⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-19 更新
DiffBoost: Enhancing Medical Image Segmentation via Text-Guided Diffusion Model
Authors:Zheyuan Zhang, Lanhong Yao, Bin Wang, Debesh Jha, Gorkem Durak, Elif Keles, Alpay Medetalibeyoglu, Ulas Bagci
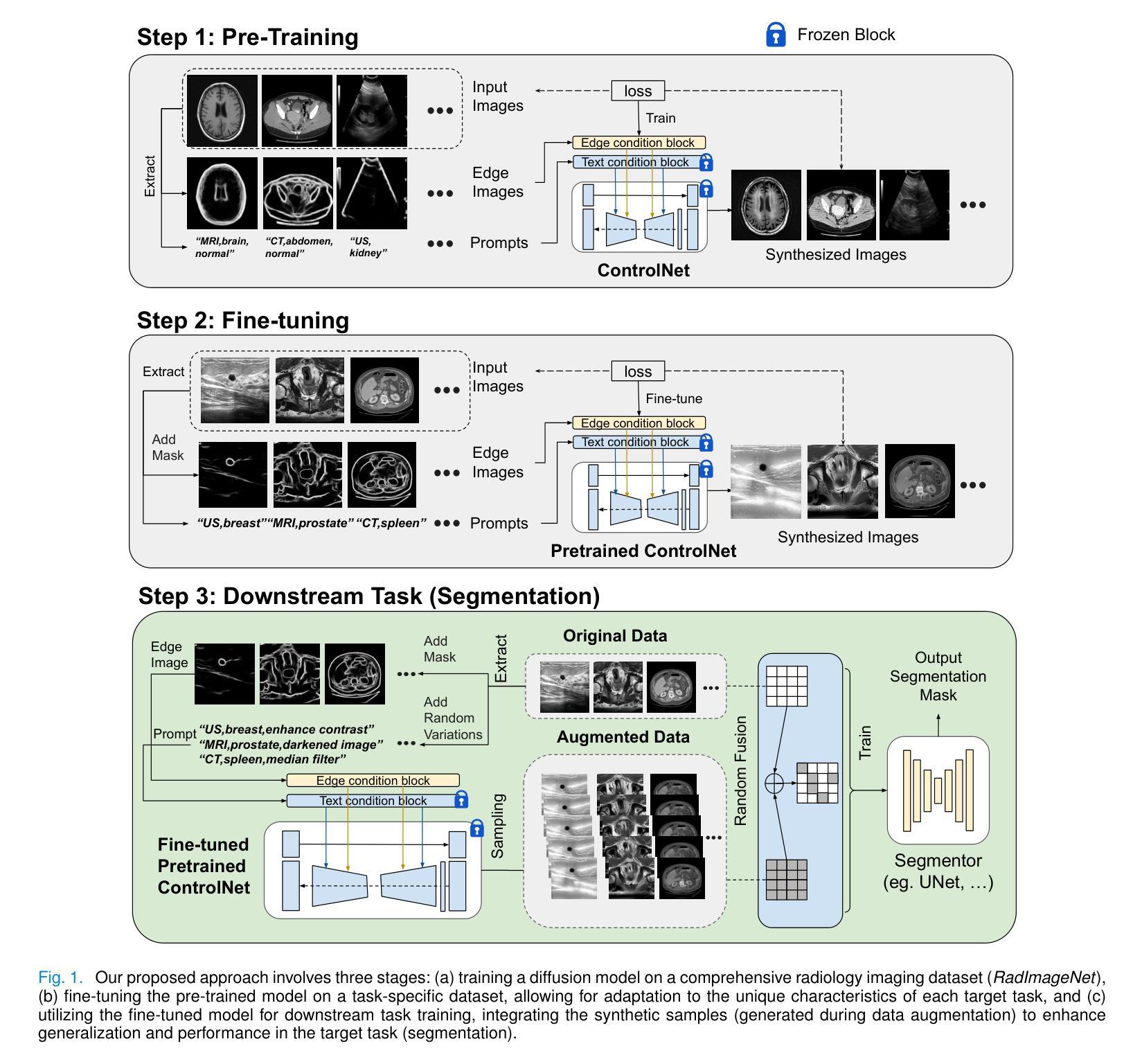
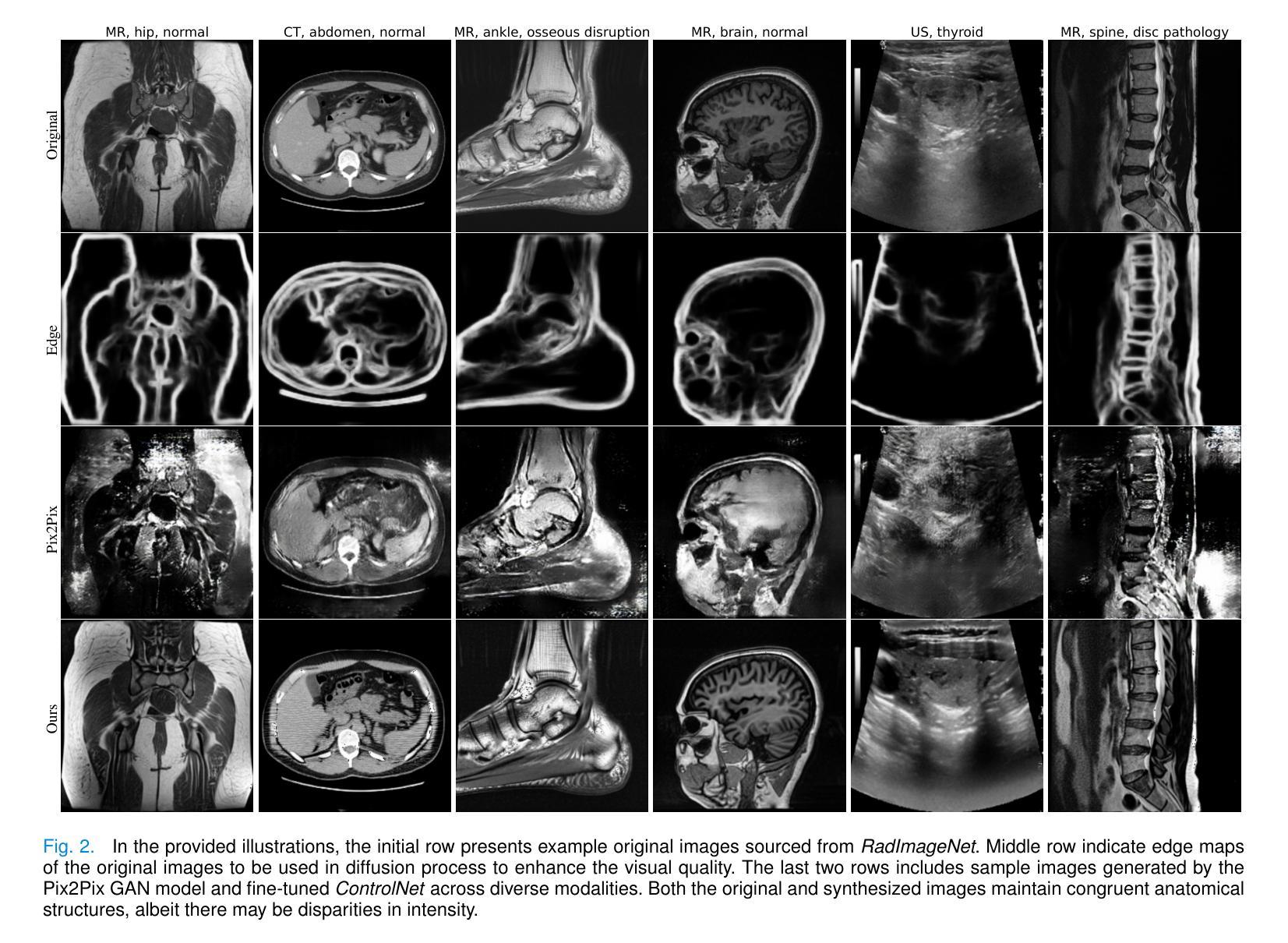
Large-scale, big-variant, high-quality data are crucial for developing robust and successful deep-learning models for medical applications since they potentially enable better generalization performance and avoid overfitting. However, the scarcity of high-quality labeled data always presents significant challenges. This paper proposes a novel approach to address this challenge by developing controllable diffusion models for medical image synthesis, called DiffBoost. We leverage recent diffusion probabilistic models to generate realistic and diverse synthetic medical image data that preserve the essential characteristics of the original medical images by incorporating edge information of objects to guide the synthesis process. In our approach, we ensure that the synthesized samples adhere to medically relevant constraints and preserve the underlying structure of imaging data. Due to the random sampling process by the diffusion model, we can generate an arbitrary number of synthetic images with diverse appearances. To validate the effectiveness of our proposed method, we conduct an extensive set of medical image segmentation experiments on multiple datasets, including Ultrasound breast (+13.87%), CT spleen (+0.38%), and MRI prostate (+7.78%), achieving significant improvements over the baseline segmentation methods. The promising results demonstrate the effectiveness of our \textcolor{black}{DiffBoost} for medical image segmentation tasks and show the feasibility of introducing a first-ever text-guided diffusion model for general medical image segmentation tasks. With carefully designed ablation experiments, we investigate the influence of various data augmentations, hyper-parameter settings, patch size for generating random merging mask settings, and combined influence with different network architectures. Source code are available at https://github.com/NUBagciLab/DiffBoost.
大规模、多样化和高质量的数据对于开发用于医学应用的稳健和成功的深度学习模型至关重要,因为它们能够提供更好的泛化性能并避免过拟合。然而,高质量标记数据的稀缺性始终是一个巨大的挑战。本文提出了一种称为DiffBoost的新型医学图像合成可控扩散模型,来解决这一挑战。我们利用最新的扩散概率模型生成逼真且多样化的合成医学图像数据,通过融入对象的边缘信息来指导合成过程,从而保留原始医学图像的基本特征。在我们的方法中,我们确保合成的样本符合医学相关的约束,并保留成像数据的基本结构。由于扩散模型的随机采样过程,我们可以生成具有不同外观的任意数量的合成图像。为了验证我们方法的有效性,我们在多个数据集上进行了大规模的医学图像分割实验,包括超声乳房(+13.87%)、CT脾脏(+0.38%)和MRI前列腺(+7.78%),在基线分割方法上取得了显著改进。这些令人鼓舞的结果证明了我们开发的DiffBoost在医学图像分割任务中的有效性,并展示了引入首个文本引导扩散模型用于一般医学图像分割任务的可行性。通过精心设计的消融实验,我们研究了各种数据增强、超参数设置、生成随机合并掩膜设置的补丁大小以及与不同网络架构的联合影响。源代码可在https://github.com/NUBagciLab/DiffBoost获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON MEDICAL IMAGING
摘要
本文提出了DiffBoost方法,通过利用可控的扩散模型进行医学图像合成,解决医学应用中高质量标注数据稀缺的问题。借助最新的扩散概率模型,生成真实且多样的合成医学图像数据,结合物体边缘信息引导合成过程,保留原始医学图像的关键特征。合成样本符合医学相关约束,并保留成像数据的基本结构。通过随机采样过程,可以生成任意数量的具有不同外观的合成图像。通过多项医学图像分割实验验证,该方法在超声乳房、CT脾脏和MRI前列腺等多个数据集上较基线分割方法取得显著改进。结果表明DiffBoost在医学图像分割任务中的有效性,并展示了引入首个文本引导的扩散模型用于一般医学图像分割任务的可行性。
关键见解
- 医学应用中高质量标注数据的稀缺性是开发稳健和成功的深度学习模型的主要挑战。
- DiffBoost方法通过可控扩散模型进行医学图像合成以应对这一挑战。
- 利用扩散概率模型生成真实且多样的合成医学图像数据。
- 合成过程结合物体边缘信息,保留原始医学图像的关键特征。
- 合成样本符合医学相关约束,并保留成像数据的基本结构。
- 通过随机采样过程,可以生成任意数量的合成图像。
- 在多个数据集上的医学图像分割实验验证了DiffBoost方法的有效性。
点此查看论文截图