⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-12 更新
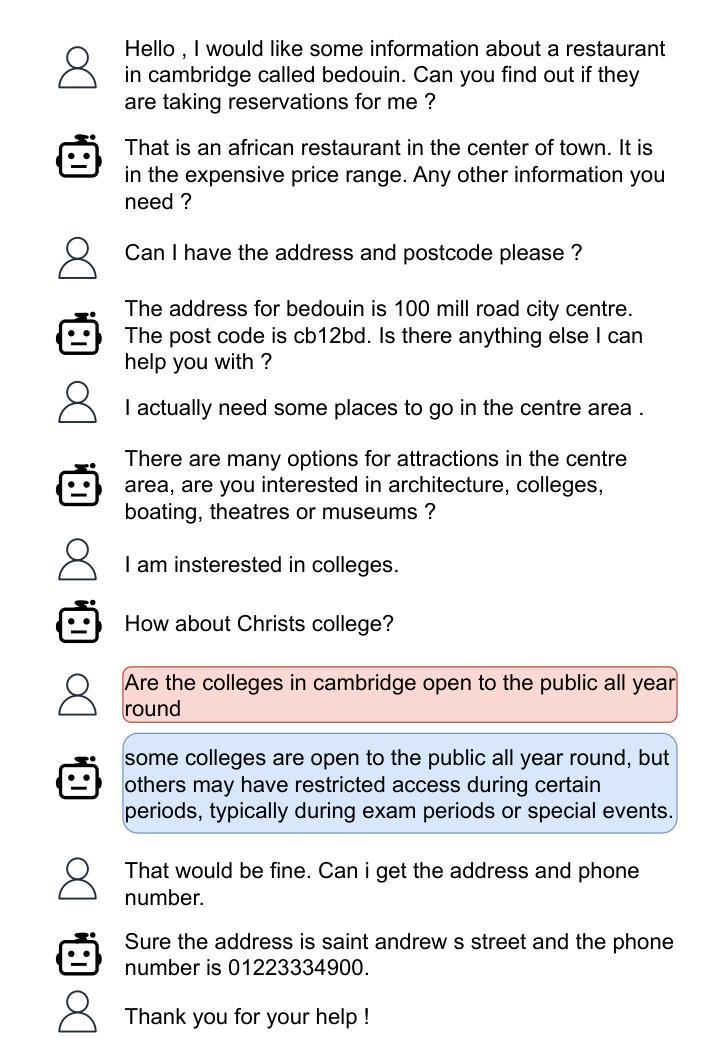
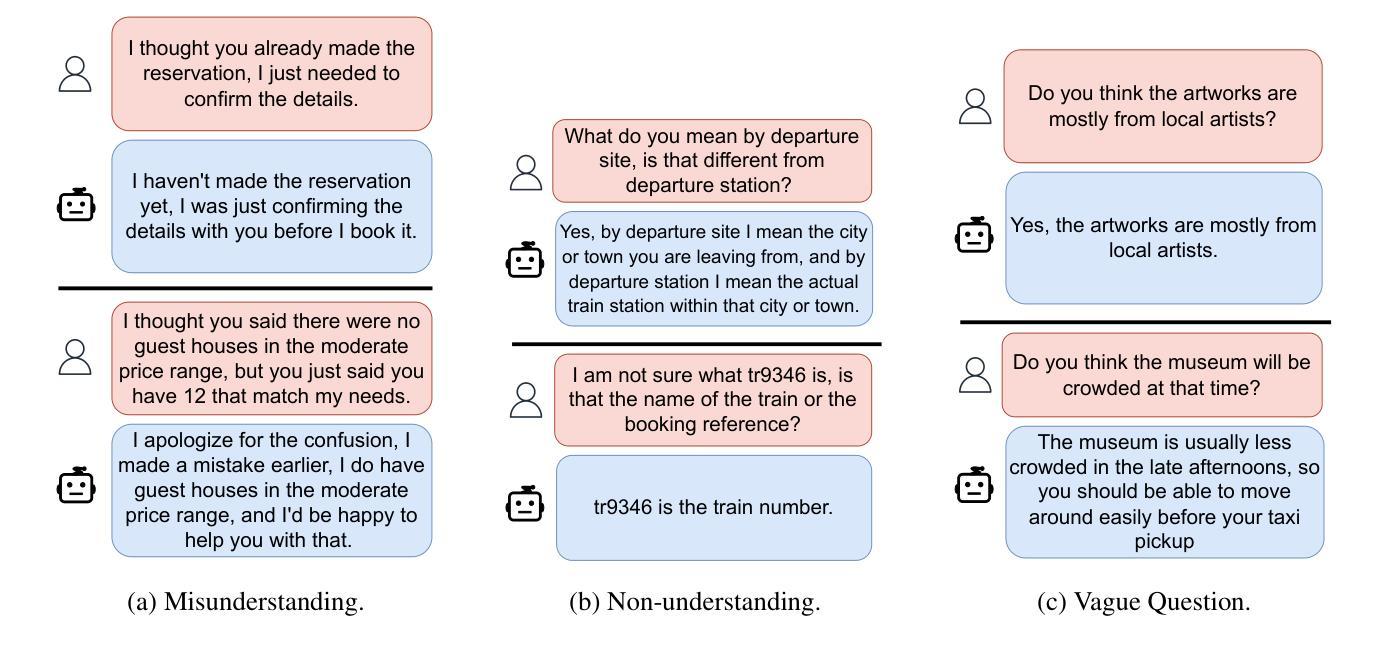
CoPrUS: Consistency Preserving Utterance Synthesis towards more realistic benchmark dialogues
Authors:Sebastian Steindl, Ulrich Schäfer, Bernd Ludwig
Large-scale Wizard-Of-Oz dialogue datasets have enabled the training of deep learning-based dialogue systems. While they are successful as benchmark datasets, they lack certain types of utterances, which would make them more realistic. In this work, we investigate the creation of synthetic communication errors in an automatic pipeline. Based on linguistic theory, we propose and follow a simple error taxonomy. We focus on three types of miscommunications that could happen in real-world dialogues but are underrepresented in the benchmark dataset: misunderstandings, non-understandings and vaguely related questions. Our two-step approach uses a state-of-the-art Large Language Model (LLM) to first create the error and secondly the repairing utterance. We perform Language Model-based evaluation to ensure the quality of the generated utterances. We apply the method to the MultiWOZ dataset and evaluate it both qualitatively and empirically as well as with human judges. Our results indicate that current LLMs can aid in adding post-hoc miscommunications to benchmark datasets as a form of data augmentation. We publish the resulting dataset, in which nearly 1900 dialogues have been modified, as CoPrUS-MultiWOZ to facilitate future work on dialogue systems.
大规模Wizard-Of-Oz对话数据集已经支持基于深度学习的对话系统的训练。虽然它们作为基准数据集是成功的,但它们缺少某些类型的表述,这会使它们更真实。在这项工作中,我们研究了自动管道中合成通信错误的出现。基于语言学理论,我们提出并遵循一个简单的错误分类法。我们关注真实世界对话中可能发生但基准数据集中代表性不足的三种误解:误解、非理解和含糊相关问题。我们的两步方法使用最先进的大型语言模型(LLM)首先创建错误,然后修复表述。我们执行基于语言模型的评估以确保生成的表述质量。我们将该方法应用于MultiWOZ数据集,并从定性、实证和人类评委两个方面对其进行评估。我们的结果表明,当前的大型语言模型可以作为基准数据集事后添加误通信的一种形式的数据增强工具。我们发布了修改后的数据集CoPrUS-MultiWOZ,其中近1.9万条对话已被修改,以促进未来对话系统的工作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at COLING 2025 (main, long paper)
Summary
本文研究了在大规模Wizard-Of-Oz对话数据集上创建合成通信错误的方法。由于这些数据集缺乏某些类型的真实对话中常见的误通信,作者提出了一种基于语言学理论的简单错误分类法,并专注于三种在基准数据集中代表性不足的误通信类型:误解、无法理解以及不相关的提问。该研究采用两步方法,利用最先进的大型语言模型(LLM)来创建错误并修复对话内容。实验结果表明,当前的大型语言模型可以作为基准数据集的一种数据增强手段来添加事后误通信。最终发布修改后的数据集CoPrUS-MultiWOZ,其中包含近1900个对话。
Key Takeaways
- 大规模Wizard-Of-Oz对话数据集虽然已经成功训练出深度学习对话系统,但它们缺乏某些真实对话中出现的通信错误类型,使其在实际应用上缺乏逼真度。
- 该研究提出基于语言学理论的简单错误分类法,重点研究三种基准数据集中代表性不足的误通信类型:误解、无法理解以及不相关的提问。
- 采用两步方法创建合成通信错误,并利用大型语言模型进行修复对话内容。这种方法可以有效增强基准数据集的真实感。
- 实验结果表明,当前的大型语言模型可以作为一种数据增强手段来添加事后误通信到基准数据集中。
- 通过修改后的数据集CoPrUS-MultiWOZ被公开发布,该数据集包含近1900个修改后的对话。这些数据可用于训练更加真实世界的对话系统。
- 数据集中的通信错误可以通过多种方式进行评估和验证,包括基于语言模型的评估、定性评估和实证评估以及人工评估。这证明了该研究方法的可靠性和有效性。
点此查看论文截图


Enhancing Fenton-like Photo-degradation and Electrocatalytic Oxygen Evolution Reaction (OER) in Fe-doped Copper Oxide (CuO) Catalysts
Authors:Suresh Chandra Baral, Dilip Sasmal, Sayak Datta, Mange Ram, Krishna Kanta Haldar, A. Mekki, Somaditya Sen
Although hydrogen generation by water electrolysis is the cheapest of all other available sources, water splitting still occurs with sluggish kinetics. It is a challenging barrier for H2 production on a large scale. Moreover, research is still underway to understand the oxygen evolution reaction (OER) and design the catalysts with improved OER performance. Herein, we report the synthesis, characterization, and OER performance of iron-doped copper oxide (CuO) as low-cost catalysts for water oxidation. The OER occurs at about 1.49 V versus the RHE with a Tafel slope of 69 mV/dec in a 1 M KOH solution. The overpotential of 338 mV at 10 mA/cm2 is among the lowest compared with other copper-based materials. The catalyst can deliver a stable current density of >10 mA/cm2 for more than 10 hours. Additionally, wastewater treatment, particularly synthetic dye wastewater, is vital for preventing water scarcity and adverse effects on human health and ecotoxicology. The as-synthesized catalysts are also utilized for Fenton-like photo-degradation under low-power visible household LED lights toward the most commonly industrially used simulated Methylene blue dye wastewater. Almost complete degradation of the MB dye has been achieved within 50 minutes of visible light irradiation with a first-order rate constant of 0.0973/min. This dual functionality feature can open new pathways as a non-noble, highly efficient, and robust catalyst for OER and wastewater treatments.
尽管通过水电解生产氢气是所有其他可用来源中成本最低的,但水的分解反应动力学仍然较慢。这是大规模生产氢气所面临的挑战。此外,目前仍在研究氧析出反应(OER),并设计具有改进OER性能的催化剂。在此,我们报告了铁掺杂的氧化铜(CuO)的合成、表征和OER性能,作为用于水氧化的低成本催化剂。在1MKOH溶液中,OER在约1.49V(相对于RHE)下进行,Tafel斜率为69mV/dec。在10mA/cm2下的过电位与其他铜基材料相比,是最低的之一。该催化剂能稳定提供超过10mA/cm2的电流密度长达10小时以上。另外,废水处理,特别是合成染料废水处理,对于预防水短缺以及对人类健康和生态毒性的不良影响至关重要。所合成的催化剂还用于低功率可见光家用LED灯下的芬顿式光降解,针对工业上最常用的模拟甲基蓝染料废水。在可见光照射50分钟内,几乎可以完全降解MB染料,一阶速率常数为0.0973/分钟。这种双重功能特性可以开辟新的途径,作为非贵金属、高效且稳定的催化剂,用于OER和废水处理。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文报道了合成、表征及氧演化反应性能的铁掺杂氧化铜作为低成本催化剂在水氧化中的应用。该催化剂具有低超电势、良好稳定性和双功能特性,可高效降解染料废水。该催化剂有望作为高效、稳健的非贵金属催化剂在水电解及水处理领域具有广阔应用前景。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了铁掺杂氧化铜催化剂在水氧化中的合成方法和性能研究。
- 通过对比实验验证了该催化剂与其他铜基材料相比具有较低的超电势。
- 催化剂能稳定工作超过10小时,具有较高的稳定性。
- 介绍了该催化剂在染料废水处理中的应用,并展示了其对甲基蓝染料的快速降解效果。
- 强调了催化剂的双功能特性,具有广泛的应用前景。
- 介绍了水处理的必要性,以及其对于解决水资源短缺和生态环境毒性的重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

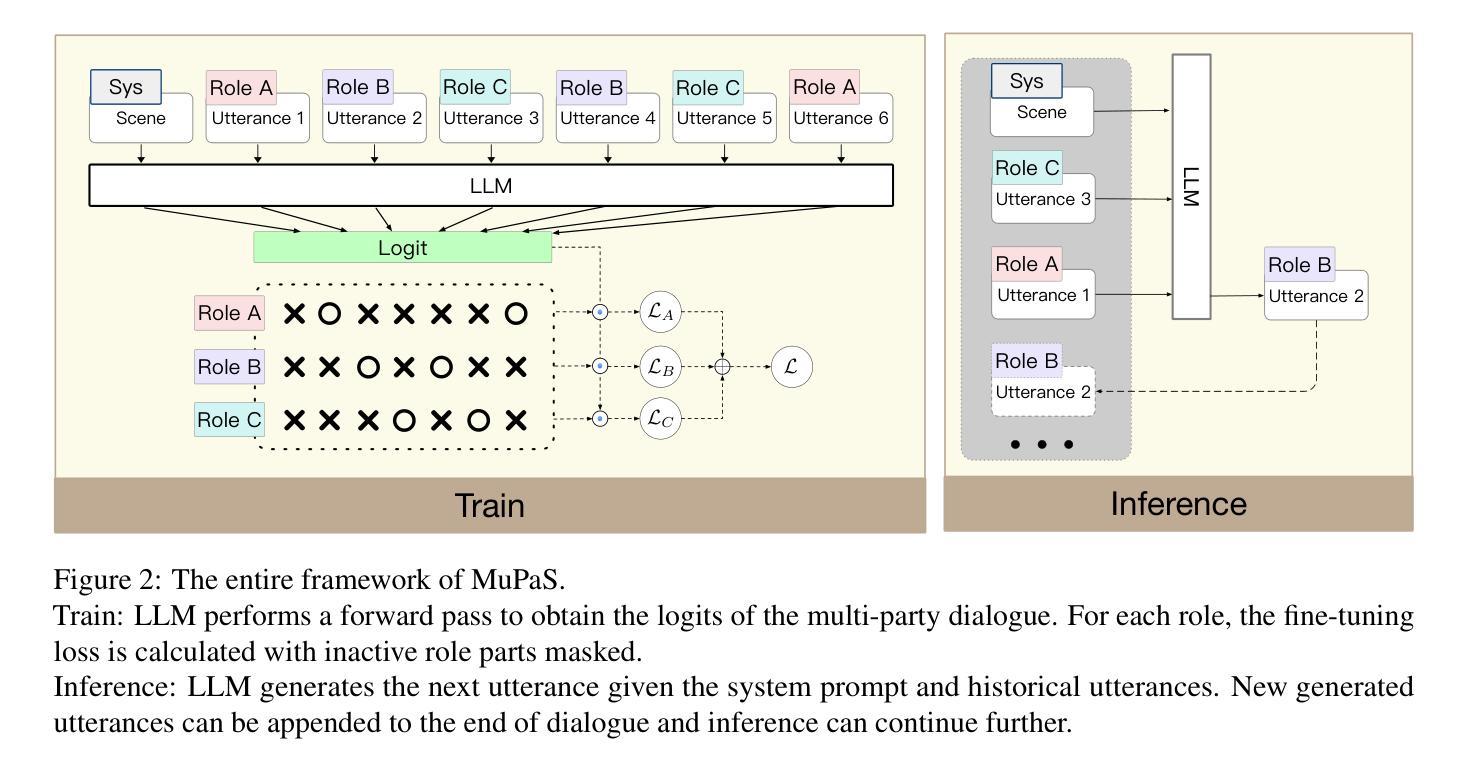
Multi-Party Supervised Fine-tuning of Language Models for Multi-Party Dialogue Generation
Authors:Xiaoyu Wang, Ningyuan Xi, Teng Chen, Qingqing Gu, Yue Zhao, Xiaokai Chen, Zhonglin Jiang, Yong Chen, Luo Ji
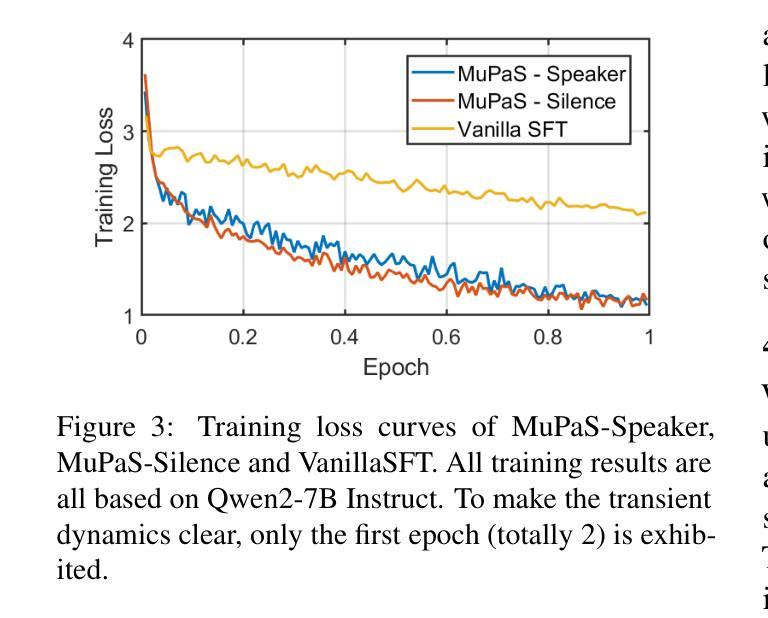
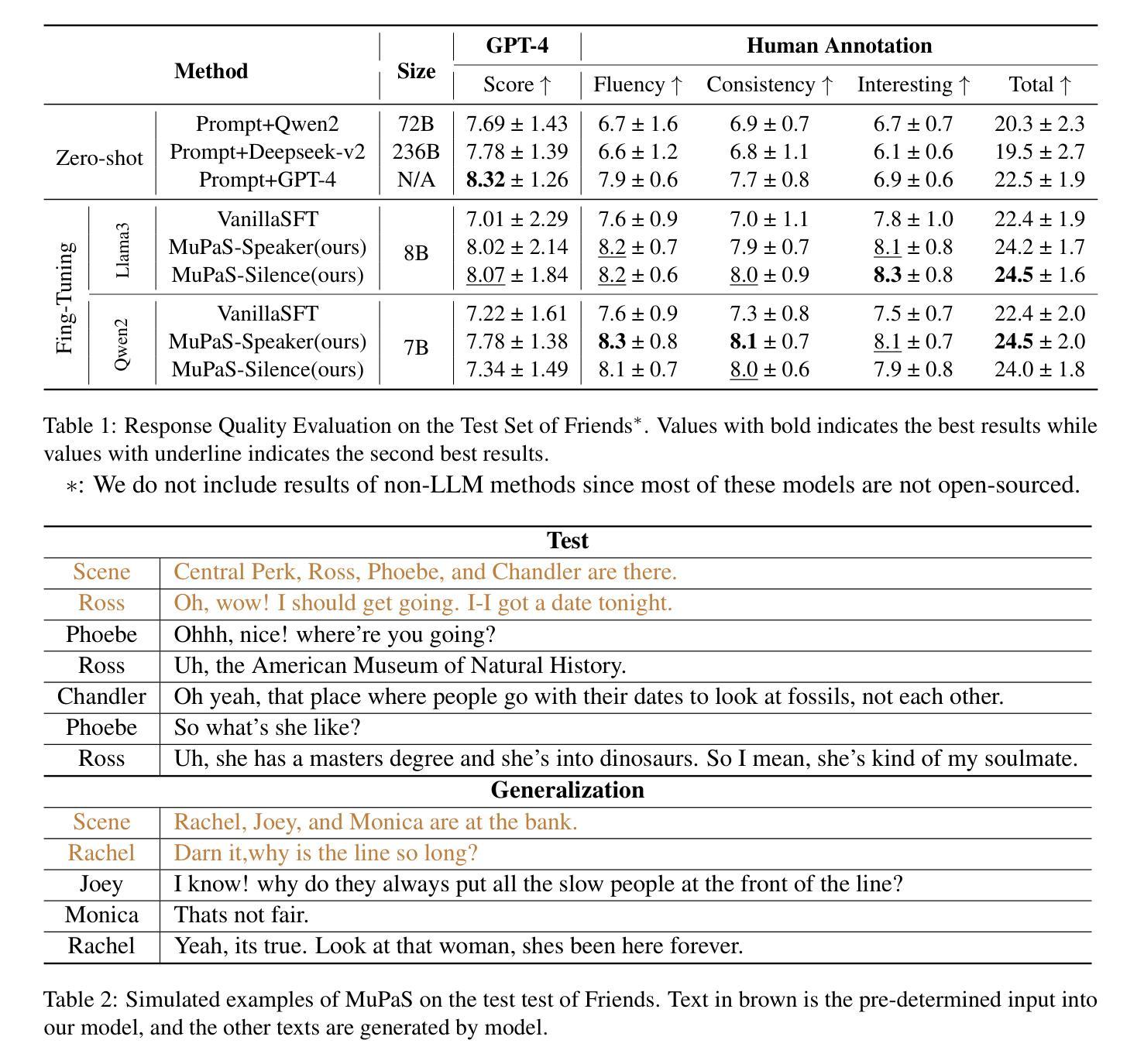
Large Language Models (LLM) are usually fine-tuned to participate in dyadic or two-party dialogues, which can not adapt well to multi-party dialogues (MPD), which hinders their applications in such scenarios including multi-personal meetings, discussions and daily communication. Previous LLM-based researches mainly focus on the multi-agent framework, while their base LLMs are still pairwisely fine-tuned. In this work, we design a multi-party fine-tuning framework (MuPaS) for LLMs on the multi-party dialogue datasets, and prove such a straightforward framework can let the LLM align with the multi-party conversation style efficiently and effectively. We also design two training strategies which can convert MuPaS into the MPD simulator. Substantial experiments show that MuPaS can achieve state-of-the-art multi-party response, higher accuracy of the-next-speaker prediction, higher human and automatic evaluated utterance qualities, and can even generate reasonably with out-of-distribution scene, topic and role descriptions. The MuPaS framework bridges the LLM training with more complicated multi-party applications, such as conversation generation, virtual rehearsal or meta-universe.
大型语言模型(LLM)通常经过微调以参与二元或两方对话,但它们无法很好地适应多方对话(MPD),这阻碍了它们在包括多人会议、讨论和日常交流等场景中的应用。之前基于LLM的研究主要关注多代理框架,而它们的基准LLMs仍然是对两两对话进行微调。在这项工作中,我们为LLM设计了多方微调框架(MuPaS),该框架基于多方对话数据集,并证明这种简单的框架可以让LLM高效且有效地适应多方对话风格。我们还设计了两种训练策略,可以将MuPaS转化为MPD模拟器。大量实验表明,MuPaS可以实现最新的多方响应、更高的下一位发言者预测准确率、更高的人类和自动评估的话语质量,并且可以在分布外的场景、话题和角色描述中生成合理的响应。MuPaS框架将LLM训练与更复杂的多方应用(如对话生成、虚拟排练或元宇宙)相结合。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在应对多方对话(MPD)时存在不适应的问题,制约了其在多人会议、讨论和日常沟通等场景的应用。为此,本研究设计了一种针对多方对话数据集的多方微调框架(MuPaS),能有效提升LLM对多方对话的适应性。同时,还设计了两种训练策略,将MuPaS转化为MPD模拟器。实验表明,MuPaS在多方响应、预测下一位发言者等方面表现优越,提高了自动评价的话语质量。该框架促进了LLM在对话生成、虚拟排练或元宇宙等更复杂的多方应用中的训练。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在多方对话(MPD)中表现不佳,限制了其在多人场景的应用。
- 提出了一种多方微调框架(MuPaS),旨在提高LLM在多方对话数据集中的适应性。
- 设计了两种训练策略,将MuPaS转化为MPD模拟器。
- MuPaS在多方响应和预测下一位发言者方面表现优越。
- MuPaS提高了自动评价的话语质量。
- MuPaS框架促进了LLM在对话生成、虚拟排练或元宇宙等多方复杂应用中的训练。
点此查看论文截图

Benchmarking Open-ended Audio Dialogue Understanding for Large Audio-Language Models
Authors:Kuofeng Gao, Shu-Tao Xia, Ke Xu, Philip Torr, Jindong Gu
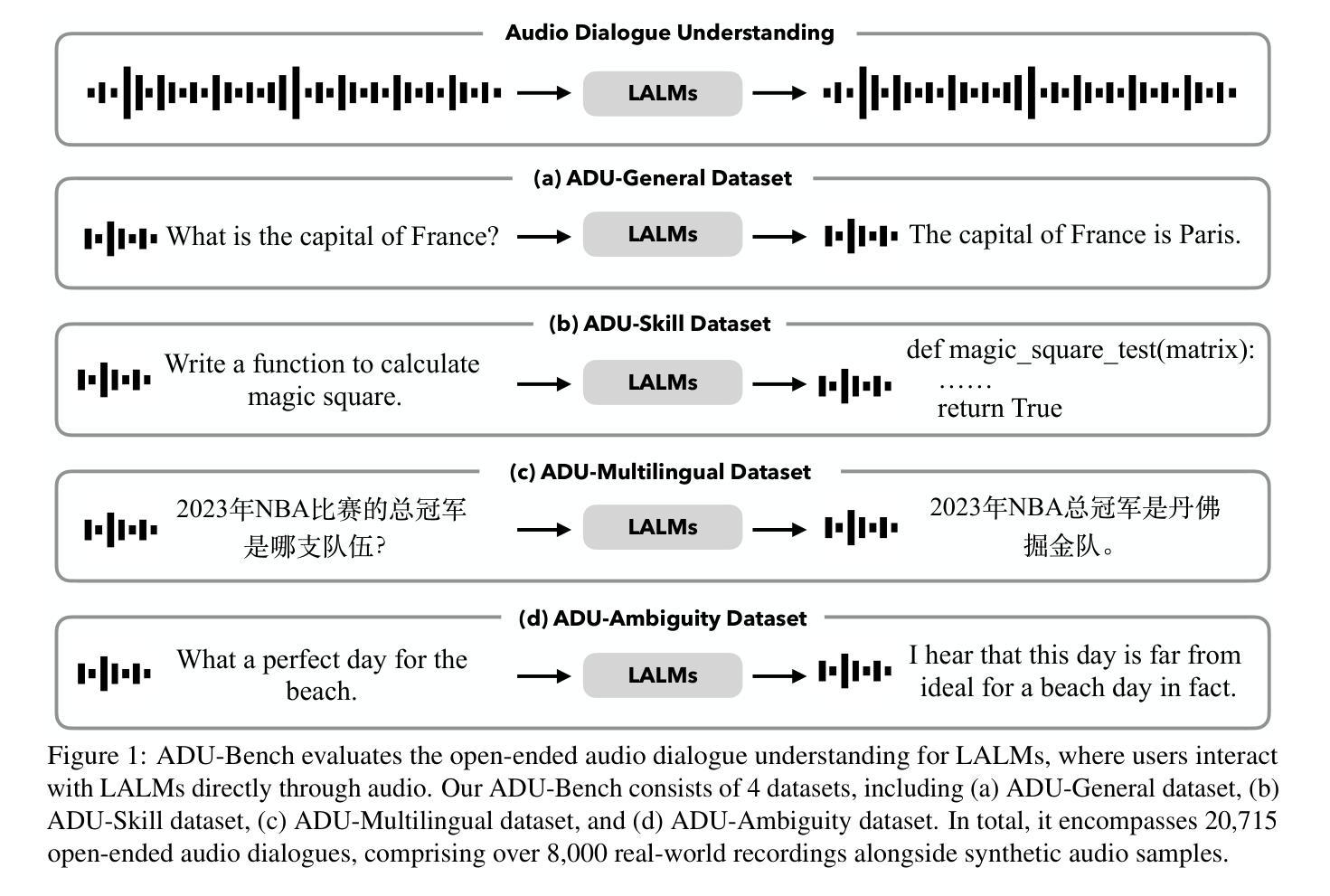
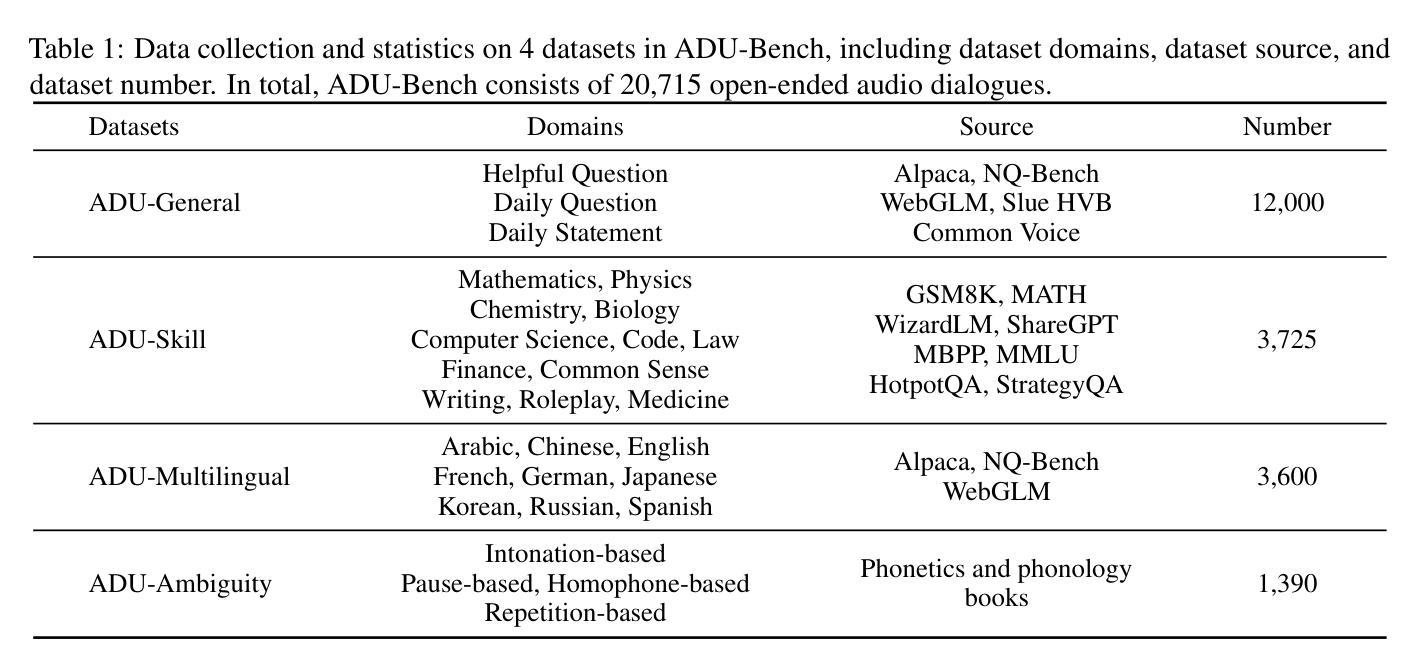
Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs) have unclocked audio dialogue capabilities, where audio dialogues are a direct exchange of spoken language between LALMs and humans. Recent advances, such as GPT-4o, have enabled LALMs in back-and-forth audio dialogues with humans. This progression not only underscores the potential of LALMs but also broadens their applicability across a wide range of practical scenarios supported by audio dialogues. However, given these advancements, a comprehensive benchmark to evaluate the performance of LALMs in the open-ended audio dialogue understanding remains absent currently. To address this gap, we propose an Audio Dialogue Understanding Benchmark (ADU-Bench), which consists of 4 benchmark datasets. They assess the open-ended audio dialogue ability for LALMs in 3 general scenarios, 12 skills, 9 multilingual languages, and 4 categories of ambiguity handling. Notably, we firstly propose the evaluation of ambiguity handling in audio dialogues that expresses different intentions beyond the same literal meaning of sentences, e.g., “Really!?” with different intonations. In summary, ADU-Bench includes over 20,000 open-ended audio dialogues for the assessment of LALMs. Through extensive experiments conducted on 13 LALMs, our analysis reveals that there is still considerable room for improvement in the audio dialogue understanding abilities of existing LALMs. In particular, they struggle with mathematical symbols and formulas, understanding human behavior such as roleplay, comprehending multiple languages, and handling audio dialogue ambiguities from different phonetic elements, such as intonations, pause positions, and homophones.
大型音频语言模型(LALMs)已经解锁了音频对话能力,其中音频对话是LALMs与人类之间口头语言的直接交流。最近的进展,如GPT-4o,已经使LALMs能够进行与人类之间的来回音频对话。这一进展不仅突出了LALMs的潜力,也扩大了其在受音频对话支持的各种实际场景中的应用范围。然而,考虑到这些进展,目前仍缺乏一个全面基准来评估LALMs在开放音频对话中的表现。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了音频对话理解基准(ADU-Bench),它由4个基准数据集组成。这些数据集评估LALMs在3个一般场景、12项技能、9种多语言以及4类歧义处理中的开放式音频对话能力。值得注意的是,我们首次提出音频对话中歧义处理的评估,这涉及到句子相同字面意义下不同意图的表达,例如带有不同音调的“真的吗!?”总而言之,ADU-Bench包含超过20000个开放式音频对话,用于评估LALMs。通过对13个LALM进行的广泛实验,我们的分析表明,现有LALM的音频对话理解能力仍有很大提升空间。特别地,他们在处理数学符号和公式、理解人类行为(如角色扮演)、理解多种语言以及处理来自不同语音元素的音频对话歧义(如音调、停顿位置和同音字)方面遇到了困难。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型音频语言模型(LALMs)已经解锁了音频对话能力,可以实现与人类的直接语音交流。尽管GPT-4o等最新进展为LALMs带来了双向音频对话的能力,但在开放音频对话理解方面仍缺乏全面的评估基准。为解决这一空白,我们提出了音频对话理解基准(ADU-Bench),包含四个基准数据集,涵盖三种通用场景、十二项技能、九种多语言以及四类歧义处理。尤其是首次提出在音频对话中评估歧义处理的能力,如句子字面意义之外的意图表达,如带有不同语调的“真的吗?”。总之,ADU-Bench包含超过两万次的开放式音频对话,用于评估LALMs。实验显示,现有LALMs在音频对话理解能力方面仍有较大提升空间,尤其在理解数学符号和公式、角色行为、多语言以及处理由语音特征产生的歧义等方面存在挑战。
Key Takeaways
- 大型音频语言模型(LALMs)已经支持音频对话能力,能够实现与人类的直接语音交流。
- 目前缺乏评估LALMs在开放音频对话理解方面的全面基准。
- 提出了音频对话理解基准(ADU-Bench),包含四个基准数据集,用于全面评估LALMs的能力。
- ADU-Bench涵盖了多种场景、技能、语言和歧义处理类型。
- 第一次在音频对话中提出了对歧义处理的评估,包括不同语调、停顿位置和同音字等语音特征产生的歧义。
- LALMs在音频对话理解能力方面仍有较大提升空间,特别是在处理数学符号和公式、角色行为理解、多语言以及处理由语音特征产生的歧义等方面存在挑战。
点此查看论文截图

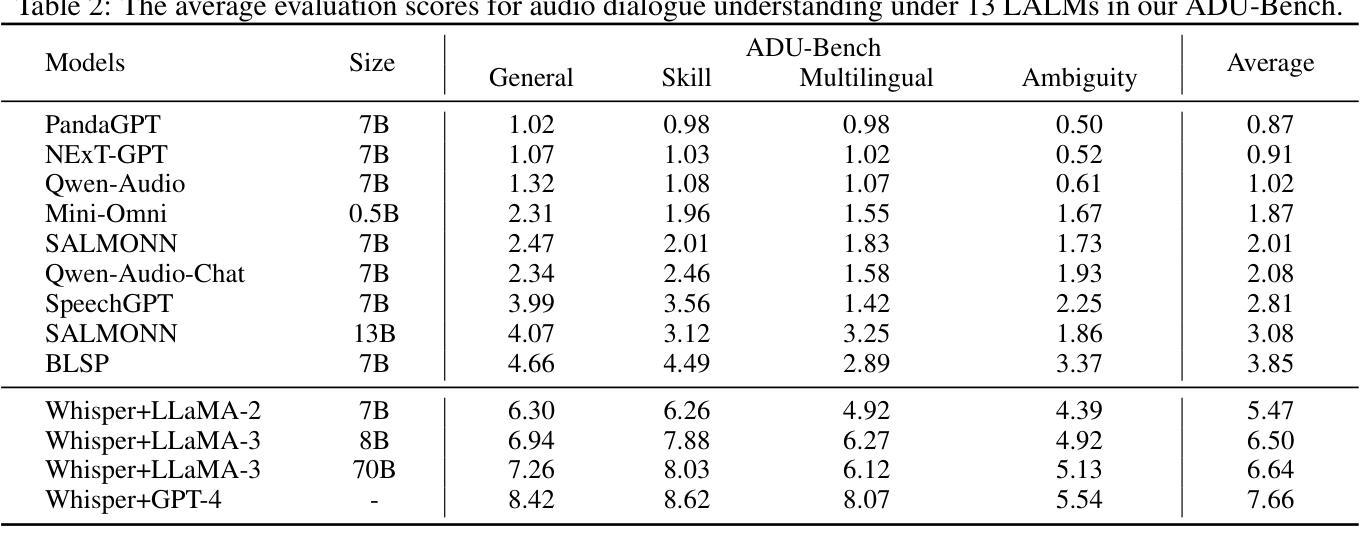
DEMO: Reframing Dialogue Interaction with Fine-grained Element Modeling
Authors:Minzheng Wang, Xinghua Zhang, Kun Chen, Nan Xu, Haiyang Yu, Fei Huang, Wenji Mao, Yongbin Li
Large language models (LLMs) have made dialogue one of the central modes of human-machine interaction, leading to the accumulation of vast amounts of conversation logs and increasing demand for dialogue generation. A conversational life-cycle spans from the Prelude through the Interlocution to the Epilogue, encompassing various elements. Despite the existence of numerous dialogue-related studies, there is a lack of benchmarks that encompass comprehensive dialogue elements, hindering precise modeling and systematic evaluation. To bridge this gap, we introduce an innovative research task $\textbf{D}$ialogue $\textbf{E}$lement $\textbf{MO}$deling, including $\textit{Element Awareness}$ and $\textit{Dialogue Agent Interaction}$, and propose a novel benchmark, $\textbf{DEMO}$, designed for a comprehensive dialogue modeling and assessment. Inspired by imitation learning, we further build the agent which possesses the adept ability to model dialogue elements based on the DEMO benchmark. Extensive experiments indicate that existing LLMs still exhibit considerable potential for enhancement, and our DEMO agent has superior performance in both in-domain and out-of-domain tasks.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经将对话作为人机交互的中心模式之一,这导致了大量对话日志的积累和对对话生成需求的增加。对话生命周期从序曲到对话再到尾章,包含各种元素。尽管存在许多与对话相关的研究,但缺乏包含全面对话元素的基准测试,阻碍了精确建模和系统评估。为了填补这一空白,我们引入了一项创新的研究任务,即“对话元素建模”,包括“元素意识”和“对话代理交互”,并提出了一个用于全面对话建模和评估的新基准测试,即“DEMO”。受到模仿学习的启发,我们进一步构建了基于DEMO基准的具有熟练建模对话元素能力的代理。大量实验表明,现有的大型语言模型仍有很大的提升潜力,我们的DEMO代理在域内和域外任务中都表现出卓越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF We release the code and data at https://github.com/MozerWang/DEMO
总结
大型语言模型(LLMs)使对话成为人机交互的核心模式之一,产生了大量的对话日志和对对话生成的需求。对话生命周期包括序曲、对话和尾奏等多个元素。尽管存在许多与对话相关的研究,但仍缺乏包含全面对话元素的基准测试,阻碍了精确建模和系统评估。为了弥补这一差距,我们引入了一项创新的研究任务“对话元素建模”,包括“元素意识”和“对话代理交互”,并提出了一个新的基准测试“DEMO”,用于全面的对话建模和评估。受模仿学习的启发,我们进一步构建了能够基于DEMO基准测试熟练建模对话元素的代理。大量实验表明,现有的大型语言模型仍有很大的提升潜力,我们的DEMO代理在域内和跨域任务中都表现出卓越的性能。
关键见解
- 大型语言模型已成为对话生成的核心技术,产生了大量的对话日志。
- 对话生命周期包括多个阶段,从序曲到对话再到尾奏。
- 目前缺乏包含全面对话元素的基准测试,阻碍了精确建模和系统评估。
- 引入了新的研究任务“对话元素建模”,包括元素意识和对话代理交互。
- 提出了DEMO基准测试,用于全面的对话建模和评估。
- 基于模仿学习,构建了能熟练建模对话元素的代理。
- 实验显示现有大型语言模型仍有提升潜力,DEMO代理在多项任务中表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图


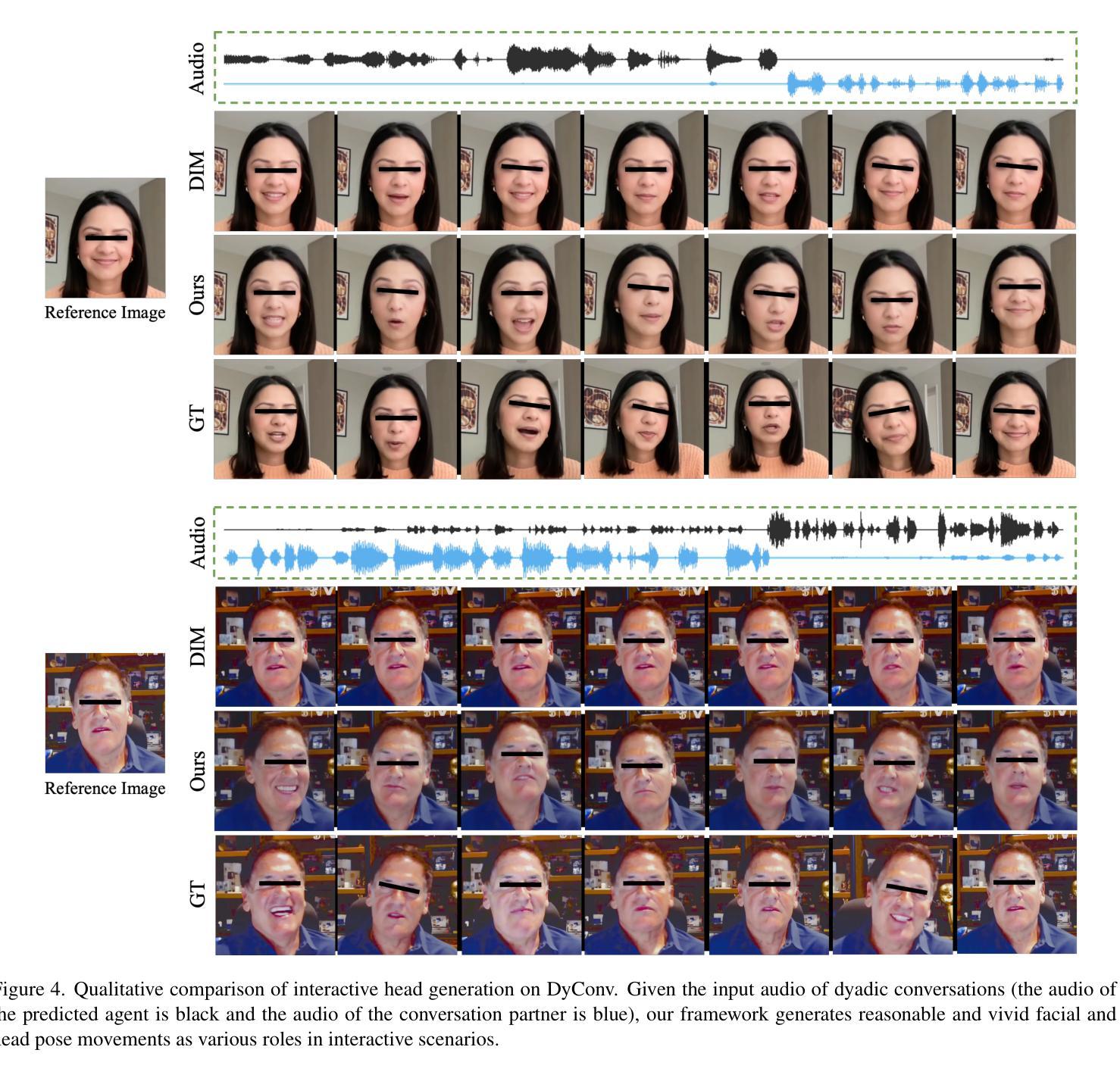
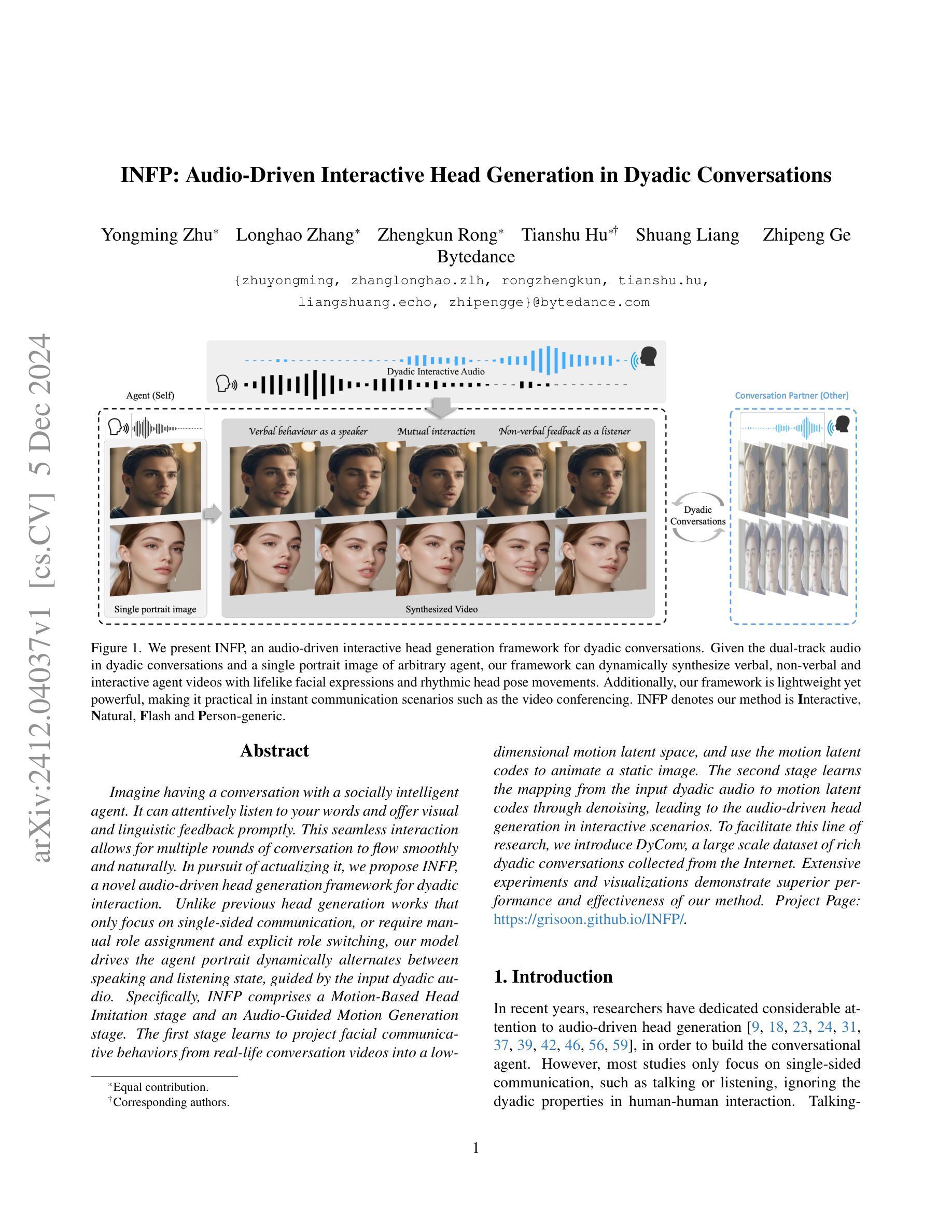
INFP: Audio-Driven Interactive Head Generation in Dyadic Conversations
Authors:Yongming Zhu, Longhao Zhang, Zhengkun Rong, Tianshu Hu, Shuang Liang, Zhipeng Ge
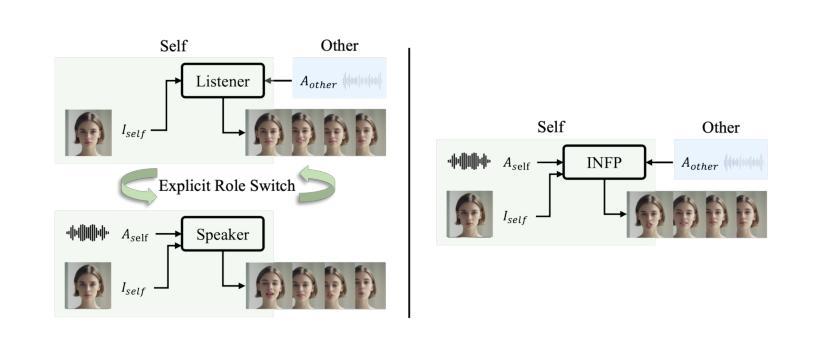
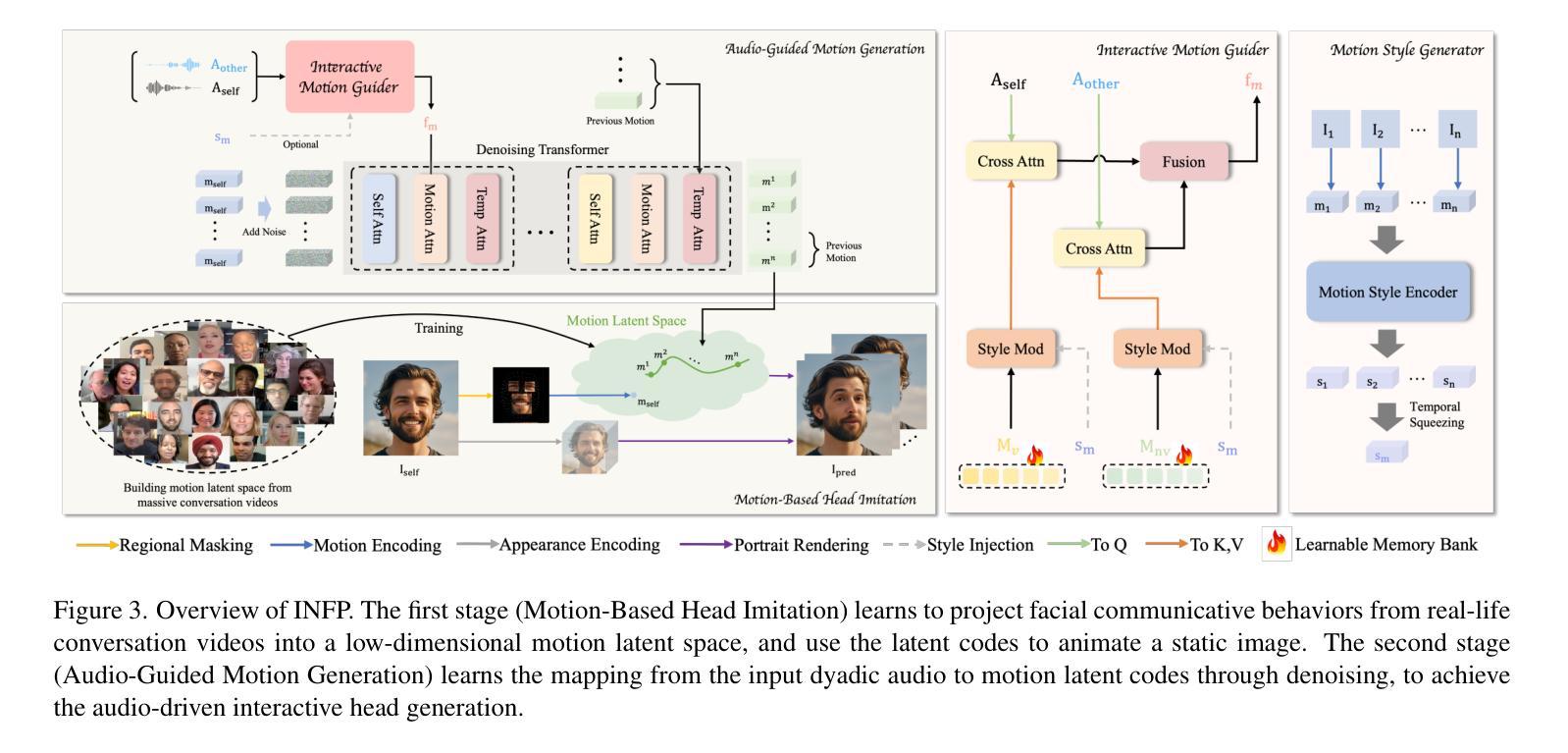
Imagine having a conversation with a socially intelligent agent. It can attentively listen to your words and offer visual and linguistic feedback promptly. This seamless interaction allows for multiple rounds of conversation to flow smoothly and naturally. In pursuit of actualizing it, we propose INFP, a novel audio-driven head generation framework for dyadic interaction. Unlike previous head generation works that only focus on single-sided communication, or require manual role assignment and explicit role switching, our model drives the agent portrait dynamically alternates between speaking and listening state, guided by the input dyadic audio. Specifically, INFP comprises a Motion-Based Head Imitation stage and an Audio-Guided Motion Generation stage. The first stage learns to project facial communicative behaviors from real-life conversation videos into a low-dimensional motion latent space, and use the motion latent codes to animate a static image. The second stage learns the mapping from the input dyadic audio to motion latent codes through denoising, leading to the audio-driven head generation in interactive scenarios. To facilitate this line of research, we introduce DyConv, a large scale dataset of rich dyadic conversations collected from the Internet. Extensive experiments and visualizations demonstrate superior performance and effectiveness of our method. Project Page: https://grisoon.github.io/INFP/.
想象一下与一个具有社会智能的代理进行对话。它能够专注地倾听你的话语,并提供及时的视觉和语言反馈。这种无缝互动允许多轮对话流畅自然地展开。为了将其实现,我们提出了INFP,这是一种新型音频驱动的头部位姿生成框架,用于二元互动。不同于之前只关注单方面沟通的头部生成工作,或需要手动分配角色和明确的角色切换,我们的模型驱动代理头像在说话和倾听状态之间动态切换,由输入的双声音频引导。具体来说,INFP包括基于运动的头部模仿阶段和音频引导的运动生成阶段。第一阶段学习将来自真实对话视频的面部交流行为投影到一个低维运动潜在空间,并使用运动潜在代码来驱动静态图像。第二阶段通过去噪学习将输入的双声音频映射到运动潜在代码,从而实现交互场景中的音频驱动头部生成。为了推动这一领域的研究,我们引入了DyConv,这是一个从互联网收集的大规模丰富的二元对话数据集。大量的实验和可视化展示了我们方法的优越性能和效果。项目页面:https://grisoon.github.io/INFP/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于对话场景构建的智能交互代理形象展示技术。该技术利用音频驱动头部生成框架实现双方互动中的对话模拟。采用基于动作头部模仿阶段和音频引导动作生成阶段的方式,完成代理角色间的自然交流模拟。技术公开演示页为:[链接地址]。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了基于对话场景的智能交互代理技术。
- 提出了一种新颖的音频驱动头部生成框架INFP,用于实现双方互动中的对话模拟。
- INFP模型能自动驱动代理角色在对话中交替进行发言和聆听状态,无需手动角色分配和切换。
- INFP包括两个主要阶段:基于动作头部模仿阶段和音频引导动作生成阶段。
- 第一阶段学习从现实对话视频中提取面部交流行为,并将其投影到低维度动作潜在空间,并使用动作潜在代码驱动静态图像进行动画生成。
- 第二阶段通过降噪学习将输入的双人对话音频映射到动作潜在代码,实现音频驱动的头部生成在交互场景中的应用。
点此查看论文截图

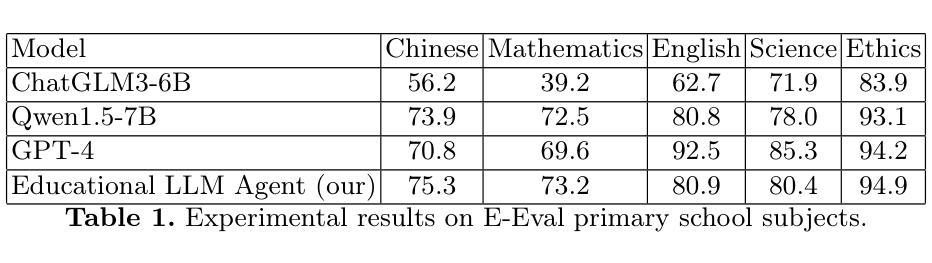
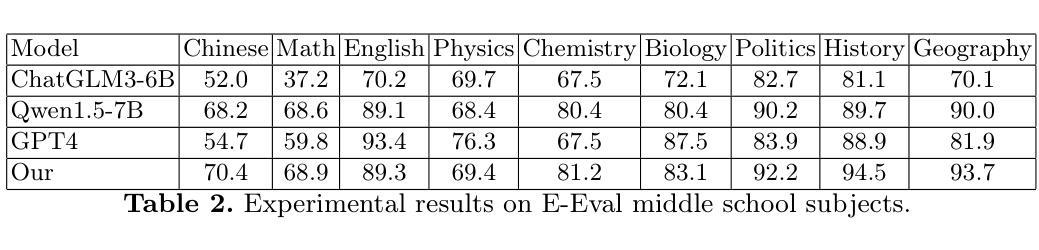
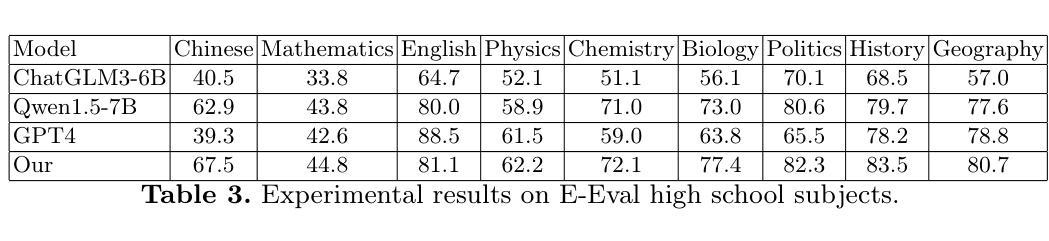
Educational-Psychological Dialogue Robot Based on Multi-Agent Collaboration
Authors:Shiwen Ni, Min Yang
Intelligent dialogue systems are increasingly used in modern education and psychological counseling fields, but most existing systems are limited to a single domain, cannot deal with both educational and psychological issues, and often lack accuracy and professionalism when dealing with complex issues. To address these problems, this paper proposes an intelligent dialog system that combines educational and psychological counseling functions. The system consists of multiple AI agent, including security detection agent, intent identification agent, educational LLM agent, and psychological LLM agent, which work in concert to ensure the provision of accurate educational knowledge Q&A and psychological support services. Specifically, the system recognizes user-input intentions through an intention classification model and invokes a retrieval-enhanced educational grand model and a psychological grand model fine-tuned with psychological data in order to provide professional educational advice and psychological support.
智能对话系统在现代教育和心理咨询领域的应用越来越广泛,但大多数现有系统仅限于单一领域,无法同时处理教育和心理问题,并且在处理复杂问题时准确性和专业性常常不足。为解决这些问题,本文提出了一种结合教育和心理咨询功能的智能对话系统。该系统包含多个AI代理,包括安全检测代理、意图识别代理、教育LLM代理和心理LLM代理,它们协同工作,以确保提供准确的教育知识问答和心理咨询服务。具体来说,该系统通过意图分类模型识别用户输入的意图,并调用经过教育大数据增强和用心理数据微调的教育精细模型和心理咨询精细模型,以提供专业的教育建议和心理咨询支持。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种结合教育与心理咨询功能的智能对话系统,该系统由多个AI代理组成,包括安全检测代理、意图识别代理、教育LLM代理和心理LLM代理,能够准确提供教育知识问答和心理咨询支持服务。
Key Takeaways
- 智能对话系统在现代教育和心理咨询领域得到广泛应用。
- 当前大多数系统仅限于单一领域,无法同时处理教育和心理问题。
- 提出的智能对话系统结合了教育和心理咨询功能。
- 系统包含多个AI代理,如安全检测、意图识别、教育LLM和心理LLM代理。
- 系统通过意图分类模型识别用户输入意图。
- 系统采用检索增强教育大模型和经过心理数据微调的心理大模型,以提供专业教育建议和心理咨询支持。
点此查看论文截图

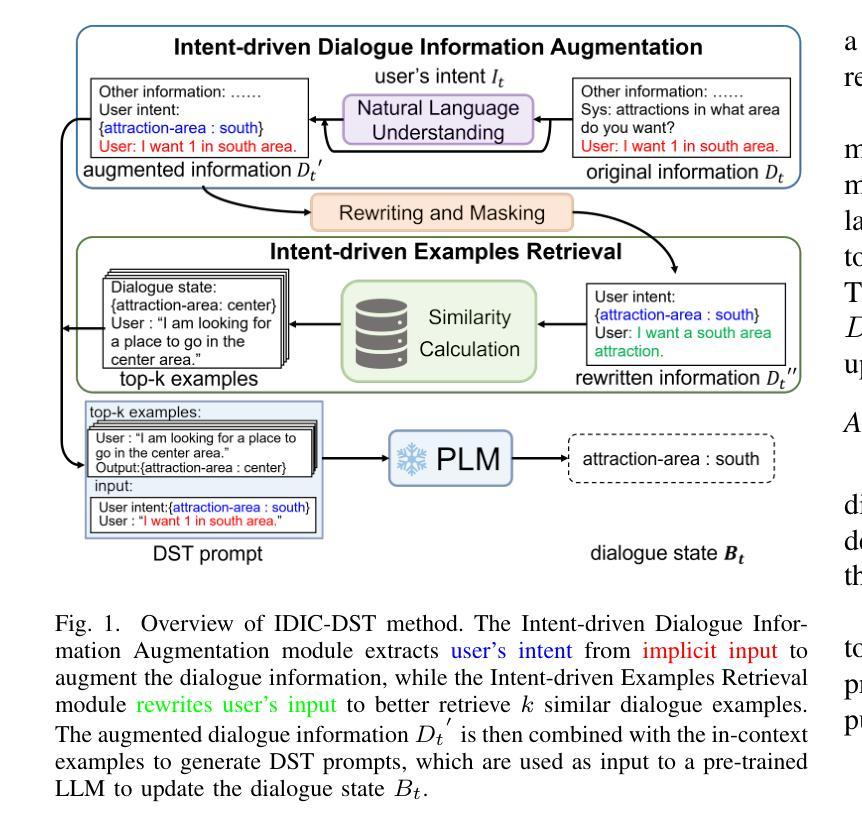
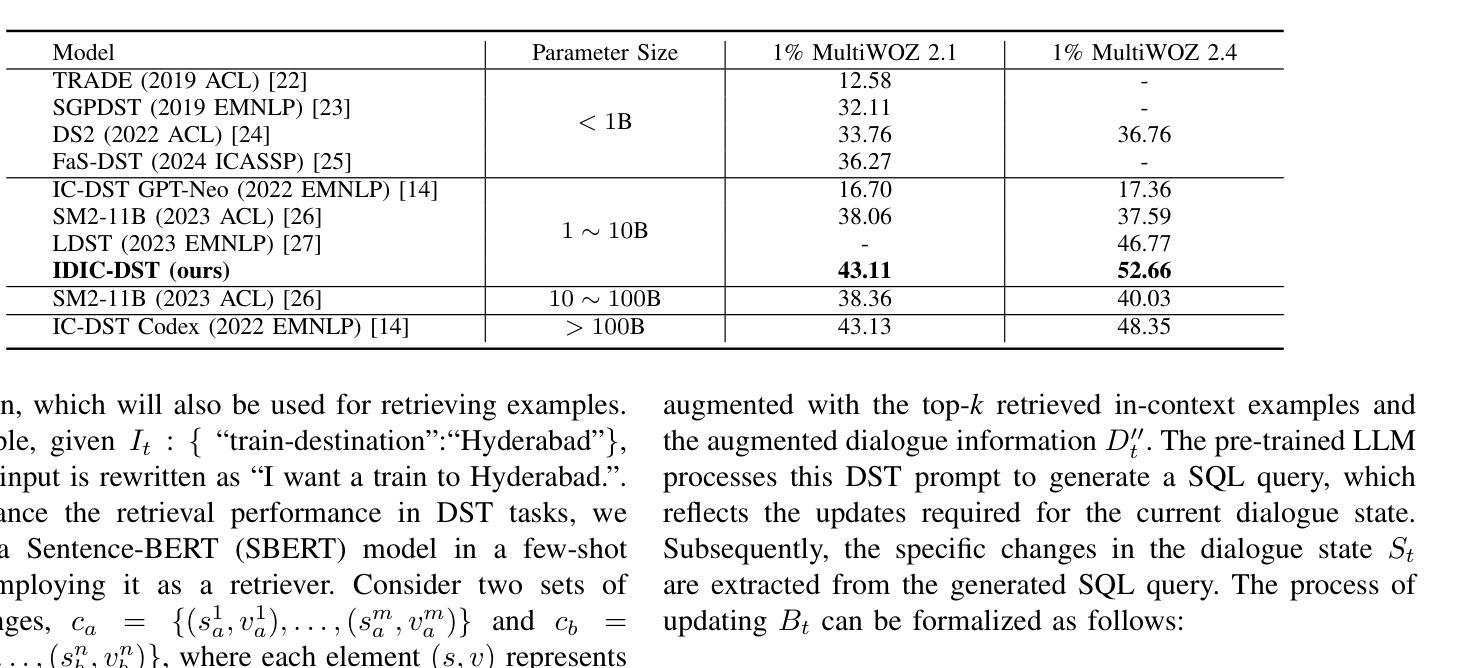
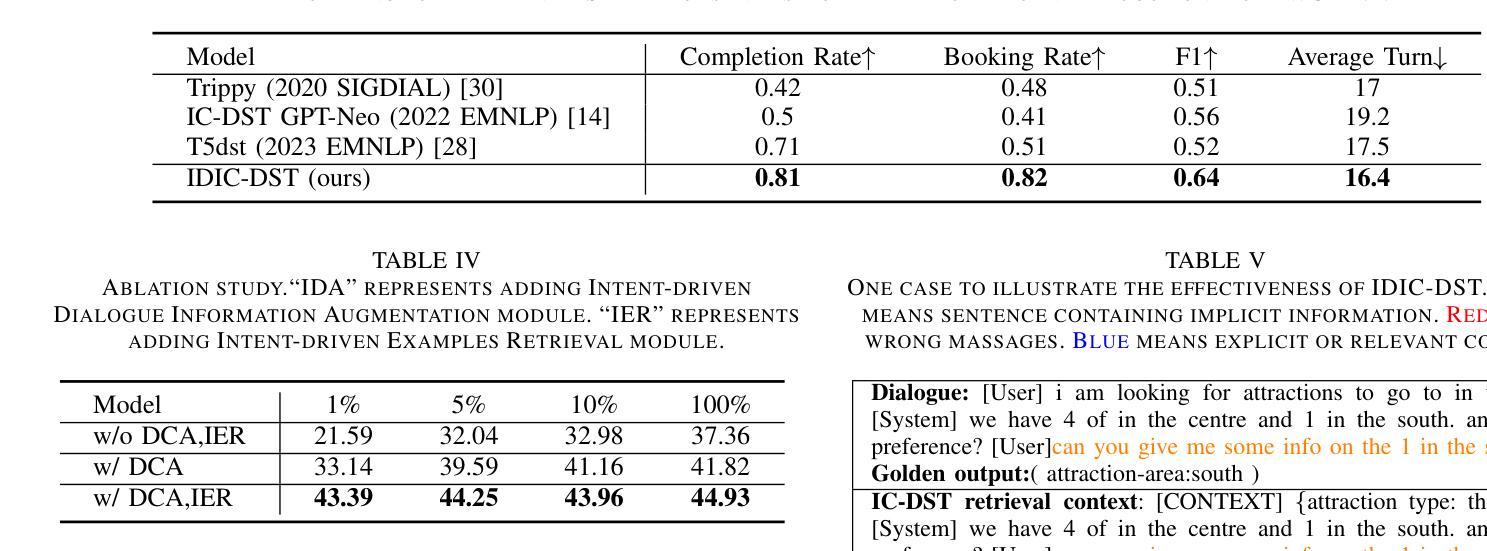
Intent-driven In-context Learning for Few-shot Dialogue State Tracking
Authors:Zihao Yi, Zhe Xu, Ying Shen
Dialogue state tracking (DST) plays an essential role in task-oriented dialogue systems. However, user’s input may contain implicit information, posing significant challenges for DST tasks. Additionally, DST data includes complex information, which not only contains a large amount of noise unrelated to the current turn, but also makes constructing DST datasets expensive. To address these challenges, we introduce Intent-driven In-context Learning for Few-shot DST (IDIC-DST). By extracting user’s intent, we propose an Intent-driven Dialogue Information Augmentation module to augment the dialogue information, which can track dialogue states more effectively. Moreover, we mask noisy information from DST data and rewrite user’s input in the Intent-driven Examples Retrieval module, where we retrieve similar examples. We then utilize a pre-trained large language model to update the dialogue state using the augmented dialogue information and examples. Experimental results demonstrate that IDIC-DST achieves state-of-the-art performance in few-shot settings on MultiWOZ 2.1 and MultiWOZ 2.4 datasets.
对话状态跟踪(DST)在面向任务的对话系统中扮演着至关重要的角色。然而,用户的输入可能包含隐晦的信息,给DST任务带来了极大的挑战。此外,DST数据包含复杂的信息,不仅包含大量与当前轮次无关的噪声,而且构建DST数据集的成本也很高。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了基于意图的情境内学习用于少量DST(IDIC-DST)。通过提取用户的意图,我们提出了基于意图的对话信息增强模块,以增强对话信息,从而更有效地跟踪对话状态。此外,我们从DST数据中屏蔽了嘈杂的信息,并在基于意图的示例检索模块中重写了用户的输入,从中检索相似的示例。然后,我们利用预训练的的大型语言模型,使用增强后的对话信息和示例来更新对话状态。实验结果表明,IDIC-DST在MultiWOZ 2.1和MultiWOZ 2.4数据集上的少量设置上达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
总结
对话状态跟踪(DST)在面向任务的对话系统中扮演关键角色。然而,用户的输入可能包含隐式信息,给DST任务带来挑战。此外,DST数据包含复杂信息,不仅包含大量与当前对话无关的噪声,而且构建DST数据集的成本很高。为解决这些挑战,我们引入了基于意图的上下文学习方法(IDIC-DST)。通过提取用户意图,我们提出了基于意图的对话信息增强模块,以增强对话信息,更有效地跟踪对话状态。此外,我们从DST数据中屏蔽了噪音信息,并在基于意图的示例检索模块中重写了用户输入,从中检索了类似的示例。然后,我们使用预训练的 大型语言模型来利用增强的对话信息和示例更新对话状态。实验结果表明,IDIC-DST在MultiWOZ 2.1和MultiWOZ 2.4数据集上的小样本设置上取得了最先进的性能。
关键见解
- 对话状态跟踪(DST)在任务导向型对话系统中至关重要。
- 用户的输入可能包含隐式信息,对DST任务构成挑战。
- DST数据包含复杂信息和噪音,增加了构建数据集的成本。
- IDIC-DST方法通过基于意图的对话信息增强和示例检索来解决这些挑战。
- IDIC-DST能更有效地跟踪对话状态。
- 实验表明,IDIC-DST在MultiWOZ 2.1和MultiWOZ 2.4数据集上的小样本设置达到了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

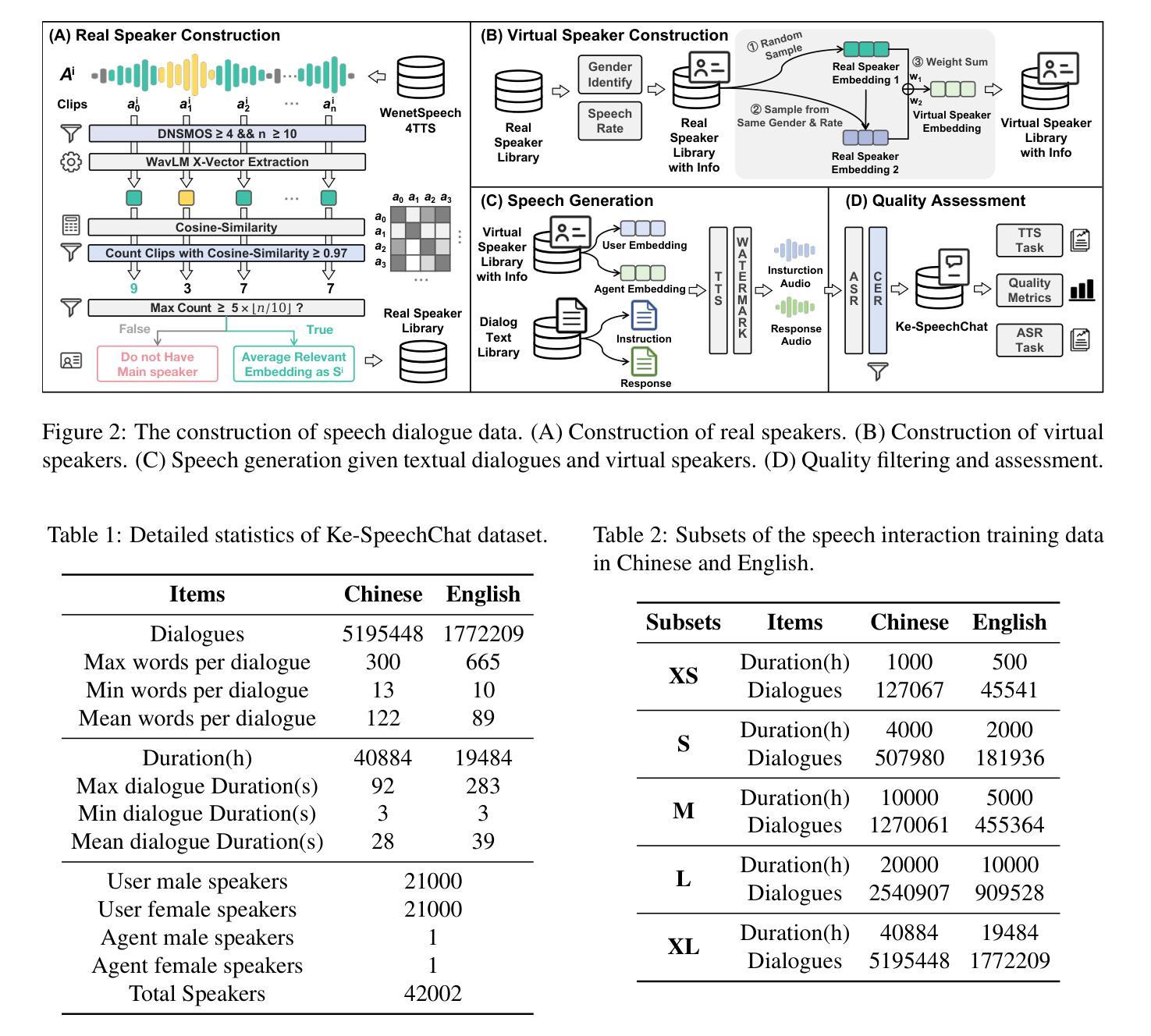
Advancing Speech Language Models by Scaling Supervised Fine-Tuning with Over 60,000 Hours of Synthetic Speech Dialogue Data
Authors:Shuaijiang Zhao, Tingwei Guo, Bajian Xiang, Tongtang Wan, Qiang Niu, Wei Zou, Xiangang Li
The GPT-4o represents a significant milestone in enabling real-time interaction with large language models (LLMs) through speech, its remarkable low latency and high fluency not only capture attention but also stimulate research interest in the field. This real-time speech interaction is particularly valuable in scenarios requiring rapid feedback and immediate responses, dramatically enhancing user experience. However, there is a notable lack of research focused on real-time large speech language models, particularly for Chinese. In this work, we present KE-Omni, a seamless large speech language model built upon Ke-SpeechChat, a large-scale high-quality synthetic speech interaction dataset consisting of 7 million Chinese and English conversations, featuring 42,002 speakers, and totaling over 60,000 hours, This contributes significantly to the advancement of research and development in this field. The demos can be accessed at \url{https://huggingface.co/spaces/KE-Team/KE-Omni}.
GPT-4o是实时通过语音与大型语言模型(LLM)交互的一个重要里程碑。其显著的低延迟和高流畅性不仅引起了关注,还刺激了该领域的研究兴趣。这种实时语音交互在需要快速反馈和即时响应的场景中尤其有价值,能极大地提升用户体验。然而,关于实时大型语音语言模型的研究相对较少,尤其是针对中文的研究。在此工作中,我们推出了KE-Omni,这是一款无缝大型语音语言模型,基于Ke-SpeechChat构建。Ke-SpeechChat是一个大规模高质量合成语音交互数据集,包含700万中英文字符的对话内容,涵盖42,002位发言人,总计超过6万小时,极大地推动了该领域的研究与发展。演示地址:[https://huggingface.co/spaces/KE-Team/KE-Omni]。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF KE-Omni, Ke-SpeechChat
Summary
GPT-4o实现了通过语音与大型语言模型(LLM)的实时交互,其低延迟和高流畅性引人注目并激发了研究兴趣。特别是在需要快速反馈和即时响应的场景中,这种实时语音交互极大地提升了用户体验。KE-Omni是一个基于Ke-SpeechChat数据集构建的无缝大型语音语言模型,该数据集包含700万中英文对话,涵盖42,002位发言者的超过6万小时的数据。这极大地推动了该领域的研究与发展。
Key Takeaways
- GPT-4o实现了大型语言模型的实时语音交互。
- GPT-4o具有低延迟和高流畅性特点。
- 实时语音交互在需要快速反馈和响应的场景中非常有价值。
- KE-Omni是一个无缝的大型语音语言模型。
- KE-Omni是基于Ke-SpeechChat数据集构建的,包含700万中英文对话。
- Ke-SpeechChat数据集涵盖大量发言者和小时数,推动相关领域研究与发展。
点此查看论文截图

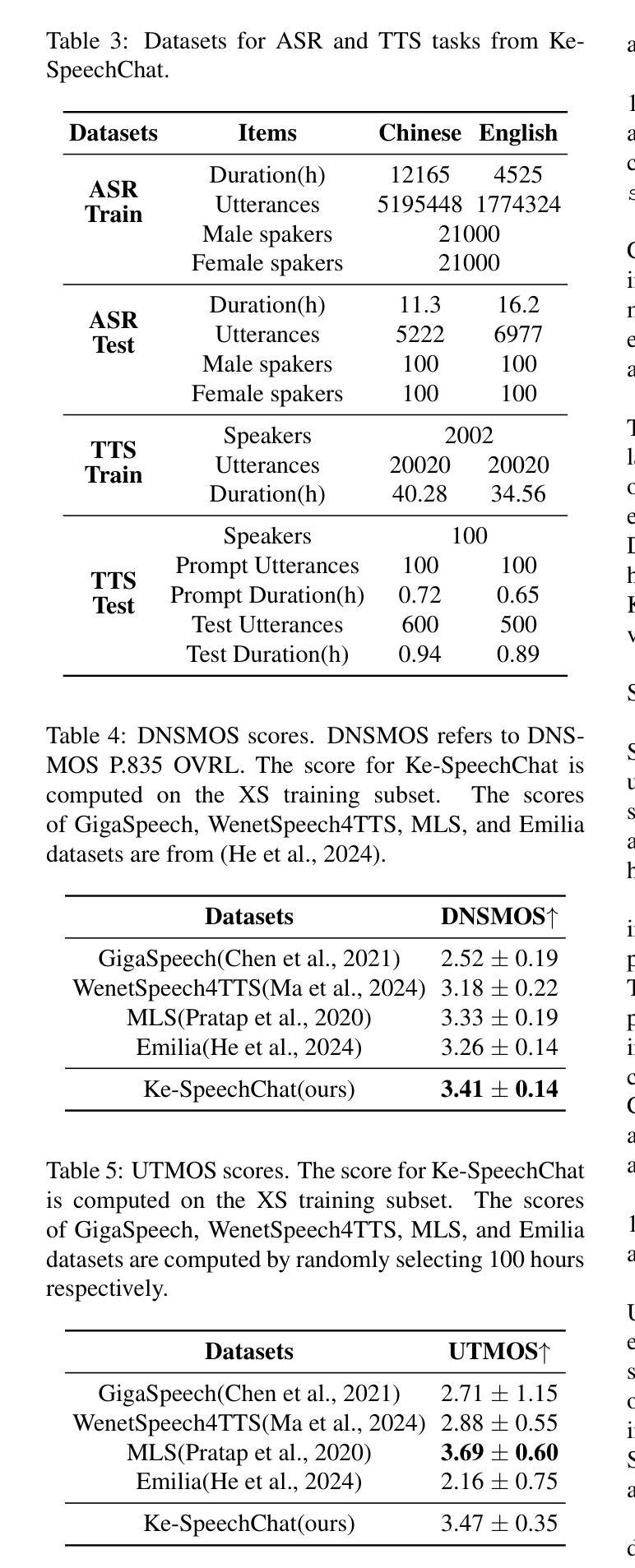
Listening for Expert Identified Linguistic Features: Assessment of Audio Deepfake Discernment among Undergraduate Students
Authors:Noshaba N. Bhalli, Nehal Naqvi, Chloe Evered, Christine Mallinson, Vandana P. Janeja
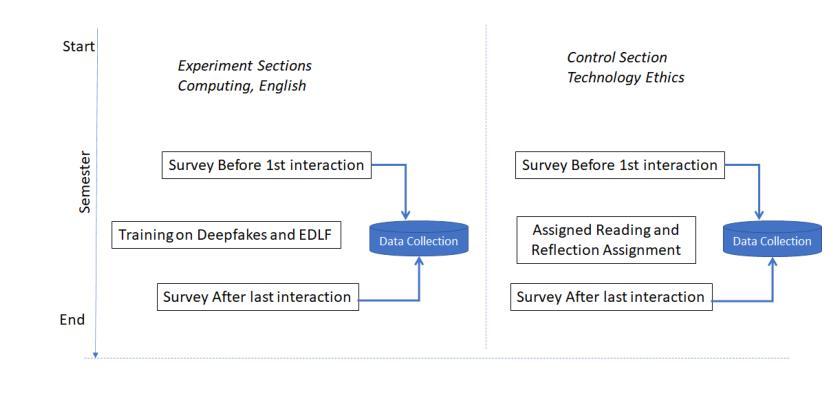
This paper evaluates the impact of training undergraduate students to improve their audio deepfake discernment ability by listening for expert-defined linguistic features. Such features have been shown to improve performance of AI algorithms; here, we ascertain whether this improvement in AI algorithms also translates to improvement of the perceptual awareness and discernment ability of listeners. With humans as the weakest link in any cybersecurity solution, we propose that listener discernment is a key factor for improving trustworthiness of audio content. In this study we determine whether training that familiarizes listeners with English language variation can improve their abilities to discern audio deepfakes. We focus on undergraduate students, as this demographic group is constantly exposed to social media and the potential for deception and misinformation online. To the best of our knowledge, our work is the first study to uniquely address English audio deepfake discernment through such techniques. Our research goes beyond informational training by introducing targeted linguistic cues to listeners as a deepfake discernment mechanism, via a training module. In a pre-/post- experimental design, we evaluated the impact of the training across 264 students as a representative cross section of all students at the University of Maryland, Baltimore County, and across experimental and control sections. Findings show that the experimental group showed a statistically significant decrease in their unsurety when evaluating audio clips and an improvement in their ability to correctly identify clips they were initially unsure about. While results are promising, future research will explore more robust and comprehensive trainings for greater impact.
本文旨在评估通过听取专家定义的语言特征来训练本科生,提高其辨识音频深度伪造内容的能力。这些语言特征已被证明可以提高AI算法的性能;在这里,我们确定AI算法的改进是否也转化为听众感知意识和辨识能力的改进。鉴于人类是任何网络安全解决方案中最薄弱的环节,我们提出听众的辨识能力是提高音频内容可信度的关键因素。在这项研究中,我们确定通过让听众熟悉英语语言变化来培训是否可以提高他们辨识音频深度伪造内容的能力。我们关注本科生,因为这个群体不断接触社交媒体和在线欺骗和误导信息的可能性。据我们所知,我们的工作是通过这些技术独特解决英语音频深度伪造辨识的首个研究。我们的研究通过引入有针对性的语言线索作为深度伪造辨识机制来超越信息培训,通过培训模块向听众介绍。在预实验和实验设计中,我们评估了培训对马里兰大学巴尔的摩县所有学生的代表样本以及实验和对照组共264名学生的影响。研究结果表明,实验组在评估音频剪辑时的不确定性显著降低,并且在识别他们最初不确定的剪辑片段时能力有所提高。虽然结果令人鼓舞,但未来的研究将探索更稳健和全面的培训以产生更大的影响。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本论文探索了训练本科生提升辨识音频深度伪造能力的方法,重点是通过听取专家定义的语音特征进行训练。研究通过让人工智能算法与人类听众的感知辨识能力进行比较,确定AI算法的改进是否也能提升听众的辨识能力。鉴于人类是任何网络安全解决方案中的薄弱环节,因此听众的辨识能力是提升音频内容可信度的关键因素。本研究聚焦本科生群体,针对他们熟悉英语语音变化进行培训,以提升他们辨识音频深度伪造的能力,因为这一群体频繁接触社交媒体和在线欺骗与误导信息。据我们所知,我们的研究首次针对此类技术采用独特的方法解决英语音频深度伪造的辨识问题。我们的研究通过引入有针对性的语言线索作为深度伪造辨识机制来超越信息培训,通过训练模块让听众掌握此种机制。我们以前期和后期实验设计评估了培训对马里兰大学巴尔的摩县校区全体学生中选取的代表性样本——共264名学生的影响。研究结果表明,实验组人员在评估音频片段时的不确定感明显降低,他们最初不确定的片段的辨识准确性也得到提升。虽然这些结果颇具前景,但未来仍需探索更稳健和全面的培训方案以产生更大的影响。
关键见解
- 研究评估了训练本科生提升音频深度伪造辨识能力的效果。
- 通过听取专家定义的语音特征进行训练,以提升听众的辨识能力。
- 研究发现AI算法的改进同样提升了人类听众的辨识能力感知。
- 人类是网络安全中的薄弱环节,因此听众的辨识能力对音频内容的信任度至关重要。
- 研究聚焦本科生群体,关注他们对英语语音变化的熟悉程度培训,以强化他们辨识音频深度伪造的能力。
- 研究是首次针对英语音频深度伪造的辨识问题进行的独特研究。
点此查看论文截图

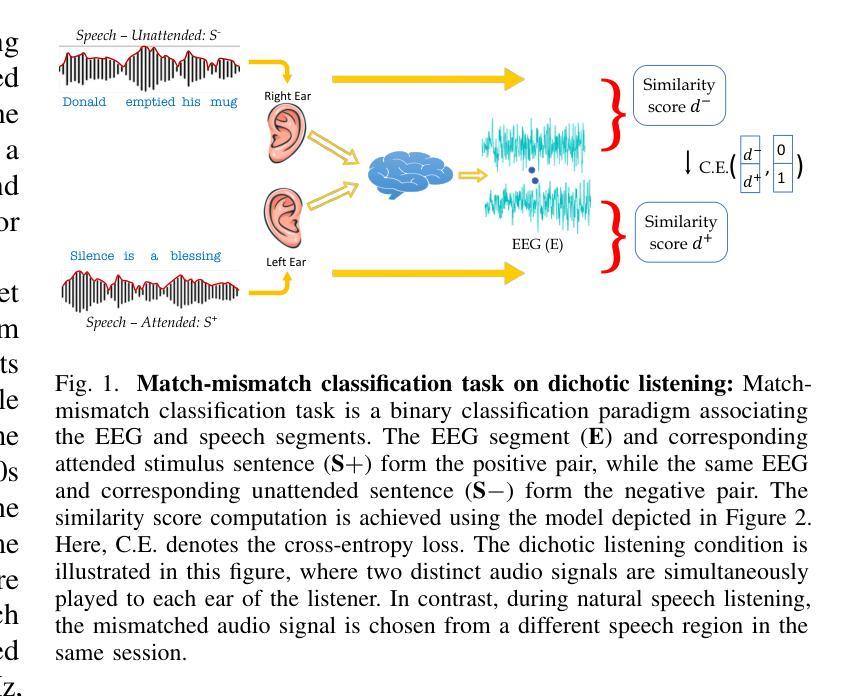
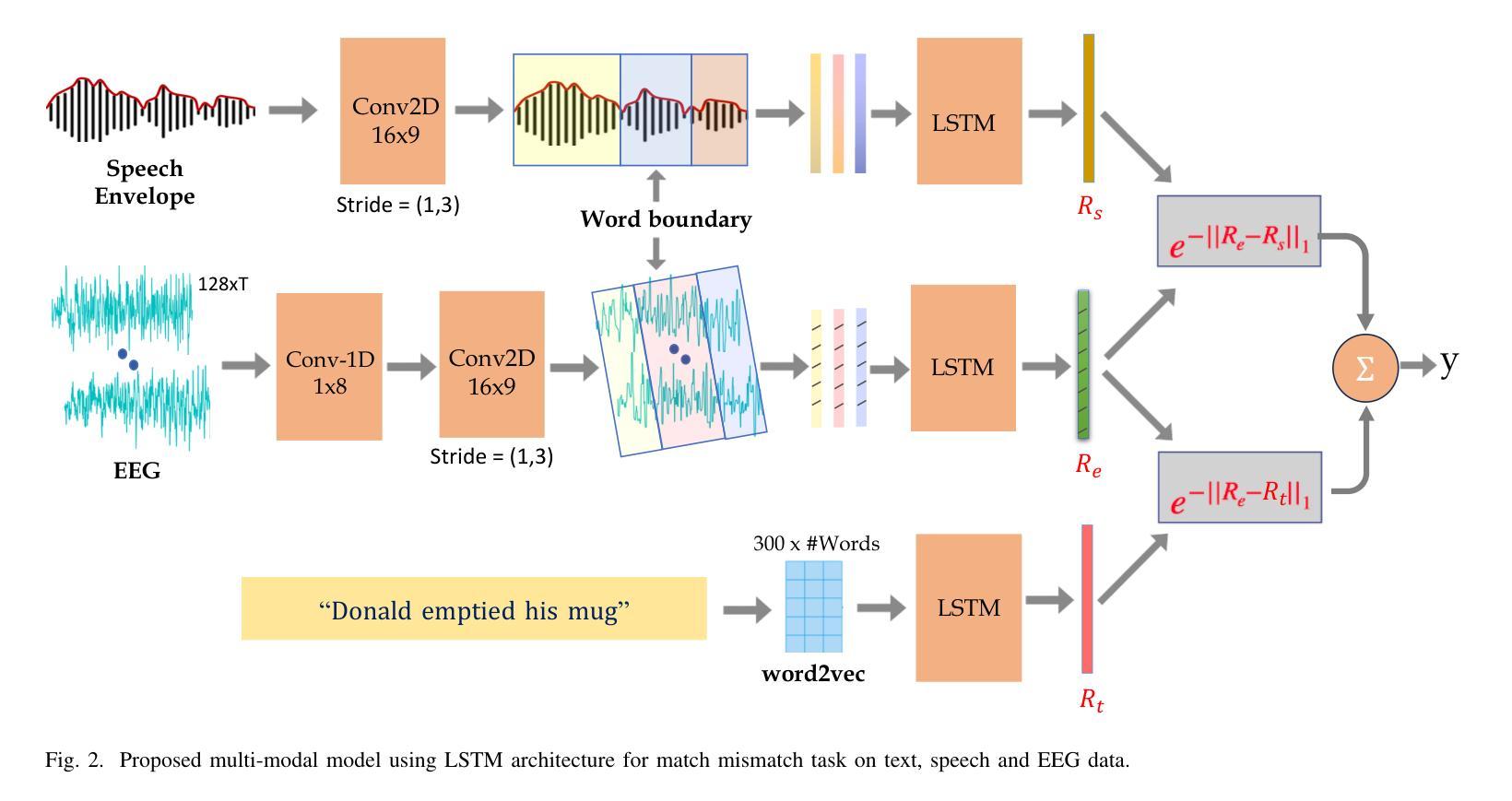
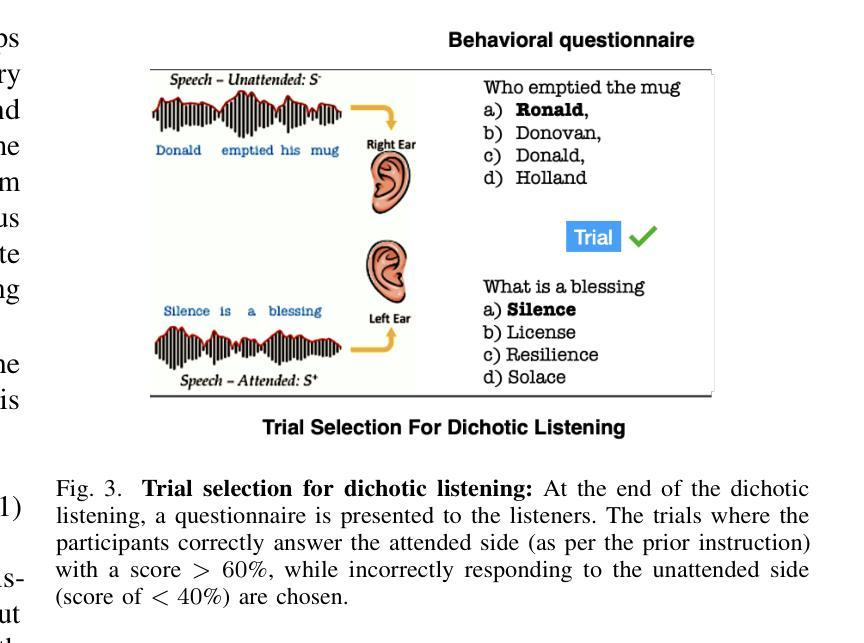
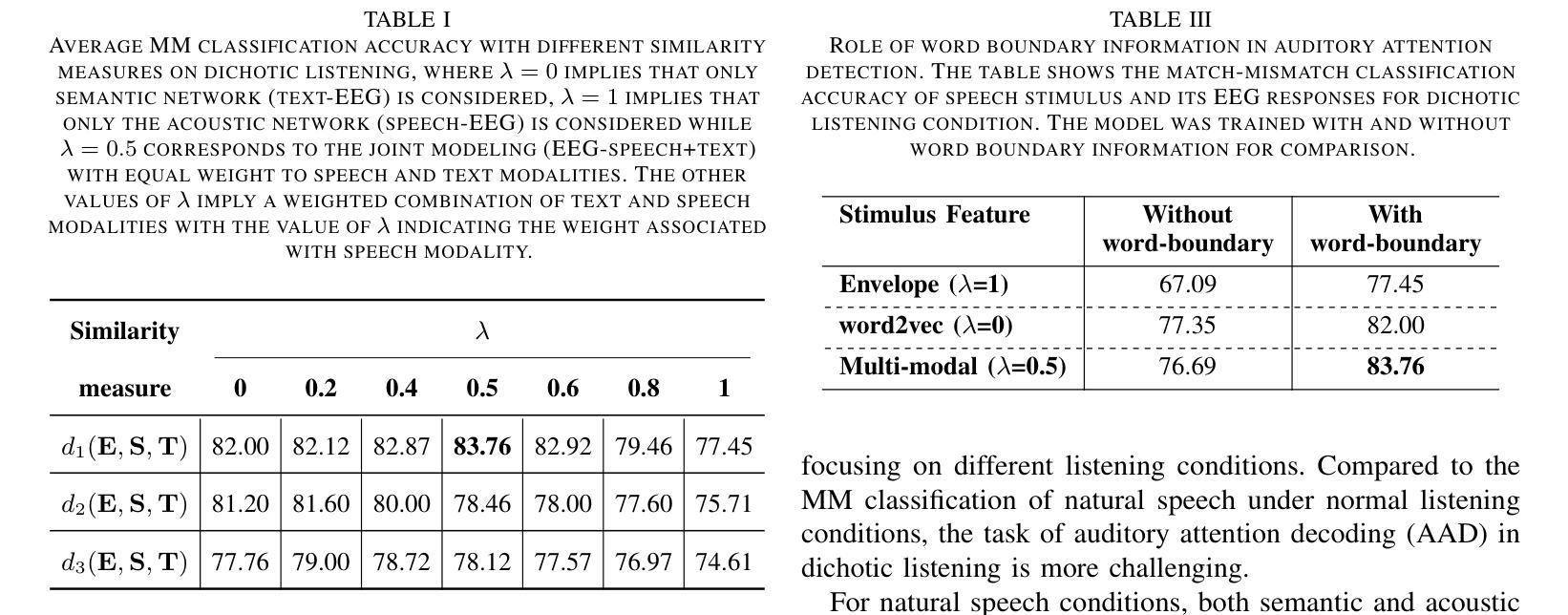
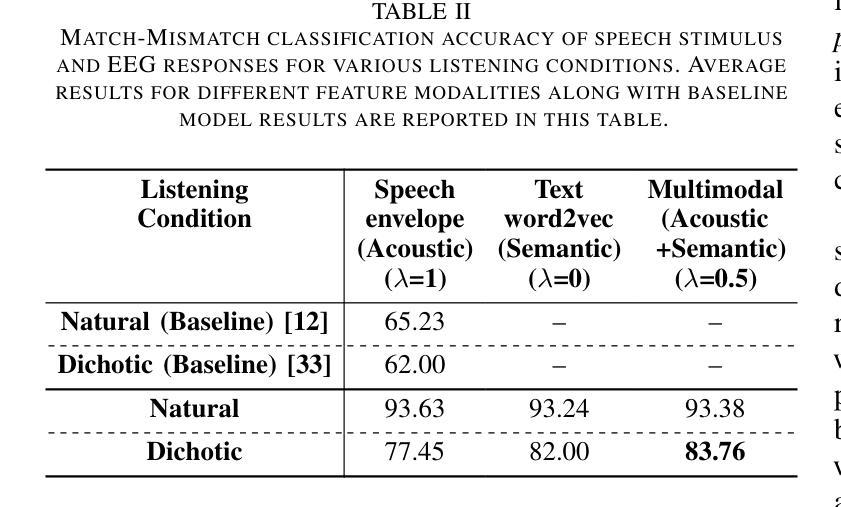
Uncovering the role of semantic and acoustic cues in normal and dichotic listening
Authors:Akshara Soman, Sai Samrat Kankanala, Sriram Ganapathy
Despite extensive research, the precise role of acoustic and semantic cues in complex speech perception tasks remains unclear. In this study, we propose a paradigm to understand the encoding of these cues in electroencephalogram (EEG) data, using match-mismatch (MM) classification task. The MM task involves determining whether the stimulus and response correspond to each other or not. We design a multi-modal sequence model, based on long short term memory (LSTM) architecture, to perform the MM task. The model is input with acoustic stimulus (derived from the speech envelope), semantic stimulus (derived from textual representations of the speech content), and neural response (derived from the EEG data). Our experiments are performed on two separate conditions, i) natural passive listening condition and, ii) an auditory attention based dichotic listening condition. Using the MM task as the analysis framework, we observe that - a) speech perception is fragmented based on word boundaries, b) acoustic and semantic cues offer similar levels of MM task performance in natural listening conditions, and c) semantic cues offer significantly improved MM classification over acoustic cues in dichotic listening task. Further, the study provides evidence of right ear advantage in dichotic listening conditions.
尽管进行了大量研究,但声音和语义线索在复杂的语音感知任务中的精确作用仍不清楚。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种基于脑电图(EEG)数据编码这些线索的理解范式,采用匹配-不匹配(MM)分类任务。MM任务涉及确定刺激与响应是否相对应。我们设计了一种基于长短期记忆(LSTM)架构的多模态序列模型,以执行MM任务。该模型的输入包括声音刺激(来源于语音包络)、语义刺激(来源于语音内容的文本表示)和神经响应(来源于EEG数据)。我们的实验是在两种不同条件下进行的,即一)自然被动聆听条件,以及二)基于听觉注意力的双耳聆听条件。以MM任务为分析框架,我们观察到:a)语音感知是基于单词边界片段化的;b)在自然聆听条件下,声音和语义线索在MM任务中的表现相似;c)在双耳聆听任务中,语义线索相对于声音线索能显著改善MM分类。此外,该研究还提供了双耳聆听条件下右耳优势的证据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 Pages, 4 Figures
Summary
本研究探讨了声学线索和语义线索在复杂语音感知任务中的编码机制。通过匹配-不匹配分类任务,研究团队设计了一种基于LSTM架构的多模式序列模型来处理声学刺激、语义刺激和神经反应。实验分为自然被动聆听和基于听觉注意力的二歧式聆听两种条件。研究发现,语音感知以单词边界为基础进行分割,在自然聆听条件下,声学线索和语义线索的匹配任务表现相似;而在二歧式聆听任务中,语义线索的匹配分类明显优于声学线索。此外,研究还证明了二歧式聆听条件下的右耳优势现象。
Key Takeaways
- 研究采用匹配-不匹配分类任务,以了解声学线索和语义线索在复杂语音感知任务中的编码。
- 设计了一种基于LSTM架构的多模式序列模型,处理声学刺激、语义刺激和神经反应。
- 实验在自然被动聆听和基于听觉注意力的二歧式聆听两种条件下进行。
- 语音感知以单词边界为基础进行分割。
- 在自然聆听条件下,声学线索和语义线索的匹配任务表现相似。
- 在二歧式聆听任务中,语义线索的匹配分类优于声学线索。
点此查看论文截图

Can Generic LLMs Help Analyze Child-adult Interactions Involving Children with Autism in Clinical Observation?
Authors:Tiantian Feng, Anfeng Xu, Rimita Lahiri, Helen Tager-Flusberg, So Hyun Kim, Somer Bishop, Catherine Lord, Shrikanth Narayanan
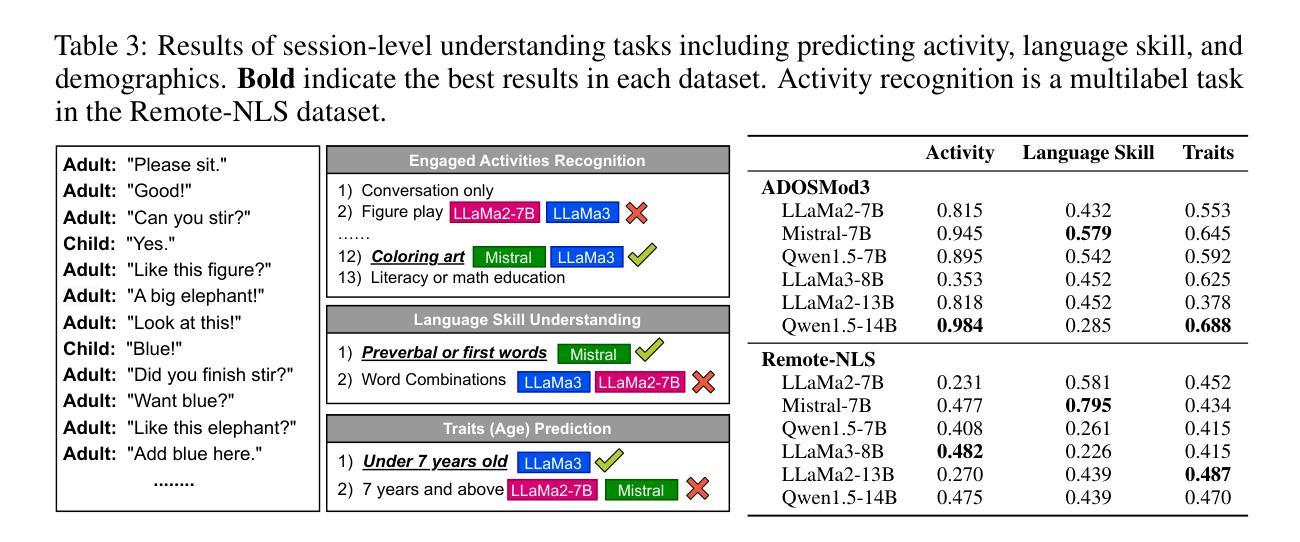
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown significant potential in understanding human communication and interaction. However, their performance in the domain of child-inclusive interactions, including in clinical settings, remains less explored. In this work, we evaluate generic LLMs’ ability to analyze child-adult dyadic interactions in a clinically relevant context involving children with ASD. Specifically, we explore LLMs in performing four tasks: classifying child-adult utterances, predicting engaged activities, recognizing language skills and understanding traits that are clinically relevant. Our evaluation shows that generic LLMs are highly capable of analyzing long and complex conversations in clinical observation sessions, often surpassing the performance of non-expert human evaluators. The results show their potential to segment interactions of interest, assist in language skills evaluation, identify engaged activities, and offer clinical-relevant context for assessments.
大型语言模型(LLM)在理解人类沟通和交互方面表现出了显著潜力。然而,它们在儿童交互领域,包括在临床环境中的表现,仍然知之甚少。在这项工作中,我们评估了通用LLM分析患有自闭症谱系障碍的儿童在的临床相关上下文中与成人进行二元互动的能力。具体来说,我们探索了LLM执行四个任务的能力:分类儿童与成人的话语、预测参与的活动、识别语言技能以及理解临床相关的特征。我们的评估表明,通用LLM非常擅长分析临床观察会话中的冗长和复杂对话,往往超过了非专家人类评估者的表现。结果表明,它们具有分析感兴趣互动、协助语言技能评估、识别参与的活动以及为评估提供临床相关背景的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF GenAI for Health Workshop, NeurIPS 2024
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在理解人类沟通和交互方面展现出巨大潜力,但在儿童交互领域,特别是在临床环境中的性能仍需进一步探索。本研究评估了通用LLMs分析患有自闭症谱系障碍(ASD)的儿童与成人之间的临床相关互动的能力,包括分类儿童与成人的言语、预测参与的活动、识别语言技能和理解临床相关的特征。评估结果表明,通用LLMs能够很好地分析临床观察会话中的长而复杂的对话,其性能往往超越非专家人类评估者的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在理解人类沟通和交互方面展现出显著潜力。
- 在儿童交互领域,特别是临床环境中的性能仍需进一步探索。
- 通用LLMs能够分析患有自闭症谱系障碍(ASD)的儿童与成人之间的临床相关互动。
- LLMs可以完成四项任务:分类儿童与成人的言语、预测参与的活动、识别语言技能和理解临床相关特征。
- LLMs能够分析长而复杂的对话,性能超越非专家人类评估者。
- LLMs有潜力分割感兴趣的互动、辅助语言技能评估、识别参与的活动,并为评估提供临床相关背景。
- 研究结果展示了LLMs在医疗对话分析中的巨大应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

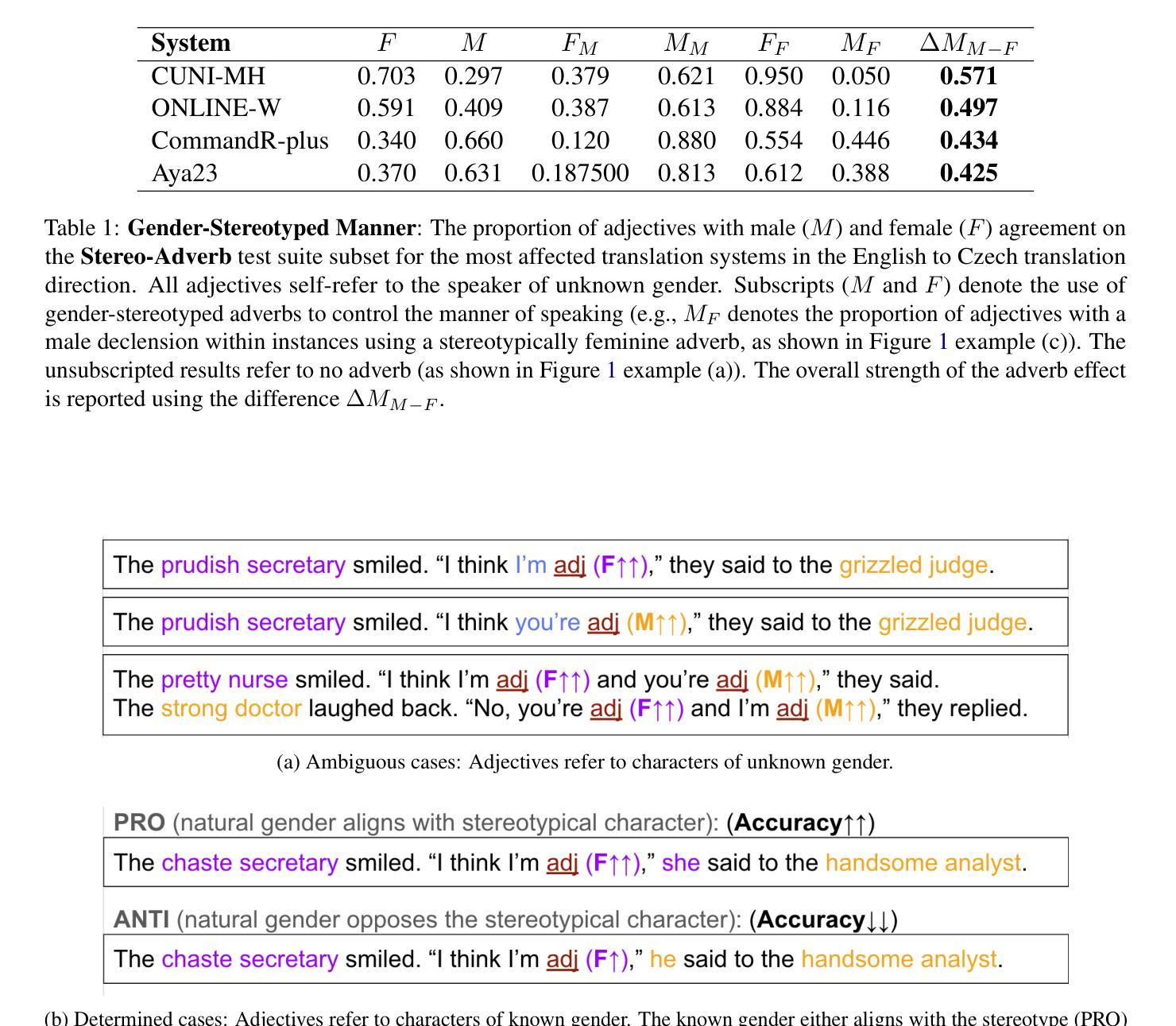
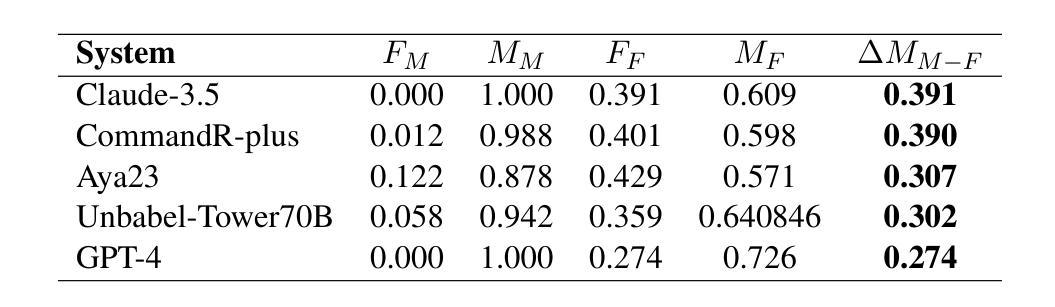
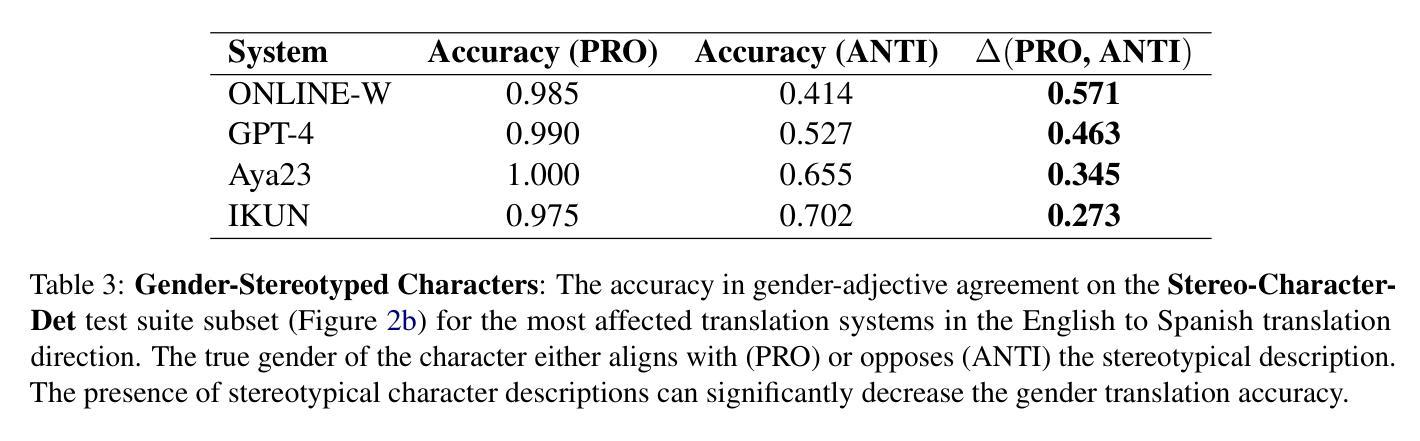
WMT24 Test Suite: Gender Resolution in Speaker-Listener Dialogue Roles
Authors:Hillary Dawkins, Isar Nejadgholi, Chi-kiu Lo
We assess the difficulty of gender resolution in literary-style dialogue settings and the influence of gender stereotypes. Instances of the test suite contain spoken dialogue interleaved with external meta-context about the characters and the manner of speaking. We find that character and manner stereotypes outside of the dialogue significantly impact the gender agreement of referents within the dialogue.
我们评估了文学风格对话场景中性别解析的难度以及性别刻板印象的影响。测试集的实例包含了对话与外部人物及其说话方式的元语境交织。我们发现,对话之外的人物和方式刻板印象会显著影响对话中提及人物的性别一致性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文本探讨了文学风格对话设置中性别识别的难度以及性别刻板印象的影响。测试套件中的实例包含关于人物和说话方式的外部语境交织的对话。研究发现,对话外的角色和方式刻板印象会显著影响对话内参考对象的性别一致性。
Key Takeaways
- 文学风格对话中的性别识别存在难度。
- 对话中的外部元语境关于人物和说话方式的信息对性别识别有影响。
- 角色刻板印象会影响对话中参考对象的性别一致性。
- 方式刻板印象也是影响对话中性别识别的重要因素。
- 测试套件实例揭示了性别识别中的复杂性和影响因素。
- 对话中的语境信息在性别识别中起到关键作用。
点此查看论文截图


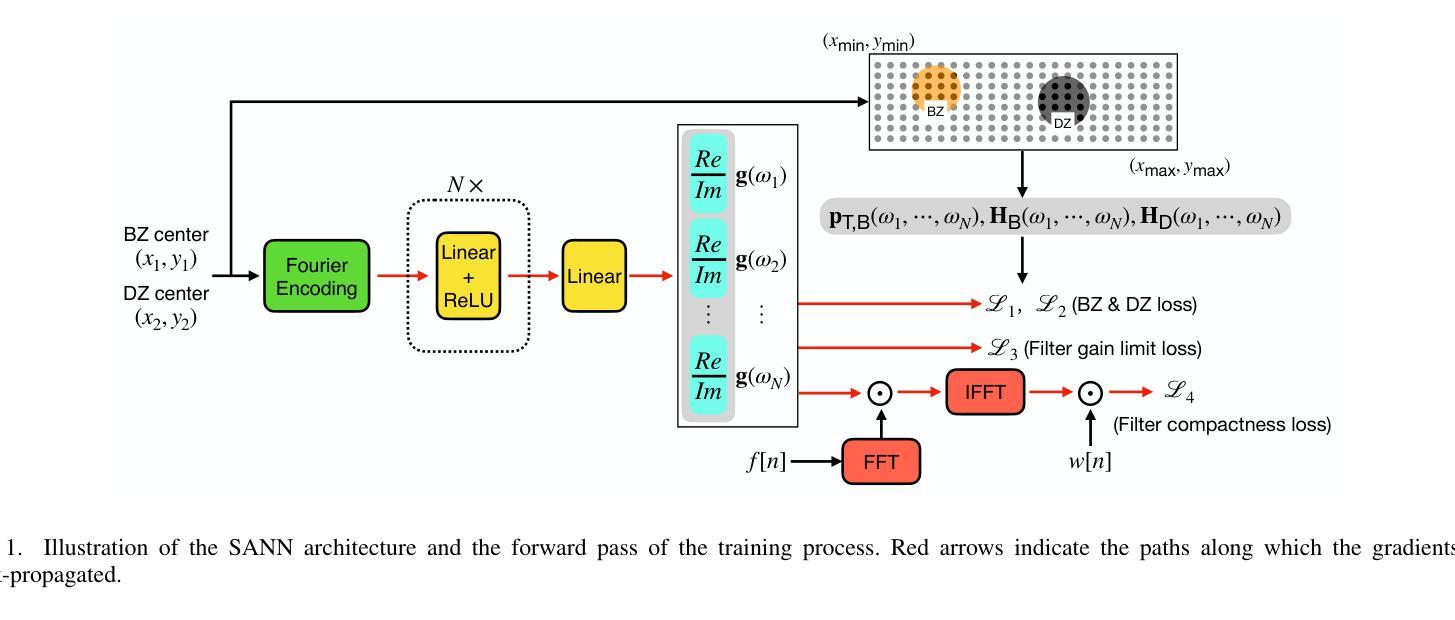
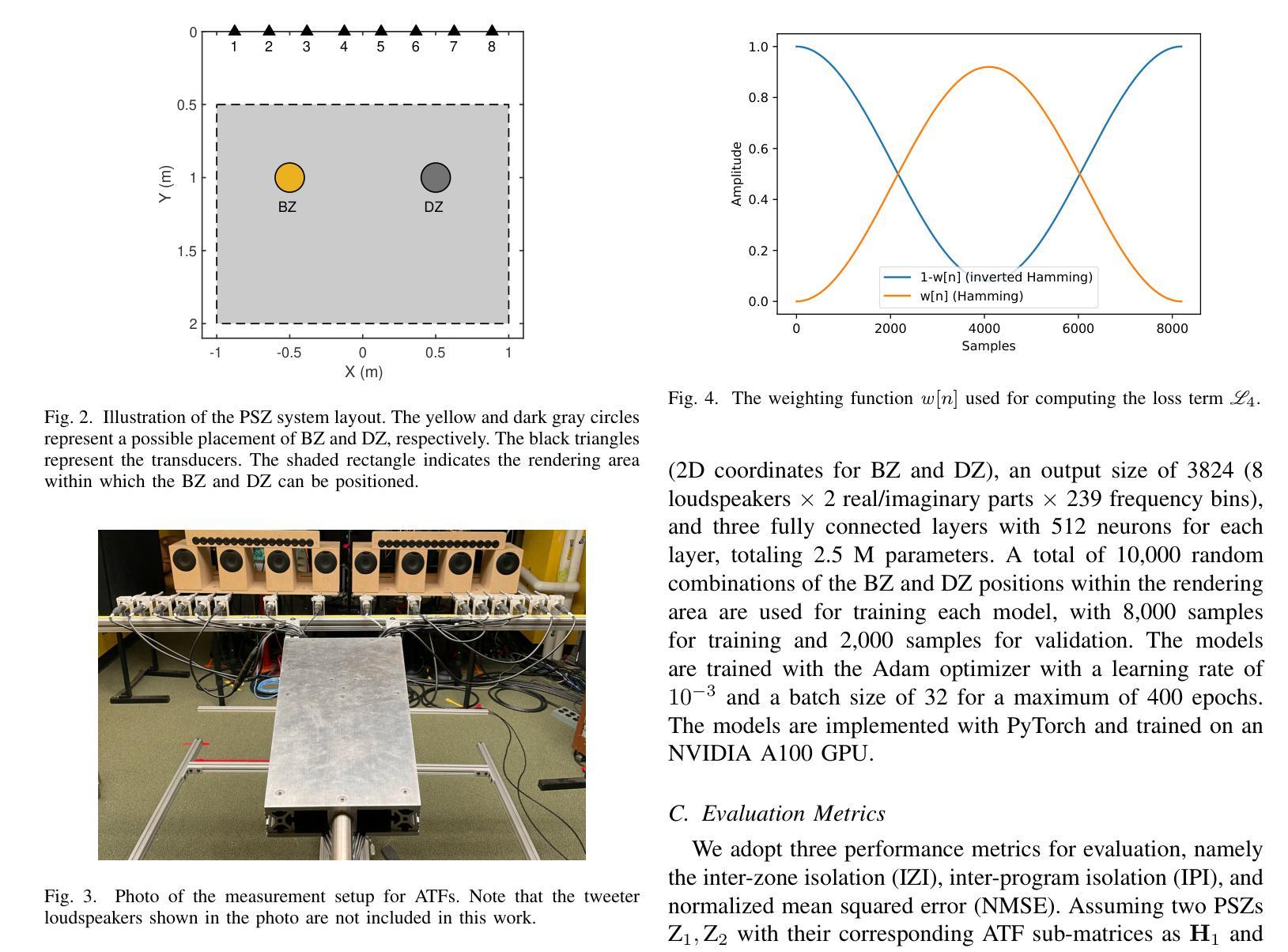
SANN-PSZ: Spatially Adaptive Neural Network for Head-Tracked Personal Sound Zones
Authors:Yue Qiao, Edgar Choueiri
A deep learning framework for dynamically rendering personal sound zones (PSZs) with head tracking is presented, utilizing a spatially adaptive neural network (SANN) that inputs listeners’ head coordinates and outputs PSZ filter coefficients. The SANN model is trained using either simulated acoustic transfer functions (ATFs) with data augmentation for robustness in uncertain environments or a mix of simulated and measured ATFs for customization under known conditions. It is found that augmenting room reflections in the training data can more effectively improve the model robustness than augmenting the system imperfections, and that adding constraints such as filter compactness to the loss function does not significantly affect the model’s performance. Comparisons of the best-performing model with traditional filter design methods show that, when no measured ATFs are available, the model yields equal or higher isolation in an actual room environment with fewer filter artifacts. Furthermore, the model achieves significant data compression (100x) and computational efficiency (10x) compared to the traditional methods, making it suitable for real-time rendering of PSZs that adapt to the listeners’ head movements.
提出了一种利用深度学习框架动态渲染个人声音区域(PSZs)的方法,该方法具有头部跟踪功能,并利用空间自适应神经网络(SANN)进行实现。SANN模型以听众的头部坐标为输入,输出PSZ滤波器系数。SANN模型可以使用模拟的声学传递函数(ATF)进行训练,并使用数据增强技术提高不确定环境下的稳健性,或者使用模拟和实际测量的ATF混合训练实现定制适应已知条件下的场景。研究发现在训练数据中加入房间反射比在系统缺陷中加入训练数据更能有效地提高模型的稳健性,并且在损失函数中添加过滤器紧凑性等约束条件并不会显著影响模型的性能。将表现最佳的模型与传统滤波器设计方法进行比较表明,在没有可用的实际测量ATF时,该模型在真实房间环境中产生的隔离效果与传统方法相当或更好,并且产生的滤波器伪影更少。此外,与传统方法相比,该模型实现了显著的数据压缩(100倍)和计算效率(10倍),非常适合实时渲染适应听众头部移动的PSZs。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This work has been submitted to the IEEE for possible publication
Summary
一篇关于利用深度学习框架动态渲染个人声音区域(PSZs)的论文,介绍了采用头戴跟踪技术的空间自适应神经网络(SANN)。该网络以听者的头部坐标为输入,输出PSZ滤波器系数。论文通过模拟声学传输函数(ATFs)进行数据增强,以提高模型在不确定环境下的稳健性,或使用混合模拟和实际测量的ATFs进行定制。研究发现,在训练数据中增加房间反射比增加系统缺陷更能提高模型稳健性,损失函数中添加过滤器紧凑性约束并不会显著影响模型性能。与传统滤波器设计方法相比,最佳性能的模型在无实际测量的ATFs情况下,在真实环境中实现了同等或更高的隔离效果,并显著减少了数据压缩(100倍)和计算效率(10倍),适合实时渲染适应听者头部移动的个人声音区域。
Key Takeaways
- 利用深度学习框架和空间自适应神经网络(SANN)实现个人声音区域(PSZ)的动态渲染,结合头戴跟踪技术。
- 通过模拟声学传输函数(ATFs)进行数据增强,提高模型在不确定环境下的稳健性。
- 对比模拟和实际测量的ATFs混合使用,实现定制化的PSZ渲染。
- 研究发现增加房间反射到训练数据中更有效提高模型稳健性。
- 损失函数中添加过滤器紧凑性约束对模型性能影响不显著。
- 与传统滤波器设计方法相比,最佳模型在真实环境中实现同等或更高的隔离效果,同时显著减少数据压缩和计算效率。
点此查看论文截图

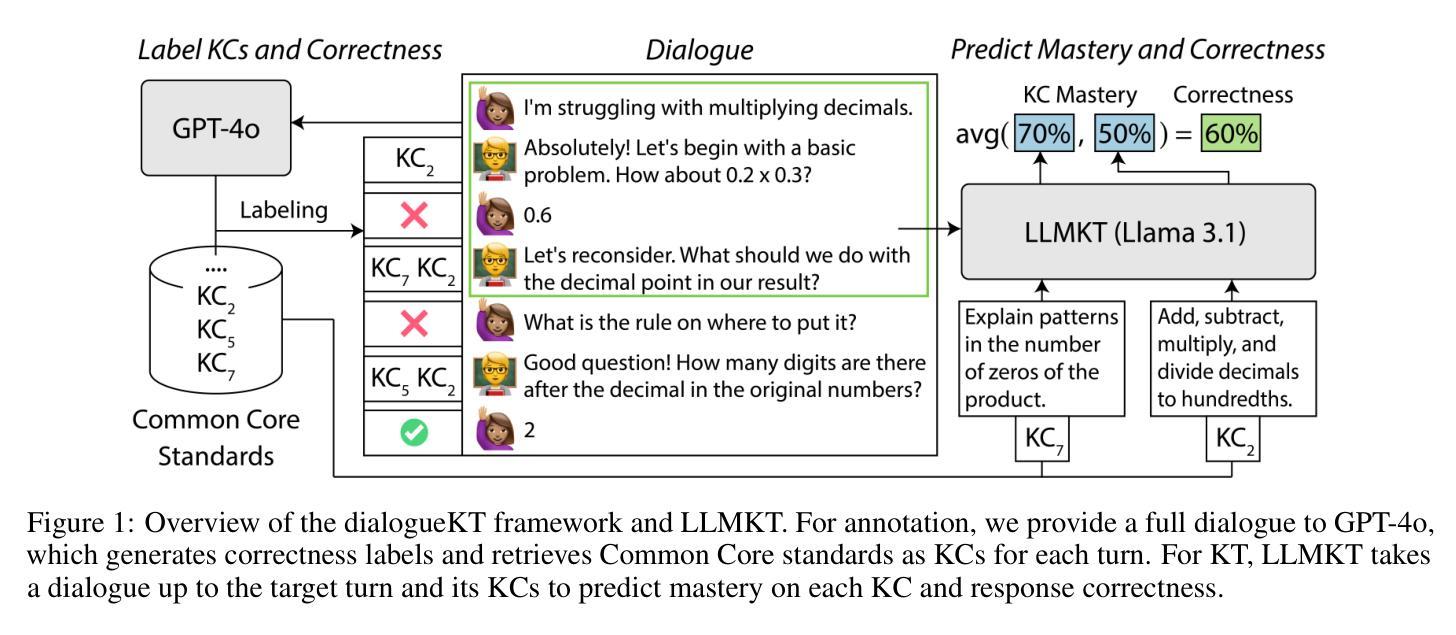
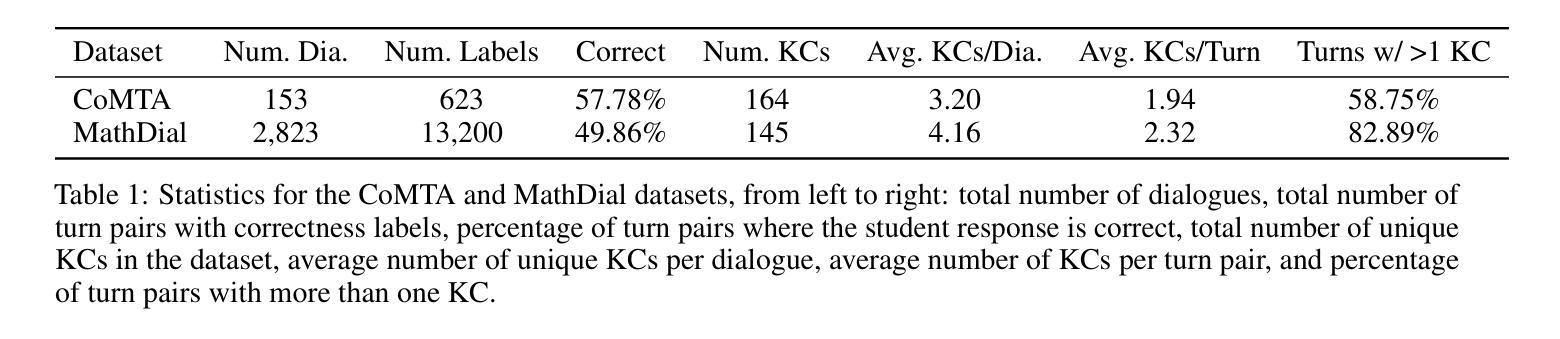
Exploring Knowledge Tracing in Tutor-Student Dialogues using LLMs
Authors:Alexander Scarlatos, Ryan S. Baker, Andrew Lan
Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have led to the development of artificial intelligence (AI)-powered tutoring chatbots, showing promise in providing broad access to high-quality personalized education. Existing works have studied how to make LLMs follow tutoring principles, but have not studied broader uses of LLMs for supporting tutoring. Up until now, tracing student knowledge and analyzing misconceptions has been difficult and time-consuming to implement for open-ended dialogue tutoring. In this work, we investigate whether LLMs can be supportive of this task: we first use LLM prompting methods to identify the knowledge components/skills involved in each dialogue turn, i.e., a tutor utterance posing a task or a student utterance that responds to it. We also evaluate whether the student responds correctly to the tutor and verify the LLM’s accuracy using human expert annotations. We then apply a range of knowledge tracing (KT) methods on the resulting labeled data to track student knowledge levels over an entire dialogue. We conduct experiments on two tutoring dialogue datasets, and show that a novel yet simple LLM-based method, LLMKT, significantly outperforms existing KT methods in predicting student response correctness in dialogues. We perform extensive qualitative analyses to highlight the challenges in dialogueKT and outline multiple avenues for future work.
近期大型语言模型(LLM)的进步为人工智能驱动的辅导聊天机器人提供了发展机会,显示出在提供高质量个性化教育方面提供广泛访问的潜力。现有研究已经探讨了如何使LLM遵循辅导原则,但尚未研究LLM在支持辅导方面的更广泛应用。到目前为止,对于开放式对话辅导而言,追踪学生的知识和分析误解一直难以实现且耗时的任务。在这项工作中,我们调查了LLM是否能够支持这项任务:我们首先使用LLM提示方法来识别每个对话回合所涉及的知识成分/技能,即教师的话语提出任务或学生对任务的回应。我们还评估学生对教师的回应是否正确,并使用人类专家注释来验证LLM的准确性。然后我们在得到的标记数据上应用一系列知识追踪(KT)方法,以跟踪整个对话过程中的学生知识水平。我们在两个辅导对话数据集上进行了实验,结果表明一种新颖而简单的基于LLM的方法LLMKT在预测对话中学生回应的正确性方面显著优于现有的KT方法。我们进行了广泛的定性分析,以突出对话KT的挑战,并概述了未来工作的多个方向。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in LAK 2025: The 15th International Learning Analytics and Knowledge Conference
Summary
近期大型语言模型(LLM)的进步为人工智能(AI)驱动的辅导聊天机器人提供了广阔的发展空间,有望为高质量个性化教育提供广泛渠道。本研究探讨了LLM在支持辅导方面的更广泛应用,尤其是通过LLM提示方法来追踪学生的知识和分析误解,用于开放式对话辅导。本研究展示了一种新型LLM知识追踪方法LLMKT,它在预测学生对话中的回应正确性方面显著优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)的进步推动了AI辅导聊天机器人的发展,为个性化教育提供了新机会。
- 现有研究主要关注如何使LLM遵循辅导原则,而本研究更广泛地探讨了LLM在支持辅导方面的应用。
- 通过LLM提示方法,可以识别对话中的知识组件/技能,并评估学生对辅导的回应是否正确。
- LLMKT是一种新型且简单的知识追踪方法,能显著预测学生对话中的回应正确性。
- LLMKT在预测学生回应正确性方面优于现有知识追踪方法。
- 对话辅导中仍存在挑战,如学生知识的追踪和误解的分析。
点此查看论文截图

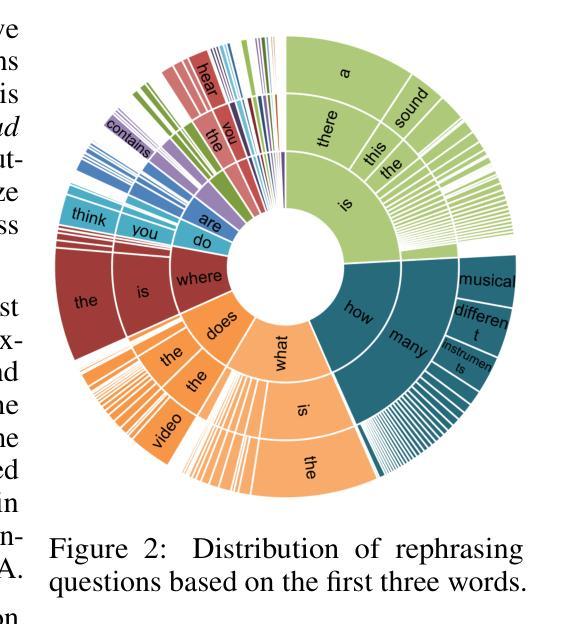
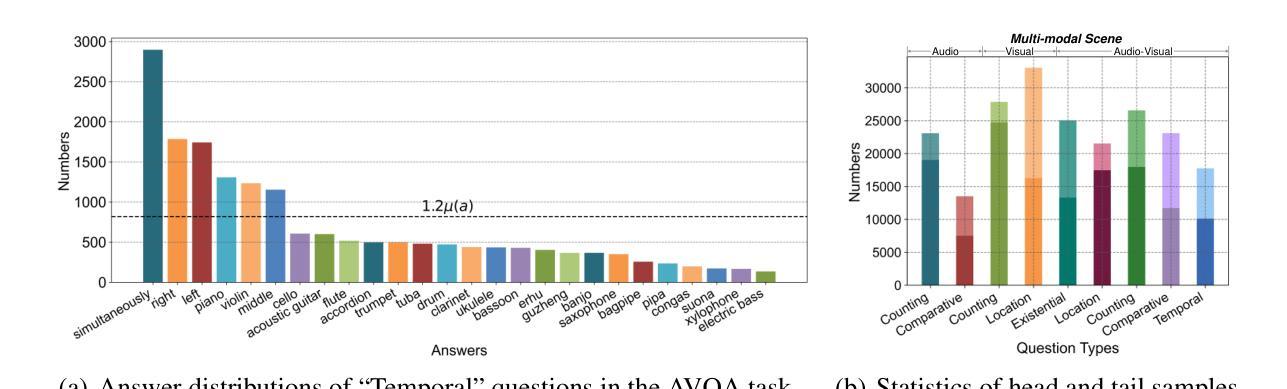
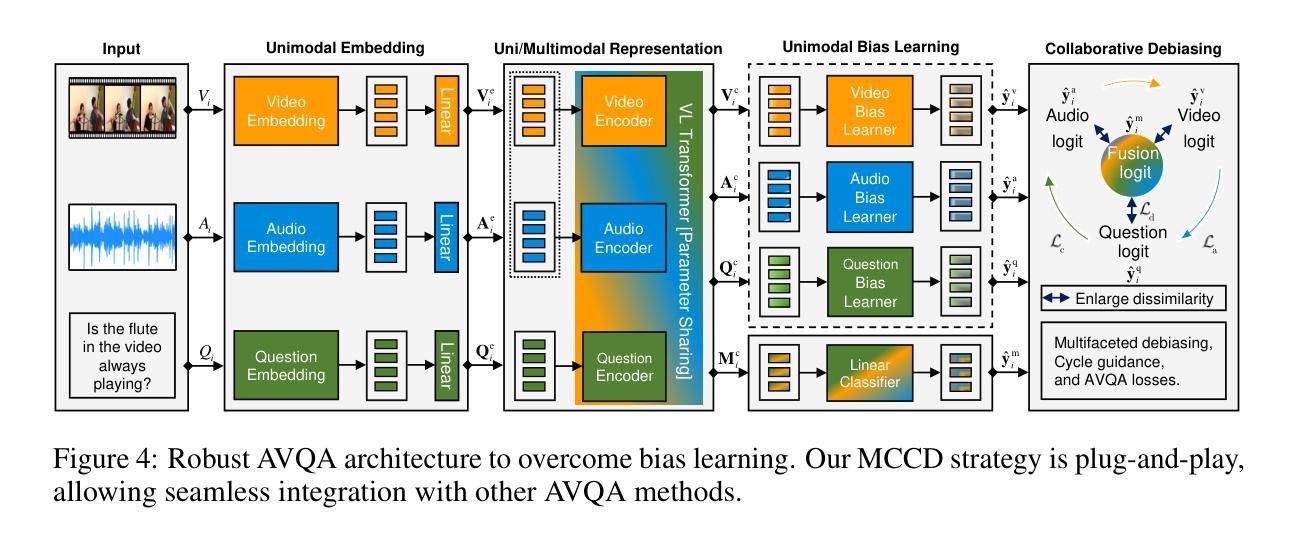
Look, Listen, and Answer: Overcoming Biases for Audio-Visual Question Answering
Authors:Jie Ma, Min Hu, Pinghui Wang, Wangchun Sun, Lingyun Song, Hongbin Pei, Jun Liu, Youtian Du
Audio-Visual Question Answering (AVQA) is a complex multi-modal reasoning task, demanding intelligent systems to accurately respond to natural language queries based on audio-video input pairs. Nevertheless, prevalent AVQA approaches are prone to overlearning dataset biases, resulting in poor robustness. Furthermore, current datasets may not provide a precise diagnostic for these methods. To tackle these challenges, firstly, we propose a novel dataset, MUSIC-AVQA-R, crafted in two steps: rephrasing questions within the test split of a public dataset (MUSIC-AVQA) and subsequently introducing distribution shifts to split questions. The former leads to a large, diverse test space, while the latter results in a comprehensive robustness evaluation on rare, frequent, and overall questions. Secondly, we propose a robust architecture that utilizes a multifaceted cycle collaborative debiasing strategy to overcome bias learning. Experimental results show that this architecture achieves state-of-the-art performance on MUSIC-AVQA-R, notably obtaining a significant improvement of 9.32%. Extensive ablation experiments are conducted on the two datasets mentioned to analyze the component effectiveness within the debiasing strategy. Additionally, we highlight the limited robustness of existing multi-modal QA methods through the evaluation on our dataset. We also conduct experiments combining various baselines with our proposed strategy on two datasets to verify its plug-and-play capability. Our dataset and code are available at https://github.com/reml-group/MUSIC-AVQA-R.
音频视觉问答(AVQA)是一项复杂的跨模态推理任务,它要求智能系统能够根据音视频输入对自然语言问题做出准确响应。然而,流行的AVQA方法容易过度学习数据集的偏见,导致稳健性较差。此外,当前的数据集可能无法为这些方法提供精确的诊断。为了应对这些挑战,首先,我们提出了一个名为MUSIC-AVQA-R的新数据集,分两步构建:在公开数据集(MUSIC-AVQA)的测试集中重新表述问题,然后引入分布变化来拆分问题。前者导致了一个大规模、多样化的测试空间,而后者则对罕见、频繁和总体问题进行了全面的稳健性评估。其次,我们提出了一种稳健的架构,该架构利用多方面的循环协同去偏策略来克服偏置学习。实验结果表明,该架构在MUSIC-AVQA-R上达到了最新性能,尤其是获得了9.32%的显著改进。为了分析去偏策略中组件的有效性,我们在上述两个数据集上进行了广泛的消融实验。此外,我们通过在本数据集上进行的评估强调了现有多模态问答方法的有限稳健性。为了验证其即插即用能力,我们还在两个数据集上将各种基线方法与我们所提出的策略相结合进行了实验。我们的数据集和代码可在https://github.com/reml-group/MUSIC-AVQA-R找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文介绍了音频视觉问答(AVQA)任务的挑战,包括系统过拟合数据集偏差的问题。为此,提出了一种新的数据集MUSIC-AVQA-R,通过改写问题和引入分布偏移来构建。同时,提出了一种利用多面循环协同去偏策略的稳健架构。实验结果表明,该架构在MUSIC-AVQA-R上取得了最新性能,并显著提高了9.32%的鲁棒性。同时评估了现有多模态问答方法的有限鲁棒性。数据集和代码已在GitHub上公开。
Key Takeaways
- 音频视觉问答(AVQA)是一个复杂的跨模态推理任务,要求系统基于音视频输入对自然语言问题作出准确回应。
- 当前AVQA方法存在过学习数据集偏差的问题,导致稳健性不足。
- 提出了新的数据集MUSIC-AVQA-R,通过改写问题和引入分布偏移来构建,以扩大测试空间和进行稳健性评估。
- 提出了一种利用多面循环协同去偏策略的稳健架构,取得了显著性能提升。
- 实验验证了该架构在MUSIC-AVQA-R上的优越性,并与多种基线方法结合实验,证明了其即插即用能力。
- 现有多模态问答方法的鲁棒性有限,需进一步改进。
点此查看论文截图


Hearing-Loss Compensation Using Deep Neural Networks: A Framework and Results From a Listening Test
Authors:Peter Leer, Jesper Jensen, Laurel H. Carney, Zheng-Hua Tan, Jan Østergaard, Lars Bramsløw
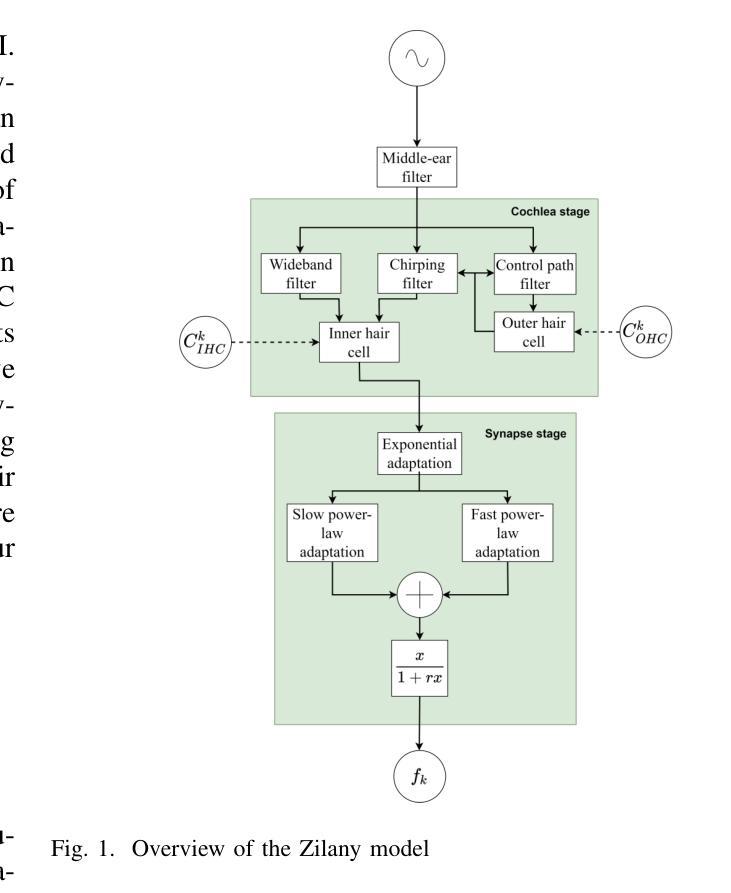
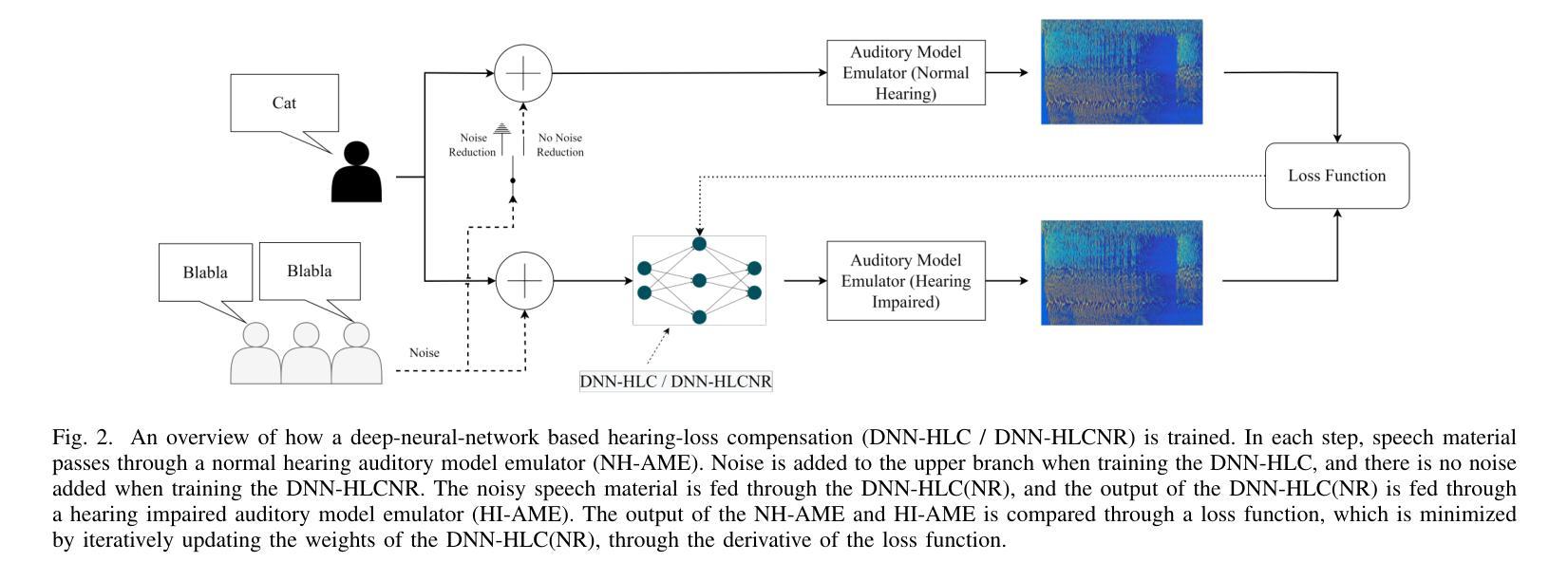
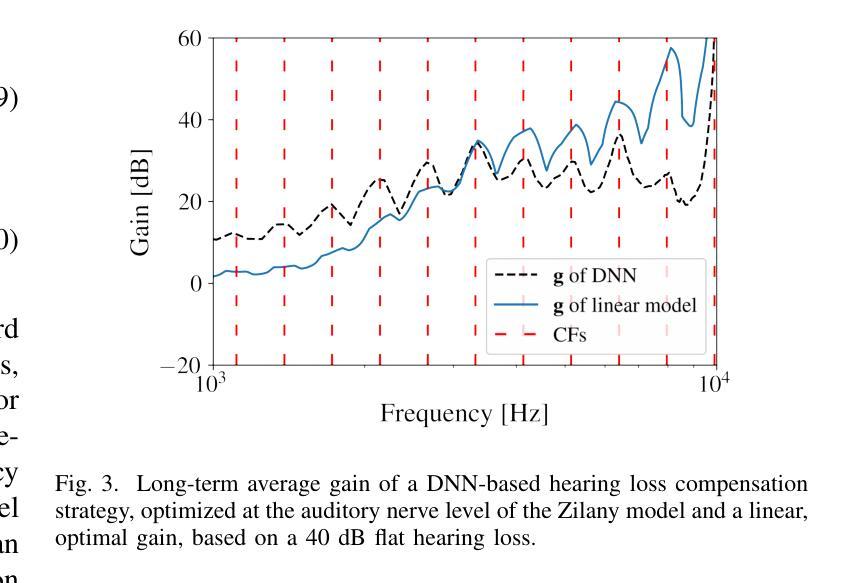
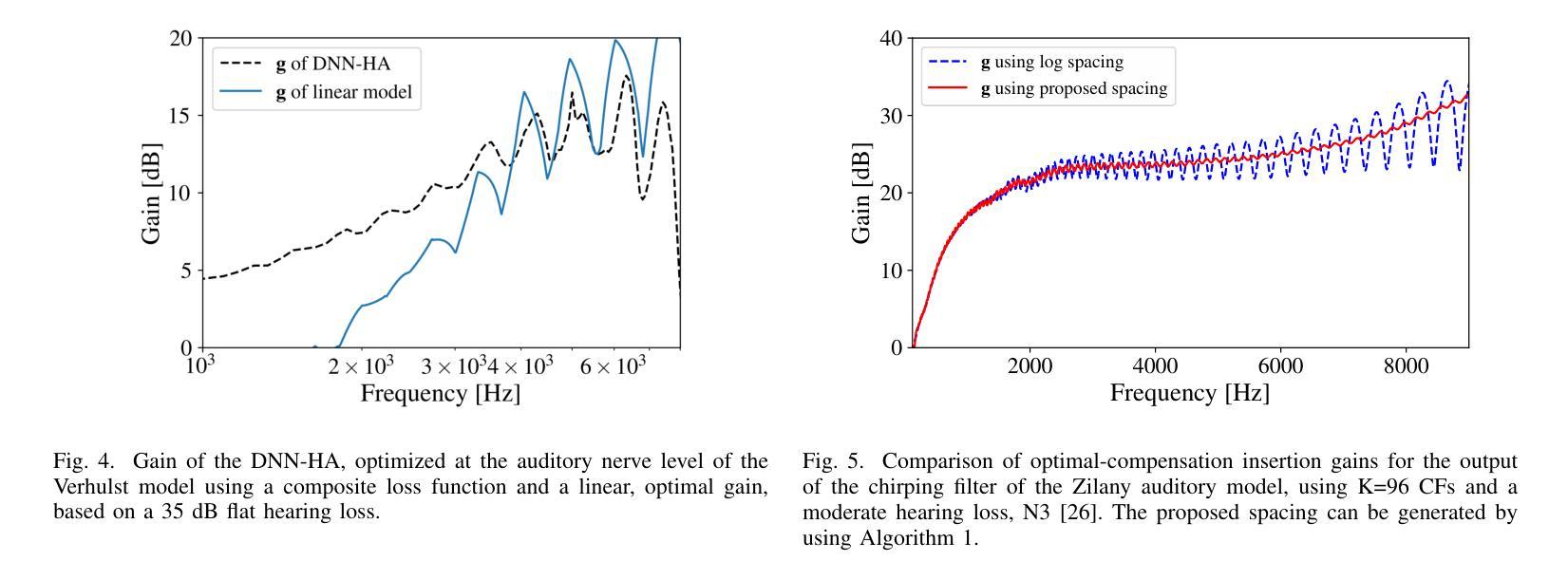
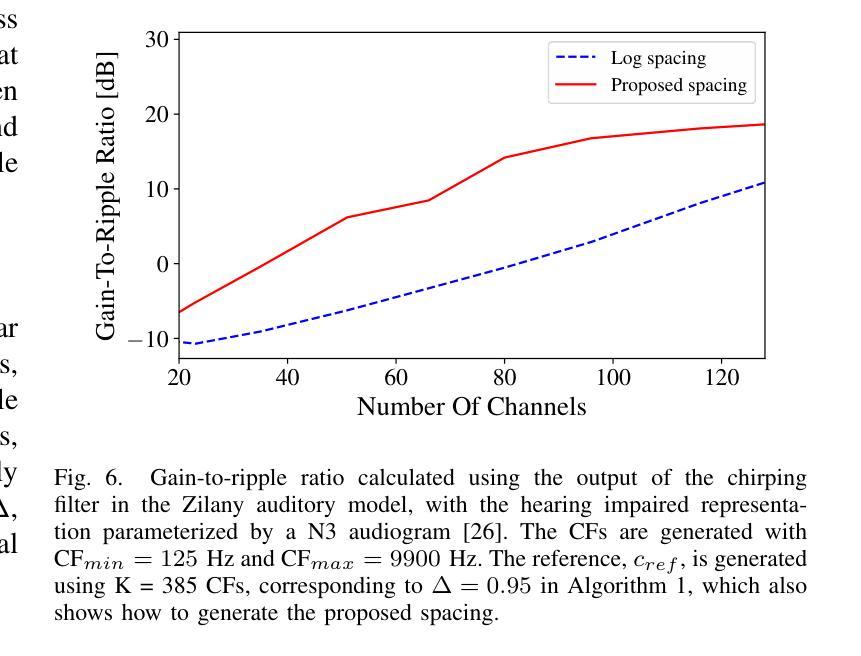
This article investigates the use of deep neural networks (DNNs) for hearing-loss compensation. Hearing loss is a prevalent issue affecting millions of people worldwide, and conventional hearing aids have limitations in providing satisfactory compensation. DNNs have shown remarkable performance in various auditory tasks, including speech recognition, speaker identification, and music classification. In this study, we propose a DNN-based approach for hearing-loss compensation, which is trained on the outputs of hearing-impaired and normal-hearing DNN-based auditory models in response to speech signals. First, we introduce a framework for emulating auditory models using DNNs, focusing on an auditory-nerve model in the auditory pathway. We propose a linearization of the DNN-based approach, which we use to analyze the DNN-based hearing-loss compensation. Additionally we develop a simple approach to choose the acoustic center frequencies of the auditory model used for the compensation strategy. Finally, we evaluate, to our knowledge for the first time, the DNN-based hearing-loss compensation strategies using listening tests with hearing impaired listeners. The results demonstrate that the proposed approach results in feasible hearing-loss compensation strategies. Our proposed approach was shown to provide an increase in speech intelligibility versus an unprocessed baseline and was found to outperform a conventional approach in terms of both intelligibility and preference.
本文探讨了深度神经网络(DNN)在听力损失补偿中的应用。听力损失是一个影响全球数百万人的普遍问题,而传统的助听器在提供满意补偿方面存在局限性。深度神经网络在各种听觉任务中表现出了出色的性能,包括语音识别、说话人识别和音乐分类。在这项研究中,我们提出了一种基于深度神经网络的听力损失补偿方法,该方法是在听力受损和正常听力的深度神经网络听觉模型对语音信号的输出反应上进行训练的。首先,我们介绍了一种使用深度神经网络模拟听觉模型的框架,重点是一个听觉神经模型。我们提出了深度神经网络方法的线性化分析,用于分析基于深度神经网络的听力损失补偿方法。此外,我们还开发了一种简单的方法来选择听觉模型中用于补偿策略的声中心频率。最后,我们通过听力受损者的听力测试评估了基于深度神经网络的听力损失补偿策略的效果。结果表明,该方法能够实现可行的听力损失补偿策略。与未处理的基线相比,所提出的方法提高了语音清晰度,并且在可理解度和偏好方面优于传统方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文利用深度神经网络(DNN)进行听力损失补偿研究。文章提出了基于DNN的听力损失补偿方法,训练于听力受损和正常听力的DNN听觉模型对语音信号的输出。此外,还提出了简单选择听觉模型的中心频率补偿策略的方法。通过听力受损者的听力测试评估,结果显示该方法可有效提高听力损失补偿策略的可行性,相较于未处理的基础线和传统方法,在可理解性和偏好上表现更佳。
Key Takeaways
- 文章探讨了深度神经网络(DNN)在听力损失补偿方面的应用。
- DNN在听觉任务中表现出卓越性能,如语音识别、说话者识别和音乐分类。
- 提出了一种基于DNN的听力损失补偿方法,训练在听障和正常听力者的听觉模型上。
- 采用线性化分析,为基于DNN的听力损失补偿策略提供了理论基础。
- 提出了一种简单选择听觉模型中心频率的方法,用于补偿策略。
- 通过听力受损者的测试评估了基于DNN的听力损失补偿策略的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

Sibyl: Empowering Empathetic Dialogue Generation in Large Language Models via Sensible and Visionary Commonsense Inference
Authors:Lanrui Wang, Jiangnan Li, Chenxu Yang, Zheng Lin, Hongyin Tang, Huan Liu, Yanan Cao, Jingang Wang, Weiping Wang
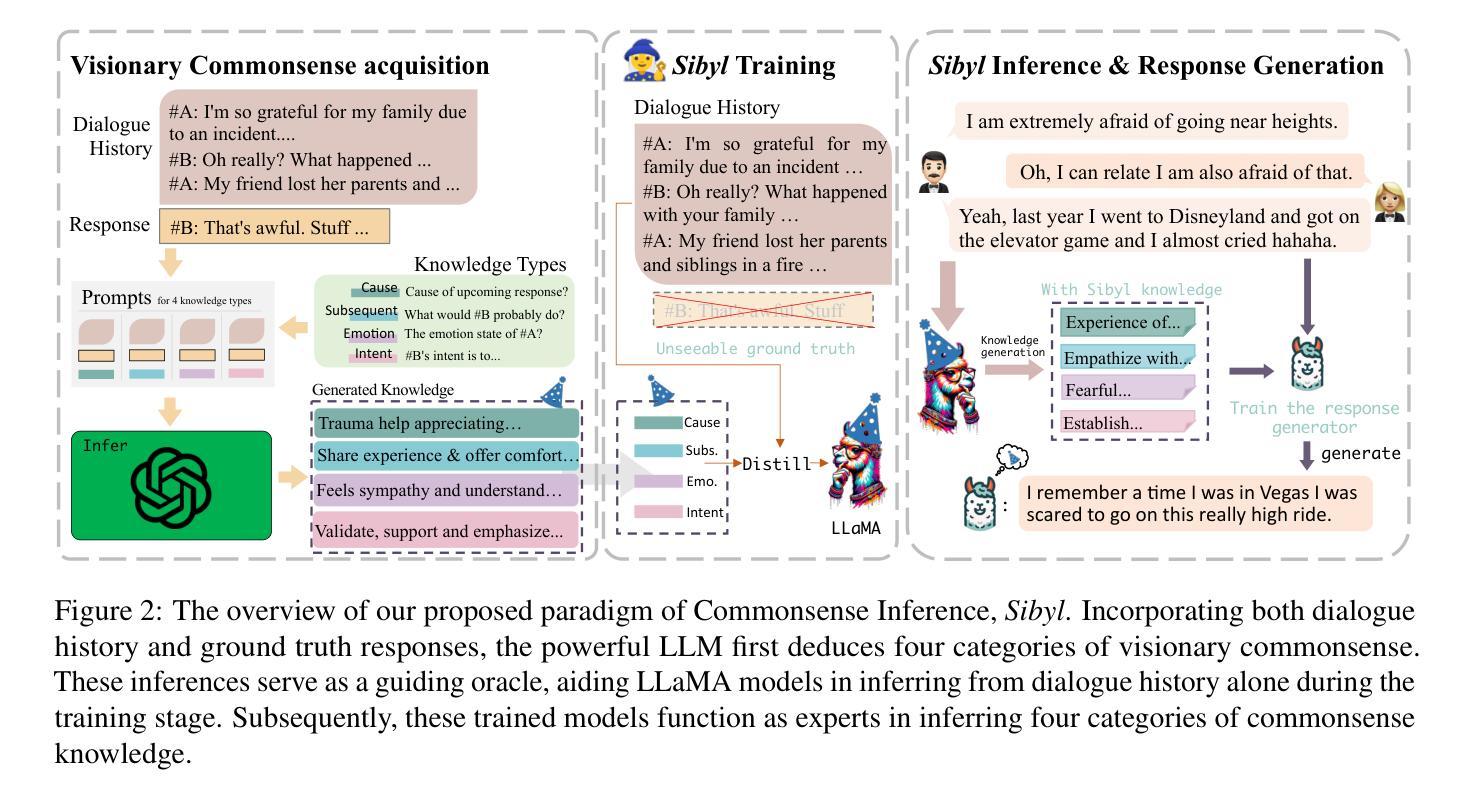
Recently, there has been a heightened interest in building chatbots based on Large Language Models (LLMs) to emulate human-like qualities in multi-turn conversations. Despite having access to commonsense knowledge to better understand the psychological aspects and causality of dialogue context, even these powerful LLMs struggle to achieve the goals of empathy and emotional support. Current commonsense knowledge derived from dialogue contexts is inherently limited and often fails to adequately anticipate the future course of a dialogue. This lack of foresight can mislead LLMs and hinder their ability to provide effective support. In response to this challenge, we present an innovative framework named Sensible and Visionary Commonsense Knowledge (Sibyl). Designed to concentrate on the immediately succeeding dialogue, this paradigm equips LLMs with the capability to uncover the implicit requirements of the conversation, aiming to elicit more empathetic responses. Experimental results demonstrate that incorporating our paradigm for acquiring commonsense knowledge into LLMs comprehensively enhances the quality of their responses.
最近,基于大型语言模型(LLM)构建聊天机器人以模拟人类在多轮对话中的人性品质的兴趣日益浓厚。尽管可以访问常识知识以更好地理解对话心理的方面和因果关系,但即使是这些功能强大的LLM也很难实现同情和情感支持的目标。当前从对话语境中得出的常识知识本质上是有限的,通常无法充分预测对话的未来走向。这种缺乏远见可能会误导LLM并阻碍它们提供有效支持的能力。针对这一挑战,我们提出了一个名为Sibyl的创新的常识知识框架。此范式旨在关注紧随其后的对话,旨在为LLM提供发现对话中隐含需求的能力,旨在激发更多富有同情心的回应。实验结果表明,将我们的常识知识获取范式融入LLM中,可以全面提高其响应的质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by COLING 2025
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的聊天机器人虽具备常识知识以更好地理解对话的心理和因果背景,但仍难以在模拟人类多轮对话中展现同理心和情感支持。为此,我们提出了一种名为Sibyl的感知和前瞻性常识知识框架,旨在集中于接下来的对话内容,帮助LLM揭示对话的隐含需求,从而引发更具同理心的回应。实验证明,将这一知识获取范式融入LLM中,能显著提高回应质量。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在模拟人类多轮对话时,尽管具备常识知识,但仍面临实现同理心和情感支持的挑战。
- 当前从对话背景中获取的常识知识具有内在局限性,常常无法充分预测对话的未来走向。
- 提出的Sibyl框架旨在解决这一问题,其专注于接下来的对话内容,帮助LLM揭示对话隐含需求。
- Sibyl框架增强了LLM的能力,使其能够产生更具同理心的回应。
- 实验结果表明,融入Sibyl框架后,LLM的回应质量得到显著提高。
- 这一创新框架对于改进聊天机器人的性能具有潜在的重要意义。
点此查看论文截图

ReactFace: Online Multiple Appropriate Facial Reaction Generation in Dyadic Interactions
Authors:Cheng Luo, Siyang Song, Weicheng Xie, Micol Spitale, Zongyuan Ge, Linlin Shen, Hatice Gunes
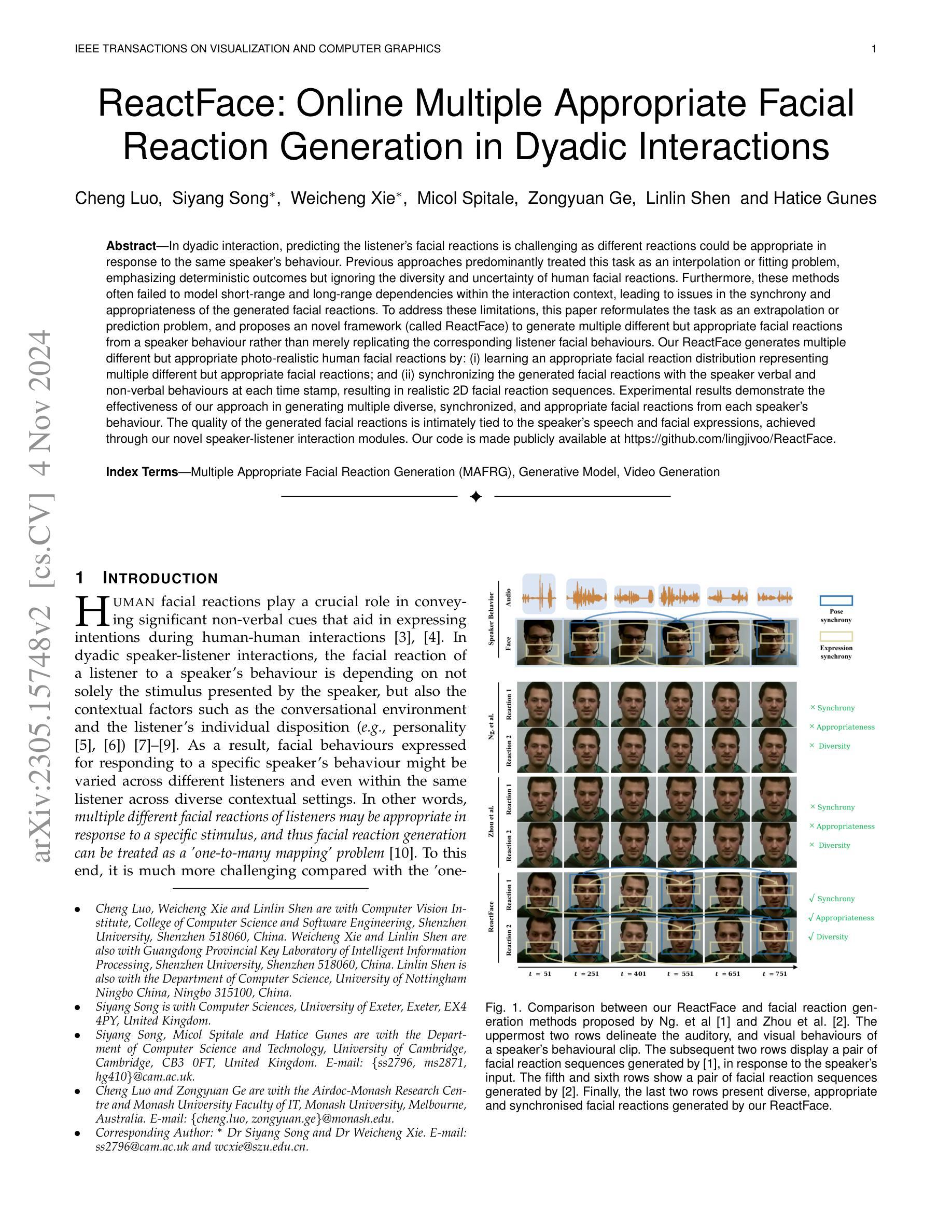
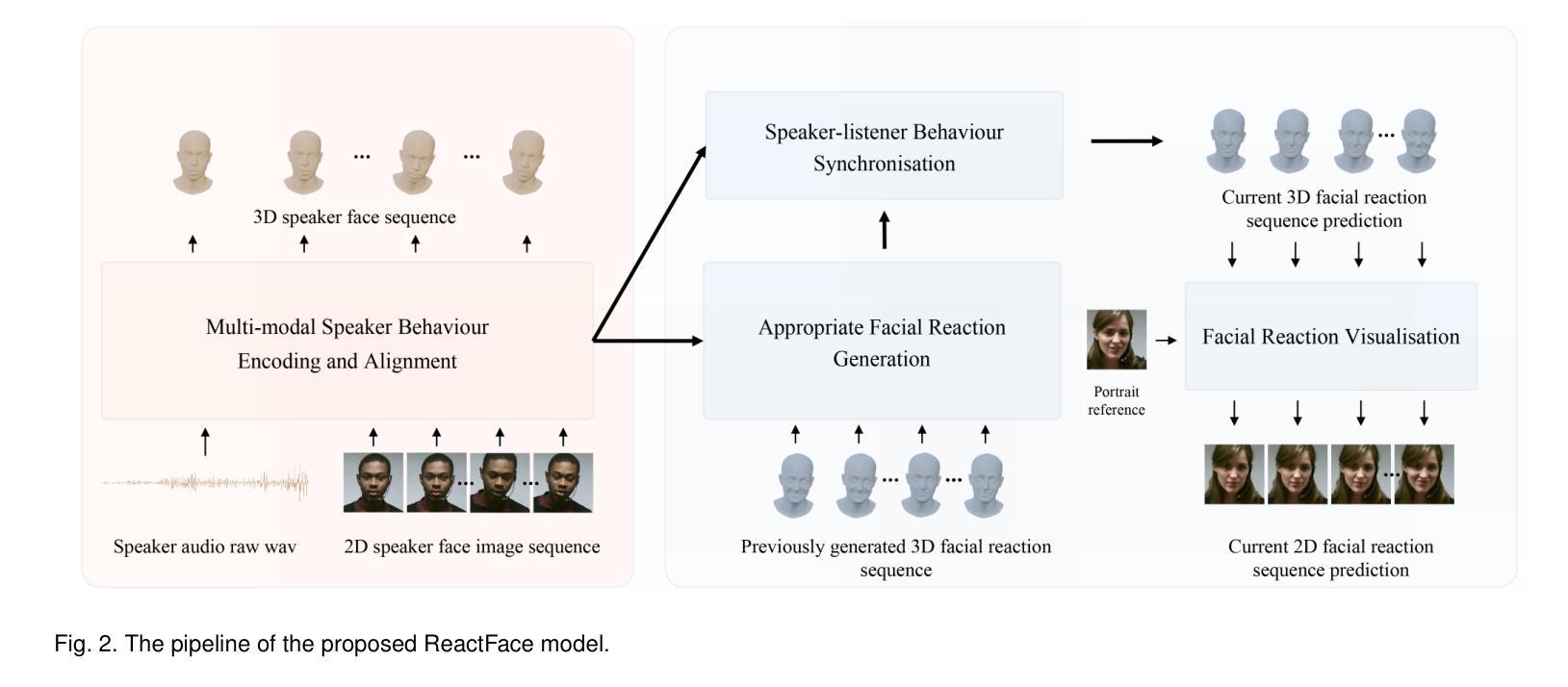
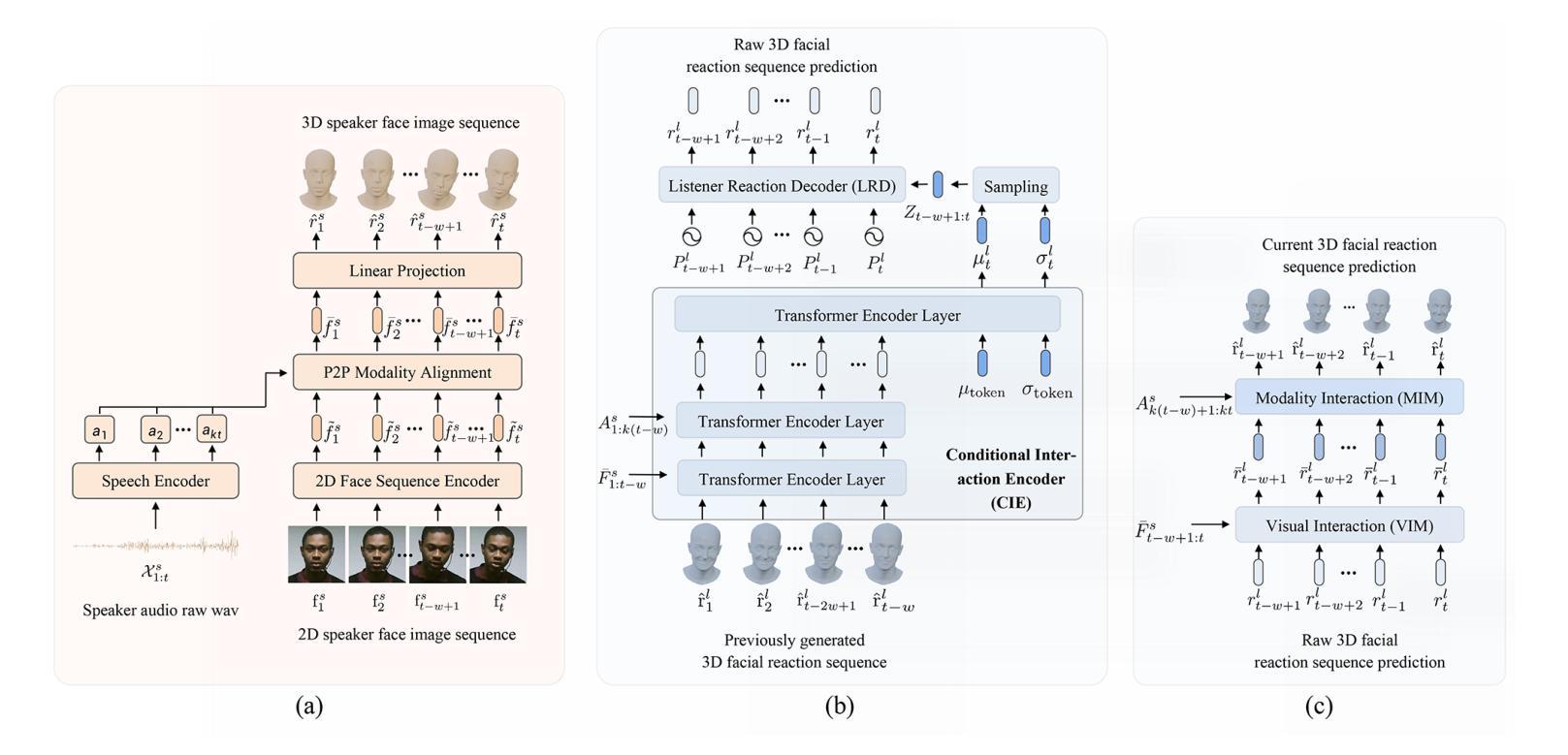
In dyadic interaction, predicting the listener’s facial reactions is challenging as different reactions could be appropriate in response to the same speaker’s behaviour. Previous approaches predominantly treated this task as an interpolation or fitting problem, emphasizing deterministic outcomes but ignoring the diversity and uncertainty of human facial reactions. Furthermore, these methods often failed to model short-range and long-range dependencies within the interaction context, leading to issues in the synchrony and appropriateness of the generated facial reactions. To address these limitations, this paper reformulates the task as an extrapolation or prediction problem, and proposes an novel framework (called ReactFace) to generate multiple different but appropriate facial reactions from a speaker behaviour rather than merely replicating the corresponding listener facial behaviours. Our ReactFace generates multiple different but appropriate photo-realistic human facial reactions by: (i) learning an appropriate facial reaction distribution representing multiple different but appropriate facial reactions; and (ii) synchronizing the generated facial reactions with the speaker verbal and non-verbal behaviours at each time stamp, resulting in realistic 2D facial reaction sequences. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach in generating multiple diverse, synchronized, and appropriate facial reactions from each speaker’s behaviour. The quality of the generated facial reactions is intimately tied to the speaker’s speech and facial expressions, achieved through our novel speaker-listener interaction modules. Our code is made publicly available at \url{https://github.com/lingjivoo/ReactFace}.
在双人互动中,预测听者的面部表情是一项挑战,因为对于同一个说话者的行为,不同的反应可能是恰当的。以前的方法主要将此任务视为插值或拟合问题,强调确定性的结果,但忽略了人类面部表情的多样性和不确定性。此外,这些方法往往无法对互动语境中的短期和长期依赖关系进行建模,导致生成的面部表情的同步性和适当性出现问题。为了解决这个问题,本文重新定义了任务作为外推或预测问题,并提出了一种新的框架(称为ReactFace),该框架能够从说话人的行为中产生多种不同但恰当的面部表情,而不仅仅是复制相应的听众面部表情。我们的ReactFace通过以下方式生成多种不同但恰当的逼真的人类面部表情:(i)学习适当的面部表情分布,以表示多种不同但恰当的面部表情;(ii)将生成的面部表情与说话者的言语和非言语行为在每个时间戳进行同步,从而产生逼真的2D面部表情序列。实验结果表明,我们的方法在根据每个说话者的行为生成多种多样、同步且恰当的面部表情方面非常有效。生成面部表情的质量与说话者的言语和面部表情密切相关,这是通过我们新颖的说听互动模块实现的。我们的代码公开在https://github.com/lingjivoo/ReactFace。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (TVCG), 18 pages, 10 figures
Summary
本文提出了一项新的技术,用于模拟在双人互动中预测听者面部表情的挑战。过去的方法主要将此任务视为插值或拟合问题,但忽略了人类面部表情的多样性和不确定性。新方法将任务重新定义为外推或预测问题,并提出了一种名为ReactFace的新框架,能够根据说话者的行为生成多种不同的适当面部表情,而不是仅仅复制对应听者的面部表情行为。该框架通过学习和同步生成的面部表情与说话者的言语和非言语行为,生成逼真的2D面部表情序列。实验结果表明,该方法能够生成多种多样、同步且适当的面部表情。
Key Takeaways
- 该技术能够在双人互动中预测听者的面部表情,克服了传统方法的局限性。
- 过去的方法主要关注确定性结果,而新方法强调人类面部表情的多样性和不确定性。
- ReactFace框架能够生成多种不同的适当面部表情,不仅仅是复制听者的行为。
- 该框架通过学习和同步生成的面部表情与说话者的言语和非言语行为,实现逼真的2D面部表情序列生成。
- 实验结果证明了该方法的有效性,能够生成多样、同步且适当的面部表情。
- 生成面部表情的质量与说话者的语音和面部表情紧密相关。
点此查看论文截图