⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-19 更新
Prompt Categories Cluster for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Wangyu Wu, Xianglin Qiu, Siqi Song, Xiaowei Huang, Fei Ma, Jimin Xiao
Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS), which leverages image-level labels, has garnered significant attention due to its cost-effectiveness. The previous methods mainly strengthen the inter-class differences to avoid class semantic ambiguity which may lead to erroneous activation. However, they overlook the positive function of some shared information between similar classes. Categories within the same cluster share some similar features. Allowing the model to recognize these features can further relieve the semantic ambiguity between these classes. To effectively identify and utilize this shared information, in this paper, we introduce a novel WSSS framework called Prompt Categories Clustering (PCC). Specifically, we explore the ability of Large Language Models (LLMs) to derive category clusters through prompts. These clusters effectively represent the intrinsic relationships between categories. By integrating this relational information into the training network, our model is able to better learn the hidden connections between categories. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, showing its ability to enhance performance on the PASCAL VOC 2012 dataset and surpass existing state-of-the-art methods in WSSS.
弱监督语义分割(WSSS)利用图像级别的标签,因其成本效益而备受关注。之前的方法主要是加强类之间的差异,以避免可能导致错误激活的类语义模糊。然而,他们忽视了相似类别之间共享信息的积极作用。同一聚类中的类别共享一些相似特征。允许模型识别这些特征可以进一步缓解这些类别之间的语义模糊。为了有效地识别和利用这些共享信息,本文引入了一种新型的WSSS框架,称为提示类别聚类(PCC)。具体来说,我们探索了大型语言模型(LLM)通过提示推导类别聚类的能力。这些聚类有效地代表了类别之间的内在关系。通过将这种关系信息集成到训练网络中,我们的模型能够更好地学习类别之间的隐藏连接。实验结果证明了我们的方法的有效性,表明其在PASCAL VOC 2012数据集上的性能提升,并超越了现有的WSSS先进方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
利用图像级标签的弱监督语义分割(WSSS)因其成本效益而受到广泛关注。以往方法主要强化类间差异以避免语义模糊导致的错误激活,但忽视了相似类别间共享信息的积极作用。本文提出一种名为Prompt Categories Clustering(PCC)的新型WSSS框架,通过大型语言模型(LLM)的提示能力来识别类别集群,有效代表类别之间的内在关系。通过将此关系信息整合到训练网络中,模型能更好地学习类别之间的隐藏联系。实验结果表明,该方法在PASCAL VOC 2012数据集上表现优异,超越了现有的弱监督语义分割方法。
Key Takeaways:
- WSSS利用图像级标签,成本效益高,受到广泛关注。
- 以往方法主要强化类间差异,避免语义模糊导致的错误激活。
- 相似类别间存在共享信息,可有效缓解语义模糊。
- 本文提出一种新的WSSS框架——Prompt Categories Clustering(PCC)。
- PCC利用大型语言模型的提示能力来识别类别集群,代表类别间的内在关系。
- 将关系信息整合到训练网络中,使模型更好地学习类别间的隐藏联系。
点此查看论文截图


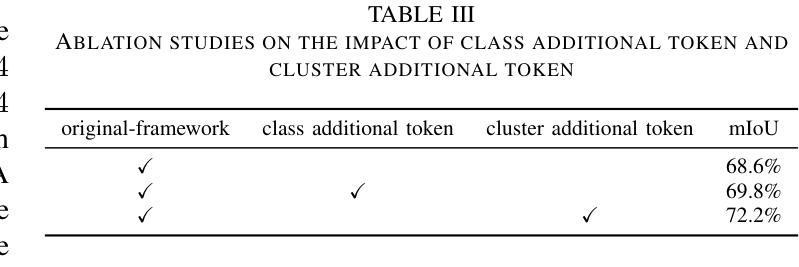
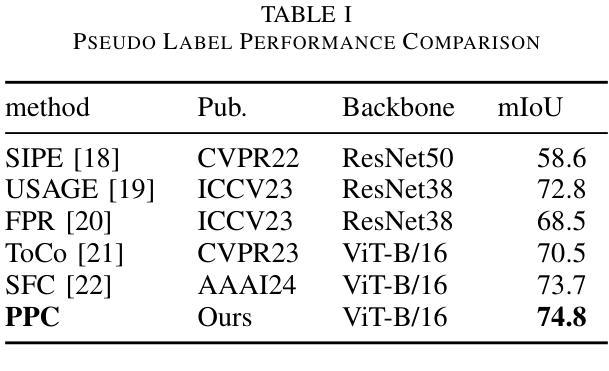
S2S2: Semantic Stacking for Robust Semantic Segmentation in Medical Imaging
Authors:Yimu Pan, Sitao Zhang, Alison D. Gernand, Jeffery A. Goldstein, James Z. Wang
Robustness and generalizability in medical image segmentation are often hindered by scarcity and limited diversity of training data, which stands in contrast to the variability encountered during inference. While conventional strategies – such as domain-specific augmentation, specialized architectures, and tailored training procedures – can alleviate these issues, they depend on the availability and reliability of domain knowledge. When such knowledge is unavailable, misleading, or improperly applied, performance may deteriorate. In response, we introduce a novel, domain-agnostic, add-on, and data-driven strategy inspired by image stacking in image denoising. Termed ``semantic stacking,’’ our method estimates a denoised semantic representation that complements the conventional segmentation loss during training. This method does not depend on domain-specific assumptions, making it broadly applicable across diverse image modalities, model architectures, and augmentation techniques. Through extensive experiments, we validate the superiority of our approach in improving segmentation performance under diverse conditions. Code is available at https://github.com/ymp5078/Semantic-Stacking.
医学图像分割的稳健性和通用性常常受到训练数据稀缺和多样性有限的阻碍,这与推理过程中遇到的变量形成对比。虽然传统的策略——如特定领域的增强、专用架构和定制训练程序——可以缓解这些问题,但它们依赖于领域知识的可用性和可靠性。当这种知识不可用、误导或应用不当时,性能可能会恶化。为此,我们引入了一种新型、非特定领域的附加数据驱动策略,该策略受到图像去噪中图像堆叠的启发。我们将其称为“语义堆叠”,该方法估计去噪的语义表示,以补充训练过程中的常规分割损失。该方法不依赖于特定领域的假设,因此可广泛应用于不同的图像模式、模型架构和增强技术。通过广泛的实验,我们验证了该方法在改善不同条件下的分割性能方面的优越性。代码可在https://github.com/ymp5078/Semantic-Stacking获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI2025
Summary
医学图像分割中,训练数据的稀缺和有限多样性常导致模型的稳健性和泛化能力受限。为应对此问题,本文提出一种新型、领域无关的、附加的、数据驱动策略,受图像去噪中的图像堆叠启发,称为“语义堆叠”。该方法估计去噪的语义表示,在训练过程中补充传统分割损失,可广泛应用于不同图像模态、模型架构和增强技术。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割面临训练数据稀缺和有限多样性问题,影响模型稳健性和泛化能力。
- 传统策略如领域特定增强、专门架构和定制训练程序可缓解这些问题,但依赖领域知识的可用性、可靠性。
- 当领域知识不可用、误导或不当应用时,性能可能下降。
- 本文提出一种新型、领域无关的、附加的、数据驱动策略——“语义堆叠”,估计去噪语义表示,补充传统分割损失。
- “语义堆叠”方法不受特定领域假设的限制,可广泛应用于不同图像模态、模型架构和增强技术。
- 通过广泛实验,验证了该方法在改善分割性能方面的优越性。
点此查看论文截图

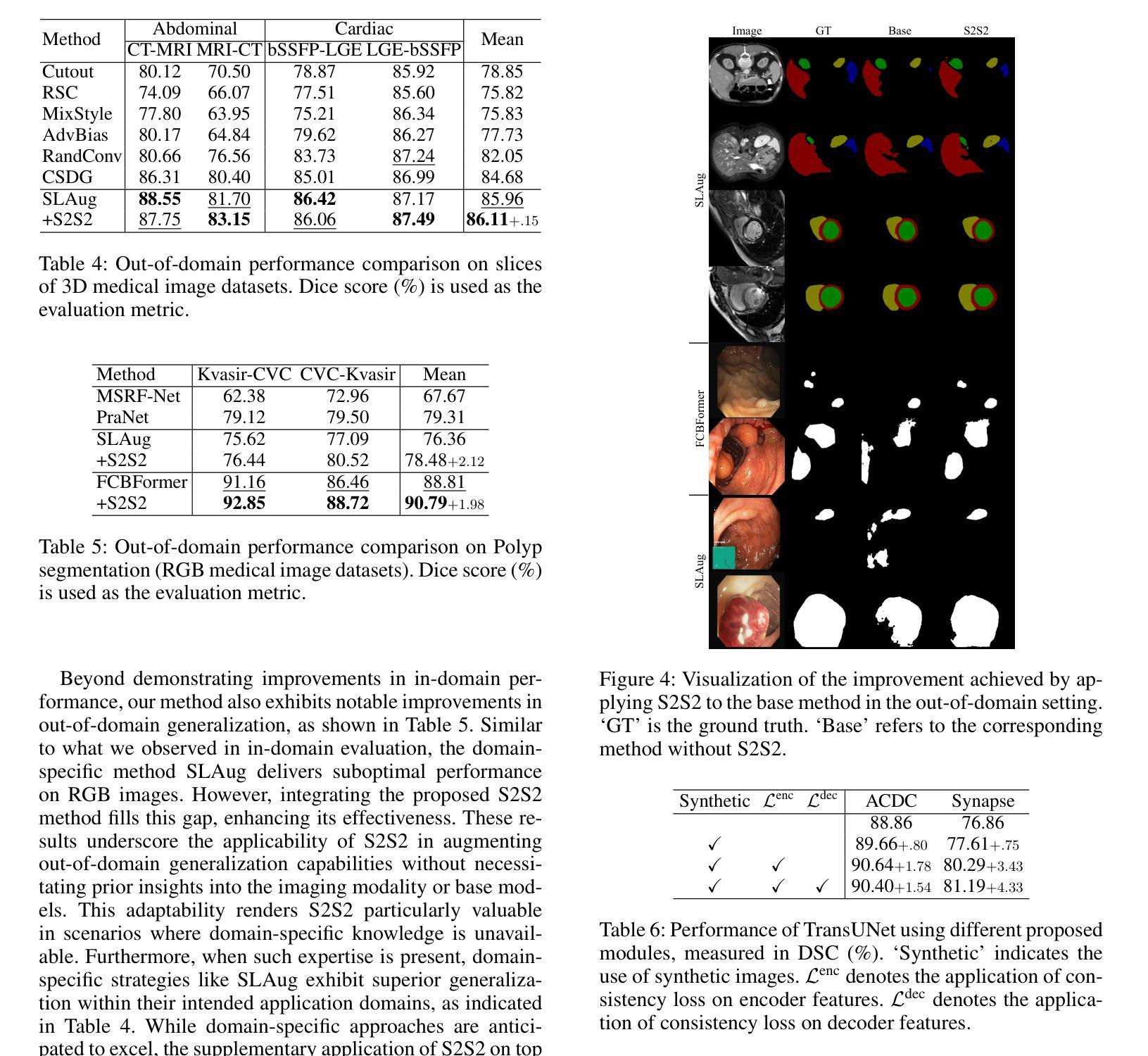
A New Adversarial Perspective for LiDAR-based 3D Object Detection
Authors:Shijun Zheng, Weiquan Liu, Yu Guo, Yu Zang, Siqi Shen, Cheng Wang
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) rely on LiDAR sensors for environmental perception and decision-making in driving scenarios. However, ensuring the safety and reliability of AVs in complex environments remains a pressing challenge. To address this issue, we introduce a real-world dataset (ROLiD) comprising LiDAR-scanned point clouds of two random objects: water mist and smoke. In this paper, we introduce a novel adversarial perspective by proposing an attack framework that utilizes water mist and smoke to simulate environmental interference. Specifically, we propose a point cloud sequence generation method using a motion and content decomposition generative adversarial network named PCS-GAN to simulate the distribution of random objects. Furthermore, leveraging the simulated LiDAR scanning characteristics implemented with Range Image, we examine the effects of introducing random object perturbations at various positions on the target vehicle. Extensive experiments demonstrate that adversarial perturbations based on random objects effectively deceive vehicle detection and reduce the recognition rate of 3D object detection models.
自动驾驶车辆(AV)在驾驶场景中依赖于激光雷达传感器进行环境感知和决策。然而,在复杂环境中确保自动驾驶车辆的安全和可靠性仍然是一个紧迫的挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了一个包含激光雷达扫描的两种随机对象点云数据的真实世界数据集(ROLiD):水雾和烟雾。在本文中,我们提出了一种利用水雾和烟雾模拟环境干扰的攻击框架,从而引入了对抗性视角。具体来说,我们提出了一种使用名为PCS-GAN的运动和内容分解生成对抗网络来点云序列生成方法,以模拟随机对象的分布。此外,利用模拟的激光雷达扫描特性结合范围图像,我们研究了在目标车辆的不同位置引入随机对象扰动的影响。大量实验表明,基于随机对象的对抗性扰动可以有效地欺骗车辆检测,降低3D对象检测模型的识别率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 7 figures, AAAI2025
Summary
本文介绍了自动驾驶车辆(AVs)在复杂环境中面临的挑战,为此引入了真实世界数据集(ROLiD),包含激光雷达扫描的水雾和烟雾点云。文章提出一种利用水雾和烟雾模拟环境干扰的对抗性视角,并开发了一种名为PCS-GAN的生成对抗网络来模拟随机对象的点云序列生成。该网络结合运动和内容分解技术,模拟随机对象分布。实验表明,基于随机对象的对抗性扰动可有效欺骗车辆检测并降低三维目标检测模型的识别率。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶车辆在复杂环境中面临安全可靠性挑战。
- 引入真实世界数据集(ROLiD),包含水雾和烟雾的激光雷达点云数据。
- 提出利用水雾和烟雾模拟环境干扰的对抗性视角。
- 开发名为PCS-GAN的生成对抗网络来模拟随机对象的点云序列生成。
- 该网络通过运动和内容分解技术模拟随机对象的分布特性。
- 对抗性扰动能模拟随机对象干扰车辆检测。
点此查看论文截图

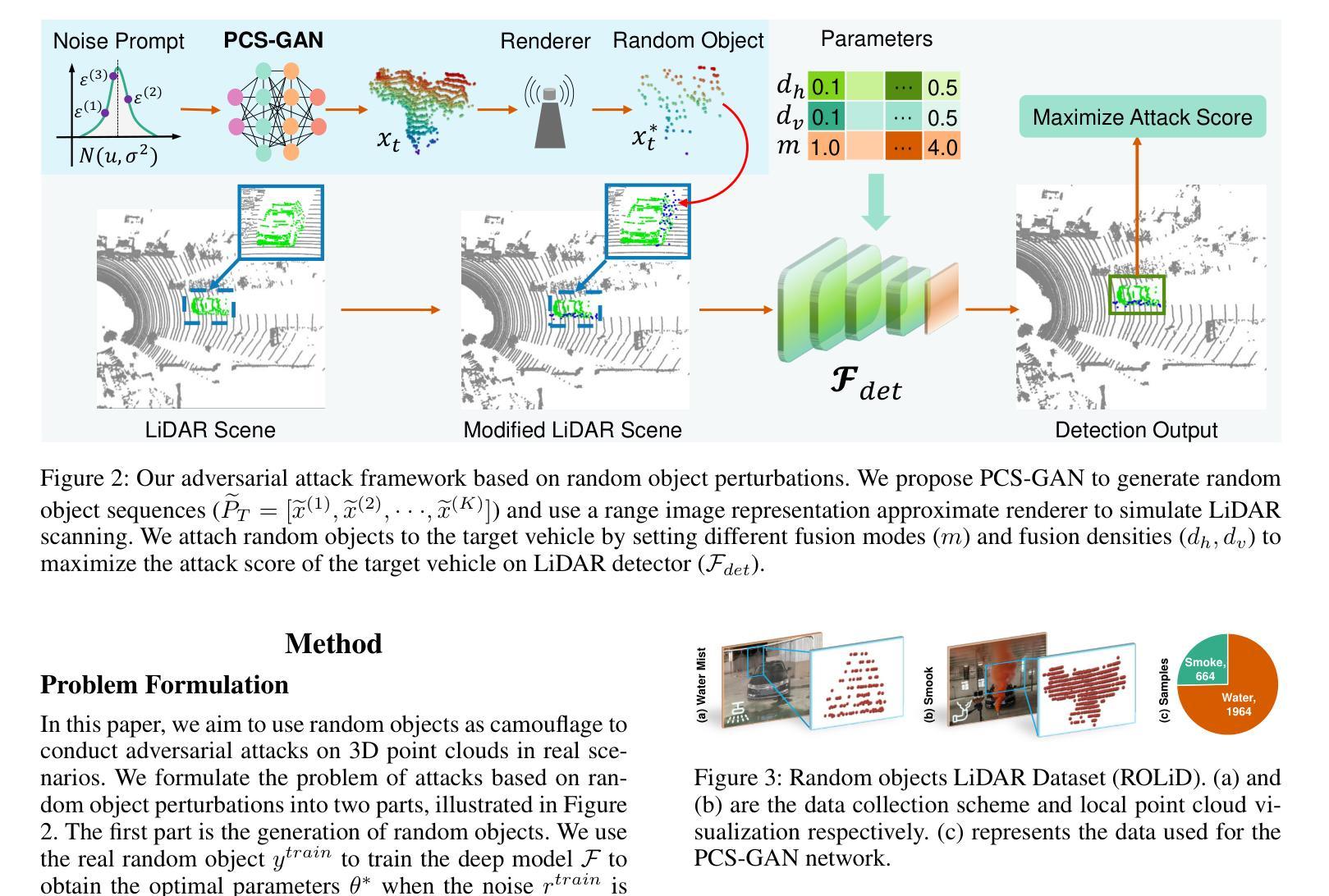
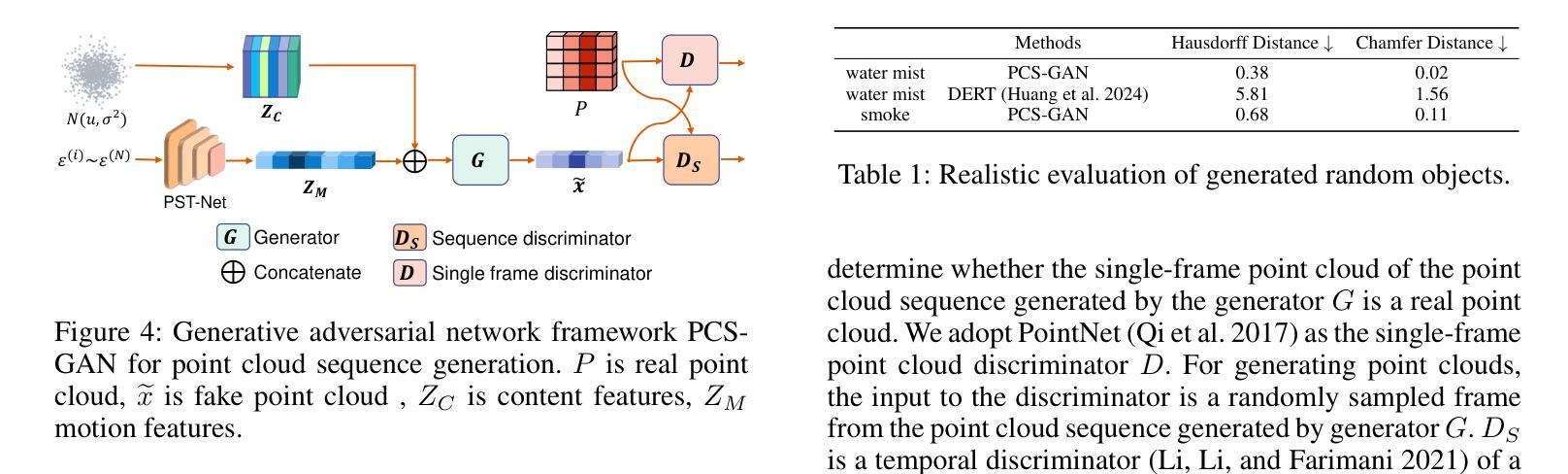

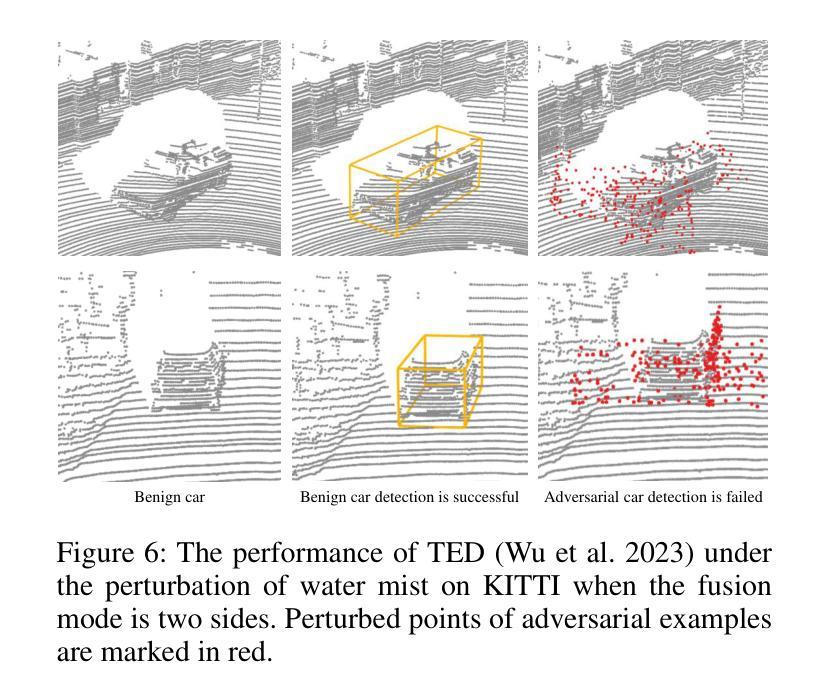
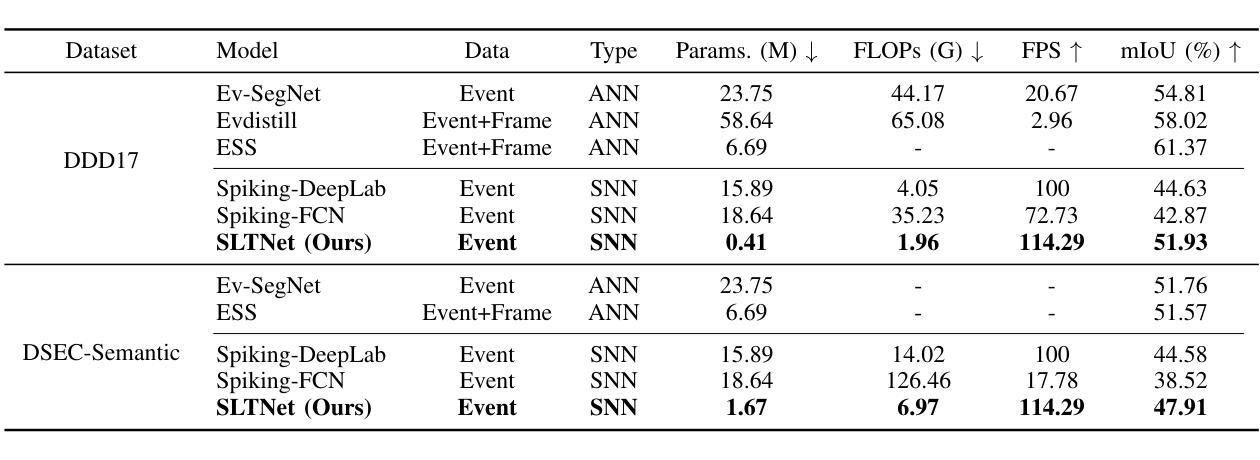
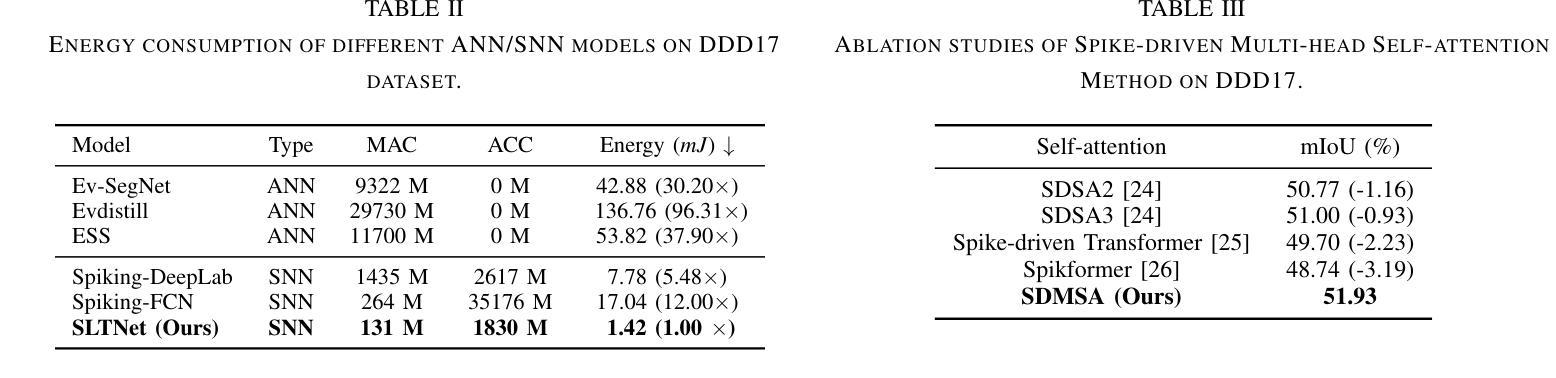
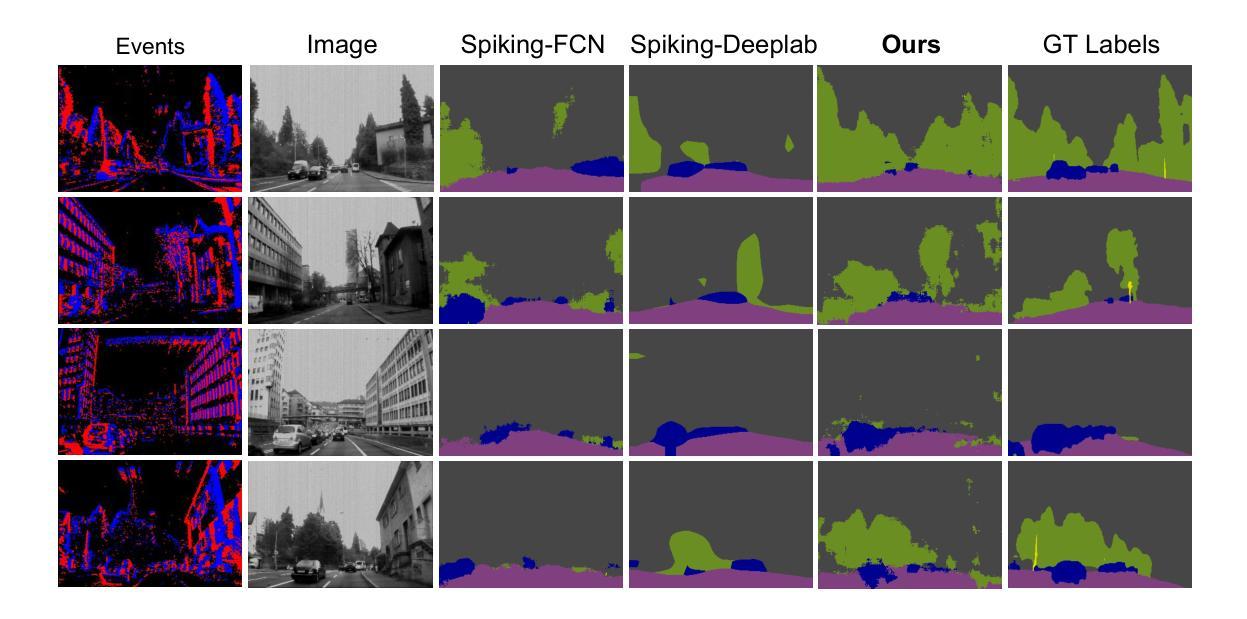
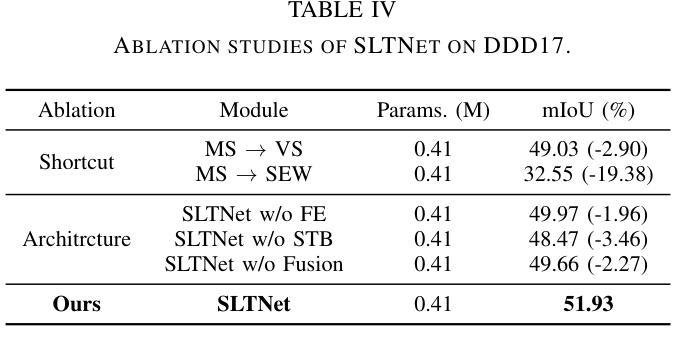
Efficient Event-based Semantic Segmentation with Spike-driven Lightweight Transformer-based Networks
Authors:Xiaxin Zhu, Fangming Guo, Xianlei Long, Qingyi Gu, Chao Chen, Fuqiang Gu
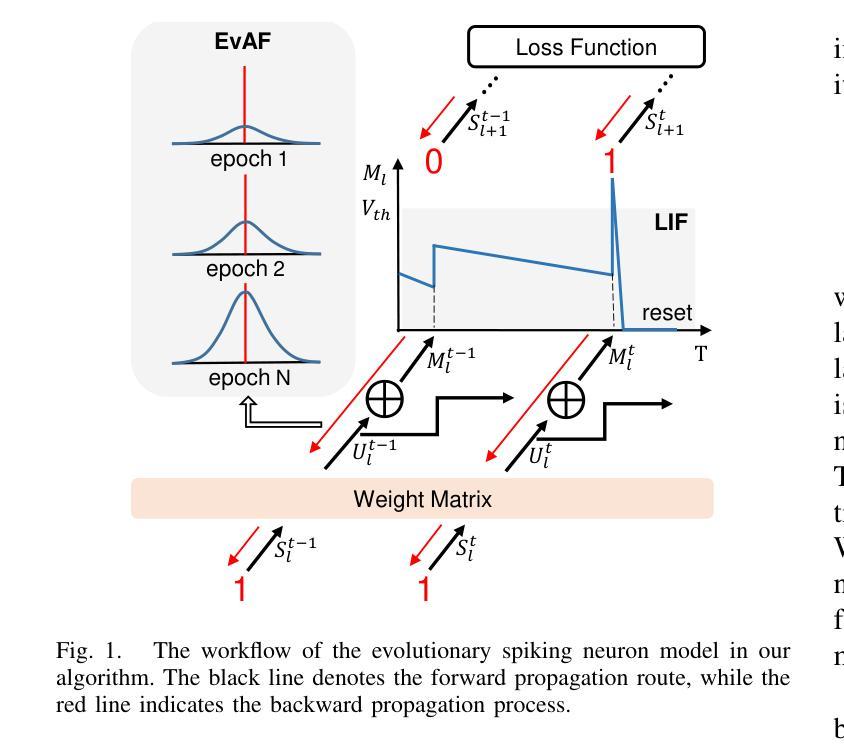
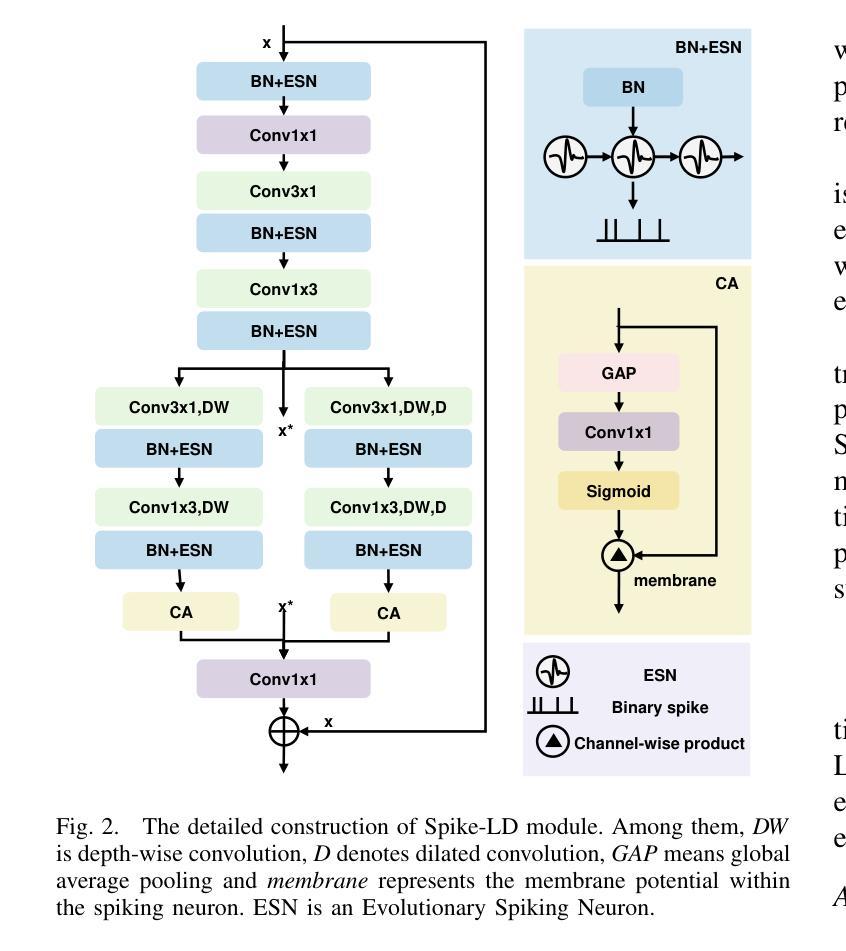
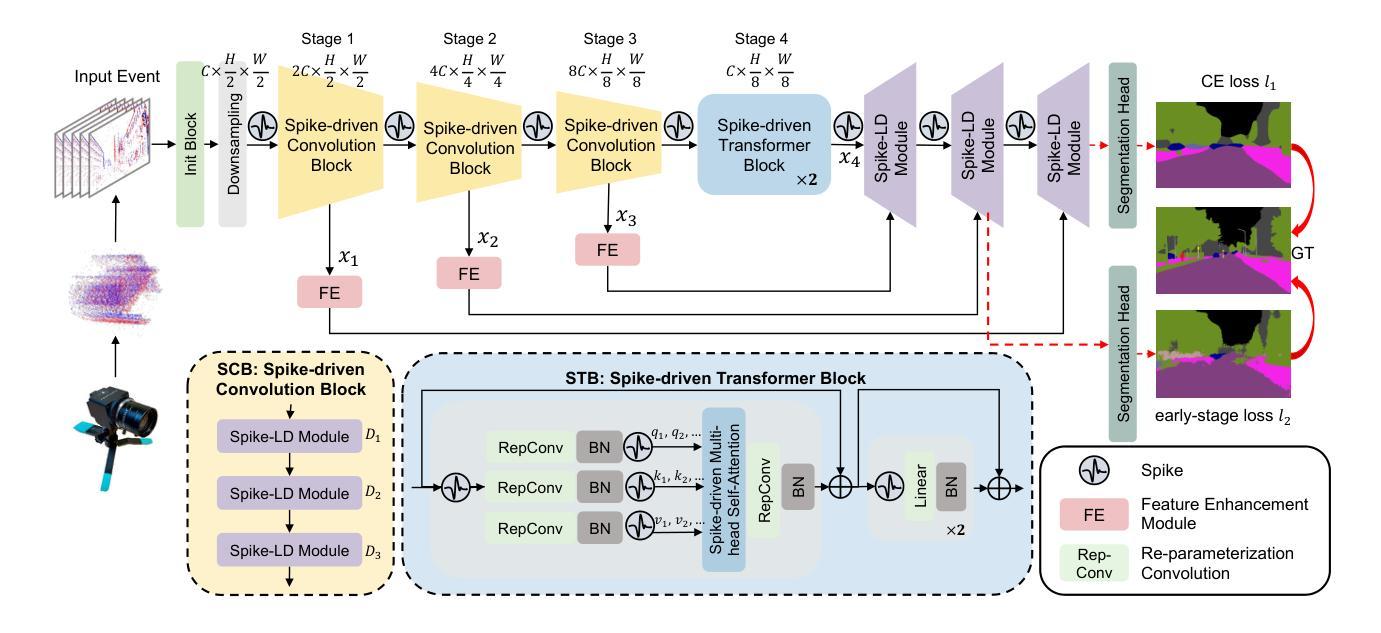
Event-based semantic segmentation has great potential in autonomous driving and robotics due to the advantages of event cameras, such as high dynamic range, low latency, and low power cost. Unfortunately, current artificial neural network (ANN)-based segmentation methods suffer from high computational demands, the requirements for image frames, and massive energy consumption, limiting their efficiency and application on resource-constrained edge/mobile platforms. To address these problems, we introduce SLTNet, a spike-driven lightweight transformer-based network designed for event-based semantic segmentation. Specifically, SLTNet is built on efficient spike-driven convolution blocks (SCBs) to extract rich semantic features while reducing the model’s parameters. Then, to enhance the long-range contextural feature interaction, we propose novel spike-driven transformer blocks (STBs) with binary mask operations. Based on these basic blocks, SLTNet employs a high-efficiency single-branch architecture while maintaining the low energy consumption of the Spiking Neural Network (SNN). Finally, extensive experiments on DDD17 and DSEC-Semantic datasets demonstrate that SLTNet outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) SNN-based methods by at least 7.30% and 3.30% mIoU, respectively, with extremely 5.48x lower energy consumption and 1.14x faster inference speed.
基于事件的语义分割在自动驾驶和机器人技术方面有着巨大的潜力,这是由于事件相机具有诸如高动态范围、低延迟和低功耗等优点。然而,目前基于人工神经网络(ANN)的分割方法存在着计算量大、对图像帧的要求高以及能耗巨大的问题,这在资源受限的边缘/移动平台上限制了其效率和应用。为了解决这些问题,我们引入了SLTNet,这是一个基于脉冲驱动的轻量级变压器网络,用于基于事件的语义分割。具体而言,SLTNet是建立在高效的脉冲驱动卷积块(SCB)基础上的,旨在提取丰富的语义特征,同时减少模型的参数。然后,为了增强长程纹理特征的交互,我们提出了新型脉冲驱动变压器块(STB),采用二进制掩码操作。基于这些基本块,SLTNet采用了高效的单分支架构,同时保持了脉冲神经网络(SNN)的低能耗。最后在DDD17和DSEC-Semantic数据集上的大量实验表明,SLTNet比最先进的SNN方法至少高出7.30%和3.30%的mIoU,同时能耗降低了5.48倍,推理速度提高了1.14倍。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to IEEE ICRA 2025
Summary
事件驱动的语义分割在自动驾驶和机器人领域具有巨大潜力,得益于事件相机的高动态范围、低延迟和低能耗优势。为解决当前人工神经网络(ANN)分割方法计算量大、对图像帧的要求以及能耗高的问题,我们提出了SLTNet,一个基于脉冲驱动轻量级Transformer的事件驱动语义分割网络。通过高效的脉冲驱动卷积块(SCB)提取丰富的语义特征并减少模型参数,同时提出新颖的脉冲驱动Transformer块(STB)进行长距离上下文特征交互。实验表明,SLTNet在DDD17和DSEC-Semantic数据集上的性能优于最新SNN方法,至少提高了7.30%和3.30%的mIoU,同时能耗降低了5.48倍,推理速度提高了1.14倍。
Key Takeaways
- 事件驱动的语义分割在自动驾驶和机器人领域有潜力,因事件相机的高动态范围、低延迟和低能耗优势。
- 当前ANN方法在计算需求、图像帧要求和能耗方面存在问题。
- SLTNet是一个基于脉冲驱动的轻量级Transformer网络,用于事件驱动的语义分割。
- SLTNet使用高效的脉冲驱动卷积块(SCB)提取语义特征并减少模型参数。
- 提出了脉冲驱动Transformer块(STB)进行长距离上下文特征交互。
点此查看论文截图

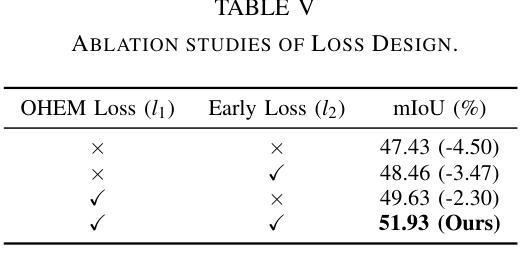
Differential Alignment for Domain Adaptive Object Detection
Authors:Xinyu He, Xinhui Li, Xiaojie Guo
Domain adaptive object detection (DAOD) aims to generalize an object detector trained on labeled source-domain data to a target domain without annotations, the core principle of which is \emph{source-target feature alignment}. Typically, existing approaches employ adversarial learning to align the distributions of the source and target domains as a whole, barely considering the varying significance of distinct regions, say instances under different circumstances and foreground \emph{vs} background areas, during feature alignment. To overcome the shortcoming, we investigates a differential feature alignment strategy. Specifically, a prediction-discrepancy feedback instance alignment module (dubbed PDFA) is designed to adaptively assign higher weights to instances of higher teacher-student detection discrepancy, effectively handling heavier domain-specific information. Additionally, an uncertainty-based foreground-oriented image alignment module (UFOA) is proposed to explicitly guide the model to focus more on regions of interest. Extensive experiments on widely-used DAOD datasets together with ablation studies are conducted to demonstrate the efficacy of our proposed method and reveal its superiority over other SOTA alternatives. Our code is available at https://github.com/EstrellaXyu/Differential-Alignment-for-DAOD.
领域自适应目标检测(DAOD)旨在将训练有标签的源域数据的目标检测器推广到无注释的目标域。其核心原理是“源域到目标域的特征对齐”。通常,现有的方法采用对抗性学习来整体对齐源域和目标域的整体分布,几乎不考虑不同区域在特征对齐过程中的不同重要性,例如在不同情境下的实例以及前景与背景区域之间的差异。为了克服这一缺点,我们研究了一种差异特征对齐策略。具体来说,设计了一个预测差异反馈实例对齐模块(简称PDFA),该模块能够自适应地为具有较高教师-学生检测差异的实例分配更高的权重,从而有效地处理更重的特定领域信息。此外,还提出了一种基于不确定性的面向前景的图像对齐模块(UFOA),以明确指导模型更多地关注感兴趣区域。我们在广泛使用的DAOD数据集上进行了大量实验,同时进行了消融研究,以证明我们提出的方法的有效性,并揭示其在其他最新替代方案中的优越性。我们的代码可在https://github.com/EstrellaXyu/Differential-Alignment-for-DAOD找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 8 figures, accepted by aaai25
Summary
领域自适应目标检测(DAOD)旨在将训练有标签的源域数据的目标检测器推广到无标注的目标域。其核心原理是源域和目标域的特征对齐。现有方法通常采用对抗性学习来整体对齐源域和目标域分布,但很少考虑不同区域(如不同情境下的实例和前景与背景区域)的不同重要性。为了克服这一不足,我们提出了一种差异化特征对齐策略,并设计了预测差异反馈实例对齐模块(PDFA),该模块能够自适应地为具有较高教师-学生检测差异的实例分配更高的权重,有效处理特定域信息。此外,还提出了基于不确定性的面向前景的图像对齐模块(UFOA),以指导模型更多地关注感兴趣区域。通过广泛的DAOD数据集实验和消融研究,验证了所提方法的有效性,并展示了其在其他先进替代方案中的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 领域自适应目标检测(DAOD)关注源域检测器在目标域的推广。
- 核心是源域和目标域的特征对齐。
- 现有方法整体对齐源域和目标域分布,忽略了不同区域的重要性差异。
- 提出了差异化特征对齐策略,包括预测差异反馈实例对齐模块(PDFA)。
- PDFA能自适应地处理特定域信息并为重要实例分配更高权重。
- 提出了基于不确定性的面向前景的图像对齐模块(UFOA),引导模型关注感兴趣区域。
点此查看论文截图

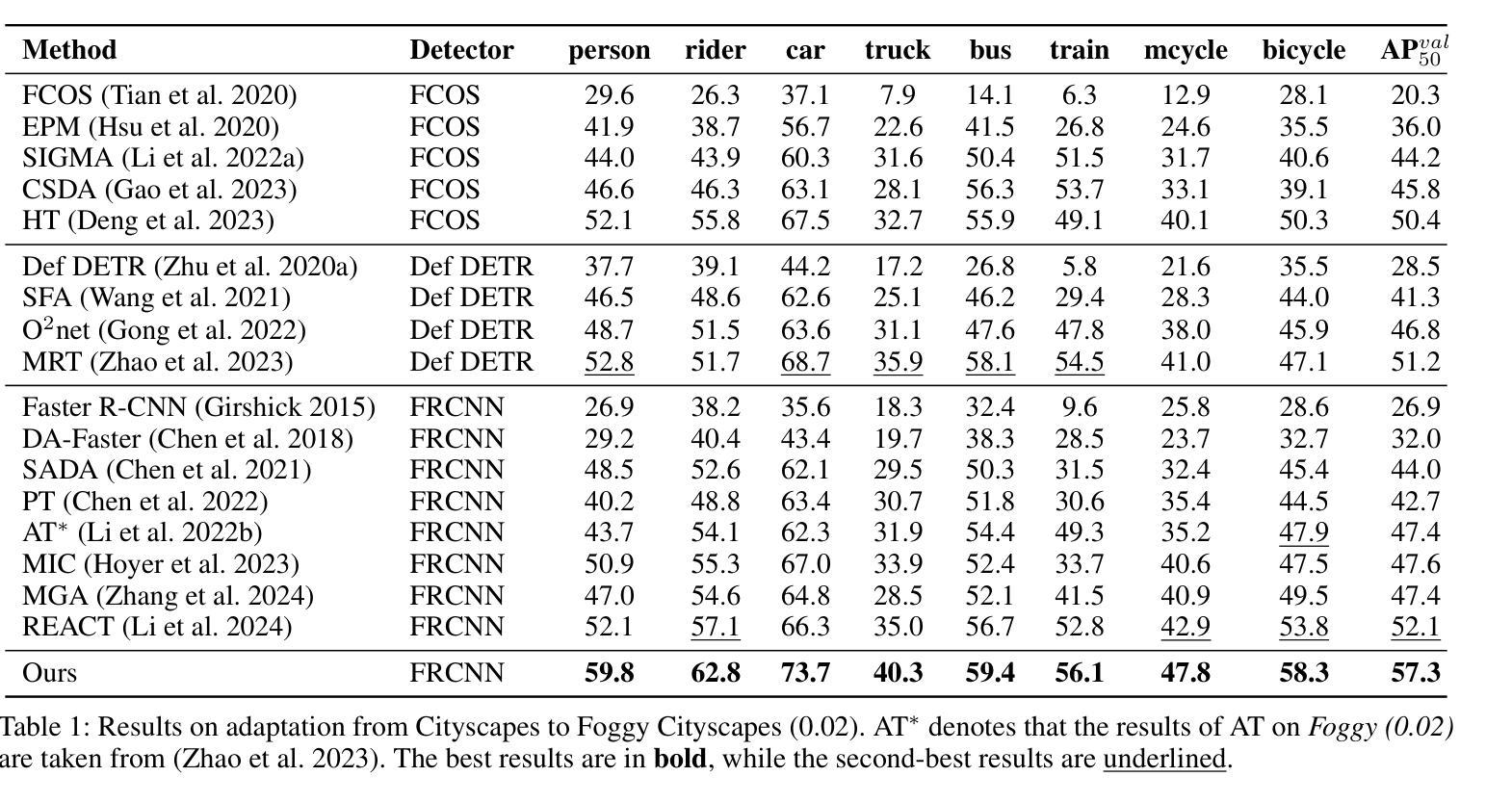
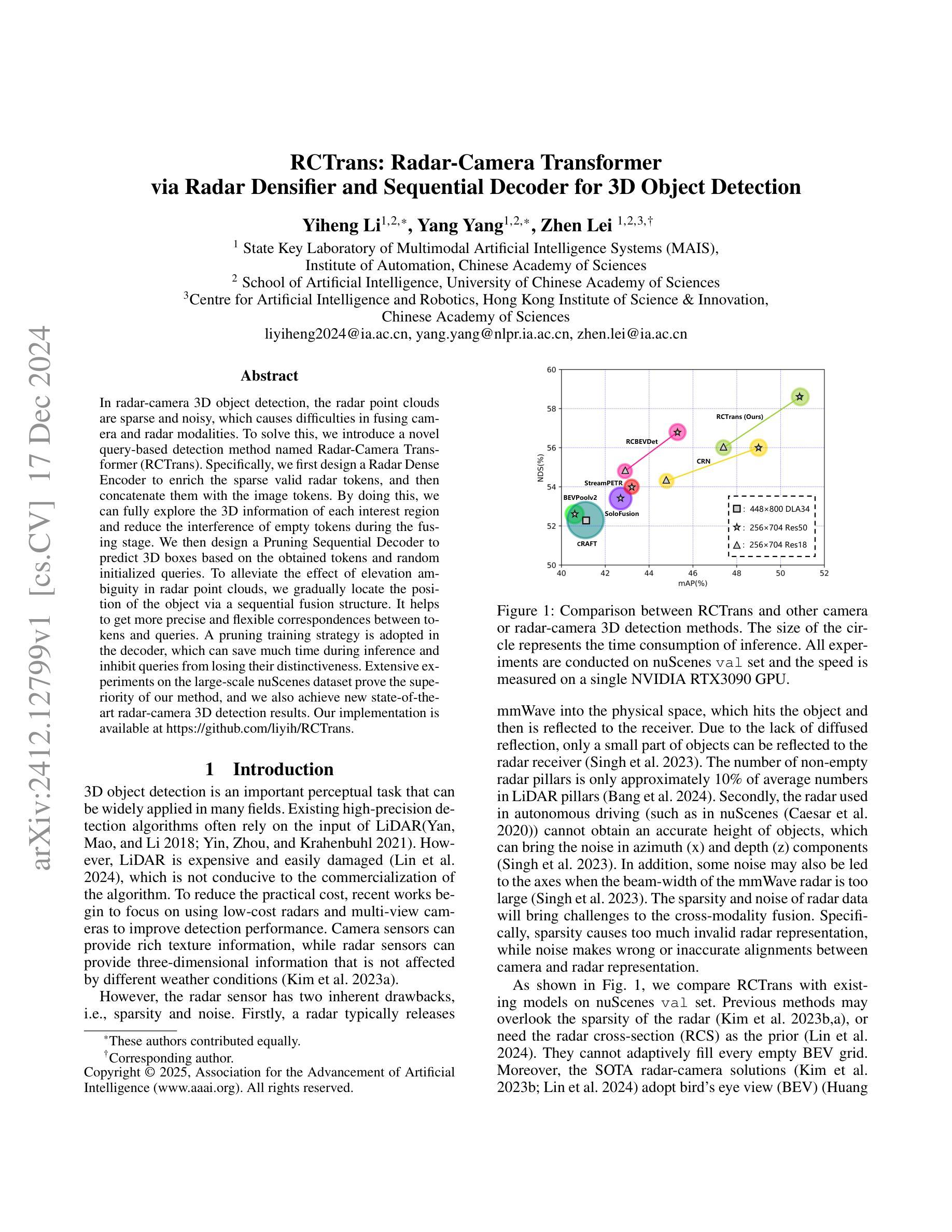
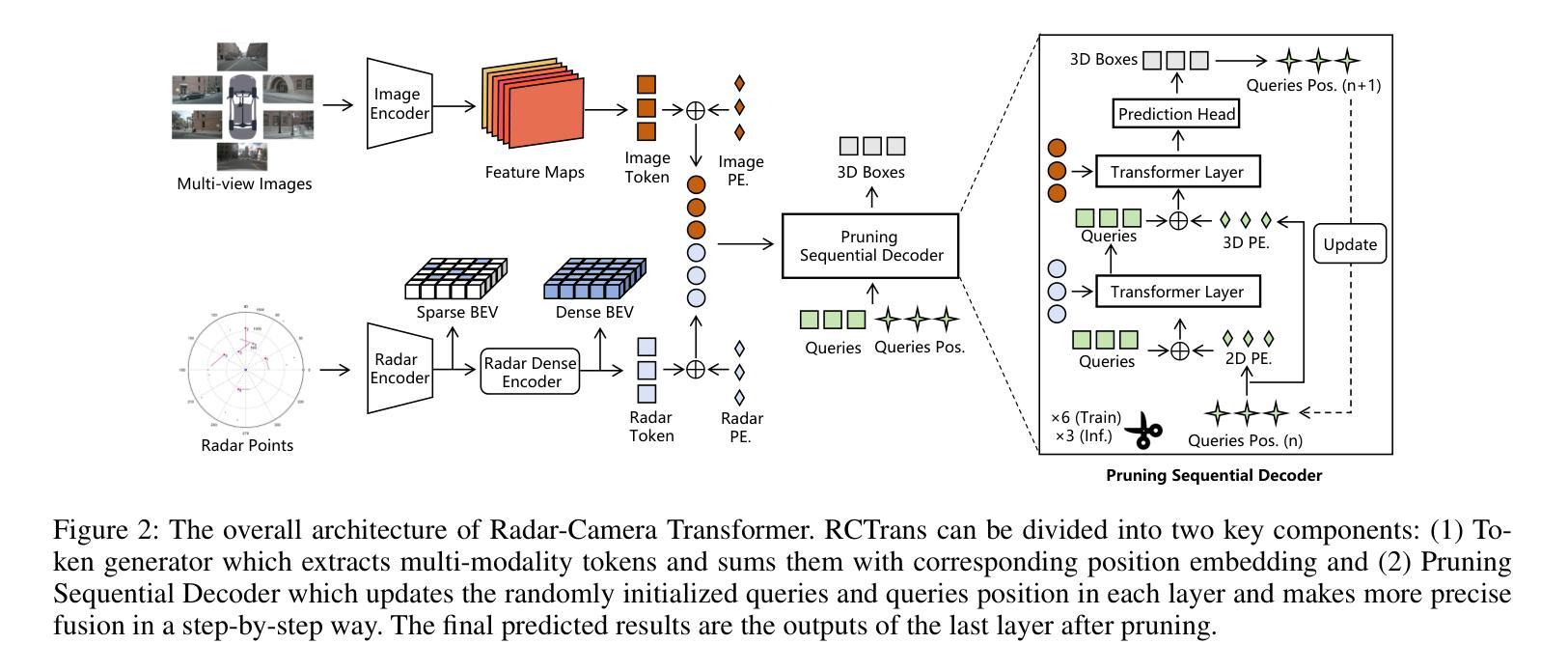
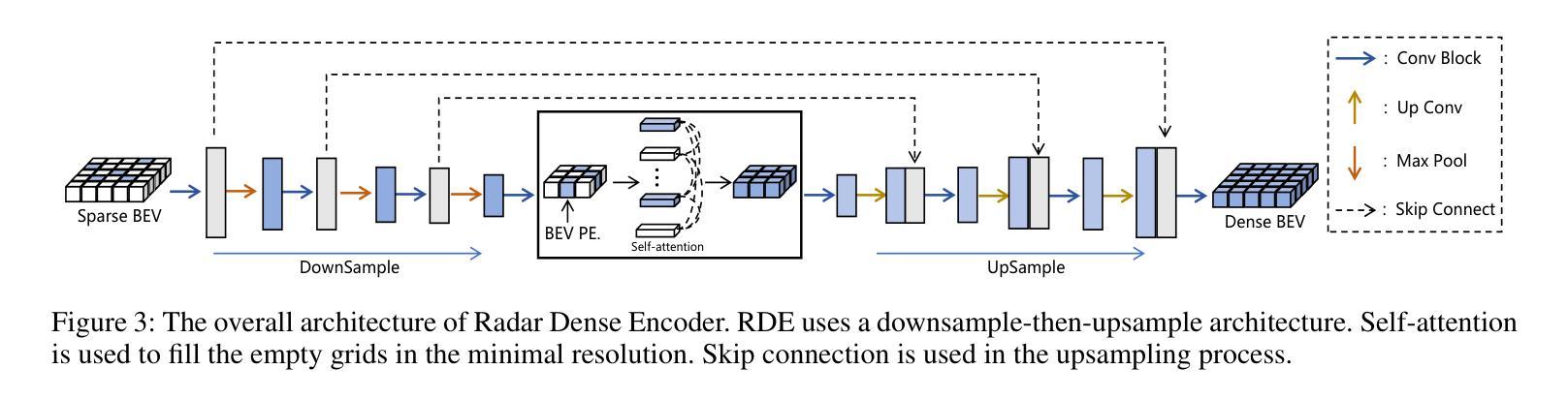
RCTrans: Radar-Camera Transformer via Radar Densifier and Sequential Decoder for 3D Object Detection
Authors:Yiheng Li, Yang Yang, Zhen Lei
In radar-camera 3D object detection, the radar point clouds are sparse and noisy, which causes difficulties in fusing camera and radar modalities. To solve this, we introduce a novel query-based detection method named Radar-Camera Transformer (RCTrans). Specifically, we first design a Radar Dense Encoder to enrich the sparse valid radar tokens, and then concatenate them with the image tokens. By doing this, we can fully explore the 3D information of each interest region and reduce the interference of empty tokens during the fusing stage. We then design a Pruning Sequential Decoder to predict 3D boxes based on the obtained tokens and random initialized queries. To alleviate the effect of elevation ambiguity in radar point clouds, we gradually locate the position of the object via a sequential fusion structure. It helps to get more precise and flexible correspondences between tokens and queries. A pruning training strategy is adopted in the decoder, which can save much time during inference and inhibit queries from losing their distinctiveness. Extensive experiments on the large-scale nuScenes dataset prove the superiority of our method, and we also achieve new state-of-the-art radar-camera 3D detection results. Our implementation is available at https://github.com/liyih/RCTrans.
在雷达摄像头3D目标检测中,雷达点云稀疏且存在噪声,这给摄像头和雷达模式的融合带来了困难。针对这一问题,我们引入了一种基于查询的新型检测方法,名为Radar-Camera Transformer(RCTrans)。具体来说,我们首先设计了一个Radar Dense Encoder来丰富稀疏有效的雷达令牌,然后将其与图像令牌连接起来。通过这样做,我们可以充分探索每个感兴趣区域的3D信息,并在融合阶段减少空令牌的影响。接着,我们设计了一个Pruning Sequential Decoder,基于获得的令牌和随机初始化的查询来预测3D边界框。为了减轻雷达点云中高度模糊的影响,我们通过顺序融合结构逐渐定位目标位置。这有助于获得令牌和查询之间更准确、更灵活的对齐关系。解码器采用了一种修剪训练策略,这可以在推理过程中节省大量时间并防止查询失去其独特性。在大规模nuScenes数据集上的大量实验证明了我们的方法的优越性,我们还实现了最新的雷达摄像头3D检测结果。我们的实现可访问于https://github.com/liyih/RCTrans。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary:针对雷达点云稀疏和噪声问题,提出一种基于查询的雷达-相机Transformer(RCTrans)融合方法。设计雷达密集编码器(Radar Dense Encoder)对稀疏雷达点云进行增强处理,与图像标记符进行结合,利用3D信息探测兴趣区域并减少空标记符的干扰。同时采用修剪序列解码器(Pruning Sequential Decoder)预测基于获得的标记符和随机初始化查询的3D边界框。通过序列融合结构逐步定位物体位置,提高了标记符与查询之间的精确性和灵活性对应。采用修剪训练策略在解码器中节省推理时间并防止查询失去独特性。在大型nuScenes数据集上进行的大量实验证明了该方法在雷达相机3D检测中的优越性。
Key Takeaways:
- 雷达点云稀疏性和噪声导致雷达和相机模态融合困难。
- 提出了一种新的基于查询的雷达-相机Transformer(RCTrans)方法来解决这一问题。
- 设计了雷达密集编码器来增强稀疏雷达点云,并将其与图像标记符结合,以利用每个兴趣区域的3D信息并减少干扰。
- 采用修剪序列解码器预测基于标记符和随机查询的3D边界框。
- 通过序列融合结构逐步定位物体位置,提高了标记符与查询之间的精确性和灵活性对应。
- 采用修剪训练策略以提高推理效率并防止查询失去独特性。
点此查看论文截图
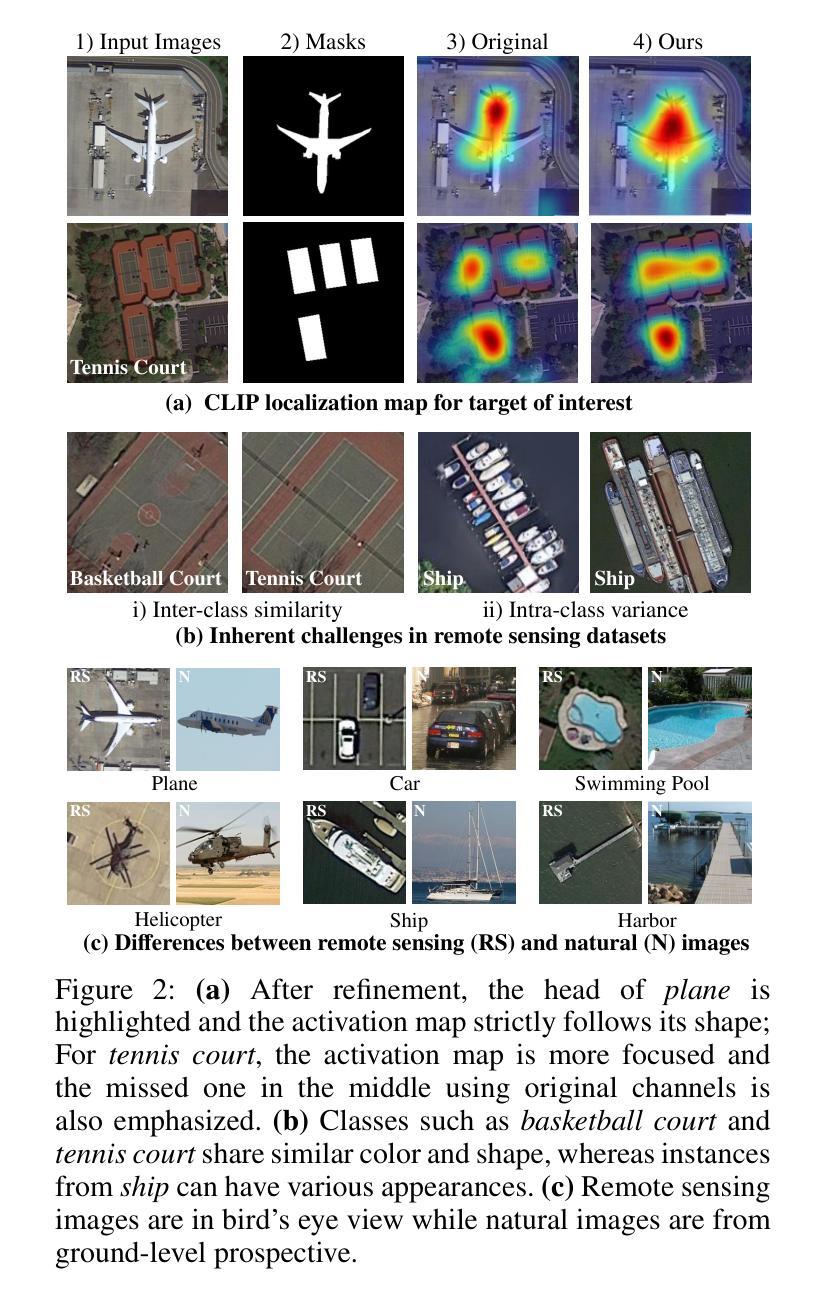
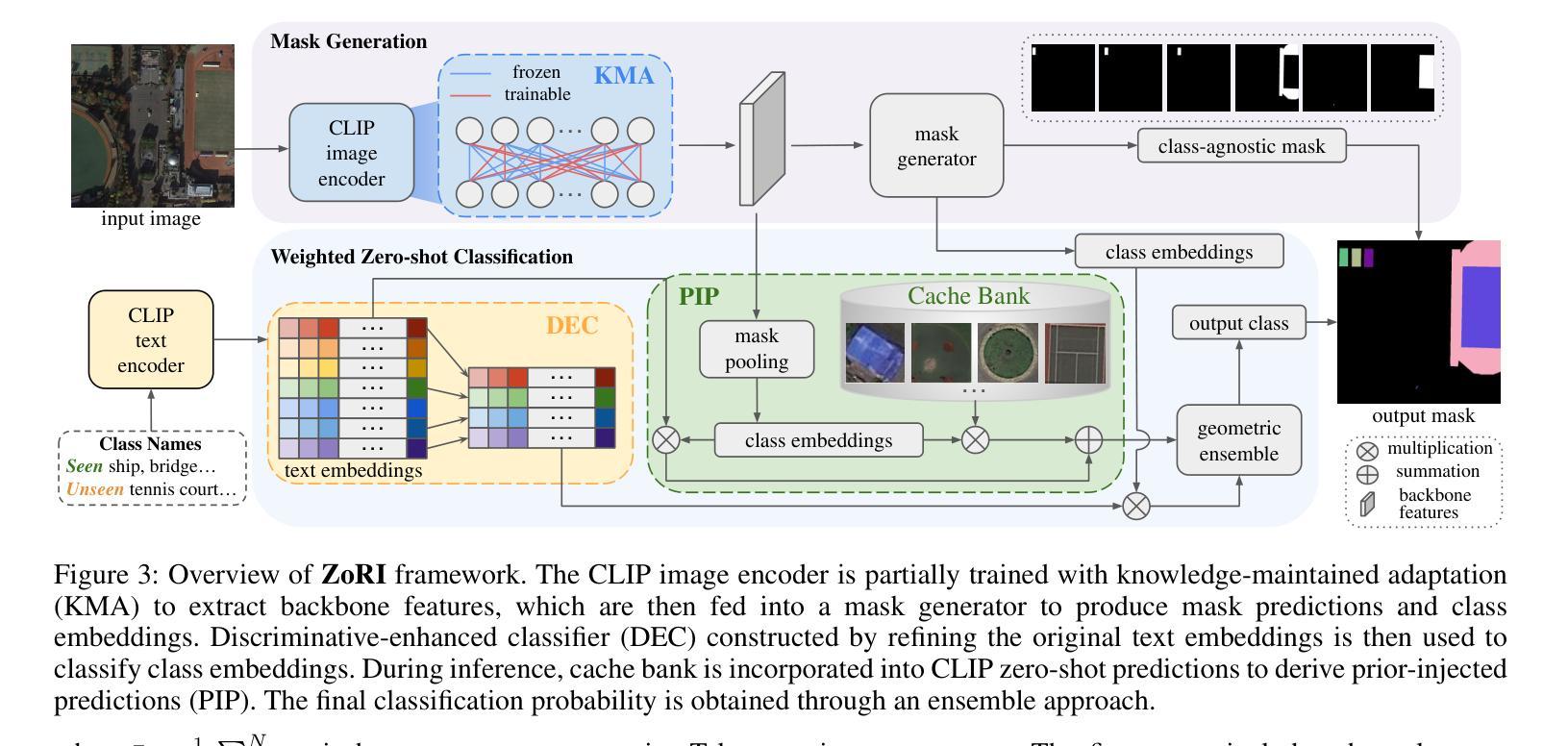
ZoRI: Towards Discriminative Zero-Shot Remote Sensing Instance Segmentation
Authors:Shiqi Huang, Shuting He, Bihan Wen
Instance segmentation algorithms in remote sensing are typically based on conventional methods, limiting their application to seen scenarios and closed-set predictions. In this work, we propose a novel task called zero-shot remote sensing instance segmentation, aimed at identifying aerial objects that are absent from training data. Challenges arise when classifying aerial categories with high inter-class similarity and intra-class variance. Besides, the domain gap between vision-language models’ pretraining datasets and remote sensing datasets hinders the zero-shot capabilities of the pretrained model when it is directly applied to remote sensing images. To address these challenges, we propose a $\textbf{Z}$ero-Sh$\textbf{o}$t $\textbf{R}$emote Sensing $\textbf{I}$nstance Segmentation framework, dubbed $\textbf{ZoRI}$. Our approach features a discrimination-enhanced classifier that uses refined textual embeddings to increase the awareness of class disparities. Instead of direct fine-tuning, we propose a knowledge-maintained adaptation strategy that decouples semantic-related information to preserve the pretrained vision-language alignment while adjusting features to capture remote sensing domain-specific visual cues. Additionally, we introduce a prior-injected prediction with cache bank of aerial visual prototypes to supplement the semantic richness of text embeddings and seamlessly integrate aerial representations, adapting to the remote sensing domain. We establish new experimental protocols and benchmarks, and extensive experiments convincingly demonstrate that ZoRI achieves the state-of-art performance on the zero-shot remote sensing instance segmentation task. Our code is available at https://github.com/HuangShiqi128/ZoRI.
遥感领域的实例分割算法通常基于传统方法,将其应用限制在已知场景和封闭集预测上。在这项工作中,我们提出了一项名为零样本遥感实例分割的新型任务,旨在识别训练数据中不存在的航空物体。在分类具有高度类间相似性和类内差异的航空类别时,会出现挑战。此外,视觉语言模型预训练数据集和遥感数据集之间的域差距,阻碍了预训练模型在直接应用于遥感图像时的零样本能力。为解决这些挑战,我们提出了一个名为$\textbf{ZoRI}$(零样本遥感实例分割)的框架。我们的方法采用增强判别力的分类器,利用精细文本嵌入来提高对类别差异的认识。我们并未采用直接微调的方法,而是提出了一种知识保持适应策略,该策略可以解耦语义相关信息,在保持预训练的视觉语言对齐的同时调整特征以捕获遥感领域特定的视觉线索。此外,我们引入了基于航空视觉原型的先验注入预测缓存库,以补充文本嵌入的语义丰富性并无缝集成航空表示,适应遥感领域。我们建立了新的实验协议和基准测试,大量实验有力地证明,在零样本遥感实例分割任务上,ZoRI达到了最先进的性能。我们的代码位于https://github.com/HuangShiqi128/ZoRI。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025, code see https://github.com/HuangShiqi128/ZoRI
Summary
该文介绍了一种新型遥感实例分割任务——零样本遥感实例分割,旨在识别训练数据中不存在的空中目标。针对遥感图像中的类别分类难题和领域差距问题,提出了名为ZoRI的零样本遥感实例分割框架。该框架采用增强判别力的分类器,使用精细文本嵌入提高类别差异的感知能力。同时,提出了一种知识保持适应策略,以解耦语义相关信息并保留预训练的视觉语言对齐,调整特征以捕捉遥感特定视觉线索。此外,引入了基于空中视觉原型的先验注入预测缓存库,以补充文本嵌入的语义丰富性并无缝集成空中表示,适应遥感领域。实验证明ZoRI在零样本遥感实例分割任务上达到了最新性能。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种新型遥感实例分割任务——零样本遥感实例分割,针对训练数据中未出现的空中目标进行识别。
- 提出了名为ZoRI的框架来解决零样本遥感实例分割的挑战,包括类别分类难题和领域差距问题。
- ZoRI框架采用增强判别力的分类器,利用精细文本嵌入来提高类别差异的感知能力。
- 提出了一种知识保持适应策略,通过解耦语义相关信息来保留预训练的视觉语言对齐,并调整特征以捕捉遥感特定视觉线索。
- 引入了基于空中视觉原型的先验注入预测缓存库,以丰富语义信息和无缝集成空中表示,适应遥感领域。
- 实验证明ZoRI在零样本遥感实例分割任务上达到了最新性能。
点此查看论文截图

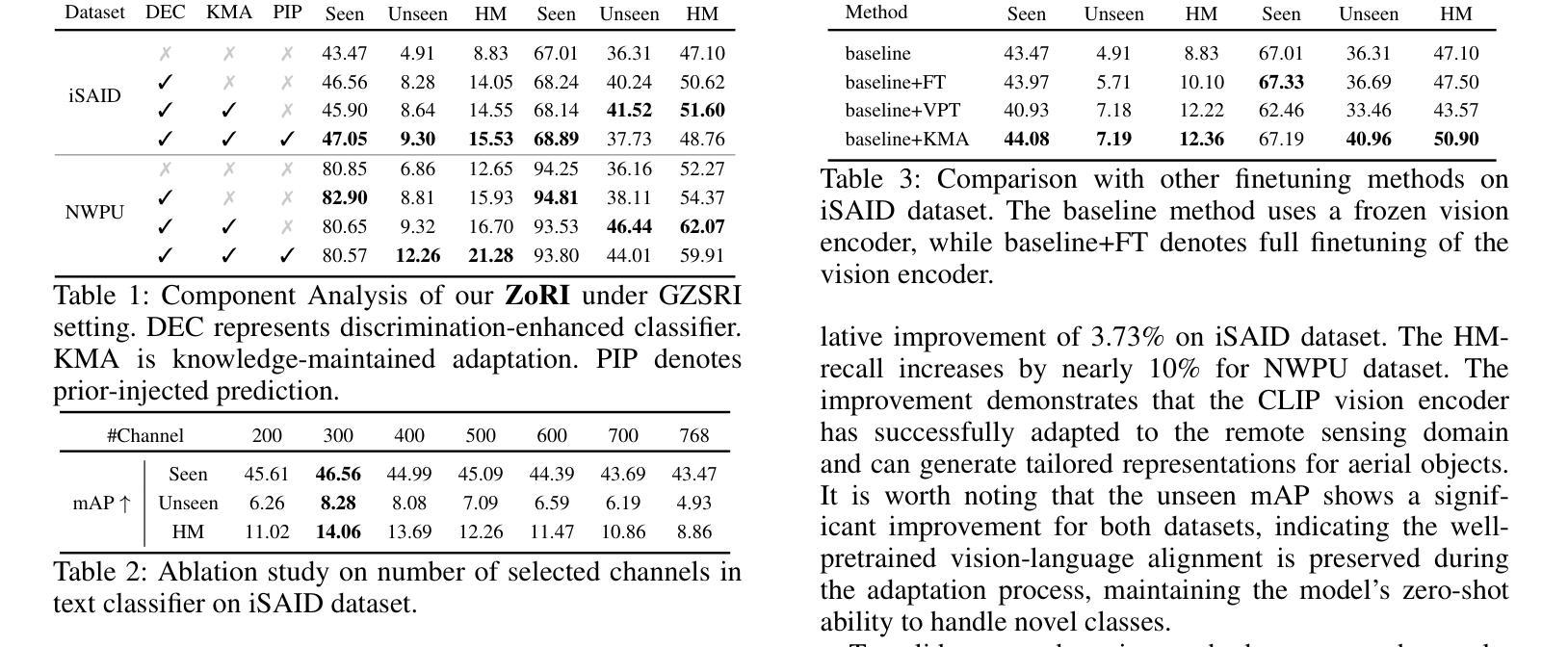
Structural Pruning via Spatial-aware Information Redundancy for Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Dongyue Wu, Zilin Guo, Li Yu, Nong Sang, Changxin Gao
In recent years, semantic segmentation has flourished in various applications. However, the high computational cost remains a significant challenge that hinders its further adoption. The filter pruning method for structured network slimming offers a direct and effective solution for the reduction of segmentation networks. Nevertheless, we argue that most existing pruning methods, originally designed for image classification, overlook the fact that segmentation is a location-sensitive task, which consequently leads to their suboptimal performance when applied to segmentation networks. To address this issue, this paper proposes a novel approach, denoted as Spatial-aware Information Redundancy Filter Pruning(SIRFP), which aims to reduce feature redundancy between channels. First, we formulate the pruning process as a maximum edge weight clique problem(MEWCP) in graph theory, thereby minimizing the redundancy among the remaining features after pruning. Within this framework, we introduce a spatial-aware redundancy metric based on feature maps, thus endowing the pruning process with location sensitivity to better adapt to pruning segmentation networks. Additionally, based on the MEWCP, we propose a low computational complexity greedy strategy to solve this NP-hard problem, making it feasible and efficient for structured pruning. To validate the effectiveness of our method, we conducted extensive comparative experiments on various challenging datasets. The results demonstrate the superior performance of SIRFP for semantic segmentation tasks.
近年来,语义分割在各种应用中蓬勃发展。然而,高计算成本仍然是阻碍其进一步采用的一大挑战。针对结构化网络瘦身(structured network slimming)的滤波器剪枝方法为解决分割网络的减少问题提供了直接有效的解决方案。然而,我们认为大多数现有的剪枝方法最初是为图像分类而设计的,忽略了分割是一个位置敏感的任务这一事实,因此当应用于分割网络时,其性能表现并不理想。为了解决这一问题,本文提出了一种新的方法,称为空间感知信息冗余滤波器剪枝(SIRFP),旨在减少通道之间的特征冗余。首先,我们将剪枝过程公式化为图论中的最大边权重集团问题(MEWCP),从而最小化剪枝后剩余特征之间的冗余。在这个框架内,我们引入了基于特征图的具有空间感知的冗余度量指标,从而使剪枝过程具有位置敏感性,更好地适应分割网络的剪枝。此外,基于MEWCP,我们提出了一种低计算复杂度的贪婪策略来解决这个NP难题,使结构化剪枝变得可行且高效。为了验证我们方法的有效性,我们在各种具有挑战性的数据集上进行了广泛的对比实验。结果表明SIRFP在语义分割任务上的性能优越。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
本文提出一种名为SIRFP的空间感知信息冗余滤波器剪枝方法,旨在减少分割网络中的特征冗余。通过图论中的最大边权重集团问题来表述剪枝过程,并提出一种基于特征图的空感知冗余度量,使剪枝过程具有位置敏感性,从而更好地适应分割网络的剪枝。实验结果表明,SIRFP在语义分割任务上具有出色的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 语义分割在多个应用领域中蓬勃发展,但高计算成本仍是其进一步应用的重大挑战。
- 过滤器剪枝方法可作为结构化网络瘦身的一种直接和有效的解决方案。
- 现有的剪枝方法忽略了分割是位置敏感的任务,导致在分割网络中的应用表现不佳。
- 本文提出的SIRFP方法旨在减少通道间的特征冗余,将剪枝过程表述为图论中的最大边权重集团问题。
- 引入基于特征图的空感知冗余度量,使剪枝过程具有位置敏感性。
- 提出一种低计算复杂度的贪婪策略来解决NP难题,实现结构化剪枝的可行性和效率。
点此查看论文截图

SEG-SAM: Semantic-Guided SAM for Unified Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Shuangping Huang, Hao Liang, Qingfeng Wang, Chulong Zhong, Zijian Zhou, Miaojing Shi
Recently, developing unified medical image segmentation models gains increasing attention, especially with the advent of the Segment Anything Model (SAM). SAM has shown promising binary segmentation performance in natural domains, however, transferring it to the medical domain remains challenging, as medical images often possess substantial inter-category overlaps. To address this, we propose the SEmantic-Guided SAM (SEG-SAM), a unified medical segmentation model that incorporates semantic medical knowledge to enhance medical segmentation performance. First, to avoid the potential conflict between binary and semantic predictions, we introduce a semantic-aware decoder independent of SAM’s original decoder, specialized for both semantic segmentation on the prompted object and classification on unprompted objects in images. To further enhance the model’s semantic understanding, we solicit key characteristics of medical categories from large language models and incorporate them into SEG-SAM through a text-to-vision semantic module, adaptively transferring the language information into the visual segmentation task. In the end, we introduce the cross-mask spatial alignment strategy to encourage greater overlap between the predicted masks from SEG-SAM’s two decoders, thereby benefiting both predictions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SEG-SAM outperforms state-of-the-art SAM-based methods in unified binary medical segmentation and task-specific methods in semantic medical segmentation, showcasing promising results and potential for broader medical applications.
近期,开发统一医学图像分割模型越来越受到关注,尤其是随着Segment Anything Model(SAM)的出现。SAM在自然领域的二进制分割性能方面表现出良好的前景,然而将其转移到医学领域仍然具有挑战性,因为医学图像通常存在大量的类别间重叠。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了SEmantic-Guided SAM(SEG-SAM),这是一种结合语义医学知识来增强医学分割性能的统一的医学分割模型。首先,为了避免二进制和语义预测之间的潜在冲突,我们引入了一个独立于SAM原始解码器的语义感知解码器,专门用于图像中对提示对象的语义分割以及对未提示对象的分类。为了进一步增强模型的语义理解,我们从大型语言模型中提取医学类别的关键特征,并通过文本到视觉语义模块将其融入SEG-SAM中,自适应地将语言信息转移到视觉分割任务中。最后,我们引入了跨掩膜空间对齐策略,以鼓励SEG-SAM的两个解码器产生的预测掩膜之间更大的重叠,从而有利于两种预测。大量实验表明,SEG-SAM在统一的二元医学分割方面优于最先进SAM方法,在特定任务的语义医学分割方面也表现出色,显示出广阔的应用前景和潜在的医学应用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 3 figures
Summary
SAM模型在自然领域已展现出有前景的二元分割性能,但将其应用于医学领域面临挑战。为此,我们提出SEG-SAM模型,结合语义医学知识提升医学分割性能。通过引入语义感知解码器避免二元和语义预测之间的潜在冲突,借助大型语言模型获取医学类别的关键特征,并通过文本到视觉的语义模块将其融入SEG-SAM。实验表明,SEG-SAM在统一二元医学分割和语义医学分割任务上表现优异。
Key Takeaways
- SAM模型在医学领域应用面临挑战,主要由于医学图像存在大量的类别间重叠。
- SEG-SAM模型通过结合语义医学知识提升医学分割性能。
- SEG-SAM引入语义感知解码器,独立于SAM原始解码器,能同时进行语义分割和未提示对象的分类。
- 利用大型语言模型获取医学类别的关键特征,并通过文本到视觉的语义模块融入SEG-SAM,增强模型对语义的理解。
- SEG-SAM采用跨掩膜空间对齐策略,鼓励两个解码器产生的预测掩膜更大程度重叠,从而有利于两种预测。
- 实验显示,SEG-SAM在统一二元医学分割和语义医学分割任务上表现优于其他先进SAM方法和特定任务方法。
点此查看论文截图

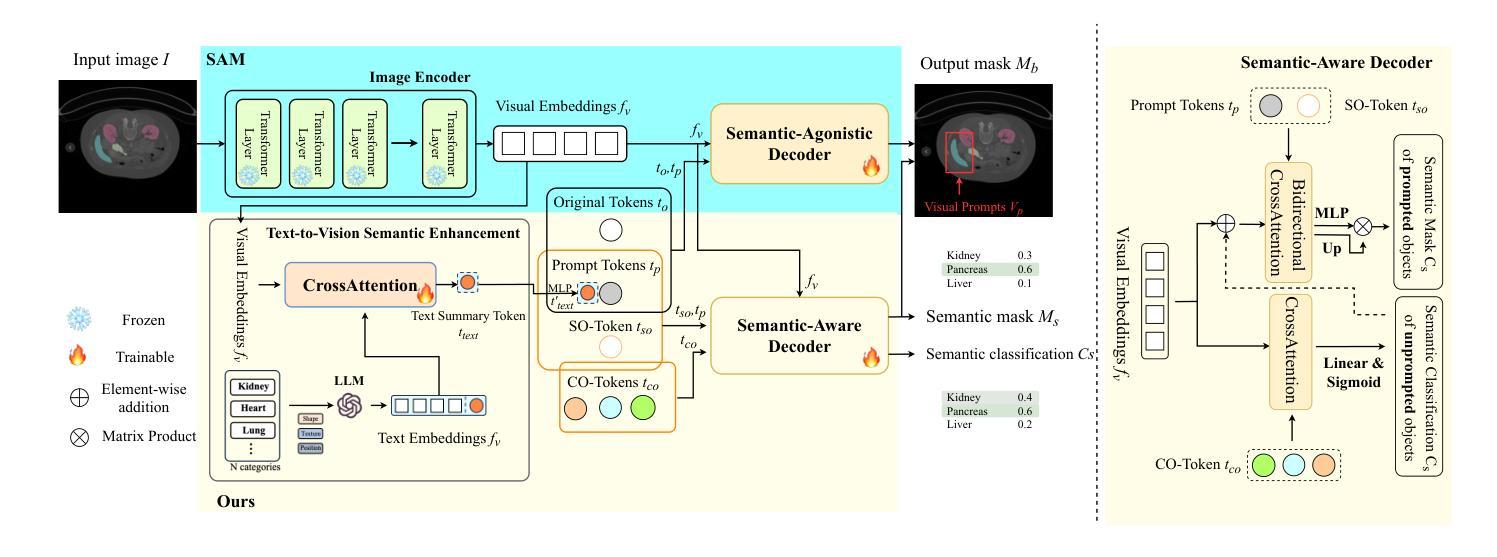
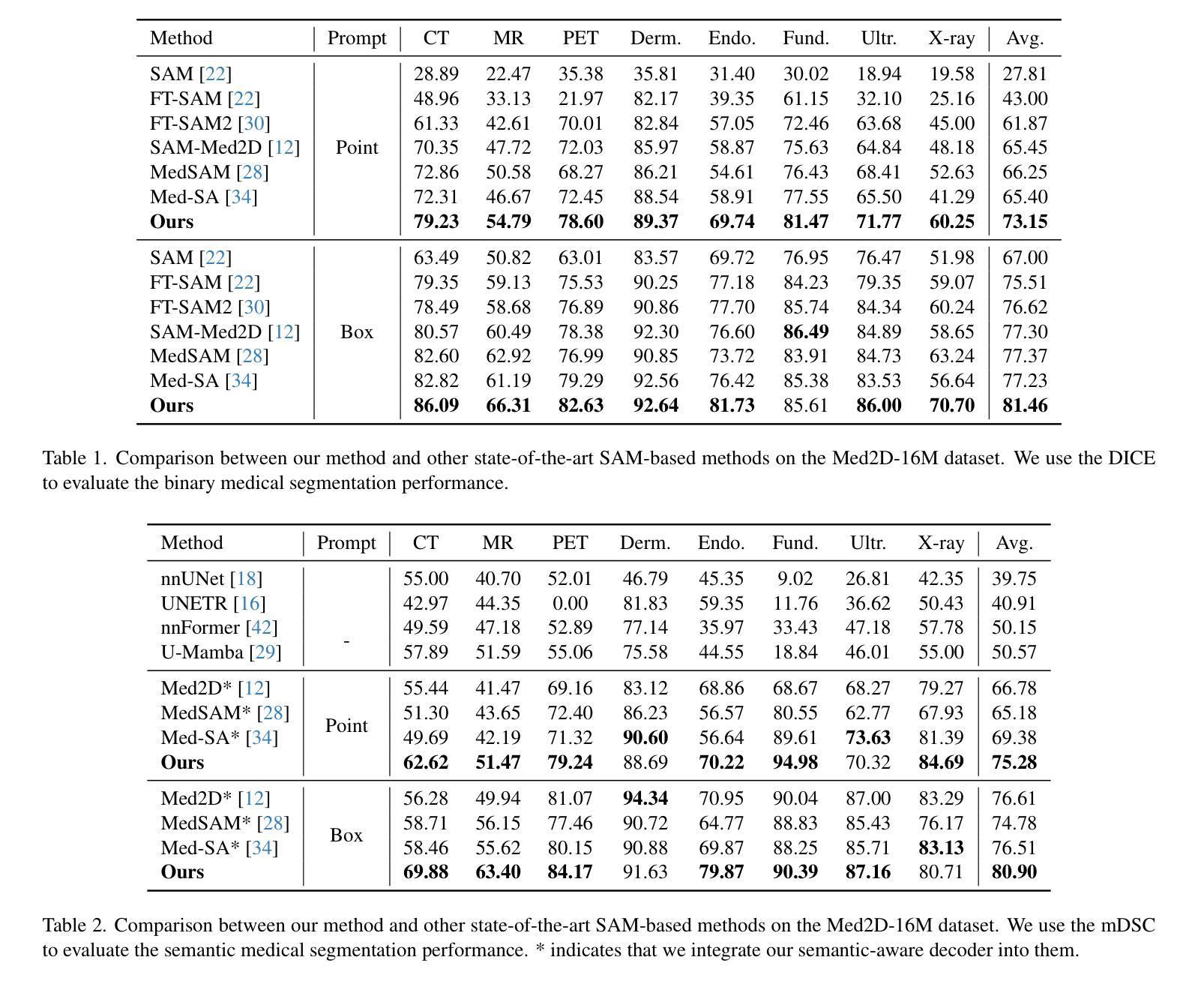
DuSSS: Dual Semantic Similarity-Supervised Vision-Language Model for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Qingtao Pan, Wenhao Qiao, Jingjiao Lou, Bing Ji, Shuo Li
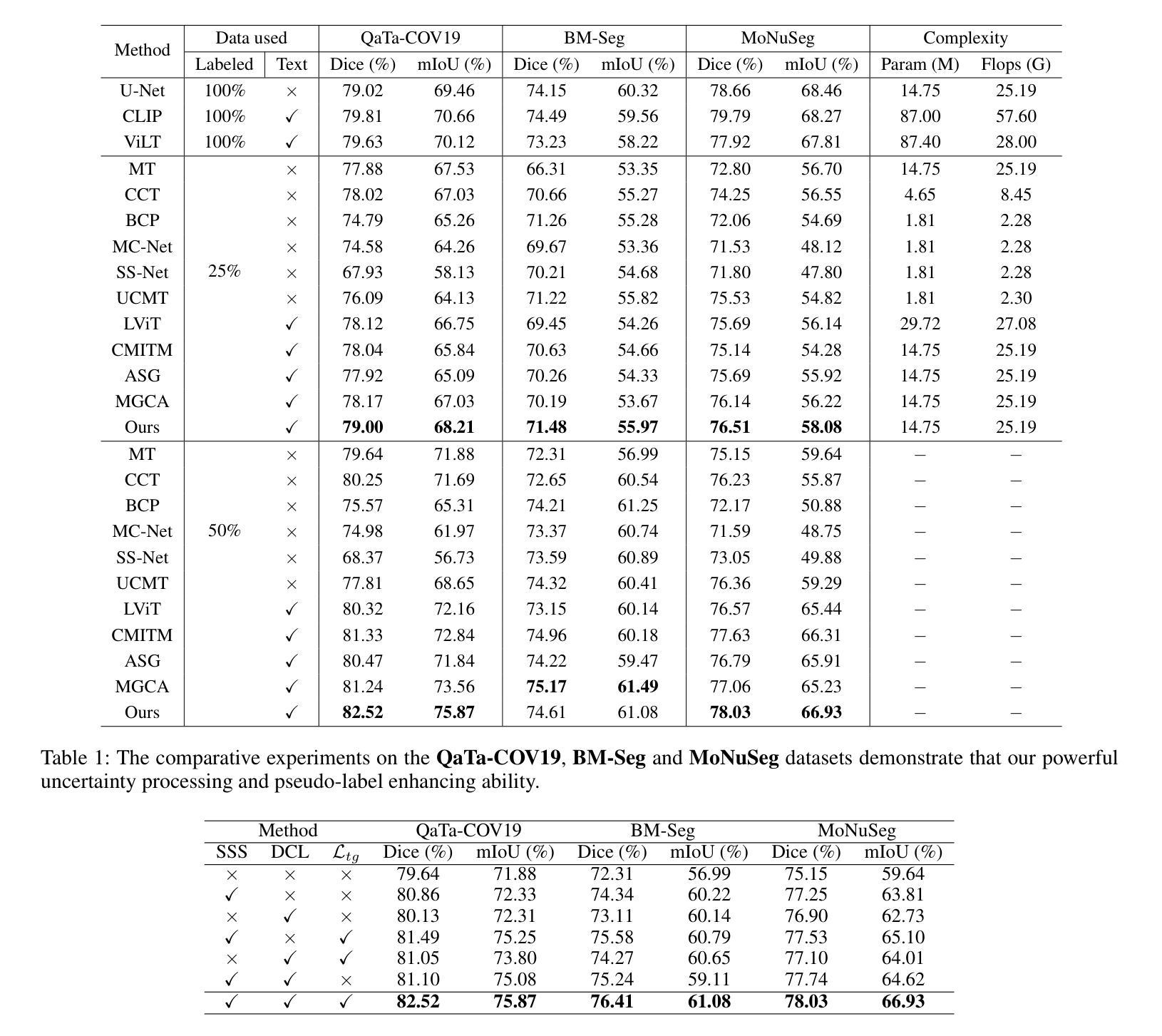
Semi-supervised medical image segmentation (SSMIS) uses consistency learning to regularize model training, which alleviates the burden of pixel-wise manual annotations. However, it often suffers from error supervision from low-quality pseudo labels. Vision-Language Model (VLM) has great potential to enhance pseudo labels by introducing text prompt guided multimodal supervision information. It nevertheless faces the cross-modal problem: the obtained messages tend to correspond to multiple targets. To address aforementioned problems, we propose a Dual Semantic Similarity-Supervised VLM (DuSSS) for SSMIS. Specifically, 1) a Dual Contrastive Learning (DCL) is designed to improve cross-modal semantic consistency by capturing intrinsic representations within each modality and semantic correlations across modalities. 2) To encourage the learning of multiple semantic correspondences, a Semantic Similarity-Supervision strategy (SSS) is proposed and injected into each contrastive learning process in DCL, supervising semantic similarity via the distribution-based uncertainty levels. Furthermore, a novel VLM-based SSMIS network is designed to compensate for the quality deficiencies of pseudo-labels. It utilizes the pretrained VLM to generate text prompt guided supervision information, refining the pseudo label for better consistency regularization. Experimental results demonstrate that our DuSSS achieves outstanding performance with Dice of 82.52%, 74.61% and 78.03% on three public datasets (QaTa-COV19, BM-Seg and MoNuSeg).
半监督医学图像分割(SSMIS)利用一致性学习来规范模型训练,减轻了像素级手动标注的负担。然而,它常常受到低质量伪标签的错误监督的影响。视觉语言模型(VLM)通过引入文本提示引导的多模态监督信息来提高伪标签的潜力。然而,它面临着跨模态的问题:获取的信息往往对应多个目标。为了解决上述问题,我们提出了用于SSMIS的双语义相似性监督VLM(DuSSS)。具体来说,1)设计了双对比学习(DCL),通过捕捉每种模态的内在表示和跨模态的语义关联,提高跨模态语义一致性。2)为了鼓励学习多个语义对应关系,提出了语义相似性监督策略(SSS),并将其注入DCL中的每个对比学习过程中,通过基于分布的的不确定性水平监督语义相似性。此外,设计了一个基于VLM的SSMIS网络,以弥补伪标签的质量缺陷。它利用预训练的VLM生成文本提示引导的监督信息,对伪标签进行细化,以更好地实现一致性正则化。实验结果证明,我们的DuSSS在三个公共数据集(QaTa-COV19、BM-Seg和MoNuSeg)上取得了出色的性能,Dice分别为82.52%、74.61%和78.03%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
医学图像半监督分割(SSMIS)通过一致性学习进行模型训练,减轻像素级手动标注的负担。然而,它常常受到低质量伪标签的错误监督影响。本研究提出一种基于双重语义相似性监督的跨模态视觉语言模型(DuSSS),通过双重对比学习(DCL)提高跨模态语义一致性,通过语义相似性监督策略(SSS)鼓励学习多个语义对应关系,并设计新型SSMIS网络以补偿伪标签质量不足。实验结果显示,DuSSS在三个公开数据集上实现了优异的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 半监督医学图像分割利用一致性学习减轻手动标注负担。
- 低质量伪标签可能导致错误监督的问题。
- 提出DuSSS方法,结合视觉语言模型(VLM)增强伪标签质量。
- DuSSS使用双重对比学习(DCL)提高跨模态语义一致性。
- 语义相似性监督策略(SSS)鼓励学习多个语义对应关系。
- 设计新型SSMIS网络以补偿伪标签质量不足。
点此查看论文截图

Exploring Semantic Consistency and Style Diversity for Domain Generalized Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Hongwei Niu, Linhuang Xie, Jianghang Lin, Shengchuan Zhang
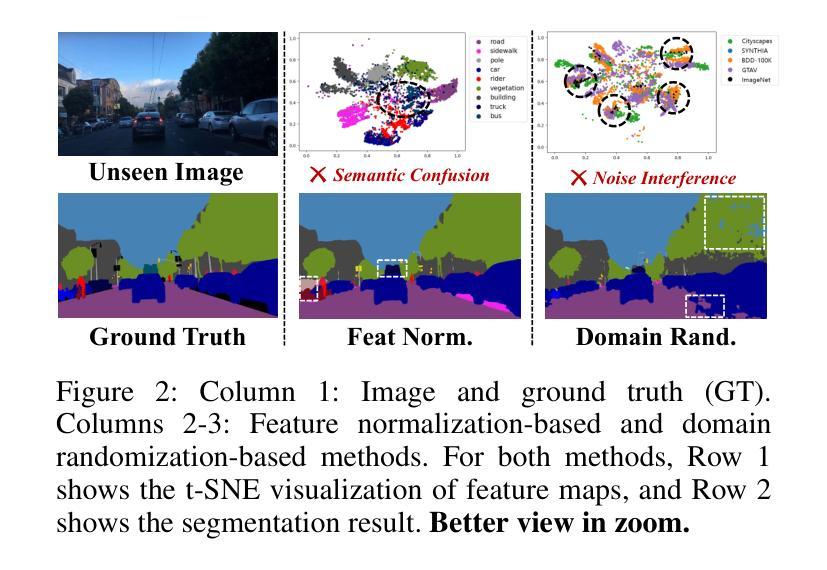
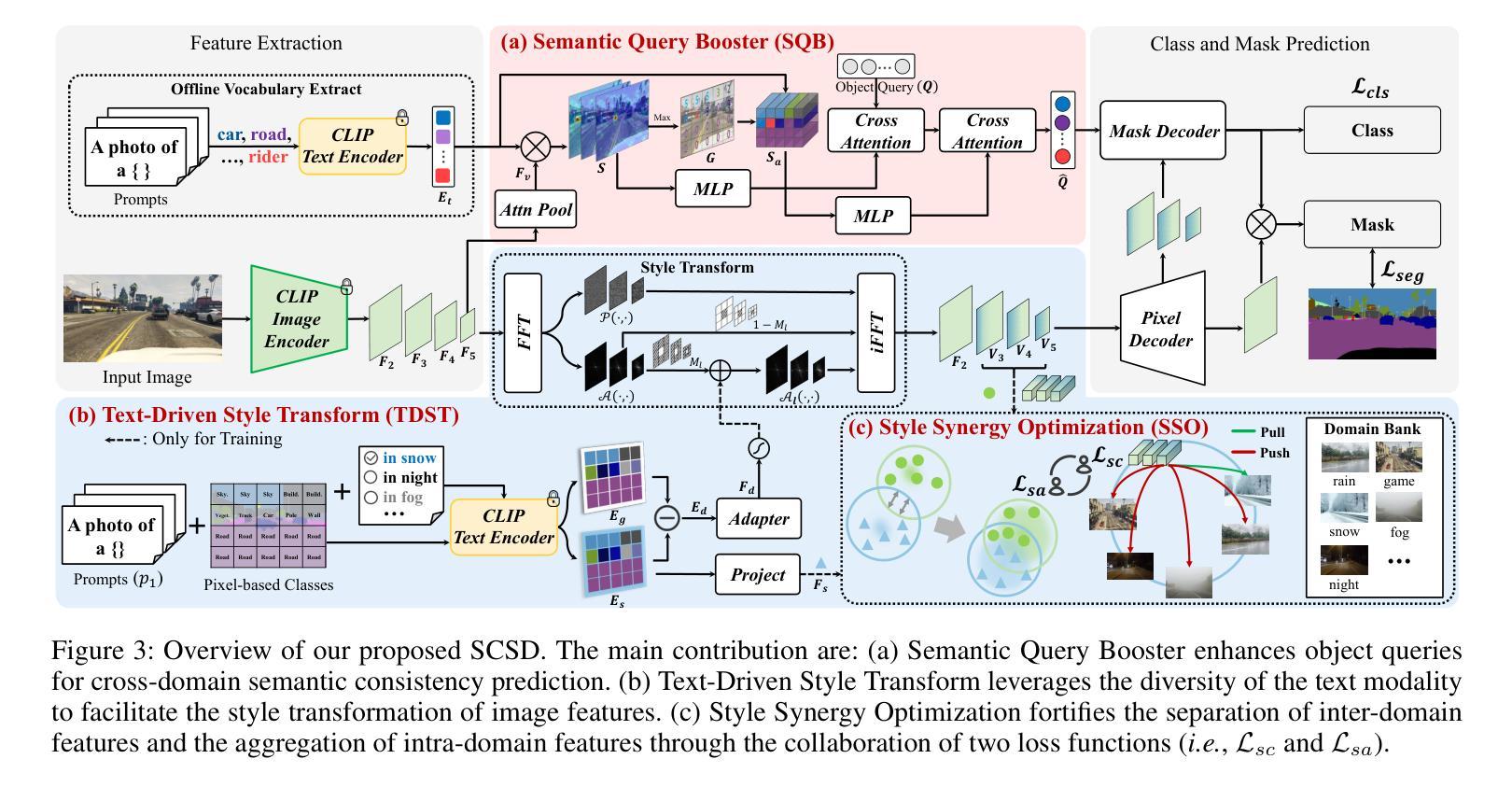
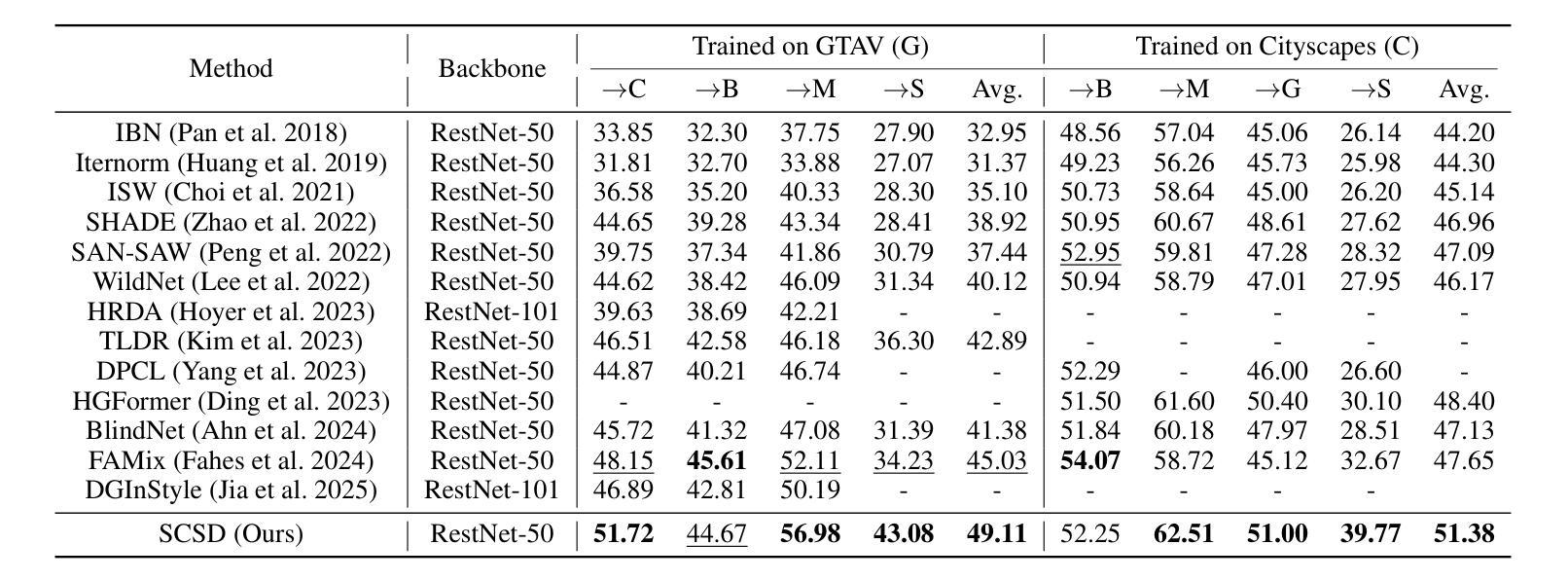
Domain Generalized Semantic Segmentation (DGSS) seeks to utilize source domain data exclusively to enhance the generalization of semantic segmentation across unknown target domains. Prevailing studies predominantly concentrate on feature normalization and domain randomization, these approaches exhibit significant limitations. Feature normalization-based methods tend to confuse semantic features in the process of constraining the feature space distribution, resulting in classification misjudgment. Domain randomization-based methods frequently incorporate domain-irrelevant noise due to the uncontrollability of style transformations, resulting in segmentation ambiguity. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel framework, named SCSD for Semantic Consistency prediction and Style Diversity generalization. It comprises three pivotal components: Firstly, a Semantic Query Booster is designed to enhance the semantic awareness and discrimination capabilities of object queries in the mask decoder, enabling cross-domain semantic consistency prediction. Secondly, we develop a Text-Driven Style Transform module that utilizes domain difference text embeddings to controllably guide the style transformation of image features, thereby increasing inter-domain style diversity. Lastly, to prevent the collapse of similar domain feature spaces, we introduce a Style Synergy Optimization mechanism that fortifies the separation of inter-domain features and the aggregation of intra-domain features by synergistically weighting style contrastive loss and style aggregation loss. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed SCSD significantly outperforms existing state-of-theart methods. Notably, SCSD trained on GTAV achieved an average of 49.11 mIoU on the four unseen domain datasets, surpassing the previous state-of-the-art method by +4.08 mIoU. Code is available at https://github.com/nhw649/SCSD.
领域通用语义分割(DGSS)旨在仅利用源域数据来提高在未知目标域上语义分割的泛化能力。目前的研究主要集中在特征归一化和领域随机化上,但这些方法存在显著局限性。基于特征归一化的方法往往会在约束特征空间分布的过程中混淆语义特征,导致分类判断错误。而基于领域随机化的方法由于风格转换的不可控性,经常引入与领域无关的噪声,导致分割模糊。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了一个名为SCSD(语义一致性预测和风格多样性泛化)的新框架。它包含三个关键组件:首先,设计了一种语义查询增强器,用于提高掩膜解码器中对象查询的语义意识和辨别能力,从而实现跨域语义一致性预测。其次,我们开发了一个文本驱动的风格转换模块,该模块利用领域差异文本嵌入来可控地指导图像特征的样式转换,从而增加跨领域的风格多样性。最后,为了防止类似领域特征空间的崩溃,我们引入了一种风格协同优化机制,通过协同权重风格对比损失和风格聚合损失,加强了跨领域特征的分离和领域内特征的聚合。大量实验表明,所提出的SCSD显著优于现有的最先进的方法。值得注意的是,SCSD在GTAV上训练,在四个未见过的领域数据集上平均达到49.11 mIoU,比之前的最佳方法高出+4.08 mIoU。代码可在https://github.com/nhw649/SCSD获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
领域通用语义分割(DGSS)利用源域数据提升在未知目标域上的语义分割泛化能力。当前主流方法集中在特征归一化和领域随机化上,但存在混淆语义特征和引入领域不相关噪声的问题。为解决这些问题,提出了SCSD框架,包含语义查询增强器、文本驱动风格转换模块以及风格协同优化机制。SCSD在四个未见域数据集上的平均mIoU达到49.11,超越了现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- DGSS旨在利用源域数据提升语义分割在未知目标域的泛化能力。
- 当前方法主要关注特征归一化和领域随机化,但存在语义特征混淆和引入不相关噪声的问题。
- SCSD框架包含三个关键组件:语义查询增强器、文本驱动风格转换模块和风格协同优化机制。
- 语义查询增强器提升对象查询的语义意识和辨别能力,实现跨域语义一致性预测。
- 文本驱动风格转换模块利用领域差异文本嵌入来可控地引导图像特征的样式转换,增加跨域风格多样性。
- 风格协同优化机制通过协同加权风格对比损失和风格聚合损失,强化域间特征分离和域内特征聚合。
- SCSD在四个未见域数据集上的表现显著优于现有方法,平均mIoU达到49.11。
点此查看论文截图

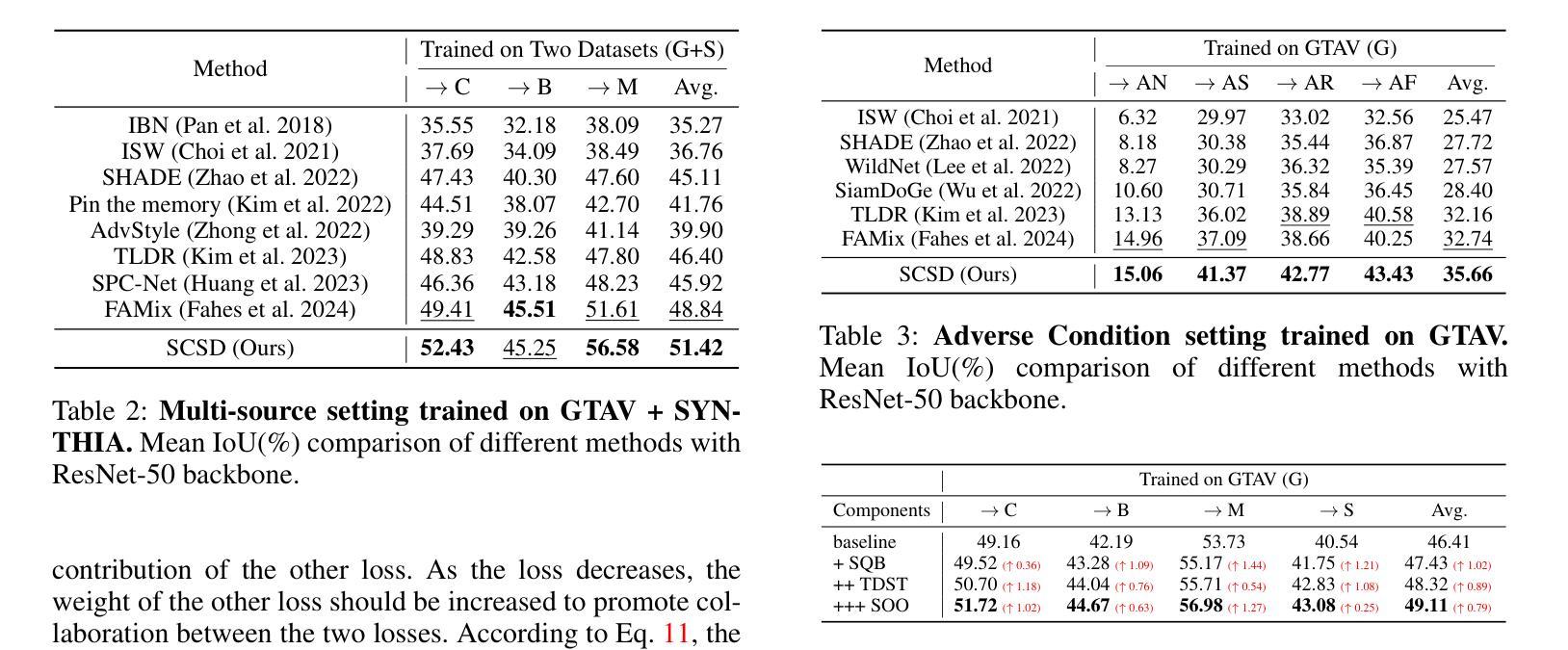
Coconut Palm Tree Counting on Drone Images with Deep Object Detection and Synthetic Training Data
Authors:Tobias Rohe, Barbara Böhm, Michael Kölle, Jonas Stein, Robert Müller, Claudia Linnhoff-Popien
Drones have revolutionized various domains, including agriculture. Recent advances in deep learning have propelled among other things object detection in computer vision. This study utilized YOLO, a real-time object detector, to identify and count coconut palm trees in Ghanaian farm drone footage. The farm presented has lost track of its trees due to different planting phases. While manual counting would be very tedious and error-prone, accurately determining the number of trees is crucial for efficient planning and management of agricultural processes, especially for optimizing yields and predicting production. We assessed YOLO for palm detection within a semi-automated framework, evaluated accuracy augmentations, and pondered its potential for farmers. Data was captured in September 2022 via drones. To optimize YOLO with scarce data, synthetic images were created for model training and validation. The YOLOv7 model, pretrained on the COCO dataset (excluding coconut palms), was adapted using tailored data. Trees from footage were repositioned on synthetic images, with testing on distinct authentic images. In our experiments, we adjusted hyperparameters, improving YOLO’s mean average precision (mAP). We also tested various altitudes to determine the best drone height. From an initial mAP@.5 of $0.65$, we achieved 0.88, highlighting the value of synthetic images in agricultural scenarios.
无人机已经彻底改变了包括农业在内的各个领域。深度学习领域的最新进展推动了计算机视觉中的物体检测等技术。本研究使用YOLO实时物体检测器来识别和计数加纳农场无人机影像中的椰子树。由于种植阶段不同,该农场无法追踪其树木。虽然手动计数非常繁琐且容易出错,但准确确定树木数量对于高效规划和农业过程管理至关重要,特别是对于优化产量和预测生产。我们在半自动化框架内评估了YOLO检测棕榈树的性能,评估了准确性增强情况,并考虑了其对农民的潜力。数据是通过无人机在2022年9月捕获的。为了利用稀缺数据优化YOLO,我们创建了合成图像用于模型训练和验证。我们使用预训练的COCO数据集(不包括椰子树)上的YOLOv7模型,并使用定制数据进行了适应。将影像中的树木重新定位到合成图像上,并在不同的真实图像上进行测试。在实验中,我们调整了超参数,提高了YOLO的平均精度均值(mAP)。我们还测试了各种高度以确定最佳的无人机高度。从最初的mAP@.5的0.65,我们达到了0.88,突显了合成图像在农业场景中的价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages
Summary
本研究利用深度学习中的YOLO实时目标检测算法,在加纳的农业无人机影像中对椰子树进行检测和计数。通过合成图像优化YOLO模型,提高模型精度,解决了因种植阶段不同导致的树木跟踪丢失问题。准确计树对农业管理和生产优化至关重要。
Key Takeaways
- 研究背景:研究展示了无人机在农业领域的应用,特别是在椰子树的计数方面的应用。
- 技术应用:使用YOLO实时目标检测算法对椰子树进行识别和计数。
- 数据挑战与对策:针对数据稀缺的问题,研究通过合成图像来优化YOLO模型,提高模型的精度。
- 模型优化结果:从初始的mAP@.5值为0.65提高到0.88,证明了合成图像在农业场景中的价值。
- 模型适用性:研究了不同海拔下的无人机拍摄效果,以确定最佳的无人机高度。
- 研究意义:准确计树对农业管理和生产优化至关重要,该研究的成果可为农民提供有力的工具支持。
点此查看论文截图




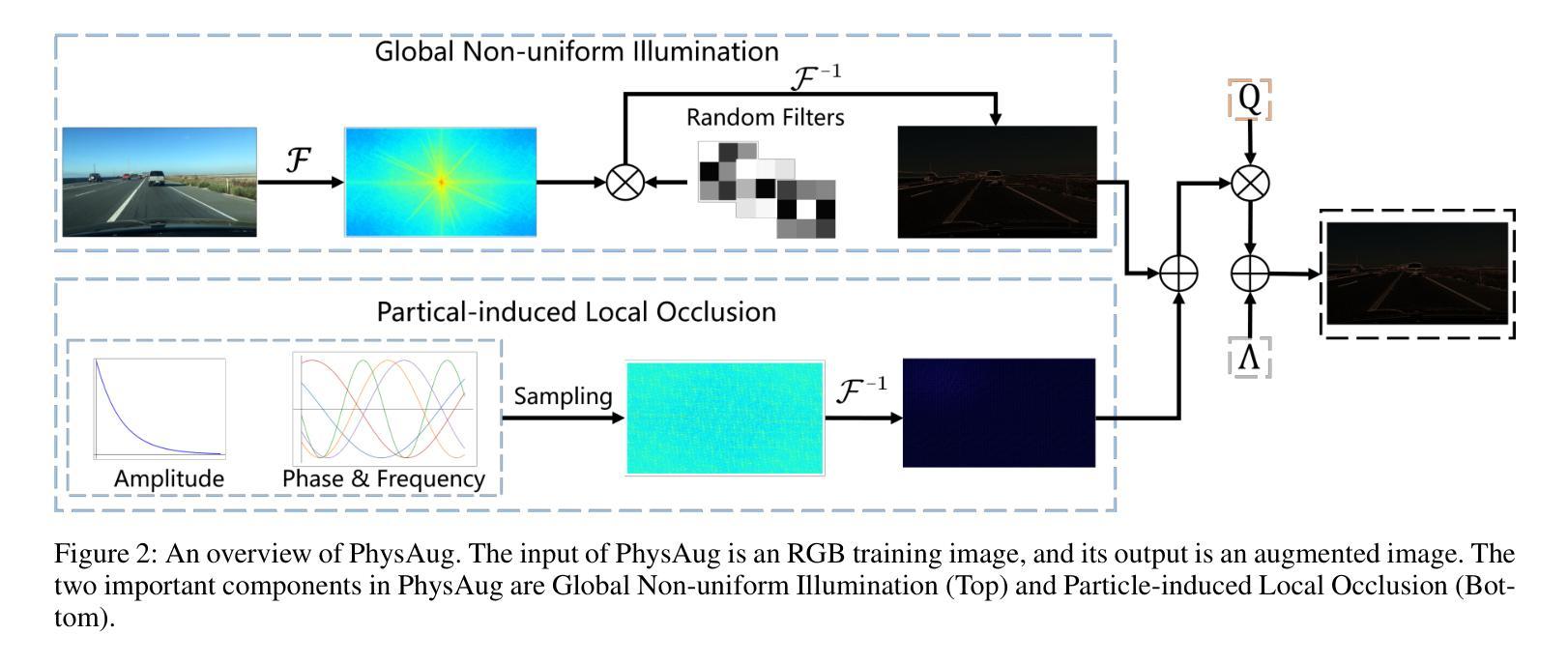
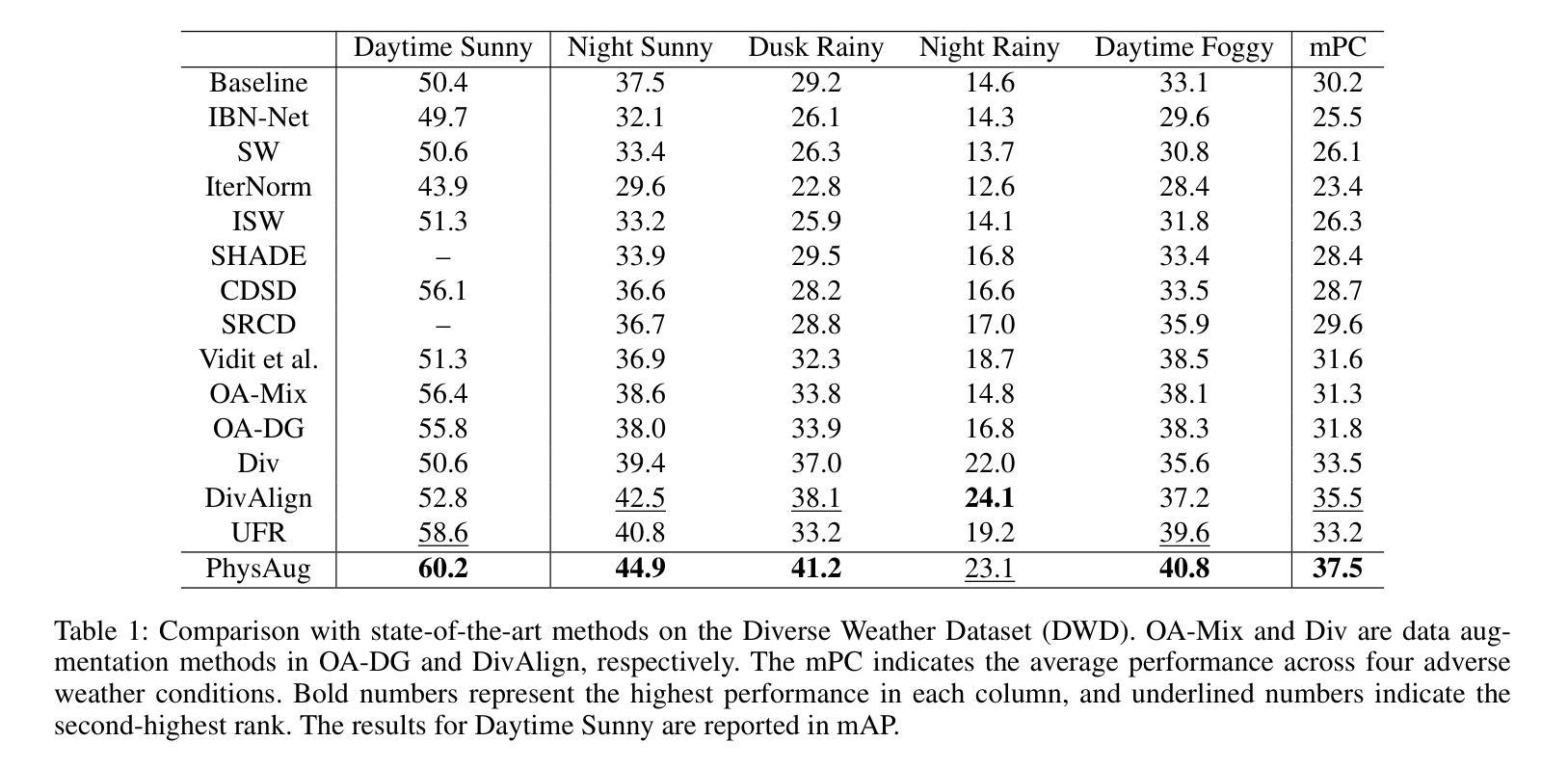
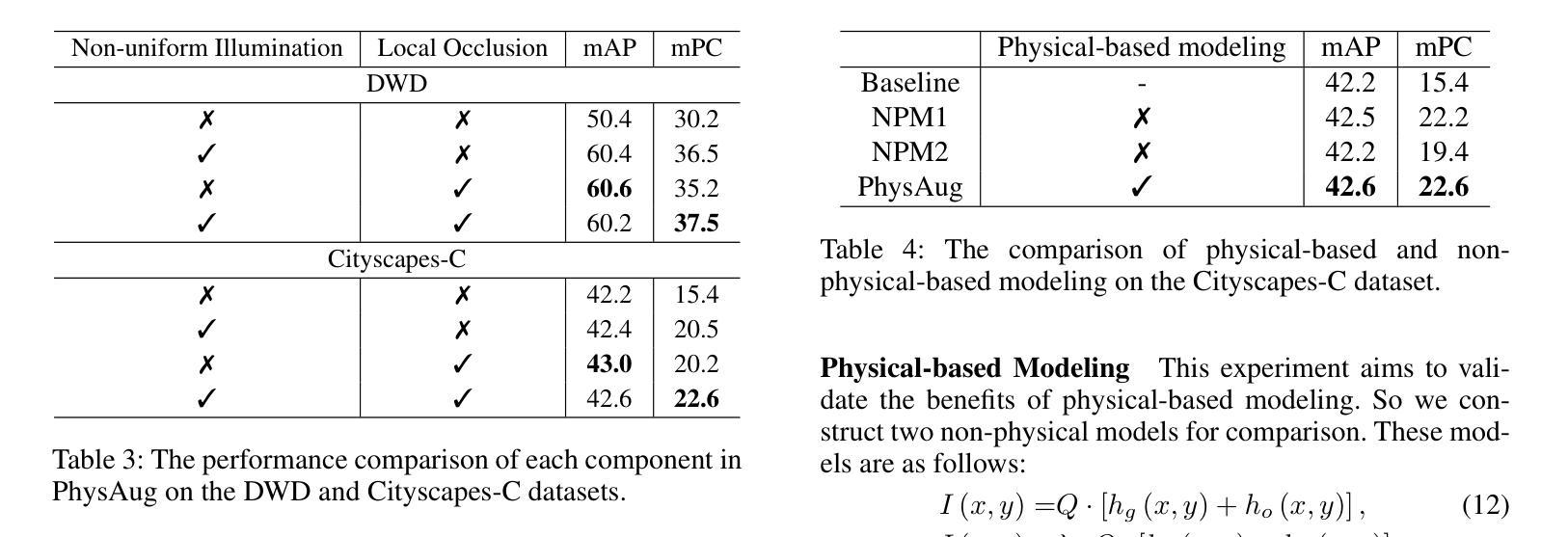
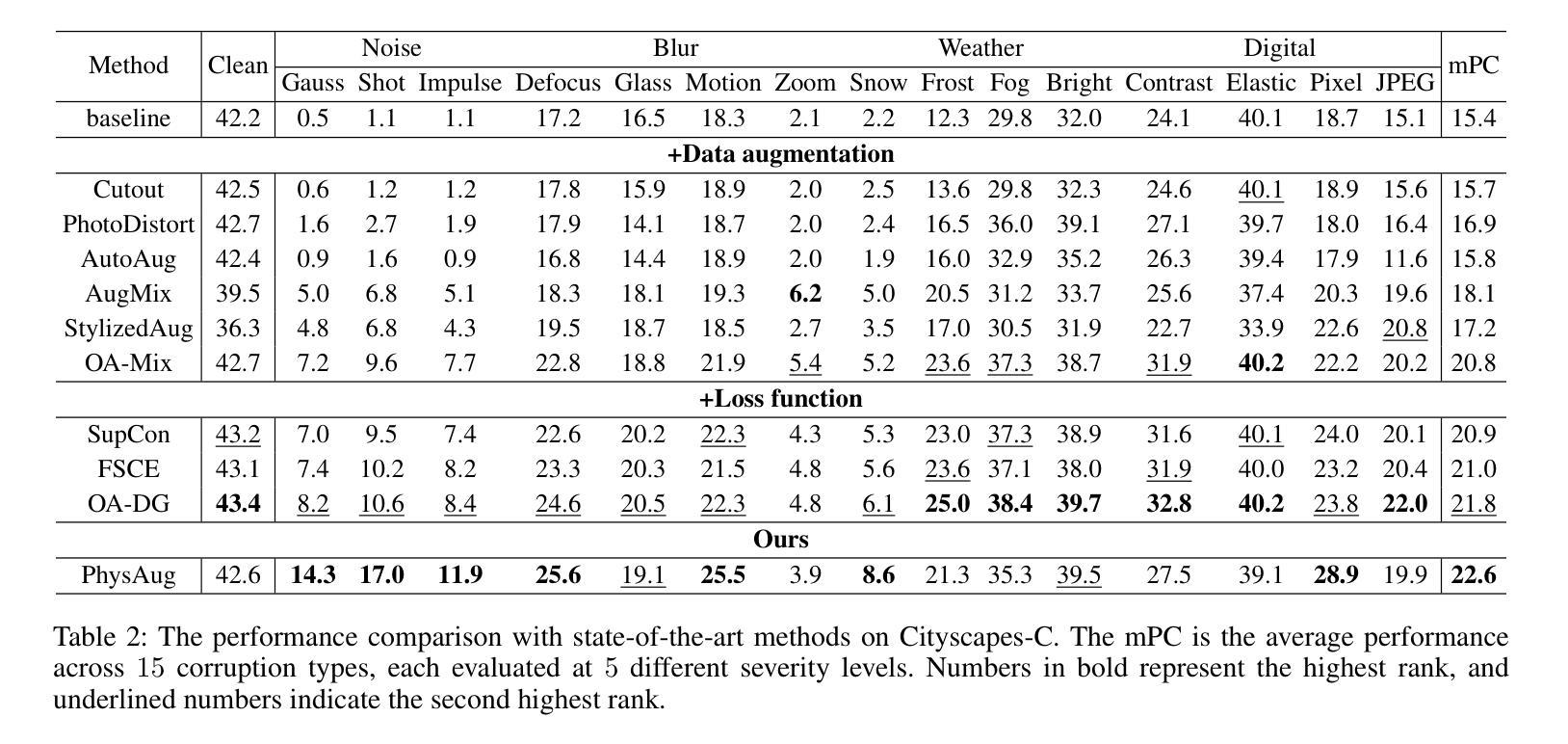
PhysAug: A Physical-guided and Frequency-based Data Augmentation for Single-Domain Generalized Object Detection
Authors:Xiaoran Xu, Jiangang Yang, Wenhui Shi, Siyuan Ding, Luqing Luo, Jian Liu
Single-Domain Generalized Object Detection~(S-DGOD) aims to train on a single source domain for robust performance across a variety of unseen target domains by taking advantage of an object detector. Existing S-DGOD approaches often rely on data augmentation strategies, including a composition of visual transformations, to enhance the detector’s generalization ability. However, the absence of real-world prior knowledge hinders data augmentation from contributing to the diversity of training data distributions. To address this issue, we propose PhysAug, a novel physical model-based non-ideal imaging condition data augmentation method, to enhance the adaptability of the S-DGOD tasks. Drawing upon the principles of atmospheric optics, we develop a universal perturbation model that serves as the foundation for our proposed PhysAug. Given that visual perturbations typically arise from the interaction of light with atmospheric particles, the image frequency spectrum is harnessed to simulate real-world variations during training. This approach fosters the detector to learn domain-invariant representations, thereby enhancing its ability to generalize across various settings. Without altering the network architecture or loss function, our approach significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art across various S-DGOD datasets. In particular, it achieves a substantial improvement of $7.3%$ and $7.2%$ over the baseline on DWD and Cityscape-C, highlighting its enhanced generalizability in real-world settings.
单域广义对象检测(S-DGOD)旨在通过对象检测器在单一源域上进行训练,以便在各种未见过的目标域上实现稳健性能。现有的S-DGOD方法通常依赖于数据增强策略,包括视觉转换的组合,以增强检测器的泛化能力。然而,缺乏真实世界的先验知识阻碍了数据增强对训练数据分布多样性的贡献。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了PhysAug,这是一种基于物理模型的新型非理想成像条件数据增强方法,以提高S-DGOD任务的适应性。基于大气光学原理,我们开发了一个通用扰动模型,作为我们提出的PhysAug的基础。鉴于视觉扰动通常是由光与大气粒子的相互作用而产生的,因此我们利用图像频谱来模拟训练过程中的真实世界变化。这种方法促进了检测器学习域不变表示,从而提高了其在各种设置中的泛化能力。在不改变网络架构或损失函数的情况下,我们的方法在多个S-DGOD数据集上显著优于当前最新技术。特别是在DWD和Cityscape-C上,与基线相比,它实现了7.3%和7.2%的大幅改进,凸显了其在真实世界环境中的增强泛化能力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了单域广义目标检测(S-DGOD)面临的挑战,并提出了基于物理模型的非理想成像条件数据增强方法PhysAug,旨在提高S-DGOD任务的适应性。通过模拟真实世界中的视觉扰动,该方法促进检测器学习域不变表示,从而提高其在不同设置中的泛化能力。在不改变网络架构或损失函数的情况下,该方法在多个S-DGOD数据集上显著优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- S-DGOD旨在通过单一源域训练,实现在多种未见目标域上的稳健性能。
- 现有S-DGOD方法常依赖数据增强策略来提高检测器的泛化能力。
- 真实世界先验知识的缺失阻碍了数据增强对训练数据分布多样性的贡献。
- 提出了基于物理模型的非理想成像条件数据增强方法PhysAug,模拟真实世界中的视觉扰动。
- PhysAug利用大气光学原理,建立通用扰动模型,促进检测器学习域不变表示。
- 该方法在不改变网络架构或损失函数的情况下,显著提高了S-DGOD任务在多个数据集上的性能。
点此查看论文截图

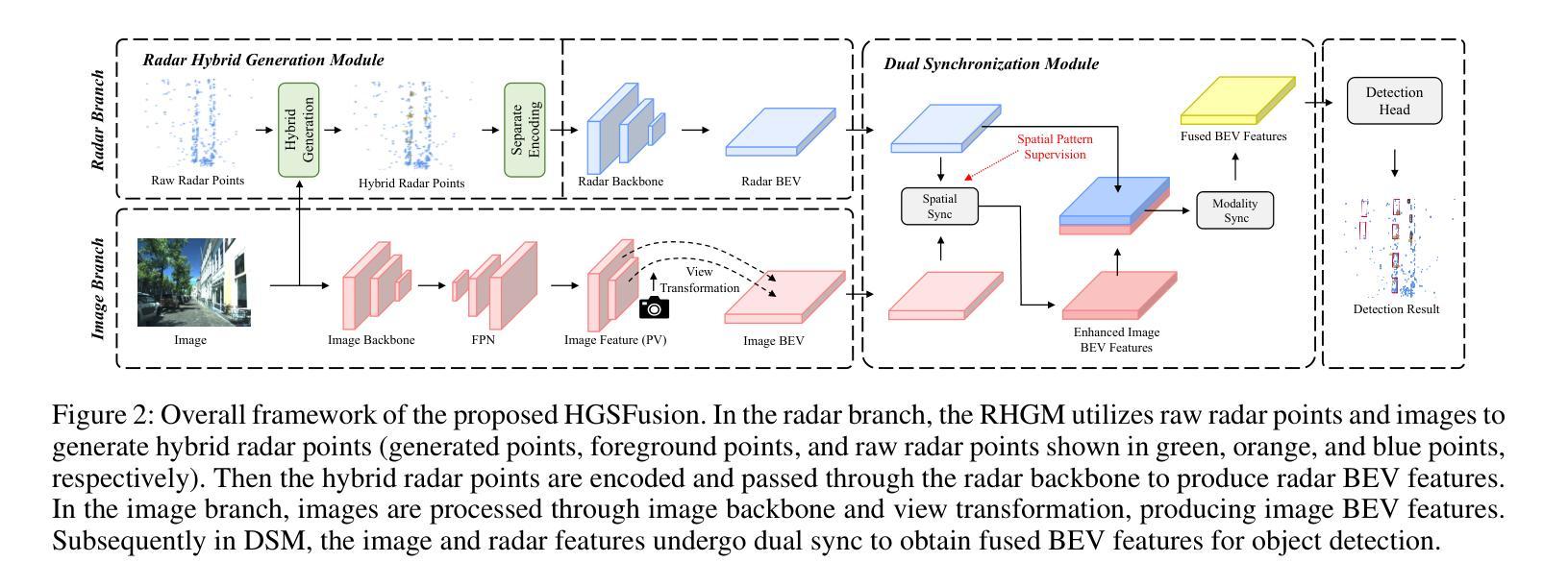
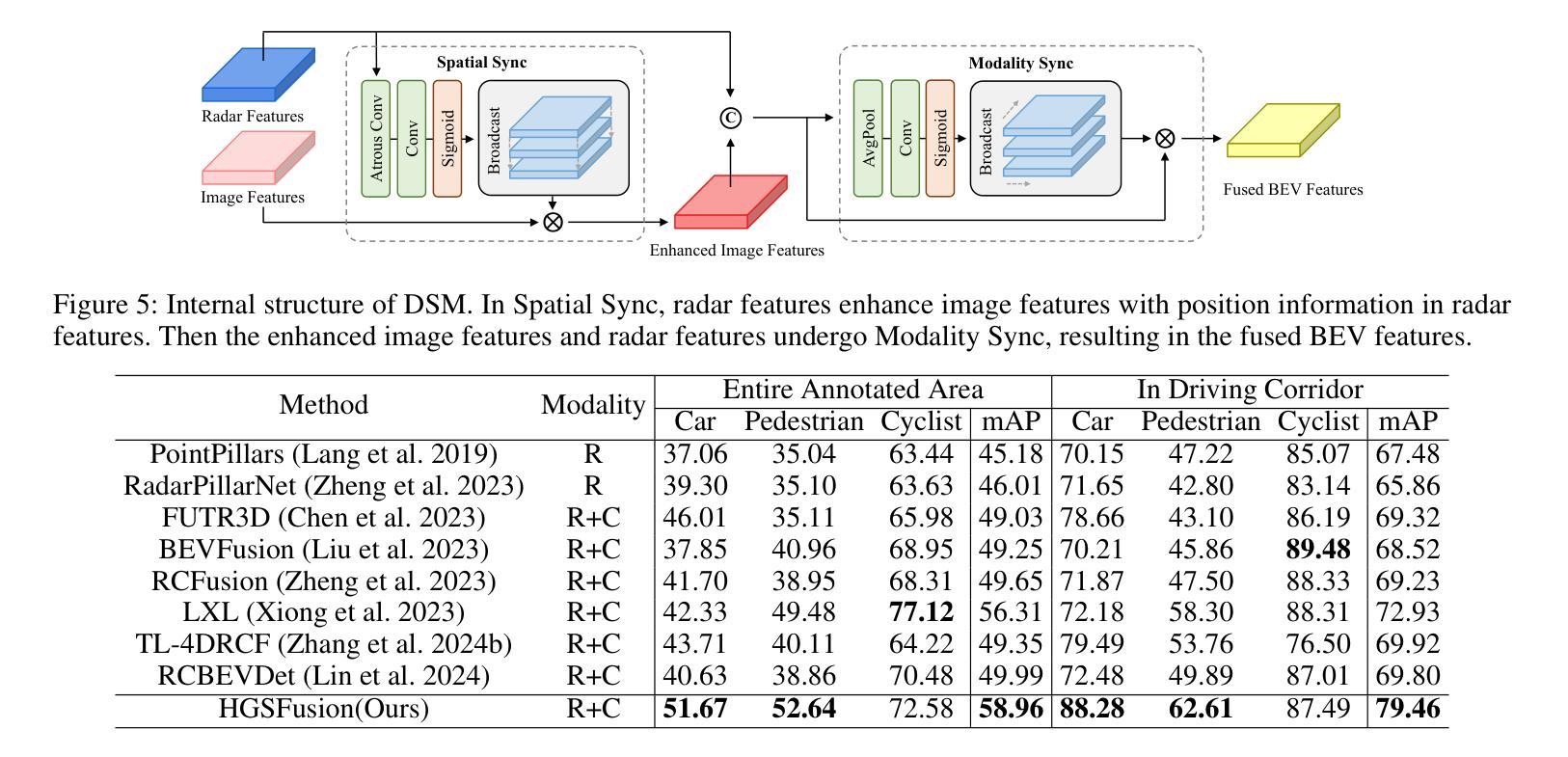
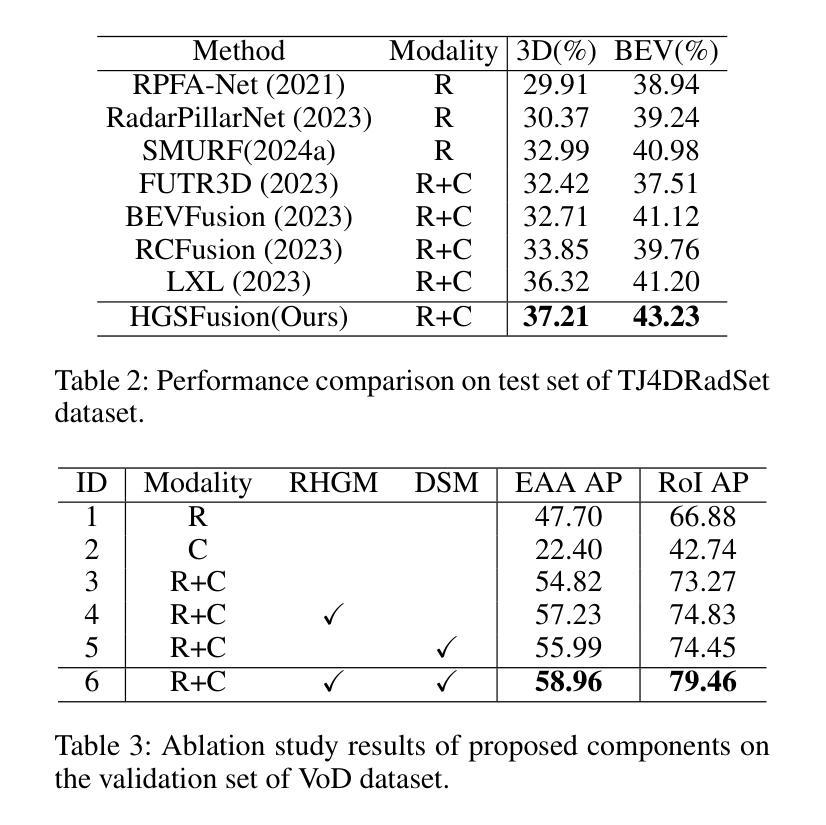
HGSFusion: Radar-Camera Fusion with Hybrid Generation and Synchronization for 3D Object Detection
Authors:Zijian Gu, Jianwei Ma, Yan Huang, Honghao Wei, Zhanye Chen, Hui Zhang, Wei Hong
Millimeter-wave radar plays a vital role in 3D object detection for autonomous driving due to its all-weather and all-lighting-condition capabilities for perception. However, radar point clouds suffer from pronounced sparsity and unavoidable angle estimation errors. To address these limitations, incorporating a camera may partially help mitigate the shortcomings. Nevertheless, the direct fusion of radar and camera data can lead to negative or even opposite effects due to the lack of depth information in images and low-quality image features under adverse lighting conditions. Hence, in this paper, we present the radar-camera fusion network with Hybrid Generation and Synchronization (HGSFusion), designed to better fuse radar potentials and image features for 3D object detection. Specifically, we propose the Radar Hybrid Generation Module (RHGM), which fully considers the Direction-Of-Arrival (DOA) estimation errors in radar signal processing. This module generates denser radar points through different Probability Density Functions (PDFs) with the assistance of semantic information. Meanwhile, we introduce the Dual Sync Module (DSM), comprising spatial sync and modality sync, to enhance image features with radar positional information and facilitate the fusion of distinct characteristics in different modalities. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, outperforming the state-of-the-art methods in the VoD and TJ4DRadSet datasets by $6.53%$ and $2.03%$ in RoI AP and BEV AP, respectively. The code is available at https://github.com/garfield-cpp/HGSFusion.
毫米波雷达因其全天候和全光照条件下的感知能力,在自动驾驶的3D目标检测中发挥着至关重要的作用。然而,雷达点云存在明显的稀疏性和不可避免的角度估计误差。为了克服这些局限性,融入相机可能有助于部分弥补这些不足。然而,雷达和相机数据的直接融合可能导致负面甚至相反的效果,因为图像缺乏深度信息,且在不良光照条件下图像特征质量较低。因此,本文提出了融合雷达和相机的网络Hybrid Generation and Synchronization(HGSFusion),旨在更好地融合雷达潜力和图像特征进行3D目标检测。具体来说,我们提出了Radar Hybrid Generation Module(RHGM),它充分考虑了雷达信号处理中的到达方向(DOA)估计误差。该模块通过不同的概率密度函数(PDF)生成更密集的雷达点,并借助语义信息。同时,我们引入了包含空间同步和模态同步的Dual Sync Module(DSM),以增强图像特征中的雷达位置信息,并促进不同模态中不同特征的融合。大量实验表明,我们的方法非常有效,在VoD和TJ4DRadSet数据集上的RoI AP和BEV AP分别提高了6.53%和2.03%,超越了最先进的方法。代码可用在https://github.com/garfield-cpp/HGSFusion。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 12 pages, 8 figures, 7 tables. Accepted by AAAI 2025 , the 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence
Summary:
毫米波雷达在自主驾驶的3D目标检测中扮演着重要角色,得益于其在各种天气和光照条件下的感知能力。但雷达点云存在显著的稀疏性和角度估计误差。为了解决这个问题,引入摄像机有助于部分弥补不足。针对雷达与摄像机数据直接融合可能带来的负面效果,本文提出了融合雷达与摄像机数据的雷达-摄像机融合网络(HGSFusion)。该网络包括雷达混合生成模块(RHGM)和双重同步模块(DSM),旨在更好地融合雷达潜力和图像特征进行3D目标检测。RHGM模块考虑了雷达信号处理中的方向到达(DOA)估计误差,通过不同的概率密度函数生成更密集的雷达点。DSM模块则通过空间同步和模态同步增强图像特征并促进不同模态的融合。实验证明,该方法优于现有方法,在VoD和TJ4DRadSet数据集上的检测精度分别提高了$6.53%$和$2.03%$。相关代码可通过GitHub获取。
Key Takeaways:
- 毫米波雷达在自主驾驶的3D目标检测中起到关键作用,因其具备全天候和全光照条件下的感知能力。
- 雷达点云存在稀疏性和角度估计误差的问题,需要寻找解决方案来改进。
- 通过引入摄像机来融合数据有助于部分弥补雷达的不足,但同时也需要注意二者直接融合可能带来的问题,如缺乏深度信息和不良光照条件下图像质量差等。
- 提出了雷达-摄像机融合网络HGSFusion,包括雷达混合生成模块RHGM和双重同步模块DSM,以更好地融合雷达和图像特征进行3D目标检测。
- RHGM考虑了雷达信号处理中的DOA估计误差,并可通过不同的概率密度函数生成更密集的雷达点。
- DSM模块旨在通过空间同步和模态同步增强图像特征并促进不同模态数据的融合。
点此查看论文截图


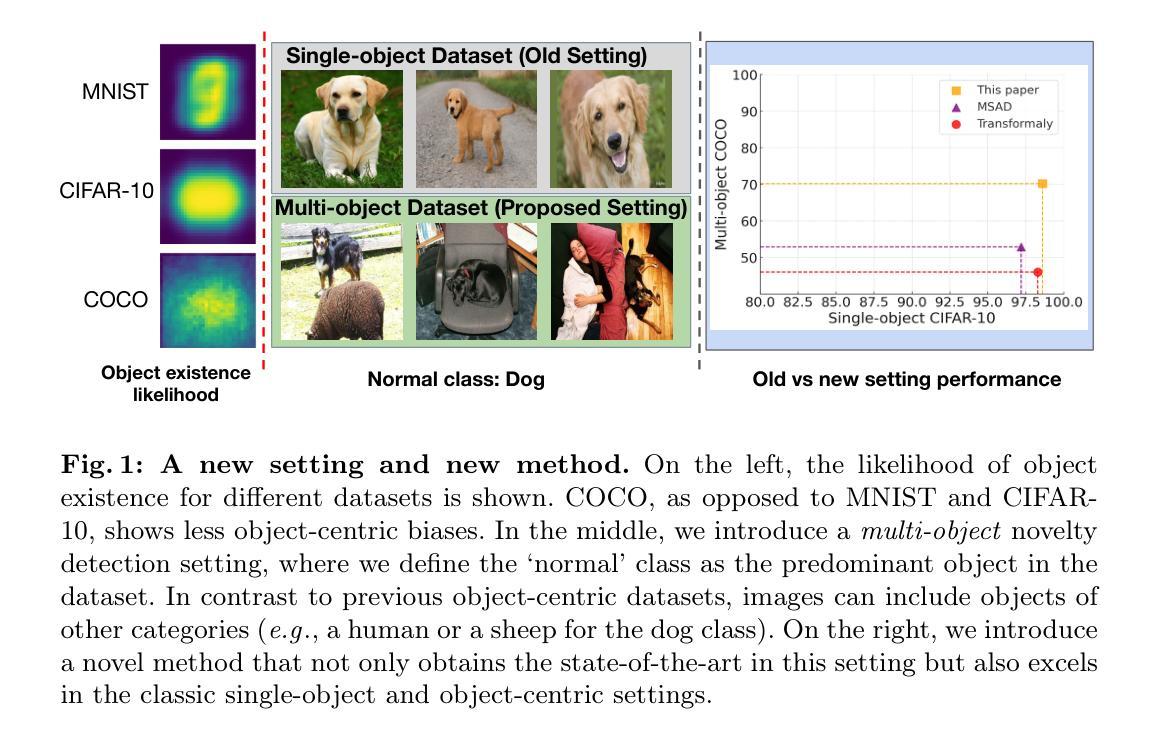
Redefining Normal: A Novel Object-Level Approach for Multi-Object Novelty Detection
Authors:Mohammadreza Salehi, Nikolaos Apostolikas, Efstratios Gavves, Cees G. M. Snoek, Yuki M. Asano
In the realm of novelty detection, accurately identifying outliers in data without specific class information poses a significant challenge. While current methods excel in single-object scenarios, they struggle with multi-object situations due to their focus on individual objects. Our paper suggests a novel approach: redefining normal' at the object level in training datasets. Rather than the usual image-level view, we consider the most dominant object in a dataset as the norm, offering a perspective that is more effective for real-world scenarios. Adapting to our object-level definition of normal’, we modify knowledge distillation frameworks, where a student network learns from a pre-trained teacher network. Our first contribution, DeFeND(Dense Feature Fine-tuning on Normal Data), integrates dense feature fine-tuning into the distillation process, allowing the teacher network to focus on object-level features with a self-supervised loss. The second is masked knowledge distillation, where the student network works with partially hidden inputs, honing its ability to deduce and generalize from incomplete data. This approach not only fares well in single-object novelty detection but also considerably surpasses existing methods in multi-object contexts. The implementation is available at: https://github.com/SMSD75/Redefining_Normal_ACCV24/tree/main
在新型检测领域,没有特定类别信息的情况下准确识别数据中的异常值是一个巨大的挑战。当前的方法在单一对象场景中表现出色,但在多对象场景中却表现不佳,因为它们侧重于单个对象。我们的论文提出了一种新方法:在训练数据集中重新定义对象级别的“正常”。我们不再采用通常的图像级别视角,而是考虑数据集中最主导的对象为正常标准,这为现实世界场景提供了更有效的视角。根据我们对“正常”的对象级别定义,我们修改了知识蒸馏框架,学生网络从中学习预训练的教师网络。我们的第一个贡献是DeFeND(在正常数据上进行密集特征微调),它将密集特征微调集成到蒸馏过程中,使教师网络能够通过自我监督损失关注对象级别特征。第二个是掩膜知识蒸馏,学生网络对部分隐藏输入进行操作,提高了从不完整数据中推断和概括的能力。这种方法不仅在单一对象的新颖性检测中表现良好,而且在多对象环境中也大大超越了现有方法。具体实现可访问:https://github.com/SMSD75/Redefining_Normal_ACCV24/tree/main
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ACCV24(Oral)
Summary:
本文提出了一种新的方法来解决无特定类别信息下的异常检测问题。在训练数据集上重新定义对象级别的“正常”,以适应真实场景中的多对象情况。通过修改知识蒸馏框架并引入密集特征微调,实现对象级别的特征学习。此外,还提出了掩膜知识蒸馏方法,该方法不仅适用于单对象异常检测,而且在多对象场景中表现优异。
Key Takeaways:
- 当前方法在异常检测中面临处理多对象情况的挑战。
- 本文通过重新定义对象级别的“正常”来解决这一问题。
- 引入密集特征微调的知识蒸馏方法,帮助网络进行对象级别的特征学习。
- 提出掩膜知识蒸馏,提高网络从不完整数据中推断和泛化的能力。
- 该方法不仅在单对象异常检测中表现良好,而且在多对象场景中也有显著优势。
- 论文中的实现细节和代码已公开,便于他人参考和使用。
点此查看论文截图

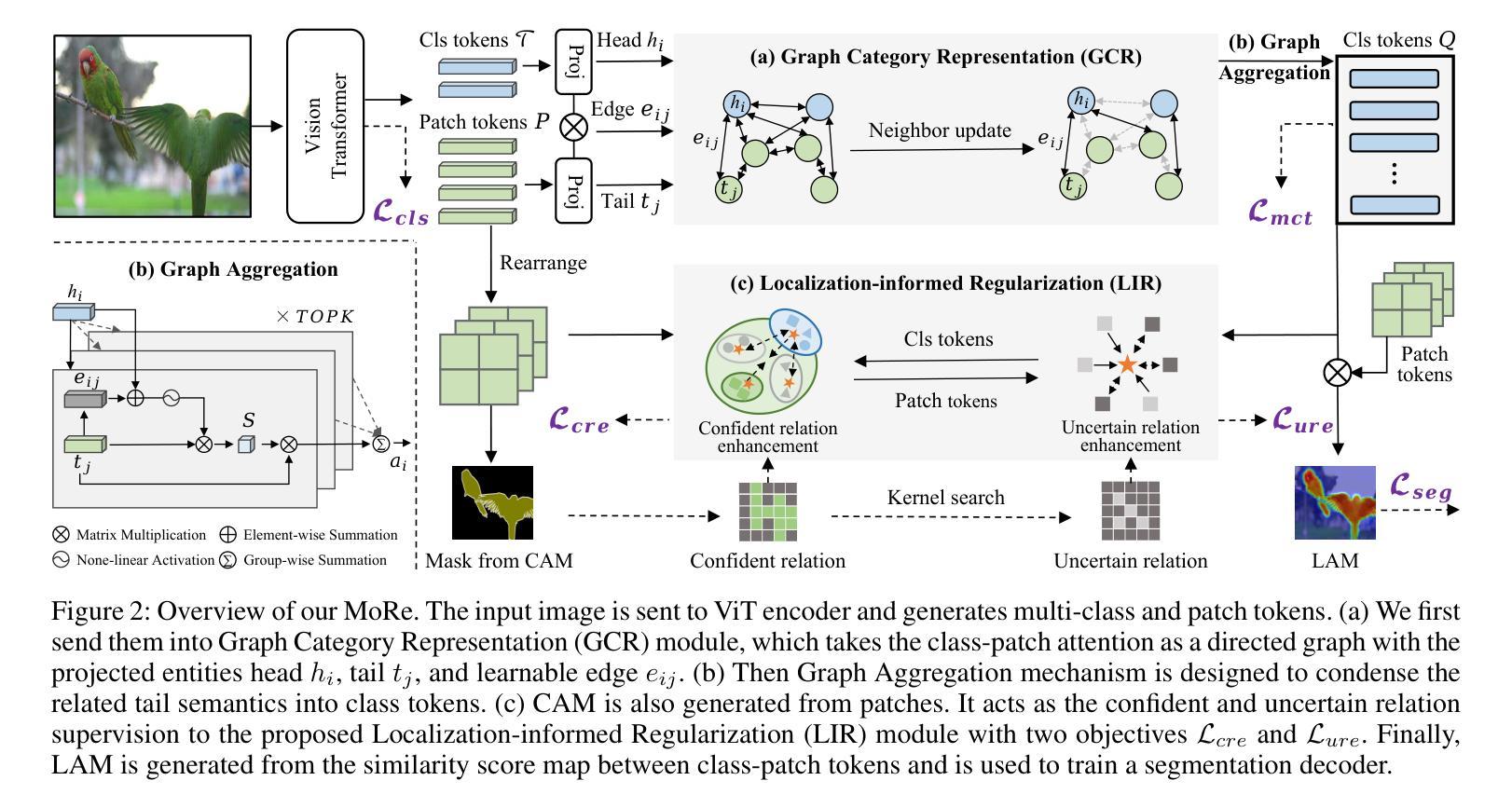
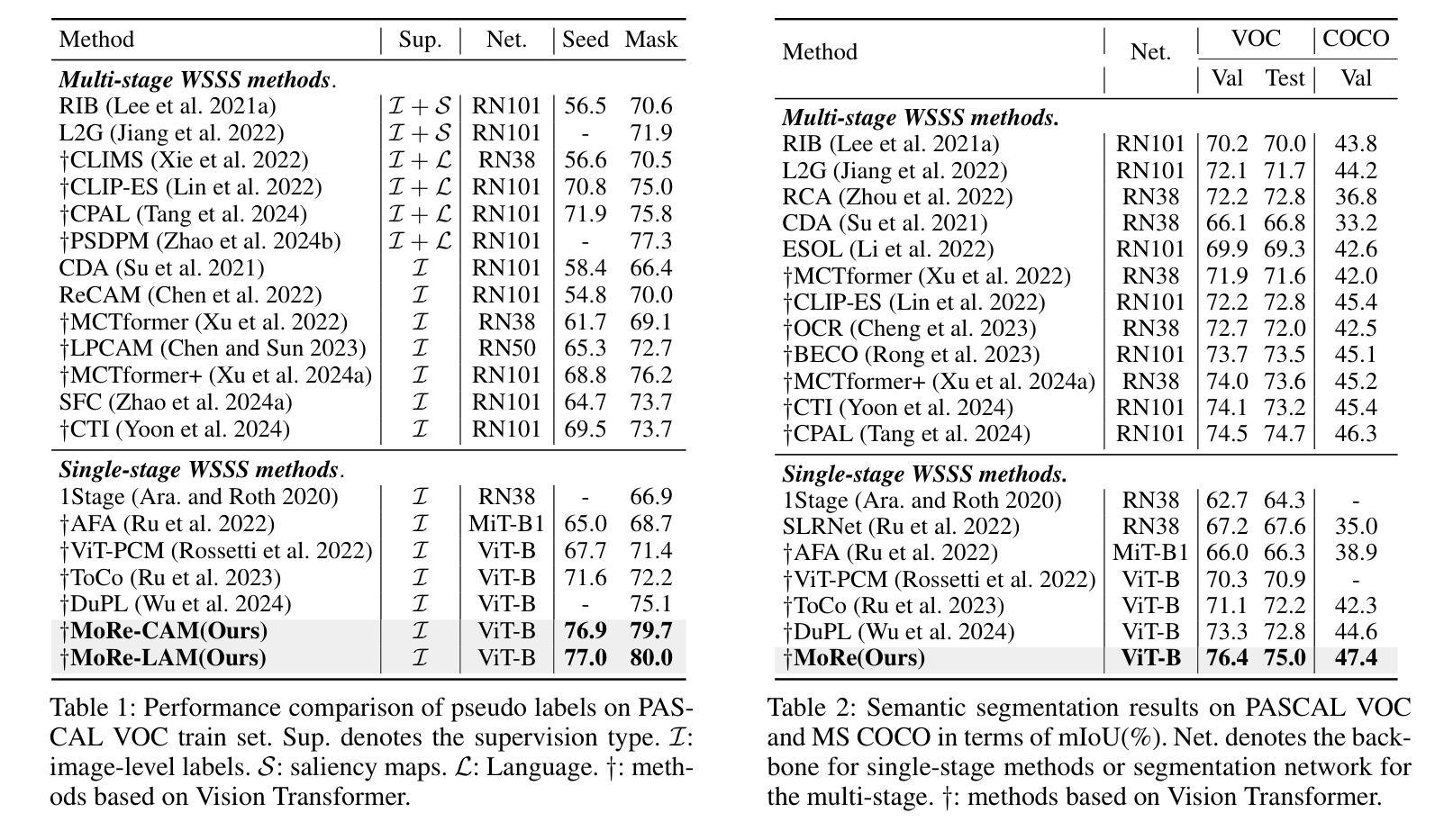
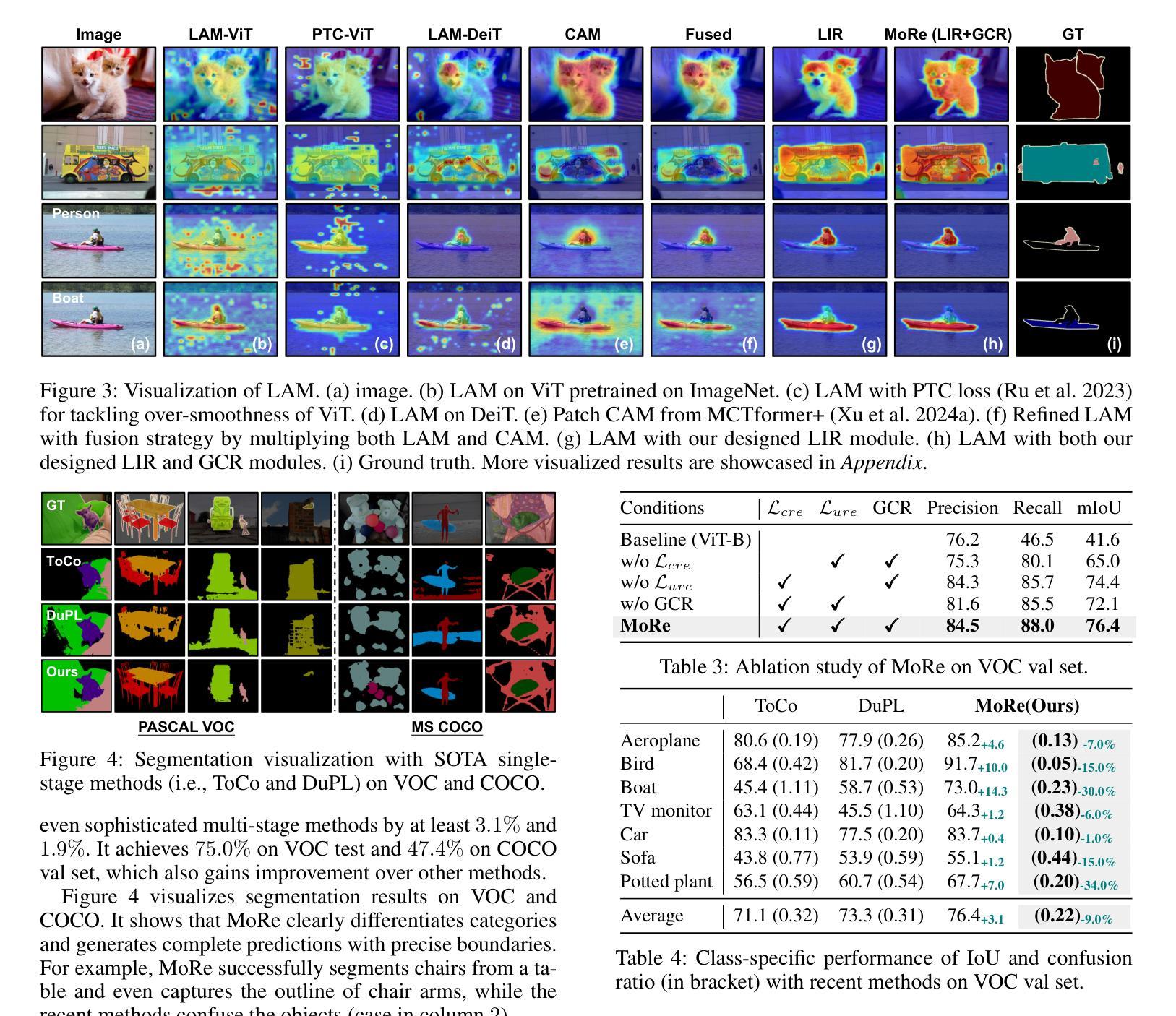
MoRe: Class Patch Attention Needs Regularization for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Zhiwei Yang, Yucong Meng, Kexue Fu, Shuo Wang, Zhijian Song
Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) with image-level labels typically uses Class Activation Maps (CAM) to achieve dense predictions. Recently, Vision Transformer (ViT) has provided an alternative to generate localization maps from class-patch attention. However, due to insufficient constraints on modeling such attention, we observe that the Localization Attention Maps (LAM) often struggle with the artifact issue, i.e., patch regions with minimal semantic relevance are falsely activated by class tokens. In this work, we propose MoRe to address this issue and further explore the potential of LAM. Our findings suggest that imposing additional regularization on class-patch attention is necessary. To this end, we first view the attention as a novel directed graph and propose the Graph Category Representation module to implicitly regularize the interaction among class-patch entities. It ensures that class tokens dynamically condense the related patch information and suppress unrelated artifacts at a graph level. Second, motivated by the observation that CAM from classification weights maintains smooth localization of objects, we devise the Localization-informed Regularization module to explicitly regularize the class-patch attention. It directly mines the token relations from CAM and further supervises the consistency between class and patch tokens in a learnable manner. Extensive experiments are conducted on PASCAL VOC and MS COCO, validating that MoRe effectively addresses the artifact issue and achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing recent single-stage and even multi-stage methods. Code is available at https://github.com/zwyang6/MoRe.
使用图像级标签的弱监督语义分割(WSSS)通常使用类激活图(CAM)来实现密集预测。最近,视觉转换器(ViT)提供了一种从类补丁注意力生成定位图的替代方案。然而,由于对这类注意力的建模约束不足,我们观察到定位注意力图(LAM)经常面临伪影问题,即语义相关性极小的补丁区域会被类令牌错误激活。在这项工作中,我们提出MoRe来解决这个问题,并进一步研究LAM的潜力。我们的研究结果表明,对类补丁注意力施加额外的正则化是必要的。为此,我们首先将注意力视为一种新型的有向图,并提出图类别表示模块,以隐式地规范类补丁实体之间的交互。它确保类令牌能够动态地凝聚相关的补丁信息,并在图级别抑制无关伪影。其次,受分类权重CAM能保持对象定位平滑的启发,我们设计了定位感知正则化模块,以显式地规范类补丁注意力。它直接从CAM挖掘令牌关系,并以可学习的方式监督类和补丁令牌之间的一致性。在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO上进行了大量实验,验证了MoRe有效地解决了伪影问题,实现了最先进的性能,超越了最近的单阶段甚至多阶段方法。代码可在https://github.com/zwyang6/MoRe找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025
Summary
本文探讨了基于图像级别标签的弱监督语义分割(WSSS)问题。文章指出,使用Vision Transformer(ViT)生成的Localization Attention Maps(LAM)存在误激活非语义相关区域的问题。为此,本文提出了MoRe方法,通过额外的正则化来优化LAM的性能。MoRe包括两个模块:Graph Category Representation模块和Localization-informed Regularization模块,分别通过隐式和显式的方式对类补丁注意力进行正则化。实验表明,MoRe在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO数据集上取得了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 弱监督语义分割(WSSS)通常使用Class Activation Maps(CAM)实现密集预测。
- Vision Transformer(ViT)可生成Localization Attention Maps(LAM)。
- LAM存在误激活非语义相关区域的问题。
- MoRe方法通过额外的正则化来解决LAM的问题。
- MoRe包括Graph Category Representation模块和Localization-informed Regularization模块。
- MoRe在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO数据集上实现了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

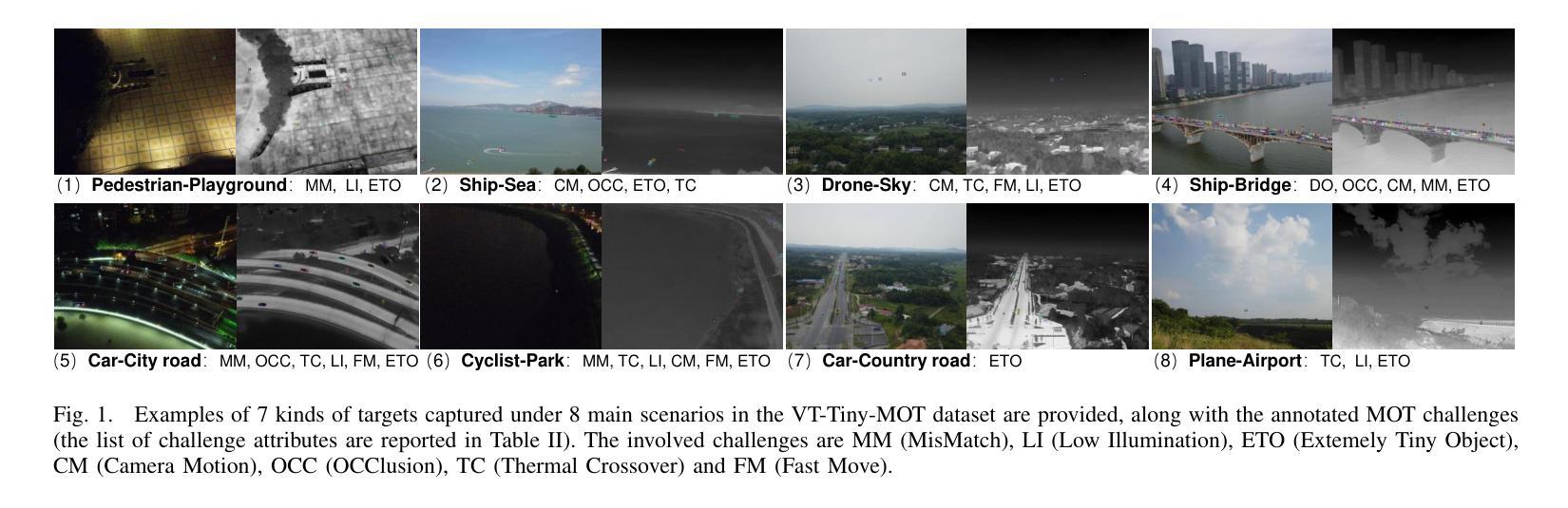
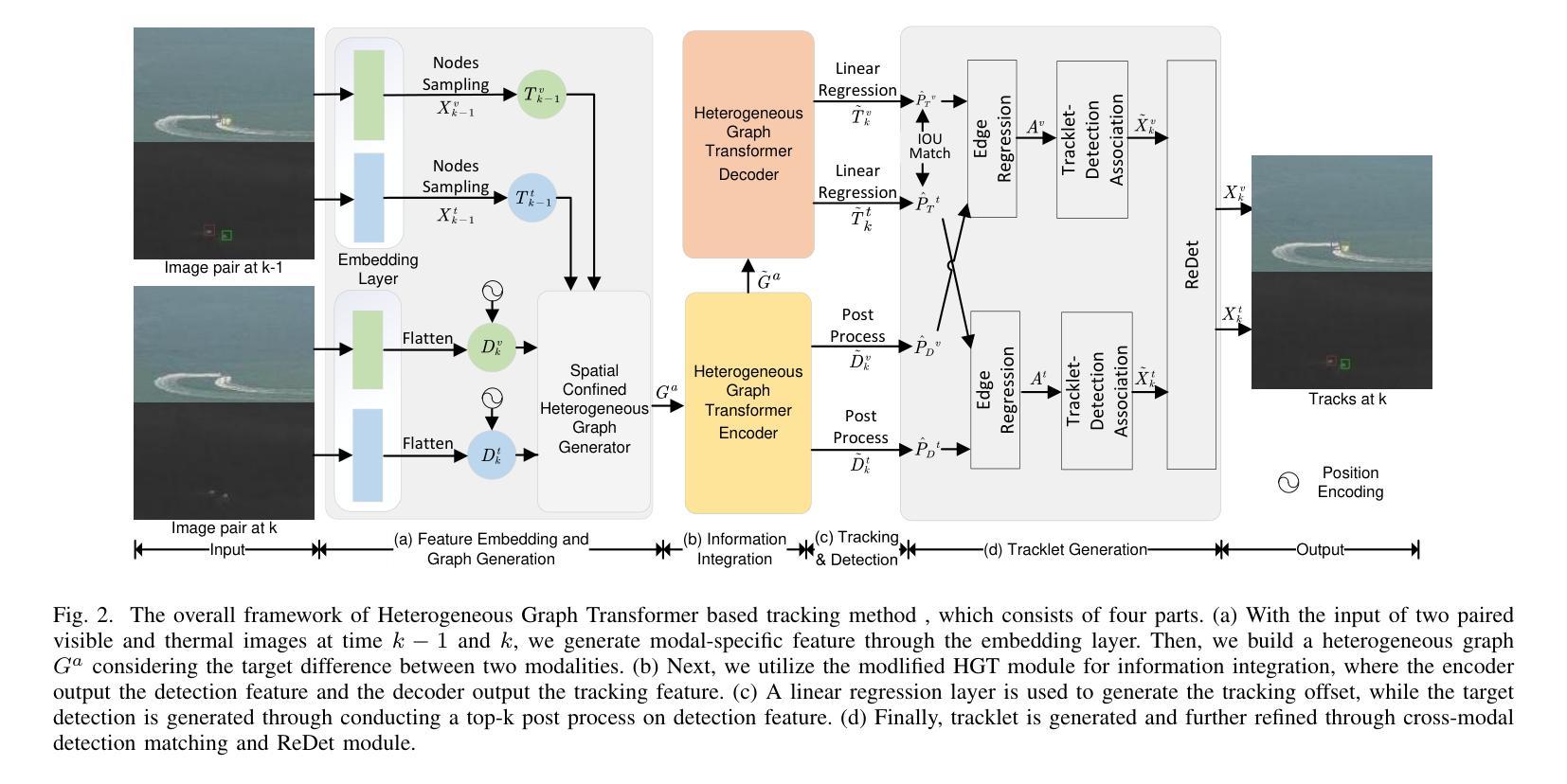
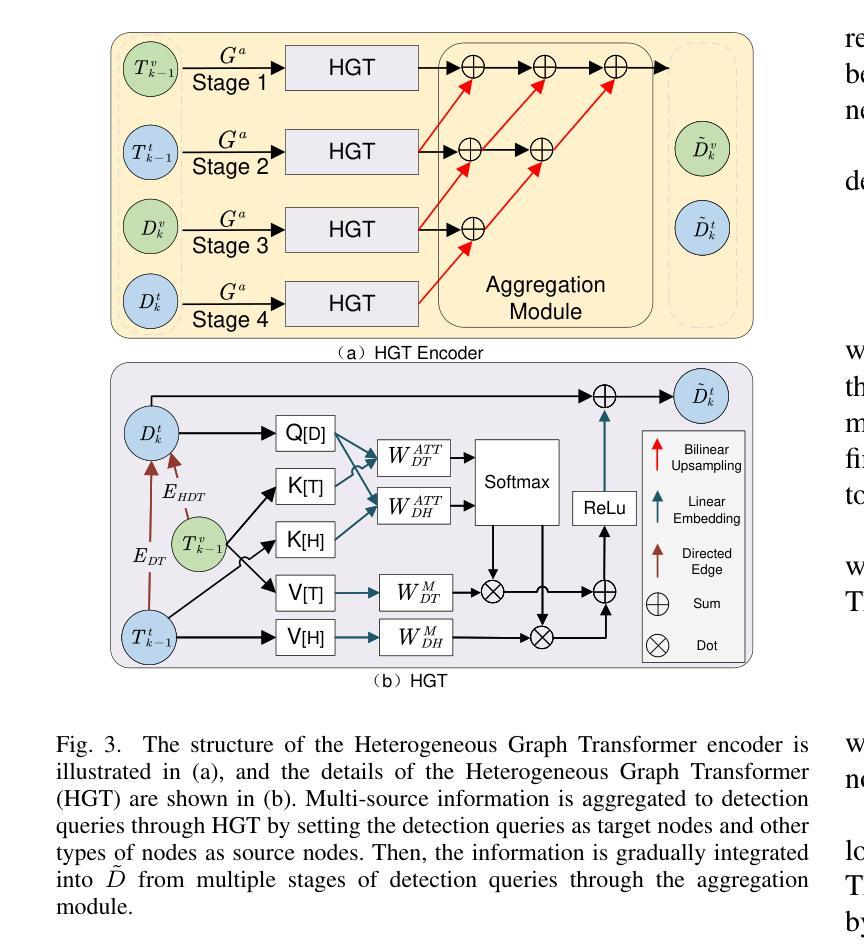
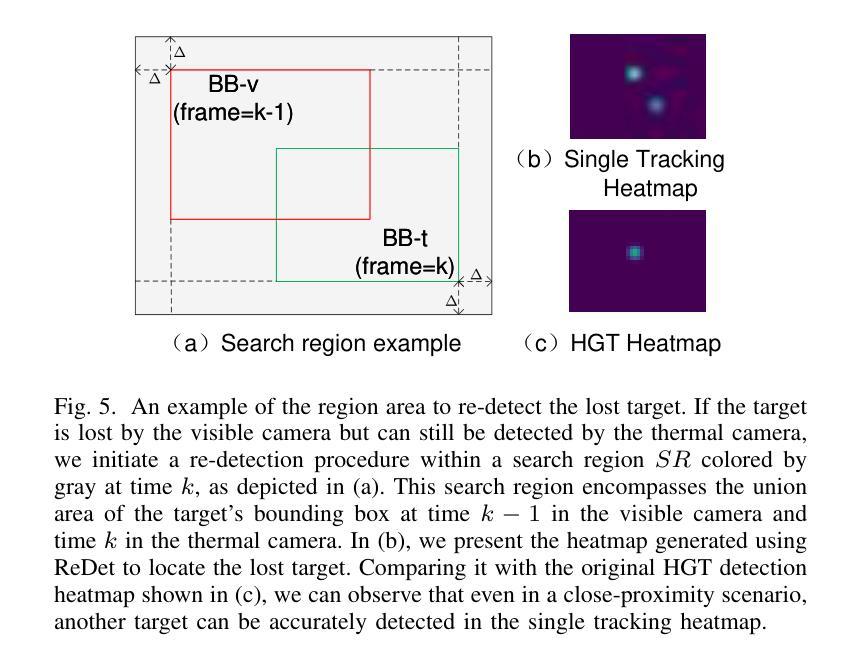
Heterogeneous Graph Transformer for Multiple Tiny Object Tracking in RGB-T Videos
Authors:Qingyu Xu, Longguang Wang, Weidong Sheng, Yingqian Wang, Chao Xiao, Chao Ma, Wei An
Tracking multiple tiny objects is highly challenging due to their weak appearance and limited features. Existing multi-object tracking algorithms generally focus on single-modality scenes, and overlook the complementary characteristics of tiny objects captured by multiple remote sensors. To enhance tracking performance by integrating complementary information from multiple sources, we propose a novel framework called {HGT-Track (Heterogeneous Graph Transformer based Multi-Tiny-Object Tracking)}. Specifically, we first employ a Transformer-based encoder to embed images from different modalities. Subsequently, we utilize Heterogeneous Graph Transformer to aggregate spatial and temporal information from multiple modalities to generate detection and tracking features. Additionally, we introduce a target re-detection module (ReDet) to ensure tracklet continuity by maintaining consistency across different modalities. Furthermore, this paper introduces the first benchmark VT-Tiny-MOT (Visible-Thermal Tiny Multi-Object Tracking) for RGB-T fused multiple tiny object tracking. Extensive experiments are conducted on VT-Tiny-MOT, and the results have demonstrated the effectiveness of our method. Compared to other state-of-the-art methods, our method achieves better performance in terms of MOTA (Multiple-Object Tracking Accuracy) and ID-F1 score. The code and dataset will be made available at https://github.com/xuqingyu26/HGTMT.
针对多个微小目标的跟踪由于其外观微弱、特征有限而面临巨大挑战。现有的多目标跟踪算法通常专注于单模态场景,忽略了多个远程传感器捕获的微小对象的互补特性。为了通过整合来自多个源头的互补信息来提高跟踪性能,我们提出了一种新型框架,称为HGT-Track(基于异构图变换器的多微小目标跟踪)。具体而言,我们首先采用基于Transformer的编码器对不同模态的图像进行嵌入。然后,我们利用异构图变换器聚合多个模态的空间和时间信息,以生成检测和跟踪特征。此外,我们引入了一个目标再检测模块(ReDet),以确保在不同模态之间保持一致性,从而实现轨迹连续性。此外,本文还介绍了首个RGB-T融合多微小目标跟踪的基准测试VT-Tiny-MOT(可见热微小多目标跟踪)。在VT-Tiny-MOT上进行了大量实验,结果证明了我们的方法的有效性。与其他最先进的方法相比,我们的方法在多目标跟踪准确度(MOTA)和ID-F1分数方面取得了更好的性能。代码和数据集将在https://github.com/xuqingyu26/HGTMT上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF N/A
Summary
针对多模态场景中的多个微小目标跟踪问题,本文提出了一个名为HGT-Track的新型框架,该框架利用异质图变换技术集成多源信息以提升跟踪性能。框架包括多模态图像嵌入、异质图变换器进行时空信息聚合、目标重新检测模块确保轨迹连续性,并在RGB-T融合的多微小目标跟踪上引入首个基准测试VT-Tiny-MOT。实验结果表明,该方法在MOTA和ID-F1分数上较其他先进方法表现更优。
Key Takeaways
- 本文针对多模态场景中的多个微小目标跟踪问题,提出了一种新型框架HGT-Track。
- HGT-Track利用Transformer编码器嵌入不同模态的图像。
- 引入异质图变换器来聚合多模态的时空信息,以生成检测和跟踪特征。
- 目标重新检测模块(ReDet)确保轨迹连续性,维持不同模态间的一致性。
- 介绍了首个RGB-T融合的多微小目标跟踪基准测试VT-Tiny-MOT。
- 在VT-Tiny-MOT上的实验证明了HGT-Track的有效性,其在MOTA和ID-F1分数上较其他方法表现更优。
点此查看论文截图

Analysis of Object Detection Models for Tiny Object in Satellite Imagery: A Dataset-Centric Approach
Authors:Kailas PS, Selvakumaran R, Palani Murugan, Ramesh Kumar V, Malaya Kumar Biswal M
In recent years, significant advancements have been made in deep learning-based object detection algorithms, revolutionizing basic computer vision tasks, notably in object detection, tracking, and segmentation. This paper delves into the intricate domain of Small-Object-Detection (SOD) within satellite imagery, highlighting the unique challenges stemming from wide imaging ranges, object distribution, and their varying appearances in bird’s-eye-view satellite images. Traditional object detection models face difficulties in detecting small objects due to limited contextual information and class imbalances. To address this, our research presents a meticulously curated dataset comprising 3000 images showcasing cars, ships, and airplanes in satellite imagery. Our study aims to provide valuable insights into small object detection in satellite imagery by empirically evaluating state-of-the-art models. Furthermore, we tackle the challenges of satellite video-based object tracking, employing the Byte Track algorithm on the SAT-MTB dataset. Through rigorous experimentation, we aim to offer a comprehensive understanding of the efficacy of state-of-the-art models in Small-Object-Detection for satellite applications. Our findings shed light on the effectiveness of these models and pave the way for future advancements in satellite imagery analysis.
近年来,基于深度学习的目标检测算法取得了重大进展,为计算机视觉的基本任务(特别是在目标检测、跟踪和分割方面)带来了革命性的变革。本文深入探讨了卫星图像中的小目标检测(SOD)的复杂领域,重点介绍了由于成像范围广泛、目标分布及其俯视图卫星图像中外观变化所带来的独特挑战。传统目标检测模型由于上下文信息有限和类别不平衡,在检测小目标时面临困难。为了解决这一问题,我们的研究呈现了一个精心策划的数据集,包含3000张展示卫星图像中的汽车、船只和飞机的图像。本研究旨在通过实证评估最新模型,为卫星图像中的小目标检测提供有价值的见解。此外,我们解决了基于卫星视频的跟踪挑战,在SAT-MTB数据集上采用Byte Track算法。通过严格的实验,我们旨在全面理解最新模型在小目标检测中的有效性,为卫星应用提供宝贵洞察。我们的研究为这些模型的有效性提供了有力的证据,并为未来的卫星图像分析进步铺平了道路。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Conference Proceesings of AIAA SciTech Forum 2025 and Exposition
Summary
随着深度学习技术的发展,小目标检测已成为卫星图像分析中的研究热点。本研究介绍了一个专门的数据集,并通过实验评估了当前先进模型在小目标检测中的性能。此外,本研究还探讨了卫星视频中的目标跟踪问题,采用了Byte Track算法在SAT-MTB数据集上进行实验。研究结果表明这些模型的有效性,为后续卫星图像分析的研究提供了新的方向。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习技术在小目标检测领域取得显著进展,尤其在卫星图像分析中应用广泛。
- 介绍了专门用于卫星图像中小目标检测的数据集,包含3000张图像。
- 指出小目标检测在卫星图像中的独特挑战,如成像范围广泛、目标分布和外观变化等。
- 传统目标检测模型在检测小目标时面临困难,如上下文信息有限和类别不平衡等问题。
- 采用Byte Track算法在SAT-MTB数据集上进行实验,以探讨卫星视频中的目标跟踪问题。
- 通过实验评估了当前先进模型在小目标检测和跟踪中的性能。
点此查看论文截图


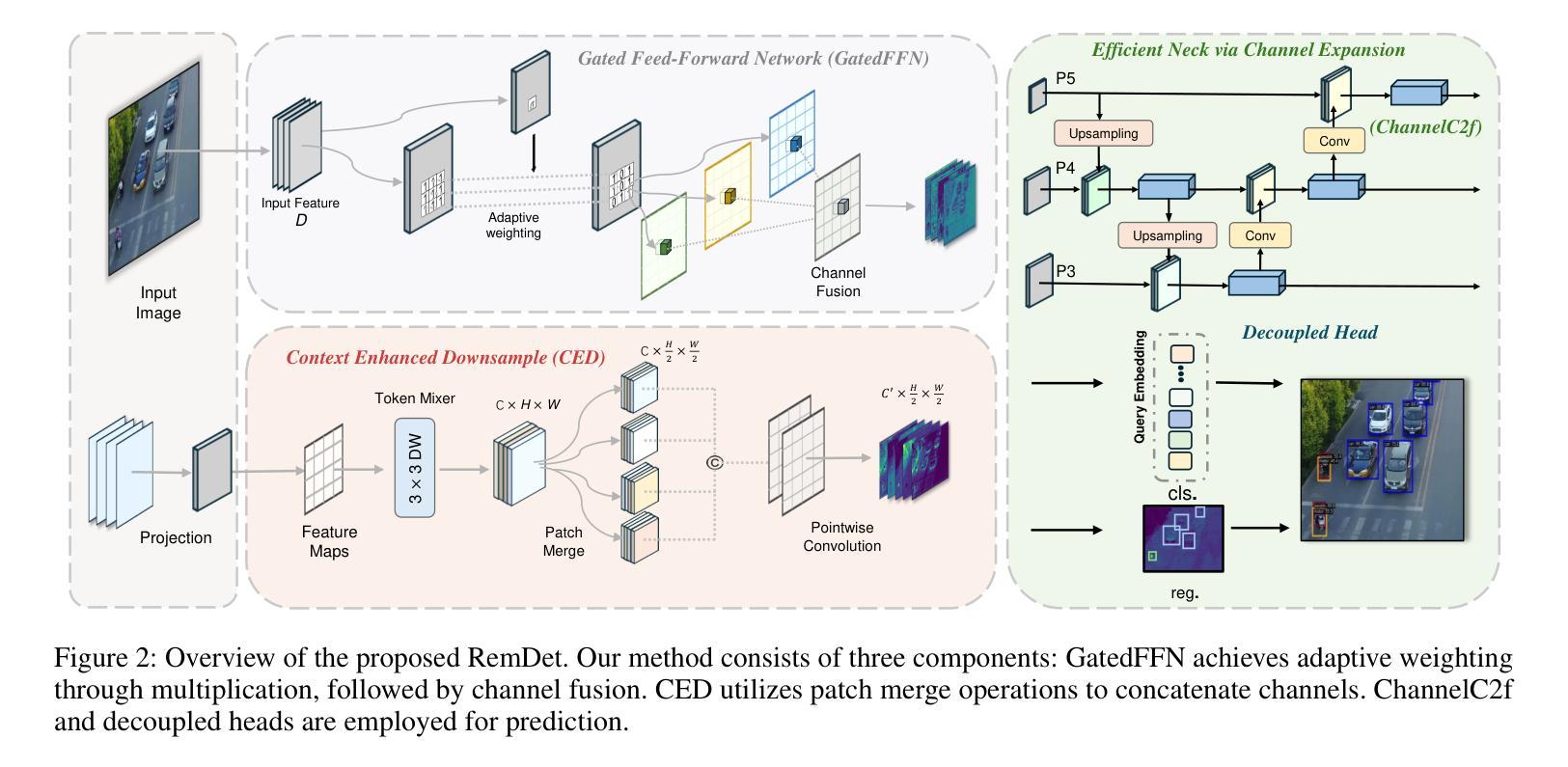
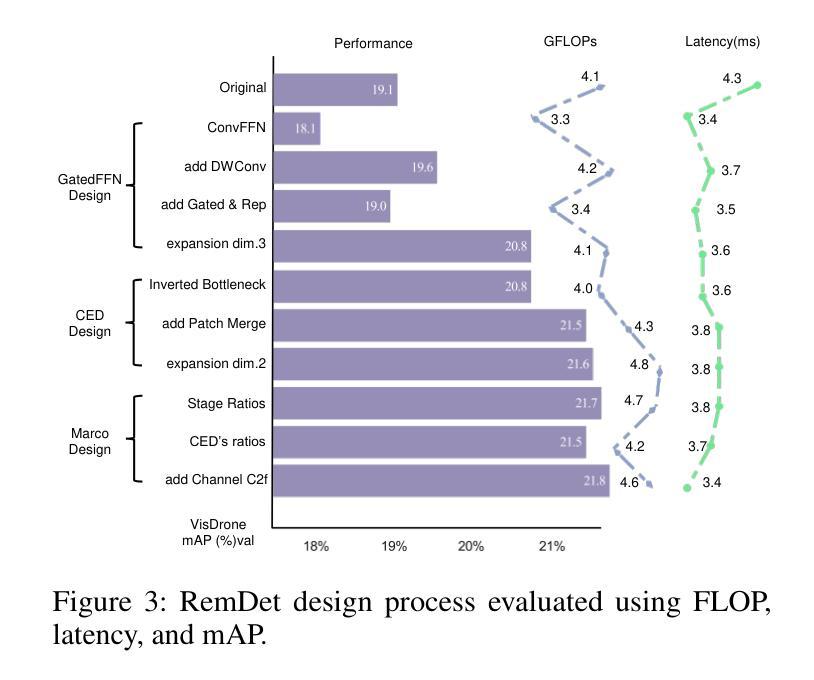
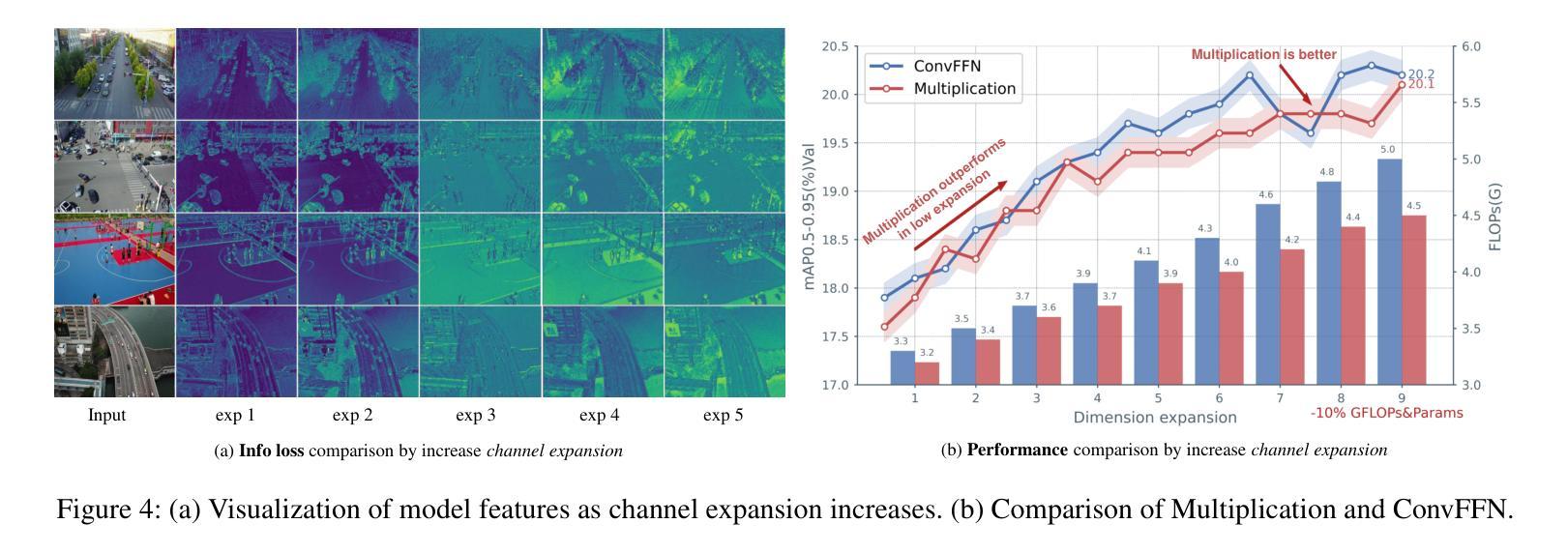
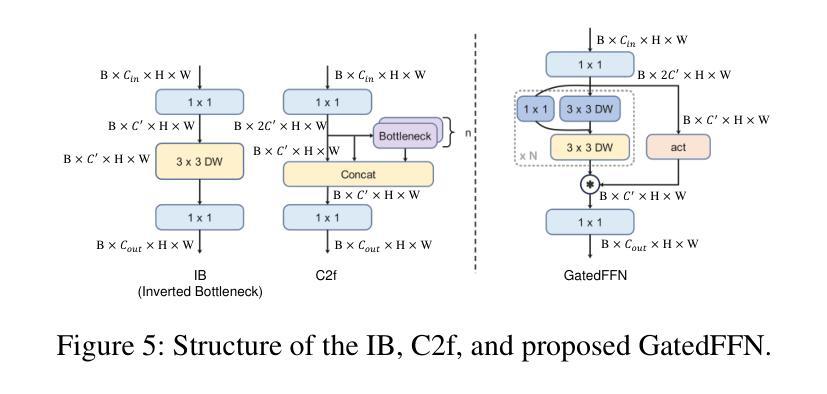
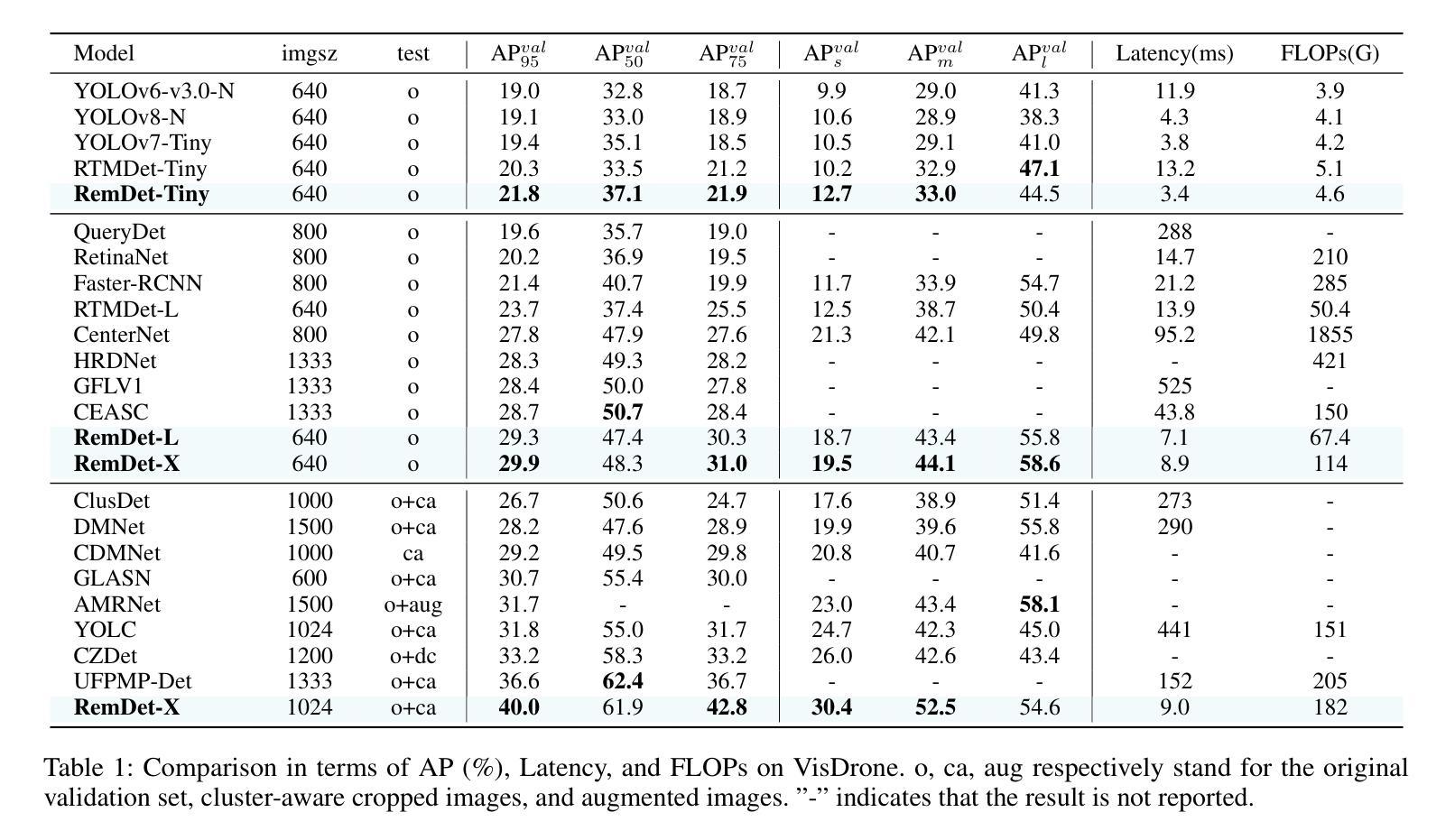
RemDet: Rethinking Efficient Model Design for UAV Object Detection
Authors:Chen Li, Rui Zhao, Zeyu Wang, Huiying Xu, Xinzhong Zhu
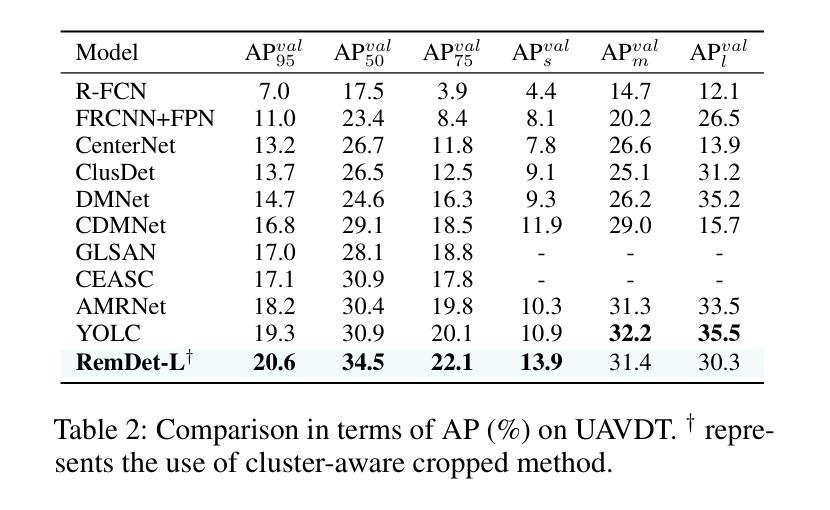
Object detection in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) images has emerged as a focal area of research, which presents two significant challenges: i) objects are typically small and dense within vast images; ii) computational resource constraints render most models unsuitable for real-time deployment. Current real-time object detectors are not optimized for UAV images, and complex methods designed for small object detection often lack real-time capabilities. To address these challenges, we propose a novel detector, RemDet (Reparameter efficient multiplication Detector). Our contributions are as follows: 1) Rethinking the challenges of existing detectors for small and dense UAV images, and proposing information loss as a design guideline for efficient models. 2) We introduce the ChannelC2f module to enhance small object detection performance, demonstrating that high-dimensional representations can effectively mitigate information loss. 3) We design the GatedFFN module to provide not only strong performance but also low latency, effectively addressing the challenges of real-time detection. Our research reveals that GatedFFN, through the use of multiplication, is more cost-effective than feed-forward networks for high-dimensional representation. 4) We propose the CED module, which combines the advantages of ViT and CNN downsampling to effectively reduce information loss. It specifically enhances context information for small and dense objects. Extensive experiments on large UAV datasets, Visdrone and UAVDT, validate the real-time efficiency and superior performance of our methods. On the challenging UAV dataset VisDrone, our methods not only provided state-of-the-art results, improving detection by more than 3.4%, but also achieve 110 FPS on a single 4090.
无人机(UAV)图像中的目标检测已成为研究的重要领域,这带来了两大挑战:一是对大部分目标通常很小且密集地分布在大型图像中;二是计算资源限制使得大多数模型不适合实时部署。现有的实时目标检测器并不适用于无人机图像,而针对小目标检测设计的复杂方法往往缺乏实时性能。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型检测器RemDet(重参数高效乘法检测器)。我们的贡献如下:首先,我们重新思考了现有检测器在小型且密集的无人机图像上所面临的挑战,并提出了信息损失作为高效模型设计的指导原则。其次,我们引入了ChannelC2f模块以提高小目标检测性能,证明了高维表示可以有效地减轻信息损失。第三,我们设计了GatedFFN模块,不仅提供强大的性能,而且具有低延迟,有效地解决了实时检测的挑战。我们的研究表明,通过乘法运算的GatedFFN比前馈网络更经济高效,用于高维表示。第四,我们提出了CED模块,它结合了ViT和CNN下采样的优点,有效地减少了信息损失。特别是提高了小且密集目标的上下文信息。在大规模无人机数据集Visdrone和UAVDT上的大量实验验证了我们方法的实时效率和卓越性能。在具有挑战性的VisDrone无人机数据集上,我们的方法不仅提供了优于其他方法的最新结果,提高了超过3.4%的检测性能,而且在单个4090上实现了110 FPS。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to AAAI25
Summary:针对无人机图像中的目标检测面临的小目标检测与实时计算资源限制两大挑战,提出了一种新型检测器RemDet。通过引入ChannelC2f模块增强小目标检测性能,设计GatedFFN模块实现强性能与低延迟,提出CED模块结合ViT和CNN下采样的优势以减少信息损失。在大型无人机数据集上的实验验证了其方法和性能的优越性。
Key Takeaways:
- 无人机图像中的目标检测面临小目标检测和实时计算资源限制两大挑战。
- 提出了一种新型检测器RemDet,通过信息损失作为设计高效模型的原则。
- 通过引入ChannelC2f模块增强小目标检测性能。
- GatedFFN模块设计实现了高性能与低延迟,解决了实时检测的挑战。
- CED模块结合了ViT和CNN下采样的优点,旨在减少信息损失并增强上下文信息。
- 在大型无人机数据集上的实验验证了RemDet的优越性能和实时效率。
点此查看论文截图

No Annotations for Object Detection in Art through Stable Diffusion
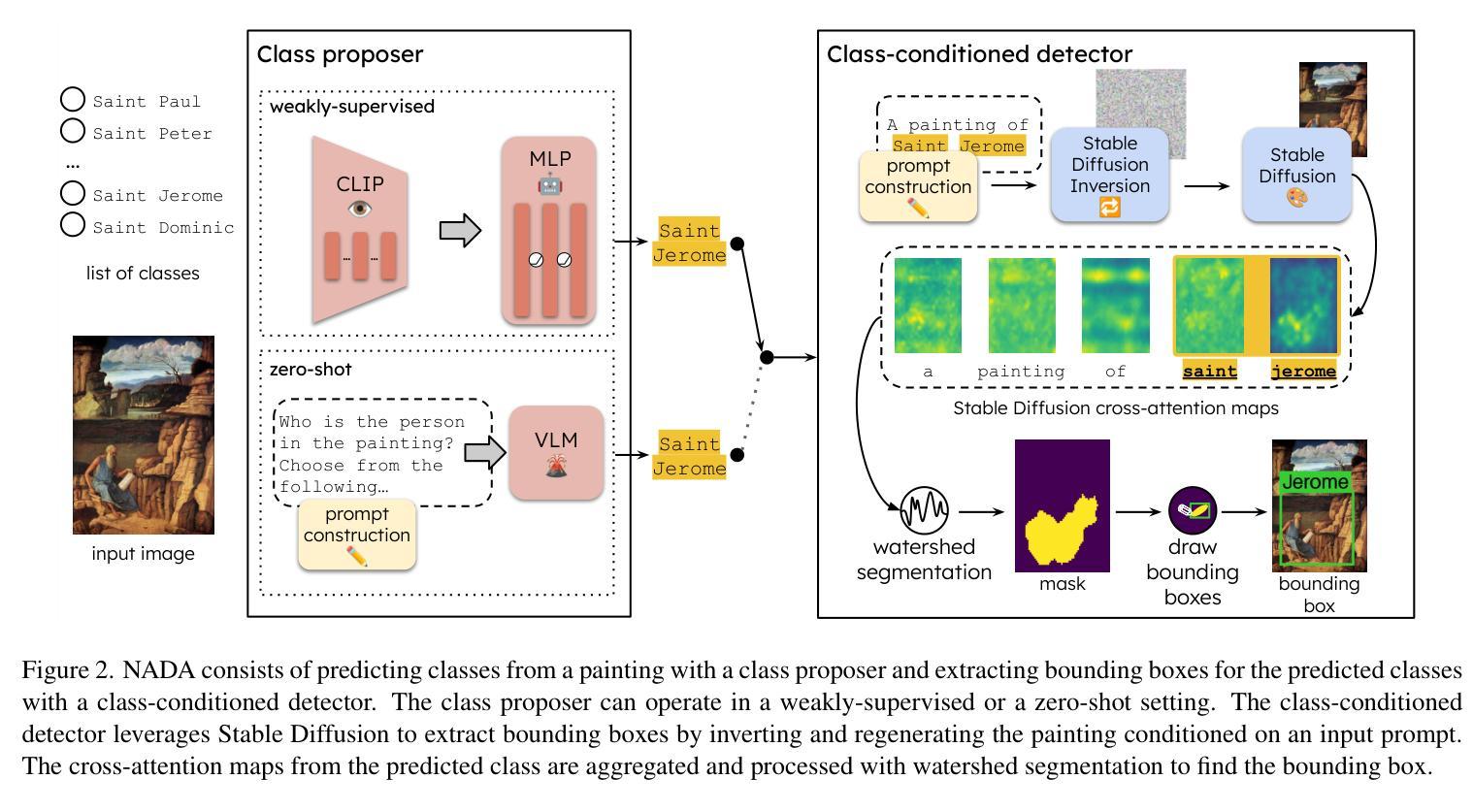
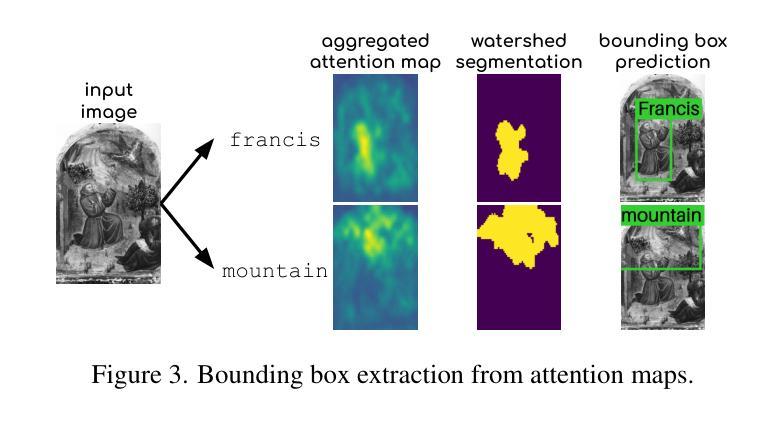
Authors:Patrick Ramos, Nicolas Gonthier, Selina Khan, Yuta Nakashima, Noa Garcia
Object detection in art is a valuable tool for the digital humanities, as it allows for faster identification of objects in artistic and historical images compared to humans. However, annotating such images poses significant challenges due to the need for specialized domain expertise. We present NADA (no annotations for detection in art), a pipeline that leverages diffusion models’ art-related knowledge for object detection in paintings without the need for full bounding box supervision. Our method, which supports both weakly-supervised and zero-shot scenarios and does not require any fine-tuning of its pretrained components, consists of a class proposer based on large vision-language models and a class-conditioned detector based on Stable Diffusion. NADA is evaluated on two artwork datasets, ArtDL 2.0 and IconArt, outperforming prior work in weakly-supervised detection, while being the first work for zero-shot object detection in art. Code is available at https://github.com/patrick-john-ramos/nada
艺术品中的目标检测对于数字人文来说是一个有价值的工具,因为它与人类相比,可以更快地识别艺术和历史图像中的目标。然而,对这些图像进行标注却带来了很大的挑战,因为需要专业的领域知识。我们提出了NADA(艺术品检测无需标注),这是一种无需完整边界框监督即可在绘画中进行目标检测的管道,利用扩散模型的与艺术相关的知识。我们的方法支持弱监督和无源场景,并且不需要对其预训练组件进行任何微调,它由基于大型视觉语言模型的类提出者和基于Stable Diffusion的类条件检测器组成。NADA在ArtDL 2.0和IconArt两个艺术品数据集上进行了评估,在弱监督检测方面优于先前的工作,同时是艺术品零样本目标检测的第一项工作。代码可在https://github.com/patrick-john-ramos/nada找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures, to be published in WACV 2025
Summary
对象检测在艺术领域是数字人文的重要工具,能更快地在艺术和历史图像中识别物体。然而,对这类图像进行标注需要特定领域的专业知识,存在巨大挑战。我们提出了NADA(艺术中无需标注的检测),这是一种利用扩散模型的与艺术相关的知识,在画作中进行物体检测的方法,无需完整的边界框监督。我们的方法支持弱监督和无源场景,且不需要对预训练组件进行微调,它由基于大型视觉语言模型的类提议器和基于Stable Diffusion的类条件检测器组成。NADA在ArtDL 2.0和IconArt两个艺术品数据集上进行了评估,在弱监督检测方面优于以前的工作,并且是艺术中零样本对象检测的首次工作。
Key Takeaways
- 对象检测在艺术领域具有重要价值,可以快速识别艺术和历史图像中的物体。
- 标注艺术图像面临需要特定领域专业知识的挑战。
- NADA方法利用扩散模型的与艺术相关的知识,实现了在画作中的物体检测,无需完整的边界框监督。
- NADA方法支持弱监督和无源场景,且预训练组件无需微调。
- NADA由基于大型视觉语言模型的类提议器和基于Stable Diffusion的类条件检测器组成。
- NADA在ArtDL 2.0和IconArt两个艺术品数据集上表现出色,优于先前的弱监督检测方法。
- NADA是首次尝试在艺术品检测中实现零样本对象检测的工作。
点此查看论文截图

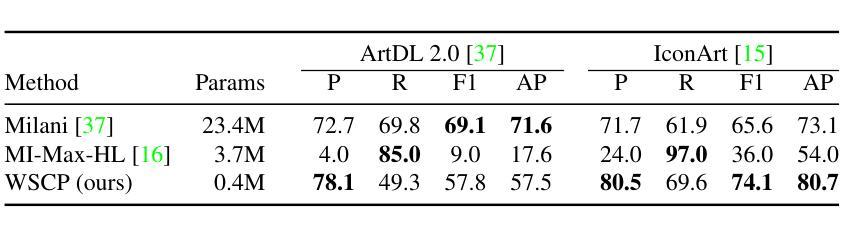
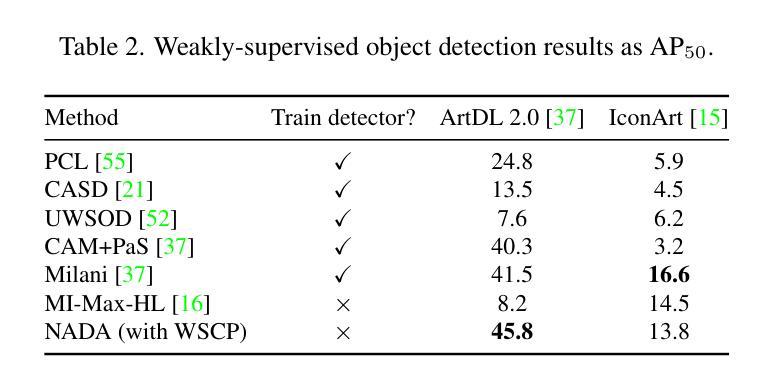
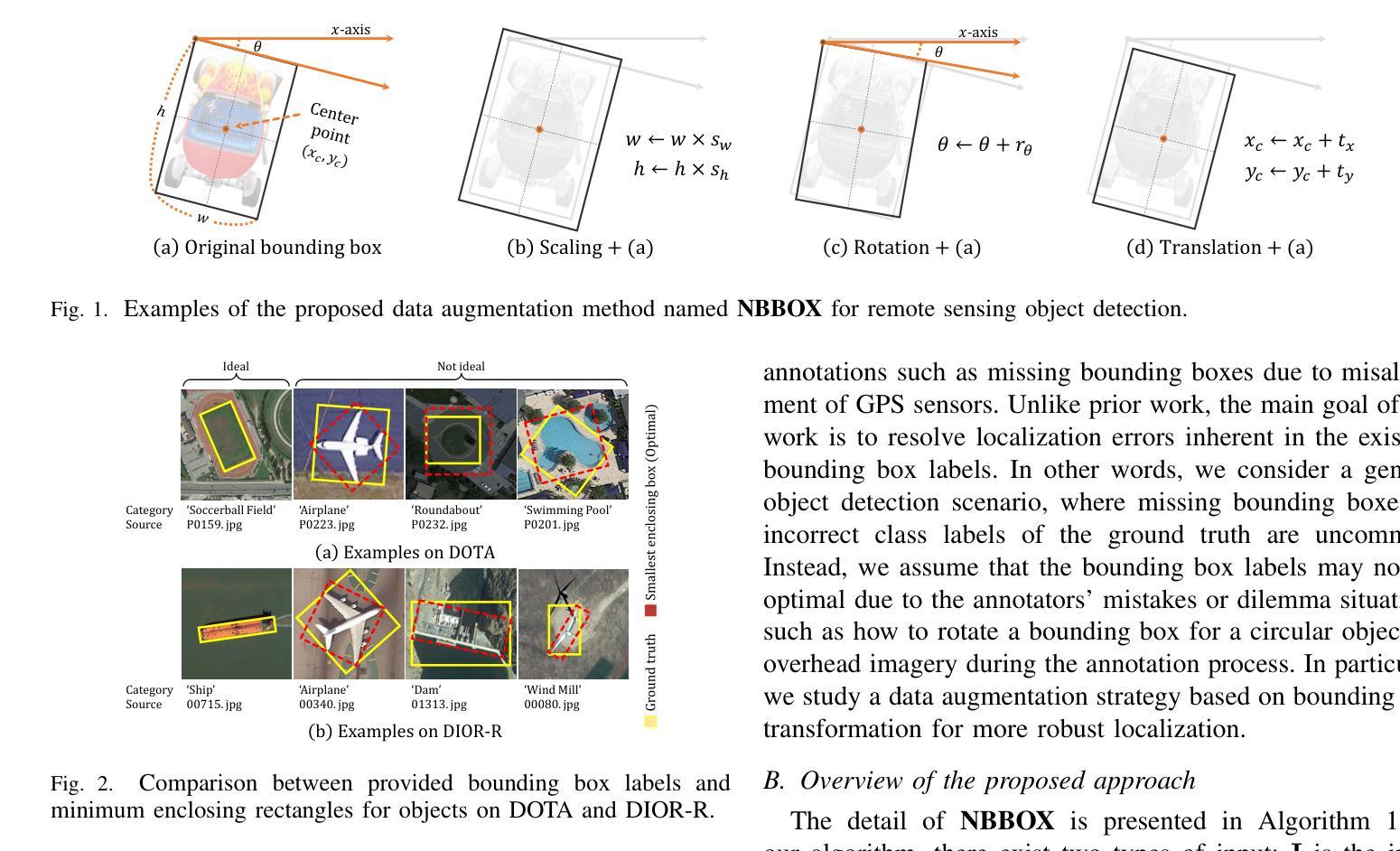
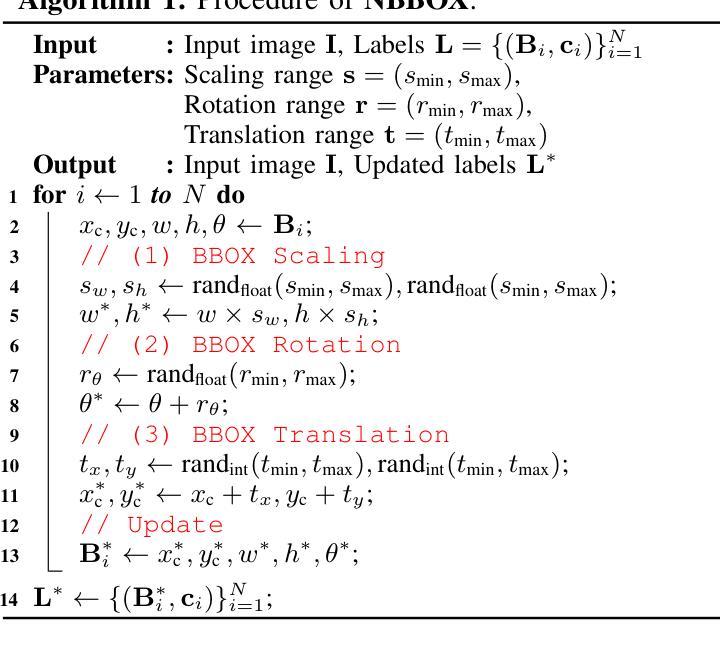
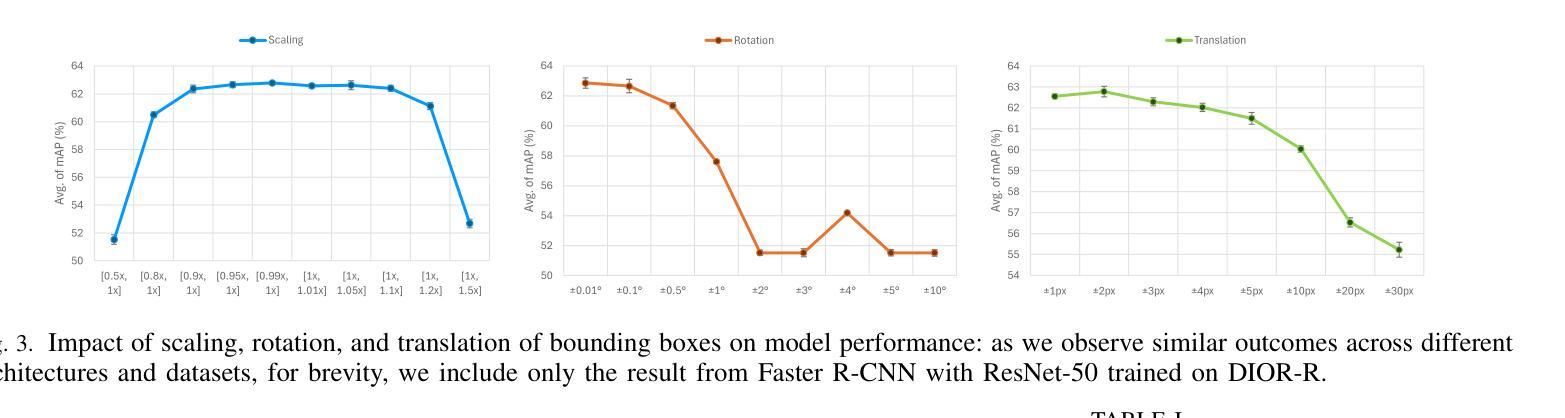
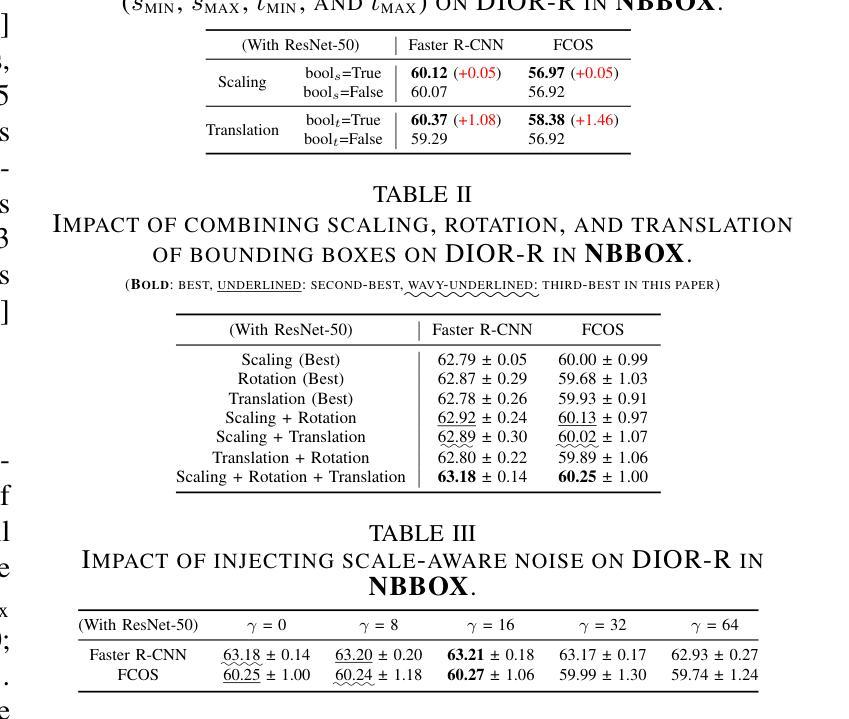
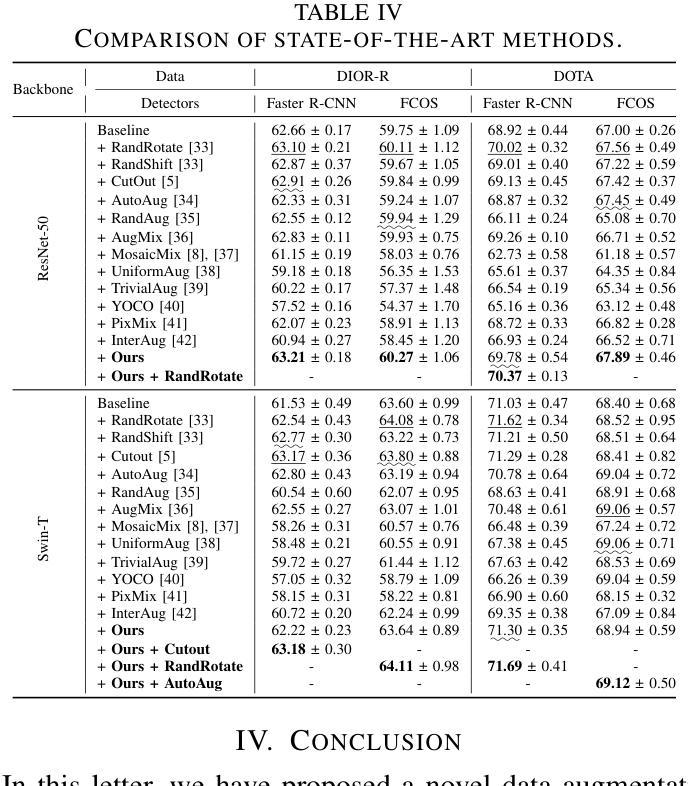
NBBOX: Noisy Bounding Box Improves Remote Sensing Object Detection
Authors:Yechan Kim, SooYeon Kim, Moongu Jeon
Data augmentation has shown significant advancements in computer vision to improve model performance over the years, particularly in scenarios with limited and insufficient data. Currently, most studies focus on adjusting the image or its features to expand the size, quality, and variety of samples during training in various tasks including object detection. However, we argue that it is necessary to investigate bounding box transformations as a data augmentation technique rather than image-level transformations, especially in aerial imagery due to potentially inconsistent bounding box annotations. Hence, this letter presents a thorough investigation of bounding box transformation in terms of scaling, rotation, and translation for remote sensing object detection. We call this augmentation strategy NBBOX (Noise Injection into Bounding Box). We conduct extensive experiments on DOTA and DIOR-R, both well-known datasets that include a variety of rotated generic objects in aerial images. Experimental results show that our approach significantly improves remote sensing object detection without whistles and bells and it is more time-efficient than other state-of-the-art augmentation strategies.
数据增强在计算机视觉领域已经取得了显著进展,多年来在提高模型性能,特别是在数据有限和不足的场景下,发挥了重要作用。目前,大多数研究都集中在调整图像或其特征上,以扩大样本的大小、质量和多样性,用于各种任务,包括目标检测。然而,我们认为有必要研究边界框变换作为一种数据增强技术,而不是图像级别的变换,特别是在航空图像中,因为边界框注释可能存在潜在的不一致性。因此,本文全面研究了边界框变换在缩放、旋转和平移方面的遥感目标检测。我们将这种增强策略称为NBBOX(噪声注入边界框)。我们在DOTA和DIOR-R这两个数据集上进行了大量实验,这两个数据集都包含航空图像中的多种旋转通用对象。实验结果表明,我们的方法在不需要过多修饰的情况下,显著提高了遥感目标检测性能,并且与其他最先进的增强策略相比,更加高效省时。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
数据增强在计算机视觉领域已经取得了显著进展,特别是在数据有限和不足的情境下提高模型性能。当前研究主要集中在调整图像或其特征以扩大样本大小、质量和多样性,用于各种任务中的训练,包括目标检测。然而,我们认为有必要研究边界框变换作为一种数据增强技术,而不是图像级别的变换,特别是在航空图像中,因为边界框注释可能存在不一致的情况。因此,本文全面研究了边界框变换在缩放、旋转和翻译方面的遥感目标检测。我们将这种增强策略称为NBBOX(噪声注入边界框)。我们在DOTA和DIOR-R这两个包含航空图像中各种旋转通用目标的数据集上进行了广泛的实验。实验结果表明,我们的方法在不需要复杂操作的情况下显著提高了遥感目标检测的精度,并且与其他最先进的增强策略相比更加省时高效。
关键见解
- 数据增强在改进模型性能上发挥了重要作用,特别是在数据有限的情况下。
- 当前研究主要集中在图像级别的数据增强,但边界框变换同样重要。
- 边界框注释在航空图像中可能存在不一致的情况,需要进行深入研究。
- 介绍了NBBOX策略,它通过边界框的缩放、旋转和翻译来进行数据增强。
- 在DOTA和DIOR-R数据集上的实验表明,NBBOX策略在遥感目标检测任务中显著提高了性能。
点此查看论文截图


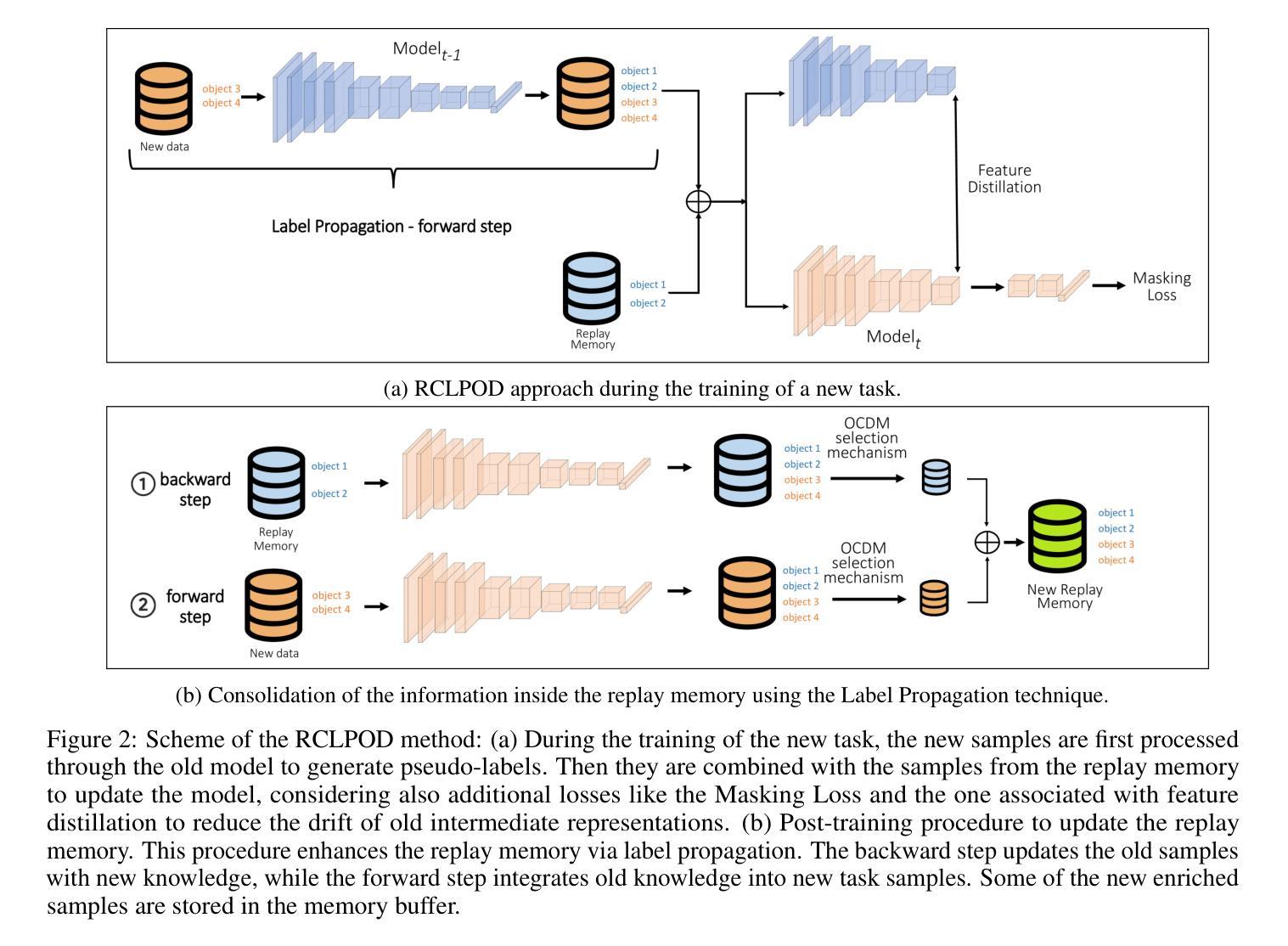
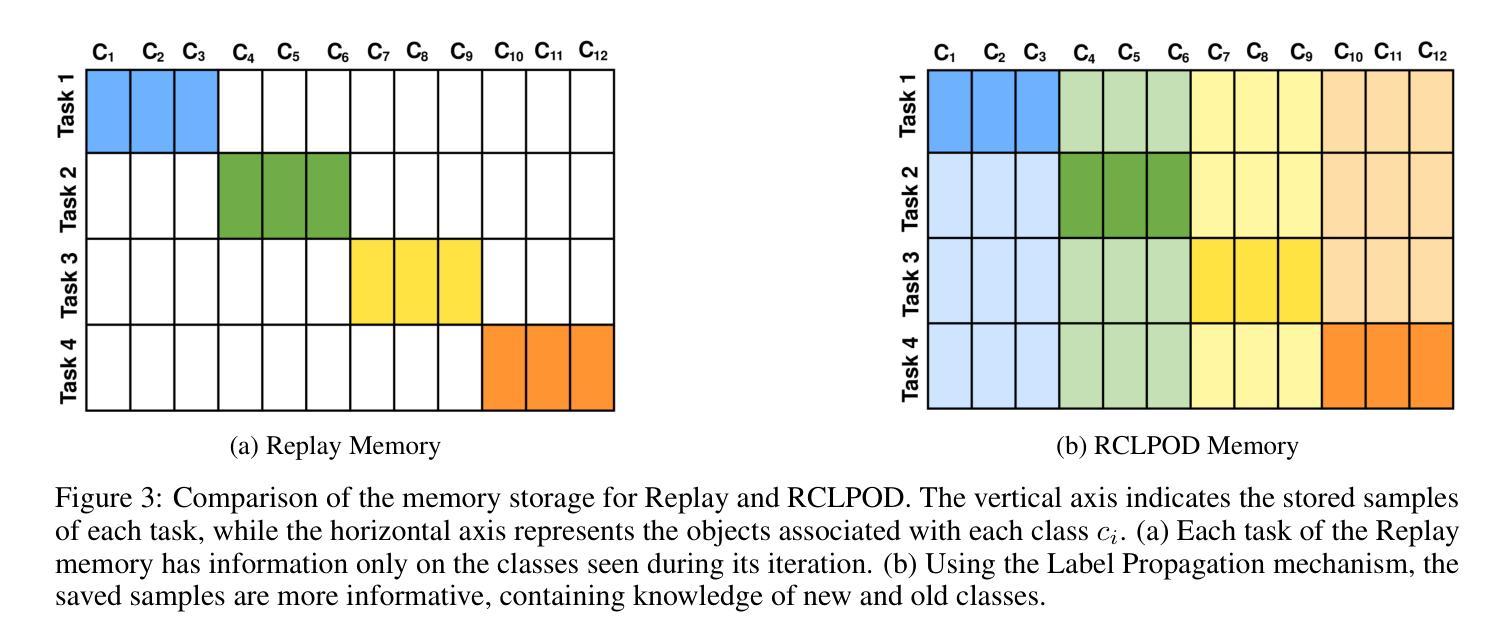
Replay Consolidation with Label Propagation for Continual Object Detection
Authors:Riccardo De Monte, Davide Dalle Pezze, Marina Ceccon, Francesco Pasti, Francesco Paissan, Elisabetta Farella, Gian Antonio Susto, Nicola Bellotto
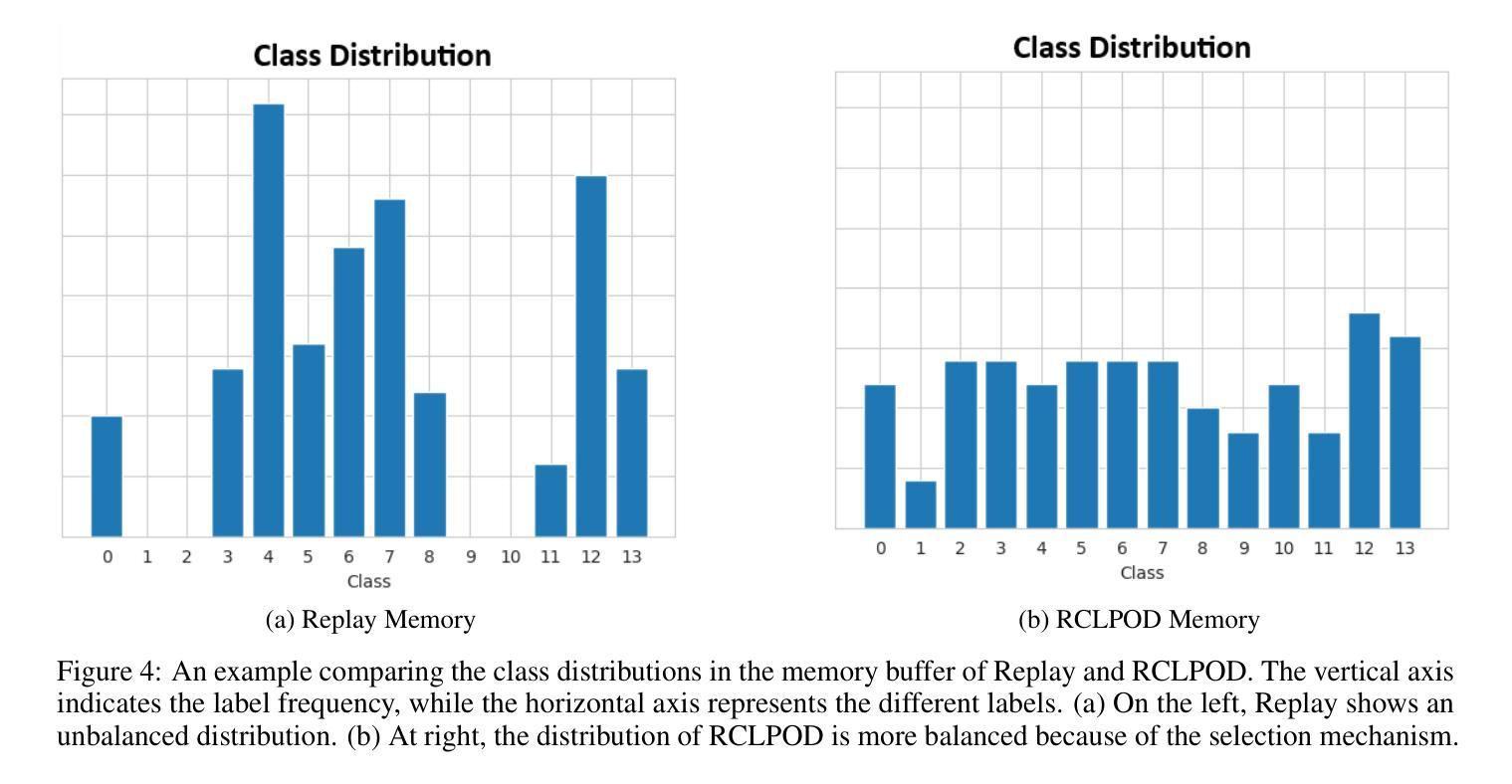
Continual Learning (CL) aims to learn new data while remembering previously acquired knowledge. In contrast to CL for image classification, CL for Object Detection faces additional challenges such as the missing annotations problem. In this scenario, images from previous tasks may contain instances of unknown classes that could reappear as labeled in future tasks, leading to task interference in replay-based approaches. Consequently, most approaches in the literature have focused on distillation-based techniques, which are effective when there is a significant class overlap between tasks. In our work, we propose an alternative to distillation-based approaches with a novel approach called Replay Consolidation with Label Propagation for Object Detection (RCLPOD). RCLPOD enhances the replay memory by improving the quality of the stored samples through a technique that promotes class balance while also improving the quality of the ground truth associated with these samples through a technique called label propagation. RCLPOD outperforms existing techniques on well-established benchmarks such as VOC and COC. Moreover, our approach is developed to work with modern architectures like YOLOv8, making it suitable for dynamic, real-world applications such as autonomous driving and robotics, where continuous learning and resource efficiency are essential.
持续学习(CL)旨在学习新数据的同时保留之前获得的知识。与用于图像分类的CL不同,用于目标检测的CL面临额外的挑战,例如缺失注释问题。在这种情况下,来自先前任务的图像可能包含未知类的实例,这些实例可能在未来任务中被标记为重现,导致基于重播的方法出现任务干扰。因此,文献中的大多数方法都集中在基于蒸馏的技术上,这在任务之间存在大量类重叠时非常有效。在我们的工作中,我们提出了一种基于蒸馏方法的替代方案,采用了一种新型方法,称为用于目标检测的回放巩固与标签传播(RCLPOD)。RCLPOD通过提高存储样本的质量来增强回放记忆,采用一种促进类平衡的技术,同时通过标签传播技术提高与这些样本相关的地面真实性的质量。RCLPOD在VOC和COC等既定基准测试上的表现优于现有技术。此外,我们的方法是为现代架构(如YOLOv8)而开发的,因此非常适合动态、现实世界的应用(如自动驾驶和机器人技术),在这里,持续学习和资源效率至关重要。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了持续学习(CL)在目标检测领域的应用及其所面临的挑战。针对图像分类的CL方法不适用于目标检测,因为目标检测面临缺少注释的问题。因此,大多数文献中的方法都集中在基于蒸馏的技术上,但当任务间存在大量类别重叠时,这些方法的效果可能有限。本文提出了一种替代方法——回放整合与标签传播相结合的目标检测(RCLPOD)。RCLPOD通过提高存储样本的质量和与其关联的地面真实度来改善回放记忆。它推广了类别平衡,改进了样本标记过程,并取得了现有技术在基准测试中的出色表现。此外,该方法与现代架构(如YOLOv8)兼容,适用于自主驾驶和机器人等动态实际应用场景。这些场景中,持续学习和资源效率至关重要。
Key Takeaways
持续学习(CL)旨在学习新数据的同时保留先前获得的知识。在目标检测领域应用时面临缺少注释等挑战。
传统基于蒸馏的方法在处理存在大量类别重叠的任务时效果有限。这意味着单纯依赖这些方法无法在所有场景中取得理想结果。现有的研究多集中于这种背景下进行目标检测的技术突破。在需要跨不同任务进行学习的情况下,某些领域技术面临着识别准确率不高的问题。我们面临对适用于真实世界的解决方案的需求增长趋势以及创新压力和挑战在不断加剧的情形下进行这些探索和技术研究是一大关键领域(点)(因为迫切需要满足社会实际应用的连续学习和预测准确度的双重要求)。文中强调自主驾驶和机器人领域等对持续学习和资源效率的极高要求表明实际生活中解决该领域的问题紧迫性不断提高也显示现实需求和不断增长的压力表明缺乏实时精准和精确标注的高质量数据源正在限制这类系统的成功因此面临的挑战也很大意味着应对场景适应性弱高准确率可集成现实环境的自动化程度尚需进一步加强整体发展趋势来看实现高质量持续学习在目标检测领域是当下迫切的需求和发展趋势的重要体现点)。具体来说在解决缺少注释问题时构建一套灵活可靠的样本收集和标记流程以及应对模型过度适应当前任务的策略就显得尤为重要同时也为未来的技术发展和实际应用提供了重要的思路和方向因此建立更加智能灵活的标注系统对于未来的持续学习和目标检测技术的发展至关重要对于实际应用场景而言在动态环境中进行精准的目标检测和持续学习是一个重要的研究方向。现有基于回放的技术可通过多种途径提高准确性和适用性意味着创新的目标检测方法与成熟应用的集成是非常重要的这在扩大市场应用范围推动技术创新发展增强对社会的适应性方面有着重要潜力我们需要致力于在继续应对关键领域问题的同时研究先进的机器学习和计算机视觉技术在以无人驾驶系统为首的新技术和现代化平台上确保可靠性维护措施等因素在整个研究和产品开发过程中的综合考量确保了其持续学习系统的有效性这些创新对于保持模型效能同时确保性能一致性以符合用户期望将发挥关键作用在复杂多变的环境中保证模型的有效性和准确性并减少人为干预的需求以优化整个系统的性能实现未来技术应用的关键目标之一是优化和自动化决策过程的复杂性降低对用户参与度的依赖以便能高效运行并保证高可用性这意味着该领域未来会向智能化发展并解决相关实际问题进一步推进该技术的商业化进程和市场普及度推动其在目标检测领域的商业化推广从社会发展视角表明公众和技术市场对于继续实现关键技术飞跃的重视是非常积极的改进进步乃至质的飞跃行业总体朝着更高的集成度自动化以及灵活性和智能化的方向发展并为适应不同需求提供更丰富的选择这符合整个行业的未来发展趋势并有望推动相关领域的进一步突破和创新发展。我们的方法通过改进回放记忆和标签传播策略从而有效应对以上挑战不仅使新应用场景和技术的进步相辅相成还将激发进一步的科技创新促使该技术进入更高层次的智能应用阶段为实现更加智能高效的社会生活提供了可能性。Key Takeaways的具体内容需要基于原文内容精简提炼出最重要的几点即可。以下是根据原文提炼出的关键要点:
持续学习在目标检测领域面临缺少注释的挑战。
基于蒸馏的方法在处理类别重叠任务时存在局限性。
本文提出的RCLPOD方法通过改进回放记忆和标签传播策略来增强模型性能。
点此查看论文截图



ESOD: Efficient Small Object Detection on High-Resolution Images
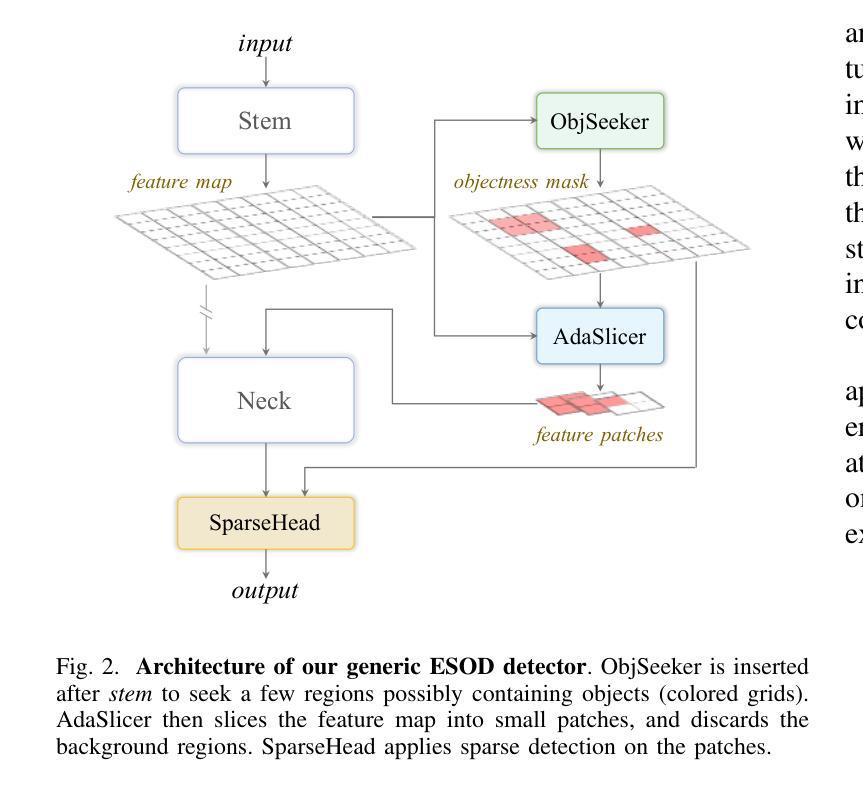
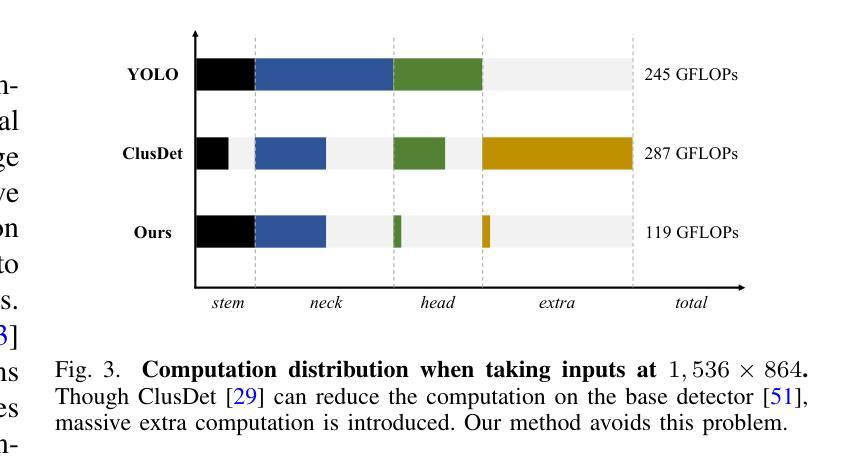
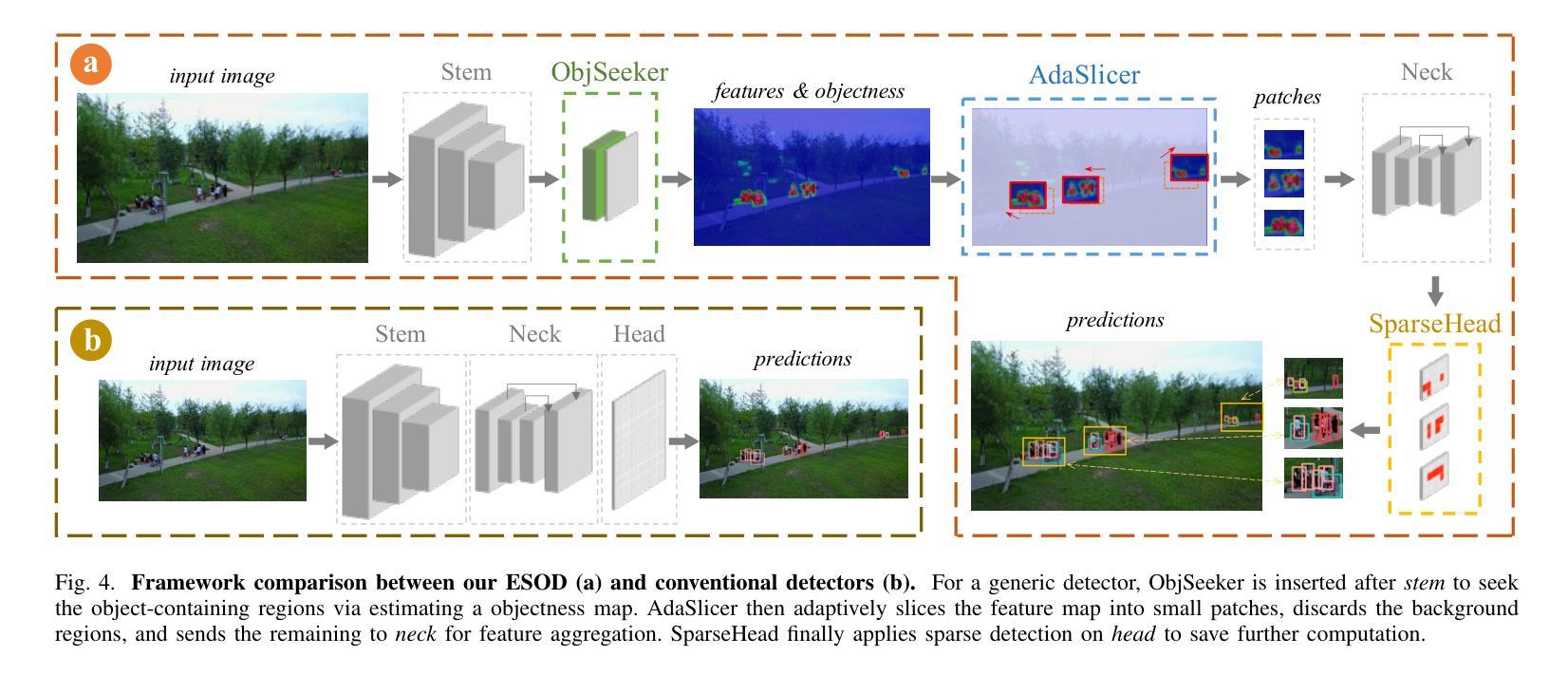
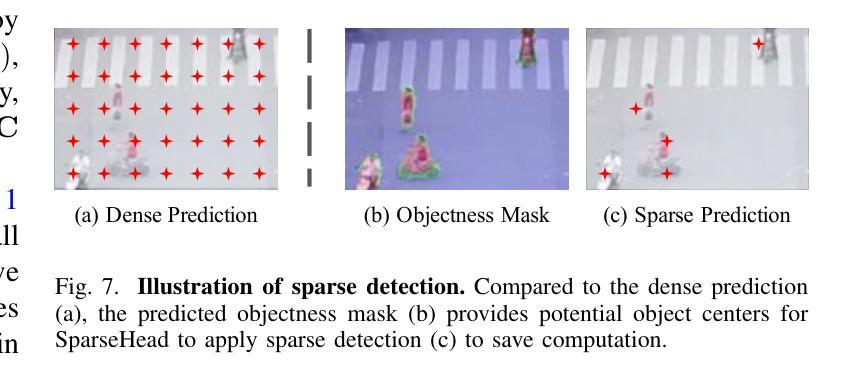
Authors:Kai Liu, Zhihang Fu, Sheng Jin, Ze Chen, Fan Zhou, Rongxin Jiang, Yaowu Chen, Jieping Ye
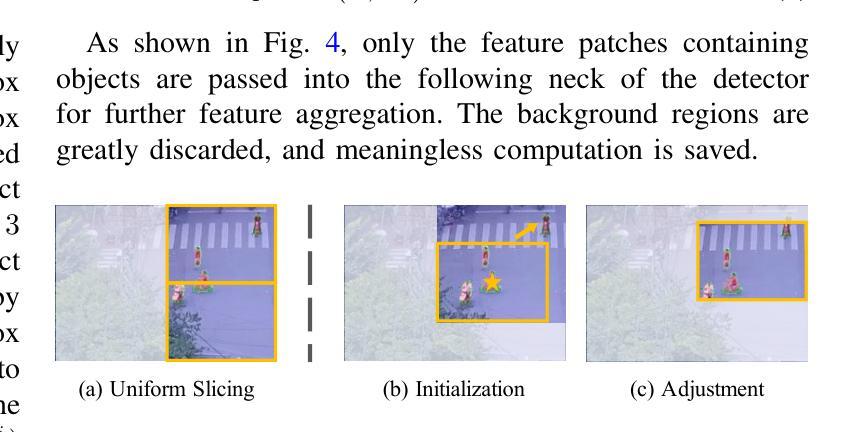
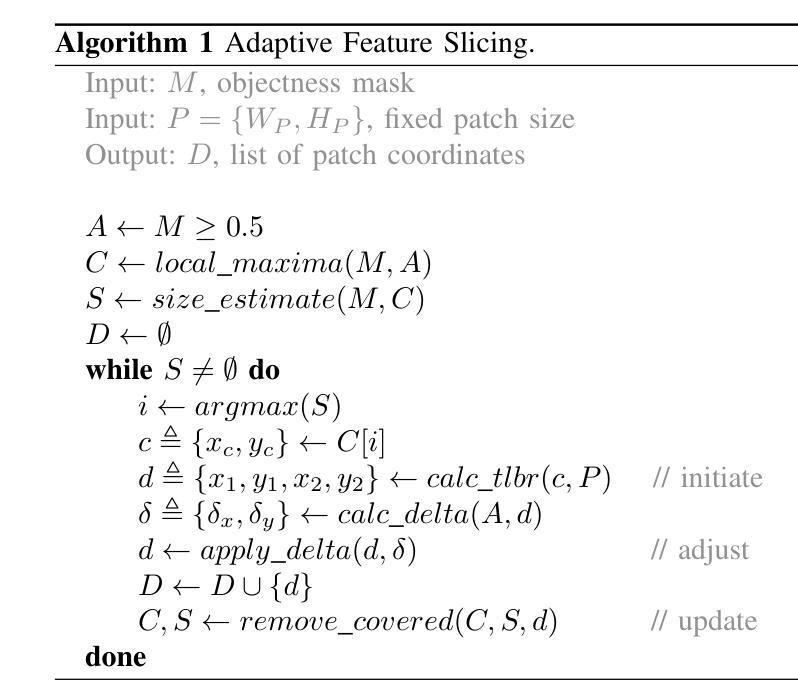
Enlarging input images is a straightforward and effective approach to promote small object detection. However, simple image enlargement is significantly expensive on both computations and GPU memory. In fact, small objects are usually sparsely distributed and locally clustered. Therefore, massive feature extraction computations are wasted on the non-target background area of images. Recent works have tried to pick out target-containing regions using an extra network and perform conventional object detection, but the newly introduced computation limits their final performance. In this paper, we propose to reuse the detector’s backbone to conduct feature-level object-seeking and patch-slicing, which can avoid redundant feature extraction and reduce the computation cost. Incorporating a sparse detection head, we are able to detect small objects on high-resolution inputs (e.g., 1080P or larger) for superior performance. The resulting Efficient Small Object Detection (ESOD) approach is a generic framework, which can be applied to both CNN- and ViT-based detectors to save the computation and GPU memory costs. Extensive experiments demonstrate the efficacy and efficiency of our method. In particular, our method consistently surpasses the SOTA detectors by a large margin (e.g., 8% gains on AP) on the representative VisDrone, UAVDT, and TinyPerson datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/alibaba/esod.
放大输入图像是一种简单有效的促进小目标检测的方法。然而,简单的图像放大在计算和GPU内存方面成本高昂。实际上,小目标通常稀疏分布且局部聚集。因此,在非目标背景区域的图像上进行了大量特征提取计算,造成了浪费。近期的研究工作尝试使用额外的网络来挑选出包含目标的区域,并进行传统的目标检测,但新引入的计算限制了其最终性能。在本文中,我们提出重用检测器的主干网络进行特征级的目标搜索和补丁切片,这可以避免冗余的特征提取,并降低计算成本。通过结合稀疏检测头,我们能够在高分辨率输入(例如1080P或更大)上检测小目标,以实现卓越的性能。所得的Efficient Small Object Detection(ESOD)方法是一个通用框架,可应用于基于CNN和ViT的检测器,以节省计算和GPU内存成本。大量实验证明了我们的方法的有效性和效率。特别是,我们的方法在代表性的VisDrone、UAVDT和TinyPerson数据集上始终大幅度超越最新检测器(例如在AP上获得8%的增益)。代码可在https://github.com/alibaba/esod 获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been recerived by IEEE TIP 2024. Code is available at https://github.com/alibaba/esod
Summary:
该文提出了一种高效的检测小对象的方法,通过重用检测器的主干网络进行特征层面的目标搜索和补丁切片,避免了冗余的特征提取,降低了计算成本。该方法结合了稀疏检测头,能够在高分辨率输入上检测小目标,从而提高性能。提出的Efficient Small Object Detection(ESOD)方法是一个通用框架,可应用于CNN和ViT基检测器,节省计算和GPU内存成本。实验表明,该方法在代表性数据集上超过了最先进的目标检测方法。
Key Takeaways:
- 简单图像放大对小目标检测并不高效,存在计算和GPU内存成本高昂的问题。
- 小目标在图像中通常稀疏分布且局部聚集。
- 现有方法试图通过额外的网络挑选出包含目标的区域进行常规目标检测,但新引入的计算限制了其最终性能。
- 本文提出了一个高效的检测方法——Efficient Small Object Detection(ESOD)。该方法重用检测器的主干网络进行特征层面的目标搜索和补丁切片,避免冗余特征提取并降低计算成本。
- ESOD方法结合了稀疏检测头,能够在高分辨率输入上检测小目标,实现优越性能。
- ESOD是一个通用框架,适用于CNN和ViT基检测器,能有效节省计算和GPU内存成本。
点此查看论文截图