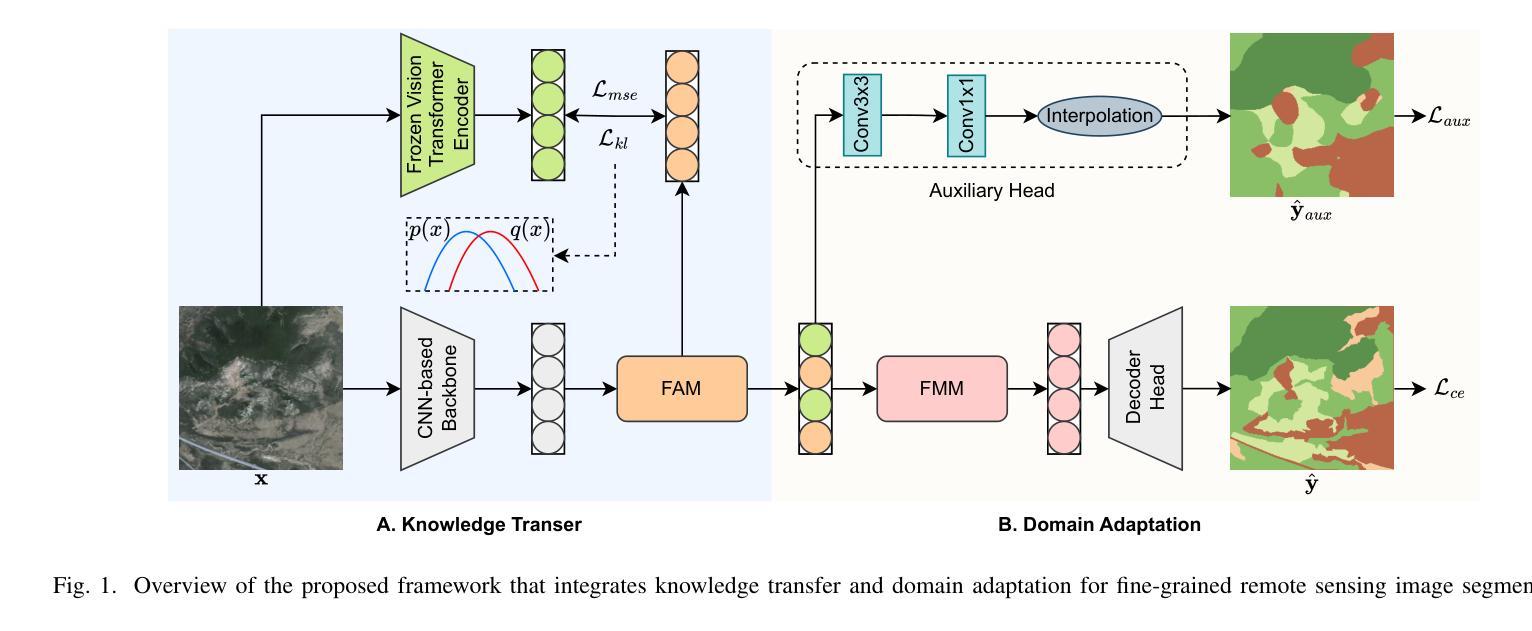
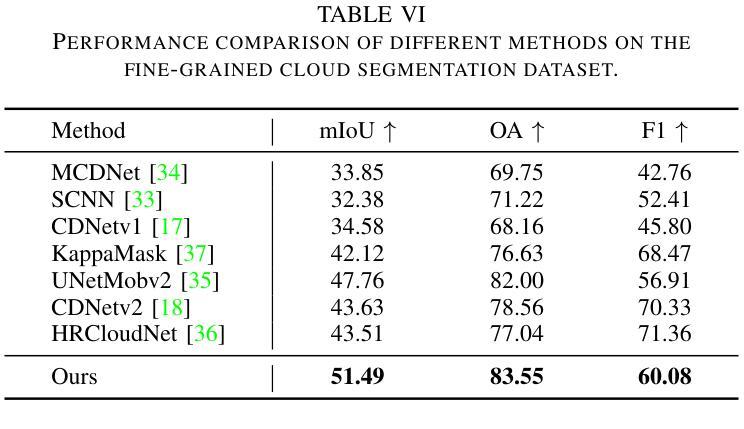
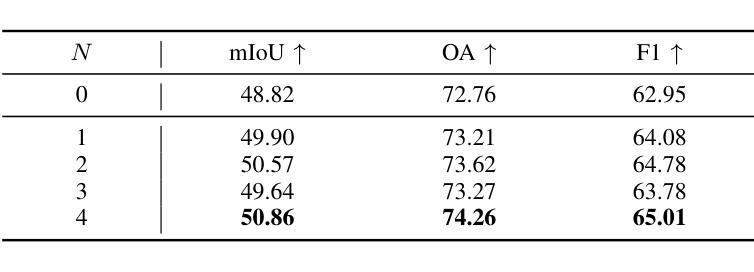
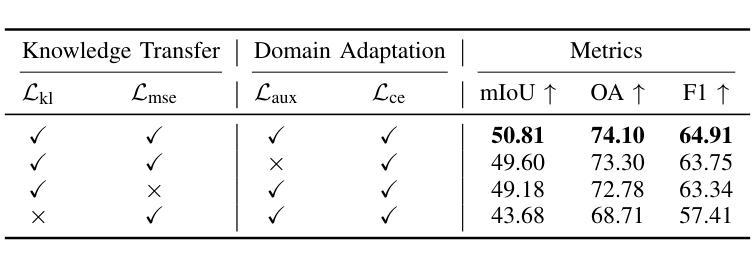
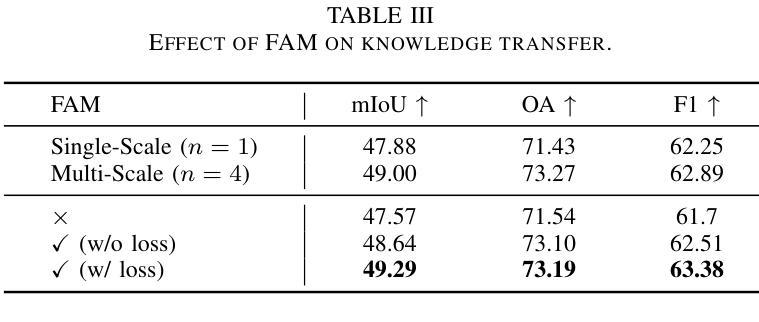
Knowledge Transfer and Domain Adaptation for Fine-Grained Remote Sensing Image Segmentation
Authors:Shun Zhang, Xuechao Zou, Kai Li, Congyan Lang, Shiying Wang, Pin Tao, Tengfei Cao
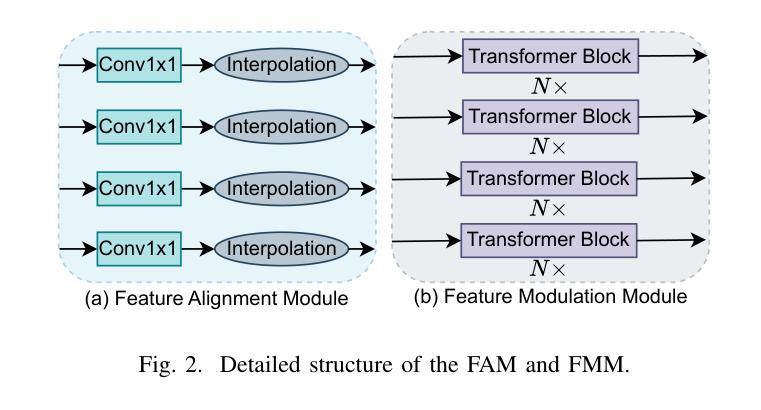
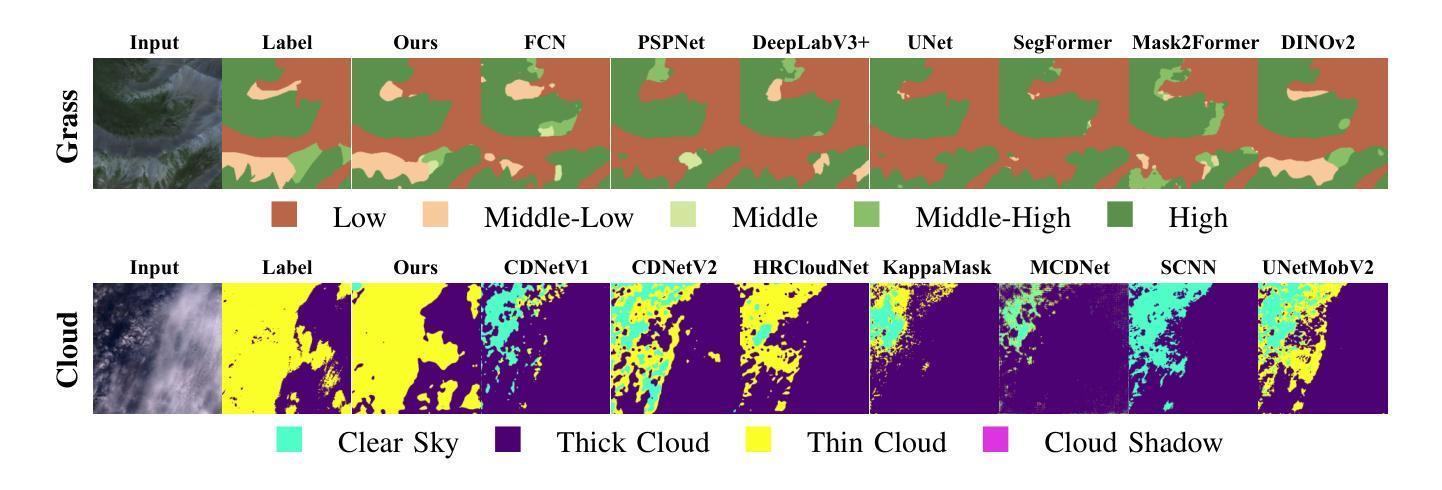
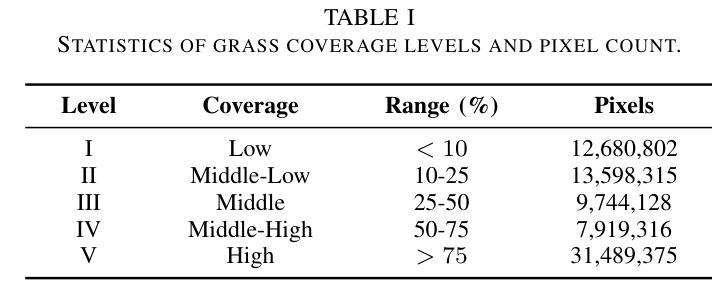
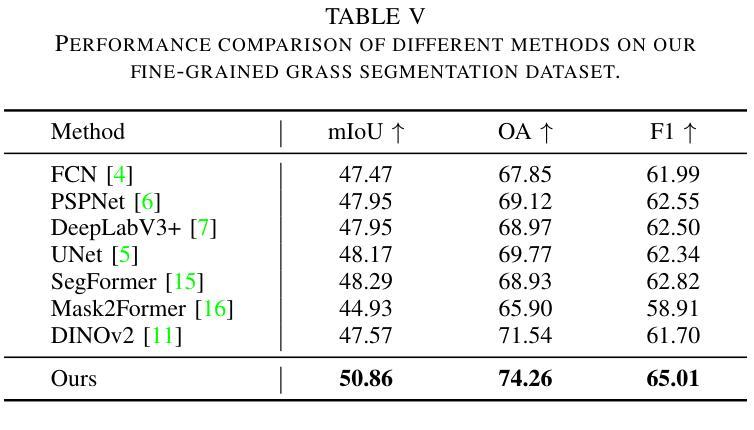
Fine-grained remote sensing image segmentation is essential for accurately identifying detailed objects in remote sensing images. Recently, vision transformer models (VTMs) pre-trained on large-scale datasets have demonstrated strong zero-shot generalization. However, directly applying them to specific tasks may lead to domain shift. We introduce a novel end-to-end learning paradigm combining knowledge guidance with domain refinement to enhance performance. We present two key components: the Feature Alignment Module (FAM) and the Feature Modulation Module (FMM). FAM aligns features from a CNN-based backbone with those from the pretrained VTM’s encoder using channel transformation and spatial interpolation, and transfers knowledge via KL divergence and L2 normalization constraint. FMM further adapts the knowledge to the specific domain to address domain shift. We also introduce a fine-grained grass segmentation dataset and demonstrate, through experiments on two datasets, that our method achieves a significant improvement of 2.57 mIoU on the grass dataset and 3.73 mIoU on the cloud dataset. The results highlight the potential of combining knowledge transfer and domain adaptation to overcome domain-related challenges and data limitations. The project page is available at https://xavierjiezou.github.io/KTDA/.
精细遥感图像分割对于准确识别遥感图像中的详细物体至关重要。最近,在大型数据集上预训练的视觉转换器模型(VTM)表现出强大的零样本泛化能力。然而,直接将其应用于特定任务可能会导致领域偏移。我们引入了一种结合知识引导和领域精炼的新型端到端学习范式,以提高性能。我们提出了两个关键组件:特征对齐模块(FAM)和特征调制模块(FMM)。FAM通过通道变换和空间插值,将对来自基于CNN的骨干网的特征与预训练VTM编码器的特征进行对齐,并通过KL散度和L2归一化约束进行知识转移。FMM进一步将知识适应到特定领域,以解决领域偏移问题。我们还介绍了一个精细的草分割数据集,并通过两个数据集的实验证明,我们的方法在草数据集上实现了2.57 mIoU的显著改进,在云数据集上实现了3.73 mIoU。结果突出了结合知识转移和领域适应的潜力,可以克服与领域相关的挑战和数据限制。项目页面可在[https://xavierjiezou.github.io/KTDA/]访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 3 figures, 6 tables
Summary
远程精细遥感图像分割需要准确识别遥感图像中的详细物体。本研究结合知识指导和领域精炼,提出了一种新型端到端学习范式。研究中关键部分包括特征对齐模块(FAM)和特征调制模块(FMM)。FAM通过对通道变换和空间插值,对齐基于CNN的主干网络与预训练VTM编码器的特征,并通过KL散度和L2归一化约束转移知识。FMM进一步适应知识以应对领域偏移。实验表明,结合知识转移和领域适应的方法在草类数据集上提高了2.57 mIoU,在云数据集上提高了3.73 mIoU。该方法的潜力在于克服领域相关挑战和应对数据局限性。项目页面可在链接https://xavierjiezou.github.io/KTDA/找到。
Key Takeaways
- 精细遥感图像分割对于准确识别遥感图像中的详细物体至关重要。
- 引入了一种新型端到端学习范式,结合了知识指导和领域精炼。
- 特征对齐模块(FAM)通过通道变换和空间插值对齐特征,并通过KL散度和L2归一化约束转移知识。
- 特征调制模块(FMM)进一步适应知识以解决领域偏移问题。
- 研究人员还引入了一个精细的草地分割数据集进行实验验证。
- 实验结果显示,该方法在草类数据集上提高了2.57 mIoU,在云数据集上提高了3.73 mIoU。
点此查看论文截图

Semantic Consistency-Based Uncertainty Quantification for Factuality in Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Chenyu Wang, Weichao Zhou, Shantanu Ghosh, Kayhan Batmanghelich, Wenchao Li
Radiology report generation (RRG) has shown great potential in assisting radiologists by automating the labor-intensive task of report writing. While recent advancements have improved the quality and coherence of generated reports, ensuring their factual correctness remains a critical challenge. Although generative medical Vision Large Language Models (VLLMs) have been proposed to address this issue, these models are prone to hallucinations and can produce inaccurate diagnostic information. To address these concerns, we introduce a novel Semantic Consistency-Based Uncertainty Quantification framework that provides both report-level and sentence-level uncertainties. Unlike existing approaches, our method does not require modifications to the underlying model or access to its inner state, such as output token logits, thus serving as a plug-and-play module that can be seamlessly integrated with state-of-the-art models. Extensive experiments demonstrate the efficacy of our method in detecting hallucinations and enhancing the factual accuracy of automatically generated radiology reports. By abstaining from high-uncertainty reports, our approach improves factuality scores by $10$%, achieved by rejecting $20$% of reports using the Radialog model on the MIMIC-CXR dataset. Furthermore, sentence-level uncertainty flags the lowest-precision sentence in each report with an $82.9$% success rate.
医学影像报告生成(RRG)在协助放射科医生自动化报告撰写方面展现出巨大潜力。虽然近期的发展提高了生成报告的质量和连贯性,但确保其实事求是的正确性仍是关键挑战。尽管已经提出了生成式医学影像大型语言模型(VLLM)来解决这个问题,但这些模型容易出现虚构现象,可能产生不准确的诊断信息。为了解决这些担忧,我们引入了一种新型的基于语义一致性的不确定性量化框架,该框架能够提供报告级别和句子级别的不确定性。与现有方法不同,我们的方法不需要修改底层模型或访问其内部状态,如输出令牌对数几率等,因此可以作为无缝集成最新技术的即插即用模块。大量实验证明了我们方法在检测虚构现象和提高自动生成的医学影像报告的事实准确性方面的有效性。通过避免高不确定性的报告,我们的方法在MIMIC-CXR数据集上使用Radialog模型拒绝20%的报告,提高了事实得分10%。此外,句子级别的不确定性可以成功标记每个报告中精度最低的那句,成功率为82.9%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了放射报告生成(RRG)的潜力与挑战,包括自动生成报告的准确性和事实正确性。提出了一种新的基于语义一致性的不确定性量化框架,该框架可以在不需要修改底层模型或访问其内部状态的情况下,提供报告级别和句子级别的不确定性,从而提高报告的准确性并检测出虚构信息。实验证明,该方法能有效提高自动生成的放射报告的准确性,并在MIMIC-CXR数据集上实现了较高的成功率。
Key Takeaways
- 放射报告生成(RRG)具有辅助放射科医生自动生成报告的潜力,但确保报告的事实正确性仍是关键挑战。
- 生成式医学视觉大型语言模型(VLLMs)虽然有助于提高报告质量和连贯性,但容易产生虚构信息。
- 引入了一种新的基于语义一致性的不确定性量化框架,该框架能够提供报告级别和句子级别的不确定性,从而提高报告的准确性。
- 该方法与底层模型兼容,无需进行修改或访问其内部状态,可无缝集成到最新模型中。
- 实验证明,该方法能有效检测出虚构信息,提高报告的准确性。
- 通过拒绝高不确定性的报告,使用该方法在MIMIC-CXR数据集上的事实性得分提高了10%,同时拒绝了20%的报告。
点此查看论文截图

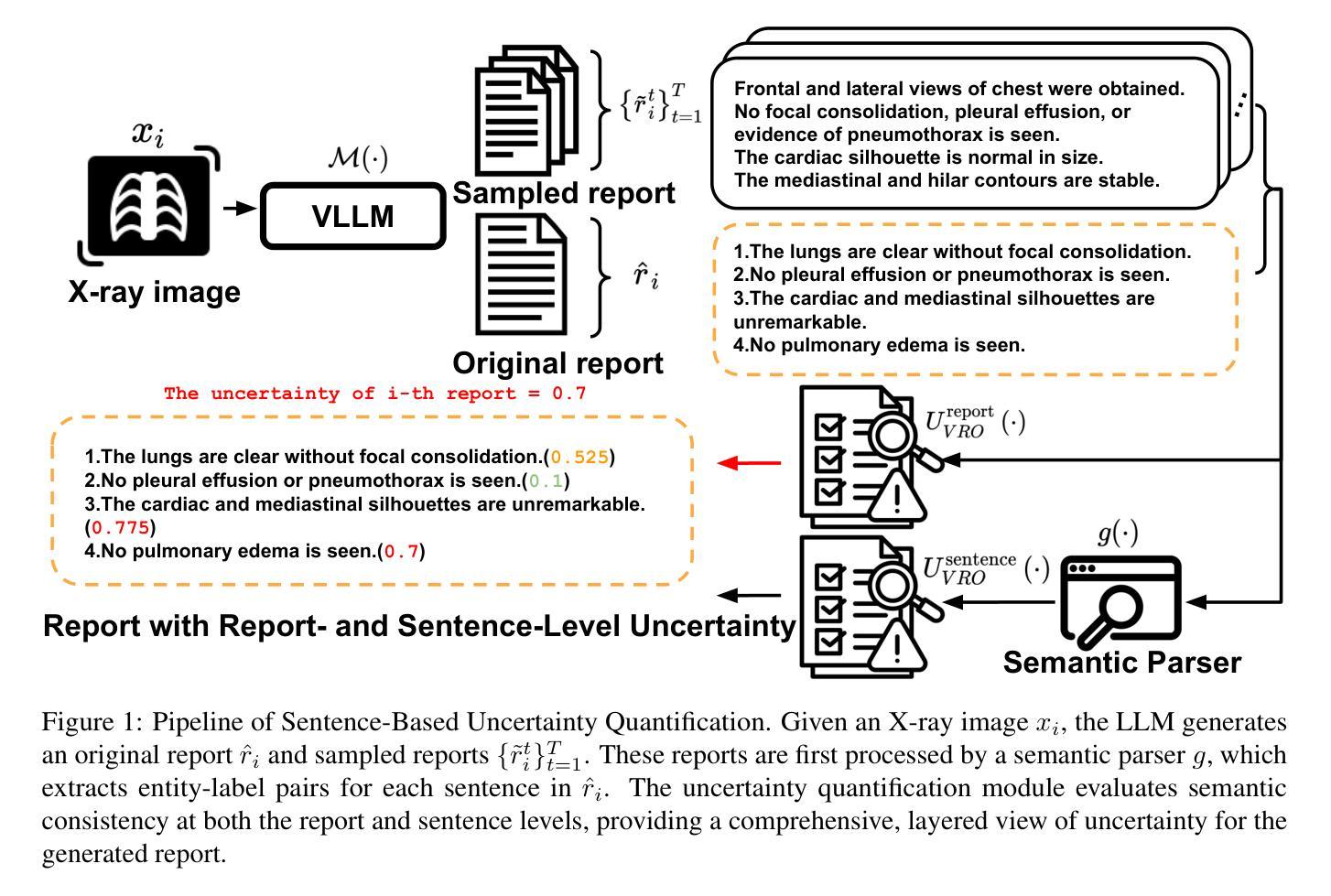
Mask of truth: model sensitivity to unexpected regions of medical images
Authors:Théo Sourget, Michelle Hestbek-Møller, Amelia Jiménez-Sánchez, Jack Junchi Xu, Veronika Cheplygina
The development of larger models for medical image analysis has led to increased performance. However, it also affected our ability to explain and validate model decisions. Models can use non-relevant parts of images, also called spurious correlations or shortcuts, to obtain high performance on benchmark datasets but fail in real-world scenarios. In this work, we challenge the capacity of convolutional neural networks (CNN) to classify chest X-rays and eye fundus images while masking out clinically relevant parts of the image. We show that all models trained on the PadChest dataset, irrespective of the masking strategy, are able to obtain an Area Under the Curve (AUC) above random. Moreover, the models trained on full images obtain good performance on images without the region of interest (ROI), even superior to the one obtained on images only containing the ROI. We also reveal a possible spurious correlation in the Chaksu dataset while the performances are more aligned with the expectation of an unbiased model. We go beyond the performance analysis with the usage of the explainability method SHAP and the analysis of embeddings. We asked a radiology resident to interpret chest X-rays under different masking to complement our findings with clinical knowledge. Our code is available at https://github.com/TheoSourget/MMC_Masking and https://github.com/TheoSourget/MMC_Masking_EyeFundus
开发用于医学图像分析的大型模型已经提高了性能。然而,这也影响了我们解释和验证模型决策的能力。模型可能会使用图像的非关键部分,也称为偶然关联或捷径,在基准数据集上获得高性能,但在现实场景中却会失败。在这项工作中,我们挑战卷积神经网络(CNN)对胸部X光片和眼底图像进行分类的能力,同时屏蔽图像中临床关键的部分。我们表明,所有在PadChest数据集上训练的模型,无论采用何种屏蔽策略,都能够获得高于随机的曲线下面积(AUC)。此外,在完整图像上训练的模型在无感兴趣区域(ROI)的图像上表现出良好的性能,即使在只包含ROI的图像上的表现也要优越。我们还揭示了Chaksu数据集中可能存在的偶然关联,同时性能更加符合无偏见模型的预期。除了性能分析,我们还使用了SHAP解释方法和嵌入分析。我们邀请了一名放射科医生在不同屏蔽条件下解读胸部X光片,以补充我们的临床知识发现。我们的代码可在https://github.com/TheoSourget/MMC_Masking和https://github.com/TheoSurget/MMC_Masking_EyeFundus获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像分析模型发展提升性能,但难以解释和验证决策。模型可能利用图像的非关键部分获得高基准数据集性能,但在真实世界场景中失败。研究挑战卷积神经网络对胸部X光和眼底图像的分类能力,同时掩盖临床上关键部分。训练于全图像的模型在不含感兴趣区域的图像上表现良好,甚至优于仅含感兴趣区域的图像。分析显示Chaksu数据集存在可能的偶然关联,性能更符合无偏见模型的预期。结合SHAP解释方法和嵌入分析,补充临床知识解读胸部X光的不同掩盖情况。相关代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分析模型性能提升同时,存在难以解释和验证决策的问题。
- 模型可能利用非关键图像部分(即偶然关联或捷径)获得高基准数据集性能。
- 在胸部X光和眼底图像分类中,掩盖临床上关键部分的研究挑战卷积神经网络的分类能力。
- 训练于全图像的模型在不含感兴趣区域的图像上表现良好。
- 分析显示某些医学图像数据集中存在可能的偶然关联。
- 结合SHAP解释方法和嵌入分析来评估模型性能。
点此查看论文截图

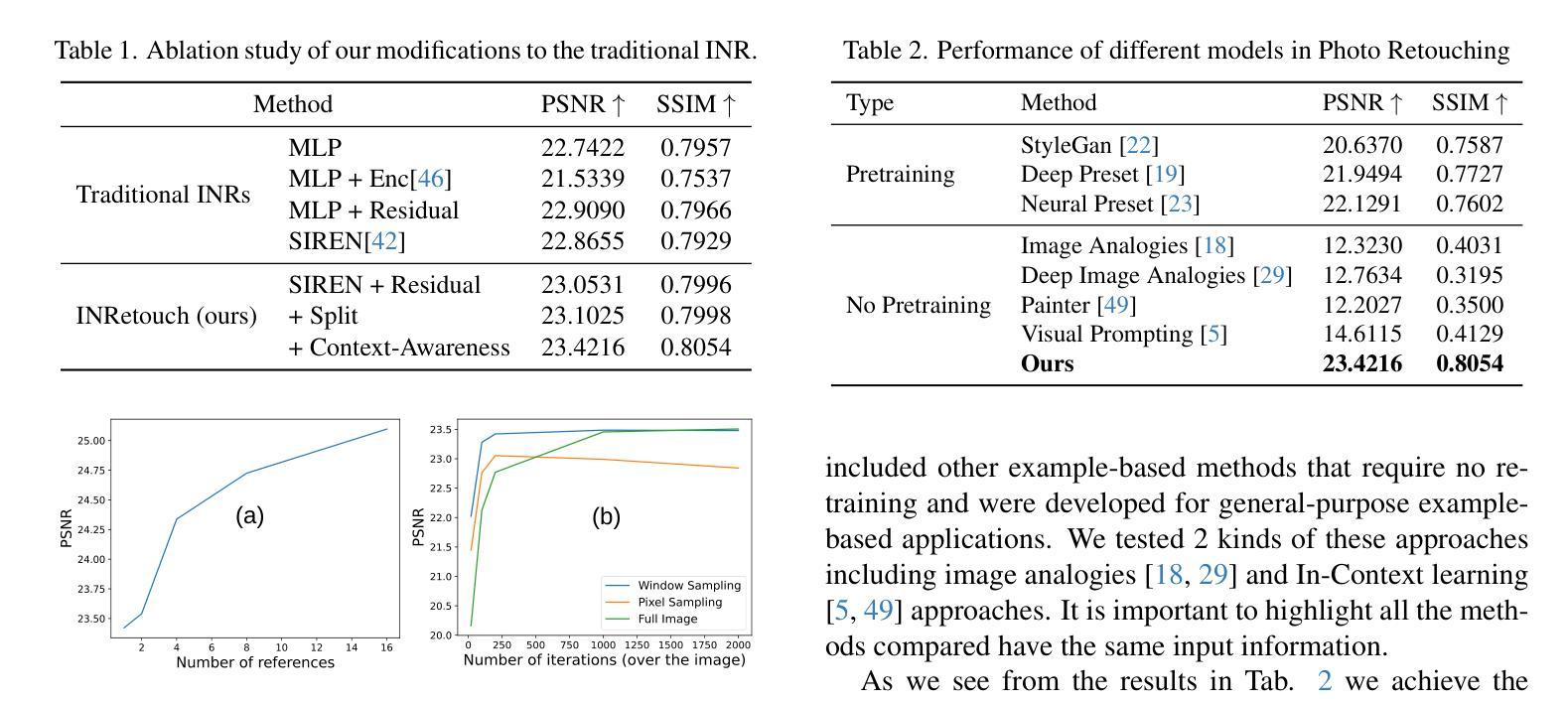
INRetouch: Context Aware Implicit Neural Representation for Photography Retouching
Authors:Omar Elezabi, Marcos V. Conde, Zongwei Wu, Radu Timofte
Professional photo editing remains challenging, requiring extensive knowledge of imaging pipelines and significant expertise. With the ubiquity of smartphone photography, there is an increasing demand for accessible yet sophisticated image editing solutions. While recent deep learning approaches, particularly style transfer methods, have attempted to automate this process, they often struggle with output fidelity, editing control, and complex retouching capabilities. We propose a novel retouch transfer approach that learns from professional edits through before-after image pairs, enabling precise replication of complex editing operations. To facilitate this research direction, we introduce a comprehensive Photo Retouching Dataset comprising 100,000 high-quality images edited using over 170 professional Adobe Lightroom presets. We develop a context-aware Implicit Neural Representation that learns to apply edits adaptively based on image content and context, requiring no pretraining and capable of learning from a single example. Our method extracts implicit transformations from reference edits and adaptively applies them to new images. Through extensive evaluation, we demonstrate that our approach not only surpasses existing methods in photo retouching but also enhances performance in related image reconstruction tasks like Gamut Mapping and Raw Reconstruction. By bridging the gap between professional editing capabilities and automated solutions, our work presents a significant step toward making sophisticated photo editing more accessible while maintaining high-fidelity results. Check the Project Page at https://omaralezaby.github.io/inretouch for more Results and information about Code and Dataset availability.
专业照片编辑仍然具有挑战性,需要深入了解成像管道和丰富的专业知识。随着智能手机摄影的普及,人们对易于使用且高级的图像编辑解决方案的需求不断增加。虽然最近的深度学习技术,特别是风格迁移方法,已经尝试自动化这一过程,但它们在输出保真度、编辑控制和复杂润饰功能方面往往面临挑战。我们提出了一种新型的润饰迁移方法,它通过专业编辑的前后图像对来学习,能够精确复制复杂的编辑操作。为了促进这一研究方向,我们引入了一个全面的照片润饰数据集,包含使用超过170个专业Adobe Lightroom预设编辑的10万张高质量图像。我们开发了一种上下文感知的隐式神经表示方法,该方法能够基于图像内容和上下文自适应地应用编辑操作,无需预先训练,并且能够从单个示例中学习。我们的方法从参考编辑中提取隐式转换,并自适应地应用于新图像。通过广泛评估,我们证明我们的方法不仅在照片润饰方面超越了现有方法,而且在相关图像重建任务(如色域映射和原始重建)方面也提高了性能。通过缩小专业编辑能力和自动化解决方案之间的差距,我们的工作是在保持高保真结果的同时,使高级照片编辑更加易于访问的重要一步。有关更多结果和关于代码和数据集可用性的信息,请访问https://omaralezaby.github.io/inretouch。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型的照片修饰转换方法,通过学习和复制专业编辑的操作,提高了自动化照片编辑的精度和效率。为此,研究团队建立了一个包含十万张高质量图片的数据集,使用超过170种Adobe Lightroom预设进行编辑。他们开发了一种基于上下文感知的隐式神经网络表示方法,能够根据图像内容和上下文自适应地应用编辑操作,无需预先训练且能从单个示例中学习。评估结果表明,该方法不仅在照片修饰方面超越现有技术,还在相关图像重建任务如色域映射和原始重建中提升了性能,是专业编辑与自动化解决方案之间的桥梁。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究提出了一种新型照片修饰转换方法,能学习和复制专业编辑的操作。
- 建立了一个包含十万张高质量图片的数据集,用于训练和评估照片编辑技术。
- 利用隐式神经网络表示方法,能根据图像内容和上下文自适应应用编辑操作。
- 方法无需预先训练且能从单个示例中学习。
- 该方法在照片修饰和图像重建任务上表现优越。
- 该研究促进了专业编辑与自动化解决方案的融合,使高质量照片编辑更加普及和便捷。
点此查看论文截图



INSIGHT: Explainable Weakly-Supervised Medical Image Analysis
Authors:Wenbo Zhang, Junyu Chen, Christopher Kanan
Due to their large sizes, volumetric scans and whole-slide pathology images (WSIs) are often processed by extracting embeddings from local regions and then an aggregator makes predictions from this set. However, current methods require post-hoc visualization techniques (e.g., Grad-CAM) and often fail to localize small yet clinically crucial details. To address these limitations, we introduce INSIGHT, a novel weakly-supervised aggregator that integrates heatmap generation as an inductive bias. Starting from pre-trained feature maps, INSIGHT employs a detection module with small convolutional kernels to capture fine details and a context module with a broader receptive field to suppress local false positives. The resulting internal heatmap highlights diagnostically relevant regions. On CT and WSI benchmarks, INSIGHT achieves state-of-the-art classification results and high weakly-labeled semantic segmentation performance. Project website and code are available at: https://zhangdylan83.github.io/ewsmia/
由于体积扫描和全幻灯片病理图像(WSI)的尺寸较大,通常通过对局部区域提取嵌入进行加工,然后由聚合器根据此集合进行预测。然而,当前的方法需要事后可视化技术(例如Grad-CAM),并且往往无法定位虽小但临床上至关重要的细节。为了解决这些局限性,我们引入了INSIGHT,这是一种新型的弱监督聚合器,它将热图生成作为归纳偏见进行集成。从预训练的特征图开始,INSIGHT使用具有较小卷积核的检测模块来捕捉细节,并使用具有更广泛接受域的上文模块来抑制局部误报。结果内部热图突出了与诊断相关的区域。在CT和WSI基准测试中,INSIGHT取得了最先进的分类结果,并在弱标签语义分割方面表现出色。项目网站和代码可通过以下链接获取:[https://zhangdylan83.github.io/ewsmia/] 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了处理大型医学图像的新方法——INSIGHT。该方法采用弱监督聚合技术,结合生成的热图作为归纳偏置,以改进现有的医学图像处理方法。INSIGHT能够从预训练的特征图中提取细节,并生成内部热图突出显示诊断相关区域。在CT和WSI基准测试中,INSIGHT取得了最先进的分类结果和高性能的弱标签语义分割效果。
Key Takeaways
- INSIGHT是一种处理大型医学图像的新方法,采用弱监督聚合技术改进现有的处理方法。
- INSIGHT集成了生成热图作为归纳偏置,能够从预训练的特征图中提取细节。
- INSIGHT通过检测模块和上下文模块的设计,能够捕捉精细细节并抑制局部误报。
- 内部热图突出了诊断相关的区域。
- 在CT和WSI基准测试中,INSIGHT实现了最先进的分类结果。
- INSIGHT在弱标签语义分割方面也表现出高性能。
点此查看论文截图
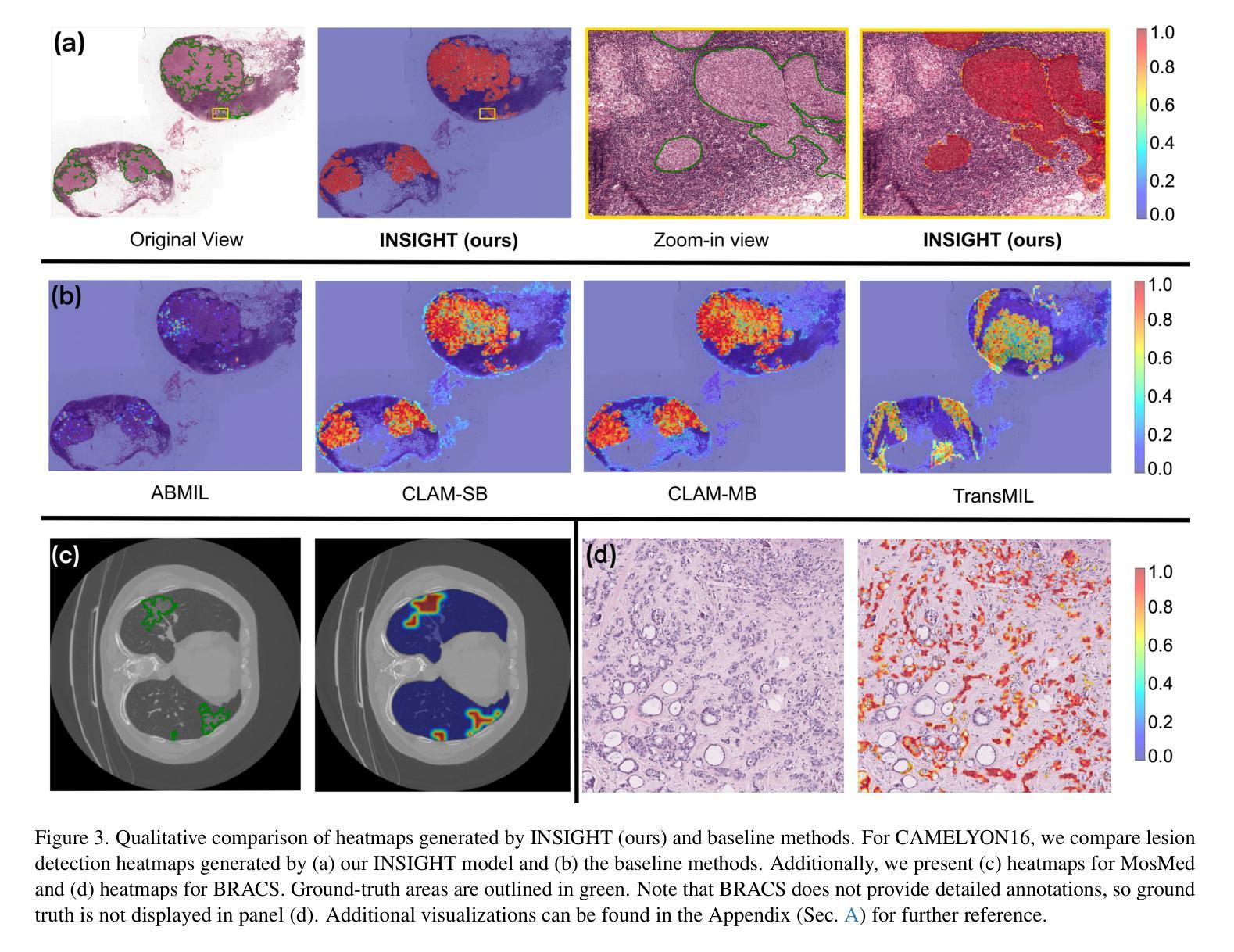
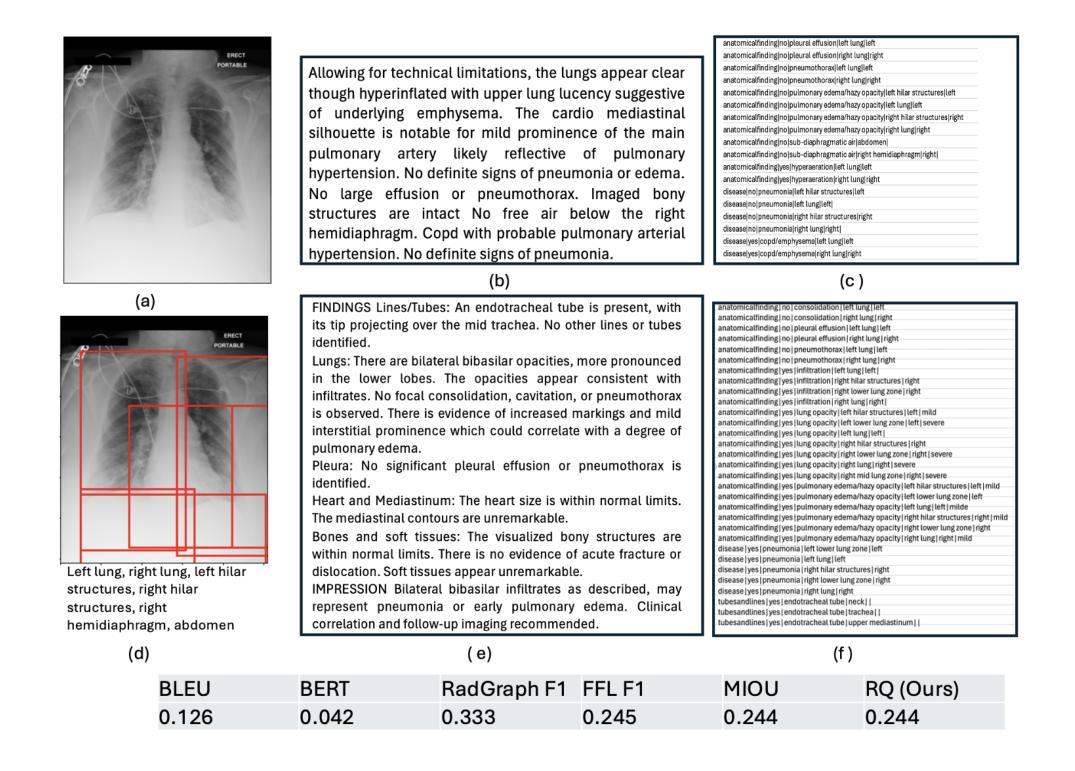
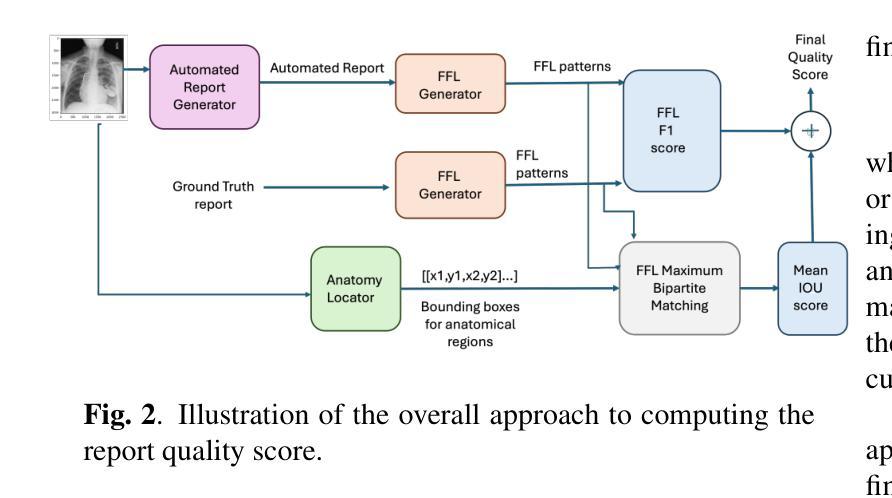
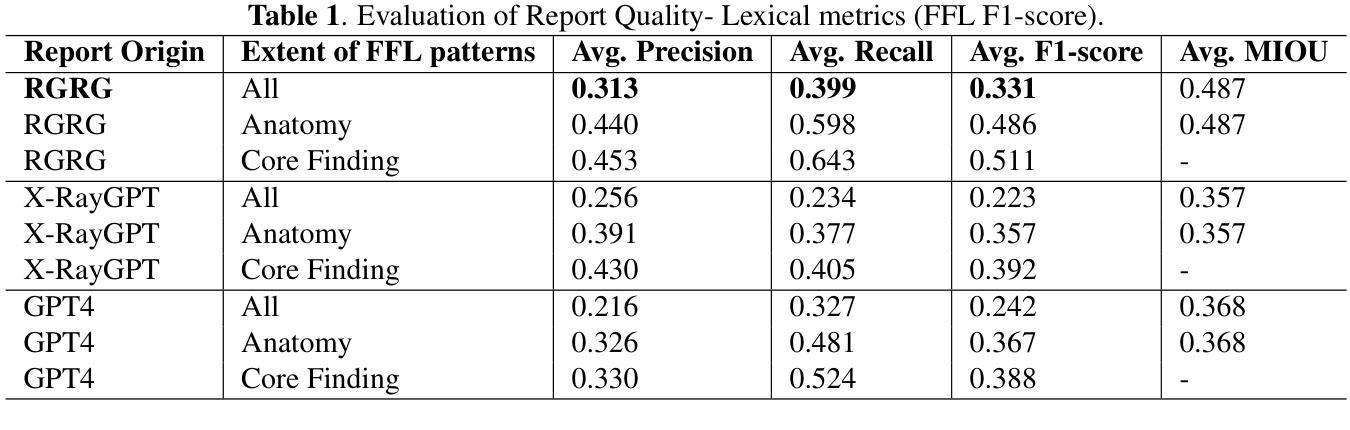
Evaluating Automated Radiology Report Quality through Fine-Grained Phrasal Grounding of Clinical Findings
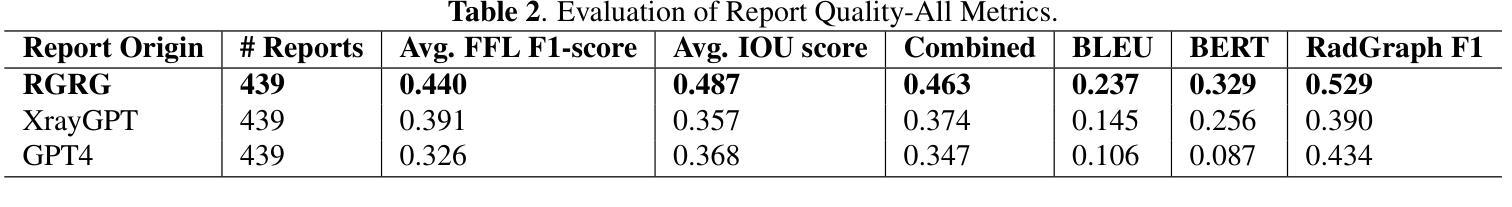
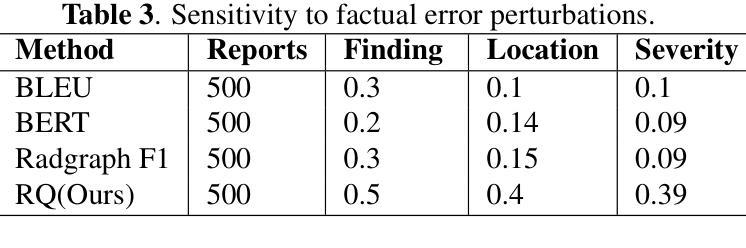
Authors:Razi Mahmood, Pingkun Yan, Diego Machado Reyes, Ge Wang, Mannudeep K. Kalra, Parisa Kaviani, Joy T. Wu, Tanveer Syeda-Mahmood
Several evaluation metrics have been developed recently to automatically assess the quality of generative AI reports for chest radiographs based only on textual information using lexical, semantic, or clinical named entity recognition methods. In this paper, we develop a new method of report quality evaluation by first extracting fine-grained finding patterns capturing the location, laterality, and severity of a large number of clinical findings. We then performed phrasal grounding to localize their associated anatomical regions on chest radiograph images. The textual and visual measures are then combined to rate the quality of the generated reports. We present results that compare this evaluation metric with other textual metrics on a gold standard dataset derived from the MIMIC collection and show its robustness and sensitivity to factual errors.
近期已经开发了一些评估指标,用于仅基于文本信息,使用词汇、语义或临床命名实体识别方法,自动评估胸部放射学报告中生成式人工智能报告的质量。在本文中,我们开发了一种新的报告质量评估方法,首先提取精细的检测结果模式,捕捉大量临床检测结果的部位、单侧性和严重性。然后我们对短语进行定位,以确定其在胸部放射图像上的相关解剖区域。然后将文本和视觉度量结合起来评估生成的报告质量。我们在由MIMIC集合衍生的黄金标准数据集上,对比这种评估指标与其他文本指标的对比结果,展示其稳健性和对事实错误的敏感性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于文本信息评估生成式AI报告质量的新方法。该方法通过提取精细的病变模式捕捉大量临床发现的部位、单侧性和严重程度,在胸部放射图像上进行短语定位,并融合文本和视觉指标来评估报告质量。实验结果表明,该评估指标与其他文本指标相比,在MIMIC数据集上具有稳健性和事实错误的敏感性。
Key Takeaways
- 文章提出了一种基于文本信息的自动生成报告质量评估新方法。
- 方法包括提取临床发现的精细模式并定位其相关解剖区域。
- 结合文本和视觉指标评估生成的报告质量。
- 实验在MIMIC数据集上进行,显示新评估指标的稳健性和事实错误的敏感性。
- 该方法能够自动评估生成式AI报告的准确性。
- 文章展示了如何将新方法与其他文本指标进行比较。
点此查看论文截图

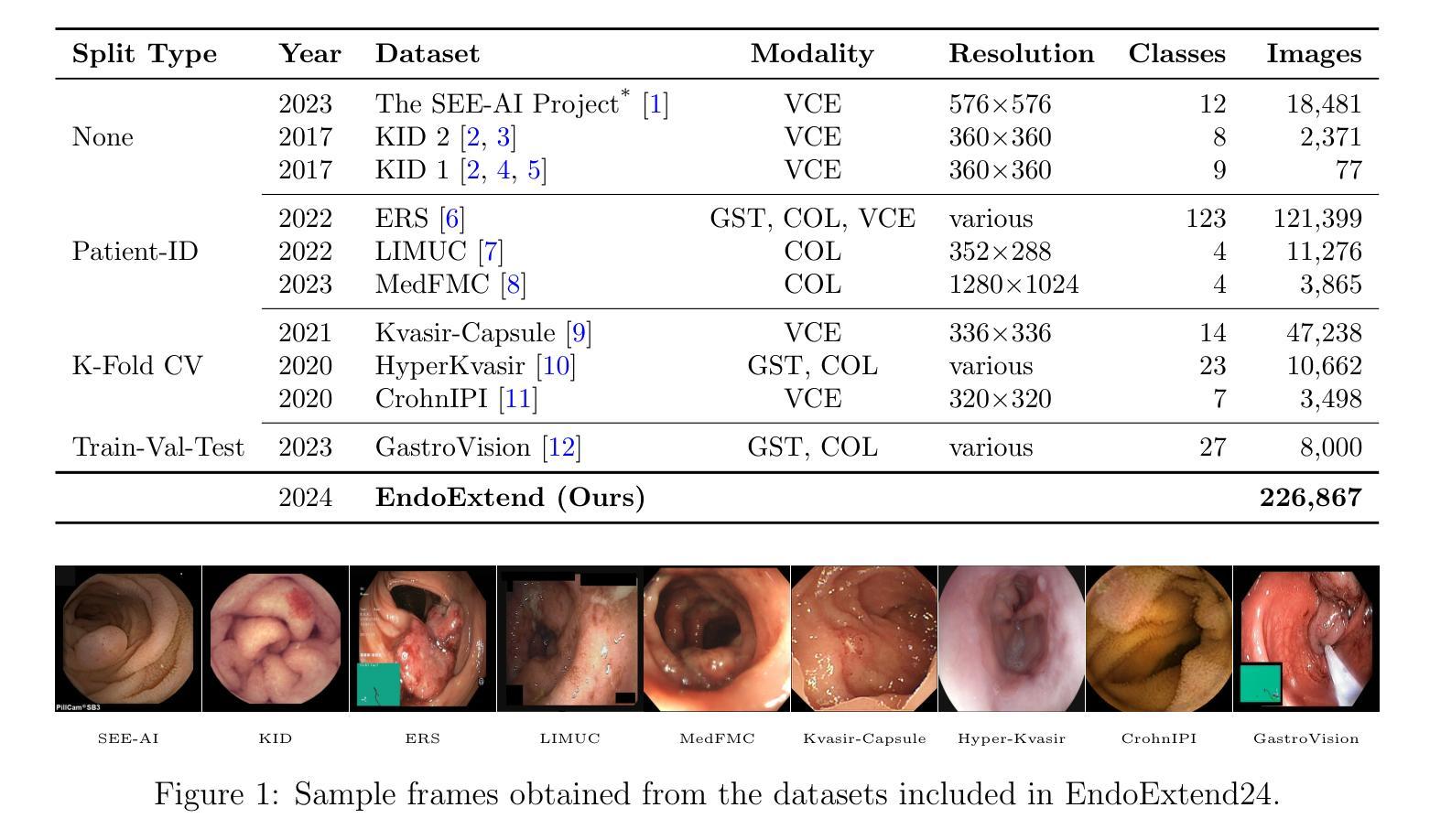
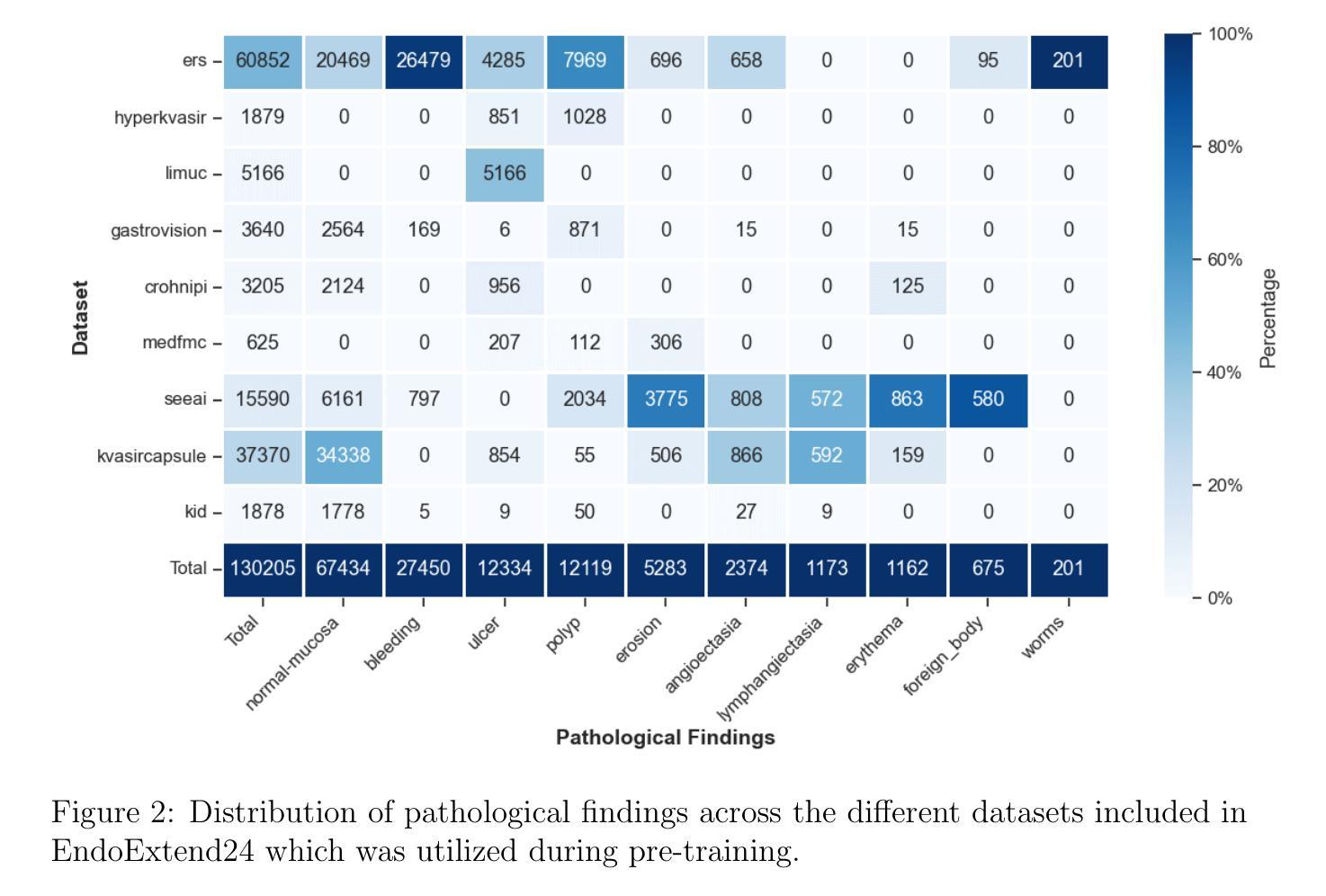
Domain-Adaptive Pre-training of Self-Supervised Foundation Models for Medical Image Classification in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Authors:Marcel Roth, Micha V. Nowak, Adrian Krenzer, Frank Puppe
Video capsule endoscopy has transformed gastrointestinal endoscopy (GIE) diagnostics by offering a non-invasive method for capturing detailed images of the gastrointestinal tract, enabling early disease detection. However, its potential is limited by the sheer volume of images generated during the imaging procedure, which can take anywhere from 6-8 hours and often produce up to 1 million images, necessitating automated analysis. Additionally, the variability of these images, combined with the need for expert annotations and the scarcity of large, high-quality labeled datasets, constrains the effectiveness of current medical image analysis models. To address this, we introduce a novel large GIE dataset, called EndoExtend24, created by merging ten existing public and private datasets, ensuring patient integrity across splits. EndoExtend24 includes over 226,000 labeled images, as well as dynamic class mappings, which allow unified training across datasets with differing labeling granularity, supporting up to 123 distinct pathological findings. Further, we propose to leverage domain adaptive pre-training of foundation models trained with self-supervision on generic image data, to adapt them to the task of GIE medical image diagnosis. Specifically, the EVA-02 model, which is based on the ViT architecture and trained on ImageNet-22k with masked image modeling (using EVA-CLIP as a MIM teacher), is pre-trained on the EndoExtend24 dataset to achieve domain adaptation, and finally trained on the Capsule Endoscopy 2024 Challenge dataset. Our model demonstrates robust performance, securing third place in the Capsule Endoscopy 2024 Challenge. We achieved a macro AUC of 0.762 and a balanced accuracy of 37.1% on the test set. These results emphasize the effectiveness of our domain-adaptive pre-training approach and the enriched EndoExtend24 dataset in advancing gastrointestinal endoscopy diagnostics.
视频胶囊内镜技术为胃肠道内镜(GIE)诊断提供了一种非侵入性的方法,能够捕捉胃肠道的详细图像,从而实现早期疾病的检测。然而,其潜力受限于成像过程中产生的图像数量庞大,成像过程可能需要6-8小时,并可能产生高达100万张图像,因此需要进行自动化分析。此外,这些图像的差异性,加上需要专家标注以及大规模高质量标注数据集的稀缺,限制了当前医学图像分析模型的有效性。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了一个名为EndoExtend24的大型GIE数据集,该数据集是通过合并十个现有的公共和私有数据集创建的,可确保跨分割的患者完整性。EndoExtend24包含超过22万张标记图像,以及动态类映射,允许在不同标签粒度的数据集上进行统一训练,支持多达123种不同的病理发现。此外,我们提议利用基于自监督的通用图像数据对基础模型进行域自适应预训练,以适应GIE医学图像诊断的任务。具体来说,EVA-02模型基于ViT架构构建,在ImageNet-22k数据集上进行遮掩图像建模(使用EVA-CLIP作为遮掩图像建模的教师),在EndoExtend24数据集上进行预训练以实现域适应,并最终在Capsule Endoscopy 2024挑战赛数据集上进行训练。我们的模型表现出稳健的性能,在Capsule Endoscopy 2024挑战赛中荣获第三名。在测试集上,我们的宏观AUC达到0.762,平衡精度为37.1%。这些结果强调了我们域自适应预训练方法和丰富的EndoExtend24数据集在推进胃肠道内窥镜诊断方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视频胶囊内镜为胃肠道内窥镜检查(GIE)提供了一种非侵入性的成像方法,能够详细捕捉胃肠道的影像,有助于早期疾病检测。然而,由于成像过程产生的图像数量庞大,分析过程需要自动化处理。为此,研究者们引入了EndoExtend24数据集,并尝试通过基于域自适应预训练的模型进行诊断。其中EVA-02模型在GIE医学图像诊断任务中表现出良好的性能,在Capsule Endoscopy 2024 Challenge中取得了第三名的好成绩。该模型的表现在宏观AUC和平衡精度方面都达到了显著水平。这凸显了我们的域自适应预训练方法和丰富的EndoExtend24数据集在推动胃肠道内窥镜诊断方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 视频胶囊内镜为胃肠道内窥镜诊断提供了非侵入性的详细图像捕获方法,有助于早期疾病检测。
- 成像过程中产生的海量图像数据需要自动化分析处理。
- EndoExtend24数据集通过合并多个公共和私有数据集,确保了患者数据的完整性。
- 该数据集包含超过226,000张标记图像和动态类映射,支持多达123种不同的病理发现。
- 研究者提出利用基于域自适应预训练的模型进行GIE医学图像诊断。
- EVA-02模型在GIE医学图像诊断任务中表现出良好性能,在比赛中获得了第三名。
点此查看论文截图

The Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS-METS) Challenge 2023: Brain Metastasis Segmentation on Pre-treatment MRI
Authors:Ahmed W. Moawad, Anastasia Janas, Ujjwal Baid, Divya Ramakrishnan, Rachit Saluja, Nader Ashraf, Nazanin Maleki, Leon Jekel, Nikolay Yordanov, Pascal Fehringer, Athanasios Gkampenis, Raisa Amiruddin, Amirreza Manteghinejad, Maruf Adewole, Jake Albrecht, Udunna Anazodo, Sanjay Aneja, Syed Muhammad Anwar, Timothy Bergquist, Veronica Chiang, Verena Chung, Gian Marco Conte, Farouk Dako, James Eddy, Ivan Ezhov, Nastaran Khalili, Keyvan Farahani, Juan Eugenio Iglesias, Zhifan Jiang, Elaine Johanson, Anahita Fathi Kazerooni, Florian Kofler, Kiril Krantchev, Dominic LaBella, Koen Van Leemput, Hongwei Bran Li, Marius George Linguraru, Xinyang Liu, Zeke Meier, Bjoern H Menze, Harrison Moy, Klara Osenberg, Marie Piraud, Zachary Reitman, Russell Takeshi Shinohara, Chunhao Wang, Benedikt Wiestler, Walter Wiggins, Umber Shafique, Klara Willms, Arman Avesta, Khaled Bousabarah, Satrajit Chakrabarty, Nicolo Gennaro, Wolfgang Holler, Manpreet Kaur, Pamela LaMontagne, MingDe Lin, Jan Lost, Daniel S. Marcus, Ryan Maresca, Sarah Merkaj, Gabriel Cassinelli Pedersen, Marc von Reppert, Aristeidis Sotiras, Oleg Teytelboym, Niklas Tillmans, Malte Westerhoff, Ayda Youssef, Devon Godfrey, Scott Floyd, Andreas Rauschecker, Javier Villanueva-Meyer, Irada Pfluger, Jaeyoung Cho, Martin Bendszus, Gianluca Brugnara, Justin Cramer, Gloria J. Guzman Perez-Carillo, Derek R. Johnson, Anthony Kam, Benjamin Yin Ming Kwan, Lillian Lai, Neil U. Lall, Fatima Memon, Mark Krycia, Satya Narayana Patro, Bojan Petrovic, Tiffany Y. So, Gerard Thompson, Lei Wu, E. Brooke Schrickel, Anu Bansal, Frederik Barkhof, Cristina Besada, Sammy Chu, Jason Druzgal, Alexandru Dusoi, Luciano Farage, Fabricio Feltrin, Amy Fong, Steve H. Fung, R. Ian Gray, Ichiro Ikuta, Michael Iv, Alida A. Postma, Amit Mahajan, David Joyner, Chase Krumpelman, Laurent Letourneau-Guillon, Christie M. Lincoln, Mate E. Maros, Elka Miller, Fanny Moron, Esther A. Nimchinsky, Ozkan Ozsarlak, Uresh Patel, Saurabh Rohatgi, Atin Saha, Anousheh Sayah, Eric D. Schwartz, Robert Shih, Mark S. Shiroishi, Juan E. Small, Manoj Tanwar, Jewels Valerie, Brent D. Weinberg, Matthew L. White, Robert Young, Vahe M. Zohrabian, Aynur Azizova, Melanie Maria Theresa Bruseler, Mohanad Ghonim, Mohamed Ghonim, Abdullah Okar, Luca Pasquini, Yasaman Sharifi, Gagandeep Singh, Nico Sollmann, Theodora Soumala, Mahsa Taherzadeh, Philipp Vollmuth, Martha Foltyn-Dumitru, Ajay Malhotra, Aly H. Abayazeed, Francesco Dellepiane, Philipp Lohmann, Victor M. Perez-Garcia, Hesham Elhalawani, Maria Correia de Verdier, Sanaria Al-Rubaiey, Rui Duarte Armindo, Kholod Ashraf, Moamen M. Asla, Mohamed Badawy, Jeroen Bisschop, Nima Broomand Lomer, Jan Bukatz, Jim Chen, Petra Cimflova, Felix Corr, Alexis Crawley, Lisa Deptula, Tasneem Elakhdar, Islam H. Shawali, Shahriar Faghani, Alexandra Frick, Vaibhav Gulati, Muhammad Ammar Haider, Fatima Hierro, Rasmus Holmboe Dahl, Sarah Maria Jacobs, Kuang-chun Jim Hsieh, Sedat G. Kandemirli, Katharina Kersting, Laura Kida, Sofia Kollia, Ioannis Koukoulithras, Xiao Li, Ahmed Abouelatta, Aya Mansour, Ruxandra-Catrinel Maria-Zamfirescu, Marcela Marsiglia, Yohana Sarahi Mateo-Camacho, Mark McArthur, Olivia McDonnell, Maire McHugh, Mana Moassefi, Samah Mostafa Morsi, Alexander Munteanu, Khanak K. Nandolia, Syed Raza Naqvi, Yalda Nikanpour, Mostafa Alnoury, Abdullah Mohamed Aly Nouh, Francesca Pappafava, Markand D. Patel, Samantha Petrucci, Eric Rawie, Scott Raymond, Borna Roohani, Sadeq Sabouhi, Laura M. Sanchez-Garcia, Zoe Shaked, Pokhraj P. Suthar, Talissa Altes, Edvin Isufi, Yaseen Dhemesh, Jaime Gass, Jonathan Thacker, Abdul Rahman Tarabishy, Benjamin Turner, Sebastiano Vacca, George K. Vilanilam, Daniel Warren, David Weiss, Fikadu Worede, Sara Yousry, Wondwossen Lerebo, Alejandro Aristizabal, Alexandros Karargyris, Hasan Kassem, Sarthak Pati, Micah Sheller, Katherine E. Link, Evan Calabrese, Nourel hoda Tahon, Ayman Nada, Yuri S. Velichko, Spyridon Bakas, Jeffrey D. Rudie, Mariam Aboian
The translation of AI-generated brain metastases (BM) segmentation into clinical practice relies heavily on diverse, high-quality annotated medical imaging datasets. The BraTS-METS 2023 challenge has gained momentum for testing and benchmarking algorithms using rigorously annotated internationally compiled real-world datasets. This study presents the results of the segmentation challenge and characterizes the challenging cases that impacted the performance of the winning algorithms. Untreated brain metastases on standard anatomic MRI sequences (T1, T2, FLAIR, T1PG) from eight contributed international datasets were annotated in stepwise method: published UNET algorithms, student, neuroradiologist, final approver neuroradiologist. Segmentations were ranked based on lesion-wise Dice and Hausdorff distance (HD95) scores. False positives (FP) and false negatives (FN) were rigorously penalized, receiving a score of 0 for Dice and a fixed penalty of 374 for HD95. Eight datasets comprising 1303 studies were annotated, with 402 studies (3076 lesions) released on Synapse as publicly available datasets to challenge competitors. Additionally, 31 studies (139 lesions) were held out for validation, and 59 studies (218 lesions) were used for testing. Segmentation accuracy was measured as rank across subjects, with the winning team achieving a LesionWise mean score of 7.9. Common errors among the leading teams included false negatives for small lesions and misregistration of masks in space.The BraTS-METS 2023 challenge successfully curated well-annotated, diverse datasets and identified common errors, facilitating the translation of BM segmentation across varied clinical environments and providing personalized volumetric reports to patients undergoing BM treatment.
将AI生成的脑转移(BM)分段翻译应用于临床实践,很大程度上依赖于多样化、高质量标注的医学影像数据集。BraTS-METS 2023挑战赛通过使用严格标注的国际汇编真实世界数据集,测试并评估算法性能。本研究介绍了分割挑战的结果,并对影响获胜算法性能的挑战性病例进行了特征描述。对来自八个国际数据集的未经处理的脑转移瘤在标准解剖MRI序列(T1、T2、FLAIR、T1PG)上采用逐步方法进行标注:公开UNET算法、学生、神经放射学家、最终审批神经放射学家。根据病灶Dice和Hausdorff距离(HD95)得分对分割进行排名。假阳性(FP)和假阴性(FN)受到严格惩罚,Dice得分为0,HD95固定惩罚为374。八个数据集共标注了1303项研究,其中402项研究(3076个病灶)在Synapse上作为公开数据集向参赛者发布。此外,还留出31项研究(139个病灶)用于验证,59项研究(218个病灶)用于测试。分割准确度通过受试者排名来衡量,第一名团队的病灶级平均得分为7.9。领先团队的常见错误包括小病灶的假阴性和口罩的空间错位。BraTS-METS 2023挑战赛成功筛选了标注良好、多样化的数据集,并识别了常见错误,促进了BM分段的临床翻译应用于各种临床环境,并为接受BM治疗的患者提供个性化的体积报告。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了BraTS-METS 2023挑战赛的结果,该挑战赛使用严格注释的国际汇编真实世界数据集来测试和评估算法在大脑转移瘤分割方面的性能。研究通过对未治疗的大脑转移瘤进行逐步标注,评估了分割挑战中的算法性能,并指出了影响算法性能的挑战性案例。该挑战成功地整理了经过良好注释的多样化数据集,并确定了常见错误,促进了大脑转移瘤分割在临床实践中的应用,为患者提供个性化的体积报告。
Key Takeaways
- BraTS-METS 2023挑战赛使用严格注释的国际汇编真实世界数据集进行测试和评估。
- 研究采用逐步标注法对未治疗的大脑转移瘤进行标注,并评估了分割算法的效能。
- 挑战赛中存在影响算法性能的挑战性案例,如小病灶的漏检和面具的空间错位等。
- 挑战赛成功整理出多样化且经过良好注释的数据集,有助于推动大脑转移瘤分割技术在不同临床环境中的实际应用。
- 挑战赛确定了常见错误,如误分割和漏分割,这有助于提高算法性能。
- 通过挑战赛的成果,促进了医学图像分割技术的发展,为患者提供更准确的个性化体积报告。
点此查看论文截图