⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-12 更新
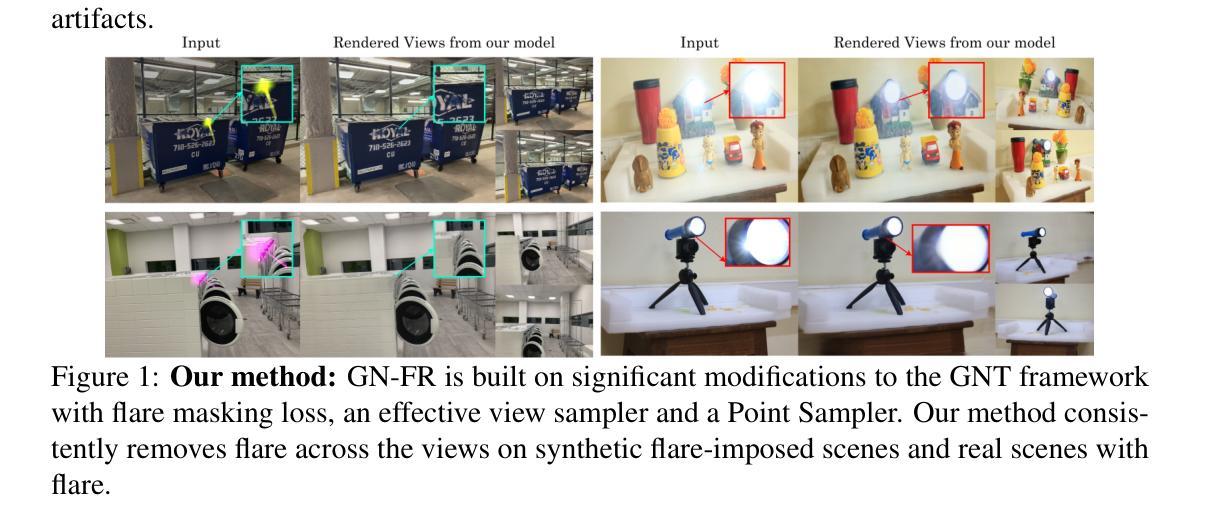
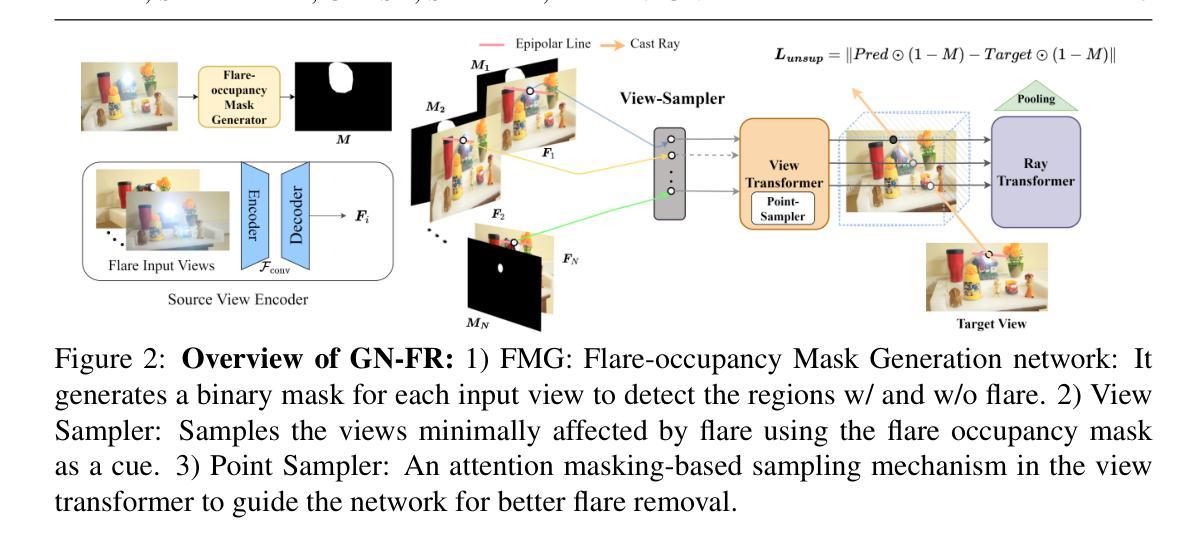
GN-FR:Generalizable Neural Radiance Fields for Flare Removal
Authors:Gopi Raju Matta, Rahul Siddartha, Rongali Simhachala Venkata Girish, Sumit Sharma, Kaushik Mitra
Flare, an optical phenomenon resulting from unwanted scattering and reflections within a lens system, presents a significant challenge in imaging. The diverse patterns of flares, such as halos, streaks, color bleeding, and haze, complicate the flare removal process. Existing traditional and learning-based methods have exhibited limited efficacy due to their reliance on single-image approaches, where flare removal is highly ill-posed. We address this by framing flare removal as a multi-view image problem, taking advantage of the view-dependent nature of flare artifacts. This approach leverages information from neighboring views to recover details obscured by flare in individual images. Our proposed framework, GN-FR (Generalizable Neural Radiance Fields for Flare Removal), can render flare-free views from a sparse set of input images affected by lens flare and generalizes across different scenes in an unsupervised manner. GN-FR incorporates several modules within the Generalizable NeRF Transformer (GNT) framework: Flare-occupancy Mask Generation (FMG), View Sampler (VS), and Point Sampler (PS). To overcome the impracticality of capturing both flare-corrupted and flare-free data, we introduce a masking loss function that utilizes mask information in an unsupervised setting. Additionally, we present a 3D multi-view flare dataset, comprising 17 real flare scenes with 782 images, 80 real flare patterns, and their corresponding annotated flare-occupancy masks. To our knowledge, this is the first work to address flare removal within a Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) framework.
炫光作为一种由镜头系统内的不必要散射和反射引起的光学现象,在成像中构成重大挑战。炫光图案多种多样,例如光晕、条纹、色彩溢出和朦胧,这些都使炫光去除过程复杂化。由于依赖于单图像方法,现有的传统和基于学习的方法在炫光去除方面的表现往往有限,而炫光去除是一个高度不适定的问题。我们通过将炫光去除构造成多视图图像问题来解决这一问题,利用炫光伪影的视图相关性。这种方法利用相邻视图的详细信息来恢复被炫光遮挡的单幅图像中的细节。我们提出的框架GN-FR(用于炫光去除的可泛化神经辐射场)能够从受镜头炫光影响的稀疏输入图像集中呈现无炫光的视图,并以无监督的方式在不同的场景中泛化。GN-FR在可泛化NeRF转换器(GNT)框架内结合了多个模块:炫光占用掩模生成器(FMG)、视图采样器(VS)和点采样器(PS)。为了克服同时获取受炫光破坏和未受破坏的数据的不实际性,我们引入了一个掩模损失函数,该函数在无监督环境中利用掩模信息。此外,我们还推出了一个3D多视图炫光数据集,包含17个真实炫光场景、包含共782幅图像的图像以及与其相对应的带注释的炫光占用掩模。据我们所知,这是首次在神经辐射场(NeRF)框架内解决炫光去除问题的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
光学现象中的耀斑,由于镜头系统中的意外散射和反射而产生,对成像造成了重大挑战。耀斑的多样表现形态,如光晕、条纹、色彩溢出和雾霾等,使得耀斑去除过程变得复杂。现有的传统和基于学习的方法表现出有限的效率,因为它们依赖于单图像方法,而耀斑去除在此情况下高度不适定。我们通过将耀斑去除作为多视图图像问题来解决这一问题,利用耀斑伪影的视图相关性。这种方法利用邻近视图的资讯来恢复被耀斑遮挡的单幅图像中的细节。我们提出的框架GN-FR(用于耀斑去除的可泛化神经辐射场),可以从一组稀疏的受镜头耀斑影响的输入图像中渲染无耀斑的视图,并以无监督的方式泛化到不同的场景。GN-FR在Generalizable NeRF Transformer(GNT)框架内结合了多个模块:耀斑占用掩模生成(FMG)、视图采样器(VS)和点采样器(PS)。为了克服同时捕获受耀斑损坏和无耀斑数据的不切实际性,我们引入了一个掩模损失函数,该函数在无监督设置中使用掩模信息。此外,我们还推出了一个包含17个真实耀斑场景、包含782张图像和80个真实耀斑模式及其相应的标注耀斑占用掩模的3D多视图耀斑数据集。据我们所知,这是首次在神经辐射场(NeRF)框架内解决耀斑去除问题的研究。
关键见解
- 引入了一种新的方法来解决镜头中的耀斑问题,通过将其视为多视图图像问题并利用视图间的相关性。
- 提出了一种基于神经辐射场的框架GN-FR,可从受影响的稀疏图像集中有效去除耀斑,并可在不同场景中泛化。
- GN-FR框架结合了多个模块,包括用于生成耀斑占用掩模的FMG模块、视图采样器VS和点采样器PS模块。
- 开发了一个用于训练和评估GN-FR的新的数据集。这是一个涵盖广泛耀斑模式的全面数据集,适合支持对该问题的深入研究。
- 提出了一种新的掩模损失函数,可以在没有配对无耀斑数据的情况下进行训练,这是一种创新的无监督学习方法。
点此查看论文截图


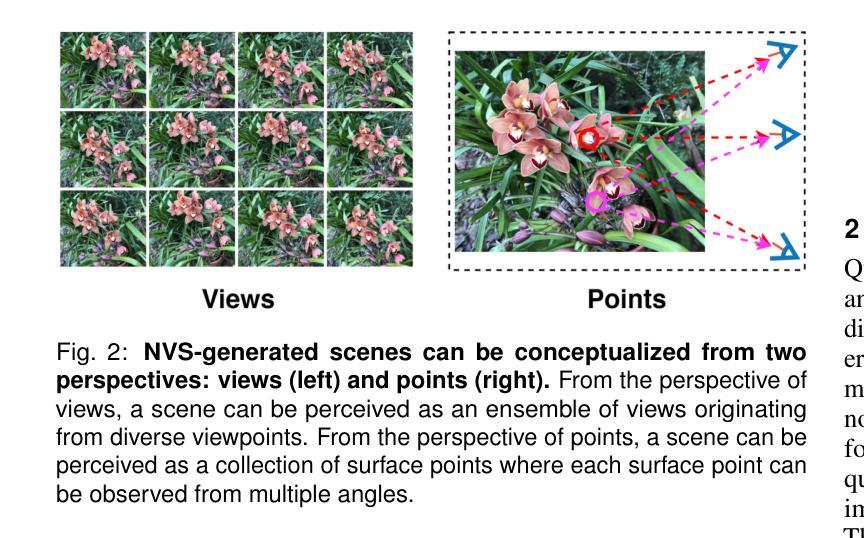
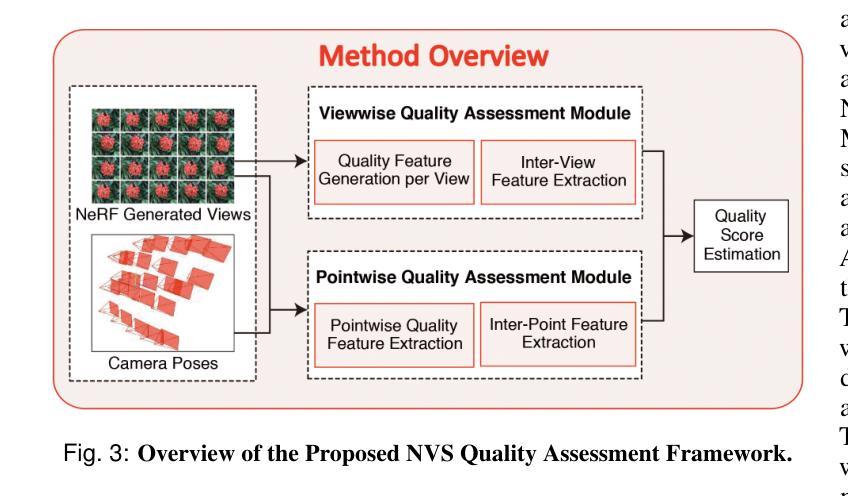
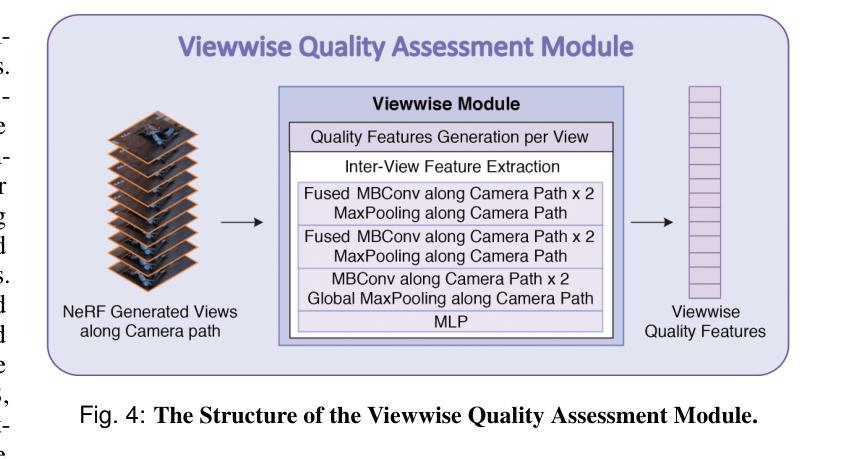
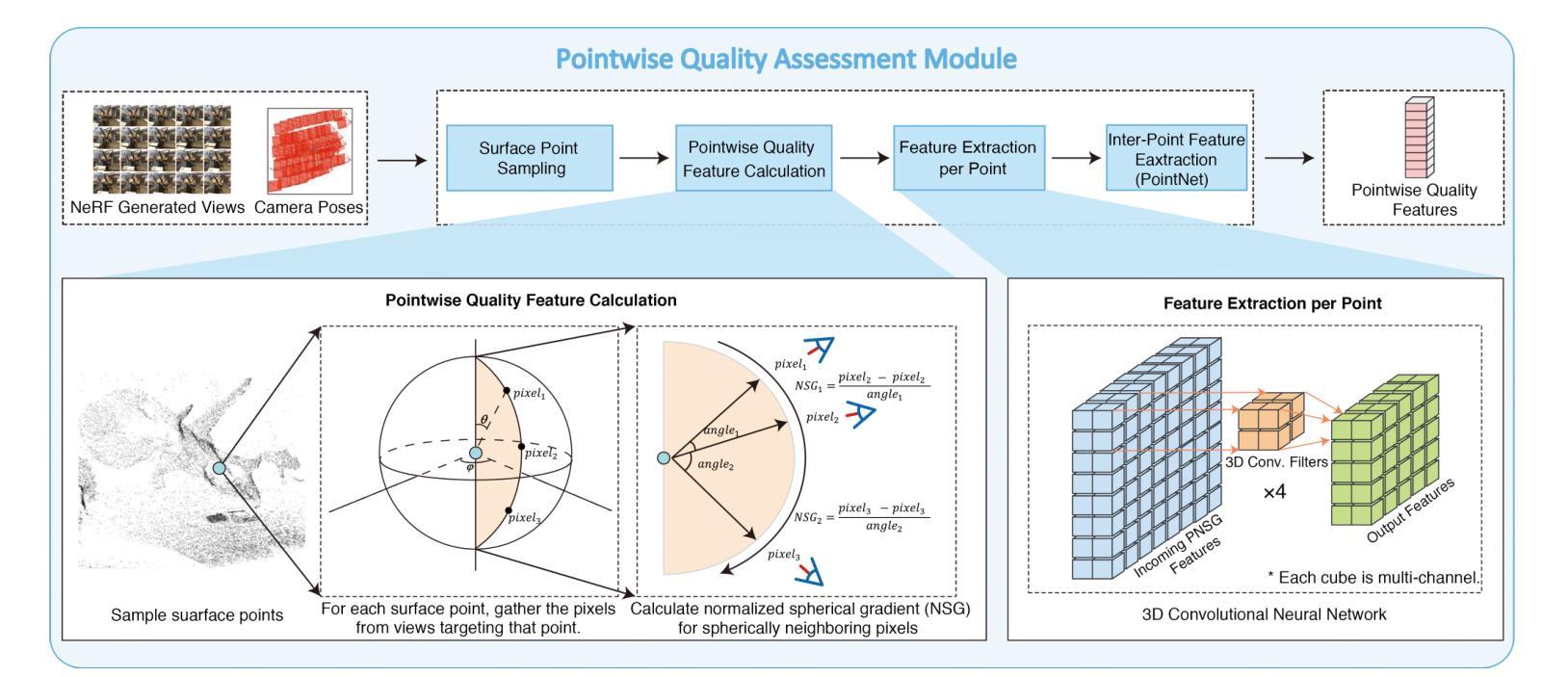
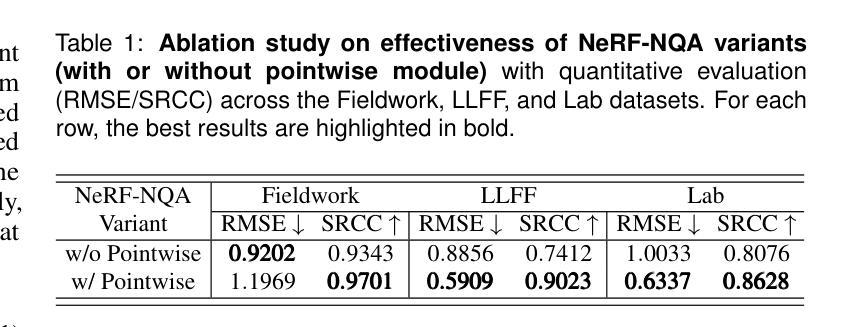
NeRF-NQA: No-Reference Quality Assessment for Scenes Generated by NeRF and Neural View Synthesis Methods
Authors:Qiang Qu, Hanxue Liang, Xiaoming Chen, Yuk Ying Chung, Yiran Shen
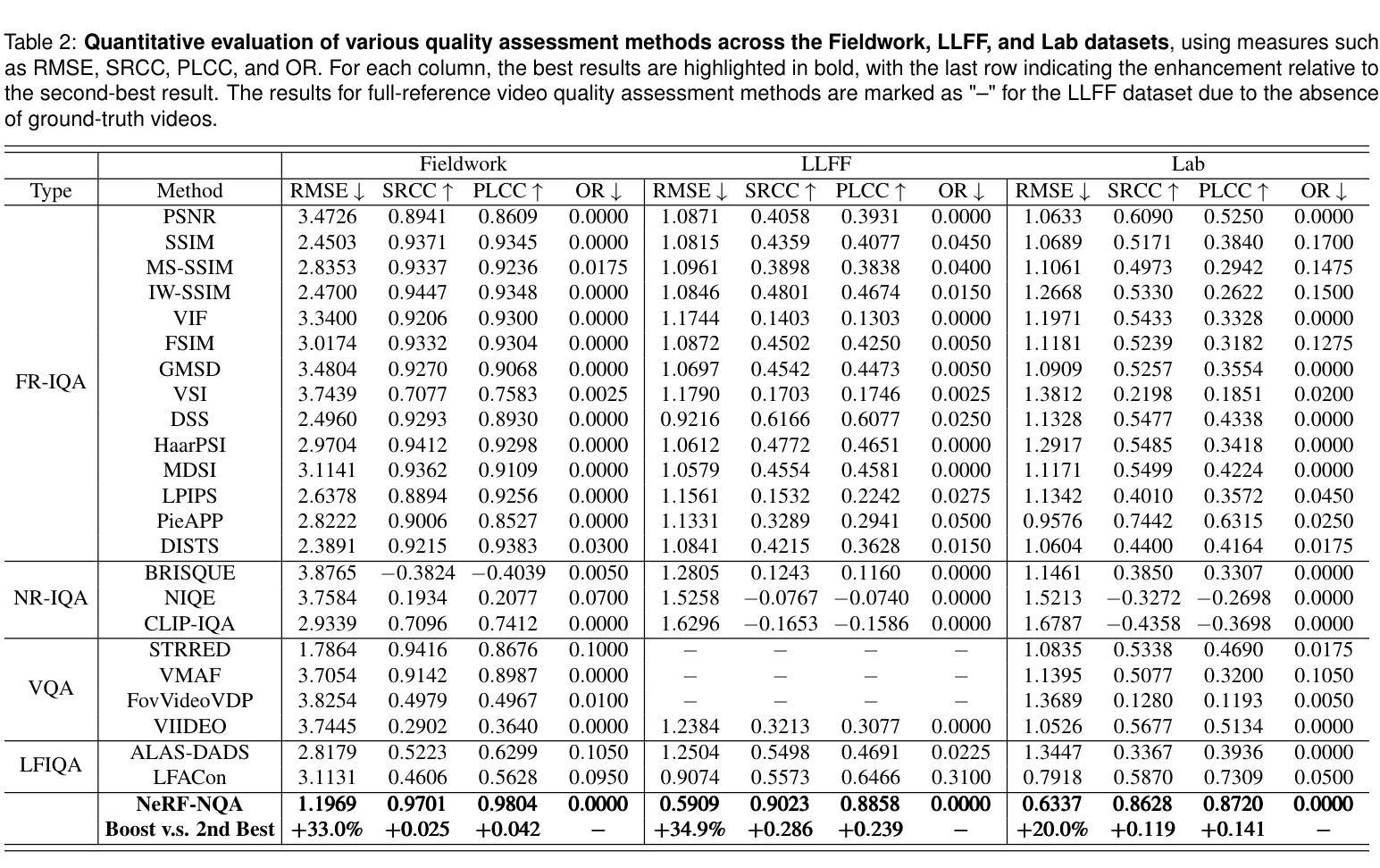
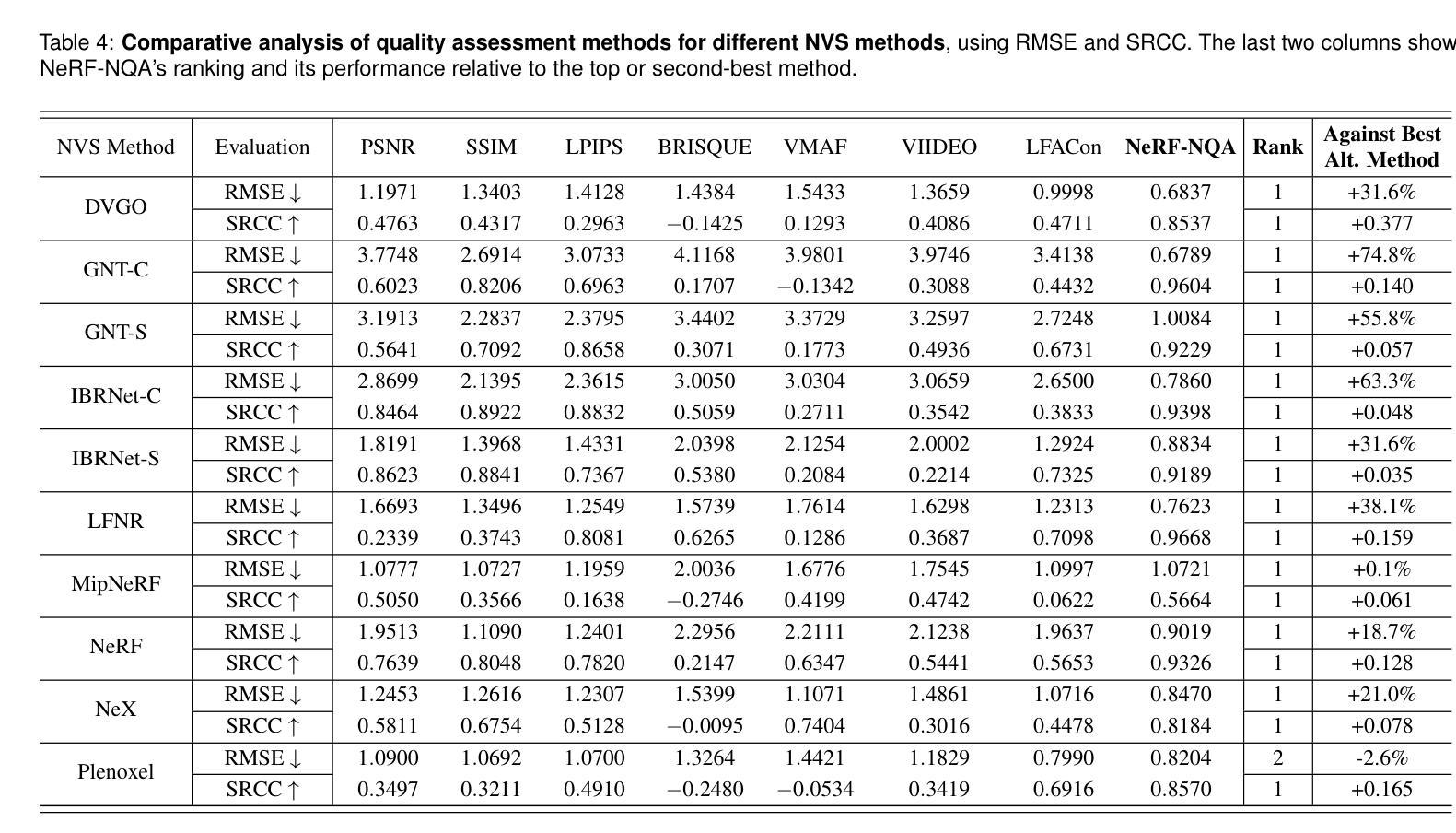
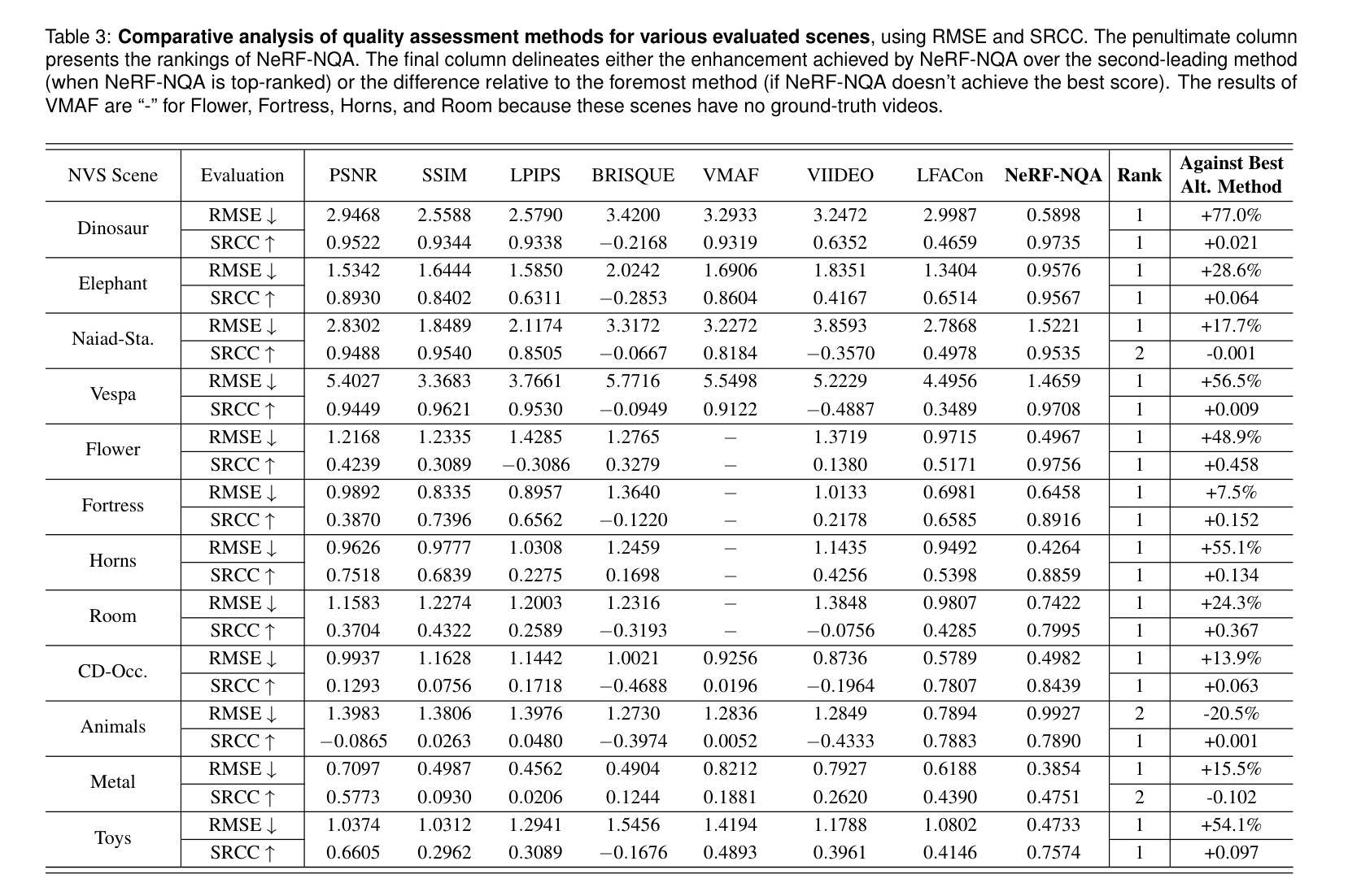
Neural View Synthesis (NVS) has demonstrated efficacy in generating high-fidelity dense viewpoint videos using a image set with sparse views. However, existing quality assessment methods like PSNR, SSIM, and LPIPS are not tailored for the scenes with dense viewpoints synthesized by NVS and NeRF variants, thus, they often fall short in capturing the perceptual quality, including spatial and angular aspects of NVS-synthesized scenes. Furthermore, the lack of dense ground truth views makes the full reference quality assessment on NVS-synthesized scenes challenging. For instance, datasets such as LLFF provide only sparse images, insufficient for complete full-reference assessments. To address the issues above, we propose NeRF-NQA, the first no-reference quality assessment method for densely-observed scenes synthesized from the NVS and NeRF variants. NeRF-NQA employs a joint quality assessment strategy, integrating both viewwise and pointwise approaches, to evaluate the quality of NVS-generated scenes. The viewwise approach assesses the spatial quality of each individual synthesized view and the overall inter-views consistency, while the pointwise approach focuses on the angular qualities of scene surface points and their compound inter-point quality. Extensive evaluations are conducted to compare NeRF-NQA with 23 mainstream visual quality assessment methods (from fields of image, video, and light-field assessment). The results demonstrate NeRF-NQA outperforms the existing assessment methods significantly and it shows substantial superiority on assessing NVS-synthesized scenes without references. An implementation of this paper are available at https://github.com/VincentQQu/NeRF-NQA.
神经视图合成(NVS)已经显示出使用稀疏视图图像集生成高保真密集视点视频的效能。然而,现有的质量评估方法,如PSNR、SSIM和LPIPS,并不适用于由NVS和NeRF变体合成的密集视点场景,因此,它们在捕捉感知质量方面常常不足,包括NVS合成场景的空间和角度方面。此外,缺乏密集的地面真实视图使得对NVS合成场景进行全参考质量评估具有挑战性。例如,LLFF等数据集只提供稀疏图像,不足以进行完整的全参考评估。为了解决上述问题,我们提出了NeRF-NQA,这是第一种用于由NVS和NeRF变体合成的密集观察场景的无参考质量评估方法。NeRF-NQA采用联合质量评估策略,结合了视图方法和点方法,以评估NVS生成场景的质量。视图方法评估每个单独合成视图的空质量以及整体视图间的一致性,而点方法则侧重于场景表面点的角度质量以及它们的复合点间质量。进行了广泛评估,将NeRF-NQA与23种主流视觉质量评估方法(来自图像、视频和光场评估领域)进行比较。结果表明,NeRF-NQA在评估NVS合成场景方面显著优于现有评估方法,并且在无参考评估方面表现出极大的优势。该论文的实现可访问https://github.com/VincentQQu/NeRF-NQA。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
NeRF-NQA作为一种无参考质量评估方法,针对密集观测场景合成的质量评估问题进行了创新。该方法结合了视点方法和点方法,旨在评估NVS生成的场景质量。与传统的质量评估方法相比,NeRF-NQA能更好地捕捉合成场景的感知质量,包括空间与角度方面。研究成果在广泛评估中验证了其优越性。具体实现可参见相关GitHub仓库。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF-NQA是首个针对由NVS和NeRF变体合成的密集观测场景的无参考质量评估方法。
- NeRF-NQA采用联合质量评估策略,包括视点方法和点方法,以全面评估NVS生成的场景质量。
- NeRF-NQA能够评估每个合成视点的空间质量和视点间的整体一致性。
- NeRF-NQA可以关注场景表面点的角度质量以及各点之间的复合质量。
- 与主流视觉质量评估方法相比,NeRF-NQA在评估NVS合成的场景时表现出显著优势。
- 缺乏密集地面真实视图给NVS合成的场景全参考质量评估带来挑战,而NeRF-NQA解决了这一问题。
点此查看论文截图

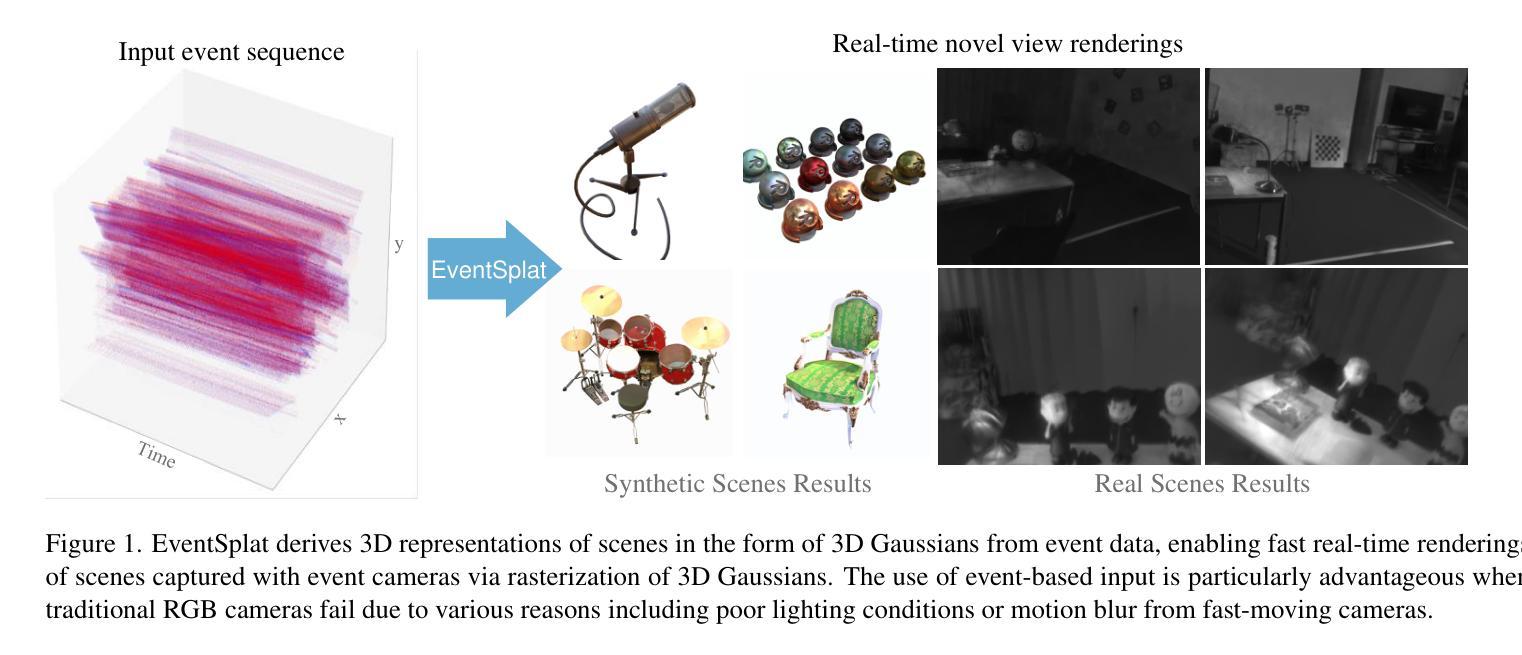
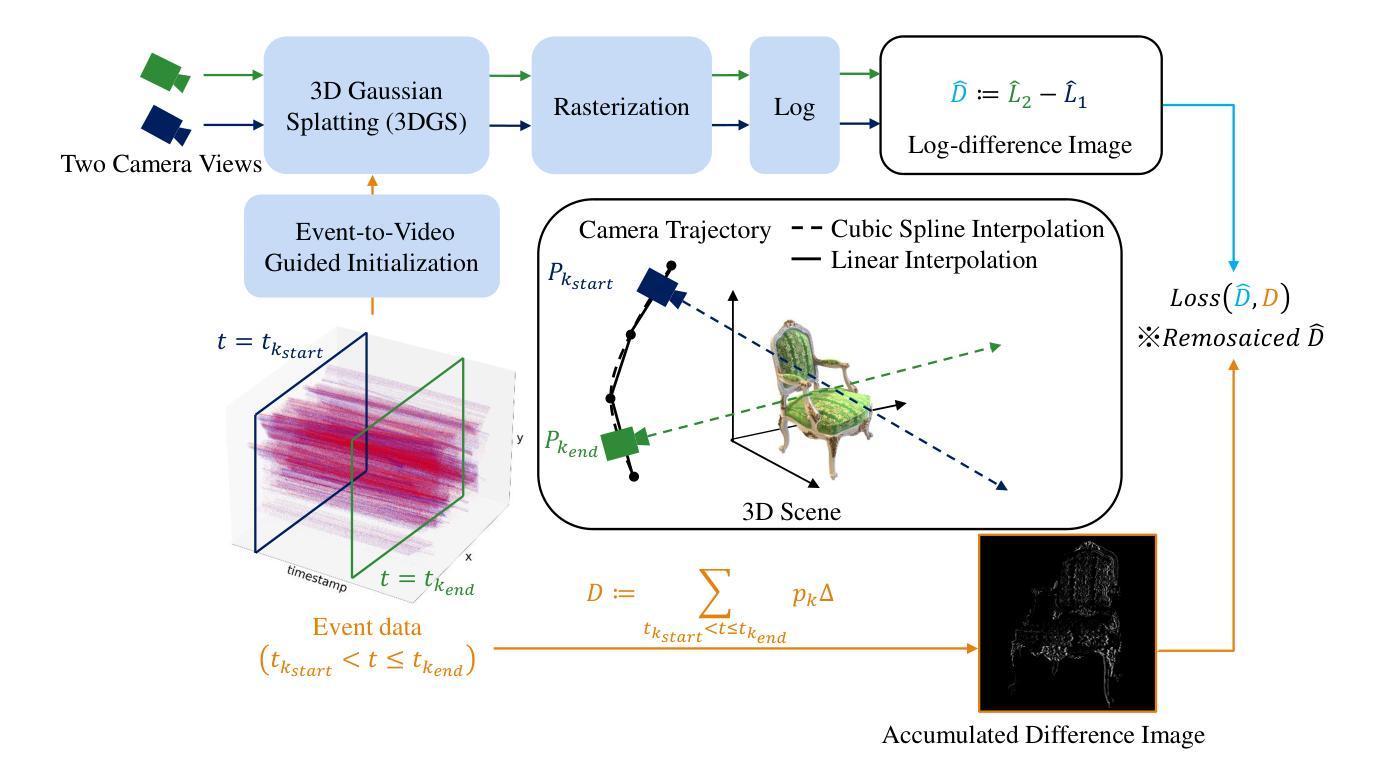
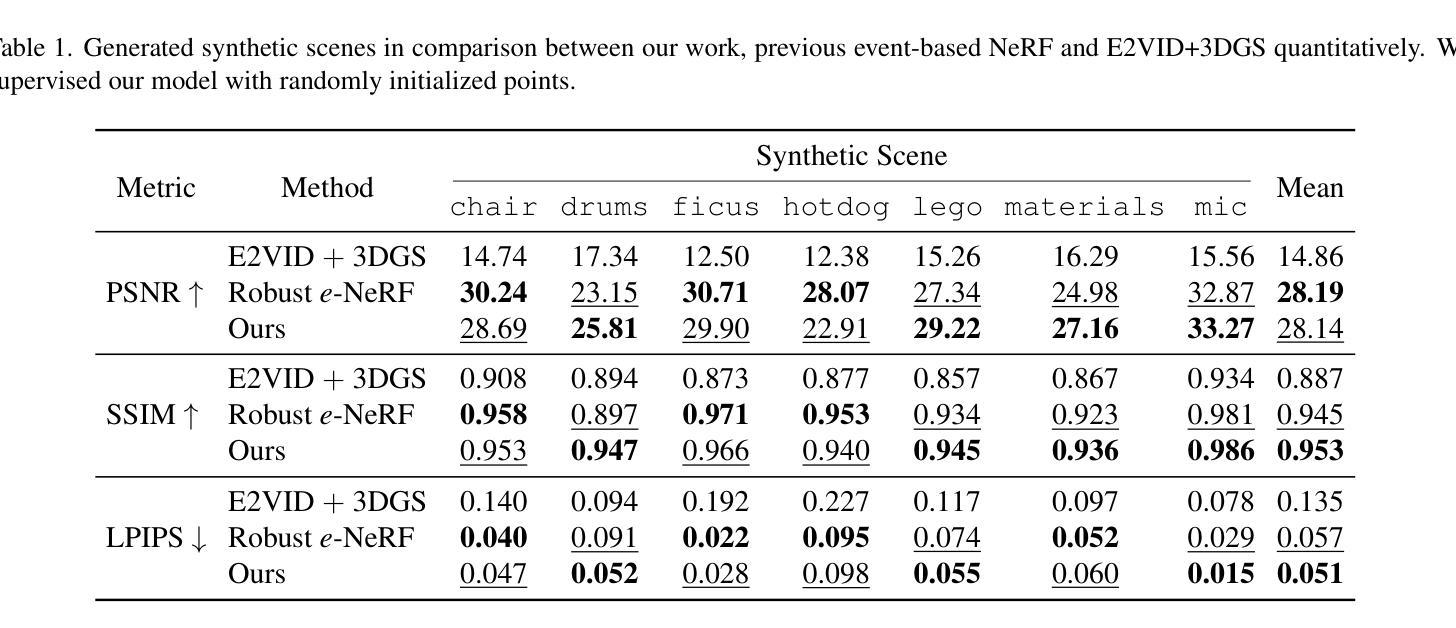
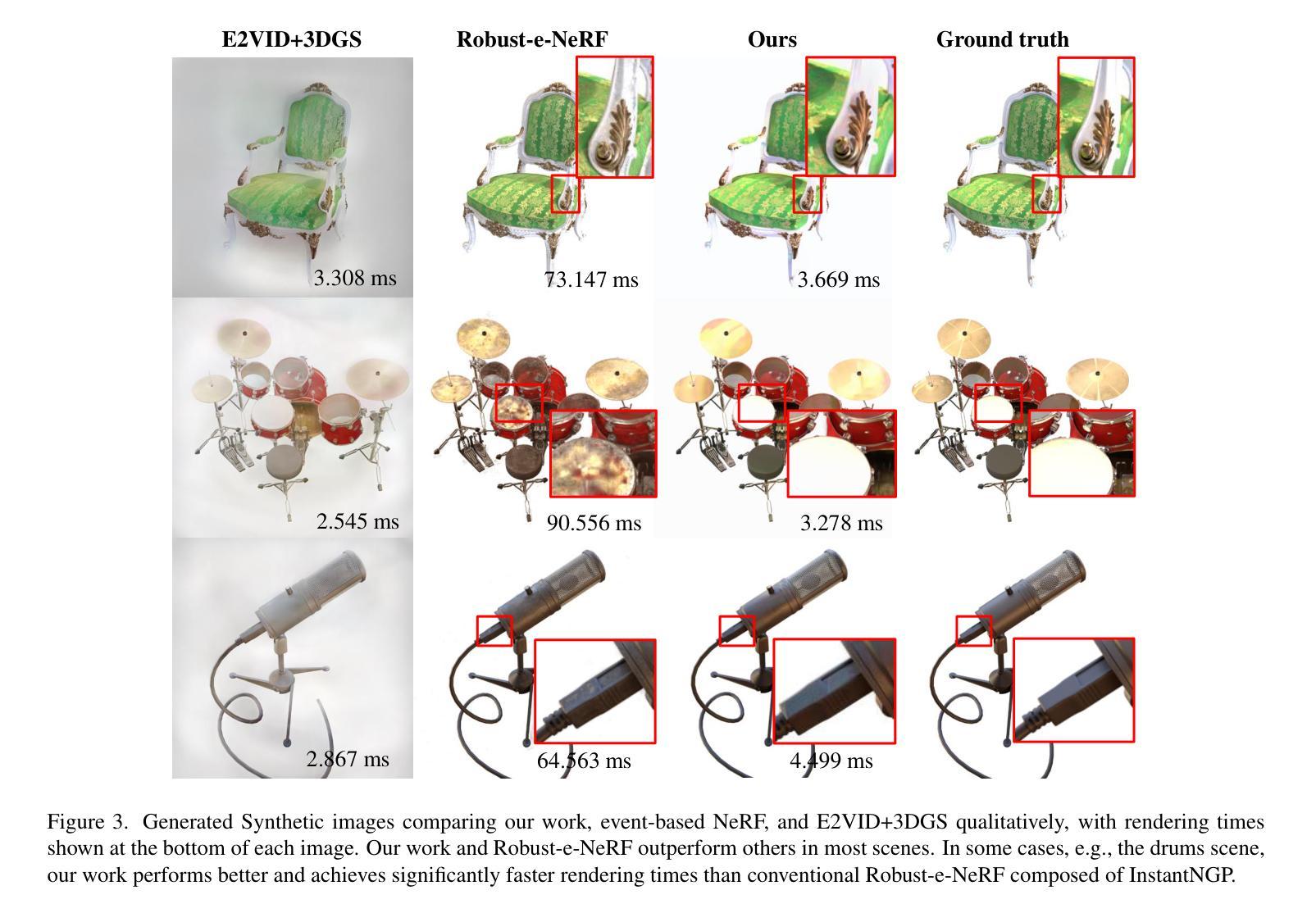
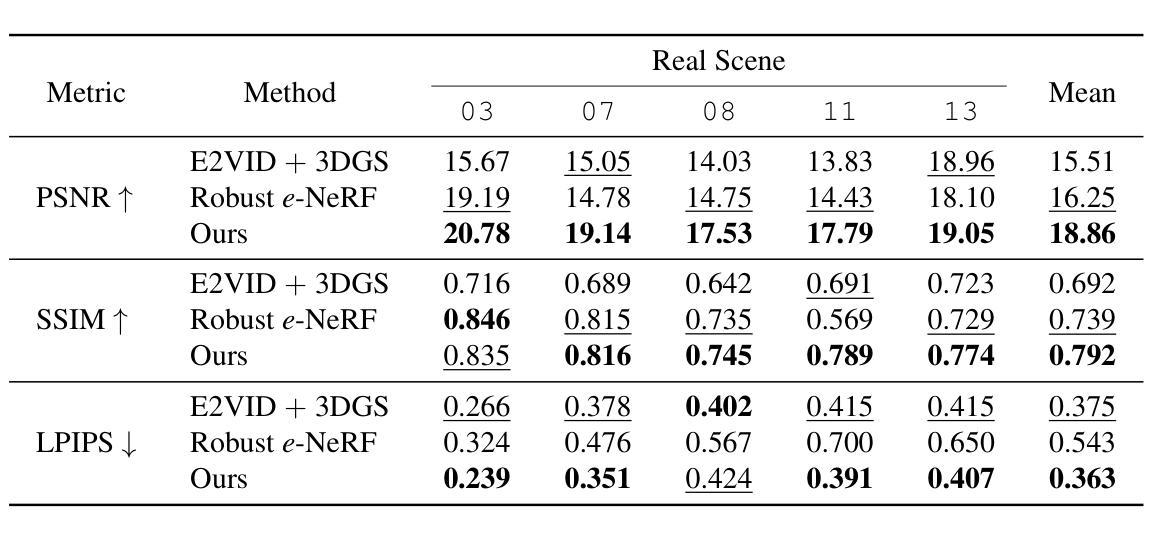
EventSplat: 3D Gaussian Splatting from Moving Event Cameras for Real-time Rendering
Authors:Toshiya Yura, Ashkan Mirzaei, Igor Gilitschenski
We introduce a method for using event camera data in novel view synthesis via Gaussian Splatting. Event cameras offer exceptional temporal resolution and a high dynamic range. Leveraging these capabilities allows us to effectively address the novel view synthesis challenge in the presence of fast camera motion. For initialization of the optimization process, our approach uses prior knowledge encoded in an event-to-video model. We also use spline interpolation for obtaining high quality poses along the event camera trajectory. This enhances the reconstruction quality from fast-moving cameras while overcoming the computational limitations traditionally associated with event-based Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) methods. Our experimental evaluation demonstrates that our results achieve higher visual fidelity and better performance than existing event-based NeRF approaches while being an order of magnitude faster to render.
我们介绍了一种利用事件相机数据通过高斯点积进行新颖视角合成的方法。事件相机提供卓越的时间分辨率和高动态范围。利用这些功能,我们能够有效地解决快速摄像机运动下的新颖视角合成挑战。为了优化过程的初始化,我们的方法使用事件到视频的模型中的先验知识。我们还使用样条插值来获得事件相机轨迹的高质量姿态。这提高了从快速移动的相机进行重建的质量,同时克服了传统上与基于事件的神视辐射场(NeRF)方法相关的计算限制。我们的实验评估表明,我们的结果达到了更高的视觉保真度和性能,并且渲染速度比现有的基于事件的NeRF方法快一个数量级。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用事件相机数据进行新型视图合成的方法,通过高斯点云技术实现。事件相机具有出色的时间分辨率和高动态范围,使得在快速相机运动的情况下,能够有效地应对视图合成挑战。该方法使用事件到视频的模型编码先验知识来进行优化过程的初始化,并使用样条插值来获得事件相机轨迹的高质量姿态。这提高了快速移动相机的重建质量,并克服了传统事件基础神经辐射场(NeRF)方法的计算限制。实验评估表明,该方法的结果具有更高的视觉保真度和更好的性能,并且渲染速度比现有事件基础NeRF方法快一个数量级。
Key Takeaways
- 利用事件相机的优秀时间分辨率和高动态范围进行新型视图合成。
- 使用事件到视频的模型编码先验知识优化过程。
- 通过样条插值获得高质量姿态,提高快速移动相机的重建质量。
- 克服了传统事件基础神经辐射场(NeRF)方法的计算限制。
- 实现高视觉保真度和良好性能的结果。
- 相比现有事件基础NeRF方法,渲染速度更快。
点此查看论文截图

Diffusing Differentiable Representations
Authors:Yash Savani, Marc Finzi, J. Zico Kolter
We introduce a novel, training-free method for sampling differentiable representations (diffreps) using pretrained diffusion models. Rather than merely mode-seeking, our method achieves sampling by “pulling back” the dynamics of the reverse-time process–from the image space to the diffrep parameter space–and updating the parameters according to this pulled-back process. We identify an implicit constraint on the samples induced by the diffrep and demonstrate that addressing this constraint significantly improves the consistency and detail of the generated objects. Our method yields diffreps with substantially improved quality and diversity for images, panoramas, and 3D NeRFs compared to existing techniques. Our approach is a general-purpose method for sampling diffreps, expanding the scope of problems that diffusion models can tackle.
我们介绍了一种利用预训练的扩散模型进行可微分表示(diffrep)采样的新型无训练方法。我们的方法不是单纯地寻求模式,而是通过“拉回”反向时间过程的动态来实现采样——从图像空间到diffrep参数空间,并根据拉回的流程更新参数。我们识别出由diffrep引起的样本的隐式约束,并证明解决这一约束可以显著提高生成对象的连贯性和细节。与现有技术相比,我们的方法在图像、全景图和3D NeRF的diffrep生成方面,具有更高质量和多样性的表现。我们的方法是通用的diffrep采样方法,扩大了扩散模型所能解决的问题范围。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published at NeurIPS 2024
摘要
基于预训练的扩散模型,我们提出了一种无需训练的可采样可微表示(diffrep)的新方法。与其他方法不同,我们的方法通过“拉回”反向时间过程的动态来实现采样,从图像空间到diffrep参数空间,并根据拉回的过程更新参数。我们确定了diffrep所隐含的样本约束,并证明解决这一约束能显著提高生成对象的连贯性和细节。相比于现有技术,我们的方法在图像、全景和三维NeRF的diffrep生成方面有着显著的质量提升和多样性。此外,我们的方法为采样diffrep提供了一种通用方法,扩大了扩散模型可解决的问题范围。
要点摘要
- 提出了一种全新的无需训练的可采样可微表示(diffrep)方法。
- 通过“拉回”反向时间过程的动态实现从图像空间到diffrep参数空间的采样。
- 确定并解决了diffrep采样中的隐含约束问题。
- 在图像、全景和三维NeRF的diffrep生成方面,显著提高了生成对象的质量和多样性。
- 通过扩散模型实现了高质量的diffrep采样,扩展了其应用范围。
- 该方法具有广泛的应用前景,为采样diffrep提供了一种通用方法。
点此查看论文截图

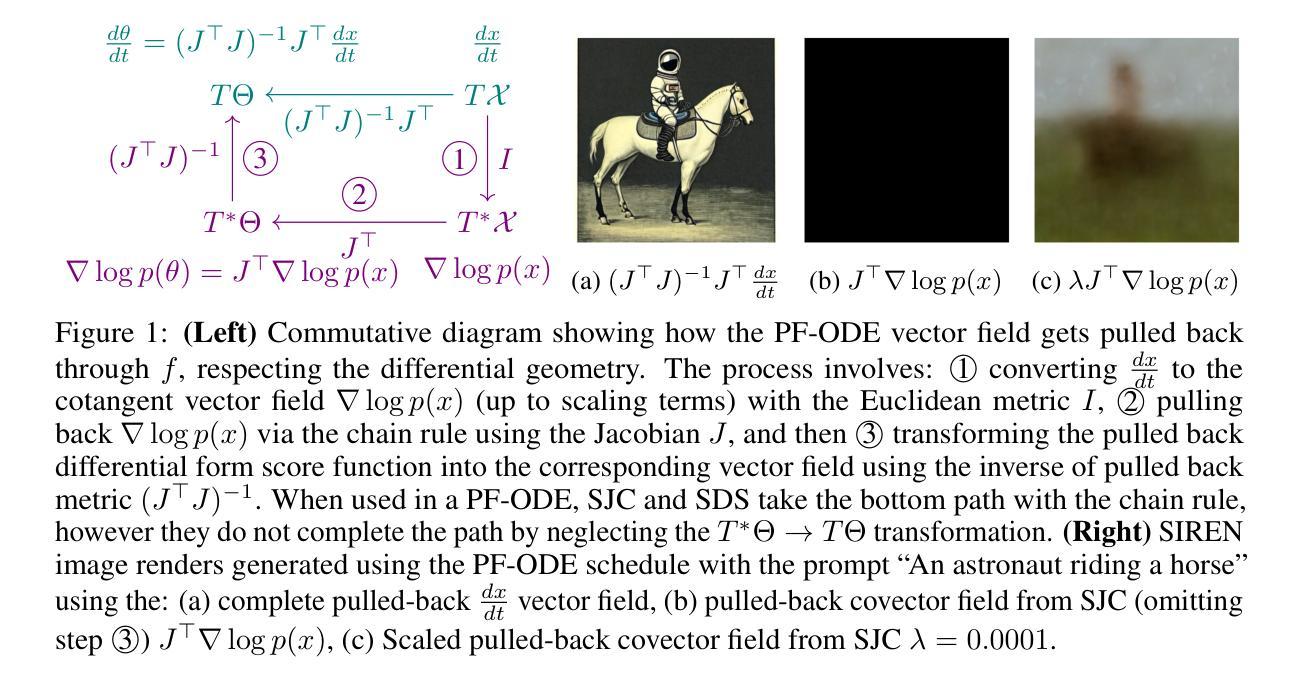
Enhancing operational wind downscaling capabilities over Canada: Application of a Conditional Wasserstein GAN methodology
Authors:Jorge Guevara, Victor Nascimento, Johannes Schmude, Daniel Salles, Simon Corbeil-Létourneau, Madalina Surcel, Dominique Brunet
Wind downscaling is essential for improving the spatial resolution of weather forecasts, particularly in operational Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP). This study advances wind downscaling by extending the DownGAN framework introduced by Annau et al.,to operational datasets from the Global Deterministic Prediction System (GDPS) and High-Resolution Deterministic Prediction System (HRDPS), covering the entire Canadian domain. We enhance the model by incorporating high-resolution static covariates, such as HRDPS-derived topography, into a Conditional Wasserstein Generative Adversarial Network with Gradient Penalty, implemented using a UNET-based generator. Following the DownGAN framework, our methodology integrates low-resolution GDPS forecasts (15 km, 10-day horizon) and high-resolution HRDPS forecasts (2.5 km, 48-hour horizon) with Frequency Separation techniques adapted from computer vision. Through robust training and inference over the Canadian region, we demonstrate the operational scalability of our approach, achieving significant improvements in wind downscaling accuracy. Statistical validation highlights reductions in root mean square error (RMSE) and log spectral distance (LSD) metrics compared to the original DownGAN. High-resolution conditioning covariates and Frequency Separation strategies prove instrumental in enhancing model performance. This work underscores the potential for extending high-resolution wind forecasts beyond the 48-hour horizon, bridging the gap to the 10-day low resolution global forecast window.
风场降尺度化对于提高天气预报的空间分辨率至关重要,特别是在业务数值天气预报(NWP)中。本研究通过扩展Annau等人介绍的DownGAN框架,将风场降尺度化技术应用于全球确定性预测系统(GDPS)和高分辨率确定性预测系统(HRDPS)的业务数据集,覆盖整个加拿大区域。我们通过将高分辨率静态协变量(如HRDPS衍生的地形)纳入带有梯度惩罚的条件Wasserstein生成对抗网络,增强了模型的功能。该网络采用基于UNET的生成器实现。遵循DownGAN框架,我们的方法结合了低分辨率GDPS预测(15公里,10天视野)和高分辨率HRDPS预测(2.5公里,48小时视野),并采用了从计算机视觉中改编的频率分离技术。通过在加拿大地区的稳健训练和推理,我们展示了该方法在业务规模上的可扩展性,在风场降尺度化精度方面取得了显著提高。统计验证结果显示,与原始DownGAN相比,均方根误差(RMSE)和对数谱距离(LSD)指标有所降低。高分辨率条件协变量和频率分离策略对于提高模型性能起到了关键作用。这项工作突出了将高分辨率风场预测扩展到48小时视野之外的可能性,缩小了与10天低分辨率全球预测窗口的差距。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本主要介绍了对天气预测的风场精细化的研究。通过扩展DownGAN框架并融合静态协变量和高分辨率地形数据,研究人员提高了风场精细化的准确性。该模型在加拿大区域进行了稳健的训练和推理,显著提升了长期天气预报的精细化水平,并降低了预测误差。
Key Takeaways
- 研究人员扩展了DownGAN框架,将其应用于全球确定性预测系统和高分辨率确定性预测系统的操作数据集。
- 通过融合高分辨率静态协变量如地形数据,增强了模型的性能。
- 模型采用条件瓦瑟斯坦生成对抗网络,结合了梯度惩罚,提高了精细化水平。
- 在加拿大区域内进行了模型的稳健训练和推理,展示了方法在实际操作中的可扩展性。
- 通过频率分离技术提高了模型性能,与计算机视觉中的技术相结合,降低了根均方误差和对数谱距离指标。
- 高分辨率协变量和频率分离策略对于提高模型性能起到了关键作用。
点此查看论文截图

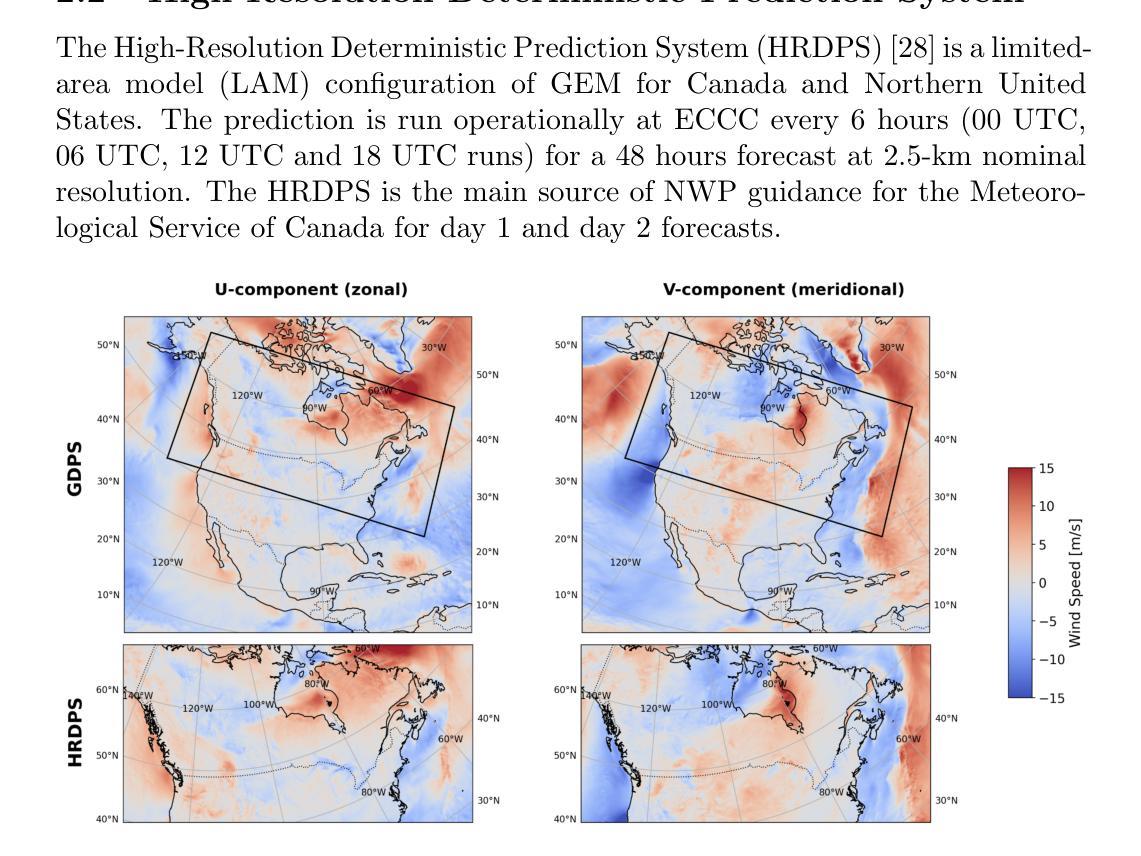
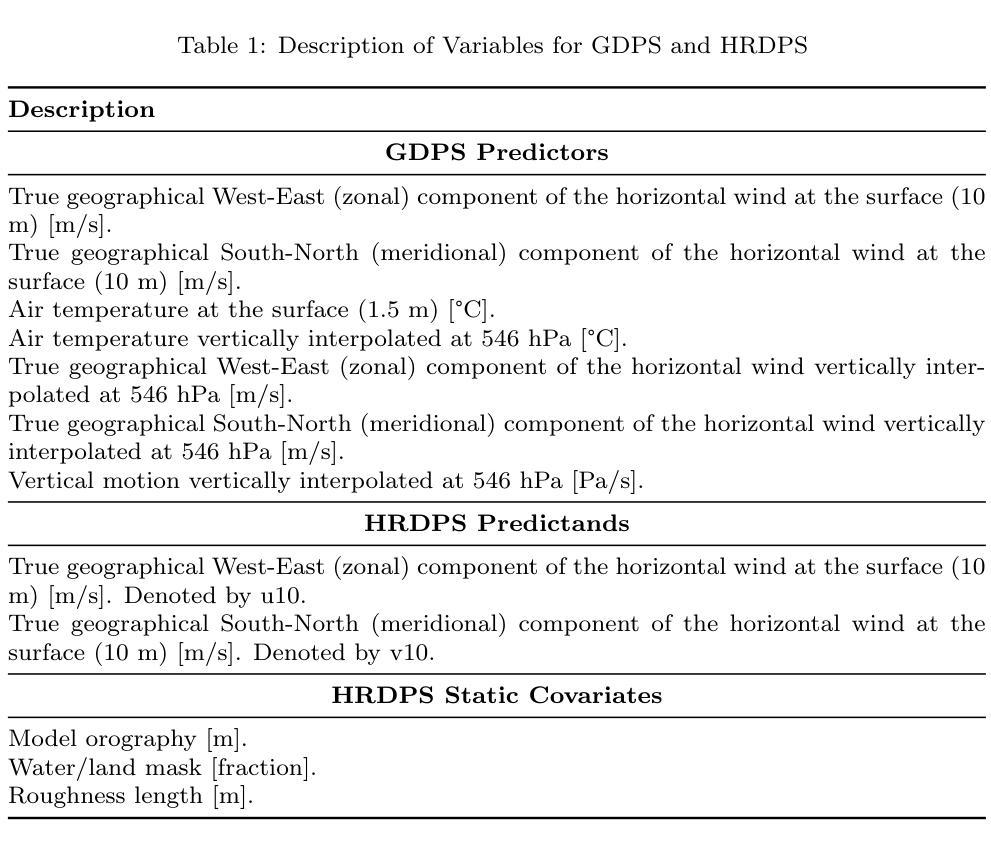
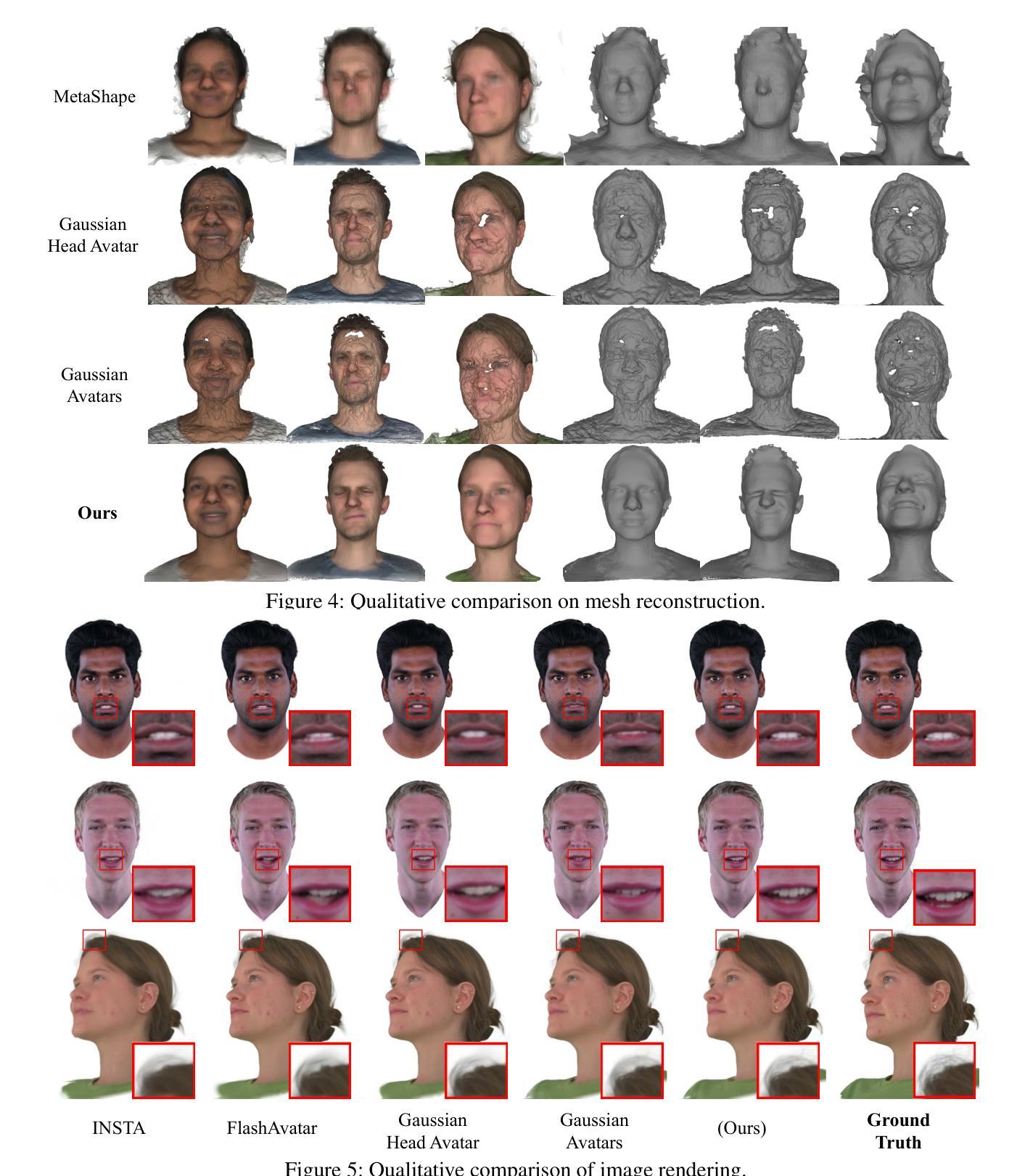
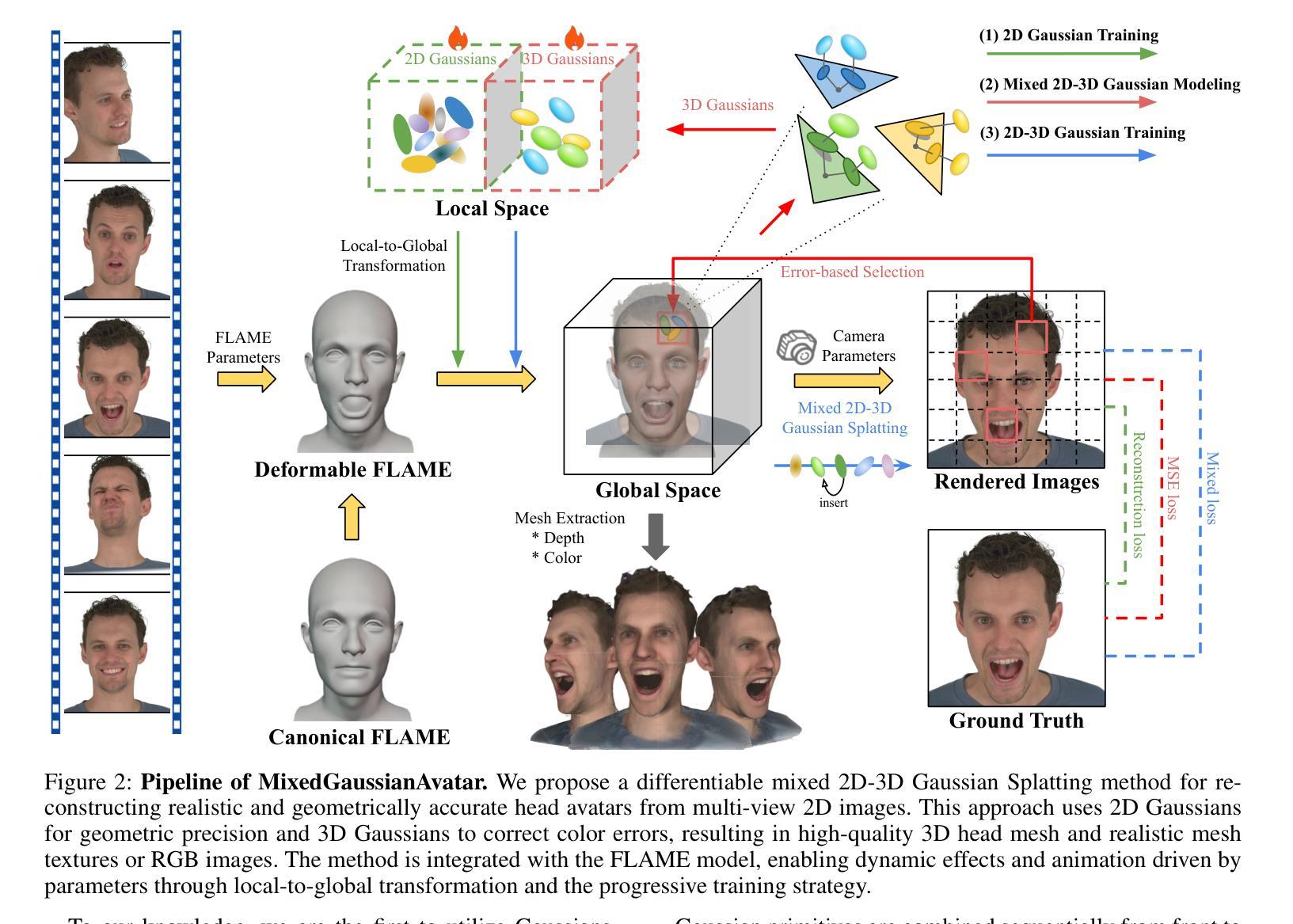
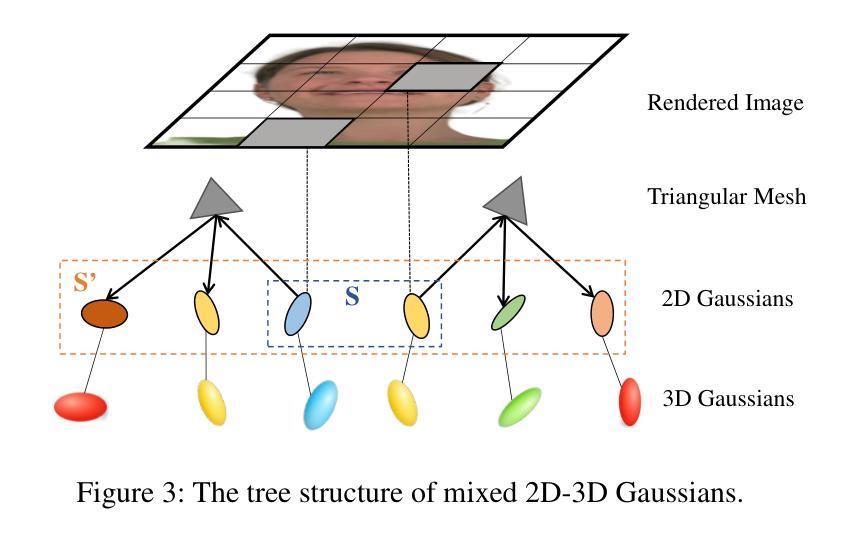
MixedGaussianAvatar: Realistically and Geometrically Accurate Head Avatar via Mixed 2D-3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Peng Chen, Xiaobao Wei, Qingpo Wuwu, Xinyi Wang, Xingyu Xiao, Ming Lu
Reconstructing high-fidelity 3D head avatars is crucial in various applications such as virtual reality. The pioneering methods reconstruct realistic head avatars with Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), which have been limited by training and rendering speed. Recent methods based on 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) significantly improve the efficiency of training and rendering. However, the surface inconsistency of 3DGS results in subpar geometric accuracy; later, 2DGS uses 2D surfels to enhance geometric accuracy at the expense of rendering fidelity. To leverage the benefits of both 2DGS and 3DGS, we propose a novel method named MixedGaussianAvatar for realistically and geometrically accurate head avatar reconstruction. Our main idea is to utilize 2D Gaussians to reconstruct the surface of the 3D head, ensuring geometric accuracy. We attach the 2D Gaussians to the triangular mesh of the FLAME model and connect additional 3D Gaussians to those 2D Gaussians where the rendering quality of 2DGS is inadequate, creating a mixed 2D-3D Gaussian representation. These 2D-3D Gaussians can then be animated using FLAME parameters. We further introduce a progressive training strategy that first trains the 2D Gaussians and then fine-tunes the mixed 2D-3D Gaussians. We demonstrate the superiority of MixedGaussianAvatar through comprehensive experiments. The code will be released at: https://github.com/ChenVoid/MGA/.
重建高保真3D头像对于虚拟现实等应用至关重要。开创性的方法使用神经辐射场(NeRF)重建逼真的头像,但受限于训练和渲染速度。基于3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)的最近的方法显著提高了训练和渲染的效率。然而,3DGS的表面不一致导致几何精度不佳;后来的2DGS使用2D surfels来提高几何精度,但牺牲了渲染保真度。为了结合2DGS和3DGS的优点,我们提出了一种名为MixedGaussianAvatar的新方法,用于真实且几何精确的头像重建。我们的主要想法是使用2D高斯重建3D头像的表面,以确保几何精度。我们将2D高斯附加到FLAME模型的三角网格上,并在2DGS的渲染质量不足的地方连接到额外的3D高斯,创建混合的2D-3D高斯表示。这些2D-3D高斯可以使用FLAME参数进行动画处理。我们还引入了一种渐进的训练策略,首先训练2D高斯,然后对混合的2D-3D高斯进行微调。我们通过全面的实验展示了MixedGaussianAvatar的优势。代码将在以下网址发布:https://github.com/ChenVoid/MGA/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project: https://chenvoid.github.io/MGA/
Summary
本文提出了一个名为MixedGaussianAvatar的新方法,用于基于Neural Radiance Fields(NeRF)技术重建高保真三维头像。该方法结合了二维Gaussians和三维Gaussians的优点,确保了几何准确性并提高了渲染质量。通过将二维Gaussians附着在FLAME模型的三角网格上,并在需要时添加额外的三维Gaussians,创建了一个混合的二维-三维高斯表示。此外,还采用了一种渐进式的训练策略,首先训练二维Gaussians,然后对混合的二维-三维Gaussians进行微调。MixedGaussianAvatar通过一系列实验证明了其优越性。
Key Takeaways
- MixedGaussianAvatar方法结合了二维Gaussians和三维Gaussians的优势,旨在重建高保真三维头像。
- 方法利用二维Gaussians重建三维头部的表面,确保几何准确性。
- 通过将二维Gaussians附着在FLAME模型的三角网格上,并在必要时添加额外的三维Gaussians,创建了混合的二维-三维高斯表示。
- 引入了渐进式的训练策略,首先训练二维Gaussians,再对混合的二维-三维Gaussians进行微调。
- 该方法可以提高渲染速度并改善几何准确性。
- MixedGaussianAvatar的优越性通过一系列实验得到了验证。
点此查看论文截图


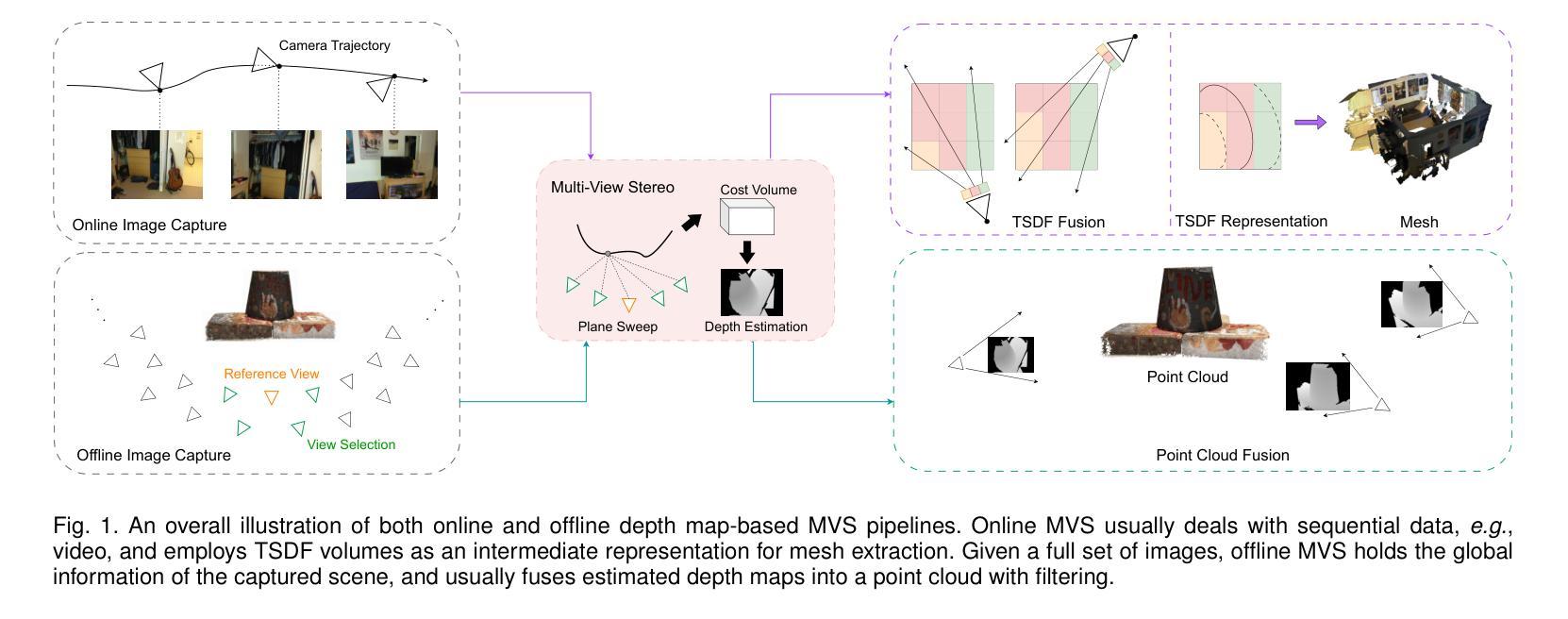
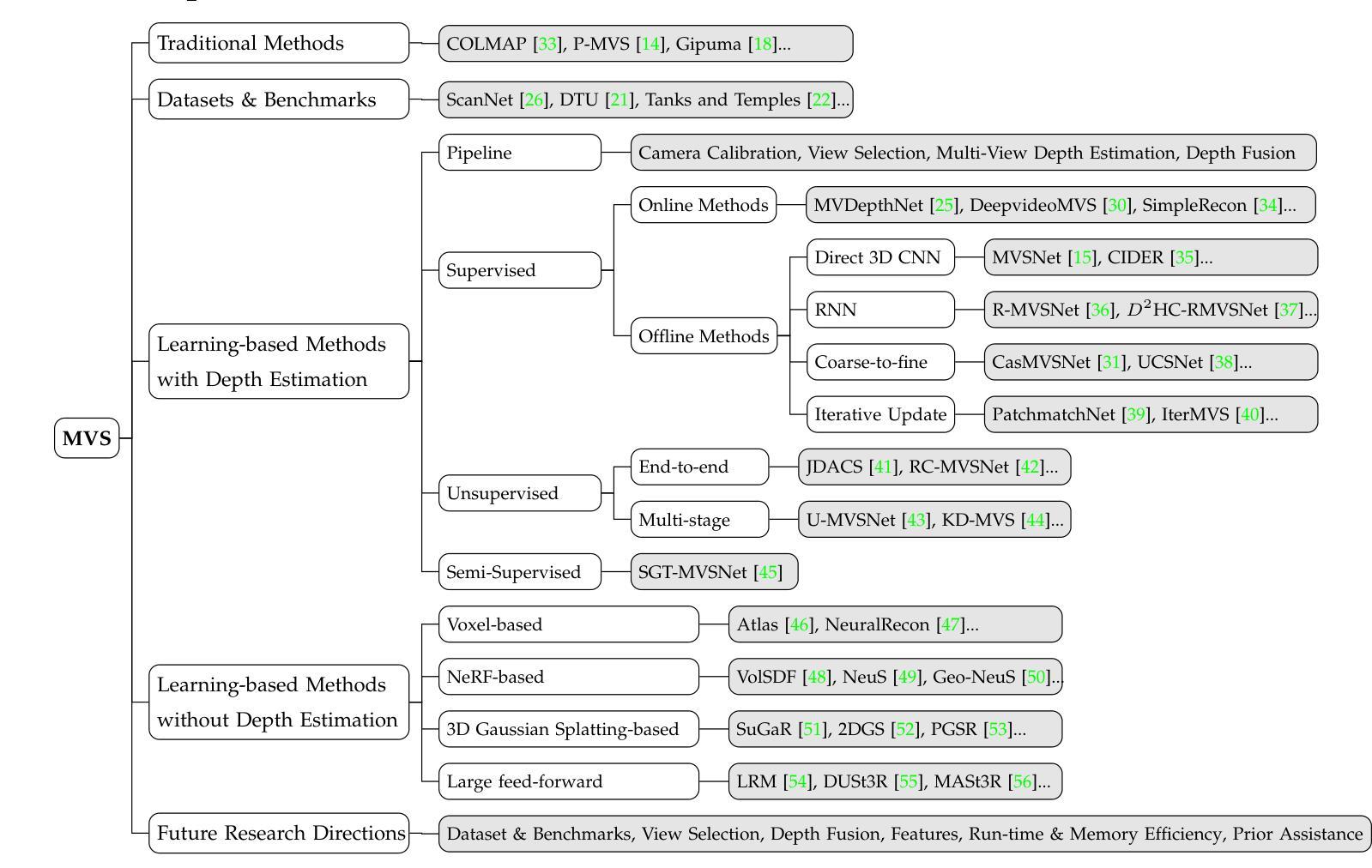
Learning-based Multi-View Stereo: A Survey
Authors:Fangjinhua Wang, Qingtian Zhu, Di Chang, Quankai Gao, Junlin Han, Tong Zhang, Richard Hartley, Marc Pollefeys
3D reconstruction aims to recover the dense 3D structure of a scene. It plays an essential role in various applications such as Augmented/Virtual Reality (AR/VR), autonomous driving and robotics. Leveraging multiple views of a scene captured from different viewpoints, Multi-View Stereo (MVS) algorithms synthesize a comprehensive 3D representation, enabling precise reconstruction in complex environments. Due to its efficiency and effectiveness, MVS has become a pivotal method for image-based 3D reconstruction. Recently, with the success of deep learning, many learning-based MVS methods have been proposed, achieving impressive performance against traditional methods. We categorize these learning-based methods as: depth map-based, voxel-based, NeRF-based, 3D Gaussian Splatting-based, and large feed-forward methods. Among these, we focus significantly on depth map-based methods, which are the main family of MVS due to their conciseness, flexibility and scalability. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive review of the literature at the time of this writing. We investigate these learning-based methods, summarize their performances on popular benchmarks, and discuss promising future research directions in this area.
三维重建旨在恢复场景的密集三维结构。它在增强/虚拟现实(AR/VR)、自动驾驶和机器人技术等各种应用中发挥着至关重要的作用。利用从不同视角捕捉的场景的多个视图,多视图立体(MVS)算法合成全面的三维表示,实现在复杂环境中的精确重建。由于其效率和有效性,MVS已成为基于图像的3D重建的关键方法。最近,随着深度学习取得的成功,已经提出了许多基于学习的MVS方法,与传统方法相比,这些方法取得了令人印象深刻的效果。我们将这些基于学习的方法分为以下几类:基于深度图的方法、基于体素的方法、基于NeRF的方法、基于三维高斯贴图的方法和大型前馈方法。其中,我们重点关注基于深度图的方法,由于其简洁性、灵活性和可扩展性,它们成为MVS的主要家族。在本文综述中,我们全面回顾了截至当前文献的情况。我们调查了这些基于学习的方法,总结了它们在流行基准测试上的性能,并讨论了该领域未来研究的富有希望的方向。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度学习的多视角立体(MVS)方法在3D重建领域取得了显著进展。本文主要关注基于深度图的MVS方法,它们具有简洁性、灵活性和可扩展性,是MVS的主要家族。本文提供了对这些学习方法的全面综述,总结了它们在流行基准测试上的性能,并讨论了该领域的未来研究方向。
Key Takeaways
- 3D重建旨在恢复场景的密集3D结构,在增强/虚拟现实、自动驾驶和机器人技术等领域有广泛应用。
- 多视角立体(MVS)算法通过从不同视角捕捉场景的多视角图像,合成全面的3D表示,实现在复杂环境中的精确重建。
- MVS已成为图像3D重建的关键方法,因其高效性和效果性。
- 深度学习在MVS方法中的应用已经取得了令人印象深刻的性能,产生了多种学习基于的方法,如深度图基于、体素基于、NeRF基于等。
- 深度图基于的方法是MVS的主要家族,因其简洁性、灵活性和可扩展性而受到关注。
- 本文提供了学习基于的MVS方法的全面综述,总结了它们在流行基准测试上的性能。
点此查看论文截图

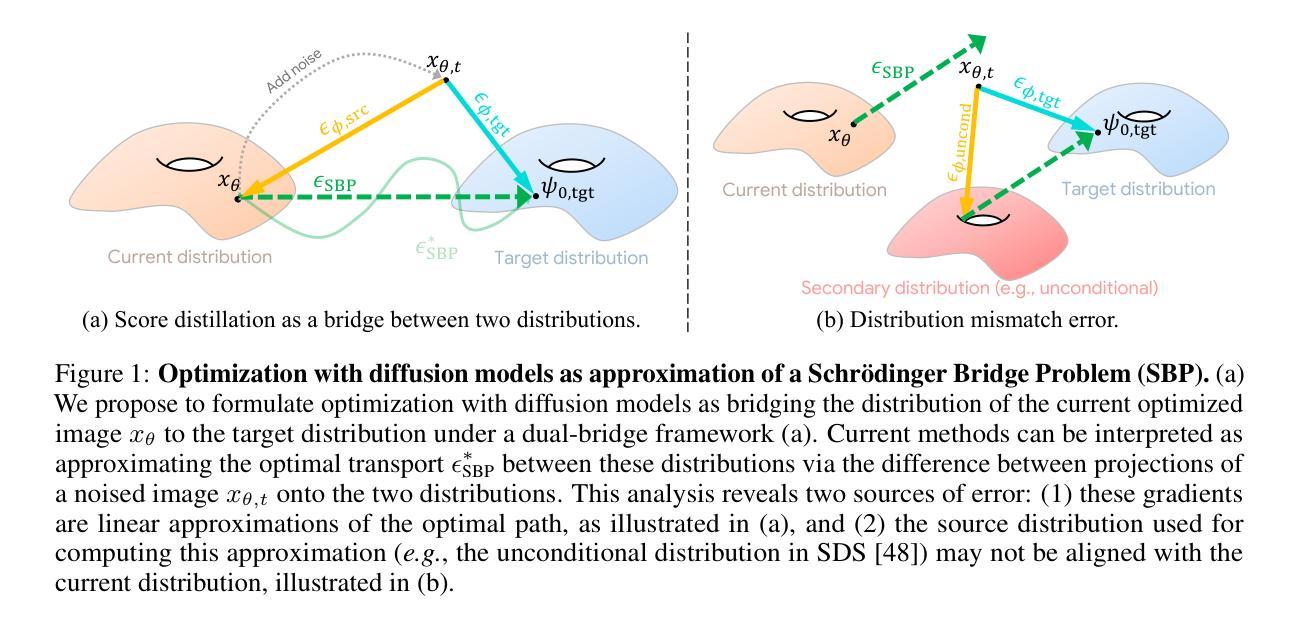
Rethinking Score Distillation as a Bridge Between Image Distributions
Authors:David McAllister, Songwei Ge, Jia-Bin Huang, David W. Jacobs, Alexei A. Efros, Aleksander Holynski, Angjoo Kanazawa
Score distillation sampling (SDS) has proven to be an important tool, enabling the use of large-scale diffusion priors for tasks operating in data-poor domains. Unfortunately, SDS has a number of characteristic artifacts that limit its usefulness in general-purpose applications. In this paper, we make progress toward understanding the behavior of SDS and its variants by viewing them as solving an optimal-cost transport path from a source distribution to a target distribution. Under this new interpretation, these methods seek to transport corrupted images (source) to the natural image distribution (target). We argue that current methods’ characteristic artifacts are caused by (1) linear approximation of the optimal path and (2) poor estimates of the source distribution. We show that calibrating the text conditioning of the source distribution can produce high-quality generation and translation results with little extra overhead. Our method can be easily applied across many domains, matching or beating the performance of specialized methods. We demonstrate its utility in text-to-2D, text-based NeRF optimization, translating paintings to real images, optical illusion generation, and 3D sketch-to-real. We compare our method to existing approaches for score distillation sampling and show that it can produce high-frequency details with realistic colors.
得分蒸馏采样(SDS)已被证明是执行数据贫乏域任务时使用大规模扩散先验的重要工具。然而,SDS存在许多特征性伪影,限制了其在通用应用中的实用性。在本文中,我们通过将其视为从源分布到目标分布的最佳成本传输路径的解决方式,取得了理解SDS及其变体行为的进展。在这种新解释下,这些方法试图将损坏的图像(源)传输到自然图像分布(目标)。我们认为当前方法的特征性伪影是由(1)最佳路径的线性近似和(2)源分布估计不佳引起的。我们表明,校准源分布的文本条件可以在几乎不增加额外开销的情况下产生高质量生成和翻译结果。我们的方法可以轻松应用于多个领域,达到或超过专业方法的性能。我们在文本到2D、基于文本的NeRF优化、绘画到现实图像的翻译、光学幻觉生成和3D草图到现实等任务中展示了其实用性。我们将方法与现有的分数蒸馏采样方法进行了比较,并证明它可以生成具有逼真颜色的高频细节。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024. Project webpage: https://sds-bridge.github.io/
Summary
本文探讨了基于评分蒸馏采样(SDS)的技术在数据稀缺领域的应用。通过将其视为从源分布到目标分布的最佳成本传输路径的解决方法,本文深入理解了SDS及其变体在图像转换方面的行为。文章指出当前方法的特征缺陷源于线性近似最优路径和源分布估计不佳,并提出通过校准源分布的文本条件来提高生成和转换质量。此方法可广泛应用于多个领域,与专项方法相比具有竞争力,并在文本到二维图像转换、基于文本的NeRF优化、绘画到现实图像翻译、光学幻觉生成和三维草图到现实场景等任务中展现出优越性能。本文还与现有评分蒸馏采样方法进行了比较,显示出在高频细节和真实色彩生成方面的优势。
Key Takeaways
- 评分蒸馏采样(SDS)已成为解决数据稀缺领域问题的关键工具。
- SDS和其他方法可视为从源分布到目标分布的最佳成本传输路径的解决方法。
- 当前SDS方法的特征缺陷源于线性近似最优路径和源分布估计不佳。
- 通过校准源分布的文本条件,可以提高生成和转换质量,且几乎无需额外开销。
- 该方法具有广泛的应用性,可在多个领域进行应用,如文本到二维图像转换、基于文本的NeRF优化等。
- 与现有评分蒸馏采样方法相比,该方法在高频细节和真实色彩生成方面表现出优势。
点此查看论文截图

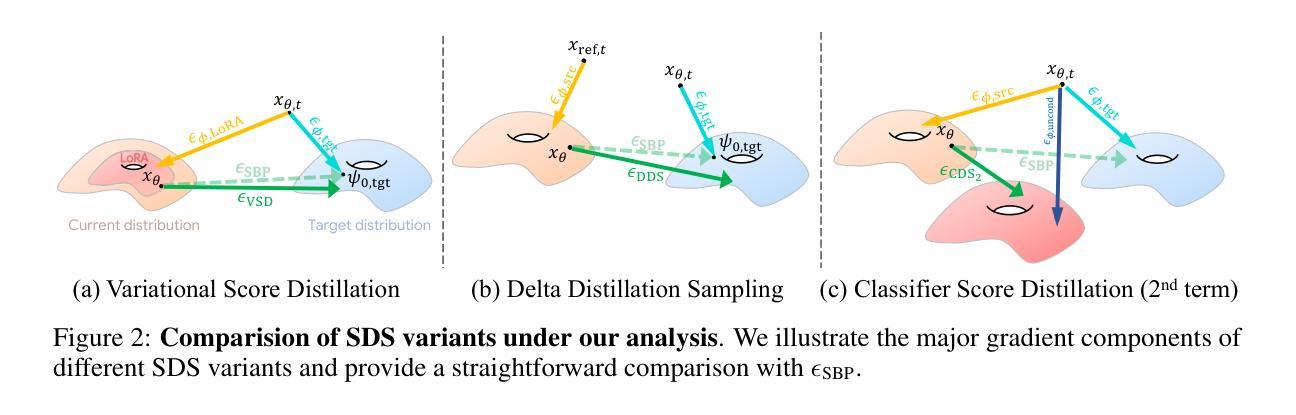
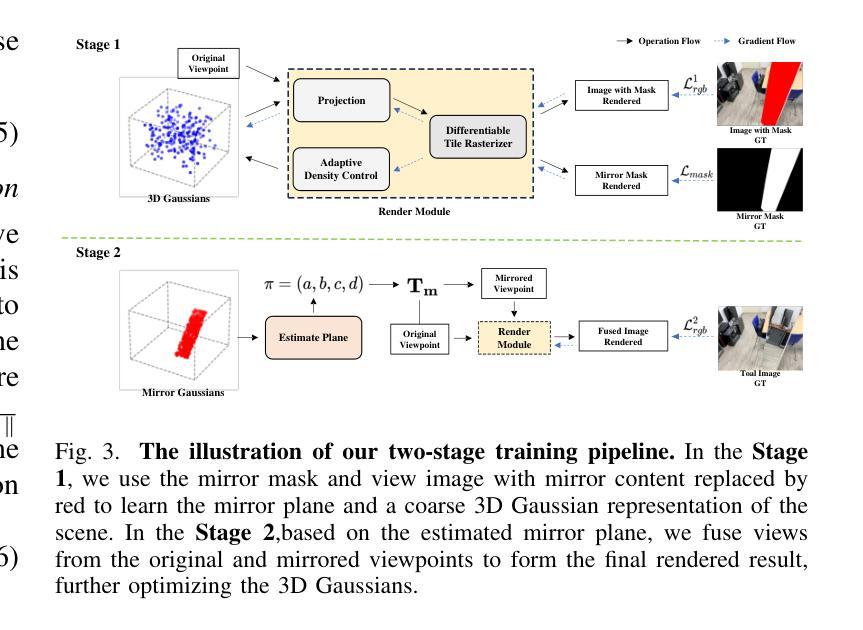
Mirror-3DGS: Incorporating Mirror Reflections into 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jiarui Meng, Haijie Li, Yanmin Wu, Qiankun Gao, Shuzhou Yang, Jian Zhang, Siwei Ma
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has significantly advanced 3D scene reconstruction and novel view synthesis. However, like Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), 3DGS struggles with accurately modeling physical reflections, particularly in mirrors, leading to incorrect reconstructions and inconsistent reflective properties. To address this challenge, we introduce Mirror-3DGS, a novel framework designed to accurately handle mirror geometries and reflections, thereby generating realistic mirror reflections. By incorporating mirror attributes into 3DGS and leveraging plane mirror imaging principles, Mirror-3DGS simulates a mirrored viewpoint from behind the mirror, enhancing the realism of scene renderings. Extensive evaluations on both synthetic and real-world scenes demonstrate that our method can render novel views with improved fidelity in real-time, surpassing the state-of-the-art Mirror-NeRF, especially in mirror regions.
3D高斯摊铺(3DGS)在三维场景重建和新型视图合成方面取得了显著进展。然而,与神经辐射场(NeRF)一样,3DGS在准确模拟物理反射方面存在困难,特别是在镜子中,导致重建不准确和反射属性不一致。为了应对这一挑战,我们引入了Mirror-3DGS,这是一个专为准确处理镜子几何形状和反射而设计的新型框架,从而生成逼真的镜子反射。通过将镜子属性融入3DGS并利用平面镜像成像原理,Mirror-3DGS可以模拟镜子后面的视角,增强场景渲染的逼真度。对合成场景和真实场景的大量评估表明,我们的方法能够在实时中以更高的保真度呈现新颖观点,超越了最先进的Mirror-NeRF,特别是在镜子区域。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE International Conference on Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP 2024, Oral)
Summary
该文介绍了针对三维场景重建和新型视角合成中的反射问题,提出了一种名为Mirror-3DGS的新型框架。该框架通过融入镜像属性并利用平面镜像成像原理,准确处理镜像几何和反射,生成逼真的镜面反射效果。相较于当前最先进的Mirror-NeRF,该方法在合成和真实场景下的评估表现更优秀,特别是在镜像区域的实时渲染中提高了保真度。
Key Takeaways
- Mirror-3DGS框架被设计用于解决三维场景重建和新型视角合成中的镜像反射问题。
- 该框架结合镜像属性,利用平面镜像成像原理,模拟了镜子后的视角,增强了场景渲染的逼真度。
- Mirror-3DGS能够在实时渲染中生成更高保真的镜像区域,超越当前最先进的Mirror-NeRF方法。
- 通过在合成和真实场景下的广泛评估,验证了Mirror-3DGS的有效性。
- 该方法对于改进三维场景重建和视角合成的质量具有重大意义。
- Mirror-3DGS的引入进一步推动了三维场景建模和渲染技术的发展。
点此查看论文截图

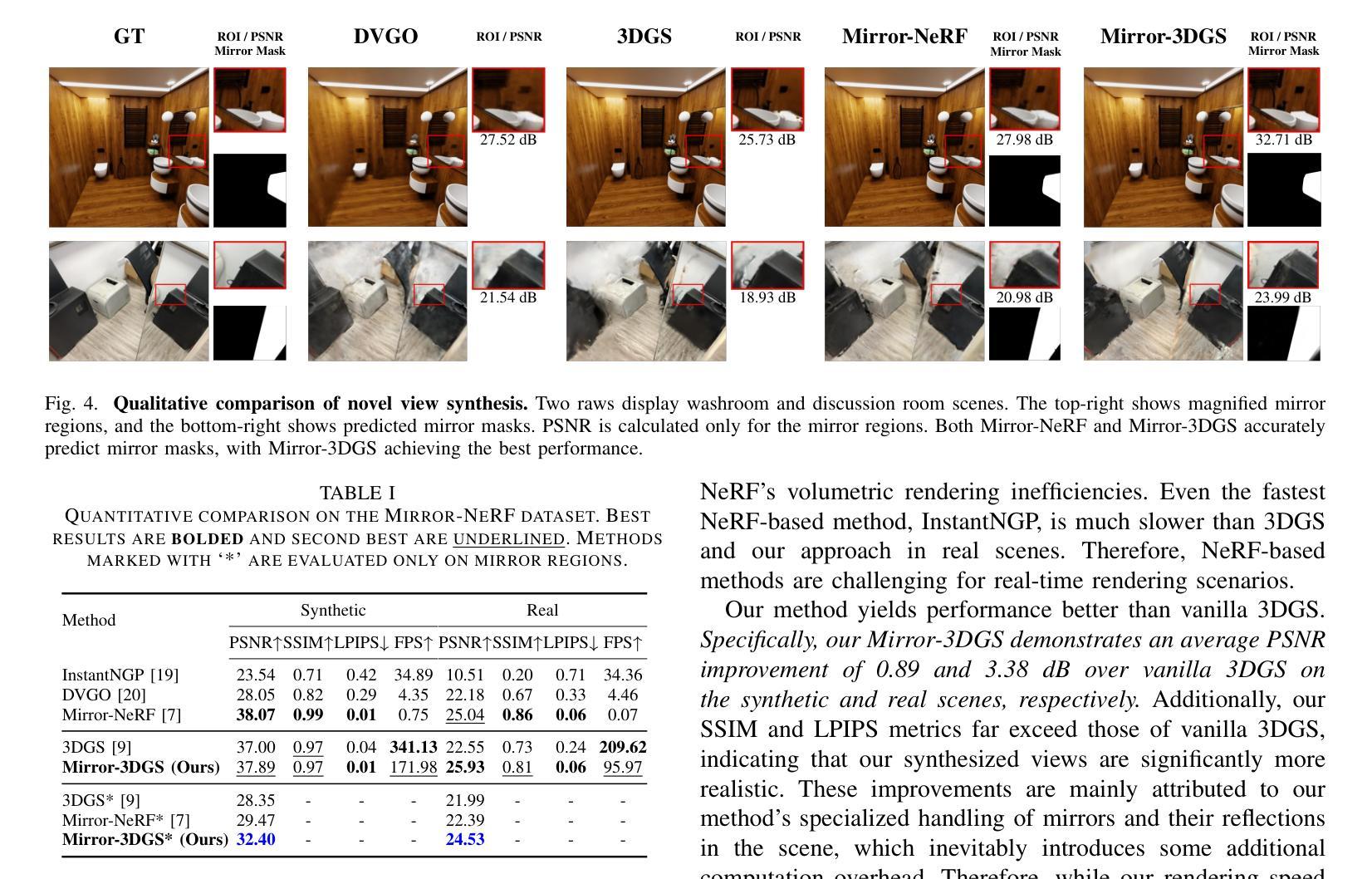
UniSDF: Unifying Neural Representations for High-Fidelity 3D Reconstruction of Complex Scenes with Reflections
Authors:Fangjinhua Wang, Marie-Julie Rakotosaona, Michael Niemeyer, Richard Szeliski, Marc Pollefeys, Federico Tombari
Neural 3D scene representations have shown great potential for 3D reconstruction from 2D images. However, reconstructing real-world captures of complex scenes still remains a challenge. Existing generic 3D reconstruction methods often struggle to represent fine geometric details and do not adequately model reflective surfaces of large-scale scenes. Techniques that explicitly focus on reflective surfaces can model complex and detailed reflections by exploiting better reflection parameterizations. However, we observe that these methods are often not robust in real scenarios where non-reflective as well as reflective components are present. In this work, we propose UniSDF, a general purpose 3D reconstruction method that can reconstruct large complex scenes with reflections. We investigate both camera view as well as reflected view-based color parameterization techniques and find that explicitly blending these representations in 3D space enables reconstruction of surfaces that are more geometrically accurate, especially for reflective surfaces. We further combine this representation with a multi-resolution grid backbone that is trained in a coarse-to-fine manner, enabling faster reconstructions than prior methods. Extensive experiments on object-level datasets DTU, Shiny Blender as well as unbounded datasets Mip-NeRF 360 and Ref-NeRF real demonstrate that our method is able to robustly reconstruct complex large-scale scenes with fine details and reflective surfaces, leading to the best overall performance. Project page: \url{https://fangjinhuawang.github.io/UniSDF}.
神经三维场景表示在从无到有构建从二维图像中获得了巨大潜力的三维重建。然而,重建现实世界中的复杂场景仍然是一个挑战。现有的通用三维重建方法往往难以表示精细的几何细节,并且在大规模场景的反射表面建模方面存在不足。专注于反射表面的技术可以通过利用更好的反射参数化来模拟复杂和详细的反射。然而,我们观察到这些方法在非反射和反射成分都存在的真实场景中并不稳健。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种通用目的的三维重建方法UniSDF,能够重建带有反射的大型复杂场景。我们研究了基于相机视角和反射视角的颜色参数化技术,并发现通过在三维空间中显式混合这些表示,能够重建出更准确的几何表面,特别是对于反射表面。我们进一步将这种表示与以从粗糙到精细的方式训练的多分辨率网格主干相结合,使得比现有方法更快的重建速度。在对象级别的数据集DTU和Shiny Blender以及无边界数据集Mip-NeRF 360和Ref-NeRF real上的大量实验表明,我们的方法能够稳健地重建具有精细细节和反射表面的复杂大规模场景,取得了最佳的整体性能。项目页面:https://fangjinhuawang.github.io/UniSDF。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024 camera ready
Summary
该文提出一种名为UniSDF的通用三维重建方法,可重建具有反射特性的大型复杂场景。该方法结合相机视角和反射视角的颜色参数化技术,能在三维空间中显式融合这些表示,从而更精确地重建几何表面,尤其适用于反射表面。此外,该方法结合了多分辨率网格主干,采用由粗到细的训练方式,实现了比现有方法更快的重建速度。实验结果显示,该方法在物体级别数据集DTU、Shiny Blender以及无界数据集Mip-NeRF 360和Ref-NeRF real上表现最佳,能够稳健地重建具有精细细节和反射特性的大型场景。
Key Takeaways
- UniSDF是一种用于重建具有反射特性的大型复杂场景的三维重建方法。
- 该方法结合相机视角和反射视角的颜色参数化技术,以提高几何表面的重建精度。
- UniSDF采用多分辨率网格主干,实现了快速的三维重建。
- 该方法在多种数据集上的实验表现优秀,能够稳健地重建具有精细细节和反射特性的场景。
- UniSDF方法具有通用性,适用于不同的复杂场景。
- 显式融合反射和非反射组件在现实场景中的表现是该方法的一个关键优点。
点此查看论文截图


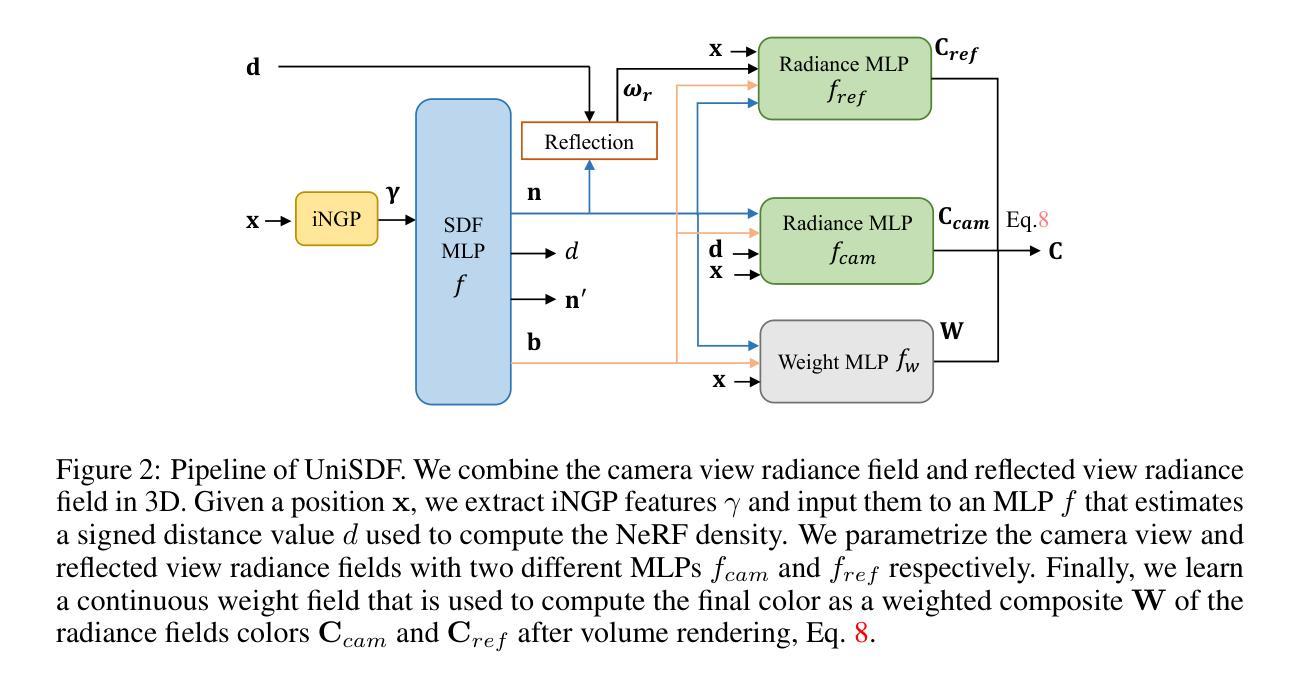

Unpaired Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography Image Super-Resolution via Frequency-Aware Inverse-Consistency GAN
Authors:Weiwen Zhang, Dawei Yang, Haoxuan Che, An Ran Ran, Carol Y. Cheung, Hao Chen
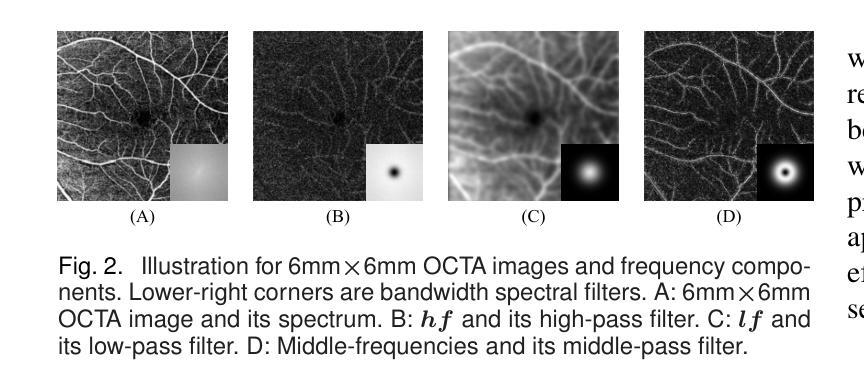
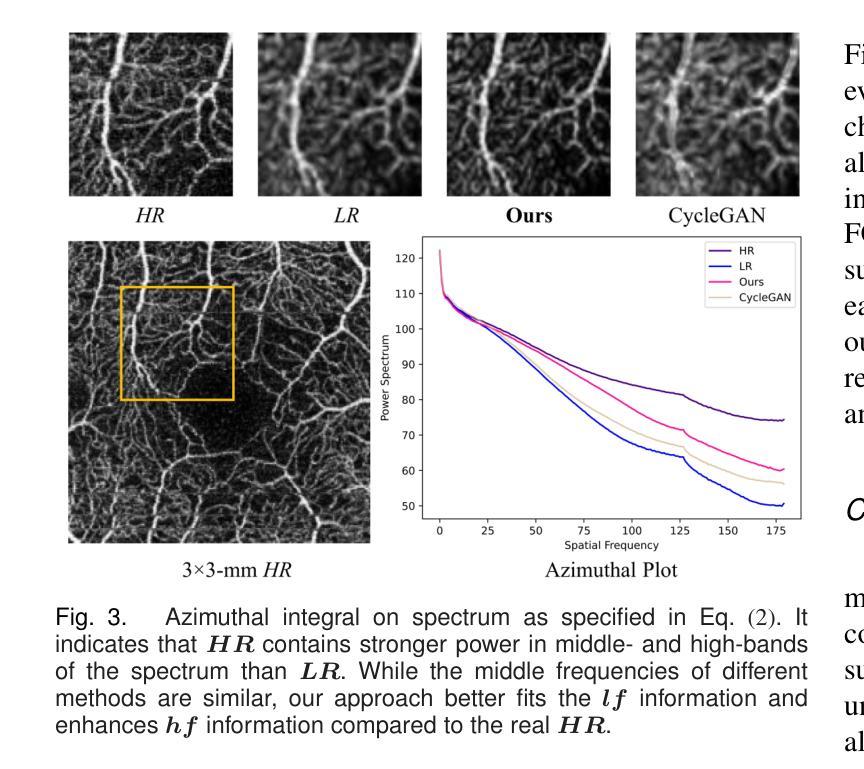
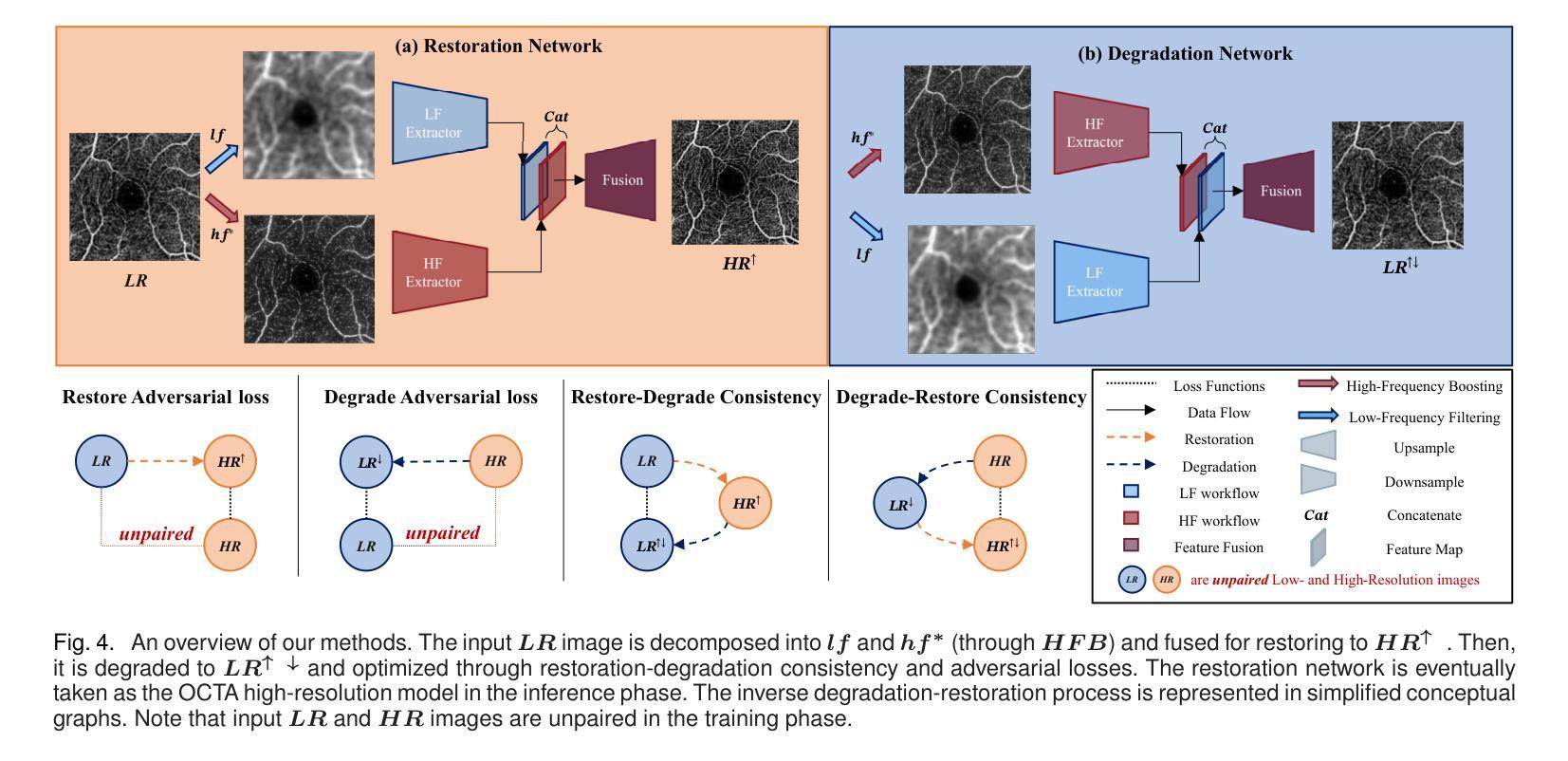
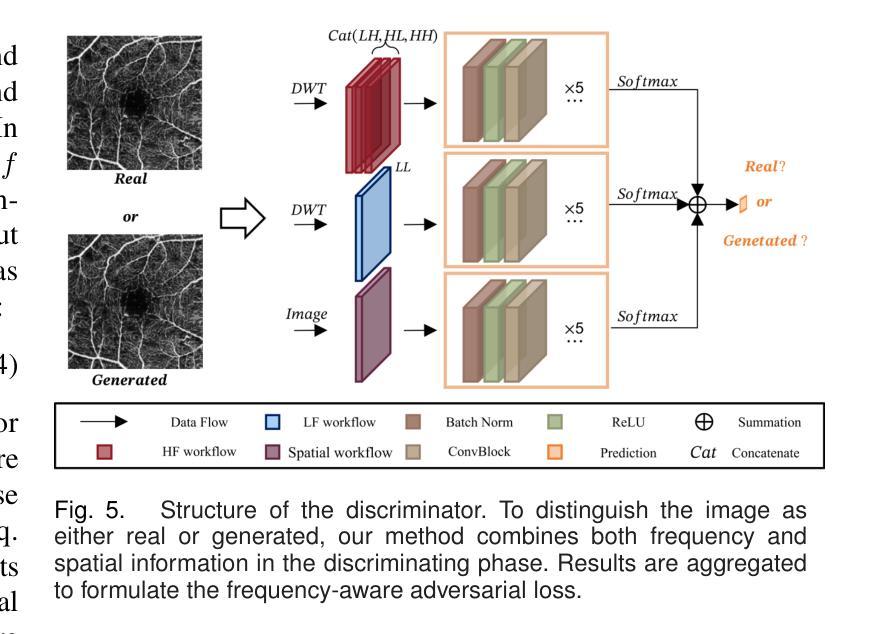
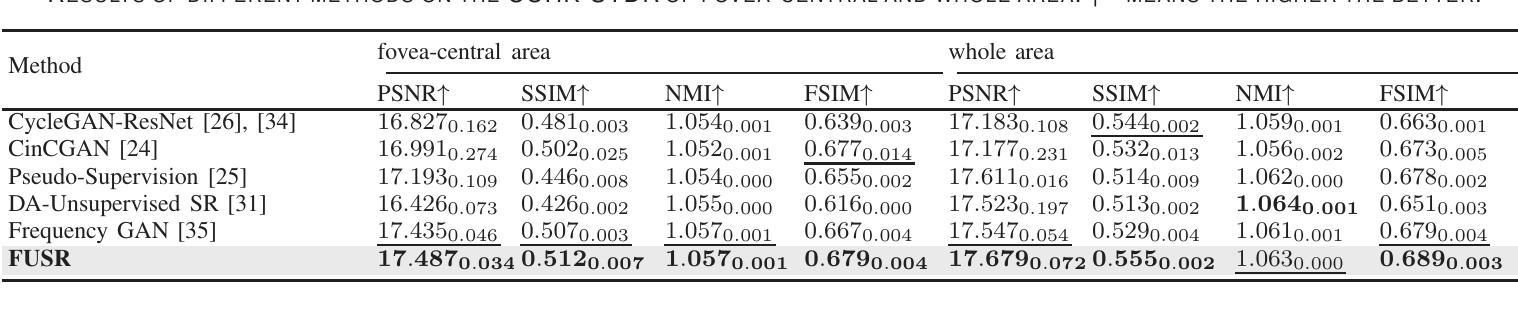
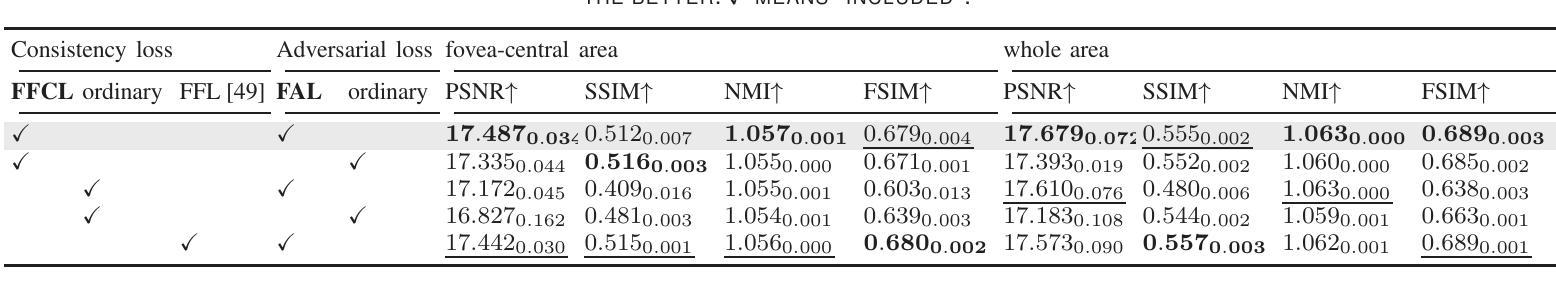
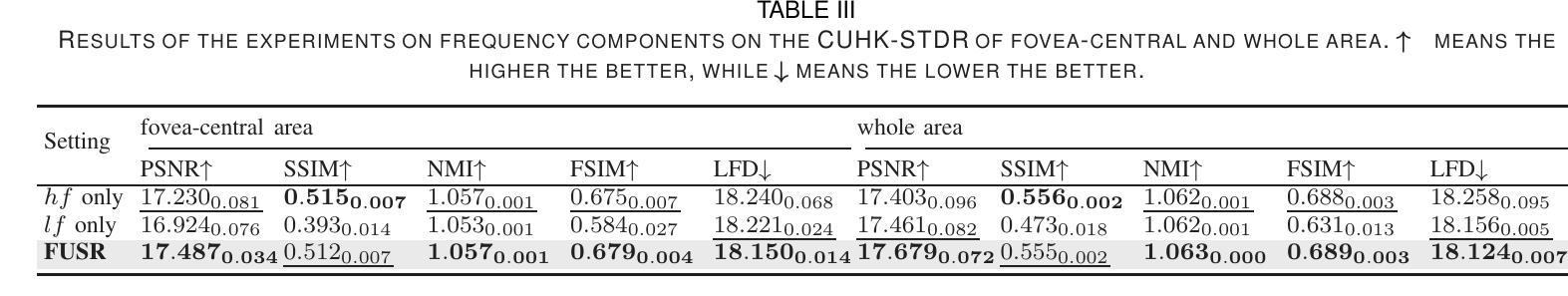
For optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) images, a limited scanning rate leads to a trade-off between field-of-view (FOV) and imaging resolution. Although larger FOV images may reveal more parafoveal vascular lesions, their application is greatly hampered due to lower resolution. To increase the resolution, previous works only achieved satisfactory performance by using paired data for training, but real-world applications are limited by the challenge of collecting large-scale paired images. Thus, an unpaired approach is highly demanded. Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) has been commonly used in the unpaired setting, but it may struggle to accurately preserve fine-grained capillary details, which are critical biomarkers for OCTA. In this paper, our approach aspires to preserve these details by leveraging the frequency information, which represents details as high-frequencies ($\textbf{hf}$) and coarse-grained backgrounds as low-frequencies ($\textbf{lf}$). In general, we propose a GAN-based unpaired super-resolution method for OCTA images and exceptionally emphasize $\textbf{hf}$ fine capillaries through a dual-path generator. To facilitate a precise spectrum of the reconstructed image, we also propose a frequency-aware adversarial loss for the discriminator and introduce a frequency-aware focal consistency loss for end-to-end optimization. Experiments show that our method outperforms other state-of-the-art unpaired methods both quantitatively and visually.
对于光学相干断层扫描血管造影(OCTA)图像,有限的扫描速率导致视野(FOV)与成像分辨率之间的权衡。虽然较大的FOV图像可能会揭示更多的旁中心凹血管病变,但由于分辨率较低,其应用受到很大阻碍。为了提升分辨率,之前的工作只有在使用配对数据进行训练时才能达到令人满意的效果,但现实世界的实际应用受限于收集大规模配对图像的挑战。因此,对未配对的方法有着极高的需求。生成对抗网络(GAN)已在未配对设置中广泛使用,但在准确保留精细毛细血管细节方面可能面临困难,这对于OCTA来说是非常重要的生物标志物。在本文中,我们的方法旨在通过利用频率信息来保留这些详细信息,将精细的毛细血管作为高频(hf)和粗粒度的背景作为低频(lf)来表示。总的来说,我们提出了一种基于GAN的未配对超分辨率方法用于OCTA图像,并通过双路径生成器特别强调了高频的精细毛细血管。为了促进重建图像的精确光谱,我们还为鉴别器提出了频率感知对抗性损失,并引入了频率感知焦点一致性损失来进行端到端的优化。实验表明,我们的方法在定量和视觉上超越了其他最先进的未配对方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 10 figures, in IEEE J-BHI, 2024
Summary
针对光学相干断层扫描血管造影(OCTA)图像,因扫描速率有限,需在视野(FOV)与成像分辨率之间进行权衡。为提升分辨率,先前研究仅通过对配对数据进行训练获得满意结果,但实际应用受限于大规模配对图像采集的挑战。因此,对无需配对的方法有迫切需求。本文利用频率信息,采用生成对抗网络(GAN)进行OCTA图像的无需配对超分辨率处理,并特别强调高频细节毛细血管的保留。通过双路径生成器、频率感知对抗损失和端到端优化的频率感知焦点一致性损失等方法,实现了精确的图像重建。实验表明,该方法在无需配对的方法中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- OCTA图像面临扫描速率与视野和成像分辨率之间的权衡。
- 先前方法依赖配对数据进行训练,但配对图像采集困难,故需求无需配对的方法。
- 本文采用GAN进行OCTA图像超分辨率处理,并特别关注高频细节毛细血管的保留。
- 提出双路径生成器、频率感知对抗损失和频率感知焦点一致性损失等方法提升图像重建精度。
点此查看论文截图
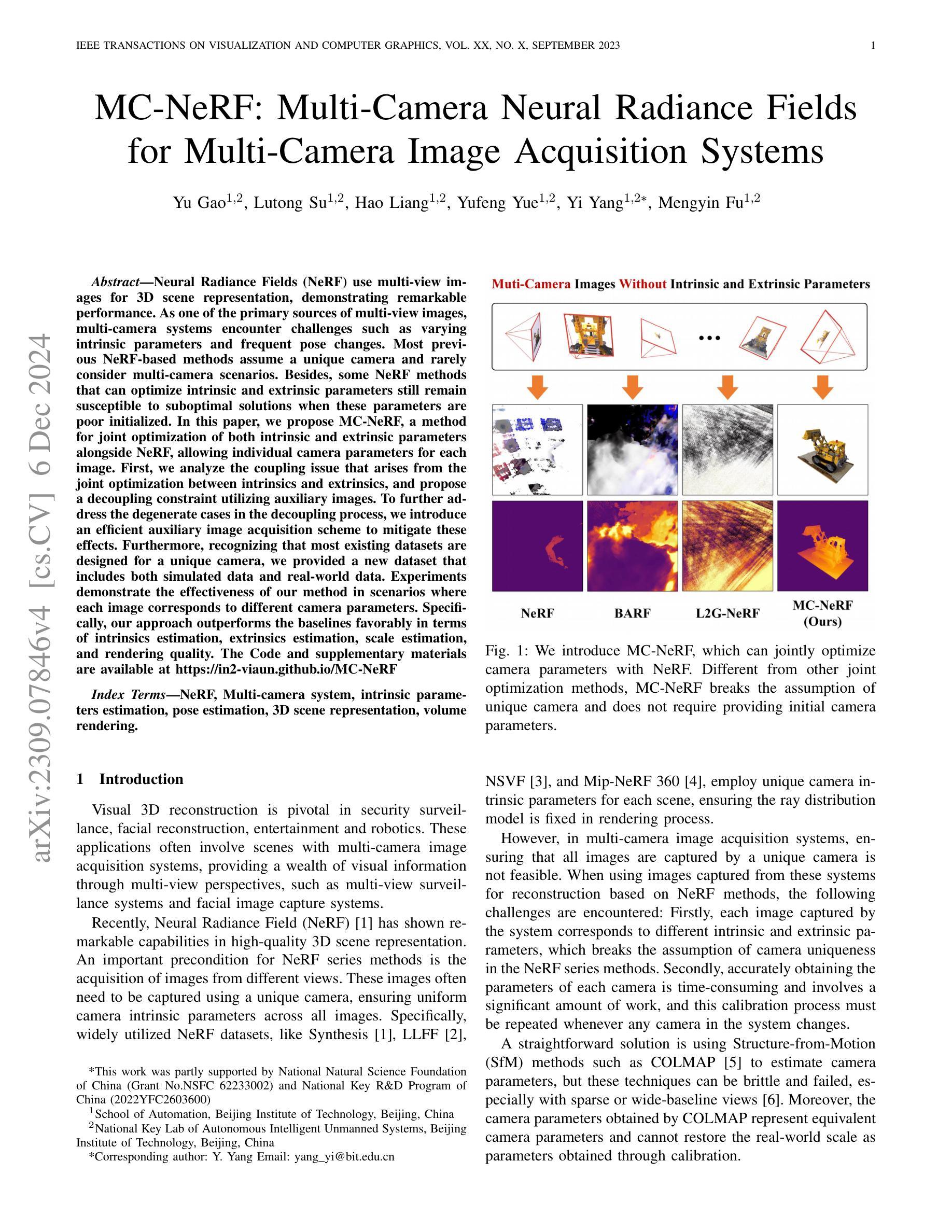
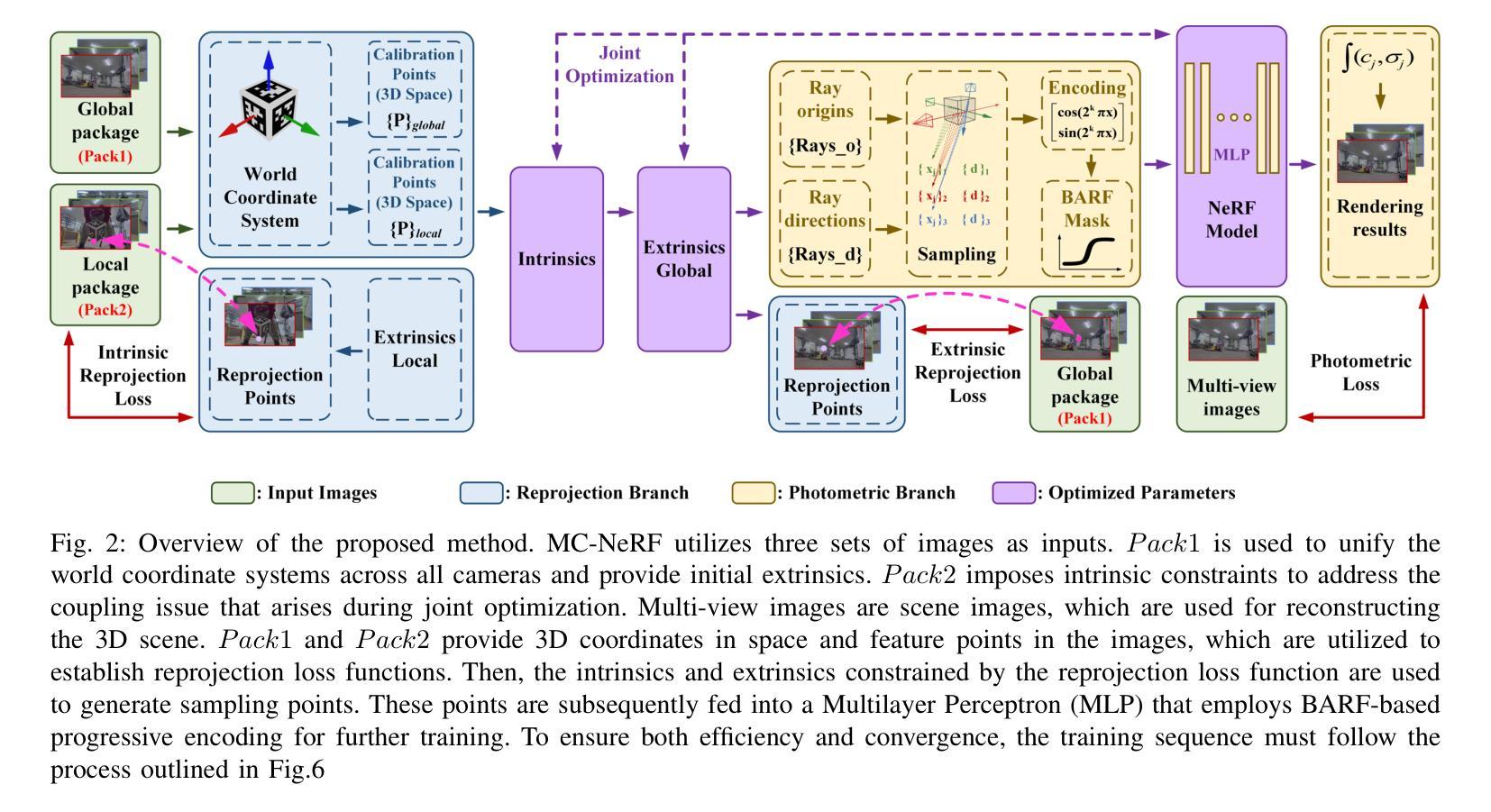
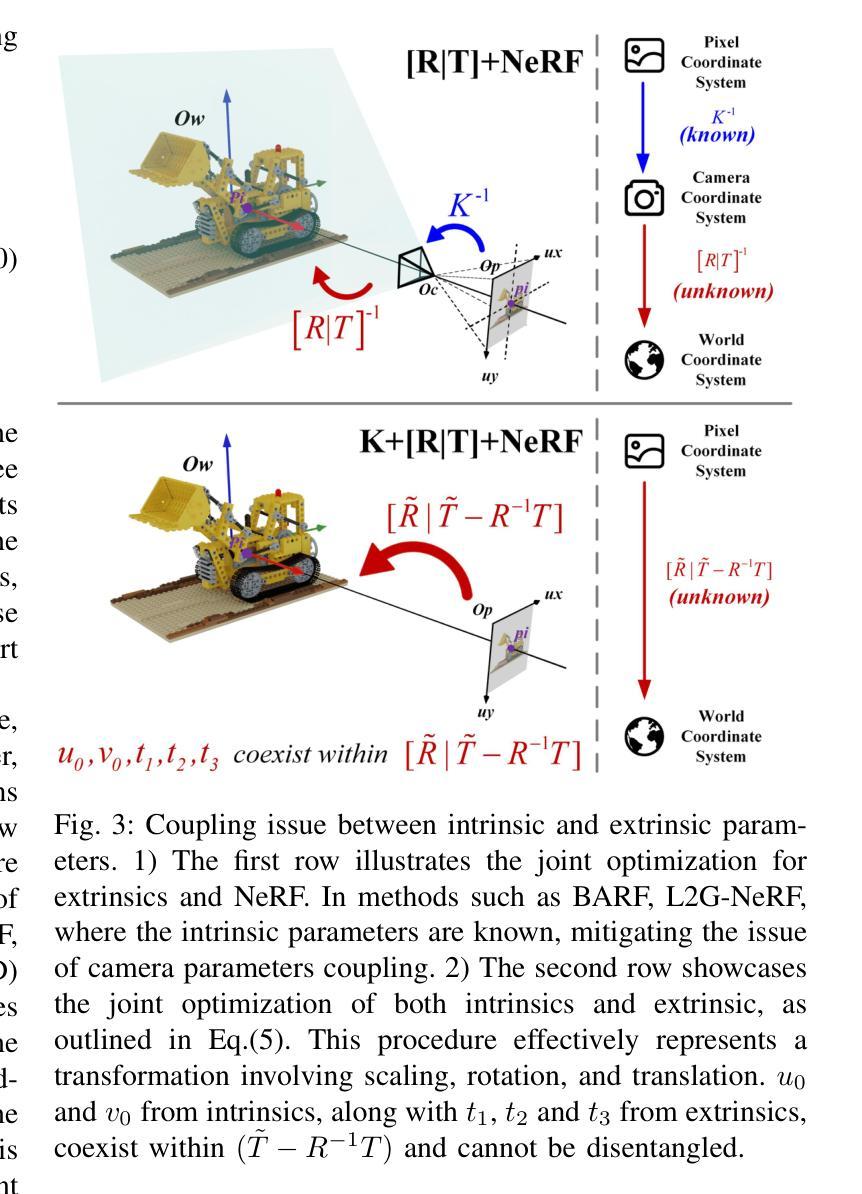
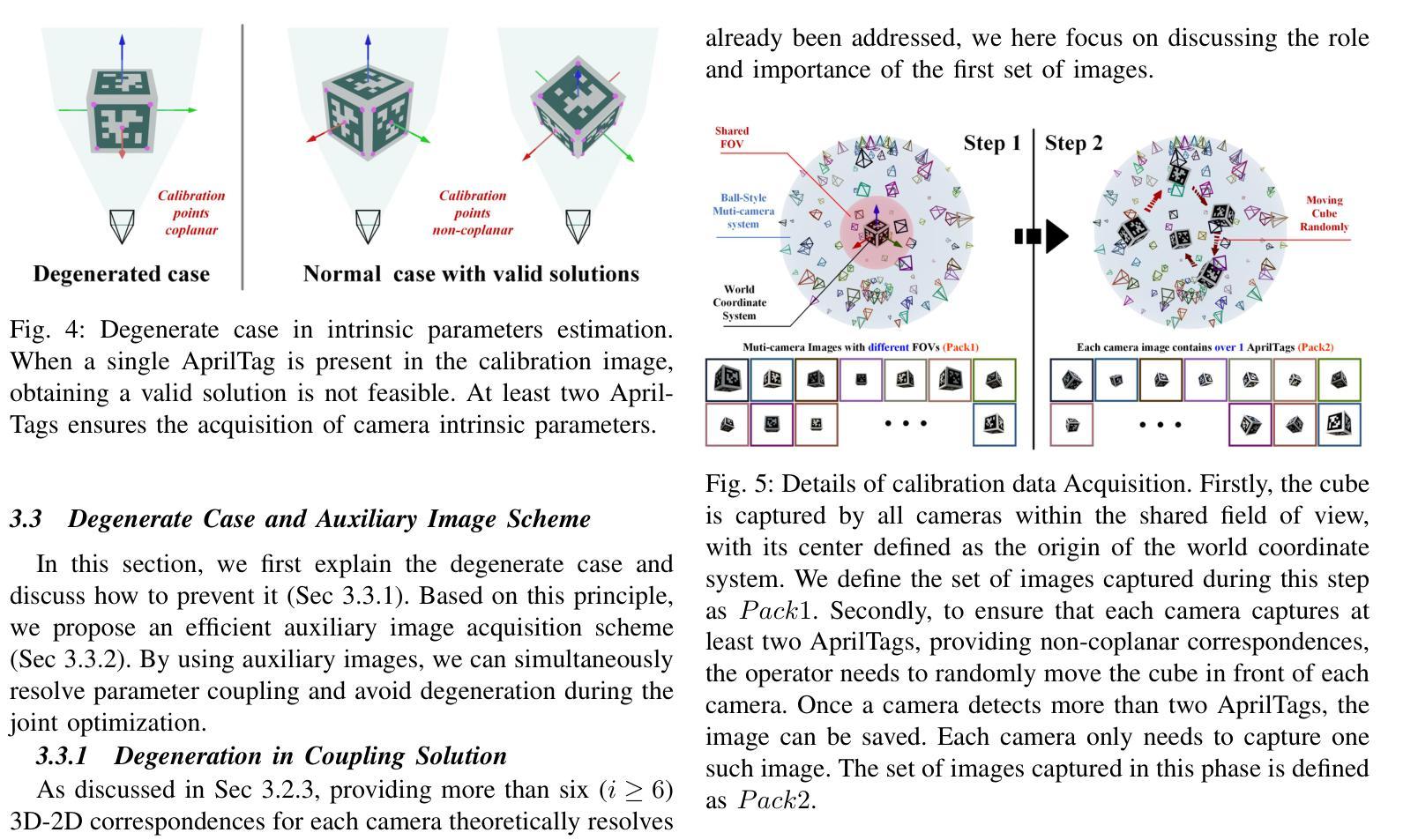
MC-NeRF: Multi-Camera Neural Radiance Fields for Multi-Camera Image Acquisition Systems
Authors:Yu Gao, Lutong Su, Hao Liang, Yufeng Yue, Yi Yang, Mengyin Fu
Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) use multi-view images for 3D scene representation, demonstrating remarkable performance. As one of the primary sources of multi-view images, multi-camera systems encounter challenges such as varying intrinsic parameters and frequent pose changes. Most previous NeRF-based methods assume a unique camera and rarely consider multi-camera scenarios. Besides, some NeRF methods that can optimize intrinsic and extrinsic parameters still remain susceptible to suboptimal solutions when these parameters are poor initialized. In this paper, we propose MC-NeRF, a method that enables joint optimization of both intrinsic and extrinsic parameters alongside NeRF. The method also supports each image corresponding to independent camera parameters. First, we tackle coupling issue and the degenerate case that arise from the joint optimization between intrinsic and extrinsic parameters. Second, based on the proposed solutions, we introduce an efficient calibration image acquisition scheme for multi-camera systems, including the design of calibration object. Finally, we present an end-to-end network with training sequence that enables the estimation of intrinsic and extrinsic parameters, along with the rendering network. Furthermore, recognizing that most existing datasets are designed for a unique camera, we construct a real multi-camera image acquisition system and create a corresponding new dataset, which includes both simulated data and real-world captured images. Experiments confirm the effectiveness of our method when each image corresponds to different camera parameters. Specifically, we use multi-cameras, each with different intrinsic and extrinsic parameters in real-world system, to achieve 3D scene representation without providing initial poses.
神经辐射场(NeRF)利用多视角图像进行三维场景表示,并表现出卓越的性能。作为多视角图像的主要来源之一,多相机系统面临着诸如内在参数变化以及姿态变化频繁等挑战。大多数基于NeRF的方法都假设有一个独特的相机,很少考虑多相机场景。此外,有些NeRF方法可以优化内在和外在参数,但当这些参数初始化不佳时,仍然容易陷入次优解。在本文中,我们提出了MC-NeRF方法,该方法能够同时优化内在和外在参数,并与NeRF相结合。该方法还支持每张图像对应独立的相机参数。首先,我们解决了由内在和外在参数的联合优化产生的耦合问题和退化情况。其次,基于这些解决方案,我们为多相机系统引入了有效的校准图像采集方案,包括校准对象的设计。最后,我们提出了一个端到端的网络训练序列,该序列能够估计内在和外在参数,以及渲染网络。此外,我们认识到大多数现有数据集都是为单一相机设计的,因此我们构建了一个真正的多相机图像采集系统,并创建了一个相应的新数据集,该数据集包括模拟数据和真实捕获的图像。实验证实,当每张图像对应不同的相机参数时,我们的方法非常有效。具体来说,我们使用具有不同内在和外在参数的多相机真实系统,无需提供初始姿态即可实现三维场景表示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This manuscript is currently under review
Summary
本文提出了MC-NeRF方法,实现了对NeRF中的内在参数和外在参数的联合优化支持,每一张图像都有独立的相机参数。通过解决内在和外在参数联合优化带来的耦合问题和退化情况,引入了高效的多相机系统校准图像采集方案。同时,构建了一个真实的多相机图像采集系统并创建了对应的新数据集,实验验证了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- MC-NeRF方法实现了对NeRF的内在参数和外在参数的联合优化,使得每一张图像都可以有独立的相机参数。
- 该方法解决了在联合优化内在和外在参数时出现的耦合问题和退化情况。
- 引入了一种高效的多相机系统校准图像采集方案,包括校准对象的设计。
- 构建了一个真实的多相机图像采集系统并创建了对应的新数据集,包含模拟数据和真实捕获的图像。
- 实验验证了该方法在真实世界系统中使用多相机,每个相机具有不同的内在和外在参数,实现3D场景表示的有效性。
- 该方法能够在不提供初始姿态的情况下实现3D场景表示。
点此查看论文截图
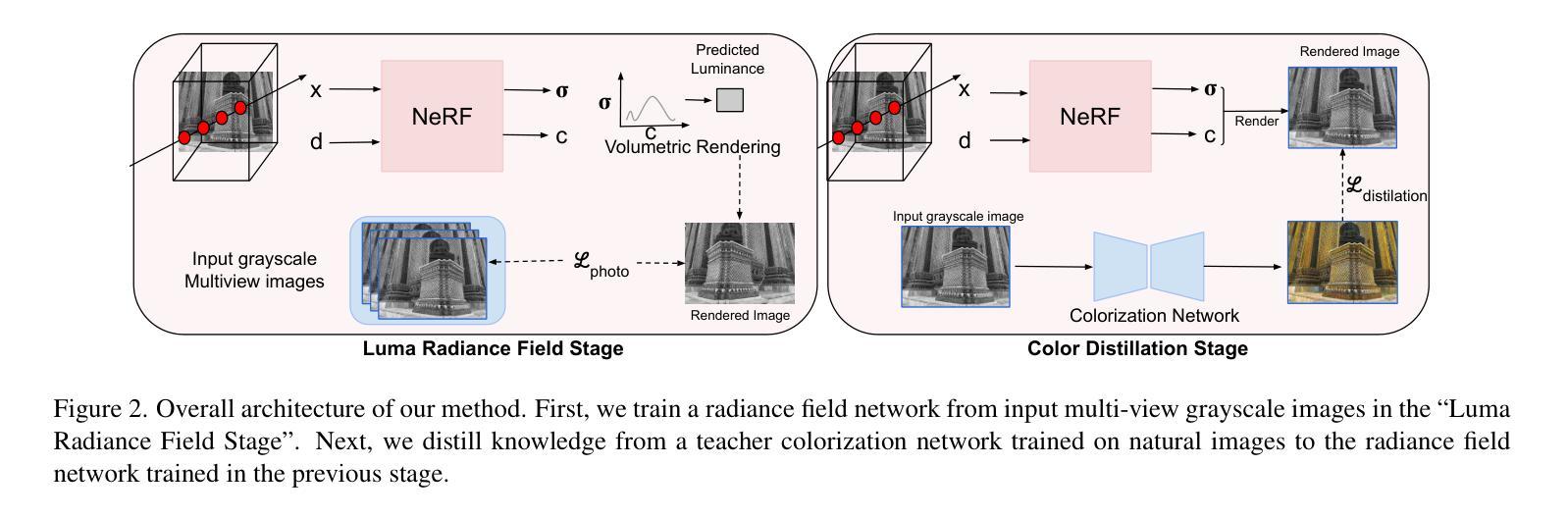
ChromaDistill: Colorizing Monochrome Radiance Fields with Knowledge Distillation
Authors:Ankit Dhiman, R Srinath, Srinjay Sarkar, Lokesh R Boregowda, R Venkatesh Babu
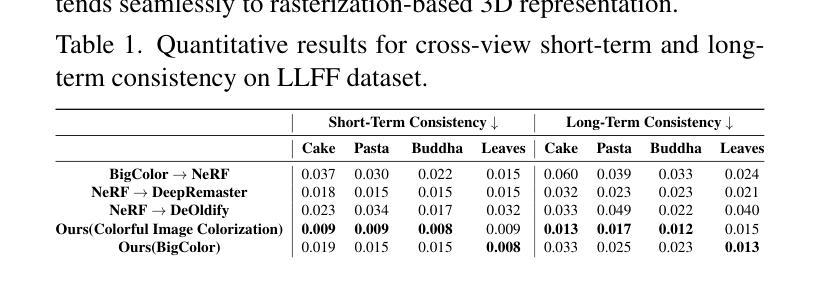
Colorization is a well-explored problem in the domains of image and video processing. However, extending colorization to 3D scenes presents significant challenges. Recent Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) and Gaussian-Splatting(3DGS) methods enable high-quality novel-view synthesis for multi-view images. However, the question arises: How can we colorize these 3D representations? This work presents a method for synthesizing colorized novel views from input grayscale multi-view images. Using image or video colorization methods to colorize novel views from these 3D representations naively will yield output with severe inconsistencies. We introduce a novel method to use powerful image colorization models for colorizing 3D representations. We propose a distillation-based method that transfers color from these networks trained on natural images to the target 3D representation. Notably, this strategy does not add any additional weights or computational overhead to the original representation during inference. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method produces high-quality colorized views for indoor and outdoor scenes, showcasing significant cross-view consistency advantages over baseline approaches. Our method is agnostic to the underlying 3D representation and easily generalizable to NeRF and 3DGS methods. Further, we validate the efficacy of our approach in several diverse applications: 1.) Infra-Red (IR) multi-view images and 2.) Legacy grayscale multi-view image sequences. Project Webpage: https://val.cds.iisc.ac.in/chroma-distill.github.io/
着色是图像和视频处理领域已经得到很好研究的问题。然而,将着色技术扩展到三维场景面临重大挑战。最近的神经辐射场(NeRF)和高斯模板(Gaussian Splatting,简称3DGS)方法能够实现高质量的多视角图像新视角合成。但问题是:我们如何对这些三维表示进行着色?这项工作提出了一种从输入灰度多视角图像合成彩色新视角的方法。使用图像或视频着色方法来直观地对着这些三维表示的新视角进行着色会导致输出具有严重的色差。我们引入了一种使用强大的图像着色模型为三维表示着色的新方法。我们提出了一种基于蒸馏的方法,将自然图像训练的网络中的颜色转移到目标三维表示上。值得注意的是,这种策略在推理期间不会给原始表示增加任何额外的权重或计算开销。大量实验表明,我们的方法为室内和室外场景生成了高质量彩色视图,相较于基准方法展现出显著的跨视图一致性优势。我们的方法对于底层的三维表示持中立态度,并易于推广到NeRF和3DGS方法。此外,我们通过几个不同的应用验证了我们的方法的有效性:包括红外(IR)多视角图像和遗留灰度多视角图像序列的应用场景。项目网页链接:https://val.cds.iisc.ac.in/chroma-distill.github.io/(中文官网链接可能无法直接打开,请尝试其他途径获取更多详细信息。)
论文及项目相关链接
PDF WACV 2025, AI3DCC @ ICCV 2023
Summary
本文探讨了将颜色化技术应用于三维场景的问题。尽管Neural Radiance Field(NeRF)和Gaussian-Splatting(3DGS)等方法能够实现多视角图像的高质量新型视图合成,但如何在这些三维表示中进行颜色化仍是一个问题。本研究提出了一种从输入灰度多视角图像合成彩色新型视图的方法。直接使用图像或视频颜色化方法对三维表示进行颜色化会导致输出存在严重的不一致性。本研究引入了一种基于蒸馏的方法,将从自然图像训练的图像颜色化模型中的颜色转移到目标三维表示中。值得注意的是,在推理过程中,此策略不会给原始表示增加任何额外的权重或计算开销。实验表明,该方法在室内和室外场景的颜色化视图中表现出色,与基准方法相比具有显著的跨视图一致性优势。该方法对底层三维表示具有通用性,可轻松推广到NeRF和3DGS方法。此外,该研究还在红外多视角图像和遗留灰度多视角图像序列等多样化应用中验证了其方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 本文解决了在三维场景中颜色化的问题,尤其是针对Neural Radiance Field(NeRF)和Gaussian-Splatting(3DGS)方法生成的三维表示。
- 直接使用图像或视频颜色化方法对三维表示进行颜色化会导致输出存在严重的不一致性。
- 研究提出了一种基于蒸馏的方法,将从自然图像训练的颜色化模型中的颜色转移到目标三维表示中,提高了颜色化质量并保持了跨视图的一致性。
- 该方法在室内和室外场景的颜色化视图中表现优异,相比基准方法具有显著优势。
- 方法对底层三维表示具有通用性,可适用于多种三维表示方法,包括NeRF和3DGS。
- 研究在多种应用中验证了其方法的有效性,包括红外多视角图像和遗留灰度多视角图像序列等。
点此查看论文截图




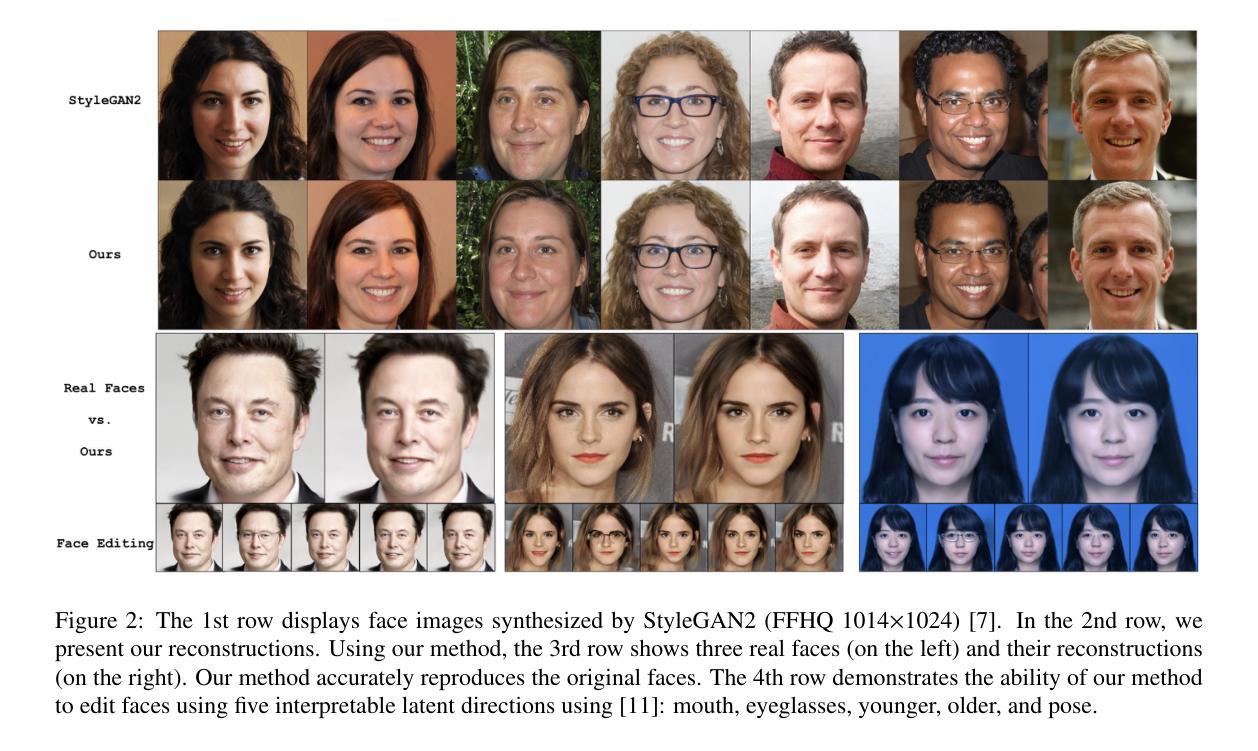
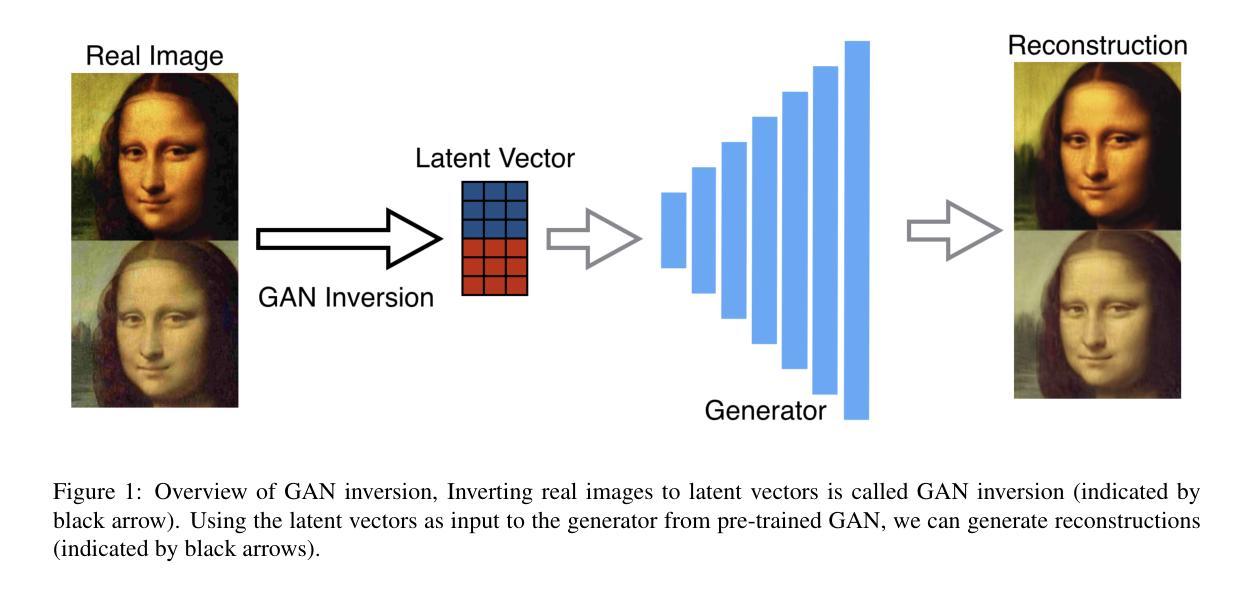
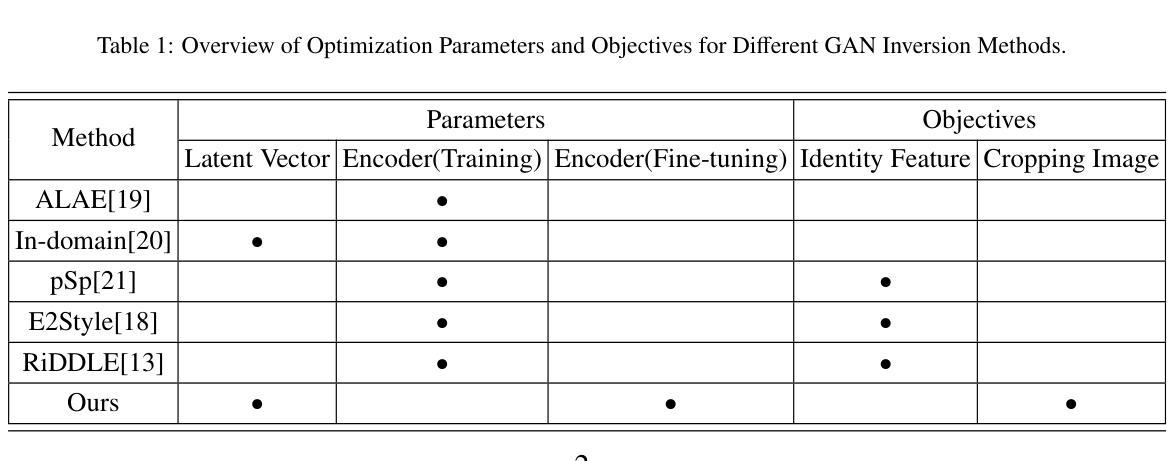
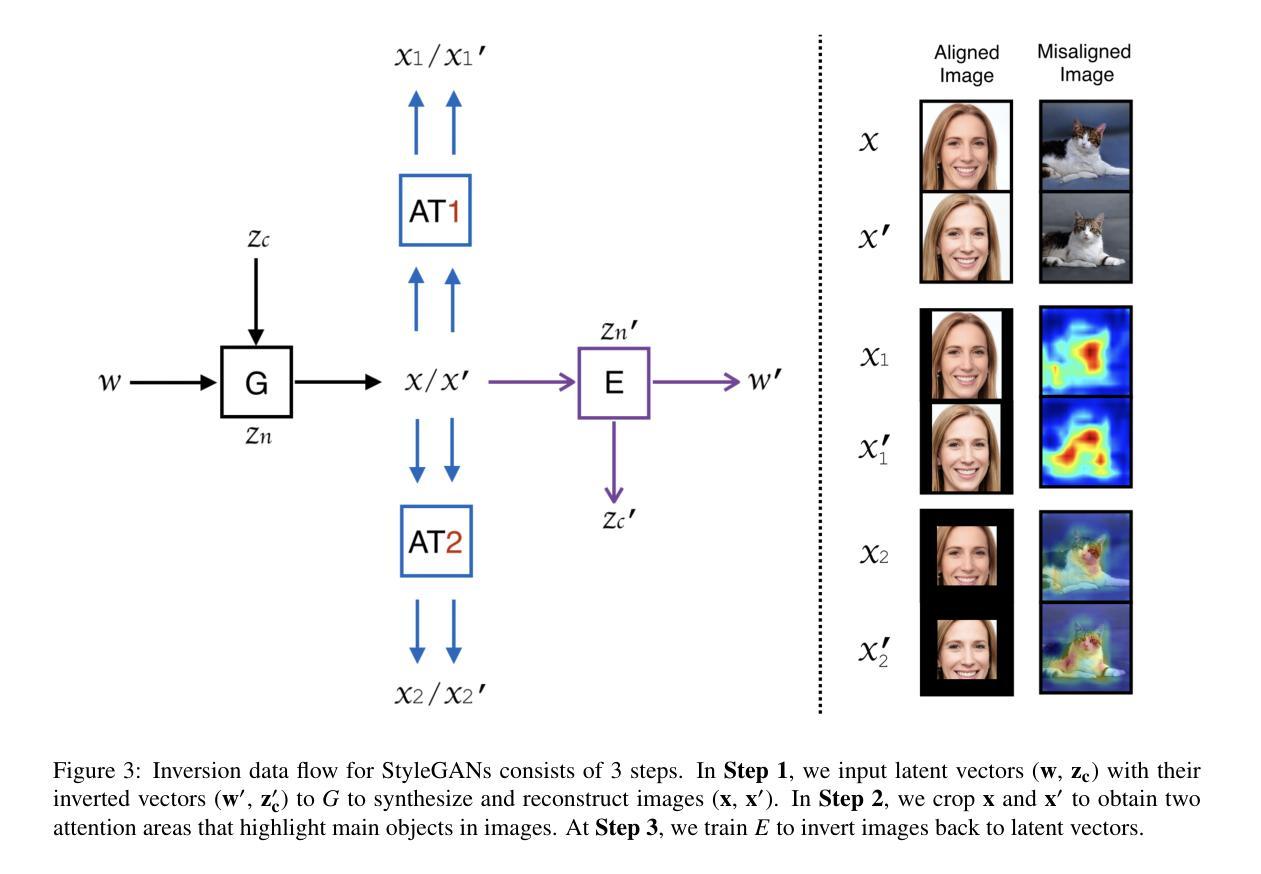
Diverse Similarity Encoder for Deep GAN Inversion
Authors:Cheng Yu, Wenmin Wang, Roberto Bugiolacchi
Current deep generative adversarial networks (GANs) can synthesize high-quality (HQ) images, so learning representation with GANs is favorable. GAN inversion is one of emerging approaches that study how to invert images into latent space. Existing GAN encoders can invert images on StyleGAN, but cannot adapt to other deep GANs. We propose a novel approach to address this issue. By evaluating diverse similarity in latent vectors and images, we design an adaptive encoder, named diverse similarity encoder (DSE), that can be expanded to a variety of state-of-the-art GANs. DSE makes GANs reconstruct higher fidelity images from HQ images, no matter whether they are synthesized or real images. DSE has unified convolutional blocks and adapts well to mainstream deep GANs, e.g., PGGAN, StyleGAN, and BigGAN.
当前深度生成对抗网络(GANs)能够合成高质量(HQ)图像,因此使用GANs学习表示是有利的。GAN反演是新兴方法之一,研究如何将图像反演到潜在空间。现有的GAN编码器可以在StyleGAN上反演图像,但不能适应其他深度GAN。我们提出了一种解决此问题的新方法。通过评估潜在向量和图像中的多种相似性,我们设计了一种自适应编码器,名为多样化相似性编码器(DSE),可以扩展到多种最新GAN技术。DSE无论图像是合成还是真实图像,都能使GAN从高质量图像中重建更高保真度的图像。DSE具有统一的卷积块,能很好地适应主流深度GAN,例如PGGAN、StyleGAN和BigGAN。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种名为DSE(多样相似性编码器)的新方法,解决了现有GAN编码器不能适应多种先进的GANs的问题。DSE通过评估潜在向量和图像之间的多样相似性,能够扩展到各种最先进的GANs。DSE提高了GANs从高质量图像(无论是合成还是真实图像)重建高保真图像的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 当前深度生成对抗网络(GANs)可以合成高质量图像,使用GANs学习表示受到青睐。
- GAN反演是新兴方法之一,研究如何将图像反演到潜在空间。
- 现有GAN编码器可以在StyleGAN上进行图像反演,但不能适应其他深度GANs。
- 提出了一种新的方法——多样相似性编码器(DSE),可以解决此问题。
- DSE通过评估潜在向量和图像之间的多样相似性进行设计。
- DSE可以扩展到各种最先进的GANs,如PGGAN、StyleGAN和BigGAN。
点此查看论文截图