⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-12 更新
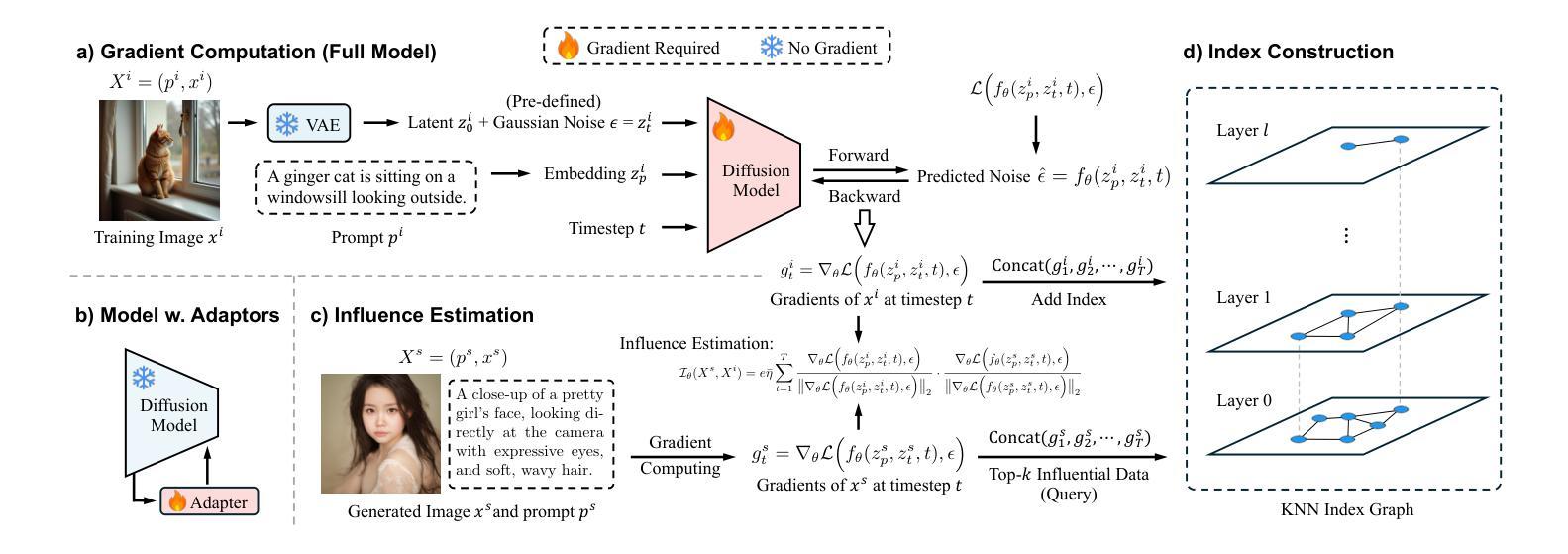
DMin: Scalable Training Data Influence Estimation for Diffusion Models
Authors:Huawei Lin, Yingjie Lao, Weijie Zhao
Identifying the training data samples that most influence a generated image is a critical task in understanding diffusion models, yet existing influence estimation methods are constrained to small-scale or LoRA-tuned models due to computational limitations. As diffusion models scale up, these methods become impractical. To address this challenge, we propose DMin (Diffusion Model influence), a scalable framework for estimating the influence of each training data sample on a given generated image. By leveraging efficient gradient compression and retrieval techniques, DMin reduces storage requirements from 339.39 TB to only 726 MB and retrieves the top-k most influential training samples in under 1 second, all while maintaining performance. Our empirical results demonstrate DMin is both effective in identifying influential training samples and efficient in terms of computational and storage requirements.
识别和评估对生成图像影响最大的训练数据样本是理解扩散模型的关键任务。然而,由于计算限制,现有的影响评估方法仅限于小规模或经过LoRA调整模型的应用。随着扩散模型的规模扩大,这些方法变得不切实际。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了DMin(扩散模型影响),这是一个可扩展的框架,用于估计每个训练数据样本对给定生成图像的影响。通过利用高效的梯度压缩和检索技术,DMin将存储需求从339.39TB减少到仅726MB,并在不到1秒内检索到前k个最具影响力的训练样本,同时保持性能。我们的经验结果表明,DMin在识别有影响力的训练样本方面非常有效,同时在计算和存储需求方面也非常高效。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 6 figures, 8 tables. Under Review
Summary
训练数据样本对生成图像的影响评估是理解扩散模型的关键任务。然而,由于计算限制,现有影响评估方法仅限于小规模或经过LoRA调整模型的使用。随着扩散模型的扩展,这些方法变得不切实际。为解决此挑战,我们提出了DMin(扩散模型影响)框架,用于估算每个训练数据样本对给定生成图像的影响。通过利用高效的梯度压缩和检索技术,DMin将存储需求从339.39TB减少到仅726MB,并在不到1秒内检索到前k个最具影响力的训练样本,同时保持性能。经验结果表明,DMin在识别具有影响力的训练样本方面既有效,又在计算和存储需求方面高效。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型中,评估训练数据样本对生成图像的影响是关键任务。
- 现有影响评估方法因计算限制而局限于小规模或特定模型应用。
- DMin框架旨在解决大规模扩散模型的训练数据影响评估挑战。
- DMin利用梯度压缩和检索技术,显著减少存储需求并加快检索速度。
- DMin能够高效地在不到一秒内检索到最具影响力的训练样本。
- DMin在识别具有影响力的训练样本方面表现出良好的效果。
- DMin在降低计算和存储需求的同时保持性能。
点此查看论文截图


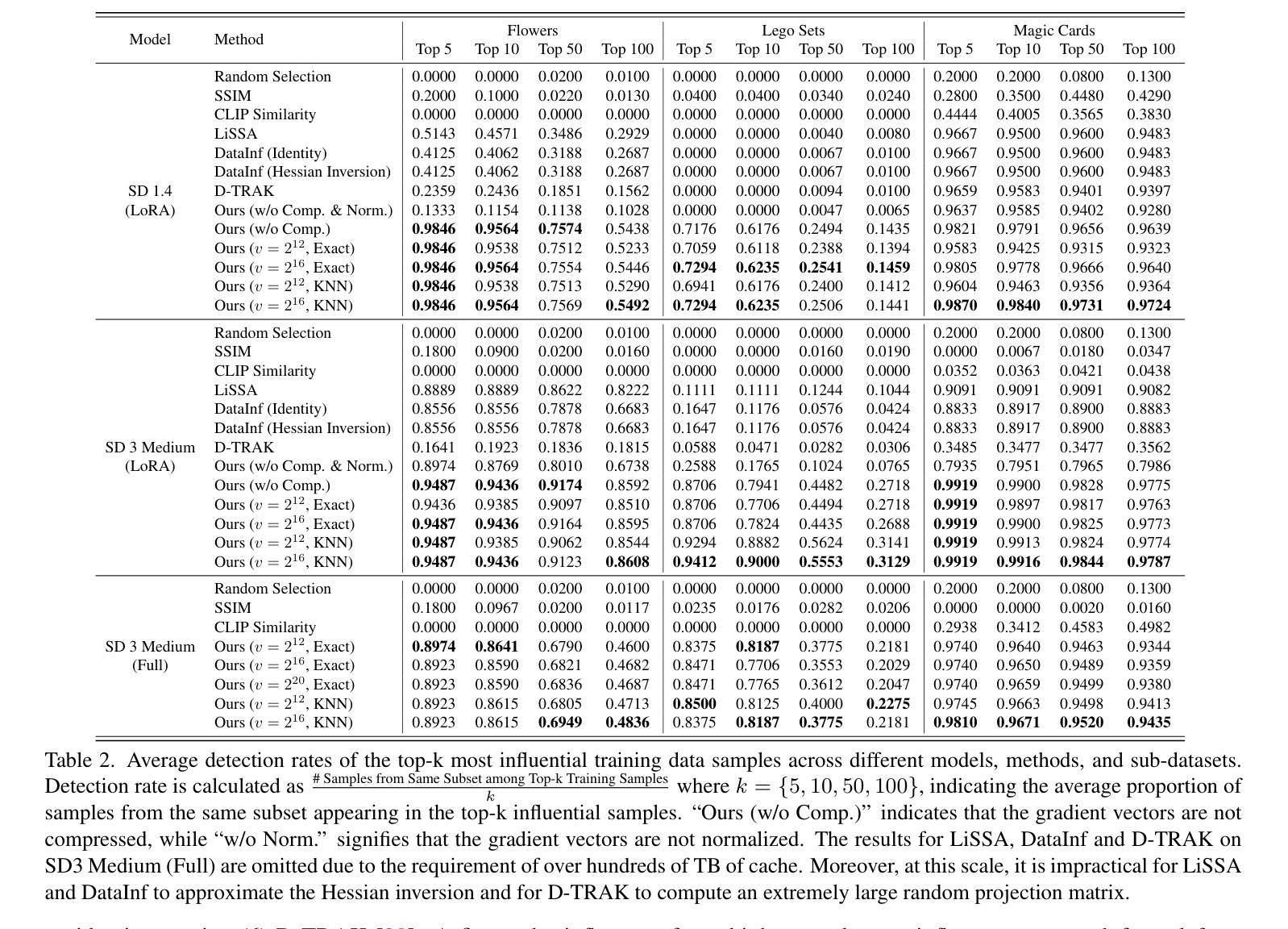
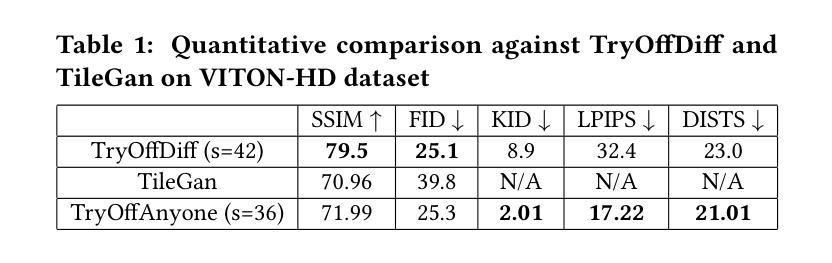
TryOffAnyone: Tiled Cloth Generation from a Dressed Person
Authors:Ioannis Xarchakos, Theodoros Koukopoulos
The fashion industry is increasingly leveraging computer vision and deep learning technologies to enhance online shopping experiences and operational efficiencies. In this paper, we address the challenge of generating high-fidelity tiled garment images essential for personalized recommendations, outfit composition, and virtual try-on systems from photos of garments worn by models. Inspired by the success of Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) in image-to-image translation, we propose a novel approach utilizing a fine-tuned StableDiffusion model. Our method features a streamlined single-stage network design, which integrates garmentspecific masks to isolate and process target clothing items effectively. By simplifying the network architecture through selective training of transformer blocks and removing unnecessary crossattention layers, we significantly reduce computational complexity while achieving state-of-the-art performance on benchmark datasets like VITON-HD. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in producing high-quality tiled garment images for both full-body and half-body inputs. Code and model are available at: https://github.com/ixarchakos/try-off-anyone
时尚产业正越来越多地利用计算机视觉和深度学习技术,以提升在线购物体验和运营效率。本文旨在解决从模特所穿衣物照片生成高质量平铺衣物图像的挑战,这些图像对于个性化推荐、服装搭配和虚拟试穿系统至关重要。受潜在扩散模型(Latent Diffusion Models,简称LDMs)在图到图翻译中的成功的启发,我们提出了一种利用微调过的StableDiffusion模型的新方法。我们的方法采用简洁的单阶段网络设计,结合衣物特定掩膜,有效隔离和处理目标衣物项目。通过选择性训练变压器块并去除不必要的交叉注意层,简化网络架构,我们在降低计算复杂性的同时,在VITON-HD等基准数据集上实现了最先进的性能。实验结果表明,我们的方法在全身体和半身体输入情况下,生成高质量平铺衣物图像的有效性。代码和模型可在https://github.com/ixarchakos/try-off-anyone找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
时尚产业正积极运用计算机视觉和深度学习技术,以提升在线购物体验和运营效率。本文解决生成高保真平铺服装图片的挑战,这些图片对于个性化推荐、搭配组合和虚拟试衣系统至关重要。受潜在扩散模型(Latent Diffusion Models,简称LDMs)在图转图成功的启发,本文提出了一种利用微调StableDiffusion模型的新方法。该方法采用简洁的单阶段网络设计,结合服装特定掩膜,有效隔离和处理目标服装项目。通过选择性训练变压器块并去除不必要的交叉注意力层,简化网络架构,在降低计算复杂性的同时,实现在VITON-HD等基准数据集上的卓越性能。实验结果证明,该方法在全身体和半身输入的情况下,都能生成高质量的平铺服装图像。
Key Takeaways:
- 时尚产业正在利用计算机视觉和深度学习技术提升在线购物体验和运营效率。
- 生成高保真平铺服装图像对于个性化推荐、搭配组合和虚拟试衣系统至关重要。
- 潜在扩散模型(Latent Diffusion Models,简称LDMs)在图转图方面的成功应用为解决问题提供了灵感。
- 提出一种利用微调StableDiffusion模型的新方法,采用简洁的单阶段网络设计。
- 该方法结合服装特定掩膜,有效隔离和处理目标服装项目。
- 通过简化网络架构,实现了在降低计算复杂性的同时,在基准数据集上实现卓越性能。
- 实验结果证明该方法能生成高质量的平铺服装图像,适用于全身体和半身输入。
点此查看论文截图



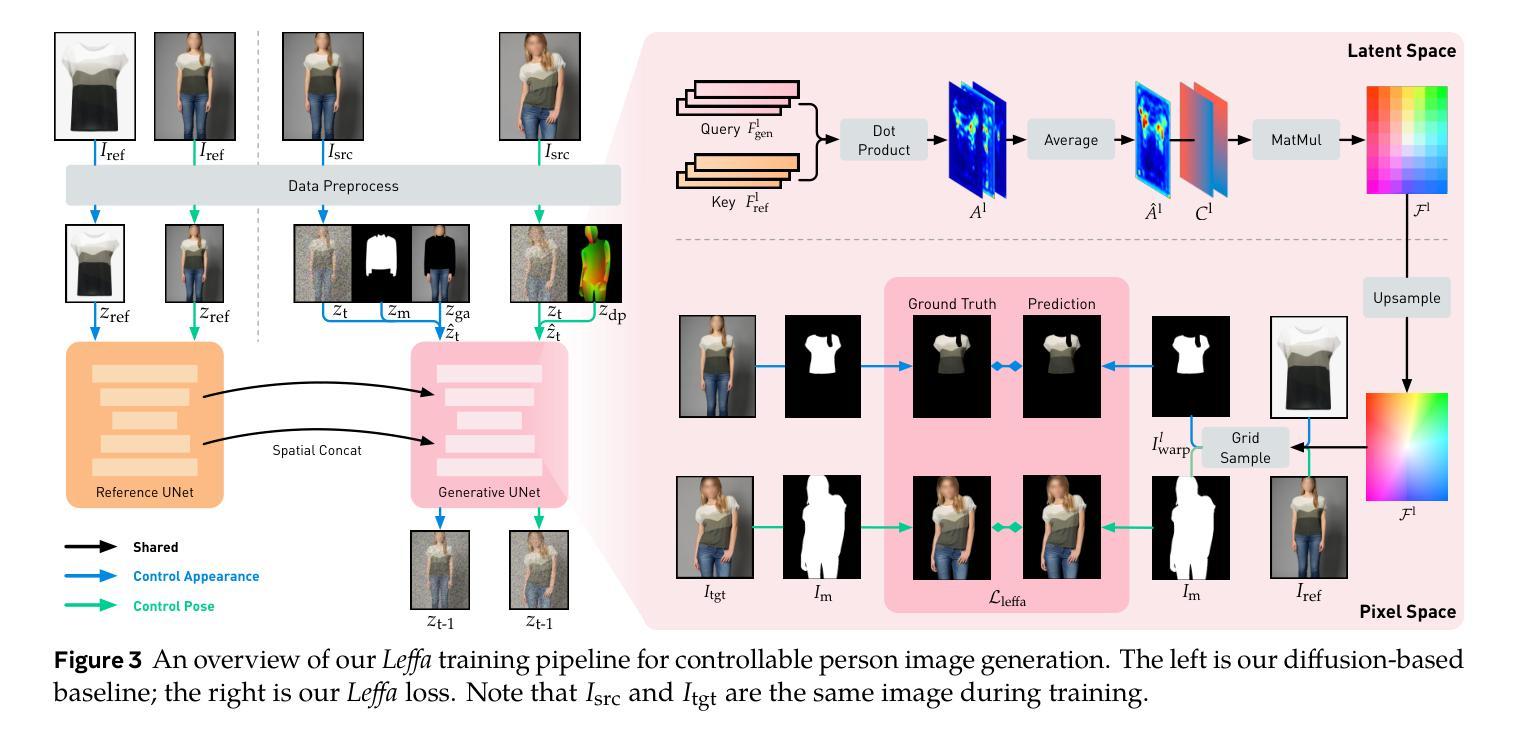
Learning Flow Fields in Attention for Controllable Person Image Generation
Authors:Zijian Zhou, Shikun Liu, Xiao Han, Haozhe Liu, Kam Woh Ng, Tian Xie, Yuren Cong, Hang Li, Mengmeng Xu, Juan-Manuel Pérez-Rúa, Aditya Patel, Tao Xiang, Miaojing Shi, Sen He
Controllable person image generation aims to generate a person image conditioned on reference images, allowing precise control over the person’s appearance or pose. However, prior methods often distort fine-grained textural details from the reference image, despite achieving high overall image quality. We attribute these distortions to inadequate attention to corresponding regions in the reference image. To address this, we thereby propose learning flow fields in attention (Leffa), which explicitly guides the target query to attend to the correct reference key in the attention layer during training. Specifically, it is realized via a regularization loss on top of the attention map within a diffusion-based baseline. Our extensive experiments show that Leffa achieves state-of-the-art performance in controlling appearance (virtual try-on) and pose (pose transfer), significantly reducing fine-grained detail distortion while maintaining high image quality. Additionally, we show that our loss is model-agnostic and can be used to improve the performance of other diffusion models.
可控人物图像生成旨在根据参考图像生成人物图像,实现对人物外观或姿态的精确控制。然而,尽管先前的方法在整体图像质量上取得了较高的水平,但它们往往会扭曲参考图像的细微纹理细节。我们将这些扭曲归因于对参考图像中相应区域的关注不足。为解决这一问题,我们提出了学习注意力流场(Leffa),通过在训练过程中明确引导目标查询在注意力层关注正确的参考键,以实现精准控制。具体而言,它是通过基于扩散基准的注意力图上的正则化损失来实现的。我们的大量实验表明,Leffa在控制外观(虚拟试穿)和姿态(姿态迁移)方面达到了最新技术水平,显著减少了细微细节失真,同时保持了高图像质量。此外,我们还证明了我们的损失模型具有模型无关性,可用于提高其他扩散模型的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF github: https://github.com/franciszzj/Leffa, demo: https://huggingface.co/spaces/franciszzj/Leffa, model: https://huggingface.co/franciszzj/Leffa
Summary
基于参考图像生成可控人物图像的方法旨在根据参考图像生成人物图像,并能精确控制人物的外观或姿态。然而,先前的方法常常在保持整体图像质量的同时忽视了细节处的纹理失真。我们将这种失真归因于对参考图像中对应区域的关注度不足。为此,我们提出了学习注意力流场(Leffa)的方法,通过训练过程中的注意力层明确引导目标查询关注正确的参考关键信息。具体来说,它通过扩散基准模型上的注意力图实现正则化损失。广泛的实验表明,Leffa在控制外观(虚拟试穿)和姿态(姿态转移)方面达到了最先进的性能,显著减少了细节失真并保持高质量图像。此外,我们的损失模型具有模型无关性,可用于提高其他扩散模型的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 可控人物图像生成旨在根据参考图像生成人物图像,并精确控制其外观或姿态。
- 现有方法在处理细节纹理时存在失真问题。
- 纹理失真的原因是对参考图像中对应区域的关注度不足。
- 学习注意力流场(Leffa)方法通过训练过程中的注意力层明确引导目标查询关注正确的参考关键信息。
- Leffa方法通过扩散基准模型上的注意力图实现正则化损失。
- Leffa在控制外观和姿态方面达到了最先进的性能,显著减少了细节失真。
点此查看论文截图


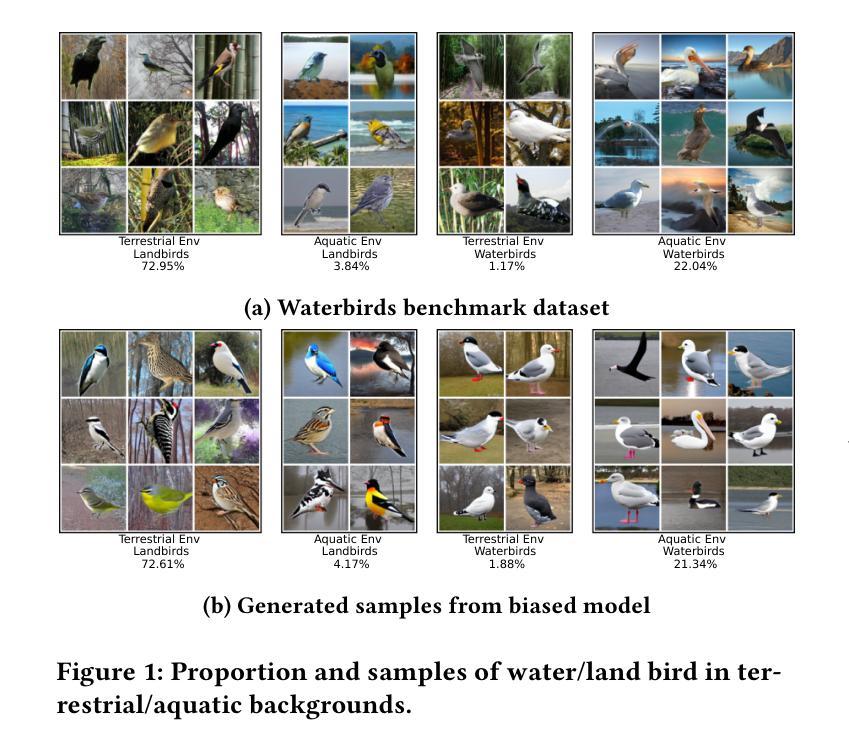
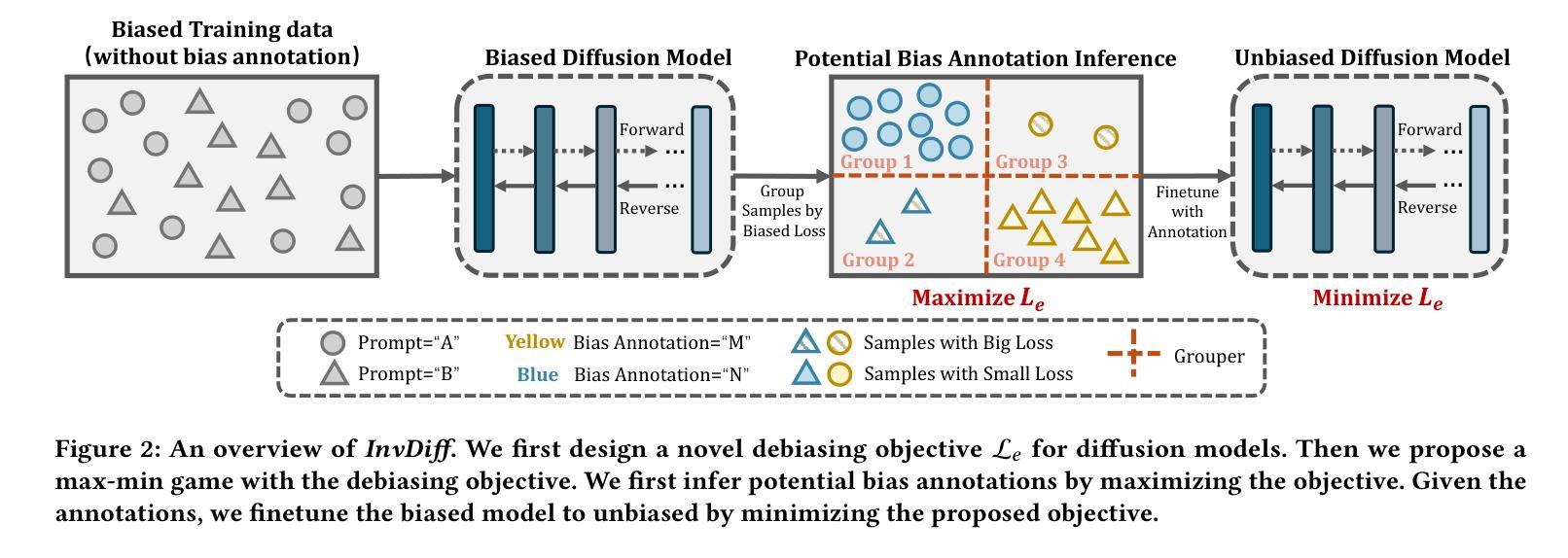
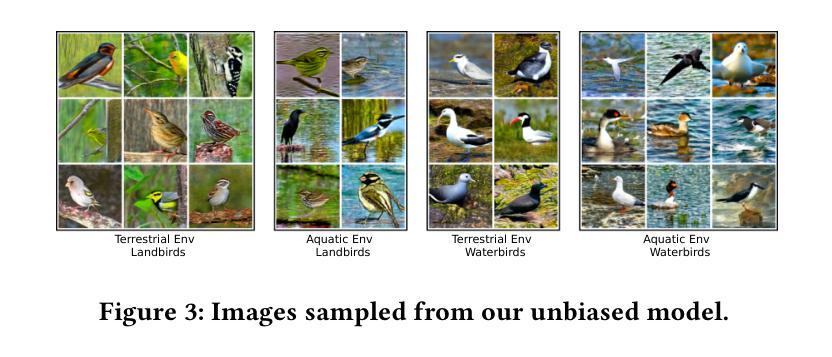
InvDiff: Invariant Guidance for Bias Mitigation in Diffusion Models
Authors:Min Hou, Yueying Wu, Chang Xu, Yu-Hao Huang, Chenxi Bai, Le Wu, Jiang Bian
As one of the most successful generative models, diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in synthesizing high-quality images. These models learn the underlying high-dimensional data distribution in an unsupervised manner. Despite their success, diffusion models are highly data-driven and prone to inheriting the imbalances and biases present in real-world data. Some studies have attempted to address these issues by designing text prompts for known biases or using bias labels to construct unbiased data. While these methods have shown improved results, real-world scenarios often contain various unknown biases, and obtaining bias labels is particularly challenging. In this paper, we emphasize the necessity of mitigating bias in pre-trained diffusion models without relying on auxiliary bias annotations. To tackle this problem, we propose a framework, InvDiff, which aims to learn invariant semantic information for diffusion guidance. Specifically, we propose identifying underlying biases in the training data and designing a novel debiasing training objective. Then, we employ a lightweight trainable module that automatically preserves invariant semantic information and uses it to guide the diffusion model’s sampling process toward unbiased outcomes simultaneously. Notably, we only need to learn a small number of parameters in the lightweight learnable module without altering the pre-trained diffusion model. Furthermore, we provide a theoretical guarantee that the implementation of InvDiff is equivalent to reducing the error upper bound of generalization. Extensive experimental results on three publicly available benchmarks demonstrate that InvDiff effectively reduces biases while maintaining the quality of image generation. Our code is available at https://github.com/Hundredl/InvDiff.
作为最成功的生成模型之一,扩散模型在合成高质量图像方面表现出了显著的效率。这些模型以无监督的方式学习潜在的高维数据分布。尽管它们很成功,但扩散模型是高度数据驱动的,很容易继承现实数据中存在的不平衡和偏见。一些研究试图通过为已知偏见设计文本提示或使用偏见标签来构建无偏见数据来解决这些问题。虽然这些方法已经显示出改进的结果,但现实世界的场景通常包含各种未知的偏见,并且获取偏见标签具有挑战性。在本文中,我们强调了在预训练的扩散模型中减轻偏见的重要性,无需依赖辅助偏见注释。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种名为InvDiff的框架,旨在学习扩散指导的不变语义信息。具体来说,我们提出识别训练数据中的潜在偏见并设计一种新的去偏见训练目标。然后,我们采用轻量级的可训练模块自动保留不变语义信息,并将其用于指导扩散模型的采样过程,以产生无偏见的输出。值得注意的是,我们只需要在轻量级的可训练模块中学习少量的参数,无需更改预训练的扩散模型。此外,我们提供了理论保证,证明InvDiff的实现等同于降低了泛化误差的上界。在三个公开可用基准上的广泛实验结果表明,InvDiff在减少偏见的同时保持了图像生成的品质。我们的代码位于https://github.com/Hundredl/InvDiff。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF KDD 2025
Summary
扩散模型在合成高质量图像方面表现出显著的效果,但它们高度依赖数据,并可能继承现实世界的偏见。针对这一问题,本文提出了一种无需依赖辅助偏见注释的框架InvDiff,旨在学习扩散指导的不变语义信息。通过识别训练数据中的潜在偏见并设计新的去偏见训练目标,使用轻量级可训练模块自动保留不变语义信息,并用于指导扩散模型的采样过程,实现无偏见的结果。只需在轻量级可训练模块中学习少量参数,无需更改预训练的扩散模型。实验结果表明,InvDiff在减少偏见的同时保持了图像生成的品质。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在合成高质量图像方面表现出卓越性能,但存在数据驱动的问题,可能继承现实世界的偏见。
- 现有方法尝试通过文本提示或偏见标签来解决偏见问题,但面对未知偏见时效果有限,且获取偏见标签具有挑战性。
- 本文强调无需依赖辅助偏见注释来减轻预训练扩散模型中的偏见的重要性。
- 提出了一种名为InvDiff的框架,旨在学习扩散指导的不变语义信息来应对偏见问题。
- InvDiff通过识别训练数据中的潜在偏见并设计去偏见训练目标来实现其目标。
- 使用轻量级可训练模块自动保留不变语义信息,指导扩散模型的采样过程以实现无偏见结果。
点此查看论文截图

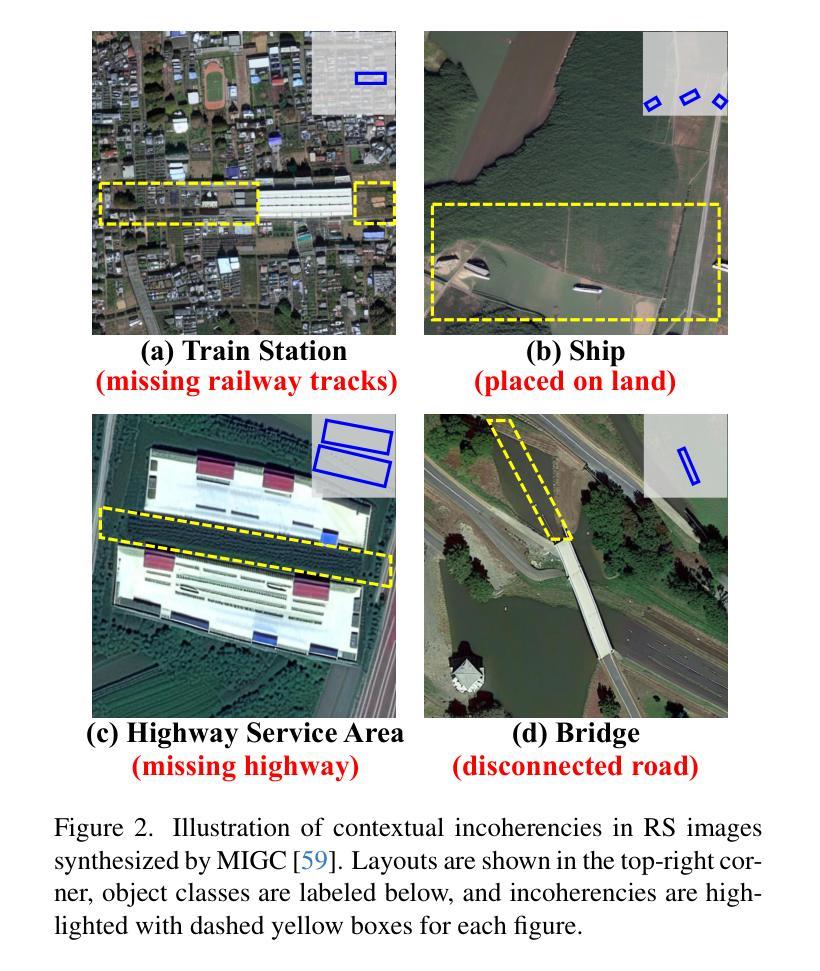
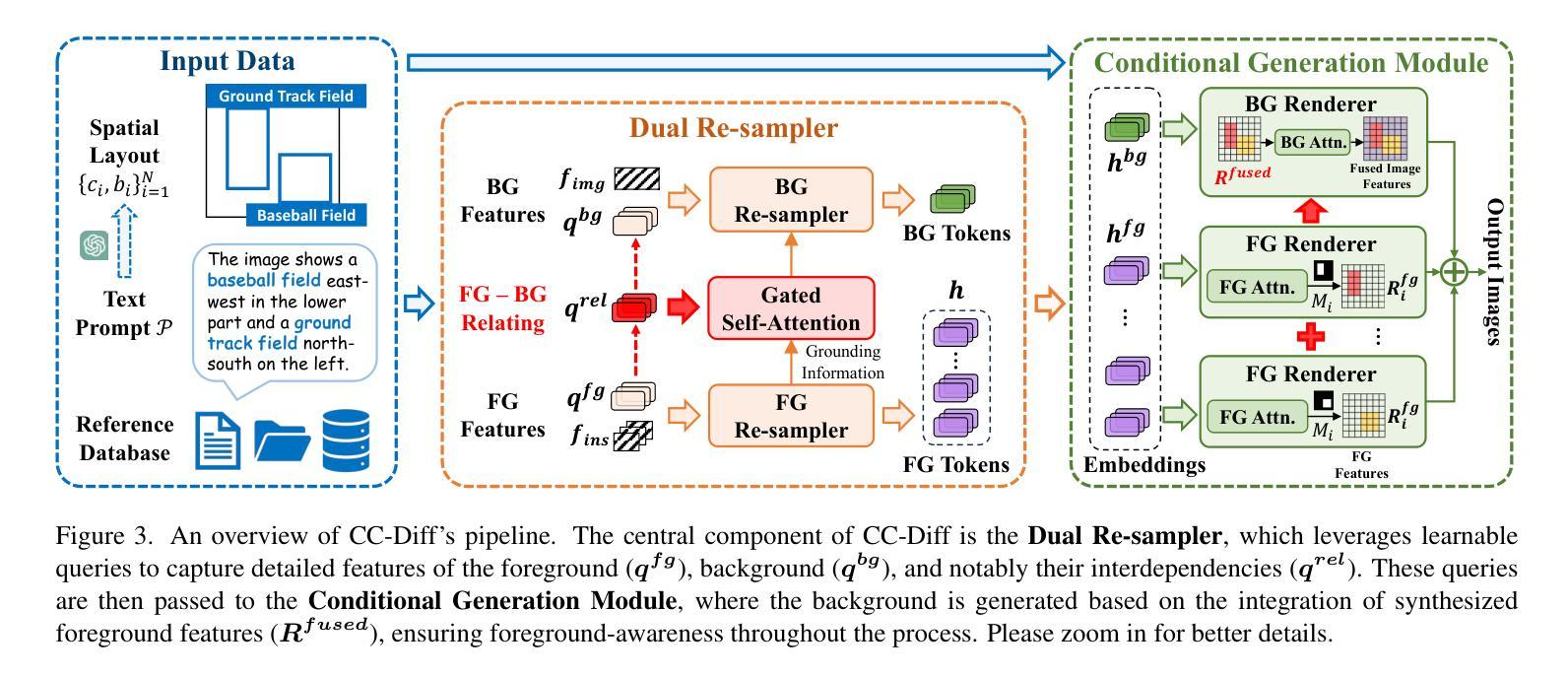
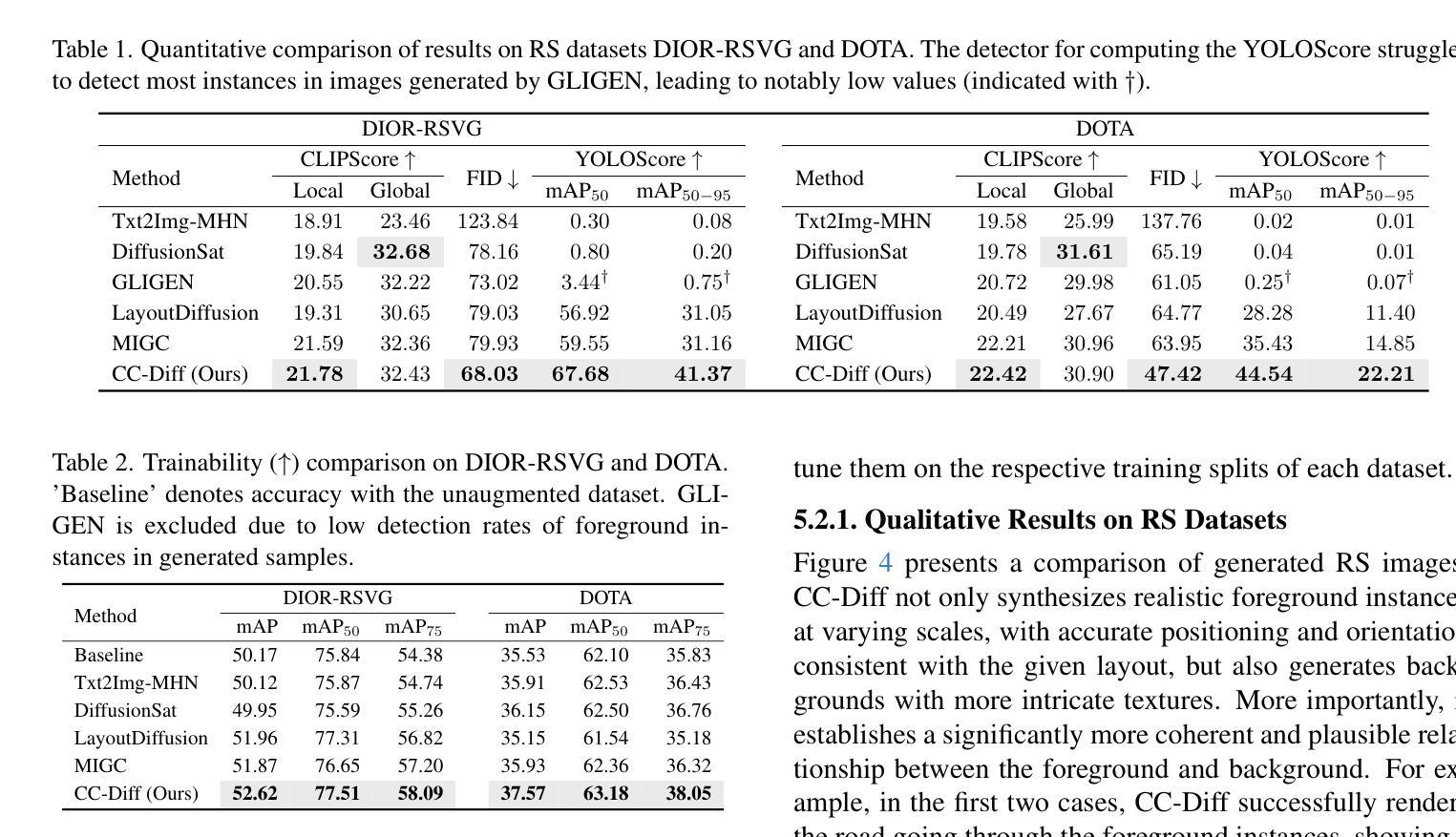
CC-Diff: Enhancing Contextual Coherence in Remote Sensing Image Synthesis
Authors:Mu Zhang, Yunfan Liu, Yue Liu, Hongtian Yu, Qixiang Ye
Accurately depicting real-world landscapes in remote sensing (RS) images requires precise alignment between objects and their environment. However, most existing synthesis methods for natural images prioritize foreground control, often reducing the background to plain textures. This neglects the interaction between foreground and background, which can lead to incoherence in RS scenarios. In this paper, we introduce CC-Diff, a Diffusion Model-based approach for RS image generation with enhanced Context Coherence. To capture spatial interdependence, we propose a sequential pipeline where background generation is conditioned on synthesized foreground instances. Distinct learnable queries are also employed to model both the complex background texture and its semantic relation to the foreground. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CC-Diff outperforms state-of-the-art methods in visual fidelity, semantic accuracy, and positional precision, excelling in both RS and natural image domains. CC-Diff also shows strong trainability, improving detection accuracy by 2.04 mAP on DOTA and 2.25 mAP on the COCO benchmark.
在遥感(RS)图像中准确描绘真实世界的景观要求物体与其环境之间有精确的对齐。然而,大多数现有的自然图像合成方法优先对前景进行控制,通常将背景简化为平原纹理。这忽略了前景和背景之间的交互,可能导致遥感场景中的不连贯性。在本文中,我们介绍了CC-Diff,这是一种基于扩散模型的遥感图像生成方法,具有增强的上下文一致性。为了捕获空间相关性,我们提出了一个顺序流程,其中背景生成是在合成的前景实例条件下进行的。我们还使用不同的可学习查询来对复杂的背景纹理及其与前景的语义关系进行建模。大量实验表明,CC-Diff在视觉保真度、语义准确性和定位精度方面优于最先进的方法,在遥感和自然图像领域都表现出色。CC-Diff还显示出强大的可训练性,在DOTA和COCO基准测试上的检测准确率分别提高了2.04 mAP和2.25 mAP。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
远程遥感图像中的真实世界景观准确描绘需要物体与其环境之间的精确对齐。现有大多数自然图像合成方法侧重于前景控制,常常将背景简化为单一纹理,忽略了前景与背景之间的交互作用,导致遥感场景中的不连贯性。本文提出基于扩散模型的CC-Diff方法,用于遥感图像生成,增强上下文连贯性。通过采用条件背景生成的顺序流程以及使用不同的可学习查询来建模复杂背景纹理及其与前景的语义关系,实现空间依赖性捕捉。实验表明,CC-Diff在视觉保真度、语义准确性和定位精度方面均优于现有先进技术,并在遥感和自然图像领域均有卓越表现,提高了DOTA和COCO基准测试中的检测精度。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感图像准确描绘需要前景与背景间的精确对齐。
- 现有自然图像合成方法常忽略背景,导致遥感场景中的不连贯性。
- CC-Diff方法基于扩散模型,用于遥感图像生成,增强上下文连贯性。
- 采用顺序流程实现背景生成的条件化,以及使用不同的可学习查询建模复杂背景纹理及其与前景的关系。
- CC-Diff在视觉、语义和定位精度方面表现优异。
- CC-Diff在遥感和自然图像领域均展现出优势。
点此查看论文截图


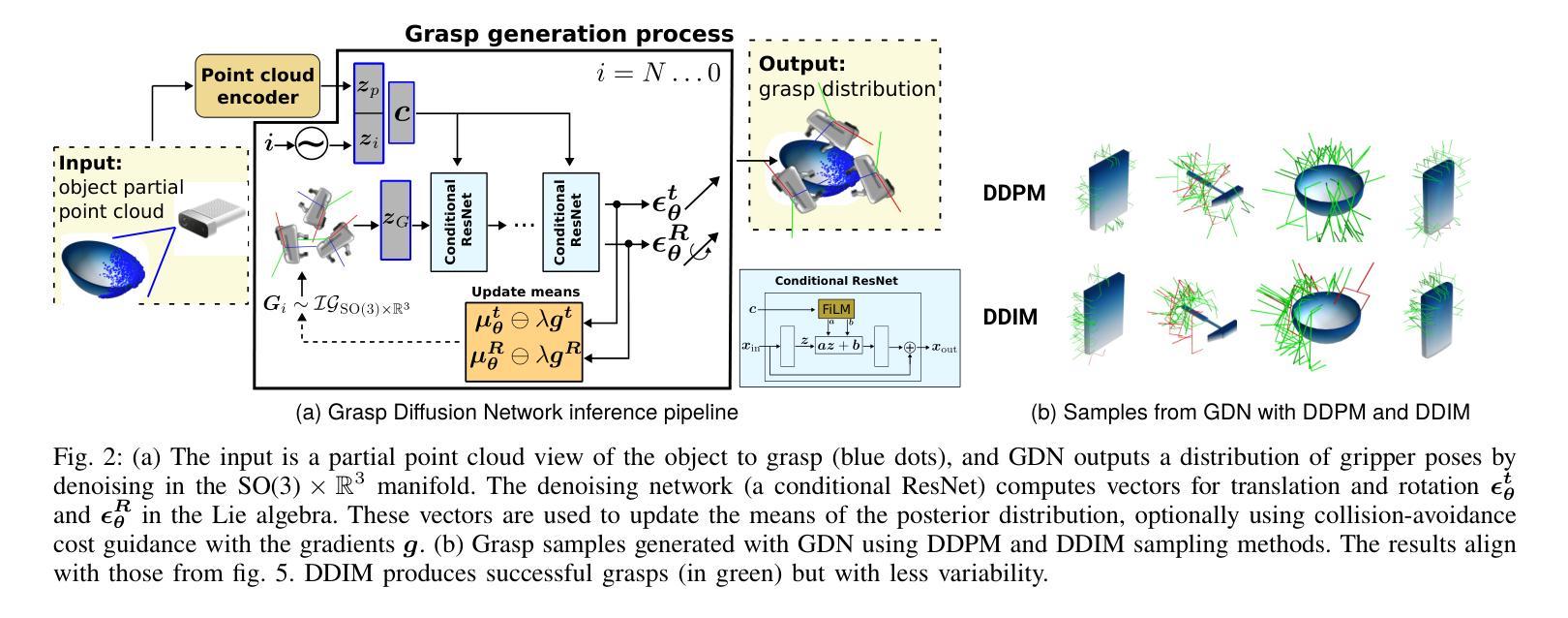
Grasp Diffusion Network: Learning Grasp Generators from Partial Point Clouds with Diffusion Models in SO(3)xR3
Authors:Joao Carvalho, An T. Le, Philipp Jahr, Qiao Sun, Julen Urain, Dorothea Koert, Jan Peters
Grasping objects successfully from a single-view camera is crucial in many robot manipulation tasks. An approach to solve this problem is to leverage simulation to create large datasets of pairs of objects and grasp poses, and then learn a conditional generative model that can be prompted quickly during deployment. However, the grasp pose data is highly multimodal since there are several ways to grasp an object. Hence, in this work, we learn a grasp generative model with diffusion models to sample candidate grasp poses given a partial point cloud of an object. A novel aspect of our method is to consider diffusion in the manifold space of rotations and to propose a collision-avoidance cost guidance to improve the grasp success rate during inference. To accelerate grasp sampling we use recent techniques from the diffusion literature to achieve faster inference times. We show in simulation and real-world experiments that our approach can grasp several objects from raw depth images with $90%$ success rate and benchmark it against several baselines.
在众多的机器人操作任务中,从单视角摄像机成功抓取物体至关重要。一种解决此问题的方法是利用模拟技术创建大量物体和抓取姿态的数据集,然后学习一种条件生成模型,在部署期间可以快速进行提示。然而,由于抓取物体的方式有多种,抓取姿态数据具有多模态性。因此,在这项工作中,我们利用扩散模型学习抓取生成模型,以给定物体的部分点云来采样候选抓取姿态。我们方法的一个新颖之处在于考虑在旋转流形空间中的扩散,并提出一种避碰成本引导来提高推理过程中的抓取成功率。为了加快抓取采样速度,我们采用了扩散文献中的最新技术来实现更快的推理时间。我们在模拟和真实世界的实验中证明,我们的方法能够从原始深度图像中抓取多种物体,成功率达到90%,并且与几个基准方法进行了比较。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文探讨了如何利用扩散模型解决机器人抓取任务中的单视角相机抓取问题。通过仿真创建大量对象与抓取姿态的数据集,学习条件生成模型,在部署时快速提示。由于抓取姿态数据具有多模态性,本文采用扩散模型学习抓取生成模型,对给定对象的局部点云进行采样候选抓取姿态。方法的创新之处在于考虑旋转流形空间的扩散,并提出碰撞避免成本指导以提高推理阶段的抓取成功率。利用扩散文献中的最新技术加速抓取采样,实现在模拟和真实环境中的高效抓取,成功率为90%,与其他基线方法相比具有优势。
Key Takeaways
- 利用仿真创建大量对象与抓取姿态的数据集,解决单视角相机抓取问题。
- 学习条件生成模型,能够在部署时快速提示。
- 抓取姿态数据具有多模态性,采用扩散模型学习抓取生成模型。
- 方法的创新点在于考虑旋转流形空间的扩散。
- 提出碰撞避免成本指导,提高推理阶段的抓取成功率。
- 利用最新技术加速抓取采样,提高推理效率。
- 在模拟和真实环境中实现高效抓取,成功率为90%。
点此查看论文截图

Unicorn: Unified Neural Image Compression with One Number Reconstruction
Authors:Qi Zheng, Haozhi Wang, Zihao Liu, Jiaming Liu, Peiye Liu, Zhijian Hao, Yanheng Lu, Dimin Niu, Jinjia Zhou, Minge Jing, Yibo Fan
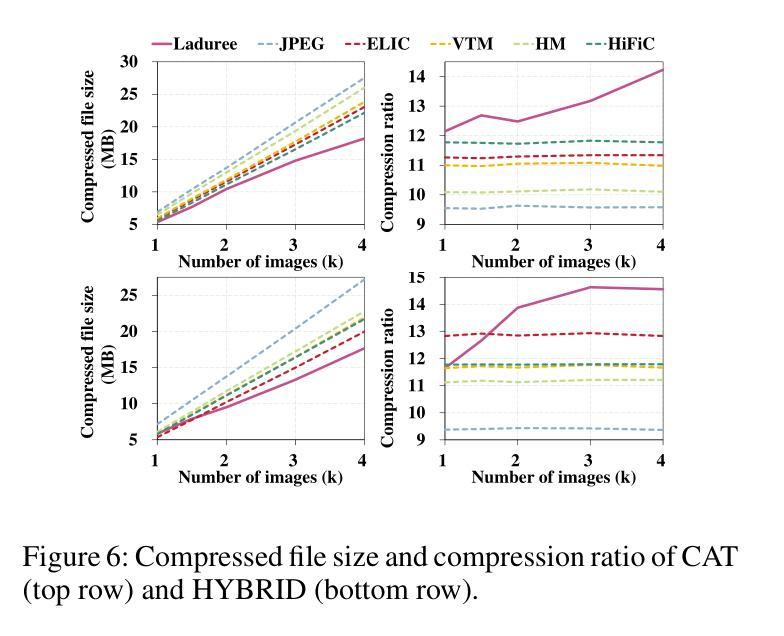
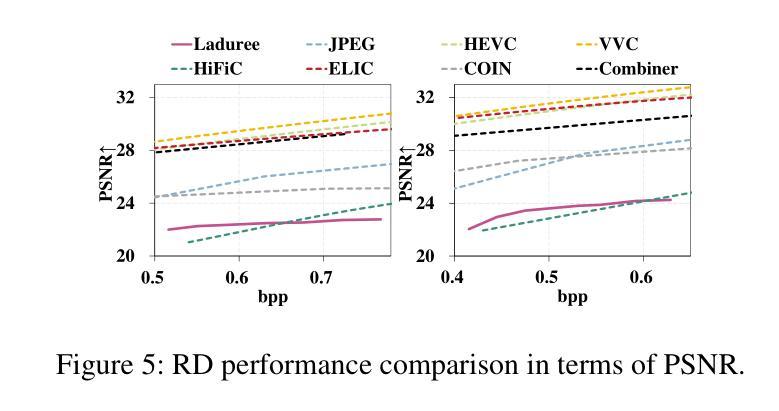
Prevalent lossy image compression schemes can be divided into: 1) explicit image compression (EIC), including traditional standards and neural end-to-end algorithms; 2) implicit image compression (IIC) based on implicit neural representations (INR). The former is encountering impasses of either leveling off bitrate reduction at a cost of tremendous complexity while the latter suffers from excessive smoothing quality as well as lengthy decoder models. In this paper, we propose an innovative paradigm, which we dub \textbf{Unicorn} (\textbf{U}nified \textbf{N}eural \textbf{I}mage \textbf{C}ompression with \textbf{O}ne \textbf{N}number \textbf{R}econstruction). By conceptualizing the images as index-image pairs and learning the inherent distribution of pairs in a subtle neural network model, Unicorn can reconstruct a visually pleasing image from a randomly generated noise with only one index number. The neural model serves as the unified decoder of images while the noises and indexes corresponds to explicit representations. As a proof of concept, we propose an effective and efficient prototype of Unicorn based on latent diffusion models with tailored model designs. Quantitive and qualitative experimental results demonstrate that our prototype achieves significant bitrates reduction compared with EIC and IIC algorithms. More impressively, benefitting from the unified decoder, our compression ratio escalates as the quantity of images increases. We envision that more advanced model designs will endow Unicorn with greater potential in image compression. We will release our codes in \url{https://github.com/uniqzheng/Unicorn-Laduree}.
当前流行的有损图像压缩方案可分为两类:一是显式图像压缩(EIC),包括传统标准和神经端到端算法;二是基于隐式神经表示(INR)的隐式图像压缩(IIC)。前者在降低比特率时面临着巨大的复杂性,而后者则存在过度平滑质量和过长的解码器模型问题。在本文中,我们提出了一种创新的方法,我们称之为“独角兽”(Unicorn)(统一神经网络图像压缩)。通过将图像概念化为索引图像对,并在微妙的神经网络模型中学习对之间的内在分布,独角兽可以从随机生成的噪声中仅用单个索引号重建出令人愉悦的图像。神经网络模型充当图像的统一解码器,而噪声和索引对应于显式表示。作为概念验证,我们基于潜在扩散模型提出了一个有效且高效的独角兽原型,并进行了量身定制的模型设计。定量和定性的实验结果表明,我们的原型与EIC和IIC算法相比实现了显著的码率降低。更令人印象深刻的是,得益于统一的解码器,随着图像数量的增加,我们的压缩比也随之提高。我们预计更先进的模型设计将赋予独角兽在图像压缩方面的更大潜力。我们会在https://github.com/uniqzheng/Unicorn-Laduree上发布我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为Unicorn的统一神经网络图像压缩方法,通过把图像视为索引-图像对,并在微妙的神经网络模型中学习这些对的内在分布,能够从随机生成的噪声中仅用单个索引号重建出视觉上令人满意的图像。该方法基于潜在扩散模型设计原型,与现有图像压缩算法相比,实现了显著的码率降低,且随着图像数量的增加,压缩比有所提高。
Key Takeaways
- 论文对现有的有损图像压缩方案进行了分类,包括显式图像压缩(EIC)和隐式图像压缩(IIC)。
- EIC面临在降低比特率时复杂度急剧增加的问题,而IIC则存在图像质量过于平滑和解码器模型过长的问题。
- Unicorn方法通过把图像视为索引-图像对,并利用神经网络学习其内在分布,实现了从随机噪声中重建图像的能力。
- Unicorn基于潜在扩散模型设计原型,实现了与现有算法相比的显著码率降低。
- Unicorn具有随着图像数量增加,压缩比提高的特点。
- 论文提出的Unicorn方法具有潜在图像压缩的巨大潜力。
点此查看论文截图

Diffusion-Based Attention Warping for Consistent 3D Scene Editing
Authors:Eyal Gomel, Lior Wolf
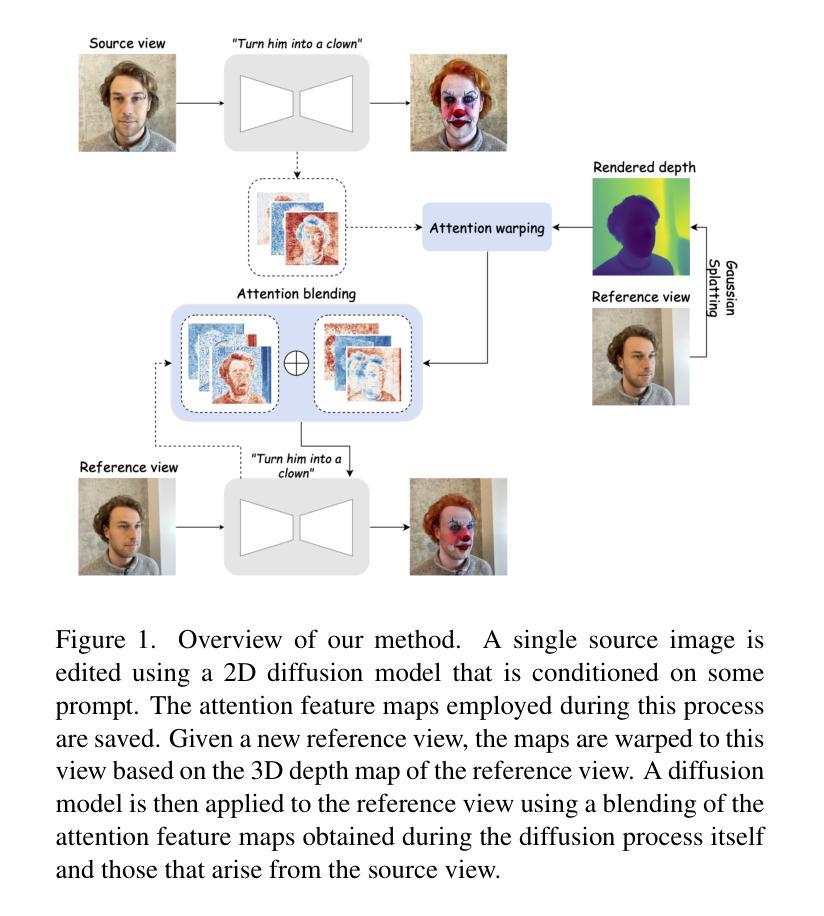
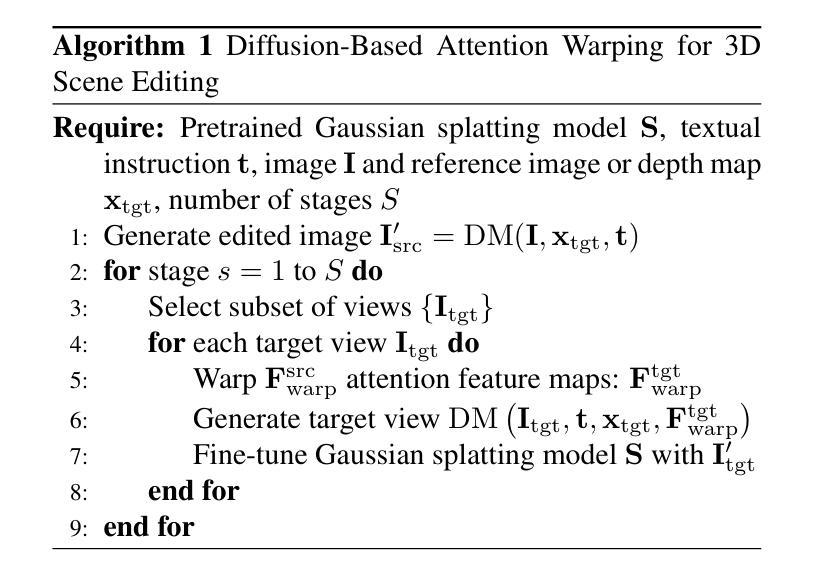
We present a novel method for 3D scene editing using diffusion models, designed to ensure view consistency and realism across perspectives. Our approach leverages attention features extracted from a single reference image to define the intended edits. These features are warped across multiple views by aligning them with scene geometry derived from Gaussian splatting depth estimates. Injecting these warped features into other viewpoints enables coherent propagation of edits, achieving high fidelity and spatial alignment in 3D space. Extensive evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in generating versatile edits of 3D scenes, significantly advancing the capabilities of scene manipulation compared to the existing methods. Project page: \url{https://attention-warp.github.io}
我们提出了一种利用扩散模型进行3D场景编辑的新方法,旨在确保不同视角下的视图一致性和逼真性。我们的方法利用从单一参考图像中提取的注意力特征来定义预期的编辑。通过将这些特征与从高斯展布深度估计中得出的场景几何结构进行对齐,将它们变形到多个视角。将这些变形的特征注入到其他视角,能够实现编辑的连贯传播,在3D空间中实现高保真和空间对齐。大量评估表明,我们的方法在生成3D场景的通用编辑方面非常有效,与现有方法相比,显著提高了场景操作的能力。项目页面:https://attention-warp.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:我们提出了一种使用扩散模型进行3D场景编辑的新方法,通过利用注意力特征确保从不同角度观看时场景的一致性和逼真性。该方法通过从参考图像中提取注意力特征来定义预期的编辑,然后将这些特征通过高斯模糊深度估计的场景几何进行对齐,在不同视角进行变形。将这些变形的特征注入到其他视角,实现了编辑的连贯传播,在3D空间中实现了高保真和空间对齐。评估表明,我们的方法在生成多样化的3D场景编辑方面非常有效,与现有方法相比,大大提升了场景操作的能力。
Key Takeaways:
- 提出了一种基于扩散模型的新方法进行3D场景编辑。
- 利用注意力特征确保不同视角观看场景的一致性和逼真性。
- 通过高斯模糊深度估计的场景几何对注意力特征进行变形。
- 将变形的特征注入到其他视角,实现编辑的连贯传播。
- 在3D空间中实现了高保真和空间对齐的编辑效果。
- 评估表明该方法在生成多样化的3D场景编辑方面非常有效。
点此查看论文截图


Non-Normal Diffusion Models
Authors:Henry Li
Diffusion models generate samples by incrementally reversing a process that turns data into noise. We show that when the step size goes to zero, the reversed process is invariant to the distribution of these increments. This reveals a previously unconsidered parameter in the design of diffusion models: the distribution of the diffusion step $\Delta x_k := x_{k} - x_{k + 1}$. This parameter is implicitly set by default to be normally distributed in most diffusion models. By lifting this assumption, we generalize the framework for designing diffusion models and establish an expanded class of diffusion processes with greater flexibility in the choice of loss function used during training. We demonstrate the effectiveness of these models on density estimation and generative modeling tasks on standard image datasets, and show that different choices of the distribution of $\Delta x_k$ result in qualitatively different generated samples.
扩散模型通过逐步反转将数据转化为噪声的过程来生成样本。我们证明,当步长趋于零时,反转过程对这些增量的分布是不变的。这揭示了扩散模型设计中一个以前未被考虑过的参数:扩散步长$\Delta x_k := x_{k} - x_{k + 1}$的分布。这个参数在大多数扩散模型中默认被设为正态分布。通过取消这个假设,我们推广了设计扩散模型的框架,并建立了一个具有更大灵活性的扩散过程类,在训练过程中可以选择更大的损失函数。我们在标准图像数据集上展示了这些模型在密度估计和生成建模任务上的有效性,并证明了不同的$\Delta x_k$分布选择会导致定性不同的生成样本。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了扩散模型通过逐步反转将数据转化为噪声的过程来生成样本。当步长趋于零时,反转过程对增量分布具有不变性,揭示出扩散模型设计中一个未被考虑过的参数:扩散步长Δxk的分布。大多数扩散模型默认将其设为正态分布。通过取消这一假设,本文推广了扩散模型的设计框架,并建立了一个具有更大灵活性的扩散过程类,可在训练过程中选择不同的损失函数。在标准图像数据集上进行密度估计和生成建模任务时,本文展示了不同Δxk分布选择对生成样本质量的影响。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型通过逐步反转数据到噪声的过程生成样本。
- 扩散步长Δxk的分布是一个未被充分研究的参数。
- 大多数扩散模型默认将扩散步长Δxk设为正态分布。
- 取消这一假设可以推广扩散模型的设计框架,并建立更灵活的扩散过程类。
- 不同的Δxk分布选择会影响生成样本的质量。
- 在标准图像数据集上,新的扩散模型在密度估计和生成建模任务中表现出效果。
点此查看论文截图


Efficient Diversity-Preserving Diffusion Alignment via Gradient-Informed GFlowNets
Authors:Zhen Liu, Tim Z. Xiao, Weiyang Liu, Yoshua Bengio, Dinghuai Zhang
While one commonly trains large diffusion models by collecting datasets on target downstream tasks, it is often desired to align and finetune pretrained diffusion models on some reward functions that are either designed by experts or learned from small-scale datasets. Existing methods for finetuning diffusion models typically suffer from lack of diversity in generated samples, lack of prior preservation, and/or slow convergence in finetuning. Inspired by recent successes in generative flow networks (GFlowNets), a class of probabilistic models that sample with the unnormalized density of a reward function, we propose a novel GFlowNet method dubbed Nabla-GFlowNet (abbreviated as $\nabla$-GFlowNet), the first GFlowNet method that leverages the rich signal in reward gradients, together with an objective called $\nabla$-DB plus its variant residual $\nabla$-DB designed for prior-preserving diffusion alignment. We show that our proposed method achieves fast yet diversity- and prior-preserving alignment of Stable Diffusion, a large-scale text-conditioned image diffusion model, on different realistic reward functions.
通常人们通过收集目标下游任务的数据集来训练大型扩散模型,但往往希望将预训练的扩散模型与某些奖励函数对齐并进行微调,这些奖励函数是专家设计的或者是从小规模数据集中学习得到的。现有的微调扩散模型的方法通常存在生成样本缺乏多样性、缺乏先验知识保留以及微调过程中收敛速度慢等问题。受到生成流网络(GFlowNets)领域的最新成功的启发,一类使用奖励函数未归一化密度进行采样的概率模型,我们提出了一种新型的GFlowNet方法,称为Nabla-GFlowNet(简称$\nabla$-GFlowNet),它是第一个利用奖励梯度丰富信号以及一个称为$\nabla$-DB的目标及其为保留先验设计的变体残差$\nabla$-DB的GFlowNet方法,以实现扩散对齐。我们展示了我们提出的方法在多种真实奖励函数上快速实现了大规模文本条件图像扩散模型的多样性和先验知识保留对齐。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report (35 pages, 31 figures)
Summary
大型扩散模型的训练通常是通过在目标下游任务上收集数据集来进行的,然而,人们更希望将预训练的扩散模型调整并对齐到某些奖励函数上,这些奖励函数是由专家设计的或者是从小规模数据集中学习得到的。现有的微调扩散模型的方法通常存在生成样本缺乏多样性、缺乏先验知识保留以及微调过程中收敛速度慢的问题。受生成流网络(GFlowNets)近期成功的启发,我们提出了一种名为Nabla-GFlowNet的新方法,它是第一个利用奖励梯度丰富信号并结合称为$\nabla$-DB的目标及其变体的GFlowNet方法,即用于先验保留扩散对齐的剩余$\nabla$-DB。我们的方法能够在不同的现实奖励函数上快速实现对Stable Diffusion等大型文本条件图像扩散模型的对齐,同时保持多样性和先验知识。
Key Takeaways
- 大型扩散模型的训练通常集中在目标下游任务的数据集上,但专家设计的奖励函数或从小规模数据集中学习的奖励函数的对齐和微调是常见的需求。
- 现有微调扩散模型的方法存在生成样本缺乏多样性、缺乏先验知识保留和收敛速度慢的问题。
- Nabla-GFlowNet是首个结合奖励梯度信号的GFlowNet方法。
- Nabla-GFlowNet利用丰富的奖励梯度信号,有助于快速对齐大型文本条件图像扩散模型。
- 该方法设计的目标是实现多样性和先验知识保留的对齐。
- 通过实验验证,Nabla-GFlowNet在多种现实奖励函数上成功实现了Stable Diffusion模型的对齐。
点此查看论文截图


From Slow Bidirectional to Fast Causal Video Generators
Authors:Tianwei Yin, Qiang Zhang, Richard Zhang, William T. Freeman, Fredo Durand, Eli Shechtman, Xun Huang
Current video diffusion models achieve impressive generation quality but struggle in interactive applications due to bidirectional attention dependencies. The generation of a single frame requires the model to process the entire sequence, including the future. We address this limitation by adapting a pretrained bidirectional diffusion transformer to a causal transformer that generates frames on-the-fly. To further reduce latency, we extend distribution matching distillation (DMD) to videos, distilling 50-step diffusion model into a 4-step generator. To enable stable and high-quality distillation, we introduce a student initialization scheme based on teacher’s ODE trajectories, as well as an asymmetric distillation strategy that supervises a causal student model with a bidirectional teacher. This approach effectively mitigates error accumulation in autoregressive generation, allowing long-duration video synthesis despite training on short clips. Our model supports fast streaming generation of high quality videos at 9.4 FPS on a single GPU thanks to KV caching. Our approach also enables streaming video-to-video translation, image-to-video, and dynamic prompting in a zero-shot manner. We will release the code based on an open-source model in the future.
当前的视频扩散模型在生成质量方面表现令人印象深刻,但由于双向注意力依赖性,在交互式应用中表现挣扎。单个帧的生成需要模型处理整个序列,包括未来信息。我们通过将预训练的双向扩散变压器适应为因果变压器来解决这一限制,该因果变压器可以即时生成帧。为了进一步降低延迟,我们将分布匹配蒸馏(DMD)扩展到视频领域,将50步扩散模型精炼为4步生成器。为了实现稳定和高质量的蒸馏,我们引入了基于教师ODE轨迹的学生初始化方案,以及一种不对称的蒸馏策略,即使用双向教师监督因果学生模型。这种方法有效地缓解了自回归生成中的误差累积,即使在短片段训练的情况下也能实现长期视频合成。我们的模型支持在单个GPU上以9.4 FPS的速度快速流式生成高质量视频,这得益于KV缓存。我们的方法还实现了流式视频到视频的转换、图像到视频以及零样本方式的动态提示。未来,我们将基于开源模型发布代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://causvid.github.io/
Summary
针对当前视频扩散模型在交互式应用中由于双向注意力依赖而产生的瓶颈,研究团队通过将一个预训练的双向扩散转换器改编为因果转换器来解决这一问题,实现了即时生成帧。为进一步提高效率,研究团队将分布匹配蒸馏法(DMD)扩展到视频领域,将50步扩散模型浓缩为4步生成器。此外,通过引入基于教师常微分方程轨迹的学生初始化方案以及不对称蒸馏策略,有效实现了稳定且高质量的蒸馏,减少了自回归生成中的误差积累。该研究模型支持在单个GPU上以9.4 FPS的速度快速生成高质量视频,并实现视频到视频的流式转换、图像到视频以及零样本动态提示等功能。
Key Takeaways
- 双向注意力依赖是视频扩散模型在交互式应用中的瓶颈。
- 研究团队通过改编预训练的双向扩散转换器为因果转换器来解决这一问题。
- 分布匹配蒸馏法(DMD)被成功扩展到视频领域,将扩散模型的步骤从50步减少到4步。
- 引入基于教师常微分方程轨迹的学生初始化方案和不对称蒸馏策略,实现了稳定且高质量的蒸馏。
- 模型支持快速生成高质量视频,并能在单个GPU上以9.4 FPS的速度进行流式传输。
- 模型能够实现视频到视频的流式转换、图像到视频转换以及零样本动态提示功能。
- 研究团队计划基于开源模型发布代码。
点此查看论文截图




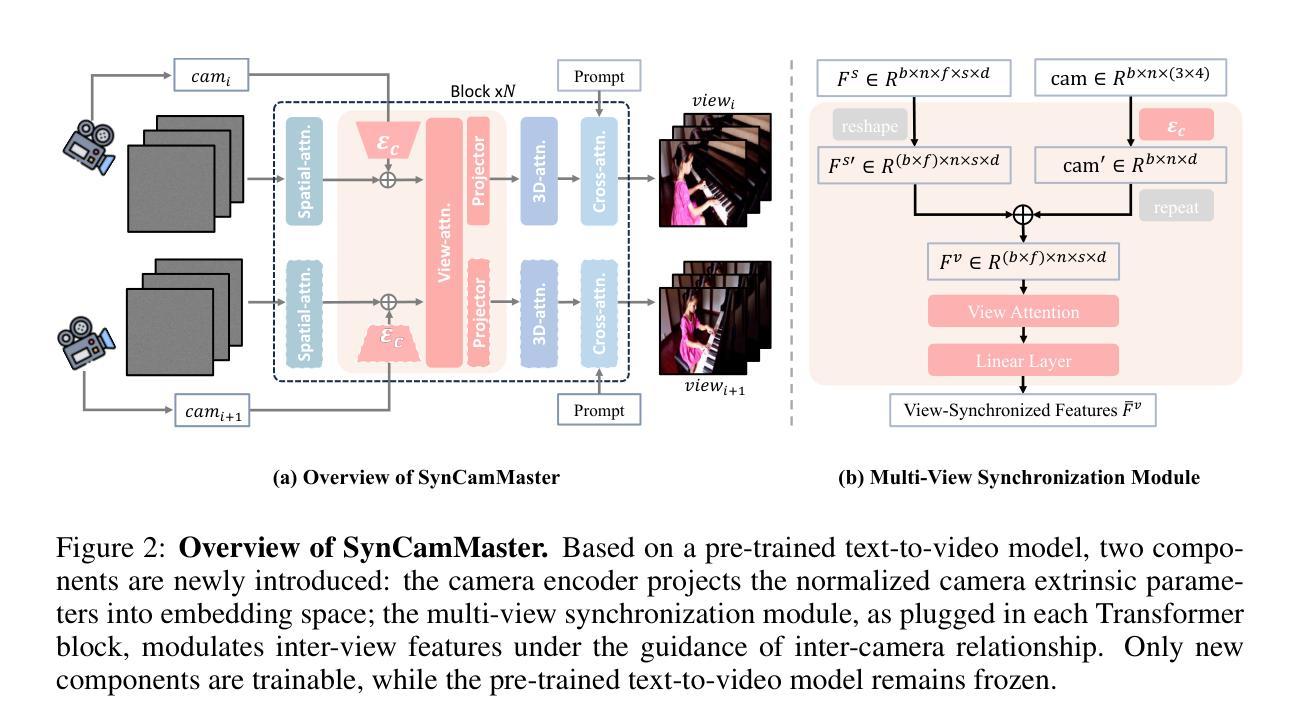
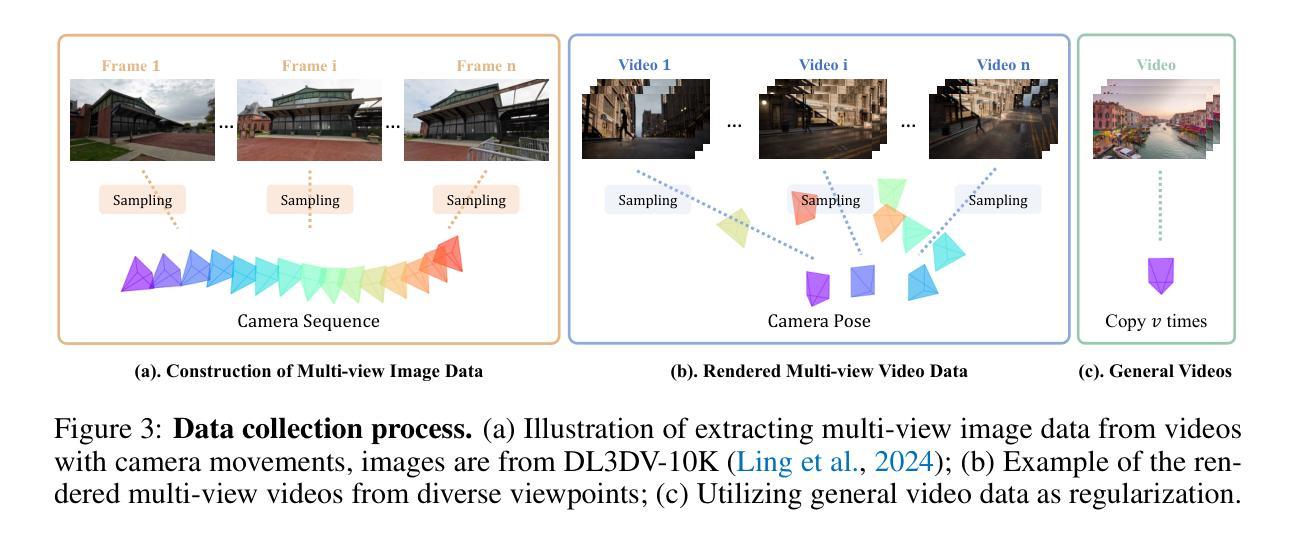
SynCamMaster: Synchronizing Multi-Camera Video Generation from Diverse Viewpoints
Authors:Jianhong Bai, Menghan Xia, Xintao Wang, Ziyang Yuan, Xiao Fu, Zuozhu Liu, Haoji Hu, Pengfei Wan, Di Zhang
Recent advancements in video diffusion models have shown exceptional abilities in simulating real-world dynamics and maintaining 3D consistency. This progress inspires us to investigate the potential of these models to ensure dynamic consistency across various viewpoints, a highly desirable feature for applications such as virtual filming. Unlike existing methods focused on multi-view generation of single objects for 4D reconstruction, our interest lies in generating open-world videos from arbitrary viewpoints, incorporating 6 DoF camera poses. To achieve this, we propose a plug-and-play module that enhances a pre-trained text-to-video model for multi-camera video generation, ensuring consistent content across different viewpoints. Specifically, we introduce a multi-view synchronization module to maintain appearance and geometry consistency across these viewpoints. Given the scarcity of high-quality training data, we design a hybrid training scheme that leverages multi-camera images and monocular videos to supplement Unreal Engine-rendered multi-camera videos. Furthermore, our method enables intriguing extensions, such as re-rendering a video from novel viewpoints. We also release a multi-view synchronized video dataset, named SynCamVideo-Dataset. Project page: https://jianhongbai.github.io/SynCamMaster/.
近期视频扩散模型的进展在模拟真实世界动态和保持3D一致性方面展现出卓越的能力。这一进展激发我们研究这些模型在跨不同视角确保动态一致性的潜力,这对于虚拟拍摄等应用来说是一个高度理想的功能。不同于现有方法专注于单一对象的多个视角生成用于4D重建,我们的兴趣在于从任意视角生成开放世界视频,结合采用自由度为六的视角摄像头姿态。为此,我们提出了一个随插随玩的模块,它可增强文本至视频的预训练模型进行多摄像头视频生成的能力,以确保不同视角间的内容一致性。具体来说,我们引入了一个多视角同步模块以保持这些视角之间外观和几何的一致性。考虑到高质量训练数据的稀缺性,我们设计了一种混合训练方案,该方案利用多摄像头图像和单目视频来补充由虚幻引擎渲染的多摄像头视频。此外,我们的方法还启用了有趣的扩展功能,如从新颖视角重新渲染视频。我们还发布了一个名为SynCamVideo-Dataset的多视角同步视频数据集。项目页面:https://jianhongbai.github.io/SynCamMaster/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://jianhongbai.github.io/SynCamMaster/
Summary
本文介绍了视频扩散模型的新进展,该模型能够在模拟真实世界动态和保持3D一致性方面表现出卓越的能力。研究团队探讨了该模型在虚拟拍摄等应用中确保从不同视角动态一致性的潜力。该研究提出了一种即插即用模块,可以增强预训练文本到视频模型的多相机视频生成能力,确保不同视角的内容一致性。该研究引入了多视角同步模块,并设计了一种混合训练方案来利用多相机图像和单目视频来补充虚幻引擎渲染的多相机视频。此外,该研究的方法还可以进行有趣的扩展,例如从新颖的视角重新渲染视频。同时发布了一个名为SynCamVideo-Dataset的多视角同步视频数据集。
Key Takeaways
- 视频扩散模型在模拟真实世界动态和保持3D一致性方面表现出卓越的能力。
- 研究团队关注模型在虚拟拍摄中确保不同视角动态一致性的潜力。
- 提出了一种即插即用模块,增强预训练文本到视频模型的多相机视频生成能力。
- 引入了多视角同步模块以维持不同视角的外观和几何一致性。
- 设计了一种混合训练方案,利用多相机图像和单目视频来补充虚幻引擎渲染的多相机视频。
- 方法支持从新颖视角重新渲染视频,提供了更大的创作自由度。
点此查看论文截图


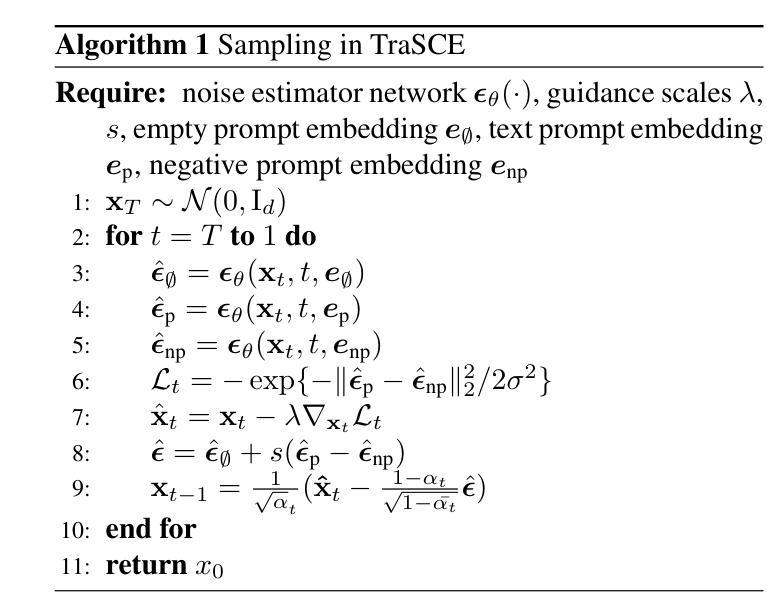
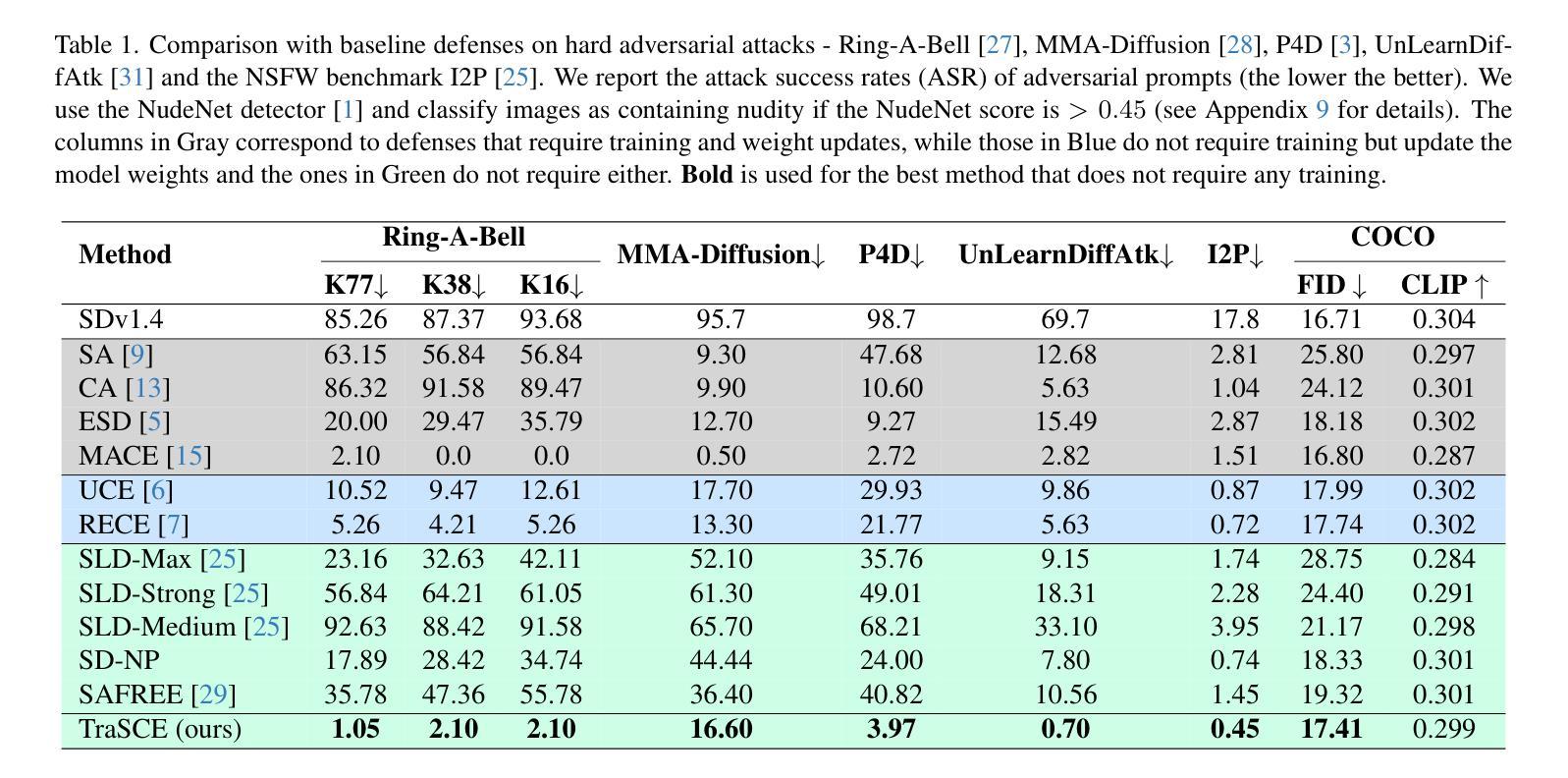
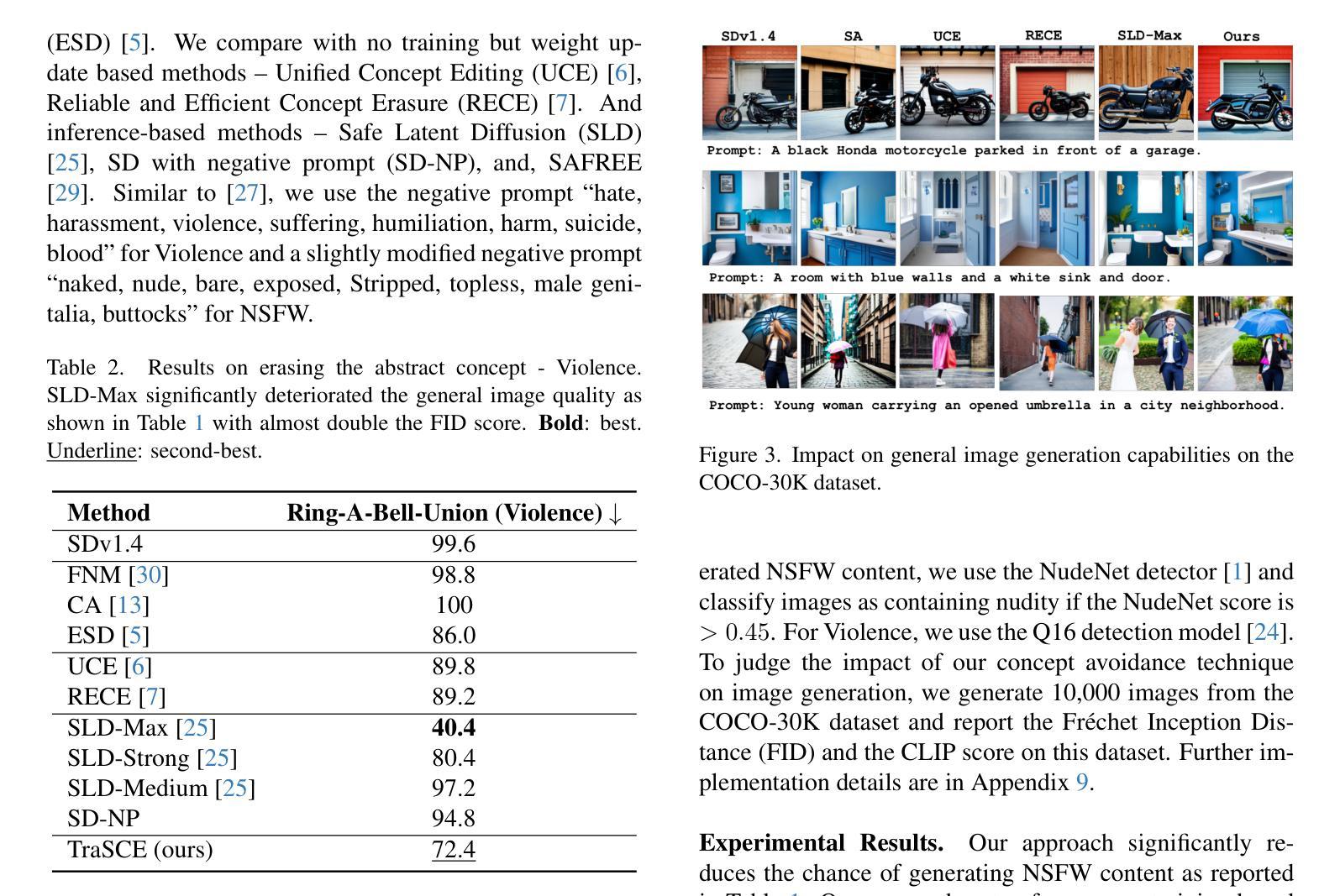
TraSCE: Trajectory Steering for Concept Erasure
Authors:Anubhav Jain, Yuya Kobayashi, Takashi Shibuya, Yuhta Takida, Nasir Memon, Julian Togelius, Yuki Mitsufuji
Recent advancements in text-to-image diffusion models have brought them to the public spotlight, becoming widely accessible and embraced by everyday users. However, these models have been shown to generate harmful content such as not-safe-for-work (NSFW) images. While approaches have been proposed to erase such abstract concepts from the models, jail-breaking techniques have succeeded in bypassing such safety measures. In this paper, we propose TraSCE, an approach to guide the diffusion trajectory away from generating harmful content. Our approach is based on negative prompting, but as we show in this paper, conventional negative prompting is not a complete solution and can easily be bypassed in some corner cases. To address this issue, we first propose a modification of conventional negative prompting. Furthermore, we introduce a localized loss-based guidance that enhances the modified negative prompting technique by steering the diffusion trajectory. We demonstrate that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art results on various benchmarks in removing harmful content including ones proposed by red teams; and erasing artistic styles and objects. Our proposed approach does not require any training, weight modifications, or training data (both image or prompt), making it easier for model owners to erase new concepts.
文本到图像扩散模型的最新进展使其受到公众关注,并逐渐被日常用户广泛接受和使用。然而,这些模型已被证明可以生成有害内容,如不适合工作场合(NSFW)的图像。虽然已有方法试图从模型中消除这些抽象概念,但破解技术已成功绕过这些安全措施。在本文中,我们提出TraSCE方法,通过引导扩散轨迹远离生成有害内容。我们的方法基于负提示,但正如我们在本文中所展示的,传统的负提示并不构成完整解决方案,在某些特定情况下容易被绕过。为了解决这个问题,我们首先提出对常规负提示的修改。此外,我们还引入了一种基于局部损失的指导方法,通过引导扩散轨迹来增强改进后的负提示技术。我们证明,我们的方法在去除有害内容方面达到了最新水平,包括红队提出的各种基准测试中的有害内容;以及消除艺术风格和物体。我们提出的方法不需要任何训练、权重修改或训练数据(无论是图像还是提示),这使得模型所有者更容易消除新概念。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到图像扩散模型近期受到广泛关注,但其生成不适当内容(如不适宜工作场合的图像)的问题引发担忧。现有方法试图从模型中移除这些抽象概念,但存在绕过安全措施的越狱技术。本文提出TraSCE方法,通过负提示和引导扩散轨迹,避免生成有害内容。TraSCE方法改进了传统负提示,并引入基于局部损失的指导,改进后的技术能更有效地引导扩散轨迹。实验证明,该方法在去除有害内容、消除艺术风格和物体方面达到最新水平,且无需任何训练、权重修改或训练数据,便于模型所有者移除新概念。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像扩散模型受到广泛关注,但生成不适当内容的问题引发担忧。
- 现有方法试图从模型中移除有害内容,但存在绕过安全措施的技术。
- TraSCE方法基于负提示和改进的扩散轨迹指导,避免生成有害内容。
- TraSCE方法改进了传统负提示,并引入局部损失指导机制。
- 实验证明TraSCE方法在去除有害内容方面达到最新水平。
- TraSCE方法无需任何训练、权重修改或训练数据,易于实施新概念移除。
点此查看论文截图


Motion Artifact Removal in Pixel-Frequency Domain via Alternate Masks and Diffusion Model
Authors:Jiahua Xu, Dawei Zhou, Lei Hu, Jianfeng Guo, Feng Yang, Zaiyi Liu, Nannan Wang, Xinbo Gao
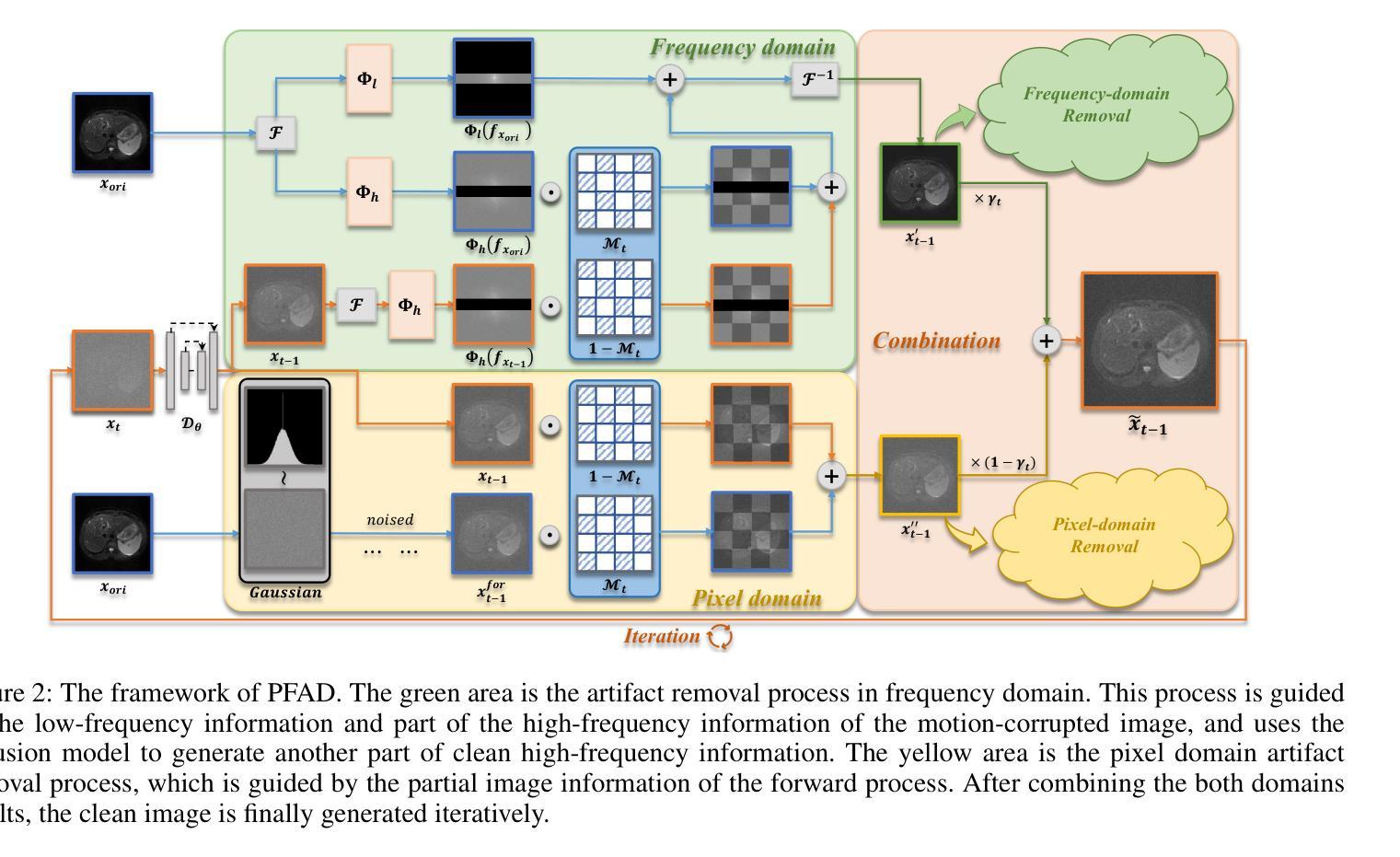
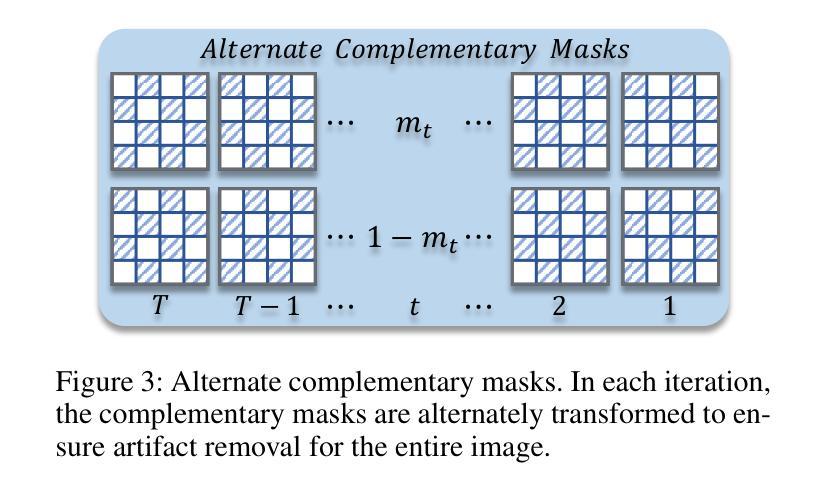
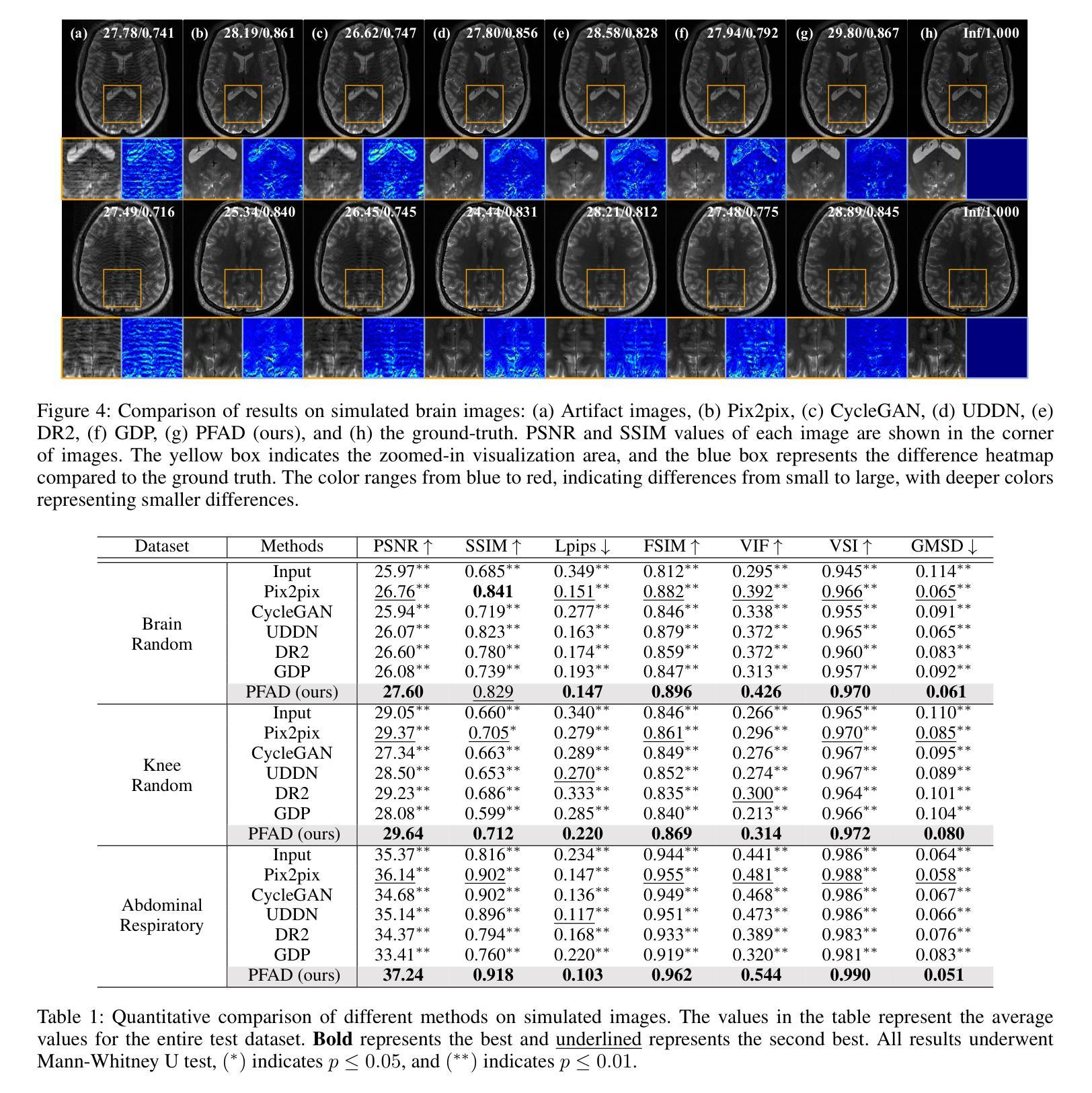
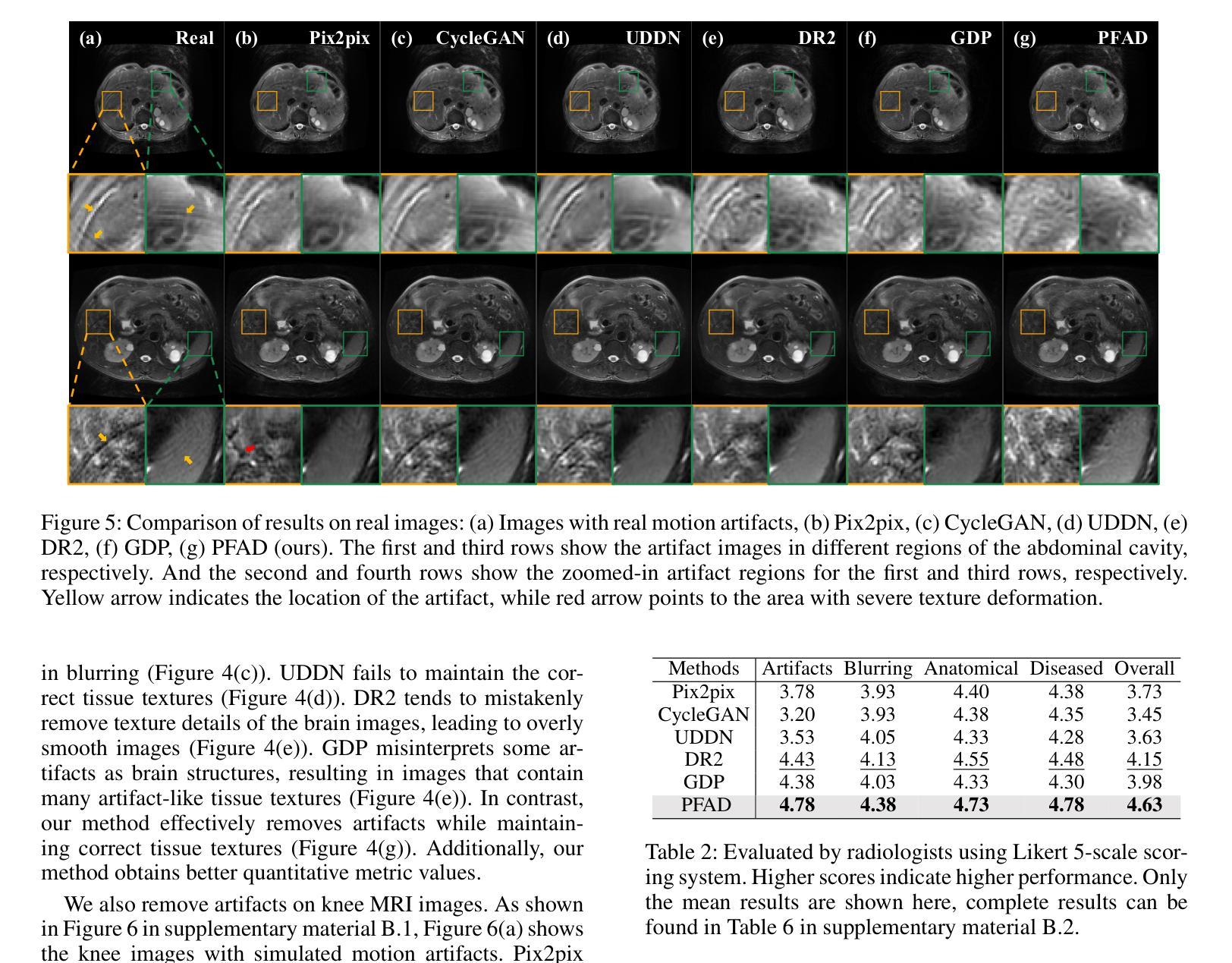
Motion artifacts present in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can seriously interfere with clinical diagnosis. Removing motion artifacts is a straightforward solution and has been extensively studied. However, paired data are still heavily relied on in recent works and the perturbations in k-space (frequency domain) are not well considered, which limits their applications in the clinical field. To address these issues, we propose a novel unsupervised purification method which leverages pixel-frequency information of noisy MRI images to guide a pre-trained diffusion model to recover clean MRI images. Specifically, considering that motion artifacts are mainly concentrated in high-frequency components in k-space, we utilize the low-frequency components as the guide to ensure correct tissue textures. Additionally, given that high-frequency and pixel information are helpful for recovering shape and detail textures, we design alternate complementary masks to simultaneously destroy the artifact structure and exploit useful information. Quantitative experiments are performed on datasets from different tissues and show that our method achieves superior performance on several metrics. Qualitative evaluations with radiologists also show that our method provides better clinical feedback. Our code is available at https://github.com/medcx/PFAD.
磁共振成像(MRI)中的运动伪影会严重干扰临床诊断。去除运动伪影是一种直接解决方案,已经得到了广泛的研究。然而,最近的研究仍然严重依赖于配对数据,而k空间(频率域)中的扰动并未得到很好的考虑,这限制了其在临床领域的应用。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新型的无监督净化方法,该方法利用带噪声的MRI图像的像素频率信息来指导预训练的扩散模型恢复清洁的MRI图像。具体来说,考虑到运动伪影主要集中在k空间的高频成分中,我们利用低频成分作为指导,以确保正确的纹理组织。此外,鉴于高频和像素信息有助于恢复形状和细节纹理,我们设计了交替的互补掩膜来同时破坏伪影结构并利用有用信息。在不同组织数据集上进行的定量实验表明,我们的方法在多个指标上实现了卓越的性能。与放射科医生进行的定性评估也表明,我们的方法提供了更好的临床反馈。我们的代码可在https://github.com/medcx/PFAD找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures, AAAI 2025
Summary
本文提出一种新型的无监督净化方法,利用噪声磁共振成像(MRI)图像的像素频率信息引导预训练的扩散模型恢复清洁的MRI图像,以解决MRI中的运动伪影问题。该方法考虑运动伪影主要集中在k空间的高频成分上,利用低频成分作为指导以确保正确的组织纹理。同时,设计交替互补掩膜同时破坏伪影结构并提取有用信息,以提高图像恢复质量。实验结果表明,该方法在多个指标上表现优异,获得放射科医师的积极评价。
Key Takeaways
- 磁共振成像(MRI)中的运动伪影会干扰临床诊断,去除伪影是亟待解决的问题。
- 现有方法多依赖配对数据,对k空间频率扰动考虑不足,限制了其在临床的应用。
- 新型无监督净化方法利用像素频率信息引导预训练扩散模型恢复清洁MRI图像。
- 方法针对运动伪影主要集中在k空间高频成分的问题,使用低频成分作为指导。
- 设计交替互补掩膜以同时破坏伪影结构和提取有用信息。
- 实验在多个数据集和指标上表现出优异性能,获得放射科医师的积极评价。
点此查看论文截图

[MASK] is All You Need
Authors:Vincent Tao Hu, Björn Ommer
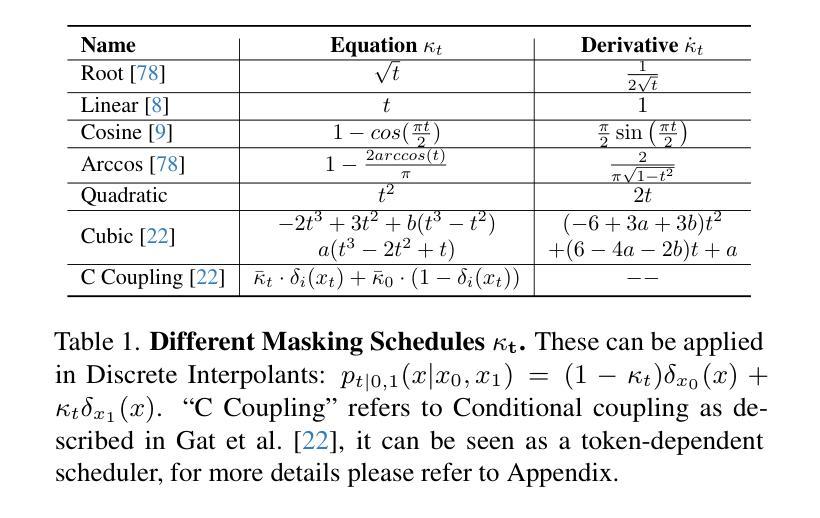
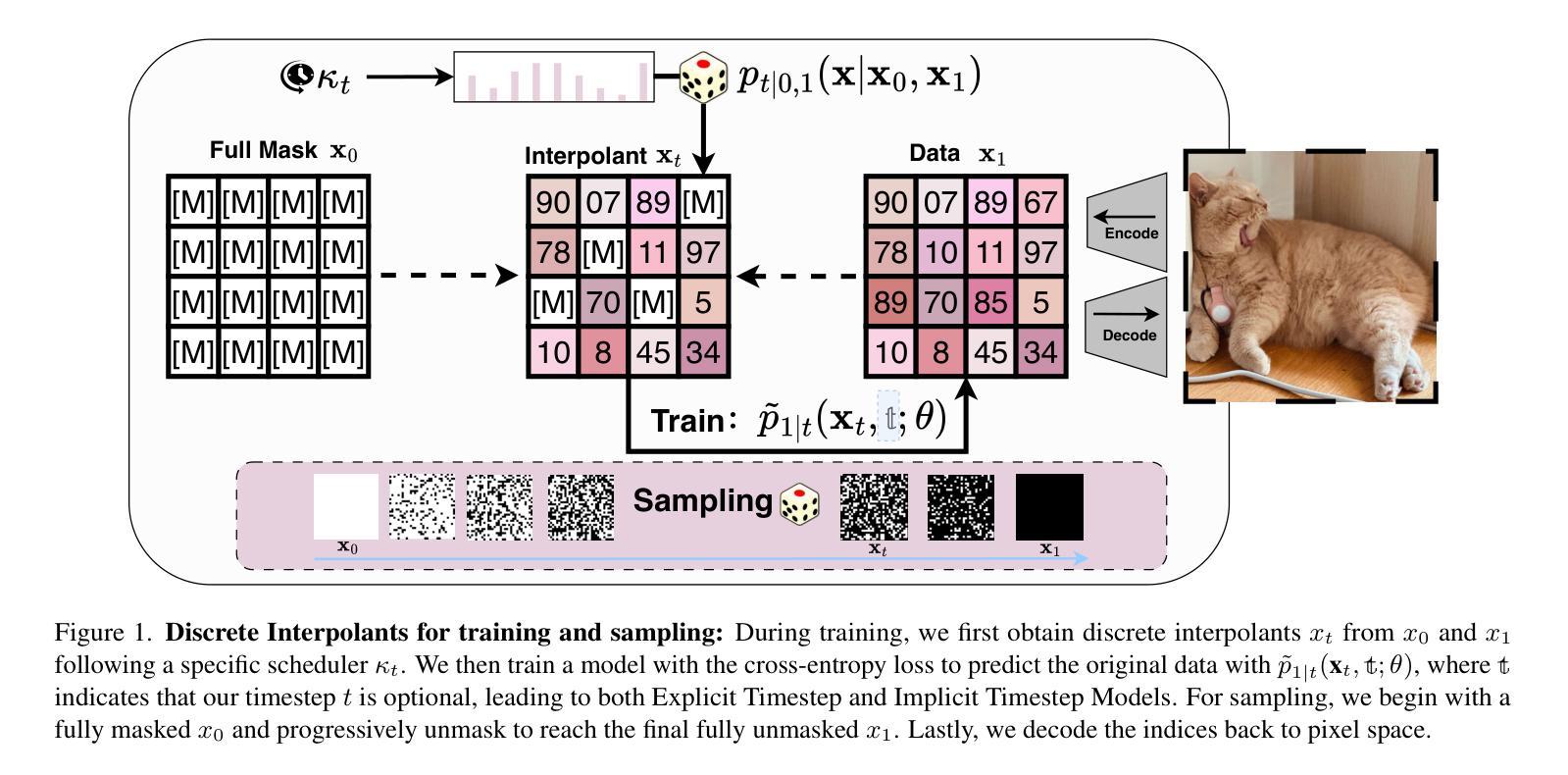
In generative models, two paradigms have gained attraction in various applications: next-set prediction-based Masked Generative Models and next-noise prediction-based Non-Autoregressive Models, e.g., Diffusion Models. In this work, we propose using discrete-state models to connect them and explore their scalability in the vision domain. First, we conduct a step-by-step analysis in a unified design space across two types of models including timestep-independence, noise schedule, temperature, guidance strength, etc in a scalable manner. Second, we re-cast typical discriminative tasks, e.g., image segmentation, as an unmasking process from [MASK] tokens on a discrete-state model. This enables us to perform various sampling processes, including flexible conditional sampling by only training once to model the joint distribution. All aforementioned explorations lead to our framework named Discrete Interpolants, which enables us to achieve state-of-the-art or competitive performance compared to previous discrete-state based methods in various benchmarks, like ImageNet256, MS COCO, and video dataset FaceForensics. In summary, by leveraging [MASK] in discrete-state models, we can bridge Masked Generative and Non-autoregressive Diffusion models, as well as generative and discriminative tasks.
在生成模型中,有两种范式在各种应用中受到了关注:基于下一个集合预测的Masked Generative Models和基于下一个噪声预测的非自回归模型(例如扩散模型)。在这项工作中,我们提出使用离散状态模型来连接它们,并探索它们在视觉领域的可扩展性。首先,我们在统一的设计空间中对两种类型的模型进行了逐步分析,包括时间步独立性、噪声时间表、温度、指导强度等,以一种可扩展的方式。其次,我们将典型的判别任务(例如图像分割)重新定位为离散状态模型上的去遮掩过程。这使得我们能够执行各种采样过程,包括通过仅训练一次来对联合分布进行建模,从而实现灵活的条件采样。所有上述探索都引领我们构建了名为“离散插值”的框架,该框架使我们能够在各种基准测试(例如ImageNet256、MS COCO和视频数据集FaceForensics)上达到或超过基于离散状态的方法的先进水平。总的来说,通过利用离散状态模型中的[MASK],我们可以架起Masked Generative和Non-autoregressive Diffusion模型之间的桥梁,以及生成任务和判别任务之间的桥梁。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report (WIP), Project Page(code, model, dataset): https://compvis.github.io/mask/
Summary:
本文探讨了生成模型中的两种范式:基于下一步预测的Masked Generative模型和基于下一步噪声预测的非自回归模型,例如扩散模型。研究人员使用离散状态模型将两者联系起来,并在视觉领域探索其可扩展性。通过对两种模型的统一设计空间进行逐步分析,包括时间步独立性、噪声时间表、温度、指导强度等,并将典型的判别任务重新定义为离散状态模型上的去遮掩过程。这启用了各种采样过程,包括通过仅训练一次来对联合分布进行灵活的条件采样。所有这些探索都引领了一个名为“离散插值”的框架,该框架在ImageNet256、MS COCO和FaceForensics视频数据集上达到了最新的或具有竞争力的性能。总之,通过利用离散状态模型中的[MASK],可以桥接Masked Generative和Non-autoregressive Diffusion模型,以及生成和判别任务。
Key Takeaways:
- 工作中探讨了生成模型中的两种范式:Masked Generative模型和Non-Autoregressive Models(例如扩散模型)。
- 使用离散状态模型将这两种范式连接起来,并在视觉领域探索其可扩展性。
- 在统一设计空间中对两种模型进行逐步分析,包括时间步独立性、噪声时间表等。
- 将判别任务重新定义为离散状态模型上的去遮掩过程,实现了灵活的采样过程。
- 提出了名为“离散插值”的框架,在多个数据集上实现了具有竞争力的性能。
- 通过利用离散状态模型中的[MASK],桥接了不同类型的生成模型和任务。
点此查看论文截图

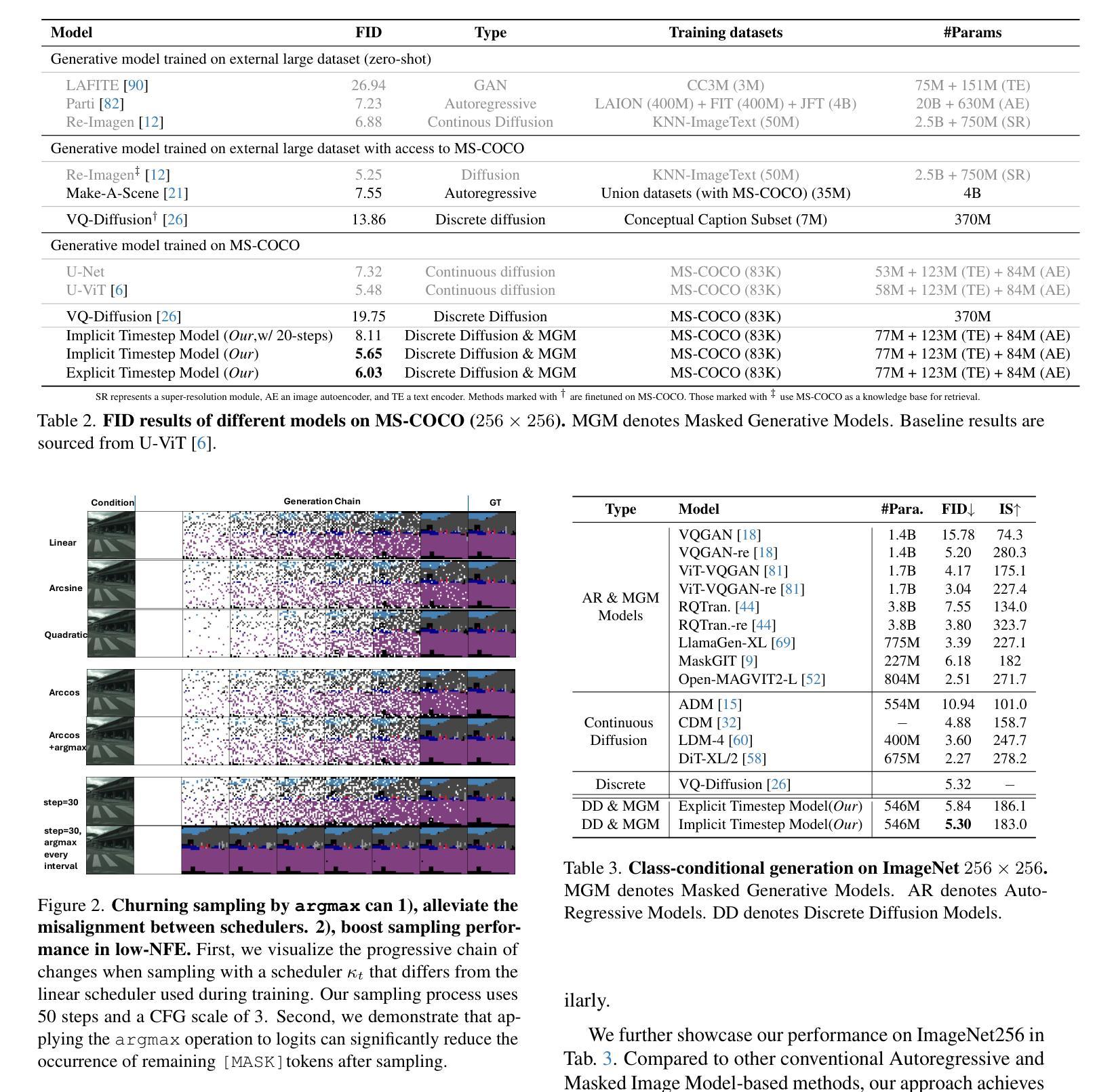
ContRail: A Framework for Realistic Railway Image Synthesis using ControlNet
Authors:Andrei-Robert Alexandrescu, Razvan-Gabriel Petec, Alexandru Manole, Laura-Silvia Diosan
Deep Learning became an ubiquitous paradigm due to its extraordinary effectiveness and applicability in numerous domains. However, the approach suffers from the high demand of data required to achieve the potential of this type of model. An ever-increasing sub-field of Artificial Intelligence, Image Synthesis, aims to address this limitation through the design of intelligent models capable of creating original and realistic images, endeavour which could drastically reduce the need for real data. The Stable Diffusion generation paradigm recently propelled state-of-the-art approaches to exceed all previous benchmarks. In this work, we propose the ContRail framework based on the novel Stable Diffusion model ControlNet, which we empower through a multi-modal conditioning method. We experiment with the task of synthetic railway image generation, where we improve the performance in rail-specific tasks, such as rail semantic segmentation by enriching the dataset with realistic synthetic images.
深度学习因其在众多领域的卓越效果和适用性而成为无处不在的范例。然而,这种方法需要大量的数据来实现该类型模型的潜力。人工智能的一个日益增长的子领域——图像合成,旨在通过设计能够创建原创和逼真图像的智能模型来解决这一局限性,从而大幅减少对真实数据的需求。最近,Stable Diffusion生成范式推动了最先进的方法超越了所有之前的基准测试。在这项工作中,我们提出了基于新型Stable Diffusion模型ControlNet的ContRail框架,我们通过多模态条件方法对其进行赋能。我们尝试铁路图像合成任务,通过用逼真的合成图像丰富数据集,改进铁路特定任务(如铁路语义分割)的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 5 figures, 2 tables
Summary
深度学习因其跨多个领域的出色效果和适用性而成为无处不在的范例。然而,这种方法对数据的需求极高,限制了其潜力。图像合成作为人工智能的一个日益增长的子领域,旨在通过设计能够创建原始和逼真图像的智能模型来解决这一局限性。最近的Stable Diffusion生成范式推动最先进的技术超越了所有先前的基准测试。在这项工作中,我们基于新型的Stable Diffusion模型ControlNet提出ContRail框架,并通过多模态条件方法增强其能力。我们尝试铁路图像生成任务,通过丰富数据集与逼真的合成图像,提高了铁路特定任务(如铁路语义分割)的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习已成为多个领域的标准范例,但其对数据的高需求限制了其潜力。
- 图像合成子领域旨在通过智能模型创建逼真图像来解决此问题。
- Stable Diffusion生成范式已成为最先进的图像生成技术。
- ContRail框架基于ControlNet模型,通过多模态条件方法增强性能。
- 在铁路图像生成任务中,ContRail框架通过丰富数据集与合成图像提高了铁路特定任务(如铁路语义分割)的性能。
- ContRail框架可能有助于减少真实数据的需求,提高模型的性能和适用性。
点此查看论文截图

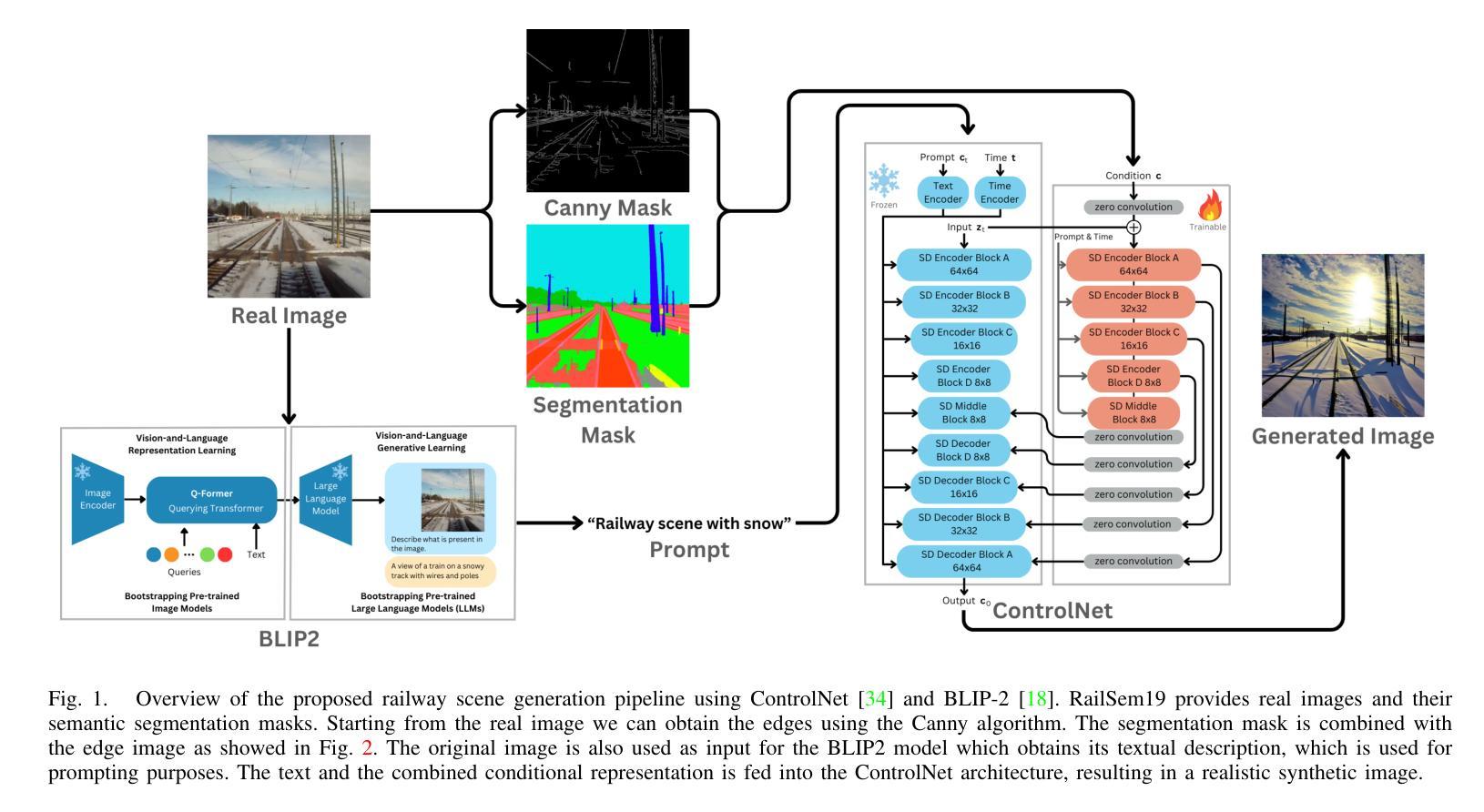
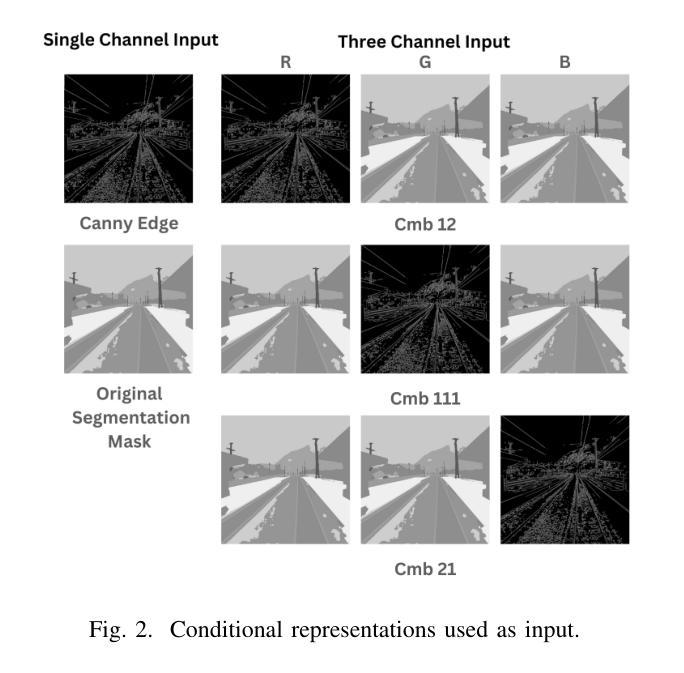

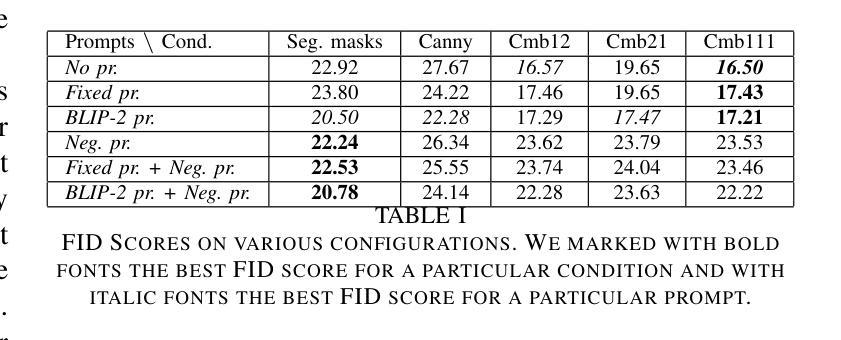
Open-Source Acceleration of Stable-Diffusion.cpp
Authors:Jingxu Ng, Cheng Lv, Pu Zhao, Wei Niu, Juyi Lin, Minzhou Pan, Yun Liang, Yanzhi Wang
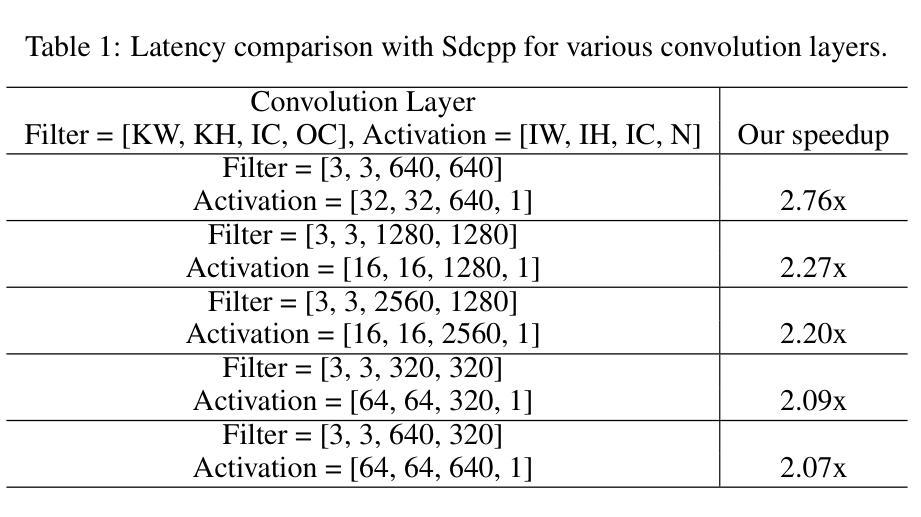
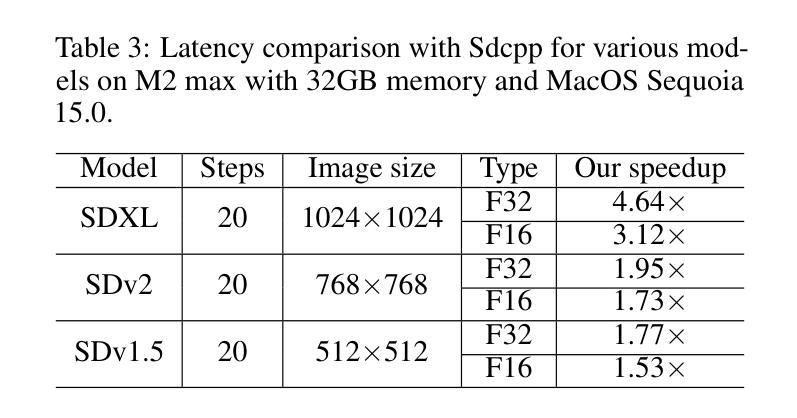
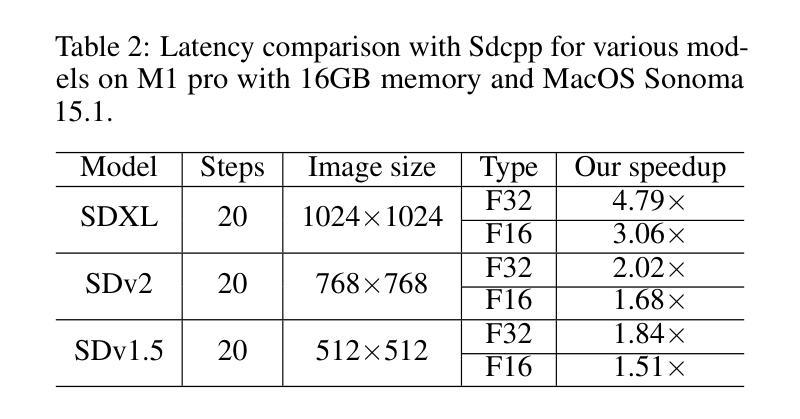
Stable diffusion plays a crucial role in generating high-quality images. However, image generation is time-consuming and memory-intensive. To address this, stable-diffusion.cpp (Sdcpp) emerges as an efficient inference framework to accelerate the diffusion models. Although it is lightweight, the current implementation of ggml_conv_2d operator in Sdcpp is suboptimal, exhibiting both high inference latency and massive memory usage. To address this, in this work, we present an optimized version of Sdcpp leveraging the Winograd algorithm to accelerate 2D convolution operations, which is the primary bottleneck in the pipeline. By analyzing both dependent and independent computation graphs, we exploit the device’s locality and parallelism to achieve substantial performance improvements. Our framework delivers correct end-to-end results across various stable diffusion models, including SDv1.4, v1.5, v2.1, SDXL, and SDXL-Turbo. Our evaluation results demonstrate a speedup up to 2.76x for individual convolutional layers and an inference speedup up to 4.79x for the overall image generation process, compared with the original Sdcpp on M1 pro. Homepage: https://github.com/SealAILab/stable-diffusion-cpp
稳定扩散在生成高质量图像中扮演着至关重要的角色。然而,图像生成是耗时且内存密集型的。为了解决这一问题,stable-diffusion.cpp(Sdcpp)作为一个高效的推理框架应运而生,以加速扩散模型。虽然它很轻便,但Sdcpp中ggml_conv_2d算子的当前实现并不理想,存在推理延迟高和内存使用量大的问题。针对这一问题,我们在工作中提出了一个优化版的Sdcpp,它利用Winograd算法加速2D卷积操作,这是管道中的主要瓶颈。通过分析有向和无向计算图,我们利用设备的局部性和并行性实现了显著的性能提升。我们的框架在各种稳定扩散模型中都能提供正确的端到端结果,包括SDv1.4、v1.5、v2.1、SDXL和SDXL-Turbo。我们的评估结果表明,与原始Sdcpp在M1 Pro上的表现相比,我们的方法在单个卷积层上实现了最高达2.76倍的速度提升,整体图像生成过程实现了最高达4.79倍的推理速度提升。主页:https://github.com/SealAILab/stable-diffusion-cpp
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
稳定扩散在生成高质量图像中起到关键作用,但图像生成耗时且占用大量内存。为解决这个问题,出现了stable-diffusion.cpp(Sdcpp)这一高效推理框架来加速扩散模型。然而,Sdcpp中ggml_conv_2d算子的当前实现并不理想,存在推理延迟高和内存使用量大等问题。本研究中,我们利用Winograd算法优化Sdcpp版本,加速2D卷积操作,这是管道中的主要瓶颈。通过分析有依赖性和无依赖性的计算图,我们利用设备的局部性和并行性实现显著的性能提升。该框架可在各种稳定扩散模型(包括SDv1.4、v1.5、v2.1、SDXL和SDXL-Turbo)中提供正确的端到端结果。评估结果显示,与原始Sdcpp相比,单个卷积层的速度提升可达2.76倍,整体图像生成过程的推理速度提升可达4.79倍。
Key Takeaways
- 稳定扩散在生成高质量图像中很重要,但存在时间和内存消耗大的问题。
- stable-diffusion.cpp(Sdcpp)框架旨在加速扩散模型的推理过程。
- Sdcpp中ggml_conv_2d算子的当前实现存在性能瓶颈。
- 利用Winograd算法优化Sdcpp,加速2D卷积操作。
- 通过分析计算图,利用设备局部性和并行性提升性能。
- 优化的框架适用于多种稳定扩散模型。
- 评估结果显示,该优化显著提升了推理速度和图像生成效率。
点此查看论文截图


BudgetFusion: Perceptually-Guided Adaptive Diffusion Models
Authors:Qinchan Li, Kenneth Chen, Changyue Su, Qi Sun
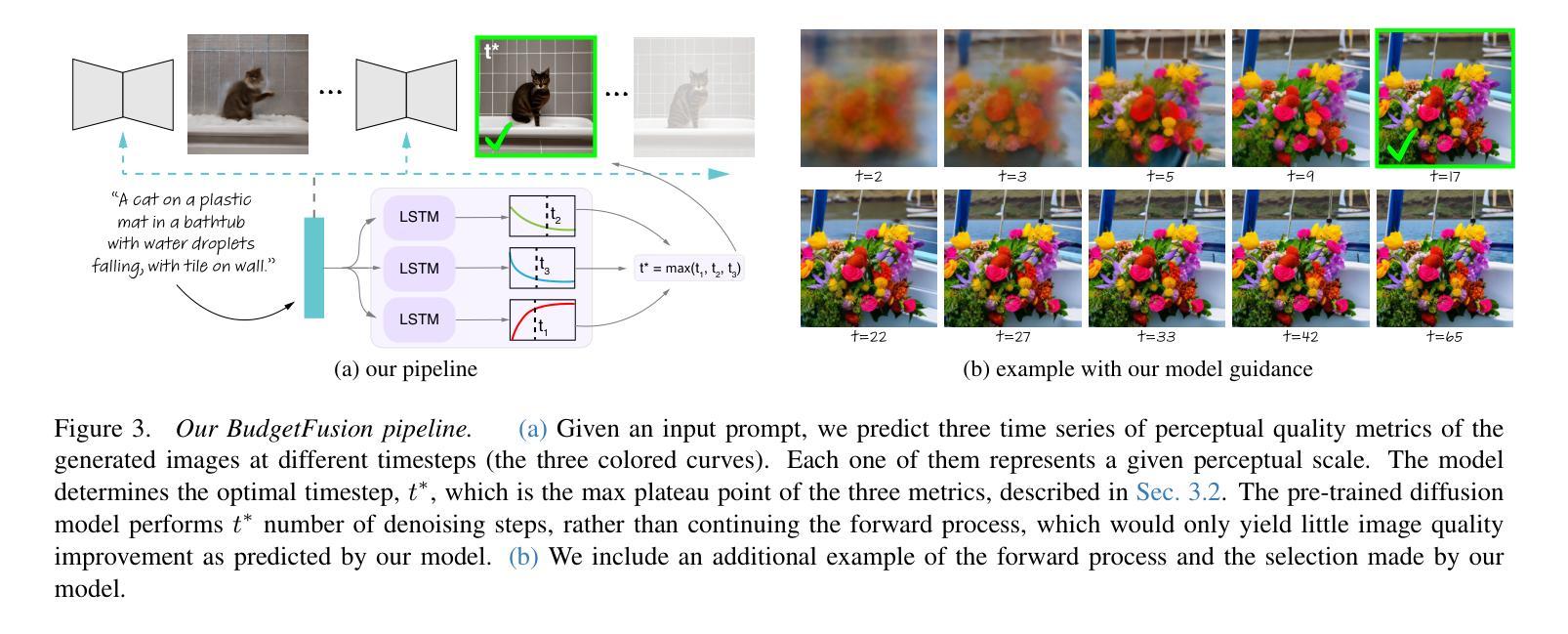
Diffusion models have shown unprecedented success in the task of text-to-image generation. While these models are capable of generating high-quality and realistic images, the complexity of sequential denoising has raised societal concerns regarding high computational demands and energy consumption. In response, various efforts have been made to improve inference efficiency. However, most of the existing efforts have taken a fixed approach with neural network simplification or text prompt optimization. Are the quality improvements from all denoising computations equally perceivable to humans? We observed that images from different text prompts may require different computational efforts given the desired content. The observation motivates us to present BudgetFusion, a novel model that suggests the most perceptually efficient number of diffusion steps before a diffusion model starts to generate an image. This is achieved by predicting multi-level perceptual metrics relative to diffusion steps. With the popular Stable Diffusion as an example, we conduct both numerical analyses and user studies. Our experiments show that BudgetFusion saves up to five seconds per prompt without compromising perceptual similarity. We hope this work can initiate efforts toward answering a core question: how much do humans perceptually gain from images created by a generative model, per watt of energy?
扩散模型在文本到图像生成任务中取得了前所未有的成功。虽然这些模型能够生成高质量和逼真的图像,但序列去噪的复杂性引发了社会对提高计算效率和降低能源消耗的关注。作为回应,人们已经做出了各种努力提高推理效率。然而,现有的大多数努力都采取了固定的方法,如神经网络简化或文本提示优化。来自所有去噪计算的质量提升是否对人类的感知具有同等的认知效果?我们发现,根据所需内容,来自不同文本提示的图像可能需要不同的计算工作量。这一观察促使我们提出了BudgetFusion模型,该模型能够在扩散模型开始生成图像之前,预测出感知效率最高的扩散步骤数量。这是通过预测与扩散步骤相关的多级感知指标来实现的。以流行的Stable Diffusion为例,我们进行了数值分析和用户研究。实验表明,BudgetFusion能在不损害感知相似性的情况下,为每个提示节省多达五秒的时间。我们希望这项工作能够引发对核心问题的思考:人类从每瓦特能量所生成的图像中获得多少感知收益?
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
扩散模型在文本到图像生成任务中取得了前所未有的成功。然而,由于其复杂的去噪过程,社会对高计算需求和能源消耗表示担忧。为提高推理效率,已做出多种努力。大多数现有方法通过简化神经网络或优化文本提示来实现。人类是否对所有的去噪计算改进有同等的感知效果?研究发现,不同的文本提示可能因所需内容不同而需要不同的计算量。基于此观察,我们提出了BudgetFusion模型,该模型建议在扩散模型开始生成图像之前,以最符合人类感知效率的方式执行不同数量的扩散步骤。这是通过预测与扩散步骤相关的多级感知度量来实现的。以流行的Stable Diffusion为例,我们进行了数值分析和用户研究。实验表明,BudgetFusion可以在不损害感知相似性的情况下,每个提示节省多达五秒时间。希望通过这项工作能引发回答一个核心问题的努力:人类从生成模型创建的图像中感知到的收益与其消耗的每瓦能量相比是多少?
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在文本到图像生成任务中表现出强大的能力,但计算需求和能源消耗较高。
- 提高推理效率是当前的研究重点,现有方法主要集中在神经网络简化和文本提示优化上。
- 人类对不同去噪计算改进的感知效果可能不同,不同文本提示可能需要不同的计算量。
- BudgetFusion模型建议最符合人类感知效率的去噪步骤数量,以提高图像生成效率。
- BudgetFusion以Stable Diffusion为例,通过数值分析和用户研究验证了其有效性。
- BudgetFusion可节省大量时间,同时不损害图像的感知相似性。
点此查看论文截图


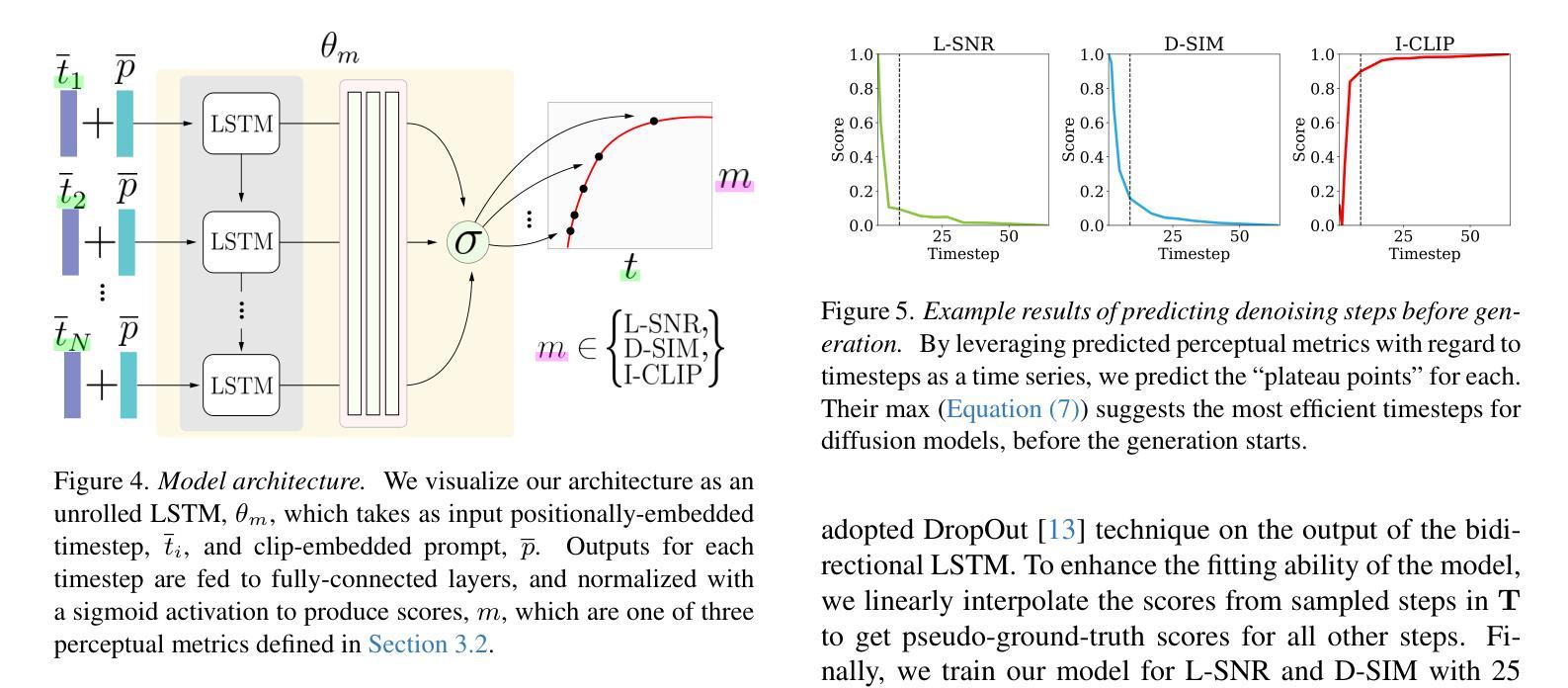

Hidden in the Noise: Two-Stage Robust Watermarking for Images
Authors:Kasra Arabi, Benjamin Feuer, R. Teal Witter, Chinmay Hegde, Niv Cohen
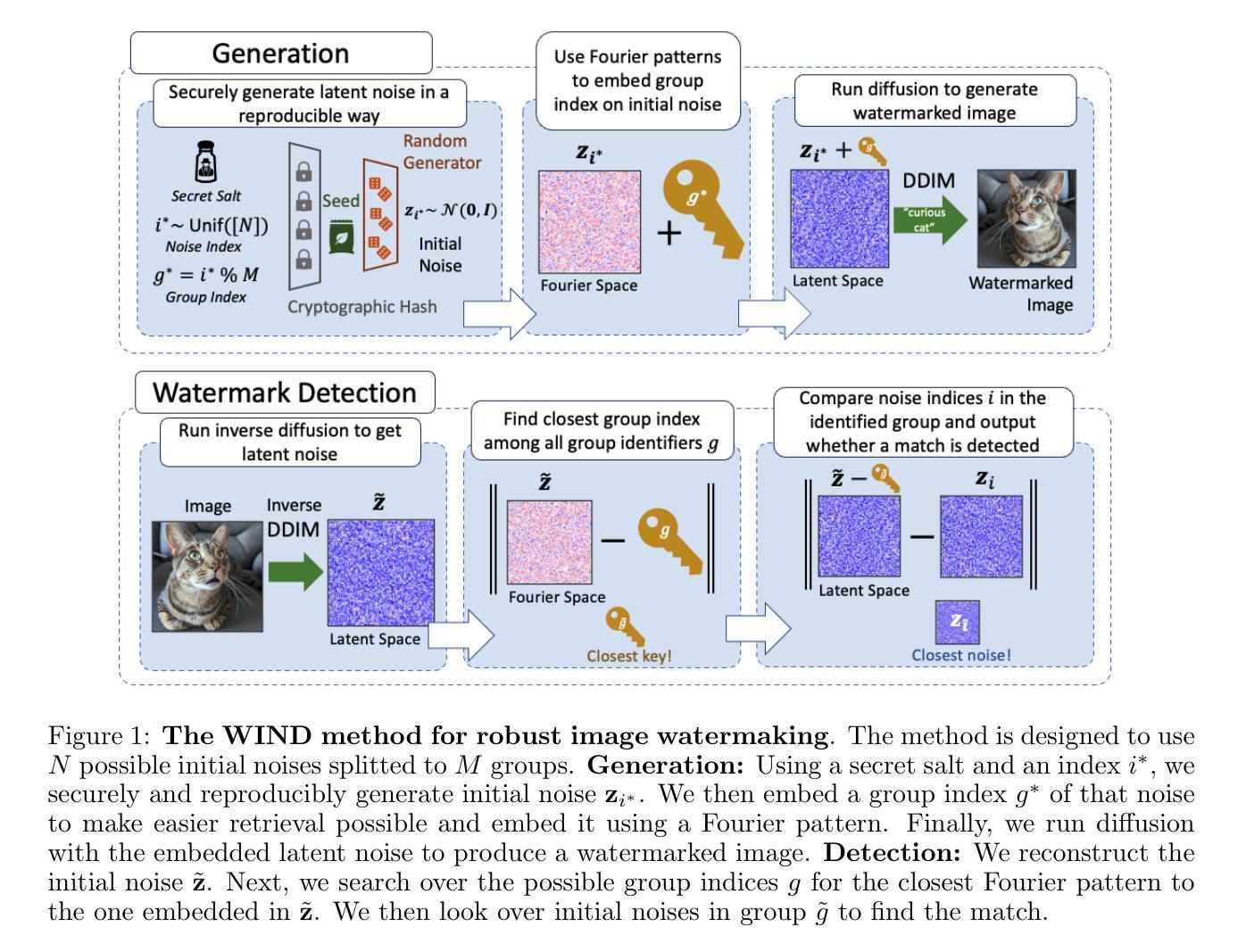
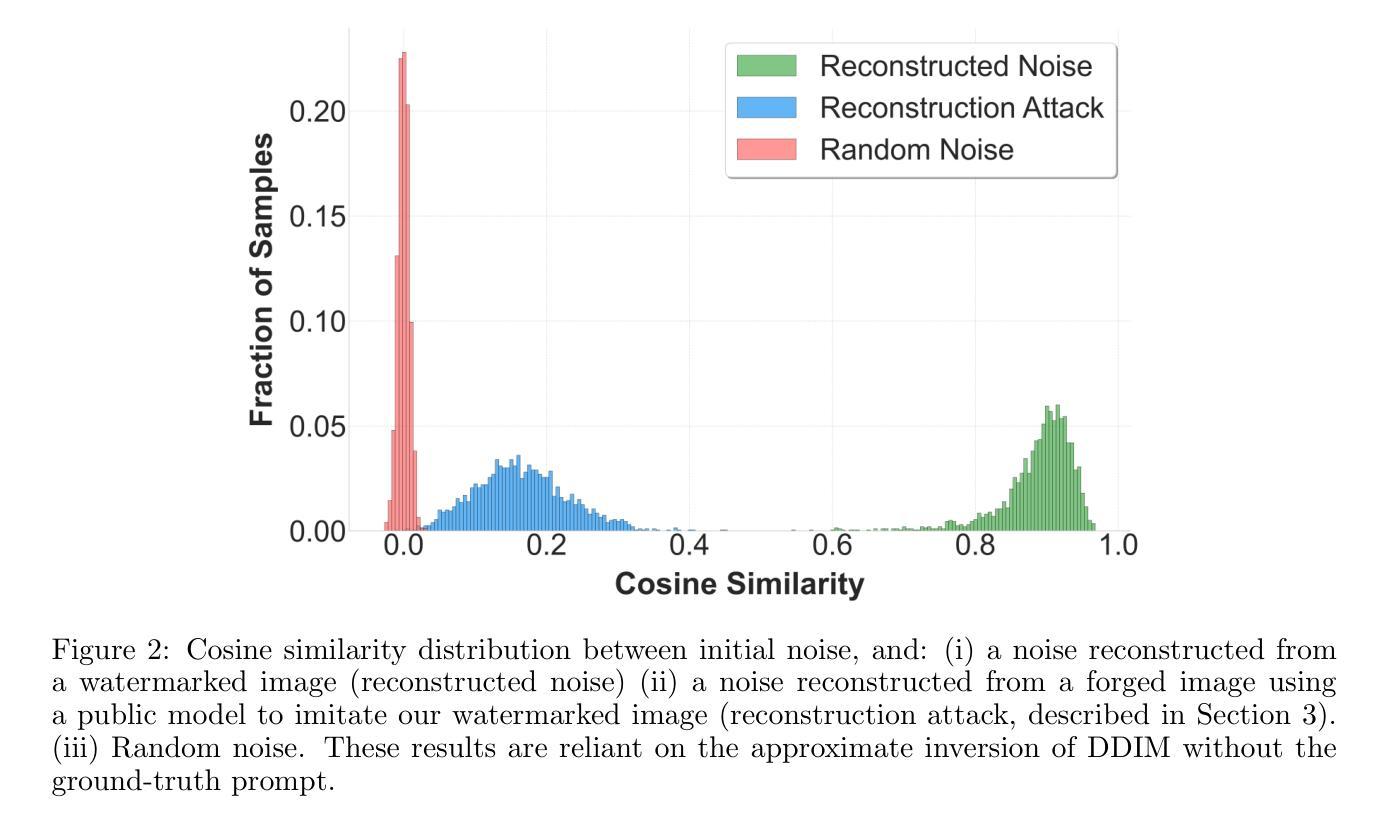
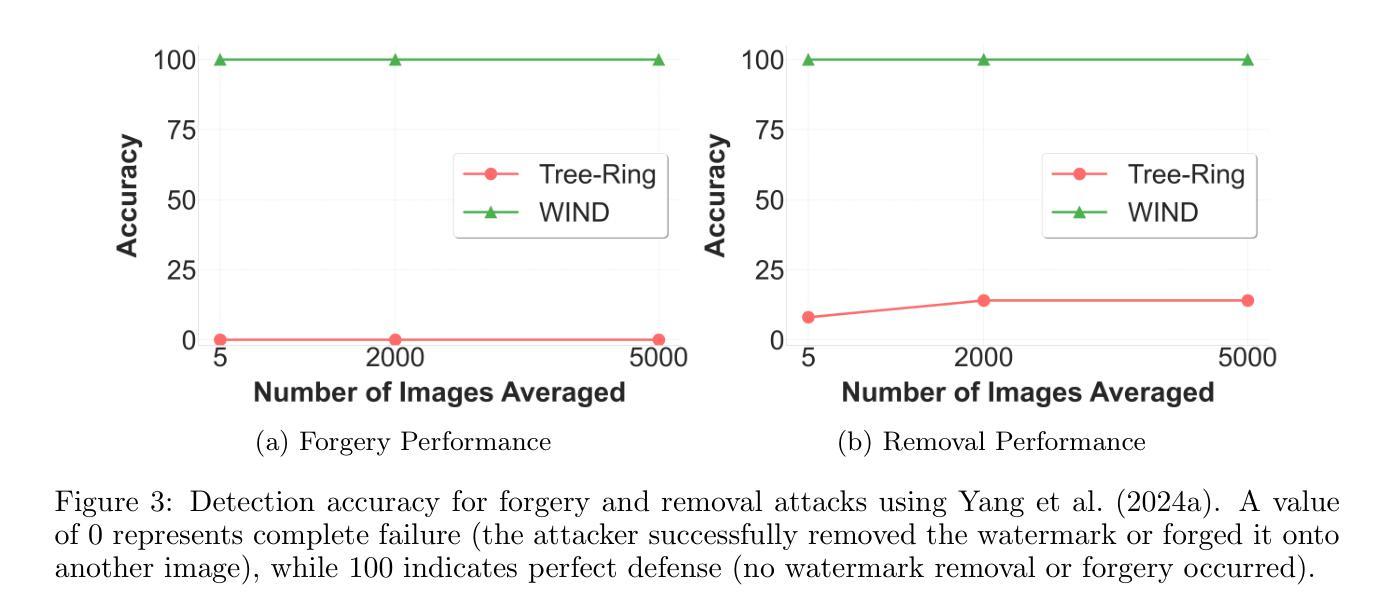
As the quality of image generators continues to improve, deepfakes become a topic of considerable societal debate. Image watermarking allows responsible model owners to detect and label their AI-generated content, which can mitigate the harm. Yet, current state-of-the-art methods in image watermarking remain vulnerable to forgery and removal attacks. This vulnerability occurs in part because watermarks distort the distribution of generated images, unintentionally revealing information about the watermarking techniques. In this work, we first demonstrate a distortion-free watermarking method for images, based on a diffusion model’s initial noise. However, detecting the watermark requires comparing the initial noise reconstructed for an image to all previously used initial noises. To mitigate these issues, we propose a two-stage watermarking framework for efficient detection. During generation, we augment the initial noise with generated Fourier patterns to embed information about the group of initial noises we used. For detection, we (i) retrieve the relevant group of noises, and (ii) search within the given group for an initial noise that might match our image. This watermarking approach achieves state-of-the-art robustness to forgery and removal against a large battery of attacks.
随着图像生成器的质量不断提高,深度伪造技术成为社会热议的话题。图像水印允许负责任的模型所有者检测和标记其AI生成的内容,从而减轻潜在的伤害。然而,当前最先进的水印嵌入技术仍然容易受到伪造和移除攻击的影响。这种脆弱性部分是因为水印会扭曲生成的图像的分布,从而无意中泄露有关水印技术的信息。在这项工作中,我们首先展示了一种基于扩散模型的初始噪声的无失真水印嵌入方法。然而,检测水印需要对比图像重建的初始噪声与所有之前使用的初始噪声。为了缓解这些问题,我们提出了一种用于高效检测的两阶段水印框架。在生成过程中,我们通过将生成的傅里叶模式与初始噪声相结合,嵌入有关我们所使用的初始噪声组的信息。对于检测,我们(i)检索相关的噪声组,(ii)在给定组内搜索可能与我们的图像匹配的初始噪声。这种水印方法达到了对抗大量攻击的伪造和移除的最新稳健性标准。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
新一代图像生成器质量不断提升,深度伪造技术引发了社会热议。图像水印技术能让模型所有者对其AI生成内容进行检测和标注,从而减轻潜在危害。然而,当前最先进的水印方法仍易受到伪造和移除攻击。本文提出了一种基于扩散模型初始噪声的无失真图像水印方法,但检测水印需要对比图像重建的初始噪声与所有已使用的初始噪声。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一个两阶段的水印检测框架以提高效率。生成阶段我们通过嵌入生成的傅里叶模式增强初始噪声以携带信息,检测阶段则首先找到相关噪声组并在该组内搜索匹配的初始噪声。该方法在水印防伪造和防移除方面达到了业界领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 图像生成器质量提升引发深度伪造技术社会关注。
- 图像水印技术允许模型所有者标注AI生成内容以减轻潜在危害。
- 当前水印方法易受到伪造和移除攻击。
- 提出了一种基于扩散模型初始噪声的无失真图像水印方法。
- 检测水印需要对比图像重建的初始噪声与所有已使用的初始噪声,存在效率问题。
- 提出两阶段水印检测框架以提高效率。
点此查看论文截图


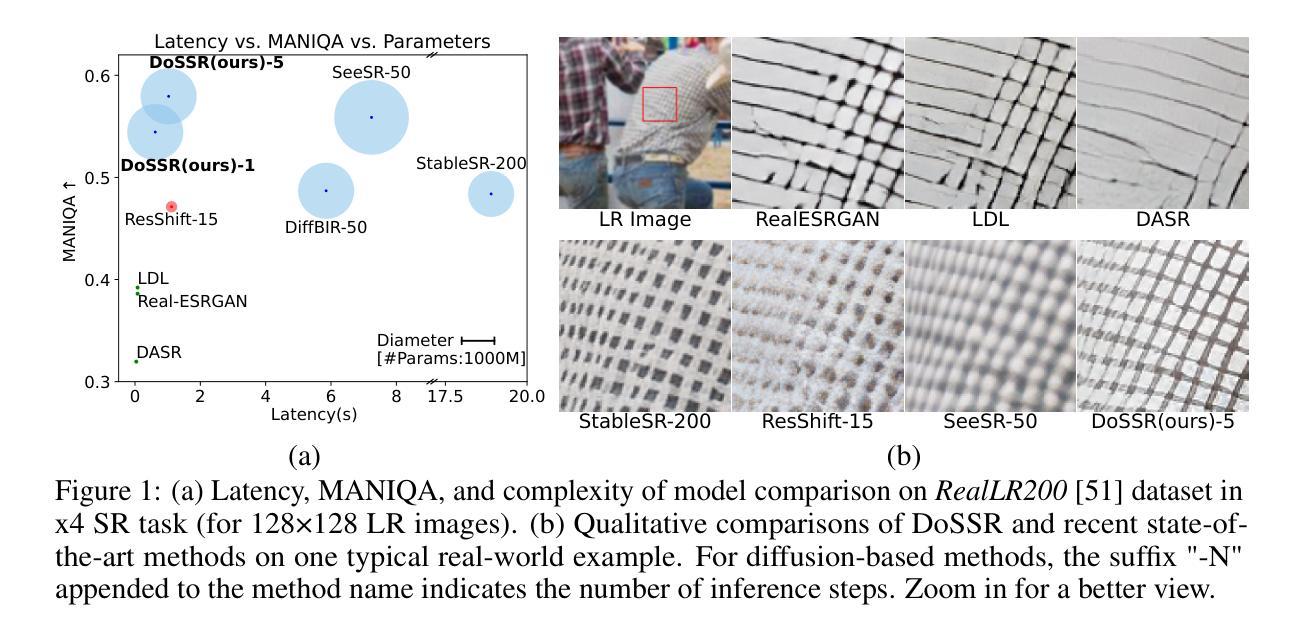
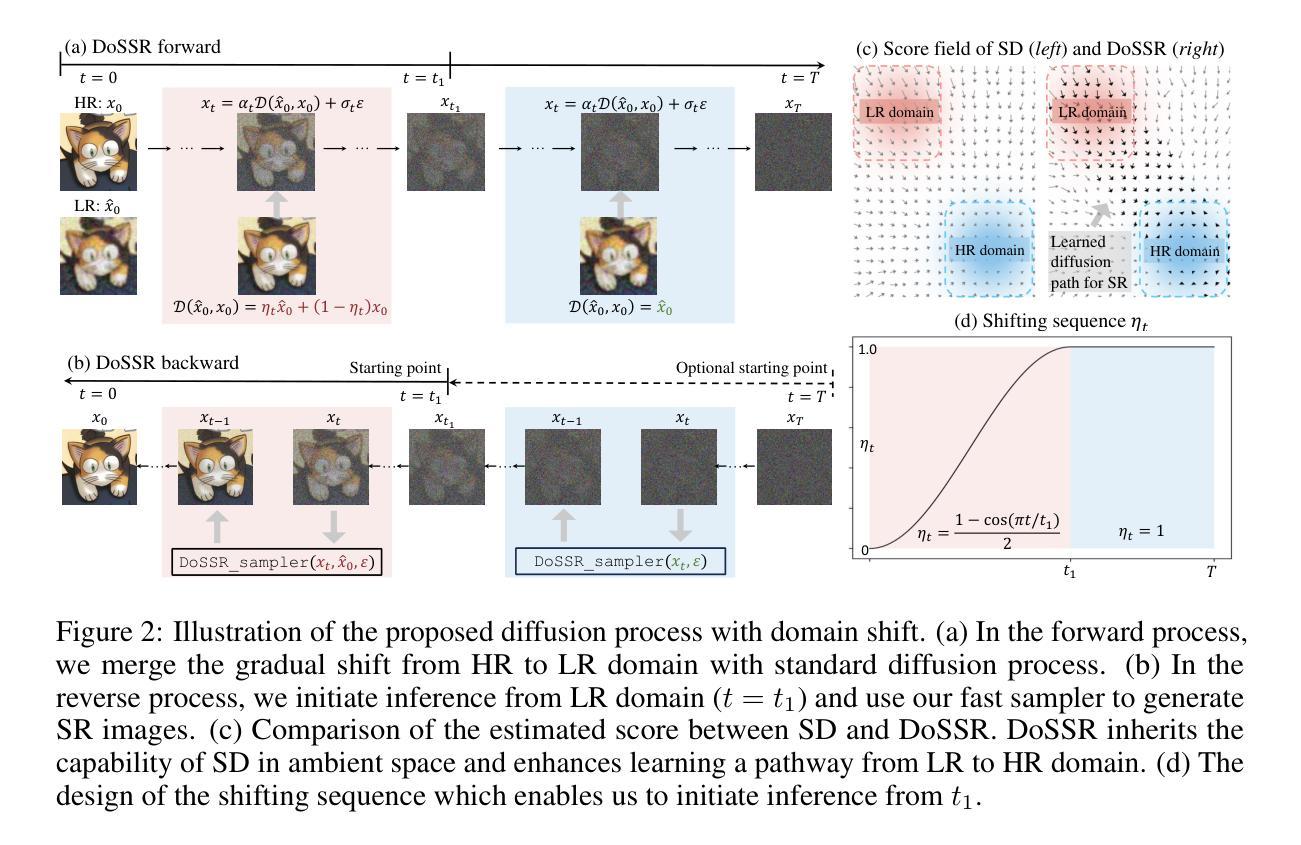
Taming Diffusion Prior for Image Super-Resolution with Domain Shift SDEs
Authors:Qinpeng Cui, Yixuan Liu, Xinyi Zhang, Qiqi Bao, Qingmin Liao, Li Wang, Tian Lu, Zicheng Liu, Zhongdao Wang, Emad Barsoum
Diffusion-based image super-resolution (SR) models have attracted substantial interest due to their powerful image restoration capabilities. However, prevailing diffusion models often struggle to strike an optimal balance between efficiency and performance. Typically, they either neglect to exploit the potential of existing extensive pretrained models, limiting their generative capacity, or they necessitate a dozens of forward passes starting from random noises, compromising inference efficiency. In this paper, we present DoSSR, a Domain Shift diffusion-based SR model that capitalizes on the generative powers of pretrained diffusion models while significantly enhancing efficiency by initiating the diffusion process with low-resolution (LR) images. At the core of our approach is a domain shift equation that integrates seamlessly with existing diffusion models. This integration not only improves the use of diffusion prior but also boosts inference efficiency. Moreover, we advance our method by transitioning the discrete shift process to a continuous formulation, termed as DoS-SDEs. This advancement leads to the fast and customized solvers that further enhance sampling efficiency. Empirical results demonstrate that our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on synthetic and real-world datasets, while notably requiring only 5 sampling steps. Compared to previous diffusion prior based methods, our approach achieves a remarkable speedup of 5-7 times, demonstrating its superior efficiency. Code: https://github.com/QinpengCui/DoSSR.
基于扩散的图像超分辨率(SR)模型因其强大的图像恢复能力而备受关注。然而,流行的扩散模型往往难以在效率和性能之间取得最佳平衡。通常,它们要么忽视利用现有预训练模型的潜力,限制了其生成能力,要么需要从随机噪声开始多次前向传递,从而影响推理效率。在本文中,我们提出了DoSSR,这是一种基于域迁移的扩散SR模型,它利用预训练扩散模型的生成能力,同时通过以低分辨率(LR)图像开始扩散过程来显著提高效率。我们的方法的核心是一个域迁移方程,它能与现有的扩散模型无缝集成。这种集成不仅改善了扩散优先的使用,还提高了推理效率。此外,我们通过将离散迁移过程转变为连续公式,即DoS-SDEs,进一步推进了我们的方法。这种进展导致了快速、定制的求解器,进一步提高了采样效率。经验结果表明,我们提出的方法在合成和真实世界数据集上达到了最先进的性能,仅需要5个采样步骤。与之前基于扩散优先的方法相比,我们的方法实现了5-7倍的显著加速,证明了其卓越的效率。代码地址:https://github.com/QinpengCui/DoSSR。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper is accepted by NeurIPS 2024
Summary
域转移扩散模型(DoSSR)实现了基于扩散的超分辨率重建,利用了预训练模型的生成能力并显著提高了效率,通过对低分辨率图像启动扩散过程。新方法通过连续化离散转移过程,进一步提高了采样效率。在合成和真实数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法实现了最先进的性能,仅需要5个采样步骤,与之前基于扩散先验的方法相比,速度提高了5-7倍。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像超分辨率重建中表现出强大的图像恢复能力。
- 现有扩散模型在效率和性能之间难以达到平衡。
- DoSSR模型利用预训练模型的生成能力,提高了扩散模型的效率。
- DoSSR通过域转移方程与现有扩散模型无缝集成,改进了扩散先验的使用并提高了推理效率。
- DoSSR将离散转移过程转化为连续形式,提高了采样效率。
- 实证结果表明,DoSSR在合成和真实数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
- DoSSR仅需5个采样步骤,相比之前的扩散先验方法,速度提高了5-7倍。
点此查看论文截图

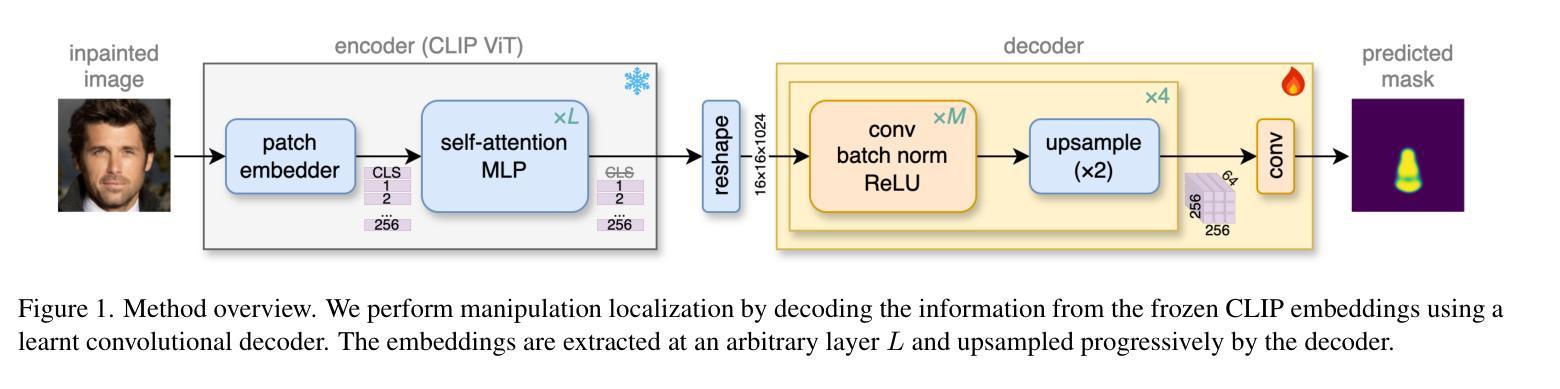
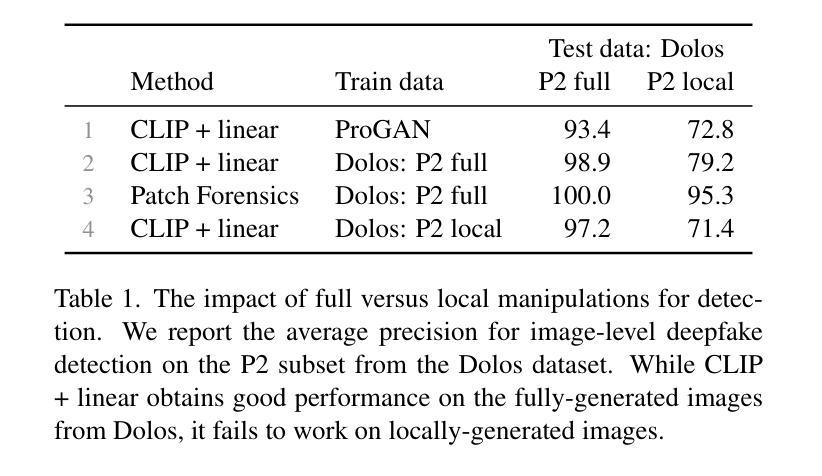
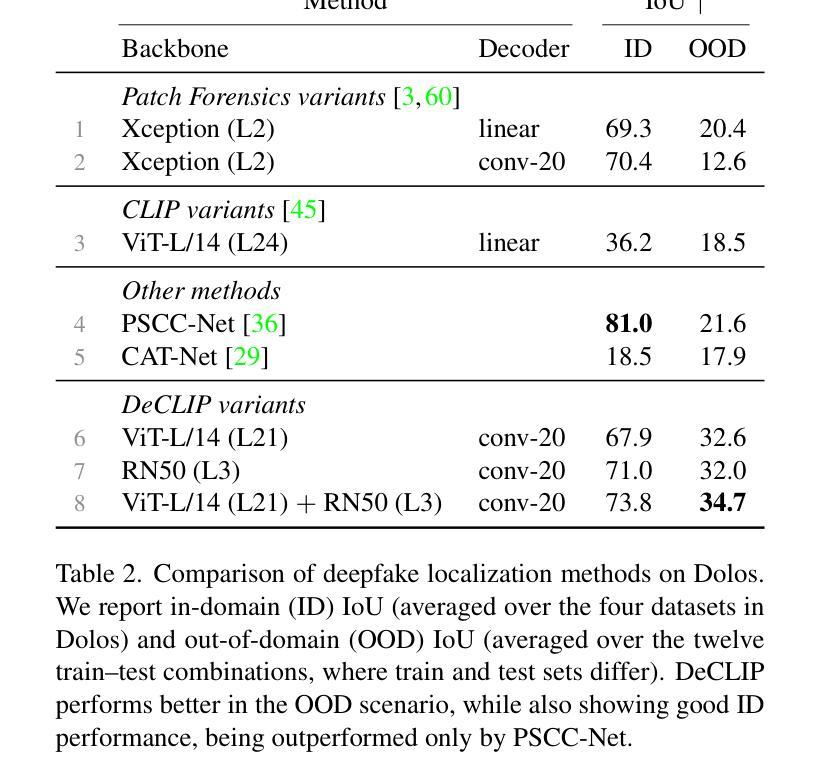
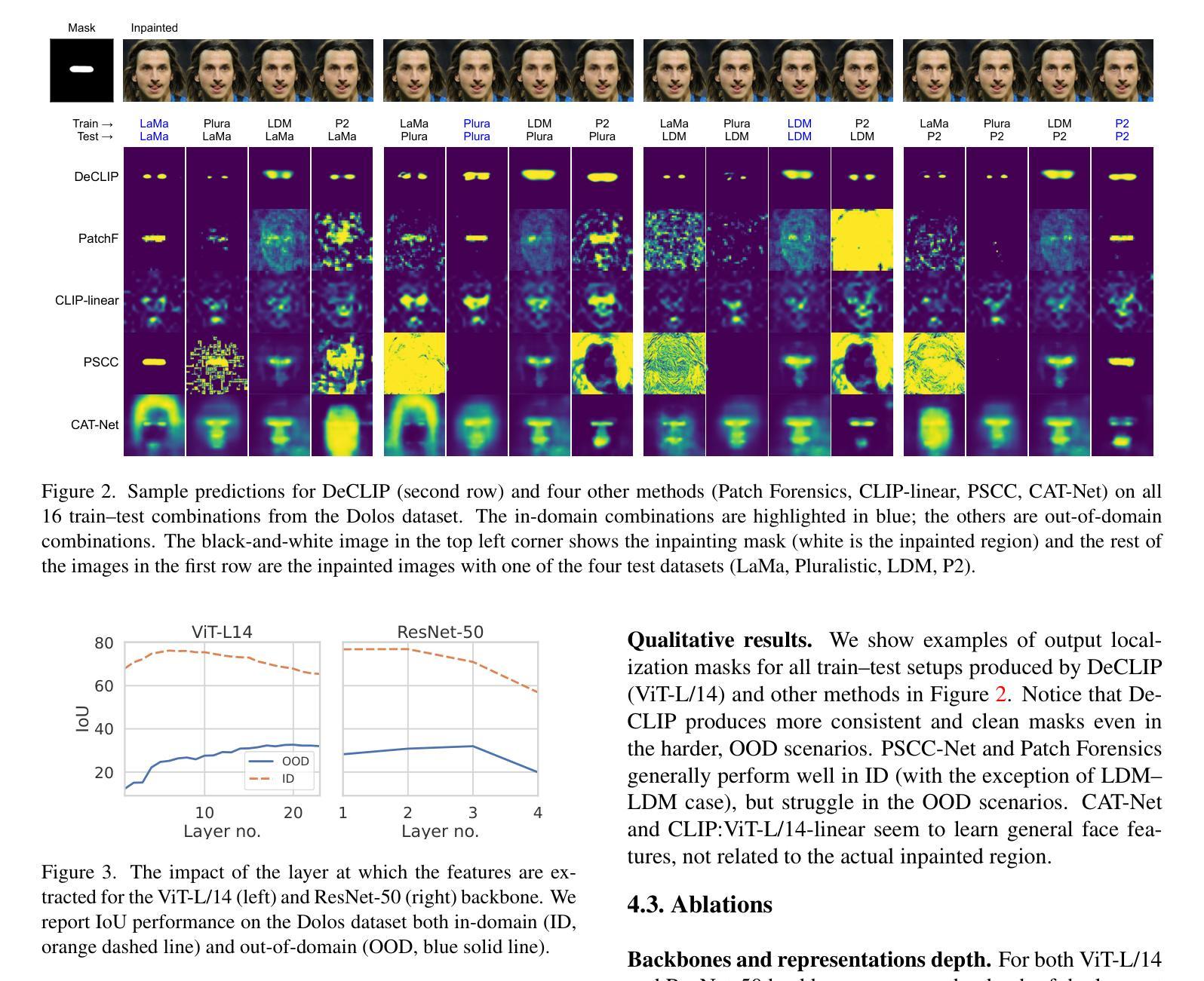
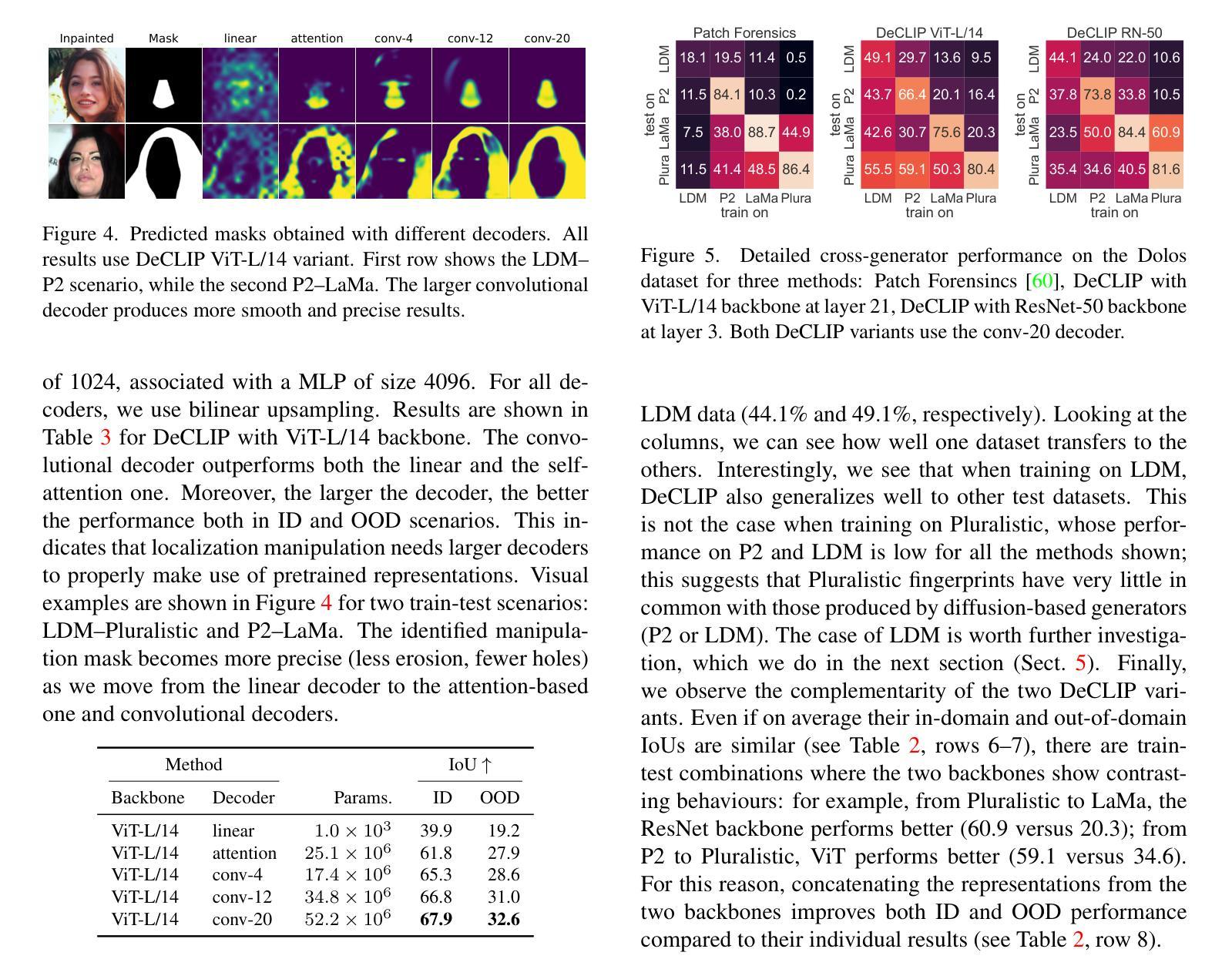
DeCLIP: Decoding CLIP representations for deepfake localization
Authors:Stefan Smeu, Elisabeta Oneata, Dan Oneata
Generative models can create entirely new images, but they can also partially modify real images in ways that are undetectable to the human eye. In this paper, we address the challenge of automatically detecting such local manipulations. One of the most pressing problems in deepfake detection remains the ability of models to generalize to different classes of generators. In the case of fully manipulated images, representations extracted from large self-supervised models (such as CLIP) provide a promising direction towards more robust detectors. Here, we introduce DeCLIP, a first attempt to leverage such large pretrained features for detecting local manipulations. We show that, when combined with a reasonably large convolutional decoder, pretrained self-supervised representations are able to perform localization and improve generalization capabilities over existing methods. Unlike previous work, our approach is able to perform localization on the challenging case of latent diffusion models, where the entire image is affected by the fingerprint of the generator. Moreover, we observe that this type of data, which combines local semantic information with a global fingerprint, provides more stable generalization than other categories of generative methods.
生成模型可以创建全新的图像,但它们也可以以人类眼睛无法察觉的方式部分修改真实图像。在本文中,我们解决了自动检测此类局部操作挑战的问题。在深度伪造检测中,仍然存在模型能否推广到不同类别生成器的问题。在完全操作的图像情况下,从大型自监督模型(如CLIP)中提取的表示,为构建更稳健的检测器提供了很有前景的方向。在这里,我们介绍了DeCLIP,这是首次尝试利用此类大型预训练特征来检测局部操作。我们证明,当与合理的卷积解码器结合时,预训练的自监督表示能够执行定位任务并改进现有方法的泛化能力。与之前的工作不同,我们的方法能够在潜扩散模型的挑战性案例中执行定位任务,整个图像受到生成器指纹的影响。此外,我们发现此类结合了局部语义信息和全局指纹的数据,相比其他类别的生成方法,能够提供更为稳定的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为DeCLIP的方法,该方法利用大型预训练模型的特征来检测图像中的局部操作。通过结合大型卷积解码器,该方法能够实现定位,并改进对现有方法的泛化能力。此方法能够在潜在扩散模型的挑战情况下进行定位,且此种数据类型结合了局部语义信息和全局指纹,提供了比其他类别生成方法更稳定的泛化性能。
Key Takeaways
- DeCLIP方法利用大型预训练模型的特征进行图像局部操作的检测。
- 通过结合卷积解码器,DeCLIP能够实现定位并改进泛化能力。
- DeCLIP方法能够在潜在扩散模型的挑战情况下进行定位。
- 局部操作检测需要同时考虑局部语义信息和全局指纹。
- 大型自监督模型(如CLIP)在图像检测中表现出良好的潜力。
- DeCLIP方法在处理生成模型创建的图像时,展现出强大的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

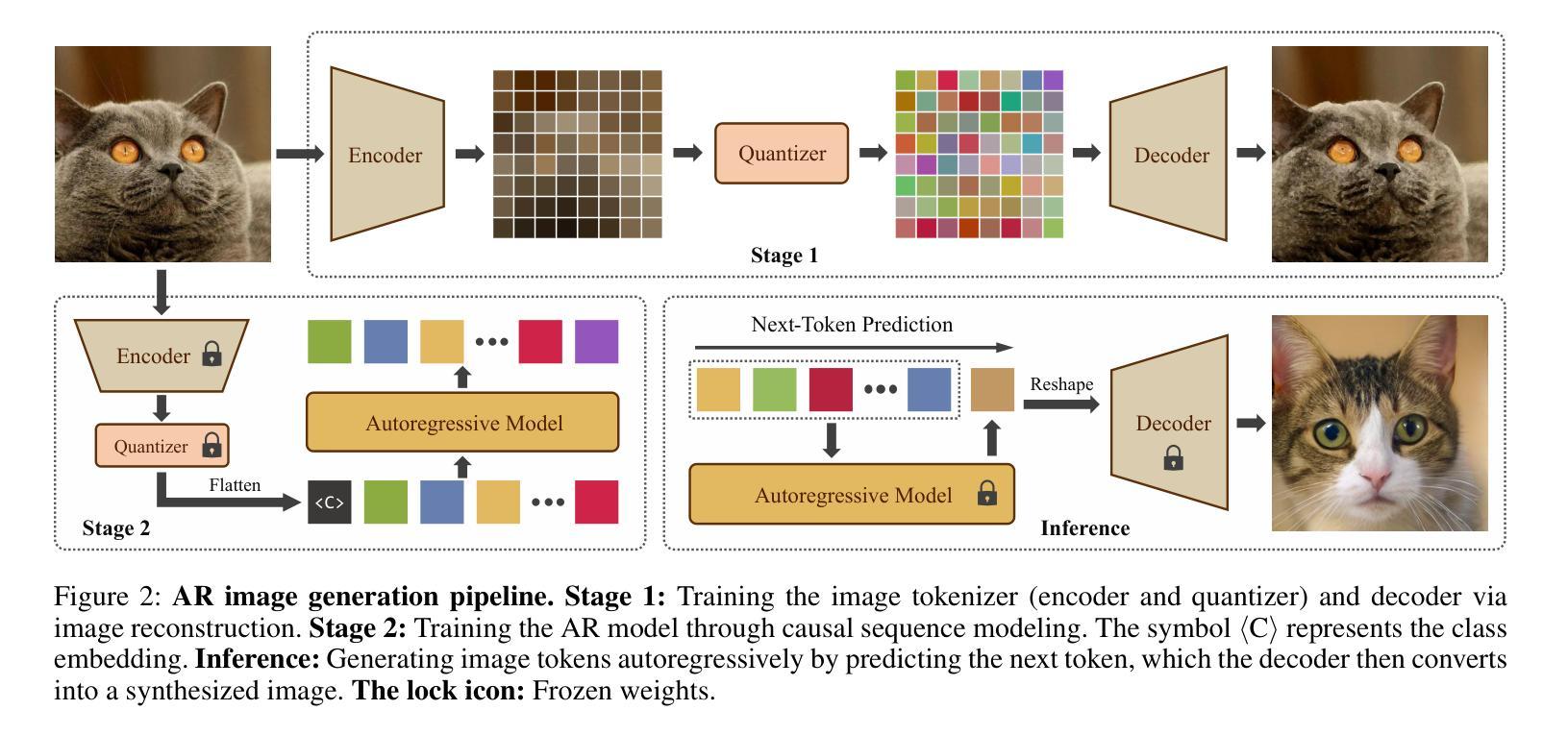
Scalable Autoregressive Image Generation with Mamba
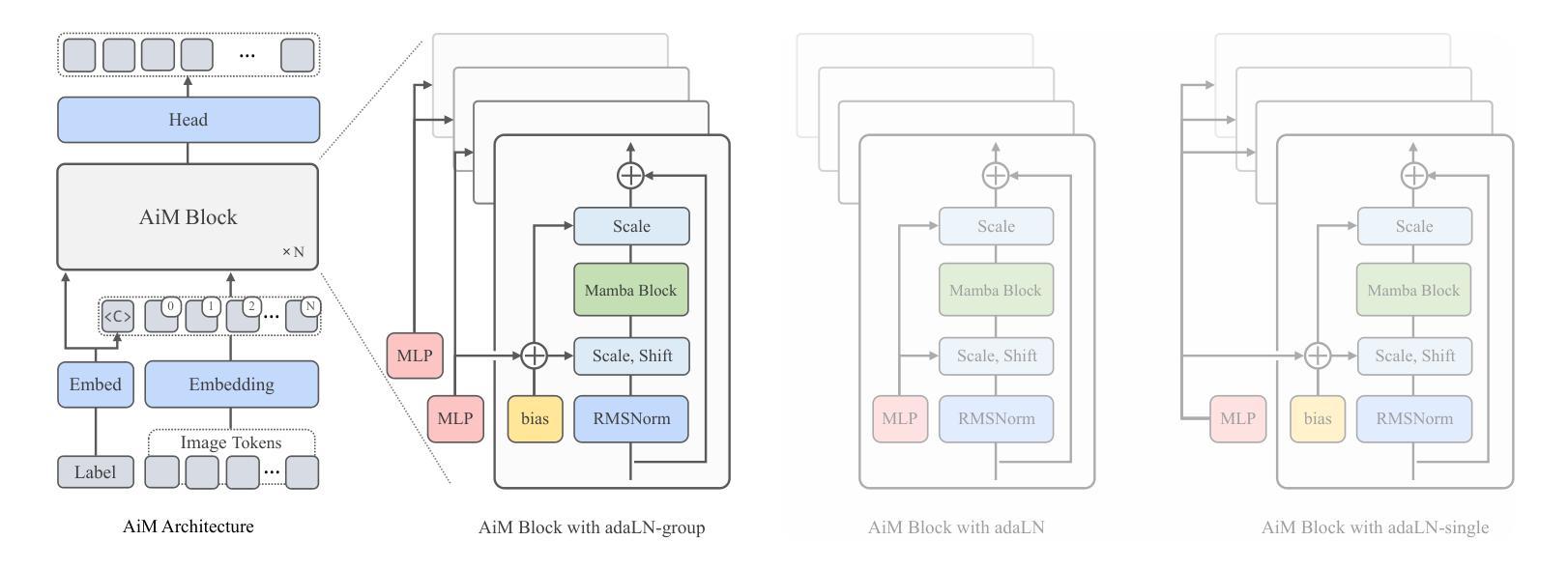
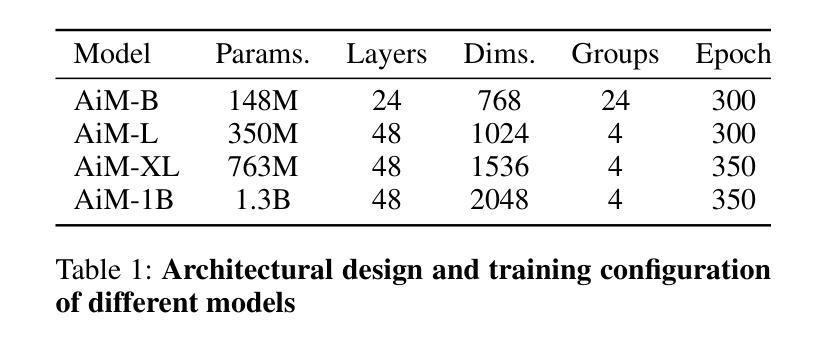
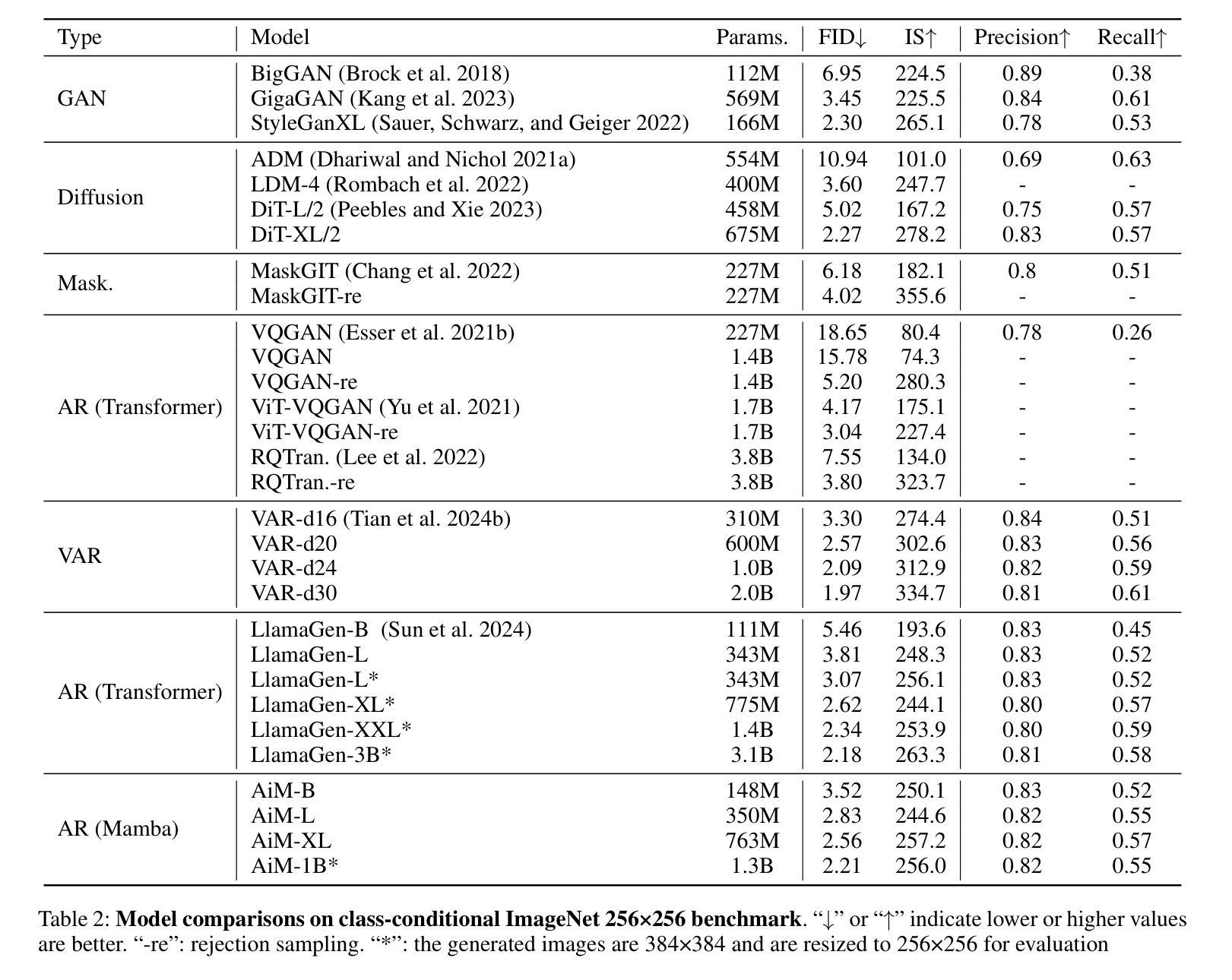
Authors:Haopeng Li, Jinyue Yang, Kexin Wang, Xuerui Qiu, Yuhong Chou, Xin Li, Guoqi Li
We introduce AiM, an autoregressive (AR) image generative model based on Mamba architecture. AiM employs Mamba, a novel state-space model characterized by its exceptional performance for long-sequence modeling with linear time complexity, to supplant the commonly utilized Transformers in AR image generation models, aiming to achieve both superior generation quality and enhanced inference speed. Unlike existing methods that adapt Mamba to handle two-dimensional signals via multi-directional scan, AiM directly utilizes the next-token prediction paradigm for autoregressive image generation. This approach circumvents the need for extensive modifications to enable Mamba to learn 2D spatial representations. By implementing straightforward yet strategically targeted modifications for visual generative tasks, we preserve Mamba’s core structure, fully exploiting its efficient long-sequence modeling capabilities and scalability. We provide AiM models in various scales, with parameter counts ranging from 148M to 1.3B. On the ImageNet1K 256*256 benchmark, our best AiM model achieves a FID of 2.21, surpassing all existing AR models of comparable parameter counts and demonstrating significant competitiveness against diffusion models, with 2 to 10 times faster inference speed. Code is available at https://github.com/hp-l33/AiM
我们介绍了基于Mamba架构的自回归(AR)图像生成模型AiM。AiM采用Mamba这一新型状态空间模型,具有对长序列进行线性时间复杂度建模的卓越性能,取代了AR图像生成模型中常用的Transformer,旨在实现更高的生成质量和更快的推理速度。与现有方法不同,这些方法通过多方向扫描使Mamba适应处理二维信号,AiM则直接使用下一个令牌预测范式进行自回归图像生成。这种方法避免了需要对Mamba进行大量修改以学习二维空间表示的需要。我们对视觉生成任务进行了简单而战略性的修改,充分利用了Mamba的核心结构、高效的长序列建模能力和可扩展性。我们提供了各种规模的AiM模型,参数数量从148M到1.3B不等。在ImageNet1K 256*256基准测试上,我们最好的AiM模型实现了FID为2.21,超越了所有现有参数数量相当的AR模型,并在推理速度上表现出显著竞争力,为扩散模型的2到10倍。代码可在https://github.com/hp-l33/AiM找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 8 figures
Summary
基于Mamba架构的AiM图像生成模型具有出色的性能和线性时间复杂度,可实现高质量图像生成和快速推理。通过直接利用下一个令牌预测范式进行自回归图像生成,无需对Mamba进行大量修改即可学习二维空间表示。同时,提供不同规模的AiM模型,参数范围从148M到1.3B,最佳模型在ImageNet 256*256基准测试中FID为2.21,超越现有同类参数规模的AR模型,并与扩散模型具有竞争力,推理速度提高2至10倍。
Key Takeaways
- AiM是一个基于Mamba架构的自回归图像生成模型,具有出色的性能和线性时间复杂度。
- AiM通过直接利用下一个令牌预测范式进行自回归图像生成,无需对Mamba进行大量修改即可处理二维信号。
- AiM模型参数范围从148M到1.3B,可在不同规模下提供。
- 在ImageNet 256*256基准测试中,最佳AiM模型的FID达到2.21,性能优越。
- AiM超越现有同类参数规模的AR模型,显示其显著的优势。
- AiM与扩散模型具有竞争力,并提供了更快的推理速度。
点此查看论文截图


EvolvED: Evolutionary Embeddings to Understand the Generation Process of Diffusion Models
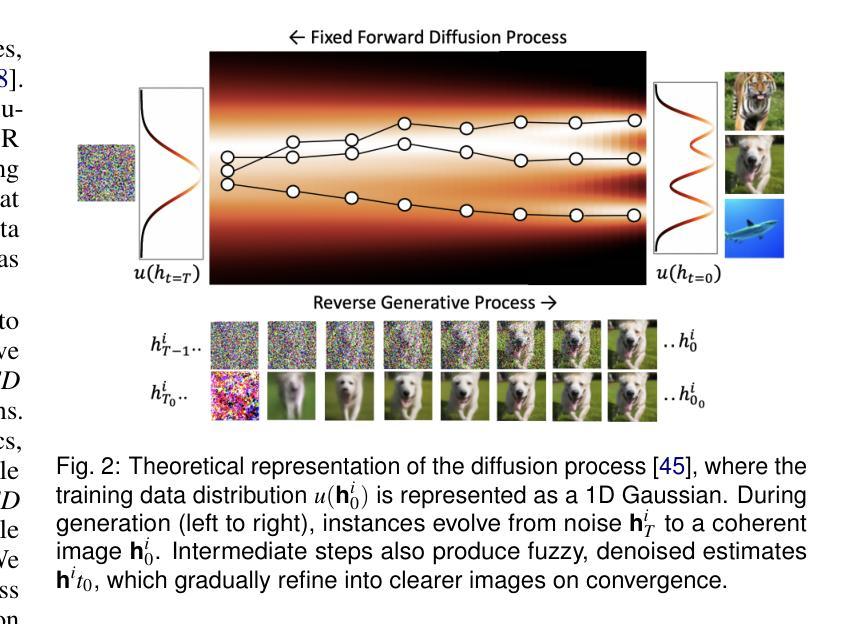
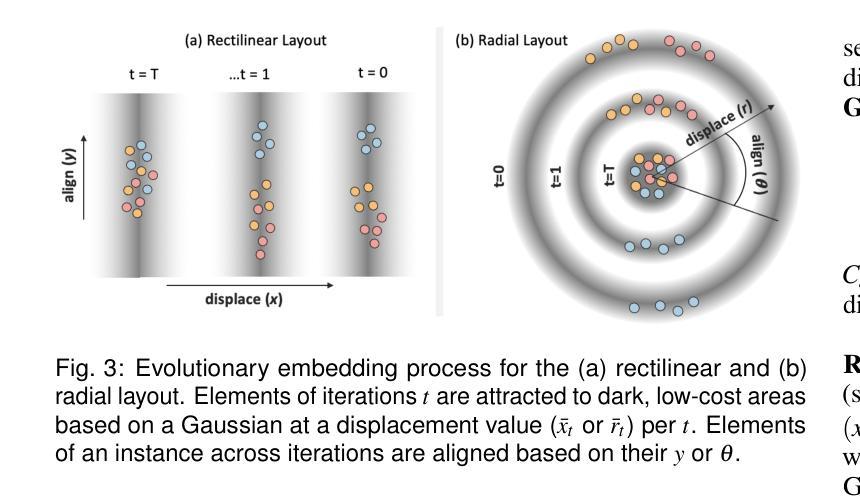
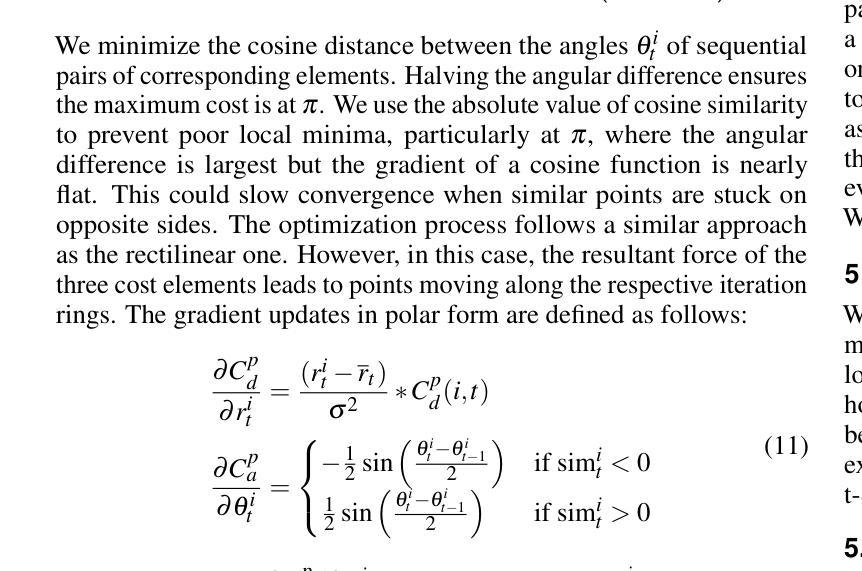
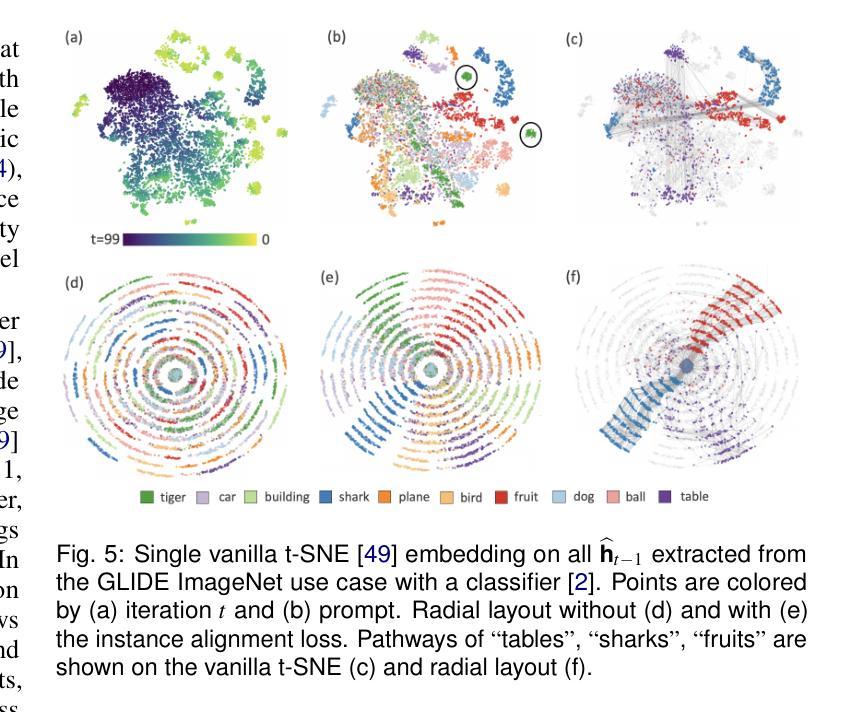
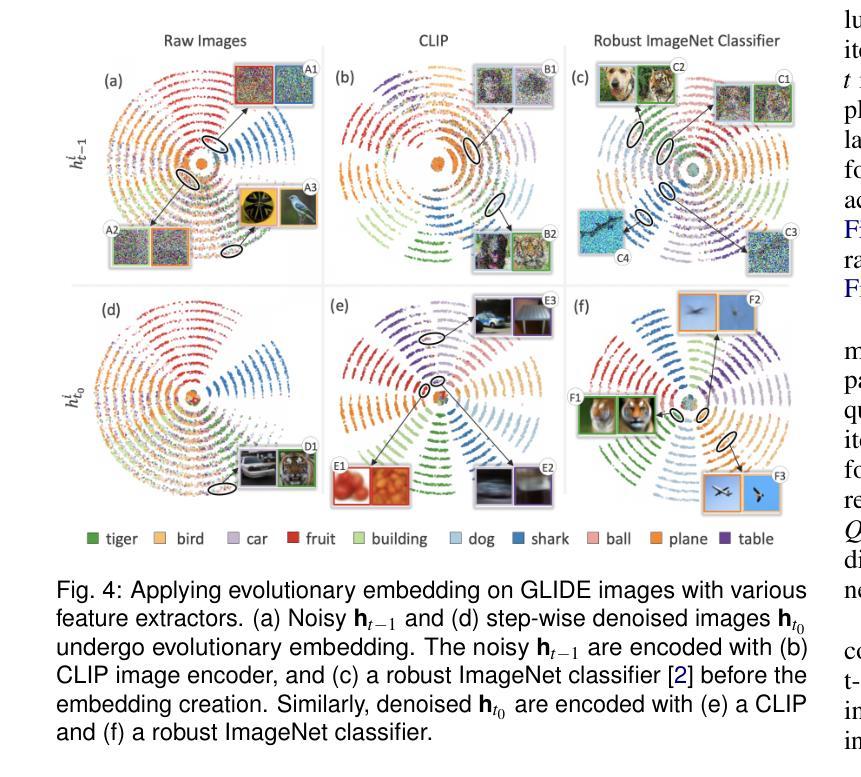
Authors:Vidya Prasad, Hans van Gorp, Christina Humer, Ruud J. G. van Sloun, Anna Vilanova, Nicola Pezzotti
Diffusion models, widely used in image generation, rely on iterative refinement to generate images from noise. Understanding this data evolution is important for model development and interpretability, yet challenging due to its high-dimensional, iterative nature. Prior works often focus on static or instance-level analyses, missing the iterative and holistic aspects of the generative path. While dimensionality reduction can visualize image evolution for few instances, it does preserve the iterative structure. To address these gaps, we introduce EvolvED, a method that presents a holistic view of the iterative generative process in diffusion models. EvolvED goes beyond instance exploration by leveraging predefined research questions to streamline generative space exploration. Tailored prompts aligned with these questions are used to extract intermediate images, preserving iterative context. Targeted feature extractors trace the evolution of key image attribute evolution, addressing the complexity of high-dimensional outputs. Central to EvolvED is a novel evolutionary embedding algorithm that encodes iterative steps while maintaining semantic relations. It enhances the visualization of data evolution by clustering semantically similar elements within each iteration with t-SNE, grouping elements by iteration, and aligning an instance’s elements across iterations. We present rectilinear and radial layouts to represent iterations and support exploration. We apply EvolvED to diffusion models like GLIDE and Stable Diffusion, demonstrating its ability to provide valuable insights into the generative process.
扩散模型广泛应用于图像生成,依赖于迭代优化从噪声中生成图像。了解数据的演化对于模型发展和可解释性很重要,但由于其高维度、迭代性质,这具有挑战性。早期的研究经常关注静态或实例级别的分析,忽略了生成路径的迭代和整体方面。尽管降维可以可视化少数实例的图像演化,但它并不保留迭代结构。为了解决这些差距,我们引入了EvolvED方法,它为扩散模型中的迭代生成过程提供了整体视图。EvolvED超越了实例探索,利用预先定义的研究问题来简化生成空间探索。针对这些问题量身定制的提示用于提取中间图像,保留迭代上下文。目标特征提取器追踪关键图像属性演变的历程,解决高维度输出的复杂性。EvolvED的核心是一种新型进化嵌入算法,该算法在维持语义关系的同时编码迭代步骤。它通过t-SNE将每个迭代中语义上相似的元素进行聚类,按迭代对元素进行分组,并对齐各迭代的实例元素。我们采用直线和径向布局来表示迭代并支持探索。我们将EvolvED应用于GLIDE和Stable Diffusion等扩散模型,展示了它在了解生成过程中的有价值见解的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
扩散模型在图像生成领域广泛应用,通过迭代优化从噪声生成图像。了解数据演化对模型发展和可解释性重要,但因其高维、迭代性质,挑战较大。以前的研究多关注静态或实例层面的分析,忽略了生成路径的迭代和整体方面。EvolvED方法通过利用预设的研究问题,对扩散模型的迭代生成过程进行全面观察。通过针对性提示提取中间图像,保留迭代上下文。目标特征提取器追踪关键图像属性演变,解决高维输出的复杂性。EvolvED的核心是一种新型演化嵌入算法,可在编码迭代步骤的同时维持语义关系。该算法采用t-SNE聚类,将语义相似的元素聚集在每次迭代中,通过实例元素对齐其迭代过程。本文提出了直线和径向布局来代表迭代并支持探索。应用EvolvED于GLIDE和Stable Diffusion等扩散模型,证明其能为生成过程提供有价值的见解。
Key Takeaways:
- 扩散模型通过迭代优化从噪声生成图像,理解其数据演化对模型发展和可解释性至关重要。
- 现有研究多关注静态或实例层面的分析,忽略了扩散模型的迭代和整体生成路径。
- EvolvED方法提供对扩散模型迭代生成过程的全面观察,利用预设研究问题和针对性提示进行空间探索。
- 目标特征提取器追踪关键图像属性演变,解决高维数据复杂性。
- EvolvED采用新型演化嵌入算法,编码迭代步骤同时维持语义关系,增强数据演化的可视化。
- 应用EvolvED于GLIDE和Stable Diffusion等模型,证明其有效性。
点此查看论文截图

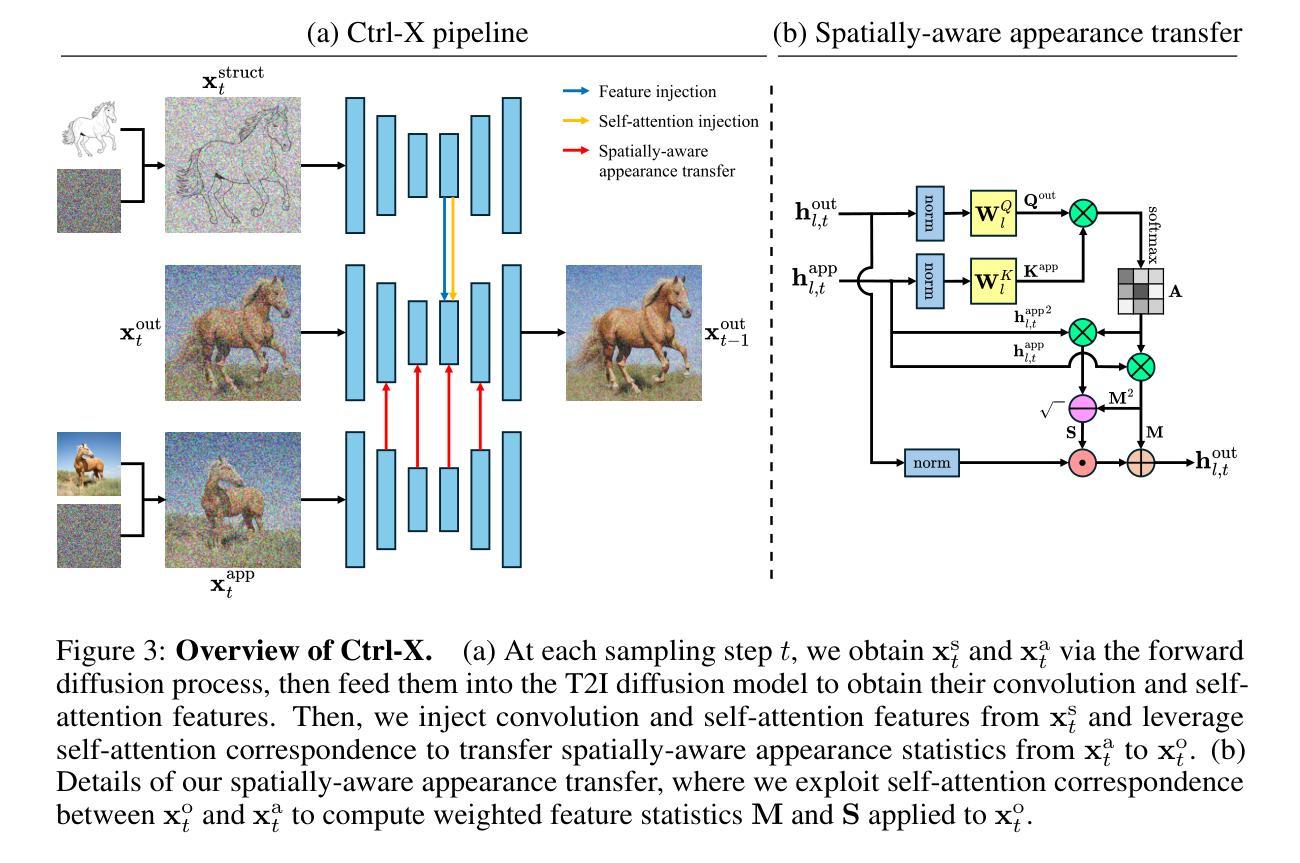
Ctrl-X: Controlling Structure and Appearance for Text-To-Image Generation Without Guidance
Authors:Kuan Heng Lin, Sicheng Mo, Ben Klingher, Fangzhou Mu, Bolei Zhou
Recent controllable generation approaches such as FreeControl and Diffusion Self-Guidance bring fine-grained spatial and appearance control to text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models without training auxiliary modules. However, these methods optimize the latent embedding for each type of score function with longer diffusion steps, making the generation process time-consuming and limiting their flexibility and use. This work presents Ctrl-X, a simple framework for T2I diffusion controlling structure and appearance without additional training or guidance. Ctrl-X designs feed-forward structure control to enable the structure alignment with a structure image and semantic-aware appearance transfer to facilitate the appearance transfer from a user-input image. Extensive qualitative and quantitative experiments illustrate the superior performance of Ctrl-X on various condition inputs and model checkpoints. In particular, Ctrl-X supports novel structure and appearance control with arbitrary condition images of any modality, exhibits superior image quality and appearance transfer compared to existing works, and provides instant plug-and-play functionality to any T2I and text-to-video (T2V) diffusion model. See our project page for an overview of the results: https://genforce.github.io/ctrl-x
最近的可控生成方法,如FreeControl和Diffusion Self-Guidance,为文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型带来了精细的时空和控制力,而无需训练辅助模块。然而,这些方法针对每种类型的得分函数优化潜在嵌入,并增加了扩散步骤,使得生成过程变得耗时,并限制了其灵活性和使用。本研究提出了Ctrl-X,这是一个用于T2I扩散控制结构和外观的简单框架,无需额外的训练或指导。Ctrl-X设计前馈结构控制以实现与结构图像的结构对齐和用户输入图像的语义感知外观转移,以促进外观转移。广泛的定性和定量实验表明,Ctrl-X在各种条件输入和模型检查点上的性能优越。特别地,Ctrl-X支持使用任意模态的条件图像进行新颖的结构和外观控制,与现有作品相比展现出更高的图像质量和外观转移效果,并为任何T2I和文本到视频(T2V)的扩散模型提供了即时即用的功能。有关结果的概述,请参见我们的项目页面:https://genforce.github.io/ctrl-x
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 17 figures, see project page at https://genforce.github.io/ctrl-x
Summary
近期可控生成方法如FreeControl和Diffusion Self-Guidance为文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型带来了精细的时空和外观控制,无需训练辅助模块。然而,这些方法针对每种类型的得分函数优化潜在嵌入,扩散步骤较长,使得生成过程耗时,且限制了其灵活性和使用。本研究提出Ctrl-X,一个无需额外训练或指导的T2I扩散控制框架。Ctrl-X设计前馈结构控制以实现结构图像的对齐,并设计语义感知的外观转移以促进从用户输入图像进行外观转移。广泛的定性和定量实验表明,Ctrl-X在各种条件输入和模型检查点上表现出卓越的性能。特别是,Ctrl-X支持具有任意模态条件图像的新颖结构和外观控制,与现有作品相比展现出卓越的图片质量和外观转移效果,并且能为任何T2I和文本到视频(T2V)扩散模型提供即时即用的功能。
Key Takeaways
- Ctrl-X是一个用于文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型的控制框架,可实现结构和外观的精细控制。
- Ctrl-X不需要额外的训练或指导,能够实现快速且灵活的控制。
- Ctrl-X通过前馈结构控制和语义感知的外观转移设计,实现对结构图像的对齐和外观从用户输入图像的转移。
- Ctrl-X在多种条件输入和模型检查点上的表现优于其他方法。
- Ctrl-X支持具有任意模态条件图像的新颖结构和外观控制。
- Ctrl-X在图像质量和外观转移方面表现出卓越的效果。
点此查看论文截图



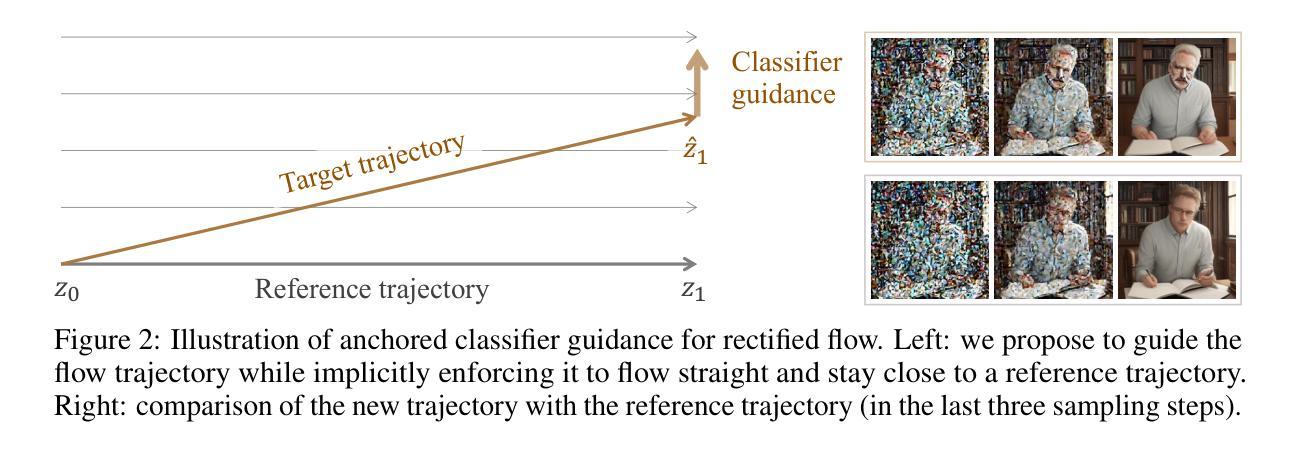
RectifID: Personalizing Rectified Flow with Anchored Classifier Guidance
Authors:Zhicheng Sun, Zhenhao Yang, Yang Jin, Haozhe Chi, Kun Xu, Kun Xu, Liwei Chen, Hao Jiang, Yang Song, Kun Gai, Yadong Mu
Customizing diffusion models to generate identity-preserving images from user-provided reference images is an intriguing new problem. The prevalent approaches typically require training on extensive domain-specific images to achieve identity preservation, which lacks flexibility across different use cases. To address this issue, we exploit classifier guidance, a training-free technique that steers diffusion models using an existing classifier, for personalized image generation. Our study shows that based on a recent rectified flow framework, the major limitation of vanilla classifier guidance in requiring a special classifier can be resolved with a simple fixed-point solution, allowing flexible personalization with off-the-shelf image discriminators. Moreover, its solving procedure proves to be stable when anchored to a reference flow trajectory, with a convergence guarantee. The derived method is implemented on rectified flow with different off-the-shelf image discriminators, delivering advantageous personalization results for human faces, live subjects, and certain objects. Code is available at https://github.com/feifeiobama/RectifID.
定制扩散模型以从用户提供的参考图像生成身份保留图像是一个引人入胜的新问题。流行的方法通常需要在对特定领域的大量图像上进行训练以实现身份保留,这在不同的使用情况下缺乏灵活性。为了解决这一问题,我们利用分类器指导这一无需训练的技术,使用现有分类器来引导扩散模型进行个性化图像生成。我们的研究表明,基于最新的校正流框架,普通分类器指导的主要局限性在于需要特殊分类器,可以通过简单的定点解决策略来解决,允许使用现成的图像鉴别器进行灵活的个性化设置。而且,当其解决方案固定在参考流轨迹上时,证明其解决程序是稳定的,并且有收敛性的保证。所推导的方法在不同的现成图像鉴别器上应用于校正流,为人脸、活体主体和某些物体生成了有利的个性化结果。代码可在https://github.com/feifeiobama/RectifID找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024
Summary
扩散模型根据用户提供的参考图像生成身份保留图像是一个新的研究问题。为了解决这个问题,研究团队采用了无训练的分类器指导技术,该技术使用现有的分类器来引导扩散模型进行个性化图像生成。该研究解决了原始分类器指导方法的主要限制,使用简单的定点解决方案,并证明其在参考流轨迹锚定下的稳定性,并提供了收敛保证。该方法在人脸、活体生物和某些物体上实现了有利的个性化结果。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型能够根据用户提供的参考图像生成身份保留图像。
- 研究团队首次尝试使用无训练的分类器指导技术来解决这个问题。
- 研究解决了原始分类器指导方法的主要限制,使其更加灵活。
- 研究证明方法在使用参考流轨迹时的稳定性,并提供收敛保证。
- 该方法在不同的对象(如人脸、活体生物和某些物体)上都实现了良好的个性化结果。
- 该方法的实现代码已公开在GitHub上供公众查阅和使用。
点此查看论文截图