⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-12 更新
BLADE: Single-view Body Mesh Learning through Accurate Depth Estimation
Authors:Shengze Wang, Jiefeng Li, Tianye Li, Ye Yuan, Henry Fuchs, Koki Nagano, Shalini De Mello, Michael Stengel
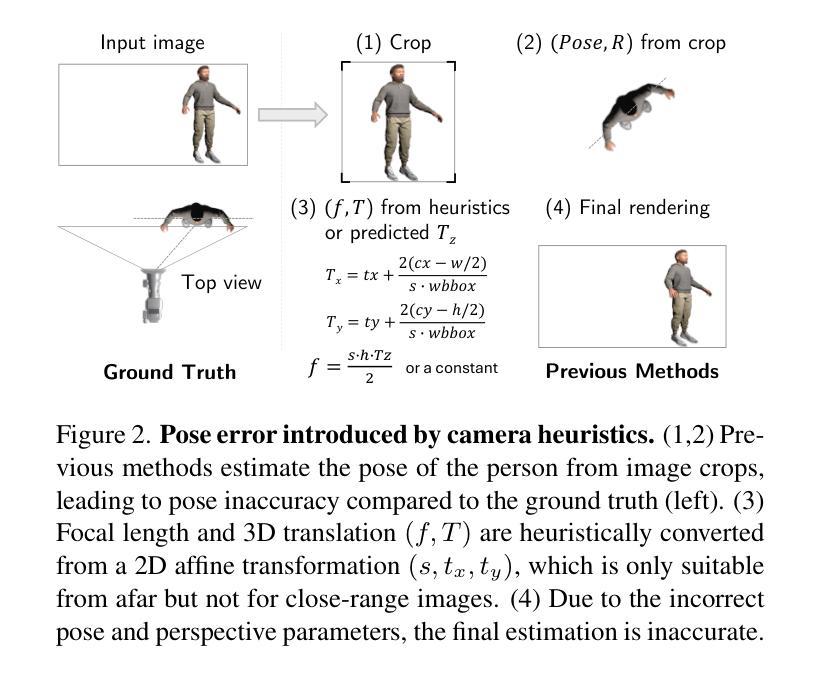
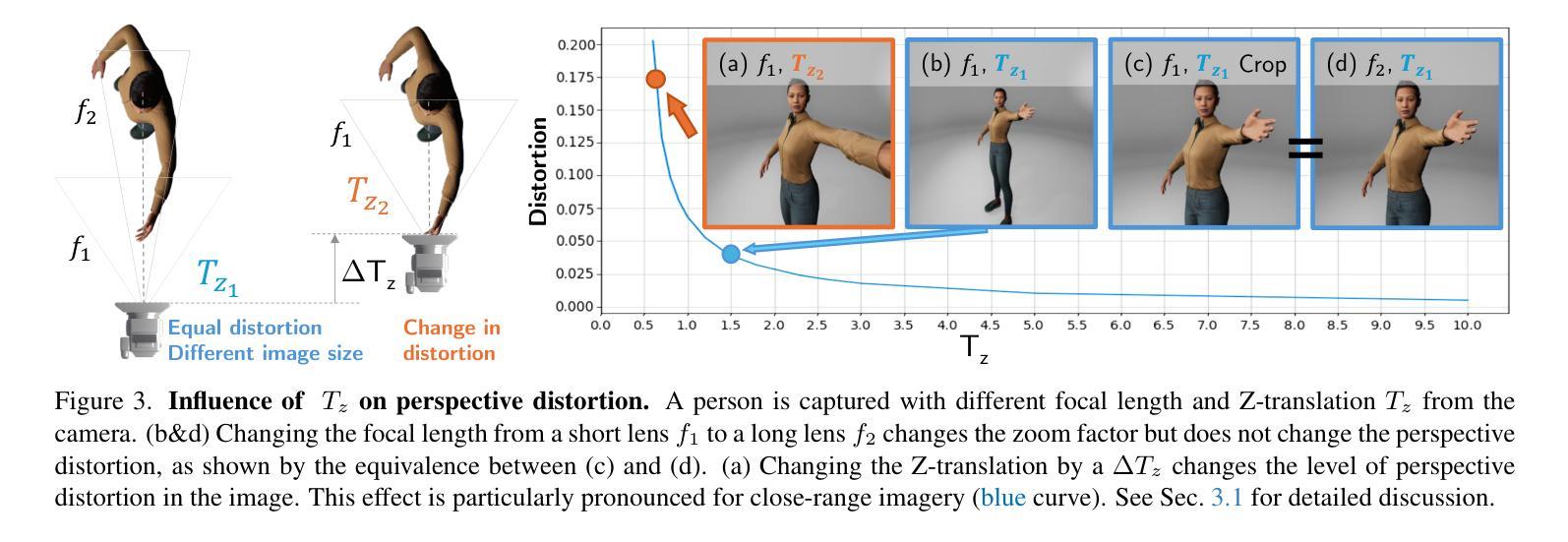
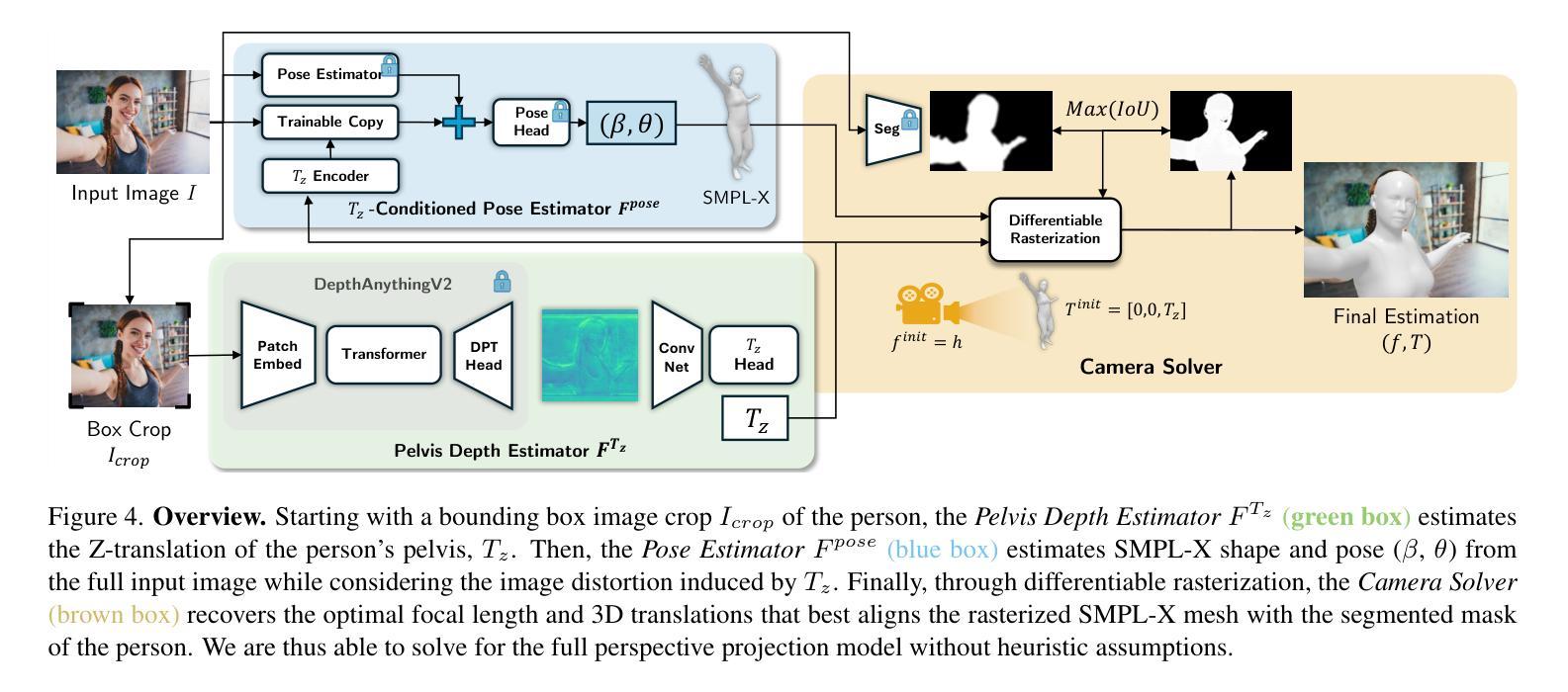
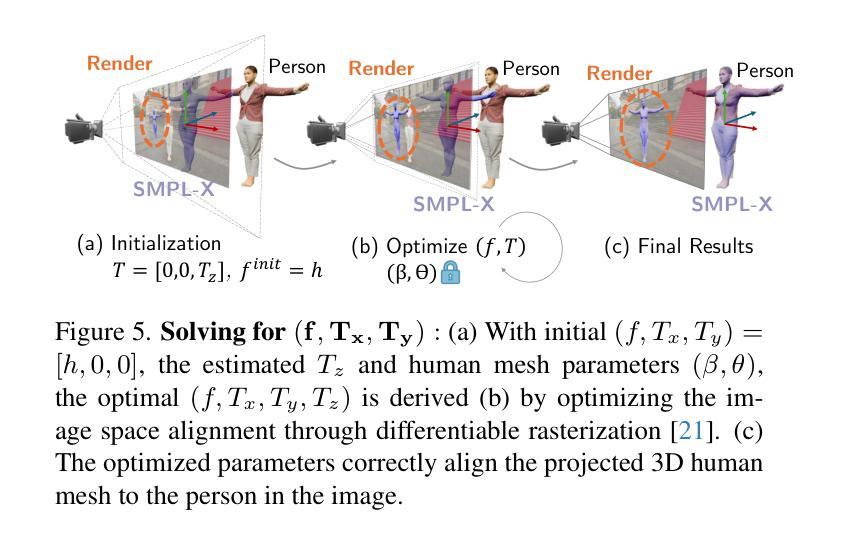
Single-image human mesh recovery is a challenging task due to the ill-posed nature of simultaneous body shape, pose, and camera estimation. Existing estimators work well on images taken from afar, but they break down as the person moves close to the camera. Moreover, current methods fail to achieve both accurate 3D pose and 2D alignment at the same time. Error is mainly introduced by inaccurate perspective projection heuristically derived from orthographic parameters. To resolve this long-standing challenge, we present our method BLADE which accurately recovers perspective parameters from a single image without heuristic assumptions. We start from the inverse relationship between perspective distortion and the person’s Z-translation Tz, and we show that Tz can be reliably estimated from the image. We then discuss the important role of Tz for accurate human mesh recovery estimated from close-range images. Finally, we show that, once Tz and the 3D human mesh are estimated, one can accurately recover the focal length and full 3D translation. Extensive experiments on standard benchmarks and real-world close-range images show that our method is the first to accurately recover projection parameters from a single image, and consequently attain state-of-the-art accuracy on 3D pose estimation and 2D alignment for a wide range of images. https://research.nvidia.com/labs/amri/projects/blade/
单图像人体网格恢复是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为同时进行身体形状、姿势和相机估计的性质是不确定的。现有的估计器在远距离拍摄的图像上表现良好,但当人物靠近相机时,它们就会失效。此外,当前的方法无法同时实现准确的3D姿势和2D对齐。误差主要是由透视投影引起的,透视投影是根据正射参数启发式推导出来的,但推导并不准确。为了解决这一长期存在的挑战,我们提出了方法BLADE,它可以从单幅图像中准确地恢复透视参数,而无需做出启发式假设。我们从透视失真与人的Z平移Tz之间的反向关系入手,并展示可以从图像中可靠地估计Tz。然后,我们讨论了Tz在从近距离图像准确估计人体网格恢复中的重要作用。最后,我们展示了一旦估计出Tz和3D人体网格,就可以准确恢复焦距和完整的3D平移。在标准基准测试和真实世界的近距离图像上的大量实验表明,我们的方法首次从单幅图像中准确恢复了投影参数,并在广泛的图像上实现了最先进的3D姿势估计和2D对齐精度。[详情链接:https://research.nvidia.com/labs/amri/projects/blade/]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
单图像人体网格恢复是一项具有挑战性的任务,需要同时估计身体形状、姿势和相机参数。现有方法对于远距离拍摄的人体图像效果较好,但在近距离拍摄时则表现不佳。本文提出了一种新的方法BLADE,可以从单幅图像准确恢复透视参数,无需启发式假设。该方法基于透视畸变与人的Z平移Tz之间的逆向关系,可靠估计Tz,并讨论其在近距离图像的人体网格恢复中的重要作用。实验表明,在估计Tz和3D人体网格后,可以准确恢复焦距和完整的3D平移。该方法在标准基准测试和真实世界近距离图像上的实验表现均达到了领先水平。
Key Takeaways
- 单图像人体网格恢复具有挑战性,需同时估计身体形状、姿势和相机参数。
- 现有方法在近距离拍摄时效果不佳。
- 本文提出了BLADE方法,可从单幅图像准确恢复透视参数。
- BLADE利用透视畸变与人的Z平移Tz之间的逆向关系进行估计。
- Tz的准确估计是实现近距离图像人体网格恢复的关键。
- 在估计Tz和3D人体网格后,可以准确恢复焦距和完整的3D平移。
- 实验表明,BLADE方法在标准基准测试和真实世界近距离图像上均达到了领先水平。
点此查看论文截图


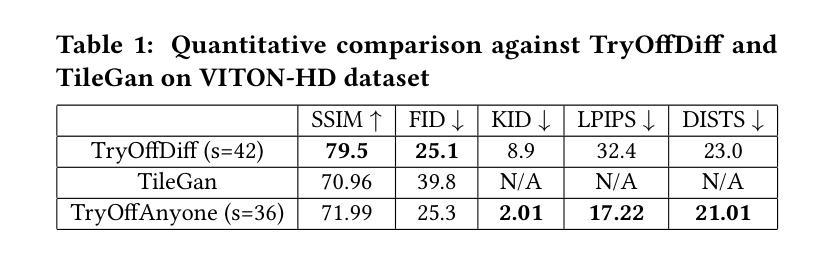
TryOffAnyone: Tiled Cloth Generation from a Dressed Person
Authors:Ioannis Xarchakos, Theodoros Koukopoulos
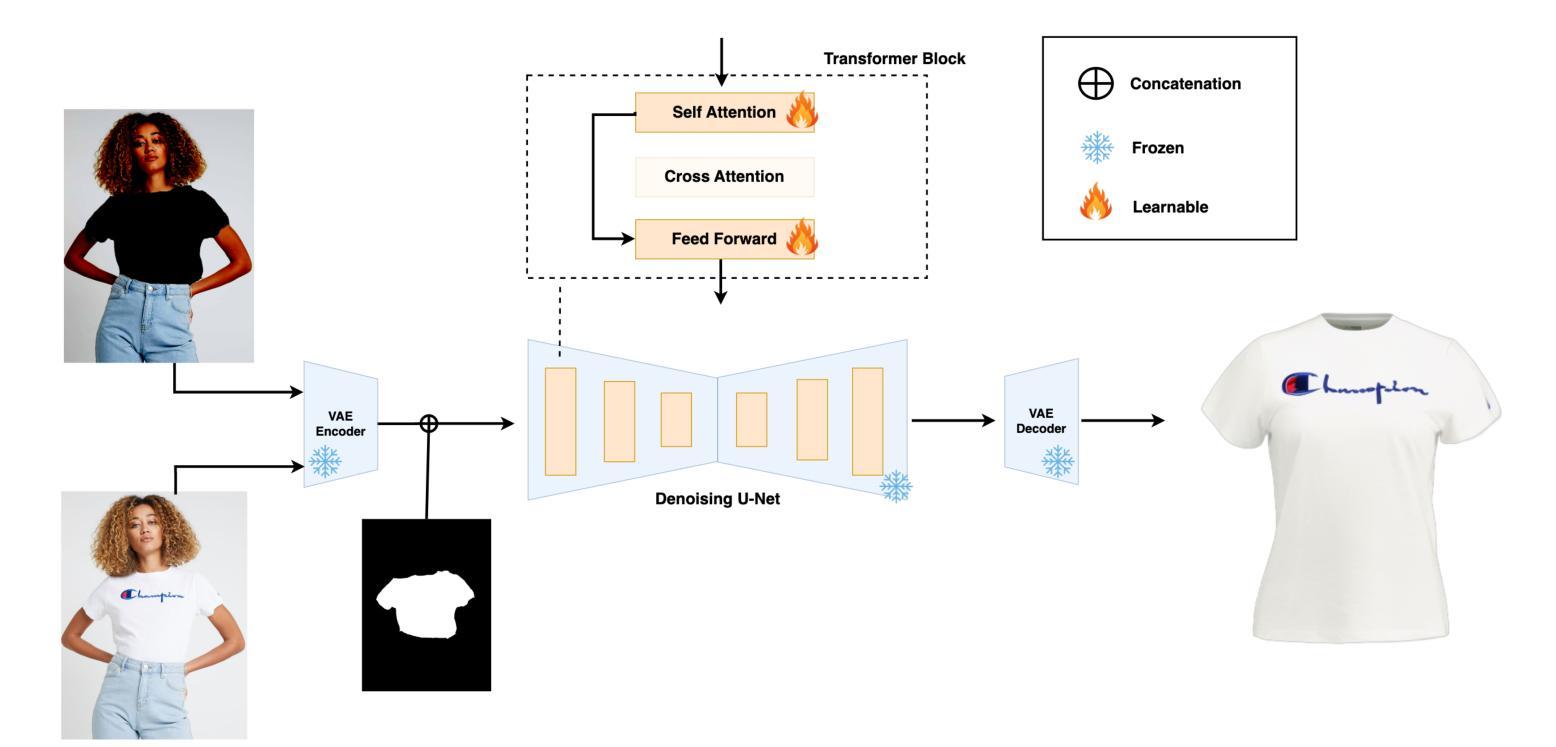
The fashion industry is increasingly leveraging computer vision and deep learning technologies to enhance online shopping experiences and operational efficiencies. In this paper, we address the challenge of generating high-fidelity tiled garment images essential for personalized recommendations, outfit composition, and virtual try-on systems from photos of garments worn by models. Inspired by the success of Latent Diffusion Models (LDMs) in image-to-image translation, we propose a novel approach utilizing a fine-tuned StableDiffusion model. Our method features a streamlined single-stage network design, which integrates garmentspecific masks to isolate and process target clothing items effectively. By simplifying the network architecture through selective training of transformer blocks and removing unnecessary crossattention layers, we significantly reduce computational complexity while achieving state-of-the-art performance on benchmark datasets like VITON-HD. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in producing high-quality tiled garment images for both full-body and half-body inputs. Code and model are available at: https://github.com/ixarchakos/try-off-anyone
时尚产业正越来越多地利用计算机视觉和深度学习技术,以提升在线购物体验和运营效率。在本文中,我们面临从模特穿着的服装照片生成高质量拼贴服装图像的挑战,这对于个性化推荐、服装搭配和虚拟试穿系统至关重要。受到潜在扩散模型(Latent Diffusion Models,简称LDMs)在图到图翻译中的成功的启发,我们提出了一种利用微调过的StableDiffusion模型的新方法。我们的方法采用了简化的单阶段网络设计,通过集成服装特定掩膜来有效地隔离和处理目标服装项目。通过有选择地训练变压器块并去除不必要的交叉注意层,简化了网络架构,我们在降低计算复杂性的同时,在VITON-HD等基准数据集上实现了最先进的性能。实验结果表明,我们的方法在全身体和半身体输入情况下生成高质量拼贴服装图像方面非常有效。代码和模型可在https://github.com/ixarchakos/try-off-anyone找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
时尚产业正利用计算机视觉和深度学习技术提升在线购物体验和运营效率。本文提出一种利用潜在扩散模型(Latent Diffusion Models,简称LDMs)生成高质量服装平铺图像的新方法,这对于个性化推荐、搭配组合和虚拟试衣系统至关重要。该方法通过简化的单阶段网络设计,结合服装特定掩膜,有效隔离和处理目标服装项目。通过选择性训练变压器块并去除不必要的交叉注意力层,在简化网络架构的同时,我们在基准数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 时尚产业正在整合计算机视觉和深度学习技术以提升在线购物和运营效率。
- 该论文关注于生成高质量服装平铺图像的挑战性问题,这对于个性化推荐、搭配和虚拟试衣至关重要。
- 论文提出了一种基于潜在扩散模型的新方法,用于从模特穿着的服装照片生成平铺图像。
- 该方法通过简化的单阶段网络设计和服装特定掩膜有效处理目标服装项目。
- 通过选择性训练和优化网络架构,该研究在基准数据集上实现了卓越性能。
- 实验结果证明了该方法在全身体和半身体输入下生成高质量服装平铺图像的有效性。
点此查看论文截图



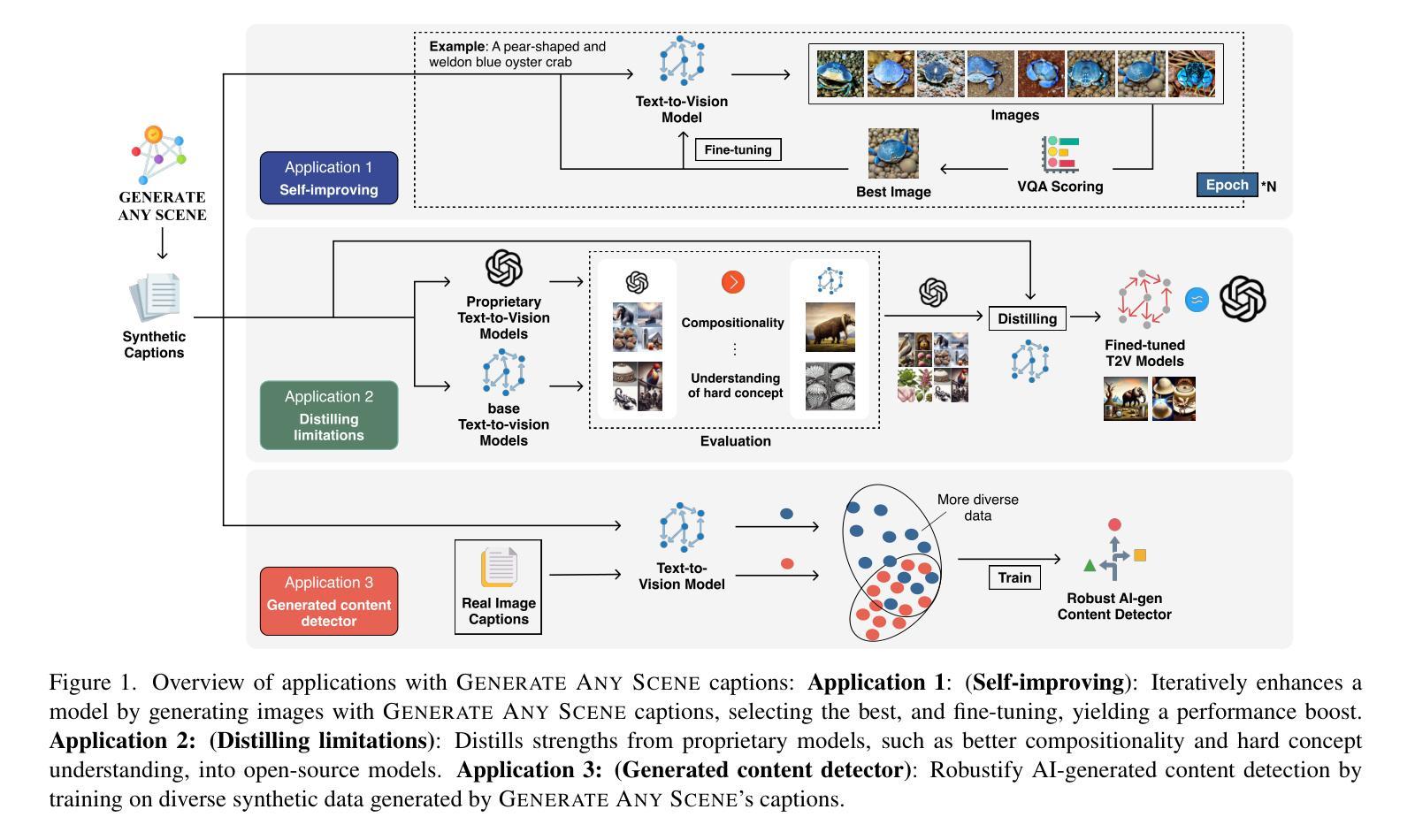
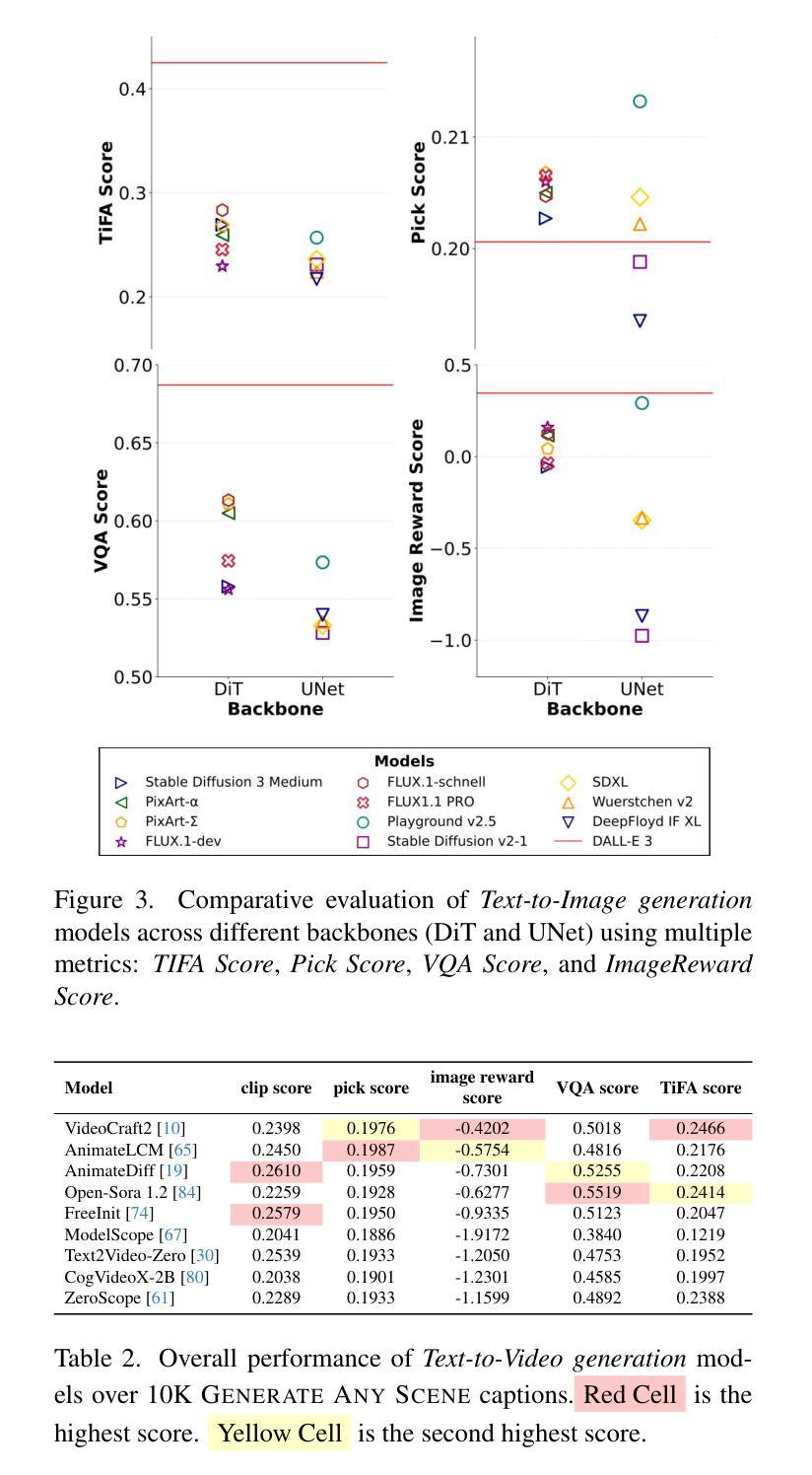
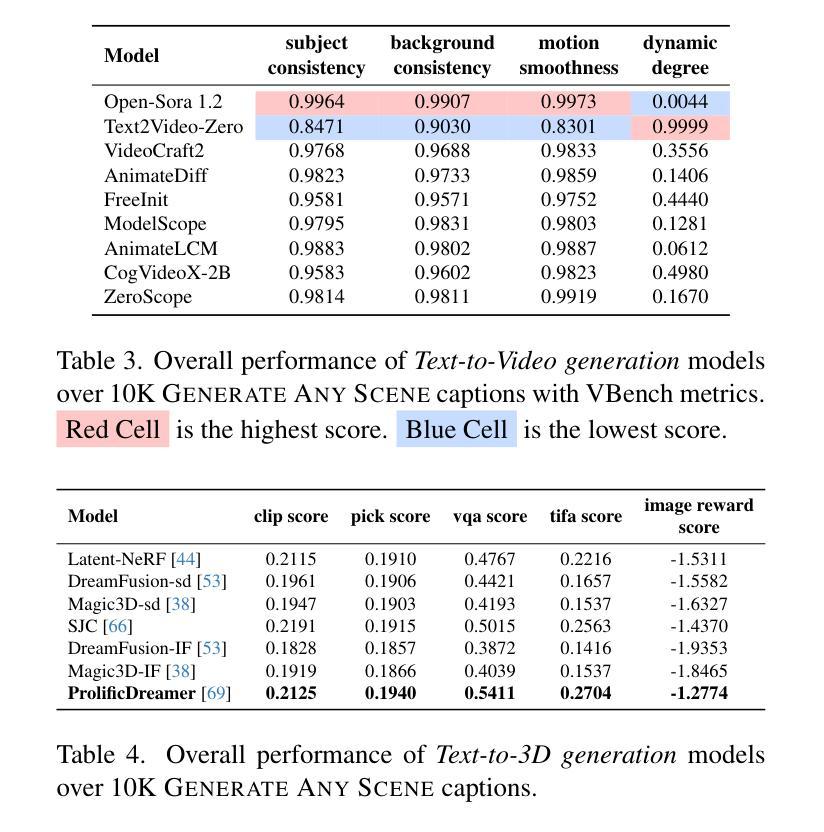
Generate Any Scene: Evaluating and Improving Text-to-Vision Generation with Scene Graph Programming
Authors:Ziqi Gao, Weikai Huang, Jieyu Zhang, Aniruddha Kembhavi, Ranjay Krishna
DALL-E and Sora have gained attention by producing implausible images, such as “astronauts riding a horse in space.” Despite the proliferation of text-to-vision models that have inundated the internet with synthetic visuals, from images to 3D assets, current benchmarks predominantly evaluate these models on real-world scenes paired with captions. We introduce Generate Any Scene, a framework that systematically enumerates scene graphs representing a vast array of visual scenes, spanning realistic to imaginative compositions. Generate Any Scene leverages ‘scene graph programming’, a method for dynamically constructing scene graphs of varying complexity from a structured taxonomy of visual elements. This taxonomy includes numerous objects, attributes, and relations, enabling the synthesis of an almost infinite variety of scene graphs. Using these structured representations, Generate Any Scene translates each scene graph into a caption, enabling scalable evaluation of text-to-vision models through standard metrics. We conduct extensive evaluations across multiple text-to-image, text-to-video, and text-to-3D models, presenting key findings on model performance. We find that DiT-backbone text-to-image models align more closely with input captions than UNet-backbone models. Text-to-video models struggle with balancing dynamics and consistency, while both text-to-video and text-to-3D models show notable gaps in human preference alignment. We demonstrate the effectiveness of Generate Any Scene by conducting three practical applications leveraging captions generated by Generate Any Scene: 1) a self-improving framework where models iteratively enhance their performance using generated data, 2) a distillation process to transfer specific strengths from proprietary models to open-source counterparts, and 3) improvements in content moderation by identifying and generating challenging synthetic data.
DALL-E和Sora通过生成不可信的图像,如“宇航员在太空中骑马”,引起了人们的关注。尽管文本到视觉的模型已经生成了大量的合成视觉,从图像到3D资产,但目前的基准测试主要还是对现实世界场景与配文的配对进行评估。我们介绍了Generate Any Scene框架,该框架系统地枚举了代表各种视觉场景的场景图,涵盖了从现实到想象的各种组合。Generate Any Scene利用“场景图编程”的方法,这是一种从视觉元素的结构化分类中动态构建场景图的方法,这些场景图具有不同的复杂性。此分类包括许多对象、属性和关系,能够合成几乎无限多种场景图。通过使用这些结构化表示,Generate Any Scene将每个场景图翻译为配文,通过标准指标实现对文本到视觉模型的可扩展评估。我们对多个文本到图像、文本到视频和文本到3D模型进行了广泛评估,并呈现了关于模型性能的关键发现。我们发现,DiT主干文本到图像模型的输入配文对齐程度高于UNet主干模型。文本到视频模型在平衡动态和一致性方面遇到困难,而文本到视频和文本到3D模型在人的偏好对齐方面都存在明显的差距。我们通过开展三项实际应用,展示了Generate Any Scene的有效性,这些应用利用Generate Any Scene生成的配文:1)一个自我完善框架,模型使用生成的数据迭代地提高其性能;2)一个蒸馏过程,将专有模型的具体优势转移到开源模型;3)通过识别和生成具有挑战性的合成数据,改进内容审核。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了两个文本转图像模型DALL-E和Sora,它们能够生成不可思议的图像,如“宇航员在太空骑乘马匹”。针对当前文本转视觉模型主要基于现实场景配对的评价基准,作者提出了一种名为Generate Any Scene的框架。该框架通过系统地列举代表各种视觉场景的场景图,从结构化的分类元素中进行动态构建场景图的方法,涵盖了从现实到想象的各种组合。该框架还包括将每个场景图转换为描述文本的模块,使得能够通过标准指标对文本转视觉模型进行大规模评估。作者在多个文本转图像、文本转视频和文本转3D模型上进行了广泛评估,发现了一些关键发现。最后,作者展示了Generate Any Scene框架通过生成场景描述文本的实际应用效果,包括自我改进框架、蒸馏过程和内容审核改进。
Key Takeaways
- DALL-E和Sora等文本转图像模型能够生成超乎想象的图像。
- 当前文本转视觉模型的评价主要基于现实场景配对,但作者提出了一种名为Generate Any Scene的框架,以系统地评估模型的表现。
- Generate Any Scene框架利用场景图编程方法,从结构化的分类元素中构建复杂的场景图。
- 该框架能够涵盖从现实到想象的各种场景组合,并将场景图转换为描述文本。
- 作者对多种文本转图像、文本转视频和文本转3D模型进行了广泛评估,发现DiT骨架的文本转图像模型与输入描述更为一致,而UNet骨架的模型存在差距。
- 文本转视频模型在平衡动态和一致性方面存在挑战。
点此查看论文截图


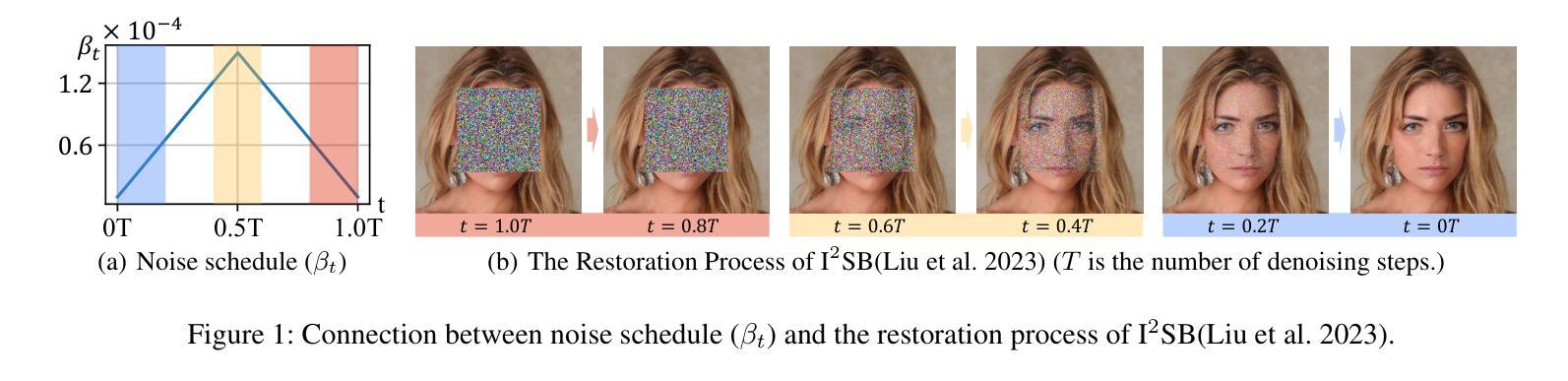
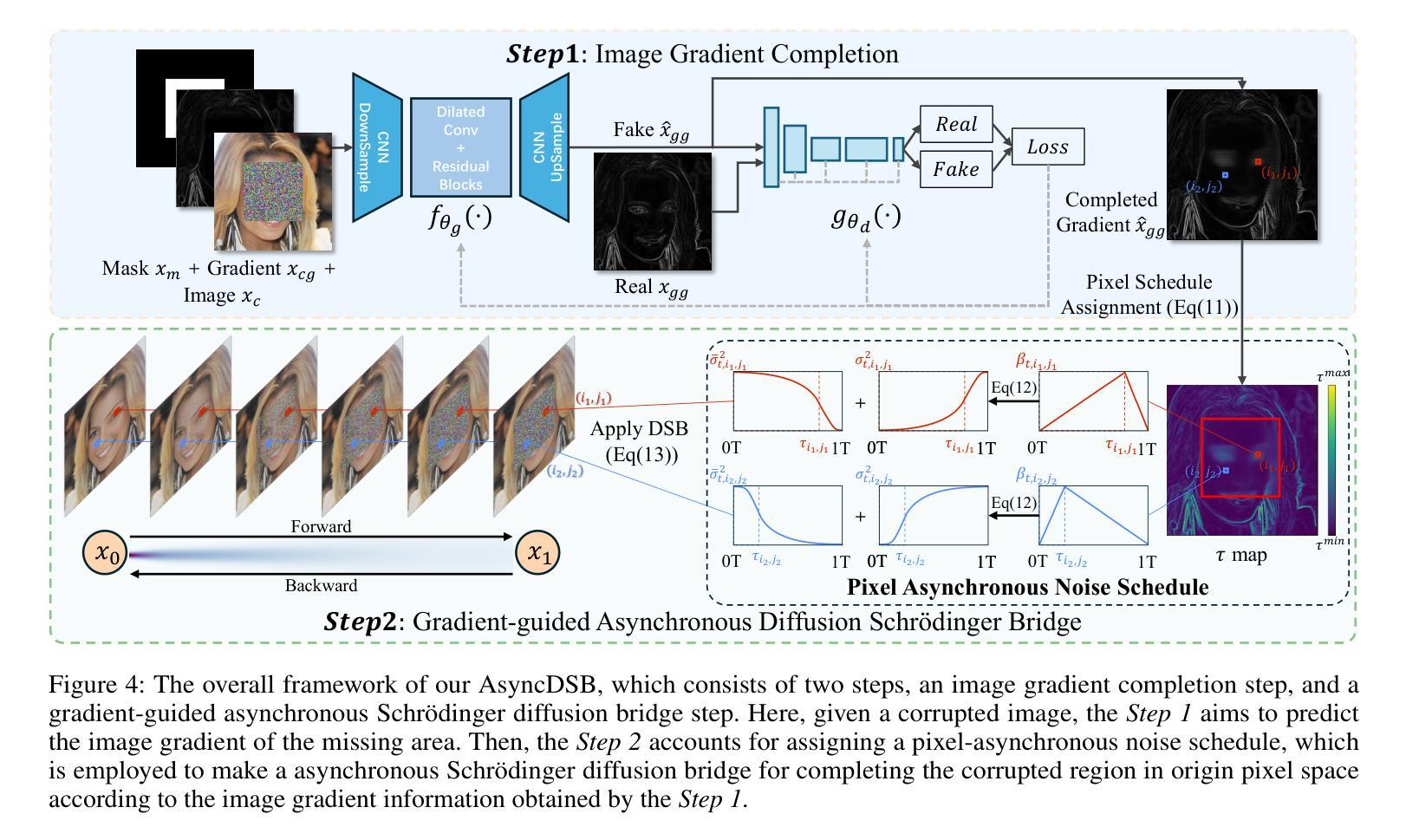
AsyncDSB: Schedule-Asynchronous Diffusion Schrödinger Bridge for Image Inpainting
Authors:Zihao Han, Baoquan Zhang, Lisai Zhang, Shanshan Feng, Kenghong Lin, Guotao Liang, Yunming Ye, Xiaochen Qi, Guangming Ye
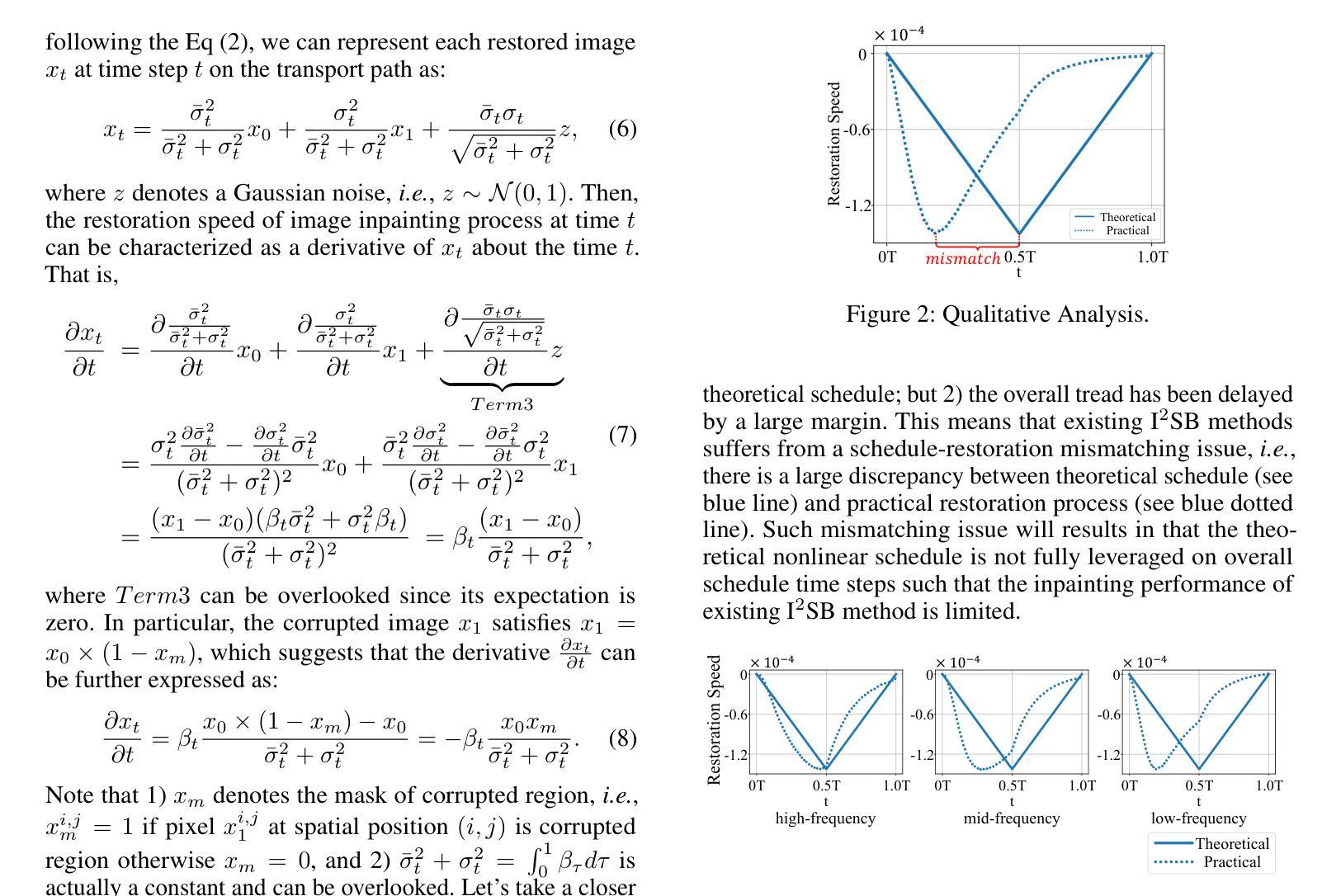
Image inpainting is an important image generation task, which aims to restore corrupted image from partial visible area. Recently, diffusion Schr"odinger bridge methods effectively tackle this task by modeling the translation between corrupted and target images as a diffusion Schr"odinger bridge process along a noising schedule path. Although these methods have shown superior performance, in this paper, we find that 1) existing methods suffer from a schedule-restoration mismatching issue, i.e., the theoretical schedule and practical restoration processes usually exist a large discrepancy, which theoretically results in the schedule not fully leveraged for restoring images; and 2) the key reason causing such issue is that the restoration process of all pixels are actually asynchronous but existing methods set a synchronous noise schedule to them, i.e., all pixels shares the same noise schedule. To this end, we propose a schedule-Asynchronous Diffusion Schr"odinger Bridge (AsyncDSB) for image inpainting. Our insight is preferentially scheduling pixels with high frequency (i.e., large gradients) and then low frequency (i.e., small gradients). Based on this insight, given a corrupted image, we first train a network to predict its gradient map in corrupted area. Then, we regard the predicted image gradient as prior and design a simple yet effective pixel-asynchronous noise schedule strategy to enhance the diffusion Schr"odinger bridge. Thanks to the asynchronous schedule at pixels, the temporal interdependence of restoration process between pixels can be fully characterized for high-quality image inpainting. Experiments on real-world datasets show that our AsyncDSB achieves superior performance, especially on FID with around 3% - 14% improvement over state-of-the-art baseline methods.
图像补全是一项重要的图像生成任务,旨在从部分可见区域恢复受损图像。最近,扩散Schrödinger桥方法通过将在损坏图像和目标图像之间的转换建模为沿噪声调度路径的扩散Schrödinger桥过程,有效地解决了此任务。尽管这些方法已经显示出卓越的性能,但在本文中,我们发现现有方法存在以下问题:1)存在调度恢复不匹配的问题,即理论调度和实际恢复过程通常存在较大差异,这从理论上导致调度在恢复图像时未得到充分利用;2)造成这一问题的主要原因是所有像素的恢复过程实际上是异步的,但现有方法会对它们设置同步噪声调度,即所有像素共享相同的噪声调度。为此,我们针对图像补全提出了一种异步调度扩散Schrödinger桥(AsyncDSB)。我们的见解是优先调度高频(即大梯度)像素,然后是低频(即小梯度)像素。基于这一见解,对于给定的损坏图像,我们首先训练一个网络来预测其损坏区域的梯度图。然后,我们将预测的图像梯度视为先验,并设计了一种简单有效的像素异步噪声调度策略,以增强扩散Schrödinger桥。由于像素的异步调度,可以充分刻画像素之间恢复过程的时序相关性,从而实现高质量图像补全。在真实数据集上的实验表明,我们的AsyncDSB达到了卓越的性能,特别是在FID上,较最新基线方法有约3%-14%的提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
本文探讨了图像修复任务中的扩散薛定谔桥方法存在的问题,并提出了新的解决方案。现有方法存在理论恢复计划与实际操作不匹配的问题,原因在于对所有像素的恢复过程是异步的,但现有方法设定了同步噪声计划。为此,本文提出了异步扩散薛定谔桥(AsyncDSB)方法,优先调度高频像素,再调度低频像素。实验结果表明,AsyncDSB在真实数据集上的性能优于现有方法,特别是在FID指标上,有约3%-14%的提升。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散薛定谔桥方法在图像修复任务中表现优越。
- 现有方法存在理论恢复计划与实际操作不匹配的问题。
- 问题根源在于对所有像素设定了同步噪声计划,而实际恢复过程是异步的。
- 本文提出了异步扩散薛定谔桥(AsyncDSB)方法,优先处理高频像素。
- AsyncDSB方法通过设计像素异步噪声计划,能充分表征像素间恢复的时空依赖性。
- 实验结果表明,AsyncDSB在真实数据集上的性能优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图


From Slow Bidirectional to Fast Causal Video Generators
Authors:Tianwei Yin, Qiang Zhang, Richard Zhang, William T. Freeman, Fredo Durand, Eli Shechtman, Xun Huang
Current video diffusion models achieve impressive generation quality but struggle in interactive applications due to bidirectional attention dependencies. The generation of a single frame requires the model to process the entire sequence, including the future. We address this limitation by adapting a pretrained bidirectional diffusion transformer to a causal transformer that generates frames on-the-fly. To further reduce latency, we extend distribution matching distillation (DMD) to videos, distilling 50-step diffusion model into a 4-step generator. To enable stable and high-quality distillation, we introduce a student initialization scheme based on teacher’s ODE trajectories, as well as an asymmetric distillation strategy that supervises a causal student model with a bidirectional teacher. This approach effectively mitigates error accumulation in autoregressive generation, allowing long-duration video synthesis despite training on short clips. Our model supports fast streaming generation of high quality videos at 9.4 FPS on a single GPU thanks to KV caching. Our approach also enables streaming video-to-video translation, image-to-video, and dynamic prompting in a zero-shot manner. We will release the code based on an open-source model in the future.
当前的视频扩散模型虽然实现了令人印象深刻的生成质量,但由于双向注意力依赖性,在交互式应用中表现困难。生成单个帧需要模型处理整个序列,包括未来信息。我们通过将预训练的双向扩散变压器适应为因果变压器来解决这个问题,该因果变压器可以即时生成帧。为了进一步降低延迟,我们将分布匹配蒸馏(DMD)扩展到视频领域,将50步扩散模型蒸馏为4步生成器。为了实现稳定和高质量的蒸馏,我们引入了基于教师ODE轨迹的学生初始化方案,以及一种不对称的蒸馏策略,即用双向教师监督因果学生模型。这种方法有效地减轻了自回归生成中的误差累积,即使在短片段上进行训练也能实现长时长视频合成。我们的模型支持在单个GPU上以9.4 FPS的速度快速流式生成高质量视频,这得益于KV缓存。我们的方法还实现了流式视频到视频的翻译、图像到视频以及零样本方式的动态提示。未来,我们将基于开源模型发布代码。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://causvid.github.io/
Summary
本文主要介绍了一种解决视频扩散模型在交互式应用中的双向注意力依赖问题的方法。通过将预训练的双向扩散变压器适配器调整为因果变压器,实现在线生成帧,减少了对整个序列的处理需求。为进一步提高效率,研究团队将分布匹配蒸馏法扩展到视频领域,将50步扩散模型简化为4步生成器。通过引入基于教师常微分方程轨迹的学生初始化方案和不对称蒸馏策略,有效实现了稳定高质量的蒸馏,减少了自回归生成中的误差累积。该方法支持在单个GPU上以9.4 FPS的速度快速生成高质量视频,并实现视频转视频、图像转视频的流式翻译以及零样本动态提示。未来,研究团队计划基于开源模型发布相关代码。
Key Takeaways
- 当前视频扩散模型在交互式应用中面临双向注意力依赖问题。
- 通过将双向扩散模型调整为因果模型,实现在线生成帧,减少了对整个序列的处理需求。
- 首次将分布匹配蒸馏法扩展到视频领域,简化了模型步骤。
- 引入基于教师常微分方程轨迹的学生初始化方案和不对称蒸馏策略,提高了模型的稳定性和蒸馏质量。
- 方法有效减少了自回归生成中的误差累积,支持长时长视频合成。
- 模型支持快速生成高质量视频,并实现了视频流式翻译和动态提示功能。
点此查看论文截图




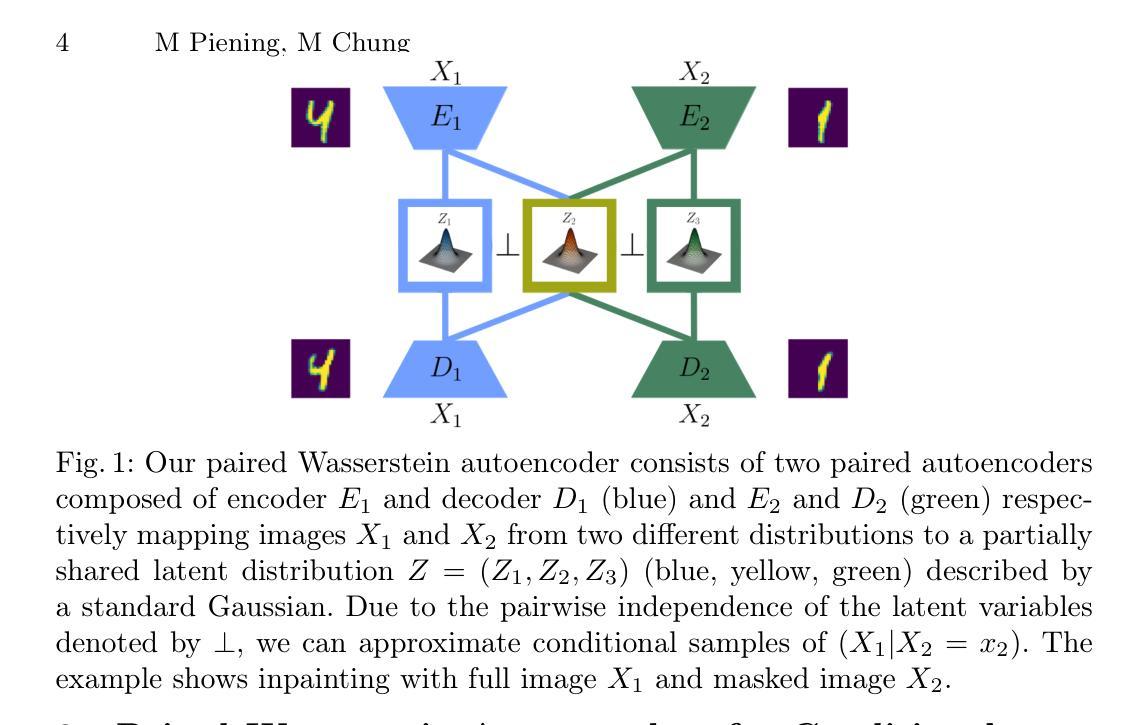
Paired Wasserstein Autoencoders for Conditional Sampling
Authors:Moritz Piening, Matthias Chung
Wasserstein distances greatly influenced and coined various types of generative neural network models. Wasserstein autoencoders are particularly notable for their mathematical simplicity and straight-forward implementation. However, their adaptation to the conditional case displays theoretical difficulties. As a remedy, we propose the use of two paired autoencoders. Under the assumption of an optimal autoencoder pair, we leverage the pairwise independence condition of our prescribed Gaussian latent distribution to overcome this theoretical hurdle. We conduct several experiments to showcase the practical applicability of the resulting paired Wasserstein autoencoders. Here, we consider imaging tasks and enable conditional sampling for denoising, inpainting, and unsupervised image translation. Moreover, we connect our image translation model to the Monge map behind Wasserstein-2 distances.
Wasserstein距离对各种生成神经网络模型产生了深远影响,并创造了各种类型。Wasserstein自编码器因其数学简单性和直接实现性而尤为引人注目。然而,它们对条件情况的适应却显示出理论上的困难。作为一种补救措施,我们提出了使用两个配对自编码器。在假设最优自编码器对的情况下,我们利用指定的高斯潜在分布的配对独立性条件来克服这一理论障碍。我们进行了多次实验,以展示所得配对Wasserstein自编码器的实际适用性。在此,我们考虑成像任务,实现去噪、图像修复和无监督图像翻译的条件采样。此外,我们将图像翻译模型与Wasserstein-2距离背后的Monge图连接起来。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文介绍了Wasserstein距离对各种生成神经网络模型的影响,特别是Wasserstein自编码器在数学上的简洁性和直接实现性。然而,将其适应于条件情况存在理论困难。为此,我们提出了使用两个配对自编码器的方法。在假设最优自编码器对的基础上,我们利用规定的Gaussian潜在分布的配对独立性条件来克服这一理论障碍。我们通过实验展示了配对Wasserstein自编码器的实际应用,在成像任务中实现了去噪、图像补全和无需监督的图像翻译的条件采样。此外,我们将图像翻译模型与Wasserstein-2距离背后的Monge图联系起来。
Key Takeaways
- Wasserstein距离对生成神经网络模型有重要影响,特别是Wasserstein自编码器。
- Wasserstein自编码器在条件情况下的适应存在理论困难。
- 提出使用两个配对自编码器的方法来解决这一理论困难。
- 假设最优自编码器对,并利用Gaussian潜在分布的配对独立性条件。
- 配对Wasserstein自编码器在成像任务中有实际应用,包括去噪、图像补全和无需监督的图像翻译的条件采样。
- 实验证明了配对Wasserstein自编码器的实用性。
点此查看论文截图

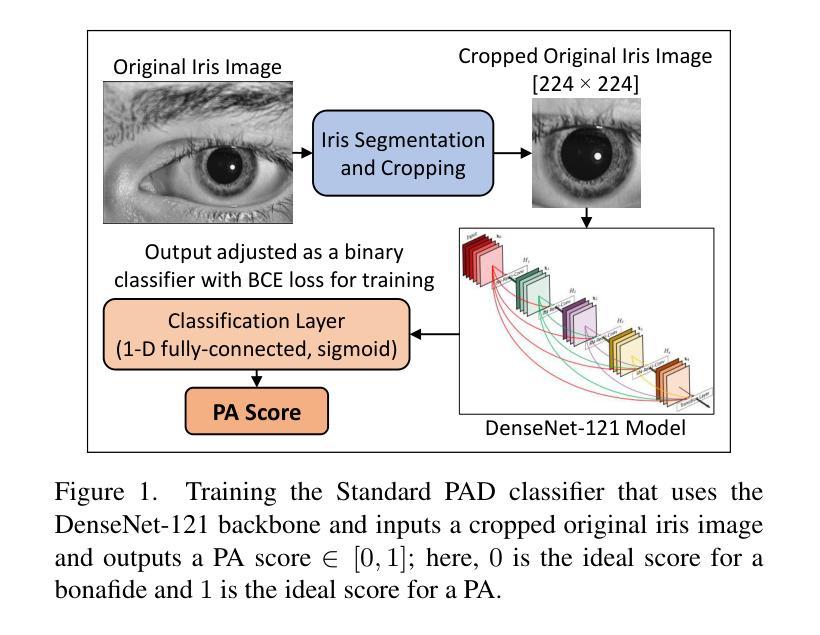
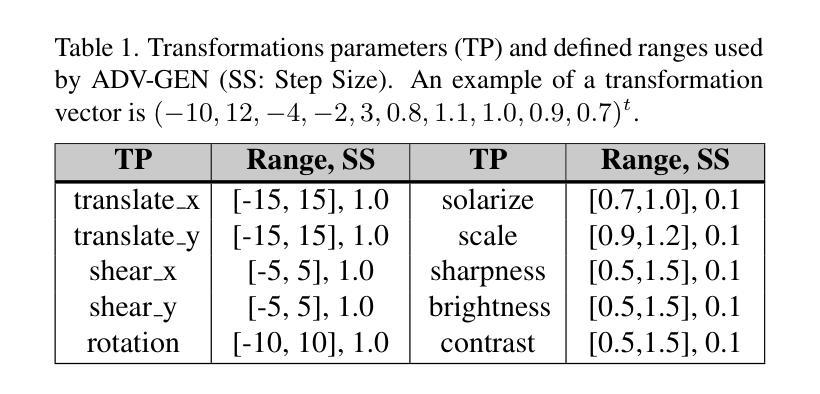
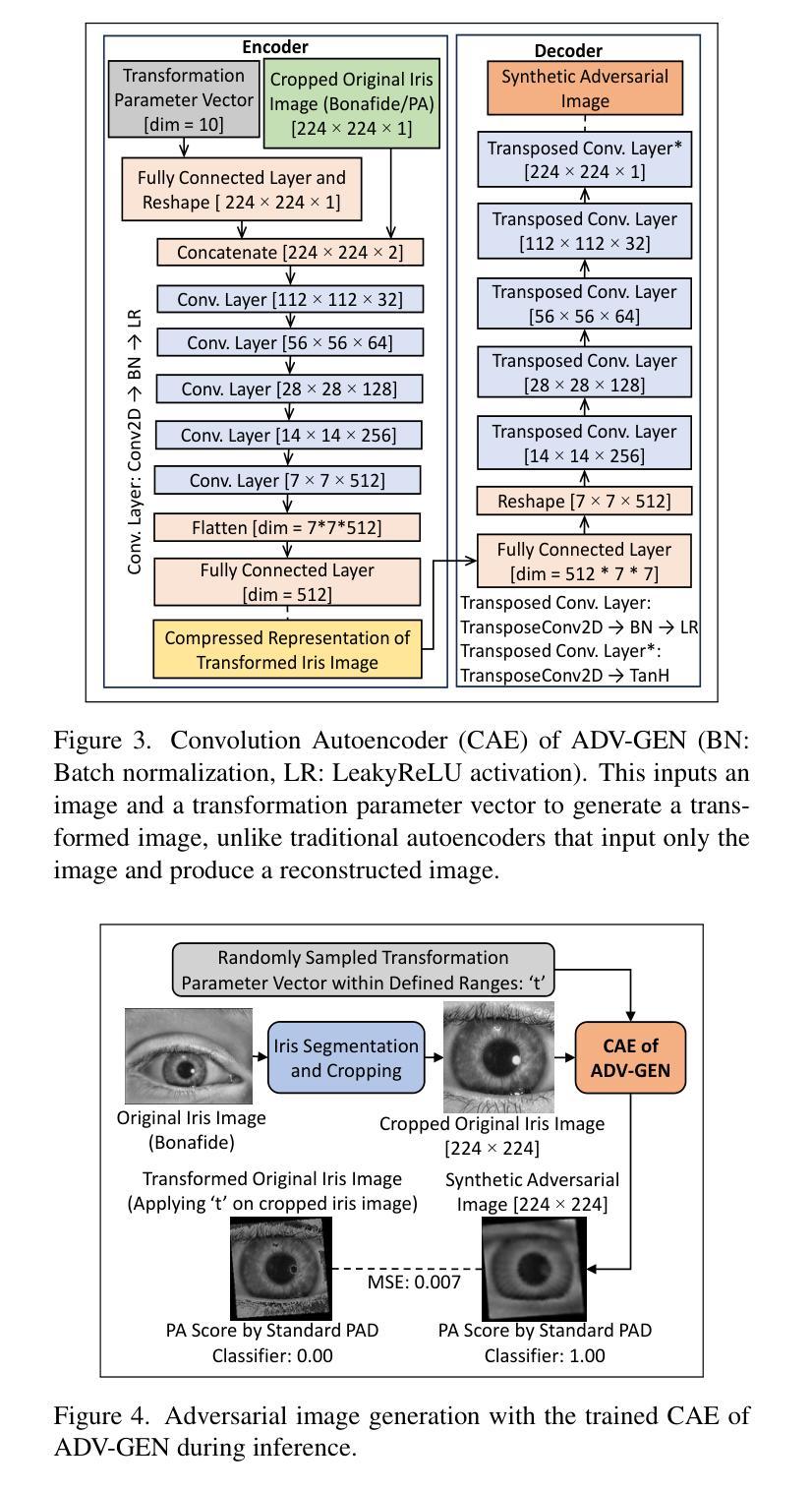
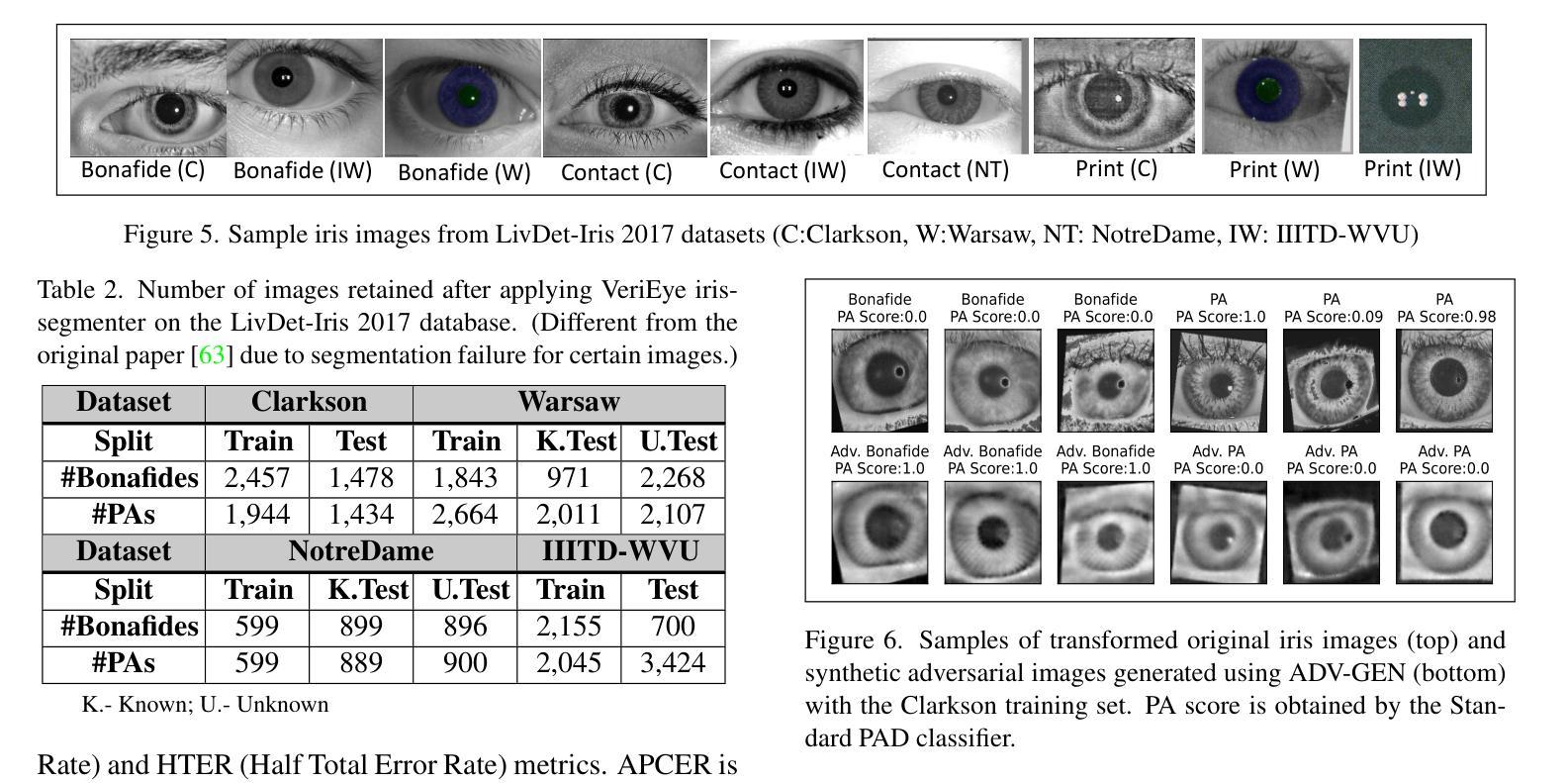
A Parametric Approach to Adversarial Augmentation for Cross-Domain Iris Presentation Attack Detection
Authors:Debasmita Pal, Redwan Sony, Arun Ross
Iris-based biometric systems are vulnerable to presentation attacks (PAs), where adversaries present physical artifacts (e.g., printed iris images, textured contact lenses) to defeat the system. This has led to the development of various presentation attack detection (PAD) algorithms, which typically perform well in intra-domain settings. However, they often struggle to generalize effectively in cross-domain scenarios, where training and testing employ different sensors, PA instruments, and datasets. In this work, we use adversarial training samples of both bonafide irides and PAs to improve the cross-domain performance of a PAD classifier. The novelty of our approach lies in leveraging transformation parameters from classical data augmentation schemes (e.g., translation, rotation) to generate adversarial samples. We achieve this through a convolutional autoencoder, ADV-GEN, that inputs original training samples along with a set of geometric and photometric transformations. The transformation parameters act as regularization variables, guiding ADV-GEN to generate adversarial samples in a constrained search space. Experiments conducted on the LivDet-Iris 2017 database, comprising four datasets, and the LivDet-Iris 2020 dataset, demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed method. The code is available at https://github.com/iPRoBe-lab/ADV-GEN-IrisPAD.
基于虹膜的生物识别系统容易受到呈现攻击(PAs)的影响,攻击者会展示物理伪制品(例如打印的虹膜图像、纹理隐形眼镜)来击败系统。这促使了多种呈现攻击检测(PAD)算法的发展,这些算法通常在域内设置中表现良好。然而,当训练和测试使用不同的传感器、呈现攻击工具和数据集时,它们在跨域场景中的通用化能力往往不足。在这项工作中,我们使用真实虹膜和呈现攻击的对抗性训练样本,以提高PAD分类器在跨域方面的性能。我们方法的新颖之处在于利用经典数据增强方案(例如平移、旋转)的转换参数来生成对抗性样本。我们通过卷积自编码器ADV-GEN实现这一点,该自编码器输入原始训练样本以及一组几何和光度转换。转换参数作为正则化变量,指导ADV-GEN在受限的搜索空间中生成对抗性样本。在LivDet-Iris 2017数据库(包含四个数据集)和LivDet-Iris 2020数据集上进行的实验证明了我们的方法的有效性。代码可在https://github.com/iPRoBe-lab/ADV-GEN-IrisPAD找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), 2025
Summary
本文介绍了基于虹膜的生物识别系统易受到表现攻击(PAs)的问题,针对此问题提出了利用对抗性训练样本改进跨域表现攻击检测(PAD)分类器性能的方法。该方法利用经典数据增强方案中的转换参数生成对抗样本,通过卷积自编码器ADV-GEN实现。转换参数作为正则化变量,指导ADV-GEN在约束搜索空间内生成对抗样本。在LivDet-Iris 2017和LivDet-Iris 2020数据集上的实验证明了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 虹膜生物识别系统易受到表现攻击(PAs),需要更有效的PAD算法。
- 对抗性训练样本用于改进跨域PAD分类器的性能。
- 利用经典数据增强方案中的转换参数生成对抗样本。
- 卷积自编码器ADV-GEN用于实现这一方法。
- 转换参数作为正则化变量,指导ADV-GEN生成对抗样本。
- 在LivDet-Iris 2017和LivDet-Iris 2020数据集上的实验证明了该方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

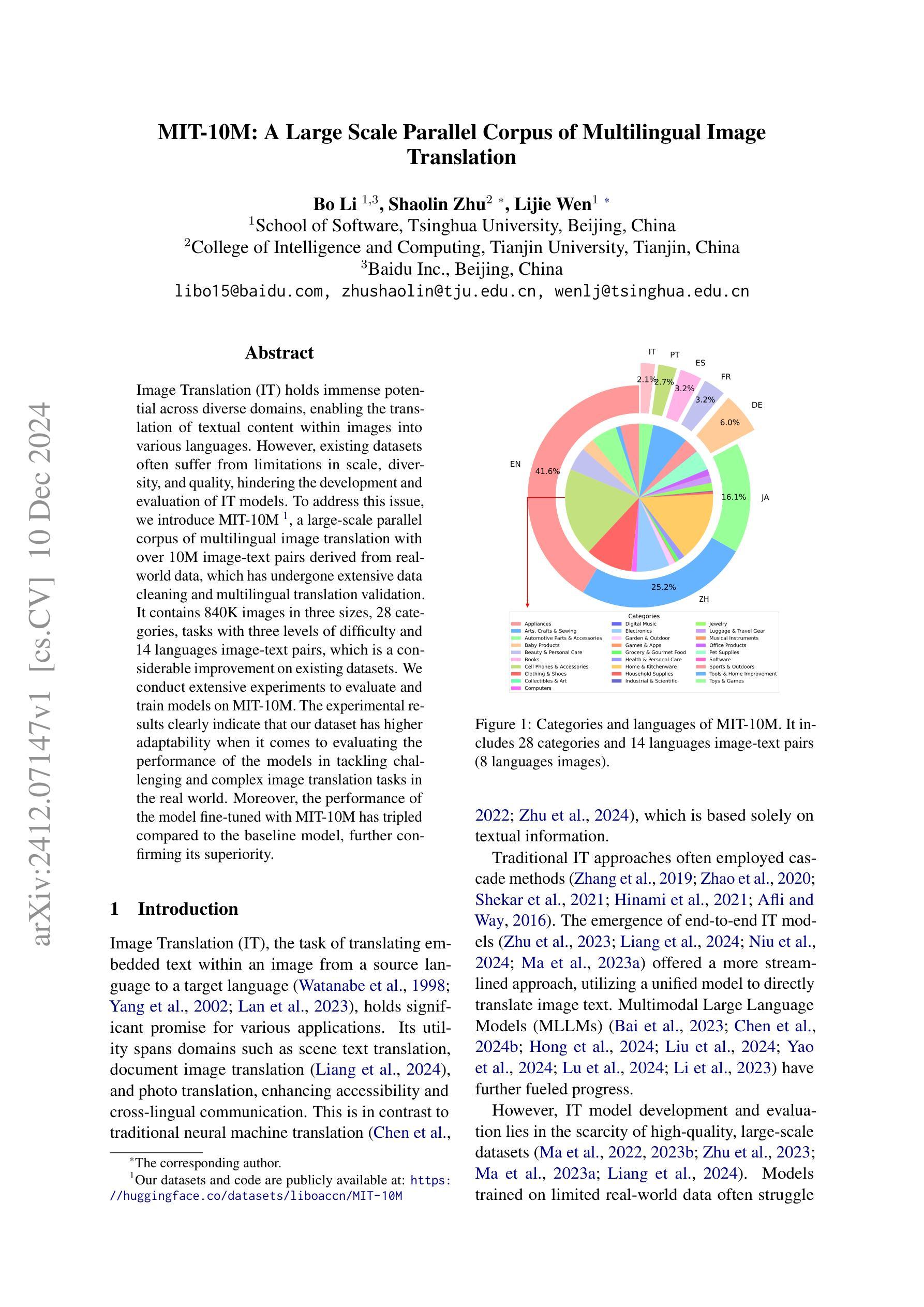
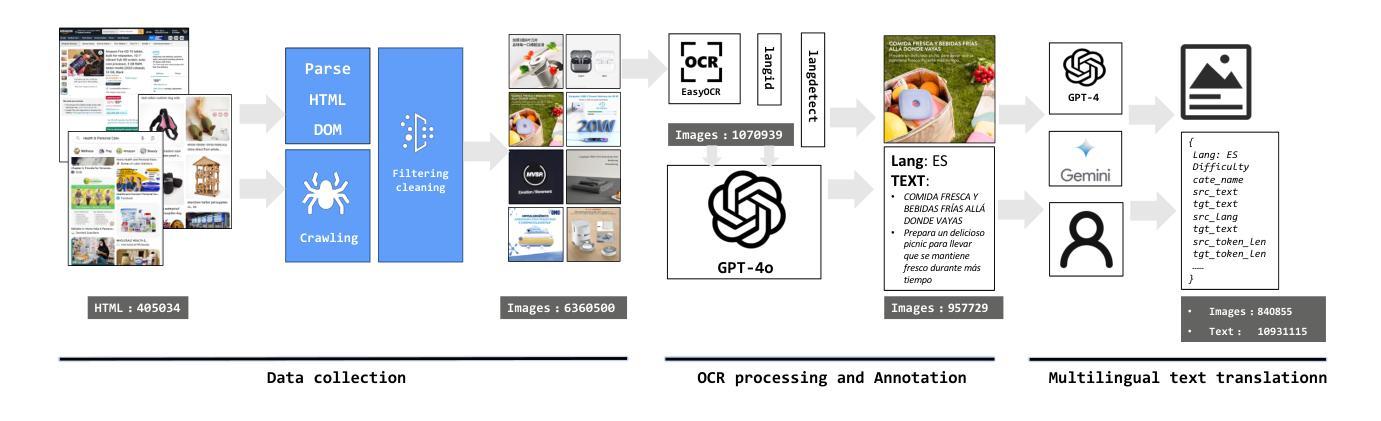
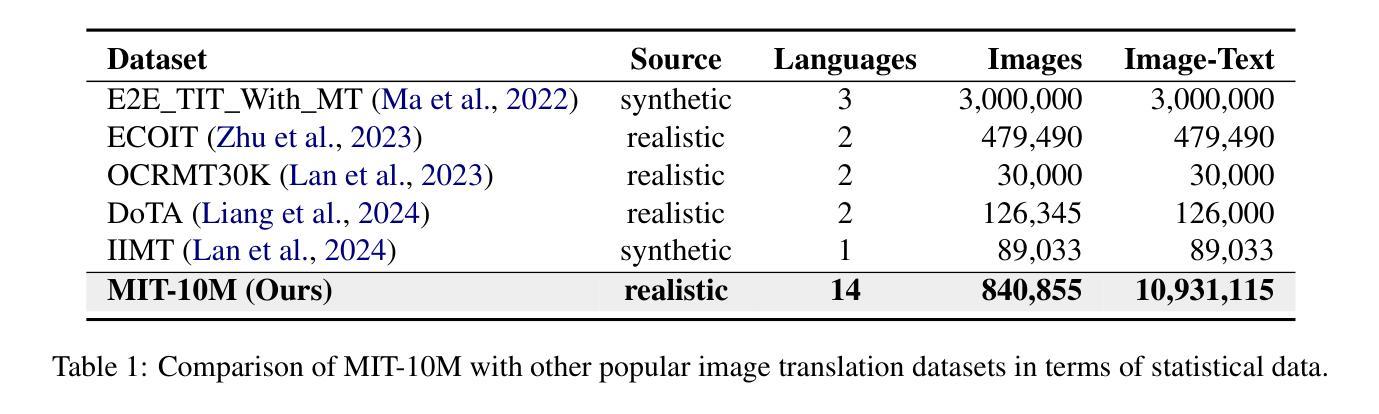
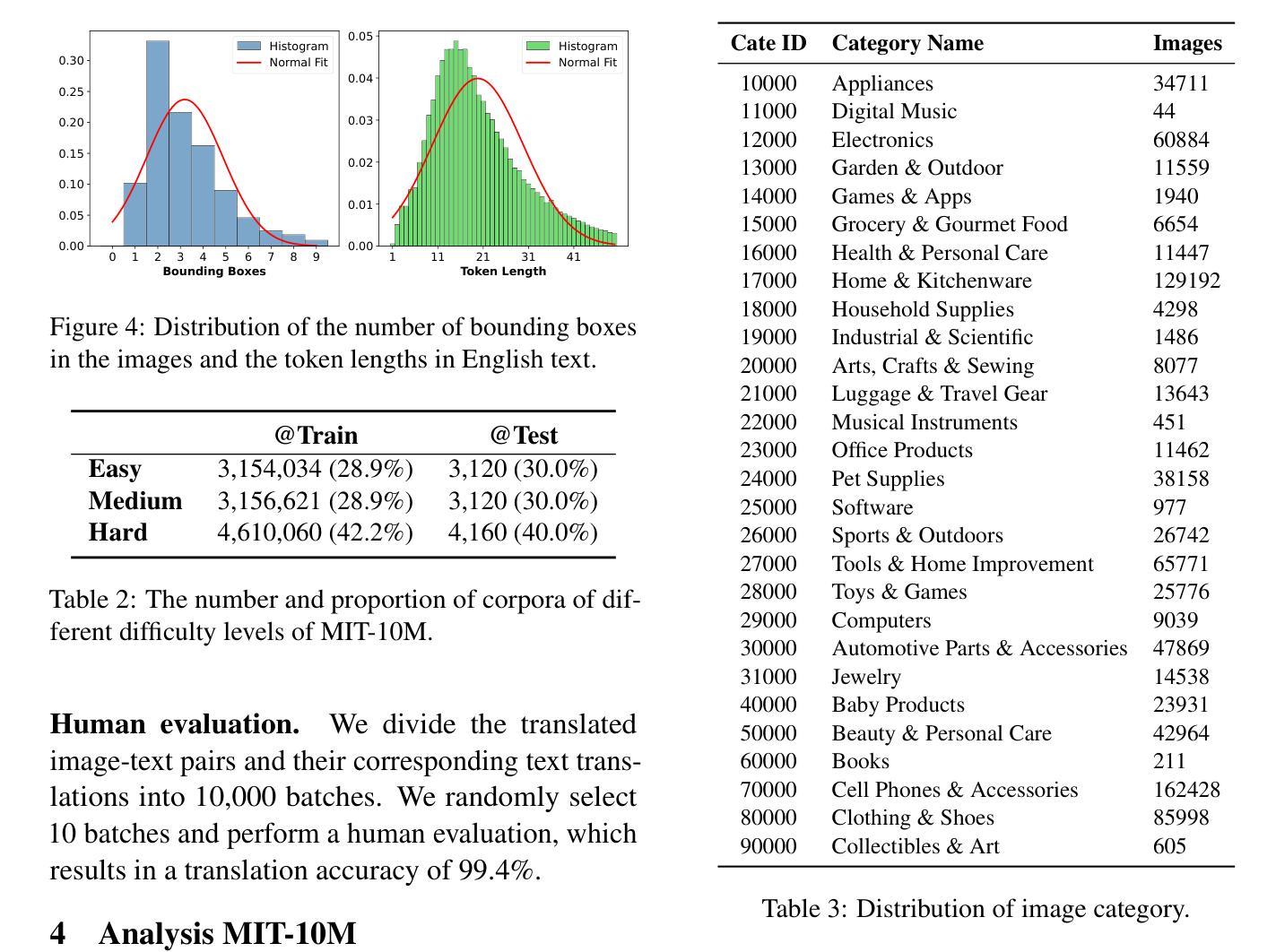
MIT-10M: A Large Scale Parallel Corpus of Multilingual Image Translation
Authors:Bo Li, Shaolin Zhu, Lijie Wen
Image Translation (IT) holds immense potential across diverse domains, enabling the translation of textual content within images into various languages. However, existing datasets often suffer from limitations in scale, diversity, and quality, hindering the development and evaluation of IT models. To address this issue, we introduce MIT-10M, a large-scale parallel corpus of multilingual image translation with over 10M image-text pairs derived from real-world data, which has undergone extensive data cleaning and multilingual translation validation. It contains 840K images in three sizes, 28 categories, tasks with three levels of difficulty and 14 languages image-text pairs, which is a considerable improvement on existing datasets. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate and train models on MIT-10M. The experimental results clearly indicate that our dataset has higher adaptability when it comes to evaluating the performance of the models in tackling challenging and complex image translation tasks in the real world. Moreover, the performance of the model fine-tuned with MIT-10M has tripled compared to the baseline model, further confirming its superiority.
图像翻译(IT)在各个领域具有巨大的潜力,能够实现图像内文本内容的跨语言翻译。然而,现有数据集在规模、多样性和质量方面存在诸多局限,阻碍了IT模型的开发与评估。为了解决这一问题,我们推出了MIT-10M,这是一个大规模的多语言图像翻译平行语料库,包含超过1000万个图像文本对,这些数据均来源于现实世界,并经过了严格的数据清洗和多语言翻译验证。它包含三种尺寸的84万个图像、28个类别、三个难度等级的任务,以及14种语言的图像文本对,对现有数据集来说是一个巨大的改进。我们在MIT-10M上进行了广泛的实验来评估和训练模型。实验结果清楚地表明,我们的数据集在评估模型应对现实世界中具有挑战性和复杂性的图像翻译任务的性能时具有更高的适应性。此外,使用MIT-10M进行微调的模型性能是基线模型的三倍,这进一步证明了其优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in COLING 2025
Summary
图像翻译(IT)在多个领域具有巨大潜力,可实现图像内文本的跨语言翻译。然而,现有数据集在规模、多样性和质量方面存在局限性,阻碍了IT模型的开发和评估。为此,我们推出了MIT-10M,这是一个包含超过1000万张图像文本对的大型多语言图像翻译平行语料库,源于现实世界数据,并经过严格的数据清洗和多语言翻译验证。它在图像大小、类别、任务难度和语言多样性方面都有显著改进。实验表明,MIT-10M在应对现实世界中的复杂图像翻译任务时表现出更高的适应性,使用MIT-10M微调的模型性能是基线模型的三倍。
Key Takeaways
- 图像翻译(IT)在多个领域具有应用潜力,能够实现图像内文本的跨语言翻译。
- 现有数据集存在规模、多样性和质量方面的局限性,影响IT模型的发展。
- MIT-10M是一个大型多语言图像翻译平行语料库,包含超过1000万张图像文本对。
- MIT-10M从现实世界数据派生,经过严格的数据清洗和翻译验证。
- MIT-10M在图像大小、类别、任务难度和语言方面都有显著改进,更具多样性。
- 实验表明MIT-10M在评估模型性能和处理复杂图像翻译任务时表现出更高的适应性。
点此查看论文截图


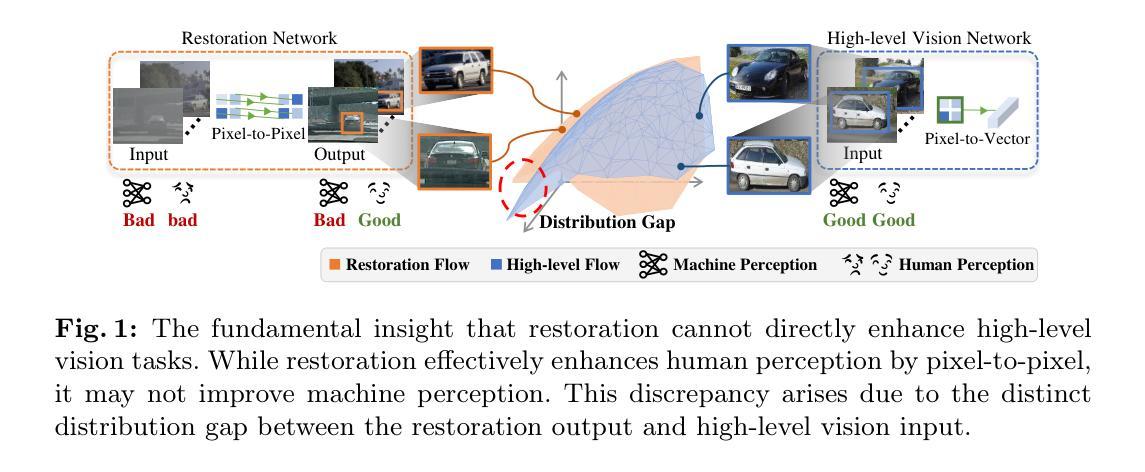
Unsupervised Variational Translator for Bridging Image Restoration and High-Level Vision Tasks
Authors:Jiawei Wu, Zhi Jin
Recent research tries to extend image restoration capabilities from human perception to machine perception, thereby enhancing the performance of high-level vision tasks in degraded environments. These methods, primarily based on supervised learning, typically involve the retraining of restoration networks or high-level vision networks. However, collecting paired data in real-world scenarios and retraining large-scale models are challenge. To this end, we propose an unsupervised learning method called \textbf{Va}riational \textbf{T}ranslator (VaT), which does not require retraining existing restoration and high-level vision networks. Instead, it establishes a lightweight network that serves as an intermediate bridge between them. By variational inference, VaT approximates the joint distribution of restoration output and high-level vision input, dividing the optimization objective into preserving content and maximizing marginal likelihood associated with high-level vision tasks. By cleverly leveraging self-training paradigms, VaT achieves the above optimization objective without requiring labels. As a result, the translated images maintain a close resemblance to their original content while also demonstrating exceptional performance on high-level vision tasks. Extensive experiments in dehazing and low-light enhancement for detection and classification show the superiority of our method over other state-of-the-art unsupervised counterparts, even significantly surpassing supervised methods in some complex real-world scenarios.Code is available at https://github.com/Fire-friend/VaT.
最近的研究尝试将从人类感知到机器感知的图像恢复能力进行扩展,从而提高在恶劣环境下高级视觉任务的性能。这些方法主要基于有监督学习,通常涉及恢复网络或高级视觉网络的再训练。然而,在真实场景收集配对数据并重新训练大规模模型是挑战。为此,我们提出了一种无需监督学习方法,称为“变分翻译器(VaT)”,它不需要重新训练现有的恢复和高级视觉网络。相反,它建立了一个轻量级网络,作为它们之间的中间桥梁。通过变分推理,VaT近似恢复输出和高级视觉输入的共同分布,将优化目标分为保持内容和最大化与高级视觉任务相关的边缘可能性。通过巧妙地利用自训练模式,VaT在不要求标签的情况下实现了上述优化目标。因此,翻译后的图像保持与原始内容密切相似,同时在高级视觉任务上表现出卓越的性能。去雾和低光增强检测和分类的广泛实验表明,我们的方法在与其他最先进的无监督方法相比具有优势,甚至在某些复杂的真实场景中显著超过了有监督方法。代码可用在https://github.com/Fire-friend/VaT。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
最新研究尝试将图像恢复能力从人类感知扩展到机器感知,从而提高退化环境下高级视觉任务的表现。该研究提出了一种无需重新训练现有恢复和高级视觉网络的监督学习方法——变分翻译器(VaT)。它通过变分推理来近似恢复输出和高级视觉输入的联合分布,将优化目标分为保持内容和最大化与高级视觉任务相关的边缘概率。通过巧妙地利用自训练模式,VaT在不依赖标签的情况下实现了上述优化目标。实验证明,翻译后的图像在保持原始内容的同时,在高级视觉任务上表现出卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 研究致力于将图像恢复从人类感知扩展到机器感知,以增强机器在恶劣环境下的视觉任务性能。
- 提出了一种名为变分翻译器(VaT)的无监督学习方法。
- VaT不需要重新训练现有的恢复和高级视觉网络,而是建立一个轻量级网络作为它们之间的桥梁。
- 通过变分推理,VaT可以近似恢复输出和高级视觉输入的联合分布。
- VaT将优化目标分为保持图像内容和最大化与高级视觉任务相关的边缘概率。
- 通过自训练模式,VaT在不依赖标签的情况下实现了优化目标。
点此查看论文截图

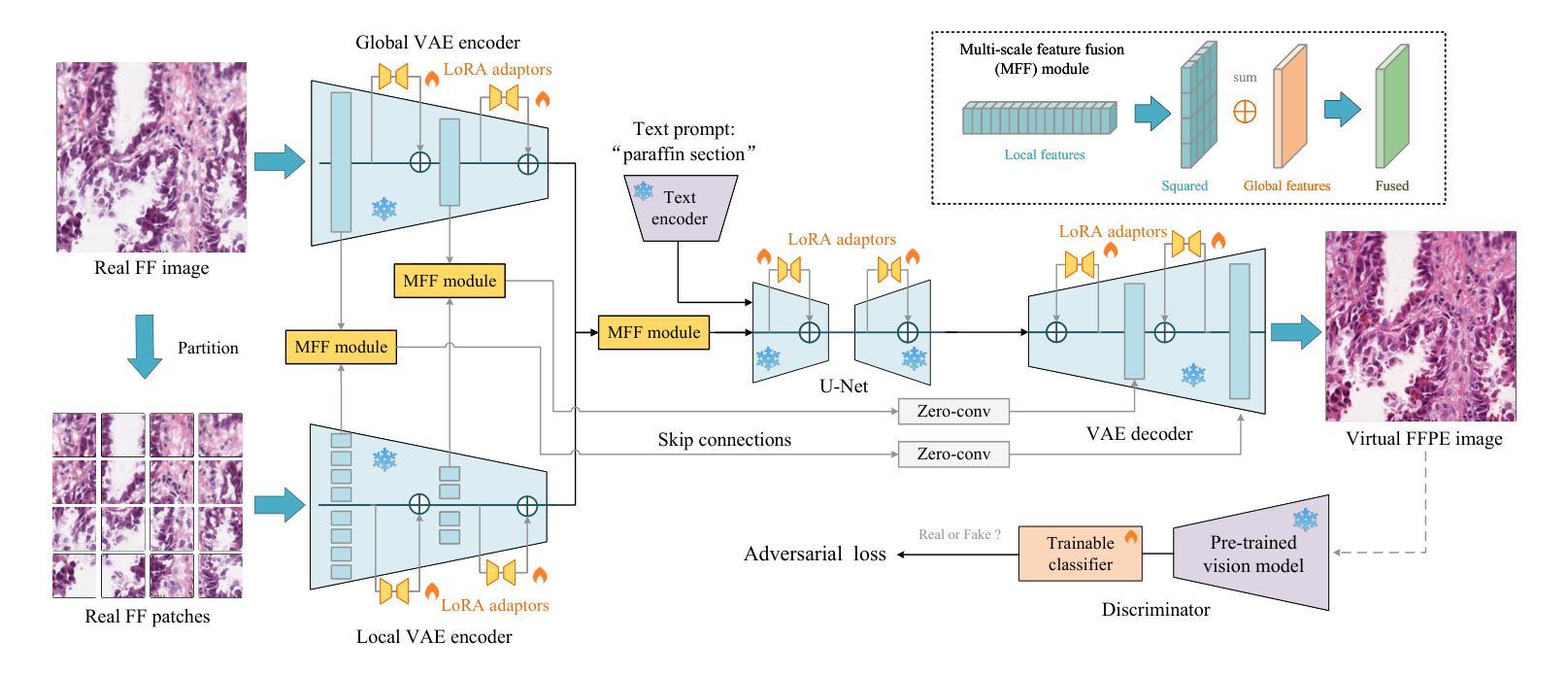
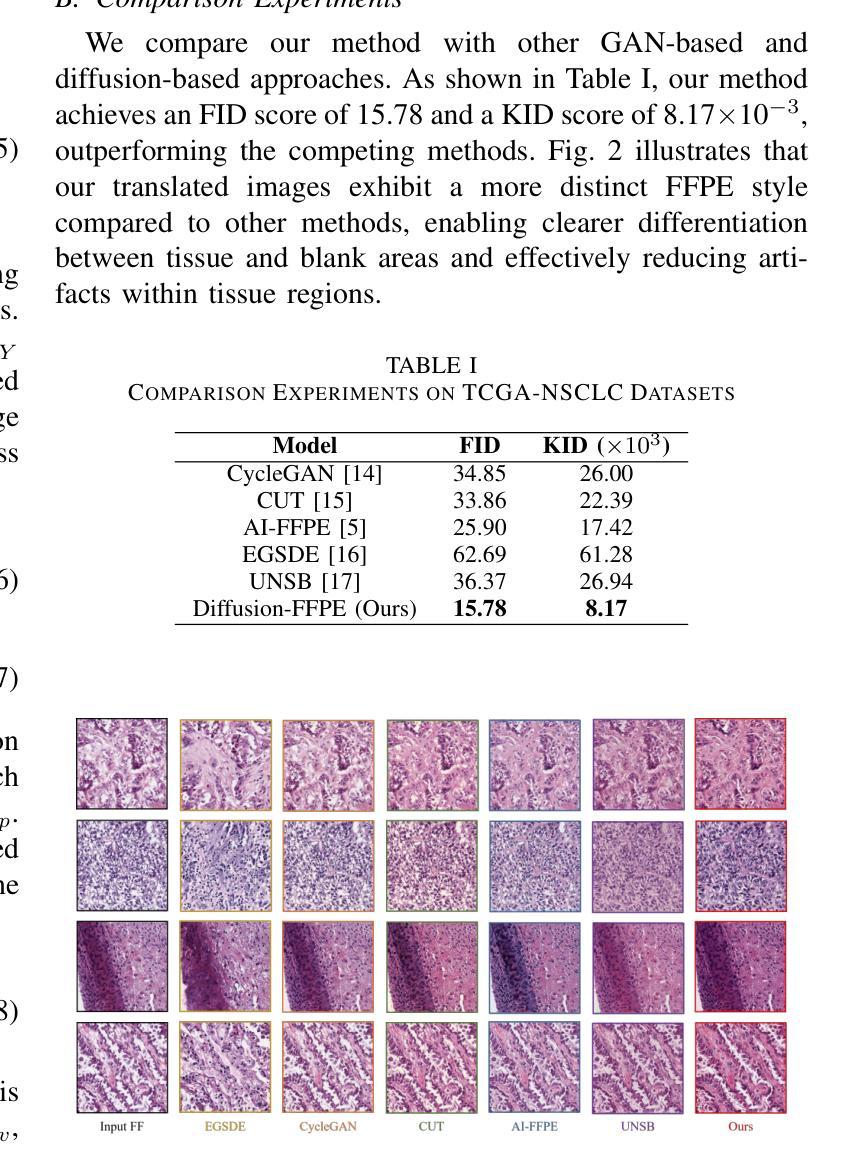
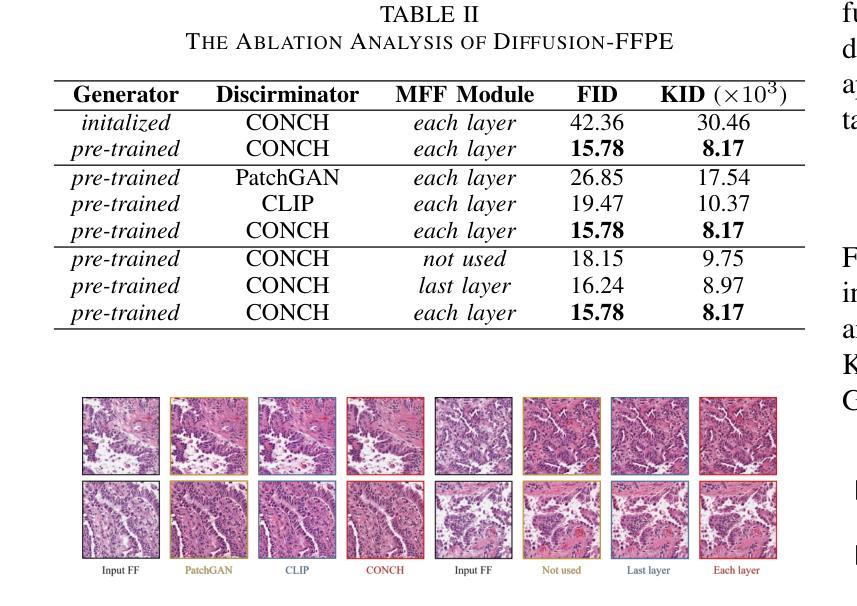
Leveraging Pre-trained Models for FF-to-FFPE Histopathological Image Translation
Authors:Qilai Zhang, Jiawen Li, Peiran Liao, Jiali Hu, Tian Guan, Anjia Han, Yonghong He
The two primary types of Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) slides in histopathology are Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) and Fresh Frozen (FF). FFPE slides offer high quality histopathological images but require a labor-intensive acquisition process. In contrast, FF slides can be prepared quickly, but the image quality is relatively poor. Our task is to translate FF images into FFPE style, thereby improving the image quality for diagnostic purposes. In this paper, we propose Diffusion-FFPE, a method for FF-to-FFPE histopathological image translation using a pre-trained diffusion model. Specifically, we utilize a one-step diffusion model as the generator, which we fine-tune using LoRA adapters within an adversarial learning framework. To enable the model to effectively capture both global structural patterns and local details, we introduce a multi-scale feature fusion module that leverages two VAE encoders to extract features at different image resolutions, performing feature fusion before inputting them into the UNet. Additionally, a pre-trained vision-language model for histopathology serves as the backbone for the discriminator, enhancing model performance. Our FF-to-FFPE translation experiments on the TCGA-NSCLC dataset demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms existing methods. The code and models are released at https://github.com/QilaiZhang/Diffusion-FFPE.
组织病理学中的两种主要类型的苏木精和伊红(H&E)切片包括福尔马林固定石蜡包埋(FFPE)和新鲜冷冻(FF)。FFPE切片提供高质量的组织病理学图像,但需要劳动密集型的采集过程。相比之下,FF切片可以快速制备,但图像质量相对较差。我们的任务是将FF图像转换为FFPE风格,从而提高图像质量,用于诊断目的。在本文中,我们提出了Diffusion-FFPE方法,这是一种使用预训练的扩散模型进行FF到FFPE组织病理学图像翻译的方法。具体来说,我们利用一步扩散模型作为生成器,在一个对抗性学习框架内使用LoRA适配器对其进行微调。为了允许模型有效地捕捉全局结构模式和局部细节,我们引入了一个多尺度特征融合模块,该模块利用两个VAE编码器在不同图像分辨率下提取特征,在将它们输入到UNet之前进行特征融合。此外,一个预训练的组织病理学视觉语言模型作为判别器的骨干,增强了模型性能。我们在TCGA-NSCLC数据集上进行的FF到FFPE翻译实验表明,所提出的方法优于现有方法。相关代码和模型已发布在:https://github.com/QilaiZhang/Diffusion-FFPE。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at IEEE BIBM 2024
Summary
本文介绍了两种主要的病理切片类型:FFPE和FF。FFPE切片图像质量高但制作过程繁琐,而FF切片制作快速但图像质量较差。本文的目标是提出一种将FF图像转换为FFPE风格的方法,以提高诊断用图像质量。具体提出了Diffusion-FFPE方法,使用预训练的扩散模型进行FF到FFPE的病理图像翻译,通过引入多尺度特征融合模块和对抗性学习框架中的LoRA适配器进行微调。实验证明该方法在TCGA-NSCLC数据集上的FF-to-FFPE翻译效果优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍两种主要的病理切片类型:FFPE和FF,分别具有高质量和快速制作的特点,但存在图像质量和制作难度的权衡问题。
- 任务是开发一种将FF图像转换为FFPE风格的方法,以提高诊断用图像质量。
- 提出了Diffusion-FFPE方法,使用预训练的扩散模型进行病理图像翻译。
- 通过引入多尺度特征融合模块,模型能够捕捉图像的全局结构模式和局部细节。
- 对抗性学习框架和LoRA适配器用于微调模型,提高模型的性能。
- 在TCGA-NSCLC数据集上的实验证明,Diffusion-FFPE方法在FF-to-FFPE翻译方面优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图

SurgeMOD: Translating image-space tissue motions into vision-based surgical forces
Authors:Mikel De Iturrate Reyzabal, Dionysios Malas, Shuai Wang, Sebastien Ourselin, Hongbin Liu
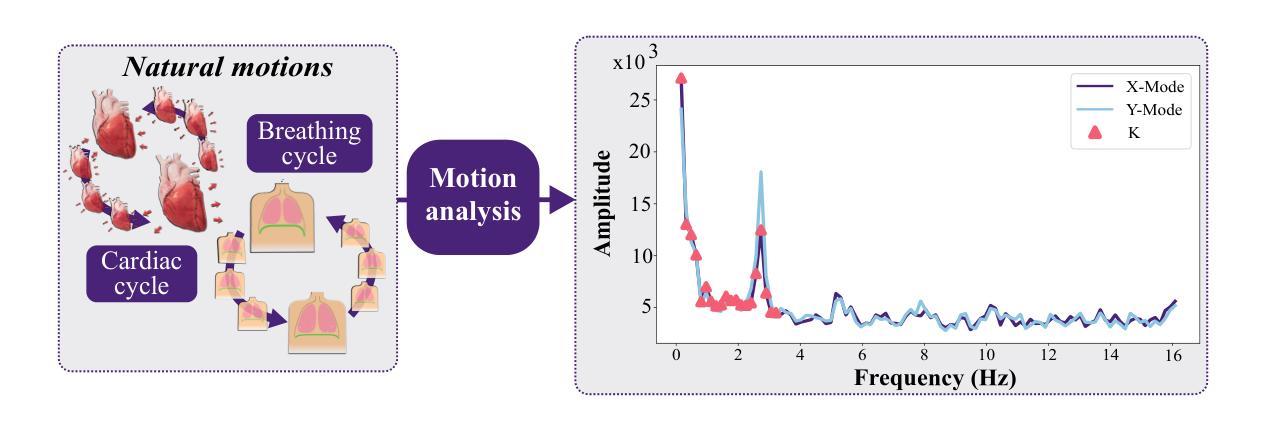
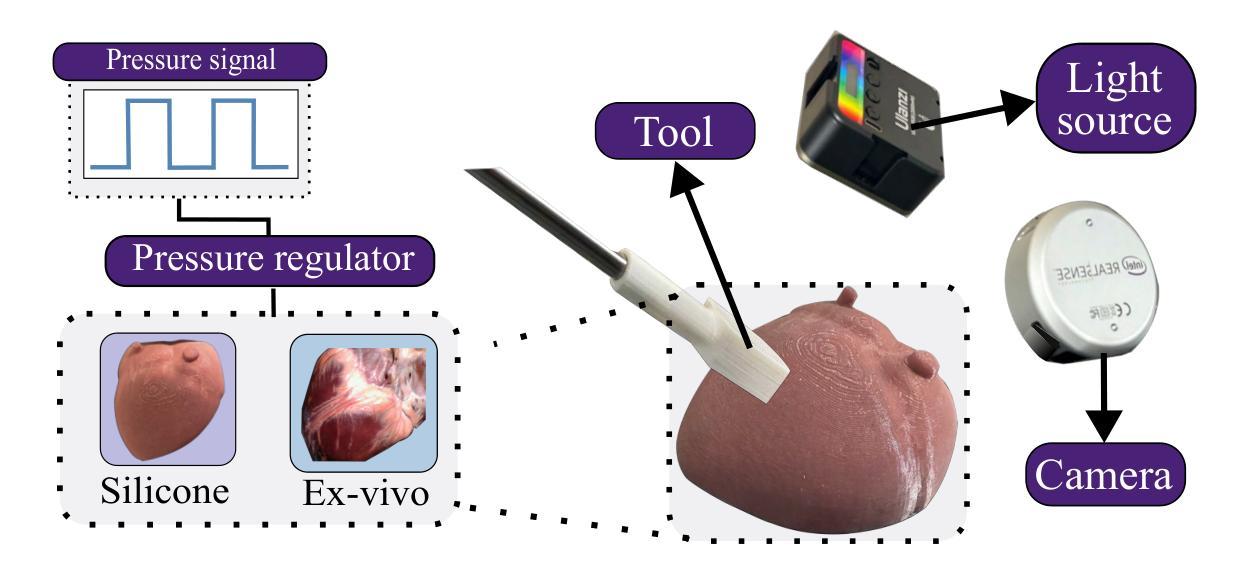
We present a new approach for vision-based force estimation in Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery based on frequency domain basis of motion of organs derived directly from video. Using internal movements generated by natural processes like breathing or the cardiac cycle, we infer the image-space basis of the motion on the frequency domain. As we are working with this representation, we discretize the problem to a limited amount of low-frequencies to build an image-space mechanical model of the environment. We use this pre-built model to define our force estimation problem as a dynamic constraint problem. We demonstrate that this method can estimate point contact forces reliably for silicone phantom and ex-vivo experiments, matching real readings from a force sensor. In addition, we perform qualitative experiments in which we synthesize coherent force textures from surgical videos over a certain region of interest selected by the user. Our method demonstrates good results for both quantitative and qualitative analysis, providing a good starting point for a purely vision-based method for surgical force estimation.
我们提出了一种基于视频直接导出器官运动频率域特征的最小侵入式机器人手术中的基于视觉的力估计新方法。我们利用自然过程(如呼吸或心脏周期)产生的内部运动,推断频率域上的运动图像空间基础。由于我们采用这种表示形式,我们将问题离散化为有限数量的低频,以建立图像空间环境机械模型。我们使用此预构建模型将力估计问题定义为动态约束问题。我们证明该方法可以可靠地估计硅胶幻影和离体实验中的点接触力,与来自力传感器的实际读数相匹配。此外,我们在用户选择的特定感兴趣区域上对手术视频进行了连贯的力纹理合成实验。我们的方法在为定量和定性分析均取得良好结果的同时,为纯粹的基于视觉的力估计方法提供了一个良好的起点。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种基于视频的新方法,用于微创机器人手术中的基于视觉的力估计。该方法利用器官运动的频率域基础,直接从视频中提取运动信息。利用自然过程(如呼吸或心脏周期)产生的内部运动,推断图像空间在频率域的运动基础。在构建图像空间环境机械模型时,将问题简化为有限低频问题。使用此预构建模型将力估计问题定义为动态约束问题。该方法可以可靠地估计硅胶假体和离体实验的点接触力,与力传感器的实际读数相匹配。此外,还对用户选择的特定感兴趣区域进行了连贯的力纹理合成实验。该方法在定量和定性分析中均取得了良好结果,为纯粹的基于视觉的力估计方法提供了一个良好的起点。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种基于视频的新方法用于微创机器人手术中的力估计。
- 该方法利用器官运动的频率域信息进行力估计。
- 利用自然过程产生的内部运动信息来推断图像空间在频率域的运动基础。
- 方法通过离散化问题到低频来构建图像空间机械模型。
- 力估计问题被定义为一个动态约束问题。
- 该方法在硅胶假体和离体实验中能够可靠估计点接触力,并与实际读数相匹配。
点此查看论文截图

Rethinking Score Distillation as a Bridge Between Image Distributions
Authors:David McAllister, Songwei Ge, Jia-Bin Huang, David W. Jacobs, Alexei A. Efros, Aleksander Holynski, Angjoo Kanazawa
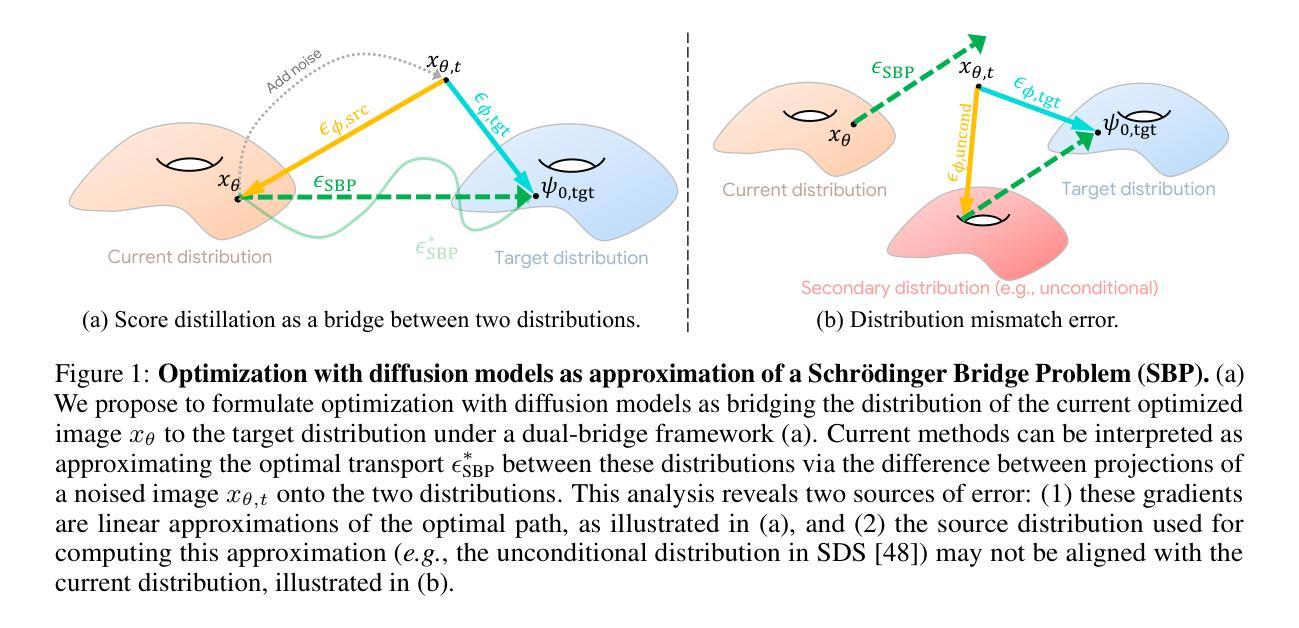
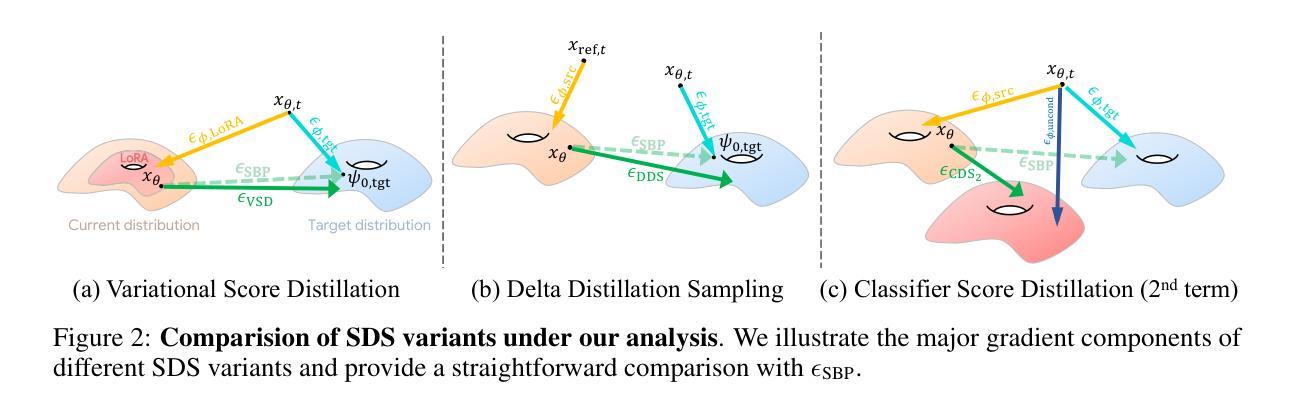
Score distillation sampling (SDS) has proven to be an important tool, enabling the use of large-scale diffusion priors for tasks operating in data-poor domains. Unfortunately, SDS has a number of characteristic artifacts that limit its usefulness in general-purpose applications. In this paper, we make progress toward understanding the behavior of SDS and its variants by viewing them as solving an optimal-cost transport path from a source distribution to a target distribution. Under this new interpretation, these methods seek to transport corrupted images (source) to the natural image distribution (target). We argue that current methods’ characteristic artifacts are caused by (1) linear approximation of the optimal path and (2) poor estimates of the source distribution. We show that calibrating the text conditioning of the source distribution can produce high-quality generation and translation results with little extra overhead. Our method can be easily applied across many domains, matching or beating the performance of specialized methods. We demonstrate its utility in text-to-2D, text-based NeRF optimization, translating paintings to real images, optical illusion generation, and 3D sketch-to-real. We compare our method to existing approaches for score distillation sampling and show that it can produce high-frequency details with realistic colors.
得分蒸馏采样(SDS)已被证明是处理数据稀缺领域任务的重要工具,可实现大规模扩散先验的使用。然而,SDS存在一些特征伪影,限制了其在通用应用中的实用性。在本文中,我们通过将SDS及其变体视为从源分布到目标分布的最优成本传输路径的解决方式,取得了理解其行为方面的进展。在这种新的解释下,这些方法试图将损坏的图像(源)传输到自然图像分布(目标)。我们认为当前方法的特征伪影是由(1)最优路径的线性近似和(2)源分布的不良估计引起的。我们表明,校准源分布的文本条件可以产生高质量的产生和翻译结果,且只需很少额外开销。我们的方法可轻松应用于多个领域,达到或超过专业方法的性能。我们在文本到二维、基于文本的NeRF优化、绘画到真实图像的翻译、光学错觉生成以及三维草图到现实的应用中展示了其实用性。我们将我们的方法与现有的分数蒸馏采样方法进行了比较,并证明它能够产生具有逼真颜色的高频细节。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024. Project webpage: https://sds-bridge.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了得分蒸馏采样(SDS)在处理数据稀缺领域任务时的重要性,但其存在的特征缺陷限制了其在通用应用中的实用性。文章通过将其视为从源分布到目标分布的最优成本传输路径的解决方案来推动对SDS及其变种行为的理解。文章认为当前方法的特征缺陷是由线性近似最优路径和源分布估计不良引起的。通过校准源分布的文本条件,可以产生高质量生成和翻译结果,且几乎不需要额外开销。该方法可轻松应用于多个领域,达到或超越专业方法的性能水平。实验展示了它在文本到二维、基于文本的NeRF优化、将绘画转换为真实图像、光学幻象生成以及从草图到现实的逼真性上的优势,并将本方法与现有的分数蒸馏采样方法进行比较,显示其在高频率细节和真实色彩方面可生成高质量的图像。简而言之,通过解决数据传输问题的方法优化了得分蒸馏采样。该方法应用广泛,能够在多种场景下实现高质量的图像生成和翻译效果。通过对比实验证明,此方法能够提升高频率细节的真实色彩表现。
Key Takeaways
- SDS在处理数据稀缺领域的任务时具有关键作用,但存在特征缺陷限制了其在通用应用中的实用性。
点此查看论文截图

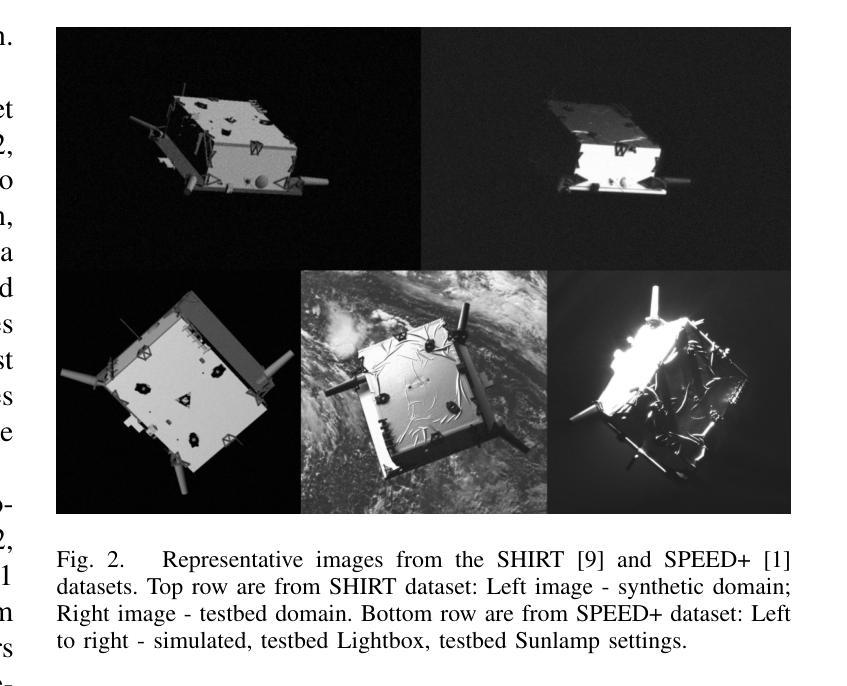
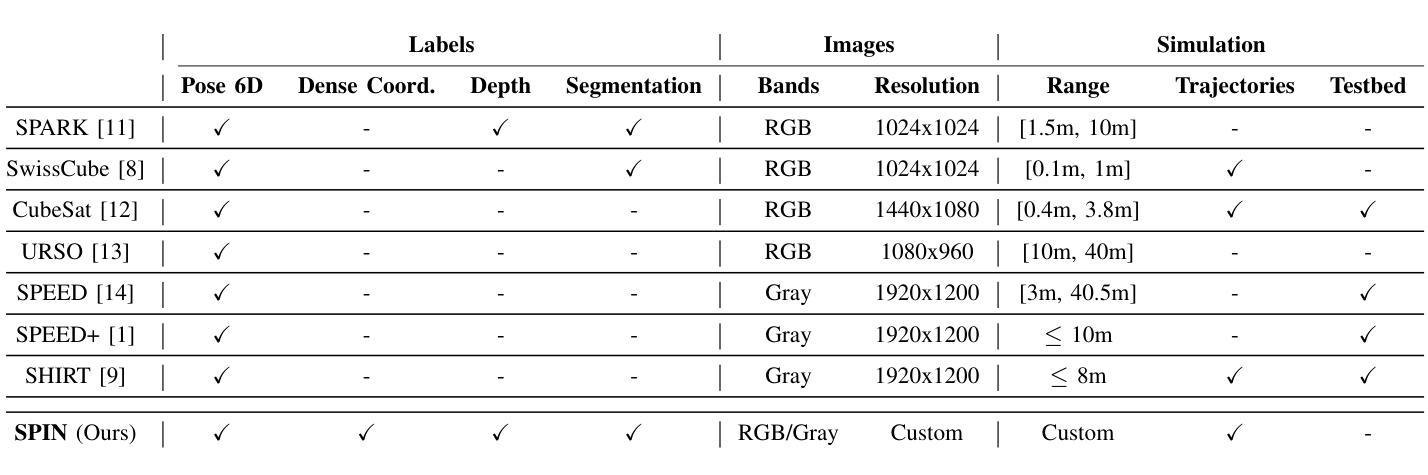
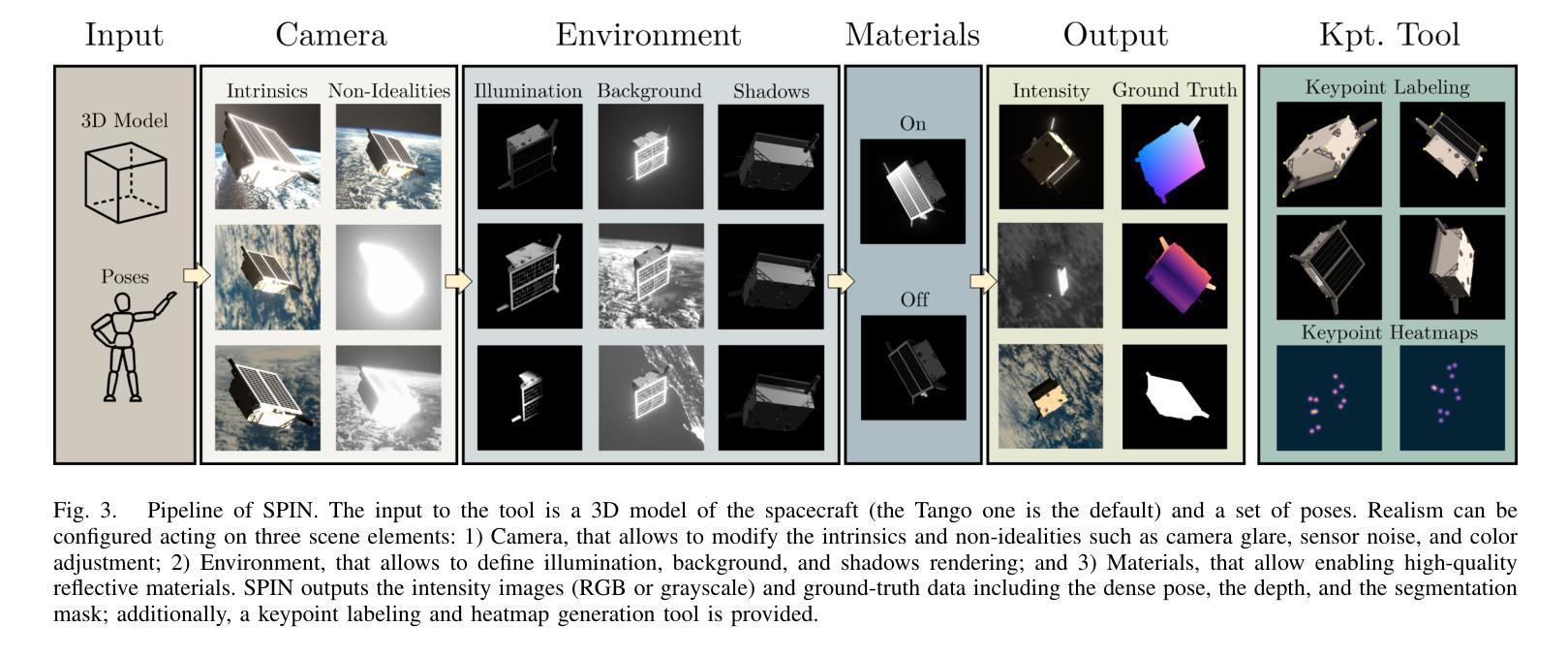
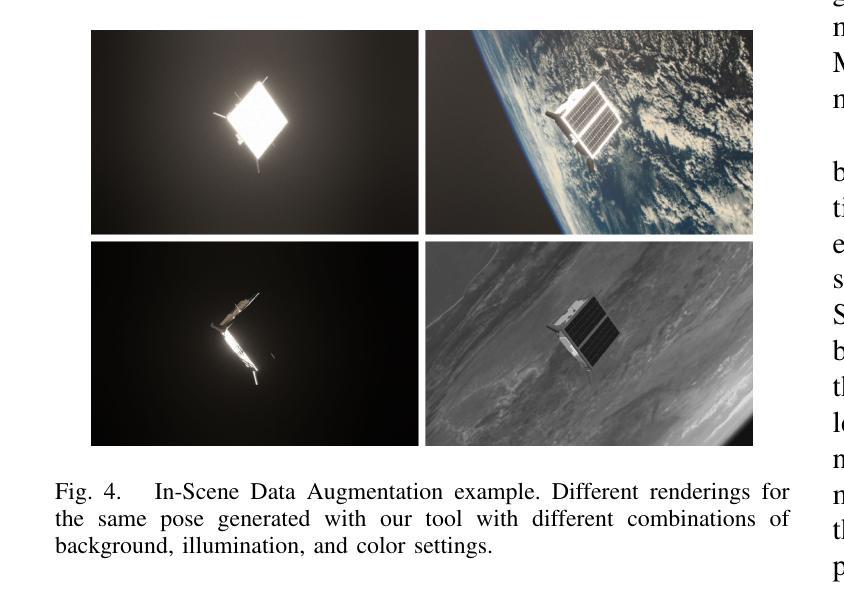
SPIN: Spacecraft Imagery for Navigation
Authors:Javier Montalvo, Juan Ignacio Bravo Pérez-Villar, Álvaro García-Martín, Pablo Carballeira, Jesús Bescós
The scarcity of data acquired under actual space operational conditions poses a significant challenge for developing learning-based visual navigation algorithms crucial for autonomous spacecraft navigation. This data shortage is primarily due to the prohibitive costs and inherent complexities of space operations. While existing datasets, predominantly relying on computer-simulated data, have partially addressed this gap, they present notable limitations. Firstly, these datasets often utilize proprietary image generation tools, restricting the evaluation of navigation methods in novel, unseen scenarios. Secondly, they provide limited ground-truth data, typically focusing solely on the spacecraft’s translation and rotation relative to the camera. To address these limitations, we present SPIN (SPacecraft Imagery for Navigation), an open-source spacecraft image generation tool designed to support a wide range of visual navigation scenarios in space, with a particular focus on relative navigation tasks. SPIN provides multiple modalities of ground-truth data and allows researchers to employ custom 3D models of satellites, define specific camera-relative poses, and adjust settings such as camera parameters or environmental illumination conditions. We also propose a method for exploiting our tool as a data augmentation module. We validate our tool on the spacecraft pose estimation task by training with a SPIN-generated replica of SPEED+, reaching a 47% average error reduction on SPEED+ testbed data (that simulates realistic space conditions), further reducing it to a 60% error reduction when using SPIN as a data augmentation method. Both the SPIN tool (and source code) and our SPIN-generated version of SPEED+ will be publicly released upon paper acceptance on GitHub. https://github.com/vpulab/SPIN
在真实的太空操作条件下获取的数据稀缺,对于开发基于学习的视觉导航算法构成了重大挑战,这些算法对于自主航天器导航至关重要。这一数据短缺主要是由于太空操作的高昂成本和固有复杂性。虽然现有的数据集主要依赖于计算机模拟数据,并已部分解决了这一差距,但它们存在明显的局限性。
首先,这些数据集经常使用专有图像生成工具,限制了在新颖、未见过的场景中对导航方法的评估。其次,它们提供的真实数据有限,通常只专注于航天器相对于相机的平移和旋转。
为了解决这些局限性,我们推出了SPIN(航天器图像导航),这是一款开源的航天器图像生成工具,旨在支持广泛的太空视觉导航场景,特别侧重于相对导航任务。SPIN提供了多种模式的真实数据,并允许研究人员使用定制的卫星3D模型,定义特定的相机相对姿态,并调整相机参数或环境照明条件等设置。我们还提出了一种利用该工具作为数据增强模块的方法。我们通过使用SPIN生成的SPEED+复制品对航天器姿态估计任务进行训练,在模拟真实太空条件的SPEED+测试床上将平均误差减少了47%,在使用SPIN作为数据增强方法时,误差进一步减少了60%。
SPIN工具(及源代码)和我们使用SPIN生成的SPEED+版本将在论文被接受后公开发布在GitHub上。https://github.com/vpulab/SPIN
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
空间操作条件下实际数据稀缺,为自主航天器导航的视觉导航算法开发带来挑战。现有数据集主要依赖计算机模拟数据,存在显著局限性。为此,提出SPIN工具,支持多种太空视觉导航场景,特别是相对导航任务,提供多种模态的地面真实数据,并允许研究使用自定义卫星模型、特定相机姿态和可调环境照明条件等。验证显示,使用SPIN工具数据增强方法可降低姿态估计错误率。
Key Takeaways
- 空间操作条件下实际数据稀缺,对视觉导航算法开发构成挑战。
- 现有数据集主要依赖计算机模拟数据,存在局限性。
- SPIN工具旨在支持多种太空视觉导航场景,特别是相对导航任务。
- SPIN工具提供多种模态的地面真实数据。
- SPIN允许使用自定义卫星模型、特定相机姿态和可调环境照明条件。
- 使用SPIN工具作为数据增强方法可降低姿态估计错误率。
点此查看论文截图

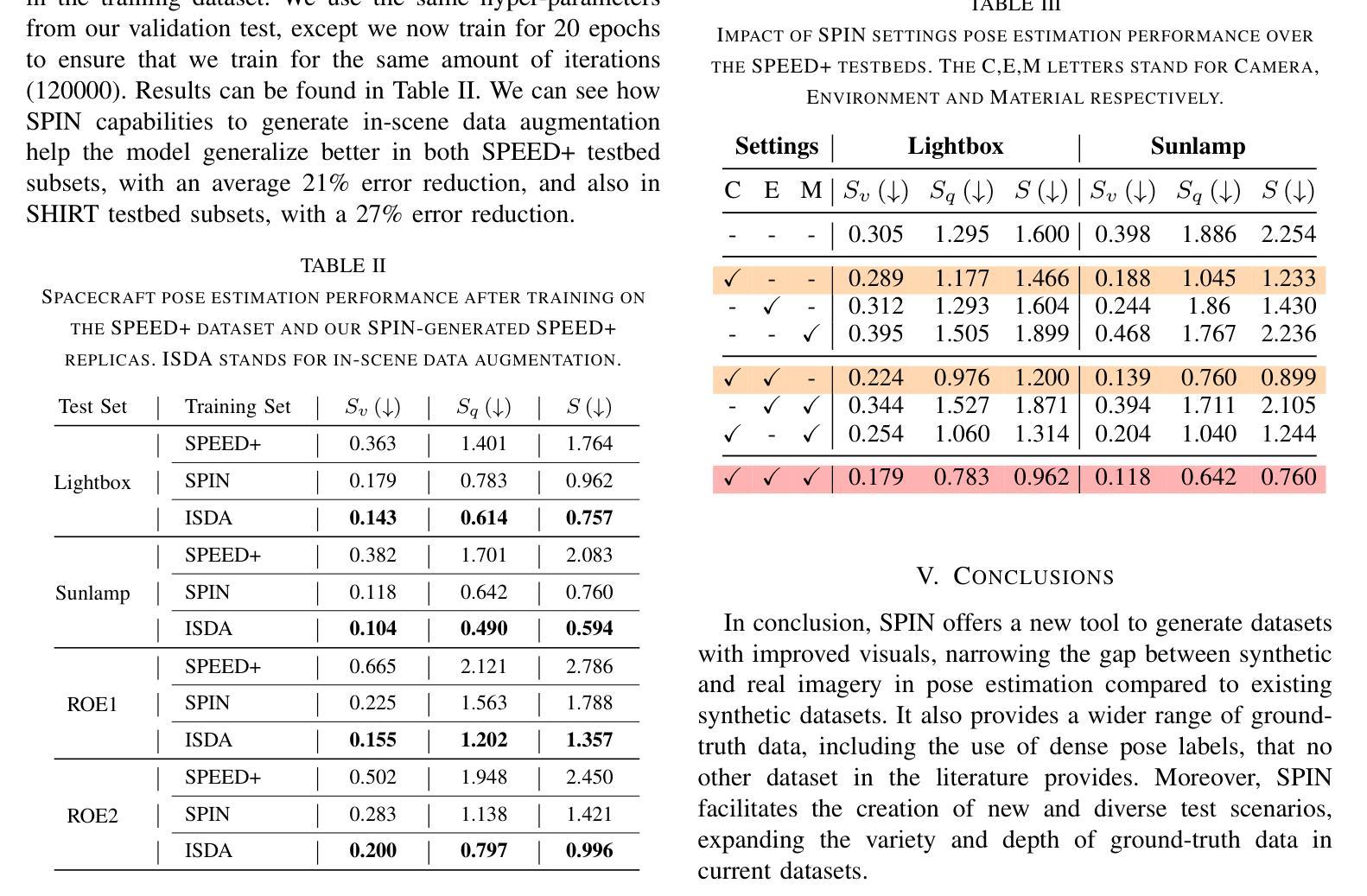
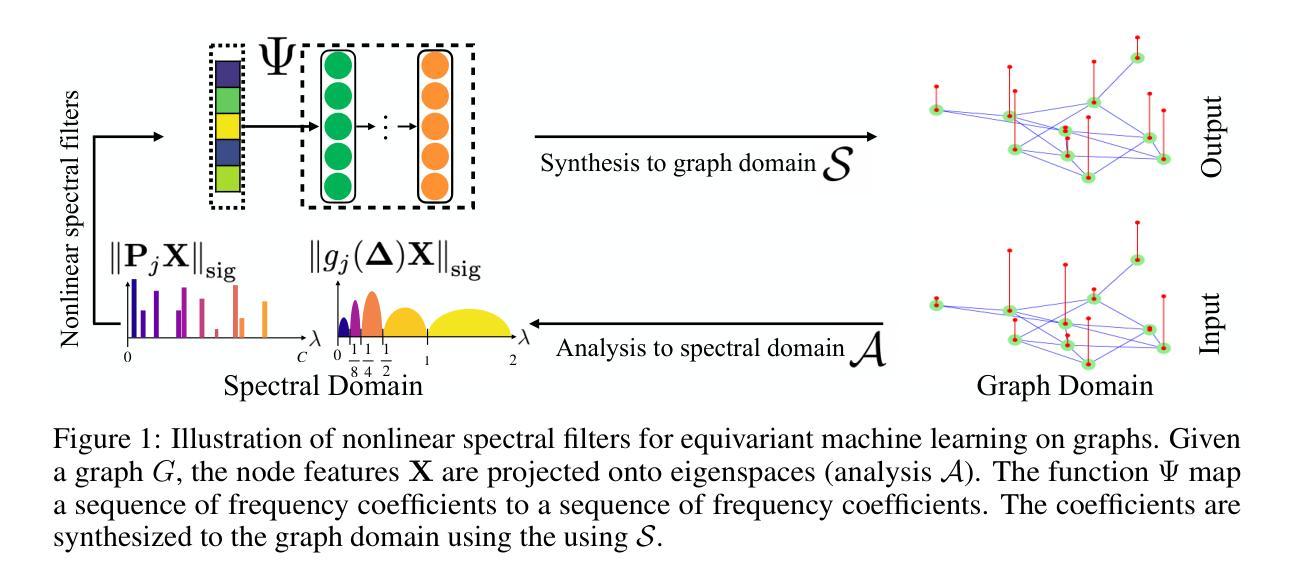
Equivariant Machine Learning on Graphs with Nonlinear Spectral Filters
Authors:Ya-Wei Eileen Lin, Ronen Talmon, Ron Levie
Equivariant machine learning is an approach for designing deep learning models that respect the symmetries of the problem, with the aim of reducing model complexity and improving generalization. In this paper, we focus on an extension of shift equivariance, which is the basis of convolution networks on images, to general graphs. Unlike images, graphs do not have a natural notion of domain translation. Therefore, we consider the graph functional shifts as the symmetry group: the unitary operators that commute with the graph shift operator. Notably, such symmetries operate in the signal space rather than directly in the spatial space. We remark that each linear filter layer of a standard spectral graph neural network (GNN) commutes with graph functional shifts, but the activation function breaks this symmetry. Instead, we propose nonlinear spectral filters (NLSFs) that are fully equivariant to graph functional shifts and show that they have universal approximation properties. The proposed NLSFs are based on a new form of spectral domain that is transferable between graphs. We demonstrate the superior performance of NLSFs over existing spectral GNNs in node and graph classification benchmarks.
等价机器学习是一种设计深度学习模型的方法,它尊重问题的对称性,旨在降低模型复杂性并改善泛化能力。在本文中,我们重点关注将平移等价性(卷积网络图像的基础)扩展到一般图上的扩展。与图像不同,图没有自然域平移的概念。因此,我们将图功能平移视为对称群:与图平移算子对易的酉算子。值得注意的是,这种对称性在信号空间而不是直接在空间空间中起作用。我们注意到,标准谱图神经网络(GNN)的每一层线性滤波器都与图功能平移对易,但激活函数会破坏这种对称性。相反,我们提出了完全等价于图功能平移的非线性谱滤波器(NLSFs),并证明了它们具有通用逼近属性。所提出的NLSFs基于一种可在图之间转移的新型谱域。我们在节点和图分类基准测试中展示了NLSFs相对于现有谱GNN的优越性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文研究了等变机器学习在设计深度学习模型中的应用,通过尊重问题的对称性来降低模型复杂性并提高泛化能力。文章重点关注了从图像卷积网络基础的平移等变性的扩展到一般图的等变性。文章提出了基于图功能转换作为对称群的新思路,即与图转换算子交换的酉算子。这种对称性在信号空间而非直接的空间上操作。文章还讨论了标准谱图神经网络(GNN)的每一层线性滤波器都与图功能转换交换,但激活函数破坏了这种对称性。因此,文章提出了完全对图功能转换等变的非线性谱滤波器(NLSFs),并展示了其通用逼近属性。NLSFs基于可在不同图之间转移的新型谱域,并在节点和图形分类基准测试中表现出优于现有谱GNN的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 等变机器学习通过尊重问题的对称性来设计深度学习模型,以降低模型复杂性并提高泛化能力。
- 文章将图像卷积网络的平移等变性扩展到了一般图的等变性研究。
- 文章提出了基于图功能转换作为对称群的新思路,并指出对称操作在信号空间进行而非直接在空间上。
- 标准谱图神经网络的每一层线性滤波器都与图功能转换交换,但激活函数破坏了这种对称性。
- 文章提出了非线性谱滤波器(NLSFs),它们完全对图功能转换等变并具有通用逼近属性。
- NLSFs基于新型谱域,可在不同图之间进行转移。
点此查看论文截图

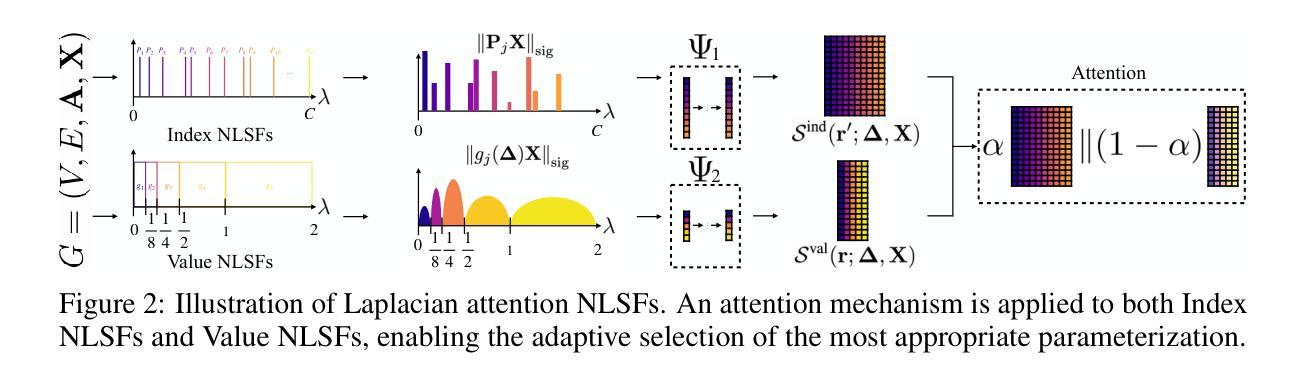
Imitating the Functionality of Image-to-Image Models Using a Single Example
Authors:Nurit Spingarn-Eliezer, Tomer Michaeli
We study the possibility of imitating the functionality of an image-to-image translation model by observing input-output pairs. We focus on cases where training the model from scratch is impossible, either because training data are unavailable or because the model architecture is unknown. This is the case, for example, with commercial models for biological applications. Since the development of these models requires large investments, their owners commonly keep them confidential, and reveal only a few input-output examples on the company’s website or in an academic paper. Surprisingly, we find that even a single example typically suffices for learning to imitate the model’s functionality, and that this can be achieved using a simple distillation approach. We present an extensive ablation study encompassing a wide variety of model architectures, datasets and tasks, to characterize the factors affecting vulnerability to functionality imitation, and provide a preliminary theoretical discussion on the reasons for this unwanted behavior.
我们研究了通过观察输入-输出对来模仿图像到图像翻译模型功能的可能性。我们关注的是那些从零开始训练模型不可行的情况,这可能是因为训练数据不可用,或者模型架构未知。这种情况常见于生物应用方面的商业模型。由于开发这些模型需要大量的投资,因此其所有者通常将其保密,仅在公司的网站或学术论文中展示少数输入-输出示例。令人惊讶的是,我们发现即使是一个示例通常也足以学习模仿模型的功能,而且可以通过简单的蒸馏方法实现这一点。我们进行了一项广泛的消融研究,涵盖了各种模型架构、数据集和任务,以描述影响功能模仿脆弱性的因素,并就这种不想要的行为的原因进行了初步的理论讨论。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究的重点是探究通过观察输入-输出对来模仿图像到图像翻译模型的功能的可能性。特别是在无法从头开始训练模型的情况下,如训练数据不可用或模型架构未知等情境。商业模型中应用于生物学的场景便是如此。模型开发需要大量的投入,因此其所有者通常将其保密,仅在公司的网站或学术论文中展示少量的输入-输出示例。令人惊讶的是,我们发现即使是一个示例也足以学习模仿模型的功能,并且这可以通过简单的蒸馏方法实现。本文进行了一项广泛的消融研究,涵盖了多种模型架构、数据集和任务,以探究影响功能模仿脆弱性的因素,并初步从理论上探讨了这种行为背后的原因。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注在无法从头开始训练模型的情况下,模仿图像到图像翻译模型的功能的可能性。
- 在训练数据不可用或模型架构未知时,可以通过观察输入-输出对来模仿模型功能。
- 商业模型中应用于生物学的场景是这一问题的典型应用背景。
- 模型所有者通常保密其模型,仅展示少量输入-输出示例。
- 一个示例即可学习模仿模型功能,可通过简单的蒸馏方法实现。
- 研究通过广泛的消融研究多种模型架构、数据集和任务,以探究影响功能模仿脆弱性的因素。
点此查看论文截图
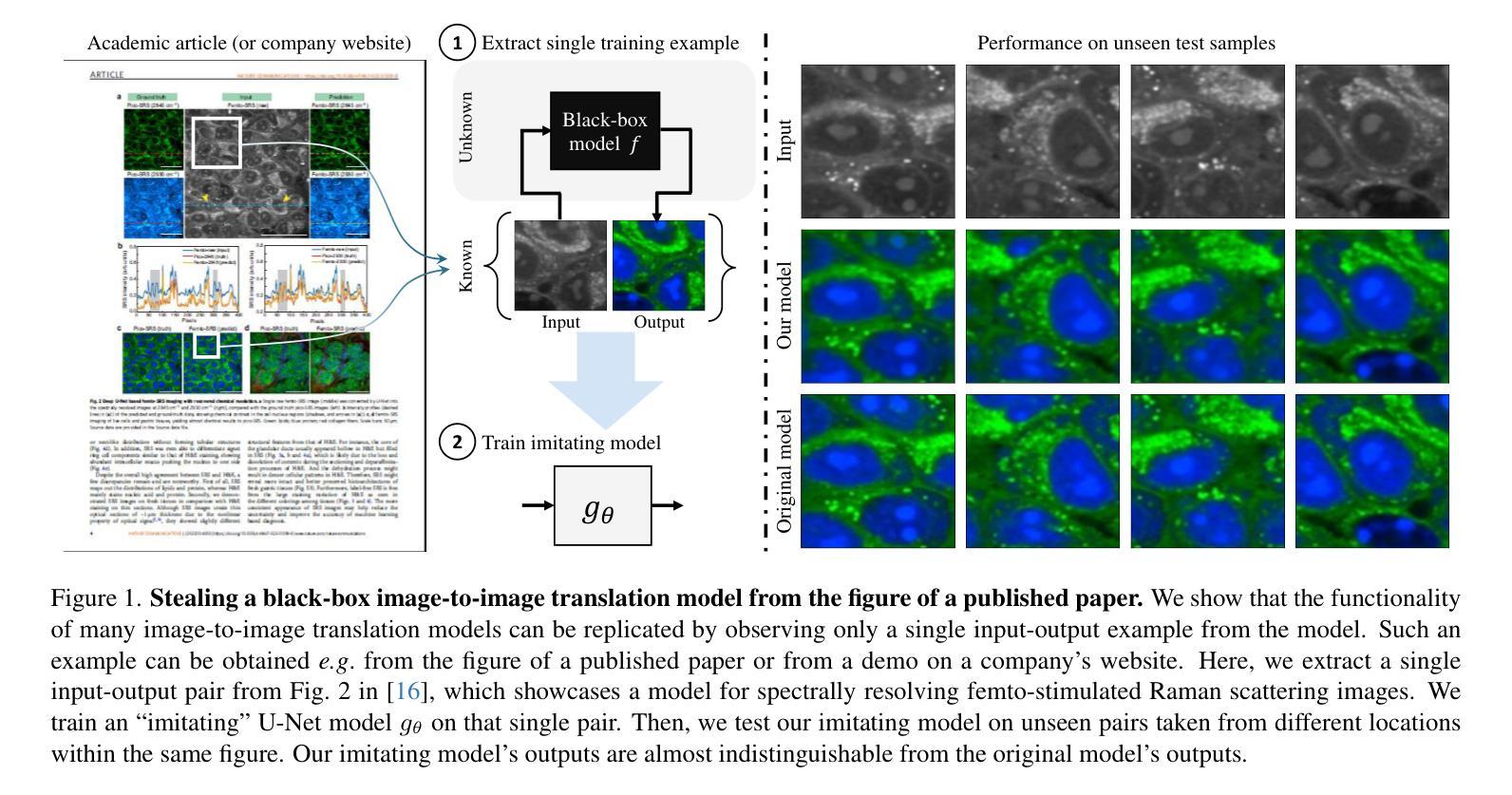


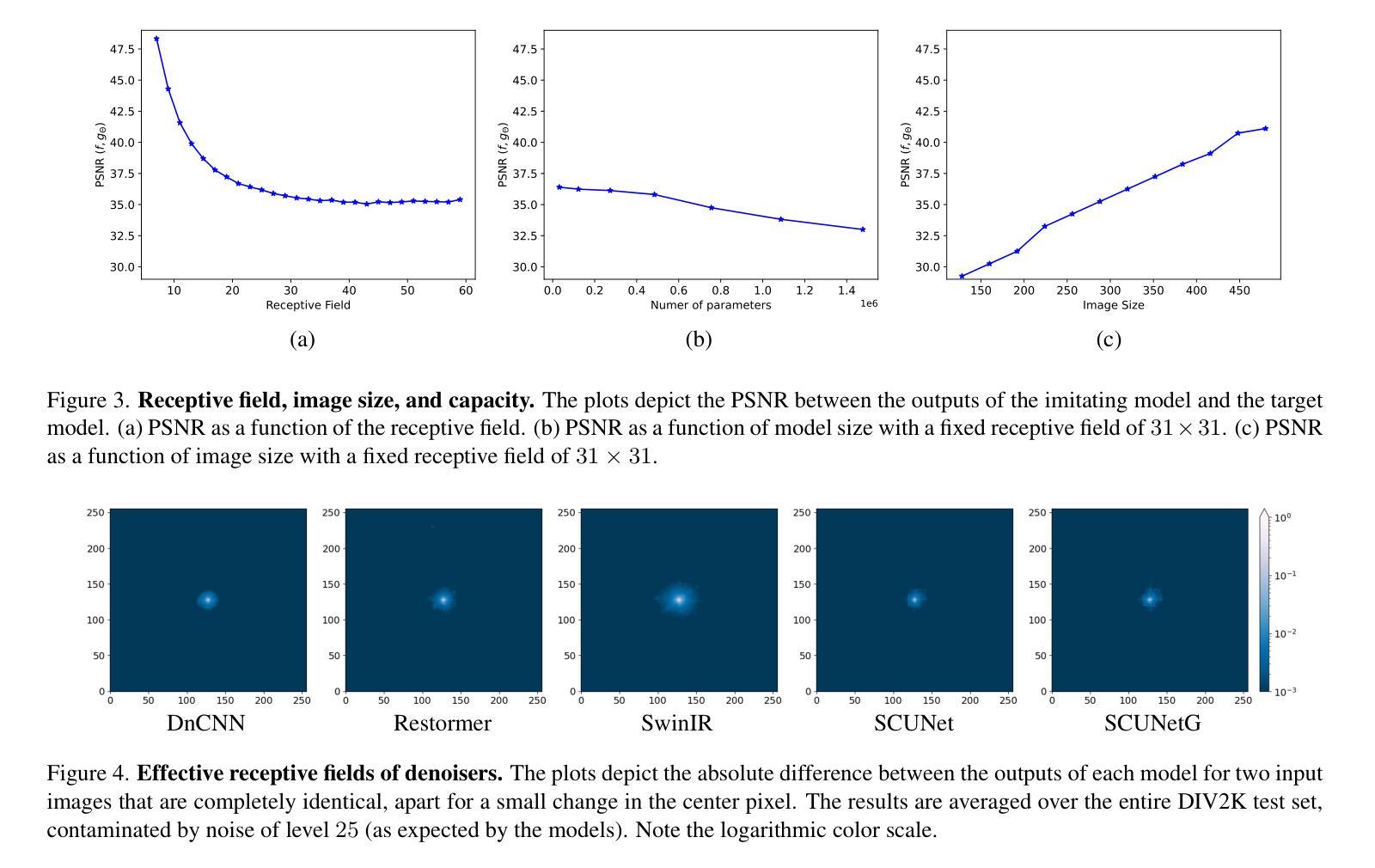
Multi-Sensor Diffusion-Driven Optical Image Translation for Large-Scale Applications
Authors:João Gabriel Vinholi, Marco Chini, Anis Amziane, Renato Machado, Danilo Silva, Patrick Matgen
Comparing images captured by disparate sensors is a common challenge in remote sensing. This requires image translation – converting imagery from one sensor domain to another while preserving the original content. Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models (DDIM) are potential state-of-the-art solutions for such domain translation due to their proven superiority in multiple image-to-image translation tasks in computer vision. However, these models struggle with reproducing radiometric features of large-scale multi-patch imagery, resulting in inconsistencies across the full image. This renders downstream tasks like Heterogeneous Change Detection impractical. To overcome these limitations, we propose a method that leverages denoising diffusion for effective multi-sensor optical image translation over large areas. Our approach super-resolves large-scale low spatial resolution images into high-resolution equivalents from disparate optical sensors, ensuring uniformity across hundreds of patches. Our contributions lie in new forward and reverse diffusion processes that address the challenges of large-scale image translation. Extensive experiments using paired Sentinel-II (10m) and Planet Dove (3m) images demonstrate that our approach provides precise domain adaptation, preserving image content while improving radiometric accuracy and feature representation. A thorough image quality assessment and comparisons with the standard DDIM framework and five other leading methods are presented. We reach a mean Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (mLPIPS) of 0.1884 and a Fr'echet Inception Distance (FID) of 45.64, expressively outperforming all compared methods, including DDIM, ShuffleMixer, and SwinIR. The usefulness of our approach is further demonstrated in two Heterogeneous Change Detection tasks.
在遥感领域,比较由不同传感器捕获的图像是一个常见的挑战。这需要进行图像翻译,即将图像从一个传感器领域转换到另一个传感器领域,同时保留原始内容。去噪扩散隐式模型(DDIM)是此类领域翻译中潜在的先进解决方案,因为它们在计算机视觉的多个图像到图像翻译任务中表现出了优越性。然而,这些模型在再现大规模多补丁图像的辐射特征方面存在困难,导致整个图像的不一致性。这使得下游任务(例如异质变化检测)变得不切实际。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了一种利用去噪扩散进行多传感器光学图像有效翻译的方法,该方法适用于大规模区域。我们的方法将大规模低空间分辨率图像超分辨率转化为来自不同光学传感器的高分辨率等效图像,确保数百个补丁的一致性。我们的贡献在于新的前向和反向扩散过程,解决了大规模图像翻译的挑战。使用配对的Sentinel-II(10米)和Planet Dove(3米)图像进行的广泛实验表明,我们的方法提供了精确的领域适应性,在保留图像内容的同时提高了辐射精度和特征表示。对图像质量进行了全面的评估,并与标准DDIM框架和其他五种领先方法进行了比较。我们达到了平均学习感知图像补丁相似性(mLPIPS)为0.1884,Fréchet Inception Distance(FID)为45.64,显著优于所有比较方法,包括DDIM、ShuffleMixer和SwinIR。我们的方法的有用性在两项异质变化检测任务中得到了进一步证明。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This is the accepted version of the manuscript published in IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing (JSTARS). Please access the final version at IEEEXplore (Open Access). DOI 10.1109/JSTARS.2024.3506032. This technology is protected by a patent filed on 23 december 2023 at Office Luxembourgeois de la propri'et'e intellectuelle (LU505861)
Summary
针对遥感领域不同传感器图像转换的挑战,提出一种基于去噪扩散模型的大型多传感器光学图像翻译方法。该方法能够有效解决大型多斑块图像的放射特征再现问题,提高图像翻译的辐射精度和特征表示能力。通过对比实验,该方法在图像质量评估指标上表现出优异性能,显著优于其他对比方法。
Key Takeaways
- 遥感领域中,不同传感器图像的比较和转换是一个常见挑战。
- Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models(DDIM)在图像到图像翻译任务中表现出卓越性能,但处理大型多斑块图像时存在困难。
- 提出一种基于去噪扩散模型的大型多传感器光学图像翻译方法,解决了DDIM在处理大型图像时的局限性。
- 方法通过超级解析技术将大规模低空间分辨率图像转换为高分辨率等效物,确保数百个斑块之间的均匀性。
- 通过广泛的实验验证,该方法在图像质量评估指标上表现出优异性能,如Learned Perceptual Image Patch Similarity (mLPIPS)和Fréchet Inception Distance (FID)。
- 与其他方法相比,包括DDIM、ShuffleMixer和SwinIR等,该方法在图像翻译方面表现出更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图
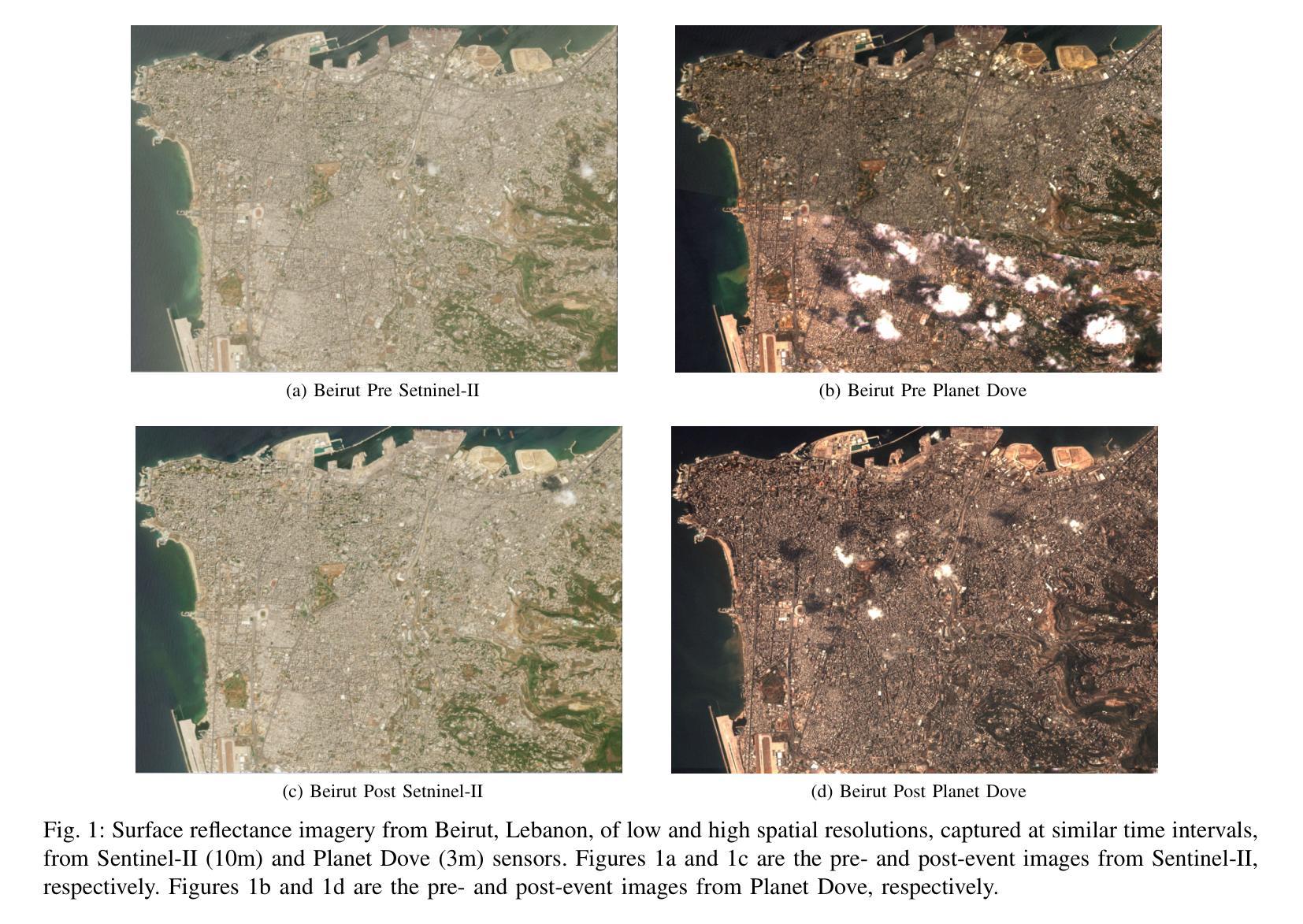


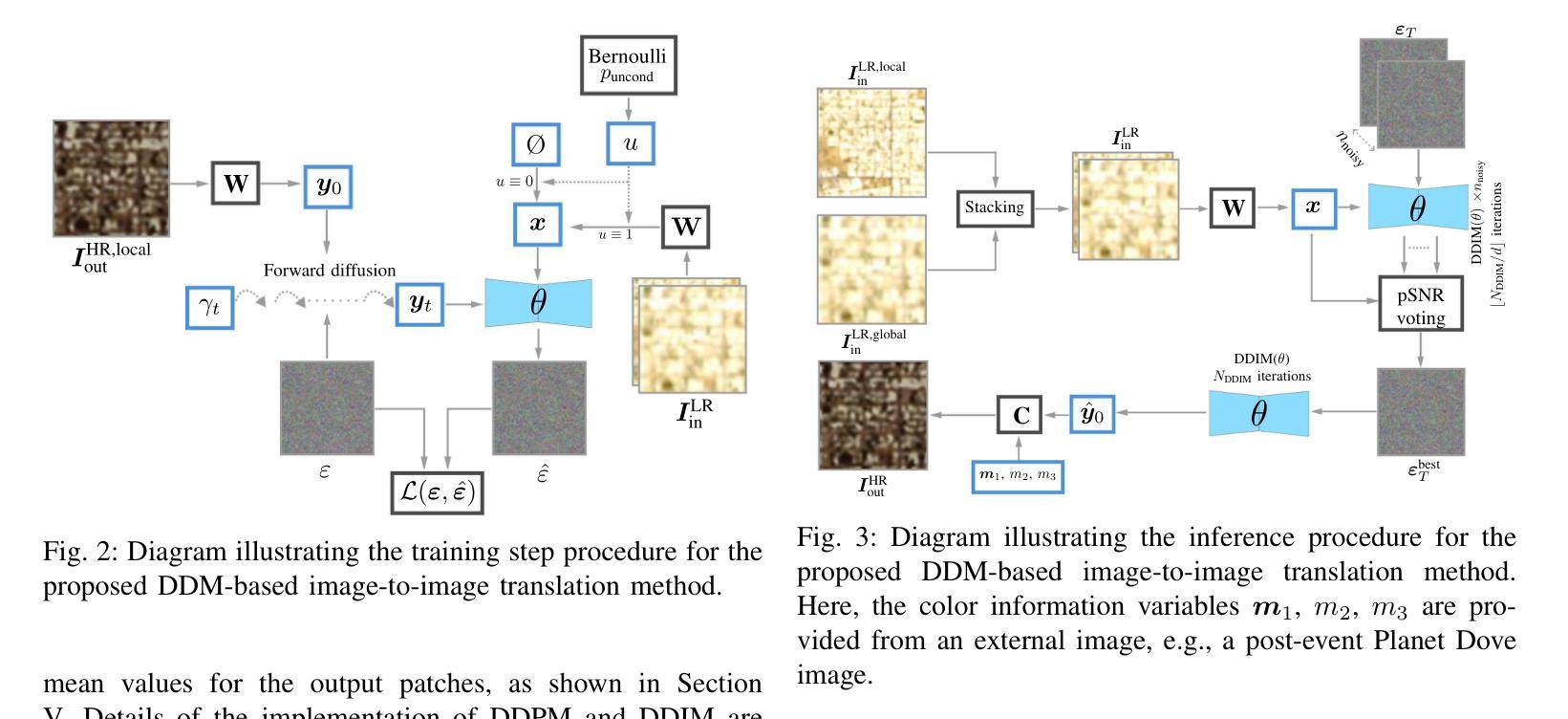

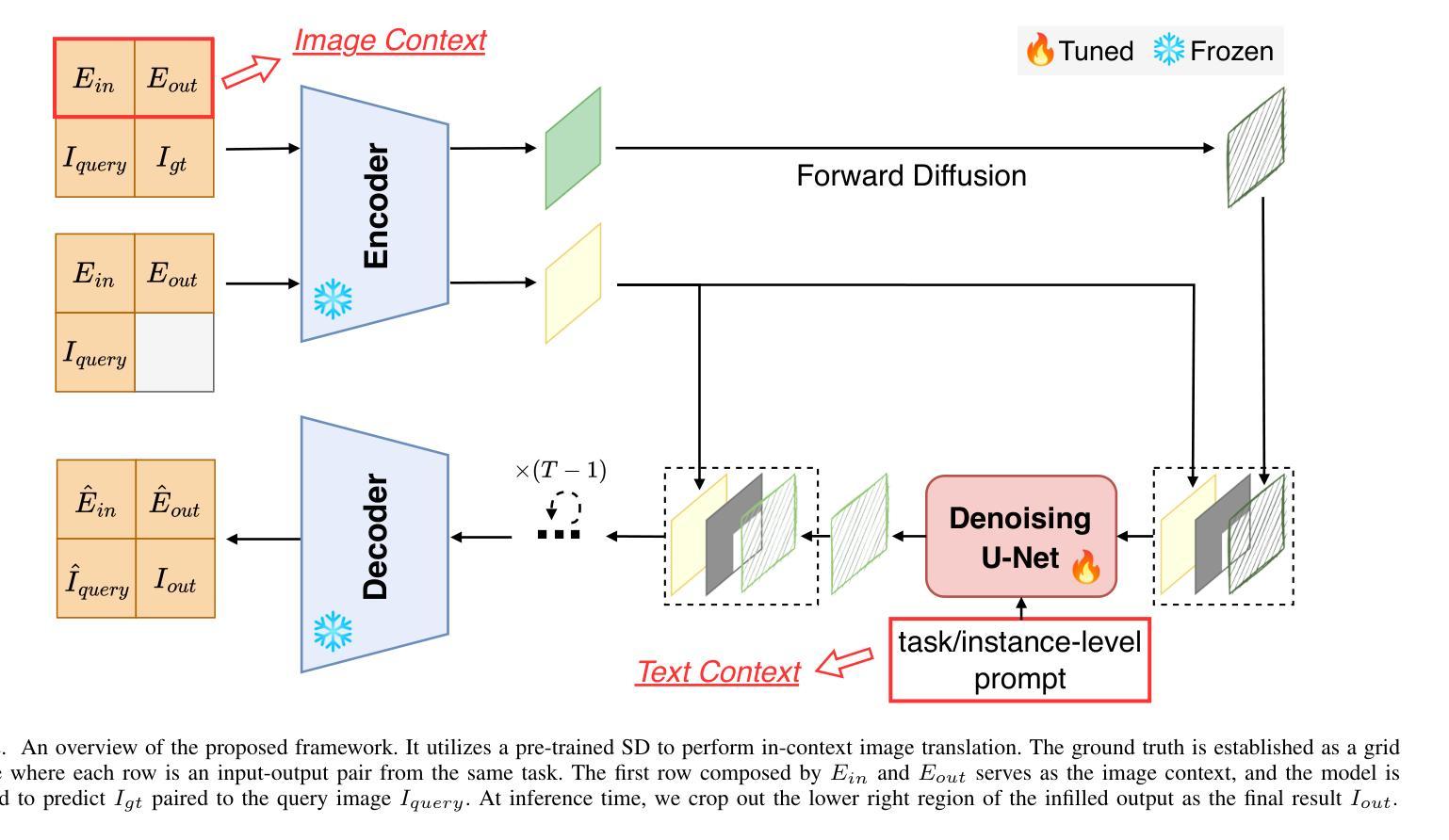
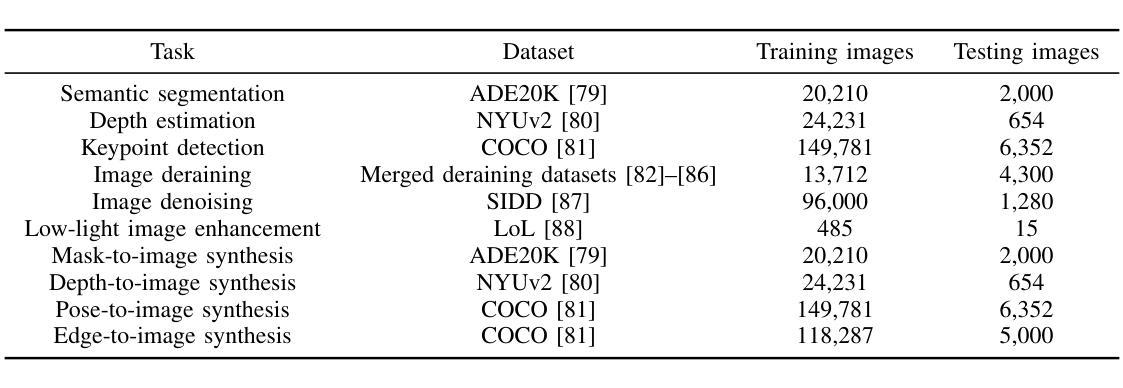
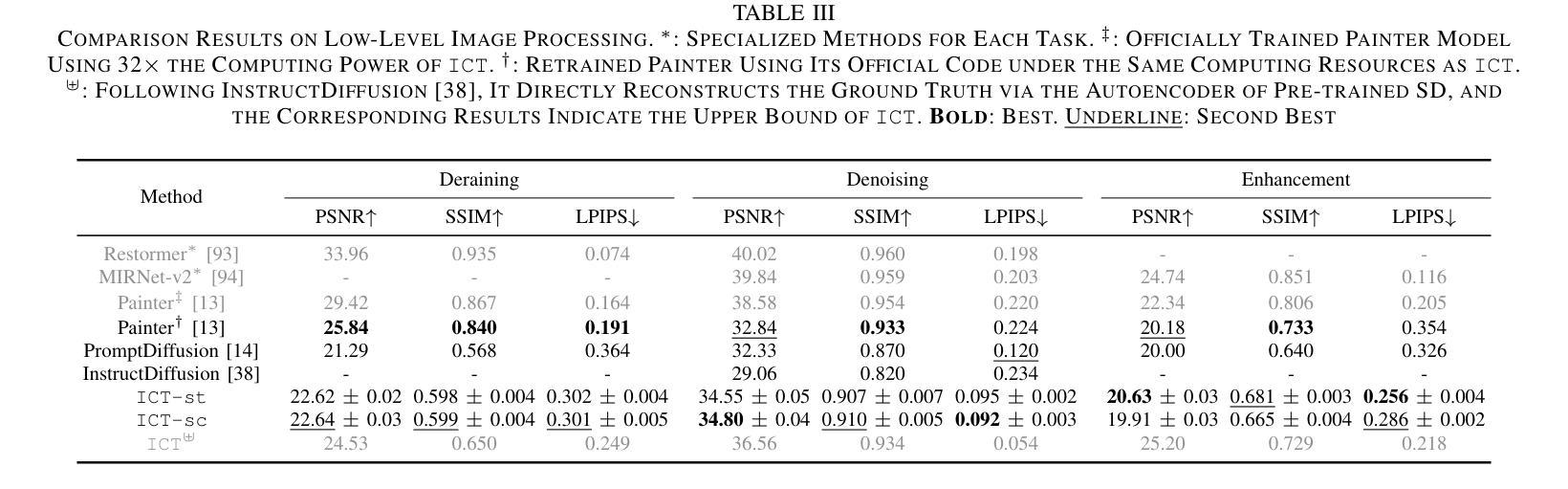
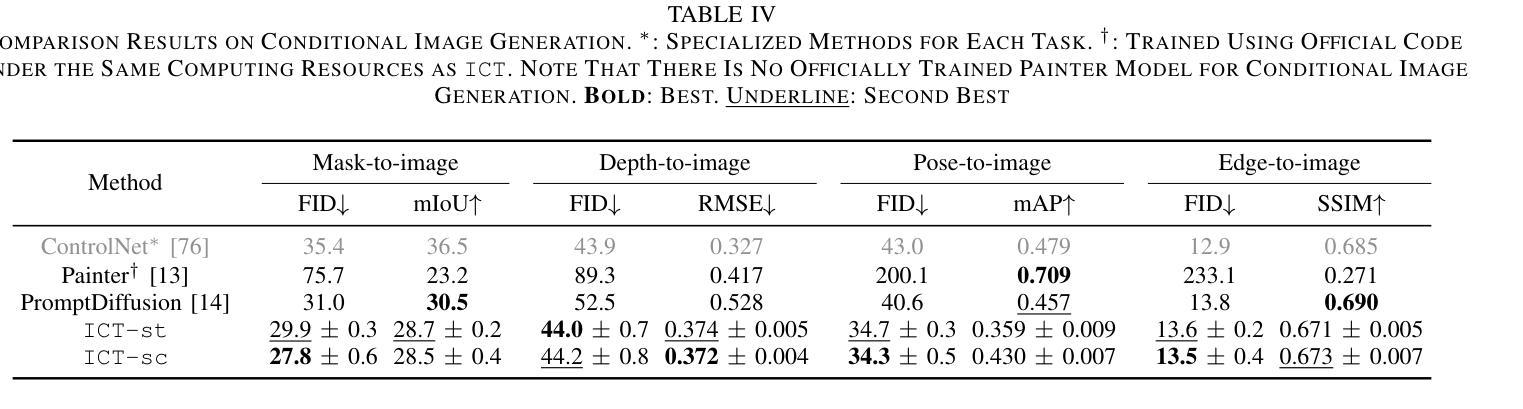
In-Context Translation: Towards Unifying Image Recognition, Processing, and Generation
Authors:Han Xue, Qianru Sun, Li Song, Wenjun Zhang, Zhiwu Huang
We propose In-Context Translation (ICT), a general learning framework to unify visual recognition (e.g., semantic segmentation), low-level image processing (e.g., denoising), and conditional image generation (e.g., edge-to-image synthesis). Thanks to unification, ICT significantly reduces the inherent inductive bias that comes with designing models for specific tasks, and it maximizes mutual enhancement across similar tasks. However, the unification across a large number of tasks is non-trivial due to various data formats and training pipelines. To this end, ICT introduces two designs. Firstly, it standardizes input-output data of different tasks into RGB image pairs, e.g., semantic segmentation data pairs an RGB image with its segmentation mask in the same RGB format. This turns different tasks into a general translation task between two RGB images. Secondly, it standardizes the training of different tasks into a general in-context learning, where “in-context” means the input comprises an example input-output pair of the target task and a query image. The learning objective is to generate the “missing” data paired with the query. The implicit translation process is thus between the query and the generated image. In experiments, ICT unifies ten vision tasks and showcases impressive performance on their respective benchmarks. Notably, ICT performs well across three major categories of computer vision tasks, while its two competitors (Painter and PromptDiffusion) are only effective in at most two of these task categories. In addition, compared to its competitors, ICT trained on only 4 RTX 3090 GPUs is shown to be more efficient and less costly in training.
我们提出了上下文翻译(ICT)这一通用学习框架,旨在统一视觉识别(例如语义分割)、低级图像处理(例如去噪)和条件图像生成(例如边缘到图像的合成)。由于统一化,ICT极大地减少了为特定任务设计模型时固有的归纳偏见,并最大限度地提高了类似任务之间的相互促进。然而,由于各种数据格式和训练管道,在大量任务之间进行统一并不容易。为此,ICT引入了两种设计。首先,它将不同任务的输入-输出数据标准化为RGB图像对。例如,语义分割数据将RGB图像与其分割掩码配对成相同的RGB格式。这将不同的任务转变为两个RGB图像之间的通用翻译任务。其次,它将不同任务的训练标准化为通用的上下文内学习。在这里,“上下文内”是指输入包含目标任务的示例输入-输出对和查询图像。学习目标是生成与查询相匹配的“缺失”数据。因此,隐式翻译过程发生在查询和生成的图像之间。在实验中,ICT统一了十种视觉任务,并在各自的基准测试中取得了令人印象深刻的性能。值得注意的是,ICT在三个主要计算机视觉任务类别中都表现良好,而它的两个竞争对手(Painter和PromptDiffusion)最多只能在两个任务类别中有效。此外,与竞争对手相比,ICT仅在4个RTX 3090 GPU上进行训练,显示出更高的训练效率和更低的成本。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
提出一种名为In-Context Translation(ICT)的统一学习框架,涵盖视觉识别、低级图像处理和条件图像生成等多个任务。通过标准化输入/输出数据和训练流程,ICT减少任务特定模型的固有偏见,最大化相似任务间的相互增强。实验表明,ICT在十大视觉任务上表现出色,并在主要计算机视觉任务类别中表现优异,相较于其他两个竞争对手更高效且训练成本更低。
Key Takeaways
- ICT是一个用于统一多种计算机视觉任务的学习框架,包括视觉识别、低级图像处理和条件图像生成等。
- ICT通过标准化输入/输出数据和训练流程来减少任务特定模型的偏见,并实现任务间的相互增强。
- ICT将不同任务的标准化为RGB图像对,便于进行翻译任务。
- ICT引入了一种名为“上下文学习”的训练方式,通过示例输入输出对和查询图像生成缺失数据。
- ICT在多个视觉任务上的实验表现出色,统一了十大视觉任务并在各大基准测试中取得优异性能。
- ICT在主要计算机视觉任务类别中表现优异,相较于其他竞争对手有更广泛的应用。
点此查看论文截图

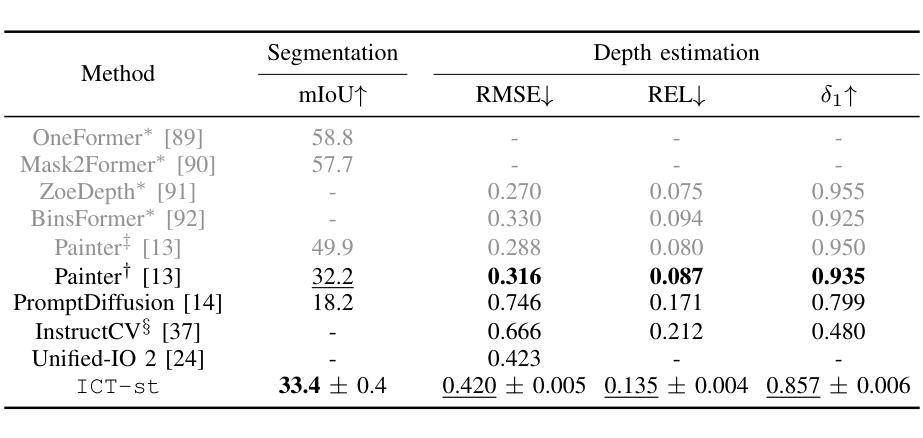
ContourDiff: Unpaired Image-to-Image Translation with Structural Consistency for Medical Imaging
Authors:Yuwen Chen, Nicholas Konz, Hanxue Gu, Haoyu Dong, Yaqian Chen, Lin Li, Jisoo Lee, Maciej A. Mazurowski
Preserving object structure through image-to-image translation is crucial, particularly in applications such as medical imaging (e.g., CT-to-MRI translation), where downstream clinical and machine learning applications will often rely on such preservation. However, typical image-to-image translation algorithms prioritize perceptual quality with respect to output domain features over the preservation of anatomical structures. To address these challenges, we first introduce a novel metric to quantify the structural bias between domains which must be considered for proper translation. We then propose ContourDiff, a novel image-to-image translation algorithm that leverages domain-invariant anatomical contour representations of images to preserve the anatomical structures during translation. These contour representations are simple to extract from images, yet form precise spatial constraints on their anatomical content. ContourDiff applies an input image contour representation as a constraint at every sampling step of a diffusion model trained in the output domain, ensuring anatomical content preservation for the output image. We evaluate our method on challenging lumbar spine and hip-and-thigh CT-to-MRI translation tasks, via (1) the performance of segmentation models trained on translated images applied to real MRIs, and (2) the foreground FID and KID of translated images with respect to real MRIs. Our method outperforms other unpaired image translation methods by a significant margin across almost all metrics and scenarios. Moreover, it achieves this without the need to access any input domain information during training.
通过图像到图像的翻译来保留对象结构至关重要,特别是在医疗成像(例如CT到MRI的翻译)等应用中。下游的临床和机器学习应用通常会依赖于这种保留。然而,典型的图像到图像的翻译算法会优先考虑输出域特征的感知质量,而不是保留解剖结构。为了解决这些挑战,我们首先引入了一种新的度量标准,来量化翻译时必须要考虑的域之间的结构偏差。然后,我们提出了ContourDiff,这是一种新型的图像到图像翻译算法,它利用图像的域不变解剖轮廓表示在翻译过程中保留解剖结构。这些轮廓表示法可以从图像中轻松提取,却能为它们的解剖内容形成精确的空间约束。ContourDiff将输入图像的轮廓表示作为扩散模型在每个采样步骤中的约束,该模型在输出域中进行训练,确保输出图像的解剖内容保留。我们通过具有挑战性的腰椎和髋关节及大腿CT到MRI的翻译任务来评估我们的方法,包括(1)在真实MRI上应用翻译图像训练的分割模型的性能,(2)翻译图像相对于真实MRI的前景FID和KID。我们的方法在几乎所有指标和场景中显著优于其他非配对图像翻译方法,而且,它在训练过程中无需访问任何输入域信息。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新型图像到图像翻译算法ContourDiff,用于在医学成像等应用中保持对象结构。它通过利用图像的域不变解剖轮廓表示来精确模拟解剖结构,并在翻译过程中保持这些结构。在腰椎和髋关节CT到MRI的翻译任务上进行了评估,结果表明该方法在大多数指标和场景下都显著优于其他非配对图像翻译方法,且无需访问训练过程中的输入域信息。
Key Takeaways
- 图像到图像翻译中保持对象结构至关重要,特别是在医学成像等应用中。
- 现有的图像到图像翻译算法通常更侧重于输出域特征的感知质量,而忽视了解剖结构的保持。
- 引入了一种新型指标来量化域之间的结构偏差,这对于正确的翻译是必要的。
- 提出了ContourDiff算法,利用图像的域不变解剖轮廓表示来模拟和保持解剖结构。
- ContourDiff通过在扩散模型的每个采样步骤中应用输入图像的轮廓表示作为约束,确保输出图像的解剖内容得到保留。
- 在具有挑战性的腰椎和髋关节CT到MRI的翻译任务上进行了评估,证明该方法显著优于其他非配对图像翻译方法。
点此查看论文截图

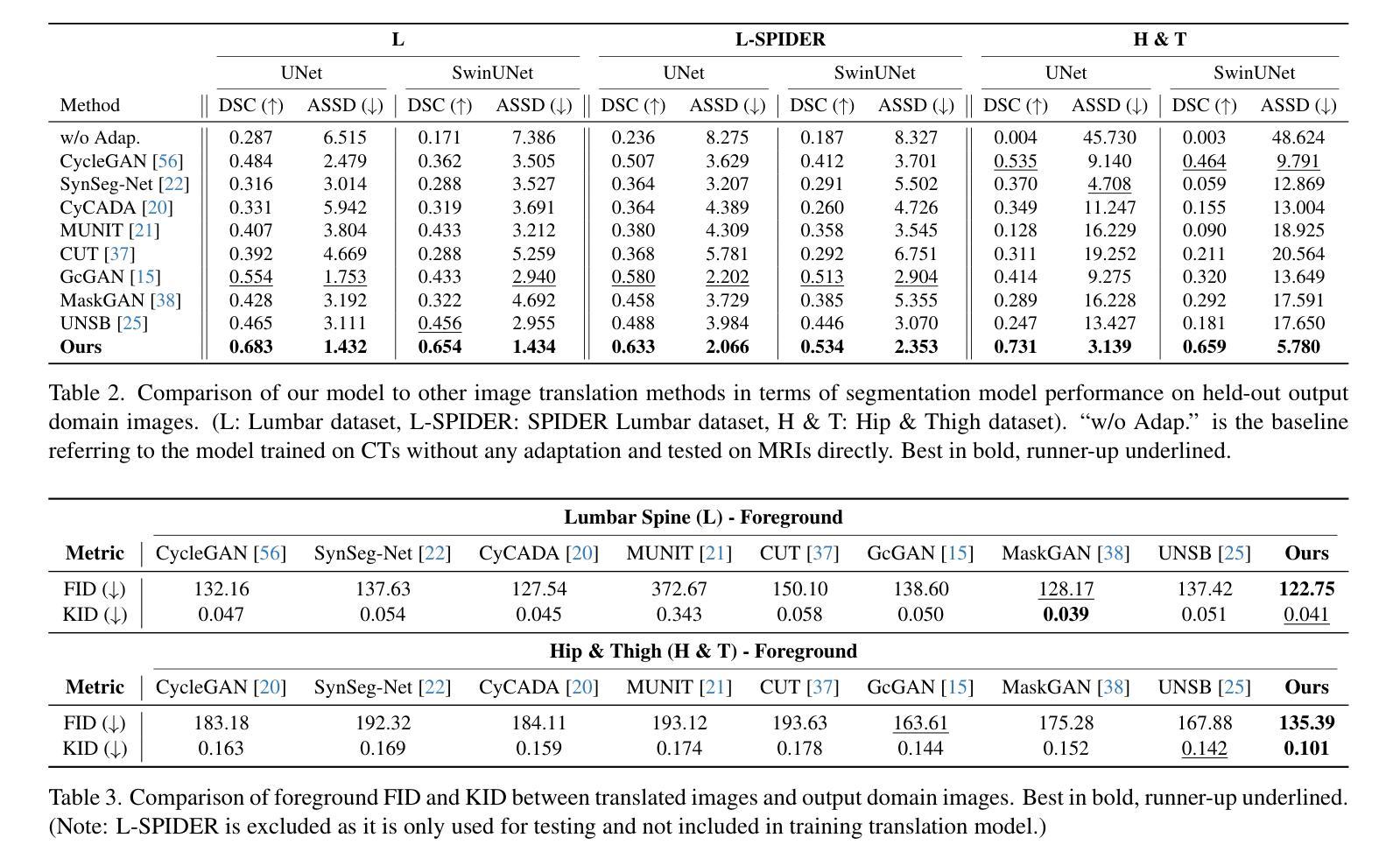
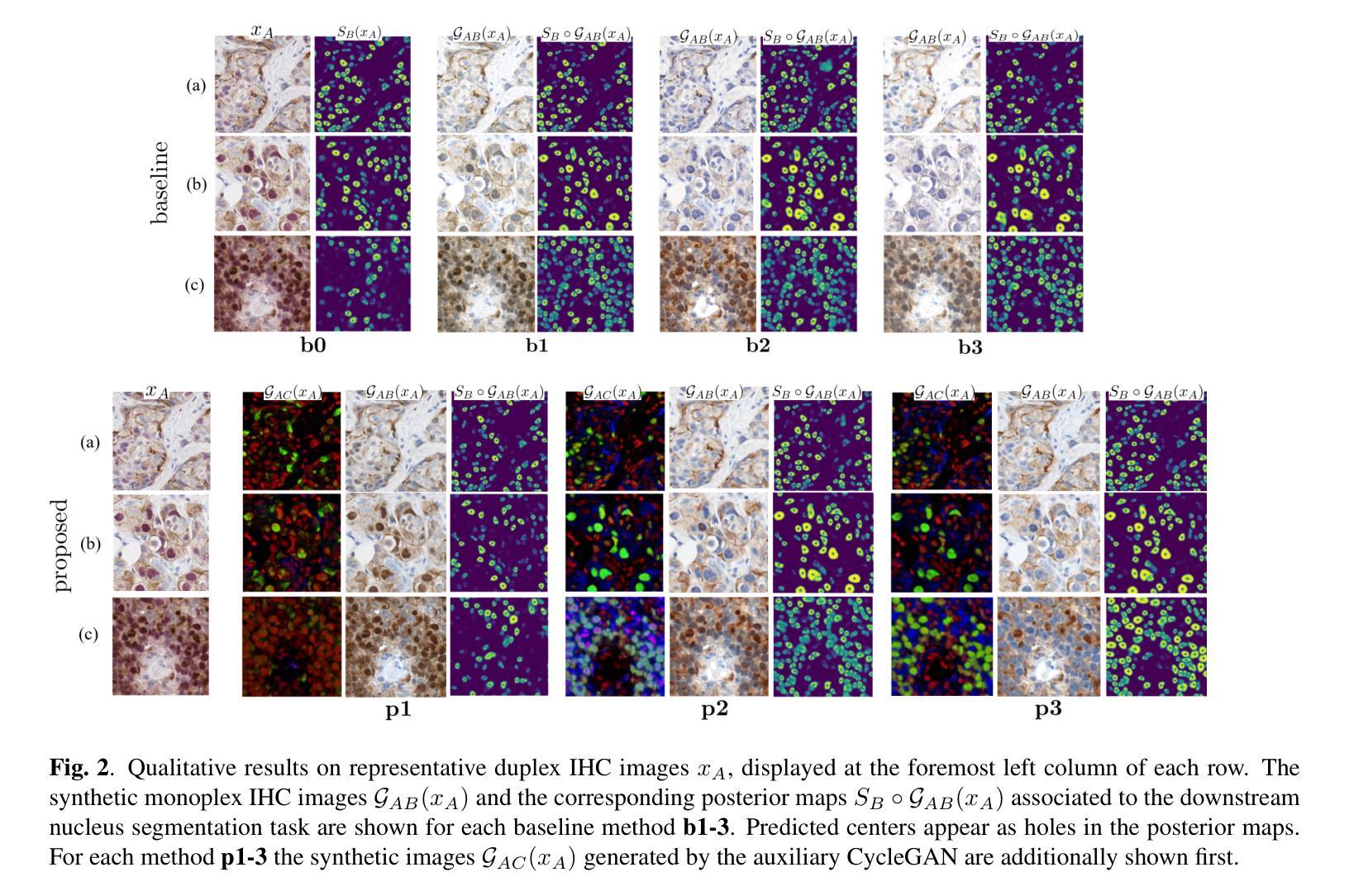
Auxiliary CycleGAN-guidance for Task-Aware Domain Translation from Duplex to Monoplex IHC Images
Authors:Nicolas Brieu, Nicolas Triltsch, Philipp Wortmann, Dominik Winter, Shashank Saran, Marlon Rebelatto, Günter Schmidt
Generative models enable the translation from a source image domain where readily trained models are available to a target domain unseen during training. While Cycle Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are well established, the associated cycle consistency constrain relies on that an invertible mapping exists between the two domains. This is, however, not the case for the translation between images stained with chromogenic monoplex and duplex immunohistochemistry (IHC) assays. Focusing on the translation from the latter to the first, we propose - through the introduction of a novel training design, an alternative constrain leveraging a set of immunofluorescence (IF) images as an auxiliary unpaired image domain. Quantitative and qualitative results on a downstream segmentation task show the benefit of the proposed method in comparison to baseline approaches.
生成模型能够实现从易于训练模型得到的源图像域到训练期间未见的目标域的转换。虽然循环生成对抗网络(GANs)已经建立,但相关的循环一致性约束依赖于两个域之间存在可逆映射。然而,在染色单用和多用免疫组织化学(IHC)检测图像之间的转换并非如此。我们专注于从后者到前者的转换,通过引入新型训练设计,利用一组免疫荧光(IF)图像作为非配对图像域,提出一种替代约束。在下游分割任务上的定量和定性结果表明,与基准方法相比,所提出的方法具有优势。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 5 pages
Summary
本文介绍了生成模型在图像域转换中的应用,特别是在源图像域和目标域之间不存在可逆映射的情况下。虽然循环生成对抗网络(Cycle GANs)已经得到了广泛应用,但它们依赖于循环一致性约束,这在某些情况下可能不适用。针对免疫组织化学染色图像(IHC)向明场图像转换的问题,提出了一种利用免疫荧光(IF)图像作为辅助非配对图像域的新训练设计方法,该方法在下游分割任务中的定量和定性结果均优于基准方法。
Key Takeaways
- 生成模型能够实现从已训练的源图像域到未见过的新目标域的翻译。
- 循环生成对抗网络(Cycle GANs)中的循环一致性约束依赖于两个域间可逆映射的存在。
- 在某些情况(例如免疫组织化学染色图像与明场图像的转换)下,可能不存在这样的可逆映射。
- 针对这一问题,提出了一种利用免疫荧光(IF)图像作为辅助非配对图像域的新训练设计方法。
- 该方法提高了图像转换的准确性和质量。
- 通过下游分割任务的定量和定性结果验证了该方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

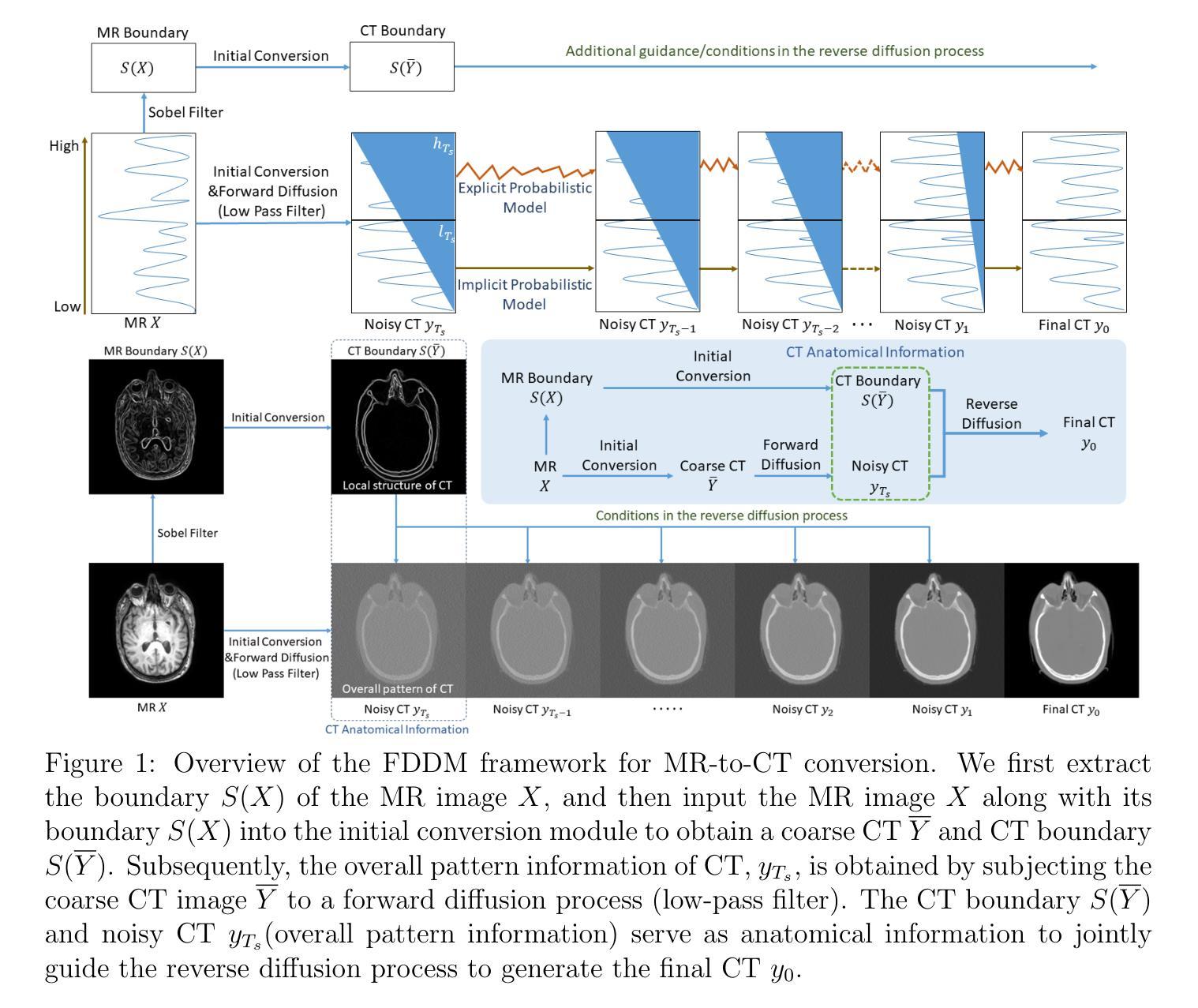
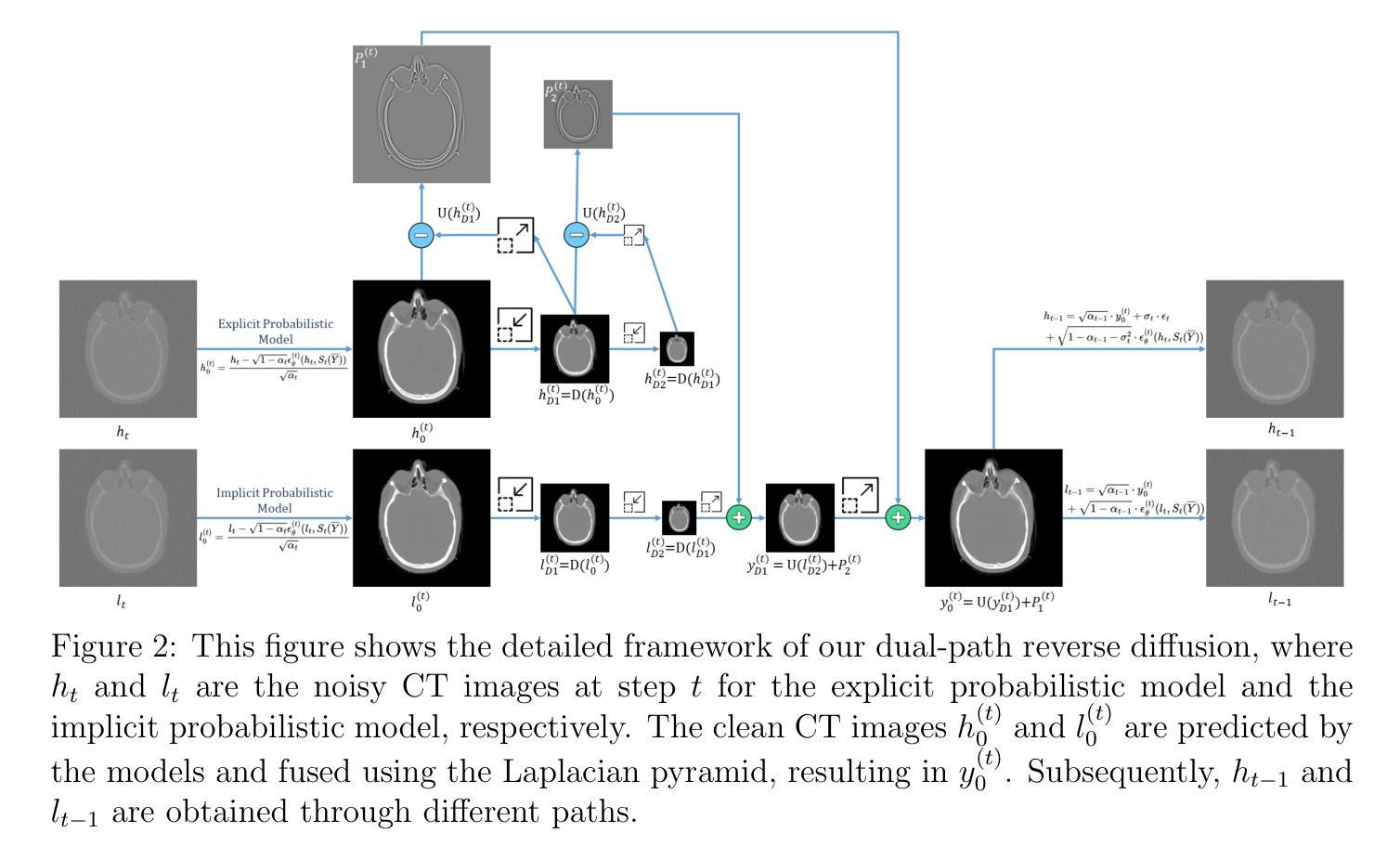
FDDM: Unsupervised Medical Image Translation with a Frequency-Decoupled Diffusion Model
Authors:Yunxiang Li, Hua-Chieh Shao, Xiaoxue Qian, You Zhang
Diffusion models have demonstrated significant potential in producing high-quality images in medical image translation to aid disease diagnosis, localization, and treatment. Nevertheless, current diffusion models have limited success in achieving faithful image translations that can accurately preserve the anatomical structures of medical images, especially for unpaired datasets. The preservation of structural and anatomical details is essential to reliable medical diagnosis and treatment planning, as structural mismatches can lead to disease misidentification and treatment errors. In this study, we introduce the Frequency Decoupled Diffusion Model (FDDM) for MR-to-CT conversion. FDDM first obtains the anatomical information of the CT image from the MR image through an initial conversion module. This anatomical information then guides a subsequent diffusion model to generate high-quality CT images. Our diffusion model uses a dual-path reverse diffusion process for low-frequency and high-frequency information, achieving a better balance between image quality and anatomical accuracy. We extensively evaluated FDDM using public datasets for brain MR-to-CT and pelvis MR-to-CT translations, demonstrating its superior performance to other GAN-based, VAE-based, and diffusion-based models. The evaluation metrics included Frechet Inception Distance (FID), Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), and Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM). FDDM achieved the best scores on all metrics for both datasets, particularly excelling in FID, with scores of 25.9 for brain data and 29.2 for pelvis data, significantly outperforming other methods. These results demonstrate that FDDM can generate high-quality target domain images while maintaining the accuracy of translated anatomical structures.
扩散模型在医学图像翻译中生成高质量图像以辅助疾病诊断、定位和治疗的潜力巨大。然而,当前扩散模型在忠实图像翻译方面取得的成功有限,无法准确保留医学图像的结构信息,特别是在非配对数据集上。保留结构和解剖细节对于可靠的医学诊断和治疗计划至关重要,结构不匹配可能导致疾病误判和治疗错误。本研究中,我们引入了频率解耦扩散模型(FDDM)用于MR到CT的转换。FDDM首先通过初始转换模块从MR图像中获取CT图像的解剖信息。然后,此解剖信息引导后续的扩散模型生成高质量的CT图像。我们的扩散模型采用双路径反向扩散过程来处理低频和高频信息,实现了图像质量和解剖准确性之间的更好平衡。我们使用公共数据集对大脑MR到CT和骨盆MR到CT的转换全面评估了FDDM,证明了其优于其他基于GAN、基于VAE和基于扩散的模型。评估指标包括Frechet Inception Distance(FID)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)和结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)。FDDM在两个数据集上的所有指标均获得最佳分数,特别是在FID上表现尤为出色,大脑数据得分为25.9,骨盆数据得分为29.2,显著优于其他方法。这些结果表明,FDDM可以在保持翻译后的解剖结构准确性的同时,生成高质量的目标域图像。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该研究介绍了频率解耦扩散模型(FDDM)在MR到CT转换中的应用。该模型通过初始转换模块获取CT图像的解剖学信息,然后指导后续的扩散模型生成高质量的CT图像。使用双路径反向扩散过程平衡图像质量和解剖学准确性,并在脑部和骨盆MR到CT转换的公开数据集上进行了广泛评估,表现出优于其他GAN、VAE和扩散模型的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在医学图像翻译中生成高质量图像方面具有显著潜力,有助于疾病诊断、定位和治疗的辅助。
- 当前扩散模型在忠实图像翻译方面存在局限性,难以准确保留医学图像的结构和解剖细节。
- 结构和解剖细节的保留对可靠的医学诊断和治疗计划至关重要。
- FDDM模型通过初始转换模块获取CT图像的解剖学信息,并用于指导扩散模型生成高质量CT图像。
- FDDM使用双路径反向扩散过程平衡图像质量和解剖学准确性。
- FDDM在脑部数据和骨盆数据的MR到CT转换中表现出最佳性能,特别是在FID指标上得分显著。
点此查看论文截图

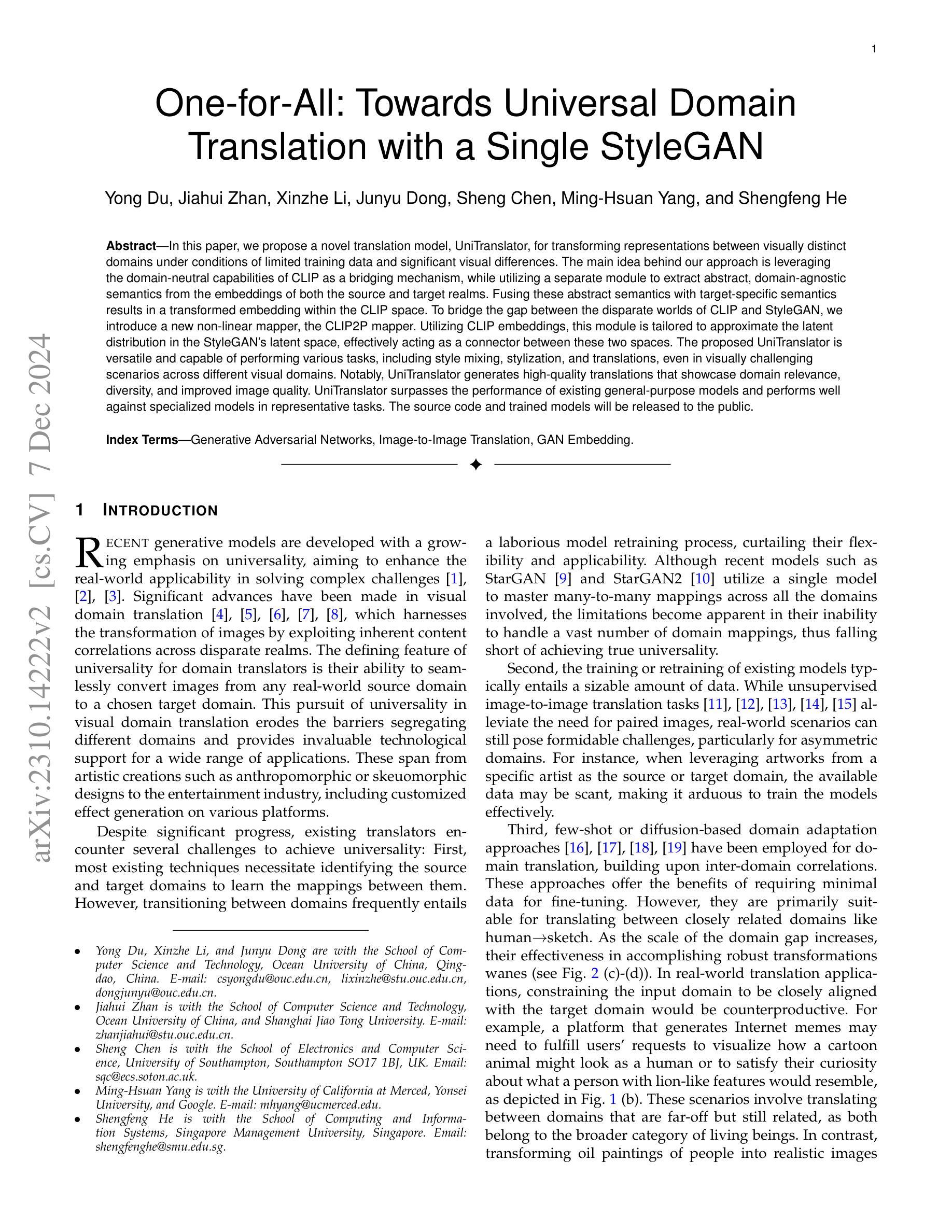
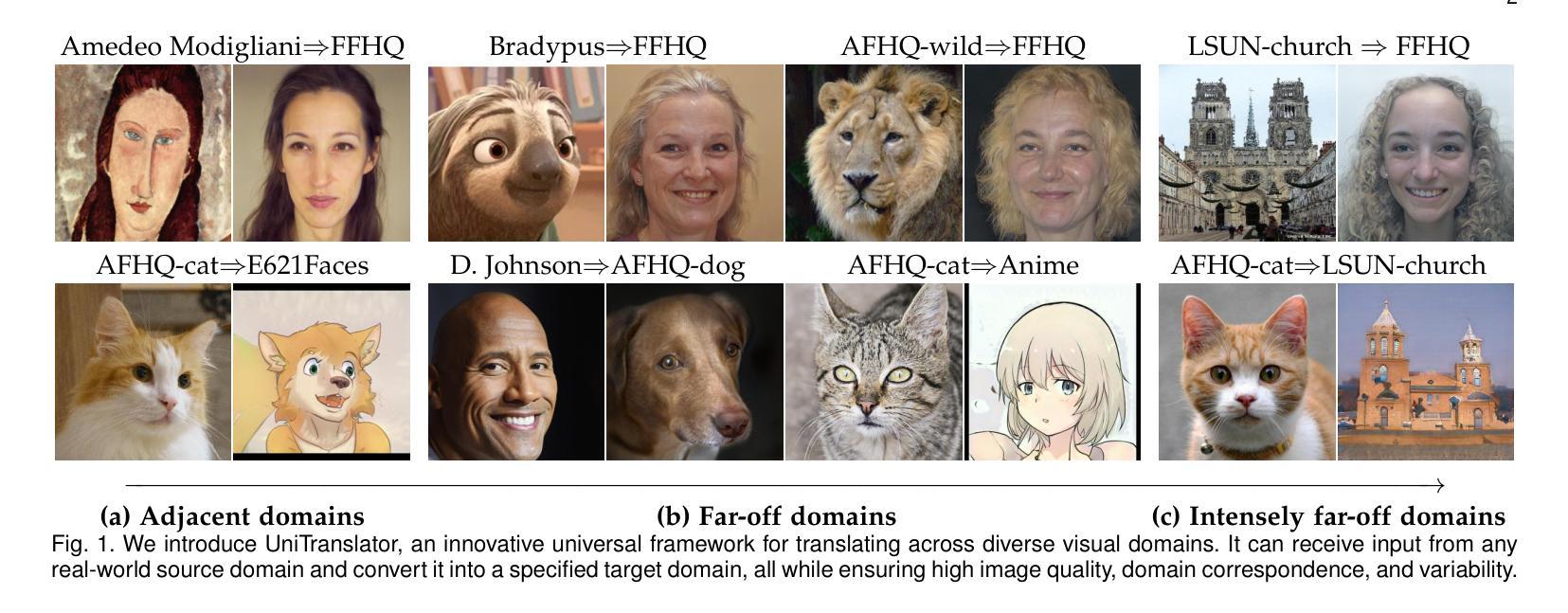
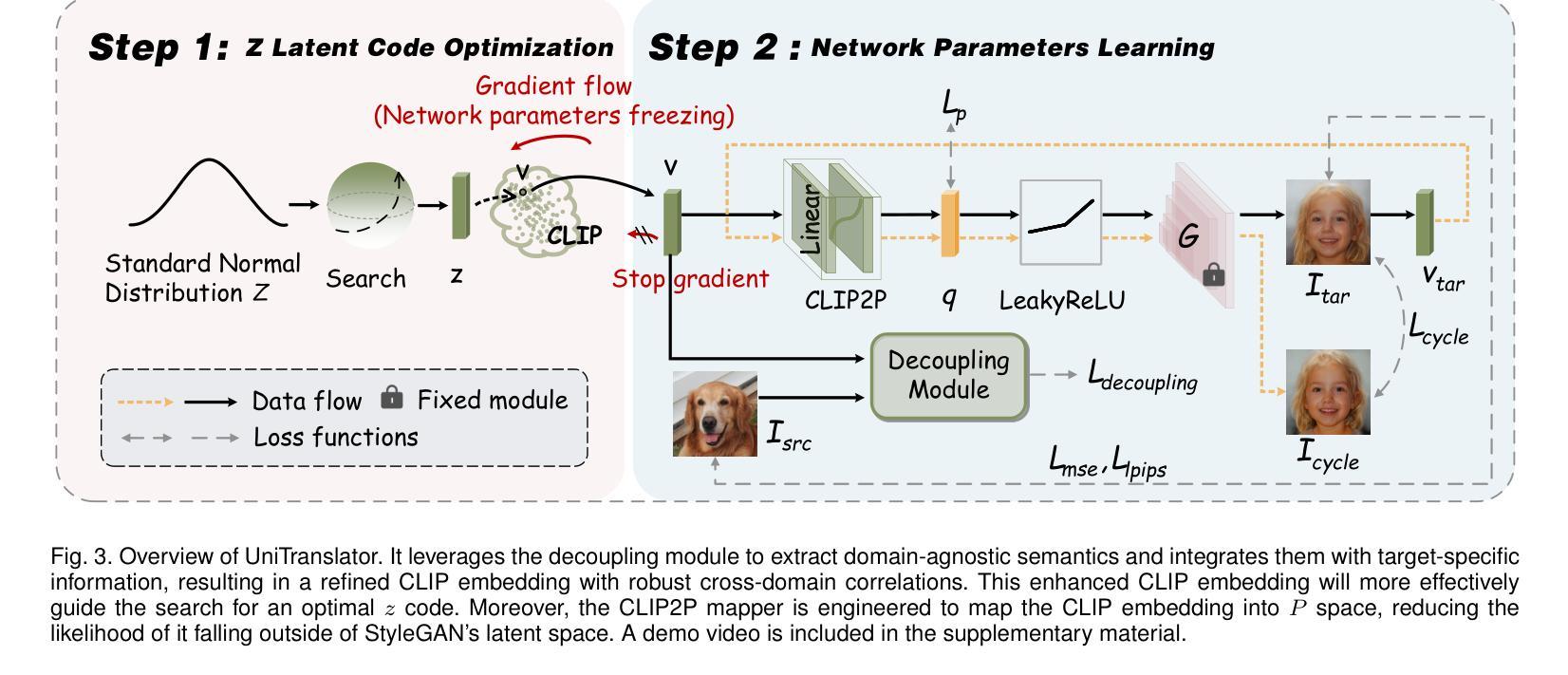
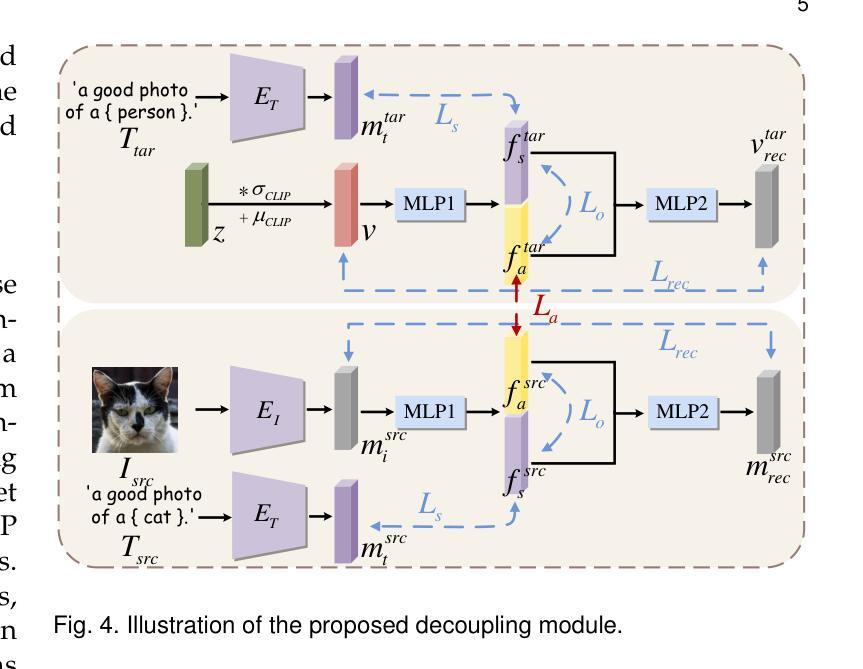
One-for-All: Towards Universal Domain Translation with a Single StyleGAN
Authors:Yong Du, Jiahui Zhan, Xinzhe Li, Junyu Dong, Sheng Chen, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Shengfeng He
In this paper, we propose a novel translation model, UniTranslator, for transforming representations between visually distinct domains under conditions of limited training data and significant visual differences. The main idea behind our approach is leveraging the domain-neutral capabilities of CLIP as a bridging mechanism, while utilizing a separate module to extract abstract, domain-agnostic semantics from the embeddings of both the source and target realms. Fusing these abstract semantics with target-specific semantics results in a transformed embedding within the CLIP space. To bridge the gap between the disparate worlds of CLIP and StyleGAN, we introduce a new non-linear mapper, the CLIP2P mapper. Utilizing CLIP embeddings, this module is tailored to approximate the latent distribution in the StyleGAN’s latent space, effectively acting as a connector between these two spaces. The proposed UniTranslator is versatile and capable of performing various tasks, including style mixing, stylization, and translations, even in visually challenging scenarios across different visual domains. Notably, UniTranslator generates high-quality translations that showcase domain relevance, diversity, and improved image quality. UniTranslator surpasses the performance of existing general-purpose models and performs well against specialized models in representative tasks. The source code and trained models will be released to the public.
本文提出了一种新型翻译模型UniTranslator,用于在训练数据有限和视觉差异显著的情况下,实现不同视觉领域之间的表示转换。我们的方法的主要思想是利用CLIP的中立域能力作为桥梁机制,同时使用一个单独的模块从源领域和目标领域的嵌入中提取抽象、领域无关的语义。将这些抽象语义与目标特定语义融合,得到CLIP空间内的转换嵌入。为了弥合CLIP和StyleGAN之间不同世界的差距,我们引入了一种新的非线性映射器——CLIP2P映射器。该模块利用CLIP嵌入进行定制,以近似StyleGAN潜在空间中的潜在分布,有效地作为这两个空间之间的连接器。所提出的UniTranslator通用性强,能够执行各种任务,包括风格混合、风格化和翻译,即使在跨越不同视觉领域的视觉挑战场景中也是如此。值得注意的是,UniTranslator生成的翻译结果具有高质量,展示了领域相关性、多样性和改进的图像质量。UniTranslator超越了现有通用模型的性能,并在代表性任务中表现良好,甚至超过了专业模型。源代码和训练好的模型将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新型翻译模型UniTranslator,该模型可在训练数据有限且视觉差异显著的情况下,实现不同视觉领域间的表示转换。它通过利用CLIP的域中性能力作为桥梁机制,同时运用单独模块从源域和目标域嵌入中提取抽象、领域无关的语义,再将这些抽象语义与特定目标的语义融合,生成在CLIP空间内的转换嵌入。为缩小CLIP和StyleGAN之间鸿沟,引入了新的非线性映射器CLIP2P mapper。该模块利用CLIP嵌入,旨在近似StyleGAN潜在空间中的潜在分布,从而在这两个空间之间发挥连接作用。UniTranslator功能强大,能执行风格混合、风格化和翻译等任务,甚至在视觉挑战性场景下也能在不同视觉领域之间实现高质量翻译。总的来说,UniTranslator超越了现有通用模型的表现,并在代表性任务中表现良好。源代码和训练模型将公开发布。
Key Takeaways
- UniTranslator是一个用于在不同视觉领域间进行表示转换的新型翻译模型。
- 它利用CLIP的域中性能力作为桥梁机制。
- UniTranslator通过融合抽象和特定目标的语义生成转换嵌入。
- 引入了新的非线性映射器CLIP2P mapper以连接CLIP和StyleGAN。
- UniTranslator能够在风格混合、风格化和翻译等任务中表现出强大的能力。
- 它在视觉挑战性场景下也能实现高质量翻译。
点此查看论文截图
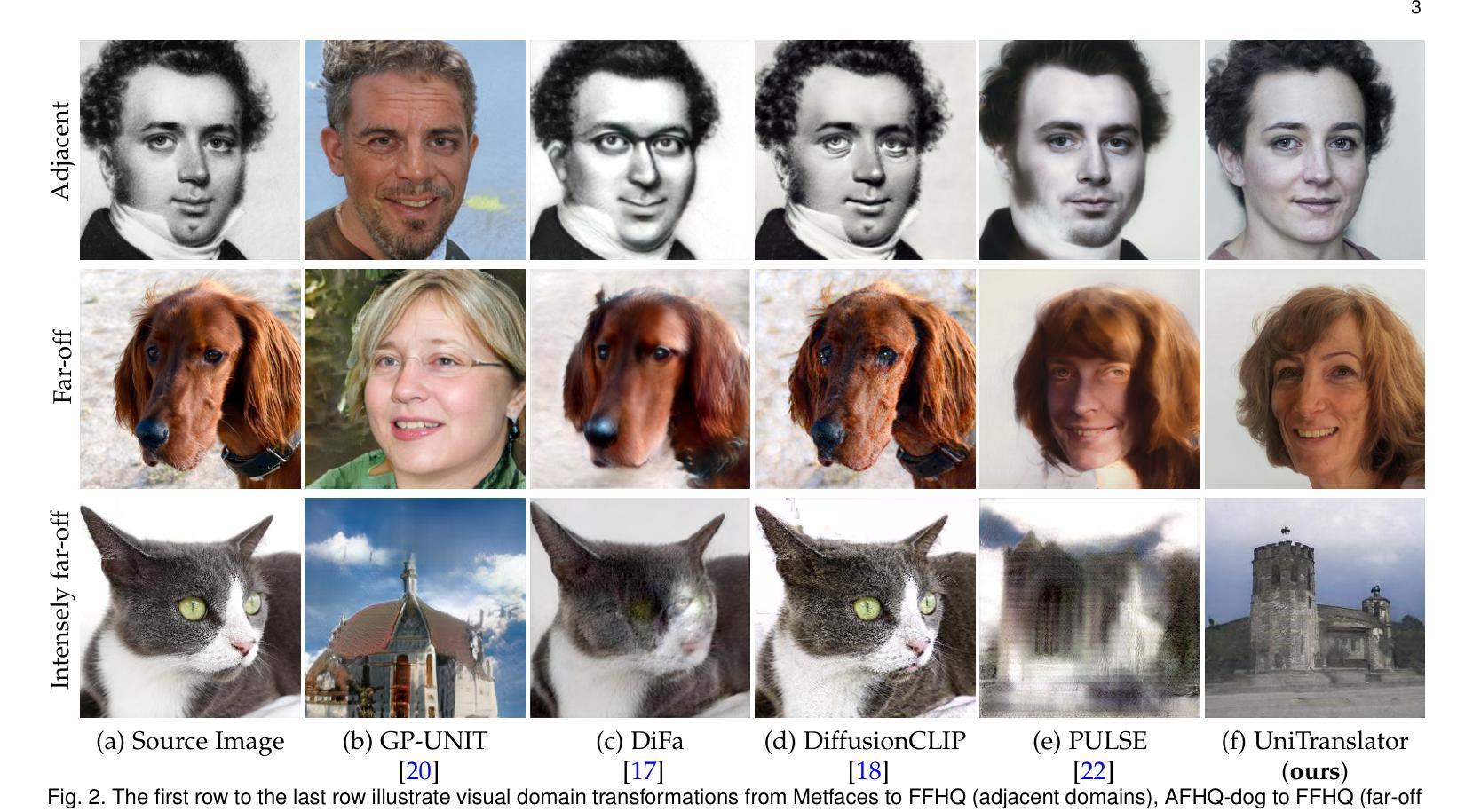

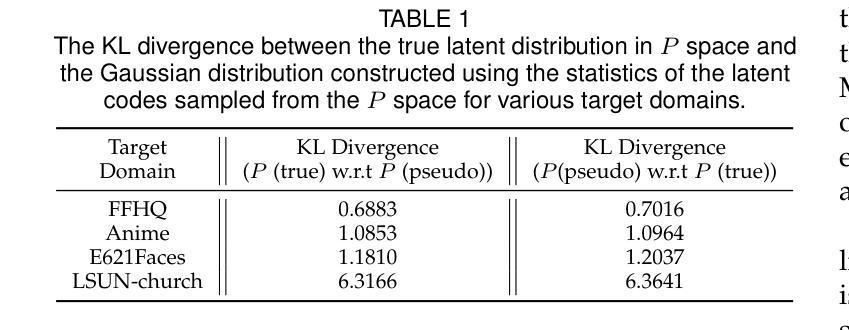
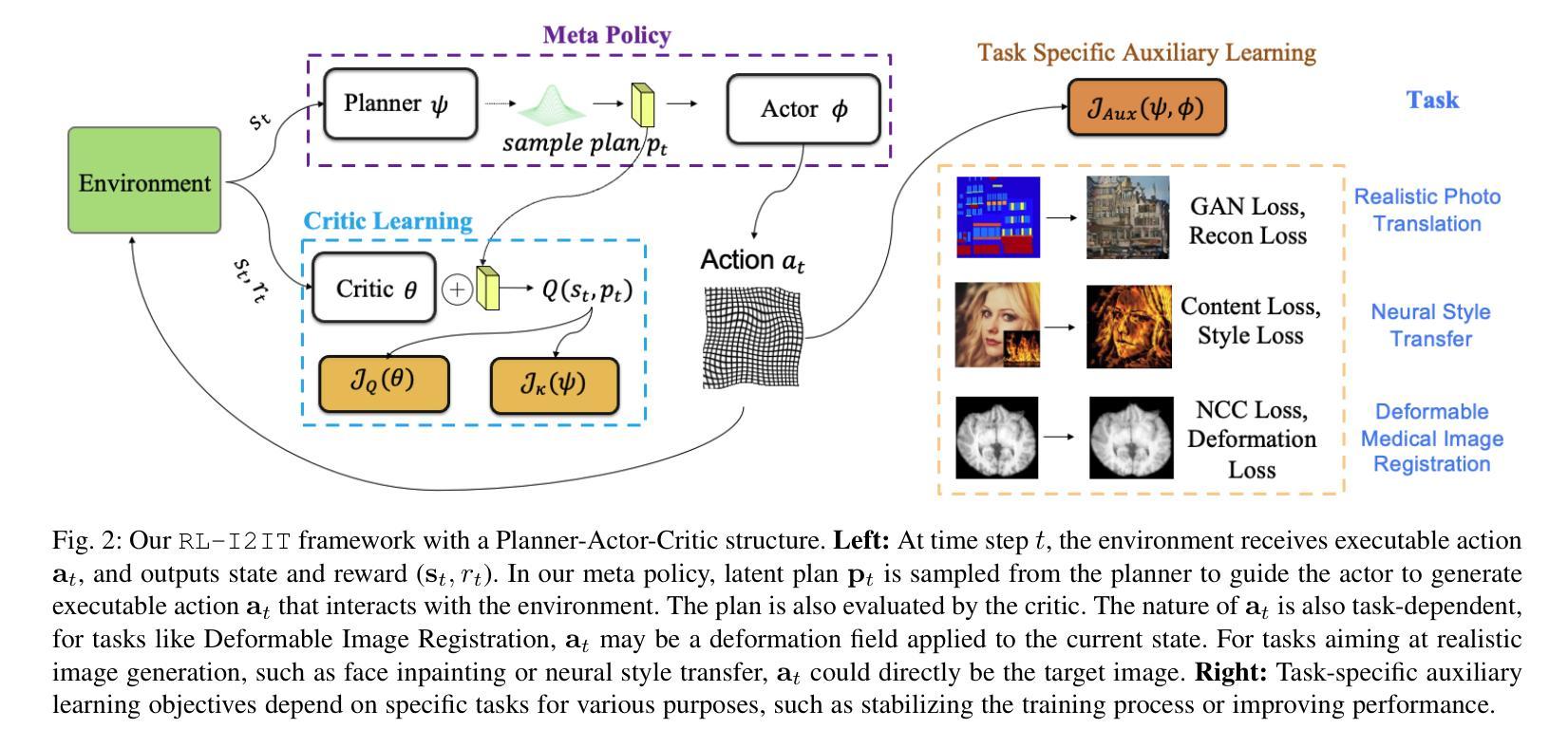
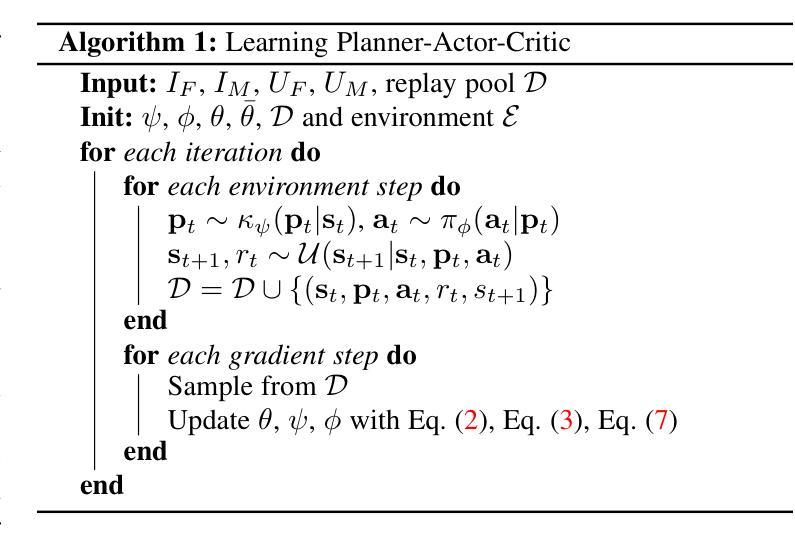
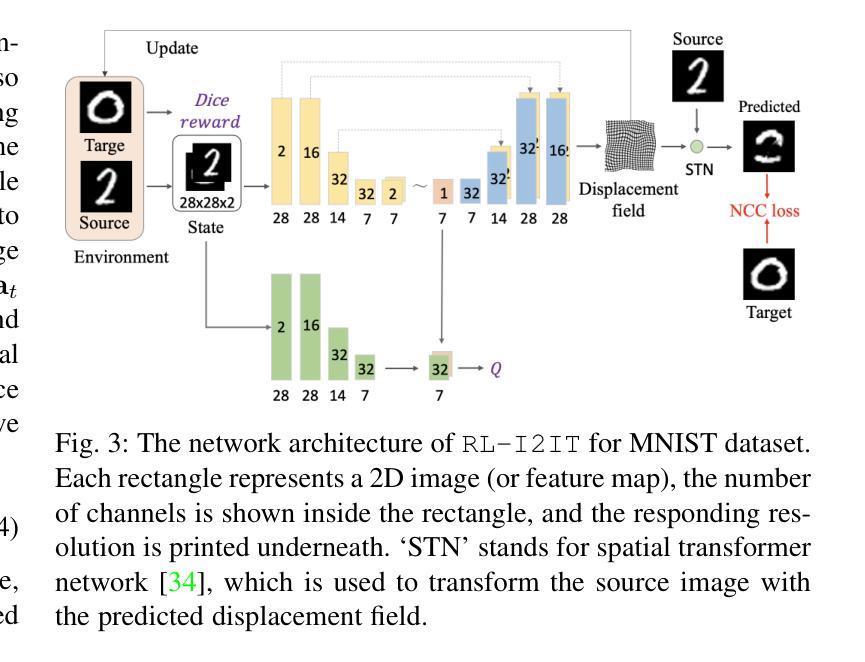
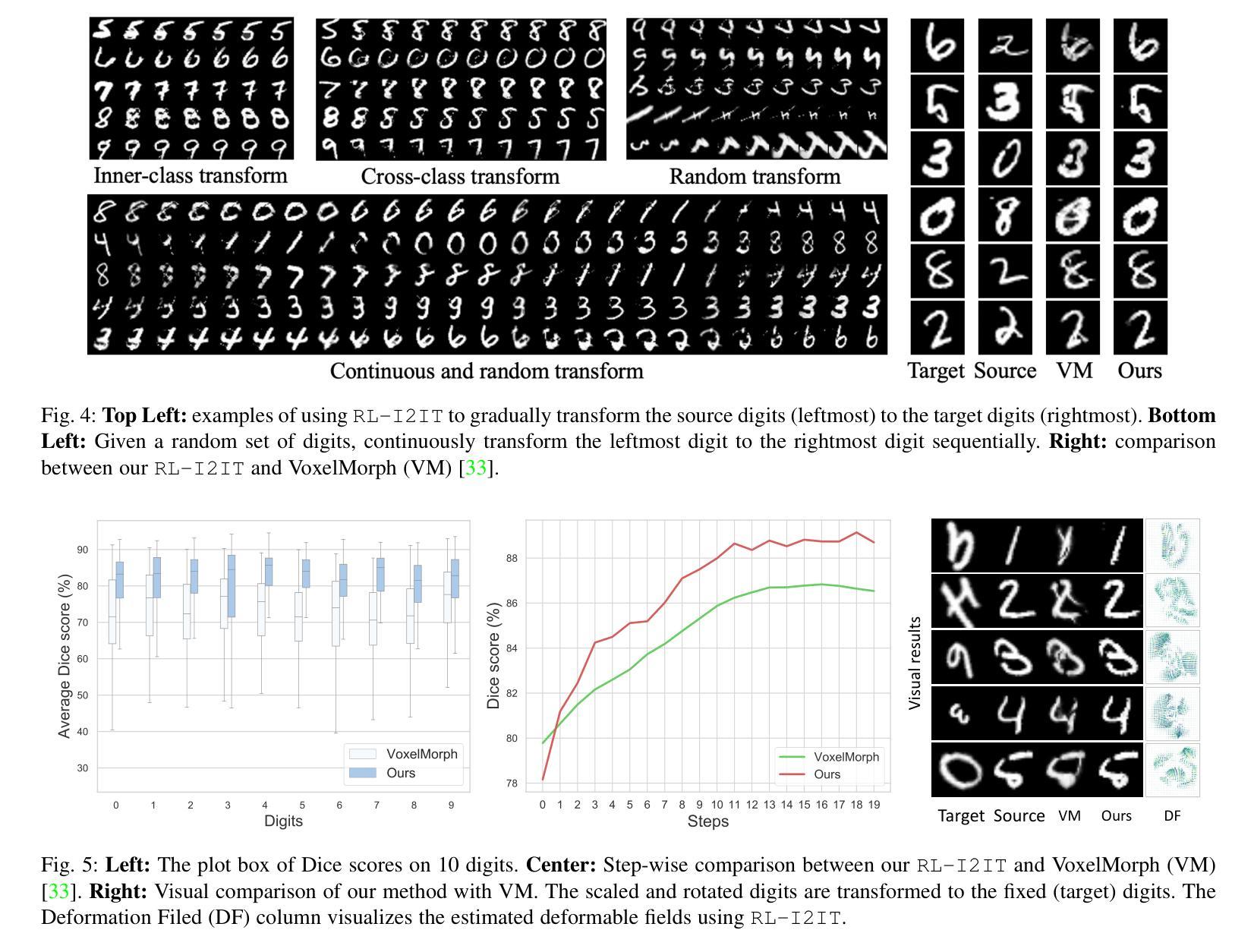
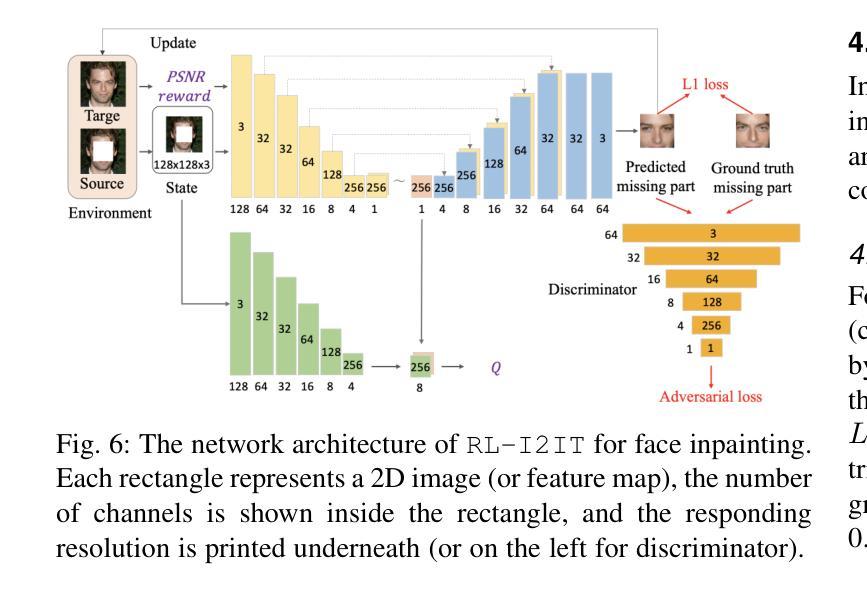
RL-I2IT: Image-to-Image Translation with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Authors:Xin Wang, Ziwei Luo, Jing Hu, Chengming Feng, Shu Hu, Bin Zhu, Xi Wu, Hongtu Zhu, Xin Li, Siwei Lyu
Most existing Image-to-Image Translation (I2IT) methods generate images in a single run of a deep learning (DL) model. However, designing such a single-step model is always challenging, requiring a huge number of parameters and easily falling into bad global minimums and overfitting. In this work, we reformulate I2IT as a step-wise decision-making problem via deep reinforcement learning (DRL) and propose a novel framework that performs RL-based I2IT (RL-I2IT). The key feature in the RL-I2IT framework is to decompose a monolithic learning process into small steps with a lightweight model to progressively transform a source image successively to a target image. Considering that it is challenging to handle high dimensional continuous state and action spaces in the conventional RL framework, we introduce meta policy with a new concept Plan to the standard Actor-Critic model, which is of a lower dimension than the original image and can facilitate the actor to generate a tractable high dimensional action. In the RL-I2IT framework, we also employ a task-specific auxiliary learning strategy to stabilize the training process and improve the performance of the corresponding task. Experiments on several I2IT tasks demonstrate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed method when facing high-dimensional continuous action space problems. Our implementation of the RL-I2IT framework is available at https://github.com/Algolzw/SPAC-Deformable-Registration.
现有的大多数图像到图像翻译(I2IT)方法都是使用深度学习(DL)模型在一次运行中生成图像。然而,设计这样的单步模型总是具有挑战性,需要大量的参数,并且容易陷入糟糕的全局最小值和过度拟合。在这项工作中,我们通过深度强化学习(DRL)重新制定I2IT作为逐步决策问题,并提出了一种基于强化学习的I2IT(RL-I2IT)的新框架。RL-I2IT框架的关键功能是将单一的学习过程分解为使用轻型模型的小步骤,以逐步将源图像连续变换为目标图像。考虑到在常规强化学习框架中处理高维连续状态和动作空间的挑战,我们向标准的Actor-Critic模型引入了元策略和新的计划概念。该概念具有比原始图像更低的维度,并且可以促进Actor生成可控制的高维动作。在RL-I2IT框架中,我们还采用特定任务的辅助学习策略来稳定训练过程并改善相应任务的性能。在几个I2IT任务上的实验表明,面对高维连续动作空间问题时,所提出的方法是有效和稳健的。有关RL-I2IT框架的实现可以在 https://github.com/Algolzw/SPAC-Deformable-Registration 找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:通过深度强化学习(DRL)实现基于步决策的图像到图像翻译(I2IT),将单一学习进程分解为多个小步骤,用轻量级模型逐步将源图像转换为目标图像。引入元政策和计划概念,解决高维连续状态和动作空间处理问题。采用特定任务辅助学习策略,稳定训练过程,提高任务性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 该研究将图像到图像翻译(I2IT)重新定义为一种基于步决策的强化学习问题。
- 提出了一种新颖的强化学习I2IT(RL-I2IT)框架,该框架将单一深度学习模型分解为多个小步骤。
- 在RL-I2IT框架中引入了元政策和计划的新概念来处理高维连续状态和动作空间。
- 通过采用特定任务的辅助学习策略,提高了训练的稳定性和任务性能。
- 该方法在多种I2IT任务上的实验验证了其面对高维连续动作空间问题时的有效性和稳健性。
- 研究者可从公开的代码库中获取RL-I2IT框架的实现。
点此查看论文截图

The Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS-METS) Challenge 2023: Brain Metastasis Segmentation on Pre-treatment MRI
Authors:Ahmed W. Moawad, Anastasia Janas, Ujjwal Baid, Divya Ramakrishnan, Rachit Saluja, Nader Ashraf, Nazanin Maleki, Leon Jekel, Nikolay Yordanov, Pascal Fehringer, Athanasios Gkampenis, Raisa Amiruddin, Amirreza Manteghinejad, Maruf Adewole, Jake Albrecht, Udunna Anazodo, Sanjay Aneja, Syed Muhammad Anwar, Timothy Bergquist, Veronica Chiang, Verena Chung, Gian Marco Conte, Farouk Dako, James Eddy, Ivan Ezhov, Nastaran Khalili, Keyvan Farahani, Juan Eugenio Iglesias, Zhifan Jiang, Elaine Johanson, Anahita Fathi Kazerooni, Florian Kofler, Kiril Krantchev, Dominic LaBella, Koen Van Leemput, Hongwei Bran Li, Marius George Linguraru, Xinyang Liu, Zeke Meier, Bjoern H Menze, Harrison Moy, Klara Osenberg, Marie Piraud, Zachary Reitman, Russell Takeshi Shinohara, Chunhao Wang, Benedikt Wiestler, Walter Wiggins, Umber Shafique, Klara Willms, Arman Avesta, Khaled Bousabarah, Satrajit Chakrabarty, Nicolo Gennaro, Wolfgang Holler, Manpreet Kaur, Pamela LaMontagne, MingDe Lin, Jan Lost, Daniel S. Marcus, Ryan Maresca, Sarah Merkaj, Gabriel Cassinelli Pedersen, Marc von Reppert, Aristeidis Sotiras, Oleg Teytelboym, Niklas Tillmans, Malte Westerhoff, Ayda Youssef, Devon Godfrey, Scott Floyd, Andreas Rauschecker, Javier Villanueva-Meyer, Irada Pfluger, Jaeyoung Cho, Martin Bendszus, Gianluca Brugnara, Justin Cramer, Gloria J. Guzman Perez-Carillo, Derek R. Johnson, Anthony Kam, Benjamin Yin Ming Kwan, Lillian Lai, Neil U. Lall, Fatima Memon, Mark Krycia, Satya Narayana Patro, Bojan Petrovic, Tiffany Y. So, Gerard Thompson, Lei Wu, E. Brooke Schrickel, Anu Bansal, Frederik Barkhof, Cristina Besada, Sammy Chu, Jason Druzgal, Alexandru Dusoi, Luciano Farage, Fabricio Feltrin, Amy Fong, Steve H. Fung, R. Ian Gray, Ichiro Ikuta, Michael Iv, Alida A. Postma, Amit Mahajan, David Joyner, Chase Krumpelman, Laurent Letourneau-Guillon, Christie M. Lincoln, Mate E. Maros, Elka Miller, Fanny Moron, Esther A. Nimchinsky, Ozkan Ozsarlak, Uresh Patel, Saurabh Rohatgi, Atin Saha, Anousheh Sayah, Eric D. Schwartz, Robert Shih, Mark S. Shiroishi, Juan E. Small, Manoj Tanwar, Jewels Valerie, Brent D. Weinberg, Matthew L. White, Robert Young, Vahe M. Zohrabian, Aynur Azizova, Melanie Maria Theresa Bruseler, Mohanad Ghonim, Mohamed Ghonim, Abdullah Okar, Luca Pasquini, Yasaman Sharifi, Gagandeep Singh, Nico Sollmann, Theodora Soumala, Mahsa Taherzadeh, Philipp Vollmuth, Martha Foltyn-Dumitru, Ajay Malhotra, Aly H. Abayazeed, Francesco Dellepiane, Philipp Lohmann, Victor M. Perez-Garcia, Hesham Elhalawani, Maria Correia de Verdier, Sanaria Al-Rubaiey, Rui Duarte Armindo, Kholod Ashraf, Moamen M. Asla, Mohamed Badawy, Jeroen Bisschop, Nima Broomand Lomer, Jan Bukatz, Jim Chen, Petra Cimflova, Felix Corr, Alexis Crawley, Lisa Deptula, Tasneem Elakhdar, Islam H. Shawali, Shahriar Faghani, Alexandra Frick, Vaibhav Gulati, Muhammad Ammar Haider, Fatima Hierro, Rasmus Holmboe Dahl, Sarah Maria Jacobs, Kuang-chun Jim Hsieh, Sedat G. Kandemirli, Katharina Kersting, Laura Kida, Sofia Kollia, Ioannis Koukoulithras, Xiao Li, Ahmed Abouelatta, Aya Mansour, Ruxandra-Catrinel Maria-Zamfirescu, Marcela Marsiglia, Yohana Sarahi Mateo-Camacho, Mark McArthur, Olivia McDonnell, Maire McHugh, Mana Moassefi, Samah Mostafa Morsi, Alexander Munteanu, Khanak K. Nandolia, Syed Raza Naqvi, Yalda Nikanpour, Mostafa Alnoury, Abdullah Mohamed Aly Nouh, Francesca Pappafava, Markand D. Patel, Samantha Petrucci, Eric Rawie, Scott Raymond, Borna Roohani, Sadeq Sabouhi, Laura M. Sanchez-Garcia, Zoe Shaked, Pokhraj P. Suthar, Talissa Altes, Edvin Isufi, Yaseen Dhemesh, Jaime Gass, Jonathan Thacker, Abdul Rahman Tarabishy, Benjamin Turner, Sebastiano Vacca, George K. Vilanilam, Daniel Warren, David Weiss, Fikadu Worede, Sara Yousry, Wondwossen Lerebo, Alejandro Aristizabal, Alexandros Karargyris, Hasan Kassem, Sarthak Pati, Micah Sheller, Katherine E. Link, Evan Calabrese, Nourel hoda Tahon, Ayman Nada, Yuri S. Velichko, Spyridon Bakas, Jeffrey D. Rudie, Mariam Aboian
The translation of AI-generated brain metastases (BM) segmentation into clinical practice relies heavily on diverse, high-quality annotated medical imaging datasets. The BraTS-METS 2023 challenge has gained momentum for testing and benchmarking algorithms using rigorously annotated internationally compiled real-world datasets. This study presents the results of the segmentation challenge and characterizes the challenging cases that impacted the performance of the winning algorithms. Untreated brain metastases on standard anatomic MRI sequences (T1, T2, FLAIR, T1PG) from eight contributed international datasets were annotated in stepwise method: published UNET algorithms, student, neuroradiologist, final approver neuroradiologist. Segmentations were ranked based on lesion-wise Dice and Hausdorff distance (HD95) scores. False positives (FP) and false negatives (FN) were rigorously penalized, receiving a score of 0 for Dice and a fixed penalty of 374 for HD95. Eight datasets comprising 1303 studies were annotated, with 402 studies (3076 lesions) released on Synapse as publicly available datasets to challenge competitors. Additionally, 31 studies (139 lesions) were held out for validation, and 59 studies (218 lesions) were used for testing. Segmentation accuracy was measured as rank across subjects, with the winning team achieving a LesionWise mean score of 7.9. Common errors among the leading teams included false negatives for small lesions and misregistration of masks in space.The BraTS-METS 2023 challenge successfully curated well-annotated, diverse datasets and identified common errors, facilitating the translation of BM segmentation across varied clinical environments and providing personalized volumetric reports to patients undergoing BM treatment.
将AI生成的脑转移瘤(BM)分割应用于临床实践,在很大程度上依赖于多样化、高质量标注的医学影像数据集。BraTS-METS 2023挑战赛通过使用严格标注的国际真实世界数据集测试和比较算法而势头正劲。本研究呈现了分割挑战的结果,并描述了对获胜算法性能产生影响的具有挑战性的病例。对来自八个国际数据集的未经治疗的脑转移瘤在标准解剖MRI序列(T1、T2、FLAIR、T1PG)上采用逐步方法进行标注:公开UNET算法、学生、神经放射学家、最终审批的神经放射学家。根据病灶级Dice和Hausdorff距离(HD95)评分对分割进行排名。假阳性(FP)和假阴性(FN)受到严格惩罚,Dice得分为0,HD95的固定惩罚为374。八个数据集共标注了1303项研究,其中402项研究(3076个病灶)在Synapse上作为公开数据集向参赛者发布。此外,还留出31项研究(139个病灶)用于验证,59项研究(218个病灶)用于测试。分割精度通过受试者排名来衡量,冠军团队的病灶级平均得分为7.9。领先团队常见的错误包括小病灶的假阴性以及口罩在空间上的错位。BraTS-METS 2023挑战赛成功筛选出了标注良好、多样化的数据集,并发现了常见错误,推动了BM分割在不同临床环境中的转化,并为接受BM治疗的病人提供个性化的体积报告。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文本介绍了BraTS-METS 2023挑战赛的结果及影响获胜算法性能的挑战性病例。该挑战赛使用严格注释的国际汇编真实世界数据集来测试和评估算法。文中指出,将人工智能生成的脑转移瘤分割结果转化为临床实践依赖于多样且高质量的医疗成像数据集。通过该挑战,成功整理出经过良好注释的多样化数据集,并识别出常见错误,促进了脑转移瘤分割在临床环境中的转化,为患者提供个性化的体积报告。
Key Takeaways
- BraTS-METS 2023挑战赛利用严格注释的国际汇编真实世界数据集测试和评估算法,推动AI在医疗领域的应用。
- 该研究呈现分割挑战的结果,并描述了影响获胜算法性能的挑战性病例。
- 将AI生成的脑转移瘤(BM)分割结果转化为临床实践依赖于高质量、多样化的医学成像数据集。
- 挑战赛中发现的问题包括小病灶的漏检以及口罩在空间上的错位等。
- BraTS-METS 2023挑战成功地整理出经过良好注释的多样化数据集,有助于算法的进一步发展。
- 挑战赛有助于将BM分割结果转化为临床实践,为接受BM治疗的患者提供个性化的体积报告。
点此查看论文截图

Vision-and-Language Pretraining
Authors:Thong Nguyen, Cong-Duy Nguyen, Xiaobao Wu, See-Kiong Ng, Anh Tuan Luu
With the burgeoning amount of data of image-text pairs and diversity of Vision-and-Language (V&L) tasks, scholars have introduced an abundance of deep learning models in this research domain. Furthermore, in recent years, transfer learning has also shown tremendous success in Computer Vision for tasks such as Image Classification, Object Detection, etc., and in Natural Language Processing for Question Answering, Machine Translation, etc. Inheriting the spirit of Transfer Learning, research works in V&L have devised multiple pretraining techniques on large-scale datasets in order to enhance the performance of downstream tasks. The aim of this article is to provide a comprehensive revision of contemporary V&L pretraining models. In particular, we categorize and delineate pretraining approaches, along with the summary of state-of-the-art vision-and-language pretrained models. Moreover, a list of training datasets and downstream tasks is supplied to further polish the perspective into V&L pretraining. Lastly, we decided to take a further step to discuss numerous directions for future research.
随着图像文本对数据的不断增加和视觉与语言(V&L)任务的多样性,学者们在这个研究领域中已经引入了大量的深度学习模型。此外,近年来,迁移学习在计算机视觉的图像分类、目标检测等任务以及自然语言处理的问答、机器翻译等任务中也取得了巨大的成功。秉承迁移学习的精神,视觉与语言领域的研究工作在大规模数据集上设计了多种预训练技术,以提高下游任务的性能。本文的目的是对当代视觉与语言预训练模型进行全面回顾。特别是,我们对预训练方法进行分类和描述,以及对最先进的视觉和语言预训练模型进行总结。此外,还提供了一系列训练数据集和下游任务,以进一步深入了解视觉与语言的预训练。最后,我们决定进一步讨论未来研究的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The content of the paper has been outdated. I would like to rewrite a new version with completely new information.
Summary
随着图像文本对数据的激增和视觉与语言(V&L)任务的多样性,学者已引入大量深度学习模型。借助迁移学习的成功,V&L研究在大型数据集上设计了多种预训练技术,以提高下游任务性能。本文旨在全面回顾当代的V&L预训练模型,分类并概述先进的视觉与语言预训练模型,并提供训练数据集和下游任务列表,为进一步探讨V&L预训练提供视角。
Key Takeaways
- 视觉与语言(V&L)领域引入大量深度学习模型以应对图像文本对数据的激增和任务多样性。
- 迁移学习在计算机视觉和自然语言处理任务中取得了巨大成功。
- V&L研究利用迁移学习的精神,在大型数据集上采用多种预训练技术以提高下游任务性能。
- 本文全面回顾了当代的V&L预训练模型,并进行分类概述。
- 文章提供了先进的视觉与语言预训练模型的总结。
- 列出了训练数据集和下游任务,为深入研究V&L预训练提供了视角。
点此查看论文截图