⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-12 更新
Enhancing 3D Object Detection in Autonomous Vehicles Based on Synthetic Virtual Environment Analysis
Authors:Vladislav Li, Ilias Siniosoglou, Thomai Karamitsou, Anastasios Lytos, Ioannis D. Moscholios, Sotirios K. Goudos, Jyoti S. Banerjee, Panagiotis Sarigiannidi, Vasileios Argyriou
Autonomous Vehicles (AVs) use natural images and videos as input to understand the real world by overlaying and inferring digital elements, facilitating proactive detection in an effort to assure safety. A crucial aspect of this process is real-time, accurate object recognition through automatic scene analysis. While traditional methods primarily concentrate on 2D object detection, exploring 3D object detection, which involves projecting 3D bounding boxes into the three-dimensional environment, holds significance and can be notably enhanced using the AR ecosystem. This study examines an AI model’s ability to deduce 3D bounding boxes in the context of real-time scene analysis while producing and evaluating the model’s performance and processing time, in the virtual domain, which is then applied to AVs. This work also employs a synthetic dataset that includes artificially generated images mimicking various environmental, lighting, and spatiotemporal states. This evaluation is oriented in handling images featuring objects in diverse weather conditions, captured with varying camera settings. These variations pose more challenging detection and recognition scenarios, which the outcomes of this work can help achieve competitive results under most of the tested conditions.
自动驾驶车辆(AV)使用自然图像和视频作为输入,通过叠加和推断数字元素来理解现实世界,促进主动检测,以确保安全。此过程的一个重要方面是实时、准确的物体识别,通过自动场景分析实现。虽然传统方法主要集中在2D目标检测上,但探索3D目标检测具有重要意义,涉及将3D边界框投影到三维环境中,并且可以利用AR生态系统显著增强。本研究旨在研究AI模型在实时场景分析背景下推断3D边界框的能力,同时在虚拟域中生成并评估模型的性能和处理时间,然后将其应用于自动驾驶车辆。这项工作还采用合成数据集,包括模拟各种环境、照明和时空状态的人工生成图像。该评估侧重于处理在不同天气条件下拍摄的包含物体的图像,使用不同的相机设置。这些变化带来了更具挑战的检测和识别场景,本工作的结果可以在大多数测试条件下实现有竞争力的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
自动驾驶车辆利用自然图像和视频作为输入,通过叠加和推断数字元素理解现实世界,以实现主动检测并确保安全。关键过程在于通过自动场景分析进行实时、精确的目标识别。本研究探讨了人工智能模型在实时场景分析中推断三维边界框的能力,并在虚拟领域产生并评估了模型的性能和运行时间,然后将其应用于自动驾驶车辆。该研究还采用了合成数据集,包括模拟各种环境、光照和时空状态的合成图像。此评估主要处理在不同天气条件下拍摄的物体图像,采用各种相机设置。这些变化带来了更具挑战性的检测和识别场景,而这项工作的成果可以在大多数测试条件下实现具有竞争力的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶车辆(AVs)依赖自然图像和视频作为输入来理解现实世界,并采用数字元素叠加进行实时检测以确保安全。
- 实时、精确的目标识别是自动驾驶中的关键过程,主要通过自动场景分析实现。
- 传统方法主要关注二维目标检测,而三维目标检测(涉及在三维环境中投影三维边界框)对自动驾驶尤为重要。
- 增强现实(AR)生态系统可以显著增强三维目标检测的准确性。
- 本研究探讨了AI模型在实时场景分析中推断三维边界框的能力,并在虚拟环境中评估了其性能和运行时间。
- 研究采用了合成数据集,模拟了各种环境、光照和时空条件下的图像,以评估模型在各种天气和相机设置下的性能。
点此查看论文截图

LUIEO: A Lightweight Model for Integrating Underwater Image Enhancement and Object Detection
Authors:Bin Li, Li Li, Zhenwei Zhang, Yuping Duan
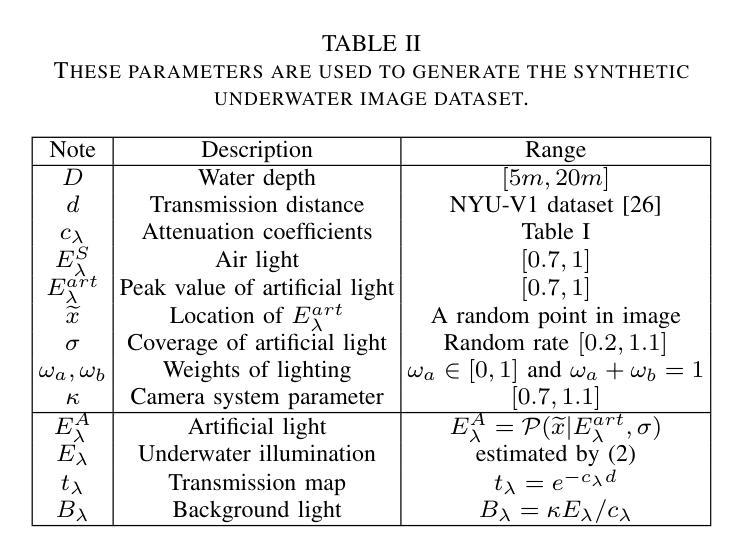
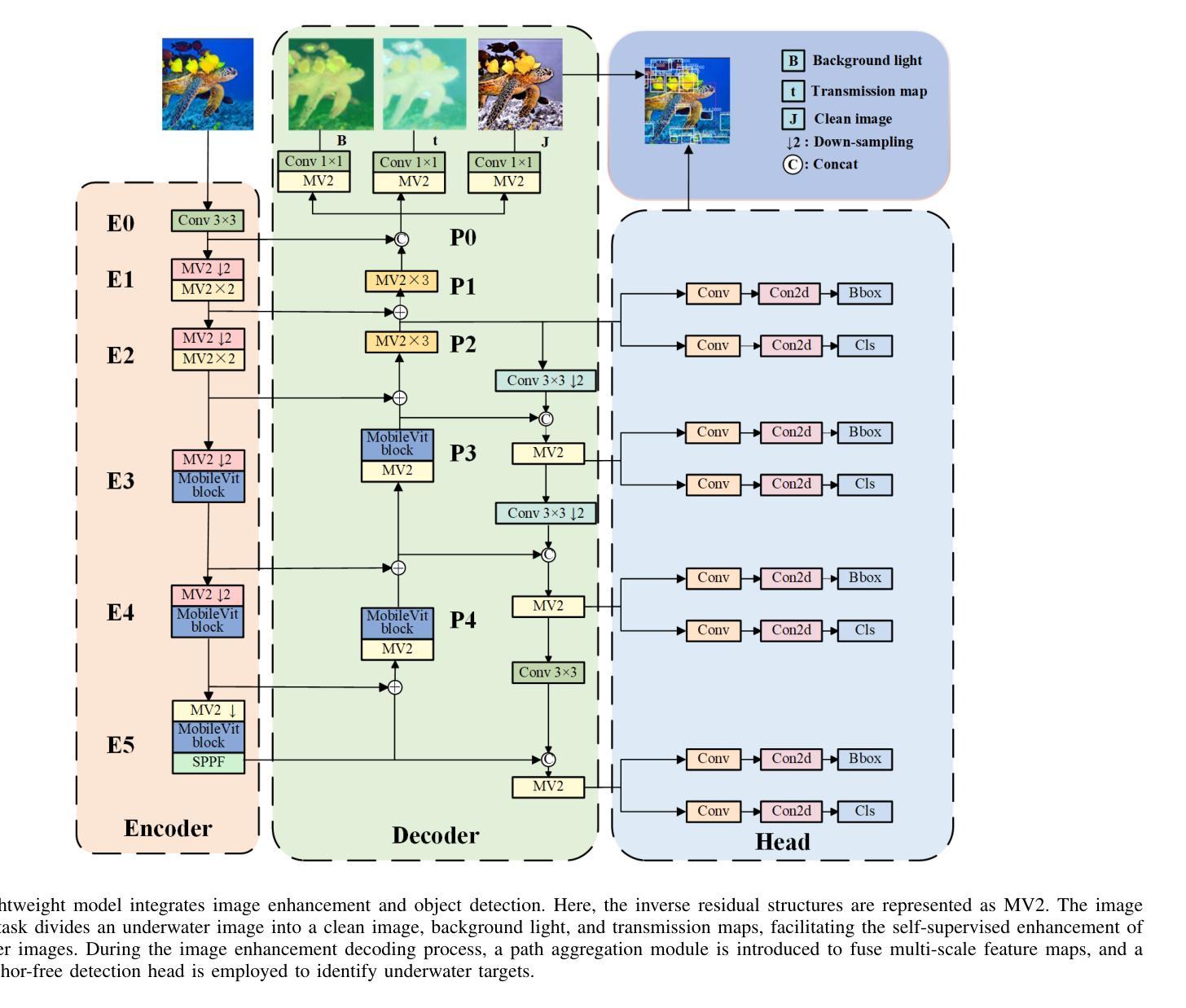
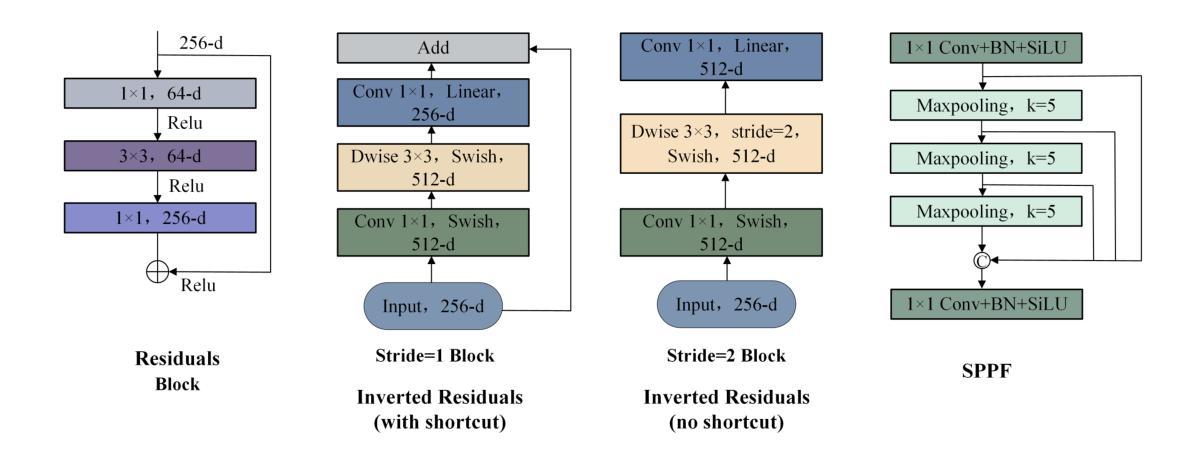
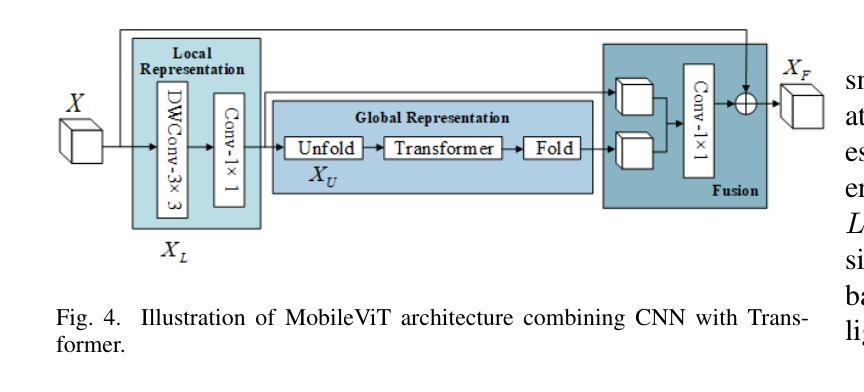
Underwater optical images inevitably suffer from various degradation factors such as blurring, low contrast, and color distortion, which hinder the accuracy of object detection tasks. Due to the lack of paired underwater/clean images, most research methods adopt a strategy of first enhancing and then detecting, resulting in a lack of feature communication between the two learning tasks. On the other hand, due to the contradiction between the diverse degradation factors of underwater images and the limited number of samples, existing underwater enhancement methods are difficult to effectively enhance degraded images of unknown water bodies, thereby limiting the improvement of object detection accuracy. Therefore, most underwater target detection results are still displayed on degraded images, making it difficult to visually judge the correctness of the detection results. To address the above issues, this paper proposes a multi-task learning method that simultaneously enhances underwater images and improves detection accuracy. Compared with single-task learning, the integrated model allows for the dynamic adjustment of information communication and sharing between different tasks. Due to the fact that real underwater images can only provide annotated object labels, this paper introduces physical constraints to ensure that object detection tasks do not interfere with image enhancement tasks. Therefore, this article introduces a physical module to decompose underwater images into clean images, background light, and transmission images and uses a physical model to calculate underwater images for self-supervision. Numerical experiments demonstrate that the proposed model achieves satisfactory results in visual performance, object detection accuracy, and detection efficiency compared to state-of-the-art comparative methods.
水下光学图像不可避免地受到模糊、低对比度和颜色失真等多种降质因素的影响,这些因素影响目标检测任务的准确性。由于缺少配对的水下/清洁图像,大多数研究方法采用先增强后检测的策略,导致两个学习任务之间缺乏特征交流。另一方面,由于水下图像的各种降质因素与样本数量有限的矛盾,现有的水下增强方法难以有效增强未知水体的退化图像,从而限制了目标检测准确性的提高。因此,大多数水下目标检测结果仍显示在退化图像上,很难直观地判断检测结果的正确性。为了解决上述问题,本文提出了一种多任务学习方法,可以同时增强水下图像并提高检测准确性。与单任务学习相比,集成模型允许不同任务之间动态调整信息交流和共享。由于真实水下图像只能提供注释的目标标签,本文引入物理约束以确保目标检测任务不会干扰图像增强任务。因此,本文引入了一个物理模块来将水下图像分解为清洁图像、背景光和透射图像,并使用物理模型计算水下图像进行自监督。数值实验表明,与最先进的比较方法相比,该模型在视觉性能、目标检测准确性和检测效率方面取得了令人满意的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本指出水下光学图像存在模糊、低对比度和色彩失真等退化问题,影响目标检测的准确性。由于没有配对的水下/清洁图像,大多数研究方法采用先增强后检测的策略,导致两个学习任务之间缺乏特征交流。为解决上述问题,本文提出一种多任务学习方法,可同时增强水下图像并提高检测准确性。与单任务学习相比,集成模型可实现不同任务间信息通信和共享的动态调整。此外,本文引入物理约束来确保目标检测任务不与图像增强任务相互干扰,并采用物理模块对水下图像进行分解为清洁图像、背景光和透射图像,并使用物理模型计算水下图像进行自监督。实验表明,该模型在视觉性能、目标检测准确性和检测效率方面均取得令人满意的结果。
Key Takeaways
- 水下光学图像存在多种退化因素,影响目标检测的准确性。
- 缺乏配对的水下/清洁图像使得先增强后检测的策略导致特征交流不足。
- 本文提出一种多任务学习方法,可同时增强水下图像并提高检测准确性。
- 与单任务学习相比,集成模型可实现信息交流和共享的动态调整。
- 为确保目标检测任务不与图像增强任务相互干扰,引入物理约束。
- 使用物理模块对水下图像进行分解,并采用物理模型进行自监督计算。
点此查看论文截图

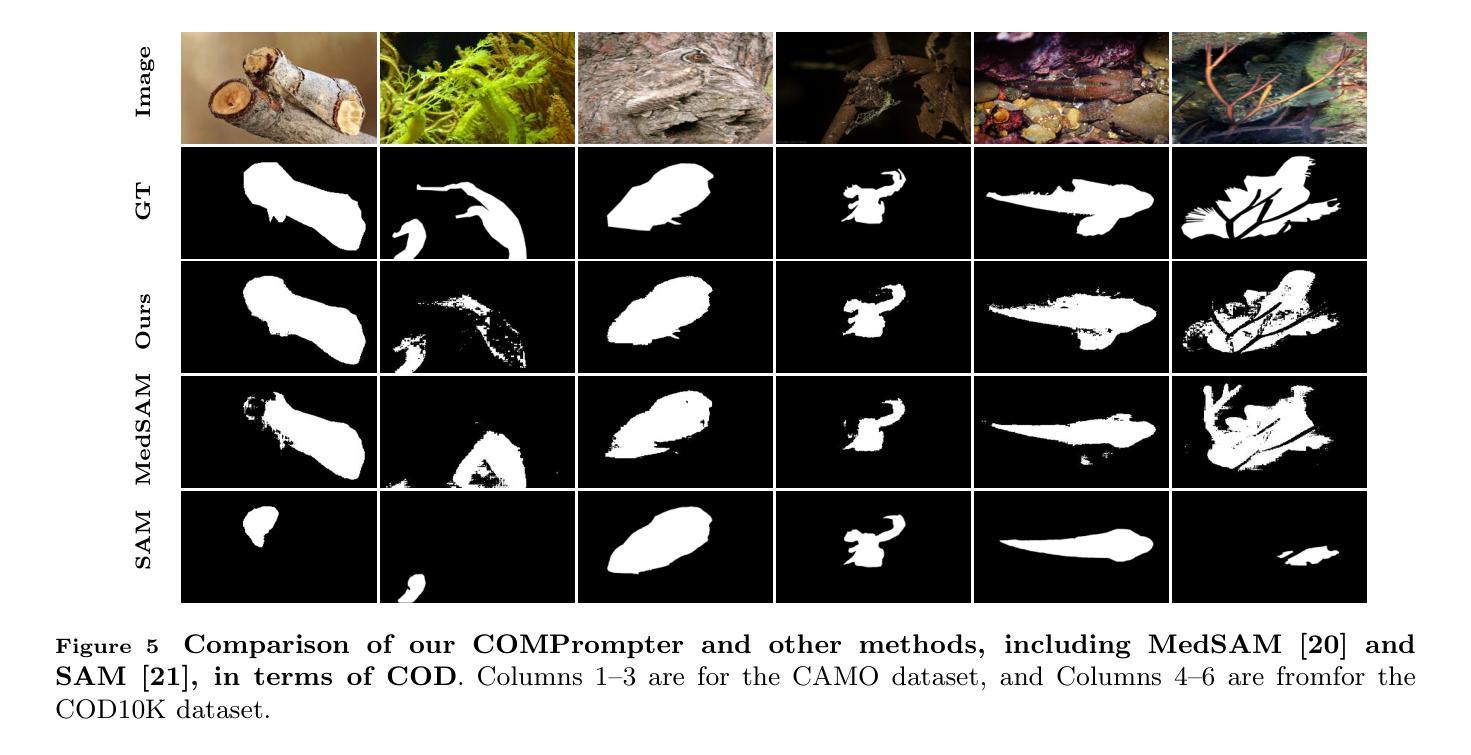
COMPrompter: reconceptualized segment anything model with multiprompt network for camouflaged object detection
Authors:Xiaoqin Zhang, Zhenni Yu, Li Zhao, Deng-Ping Fan, Guobao Xiao
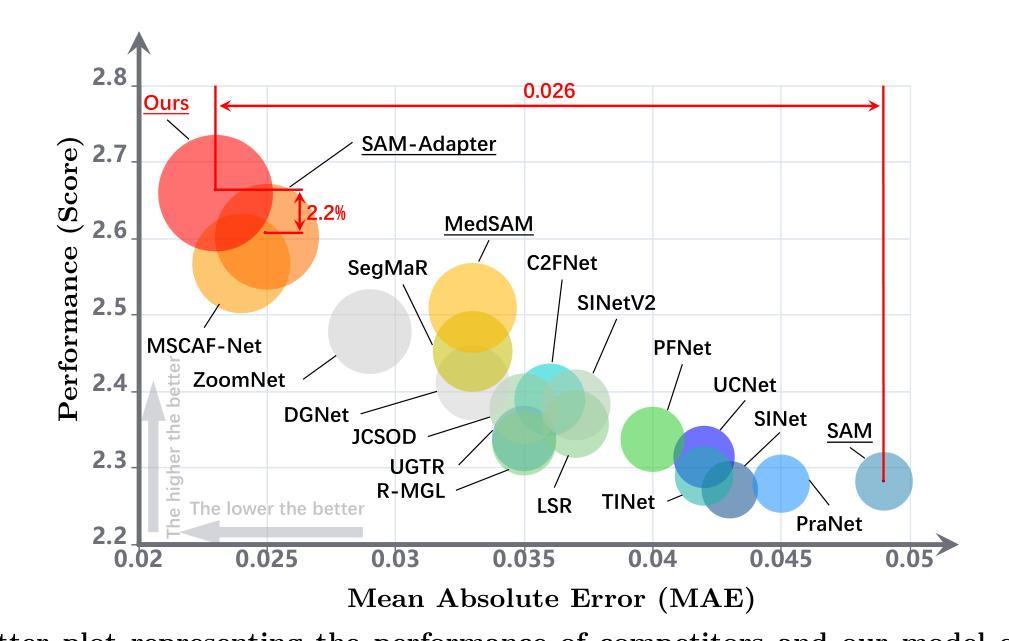
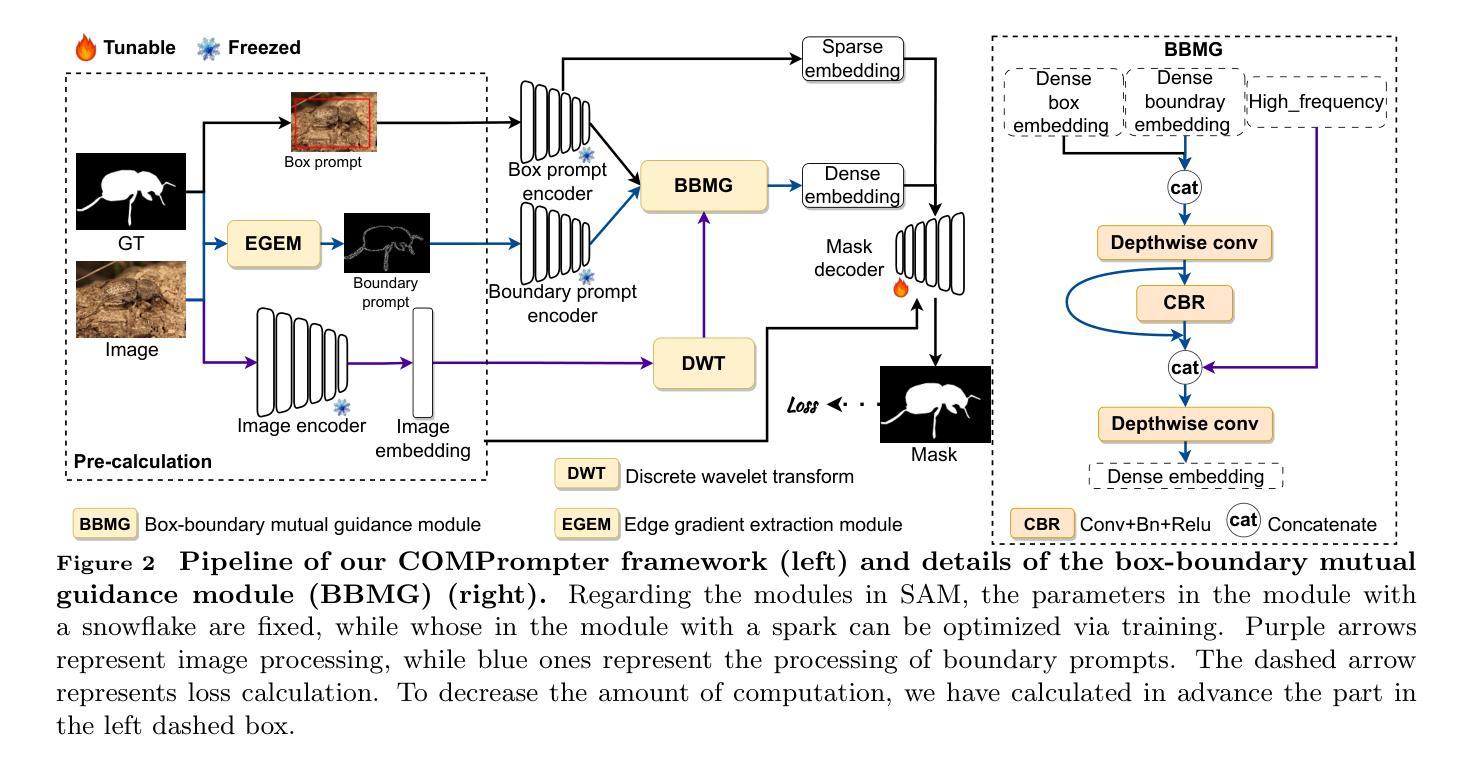
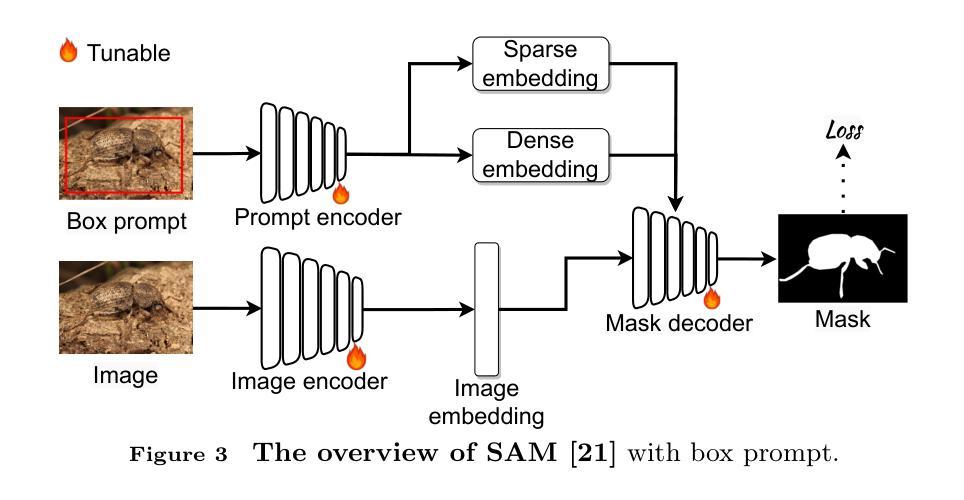
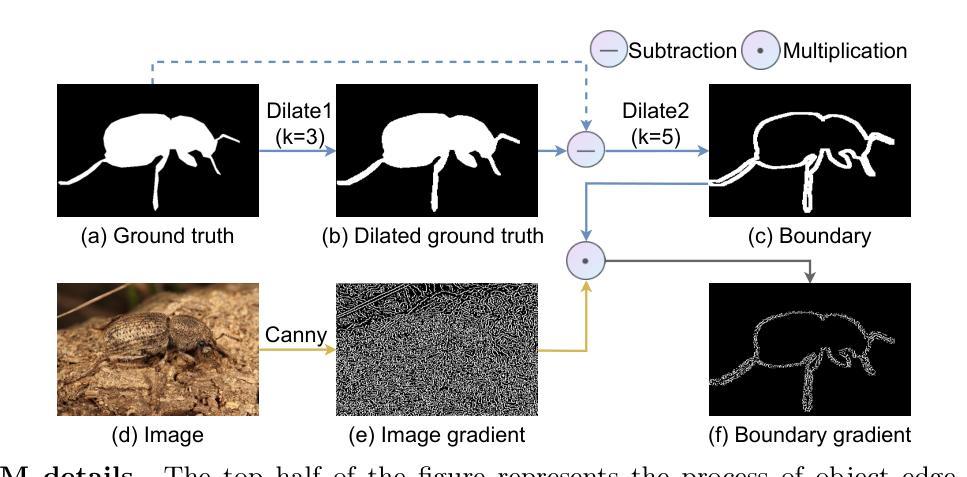
We rethink the segment anything model (SAM) and propose a novel multiprompt network called COMPrompter for camouflaged object detection (COD). SAM has zero-shot generalization ability beyond other models and can provide an ideal framework for COD. Our network aims to enhance the single prompt strategy in SAM to a multiprompt strategy. To achieve this, we propose an edge gradient extraction module, which generates a mask containing gradient information regarding the boundaries of camouflaged objects. This gradient mask is then used as a novel boundary prompt, enhancing the segmentation process. Thereafter, we design a box-boundary mutual guidance module, which fosters more precise and comprehensive feature extraction via mutual guidance between a boundary prompt and a box prompt. This collaboration enhances the model’s ability to accurately detect camouflaged objects. Moreover, we employ the discrete wavelet transform to extract high-frequency features from image embeddings. The high-frequency features serve as a supplementary component to the multiprompt system. Finally, our COMPrompter guides the network to achieve enhanced segmentation results, thereby advancing the development of SAM in terms of COD. Experimental results across COD benchmarks demonstrate that COMPrompter achieves a cutting-edge performance, surpassing the current leading model by an average positive metric of 2.2% in COD10K. In the specific application of COD, the experimental results in polyp segmentation show that our model is superior to top-tier methods as well. The code will be made available at https://github.com/guobaoxiao/COMPrompter.
我们对任意分割模型(SAM)进行了重新思考,并针对伪装目标检测(COD)提出了一种新的多提示网络,名为COMPrompter。SAM具有超越其他模型的零样本泛化能力,可为COD提供理想框架。我们的网络旨在增强SAM中的单提示策略为多提示策略。为此,我们提出了边缘梯度提取模块,该模块生成包含关于伪装目标边界的梯度信息的掩膜。然后,将这个梯度掩膜用作一个新的边界提示,以增强分割过程。之后,我们设计了一个盒子边界相互引导模块,通过边界提示和盒子提示之间的相互引导,实现更精确和全面的特征提取。这种协作增强了模型精确检测伪装目标的能力。此外,我们采用离散小波变换从图像嵌入中提取高频特征。高频特征作为多提示系统的补充成分。最终,我们的COMPrompter引导网络实现增强的分割结果,从而促进了SAM在COD方面的发展。在COD基准测试上的实验结果表明,COMPrompter达到了领先水平,在COD10K上的平均正面指标超越了当前领先模型2.2%。在COD的特定应用——息肉分割的实验结果也表明,我们的模型优于顶级方法。代码将在https://github.com/guobaoxiao/COMPrompter上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SCIENCE CHINA Information Sciences 2024
Summary
该文提出一种新型的多提示网络,名为COMPrompter,用于伪装目标检测(COD)。该方法在分段任何东西模型(SAM)的基础上进行了改进,通过引入边缘梯度提取模块和高频特征提取方法,提高了伪装目标检测的准确性。COMPrompter在多个COD基准测试中表现出卓越性能,较现有领先模型平均提高了2.2%的阳性指标。同时,在特定应用如息肉分割中,该模型也表现出优越性。相关代码可通过链接访问。
Key Takeaways
- COMPrompter是一种基于SAM的多提示网络,用于伪装目标检测。
- 引入边缘梯度提取模块,生成包含目标边界梯度信息的掩膜,作为新的边界提示,增强分割过程。
- 设计了盒边界相互引导模块,通过边界提示和盒提示之间的相互引导,实现更精确和全面的特征提取。
- 采用离散小波变换提取图像嵌入中的高频特征,作为多提示系统的补充。
- COMPrompter提高了伪装目标检测的准确性,并在多个基准测试中表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

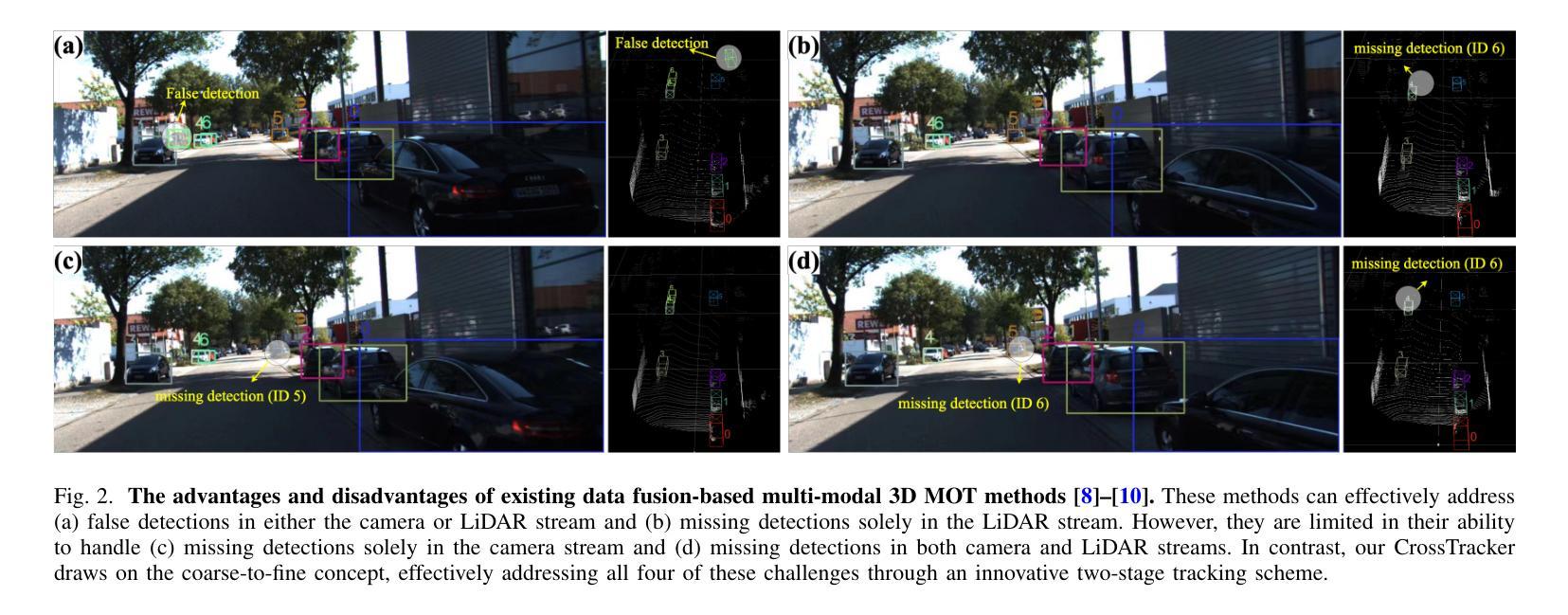
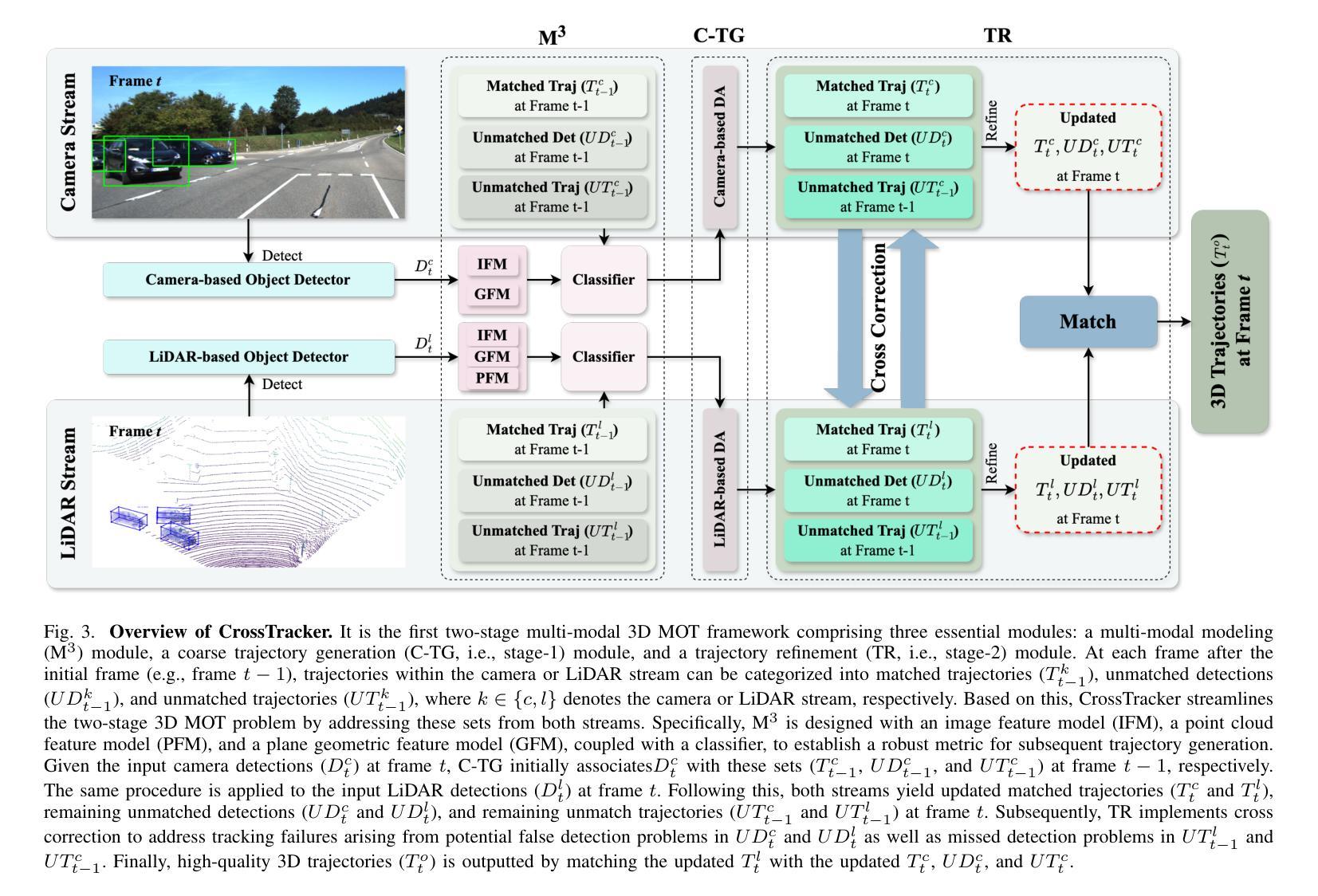
CrossTracker: Robust Multi-modal 3D Multi-Object Tracking via Cross Correction
Authors:Lipeng Gu, Xuefeng Yan, Weiming Wang, Honghua Chen, Dingkun Zhu, Liangliang Nan, Mingqiang Wei
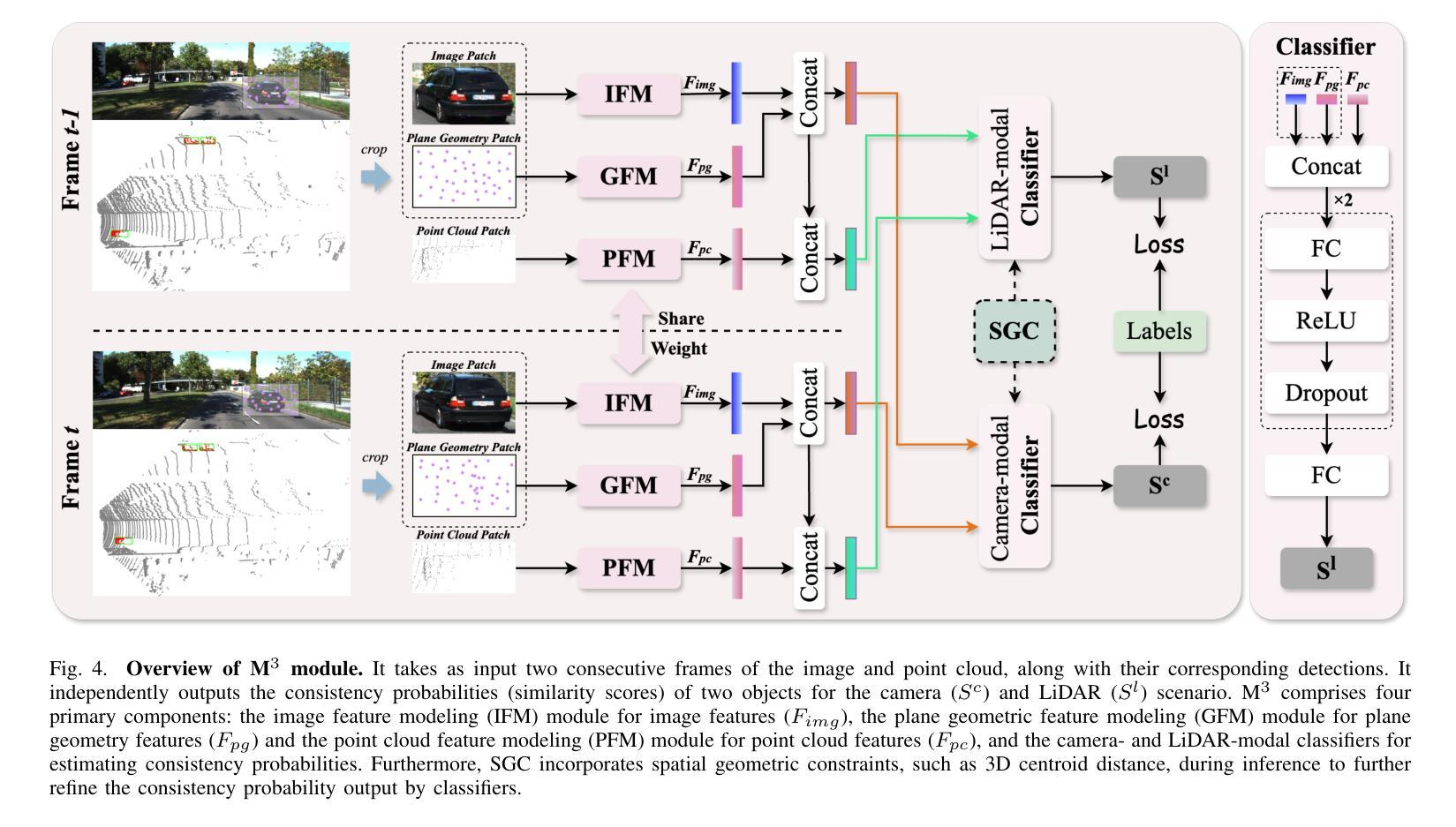
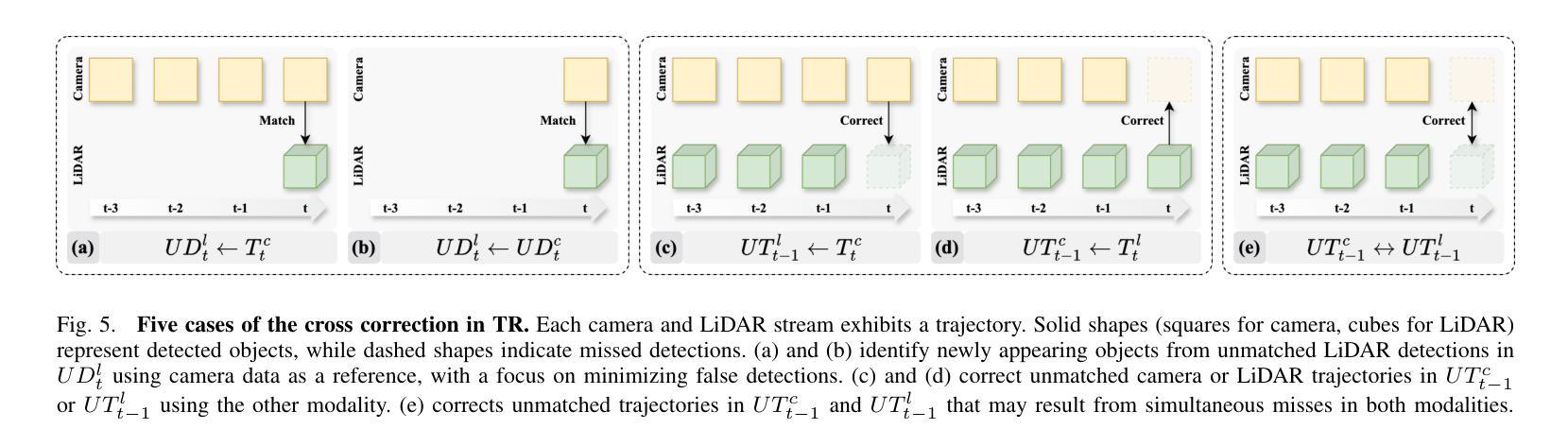
The fusion of camera- and LiDAR-based detections offers a promising solution to mitigate tracking failures in 3D multi-object tracking (MOT). However, existing methods predominantly exploit camera detections to correct tracking failures caused by potential LiDAR detection problems, neglecting the reciprocal benefit of refining camera detections using LiDAR data. This limitation is rooted in their single-stage architecture, akin to single-stage object detectors, lacking a dedicated trajectory refinement module to fully exploit the complementary multi-modal information. To this end, we introduce CrossTracker, a novel two-stage paradigm for online multi-modal 3D MOT. CrossTracker operates in a coarse-to-fine manner, initially generating coarse trajectories and subsequently refining them through an independent refinement process. Specifically, CrossTracker incorporates three essential modules: i) a multi-modal modeling (M^3) module that, by fusing multi-modal information (images, point clouds, and even plane geometry extracted from images), provides a robust metric for subsequent trajectory generation. ii) a coarse trajectory generation (C-TG) module that generates initial coarse dual-stream trajectories, and iii) a trajectory refinement (TR) module that refines coarse trajectories through cross correction between camera and LiDAR streams. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of our CrossTracker over its eighteen competitors, underscoring its effectiveness in harnessing the synergistic benefits of camera and LiDAR sensors for robust multi-modal 3D MOT.
融合相机和激光雷达检测为解决三维多目标跟踪(MOT)中的跟踪失败问题提供了有前途的解决方案。然而,现有方法主要利用相机检测来纠正由潜在的激光雷达检测问题引起的跟踪失败,忽略了利用激光雷达数据优化相机检测的互惠效益。这一局限性源于其类似于单阶段目标检测器的单一阶段架构,缺乏专门的轨迹优化模块,无法充分利用互补的多模式信息。为此,我们引入了CrossTracker,这是一种用于在线多模式三维MOT的新型两阶段范式。CrossTracker按由粗到细的方式运行,首先生成粗略轨迹,然后通过独立的优化过程对其进行细化。具体来说,CrossTracker包含了三个基本模块:i)多模式建模(M^3)模块,它通过融合多模式信息(图像、点云以及甚至从图像中提取的平面几何),为后续轨迹生成提供稳健的度量标准。ii)粗略轨迹生成(C-TG)模块,用于生成初始的粗略双流轨迹;iii)轨迹优化(TR)模块,通过相机和激光雷达流之间的交叉校正来优化粗略轨迹。综合实验表明,我们的CrossTracker在18个竞争对手中表现出卓越性能,突显了其在利用相机和激光雷达传感器的协同优势进行稳健多模式三维MOT方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了跨模态追踪(CrossTracker)技术,这是一种新型的在线多模态三维多目标追踪(3D MOT)的两阶段框架。它通过融合相机和激光雷达数据,旨在解决追踪失败的问题。CrossTracker通过粗到细的流程操作,首先生成粗略轨迹,然后通过独立的细化过程进行改进。实验表明,CrossTracker在十八个竞争对手中表现出卓越性能,有效实现了相机和激光雷达传感器的协同优势,为稳健的多模态3D MOT提供了强有力的支持。
Key Takeaways
- 跨模态追踪技术通过融合相机和激光雷达检测,弥补了单一传感器追踪的缺陷。
- 现有方法主要依赖相机检测来纠正由潜在激光雷达检测问题引起的跟踪失败,而CrossTracker利用双向优势,即使用激光雷达数据来优化相机检测。
- CrossTracker引入了一种新型的两阶段框架,以在线多模态3D MOT为目标。
- 该技术通过粗到细的流程操作,首先生成粗略轨迹,然后通过独立的细化过程进行改进。
- CrossTracker包括三个关键模块:多模态建模(M^3)、粗轨迹生成(C-TG)和轨迹细化(TR)。
- M^3模块通过融合多模态信息(图像、点云甚至从图像中提取的平面几何),为后续轨迹生成提供稳健指标。
点此查看论文截图


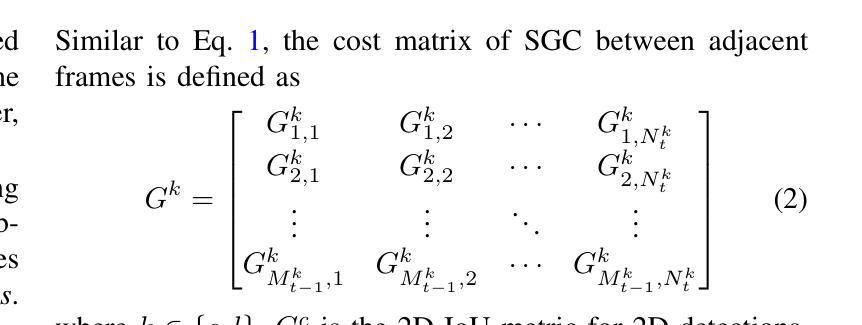
Leveraging Semantic Asymmetry for Precise Gross Tumor Volume Segmentation of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Planning CT
Authors:Zi Li, Ying Chen, Zeli Chen, Yanzhou Su, Tai Ma, Tony C. W. Mok, Yan-Jie Zhou, Yunhai Bai, Zhinlin Zheng, Le Lu, Yirui Wang, Jia Ge, Xianghua Ye, Senxiang Yan, Dakai Jin
In the radiation therapy of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), clinicians typically delineate the gross tumor volume (GTV) using non-contrast planning computed tomography to ensure accurate radiation dose delivery. However, the low contrast between tumors and adjacent normal tissues necessitates that radiation oncologists manually delineate the tumors, often relying on diagnostic MRI for guidance. % In this study, we propose a novel approach to directly segment NPC gross tumors on non-contrast planning CT images, circumventing potential registration errors when aligning MRI or MRI-derived tumor masks to planning CT. To address the low contrast issues between tumors and adjacent normal structures in planning CT, we introduce a 3D Semantic Asymmetry Tumor segmentation (SATs) method. Specifically, we posit that a healthy nasopharyngeal region is characteristically bilaterally symmetric, whereas the emergence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma disrupts this symmetry. Then, we propose a Siamese contrastive learning segmentation framework that minimizes the voxel-wise distance between original and flipped areas without tumor and encourages a larger distance between original and flipped areas with tumor. Thus, our approach enhances the sensitivity of features to semantic asymmetries. % Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed SATs achieves the leading NPC GTV segmentation performance in both internal and external testing, \emph{e.g.}, with at least 2% absolute Dice score improvement and 12% average distance error reduction when compared to other state-of-the-art methods in the external testing.
在鼻咽癌(NPC)的放射治疗过程中,临床医生通常使用非对比计划计算机断层扫描(planning CT)来划定大体肿瘤体积(GTV),以确保准确的辐射剂量传递。然而,肿瘤与相邻正常组织之间的对比度较低,迫使放疗科医生手动划定肿瘤,通常依赖诊断磁共振成像(MRI)进行引导。本研究提出了一种在无需对比剂的非对比计划CT图像上直接分割鼻咽癌大体肿瘤的新方法,避免了将MRI或基于MRI的肿瘤掩膜与计划CT对齐时可能出现的注册误差。为了解决在计划CT中肿瘤与相邻正常结构之间的低对比度问题,我们引入了三维语义不对称肿瘤分割(SATs)方法。具体而言,我们认为健康的咽腔区域具有典型的双侧对称性,而鼻咽癌的出现会破坏这种对称性。然后,我们提出了一种Siamese对比学习分割框架,该框架通过最小化原始和翻转区域(无肿瘤)之间的体素距离以及鼓励原始和翻转区域(有肿瘤)之间的距离来增强特征对语义不对称的敏感性。广泛的实验表明,所提出的SATs在内部和外部测试中均实现了领先的NPC GTV分割性能,例如与外部测试中的其他最先进的方法相比,至少提高了2%的绝对Dice得分并减少了12%的平均距离误差。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:在鼻咽癌放射治疗领域,本研究提出了一种新的方法,即基于非对比剂规划计算机断层扫描(CT)直接分割鼻咽癌肿瘤体积(GTV)。通过利用健康的鼻咽区域具有双侧对称性的特征,本研究引入了一种三维语义不对称肿瘤分割(SATs)方法来解决肿瘤与邻近正常组织之间的对比度低的问题。同时,研究还提出了一种Siamese对比学习分割框架,该框架可以缩小无肿瘤区域的原始和翻转区域之间的像素距离,并鼓励有肿瘤区域的原始和翻转区域之间的距离更大。通过大量实验验证,本研究提出的SATs方法在内部和外部测试中均实现了领先的NPC GTV分割性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 本研究提出了一种基于非对比剂规划CT直接分割鼻咽癌肿瘤体积的新方法。
- 研究引入了三维语义不对称肿瘤分割(SATs)方法来解决肿瘤与邻近正常组织之间的对比度低的问题。
- SATs方法利用了健康的鼻咽区域具有的双侧对称性特征来区分肿瘤和正常组织。
- 研究还提出了一种Siamese对比学习分割框架来增强特征的敏感性。
- SATs方法在实际应用中的性能显著优于其他最先进的方法,如在外部测试中实现了至少2%的绝对Dice得分提高和平均距离误差减少12%。
点此查看论文截图

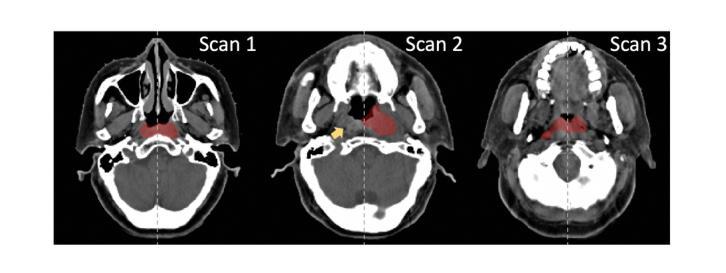
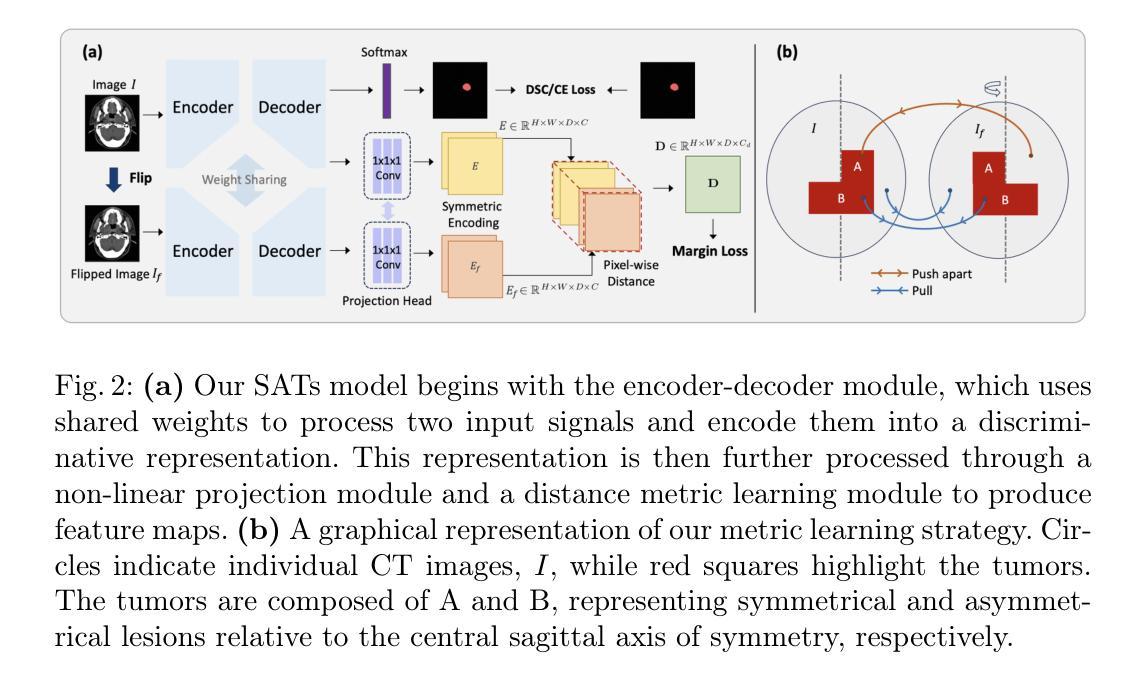
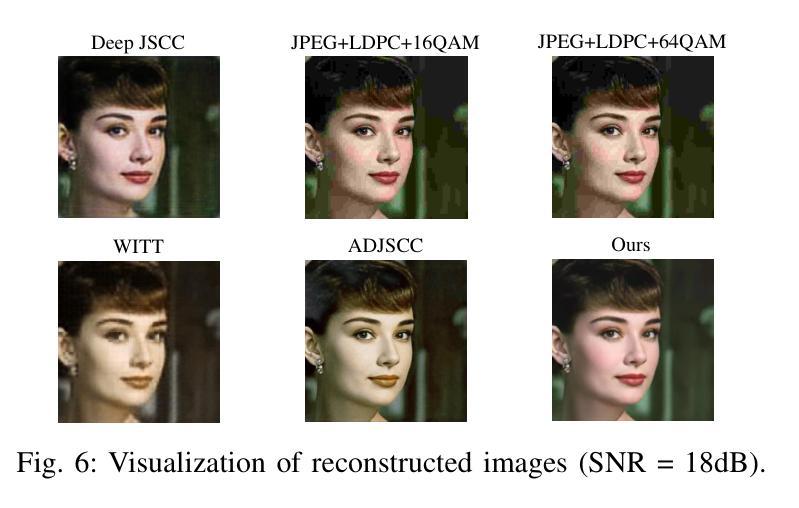
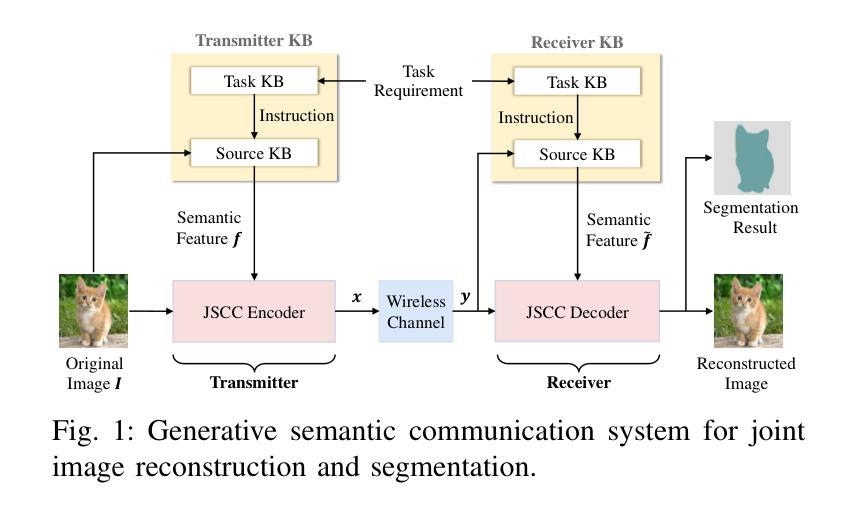
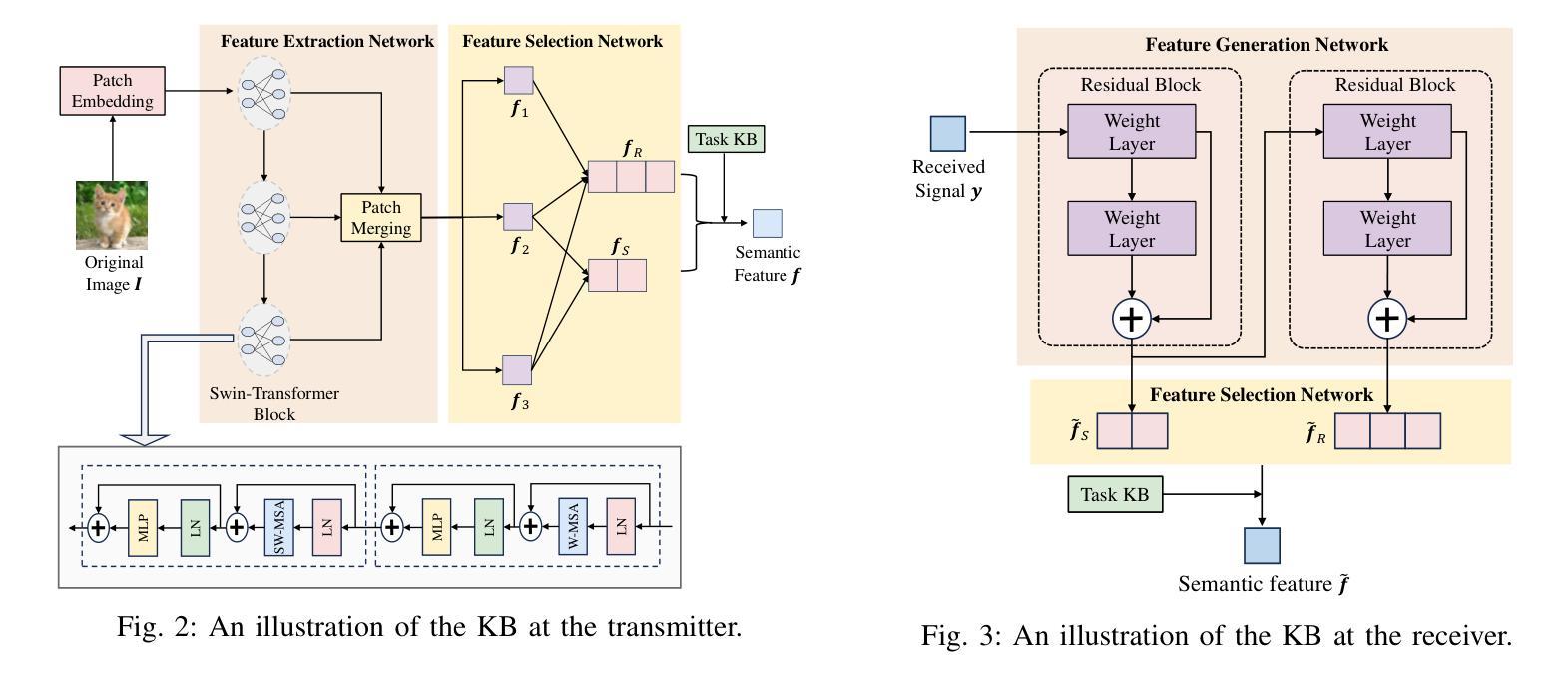
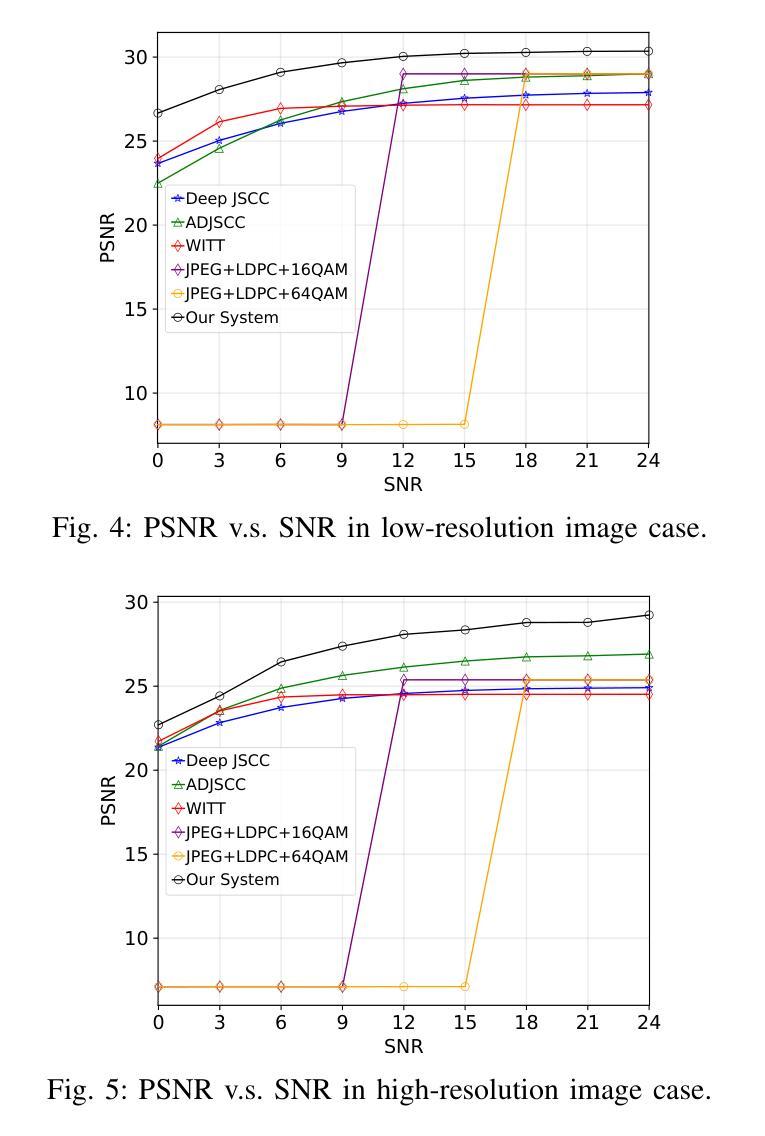
Generative Semantic Communication for Joint Image Transmission and Segmentation
Authors:Weiwen Yuan, Jinke Ren, Chongjie Wang, Ruichen Zhang, Jun Wei, Dong In Kim, Shuguang Cui
Semantic communication has emerged as a promising technology for enhancing communication efficiency. However, most existing research emphasizes single-task reconstruction, neglecting model adaptability and generalization across multi-task systems. In this paper, we propose a novel generative semantic communication system that supports both image reconstruction and segmentation tasks. Our approach builds upon semantic knowledge bases (KBs) at both the transmitter and receiver, with each semantic KB comprising a source KB and a task KB. The source KB at the transmitter leverages a hierarchical Swin-Transformer, a generative AI scheme, to extract multi-level features from the input image. Concurrently, the counterpart source KB at the receiver utilizes hierarchical residual blocks to generate task-specific knowledge. Furthermore, the two task KBs adopt a semantic similarity model to map different task requirements into pre-defined task instructions, thereby facilitating the feature selection of the source KBs. Additionally, we develop a unified residual block-based joint source and channel (JSCC) encoder and two task-specific JSCC decoders to achieve the two image tasks. In particular, a generative diffusion model is adopted to construct the JSCC decoder for the image reconstruction task. Experimental results demonstrate that our multi-task generative semantic communication system outperforms previous single-task communication systems in terms of peak signal-to-noise ratio and segmentation accuracy.
语义通信作为一种提高通信效率的有前途的技术已经崭露头角。然而,大多数现有研究强调单任务重建,忽略了模型在多任务系统中的适应性和泛化能力。本文中,我们提出了一种支持图像重建和分割任务的新型生成语义通信系统。我们的方法基于发射器和接收器双方的语义知识库(KBs),每个语义知识库包括源知识库和任务知识库。发射器端的源知识库利用分层Swin-Transformer(一种生成人工智能方案)从输入图像中提取多层次特征。同时,接收器端的对应源知识库利用分层残差块生成特定任务的知识。此外,两个任务知识库采用语义相似性模型,将不同的任务要求映射到预定义的任务指令中,从而促进源知识库的特征选择。此外,我们开发了一种基于统一残差块的联合源信道(JSCC)编码器,以及两个针对特定任务的JSCC解码器,以实现两个图像任务。特别是,采用生成扩散模型构建图像重建任务的JSCC解码器。实验结果表明,我们的多任务生成语义通信系统相对于之前的单任务通信系统在峰值信噪比和分割精度方面表现出更好的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种支持图像重建和分割任务的多任务生成语义通信系统。该系统基于发送器和接收器端的语义知识库,利用生成人工智能方案提取输入图像的多层次特征,并实现任务特定知识的生成。通过语义相似性模型映射不同任务要求,并开发统一的联合源信道编码器与两个任务特定解码器,实现图像重建和分割任务。实验结果表明,该系统在峰值信噪比和分割精度方面优于以前的单任务通信系统。
Key Takeaways
- 语义通信技术能提高通信效率,但现有研究主要关注单任务重建,忽视了模型在多任务系统中的适应性和泛化能力。
- 本文提出了一种新的生成语义通信系统,支持图像重建和分割任务。
- 系统利用语义知识库来提取输入图像的多层次特征,并生成任务特定知识。
- 通过语义相似性模型映射不同任务要求,促进特征选择。
- 开发了联合源和信道编码器及两个任务特定解码器,用于实现两个图像任务。
- 采用生成扩散模型构建图像重建任务的解码器。
点此查看论文截图


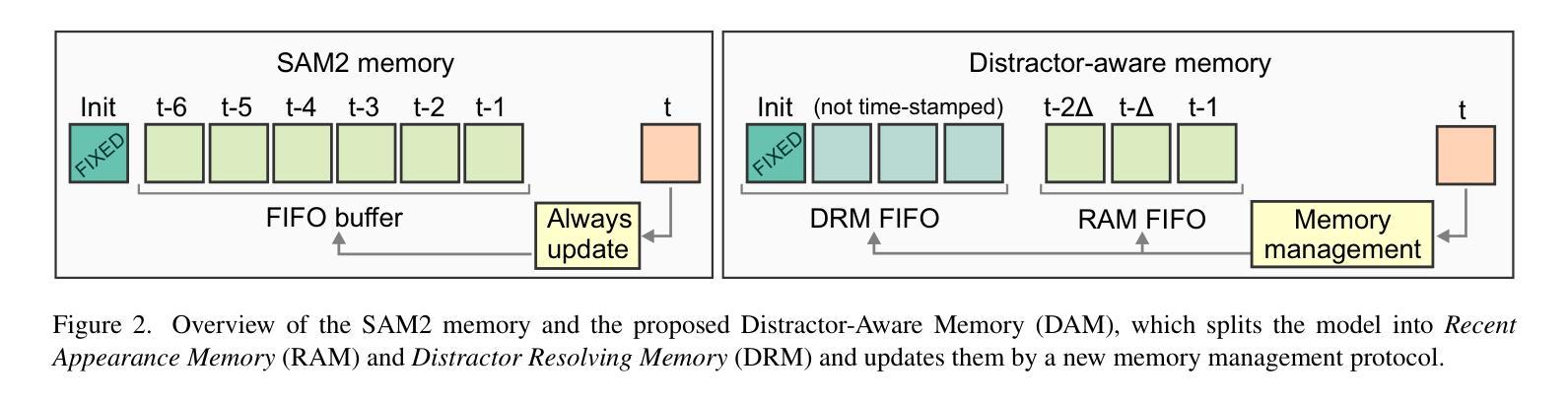
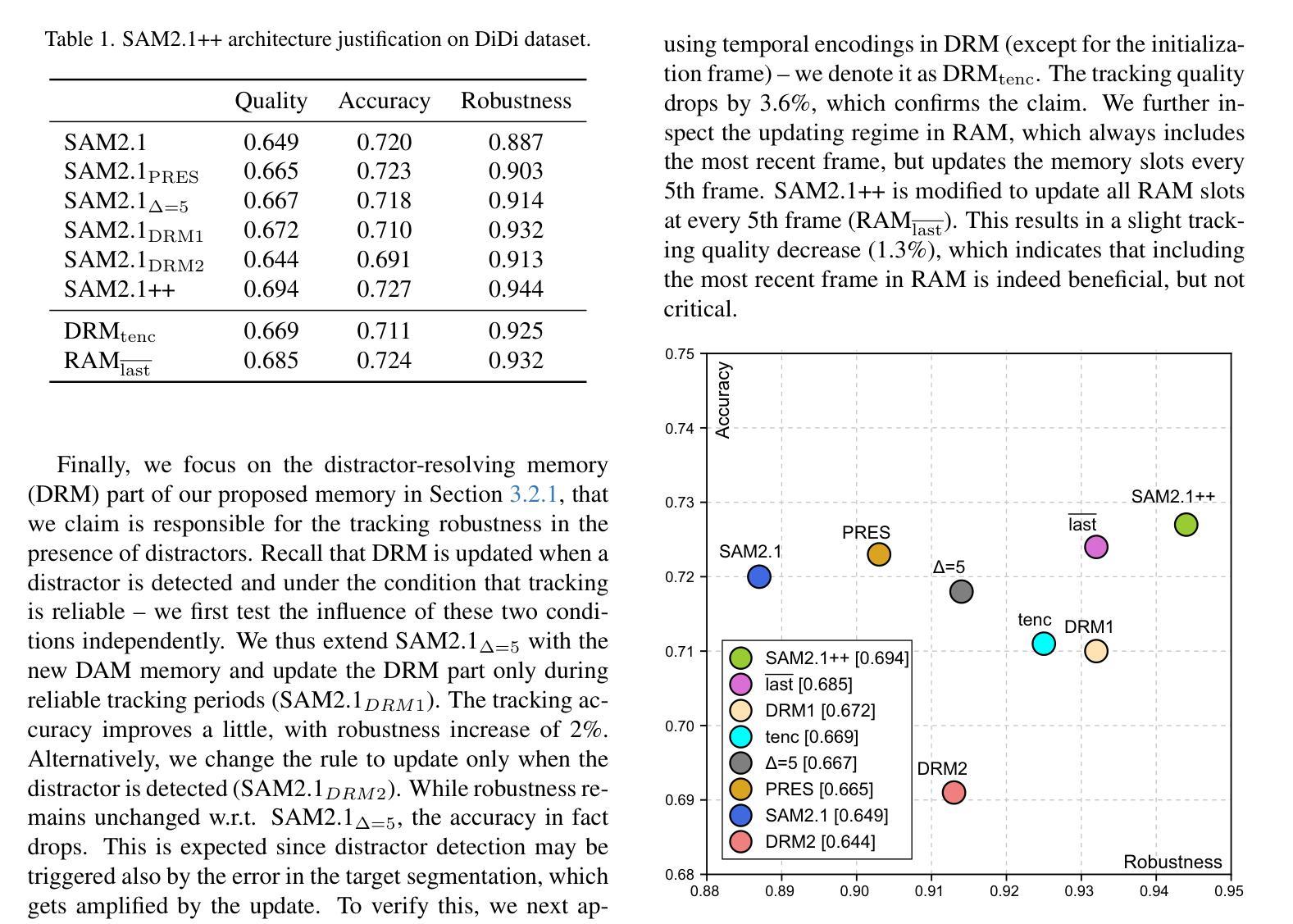
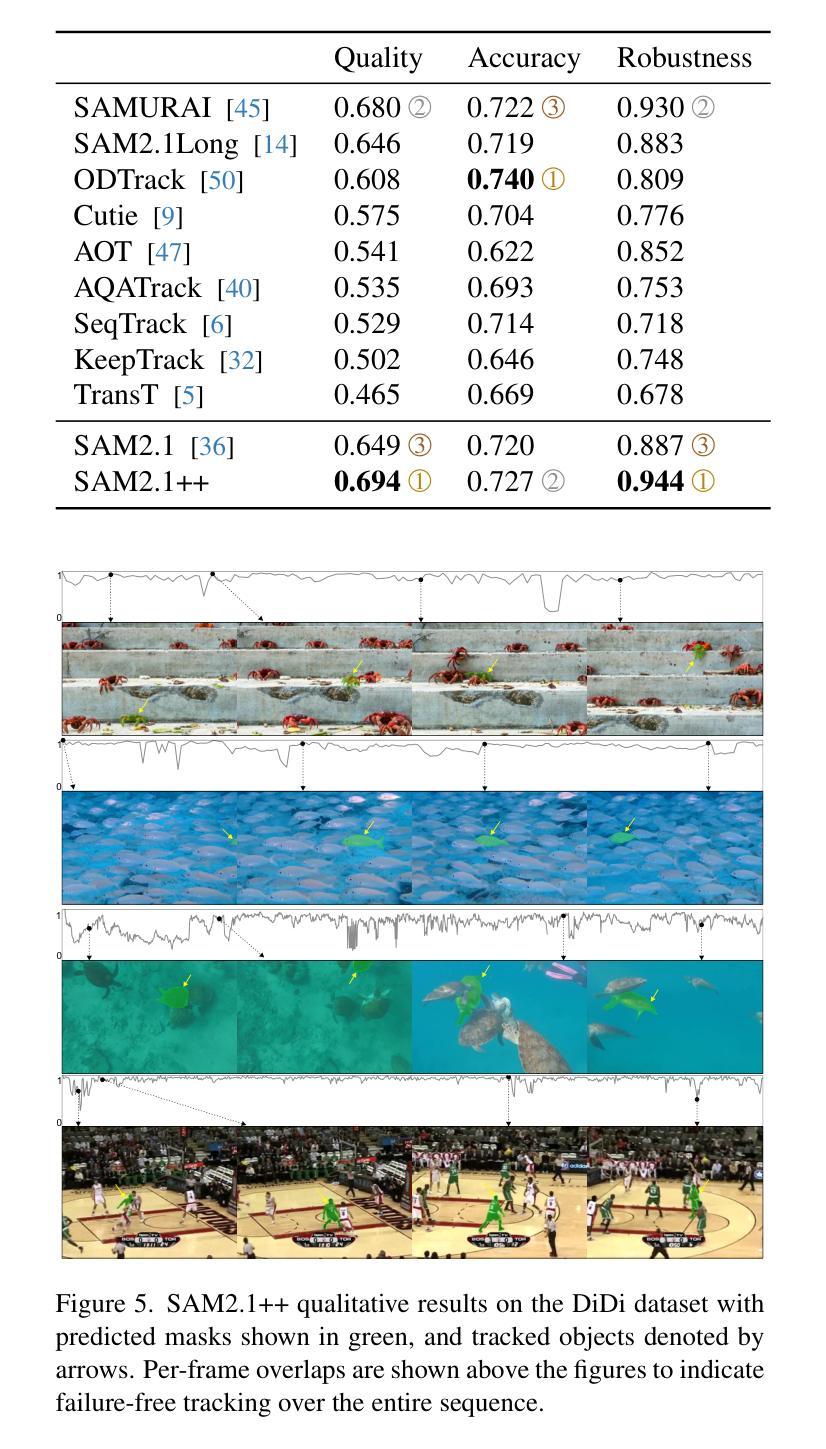
A Distractor-Aware Memory for Visual Object Tracking with SAM2
Authors:Jovana Videnovic, Alan Lukezic, Matej Kristan
Memory-based trackers are video object segmentation methods that form the target model by concatenating recently tracked frames into a memory buffer and localize the target by attending the current image to the buffered frames. While already achieving top performance on many benchmarks, it was the recent release of SAM2 that placed memory-based trackers into focus of the visual object tracking community. Nevertheless, modern trackers still struggle in the presence of distractors. We argue that a more sophisticated memory model is required, and propose a new distractor-aware memory model for SAM2 and an introspection-based update strategy that jointly addresses the segmentation accuracy as well as tracking robustness. The resulting tracker is denoted as SAM2.1++. We also propose a new distractor-distilled DiDi dataset to study the distractor problem better. SAM2.1++ outperforms SAM2.1 and related SAM memory extensions on seven benchmarks and sets a solid new state-of-the-art on six of them.
基于内存的跟踪器是一种视频目标分割方法,它通过将近来跟踪的帧拼接到内存缓冲区中并形成目标模型,然后通过关注当前图像与缓冲帧来定位目标。尽管基于内存的跟踪器已在许多基准测试上取得了顶尖性能,但SAM2的最近发布还是使其成为视觉目标跟踪社区的关注焦点。然而,在现代跟踪器面前,干扰物的存在仍然是一个挑战。我们认为需要一个更复杂的内存模型,因此为SAM2提出了一个新的干扰物感知内存模型,以及一种基于自省策略的更新策略,共同解决分割精度和跟踪稳健性问题。所得的跟踪器被标记为SAM2.1 ++。我们还提出了一个新的干扰物精炼数据集DiDi,以更好地研究干扰物问题。SAM2.1 ++ 在七个基准测试上超越了SAM2.1和相关的SAM内存扩展,并在其中六个上创下了最新的先进技术成果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review. Code available on Github: https://github.com/jovanavidenovic/DAM4SAM
Summary
基于内存的跟踪器是一种视频目标分割方法,它通过连接最近跟踪的帧到内存缓冲区来形成目标模型,并通过关注当前图像和缓冲帧来定位目标。尽管已经在许多基准测试中取得了顶尖性能,但最近SAM2的发布使基于内存的跟踪器成为视觉目标跟踪社区的关注焦点。然而,现代跟踪器在存在干扰物时仍面临挑战。本文提出一种新型的干扰物感知内存模型用于SAM2,以及一种基于内省的更新策略,旨在解决分割精度和跟踪稳健性问题。所得跟踪器称为SAM2.1++。同时,本文还提出了一种新型的干扰物蒸馏DiDi数据集,以更好地研究干扰物问题。SAM2.1++在七个基准测试中超越了SAM2.1和相关SAM内存扩展,并在其中六个基准测试上创下了新的最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 基于内存的跟踪器通过连接最近跟踪的帧到内存缓冲区形成目标模型,并定位目标。
- SAM2的发布使基于内存的跟踪器成为视觉目标跟踪的焦点。
- 现代跟踪器在存在干扰物时仍面临挑战。
- 提出了一种新型的干扰物感知内存模型用于SAM2,解决分割精度和跟踪稳健性问题。
- SAM2.1++性能超越了SAM2.1和相关SAM内存扩展。
- SAM2.1++在多个基准测试上创下了新的最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图


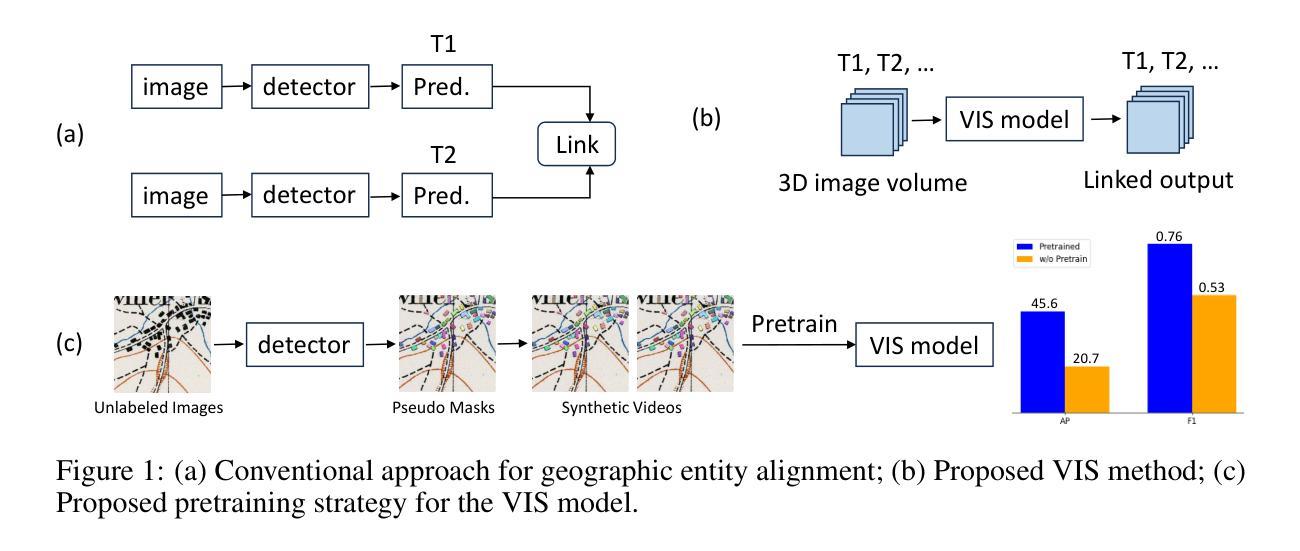
Self-supervised Video Instance Segmentation Can Boost Geographic Entity Alignment in Historical Maps
Authors:Xue Xia, Randall Balestriero, Tao Zhang, Lorenz Hurni
Tracking geographic entities from historical maps, such as buildings, offers valuable insights into cultural heritage, urbanization patterns, environmental changes, and various historical research endeavors. However, linking these entities across diverse maps remains a persistent challenge for researchers. Traditionally, this has been addressed through a two-step process: detecting entities within individual maps and then associating them via a heuristic-based post-processing step. In this paper, we propose a novel approach that combines segmentation and association of geographic entities in historical maps using video instance segmentation (VIS). This method significantly streamlines geographic entity alignment and enhances automation. However, acquiring high-quality, video-format training data for VIS models is prohibitively expensive, especially for historical maps that often contain hundreds or thousands of geographic entities. To mitigate this challenge, we explore self-supervised learning (SSL) techniques to enhance VIS performance on historical maps. We evaluate the performance of VIS models under different pretraining configurations and introduce a novel method for generating synthetic videos from unlabeled historical map images for pretraining. Our proposed self-supervised VIS method substantially reduces the need for manual annotation. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed self-supervised VIS approach, achieving a 24.9% improvement in AP and a 0.23 increase in F1 score compared to the model trained from scratch.
从历史地图中追踪地理实体,如建筑等,为文化遗产、城市化模式、环境变化以及各种历史研究提供了宝贵的见解。然而,如何在不同的地图之间将这些实体关联起来一直是研究人员面临的挑战。传统上,这通过两步过程来解决:先在单个地图内检测实体,然后通过基于启发式的后处理步骤将它们关联起来。在本文中,我们提出了一种新方法,该方法结合了历史地图中的地理实体分割和关联,使用视频实例分割(VIS)技术。这种方法极大地简化了地理实体的对齐过程,提高了自动化程度。然而,为VIS模型获取高质量的视频格式训练数据成本高昂,尤其是历史地图通常包含数百或数千个地理实体。为了缓解这一挑战,我们探索了自监督学习(SSL)技术,以提高历史地图上的VIS性能。我们评估了VIS模型在不同预训练配置下的性能,并引入了一种从无标签的历史地图图像生成合成视频的新方法,用于预训练。我们提出的自监督VIS方法大大降低了对手动标注的需求。实验结果表明,与从头开始训练的模型相比,所提出的自监督VIS方法在AP上提高了24.9%,F1分数提高了0.23。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:利用视频实例分割技术结合历史地图中的地理实体分割与关联,为文化继承、城市化模式、环境变化等领域提供有价值的见解。针对历史地图中实体对齐的难题,提出一种新方法,通过自监督学习技术提高视频实例分割性能,减少人工标注需求,显著提高模型性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 历史地图中的地理实体跟踪对于文化研究、城市规划等领域具有价值。
- 传统的地理实体关联方法需要两步处理,存在效率不高的问题。
- 视频实例分割技术被应用于历史地图的地理实体分割与关联,提高了效率。
- 获取高质量的视频格式训练数据对于VIS模型来说成本高昂。
- 采用自监督学习技术解决VIS模型训练数据不足的问题。
- 通过对不同预训练配置进行评估,提出了新的方法生成合成视频用于预训练。
点此查看论文截图

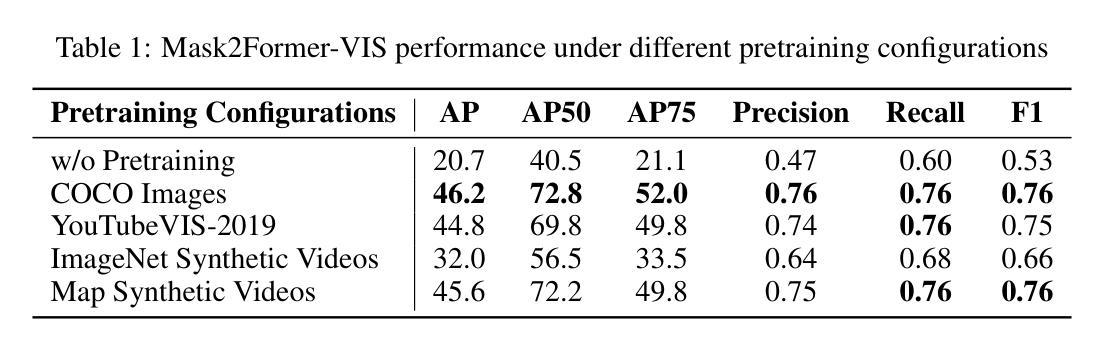

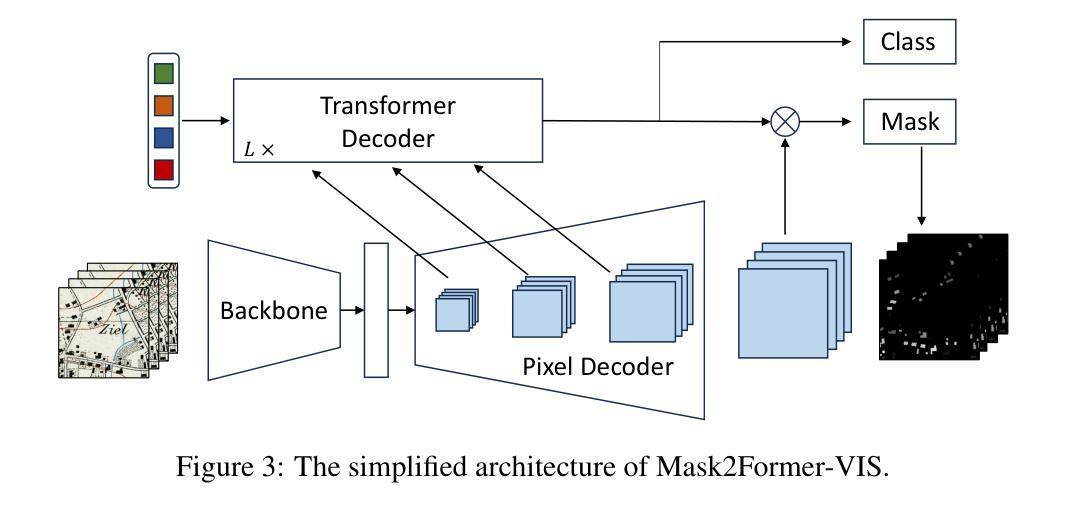
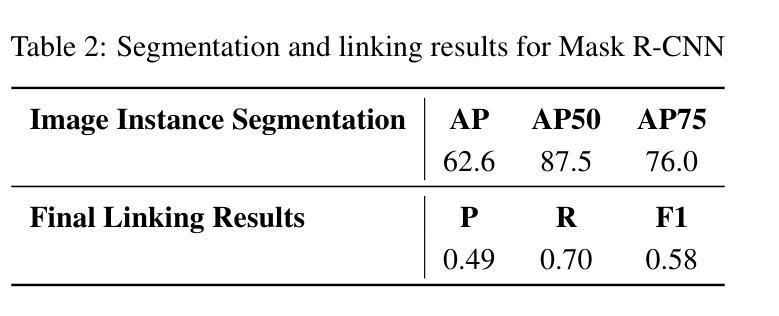
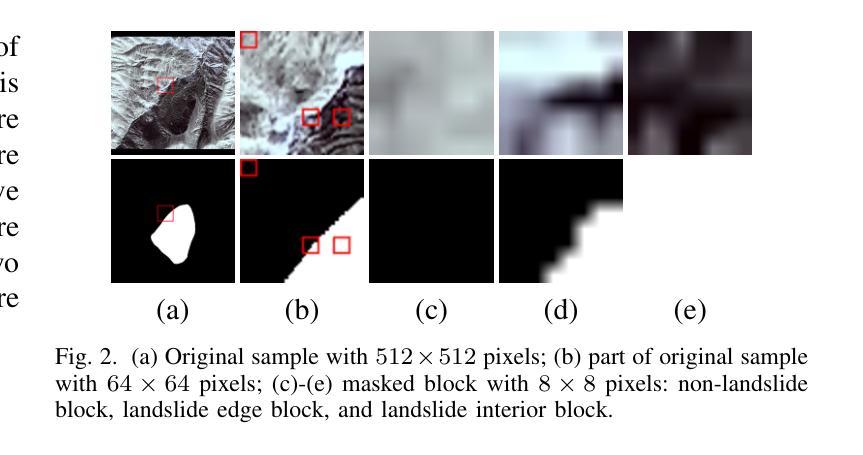
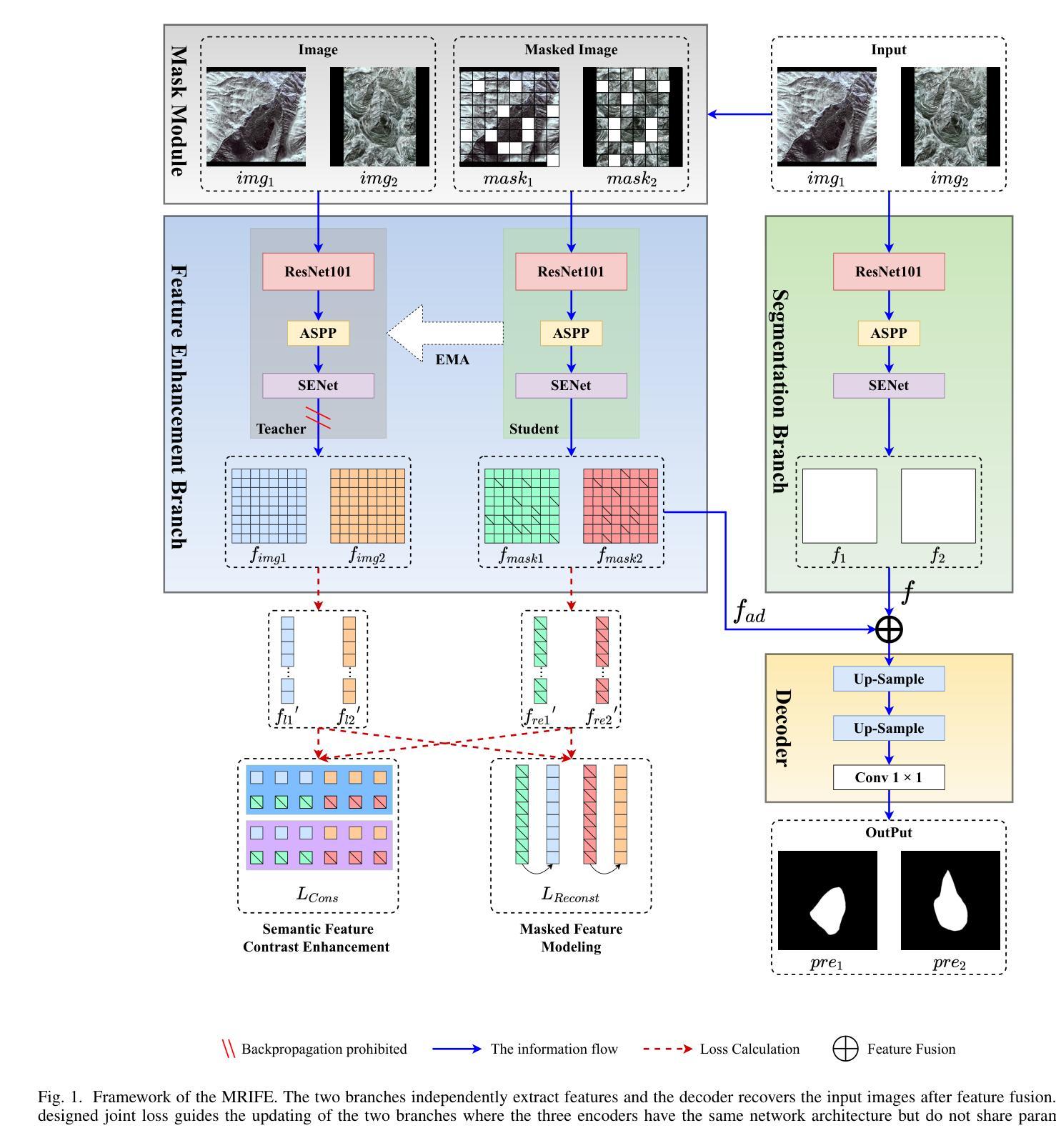
MRIFE: A Mask-Recovering and Interactive-Feature-Enhancing Semantic Segmentation Network For Relic Landslide Detection
Authors:Juefei He, Yuexing Peng, Wei Li, Junchuan Yu, Daqing Ge, Wei Xiang
Relic landslide, formed over a long period, possess the potential for reactivation, making them a hazardous geological phenomenon. While reliable relic landslide detection benefits the effective monitoring and prevention of landslide disaster, semantic segmentation using high-resolution remote sensing images for relic landslides faces many challenges, including the object visual blur problem, due to the changes of appearance caused by prolonged natural evolution and human activities, and the small-sized dataset problem, due to difficulty in recognizing and labelling the samples. To address these challenges, a semantic segmentation model, termed mask-recovering and interactive-feature-enhancing (MRIFE), is proposed for more efficient feature extraction and separation. Specifically, a contrastive learning and mask reconstruction method with locally significant feature enhancement is proposed to improve the ability to distinguish between the target and background and represent landslide semantic features. Meanwhile, a dual-branch interactive feature enhancement architecture is used to enrich the extracted features and address the issue of visual ambiguity. Self-distillation learning is introduced to leverage the feature diversity both within and between samples for contrastive learning, improving sample utilization, accelerating model convergence, and effectively addressing the problem of the small-sized dataset. The proposed MRIFE is evaluated on a real relic landslide dataset, and experimental results show that it greatly improves the performance of relic landslide detection. For the semantic segmentation task, compared to the baseline, the precision increases from 0.4226 to 0.5347, the mean intersection over union (IoU) increases from 0.6405 to 0.6680, the landslide IoU increases from 0.3381 to 0.3934, and the F1-score increases from 0.5054 to 0.5646.
遗迹滑坡经历了长期形成过程,具有重新活动的潜力,成为一种危险的地质现象。可靠的遗迹滑坡检测有助于有效监测和预防滑坡灾害,然而,使用高分辨率遥感图像对遗迹滑坡进行语义分割面临诸多挑战,其中包括由于长期自然演变和人类活动导致的外观变化引起的目标视觉模糊问题,以及由于识别和标记样本困难而导致的小规模数据集问题。为了解决这些挑战,提出了一种名为掩膜恢复和交互特征增强(MRIFE)的语义分割模型,以更有效地提取和分离特征。具体来说,提出了一种对比学习和掩膜重建方法,具有局部重要特征增强的能力,以提高区分目标和背景的能力,并表现滑坡语义特征。同时,使用双分支交互特征增强架构来丰富提取的特征并解决视觉模糊问题。引入了自蒸馏学习,以利用样本内的特征多样性进行对比学习,提高样本利用率,加速模型收敛,有效解决小规模数据集的问题。提出的MRIFE方法在真实的遗迹滑坡数据集上进行了评估,实验结果表明,它大大提高了遗迹滑坡检测的性能。对于语义分割任务,与基线相比,精确度从0.4226提高到0.5347,平均交并比(IoU)从0.6405提高到0.6680,滑坡IoU从0.3381提高到0.3934,F1分数从0.5054提高到0.5646。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于长期形成的遗迹滑坡具有重新激活的潜力,因此对其进行可靠的检测对于有效的灾害监测和预防至关重要。面对遗迹滑坡在视觉上的模糊性以及小样本数据集带来的挑战,提出了一个名为MRIFE的语义分割模型,通过对比学习和掩膜重建方法提高目标背景区分能力,并采用双分支交互特征增强架构来丰富提取的特征并解决视觉模糊问题。此外,还引入了自蒸馏学习来提高样本利用率和模型收敛速度。在真实遗迹滑坡数据集上的实验结果表明,MRIFE模型大大提高了遗迹滑坡检测的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 遗迹滑坡具有重新激活的潜力,可靠的检测对于灾害监测和预防至关重要。
- 遗迹滑坡在视觉上存在模糊问题,小样本数据集也是一大挑战。
- 提出了MRIFE语义分割模型,通过对比学习和掩膜重建提高目标背景区分能力。
- 双分支交互特征增强架构用于丰富提取的特征并解决视觉模糊。
- 自蒸馏学习提高样本利用率和模型收敛速度。
- MRIFE模型在真实遗迹滑坡数据集上的实验性能显著提升。
点此查看论文截图


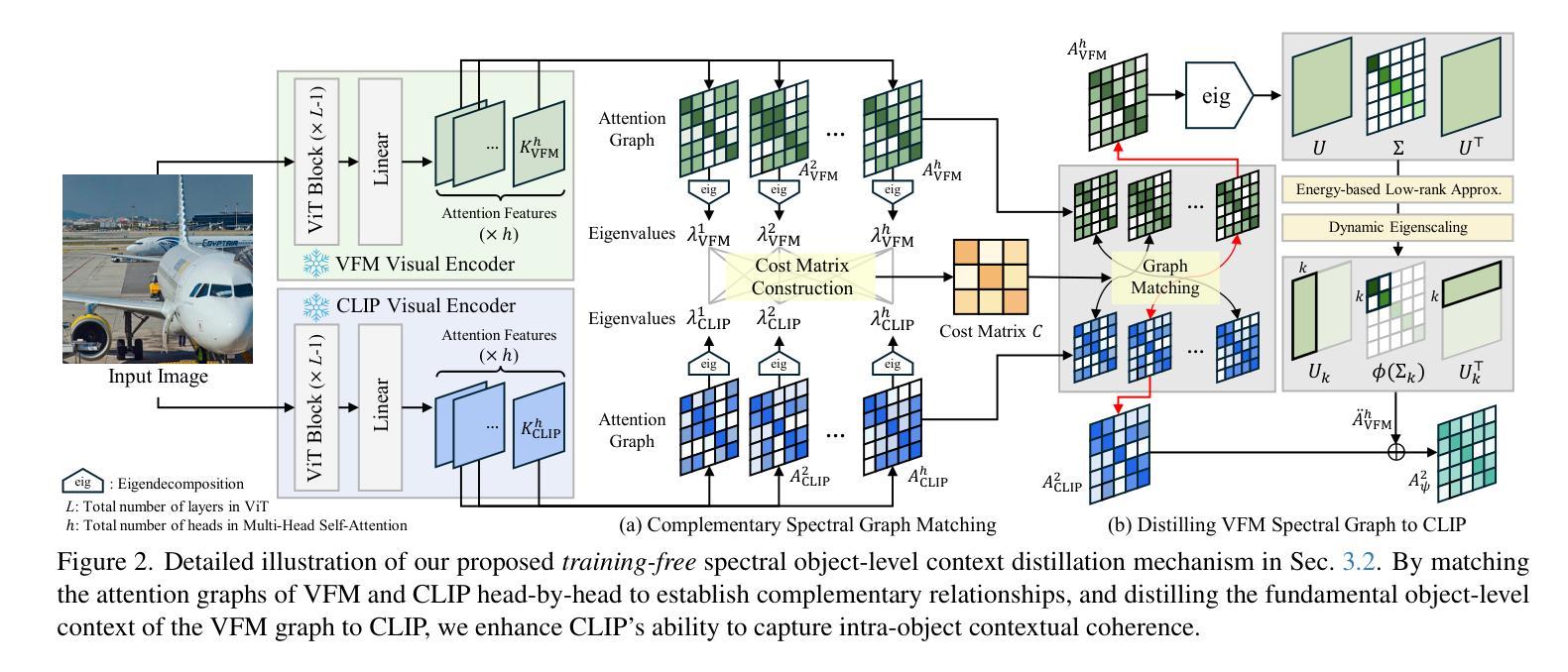
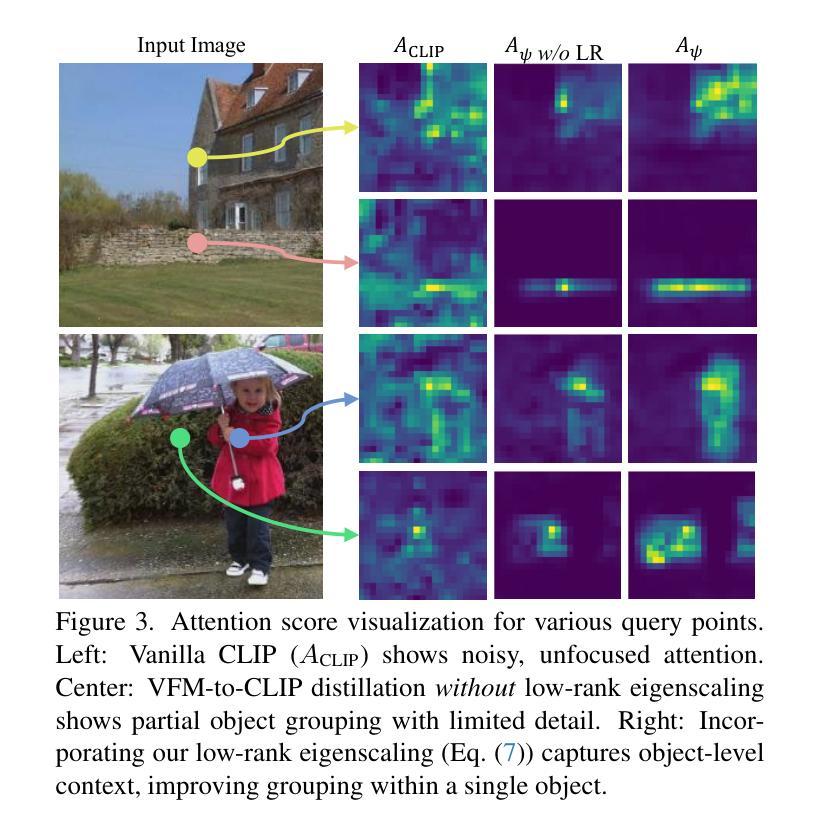
Distilling Spectral Graph for Object-Context Aware Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Chanyoung Kim, Dayun Ju, Woojung Han, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Seong Jae Hwang
Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation (OVSS) has advanced with recent vision-language models (VLMs), enabling segmentation beyond predefined categories through various learning schemes. Notably, training-free methods offer scalable, easily deployable solutions for handling unseen data, a key goal of OVSS. Yet, a critical issue persists: lack of object-level context consideration when segmenting complex objects in the challenging environment of OVSS based on arbitrary query prompts. This oversight limits models’ ability to group semantically consistent elements within object and map them precisely to user-defined arbitrary classes. In this work, we introduce a novel approach that overcomes this limitation by incorporating object-level contextual knowledge within images. Specifically, our model enhances intra-object consistency by distilling spectral-driven features from vision foundation models into the attention mechanism of the visual encoder, enabling semantically coherent components to form a single object mask. Additionally, we refine the text embeddings with zero-shot object presence likelihood to ensure accurate alignment with the specific objects represented in the images. By leveraging object-level contextual knowledge, our proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance with strong generalizability across diverse datasets.
开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)随着最近的视觉语言模型(VLMs)的发展而进步,通过各种学习方案实现了超出预定类别的分割。值得注意的是,无训练方法为处理未见数据提供了可扩展、易于部署的解决方案,这是OVSS的关键目标。然而,一个关键问题依然存在:在基于任意查询提示的OVSS的复杂环境中,对复杂对象进行分割时缺乏对象级别的上下文考虑。这一疏忽限制了模型在对象内组合语义一致元素的能力,并准确地将它们映射到用户定义的任意类别。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种通过结合图像中的对象级上下文知识来克服这一限制的新方法。具体来说,我们的模型通过将从视觉基础模型提炼的谱驱动特征蒸馏到视觉编码器的注意力机制中,增强了对象内部的连贯性,使得语义一致的组件能够形成单个对象掩码。此外,我们还通过零样本对象存在概率对文本嵌入进行了精炼,以确保与图像中表示的特定对象的准确对齐。通过利用对象级的上下文知识,我们提出的方法在多个数据集上实现了最先进的性能,并具有较强的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)在最近的视觉语言模型(VLMs)的支持下得到了发展,可以通过不同的学习方案实现超出预定类别的分割。本文介绍了一种新的方法,通过引入对象级别的上下文知识来解决复杂对象在OVSS环境中的分割问题,从而实现更精确的语义分割。
Key Takeaways
- 开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)允许超越预定类别的分割,通过不同的学习方案实现更广泛的语义理解。
- 训练免费的方法为处理未见过的数据提供了可扩展和易于部署的解决方案,是OVSS的关键目标之一。
- 当前方法缺乏对象级别的上下文考虑,在基于任意查询提示的OVSS环境中分割复杂对象时存在限制。
- 新方法通过引入对象级别的上下文知识来解决这个问题,增强了对象内部的一致性。
- 方法通过提炼视觉基础模型的频谱驱动特征到视觉编码器的注意力机制,使语义上一致的分量形成单个对象掩膜。
- 通过改进文本嵌入和零样本对象存在可能性,确保与图像中表示的特定对象的准确对齐。
点此查看论文截图

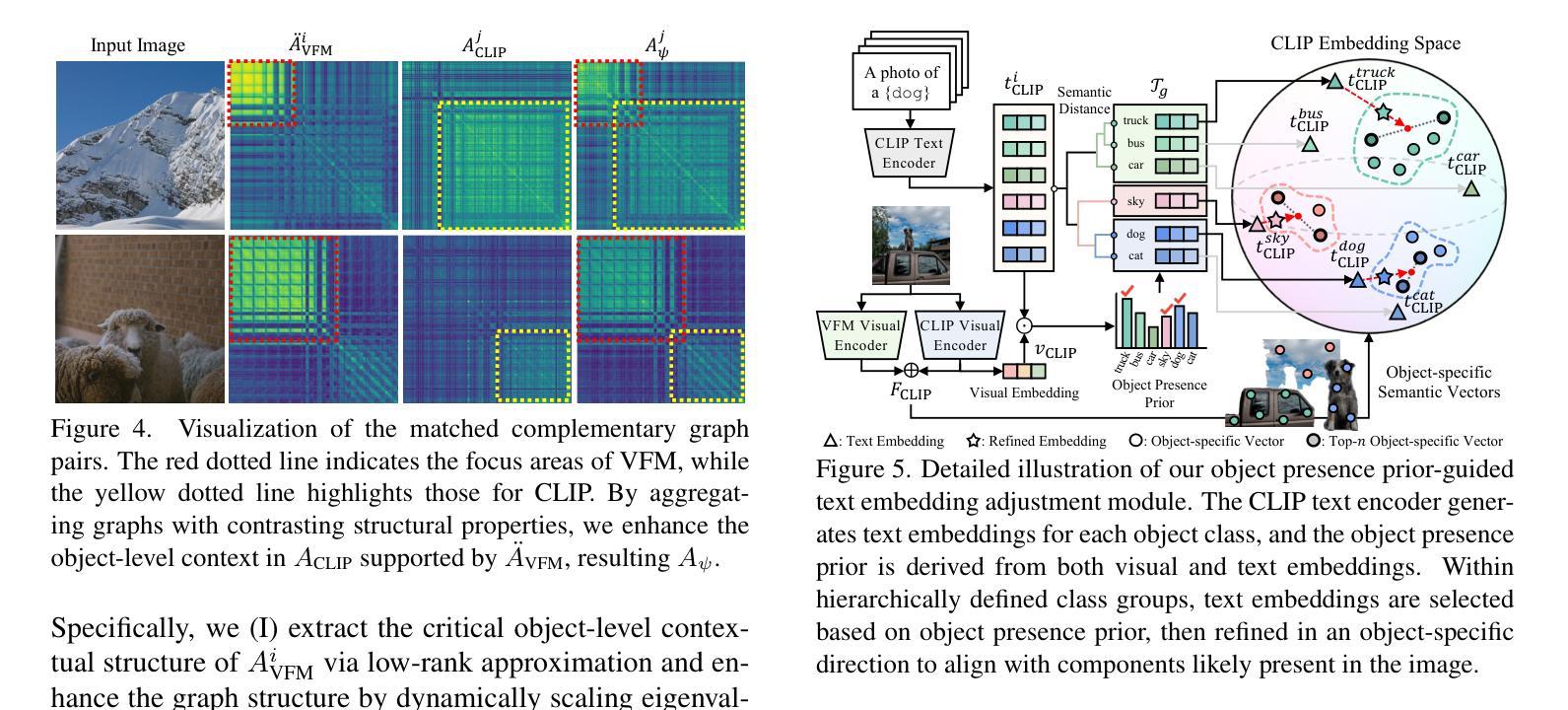
SynDiff-AD: Improving Semantic Segmentation and End-to-End Autonomous Driving with Synthetic Data from Latent Diffusion Models
Authors:Harsh Goel, Sai Shankar Narasimhan, Oguzhan Akcin, Sandeep Chinchali
In recent years, significant progress has been made in collecting large-scale datasets to improve segmentation and autonomous driving models. These large-scale datasets are often dominated by common environmental conditions such as “Clear and Day” weather, leading to decreased performance in under-represented conditions like “Rainy and Night”. To address this issue, we introduce SynDiff-AD, a novel data augmentation pipeline that leverages diffusion models (DMs) to generate realistic images for such subgroups. SynDiff-AD uses ControlNet-a DM that guides data generation conditioned on semantic maps-along with a novel prompting scheme that generates subgroup-specific, semantically dense prompts. By augmenting datasets with SynDiff-AD, we improve the performance of segmentation models like Mask2Former and SegFormer by up to 1.2% and 2.3% on the Waymo dataset, and up to 1.4% and 0.7% on the DeepDrive dataset, respectively. Additionally, we demonstrate that our SynDiff-AD pipeline enhances the driving performance of end-to-end autonomous driving models, like AIM-2D and AIM-BEV, by up to 20% across diverse environmental conditions in the CARLA autonomous driving simulator, providing a more robust model.
近年来,在收集大规模数据集以改进分割和自动驾驶模型方面取得了重大进展。这些大规模数据集通常以“晴朗和白天”等常见环境条件为主,导致在代表性不足的条件(如“雨天夜间”)下的性能下降。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了SynDiff-AD,这是一种新型数据增强管道,它利用扩散模型(DM)生成此类子组的现实图像。SynDiff-AD使用ControlNet(一种基于语义地图引导数据生成的DM),以及一种新型提示方案,该方案可以生成子组特定的语义密集提示。通过SynDiff-AD增强数据集,我们改进了Mask2Former和SegFormer等分割模型的性能,在Waymo数据集上分别提高了1.2%和2.3%,在DeepDrive数据集上分别提高了1.4%和0.7%。此外,我们还证明了我们的SynDiff-AD管道在CARLA自动驾驶模拟器中的多种环境条件下,提高了端到端自动驾驶模型(如AIM-2D和AIM-BEV)的驾驶性能,最高提高了20%,为更稳健的模型提供了支持。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文介绍了针对大规模数据集在自动驾驶模型中的使用问题,提出了一种新的数据增强方法SynDiff-AD。该方法利用扩散模型生成针对特定环境条件下的真实图像,解决了因天气条件导致模型性能下降的问题。实验表明,通过SynDiff-AD方法的数据增强,可以提升分割模型的性能,并在CARLA自动驾驶模拟器中提高了端到端的自动驾驶模型的驾驶性能。
Key Takeaways
- 引入大规模数据集提高了分割和自动驾驶模型的性能。
- 常见环境条件下的数据集可能导致模型在特定环境下的性能下降。
- SynDiff-AD是一种新的数据增强方法,利用扩散模型生成真实图像。
- SynDiff-AD可以解决特定环境条件下的模型性能问题。
- 通过SynDiff-AD的数据增强,可以提高分割模型的性能。
- 在CARLA自动驾驶模拟器中,SynDiff-AD提高了端到端的自动驾驶模型的驾驶性能。
点此查看论文截图

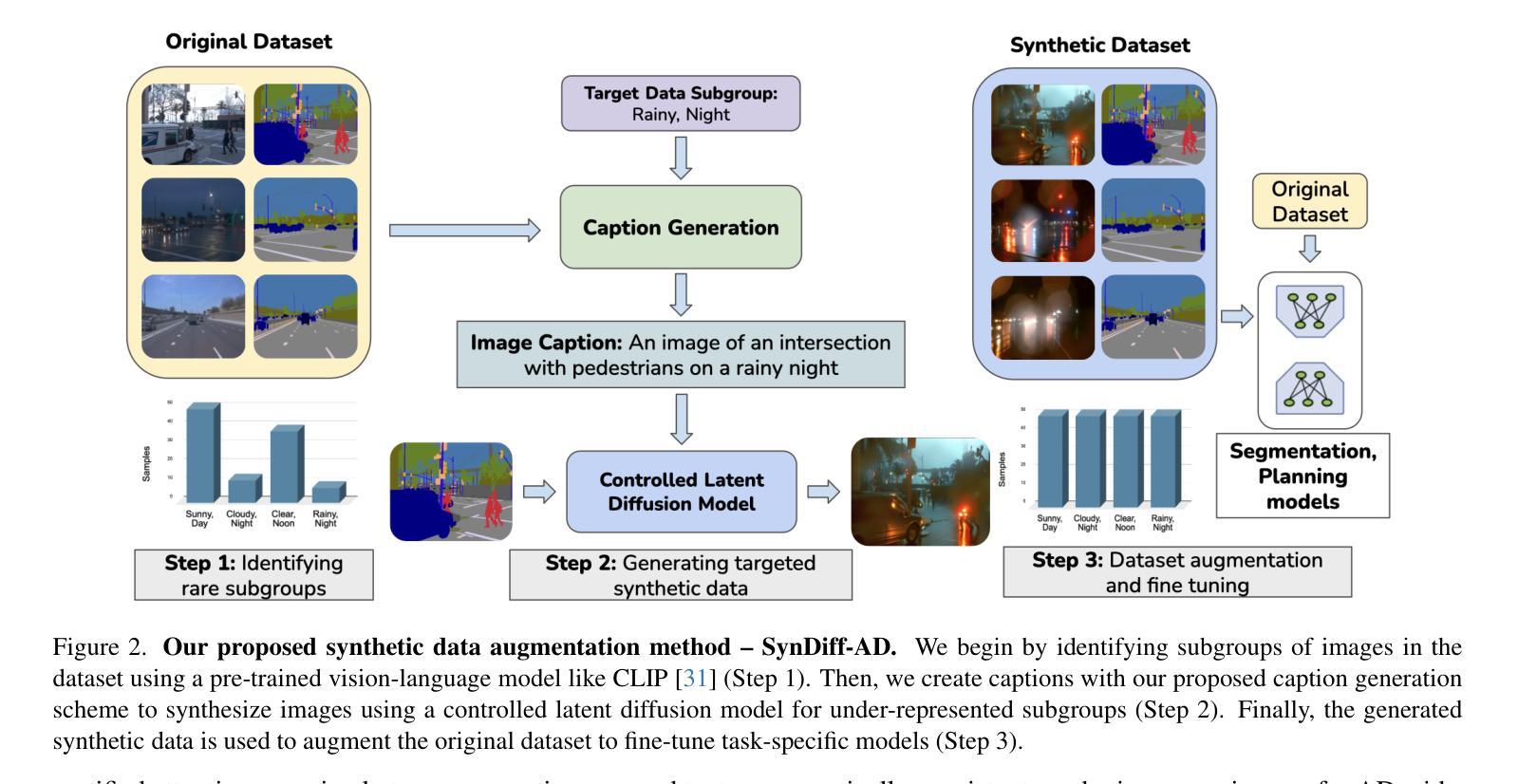

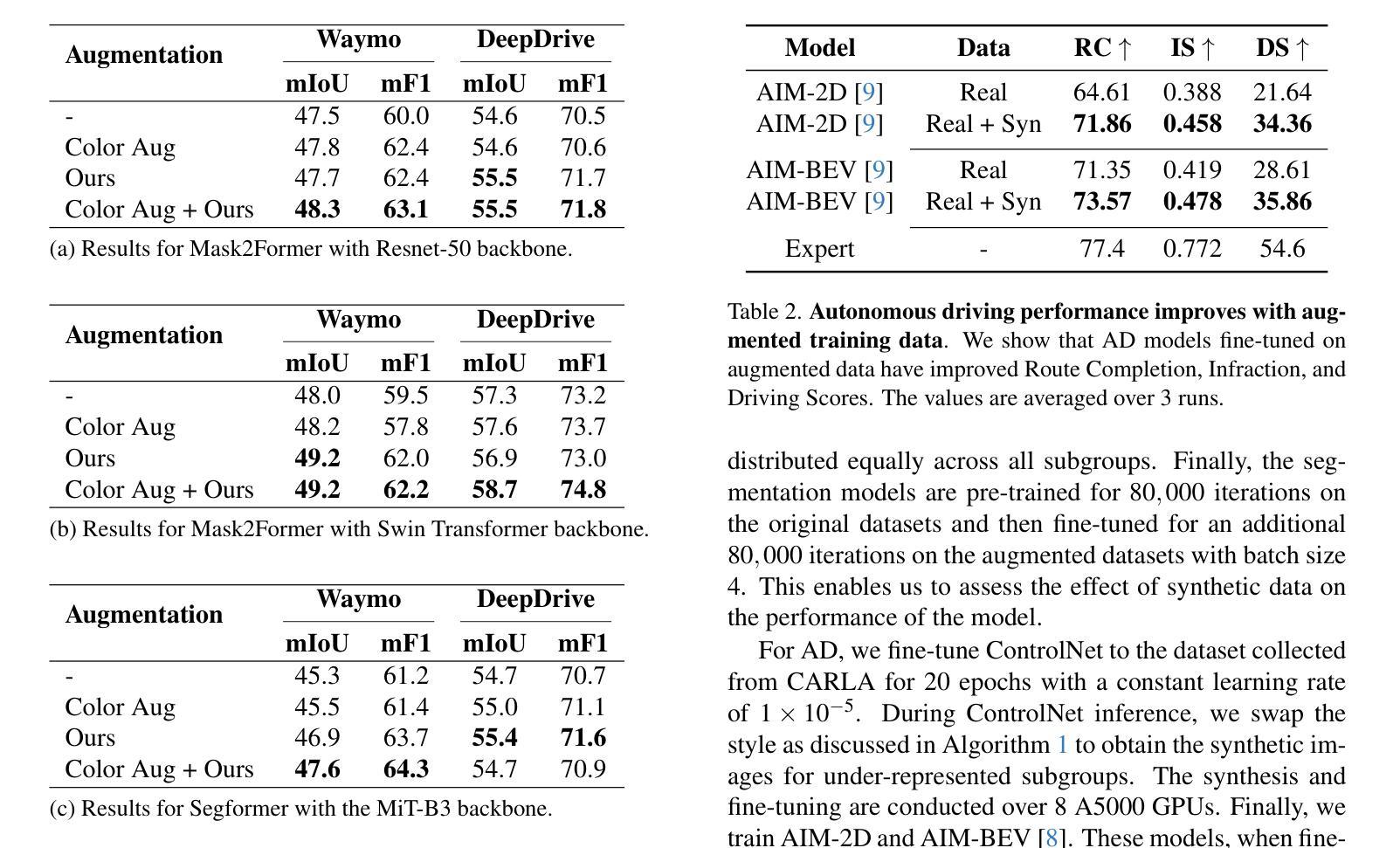
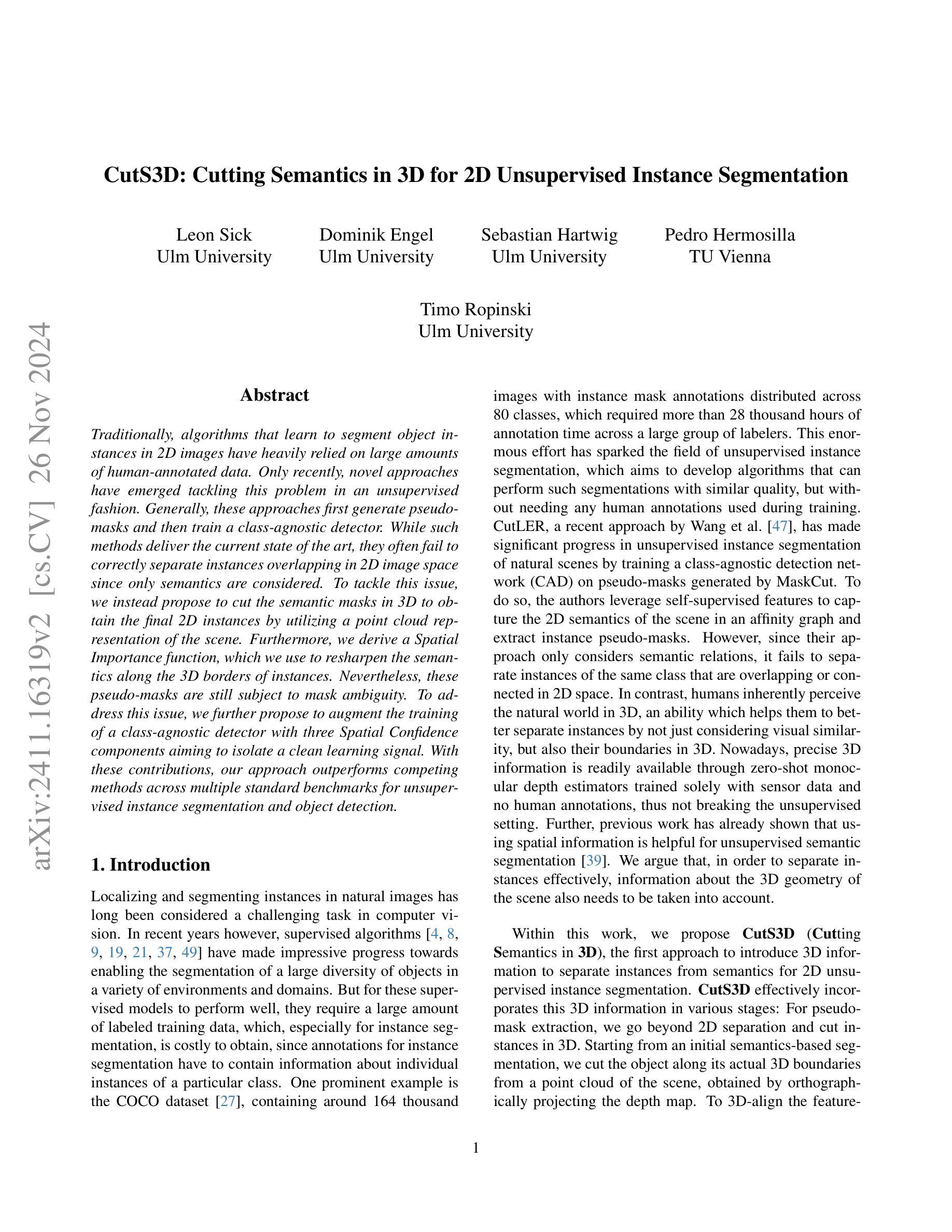
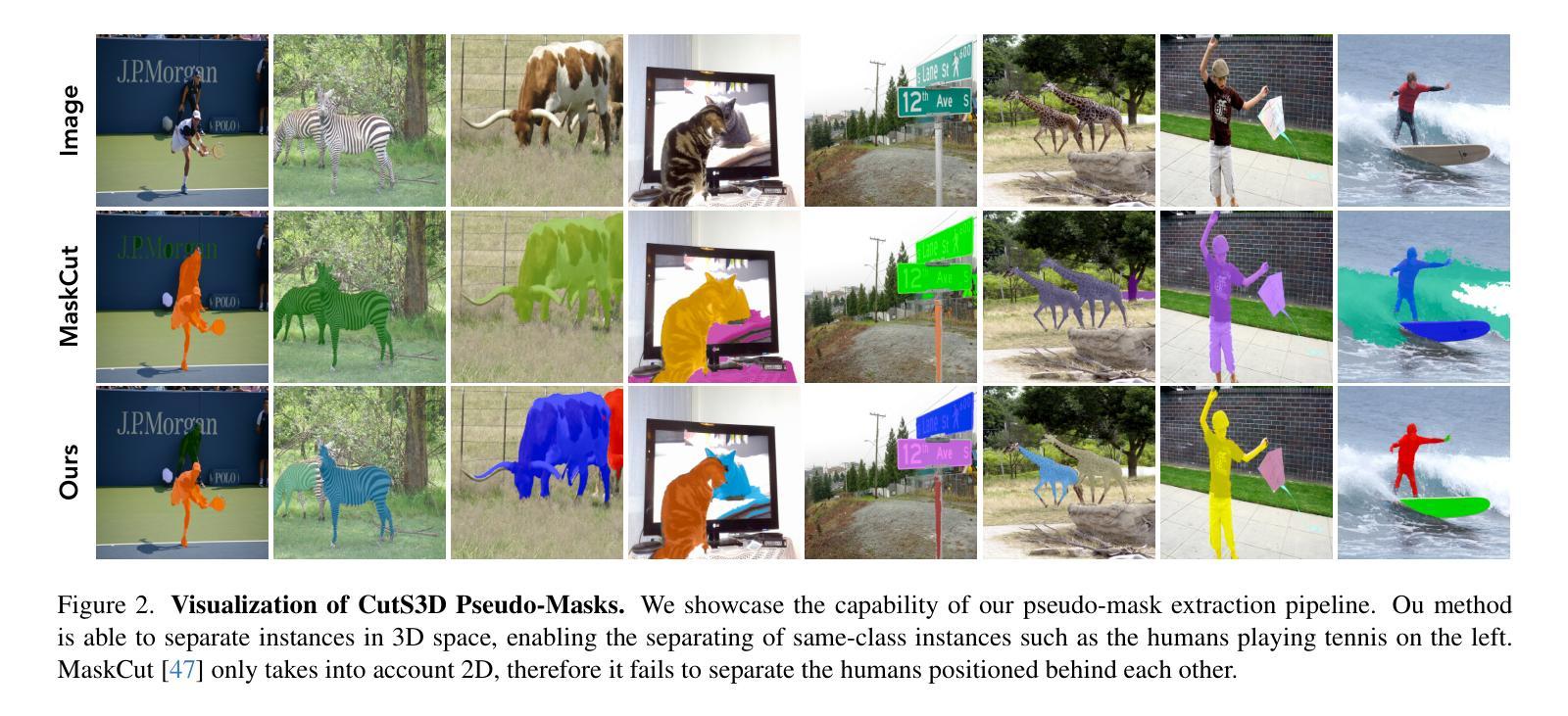
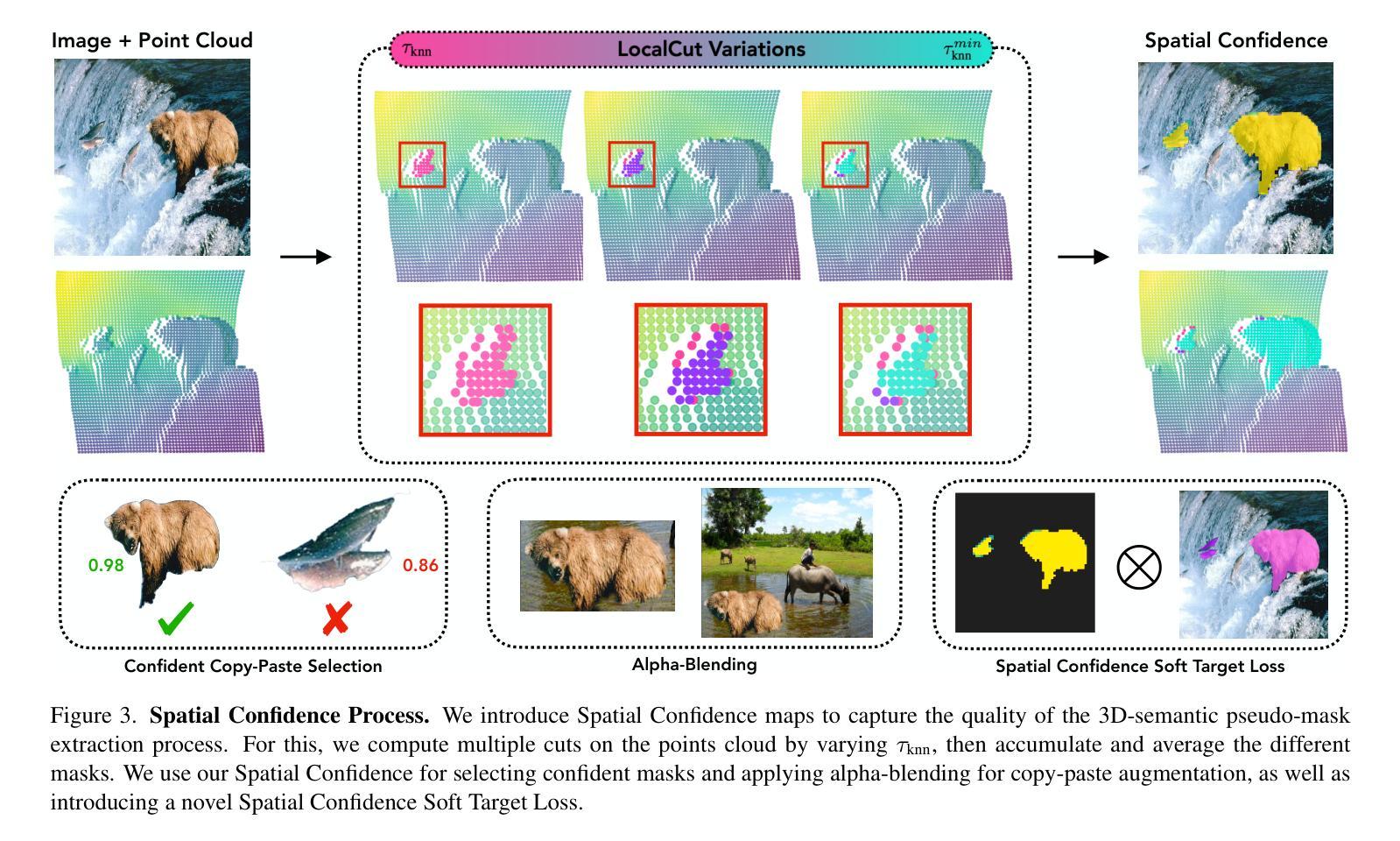
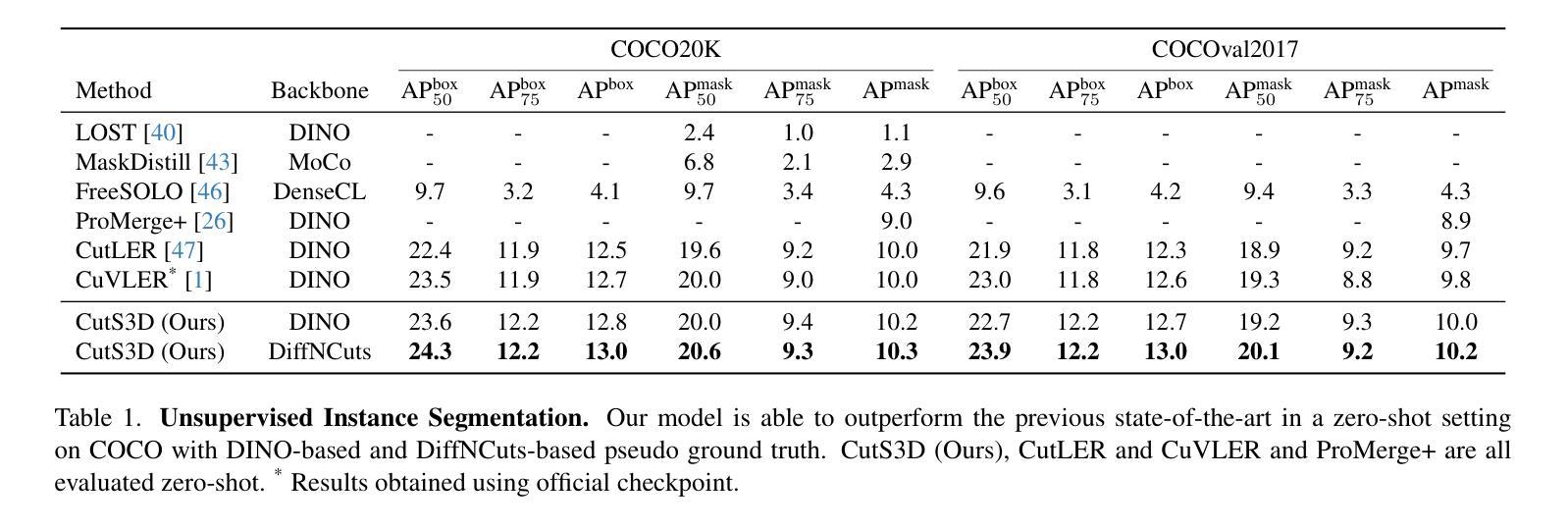
CutS3D: Cutting Semantics in 3D for 2D Unsupervised Instance Segmentation
Authors:Leon Sick, Dominik Engel, Sebastian Hartwig, Pedro Hermosilla, Timo Ropinski
Traditionally, algorithms that learn to segment object instances in 2D images have heavily relied on large amounts of human-annotated data. Only recently, novel approaches have emerged tackling this problem in an unsupervised fashion. Generally, these approaches first generate pseudo-masks and then train a class-agnostic detector. While such methods deliver the current state of the art, they often fail to correctly separate instances overlapping in 2D image space since only semantics are considered. To tackle this issue, we instead propose to cut the semantic masks in 3D to obtain the final 2D instances by utilizing a point cloud representation of the scene. Furthermore, we derive a Spatial Importance function, which we use to resharpen the semantics along the 3D borders of instances. Nevertheless, these pseudo-masks are still subject to mask ambiguity. To address this issue, we further propose to augment the training of a class-agnostic detector with three Spatial Confidence components aiming to isolate a clean learning signal. With these contributions, our approach outperforms competing methods across multiple standard benchmarks for unsupervised instance segmentation and object detection.
传统上,学习在2D图像中分割对象实例的算法严重依赖于大量的人工标注数据。仅最近,新兴的方法开始以无监督的方式处理这一问题。一般来说,这些方法首先生成伪掩膜,然后训练一种类无关的探测器。虽然这些方法达到了当前的最佳水平,但由于只考虑语义,它们往往无法正确分离在2D图像空间中重叠的实例。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种在3D空间中对语义掩膜进行切割的方法,利用场景的点云表示来获得最终的2D实例。此外,我们推导出了一个空间重要性函数,我们用它来锐化实例的3D边界处的语义。然而,这些伪掩膜仍然存在掩膜模糊的问题。为了解决这一问题,我们进一步提出在类无关的探测器训练中增加三个空间置信度分量,旨在产生一个清晰的学习信号。通过以上的贡献,我们的方法在多个人工分割、实例分割和对象检测的基准测试中均优于其他方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
近期新兴的无监督方法开始尝试解决二维图像中的实例分割问题,它们先生成伪掩膜再训练类别无关的探测器以达到当前最优效果。然而,这些方法在分离重叠实例时存在缺陷,仅考虑语义而未充分利用三维空间信息。为此,我们提出利用点云表示场景,在三维空间进行语义掩膜的切割以获得最终的二维实例。同时,我们引入空间重要性函数以强化三维边界处的语义信息。为解决伪掩膜存在的模糊问题,我们还通过添加三个空间置信度组件来增强类别无关探测器的训练效果。该方法在多个标准基准测试中表现优越。
Key Takeaways:
- 无监督方法开始应用于二维图像实例分割问题。
- 传统方法依赖大量人工标注数据,而新兴方法通过生成伪掩膜训练类别无关探测器以达成最优效果。
- 当前方法在处理重叠实例时存在困难,仅考虑语义未充分利用三维空间信息。
- 提出利用点云表示场景进行三维语义掩膜切割以获得二维实例。
- 引入空间重要性函数强化三维边界处的语义信息。
- 伪掩膜存在模糊问题,为解决此问题添加了三个空间置信度组件以增强探测器训练效果。
点此查看论文截图
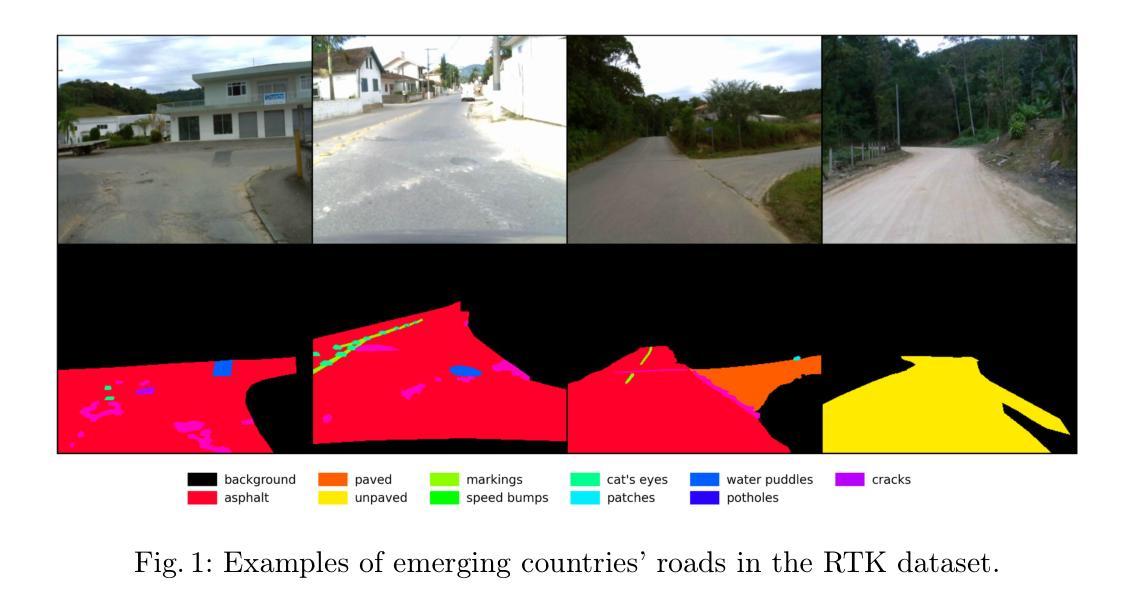
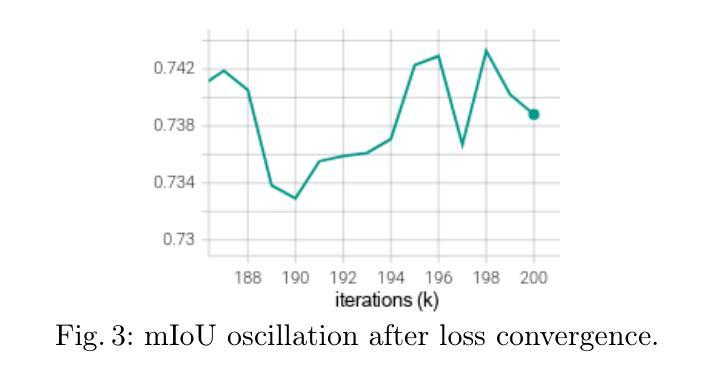
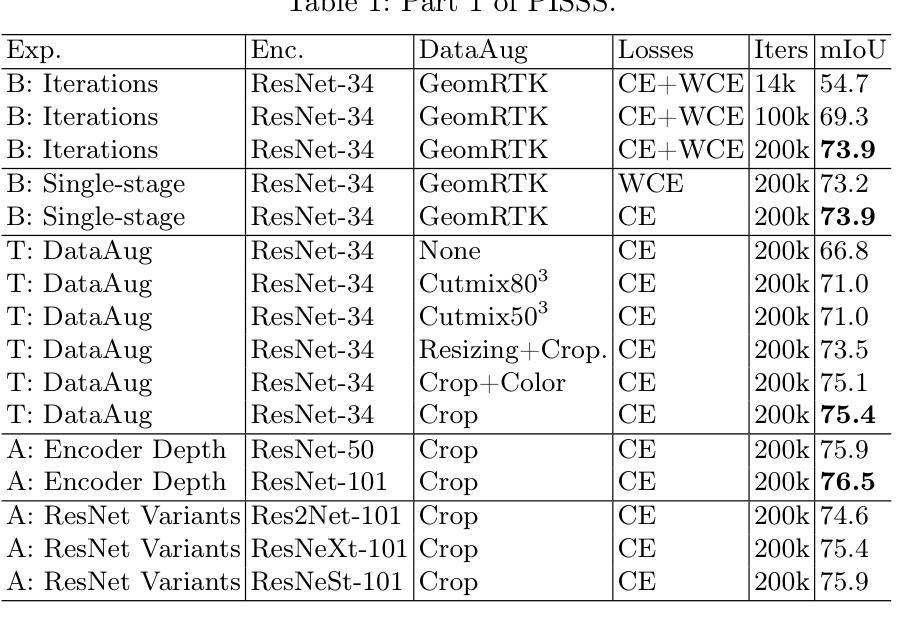
A Performance Increment Strategy for Semantic Segmentation of Low-Resolution Images from Damaged Roads
Authors:Rafael S. Toledo, Cristiano S. Oliveira, Vitor H. T. Oliveira, Eric A. Antonelo, Aldo von Wangenheim
Autonomous driving needs good roads, but 85% of Brazilian roads have damages that deep learning models may not regard as most semantic segmentation datasets for autonomous driving are high-resolution images of well-maintained urban roads. A representative dataset for emerging countries consists of low-resolution images of poorly maintained roads and includes labels of damage classes; in this scenario, three challenges arise: objects with few pixels, objects with undefined shapes, and highly underrepresented classes. To tackle these challenges, this work proposes the Performance Increment Strategy for Semantic Segmentation (PISSS) as a methodology of 14 training experiments to boost performance. With PISSS, we reached state-of-the-art results of 79.8 and 68.8 mIoU on the Road Traversing Knowledge (RTK) and Technik Autonomer Systeme 500 (TAS500) test sets, respectively. Furthermore, we also offer an analysis of DeepLabV3+ pitfalls for small object segmentation.
自动驾驶需要良好的道路,但巴西有85%的道路存在损坏,深度学习模型可能无法识别,因为大多数自动驾驶的语义分割数据集都是高分辨率的良好维护的城市道路图像。对于新兴国家而言,一个典型的数据集包含低分辨率的破损道路图像,并包括损坏类别的标签;在这种情况下,出现了三个挑战:像素少的物体、形状不确定的物体以及高度欠代表的类别。为了应对这些挑战,这项工作提出了语义分割性能提升策略(PISSS)作为一种包含14个训练实验的方法来提高性能。通过PISSS,我们在Road Traversing Knowledge(RTK)和Technik Autonomer Systeme 500(TAS500)测试集上达到了最先进的79.8%和68.8%的mIoU结果。此外,我们还对DeepLabV3+在小型对象分割中的陷阱进行了分析。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文指出,自主驾驶需要良好的道路环境,但巴西约有85%的道路存在损坏情况。现有的语义分割数据集多为高分辨率的良好城市道路图像,不适用于此场景。为此,本文提出了针对新兴国家道路情况的代表性数据集,并指出了其中的三大挑战:像素少的物体、形状不确定的物体以及高度未被充分代表的类别。为解决这些挑战,本文提出了语义分割性能提升策略(PISSS),通过14个训练实验提升了模型性能。在RTK和TAS500测试集上分别达到了79.8和68.8 mIoU的先进水平。同时,本文也对DeepLabV3+在小目标分割中的陷阱进行了分析。
Key Takeaways
- 巴西大部分道路存在损坏情况(占比约为85%),对自主驾驶构成挑战。
- 现存的语义分割数据集主要关注良好维护的城市道路的高分辨率图像,不适用于新兴国家的道路状况。
- 针对新兴国家道路状况,存在三大挑战:像素少的物体、形状不确定的物体以及高度未被充分代表的类别。
- 为应对这些挑战,提出了语义分割性能提升策略(PISSS),并通过训练实验验证了其有效性。
- 在RTK和TAS500测试集上,使用PISSS策略达到了领先水平,mIoU分别为79.8和68.8。
- 文章还探讨了DeepLabV3+在小目标分割中的潜在问题。
点此查看论文截图

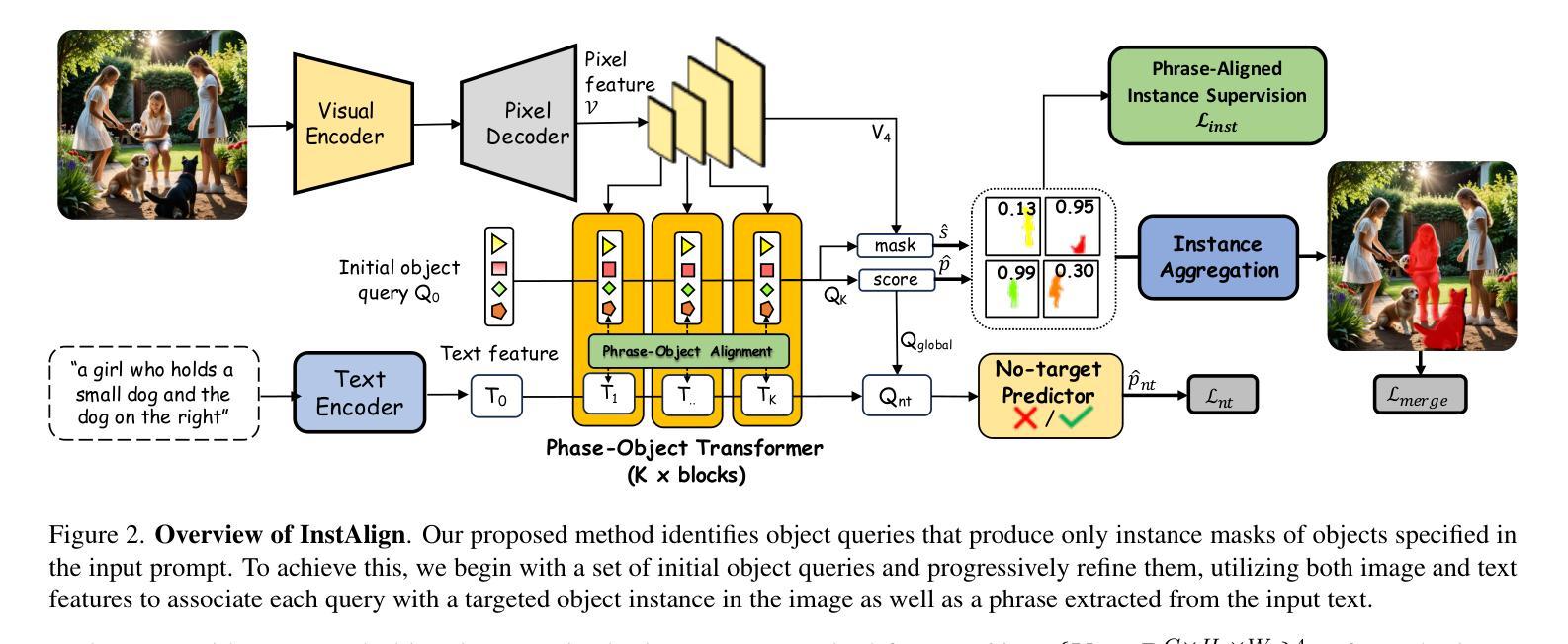
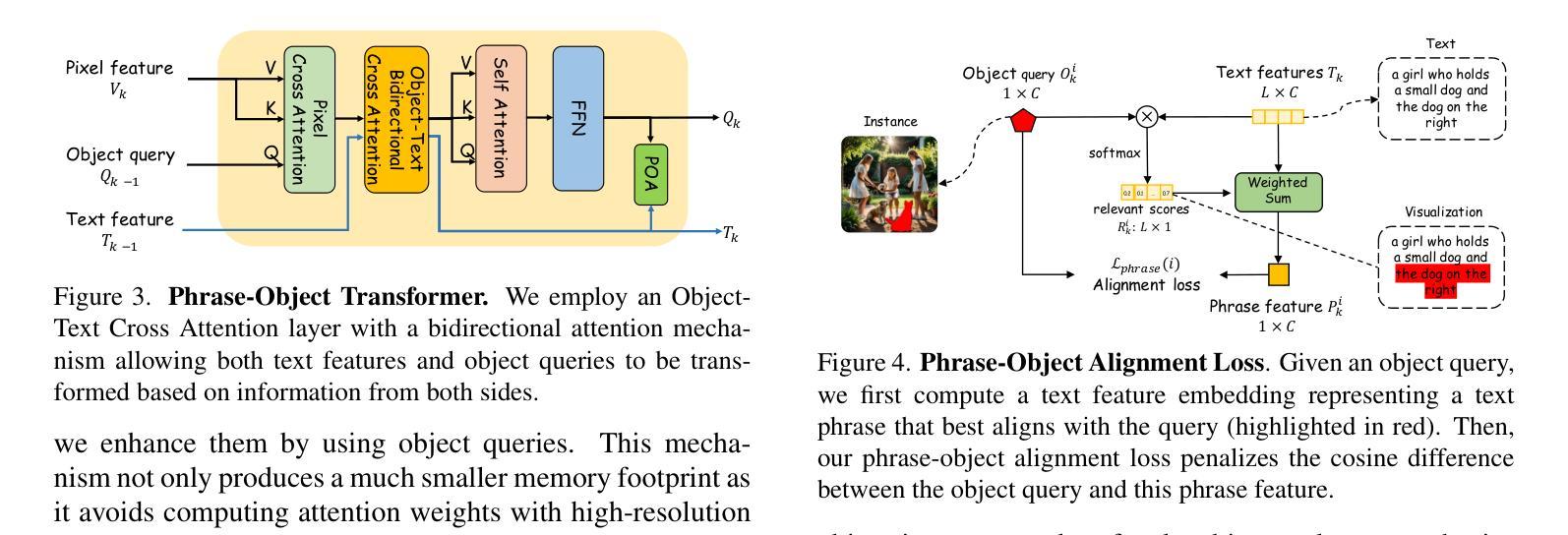
Instance-Aware Generalized Referring Expression Segmentation
Authors:E-Ro Nguyen, Hieu Le, Dimitris Samaras, Michael Ryoo
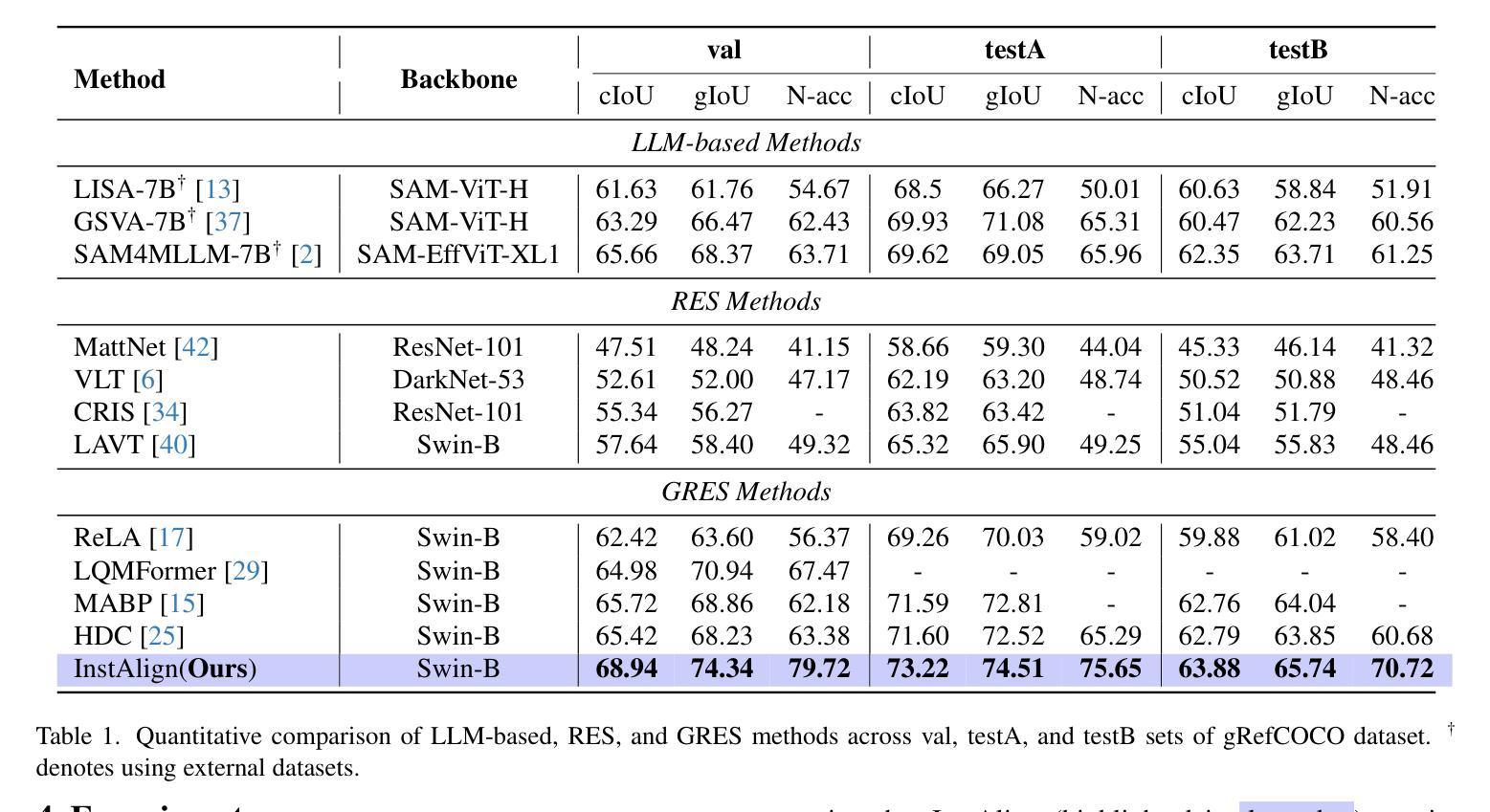
Recent works on Generalized Referring Expression Segmentation (GRES) struggle with handling complex expressions referring to multiple distinct objects. This is because these methods typically employ an end-to-end foreground-background segmentation and lack a mechanism to explicitly differentiate and associate different object instances to the text query. To this end, we propose InstAlign, a method that incorporates object-level reasoning into the segmentation process. Our model leverages both text and image inputs to extract a set of object-level tokens that capture both the semantic information in the input prompt and the objects within the image. By modeling the text-object alignment via instance-level supervision, each token uniquely represents an object segment in the image, while also aligning with relevant semantic information from the text. Extensive experiments on the gRefCOCO and Ref-ZOM benchmarks demonstrate that our method significantly advances state-of-the-art performance, setting a new standard for precise and flexible GRES.
关于广义引用表达式分割(GRES)的最新研究在处理引用多个不同对象的复杂表达式时遇到了困难。这是因为这些方法通常采用端到端的前景背景分割,并且缺乏一种机制来明确区分和关联不同的对象实例到文本查询。为此,我们提出了InstAlign方法,它将对象级别的推理融入到分割过程中。我们的模型利用文本和图像输入来提取一组对象级别的标记,这些标记既捕获输入提示中的语义信息,也捕获图像中的对象。通过对文本对象对齐进行实例级监督建模,每个标记唯一地代表图像中的一个对象段,同时与文本中的相关语义信息对齐。在gRefCOCO和Ref-ZOM基准测试上的大量实验表明,我们的方法显著提高了最新技术的性能,为精确灵活的GRES设定了新的标准。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文提出一种名为InstAlign的方法,用于处理广义指代表达式分割(GRES)中的复杂问题。该方法结合了文本和图像输入,提取对象级标记,以捕捉输入提示中的语义信息和图像中的对象。通过实例级监督建模文本对象对齐,每个标记唯一代表图像中的一个对象段,并与文本中的相关语义信息对齐。在gRefCOCO和Ref-ZOM基准测试上进行了广泛实验,表明该方法在最新技术的基础上取得了显著进展,为精确灵活的GRES设定了新的标准。
Key Takeaways
- 广义指代表达式分割(GRES)在处理复杂表达式时面临挑战,这些表达式可能指代多个不同对象。
- 当前方法通常采用端到前的前台后台分割方式,缺乏明确区分和关联不同对象实例的机制。
- InstAlign方法结合了文本和图像输入,提取对象级标记以捕捉语义信息和图像中的对象。
- 通过实例级监督建模文本与对象的对齐关系。
- 每个标记唯一代表图像中的一个对象段,并与文本的语义信息对齐。
- 在gRefCOCO和Ref-ZOM基准测试上的实验表明,InstAlign方法显著提高了最新技术的性能。
点此查看论文截图

Effective SAM Combination for Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Minhyeok Lee, Suhwan Cho, Jungho Lee, Sunghun Yang, Heeseung Choi, Ig-Jae Kim, Sangyoun Lee
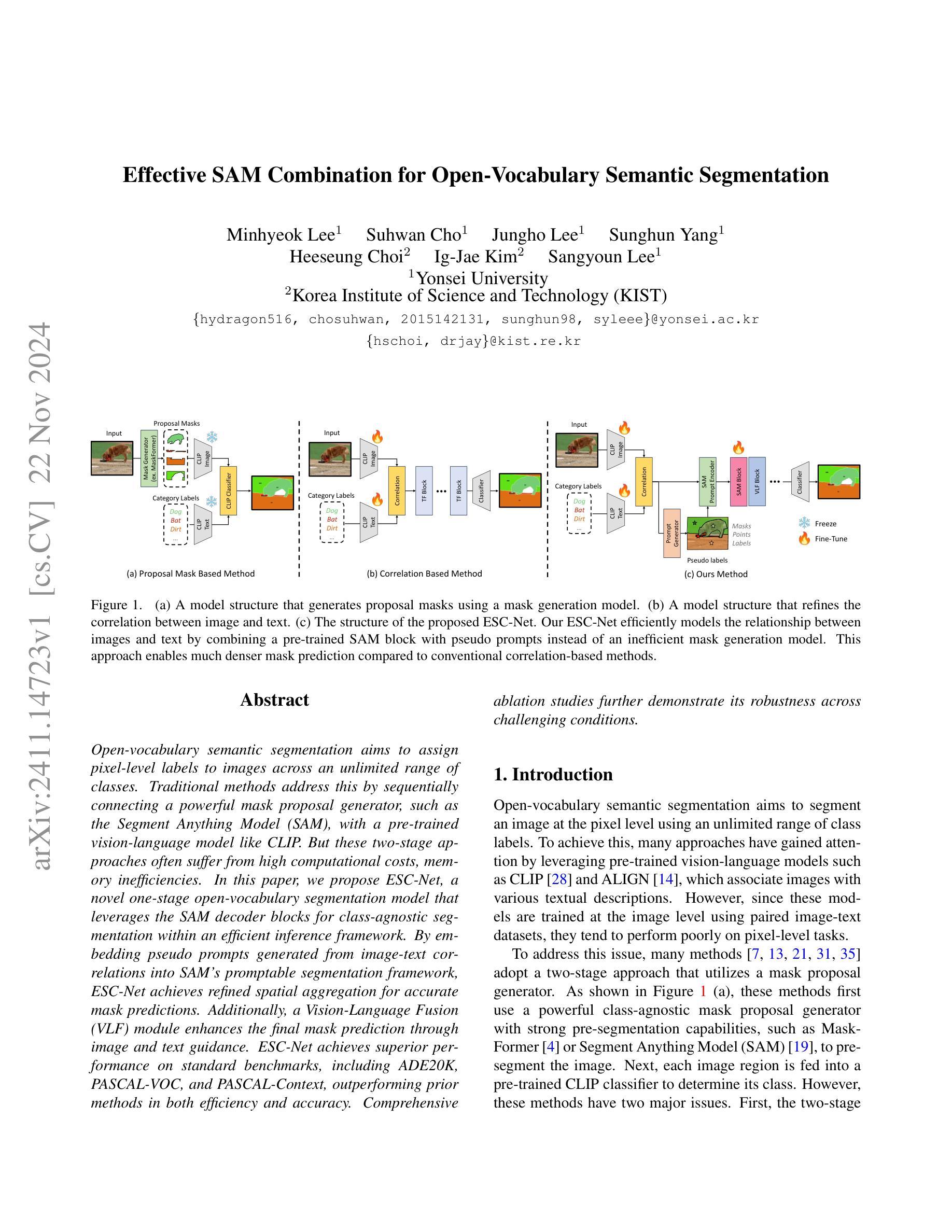
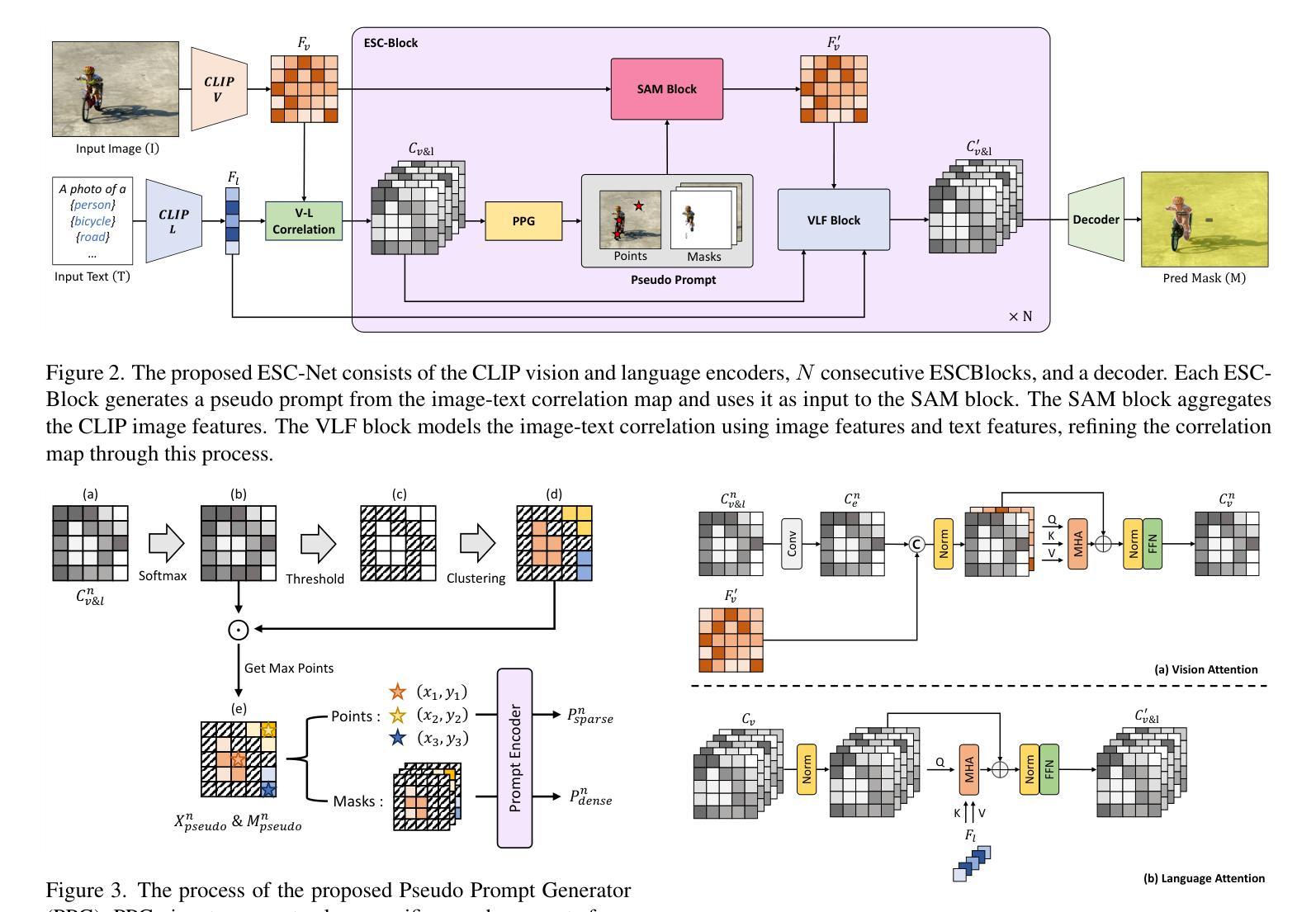
Open-vocabulary semantic segmentation aims to assign pixel-level labels to images across an unlimited range of classes. Traditional methods address this by sequentially connecting a powerful mask proposal generator, such as the Segment Anything Model (SAM), with a pre-trained vision-language model like CLIP. But these two-stage approaches often suffer from high computational costs, memory inefficiencies. In this paper, we propose ESC-Net, a novel one-stage open-vocabulary segmentation model that leverages the SAM decoder blocks for class-agnostic segmentation within an efficient inference framework. By embedding pseudo prompts generated from image-text correlations into SAM’s promptable segmentation framework, ESC-Net achieves refined spatial aggregation for accurate mask predictions. ESC-Net achieves superior performance on standard benchmarks, including ADE20K, PASCAL-VOC, and PASCAL-Context, outperforming prior methods in both efficiency and accuracy. Comprehensive ablation studies further demonstrate its robustness across challenging conditions.
开放词汇语义分割旨在给无限范围的类别中的图像分配像素级标签。传统方法通过顺序连接强大的掩膜提案生成器(如Anything分段模型(SAM))和预训练的视觉语言模型(如CLIP)来解决这个问题。但这些两阶段方法往往存在计算成本高、内存效率低的问题。在本文中,我们提出了ESC-Net,这是一种新型的一阶段开放词汇分割模型,它利用SAM解码器块在有效的推理框架内进行类别无关的分割。通过将由图像文本相关性生成的伪提示嵌入到SAM的可提示分割框架中,ESC-Net实现了精细的空间聚合,以获得准确的掩膜预测。ESC-Net在包括ADE20K、PASCAL-VOC和PASCAL-Context在内的标准基准测试上实现了卓越的性能,在效率和准确性方面均优于以前的方法。全面的消融研究进一步证明了其在具有挑战的条件下的稳健性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
该文提出了一种新型的一站式开放词汇语义分割模型ESC-Net。结合Segment Anything Model(SAM)解码器块,该模型可在高效推理框架内进行类别无关的分割。通过嵌入由图像文本相关性生成的伪提示,ESC-Net实现了精细的空间聚合,用于准确的掩膜预测。在多个标准基准测试中,ESC-Net表现出卓越的性能,包括ADE20K、PASCAL-VOC和PASCAL-Context,在效率和准确性方面均优于以前的方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 开放词汇语义分割的目标是为图像中的每个像素分配标签,涵盖无限类别范围。
- 传统方法通常使用两阶段方法,包括强大的掩膜提案生成器(如SAM)和预训练的视觉语言模型(如CLIP)。
- 两阶段方法存在计算成本高和内存效率低的问题。
- ESC-Net是一个新型的一站式开放词汇分割模型,利用SAM解码器块在高效推理框架内进行类别无关的分割。
- ESC-Net通过嵌入伪提示,实现精细的空间聚合,用于准确的掩膜预测。
- ESC-Net在多个基准测试中表现出卓越性能,包括ADE20K、PASCAL-VOC和PASCAL-Context。
点此查看论文截图
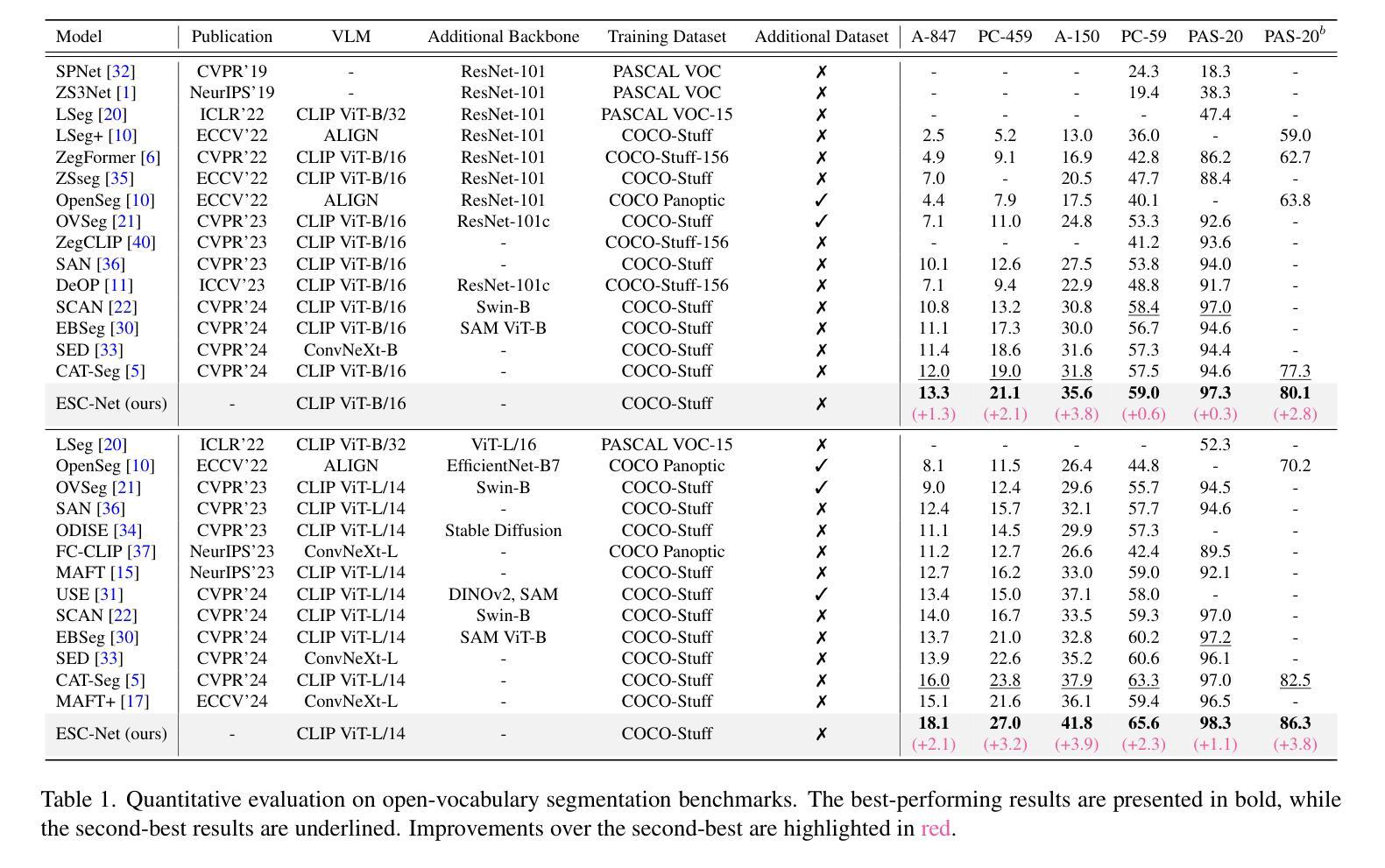
DINO-X: A Unified Vision Model for Open-World Object Detection and Understanding
Authors:Tianhe Ren, Yihao Chen, Qing Jiang, Zhaoyang Zeng, Yuda Xiong, Wenlong Liu, Zhengyu Ma, Junyi Shen, Yuan Gao, Xiaoke Jiang, Xingyu Chen, Zhuheng Song, Yuhong Zhang, Hongjie Huang, Han Gao, Shilong Liu, Hao Zhang, Feng Li, Kent Yu, Lei Zhang
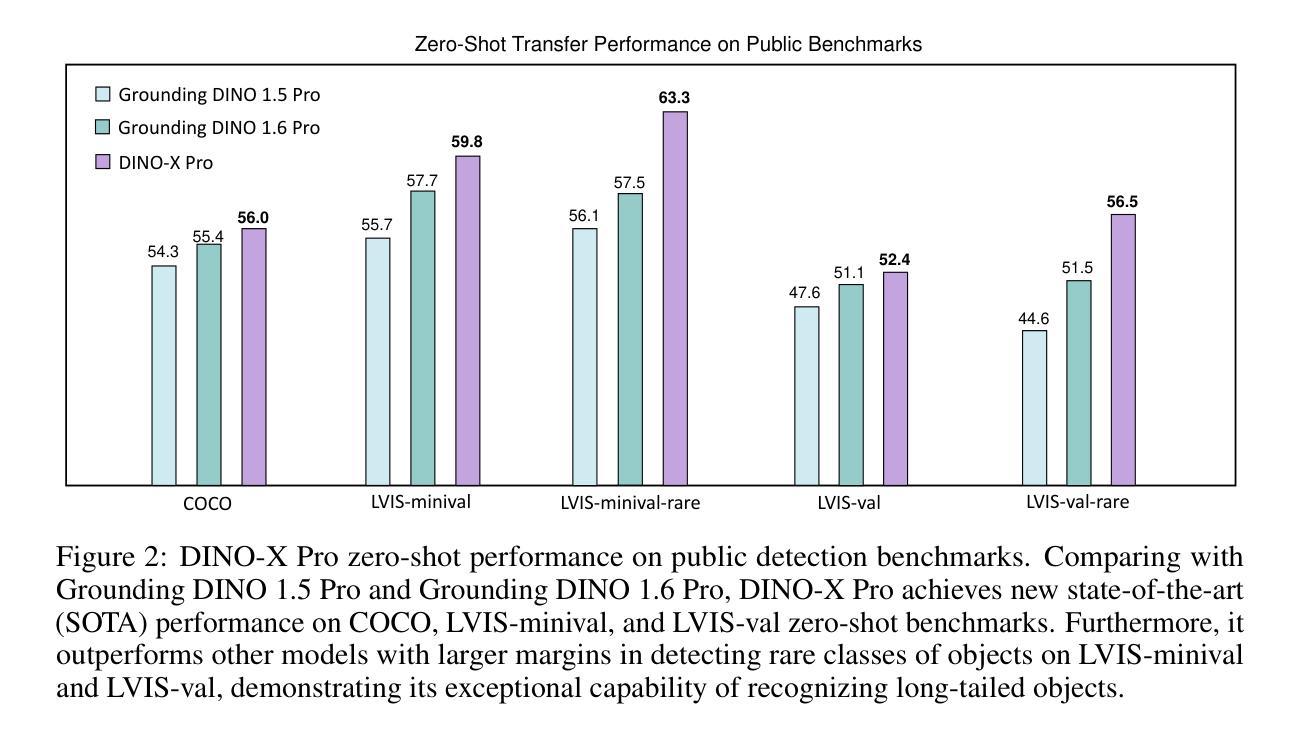
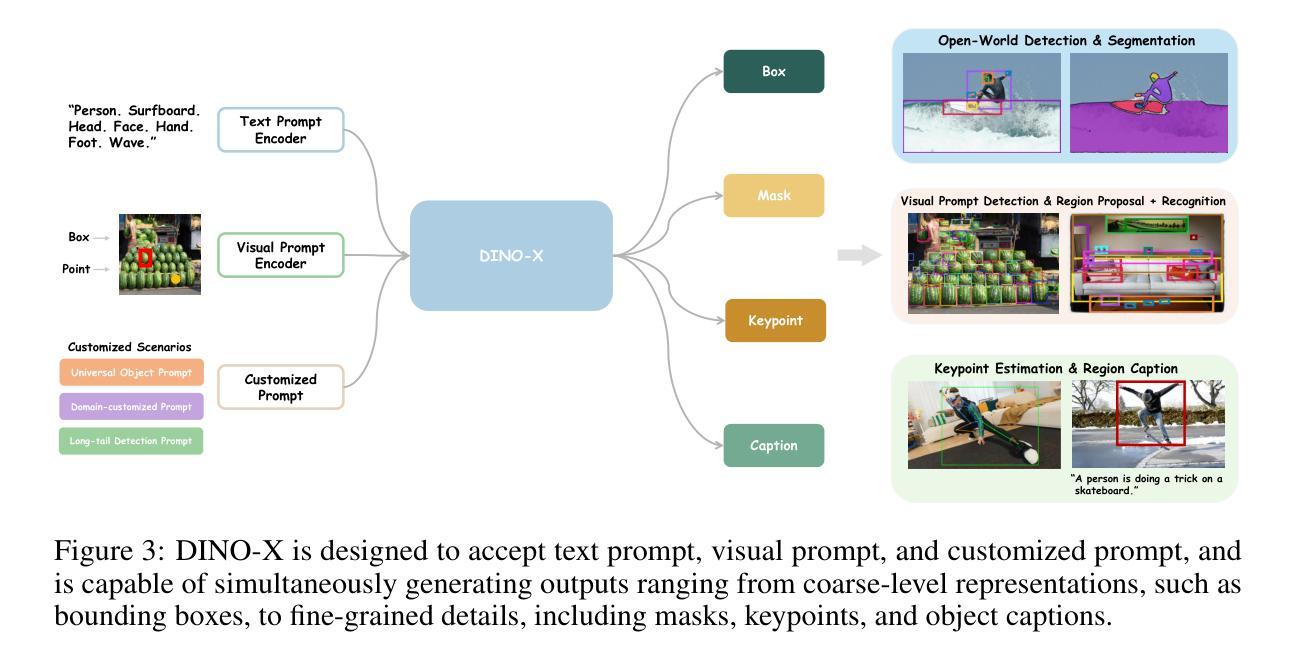
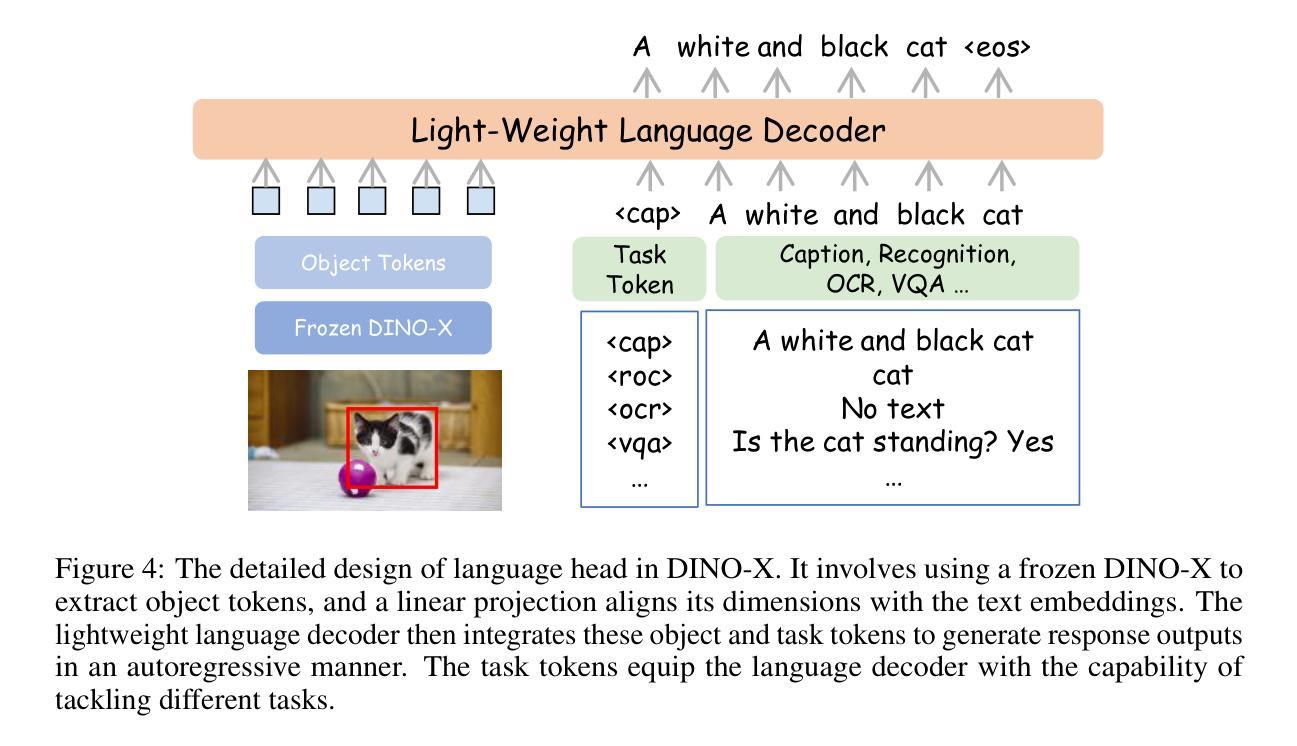
In this paper, we introduce DINO-X, which is a unified object-centric vision model developed by IDEA Research with the best open-world object detection performance to date. DINO-X employs the same Transformer-based encoder-decoder architecture as Grounding DINO 1.5 to pursue an object-level representation for open-world object understanding. To make long-tailed object detection easy, DINO-X extends its input options to support text prompt, visual prompt, and customized prompt. With such flexible prompt options, we develop a universal object prompt to support prompt-free open-world detection, making it possible to detect anything in an image without requiring users to provide any prompt. To enhance the model’s core grounding capability, we have constructed a large-scale dataset with over 100 million high-quality grounding samples, referred to as Grounding-100M, for advancing the model’s open-vocabulary detection performance. Pre-training on such a large-scale grounding dataset leads to a foundational object-level representation, which enables DINO-X to integrate multiple perception heads to simultaneously support multiple object perception and understanding tasks, including detection, segmentation, pose estimation, object captioning, object-based QA, etc. Experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of DINO-X. Specifically, the DINO-X Pro model achieves 56.0 AP, 59.8 AP, and 52.4 AP on the COCO, LVIS-minival, and LVIS-val zero-shot object detection benchmarks, respectively. Notably, it scores 63.3 AP and 56.5 AP on the rare classes of LVIS-minival and LVIS-val benchmarks, improving the previous SOTA performance by 5.8 AP and 5.0 AP. Such a result underscores its significantly improved capacity for recognizing long-tailed objects.
本文介绍了由IDEA Research开发的DINO-X,这是一个统一的以对象为中心的视觉模型,具有迄今为止最佳的开放世界对象检测性能。DINO-X采用与Grounding DINO 1.5相同的基于Transformer的编码器-解码器架构,追求开放世界对象理解的对象级表示。为了简化长尾对象检测,DINO-X扩展了其输入选项,支持文本提示、视觉提示和自定义提示。通过这样灵活的提示选项,我们开发了一种通用对象提示,支持无提示的开放世界检测,使得在图像中检测任何对象成为可能,而无需用户提供任何提示。为了提高模型的核心定位能力,我们构建了一个大规模数据集,称为Grounding-100M,包含超过1亿个高质量定位样本,以提升模型的开放词汇检测性能。在如此大规模的定位数据集上进行预训练,得到了一个基础的对象级表示,使DINO-X能够集成多个感知头,同时支持多个对象感知和理解任务,包括检测、分割、姿态估计、对象描述、基于对象的问答等。实验结果表明DINO-X的性能优越。具体来说,DINO-X Pro模型在COCO、LVIS-minival和LVIS-val零样本对象检测基准测试上的AP值分别达到56.0、59.8和52.4。特别是在LVIS-minival和LVIS-val基准的稀有类别上,其AP值达到63.3和56.5,比之前的最佳性能提高了5.8 AP和5.0 AP。这一结果凸显了其在识别长尾对象方面的显著改善能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report
Summary
本文介绍了由IDEA Research开发的DINO-X统一对象级视觉模型,具有最佳开放世界目标检测性能。DINO-X采用与Grounding DINO 1.5相同的Transformer编码器-解码器架构,追求对象级表示以实现开放世界对象理解。它通过扩展输入选项以支持文本提示、视觉提示和自定义提示,简化了长尾目标检测。此外,DINO-X具有通用对象提示,支持无提示开放世界检测,可在不需要用户提供任何提示的情况下检测图像中的任何内容。通过构建大规模接地数据集Grounding-100M,增强了模型的核心接地能力,并提高了开放词汇检测性能。预训练这样的大型接地数据集为DINO-X提供了基础的对象级表示,使其能够集成多个感知头,同时支持多个对象感知和理解任务。实验结果表明DINO-X性能卓越。
Key Takeaways
- DINO-X是IDEA Research开发的统一对象级视觉模型,具有出色的开放世界目标检测性能。
- DINO-X采用与Grounding DINO 1.5相同的Transformer架构。
- DINO-X支持多种提示方式,包括文本、视觉和自定义提示,简化了长尾目标检测。
- 通用对象提示支持无提示开放世界检测。
- 通过大规模接地数据集Grounding-100M提高模型核心接地能力和开放词汇检测性能。
- 预训练大型接地数据集为DINO-X提供基础对象级表示。
- DINO-X能同时支持多个对象感知和理解任务,包括检测、分割、姿态估计等,且实验结果表明其性能卓越。
点此查看论文截图

DIS-Mine: Instance Segmentation for Disaster-Awareness in Poor-Light Condition in Underground Mines
Authors:Mizanur Rahman Jewel, Mohamed Elmahallawy, Sanjay Madria, Samuel Frimpong
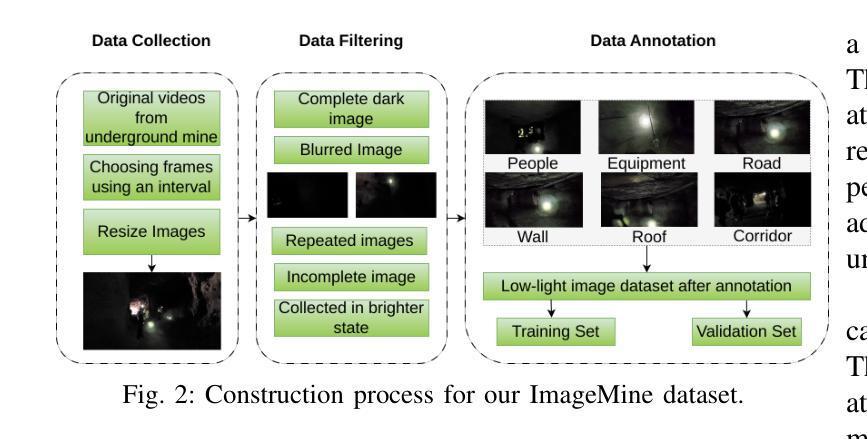
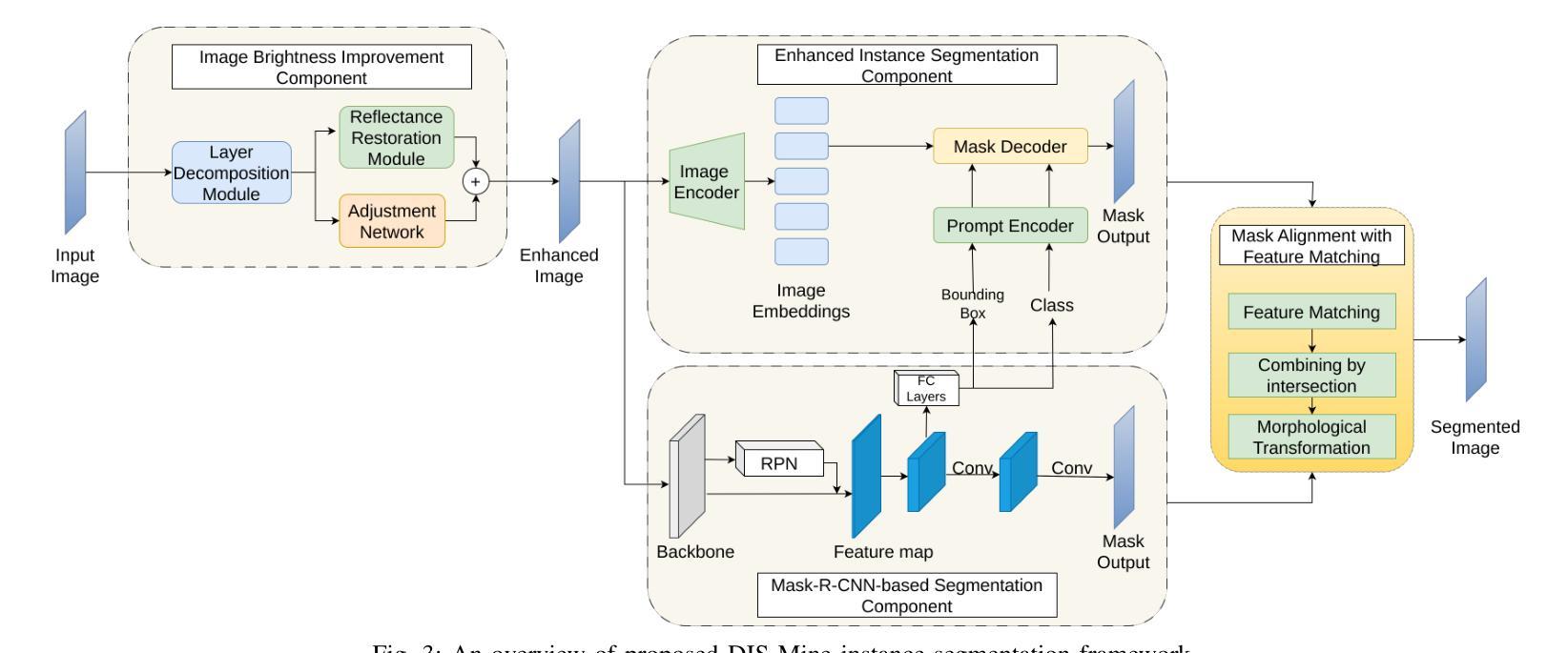
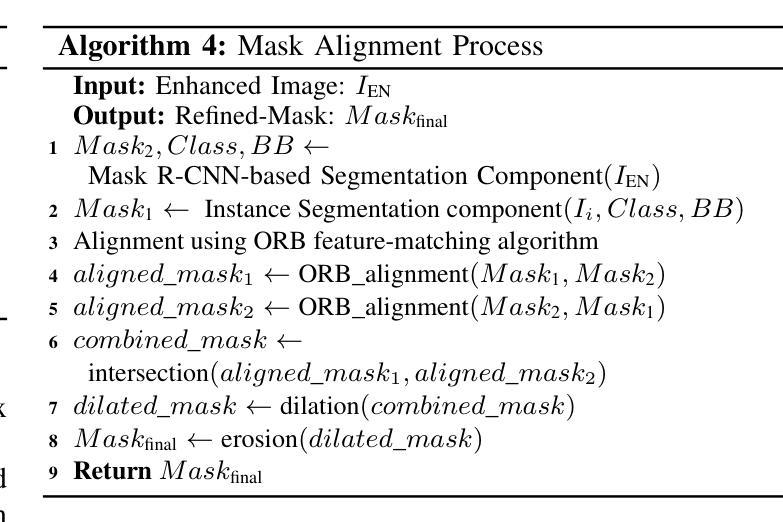
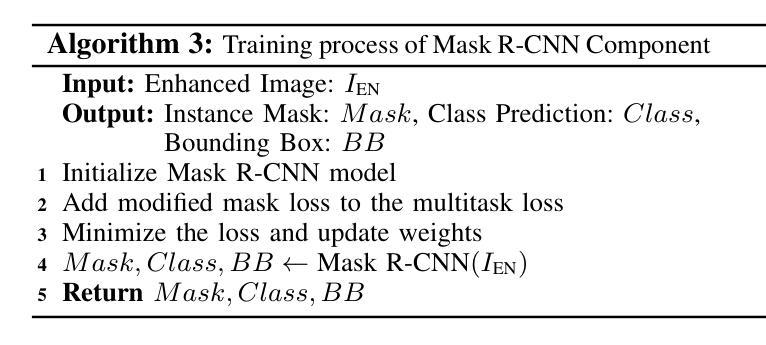
Detecting disasters in underground mining, such as explosions and structural damage, has been a persistent challenge over the years. This problem is compounded for first responders, who often have no clear information about the extent or nature of the damage within the mine. The poor-light or even total darkness inside the mines makes rescue efforts incredibly difficult, leading to a tragic loss of life. In this paper, we propose a novel instance segmentation method called DIS-Mine, specifically designed to identify disaster-affected areas within underground mines under low-light or poor visibility conditions, aiding first responders in rescue efforts. DIS-Mine is capable of detecting objects in images, even in complete darkness, by addressing challenges such as high noise, color distortions, and reduced contrast. The key innovations of DIS-Mine are built upon four core components: i) Image brightness improvement, ii) Instance segmentation with SAM integration, iii) Mask R-CNN-based segmentation, and iv) Mask alignment with feature matching. On top of that, we have collected real-world images from an experimental underground mine, introducing a new dataset named ImageMine, specifically gathered in low-visibility conditions. This dataset serves to validate the performance of DIS-Mine in realistic, challenging environments. Our comprehensive experiments on the ImageMine dataset, as well as on various other datasets demonstrate that DIS-Mine achieves a superior F1 score of 86.0% and mIoU of 72.0%, outperforming state-of-the-art instance segmentation methods, with at least 15x improvement and up to 80% higher precision in object detection.
检测地下采矿中的灾害,如爆炸和结构破坏,一直是多年来的一个持续挑战。对于经常没有关于矿内损害程度或性质的明确信息的一线救援人员来说,这个问题更为严重。矿内光线昏暗甚至完全黑暗,使得救援工作极为困难,并导致生命悲剧。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的实例分割方法,称为DIS-Mine,专门用于在光线不足或能见度差的条件下识别地下矿藏中的受灾区域,以协助一线救援人员进行救援工作。DIS-Mine能够在图像中检测物体,甚至在完全黑暗中也能如此,通过解决高噪声、色彩失真和对比度降低等挑战。DIS-Mine的关键创新点基于四个核心组件:i)图像亮度改进,ii)带SAM集成的实例分割,iii)基于Mask R-CNN的分割,以及iv)与特征匹配的掩膜对齐。除此之外,我们从实验性地下矿场收集了现实世界图像,引入了一个名为ImageMine的新数据集,该数据集是在低能见度条件下专门收集的。该数据集用于验证DIS-Mine在真实且具有挑战性的环境中的性能。我们在ImageMine数据集以及其他各个数据集上的综合实验表明,DIS-Mine的F1分数达到86.0%,mIoU达到72.0%,优于最先进实例分割方法,在目标检测方面至少有15倍的改进,最高可达80%的精确度提高。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:地下矿山灾难检测,如爆炸和结构损坏,一直是一个挑战性问题。本文提出了一种新型的实例分割方法DIS-Mine,能在低光照或低可见性条件下识别矿山内的受灾区域,有助于救援人员开展救援工作。该方法解决了图像中的高噪声、色彩失真和对比度降低等问题,由图像亮度改进、实例分割与SAM集成等四个核心组件构成。此外,还收集了一个名为ImageMine的新数据集来验证DIS-Mine在真实环境中的性能。实验表明,DIS-Mine在ImageMine和其他数据集上的表现优于其他实例分割方法,实现了F1分数为86.0%,mIoU为72.0%,在目标检测方面的精度至少提高了15倍,最高提高了80%。
Key Takeaways:
- 地下矿山灾难检测是一个重要的挑战性问题,特别是在低光照或低可见性条件下。
- DIS-Mine是一种新型的实例分割方法,旨在解决地下矿山灾难检测中的难题。
- DIS-Mine具有在恶劣环境下检测图像中物体的能力,包括高噪声、色彩失真和对比度降低的环境。
- DIS-Mine包括四个核心组件:图像亮度改进、实例分割与SAM集成等。
- 引入了新的数据集ImageMine来验证DIS-Mine的性能。
- 实验表明,DIS-Mine在多个数据集上的表现优于其他实例分割方法。
点此查看论文截图


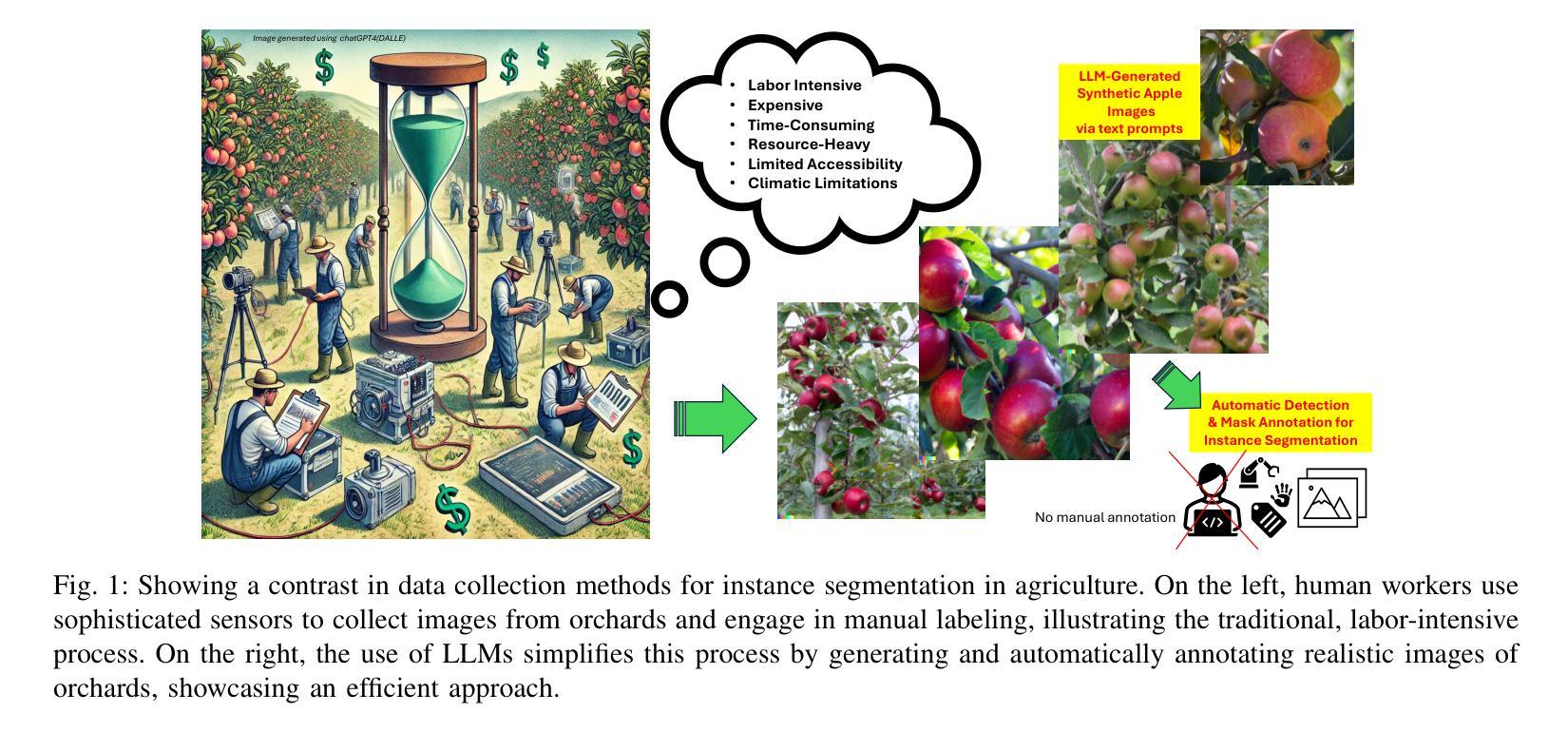
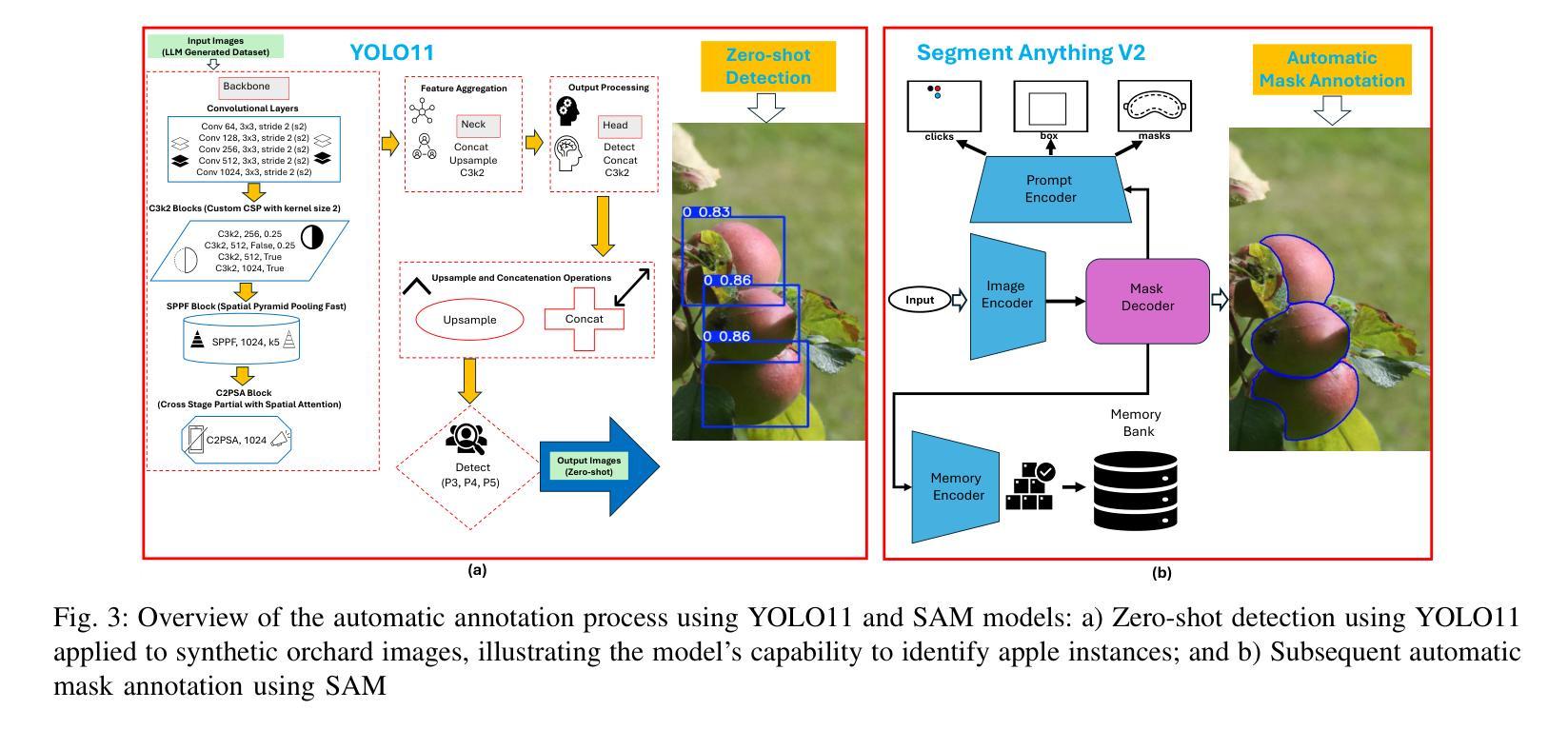
Zero-Shot Automatic Annotation and Instance Segmentation using LLM-Generated Datasets: Eliminating Field Imaging and Manual Annotation for Deep Learning Model Development
Authors:Ranjan Sapkota, Achyut Paudel, Manoj Karkee
Currently, deep learning-based instance segmentation for various applications (e.g., Agriculture) is predominantly performed using a labor-intensive process involving extensive field data collection using sophisticated sensors, followed by careful manual annotation of images, presenting significant logistical and financial challenges to researchers and organizations. The process also slows down the model development and training process. In this study, we presented a novel method for deep learning-based instance segmentation of apples in commercial orchards that eliminates the need for labor-intensive field data collection and manual annotation. Utilizing a Large Language Model (LLM), we synthetically generated orchard images and automatically annotated them using the Segment Anything Model (SAM) integrated with a YOLO11 base model. This method significantly reduces reliance on physical sensors and manual data processing, presenting a major advancement in “Agricultural AI”. The synthetic, auto-annotated dataset was used to train the YOLO11 model for Apple instance segmentation, which was then validated on real orchard images. The results showed that the automatically generated annotations achieved a Dice Coefficient of 0.9513 and an IoU of 0.9303, validating the accuracy and overlap of the mask annotations. All YOLO11 configurations, trained solely on these synthetic datasets with automated annotations, accurately recognized and delineated apples, highlighting the method’s efficacy. Specifically, the YOLO11m-seg configuration achieved a mask precision of 0.902 and a mask mAP@50 of 0.833 on test images collected from a commercial orchard. Additionally, the YOLO11l-seg configuration outperformed other models in validation on 40 LLM-generated images, achieving the highest mask precision and mAP@50 metrics. Keywords: YOLO, SAM, SAMv2, YOLO11, YOLOv11, Segment Anything, YOLO-SAM
目前,基于深度学习的各种应用(例如农业)中的实例分割主要采用劳动密集型的流程,涉及使用精密传感器进行大量的田间数据收集,以及对图像进行仔细的手动标注,这给研究者和组织带来了重大的后勤和财务挑战,同时也减缓了模型和训练的开发过程。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种基于深度学习的商业果园苹果实例分割的新方法,该方法无需进行劳动密集型的田间数据收集和手动标注。我们利用大型语言模型(LLM)合成生成果园图像,并使用与YOLO11基础模型集成的Segment Anything Model(SAM)进行自动标注。该方法显著减少了对物理传感器和手动数据处理的依赖,是“农业人工智能”领域的一项重大进展。合成的自动标注数据集用于训练YOLO11苹果实例分割模型,并在真实的果园图像上进行了验证。结果显示,自动生成的标注达到了Dice系数为0.9513和IoU为0.9303,验证了掩膜标注的准确性和重叠度。所有仅在自动标注的合成数据集上训练的YOLO11配置,都能准确识别和划分苹果,突显了该方法的有效性。特别是YOLO11m-seg配置在来自商业果园的测试图像上达到了0.902的掩膜精度和0.833的mAP@50指标。此外,YOLO11l-seg配置在40张LLM生成的图像验证中表现优于其他模型,获得了最高的掩膜精度和mAP@50指标。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于深度学习和大型语言模型(LLM)的苹果实例分割方法,该方法通过合成图像自动生成和自动标注技术,大幅减少了人力密集型的实地数据收集与手动标注工作。研究利用Segment Anything Model (SAM)与YOLO11基础模型,实现对苹果实例的自动分割,并在商业果园的实拍图像中验证了其有效性。此方法显著减少了对传统物理传感器和手动数据处理的依赖,是农业人工智能领域的一大进步。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了一种基于深度学习和大型语言模型的苹果实例分割方法,实现了图像的自动标注和分割。
- 方法通过合成图像生成技术,大幅减少了实地数据收集和手动标注的工作量。
- 研究利用了Segment Anything Model (SAM)与YOLO11模型进行苹果实例的自动分割。
- 自动化生成的注释在真实果园图像上取得了较高的分割效果,Dice系数为0.9513,IoU为0.9303。
- YOLO11模型的不同配置在仅使用合成数据集和自动注释的情况下,均能准确识别和分割苹果。
- YOLO11m-seg配置在测试图像上取得了较高的掩膜精度和mAP@50指标。
点此查看论文截图


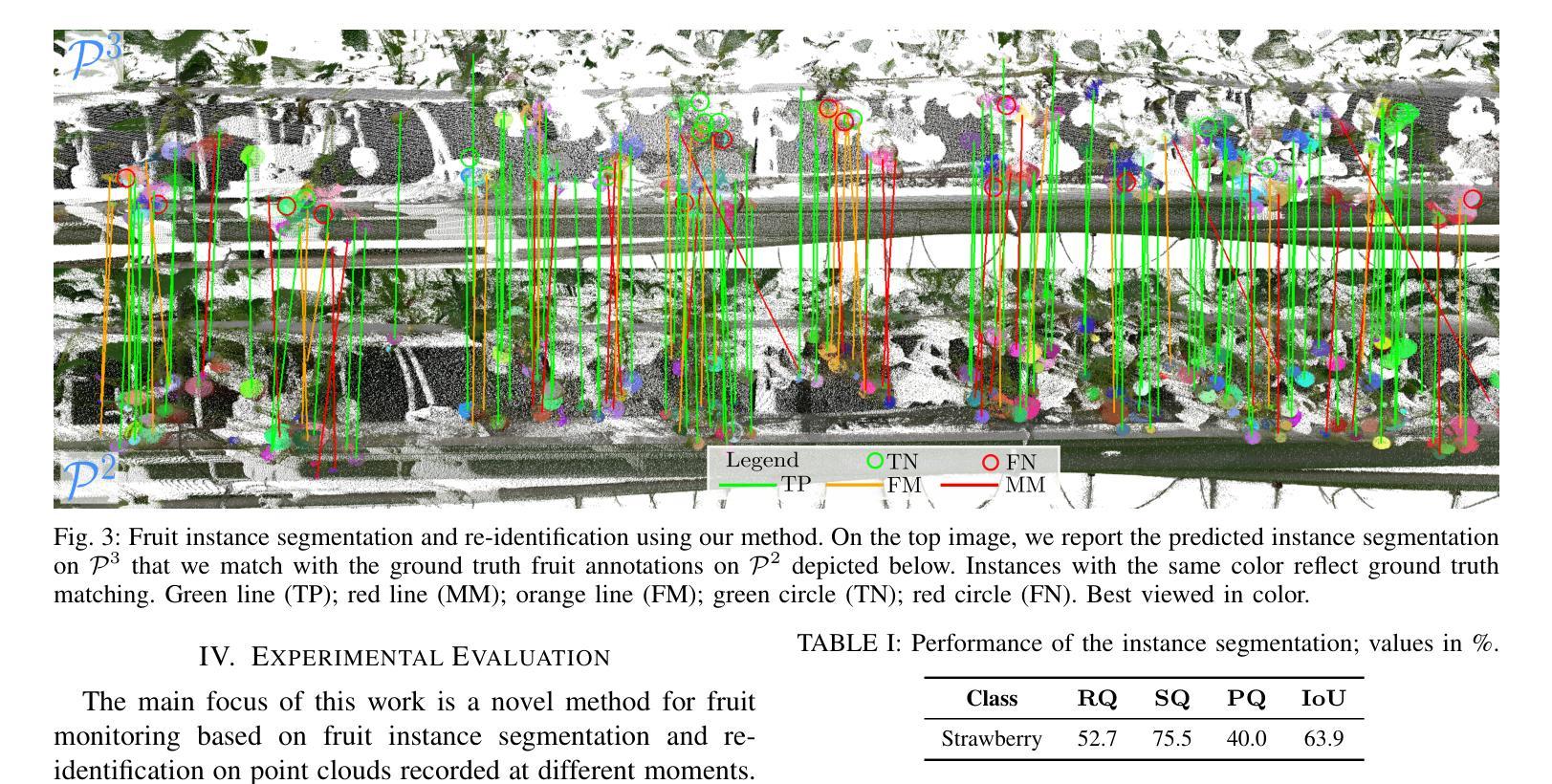
Horticultural Temporal Fruit Monitoring via 3D Instance Segmentation and Re-Identification using Point Clouds
Authors:Daniel Fusaro, Federico Magistri, Jens Behley, Alberto Pretto, Cyrill Stachniss
Robotic fruit monitoring is a key step toward automated agricultural production systems. Robots can significantly enhance plant and temporal fruit monitoring by providing precise, high-throughput assessments that overcome the limitations of traditional manual methods. Fruit monitoring is a challenging task due to the significant variation in size, shape, orientation, and occlusion of fruits. Also, fruits may be harvested or newly grown between recording sessions. Most methods are 2D image-based and they lack the 3D structure, depth, and spatial information, which represent key aspects of fruit monitoring. 3D colored point clouds, instead, can offer this information but they introduce challenges such as their sparsity and irregularity. In this paper, we present a novel approach for temporal fruit monitoring that addresses point clouds collected in a greenhouse over time. Our method segments fruits using a learning-based instance segmentation approach directly on the point cloud. Each segmented fruit is processed by a 3D sparse convolutional neural network to extract descriptors, which are used in an attention-based matching network to associate fruits with their instances from previous data collections. Experimental results on a real dataset of strawberries demonstrate that our approach outperforms other methods for fruits re-identification over time, allowing for precise temporal fruit monitoring in real and complex scenarios.
机器人水果监测是向自动化农业生产系统迈进的关键一步。机器人通过提供精确、高通量的评估,能够极大地增强植物和临时水果监测,克服传统人工方法的局限性。水果监测是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为水果的大小、形状、方向和遮挡存在很大差异。此外,在记录期间可能会有水果被采摘或新长出来。大多数方法都是基于2D图像的,缺乏3D结构、深度和空间信息,这些正是水果监测的关键方面。相反,3D彩色点云可以提供这些信息,但它们带来了稀疏性和不规则性等挑战。在本文中,我们提出了一种用于临时水果监测的新方法,该方法处理在温室中随时间收集的点云。我们的方法直接在点云上使用基于学习的实例分割方法进行水果分割。每个分割出来的水果都会通过3D稀疏卷积神经网络进行处理,以提取描述符,这些描述符用于基于注意力的匹配网络,将水果与以前的数据收集中的实例进行关联。在草莓的实际数据集上的实验结果表明,我们的方法在长时间水果再识别方面优于其他方法,允许在真实和复杂场景中进行精确的临时水果监测。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于点云的时空水果监测新方法,该方法直接在点云上进行学习型的实例分割,并通过3D稀疏卷积神经网络处理每个分割的水果,以提取描述符号。这些描述符号用于基于注意力的匹配网络,将与以前的数据收集中的水果实例进行关联。在草莓的真实数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在复杂的现实场景中,对水果的再识别能力优于其他方法,可实现精确的时空水果监测。
Key Takeaways
- 水果监测是农业自动化生产系统中的关键步骤,机器人可以克服传统手动方法的局限性,提供精确、高通量的评估结果。
- 水果监测具有挑战性,因为水果的大小、形状、方向和遮挡有很大的变化,且可能在记录期间被采摘或新长出来。
- 大多数方法基于二维图像,缺乏三维结构和深度空间信息。
- 点云技术可以克服二维图像的限制,提供三维结构信息,但点云的稀疏性和不规则性引入新的挑战。
- 本文提出了一种基于点云的水果监测新方法,通过实例分割和卷积神经网络处理水果,实现精确监测。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在复杂的现实场景中表现出色,能够识别随时间变化的水果。
点此查看论文截图

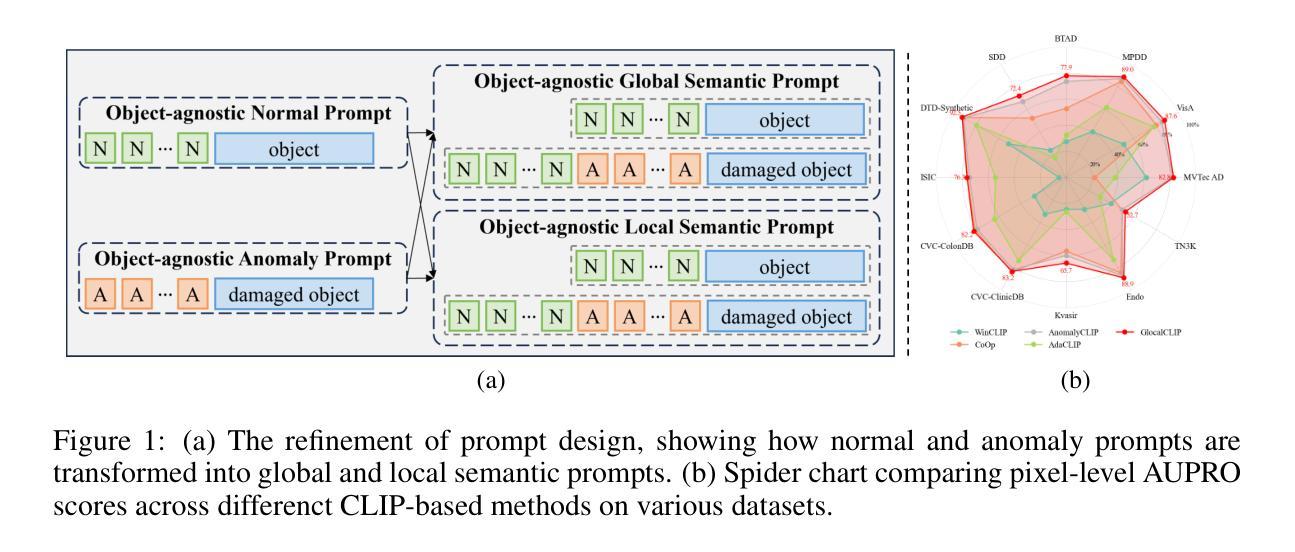
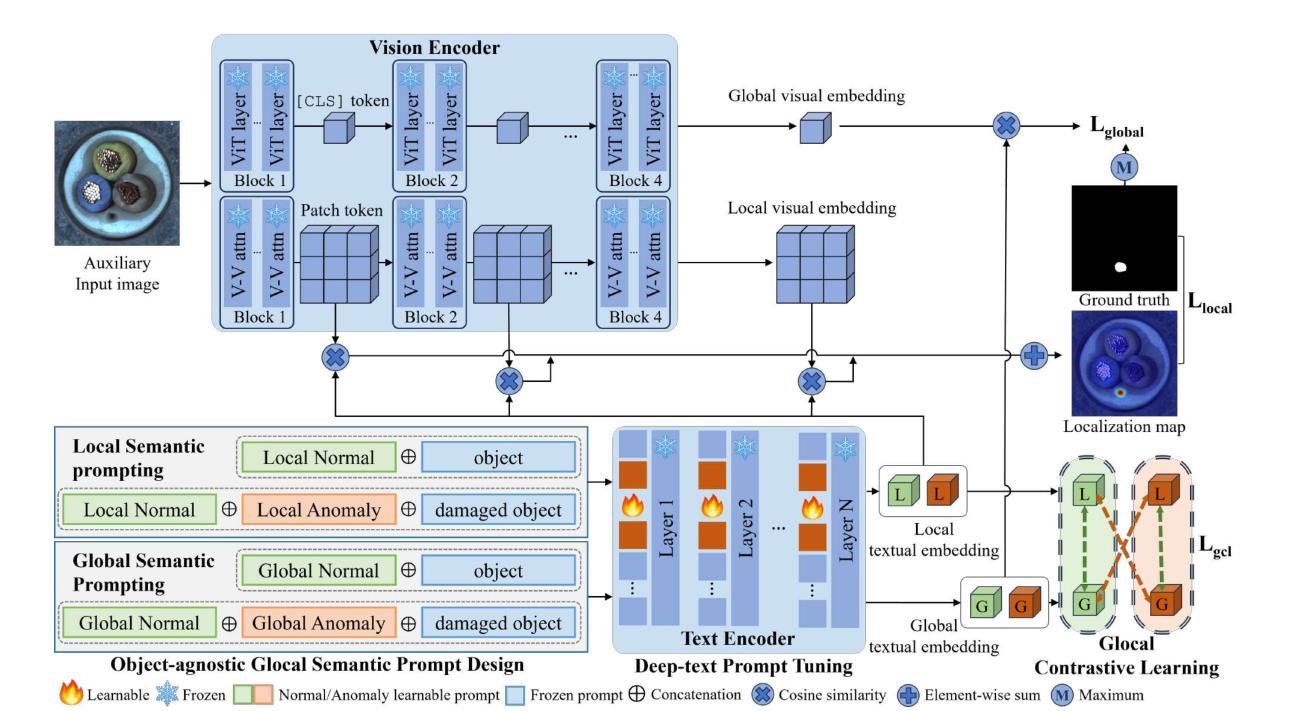
GlocalCLIP: Object-agnostic Global-Local Prompt Learning for Zero-shot Anomaly Detection
Authors:Jiyul Ham, Yonggon Jung, Jun-Geol Baek
Zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD) is crucial for detecting anomalous patterns in target datasets without using training samples, specifically in scenarios where there are distributional differences between the target domain and training data or where data scarcity arises because of restricted access. Although recently pretrained vision-language models demonstrate strong zero-shot performance across various visual tasks, they focus on learning class semantics, which makes their direct application to ZSAD challenging. To address this scenario, we propose GlocalCLIP, which uniquely separates global and local prompts and jointly optimizes them. This approach enables the object-agnostic glocal semantic prompt to effectively capture general normal and anomalous patterns without dependency on specific objects in the image. We refine the text prompts for more precise adjustments by utilizing deep-text prompt tuning in the text encoder. In the vision encoder, we apply V-V attention layers to capture detailed local image features. Finally, we introduce glocal contrastive learning to improve the complementary learning of global and local prompts, effectively detecting anomalous patterns across various domains. The generalization performance of GlocalCLIP in ZSAD was demonstrated on 15 real-world datasets from both the industrial and medical domains, achieving superior performance compared to existing methods. Code will be made available at https://github.com/YUL-git/GlocalCLIP.
零样本异常检测(ZSAD)对于在无需训练样本的情况下检测目标数据集中的异常模式至关重要,特别是在目标域与训练数据之间存在分布差异或由于访问受限而导致数据稀缺的场景中。尽管最近预训练的视觉语言模型在各种视觉任务中表现出强大的零样本性能,但它们主要关注类别语义的学习,这使得它们直接应用于ZSAD具有挑战性。为了应对这一场景,我们提出了GlocalCLIP方法,该方法独特地分离全局和局部提示并进行联合优化。这一方法使得对象无关的局部语义提示能够有效地捕捉通用正常和异常模式,而无需依赖图像中的特定对象。我们通过利用文本编码器的深度文本提示调整来完善文本提示,以实现更精确的调整。在视觉编码器方面,我们应用V-V注意力层来捕捉详细的局部图像特征。最后,我们引入了局部对比学习,以提高全局和局部提示的互补学习,有效检测不同领域的异常模式。GlocalCLIP在ZSAD中的泛化性能在15个来自工业和医疗领域的真实世界数据集上得到了验证,相较于现有方法表现出卓越的性能。代码将发布在https://github.com/YUL-git/GlocalCLIP。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 29 pages, 36 figures
Summary
针对零样本异常检测(ZSAD)问题,尤其是当目标数据集与训练数据存在分布差异或数据稀缺时,提出一种名为GlocalCLIP的方法。该方法通过分离全局和局部提示并进行联合优化,有效捕捉正常和异常模式。此外,使用深度文本提示调整和V-V注意力层增强学习性能。最后通过对比实验验证了GlocalCLIP在不同领域的实际数据集中的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- ZSAD在处理存在分布差异或数据稀缺的问题时面临挑战。
- GlocalCLIP方法通过分离全局和局部提示进行优化,能够捕捉正常和异常模式。
- 深度文本提示调整提高了精度。
- V-V注意力层有助于捕捉局部图像特征。
- GlocalCLIP引入对比学习以增强全局和局部提示的互补学习。
- 在多个真实世界数据集上验证了GlocalCLIP的优越性能。
点此查看论文截图

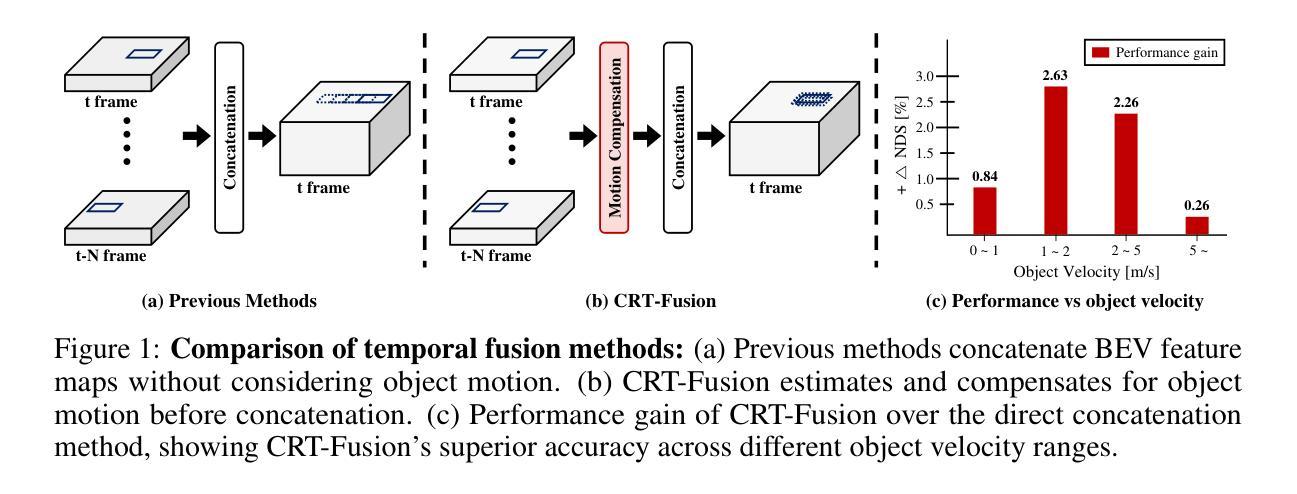
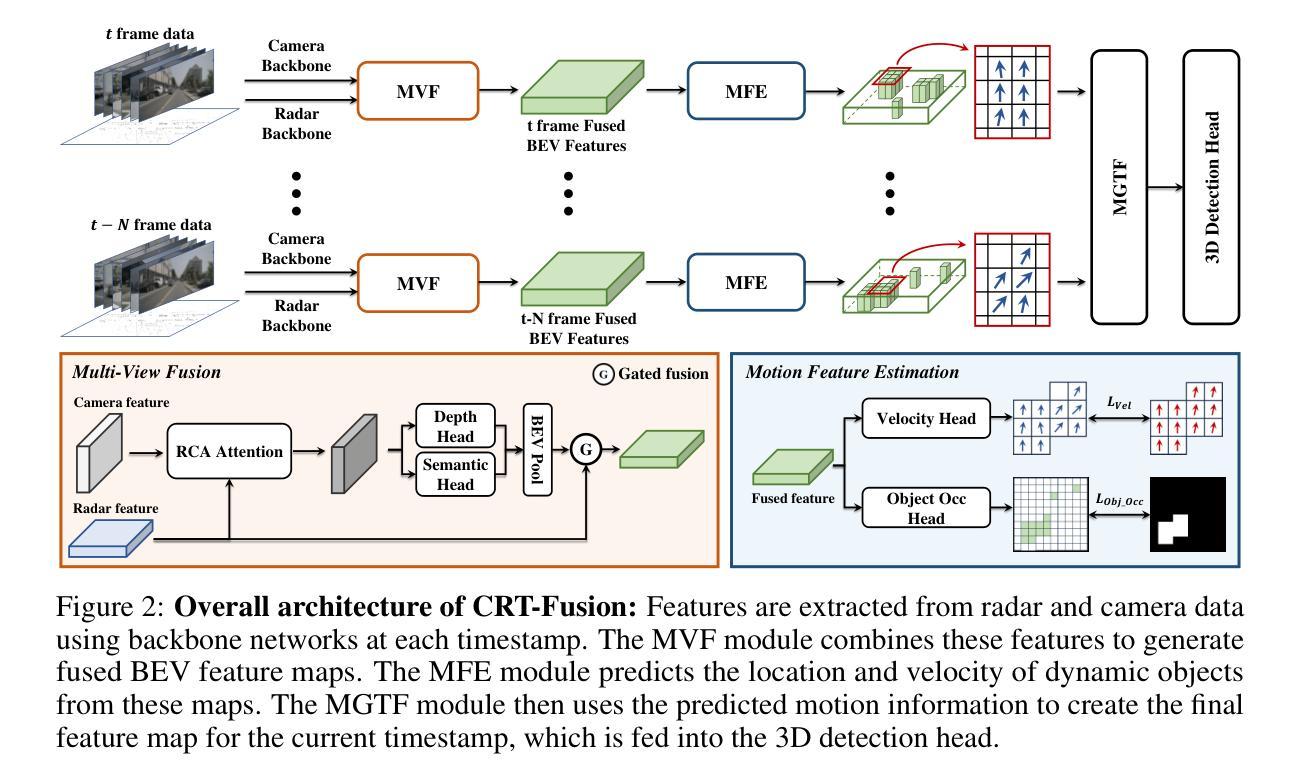
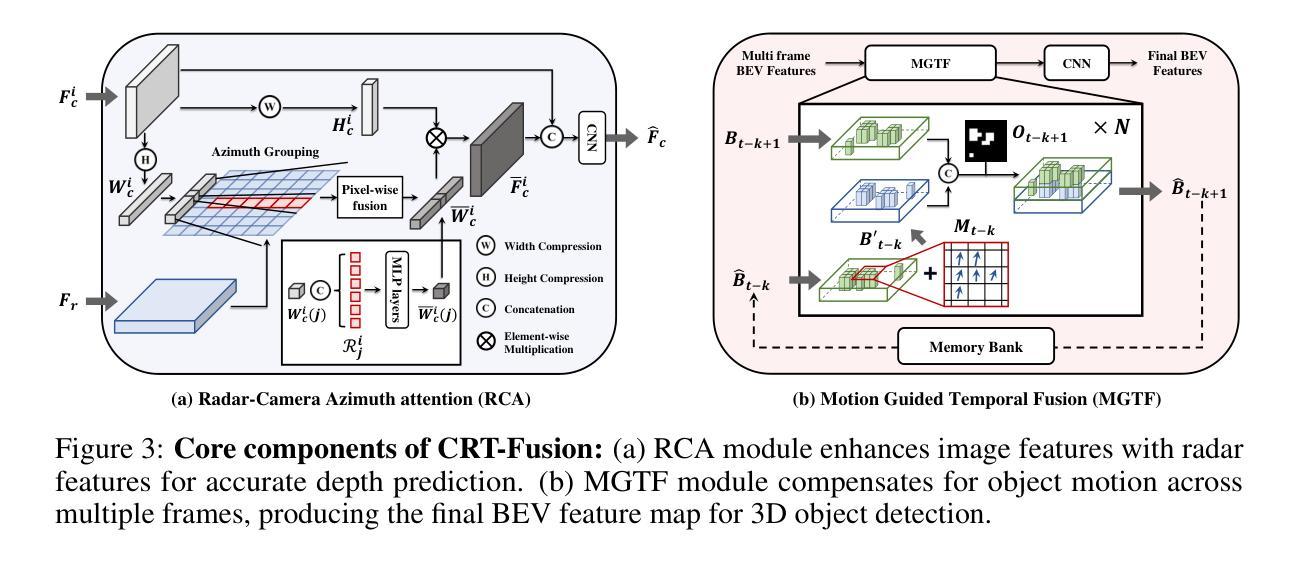
CRT-Fusion: Camera, Radar, Temporal Fusion Using Motion Information for 3D Object Detection
Authors:Jisong Kim, Minjae Seong, Jun Won Choi
Accurate and robust 3D object detection is a critical component in autonomous vehicles and robotics. While recent radar-camera fusion methods have made significant progress by fusing information in the bird’s-eye view (BEV) representation, they often struggle to effectively capture the motion of dynamic objects, leading to limited performance in real-world scenarios. In this paper, we introduce CRT-Fusion, a novel framework that integrates temporal information into radar-camera fusion to address this challenge. Our approach comprises three key modules: Multi-View Fusion (MVF), Motion Feature Estimator (MFE), and Motion Guided Temporal Fusion (MGTF). The MVF module fuses radar and image features within both the camera view and bird’s-eye view, thereby generating a more precise unified BEV representation. The MFE module conducts two simultaneous tasks: estimation of pixel-wise velocity information and BEV segmentation. Based on the velocity and the occupancy score map obtained from the MFE module, the MGTF module aligns and fuses feature maps across multiple timestamps in a recurrent manner. By considering the motion of dynamic objects, CRT-Fusion can produce robust BEV feature maps, thereby improving detection accuracy and robustness. Extensive evaluations on the challenging nuScenes dataset demonstrate that CRT-Fusion achieves state-of-the-art performance for radar-camera-based 3D object detection. Our approach outperforms the previous best method in terms of NDS by +1.7%, while also surpassing the leading approach in mAP by +1.4%. These significant improvements in both metrics showcase the effectiveness of our proposed fusion strategy in enhancing the reliability and accuracy of 3D object detection.
准确且稳定的3D物体检测是自动驾驶汽车和机器人技术中的关键组成部分。虽然最近的雷达-相机融合方法在鸟瞰图(BEV)表示的信息融合方面取得了显著进展,但它们往往难以有效地捕捉动态物体的运动,导致在真实场景中的性能受限。针对这一挑战,我们在本文中介绍了CRT-Fusion,这是一个将时间信息融入雷达-相机融合的新型框架。我们的方法包括三个关键模块:多视图融合(MVF)、运动特征估计器(MFE)和运动引导时间融合(MGTF)。MVF模块在相机视图和鸟瞰图中融合雷达和图像特征,从而生成更精确的统一BEV表示。MFE模块同时执行两个任务:像素级速度信息估计和BEV分割。基于MFE模块获得的速度和占用分数图,MGTF模块以递归方式对齐和融合多个时间戳的特征图。通过考虑动态物体的运动,CRT-Fusion可以生成稳定的BEV特征图,从而提高检测准确性和稳健性。在具有挑战性的nuScenes数据集上的广泛评估表明,CRT-Fusion在基于雷达-相机的3D物体检测方面达到了最新技术水平。我们的方法在NDS方面较之前最佳方法提高了+1.7%,同时在mAP方面也超越了领先方法+1.4%。这两个指标的大幅提升展示了我们的融合策略在提高3D物体检测的可靠性和准确性方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at NeurIPS2024
Summary
雷达与相机融合技术在三维物体检测中取得了显著进展,但仍存在对动态物体运动捕捉不足的问题。本文提出的CRT-Fusion框架通过集成时间信息,解决了这一问题。它包含三个关键模块:多视角融合(MVF)、运动特征估计器(MFE)和运动引导时间融合(MGTF)。CRT-Fusion在nuScenes数据集上的评估结果表明,其在雷达-相机基的三维物体检测方面达到了最新技术水平,显著提高了检测准确性和鲁棒性。
Key Takeaways
- CRT-Fusion框架通过整合时间信息,提高了雷达与相机融合技术的三维物体检测性能。
- MVF模块在相机视角和鸟瞰视角融合雷达和图像特征,生成更精确的统一鸟瞰视图表示。
- MFE模块同时执行像素级速度信息估计和鸟瞰视图分割两个任务。
- MGTF模块基于速度和占用分数图,对跨多个时间戳的特征图进行对齐和融合。
- CRT-Fusion在nuScenes数据集上的表现优于其他方法,在NDS和mAP指标上实现了显著改进。
- 该框架增强了三维物体检测的可靠性和准确性。
点此查看论文截图

On the Black-box Explainability of Object Detection Models for Safe and Trustworthy Industrial Applications
Authors:Alain Andres, Aitor Martinez-Seras, Ibai Laña, Javier Del Ser
In the realm of human-machine interaction, artificial intelligence has become a powerful tool for accelerating data modeling tasks. Object detection methods have achieved outstanding results and are widely used in critical domains like autonomous driving and video surveillance. However, their adoption in high-risk applications, where errors may cause severe consequences, remains limited. Explainable Artificial Intelligence methods aim to address this issue, but many existing techniques are model-specific and designed for classification tasks, making them less effective for object detection and difficult for non-specialists to interpret. In this work we focus on model-agnostic explainability methods for object detection models and propose D-MFPP, an extension of the Morphological Fragmental Perturbation Pyramid (MFPP) technique based on segmentation-based masks to generate explanations. Additionally, we introduce D-Deletion, a novel metric combining faithfulness and localization, adapted specifically to meet the unique demands of object detectors. We evaluate these methods on real-world industrial and robotic datasets, examining the influence of parameters such as the number of masks, model size, and image resolution on the quality of explanations. Our experiments use single-stage object detection models applied to two safety-critical robotic environments: i) a shared human-robot workspace where safety is of paramount importance, and ii) an assembly area of battery kits, where safety is critical due to the potential for damage among high-risk components. Our findings evince that D-Deletion effectively gauges the performance of explanations when multiple elements of the same class appear in a scene, while D-MFPP provides a promising alternative to D-RISE when fewer masks are used.
在人机互动领域,人工智能已成为加速数据建模任务的强大工具。物体检测方法已经取得了显著成果,并广泛应用于自动驾驶和视频监控等重要领域。然而,其在高风险应用中的采用仍然有限,因为错误可能会导致严重后果。可解释人工智能方法旨在解决这个问题,但许多现有技术都是针对特定模型的分类任务,对于物体检测而言效果较差,且非专业人员难以解释。在这项工作中,我们专注于针对物体检测模型的模型无关可解释性方法,并提出D-MFPP,它是基于分割掩膜扩展的形态学片段扰动金字塔(MFPP)技术,用于生成解释。此外,我们引入了D-Deletion,这是一个结合了忠实性和定位性的新型指标,专门为物体检测器的独特需求而设计。我们在真实的工业和机器人数据集上评估了这些方法,研究了掩膜数量、模型大小和图像分辨率等参数对解释质量的影响。我们的实验使用了应用于两个安全关键的机器人环境的单阶段物体检测模型:一是对人的安全至关重要的共享人机工作空间;二是电池组件装配区,由于高风险组件的存在,安全至关重要。我们的研究结果表明,当场景中出现同一类的多个元素时,D-Deletion有效地衡量了解释的性能,而D-MFPP在使用的掩膜数量较少时提供了一个有前途的替代方案。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 10 figures, 6 tables
摘要
在人机互动领域,人工智能已成为加速数据建模任务的强大工具。对象检测方法取得了显著成果,广泛应用于自动驾驶和视频监控等重要领域。然而,它们在高风险应用中的采用仍受到限制,因为一旦出现错误可能会带来严重后果。可解释性人工智能方法旨在解决这一问题,但许多现有技术都是针对特定模型的分类任务,对于对象检测的应用效果较差,并且难以被非专业人士解读。本研究专注于模型不可知的可解释性方法用于对象检测模型,并提出D-MFPP,它是基于分割掩膜技术的Morphological Fragmental Perturbation Pyramid(MFPP)技术的扩展,用于生成解释。此外,我们引入了D-Deletion,这是一个结合了忠实性和定位的新指标,专为满足对象检测器的独特需求而设计。我们在真实的工业界和机器人数据集上评估了这些方法,研究了掩膜数量、模型大小和图像分辨率等参数对解释质量的影响。我们的实验使用了单阶段对象检测模型,并应用于两个安全至关重要的机器人环境:一是对人机器人共享工作空间内的装配电池组件区域。我们的研究结果表明,当场景中同一类的元素出现多次时,D-Deletion能有效衡量解释的性能,而D-MFPP在掩膜数量较少时提供了一个有前景的替代方案。
关键见解
- 人工智能在数据建模任务中表现出强大的加速能力,尤其在对象检测领域取得了显著成果。
- 对象检测方法在高风险应用中的采用受到限制,因为错误可能导致严重后果。
- 可解释性人工智能方法在对象检测领域的应用至关重要,但现有技术多针对特定模型,难以被非专业人士解读。
- 本研究提出D-MFPP和D-Deletion方法,分别用于生成解释和评估对象检测模型的可解释性。
- 实验表明,D-Deletion能有效衡量在场景中同一类元素出现多次时的解释性能。
- D-MFPP在较少掩膜使用时提供了一个有前景的替代方案。
点此查看论文截图

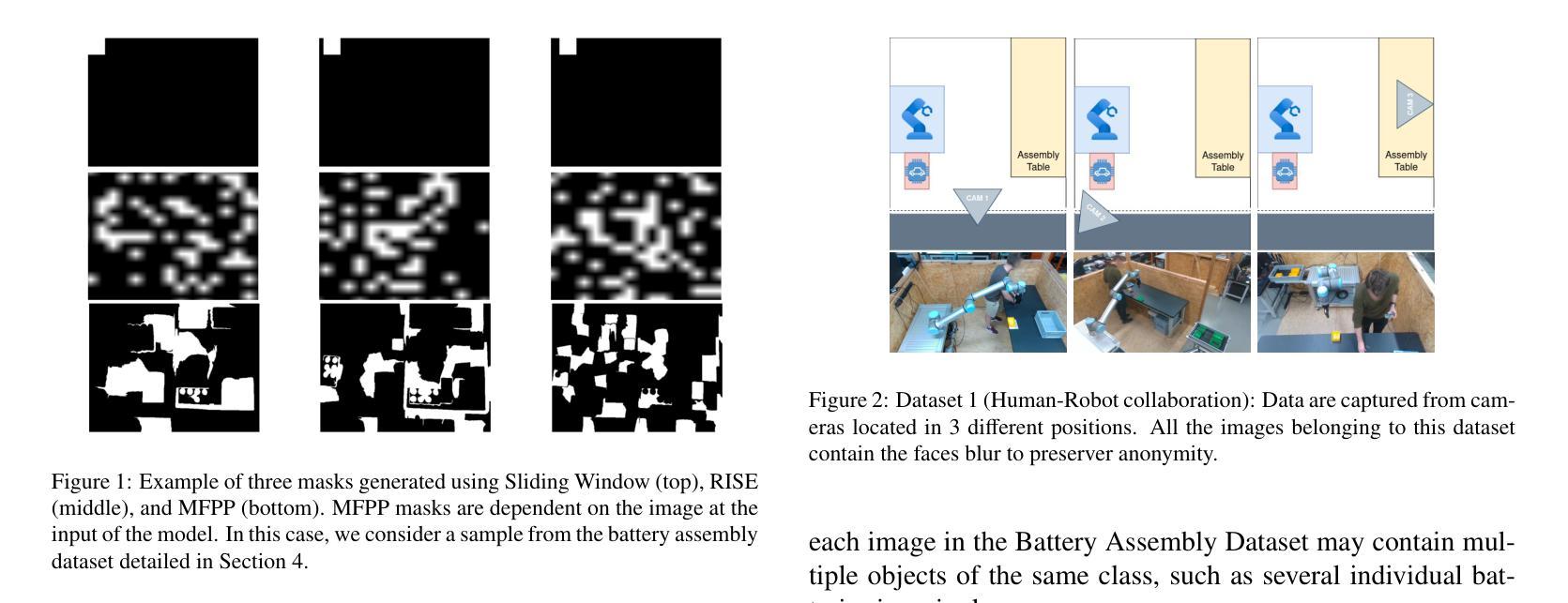
MV-Adapter: Enhancing Underwater Instance Segmentation via Adaptive Channel Attention
Authors:Lianjun Liu
Underwater instance segmentation is a fundamental and critical step in various underwater vision tasks. However, the decline in image quality caused by complex underwater environments presents significant challenges to existing segmentation models. While the state-of-the-art USIS-SAM model has demonstrated impressive performance, it struggles to effectively adapt to feature variations across different channels in addressing issues such as light attenuation, color distortion, and complex backgrounds. This limitation hampers its segmentation performance in challenging underwater scenarios. To address these issues, we propose the MarineVision Adapter (MV-Adapter). This module introduces an adaptive channel attention mechanism that enables the model to dynamically adjust the feature weights of each channel based on the characteristics of underwater images. By adaptively weighting features, the model can effectively handle challenges such as light attenuation, color shifts, and complex backgrounds. Experimental results show that integrating the MV-Adapter module into the USIS-SAM network architecture further improves the model’s overall performance, especially in high-precision segmentation tasks. On the USIS10K dataset, the module achieves improvements in key metrics such as mAP, AP50, and AP75 compared to competitive baseline models.
水下实例分割是各种水下视觉任务中的一项基本且关键步骤。然而,由于水下环境的复杂性导致的图像质量下降,给现有的分割模型带来了巨大的挑战。虽然目前最先进的USIS-SAM模型已经表现出了令人印象深刻的表现,但在处理光衰减、色彩失真和复杂背景等问题时,它在适应不同通道的特征变化方面仍存在困难。这一局限性阻碍了它在具有挑战性的水下场景中的分割性能。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了MarineVision Adapter(MV-Adapter)。该模块引入了一种自适应通道注意力机制,使模型能够根据水下图像的特性动态调整每个通道的特征权重。通过自适应地加权特征,该模型可以有效地应对光衰减、色彩偏移和复杂背景等挑战。实验结果表明,将MV-Adapter模块集成到USIS-SAM网络架构中,可以进一步提高模型的总体性能,特别是在高精度分割任务中。在USIS10K数据集上,该模块在主要指标mAP、AP50和AP75上相对于竞争基准模型取得了改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
水下实例分割是水下视觉任务中的基础且关键的一步。复杂的水下环境导致的图像质量下降给现有的分割模型带来了挑战。虽然目前最先进的USIS-SAM模型表现出令人印象深刻的性能,但在处理光衰减、色彩失真和复杂背景等问题时,它难以适应不同通道的特征变化。为解决这些问题,我们提出了MarineVision Adapter(MV-Adapter)模块。该模块引入了一种自适应通道注意力机制,使模型能够根据水下图像的特性动态调整每个通道的特征权重。通过自适应地加权特征,模型可以有效地应对光衰减、色彩偏移和复杂背景等挑战。实验结果表明,将MV-Adapter模块集成到USIS-SAM网络架构中,进一步提高了模型的总体性能,特别是在高精度分割任务中。在USIS10K数据集上,该模块与基线模型相比,在关键指标mAP、AP50和AP75上取得了改进。
Key Takeaways
- 水下实例分割是水下视觉任务的基础且关键步骤,但复杂的水下环境导致的图像质量下降给现有模型带来挑战。
- USIS-SAM模型虽表现出卓越性能,但在适应不同通道特征变化方面存在困难,难以应对光衰减、色彩失真和复杂背景等问题。
- MarineVision Adapter(MV-Adapter)模块通过引入自适应通道注意力机制,使模型能根据水下图像特性动态调整通道特征权重。
- MV-Adapter模块集成到USIC-SAM网络架构中,提高了模型的总体性能,特别是在高精度分割任务中。
- 在USIS10K数据集上,MV-Adapter模块在关键指标上改进了模型的性能,如mAP、AP50和AP75。
- MV-Adapter模块的出现是为了解决现有模型在应对水下图像挑战时的不足。
点此查看论文截图

NT-VOT211: A Large-Scale Benchmark for Night-time Visual Object Tracking
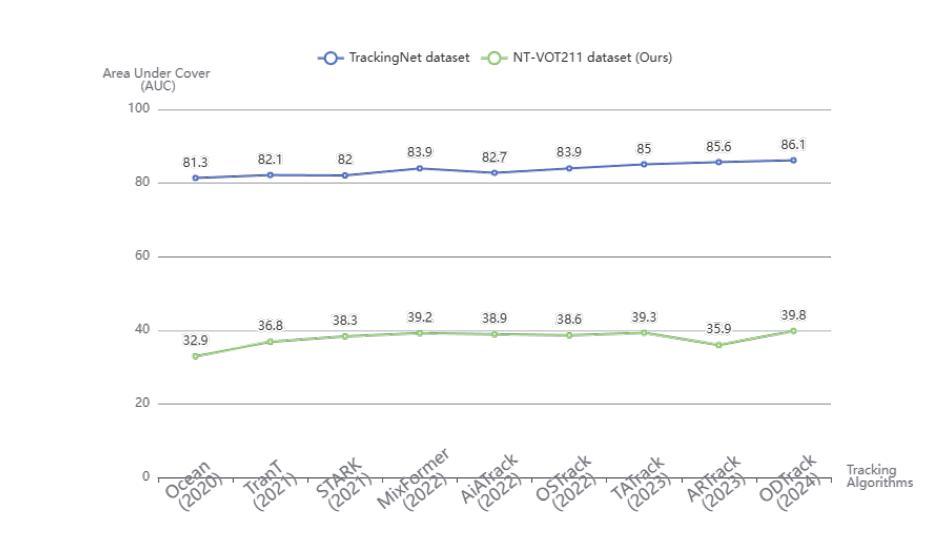
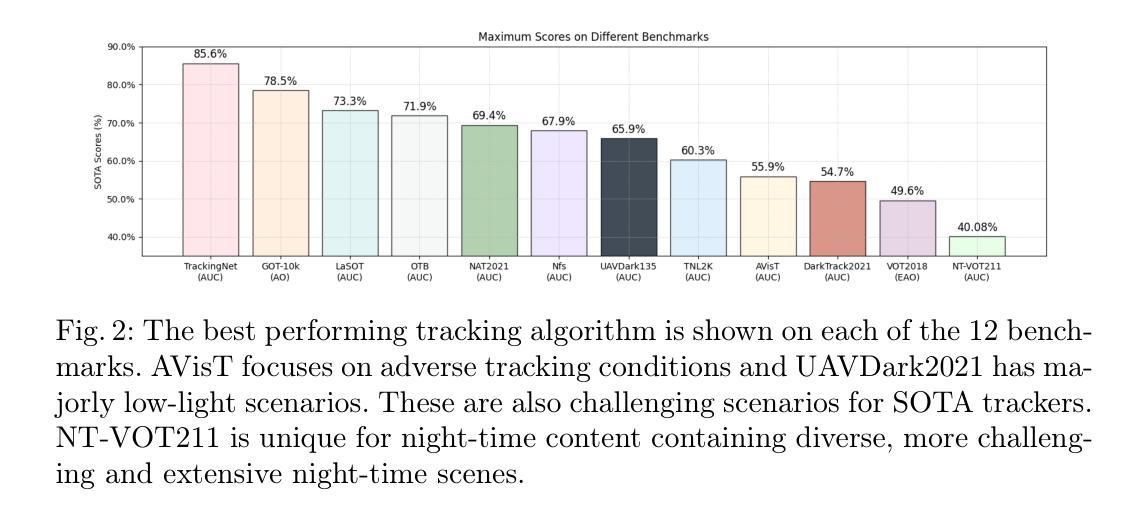
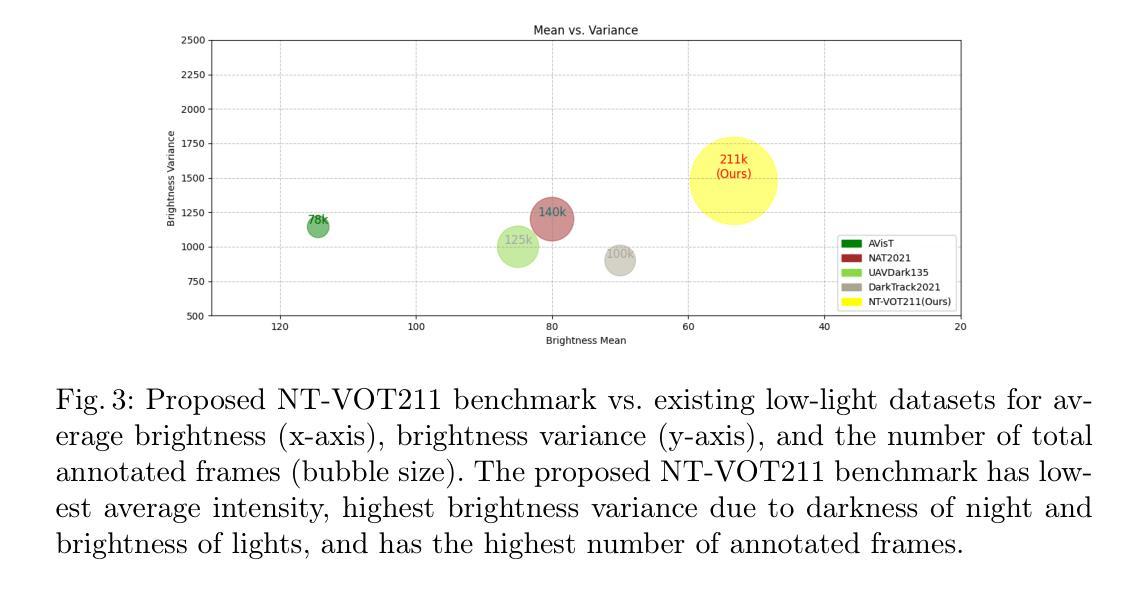
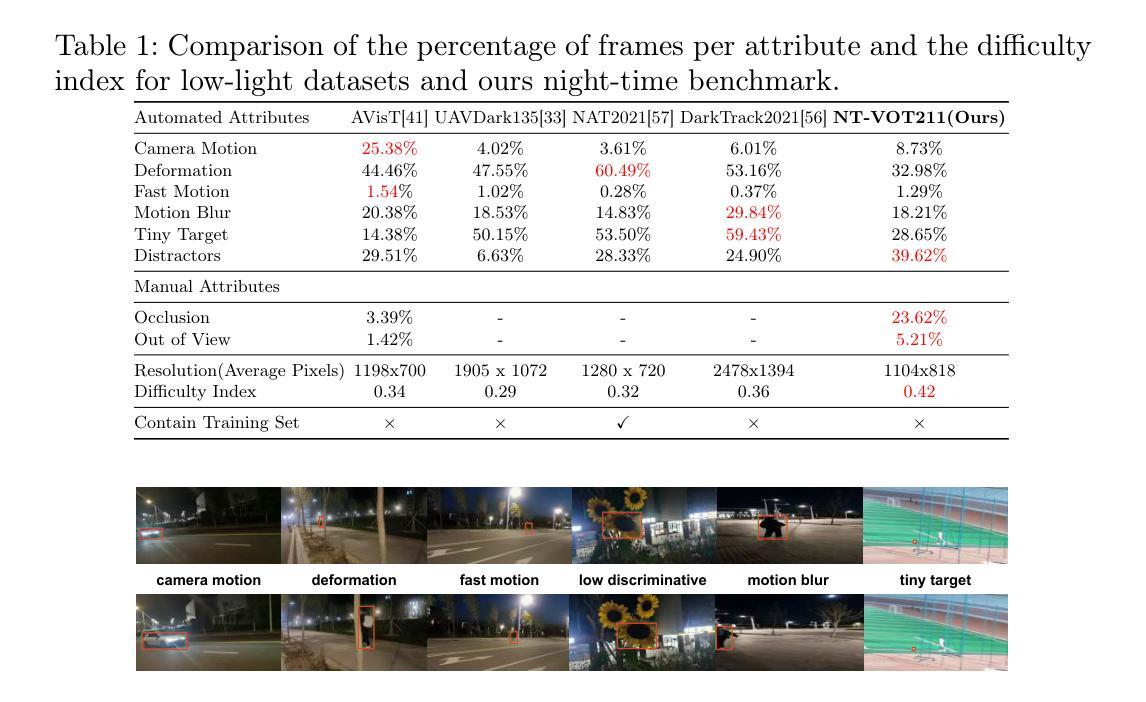
Authors:Yu Liu, Arif Mahmood, Muhammad Haris Khan
Many current visual object tracking benchmarks such as OTB100, NfS, UAV123, LaSOT, and GOT-10K, predominantly contain day-time scenarios while the challenges posed by the night-time has been less investigated. It is primarily because of the lack of a large-scale, well-annotated night-time benchmark for rigorously evaluating tracking algorithms. To this end, this paper presents NT-VOT211, a new benchmark tailored for evaluating visual object tracking algorithms in the challenging night-time conditions. NT-VOT211 consists of 211 diverse videos, offering 211,000 well-annotated frames with 8 attributes including camera motion, deformation, fast motion, motion blur, tiny target, distractors, occlusion and out-of-view. To the best of our knowledge, it is the largest night-time tracking benchmark to-date that is specifically designed to address unique challenges such as adverse visibility, image blur, and distractors inherent to night-time tracking scenarios. Through a comprehensive analysis of results obtained from 42 diverse tracking algorithms on NT-VOT211, we uncover the strengths and limitations of these algorithms, highlighting opportunities for enhancements in visual object tracking, particularly in environments with suboptimal lighting. Besides, a leaderboard for revealing performance rankings, annotation tools, comprehensive meta-information and all the necessary code for reproducibility of results is made publicly available. We believe that our NT-VOT211 benchmark will not only be instrumental in facilitating field deployment of VOT algorithms, but will also help VOT enhancements and it will unlock new real-world tracking applications. Our dataset and other assets can be found at: {https://github.com/LiuYuML/NV-VOT211.
当前许多视觉目标跟踪基准测试,如OTB100、NfS、UAV123、LaSOT和GOT-10K等,主要包含日间场景,而夜间场景所带来的挑战却研究较少。这主要是因为缺乏大规模、标注良好的夜间基准测试,以严格评估跟踪算法。为此,本文提出了NV-VOT211,一个新的基准测试,旨在评估夜间条件下视觉目标跟踪算法的性能。NV-VOT211包含211个多样化的视频,提供211,000个标注良好的帧,包括8个属性,如相机运动、变形、快速运动、运动模糊、微小目标、干扰物、遮挡和视野外等。据我们所知,它是迄今为止最大的夜间跟踪基准测试,专门设计用于解决夜间跟踪场景所特有的独特挑战,如能见度不良、图像模糊和干扰物等。通过对42种不同的跟踪算法在NV-VOT211上的结果进行全面分析,我们揭示了这些算法的优点和局限性,突显了视觉目标跟踪在光线不足环境中的增强机会。此外,我们还提供了一个排行榜,展示性能排名、标注工具、综合元信息和所有必要代码以供结果复现,现已公开可用。我们相信,我们的NV-VOT211基准测试不仅将有助于促进VOT算法的实地部署,还将有助于VOT的改进,并将解锁新的现实世界跟踪应用程序。我们的数据集和其他资产可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/LiuYuML/NV-VOT211。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Oral Acceptance at the Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV) 2024, Hanoi, Vietnam
Summary:
本文介绍了一个针对夜间视觉目标跟踪的新基准数据集NT-VOT211。该数据集包含211个视频和超过21万个标注良好的帧,涵盖8种属性,是目前最大的专门用于应对夜间跟踪挑战的基准数据集。通过对42种不同的跟踪算法在NT-VOT211上的结果进行分析,揭示了它们的优缺点,强调了次优光照环境下视觉目标跟踪的改进机会。此外,还提供了性能排行榜、标注工具、综合元信息和所有必要代码供公众使用。NT-VOT211有望推动视觉目标跟踪算法的部署,促进算法改进,并推动新的实际应用发展。
Key Takeaways:
- 当前视觉目标跟踪基准数据集主要关注白天场景,夜间挑战的研究较少。
- 缺乏大规模、标注良好的夜间基准数据集来评估跟踪算法。
- NT-VOT211是一个新的夜间视觉目标跟踪基准数据集,包含多样化的视频和标注良好的帧。
- NT-VOT211专门针对夜间跟踪的挑战,如不良能见度、图像模糊和干扰物等。
- 对42种跟踪算法在NT-VOT211上的结果分析揭示了算法的优缺点和改进机会。
- NT-VOT211提供了性能排行榜、标注工具等公共资源。
点此查看论文截图

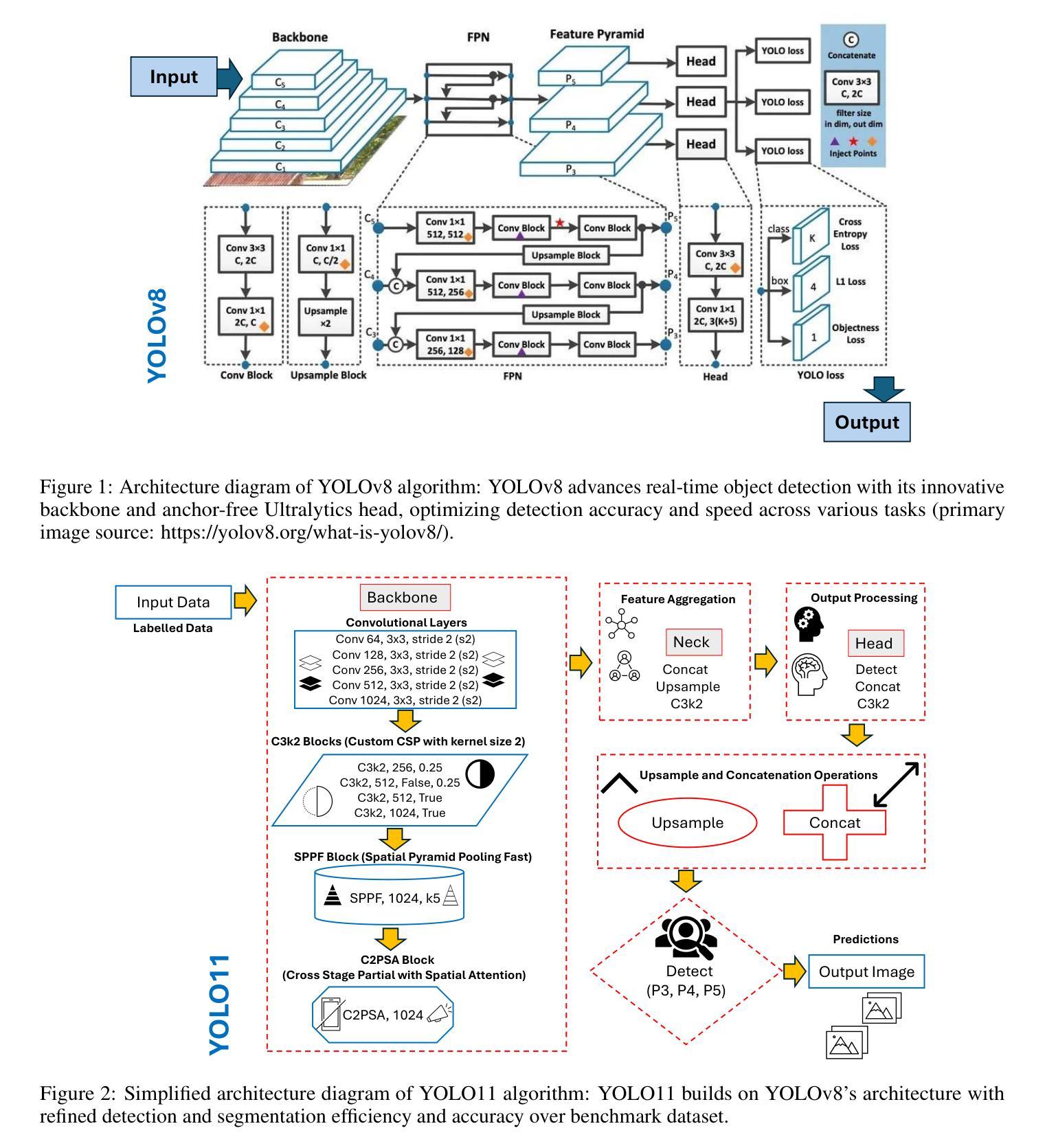
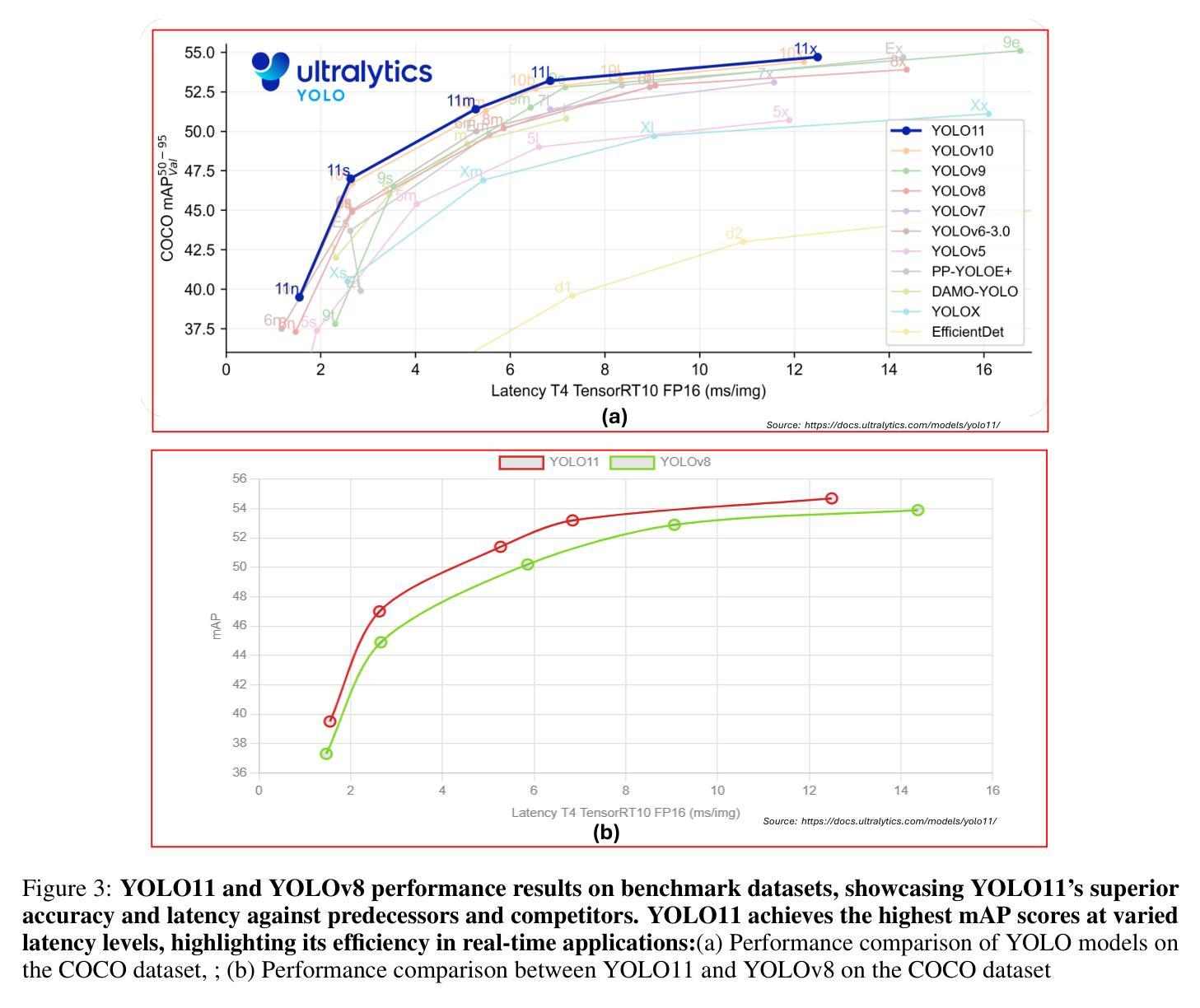
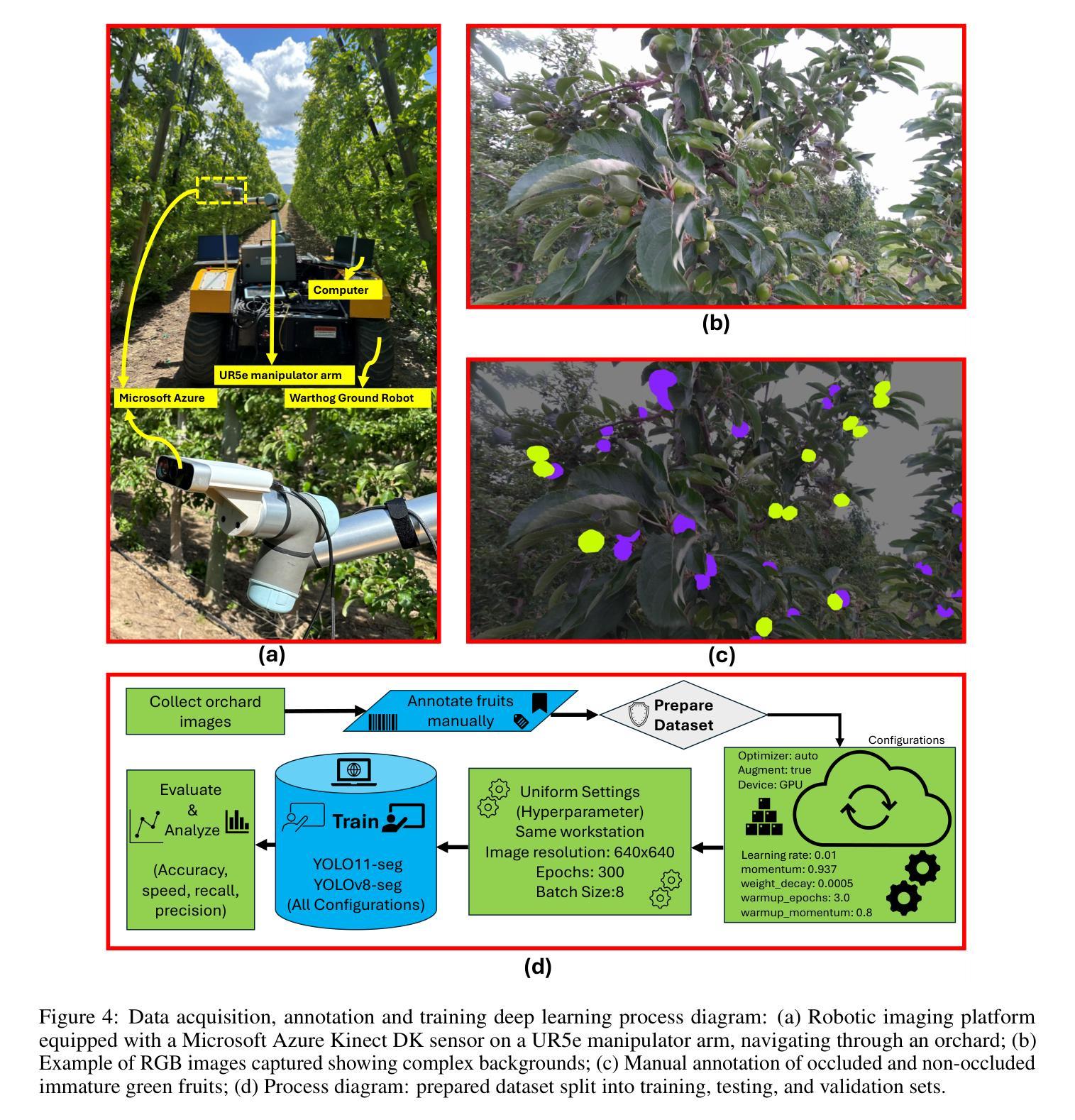
Comparing YOLO11 and YOLOv8 for instance segmentation of occluded and non-occluded immature green fruits in complex orchard environment
Authors:Ranjan Sapkota, Manoj Karkee
This study conducted a comprehensive performance evaluation on YOLO11 and YOLOv8, the latest in the “You Only Look Once” (YOLO) series, focusing on their instance segmentation capabilities for immature green apples in orchard environments. YOLO11n-seg achieved the highest mask precision across all categories with a notable score of 0.831, highlighting its effectiveness in fruit detection. YOLO11m-seg and YOLO11l-seg excelled in non-occluded and occluded fruitlet segmentation with scores of 0.851 and 0.829, respectively. Additionally, YOLO11x-seg led in mask recall for all categories, achieving a score of 0.815, with YOLO11m-seg performing best for non-occluded immature green fruitlets at 0.858 and YOLOv8x-seg leading the occluded category with 0.800. In terms of mean average precision at a 50% intersection over union (mAP@50), YOLO11m-seg consistently outperformed, registering the highest scores for both box and mask segmentation, at 0.876 and 0.860 for the “All” class and 0.908 and 0.909 for non-occluded immature fruitlets, respectively. YOLO11l-seg and YOLOv8l-seg shared the top box mAP@50 for occluded immature fruitlets at 0.847, while YOLO11m-seg achieved the highest mask mAP@50 of 0.810. Despite the advancements in YOLO11, YOLOv8n surpassed its counterparts in image processing speed, with an impressive inference speed of 3.3 milliseconds, compared to the fastest YOLO11 series model at 4.8 milliseconds, underscoring its suitability for real-time agricultural applications related to complex green fruit environments.
本研究对最新的“You Only Look Once”(YOLO)系列中的YOLO11和YOLOv8进行了全面的性能评估,重点关注它们在果园环境中对未成熟绿苹果的实例分割能力。YOLO11n-seg在所有类别中获得了最高的掩膜精度,达到了0.831的显著分数,突显其在水果检测方面的有效性。YOLO11m-seg和YOLO11l-seg在非遮挡和遮挡的幼果分割方面表现出色,分别获得了0.851和0.829的分数。此外,YOLO11x-seg在所有类别的掩膜召回率方面名列前茅,得分为0.815,其中YOLO11m-seg在非遮挡的未成熟绿苹上表现最佳,得分为0.858,而YOLOv8x-seg在遮挡类别中领先,得分为0.800。在50%交集上的平均精度均值(mAP@50)方面,YOLO11m-seg表现一直较好,在“全部”类别中,框和掩膜分割的最高分数分别为0.876和0.860,在未遮挡的未成熟果类中分别为0.908和0.909。YOLO11l-seg和YOLOv8l-seg在遮挡的未成熟果类中共享了最高的框mAP@50,得分为0.847,而YOLO11m-seg获得了最高的掩膜mAP@50,得分为0.810。尽管YOLO11有所进步,但在图像处理速度方面,YOLOv8n超越了其他模型,其推理速度达到了惊人的3.3毫秒,而最快的YOLO11系列模型为4.8毫秒,这表明YOLOv8n非常适合与复杂绿色水果环境相关的实时农业应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 Pages, 10 Figures, 3 Tables
摘要
本研究对YOLO系列的最新版本YOLO11和YOLOv8进行了全面的性能评估,重点考察它们在果园环境中对未成熟绿苹果的实例分割能力。YOLO11系列在各类别中均取得了最高的掩膜精度,其中YOLO11n-seg以0.831的显著分数脱颖而出,凸显其在果实检测方面的有效性。YOLO11m-seg和YOLO11l-seg在非遮挡和遮挡果实分割方面表现出色,分数分别为0.851和0.829。此外,YOLO11x-seg在所有类别中领先,在掩膜召回方面得分为0.815。在平均精度均值(mAP@50)方面,YOLO11m-seg表现卓越,在“所有”类别和非遮挡未成熟果实中分别获得0.876和0.860的高分。尽管YOLO1在多个评估中表现优异,但YOLOv8n在图像处理速度方面更胜一筹,其推理速度为3.3毫秒,与速度最快的YOLOi系列模型相比有显著优势,使其适用于复杂的绿色水果环境的实时农业应用。
要点提炼
- YOLO系列的最新模型YOLO11和YOLOv8在果实检测领域进行了全面的性能评估。
- YOLO11系列在果实掩膜精度方面表现最佳,特别在各类别中YOLO1ln-seg取得了显著成绩。
- YOLO1lm-seg和YOLOlxl-seg在非遮挡和遮挡条件下的果实分割表现优秀。
- YOLOll系列在掩膜召回方面表现出色,其中YOLOllx-seg在所有类别中领先。
- 在平均精度均值(mAP@50)评估中,YOLOllm-seg获得最高分数,显示出卓越的性能。
- 研究表明,尽管YOLOll具有许多优势,但YOLOv8n在图像处理速度方面更胜一筹,具有更快的推理速度。
点此查看论文截图

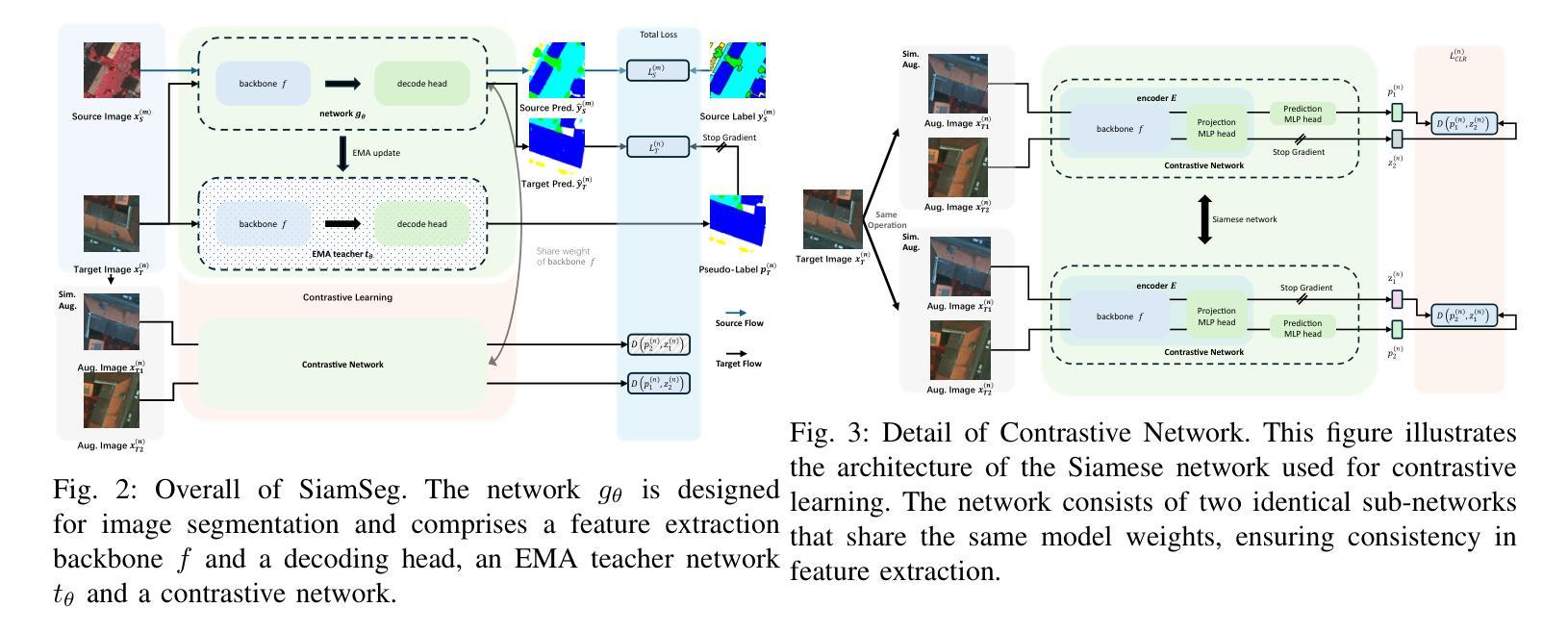
SiamSeg: Self-Training with Contrastive Learning for Unsupervised Domain Adaptation Semantic Segmentation in Remote Sensing
Authors:Bin Wang, Fei Deng, Shuang Wang, Wen Luo, Zhixuan Zhang, Peifan Jiang
Semantic segmentation of remote sensing (RS) images is a challenging yet essential task with broad applications. While deep learning, particularly supervised learning with large-scale labeled datasets, has significantly advanced this field, the acquisition of high-quality labeled data remains costly and time-intensive. Unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA) provides a promising alternative by enabling models to learn from unlabeled target domain data while leveraging labeled source domain data. Recent self-training (ST) approaches employing pseudo-label generation have shown potential in mitigating domain discrepancies. However, the application of ST to RS image segmentation remains underexplored. Factors such as variations in ground sampling distance, imaging equipment, and geographic diversity exacerbate domain shifts, limiting model performance across domains. In that case, existing ST methods, due to significant domain shifts in cross-domain RS images, often underperform. To address these challenges, we propose integrating contrastive learning into UDA, enhancing the model’s ability to capture semantic information in the target domain by maximizing the similarity between augmented views of the same image. This additional supervision improves the model’s representational capacity and segmentation performance in the target domain. Extensive experiments conducted on RS datasets, including Potsdam, Vaihingen, and LoveDA, demonstrate that our method, SimSeg, outperforms existing approaches, achieving state-of-the-art results. Visualization and quantitative analyses further validate SimSeg’s superior ability to learn from the target domain. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/woldier/SiamSeg.
遥感(RS)图像的语义分割是一项具有广泛应用挑战性的且必不可少的任务。尽管深度学习,特别是利用大规模标记数据集进行监督学习,已经显著推动了这一领域的发展,但获取高质量标记数据仍然成本高昂且耗时。无监督域自适应(UDA)提供了一种有前途的替代方案,使模型能够利用标记的源域数据的同时从未标记的目标域数据进行学习。最近采用伪标签生成的自训练(ST)方法显示出在减少域差异方面的潜力。然而,将ST应用于遥感图像分割仍然鲜有研究。诸如地面采样距离、成像设备和地理多样性的变化等因素加剧了域偏移,限制了模型在不同域之间的性能。在这种情况下,由于跨域遥感图像中的域偏移较大,现有的ST方法往往表现不佳。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出将对比学习整合到UDA中,通过最大化同一图像的增强视图之间的相似性,增强模型在目标域中捕获语义信息的能力。这种额外的监督提高了模型的表示能力和目标域的分割性能。在包括Potsdam、Vaihingen和LoveDA的遥感数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,我们的SimSeg方法优于现有方法,取得了最新结果。可视化和定量分析进一步验证了SimSeg从目标域学习的高级能力。代码公开在https://github.com/woldier/SiamSeg。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了遥感图像语义分割的挑战,包括跨域数据的高成本标注和领域差异问题。提出了一种结合对比学习和无监督域自适应的方法,通过最大化同一图像的不同视图之间的相似性,增强模型在目标域捕捉语义信息的能力。实验证明,该方法在多个遥感数据集上实现了最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像语义分割是一项具有挑战性的任务,但具有广泛的应用价值。
- 深度学习在遥感图像分割领域取得了显著进展,但标注高质量数据成本高昂且耗时。
- 无监督域自适应(UDA)提供了一种利用未标记目标域数据和标记源域数据的模型学习方法。
- 自训练(ST)方法通过伪标签生成具有减轻域差异潜力,但在遥感图像分割中应用有限。
- 领域漂移问题在遥感图像中尤为严重,现有自训练方法往往因跨域遥感图像的显著领域漂移而表现不佳。
- 结合对比学习可以增强模型在目标域捕捉语义信息的能力,通过最大化同一图像的不同视图之间的相似性来提高模型的表示能力和分割性能。
点此查看论文截图

Adapting Vision-Language Model with Fine-grained Semantics for Open-Vocabulary Segmentation
Authors:Yong Xien Chng, Xuchong Qiu, Yizeng Han, Kai Ding, Wan Ding, Gao Huang
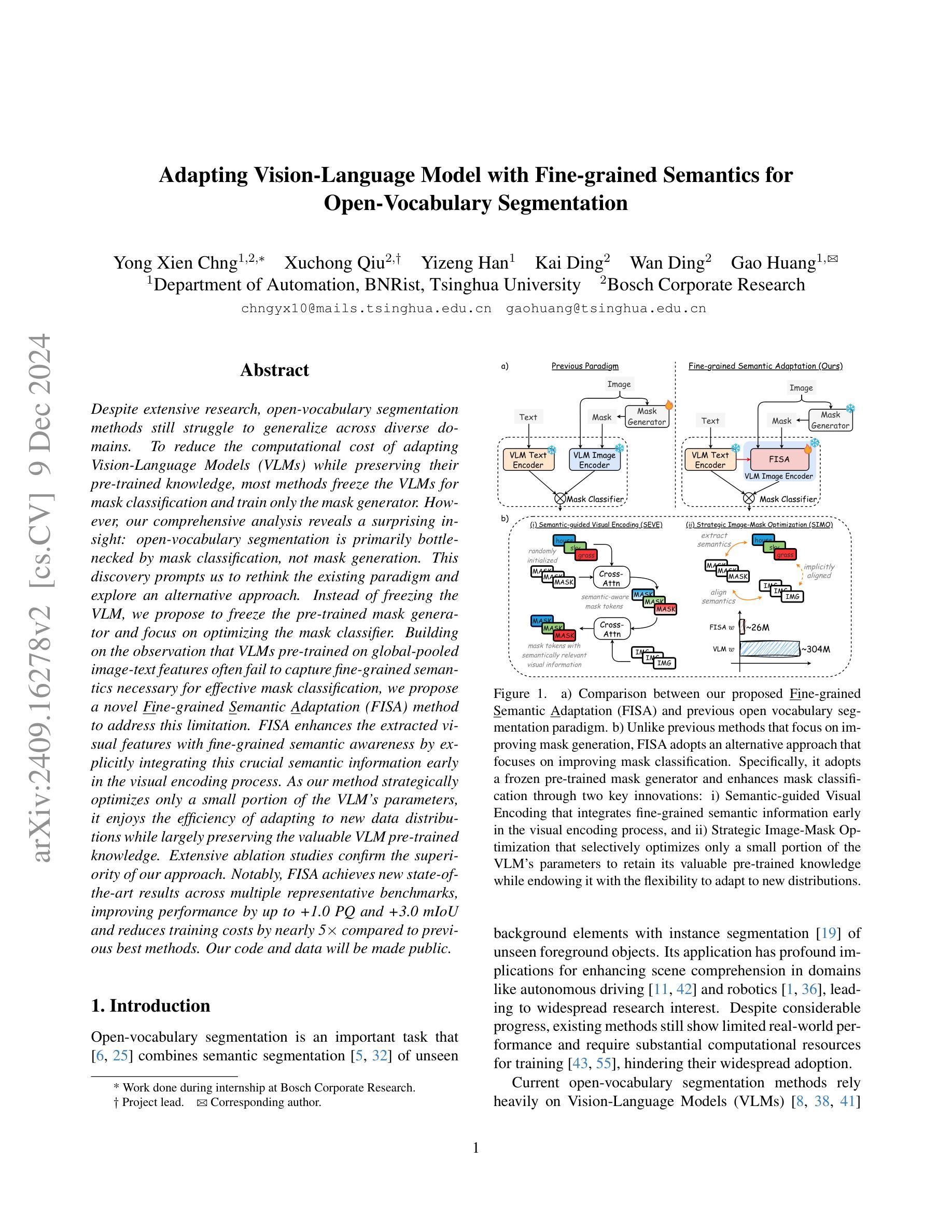
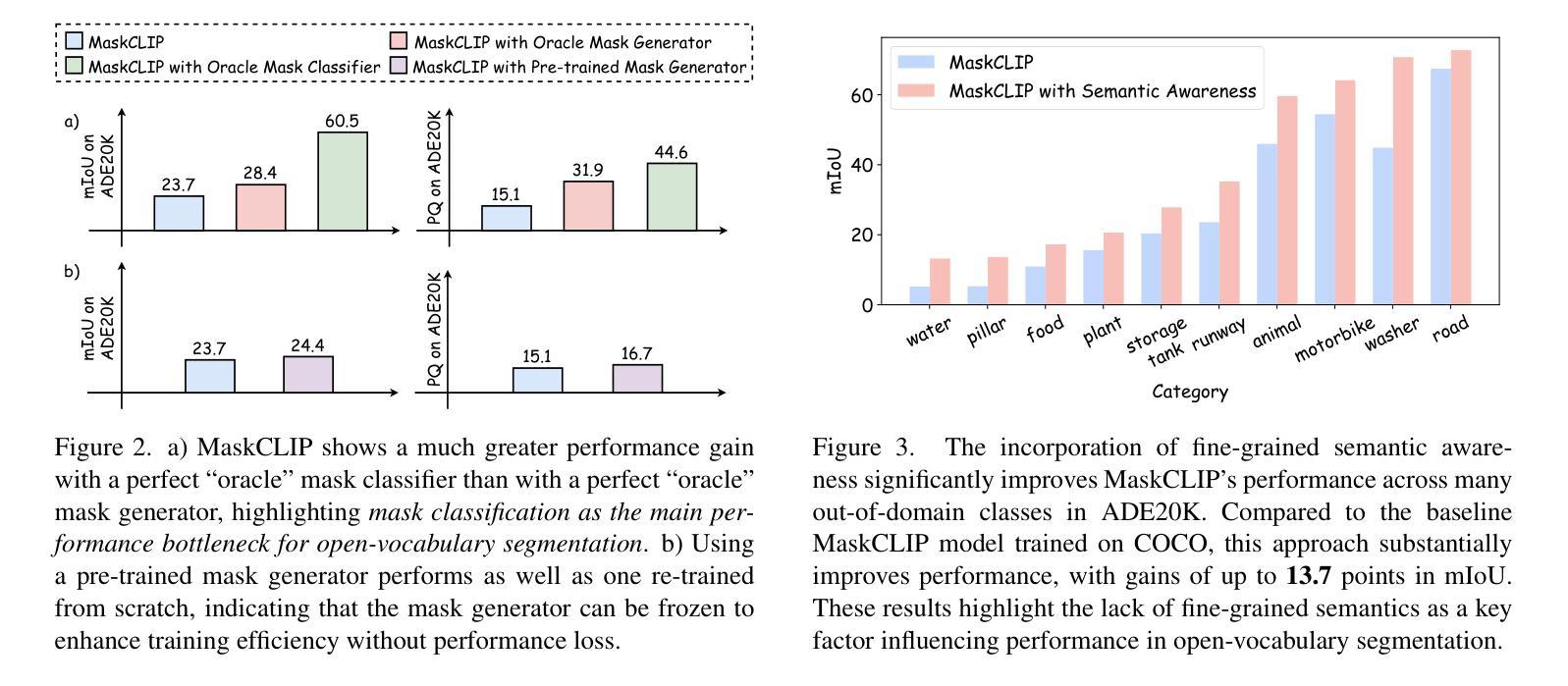
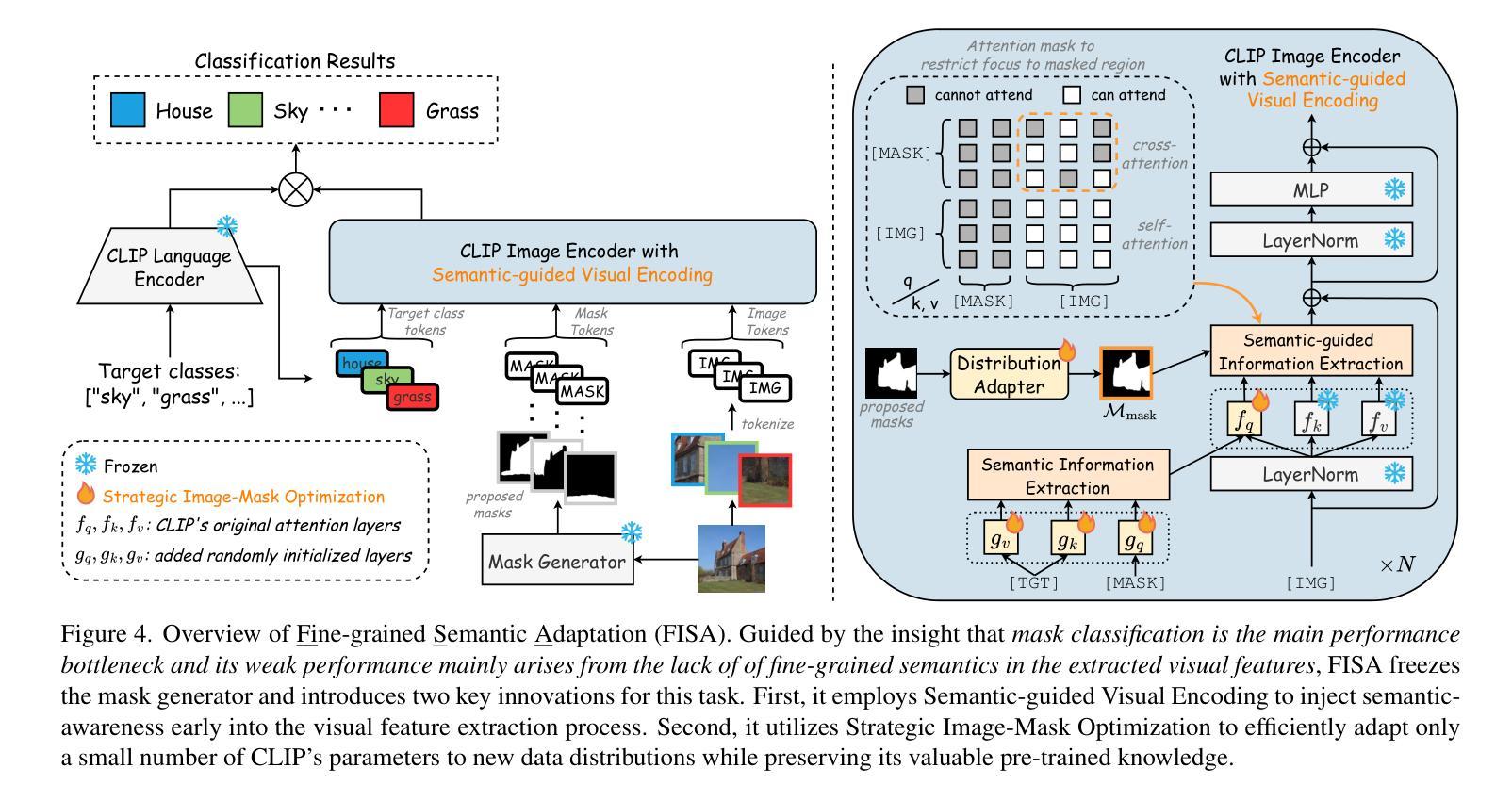
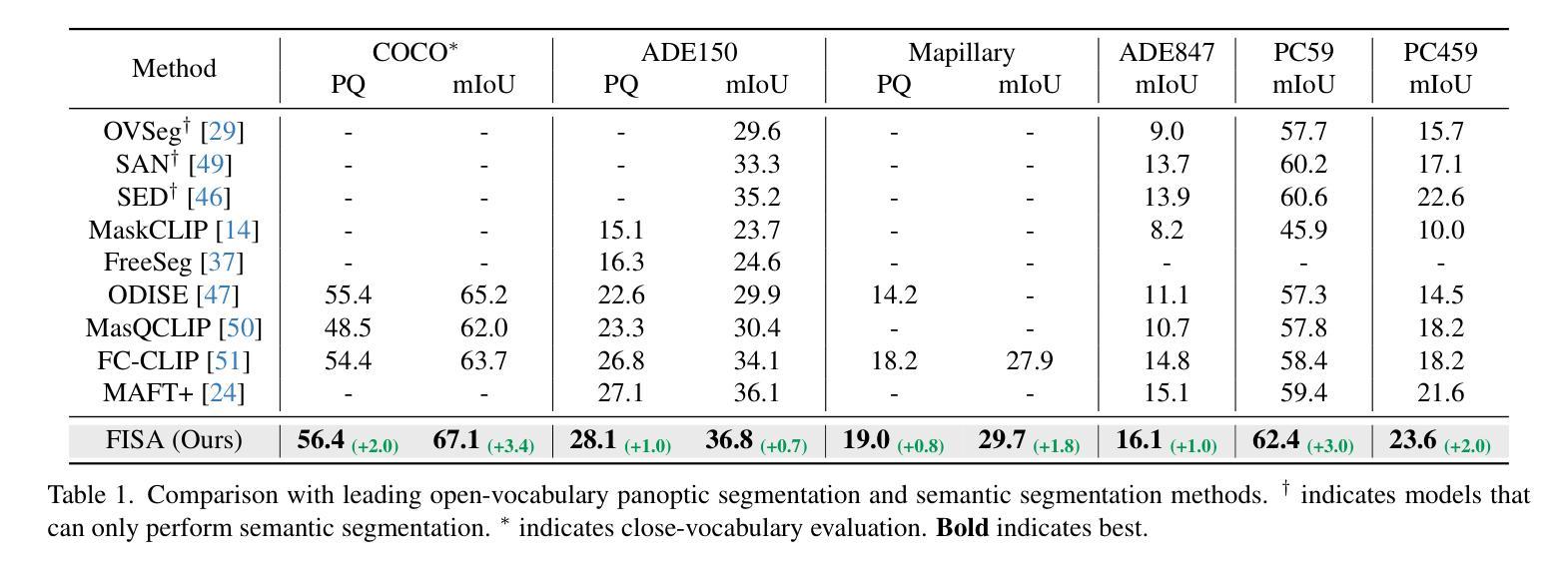
Despite extensive research, open-vocabulary segmentation methods still struggle to generalize across diverse domains. To reduce the computational cost of adapting Vision-Language Models (VLMs) while preserving their pre-trained knowledge, most methods freeze the VLMs for mask classification and train only the mask generator. However, our comprehensive analysis reveals a surprising insight: open-vocabulary segmentation is primarily bottlenecked by mask classification, not mask generation. This discovery prompts us to rethink the existing paradigm and explore an alternative approach. Instead of freezing the VLM, we propose to freeze the pre-trained mask generator and focus on optimizing the mask classifier. Building on the observation that VLMs pre-trained on global-pooled image-text features often fail to capture fine-grained semantics necessary for effective mask classification, we propose a novel Fine-grained Semantic Adaptation (FISA) method to address this limitation. FISA enhances the extracted visual features with fine-grained semantic awareness by explicitly integrating this crucial semantic information early in the visual encoding process. As our method strategically optimizes only a small portion of the VLM’s parameters, it enjoys the efficiency of adapting to new data distributions while largely preserving the valuable VLM pre-trained knowledge. Extensive ablation studies confirm the superiority of our approach. Notably, FISA achieves new state-of-the-art results across multiple representative benchmarks, improving performance by up to +1.0 PQ and +3.0 mIoU and reduces training costs by nearly 5x compared to previous best methods. Our code and data will be made public.
尽管进行了广泛的研究,开放词汇分割方法仍然难以在不同领域进行推广。为了降低适应视觉语言模型(VLM)的计算成本,同时保留其预训练知识,大多数方法会冻结VLM进行掩膜分类,并且只训练掩膜生成器。然而,我们的综合分析揭示了一个令人惊讶的见解:开放词汇分割主要受到掩膜分类的瓶颈限制,而不是掩膜生成。这一发现促使我们重新思考现有的范式,并探索一种替代方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 13 pages, 10 figures
摘要
该文本提出了在视觉语言模型中对开放词汇分割方法的瓶颈不在于面具生成,而在于面具分类。为解决此问题,提出一种新的方法,冻结预训练的面具生成器并专注于优化面具分类器。为此引入了一种名为“精细语义适应”(FISA)的方法,通过早期在视觉编码过程中明确集成关键语义信息,增强提取的视觉特征的精细语义意识。由于该方法仅优化VLM一小部分参数,因此在适应新数据分布时保持了高效性,同时保留了宝贵的VLM预训练知识。经过广泛的消融研究,证实了该方法在多个代表性基准测试上的优越性。尤其是FISA相较于以前最佳方法取得了+1.0 PQ和+3.0 mIoU的性能提升,并将训练成本降低了近5倍。我们的代码和数据将公开。
关键见解
- 开放词汇分割方法的瓶颈在于面具分类而非面具生成。
- 提出冻结预训练的面具生成器并优化面具分类器的策略。
- 介绍了一种名为“精细语义适应”(FISA)的方法,增强了视觉特征的精细语义意识。
- FISA通过早期集成关键语义信息在视觉编码过程中提高了性能。
- FISA方法仅优化VLM一小部分参数,保留预训练知识的同时适应新数据分布。
- 经过消融研究证实FISA方法的优越性。
点此查看论文截图
PolarBEVDet: Exploring Polar Representation for Multi-View 3D Object Detection in Bird’s-Eye-View
Authors:Zichen Yu, Quanli Liu, Wei Wang, Liyong Zhang, Xiaoguang Zhao
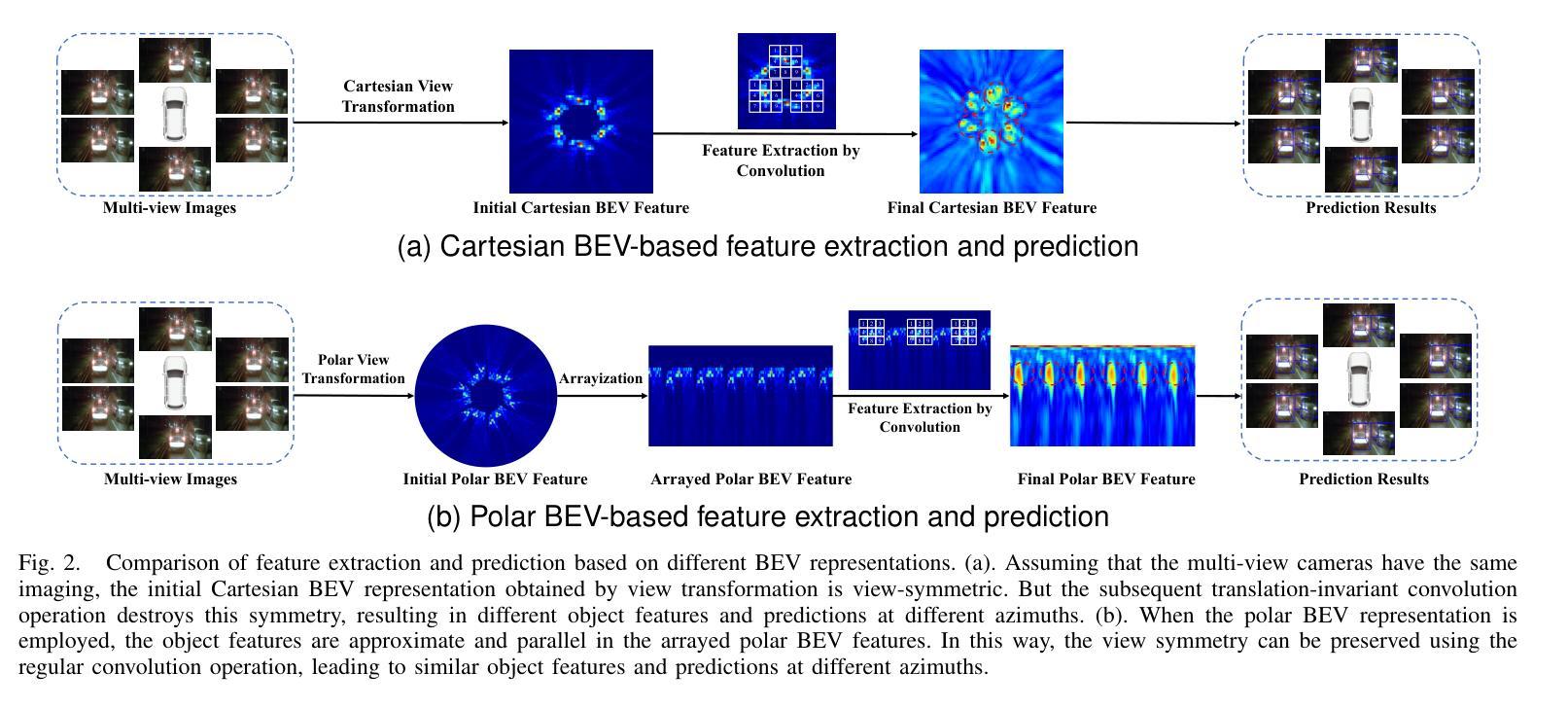
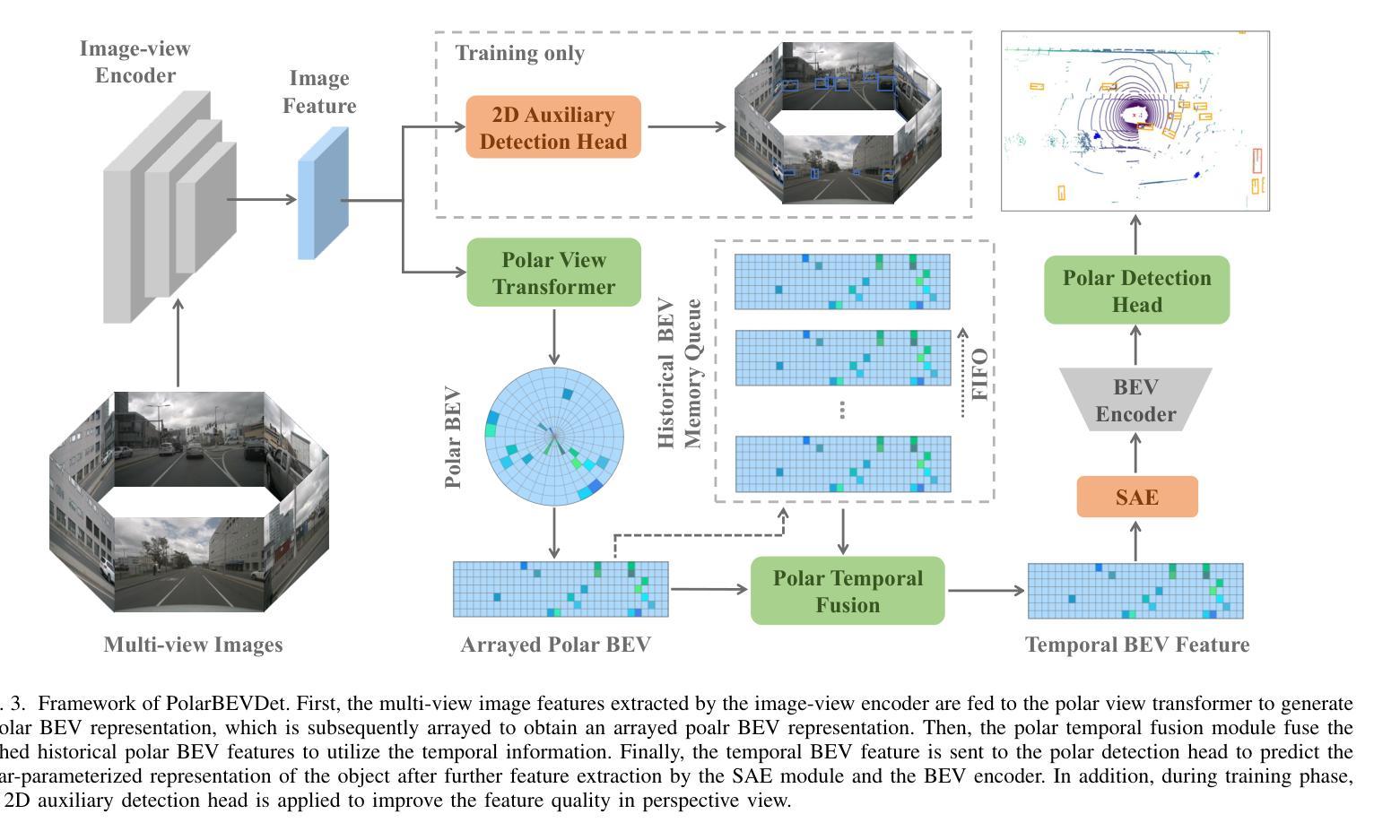
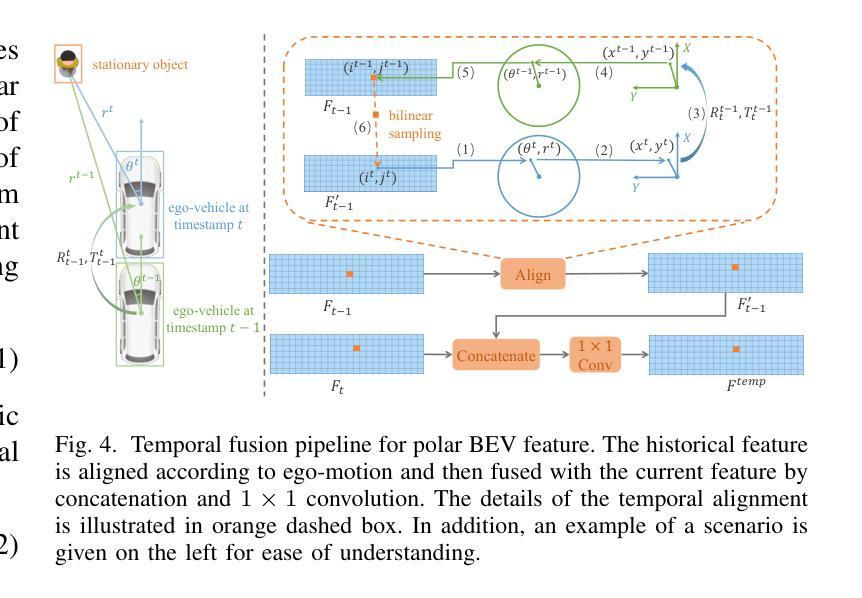
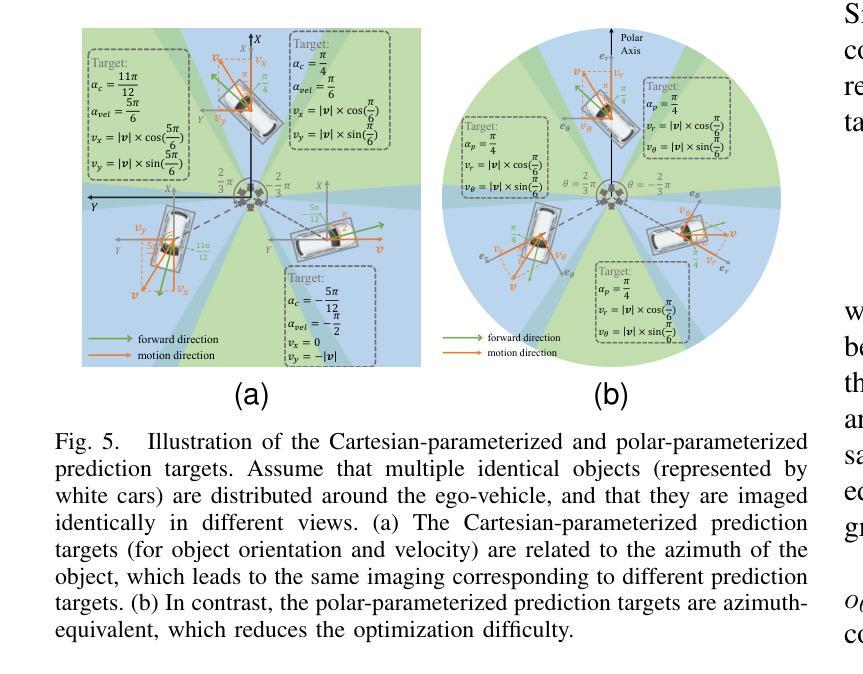
Recently, LSS-based multi-view 3D object detection provides an economical and deployment-friendly solution for autonomous driving. However, all the existing LSS-based methods transform multi-view image features into a Cartesian Bird’s-Eye-View(BEV) representation, which does not take into account the non-uniform image information distribution and hardly exploits the view symmetry. In this paper, in order to adapt the image information distribution and preserve the view symmetry by regular convolution, we propose to employ the polar BEV representation to substitute the Cartesian BEV representation. To achieve this, we elaborately tailor three modules: a polar view transformer to generate the polar BEV representation, a polar temporal fusion module for fusing historical polar BEV features and a polar detection head to predict the polar-parameterized representation of the object. In addition, we design a 2D auxiliary detection head and a spatial attention enhancement module to improve the quality of feature extraction in perspective view and BEV, respectively. Finally, we integrate the above improvements into a novel multi-view 3D object detector, PolarBEVDet. Experiments on nuScenes show that PolarBEVDet achieves the superior performance. The code is available at https://github.com/Yzichen/PolarBEVDet.git.(This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication. Copyright may be transferred without notice, after which this version may no longer be accessible)
近期,基于LSS的多视角3D目标检测为自动驾驶提供了一种经济且易于部署的解决方案。然而,现有的所有基于LSS的方法都将多视角图像特征转换为笛卡尔鸟瞰(BEV)表示,这种方法没有考虑到图像信息分布的不均匀性,且几乎不能利用视角对称性。在本文中,为了适应图像信息分布并保留常规卷积的视图对称性,我们提出使用极坐标BEV表示来替代笛卡尔BEV表示。为此,我们精心设计了三个模块:极视图变换器,用于生成极坐标BEV表示;极时间融合模块,用于融合历史极BEV特征;以及极检测头,用于预测对象的极参数表示。此外,我们设计了一个2D辅助检测头和空间注意力增强模块,分别提高了透视图和BEV的特征提取质量。最后,我们将上述改进整合到新型多视角3D目标检测器PolarBEVDet中。在nuScenes上的实验表明,PolarBEVDet达到了卓越的性能。代码可访问https://github.com/Yzichen/PolarBEVDet.git。(这项工作已提交至IEEE以待发表。在版权转让通知后,此版本可能不再可用)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
基于LSS的多视角3D对象检测为自动驾驶提供了经济且易于部署的解决方案。但现有方法将多视角图像特征转换为笛卡尔鸟瞰图表示,忽略了非均匀图像信息分布,难以利用视角对称性。本文提出使用极坐标鸟瞰图表示替代笛卡尔鸟瞰图表示,为此精心设计三个模块:极视角变换器生成极坐标鸟瞰图表示、极时序融合模块融合历史极坐标鸟瞰图特征、极检测头预测对象的极参数表示。此外,设计了一个二维辅助检测头和空间注意力增强模块,以提高透视图和鸟瞰图特征提取的质量。最终将上述改进整合到新型多视角三维目标检测器PolarBEVDet中,在nuScenes上的实验表明其性能卓越。
Key Takeaways
- LSS为基础的多视角3D目标检测为自动驾驶提供了有效解决方案。
- 现有方法使用笛卡尔鸟瞰图表示存在信息分布不均和视角对称性利用不足的问题。
- 引入极坐标鸟瞰图表示法,以更好地适应图像信息分布并保留视角对称性。
- 包括三个核心模块:极视角变换器、极时序融合模块和极检测头。
- 设计二维辅助检测头和空间注意力增强模块提升特征提取质量。
- 新型检测器PolarBEVDet集成了上述改进,并在nuScenes上表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

A Review of Human-Object Interaction Detection
Authors:Yuxiao Wang, Qiwei Xiong, Yu Lei, Weiying Xue, Qi Liu, Zhenao Wei
Human-object interaction (HOI) detection plays a key role in high-level visual understanding, facilitating a deep comprehension of human activities. Specifically, HOI detection aims to locate the humans and objects involved in interactions within images or videos and classify the specific interactions between them. The success of this task is influenced by several key factors, including the accurate localization of human and object instances, as well as the correct classification of object categories and interaction relationships. This paper systematically summarizes and discusses the recent work in image-based HOI detection. First, the mainstream datasets involved in HOI relationship detection are introduced. Furthermore, starting with two-stage methods and end-to-end one-stage detection approaches, this paper comprehensively discusses the current developments in image-based HOI detection, analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of these two methods. Additionally, the advancements of zero-shot learning, weakly supervised learning, and the application of large-scale language models in HOI detection are discussed. Finally, the current challenges in HOI detection are outlined, and potential research directions and future trends are explored.
人机交互(HOI)检测在高层次视觉理解中扮演着关键角色,有助于对人类活动进行深度学习理解。具体而言,HOI检测的目标是定位图像或视频中参与交互的人和物体,并分类它们之间的特定交互。该任务的成功受到几个关键因素的影响,包括人和物体实例的准确定位,以及物体类别和交互关系的正确分类。本文系统地总结和讨论了基于图像的HOI检测的近期工作。首先,介绍了HOI关系检测涉及的主流数据集。此外,本文综合讨论了基于图像的HOI检测的当前发展,从两阶段方法和端到端单阶段检测方法开始,分析了这两种方法的优缺点。另外,还讨论了零样本学习、弱监督学习以及大规模语言模型在HOI检测中的应用。最后,概述了HOI检测当前的挑战,并探讨了潜在的研究方向和未来趋势。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期关于基于图像的HOI检测的研究总结。文章介绍了主流数据集,探讨了从两阶段方法到端到端的一阶段检测方法的最新进展,并分析了两者优缺点。此外,还讨论了零样本学习、弱监督学习和大规模语言模型在HOI检测中的应用。最后,文章指出了当前面临的挑战和潜在的研究方向及未来趋势。
Key Takeaways
- HOI检测在高层次视觉理解中扮演重要角色,旨在定位图像或视频中人类与物体间的交互,并分类它们之间的特定交互。
- 主流数据集在HOI关系检测中的应用被介绍。
- 当前图像基于HOI检测的方法包括两阶段方法和端到端的一阶段检测方法,两者各有优缺点。
- 零样本学习、弱监督学习和大规模语言模型在HOI检测中的应用得到探讨。
- HOI检测当前面临一些挑战,如准确的人类和物体实例定位、物体类别和交互关系的正确分类等。
- 文章指出了未来HOI检测的研究方向和趋势,包括技术方法的改进、新数据集和评估标准的探索等。
点此查看论文截图

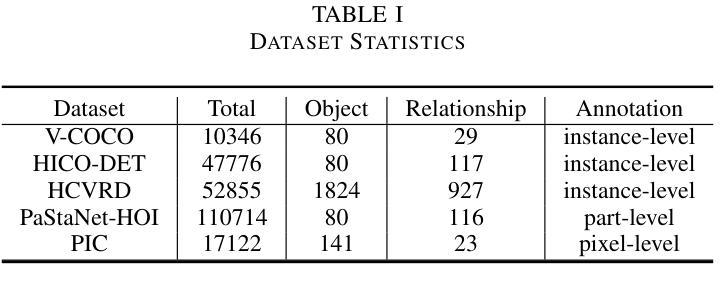
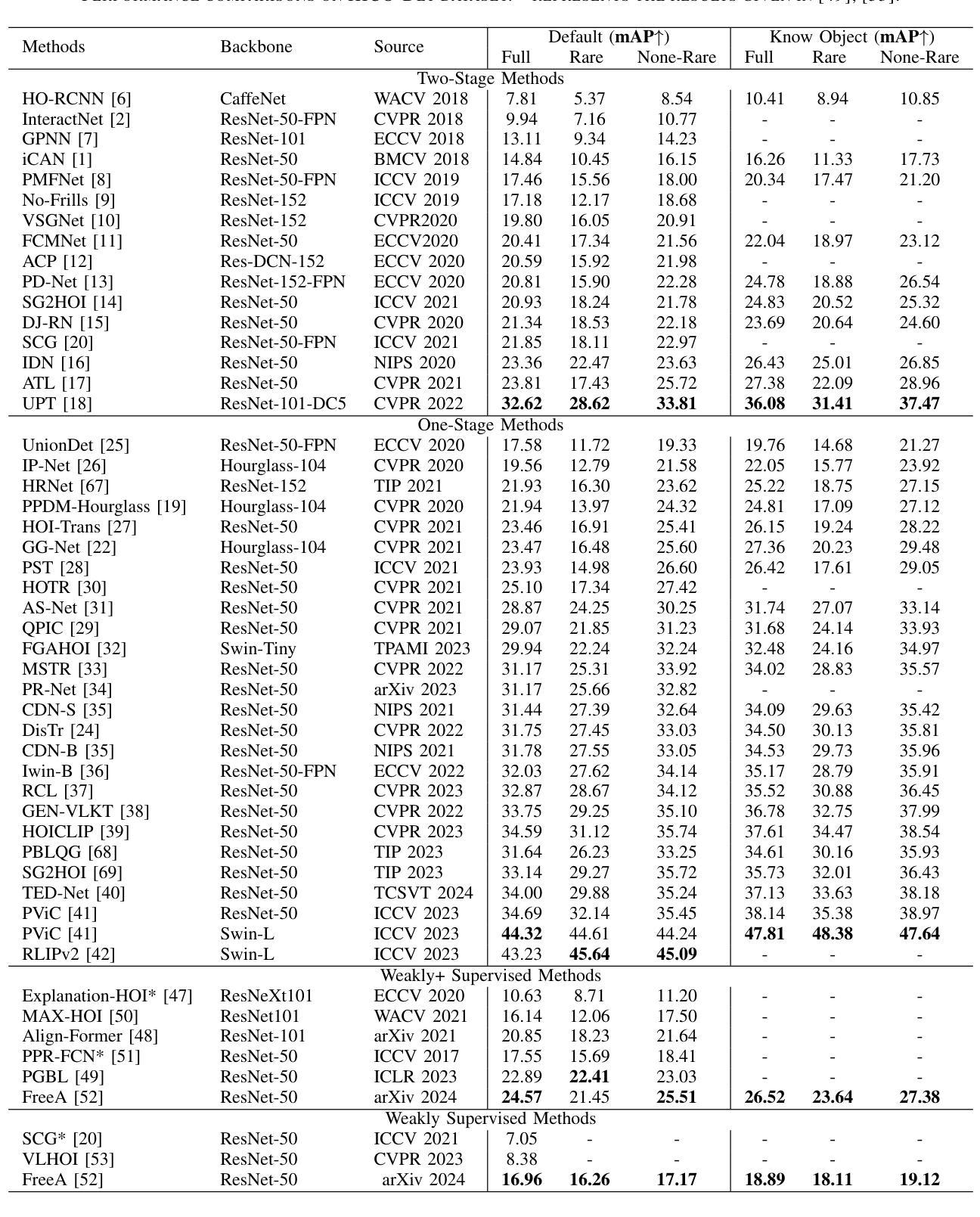
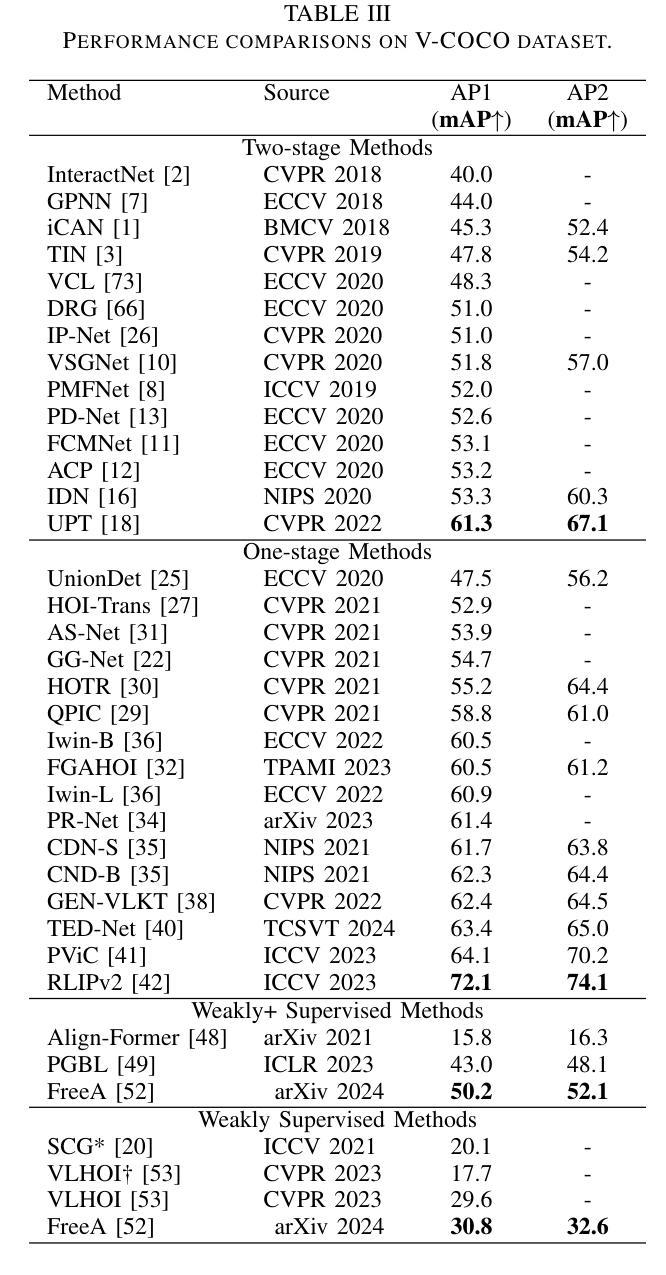
PADetBench: Towards Benchmarking Physical Attacks against Object Detection
Authors:Jiawei Lian, Jianhong Pan, Lefan Wang, Yi Wang, Lap-Pui Chau, Shaohui Mei
Physical attacks against object detection have gained increasing attention due to their significant practical implications. However, conducting physical experiments is extremely time-consuming and labor-intensive. Moreover, physical dynamics and cross-domain transformation are challenging to strictly regulate in the real world, leading to unaligned evaluation and comparison, severely hindering the development of physically robust models. To accommodate these challenges, we explore utilizing realistic simulation to thoroughly and rigorously benchmark physical attacks with fairness under controlled physical dynamics and cross-domain transformation. This resolves the problem of capturing identical adversarial images that cannot be achieved in the real world. Our benchmark includes 20 physical attack methods, 48 object detectors, comprehensive physical dynamics, and evaluation metrics. We also provide end-to-end pipelines for dataset generation, detection, evaluation, and further analysis. In addition, we perform 8064 groups of evaluation based on our benchmark, which includes both overall evaluation and further detailed ablation studies for controlled physical dynamics. Through these experiments, we provide in-depth analyses of physical attack performance and physical adversarial robustness, draw valuable observations, and discuss potential directions for future research. Codebase: https://github.com/JiaweiLian/Benchmarking_Physical_Attack
针对目标检测的物理攻击因其在实际应用中的重要意义而备受关注。然而,进行物理实验极其耗费时间和人力。此外,在真实世界中,物理动态和跨域转换的严格调控具有挑战性,导致评估与比较的不对齐,严重阻碍物理稳健型模型的发展。为了应对这些挑战,我们探索利用现实仿真来在受控的物理动态和跨域转换下,公平、全面、严格地评估物理攻击。这解决了在真实世界中无法捕获相同对抗图像的问题。我们的基准测试包括20种物理攻击方法、48种目标检测器、全面的物理动态和评估指标。我们还提供了用于数据集生成、检测、评估和进一步分析的端到端管道。此外,我们基于基准测试进行了8064组评估,包括整体评估和受控物理动态的进一步详细消融研究。通过这些实验,我们对物理攻击性能和物理对抗稳健性进行了深入分析,观察并讨论了未来研究潜在方向。代码库:https://github.com/JiaweiLian/Benchmarking_Physical_Attack
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本主要介绍了针对物理攻击下的目标检测挑战,通过利用现实仿真技术来建立基准测试,模拟物理攻击并控制物理动态和跨域转换,以公平地评估模型在现实世界中的鲁棒性。该基准测试包括多种物理攻击方法和目标检测器,提供数据集生成、检测、评估和进一步分析的端到端流程。通过实验,对物理攻击性能和物理对抗稳健性进行了深入分析,为未来的研究提供了潜在方向。
Key Takeaways
- 物理攻击对目标检测的挑战在于现实世界中的时间消耗和劳动力需求大,且物理动态和跨域转换难以严格调控。
- 利用现实仿真技术建立基准测试,以模拟物理攻击并控制物理动态和跨域转换,从而实现公平评估。
- 基准测试包含多种物理攻击方法和目标检测器,提供全面的评估指标。
- 提供数据集生成、检测、评估和进一步分析的端到端流程。
- 通过实验对物理攻击性能和物理对抗稳健性进行了深入分析。
- 该研究提供的基准测试有助于深入了解物理攻击的影响并推动相关研究的进一步发展。
点此查看论文截图

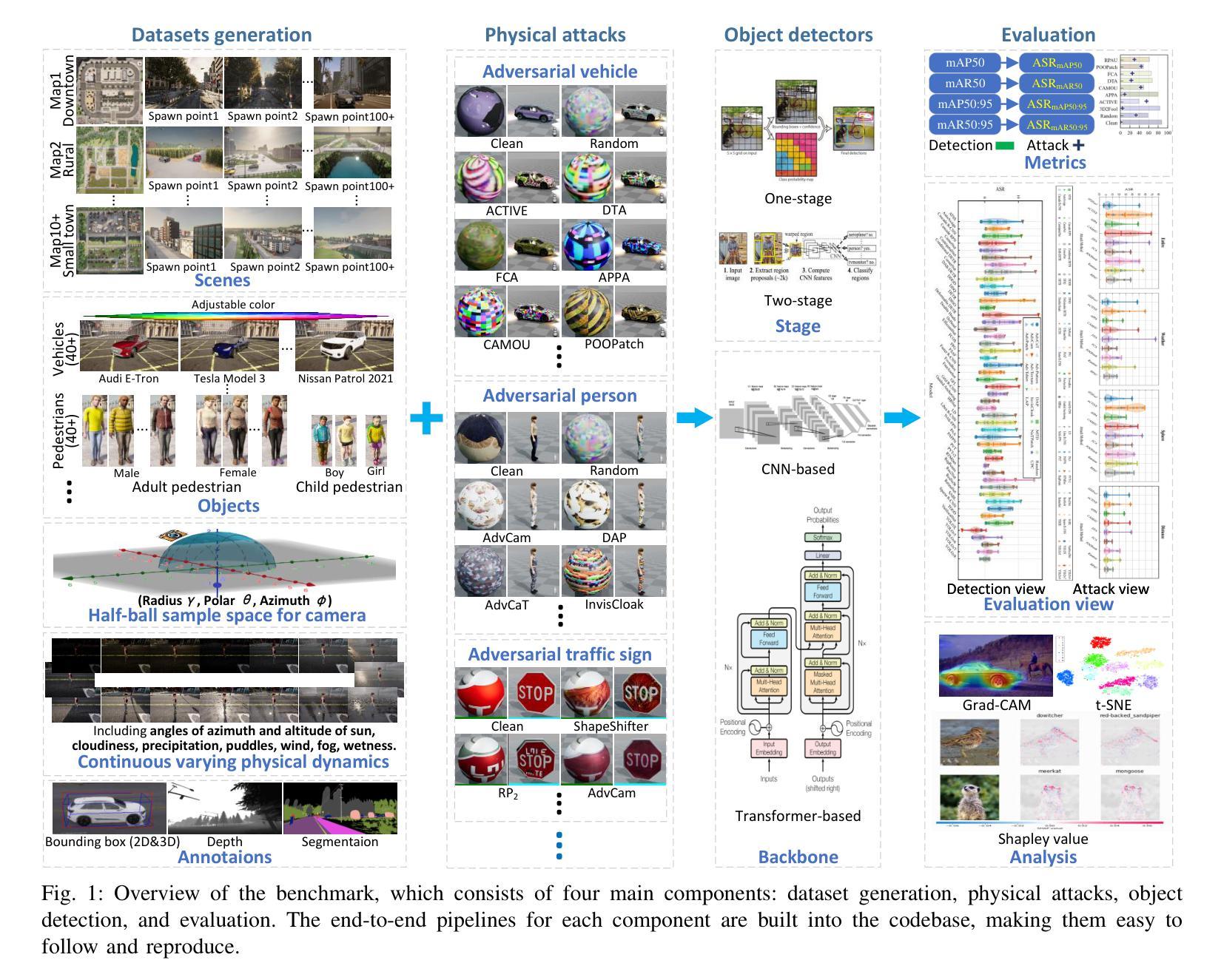




Adaptive Patch Contrast for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Wangyu Wu, Tianhong Dai, Zhenhong Chen, Xiaowei Huang, Jimin Xiao, Fei Ma, Renrong Ouyang
Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) using only image-level labels has gained significant attention due to its cost-effectiveness. The typical framework involves using image-level labels as training data to generate pixel-level pseudo-labels with refinements. Recently, methods based on Vision Transformers (ViT) have demonstrated superior capabilities in generating reliable pseudo-labels, particularly in recognizing complete object regions, compared to CNN methods. However, current ViT-based approaches have some limitations in the use of patch embeddings, being prone to being dominated by certain abnormal patches, as well as many multi-stage methods being time-consuming and lengthy in training, thus lacking efficiency. Therefore, in this paper, we introduce a novel ViT-based WSSS method named \textit{Adaptive Patch Contrast} (APC) that significantly enhances patch embedding learning for improved segmentation effectiveness. APC utilizes an Adaptive-K Pooling (AKP) layer to address the limitations of previous max pooling selection methods. Additionally, we propose a Patch Contrastive Learning (PCL) to enhance patch embeddings, thereby further improving the final results. Furthermore, we improve upon the existing multi-stage training framework without CAM by transforming it into an end-to-end single-stage training approach, thereby enhancing training efficiency. The experimental results show that our approach is effective and efficient, outperforming other state-of-the-art WSSS methods on the PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 dataset within a shorter training duration.
使用仅图像级标签的弱监督语义分割(WSSS)因其成本效益而备受关注。典型的框架是使用图像级标签作为训练数据,通过不断优化来生成像素级伪标签。最近,基于视觉转换器(ViT)的方法在生成可靠的伪标签方面表现出了出色的能力,特别是在识别完整的对象区域方面优于CNN方法。然而,当前的ViT方法在使用补丁嵌入时存在一些局限性,容易受到某些异常补丁的主导,而且许多多阶段方法在训练和推理上耗时较长,缺乏效率。因此,本文介绍了一种新型的基于ViT的WSSS方法,名为自适应补丁对比(APC),该方法显著增强了补丁嵌入学习,提高了分割效果。APC利用自适应K池化(AKP)层解决了以前最大池化选择方法的局限性。此外,我们提出了补丁对比学习(PCL)来增强补丁嵌入,从而进一步提高最终结果。此外,我们改进了现有的多阶段训练框架,将其转变为端到端的单阶段训练方法,提高了训练效率。实验结果表明,我们的方法有效且高效,在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上超越了其他最先进的WSSS方法,并且在较短的训练时间内取得了良好效果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the EAAI Journal
Summary
基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的弱监督语义分割(WSSS)方法通过使用图像级别的标签生成可靠的伪标签来识别完整的对象区域,表现出卓越的性能。然而,当前ViT方法存在局限,如易受异常补丁主导以及多阶段方法训练时间长、效率低下。本文提出一种名为“自适应补丁对比”(APC)的新型ViT-based WSSS方法,通过自适应K池化(AKP)层和补丁对比学习(PCL)增强补丁嵌入学习,提高分割效果。此外,我们还改进了现有的多阶段训练框架,将其转变为端到端的单阶段训练方式,提高了训练效率。实验结果表明,我们的方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上表现优异,训练时间短。
Key Takeaways
- WSSS利用图像级标签生成像素级伪标签进行训练,成本效益显著。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)在生成可靠伪标签方面表现出卓越性能,特别是在识别完整对象区域方面。
- 当前ViT方法存在局限,易受到异常补丁主导以及训练时间长、效率低下的问题。
- 本文提出的“自适应补丁对比”(APC)方法通过自适应K池化(AKP)层和补丁对比学习(PCL)增强补丁嵌入学习,提高分割效果。
- APC改进了现有的多阶段训练框架,采用端到端的单阶段训练方式,提高了训练效率。
- 实验结果表明,APC方法在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO 2014数据集上表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

BiCo-Fusion: Bidirectional Complementary LiDAR-Camera Fusion for Semantic- and Spatial-Aware 3D Object Detection
Authors:Yang Song, Lin Wang
3D object detection is an important task that has been widely applied in autonomous driving. To perform this task, a new trend is to fuse multi-modal inputs, i.e., LiDAR and camera. Under such a trend, recent methods fuse these two modalities by unifying them in the same 3D space. However, during direct fusion in a unified space, the drawbacks of both modalities (LiDAR features struggle with detailed semantic information and the camera lacks accurate 3D spatial information) are also preserved, diluting semantic and spatial awareness of the final unified representation. To address the issue, this letter proposes a novel bidirectional complementary LiDAR-camera fusion framework, called BiCo-Fusion that can achieve robust semantic- and spatial-aware 3D object detection. The key insight is to fuse LiDAR and camera features in a bidirectional complementary way to enhance the semantic awareness of the LiDAR and the 3D spatial awareness of the camera. The enhanced features from both modalities are then adaptively fused to build a semantic- and spatial-aware unified representation. Specifically, we introduce Pre-Fusion consisting of a Voxel Enhancement Module (VEM) to enhance the semantic awareness of voxel features from 2D camera features and Image Enhancement Module (IEM) to enhance the 3D spatial awareness of camera features from 3D voxel features. We then introduce Unified Fusion (U-Fusion) to adaptively fuse the enhanced features from the last stage to build a unified representation. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our BiCo-Fusion against the prior arts. Project page: https://t-ys.github.io/BiCo-Fusion/.
三维物体检测是一项在自动驾驶中广泛应用的重要任务。为了完成这项任务,目前的一个新趋势是融合多模态输入,即激光雷达和摄像机。在这种趋势下,最近的方法通过将这两种模态统一到同一三维空间中进行融合。然而,在统一空间中进行直接融合时,两种模态的缺点(激光雷达特征难以获取详细的语义信息,而摄像机缺乏准确的三维空间信息)也会被保留下来,导致最终统一表示的语义和空间感知能力减弱。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 5 figures
Summary
该文探讨了三维物体检测在自动驾驶领域的重要性,并指出当前融合激光雷达和相机进行多模态输入的新趋势。然而,直接在同一三维空间中进行融合会导致两种模态的缺点(激光雷达特征缺乏详细语义信息,相机缺乏准确的3D空间信息)都被保留下来,影响最终统一表示的语义和空间感知能力。为解决这一问题,本文提出了一种双向互补的激光雷达-相机融合框架——BiCo-Fusion,该框架能够实现稳健的语义和空间感知三维物体检测。通过双向互补的方式融合激光雷达和相机特征,增强激光雷达的语义感知能力和相机的三维空间感知能力。然后自适应地融合来自两个模态的增强特征,构建具有语义和空间感知的统一表示。实验证明,该方法优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 3D物体检测在自动驾驶中扮演重要角色。
- 当前趋势是融合多模态输入(如激光雷达和相机)进行三维物体检测。
- 直接在统一空间融合两种模态会导致语义和空间感知的缺陷。
- 双向互补的激光雷达-相机融合框架——BiCo-Fusion被提出以解决这个问题。
- BiCo-Fusion增强了激光雷达的语义感知和相机的三维空间感知能力。
- 通过自适应融合增强特征,构建具有语义和空间感知的统一表示。
点此查看论文截图

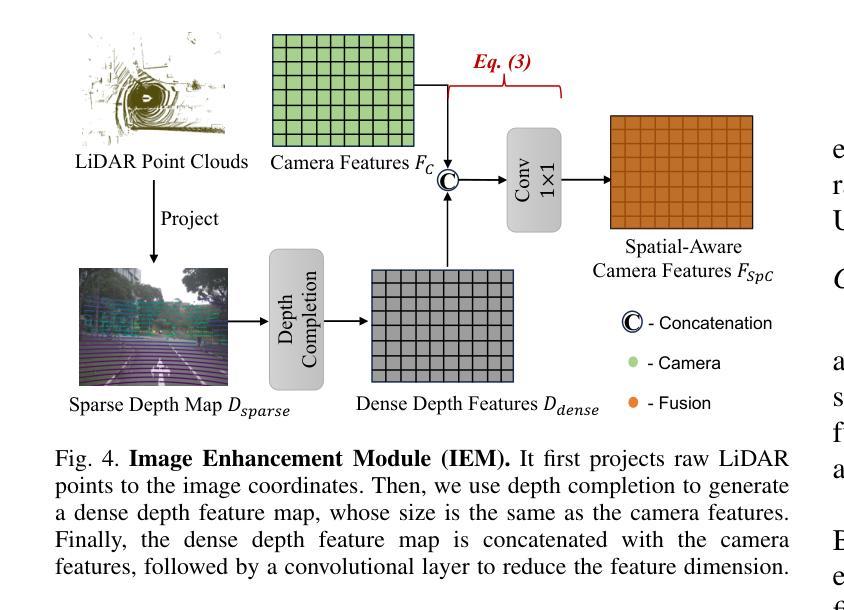
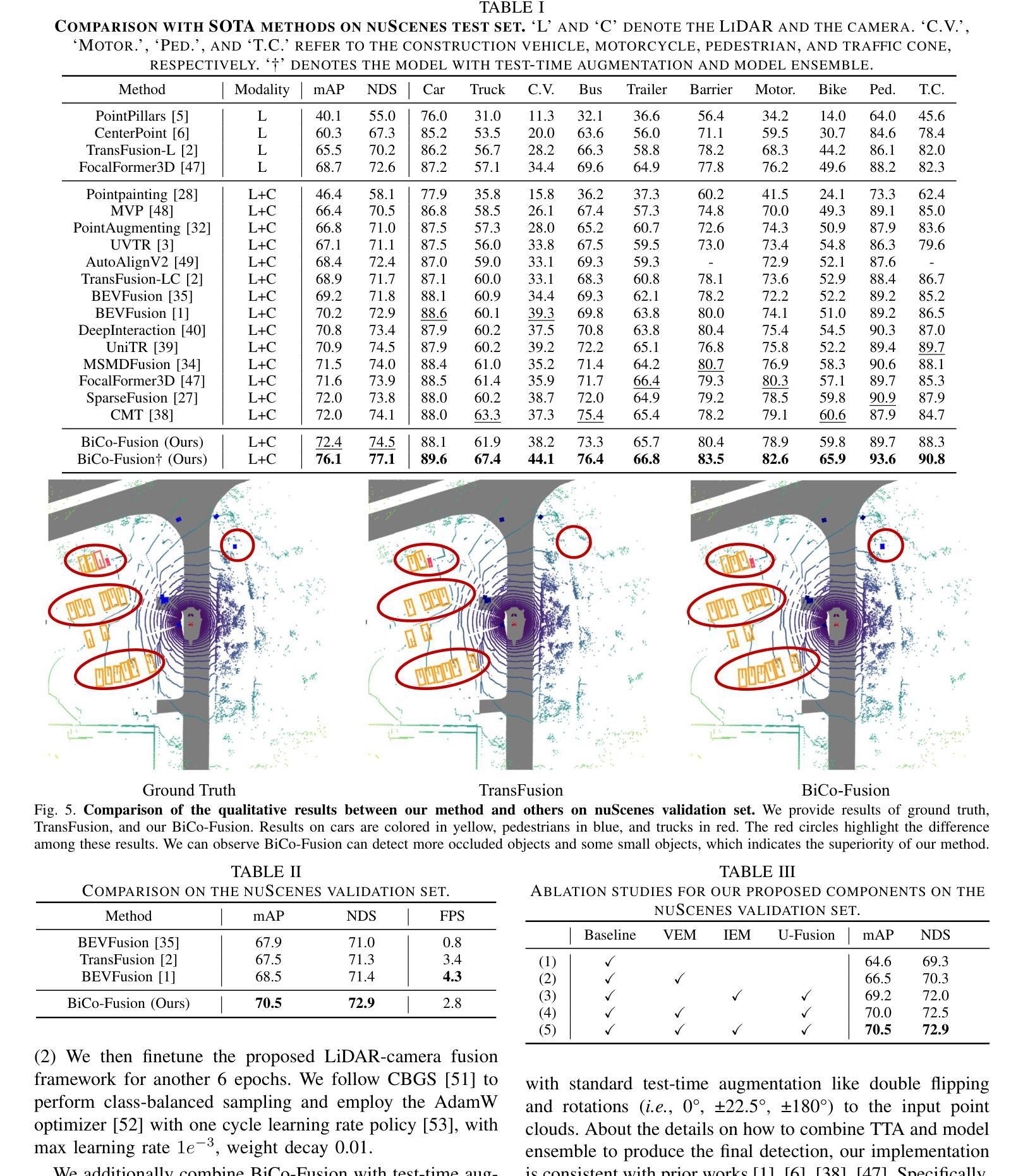
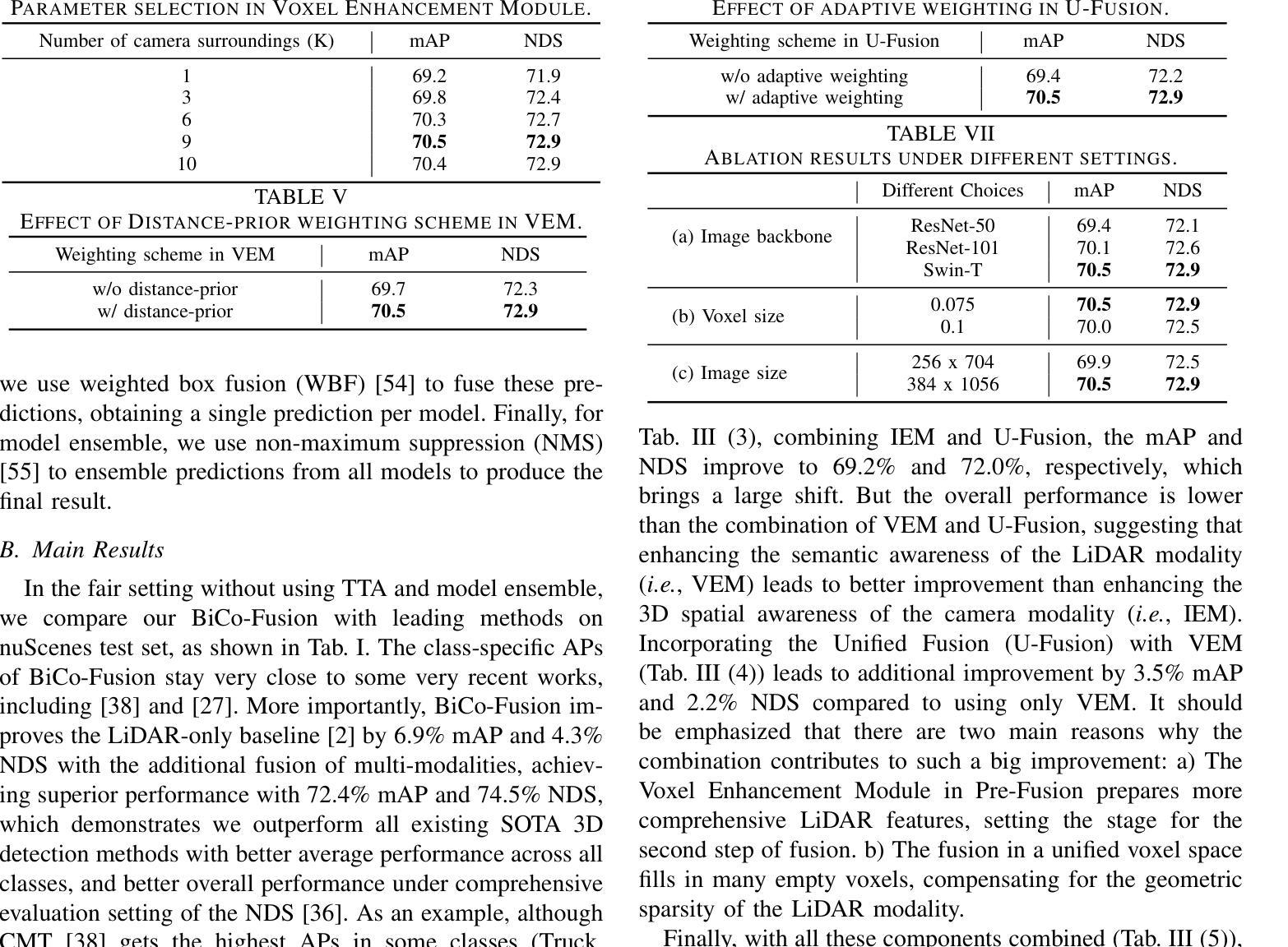
SemFlow: Binding Semantic Segmentation and Image Synthesis via Rectified Flow
Authors:Chaoyang Wang, Xiangtai Li, Lu Qi, Henghui Ding, Yunhai Tong, Ming-Hsuan Yang
Semantic segmentation and semantic image synthesis are two representative tasks in visual perception and generation. While existing methods consider them as two distinct tasks, we propose a unified framework (SemFlow) and model them as a pair of reverse problems. Specifically, motivated by rectified flow theory, we train an ordinary differential equation (ODE) model to transport between the distributions of real images and semantic masks. As the training object is symmetric, samples belonging to the two distributions, images and semantic masks, can be effortlessly transferred reversibly. For semantic segmentation, our approach solves the contradiction between the randomness of diffusion outputs and the uniqueness of segmentation results. For image synthesis, we propose a finite perturbation approach to enhance the diversity of generated results without changing the semantic categories. Experiments show that our SemFlow achieves competitive results on semantic segmentation and semantic image synthesis tasks. We hope this simple framework will motivate people to rethink the unification of low-level and high-level vision.
语义分割和语义图像合成是视觉感知和生成中的两个代表性任务。虽然现有方法将它们视为两个独立的任务,但我们提出了一个统一的框架(SemFlow)并将它们建模为一对反向问题。具体来说,受正则流理论的启发,我们训练一个常微分方程(ODE)模型,在真实图像和语义蒙版分布之间进行传输。由于训练对象是对称的,属于两个分布(即图像和语义蒙版)的样本可以很容易地进行可逆转换。对于语义分割,我们的方法解决了扩散输出随机性和分割结果唯一性之间的矛盾。对于图像合成,我们提出了一种有限扰动方法,以提高生成结果的多样性,而不改变语义类别。实验表明,我们的SemFlow在语义分割和语义图像合成任务上取得了具有竞争力的结果。我们希望这个简单的框架能激励人们重新思考低级别和高级别视觉任务的统一。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024
Summary:
提出一种统一框架(SemFlow),将语义分割和语义图像合成视为一对反向问题。利用常微分方程(ODE)模型实现真实图像和语义掩膜之间的转换,实现可逆转换。解决扩散输出随机性与分割结果唯一性之间的矛盾,提出有限扰动方法提高生成结果的多样性。在语义分割和语义图像合成任务上取得有竞争力的结果。
Key Takeaways:
- 提出统一框架SemFlow,将语义分割和语义图像合成视为反向问题。
- 利用常微分方程(ODE)模型实现真实图像和语义掩膜之间的转换。
- 解决扩散输出随机性与分割结果唯一性的矛盾。
- 提出有限扰动方法,提高生成结果的多样性。
- 在语义分割和语义图像合成任务上取得有竞争力的结果。
- 希望此简单框架能激励人们重新思考低级别和高级别视觉任务的统一。
点此查看论文截图

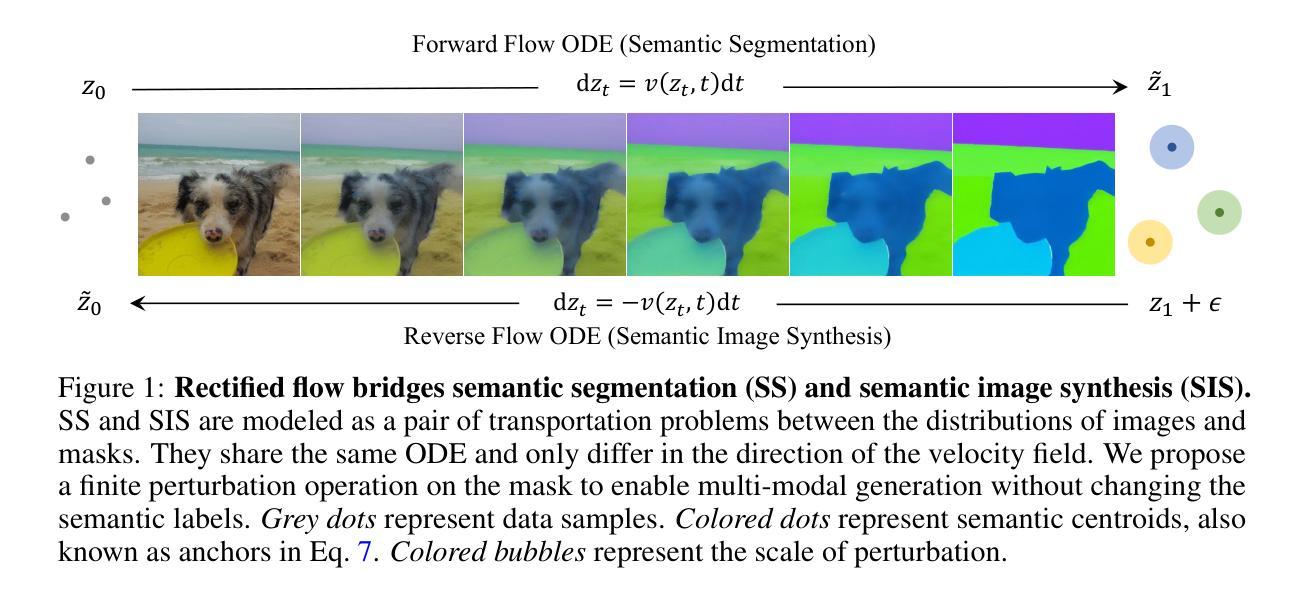
Weakly-Supervised Semantic Segmentation with Image-Level Labels: from Traditional Models to Foundation Models
Authors:Zhaozheng Chen, Qianru Sun
The rapid development of deep learning has driven significant progress in image semantic segmentation - a fundamental task in computer vision. Semantic segmentation algorithms often depend on the availability of pixel-level labels (i.e., masks of objects), which are expensive, time-consuming, and labor-intensive. Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) is an effective solution to avoid such labeling. It utilizes only partial or incomplete annotations and provides a cost-effective alternative to fully-supervised semantic segmentation. In this journal, our focus is on the WSSS with image-level labels, which is the most challenging form of WSSS. Our work has two parts. First, we conduct a comprehensive survey on traditional methods, primarily focusing on those presented at premier research conferences. We categorize them into four groups based on where their methods operate: pixel-wise, image-wise, cross-image, and external data. Second, we investigate the applicability of visual foundation models, such as the Segment Anything Model (SAM), in the context of WSSS. We scrutinize SAM in two intriguing scenarios: text prompting and zero-shot learning. We provide insights into the potential and challenges of deploying visual foundational models for WSSS, facilitating future developments in this exciting research area.
深度学习技术的快速发展推动了图像语义分割在计算机视觉领域中的重大进步。语义分割算法通常依赖于像素级标签(即对象掩膜)的可用性,而这些标签的获取成本高昂、耗时且劳动密集。弱监督语义分割(WSSS)是解决避免此类标注的有效方法。它仅利用部分或不完整的注释,为完全监督的语义分割提供了成本效益更高的替代方案。在本期刊中,我们的重点是有图像级标签的WSSS,这是WSSS中最具挑战性的形式。我们的工作分为两部分。首先,我们对传统方法进行了全面的综述,主要集中在主要研究会议上发表的方法。我们根据它们的方法操作位置将它们分为四类:像素级、图像级、跨图像和外部数据。其次,我们探讨了视觉基础模型(如万物分割模型SAM)在WSSS背景下的适用性。我们对SAM在两个有趣的场景:文本提示和零样本学习进行了审查。我们深入探讨了将视觉基础模型用于WSSS的潜力和挑战,有助于这一激动人心的研究领域未来的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM Computing Surveys
Summary
深度学习的发展推动了图像语义分割领域的显著进步,这是计算机视觉中的一项基础任务。语义分割算法通常依赖于像素级标签(即对象掩膜),这些标签的获取成本高、耗时长且劳力密集。弱监督语义分割(WSSS)是避免这种标注的有效解决方案,它仅利用部分或不完整的注释,为全监督语义分割提供了成本效益高的替代方案。本文重点关注具有图像级标签的WSSS,这是WSSS中最具挑战性的形式。文章首先全面回顾了传统方法,主要关注顶级研究会议提出的方法,将它们分为四类:像素级、图像级、跨图像和外部数据。其次,调查了视觉基础模型(如Segment Anything Model,SAM)在WSSS中的应用。本文详细分析了SAM在两个有趣场景:文本提示和零样本学习中的表现。为视觉基础模型在WSSS中的应用提供了见解和挑战,有助于该领域的未来发展。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习推动了图像语义分割的进步。
- 语义分割算法依赖于像素级标签,但这些标签获取成本高且耗时。
- 弱监督语义分割(WSSS)是避免密集标注的有效解决方案。
- WSSS的研究重点在于如何利用图像级标签,这是最具挑战性的形式。
- 文章回顾了传统方法,并将其分为像素级、图像级、跨图像和外部数据四类。
- 视觉基础模型(如SAM)在WSSS中的应用被详细调查。
点此查看论文截图