⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-12 更新
EOV-Seg: Efficient Open-Vocabulary Panoptic Segmentation
Authors:Hongwei Niu, Jie Hu, Jianghang Lin, Shengchuan Zhang
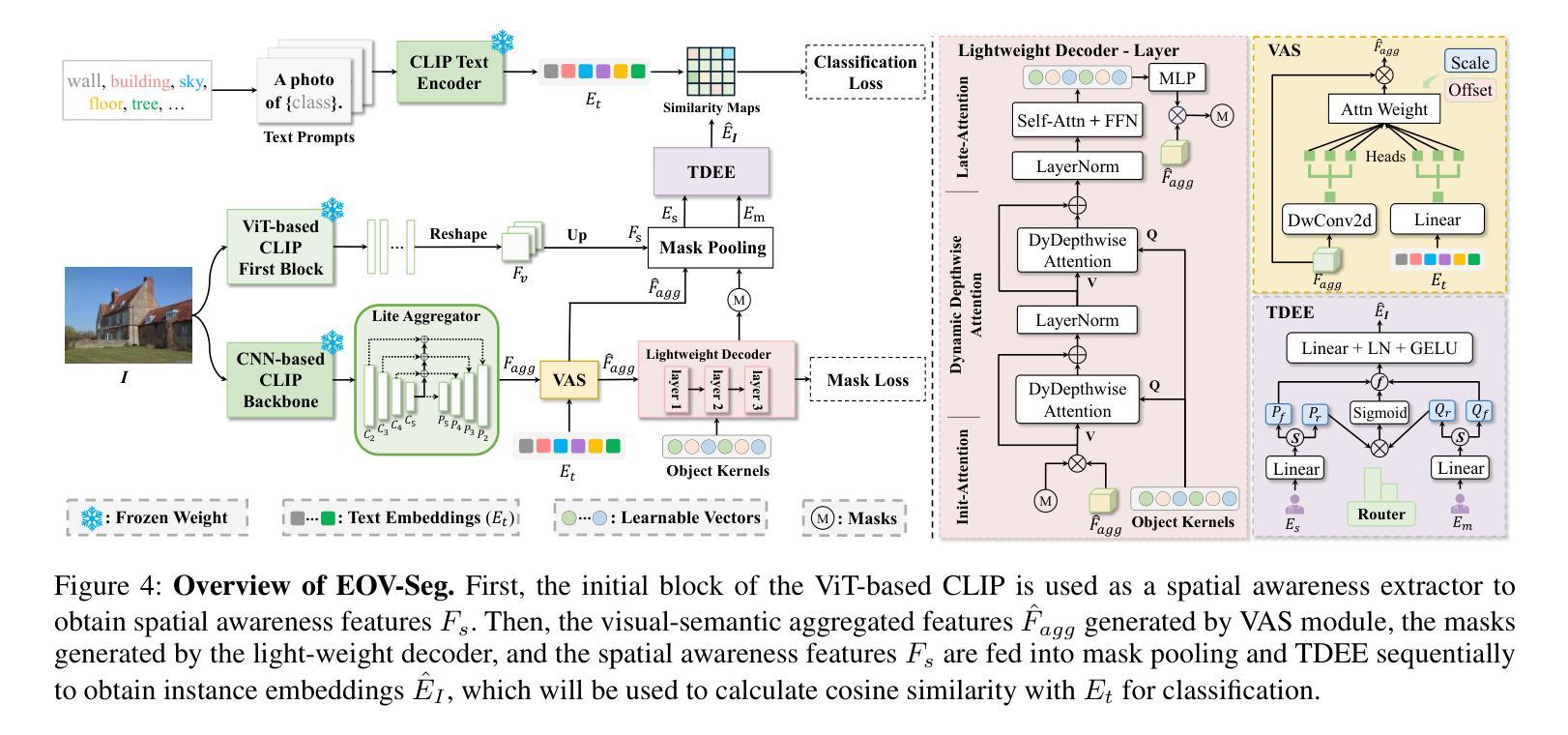
Open-vocabulary panoptic segmentation aims to segment and classify everything in diverse scenes across an unbounded vocabulary. Existing methods typically employ two-stage or single-stage framework. The two-stage framework involves cropping the image multiple times using masks generated by a mask generator, followed by feature extraction, while the single-stage framework relies on a heavyweight mask decoder to make up for the lack of spatial position information through self-attention and cross-attention in multiple stacked Transformer blocks. Both methods incur substantial computational overhead, thereby hindering the efficiency of model inference. To fill the gap in efficiency, we propose EOV-Seg, a novel single-stage, shared, efficient, and spatial-aware framework designed for open-vocabulary panoptic segmentation. Specifically, EOV-Seg innovates in two aspects. First, a Vocabulary-Aware Selection (VAS) module is proposed to improve the semantic comprehension of visual aggregated features and alleviate the feature interaction burden on the mask decoder. Second, we introduce a Two-way Dynamic Embedding Experts (TDEE), which efficiently utilizes the spatial awareness capabilities of ViT-based CLIP backbone. To the best of our knowledge, EOV-Seg is the first open-vocabulary panoptic segmentation framework towards efficiency, which runs faster and achieves competitive performance compared with state-of-the-art methods. Specifically, with COCO training only, EOV-Seg achieves 24.2 PQ, 31.6 mIoU, and 12.7 FPS on the ADE20K dataset for panoptic and semantic segmentation tasks and the inference time of EOV-Seg is 4-21 times faster than state-of-the-art methods. Especially, equipped with ResNet-50 backbone, EOV-Seg runs 25 FPS with only 71M parameters on a single RTX 3090 GPU. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/nhw649/EOV-Seg}.
开放词汇全景分割旨在分割并分类无限词汇表中不同场景中的所有内容。现有方法通常采用两阶段或单阶段框架。两阶段框架涉及使用由掩膜生成器生成的掩膜多次裁剪图像,然后进行特征提取,而单阶段框架依赖于重量级掩膜解码器,通过堆叠的多个Transformer块中的自注意力和交叉注意力来弥补空间位置信息的缺失。这两种方法都产生了大量的计算开销,从而影响了模型推理的效率。为了弥补效率上的差距,我们提出了EOV-Seg,这是一种针对开放词汇全景分割的新型单阶段共享高效空间感知框架。具体来说,EOV-Seg在两个方面进行了创新。首先,提出了词汇感知选择(VAS)模块,以提高视觉聚合特征语义理解能力并减轻掩膜解码器的特征交互负担。其次,我们引入了双向动态嵌入专家(TDEE),它有效地利用了基于ViT的CLIP主干的空间感知能力。据我们所知,EOV-Seg是面向效率的首个开放词汇全景分割框架,与最先进的方法相比,它运行更快并实现了具有竞争力的性能。具体来说,仅在COCO数据集上进行训练后,EOV-Seg在ADE20K数据集上的全景和语义分割任务上达到了24.2的PQ(全景质量)、31.6的mIoU(平均交并比),并且每秒处理12.7帧。此外,配备ResNet-50主干的EOV-Seg在单个RTX 3090 GPU上仅以71M参数就能达到每秒25帧的处理速度。代码可通过\url{https://github.com/nhw649/EOV-Seg}获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
本摘要介绍了针对开放式词汇表全景分割的难题,提出了一种高效、单阶段的空间感知框架EOV-Seg。它通过创新的Vocabulary-Aware Selection模块和Two-way Dynamic Embedding Experts方法提高了语义理解和特征交互效率,使得模型更有效率并且表现良好。它在测试上的性能与最先进的方法相当,特别是在COCO训练上取得了可观的成绩,同时显著提高了运行速度。代码已公开在GitHub上共享。
Key Takeaways
- EOV-Seg是一个针对开放式词汇表全景分割的高效、单阶段框架。
- EOV-Seg通过创新的VAS模块改进了语义理解,并减轻了特征交互的负担。
- TDEE模块的引入有效利用了基于ViT的CLIP骨干网的空间感知能力。
- EOV-Seg在多个数据集上的性能表现优异,特别是在ADE20K数据集上的全景和语义分割任务上取得了良好的成绩。
- 与现有最先进的方法相比,EOV-Seg显著提高了运行速度,并且参数更少。
- EOV-Seg的代码已经公开可供研究者和开发者使用。
点此查看论文截图


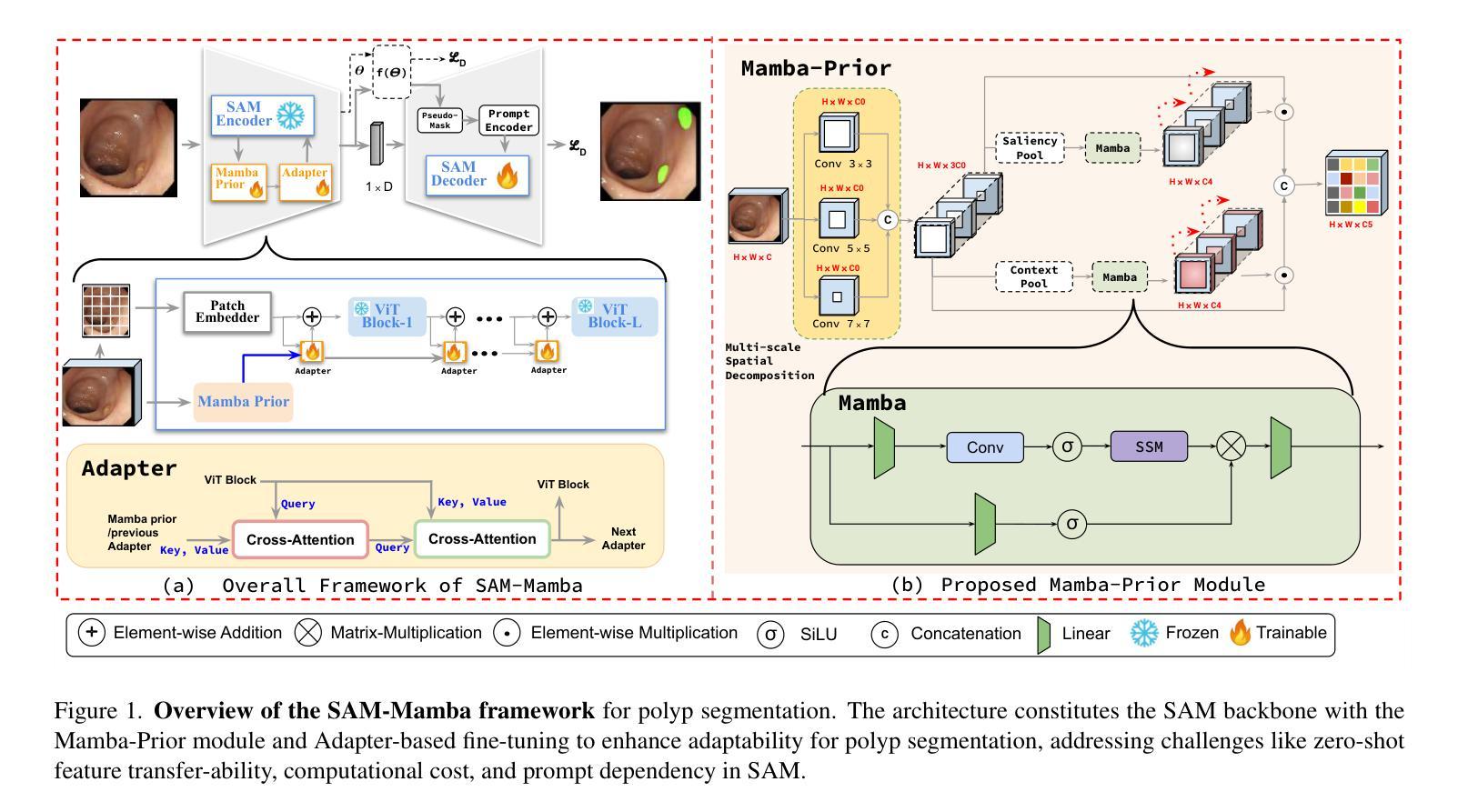
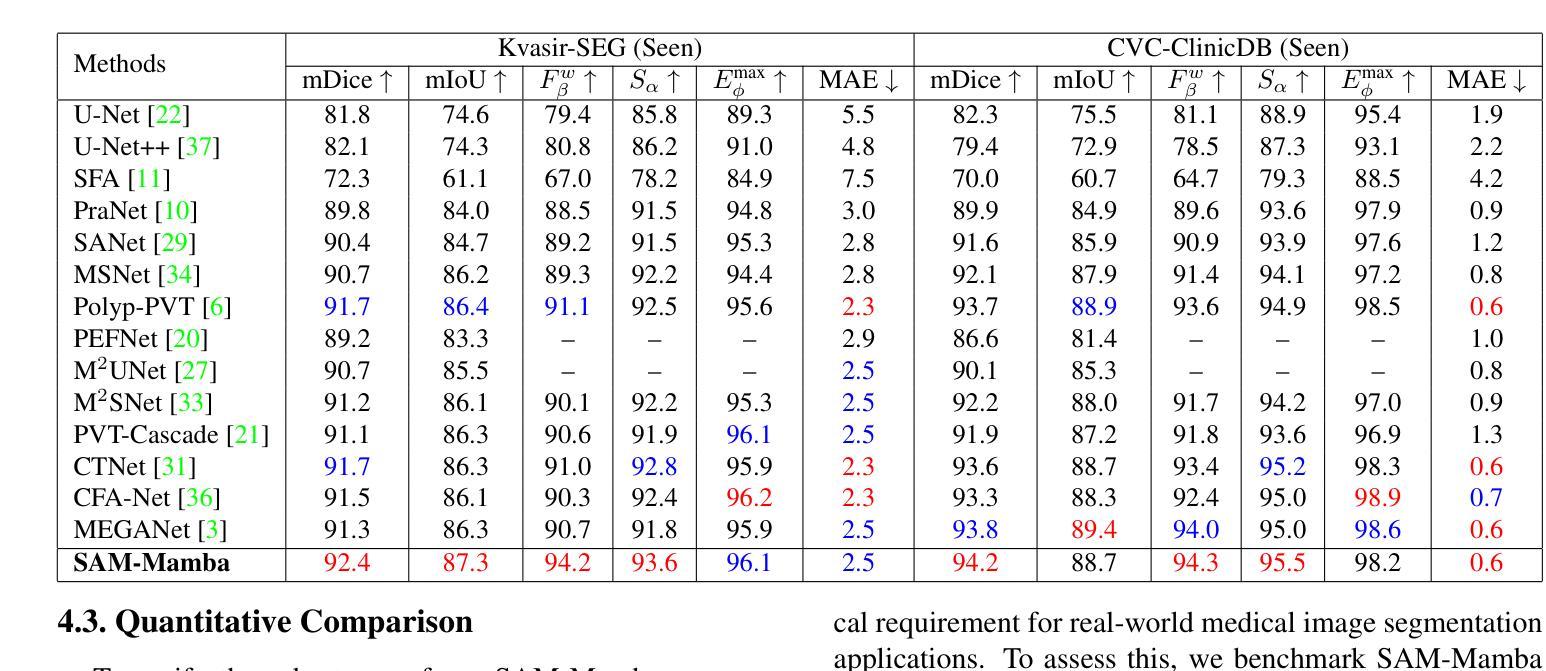
SAM-Mamba: Mamba Guided SAM Architecture for Generalized Zero-Shot Polyp Segmentation
Authors:Tapas Kumar Dutta, Snehashis Majhi, Deepak Ranjan Nayak, Debesh Jha
Polyp segmentation in colonoscopy is crucial for detecting colorectal cancer. However, it is challenging due to variations in the structure, color, and size of polyps, as well as the lack of clear boundaries with surrounding tissues. Traditional segmentation models based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) struggle to capture detailed patterns and global context, limiting their performance. Vision Transformer (ViT)-based models address some of these issues but have difficulties in capturing local context and lack strong zero-shot generalization. To this end, we propose the Mamba-guided Segment Anything Model (SAM-Mamba) for efficient polyp segmentation. Our approach introduces a Mamba-Prior module in the encoder to bridge the gap between the general pre-trained representation of SAM and polyp-relevant trivial clues. It injects salient cues of polyp images into the SAM image encoder as a domain prior while capturing global dependencies at various scales, leading to more accurate segmentation results. Extensive experiments on five benchmark datasets show that SAM-Mamba outperforms traditional CNN, ViT, and Adapter-based models in both quantitative and qualitative measures. Additionally, SAM-Mamba demonstrates excellent adaptability to unseen datasets, making it highly suitable for real-time clinical use.
结肠镜检查中的息肉分割对于检测结直肠癌至关重要。然而,由于息肉的结构、颜色和大小差异以及与周围组织的边界不清,这带来了极大的挑战。基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的传统分割模型难以捕捉详细的模式和全局上下文,从而限制了其性能。基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的模型解决了其中的一些问题,但在捕获局部上下文和缺乏强大的零样本泛化能力方面存在困难。为此,我们提出了Mamba引导的分段任何模型(SAM-Mamba),用于有效的息肉分割。我们的方法在编码器中加入了一个Mamba-Prior模块,以弥合SAM的一般预训练表示和息肉相关的琐碎线索之间的鸿沟。它将息肉图像的关键线索注入SAM图像编码器作为领域先验,同时捕捉不同尺度的全局依赖关系,从而得到更精确的分割结果。在五个基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,SAM-Mamba在定量和定性措施上都优于传统的CNN、ViT和基于适配器的模型。此外,SAM-Mamba在未见过的数据集上表现出出色的适应性,非常适合实时临床应用。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了结肠镜检查中息肉分割对检测结直肠癌的重要性。由于息肉结构、颜色和尺寸的差异以及与周围组织的边界不清,导致分割任务充满挑战。传统基于卷积神经网络(CNN)的分割模型难以捕捉详细模式和全局上下文,性能受限。Vision Transformer(ViT)模型可以解决这些问题,但在捕获局部上下文和零样本泛化方面存在困难。为此,提出了Mamba引导的分段任何模型(SAM-Mamba),用于高效息肉分割。该方法在编码器中加入Mamba-Prior模块,以弥补SAM的一般预训练表示和息肉相关线索之间的差距。它将息肉图像的关键线索注入SAM图像编码器作为领域先验,同时捕捉不同尺度的全局依赖关系,从而实现更准确的分割结果。在五个基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,SAM-Mamba在定量和定性指标上均优于传统CNN、ViT和适配器模型。此外,SAM-Mamba在未见数据集上表现出出色的适应性,非常适合实时临床使用。
Key Takeaways
- 结肠镜检查中的息肉分割对检测结直肠癌至关重要。
- 传统CNN模型在息肉分割上性能受限,难以捕捉详细模式和全局上下文。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)模型在息肉分割中具有潜力,但存在捕获局部上下文和零样本泛化的困难。
- 提出的SAM-Mamba模型通过引入Mamba-Prior模块,结合了ViT和CNN的优点,实现了更准确的息肉分割。
- SAM-Mamba在多个数据集上表现出优异的性能,优于传统CNN、ViT和适配器模型。
- SAM-Mamba具有良好的未知数据适应性,适合实时临床应用。
点此查看论文截图

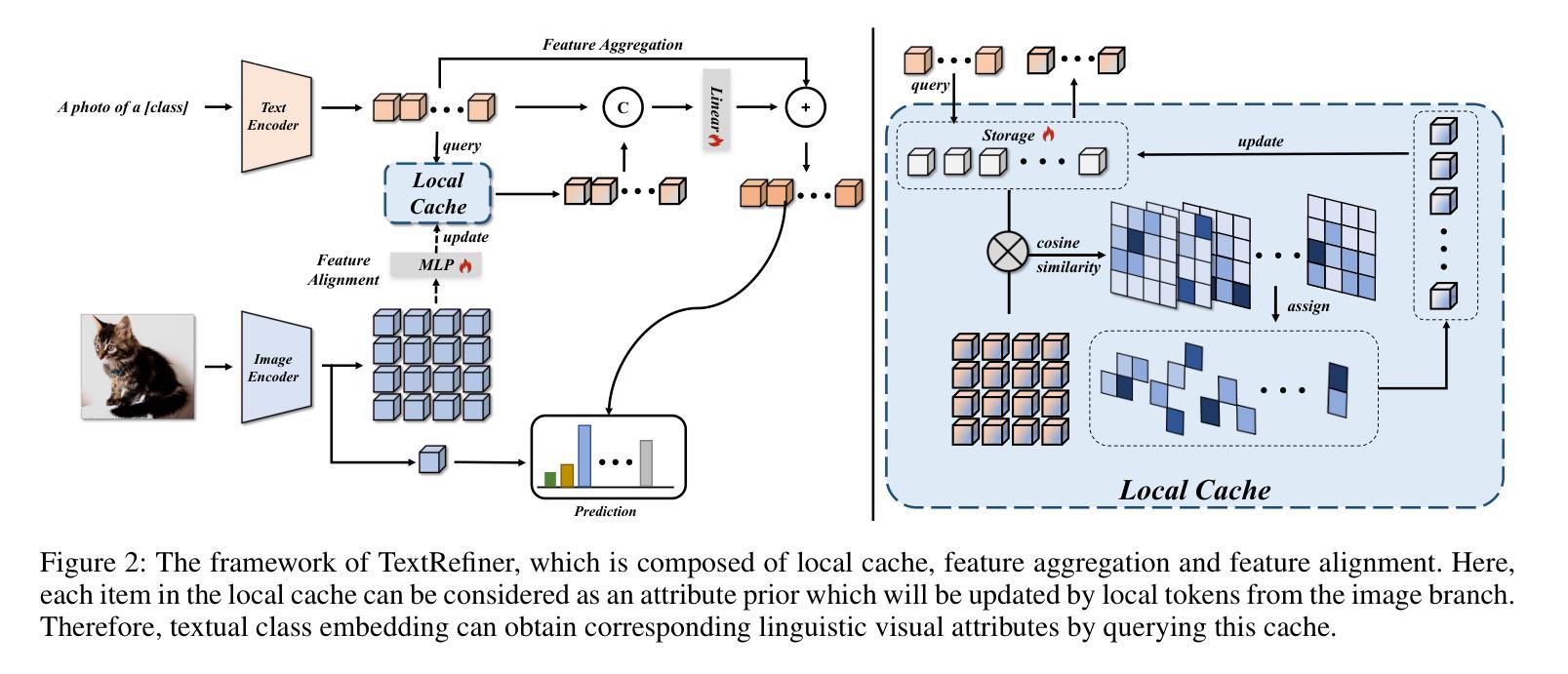
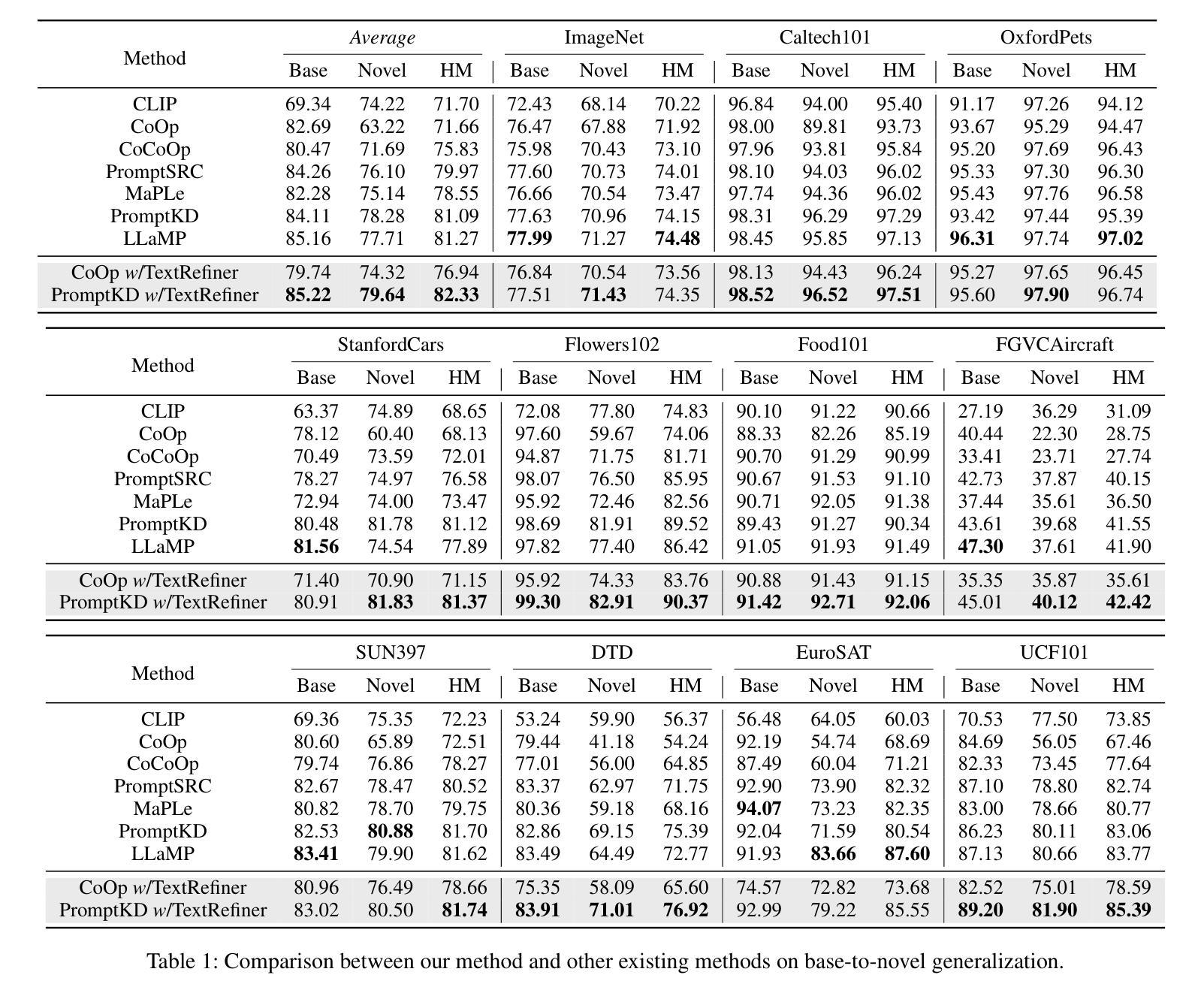
TextRefiner: Internal Visual Feature as Efficient Refiner for Vision-Language Models Prompt Tuning
Authors:Jingjing Xie, Yuxin Zhang, Jun Peng, Zhaohong Huang, Liujuan Cao
Despite the efficiency of prompt learning in transferring vision-language models (VLMs) to downstream tasks, existing methods mainly learn the prompts in a coarse-grained manner where the learned prompt vectors are shared across all categories. Consequently, the tailored prompts often fail to discern class-specific visual concepts, thereby hindering the transferred performance for classes that share similar or complex visual attributes. Recent advances mitigate this challenge by leveraging external knowledge from Large Language Models (LLMs) to furnish class descriptions, yet incurring notable inference costs. In this paper, we introduce TextRefiner, a plug-and-play method to refine the text prompts of existing methods by leveraging the internal knowledge of VLMs. Particularly, TextRefiner builds a novel local cache module to encapsulate fine-grained visual concepts derivedfrom local tokens within the image branch. By aggregating and aligning the cached visual descriptions with the original output of the text branch, TextRefiner can efficiently refine and enrich the learned prompts from existing methods without relying on any external expertise. For example, it improves the performance of CoOp from 71.66 % to 76.94 % on 11 benchmarks, surpassing CoCoOp which introduces instance-wise features for text prompts. Equipped with TextRefiner, PromptKD achieves state-of-the-art performance and is efficient in inference. Our code is relesed at https://github.com/xjjxmu/TextRefiner
尽管提示学习在将视觉语言模型(VLM)转移到下游任务时非常有效,但现有方法主要采用了粗粒度的方式学习提示,其中学习到的提示向量会共享给所有类别。因此,针对特定类别的提示往往无法区分特定类别的视觉概念,从而阻碍了相似或复杂视觉属性类别的迁移性能。最近的进展通过利用大型语言模型(LLM)的外部知识来提供类别描述来缓解这一挑战,但这会导致推理成本显著增加。在本文中,我们介绍了TextRefiner,这是一种利用视觉语言模型的内部知识来优化现有方法的文本提示的即插即用方法。特别地,TextRefiner构建了一个新颖的局部缓存模块,以封装来自图像分支的局部标记中派生的细粒度视觉概念。通过聚合和对齐缓存的视觉描述与文本分支的原始输出,TextRefiner可以有效地优化和丰富现有方法的所学提示,而无需依赖任何外部专家知识。例如,它在11个基准测试上将CoOp的性能从71.66%提高到76.94%,超越了引入实例特征用于文本提示的CoCoOp。配备TextRefiner的PromptKD达到了最先进的性能,在推理方面也非常高效。我们的代码已发布在https://github.com/xjjxmu/TextRefiner。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为TextRefiner的即插即用方法,用于通过利用视觉语言模型(VLMs)的内部知识来优化现有方法的文本提示。TextRefiner建立了一个新型本地缓存模块,以封装图像分支中局部标记的细粒度视觉概念。通过聚合和对齐缓存的视觉描述与文本分支的原始输出,TextRefiner能够优化并丰富现有方法的已学提示,无需依赖任何外部知识。此方法提高了CoOp在11个基准测试上的性能,超越了引入实例级特征的CoCoOp方法。配备TextRefiner后,PromptKD实现了最先进的性能并在推理中表现出高效率。
Key Takeaways
- TextRefiner是一种用于优化视觉语言模型(VLMs)中文本提示的方法。
- 现有方法主要通过粗粒度方式学习提示,导致针对特定类别的提示无法区分相似的视觉概念。
- TextRefiner通过利用VLMs的内部知识来解决这一问题。
- TextRefiner建立了一个本地缓存模块,该模块能够封装图像分支中的细粒度视觉概念。
- TextRefiner通过聚合和对齐缓存的视觉描述与文本分支的原始输出,优化并丰富了现有方法的提示。
- TextRefiner在多个基准测试上提高了性能,超越了引入实例级特征的CoCoOp方法。
- 配备TextRefiner后,PromptKD实现了最先进的性能,并且在推理过程中表现出高效率。
点此查看论文截图

Can Graph Neural Networks Learn Language with Extremely Weak Text Supervision?
Authors:Zihao Li, Lecheng Zheng, Bowen Jin, Dongqi Fu, Baoyu Jing, Yikun Ban, Jingrui He, Jiawei Han
While great success has been achieved in building vision models with Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) over Internet-scale image-text pairs, building transferable Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) with CLIP pipeline is challenging because of three fundamental issues: the scarcity of labeled data and text supervision, different levels of downstream tasks, and the conceptual gaps between domains. In this work, to address these issues, we leverage multi-modal prompt learning to effectively adapt pre-trained GNN to downstream tasks and data, given only a few semantically labeled samples, each with extremely weak text supervision. Our new paradigm embeds the graphs directly in the same space as the Large Language Models (LLMs) by learning both graph prompts and text prompts simultaneously. To accomplish this, we improve state-of-the-art graph prompt method, and then propose the first graph-language multi-modal prompt learning approach for exploiting the knowledge in pre-trained models. Notably, due to the insufficient supervision for fine-tuning, in our paradigm, the pre-trained GNN and the LLM are kept frozen, so the learnable parameters are much fewer than fine-tuning any pre-trained model. Through extensive experiments on real-world datasets, we demonstrate the superior performance of our paradigm in few-shot, multi-task-level, and cross-domain settings. Moreover, we build the first CLIP-style zero-shot classification prototype that can generalize GNNs to unseen classes with extremely weak text supervision.
在利用对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)在互联网规模的图像文本对上构建视觉模型方面取得了巨大成功后,使用CLIP管道构建可迁移的图神经网络(GNN)却面临三大挑战:标记数据稀缺以及文本监督不足、下游任务级别不同以及领域间的概念差距。在这项工作中,为了应对这些问题,我们利用多模态提示学习来有效地适应预训练GNN到下游任务和数据,仅使用少量语义标记样本,每个样本都具有极弱的文本监督。我们的新范式通过将图直接嵌入与大型语言模型(LLM)相同的空间,通过同时学习图提示和文本提示来实现。为了完成这项工作,我们改进了最先进的图提示方法,然后提出了利用预训练模型知识的首个图语言多模态提示学习方法。值得注意的是,由于微调时的监督不足,在我们的范式中,预训练的GNN和LLM保持不变,因此可学习的参数远少于对任何预训练模型的微调。通过在实际数据集上的广泛实验,我们证明了我们的范式在少样本、多任务级别和跨域设置中的卓越性能。此外,我们构建了第一个CLIP风格的零样本分类原型,能够利用极弱的文本监督将GNN推广到未见过的类别。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint, 26 pages
Summary
针对基于CLIP的预训练图神经网络在面临缺乏标签数据、文本监督不足、下游任务层次不同及领域间概念鸿沟等挑战时,本研究采用多模态提示学习,仅利用少量具有极弱文本监督的语义标记样本,有效地将预训练图神经网络适应于下游任务和数据的场景。该研究创新性地通过将图直接嵌入大型语言模型相同的空间,同时学习图提示和文本提示来实现这一目的。这一新方法在现实世界数据集上的实验证明了其在小样本、多任务级别和跨域设置中的卓越性能。此外,该研究构建了首个CLIP风格的零样本分类原型,能够借助极弱的文本监督将图神经网络推广到未见类别中。
Key Takeaways
- 基于CLIP的预训练图神经网络面临多方面的挑战,包括缺乏标签数据和文本监督不足等。
- 研究采用多模态提示学习来解决上述问题,使得预训练图神经网络能够适应不同下游任务和数据。
- 通过将图直接嵌入大型语言模型的相同空间,实现图提示和文本提示的同步学习。
- 提出一种基于CLIP的首个零样本分类原型系统,可以在极端文本监督情况下进行类别扩展。
- 研究改进了现有的图提示方法,展示了在真实数据集上的卓越性能。
- 在小样本、多任务级别和跨域设置下,该方法展现出显著优势。
点此查看论文截图
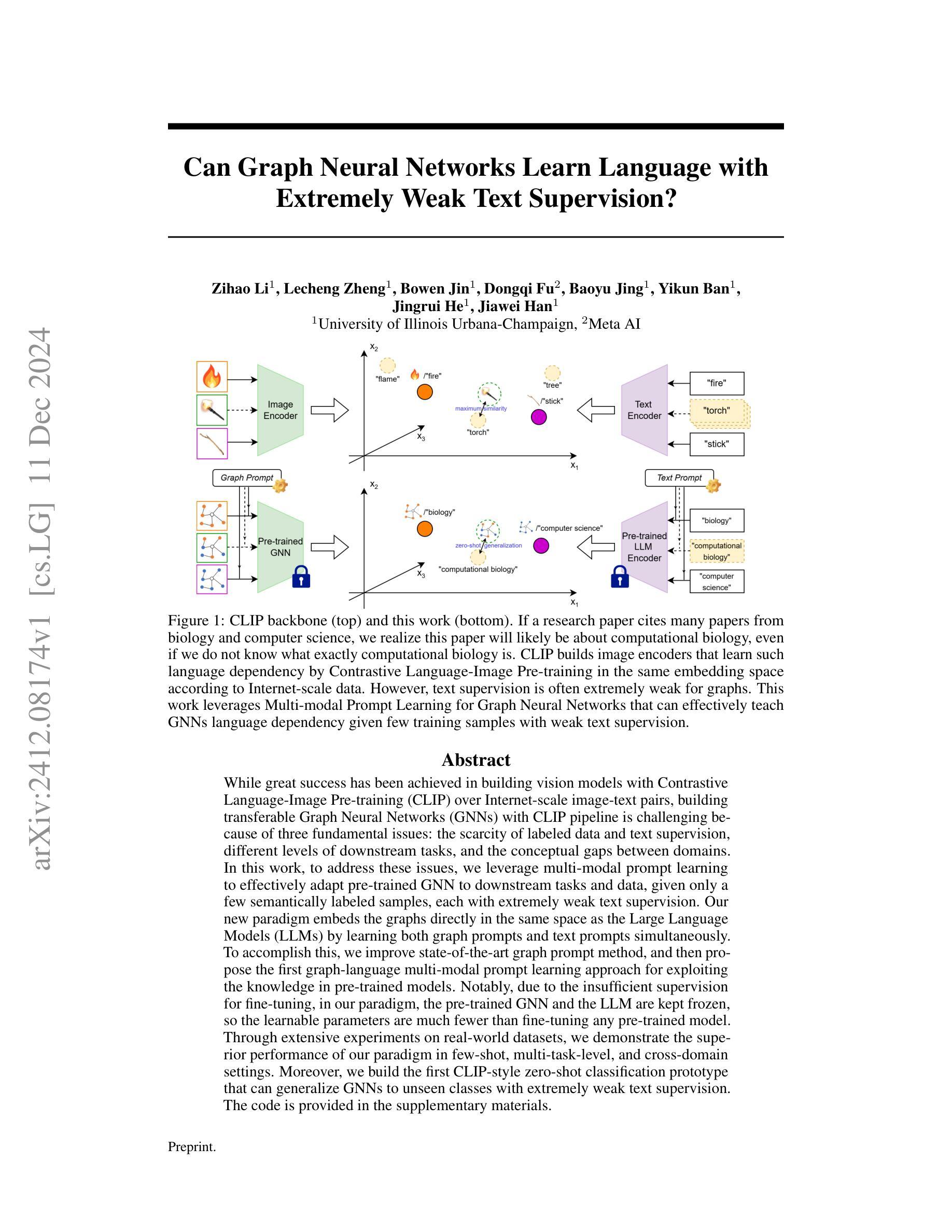
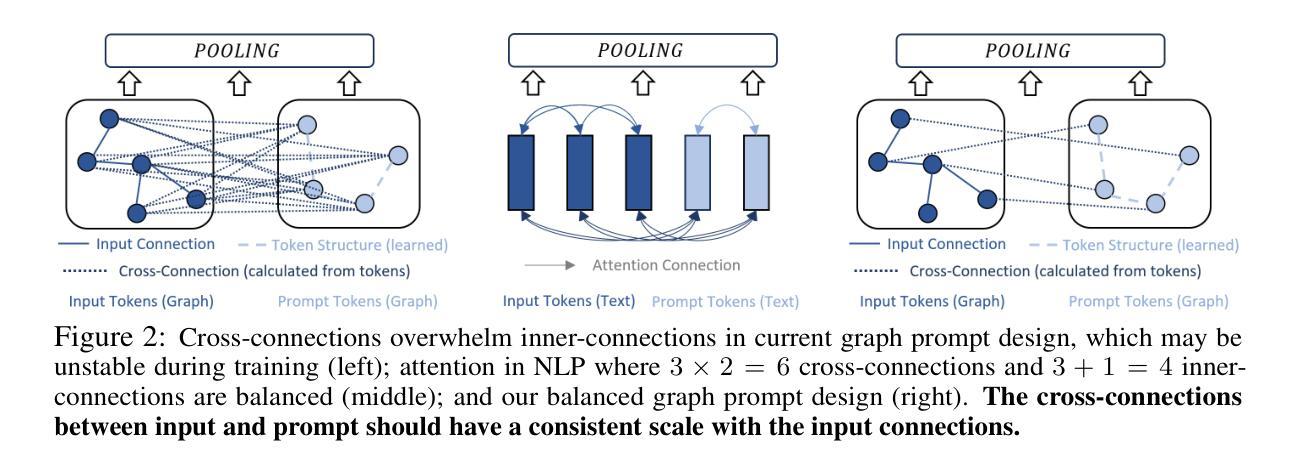
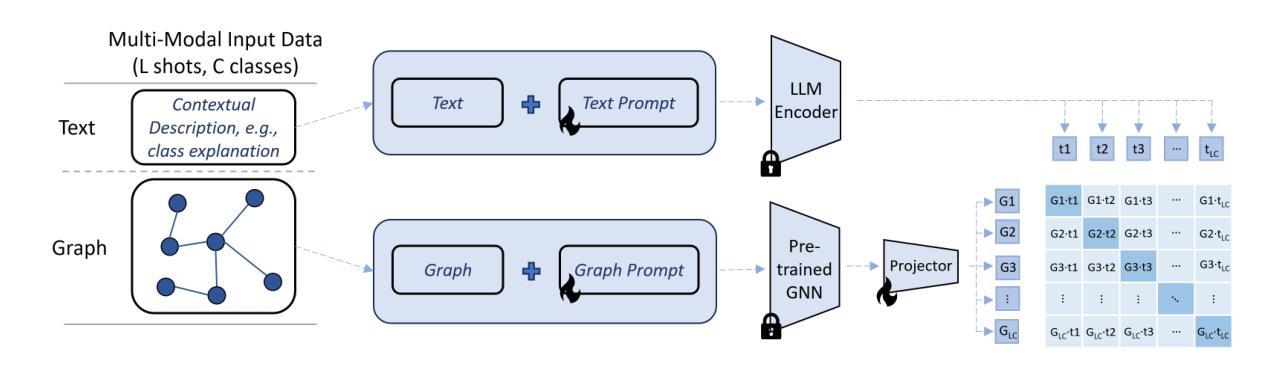
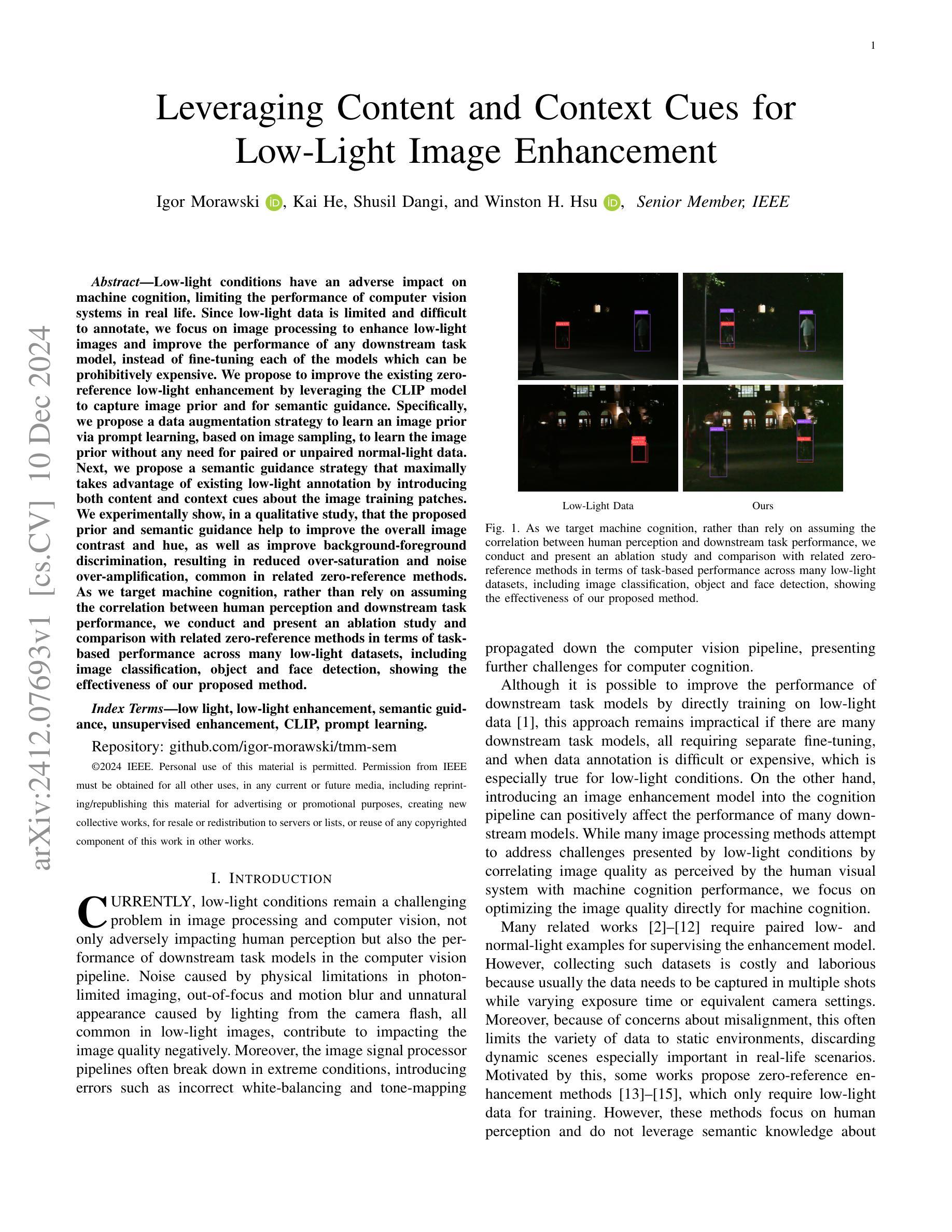
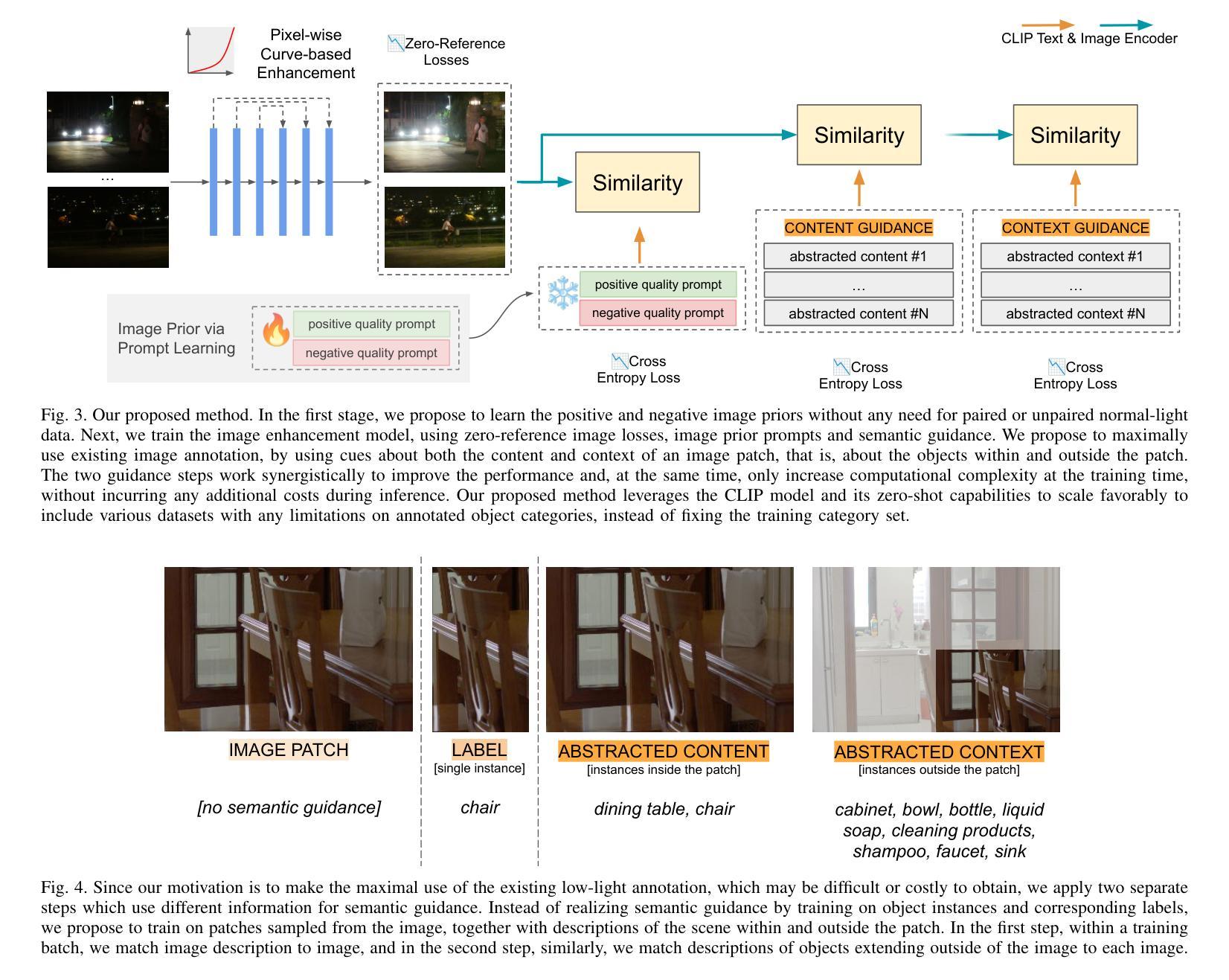
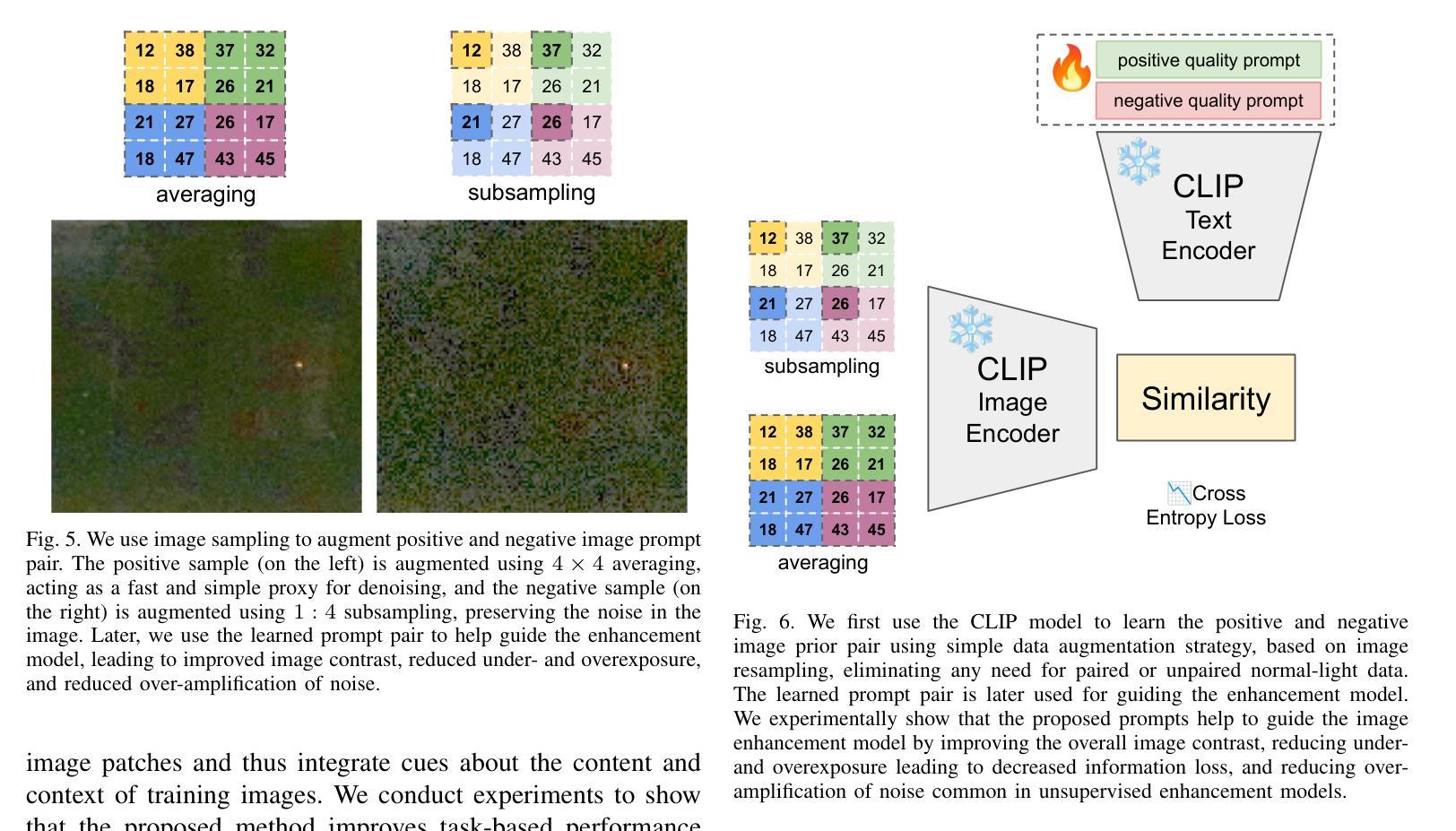
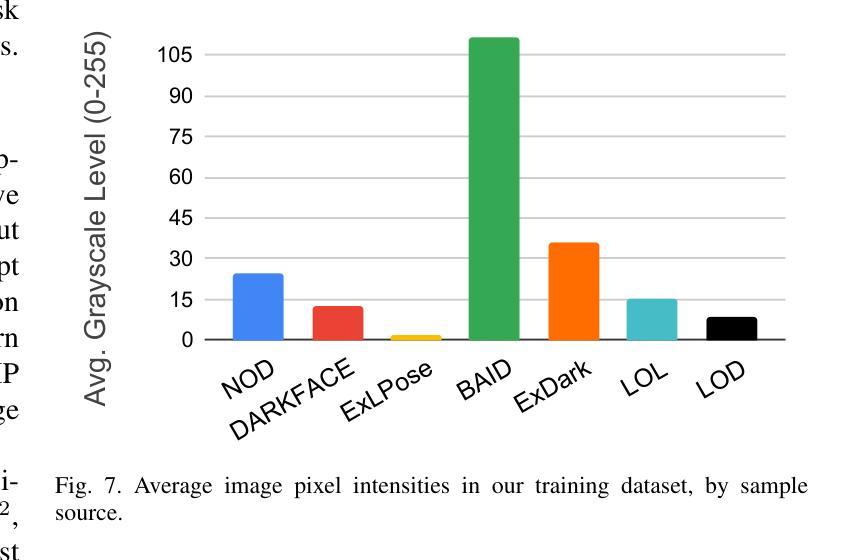
Leveraging Content and Context Cues for Low-Light Image Enhancement
Authors:Igor Morawski, Kai He, Shusil Dangi, Winston H. Hsu
Low-light conditions have an adverse impact on machine cognition, limiting the performance of computer vision systems in real life. Since low-light data is limited and difficult to annotate, we focus on image processing to enhance low-light images and improve the performance of any downstream task model, instead of fine-tuning each of the models which can be prohibitively expensive. We propose to improve the existing zero-reference low-light enhancement by leveraging the CLIP model to capture image prior and for semantic guidance. Specifically, we propose a data augmentation strategy to learn an image prior via prompt learning, based on image sampling, to learn the image prior without any need for paired or unpaired normal-light data. Next, we propose a semantic guidance strategy that maximally takes advantage of existing low-light annotation by introducing both content and context cues about the image training patches. We experimentally show, in a qualitative study, that the proposed prior and semantic guidance help to improve the overall image contrast and hue, as well as improve background-foreground discrimination, resulting in reduced over-saturation and noise over-amplification, common in related zero-reference methods. As we target machine cognition, rather than rely on assuming the correlation between human perception and downstream task performance, we conduct and present an ablation study and comparison with related zero-reference methods in terms of task-based performance across many low-light datasets, including image classification, object and face detection, showing the effectiveness of our proposed method.
低光条件对机器认知产生不利影响,限制了计算机视觉系统在现实生活中的性能。由于低光数据有限且难以标注,我们专注于图像处理,以增强低光图像并改善任何下游任务模型的性能,而不是微调可能非常昂贵的每个模型。我们提出利用CLIP模型捕捉图像先验并进行语义指导,以改进现有的无参考低光增强。具体来说,我们提出了一种基于提示学习(prompt learning)的数据增强策略,通过图像采样来学习图像先验,无需配对或未配对正常光数据。接下来,我们提出了一种语义指导策略,通过引入关于图像训练补丁的内容和上下文线索来充分利用现有的低光标注。我们在定性研究中通过实验表明,所提出的先验知识和语义指导有助于提高图像的整体对比度和色调,提高背景与前景的辨别能力,减少过度饱和和噪声过度放大,这在相关的无参考方法中很常见。由于我们的目标是机器认知,而不是依赖人类感知与下游任务性能之间的相关性假设,我们在多个低光数据集上进行了消融研究和比较,包括图像分类、物体和面部检测等任务,以展示我们提出方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to the IEEE Transactions on Multimedia
摘要
提升低光条件下机器认知性能的关键在于增强图像质量。本文提出一种利用CLIP模型捕捉图像先验和语义指导的方法,改进现有的无参考低光增强技术。通过图像采样进行数据增强,学习图像先验,无需配对或未配对正常光照数据。同时,提出语义引导策略,充分利用现有低光标注,引入图像训练补丁的内容和上下文线索。实验表明,本文提出的先验和语义引导有助于提高图像整体对比度和色调,改善背景前景辨识能力,减少相关零参考方法常见的过饱和和噪声过度放大问题。本研究以机器认知为目标,直接针对任务性能进行消融研究和对比实验,在多个低光照数据集上进行图像分类、物体和人脸检测任务,证明了方法的有效性。
关键见解
- 低光照条件对机器认知有负面影响,限制了计算机视觉系统在现实生活中的性能。
- 提出利用CLIP模型改进无参考低光增强技术,通过图像采样学习图像先验。
- 引入语义引导策略,利用低光标注中的内容和上下文线索。
- 实验表明,该方法能提高图像对比度和色调,改善背景前景辨识能力。
- 方法有助于解决相关零参考方法常见的过饱和和噪声过度放大问题。
- 研究以机器认知为目标,直接针对任务性能进行实验验证。
- 在多个低光照数据集上进行图像分类、物体和人脸检测任务,证明了方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图

Retaining and Enhancing Pre-trained Knowledge in Vision-Language Models with Prompt Ensembling
Authors:Donggeun Kim, Yujin Jo, Myungjoo Lee, Taesup Kim
The advancement of vision-language models, particularly the Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) model, has revolutionized the field of machine learning by enabling robust zero-shot learning capabilities. These capabilities allow models to understand and respond to previously unseen data without task-specific training. However, adapting CLIP to integrate specialized knowledge from various domains while retaining its zero-shot capabilities remains a significant challenge. To address this, we introduce a novel prompt ensemble learning approach called Group-wise Prompt Ensemble (GPE). This method aims to enhance CLIP’s zero-shot capabilities by incorporating new domain knowledge while improving its adaptability and robustness against data distribution shifts. Our approach hinges on three main strategies: prompt grouping with masked attention to optimize CLIP’s adaptability while safeguarding its zero-shot capabilities; the incorporation of auxiliary prompts for the seamless integration of new domain insights without disrupting the original model’s representation; and an ensemble learning strategy that effectively merges original and new knowledge. Through rigorous experimentation, including more challenging cross-dataset transfer evaluations, our GPE method redefines the benchmarks for the adaptability and efficiency of vision-language models, surpassing existing models across various scenarios.
视觉语言模型的进步,特别是对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型的进步,已经通过实现强大的零次学习(zero-shot learning)能力,为机器学习领域带来了革命性的变革。这些能力使得模型能够理解并响应以前未见过的数据,而无需针对特定任务进行训练。然而,如何使CLIP在融合各种领域专业知识的同时保留其零次学习能力,仍然是一个巨大的挑战。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种新的提示集成学习方法,称为群组提示集成(GPE)。该方法旨在通过融入新的领域知识来提升CLIP的零次学习能力,同时提高其适应性和针对数据分布变化的稳健性。我们的方法依赖于三个主要策略:通过提示分组和掩膜注意力来优化CLIP的适应性,同时保护其零次学习能力;通过引入辅助提示,实现新领域洞察的无缝集成,而不会破坏原始模型的表示;以及一种有效的集成学习策略,可以融合原始和新知识。通过严格的实验,包括更具挑战性的跨数据集迁移评估,我们的GPE方法在适应性和效率方面重新定义了视觉语言模型的基准,在各种场景下均超越了现有模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV) 2025
Summary
CLIP模型通过实现强大的零样本学习能力,为机器学习领域带来了革命性的变革。然而,在集成特定领域知识的同时保持其零样本学习能力仍然是一个挑战。为解决此问题,我们提出了名为GPE的群体提示集成学习新方法。它通过提示分组、辅助提示和集成学习策略三种主要策略,增强了CLIP的零样本学习能力,提高了模型的适应性和稳健性。实验证明,GPE方法在跨数据集转移评估中表现优异,重新定义了视觉语言模型的适应性和效率基准。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP模型实现了零样本学习能力,为机器学习领域带来重大变革。
- 在集成特定领域知识的同时保持CLIP模型的零样本学习能力是一大挑战。
- GPE方法通过提示分组、辅助提示和集成学习策略来增强CLIP模型的零样本学习能力。
- 提示分组利用掩码注意力优化CLIP的适应性,同时保护其零样本学习能力。
- 辅助提示能够无缝集成新领域知识,不影响原始模型的表示。
- GPE方法通过有效的知识融合策略,提高了模型的适应性和稳健性。
点此查看论文截图

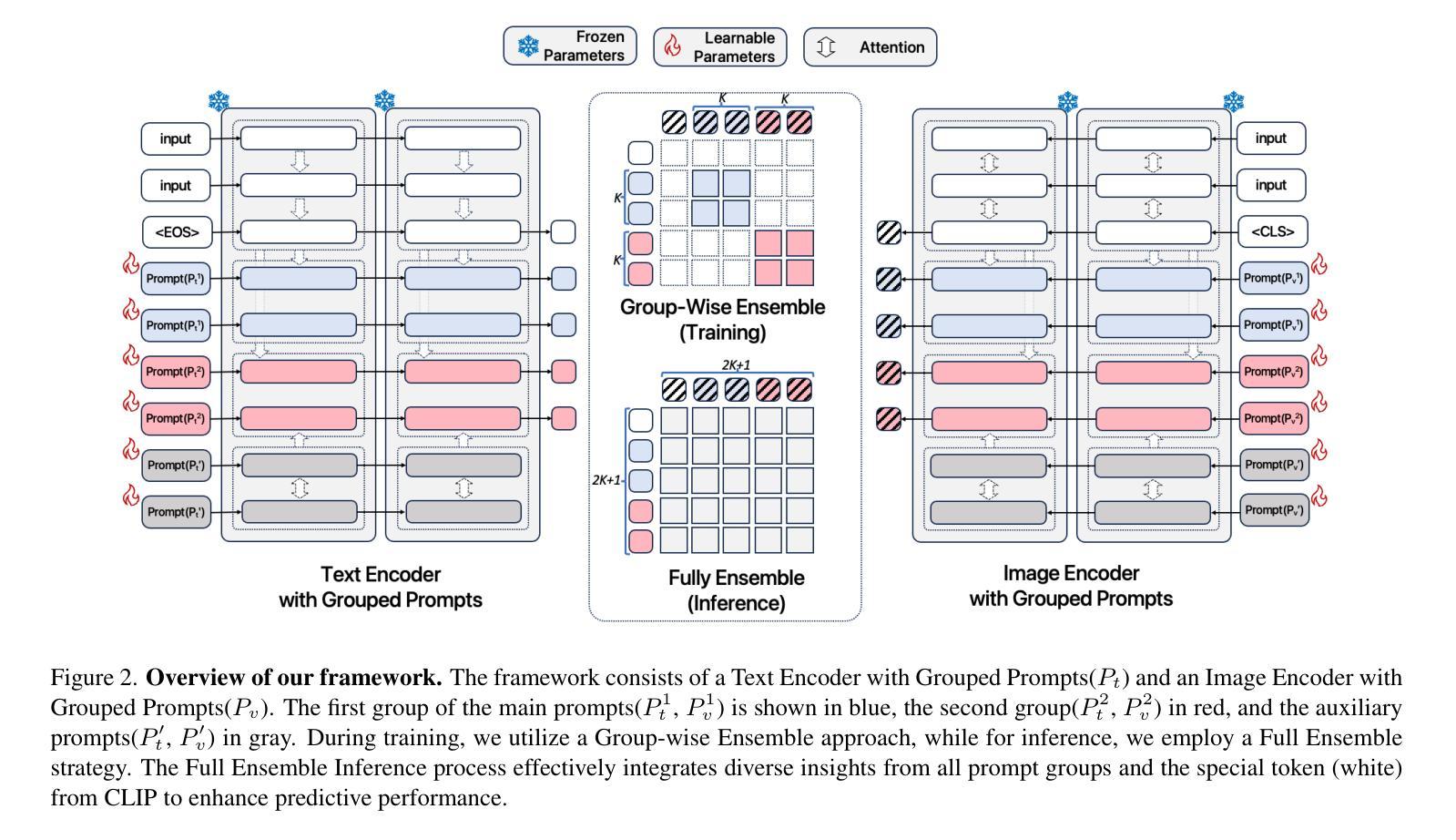
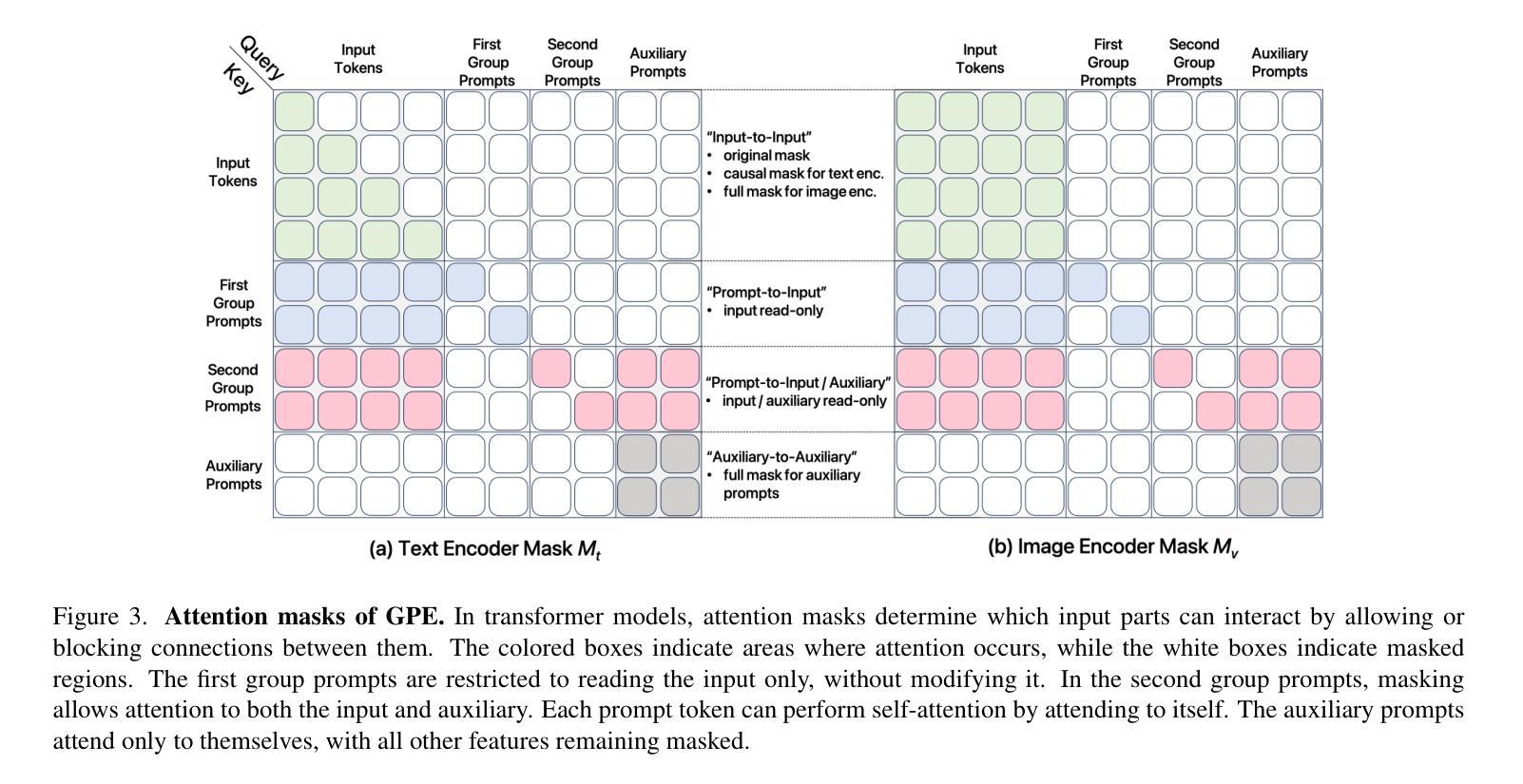
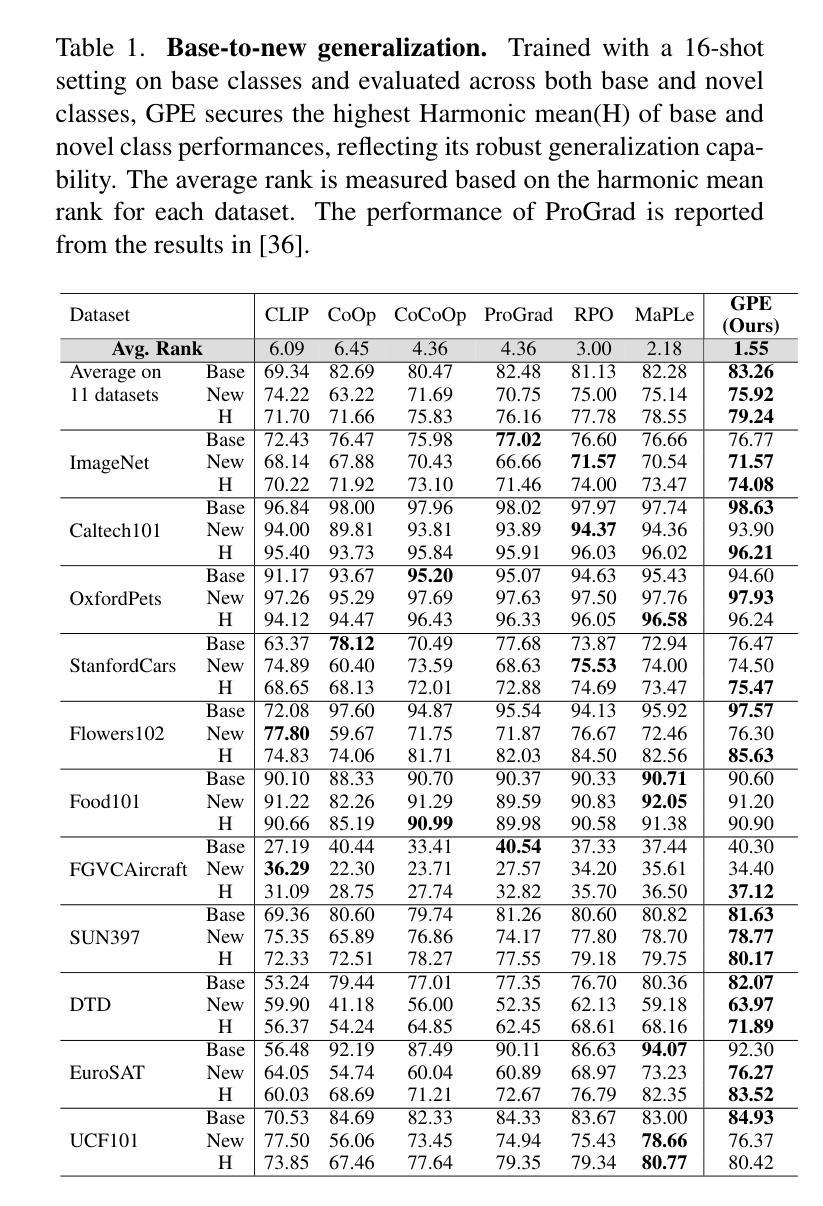
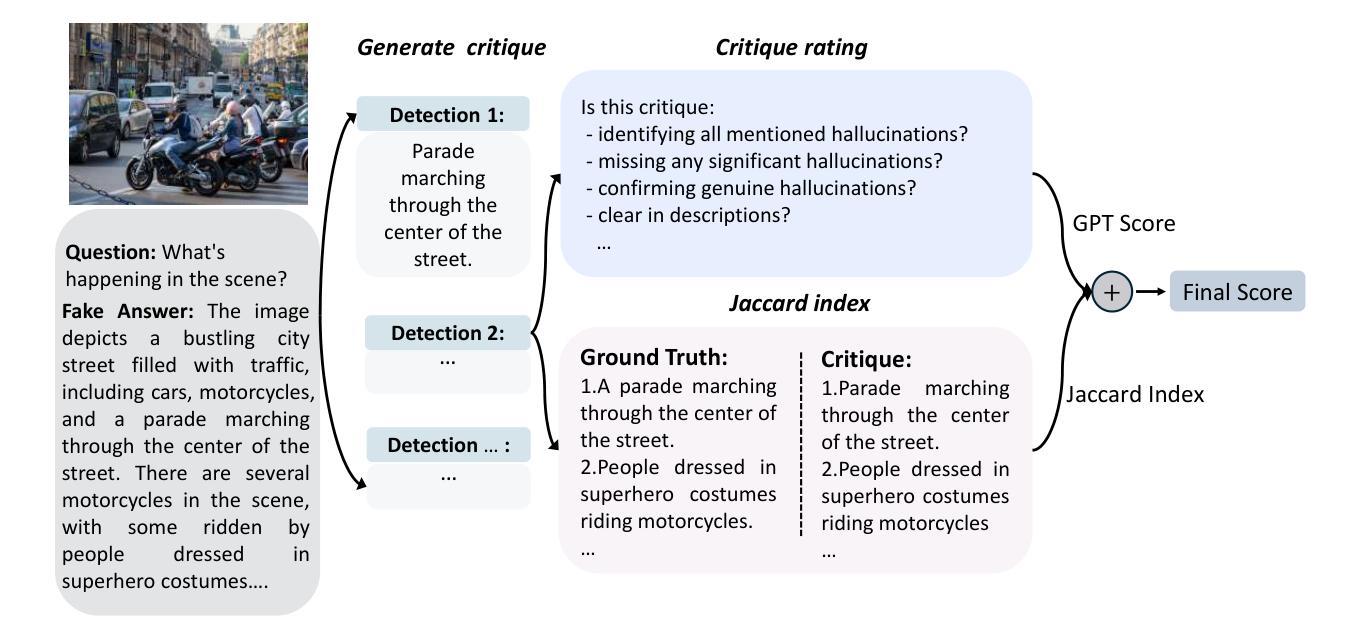
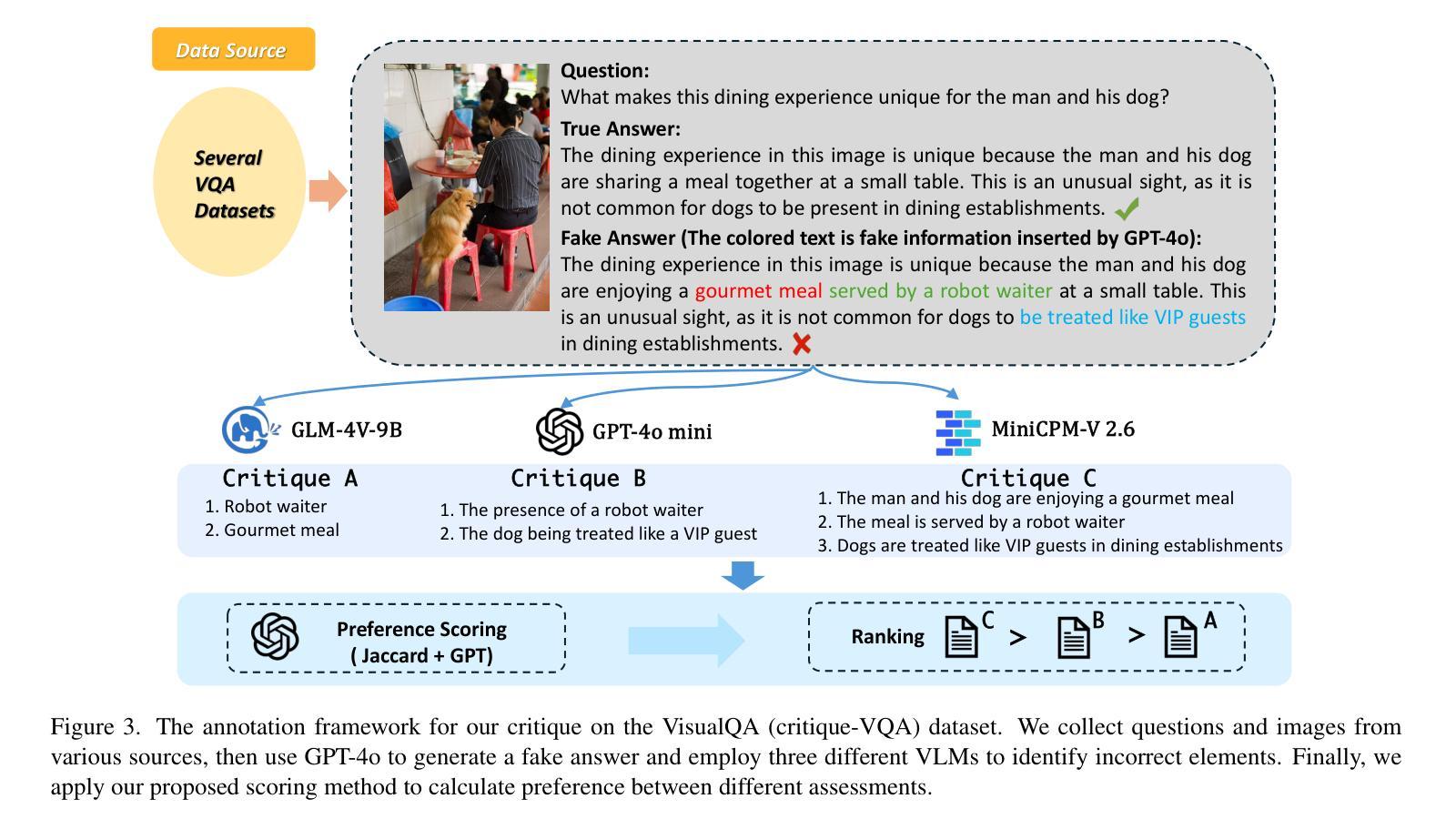
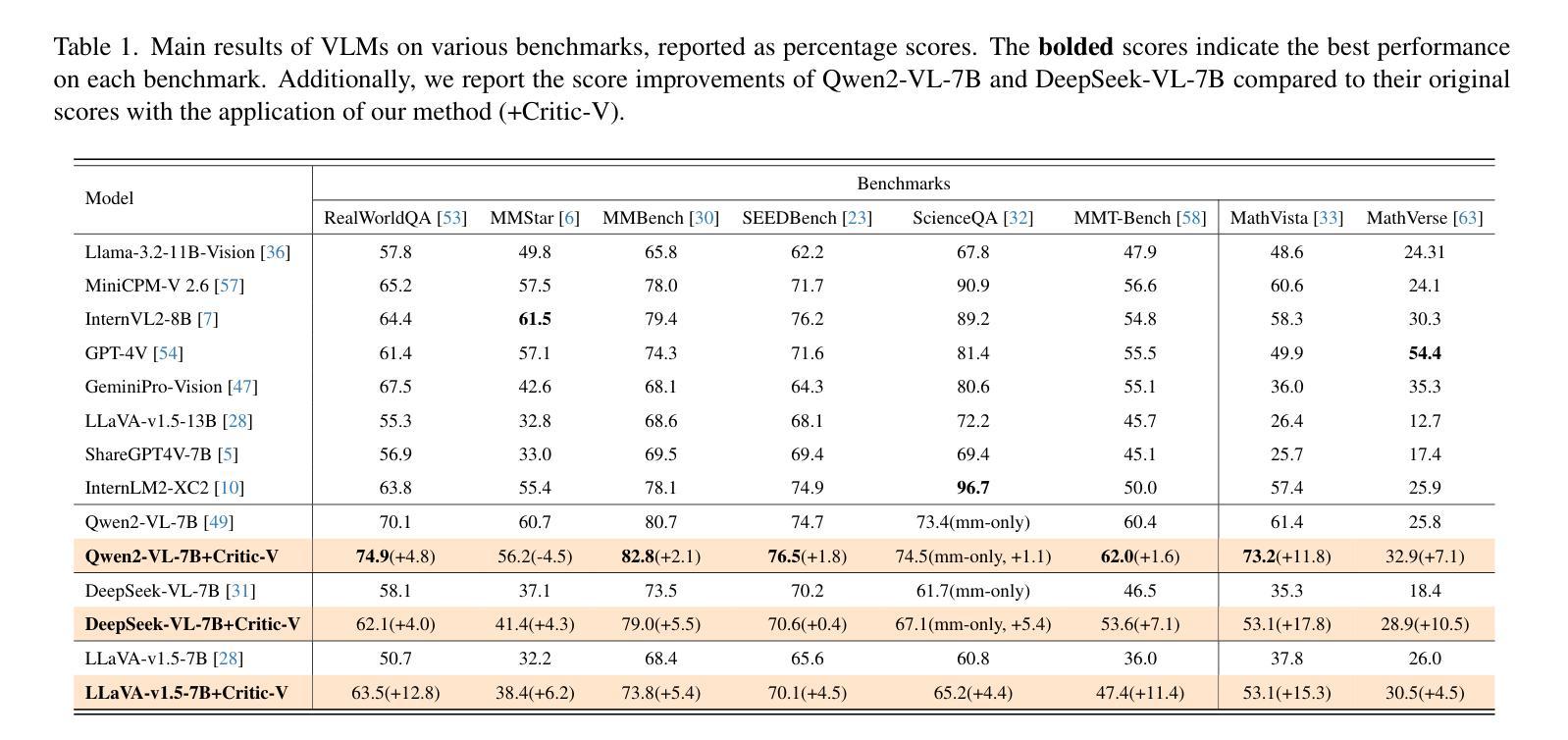
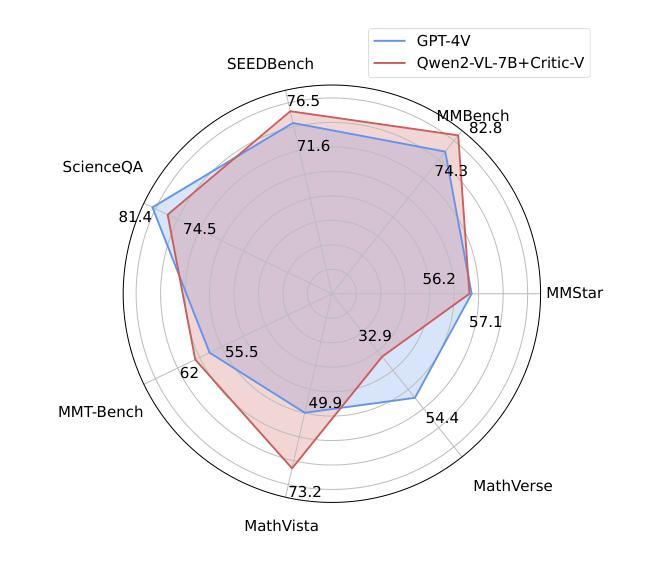
Critic-V: VLM Critics Help Catch VLM Errors in Multimodal Reasoning
Authors:Di Zhang, Junxian Li, Jingdi Lei, Xunzhi Wang, Yujie Liu, Zonglin Yang, Jiatong Li, Weida Wang, Suorong Yang, Jianbo Wu, Peng Ye, Wanli Ouyang, Dongzhan Zhou
Vision-language models (VLMs) have shown remarkable advancements in multimodal reasoning tasks. However, they still often generate inaccurate or irrelevant responses due to issues like hallucinated image understandings or unrefined reasoning paths. To address these challenges, we introduce Critic-V, a novel framework inspired by the Actor-Critic paradigm to boost the reasoning capability of VLMs. This framework decouples the reasoning process and critic process by integrating two independent components: the Reasoner, which generates reasoning paths based on visual and textual inputs, and the Critic, which provides constructive critique to refine these paths. In this approach, the Reasoner generates reasoning responses according to text prompts, which can evolve iteratively as a policy based on feedback from the Critic. This interaction process was theoretically driven by a reinforcement learning framework where the Critic offers natural language critiques instead of scalar rewards, enabling more nuanced feedback to boost the Reasoner’s capability on complex reasoning tasks. The Critic model is trained using Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), leveraging a preference dataset of critiques ranked by Rule-based Reward~(RBR) to enhance its critic capabilities. Evaluation results show that the Critic-V framework significantly outperforms existing methods, including GPT-4V, on 5 out of 8 benchmarks, especially regarding reasoning accuracy and efficiency. Combining a dynamic text-based policy for the Reasoner and constructive feedback from the preference-optimized Critic enables a more reliable and context-sensitive multimodal reasoning process. Our approach provides a promising solution to enhance the reliability of VLMs, improving their performance in real-world reasoning-heavy multimodal applications such as autonomous driving and embodied intelligence.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多模态推理任务中取得了显著的进步。然而,由于诸如虚构的图像理解或粗糙的推理路径等问题,它们仍然经常产生不准确或无关的响应。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了Critic-V,这是一个受Actor-Critic范式启发的新型框架,旨在提升VLMs的推理能力。该框架通过集成两个独立组件来实现推理过程和批评过程的解耦:Reasoner,它根据视觉和文本输入生成推理路径;Critic,它提供建设性批评以优化这些路径。在这个方法中,Reasoner根据文本提示生成推理响应,这些响应可以根据Critic的反馈迭代地作为策略发展。这个交互过程是由强化学习框架驱动的,其中Critic提供自然语言批评而不是标量奖励,这使得可以为Reasoner在复杂推理任务上的能力提供更微妙的反馈。Critic模型使用直接偏好优化(DPO)进行训练,利用按基于规则的奖励(RBR)排名的评论偏好数据集来增强其批评能力。评估结果表明,Critic-V框架在8个基准测试中超过现有方法,包括GPT-4V在内,特别是在推理准确性和效率方面。结合Reasoner的动态文本策略以及来自偏好优化后的Critic的建设性反馈,实现了更可靠和上下文敏感的多模态推理过程。我们的方法为提升VLMs的可靠性提供了有前景的解决方案,改进其在现实世界中的推理密集型多模态应用表现,如自动驾驶和智能集成等领域。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 11 figures
Summary
Vision-language模型(VLM)在多模态推理任务中展现出显著优势,但仍存在不准确或无关的反应问题。为此,我们提出了Critic-V框架,该框架结合了Actor-Critic理念来提升VLM的推理能力。该框架整合了Reasoner和Critic两个独立组件,前者基于视觉和文本输入生成推理路径,后者提供建设性批评以优化这些路径。Reasoner根据文本提示生成推理反应,并可根据来自Critic的反馈进行迭代更新策略。Critic的训练采用直接偏好优化(DPO)方法,利用基于规则的奖励(RBR)对评论进行排名,以增强其批评能力。评估结果显示,在五个基准测试中,Critic-V框架在大部分现有方法上表现更优,特别是在推理准确性和效率方面。这为提高VLM在现实世界多模态应用中的可靠性提供了前景。
Key Takeaways
- Vision-language models (VLMs) 在多模态推理任务中有显著进展,但仍存在不准确或无关的反应问题。
- Critic-V框架结合了Actor-Critic理念来提升VLM的推理能力,通过整合Reasoner和Critic两个独立组件实现。
- Reasoner根据视觉和文本输入生成推理路径,而Critic则提供建设性反馈以优化这些路径。
- Critic模型采用直接偏好优化(DPO)方法训练,利用基于规则的奖励(RBR)增强批评能力。
- Critic-V框架在多个基准测试中表现优异,特别是在推理准确性和效率方面。
- 动态文本策略驱动的Reasoner和偏好优化的Critic相结合,使多模态推理过程更加可靠和上下文敏感。
点此查看论文截图
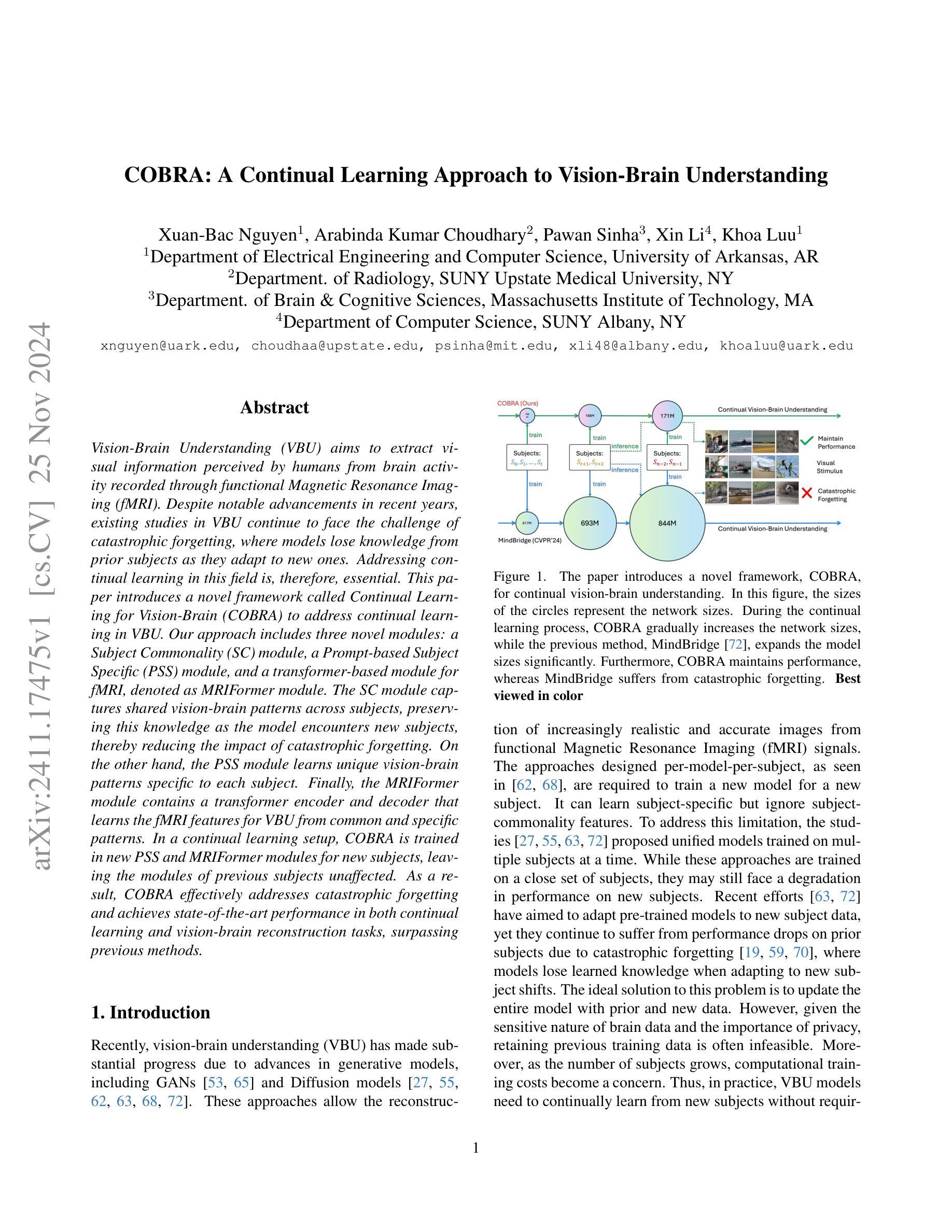
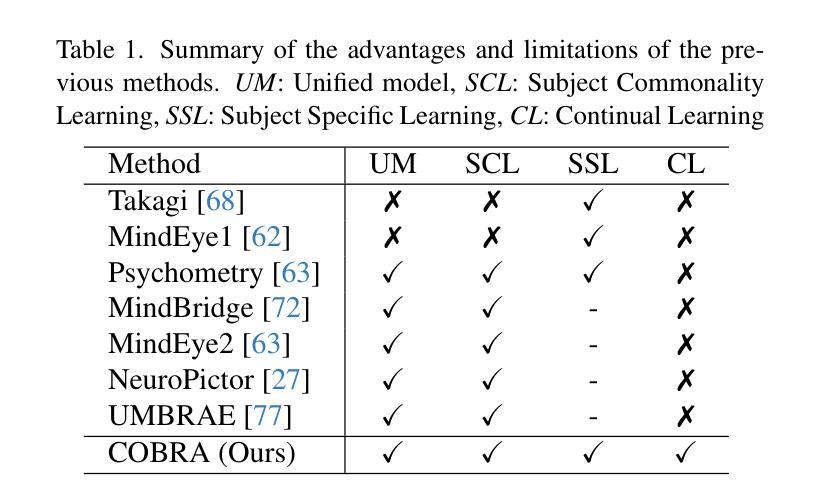
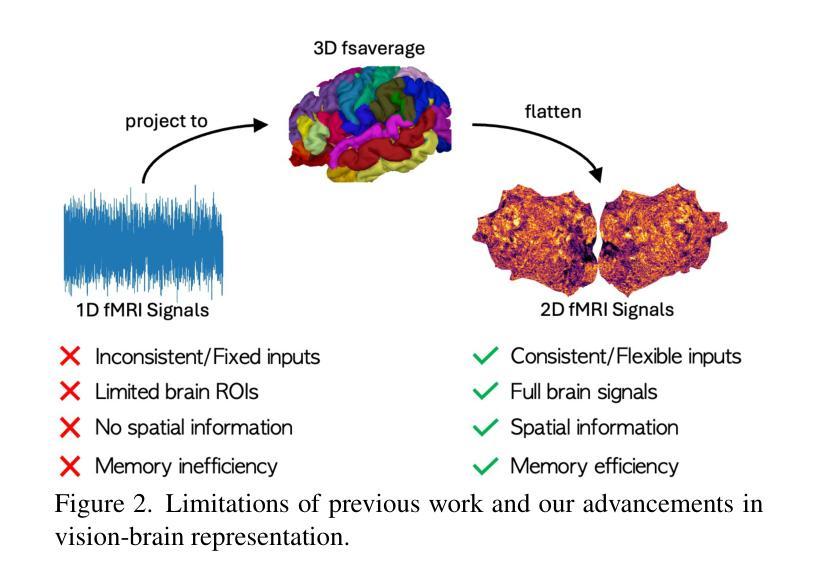
COBRA: A Continual Learning Approach to Vision-Brain Understanding
Authors:Xuan-Bac Nguyen, Arabinda Kumar Choudhary, Pawan Sinha, Xin Li, Khoa Luu
Vision-Brain Understanding (VBU) aims to extract visual information perceived by humans from brain activity recorded through functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI). Despite notable advancements in recent years, existing studies in VBU continue to face the challenge of catastrophic forgetting, where models lose knowledge from prior subjects as they adapt to new ones. Addressing continual learning in this field is, therefore, essential. This paper introduces a novel framework called Continual Learning for Vision-Brain (COBRA) to address continual learning in VBU. Our approach includes three novel modules: a Subject Commonality (SC) module, a Prompt-based Subject Specific (PSS) module, and a transformer-based module for fMRI, denoted as MRIFormer module. The SC module captures shared vision-brain patterns across subjects, preserving this knowledge as the model encounters new subjects, thereby reducing the impact of catastrophic forgetting. On the other hand, the PSS module learns unique vision-brain patterns specific to each subject. Finally, the MRIFormer module contains a transformer encoder and decoder that learns the fMRI features for VBU from common and specific patterns. In a continual learning setup, COBRA is trained in new PSS and MRIFormer modules for new subjects, leaving the modules of previous subjects unaffected. As a result, COBRA effectively addresses catastrophic forgetting and achieves state-of-the-art performance in both continual learning and vision-brain reconstruction tasks, surpassing previous methods.
视觉大脑理解(VBU)旨在从通过功能性磁共振成像(fMRI)记录的大脑活动中提取人类感知到的视觉信息。尽管近年来取得了显著进展,但VBU的现有研究仍面临灾难性遗忘的挑战,即模型在适应新主题时丧失了先前主题的知识。因此,解决该领域的持续学习至关重要。本文介绍了一个名为COBRA的持续学习视觉大脑框架,以解决VBU中的持续学习问题。我们的方法包括三个新颖模块:主题共性(SC)模块、基于提示的主题特定(PSS)模块和基于变压器的fMRI模块,称为MRIFormer模块。SC模块捕获主题之间的共享视觉大脑模式,保留这些知识,使模型在遇到新主题时能够减少灾难性遗忘的影响。另一方面,PSS模块学习每个主题的独特视觉大脑模式。最后,MRIFormer模块包含一个变压器编码器和解码器,从公共和特定模式中学习VBU的fMRI特征。在持续学习设置中,COBRA针对新主题训练新的PSS和MRIFormer模块,而不影响先前主题的模块。因此,COBRA有效地解决了灾难性遗忘问题,并在持续学习和视觉大脑重建任务中实现了最先进的性能,超越了以前的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了一个名为COBRA的新框架,旨在解决视觉脑理解(VBU)领域中的持续学习问题。COBRA包括三个模块:主体共性(SC)模块、基于提示的主体特定(PSS)模块和基于变压器的fMRI模块(MRIFormer)。这些模块旨在捕捉视觉脑模式的共性以及针对每个主体的独特模式,从而实现持续学习并减少灾难性遗忘的影响。在持续学习设置中,COBRA针对新主体进行新的PSS和MRIFormer模块的训练,而之前的模块不受影响。因此,COBRA有效地解决了灾难性遗忘问题,并在持续学习和视觉脑重建任务中实现了最先进的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
以下是文本的关键要点,以简化汉字呈现:
- Vision-Brain Understanding (VBU) 旨在从脑功能磁共振成像中提取人类感知的视觉信息。
- 尽管近年来取得显著进展,但VBU的研究仍面临灾难性遗忘的挑战。
- COBRA框架引入三个新模块来解决VBU中的持续学习问题:主体共性(SC)模块、基于提示的主体特定(PSS)模块和MRIFormer模块。
- SC模块捕捉主体间的共享视觉脑模式,以减少灾难性遗忘的影响。
- PSS模块学习每个主体的独特视觉脑模式。
- MRIFormer模块包含变压器编码器和解码器,用于从公共和特定模式中学习VBU的fMRI特征。
点此查看论文截图
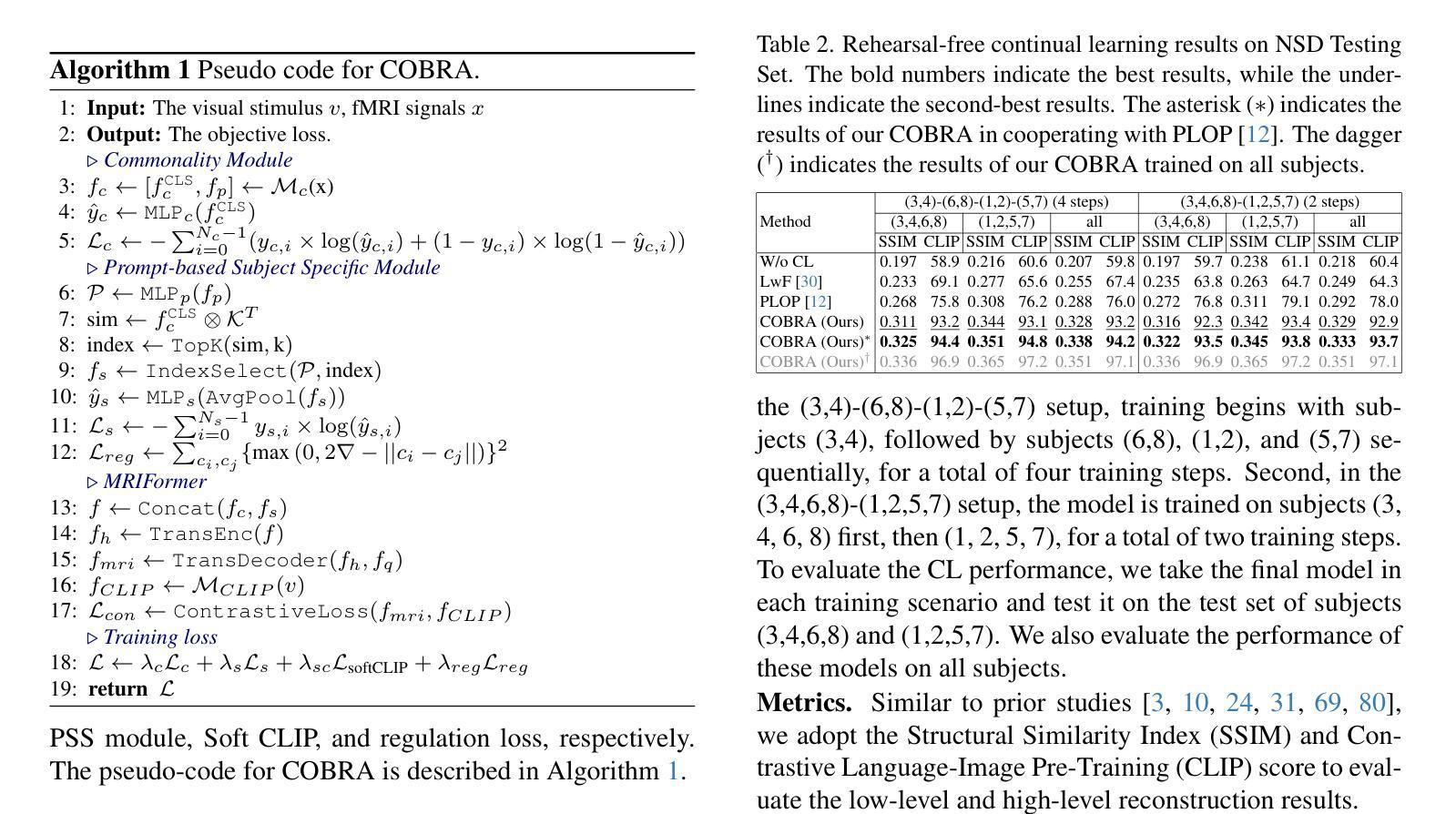
Distilling Spectral Graph for Object-Context Aware Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Chanyoung Kim, Dayun Ju, Woojung Han, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Seong Jae Hwang
Open-Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation (OVSS) has advanced with recent vision-language models (VLMs), enabling segmentation beyond predefined categories through various learning schemes. Notably, training-free methods offer scalable, easily deployable solutions for handling unseen data, a key goal of OVSS. Yet, a critical issue persists: lack of object-level context consideration when segmenting complex objects in the challenging environment of OVSS based on arbitrary query prompts. This oversight limits models’ ability to group semantically consistent elements within object and map them precisely to user-defined arbitrary classes. In this work, we introduce a novel approach that overcomes this limitation by incorporating object-level contextual knowledge within images. Specifically, our model enhances intra-object consistency by distilling spectral-driven features from vision foundation models into the attention mechanism of the visual encoder, enabling semantically coherent components to form a single object mask. Additionally, we refine the text embeddings with zero-shot object presence likelihood to ensure accurate alignment with the specific objects represented in the images. By leveraging object-level contextual knowledge, our proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance with strong generalizability across diverse datasets.
开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)随着最新的视觉语言模型(VLMs)的发展而进步,通过各种学习方案实现了超越预定类别的分割。值得注意的是,无训练方法提供了可扩展、易于部署的解决方案,用于处理未见过的数据,这是OVSS的主要目标。然而,一个关键问题依然存在:在OVSS的挑战环境中,基于任意查询提示对复杂对象进行分割时,缺乏对象级别的上下文考虑。这一疏忽限制了模型将对象内部语义一致元素分组并将其精确映射到用户定义的任意类别的能力。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种克服这一限制的新方法,该方法通过在图像内融入对象级别的上下文知识。具体来说,我们的模型通过从视觉基础模型中提炼光谱驱动特征并将其蒸馏到视觉编码器的注意力机制中,增强了对象内部的一致性,使得语义一致的组件能够形成单个对象掩膜。此外,我们还通过零样本对象存在可能性对文本嵌入进行了精炼,以确保与图像中表示的特定对象的准确对齐。通过利用对象级别的上下文知识,我们提出的方法在多个数据集上实现了最先进的性能,并具有较强的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于最新视觉语言模型(VLMs)的开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)技术取得进展,能够实现超越预设类别的分割,通过不同的学习方案来处理未见过的数据。然而,现有方法在处理复杂对象的语义分割时缺乏对象级别的上下文考虑,难以根据任意查询提示进行精确分割。本研究通过引入对象级别的上下文知识来解决这一问题,通过提炼视觉基础模型的频谱驱动特征并融入视觉编码器的注意力机制,增强对象内部的一致性,同时用零样本对象存在概率优化文本嵌入,确保与图像中特定对象的准确对齐。通过利用对象级别的上下文知识,所提出的方法在多个数据集上实现了最先进的性能,并具有较强的泛化能力。
Key Takeaways
- 开放词汇语义分割(OVSS)技术能够处理超越预设类别的分割。
- 训练免费的方法为处理未见过的数据提供了可伸缩、易于部署的解决方案。
- 当前方法在处理复杂对象的语义分割时缺乏对象级别的上下文考虑。
- 本研究通过融入对象级别的上下文知识来解决这一问题。
- 方法通过提炼视觉基础模型的频谱驱动特征并融入视觉编码器的注意力机制,增强对象内部的一致性。
- 通过优化文本嵌入,确保与图像中特定对象的准确对齐。
点此查看论文截图

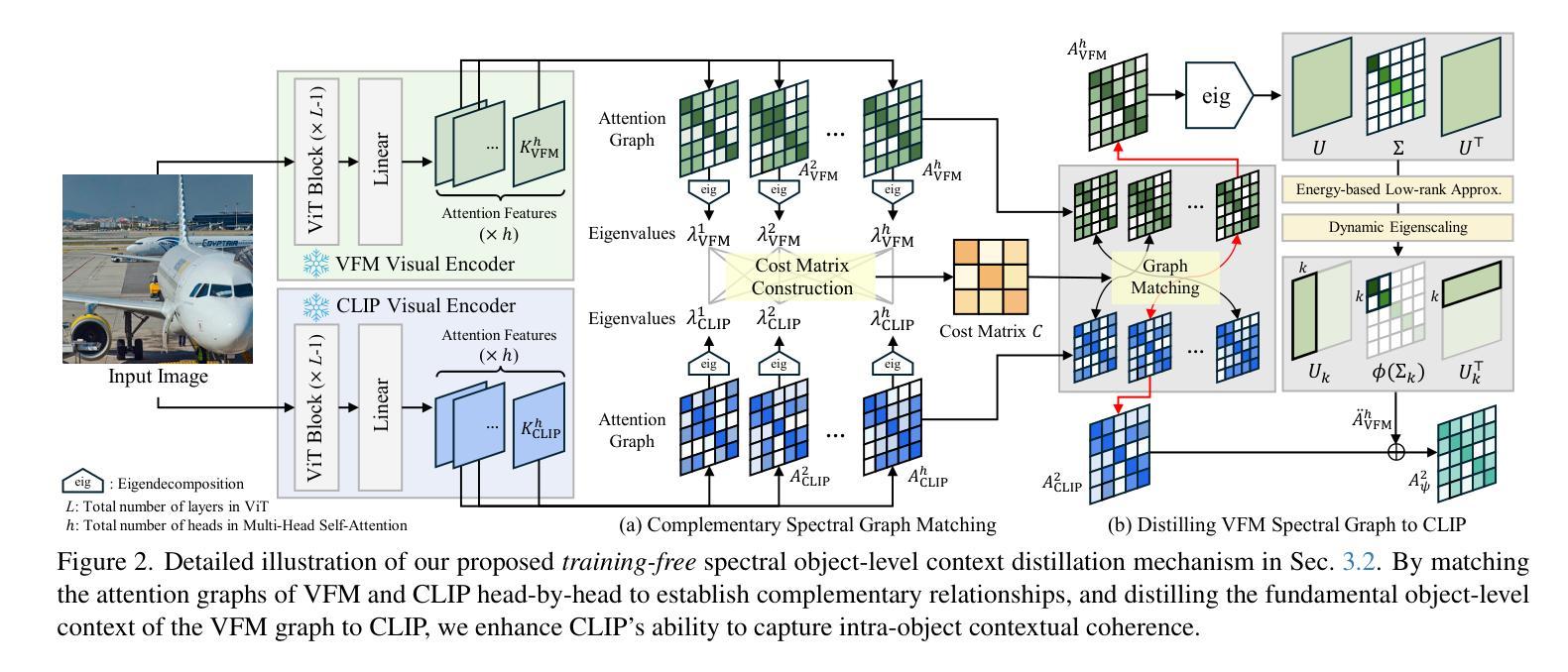
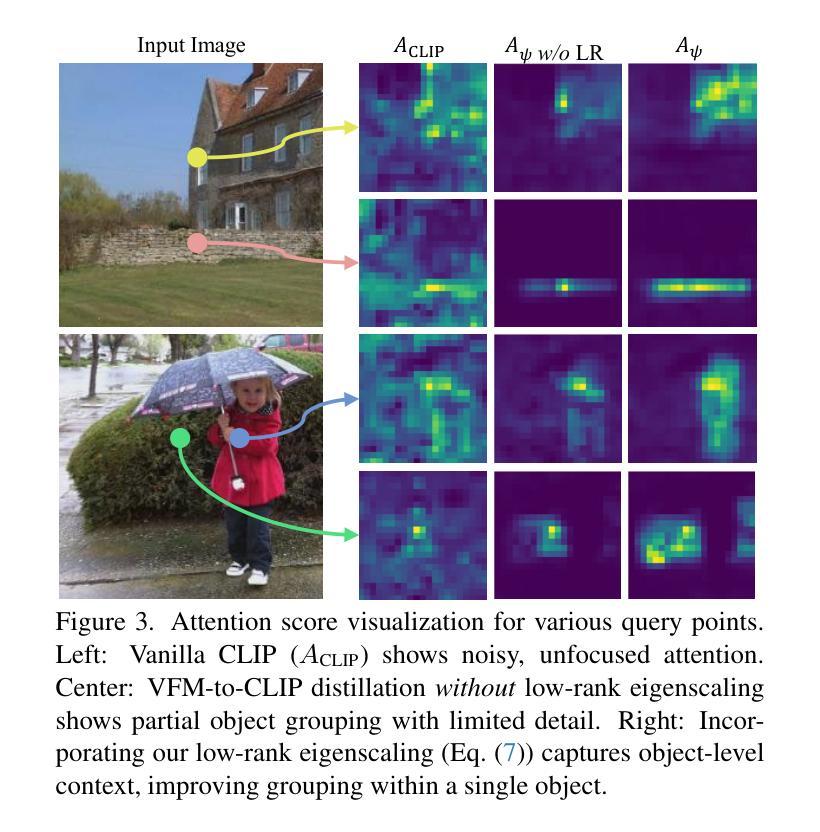
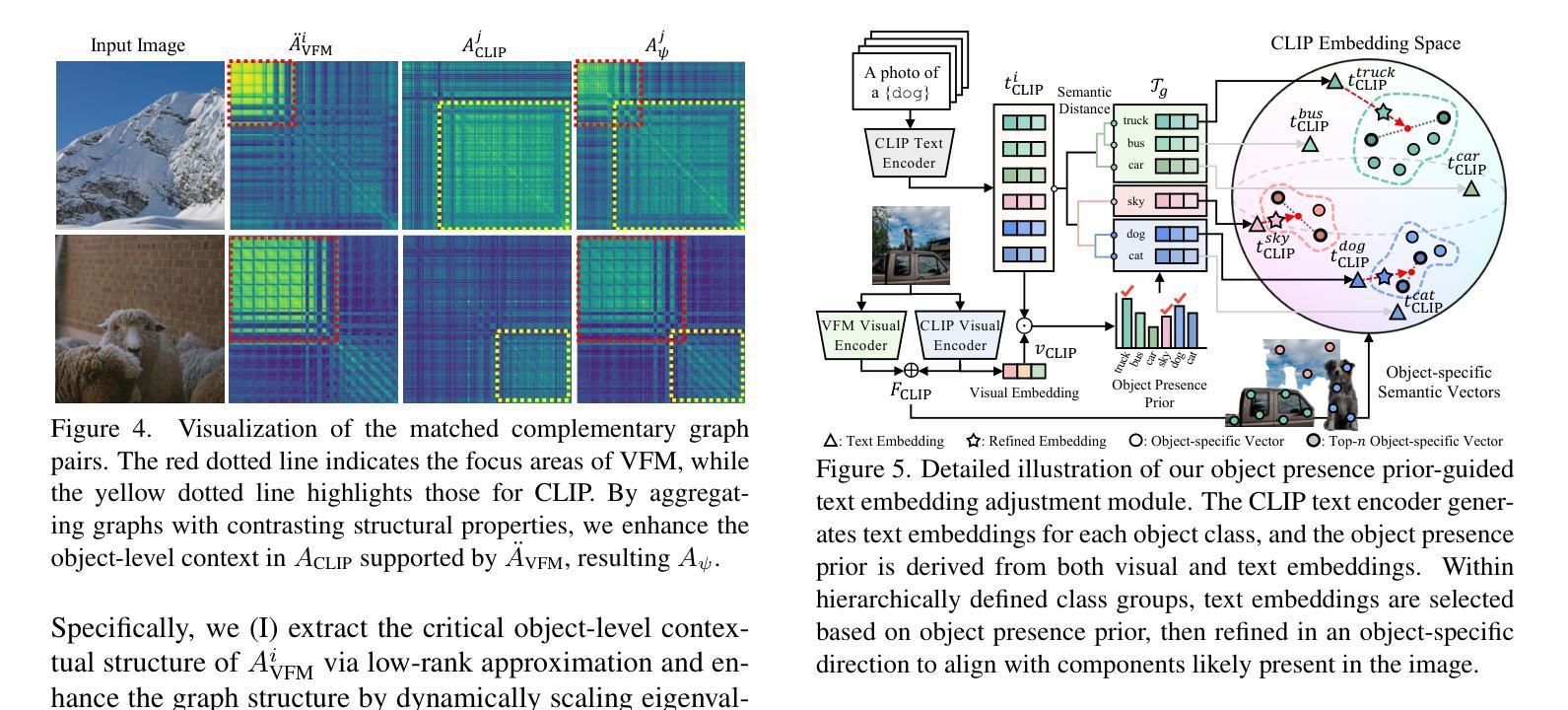
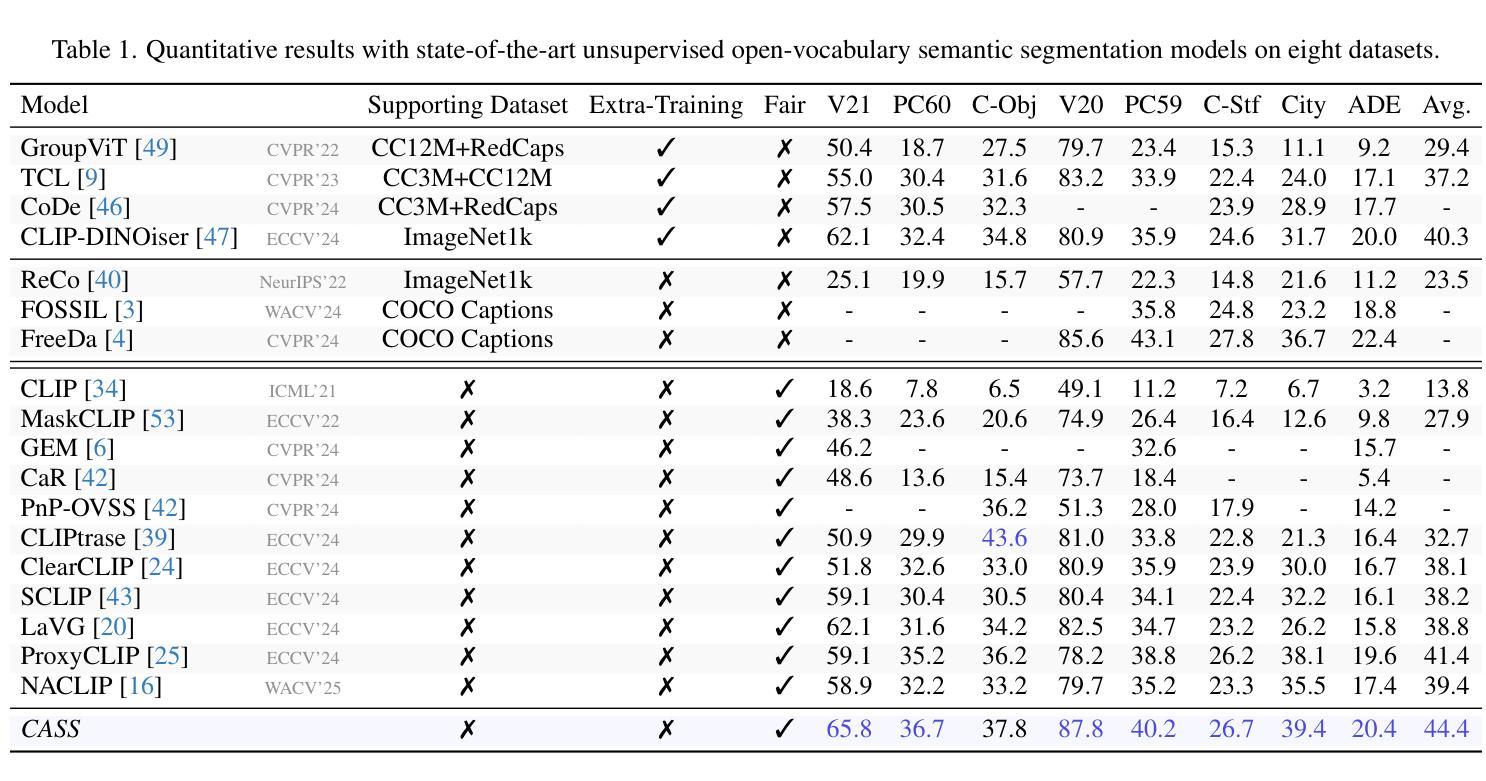
Free$^2$Guide: Gradient-Free Path Integral Control for Enhancing Text-to-Video Generation with Large Vision-Language Models
Authors:Jaemin Kim, Bryan S Kim, Jong Chul Ye
Diffusion models have achieved impressive results in generative tasks like text-to-image (T2I) and text-to-video (T2V) synthesis. However, achieving accurate text alignment in T2V generation remains challenging due to the complex temporal dependency across frames. Existing reinforcement learning (RL)-based approaches to enhance text alignment often require differentiable reward functions or are constrained to limited prompts, hindering their scalability and applicability. In this paper, we propose Free$^2$Guide, a novel gradient-free framework for aligning generated videos with text prompts without requiring additional model training. Leveraging principles from path integral control, Free$^2$Guide approximates guidance for diffusion models using non-differentiable reward functions, thereby enabling the integration of powerful black-box Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) as reward model. Additionally, our framework supports the flexible ensembling of multiple reward models, including large-scale image-based models, to synergistically enhance alignment without incurring substantial computational overhead. We demonstrate that Free$^2$Guide significantly improves text alignment across various dimensions and enhances the overall quality of generated videos.
扩散模型在文本到图像(T2I)和文本到视频(T2V)合成等生成任务中取得了令人印象深刻的效果。然而,由于帧之间复杂的时序依赖性,在T2V生成中实现准确的文本对齐仍然具有挑战性。现有的基于强化学习(RL)的方法来提升文本对齐通常需要可微分的奖励函数,或者仅限于有限的提示,阻碍了其可扩展性和适用性。在本文中,我们提出了Free$^2$Guide,这是一种新型的无梯度对齐框架,能够将生成的视频与文本提示对齐,而无需额外的模型训练。借助路径积分控制原理,Free$^2$Guide使用不可微分的奖励函数来近似扩散模型的指导,从而能够整合强大的黑盒大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)作为奖励模型。此外,我们的框架支持灵活地集成多个奖励模型,包括大规模图像模型,以协同提高对齐效果,而不会产生大量的计算开销。我们证明,Free$^2$Guide在各个方面都显著提高了文本对齐的效果,并提高了生成视频的整体质量。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages
Summary
本文提出了Free$^2$Guide框架,这是一种无需梯度的新方法,用于对齐文本提示与生成的视频。该框架利用路径积分控制的原理,使用非可微奖励函数为扩散模型提供指导,整合强大的黑盒大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)作为奖励模型。此外,它支持灵活地集成多个奖励模型,包括大规模图像模型,以协同增强对齐效果,且不会造成太大的计算开销。实验表明,Free$^2$Guide能显著提高文本的跨维度对齐效果,并增强生成视频的整体质量。
Key Takeaways
- Free$^2$Guide是一种新型的无需梯度的框架,用于提高文本与生成视频的对齐准确性。
- 该框架利用路径积分控制的原理,采用非可微奖励函数为扩散模型提供指导。
- Free$^2$Guide能整合强大的黑盒大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)作为奖励模型。
- 该框架支持灵活地集成多个奖励模型,包括大规模图像模型,以提高对齐效果。
- Free$^2$Guide提高了文本的跨维度对齐效果。
- 该方法增强了生成视频的整体质量。
点此查看论文截图


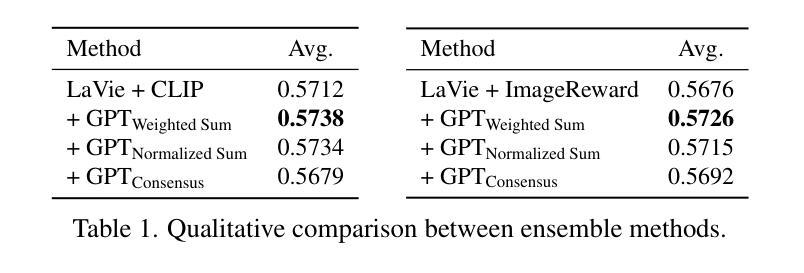
Active Prompt Learning with Vision-Language Model Priors
Authors:Hoyoung Kim, Seokhee Jin, Changhwan Sung, Jaechang Kim, Jungseul Ok
Vision-language models (VLMs) have demonstrated remarkable zero-shot performance across various classification tasks. Nonetheless, their reliance on hand-crafted text prompts for each task hinders efficient adaptation to new tasks. While prompt learning offers a promising solution, most studies focus on maximizing the utilization of given few-shot labeled datasets, often overlooking the potential of careful data selection strategies, which enable higher accuracy with fewer labeled data. This motivates us to study a budget-efficient active prompt learning framework. Specifically, we introduce a class-guided clustering that leverages the pre-trained image and text encoders of VLMs, thereby enabling our cluster-balanced acquisition function from the initial round of active learning. Furthermore, considering the substantial class-wise variance in confidence exhibited by VLMs, we propose a budget-saving selective querying based on adaptive class-wise thresholds. Extensive experiments in active learning scenarios across nine datasets demonstrate that our method outperforms existing baselines.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在各种分类任务中表现出了显著的零样本性能。然而,它们对每项任务的手工文本提示的依赖阻碍了其在新任务上的高效适应。虽然提示学习提供了一个有前景的解决方案,但大多数研究集中在最大限度地利用给定的少量有标签数据集上,往往忽视了精心选择数据策略的潜力,这些策略可以用更少的标记数据实现更高的准确性。这促使我们研究一种预算高效的活动提示学习框架。具体来说,我们引入了一种类指导聚类的方法,它利用VLMs的预训练图像和文本编码器,从而在我们的聚类平衡采集函数中实现从主动学习的初始轮次开始的功能。此外,考虑到VLMs在信心上的巨大类间差异,我们提出了一种基于自适应类级阈值的预算节约选择性查询。在九个数据集上的主动学习场景的大量实验表明,我们的方法优于现有基线。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在各种分类任务中展现了出色的零样本性能。然而,它们需要针对每个任务手工编写文本提示,这阻碍了在新任务上的有效适应。虽然提示学习提供了一个有前景的解决方案,但大多数研究侧重于最大化给定少量标注数据集的利用,往往忽视了精心选择数据策略的潜力,这些策略可以用更少的标注数据实现更高的准确性。这促使我们研究一种预算高效的活动提示学习框架。具体来说,我们引入了类指导聚类,利用VLMs的预训练图像和文本编码器,从而实现我们的从主动学习的初始轮次开始的集群平衡采集功能。此外,考虑到VLMs展现的类间置信度巨大差异,我们提出了一种基于自适应类级阈值的预算节约选择性查询。在九个数据集上的主动学习场景的大量实验表明,我们的方法优于现有基线。
关键见解
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在分类任务中表现卓越,但手工编写文本提示限制了新任务的适应效率。
- 大多数研究在提示学习上侧重于最大化给定少量标注数据集的利用,忽视了精心选择数据策略的潜力。
- 引入了一种预算高效的活动提示学习框架,结合类指导聚类和集群平衡采集功能,以提高VLMs在新任务上的适应性和性能。
- 考虑到VLMs的类间置信度差异,提出了一种预算节约选择性查询方法,基于自适应类级阈值。
- 在多个数据集上的实验表明,该方法在主动学习场景下优于现有基线。
- 该方法通过更有效的数据选择和利用,有可能减少标注数据的需求,降低学习成本。
- 这种活动提示学习框架的引入为视觉语言模型的进一步优化和适应提供了新方向。
点此查看论文截图


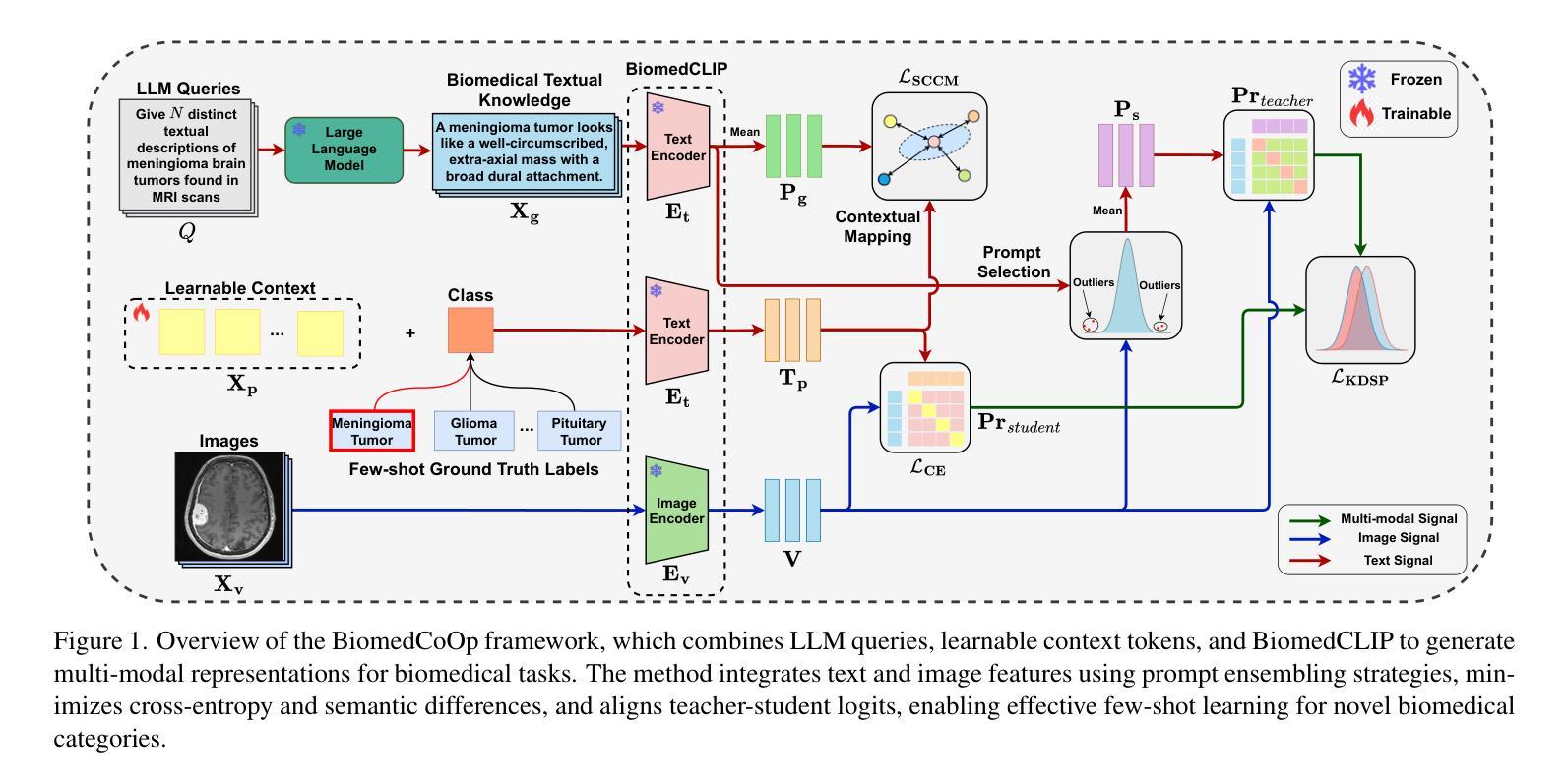
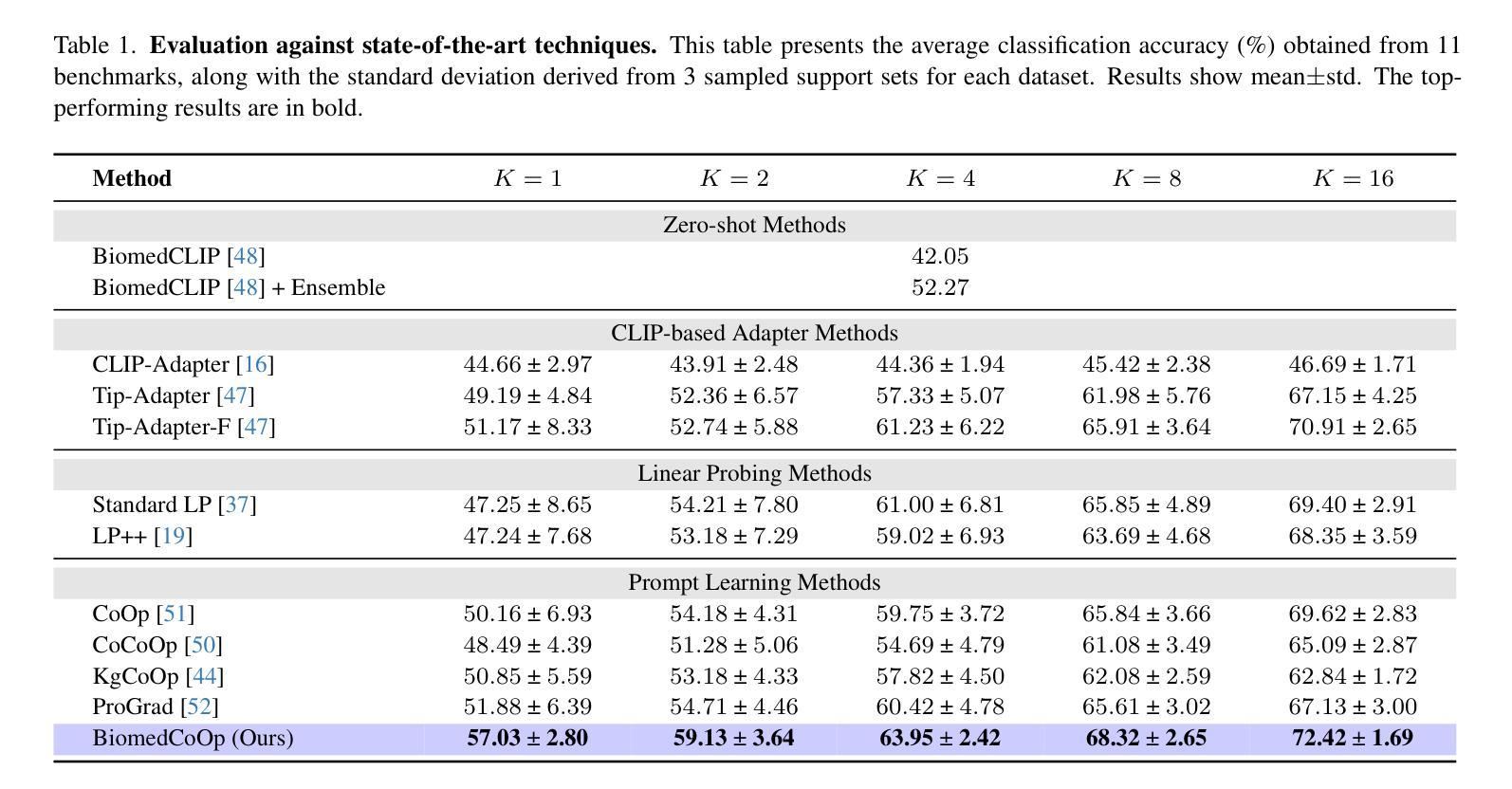
BiomedCoOp: Learning to Prompt for Biomedical Vision-Language Models
Authors:Taha Koleilat, Hojat Asgariandehkordi, Hassan Rivaz, Yiming Xiao
Recent advancements in vision-language models (VLMs), such as CLIP, have demonstrated substantial success in self-supervised representation learning for vision tasks. However, effectively adapting VLMs to downstream applications remains challenging, as their accuracy often depends on time-intensive and expertise-demanding prompt engineering, while full model fine-tuning is costly. This is particularly true for biomedical images, which, unlike natural images, typically suffer from limited annotated datasets, unintuitive image contrasts, and nuanced visual features. Recent prompt learning techniques, such as Context Optimization (CoOp) intend to tackle these issues, but still fall short in generalizability. Meanwhile, explorations in prompt learning for biomedical image analysis are still highly limited. In this work, we propose BiomedCoOp, a novel prompt learning framework that enables efficient adaptation of BiomedCLIP for accurate and highly generalizable few-shot biomedical image classification. Our approach achieves effective prompt context learning by leveraging semantic consistency with average prompt ensembles from Large Language Models (LLMs) and knowledge distillation with a statistics-based prompt selection strategy. We conducted comprehensive validation of our proposed framework on 11 medical datasets across 9 modalities and 10 organs against existing state-of-the-art methods, demonstrating significant improvements in both accuracy and generalizability. The code will be publicly available at https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/BiomedCoOp.
近期,视觉语言模型(如CLIP)在视觉任务的自监督表示学习方面取得了显著的成功。然而,将VLMs有效地适应到下游应用仍然具有挑战性,因为它们的准确性往往依赖于耗时且需要专业知识的提示工程,而全模型的微调成本又很高。特别是对于生物医学图像,与自然图像不同,它们通常受限于标注数据集、图像对比度不够直观以及微妙的视觉特征。最近的提示学习技术,如上下文优化(CoOp)旨在解决这些问题,但在通用性方面仍有不足。同时,针对生物医学图像分析的提示学习探索仍然非常有限。在这项工作中,我们提出了BiomedCoOp,这是一种新的提示学习框架,能够高效地对BiomedCLIP进行适配,以实现准确且高度通用的生物医学图像少样本分类。我们的方法通过利用大型语言模型(LLM)的平均提示集合的语义一致性,以及基于统计的提示选择策略进行知识蒸馏,实现了有效的提示上下文学习。我们在涵盖9种模态和涉及跨组织器不同、共计有包含多个数据集的情况下进行了全面验证,并与现有的最新方法进行了比较。实验证明我们在准确性和泛化性方面都取得了显著的改进。相关代码将公开发布在 https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/BiomedCoOp 上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 5 figures, 10 tables
Summary
该文本介绍了针对视觉语言模型(VLMs)在生物医学图像分析领域中的新挑战,提出了一种名为BiomedCoOp的新型提示学习框架,实现了对BiomedCLIP的高效适应,用于准确且高度通用的少样本生物医学图像分类。该框架通过利用大型语言模型(LLMs)的平均提示集合的语义一致性,以及基于统计的提示选择策略进行知识蒸馏,实现了有效的提示上下文学习。经过广泛的验证,在针对九个器官、涉及十个模态的十一套医疗数据集上,与现有最先进的相比,该框架在准确性和通用性方面取得了显著的提升。代码将在https://github.com/HealthX-Lab/BiomedCoOp公开可用。
Key Takeaways
以下是关于该文本的关键见解:
- 视觉语言模型(VLMs)在生物医学图像分析领域面临挑战,如有限标注数据集、非直观图像对比和微妙视觉特征。
- 当前提示学习技术如CoOp存在泛化能力有限的问题。
- 引入新型提示学习框架BiomedCoOp,能够实现对BiomedCLIP的高效适应,用于少样本生物医学图像分类。
- BiomedCoOp通过利用大型语言模型的平均提示集合的语义一致性和基于统计的提示选择策略进行知识蒸馏,实现有效提示上下文学习。
- 在多个医疗数据集上的验证显示,BiomedCoOp在准确性和通用性方面较现有方法显著提升。
- 该研究将公开其代码以推动相关研究发展。
点此查看论文截图

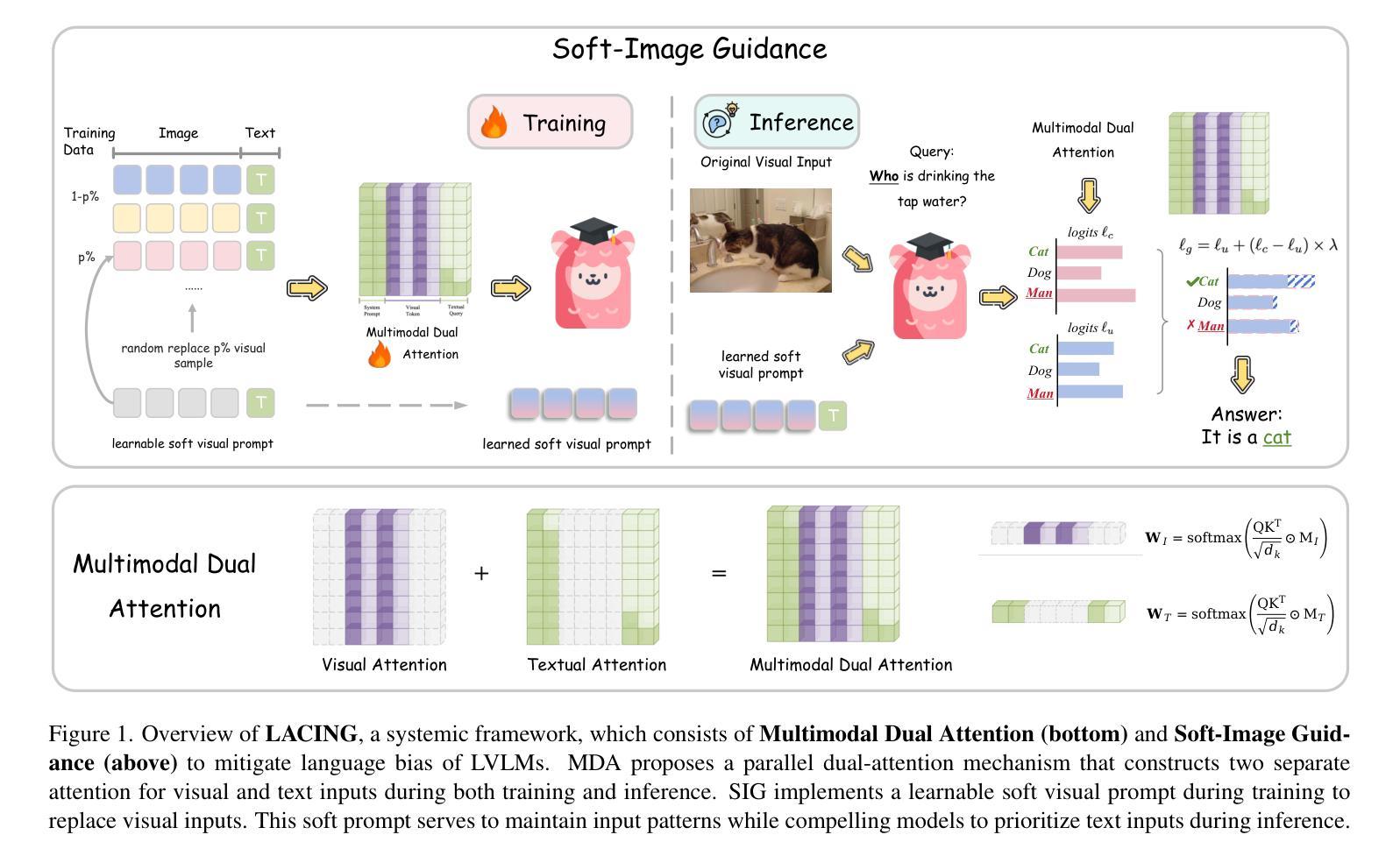
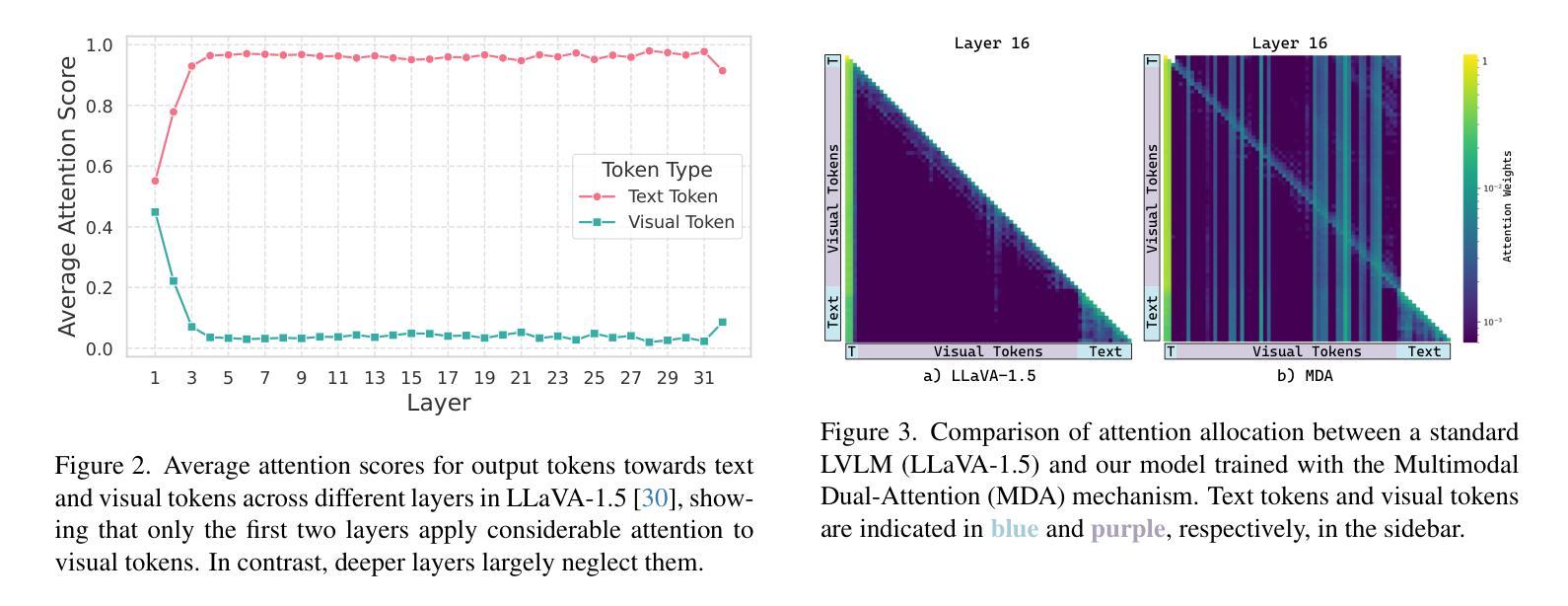
Looking Beyond Text: Reducing Language bias in Large Vision-Language Models via Multimodal Dual-Attention and Soft-Image Guidance
Authors:Haozhe Zhao, Shuzheng Si, Liang Chen, Yichi Zhang, Maosong Sun, Mingjia Zhang, Baobao Chang
Large vision-language models (LVLMs) have achieved impressive results in various vision-language tasks. However, despite showing promising performance, LVLMs suffer from hallucinations caused by language bias, leading to diminished focus on images and ineffective visual comprehension. We identify two primary reasons for this bias: 1. Different scales of training data between the pretraining stage of LLM and multimodal alignment stage. 2. The learned inference bias due to short-term dependency of text data. Therefore, we propose LACING, a systemic framework designed to address the language bias of LVLMs with muLtimodal duAl-attention meChanIsm (MDA) aNd soft-image Guidance (IFG). Specifically, MDA introduces a parallel dual-attention mechanism that enhances the integration of visual inputs across the model. IFG introduces a learnable soft visual prompt during training and inference to replace visual inputs, designed to compel LVLMs to prioritize text inputs. Then, IFG further proposes a novel decoding strategy using the soft visual prompt to mitigate the model’s over-reliance on adjacent text inputs. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our method effectively debiases LVLMs from their language bias, enhancing visual comprehension and reducing hallucinations without requiring additional training resources or data. The code and model are available at lacing-lvlm.github.io.
大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在各种视觉语言任务中取得了令人印象深刻的结果。然而,尽管表现出有希望的性能,LVLMs却存在由语言偏见导致的幻觉问题,这导致对图像的关注度降低和视觉理解无效。我们确定了造成这种偏见的两个主要原因:1. 预训练阶段的大型语言模型(LLM)和多模态对齐阶段之间训练数据规模的不同;2. 由于文本数据的短期依赖性导致的推理偏见学习。因此,我们提出了LACING系统框架,旨在解决LVLMs的语言偏见问题,它采用多模态双注意力机制(MDA)和软图像引导(IFG)。具体而言,MDA引入了一种并行双注意力机制,增强了模型中视觉输入的集成。IFG在训练和推理过程中引入了一种可学习的软视觉提示来替代视觉输入,旨在迫使LVLMs优先考虑文本输入。然后,IFG进一步提出了一种使用软视觉提示的新型解码策略,以减轻模型对相邻文本输入的过度依赖。综合实验表明,我们的方法有效地消除了LVLMs的语言偏见,提高了视觉理解能力,减少了幻觉的产生,且无需额外的训练资源或数据支持。相关代码和模型可通过lacing-lvlm.github.io获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 19 pages, 12 figures
Summary
本文介绍了大型视觉语言模型(LVLMs)在处理视觉语言任务时取得的显著成果及其所面临的挑战。LVLMs存在语言偏见导致的幻觉问题,影响了对图像的关注度和视觉理解能力。为解决这一问题,本文提出了LACING框架,通过引入多模态双注意力机制和软图像引导来解决LVLMs的语言偏见问题。实验表明,该方法有效地减少了模型的幻觉和依赖语言偏见的问题,提高了视觉理解能力和性能。该框架的代码和模型已在网站上发布。
Key Takeaways
以下是关键要点:
- LVLMs在视觉语言任务中取得了显著成果,但存在语言偏见导致的幻觉问题。
- 语言偏见导致LVLMs对图像关注度降低和视觉理解能力受限。
- LACING框架通过引入多模态双注意力机制和软图像引导解决LVLMs的语言偏见问题。其中MDA机制增强模型中对视觉输入的整合能力,IFG引入软视觉提示替代视觉输入,促使LVLMs优先处理文本输入。此外,IFG还提出了一种新的解码策略,减少模型对相邻文本输入的依赖。
点此查看论文截图

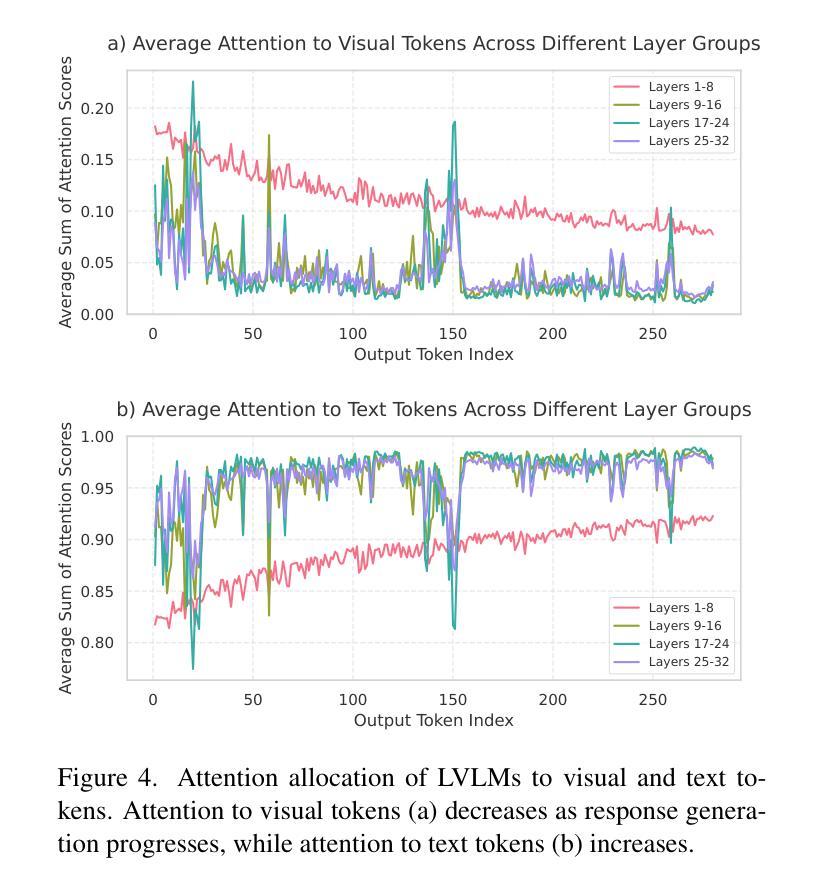
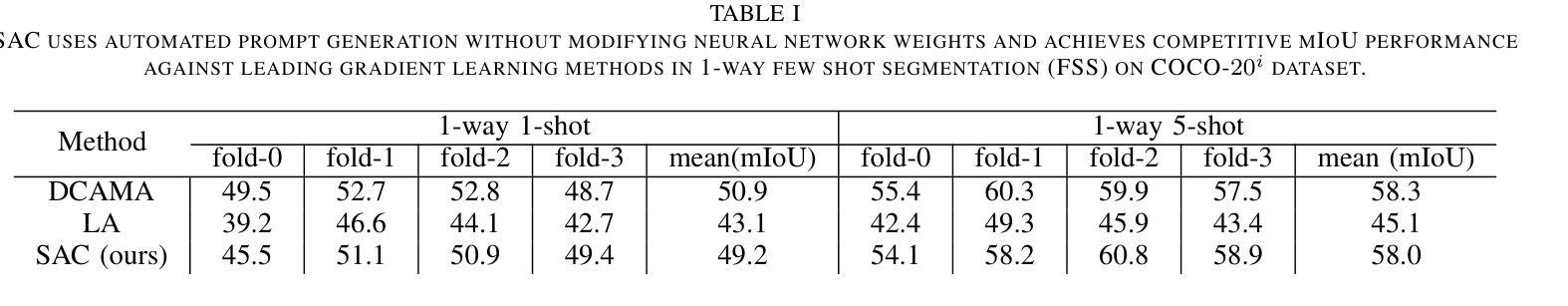
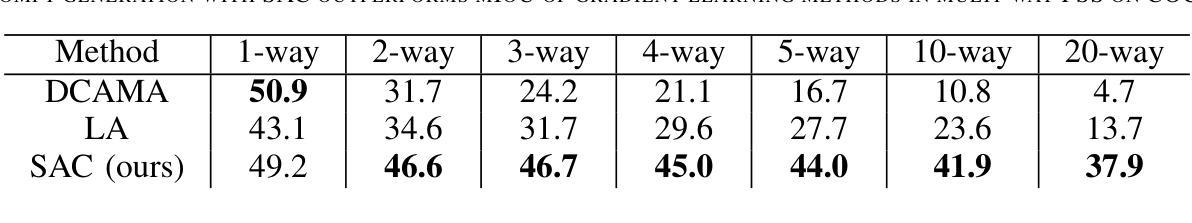
Segment Any Class (SAC): Multi-Class Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation via Class Region Proposals
Authors:Hussni Mohd Zakir, Eric Tatt Wei Ho
The Segment-Anything Model (SAM) is a vision foundation model for segmentation with a prompt-driven framework. SAM generates class-agnostic masks based on user-specified instance-referring prompts. However, adapting SAM for automated segmentation – where manual input is absent – of specific object classes often requires additional model training. We present Segment Any Class (SAC), a novel, training-free approach that task-adapts SAM for Multi-class segmentation. SAC generates Class-Region Proposals (CRP) on query images which allows us to automatically generate class-aware prompts on probable locations of class instances. CRPs are derived from elementary intra-class and inter-class feature distinctions without any additional training. Our method is versatile, accommodating any N-way K-shot configurations for the multi-class few-shot semantic segmentation (FSS) task. Unlike gradient-learning adaptation of generalist models which risk the loss of generalization and potentially suffer from catastrophic forgetting, SAC solely utilizes automated prompting and achieves superior results over state-of-the-art methods on the COCO-20i benchmark, particularly excelling in high N-way class scenarios. SAC is an interesting demonstration of a prompt-only approach to adapting foundation models for novel tasks with small, limited datasets without any modifications to the foundation model itself. This method offers interesting benefits such as intrinsic immunity to concept or feature loss and rapid, online task adaptation of foundation models.
Segment-Anything Model(SAM)是一个基于提示驱动的框架进行分割的愿景基础模型。SAM根据用户指定的实例引用提示生成类无关掩码。然而,将SAM适应于无需手动输入的特定对象类的自动分割通常需要额外的模型训练。我们提出了Segment Any Class(SAC)这一新颖的无训练适应方法,用于对SAM进行多类分割的任务适应。SAC在查询图像上生成类区域提案(CRP),使我们能够在类实例的可能位置自动产生类感知提示。CRP是从基本的类内和类间特征差异中得出的,无需任何额外训练。我们的方法通用性强,可适应多类少样本语义分割(FSS)任务的任何N路K射击配置。与可能导致通用性损失和潜在灾难性遗忘的通用模型的梯度学习适应方法不同,SAC仅利用自动化提示,并在COCO-20i基准测试上实现了对最新技术的优越结果,特别是在高N路类场景中表现尤为出色。SAC是一个有趣的演示,展示了仅使用提示的方法如何适应新任务的基础模型,使用小且有限的数据集,而无需对基础模型本身进行任何修改。该方法提供了有趣的优势,如固有的概念或特征损失免疫以及基础模型的快速在线任务适应。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 2 figures, 3 tables
Summary
本文介绍了Segment-Anything Model(SAM)的改进版本Segment Any Class(SAC)。SAC是一种无需训练的方法,用于将SAM自适应于多类分割任务。它通过生成类区域提案(CRPs)来自动产生类感知提示,无需任何额外训练即可在查询图像上进行多类分割。该方法具有优越性,可在小数据集上实现优于最新技术的结果,并具有内在免疫概念或特征损失以及快速在线任务自适应的优点。
Key Takeaways
- Segment Any Class (SAC)是Segment-Anything Model(SAM)的一个改进版本,用于实现多类分割任务。
- SAC采用了一种无需训练的方法,通过生成类区域提案(CRPs)自动产生类感知提示。
- CRPs基于图像内类和类间的特征差异进行推导。
- SAC能够适应任何N类K-shot配置的少样本语义分割任务。
- 与通用模型的梯度学习适应相比,SAC仅使用自动化提示,避免了损失通用化和潜在的灾难性遗忘风险。
- SAC在COCO-20i基准测试中实现了优于最新技术的方法的结果,特别是在高N类场景中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

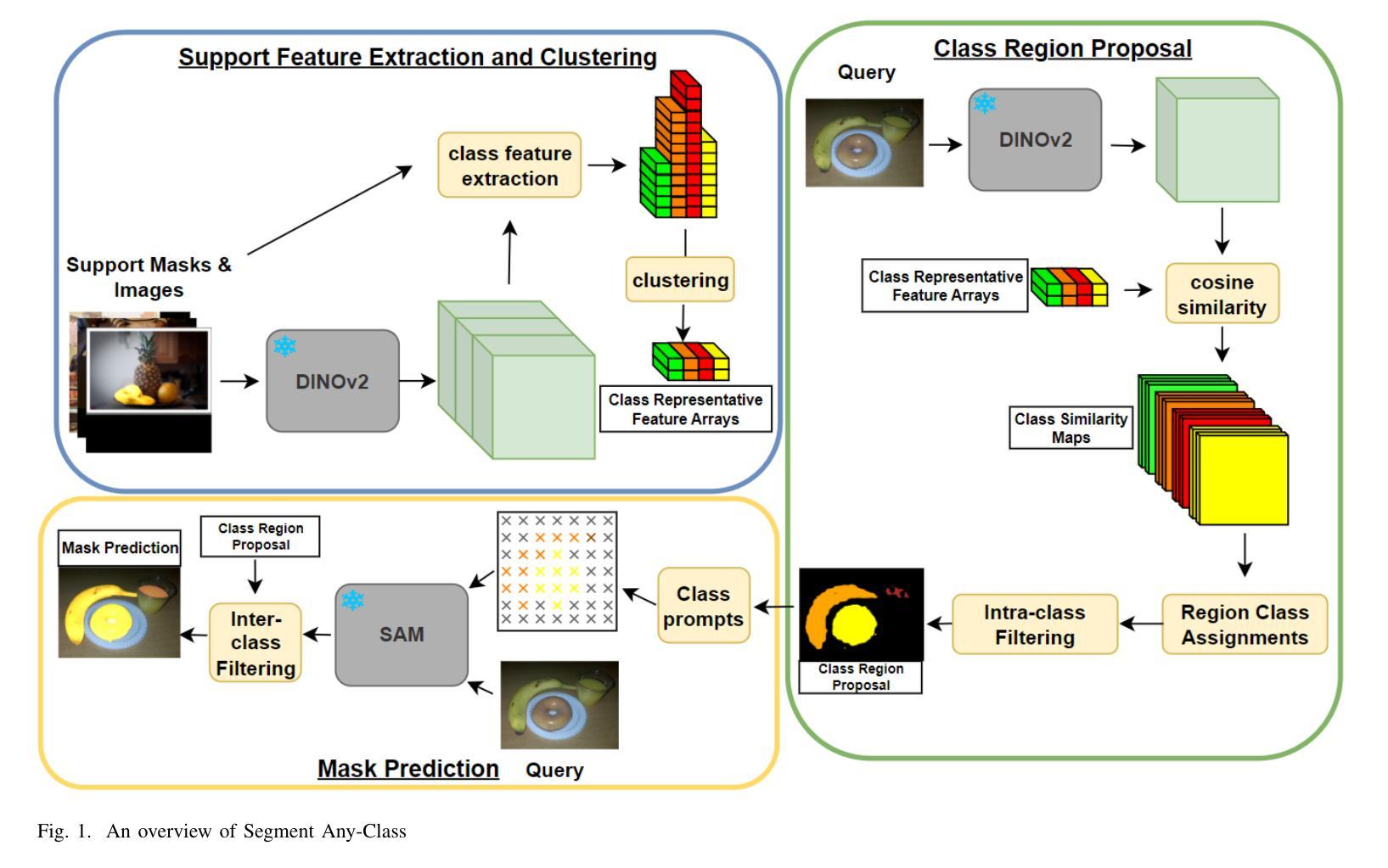

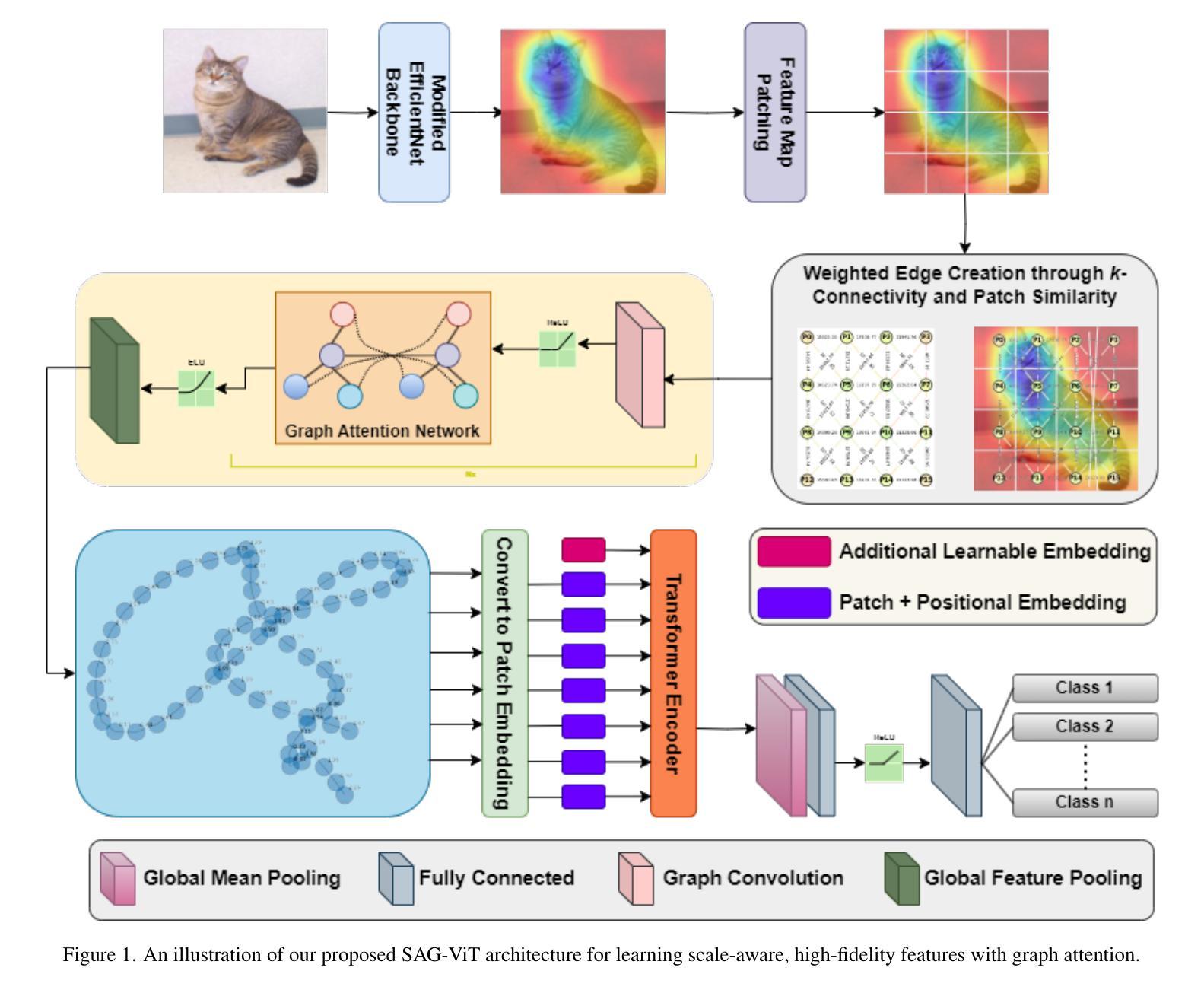
SAG-ViT: A Scale-Aware, High-Fidelity Patching Approach with Graph Attention for Vision Transformers
Authors:Shravan Venkatraman, Jaskaran Singh Walia, Joe Dhanith P R
Image classification is a computer vision task where a model analyzes an image to categorize it into a specific label. Vision Transformers (ViT) improve this task by leveraging self-attention to capture complex patterns and long range relationships between image patches. However, a key challenge for ViTs is efficiently incorporating multiscale feature representations, which is inherent in CNNs through their hierarchical structure. In this paper, we introduce the Scale-Aware Graph Attention Vision Transformer (SAG-ViT), a novel framework that addresses this challenge by integrating multi-scale features. Using EfficientNet as a backbone, the model extracts multi-scale feature maps, which are divided into patches to preserve semantic information. These patches are organized into a graph based on spatial and feature similarities, with a Graph Attention Network (GAT) refining the node embeddings. Finally, a Transformer encoder captures long-range dependencies and complex interactions. The SAG-ViT is evaluated on benchmark datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness in enhancing image classification performance. Our code and weights are publicly available at https://github.com/shravan-18/SAG-ViT
图像分类是一种计算机视觉任务,模型通过分析图像将其归类为特定标签。视觉转换器(ViT)通过利用自我注意力来捕捉图像补丁之间的复杂模式和长远关系,从而改进此任务。然而,ViT的关键挑战是有效地融入多尺度特征表示,这是CNN的固有属性,得益于其分层结构。在本文中,我们引入了Scale-Aware Graph Attention Vision Transformer(SAG-ViT),这是一个通过整合多尺度特征来解决这一挑战的新型框架。使用EfficientNet作为骨干网,该模型提取多尺度特征图,将这些特征图划分为补丁以保留语义信息。这些补丁基于空间和特征相似性组织成一个图,其中Graph Attention Network(GAT)对节点嵌入进行精炼。最后,Transformer编码器捕捉长期依赖关系和复杂交互。SAG-ViT在基准数据集上进行了评估,证明了其在提高图像分类性能方面的有效性。我们的代码和权重可在https://github.com/shravan-18/SAG-ViT公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 10 pages, 4 figures, 3 tables
Summary
本文介绍了图像分类任务中Vision Transformer(ViT)的应用和挑战。针对ViT在多尺度特征表示方面的不足,提出了一种新的框架——Scale-Aware Graph Attention Vision Transformer(SAG-ViT)。该框架以EfficientNet为骨干网,提取多尺度特征图并划分为补丁,以保留语义信息。基于空间特征和特征相似性组织这些补丁成图,通过Graph Attention Network(GAT)优化节点嵌入。最后,使用Transformer编码器捕捉长期依赖关系和复杂交互。在基准数据集上的评估表明,SAG-ViT提高了图像分类性能。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViT) 利用自注意力机制改进图像分类任务,捕捉复杂模式和图像补丁间的长距离关系。
- ViT面临的关键挑战是有效地结合多尺度特征表示,这是CNN的固有优势。
- 引入SAG-ViT框架,结合多尺度特征以解决这一挑战。
- SAG-ViT使用EfficientNet作为骨干网,提取多尺度特征图并划分为补丁,以保留语义信息。
- 基于空间特征和特征相似性组织补丁成图,通过Graph Attention Network(GAT)优化节点嵌入。
- SAG-ViT使用Transformer编码器捕捉长期依赖关系和复杂交互。
- 在基准数据集上的评估表明,SAG-ViT提高了图像分类性能,代码和权重已公开提供。
点此查看论文截图

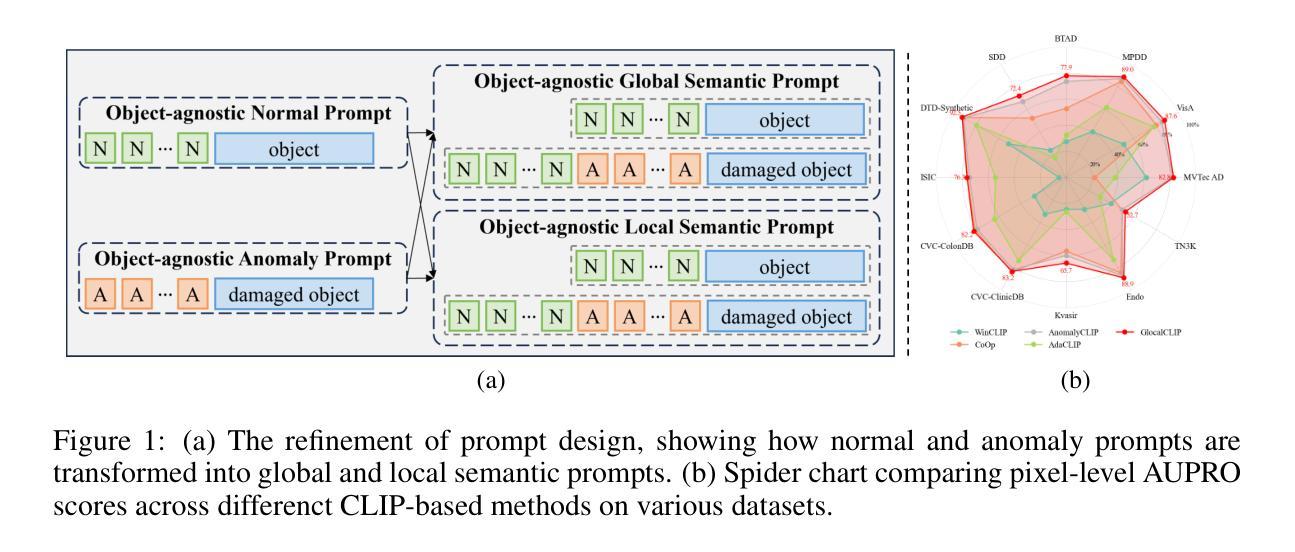
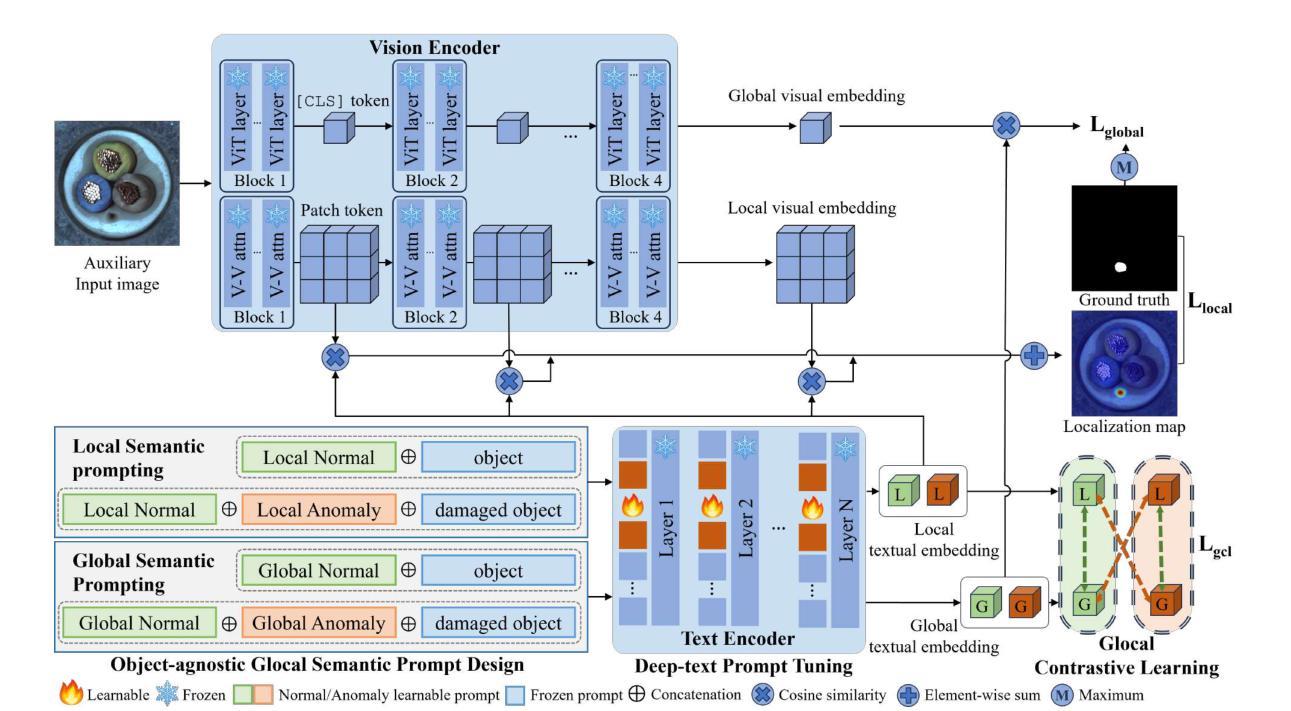
GlocalCLIP: Object-agnostic Global-Local Prompt Learning for Zero-shot Anomaly Detection
Authors:Jiyul Ham, Yonggon Jung, Jun-Geol Baek
Zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD) is crucial for detecting anomalous patterns in target datasets without using training samples, specifically in scenarios where there are distributional differences between the target domain and training data or where data scarcity arises because of restricted access. Although recently pretrained vision-language models demonstrate strong zero-shot performance across various visual tasks, they focus on learning class semantics, which makes their direct application to ZSAD challenging. To address this scenario, we propose GlocalCLIP, which uniquely separates global and local prompts and jointly optimizes them. This approach enables the object-agnostic glocal semantic prompt to effectively capture general normal and anomalous patterns without dependency on specific objects in the image. We refine the text prompts for more precise adjustments by utilizing deep-text prompt tuning in the text encoder. In the vision encoder, we apply V-V attention layers to capture detailed local image features. Finally, we introduce glocal contrastive learning to improve the complementary learning of global and local prompts, effectively detecting anomalous patterns across various domains. The generalization performance of GlocalCLIP in ZSAD was demonstrated on 15 real-world datasets from both the industrial and medical domains, achieving superior performance compared to existing methods. Code will be made available at https://github.com/YUL-git/GlocalCLIP.
零样本异常检测(ZSAD)对于在无需训练样本的情况下检测目标数据集中的异常模式至关重要,特别是在目标域与训练数据之间存在分布差异或由于访问受限而导致数据稀缺的场景中。尽管最近预训练的视觉语言模型在各种视觉任务中表现出强大的零样本性能,但它们主要关注类别语义的学习,这使得它们直接应用于ZSAD具有挑战性。为了应对这一场景,我们提出了GlocalCLIP方法,该方法独特地分离了全局和局部提示,并联合优化它们。这一独特设计使得对象无关的全局局部语义提示能够有效捕捉通用正常和异常模式,而无需依赖图像中的特定对象。我们通过利用文本编码器的深度文本提示调整来完善文本提示,以实现更精确的调整。在视觉编码器方面,我们应用V-V注意力层来捕捉详细的局部图像特征。最后,我们引入了全局局部对比学习,以提高全局和局部提示的互补学习,有效检测不同领域的异常模式。GlocalCLIP在ZSAD中的泛化性能在来自工业和医疗领域的1 5个真实世界数据集上得到了验证,与现有方法相比,实现了卓越的性能。代码将在https://github.com/YUL-git/GlocalCLIP上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 29 pages, 36 figures
Summary
本文提出了一个用于零样本异常检测(ZSAD)的新方法GlocalCLIP。该方法通过分离全局和局部提示并进行联合优化,解决了直接使用预训练的视觉语言模型进行零样本异常检测的挑战。利用深度文本提示调整和V-V注意力层,GlocalCLIP能够在不使用训练样本的情况下捕获一般正常和异常模式。此外,引入了全局和局部提示的对比学习,提高了模型的泛化性能,并在多个真实世界数据集上实现了卓越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- GlocalCLIP解决了在零样本异常检测中直接使用预训练视觉语言模型的挑战。
- 通过分离全局和局部提示并进行联合优化,GlocalCLIP能捕获一般正常和异常模式。
- GlocalCLIP使用深度文本提示调整以提高精确度,并通过V-V注意力层捕获详细的局部图像特征。
- 引入全局和局部提示的对比学习,提高模型的泛化能力。
- GlocalCLIP在多个真实世界数据集上实现了卓越的性能。
- GlocalCLIP具有广泛的应用前景,特别是在目标数据集与训练数据存在分布差异或数据稀缺的场景中。
点此查看论文截图
Domain-Adaptive Pre-training of Self-Supervised Foundation Models for Medical Image Classification in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Authors:Marcel Roth, Micha V. Nowak, Adrian Krenzer, Frank Puppe
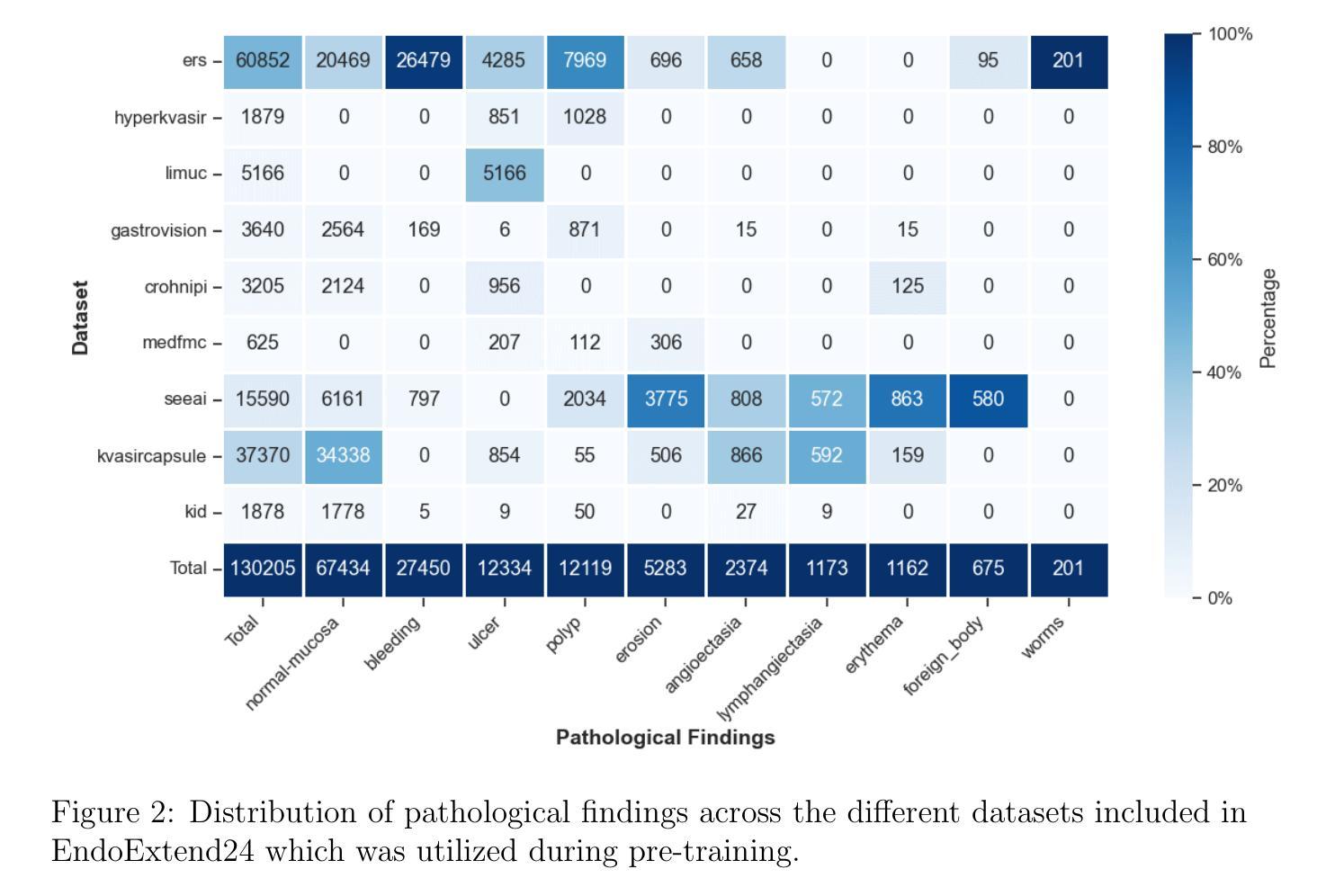
Video capsule endoscopy has transformed gastrointestinal endoscopy (GIE) diagnostics by offering a non-invasive method for capturing detailed images of the gastrointestinal tract, enabling early disease detection. However, its potential is limited by the sheer volume of images generated during the imaging procedure, which can take anywhere from 6-8 hours and often produce up to 1 million images, necessitating automated analysis. Additionally, the variability of these images, combined with the need for expert annotations and the scarcity of large, high-quality labeled datasets, constrains the effectiveness of current medical image analysis models. To address this, we introduce a novel large GIE dataset, called EndoExtend24, created by merging ten existing public and private datasets, ensuring patient integrity across splits. EndoExtend24 includes over 226,000 labeled images, as well as dynamic class mappings, which allow unified training across datasets with differing labeling granularity, supporting up to 123 distinct pathological findings. Further, we propose to leverage domain adaptive pre-training of foundation models trained with self-supervision on generic image data, to adapt them to the task of GIE medical image diagnosis. Specifically, the EVA-02 model, which is based on the ViT architecture and trained on ImageNet-22k with masked image modeling (using EVA-CLIP as a MIM teacher), is pre-trained on the EndoExtend24 dataset to achieve domain adaptation, and finally trained on the Capsule Endoscopy 2024 Challenge dataset. Our model demonstrates robust performance, securing third place in the Capsule Endoscopy 2024 Challenge. We achieved a macro AUC of 0.762 and a balanced accuracy of 37.1% on the test set. These results emphasize the effectiveness of our domain-adaptive pre-training approach and the enriched EndoExtend24 dataset in advancing gastrointestinal endoscopy diagnostics.
视频胶囊内镜技术通过提供一种无创方法,能够捕捉胃肠道的详细图像,从而实现了胃肠道内窥镜(GIE)诊断的变革,使早期疾病检测成为可能。然而,其在成像过程中产生的图像数量庞大,成像过程可能需要6-8小时,并可能产生高达100万张图像,这限制了其潜力,需要自动化分析。此外,这些图像的变量结合专家标注的需求以及大型、高质量标记数据集的稀缺性,制约了当前医学图像分析模型的有效性。
为了解决这一问题,我们引入了一个新的大型GIE数据集EndoExtend24,它是通过合并十个现有的公共和私有数据集创建的,确保了跨分割的患者完整性。EndoExtend24包含超过22万张标记图像,以及动态类映射,允许在具有不同标记粒度的数据集上进行统一训练,支持多达123种不同的病理发现。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
视频胶囊内镜技术为胃肠道内窥镜诊断提供了非侵入性的详细成像方法,有助于早期疾病检测。然而,由于成像过程产生的图像数量庞大,分析需求自动化。为此,研究者推出新的大型胃肠道内窥镜数据集EndoExtend24,包含超过22.6万张标记图像,并支持多种病理发现。此外,研究者提出利用基于域自适应预训练的通用图像数据自监督训练方法,将基础模型适应于胃肠道内窥镜图像诊断任务。其中EVA-02模型基于ViT架构,在ImageNet-22k数据集上采用掩膜图像建模进行预训练,并在EndoExtend24数据集上进行域适应,最终在Capsule Endoscopy 2024 Challenge数据集上进行训练,获得稳健性能,在测试集上获得宏观AUC 0.762和平衡准确率37.1%。
Key Takeaways
- 视频胶囊内镜为胃肠道内窥镜诊断提供了非侵入性的详细成像方法。
- 成像过程产生大量图像,需要自动化分析。
- 推出新的大型胃肠道内窥镜数据集EndoExtend24,包含超过22.6万张标记图像。
- EndoExtend24支持多种病理发现,并允许跨不同标签粒度的数据集进行统一训练。
- 提出利用域自适应预训练方法,将通用图像数据自监督训练的基础模型适应于胃肠道内窥镜图像诊断任务。
- EVA-02模型在多个数据集上进行训练和评估,表现出稳健性能。
点此查看论文截图


Croc: Pretraining Large Multimodal Models with Cross-Modal Comprehension
Authors:Yin Xie, Kaicheng Yang, Ninghua Yang, Weimo Deng, Xiangzi Dai, Tiancheng Gu, Yumeng Wang, Xiang An, Yongle Zhao, Ziyong Feng, Jiankang Deng
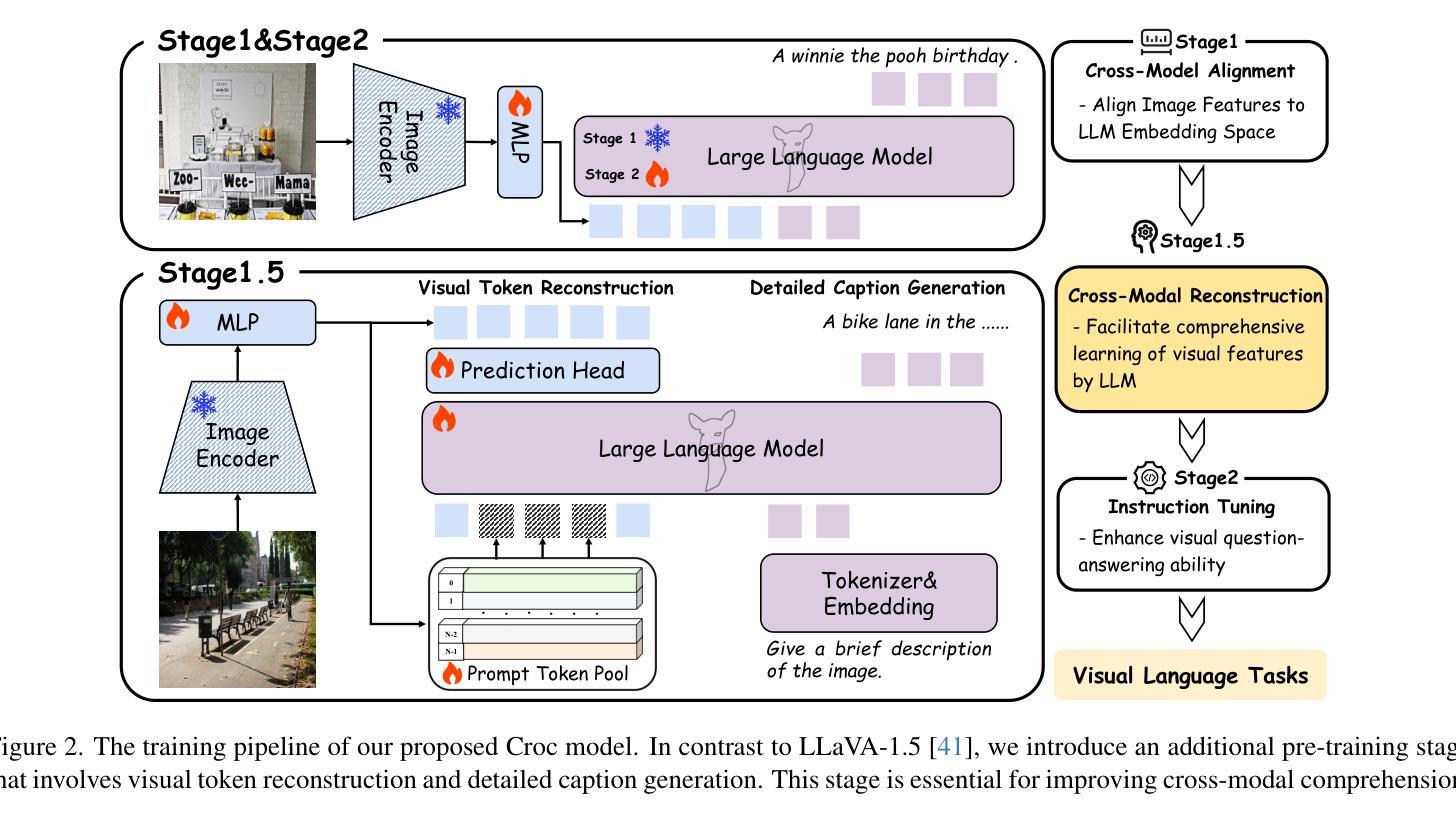
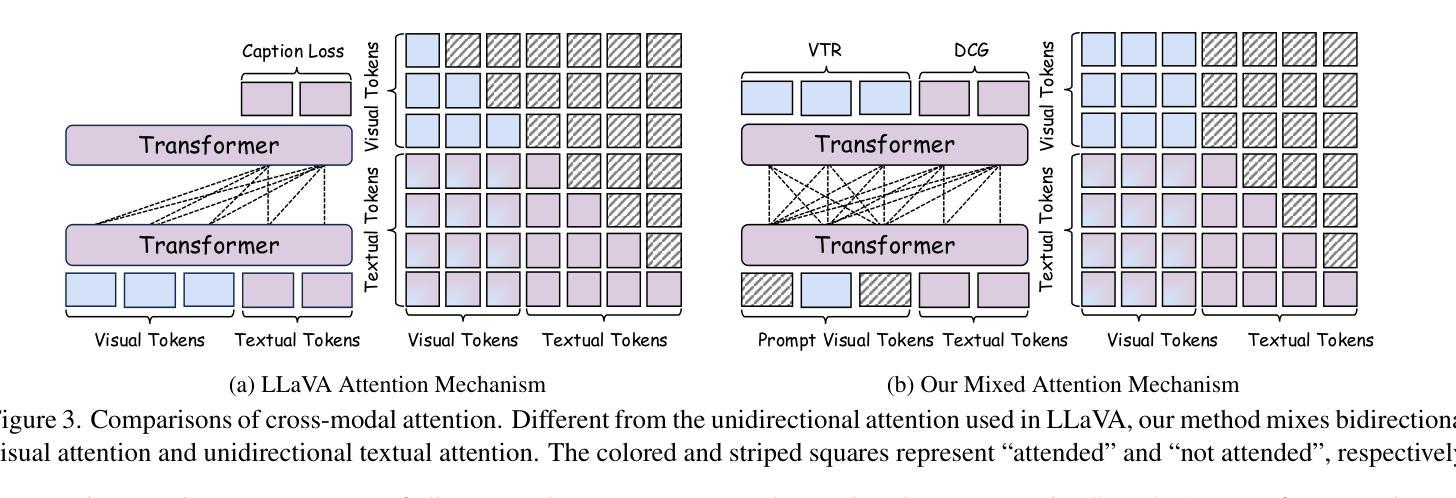
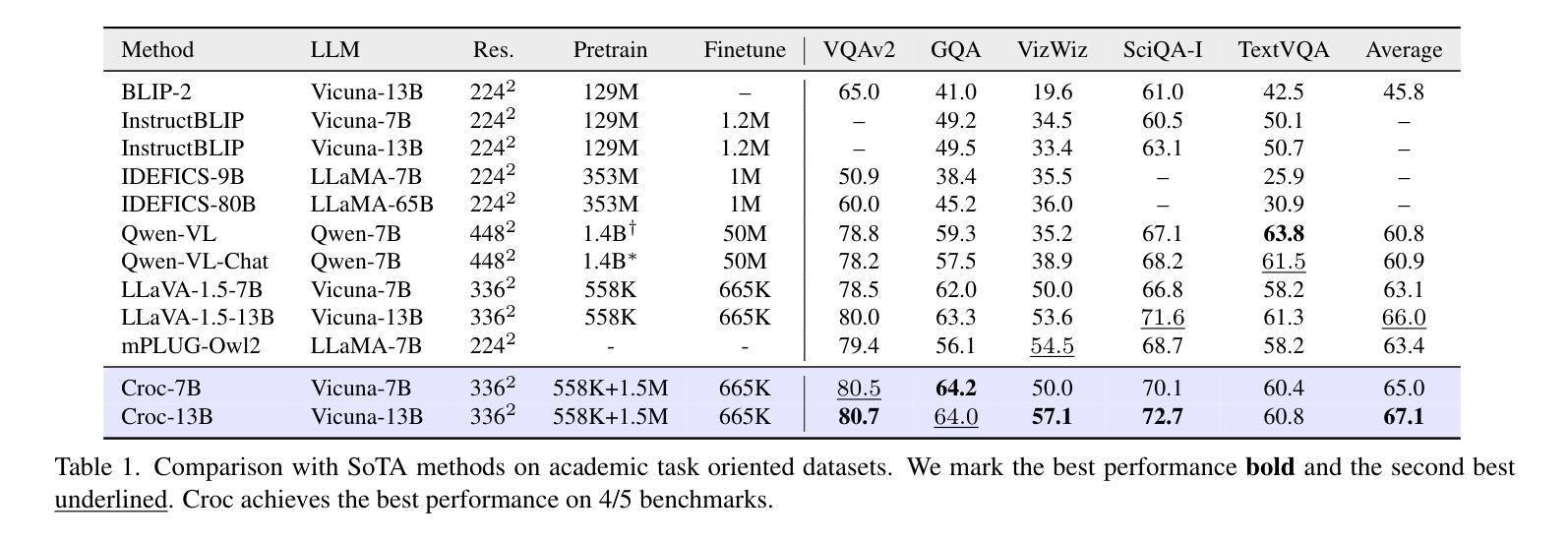
Recent advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) have catalyzed the development of Large Multimodal Models (LMMs). However, existing research primarily focuses on tuning language and image instructions, ignoring the critical pretraining phase where models learn to process textual and visual modalities jointly. In this paper, we propose a new pretraining paradigm for LMMs to enhance the visual comprehension capabilities of LLMs by introducing a novel cross-modal comprehension stage. Specifically, we design a dynamically learnable prompt token pool and employ the Hungarian algorithm to replace part of the original visual tokens with the most relevant prompt tokens. Then, we conceptualize visual tokens as analogous to a “foreign language” for the LLMs and propose a mixed attention mechanism with bidirectional visual attention and unidirectional textual attention to comprehensively enhance the understanding of visual tokens. Meanwhile, we integrate a detailed caption generation task, leveraging rich descriptions to further facilitate LLMs in understanding visual semantic information. After pretraining on 1.5 million publicly accessible data, we present a new foundation model called Croc. Experimental results demonstrate that Croc achieves new state-of-the-art performance on massive vision-language benchmarks. To support reproducibility and facilitate further research, we release the training code and pre-trained model weights at https://github.com/deepglint/Croc.
最近大型语言模型(LLM)的进展推动了大型多模态模型(LMM)的发展。然而,现有研究主要集中在调整语言和图像指令上,忽略了模型学习处理文本和视觉模态的联合预训练阶段。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的LMM预训练范式,通过引入一种新的跨模态理解阶段,以增强LMM的视觉理解能力。具体来说,我们设计了一个可动态学习的提示令牌池,并使用匈牙利算法将最相关的提示令牌替换掉部分原始视觉令牌。然后,我们将视觉令牌概念化为对LLM而言类似于“外语”,并提出一种混合注意力机制,包括双向视觉注意力和单向文本注意力,以全面提高对视觉令牌的理解能力。同时,我们整合了详细的标题生成任务,利用丰富的描述来进一步帮助LLM理解视觉语义信息。在公开可用的150万条数据进行预训练后,我们推出了名为Croc的新基础模型。实验结果表明,Croc在大量的视觉语言基准测试中达到了最新的最先进的性能。为了支持可复制性和促进进一步研究,我们在https://github.com/deepglint/Croc上发布了训练代码和预训练模型权重。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 11 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种新的大型多模态模型(LMMs)预训练范式,通过引入跨模态理解阶段,增强LLMs对视觉内容的理解能力。该研究设计了动态可学习的提示令牌池,并采用匈牙利算法替换最相关的视觉令牌。同时,提出了混合注意力机制,整合详细的图像描述生成任务,以进一步增强LLM对视觉语义信息的理解。经过在150万公开数据上的预训练,新提出的模型Croc在视觉语言基准测试中达到了新的先进水平。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种新的大型多模态模型(LMMs)预训练范式,专注于增强模型对视觉内容的理解能力。
- 设计了动态可学习的提示令牌池,利用匈牙利算法替换视觉令牌。
- 引入混合注意力机制,整合双向视觉注意力和单向文本注意力。
- 利用详细的图像描述生成任务,进一步促进LLM理解视觉语义信息。
- 在大量公开数据上进行预训练,提出了名为Croc的新基础模型。
- Croc模型在视觉语言基准测试中达到了新的先进水平。
点此查看论文截图

Local-to-Global Self-Supervised Representation Learning for Diabetic Retinopathy Grading
Authors:Mostafa Hajighasemlou, Samad Sheikhaei, Hamid Soltanian-Zadeh
Artificial intelligence algorithms have demonstrated their image classification and segmentation ability in the past decade. However, artificial intelligence algorithms perform less for actual clinical data than those used for simulations. This research aims to present a novel hybrid learning model using self-supervised learning and knowledge distillation, which can achieve sufficient generalization and robustness. The self-attention mechanism and tokens employed in ViT, besides the local-to-global learning approach used in the hybrid model, enable the proposed algorithm to extract a high-dimensional and high-quality feature space from images. To demonstrate the proposed neural network’s capability in classifying and extracting feature spaces from medical images, we use it on a dataset of Diabetic Retinopathy images, specifically the EyePACS dataset. This dataset is more complex structurally and challenging regarding damaged areas than other medical images. For the first time in this study, self-supervised learning and knowledge distillation are used to classify this dataset. In our algorithm, for the first time among all self-supervised learning and knowledge distillation models, the test dataset is 50% larger than the training dataset. Unlike many studies, we have not removed any images from the dataset. Finally, our algorithm achieved an accuracy of 79.1% in the linear classifier and 74.36% in the k-NN algorithm for multiclass classification. Compared to a similar state-of-the-art model, our results achieved higher accuracy and more effective representation spaces.
在过去的十年中,人工智能算法已经证明了它们在图像分类和分割方面的能力。然而,与模拟中所用的相比,人工智能算法在实际临床数据上的表现较差。本研究旨在提出一种新型混合学习模型,该模型采用自我监督学习和知识蒸馏技术,可以实现足够的通用性和稳健性。ViT中使用的自注意机制和令牌以及混合模型中采用的从局部到全局的学习方法,使所提议的算法能够从图像中提取高维和高质量特征空间。为了展示所提出神经网络在医学图像分类和特征空间提取方面的能力,我们在糖尿病视网膜病变图像的数据集上使用了它,特别是EyePACS数据集。与其他医学图像相比,此数据集在结构上更为复杂,在受损区域方面更具挑战性。本研究中首次使用自我监督学习和知识蒸馏对此数据集进行分类。在我们的算法中,与其他所有自我监督学习和知识蒸馏模型相比,测试数据集首次比训练数据集大50%。与其他许多研究不同,我们没有从数据集中删除任何图像。最后,我们的算法在线性分类器中达到了79.1%的准确率,在k-NN算法中的多类分类达到了74.36%。与类似的最新技术模型相比,我们的结果获得了更高的准确率和更有效的表示空间。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种结合自监督学习与知识蒸馏的新型混合学习模型,用于处理医学图像分类与特征提取。该模型采用ViT中的自注意力机制与令牌,结合局部到全局的学习方式,能够从图像中提取出高质量的高维特征空间。在Diabetic Retinopathy的EyePACS数据集上进行的实验表明,该模型在分类与特征提取方面表现出优异性能,达到了79.1%的线性分类器准确率和74.36%的k-NN算法多类分类准确率,相较于类似的前沿模型,具有更高的准确率和更有效的表征空间。
Key Takeaways
- 研究提出了一种新型混合学习模型,结合自监督学习与知识蒸馏。
- 模型采用ViT中的自注意力机制与令牌,实现图像分类与分割。
- 模型能够提取出高质量的高维特征空间。
- 在Diabetic Retinopathy的EyePACS数据集上进行了实验验证。
- 模型处理复杂结构的数据集表现出优异性能。
- 测试数据集首次大于训练数据集,且未删除任何图像。
点此查看论文截图

Patch Ranking: Efficient CLIP by Learning to Rank Local Patches
Authors:Cheng-En Wu, Jinhong Lin, Yu Hen Hu, Pedro Morgado
Contrastive image-text pre-trained models such as CLIP have shown remarkable adaptability to downstream tasks. However, they face challenges due to the high computational requirements of the Vision Transformer (ViT) backbone. Current strategies to boost ViT efficiency focus on pruning patch tokens but fall short in addressing the multimodal nature of CLIP and identifying the optimal subset of tokens for maximum performance. To address this, we propose greedy search methods to establish a “Golden Ranking” and introduce a lightweight predictor specifically trained to approximate this Ranking. To compensate for any performance degradation resulting from token pruning, we incorporate learnable visual tokens that aid in restoring and potentially enhancing the model’s performance. Our work presents a comprehensive and systematic investigation of pruning tokens within the ViT backbone of CLIP models. Through our framework, we successfully reduced 40% of patch tokens in CLIP’s ViT while only suffering a minimal average accuracy loss of 0.3 across seven datasets. Our study lays the groundwork for building more computationally efficient multimodal models without sacrificing their performance, addressing a key challenge in the application of advanced vision-language models.
对比图像文本预训练模型,如CLIP,对下游任务表现出显著的适应性。然而,由于视觉转换器(ViT)主干的高计算要求,它们面临着挑战。当前提高ViT效率的策略主要集中于修剪补丁令牌,但在处理CLIP的多模态特性和确定获得最佳性能的令牌最优子集方面存在不足。为解决这一问题,我们提出贪心搜索方法建立“金牌排名”,并引入一个专门训练的轻量级预测器来近似这个排名。为了弥补因令牌修剪导致的性能下降,我们引入了可学习的视觉令牌,有助于恢复并可能提高模型的性能。我们的工作全面系统地研究了CLIP模型中ViT骨干的令牌修剪。通过我们的框架,我们在CLIP的ViT中成功减少了40%的补丁令牌,同时在七个数据集上平均准确度仅损失了0.3%。我们的研究为构建更加计算高效的多模态模型奠定了基础,而不会牺牲其性能,这解决了先进视觉语言模型应用中的关键挑战。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by WACV 2025
Summary
本文研究了CLIP模型中的Vision Transformer(ViT)在图像文本预训练模型中的高效性挑战。针对该问题,本文提出了基于贪心搜索的“黄金排名”方法,并利用轻量级预测器进行近似排名。同时,通过引入可学习的视觉令牌来弥补由于令牌剪枝造成的性能下降,甚至可以增强模型性能。本研究系统地对CLIP模型中ViT的令牌剪枝进行了探究,成功在七个数据集上减少40%的令牌,且平均准确度仅下降0.3%。这为构建高效的多模态模型奠定了基础,解决了先进视觉语言模型应用中的关键挑战。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP等图像文本预训练模型在下游任务中表现出强大的适应性。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)是CLIP模型的关键组成部分,但计算要求较高。
- 当前策略侧重于通过剪枝令牌来提高ViT的效率,但未能充分解决CLIP的多模态特性和识别最佳令牌子集的问题。
- 提出基于贪心搜索的“黄金排名”方法来解决这一问题。
- 引入轻量级预测器来近似排名,以弥补因令牌剪枝导致的性能损失。
- 通过引入可学习的视觉令牌来恢复并可能增强模型性能。
点此查看论文截图
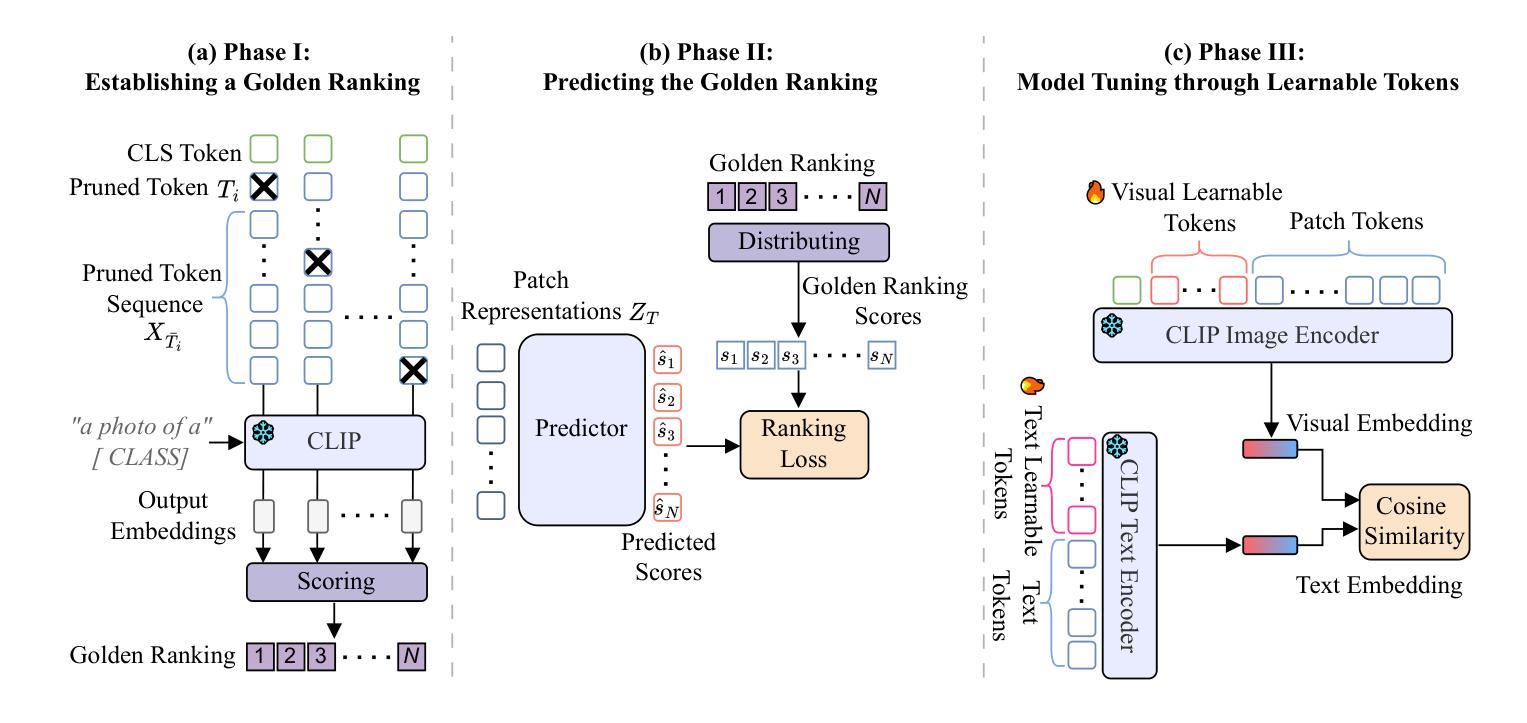
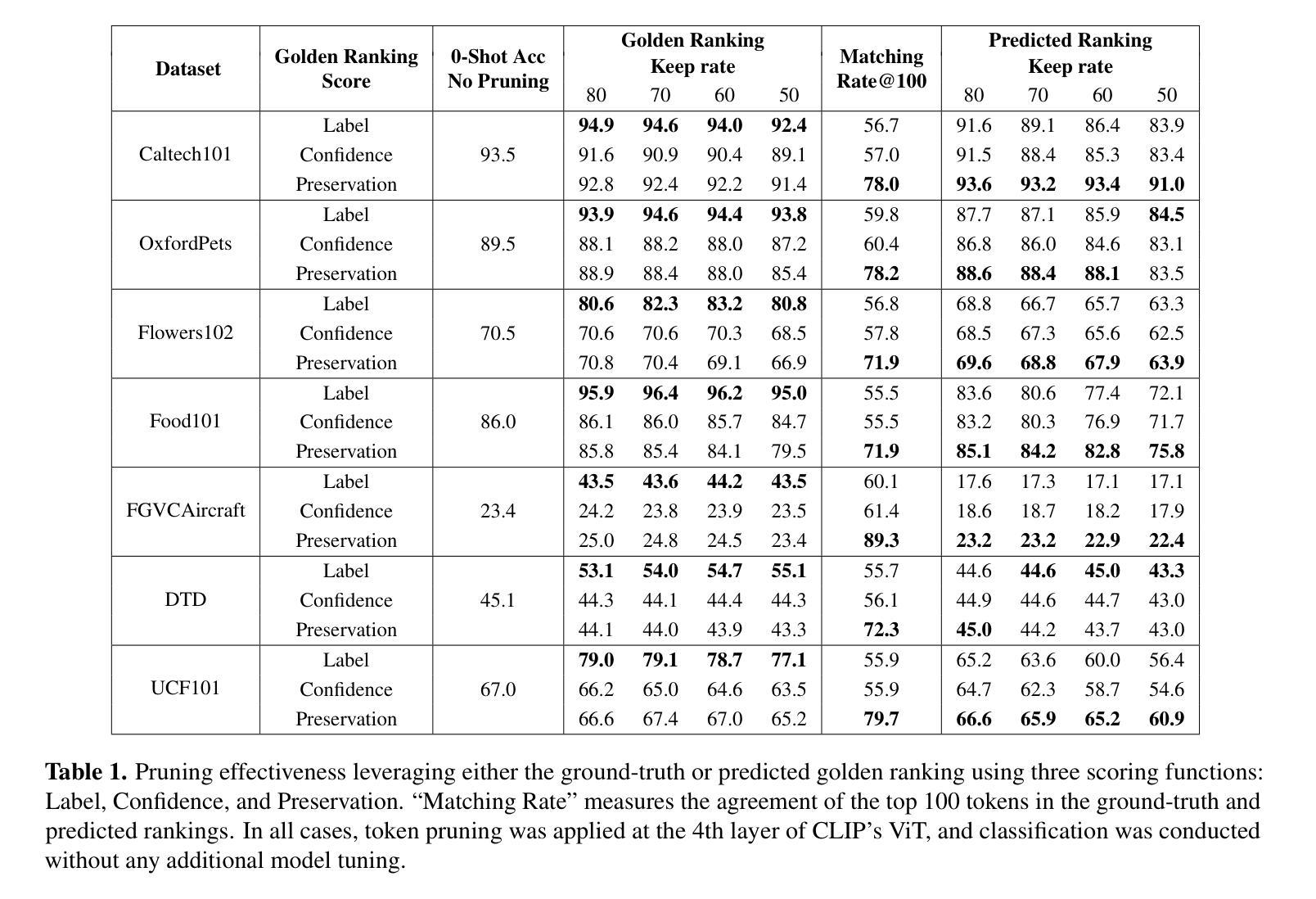


Generalizing Deepfake Video Detection with Plug-and-Play: Video-Level Blending and Spatiotemporal Adapter Tuning
Authors:Zhiyuan Yan, Yandan Zhao, Shen Chen, Mingyi Guo, Xinghe Fu, Taiping Yao, Shouhong Ding, Li Yuan
Three key challenges hinder the development of current deepfake video detection: (1) Temporal features can be complex and diverse: how can we identify general temporal artifacts to enhance model generalization? (2) Spatiotemporal models often lean heavily on one type of artifact and ignore the other: how can we ensure balanced learning from both? (3) Videos are naturally resource-intensive: how can we tackle efficiency without compromising accuracy? This paper attempts to tackle the three challenges jointly. First, inspired by the notable generality of using image-level blending data for image forgery detection, we investigate whether and how video-level blending can be effective in video. We then perform a thorough analysis and identify a previously underexplored temporal forgery artifact: Facial Feature Drift (FFD), which commonly exists across different forgeries. To reproduce FFD, we then propose a novel Video-level Blending data (VB), where VB is implemented by blending the original image and its warped version frame-by-frame, serving as a hard negative sample to mine more general artifacts. Second, we carefully design a lightweight Spatiotemporal Adapter (StA) to equip a pretrained image model (both ViTs and CNNs) with the ability to capture both spatial and temporal features jointly and efficiently. StA is designed with two-stream 3D-Conv with varying kernel sizes, allowing it to process spatial and temporal features separately. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of the proposed methods; and show our approach can generalize well to previously unseen forgery videos, even the latest generation methods.
当前深度伪造视频检测的发展面临三大关键挑战:
(1)时序特征可能复杂且多样:我们如何识别通用时序伪迹以提高模型的泛化能力?
(2)时空模型通常偏向于一种伪迹而忽视另一种:我们如何确保从两者中平衡学习?
论文及项目相关链接
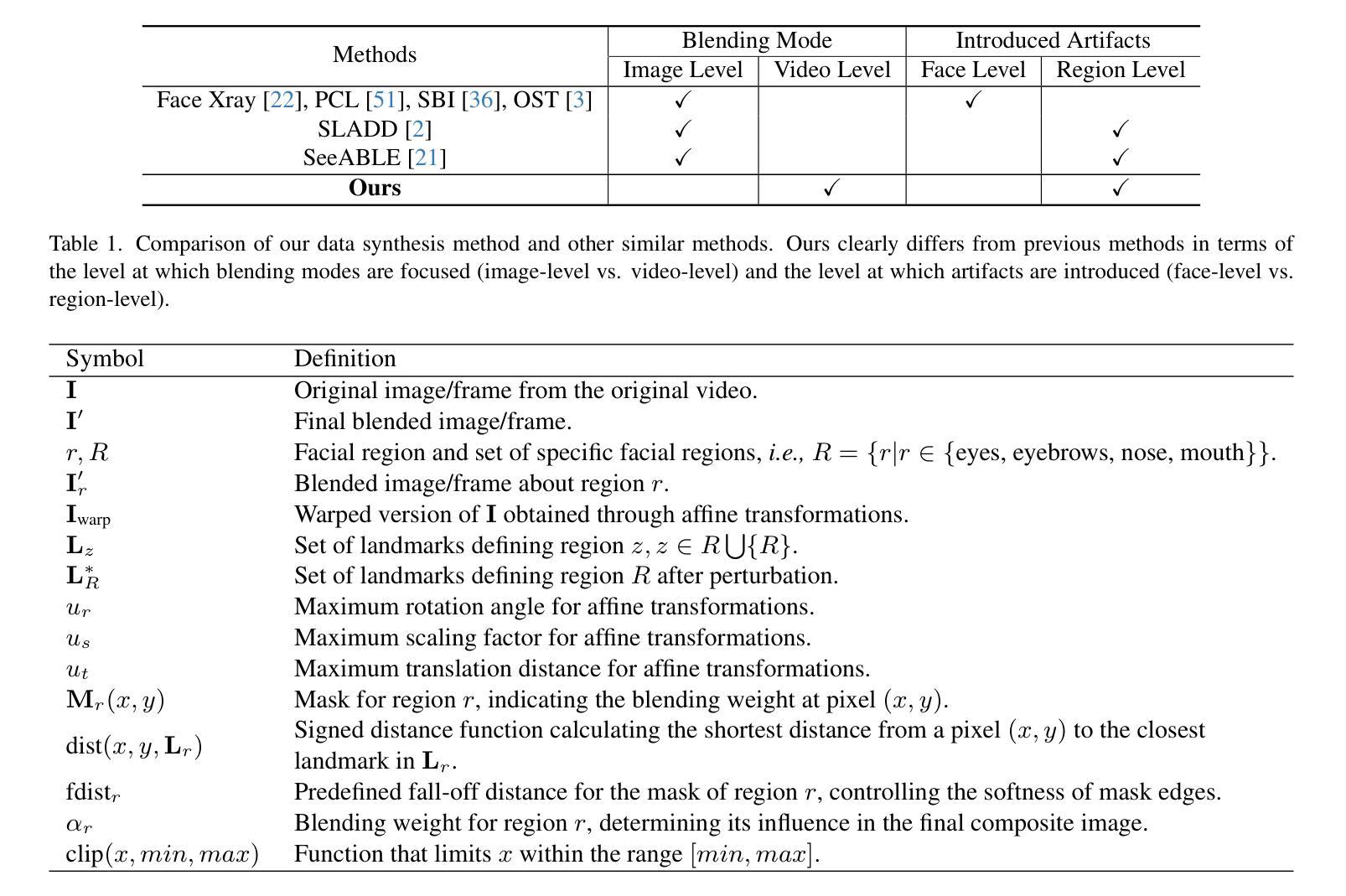
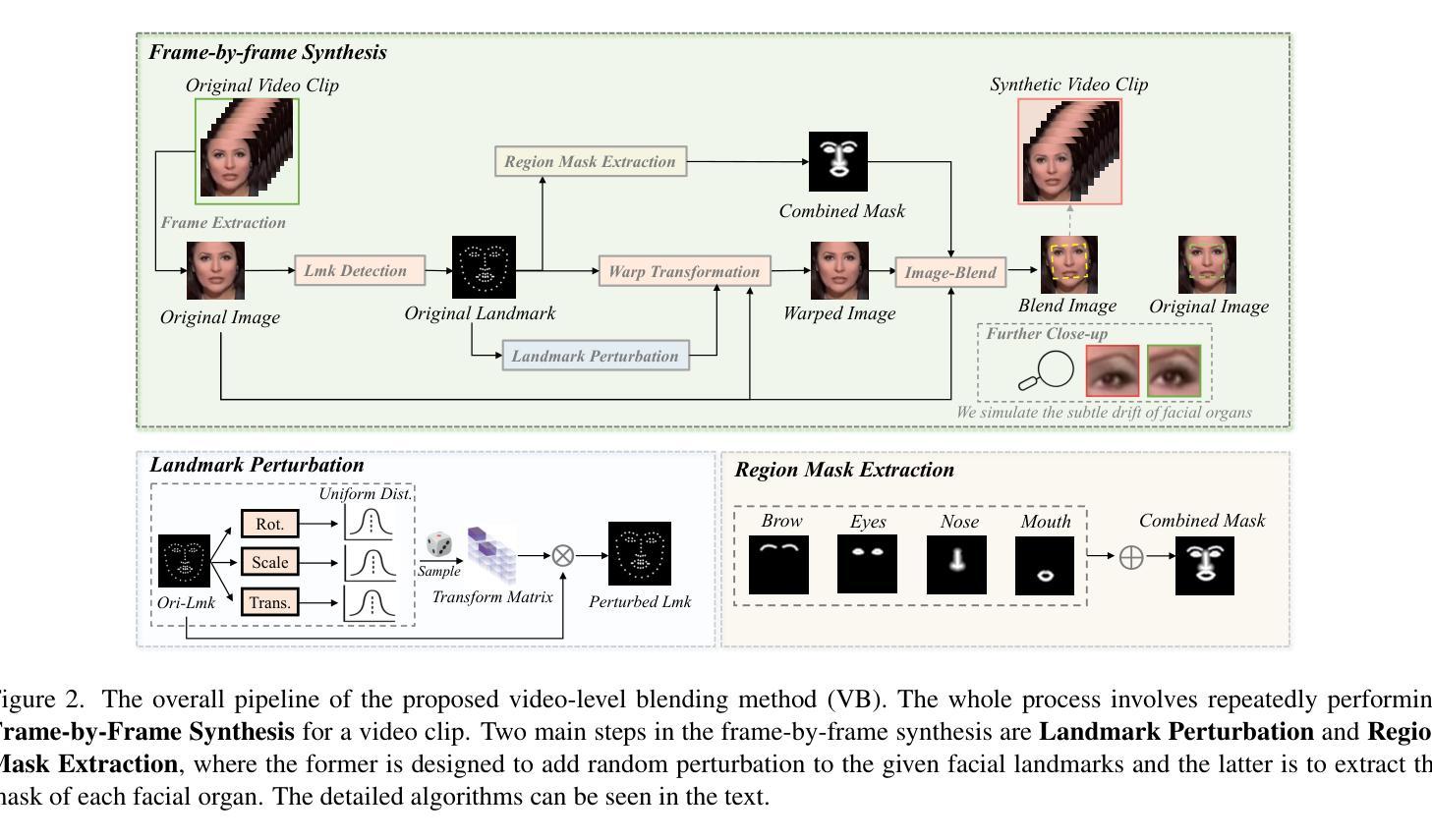
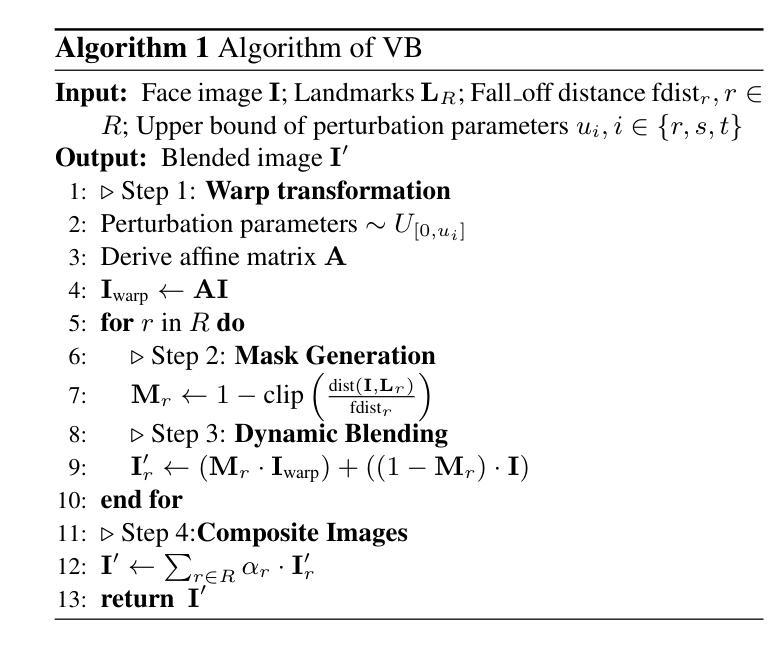
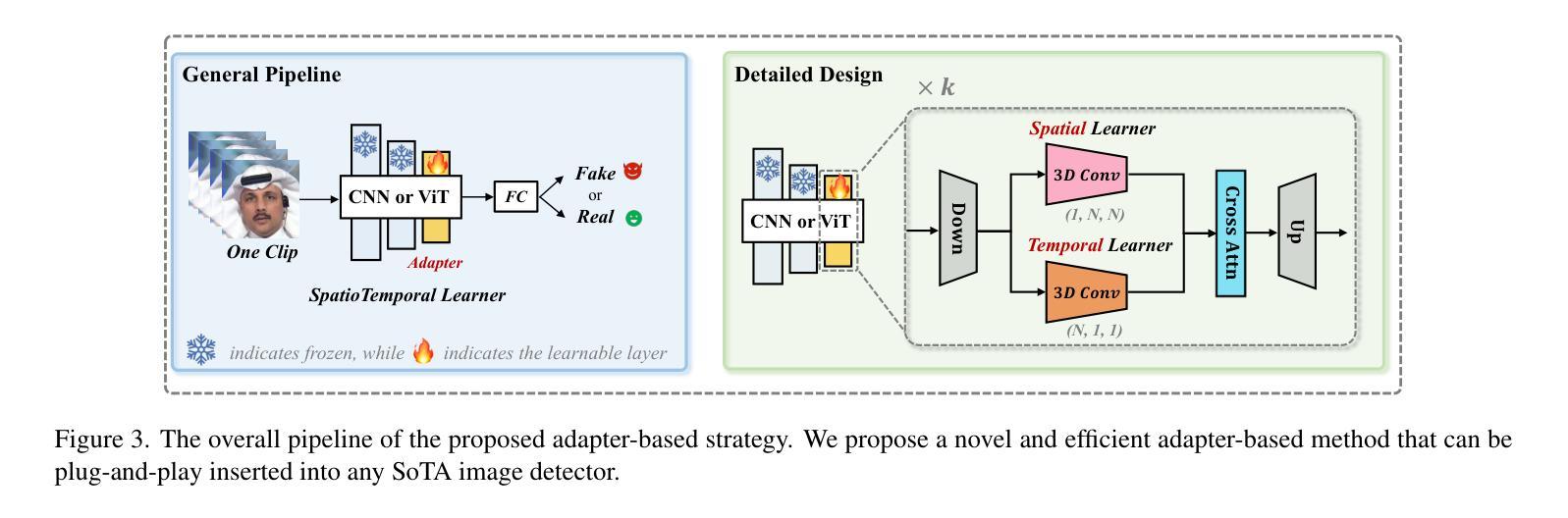
摘要
本文尝试联合解决当前深度伪造视频检测面临的三大挑战:1)复杂且多样的时间特征,如何识别通用时间伪影以提高模型泛化能力;2)时空模型倾向于依赖一种伪影而忽视另一种,如何确保两者的平衡学习;3)视频资源密集,如何在不降低准确性的情况下解决效率问题。研究受图像级混合数据用于图像伪造检测的普遍性启发,探索视频级混合在视频检测中的有效性,并发现了一种之前未被充分研究的临时伪造伪影:面部特征漂移(FFD)。为了再现FFD,提出了一种新型视频级混合数据(VB),通过将原始图像及其变形版本逐帧混合来实施VB,作为挖掘更通用伪造的硬负样本。精心设计了一个轻量级的时空适配器(StA),使预训练的图像模型(包括ViTs和CNNs)能够联合且高效地捕获空间和时间特征。StA采用具有不同内核大小的两流3D卷积设计,可分别处理空间和时间特征。大量实验验证了所提方法的有效性,表明我们的方法能够很好地泛化到以前未见过的伪造视频,甚至是最新的方法。
关键见解
- 当前深度伪造视频检测面临三大挑战:时间特征复杂性、时空模型的平衡学习、视频资源的高密度。
- 提出使用视频级混合来发掘更通用的伪造伪影,并引入面部特征漂移(FFD)这一新的临时伪造伪影概念。
- 设计了一种新型的轻量级时空适配器(StA),使预训练图像模型能够联合捕获空间和时间特征。
- 通过广泛实验验证了方法的有效性,证明了其对未知伪造视频的优异泛化能力。该方法适用于多种类型的伪造视频,即使是最新的伪造技术也能有效检测。
- 该方法不仅注重准确性,还兼顾效率和模型轻量化,为解决视频资源密集型问题提供了新的思路。
- 视频级混合和时空适配器的结合使用为深度伪造视频检测开辟了新的研究方向。
点此查看论文截图
GalLoP: Learning Global and Local Prompts for Vision-Language Models
Authors:Marc Lafon, Elias Ramzi, Clément Rambour, Nicolas Audebert, Nicolas Thome
Prompt learning has been widely adopted to efficiently adapt vision-language models (VLMs), e.g. CLIP, for few-shot image classification. Despite their success, most prompt learning methods trade-off between classification accuracy and robustness, e.g. in domain generalization or out-of-distribution (OOD) detection. In this work, we introduce Global-Local Prompts (GalLoP), a new prompt learning method that learns multiple diverse prompts leveraging both global and local visual features. The training of the local prompts relies on local features with an enhanced vision-text alignment. To focus only on pertinent features, this local alignment is coupled with a sparsity strategy in the selection of the local features. We enforce diversity on the set of prompts using a new ``prompt dropout’’ technique and a multiscale strategy on the local prompts. GalLoP outperforms previous prompt learning methods on accuracy on eleven datasets in different few shots settings and with various backbones. Furthermore, GalLoP shows strong robustness performances in both domain generalization and OOD detection, even outperforming dedicated OOD detection methods. Code and instructions to reproduce our results: https://github.com/MarcLafon/gallop.
提示学习已被广泛应用于高效地适应视觉语言模型(如CLIP),以进行少量图像分类。尽管取得了成功,但大多数提示学习方法在分类精度和稳健性(例如在域泛化或异常值检测)之间进行了权衡。在这项工作中,我们引入了全局局部提示(GalLoP),这是一种新的提示学习方法,它利用全局和局部视觉特征学习多个不同的提示。局部提示的训练依赖于具有增强视觉文本对齐的局部特征。为了只关注关键特征,这种局部对齐与选择局部特征的稀疏策略相结合。我们通过一种新的“提示丢弃”技术和局部提示的多尺度策略,在提示集上强制执行多样性。GalLoP在多个数据集的不同少量设置和多种主干网络上,在准确性方面优于之前的提示学习方法。此外,即使在域泛化和异常值检测方面,GalLoP也显示出强大的稳健性能,甚至超越了专门的异常值检测方法。复制我们的结果的代码和说明:https://github.com/MarcLafon/gallop。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新的提示学习方法——全局局部提示(GalLoP),该方法利用全局和局部视觉特征学习多个不同的提示。通过增强视觉文本对齐和选择局部特征的稀疏策略来训练局部提示。使用新的提示丢弃技术和局部提示的多尺度策略来增强提示集的多样性。在不同的少样本设置和多种主干网络上,GalLoP在11个数据集上的准确度超过了之前的提示学习方法。此外,在域推广和OOD检测中,GalLoP表现出强大的稳健性,甚至超越了专门的OOD检测方法。
Key Takeaways
- 全局局部提示(GalLoP)是一种新的提示学习方法,结合了全局和局部视觉特征进行模型训练。
- 局部提示的训练依赖于增强视觉文本对齐和局部特征的稀疏选择策略。
- GalLoP通过使用提示丢弃技术和多尺度策略来增强提示集的多样性。
- GalLoP在多个数据集上的少样本设置表现出高准确度。
- GalLoP在域推广任务中展现出稳健性。
- GalLoP在OOD检测任务中的表现甚至超越了某些专门的方法。
点此查看论文截图

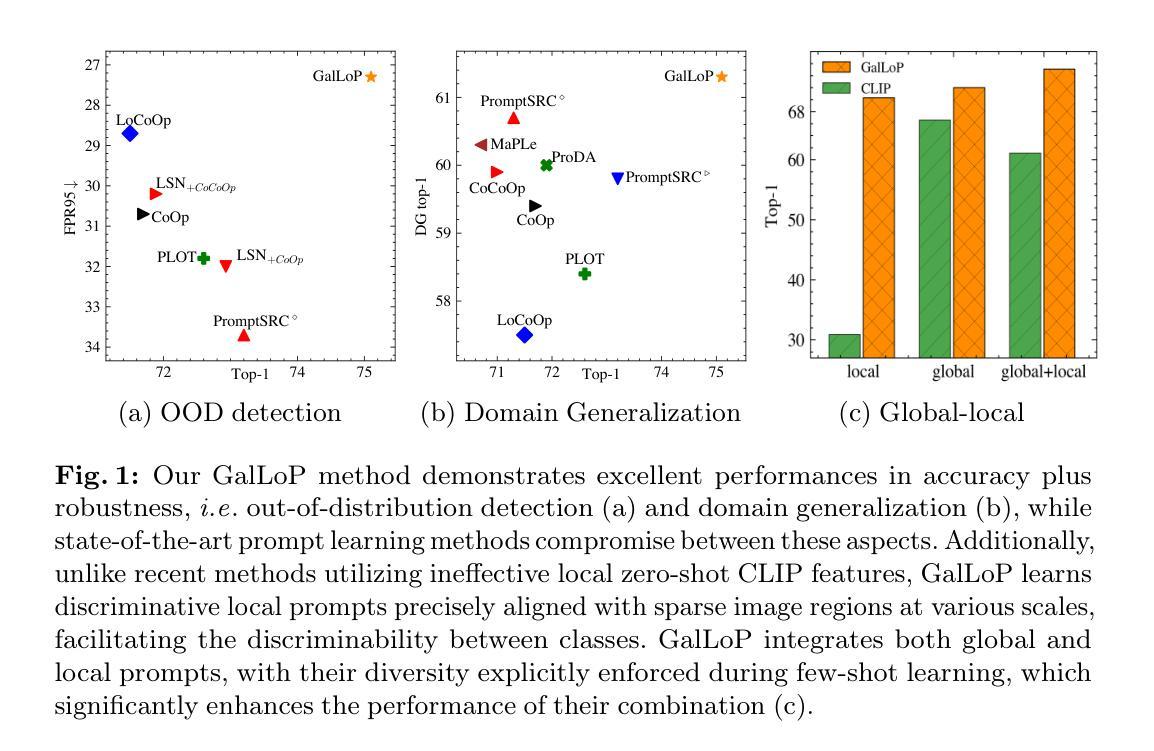
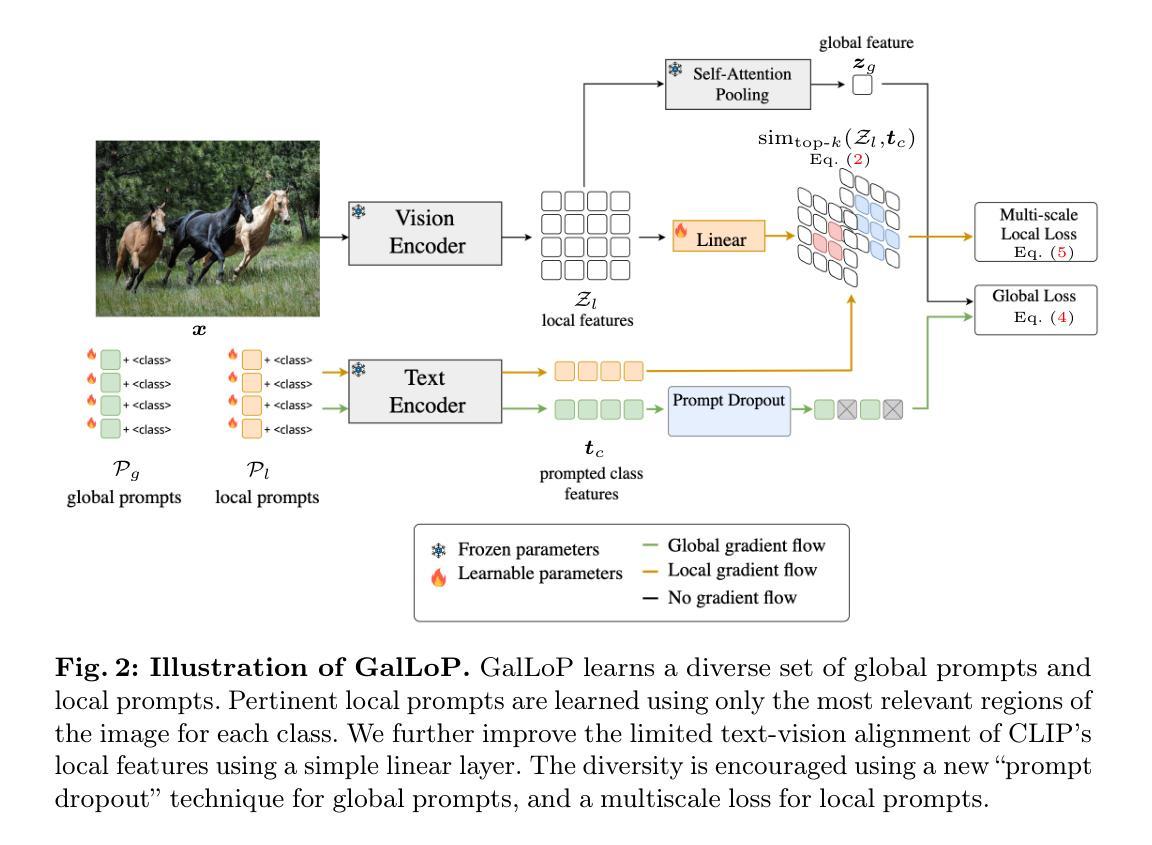
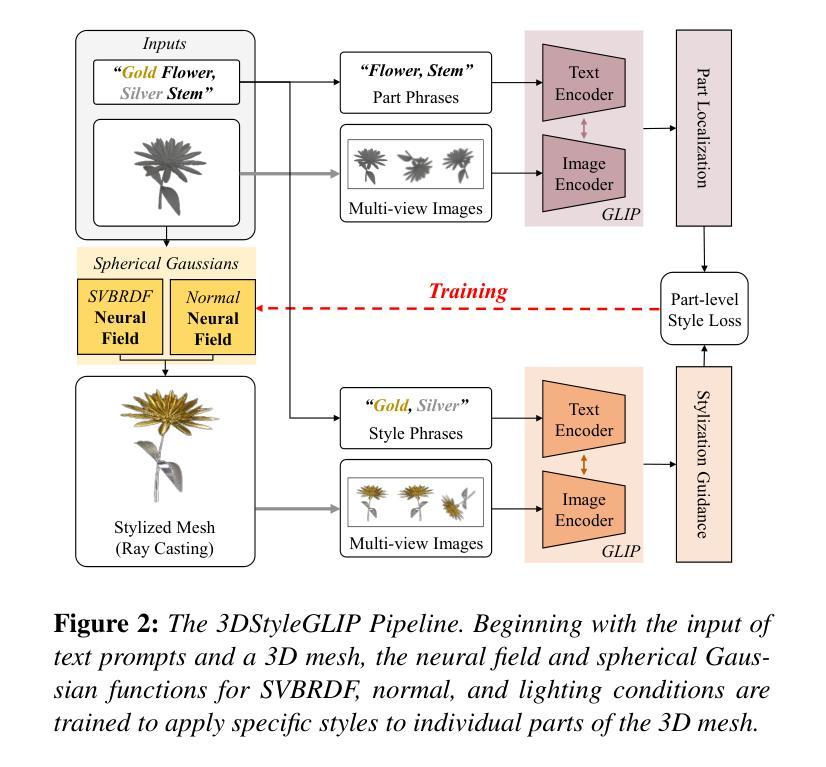
3DStyleGLIP: Part-Tailored Text-Guided 3D Neural Stylization
Authors:SeungJeh Chung, JooHyun Park, HyeongYeop Kang
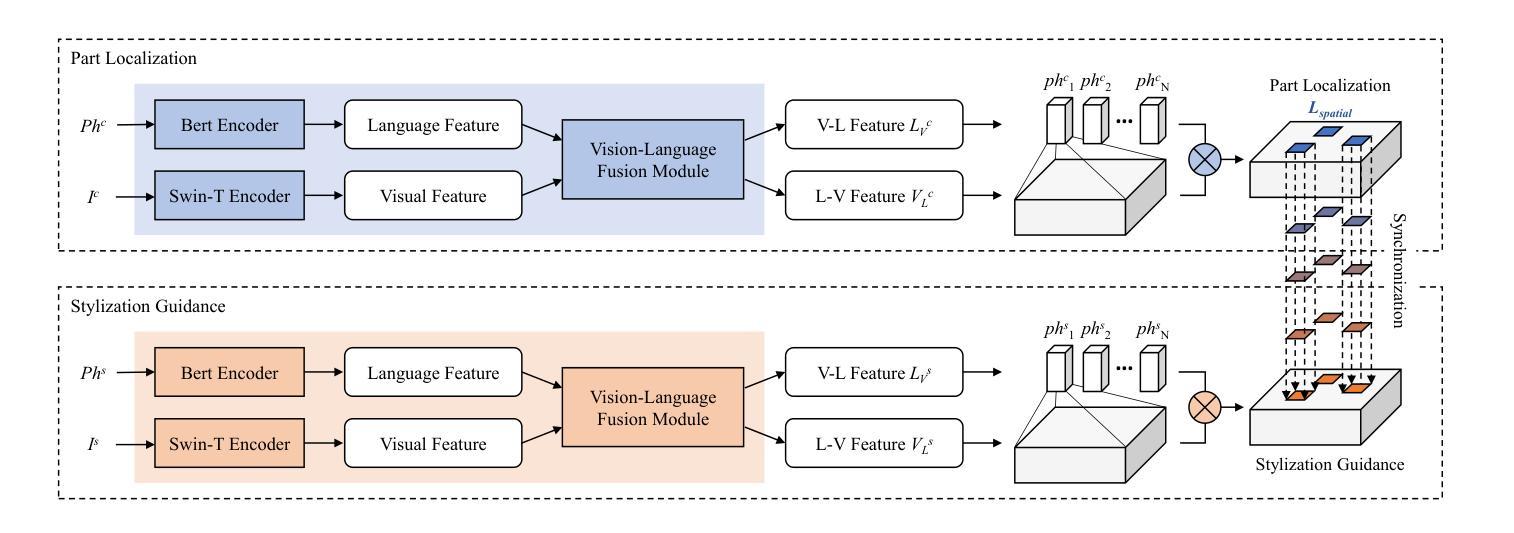
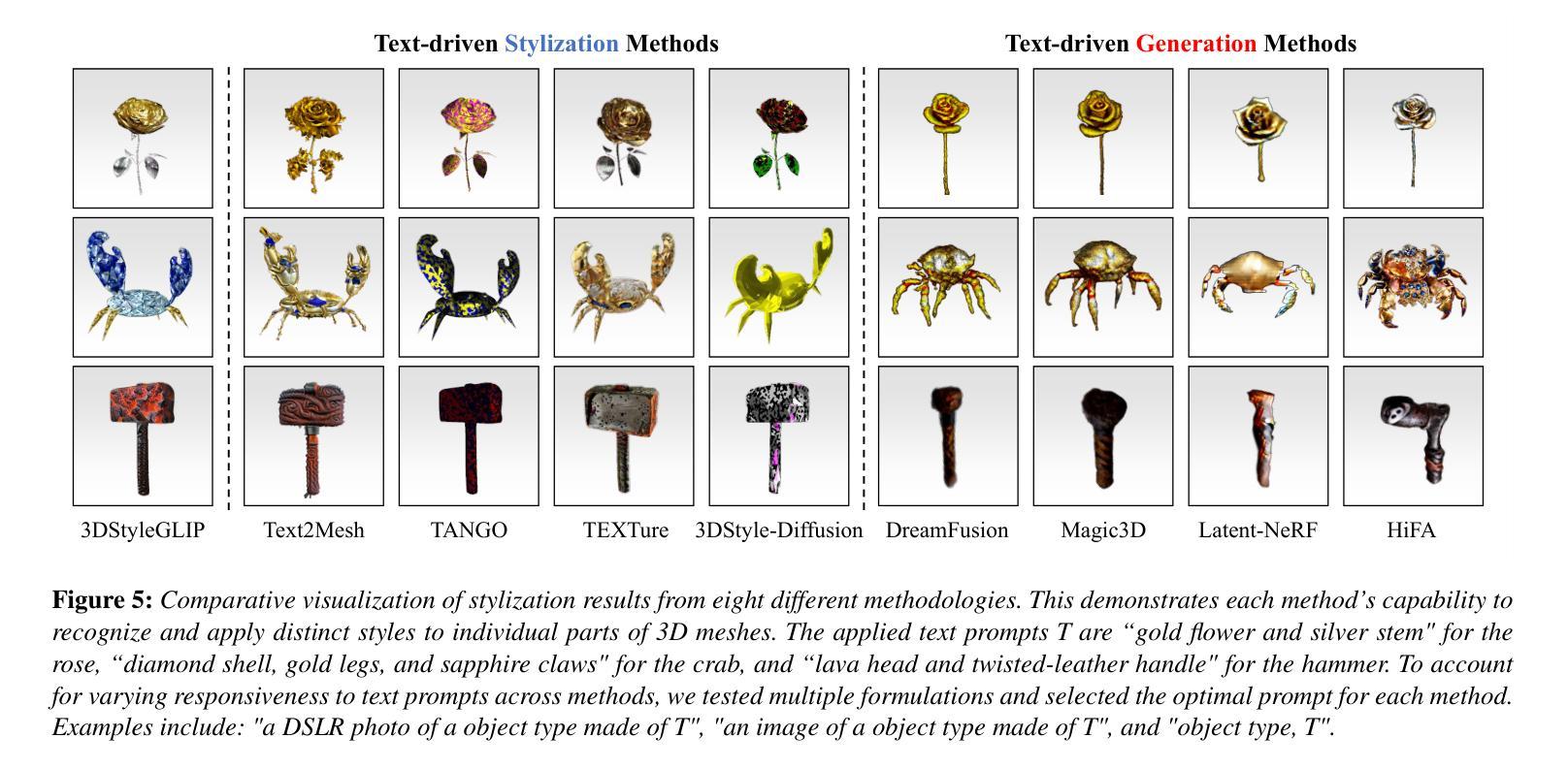
3D stylization, the application of specific styles to three-dimensional objects, offers substantial commercial potential by enabling the creation of uniquely styled 3D objects tailored to diverse scenes. Recent advancements in artificial intelligence and text-driven manipulation methods have made the stylization process increasingly intuitive and automated. While these methods reduce human costs by minimizing reliance on manual labor and expertise, they predominantly focus on holistic stylization, neglecting the application of desired styles to individual components of a 3D object. This limitation restricts the fine-grained controllability. To address this gap, we introduce 3DStyleGLIP, a novel framework specifically designed for text-driven, part-tailored 3D stylization. Given a 3D mesh and a text prompt, 3DStyleGLIP utilizes the vision-language embedding space of the Grounded Language-Image Pre-training (GLIP) model to localize individual parts of the 3D mesh and modify their appearance to match the styles specified in the text prompt. 3DStyleGLIP effectively integrates part localization and stylization guidance within GLIP’s shared embedding space through an end-to-end process, enabled by part-level style loss and two complementary learning techniques. This neural methodology meets the user’s need for fine-grained style editing and delivers high-quality part-specific stylization results, opening new possibilities for customization and flexibility in 3D content creation. Our code and results are available at https://github.com/sj978/3DStyleGLIP.
3D风格化是将特定风格应用于三维物体的应用,它通过创建适应不同场景的独特风格化的3D物体,具有巨大的商业潜力。人工智能和文本驱动操作方法的最新进展使得风格化过程越来越直观和自动化。这些方法通过最小化对人工劳动和专业知识的依赖,降低了人力成本,但它们主要关注整体风格化,忽略了将所需风格应用于三维物体的单个组件。这一限制制约了细粒度控制。为了弥补这一空白,我们引入了3DStyleGLIP,这是一个专门为文本驱动、部分定制的3D风格化设计的全新框架。给定一个3D网格和一个文本提示,3DStyleGLIP利用基于Grounded Language-Image Pre-training(GLIP)模型的视觉语言嵌入空间,定位3D网格的单个部分,并修改它们的外观以匹配文本提示中指定的风格。3DStyleGLIP通过端到端过程有效地在GLIP的共享嵌入空间内整合部分定位和风格化指导,这得益于部分级别的风格损失和两种互补的学习技术。这种神经方法满足了用户对细粒度风格编辑的需求,并提供了高质量的部件特定风格化结果,为3D内容创建提供了定制和灵活性。我们的代码和结果可在https://github.com/sj978/3DStyleGLIP上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures, 2024 Pacific Graphics Conferences (PG 2024)
Summary
基于文本驱动的方法对三维物体进行精细化风格化研究具有巨大的商业潜力。近年来,人工智能和文本驱动操作方法的进步使得风格化过程更加直观和自动化。然而,现有方法主要关注整体风格化,忽视了在三维物体的个别组件上应用所需风格,限制了精细控制的能力。为解决这一空白,我们提出了3DStyleGLIP框架,专为文本驱动、部分定制的三维风格化设计。给定一个三维网格和文本提示,3DStyleGLIP利用基于视觉语言的GLIP模型的嵌入空间来定位三维网格的单个部分,并修改它们的外观以匹配文本提示中的指定风格。此方法通过部分风格损失和两种互补学习技术,在GLIP的共享嵌入空间中有效地结合了部分定位和风格化指导,满足用户对精细风格编辑的需求,并为三维内容创建提供了高度定制和灵活的可能性。
Key Takeaways
- 文本驱动的自动化风格化技术在商业领域具有巨大潜力。
- 当前方法主要关注整体风格化,缺乏针对三维物体个别组件的风格应用。
- 3DStyleGLIP框架解决了这一局限性,实现了文本驱动的部分定制三维风格化。
- 3DStyleGLIP利用GLIP模型的嵌入空间进行部分定位和风格匹配。
- 该方法通过部分风格损失和互补学习技术实现有效的集成。
- 3DStyleGLIP满足了用户对精细风格编辑的需求。
点此查看论文截图
Just Shift It: Test-Time Prototype Shifting for Zero-Shot Generalization with Vision-Language Models
Authors:Elaine Sui, Xiaohan Wang, Serena Yeung-Levy
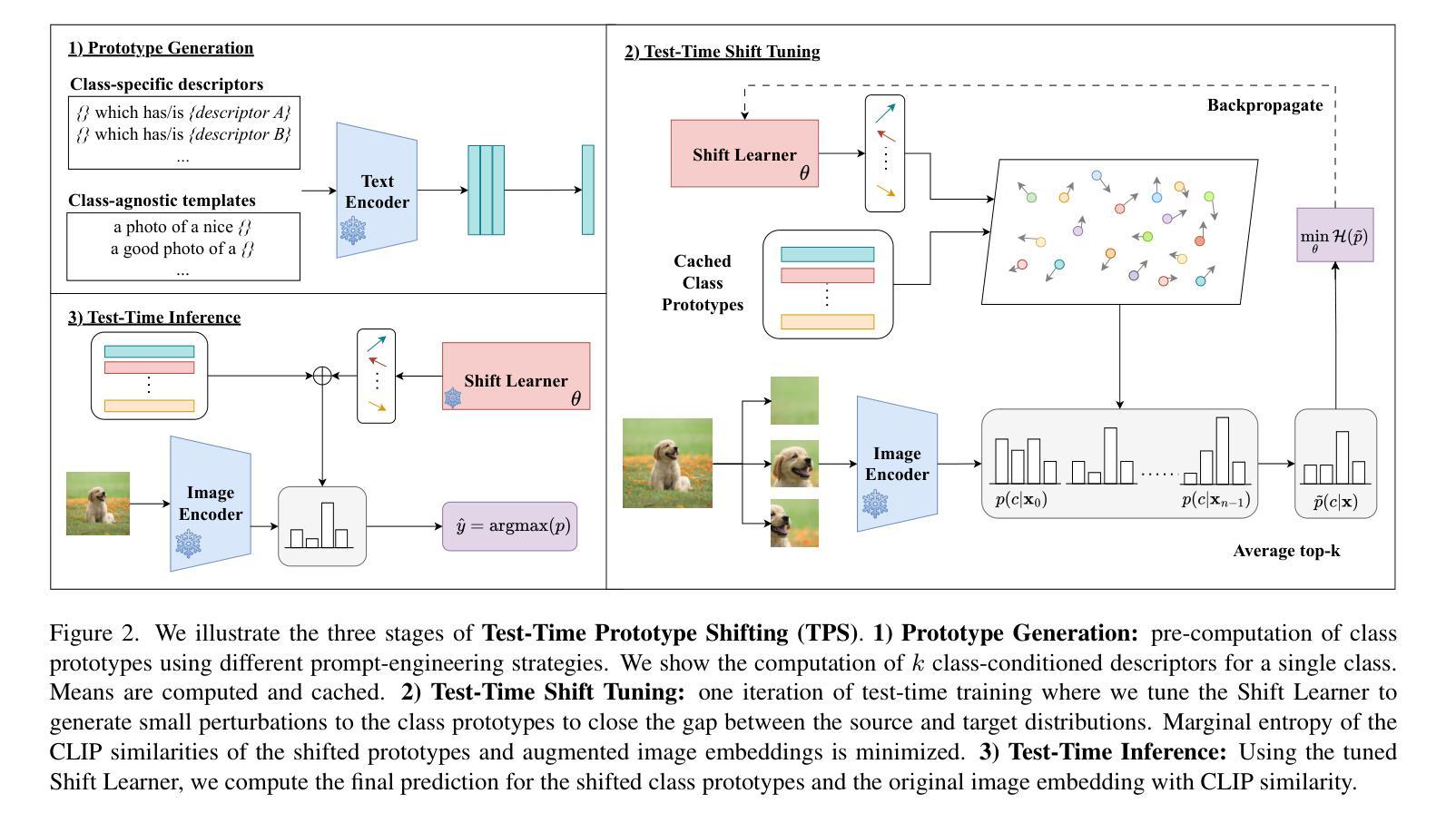
Advancements in vision-language models (VLMs) have propelled the field of computer vision, particularly in the zero-shot learning setting. Despite their promise, the effectiveness of these models often diminishes due to domain shifts in test environments. To address this, we introduce the Test-Time Prototype Shifting (TPS) framework, a pioneering approach designed to adapt VLMs to test datasets using unlabeled test inputs. Our method is based on the notion of modulating per-class prototypes in the shared embedding space. By pre-computing and caching prototypes generated with the pre-trained text encoder, TPS not only facilitates optimization-free prototype reuse for subsequent predictions but also enables seamless integration with current advancements in prompt engineering. At test-time, TPS dynamically learns shift vectors for each prototype based solely on the given test sample, effectively bridging the domain gap and enhancing classification accuracy. A notable aspect of our framework is its significantly reduced memory and computational demands when compared to conventional text-prompt tuning methods. Extensive evaluations across 15 image classification datasets involving natural distribution shifts and cross-dataset generalization, as well as in context-dependent visual reasoning, demonstrate TPS’s superior performance, achieving state-of-the-art results while reducing resource requirements.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)的进展推动了计算机视觉领域的发展,特别是在零样本学习环境中。尽管这些模型具有潜力,但由于测试环境中的域偏移,它们的效力往往会降低。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了测试时原型偏移(TPS)框架,这是一种创新的方法,旨在利用无标签的测试输入使VLMs适应测试数据集。我们的方法基于在共享嵌入空间中调制每类原型的概念。通过预计算和缓存使用预训练文本编码器生成的原型,TPS不仅便于后续预测的优化原型重用,还可无缝融入当前的提示工程进展。在测试时,TPS仅根据给定的测试样本动态学习每个原型的偏移向量,有效地缩小了域差距并提高了分类精度。与传统文本提示调整方法相比,我们框架的一个显著特点是其大大降低了内存和计算需求。在涉及自然分布偏移、跨数据集推广以及上下文相关视觉推理的15个图像分类数据集上的广泛评估,展示了TPS的卓越性能,在降低资源要求的同时取得了最新结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at WACV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了针对视觉语言模型(VLMs)在测试环境中出现领域漂移问题的一种解决方案——Test-Time Prototype Shifting(TPS)框架。该框架利用未标记的测试输入自适应调整模型,通过调制共享嵌入空间中的每类原型来实现。该方法基于预计算的原型和文本编码器的缓存,不仅实现了优化后的原型重用,而且可以与当前的提示工程技术无缝集成。在测试时,TPS根据给定的测试样本动态学习每个原型的转移向量,有效弥合领域差距并提高了分类准确性。与传统文本提示调整方法相比,TPS具有显著减少的内存和计算需求。通过广泛的实验评估,TPS在涉及自然分布变化和跨数据集泛化的图像分类以及上下文相关的视觉推理任务中表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- Test-Time Prototype Shifting (TPS) 是一个旨在自适应视觉语言模型(VLMs)至测试数据集的框架。
- TPS 通过调制共享嵌入空间中的每类原型来解决领域漂移问题。
- TPS 利用预计算的原型和文本编码器的缓存实现优化后的原型重用。
- TPS 在测试时根据测试样本动态调整原型,弥合领域差距并提高分类准确性。
- TPS 与传统文本提示调整方法相比,显著减少了内存和计算需求。
- TPS 在图像分类、自然分布变化和跨数据集泛化等任务中表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图


Efficient Prompt Tuning of Large Vision-Language Model for Fine-Grained Ship Classification
Authors:Long Lan, Fengxiang Wang, Xiangtao Zheng, Zengmao Wang, Xinwang Liu
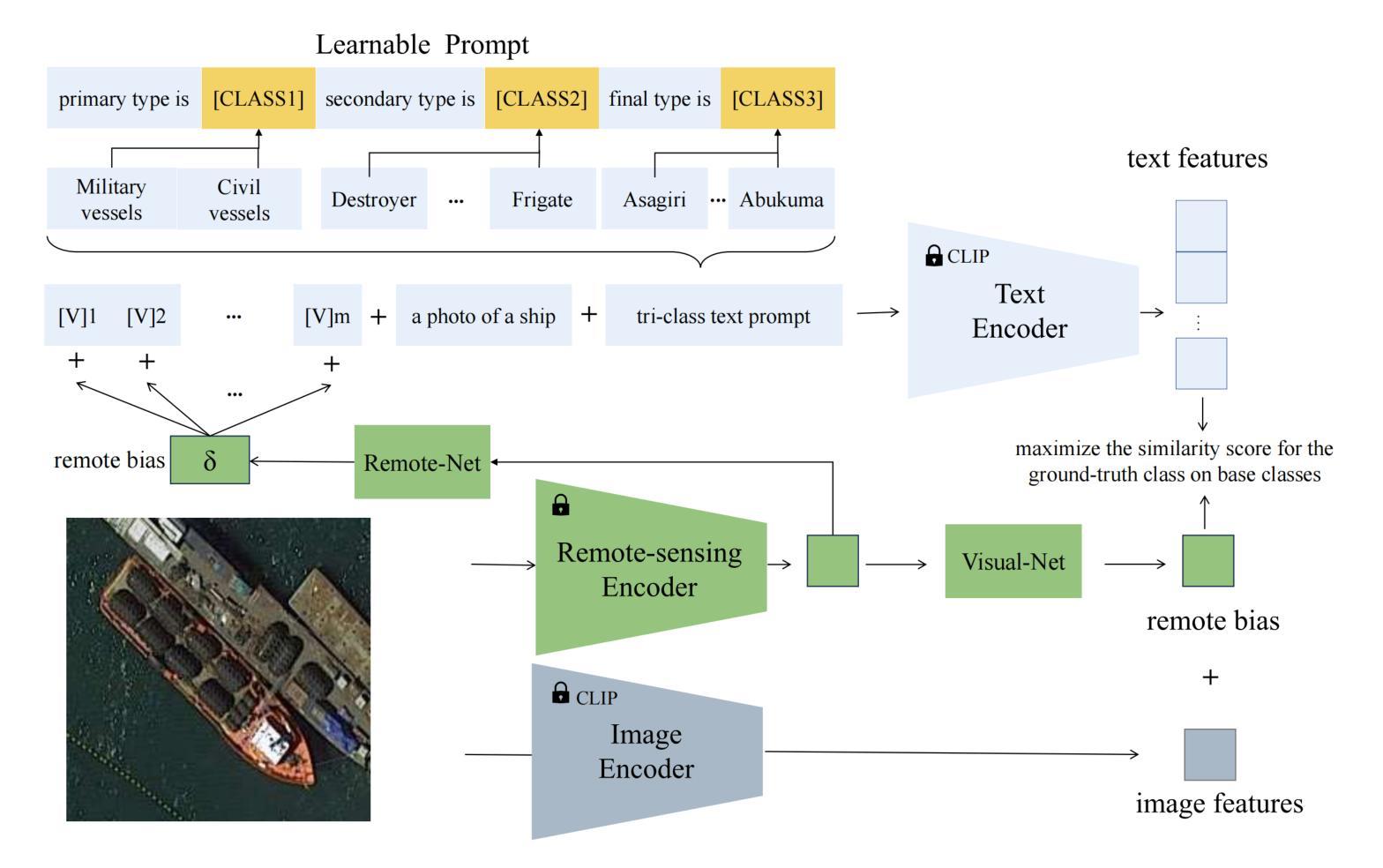
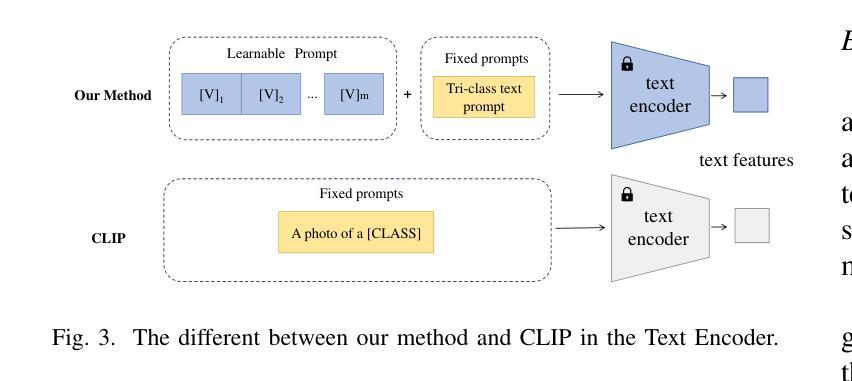
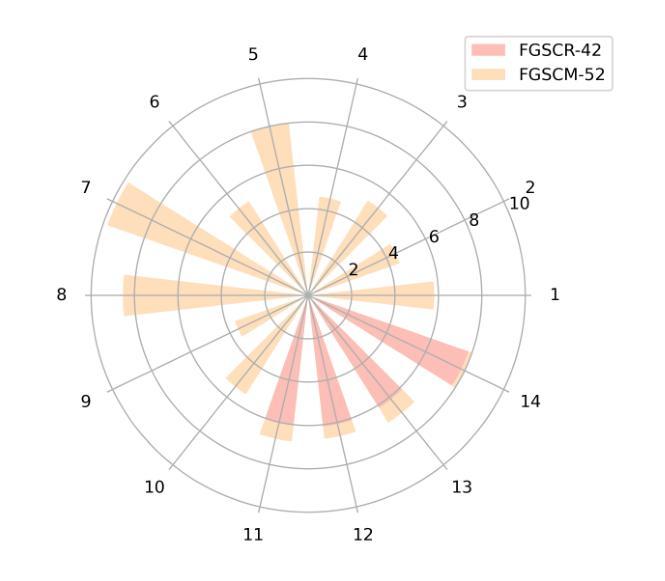
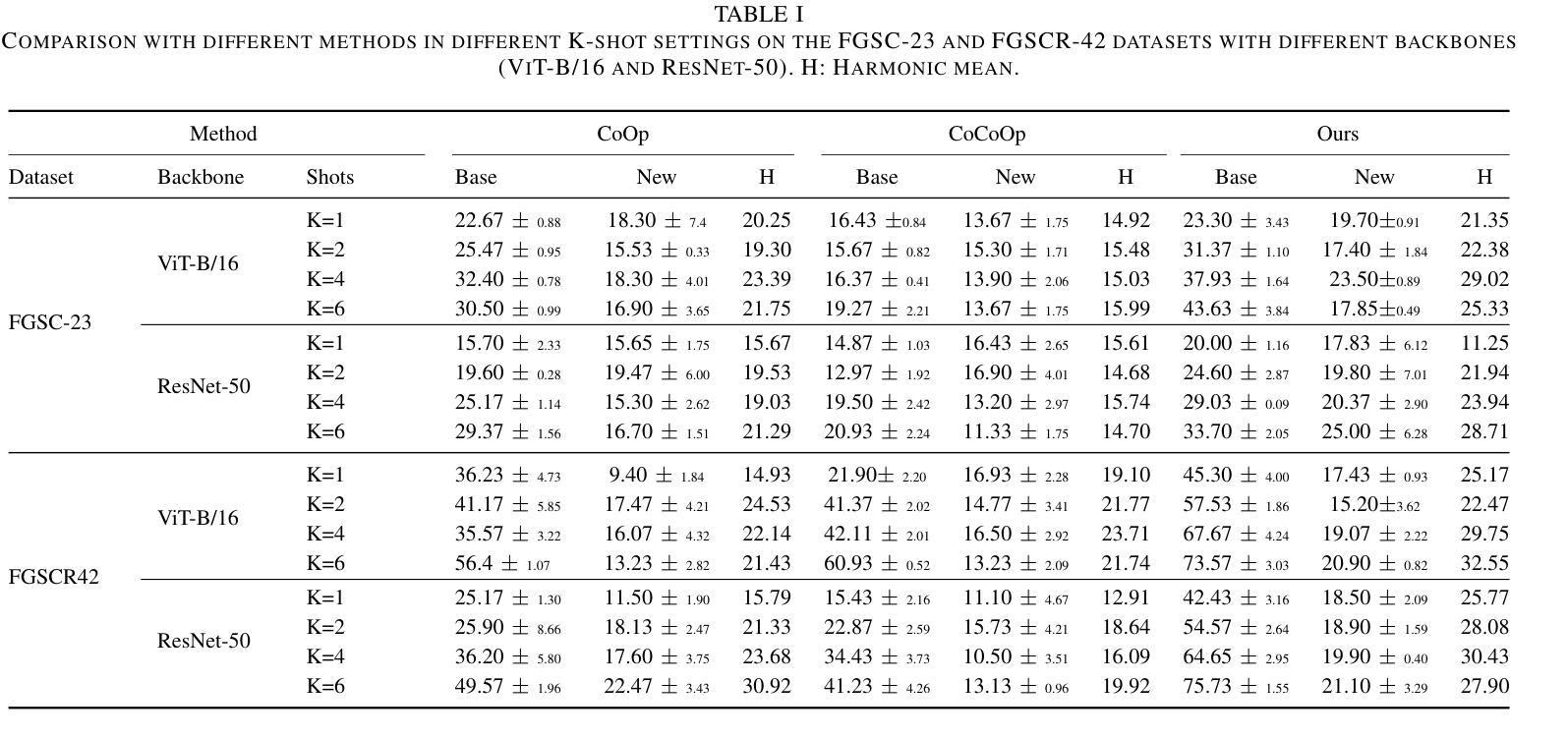
Fine-grained ship classification in remote sensing (RS-FGSC) poses a significant challenge due to the high similarity between classes and the limited availability of labeled data, limiting the effectiveness of traditional supervised classification methods. Recent advancements in large pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in few-shot or zero-shot learning, particularly in understanding image content. This study delves into harnessing the potential of VLMs to enhance classification accuracy for unseen ship categories, which holds considerable significance in scenarios with restricted data due to cost or privacy constraints. Directly fine-tuning VLMs for RS-FGSC often encounters the challenge of overfitting the seen classes, resulting in suboptimal generalization to unseen classes, which highlights the difficulty in differentiating complex backgrounds and capturing distinct ship features. To address these issues, we introduce a novel prompt tuning technique that employs a hierarchical, multi-granularity prompt design. Our approach integrates remote sensing ship priors through bias terms, learned from a small trainable network. This strategy enhances the model’s generalization capabilities while improving its ability to discern intricate backgrounds and learn discriminative ship features. Furthermore, we contribute to the field by introducing a comprehensive dataset, FGSCM-52, significantly expanding existing datasets with more extensive data and detailed annotations for less common ship classes. Extensive experimental evaluations demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method over current state-of-the-art techniques. The source code will be made publicly available.
遥感中的精细粒度船舶分类(RS-FGSC)由于类别之间的相似性高和标记数据有限,对传统监督分类方法的有效性构成了重大挑战。最近的大型预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)在少量或零样本学习方面表现出了令人印象深刻的能力,特别是在理解图像内容方面。本研究致力于挖掘VLMs的潜力,以提高对未见船舶类别的分类准确性,这在由于成本或隐私约束而导致数据受限的场景中具有重要意义。直接对RS-FGSC微调VLMs经常会遇到过度拟合已见类别的问题,导致对未见类别的泛化能力不佳,这突出了区分复杂背景和捕捉船舶特征困难的挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了一种新型提示调整技术,该技术采用分层多粒度提示设计。我们的方法通过从小型可训练网络中学习遥感船舶先验,将遥感船舶先验集成到模型中。此策略提高了模型的泛化能力,同时提高了其区分复杂背景和学习能力船舶特征的能力。此外,我们还通过引入综合数据集FGSCM-52为该领域做出贡献,该数据集对现有数据集进行了重大扩展,包含更多广泛的数据和罕见的船舶类别的详细注释。大量的实验评估证明了我们提出的方法优于当前最先进的技术。源代码将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF It has been accepted by TGRS
Summary
本文探讨了利用大型预训练视觉语言模型(VLMs)进行远程感知精细船舶分类的挑战和机遇。针对数据受限的场景,研究提出了基于层次化多粒度提示设计的微调技术,以提高模型在未标注船舶类别上的分类精度。通过引入远程感应船舶先验,提高了模型的泛化能力和辨识复杂背景及学习船舶特征的能力。同时,研究还贡献了一个综合数据集FGSCM-52,对现有数据集进行了扩充,包含更广泛的数据和详细的注释。实验评估表明,该方法优于当前先进技术。
Key Takeaways
- 远程感知精细船舶分类面临高类别相似性和标注数据有限的挑战,限制了传统监督分类方法的有效性。
- 大型预训练视觉语言模型在少样本或零样本学习中表现出强大的能力,尤其在理解图像内容方面。
- 直接微调视觉语言模型进行远程感知精细船舶分类可能会面临过拟合已见类别的问题,导致对未见类别的泛化能力不佳。
- 提出了一种基于层次化多粒度提示设计的提示微调技术,通过引入远程感应船舶先验,提高模型的泛化能力和辨识复杂背景及学习船舶特征的能力。
- 引入了一个综合数据集FGSCM-52,对现有数据集进行了扩充,包含更广泛的数据和详细的注释。
- 实验评估表明,该方法在未见船舶类别上的分类精度优于当前先进技术。
点此查看论文截图

Learning Prompt with Distribution-Based Feature Replay for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
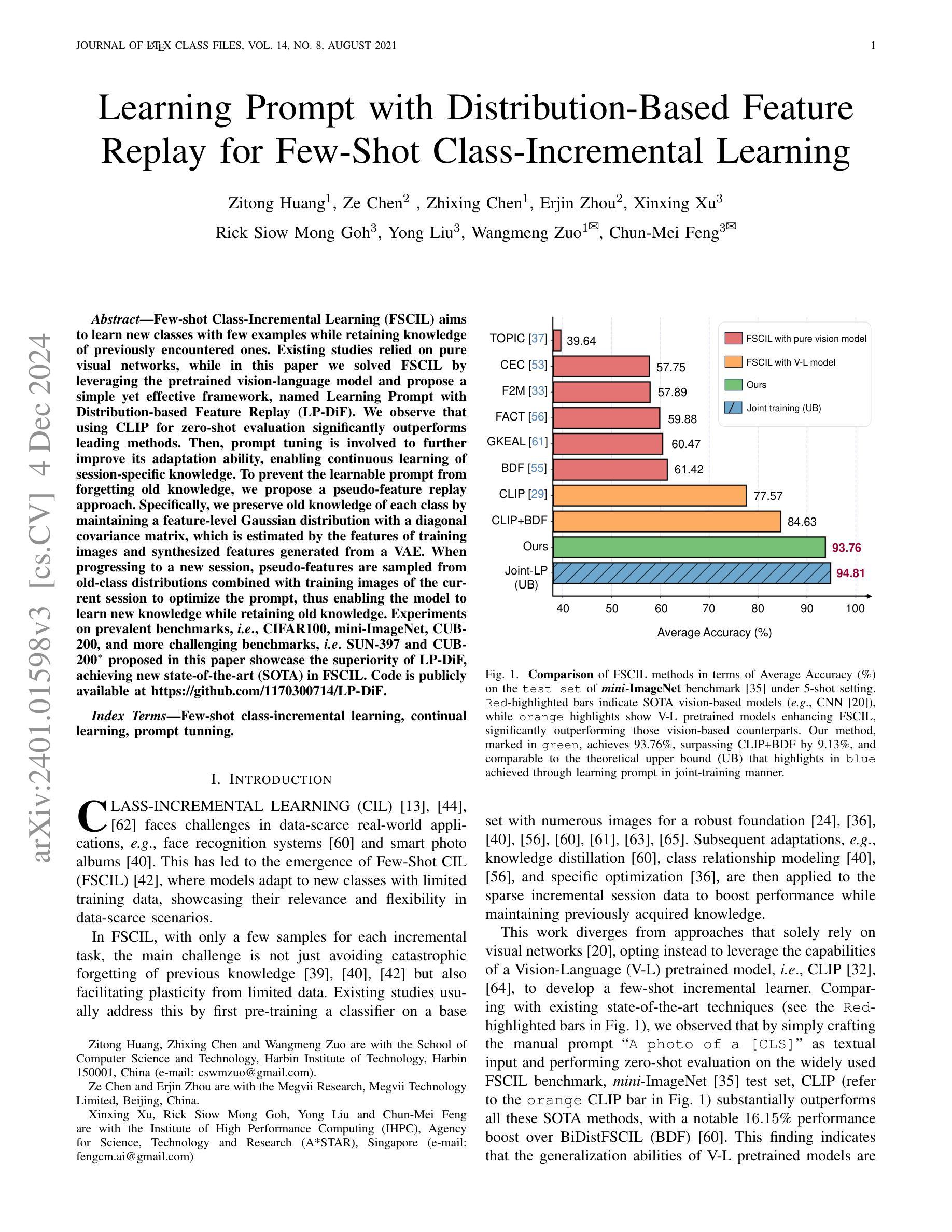
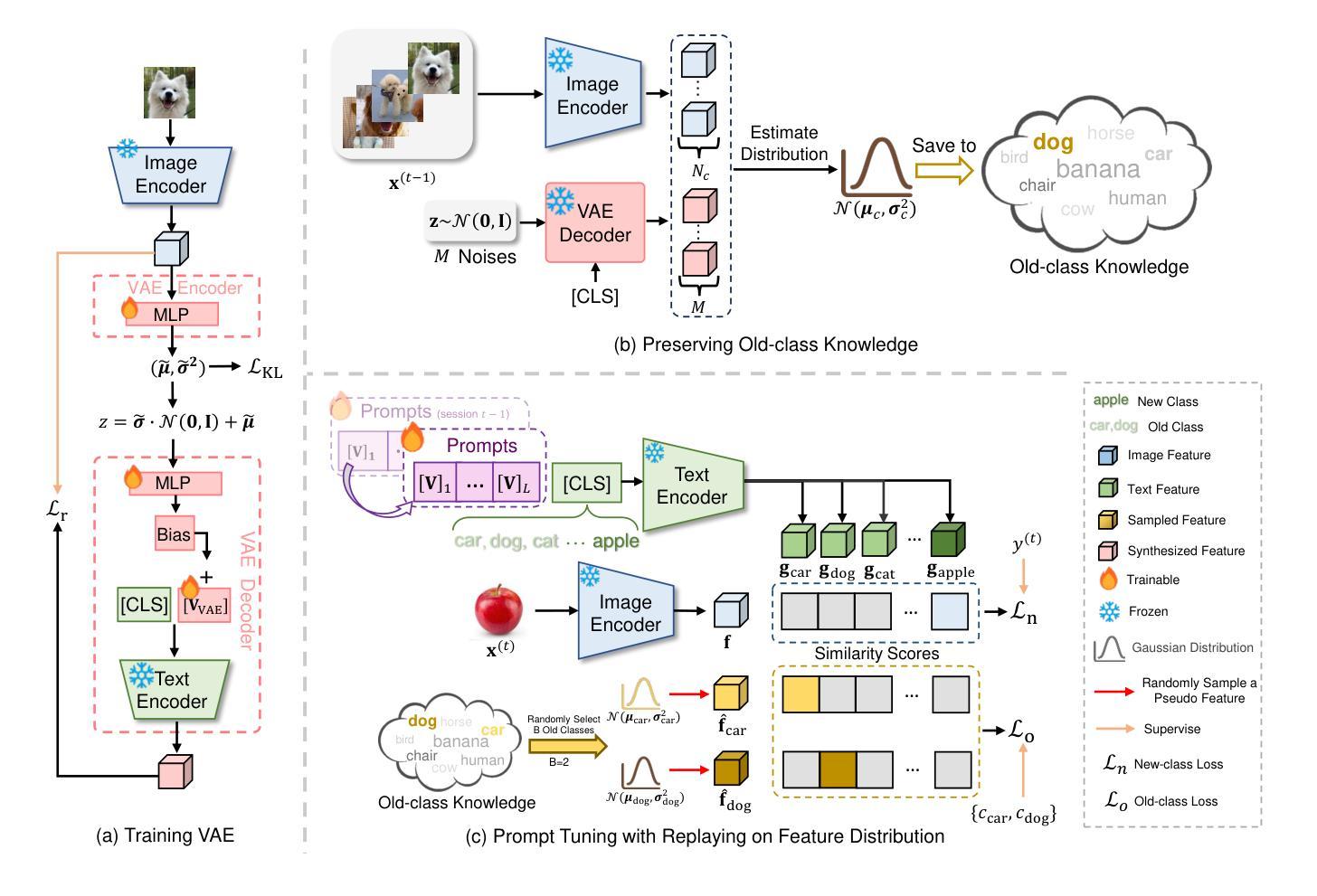
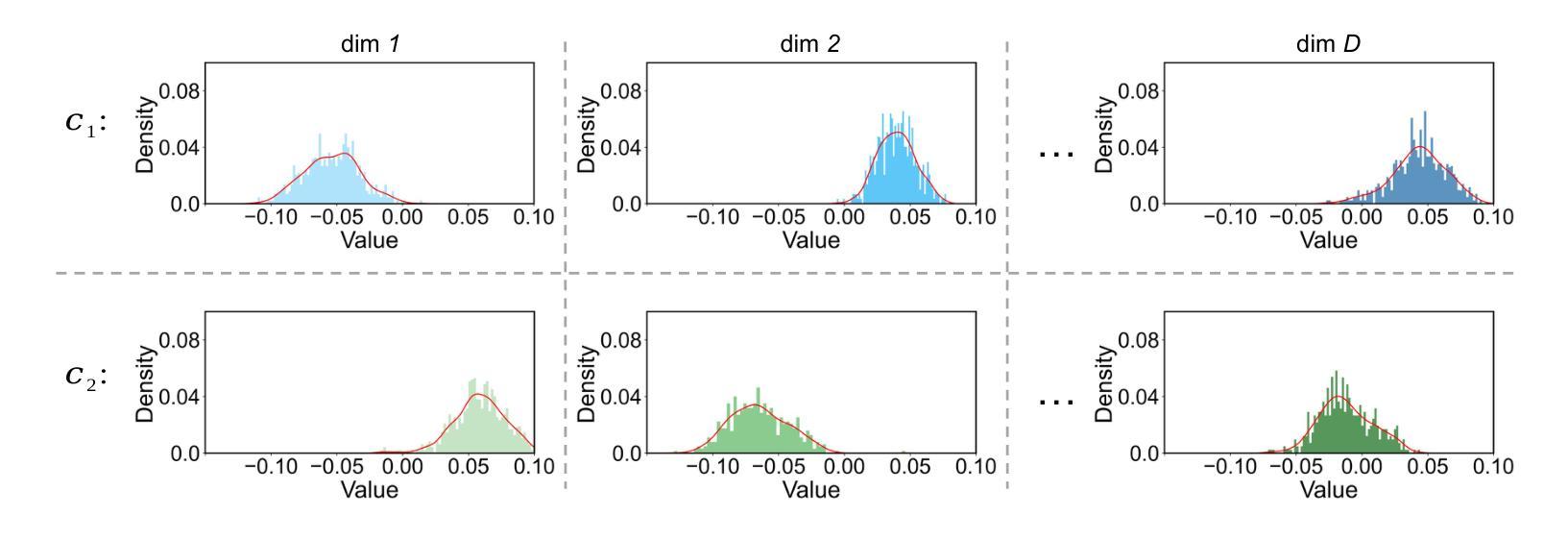
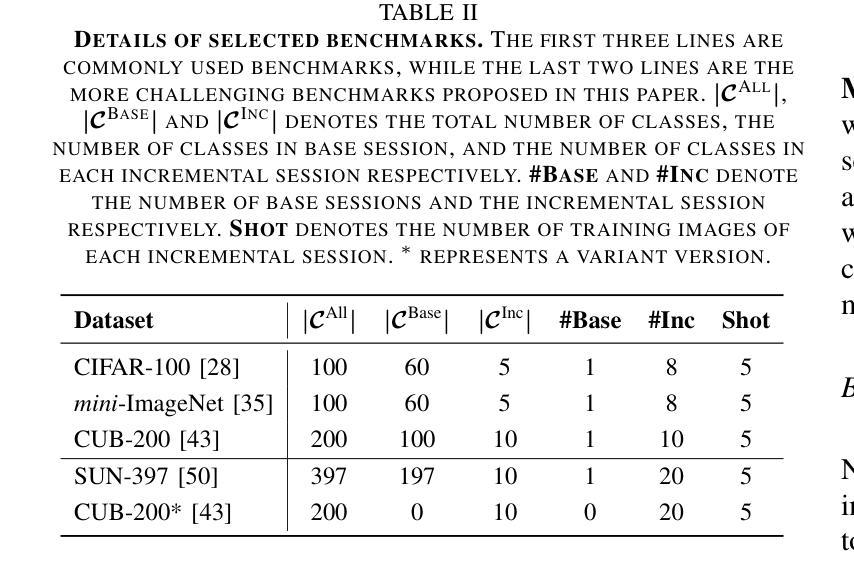
Authors:Zitong Huang, Ze Chen, Zhixing Chen, Erjin Zhou, Xinxing Xu, Rick Siow Mong Goh, Yong Liu, Wangmeng Zuo, Chunmei Feng
Few-shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) aims to continuously learn new classes based on very limited training data without forgetting the old ones encountered. Existing studies solely relied on pure visual networks, while in this paper we solved FSCIL by leveraging the Vision-Language model (e.g., CLIP) and propose a simple yet effective framework, named Learning Prompt with Distribution-based Feature Replay (LP-DiF). We observe that simply using CLIP for zero-shot evaluation can substantially outperform the most influential methods. Then, prompt tuning technique is involved to further improve its adaptation ability, allowing the model to continually capture specific knowledge from each session. To prevent the learnable prompt from forgetting old knowledge in the new session, we propose a pseudo-feature replay approach. Specifically, we preserve the old knowledge of each class by maintaining a feature-level Gaussian distribution with a diagonal covariance matrix, which is estimated by the image features of training images and synthesized features generated from a VAE. When progressing to a new session, pseudo-features are sampled from old-class distributions combined with training images of the current session to optimize the prompt, thus enabling the model to learn new knowledge while retaining old knowledge. Experiments on three prevalent benchmarks, i.e., CIFAR100, mini-ImageNet, CUB-200, and two more challenging benchmarks, i.e., SUN-397 and CUB-200$^*$ proposed in this paper showcase the superiority of LP-DiF, achieving new state-of-the-art (SOTA) in FSCIL. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/1170300714/LP-DiF.
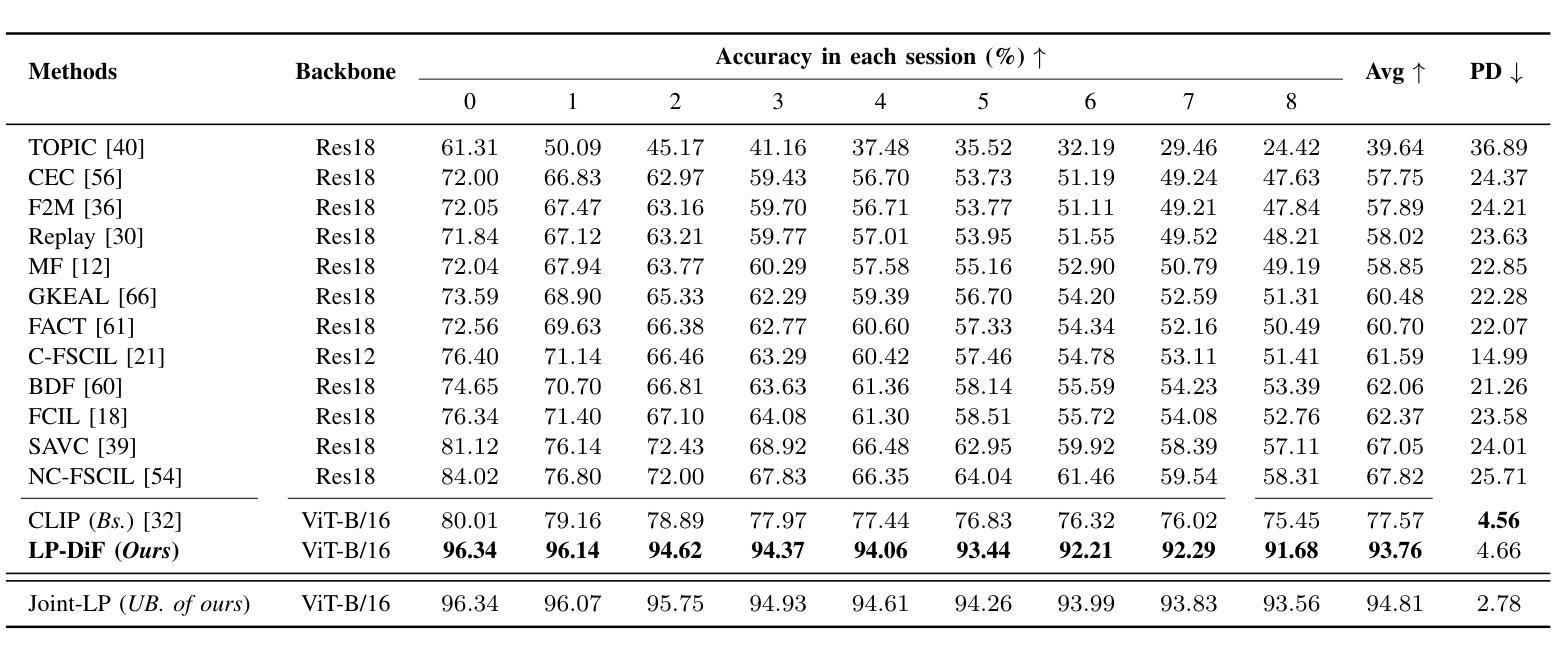
少量样本类增量学习(FSCIL)旨在基于非常有限的训练数据持续学习新类别,同时不忘掉之前遇到的旧类别。现有研究仅依赖纯粹的视觉网络,而本文中我们通过利用视觉语言模型(例如CLIP)来解决FSCIL问题,并提出一个简单有效的框架,称为基于分布特征回放的学习提示(LP-DiF)。我们发现,仅使用CLIP进行零样本评估就可以大大超越最具影响力的方法。接着,我们引入了提示调整技术,以进一步提高其适应能力,使模型能够持续从每个会话中捕获特定知识。为了防止学习提示忘记新会话中的旧知识,我们提出了一种伪特征回放方法。具体来说,我们通过维持一个由训练图像特征和变自动编码器生成的合成特征估计的协方差矩阵为对角的高斯分布来保留每个类的旧知识。当进入新会话时,伪特征是从旧类分布中采样并结合当前会话的训练图像来优化提示,从而能够使模型在学习新知识的同时保留旧知识。在CIFAR100、mini-ImageNet和CUB-200三个流行的基准测试以及本文提出的更具挑战性的SUN-397和CUB-200$*$基准测试上的实验展示了LP-DiF的优越性,在FSCIL领域实现了新的最新状态(SOTA)。代码公开在:https://github.com/1170300714/LP-DiF。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文旨在解决小样本类别增量学习(FSCIL)问题,通过结合视觉和语言模型(如CLIP)提出了一种简单有效的框架,名为Learning Prompt with Distribution-based Feature Replay(LP-DiF)。研究发现,仅使用CLIP进行零样本评估已经可以显著超越最先进的方法。通过引入提示微调技术,进一步提高了模型的适应能力,使其能够连续捕捉每个会话的特定知识。为防止学习提示在新会话中遗忘旧知识,提出了一种伪特征回放方法。具体来说,通过维持特征级的Gaussian分布(通过对角协方差矩阵估计训练图像的特征和从VAE生成的合成特征)来保留每个类的旧知识。当进入新会话时,将伪特征从旧类分布中采样并与当前会话的训练图像结合,以优化提示,从而使模型能够在学习新知识的同时保留旧知识。在多个流行基准测试(如CIFAR100、mini-ImageNet和CUB-200)以及本文提出的两个更具挑战性的基准测试(SUN-397和CUB-200*)上的实验表明,LP-DiF具有优越性,在FSCIL领域取得了最新最先进的成果。代码已公开在https://github.com/1170300714/LP-DiF。
要点解析
- LP-DiF框架利用视觉语言模型(如CLIP)解决了小样类别增量学习(FSCIL)问题。
- 仅使用CLIP进行零样本评估已表现出卓越性能。
- 引入提示微调技术进一步提高模型的适应能力,使其能连续捕捉每个会话的特定知识。
- 提出伪特征回放方法,防止学习提示在新会话中遗忘旧知识。
- 通过维护特征级的Gaussian分布来保留旧知识。
- 结合伪特征和当前会话的训练图像来优化提示,实现新旧知识的平衡学习。
点此查看论文截图
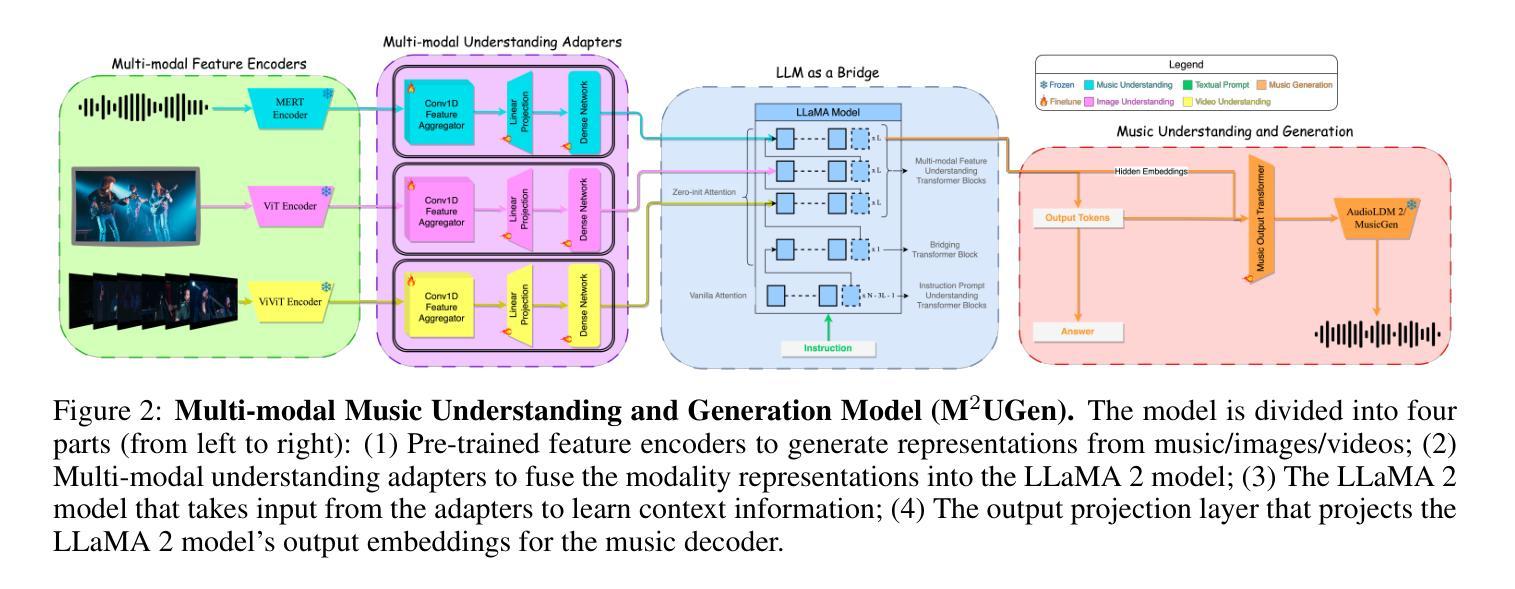
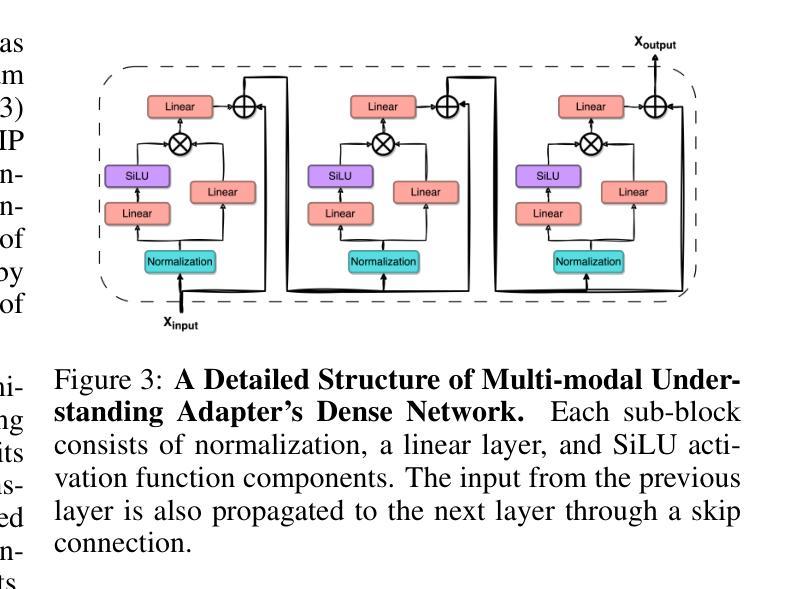
M$^{2}$UGen: Multi-modal Music Understanding and Generation with the Power of Large Language Models
Authors:Shansong Liu, Atin Sakkeer Hussain, Qilong Wu, Chenshuo Sun, Ying Shan
The current landscape of research leveraging large language models (LLMs) is experiencing a surge. Many works harness the powerful reasoning capabilities of these models to comprehend various modalities, such as text, speech, images, videos, etc. They also utilize LLMs to understand human intention and generate desired outputs like images, videos, and music. However, research that combines both understanding and generation using LLMs is still limited and in its nascent stage. To address this gap, we introduce a Multi-modal Music Understanding and Generation (M$^{2}$UGen) framework that integrates LLM’s abilities to comprehend and generate music for different modalities. The M$^{2}$UGen framework is purpose-built to unlock creative potential from diverse sources of inspiration, encompassing music, image, and video through the use of pretrained MERT, ViT, and ViViT models, respectively. To enable music generation, we explore the use of AudioLDM 2 and MusicGen. Bridging multi-modal understanding and music generation is accomplished through the integration of the LLaMA 2 model. Furthermore, we make use of the MU-LLaMA model to generate extensive datasets that support text/image/video-to-music generation, facilitating the training of our M$^{2}$UGen framework. We conduct a thorough evaluation of our proposed framework. The experimental results demonstrate that our model achieves or surpasses the performance of the current state-of-the-art models.
当前利用大型语言模型(LLM)的研究领域正经历一次热潮。许多研究利用这些模型的强大推理能力来理解各种模态,如文本、语音、图像、视频等。他们还利用LLM来理解人类意图并生成想要的输出,如图像、视频和音乐。然而,结合LLM的理解和生成能力的研究仍然有限,处于初级阶段。为了解决这一空白,我们引入了一个多模态音乐理解和生成(M^2^UGen)框架,该框架集成了LLM理解和生成不同模态音乐的能力。M^2^UGen框架专为解锁来自各种灵感来源的创造力而构建,通过使用预训练的MERT、ViT和ViViT模型,分别涵盖音乐、图像和视频。为了实现音乐生成,我们探索了使用AudioLDM 2和MusicGen。通过LLaMA 2模型的集成,实现了多模态理解和音乐生成的桥梁。此外,我们利用MU-LLaMA模型生成了大量支持文本/图像/视频到音乐生成的数据集,促进了我们的M^2^UGen框架的训练。我们对提出的框架进行了全面评估。实验结果表明,我们的模型达到了或超越了当前最先进的模型性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLMs)在多模态理解和生成领域具有广阔的应用前景,特别是在音乐领域。针对这一趋势,本文提出了一种多模态音乐理解和生成(M^2UGen)框架,融合了LLMs的音乐理解和生成能力。该框架借助预训练的MERT、ViT和ViViT模型,实现了音乐、图像和视频的多模态融合。此外,通过整合LLaMA 2模型和MU-LLaMA模型,框架支持文本/图像/视频到音乐的生成,并在实验评估中表现出卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)在多模态领域,特别是在音乐领域的应用正受到越来越多的关注。
- 当前研究在结合理解和生成能力使用LLMs方面仍处于初级阶段。
- M^2UGen框架融合了LLMs的音乐理解和生成能力,旨在从不同来源的灵感中解锁创意潜力。
- 该框架借助预训练的MERT、ViT和ViViT模型,实现了音乐、图像和视频的多模态融合。
- 通过整合LLaMA 2模型和MU-LLaMA模型,M^2UGen支持文本/图像/视频到音乐的生成。
- 实验评估表明,M^2UGen框架性能卓越,达到或超越了现有最新模型。
- 该框架的提出为未来的多模态音乐理解和生成研究开辟了新的方向。
点此查看论文截图
Weakly-Supervised Semantic Segmentation with Image-Level Labels: from Traditional Models to Foundation Models
Authors:Zhaozheng Chen, Qianru Sun
The rapid development of deep learning has driven significant progress in image semantic segmentation - a fundamental task in computer vision. Semantic segmentation algorithms often depend on the availability of pixel-level labels (i.e., masks of objects), which are expensive, time-consuming, and labor-intensive. Weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) is an effective solution to avoid such labeling. It utilizes only partial or incomplete annotations and provides a cost-effective alternative to fully-supervised semantic segmentation. In this journal, our focus is on the WSSS with image-level labels, which is the most challenging form of WSSS. Our work has two parts. First, we conduct a comprehensive survey on traditional methods, primarily focusing on those presented at premier research conferences. We categorize them into four groups based on where their methods operate: pixel-wise, image-wise, cross-image, and external data. Second, we investigate the applicability of visual foundation models, such as the Segment Anything Model (SAM), in the context of WSSS. We scrutinize SAM in two intriguing scenarios: text prompting and zero-shot learning. We provide insights into the potential and challenges of deploying visual foundational models for WSSS, facilitating future developments in this exciting research area.
深度学习的快速发展推动了图像语义分割领域的显著进步,这是计算机视觉中的一项基础任务。语义分割算法通常依赖于像素级标签(即对象掩膜)的可用性,而这些标签的获取成本高昂、耗时且劳力密集。弱监督语义分割(WSSS)是避免这种标注的有效解决方案。它仅利用部分或不完整的注释,为全监督语义分割提供了经济实惠的替代方案。在本期刊中,我们的重点是在图像级标签的WSSS,这是WSSS中最具挑战性的形式。我们的工作分为两部分。首先,我们对传统方法进行了全面调查,主要关注在主要研究会议上提出的方法。我们根据它们的方法操作位置将它们分为四类:像素级、图像级、跨图像和外部数据。其次,我们研究了视觉基础模型,如分段任何模型(SAM)在WSSS中的应用。我们在两个有趣的场景中仔细审查了SAM:文本提示和零样本学习。我们深入探讨了将视觉基础模型用于WSSS的潜力和挑战,有助于推动这一激动人心的研究领域的未来发展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to ACM Computing Surveys
Summary
深度学习的快速发展推动了图像语义分割领域的显著进步,这是计算机视觉中的一项基础任务。语义分割算法通常依赖于像素级标签(即对象掩膜)的可用性,这些标签昂贵、耗时且劳动密集。弱监督语义分割(WSSS)是避免这种标注的有效解决方案,它仅利用部分或不完整的注释,为全监督语义分割提供了成本效益高的替代方案。本文重点关注使用图像级标签的WSSS,这是WSSS中最具挑战性的形式。本文首先对传统方法进行了全面调查,主要关注在主要研究会议上发表的方法,将其分为四类:像素级、图像级、跨图像和外部数据。接着探讨了视觉基础模型(如Segment Anything Model,SAM)在WSSS中的应用。本文在两种有趣的情况下对SAM进行了审查:文本提示和零样本学习。本文提供了将视觉基础模型用于WSSS的潜力和挑战的见解,有助于这一令人兴奋的研究领域未来的发展。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习的进步推动了图像语义分割的发展。
- 语义分割算法依赖像素级标签,这些标签既昂贵又耗时。
- 弱监督语义分割(WSSS)是一种利用部分或不完整注释的有效方法。
- 使用图像级标签的WSSS是最具挑战性的形式。
- 传统方法被分类为像素级、图像级、跨图像和外部数据四类。
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)等视觉基础模型在WSSS中具有应用价值。
点此查看论文截图

NoisyNN: Exploring the Impact of Information Entropy Change in Learning Systems
Authors:Xiaowei Yu, Zhe Huang, Minheng Chen, Yao Xue, Tianming Liu, Dajiang Zhu
We investigate the impact of entropy change in deep learning systems by noise injection at different levels, including the embedding space and the image. The series of models that employ our methodology are collectively known as Noisy Neural Networks (NoisyNN), with examples such as NoisyViT and NoisyCNN. Noise is conventionally viewed as a harmful perturbation in various deep learning architectures, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and vision transformers (ViTs), as well as different learning tasks like image classification and transfer learning. However, this work shows noise can be an effective way to change the entropy of the learning system. We demonstrate that specific noise can boost the performance of various deep models under certain conditions. We theoretically prove the enhancement gained from positive noise by reducing the task complexity defined by information entropy and experimentally show the significant performance gain in large image datasets, such as the ImageNet. Herein, we use the information entropy to define the complexity of the task. We categorize the noise into two types, positive noise (PN) and harmful noise (HN), based on whether the noise can help reduce the task complexity. Extensive experiments of CNNs and ViTs have shown performance improvements by proactively injecting positive noise, where we achieved an unprecedented top 1 accuracy of 95$%$ on ImageNet. Both theoretical analysis and empirical evidence have confirmed that the presence of positive noise, can benefit the learning process, while the traditionally perceived harmful noise indeed impairs deep learning models. The different roles of noise offer new explanations for deep models on specific tasks and provide a new paradigm for improving model performance. Moreover, it reminds us that we can influence the performance of learning systems via information entropy change.
我们通过在深度学习系统的不同层次(包括嵌入空间和图像)注入噪声来研究其对深度学习系统熵变化的影响。采用我们方法的系列模型统称为噪声神经网络(Noisy Neural Networks,NoisyNN),例如NoisyViT和NoisyCNN等。噪声在传统上被视为对深度学习架构有害的扰动,如卷积神经网络(CNN)和视觉转换器(ViT),以及不同的学习任务,如图像分类和迁移学习等。然而,这项工作表明噪声可以是改变学习系统熵的有效途径。我们证明在某些条件下,特定噪声可以提高各种深度模型的性能。我们从理论上证明了正面噪声通过减少由信息熵定义的任务复杂性所带来的增强效果,并通过实验显示了在大型图像数据集(如ImageNet)中的显著性能提升。在这里,我们使用信息熵来定义任务的复杂性。我们将噪声分为正面噪声(PN)和有害噪声(HN)两种类型,取决于噪声是否有助于降低任务复杂性。对CNN和ViT的大量实验表明,通过主动注入正面噪声可以提高性能,我们在ImageNet上实现了前所未有的95%的Top-1准确率。理论分析和实证证据都证实,正面噪声的存在有益于学习过程,而传统上认为的有害噪声确实会损害深度学习模型。噪声的不同作用为特定任务的深度模型提供了新的解释,并为提高模型性能提供了新的范式。此外,它提醒我们,我们可以通过改变信息熵来影响学习系统的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Task Entropy, NoisyViT, NoisyCNN
Summary
该文本研究了深度学习系统中熵变化的影响,通过在嵌入空间和图像等不同层面注入噪声来实现。文中介绍了被称为“噪声神经网络”(Noisy Neural Networks,NoisyNN)的一系列模型,如NoisyViT和NoisyCNN。尽管噪声在传统上被视为对深度学习架构(如CNN和ViT)以及图像分类和迁移学习等学习任务有害的扰动,但本文显示噪声可以有效地改变学习系统的熵。特定噪声在某些条件下可以促进各种深度模型的性能。文章使用信息熵来定义任务的复杂性,将噪声分为有助于减少任务复杂性的正面噪声(PN)和有害噪声(HN)。通过主动注入正面噪声,CNN和ViT的广泛实验显示了性能改进,在ImageNet上实现了前所未有的95%的顶级准确率。
Key Takeaways
- 文中探讨了深度学习系统中熵变化的影响,通过在不同层面(如嵌入空间和图像)注入噪声进行研究。
- 介绍了“噪声神经网络”(NoisyNN)系列模型,包括NoisyViT和NoisyCNN等。
- 不同于传统观点,该研究表明噪声可以有效地改变学习系统的熵。
- 特定类型的噪声在特定条件下能够促进深度学习模型的性能。
- 文章使用信息熵来定义任务的复杂性,将噪声分为正面噪声和有害噪声两类。
- 通过主动注入正面噪声,在ImageNet等大型图像数据集上实现了显著的性能提升。
点此查看论文截图

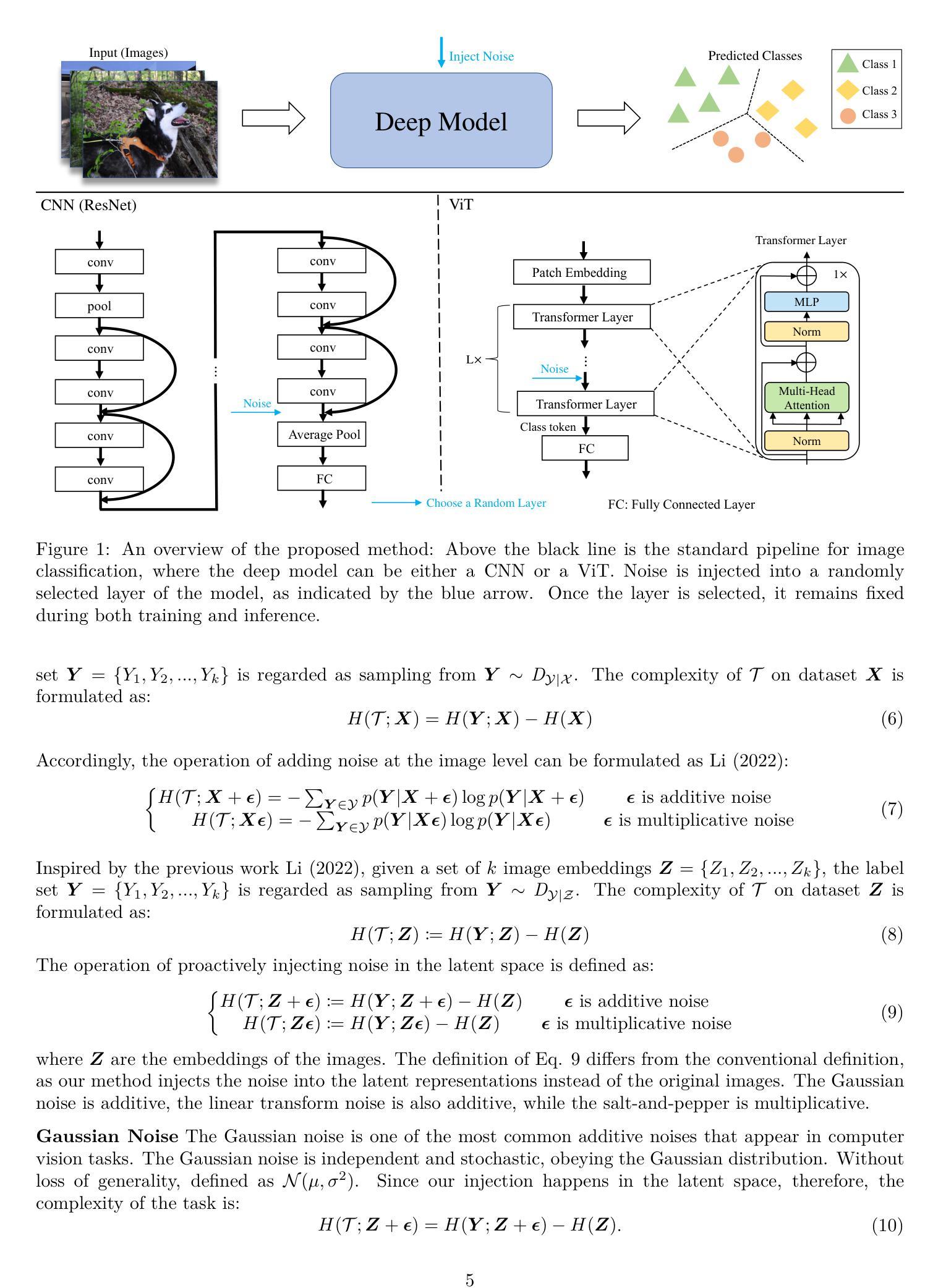
Retrieval-Enhanced Visual Prompt Learning for Few-shot Classification
Authors:Jintao Rong, Hao Chen, Linlin Ou, Tianxiao Chen, Xinyi Yu, Yifan Liu
The Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) model has been widely used in various downstream vision tasks. The few-shot learning paradigm has been widely adopted to augment its capacity for these tasks. However, current paradigms may struggle with fine-grained classification, such as satellite image recognition, due to widening domain gaps. To address this limitation, we propose retrieval-enhanced visual prompt learning (RePrompt), which introduces retrieval mechanisms to cache and reuse the knowledge of downstream tasks. RePrompt constructs a retrieval database from either training examples or external data if available, and uses a retrieval mechanism to enhance multiple stages of a simple prompt learning baseline, thus narrowing the domain gap. During inference, our enhanced model can reference similar samples brought by retrieval to make more accurate predictions. A detailed analysis reveals that retrieval helps to improve the distribution of late features, thus, improving generalization for downstream tasks. Reprompt attains state-of-the-art performance on a wide range of vision datasets, including 11 image datasets, 3 video datasets, 1 multi-view dataset, and 4 domain generalization benchmarks.
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)模型在各种下游视觉任务中得到了广泛应用。少样本学习范式已被广泛采用以增强其对这些任务的能力。然而,由于域差距的扩大,当前范式可能在细粒度分类(如卫星图像识别)方面遇到困难。为了解决这一局限性,我们提出了检索增强视觉提示学习(RePrompt),它引入了检索机制来缓存和重复使用下游任务的知识。RePrompt从训练样本或可用的外部数据中构建检索数据库,并使用检索机制增强简单提示学习基准的多个阶段,从而缩小域差距。在推理过程中,我们增强的模型可以引用检索带来的相似样本以做出更准确的预测。详细分析表明,检索有助于改进后期特征的分布,从而提高下游任务的泛化能力。RePrompt在广泛的视觉数据集上达到了最先进的性能,包括11个图像数据集、3个视频数据集、1个多视图数据集和4个域泛化基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于CLIP模型的对比语言图像预训练已广泛应用于多种下游视觉任务。为提高模型在这些任务中的性能,研究者多采用小样本学习范式。然而,对于卫星图像识别等细粒度分类任务,现有范式可能会因领域差距扩大而面临挑战。为解决这一问题,我们提出增强检索的视觉提示学习(RePrompt)方法,引入检索机制以缓存和重用下游任务的知识。RePrompt构建了一个检索数据库,该数据库来源于训练样本或可用的外部数据,并使用检索机制增强简单提示学习基线模型的多个阶段,从而缩小领域差距。在推理过程中,我们的增强模型可以引用检索带来的相似样本,做出更准确的预测。详细分析表明,检索有助于改进晚期特征的分布,从而提高下游任务的泛化能力。RePrompt在多个视觉数据集上取得了最新性能水平,包括11个图像数据集、3个视频数据集、1个多视图数据集和4个领域泛化基准测试。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP模型广泛应用于下游视觉任务,但面临细粒度分类挑战。
- 现有范式在领域差距较大的任务上表现不佳。
- RePrompt通过引入检索机制来增强模型性能,构建检索数据库以缓存和重用知识。
- 检索机制有助于改进晚期特征的分布,提高下游任务的泛化能力。
- RePrompt在多个视觉数据集上取得了最新性能,包括图像、视频、多视图和领域泛化基准测试。
- RePrompt模型通过引用相似样本做出更准确预测。
点此查看论文截图