⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-19 更新
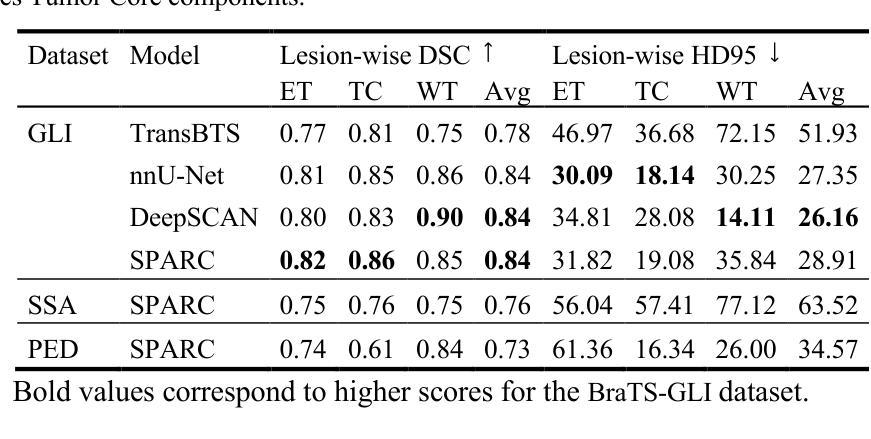
Parameter-efficient Fine-tuning for improved Convolutional Baseline for Brain Tumor Segmentation in Sub-Saharan Africa Adult Glioma Dataset
Authors:Bijay Adhikari, Pratibha Kulung, Jakesh Bohaju, Laxmi Kanta Poudel, Confidence Raymond, Dong Zhang, Udunna C Anazodo, Bishesh Khanal, Mahesh Shakya
Automating brain tumor segmentation using deep learning methods is an ongoing challenge in medical imaging. Multiple lingering issues exist including domain-shift and applications in low-resource settings which brings a unique set of challenges including scarcity of data. As a step towards solving these specific problems, we propose Convolutional adapter-inspired Parameter-efficient Fine-tuning (PEFT) of MedNeXt architecture. To validate our idea, we show our method performs comparable to full fine-tuning with the added benefit of reduced training compute using BraTS-2021 as pre-training dataset and BraTS-Africa as the fine-tuning dataset. BraTS-Africa consists of a small dataset (60 train / 35 validation) from the Sub-Saharan African population with marked shift in the MRI quality compared to BraTS-2021 (1251 train samples). We first show that models trained on BraTS-2021 dataset do not generalize well to BraTS-Africa as shown by 20% reduction in mean dice on BraTS-Africa validation samples. Then, we show that PEFT can leverage both the BraTS-2021 and BraTS-Africa dataset to obtain mean dice of 0.8 compared to 0.72 when trained only on BraTS-Africa. Finally, We show that PEFT (0.80 mean dice) results in comparable performance to full fine-tuning (0.77 mean dice) which may show PEFT to be better on average but the boxplots show that full finetuning results is much lesser variance in performance. Nevertheless, on disaggregation of the dice metrics, we find that the model has tendency to oversegment as shown by high specificity (0.99) compared to relatively low sensitivity(0.75). The source code is available at https://github.com/CAMERA-MRI/SPARK2024/tree/main/PEFT_MedNeXt
使用深度学习方法进行脑肿瘤分割自动化是医学影像领域的一个持续挑战。存在许多悬而未决的问题,包括领域迁移和在资源有限的环境中的应用,这带来了一系列独特的挑战,其中包括数据稀缺。作为解决这些特定问题的一步,我们提出了基于卷积适配器启发的MedNeXt架构参数高效微调(PEFT)方法。为了验证我们的想法,我们展示了我们的方法与全微调相比具有减少训练计算量的优势,同时使用BraTS-2021作为预训练数据集,BraTS-Africa作为微调数据集。BraTS-Africa由来自撒哈拉以南非洲人群的小数据集(60个训练样本/ 35个验证样本)组成,与BraTS-2021相比(1251个训练样本),其MRI质量有明显差异。我们首先表明,在BraTS-2021数据集上训练的模型在BraTS-Africa上表现不佳,在BraTS-Africa验证样本上的平均Dice得分降低了20%。然后,我们显示PEFT可以利用BraTS-2021和BraTS-Africa数据集获得平均Dice得分0.8(仅在BraTS-Africa上训练时为0.72)。最后,我们证明PEFT(平均Dice得分0.80)的性能与全微调(平均Dice得分0.77)相当,这可能表明PEFT在平均性能上更好,但箱线图显示全微调的结果性能波动更小。然而,在对Dice指标进行细分后,我们发现模型倾向于过度分割,表现为特异性较高(0.99),而敏感性相对较低(0.75)。源代码可在https://github.com/CAMERA-MRI/SPARK2024/tree/main/PEFT_MedNeXt找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to “The International Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) challenge organized at MICCAI 2024 conference”
Summary
本文探讨了使用深度学习自动化脑肿瘤分割的挑战,特别是在低资源环境中的挑战。为解决这些问题,提出了一种基于卷积适配器启发的参数高效微调(PEFT)的MedNeXt架构。实验表明,该方法在BraTS-Africa数据集上的表现与全微调相当,并减少了训练计算量。PEFT可利用BraTS-2021和BraTS-Africa数据集获得平均dice系数0.8,而仅在BraTS-Africa数据集上训练时则为0.72。虽然PEFT的平均性能与全微调相当,但全微调的结果表现出较小的性能差异变化。模型的性能偏向过度分割,特异性较高(0.99),而敏感性较低(0.75)。源代码已公开在相关GitHub链接上。
Key Takeaways
- 针对低资源环境下的深度学习脑肿瘤分割存在挑战,如数据稀缺和领域偏移问题。
- 提出了一种基于卷积适配器启发的参数高效微调(PEFT)的MedNeXt架构来解决这些问题。
- PEFT在BraTS-Africa数据集上的表现与全微调相当,并降低了训练计算成本。
- PEFT能够利用BraTS-2021和BraTS-Africa数据集来提高性能,获得平均dice系数0.8。
- PEFT与全微调的性能差异较小,但全微调表现出更稳定的性能表现。
- 模型有过度分割的倾向,表现出高特异性和较低的敏感性。
点此查看论文截图

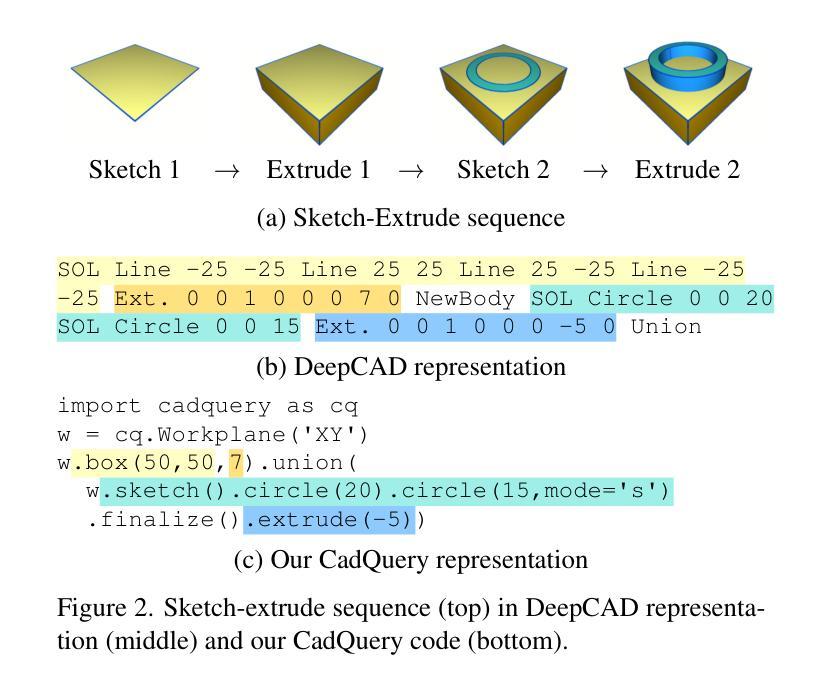
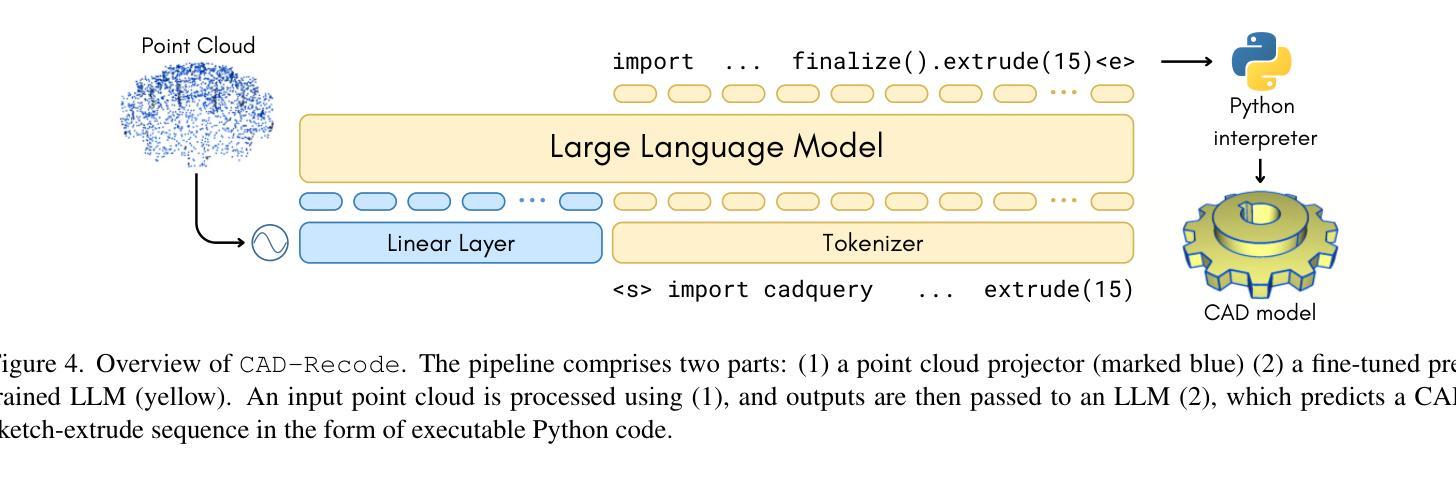
CAD-Recode: Reverse Engineering CAD Code from Point Clouds
Authors:Danila Rukhovich, Elona Dupont, Dimitrios Mallis, Kseniya Cherenkova, Anis Kacem, Djamila Aouada
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) models are typically constructed by sequentially drawing parametric sketches and applying CAD operations to obtain a 3D model. The problem of 3D CAD reverse engineering consists of reconstructing the sketch and CAD operation sequences from 3D representations such as point clouds. In this paper, we address this challenge through novel contributions across three levels: CAD sequence representation, network design, and dataset. In particular, we represent CAD sketch-extrude sequences as Python code. The proposed CAD-Recode translates a point cloud into Python code that, when executed, reconstructs the CAD model. Taking advantage of the exposure of pre-trained Large Language Models (LLMs) to Python code, we leverage a relatively small LLM as a decoder for CAD-Recode and combine it with a lightweight point cloud projector. CAD-Recode is trained solely on a proposed synthetic dataset of one million diverse CAD sequences. CAD-Recode significantly outperforms existing methods across three datasets while requiring fewer input points. Notably, it achieves 10 times lower mean Chamfer distance than state-of-the-art methods on DeepCAD and Fusion360 datasets. Furthermore, we show that our CAD Python code output is interpretable by off-the-shelf LLMs, enabling CAD editing and CAD-specific question answering from point clouds.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型通常是通过依次绘制参数草图并应用CAD操作来获得的三维模型。3D CAD逆向工程的问题在于从点云等3D表示重建草图和CAD操作序列。在本文中,我们通过三个层次的全新贡献来解决这一挑战:CAD序列表示、网络设计和数据集。特别是,我们将CAD草图挤压序列表示为Python代码。所提出的CAD-Recode将点云转换为Python代码,执行时可重建CAD模型。我们利用预训练的 大型语言模型(LLM)对Python代码的暴露,利用相对较小的LLM作为CAD-Recode的解码器,并将其与轻量级的点云投影仪相结合。CAD-Recode仅在一百万个多样化的CAD序列所构成拟合成数据集上进行训练。在三个数据集中,CAD-Recode显著优于现有方法,同时需要的输入点数更少。值得注意的是,它在DeepCAD和Fusion360数据集上实现了比最新技术低10倍的平均Chamfer距离。此外,我们展示了我们的CAD Python代码输出能被市面上的LLM所解释,从而能够有点云进行CAD编辑和特定的问答。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文解决了计算机三维CAD模型的逆向工程问题,通过创新的CAD序列表示方法、网络设计和数据集,实现从点云重建CAD模型。提出CAD-Recode方法,将点云转化为Python代码,利用预训练的LLM解码重建CAD模型。在合成数据集上训练,显著优于现有方法,实现低误差、高效率的CAD模型重建。此外,生成的CAD Python代码易于解读和编辑,增强了CAD模型的交互性和实用性。
Key Takeaways
- CAD模型逆向工程旨在从三维表示(如点云)重建草图及CAD操作序列。
- CAD-Recode方法将点云转化为Python代码,重现CAD模型。
- 利用预训练的LLM作为解码器与轻量级点云投影仪结合。
- 在合成数据集上训练,涵盖一百万个不同的CAD序列。
- 在DeepCAD和Fusion360数据集上,与现有方法相比,实现更低的Chamfer距离(平均降低了十倍)。
点此查看论文截图

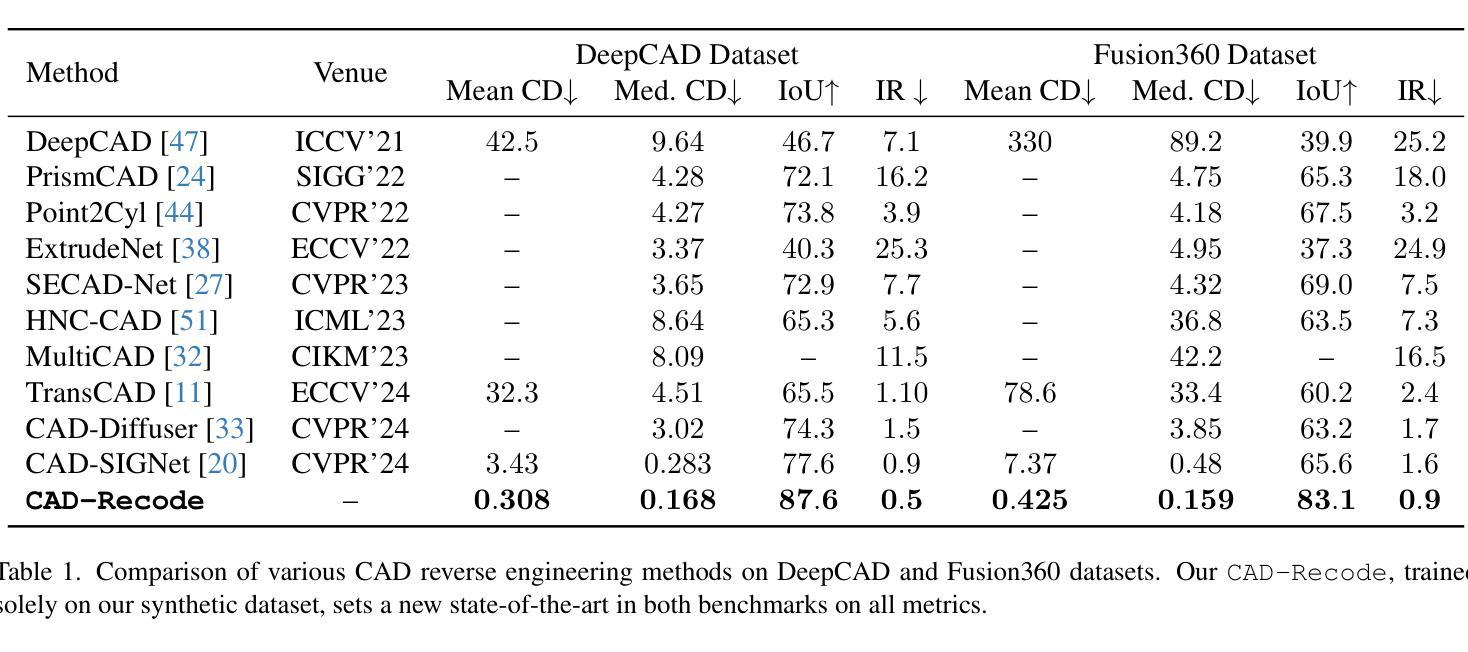
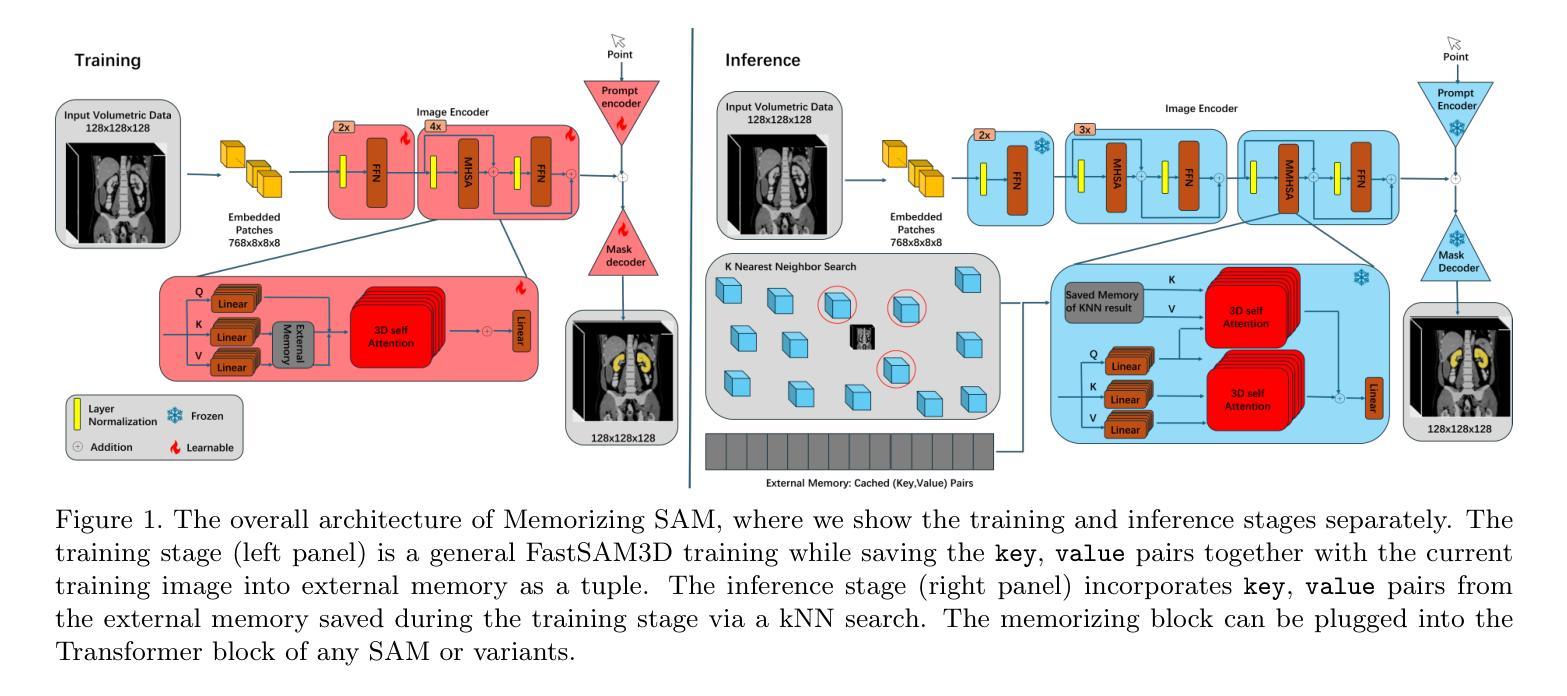
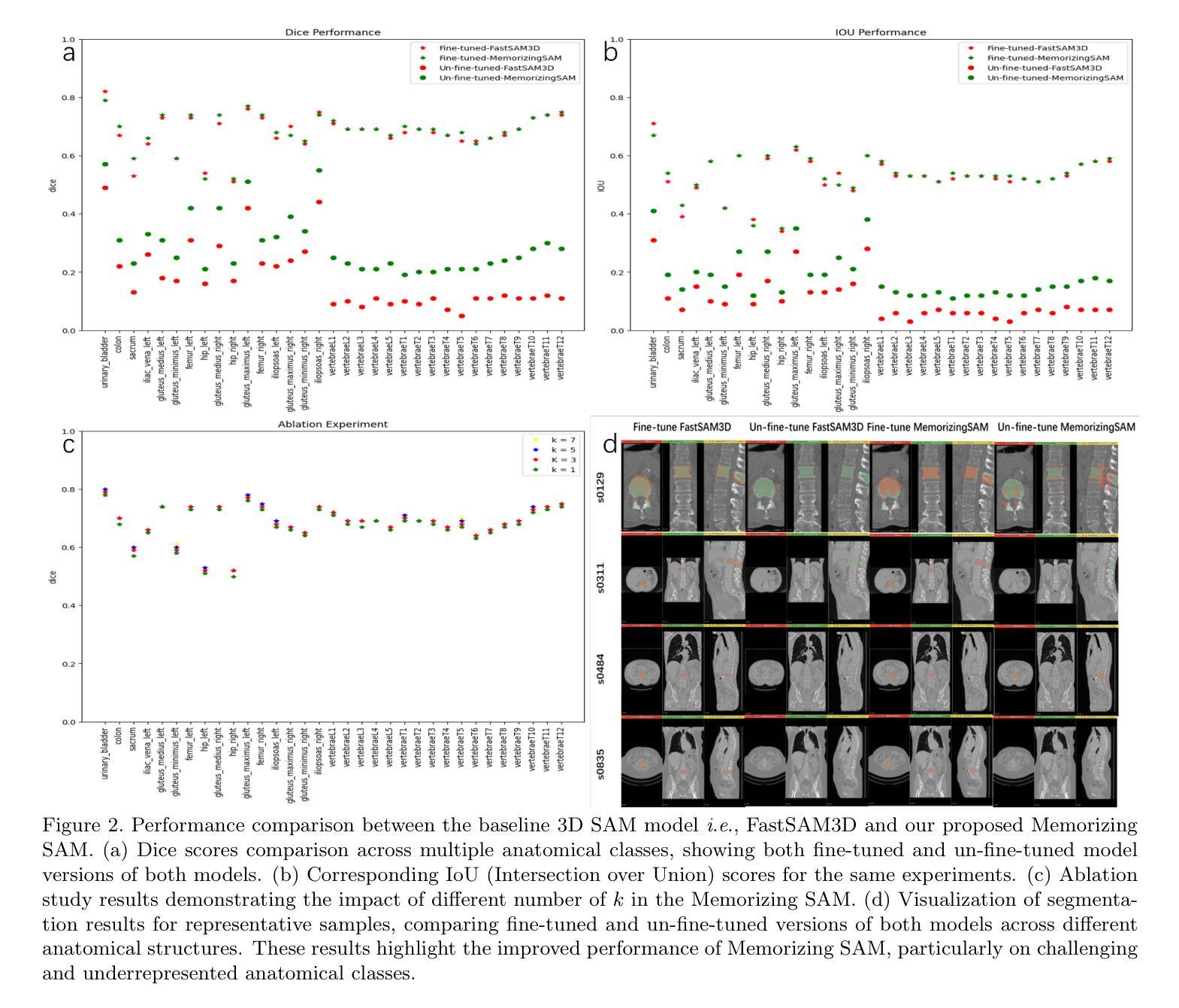
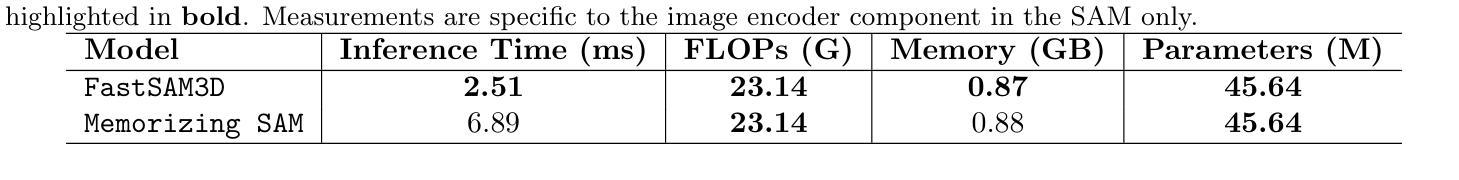
Memorizing SAM: 3D Medical Segment Anything Model with Memorizing Transformer
Authors:Xinyuan Shao, Yiqing Shen, Mathias Unberath
Segment Anything Models (SAMs) have gained increasing attention in medical image analysis due to their zero-shot generalization capability in segmenting objects of unseen classes and domains when provided with appropriate user prompts. Addressing this performance gap is important to fully leverage the pre-trained weights of SAMs, particularly in the domain of volumetric medical image segmentation, where accuracy is important but well-annotated 3D medical data for fine-tuning is limited. In this work, we investigate whether introducing the memory mechanism as a plug-in, specifically the ability to memorize and recall internal representations of past inputs, can improve the performance of SAM with limited computation cost. To this end, we propose Memorizing SAM, a novel 3D SAM architecture incorporating a memory Transformer as a plug-in. Unlike conventional memorizing Transformers that save the internal representation during training or inference, our Memorizing SAM utilizes existing highly accurate internal representation as the memory source to ensure the quality of memory. We evaluate the performance of Memorizing SAM in 33 categories from the TotalSegmentator dataset, which indicates that Memorizing SAM can outperform state-of-the-art 3D SAM variant i.e., FastSAM3D with an average Dice increase of 11.36% at the cost of only 4.38 millisecond increase in inference time. The source code is publicly available at https://github.com/swedfr/memorizingSAM
分段任何事情模型(SAM)因其零样本泛化能力而受到医学图像分析的广泛关注。当提供适当的用户提示时,它们能够分割未见类别和领域的对象。缩小这一性能差距对于充分利用SAM的预训练权重至关重要,特别是在三维医学图像分割领域,准确性至关重要,但用于微调的高精度三维医学数据有限。在这项工作中,我们调查了引入记忆机制作为插件是否可以改善SAM的性能,特别是记忆和回忆过去输入的内部表示的能力。为此,我们提出了记忆SAM,这是一种新型的三维SAM架构,它结合了记忆Transformer作为插件。与传统的保存训练或推理过程中内部表示的记忆Transformer不同,我们的记忆SAM利用现有的高精度内部表示作为内存源,以确保内存的质量。我们在TotalSegmentator数据集的33个类别中评估了记忆SAM的性能,结果表明,记忆SAM可以超越最新的三维SAM变体(即FastSAM3D),平均Dice系数提高了11.36%,而推理时间仅增加了4.38毫秒。源代码可在https://github.com/swedfr/memorizingSAM公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在医学图像分析中,通过引入记忆机制作为插件来改进Segment Anything Models(SAMs)的性能。研究团队提出了Memorizing SAM,这是一种新型的3D SAM架构,它结合了记忆Transformer作为插件。该架构利用现有的高质量内部表示作为记忆源,确保记忆的质量。在TotalSegmentator数据集上的评估表明,Memorizing SAM在平均Dice系数上优于FastSAM3D等先进模型,且推理时间仅增加毫秒级别。代码已公开分享在相关网站。
Key Takeaways
- SAMs因其零样本泛化能力而受到医学图像分析领域的关注。针对此类模型引入记忆机制以提高性能的问题进行探索。
- 提出了一种新型3D SAM架构——Memorizing SAM,结合了记忆Transformer插件。
点此查看论文截图

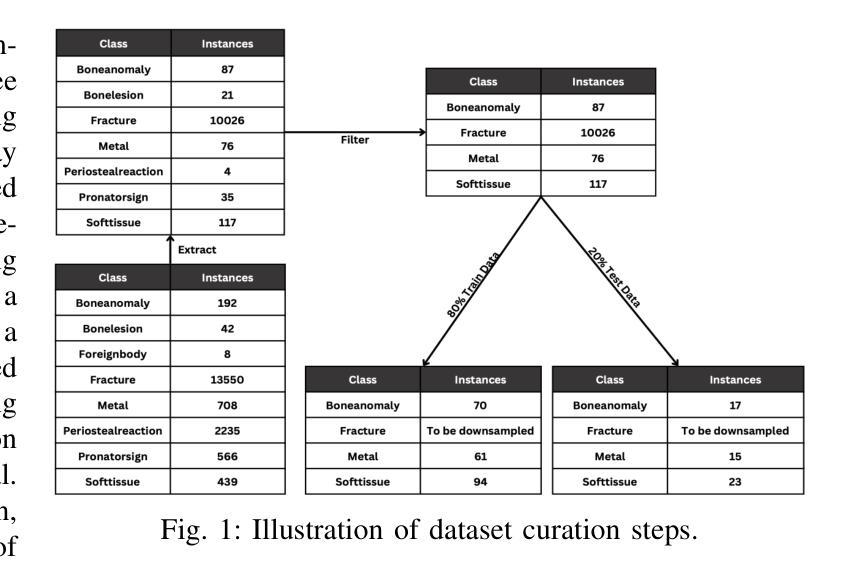
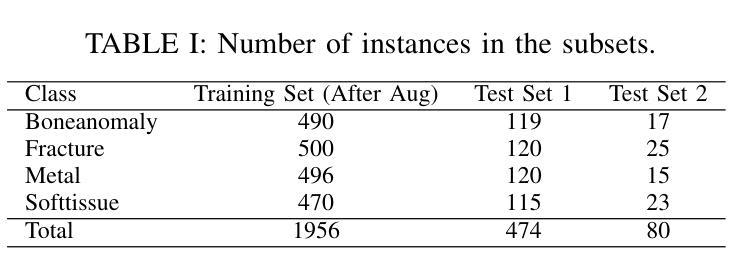
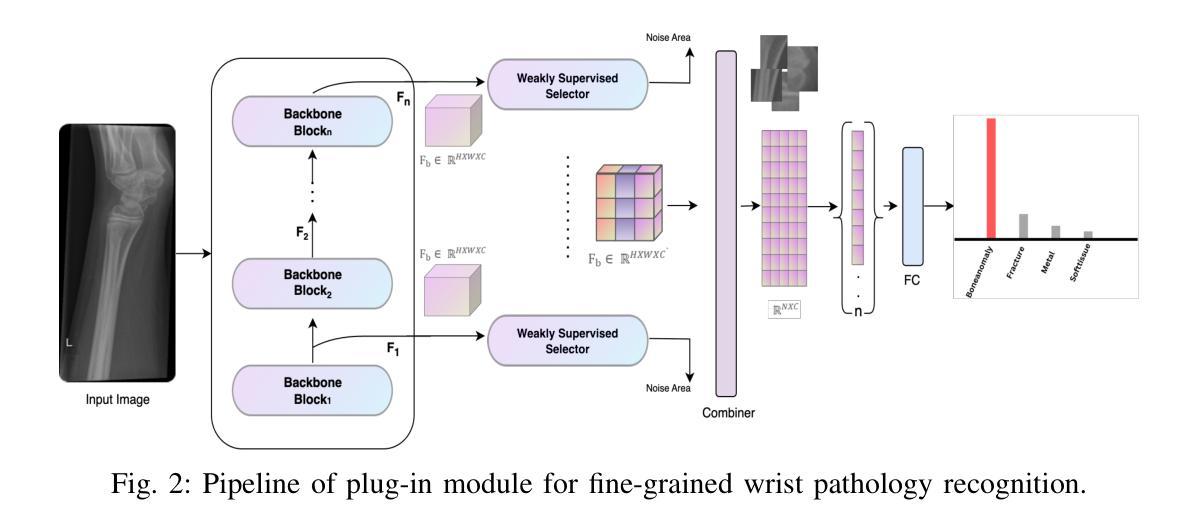
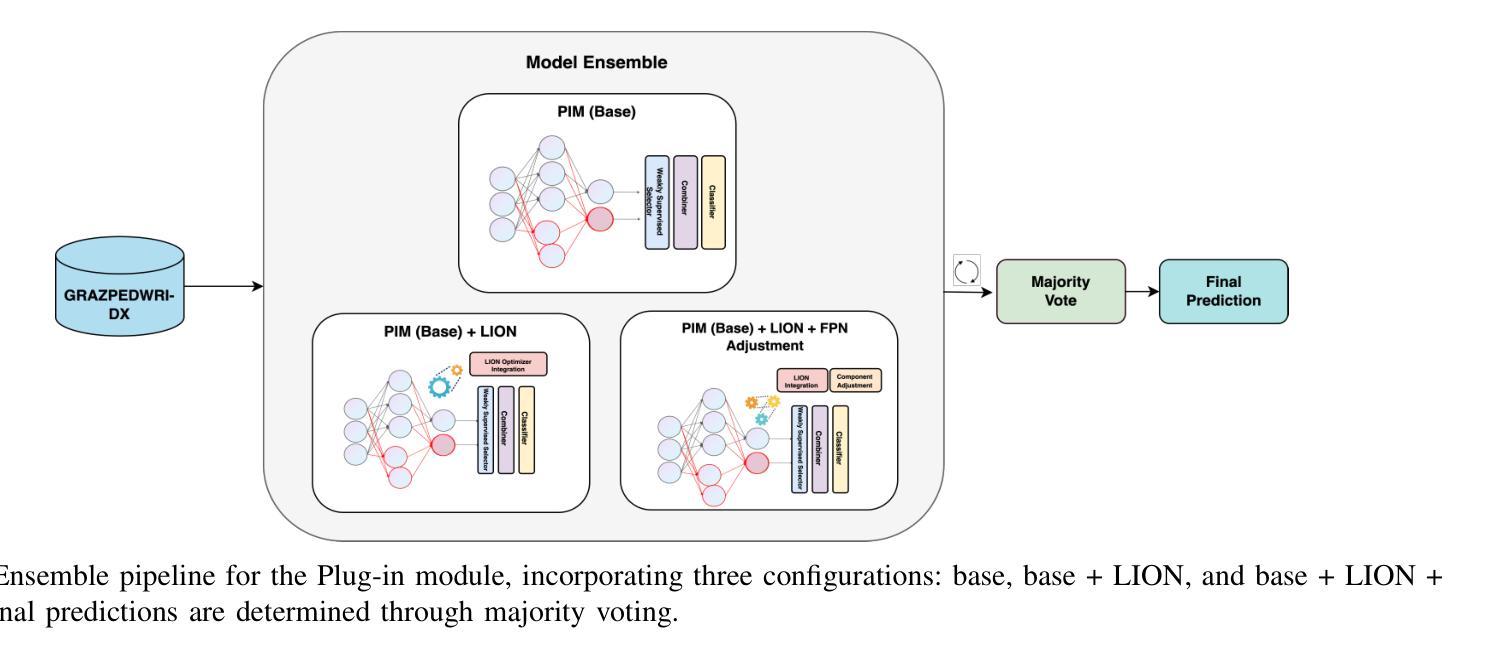
Navigating limitations with precision: A fine-grained ensemble approach to wrist pathology recognition on a limited x-ray dataset
Authors:Ammar Ahmed, Ali Shariq Imran, Mohib Ullah, Zenun Kastrati, Sher Muhammad Daudpota
The exploration of automated wrist fracture recognition has gained considerable research attention in recent years. In practical medical scenarios, physicians and surgeons may lack the specialized expertise required for accurate X-ray interpretation, highlighting the need for machine vision to enhance diagnostic accuracy. However, conventional recognition techniques face challenges in discerning subtle differences in X-rays when classifying wrist pathologies, as many of these pathologies, such as fractures, can be small and hard to distinguish. This study tackles wrist pathology recognition as a fine-grained visual recognition (FGVR) problem, utilizing a limited, custom-curated dataset that mirrors real-world medical constraints, relying solely on image-level annotations. We introduce a specialized FGVR-based ensemble approach to identify discriminative regions within X-rays. We employ an Explainable AI (XAI) technique called Grad-CAM to pinpoint these regions. Our ensemble approach outperformed many conventional SOTA and FGVR techniques, underscoring the effectiveness of our strategy in enhancing accuracy in wrist pathology recognition.
近年来,自动腕部骨折识别的研究受到了广泛关注。在实际医疗场景中,医生和外科医生可能缺乏准确解读X光片所需的专业知识,这突显了需要借助机器视觉来提高诊断准确性的必要性。然而,传统的识别技术在辨识X光片中细微差异以分类腕部疾病时面临挑战,因为这些疾病(如骨折)可能很小且难以区分。本研究将腕部疾病识别视为一项精细的视觉识别(FGVR)问题,利用一个反映现实医疗约束的定制有限数据集,仅依赖图像级别的注释。我们引入了一种基于FGVR的集成方法,用于识别X光片中的鉴别区域。我们采用名为Grad-CAM的可解释人工智能(XAI)技术来定位这些区域。我们的集成方法在许多传统的SOTA和FGVR技术上表现优越,这突显了我们的策略在提高腕部疾病识别准确性方面的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究了自动化手腕骨折识别技术的重要性及其在实际医疗场景中的应用。由于医生可能在X光解读方面缺乏专业知识,因此需要借助机器视觉技术提高诊断准确性。文章采用了一种精细粒度视觉识别(FGVR)的方法,解决手腕病理识别的问题,该方法通过使用限定且反映真实世界医疗限制的定制数据集,仅依赖图像级别的注释。通过采用Grad-CAM的可解释人工智能(XAI)技术,该策略能够识别出X光片中的鉴别区域。实验表明,该集成方法优于许多传统的SOTA和FGVR技术,证明了其在提高手腕病理识别准确性方面的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- 自动化手腕骨折识别近年来受到研究关注。
- 在实际医疗场景中,医生可能缺乏准确解读X光的专业知识。
- 手腕病理识别被视为一种精细粒度视觉识别(FGVR)问题。
- 研究采用定制数据集,反映真实世界医疗限制,仅依赖图像级别注释。
- 使用Grad-CAM的可解释人工智能(XAI)技术来识别X光片中的鉴别区域。
- 集成方法优于许多传统和FGVR技术。
点此查看论文截图

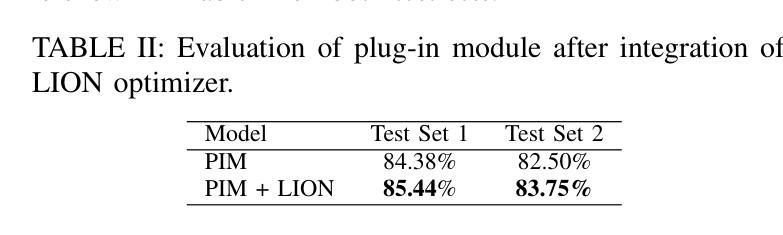
Spatial Brain Tumor Concentration Estimation for Individualized Radiotherapy Planning
Authors:Jonas Weidner, Michal Balcerak, Ivan Ezhov, André Datchev, Laurin Lux, Lucas Zimmerand Daniel Rueckert, Björn Menze, Benedikt Wiestler
Biophysical modeling of brain tumors has emerged as a promising strategy for personalizing radiotherapy planning by estimating the otherwise hidden distribution of tumor cells within the brain. However, many existing state-of-the-art methods are computationally intensive, limiting their widespread translation into clinical practice. In this work, we propose an efficient and direct method that utilizes soft physical constraints to estimate the tumor cell concentration from preoperative MRI of brain tumor patients. Our approach optimizes a 3D tumor concentration field by simultaneously minimizing the difference between the observed MRI and a physically informed loss function. Compared to existing state-of-the-art techniques, our method significantly improves predicting tumor recurrence on two public datasets with a total of 192 patients while maintaining a clinically viable runtime of under one minute - a substantial reduction from the 30 minutes required by the current best approach. Furthermore, we showcase the generalizability of our framework by incorporating additional imaging information and physical constraints, highlighting its potential to translate to various medical diffusion phenomena with imperfect data.
脑肿瘤的生物物理建模已成为一种有前景的策略,通过估计脑内肿瘤细胞的隐藏分布来个性化放射治疗计划。然而,许多目前最先进的方法计算密集,限制了它们在临床实践中的广泛应用。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种高效且直接的方法,利用软物理约束来估计脑肿瘤患者的术前MRI中的肿瘤细胞浓度。我们的方法通过同时最小化观察到的MRI与物理信息损失函数之间的差异来优化三维肿瘤浓度场。与现有的最先进技术相比,我们的方法在两个公共数据集上对192名患者的肿瘤复发预测进行了显著改善,同时保持了一分钟的临床可行运行时间——相较于当前最佳方法的30分钟,大大缩短了时间。此外,我们通过融入额外的成像信息和物理约束展示了框架的泛化能力,突显了其在处理带有缺陷数据的各种医学扩散现象中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种利用软物理约束从脑肿瘤患者的术前MRI估计肿瘤细胞浓度的高效直接方法。该方法通过优化3D肿瘤浓度场,同时最小化观测MRI与物理信息损失函数之间的差异,显著提高了在公共数据集上对192例患者的肿瘤复发预测能力,同时保持了临床可行的运行时间在一分钟以内,大大优于现有最佳方法的30分钟。此外,通过融入额外的成像信息和物理约束,展示了该框架的泛化能力,凸显其在不完美数据下应用于多种医学扩散现象的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 生物物理建模是个性化放射治疗计划的一种有前途的策略,可估计脑内隐藏的肿瘤细胞分布。
- 当前先进方法计算量大,难以广泛应用于临床实践。
- 提出了一种高效直接的方法,利用软物理约束和术前MRI来估计肿瘤细胞浓度。
- 方法在公共数据集上显著提高了肿瘤复发的预测能力,涉及192例患者。
- 相比现有技术,新方法运行时间大幅缩短至一分钟以内。
- 框架可融入额外成像信息和物理约束,展示其良好的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

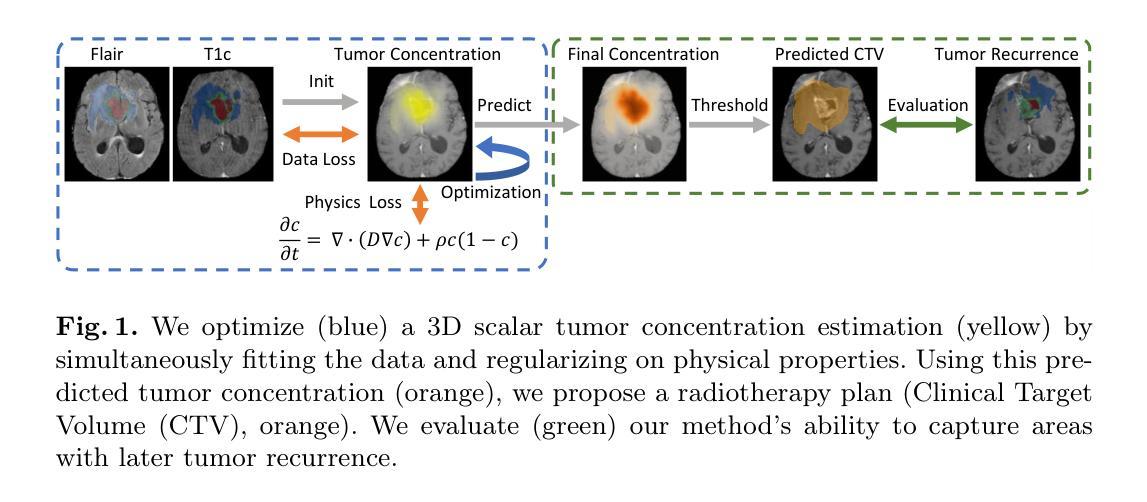
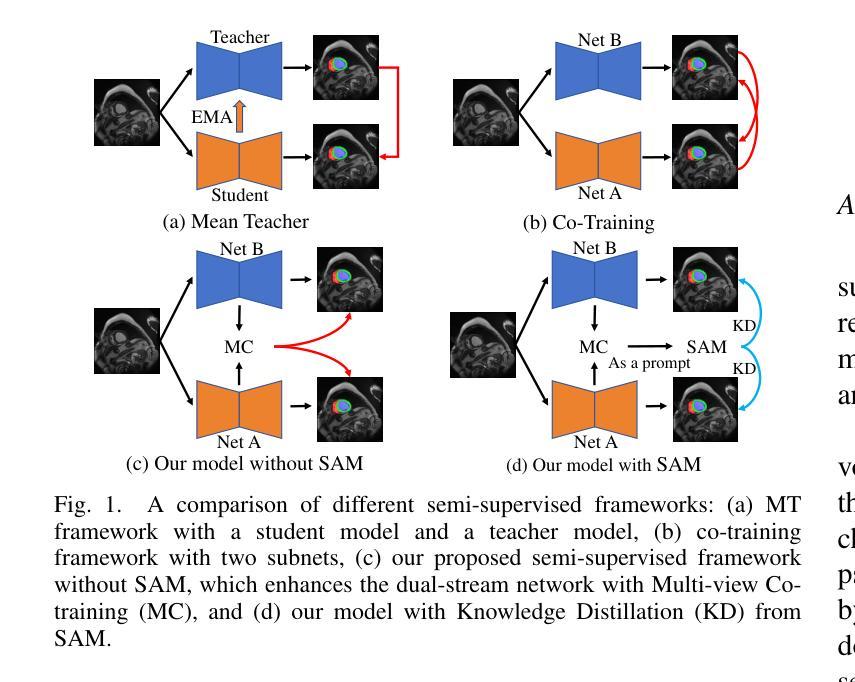
Learnable Prompting SAM-induced Knowledge Distillation for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Kaiwen Huang, Tao Zhou, Huazhu Fu, Yizhe Zhang, Yi Zhou, Chen Gong, Dong Liang
The limited availability of labeled data has driven advancements in semi-supervised learning for medical image segmentation. Modern large-scale models tailored for general segmentation, such as the Segment Anything Model (SAM), have revealed robust generalization capabilities. However, applying these models directly to medical image segmentation still exposes performance degradation. In this paper, we propose a learnable prompting SAM-induced Knowledge distillation framework (KnowSAM) for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. Firstly, we propose a Multi-view Co-training (MC) strategy that employs two distinct sub-networks to employ a co-teaching paradigm, resulting in more robust outcomes. Secondly, we present a Learnable Prompt Strategy (LPS) to dynamically produce dense prompts and integrate an adapter to fine-tune SAM specifically for medical image segmentation tasks. Moreover, we propose SAM-induced Knowledge Distillation (SKD) to transfer useful knowledge from SAM to two sub-networks, enabling them to learn from SAM’s predictions and alleviate the effects of incorrect pseudo-labels during training. Notably, the predictions generated by our subnets are used to produce mask prompts for SAM, facilitating effective inter-module information exchange. Extensive experimental results on various medical segmentation tasks demonstrate that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art semi-supervised segmentation approaches. Crucially, our SAM distillation framework can be seamlessly integrated into other semi-supervised segmentation methods to enhance performance. The code will be released upon acceptance of this manuscript at: https://github.com/taozh2017/KnowSAM
受限于标注数据的可用性推动了医学图像分割的半监督学习的进步。针对一般分割的现代化大规模模型,如Segment Anything Model(SAM),已经显示出稳健的泛化能力。然而,将这些模型直接应用于医学图像分割仍然会出现性能下降的情况。在本文中,我们提出了一种用于半监督医学图像分割的可学习提示SAM诱导知识蒸馏框架(KnowSAM)。首先,我们提出了一种多视角协同训练(MC)策略,该策略采用两个不同的子网络来采用协同教学范式,从而得到更稳健的结果。其次,我们提出了一种可学习提示策略(LPS),以动态生成密集提示并将适配器集成,以便对SAM进行微调,专门用于医学图像分割任务。此外,我们提出了SAM诱导知识蒸馏(SKD),以将SAM的有用知识转移到两个子网络中,使它们能够从SAM的预测中学习并减轻训练过程中错误伪标签的影响。值得注意的是,我们的子网产生的预测用于为SAM生成掩膜提示,促进模块间的有效信息交换。在各种医学分割任务上的大量实验结果表明,我们的模型优于最新的半监督分割方法。关键的是,我们的SAM蒸馏框架可以无缝集成到其他半监督分割方法中以提高性能。该代码将在本手稿被接受后发布在:[https://github.com/taozh2017/KnowSAM]
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 7 figures
Summary
医学图像分割领域面临标注数据有限的问题,促进了半监督学习的发展。现代大规模通用分割模型,如SAM(Segment Anything Model),展现出强大的泛化能力,但直接应用于医学图像分割性能会下降。本文提出一种基于SAM诱导知识蒸馏的半监督医学图像分割框架KnowSAM。包括多视角协同训练策略、可学习提示策略以及SAM诱导知识蒸馏方法。实验证明,该方法优于其他先进半监督分割方法,且可无缝集成到其他半监督分割方法中提高性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割面临标注数据有限的问题,促进了半监督学习技术的发展。
- SAM等大规模通用分割模型在医学图像分割中表现出强大的泛化能力,但直接应用性能不佳。
- 提出的KnowSAM框架包含多视角协同训练策略,采用两个子网络进行协同教学,提高结果稳健性。
- 引入可学习提示策略,动态生成密集提示并微调SAM以适应医学图像分割任务。
- SAM诱导知识蒸馏方法用于从SAM转移有用知识给子网络,使它们从SAM的预测中学习并减轻错误伪标签的影响。
- 子网的预测用于为SAM生成掩膜提示,实现模块间有效信息共享。
点此查看论文截图

Plug-and-Play Tri-Branch Invertible Block for Image Rescaling
Authors:Jingwei Bao, Jinhua Hao, Pengcheng Xu, Ming Sun, Chao Zhou, Shuyuan Zhu
High-resolution (HR) images are commonly downscaled to low-resolution (LR) to reduce bandwidth, followed by upscaling to restore their original details. Recent advancements in image rescaling algorithms have employed invertible neural networks (INNs) to create a unified framework for downscaling and upscaling, ensuring a one-to-one mapping between LR and HR images. Traditional methods, utilizing dual-branch based vanilla invertible blocks, process high-frequency and low-frequency information separately, often relying on specific distributions to model high-frequency components. However, processing the low-frequency component directly in the RGB domain introduces channel redundancy, limiting the efficiency of image reconstruction. To address these challenges, we propose a plug-and-play tri-branch invertible block (T-InvBlocks) that decomposes the low-frequency branch into luminance (Y) and chrominance (CbCr) components, reducing redundancy and enhancing feature processing. Additionally, we adopt an all-zero mapping strategy for high-frequency components during upscaling, focusing essential rescaling information within the LR image. Our T-InvBlocks can be seamlessly integrated into existing rescaling models, improving performance in both general rescaling tasks and scenarios involving lossy compression. Extensive experiments confirm that our method advances the state of the art in HR image reconstruction.
高分辨率(HR)图像通常会被降尺度处理成低分辨率(LR)以减少带宽,随后再对其进行上采样以恢复其原始细节。近期在图像重缩放算法方面的进展采用了可逆神经网络(INNs)来创建一个统一的框架用于降尺度和上采样,确保LR和HR图像之间的一一映射关系。传统的方法使用基于双分支的普通可逆块,分别处理高频和低频信息,通常依赖于特定的分布来模拟高频成分。然而,直接在RGB域处理低频成分会导致通道冗余,限制了图像重建的效率。为了解决这些挑战,我们提出了一种即插即用的三分支可逆块(T-InvBlocks),它将低频分支分解为亮度(Y)和色度(CbCr)成分,以减少冗余并增强特征处理。此外,我们在上采样过程中采用全零映射策略来处理高频成分,专注于在LR图像内部的关键重缩放信息。我们的T-InvBlocks可以无缝集成到现有的重缩放模型中,在一般的重缩放任务和涉及有损压缩的场景中都能提高性能。大量实验证实,我们的方法在HR图像重建方面达到了最新技术的前沿。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025. Code is available at https://github.com/Jingwei-Bao/T-InvBlocks
Summary
高分辨率图像常通过降分辨率以减少带宽,再通过图像超分辨率技术恢复其原始细节。最新图像缩放算法利用可逆神经网络(INNs)为降分辨率和升分辨率创建统一框架。传统方法使用双分支基础可逆块,分别处理高频和低频信息,常依赖特定分布来模拟高频成分。直接在RGB域处理低频成分引入通道冗余,限制了图像重建的效率。为应对这些挑战,我们提出即插即用的三分支可逆块(T-InvBlocks),将低频分支分解为亮度(Y)和色度(CbCr)成分,减少冗余并增强特征处理。此外,我们在升分辨率时采用高频成分全零映射策略,集中关键缩放信息于低分辨率图像内。T-InvBlocks可无缝集成到现有缩放模型中,提升通用缩放任务和涉及有损压缩场景的性能。实验证实,我们的方法在高分辨率图像重建方面达到业界领先。
Key Takeaways
- 高分辨率图像通过降分辨率减少带宽,再通过超分辨率技术恢复细节。
- 近期图像缩放算法使用可逆神经网络(INNs)为降分辨率和升分辨率创建统一框架。
- 传统方法处理高频和低频信息时存在通道冗余问题。
- 本文提出的三分支可逆块(T-InvBlocks)将低频成分进一步细分为亮度(Y)和色度(CbCr),以提高效率。
- 采用高频成分全零映射策略,集中关键缩放信息于低分辨率图像内。
- T-InvBlocks可集成到现有缩放模型,提升性能。
点此查看论文截图

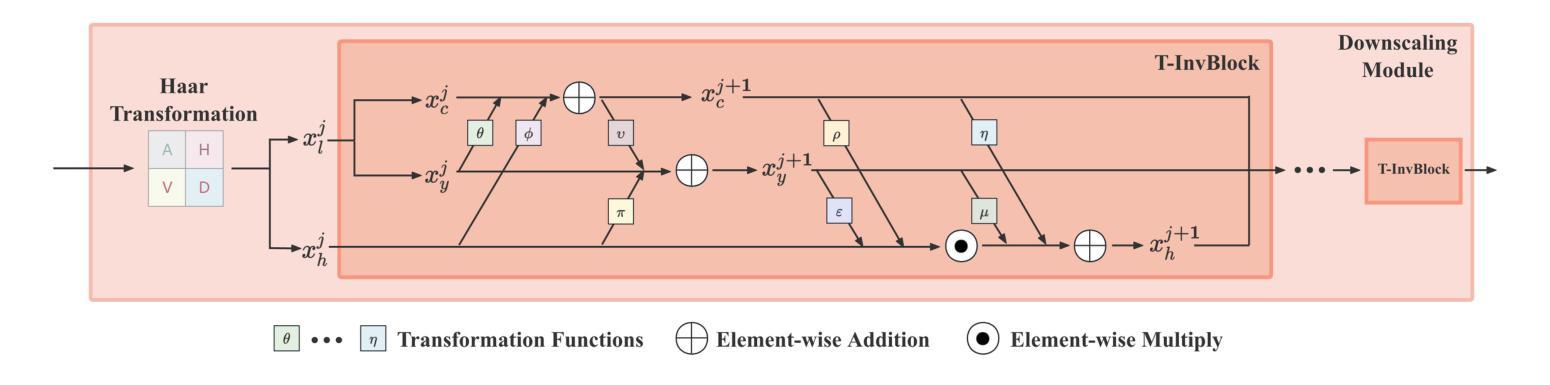
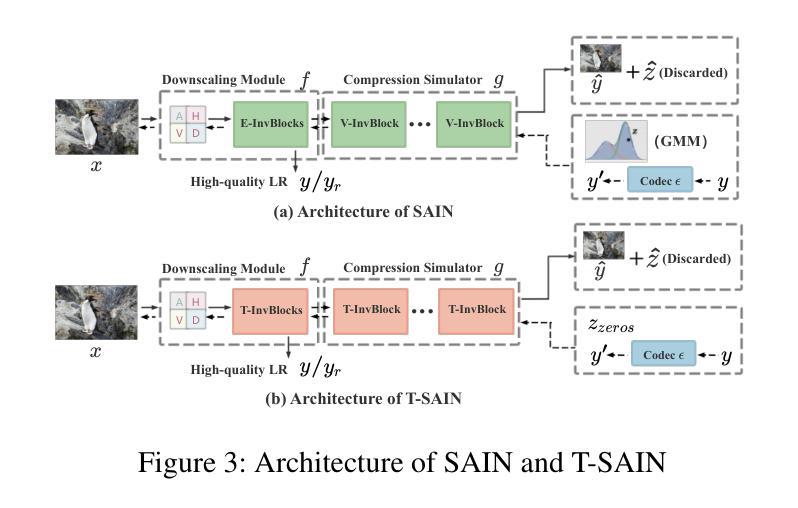
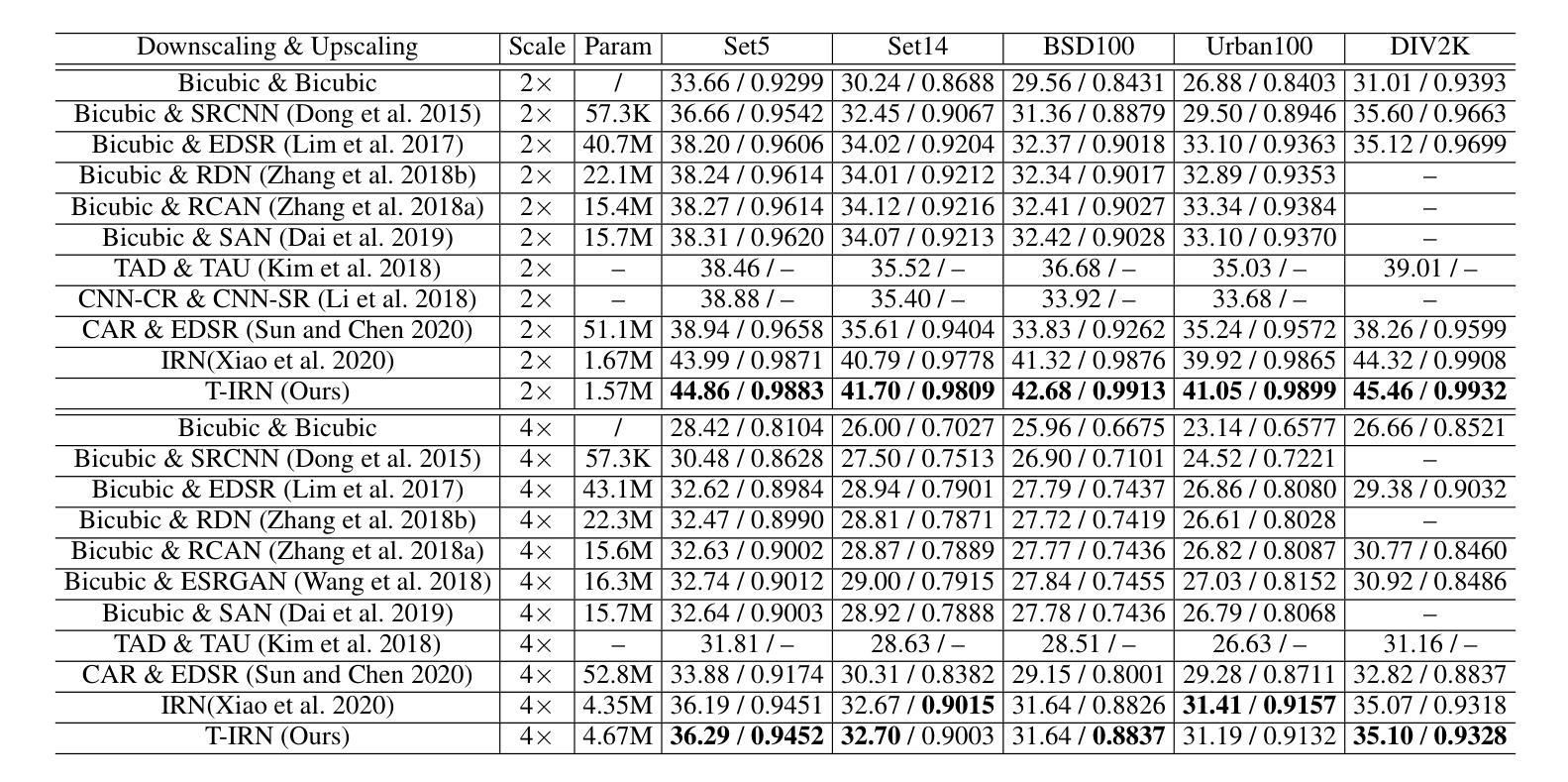
Image registration is a geometric deep learning task
Authors:Vasiliki Sideri-Lampretsa, Nil Stolt-Ansó, Martin Menten, Huaqi Qiu, Julian McGinnis, Daniel Rueckert
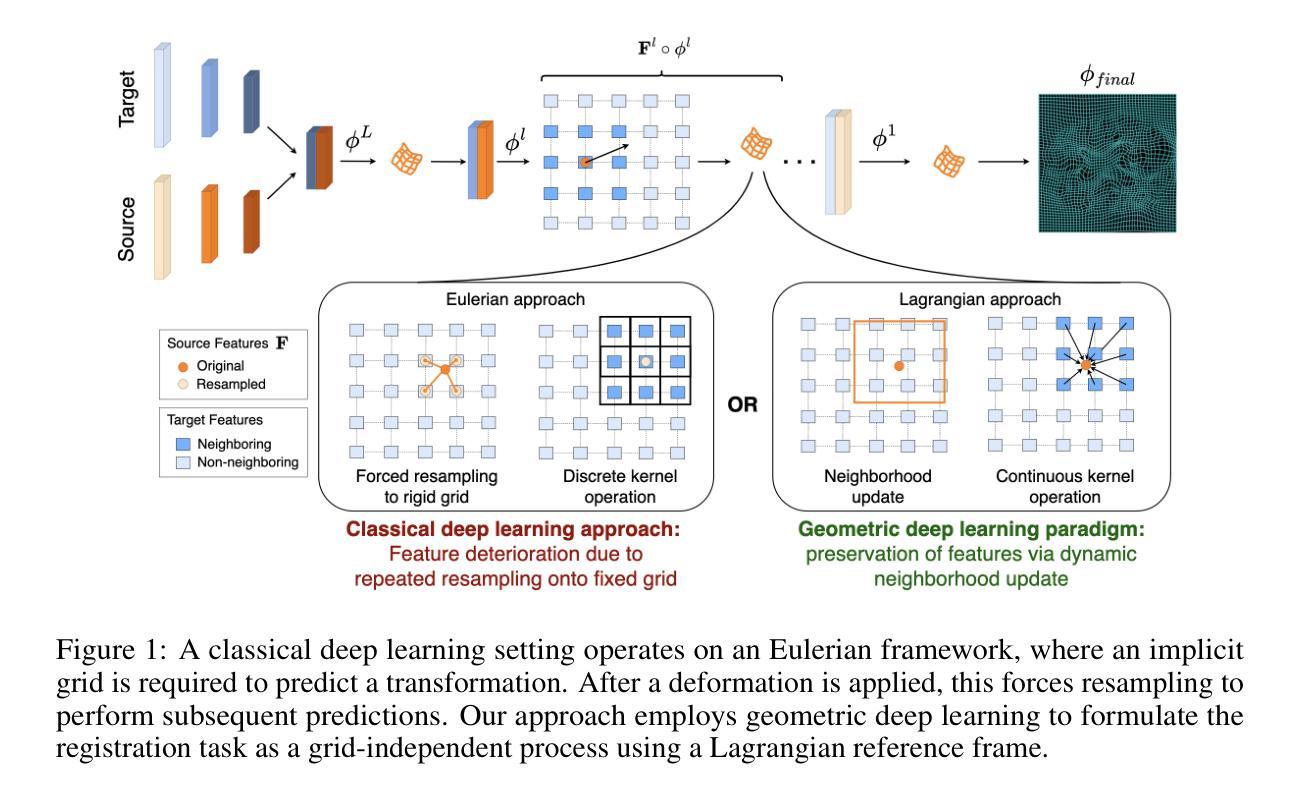
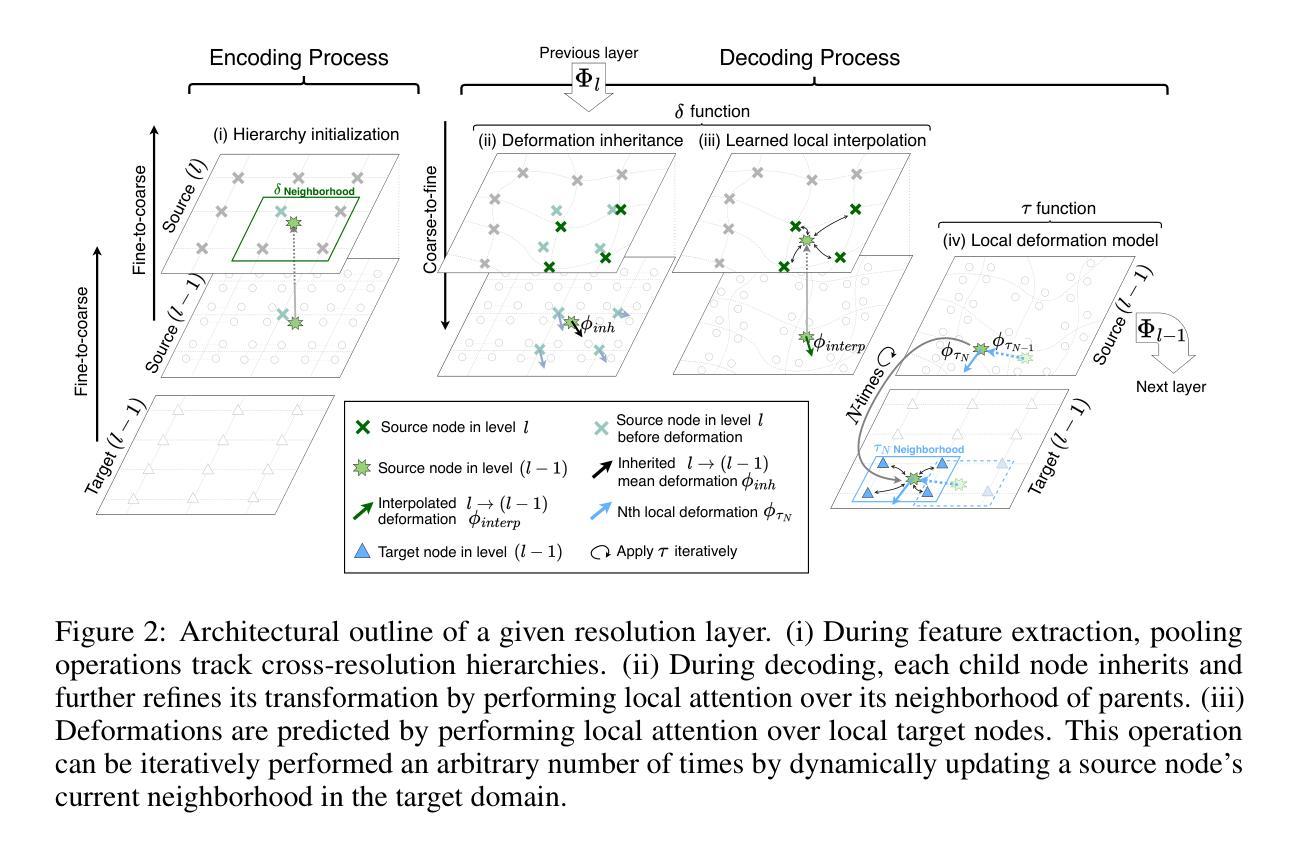
Data-driven deformable image registration methods predominantly rely on operations that process grid-like inputs. However, applying deformable transformations to an image results in a warped space that deviates from a rigid grid structure. Consequently, data-driven approaches with sequential deformations have to apply grid resampling operations between each deformation step. While artifacts caused by resampling are negligible in high-resolution images, the resampling of sparse, high-dimensional feature grids introduces errors that affect the deformation modeling process. Taking inspiration from Lagrangian reference frames of deformation fields, our work introduces a novel paradigm for data-driven deformable image registration that utilizes geometric deep-learning principles to model deformations without grid requirements. Specifically, we model image features as a set of nodes that freely move in Euclidean space, update their coordinates under graph operations, and dynamically readjust their local neighborhoods. We employ this formulation to construct a multi-resolution deformable registration model, where deformation layers iteratively refine the overall transformation at each resolution without intermediate resampling operations on the feature grids. We investigate our method’s ability to fully deformably capture large deformations across a number of medical imaging registration tasks. In particular, we apply our approach (GeoReg) to the registration of inter-subject brain MR images and inhale-exhale lung CT images, showing on par performance with the current state-of-the-art methods. We believe our contribution open up avenues of research to reduce the black-box nature of current learned registration paradigms by explicitly modeling the transformation within the architecture.
数据驱动的可变形图像注册方法主要依赖于处理网格状输入的操作。然而,将可变形转换应用于图像会产生偏离刚性网格结构的扭曲空间。因此,具有顺序变形的数据驱动方法必须在每次变形步骤之间进行网格重采样操作。虽然在高分辨率图像中重采样引起的伪影可以忽略不计,但对稀疏、高维特征网格的重采样会引入影响变形建模过程的误差。我们的工作从拉格朗日参考系变形场中获得灵感,引入了一种新型数据驱动可变形图像注册范例,该范例利用几何深度学习原理进行变形建模,无需网格要求。具体来说,我们将图像特征建模为一系列节点,这些节点在欧几里得空间中自由移动,在图形操作下更新其坐标并动态调整其局部邻域。我们利用这一公式构建了一种多分辨率可变形注册模型,其中变形层以迭代方式完善每个分辨率的整体转换,无需在特征网格上进行中间重采样操作。我们研究了我们的方法在多个医学图像注册任务中完全可变形地捕获大变形的能力。特别是,我们将我们的方法(GeoReg)应用于跨主体之间的大脑MR图像和吸气-呼气肺部CT图像的注册,显示出与当前最新方法相当的性能。我们相信我们的研究开辟了减少当前学习注册范例的黑箱性质的途径,通过在架构内显式建模转换。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 Pages
Summary
本文介绍了基于数据驱动的可变形图像注册方法的主要挑战,并提出了新的解决方案。传统方法依赖于网格输入处理,但在应用可变形转换时会产生偏离刚性网格结构的空间扭曲。本文受拉格朗日参考系变形场的启发,利用几何深度学习原理,提出了一种无需网格要求的数据驱动可变形图像注册新范式。该方法将图像特征建模为一组节点,在欧几里得空间中自由移动,在图形操作下更新其坐标,并动态调整其局部邻域。在多项医学成像注册任务中,该方法能够完全可变形地捕获大变形。
Key Takeaways
- 传统数据驱动的可变形图像注册方法主要依赖网格输入处理,但在应用可变形转换时产生空间扭曲。
- 网格重采样操作在每一步变形中都会引入误差,特别是在稀疏、高维特征网格中。
- 本文受拉格朗日参考系变形场的启发,提出了一种新的数据驱动可变形图像注册方法。
- 新方法利用几何深度学习原理,将图像特征建模为在欧几里得空间中自由移动的节点。
- 该方法通过图形操作更新节点坐标,并动态调整局部邻域,无需网格要求。
- 多分辨率可变形注册模型能够逐层精细调整转换,无需中间重采样操作。
点此查看论文截图

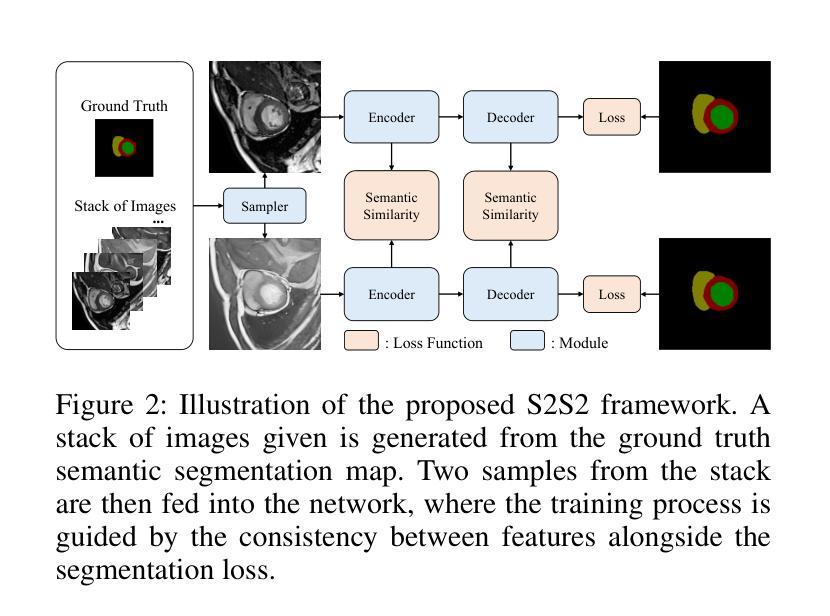
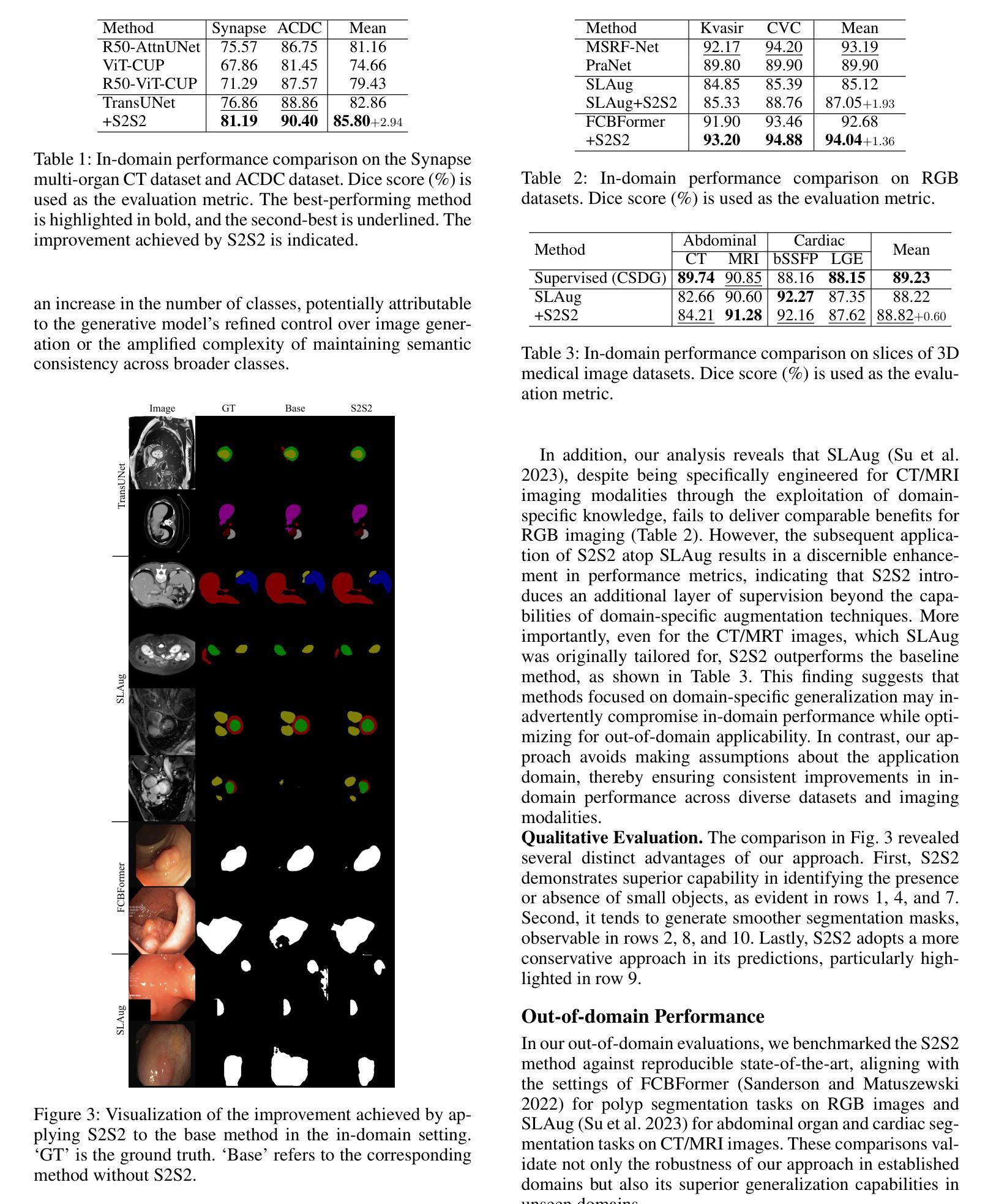
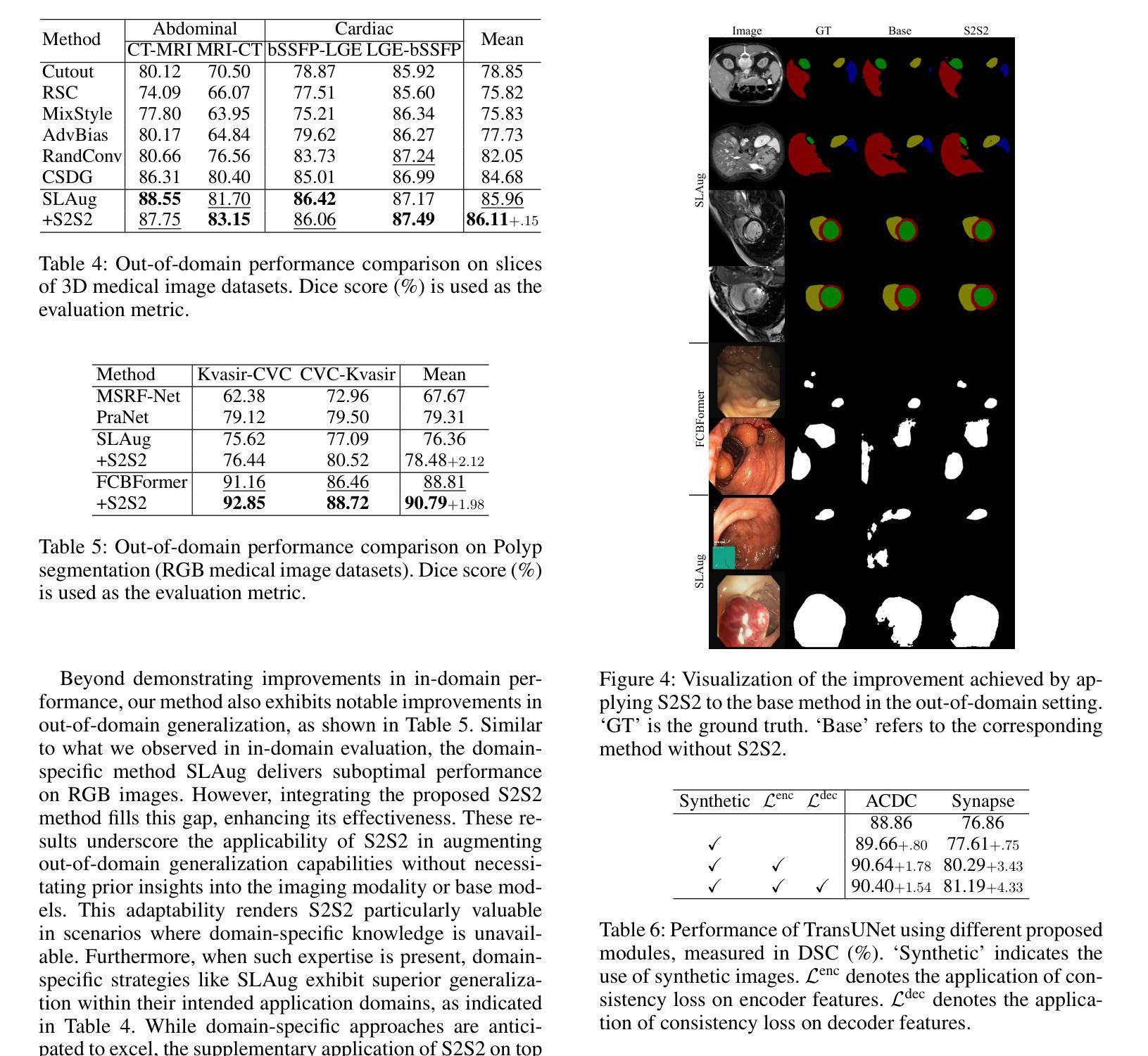
S2S2: Semantic Stacking for Robust Semantic Segmentation in Medical Imaging
Authors:Yimu Pan, Sitao Zhang, Alison D. Gernand, Jeffery A. Goldstein, James Z. Wang
Robustness and generalizability in medical image segmentation are often hindered by scarcity and limited diversity of training data, which stands in contrast to the variability encountered during inference. While conventional strategies – such as domain-specific augmentation, specialized architectures, and tailored training procedures – can alleviate these issues, they depend on the availability and reliability of domain knowledge. When such knowledge is unavailable, misleading, or improperly applied, performance may deteriorate. In response, we introduce a novel, domain-agnostic, add-on, and data-driven strategy inspired by image stacking in image denoising. Termed ``semantic stacking,’’ our method estimates a denoised semantic representation that complements the conventional segmentation loss during training. This method does not depend on domain-specific assumptions, making it broadly applicable across diverse image modalities, model architectures, and augmentation techniques. Through extensive experiments, we validate the superiority of our approach in improving segmentation performance under diverse conditions. Code is available at https://github.com/ymp5078/Semantic-Stacking.
在医学图像分割中,鲁棒性和通用性常常受到训练数据稀缺和多样性有限的阻碍,这与推理过程中遇到的变量形成对比。虽然传统的策略——如领域特定的增强、专用架构和定制训练程序——可以缓解这些问题,但它们依赖于领域知识的可用性和可靠性。当这种知识不可用、误导或应用不当时,性能可能会恶化。作为回应,我们引入了一种新型、领域无关、附加的、数据驱动的策略,该策略受到图像去噪中图像堆叠的启发。我们将其称为“语义堆叠”,该方法估计去噪的语义表示,在训练过程中补充传统的分割损失。该方法不依赖于特定领域的假设,因此可广泛应用于不同的图像模式、模型架构和增强技术。通过广泛的实验,我们验证了我们的方法在改善不同条件下的分割性能方面的优越性。代码可在 https://github.com/ymp5078/Semantic-Stacking 获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI2025
Summary
训练数据的稀缺性和多样性限制对医学图像分割的鲁棒性和泛化能力造成影响,针对这一问题,我们提出了一种新型的、领域无关的、附加的、数据驱动的策略,该策略借鉴了图像去噪中的图像堆叠技术,被称为“语义堆叠”。该方法估计去噪的语义表示,在训练过程中补充传统的分割损失,不依赖于特定领域的假设,因此可广泛应用于不同的图像模态、模型架构和增强技术。通过广泛的实验验证,该方法在多种条件下改进了分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割面临训练数据稀缺和多样性限制的挑战。
- 传统策略依赖于领域知识的可用性、可靠性和适当应用。
- 引入了一种新型的、领域无关的、附加的、数据驱动的策略——“语义堆叠”。
- “语义堆叠”方法借鉴了图像去噪中的图像堆叠技术。
- 该方法估计去噪的语义表示,在训练过程中补充传统的分割损失。
- “语义堆叠”方法具有广泛的应用性,适用于不同的图像模态、模型架构和增强技术。
点此查看论文截图

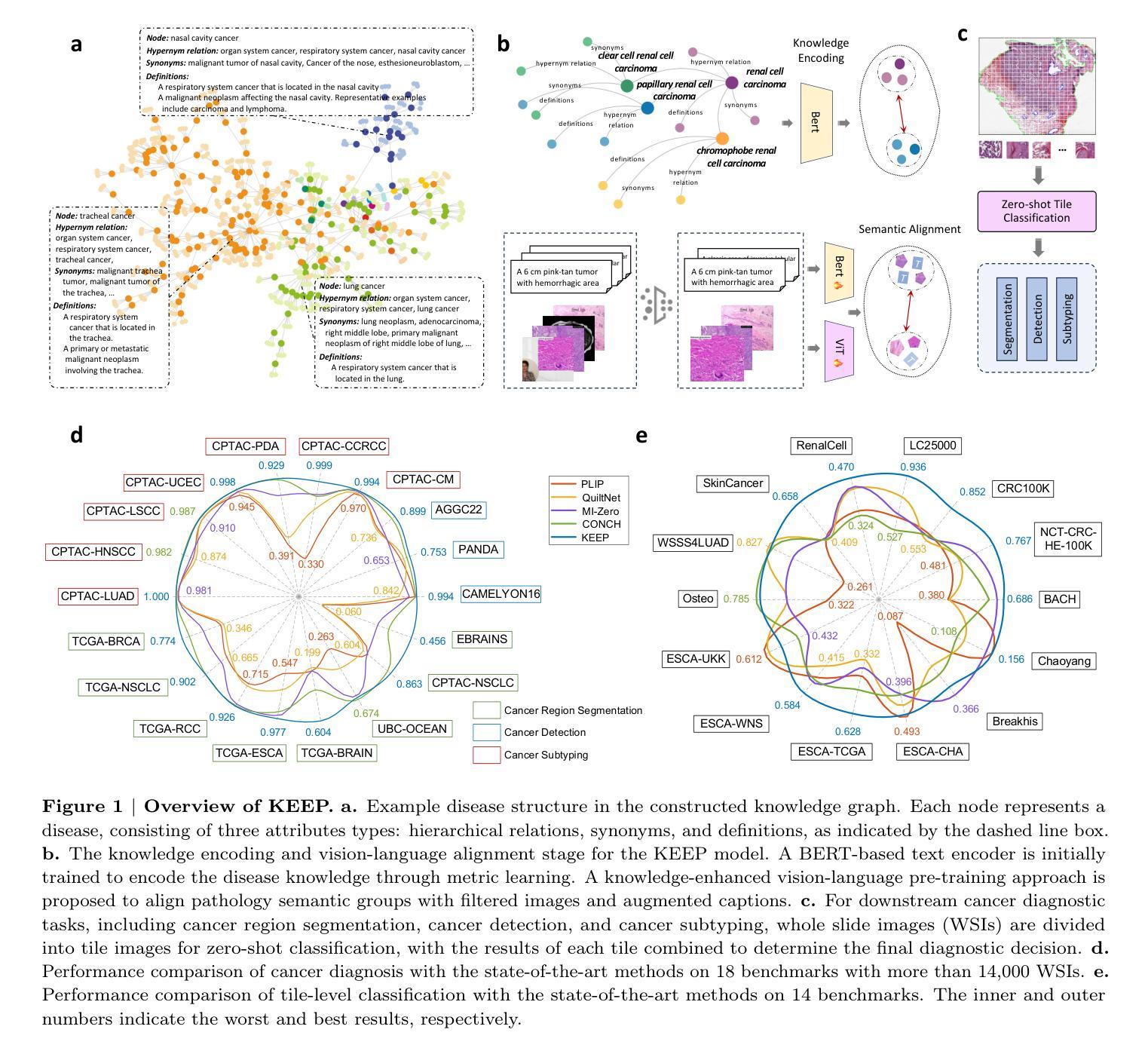
A Knowledge-enhanced Pathology Vision-language Foundation Model for Cancer Diagnosis
Authors:Xiao Zhou, Luoyi Sun, Dexuan He, Wenbin Guan, Ruifen Wang, Lifeng Wang, Xin Sun, Kun Sun, Ya Zhang, Yanfeng Wang, Weidi Xie
Deep learning has enabled the development of highly robust foundation models for various pathological tasks across diverse diseases and patient cohorts. Among these models, vision-language pre-training, which leverages large-scale paired data to align pathology image and text embedding spaces, and provides a novel zero-shot paradigm for downstream tasks. However, existing models have been primarily data-driven and lack the incorporation of domain-specific knowledge, which limits their performance in cancer diagnosis, especially for rare tumor subtypes. To address this limitation, we establish a Knowledge-enhanced Pathology (KEEP) foundation model that harnesses disease knowledge to facilitate vision-language pre-training. Specifically, we first construct a disease knowledge graph (KG) that covers 11,454 human diseases with 139,143 disease attributes, including synonyms, definitions, and hypernym relations. We then systematically reorganize the millions of publicly available noisy pathology image-text pairs, into 143K well-structured semantic groups linked through the hierarchical relations of the disease KG. To derive more nuanced image and text representations, we propose a novel knowledge-enhanced vision-language pre-training approach that integrates disease knowledge into the alignment within hierarchical semantic groups instead of unstructured image-text pairs. Validated on 18 diverse benchmarks with more than 14,000 whole slide images (WSIs), KEEP achieves state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot cancer diagnostic tasks. Notably, for cancer detection, KEEP demonstrates an average sensitivity of 89.8% at a specificity of 95.0% across 7 cancer types. For cancer subtyping, KEEP achieves a median balanced accuracy of 0.456 in subtyping 30 rare brain cancers, indicating strong generalizability for diagnosing rare tumors.
深度学习为各种疾病和不同患者群体的多种病理任务开发高度稳健的基础模型提供了可能。在这些模型中,视觉语言预训练通过利用大规模配对数据来对齐病理图像和文本嵌入空间,并为下游任务提供了一种新型零样本范式。然而,现有模型主要是数据驱动,缺乏特定领域的知识的融入,这在癌症诊断中,尤其是罕见肿瘤亚型的诊断中限制了其性能。为了解决这一局限性,我们建立了一个知识增强的病理(KEEP)基础模型,该模型利用疾病知识来促进视觉语言预训练。具体来说,我们首先构建了一个疾病知识图谱(KG),涵盖11454种人类疾病和139143个疾病属性,包括同义词、定义和上位词关系。然后,我们对数百万个公开可用的嘈杂病理图像文本对进行系统化重组,通过疾病知识图谱的层次关系将其分为14.3万组结构良好的语义组。为了得出更微妙的图像和文本表示,我们提出了一种新型的知识增强视觉语言预训练方法,该方法将疾病知识集成到层次语义组内的对齐中,而不是简单的图像文本对。在超过1.4万张全切片图像(WSIs)的18个不同基准测试集上进行验证,KEEP在零样本癌症诊断任务中达到了最新技术水平。特别是在癌症检测方面,KEEP在7种癌症类型上表现出了平均敏感性为89.8%,特异性为95.0%。在癌症亚型分析中,KEEP在30种罕见脑癌的亚型分析中达到了中位数平衡精度为0.456,显示出诊断罕见肿瘤的强泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
深度学习已推动针对多种疾病和患者群体的稳健基础模型发展。为下游任务提供零样本范式的新型预训练技术已出现,但现有模型主要依赖数据,缺乏特定领域知识的融入,在癌症诊断,尤其是罕见肿瘤亚型方面的性能受限。为解决此问题,我们建立了融合疾病知识增强(KEEP)的基础模型,通过疾病知识促进视觉语言预训练。我们在疾病知识图谱中覆盖1.1万多种人类疾病和13.9万多种疾病属性,对百万级公开病理学图像文本对进行系统重组。在18个多样基准测试超过1.4万张全幻灯片图像(WSIs)验证下,KEEP在零样本癌症诊断任务中取得最佳性能。尤其在癌症检测和癌症亚型鉴别方面表现出色。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习为各种病理任务构建了稳健的基础模型。
- 视觉语言预训练利用大规模配对数据对齐病理图像和文本嵌入空间。
- 现有模型主要依赖数据,缺乏特定领域知识融入,影响在癌症诊断尤其是罕见肿瘤亚型方面的性能。
- KEEP模型通过构建疾病知识图谱融入疾病知识,促进视觉语言预训练。
- 疾病知识图谱覆盖1.1万多种人类疾病和大量疾病属性。
- KEEP模型对病理学图像文本对进行系统性重组,通过疾病知识的层次关系进行对齐。
- KEEP模型在多个基准测试中表现优异,尤其在癌症检测和罕见肿瘤亚型鉴别方面。
- KEEP模型在零样本癌症诊断任务中平均敏感率为89.8%,特异性为95.0%。
点此查看论文截图

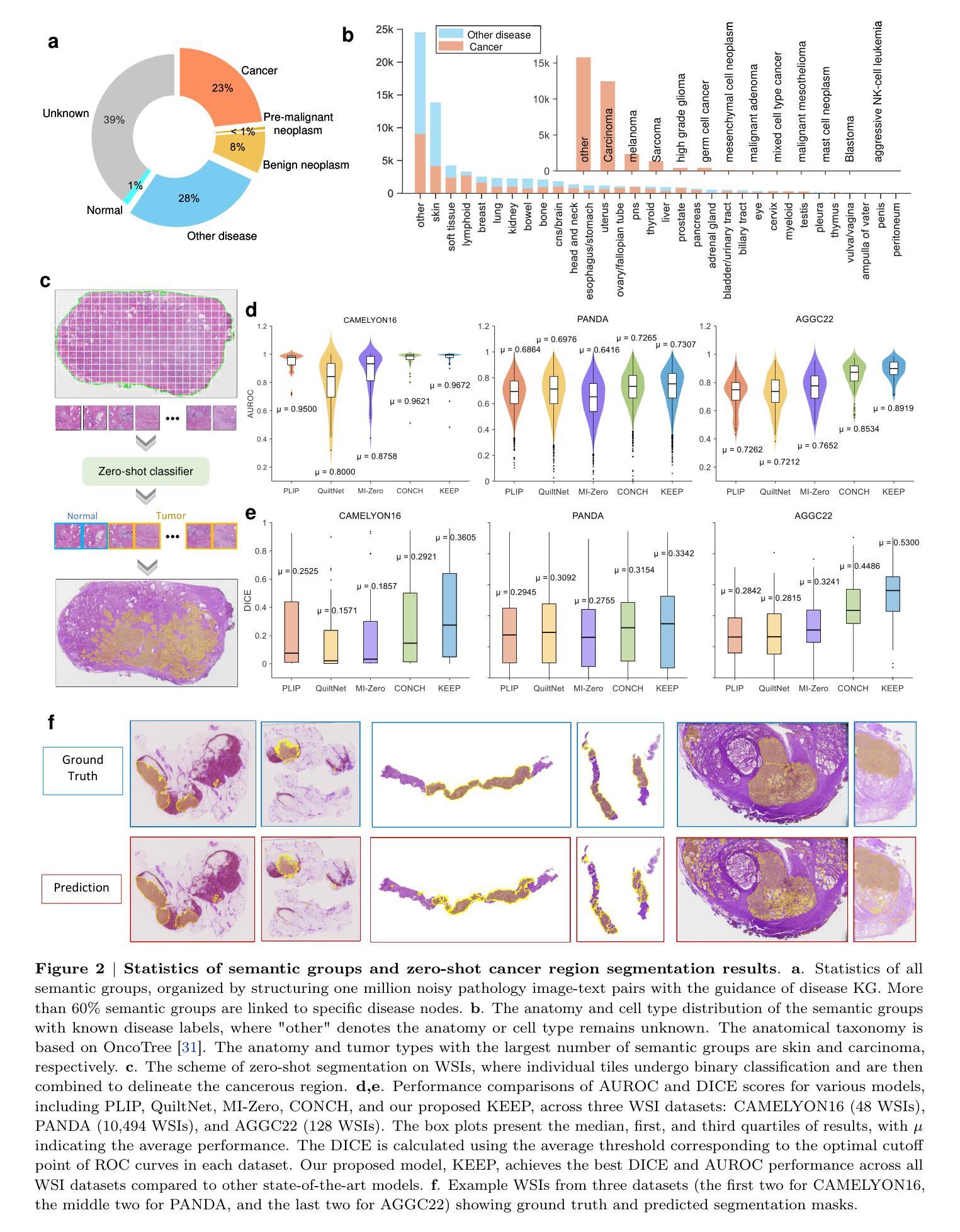
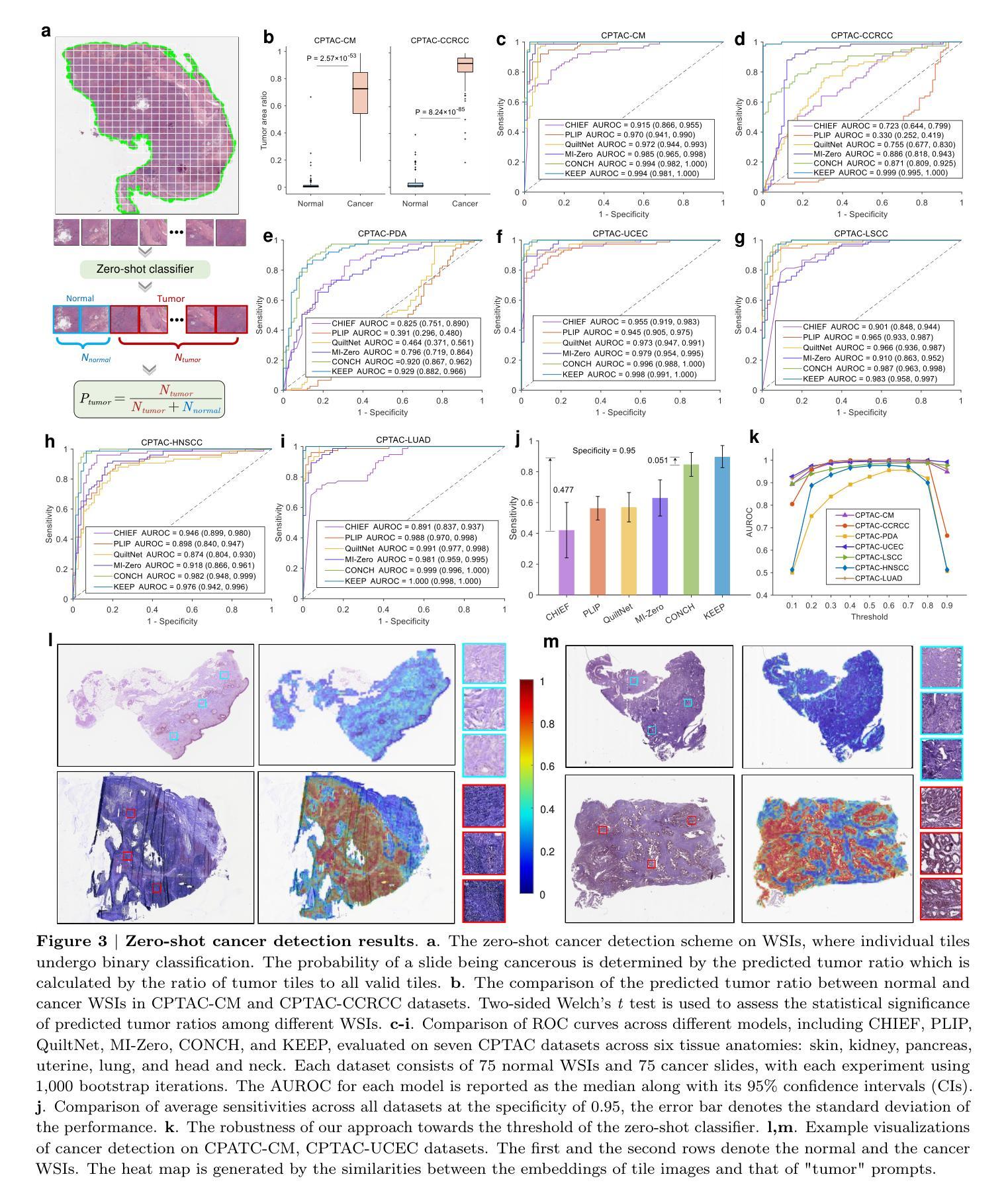
Learning of Patch-Based Smooth-Plus-Sparse Models for Image Reconstruction
Authors:Stanislas Ducotterd, Sebastian Neumayer, Michael Unser
We aim at the solution of inverse problems in imaging, by combining a penalized sparse representation of image patches with an unconstrained smooth one. This allows for a straightforward interpretation of the reconstruction. We formulate the optimization as a bilevel problem. The inner problem deploys classical algorithms while the outer problem optimizes the dictionary and the regularizer parameters through supervised learning. The process is carried out via implicit differentiation and gradient-based optimization. We evaluate our method for denoising, super-resolution, and compressed-sensing magnetic-resonance imaging. We compare it to other classical models as well as deep-learning-based methods and show that it always outperforms the former and also the latter in some instances.
我们旨在通过结合图像块的惩罚稀疏表示和无约束平滑表示来解决成像中的反问题。这允许对重建进行直接解释。我们将优化问题制定为一个双层问题。内层问题采用经典算法,外层问题通过监督学习优化字典和正则化参数。该过程通过隐式微分和基于梯度的优化来完成。我们针对去噪、超分辨率和压缩感知磁共振成像评估了我们的方法。我们将它与其它经典模型以及基于深度学习的方法进行了比较,并证明它在某些情况下总是优于前者,在某些情况下也优于后者。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文旨在解决成像中的反问题,结合惩罚稀疏图像块表示和无约束平滑表示,易于解释重建结果。优化问题被表述为双层问题,内层问题采用经典算法,外层问题通过监督学习优化字典和正则化参数。过程通过隐式分化和基于梯度的优化来实现。经去噪、超分辨率和压缩感知磁共振成像评估,该方法优于其他经典模型和某些深度学习方法。
Key Takeaways
- 结合惩罚稀疏图像块表示和无约束平滑表示,解决成像中的反问题。
- 优化问题表述为双层问题,内层采用经典算法,外层优化字典和正则化参数。
- 通过监督学习和隐式分化及基于梯度的优化实现过程。
- 方法在去噪、超分辨率和压缩感知磁共振成像应用中得到评估。
- 与其他经典模型相比,该方法表现更优。
- 在某些情况下,该方法甚至比深度学习方法表现更好。
点此查看论文截图


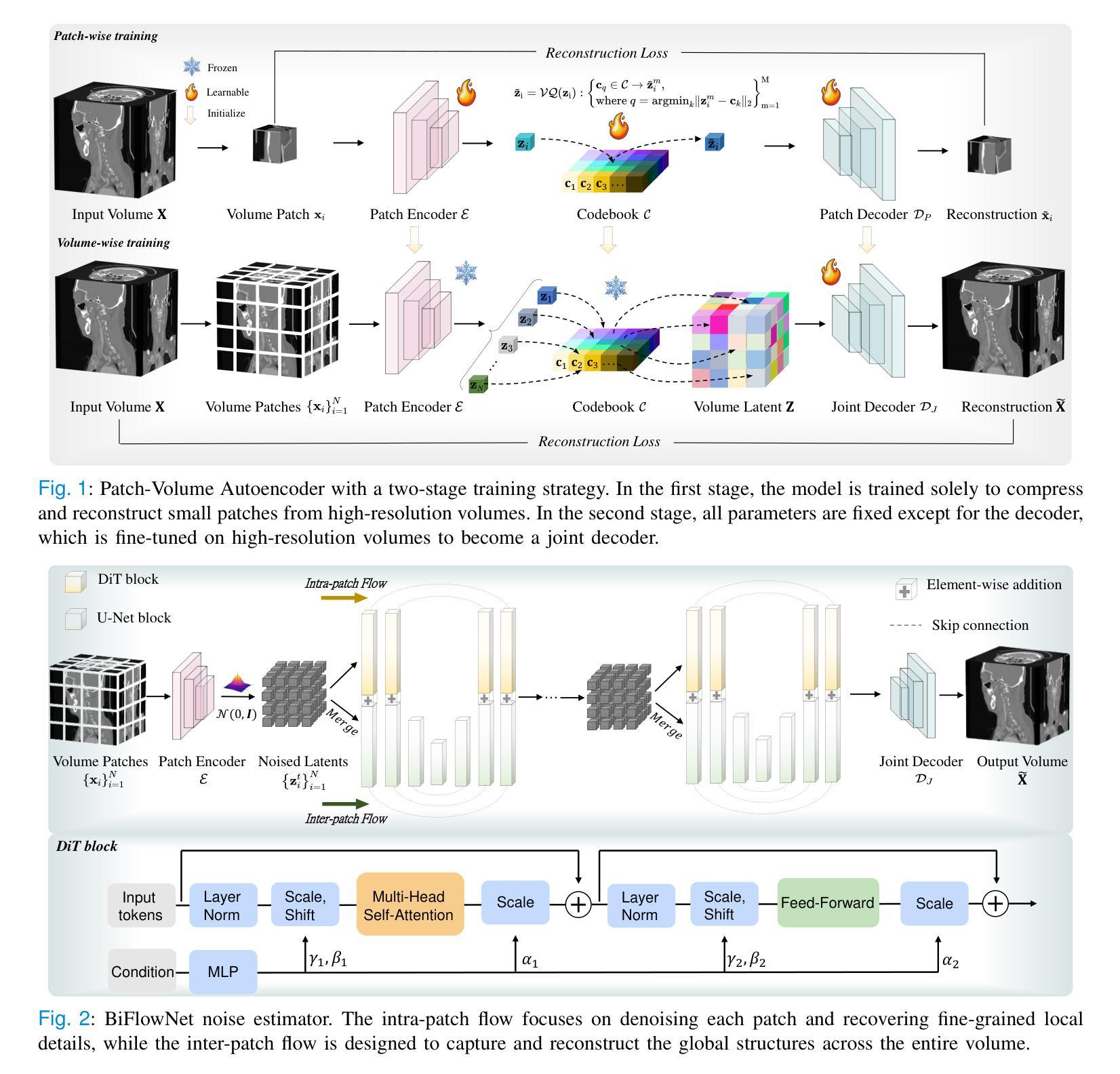
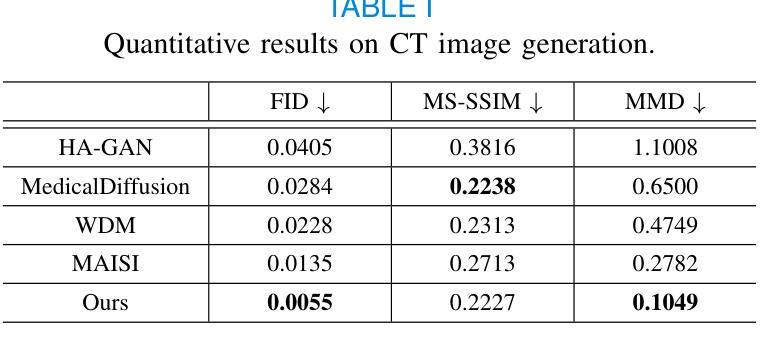
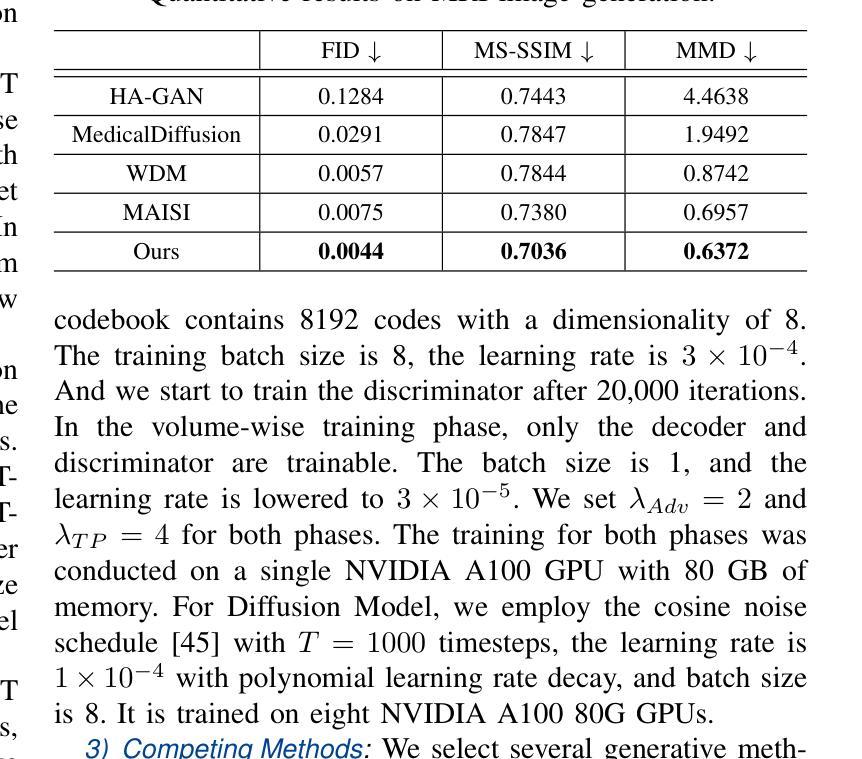
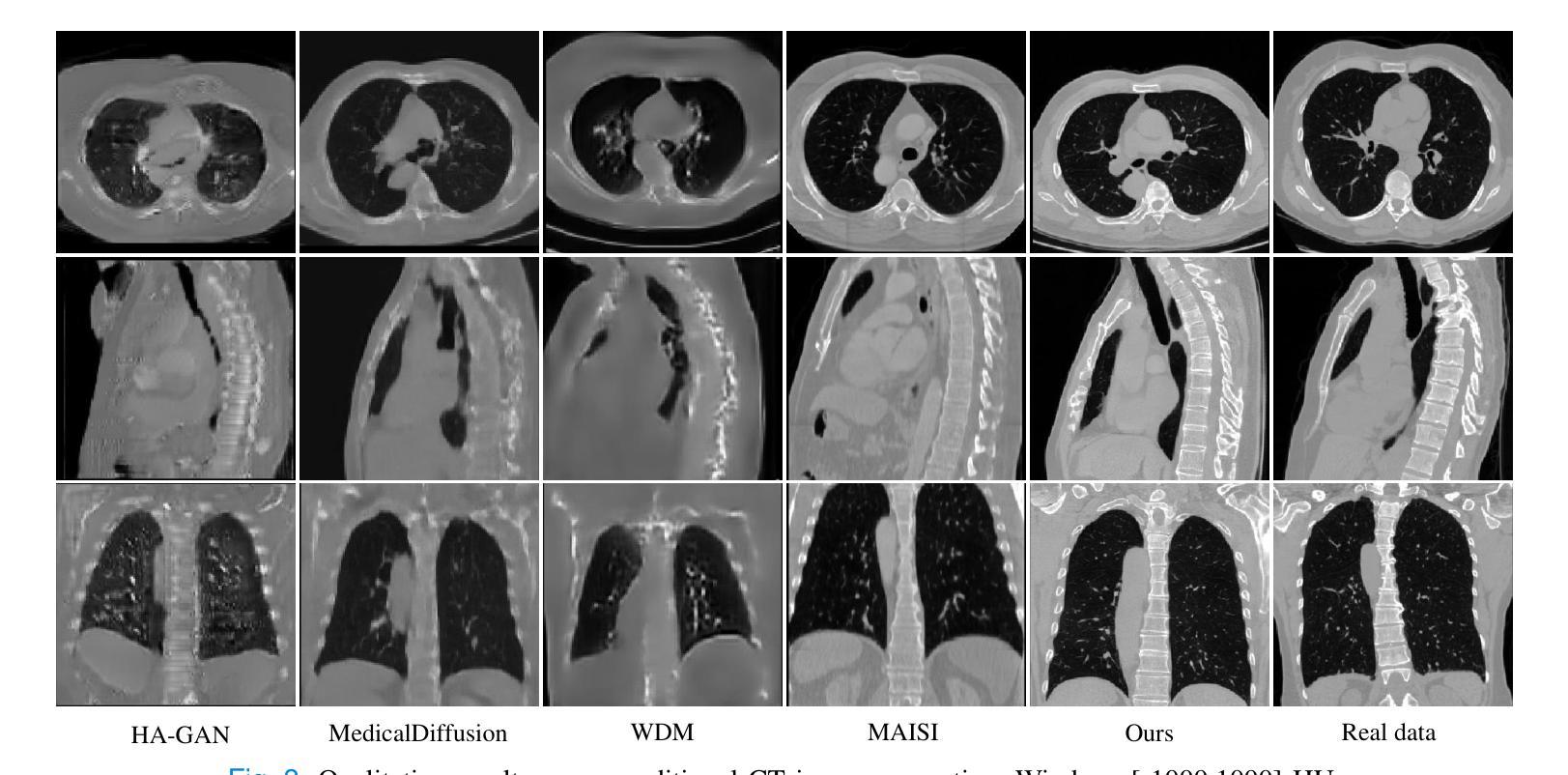
3D MedDiffusion: A 3D Medical Diffusion Model for Controllable and High-quality Medical Image Generation
Authors:Haoshen Wang, Zhentao Liu, Kaicong Sun, Xiaodong Wang, Dinggang Shen, Zhiming Cui
The generation of medical images presents significant challenges due to their high-resolution and three-dimensional nature. Existing methods often yield suboptimal performance in generating high-quality 3D medical images, and there is currently no universal generative framework for medical imaging. In this paper, we introduce the 3D Medical Diffusion (3D MedDiffusion) model for controllable, high-quality 3D medical image generation. 3D MedDiffusion incorporates a novel, highly efficient Patch-Volume Autoencoder that compresses medical images into latent space through patch-wise encoding and recovers back into image space through volume-wise decoding. Additionally, we design a new noise estimator to capture both local details and global structure information during diffusion denoising process. 3D MedDiffusion can generate fine-detailed, high-resolution images (up to 512x512x512) and effectively adapt to various downstream tasks as it is trained on large-scale datasets covering CT and MRI modalities and different anatomical regions (from head to leg). Experimental results demonstrate that 3D MedDiffusion surpasses state-of-the-art methods in generative quality and exhibits strong generalizability across tasks such as sparse-view CT reconstruction, fast MRI reconstruction, and data augmentation.
医学图像生成因其高分辨率和三维特性而面临重大挑战。现有方法常在生成高质量3D医学图像时表现不佳,目前医学成像领域尚未有通用的生成框架。在本文中,我们介绍了用于可控、高质量3D医学图像生成的3D医学扩散(3D MedDiffusion)模型。3D MedDiffusion融入了一种新颖、高效的Patch-Volume自编码器,该自编码器通过patch级编码将医学图像压缩到潜在空间,再通过volume级解码恢复到图像空间。此外,我们设计了一种新的噪声估计器,在扩散去噪过程中捕捉局部细节和全局结构信息。3D MedDiffusion可以生成细节精细、高分辨率的图像(高达512x512x512),并且在大型数据集上训练,覆盖CT和MRI模态以及不同的解剖区域(从头至脚),因此可有效适应各种下游任务。实验结果表明,3D MedDiffusion在生成质量上超越了现有最先进的方法,并在稀疏视图CT重建、快速MRI重建和数据增强等任务上表现出了强大的泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
论文介绍了一种用于可控、高质量的三维医学图像生成的新型框架,名为三维医学扩散模型(3D MedDiffusion)。它融合了新颖的Patch-Volume Autoencoder技术,能够在大型数据集上训练,生成精细、高分辨率的三维医学图像(分辨率高达512x512x512),并适应多种下游任务,如稀疏视图CT重建、快速MRI重建和数据增强等。通过这一过程,医学图像能够在潜在空间中以补丁的方式进行编码和解码,从而高效地压缩和恢复。论文设计了一种新的噪声估计器,能够在扩散去噪过程中捕捉局部细节和全局结构信息。总体而言,论文的创新成果有望在医学图像生成领域带来显著的提升和改进。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像生成面临高分辨率和三维特性的挑战。
- 当前方法生成高质量三维医学图像的性能并不理想,缺乏通用的医学成像生成框架。
- 论文提出了三维医学扩散(3D MedDiffusion)模型,这是一种可控、高质量的三维医学图像生成方法。
- 3D MedDiffusion模型融合了新颖的Patch-Volume Autoencoder技术,能够在潜在空间中以补丁的方式进行编码和解码,从而高效地压缩和恢复医学图像。
- 论文设计了一种新的噪声估计器,用于在扩散去噪过程中捕捉局部细节和全局结构信息。
- 3D MedDiffusion模型能够生成高分辨率(高达512x512x512)的精细图像,并适应多种下游任务,如稀疏视图CT重建、快速MRI重建和数据增强等。
点此查看论文截图

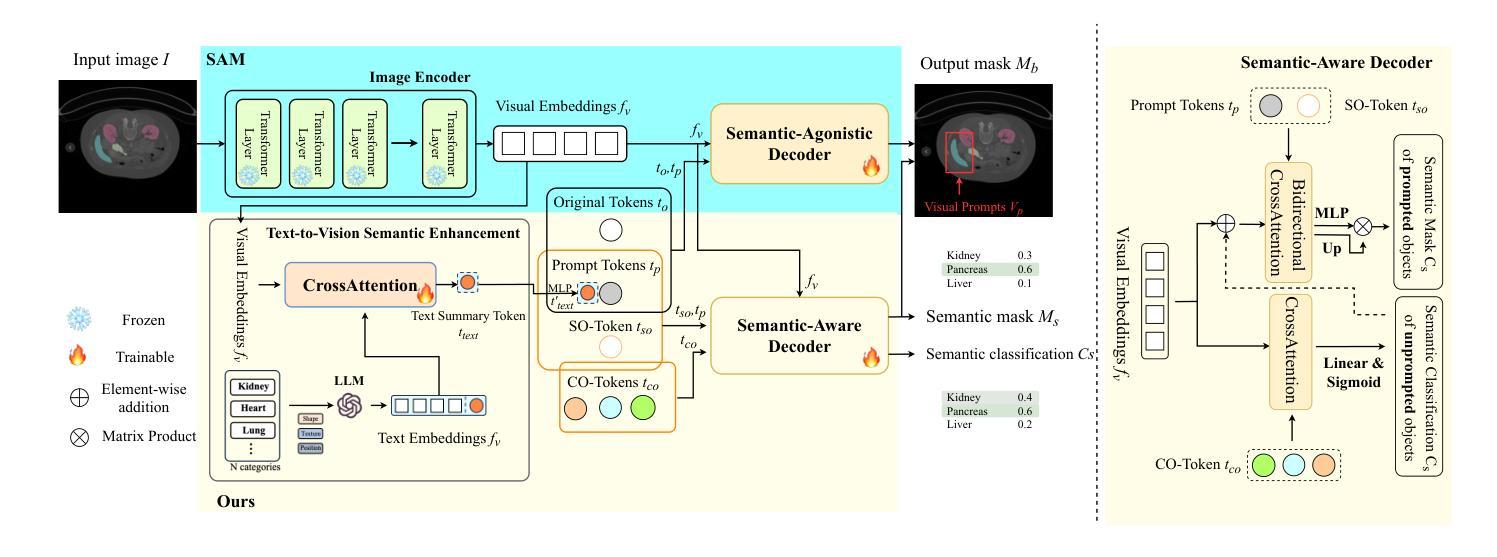
SEG-SAM: Semantic-Guided SAM for Unified Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Shuangping Huang, Hao Liang, Qingfeng Wang, Chulong Zhong, Zijian Zhou, Miaojing Shi
Recently, developing unified medical image segmentation models gains increasing attention, especially with the advent of the Segment Anything Model (SAM). SAM has shown promising binary segmentation performance in natural domains, however, transferring it to the medical domain remains challenging, as medical images often possess substantial inter-category overlaps. To address this, we propose the SEmantic-Guided SAM (SEG-SAM), a unified medical segmentation model that incorporates semantic medical knowledge to enhance medical segmentation performance. First, to avoid the potential conflict between binary and semantic predictions, we introduce a semantic-aware decoder independent of SAM’s original decoder, specialized for both semantic segmentation on the prompted object and classification on unprompted objects in images. To further enhance the model’s semantic understanding, we solicit key characteristics of medical categories from large language models and incorporate them into SEG-SAM through a text-to-vision semantic module, adaptively transferring the language information into the visual segmentation task. In the end, we introduce the cross-mask spatial alignment strategy to encourage greater overlap between the predicted masks from SEG-SAM’s two decoders, thereby benefiting both predictions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SEG-SAM outperforms state-of-the-art SAM-based methods in unified binary medical segmentation and task-specific methods in semantic medical segmentation, showcasing promising results and potential for broader medical applications.
最近,开发统一的医学图像分割模型越来越受到关注,尤其是随着Segment Anything Model(SAM)的出现。SAM在自然领域的二进制分割性能显示出良好的前景,然而,将其转移到医学领域仍然具有挑战性,因为医学图像通常存在大量的类别间重叠。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了SEmantic-Guided SAM(SEG-SAM),这是一种结合语义医学知识增强医学分割性能的统一的医学分割模型。首先,为了避免二进制和语义预测之间的潜在冲突,我们引入了一个独立于SAM原始解码器的语义感知解码器,专门用于图像中提示对象的语义分割和未提示对象的分类。为了进一步增强模型对语义的理解,我们从大型语言模型中提取医学类别的关键特征,并通过文本到视觉语义模块将其融入SEG-SAM中,自适应地将语言信息转化为视觉分割任务。最后,我们引入了跨掩膜空间对齐策略,以鼓励SEG-SAM的两个解码器产生的预测掩膜之间更大的重叠,从而有利于两种预测。大量实验表明,SEG-SAM在统一的二进制医学分割上优于最先进的SAM方法,在特定的语义医学分割任务上也表现出优越性能,展现出广阔的应用前景和潜在的医学应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 3 figures
Summary
基于医学图像统一分割模型的发展背景,介绍了SEMANTIC-GUIDED SEGMENT ANYTHING MODEL(SEG-SAM)模型的提出及其在医学图像分割中的优势。通过引入语义感知解码器,融合大型语言模型的医学类别关键特征,并采用跨掩膜空间对齐策略,SEG-SAM模型在统一二元医学分割和语义医学分割任务上表现出优异性能。
Key Takeaways
- SEG-SAM模型是基于Segment Anything Model(SAM)开发的统一医学图像分割模型,针对医学图像特有的问题进行了优化。
- 引入语义感知解码器,解决二元和语义预测之间的潜在冲突。
- 利用大型语言模型提取医学类别的关键特征,并融入SEG-SAM模型中。
- 通过文本到视觉的语义模块,自适应地将语言信息转化为视觉分割任务。
- 采用跨掩膜空间对齐策略,提升两个解码器预测的掩膜重叠度。
- SEG-SAM模型在统一二元医学分割和语义医学分割任务上均表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图

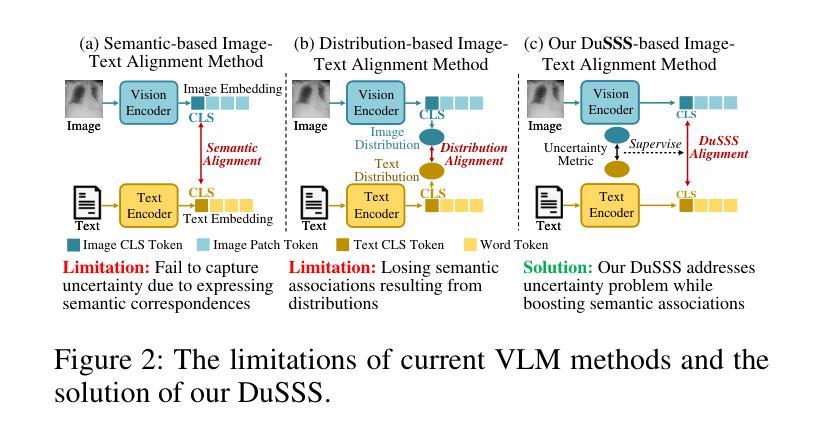
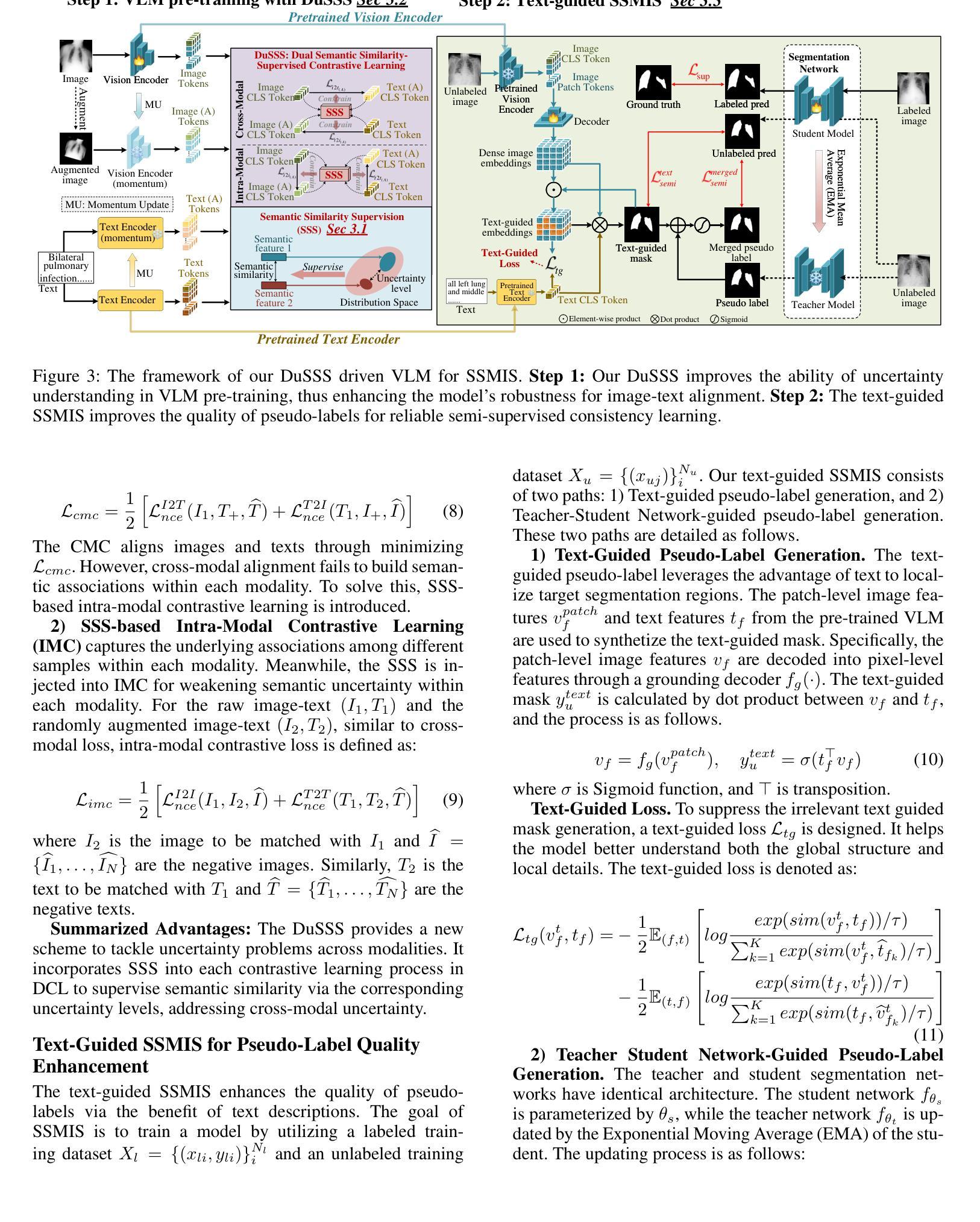
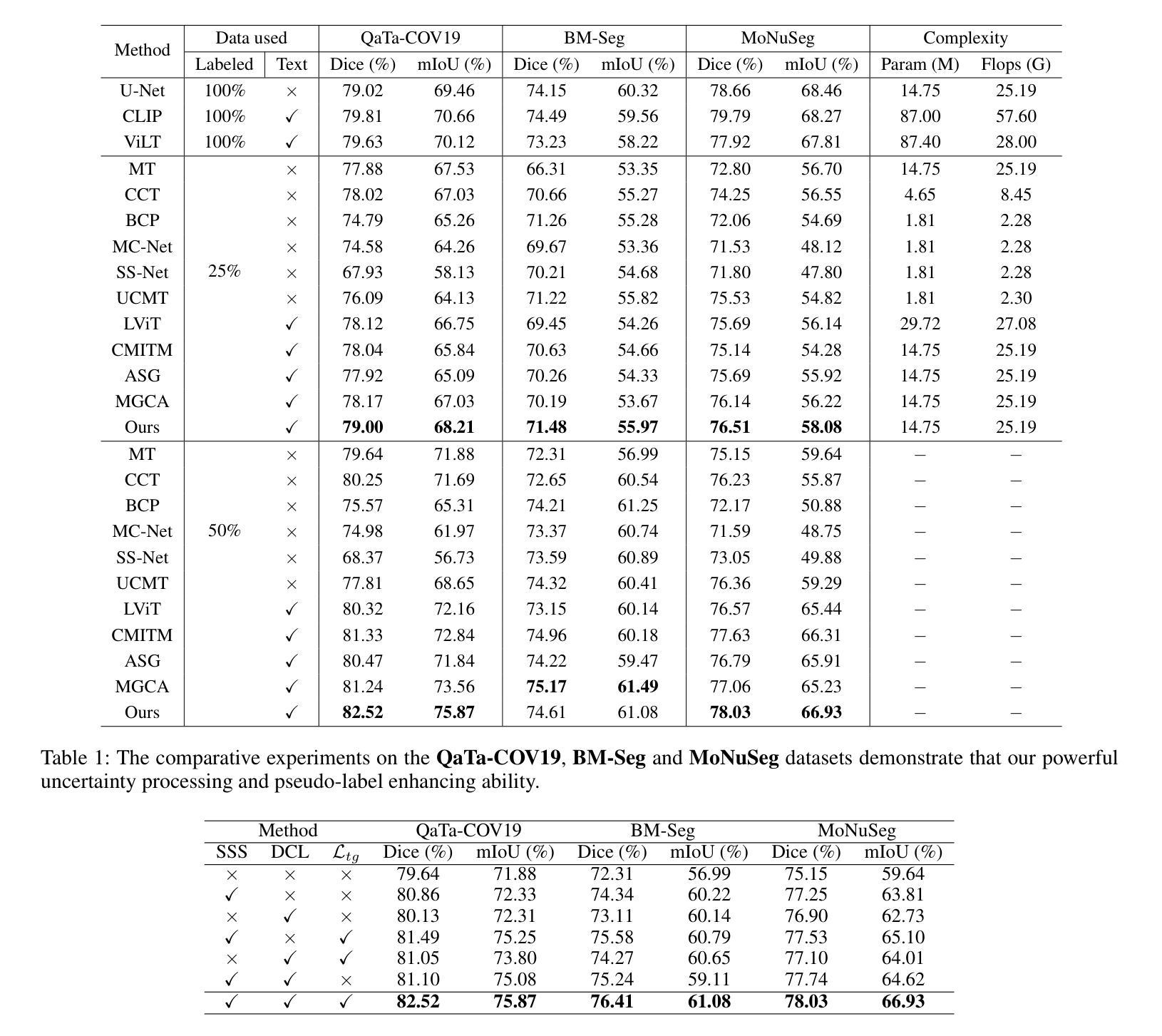
DuSSS: Dual Semantic Similarity-Supervised Vision-Language Model for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Qingtao Pan, Wenhao Qiao, Jingjiao Lou, Bing Ji, Shuo Li
Semi-supervised medical image segmentation (SSMIS) uses consistency learning to regularize model training, which alleviates the burden of pixel-wise manual annotations. However, it often suffers from error supervision from low-quality pseudo labels. Vision-Language Model (VLM) has great potential to enhance pseudo labels by introducing text prompt guided multimodal supervision information. It nevertheless faces the cross-modal problem: the obtained messages tend to correspond to multiple targets. To address aforementioned problems, we propose a Dual Semantic Similarity-Supervised VLM (DuSSS) for SSMIS. Specifically, 1) a Dual Contrastive Learning (DCL) is designed to improve cross-modal semantic consistency by capturing intrinsic representations within each modality and semantic correlations across modalities. 2) To encourage the learning of multiple semantic correspondences, a Semantic Similarity-Supervision strategy (SSS) is proposed and injected into each contrastive learning process in DCL, supervising semantic similarity via the distribution-based uncertainty levels. Furthermore, a novel VLM-based SSMIS network is designed to compensate for the quality deficiencies of pseudo-labels. It utilizes the pretrained VLM to generate text prompt guided supervision information, refining the pseudo label for better consistency regularization. Experimental results demonstrate that our DuSSS achieves outstanding performance with Dice of 82.52%, 74.61% and 78.03% on three public datasets (QaTa-COV19, BM-Seg and MoNuSeg).
半监督医学图像分割(SSMIS)利用一致性学习来规范模型训练,减轻了逐像素手动标注的负担。然而,它常常受到低质量伪标签的错误监督的影响。视觉语言模型(VLM)通过引入文本提示引导的多模态监督信息,在增强伪标签方面显示出巨大潜力。然而,它面临跨模态问题:获取的信息往往对应多个目标。为了解决上述问题,我们提出了一种用于SSMIS的双重语义相似性监督VLM(DuSSS)。具体来说,1)设计了双重对比学习(DCL),通过捕捉每种模态的内在表示和跨模态的语义关联,提高跨模态语义一致性。2)为了鼓励学习多个语义对应关系,提出了一种语义相似性监督策略(SSS),并将其注入DCL中的每个对比学习过程,通过基于分布的不确定性水平监督语义相似性。此外,设计了一种新型的基于VLM的SSMIS网络,以弥补伪标签质量缺陷。它利用预训练的VLM生成文本提示引导的监督信息,对伪标签进行细化,以得到更好的一致性正则化。实验结果证明,我们的DuSSS在三个公共数据集(QaTa-COV19、BM-Seg和MoNuSeg)上取得了出色的性能,Dice分别为82.52%、74.61%和78.03%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了半监督医学图像分割(SSMIS)中的一致性学习及面临的挑战,包括低质量伪标签导致的误差监督问题。提出使用Dual Semantic Similarity-Supervised Vision-Language Model(DuSSS)解决上述问题。该模型包括改进跨模态语义一致性的Dual Contrastive Learning(DCL),鼓励学习多重语义对应关系的Semantic Similarity-Supervision策略(SSS),并设计基于VLM的SSMIS网络以补偿伪标签的质量缺陷。实验结果显示,DuSSS在三个公共数据集上的Dice表现优秀。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督医学图像分割利用一致性学习进行模型训练,减少像素级手动标注的负担。
- 存在低质量伪标签引起的误差监督问题。
- 引入Vision-Language Model(VLM)通过文本提示引导多模态监督信息提高伪标签质量。
- 面临跨模态问题:获取的信息往往对应多个目标。
- 提出Dual Semantic Similarity-Supervised VLM(DuSSS)解决上述问题,包括改进跨模态语义一致性的Dual Contrastive Learning(DCL)。
- 引入Semantic Similarity-Supervision策略(SSS)鼓励学习多个语义对应关系,并注入到DCL的对比学习过程。
- 设计基于VLM的SSMIS网络,利用预训练的VLM生成文本提示引导的监督信息,改善伪标签质量。
点此查看论文截图

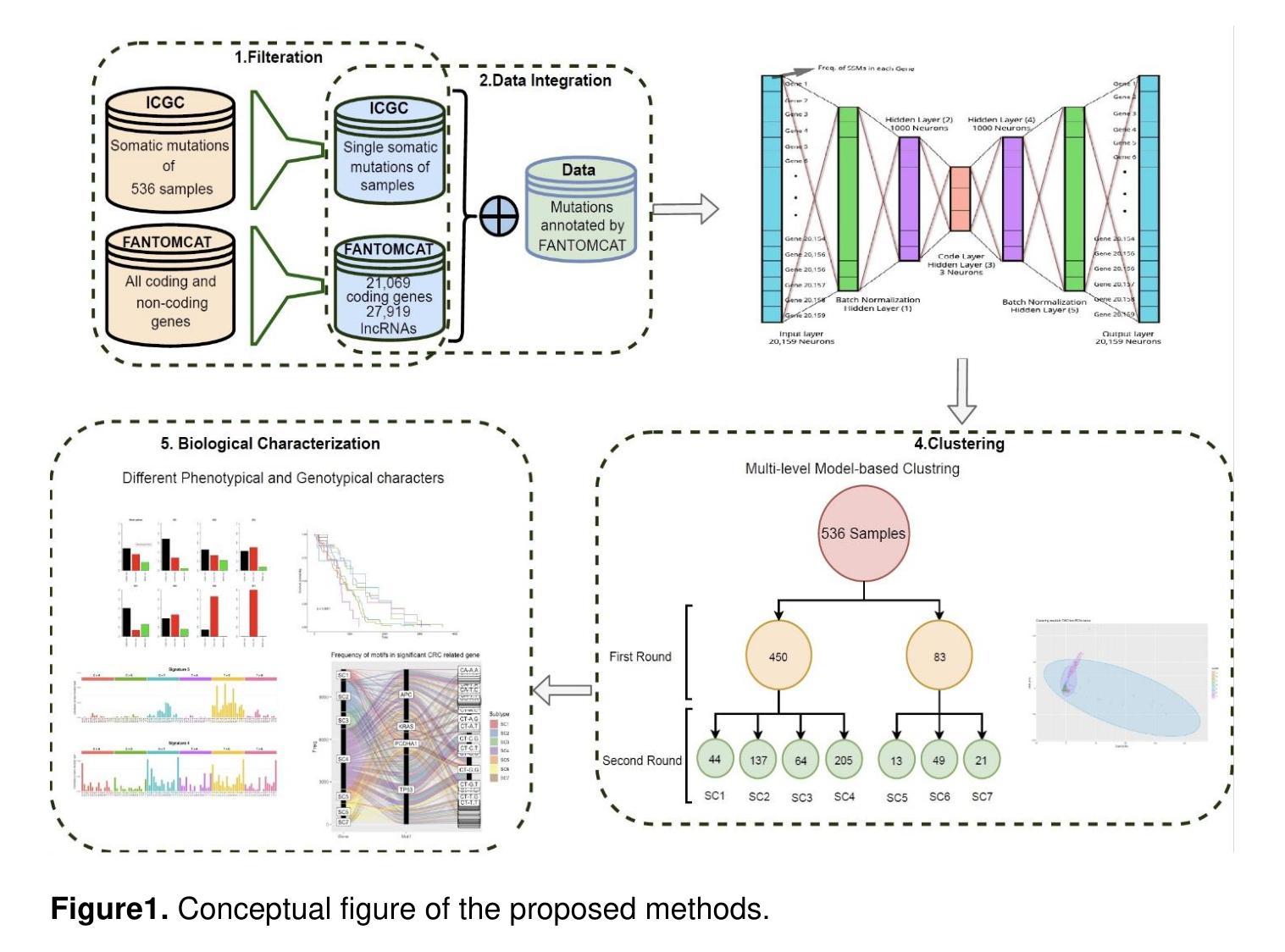
DLSOM: A Deep learning-based strategy for liver cancer subtyping
Authors:Fabio Zamio
Liver cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, with its high genetic heterogeneity complicating diagnosis and treatment. This study introduces DLSOM, a deep learning framework utilizing stacked autoencoders to analyze the complete somatic mutation landscape of 1,139 liver cancer samples, covering 20,356 protein-coding genes. By transforming high-dimensional mutation data into three low-dimensional features, DLSOM enables robust clustering and identifies five distinct liver cancer subtypes with unique mutational, functional, and biological profiles. Subtypes SC1 and SC2 exhibit higher mutational loads, while SC3 has the lowest, reflecting mutational heterogeneity. Novel and COSMIC-associated mutational signatures reveal subtype-specific molecular mechanisms, including links to hypermutation and chemotherapy resistance. Functional analyses further highlight the biological relevance of each subtype. This comprehensive framework advances precision medicine in liver cancer by enabling the development of subtype-specific diagnostics, biomarkers, and therapies, showcasing the potential of deep learning in addressing cancer complexity.
肝癌是全球癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一,其高度的遗传异质性使得诊断和治疗变得复杂。本研究介绍了DLSOM,这是一种利用堆叠自编码器进行深度学习的框架,用于分析1139个肝癌样本的完整体细胞突变图谱,覆盖20356个蛋白质编码基因。通过将高维突变数据转换为三个低维特征,DLSOM能够实现稳健的聚类,并识别出具有独特突变、功能和生物学特征的五种不同的肝癌亚型。SC1和SC2亚型表现出较高的突变负荷,而SC3的突变负荷最低,反映了突变异质性。新的和COSMIC相关的突变特征揭示了亚型特定的分子机制,包括与超突变和化疗抵抗的联系。功能分析进一步突出了每个亚型的生物学意义。这一综合框架通过开发针对亚型的诊断、生物标志和治疗手段,推动了肝癌精准医学的发展,展示了深度学习在解决癌症复杂性方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文研究利用深度学习框架DLSOM分析肝脏癌症的体细胞突变情况。通过对1,139个肝脏癌症样本的20,356个蛋白编码基因进行全面分析,DLSOM能将高维度的突变数据转化为三个低维度的特征,从而进行稳健的聚类,并识别出具有独特突变、功能和生物学特征的五种肝脏癌症亚型。这些亚型在突变负荷方面存在差异,揭示了肝脏癌症的遗传异质性。同时,研究还发现了一些亚型特有的分子机制,如超突变和化疗抵抗等。此研究为肝脏癌症的精准医疗提供了突破性的进展,有望推动开发针对特定亚型的诊断、生物标志物和疗法。
Key Takeaways
- 研究引入深度学习框架DLSOM,分析肝脏癌症的体细胞突变情况。
- DLSOM能转化高维度突变数据为低维度特征,实现稳健的聚类。
- 研究识别出五种具有不同突变、功能和生物学特征的肝脏癌症亚型。
- 不同亚型在突变负荷上存在差异,反映了肝脏癌症的遗传异质性。
- 发现了一些亚型特有的分子机制,如超突变和化疗抵抗。
- DLSOM的研究为肝脏癌症的精准医疗提供了突破性的进展。
点此查看论文截图

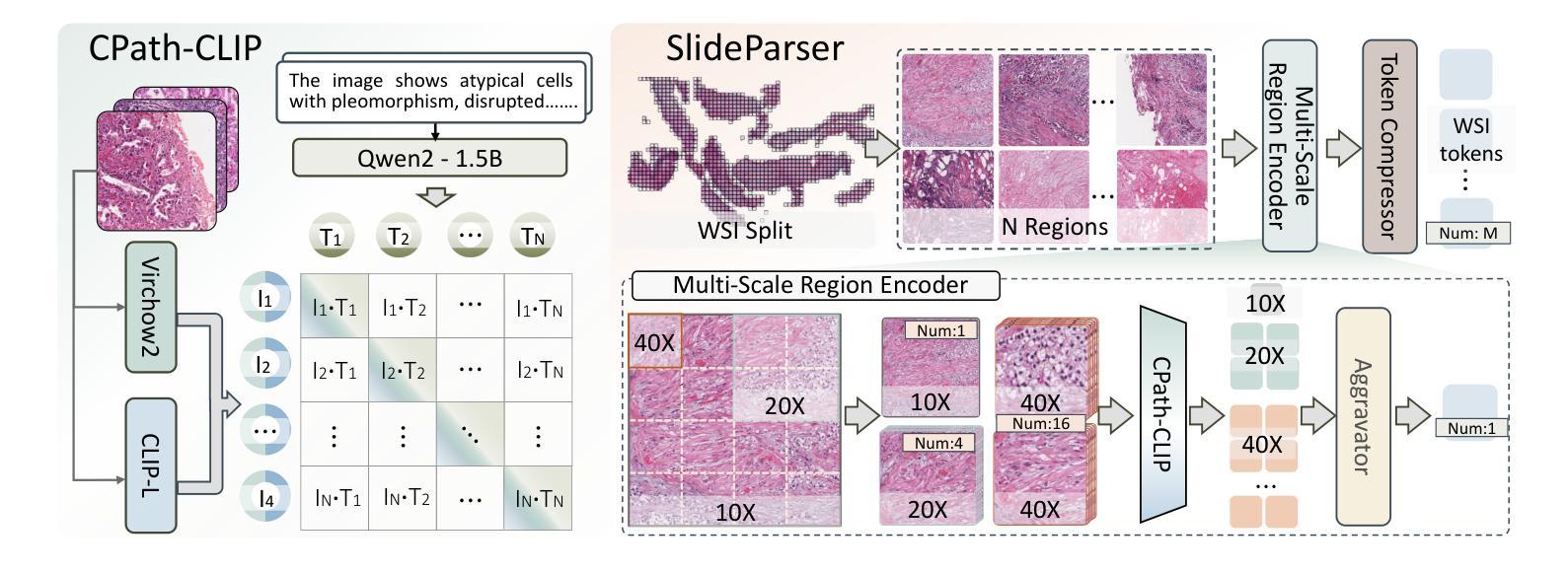
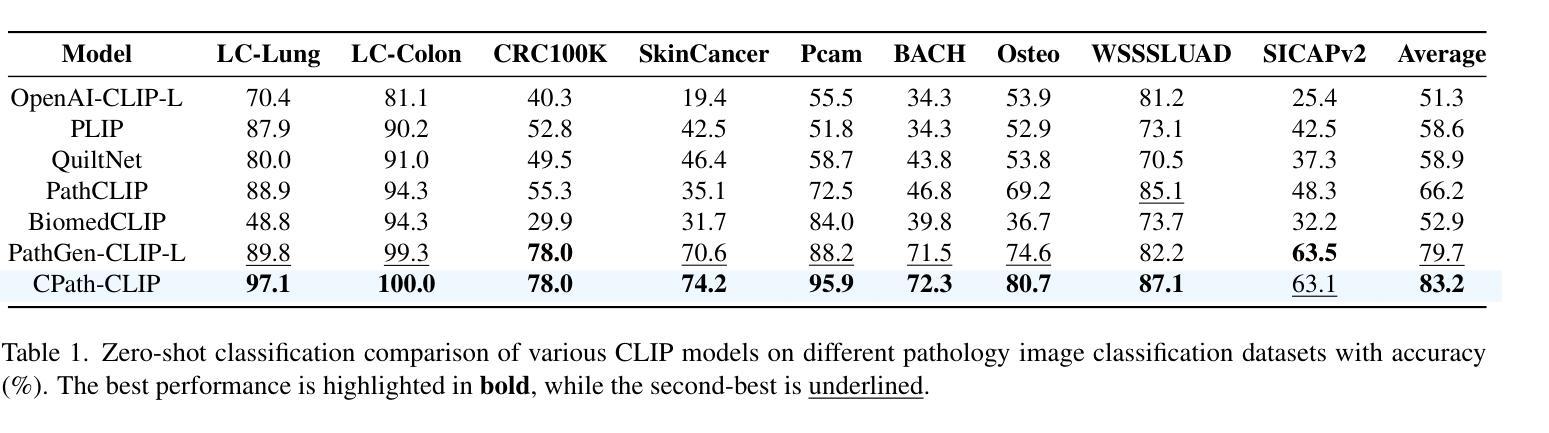
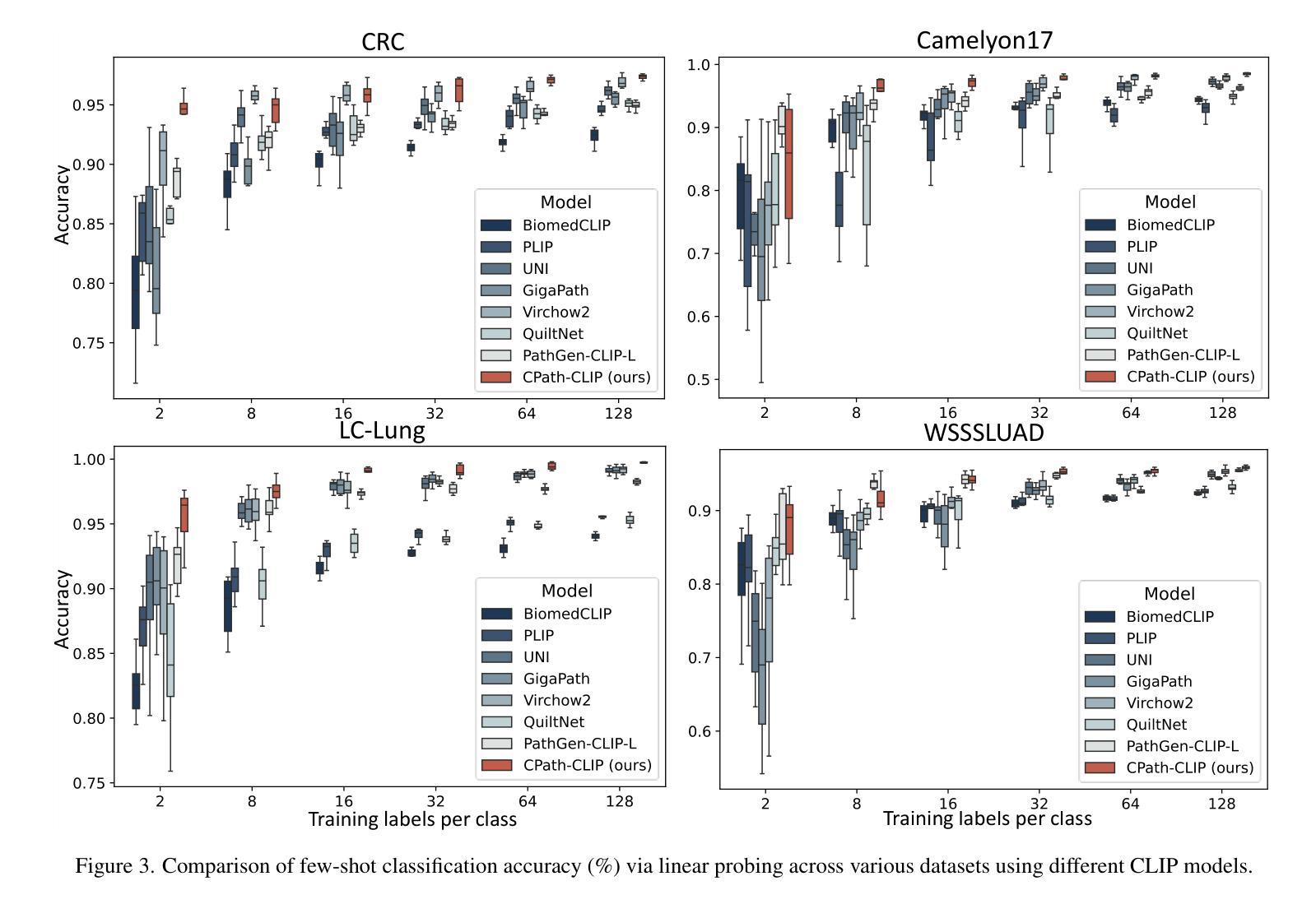
CPath-Omni: A Unified Multimodal Foundation Model for Patch and Whole Slide Image Analysis in Computational Pathology
Authors:Yuxuan Sun, Yixuan Si, Chenglu Zhu, Xuan Gong, Kai Zhang, Pingyi Chen, Ye Zhang, Zhongyi Shui, Tao Lin, Lin Yang
The emergence of large multimodal models (LMMs) has brought significant advancements to pathology. Previous research has primarily focused on separately training patch-level and whole-slide image (WSI)-level models, limiting the integration of learned knowledge across patches and WSIs, and resulting in redundant models. In this work, we introduce CPath-Omni, the first 15-billion-parameter LMM designed to unify both patch and WSI level image analysis, consolidating a variety of tasks at both levels, including classification, visual question answering, captioning, and visual referring prompting. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CPath-Omni achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance across seven diverse tasks on 39 out of 42 datasets, outperforming or matching task-specific models trained for individual tasks. Additionally, we develop a specialized pathology CLIP-based visual processor for CPath-Omni, CPath-CLIP, which, for the first time, integrates different vision models and incorporates a large language model as a text encoder to build a more powerful CLIP model, which achieves SOTA performance on nine zero-shot and four few-shot datasets. Our findings highlight CPath-Omni’s ability to unify diverse pathology tasks, demonstrating its potential to streamline and advance the field of foundation model in pathology.
多模态大型模型(LMM)的出现给病理学带来了重大进步。以往的研究主要集中在分别训练补丁级别和全幻灯片图像(WSI)级别的模型,这限制了补丁和WSIs之间学习知识的整合,并导致了冗余模型。在这项工作中,我们介绍了CPath-Omni,这是一个首个设计用于统一补丁和WSI级别图像分析的大型多模态模型,该模型集成了这两个级别的各种任务,包括分类、视觉问答、描述和视觉提示引导。大量实验表明,CPath-Omni在42个数据集的39个数据集上的七个不同任务上取得了最先进的性能,优于或与针对个别任务训练的特定任务模型相匹配。此外,我们为CPath-Omni开发了一个基于CLIP的专用病理视觉处理器CPath-CLIP,它首次整合了不同的视觉模型,并纳入大型语言模型作为文本编码器,以构建更强大的CLIP模型,该模型在九个零样本和四个少样本数据集上取得了最先进的性能。我们的研究突出了CPath-Omni统一多样化病理任务的能力,展示了其在推动病理学领域基础模型发展的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 13 figures
Summary
基于大型多模态模型(LMMs)的出现,病理学领域取得了重大进展。以往的研究主要集中在分别训练补丁级别和全幻灯片图像级别的模型,这限制了跨补丁和全幻灯片图像的知识整合,并导致模型冗余。本研究引入了CPath-Omni,这是一个旨在统一补丁和WSI级别图像分析的首个拥有15亿参数的大型多模态模型。它融合了各级别的多种任务,包括分类、视觉问答、描述和视觉引用提示等。广泛的实验表明,CPath-Omni在42个数据集的其中39个数据集的七个不同任务上取得了最佳性能。此外,我们为CPath-Omni开发了一个基于CLIP的专用病理视觉处理器CPath-CLIP,首次整合了不同的视觉模型,并引入大型语言模型作为文本编码器,构建了更强大的CLIP模型,在九个零样本和四个少样本数据集上取得了最佳性能。我们的研究突出了CPath-Omni统一多种病理任务的能力,展示了其在病理学领域基础模型应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型多模态模型(LMMs)的出现在病理学领域带来显著进展。
- 以前的研究主要关注单独训练补丁级别和全幻灯片图像级别的模型,导致知识整合受限和模型冗余。
- CPath-Omni是首个统一补丁和WSI级别图像分析的大型多模态模型,整合了各级别的多种任务。
- CPath-Omni在多个数据集上的七个任务上取得了最佳性能。
- CPath-CLIP是专门为CPath-Omni开发的病理CLIP视觉处理器,融合了不同的视觉模型和大型语言模型,增强了CLIP模型的性能。
- CPath-CLIP在多个零样本和少样本数据集上取得了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

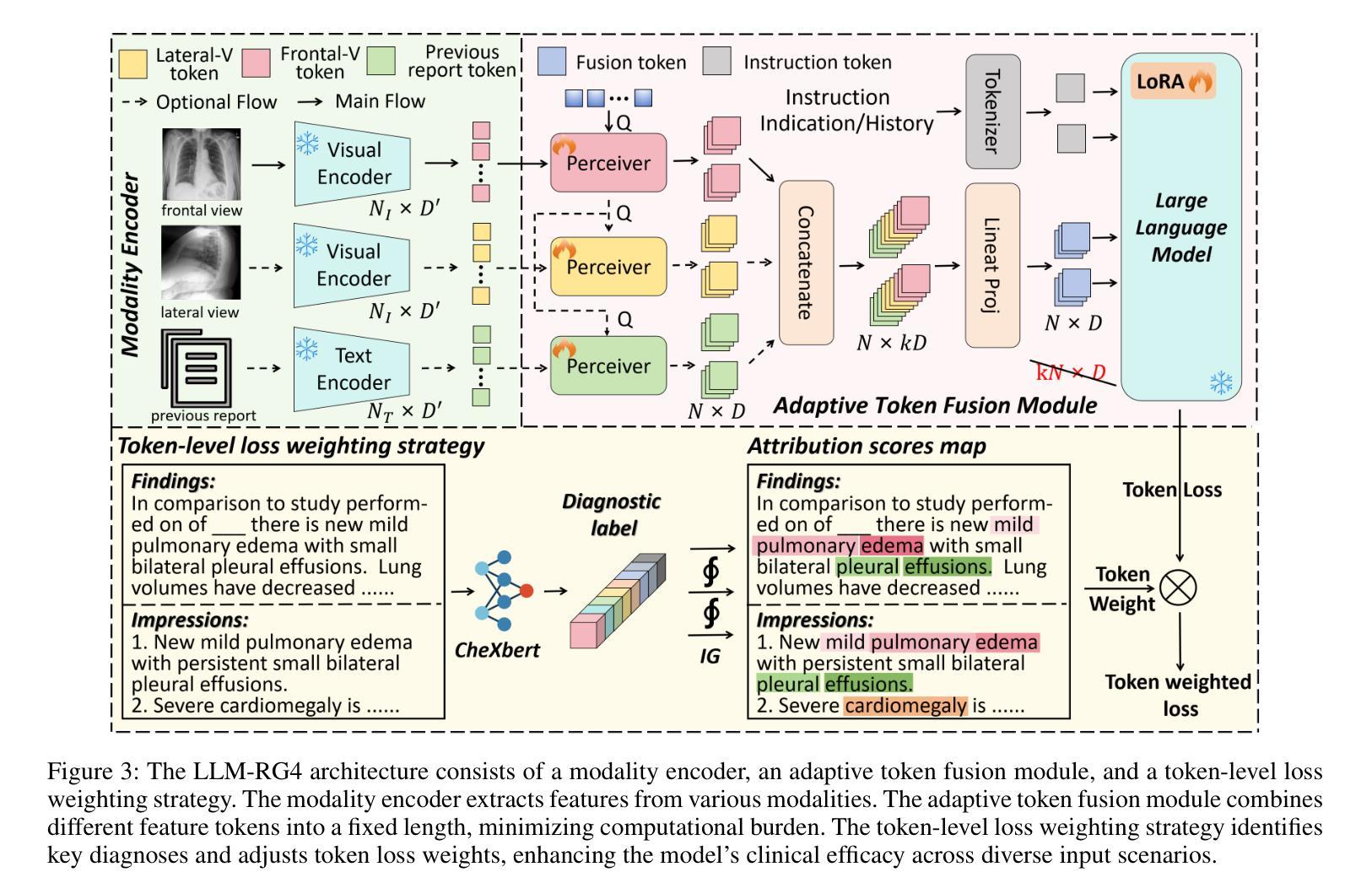
LLM-RG4: Flexible and Factual Radiology Report Generation across Diverse Input Contexts
Authors:Zhuhao Wang, Yihua Sun, Zihan Li, Xuan Yang, Fang Chen, Hongen Liao
Drafting radiology reports is a complex task requiring flexibility, where radiologists tail content to available information and particular clinical demands. However, most current radiology report generation (RRG) models are constrained to a fixed task paradigm, such as predicting the full ``finding’’ section from a single image, inherently involving a mismatch between inputs and outputs. The trained models lack the flexibility for diverse inputs and could generate harmful, input-agnostic hallucinations. To bridge the gap between current RRG models and the clinical demands in practice, we first develop a data generation pipeline to create a new MIMIC-RG4 dataset, which considers four common radiology report drafting scenarios and has perfectly corresponded input and output. Secondly, we propose a novel large language model (LLM) based RRG framework, namely LLM-RG4, which utilizes LLM’s flexible instruction-following capabilities and extensive general knowledge. We further develop an adaptive token fusion module that offers flexibility to handle diverse scenarios with different input combinations, while minimizing the additional computational burden associated with increased input volumes. Besides, we propose a token-level loss weighting strategy to direct the model’s attention towards positive and uncertain descriptions. Experimental results demonstrate that LLM-RG4 achieves state-of-the-art performance in both clinical efficiency and natural language generation on the MIMIC-RG4 and MIMIC-CXR datasets. We quantitatively demonstrate that our model has minimal input-agnostic hallucinations, whereas current open-source models commonly suffer from this problem.
起草放射学报告是一项复杂的任务,需要灵活度,其中放射科医生根据现有信息和特定临床需求定制内容。然而,当前大多数的放射学报告生成(RRG)模型受限于固定的任务范式,例如仅根据单张图像预测完整的“发现”部分,这本质上导致了输入和输出之间的不匹配。训练过的模型在应对不同输入时缺乏灵活性,并可能产生有害的、与输入无关的幻觉。为了弥合当前RRG模型与实际应用中临床需求之间的差距,我们首先开发了一个数据生成管道,创建了新的MIMIC-RG4数据集,该数据集考虑了四种常见的放射学报告起草场景,并实现了完美的输入和输出对应。其次,我们提出了一种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的RRG框架,即LLM-RG4,它利用LLM的灵活指令遵循能力和广泛的一般知识。我们进一步开发了一个自适应令牌融合模块,该模块能够提供灵活性,以处理不同场景下的不同输入组合,同时最小化增加输入量所带来的额外计算负担。此外,我们提出了一种令牌级损失加权策略,以引导模型关注正面和不确定的描述。实验结果表明,LLM-RG4在MIMIC-RG4和MIMIC-CXR数据集上达到了最新的临床效率和自然语言生成性能。我们定量证明了我们的模型具有最小的与输入无关的幻觉,而当前开源模型通常存在这个问题。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在放射学报告生成中的挑战与解决方案。由于放射学报告生成(RRG)模型受限于固定的任务模式,导致在实际应用中与临床需求存在差距。为弥补这一差距,本文开发了一个全新的数据生成管道来构建MIMIC-RG4数据集,并基于大型语言模型(LLM)提出了一个灵活的RRG框架——LLM-RG4。该框架能应对不同的输入组合场景,同时通过一个自适应的令牌融合模块减少了计算负担。此外,本文还提出了一种令牌级损失加权策略,引导模型关注正面和不确定的描述。实验结果显示,LLM-RG4在MIMIC-RG4和MIMIC-CXR数据集上达到了临床效率和自然语言生成的最新水平,且显著减少了输入无关的幻觉现象。
Key Takeaways
- 放射学报告生成(RRG)模型受限于固定任务模式,导致与临床需求不匹配。
- 提出了一种新的数据生成管道创建MIMIC-RG4数据集,涵盖四种常见的放射学报告起草场景。
- 基于大型语言模型(LLM)提出了LLM-RG4框架,具有灵活的指令遵循能力和广泛的一般知识。
- 通过自适应令牌融合模块处理不同的输入组合场景,同时减少计算负担。
- 采用令牌级损失加权策略,使模型更关注正面和不确定的描述。
- 实验证明LLM-RG4在临床效率和自然语言生成方面达到最新水平。
点此查看论文截图


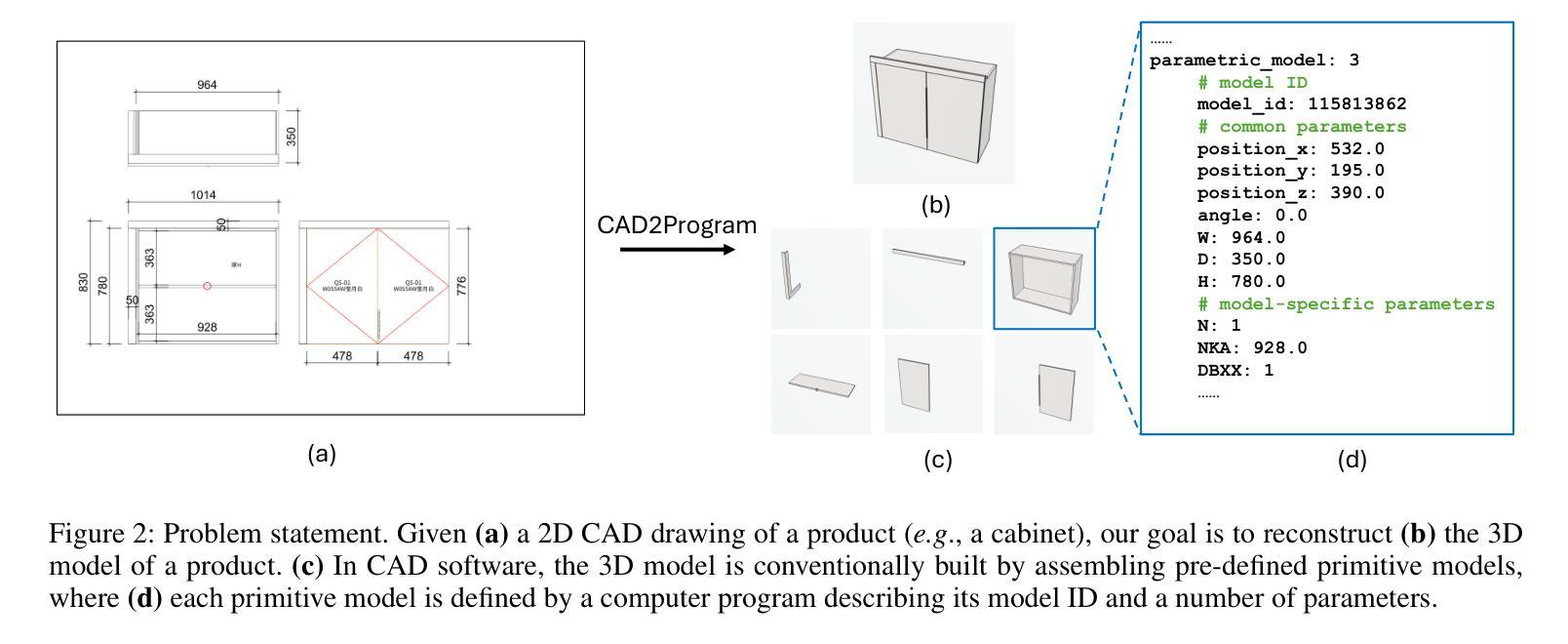
From 2D CAD Drawings to 3D Parametric Models: A Vision-Language Approach
Authors:Xilin Wang, Jia Zheng, Yuanchao Hu, Hao Zhu, Qian Yu, Zihan Zhou
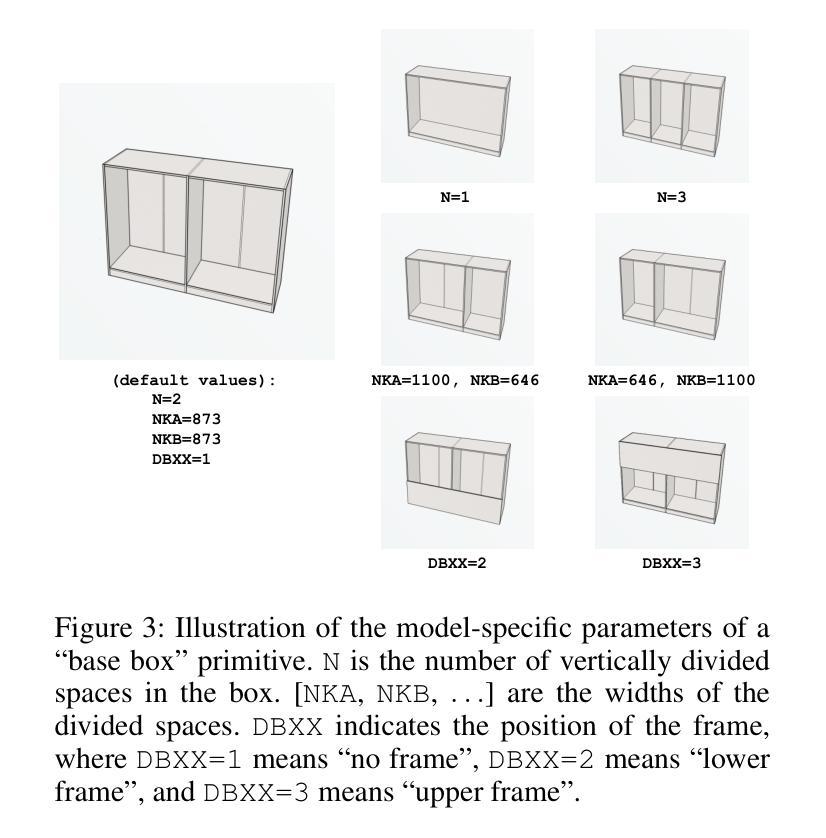
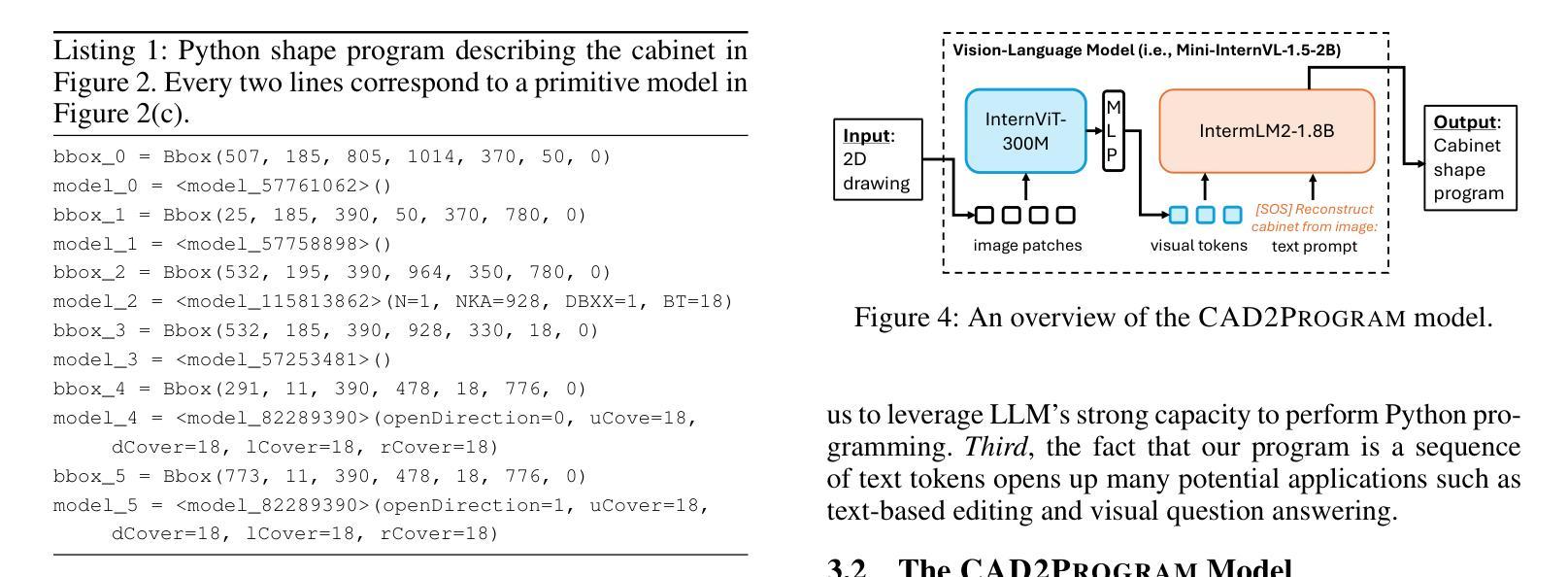
In this paper, we present CAD2Program, a new method for reconstructing 3D parametric models from 2D CAD drawings. Our proposed method is inspired by recent successes in vision-language models (VLMs), and departs from traditional methods which rely on task-specific data representations and/or algorithms. Specifically, on the input side, we simply treat the 2D CAD drawing as a raster image, regardless of its original format, and encode the image with a standard ViT model. We show that such an encoding scheme achieves competitive performance against existing methods that operate on vector-graphics inputs, while imposing substantially fewer restrictions on the 2D drawings. On the output side, our method auto-regressively predicts a general-purpose language describing 3D parametric models in text form. Compared to other sequence modeling methods for CAD which use domain-specific sequence representations with fixed-size slots, our text-based representation is more flexible, and can be easily extended to arbitrary geometric entities and semantic or functional properties. Experimental results on a large-scale dataset of cabinet models demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
本文中,我们提出了CAD2Program,这是一种从二维CAD图纸重建三维参数模型的新方法。我们提出的方法受到最近视觉语言模型(VLMs)成功的启发,与传统的依赖于特定任务数据表示和/或算法的模型截然不同。具体来说,在输入方面,我们简单地将二维CAD图纸视为光栅图像,无论其原始格式如何,并使用标准的ViT模型对其进行编码。我们证明了这种编码方案与在矢量图形输入上运行的现有方法相比具有竞争力,同时对二维图纸的约束大大减少。在输出方面,我们的方法通过自回归预测以文本形式描述三维参数模型的通用语言。与其他使用具有固定大小插槽的特定领域序列表示的CAD序列建模方法相比,我们的文本表示更加灵活,并且可轻松扩展到任意几何实体和语义或功能属性。在大型橱柜模型数据集上的实验结果证明了我们的方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To Appear in AAAI 2025. The project page is at https://manycore-research.github.io/CAD2Program
Summary
本文提出CAD2Program方法,通过借鉴视觉语言模型(VLMs)的成功经验,实现从二维CAD图纸到三维参数模型的重建。该方法将二维CAD图纸视为图像输入,使用标准ViT模型进行编码,能够兼容不同格式的图纸,预测输出描述三维参数模型的文本信息。相比传统方法和其他序列建模方法,CAD2Program更具灵活性,可以轻易扩展到任意几何实体和语义功能属性。实验证明该方法在大型橱柜模型数据集上的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- CAD2Program是一种利用视觉语言模型从二维CAD图纸重建三维参数模型的新方法。
- CAD图纸以图像形式输入,并使用标准ViT模型进行编码,兼容多种格式。
- 输出为描述三维参数模型的文本信息,相比传统方法更具灵活性。
- 方法能够扩展到任意几何实体和语义功能属性。
- 在大型橱柜模型数据集上的实验证明了该方法的有效性。
- CAD2Program受到视觉语言模型的启发,与现有的CAD处理方法不同。
点此查看论文截图

Ensemble Learning and 3D Pix2Pix for Comprehensive Brain Tumor Analysis in Multimodal MRI
Authors:Ramy A. Zeineldin, Franziska Mathis-Ullrich
Motivated by the need for advanced solutions in the segmentation and inpainting of glioma-affected brain regions in multi-modal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), this study presents an integrated approach leveraging the strengths of ensemble learning with hybrid transformer models and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), alongside the innovative application of 3D Pix2Pix Generative Adversarial Network (GAN). Our methodology combines robust tumor segmentation capabilities, utilizing axial attention and transformer encoders for enhanced spatial relationship modeling, with the ability to synthesize biologically plausible brain tissue through 3D Pix2Pix GAN. This integrated approach addresses the BraTS 2023 cluster challenges by offering precise segmentation and realistic inpainting, tailored for diverse tumor types and sub-regions. The results demonstrate outstanding performance, evidenced by quantitative evaluations such as the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC), Hausdorff Distance (HD95) for segmentation, and Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM), Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), and Mean-Square Error (MSE) for inpainting. Qualitative assessments further validate the high-quality, clinically relevant outputs. In conclusion, this study underscores the potential of combining advanced machine learning techniques for comprehensive brain tumor analysis, promising significant advancements in clinical decision-making and patient care within the realm of medical imaging.
本研究受到多模态磁共振成像(MRI)中胶质母细胞瘤影响的大脑区域分割和修复需要先进解决方案的驱动。因此,本研究提出了一种结合集成学习、混合Transformer模型和卷积神经网络(CNN)的方法,并创新性地应用了3D Pix2Pix生成对抗网络(GAN)。我们的方法结合了利用轴向注意力和Transformer编码器进行增强空间关系建模的稳健肿瘤分割能力,以及通过3D Pix2Pix GAN合成生物上合理的脑组织的能力。这一综合方法通过提供精确的分割和逼真的修复,解决了BraTS 2023集群挑战,适用于多种肿瘤类型和子区域。结果证明了其卓越性能,定量评估如用于分割的Dice相似系数(DSC)和Hausdorff距离(HD95),以及用于修复的结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)和均方误差(MSE)。定性评估进一步验证了高质量、临床相关的输出。总之,本研究强调了结合先进机器学习技术进行全面的脑肿瘤分析的可能性,有望在医学影像领域的临床决策和患者护理方面取得重大进展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the MICCAI BraTS Challenge 2023
Summary
本研究针对多模态磁共振成像(MRI)中胶质瘤受累脑区域分割和修复的需求,提出了一种结合集成学习、混合变压器模型、卷积神经网络(CNN)以及3D Pix2Pix生成对抗网络(GAN)的综合性方法。该方法不仅具备利用轴向注意力和变压器编码器进行增强空间关系建模的稳健肿瘤分割能力,而且能够通过3D Pix2Pix GAN合成具有生物学可行性的脑组织。该综合性方法针对BraTS 2023集群挑战,提供精确的分割和逼真的修复,适用于各种肿瘤类型和子区域。结果通过定量评估和定性评估证明了其卓越性能。本研究强调了结合先进机器学习技术进行全面的脑肿瘤分析的潜力,有望在医学成像领域的临床决策和患者护理方面实现重大进步。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究提出了一种结合多种机器学习技术的综合性方法,用于多模态MRI中胶质瘤脑区域的分割和修复。
- 该方法结合了集成学习、混合变压器模型、CNN以及3D Pix2Pix GAN。
- 该方法具备稳健的肿瘤分割能力,并可通过轴向注意力和变压器编码器进行空间关系建模。
- 通过合成生物学可行的脑组织,该方法具有强大的修复能力。
- 该方法在BraTS 2023集群挑战中表现出色,提供精确分割和逼真修复,适用于多种肿瘤类型和子区域。
- 结果通过定量评估(如Dice相似系数、Hausdorff距离等)和定性评估得到了验证。
点此查看论文截图

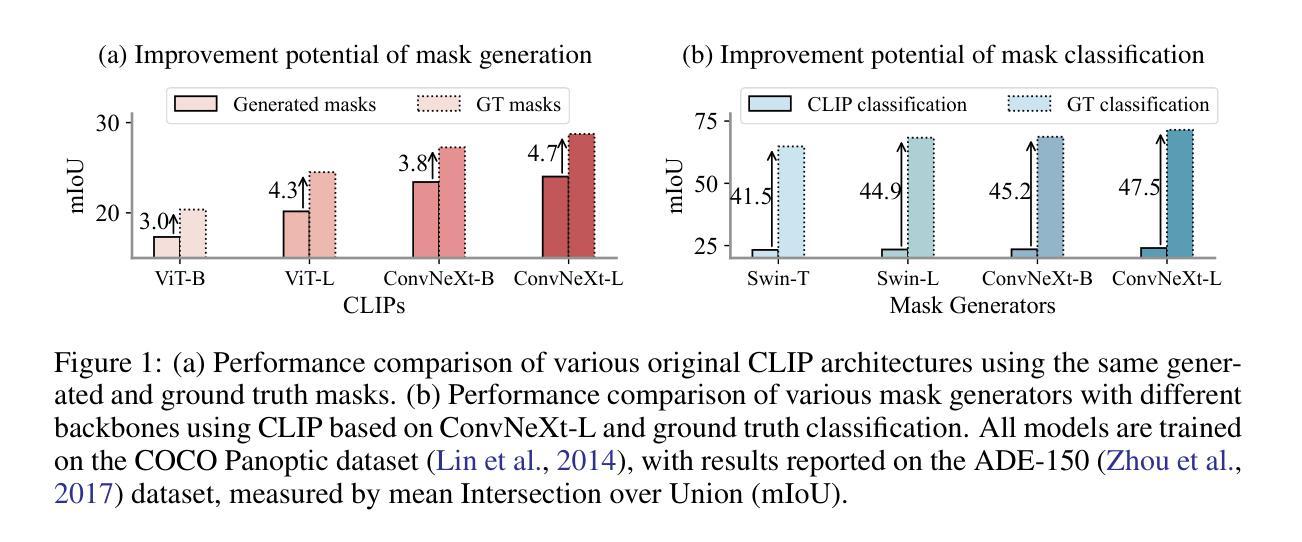
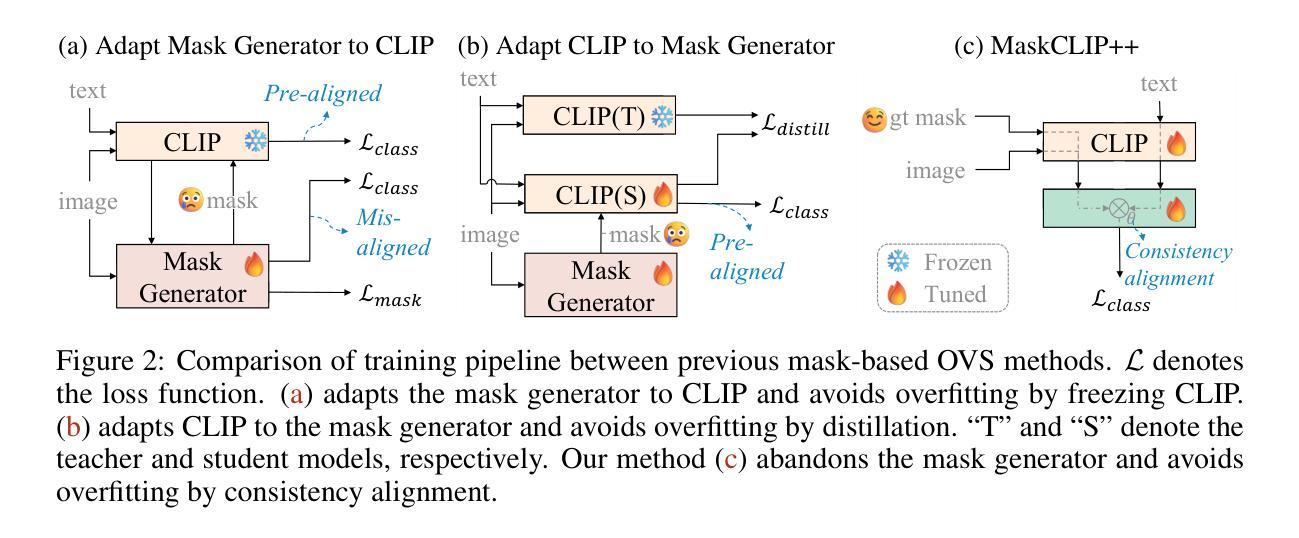
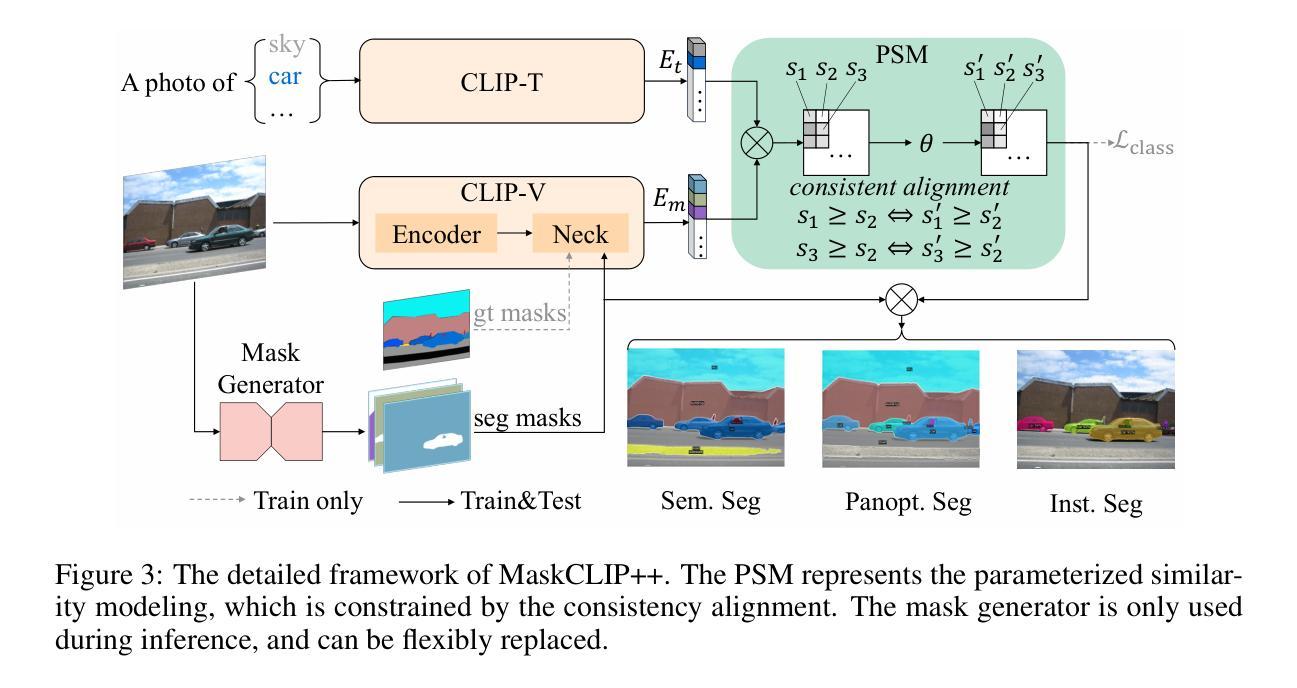
MaskCLIP++: A Mask-Based CLIP Fine-tuning Framework for Open-Vocabulary Image Segmentation
Authors:Quan-Sheng Zeng, Yunheng Li, Daquan Zhou, Guanbin Li, Qibin Hou, Ming-Ming Cheng
Open-vocabulary image segmentation has been advanced through the synergy between mask generators and vision-language models like Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP). Previous approaches focus on generating masks while aligning mask features with text embeddings during training. In this paper, we observe that relying on generated low-quality masks can weaken the alignment of vision and language in regional representations. This motivates us to present a new fine-tuning framework, named MaskCLIP++, which uses ground-truth masks instead of generated masks to enhance the mask classification capability of CLIP. Due to the limited diversity of image segmentation datasets with mask annotations, we propose incorporating a consistency alignment constraint during fine-tuning, which alleviates categorical bias toward the fine-tuning dataset. After low-cost fine-tuning, combining with the mask generator in previous state-of-the-art mask-based open vocabulary segmentation methods, we achieve performance improvements of +1.7, +2.3, +2.1, +3.1, and +0.3 mIoU on the A-847, PC-459, A-150, PC-59, and PAS-20 datasets, respectively.
开放词汇图像分割技术通过掩膜生成器和视觉语言模型(如对比语言图像预训练(CLIP))之间的协同作用取得了进展。以前的方法侧重于生成掩膜,同时在训练过程中将掩膜特征与文本嵌入对齐。在本文中,我们观察到依赖生成的低质量掩膜会削弱区域表示中的视觉和语言对齐。这促使我们提出一个新的微调框架,名为MaskCLIP++,它使用真实掩膜代替生成的掩膜,以提高CLIP的掩膜分类能力。由于带有掩膜标注的图像分割数据集多样性有限,我们提出在微调过程中引入一致性对齐约束,这减轻了对微调数据集的类别偏见。经过低成本的微调后,结合先前最先进的基于掩膜开放词汇分割方法的掩膜生成器,我们在A-847、PC-459、A-150、PC-59和PAS-20数据集上的mIoU分别提高了+1.7、+2.3、+2.1、+3.1和+0.3。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文提出一种名为MaskCLIP++的新微调框架,它使用真实掩膜代替生成的掩膜以提升CLIP的掩膜分类能力。为提高图像分割数据集掩膜标注的多样性,引入一致性对齐约束进行微调。结合先进的基于掩膜开放词汇表分割方法中的掩膜生成器,可在多个数据集上实现性能提升。
Key Takeaways
- MaskCLIP++使用真实掩膜替代生成的掩膜,以增强CLIP的掩膜分类能力。
- 真实掩膜的使用有助于提高图像分割的精度和性能。
- 一致性对齐约束在微调过程中被引入,以提高图像分割数据集的多样性并缓解分类偏向问题。
- MaskCLIP++在多个数据集上进行低成本的微调。
- 结合先进的基于掩膜开放词汇表分割方法的掩膜生成器,实现了显著的性能提升。
- 该方法在多个数据集(如A-847、PC-459、A-150、PC-59和PAS-20)上实现了性能改进,包括mIoU指标的提升。
点此查看论文截图

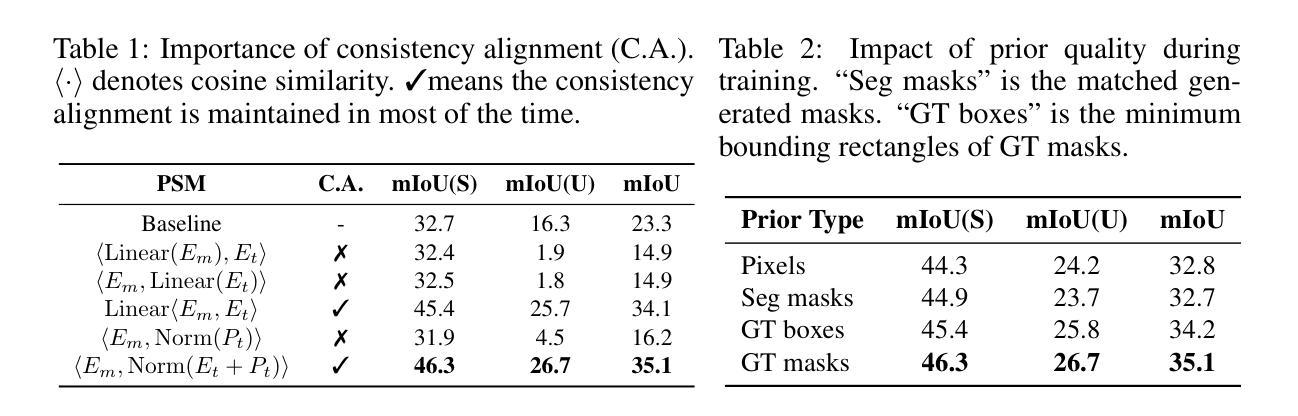
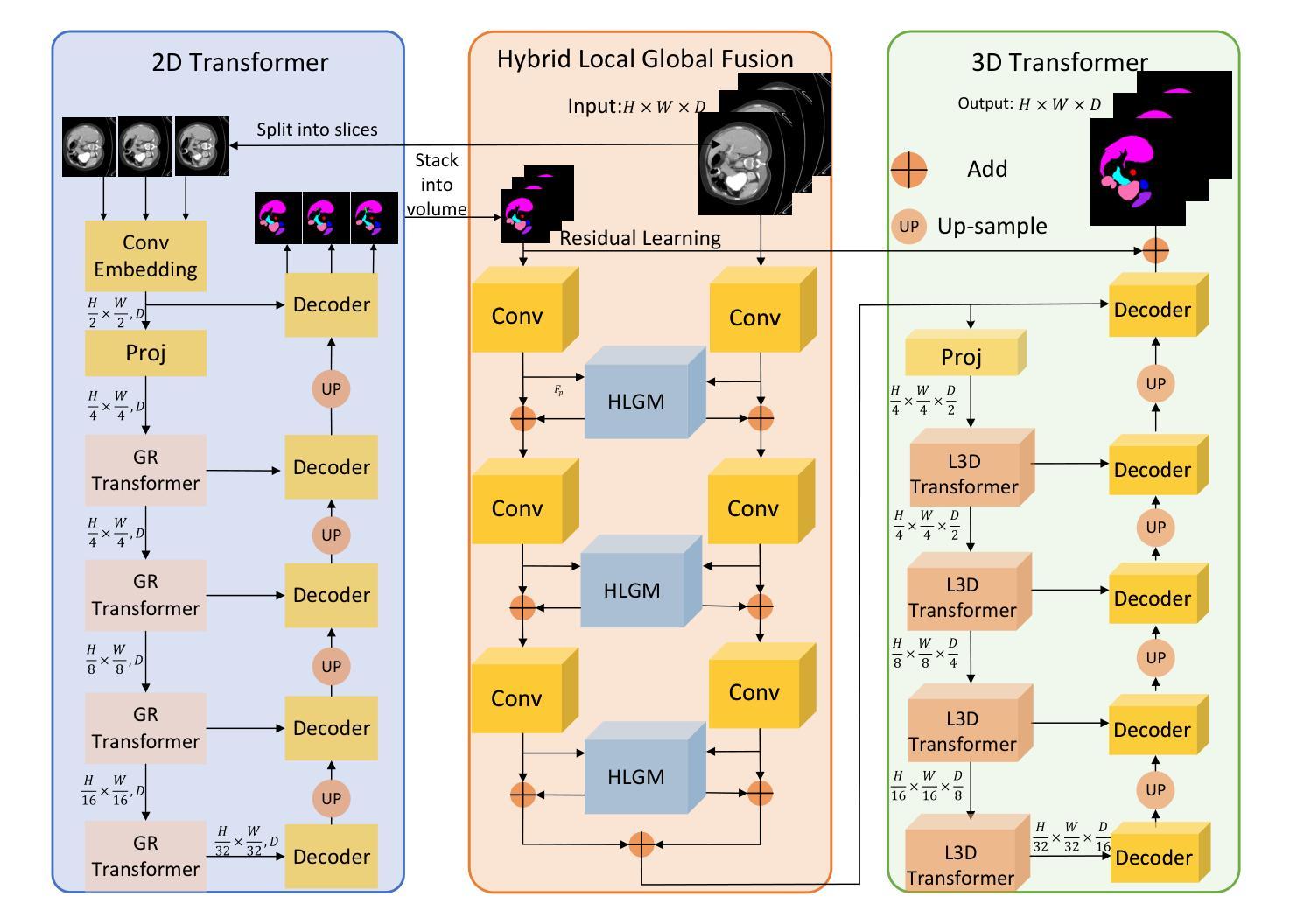
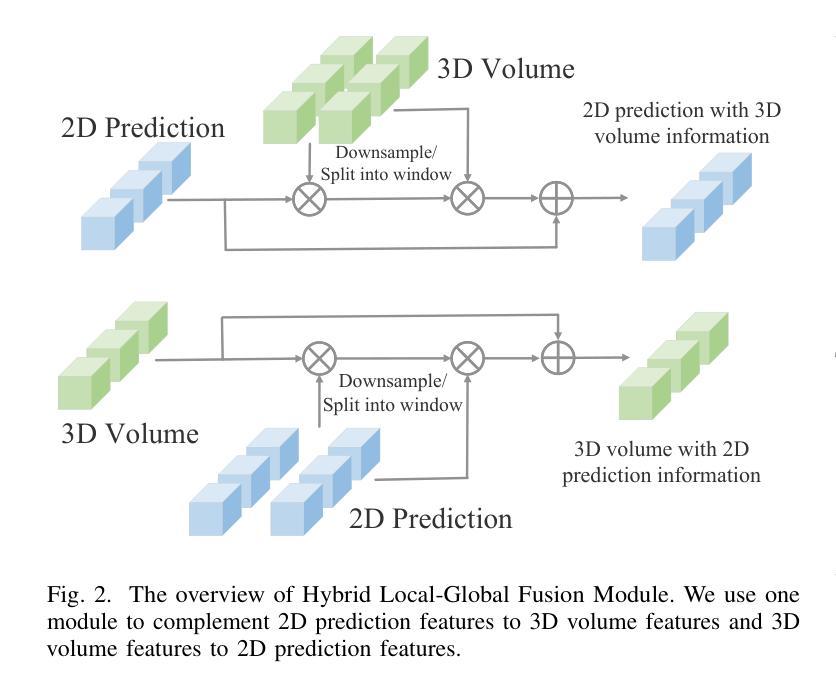
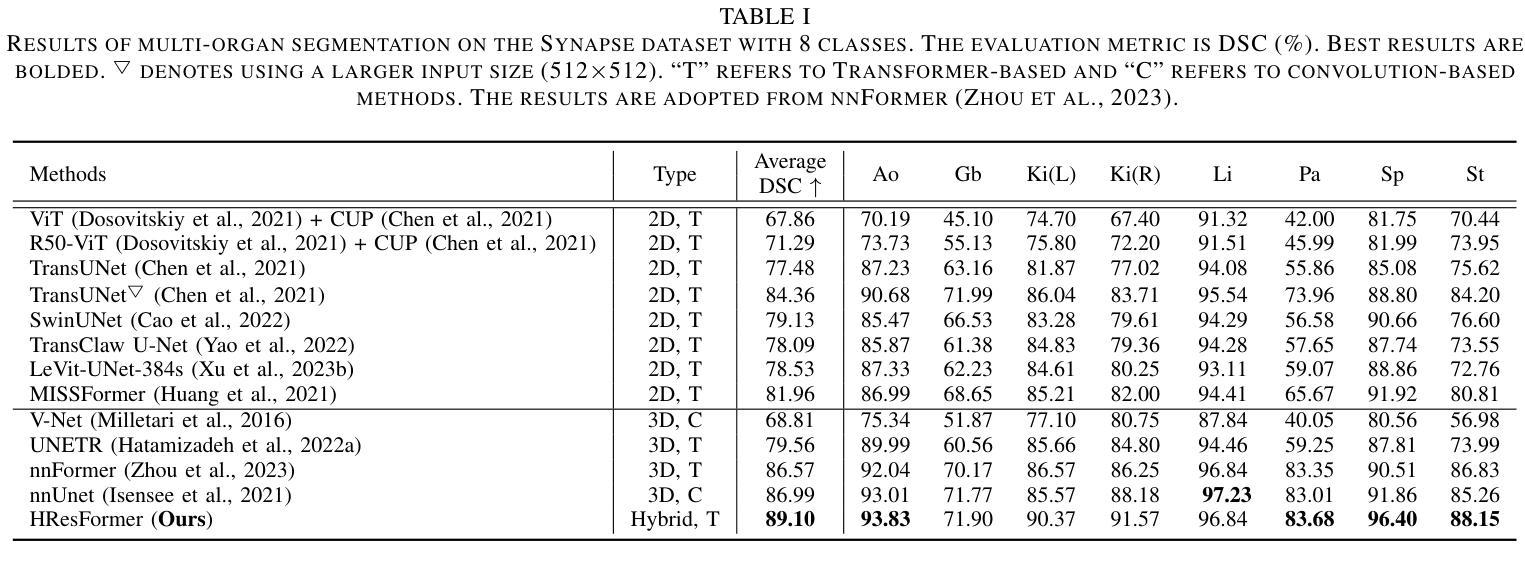
HResFormer: Hybrid Residual Transformer for Volumetric Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Sucheng Ren, Xiaomeng Li
Vision Transformer shows great superiority in medical image segmentation due to the ability in learning long-range dependency. For medical image segmentation from 3D data, such as computed tomography (CT), existing methods can be broadly classified into 2D-based and 3D-based methods. One key limitation in 2D-based methods is that the intra-slice information is ignored, while the limitation in 3D-based methods is the high computation cost and memory consumption, resulting in a limited feature representation for inner-slice information. During the clinical examination, radiologists primarily use the axial plane and then routinely review both axial and coronal planes to form a 3D understanding of anatomy. Motivated by this fact, our key insight is to design a hybrid model which can first learn fine-grained inner-slice information and then generate a 3D understanding of anatomy by incorporating 3D information. We present a novel \textbf{H}ybrid \textbf{Res}idual trans\textbf{Former} \textbf{(HResFormer)} for 3D medical image segmentation. Building upon standard 2D and 3D Transformer backbones, HResFormer involves two novel key designs: \textbf{(1)} a \textbf{H}ybrid \textbf{L}ocal-\textbf{G}lobal fusion \textbf{M}odule \textbf{(HLGM)} to effectively and adaptively fuse inner-slice information from 2D Transformer and intra-slice information from 3D volumes for 3D Transformer with local fine-grained and global long-range representation. \textbf{(2)} a residual learning of the hybrid model, which can effectively leverage the inner-slice and intra-slice information for better 3D understanding of anatomy. Experiments show that our HResFormer outperforms prior art on widely-used medical image segmentation benchmarks. This paper sheds light on an important but neglected way to design Transformers for 3D medical image segmentation.
在医学图像分割领域,由于具备学习长距离依赖关系的能力,Vision Transformer表现出了巨大的优越性。对于来自计算机断层扫描(CT)等3D数据的医学图像分割,现有方法大致可分为基于二维的方法和基于三维的方法。基于二维的方法的一个关键局限性在于忽略了切片内的信息,而基于三维的方法的局限性在于计算成本高和内存消耗大,导致对切片内信息的特征表示有限。在临床检查过程中,放射科医生主要使用轴平面,然后常规地同时查看轴平面和冠状平面,以形成对解剖结构的三维理解。受此事实的启发,我们的关键见解是设计一种混合模型,该模型首先学习精细的切片内信息,然后通过结合三维信息产生对解剖结构的三维理解。我们提出了一种新型的混合残差Transformer(HResFormer),用于三维医学图像分割。基于标准的二维和三维Transformer骨干网,HResFormer包含两个新颖的关键设计:(1)混合局部全局融合模块(HLGM),它能够有效地自适应地融合来自二维Transformer的切片内信息和来自三维体积的切片间信息,从而为三维Transformer提供局部精细和全局长距离表示。(2)混合模型的残差学习可以有效地利用切片内和切片间的信息,以更好地对解剖结构进行三维理解。实验表明,我们的HResFormer在广泛使用的医学图像分割基准测试中优于先前技术。本文揭示了设计用于三维医学图像分割的Transformer的一种重要但被忽视的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by TNNLS
Summary
针对医学图像分割领域,Vision Transformer因能学习长距离依赖关系展现出优越性。现有方法可分为基于二维和基于三维的方法,但存在忽略切片内信息和高计算成本等局限性。本文提出一种新型混合模型HResFormer,融合二维和三维Transformer骨干网络,设计Hybrid Local-Global fusion Module自适应融合切片内和体积内信息,并结合残差学习,旨在实现更好的三维解剖学理解。实验表明,HResFormer在广泛使用的医学图像分割基准测试中表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer在医学图像分割中表现优越,因能学习长距离依赖关系。
- 现有医学图像分割方法可分为基于二维和基于三维,但存在局限性。
- HResFormer是一种新型混合模型,融合二维和三维Transformer网络。
- HResFormer设计包括Hybrid Local-Global fusion Module,自适应融合切片内和体积内信息。
- HResFormer结合残差学习,实现更好的三维解剖学理解。
- 实验表明HResFormer在医学图像分割基准测试中表现优异。
点此查看论文截图


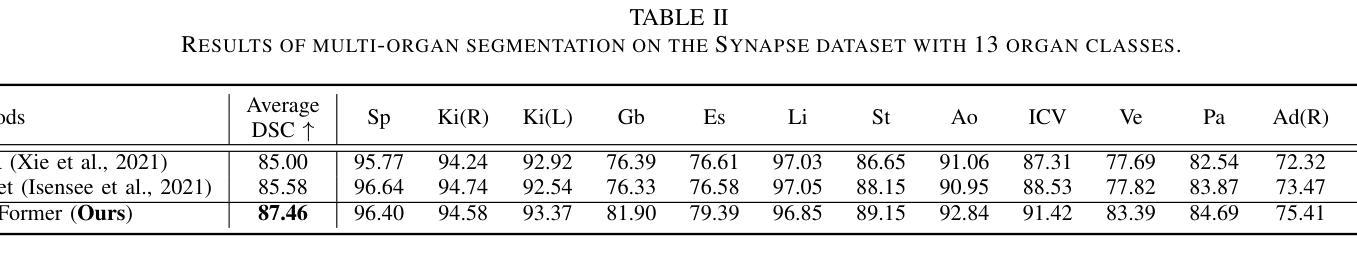
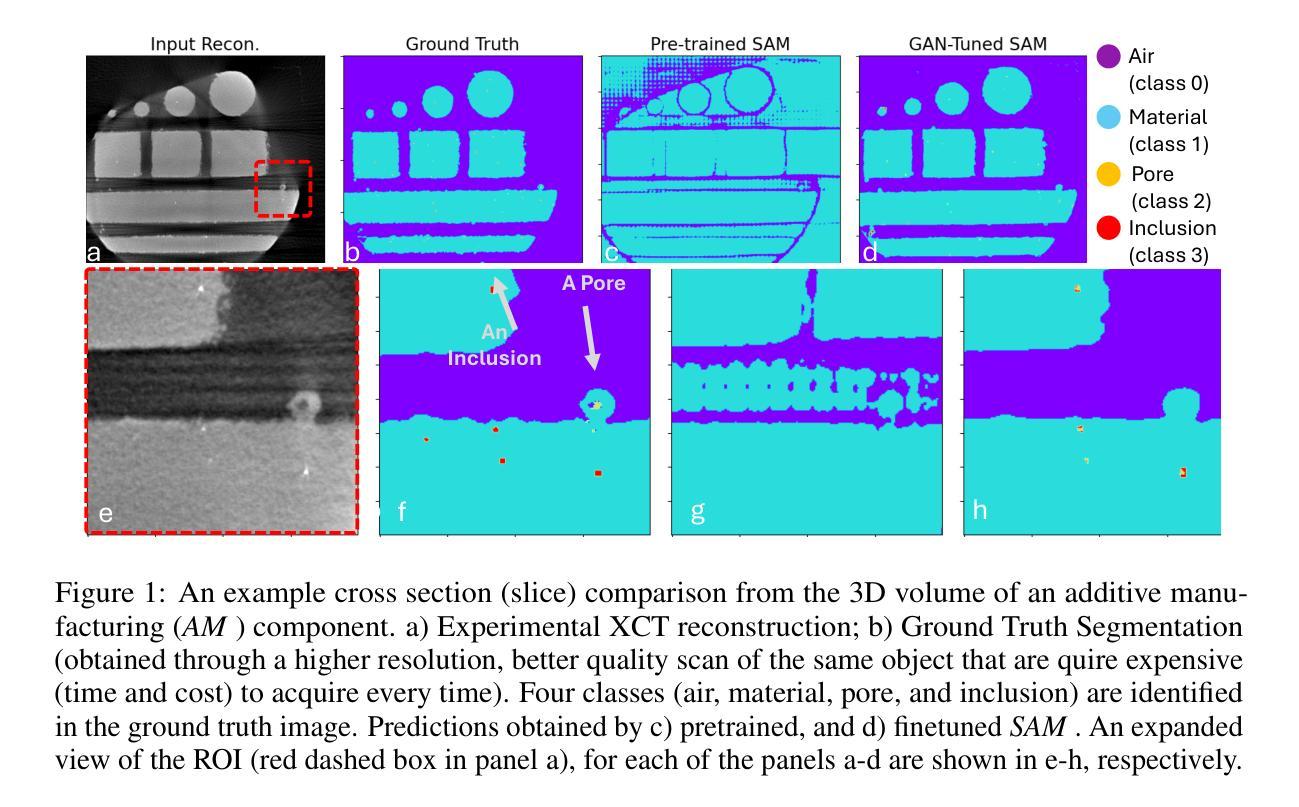
Adapting Segment Anything Model (SAM) to Experimental Datasets via Fine-Tuning on GAN-based Simulation: A Case Study in Additive Manufacturing
Authors:Anika Tabassum, Amirkoushyar Ziabari
Industrial X-ray computed tomography (XCT) is a powerful tool for non-destructive characterization of materials and manufactured components. XCT commonly accompanied by advanced image analysis and computer vision algorithms to extract relevant information from the images. Traditional computer vision models often struggle due to noise, resolution variability, and complex internal structures, particularly in scientific imaging applications. State-of-the-art foundational models, like the Segment Anything Model (SAM)-designed for general-purpose image segmentation-have revolutionized image segmentation across various domains, yet their application in specialized fields like materials science remains under-explored. In this work, we explore the application and limitations of SAM for industrial X-ray CT inspection of additive manufacturing components. We demonstrate that while SAM shows promise, it struggles with out-of-distribution data, multiclass segmentation, and computational efficiency during fine-tuning. To address these issues, we propose a fine-tuning strategy utilizing parameter-efficient techniques, specifically Conv-LoRa, to adapt SAM for material-specific datasets. Additionally, we leverage generative adversarial network (GAN)-generated data to enhance the training process and improve the model’s segmentation performance on complex X-ray CT data. Our experimental results highlight the importance of tailored segmentation models for accurate inspection, showing that fine-tuning SAM on domain-specific scientific imaging data significantly improves performance. However, despite improvements, the model’s ability to generalize across diverse datasets remains limited, highlighting the need for further research into robust, scalable solutions for domain-specific segmentation tasks.
工业X射线计算机断层扫描(XCT)是非破坏性表征材料和制造部件的强大工具。XCT通常与先进的图像分析和计算机视觉算法相结合,从图像中提取相关信息。传统计算机视觉模型经常因噪声、分辨率可变性和复杂的内部结构而面临挑战,特别是在科学成像应用中。最先进的基础模型,如用于通用图像分割的Segment Anything Model(SAM),已经彻底改变了各个领域的图像分割,但它们在材料科学等专业领域的应用仍然被探索不足。在这项工作中,我们探索了SAM在增材制造部件的工业X射线CT检测中的应用和局限性。我们证明,虽然SAM具有潜力,但在处理分布外数据、多类分割和微调过程中的计算效率时仍存在困难。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种利用参数高效技术的微调策略,特别是Conv-LoRa,以适应材料特定的数据集。此外,我们还利用生成对抗网络(GAN)生成的数据来增强训练过程,提高模型对复杂X射线CT数据的分割性能。我们的实验结果强调了定制分割模型对于准确检查的重要性,并表明在特定领域的科学成像数据上微调SAM可以显著提高性能。然而,尽管有所改进,该模型在不同数据集上的泛化能力仍然有限,这突显了对针对特定领域的分割任务的稳健、可扩展解决方案的进一步研究的必要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本研究探讨了将Segment Anything Model(SAM)应用于工业X射线CT检测增材制造部件的潜力与局限性。虽然SAM模型表现出一定潜力,但在面临超出范围的数据、多类别分割和微调过程中的计算效率问题时,其在材料特定数据集上的表现有待提高。为解决这些问题,本研究提出一种利用Conv-LoRa等参数优化技术的微调策略,同时借助生成对抗网络(GAN)生成的数据增强训练过程,提高模型对复杂X射线CT数据的分割性能。实验结果表明,针对特定科学成像数据的SAM模型微调能显著提高性能,但模型的泛化能力仍有待提升,需要进一步研究针对特定领域的稳健、可扩展解决方案。
Key Takeaways
- 工业X射线计算机断层扫描(XCT)是非破坏性材料表征和组件制造的有力工具,常与先进的图像分析和计算机视觉算法结合使用。
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)在图像分割领域具有革命性影响,但在材料科学等专业领域的应用仍待探索。
- SAM在应对工业X射线CT检测增材制造部件时面临超出范围的数据、多类别分割和计算效率的挑战。
- 利用参数优化技术(如Conv-LoRa)和生成对抗网络(GAN)生成的数据,可以提高SAM在复杂X射线CT数据上的分割性能。
- 实验表明,针对特定科学成像数据微调SAM能显著提高性能,但模型的泛化能力仍有待提升。
点此查看论文截图


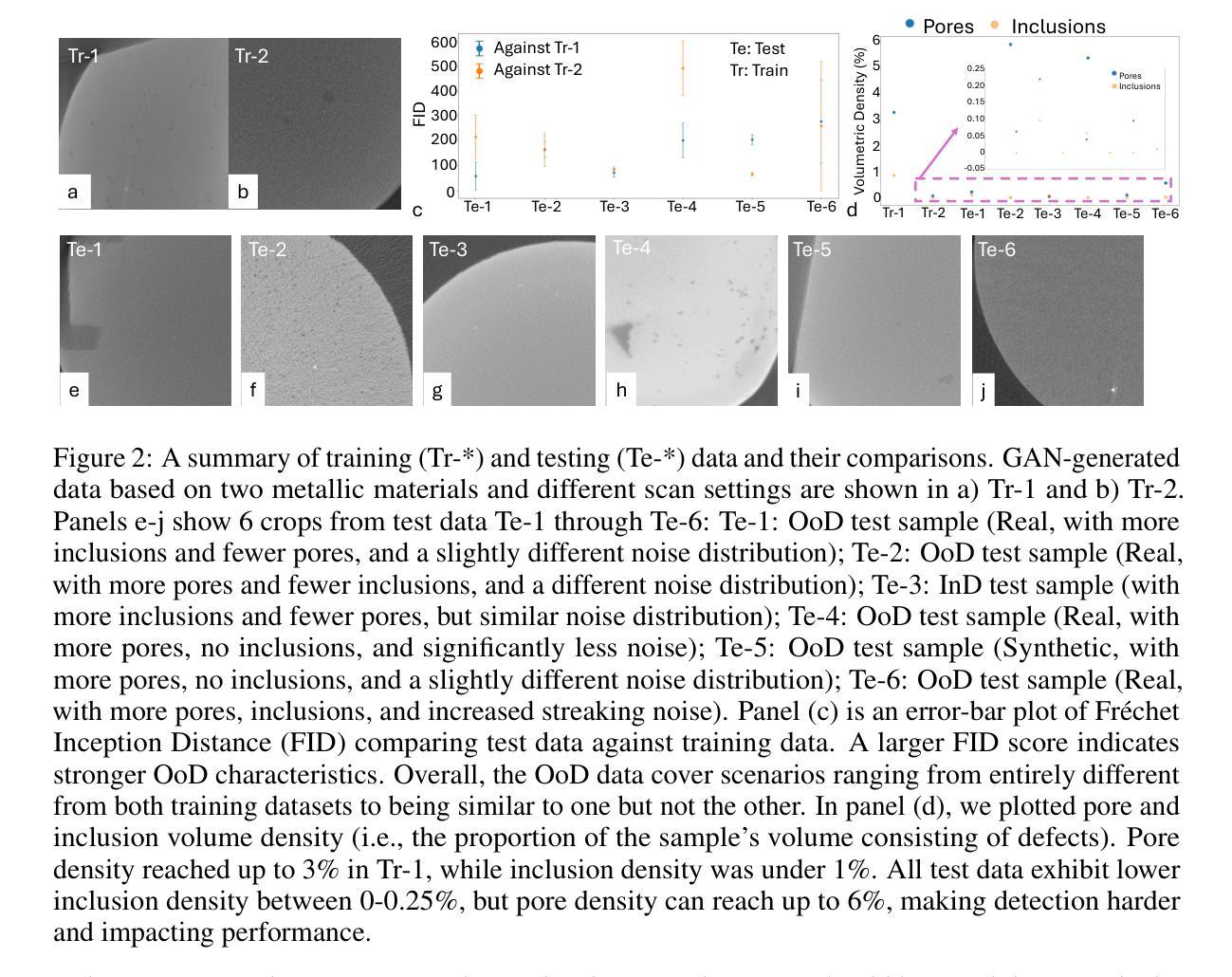
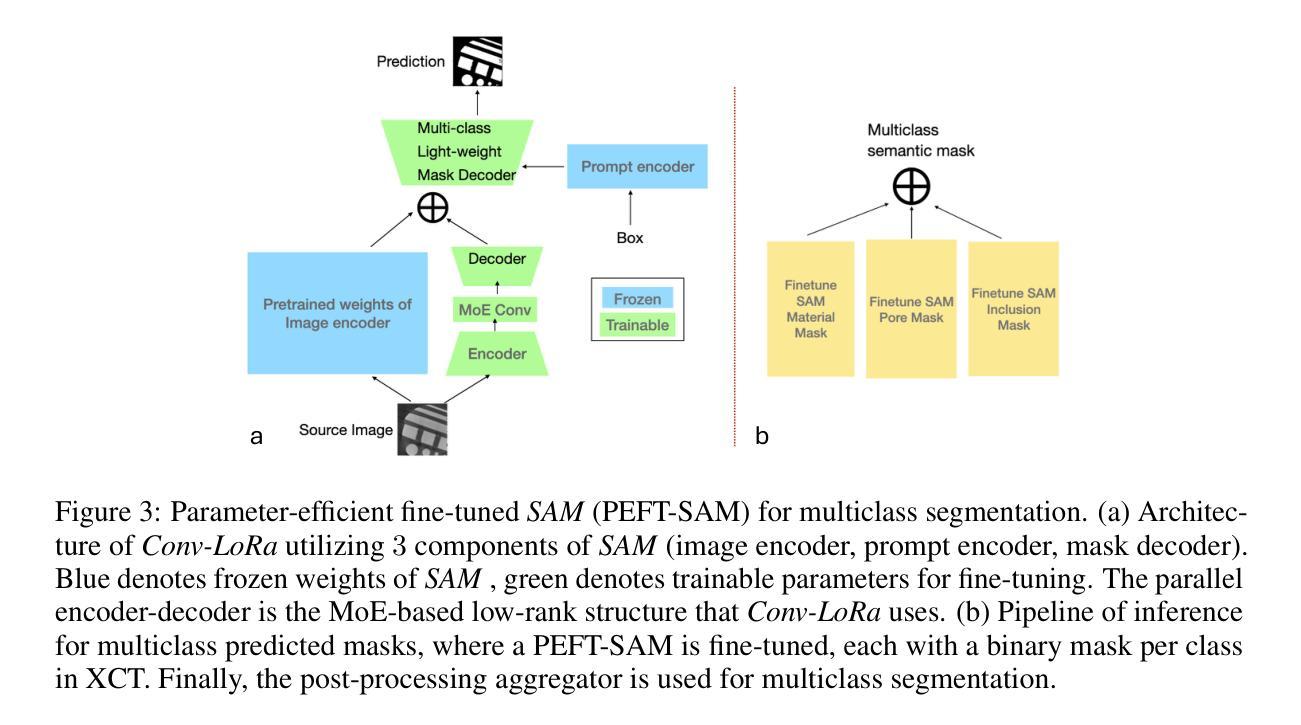
Efficient Quantization-Aware Training on Segment Anything Model in Medical Images and Its Deployment
Authors:Haisheng Lu, Yujie Fu, Fan Zhang, Le Zhang
Medical image segmentation is a critical component of clinical practice, and the state-of-the-art MedSAM model has significantly advanced this field. Nevertheless, critiques highlight that MedSAM demands substantial computational resources during inference. To address this issue, the CVPR 2024 MedSAM on Laptop Challenge was established to find an optimal balance between accuracy and processing speed. In this paper, we introduce a quantization-aware training pipeline designed to efficiently quantize the Segment Anything Model for medical images and deploy it using the OpenVINO inference engine. This pipeline optimizes both training time and disk storage. Our experimental results confirm that this approach considerably enhances processing speed over the baseline, while still achieving an acceptable accuracy level. The training script, inference script, and quantized model are publicly accessible at https://github.com/AVC2-UESTC/QMedSAM.
医学图像分割是临床实践的重要组成部分,而最新的MedSAM模型已大大推动了该领域的发展。然而,批评者指出,MedSAM在推理过程中需要大量的计算资源。为了解决这一问题,CVPR 2024 MedSAM笔记本电脑挑战赛旨在找到准确性与处理速度之间的最佳平衡。在本文中,我们介绍了一个量化感知训练管道,旨在有效地对医学图像的Segment Anything Model进行量化,并使用OpenVINO推理引擎进行部署。该管道优化了训练时间和磁盘存储。我们的实验结果证实,该方法在处理速度上明显优于基线,同时仍能达到可接受的准确性水平。训练脚本、推理脚本和量化模型可在https://github.com/AVC2-UESTC/QMedSAM公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 3 figures, to be published in LNCS
Summary
医疗图像分割是临床实践的重要组成部分,MedSAM模型为这一领域带来了显著进展。然而,批评者指出MedSAM在推理过程中需要大量的计算资源。为解决这一问题,CVPR 2024 MedSAM on Laptop Challenge旨在找到准确性与处理速度之间的平衡。本文介绍了一个量化感知训练管道,用于有效地量化医疗图像的Segment Anything Model,并使用OpenVINO推理引擎进行部署。该管道优化了训练时间和磁盘存储。实验结果表明,该方法在提高处理速度的同时,仍保持了可接受的准确性。训练脚本、推理脚本和量化模型可在AVC2-UESTC/QMedSAM公开访问。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像分割在临床实践中至关重要,MedSAM模型为该领域带来了显著进展。
- MedSAM模型在推理过程中需要大量计算资源,引发关注。
- CVPR 2024 MedSAM on Laptop Challenge旨在平衡模型的准确性和处理速度。
- 介绍了一个量化感知训练管道,用于优化医疗图像的Segment Anything Model的训练效率和部署方式。
- 训练管道的优化减少了训练时间和磁盘存储需求。
- 实验结果显示该量化方法在提高处理速度的同时维持了较高的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

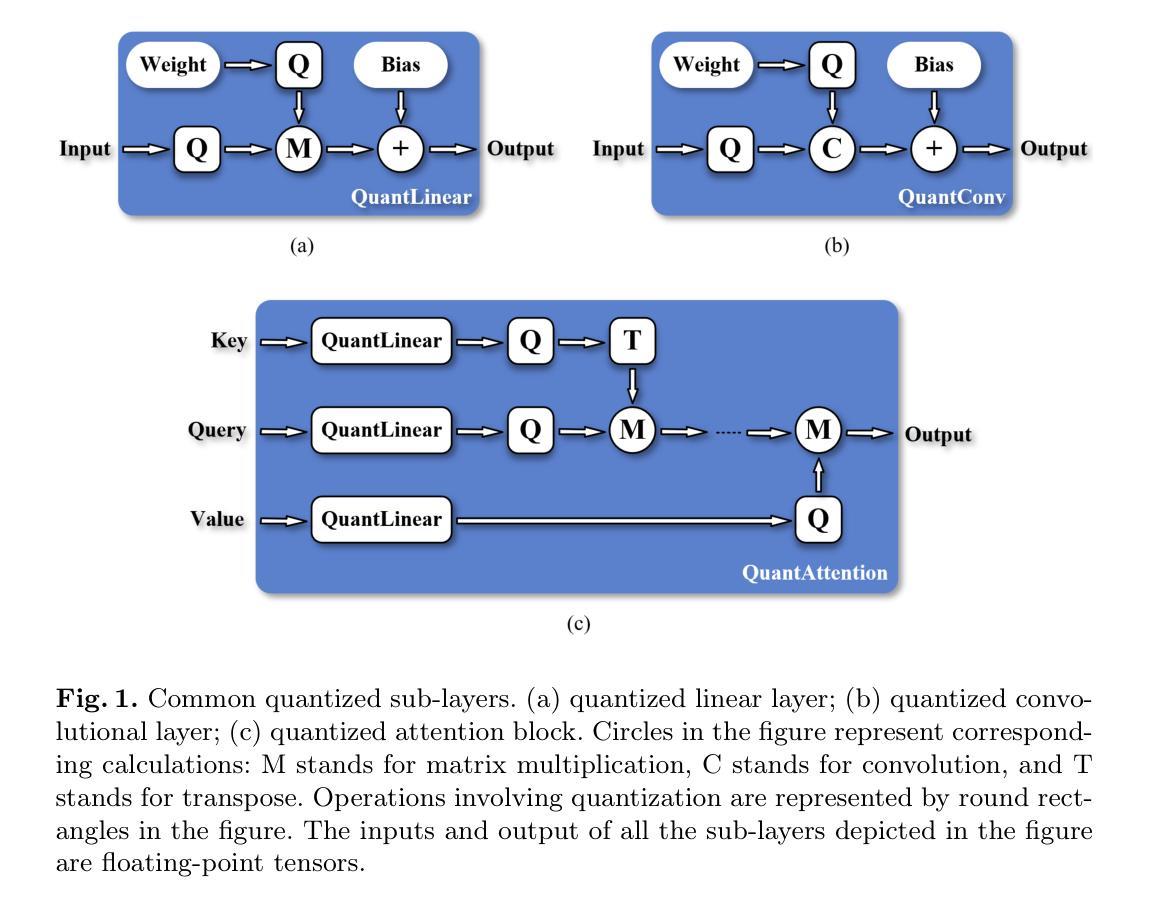
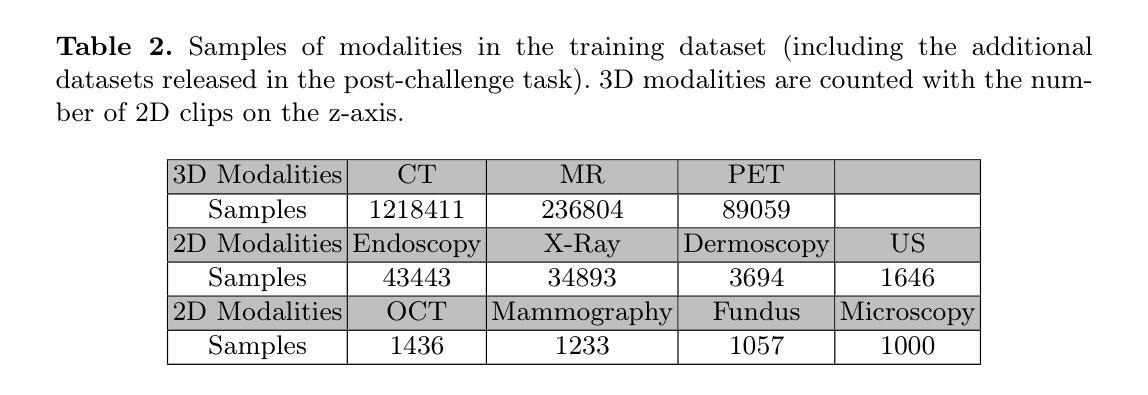
SweetTokenizer: Semantic-Aware Spatial-Temporal Tokenizer for Compact Visual Discretization
Authors:Zhentao Tan, Ben Xue, Jian Jia, Junhao Wang, Wencai Ye, Shaoyun Shi, Mingjie Sun, Wenjin Wu, Quan Chen, Peng Jiang
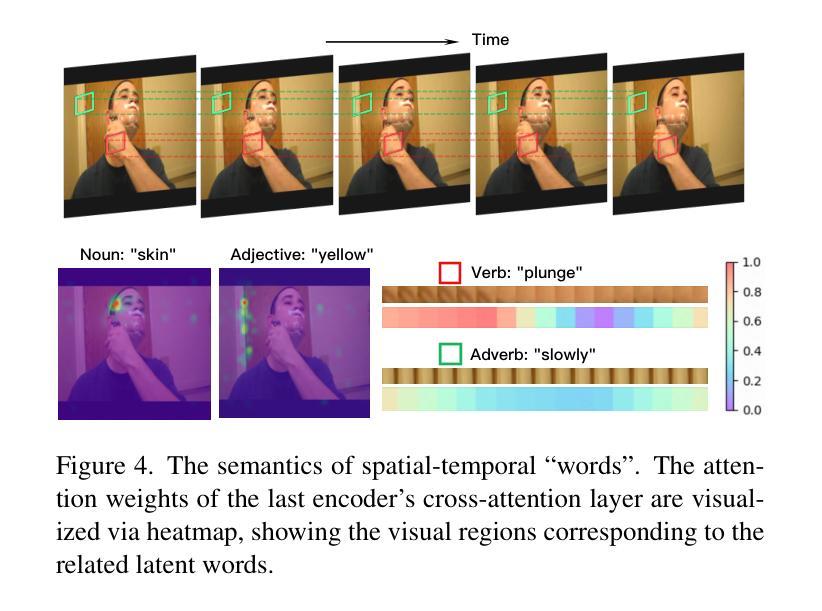
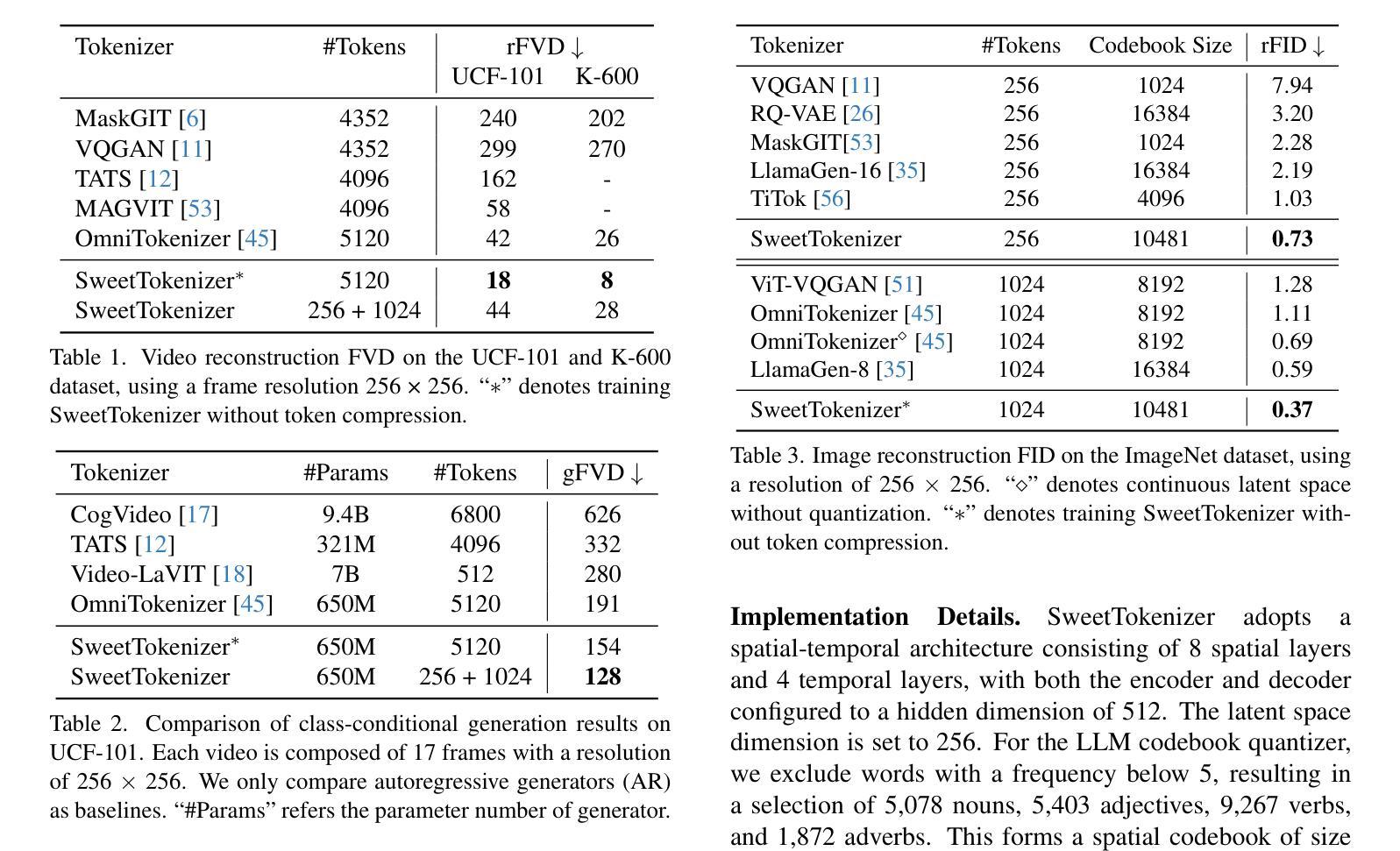
This paper presents the \textbf{S}emantic-a\textbf{W}ar\textbf{E} spatial-t\textbf{E}mporal \textbf{T}okenizer (SweetTokenizer), a compact yet effective discretization approach for vision data. Our goal is to boost tokenizers’ compression ratio while maintaining reconstruction fidelity in the VQ-VAE paradigm. Firstly, to obtain compact latent representations, we decouple images or videos into spatial-temporal dimensions, translating visual information into learnable querying spatial and temporal tokens through a \textbf{C}ross-attention \textbf{Q}uery \textbf{A}uto\textbf{E}ncoder (CQAE). Secondly, to complement visual information during compression, we quantize these tokens via a specialized codebook derived from off-the-shelf LLM embeddings to leverage the rich semantics from language modality. Finally, to enhance training stability and convergence, we also introduce a curriculum learning strategy, which proves critical for effective discrete visual representation learning. SweetTokenizer achieves comparable video reconstruction fidelity with only \textbf{25%} of the tokens used in previous state-of-the-art video tokenizers, and boost video generation results by \textbf{32.9%} w.r.t gFVD. When using the same token number, we significantly improves video and image reconstruction results by \textbf{57.1%} w.r.t rFVD on UCF-101 and \textbf{37.2%} w.r.t rFID on ImageNet-1K. Additionally, the compressed tokens are imbued with semantic information, enabling few-shot recognition capabilities powered by LLMs in downstream applications.
本文介绍了语义感知时空令牌化器(SweetTokenizer),这是一种紧凑且有效的视觉数据离散化方法。我们的目标是提高VQ-VAE架构中的token压缩比例的同时保持重建保真度。首先,为了获得紧凑的潜在表示,我们将图像或视频解耦为时空维度,并通过跨查询注意力自动编码器(CQAE)将视觉信息转化为可学习的查询空间和时间令牌。其次,为了在压缩过程中补充视觉信息,我们通过从现成的LLM嵌入中派生出的专用代码本对这些令牌进行量化,以利用语言模态的丰富语义。最后,为了提高训练稳定性和收敛性,我们还引入了一种课程学习策略,这对于有效的离散视觉表示学习至关重要。SweetTokenizer在仅使用当前视频tokenizer的百分之二十五标记的情况下取得了相当的视频重建保真度,并在GFVD指标上将视频生成结果提高了百分之三十八点九。当使用相同的标记数量时,我们在UCF-101上的视频重建结果相较于rFVD指标提升了百分之五十七点一,在ImageNet-1K上的图像重建结果相较于rFID指标提升了百分之三十七点二。此外,压缩的令牌中蕴含了语义信息,使得下游应用中能够借助LLM实现小样本识别功能。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了Semantic-Aware空间时序标记化(SweetTokenizer),这是一种紧凑而有效的针对视觉数据的离散化方法。目标是提高VQ-VAE范式中的令牌压缩率,同时保持重建保真度。首先,通过跨注意力查询自动编码器(CQAE)将图像或视频转换为可学习的查询空间和时间令牌,获得紧凑的潜在表示。其次,通过来自现成的LLM嵌入的专用代码本对这些令牌进行量化,以利用语言模态的丰富语义来补充视觉信息。最后,为了提高训练和收敛的稳定性,还引入了一种课程学习策略,这对于有效的离散视觉表示学习至关重要。SweetTokenizer以先前最先进的视频令牌器中使用的令牌的仅四分之一实现了可比的视频重建保真度,并通过GFVD将视频生成结果提高了32.9%。在使用相同令牌数量的情况下,我们在UCF-101上的视频和图像重建结果分别提高了57.1%和FID以及在ImageNet-1K上的提高了FID 37.2%。此外,压缩的令牌蕴含着语义信息,可以在下游应用中借助LLM实现少量样本识别功能。
关键见解
- SweetTokenizer是一种针对视觉数据的紧凑且有效的离散化方法,旨在提高VQ-VAE范式中的令牌压缩率并保持重建保真度。
- 通过CQAE将图像或视频转换为空间时序令牌,获得紧凑的潜在表示。
- 利用LLM嵌入的丰富语义信息通过专用代码本对令牌进行量化。
- 采用课程学习策略提高离散视觉表示学习的稳定性和有效性。
- SweetTokenizer在视频重建和生成性能上显著优于先前的技术,同时使用的令牌数量大幅减少。在视频重建中,达到了同等效果使用了仅四分之一的令牌数量;在视频生成方面,相比GFVD改进了约3成比例的结果;图像生成也取得显著改善结果。证明了少量的相同数目的标记可以有效地优化和改善处理质量和处理性能提高研究效率的效率在各种特定任务中都能实现显著的改进和提升在图像处理方面表现出了出色的效果具有显著优势且应用前景广阔可广泛应用于计算机视觉领域的各个子领域从开发流程和高效研究出发在不同模型的结构选择评估与设计工作中提供有力的支撑和技术保障
点此查看论文截图

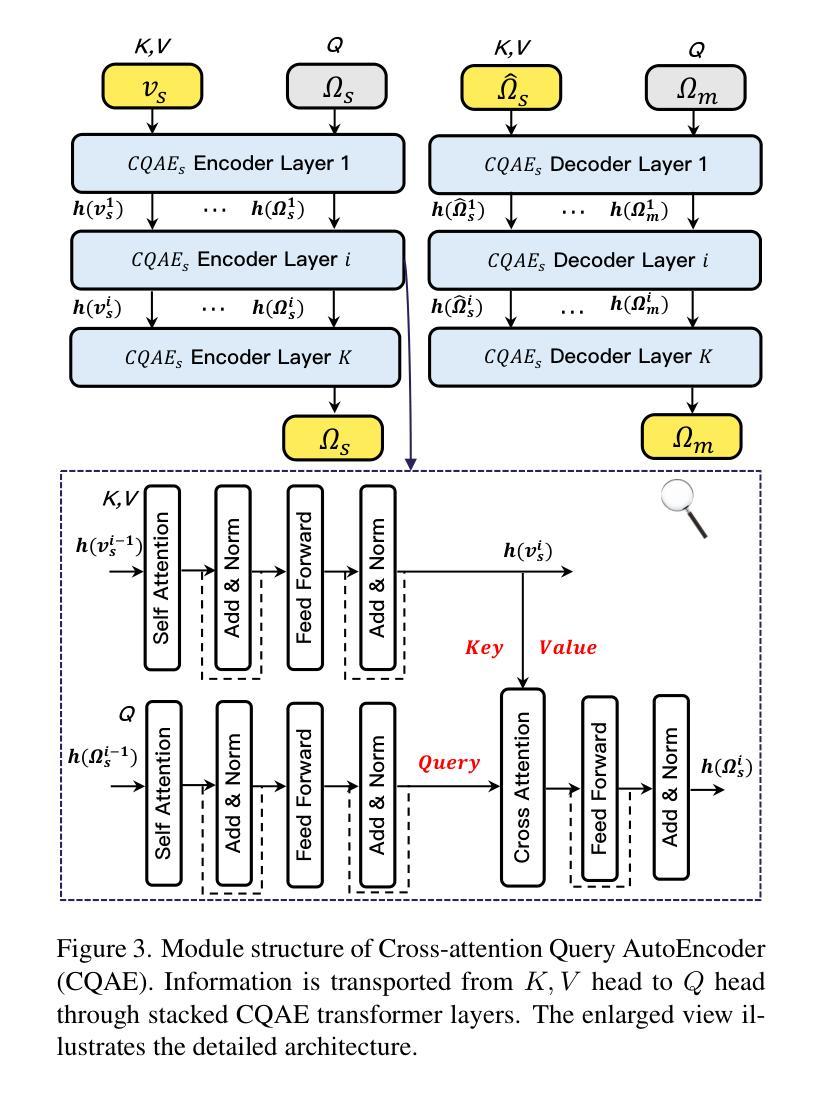
FAMNet: Frequency-aware Matching Network for Cross-domain Few-shot Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yuntian Bo, Yazhou Zhu, Lunbo Li, Haofeng Zhang
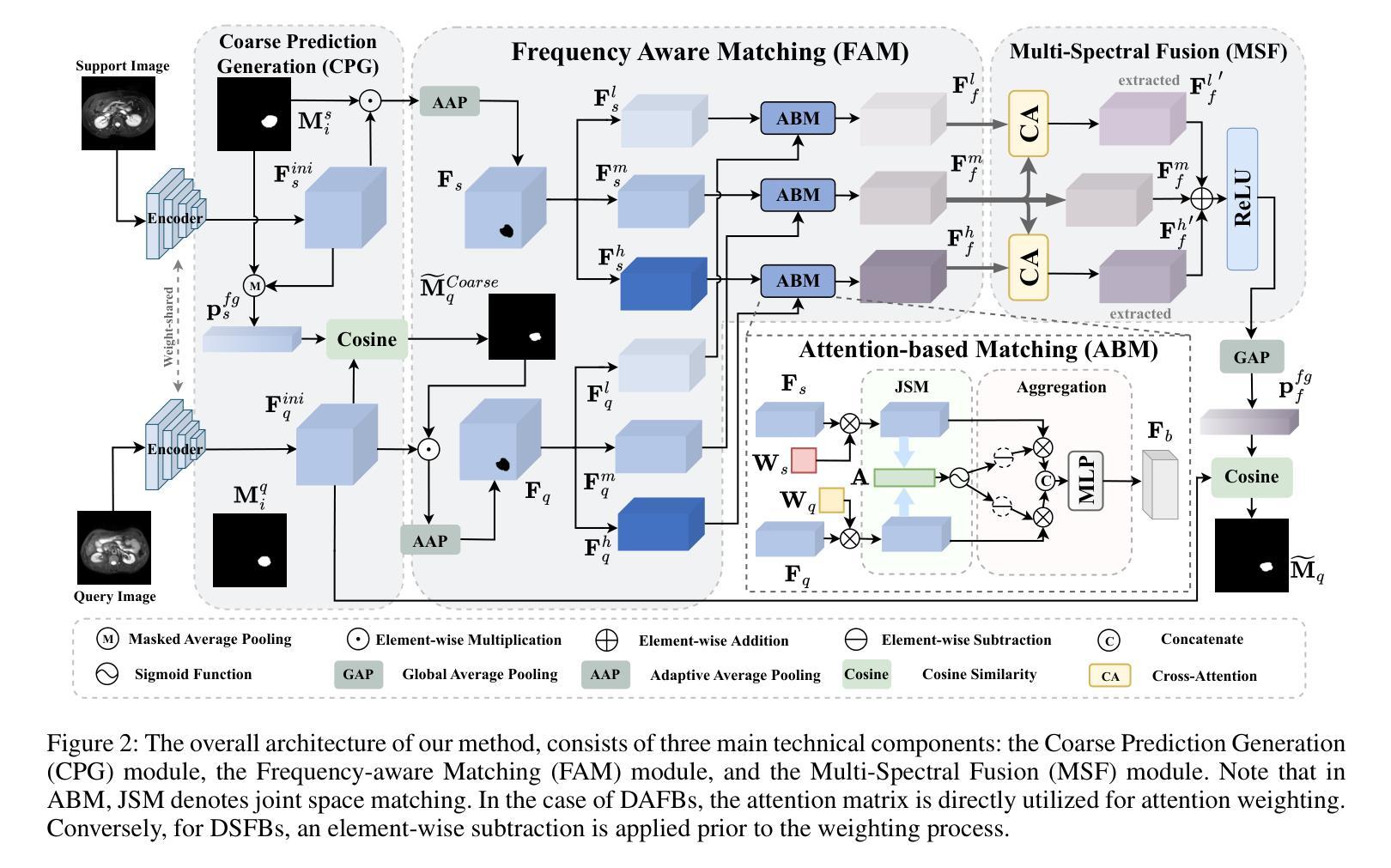
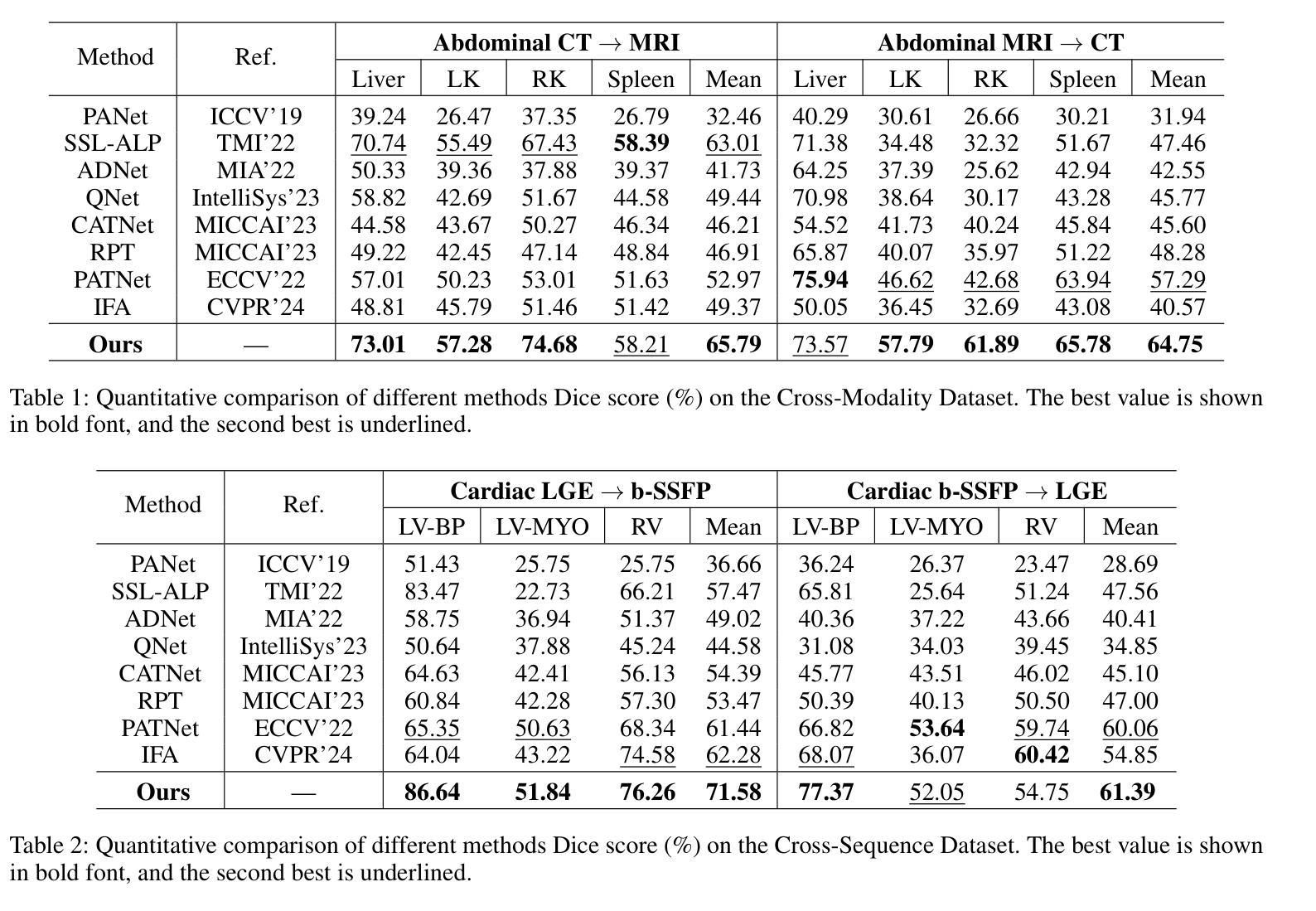
Existing few-shot medical image segmentation (FSMIS) models fail to address a practical issue in medical imaging: the domain shift caused by different imaging techniques, which limits the applicability to current FSMIS tasks. To overcome this limitation, we focus on the cross-domain few-shot medical image segmentation (CD-FSMIS) task, aiming to develop a generalized model capable of adapting to a broader range of medical image segmentation scenarios with limited labeled data from the novel target domain. Inspired by the characteristics of frequency domain similarity across different domains, we propose a Frequency-aware Matching Network (FAMNet), which includes two key components: a Frequency-aware Matching (FAM) module and a Multi-Spectral Fusion (MSF) module. The FAM module tackles two problems during the meta-learning phase: 1) intra-domain variance caused by the inherent support-query bias, due to the different appearances of organs and lesions, and 2) inter-domain variance caused by different medical imaging techniques. Additionally, we design an MSF module to integrate the different frequency features decoupled by the FAM module, and further mitigate the impact of inter-domain variance on the model’s segmentation performance. Combining these two modules, our FAMNet surpasses existing FSMIS models and Cross-domain Few-shot Semantic Segmentation models on three cross-domain datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance in the CD-FSMIS task.
现有的小样本医学图像分割(FSMIS)模型无法解决医学成像中的一个实际问题:由不同成像技术引起的域偏移,这限制了其在当前FSMIS任务中的应用。为了克服这一局限性,我们专注于跨域小样本医学图像分割(CD-FSMIS)任务,旨在开发一种通用模型,该模型能够在新的目标域中有限标记数据的情况下,适应更广泛的医学图像分割场景。受不同领域频率域相似性特征的启发,我们提出了一种频率感知匹配网络(FAMNet),它包括两个关键组件:频率感知匹配(FAM)模块和多光谱融合(MSF)模块。FAM模块解决了元学习阶段的两个问题:1)由于器官和病变的不同外观造成的域内差异导致的固有支持查询偏见;2)由于不同的医学成像技术造成的跨域差异。此外,我们设计了一个MSF模块,以整合FAM模块解耦的不同频率特征,并进一步减轻跨域差异对模型分割性能的影响。结合这两个模块,我们的FAMNet在三个跨域数据集上超越了现有的FSMIS模型和跨域小样本语义分割模型,在CD-FSMIS任务中达到了最新技术水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-25)
Summary
针对现有医疗图像分割模型在不同成像技术导致的领域偏移问题,提出一种频率感知匹配网络(FAMNet),包括频率感知匹配模块和多光谱融合模块,旨在开发一个能够适应更广泛医疗图像分割场景的通用模型,只需少量目标领域的数据。FAMNet在两个关键模块中解决跨域和内部域方差问题,并在三个跨域数据集上超越现有FSMIS模型和跨域少样本语义分割模型,实现最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 领域偏移问题是医疗图像分割中的一个实际问题,由于不同成像技术导致。
- 提出一种新型的频率感知匹配网络(FAMNet)来解决跨域少样本医疗图像分割(CD-FSMIS)任务。
- FAMNet包含两个关键组件:频率感知匹配模块和多光谱融合模块。
- FAM模块解决了元学习阶段的内部和外部领域差异问题。
- MSF模块用于整合不同频率特征,进一步减轻领域差异对模型分割性能的影响。
- FAMNet在三个跨域数据集上的性能超越了现有的FSMIS模型和跨域少样本语义分割模型。
- 该模型实现了在CD-FSMIS任务中的最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

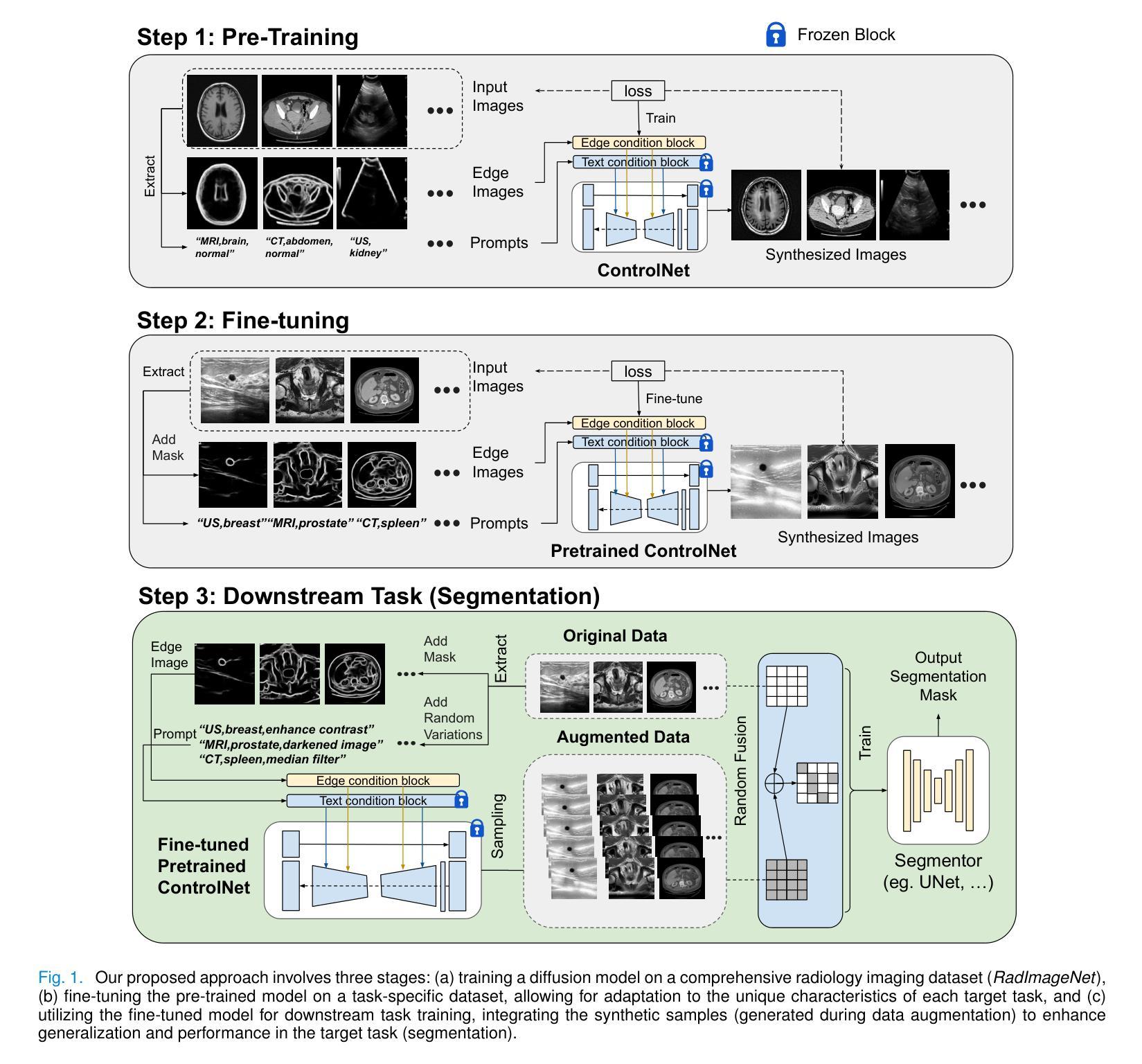
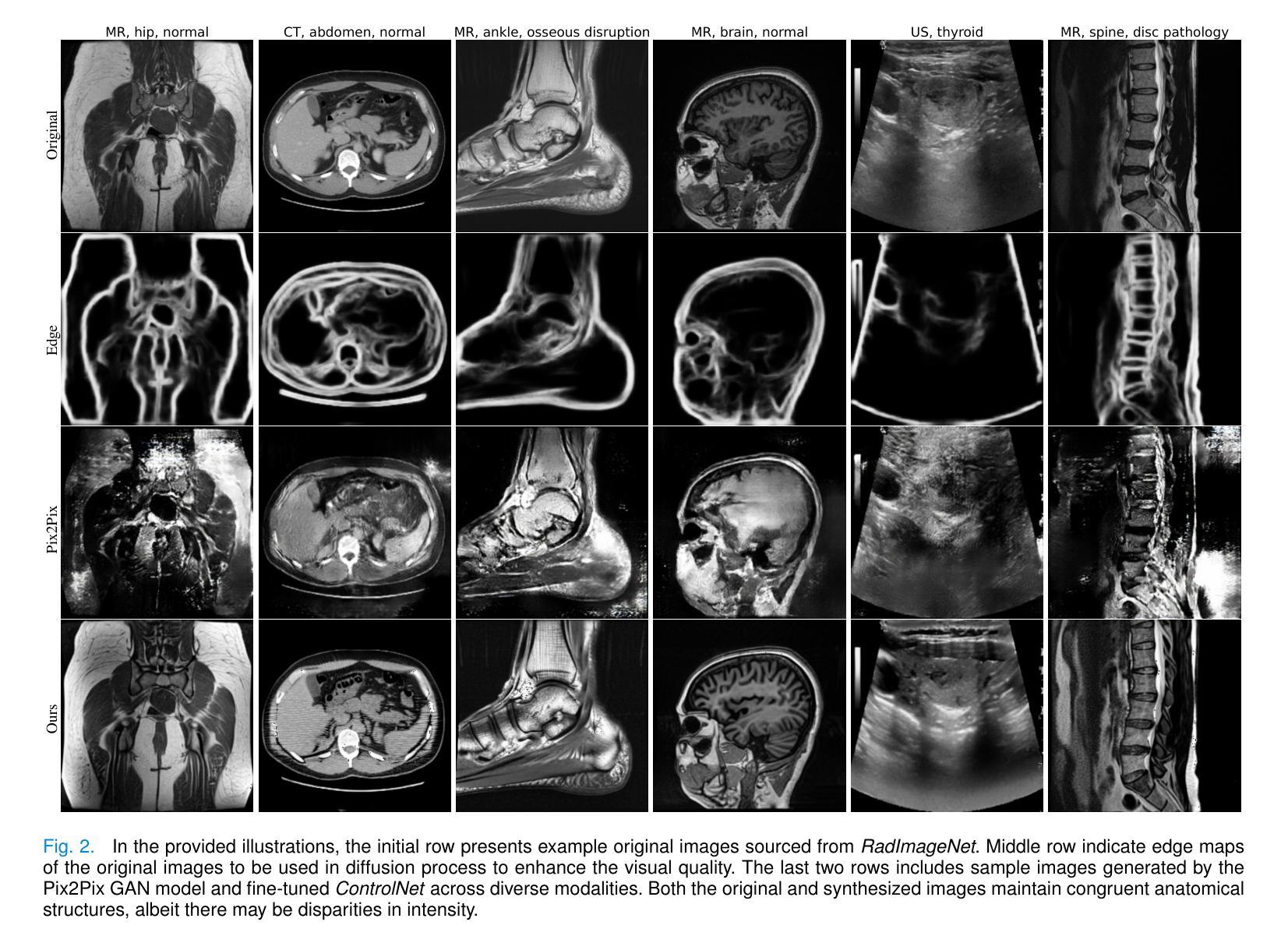
DiffBoost: Enhancing Medical Image Segmentation via Text-Guided Diffusion Model
Authors:Zheyuan Zhang, Lanhong Yao, Bin Wang, Debesh Jha, Gorkem Durak, Elif Keles, Alpay Medetalibeyoglu, Ulas Bagci
Large-scale, big-variant, high-quality data are crucial for developing robust and successful deep-learning models for medical applications since they potentially enable better generalization performance and avoid overfitting. However, the scarcity of high-quality labeled data always presents significant challenges. This paper proposes a novel approach to address this challenge by developing controllable diffusion models for medical image synthesis, called DiffBoost. We leverage recent diffusion probabilistic models to generate realistic and diverse synthetic medical image data that preserve the essential characteristics of the original medical images by incorporating edge information of objects to guide the synthesis process. In our approach, we ensure that the synthesized samples adhere to medically relevant constraints and preserve the underlying structure of imaging data. Due to the random sampling process by the diffusion model, we can generate an arbitrary number of synthetic images with diverse appearances. To validate the effectiveness of our proposed method, we conduct an extensive set of medical image segmentation experiments on multiple datasets, including Ultrasound breast (+13.87%), CT spleen (+0.38%), and MRI prostate (+7.78%), achieving significant improvements over the baseline segmentation methods. The promising results demonstrate the effectiveness of our \textcolor{black}{DiffBoost} for medical image segmentation tasks and show the feasibility of introducing a first-ever text-guided diffusion model for general medical image segmentation tasks. With carefully designed ablation experiments, we investigate the influence of various data augmentations, hyper-parameter settings, patch size for generating random merging mask settings, and combined influence with different network architectures. Source code are available at https://github.com/NUBagciLab/DiffBoost.
大规模、多变体、高质量的数据对于开发用于医学应用的稳健且成功的深度学习模型至关重要,因为它们能够潜在地实现更好的泛化性能并避免过拟合。然而,高质量标记数据的稀缺性始终是一个巨大的挑战。本文提出了一种解决这一挑战的新方法,通过开发用于医学图像合成的可控扩散模型,称为DiffBoost。我们利用最新的扩散概率模型生成逼真且多样化的合成医学图像数据,通过融入对象的边缘信息来指导合成过程,从而保留原始医学图像的基本特征。在我们的方法中,我们确保合成样本符合医学相关的约束并保留成像数据的基本结构。由于扩散模型的随机采样过程,我们可以生成具有各种外观的任意数量的合成图像。为了验证我们提出的方法的有效性,我们在多个数据集上进行了大量的医学图像分割实验,包括超声乳腺(+13.87%)、CT脾脏(+0.38%)和MRI前列腺(+7.78%),在基准分割方法上实现了显著的改进。令人鼓舞的结果证明了我们的DiffBoost在医学图像分割任务中的有效性,并展示了引入首个文本引导的扩散模型用于一般医学图像分割任务的可行性。通过精心设计的消融实验,我们研究了各种数据增强、超参数设置、用于生成随机合并蒙版的补丁大小以及不同网络架构的组合影响。源代码可在https://github.com/NUBagciLab/DiffBoost找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING
摘要
基于大规模、多变体、高质量的数据对于开发用于医学应用的稳健和成功的深度学习模型至关重要。本文提出了一种新的可控扩散模型来解决高质量标签数据稀缺的挑战,用于医学图像合成,称为DiffBoost。该模型利用最新的扩散概率模型生成逼真的、多样化的合成医学图像数据,通过融入对象的边缘信息来引导合成过程,保留原始医学图像的基本特征。通过广泛的医学图像分割实验验证,DiffBoost在超声乳房(+13.87%)、CT脾脏(+0.38%)和MRI前列腺(+7.78%)等多个数据集上取得了显著改进。结果表明DiffBoost在医学图像分割任务中的有效性,并展示了引入首个文本引导的扩散模型用于一般医学图像分割任务的可行性。
关键见解
- 大规模、高质量数据对开发稳健的深度学习模型至关重要,有助于提高模型的泛化性能和避免过拟合。
- 面临高质量标签数据的稀缺性挑战。
- 提出了一种新的可控扩散模型DiffBoost,用于生成合成医学图像数据。
- 利用扩散概率模型生成逼真的、多样化的医学图像,同时保留原始图像的基本特征。
- 通过广泛的医学图像分割实验验证,DiffBoost在多个数据集上实现了显著的改进。
- 第一个引入文本引导的扩散模型用于医学图像分割任务。
点此查看论文截图