⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-12 更新
SLGaussian: Fast Language Gaussian Splatting in Sparse Views
Authors:Kangjie Chen, BingQuan Dai, Minghan Qin, Dongbin Zhang, Peihao Li, Yingshuang Zou, Haoqian Wang
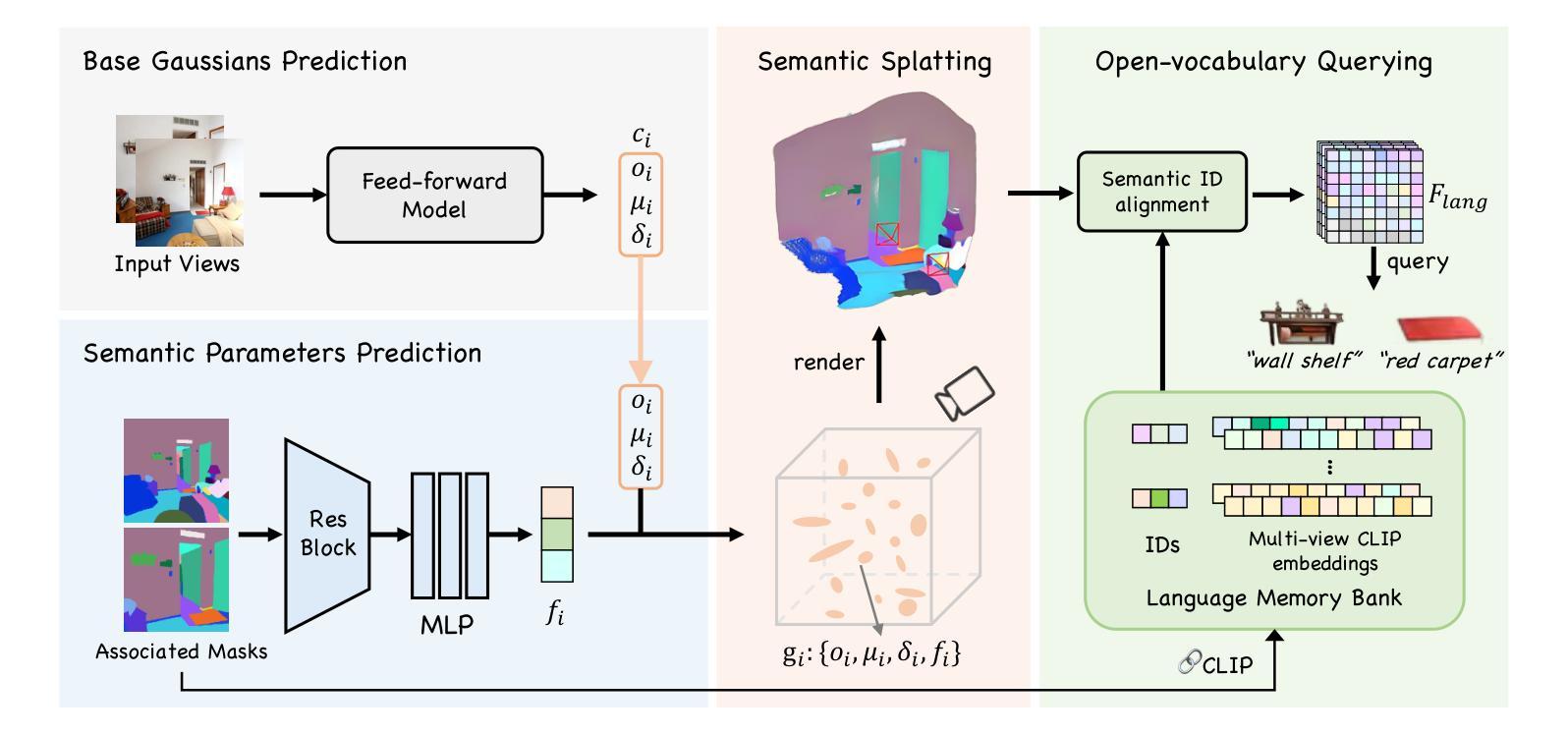
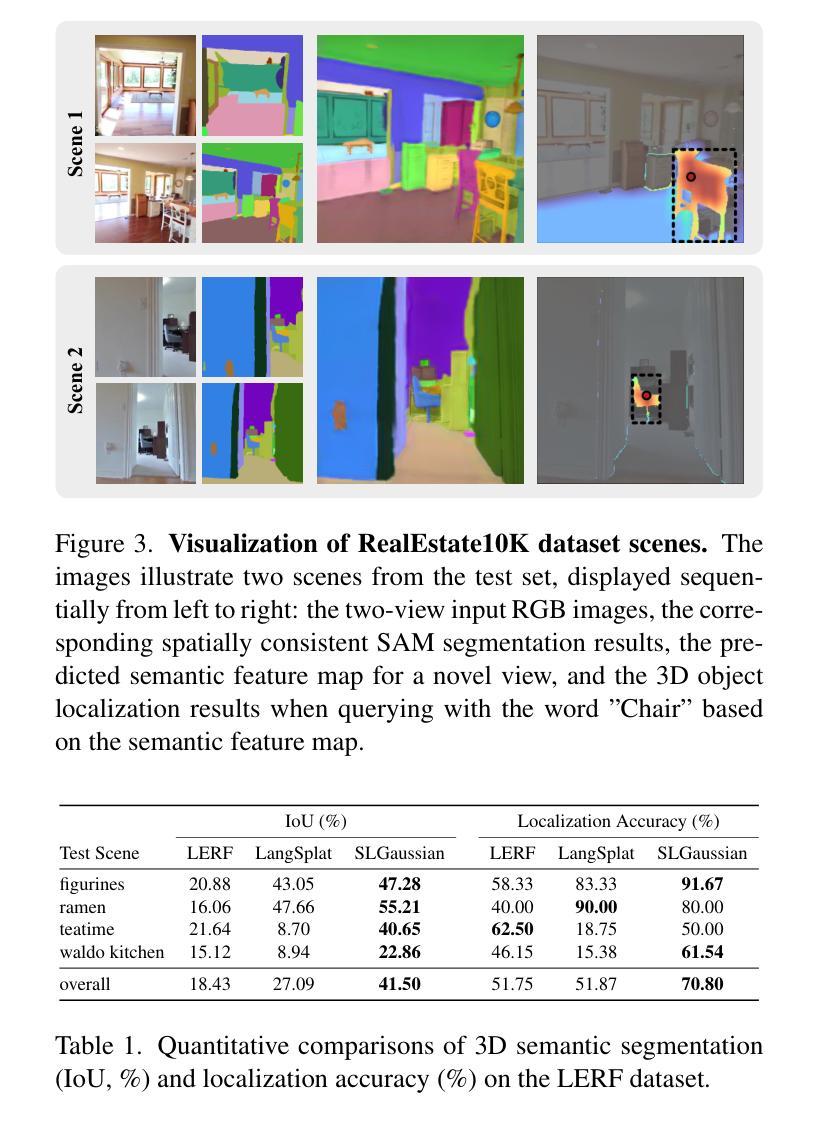
3D semantic field learning is crucial for applications like autonomous navigation, AR/VR, and robotics, where accurate comprehension of 3D scenes from limited viewpoints is essential. Existing methods struggle under sparse view conditions, relying on inefficient per-scene multi-view optimizations, which are impractical for many real-world tasks. To address this, we propose SLGaussian, a feed-forward method for constructing 3D semantic fields from sparse viewpoints, allowing direct inference of 3DGS-based scenes. By ensuring consistent SAM segmentations through video tracking and using low-dimensional indexing for high-dimensional CLIP features, SLGaussian efficiently embeds language information in 3D space, offering a robust solution for accurate 3D scene understanding under sparse view conditions. In experiments on two-view sparse 3D object querying and segmentation in the LERF and 3D-OVS datasets, SLGaussian outperforms existing methods in chosen IoU, Localization Accuracy, and mIoU. Moreover, our model achieves scene inference in under 30 seconds and open-vocabulary querying in just 0.011 seconds per query.
三维语义场学习对于自主导航、AR/VR和机器人等应用至关重要,这些应用需要有限视角对三维场景进行准确理解。现有方法在稀疏视图条件下表现不佳,依赖于不切实际的场景多视角优化,这对于许多现实世界任务来说并不实用。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了SLGaussian方法,这是一种前馈方法,可以从稀疏视角构建三维语义场,允许直接推断基于3DGS的场景。通过确保通过视频跟踪的一致SAM分割,并使用低维索引高维CLIP特征,SLGaussian能够高效地将语言信息嵌入三维空间,为稀疏视图条件下的准确三维场景理解提供了稳健的解决方案。在LERF和3D-OVS数据集上的两视图稀疏三维对象查询和分割实验中,SLGaussian在选择的IoU、定位精度和mIoU方面优于现有方法。此外,我们的模型在不到30秒内实现了场景推断,每个查询的开放词汇查询时间仅为0.011秒。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
SLGaussian能从稀疏视角构建三维语义场,实现直接对基于3DGS的场景进行推理。通过视频跟踪保证SAM分割的一致性,并利用高维CLIP特征的低维索引,SLGaussian能高效地将语言信息嵌入三维空间,为稀疏视角条件下的准确三维场景理解提供了稳健的解决方案。在LERF和3D-OVS数据集的两视图稀疏三维对象查询和分割实验中,SLGaussian在选择的IoU、定位精度和mIoU方面优于现有方法。此外,该模型场景推理用时不到30秒,开放词汇查询每秒仅0.011次。
要点提炼
- SLGaussian能够从稀疏视角进行三维语义场学习,这是自主导航、AR/VR和机器人等应用中的关键技能,其中从有限视角准确理解三维场景至关重要。
- 现有方法在稀疏视角条件下表现不佳,依赖于低效的每场景多视角优化,这在许多真实任务中不实用。
- SLGaussian通过确保SAM分割的一致性(通过视频跟踪)和使用低维索引高维CLIP特征的方法,实现了对三维场景的准确理解。
- SLGaussian能够高效地将语言信息嵌入三维空间,提供了一个稳健的解决方案。
- 在LERF和3D-OVS数据集的实验中,SLGaussian在选择的IoU、定位精度和mIoU等指标上优于现有方法。
- SLGaussian模型场景推理速度快,用时不到30秒。开放词汇查询效率高,每秒仅0.011次查询。
- 这些技术进步为未来的三维场景理解和智能应用提供了有力的支持。
点此查看论文截图

Diffusion-Based Attention Warping for Consistent 3D Scene Editing
Authors:Eyal Gomel, Lior Wolf
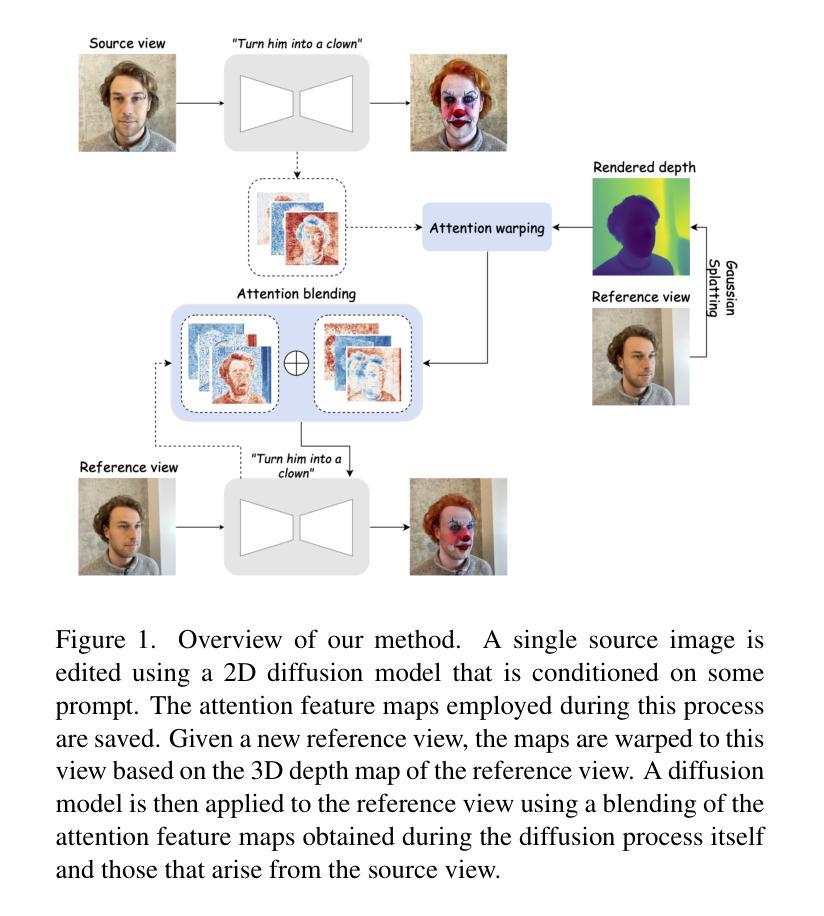
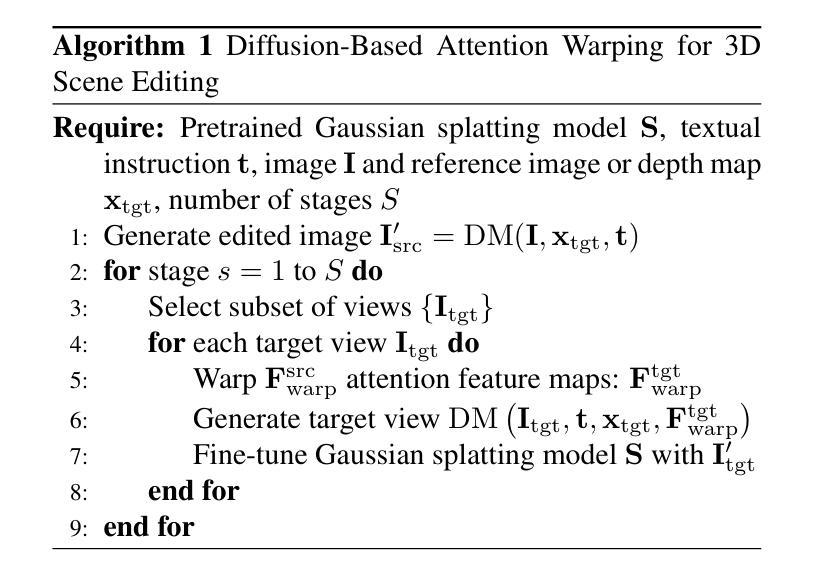
We present a novel method for 3D scene editing using diffusion models, designed to ensure view consistency and realism across perspectives. Our approach leverages attention features extracted from a single reference image to define the intended edits. These features are warped across multiple views by aligning them with scene geometry derived from Gaussian splatting depth estimates. Injecting these warped features into other viewpoints enables coherent propagation of edits, achieving high fidelity and spatial alignment in 3D space. Extensive evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in generating versatile edits of 3D scenes, significantly advancing the capabilities of scene manipulation compared to the existing methods. Project page: \url{https://attention-warp.github.io}
我们提出了一种使用扩散模型进行3D场景编辑的新方法,旨在确保不同视角下的视图一致性和逼真性。我们的方法利用从单张参考图像中提取的注意力特征来定义预期的编辑。通过将这些特征与从高斯平铺深度估计派生的场景几何进行对齐,可以在多个视角之间对这些特征进行变形。将这些变形的特征注入到其他视角中,可以实现编辑的连贯传播,在高保真和空间对齐方面实现出色的效果。大量评估表明,我们的方法在生成具有通用功能的3D场景编辑方面非常有效,与现有方法相比,大大提高了场景操作能力。项目页面:https://attention-warp.github.io
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种使用扩散模型进行3D场景编辑的新方法,该方法利用从单张参考图像提取的注意力特征来定义预期的编辑效果。通过将这些特征与从高斯泼墨深度估计得出的场景几何结构对齐,实现在多个视角间的特征变形。将这些变形后的特征注入到其他视角,实现了编辑效果的连贯传播,在3D空间中实现了高保真和空间对齐。此方法在生成3D场景的多样化编辑方面效果显著,大幅提升了场景操控能力。
Key Takeaways
- 利用扩散模型进行3D场景编辑。
- 使用单张参考图像提取注意力特征来定义编辑效果。
- 通过场景几何结构(从高斯泼墨深度估计得出)实现多视角的特征变形。
- 变形特征注入其他视角,实现连贯的编辑传播。
- 在3D空间中实现高保真和空间对齐。
- 方法生成3D场景编辑效果显著,提升场景操控能力。
点此查看论文截图


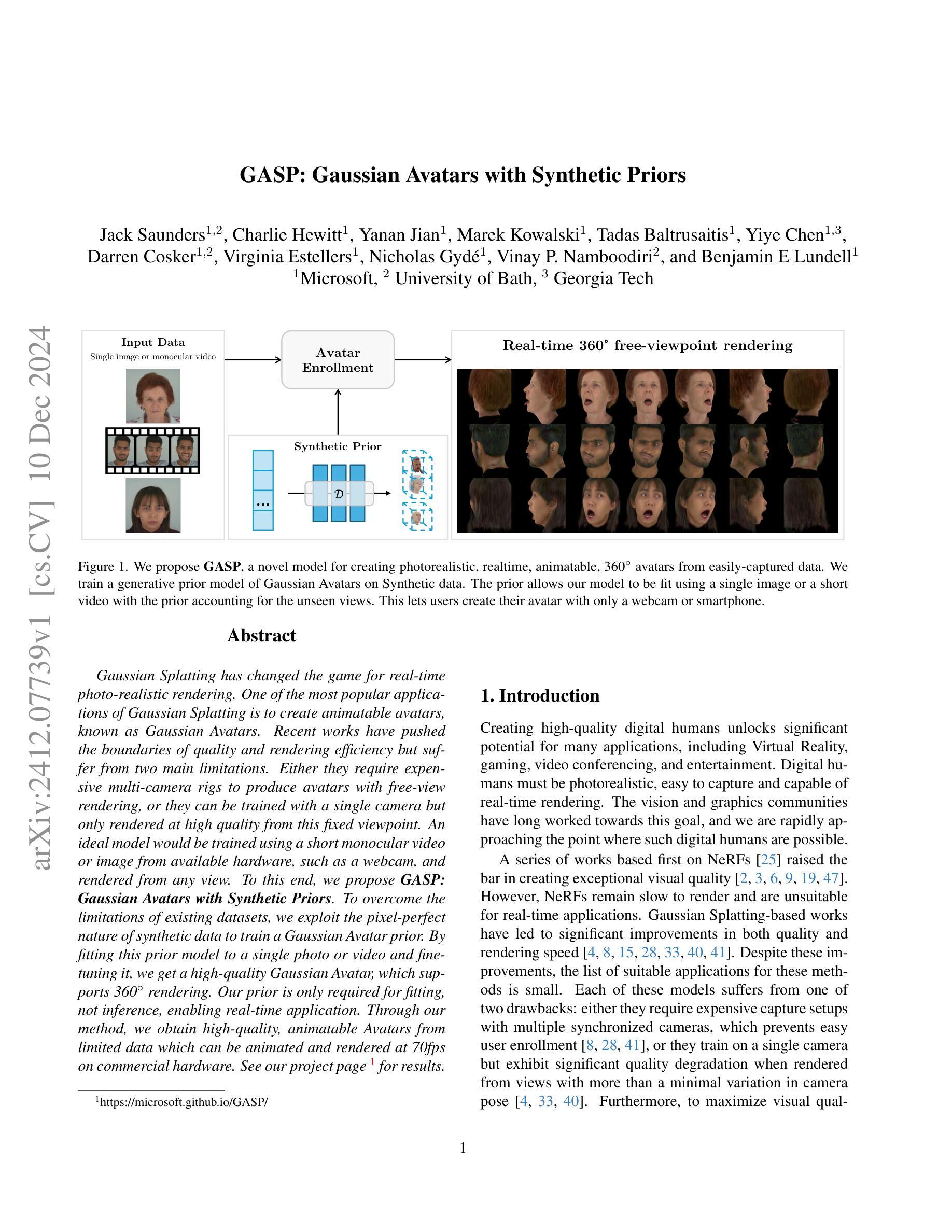
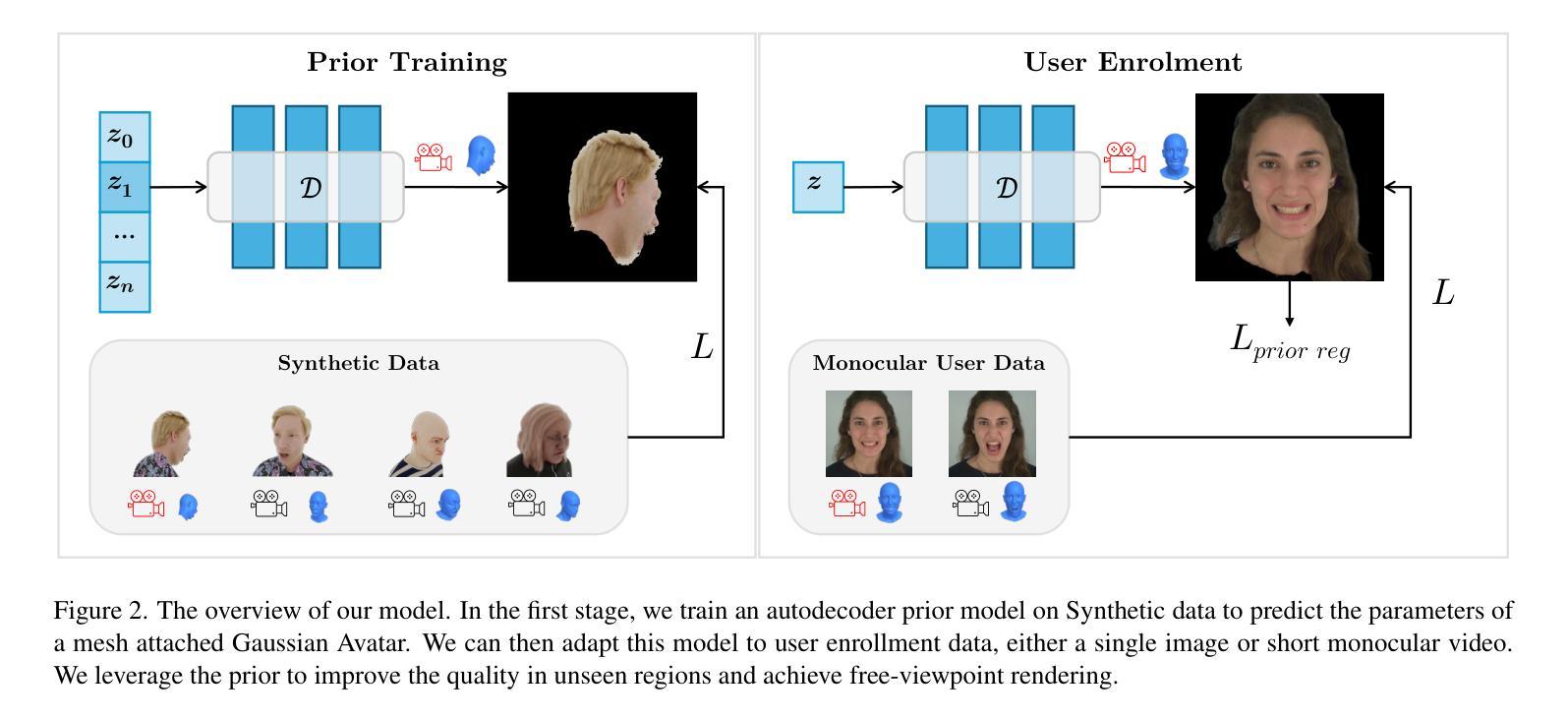
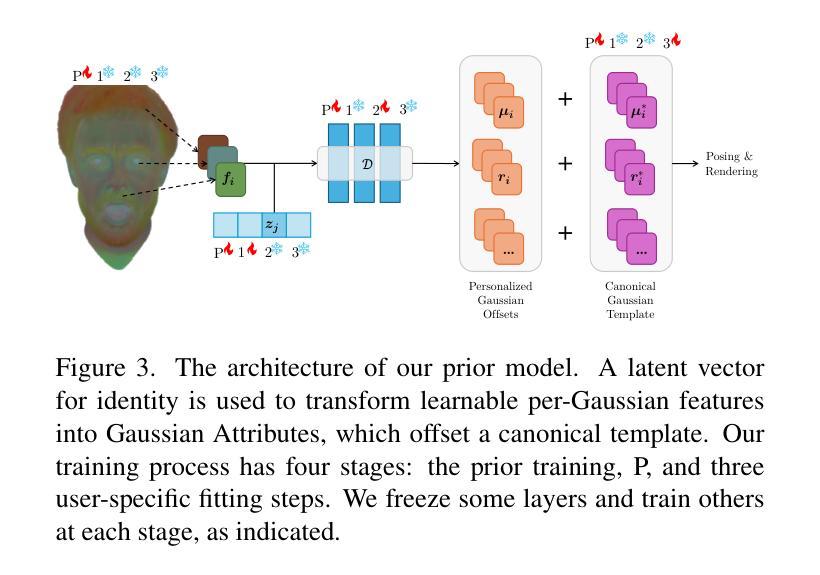
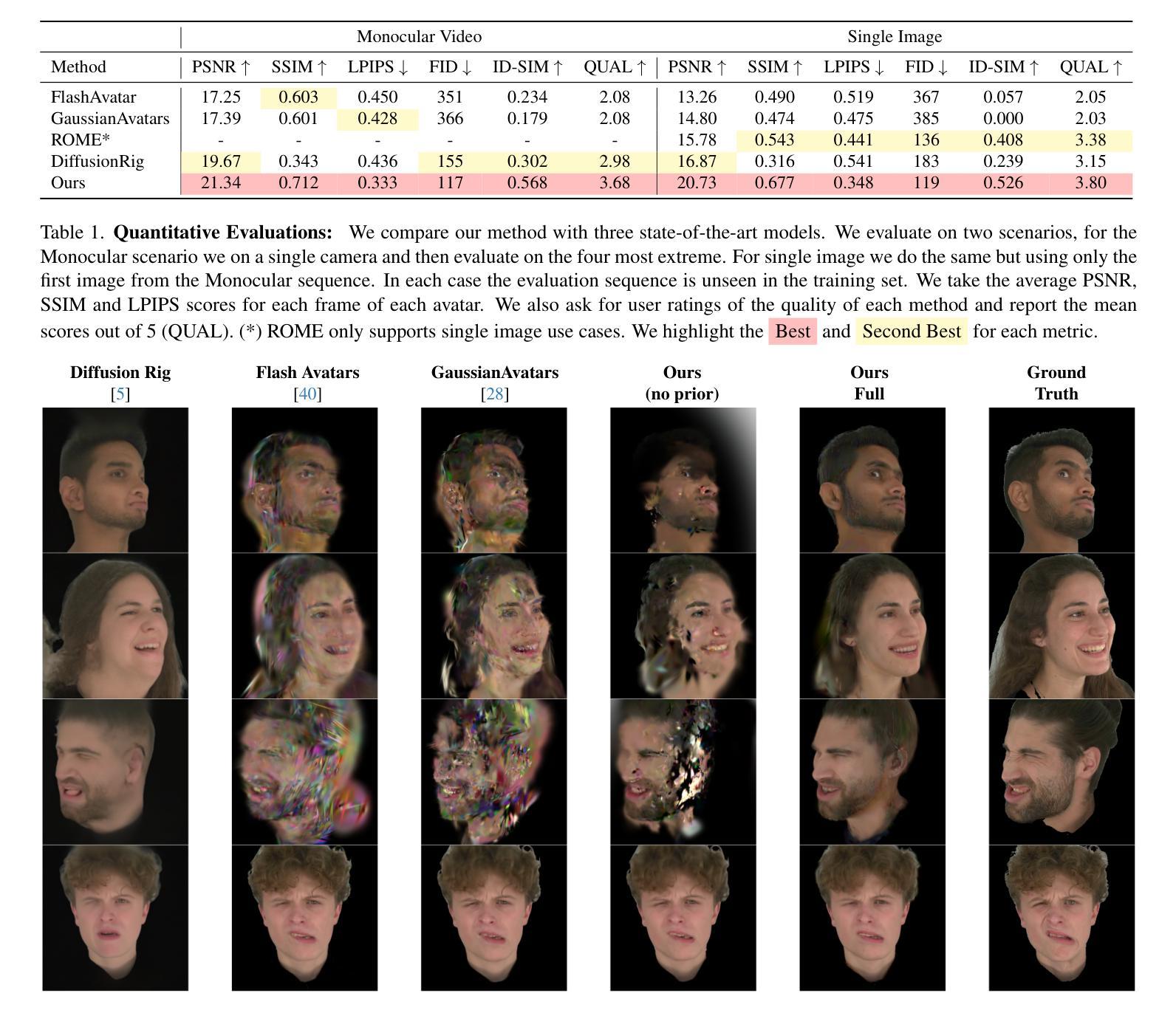
GASP: Gaussian Avatars with Synthetic Priors
Authors:Jack Saunders, Charlie Hewitt, Yanan Jian, Marek Kowalski, Tadas Baltrusaitis, Yiye Chen, Darren Cosker, Virginia Estellers, Nicholas Gyde, Vinay P. Namboodiri, Benjamin E Lundell
Gaussian Splatting has changed the game for real-time photo-realistic rendering. One of the most popular applications of Gaussian Splatting is to create animatable avatars, known as Gaussian Avatars. Recent works have pushed the boundaries of quality and rendering efficiency but suffer from two main limitations. Either they require expensive multi-camera rigs to produce avatars with free-view rendering, or they can be trained with a single camera but only rendered at high quality from this fixed viewpoint. An ideal model would be trained using a short monocular video or image from available hardware, such as a webcam, and rendered from any view. To this end, we propose GASP: Gaussian Avatars with Synthetic Priors. To overcome the limitations of existing datasets, we exploit the pixel-perfect nature of synthetic data to train a Gaussian Avatar prior. By fitting this prior model to a single photo or video and fine-tuning it, we get a high-quality Gaussian Avatar, which supports 360$^\circ$ rendering. Our prior is only required for fitting, not inference, enabling real-time application. Through our method, we obtain high-quality, animatable Avatars from limited data which can be animated and rendered at 70fps on commercial hardware. See our project page (https://microsoft.github.io/GASP/) for results.
高斯混合技术已经改变了实时逼真渲染的游戏规则。高斯混合最流行的应用之一是创建可动画的化身,称为高斯化身。近期的研究工作已经在质量和渲染效率方面取得了突破,但存在两个主要局限性。要么它们需要使用昂贵的多相机装置来产生可从任何角度进行渲染的化身,要么它们可以使用单个相机进行训练,但仅能从这个固定视角以高质量进行渲染。理想模型将使用可用的硬件(如网络摄像头)拍摄的简短单眼视频或图像进行训练,并从任何视角进行渲染。为此,我们提出了GASP:具有合成先验的高斯化身。为了克服现有数据集的限制,我们利用合成数据的完美像素特性来训练高斯化身的先验知识。通过将此先验模型拟合到一张照片或视频并进行微调,我们获得支持360°渲染的高质量高斯化身。我们的先验知识仅用于拟合,而非推理,可实现实时应用。通过我们的方法,我们从有限数据中获得了高质量的可动画化身,可以在商业硬件上以70帧/秒的速度进行动画和渲染。有关结果,请参见我们的项目页面(https://microsoft.github.io/GASP/)。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://microsoft.github.io/GASP/
Summary
高斯混合技术革新了实时逼真的渲染技术,特别是用于创建动态化虚拟角色(Gaussian Avatars)。当前的研究虽提升了质量与渲染效率,但仍存在两大局限:一需要昂贵的多相机设备来生成具有自由视角渲染效果的虚拟角色;二可借助单相机训练模型进行高质量渲染,仅限于固定视角。理想模型应该使用如网络摄像头等现有硬件设备拍摄的单眼视频或图像进行训练,并能从任何视角进行渲染。为此,我们提出GASP(高斯虚拟角色合成先验技术)。我们利用合成数据的精确像素特点训练高斯虚拟角色先验模型以克服现有数据集的局限性。通过对单张照片或视频拟合该先验模型并进行微调,我们得到了支持360°渲染的高质量高斯虚拟角色。我们的先验模型仅适用于拟合,不适用于推理,可实现实时应用。通过我们的方法,我们从有限数据中获得了高质量的动态虚拟角色,可以在商业硬件上以每秒70帧的速度进行动画和渲染。更多结果请参见项目页面(https://microsoft.github.io/GASP/)。
Key Takeaways
- Gaussian Splatting技术改变了实时逼真的渲染方式,特别是在创建动态化虚拟角色(Gaussian Avatars)方面的应用受到广泛关注。
- 当前研究在虚拟角色创建领域存在两大局限:设备成本高昂和固定视角渲染限制。
- GASP技术通过利用合成数据的精确像素特点,旨在克服现有数据集的局限性。
- 利用先验模型对单张照片或视频进行拟合和微调,实现了高质量、支持360°渲染的Gaussian Avatars。
- 该技术的先验模型仅用于拟合,不参与推理过程,确保了实时应用的可行性。
- 通过该方法,能够在有限数据下生成高质量的虚拟角色,可在商业硬件上以高帧率进行动画和渲染。
点此查看论文截图

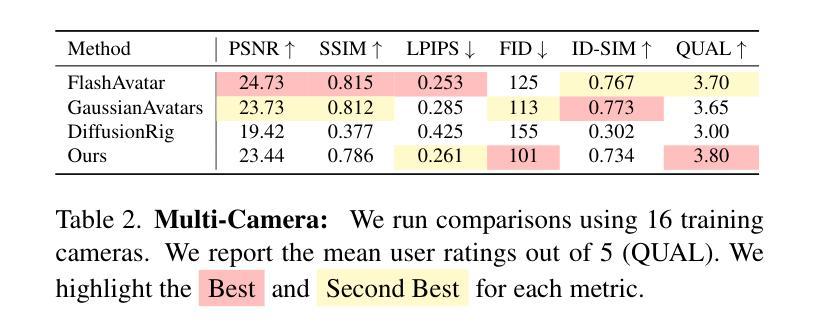
Proc-GS: Procedural Building Generation for City Assembly with 3D Gaussians
Authors:Yixuan Li, Xingjian Ran, Linning Xu, Tao Lu, Mulin Yu, Zhenzhi Wang, Yuanbo Xiangli, Dahua Lin, Bo Dai
Buildings are primary components of cities, often featuring repeated elements such as windows and doors. Traditional 3D building asset creation is labor-intensive and requires specialized skills to develop design rules. Recent generative models for building creation often overlook these patterns, leading to low visual fidelity and limited scalability. Drawing inspiration from procedural modeling techniques used in the gaming and visual effects industry, our method, Proc-GS, integrates procedural code into the 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) framework, leveraging their advantages in high-fidelity rendering and efficient asset management from both worlds. By manipulating procedural code, we can streamline this process and generate an infinite variety of buildings. This integration significantly reduces model size by utilizing shared foundational assets, enabling scalable generation with precise control over building assembly. We showcase the potential for expansive cityscape generation while maintaining high rendering fidelity and precise control on both real and synthetic cases.
建筑物是城市的主要组成部分,通常包含如窗户和门等重复元素。传统的3D建筑资产创建劳动强度大,需要制定设计规则的专业技能。最近的建筑创作生成模型往往忽略了这些模式,导致视觉逼真度低和可扩展性差。我们的方法Proc-GS从游戏和视觉效果行业中使用的程序建模技术中汲取灵感,将程序代码集成到3D高斯喷涂(3D-GS)框架中,融合了两者在高保真渲染和资产管理方面的优势。通过操作程序代码,我们可以简化这个过程并生成无限多样的建筑物。通过利用共享基础资产,这种集成显著减少了模型大小,实现了具有精确控制建筑组合的可扩展生成。我们在真实和合成案例中展示了大规模城市景观生成的高渲染保真度和精确控制的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://city-super.github.io/procgs/
Summary
本文介绍了一种将过程建模技术融入3D高斯散斑(3D-GS)框架的方法,旨在提高城市建筑生成的视觉逼真度和效率。通过操纵过程代码,可以简化建筑创建过程并生成无限多样化的建筑。该方法利用共享基础资产,显著减少模型大小,实现对建筑组合的精确控制,同时保持高渲染保真度。
Key Takeaways
- 过程建模技术被用于城市建筑生成,提高了效率和多样性。
- 将过程代码与3D高斯散斑框架结合,实现高保真渲染和资产管理。
- 通过操纵过程代码,可以简化建筑创建过程。
- 集成方法显著减少模型大小,并利用共享基础资产。
- 对建筑组合的精确控制得以实现。
- 该方法在真实和合成城市景观生成中具有潜力。
点此查看论文截图

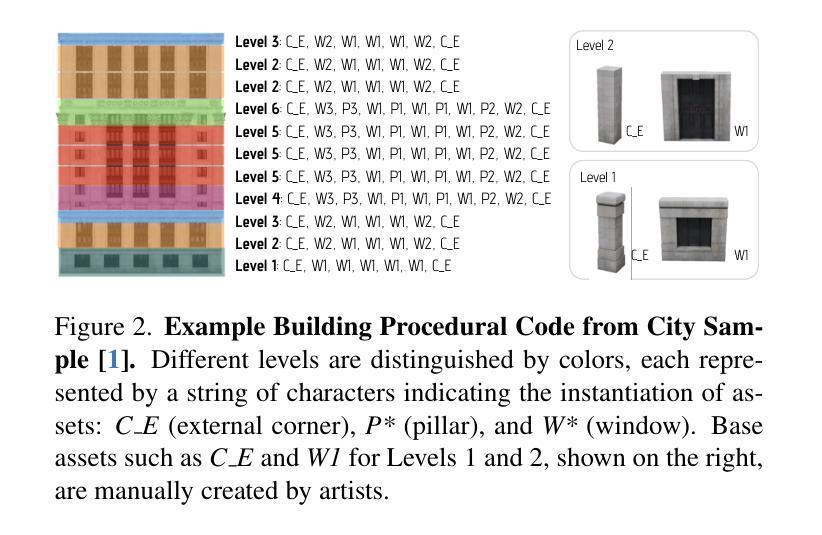
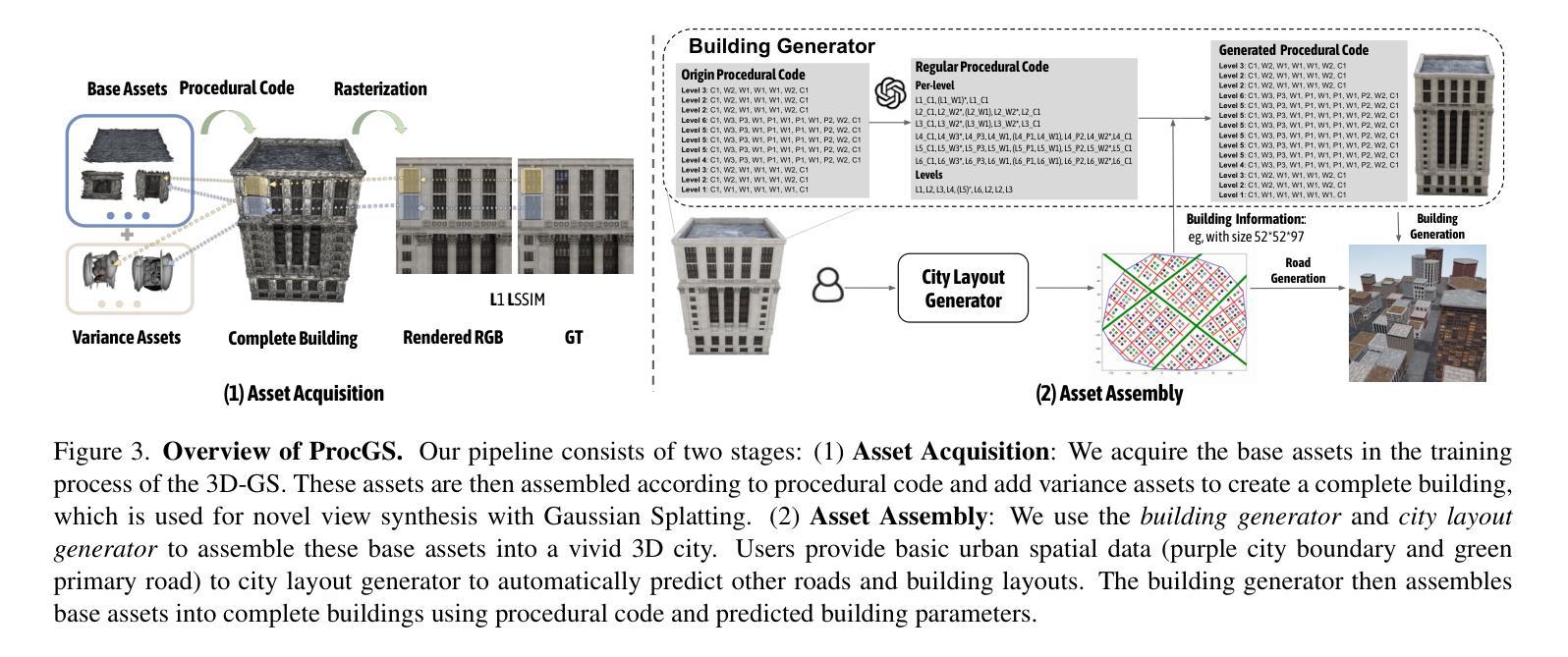
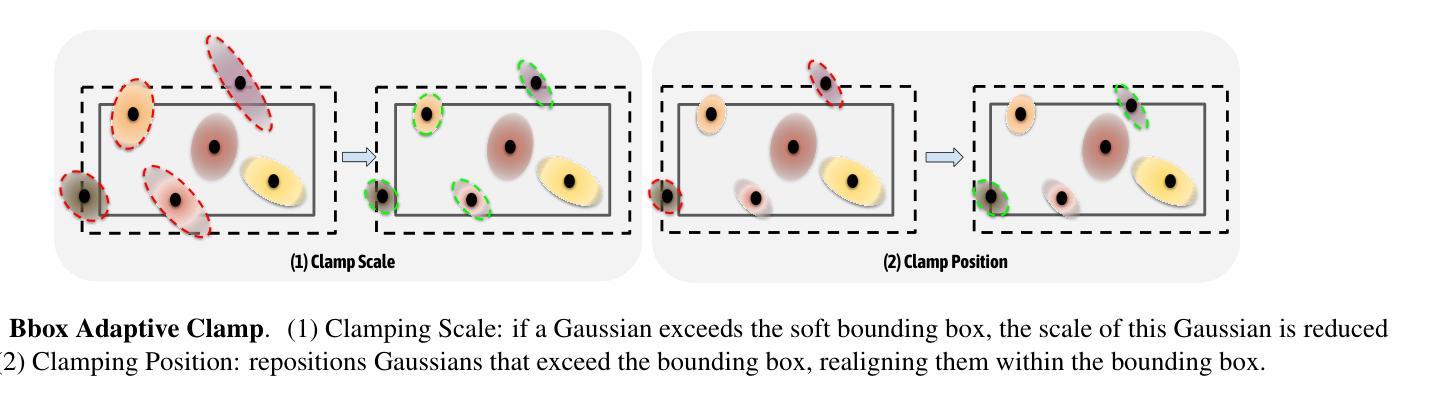
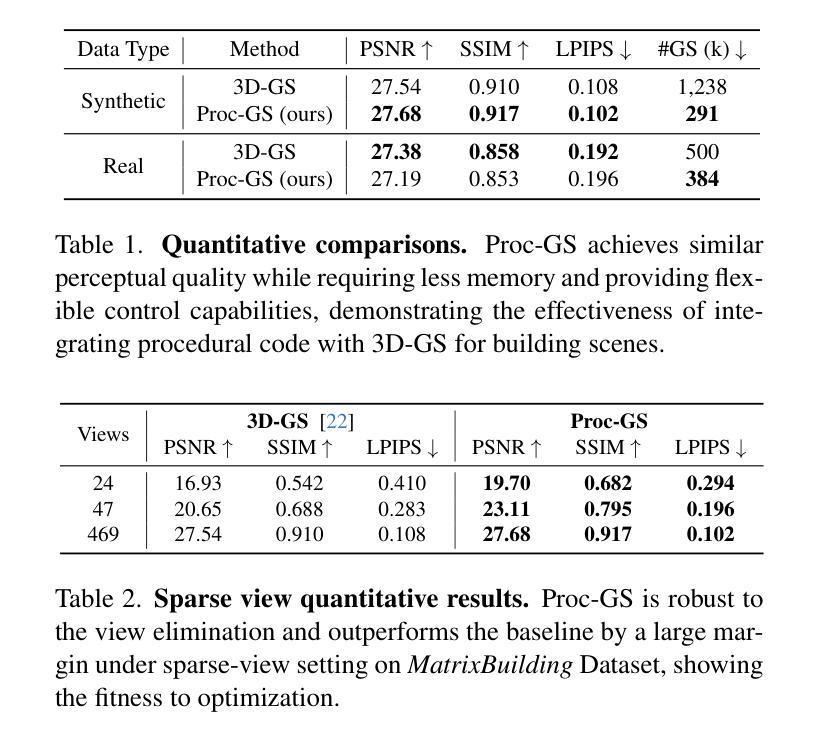
Faster and Better 3D Splatting via Group Training
Authors:Chengbo Wang, Guozheng Ma, Yifei Xue, Yizhen Lao
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has emerged as a powerful technique for novel view synthesis, demonstrating remarkable capability in high-fidelity scene reconstruction through its Gaussian primitive representations. However, the computational overhead induced by the massive number of primitives poses a significant bottleneck to training efficiency. To overcome this challenge, we propose Group Training, a simple yet effective strategy that organizes Gaussian primitives into manageable groups, optimizing training efficiency and improving rendering quality. This approach shows universal compatibility with existing 3DGS frameworks, including vanilla 3DGS and Mip-Splatting, consistently achieving accelerated training while maintaining superior synthesis quality. Extensive experiments reveal that our straightforward Group Training strategy achieves up to 30% faster convergence and improved rendering quality across diverse scenarios.
3D高斯展开技术(3DGS)作为一种强大的新型视图合成技术,已经展现出其显著的能力。它通过高斯原始表示法实现高保真场景重建。然而,大量原始数据所带来的计算开销对训练效率构成了重大瓶颈。为了克服这一挑战,我们提出了群组训练策略,该策略将高斯原始数据组织成可管理的群组,优化训练效率,提高渲染质量。该方法与现有的3DGS框架具有普遍兼容性,包括普通的3DGS和Mip-Splatting,在加速训练的同时保持优异的合成质量。大量实验表明,我们简单的群组训练策略实现了高达30%的更快收敛速度,并在各种场景中提高了渲染质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
3DGS技术因其在高保真场景重建中的卓越表现而受到广泛关注,但其计算开销大成为训练效率瓶颈。为此,提出Group Training策略,通过组织Gaussian primitives成组优化训练效率并提升渲染质量。该策略与现有3DGS框架兼容,可加速训练并保持优异合成质量。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS技术用于新型视角合成,展现高保真场景重建能力。
- 大量Gaussian primitives导致计算开销大,影响训练效率。
- 提出Group Training策略,通过组织Gaussian primitives成组以优化训练。
- Group Training策略与各种3DGS框架兼容,包括vanilla 3DGS和Mip-Splatting。
- Group Training策略可加速训练,同时保持优异的合成质量。
- 实验显示,Group Training策略可实现最快达30%的收敛速度提升。
点此查看论文截图

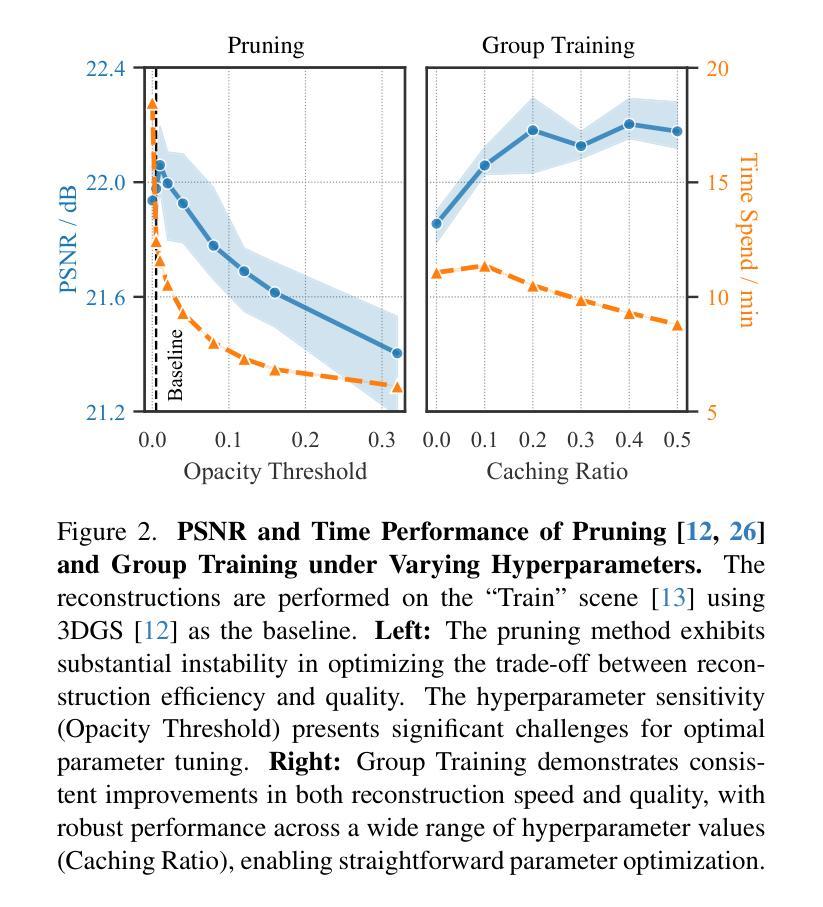

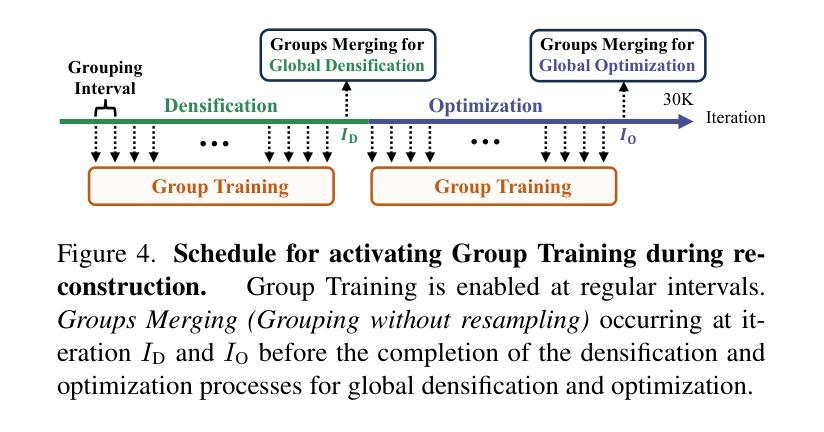
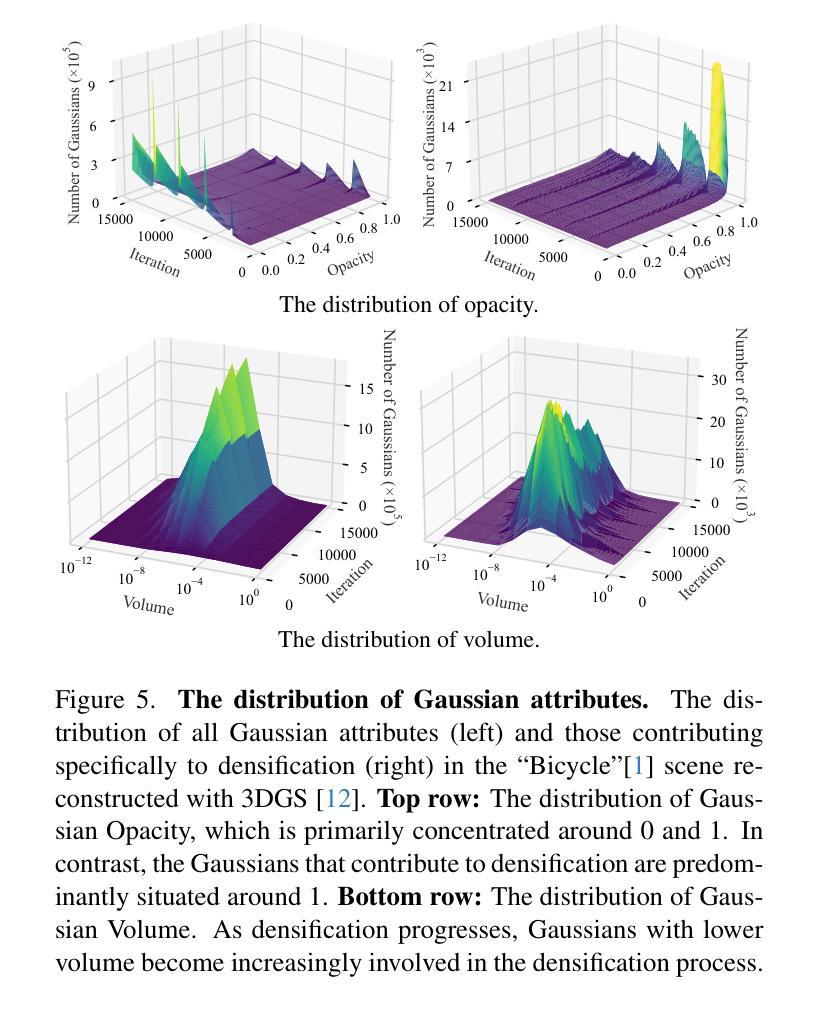
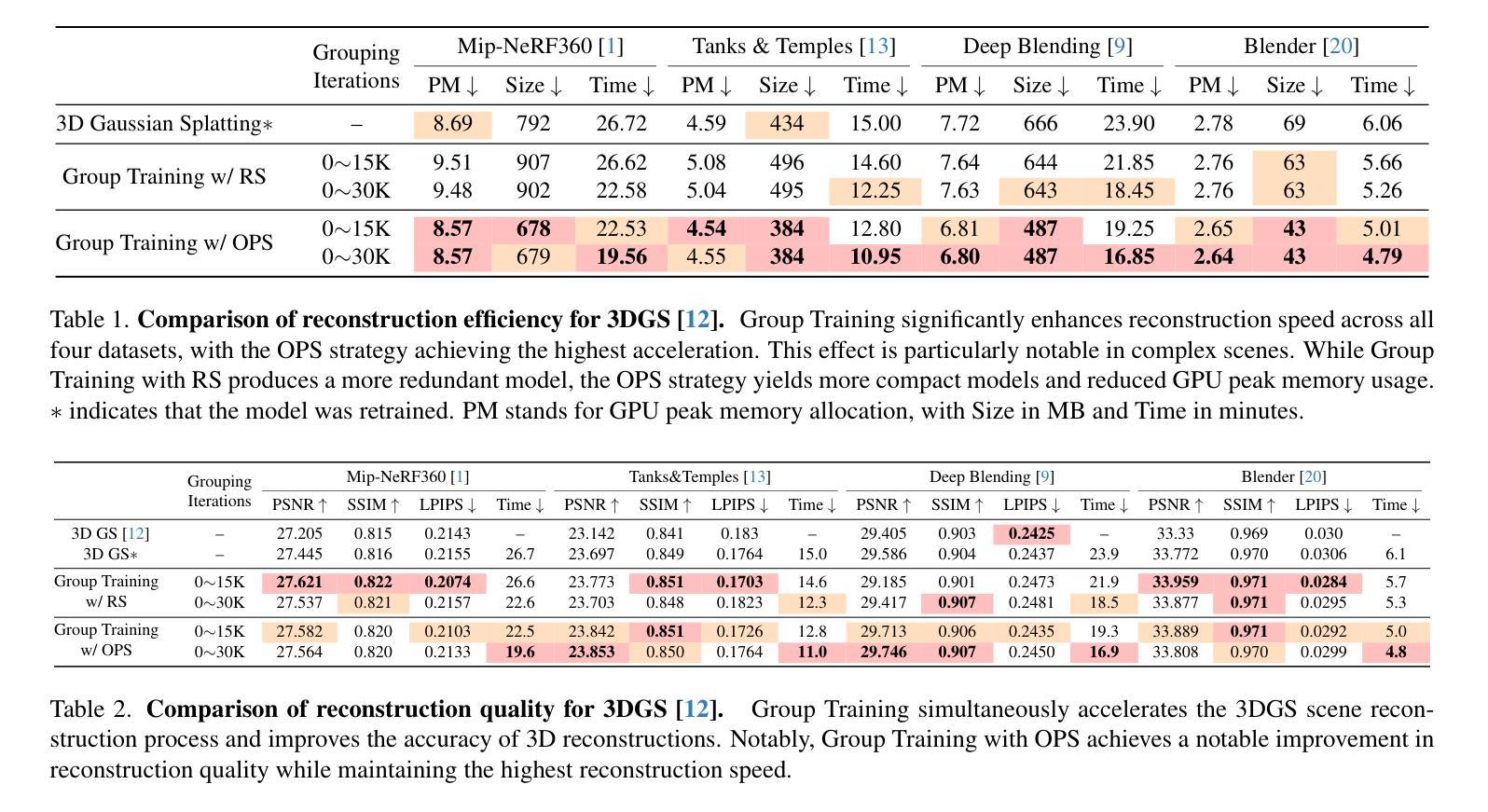
ResGS: Residual Densification of 3D Gaussian for Efficient Detail Recovery
Authors:Yanzhe Lyu, Kai Cheng, Xin Kang, Xuejin Chen
Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3D-GS) has prevailed in novel view synthesis, achieving high fidelity and efficiency. However, it often struggles to capture rich details and complete geometry. Our analysis highlights a key limitation of 3D-GS caused by the fixed threshold in densification, which balances geometry coverage against detail recovery as the threshold varies. To address this, we introduce a novel densification method, residual split, which adds a downscaled Gaussian as a residual. Our approach is capable of adaptively retrieving details and complementing missing geometry while enabling progressive refinement. To further support this method, we propose a pipeline named ResGS. Specifically, we integrate a Gaussian image pyramid for progressive supervision and implement a selection scheme that prioritizes the densification of coarse Gaussians over time. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves SOTA rendering quality. Consistent performance improvements can be achieved by applying our residual split on various 3D-GS variants, underscoring its versatility and potential for broader application in 3D-GS-based applications.
最近,3D高斯拼贴(3D-GS)在新型视图合成中盛行,实现了高保真和效率。然而,它经常难以捕捉丰富的细节和完整的几何形状。我们的分析强调了3D-GS的一个关键局限性,这是由于密集化中的固定阈值引起的,该阈值在几何覆盖与细节恢复之间取得平衡,随着阈值的变化而变化。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了一种新的密集化方法——残差分割,该方法增加了一个降标度的高斯值作为残差。我们的方法能够自适应地检索细节并补充缺失的几何形状,同时实现渐进的细化。为了进一步支持这种方法,我们提出了名为ResGS的管道。具体来说,我们结合了高斯图像金字塔进行渐进监督,并实施了一种选择方案,该方案优先对随时间推移的粗糙高斯进行密集化。大量实验表明,我们的方法达到了最先进的渲染质量。将我们的残差分割应用于各种3D-GS变体,可以实现性能的一致性提高,这证明了其在基于3D-GS的广泛应用中的通用性和潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于文本的内容,可以概括为:研究团队对现有的三维高斯分裂(3D-GS)方法进行了改进,提出了一种新的密度化方法——残差分裂(residual split)。该方法通过增加一个降尺度的高斯残差来平衡几何覆盖和细节恢复,提高了细节捕捉能力和几何完整性。同时,研究团队还提出了一种名为ResGS的管道流程,通过集成高斯图像金字塔进行渐进监督,并优先对粗糙高斯进行密度化。实验证明,新方法实现了较高的渲染质量和持续的性能改进,同时展现出在不同应用中的潜力和适应性。这一进展有望在基于三维高斯分裂的三维图形领域中得到广泛应用。
Key Takeaways
以下是基于文本内容的七个关键见解:
- 三维高斯分裂(3D-GS)在新型视图合成中受到广泛关注,具有高保真度和高效率。但其在捕捉丰富细节和完整几何上有所挑战。
- 研究团队指出固定阈值是造成三维高斯分裂中密度化过程的一个关键限制因素。阈值的变化会影响几何覆盖和细节恢复的平衡。
- 为解决此问题,研究团队引入了新的密度化方法——残差分裂(residual split),该方法通过增加一个降尺度的高斯作为残差来增强细节捕捉和补充缺失的几何信息。
- 该方法还实现了渐进的精细优化,可以通过一个名为ResGS的管道流程进行支持。这一流程结合了高斯图像金字塔进行渐进监督,并且优先对粗糙的高斯进行密度化。
点此查看论文截图

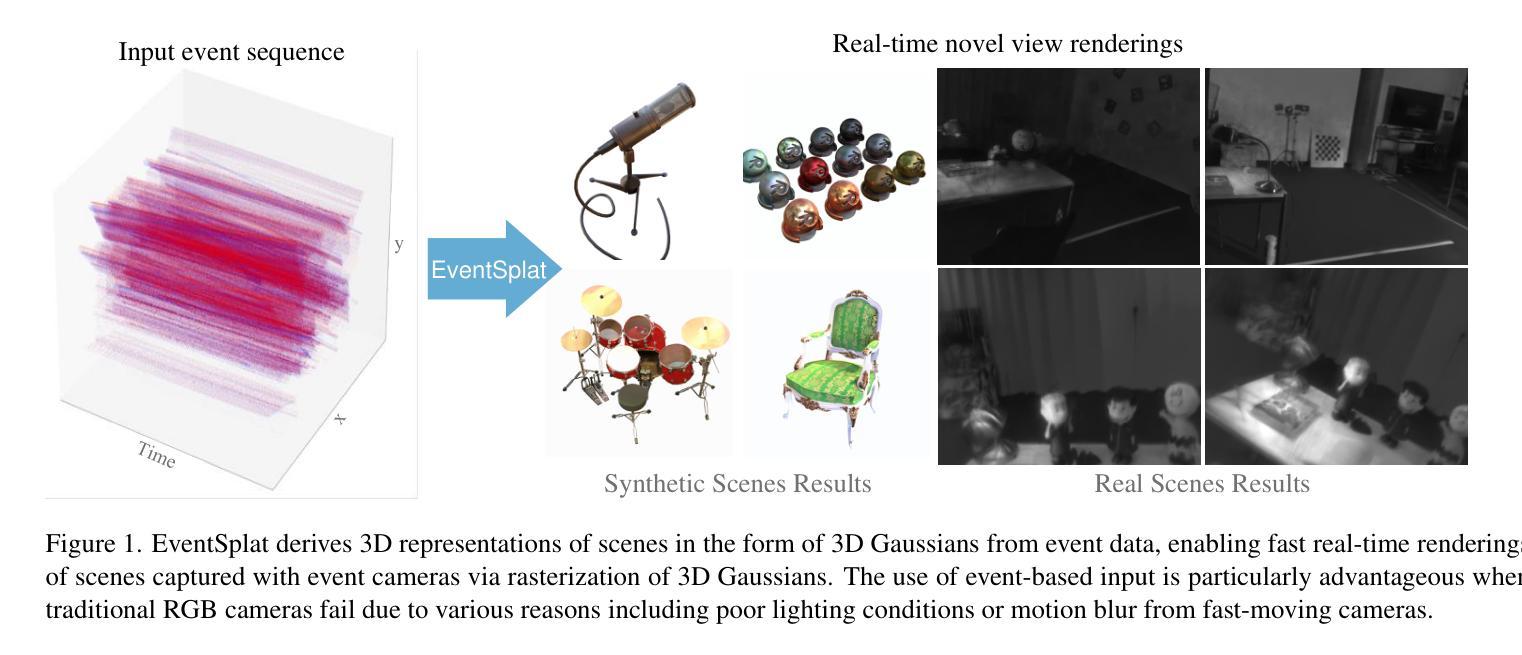
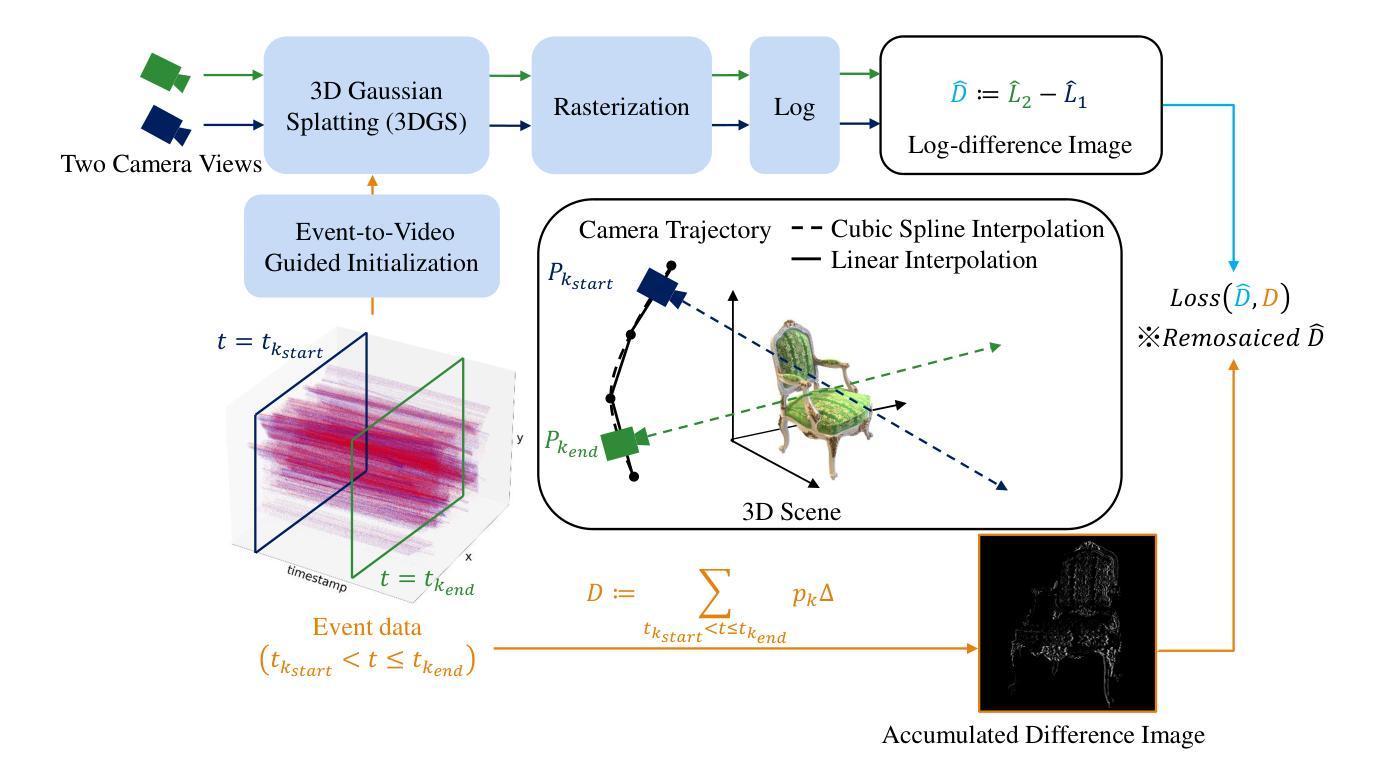
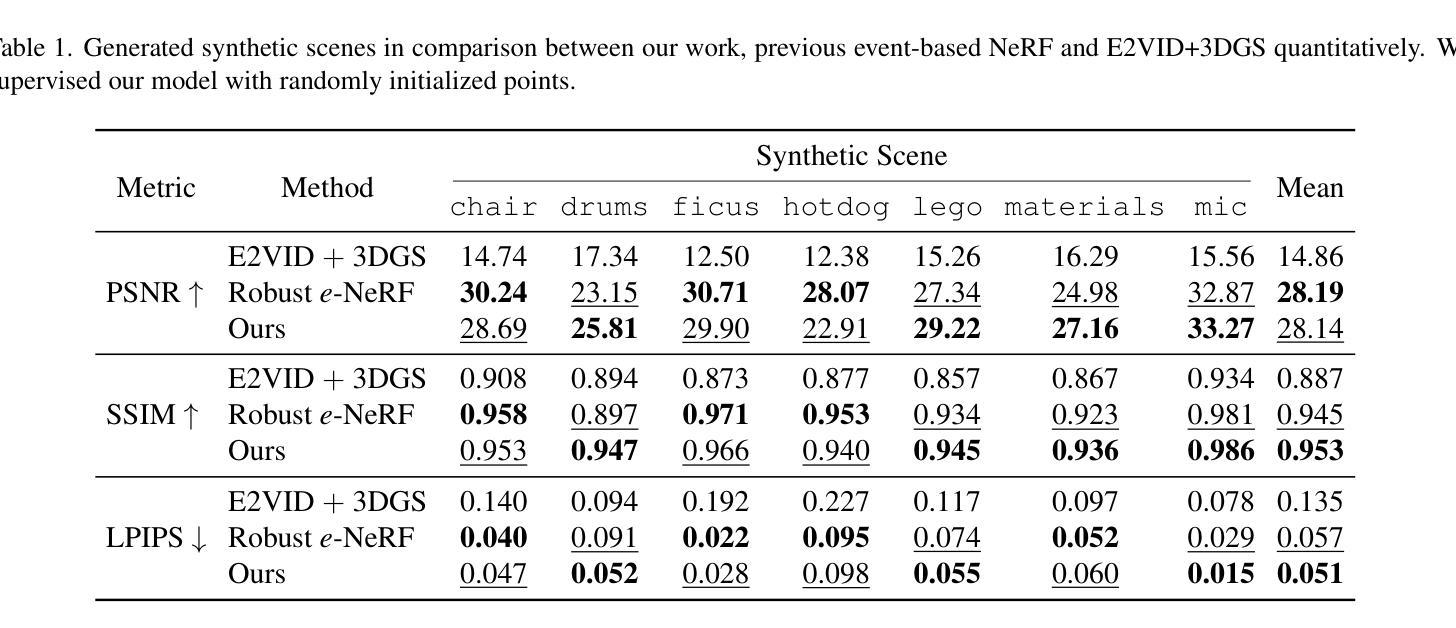
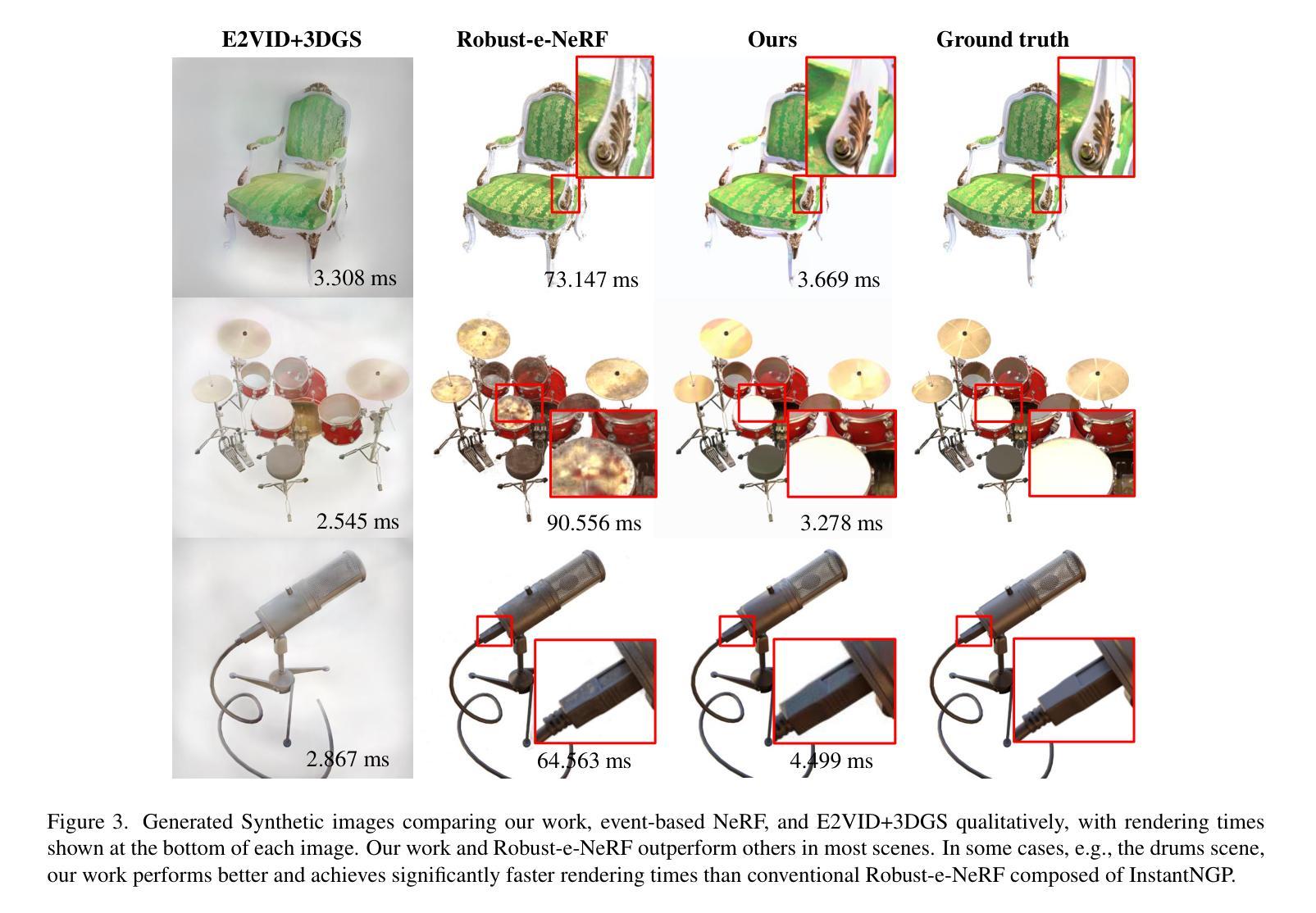
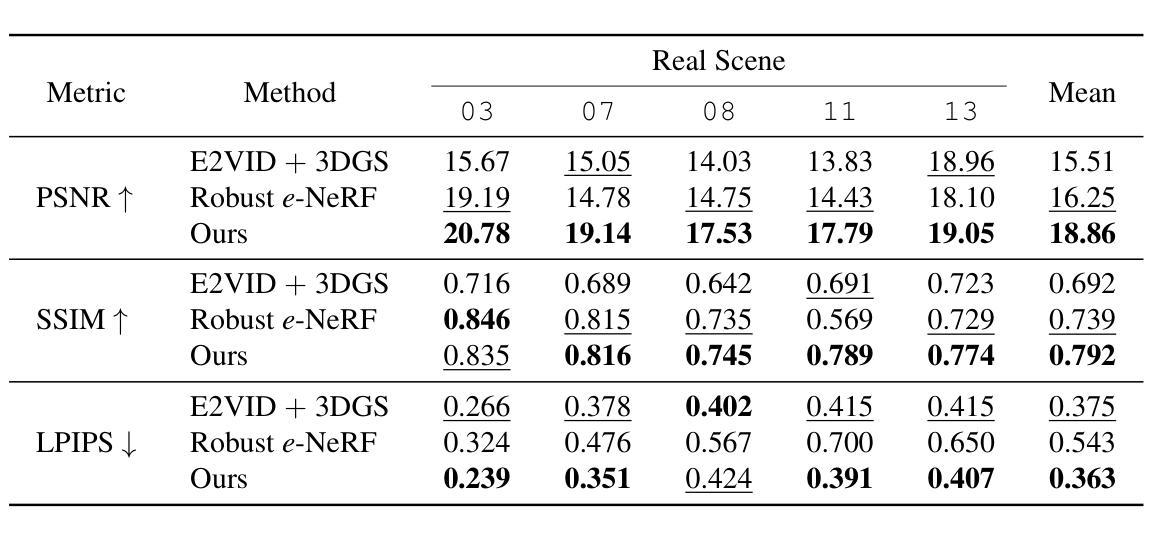
EventSplat: 3D Gaussian Splatting from Moving Event Cameras for Real-time Rendering
Authors:Toshiya Yura, Ashkan Mirzaei, Igor Gilitschenski
We introduce a method for using event camera data in novel view synthesis via Gaussian Splatting. Event cameras offer exceptional temporal resolution and a high dynamic range. Leveraging these capabilities allows us to effectively address the novel view synthesis challenge in the presence of fast camera motion. For initialization of the optimization process, our approach uses prior knowledge encoded in an event-to-video model. We also use spline interpolation for obtaining high quality poses along the event camera trajectory. This enhances the reconstruction quality from fast-moving cameras while overcoming the computational limitations traditionally associated with event-based Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) methods. Our experimental evaluation demonstrates that our results achieve higher visual fidelity and better performance than existing event-based NeRF approaches while being an order of magnitude faster to render.
我们介绍了一种利用事件相机数据通过高斯拼贴法合成新视角的方法。事件相机提供了出色的时间分辨率和高动态范围。利用这些功能,我们能够有效地解决快速相机运动下新视角合成所面临的挑战。为了初始化优化过程,我们的方法使用事件到视频的模型中编码的先验知识。我们还使用折线插值来获得事件相机轨迹的高质量姿态。这提高了快速移动相机的重建质量,并克服了传统上与基于事件的神经过辐射场(NeRF)方法相关的计算限制。我们的实验评估表明,我们的结果实现了比现有基于事件的NeRF方法更高的视觉保真度和性能,同时渲染速度提高了一个数量级。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用事件相机数据进行新颖视角合成的方法,通过高斯喷绘技术实现。事件相机具有出色的时间分辨率和高动态范围,利用这些功能,可以有效解决快速相机运动下的新颖视角合成挑战。初始化优化过程使用事件到视频的先验知识模型,同时使用样条插值获得高质量的事件相机轨迹姿态,提高了从快速移动的相机重建质量,并克服了传统事件基神经辐射场方法的计算限制。实验评估表明,该方法实现了较高的视觉保真度和性能,渲染速度比现有事件基神经辐射场方法快一个数量级。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种基于事件相机数据的新颖视角合成方法。
- 事件相机具有优秀的时间分辨率和高动态范围,有助于解决快速相机运动下的视角合成挑战。
- 利用先验知识模型初始化优化过程。
- 使用样条插值获取高质量的事件相机轨迹姿态。
- 提高了从快速移动相机重建的质量。
- 克服了传统事件基神经辐射场方法的计算限制。
- 实验评估显示,该方法视觉保真度和性能较高,渲染速度更快。
点此查看论文截图

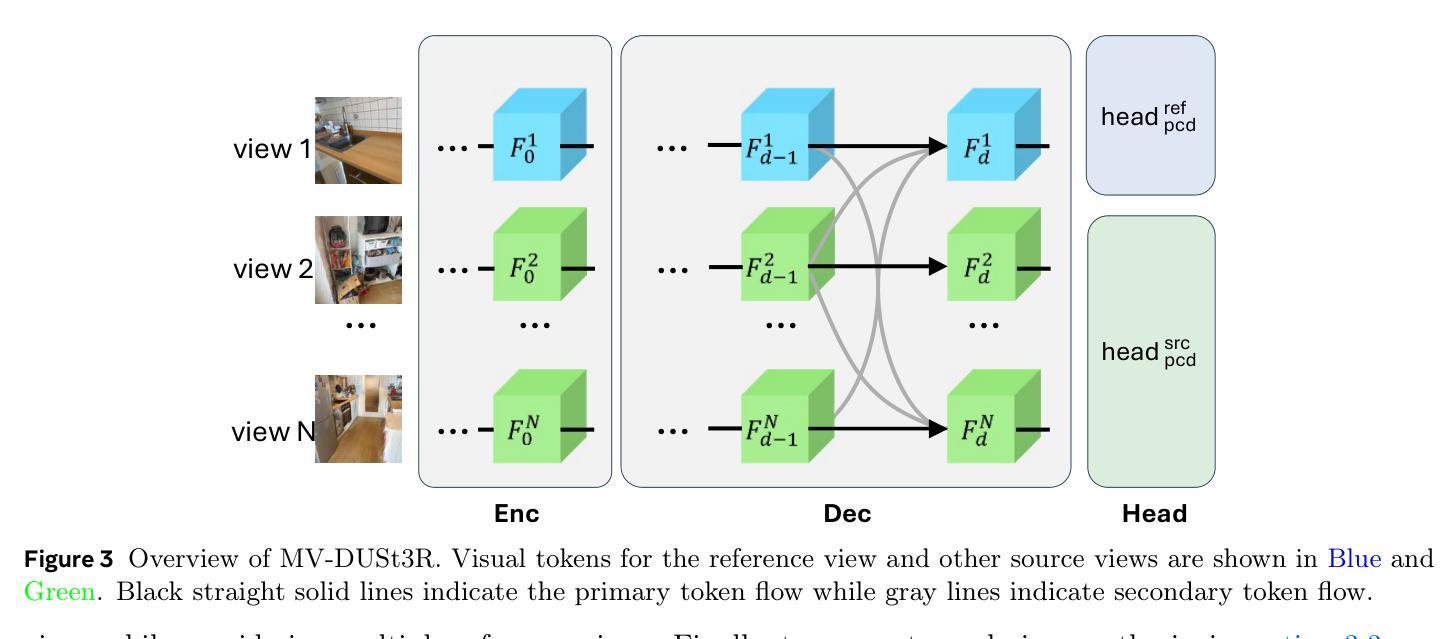
MV-DUSt3R+: Single-Stage Scene Reconstruction from Sparse Views In 2 Seconds
Authors:Zhenggang Tang, Yuchen Fan, Dilin Wang, Hongyu Xu, Rakesh Ranjan, Alexander Schwing, Zhicheng Yan
Recent sparse multi-view scene reconstruction advances like DUSt3R and MASt3R no longer require camera calibration and camera pose estimation. However, they only process a pair of views at a time to infer pixel-aligned pointmaps. When dealing with more than two views, a combinatorial number of error prone pairwise reconstructions are usually followed by an expensive global optimization, which often fails to rectify the pairwise reconstruction errors. To handle more views, reduce errors, and improve inference time, we propose the fast single-stage feed-forward network MV-DUSt3R. At its core are multi-view decoder blocks which exchange information across any number of views while considering one reference view. To make our method robust to reference view selection, we further propose MV-DUSt3R+, which employs cross-reference-view blocks to fuse information across different reference view choices. To further enable novel view synthesis, we extend both by adding and jointly training Gaussian splatting heads. Experiments on multi-view stereo reconstruction, multi-view pose estimation, and novel view synthesis confirm that our methods improve significantly upon prior art. Code will be released.
近期的稀疏多视角场景重建技术进展,如DUSt3R和MASt3R,不再需要相机标定和相机姿态估计。然而,它们仅一次处理一对视角来推断像素对齐的点图。在处理超过两个视角时,通常伴随着一系列容易出现错误的成对重建,随后是昂贵的全局优化,这往往无法纠正成对重建的错误。为了处理更多视角、减少错误并提高推理时间,我们提出了快速单阶段前馈网络MV-DUSt3R。其核心是多视角解码器块,可以在考虑任一参考视角的同时,交换任何数量的视角信息。为了使我们的方法对参考视角选择具有鲁棒性,我们进一步提出了MV-DUSt3R+,它采用跨参考视角块来融合不同参考视角选择的信息。为了进一步实现新颖视角合成,我们通过添加并联合训练高斯喷涂头来扩展两者。在多角度立体重建、多角度姿态估计和新颖视角合成方面的实验证实,我们的方法在先前技术的基础上有了显著改进。代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期,针对稀疏多视角场景重建的研究进展,如DUSt3R和MASt3R,已无需相机校准和相机姿态估计。但它们仅处理一对视图进行像素对齐的点图推断。处理多于两个视图时,常伴随组合数量的错误配对重建,随后是昂贵的全局优化,这往往无法纠正配对重建错误。为处理更多视角、减少错误并改善推断时间,我们提出了快速单阶段前馈网络MV-DUSt3R。其核心为多视角解码器块,可在任何数量的视角间交换信息,同时考虑一个参考视角。为使我们方法对参考视角选择具有稳健性,我们进一步提出MV-DUSt3R+,采用跨参考视角块来融合不同参考视角选择的信息。为实现新颖视角合成,我们扩展了两者,增加了高斯泼斑头并进行联合训练。实验证明,我们的方法在多角度立体重建、多角度姿态估计和新颖视角合成上均显著改进了先前技术。
Key Takeaways
- 近期多视角场景重建技术进展不再需要相机校准和姿态估计。
- 现有技术如DUSt3R和MASt3R仅处理两个视图,存在配对重建错误和全局优化问题。
- 为解决上述问题,提出MV-DUSt3R方法,包含多视角解码器块以交换任意视角信息。
- MV-DUSt3R+进一步增强了方法的稳健性,通过跨参考视角块融合信息。
- 为实现新颖视角合成,扩展了MV-DUSt3R和MV-DUSt3R+,增加了高斯泼斑头并进行联合训练。
- 实验证明新方法在多视角立体重建、姿态估计和新颖视角合成上有所提升。
点此查看论文截图

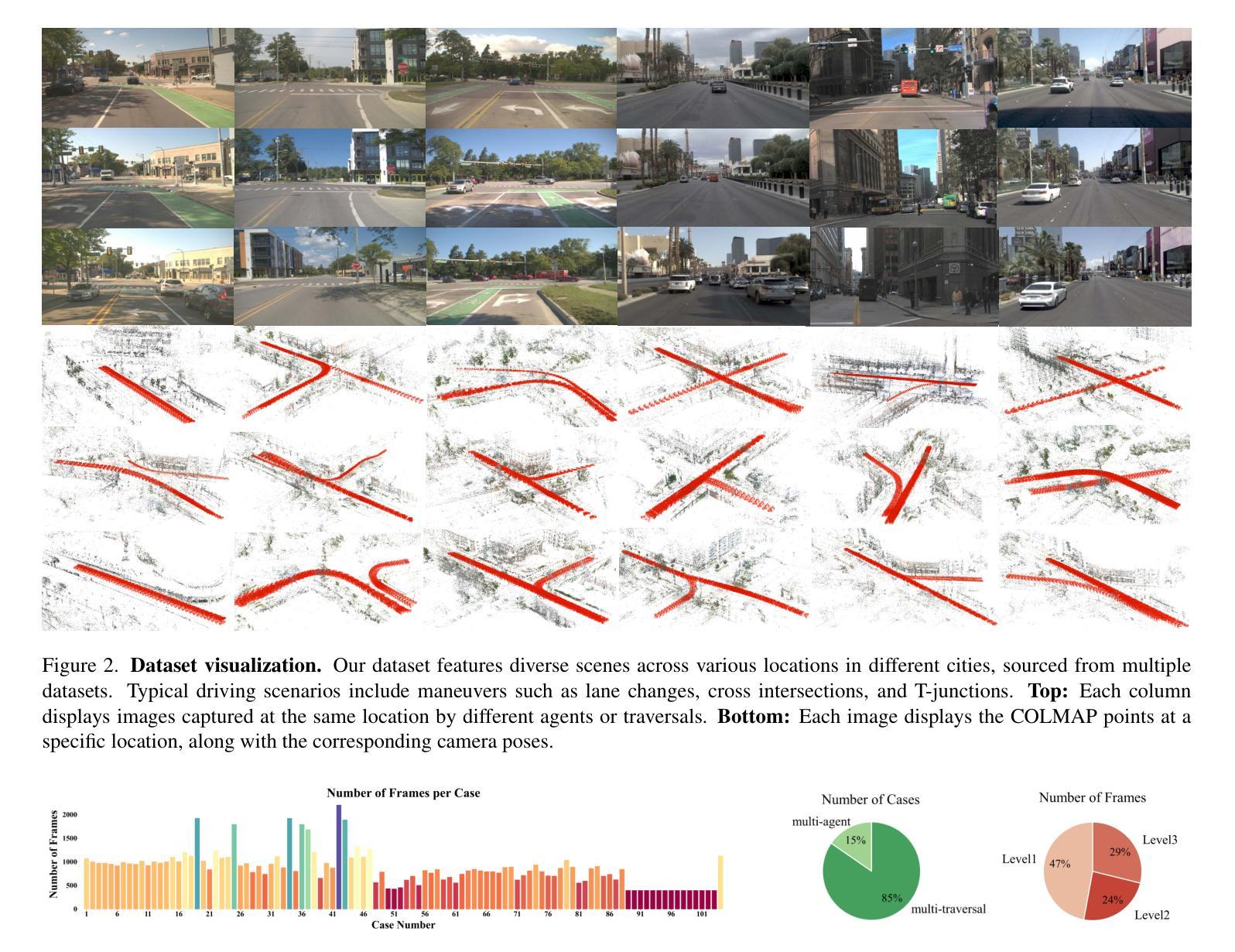
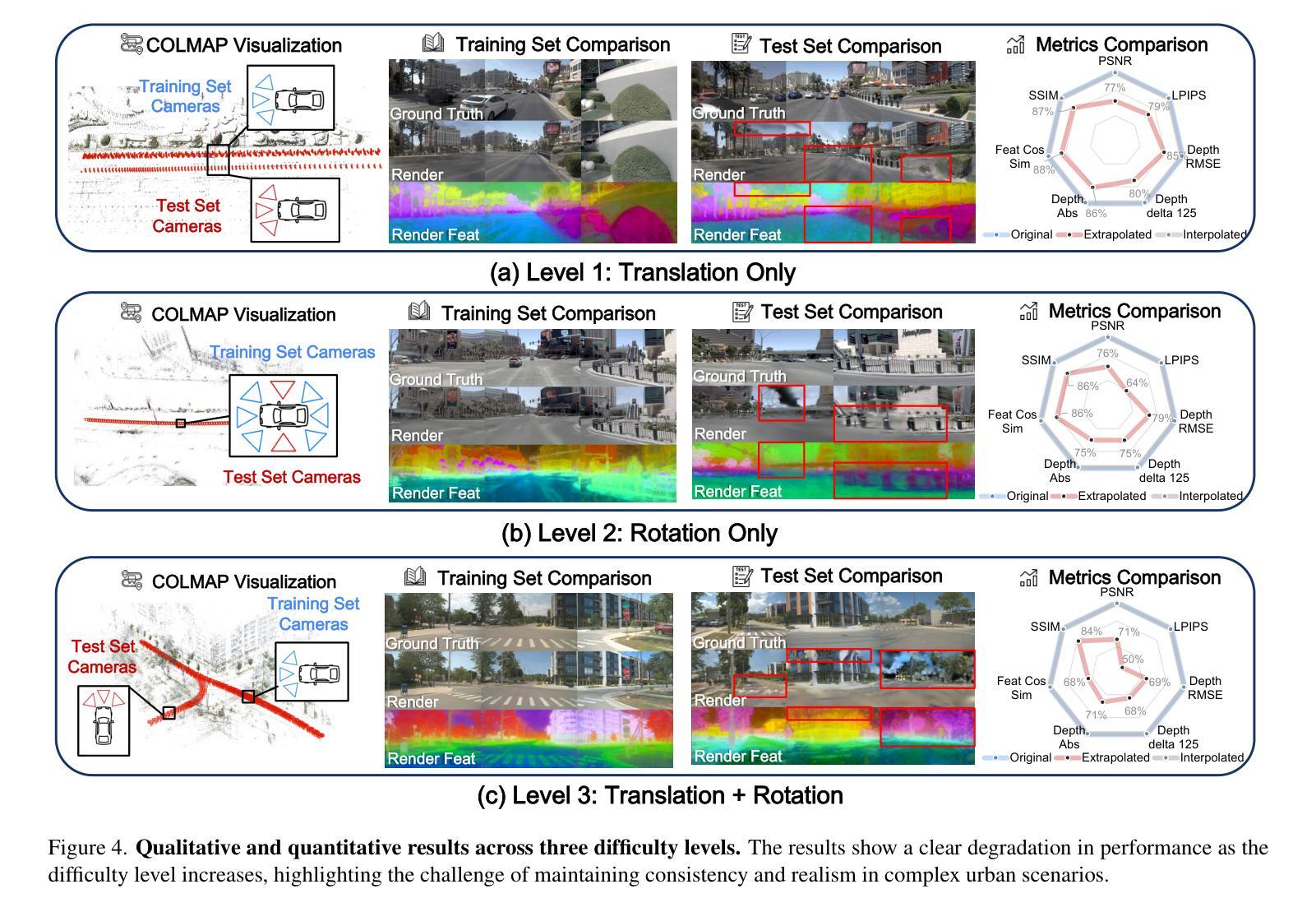
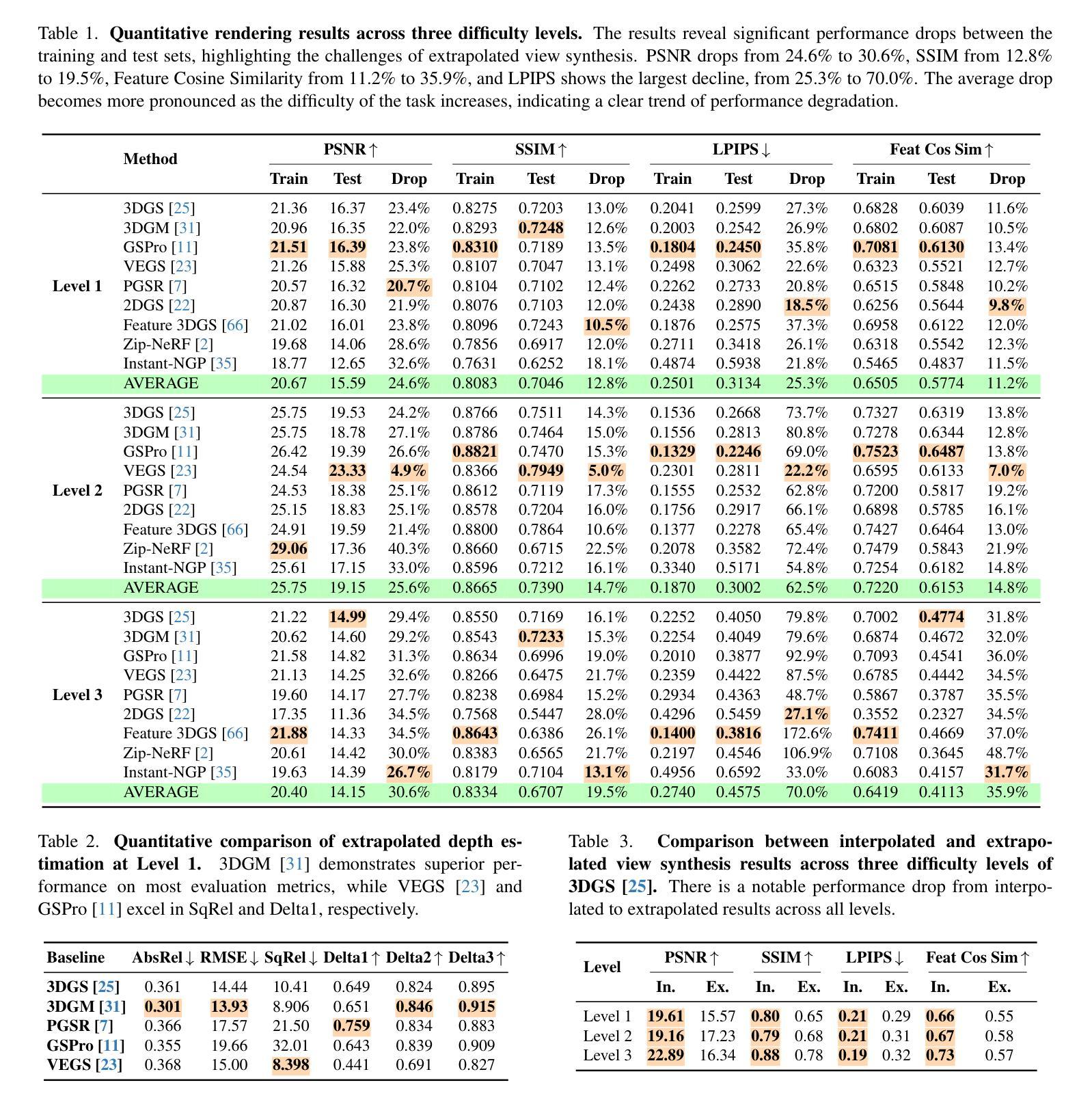
Extrapolated Urban View Synthesis Benchmark
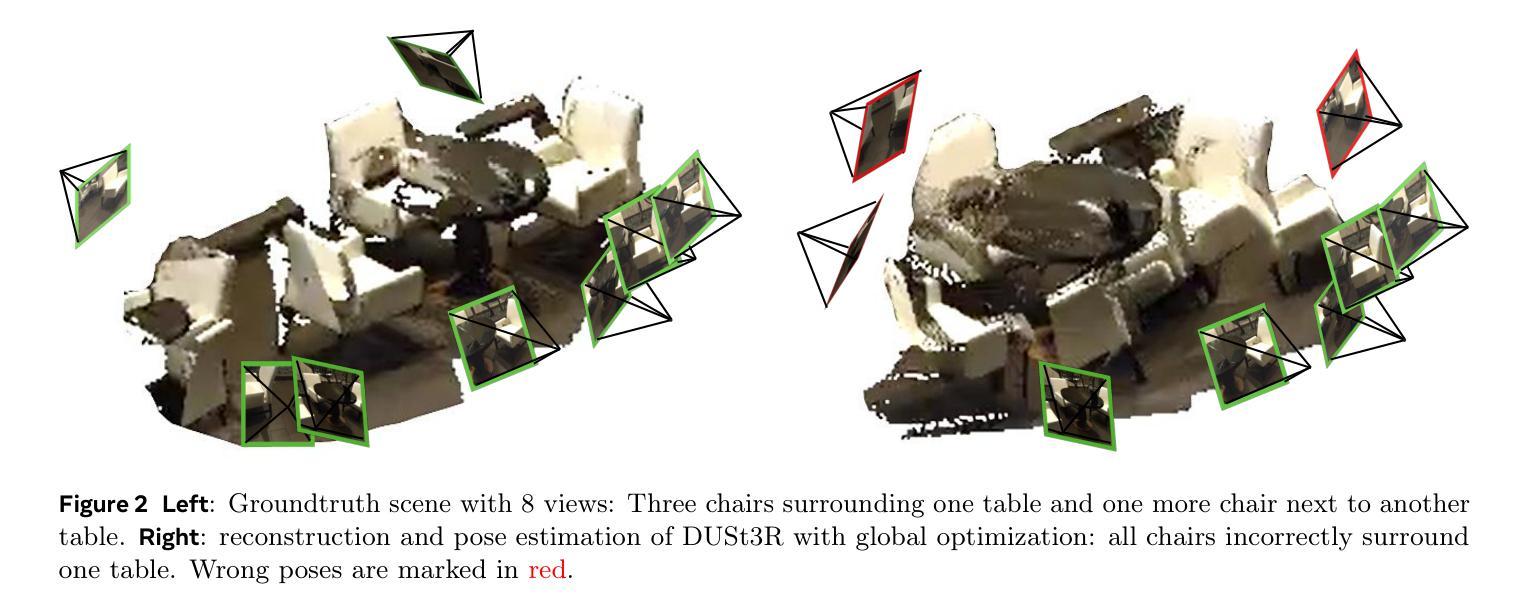
Authors:Xiangyu Han, Zhen Jia, Boyi Li, Yan Wang, Boris Ivanovic, Yurong You, Lingjie Liu, Yue Wang, Marco Pavone, Chen Feng, Yiming Li
Photorealistic simulators are essential for the training and evaluation of vision-centric autonomous vehicles (AVs). At their core is Novel View Synthesis (NVS), a crucial capability that generates diverse unseen viewpoints to accommodate the broad and continuous pose distribution of AVs. Recent advances in radiance fields, such as 3D Gaussian Splatting, achieve photorealistic rendering at real-time speeds and have been widely used in modeling large-scale driving scenes. However, their performance is commonly evaluated using an interpolated setup with highly correlated training and test views. In contrast, extrapolation, where test views largely deviate from training views, remains underexplored, limiting progress in generalizable simulation technology. To address this gap, we leverage publicly available AV datasets with multiple traversals, multiple vehicles, and multiple cameras to build the first Extrapolated Urban View Synthesis (EUVS) benchmark. Meanwhile, we conduct quantitative and qualitative evaluations of state-of-the-art Gaussian Splatting methods across different difficulty levels. Our results show that Gaussian Splatting is prone to overfitting to training views. Besides, incorporating diffusion priors and improving geometry cannot fundamentally improve NVS under large view changes, highlighting the need for more robust approaches and large-scale training. We have released our data to help advance self-driving and urban robotics simulation technology.
真实感模拟器对于以视觉为中心的自动驾驶汽车的训练和评估至关重要。其核心是新型视图合成(NVS),这是一种能够生成各种未见观点以适应自动驾驶汽车广泛且连续姿态分布的关键能力。最近,辐射场方面的进展,如3D高斯拼贴技术,实现了实时速度下的真实感渲染,并已广泛应用于大规模驾驶场景的建模。然而,它们的性能通常使用插值设置进行高度相关的训练和测试视图评估。相比之下,外推(即测试视图与训练视图存在较大偏差)的研究仍然较少,限制了通用仿真技术的进步。为了弥补这一空白,我们利用公开可用的自动驾驶数据集(包含多次遍历、多辆车和多相机)建立了第一个外推城市视图合成(EUVS)基准测试。同时,我们对不同难度水平的最新高斯拼贴方法进行了定量和定性的评估。结果表明,高斯拼贴容易过度拟合训练视图。此外,融入扩散先验知识和改进几何结构并不能在较大视角变化下从根本上改善NVS,这突显了更需要稳健的方法和大规模训练。我们已经发布我们的数据,以帮助推进自动驾驶和城市机器人仿真技术的发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://ai4ce.github.io/EUVS-Benchmark/
Summary
本文强调真实感模拟器对于以视觉为中心的自动驾驶汽车(AVs)的训练和评估至关重要。文章介绍了关键技术——Novel View Synthesis(NVS),它能生成多样的未见过视角以匹配AVs的广泛和连续的姿态分布。最新研究使用三维高斯平铺等技术实现了实时的高逼真渲染。然而,现有评估方法主要关注插值设置,测试视角与训练视角高度相关,忽视了外推评估。为了解决这个问题,文章建立了首个Extrapolated Urban View Synthesis(EUVS)基准测试平台,评估了现有高斯平铺方法在不同难度层次上的表现。结果显示高斯平铺容易过度拟合训练视角,且在大视角变化下难以根本改善NVS性能。为此,需要更稳健的方法和大规模训练数据。文章已公开数据以促进自动驾驶和城市机器人仿真技术的进步。
Key Takeaways
- 真实感模拟器对自动驾驶汽车(AVs)的训练和评估至关重要。
- Novel View Synthesis(NVS)技术生成多样的未见过视角以适应AVs的广泛姿态分布。
- 最新技术如三维高斯平铺实现了实时的高逼真渲染。
- 现有评估方法主要关注插值设置,缺乏对外推评估的研究。
- 建立了首个Extrapolated Urban View Synthesis(EUVS)基准测试平台。
- 高斯平铺技术容易过度拟合训练视角,且在大视角变化下表现不佳。
- 需要更稳健的方法和大规模训练数据来改善NVS性能。
点此查看论文截图

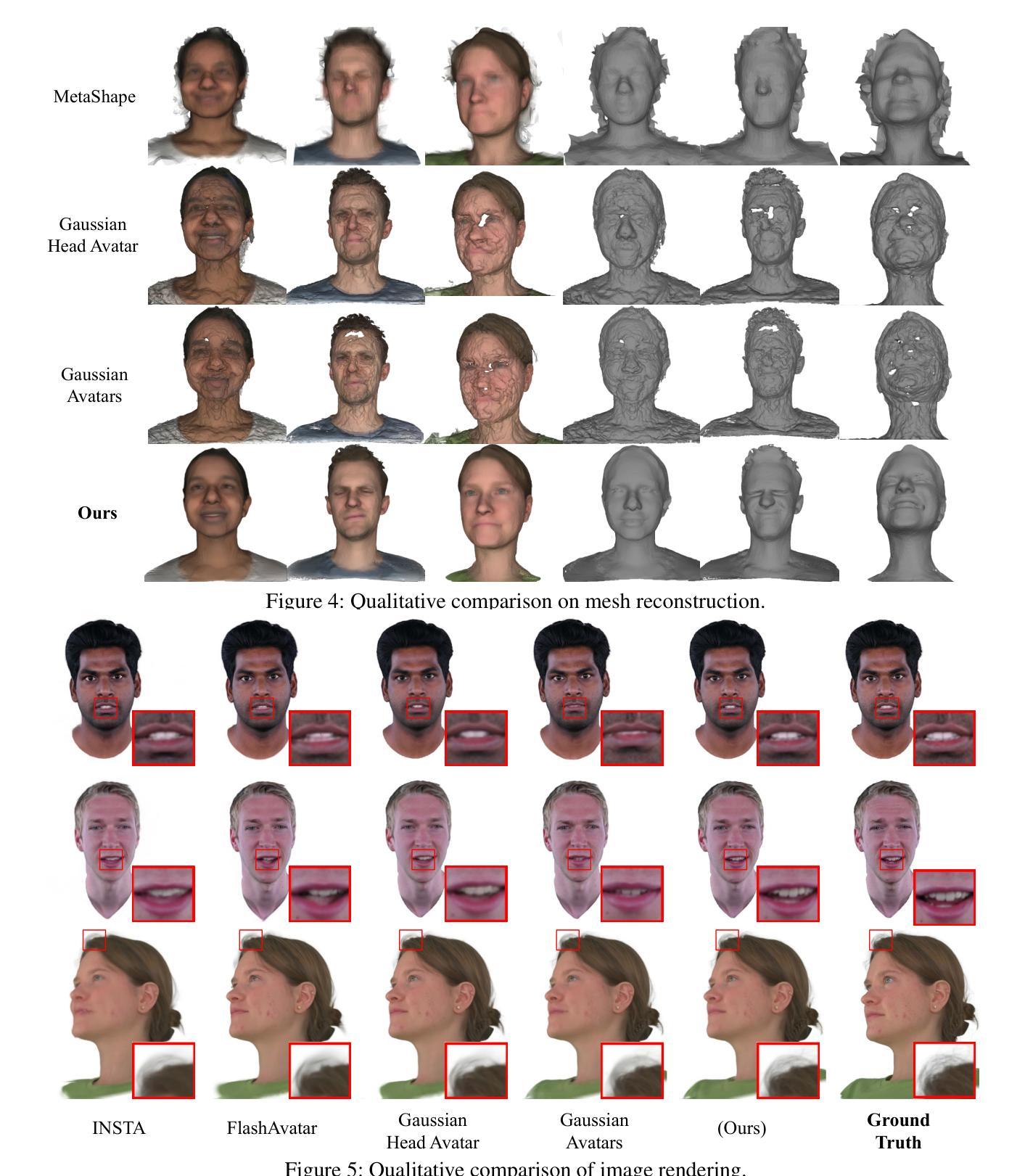
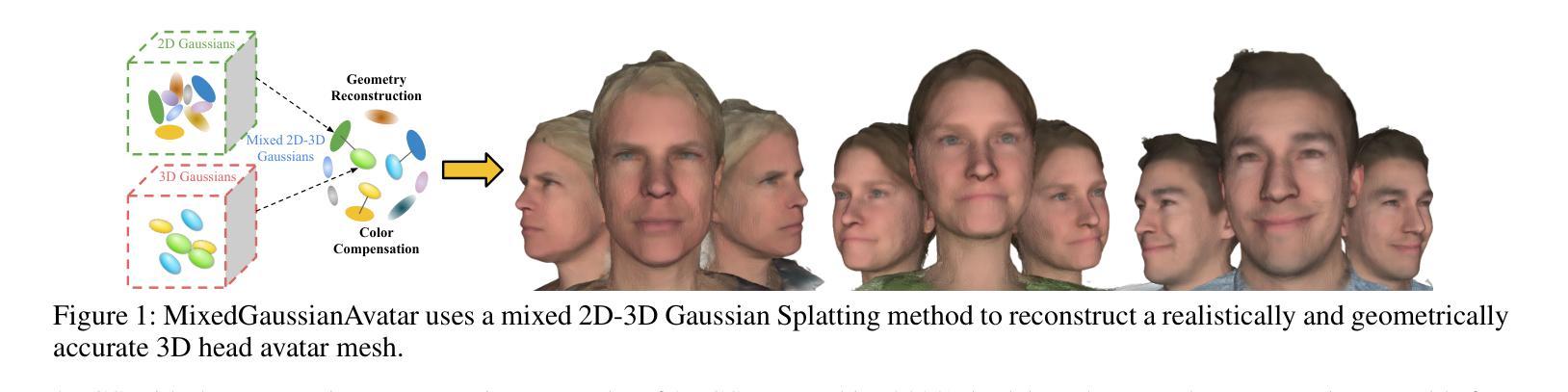
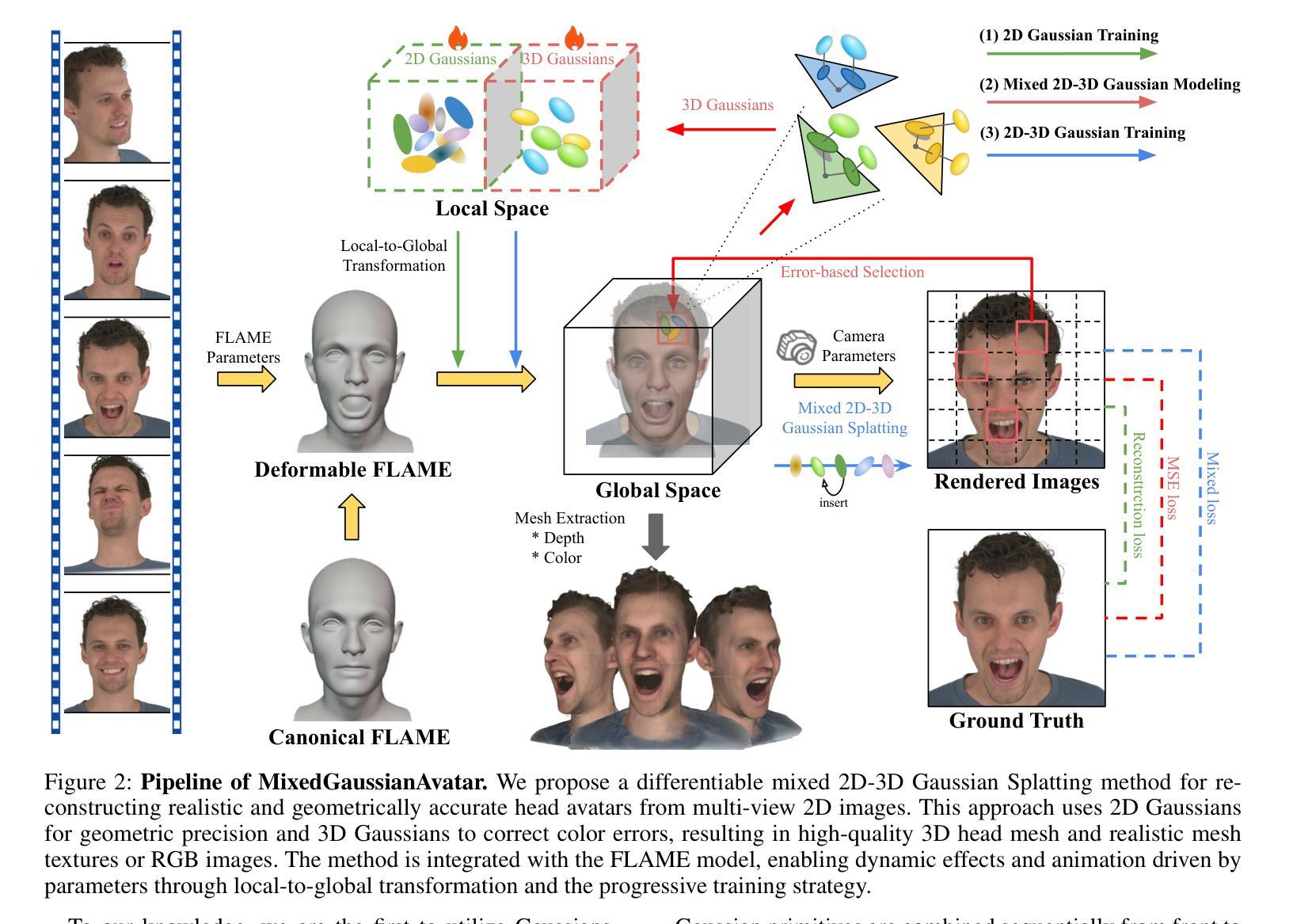
MixedGaussianAvatar: Realistically and Geometrically Accurate Head Avatar via Mixed 2D-3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Peng Chen, Xiaobao Wei, Qingpo Wuwu, Xinyi Wang, Xingyu Xiao, Ming Lu
Reconstructing high-fidelity 3D head avatars is crucial in various applications such as virtual reality. The pioneering methods reconstruct realistic head avatars with Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), which have been limited by training and rendering speed. Recent methods based on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) significantly improve the efficiency of training and rendering. However, the surface inconsistency of 3DGS results in subpar geometric accuracy; later, 2DGS uses 2D surfels to enhance geometric accuracy at the expense of rendering fidelity. To leverage the benefits of both 2DGS and 3DGS, we propose a novel method named MixedGaussianAvatar for realistically and geometrically accurate head avatar reconstruction. Our main idea is to utilize 2D Gaussians to reconstruct the surface of the 3D head, ensuring geometric accuracy. We attach the 2D Gaussians to the triangular mesh of the FLAME model and connect additional 3D Gaussians to those 2D Gaussians where the rendering quality of 2DGS is inadequate, creating a mixed 2D-3D Gaussian representation. These 2D-3D Gaussians can then be animated using FLAME parameters. We further introduce a progressive training strategy that first trains the 2D Gaussians and then fine-tunes the mixed 2D-3D Gaussians. We demonstrate the superiority of MixedGaussianAvatar through comprehensive experiments. The code will be released at: https://github.com/ChenVoid/MGA/.
重建高保真3D头像对于虚拟现实等应用至关重要。早期的方法使用神经辐射场(NeRF)重建逼真的头像,但受限于训练和渲染速度。基于3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)的最近的方法显著提高了训练和渲染的效率。然而,3DGS的表面不一致导致几何精度不佳;后来的2DGS使用2D surfels以提高几何精度,但牺牲了渲染保真度。为了结合2DGS和3DGS的优点,我们提出了一种名为MixedGaussianAvatar的新方法,用于进行真实且几何精确的头像重建。我们的主要思想是利用2D高斯重建3D头像的表面,以确保几何精度。我们将2D高斯附加到FLAME模型的三角网格上,并在2DGS渲染质量不足的地方连接额外的3D高斯,创建混合的2D-3D高斯表示。这些2D-3D高斯可以使用FLAME参数进行动画处理。我们还引入了一种渐进的训练策略,首先训练2D高斯,然后对混合的2D-3D高斯进行微调。我们通过全面的实验证明了MixedGaussianAvatar的优越性。代码将在以下网址发布:https://github.com/ChenVoid/MGA/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project: https://chenvoid.github.io/MGA/
Summary
针对三维头像重建,混合高斯体素方法(MixedGaussianAvatar)结合了二维高斯体素(2DGS)和三维高斯体素(3DGS)的优势,旨在实现真实且几何精度高的头像重建。该方法使用二维高斯重建三维头部的表面,确保几何精度,并在必要时添加三维高斯以提高渲染质量。此外,采用渐进式训练策略,先训练二维高斯,再微调混合的二维和三维高斯。该方法已在实验中表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 混合高斯体素方法结合了二维和三维高斯体素的优势,用于提高三维头像重建的真实性和几何精度。
- 方法利用二维高斯重建头部表面并确保几何精度,必要时添加三维高斯以提高渲染质量。
- 采用渐进式训练策略,先单独训练二维高斯,再对混合的二维和三维高斯进行微调。
- 该方法已在实验中表现出卓越性能,并提供了代码实现。
点此查看论文截图

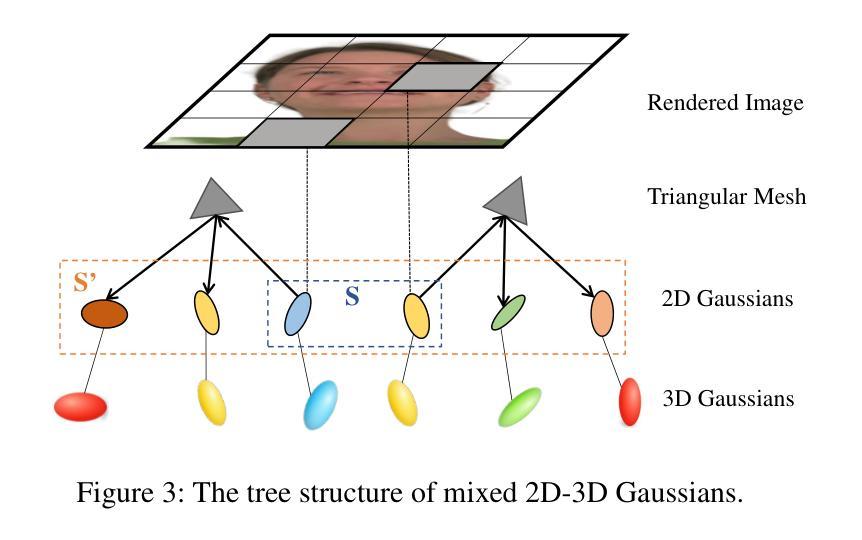

HybridGS: Decoupling Transients and Statics with 2D and 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jingyu Lin, Jiaqi Gu, Lubin Fan, Bojian Wu, Yujing Lou, Renjie Chen, Ligang Liu, Jieping Ye
Generating high-quality novel view renderings of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) in scenes featuring transient objects is challenging. We propose a novel hybrid representation, termed as HybridGS, using 2D Gaussians for transient objects per image and maintaining traditional 3D Gaussians for the whole static scenes. Note that, the 3DGS itself is better suited for modeling static scenes that assume multi-view consistency, but the transient objects appear occasionally and do not adhere to the assumption, thus we model them as planar objects from a single view, represented with 2D Gaussians. Our novel representation decomposes the scene from the perspective of fundamental viewpoint consistency, making it more reasonable. Additionally, we present a novel multi-view regulated supervision method for 3DGS that leverages information from co-visible regions, further enhancing the distinctions between the transients and statics. Then, we propose a straightforward yet effective multi-stage training strategy to ensure robust training and high-quality view synthesis across various settings. Experiments on benchmark datasets show our state-of-the-art performance of novel view synthesis in both indoor and outdoor scenes, even in the presence of distracting elements.
在包含瞬态对象的场景中,使用三维高斯点渲染(3DGS)生成高质量的新型视角渲染是一项挑战。我们提出了一种新型混合表示方法,称为HybridGS,使用针对每幅图像中的瞬态对象进行二维高斯表示,同时保持对整个静态场景的传统三维高斯表示。需要注意的是,三维高斯本身更适合于对假设多视角一致的静态场景进行建模,而瞬态对象则会出现偶然并不遵循此假设,因此我们将其建模为平面对象并从单一视角进行表示,以二维高斯形式展现。我们的新型表示方法从基本视角一致性的角度对场景进行分解,使其更加合理。此外,我们提出了一种新型的多视角调控监督方法用于三维高斯渲染技术,利用可见区域的非失真信息来进一步区分瞬态对象和静态对象。接着,我们提出了一种简单有效的多阶段训练策略,以确保在各种设置下实现稳健的训练和高质量的视角合成。在基准数据集上的实验表明,我们在室内和室外场景的视角合成方面取得了最新性能表现,即使在存在干扰元素的情况下也是如此。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://gujiaqivadin.github.io/hybridgs/
Summary
该文本介绍了针对含有瞬态物体的三维高斯模糊(3DGS)场景,提出一种名为HybridGS的新型混合表示方法。该方法使用二维高斯表示图像中的瞬态物体,同时保持对整个静态场景使用传统的三维高斯表示。提出一种新型的多视角监管方法,利用可见区域的信息,进一步区分瞬态物体和静态物体。同时,提出了一种简单有效的多阶段训练策略,确保在各种设置下实现稳健的训练和高质量视图合成。实验结果表明,该方法在室内和室外场景的新型视图合成中均表现出卓越性能,即使在存在干扰元素的情况下也是如此。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了HybridGS混合表示方法,将瞬态物体用二维高斯表示,静态场景用三维高斯表示。
- 针对含有瞬态物体的3DGS场景,采用多视角监管方法,利用可见区域信息提高瞬态物体和静态物体的区分度。
- 提出了多阶段训练策略,以提高在各种设置下的视图合成质量和稳健性。
- 引入了视角一致性分解的概念,使场景分解更为合理。
- 该方法在合成室内和室外场景的新视图时表现出卓越性能。
- 该方法能够有效处理存在干扰元素的情况。
点此查看论文截图

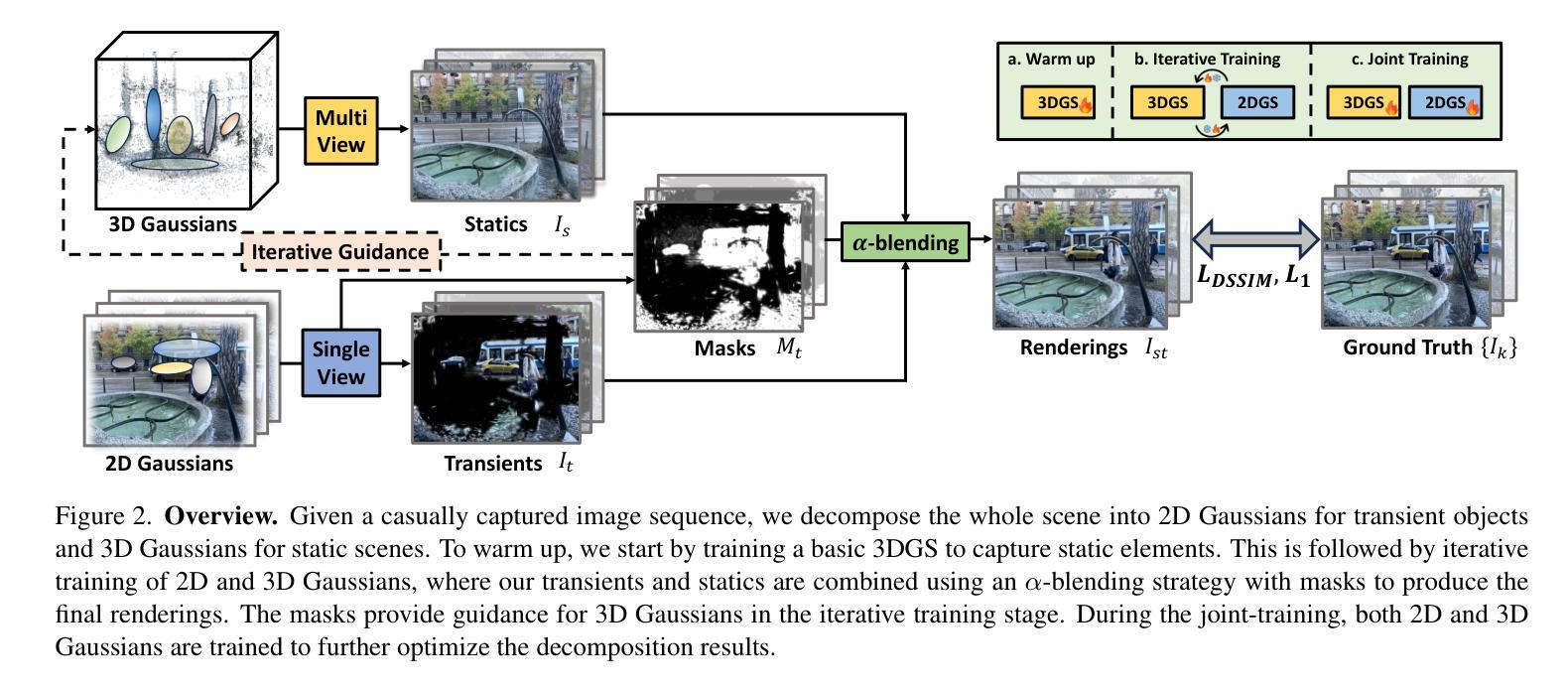
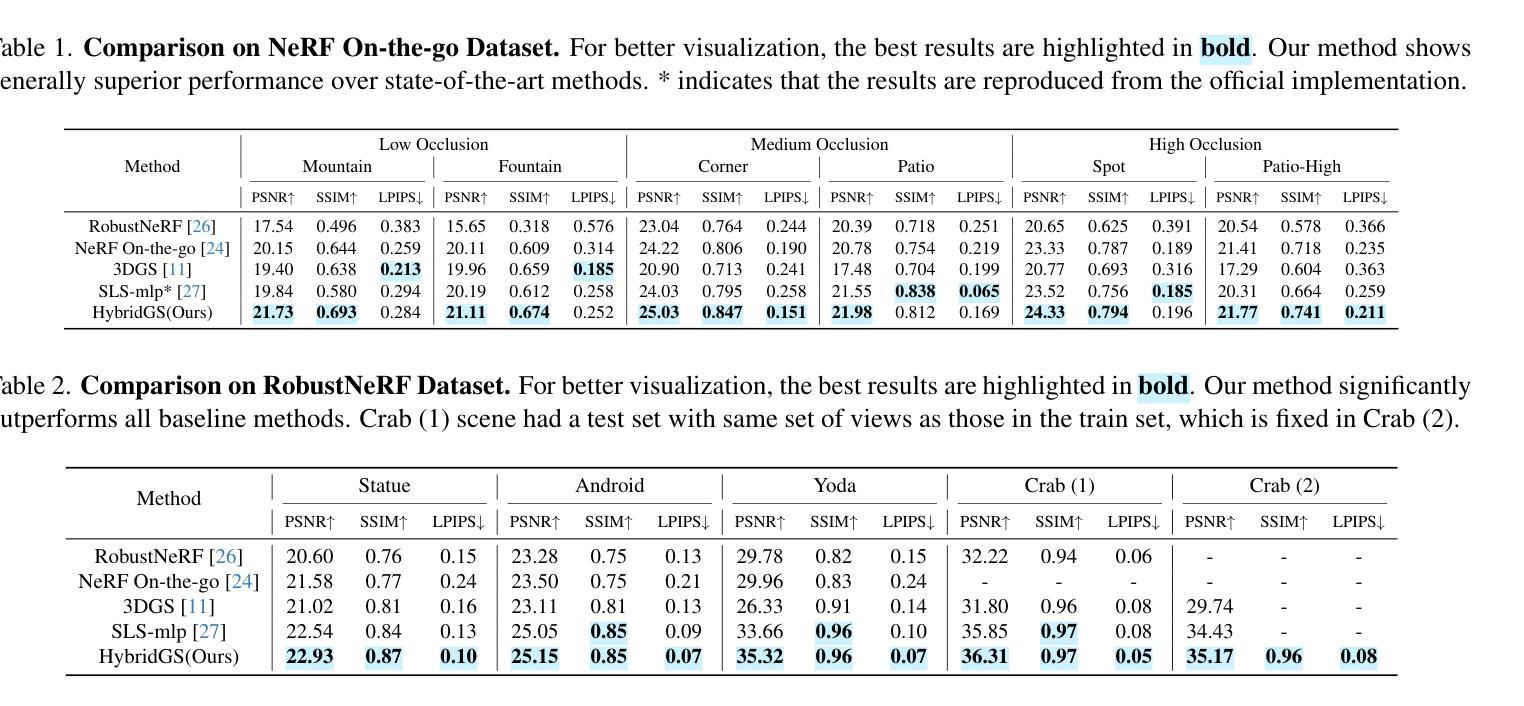
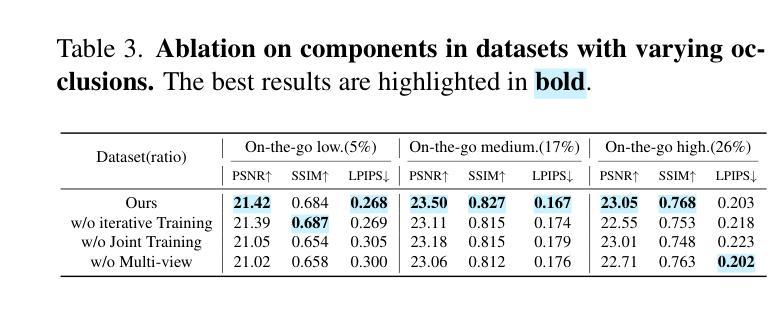
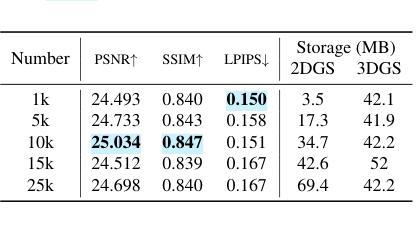
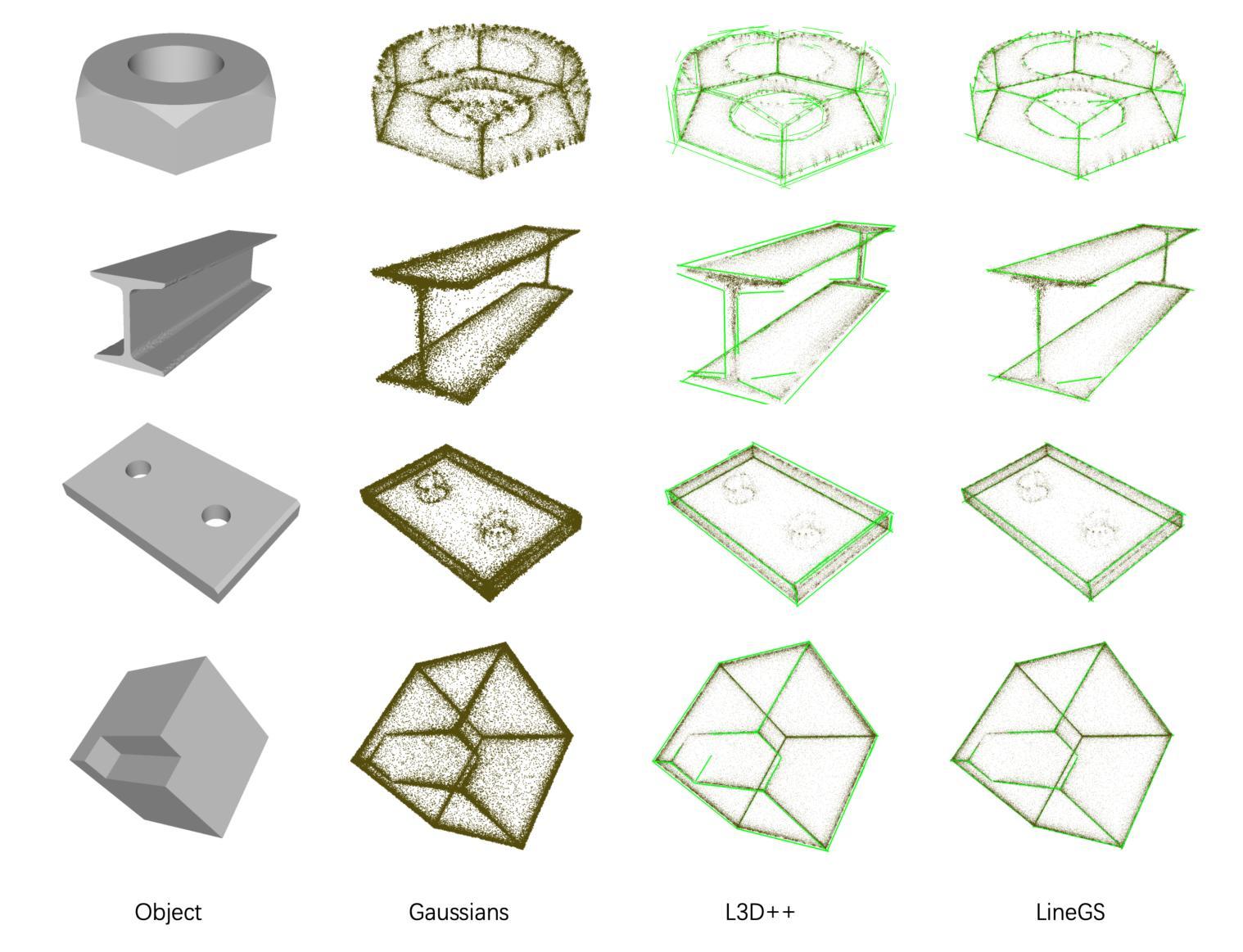
LineGS : 3D Line Segment Representation on 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Chenggang Yang, Yuang Shi, Wei Tsang Ooi
Abstract representations of 3D scenes play a crucial role in computer vision, enabling a wide range of applications such as mapping, localization, surface reconstruction, and even advanced tasks like SLAM and rendering. Among these representations, line segments are widely used because of their ability to succinctly capture the structural features of a scene. However, existing 3D reconstruction methods often face significant challenges. Methods relying on 2D projections suffer from instability caused by errors in multi-view matching and occlusions, while direct 3D approaches are hampered by noise and sparsity in 3D point cloud data. This paper introduces LineGS, a novel method that combines geometry-guided 3D line reconstruction with a 3D Gaussian splatting model to address these challenges and improve representation ability. The method leverages the high-density Gaussian point distributions along the edge of the scene to refine and optimize initial line segments generated from traditional geometric approaches. By aligning these segments with the underlying geometric features of the scene, LineGS achieves a more precise and reliable representation of 3D structures. The results show significant improvements in both geometric accuracy and model compactness compared to baseline methods.
三维场景的抽象表示在计算机视觉中发挥着至关重要的作用,能够实现如地图绘制、定位、表面重建以及高级任务如SLAM和渲染等一系列广泛的应用。在这些表示方法中,线段因其能够简洁地捕捉场景的结构特征而得到广泛应用。然而,现有的三维重建方法常常面临巨大挑战。依赖二维投影的方法受到多视角匹配和遮挡所产生的误差影响而不稳定,而直接的三维方法则受到三维点云数据中的噪声和稀疏性的阻碍。本文介绍了一种新型方法LineGS,该方法结合了几何引导的的三维线段重建和三维高斯扩展模型,以解决这些挑战并提升表示能力。该方法利用场景边缘的高密度高斯点分布来优化和改进由传统几何方法生成的初始线段。通过将这些线段与场景的基本几何特征对齐,LineGS实现了对三维结构更为精确和可靠的表现。结果表明,与基准方法相比,该方法在几何精度和模型紧凑性方面均有显著提高。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
这篇论文提出了一种名为LineGS的新方法,结合了几何指导的三维线重建与三维高斯散斑模型,以改进现有的三维重建方法面临的挑战。该方法利用场景边缘的高密度高斯点分布来优化和细化由传统几何方法生成的初始线段。通过与场景的底层几何特征对齐这些线段,LineGS实现了更准确可靠的三维结构表示。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了LineGS方法,旨在改进三维重建中的挑战。
- LineGS结合了几何指导的三维线重建和三维高斯散斑模型。
- 高密度高斯点分布用于优化和细化由传统几何方法生成的初始线段。
- LineGS通过对齐场景底层几何特征,实现了更准确可靠的三维结构表示。
- LineGS在几何精度和模型紧凑性方面相较于基线方法有显著改善。
- 该方法对于处理多视图匹配和遮挡引起的误差以及点云数据的噪声和稀疏性问题具有优势。
点此查看论文截图


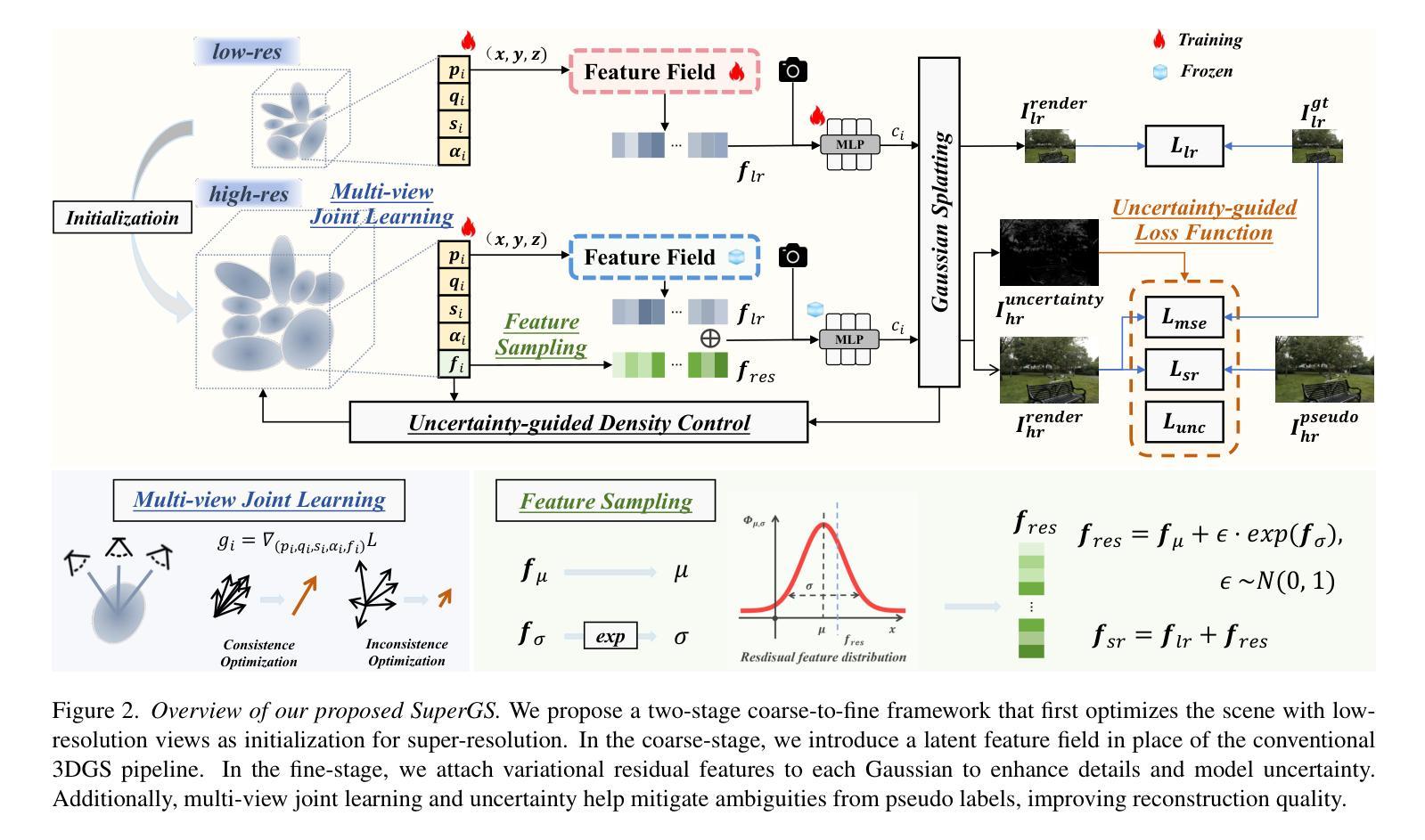
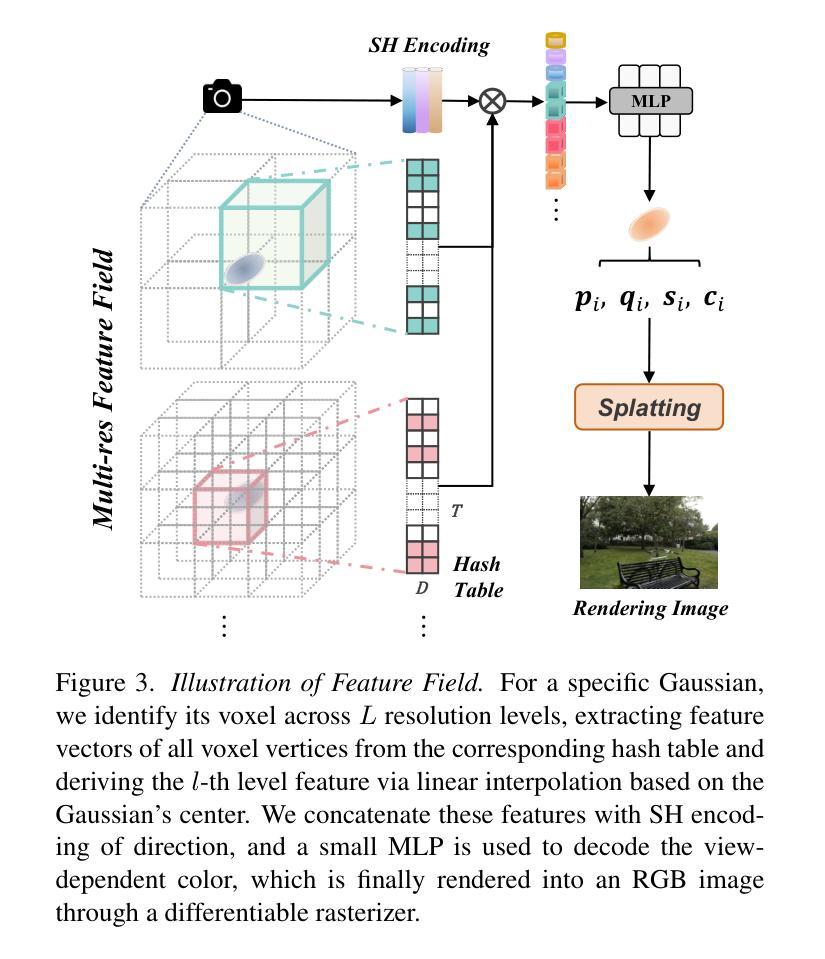
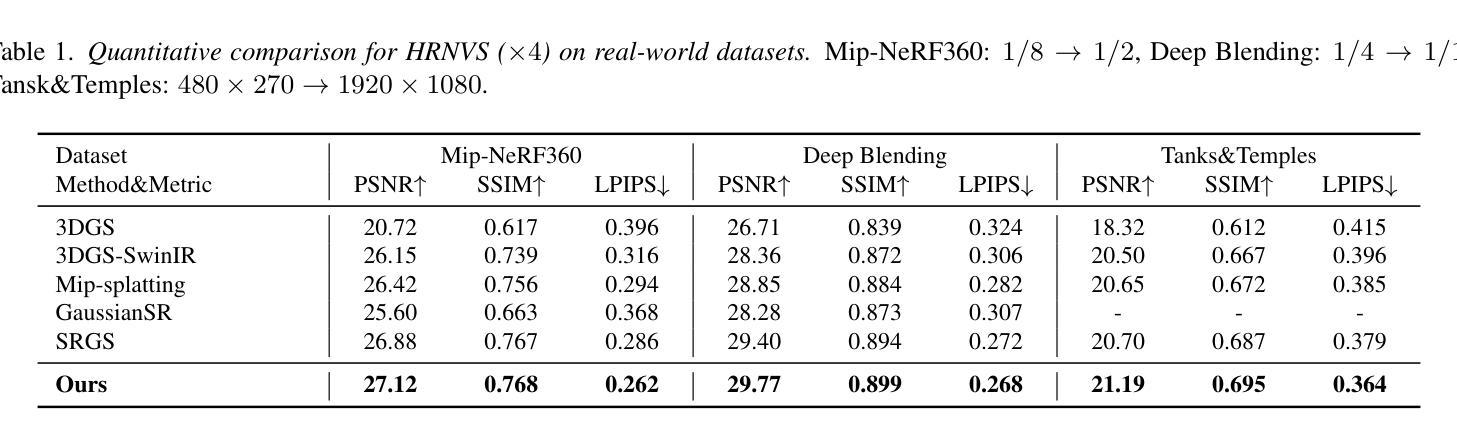
SuperGS: Super-Resolution 3D Gaussian Splatting Enhanced by Variational Residual Features and Uncertainty-Augmented Learning
Authors:Shiyun Xie, Zhiru Wang, Xu Wang, Yinghao Zhu, Chengwei Pan, Xiwang Dong
Recently, 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has exceled in novel view synthesis (NVS) with its real-time rendering capabilities and superior quality. However, it faces challenges for high-resolution novel view synthesis (HRNVS) due to the coarse nature of primitives derived from low-resolution input views. To address this issue, we propose Super-Resolution 3DGS (SuperGS), which is an expansion of 3DGS designed with a two-stage coarse-to-fine training framework. In this framework, we use a latent feature field to represent the low-resolution scene, serving as both the initialization and foundational information for super-resolution optimization. Additionally, we introduce variational residual features to enhance high-resolution details, using their variance as uncertainty estimates to guide the densification process and loss computation. Furthermore, the introduction of a multi-view joint learning approach helps mitigate ambiguities caused by multi-view inconsistencies in the pseudo labels. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SuperGS surpasses state-of-the-art HRNVS methods on both real-world and synthetic datasets using only low-resolution inputs. Code is available at https://github.com/SYXieee/SuperGS.
最近,3D高斯延展(3DGS)凭借其实时渲染能力和卓越质量在新型视图合成(NVS)方面表现出色。然而,它在高分辨率新型视图合成(HRNVS)方面面临挑战,这是由于从低分辨率输入视图派生的原始数据的粗糙性质所致。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了超级分辨率3DGS(SuperGS),它是3DGS的扩展,采用两阶段从粗到细的训练框架设计。在此框架中,我们使用潜在特征场来表示低分辨率场景,作为超分辨率优化的初始化和基础信息。此外,我们引入了变异残留特征以增强高分辨率细节,并使用其方差作为不确定性估计来指导密集化过程和损失计算。而且,引入多视图联合学习方法有助于减少由伪标签的多视图不一致性引起的歧义。大量实验表明,仅使用低分辨率输入的SuperGS在真实世界和合成数据集上的HRNVS性能超越了最新方法。代码可在https://github.com/SYXieee/SuperGS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
3DGS在新型视图合成领域具有实时渲染和高质量的优势,但面对高分辨率新型视图合成(HRNVS)的挑战。为解决此问题,提出SuperGS方法,通过两阶段精细训练框架和潜在特征场表示低分辨率场景,引入变异残差特征增强高分辨率细节,并使用方差作为不确定性估计指导优化和损失计算过程。同时采用多视角联合学习方法减少伪标签的多视角不一致性引起的模糊性。实验证明SuperGS在真实和合成数据集上均超越现有HRNVS方法。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS在新型视图合成领域表现优异,具有实时渲染和高质量的特点。
- SuperGS是对3DGS的扩展,设计了一个两阶段精细训练框架以解决高分辨率新型视图合成面临的挑战。
- 利用潜在特征场表示低分辨率场景,为后续超分辨率优化提供初始和基础信息。
- 引入变异残差特征以增强高分辨率细节,并利用其方差作为不确定性估计指导优化过程。
- 采用多视角联合学习方法减少伪标签的多视角不一致性引起的模糊性。
- 实验证明SuperGS在真实和合成数据集上的性能优于现有方法,且仅使用低分辨率输入。
点此查看论文截图

Learning-based Multi-View Stereo: A Survey
Authors:Fangjinhua Wang, Qingtian Zhu, Di Chang, Quankai Gao, Junlin Han, Tong Zhang, Richard Hartley, Marc Pollefeys
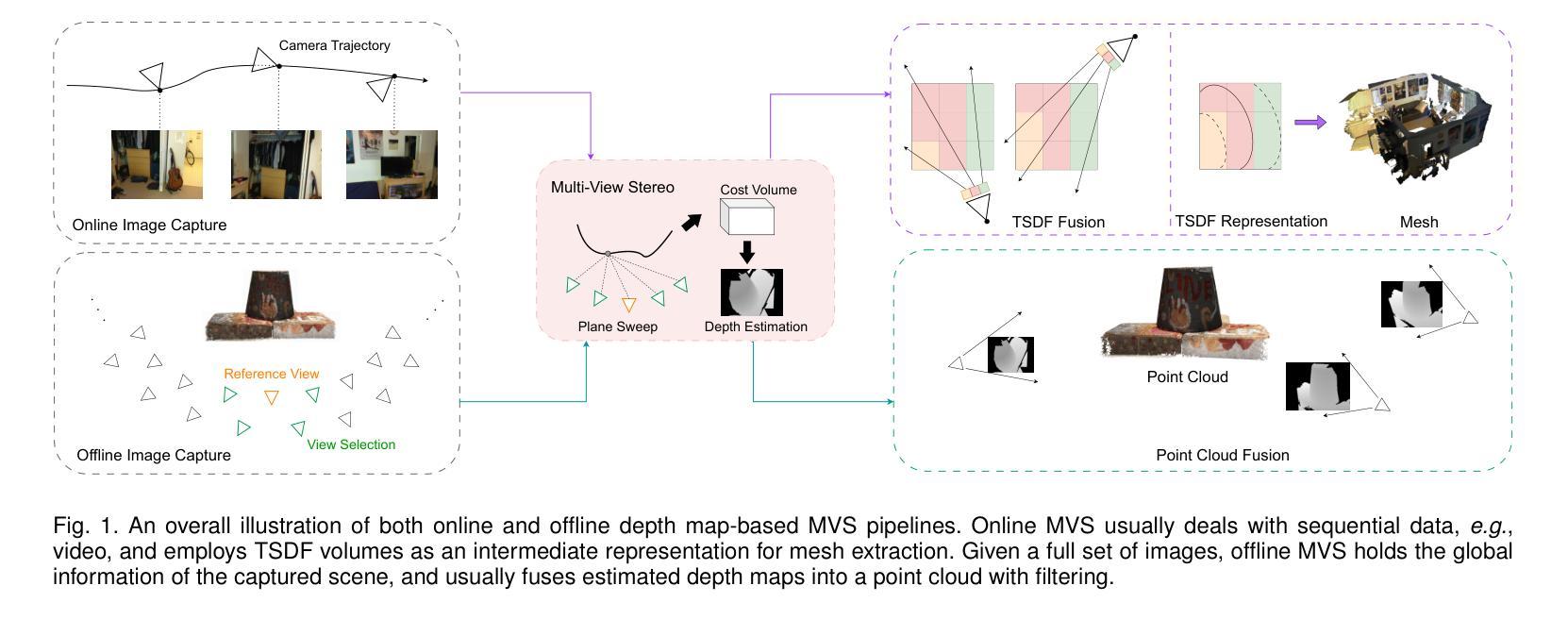
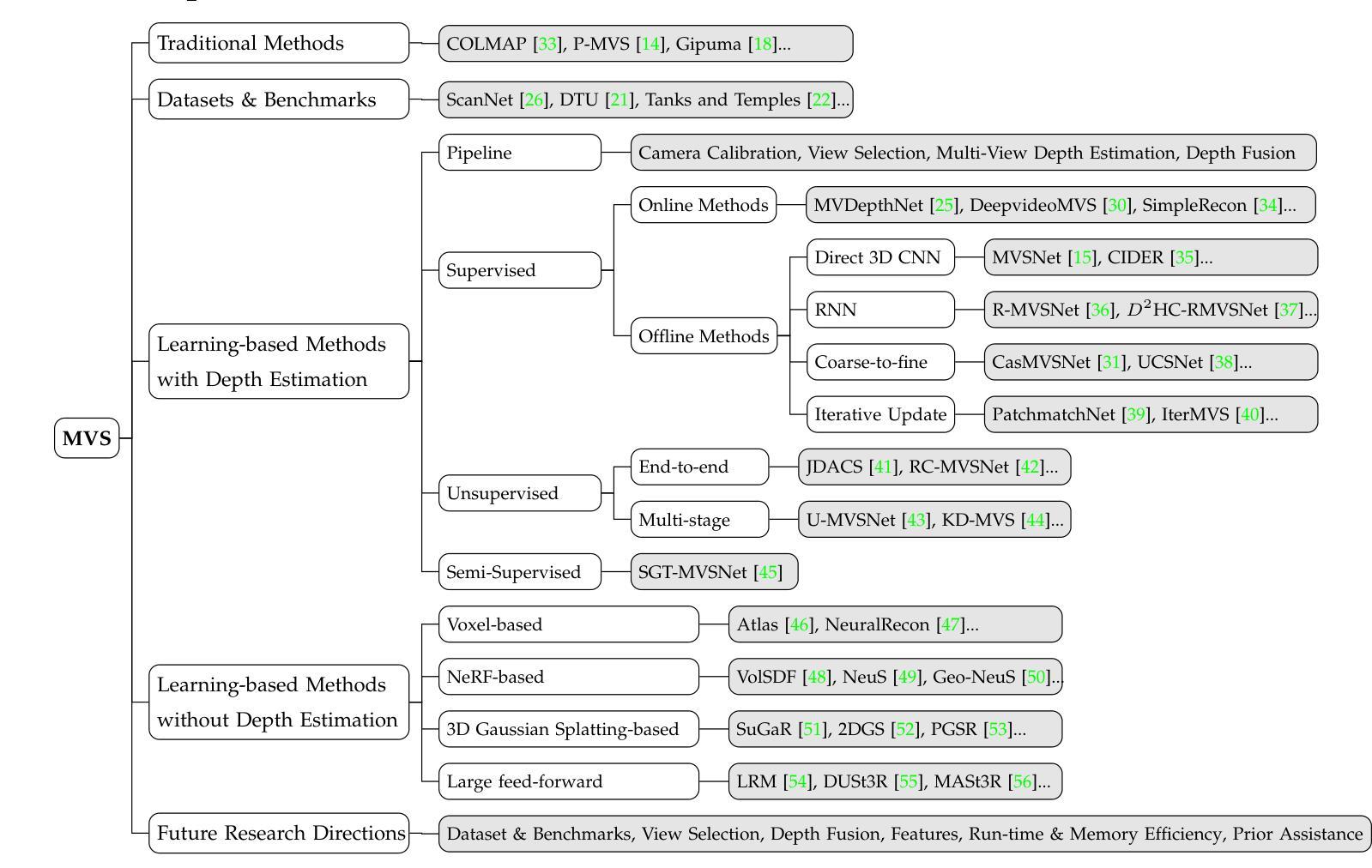
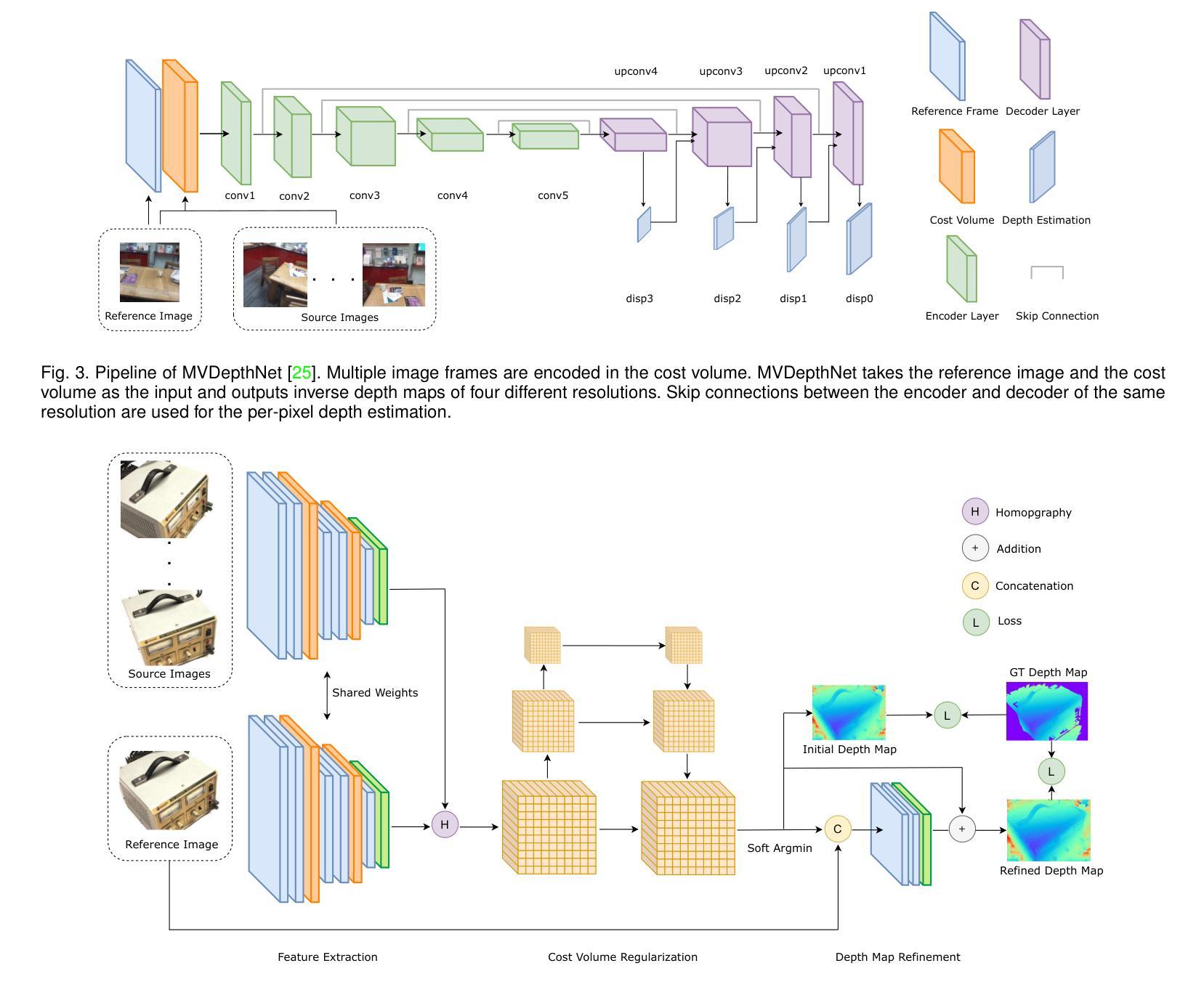
3D reconstruction aims to recover the dense 3D structure of a scene. It plays an essential role in various applications such as Augmented/Virtual Reality (AR/VR), autonomous driving and robotics. Leveraging multiple views of a scene captured from different viewpoints, Multi-View Stereo (MVS) algorithms synthesize a comprehensive 3D representation, enabling precise reconstruction in complex environments. Due to its efficiency and effectiveness, MVS has become a pivotal method for image-based 3D reconstruction. Recently, with the success of deep learning, many learning-based MVS methods have been proposed, achieving impressive performance against traditional methods. We categorize these learning-based methods as: depth map-based, voxel-based, NeRF-based, 3D Gaussian Splatting-based, and large feed-forward methods. Among these, we focus significantly on depth map-based methods, which are the main family of MVS due to their conciseness, flexibility and scalability. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive review of the literature at the time of this writing. We investigate these learning-based methods, summarize their performances on popular benchmarks, and discuss promising future research directions in this area.
三维重建旨在恢复场景的密集三维结构。它在增强/虚拟现实(AR/VR)、自动驾驶和机器人技术等各种应用中发挥着重要作用。利用从不同视角捕获的场景的多个视图,多视图立体(MVS)算法合成全面的三维表示,能够在复杂环境中实现精确重建。由于其高效性和有效性,MVS已成为基于图像的3D重建的关键方法。最近,随着深度学习取得的成功,已经提出了许多基于学习的MVS方法,与传统方法相比,这些方法取得了令人印象深刻的表现。我们将这些基于学习的方法分类为:基于深度图的方法、基于体素的方法、基于NeRF的方法、基于3D高斯喷涂的方法和大型前馈方法。其中,我们重点关注基于深度图的方法,它们是MVS的主要家族,因其简洁性、灵活性和可扩展性而闻名。在本文中,我们提供了截至当前日期的文献综述。我们调查了这些基于学习的方法,总结了它们在流行基准测试上的性能,并讨论了该领域未来有前景的研究方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了三维重建技术及其在多种应用中的重要性,如增强现实/虚拟现实(AR/VR)、自动驾驶和机器人技术。文章重点介绍了基于多视角的三维重建方法,特别是基于深度学习的学习方法。本文详细介绍了不同类型的基于学习的方法,包括深度图方法、体素方法、NeRF方法、三维高斯Splatting方法和大型前馈方法等,并重点讨论了深度图方法的特点和优势。本文总结了当前文献中的研究,评估了这些方法在流行基准测试上的性能,并探讨了该领域的未来研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 3D重建旨在恢复场景的密集三维结构,在AR/VR、自动驾驶和机器人技术等领域有广泛应用。
- 多视角立体(MVS)算法利用从不同视角捕捉的场景的多个视图,合成全面的三维表示,实现在复杂环境中的精确重建。
- 基于深度学习的学习方法在MVS中取得了显著成功,包括深度图方法、体素方法、NeRF方法等。
- 深度图方法是MVS的主要家族,具有简洁性、灵活性和可扩展性。
- 当前研究已经提供了对文献的综合回顾,评估了这些方法在流行基准测试上的性能。
点此查看论文截图

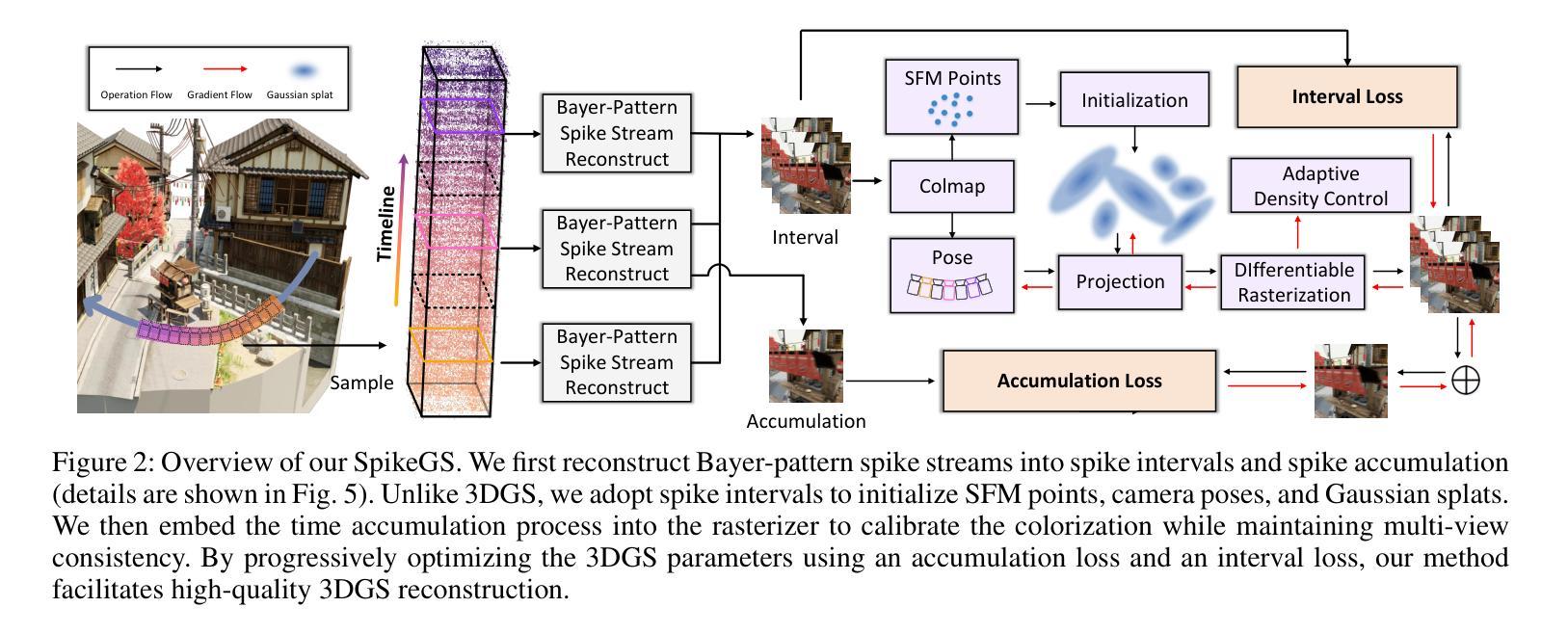
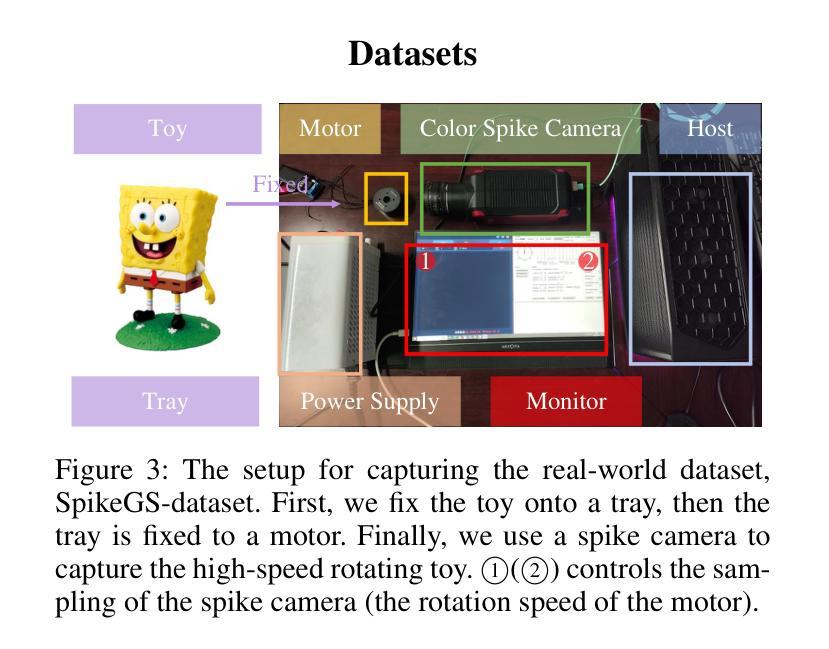
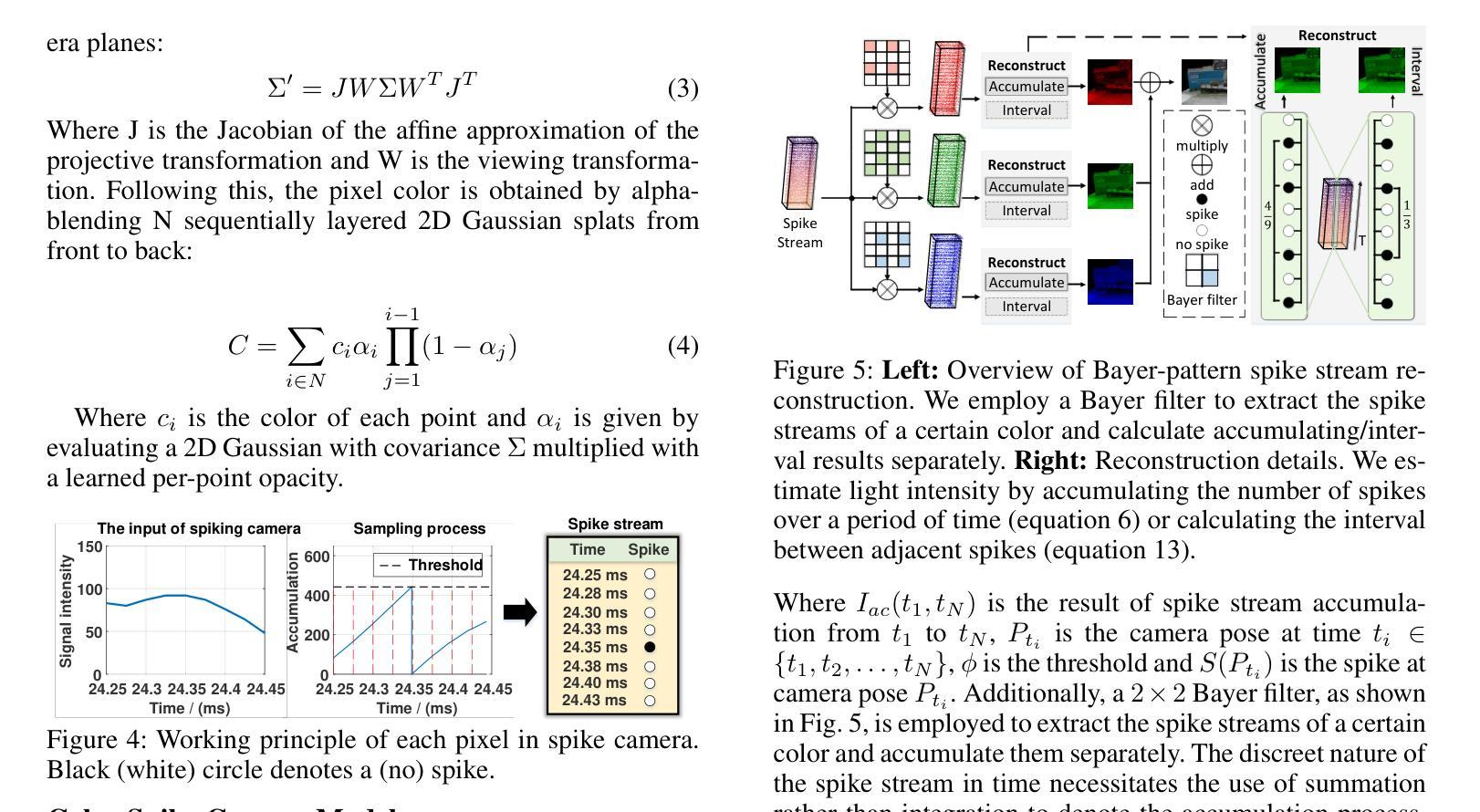
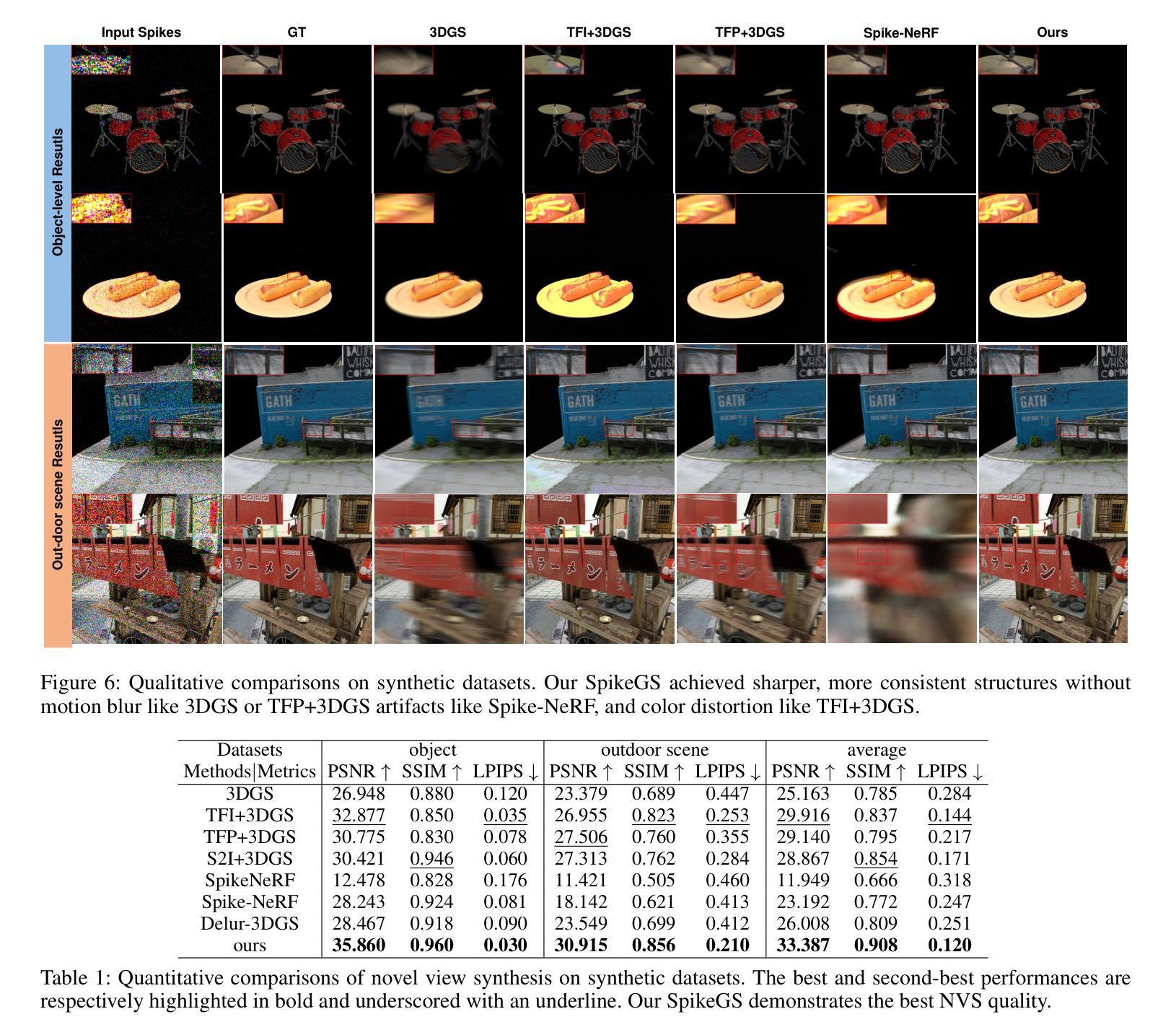
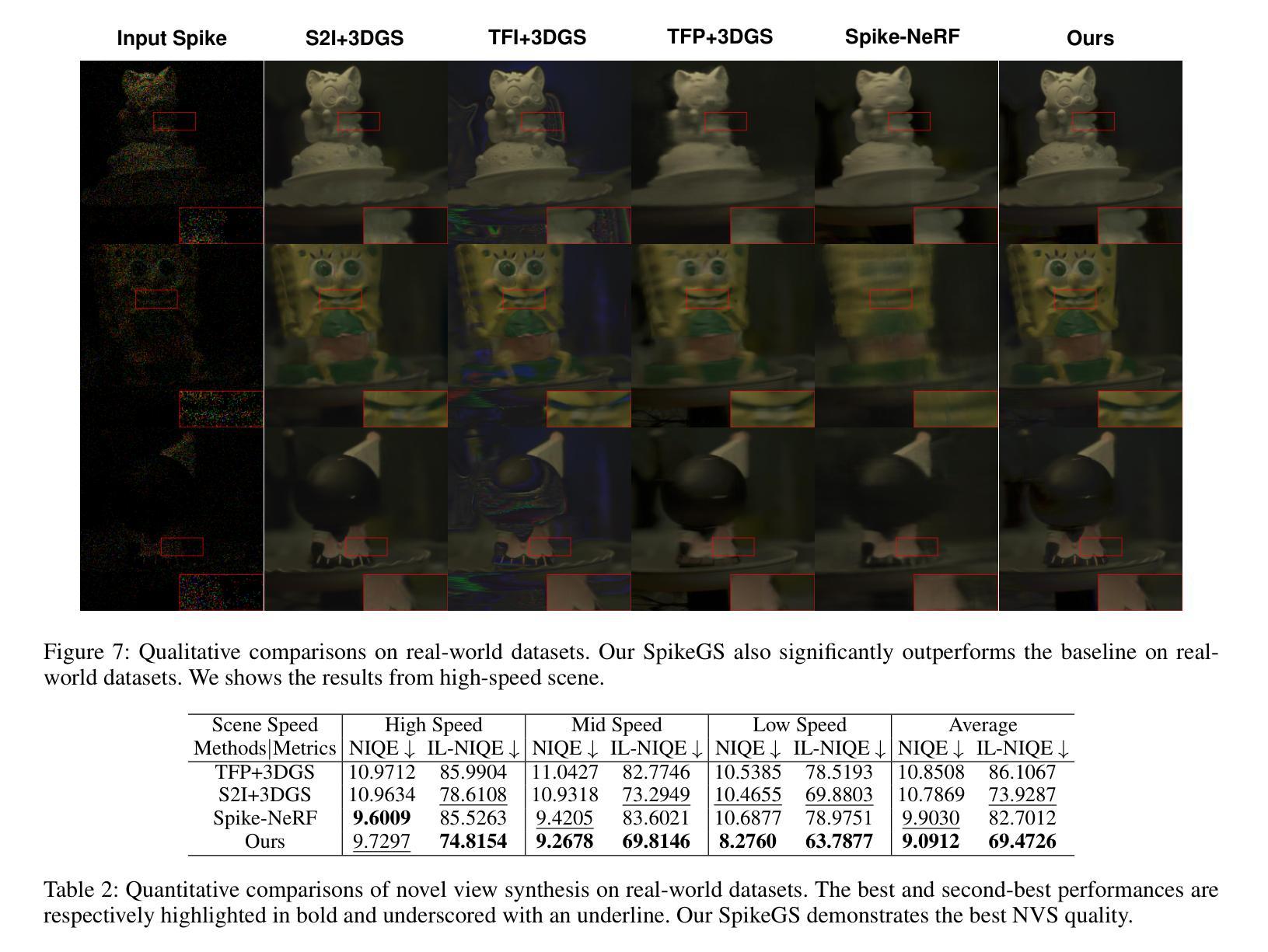
SpikeGS: Reconstruct 3D scene via fast-moving bio-inspired sensors
Authors:Yijia Guo, Liwen Hu, Yuanxi Bai, Lei Ma, Tiejun Huang
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) demonstrates unparalleled superior performance in 3D scene reconstruction. However, 3DGS heavily relies on the sharp images. Fulfilling this requirement can be challenging in real-world scenarios especially when the camera moves fast, which severely limits the application of 3DGS. To address these challenges, we proposed Spike Gausian Splatting (SpikeGS), the first framework that integrates the spike streams into 3DGS pipeline to reconstruct 3D scenes via a fast-moving bio-inspired camera. With accumulation rasterization, interval supervision, and a specially designed pipeline, SpikeGS extracts detailed geometry and texture from high temporal resolution but texture lacking spike stream, reconstructs 3D scenes captured in 1 second. Extensive experiments on multiple synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate the superiority of SpikeGS compared with existing spike-based and deblur 3D scene reconstruction methods. Codes and data will be released soon.
3D高斯融合(3DGS)在3D场景重建中表现出无与伦比的优势性能。然而,3DGS严重依赖于清晰图像。在现实世界场景中,尤其是在相机快速移动时,满足这一要求可能会具有挑战性,从而严重限制了3DGS的应用。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了Spike高斯融合(SpikeGS),这是第一个将脉冲流集成到3DGS管道中的框架,通过快速移动的仿生相机重建3D场景。通过累积光栅化、间隔监督以及专门设计的管道,SpikeGS可以从高时间分辨率但纹理缺乏的脉冲流中提取详细的几何和纹理信息,对在1秒内捕获的3D场景进行重建。在多个合成和真实数据集上的大量实验表明,与现有的基于脉冲和去模糊的3D场景重建方法相比,SpikeGS具有优越性。代码和数据将很快发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2025
Summary
3D高斯融合技术(3DGS)在三维场景重建中表现出卓越性能,但高度依赖清晰图像。在快速移动相机等现实场景中获取清晰图像是一大挑战。为解决此问题,提出Spike高斯融合(SpikeGS)框架,该框架首次将脉冲流融入3DGS流程,通过生物启发式快速移动相机重建三维场景。SpikeGS采用累积渲染、间隔监控和特殊设计流程,可从时间分辨率高但纹理缺失的脉冲流中提取详细几何和纹理信息,在1秒内重建三维场景。多项合成和真实数据集的实验结果均表明SpikeGS优于现有基于脉冲和去模糊的三维场景重建方法。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS技术具备卓越的三维场景重建性能。
- 3DGS在实际应用中面临依赖清晰图像的问题,特别是在相机快速移动的情况下。
- SpikeGS框架首次集成脉冲流技术到3DGS流程中,以应对快速移动相机带来的挑战。
- SpikeGS采用积累渲染技术,能够从高时间分辨率但纹理缺失的脉冲流中提取详细几何和纹理信息。
- SpikeGS能在短时间内(如1秒内)重建三维场景。
- 大量实验证明SpikeGS在多种合成和真实数据集上的表现均优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

Mirror-3DGS: Incorporating Mirror Reflections into 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jiarui Meng, Haijie Li, Yanmin Wu, Qiankun Gao, Shuzhou Yang, Jian Zhang, Siwei Ma
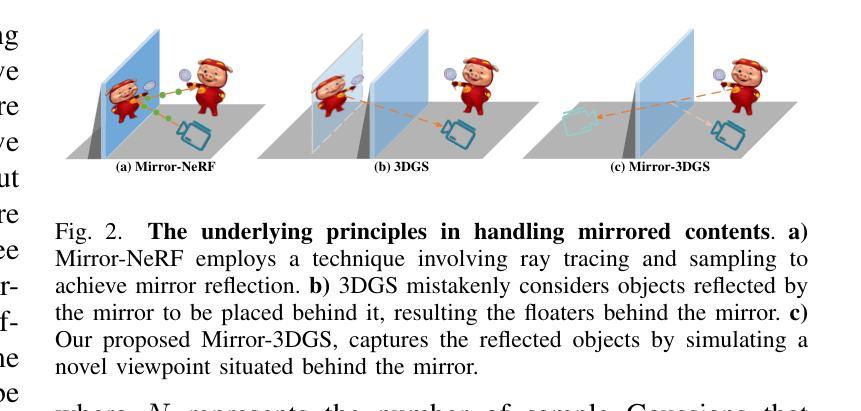
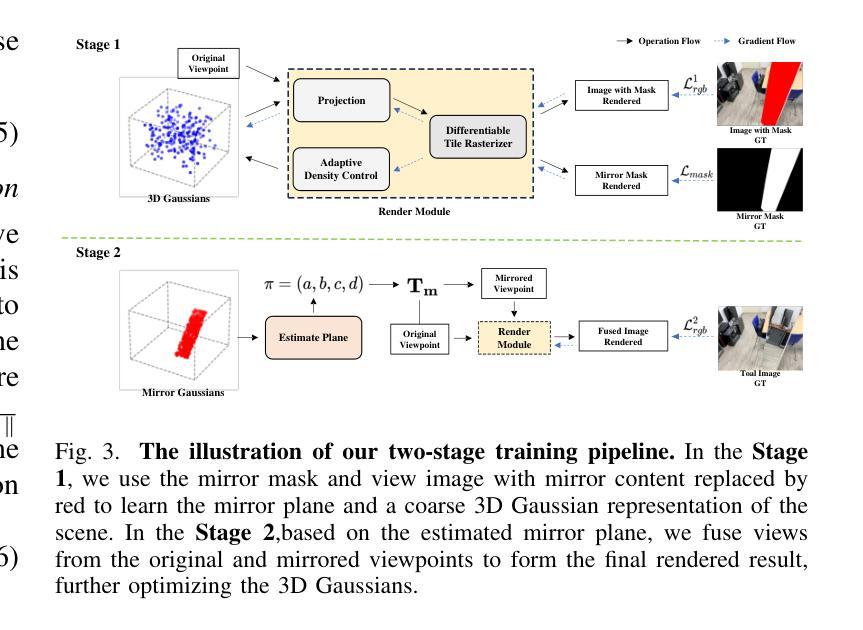
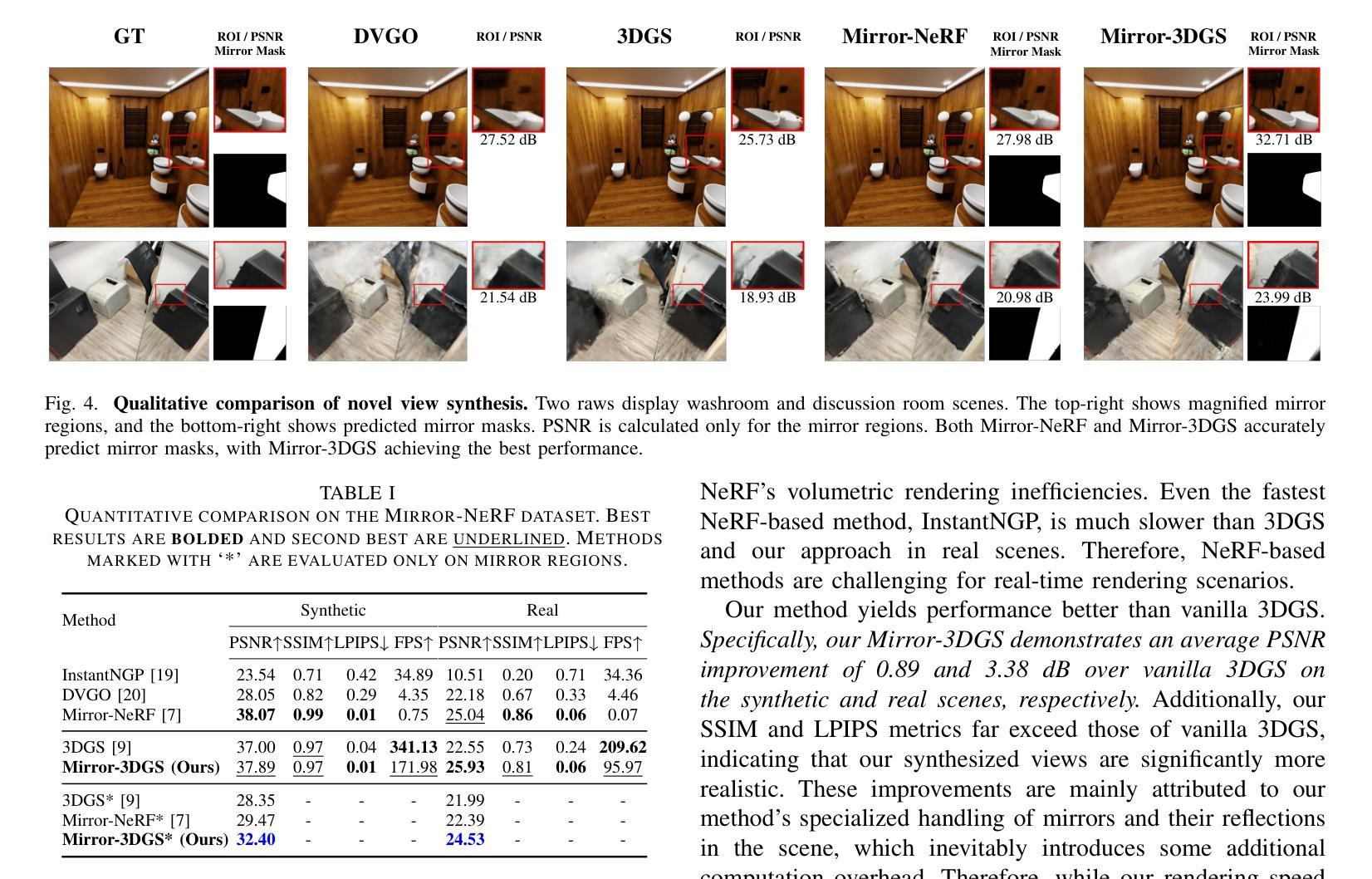
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has significantly advanced 3D scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis. However, like Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), 3DGS struggles with accurately modeling physical reflections, particularly in mirrors, leading to incorrect reconstructions and inconsistent reflective properties. To address this challenge, we introduce Mirror-3DGS, a novel framework designed to accurately handle mirror geometries and reflections, thereby generating realistic mirror reflections. By incorporating mirror attributes into 3DGS and leveraging plane mirror imaging principles, Mirror-3DGS simulates a mirrored viewpoint from behind the mirror, enhancing the realism of scene renderings. Extensive evaluations on both synthetic and real-world scenes demonstrate that our method can render novel views with improved fidelity in real-time, surpassing the state-of-the-art Mirror-NeRF, especially in mirror regions.
三维高斯延展(3DGS)在三维场景重建和新颖视角合成方面取得了显著进展。然而,与神经辐射场(NeRF)一样,3DGS在准确模拟物理反射,特别是在镜像方面存在困难,这会导致重建不准确和反射属性不一致。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了Mirror-3DGS,这是一种新型框架,旨在准确处理镜面几何和反射,从而生成逼真的镜面反射。通过将镜面属性纳入3DGS并借助平面镜像成像原理,Mirror-3DGS可以模拟镜子后面的镜像观点,增强场景渲染的逼真度。对合成场景和真实世界场景的大量评估表明,我们的方法能够在实时中以更高的保真度呈现新颖视角,超越了最先进的Mirror-NeRF,特别是在镜像区域。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE International Conference on Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP 2024, Oral)
Summary
基于三维高斯融合技术(3DGS)在处理三维场景重建和新颖视角合成方面取得了显著进展,但在处理物理反射,特别是在镜子上的反射时仍存在困难,导致重建结果不准确和反射属性不一致。为解决这一问题,我们提出了Mirror-3DGS框架,它能够准确处理镜子几何形状和反射,生成逼真的镜子反射效果。通过整合镜子属性和利用平面镜像成像原理,Mirror-3DGS模拟镜子背后的视角,增强了场景渲染的逼真度。
Key Takeaways
- 3DGS在三维场景重建和新颖视角合成方面取得显著进展。
- 3DGS在处理物理反射,特别是在镜子上的反射时存在挑战。
- Mirror-3DGS框架被设计用来准确处理镜子几何形状和反射。
- Mirror-3DGS通过整合镜子属性和利用平面镜像成像原理模拟镜子背后的视角。
- Mirror-3DGS生成的场景渲染具有更高的逼真度。
- 相比现有的Mirror-NeRF技术,Mirror-3DGS在镜子区域的渲染效果更佳。
点此查看论文截图