⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-12 更新
Utilizing Multi-step Loss for Single Image Reflection Removal
Authors:Abdelrahman Elnenaey, Marwan Torki
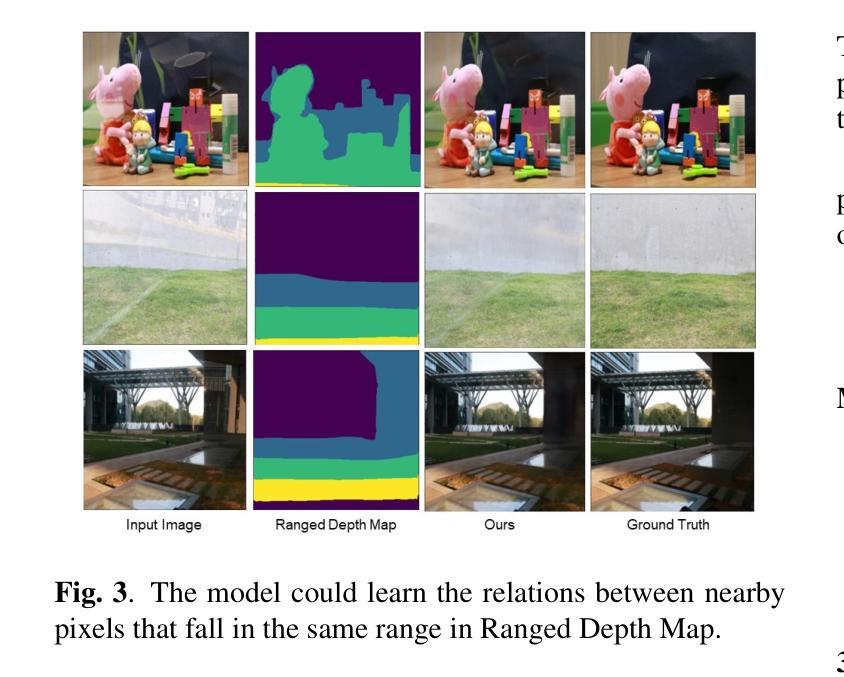
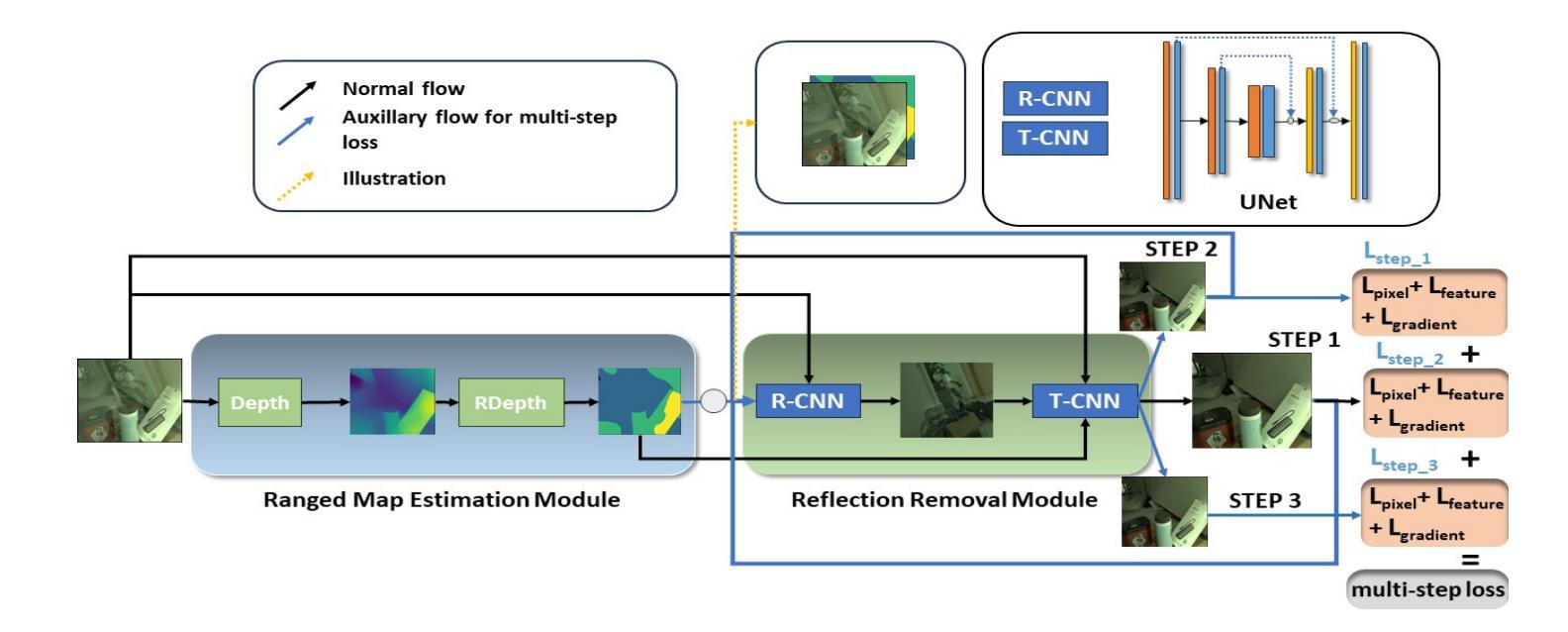
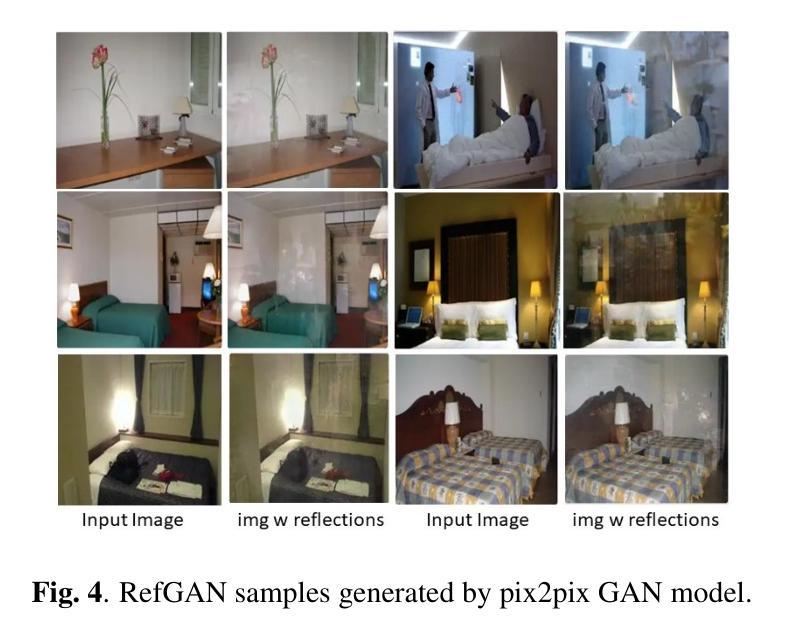
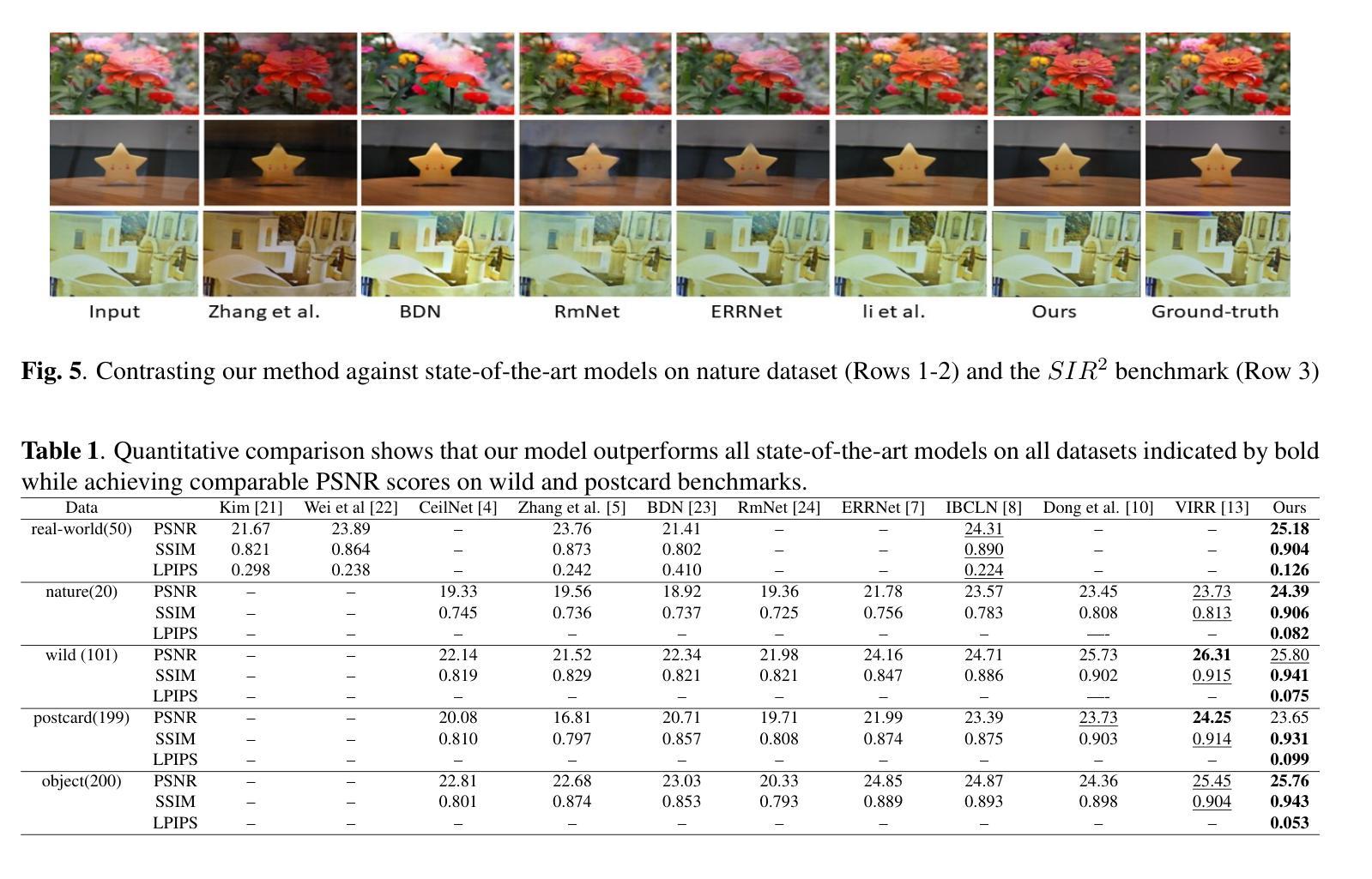
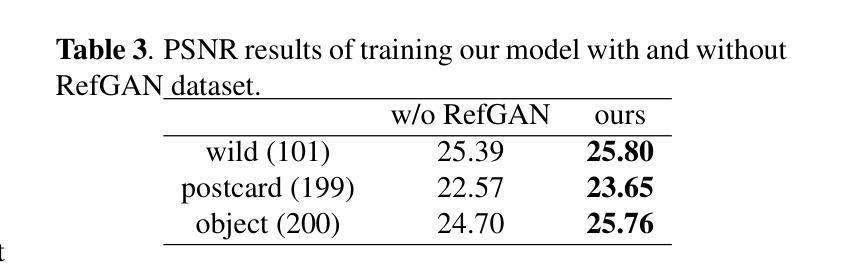
Image reflection removal is crucial for restoring image quality. Distorted images can negatively impact tasks like object detection and image segmentation. In this paper, we present a novel approach for image reflection removal using a single image. Instead of focusing on model architecture, we introduce a new training technique that can be generalized to image-to-image problems, with input and output being similar in nature. This technique is embodied in our multi-step loss mechanism, which has proven effective in the reflection removal task. Additionally, we address the scarcity of reflection removal training data by synthesizing a high-quality, non-linear synthetic dataset called RefGAN using Pix2Pix GAN. This dataset significantly enhances the model’s ability to learn better patterns for reflection removal. We also utilize a ranged depth map, extracted from the depth estimation of the ambient image, as an auxiliary feature, leveraging its property of lacking depth estimations for reflections. Our approach demonstrates superior performance on the SIR^2 benchmark and other real-world datasets, proving its effectiveness by outperforming other state-of-the-art models.
图像反射去除对于恢复图像质量至关重要。扭曲的图像会对目标检测和图像分割等任务产生负面影响。在本文中,我们提出了一种使用单幅图像进行图像反射去除的新方法。我们没有关注模型架构,而是引入了一种可推广至图像到图像问题的新训练技术,输入和输出的性质相似。这种技术体现在我们的多步损失机制中,在反射去除任务中证明了其有效性。此外,我们通过对抗生成网络(Pix2Pix GAN)合成了一种高质量的非线性合成数据集RefGan,解决了反射去除训练数据的稀缺问题。该数据集显著提高了模型学习反射去除的更好模式的能力。我们还使用从环境图像的深度估计中提取的范围深度图作为辅助特征,利用其缺乏反射深度估计的特性。我们的方法在SIR^2基准和其他真实世界数据集上表现出卓越的性能,证明了其优于其他最新模型的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 6 pages, 6 figures, IEEE ICASSP 2024
Summary
本文提出了一种利用单图像进行图像反射去除的新方法。该方法引入了一种新的训练技术,可广泛应用于同类图像转换问题。通过多步骤损失机制,该方法在反射去除任务中证明了其有效性。为解决反射去除训练数据不足的问题,研究团队还利用Pix2Pix GAN合成了一个高质量的非线性合成数据集RefGAN。此外,该研究还利用从环境图像的深度估计中提取的深度图作为辅助特征,利用其缺乏反射的特性。该方法在SIR^2基准测试和其他真实世界数据集上表现出卓越的性能,超越了其他最先进的模型。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种新的训练技术,该技术可广泛应用于同类图像转换问题。
- 通过多步骤损失机制,提高了反射去除的效果。
- 利用Pix2Pix GAN合成了一个高质量的非线性合成数据集RefGAN,解决了反射去除训练数据不足的问题。
- 利用从环境图像的深度估计中提取的深度图作为辅助特征,提高了反射去除的准确度。
- 该研究在SIR^2基准测试和其他真实世界数据集上进行了实验验证,证明了其方法的优越性。
- 该方法超越了其他最先进的模型,为图像反射去除领域提供了新的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图




Fine-grained Text to Image Synthesis
Authors:Xu Ouyang, Ying Chen, Kaiyue Zhu, Gady Agam
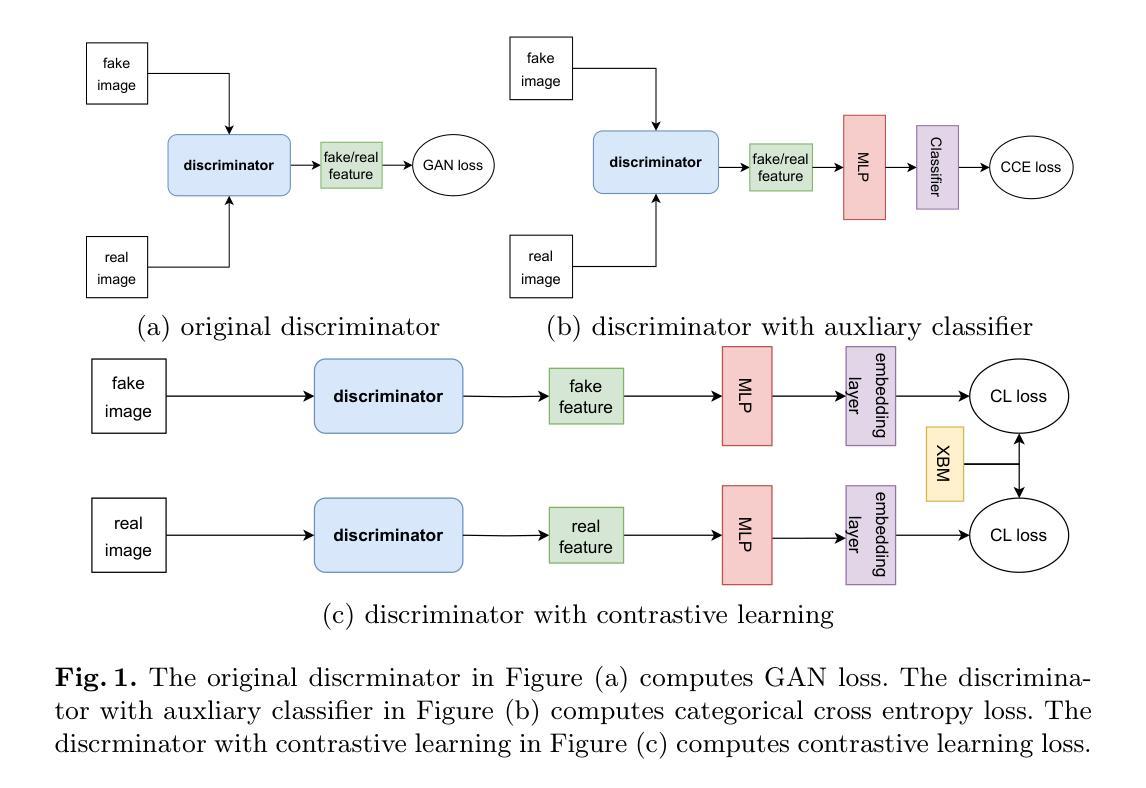
Fine-grained text to image synthesis involves generating images from texts that belong to different categories. In contrast to general text to image synthesis, in fine-grained synthesis there is high similarity between images of different subclasses, and there may be linguistic discrepancy among texts describing the same image. Recent Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN), such as the Recurrent Affine Transformation (RAT) GAN model, are able to synthesize clear and realistic images from texts. However, GAN models ignore fine-grained level information. In this paper we propose an approach that incorporates an auxiliary classifier in the discriminator and a contrastive learning method to improve the accuracy of fine-grained details in images synthesized by RAT GAN. The auxiliary classifier helps the discriminator classify the class of images, and helps the generator synthesize more accurate fine-grained images. The contrastive learning method minimizes the similarity between images from different subclasses and maximizes the similarity between images from the same subclass. We evaluate on several state-of-the-art methods on the commonly used CUB-200-2011 bird dataset and Oxford-102 flower dataset, and demonstrated superior performance.
细粒度文本到图像合成涉及从不同类别的文本生成图像。与一般的文本到图像合成相比,在细粒度合成中,不同子类的图像之间存在高相似性,描述同一图像的文本之间也可能存在语言差异。最近的生成对抗网络(GAN),如循环仿射变换(RAT)GAN模型,能够从文本中合成清晰和现实的图像。然而,GAN模型忽略了细粒度级别的信息。在本文中,我们提出了一种方法,该方法在鉴别器中融入辅助分类器,并采用对比学习方法,以提高由RAT GAN合成的图像的细粒度细节的准确性。辅助分类器帮助鉴别器对图像进行分类,并帮助生成器合成更准确的细粒度图像。对比学习方法最小化不同子类图像之间的相似性,并最大化同一子类图像之间的相似性。我们在常用的CUB-200-2011鸟类数据集和Oxford-102花卉数据集上评估了最先进的方法,并展示了卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本到图像合成技术能够根据不同的文本生成对应的图像。但在精细粒度的文本到图像合成中,不同子类别的图像间高度相似,描述相同图像的文本可能存在语言差异。为提高合成图像的精细粒度细节准确性,本文提出在判别器中加入辅助分类器并采用对比学习方法。辅助分类器帮助判别器对图像进行分类,同时帮助生成器生成更准确的精细粒度图像。对比学习方法则减少不同子类图像间的相似性并增加相同子类图像间的相似性。在常用的CUB-200-2011鸟类数据集和Oxford-102花卉数据集上,本文方法表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像合成技术可生成与文本相对应的图像。
- 精细粒度文本到图像合成面临不同子类图像高度相似的问题。
- 辅助分类器的加入有助于提高判别器的分类能力,进而提升生成图像的精细粒度细节准确性。
- 对比学习方法用于减少不同子类图像间的相似性,并增加相同子类图像间的相似性。
- 在常用的数据集上,本文提出的方法表现优越。
- 辅助分类器同时帮助生成器生成更准确的精细粒度图像。
点此查看论文截图

Creative Portraiture: Exploring Creative Adversarial Networks and Conditional Creative Adversarial Networks
Authors:Sebastian Hereu, Qianfei Hu
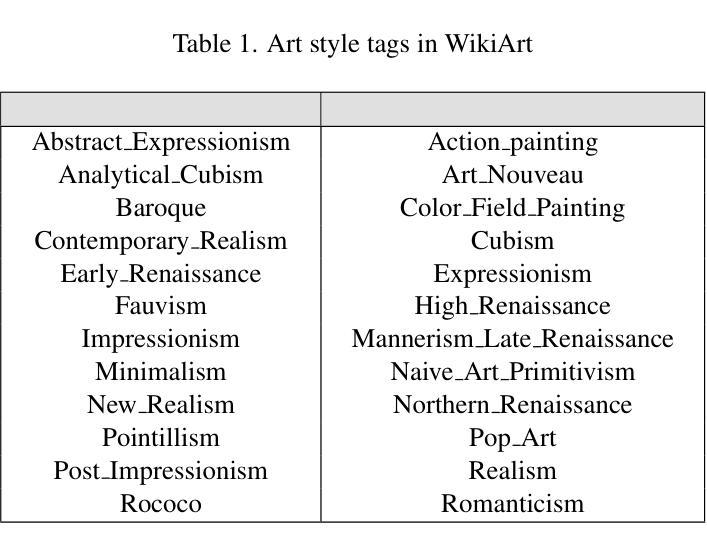
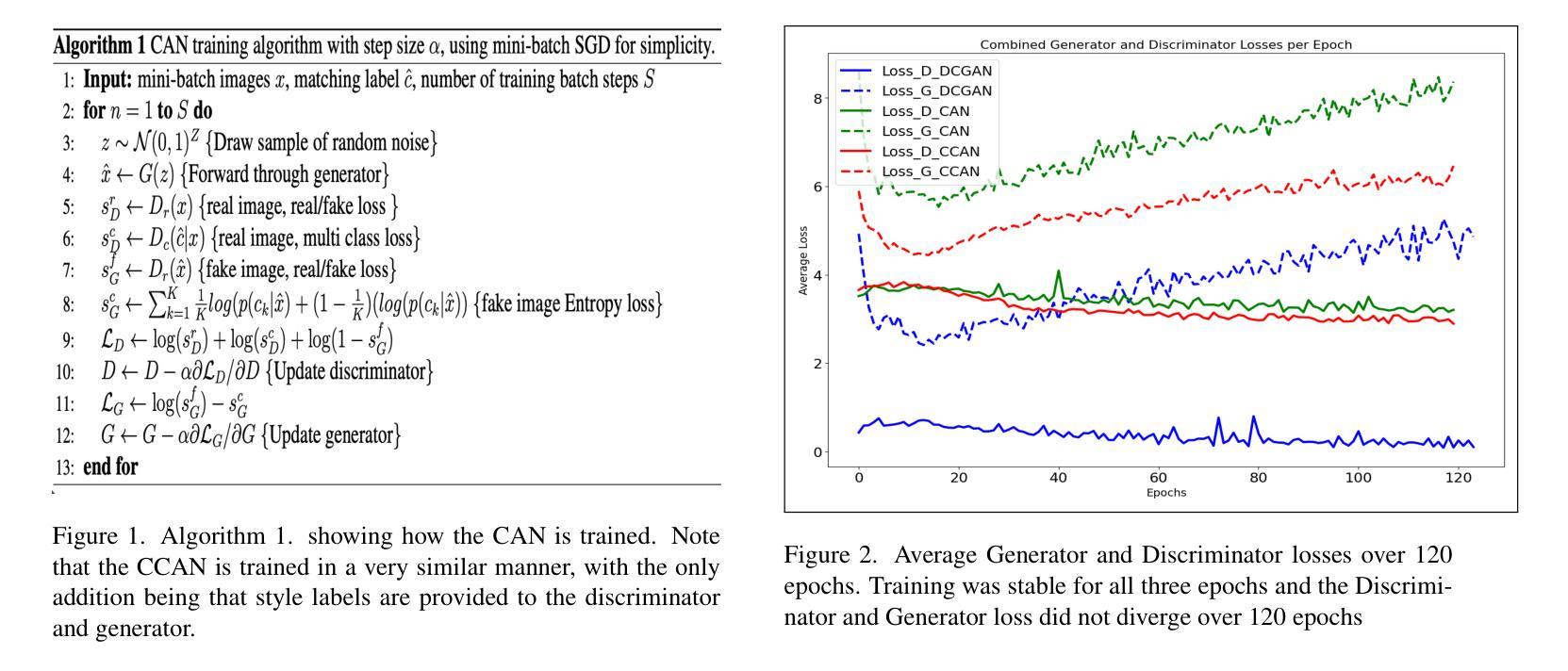
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been combined with generative adversarial networks (GANs) to create deep convolutional generative adversarial networks (DCGANs) with great success. DCGANs have been used for generating images and videos from creative domains such as fashion design and painting. A common critique of the use of DCGANs in creative applications is that they are limited in their ability to generate creative products because the generator simply learns to copy the training distribution. We explore an extension of DCGANs, creative adversarial networks (CANs). Using CANs, we generate novel, creative portraits, using the WikiArt dataset to train the network. Moreover, we introduce our extension of CANs, conditional creative adversarial networks (CCANs), and demonstrate their potential to generate creative portraits conditioned on a style label. We argue that generating products that are conditioned, or inspired, on a style label closely emulates real creative processes in which humans produce imaginative work that is still rooted in previous styles.
卷积神经网络(CNNs)与生成对抗网络(GANs)的成功结合产生了深度卷积生成对抗网络(DCGANs)。DCGANs已被用于从时尚设计和绘画等创意领域生成图像和视频。使用DCGANs在创意应用中的常见批评是,它们在生成创意产品方面的能力有限,因为生成器只是学习复制训练分布。我们探索了DCGANs的扩展版本——创意对抗网络(CANs)。我们使用CANs生成新型创意肖像,并使用WikiArt数据集来训练网络。此外,我们还介绍了CANs的扩展版本——条件创意对抗网络(CCANs),并展示了它们根据风格标签生成创意肖像的潜力。我们认为,生成基于风格标签或受其启发而产生的产品紧密模拟了真正的创意过程,人类在这种过程中会创作出根植于先前风格但又富有想象力的作品。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:卷积神经网络(CNN)与生成对抗网络(GAN)结合创建了深度卷积生成对抗网络(DCGAN),在时尚设计等领域取得了巨大成功。但DCGAN在创造性应用上被批评为局限于生成训练分布的产品。为此,我们探索了DCGAN的扩展版本——创意对抗网络(CAN),并使用WikiArt数据集生成新颖创意肖像。此外,我们还介绍了CAN的扩展版本——条件创意对抗网络(CCAN),并展示了它们根据风格标签生成创意肖像的潜力。我们认为,生成受风格标签影响或启发的产品更接近人类的真实创意过程。
Key Takeaways:
- DCGAN已成功应用于图像和视频生成,尤其在时尚设计和绘画等创意领域。
- DCGAN的一个常见批评是其生成创意产品的能力受限,仅学习复制训练分布。
- 为解决此问题,提出了创意对抗网络(CAN),使用WikiArt数据集生成新颖创意肖像。
- CAN的扩展版本——条件创意对抗网络(CCAN)能够根据风格标签生成创意肖像。
- CCAN的潜力展示了它在模拟人类真实创意过程方面的优势,即生成受风格标签影响或启发的产品。
- CCAN的应用可能推动创意领域的发展,尤其是在需要根据特定风格或要求生成内容的情况下。
点此查看论文截图




HiFiVFS: High Fidelity Video Face Swapping
Authors:Xu Chen, Keke He, Junwei Zhu, Yanhao Ge, Wei Li, Chengjie Wang
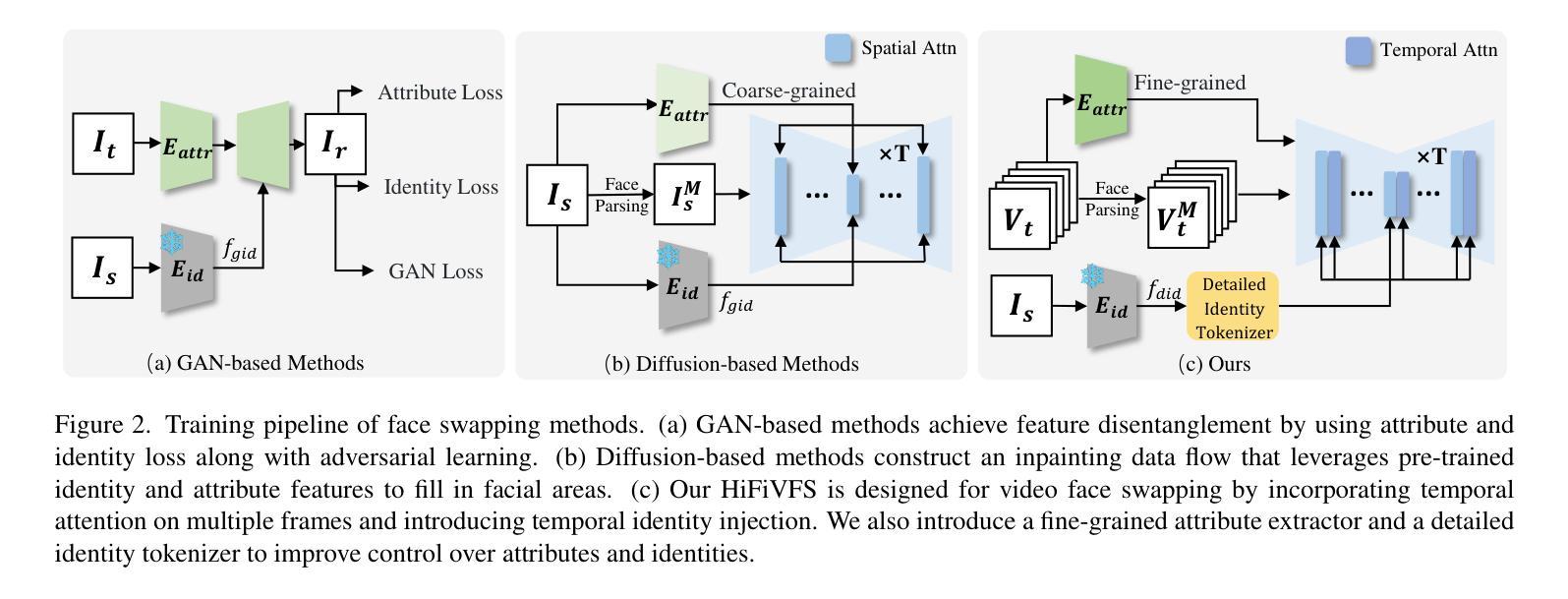
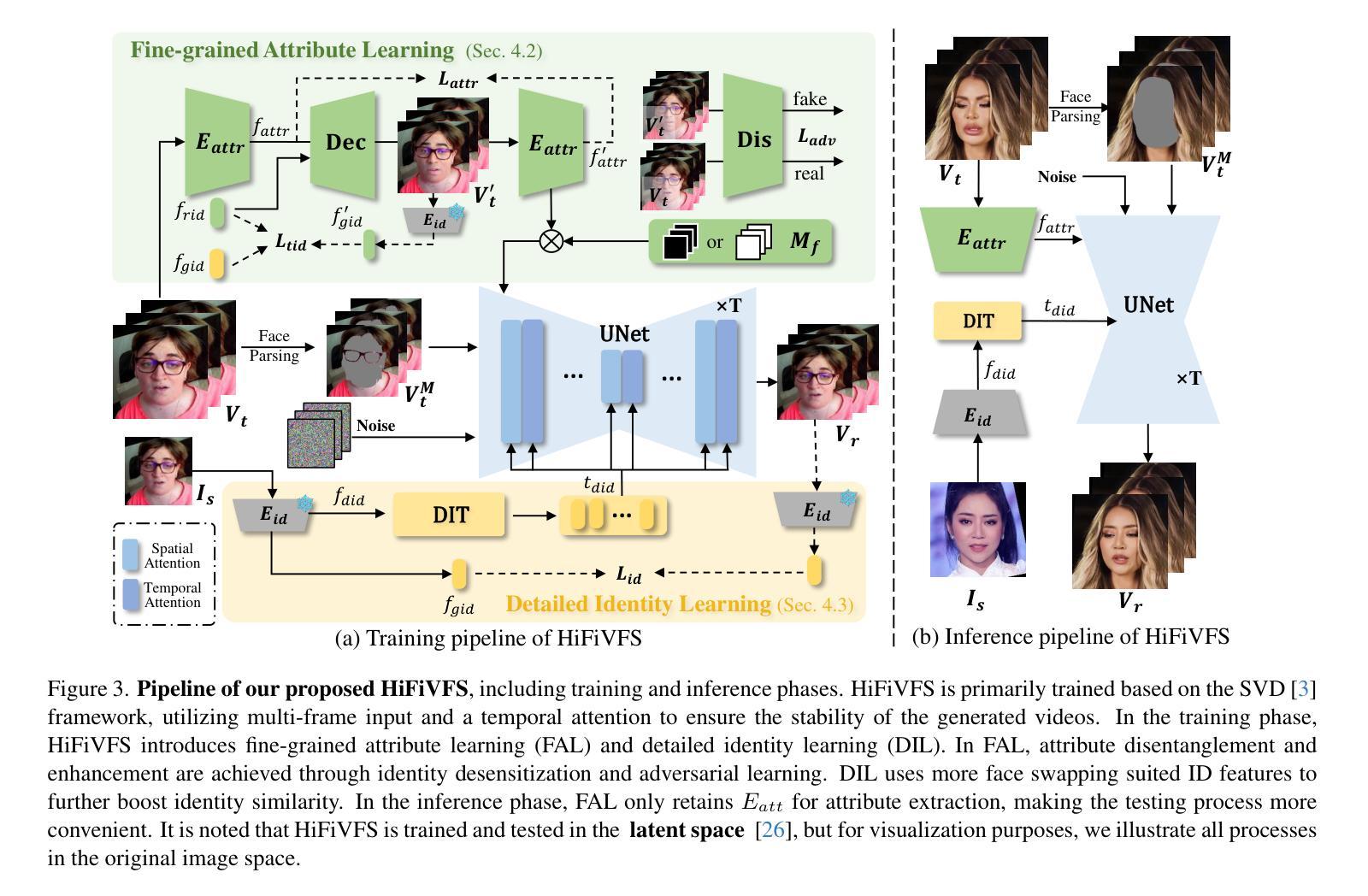
Face swapping aims to generate results that combine the identity from the source with attributes from the target. Existing methods primarily focus on image-based face swapping. When processing videos, each frame is handled independently, making it difficult to ensure temporal stability. From a model perspective, face swapping is gradually shifting from generative adversarial networks (GANs) to diffusion models (DMs), as DMs have been shown to possess stronger generative capabilities. Current diffusion-based approaches often employ inpainting techniques, which struggle to preserve fine-grained attributes like lighting and makeup. To address these challenges, we propose a high fidelity video face swapping (HiFiVFS) framework, which leverages the strong generative capability and temporal prior of Stable Video Diffusion (SVD). We build a fine-grained attribute module to extract identity-disentangled and fine-grained attribute features through identity desensitization and adversarial learning. Additionally, We introduce detailed identity injection to further enhance identity similarity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) in video face swapping, both qualitatively and quantitatively.
面部替换旨在生成结合源身份和目标属性的结果。现有方法主要集中在基于图像的面部替换上。在处理视频时,每一帧都是独立处理的,很难保证时间稳定性。从模型的角度来看,面部替换正逐渐从生成对抗网络(GANs)转向扩散模型(DMs),因为DMs显示出更强的生成能力。当前的基于扩散的方法通常采用修复技术,这在保留光照和妆容等精细属性方面存在困难。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了高保真视频面部替换(HiFiVFS)框架,它利用稳定视频扩散(SVD)的强大生成能力和时间先验。我们构建了一个精细属性模块,通过身份脱敏和对抗性学习提取身份分离和精细属性特征。此外,我们还引入了详细的身份注入,以进一步增强身份相似性。大量实验表明,我们的方法在视频面部替换中实现了定性和定量上的业界最佳水平。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于稳定视频扩散模型(SVD)的高保真视频人脸替换框架被提出,它利用扩散模型的强大生成能力和时间先验知识来解决视频人脸替换中的精细属性保留和时序稳定性问题。通过身份脱敏和对抗学习,构建了精细属性模块来提取身份分离和精细属性特征。此外,引入了详细的身份注入技术,进一步增强身份相似性。实验证明,该方法在视频人脸替换方面达到了定性和定量上的最佳效果。
Key Takeaways
- 视频人脸替换面临时序稳定性和精细属性保留的挑战。
- 现有方法主要关注图像中的人脸替换,处理视频时独立处理每一帧,难以保证时序稳定性。
- 扩散模型(DMs)具有强大的生成能力,正逐渐应用于人脸替换领域。
- 提出的HiFiVFS框架利用稳定视频扩散(SVD)的生成能力和时间先验来解决这些问题。
- 构建了一个精细属性模块,通过身份脱敏和对抗学习提取身份分离和精细属性特征。
- 引入详细身份注入技术,进一步增强身份相似性。
点此查看论文截图

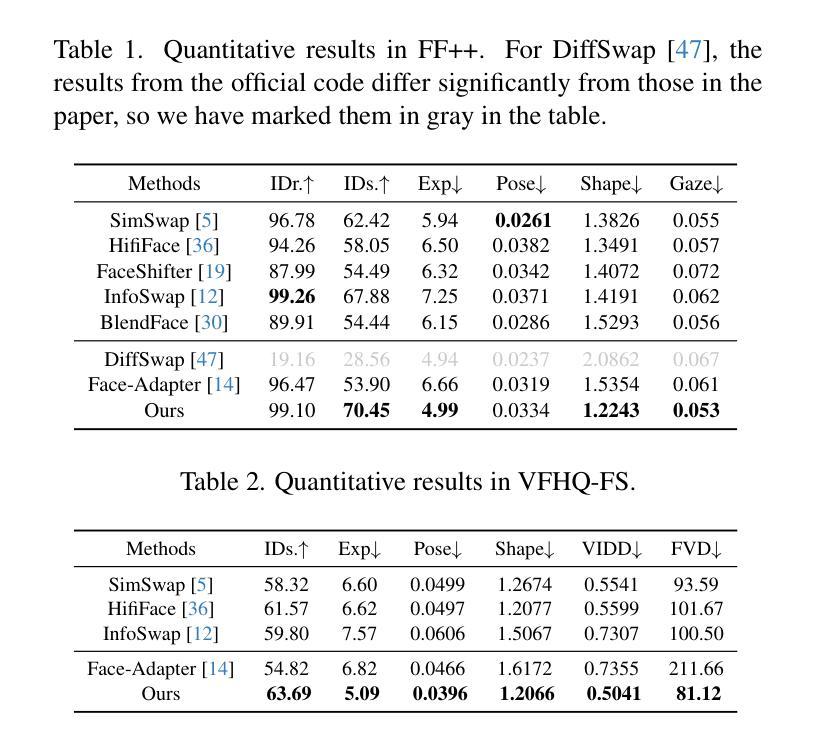
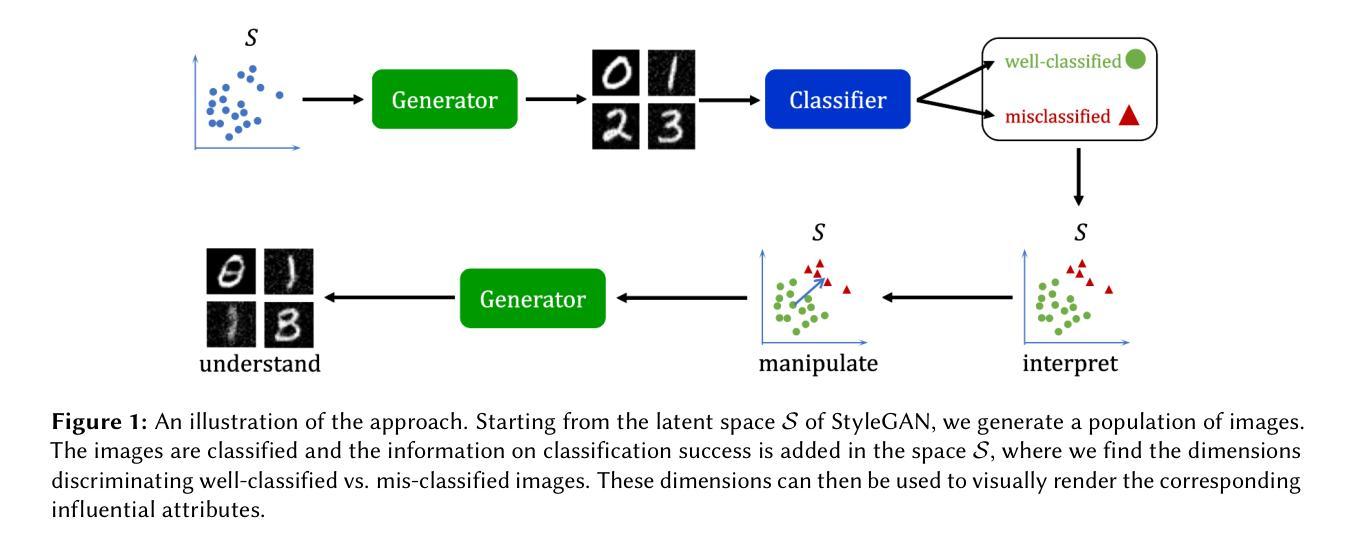
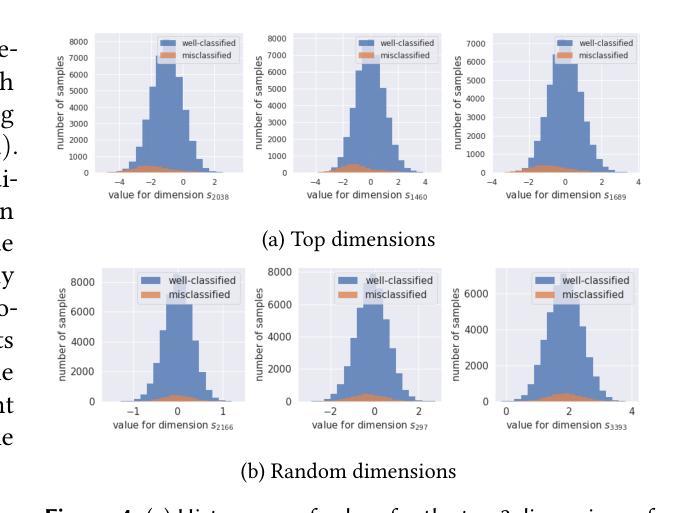
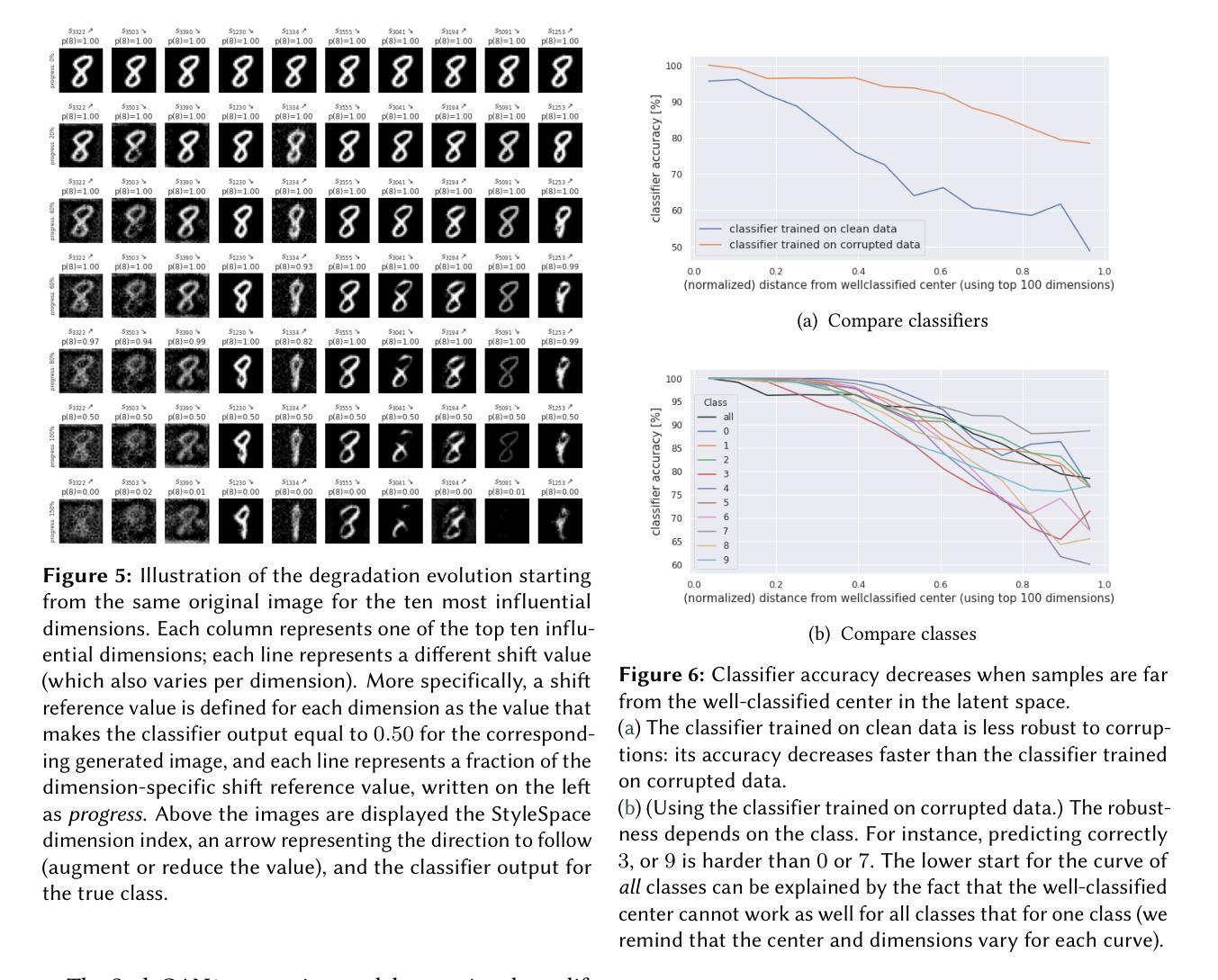
Leveraging generative models to characterize the failure conditions of image classifiers
Authors:Adrien LeCoz, Stéphane Herbin, Faouzi Adjed
We address in this work the question of identifying the failure conditions of a given image classifier. To do so, we exploit the capacity of producing controllable distributions of high quality image data made available by recent Generative Adversarial Networks (StyleGAN2): the failure conditions are expressed as directions of strong performance degradation in the generative model latent space. This strategy of analysis is used to discover corner cases that combine multiple sources of corruption, and to compare in more details the behavior of different classifiers. The directions of degradation can also be rendered visually by generating data for better interpretability. Some degradations such as image quality can affect all classes, whereas other ones such as shape are more class-specific. The approach is demonstrated on the MNIST dataset that has been completed by two sources of corruption: noise and blur, and shows a promising way to better understand and control the risks of exploiting Artificial Intelligence components for safety-critical applications.
在这项工作中,我们解决了识别给定图像分类器失效条件的问题。为此,我们利用最近出现的生成对抗网络(StyleGAN2)产生的高质量图像数据的可控分布能力:失效条件表现为生成模型潜在空间中的性能严重下降方向。这种分析策略用于发现结合多种腐败来源的极端情况,并更详细地比较不同分类器的行为。通过生成数据在视觉上呈现退化方向,以提高其可解释性。一些退化(如图像质量)可能影响所有类别,而其他一些退化(如形状)则更特定于类别。该方法在MNIST数据集上进行了演示,该数据集通过噪声和模糊两种来源进行了补充,并显示了一种更好地理解和控制将人工智能组件用于安全关键应用的风险的有前途的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了通过利用最近出现的生成对抗网络(StyleGAN2)产生的可控高质量图像数据集来识别给定图像分类器的失败条件。失败条件被表达为生成模型潜在空间中性能严重退化的方向。这种分析策略用于发现结合多种腐败来源的极端情况,并更详细地比较不同分类器的行为。通过生成数据呈现退化方向以提高可解释性。一些全局退化(如图像质量)会影响所有类别,而其他类别特定退化(如形状)则更具类别特异性。在MNIST数据集上演示了该方法,该数据集通过噪声和模糊两种来源完成,展示了一种更好地理解和控制利用人工智能组件进行安全关键应用风险的有前途的方式。
Key Takeaways
- 利用StyleGAN2生成可控的高质量图像数据集来识别图像分类器的失败条件。
- 失败条件被表达为生成模型潜在空间中性能退化的方向。
- 通过分析策略发现结合多种腐败来源的极端情况。
- 退化方向可以通过生成数据可视化,以提高解释性。
- 一些退化影响所有类别(如图像质量),而其他退化更具类别特异性(如形状)。
- 在MNIST数据集上演示了该方法,结合了噪声和模糊两种数据来源。
点此查看论文截图



Detecting Unforeseen Data Properties with Diffusion Autoencoder Embeddings using Spine MRI data
Authors:Robert Graf, Florian Hunecke, Soeren Pohl, Matan Atad, Hendrik Moeller, Sophie Starck, Thomas Kroencke, Stefanie Bette, Fabian Bamberg, Tobias Pischon, Thoralf Niendorf, Carsten Schmidt, Johannes C. Paetzold, Daniel Rueckert, Jan S Kirschke
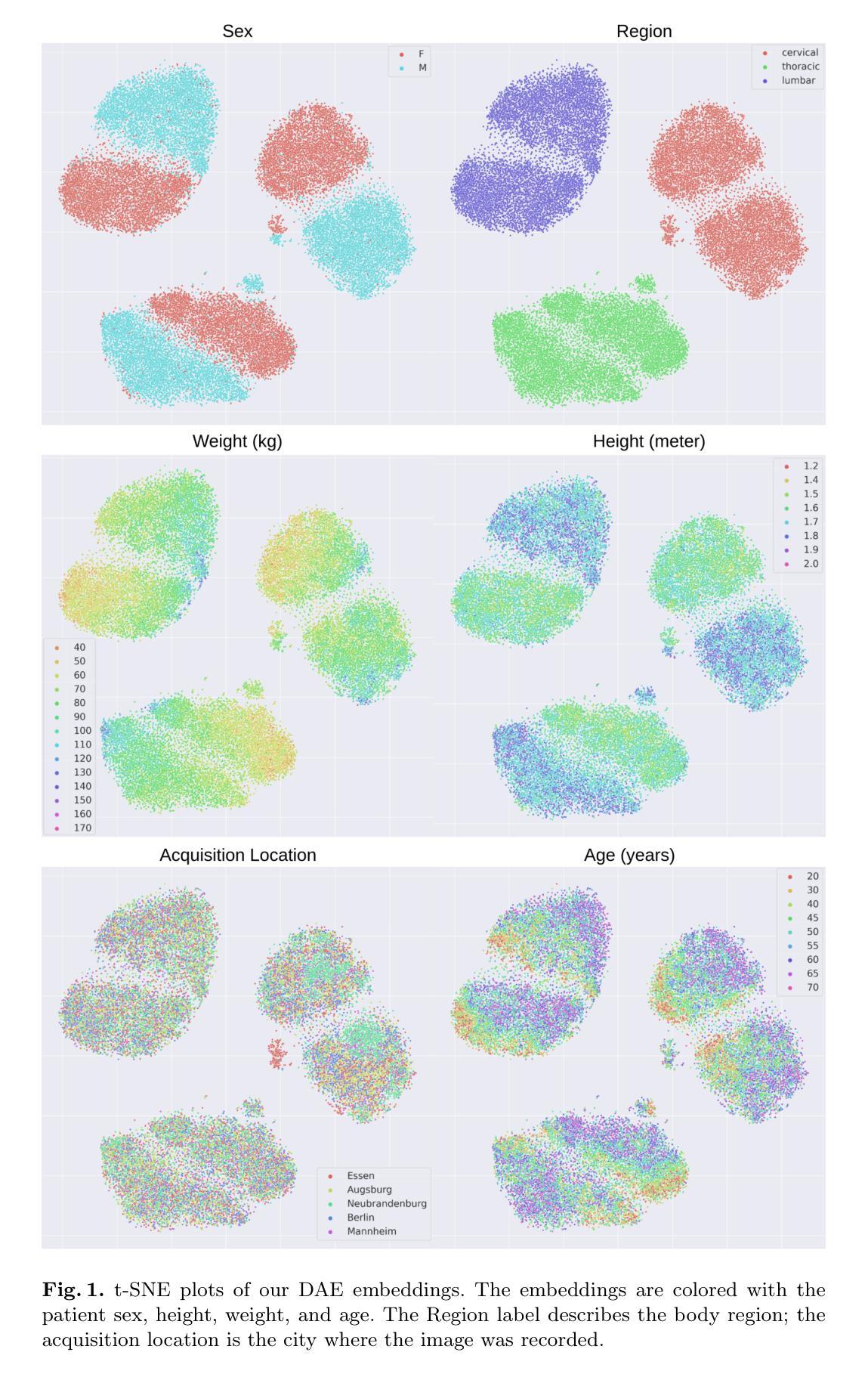
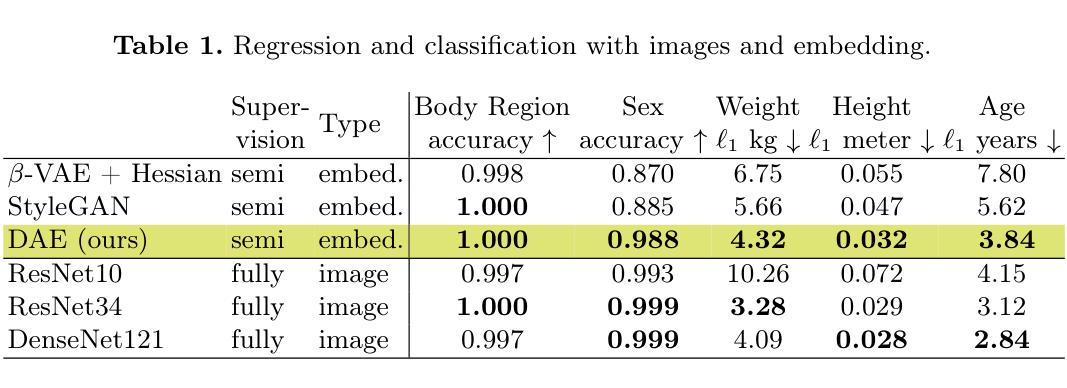
Deep learning has made significant strides in medical imaging, leveraging the use of large datasets to improve diagnostics and prognostics. However, large datasets often come with inherent errors through subject selection and acquisition. In this paper, we investigate the use of Diffusion Autoencoder (DAE) embeddings for uncovering and understanding data characteristics and biases, including biases for protected variables like sex and data abnormalities indicative of unwanted protocol variations. We use sagittal T2-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) images of the neck, chest, and lumbar region from 11186 German National Cohort (NAKO) participants. We compare DAE embeddings with existing generative models like StyleGAN and Variational Autoencoder. Evaluations on a large-scale dataset consisting of sagittal T2-weighted MR images of three spine regions show that DAE embeddings effectively separate protected variables such as sex and age. Furthermore, we used t-SNE visualization to identify unwanted variations in imaging protocols, revealing differences in head positioning. Our embedding can identify samples where a sex predictor will have issues learning the correct sex. Our findings highlight the potential of using advanced embedding techniques like DAEs to detect data quality issues and biases in medical imaging datasets. Identifying such hidden relations can enhance the reliability and fairness of deep learning models in healthcare applications, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes.
深度学习在医学成像领域取得了重大进展,利用大规模数据集来提高诊断和预后。然而,大规模数据集往往由于受试者选择和采集而带有内在错误。本文研究了使用扩散自编码器(DAE)嵌入来揭示和理解数据特征和偏见,包括性别等保护变量的偏见以及指示不需要的协议变化的异常数据。我们使用来自德国国家队列研究(NAKO)的参与者颈部、胸部和腰椎区域的矢状面T2加权磁共振(MR)图像。我们将DAE嵌入与现有的生成模型(如StyleGAN和变分自编码器)进行比较。对包含三个脊椎区域矢状面T2加权MR图像的大规模数据集的评估显示,DAE嵌入可以有效地分离保护变量,如性别和年龄。此外,我们还使用t-SNE可视化来识别成像协议中的不需要的变化,揭示头部定位的差异。我们的嵌入可以识别性别预测器在学习正确性别时会遇到问题的一些样本。我们的研究结果强调了使用先进的嵌入技术(如DAEs)检测医学成像数据集中的数据质量问题和偏见的潜力。识别这些隐藏关系可以增强深度学习模型在医疗保健应用中的可靠性和公平性,最终改善患者护理和结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper was accepted in the “Workshop on Interpretability of Machine Intelligence in Medical Image Computing” (iMIMIC) at MICCAI 2024
Summary
本研究利用扩散自编码器(DAE)嵌入技术,探究在医学成像中揭示和理解数据特性和偏见的方法,特别是对保护变量(如性别)和数据异常值的识别。通过对比StyleGAN和变分自编码器等现有生成模型,DAE嵌入在大型数据集上表现出优异性能,能有效区分保护变量,如性别和年龄。此外,该研究还利用t-SNE可视化技术识别成像协议中的意外变化,揭示了头部定位的差异。本研究揭示了使用高级嵌入技术如DAEs检测医学成像数据集数据质量问题和偏见的潜力,有助于增强深度学习模型在医疗应用中的可靠性和公平性,最终改善患者护理和结果。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散自编码器(DAE)嵌入技术用于医学成像数据的分析和理解。
- DAE嵌入能够有效区分保护变量,如性别和年龄。
- 与现有生成模型(如StyleGAN和变分自编码器)相比,DAE嵌入在大型医学图像数据集上表现出更好的性能。
- 利用t-SNE可视化技术揭示了成像协议中的意外变化。
- DAE嵌入能够识别数据质量问题和偏见,有助于增强深度学习模型在医疗应用中的可靠性和公平性。
- 该研究对于提高患者护理和结果具有潜在意义。
点此查看论文截图

Colour and Brush Stroke Pattern Recognition in Abstract Art using Modified Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Networks
Authors:Srinitish Srinivasan, Varenya Pathak, Abirami S
Abstract Art is an immensely popular, discussed form of art that often has the ability to depict the emotions of an artist. Many researchers have made attempts to study abstract art in the form of edge detection, brush stroke and emotion recognition algorithms using machine and deep learning. This papers describes the study of a wide distribution of abstract paintings using Generative Adversarial Neural Networks(GAN). GANs have the ability to learn and reproduce a distribution enabling researchers and scientists to effectively explore and study the generated image space. However, the challenge lies in developing an efficient GAN architecture that overcomes common training pitfalls. This paper addresses this challenge by introducing a modified-DCGAN (mDCGAN) specifically designed for high-quality artwork generation. The approach involves a thorough exploration of the modifications made, delving into the intricate workings of DCGANs, optimisation techniques, and regularisation methods aimed at improving stability and realism in art generation enabling effective study of generated patterns. The proposed mDCGAN incorporates meticulous adjustments in layer configurations and architectural choices, offering tailored solutions to the unique demands of art generation while effectively combating issues like mode collapse and gradient vanishing. Further this paper explores the generated latent space by performing random walks to understand vector relationships between brush strokes and colours in the abstract art space and a statistical analysis of unstable outputs after a certain period of GAN training and compare its significant difference. These findings validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, emphasising its potential to revolutionise the field of digital art generation and digital art ecosystem.
摘要艺术是一种非常流行且备受讨论的艺术形式,通常能够描绘出艺术家的情感。许多研究人员已经尝试使用机器学习和深度学习进行边缘检测、笔触和情感识别算法来研究抽象艺术。本文描述了一种使用生成对抗神经网络(GAN)研究广泛分布的抽象绘画的研究。GAN具有学习和复制分布的能力,使研究者和科学家能够有效地探索和研究生成的图像空间。然而,挑战在于开发一种有效的GAN架构,能够克服常见的训练陷阱。本文通过引入一种针对高质量艺术作品生成的改进型DCGAN(mDCGAN)来解决这一挑战。该方法涉及对所做的修改的彻底探索,深入研究DCGAN的精细工作原理、优化技术和正则化方法,旨在提高艺术生成的稳定性和真实性,从而有效研究生成的图案。所提出的mDCGAN对层配置和架构选择进行了精细调整,为艺术生成提供了量身定制的解决方案,同时有效地解决了模式崩溃和梯度消失等问题。此外,本文通过执行随机游走探索生成的潜在空间,了解抽象艺术空间中笔触和颜色之间的向量关系,并分析了GAN训练某段时间后不稳定输出的统计数据及其显著差异。这些发现验证了所提出方法的有效性,并强调其在数字艺术生成和数字艺术生态系统领域中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication by Intelligent Decision Technologies
摘要
本研究利用生成对抗神经网络(GAN)对抽象绘画进行广泛分布的研究。GANs具有学习和复制分布的能力,使研究者和科学家能够有效地探索和研究生成的图像空间。研究针对开发高效GAN架构以克服常见训练难题的挑战,提出了一种改进的DCGAN(mDCGAN),专门用于高质量艺术作品生成。该方法深入探讨了所做的修改,探讨了DCGANs的精细工作原理、优化技术和正则化方法,旨在提高艺术生成的稳定性和逼真性,从而有效地研究生成的图案。mDCGAN在层配置和架构选择方面进行了精细调整,为艺术生成的独特需求提供量身定制的解决方案,同时有效解决模式崩溃和梯度消失等问题。此外,本文还通过随机游走的方式探索了生成的潜在空间,理解抽象艺术空间中笔触和颜色之间的向量关系,并对GAN训练某一段时间后不稳定输出的统计结果进行分析和比较,验证了所提方法的有效性,强调了其在数字艺术生成和数字艺术生态系统领域的潜力。
关键见解
- 利用生成对抗神经网络(GAN)研究抽象绘画的分布。
- 提出了改进的DCGAN(mDCGAN)架构,用于高质量的艺术作品生成。
- mDCGAN在层配置和架构选择上的精细调整,满足了艺术生成的独特需求。
- mDCGAN解决了模式崩溃和梯度消失等问题,提高了艺术生成的稳定性和逼真性。
- 通过随机游走探索生成的潜在空间,理解抽象艺术空间中笔触和颜色之间的向量关系。
- 对GAN训练过程中的不稳定输出进行统计分析和比较。
- 验证了所提方法的有效性,并强调了其在数字艺术生成和数字艺术生态系统领域的潜力。
点此查看论文截图

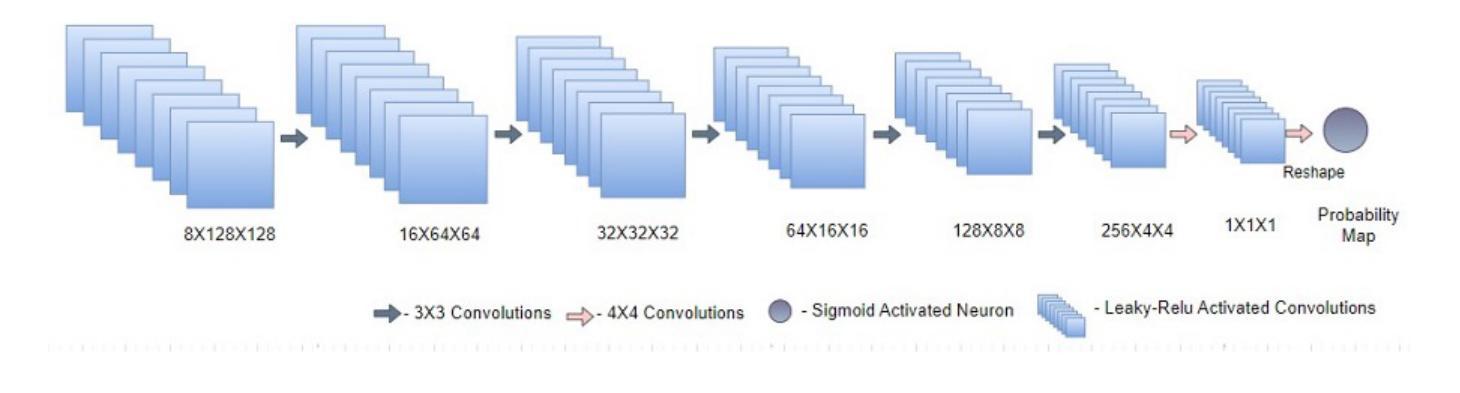
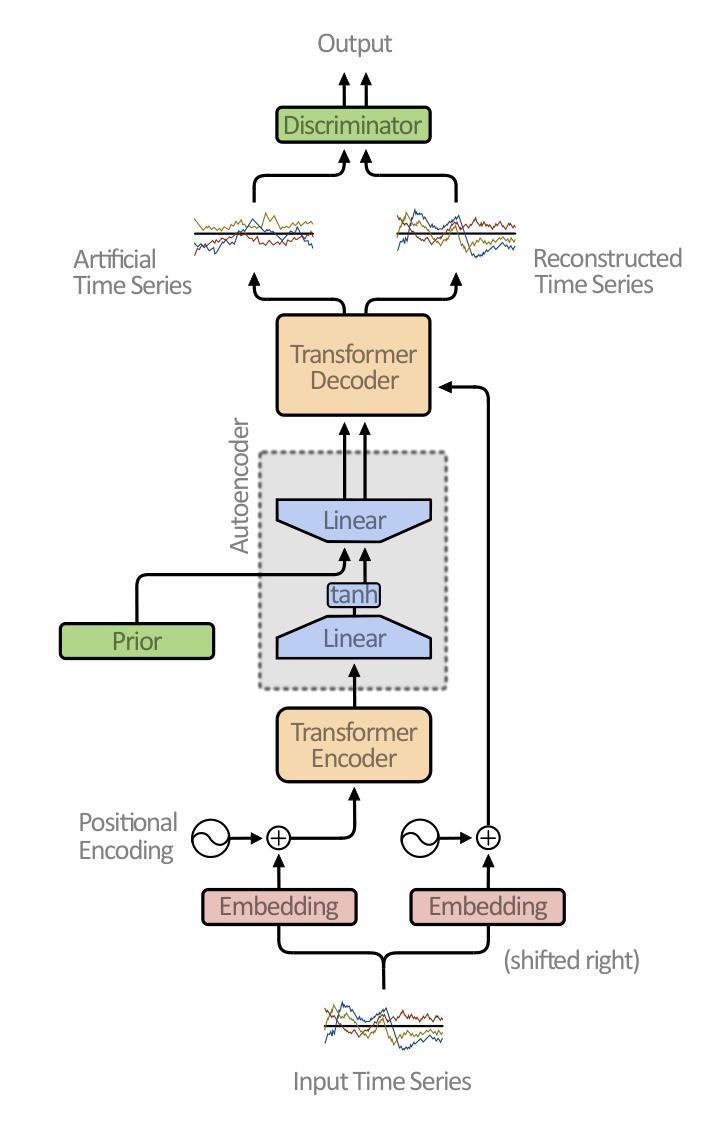
Representation Learning of Multivariate Time Series using Attention and Adversarial Training
Authors:Leon Scharwächter, Sebastian Otte
A critical factor in trustworthy machine learning is to develop robust representations of the training data. Only under this guarantee methods are legitimate to artificially generate data, for example, to counteract imbalanced datasets or provide counterfactual explanations for blackbox decision-making systems. In recent years, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have shown considerable results in forming stable representations and generating realistic data. While many applications focus on generating image data, less effort has been made in generating time series data, especially multivariate signals. In this work, a Transformer-based autoencoder is proposed that is regularized using an adversarial training scheme to generate artificial multivariate time series signals. The representation is evaluated using t-SNE visualizations, Dynamic Time Warping (DTW) and Entropy scores. Our results indicate that the generated signals exhibit higher similarity to an exemplary dataset than using a convolutional network approach.
在可信机器学习中的关键因素是开发稳健的训练数据表示。只有在这个保证下,人工生成数据的方法才是合法的,例如,对抗不平衡数据集或为黑箱决策制定系统提供反事实解释。近年来,生成对抗网络(GANs)在形成稳定表示和生成真实数据方面取得了显著成果。虽然许多应用都集中在生成图像数据上,但在生成时间序列数据方面所付出的努力较少,尤其是多元信号。在这项工作中,提出了一种基于Transformer的自编码器,通过使用对抗训练方案进行正则化来生成人工多元时间序列信号。通过t-SNE可视化、动态时间弯曲(DTW)和熵分数来评估表示方法。我们的结果表明,生成的信号与样本数据集相比,使用卷积网络方法具有更高的相似性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文强调机器学习中的稳健表示法的重要性,特别是对于生成的数据而言。通过利用生成对抗网络(GANs)技术,可以形成稳定的数据表示并生成真实的数据。尽管图像数据生成应用广泛,但在生成时间序列数据方面,尤其是多元信号生成方面的努力较少。本研究提出了一种基于Transformer的自编码器,采用对抗训练方案进行正则化,以生成人工多元时间序列信号。通过t-SNE可视化、动态时间弯曲(DTW)和熵评分对表示进行评估,结果表明生成的信号与样本数据集有较高的相似性,优于卷积网络方法。
Key Takeaways
- 机器学习中的稳健表示法对于生成数据至关重要。
- 生成对抗网络(GANs)可用于形成稳定的数据表示并生成真实数据。
- 尽管图像数据生成应用广泛,但时间序列数据的生成,特别是多元信号的生成受到的关注较少。
- 研究提出了一种基于Transformer的自编码器,采用对抗训练方案进行正则化,以生成多元时间序列信号。
- 通过多种评估方法,包括t-SNE可视化、动态时间弯曲(DTW)和熵评分,验证了生成的信号的真实性及与样本数据的高相似性。
- 该方法优于使用卷积网络的方法。
点此查看论文截图

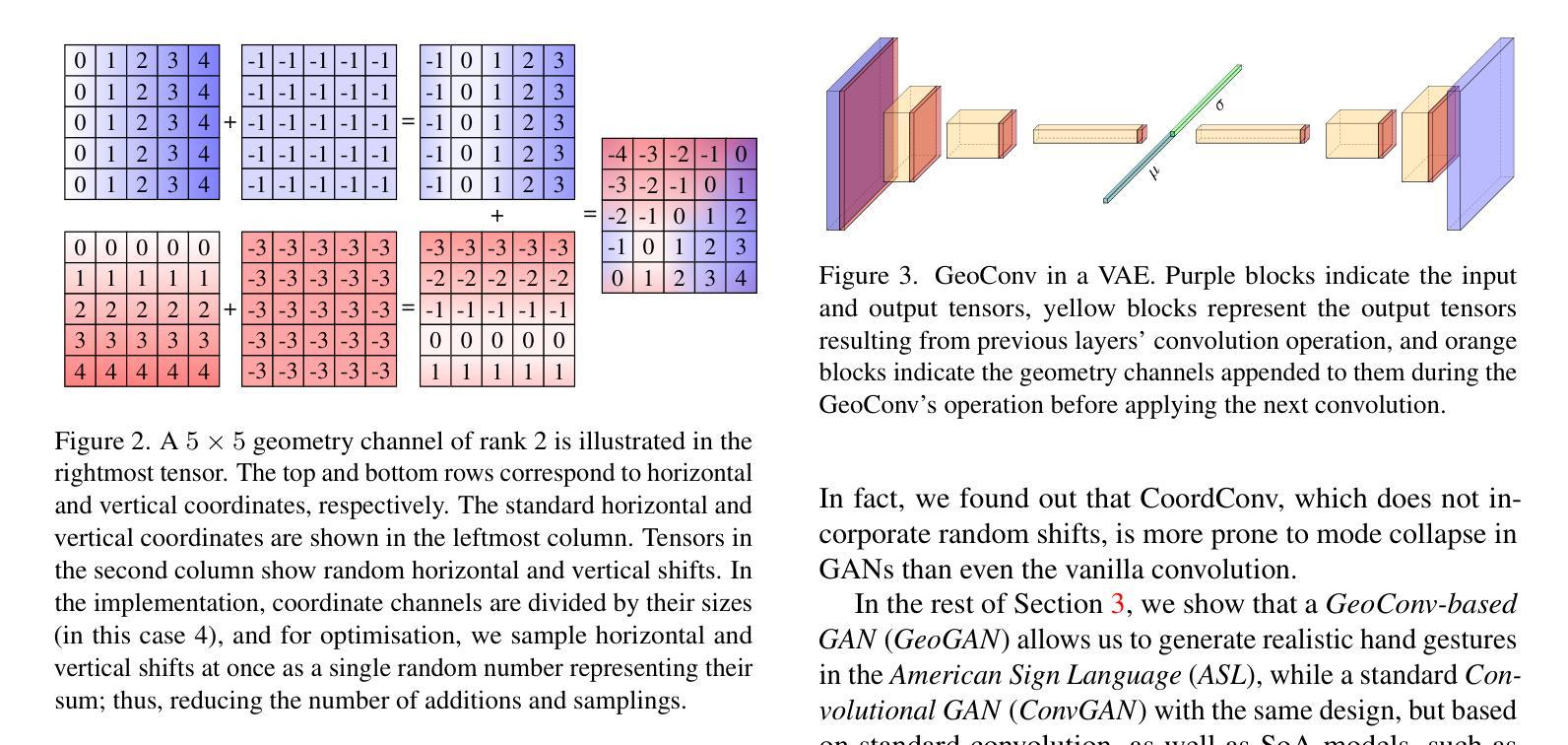
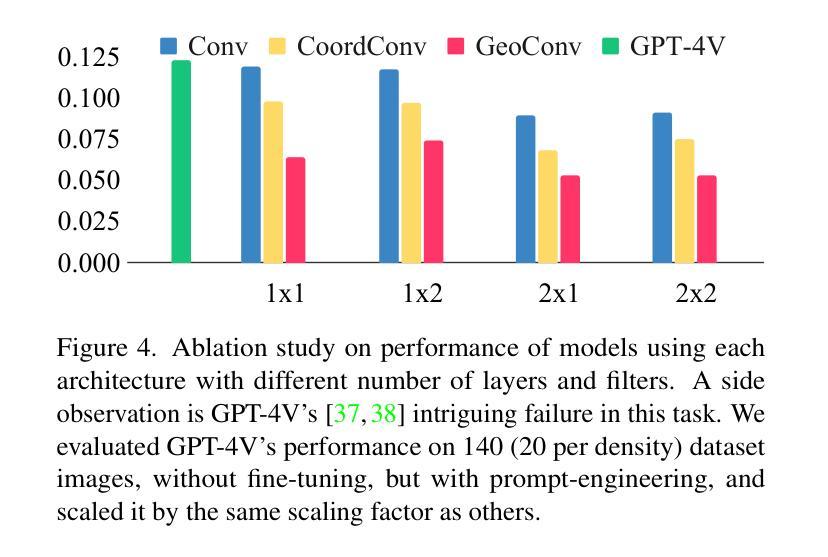
GeoPos: A Minimal Positional Encoding for Enhanced Fine-Grained Details in Image Synthesis Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Authors:Mehran Hosseini, Peyman Hosseini
The enduring inability of image generative models to recreate intricate geometric features, such as those present in human hands and fingers has been an ongoing problem in image generation for nearly a decade. While strides have been made by increasing model sizes and diversifying training datasets, this issue remains prevalent across all models, from denoising diffusion models to Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN), pointing to a fundamental shortcoming in the underlying architectures. In this paper, we demonstrate how this problem can be mitigated by augmenting convolution layers geometric capabilities through providing them with a single input channel incorporating the relative n-dimensional Cartesian coordinate system. We show this drastically improves quality of images generated by Diffusion Models, GANs, and Variational AutoEncoders (VAE).
图像生成模型长期无法重现复杂几何特征,如人类的手和手指等特征,这一问题在图像生成领域已持续近十年。尽管通过增加模型规模和多样化训练数据集,已经取得了一些进展,但这一问题在包括降噪扩散模型、生成对抗网络(GAN)在内的所有模型中依然普遍存在,这表明现有架构存在根本性不足。在本文中,我们展示了如何通过增强卷积层的几何能力来解决这一问题,具体做法是为其提供一个包含相对n维笛卡尔坐标系统的单一输入通道。我们证明了这可以极大改善扩散模型、GAN和变分自编码器(VAE)生成的图像质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at WACV 2025. Contains 19 pages, 15 figures, and 9 tables
Summary
本文探讨了图像生成模型在重建复杂几何特征(如人手和手指)方面的持续难题。尽管通过增大模型规模和多样化训练数据集已经取得了一些进展,但这一问题在包括去噪扩散模型、生成对抗网络(GAN)在内的所有模型中仍然普遍存在,这表明现有架构存在根本性缺陷。本文演示了如何通过为卷积层提供包含相对n维笛卡尔坐标系统的单一输入通道来增强其几何能力,从而缓解这一问题。此方法显著提高了扩散模型、GAN和变分自编码器(VAE)生成的图像质量。
Key Takeaways
- 图像生成模型在重建复杂几何特征方面存在持续难题,尤其是人手和手指的细节。
- 现有模型,包括扩散模型、GAN和VAE,都面临这一问题。
- 问题指向现有模型架构的根本性短板。
- 通过为卷积层提供包含n维笛卡尔坐标系统的单一输入通道,可以增强其几何能力。
- 此方法有助于改善扩散模型、GAN和VAE生成的图像质量。
- 该策略为图像生成模型的进一步发展提供了新的方向。
点此查看论文截图



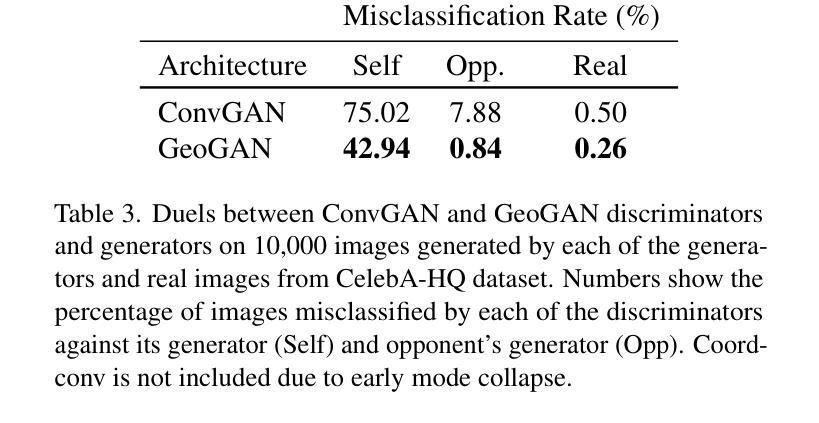
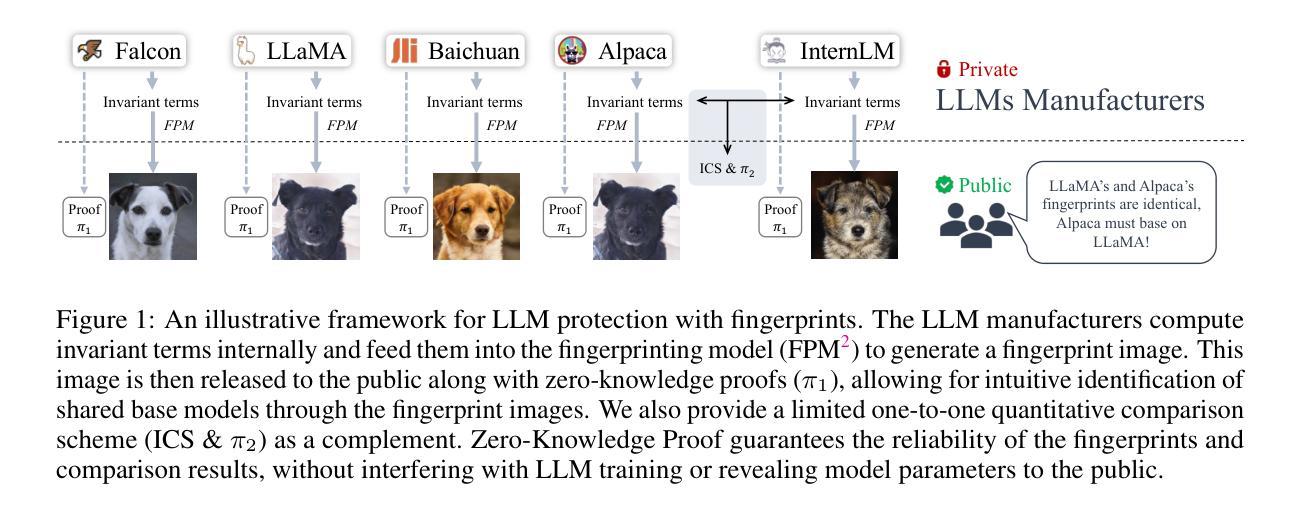
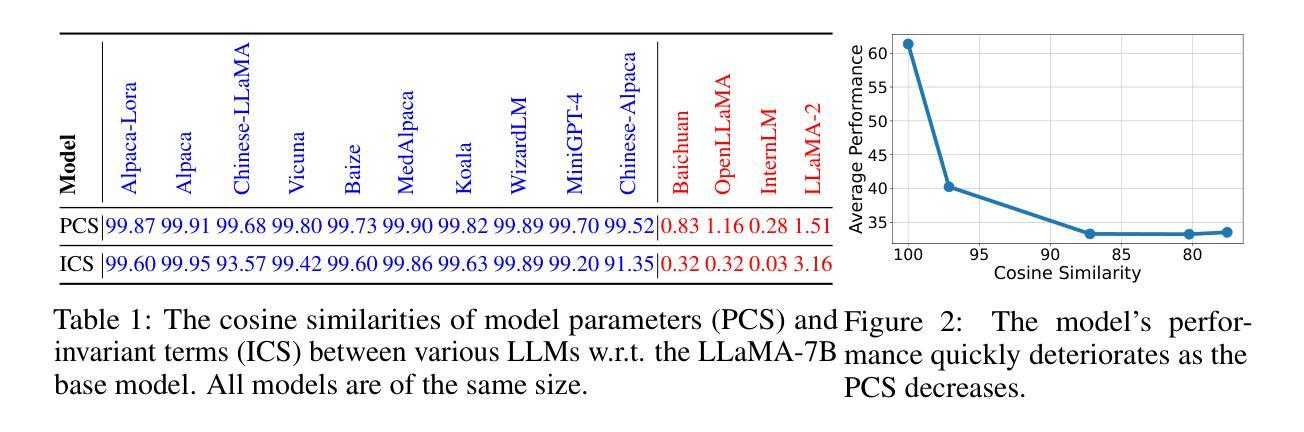
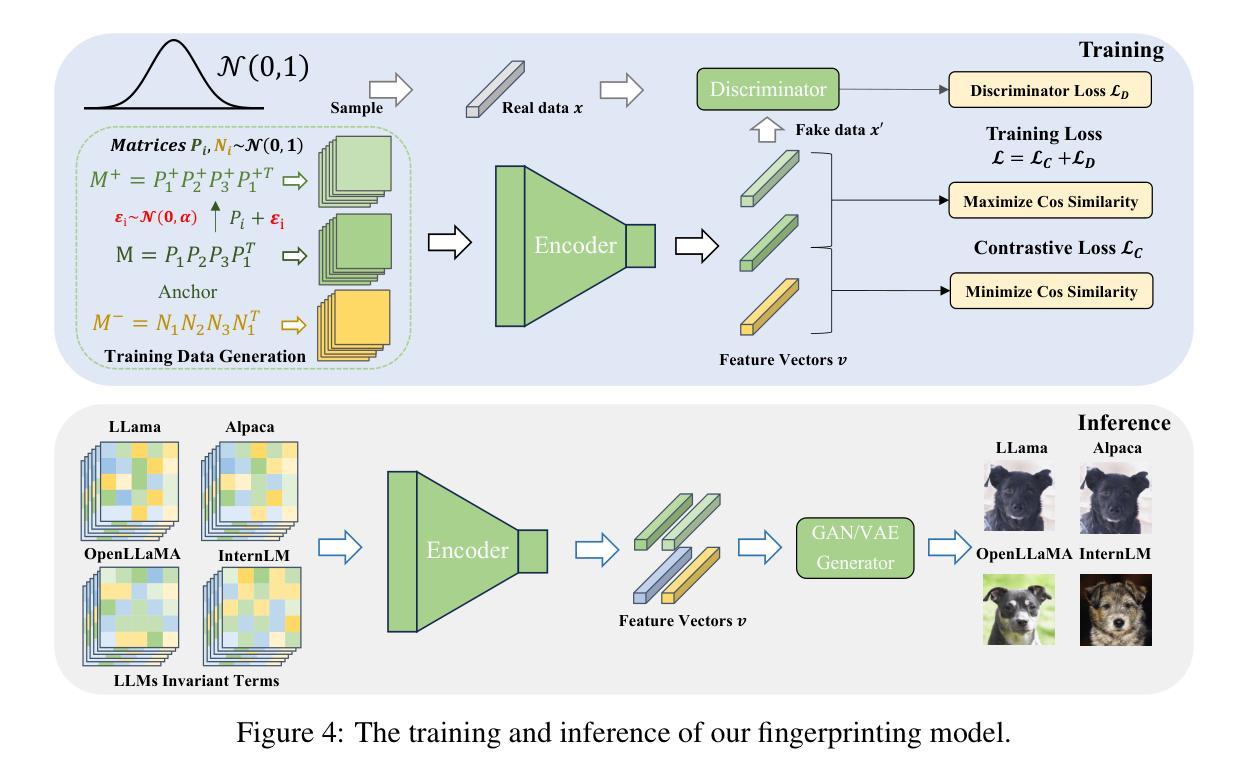
HuRef: HUman-REadable Fingerprint for Large Language Models
Authors:Boyi Zeng, Lizheng Wang, Yuncong Hu, Yi Xu, Chenghu Zhou, Xinbing Wang, Yu Yu, Zhouhan Lin
Protecting the copyright of large language models (LLMs) has become crucial due to their resource-intensive training and accompanying carefully designed licenses. However, identifying the original base model of an LLM is challenging due to potential parameter alterations. In this study, we introduce HuRef, a human-readable fingerprint for LLMs that uniquely identifies the base model without interfering with training or exposing model parameters to the public. We first observe that the vector direction of LLM parameters remains stable after the model has converged during pretraining, with negligible perturbations through subsequent training steps, including continued pretraining, supervised fine-tuning, and RLHF, which makes it a sufficient condition to identify the base model. The necessity is validated by continuing to train an LLM with an extra term to drive away the model parameters’ direction and the model becomes damaged. However, this direction is vulnerable to simple attacks like dimension permutation or matrix rotation, which significantly change it without affecting performance. To address this, leveraging the Transformer structure, we systematically analyze potential attacks and define three invariant terms that identify an LLM’s base model. Due to the potential risk of information leakage, we cannot publish invariant terms directly. Instead, we map them to a Gaussian vector using an encoder, then convert it into a natural image using StyleGAN2, and finally publish the image. In our black-box setting, all fingerprinting steps are internally conducted by the LLMs owners. To ensure the published fingerprints are honestly generated, we introduced Zero-Knowledge Proof (ZKP). Experimental results across various LLMs demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. The code is available at https://github.com/LUMIA-Group/HuRef.
保护大型语言模型(LLM)的版权对于其资源密集型训练和精心设计的许可证变得至关重要。然而,由于潜在参数改动,确定LLM的原始基础模型具有挑战性。在这项研究中,我们介绍了HuRef,这是一种人类可读的LLM指纹,可以唯一地识别基础模型,而不会干扰训练或向公众暴露模型参数。我们首先观察到,在预训练收敛后,LLM参数的向量方向保持稳定,后续训练步骤(包括继续预训练、监督微调以及RLHF)引起的扰动微乎其微,这足以成为识别基础模型的充分条件。这一必要性的验证是通过继续训练LLM并添加额外项来驱使模型参数的方向变化,导致模型受损。然而,这个方向容易受到简单的攻击,如维度置换或矩阵旋转,这些攻击会显著改变方向而不会影响性能。为了解决这个问题,我们利用Transformer结构,系统地分析了潜在攻击并定义了三个不变术语来识别LLM的基础模型。由于潜在的信息泄露风险,我们无法直接发布不变术语。相反,我们将其映射到高斯向量并使用编码器,然后使用StyleGAN2将其转换为自然图像并最终发布。在我们的黑箱设置中,所有指纹打印步骤均由LLM所有者内部进行。为了确保发布的指纹是诚实生成的,我们引入了零知识证明(ZKP)。在不同LLM上的实验结果证明了我们的方法的有效性。相关代码已发布在https://github.com/LUMIA-Group/HuRef。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对大型语言模型(LLM)的新型版权保护方法——HuRef。该方法通过生成人类可读的指纹来唯一识别LLM的基础模型,且不会干扰训练或公开模型参数。研究观察到LLM参数向量方向在预训练收敛后保持稳定,因此可作为识别基础模型的充分条件。为应对潜在攻击,研究利用Transformer结构定义了三个不变术语,并通过编码器将其映射到高斯向量,再转换成自然图像进行发布。同时引入零知识证明(ZKP)确保发布的指纹真实有效。该方法在多种LLM上的实验结果表明其有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的版权保护至关重要,因其在资源密集型的训练和精心设计的许可下。
- HuRef作为一种新型版权保护方法,能够唯一识别LLM的基础模型。
- LLM参数向量方向在预训练收敛后的稳定性为识别基础模型提供了依据。
- HuRef通过生成人类可读的指纹,既不会干扰训练,也不会公开模型参数。
- 为应对潜在攻击,研究利用Transformer结构定义了三个不变术语进行识别。
- 发布指纹时,利用编码器将其映射到高斯向量,再转换成自然图像。
点此查看论文截图

Feature Extraction for Generative Medical Imaging Evaluation: New Evidence Against an Evolving Trend
Authors:McKell Woodland, Austin Castelo, Mais Al Taie, Jessica Albuquerque Marques Silva, Mohamed Eltaher, Frank Mohn, Alexander Shieh, Suprateek Kundu, Joshua P. Yung, Ankit B. Patel, Kristy K. Brock
Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID) is a widely used metric for assessing synthetic image quality. It relies on an ImageNet-based feature extractor, making its applicability to medical imaging unclear. A recent trend is to adapt FID to medical imaging through feature extractors trained on medical images. Our study challenges this practice by demonstrating that ImageNet-based extractors are more consistent and aligned with human judgment than their RadImageNet counterparts. We evaluated sixteen StyleGAN2 networks across four medical imaging modalities and four data augmentation techniques with Fr'echet distances (FDs) computed using eleven ImageNet or RadImageNet-trained feature extractors. Comparison with human judgment via visual Turing tests revealed that ImageNet-based extractors produced rankings consistent with human judgment, with the FD derived from the ImageNet-trained SwAV extractor significantly correlating with expert evaluations. In contrast, RadImageNet-based rankings were volatile and inconsistent with human judgment. Our findings challenge prevailing assumptions, providing novel evidence that medical image-trained feature extractors do not inherently improve FDs and can even compromise their reliability. Our code is available at https://github.com/mckellwoodland/fid-med-eval.
Fréchet Inception Distance(FID)是评估合成图像质量的一个广泛使用的指标。它依赖于基于ImageNet的特征提取器,这使得其在医学影像中的应用不明确。最近的趋势是通过在医学影像上训练的特征提取器来适应FID。我们的研究通过证明基于ImageNet的提取器比RadImageNet对应的提取器在医学成像中的表现更为一致且与人类判断更吻合,挑战了这一做法。我们评估了四个医学成像模态和四种数据增强技术的十六个StyleGAN2网络,使用基于十一个ImageNet或RadImageNet训练的特征提取器计算Fréchet距离(FDs)。通过视觉图灵测试与人的判断进行比较显示,基于ImageNet的提取器产生的排名与人的判断一致,从ImageNet训练的SwAV提取器得出的FD与专家评价有着显著的相关性。相比之下,基于RadImageNet的排名波动性较大且与人类判断不一致。我们的研究结果挑战了现有的假设,提供了新的证据表明经过医学图像训练的特征提取器并不一定会提高FID,甚至可能损害其可靠性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/mckellwoodland/fid-med-eval中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This preprint has not undergone peer review or any post-submission improvements or corrections. The Version of Record of this contribution is published in LNCS vol. 15012, and is available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72390-2_9
Summary
本研究挑战了将Fréchet Inception Distance(FID)评估指标应用于医学图像质量的常规做法。通过对十六个StyleGAN2网络在不同医学成像模式和不同数据增强技术上的评估发现,基于ImageNet的特征提取器与基于RadImageNet的特征提取器相比,更为一致且与人为判断对齐。采用ImageNet训练的SwAV特征提取器计算的Fréchet距离与人类专家评价的相关性更高,而基于RadImageNet的排名则表现出不稳定且与人为判断不一致。本研究对现有的假设提出挑战,提供新的证据表明,针对医学图像训练的特征提取器并不一定能提高FID的可靠性。
Key Takeaways
- FID作为一种评估合成图像质量的指标,其适用性于医学成像领域尚不清楚。
- 目前有一种趋势是将FID适应于医学成像,通过基于医学图像的特征提取器进行训练。
- 本研究表明,基于ImageNet的特征提取器在评估医学图像质量时,相较于基于RadImageNet的特征提取器,具有更高的一致性和与人为判断的对齐度。
- 使用ImageNet训练的SwAV特征提取器计算的Fréchet距离与人类专家评价有较高的相关性。
- 基于RadImageNet的特征提取器在评估医学图像质量时表现出不稳定性和与人为判断的不一致性。
- 研究发现,针对医学图像训练的特征提取器并不一定能提高FID评估的可靠性。
点此查看论文截图

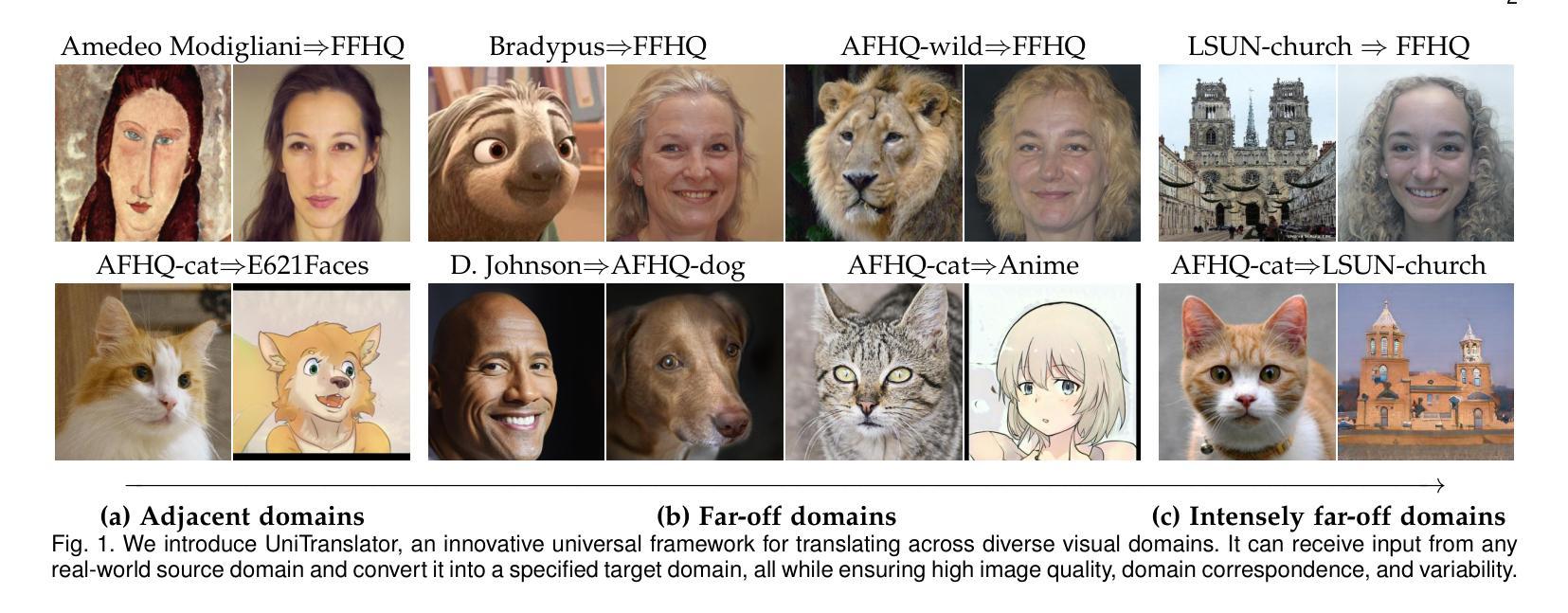
One-for-All: Towards Universal Domain Translation with a Single StyleGAN
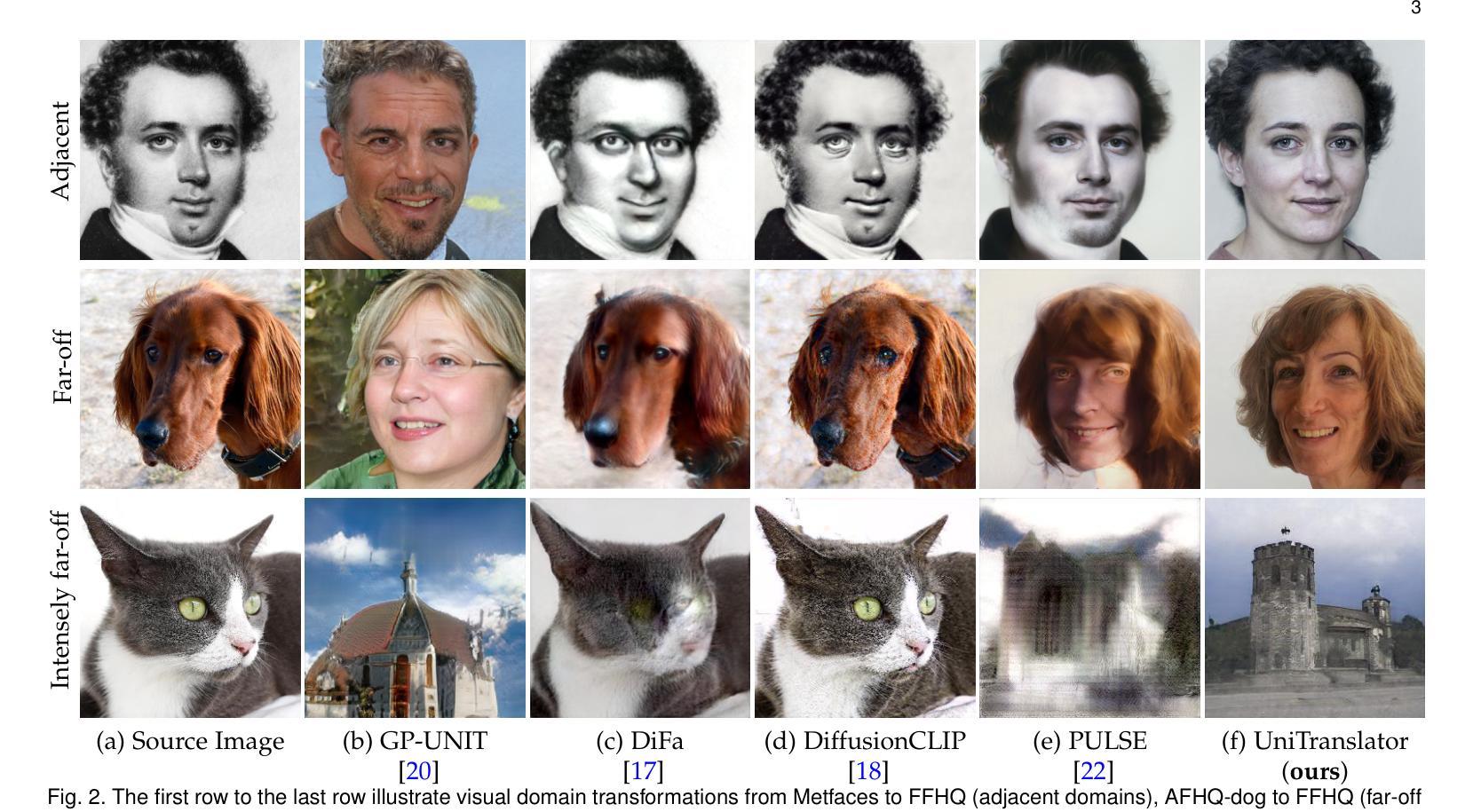
Authors:Yong Du, Jiahui Zhan, Xinzhe Li, Junyu Dong, Sheng Chen, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Shengfeng He
In this paper, we propose a novel translation model, UniTranslator, for transforming representations between visually distinct domains under conditions of limited training data and significant visual differences. The main idea behind our approach is leveraging the domain-neutral capabilities of CLIP as a bridging mechanism, while utilizing a separate module to extract abstract, domain-agnostic semantics from the embeddings of both the source and target realms. Fusing these abstract semantics with target-specific semantics results in a transformed embedding within the CLIP space. To bridge the gap between the disparate worlds of CLIP and StyleGAN, we introduce a new non-linear mapper, the CLIP2P mapper. Utilizing CLIP embeddings, this module is tailored to approximate the latent distribution in the StyleGAN’s latent space, effectively acting as a connector between these two spaces. The proposed UniTranslator is versatile and capable of performing various tasks, including style mixing, stylization, and translations, even in visually challenging scenarios across different visual domains. Notably, UniTranslator generates high-quality translations that showcase domain relevance, diversity, and improved image quality. UniTranslator surpasses the performance of existing general-purpose models and performs well against specialized models in representative tasks. The source code and trained models will be released to the public.
本文提出了一种新型翻译模型UniTranslator,用于在训练数据有限和视觉差异显著的情况下,实现不同视觉领域之间的表示转换。我们的方法的主要思想是利用CLIP的中立域能力作为桥梁机制,同时使用一个单独的模块从源领域和目标领域的嵌入中提取抽象、领域无关语义。将这些抽象语义与目标特定语义融合,得到CLIP空间内的转换嵌入。为了弥CLIP和StyleGAN之间不同世界的差距,我们引入了一种新的非线性映射器——CLIP2P映射器。该模块利用CLIP嵌入进行定制,以近似StyleGAN潜在空间中的潜在分布,有效地作为这两个空间之间的连接器。所提出的UniTranslator通用性强,能够执行各种任务,包括风格混合、风格化和翻译,即使在跨不同视觉领域的视觉挑战场景中也是如此。值得注意的是,UniTranslator生成的高质量翻译展示了领域相关性、多样性和改进的图像质量。UniTranslator超越了现有通用模型的性能,并在代表性任务中表现良好,甚至超过了专业模型。源代码和训练好的模型将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
UniTranslator模型利用CLIP的跨域中性能力,通过融合源域和目标域的抽象语义,实现在有限训练数据和显著视觉差异条件下不同视觉领域间的表示转换。引入CLIP2P非线性映射器,在CLIP和StyleGAN之间建立桥梁,实现两者空间的有效连接。UniTranslator具有多种功能,包括风格混合、风格化和翻译等,可在不同视觉领域实现高质量翻译,展示领域相关性、多样性和改善的图像质量。该模型超越现有通用模型性能,并在代表性任务中表现良好。
Key Takeaways
- UniTranslator是一个新型翻译模型,能在有限训练数据和显著视觉差异条件下实现不同视觉领域间的表示转换。
- 利用CLIP的跨域中性能力作为桥梁机制,融合源域和目标域的抽象语义。
- 引入CLIP2P非线性映射器,连接CLIP和StyleGAN空间。
- UniTranslator具备多种功能,如风格混合、风格化和翻译等。
- UniTranslator能在视觉上具有挑战性的场景中生成高质量翻译。
- UniTranslator模型性能超越现有通用模型,并在代表性任务中表现良好。
点此查看论文截图

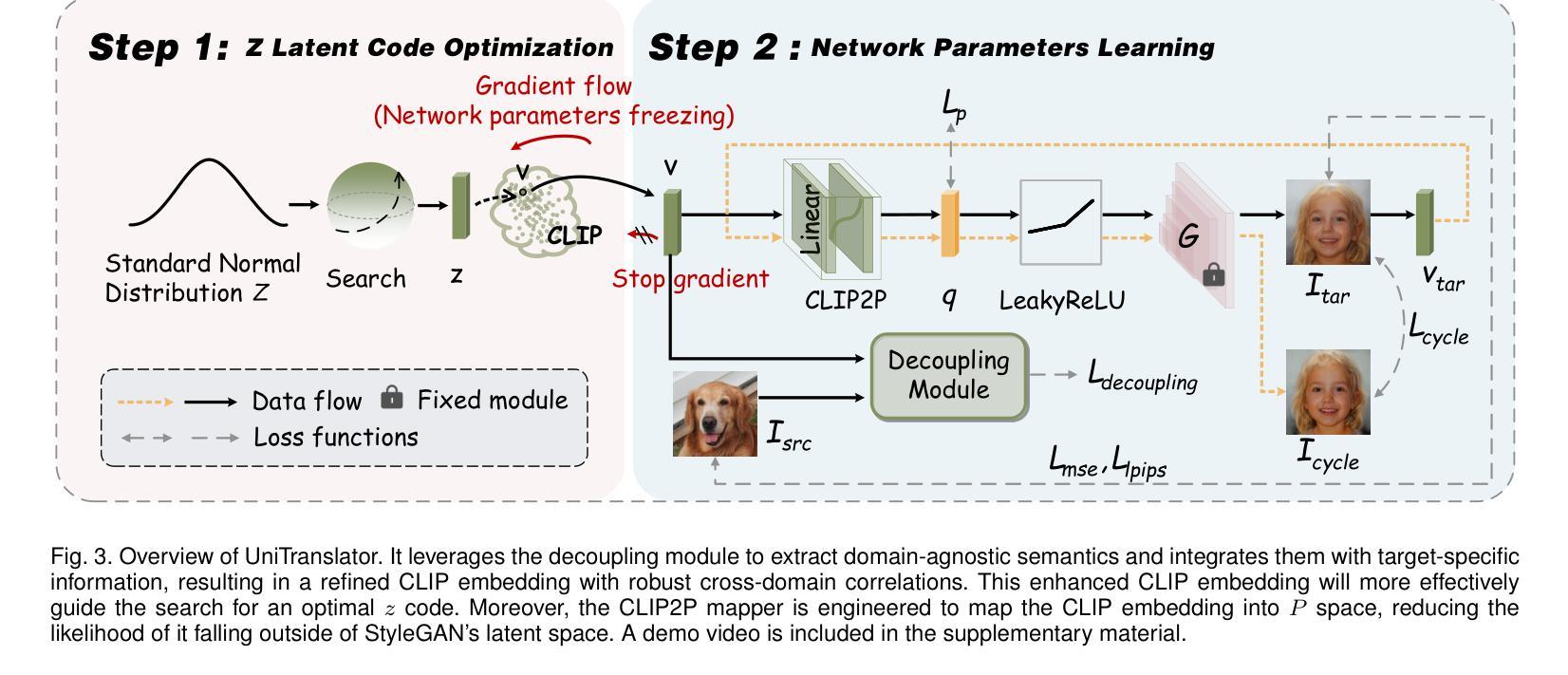
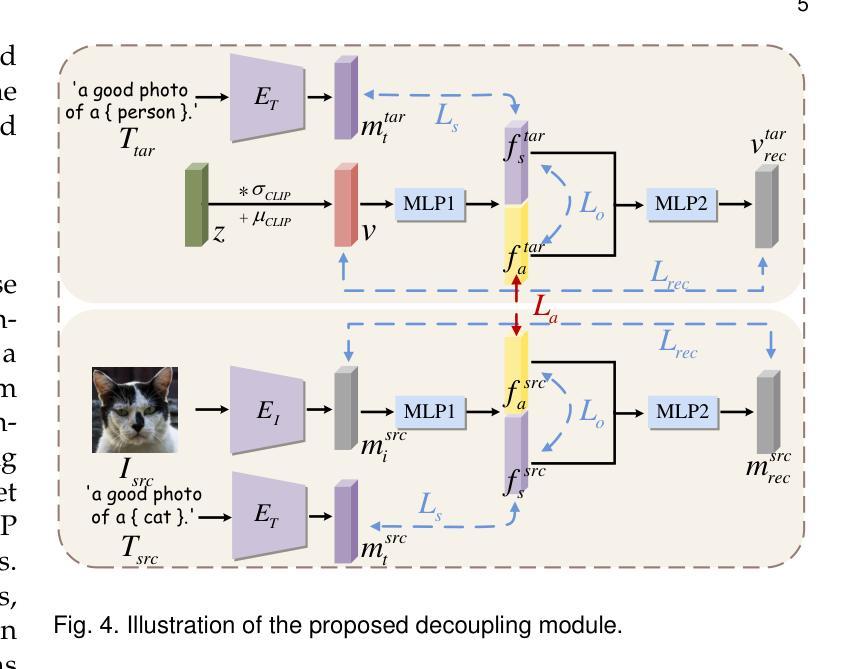
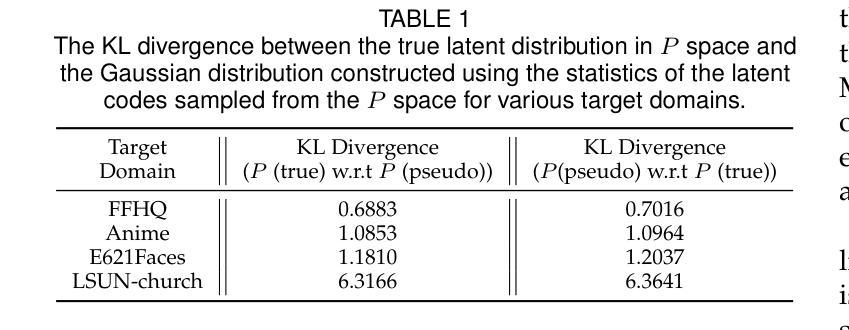
Unpaired Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Image Super-Resolution via Frequency-Aware Inverse-Consistency GAN
Authors:Weiwen Zhang, Dawei Yang, Haoxuan Che, An Ran Ran, Carol Y. Cheung, Hao Chen
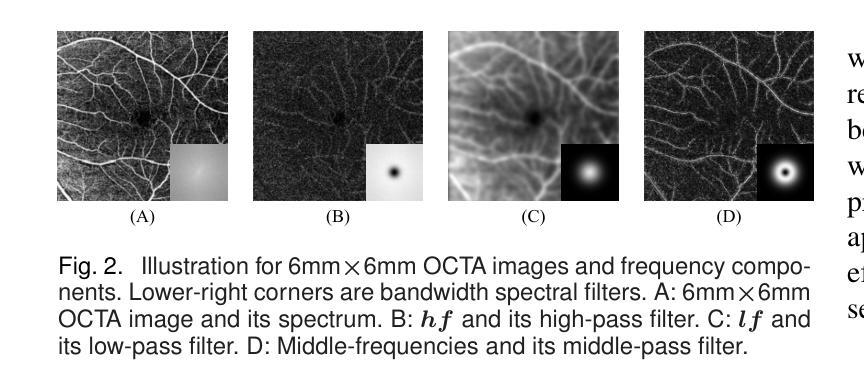
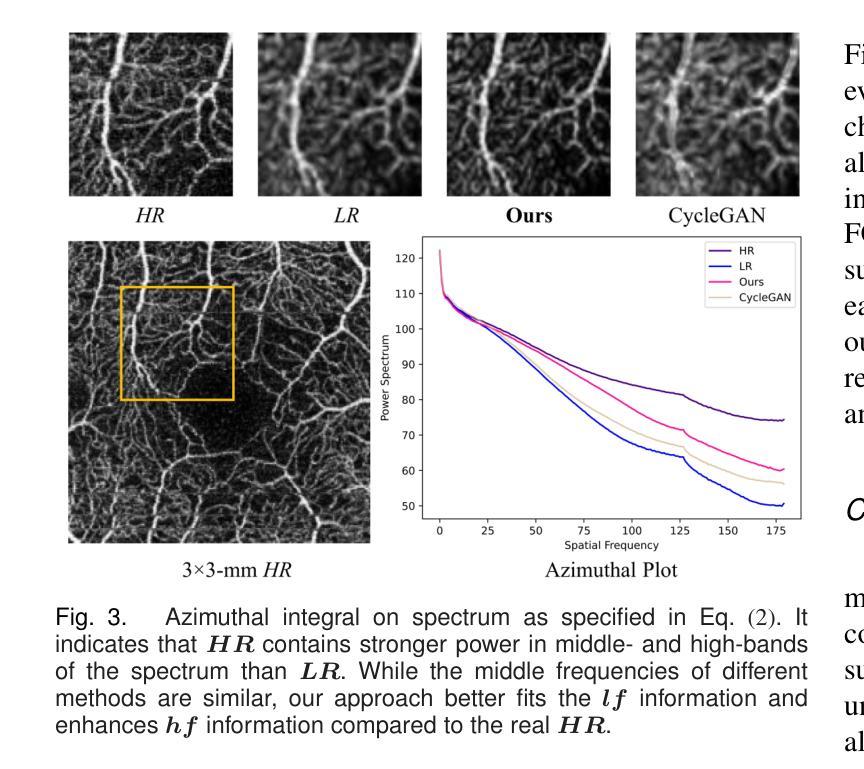
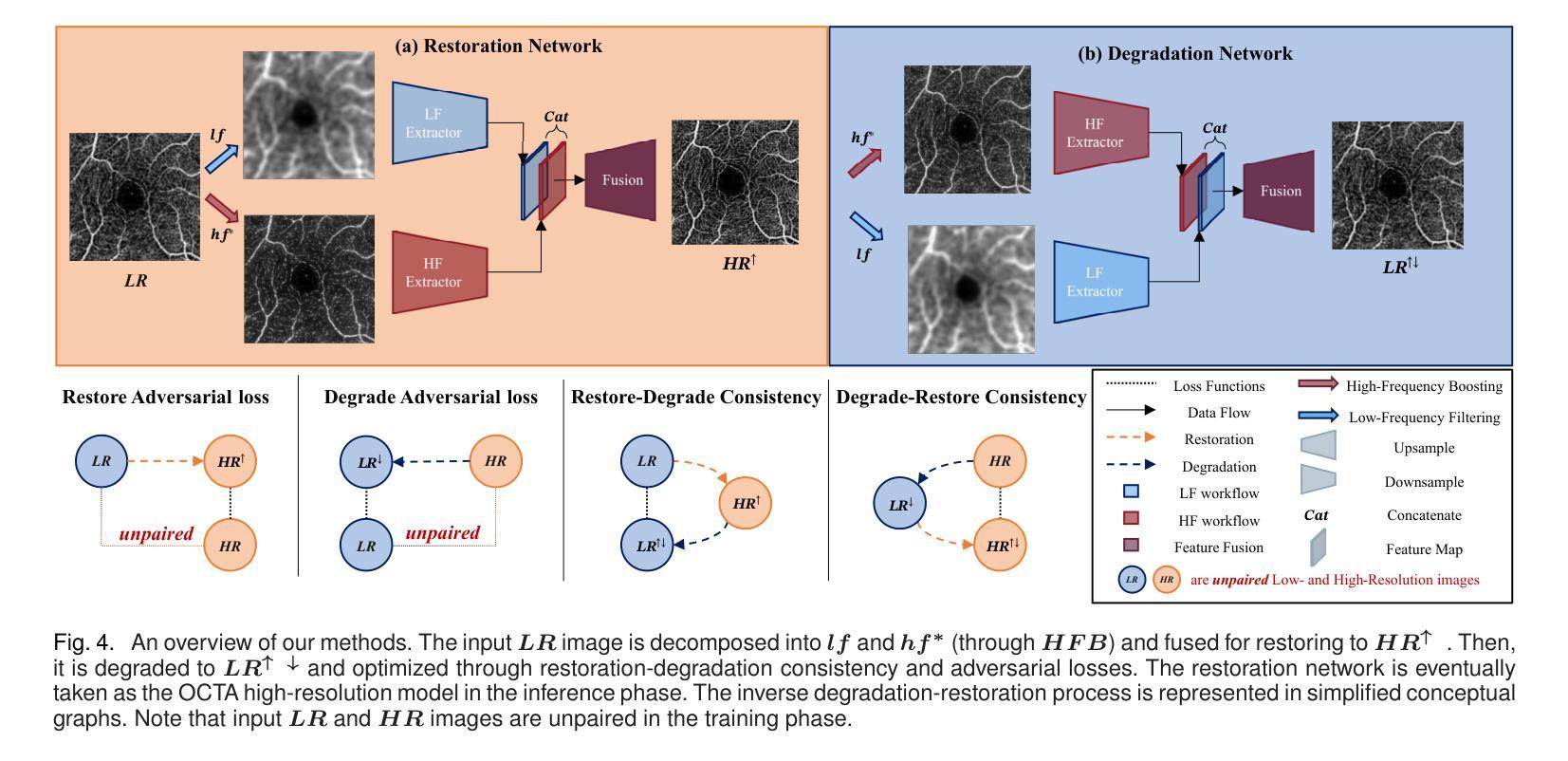
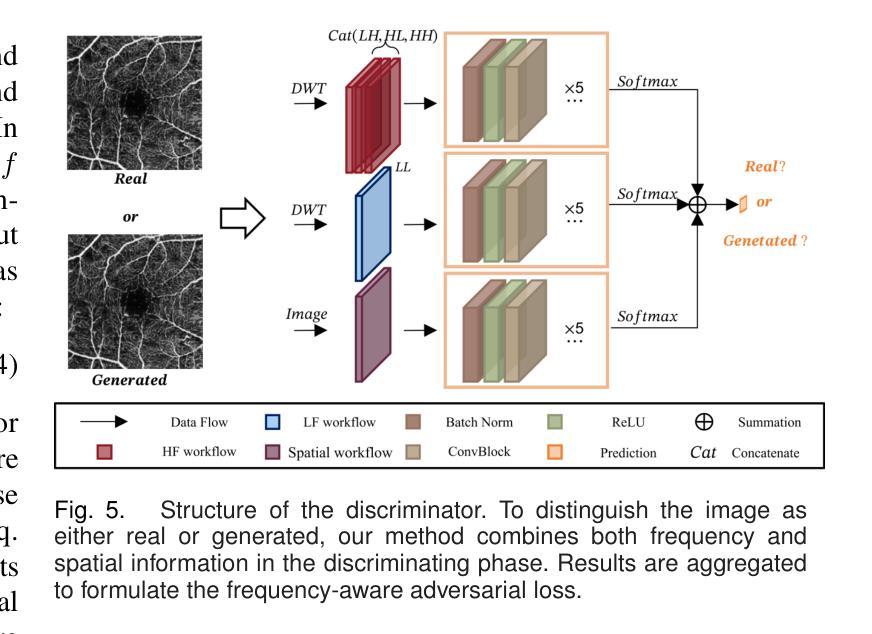
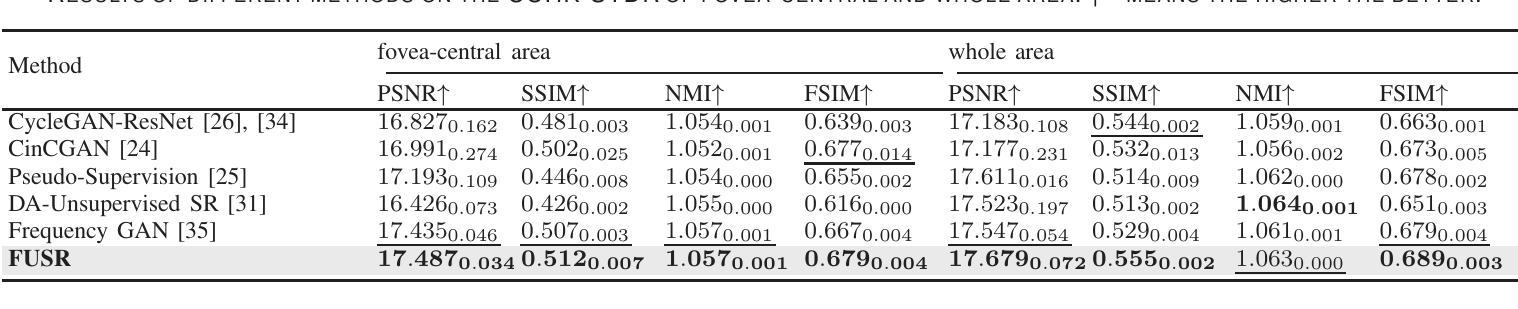
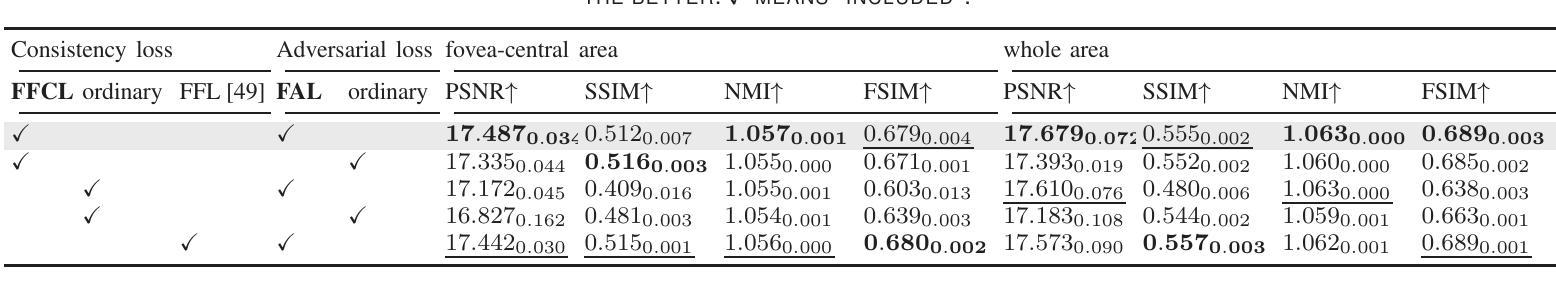
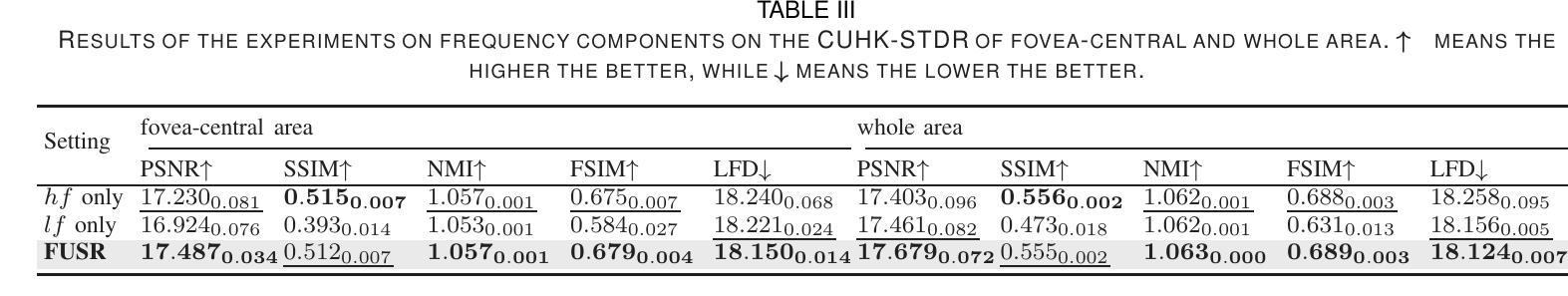
For optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) images, a limited scanning rate leads to a trade-off between field-of-view (FOV) and imaging resolution. Although larger FOV images may reveal more parafoveal vascular lesions, their application is greatly hampered due to lower resolution. To increase the resolution, previous works only achieved satisfactory performance by using paired data for training, but real-world applications are limited by the challenge of collecting large-scale paired images. Thus, an unpaired approach is highly demanded. Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) has been commonly used in the unpaired setting, but it may struggle to accurately preserve fine-grained capillary details, which are critical biomarkers for OCTA. In this paper, our approach aspires to preserve these details by leveraging the frequency information, which represents details as high-frequencies ($\textbf{hf}$) and coarse-grained backgrounds as low-frequencies ($\textbf{lf}$). In general, we propose a GAN-based unpaired super-resolution method for OCTA images and exceptionally emphasize $\textbf{hf}$ fine capillaries through a dual-path generator. To facilitate a precise spectrum of the reconstructed image, we also propose a frequency-aware adversarial loss for the discriminator and introduce a frequency-aware focal consistency loss for end-to-end optimization. Experiments show that our method outperforms other state-of-the-art unpaired methods both quantitatively and visually.
对于光学相干断层扫描血管造影(OCTA)图像,有限的扫描速率导致视野(FOV)与成像分辨率之间的权衡。虽然较大的FOV图像可能会揭示更多的旁黄斑血管病变,但由于分辨率较低,其应用受到很大阻碍。为了提升分辨率,早期的研究工作只有在利用配对数据进行训练时才能达到令人满意的效果,但现实世界的实际应用受限于收集大规模配对图像的挑战。因此,对无配对方法的需求极高。生成对抗网络(GAN)在无需配对的环境中已经得到了广泛的应用,但它可能在精确保留精细毛细血管细节方面存在困难,这对于OCTA来说是非常关键的生物标记物。在本文中,我们的方法旨在通过利用频率信息来保留这些详细信息,其中高频代表细节,低频代表粗粒背景。总的来说,我们提出了一种基于GAN的无配对超分辨率方法用于OCTA图像,并通过双路径生成器特别强调了高频的精细毛细血管。为了促进重建图像的精确频谱,我们还为鉴别器提出了一种频率感知对抗性损失,并为端到端的优化引入了一种频率感知焦点一致性损失。实验表明,我们的方法在定量和视觉方面都优于其他先进的无配对方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 10 figures, in IEEE J-BHI, 2024
Summary
本文提出了一种基于GAN的无配对超分辨率方法,用于处理OCTA图像。该方法利用频率信息,通过双路径生成器强调高频细节,并采用频率感知对抗损失和频率感知焦点一致性损失,提高了图像重建的精度和视觉效果。
Key Takeaways
- OCTA图像中,扫描率限制导致视野与成像分辨率之间的权衡。
- 较大的视野图像可能揭示更多的眼旁血管病变,但其分辨率较低。
- 以往的研究通过使用配对数据进行训练取得了令人满意的效果,但现实应用受限于收集大规模配对图像的挑战。
- 论文提出了一种基于GAN的无配对超分辨率方法,用于处理OCTA图像。
- 该方法利用频率信息,强调高频细节,并通过双路径生成器进行实现。
- 为了提高图像重建的精度,论文引入了频率感知对抗损失和频率感知焦点一致性损失。
点此查看论文截图
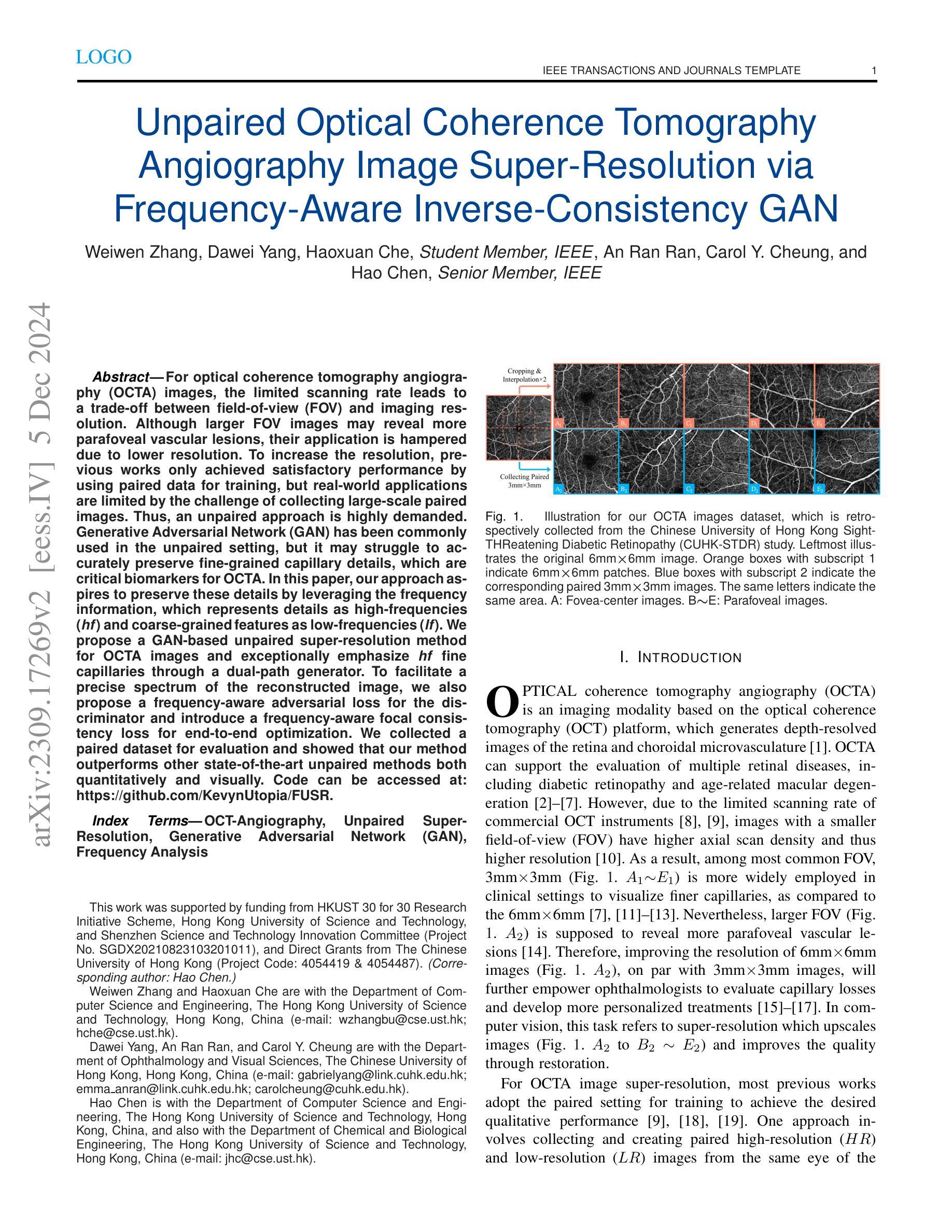
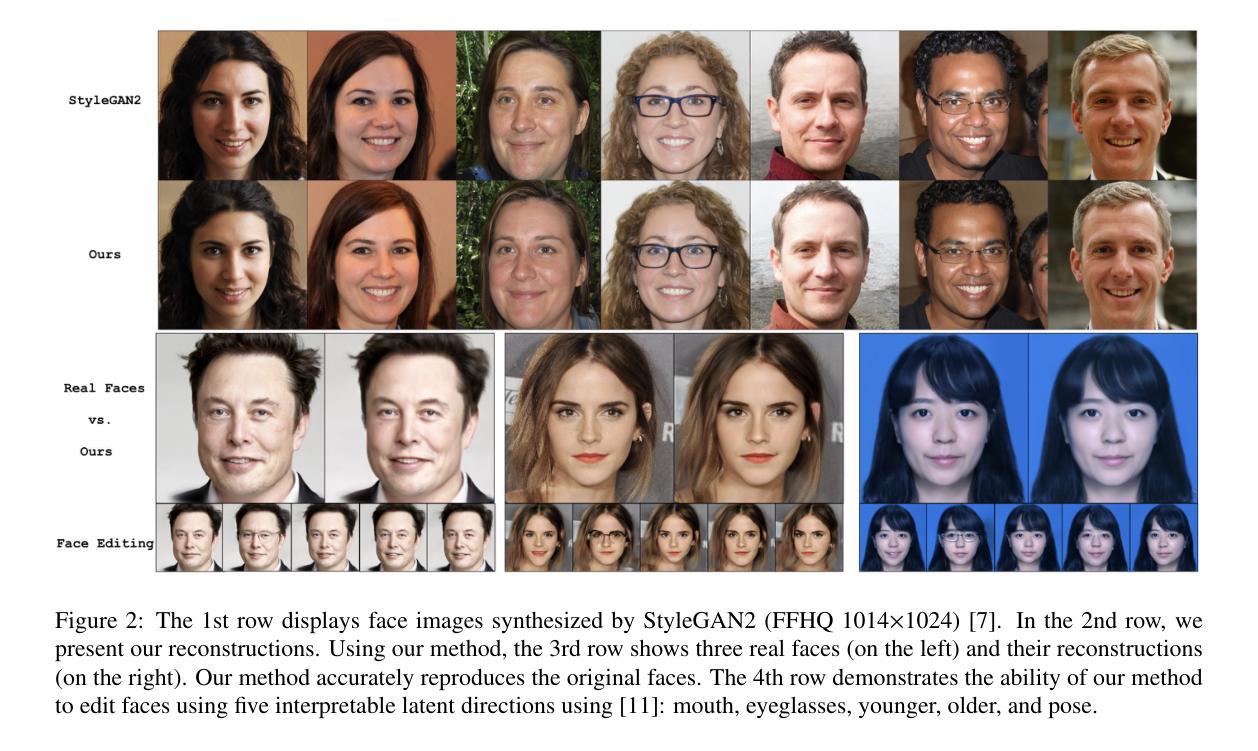
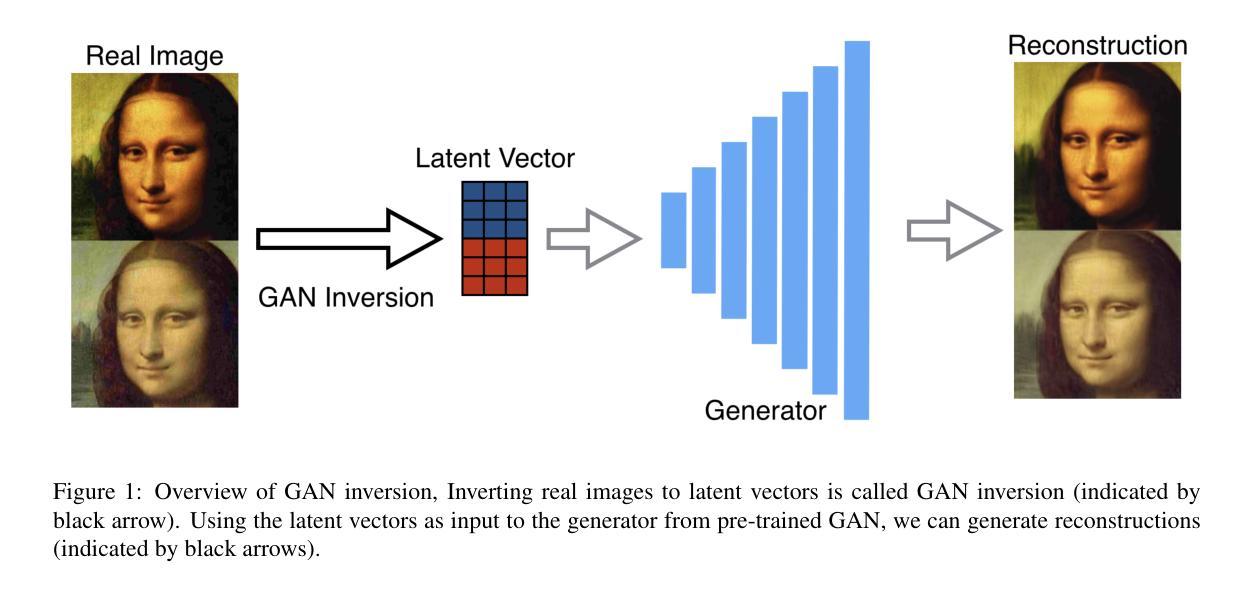
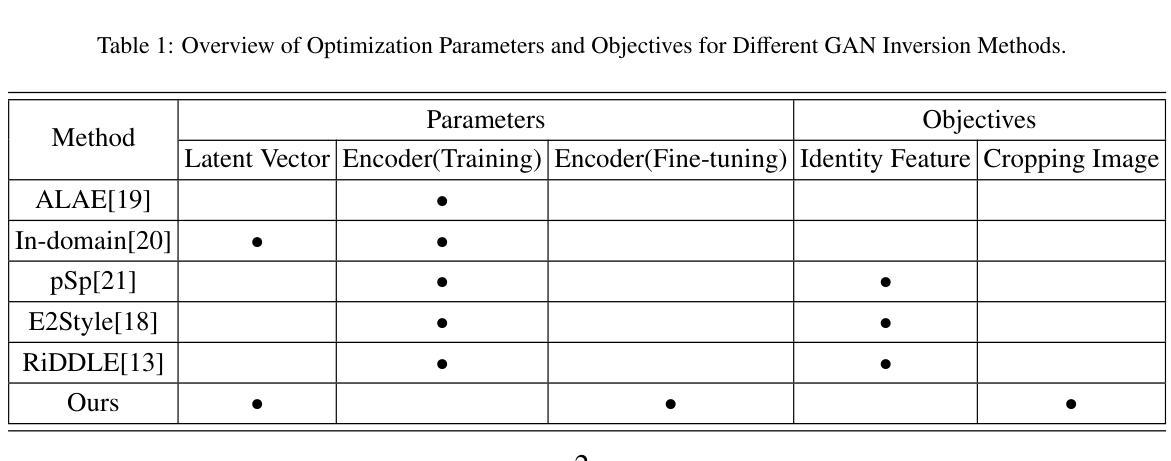
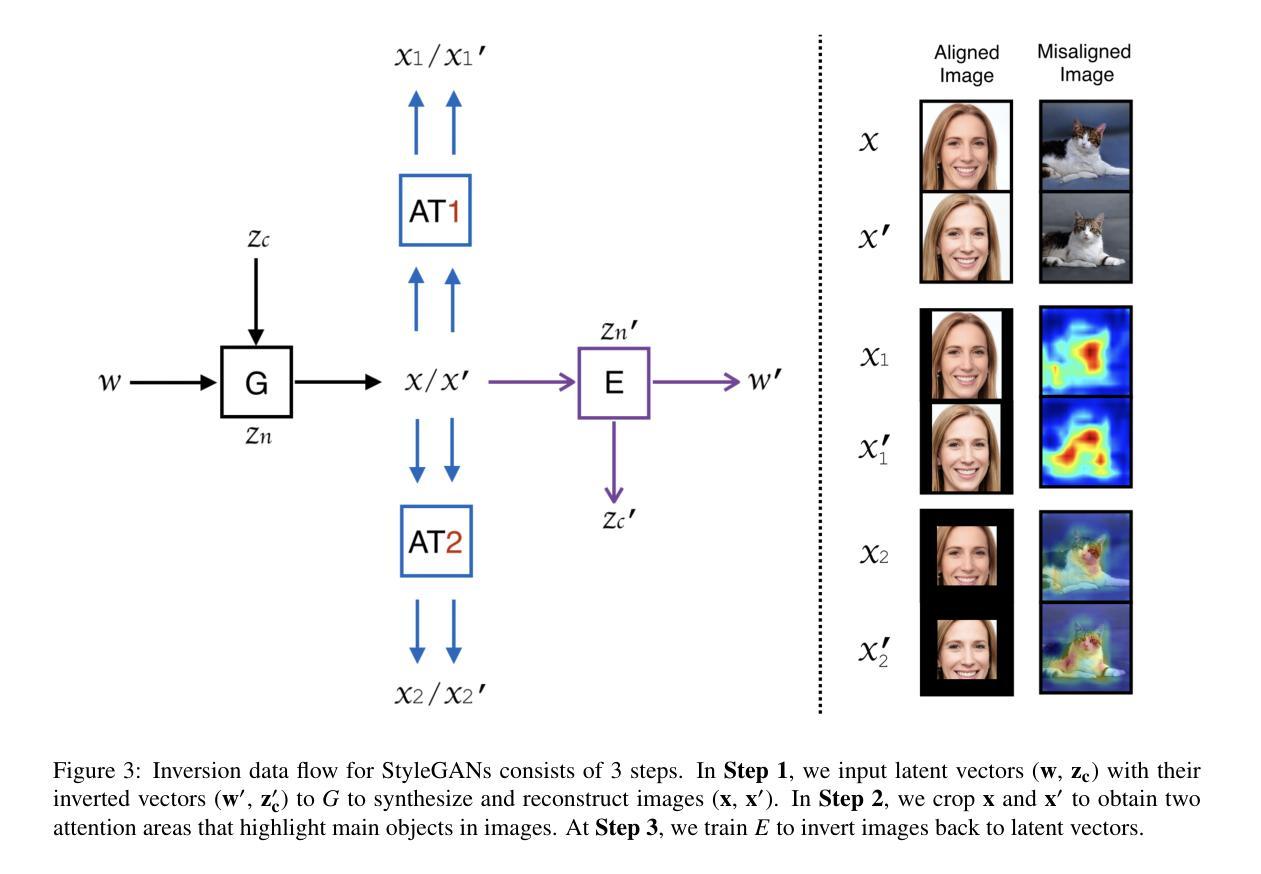
Diverse Similarity Encoder for Deep GAN Inversion
Authors:Cheng Yu, Wenmin Wang, Roberto Bugiolacchi
Current deep generative adversarial networks (GANs) can synthesize high-quality (HQ) images, so learning representation with GANs is favorable. GAN inversion is one of emerging approaches that study how to invert images into latent space. Existing GAN encoders can invert images on StyleGAN, but cannot adapt to other deep GANs. We propose a novel approach to address this issue. By evaluating diverse similarity in latent vectors and images, we design an adaptive encoder, named diverse similarity encoder (DSE), that can be expanded to a variety of state-of-the-art GANs. DSE makes GANs reconstruct higher fidelity images from HQ images, no matter whether they are synthesized or real images. DSE has unified convolutional blocks and adapts well to mainstream deep GANs, e.g., PGGAN, StyleGAN, and BigGAN.
当前深度生成对抗网络(GANs)可以合成高质量(HQ)图像,因此使用GANs学习表示是有利的。GAN反演是新兴方法之一,研究如何将图像反演到潜在空间。现有的GAN编码器可以在StyleGAN上进行图像反演,但不能适应其他深度GANs。我们提出了一种新的方法来解决这个问题。通过评估潜在向量和图像中的不同相似性,我们设计了一种自适应编码器,命名为多样相似性编码器(DSE),可以扩展到各种最先进的GANs。DSE使GANs能够从HQ图像重建更高保真度的图像,无论是合成的还是真实的图像。DSE具有统一的卷积块,并能很好地适应主流深度GANs,例如PGGAN、StyleGAN和BigGAN。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于当前深度生成对抗网络(GANs)能合成高质量图像的优势,学习其表示方法变得非常有利。针对现有GAN编码器在StyleGAN上能够倒置图像,但无法适应其他深度GAN的问题,我们提出了一种新的方法来解决这个问题。通过评估潜在向量和图像之间的不同相似性,我们设计了一种名为多样相似性编码器(DSE)的适应性编码器,它可以扩展到各种最先进的GANs。DSE使GANs能够从高质量图像中重建更高保真度的图像,无论是合成的还是真实的图像。DSE具有统一的卷积块,并很好地适应主流深度GAN,例如PGGAN、StyleGAN和BigGAN。
Key Takeaways
- 当前深度GAN能够生成高质量图像,促使研究如何借助GAN学习有效表示。
- GAN倒置成为新兴方向,旨在将图像倒置回潜在空间。
- 现有GAN编码器主要适用于StyleGAN,但缺乏对其他深度GAN的适应性。
- 提出了名为DSE的多样相似性编码器,旨在解决此问题。
- DSE通过评估潜在向量和图像之间的不同相似性进行设计。
- DSE具有广泛的应用性,可扩展到多种最先进的GANs。
- DSE能提高GANs从高质量图像重建图像的保真度,适用于合成和真实图像。
点此查看论文截图