⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-12 更新
Multimodal Latent Language Modeling with Next-Token Diffusion
Authors:Yutao Sun, Hangbo Bao, Wenhui Wang, Zhiliang Peng, Li Dong, Shaohan Huang, Jianyong Wang, Furu Wei
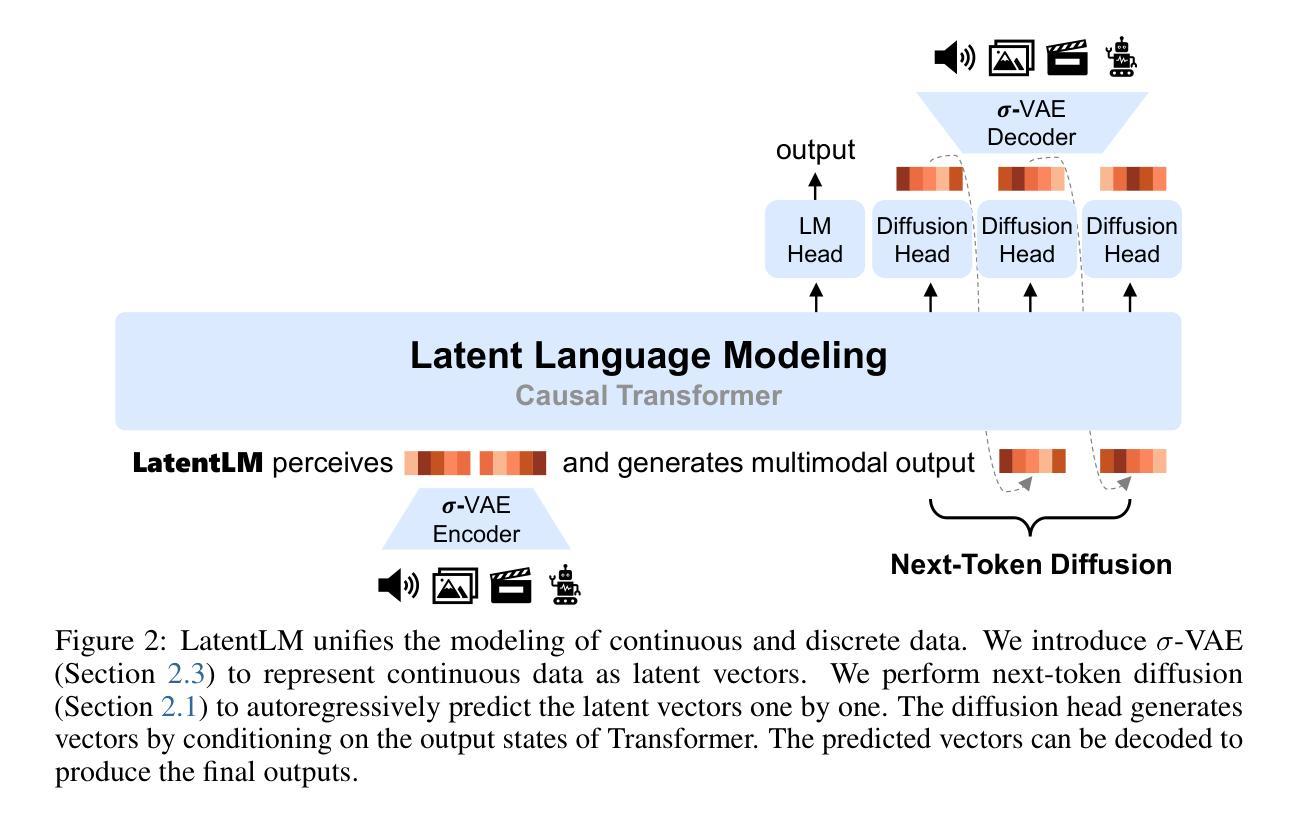
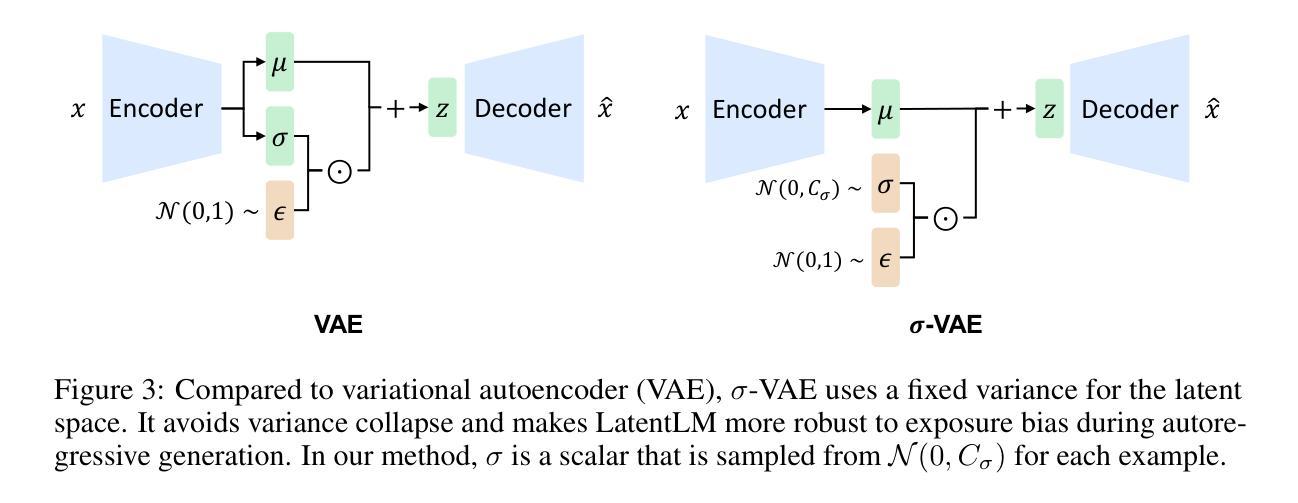
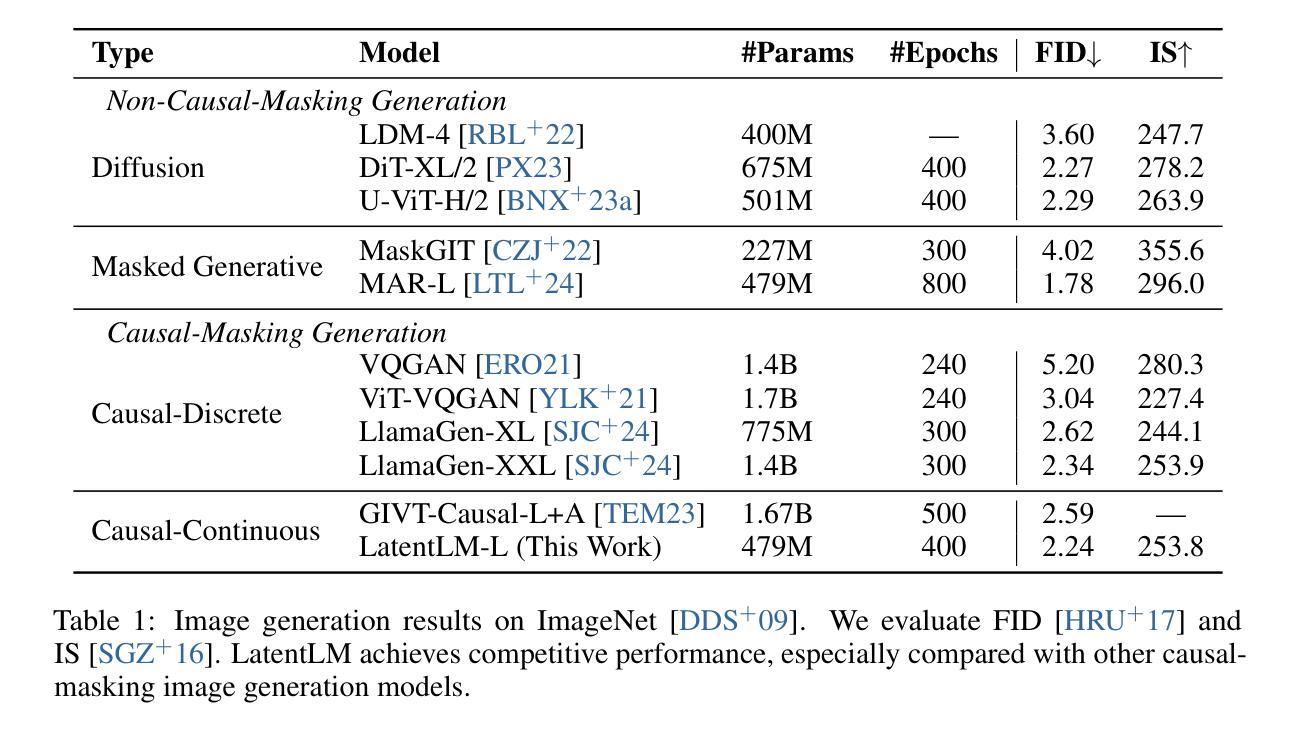
Multimodal generative models require a unified approach to handle both discrete data (e.g., text and code) and continuous data (e.g., image, audio, video). In this work, we propose Latent Language Modeling (LatentLM), which seamlessly integrates continuous and discrete data using causal Transformers. Specifically, we employ a variational autoencoder (VAE) to represent continuous data as latent vectors and introduce next-token diffusion for autoregressive generation of these vectors. Additionally, we develop $\sigma$-VAE to address the challenges of variance collapse, which is crucial for autoregressive modeling. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of LatentLM across various modalities. In image generation, LatentLM surpasses Diffusion Transformers in both performance and scalability. When integrated into multimodal large language models, LatentLM provides a general-purpose interface that unifies multimodal generation and understanding. Experimental results show that LatentLM achieves favorable performance compared to Transfusion and vector quantized models in the setting of scaling up training tokens. In text-to-speech synthesis, LatentLM outperforms the state-of-the-art VALL-E 2 model in speaker similarity and robustness, while requiring 10x fewer decoding steps. The results establish LatentLM as a highly effective and scalable approach to advance large multimodal models.
多模态生成模型需要一种统一的方法来处理离散数据(如文本和代码)和连续数据(如图像、音频和视频)。在这项工作中,我们提出了潜在语言建模(LatentLM),它利用因果Transformer无缝集成连续和离散数据。具体来说,我们采用变分自编码器(VAE)将连续数据表示为潜在向量,并引入下一个令牌扩散来进行这些向量的自回归生成。此外,我们开发出了σ-VAE,以解决方差崩溃的挑战,这对于自回归建模至关重要。大量实验表明,LatentLM在多种模态中的应用都很有效。在图像生成方面,LatentLM在性能和可扩展性方面都超越了Diffusion Transformers。当集成到多模态大型语言模型中时,LatentLM提供了一个通用接口,统一了多模态生成和理解。实验结果表明,在扩大训练令牌规模方面,LatentLM与Transfusion和向量量化模型相比取得了有利的表现。在文本到语音合成方面,LatentLM在说话人相似性和稳健性方面超越了最先进的VALL-E 2模型,同时需要10倍更少的解码步骤。这些结果证明了LatentLM在推进大型多模态模型方面是一种高效且可扩展的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
Latent Language Modeling(LatentLM)是一种多模态生成模型,能处理离散数据和连续数据。它通过变分自编码器(VAE)表示连续数据为潜在向量,并引入next-token扩散进行这些向量的自回归生成。此外,LatentLM解决了方差消失问题并提升了模型性能。实验表明,LatentLM在各种模态上表现出优越效果,超越Diffusion Transformers与Transfusion等模型。在文本到语音合成方面,LatentLM以较少的解码步骤达到或超越了现有技术。因此,LatentLM是一种高效、可扩展的多模态模型。
Key Takeaways
- Latent Language Modeling (LatentLM) 能统一处理离散和连续数据。
- 使用变分自编码器(VAE)表示连续数据为潜在向量。
- Next-token扩散用于自回归生成潜在向量。
- LatentLM解决了方差消失问题以提高模型性能。
- 在各种模态上,LatentLM表现优越,超越其他模型如Diffusion Transformers和Transfusion等。
- 在文本到语音合成方面,LatentLM效果显著,与现有技术相比需要更少的解码步骤。
点此查看论文截图

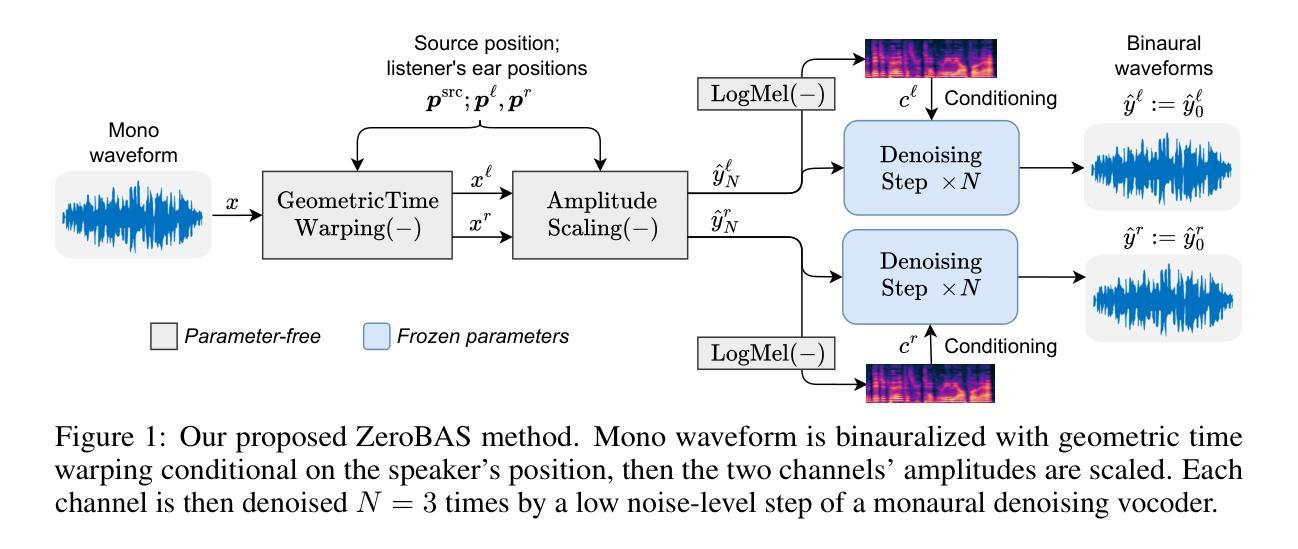
Zero-Shot Mono-to-Binaural Speech Synthesis
Authors:Alon Levkovitch, Julian Salazar, Soroosh Mariooryad, RJ Skerry-Ryan, Nadav Bar, Bastiaan Kleijn, Eliya Nachmani
We present ZeroBAS, a neural method to synthesize binaural audio from monaural audio recordings and positional information without training on any binaural data. To our knowledge, this is the first published zero-shot neural approach to mono-to-binaural audio synthesis. Specifically, we show that a parameter-free geometric time warping and amplitude scaling based on source location suffices to get an initial binaural synthesis that can be refined by iteratively applying a pretrained denoising vocoder. Furthermore, we find this leads to generalization across room conditions, which we measure by introducing a new dataset, TUT Mono-to-Binaural, to evaluate state-of-the-art monaural-to-binaural synthesis methods on unseen conditions. Our zero-shot method is perceptually on-par with the performance of supervised methods on the standard mono-to-binaural dataset, and even surpasses them on our out-of-distribution TUT Mono-to-Binaural dataset. Our results highlight the potential of pretrained generative audio models and zero-shot learning to unlock robust binaural audio synthesis.
我们提出了ZeroBAS方法,这是一种从单声道音频录制和位置信息合成双声道音频的神经方法,无需对任何双声道数据进行训练。据我们所知,这是首次发布的从零开始神经方法用于单声道到双声道的音频合成。具体来说,我们展示了基于源位置的无需参数几何时间扭曲和振幅缩放足以获得初始双声道合成,可以通过迭代应用预训练的降噪编解码器进行细化。此外,我们发现这导致了跨房间条件的泛化,我们通过引入一个新的数据集TUT Mono-to-Binaural来衡量这一点,以评估最先进单声道到双声道合成方法在未见条件上的表现。我们的零样本方法与标准单声道到双声道数据集上的有监督方法在感知上相当,甚至在我们的离群TUT Mono-to-Binaural数据集上超过了它们。我们的结果突出了预训练的生成音频模型和零样本学习在解锁稳健的双声道音频合成方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
零基音频合成方法(ZeroBAS)是一种无需训练即可从单声道音频录制和位置信息合成双声道音频的神经方法。这是首次发表的无训练双声道音频合成的神经方法。通过基于源位置的参数化几何时间扭曲和振幅缩放,可以实现初步的双声道合成,并通过迭代应用预训练的降噪编解码器进行改进。此方法可在不同房间条件下进行推广,并通过引入新的数据集TUT Mono-to-Binaural来评估其性能。零基方法在标准单声道到双声道数据集上的表现与有监督方法相当,甚至在我们的TUT Mono-to-Binaural数据集上表现更佳。结果突显了预训练生成音频模型和零样本学习的潜力,可解锁稳健的双声道音频合成。
Key Takeaways
- ZeroBAS是一种无需训练的双声道音频合成方法,可从单声道音频和位置信息合成双声道音频。
- 参数化的几何时间扭曲和振幅缩放是实现初步双声道合成的关键步骤。
- 通过迭代应用预训练的降噪编解码器,可以改进初步合成的双声道音频质量。
- 该方法可在不同房间条件下进行推广。
- 零基方法在标准数据集上的表现与有监督方法相当。
- 在新的数据集TUT Mono-to-Binaural上,零基方法的性能更佳,突显了其稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

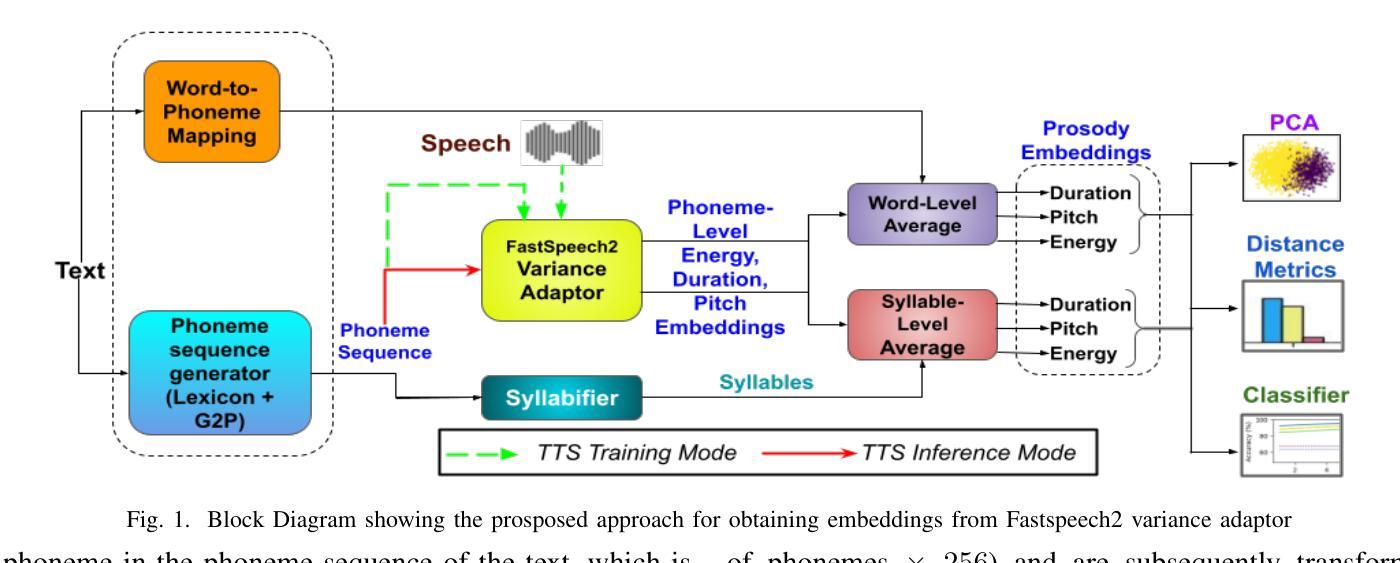
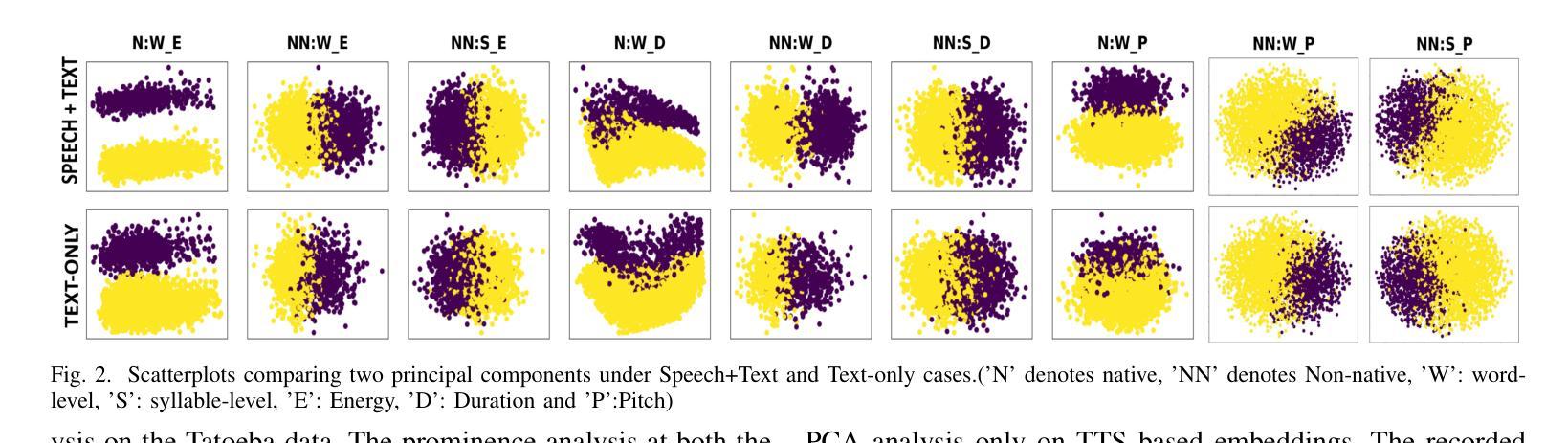
A Preliminary Analysis of Automatic Word and Syllable Prominence Detection in Non-Native Speech With Text-to-Speech Prosody Embeddings
Authors:Anindita Mondal, Rangavajjala Sankara Bharadwaj, Jhansi Mallela, Anil Kumar Vuppala, Chiranjeevi Yarra
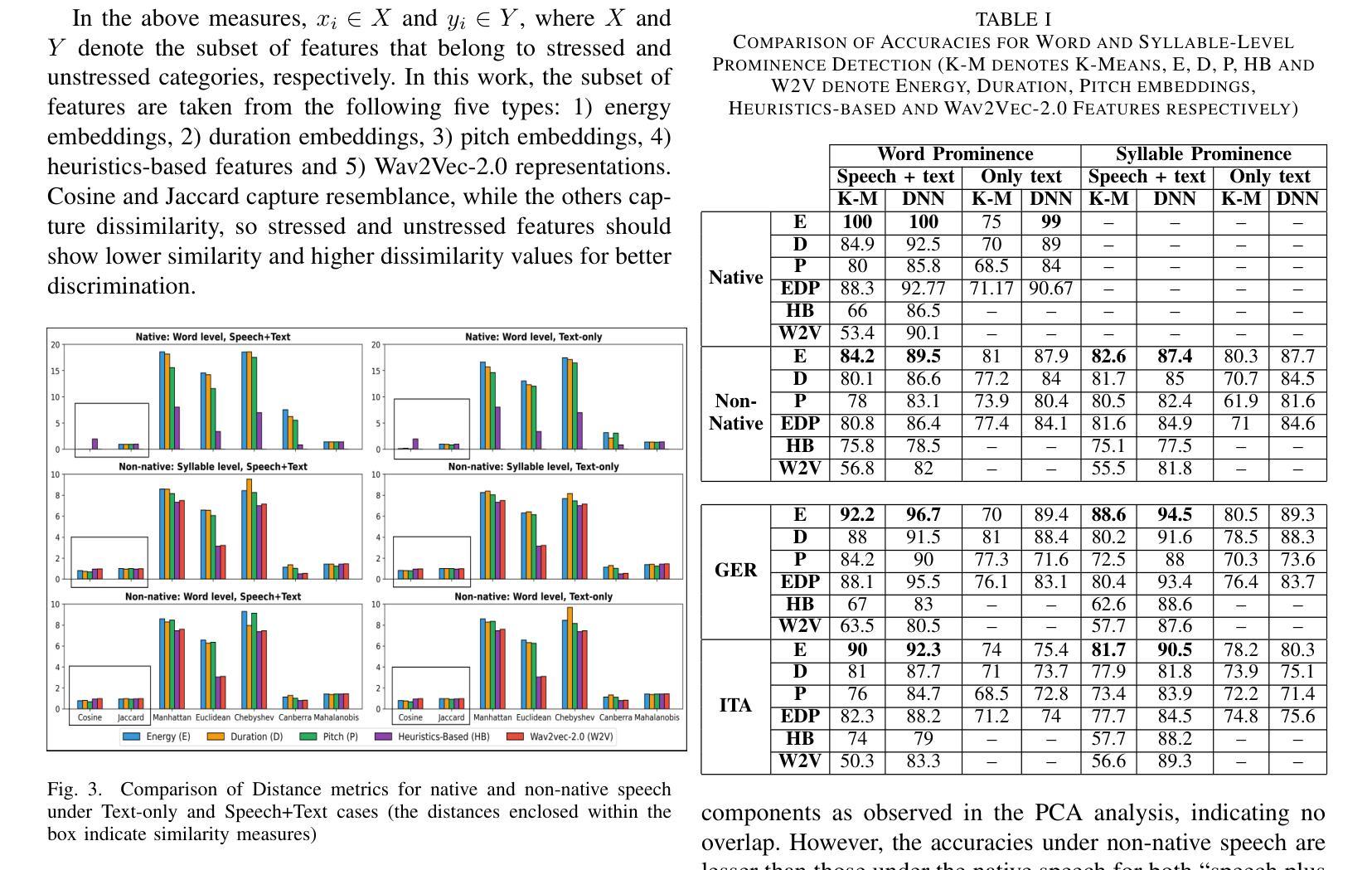
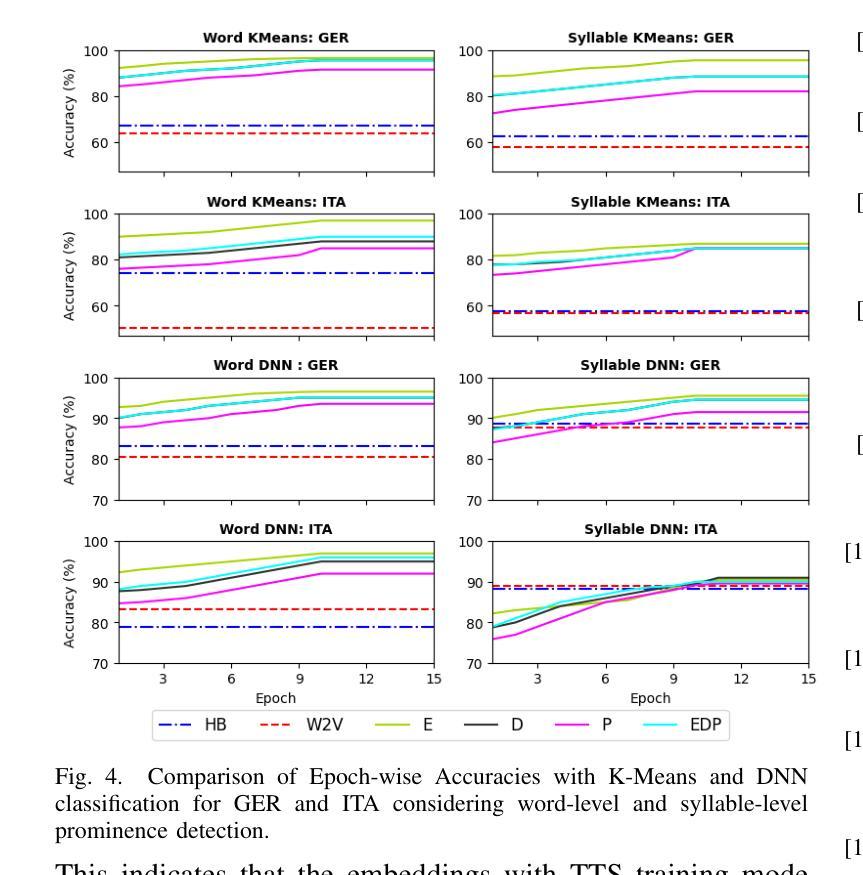
Automatic detection of prominence at the word and syllable-levels is critical for building computer-assisted language learning systems. It has been shown that prosody embeddings learned by the current state-of-the-art (SOTA) text-to-speech (TTS) systems could generate word- and syllable-level prominence in the synthesized speech as natural as in native speech. To understand the effectiveness of prosody embeddings from TTS for prominence detection under nonnative context, a comparative analysis is conducted on the embeddings extracted from native and non-native speech considering the prominence-related embeddings: duration, energy, and pitch from a SOTA TTS named FastSpeech2. These embeddings are extracted under two conditions considering: 1) only text, 2) both speech and text. For the first condition, the embeddings are extracted directly from the TTS inference mode, whereas for the second condition, we propose to extract from the TTS under training mode. Experiments are conducted on native speech corpus: Tatoeba, and non-native speech corpus: ISLE. For experimentation, word-level prominence locations are manually annotated for both corpora. The highest relative improvement on word & syllable-level prominence detection accuracies with the TTS embeddings are found to be 13.7% & 5.9% and 16.2% & 6.9% compared to those with the heuristic-based features and self-supervised Wav2Vec-2.0 representations, respectively.
自动检测单词和音节级别的突出性对于构建计算机辅助语言学习系统至关重要。研究表明,当前最先进的文本转语音(TTS)系统所学习的韵律嵌入可以在合成语音中产生与原生语音一样自然的单词和音节级别的突出性。为了了解TTS韵律嵌入在非母语环境下的突出性检测效果,对来自名为FastSpeech2的先进TTS系统提取的嵌入进行了比较分析,考虑了与突出性相关的嵌入:持续时间、能量和音调。这些嵌入是在两种条件下提取的:1)只有文本,2)语音和文本都有。对于第一种情况,嵌入直接从TTS推理模式中提取,而对于第二种情况,我们提出在TTS训练模式下提取。实验在母语语料库Tatoeba和非母语语料库ISLE上进行。为了实验,两个语料库的单词级别突出位置都进行了手动注释。与基于启发式特征和自监督Wav2Vec-2.0表示相比,使用TTS嵌入在单词和音节级别的突出性检测准确率上获得了最高相对改进,分别为13.7%和5.9%,以及16.2%和6.9%。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
基于当前最新技术(SOTA)文本转语音(TTS)系统学习到的韵律嵌入能够在合成语音中生成自然的词和音节级别的突出表达。在非母语环境下,对TTS中用于突出检测的有效性进行了对比分析,从母语和非母语语音中提取的嵌入考虑了与突出相关的嵌入因素:持续时间、能量和音调。这些嵌入是在两种情况下提取的:仅文本和语音与文本结合。对于第一种情况,直接从TTS推理模式中提取嵌入;对于第二种情况,建议在TTS训练模式下提取。实验在母语语料库Tatoeba和非母语语料库ISLE上进行。实验中,手动标注了两组语料库中词级的突出位置。相较于启发式特征和自监督的Wav2Vec-2.0表示方法,使用TTS嵌入后,词和音节级别的突出检测准确率相对提高了最高达16.2%和6.9%。
关键见解
- 文本转语音系统对韵律嵌入的理解非常重要,可生成自然的词和音节级别的突出表达。
- 对比分析了在自然和非母语环境下的韵律嵌入对于重要性检测的有效性。
- 实验考虑了在两种情境下提取嵌入:仅基于文本和同时考虑语音与文本。
点此查看论文截图

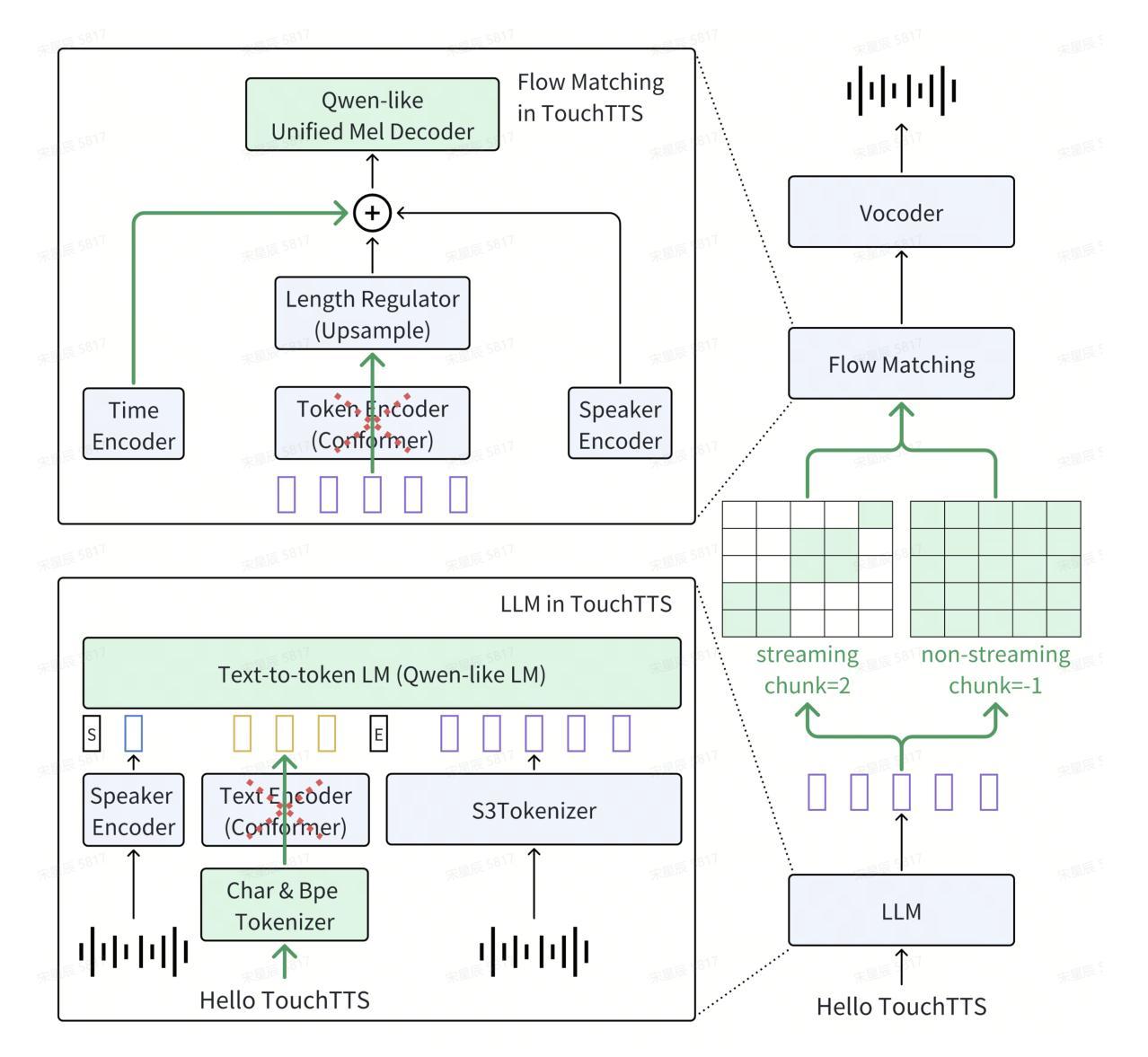
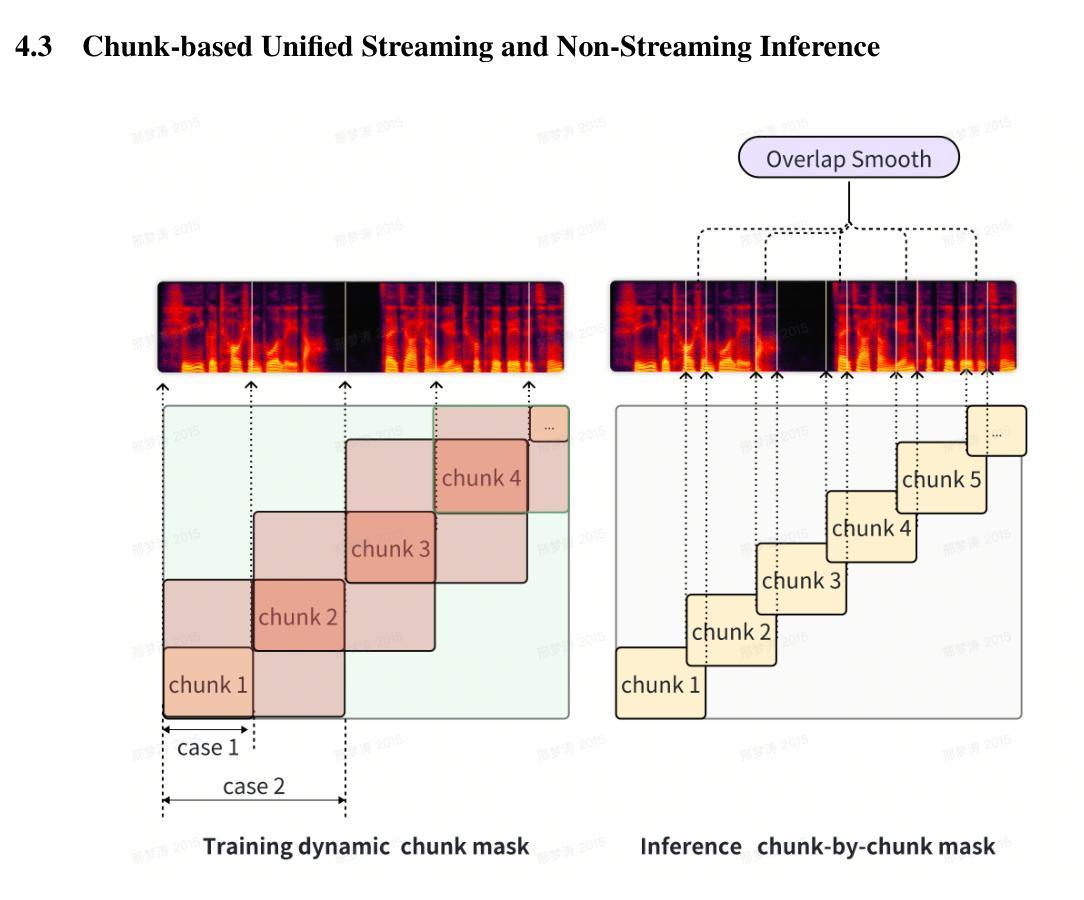
TouchTTS: An Embarrassingly Simple TTS Framework that Everyone Can Touch
Authors:Xingchen Song, Mengtao Xing, Changwei Ma, Shengqiang Li, Di Wu, Binbin Zhang, Fuping Pan, Dinghao Zhou, Yuekai Zhang, Shun Lei, Zhendong Peng, Zhiyong Wu
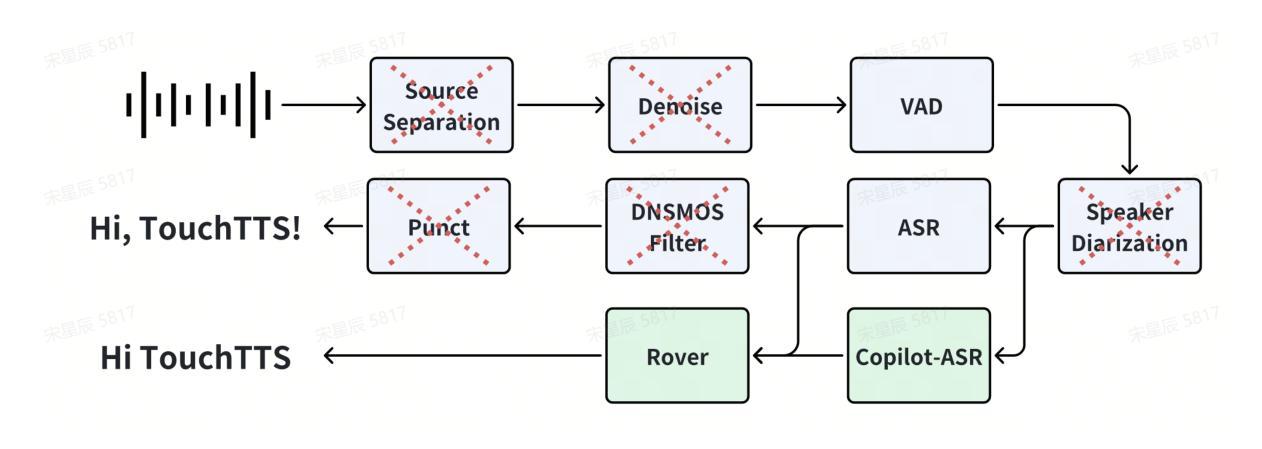
It is well known that LLM-based systems are data-hungry. Recent LLM-based TTS works typically employ complex data processing pipelines to obtain high-quality training data. These sophisticated pipelines require excellent models at each stage (e.g., speech denoising, speech enhancement, speaker diarization, and punctuation models), which themselves demand high-quality training data and are rarely open-sourced. Even with state-of-the-art models, issues persist, such as incomplete background noise removal and misalignment between punctuation and actual speech pauses. Moreover, the stringent filtering strategies often retain only 10-30% of the original data, significantly impeding data scaling efforts. In this work, we leverage a noise-robust audio tokenizer (S3Tokenizer) to design a simplified yet effective TTS data processing pipeline that maintains data quality while substantially reducing data acquisition costs, achieving a data retention rate of over 50%. Beyond data scaling challenges, LLM-based TTS systems also incur higher deployment costs compared to conventional approaches. Current systems typically use LLMs solely for text-to-token generation, while requiring separate models (e.g., flow matching models) for token-to-waveform generation, which cannot be directly executed by LLM inference engines, further complicating deployment. To address these challenges, we eliminate redundant modules in both LLM and flow components, replacing the flow model backbone with an LLM architecture. Building upon this simplified flow backbone, we propose a unified architecture for both streaming and non-streaming inference, significantly reducing deployment costs. Finally, we explore the feasibility of unifying TTS and ASR tasks using the same data for training, thanks to the simplified pipeline and the S3Tokenizer that reduces the quality requirements for TTS training data.
基于大模型的文本转语音(TTS)系统对数据有着极高的需求。近期基于大模型的TTS工作通常采用复杂的数据处理流程以获得高质量的训练数据。这些高级流程需要在每个阶段都有优秀的模型(例如语音降噪、语音增强、说话人识别和标点模型),而这些模型本身也需要高质量的训练数据并且很少开源。即使使用最先进的模型,仍存在一些问题,例如背景噪声去除不完全以及标点符号与实际语音停顿之间的不匹配。此外,严格的过滤策略通常只能保留原始数据的10-30%,极大地阻碍了数据扩展的努力。
在这项工作中,我们利用噪声鲁棒的音频标记器(S3Tokenizer)设计了一个简化而有效的TTS数据处理流程,该流程在保持数据质量的同时,大大降低了数据获取成本,实现了超过50%的数据保留率。除了数据扩展的挑战外,基于大模型的TTS系统的部署成本也高于传统方法。当前的系统通常仅使用大模型进行文本到标记的生成,但需要额外的模型(如流程匹配模型)来进行标记到波形生成的转换,这些转换无法由大模型推理引擎直接执行,进一步增加了部署的复杂性。为了应对这些挑战,我们消除了大模型和流程组件中的冗余模块,并用大模型架构替代流程模型的主干。基于这种简化的流程主干,我们提出了流式和非流式推理的统一架构,大大降低了部署成本。最后,我们借助简化的流程和S3Tokenizer,探索了使用相同数据进行TTS和语音识别(ASR)任务训练的可行性,降低了TTS训练数据的质量要求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Technical Report
摘要
基于LLM的TTS数据处理方法的新改进。通过采用噪声鲁棒的音频分词器(S3Tokenizer),简化了数据获取流程,提高了数据保留率。同时,通过优化模型架构,减少了部署成本,并探索了统一TTS和ASR任务的可行性。
关键见解
- LLM-based TTS系统对数据质量有较高要求,需复杂的数据处理流程和高质量的训练数据。
- S3Tokenizer的应用使得TTS数据处理流程简化,同时保持数据质量,并提高数据保留率至50%以上。
- LLM-based TTS系统的部署成本较高,需要通过优化模型架构来降低。
- 提出了一种统一的架构,支持流式和非流式推理,降低了部署成本。
- 简化的数据处理流程和S3Tokenizer使得TTS和ASR任务可以使用相同的数据进行训练。
- 仍存在背景噪声去除不完全和标点与语音停顿对齐问题,需要进一步完善。
- 未来的研究可以进一步探索如何优化LLM-based TTS系统的效率和性能,以应对大规模数据和复杂场景的挑战。
点此查看论文截图
LatentSpeech: Latent Diffusion for Text-To-Speech Generation
Authors:Haowei Lou, Helen Paik, Pari Delir Haghighi, Wen Hu, Lina Yao
Diffusion-based Generative AI gains significant attention for its superior performance over other generative techniques like Generative Adversarial Networks and Variational Autoencoders. While it has achieved notable advancements in fields such as computer vision and natural language processing, their application in speech generation remains under-explored. Mainstream Text-to-Speech systems primarily map outputs to Mel-Spectrograms in the spectral space, leading to high computational loads due to the sparsity of MelSpecs. To address these limitations, we propose LatentSpeech, a novel TTS generation approach utilizing latent diffusion models. By using latent embeddings as the intermediate representation, LatentSpeech reduces the target dimension to 5% of what is required for MelSpecs, simplifying the processing for the TTS encoder and vocoder and enabling efficient high-quality speech generation. This study marks the first integration of latent diffusion models in TTS, enhancing the accuracy and naturalness of generated speech. Experimental results on benchmark datasets demonstrate that LatentSpeech achieves a 25% improvement in Word Error Rate and a 24% improvement in Mel Cepstral Distortion compared to existing models, with further improvements rising to 49.5% and 26%, respectively, with additional training data. These findings highlight the potential of LatentSpeech to advance the state-of-the-art in TTS technology
基于扩散的生成人工智能(AI)因其相较于其他生成技术(如生成对抗网络和变分自编码器)的卓越性能而受到广泛关注。虽然它在计算机视觉和自然语言处理等领域取得了显著进展,但在语音生成方面的应用仍然被较少探索。主流的文本到语音(TTS)系统主要在频谱空间中把输出映射到梅尔频谱(Mel-Spectrograms),由于梅尔频谱的稀疏性,导致计算负载较高。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了LatentSpeech,这是一种利用潜在扩散模型的新型TTS生成方法。LatentSpeech通过使用潜在嵌入作为中间表示,将目标维度降低到梅尔频谱所需的5%,简化了TTS编码器与vocoder的处理过程,实现了高效高质量的语音生成。这项研究标志着潜在扩散模型在TTS中的首次集成,提高了生成语音的准确性和自然度。在基准数据集上的实验结果表明,与现有模型相比,LatentSpeech在词错误率上提高了25%,梅尔倒谱失真提高了24%,随着训练数据的增加,这两项指标分别进一步提高到49.5%和26%。这些发现凸显了LatentSpeech在推动TTS技术前沿方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于扩散的生成式AI在语音识别领域受到关注,但仍存在应用局限性。主流文本转语音系统主要映射到Mel频谱图,导致高计算负载。本研究提出LatentSpeech,一种利用潜在扩散模型的新型TTS生成方法,通过潜在嵌入作为中间表示,降低目标维度至Mel频谱图的5%,简化TTS编码器和vocoder的处理流程,实现高效高质量的语音生成。LatentSpeech集成于TTS中提高了生成语音的准确性和自然度,在基准数据集上的实验结果表明其较现有模型有所改善。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散式生成AI在多个领域表现优越,但在语音生成领域的应用仍待探索。
- 主流TTS系统主要映射到Mel频谱图,导致高计算负载。
- LatentSpeech是一种新型TTS生成方法,利用潜在扩散模型,降低目标维度至Mel频谱图的5%。
- LatentSpeech简化了TTS编码器和vocoder的处理流程,提高了语音生成的效率。
- LatentSpeech集成了扩散模型在TTS中,提高了生成语音的准确性和自然度。
- 实验结果表明,相较于现有模型,LatentSpeech在Word Error Rate上有25%的改进,在Mel Cepstral Distortion上有24%的改进。
点此查看论文截图

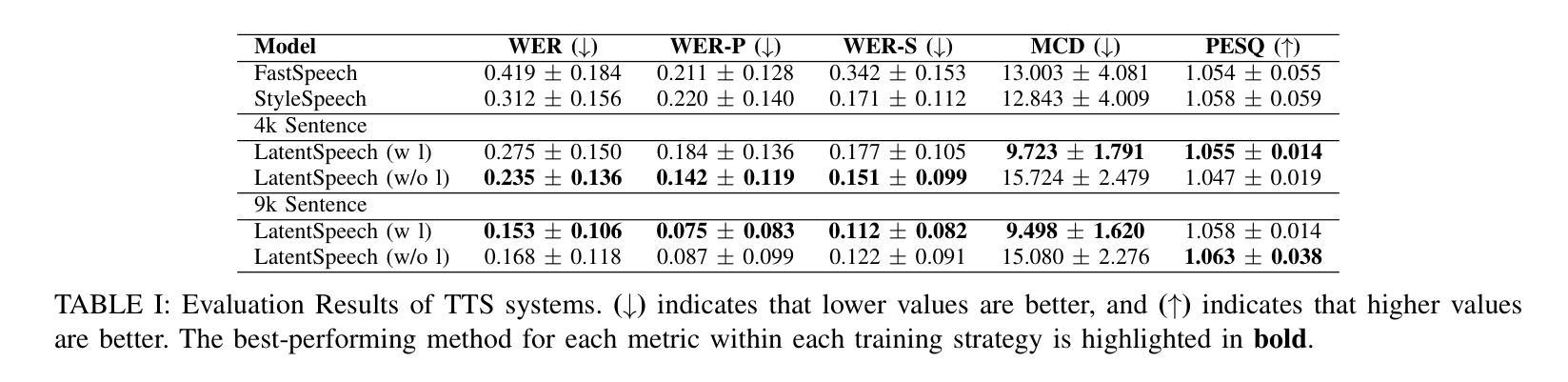
Sampling from Boltzmann densities with physics informed low-rank formats
Authors:Paul Hagemann, Janina Schütte, David Sommer, Martin Eigel, Gabriele Steidl
Our method proposes the efficient generation of samples from an unnormalized Boltzmann density by solving the underlying continuity equation in the low-rank tensor train (TT) format. It is based on the annealing path commonly used in MCMC literature, which is given by the linear interpolation in the space of energies. Inspired by Sequential Monte Carlo, we alternate between deterministic time steps from the TT representation of the flow field and stochastic steps, which include Langevin and resampling steps. These adjust the relative weights of the different modes of the target distribution and anneal to the correct path distribution. We showcase the efficiency of our method on multiple numerical examples.
我们的方法通过解决低秩张量列车(TT)格式中的基础连续性方程,有效地从未标准化的玻尔兹曼密度中生成样本。它基于MCMC文献中常用的退火路径,由能量空间中的线性插值给出。受序贯蒙特卡罗的启发,我们在确定性时间步长和流动场TT表示的随机步骤之间进行交替切换,随机步骤包括朗格文(Langevin)和重采样步骤。这些步骤调整了目标分布的各模态的相对权重,并退火到正确的路径分布。我们在多个数值示例中展示了该方法的效率。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于低秩张量列车(TT)格式的未归一化玻尔兹曼密度样本高效生成方法。该方法基于MCMC文献中常用的退火路径,通过能量空间中的线性插值给出。该方法受到序贯蒙特卡罗的启发,在流场的TT表示中交替进行确定性时间步长和随机步骤,包括朗格文重采样步骤。这些步骤调整目标分布的各模态相对权重,并退火到正确的路径分布。通过多个数值例子展示了该方法的效率。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于低秩张量列车(TT)格式的高效生成未归一化玻尔兹曼密度样本的方法。
- 方法结合了退火路径和线性插值技术,在能量空间中寻找最佳样本。
- 受到序贯蒙特卡罗的启发,该方法交替使用确定性时间步长和随机步骤。
- 确定性时间步长基于流场的TT表示,而随机步骤包括朗格文重采样步骤。
- 通过调整目标分布的各模态相对权重,实现了更精确的样本生成。
- 该方法通过退火过程达到正确的路径分布,提高了样本生成的效率。
点此查看论文截图

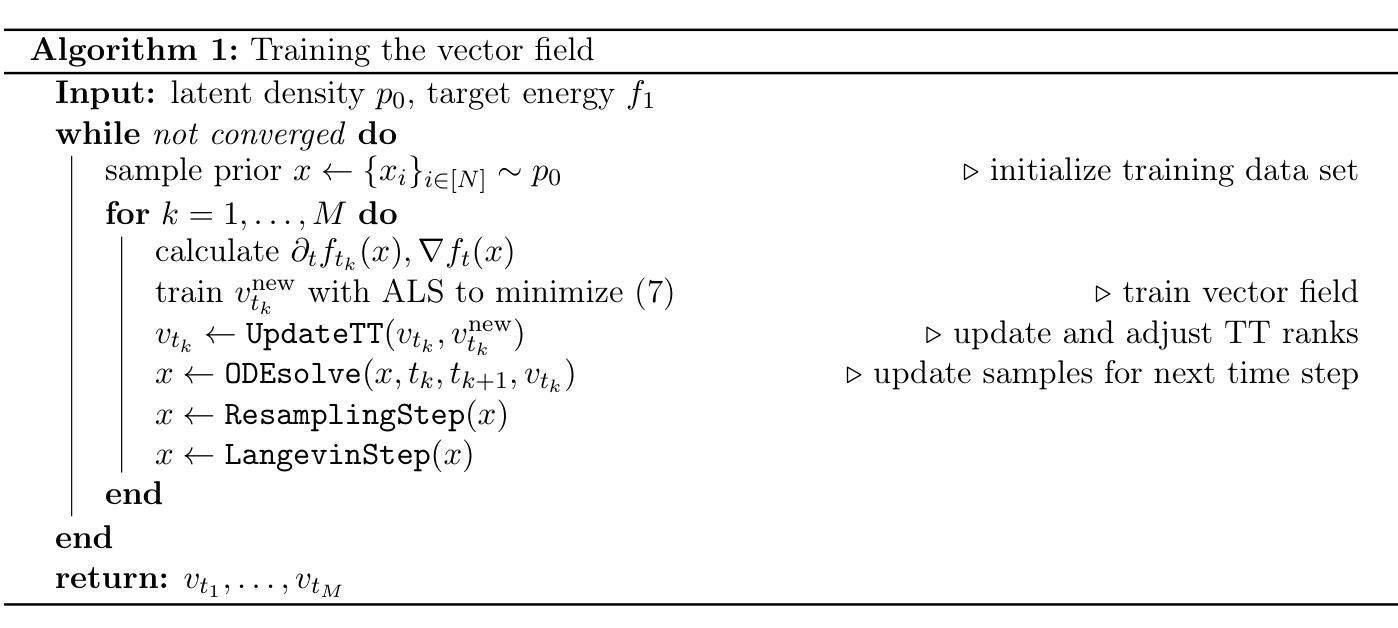
Mitigating Unauthorized Speech Synthesis for Voice Protection
Authors:Zhisheng Zhang, Qianyi Yang, Derui Wang, Pengyang Huang, Yuxin Cao, Kai Ye, Jie Hao
With just a few speech samples, it is possible to perfectly replicate a speaker’s voice in recent years, while malicious voice exploitation (e.g., telecom fraud for illegal financial gain) has brought huge hazards in our daily lives. Therefore, it is crucial to protect publicly accessible speech data that contains sensitive information, such as personal voiceprints. Most previous defense methods have focused on spoofing speaker verification systems in timbre similarity but the synthesized deepfake speech is still of high quality. In response to the rising hazards, we devise an effective, transferable, and robust proactive protection technology named Pivotal Objective Perturbation (POP) that applies imperceptible error-minimizing noises on original speech samples to prevent them from being effectively learned for text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis models so that high-quality deepfake speeches cannot be generated. We conduct extensive experiments on state-of-the-art (SOTA) TTS models utilizing objective and subjective metrics to comprehensively evaluate our proposed method. The experimental results demonstrate outstanding effectiveness and transferability across various models. Compared to the speech unclarity score of 21.94% from voice synthesizers trained on samples without protection, POP-protected samples significantly increase it to 127.31%. Moreover, our method shows robustness against noise reduction and data augmentation techniques, thereby greatly reducing potential hazards.
近年来,只需少量的语音样本,就能够完美复制一个人的声音,而恶意声音滥用(例如电信欺诈以获取非法财务收益)给我们日常生活带来了巨大的危害。因此,保护含有敏感信息(如个人语音特征)的公开语音数据至关重要。虽然大多数先前的方法侧重于欺骗说话者验证系统的音色相似性,但合成的深度伪造语音仍然具有很高的质量。为了应对日益增长的威胁,我们设计了一种有效、可迁移且稳健的主动保护技术,称为关键目标扰动(POP)。该技术对原始语音样本应用几乎无法察觉的错误最小化噪声,防止它们被有效学习用于文本到语音(TTS)合成模型,从而无法生成高质量的深度伪造语音。我们对采用客观和主观指标的先进TTS模型进行了广泛实验,全面评估了我们提出的方法。实验结果表明,该方法在各种模型中的有效性和可迁移性都很出色。与未经保护的样本训练的语音合成器的语音清晰度得分为21.94%相比,POP保护的样本得分显著提高到127.31%。此外,我们的方法显示出对降噪和数据增强技术的稳健性,从而大大减少了潜在风险。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM CCS Workshop (LAMPS) 2024
摘要
近期出现能通过少量语音样本完美复制发言人声音的技术,但同时也带来了恶意语音滥用(如电信诈骗)的巨大风险。因此,保护含有敏感信息的公开语音数据至关重要,如个人声纹。为应对风险,我们开发了一种有效、可迁移且稳健的主动保护技术——关键目标扰动(POP),通过在原始语音样本上添加几乎无法察觉的最小误差噪声,防止它们被用于文本到语音(TTS)合成模型的训练,从而防止高质量深度伪造语音的生成。我们对最先进的TTS模型进行了大量实验,用客观和主观指标全面评估了我们的方法。实验结果显示其在不同模型中的出色效果和可迁移性。相较于未经保护的样本训练的语音合成器,其语音清晰度只有21.94%,使用POP保护的样本将其显著提高到127.31%。此外,我们的方法显示出对抗降噪和数据增强技术的稳健性,大大降低了潜在风险。
关键见解
- 仅需少量语音样本即可完美复制发言人声音,同时出现恶意语音滥用风险。
- 保护公开语音数据中的敏感信息至关重要。
- 提出一种名为关键目标扰动(POP)的主动保护技术,通过添加几乎无法察觉的噪声防止语音样本被用于TTS合成。
- POP技术在各种TTS模型中表现出卓越的有效性和可迁移性。
- 与未经保护的样本相比,POP保护的样本训练的语音合成器语音清晰度显著提高。
- POP技术对抗降噪和数据增强技术具有稳健性。
- POP技术有助于大大降低因深度伪造语音带来的潜在风险。
点此查看论文截图

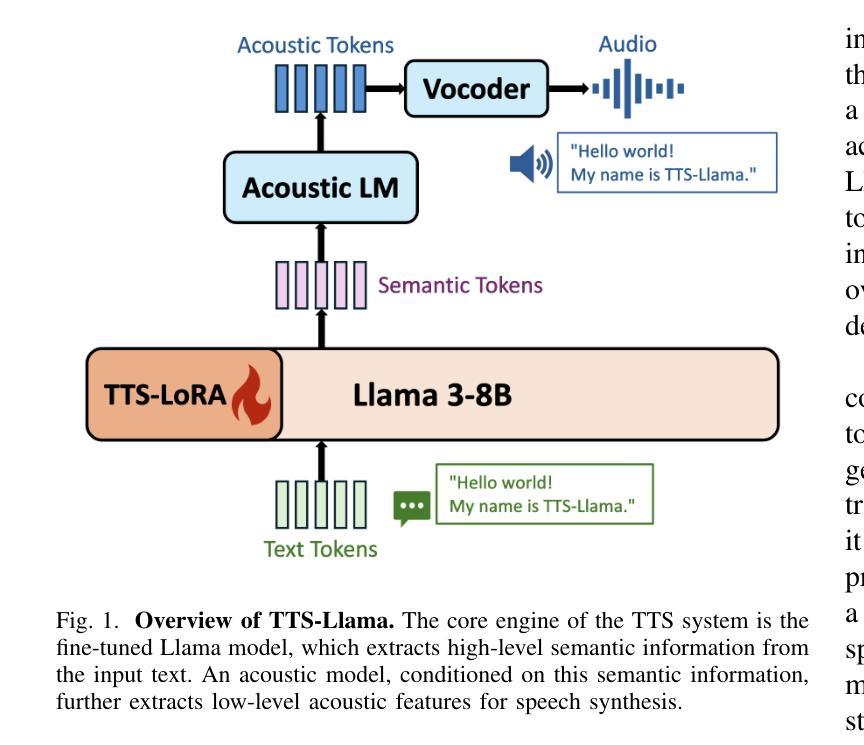
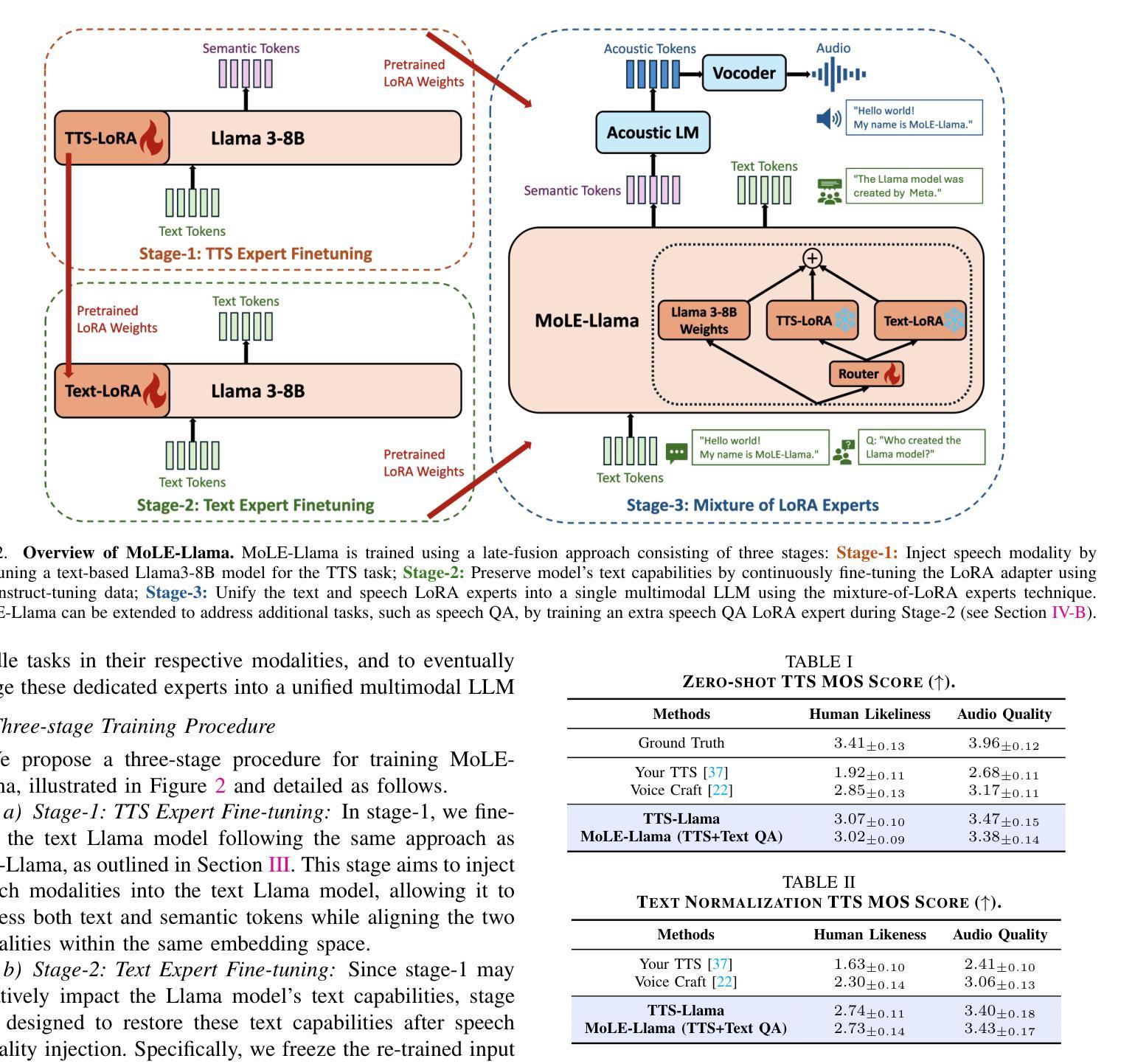
Get Large Language Models Ready to Speak: A Late-fusion Approach for Speech Generation
Authors:Maohao Shen, Shun Zhang, Jilong Wu, Zhiping Xiu, Ehab AlBadawy, Yiting Lu, Mike Seltzer, Qing He
Large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing (NLP) with impressive performance across various text-based tasks. However, the extension of text-dominant LLMs to with speech generation tasks remains under-explored. In this work, we introduce a text-to-speech (TTS) system powered by a fine-tuned Llama model, named TTS-Llama, that achieves state-of-the-art speech synthesis performance. Building on TTS-Llama, we further propose MoLE-Llama, a text-and-speech multimodal LLM developed through purely late-fusion parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) and a mixture-of-expert architecture. Extensive empirical results demonstrate MoLE-Llama’s competitive performance on both text-only question-answering (QA) and TTS tasks, mitigating catastrophic forgetting issue in either modality. Finally, we further explore MoLE-Llama in text-in-speech-out QA tasks, demonstrating its great potential as a multimodal dialog system capable of speech generation.
大型语言模型(LLM)已经凭借在各种文本相关任务中的卓越表现彻底改变了自然语言处理(NLP)的格局。然而,将文本主导的大型语言模型扩展到语音生成任务仍然有待探索。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种由精细调整的Llama模型驱动的文本到语音(TTS)系统,名为TTS-Llama,该系统实现了最先进的语音合成性能。基于TTS-Llama,我们进一步提出了MoLE-Llama,这是一个文本和语音多模态的大型语言模型,通过纯粹的后期融合参数高效微调(PEFT)和混合专家架构开发。大量的实证结果表明,MoLE-Llama在纯文本问答(QA)和TTS任务上的表现具有竞争力,减轻了任一模态中的灾难性遗忘问题。最后,我们在文本-语音问答任务中进一步探索了MoLE-Llama,证明了其作为多模态对话系统的巨大潜力,能够进行语音生成。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于大型语言模型(LLM)的文本转语音(TTS)系统取得了显著进展。本研究引入了一种基于精细调整Llama模型的TTS系统(名为TTS-Llama),实现了先进的语音合成性能。进一步构建的MoLE-Llama文本与语音混合模态LLM模型,通过纯粹的晚期融合参数效率微调(PEFT)和混合专家架构发展而来。该模型在纯文本问答(QA)和TTS任务上表现出竞争力,减轻了模态灾难遗忘问题。在文本语音问答任务中的探索表明,其作为多模态对话系统的潜力巨大。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)在文本转语音(TTS)系统的应用取得了显著进展。
- TTS-Llama系统基于精细调整的Llama模型,实现了先进的语音合成性能。
- MoLE-Llama是文本与语音混合模态LLM模型,通过PEFT和混合专家架构发展而来。
- MoLE-Llama在纯文本问答(QA)和TTS任务上表现出竞争力。
- MoLE-Llama可以减轻模态灾难遗忘问题。
- MoLE-Llama在文本语音问答任务中的探索展现出其作为多模态对话系统的潜力。
- 该研究为TTS领域提供了新方向,结合了LLM和语音技术,具有广泛的应用前景。
点此查看论文截图

Making Social Platforms Accessible: Emotion-Aware Speech Generation with Integrated Text Analysis
Authors:Suparna De, Ionut Bostan, Nishanth Sastry
Recent studies have outlined the accessibility challenges faced by blind or visually impaired, and less-literate people, in interacting with social networks, in-spite of facilitating technologies such as monotone text-to-speech (TTS) screen readers and audio narration of visual elements such as emojis. Emotional speech generation traditionally relies on human input of the expected emotion together with the text to synthesise, with additional challenges around data simplification (causing information loss) and duration inaccuracy, leading to lack of expressive emotional rendering. In real-life communications, the duration of phonemes can vary since the same sentence might be spoken in a variety of ways depending on the speakers’ emotional states or accents (referred to as the one-to-many problem of text to speech generation). As a result, an advanced voice synthesis system is required to account for this unpredictability. We propose an end-to-end context-aware Text-to-Speech (TTS) synthesis system that derives the conveyed emotion from text input and synthesises audio that focuses on emotions and speaker features for natural and expressive speech, integrating advanced natural language processing (NLP) and speech synthesis techniques for real-time applications. Our system also showcases competitive inference time performance when benchmarked against the state-of-the-art TTS models, making it suitable for real-time accessibility applications.
尽管有单音调文本到语音(TTS)屏幕阅读器等技术和表情符号的视觉元素音频叙述等辅助技术,但最近的研究概述了盲人或视障以及识字较少的人在社交网络中遇到的交互访问挑战。情感语音生成传统上依赖于人类输入的预期情感以及文本合成,还存在数据简化(导致信息丢失)和持续时间不准确等额外挑战,导致缺乏表达情感的表现。在现实生活中的通信中,由于说话人的情绪状态或口音的不同,音素的持续时间可能会有所不同(这被称为文本到语音生成的一对多问题)。因此,需要一个先进的语音合成系统来应对这种不可预测性。我们提出了一种端到端的上下文感知文本到语音(TTS)合成系统,该系统从文本输入中推导出表达的情感,并合成音频,专注于情感和说话者特征以实现自然和富有表现力的语音,集成先进的自然语言处理(NLP)和语音合成技术用于实时应用。当与最新TTS模型进行基准测试时,我们的系统还展示了具有竞争力的推理时间性能,使其适合用于实时访问性应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期研究表明,尽管有单调文本转语音(TTS)屏幕阅读器和音频叙述等辅助技术,但盲人或视障、低学历人群在使用社交网络时仍面临无障碍挑战。情感语音生成传统上依赖于预期情感和文本输入,存在数据简化导致信息丢失和持续时间不准确等问题,导致情感表达渲染不足。针对真实沟通中音素持续时间的不确定性问题,我们提出了一种端到端的语境感知文本转语音(TTS)合成系统,该系统从文本输入中推导出表达的情感,合成专注于情感和说话人特征的音频,以实现自然和富有表现力的语音。整合先进的自然语言处理(NLP)和语音合成技术,适用于实时应用。此外,我们的系统在推理时间性能上表现出竞争力,使其成为适合实时无障碍应用的理想选择。
Key Takeaways
- 盲人或视障、低学历人群在使用社交网络时仍面临无障碍挑战。
- 传统情感语音生成存在数据简化导致的信息丢失和持续时间不准确的问题。
- 真实沟通中,音素持续时间因说话人的情感状态和口音而有所不同。
- 提出一种端到端的语境感知TTS合成系统,从文本输入中推导出表达的情感。
- 系统能合成专注于情感和说话人特征的音频,实现自然和富有表现力的语音。
- 系统整合了先进的NLP和语音合成技术,适用于实时应用。
点此查看论文截图

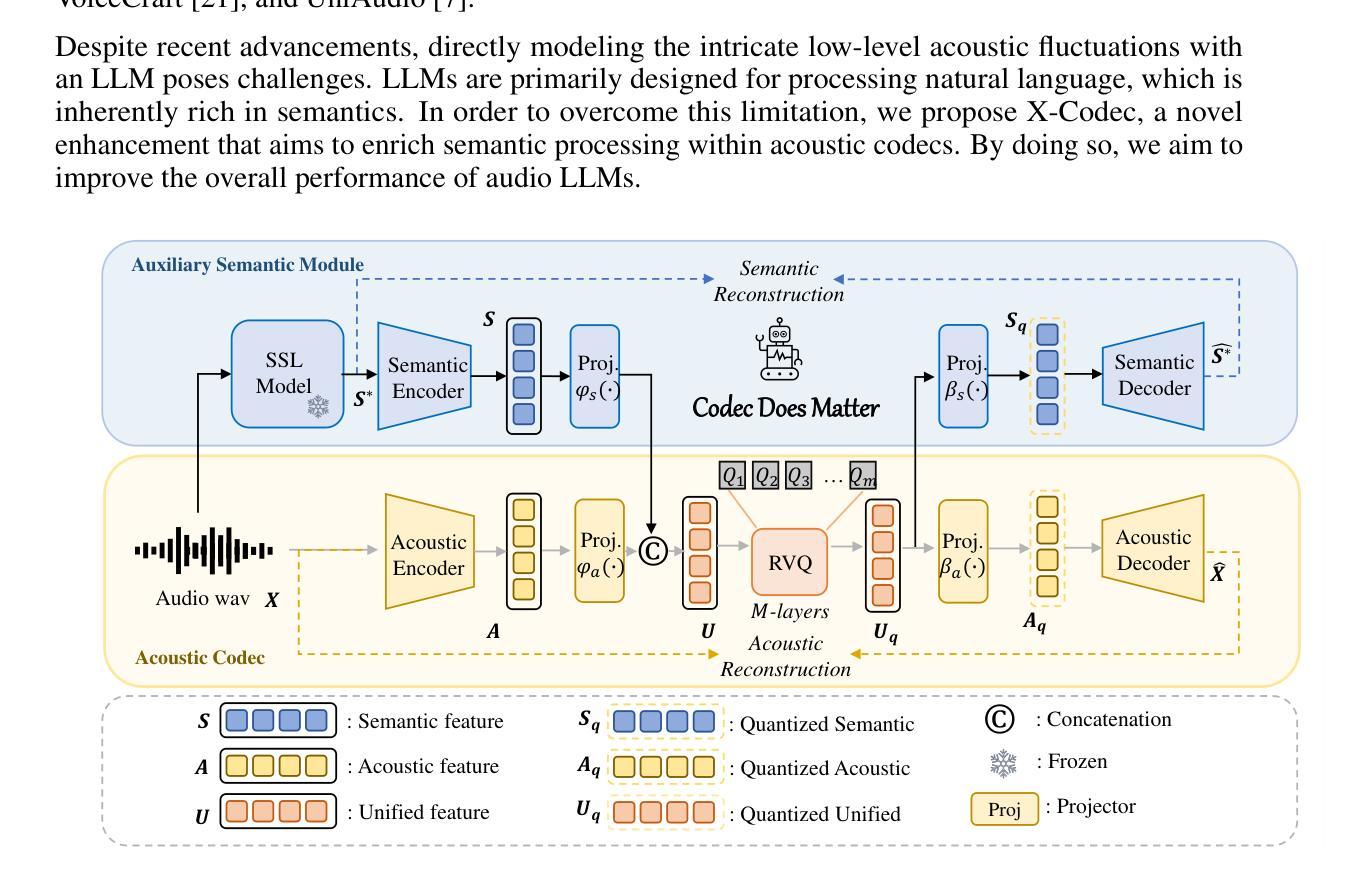
Codec Does Matter: Exploring the Semantic Shortcoming of Codec for Audio Language Model
Authors:Zhen Ye, Peiwen Sun, Jiahe Lei, Hongzhan Lin, Xu Tan, Zheqi Dai, Qiuqiang Kong, Jianyi Chen, Jiahao Pan, Qifeng Liu, Yike Guo, Wei Xue
Recent advancements in audio generation have been significantly propelled by the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). The existing research on audio LLM has primarily focused on enhancing the architecture and scale of audio language models, as well as leveraging larger datasets, and generally, acoustic codecs, such as EnCodec, are used for audio tokenization. However, these codecs were originally designed for audio compression, which may lead to suboptimal performance in the context of audio LLM. Our research aims to address the shortcomings of current audio LLM codecs, particularly their challenges in maintaining semantic integrity in generated audio. For instance, existing methods like VALL-E, which condition acoustic token generation on text transcriptions, often suffer from content inaccuracies and elevated word error rates (WER) due to semantic misinterpretations of acoustic tokens, resulting in word skipping and errors. To overcome these issues, we propose a straightforward yet effective approach called X-Codec. X-Codec incorporates semantic features from a pre-trained semantic encoder before the Residual Vector Quantization (RVQ) stage and introduces a semantic reconstruction loss after RVQ. By enhancing the semantic ability of the codec, X-Codec significantly reduces WER in speech synthesis tasks and extends these benefits to non-speech applications, including music and sound generation. Our experiments in text-to-speech, music continuation, and text-to-sound tasks demonstrate that integrating semantic information substantially improves the overall performance of language models in audio generation. Our code and demo are available (Demo: https://x-codec-audio.github.io Code: https://github.com/zhenye234/xcodec)
音频生成领域的最新进展在很大程度上得益于大型语言模型(LLM)的能力。目前关于音频LLM的研究主要集中在增强音频语言模型的架构和规模、利用更大的数据集以及一般采用音频编解码器(如EnCodec)进行音频标记化。然而,这些编解码器最初是为音频压缩而设计的,这可能导致在音频LLM的上下文中性能不佳。我们的研究旨在解决当前音频LLM编解码器的不足,特别是它们在维持生成音频的语义完整性方面所面临的挑战。例如,现有的方法如VALL-E,根据文本转录来条件化声学标记生成,由于声学标记的语义误解,经常导致内容不准确和升高的词错误率(WER),从而产生跳词和错误。为了克服这些问题,我们提出了一种简单而有效的方法,称为X-Codec。X-Codec在残差向量量化(RVQ)阶段之前融入了预训练语义编码器的语义特征,并在RVQ之后引入了语义重建损失。通过增强编解码器的语义能力,X-Codec在语音合成任务中显著降低了WER,并将这些优势扩展到了非语音应用,包括音乐和声音生成。我们在文本到语音、音乐延续和文本到声音的任务实验表明,融入语义信息能大幅提升语言模型在音频生成中的整体性能。我们的代码和演示(演示:https://x-codec-audio.github.io;代码:https://github.com/zhenye234/xcodec)已经可用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期音频生成技术的进展得益于大型语言模型(LLM)的能力。研究集中在增强音频语言模型的架构和规模、利用更大的数据集上,但现有音频LLM的编解码器如EnCodec,是为音频压缩设计的,在音频LLM语境下的表现可能不够理想。针对此问题,提出X-Codec编解码器,融入预训练语义编码器的语义特征,降低词错误率(WER),提升语音合成等任务的性能,并扩展至非语音应用。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)推动音频生成技术的最新进展。
- 现有音频LLM编解码器主要关注架构和规模的增强以及大数据集的利用。
- EnCodec等编解码器最初是为音频压缩设计的,在音频LLM语境下可能存在性能不足的问题。
- X-Codec旨在解决现有音频LLM编解码器的短板,特别是在保持生成音频的语义完整性方面。
- 现有方法如VALL-E在文本转录条件下生成声学令牌时,由于声学令牌的语义误解,会出现内容不准确和较高的词错误率(WER)。
- X-Codec通过融入预训练语义编码器的语义特征,在降低WER方面表现出色,提升语音合成任务的性能。
- X-Codec的优势不仅限于语音合成,还扩展至音乐和声效生成等非语音应用。
点此查看论文截图

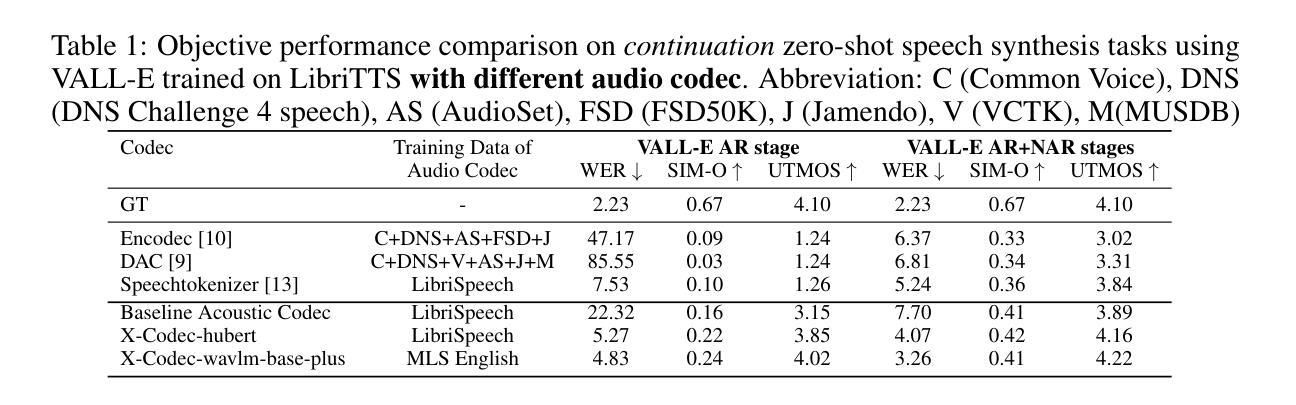
Overview of Speaker Modeling and Its Applications: From the Lens of Deep Speaker Representation Learning
Authors:Shuai Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Kong Aik Lee, Yanmin Qian, Haizhou Li
Speaker individuality information is among the most critical elements within speech signals. By thoroughly and accurately modeling this information, it can be utilized in various intelligent speech applications, such as speaker recognition, speaker diarization, speech synthesis, and target speaker extraction. In this overview, we present a comprehensive review of neural approaches to speaker representation learning from both theoretical and practical perspectives. Theoretically, we discuss speaker encoders ranging from supervised to self-supervised learning algorithms, standalone models to large pretrained models, pure speaker embedding learning to joint optimization with downstream tasks, and efforts toward interpretability. Practically, we systematically examine approaches for robustness and effectiveness, introduce and compare various open-source toolkits in the field. Through the systematic and comprehensive review of the relevant literature, research activities, and resources, we provide a clear reference for researchers in the speaker characterization and modeling field, as well as for those who wish to apply speaker modeling techniques to specific downstream tasks.
说话人的个体信息是语音信号中最关键的部分。通过对这部分信息进行全面准确的建模,可以将其应用于各种智能语音应用中,如说话人识别、说话人日记化、语音合成和目标说话人提取等。在本次概述中,我们从理论和实际两个角度对神经方法进行全面的评述,以学习说话人的表征。理论上,我们讨论了从监督到自我监督学习算法的说话人编码器,从独立模型到大型预训练模型,从纯粹的说话人嵌入学习到与下游任务的联合优化,以及向可解释性的努力。实际上,我们系统地检验了鲁棒性和有效性的方法,介绍并比较了该领域的各种开源工具包。通过对相关文献、研究活动和资源的系统和全面回顾,我们为语音特征刻画和建模领域的研究人员,以及那些希望将说话人建模技术应用于特定下游任务的人员提供了清晰的参考。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to TASLP
Summary
基于神经网络的方法对说话人特征学习进行了全面深入的探讨,从理论角度探讨了各种编码器的性能和应用范围,从实际应用角度进行了模型的鲁棒性和有效性分析,并介绍了相关的开源工具包。该综述为说话人表征和建模领域的研究人员以及希望将说话人建模技术应用于特定下游任务的人员提供了清晰的参考。
Key Takeaways
- 说话人个体信息在语音信号中占据核心地位,可用于智能语音应用如说话人识别、说话人分时段化、语音合成和目标说话人提取。
- 神经网络方法被广泛应用于说话人特征学习,包括监督学习和自监督学习算法,独立模型与大型预训练模型等。
- 说话人嵌入学习不仅关注模型性能,还努力与下游任务联合优化,提升模型的可解释性。
- 在实际应用中,说话人特征学习模型需要具备鲁棒性和有效性。
- 综述详细介绍了各种开源工具包,为研究人员提供了丰富的资源。
- 该综述为说话人表征和建模领域的研究人员提供了清晰的参考和指导。
点此查看论文截图
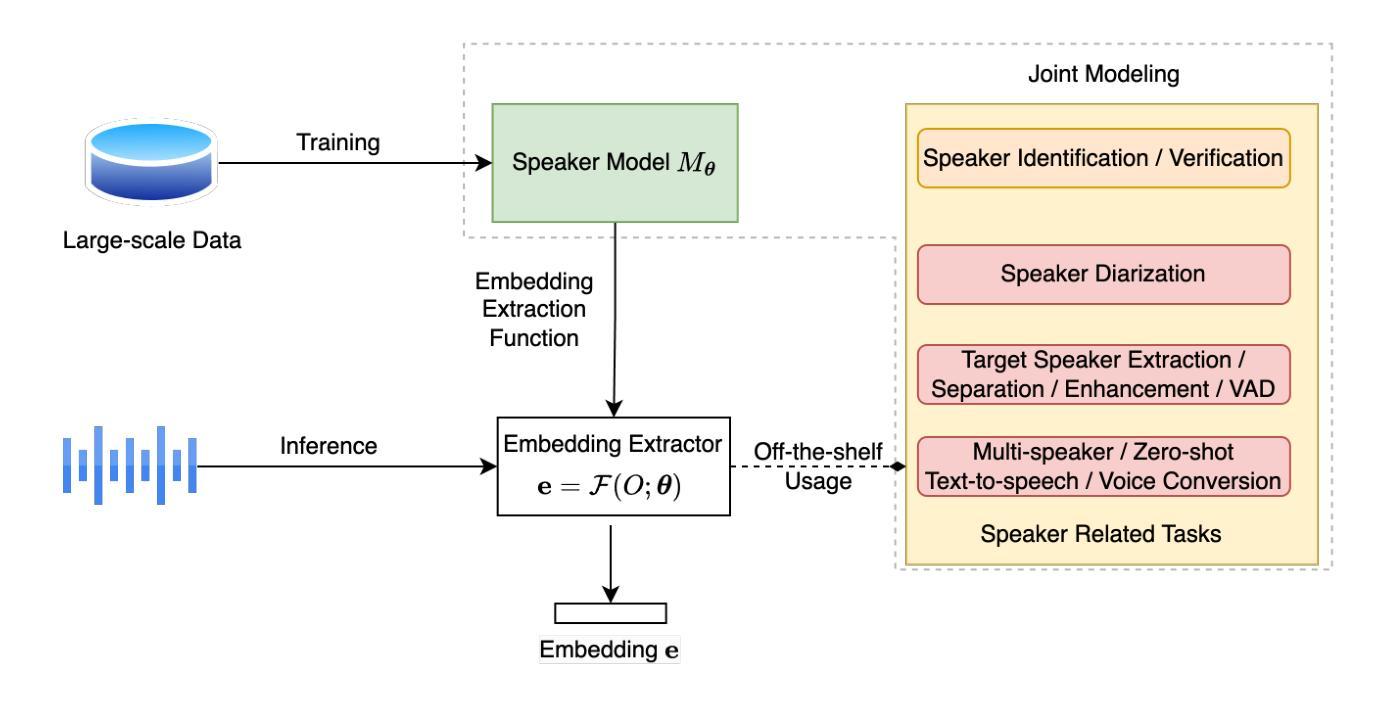

TTSDS – Text-to-Speech Distribution Score
Authors:Christoph Minixhofer, Ondřej Klejch, Peter Bell
Many recently published Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems produce audio close to real speech. However, TTS evaluation needs to be revisited to make sense of the results obtained with the new architectures, approaches and datasets. We propose evaluating the quality of synthetic speech as a combination of multiple factors such as prosody, speaker identity, and intelligibility. Our approach assesses how well synthetic speech mirrors real speech by obtaining correlates of each factor and measuring their distance from both real speech datasets and noise datasets. We benchmark 35 TTS systems developed between 2008 and 2024 and show that our score computed as an unweighted average of factors strongly correlates with the human evaluations from each time period.
许多最近发布的文本到语音(TTS)系统产生的音频接近真实语音。然而,随着新架构、方法和数据集的出现,需要重新审视TTS的评估方法,以便理解所获得的实验结果。我们提议从多个因素结合评估合成语音的质量,如语调、说话人身份和清晰度等。我们的方法通过获取每个因素的关联项,并测量它们与真实语音数据集和噪声数据集的差异来评估合成语音对真实语音的模拟程度。我们对2008年至2024年间开发的35个TTS系统进行了基准测试,并展示了我们的得分作为未加权因素平均值与每个时期的人类评估结果存在很强的相关性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF SLT 2024
Summary
近期发布的许多文本转语音(TTS)系统生成的音频已接近真实语音。然而,随着新架构、方法和数据集的出现,需要重新审视TTS的评估方法。本文提出一种评估合成语音质量的方法,综合考虑语调、说话人身份和清晰度等多个因素。该方法通过获取每个因素的相关指标,测量其与真实语音数据集和噪声数据集的差异来评估合成语音对真实语音的模拟程度。作者对2008年至2024年间开发的35个TTS系统进行了基准测试,证明其计算的无权重平均因素得分与各个时期的人类评估结果高度相关。
Key Takeaways
- TTS系统生成的音频已接近真实语音,需要重新审视其评估方法。
- 评估合成语音质量应综合考虑语调、说话人身份和清晰度等多个因素。
- 通过测量与真实语音数据集和噪声数据集的差异来评估合成语音的模拟程度。
- 本文对过去多年开发的TTS系统进行了基准测试。
- 测试结果表明,综合各因素的平均得分与人类评估结果高度相关。
- 此评估方法能够为TTS系统的进步和发展提供有力的衡量标准。
点此查看论文截图

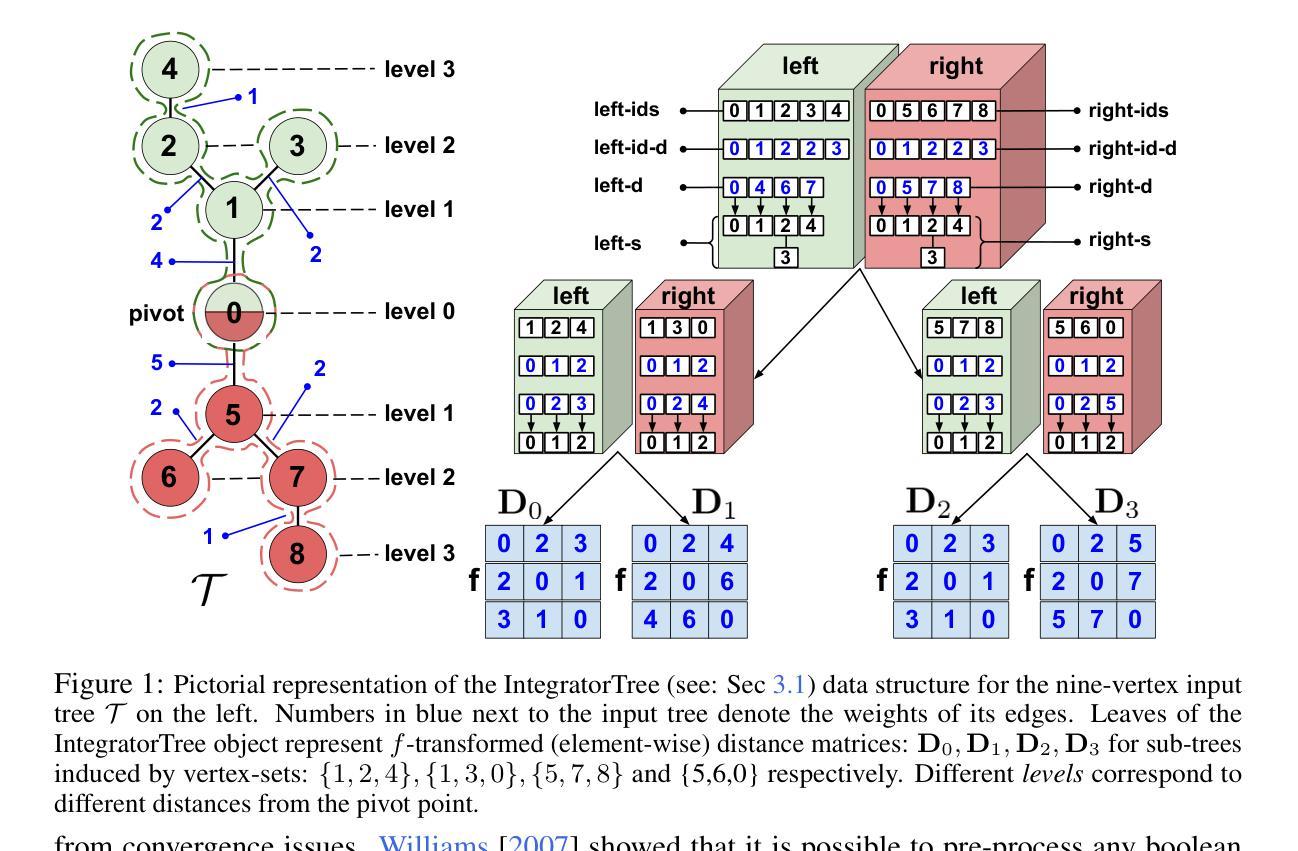
Fast Tree-Field Integrators: From Low Displacement Rank to Topological Transformers
Authors:Krzysztof Choromanski, Arijit Sehanobish, Somnath Basu Roy Chowdhury, Han Lin, Avinava Dubey, Tamas Sarlos, Snigdha Chaturvedi
We present a new class of fast polylog-linear algorithms based on the theory of structured matrices (in particular low displacement rank) for integrating tensor fields defined on weighted trees. Several applications of the resulting fast tree-field integrators (FTFIs) are presented, including (a) approximation of graph metrics with tree metrics, (b) graph classification, (c) modeling on meshes, and finally (d) Topological Transformers (TTs) (Choromanski et al., 2022) for images. For Topological Transformers, we propose new relative position encoding (RPE) masking mechanisms with as few as three extra learnable parameters per Transformer layer, leading to 1.0-1.5%+ accuracy gains. Importantly, most of FTFIs are exact methods, thus numerically equivalent to their brute-force counterparts. When applied to graphs with thousands of nodes, those exact algorithms provide 5.7-13x speedups. We also provide an extensive theoretical analysis of our methods.
我们基于结构化矩阵理论(尤其是低位移秩)提出了一种新的快速多项式对数线性算法,用于对定义在加权树上的张量场进行积分。展示了由此产生的快速树场积分器(FTFIs)的几个应用,包括(a)树度量逼近图度量,(b)图分类,(c)网格建模,以及最后(d)用于图像的拓扑转换器(TTs)(Choromanski等人,2022年)。针对拓扑转换器,我们提出了具有三个额外可学习参数的新型相对位置编码(RPE)掩码机制,带来了1.0-1.5%的准确率提升。重要的是,大多数FTFIs是精确方法,因此在数值上与暴力求解等效。当应用于具有数千个节点的图时,这些精确算法可提供5.7-13倍的加速。我们还对所用方法进行了广泛的理论分析。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024
Summary
基于结构化矩阵理论(特别是低位移秩)提出的新型快速多项式对数线性算法,用于整合定义在加权树上的张量场。该算法包含多种应用场景,如近似图指标与树指标、图分类、网格建模和图像拓扑变换器等。针对拓扑变换器,我们提出了具有更少可学习参数的新相对位置编码掩码机制,带来了额外的准确性提升。此外,大多数FTFIs算法是精确方法,在应用于具有数千个节点的图形时,提供了高达13倍的加速。
Key Takeaways
- 基于结构化矩阵理论的新型快速多项式对数线性算法用于整合张量场。
- FTFIs算法适用于多种应用场景,包括图与树指标的近似、图分类、网格建模和图像拓扑变换器。
- 针对拓扑变换器,提出了具有更少可学习参数的新相对位置编码掩码机制。
- 新机制带来了额外的准确性提升。
- 大多数FTFIs算法是精确的,等价于暴力计算方法。
- 在应用于具有数千个节点的图形时,FTFIs算法提供了显著的加速效果。
点此查看论文截图

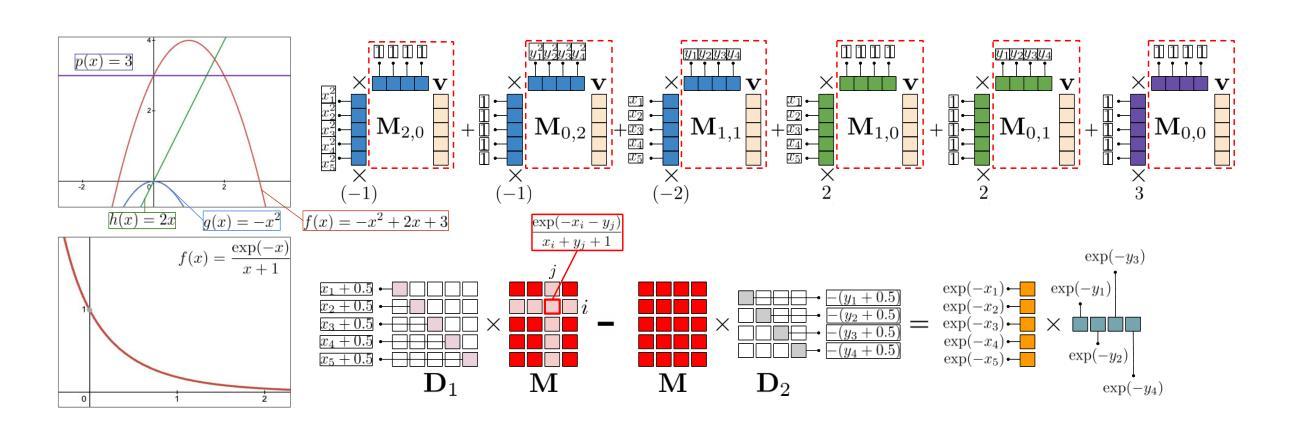
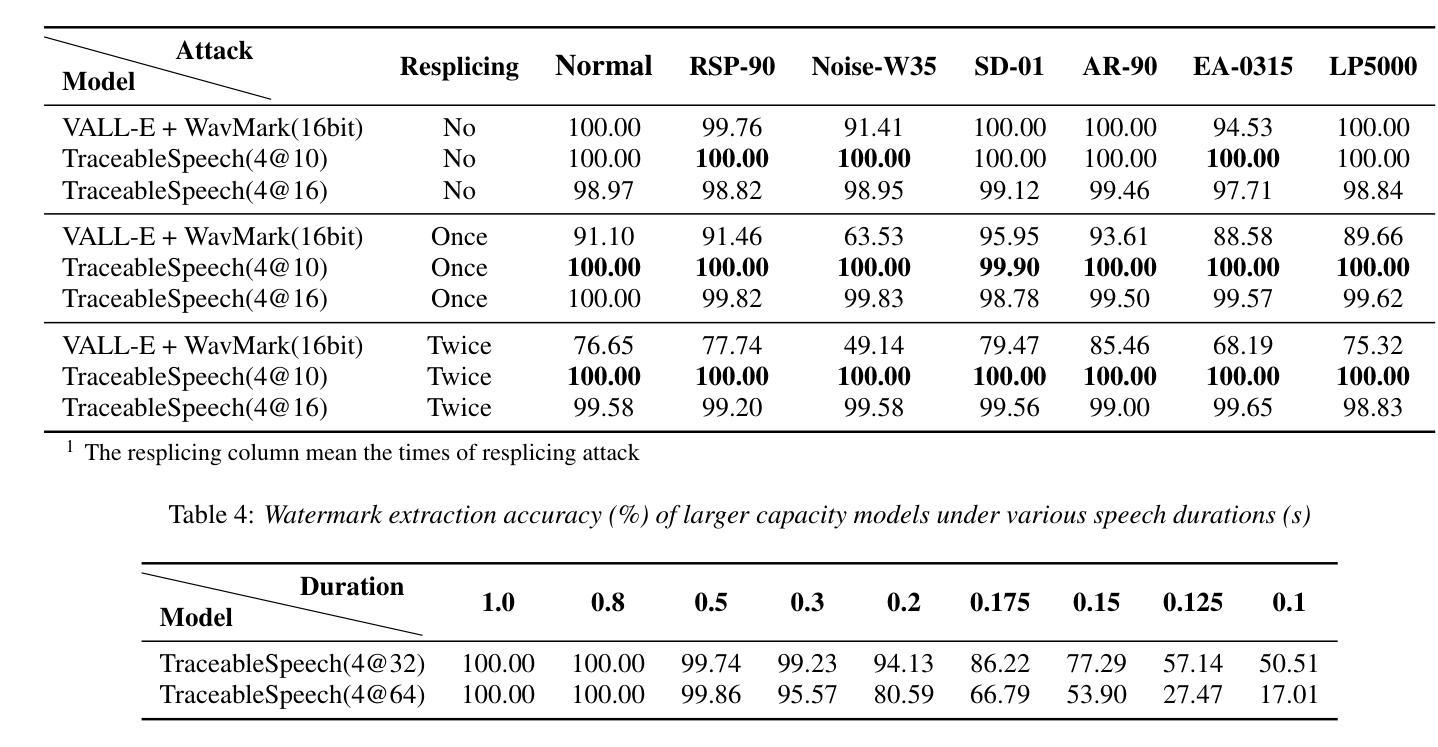
TraceableSpeech: Towards Proactively Traceable Text-to-Speech with Watermarking
Authors:Junzuo Zhou, Jiangyan Yi, Tao Wang, Jianhua Tao, Ye Bai, Chu Yuan Zhang, Yong Ren, Zhengqi Wen
Various threats posed by the progress in text-to-speech (TTS) have prompted the need to reliably trace synthesized speech. However, contemporary approaches to this task involve adding watermarks to the audio separately after generation, a process that hurts both speech quality and watermark imperceptibility. In addition, these approaches are limited in robustness and flexibility. To address these problems, we propose TraceableSpeech, a novel TTS model that directly generates watermarked speech, improving watermark imperceptibility and speech quality. Furthermore, We design the frame-wise imprinting and extraction of watermarks, achieving higher robustness against resplicing attacks and temporal flexibility in operation. Experimental results show that TraceableSpeech outperforms the strong baseline where VALL-E or HiFicodec individually uses WavMark in watermark imperceptibility, speech quality and resilience against resplicing attacks. It also can apply to speech of various durations. The code is avaliable at https://github.com/zjzser/TraceableSpeech
随着文本转语音(TTS)的进步带来的各种威胁,对合成语音的可靠追踪需求日益迫切。然而,当前的任务处理方法是在生成音频后单独添加水印,这一过程既影响了语音质量,也影响了水印的不易察觉性。此外,这些方法在稳健性和灵活性方面也存在局限。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了TraceableSpeech,这是一种新型TTS模型,能够直接生成带水印的语音,提高了水印的不易察觉性和语音质量。此外,我们设计了帧级的水印印制和提取技术,提高了对抗重新拼接攻击的稳健性和操作的时序灵活性。实验结果表明,TraceableSpeech在不易察觉性、语音质量和抵抗重新拼接攻击方面,优于VALL-E或HiFicodec等单独使用WavMark的强基线。它还可以应用于各种时长的语音。代码可在https://github.com/zjzser/TraceableSpeech找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF acceped by interspeech 2024
Summary
文本到语音(TTS)的进步带来了多种威胁,需要进行可靠的追踪合成语音。然而,现有的追踪方法通过在生成后单独添加水印到音频中,这种方法既影响语音质量又影响水印的不可察觉性。为解决这些问题,我们提出了TraceableSpeech,这是一种新型的TTS模型,可直接生成带水印的语音,提高了水印的不可察觉性和语音质量。我们还设计了帧级的水印印入和提取方法,提高了对抗拼接攻击的稳健性和操作的时效性。实验结果表明,TraceableSpeech在不可察觉性、语音质量和抗拼接攻击方面优于使用WavMark的VALL-E或HiFicodec等强基线模型,且适用于各种时长的语音。相关代码已发布在GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- TTS的进步带来了追踪合成语音的必要性,因为存在多种潜在威胁。
- 现有追踪方法通过生成后添加水印到音频中,存在语音质量和水印不可察觉性的问题。
- TraceableSpeech是一种新型的TTS模型,能直接生成带水印的语音,提高水印的不可察觉性和语音质量。
- TraceableSpeech实现了帧级的水印印入和提取,提高了对抗拼接攻击的稳健性。
- TraceableSpeech在不可察觉性、语音质量和抗拼接攻击方面优于现有基线模型。
- TraceableSpeech适用于各种时长的语音。
点此查看论文截图

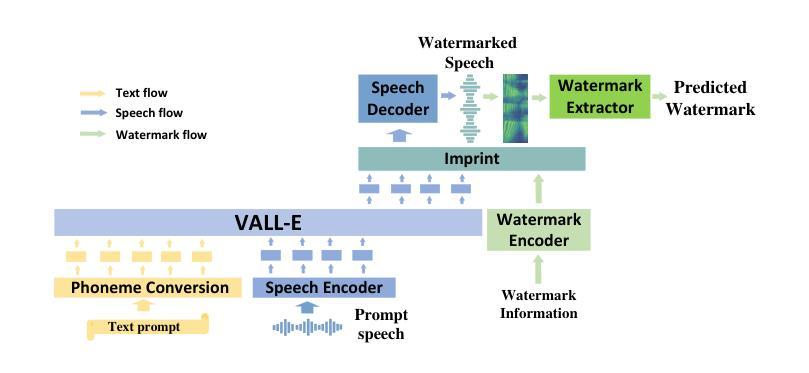
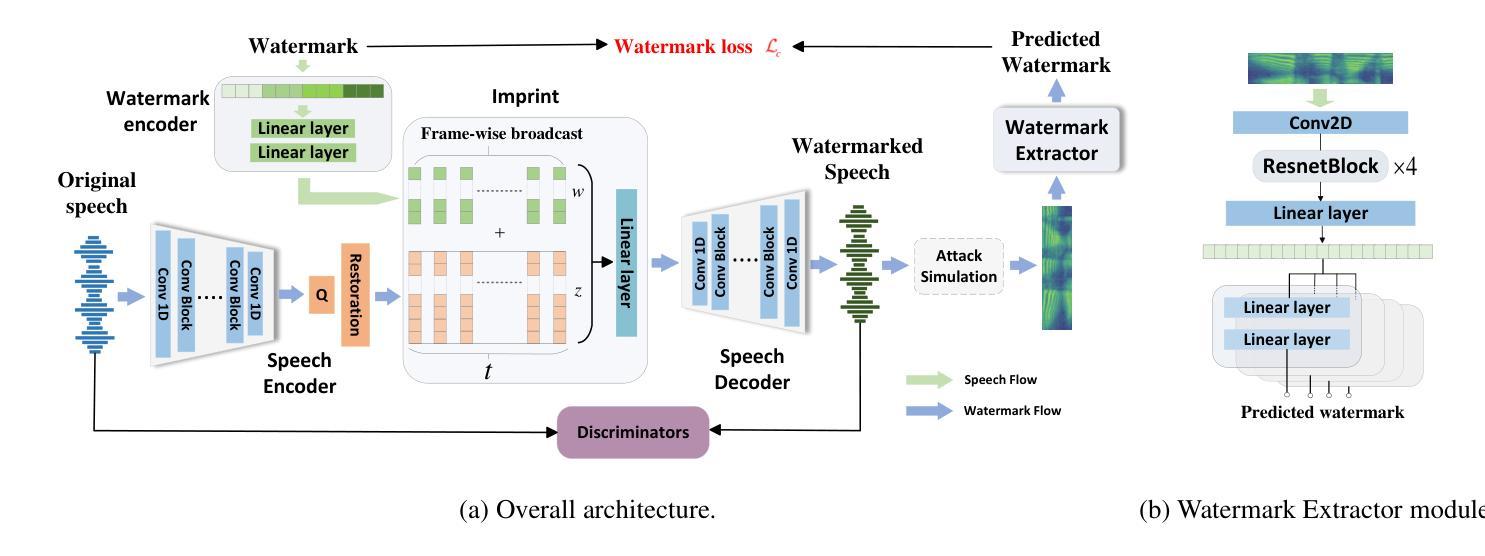
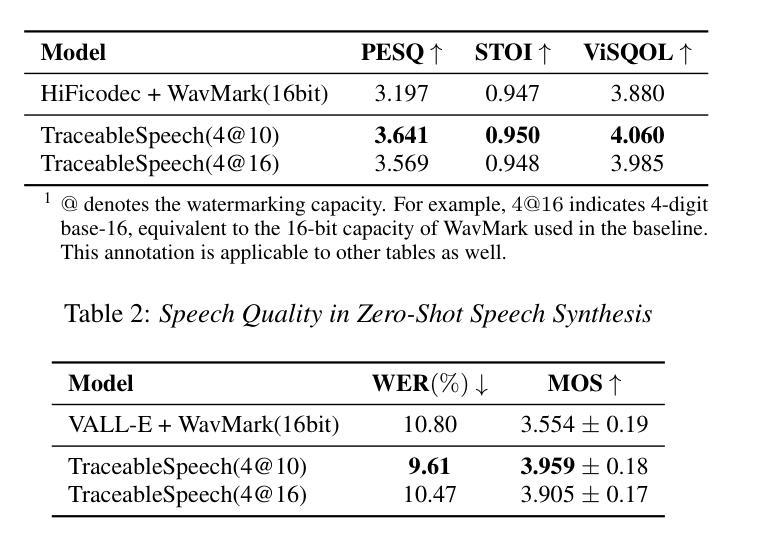
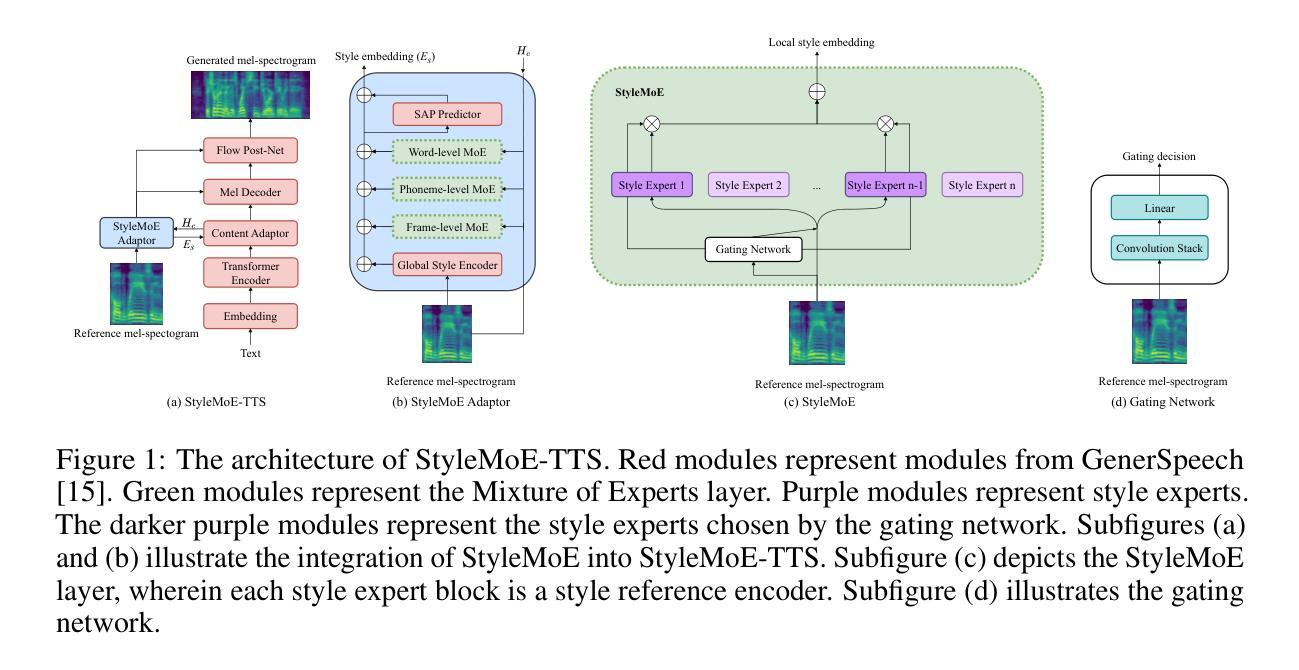
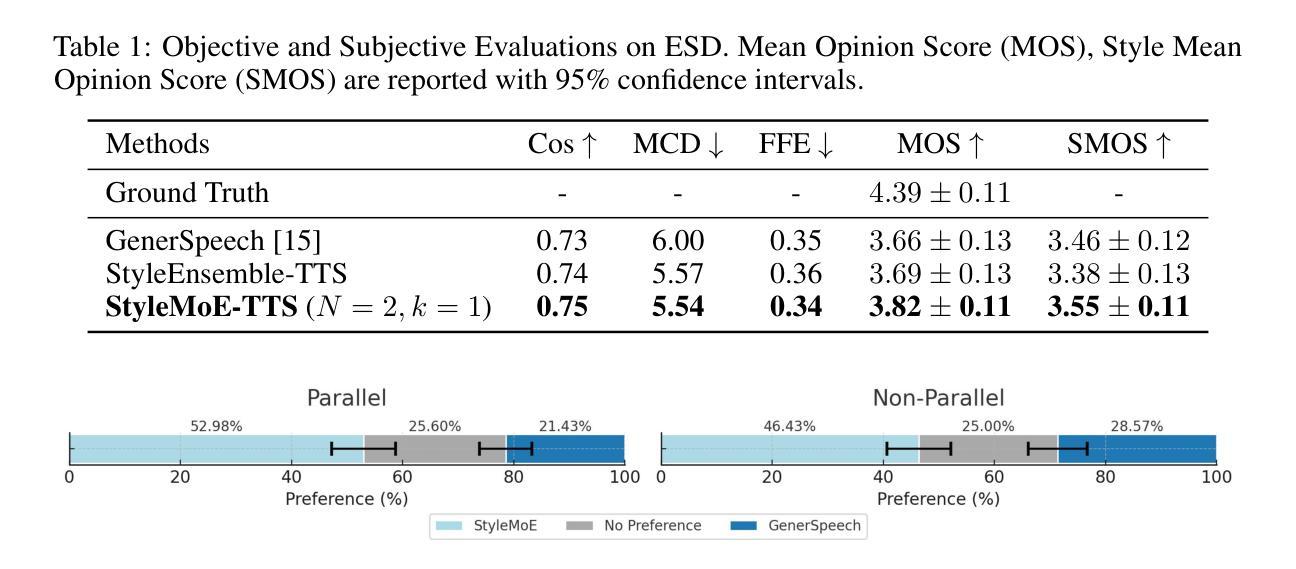
Style Mixture of Experts for Expressive Text-To-Speech Synthesis
Authors:Ahad Jawaid, Shreeram Suresh Chandra, Junchen Lu, Berrak Sisman
Recent advances in style transfer text-to-speech (TTS) have improved the expressiveness of synthesized speech. However, encoding stylistic information (e.g., timbre, emotion, and prosody) from diverse and unseen reference speech remains a challenge. This paper introduces StyleMoE, an approach that addresses the issue of learning averaged style representations in the style encoder by creating style experts that learn from subsets of data. The proposed method replaces the style encoder in a TTS framework with a Mixture of Experts (MoE) layer. The style experts specialize by learning from subsets of reference speech routed to them by the gating network, enabling them to handle different aspects of the style space. As a result, StyleMoE improves the style coverage of the style encoder for style transfer TTS. Our experiments, both objective and subjective, demonstrate improved style transfer for diverse and unseen reference speech. The proposed method enhances the performance of existing state-of-the-art style transfer TTS models and represents the first study of style MoE in TTS.
在文本到语音(TTS)的风格迁移方面最近的进展提高了合成语音的表现力。然而,从多样且未知的参考语音中编码风格信息(如音质、情感和语调)仍然是一个挑战。本文介绍了StyleMoE方法,通过创建从数据子集学习的风格专家来解决风格编码器中学习平均风格表示的问题。所提出的方法用混合专家(MoE)层替换了TTS框架中的风格编码器。风格专家通过从路由到它们的参考语音子集学习来专业化,使它们能够处理风格空间的不同方面。因此,StyleMoE提高了风格编码器在风格迁移TTS中的风格覆盖率。我们的客观和主观实验都证明了在多样且未知的参考语音中风格迁移的改进。所提出的方法提高了现有最先进的风格迁移TTS模型的性能,并且是TTS中风格MoE的首次研究。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in Audio Imagination: NeurIPS 2024 Workshop
Summary
近期文本转语音(TTS)的风格迁移技术取得了进展,提高了合成语音的表达性。然而,从多样且未知的参考语音中编码风格信息(如音质、情感和语调)仍是一个挑战。本文提出了StyleMoE方法,通过创建风格专家来解决风格编码器中学习平均风格表示的问题。该方法用专家混合(MoE)层替换TTS框架中的风格编码器。风格专家通过从路由到它们的参考语音子集学习专业知识,能够处理风格空间的不同方面。因此,StyleMoE提高了风格编码器的风格覆盖能力,改善了多样且未知参考语音的风格迁移。实验证明,该方法在主观和客观上都提高了风格迁移的效果,并增强了现有最先进的风格迁移TTS模型的性能。这是MoE在TTS中的首次研究。
Key Takeaways
- 近期TTS的风格迁移技术提高了合成语音的表达性。
- 从多样且未知的参考语音中编码风格信息是一个挑战。
- StyleMoE方法通过创建风格专家来解决这一挑战。
- 风格专家通过从路由到它们的参考语音子集学习专业知识。
- StyleMoE提高了风格编码器的风格覆盖能力。
- 实验证明StyleMoE在主观和客观上都提高了风格迁移的效果。
点此查看论文截图

DLPO: Diffusion Model Loss-Guided Reinforcement Learning for Fine-Tuning Text-to-Speech Diffusion Models
Authors:Jingyi Chen, Ju-Seung Byun, Micha Elsner, Andrew Perrault
Recent advancements in generative models have sparked a significant interest within the machine learning community. Particularly, diffusion models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in synthesizing images and speech. Studies such as those by Lee et al. (2023), Black et al. (2023), Wang et al. (2023), and Fan et al. (2024) illustrate that Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF) can enhance diffusion models for image synthesis. However, due to architectural differences between these models and those employed in speech synthesis, it remains uncertain whether RLHF could similarly benefit speech synthesis models. In this paper, we explore the practical application of RLHF to diffusion-based text-to-speech synthesis, leveraging the mean opinion score (MOS) as predicted by UTokyo-SaruLab MOS prediction system (Saeki et al., 2022) as a proxy loss. We introduce diffusion model loss-guided RL policy optimization (DLPO) and compare it against other RLHF approaches, employing the NISQA speech quality and naturalness assessment model (Mittag et al., 2021) and human preference experiments for further evaluation. Our results show that RLHF can enhance diffusion-based text-to-speech synthesis models, and, moreover, DLPO can better improve diffusion models in generating natural and high quality speech audios.
近年来,生成模型的新进展在机器学习领域引起了极大的兴趣。特别是扩散模型在图像和语音合成方面表现出了显著的能力。Lee等人(2023年)、Black等人(2023年)、Wang等人(2023年)和Fan等人(2024年)的研究表明,强化学习与人类反馈(RLHF)可以增强扩散模型在图像合成方面的性能。然而,由于这些模型与语音合成中所用模型的结构差异,尚不清楚RLHF是否也能同样有益于语音合成模型。在本文中,我们探索了RLHF在基于扩散的文本到语音合成中的实际应用,利用东京大学SaruLab的MOS预测系统所预测的均值意见分(MOS)作为代理损失。我们介绍了扩散模型损失引导RL策略优化(DLPO),并将其与其他RLHF方法进行比较,进一步采用NISQA语音质量和自然度评估模型以及人类偏好实验进行评估。我们的结果表明,RLHF可以增强基于扩散的文本到语音合成模型的性能,而且DLPO能更好地改善扩散模型生成自然、高质量语音音频的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期生成模型进展显著,特别是扩散模型在图像和语音合成方面表现出卓越能力。研究表明强化学习与人类反馈(RLHF)能提升扩散模型在图像合成方面的表现。本文探索了RLHF在基于扩散的文本到语音合成中的实际应用,采用东京大学SaruLab的MOS预测系统作为代理损失。通过对比其他RLHF方法和采用NISQA语音质量和自然度评估模型的人类偏好实验,发现RLHF能提升基于扩散的文本到语音合成模型的性能,特别是DLPO方法在生成自然高质量语音方面表现更佳。
Key Takeaways
1. 生成模型领域出现新的重要进展,扩散模型在图像和语音合成上具备出色性能。
2. 强化学习与人类反馈(RLHF)可以提升扩散模型的表现,尤其是在图像合成方面已有研究证实。
3. 本文探索了RLHF在基于扩散的文本到语音合成中的应用。
4. 采用东京大学SaruLab的MOS预测系统作为代理损失进行模型优化。
5. 对比了不同的RLHF方法和采用NISQA语音评估模型的人类偏好实验。
6. 结果显示RLHF能提升基于扩散的文本到语音合成模型的性能。
点此查看论文截图

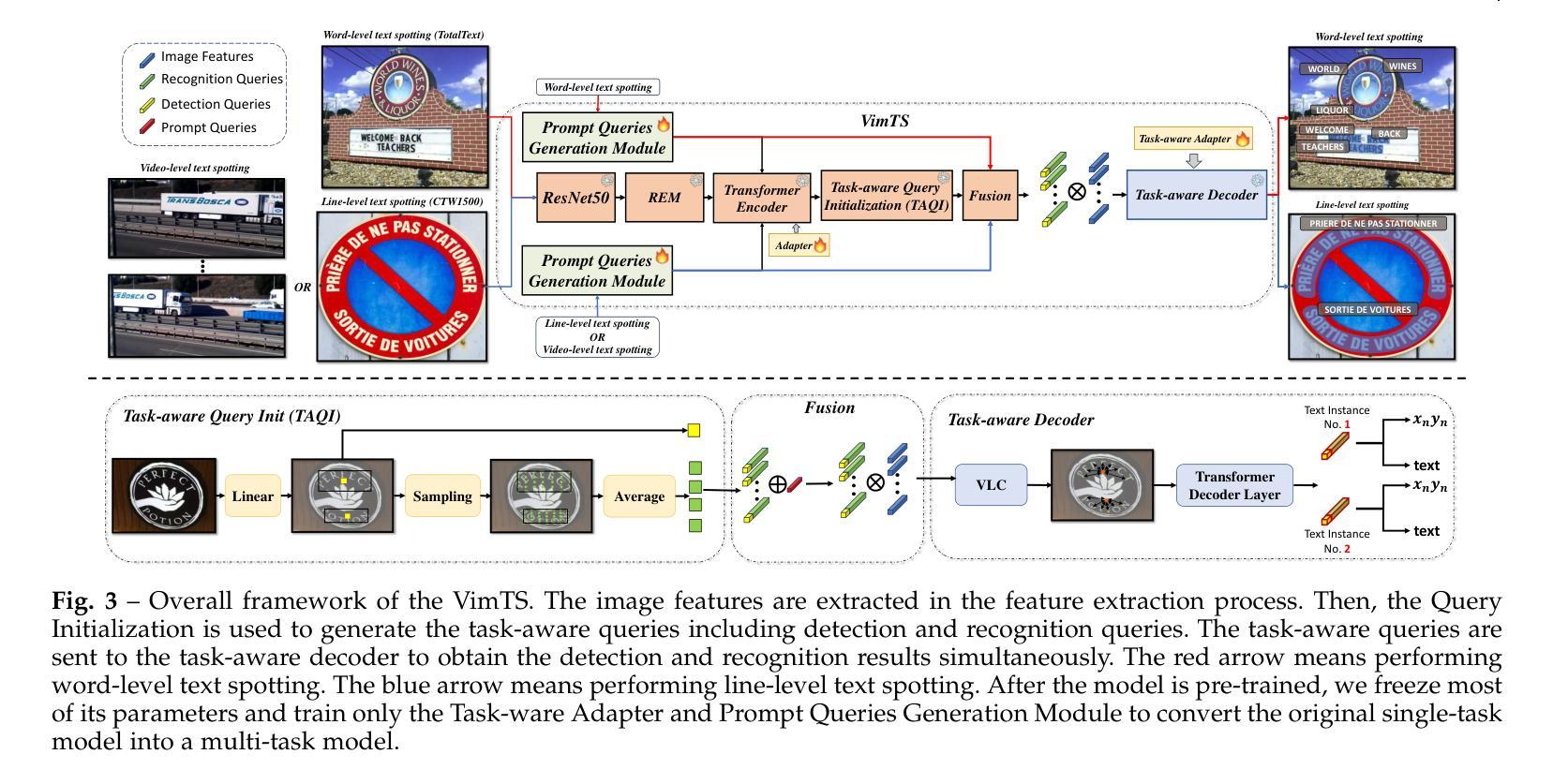
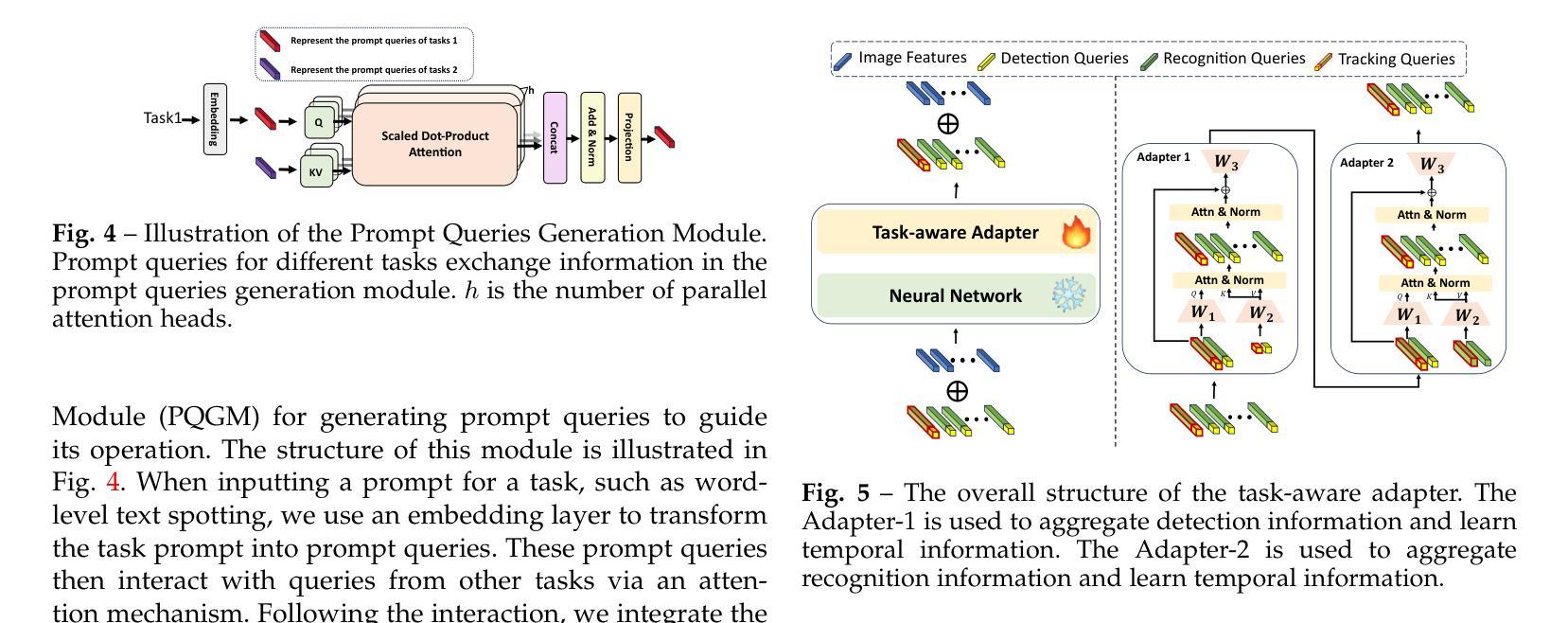
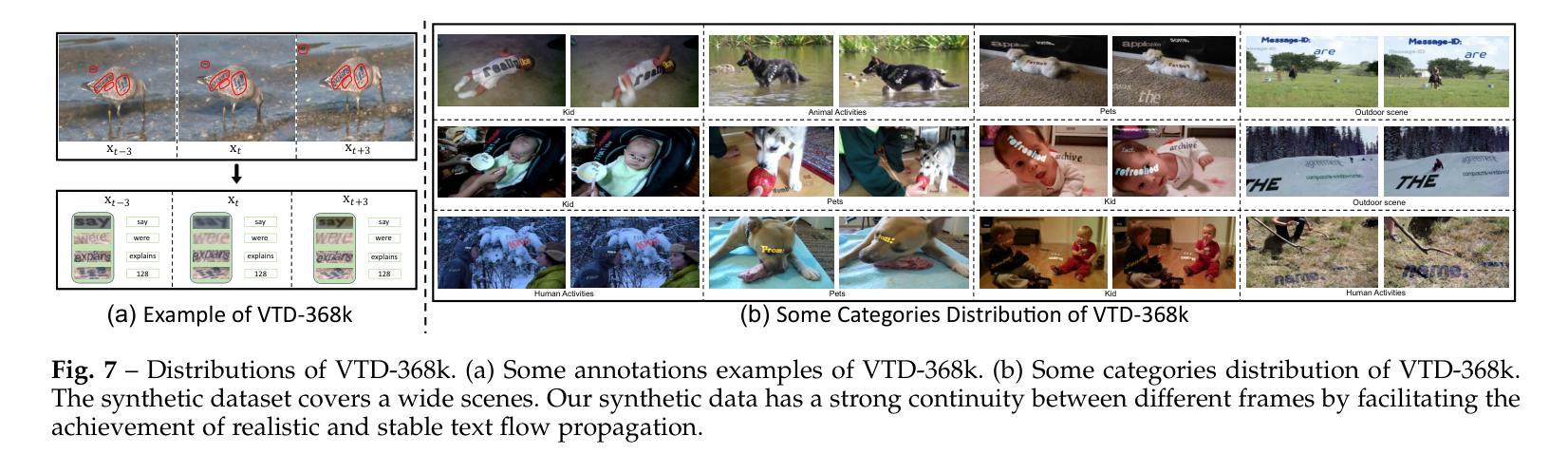
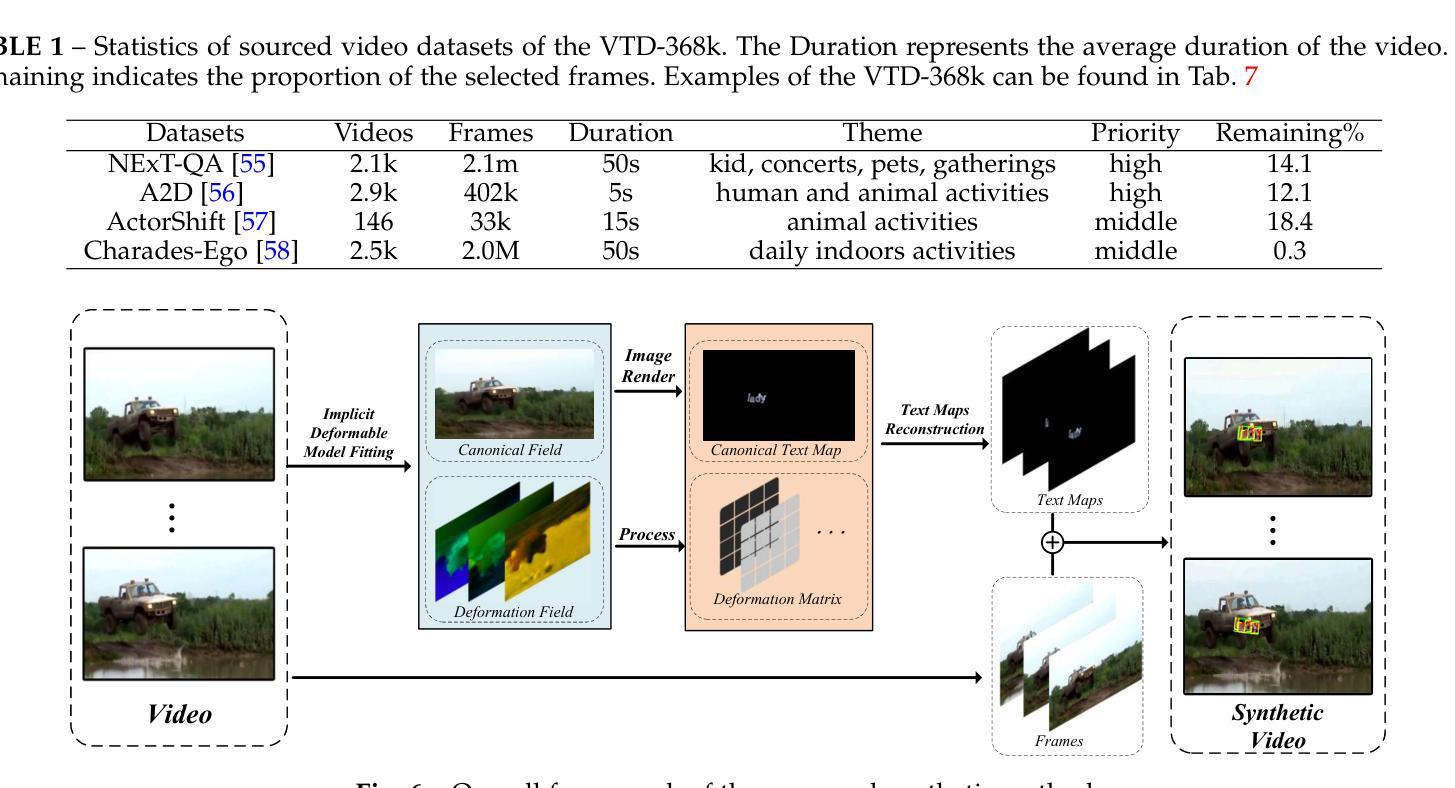
VimTS: A Unified Video and Image Text Spotter for Enhancing the Cross-domain Generalization
Authors:Yuliang Liu, Mingxin Huang, Hao Yan, Linger Deng, Weijia Wu, Hao Lu, Chunhua Shen, Lianwen Jin, Xiang Bai
Text spotting, a task involving the extraction of textual information from image or video sequences, faces challenges in cross-domain adaption, such as image-to-image and image-to-video generalization. In this paper, we introduce a new method, termed VimTS, which enhances the generalization ability of the model by achieving better synergy among different tasks. Typically, we propose a Prompt Queries Generation Module and a Tasks-aware Adapter to effectively convert the original single-task model into a multi-task model suitable for both image and video scenarios with minimal additional parameters. The Prompt Queries Generation Module facilitates explicit interaction between different tasks, while the Tasks-aware Adapter helps the model dynamically learn suitable features for each task. Additionally, to further enable the model to learn temporal information at a lower cost, we propose a synthetic video text dataset (VTD-368k) by leveraging the Content Deformation Fields (CoDeF) algorithm. Notably, our method outperforms the state-of-the-art method by an average of 2.6% in six cross-domain benchmarks such as TT-to-IC15, CTW1500-to-TT, and TT-to-CTW1500. For video-level cross-domain adaption, our method even surpasses the previous end-to-end video spotting method in ICDAR2015 video and DSText v2 by an average of 5.5% on the MOTA metric, using only image-level data. We further demonstrate that existing Large Multimodal Models exhibit limitations in generating cross-domain scene text spotting, in contrast to our VimTS model which requires significantly fewer parameters and data. The code and datasets will be made available at the https://VimTextSpotter.github.io.
文本识别涉及从图像或视频序列中提取文本信息,在跨域适应方面面临挑战,如图像到图像和图像到视频的推广。在本文中,我们介绍了一种新方法,称为VimTS。它通过实现不同任务之间的更好协同作用,增强了模型的推广能力。一般来说,我们提出了一个提示查询生成模块和任务感知适配器,有效地将原始的单任务模型转换为适合图像和视频场景的多任务模型,并且增加了极少的参数。提示查询生成模块促进了不同任务之间的显式交互,而任务感知适配器帮助模型动态学习每个任务的适当特征。此外,为了以更低的成本使模型能够学习时间序列信息,我们利用内容变形场(CoDeF)算法提出了一个合成视频文本数据集(VTD-368k)。值得注意的是,我们的方法在六个跨域基准测试上的平均表现优于最新方法约2.6%,如TT到IC15、CTW1500到TT和TT到CTW1500等。对于视频级别的跨域适应,我们的方法甚至在ICDAR2015视频和DSText v2上超越了之前的端到端视频识别方法,在MOTA指标上平均提高了约5.5%,并且仅使用图像级别的数据。我们还进一步证明了现有的大型多模态模型在生成跨域场景文本识别方面存在局限性,相比之下,我们的VimTS模型需要更少的参数和数据。代码和数据集将在VimTextSpotter.github.io上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了一种新的方法VimTS,通过实现不同任务之间的更好协同作用,提高了模型的泛化能力。为此,本文提出了Prompt Queries生成模块和任务感知适配器,以将原始单任务模型有效地转换为适合图像和视频场景的多任务模型,且只需极少量的额外参数。Prompt Queries生成模块促进了不同任务之间的显式交互,而任务感知适配器帮助模型动态学习每个任务的适当特征。此外,为了以较低的成本使模型能够学习时间序列信息,本文利用内容变形场算法提出了一个合成视频文本数据集(VTD-368k)。在六个跨域基准测试中,如TT到IC15等,本文的方法优于当前最先进的方法平均提高了2.6%。对于视频级别的跨域适应,本文的方法在ICDAR2015视频和DSText v2上甚至超过了之前的端到端视频识别方法,在MOTA指标上平均提高了5.5%,仅使用图像级别的数据。此外,本文还指出了现有大型多模态模型在跨域场景文本识别方面的局限性,与VimTS模型相比,其需要更少的参数和数据。相关代码和数据集将在https://VimTextSpotter.github.io上提供。
关键见解
- VimTS方法通过实现不同任务之间的协同作用,增强了模型的泛化能力。
- 提出了Prompt Queries生成模块和任务感知适配器,将单任务模型转换为多任务模型,适用于图像和视频场景,且参数增加少。
- Prompt Queries生成模块促进任务间的交互,而任务感知适配器使模型能动态学习每个任务的特征。
- 利用内容变形场算法提出了合成视频文本数据集VTD-368k,用于学习时间序列信息。
- VimTS方法在多个跨域基准测试中表现优越,平均提高2.6%。
- 在视频级别的跨域适应方面,VimTS方法显著超越了现有方法,平均提高5.5%。
点此查看论文截图

Bayesian Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning for Overcoming Catastrophic Forgetting
Authors:Haolin Chen, Philip N. Garner
We are motivated primarily by the adaptation of text-to-speech synthesis models; however we argue that more generic parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) is an appropriate framework to do such adaptation. Nevertheless, catastrophic forgetting remains an issue with PEFT, damaging the pre-trained model’s inherent capabilities. We demonstrate that existing Bayesian learning techniques can be applied to PEFT to prevent catastrophic forgetting as long as the parameter shift of the fine-tuned layers can be calculated differentiably. In a principled series of experiments on language modeling and speech synthesis tasks, we utilize established Laplace approximations, including diagonal and Kronecker-factored approaches, to regularize PEFT with the low-rank adaptation (LoRA) and compare their performance in pre-training knowledge preservation. Our results demonstrate that catastrophic forgetting can be overcome by our methods without degrading the fine-tuning performance, and using the Kronecker-factored approximation produces a better preservation of the pre-training knowledge than the diagonal ones.
我们主要受到文本到语音合成模型的适应性的激励;然而,我们认为更通用的参数有效微调(PEFT)是执行此类适应性的适当框架。然而,灾难性遗忘仍然是PEFT的一个问题,会损害预训练模型的固有功能。我们证明,只要可以计算微调层的参数变化是可微分的,现有的贝叶斯学习技术就可以应用于PEFT以防止灾难性遗忘。在一系列语言建模和语音合成任务的实验中,我们利用建立的拉普拉斯近似方法,包括对角线和克罗内克因子分解方法,对低秩适应(LoRA)进行正则化PEFT,并比较它们在预训练知识保留方面的性能。结果表明,我们的方法能够克服灾难性遗忘,同时不会降低微调性能,并且使用克罗内克因子分解近似比使用对角线近似能更好地保留预训练知识。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文主要探讨了文本到语音合成模型的适应性调整问题,并提出利用更通用的参数高效微调(PEFT)框架进行此类调整。然而,PEFT存在灾难性遗忘问题,会损害预训练模型的固有功能。作者展示了现有的贝叶斯学习技术可以应用于PEFT以防止灾难性遗忘,只要能够计算微调层的参数差分转移。作者在一系列语言建模和语音合成任务实验中使用Laplace近似方法(包括对角线和Kronecker分解方法)对PEFT进行正则化,并与低秩适配(LoRA)比较其保存预训练知识的效果。结果表明,该方法能克服灾难性遗忘,同时不影响微调性能,且使用Kronecker分解近似比使用对角线方法更好地保留预训练知识。
Key Takeaways
- 文章主要讨论文本到语音合成模型的适应性调整问题。
- 参数高效微调(PEFT)是一个适当的框架来进行此类调整。
- PEFT存在灾难性遗忘问题,损害预训练模型的固有功能。
- 现有的贝叶斯学习技术可以防止PEFT中的灾难性遗忘,前提是能计算微调层的参数差分转移。
- 作者使用Laplace近似方法(包括对角线和Kronecker分解)来正则化PEFT,并与低秩适配(LoRA)比较。
- 实验结果显示,使用Kronecker分解近似可以更好地保留预训练知识。
点此查看论文截图

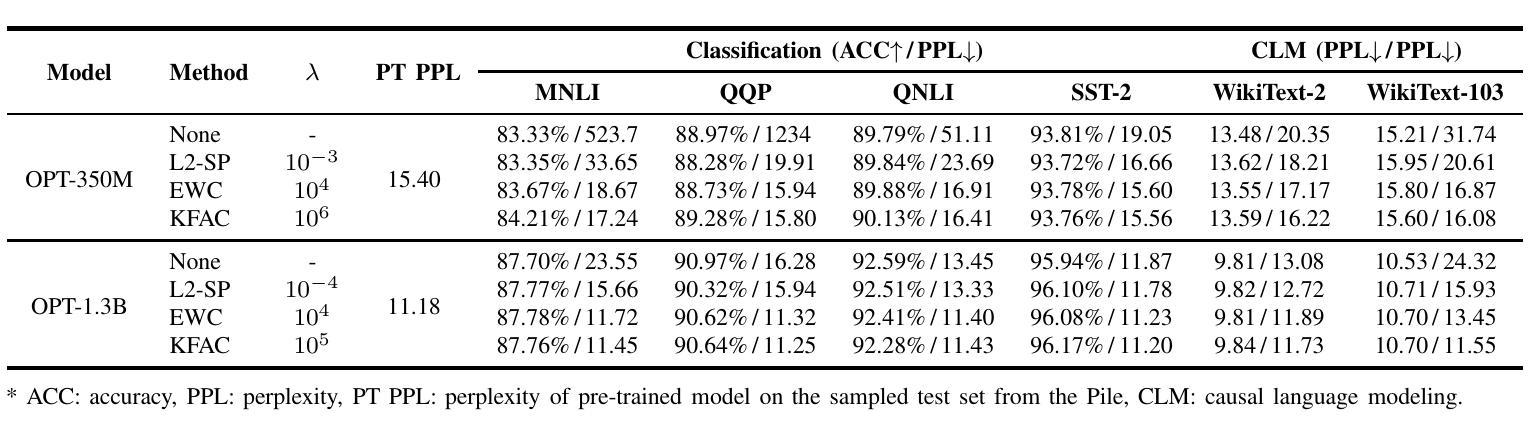
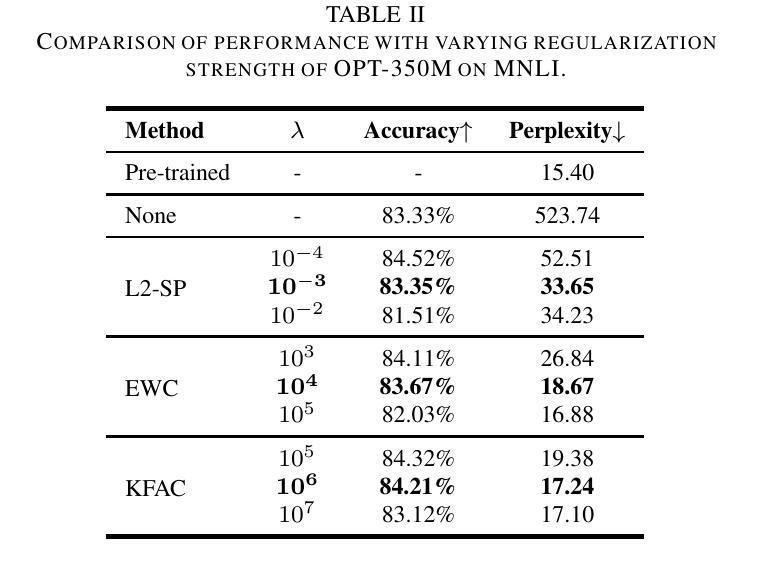
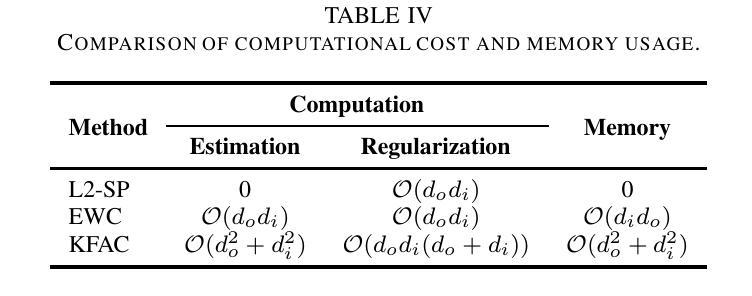
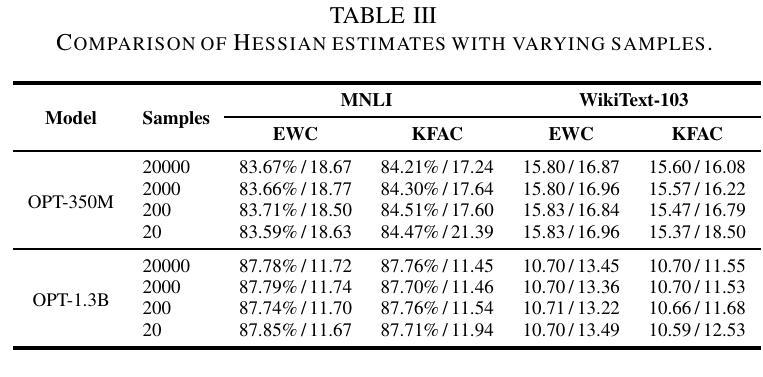
Paralinguistics-Aware Speech-Empowered Large Language Models for Natural Conversation
Authors:Heeseung Kim, Soonshin Seo, Kyeongseok Jeong, Ohsung Kwon, Soyoon Kim, Jungwhan Kim, Jaehong Lee, Eunwoo Song, Myungwoo Oh, Jung-Woo Ha, Sungroh Yoon, Kang Min Yoo
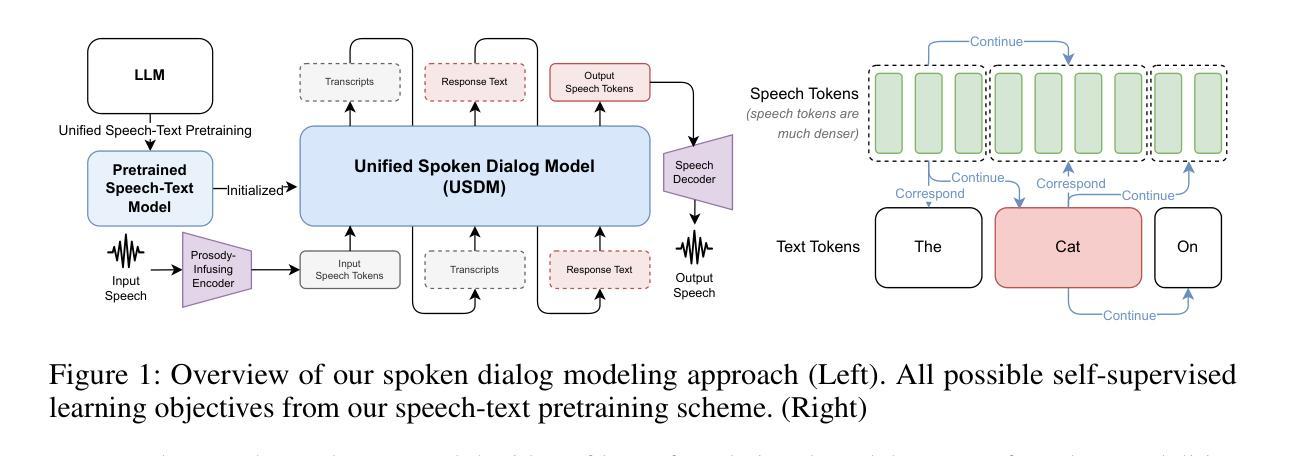
Recent work shows promising results in expanding the capabilities of large language models (LLM) to directly understand and synthesize speech. However, an LLM-based strategy for modeling spoken dialogs remains elusive, calling for further investigation. This paper introduces an extensive speech-text LLM framework, the Unified Spoken Dialog Model (USDM), designed to generate coherent spoken responses with naturally occurring prosodic features relevant to the given input speech without relying on explicit automatic speech recognition (ASR) or text-to-speech (TTS) systems. We have verified the inclusion of prosody in speech tokens that predominantly contain semantic information and have used this foundation to construct a prosody-infused speech-text model. Additionally, we propose a generalized speech-text pretraining scheme that enhances the capture of cross-modal semantics. To construct USDM, we fine-tune our speech-text model on spoken dialog data using a multi-step spoken dialog template that stimulates the chain-of-reasoning capabilities exhibited by the underlying LLM. Automatic and human evaluations on the DailyTalk dataset demonstrate that our approach effectively generates natural-sounding spoken responses, surpassing previous and cascaded baselines. Our code and checkpoints are available at https://github.com/naver-ai/usdm.
近期的研究工作显示,在扩大大型语言模型(LLM)的能力以直接理解和合成语音方面取得了有前景的结果。然而,基于LLM的建模口语对话的策略仍然难以捉摸,需要进一步的调查。本文介绍了一个全面的语音文本LLM框架,即统一口语对话模型(USDM),旨在生成与给定输入语音相关的连贯口语响应,而无需依赖自动语音识别(ASR)或文本到语音(TTS)系统。我们已经验证了包含主要含有语义信息的语音符号中的语调,并使用这个基础来构建一个注入语调的语音文本模型。此外,我们提出了一种通用的语音文本预训练方案,该方案提高了跨模式语义的捕获能力.为了构建USDM,我们使用多步骤口语对话模板对语音文本模型进行微调,该模板刺激底层LLM所展现的推理能力。在DailyTalk数据集上的自动和人类评估表明,我们的方法有效地生成了自然的口语响应,超越了先前的和级联的基准测试。我们的代码和检查点位于https://github.com/naver-ai/usdm。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024, Project Page: https://unifiedsdm.github.io/
Summary
本文提出了一种统一的口语对话模型(USDM),能够直接理解和合成语音,生成与输入语音相关的连贯口语响应,具有自然发生的韵律特征,无需依赖自动语音识别(ASR)或文本到语音(TTS)系统。通过构建包含主要语义信息的韵律语音令牌,该模型实现了韵律注入的语音文本模型。此外,还提出了一种通用的语音文本预训练方案,提高了跨模态语义的捕获能力。通过在日常对话数据集上的自动和人类评估表明,该方法生成的响应自然流畅,超越了之前的级联基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在直接理解和合成语音方面展现出有前景的结果,但仍需进一步探索建模口语对话的策略。
- USDM模型旨在生成与输入语音相关的连贯口语响应,并具备自然韵律特征。
- USDM模型通过包含主要语义信息的韵律语音令牌实现韵律注入。
- 提出了一种通用的语音文本预训练方案,增强跨模态语义捕获。
- 通过多步口语对话模板对USDM进行微调,刺激LLM的推理能力。
- 在日常对话数据集上的评估显示,USDM生成的响应自然流畅,超越级联基线方法。
点此查看论文截图


Speeding Up Speech Synthesis In Diffusion Models By Reducing Data Distribution Recovery Steps Via Content Transfer
Authors:Peter Ochieng
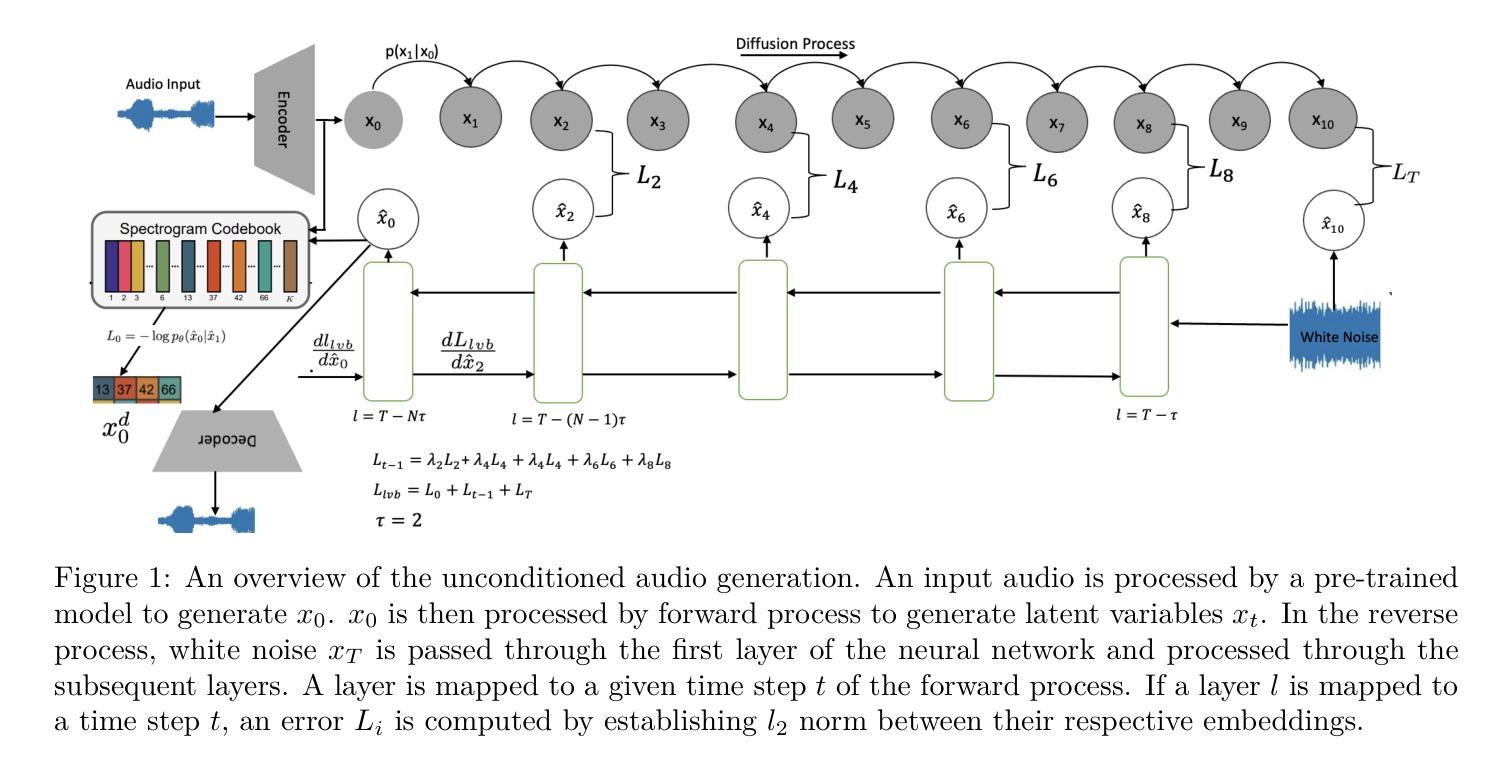
Diffusion based vocoders have been criticised for being slow due to the many steps required during sampling. Moreover, the model’s loss function that is popularly implemented is designed such that the target is the original input $x_0$ or error $\epsilon_0$. For early time steps of the reverse process, this results in large prediction errors, which can lead to speech distortions and increase the learning time. We propose a setup where the targets are the different outputs of forward process time steps with a goal to reduce the magnitude of prediction errors and reduce the training time. We use the different layers of a neural network (NN) to perform denoising by training them to learn to generate representations similar to the noised outputs in the forward process of the diffusion. The NN layers learn to progressively denoise the input in the reverse process until finally the final layer estimates the clean speech. To avoid 1:1 mapping between layers of the neural network and the forward process steps, we define a skip parameter $\tau>1$ such that an NN layer is trained to cumulatively remove the noise injected in the $\tau$ steps in the forward process. This significantly reduces the number of data distribution recovery steps and, consequently, the time to generate speech. We show through extensive evaluation that the proposed technique generates high-fidelity speech in competitive time that outperforms current state-of-the-art tools. The proposed technique is also able to generalize well to unseen speech.
基于扩散的vocoder由于采样过程中需要多个步骤,所以被批评速度较慢。此外,流行的实现中的模型的损失函数的设计目标是原始输入x_0或误差ε_0。在反向过程的早期步骤中,这会导致较大的预测误差,可能导致语音失真并增加学习时间。我们提出了一种设置,目标为正向过程时间步骤的不同输出,旨在减小预测误差的幅度并缩短训练时间。我们使用神经网络(NN)的不同层执行去噪,通过训练它们学习生成与扩散正向过程中的噪声输出相似的表示。NN层学习在反向过程中逐步对输入进行去噪,直到最终层估计出干净语音。为了避免神经网络层与正向过程步骤之间的1:1映射,我们定义了一个跳过参数τ>1,使得NN层被训练累积地去除在正向过程的τ步中注入的噪声。这显著减少了数据分布恢复步骤的数量,因此也缩短了生成语音的时间。我们通过广泛评估证明,所提出的技术在竞争时间内生成了高保真度的语音,优于当前最先进的工具。所提出的技术也能很好地推广未见过的语音。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages
Summary
本文提出一种基于扩散的vocoder改进方案,通过调整目标设定和神经网络层的设计,减少了预测误差和训练时间,生成了高质量、高保真度的语音,同时具有良好的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散vocoder因采样过程中步骤繁多而速度较慢,本文提出改进方案。
- 传统模型损失函数设计以原始输入或误差为目标,导致早期时间步骤反向过程中的预测误差较大,本文改变目标设定为前向过程时间步骤的输出,以减少预测误差和学习时间。
- 利用神经网络的不同层进行去噪训练,学习生成与扩散前向过程中的噪声输出相似的表示。
- 神经网络层逐层去噪,最终层估计清洁语音。
- 引入跳过参数τ>1,使神经网络层累计去除在τ步中注入的噪声,减少数据分布恢复步骤和时间。
- 改进方案生成的高保真语音在竞争时间内表现出优异性能,优于现有最先进的工具。
点此查看论文截图

Fast Likelihood-free Reconstruction of Gravitational Wave Backgrounds
Authors:Androniki Dimitriou, Daniel G. Figueroa, Bryan Zaldivar
We apply state-of-the-art, likelihood-free statistical inference (machine-learning-based) techniques for reconstructing the spectral shape of a gravitational wave background (GWB). We focus on the reconstruction of an arbitrarily shaped signal by the LISA detector, but the method can be easily extended to either template-dependent signals, or to other detectors, as long as a characterisation of the instrumental noise is available. As proof of the technique, we quantify the ability of LISA to reconstruct signals of arbitrary spectral shape (${\it blind}$ reconstruction), considering a diversity of frequency profiles, and including astrophysical backgrounds in some cases. As a teaser of how the method can reconstruct signals characterised by a parameter-dependent template (${\it template}$ reconstruction), we present a dedicated study for power-law signals. While our technique has several advantages with respect to traditional MCMC methods, we validate it with the latter for concrete cases. This work opens the door for both fast and accurate Bayesian parameter estimation of GWBs, with essentially no computational overhead during the inference step. Our set of tools are integrated into the package ${\tt GWBackFinder}$, which is publicly available in https://github.com/AndronikiDimitriou/GWBackFinder.
我们采用最先进的无可能性统计推断(基于机器学习)技术来重建引力波背景(GWB)的频谱形状。我们专注于利用LISA探测器对任意形状的信号进行重建,但只要有仪器噪声的特征,该方法可轻易扩展到模板依赖的信号或其他探测器。作为该技术的证明,我们量化了LISA重建任意频谱形状信号的能力(盲重建),考虑了各种频率分布,并在某些情况下包括天文背景。作为该方法可以重建参数依赖模板信号的一个提示(模板重建),我们为幂律信号进行了专项研究。虽然我们的技术相对于传统的MCMC方法有许多优势,但对于具体案例,我们还是用后者对其进行了验证。这项工作为GWBs的快速和精确贝叶斯参数估计打开了大门,在推断步骤中几乎没有计算开销。我们的工具集已集成到GWBackFinder软件包中,可在https://github.com/AndronikiDimitriou/GWBackFinder公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Published in JCAP. 29 pages plus appendices and references, 12 figures
Summary
基于最新技术,采用无需似然函数的统计推断(基于机器学习)方法,对引力波背景(GWB)的频谱形状进行重建。研究重点为LISA探测器对任意形状信号的重建,该方法可轻易扩展至模板依赖信号或其他探测器,只要具备仪器噪声特征即可。对中国技术进行了量化评估,展示了其对任意频谱形状信号的重建能力,包括多种频率分布,并在某些情况下考虑天文背景。还为参数依赖模板的信号重建提供了专项研究,重点研究了幂律信号。该技术相对于传统的MCMC方法具有多个优势,并在具体案例中进行验证。本研究为快速准确的GWB贝叶斯参数估计打开了大门,推理步骤几乎无计算开销。相关工具集已集成到公开可用的GWBackFinder软件包中。
Key Takeaways
- 采用前沿的机器学习技术,进行无需似然函数的统计推断,以重建引力波背景的频谱形状。
- 研究的焦点是LISA探测器对任意形状信号的重建能力。
- 该方法可灵活扩展到模板依赖的信号和其他探测器,前提是有仪器噪声的特征描述。
- 技术验证包括对任意频谱形状信号的重建能力,涵盖了多种频率分布,并考虑了天文背景。
- 提供了参数依赖模板的信号重建的专项研究,以幂律信号为例。
- 与传统MCMC方法相比,该技术具有显著优势,并在具体案例中得到验证。
点此查看论文截图