⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-12 更新
Can Graph Neural Networks Learn Language with Extremely Weak Text Supervision?
Authors:Zihao Li, Lecheng Zheng, Bowen Jin, Dongqi Fu, Baoyu Jing, Yikun Ban, Jingrui He, Jiawei Han
While great success has been achieved in building vision models with Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) over Internet-scale image-text pairs, building transferable Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) with CLIP pipeline is challenging because of three fundamental issues: the scarcity of labeled data and text supervision, different levels of downstream tasks, and the conceptual gaps between domains. In this work, to address these issues, we leverage multi-modal prompt learning to effectively adapt pre-trained GNN to downstream tasks and data, given only a few semantically labeled samples, each with extremely weak text supervision. Our new paradigm embeds the graphs directly in the same space as the Large Language Models (LLMs) by learning both graph prompts and text prompts simultaneously. To accomplish this, we improve state-of-the-art graph prompt method, and then propose the first graph-language multi-modal prompt learning approach for exploiting the knowledge in pre-trained models. Notably, due to the insufficient supervision for fine-tuning, in our paradigm, the pre-trained GNN and the LLM are kept frozen, so the learnable parameters are much fewer than fine-tuning any pre-trained model. Through extensive experiments on real-world datasets, we demonstrate the superior performance of our paradigm in few-shot, multi-task-level, and cross-domain settings. Moreover, we build the first CLIP-style zero-shot classification prototype that can generalize GNNs to unseen classes with extremely weak text supervision.
在利用对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)在互联网规模的图像文本对上构建视觉模型方面取得了巨大成功,但使用CLIP管道构建可迁移的图神经网络(GNN)却面临三大根本问题:缺乏标注数据和文本监督、下游任务级别不同以及领域间的概念差距。在这项工作中,为了解决这个问题,我们利用多模态提示学习来有效地适应预训练GNN到下游任务和数据,仅使用少量语义标注样本,每个样本都具有极弱的文本监督。我们的新范式通过将图直接嵌入到与大型语言模型(LLM)相同的空间中,通过同时学习图提示和文本提示来实现。为了完成这项任务,我们改进了最先进的图提示方法,然后提出了利用预训练模型知识的首个图语言多模态提示学习方法。值得注意的是,由于微调时的监督不足,在我们的范式中,预训练的GNN和LLM保持冻结状态,因此可学习的参数远远少于微调任何预训练模型。在现实数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的范式在少样本、多任务级别和跨域设置中具有卓越的性能。此外,我们构建了第一个CLIP风格的零样本分类原型,能够借助极弱的文本监督将GNN推广到未见类别。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint, 26 pages
Summary
该文本探讨了利用对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)构建视觉模型时的挑战,特别是在将预训练图神经网络(GNN)迁移到下游任务和数据时面临的三大问题。为解决这些问题,作者提出利用多模态提示学习,将图直接嵌入大型语言模型(LLM)的同一空间,同时学习图提示和文本提示。作者在改进现有图提示方法的基础上,提出了首个用于挖掘预训练模型知识的图语言多模态提示学习方法。由于微调时的监督不足,作者保持预训练的GNN和LLM冻结状态,因此可学习参数少于微调任何预训练模型。作者在真实数据集上的实验表明,该方法在少样本、多任务级别和跨域设置中具有卓越性能,并建立了首个CLIP风格的零样本分类原型,可将GNN推广到具有极弱文本监督的未见类别。
Key Takeaways
- 利用CLIP构建视觉模型时面临三大挑战:缺乏标注数据和文本监督、下游任务的不同级别、以及领域之间的概念差距。
- 提出利用多模态提示学习来适应预训练的GNN到下游任务和数据。
- 将图直接嵌入LLM的同一空间,同时学习图提示和文本提示。
- 改进了现有的图提示方法,并提出了首个图语言多模态提示学习方法,用于挖掘预训练模型的知识。
- 由于监督不足,保持预训练的GNN和LLM冻结状态,降低了可学习参数的数量。
- 在真实数据集上的实验表明,该方法在少样本、多任务级别和跨域设置中具有卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图
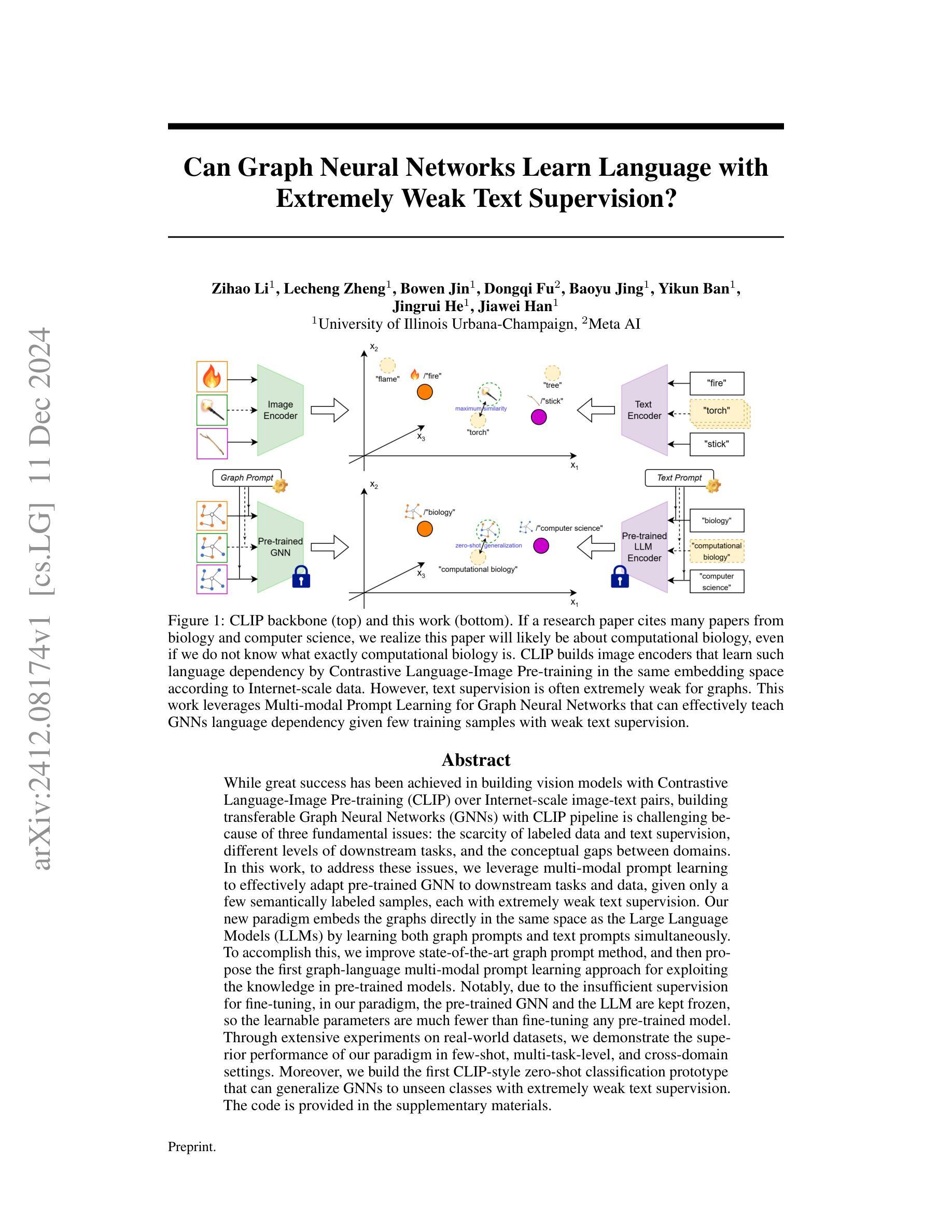
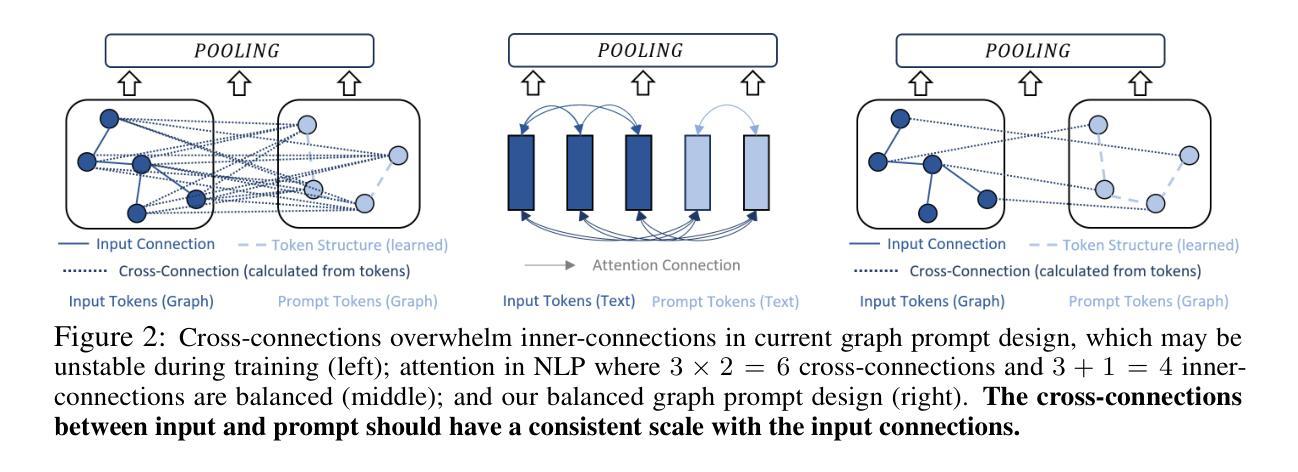
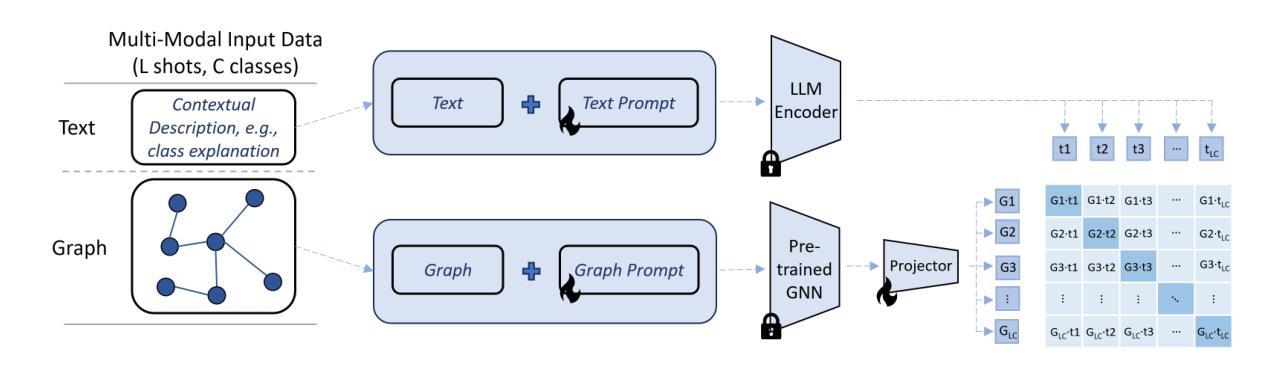
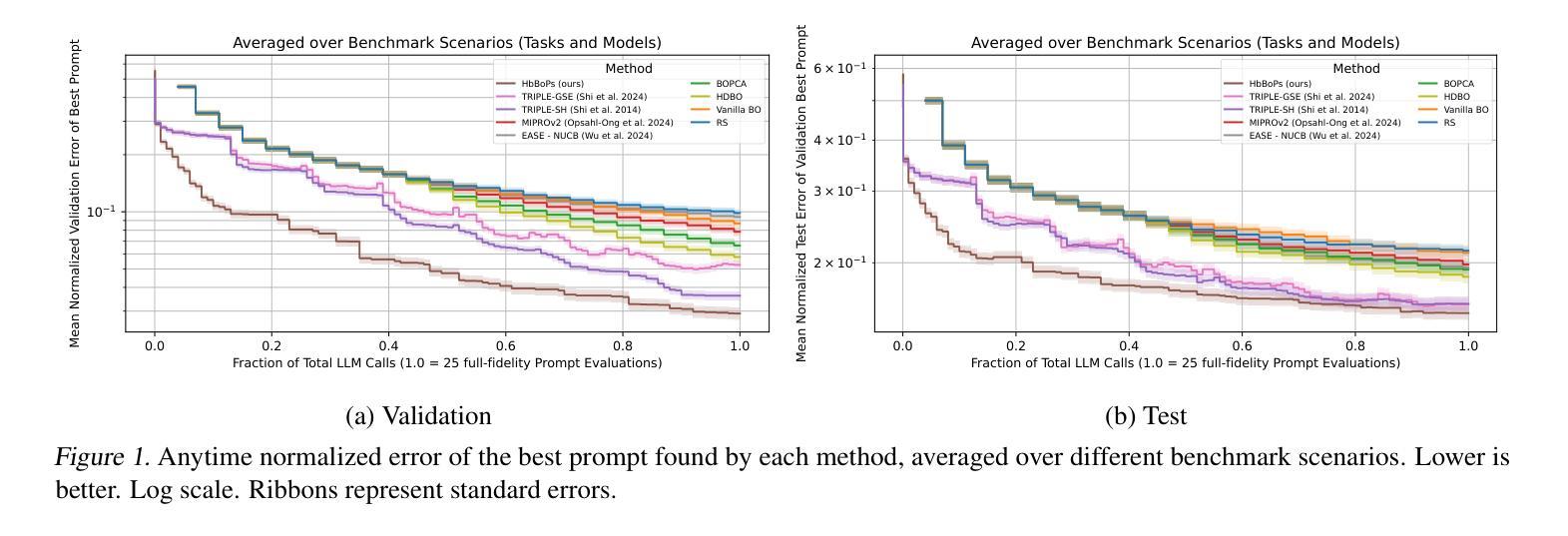
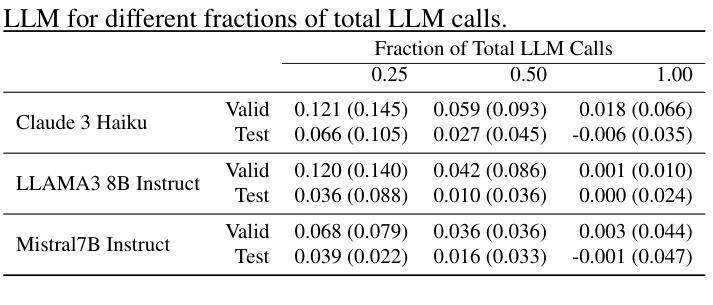
Hyperband-based Bayesian Optimization for Black-box Prompt Selection
Authors:Lennart Schneider, Martin Wistuba, Aaron Klein, Jacek Golebiowski, Giovanni Zappella, Felice Antonio Merra
Optimal prompt selection is crucial for maximizing large language model (LLM) performance on downstream tasks. As the most powerful models are proprietary and can only be invoked via an API, users often manually refine prompts in a black-box setting by adjusting instructions and few-shot examples until they achieve good performance as measured on a validation set. Recent methods addressing static black-box prompt selection face significant limitations: They often fail to leverage the inherent structure of prompts, treating instructions and few-shot exemplars as a single block of text. Moreover, they often lack query-efficiency by evaluating prompts on all validation instances, or risk sub-optimal selection of a prompt by using random subsets of validation instances. We introduce HbBoPs, a novel Hyperband-based Bayesian optimization method for black-box prompt selection addressing these key limitations. Our approach combines a structural-aware deep kernel Gaussian Process to model prompt performance with Hyperband as a multi-fidelity scheduler to select the number of validation instances for prompt evaluations. The structural-aware modeling approach utilizes separate embeddings for instructions and few-shot exemplars, enhancing the surrogate model’s ability to capture prompt performance and predict which prompt to evaluate next in a sample-efficient manner. Together with Hyperband as a multi-fidelity scheduler we further enable query-efficiency by adaptively allocating resources across different fidelity levels, keeping the total number of validation instances prompts are evaluated on low. Extensive evaluation across ten benchmarks and three LLMs demonstrate that HbBoPs outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
最优提示的选择对于下游任务中大型语言模型(LLM)的性能最大化至关重要。由于最强大的模型是专有模型,只能通过API进行调用,用户通常在一个黑箱环境中手动调整提示,通过调整指令和少量示例,直到它们在验证集上的表现良好。最近解决静态黑箱提示选择的方法存在重大局限性:它们往往未能充分利用提示的固有结构,将指令和少量示例视为一段文本。此外,它们通常通过在所有验证实例上评估提示来缺乏查询效率,或者使用验证实例的随机子集来选择提示,存在选择提示次优的风险。我们引入了HbBoPs,这是一种用于黑箱提示选择的新型基于Hyperband的贝叶斯优化方法,解决了这些关键局限性。我们的方法结合了结构感知深度内核高斯过程来对提示性能进行建模,并使用Hyperband作为多保真调度器来选择提示评估所需的验证实例数量。结构感知建模方法使用单独的嵌入来代表指令和少量示例,提高了替代模型捕捉提示性能的能力,并以样本效率高的方式预测接下来要评估哪个提示。结合Hyperband多保真调度器,我们进一步通过在不同保真度级别上自适应地分配资源来实现查询效率,同时保持评估提示所需的验证实例总数较低。在十个基准测试和三个LLM上的广泛评估表明,HbBoPs优于现有技术方法。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
大语言模型下游任务中,优质提示的选择极为关键。当前最优模型具有专有性,仅能通过API调用,用户需在黑箱设置下手动调整指令和少量示例来优化提示,直至其在验证集上的表现达到理想状态。针对静态黑箱提示选择的现有方法存在显著缺陷:它们忽略了指令和少量示例的内部结构,将其视为一段文本;同时缺乏查询效率,对所有验证实例进行评估或对提示选择产生不利影响。我们推出了HbBoPs方法,这是一种基于Hyperband的贝叶斯优化方法,旨在解决这些关键问题。我们的方法结合了结构感知深度核高斯过程来模拟提示性能与Hyperband多保真调度器来选择验证实例数量来进行提示评估。该结构感知建模方法为指令和少量示例提供独立嵌入,提高代理模型捕捉提示性能的能力,并以样本效率高的方式预测下一步应评估哪个提示。此外,Hyperband多保真调度器通过在不同保真度级别之间自适应分配资源来提高查询效率,减少验证实例数量评估提示。在十个基准测试和三个大型语言模型上的广泛评估表明,HbBoPs优于现有技术。
关键见解
- 提示选择对于大语言模型在下游任务上的性能至关重要。
- 最优模型通常只能通过API访问,用户需手动调整提示以达到最佳性能。
- 现有静态黑箱提示选择方法存在缺陷,如忽略提示的内部结构和缺乏查询效率。
- HbBoPs方法结合了结构感知建模和Hyperband多保真调度器来解决这些问题。
- 结构感知建模方法为指令和示例提供独立嵌入,提高代理模型捕捉提示性能的能力。
- Hyperband多保真调度器可自适应分配资源,提高查询效率并减少验证实例数量评估提示。
点此查看论文截图


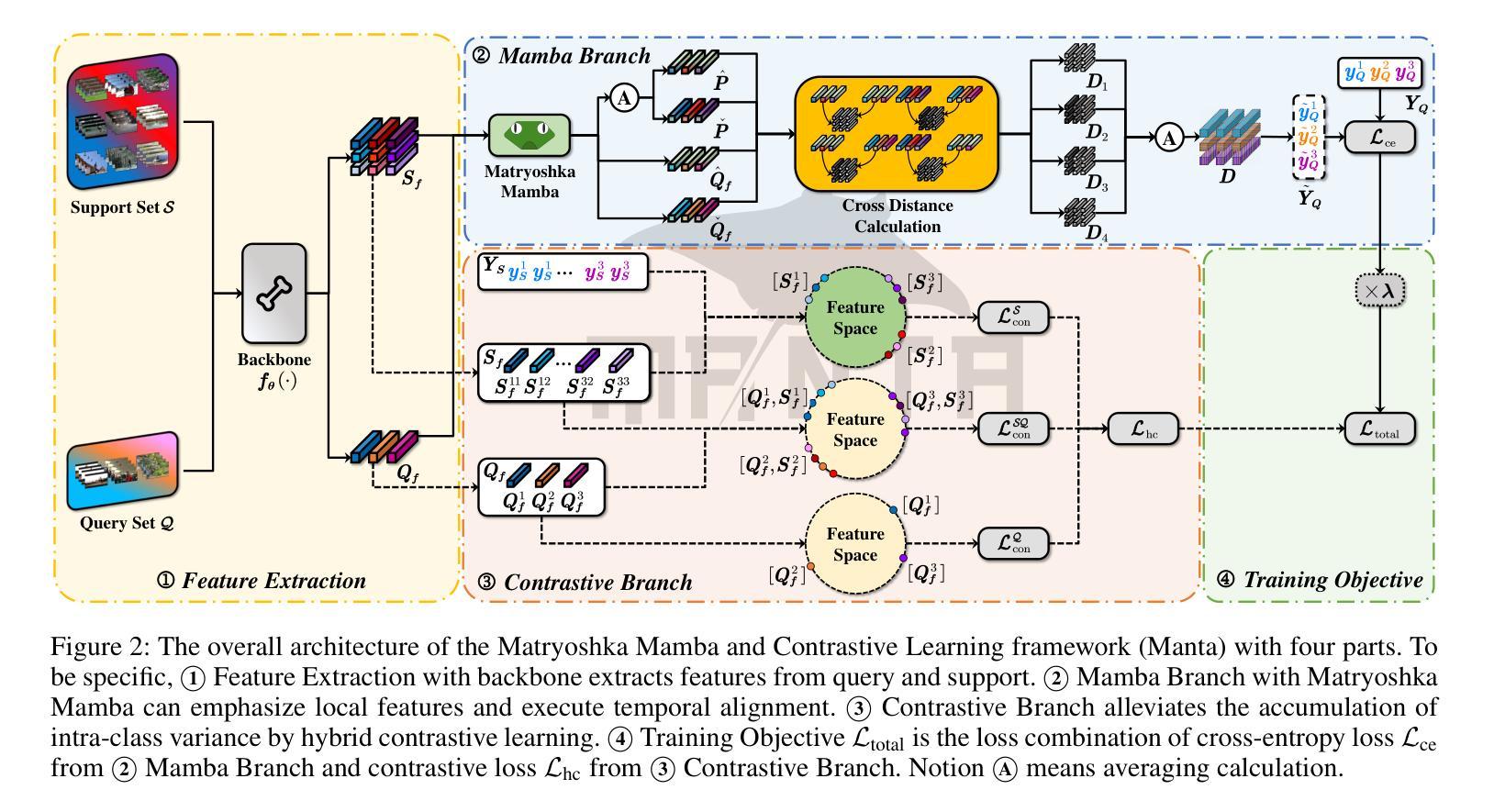
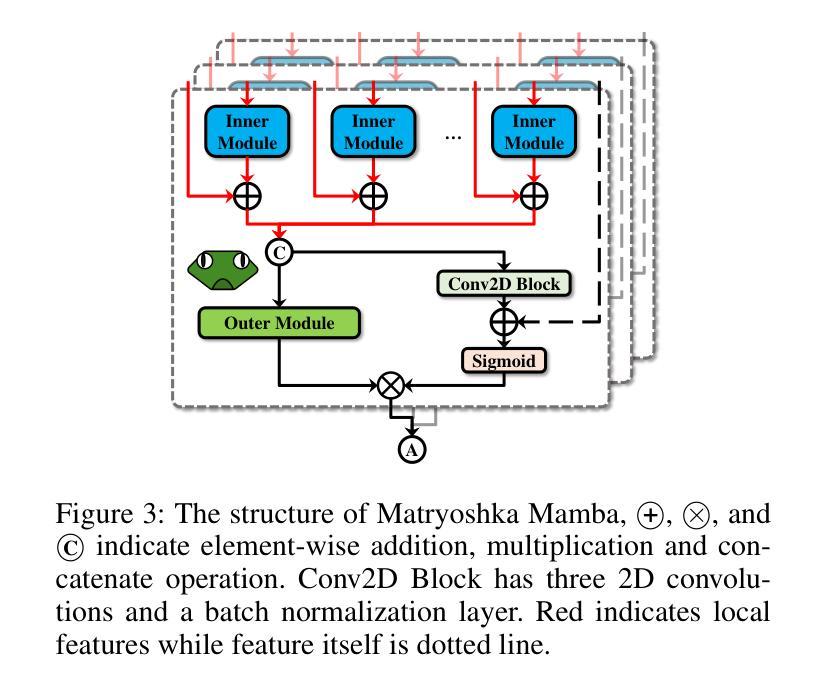
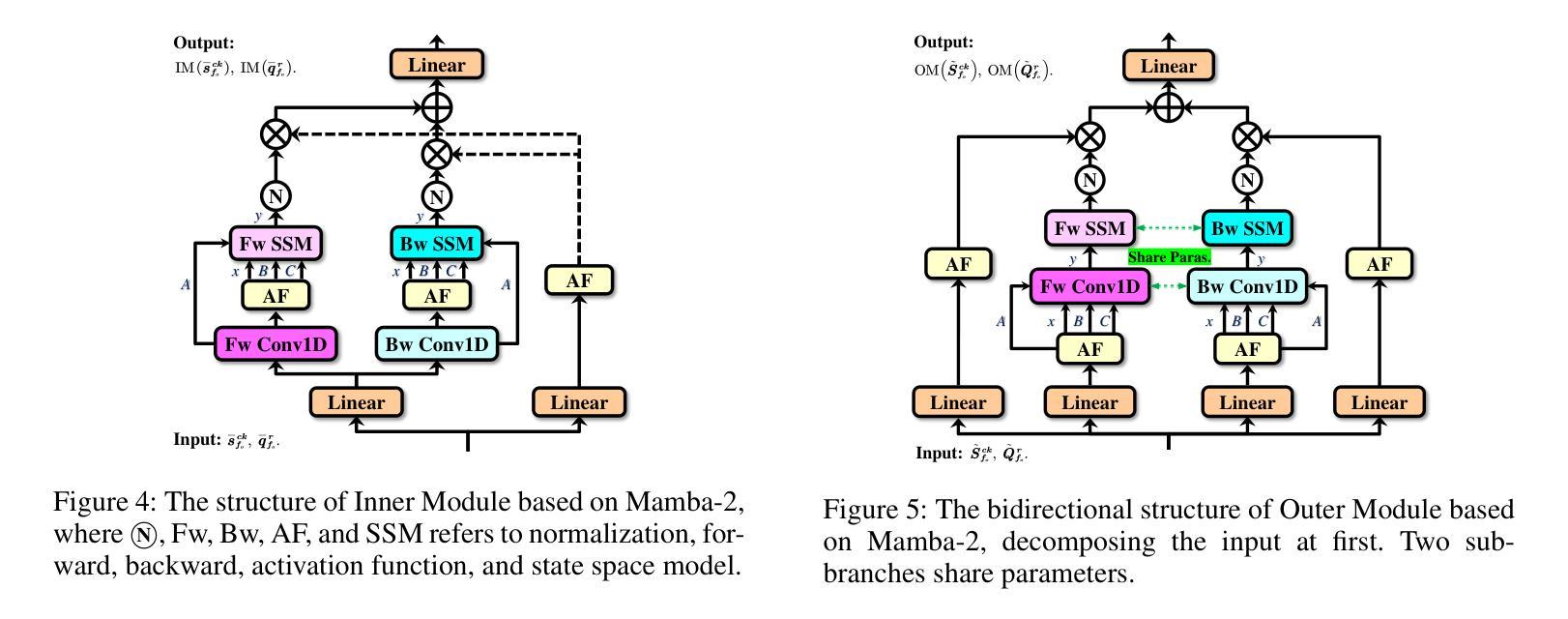
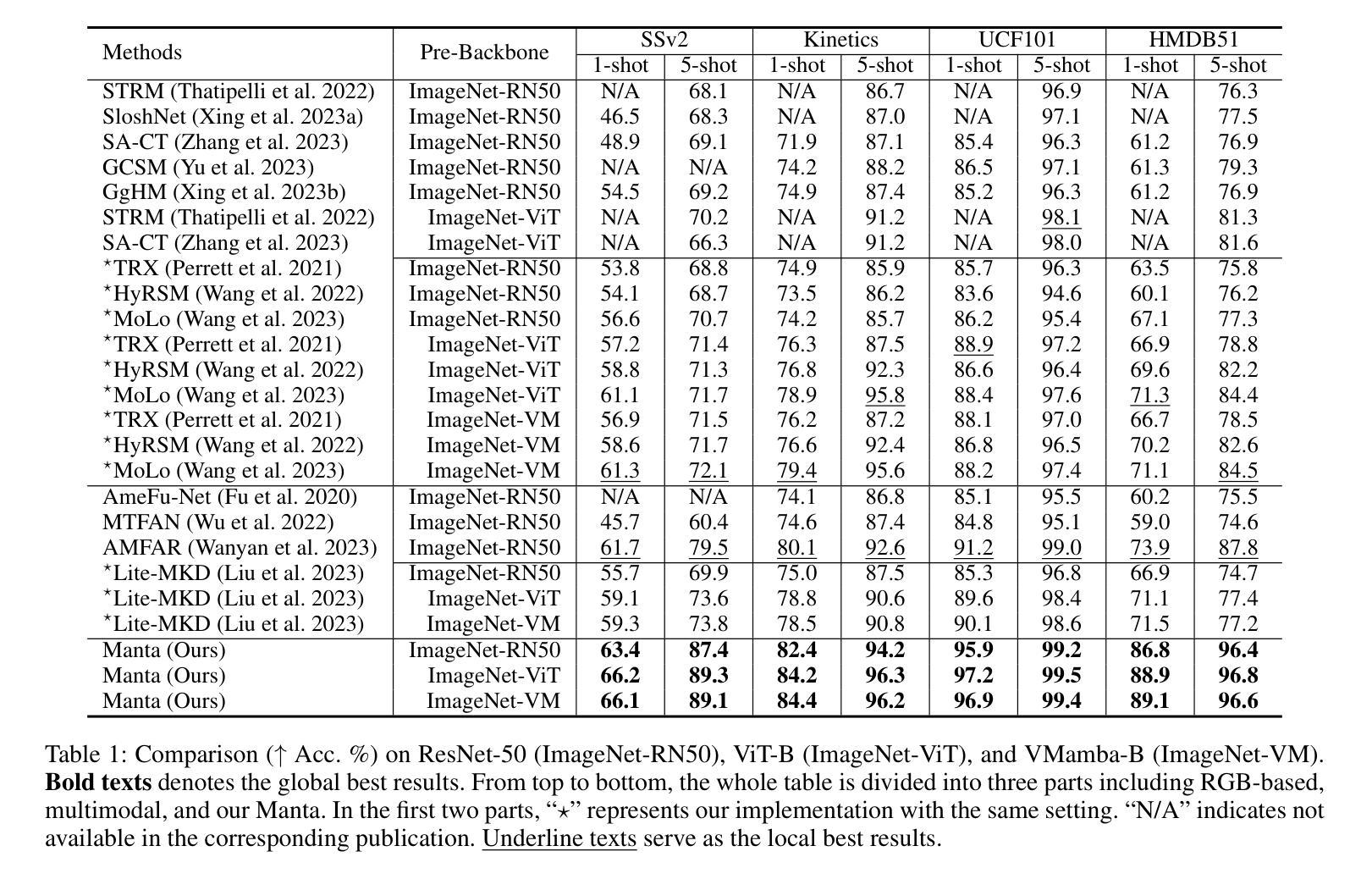
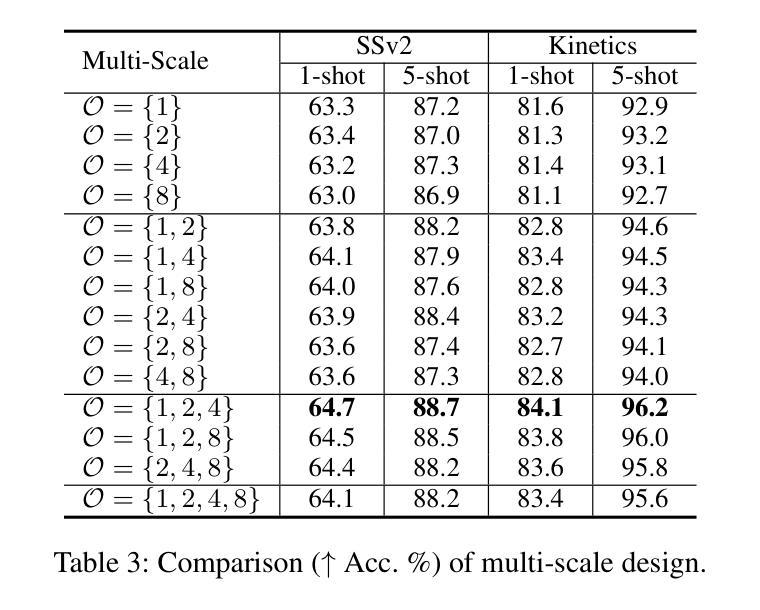
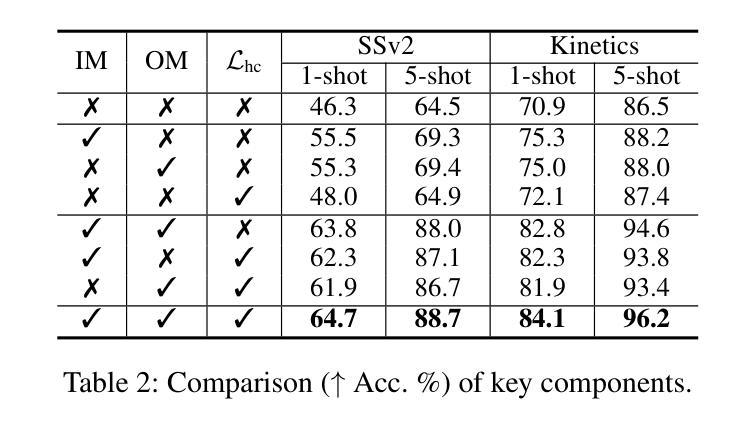
Manta: Enhancing Mamba for Few-Shot Action Recognition of Long Sub-Sequence
Authors:Wenbo Huang, Jinghui Zhang, Guang Li, Lei Zhang, Shuoyuan Wang, Fang Dong, Jiahui Jin, Takahiro Ogawa, Miki Haseyama
In few-shot action recognition(FSAR), long sub-sequences of video naturally express entire actions more effectively. However, the computational complexity of mainstream Transformer-based methods limits their application. Recent Mamba demonstrates efficiency in modeling long sequences, but directly applying Mamba to FSAR overlooks the importance of local feature modeling and alignment. Moreover, long sub-sequences within the same class accumulate intra-class variance, which adversely impacts FSAR performance. To solve these challenges, we propose a \underline{\textbf{M}}atryoshka M\underline{\textbf{A}}mba and Co\underline{\textbf{N}}tras\underline{\textbf{T}}ive Le\underline{\textbf{A}}rning framework(\textbf{Manta}). Firstly, the Matryoshka Mamba introduces multiple Inner Modules to enhance local feature representation, rather than directly modeling global features. An Outer Module captures dependencies of timeline between these local features for implicit temporal alignment. Secondly, a hybrid contrastive learning paradigm, combining both supervised and unsupervised methods, is designed to mitigate the negative effects of intra-class variance accumulation. The Matryoshka Mamba and the hybrid contrastive learning paradigm operate in parallel branches within Manta, enhancing Mamba for FSAR of long sub-sequence. Manta achieves new state-of-the-art performance on prominent benchmarks, including SSv2, Kinetics, UCF101, and HMDB51. Extensive empirical studies prove that Manta significantly improves FSAR of long sub-sequence from multiple perspectives. The code is released at https://github.com/wenbohuang1002/Manta.
在少数动作识别(FSAR)中,视频的长子序列更自然地表达整个动作。然而,主流基于Transformer的方法的计算复杂性限制了其应用。最近的Mamba在建模长序列方面表现出效率,但直接将Mamba应用于FSAR忽视了局部特征建模和对齐的重要性。此外,同一类别内的长子序列会累积类内方差,这对FSAR性能产生不利影响。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一个名为“Manta”(Matryoshka Mamba和对比性学习框架)的框架。首先,Matryoshka Mamba引入了多个内部模块来增强局部特征表示,而不是直接对全局特征进行建模。外部模块捕获这些局部特征之间的时间线依赖性,以进行隐式时间对齐。其次,结合有监督和无监督方法设计了一种混合对比学习模式,旨在减轻类内方差累积的负面影响。Matryoshka Mamba和混合对比学习模式在Manta的并行分支中运行,增强了Mamba对长子序列的FSAR能力。Manta在SSv2、Kinetics、UCF101和HMDB51等基准测试中达到了新的最先进的性能。大量的实证研究证明,Manta从多个角度显著提高了长子序列的FSAR性能。代码已发布在https://github.com/wenbohuang1002/Manta。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
该文本介绍了针对少样本动作识别(FSAR)领域的一个研究问题及其解决方案。研究者提出了一种名为Manta的新框架,结合了Matryoshka Mamba和混合对比学习策略来解决建模长序列动作的挑战。Manta通过引入多个内部模块增强局部特征表示,并设计了一种结合监督和无监督方法的混合对比学习范式来减轻同一类别内变异积累对FSAR性能的影响。该方法在多个基准测试中实现了卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- Matryoshka Mamba被引入以解决Transformer在建模长序列时面临的计算复杂性挑战。
- Matryoshka Mamba通过多个内部模块增强局部特征表示,而不是直接建模全局特征。
- 外模块用于捕捉时间序列的依赖关系,实现隐式时间对齐。
- 引入了一种混合对比学习范式,结合监督和无监督方法来减轻同一类别内变异积累带来的负面影响。
- Manta框架结合了Matryoshka Mamba和混合对比学习策略,实现了对长序列动作识别的卓越性能。
- Manta在多个基准测试中取得了最先进的性能,包括SSv2、Kinetics、UCF101和HMDB51。
点此查看论文截图

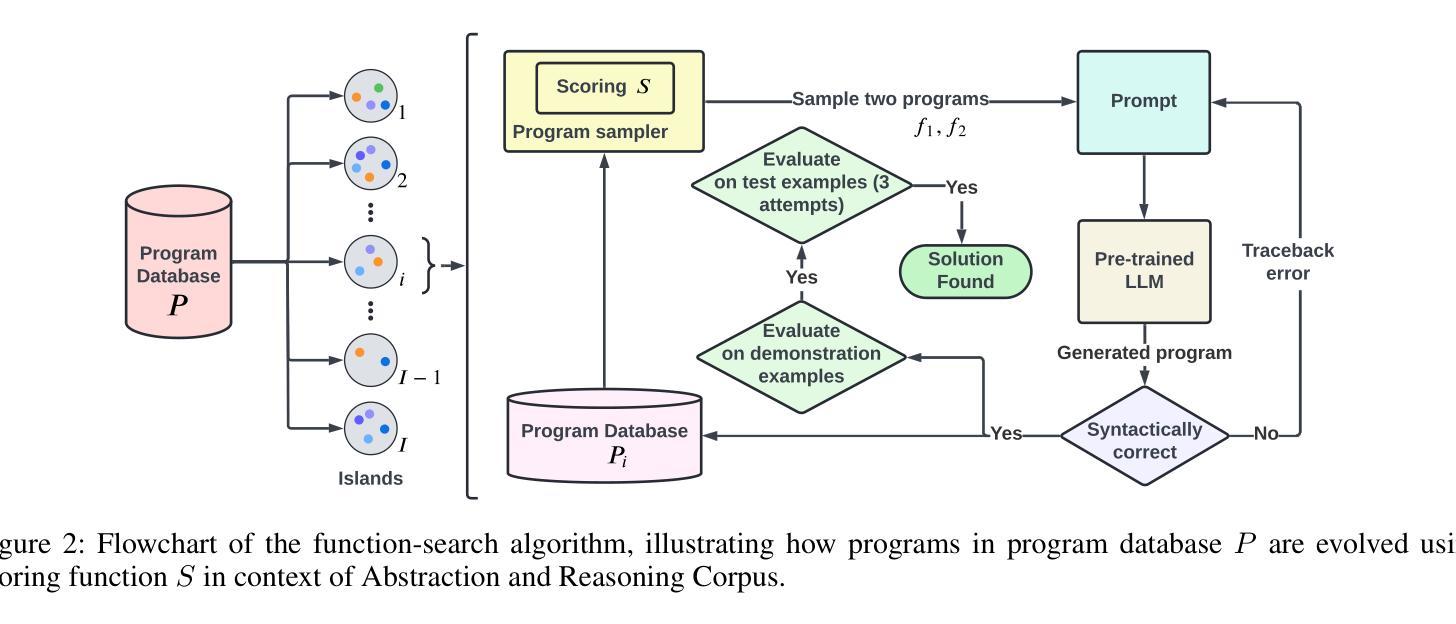
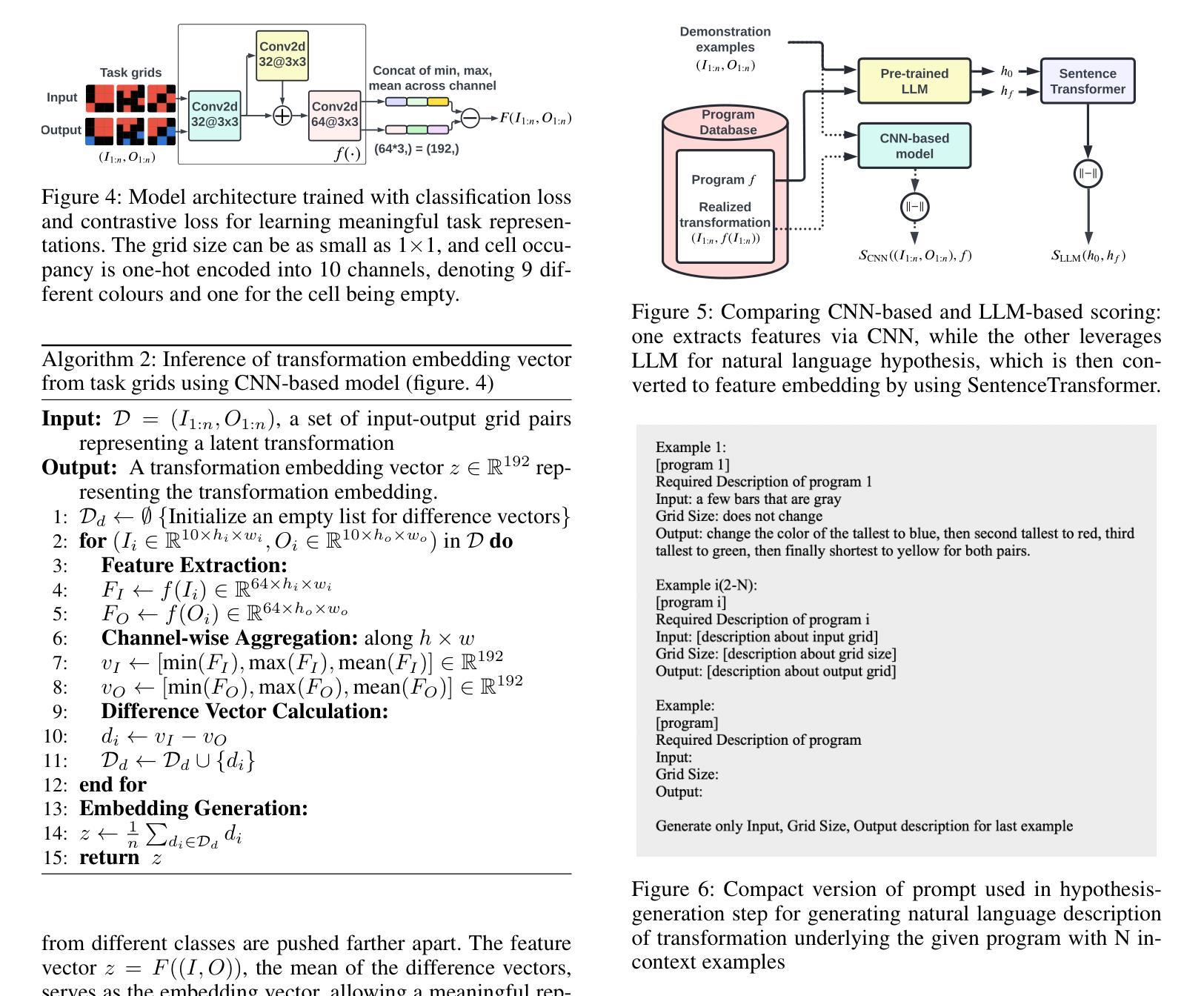
ConceptSearch: Towards Efficient Program Search Using LLMs for Abstraction and Reasoning Corpus (ARC)
Authors:Kartik Singhal, Gautam Shroff
The Abstraction and Reasoning Corpus (ARC) poses a significant challenge to artificial intelligence, demanding broad generalization and few-shot learning capabilities that remain elusive for current deep learning methods, including large language models (LLMs). While LLMs excel in program synthesis, their direct application to ARC yields limited success. To address this, we introduce ConceptSearch, a novel function-search algorithm that leverages LLMs for program generation and employs a concept-based scoring method to guide the search efficiently. Unlike simplistic pixel-based metrics like Hamming distance, ConceptSearch evaluates programs on their ability to capture the underlying transformation concept reflected in the input-output examples. We explore three scoring functions: Hamming distance, a CNN-based scoring function, and an LLM-based natural language scoring function. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of ConceptSearch, achieving a significant performance improvement over direct prompting with GPT-4. Moreover, our novel concept-based scoring exhibits up to 30% greater efficiency compared to Hamming distance, measured in terms of the number of iterations required to reach the correct solution. These findings highlight the potential of LLM-driven program search when integrated with concept-based guidance for tackling challenging generalization problems like ARC.
抽象与推理语料库(ARC)对人工智能提出了重大挑战,要求具备广泛的泛化能力和小样本学习能力,而当前深度学习方法,包括大型语言模型(LLM)都难以达到这一要求。虽然LLM在程序合成方面表现出色,但直接应用于ARC却收效甚微。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了ConceptSearch,这是一种新型的函数搜索算法,它利用LLM进行程序生成,并采用基于概念的分数计算方法,以有效地引导搜索。不同于简单的像素级度量标准(如汉明距离),ConceptSearch根据程序捕获输入输出示例中体现的基础转换概念的能力来评估程序。我们探索了三种评分函数:汉明距离、基于CNN的评分函数和基于LLM的自然语言评分函数。实验结果表明,ConceptSearch效果显著,与直接使用GPT-4提示相比,实现了显著的性能提升。此外,我们创新性的基于概念的评分方法,在达到正确解所需的迭代次数方面,与汉明距离相比,效率提高了高达30%。这些发现突显了当与基于概念的指导相结合时,LLM驱动的程序搜索在解决具有挑战性的泛化问题(如ARC)方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Pre-print of paper accepted at AAAI 2025
Summary
该文本介绍了针对人工智能领域中的抽象与推理语料库(ARC)的挑战,提出一种名为ConceptSearch的新型函数搜索算法。该算法利用大型语言模型(LLM)进行程序生成,并采用基于概念的评分方法来有效指导搜索。实验结果表明,ConceptSearch在GPT-4的直接提示下有显著的性能提升,且新型概念评分方法的效率比Hamming距离高出30%。这为解决类似ARC的具有挑战性的泛化问题提供了潜在可能性。
Key Takeaways
- ARC对人工智能提出了泛化和少样本学习的挑战,当前深度学习方法包括大型语言模型(LLMs)难以应对。
- LLMs在程序合成方面表现出色,但直接应用于ARC效果有限。
- 引入ConceptSearch算法,结合LLMs进行程序生成和概念评分方法。
- ConceptSearch通过三种评分函数进行评估:Hamming距离、基于CNN的评分函数和基于LLM的自然语言评分函数。
- 实验结果表明,ConceptSearch在GPT-4的直接提示下有显著性能提升。
- 基于概念的新型评分方法相比Hamming距离展现出更高的效率。
点此查看论文截图




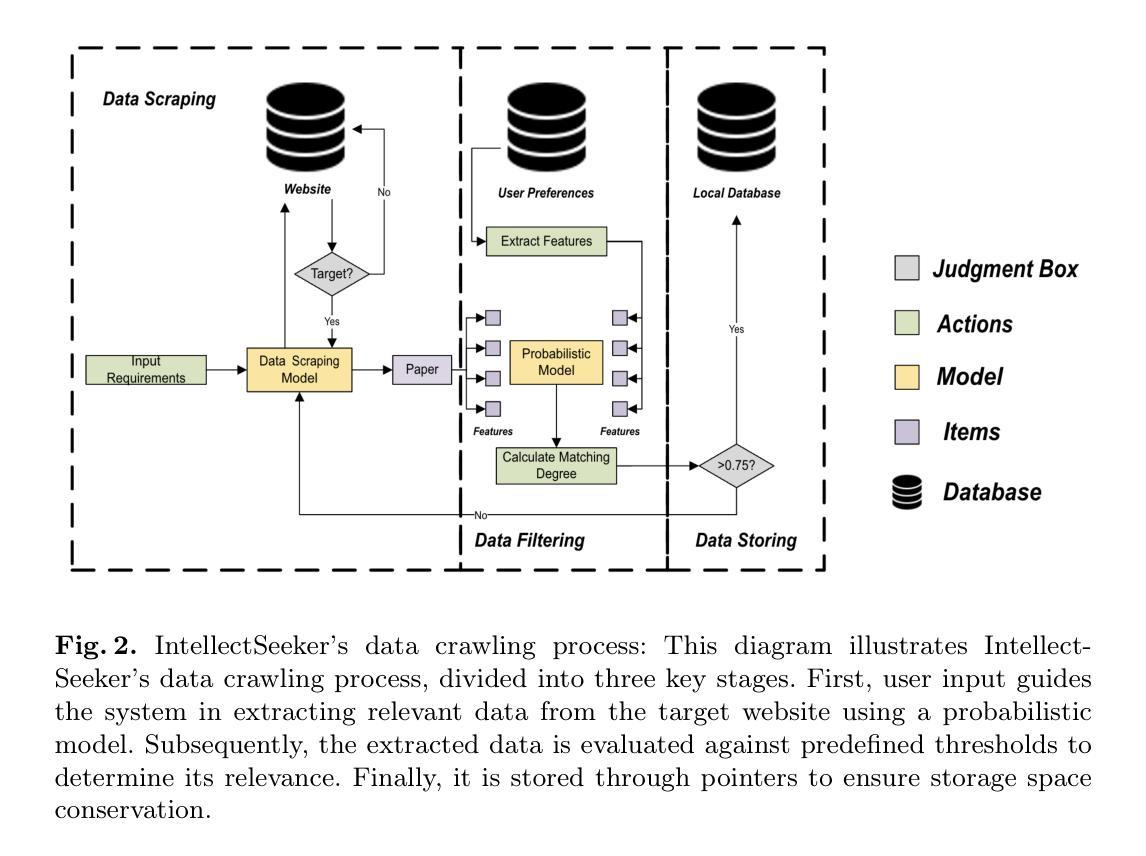
IntellectSeeker: A Personalized Literature Management System with the Probabilistic Model and Large Language Model
Authors:Weizhen Bian, Siyan Liu, Yubo Zhou, Dezhi Chen, Yijie Liao, Zhenzhen Fan, Aobo Wang
Faced with the burgeoning volume of academic literature, researchers often need help with uncertain article quality and mismatches in term searches using traditional academic engines. We introduce IntellectSeeker, an innovative and personalized intelligent academic literature management platform to address these challenges. This platform integrates a Large Language Model (LLM)–based semantic enhancement bot with a sophisticated probability model to personalize and streamline literature searches. We adopted the GPT-3.5-turbo model to transform everyday language into professional academic terms across various scenarios using multiple rounds of few-shot learning. This adaptation mainly benefits academic newcomers, effectively bridging the gap between general inquiries and academic terminology. The probabilistic model intelligently filters academic articles to align closely with the specific interests of users, which are derived from explicit needs and behavioral patterns. Moreover, IntellectSeeker incorporates an advanced recommendation system and text compression tools. These features enable intelligent article recommendations based on user interactions and present search results through concise one-line summaries and innovative word cloud visualizations, significantly enhancing research efficiency and user experience. IntellectSeeker offers academic researchers a highly customizable literature management solution with exceptional search precision and matching capabilities. The code can be found here: https://github.com/LuckyBian/ISY5001
面对日益增长的学术文献量,研究人员在文章质量不确定以及使用传统学术搜索引擎时术语搜索不匹配的问题时,常常需要帮助。我们推出IntellectSeeker,一个创新且个性化的智能学术文献管理平台,以应对这些挑战。该平台集成基于大型语言模型(LLM)的语义增强机器人和高级概率模型,以个性化和简化文献搜索。我们采用GPT-3.5 Turbo模型,通过多轮小样本学习,将日常语言转化为各种场景中的专业学术术语。这种适应主要对学术新手有益,有效地弥了一般查询和学术术语之间的差距。概率模型智能地过滤学术文章,以紧密符合用户的特定兴趣,这些兴趣来源于明确的需求和行为模式。此外,IntellectSeeker还采用了先进的推荐系统和文本压缩工具。这些功能能够根据用户交互进行智能文章推荐,并通过简洁的一行摘要和创新的词云可视化呈现搜索结果,从而显著提高研究效率和用户体验。IntellectSeeker为学术研究人员提供了高度可定制的文献管理解决方案,具有出色的搜索精度和匹配能力。代码可在以下网址找到:https://github.com/LuckyBian/ISY5001
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
学术文献数量庞大,研究者面临文章质量不确定和搜索术语不匹配的问题。IntellectSeeker是一个智能学术文献管理平台,通过大型语言模型(LLM)和概率模型,实现个性化、高效的文献搜索。采用GPT-3.5 Turbo模型进行少样本学习,将日常语言转化为专业术语。概率模型智能过滤学术文章,与用户特定兴趣紧密对齐。此外,它还包括高级推荐系统和文本压缩工具,可基于用户交互进行智能文章推荐,并通过简洁的一行总结和创新的词云可视化呈现搜索结果,提高研究效率和用户体验。
Key Takeaways
- IntellectSeeker是一个智能学术文献管理平台,解决学术文献海量、质量不确定和搜索术语不匹配的问题。
- 平台集成大型语言模型(LLM)进行语义增强,采用GPT-3.5 Turbo模型进行少样本学习,将日常语言转化为专业术语。
- 概率模型智能过滤学术文章,与用户兴趣紧密对齐,结合用户明确需求和行为模式进行推荐。
- IntellectSeeker包括高级推荐系统和文本压缩工具,提高研究效率和用户体验。
- 平台提供个性化的文献管理解决方案,具有高度的可定制性和搜索精准度。
- 通过简洁的一行总结和创新的词云可视化呈现搜索结果,帮助用户快速了解文章核心内容和研究领域。
点此查看论文截图


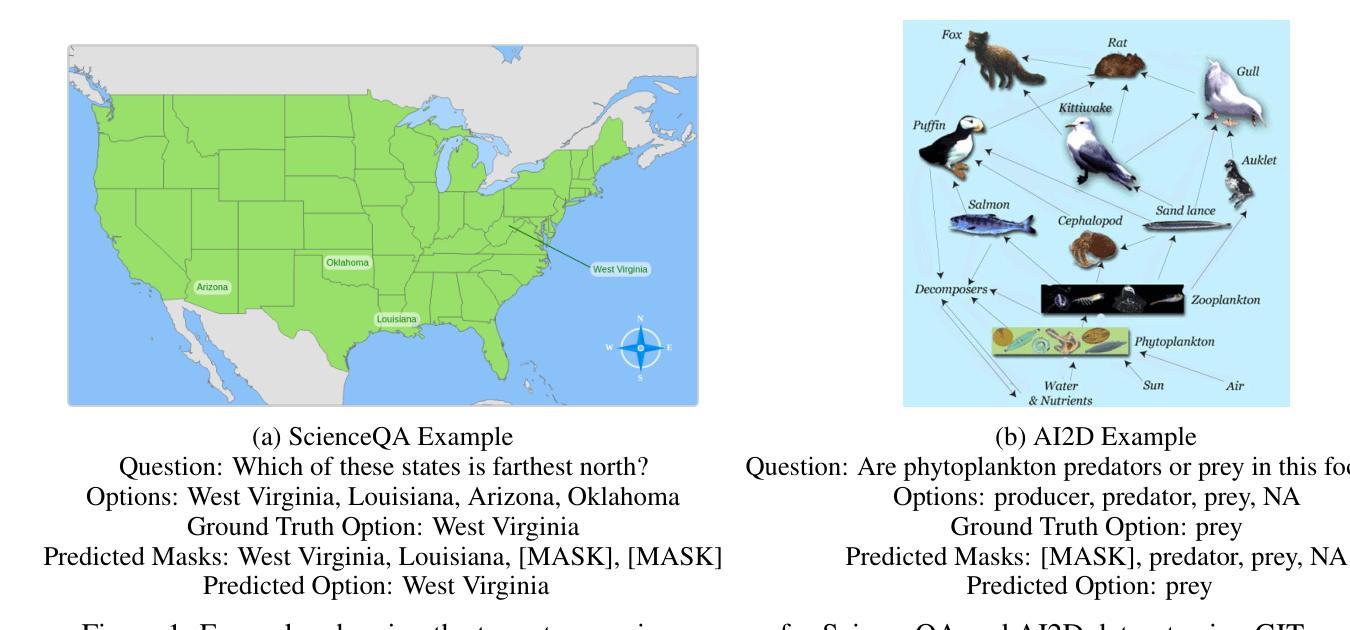
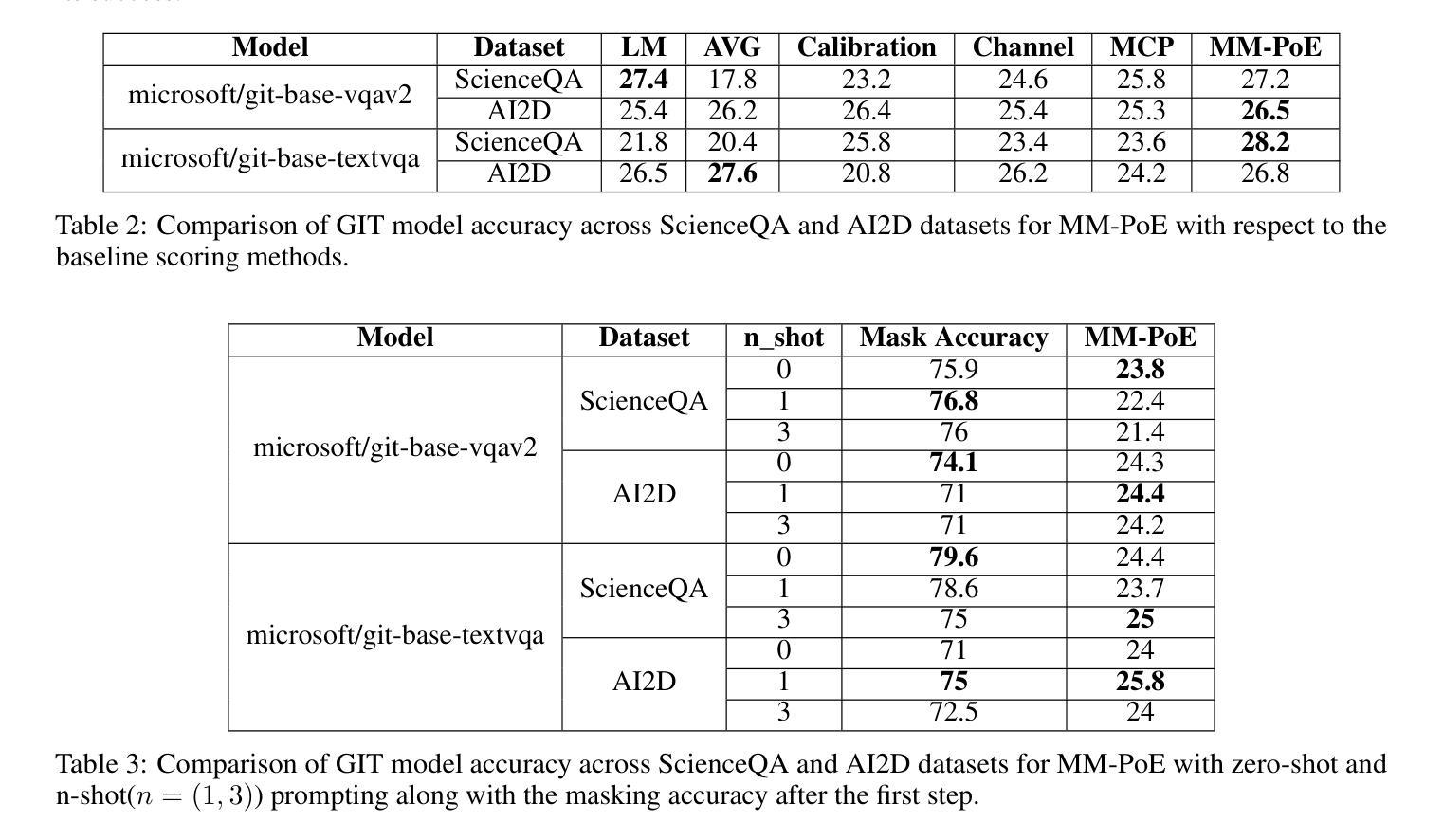
MM-PoE: Multiple Choice Reasoning via. Process of Elimination using Multi-Modal Models
Authors:Sayak Chakrabarty, Souradip Pal
This paper introduces Multiple Choice Reasoning via. Process of Elimination using Multi-Modal models, herein referred to as Multi-Modal Process of Elimination (MM-PoE). This novel methodology is engineered to augment the efficacy of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) in multiple-choice visual reasoning tasks. Diverging from conventional approaches that evaluate each option independently, MM-PoE employs a dual-step scoring paradigm that initially identifies and excludes implausible choices, subsequently concentrating on the most probable remaining options. This method emulates human test-taking strategies, where individuals typically eliminate clearly incorrect answers prior to selecting the optimal response. Our empirical evaluations, conducted across three benchmark datasets, reveal that MM-PoE significantly improves both zero-shot and few-shot performance of contemporary state-of-the-art VLMs. Critically, this approach not only broadens the application of the elimination process to multi-modal contexts but also allows few-shot experiments, thereby addressing two principal limitations concerning usage of PoE only in zero-shot settings and only with a language-only framework. As a result, MM-PoE not only refines the reasoning capabilities of VLMs but also broadens their applicability to complex visual question-answering scenarios. All code and documentation supporting our work are available at https://pypi.org/project/mm-poe/, enabling researchers and practitioners to easily integrate and further develop these techniques.
本文介绍了通过排除法(Process of Elimination)进行多模态选择推理的新方法,这里称为多模态排除法(MM-PoE)。这种新方法旨在提高视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多选项视觉推理任务中的有效性。与传统的独立评估每个选项的方法不同,MM-PoE采用双步评分范式,首先识别和排除不可能的选项,然后专注于最可能的剩余选项。这种方法模拟了人类应试策略,人们通常会在选择最佳答案之前排除明显错误的答案。我们在三个基准数据集上进行的实证评估表明,MM-PoE显著提高了当前最先进的VLMs的零样本和少样本性能。最重要的是,这种方法不仅将排除过程扩展到多模态环境,还允许进行少样本实验,从而解决了以往只将PoE用于零样本设置以及仅用于语言框架的两个主要局限性。因此,MM-PoE不仅提高了VLMs的推理能力,还扩大了其在复杂视觉问答场景中的应用范围。支持我们工作的所有代码和文档都可在https://pypi.org/project/mm-poe/上找到,使研究人员和从业者能够轻松集成并进一步开发这些技术。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了基于排除法的多模态选择推理(Multi-Modal Process of Elimination,MM-PoE)方法,旨在提高视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多选视觉推理任务中的有效性。该方法采用双步评分范式,初步排除不可能的选择,然后集中考虑最可能的选择。在三个基准数据集上的实证评估表明,MM-PoE显著提高了当前最先进的VLMs的零样本和少样本性能,并解决了以往排除法仅适用于零样本设置和仅适用于语言框架的两个主要局限。因此,MM-PoE不仅提高了VLMs的推理能力,而且扩大了其在复杂视觉问答场景中的应用范围。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了基于排除法的多模态选择推理方法(MM-PoE),用于增强视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多选视觉推理任务中的表现。
- MM-PoE采用双步评分范式,先排除不可能的选择,再集中考虑最可能的选择,这模仿了人类答题时的策略。
- 在三个基准数据集上的实证评估显示,MM-PoE显著提高了VLMs的零样本和少样本性能。
- MM-PoE解决了以往排除法仅适用于零样本设置和仅适用于语言框架的两个主要局限。
- MM-PoE提高了VLMs的推理能力,并扩大了其在复杂视觉问答场景中的应用范围。
- MM-PoE方法所有支持代码和文档都可在[https://pypi.org/project/mm-poe/]访问,便于研究人员和实践者集成和进一步发展这些技术。
点此查看论文截图

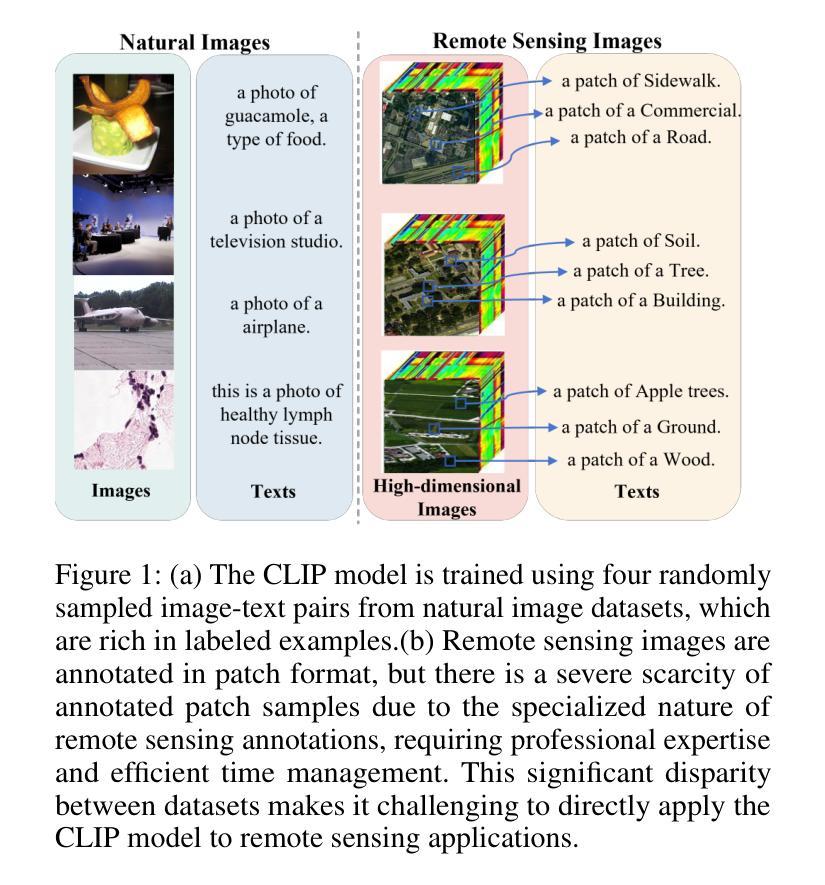
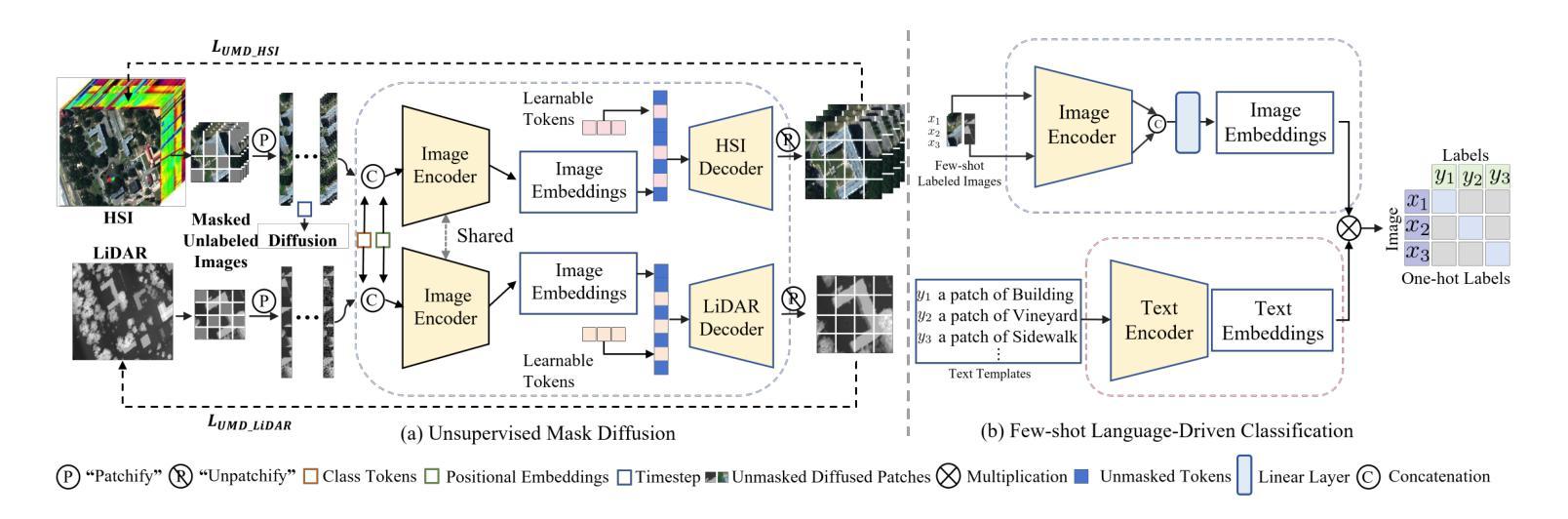
DiffCLIP: Few-shot Language-driven Multimodal Classifier
Authors:Jiaqing Zhang, Mingxiang Cao, Xue Yang, Kai Jiang, Yunsong Li
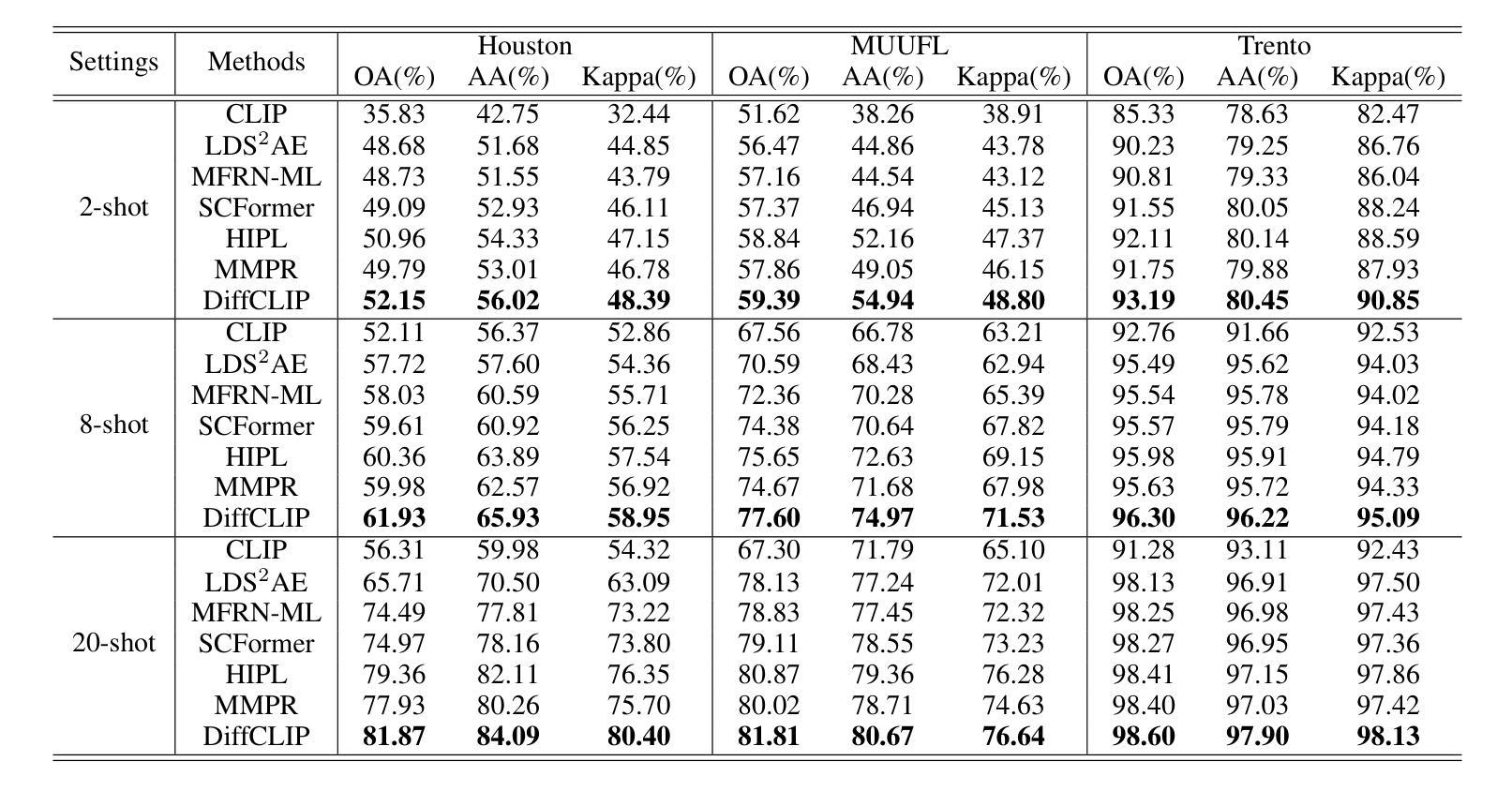
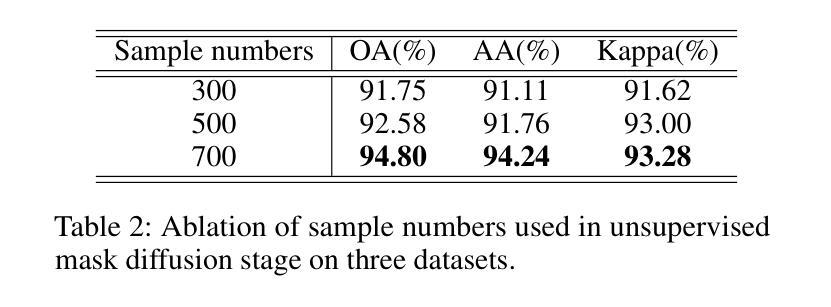
Visual language models like Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) have shown impressive performance in analyzing natural images with language information. However, these models often encounter challenges when applied to specialized domains such as remote sensing due to the limited availability of image-text pairs for training. To tackle this issue, we introduce DiffCLIP, a novel framework that extends CLIP to effectively convey comprehensive language-driven semantic information for accurate classification of high-dimensional multimodal remote sensing images. DiffCLIP is a few-shot learning method that leverages unlabeled images for pretraining. It employs unsupervised mask diffusion learning to capture the distribution of diverse modalities without requiring labels. The modality-shared image encoder maps multimodal data into a unified subspace, extracting shared features with consistent parameters across modalities. A well-trained image encoder further enhances learning by aligning visual representations with class-label text information from CLIP. By integrating these approaches, DiffCLIP significantly boosts CLIP performance using a minimal number of image-text pairs. We evaluate DiffCLIP on widely used high-dimensional multimodal datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness in addressing few-shot annotated classification tasks. DiffCLIP achieves an overall accuracy improvement of 10.65% across three remote sensing datasets compared with CLIP, while utilizing only 2-shot image-text pairs. The code has been released at https://github.com/icey-zhang/DiffCLIP.
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)等视觉语言模型在结合语言信息分析自然图像方面表现出令人印象深刻的性能。然而,当这些模型应用于遥感等特定领域时,由于可用于训练的图片文本配对数量有限,经常面临挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了DiffCLIP,这是一个将CLIP扩展到有效传达全面的语言驱动语义信息的新框架,用于对高维多模式遥感图像进行准确分类。DiffCLIP是一种小样本学习方法,利用未标记的图像进行预训练。它采用无监督的掩膜扩散学习来捕捉不同模式的分布而无需标签。模态共享图像编码器将多模式数据映射到统一子空间,提取跨模态的一致参数共享特征。经过良好训练的图像编码器通过将与CLIP中的类别标签文本信息对齐的视觉表示相结合,进一步增强了学习。通过整合这些方法,DiffCLIP使用少量的图像文本配对显著提升了CLIP的性能。我们在广泛使用的高维多模式数据集上评估了DiffCLIP的有效性,证明了它在解决小样本标注分类任务方面的效果。相较于CLIP,DiffCLIP在三个遥感数据集上的总体准确度提高了10.65%,且在仅使用2个样本的图像文本配对的情况下取得了这一成果。代码已发布在https://github.com/icey-zhang/DiffCLIP。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
一种名为DiffCLIP的新型框架扩展了CLIP模型,使其能有效传达全面的语言驱动语义信息,用于对高维多模态遥感图像进行准确分类。DiffCLIP采用无监督的掩膜扩散学习方法捕捉不同模态的分布信息,无需标签即可进行预训练。该框架采用模态共享图像编码器将多模态数据映射到统一子空间,提取跨模态的一致参数共享特征。通过结合这些技术,DiffCLIP在仅使用少量图像文本对的情况下,显著提高了CLIP的性能。
Key Takeaways
- DiffCLIP成功扩展了CLIP模型,用于处理高维多模态遥感图像的分类任务。
- DiffCLIP采用无监督的掩膜扩散学习方法,能在缺乏训练数据的情况下捕捉不同模态的分布信息。
- 模态共享图像编码器将多模态数据映射到统一子空间,提升跨模态特征提取的效果。
- DiffCLIP利用预训练的图像编码器,通过结合CLIP的类标签文本信息,强化视觉表示学习。
- 仅使用少量图像文本对,DiffCLIP就能显著提高CLIP的性能。
- 在广泛使用的高维多模态数据集上,DiffCLIP展示出了优秀的表现,特别是在解决少样本标注分类任务方面。
- DiffCLIP的代码已公开发布在GitHub上。
点此查看论文截图


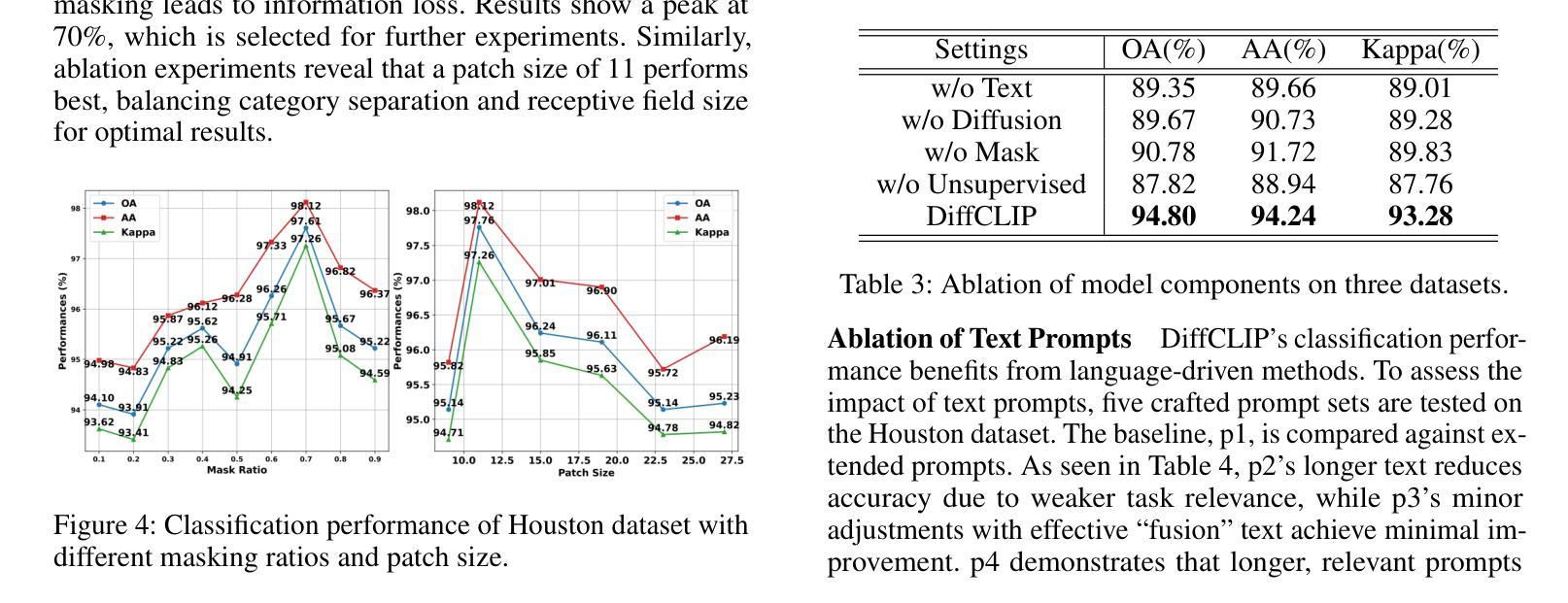
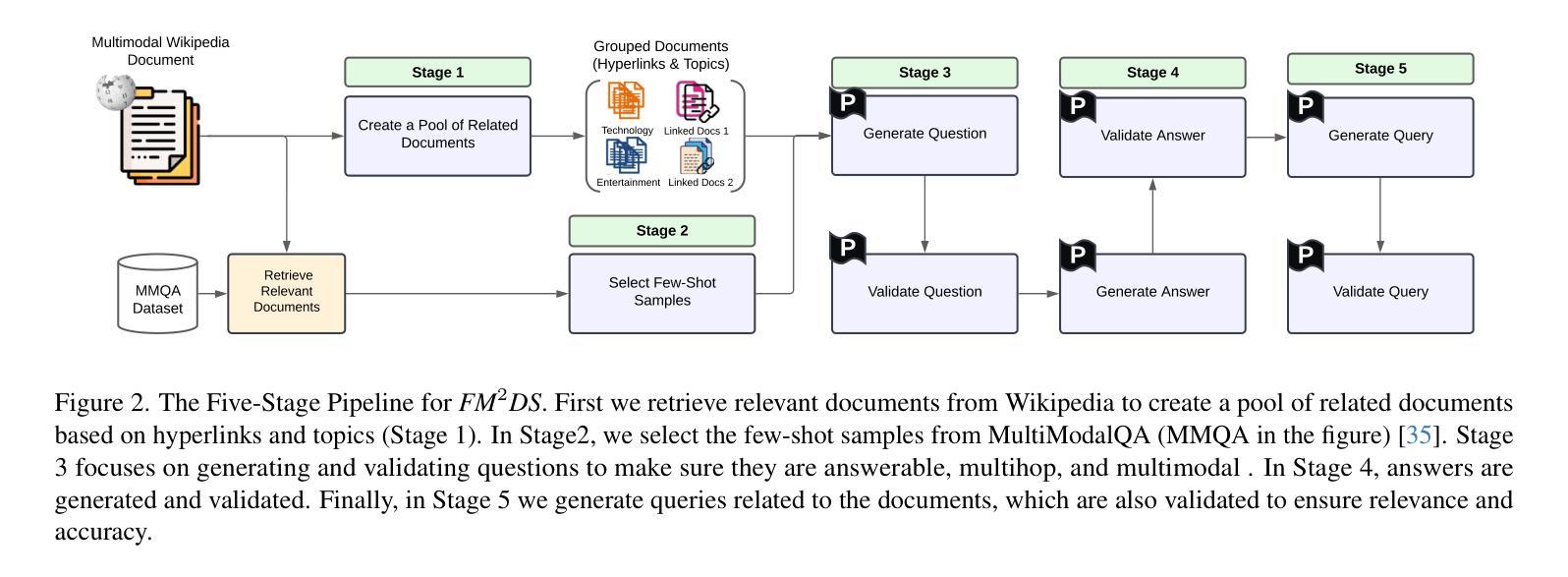
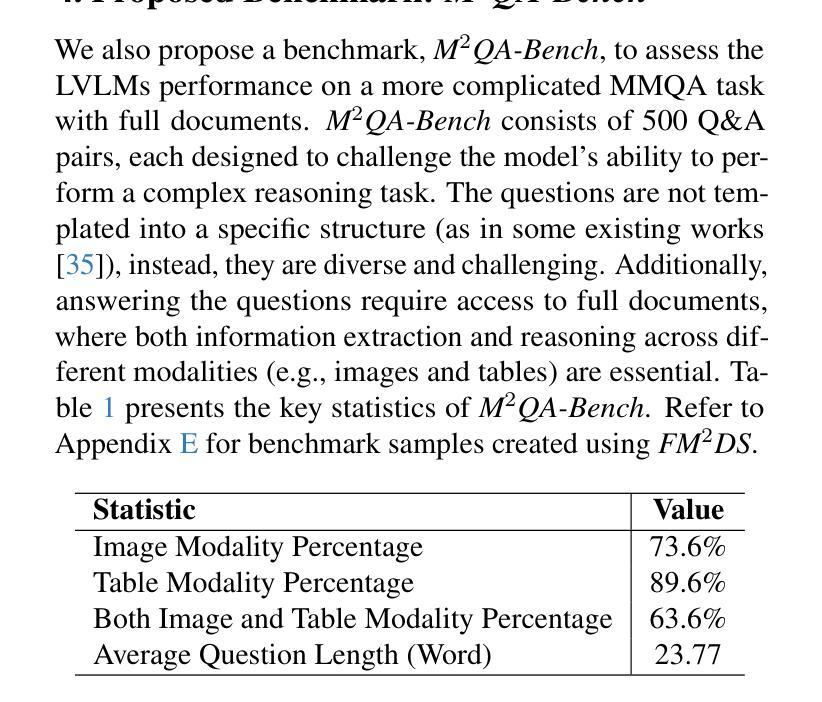
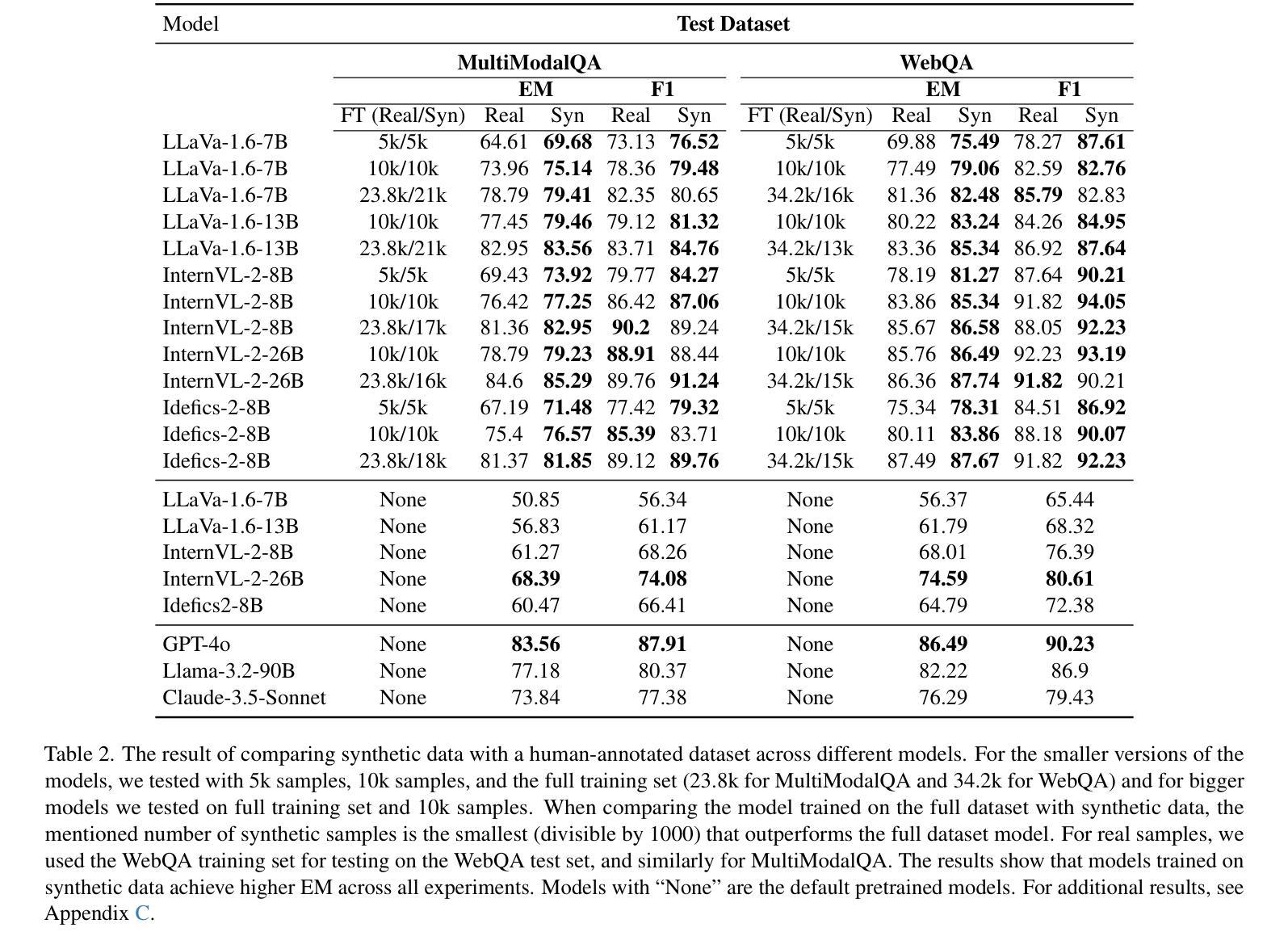
FM2DS: Few-Shot Multimodal Multihop Data Synthesis with Knowledge Distillation for Question Answering
Authors:Amirhossein Abaskohi, Spandana Gella, Giuseppe Carenini, Issam H. Laradji
Multimodal multihop question answering is a complex task that requires reasoning over multiple sources of information, such as images and text, to answer questions. While there has been significant progress in visual question answering, the multihop setting remains unexplored due to the lack of high-quality datasets. Current methods focus on single-hop question answering or a single modality, which makes them unsuitable for real-world scenarios such as analyzing multimodal educational materials, summarizing lengthy academic articles, or interpreting scientific studies that combine charts, images, and text. To address this gap, we propose a novel methodology, introducing the first framework for creating a high-quality dataset that enables training models for multimodal multihop question answering. Our approach consists of a 5-stage pipeline that involves acquiring relevant multimodal documents from Wikipedia, synthetically generating high-level questions and answers, and validating them through rigorous criteria to ensure quality data. We evaluate our methodology by training models on our synthesized dataset and testing on two benchmarks, our results demonstrate that, with an equal sample size, models trained on our synthesized data outperform those trained on human-collected data by 1.9 in exact match (EM) on average. We believe our data synthesis method will serve as a strong foundation for training and evaluating multimodal multihop question answering models.
多模态多跳问答是一项复杂的任务,它要求跨越多种信息来源(如图像和文本)进行推理以回答问题。尽管视觉问答已经取得了重大进展,但由于缺乏高质量的数据集,多跳设置仍然未被探索。当前的方法主要集中在单跳问答或单一模态,这使得它们不适合现实世界场景,如分析多模态教育材料、总结冗长的学术论文或解释结合图表、图像和文本的科学研究。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了一种新的方法,引入了创建高质量数据集的第一个框架,该框架能够训练多模态多跳问答模型。我们的方法包括一个5阶段的管道,涉及从Wikipedia获取相关的多模态文档、合成高级问题和答案、并通过严格的标准对其进行验证,以确保数据质量。我们通过在我们的合成数据集上训练模型并在两个基准上进行测试来评估我们的方法,结果表明,在样本大小相同的情况下,在我们的合成数据上训练的模型在平均精确匹配(EM)方面比在人类收集的数据上训练的模型高出1.9。我们相信我们的数据合成方法将为训练和评估多模态多跳问答模型提供坚实的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 11 figures, 10 tables, Submitted to CVPR 2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对多模态多跳问答任务的新型数据集构建方法。该方法通过5阶段管道实现,包括从Wikipedia获取相关多模态文档、合成高级问题答案并通过严格标准验证数据质量。实验表明,在相同样本量下,基于合成数据训练的模型平均精确匹配度高出人类收集数据训练的模型1.9。该数据合成方法将为多模态多跳问答模型的训练和评估提供坚实基础。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态多跳问答需要跨越多个信息源进行推理,如图像和文本。
- 当前方法主要关注单跳问答或单一模态,不适用于分析多模态教育材料、总结学术文章或解读结合图表、图像和文本的科研研究等现实场景。
- 提出了一种新型数据集构建方法,专为多模态多跳问答任务设计。
- 该方法包含5个阶段的管道,涉及从Wikipedia获取相关多模态文档、合成高级问题并验证数据质量。
- 实验显示,基于合成数据训练的模型性能优于基于人类收集数据训练的模型。
- 合成数据的方法具有潜力,为训练和评估多模态多跳问答模型提供坚实基础。
点此查看论文截图

AutoReason: Automatic Few-Shot Reasoning Decomposition
Authors:Arda Sevinc, Abdurrahman Gumus
Chain of Thought (CoT) was introduced in recent research as a method for improving step-by-step reasoning in Large Language Models. However, CoT has limited applications such as its need for hand-crafted few-shot exemplar prompts and no capability to adjust itself to different queries. In this work, we propose a system to automatically generate rationales using CoT. Our method improves multi-step implicit reasoning capabilities by decomposing the implicit query into several explicit questions. This provides interpretability for the model, improving reasoning in weaker LLMs. We test our approach with two Q&A datasets: StrategyQA and HotpotQA. We show an increase in accuracy with both, especially on StrategyQA. To facilitate further research in this field, the complete source code for this study has been made publicly available on GitHub: https://github.com/miralab-ai/autoreason.
思维链(Chain of Thought,简称CoT)最近在研究中被引入作为一种提高大型语言模型中逐步推理能力的方法。然而,CoT的应用具有一定的局限性,例如需要手工制作的少量示例提示,并且无法自行适应不同的查询。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种利用CoT自动生成理由的系统。我们的方法通过将隐式查询分解成几个显式问题来提高多步隐式推理能力。这为模型提供了可解释性,提高了较弱的大型语言模型的推理能力。我们在两个问答数据集StrategyQA和HotpotQA上测试了我们的方法。结果显示,两个数据集的准确率都有所提高,尤其是在StrategyQA上。为了促进该领域的进一步研究,本研究的完整源代码已在GitHub上公开发布:https://github.com/miralab-ai/autoreason。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大语言模型通过链式思维(CoT)改进了分步推理的方法。然而,CoT存在局限性,如需要手工制作的少数案例提示,无法适应不同的查询。本研究提出了一种自动生成理由的系统,使用CoT来提高多步推理能力。该方法将隐式查询分解成多个显式问题,从而提高模型的解释性并增强较弱的大型语言模型的推理能力。该研究已经在GitHub上公开完整源代码,方便后续研究。在StrategyQA和HotpotQA问答数据集上的测试显示,准确率有所提高,特别是在StrategyQA上。
Key Takeaways
- 链式思维(CoT)用于改进大型语言模型的分步推理能力。
- CoT存在局限性,需要手工制作的少数案例提示且无法适应不同查询。
- 提出了一种自动生成理由的系统,使用CoT提高多步推理能力。
- 将隐式查询分解成多个显式问题以提高模型解释性和推理能力。
- 在StrategyQA和HotpotQA数据集上测试,准确率有所提高。
- 系统可提高较弱的大型语言模型的推理能力。
点此查看论文截图


Fully Open Source Moxin-7B Technical Report
Authors:Pu Zhao, Xuan Shen, Zhenglun Kong, Yixin Shen, Sung-En Chang, Timothy Rupprecht, Lei Lu, Enfu Nan, Changdi Yang, Yumei He, Xingchen Xu, Yu Huang, Wei Wang, Yue Chen, Yong He, Yanzhi Wang
Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have undergone a significant transformation, marked by a rapid rise in both their popularity and capabilities. Leading this evolution are proprietary LLMs like GPT-4 and GPT-o1, which have captured widespread attention in the AI community due to their remarkable performance and versatility. Simultaneously, open-source LLMs, such as LLaMA and Mistral, have made great contributions to the ever-increasing popularity of LLMs due to the ease to customize and deploy the models across diverse applications. Although open-source LLMs present unprecedented opportunities for innovation and research, the commercialization of LLMs has raised concerns about transparency, reproducibility, and safety. Many open-source LLMs fail to meet fundamental transparency requirements by withholding essential components like training code and data, and some use restrictive licenses whilst claiming to be “open-source,” which may hinder further innovations on LLMs. To mitigate this issue, we introduce Moxin 7B, a fully open-source LLM developed in accordance with the Model Openness Framework (MOF), a ranked classification system that evaluates AI models based on model completeness and openness, adhering to principles of open science, open source, open data, and open access. Our model achieves the highest MOF classification level of “open science” through the comprehensive release of pre-training code and configurations, training and fine-tuning datasets, and intermediate and final checkpoints. Experiments show that our model achieves superior performance in zero-shot evaluation compared with popular 7B models and performs competitively in few-shot evaluation.
最近,大型语言模型(LLM)经历了重大变革,其受欢迎程度和能力都迅速上升。引领这一变革的是专有大型语言模型,如GPT-4和GPT-o1,它们由于出色的性能和多功能性而受到人工智能界的广泛关注。同时,开源的大型语言模型,如LLaMA和Mistral,由于能够在各种应用程序中轻松定制和部署模型,为大型语言模型日益普及做出了巨大贡献。尽管开源的大型语言模型为创新和研发提供了前所未有的机会,但大型语言模型的商业化引发了关于透明度、可重复性和安全性的担忧。许多开源的大型语言模型未能满足基本的透明度要求,隐瞒了关键组件,如训练代码和数据,有些则打着“开源”的口号却使用限制性许可,这可能会阻碍大型语言模型的进一步创新。为了缓解这一问题,我们推出了完全符合模型开放框架(MOF)的开源大型语言模型——Moxin 7B。MOF是一个评级分类系统,根据模型的完整性和开放性来评估人工智能模型,遵循公开科学、开源、开放数据和开放访问的原则。我们的模型通过全面发布预训练代码和配置、训练和微调数据集以及中间和最终检查点,达到了MOF分类中的最高级别“公开科学”。实验表明,与流行的大型语言模型相比,我们的模型在零样本评估中表现出卓越的性能,并在小样例评估中表现出竞争力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)经历了一次重大转变,受到广泛关注并提升了能力。GPT-4和GPT-o1等专有LLMs因出色的性能和多功能性而受到AI社区的广泛关注。同时,LLaMA和Mistral等开源LLMs通过易于定制和部署的特点推动了LLMs的普及。然而,商业化的LLMs引发了关于透明度、可复制性和安全性的担忧。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了Moxin 7B,这是一个遵循模型开放框架(MOF)开发的完全开源的LLM。该模型在预训练代码和配置、训练和微调数据集以及中间和最终检查点的全面发布方面达到了“公开科学”的最高等级。实验表明,该模型在零样本评估中取得了优于其他流行7B模型的性能,并在小样本评估中表现出竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)经历了重大转变,受到广泛关注和提升能力。
- 专有LLMs如GPT-4和GPT-o1因性能和多功能性受到关注。
- 开源LLMs推动了LLMs的普及,但存在关于商业化LLMs的透明度、可复制性和安全性的担忧。
- Moxin 7B是一个遵循模型开放框架(MOF)开发的开源LLM。
- Moxin 7B实现了全面的开放科学原则,包括预训练代码和配置的发布。
- 实验表明Moxin 7B在零样本评估中表现优越,并在小样本评估中具备竞争力。
点此查看论文截图

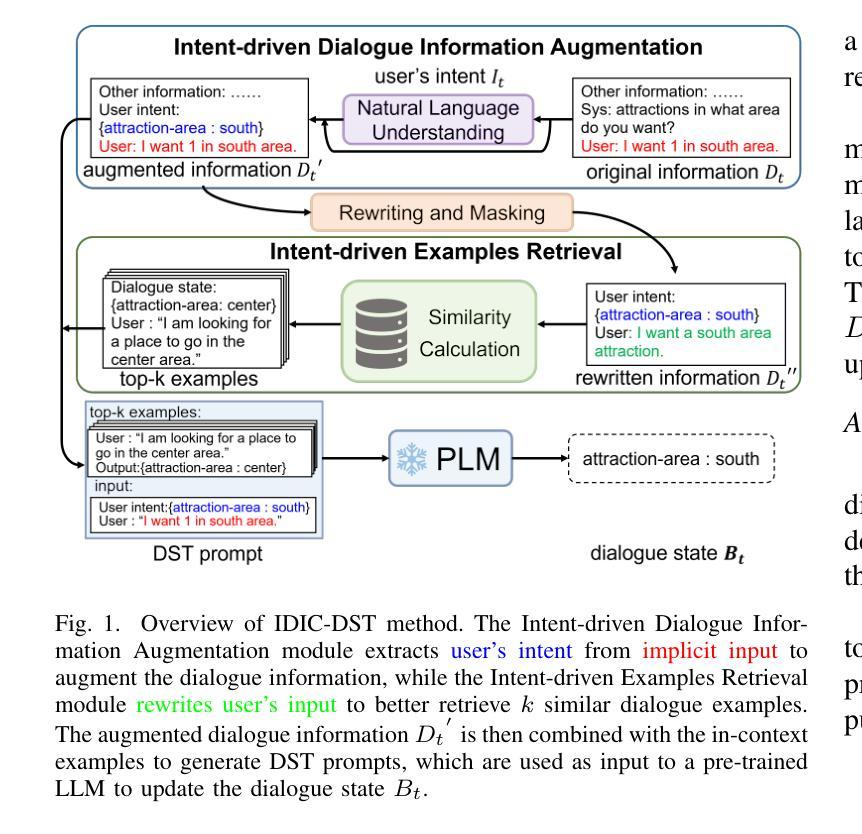
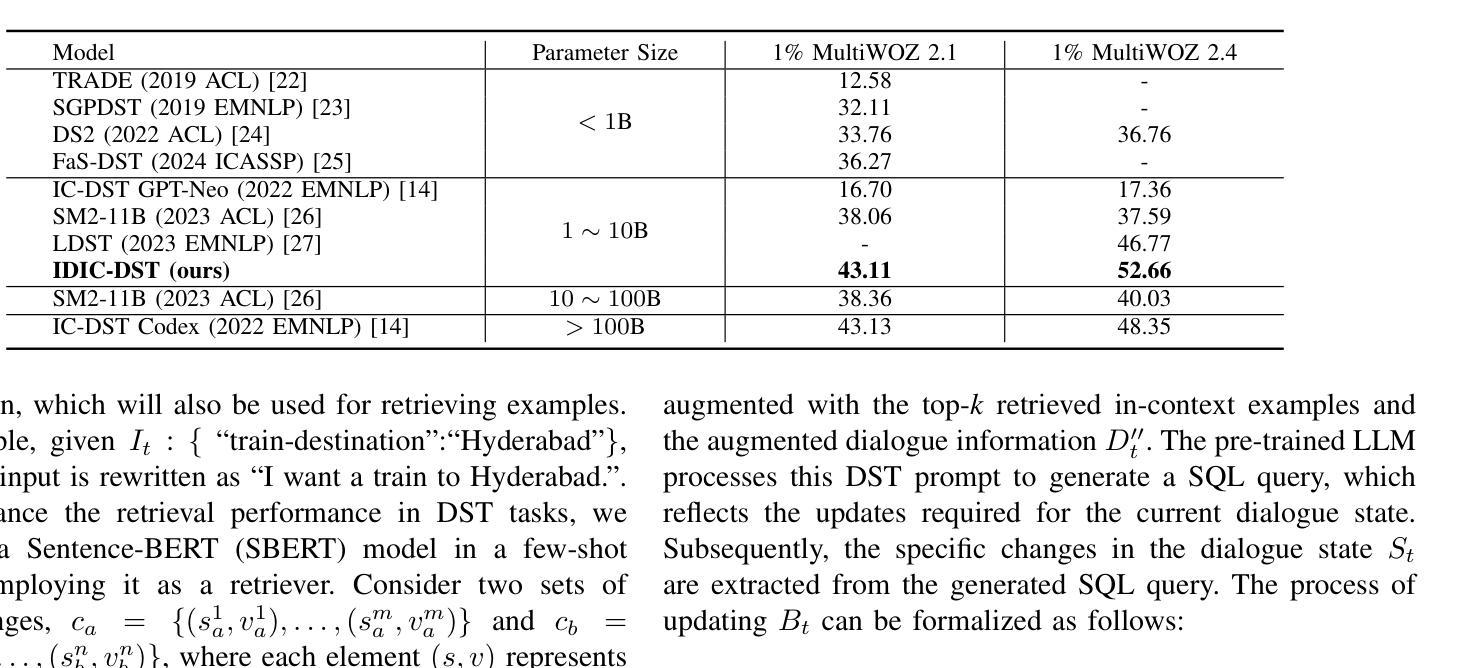
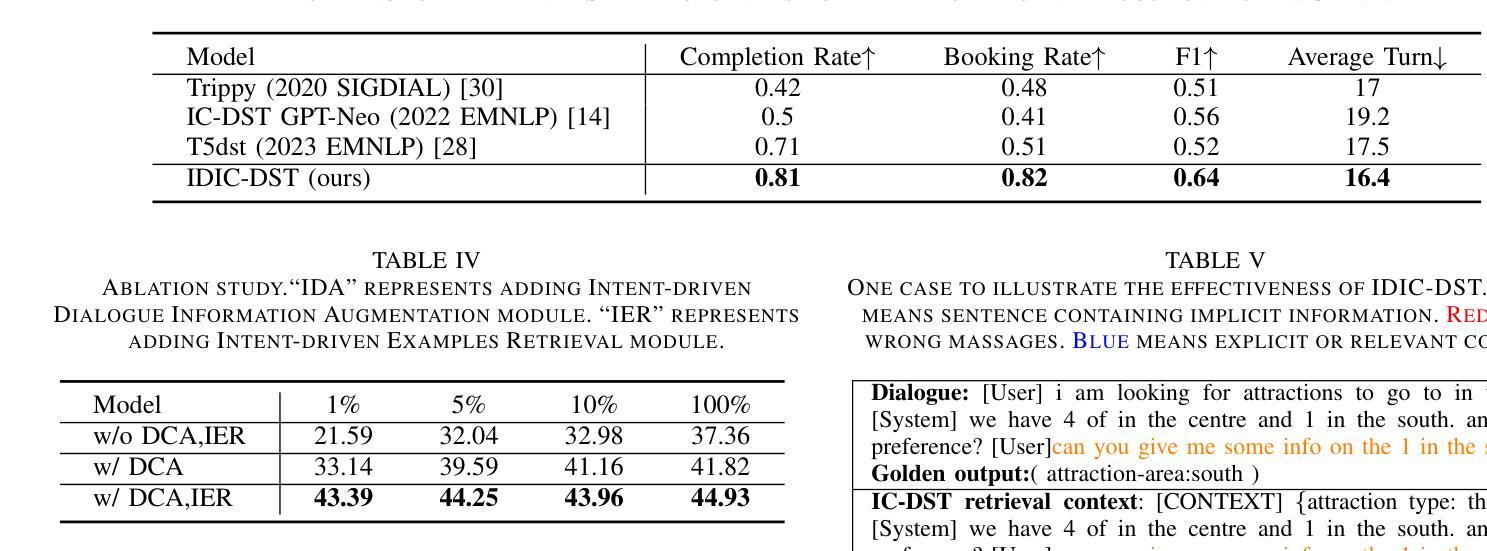
Intent-driven In-context Learning for Few-shot Dialogue State Tracking
Authors:Zihao Yi, Zhe Xu, Ying Shen
Dialogue state tracking (DST) plays an essential role in task-oriented dialogue systems. However, user’s input may contain implicit information, posing significant challenges for DST tasks. Additionally, DST data includes complex information, which not only contains a large amount of noise unrelated to the current turn, but also makes constructing DST datasets expensive. To address these challenges, we introduce Intent-driven In-context Learning for Few-shot DST (IDIC-DST). By extracting user’s intent, we propose an Intent-driven Dialogue Information Augmentation module to augment the dialogue information, which can track dialogue states more effectively. Moreover, we mask noisy information from DST data and rewrite user’s input in the Intent-driven Examples Retrieval module, where we retrieve similar examples. We then utilize a pre-trained large language model to update the dialogue state using the augmented dialogue information and examples. Experimental results demonstrate that IDIC-DST achieves state-of-the-art performance in few-shot settings on MultiWOZ 2.1 and MultiWOZ 2.4 datasets.
对话状态跟踪(DST)在面向任务的对话系统中扮演着至关重要的角色。然而,用户的输入可能包含隐含信息,给DST任务带来了巨大的挑战。此外,DST数据包含复杂信息,不仅包含大量与当前轮次无关的噪声,而且构建DST数据集的成本也很高。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了用于少量数据DST的意图驱动上下文学习(IDIC-DST)。通过提取用户的意图,我们提出了一个意图驱动对话信息增强模块,以增强对话信息,从而更有效地跟踪对话状态。此外,我们从DST数据中屏蔽了嘈杂的信息,并在意图驱动的例子检索模块中重写了用户的输入,我们检索了类似的例子。然后,我们使用预训练的的大型语言模型,利用增强的对话信息和例子来更新对话状态。实验结果表明,IDIC-DST在MultiWOZ 2.1和MultiWOZ 2.4数据集上的少量数据设置上达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
对话状态追踪(DST)在任务导向型对话系统中扮演重要角色,但用户输入可能包含隐晦信息,给DST任务带来挑战。此外,DST数据包含复杂信息,不仅包含大量与当前对话无关噪声,且构建DST数据集成本高昂。为解决这些挑战,我们提出基于意图的上下文学习(IDIC-DST)方法。通过提取用户意图,我们提出一个意图驱动对话信息增强模块来增强对话信息,更有效地追踪对话状态。同时,我们从DST数据中屏蔽噪声信息,并在意图驱动的例子检索模块中重写用户输入,检索相似例子。接着,我们使用预训练的大型语言模型,根据增强的对话信息和例子更新对话状态。实验结果表明,IDIC-DST在MultiWOZ 2.1和MultiWOZ 2.4数据集上的小样本设置上取得了最新性能。
Key Takeaways
- 对话状态追踪(DST)在任务导向型对话系统中非常重要,但面临用户输入隐晦信息和数据复杂的挑战。
- 提出基于意图的上下文学习(IDIC-DST)方法,通过意图驱动对话信息增强模块增强对话信息,提高对话状态追踪效果。
- IDIC-DST能够屏蔽与当前对话无关的噪声信息,并重写用户输入以检索相似例子。
- 利用预训练的大型语言模型更新对话状态。
- IDIC-DST在MultiWOZ 2.1和MultiWOZ 2.4数据集上的小样本设置上取得了最新性能。
- 该方法对于构建更智能、更自然的任务导向型对话系统具有重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

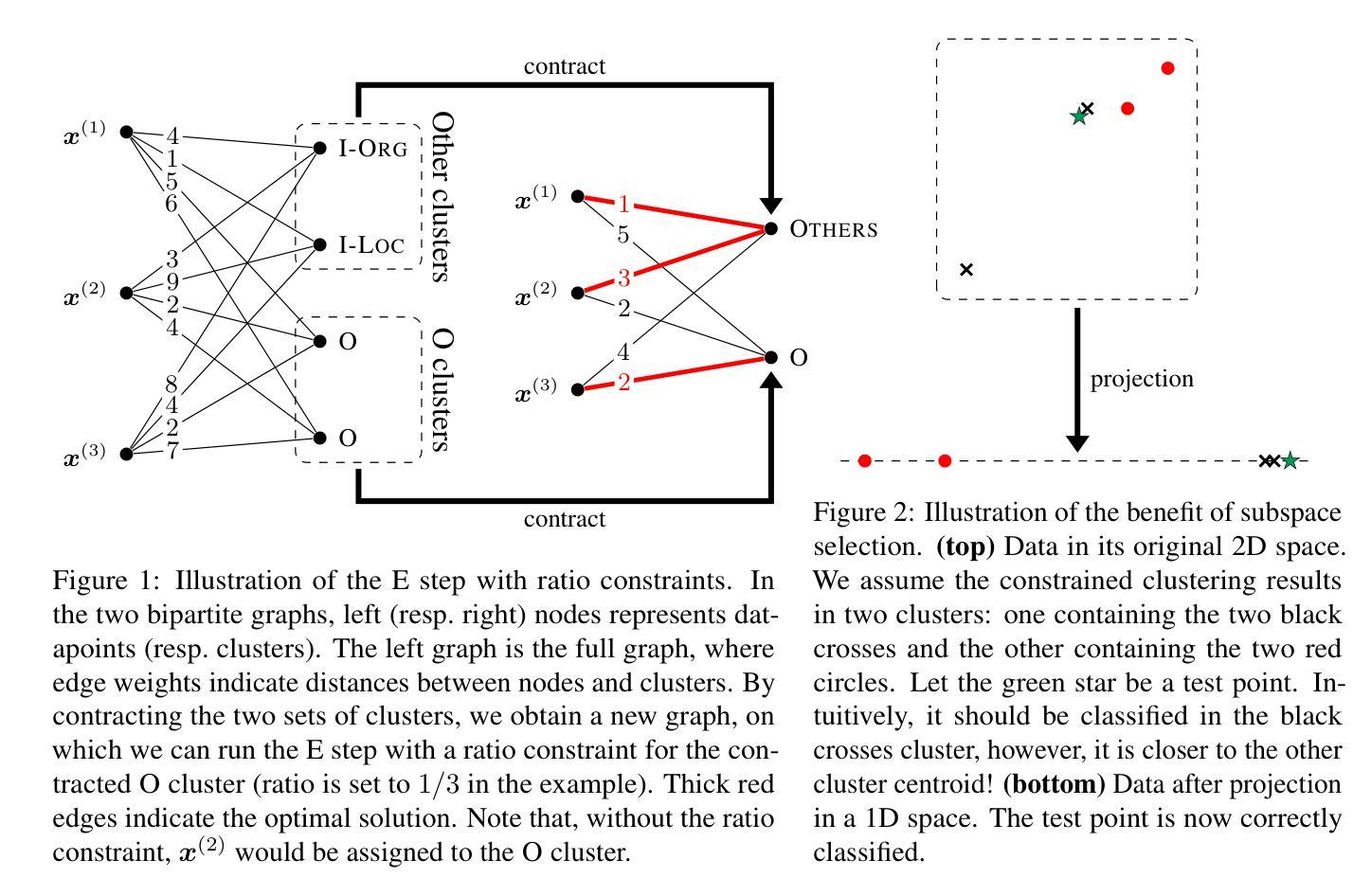
Few-Shot Domain Adaptation for Named-Entity Recognition via Joint Constrained k-Means and Subspace Selection
Authors:Ayoub Hammal, Benno Uthayasooriyar, Caio Corro
Named-entity recognition (NER) is a task that typically requires large annotated datasets, which limits its applicability across domains with varying entity definitions. This paper addresses few-shot NER, aiming to transfer knowledge to new domains with minimal supervision. Unlike previous approaches that rely solely on limited annotated data, we propose a weakly supervised algorithm that combines small labeled datasets with large amounts of unlabeled data. Our method extends the k-means algorithm with label supervision, cluster size constraints and domain-specific discriminative subspace selection. This unified framework achieves state-of-the-art results in few-shot NER on several English datasets.
命名实体识别(NER)通常需要大量的标注数据集,这限制了其在具有不同实体定义的跨域中的应用。本文针对少样本NER,旨在以最小的监督将知识转移到新领域。不同于以前仅依赖有限标注数据的方法,我们提出了一种弱监督算法,该算法将少量有标签数据集与大量无标签数据相结合。我们的方法扩展了带有标签监督、集群大小约束和特定于领域的判别子空间选择的k-means算法。这一统一框架在多个英文数据集的少样本NER上达到了最新水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF COLING 2025
Summary
本文研究了少样本命名实体识别(NER)任务,提出了一种弱监督算法来解决不同领域中的实体定义差异问题。该算法结合了少量标注数据和大量未标注数据,扩展了K-means算法,并添加了标签监督、聚类大小约束和领域特定的判别子空间选择。该统一框架在多个英文数据集上实现了少样本NER的最优结果。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文解决了命名实体识别(NER)任务中跨领域应用的问题,特别是在实体定义不同的情境下。
- 论文提出了一个弱监督算法,结合了少量标注数据和大量未标注数据来进行少样本NER。
- 该算法扩展了K-means算法,引入了标签监督、聚类大小约束以及特定领域的判别子空间选择。
- 此框架在多个英文数据集上实现了少样本NER的最优性能。
- 该方法旨在通过最少的人工监督来转移知识到新领域。
- 通过结合不同数据源和算法的优化,该论文实现了显著的结果。
点此查看论文截图

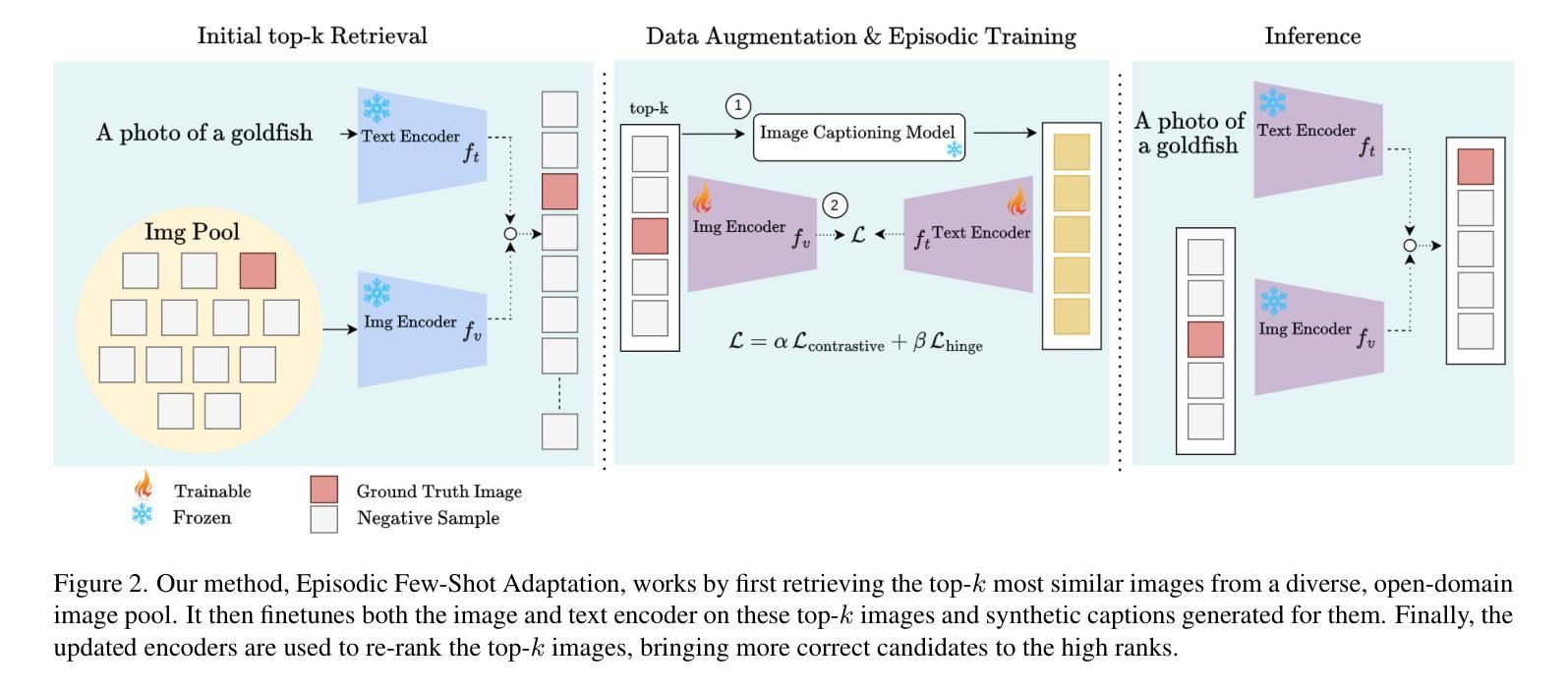
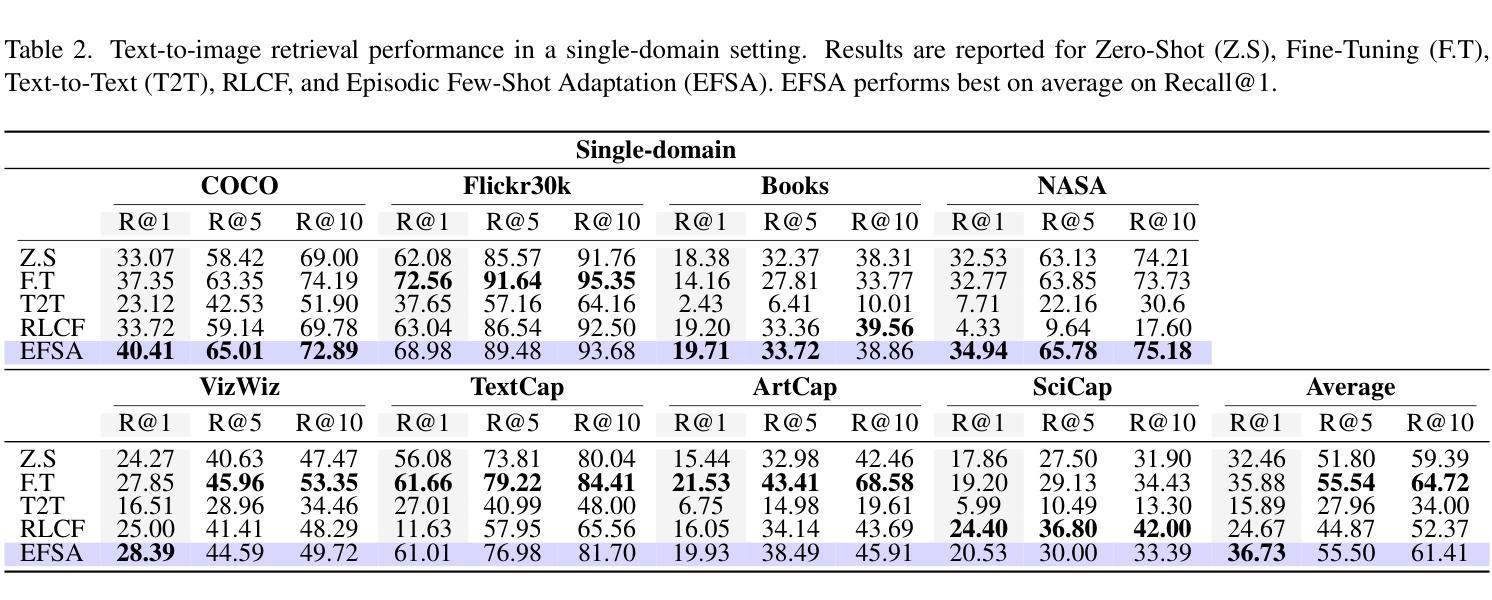
EFSA: Episodic Few-Shot Adaptation for Text-to-Image Retrieval
Authors:Muhammad Huzaifa, Yova Kementchedjhieva
Text-to-image retrieval is a critical task for managing diverse visual content, but common benchmarks for the task rely on small, single-domain datasets that fail to capture real-world complexity. Pre-trained vision-language models tend to perform well with easy negatives but struggle with hard negatives–visually similar yet incorrect images–especially in open-domain scenarios. To address this, we introduce Episodic Few-Shot Adaptation (EFSA), a novel test-time framework that adapts pre-trained models dynamically to a query’s domain by fine-tuning on top-k retrieved candidates and synthetic captions generated for them. EFSA improves performance across diverse domains while preserving generalization, as shown in evaluations on queries from eight highly distinct visual domains and an open-domain retrieval pool of over one million images. Our work highlights the potential of episodic few-shot adaptation to enhance robustness in the critical and understudied task of open-domain text-to-image retrieval.
文本转图像检索是管理多样视觉内容的关键任务,但当前常用的基准测试主要依赖于小规模、单一领域的数据集,无法捕捉真实世界的复杂性。预训练的视觉语言模型在处理简单的负样本时表现良好,但在处理视觉相似但错误的图像时,特别是在开放域场景中,往往表现不佳。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了“片段式小样本适应”(EFSA)这一新型测试时间框架。它通过微调前k个检索到的候选对象和为其生成的合成字幕,动态适应查询领域中的预训练模型。EFSA在保持泛化能力的情况下提高了跨不同领域的性能,正如在来自八个高度不同视觉领域的查询和超过一百万张图像的开放域检索池中的评估所示。我们的工作突出了片段式小样本适应在关键且尚未充分研究的开放域文本转图像检索任务中提高稳健性的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预训练的语言视觉模型在文本转图像检索任务中对于简单的负样本表现良好,但在面对视觉相似但错误的图像时,尤其是在开放域场景中,会出现挑战。为解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新的测试时间框架——Episodic Few-Shot Adaptation(EFSA),它能够根据查询的动态域对预训练模型进行微调,通过优化顶端k个检索候选和为其生成的合成字幕来实现。EFSA在多种域的查询评估和超过一百万图像的开放域检索池中展现了其提高性能的同时保持泛化的能力。我们的工作突显了阶段性少样本适应在关键的但尚未充分研究的开放域文本转图像检索任务中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 文本转图像检索是管理多样视觉内容的关键任务,但现有的基准测试通常依赖于小规模的单一领域数据集,无法捕捉现实世界的复杂性。
- 预训练的语言视觉模型在面临视觉上相似但错误的图像时(即硬负样本)会遇到挑战,特别是在开放域场景中。
- 引入了一种新的测试时间框架——Episodic Few-Shot Adaptation(EFSA),该框架能够动态适应查询的域,通过对预训练模型进行微调来提高性能。
- EFSA通过优化顶端k个检索到的候选图像和为其生成的合成字幕来实现其适应性。
- EFSA在多个不同域的查询评估和开放域检索池中展示了其提高性能的能力,同时保持了泛化性。
- EFSA的引入突显了阶段性少样本适应在开放域文本转图像检索任务中的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

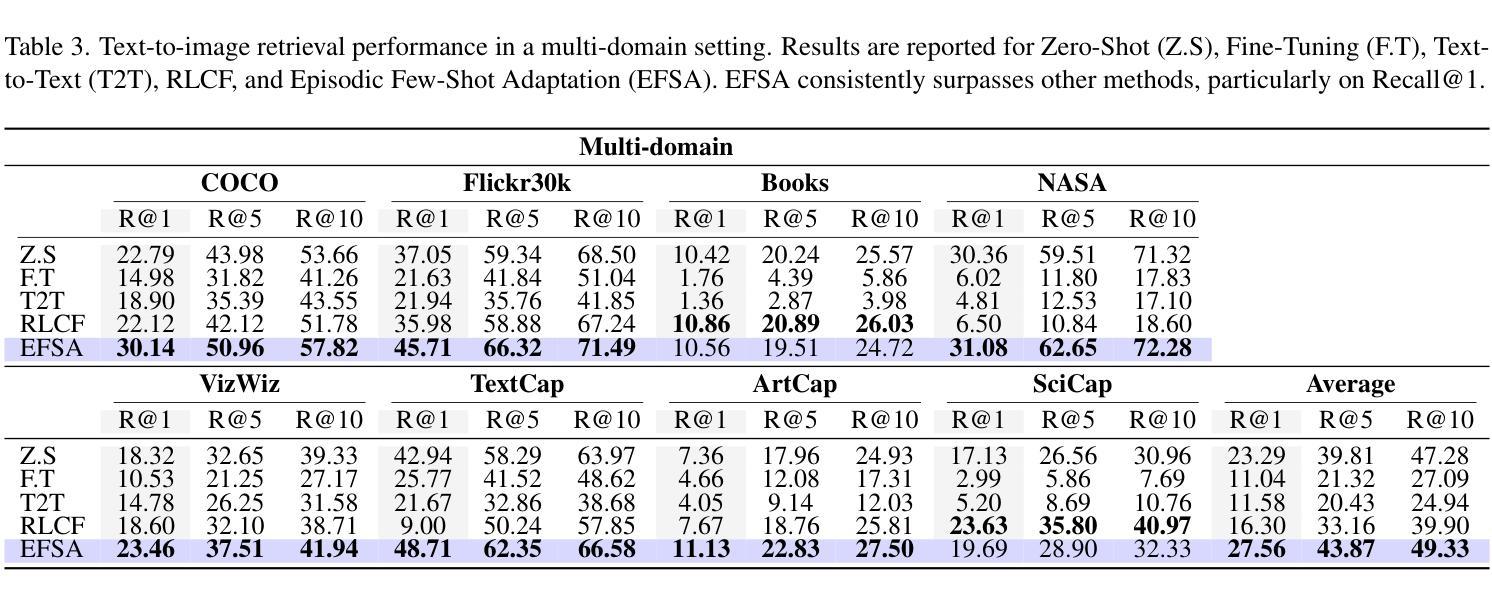
ReverseNER: A Self-Generated Example-Driven Framework for Zero-Shot Named Entity Recognition with Large Language Models
Authors:Anbang Wang, Difei Mei, Zhichao Zhang, Xiuxiu Bai, Ran Yao, Zewen Fang, Min Hu, Zhirui Cao, Haitao Sun, Yifeng Guo, Hongyao Zhou, Yu Guo
This paper presents ReverseNER, a framework aimed at overcoming the limitations of large language models (LLMs) in zero-shot Named Entity Recognition (NER) tasks, particularly in cases where certain entity types have ambiguous boundaries. ReverseNER tackles this challenge by constructing a reliable example library with the reversed process of NER. Rather than beginning with sentences, this method uses an LLM to generate entities based on their definitions and then expands them into full sentences. During sentence generation, the LLM is guided to replicate the structure of a specific ‘feature sentence’, extracted from the task sentences by clustering. This results in well-annotated sentences with clearly labeled entities, while preserving semantic and structural similarity to the task sentences. Once the example library is constructed, the method selects the most semantically similar example labels for each task sentence to support the LLM’s inference. We also propose an entity-level self-consistency scoring mechanism to improve NER performance with LLMs. Experiments show that ReverseNER significantly outperforms traditional zero-shot NER with LLMs and surpasses several few-shot methods, marking a notable improvement in NER for domains with limited labeled data.
本文介绍了ReverseNER框架,旨在克服大型语言模型(LLM)在零样本命名实体识别(NER)任务中的局限性,特别是在某些实体类型边界模糊的情况下。ReverseNER通过构建可靠的示例库来解决这一挑战,该库采用NER的逆向过程。该方法不是从句子开始,而是使用LLM根据实体定义生成实体,然后将其扩展到完整句子。在生成句子时,LLM被引导以特定的“特征句子”结构进行复制,特征句子是从任务句子中提取并通过聚类获得。这会产生带有明确标注实体的良好注释句子,同时保留与任务句子的语义和结构相似性。一旦构建了示例库,该方法就会选择每个任务句子中语义上最相似的示例标签来支持LLM的推断。我们还提出了一种实体级别的自我一致性评分机制,以提高LLM的NER性能。实验表明,与传统的零样本NER相比,ReverseNER显著提高了LLM的性能,并超越了多种小样本方法,在标签数据有限的领域,NER有了显著的改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在零样本命名实体识别(NER)任务中,大型语言模型(LLM)存在局限性,特别是在实体类型边界模糊的情况下。本文提出的ReverseNER框架通过构建可靠的示例库来解决这一问题,采用反向过程生成实体并扩展为完整句子。ReverseNER采用基于定义生成实体的方法,并指导语言模型在生成句子时复制特定特征句子的结构。此方法还提出了一种实体级别的自我一致性评分机制,以提高LLM的NER性能。实验表明,ReverseNER显著优于传统的零样本NER和几种小样本文本方法,在标签数据有限的领域取得了显著的改进。
Key Takeaways
- ReverseNER是一个针对大型语言模型(LLMs)在零样本命名实体识别(NER)任务中的局限性而设计的框架。
- ReverseNER通过构建可靠的示例库来解决实体类型边界模糊的问题。
- 该方法采用反向过程生成实体并扩展为句子,基于定义生成实体。
- ReverseNER指导语言模型在生成句子时复制特定特征句子的结构。
- ReverseNER提出了一种实体级别的自我一致性评分机制,以提高LLM的NER性能。
- 实验表明,ReverseNER在零样本和少样本情况下均表现出显著优势,特别是在标签数据有限的领域。
点此查看论文截图

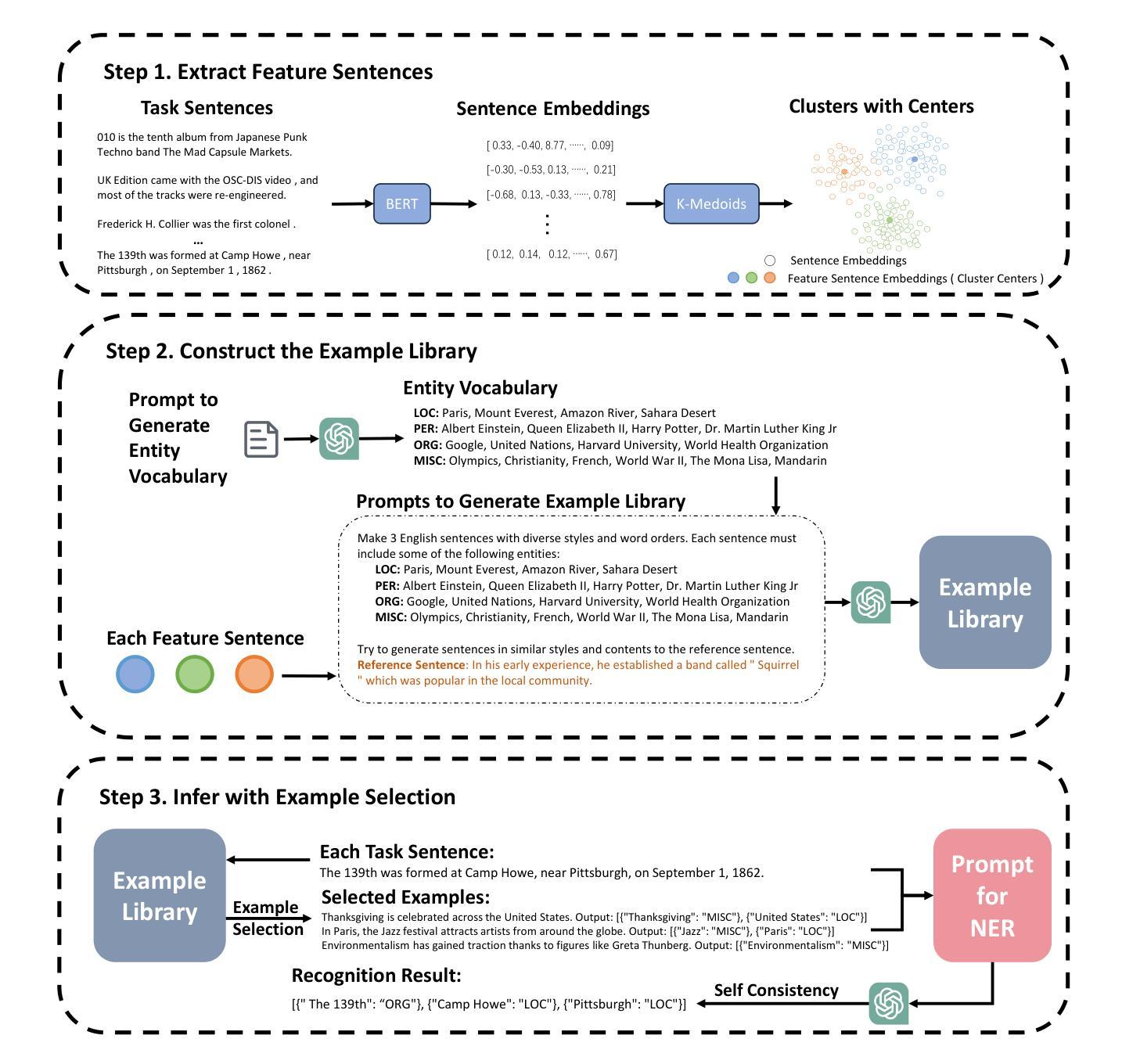
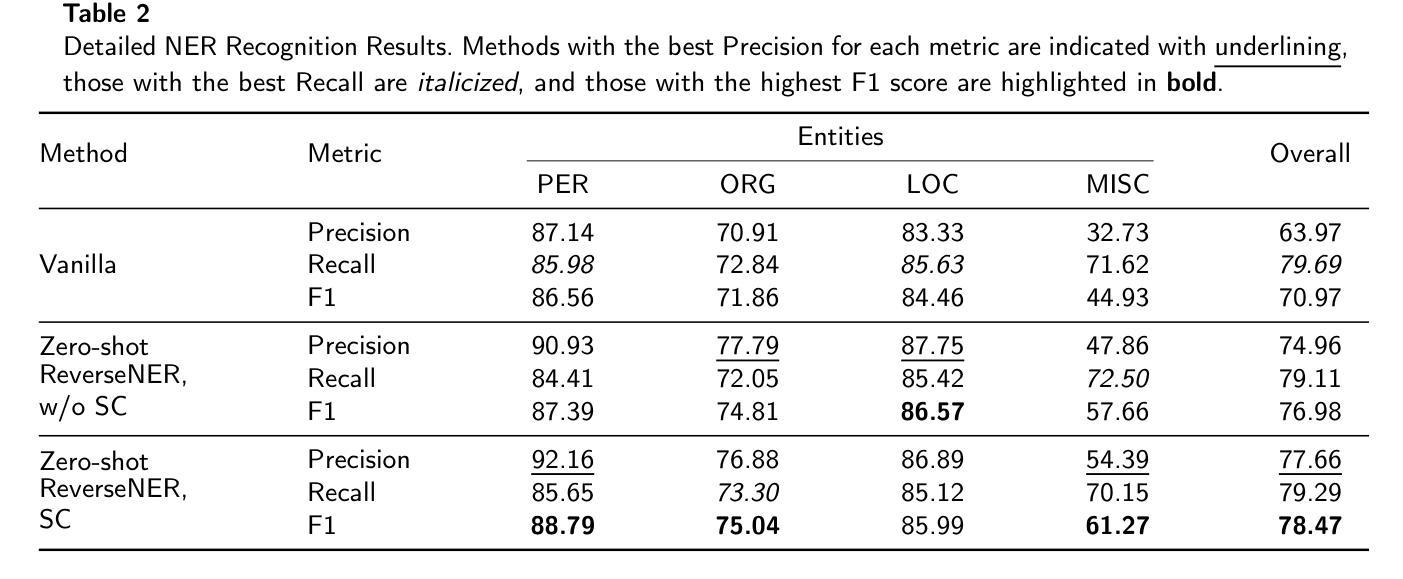
Probabilistic Language-Image Pre-Training
Authors:Sanghyuk Chun, Wonjae Kim, Song Park, Sangdoo Yun
Vision-language models (VLMs) embed aligned image-text pairs into a joint space but often rely on deterministic embeddings, assuming a one-to-one correspondence between images and texts. This oversimplifies real-world relationships, which are inherently many-to-many, with multiple captions describing a single image and vice versa. We introduce Probabilistic Language-Image Pre-training (ProLIP), the first probabilistic VLM pre-trained on a billion-scale image-text dataset using only probabilistic objectives, achieving a strong zero-shot capability (e.g., 74.6% ImageNet zero-shot accuracy with ViT-B/16). ProLIP efficiently estimates uncertainty by an “uncertainty token” without extra parameters. We also introduce a novel inclusion loss that enforces distributional inclusion relationships between image-text pairs and between original and masked inputs. Experiments demonstrate that, by leveraging uncertainty estimates, ProLIP benefits downstream tasks and aligns with intuitive notions of uncertainty, e.g., shorter texts being more uncertain and more general inputs including specific ones. Utilizing text uncertainties, we further improve ImageNet accuracy from 74.6% to 75.8% (under a few-shot setting), supporting the practical advantages of our probabilistic approach. The code is available at https://github.com/naver-ai/prolip
视觉语言模型(VLMs)将图像文本对嵌入到联合空间中,但通常依赖于确定性嵌入,假设图像和文本之间存在一对一的对应关系。这简化了真实世界中的关系,真实世界中的关系是固有的多对多关系,一个图像可以由多个字幕描述,反之亦然。我们引入了概率语言图像预训练(ProLIP),这是首个使用概率目标在百亿级图像文本数据集上进行预训练的概率VLM,它具有很强的零样本能力(例如,使用ViT-B/16的ImageNet零样本准确率为74.6%)。ProLIP通过一个“不确定性令牌”有效地估计不确定性,无需额外的参数。我们还引入了一种新型包含损失,它强制实施图像文本对之间以及原始输入和掩码输入之间的分布包含关系。实验表明,利用不确定性估计,ProLIP有助于下游任务,并与直观的不确定性概念相符,例如较短的文本具有更高的不确定性,包含特定内容的更通用输入也是如此。利用文本不确定性,我们进一步提高了ImageNet的准确率,从74.6%提高到75.8%(在小样本设置下),这支持了我们概率方法的实际优势。代码可在https://github.com/naver-ai/prolip中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Code: https://github.com/naver-ai/prolip HuggingFace Hub: https://huggingface.co/collections/SanghyukChun/prolip-6712595dfc87fd8597350291 31 pages, 4.29 MB
Summary
本文介绍了Probabilistic Language-Image Pre-training(ProLIP)模型,它是首个基于概率的视觉语言预训练模型。该模型在百亿级图像文本数据集上预训练,使用概率目标函数,实现强大的零样本能力,如以ViT-B/16模型达到74.6%的ImageNet零样本准确率。ProLIP通过“不确定性令牌”有效估计不确定性,无需额外参数。此外,引入了一种新的包含损失,强制实施图像文本对之间的分布包含关系以及原始和屏蔽输入之间的包含关系。实验表明,利用不确定性估计,ProLIP有助于下游任务,并与不确定性直观概念相符,如较短的文本具有更高的不确定性,更通用的输入包括特定的输入。利用文本不确定性,进一步将ImageNet准确率从74.6%提高到75.8%,体现了概率方法的实际优势。
Key Takeaways
- ProLIP是首个基于概率的视觉语言预训练模型(VLM),在百亿级图像文本数据集上进行预训练。
- 该模型使用概率目标函数,实现强大的零样本能力,如ImageNet零样本准确率高达74.6%。
- ProLIP通过“不确定性令牌”估计不确定性,无需额外参数。
- 引入了一种新的包含损失,用于强化图像文本对及原始和屏蔽输入之间的分布包含关系。
- 利用不确定性估计,ProLIP有助于提高下游任务的性能,符合关于不确定性的直观理解。
- 通过利用文本不确定性,进一步提升了ImageNet的准确率。
- ProLIP的代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

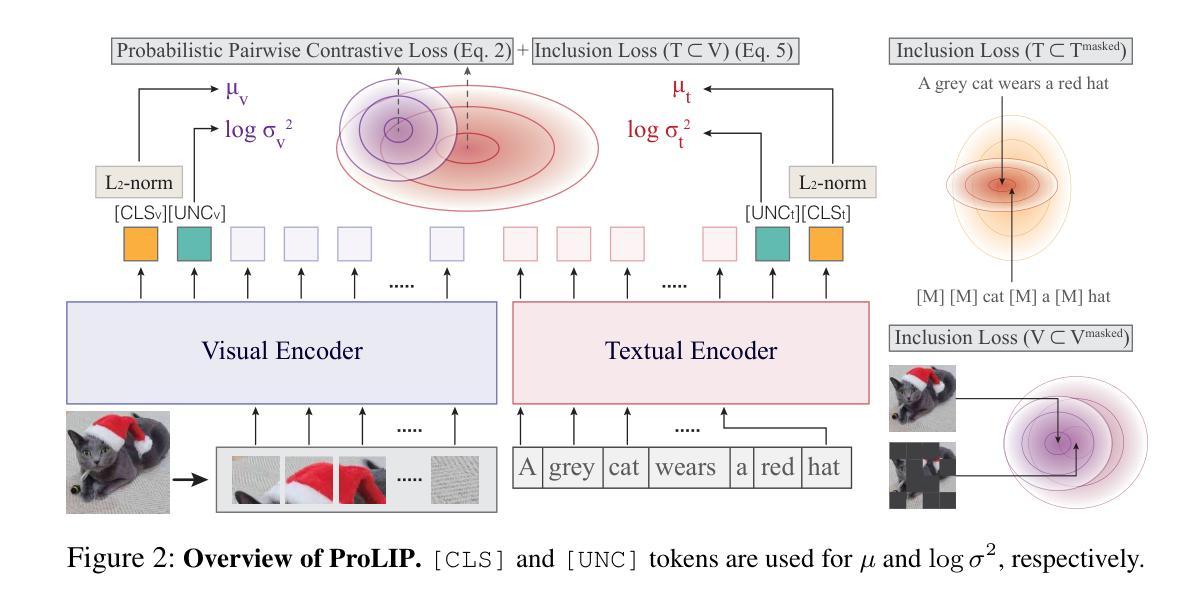
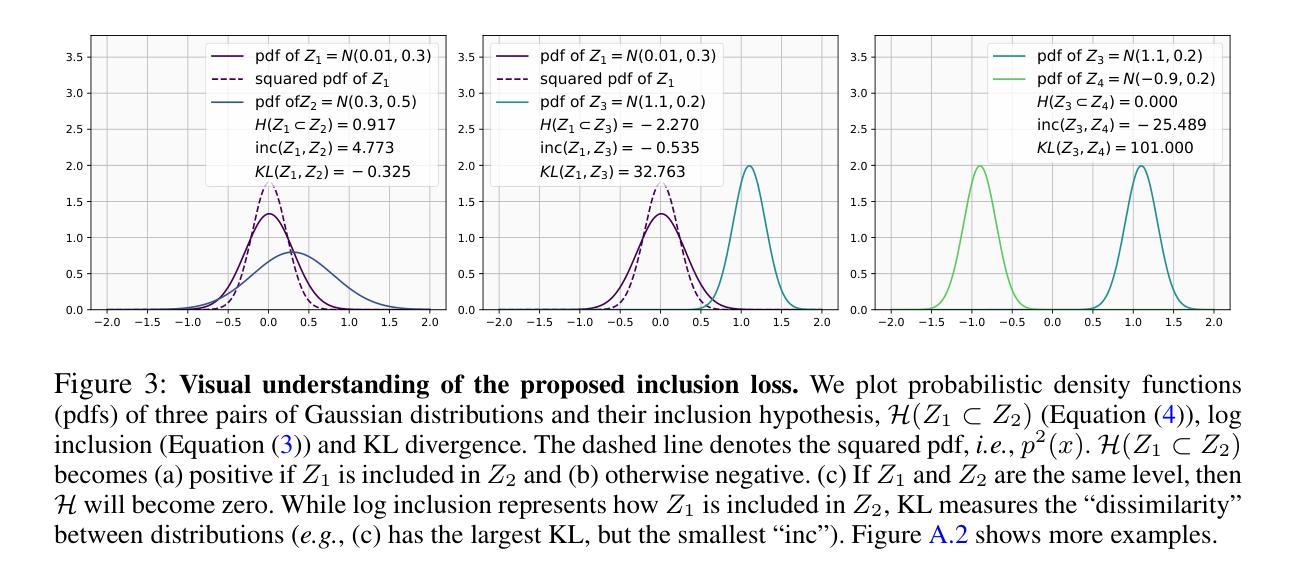
Fine-Tuning CLIP’s Last Visual Projector: A Few-Shot Cornucopia
Authors:Mohammad Fahes, Tuan-Hung Vu, Andrei Bursuc, Patrick Pérez, Raoul de Charette
We consider the problem of adapting a contrastively pretrained vision-language model like CLIP (Radford et al., 2021) for few-shot classification. The literature addresses this problem by learning a linear classifier of the frozen visual features, optimizing word embeddings, or learning external feature adapters. This paper introduces an alternative way for CLIP adaptation without adding ‘external’ parameters to optimize. We find that simply fine-tuning the last projection matrix of the vision encoder leads to performance better than all baselines. Furthermore, we show that regularizing training with the distance between the fine-tuned and pretrained matrices adds reliability for adapting CLIP. This simple approach, coined ProLIP, yields state-of-the-art performance on 11 few-shot classification benchmarks, few-shot domain generalization, cross-dataset transfer, base-to-new class generalization, and test-time adaptation. Code will be made available at: https://github.com/astra-vision/ProLIP .
我们考虑适应对比预训练视觉语言模型(如CLIP,Radford等人,2021年)进行小样本分类的问题。文献通过学习冻结视觉特征的线性分类器、优化词嵌入或学习外部特征适配器来解决这个问题。本文介绍了一种不增加优化“外部”参数的CLIP自适应替代方法。我们发现,仅仅微调视觉编码器的最后一个投影矩阵的性能超过了所有基线。此外,我们还表明,用微调后的矩阵和预训练矩阵之间的距离对训练进行正则化,可以增加CLIP的适应性。这种简单的方法被称为ProLIP,在11个小样本分类基准测试、小样本域泛化、跨数据集迁移、基础到新类别泛化和测试时间适应等方面均达到了最先进的性能。代码将在https://github.com/astra-vision/ProLIP上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
适应CLIP模型的少数镜头分类问题得到了关注,常见的策略是添加外部参数或优化单词嵌入来学习线性分类器或外部特征适配器。然而,本文提出了一种新的方法,即仅微调视觉编码器的最后一个投影矩阵,这种方法优于所有基线方法。此外,使用正则化训练可以使微调后的矩阵与预训练矩阵之间的距离增加,从而更好地适应CLIP模型。这种方法称为ProLIP,它在多个数据集上实现了最先进的性能。代码将在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
- 研究者提出了一种针对CLIP模型的少数镜头分类问题新的解决策略。该策略无需添加额外的参数,而是通过微调视觉编码器的最后一个投影矩阵来实现。这种方法的性能优于其他基线方法。
点此查看论文截图
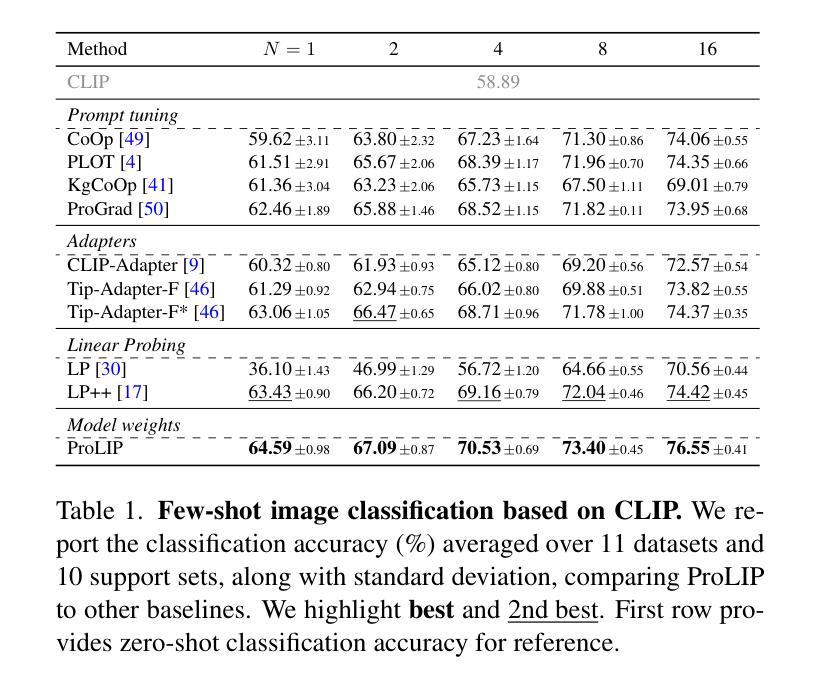
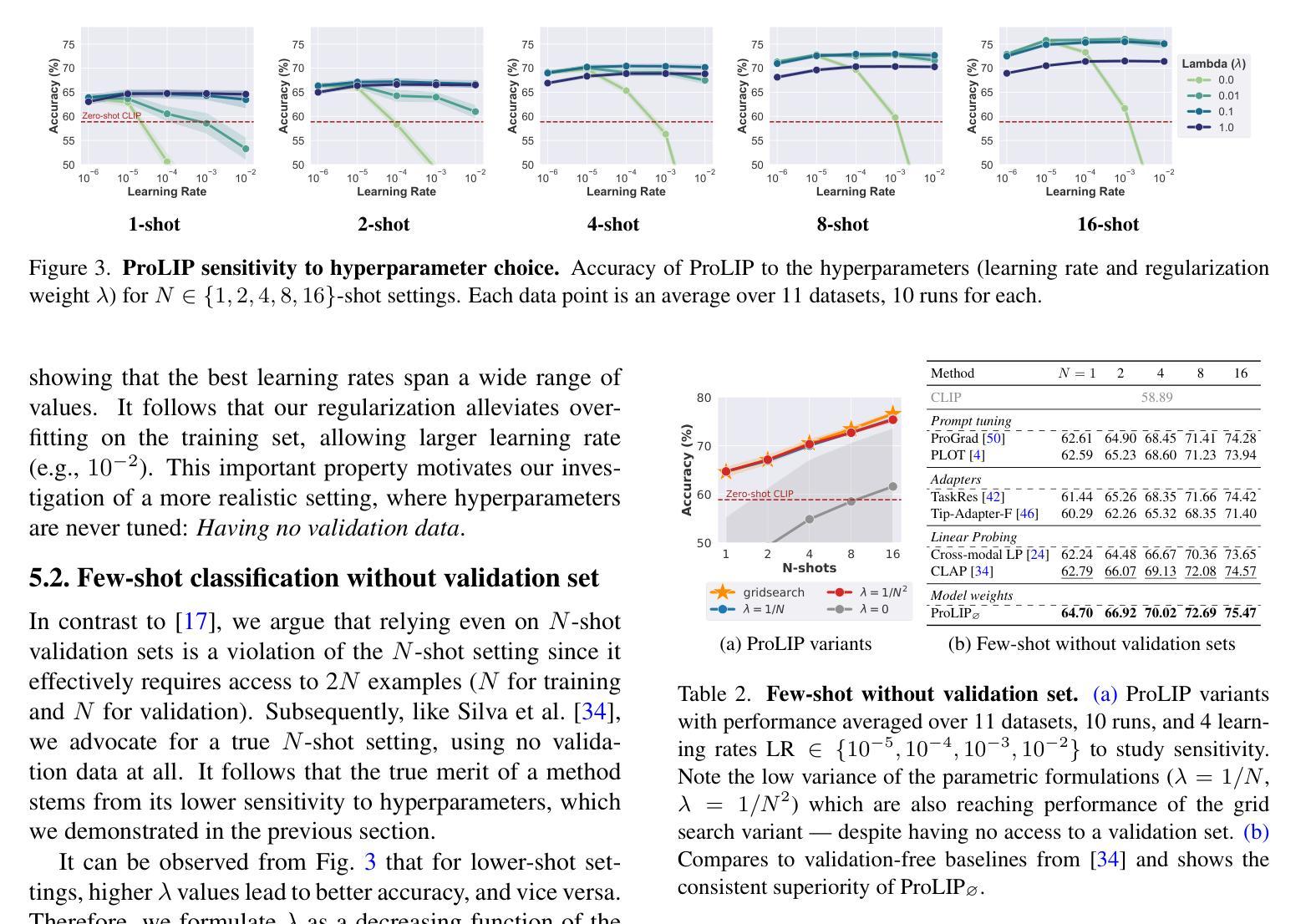
Acquiring Bidirectionality via Large and Small Language Models
Authors:Takumi Goto, Hiroyoshi Nagao, Yuta Koreeda
Using token representation from bidirectional language models (LMs) such as BERT is still a widely used approach for token-classification tasks. Even though there exist much larger unidirectional LMs such as Llama-2, they are rarely used to replace the token representation of bidirectional LMs. In this work, we hypothesize that their lack of bidirectionality is keeping them behind. To that end, we propose to newly train a small backward LM and concatenate its representations to those of existing LM for downstream tasks. Through experiments in named entity recognition, we demonstrate that introducing backward model improves the benchmark performance more than 10 points. Furthermore, we show that the proposed method is especially effective for rare domains and in few-shot learning settings.
使用来自双向语言模型(如BERT)的令牌表示,仍然是令牌分类任务的广泛使用方法。尽管存在更大的单向语言模型,如Llama-2,但它们很少被用来替代双向语言模型的令牌表示。在这项工作中,我们假设它们的双向性缺失是阻碍它们应用的关键因素。为此,我们提出新训练一个小型的反向语言模型,并将其表示与现有语言模型的表示进行拼接,以用于下游任务。通过命名实体识别的实验,我们证明了引入反向模型可以提高基准性能超过1e点以上。此外,我们还表明,该方法对于罕见领域和小样本学习设置尤其有效。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by COLING2025
Summary
本研究探讨了如何利用双向语言模型(如BERT)的令牌表示用于令牌分类任务。尽管存在更大的单向语言模型(如Llama-2),但它们很少取代双向语言模型的令牌表示。本研究假设单向性是其落后原因之一,因此提出重新训练小型反向语言模型并将其表示与现有语言模型结合用于下游任务。在命名实体识别实验中发现,引入反向模型将基准性能提高了超过10个点,尤其在罕见领域和少样本学习环境中效果尤为显著。
Key Takeaways
- 双向语言模型(如BERT)的令牌表示在令牌分类任务中仍然广泛使用。
- 尽管存在更大的单向语言模型,但它们很少取代双向语言模型的令牌表示。
- 本研究假设单向性是限制其性能的原因之一。
- 提出通过重新训练小型反向语言模型并与现有语言模型结合来提高性能。
- 在命名实体识别实验中,引入反向模型显著提高了基准性能。
- 该方法对于罕见领域特别有效。
点此查看论文截图

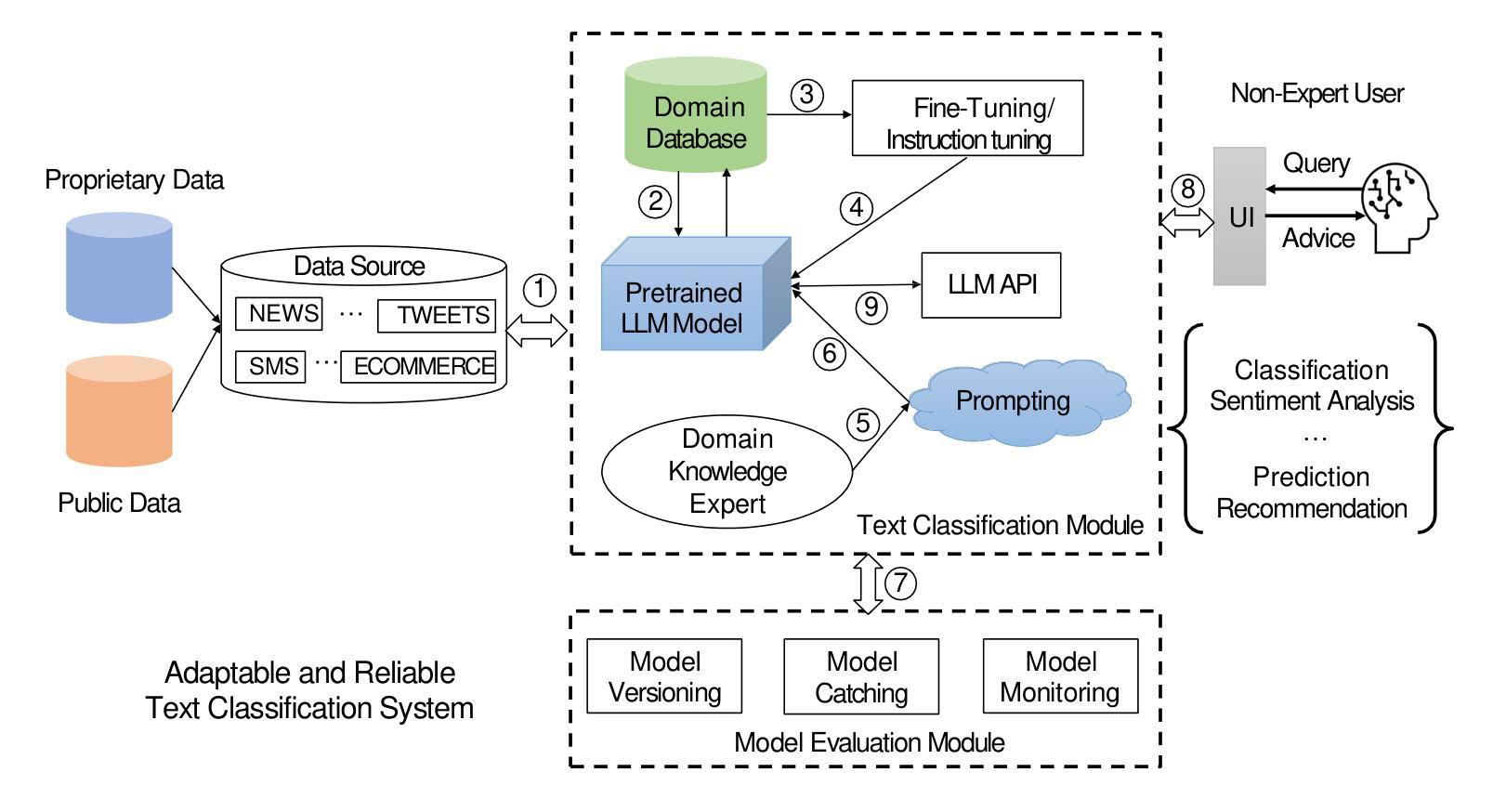
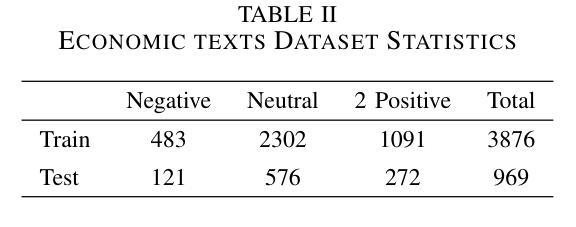
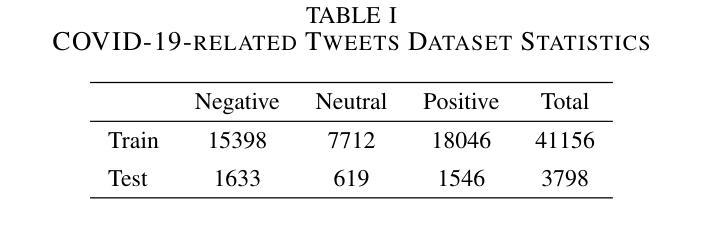
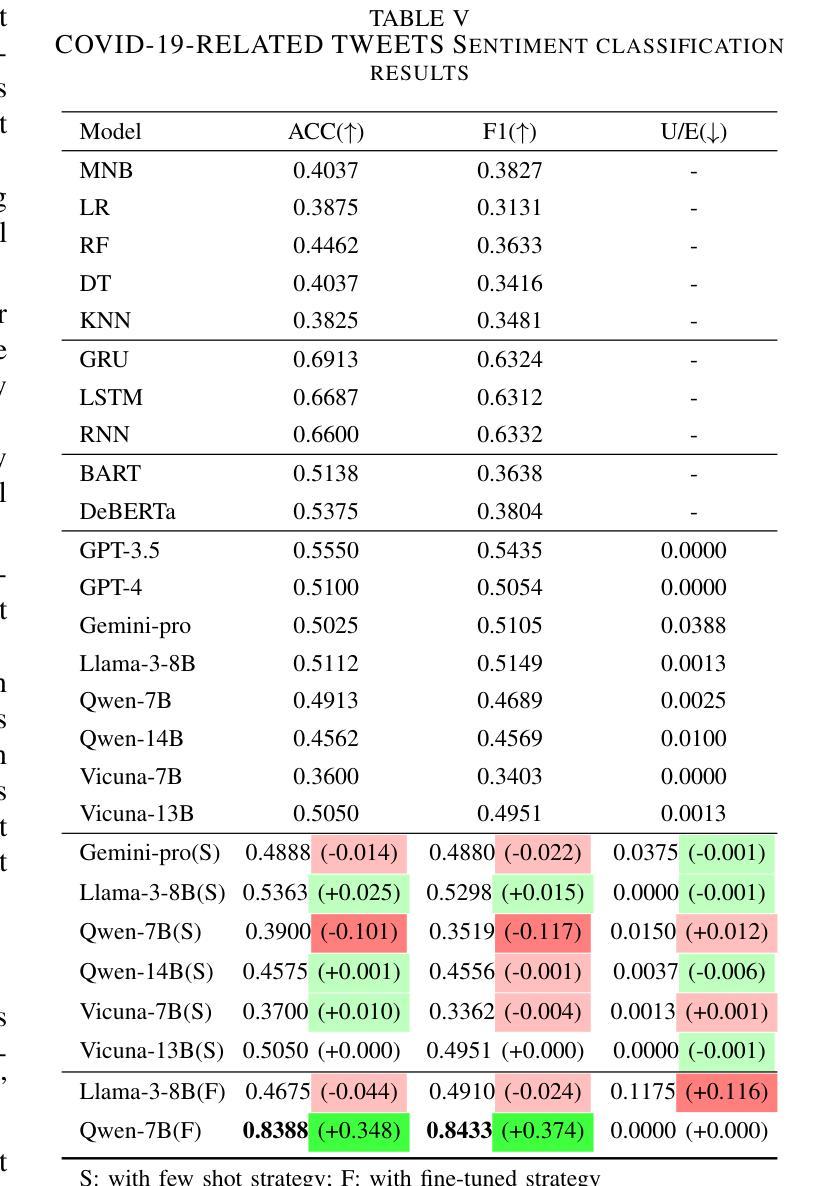
Adaptable and Reliable Text Classification using Large Language Models
Authors:Zhiqiang Wang, Yiran Pang, Yanbin Lin, Xingquan Zhu
Text classification is fundamental in Natural Language Processing (NLP), and the advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has revolutionized the field. This paper introduces an adaptable and reliable text classification paradigm, which leverages LLMs as the core component to address text classification tasks. Our system simplifies the traditional text classification workflows, reducing the need for extensive preprocessing and domain-specific expertise to deliver adaptable and reliable text classification results. We evaluated the performance of several LLMs, machine learning algorithms, and neural network-based architectures on four diverse datasets. Results demonstrate that certain LLMs surpass traditional methods in sentiment analysis, spam SMS detection, and multi-label classification. Furthermore, it is shown that the system’s performance can be further enhanced through few-shot or fine-tuning strategies, making the fine-tuned model the top performer across all datasets. Source code and datasets are available in this GitHub repository: https://github.com/yeyimilk/llm-zero-shot-classifiers.
文本分类是自然语言处理(NLP)中的一项基础工作,而随着大型语言模型(LLM)的出现,该领域已经发生了革命性的变化。本文介绍了一种灵活可靠的文本分类范式,该范式以大型语言模型为核心组件来解决文本分类任务。我们的系统简化了传统的文本分类工作流程,减少了大量预处理和特定领域专业知识需求,以提供灵活可靠的文本分类结果。我们在四个不同的数据集上评估了几种大型语言模型、机器学习算法和基于神经网络架构的性能。结果表明,某些大型语言模型在情感分析、垃圾短信检测和多媒体分类方面的表现超过了传统方法。此外,还显示可以通过少量样本或微调策略进一步提高系统性能,使微调模型成为所有数据集上的最佳表现者。源代码和数据集可在GitHub仓库中找到:https://github.com/yeyimilk/llm-zero-shot-classifiers。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICDM Workshop ARRL 2024
Summary
本文介绍了利用大型语言模型(LLMs)进行文本分类的新方法。该方法简化了传统文本分类流程,减少了预处理的需求,并能适应不同的数据集和任务。研究结果表明,某些LLM在情感分析、垃圾短信检测和多元标签分类方面超越了传统方法。通过微调策略,模型性能可进一步提升。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)已成为文本分类领域中的核心组件。
- 提出了一种新型文本分类范式,简化了流程并增强了适应性。
- 研究了LLMs在情感分析、垃圾短信检测和多元标签分类等任务上的表现。
- LLMs在某些任务上超越了传统机器学习和神经网络方法。
- 模型性能可通过微调策略进一步提升。
- 提供了一个开源GitHub仓库用于分享源代码和数据集。
点此查看论文截图

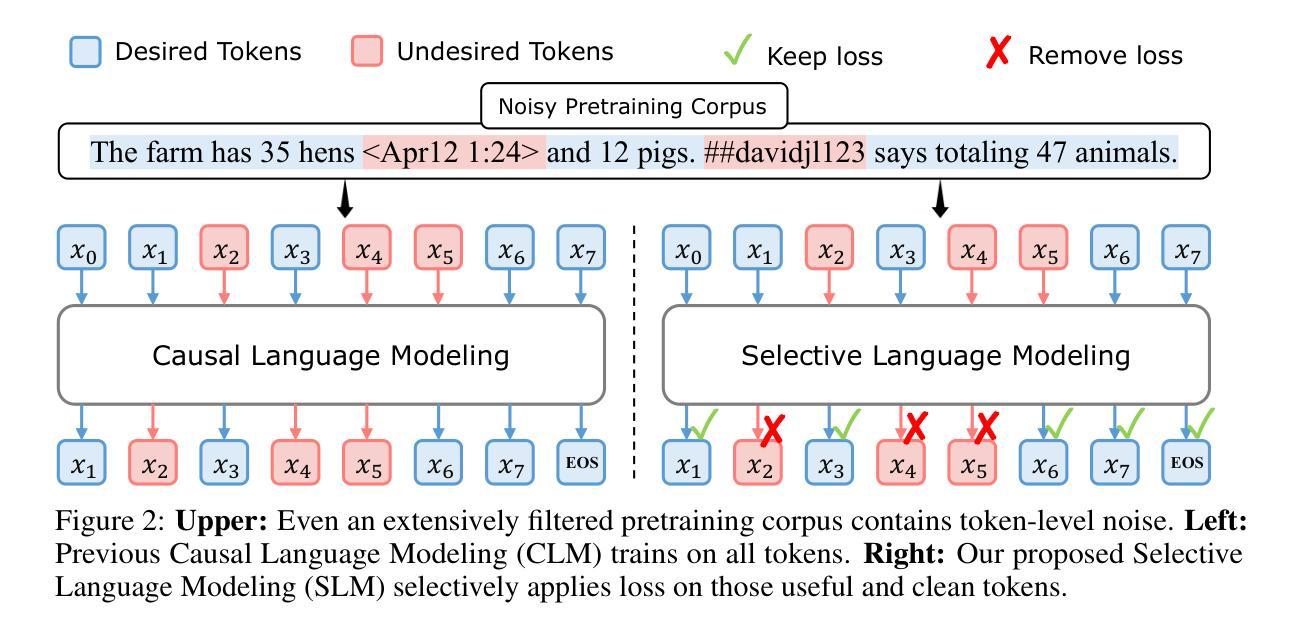
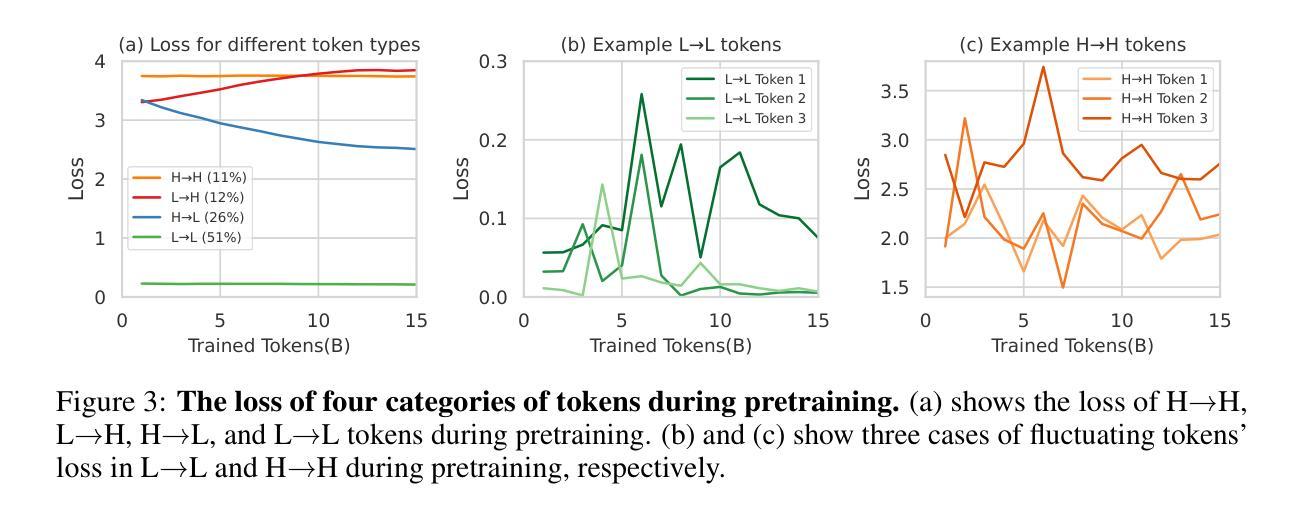
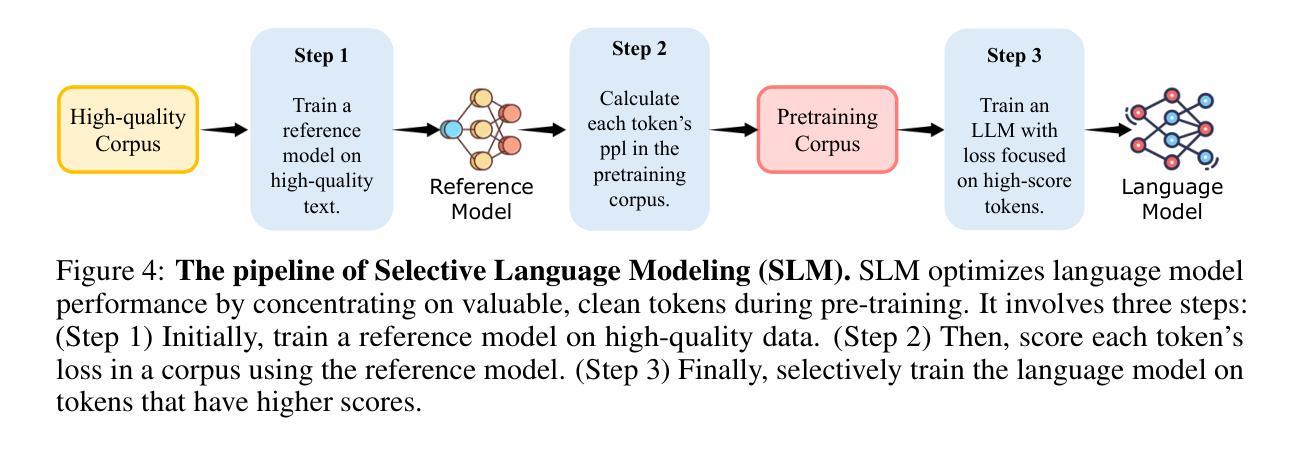
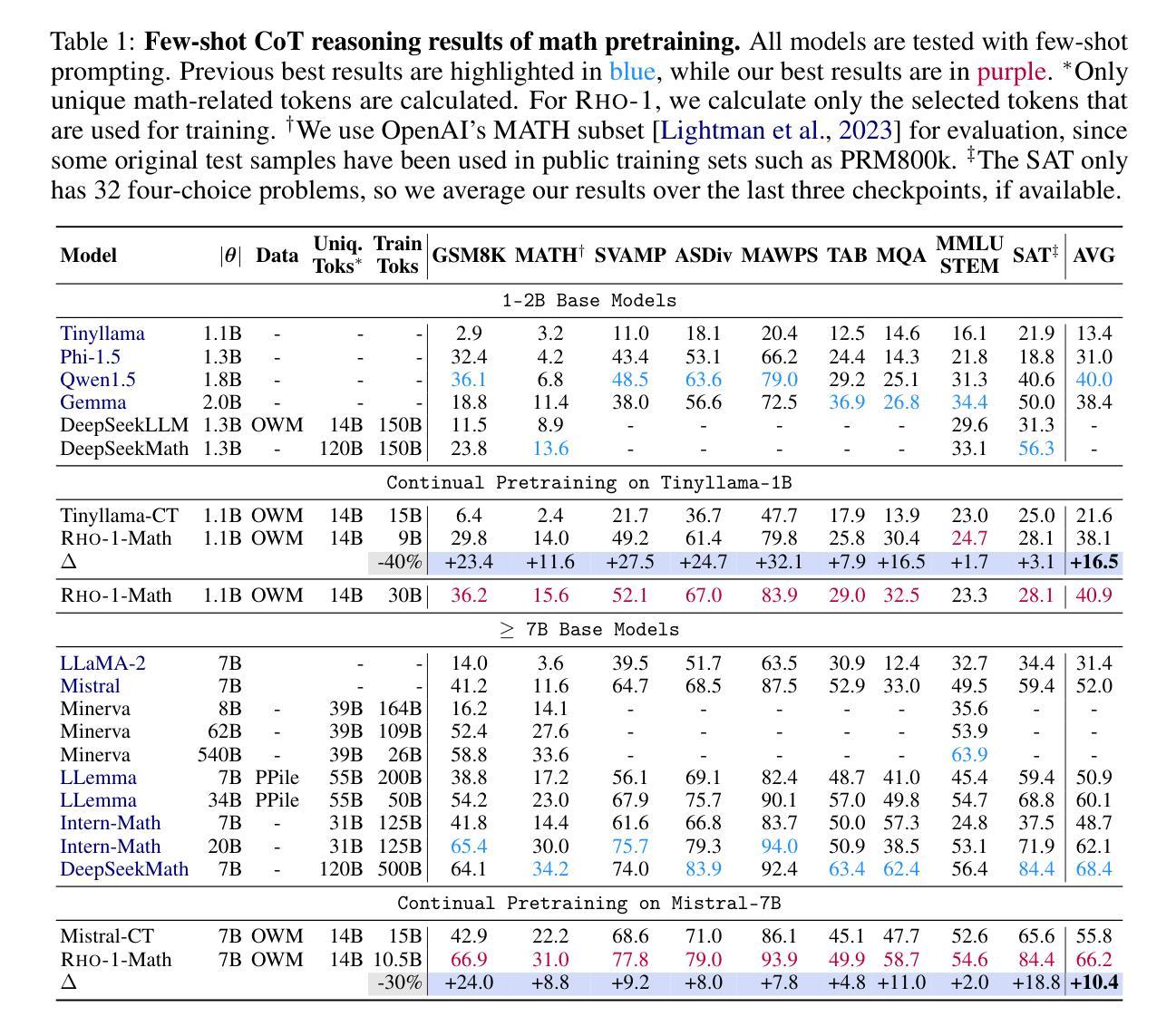
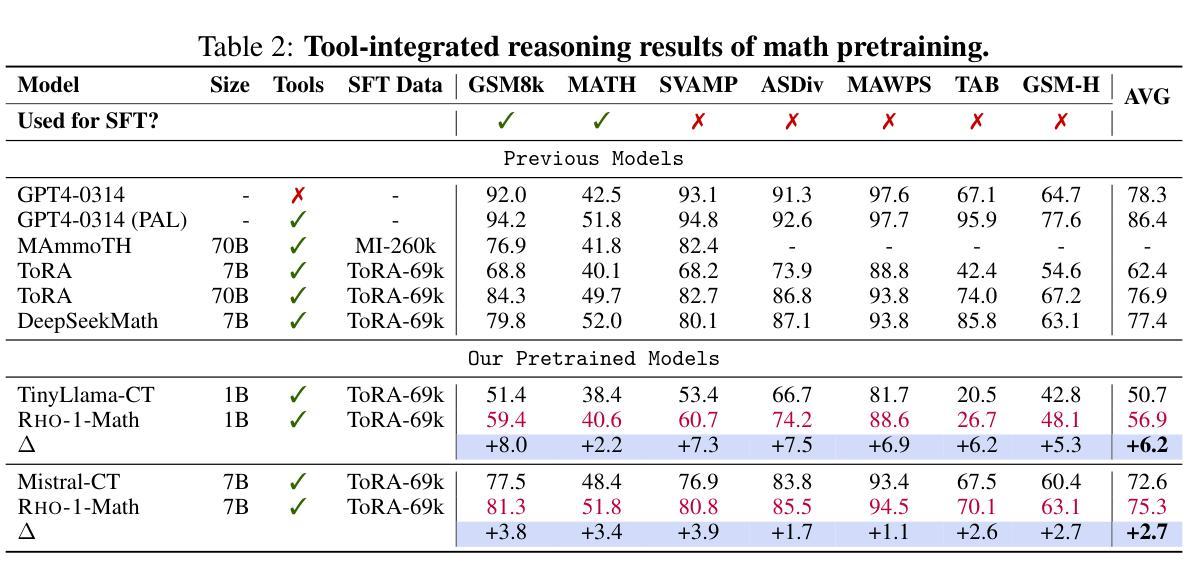
Rho-1: Not All Tokens Are What You Need
Authors:Zhenghao Lin, Zhibin Gou, Yeyun Gong, Xiao Liu, Yelong Shen, Ruochen Xu, Chen Lin, Yujiu Yang, Jian Jiao, Nan Duan, Weizhu Chen
Previous language model pre-training methods have uniformly applied a next-token prediction loss to all training tokens. Challenging this norm, we posit that ‘’9l training’’. Our initial analysis examines token-level training dynamics of language model, revealing distinct loss patterns for different tokens. Leveraging these insights, we introduce a new language model called Rho-1. Unlike traditional LMs that learn to predict every next token in a corpus, Rho-1 employs Selective Language Modeling (SLM), which selectively trains on useful tokens that aligned with the desired distribution. This approach involves scoring pretraining tokens using a reference model, and then training the language model with a focused loss on tokens with higher scores. When continual pretraining on 15B OpenWebMath corpus, Rho-1 yields an absolute improvement in few-shot accuracy of up to 30% in 9 math tasks. After fine-tuning, Rho-1-1B and 7B achieved state-of-the-art results of 40.6% and 51.8% on MATH dataset, respectively - matching DeepSeekMath with only 3% of the pretraining tokens. Furthermore, when continual pretraining on 80B general tokens, Rho-1 achieves 6.8% average enhancement across 15 diverse tasks, increasing both efficiency and performance of the language model pre-training.
之前的语言模型预训练方法都是将所有训练令牌统一应用下一个令牌的预测损失。我们挑战这一常规,并提出了“ρl训练”。我们的初步分析研究了语言模型的令牌级训练动态,发现不同令牌存在不同的损失模式。利用这些见解,我们引入了一种名为Rho-1的新语言模型。不同于传统的学习预测语料库中每个下一个令牌的LMs,Rho-1采用选择性语言建模(Selective Language Modeling,SLM),该建模方法选择性地训练有用的令牌与所需的分布对齐。这种方法涉及使用参考模型对预训练令牌进行评分,然后使用集中损失对具有较高得分的令牌进行语言模型训练。在持续使用15B OpenWebMath语料库进行预训练时,Rho-1在9个数学任务中的少样本准确度提高了高达30%。经过微调后,Rho-1-1B和7B在MATH数据集上达到了业界最佳水平的结果,分别为40.6%和51.8%,相较于DeepSeekMath只使用了其3%的预训练令牌即可与之匹敌。此外,当持续对一般令牌进行预训练达到80B时,Rho-1在涵盖不同领域的15项任务中平均提高了6.8%,提高了语言模型预训练的效率和性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF First two authors equal contribution
Summary
本文挑战了传统语言模型预训练的方法,提出了一种新的语言模型Rho-1。Rho-1采用选择性语言建模(SLM)的方式,不同于传统语言模型对每一个后续词进行预测的训练方法,而是根据期望的词汇分布,仅针对有价值的词汇进行训练。这一策略使模型能在仅有少量预训练词汇的情况下达到较高的性能水平,并在多个任务上展现出显著的提升。
Key Takeaways
- Rho-1引入了一种新的语言模型预训练方法——选择性语言建模(SLM)。
- SLM仅针对有价值的词汇进行训练,与传统的对所有词汇进行预测的方法不同。
- Rho-1在仅有少量预训练词汇的情况下,实现了较高的性能水平。在MATH数据集上取得了突破性的结果。
- Rho-1在语言模型预训练的效率上有所提升,能够在多种任务上实现平均增强效果。
点此查看论文截图
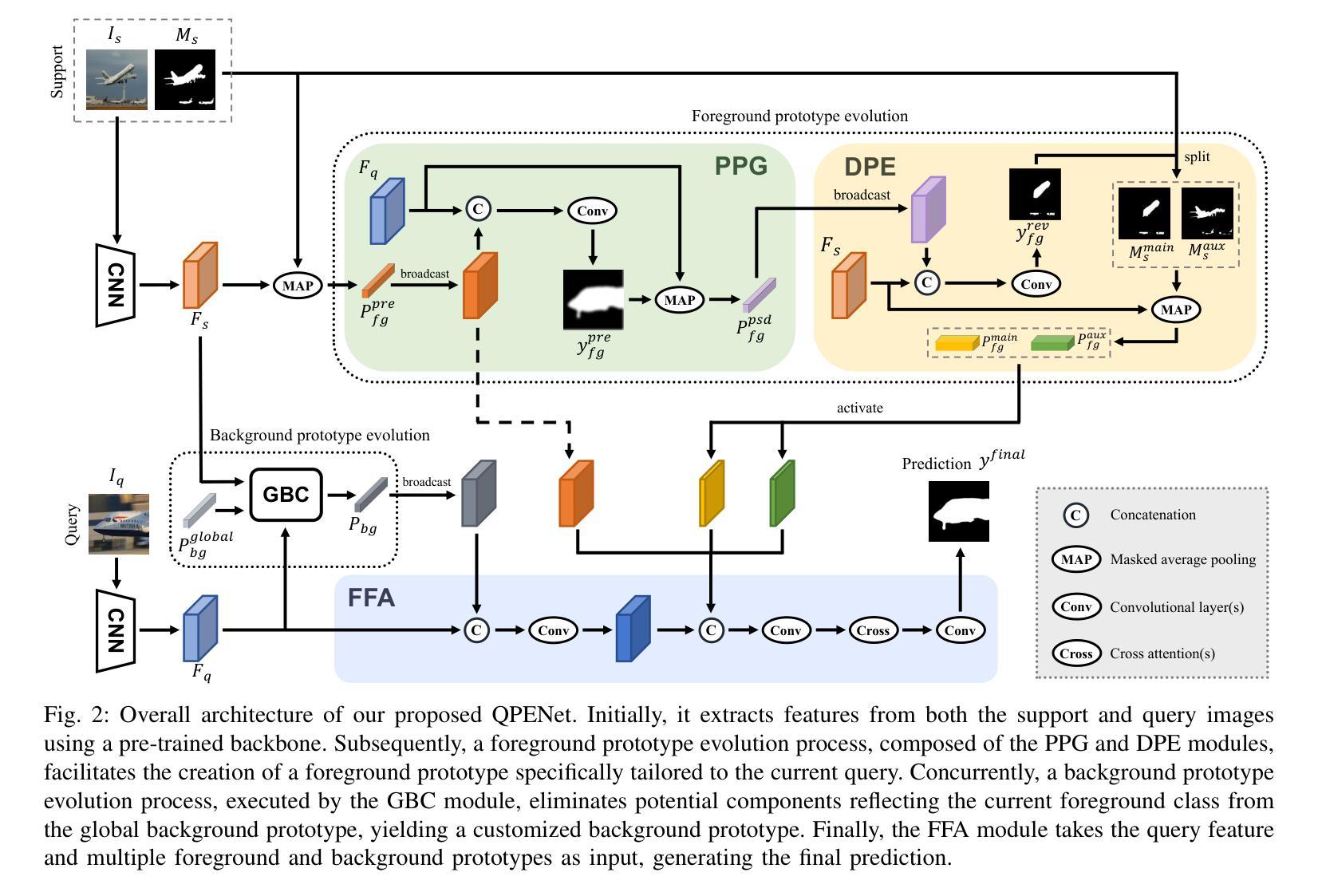
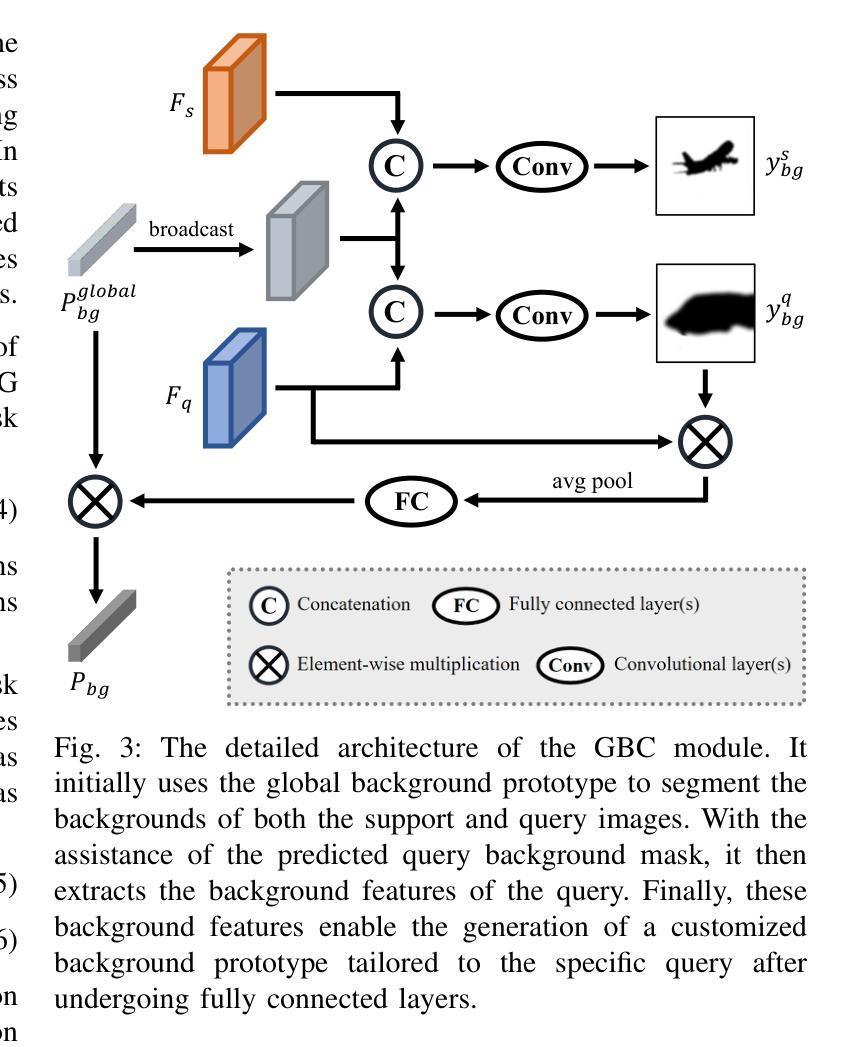
Query-guided Prototype Evolution Network for Few-Shot Segmentation
Authors:Runmin Cong, Hang Xiong, Jinpeng Chen, Wei Zhang, Qingming Huang, Yao Zhao
Previous Few-Shot Segmentation (FSS) approaches exclusively utilize support features for prototype generation, neglecting the specific requirements of the query. To address this, we present the Query-guided Prototype Evolution Network (QPENet), a new method that integrates query features into the generation process of foreground and background prototypes, thereby yielding customized prototypes attuned to specific queries. The evolution of the foreground prototype is accomplished through a \textit{support-query-support} iterative process involving two new modules: Pseudo-prototype Generation (PPG) and Dual Prototype Evolution (DPE). The PPG module employs support features to create an initial prototype for the preliminary segmentation of the query image, resulting in a pseudo-prototype reflecting the unique needs of the current query. Subsequently, the DPE module performs reverse segmentation on support images using this pseudo-prototype, leading to the generation of evolved prototypes, which can be considered as custom solutions. As for the background prototype, the evolution begins with a global background prototype that represents the generalized features of all training images. We also design a Global Background Cleansing (GBC) module to eliminate potential adverse components mirroring the characteristics of the current foreground class. Experimental results on the PASCAL-$5^i$ and COCO-$20^i$ datasets attest to the substantial enhancements achieved by QPENet over prevailing state-of-the-art techniques, underscoring the validity of our ideas.
之前的小样本分割(FSS)方法仅利用支持特征进行原型生成,忽略了查询的特定要求。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了查询引导原型演化网络(QPENet),这是一种将查询特征集成到前景和背景原型生成过程中的新方法,从而生成适应特定查询的定制原型。前景原型的演化是通过一个涉及两个新模块的\textit{支持-查询-支持}迭代过程完成的:伪原型生成(PPG)和双原型演化(DPE)。PPG模块利用支持特征为查询图像的初步分割创建初始原型,从而得到一个反映当前查询独特需求的伪原型。随后,DPE模块使用这个伪原型对支持图像进行反向分割,从而产生进化的原型,这些原型可以被视为定制解决方案。至于背景原型,演化始于代表所有训练图像通用特征的全局背景原型。我们还设计了一个全局背景清洁(GBC)模块,以消除可能的不良成分,反映当前前景类的特征。在PASCAL-$5^i$和COCO-$20^i$数据集上的实验结果证明,QPENet相较于当前最先进的技术取得了重大改进,验证了我们的想法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE TMM 2024
Summary
本文提出了一种基于查询引导的原型演化网络(QPENet)来解决小样分割问题。该方法通过引入查询特征,优化了前景和背景原型的生成过程,从而生成针对特定查询定制化的原型。通过支持特征生成伪原型,再通过反向分割生成演化后的原型,实验证明,该方法在PASCAL-5i和COCO-20i数据集上取得了显著的改进效果。
Key Takeaways
- QPENet解决了现有小样分割方法忽略查询特定需求的问题,通过集成查询特征来优化前景和背景原型的生成。
- QPENet采用支持-查询-支持的迭代过程,通过Pseudo-prototype Generation(PPG)和Dual Prototype Evolution(DPE)两个新模块实现前景原型的演化。
- PPG模块利用支持特征为查询图像生成初步分割的伪原型,反映当前查询的独特需求。
- DPE模块使用伪原型对支持图像进行反向分割,生成演化后的前景原型,这些原型可以被视为针对查询的定制解决方案。
- 背景原型的演化从代表所有训练图像通用特征的全局背景原型开始,并设计了Global Background Cleansing(GBC)模块来消除可能的不利成分,反映当前前景类的特性。
- 在PASCAL-5i和COCO-20i数据集上的实验结果证明了QPENet相较于现有技术的大幅提升。
点此查看论文截图

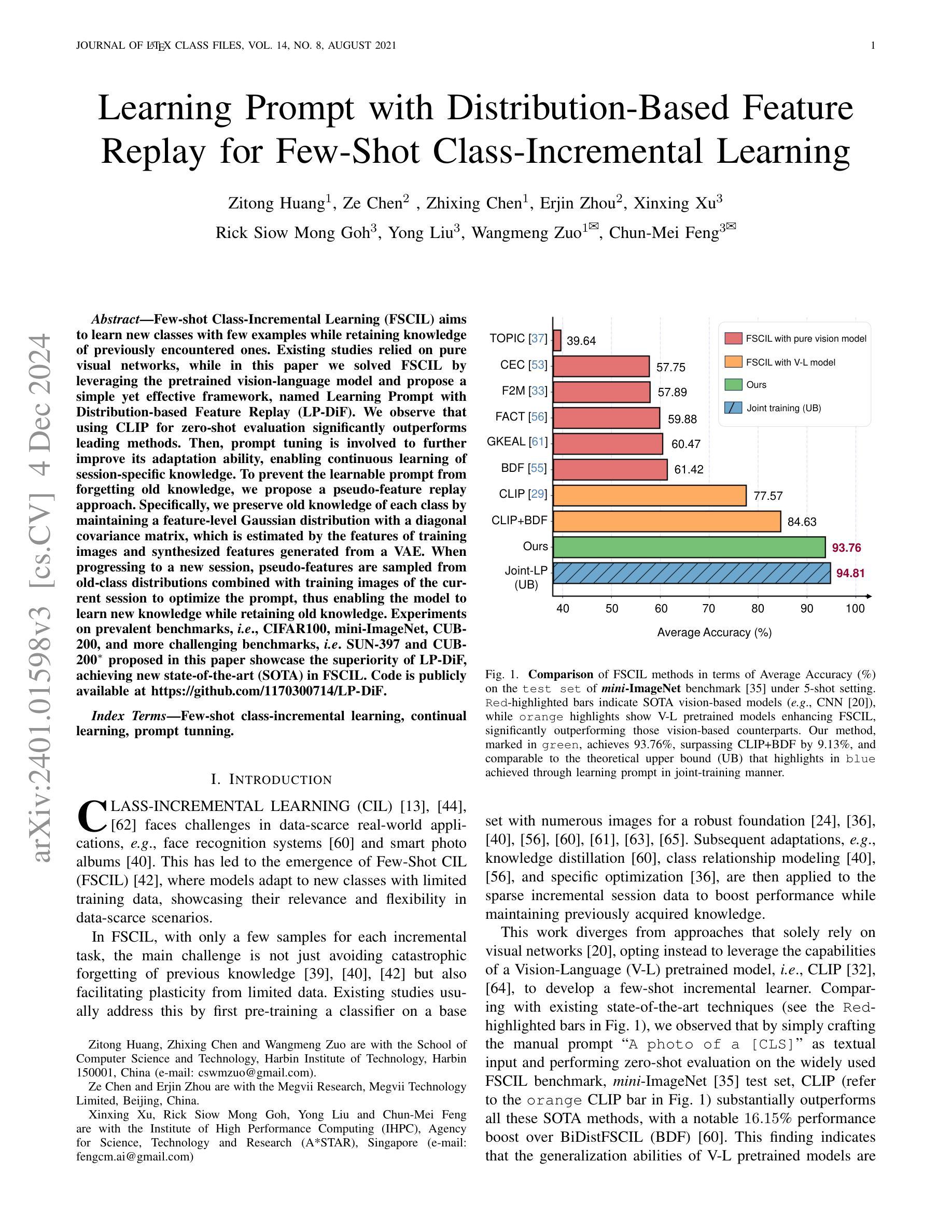
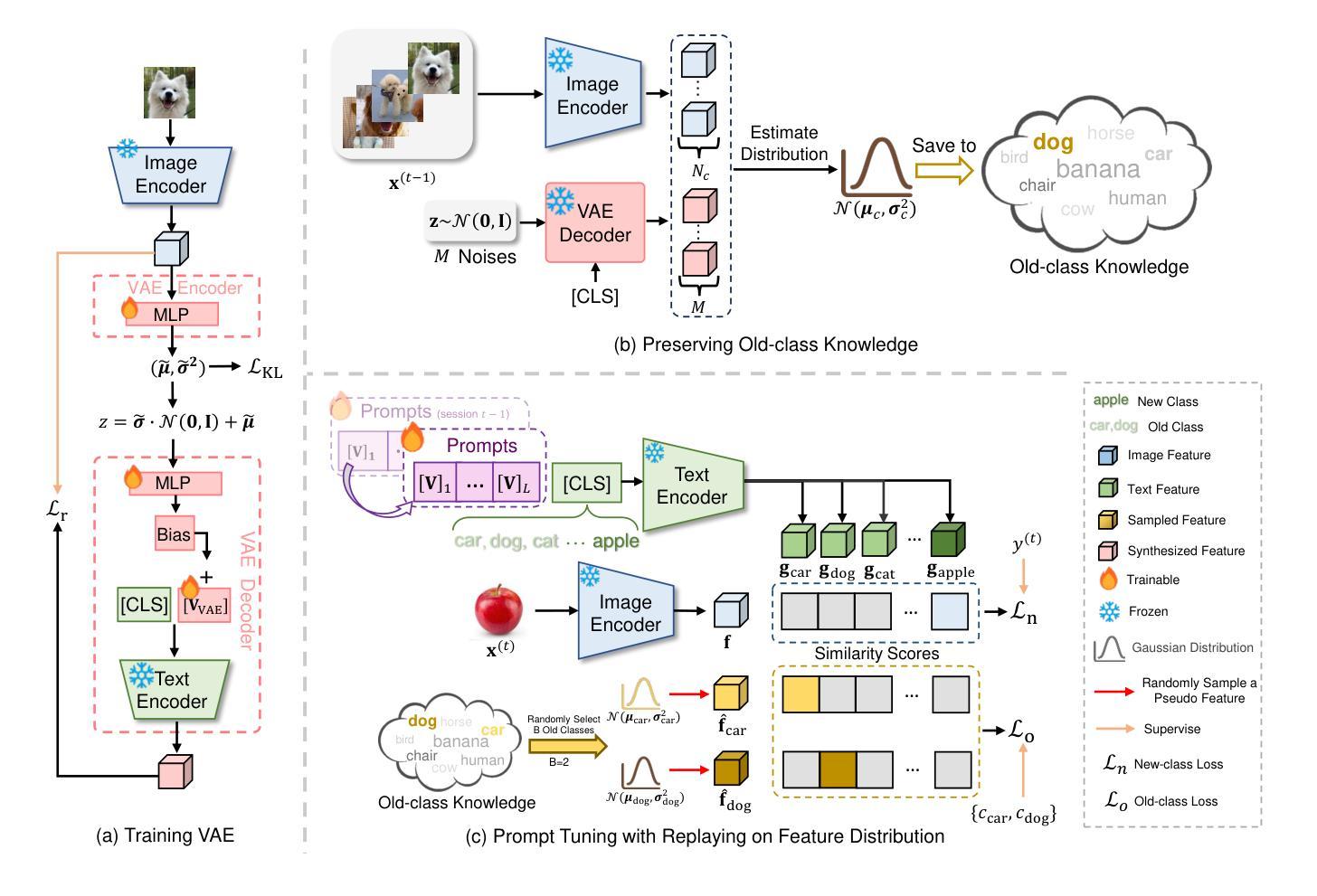
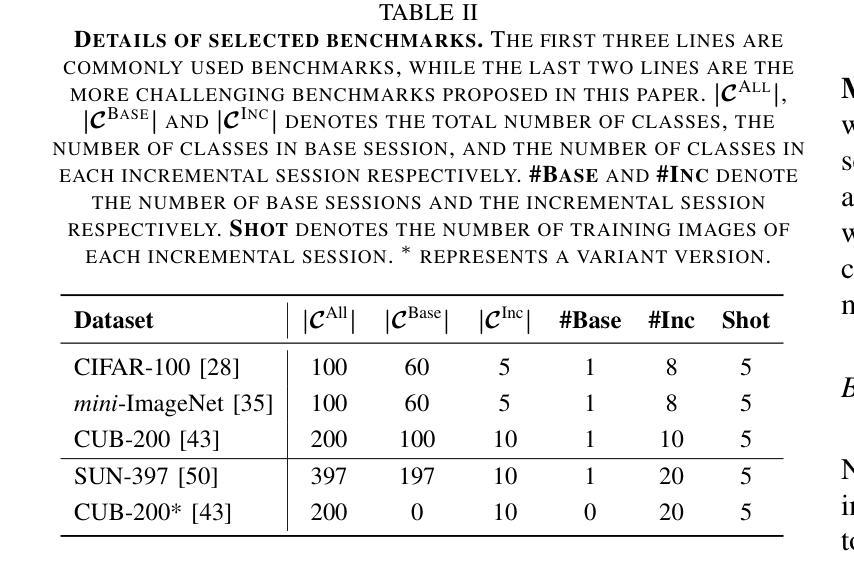
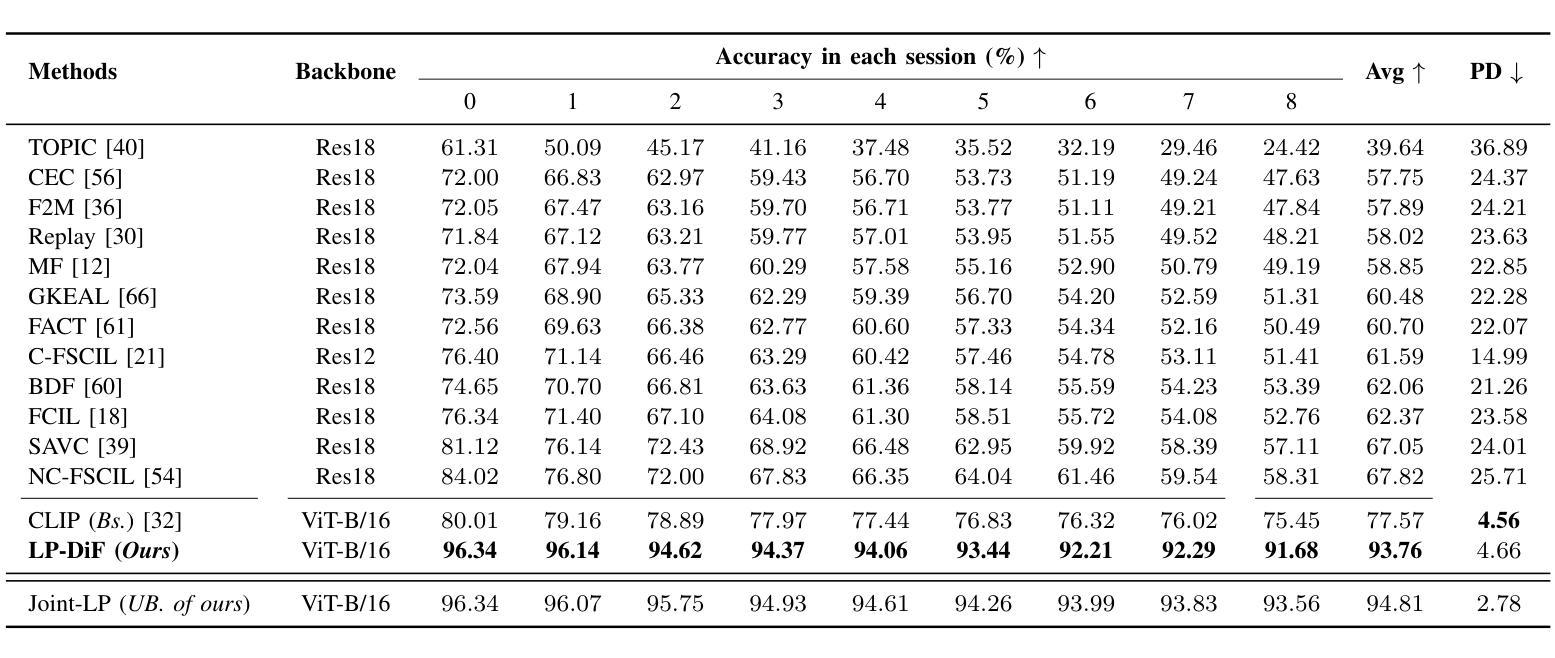
Learning Prompt with Distribution-Based Feature Replay for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Authors:Zitong Huang, Ze Chen, Zhixing Chen, Erjin Zhou, Xinxing Xu, Rick Siow Mong Goh, Yong Liu, Wangmeng Zuo, Chunmei Feng
Few-shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) aims to continuously learn new classes based on very limited training data without forgetting the old ones encountered. Existing studies solely relied on pure visual networks, while in this paper we solved FSCIL by leveraging the Vision-Language model (e.g., CLIP) and propose a simple yet effective framework, named Learning Prompt with Distribution-based Feature Replay (LP-DiF). We observe that simply using CLIP for zero-shot evaluation can substantially outperform the most influential methods. Then, prompt tuning technique is involved to further improve its adaptation ability, allowing the model to continually capture specific knowledge from each session. To prevent the learnable prompt from forgetting old knowledge in the new session, we propose a pseudo-feature replay approach. Specifically, we preserve the old knowledge of each class by maintaining a feature-level Gaussian distribution with a diagonal covariance matrix, which is estimated by the image features of training images and synthesized features generated from a VAE. When progressing to a new session, pseudo-features are sampled from old-class distributions combined with training images of the current session to optimize the prompt, thus enabling the model to learn new knowledge while retaining old knowledge. Experiments on three prevalent benchmarks, i.e., CIFAR100, mini-ImageNet, CUB-200, and two more challenging benchmarks, i.e., SUN-397 and CUB-200$^*$ proposed in this paper showcase the superiority of LP-DiF, achieving new state-of-the-art (SOTA) in FSCIL. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/1170300714/LP-DiF.
少量样本类增量学习(FSCIL)的目标是基于非常有限的训练数据持续学习新类别,同时不忘掉之前遇到的旧类别。现有研究仅依赖于纯视觉网络,而本文则通过利用视觉语言模型(例如CLIP)来解决FSCIL问题,并提出一个简单有效的框架,名为基于分布特征回放的学习提示(LP-DiF)。我们发现,仅使用CLIP进行零样本评估即可大幅超越最具影响力的方法。接着,我们采用提示调整技术来进一步提高其适应能力,使模型能够持续从每个会话中捕获特定知识。为了防止学习提示在新会话中忘记旧知识,我们提出了一种伪特征回放方法。具体来说,我们通过维持一个由训练图像特征和变自动编码器生成的合成特征估算得到的特征级对角协方差矩阵高斯分布来保留每个旧类的知识。当进入新会话时,伪特征通过从旧类分布中采样并结合当前会话的训练图像来优化提示,从而能够使模型在学习新知识的同时保留旧知识。在CIFAR100、mini-ImageNet、CUB-200三个流行基准以及本文提出的更具挑战性的SUN-397和CUB-200$*$上的实验展示了LP-DiF的优越性,在FSCIL领域达到了新的最先进的性能。代码已公开在https://github.com/1170300714/LP-DiF。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文解决了少样本类增量学习(FSCIL)问题,通过利用视觉语言模型(如CLIP)并引入Learning Prompt with Distribution-based Feature Replay(LP-DiF)框架,实现了在少量训练数据下对新类的连续学习,同时不遗忘已学类。实验结果表明,LP-DiF在多个基准测试集上表现优异,实现了新的最佳性能。
关键见解
- LP-DiF框架利用视觉语言模型(如CLIP)解决少样本类增量学习问题。
- 通过使用CLIP进行零样本评估,已显示出显著优于其他方法的效果。
- 引入提示调整技术,进一步提高模型的适应能力,使其能够连续捕捉每个会话中的特定知识。
- 提出伪特征回放方法,防止学习提示在新会话中遗忘旧知识。
- 通过维护特征级高斯分布来估计旧类的知识,并使用变分自编码器生成的合成特征进行补充。
- 伪特征与当前会话的训练图像相结合,以优化提示,使模型能够在学习新知识的同时保留旧知识。
点此查看论文截图
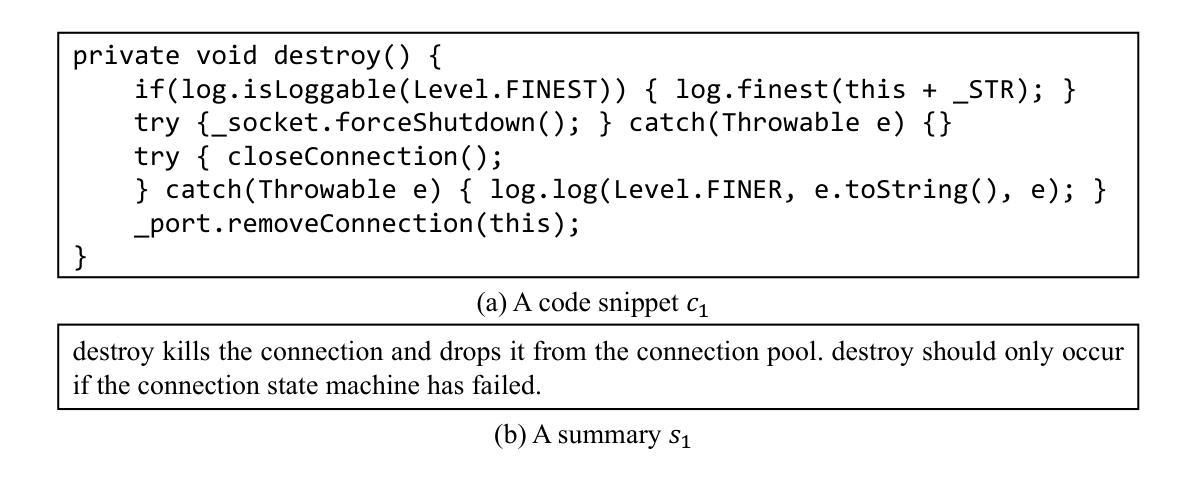
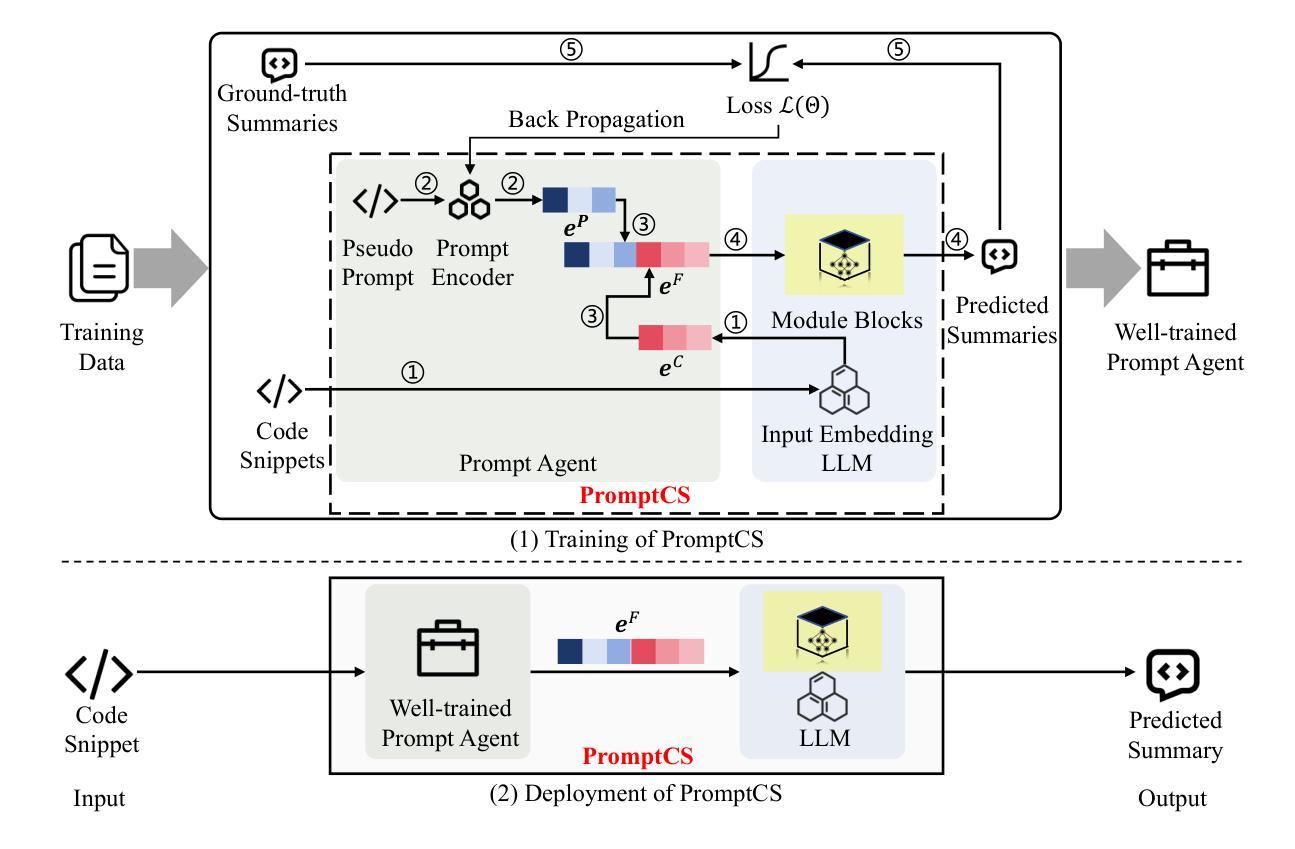
A Prompt Learning Framework for Source Code Summarization
Authors:Tingting Xu, Yun Miao, Chunrong Fang, Hanwei Qian, Xia Feng, Zhenpeng Chen, Chong Wang, Jian Zhang, Weisong Sun, Zhenyu Chen, Yang Liu
(Source) code summarization is the task of automatically generating natural language summaries (also called comments) for given code snippets. Recently, with the successful application of large language models (LLMs) in numerous fields, software engineering researchers have also attempted to adapt LLMs to solve code summarization tasks. The main adaptation schemes include instruction prompting, task-oriented (full-parameter) fine-tuning, and parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT). However, instruction prompting involves designing crafted prompts and requires users to have professional domain knowledge, while task-oriented fine-tuning requires high training costs, and effective, tailored PEFT methods for code summarization are still lacking. This paper proposes an effective prompt learning framework for code summarization called PromptCS. It no longer requires users to rack their brains to design effective prompts. Instead, PromptCS trains a prompt agent that can generate continuous prompts to unleash the potential for LLMs in code summarization. Compared to the human-written discrete prompt, the continuous prompts are produced under the guidance of LLMs and are therefore easier to understand by LLMs. PromptCS is non-invasive to LLMs and freezes the parameters of LLMs when training the prompt agent, which can greatly reduce the requirements for training resources. Our comprehensive experimental results show that PromptCS significantly outperforms instruction prompting schemes (including zero-shot learning and few-shot learning) on all four widely used metrics, and is comparable to the task-oriented fine-tuning scheme. In some base LLMs, e.g., StarCoderBase-1B and -3B, PromptCS even outperforms the task-oriented fine-tuning scheme. More importantly, the training efficiency of PromptCS is faster than the task-oriented fine-tuning scheme, with a more pronounced advantage on larger LLMs.
代码摘要任务是为给定的代码片段自动生成自然语言摘要(也称为注释)。最近,随着大型语言模型(LLM)在多个领域的成功应用,软件工程研究人员也尝试将LLM适应于解决代码摘要任务。主要的适应方案包括指令提示、面向任务(全参数)微调以及参数高效微调(PEFT)。然而,指令提示需要设计精心的提示,并要求用户具备专业领域的知识;面向任务的微调则需要高昂的训练成本,针对代码摘要的有效且定制化的PEFT方法仍然缺乏。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under review
Summary
本文介绍了代码摘要任务及大型语言模型(LLMs)在该任务中的应用。为适应代码摘要任务,提出了名为PromptCS的有效提示学习框架,该框架通过训练提示代理生成连续提示,释放LLMs在代码摘要中的潜力。相较于人工编写的离散提示,连续提示在LLMs的指导下生成,更易被LLMs理解。PromptCS减少对训练资源的需求,且在四个广泛使用的指标上显著优于指令提示方案,与任务导向的微调方案相当,甚至在某些基础LLMs上表现更佳。
Key Takeaways
- 代码摘要任务是自动生成自然语言摘要(即注释)的编程任务。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在软件工程中也被尝试用于代码摘要任务。
- 目前主要的适应方案包括指令提示、任务导向的微调以及参数高效的微调(PEFT)。
- PromptCS是一个有效的提示学习框架,通过训练提示代理生成连续提示。
- 连续提示相较于人工编写的离散提示更易被LLMs理解。
- PromptCS在多个指标上表现优于指令提示方案,与任务导向的微调方案相当或更优。
点此查看论文截图

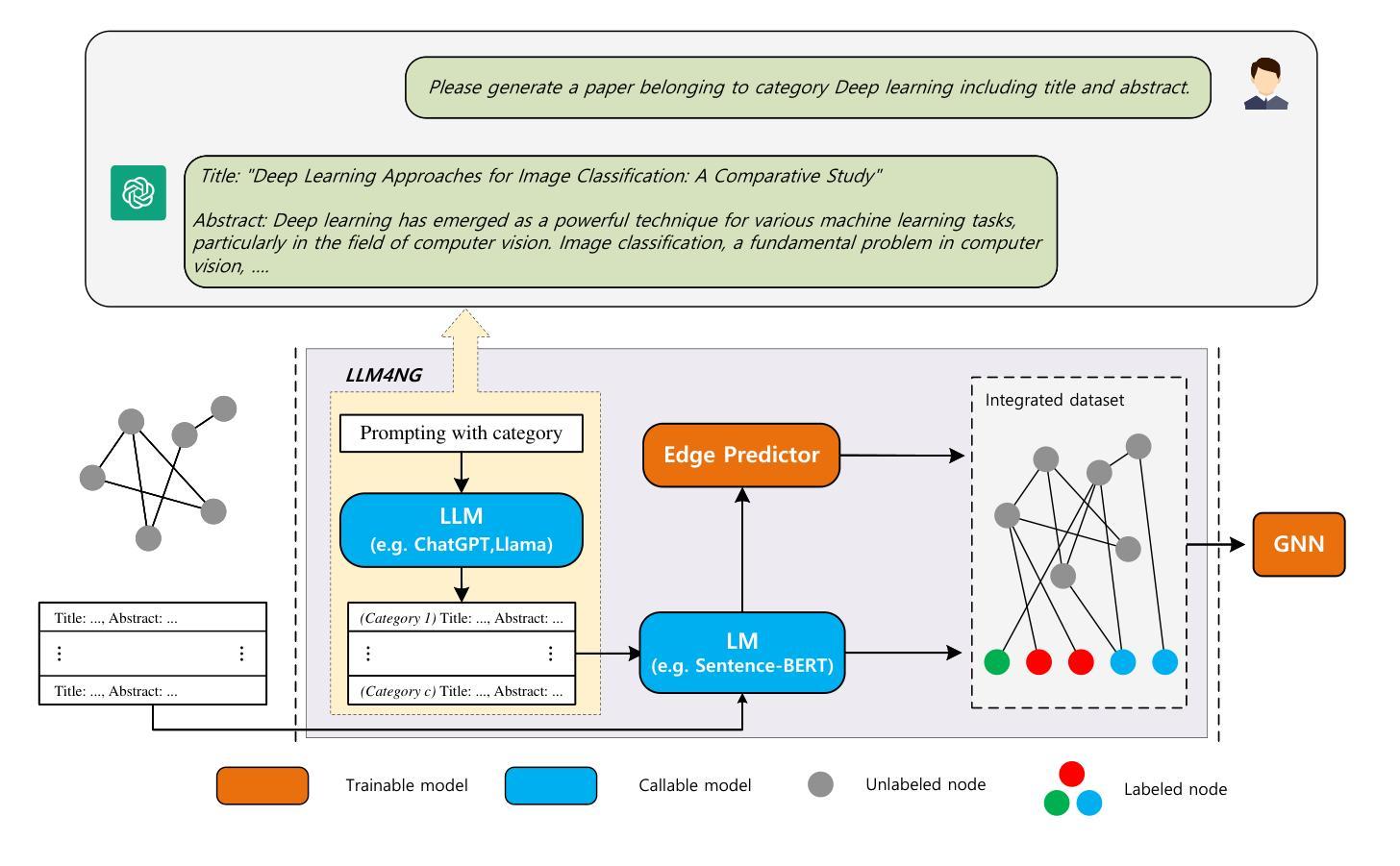
Leveraging Large Language Models for Node Generation in Few-Shot Learning on Text-Attributed Graphs
Authors:Jianxiang Yu, Yuxiang Ren, Chenghua Gong, Jiaqi Tan, Xiang Li, Xuecang Zhang
Text-attributed graphs have recently garnered significant attention due to their wide range of applications in web domains. Existing methodologies employ word embedding models for acquiring text representations as node features, which are subsequently fed into Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) for training. Recently, the advent of Large Language Models (LLMs) has introduced their powerful capabilities in information retrieval and text generation, which can greatly enhance the text attributes of graph data. Furthermore, the acquisition and labeling of extensive datasets are both costly and time-consuming endeavors. Consequently, few-shot learning has emerged as a crucial problem in the context of graph learning tasks. In order to tackle this challenge, we propose a lightweight paradigm called LLM4NG, which adopts a plug-and-play approach to empower text-attributed graphs through node generation using LLMs. Specifically, we utilize LLMs to extract semantic information from the labels and generate samples that belong to these categories as exemplars. Subsequently, we employ an edge predictor to capture the structural information inherent in the raw dataset and integrate the newly generated samples into the original graph. This approach harnesses LLMs for enhancing class-level information and seamlessly introduces labeled nodes and edges without modifying the raw dataset, thereby facilitating the node classification task in few-shot scenarios. Extensive experiments demonstrate the outstanding performance of our proposed paradigm, particularly in low-shot scenarios. For instance, in the 1-shot setting of the ogbn-arxiv dataset, LLM4NG achieves a 76% improvement over the baseline model.
文本属性图因其在网络领域的广泛应用而最近引起了人们的广泛关注。现有方法采用词嵌入模型获取文本表示作为节点特征,然后将其输入图神经网络(GNNs)进行训练。最近,大型语言模型(LLM)的出现,展现了其在信息检索和文本生成方面的强大能力,这可以极大地增强图的文本属性。此外,获取和标注大规模数据集都是成本高且耗时的任务。因此,小样本学习已成为图学习任务中的关键问题。为了解决这一挑战,我们提出了一种轻量级的范式,称为LLM4NG,它采用即插即用的方法,利用大型语言模型通过节点生成来增强文本属性图。具体来说,我们利用LLM从标签中提取语义信息,生成属于这些类别的样本作为范例。然后,我们采用边缘预测器来捕捉原始数据集固有的结构信息,并将新生成的样本集成到原始图中。这种方法利用LLM增强类级信息,并无缝地引入有标签的节点和边缘,而无需修改原始数据集,从而促进了小样本场景中的节点分类任务。大量实验表明,我们提出的范式在少样本场景中表现出卓越的性能。例如,在ogbn-arxiv数据集的1个样本设置下,LLM4NG相较于基线模型实现了7 结缘的提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2025
Summary
文本属性图因其在网页域中的广泛应用而备受关注。现有方法使用词嵌入模型获取文本表示作为节点特征,并输入图神经网络进行训练。大型语言模型的出现在信息检索和文本生成方面表现出强大的能力,可极大增强图的文本属性。为了解决数据集获取和标注的高成本和耗时问题,少样本学习成为了图学习任务中的关键。我们提出了一种名为LLM4NG的轻量级范式,通过利用大型语言模型提取标签语义信息并生成样本作为范例来赋能文本属性图。通过边缘预测器捕捉原始数据集的结构信息并将新生成的样本集成到原始图中,此范式利用大型语言模型提高类级信息,无需修改原始数据即可轻松引入标记节点和边缘,从而协助少样本场景下的节点分类任务。实验表明,特别是低样本场景下,该范式表现出卓越性能。如在ogbn-arxiv数据集的1次拍摄设置中,LLM4NG较基线模型提高了76%。
Key Takeaways
- 文本属性图因其在多种应用领域的普及而备受关注。
- 大型语言模型在信息检索和文本生成方面的强大能力可增强图的文本属性。
- 少样本学习成为图学习任务中的关键,因为数据集获取和标注成本高昂且耗时。
- LLM4NG范式利用大型语言模型提取标签语义信息并生成样本,以赋能文本属性图。
- 通过边缘预测器捕捉数据集的结构信息,并将新生成的样本集成到原始图中。
- LLM4NG利用大型语言模型提高类级信息,轻松引入标记节点和边缘,辅助少样本场景下的节点分类。
- 实验表明,特别是在低样本场景下,LLM4NG范式表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图