⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-19 更新
FocusChat: Text-guided Long Video Understanding via Spatiotemporal Information Filtering
Authors:Zheng Cheng, Rendong Wang, Zhicheng Wang
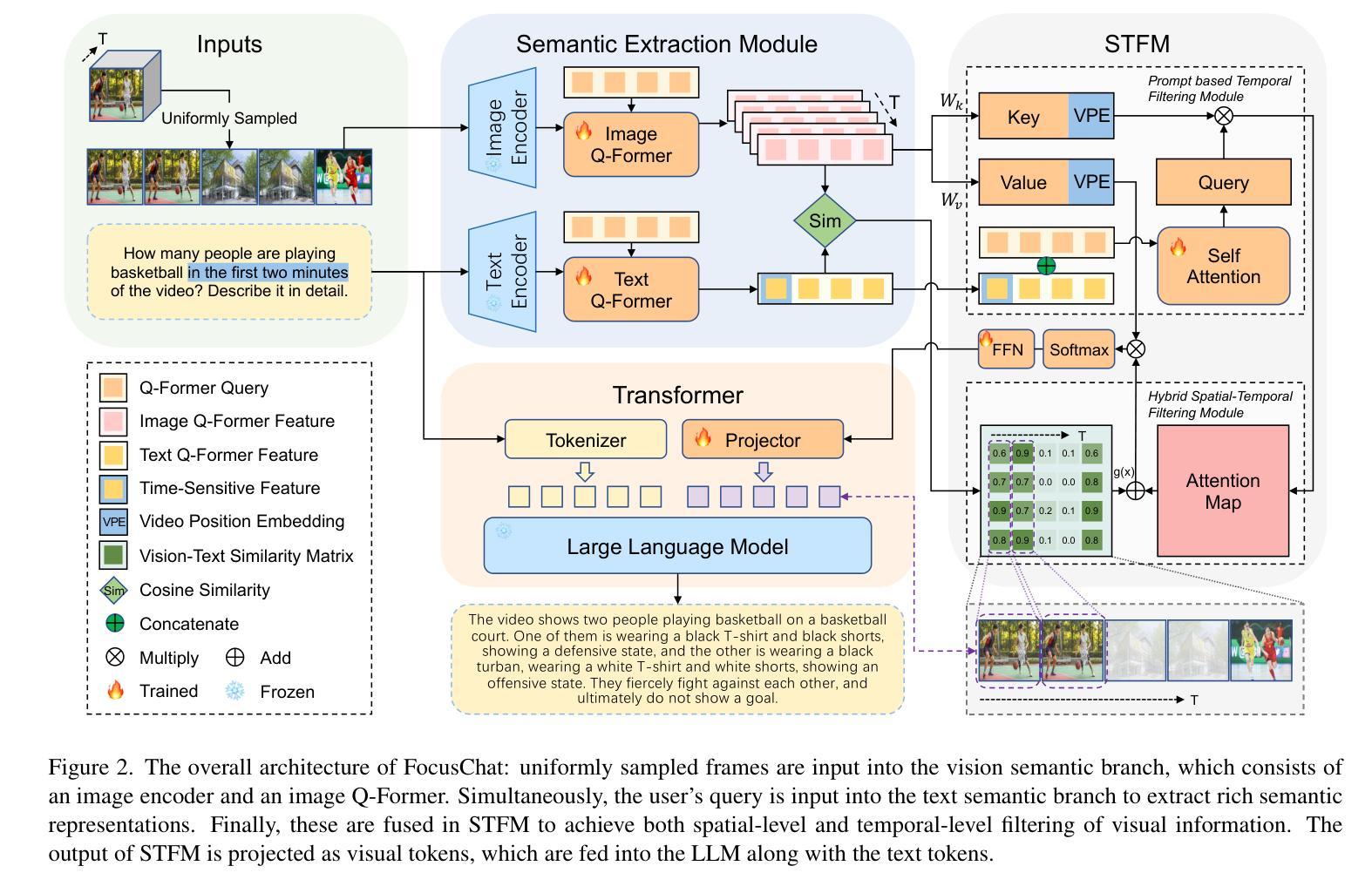
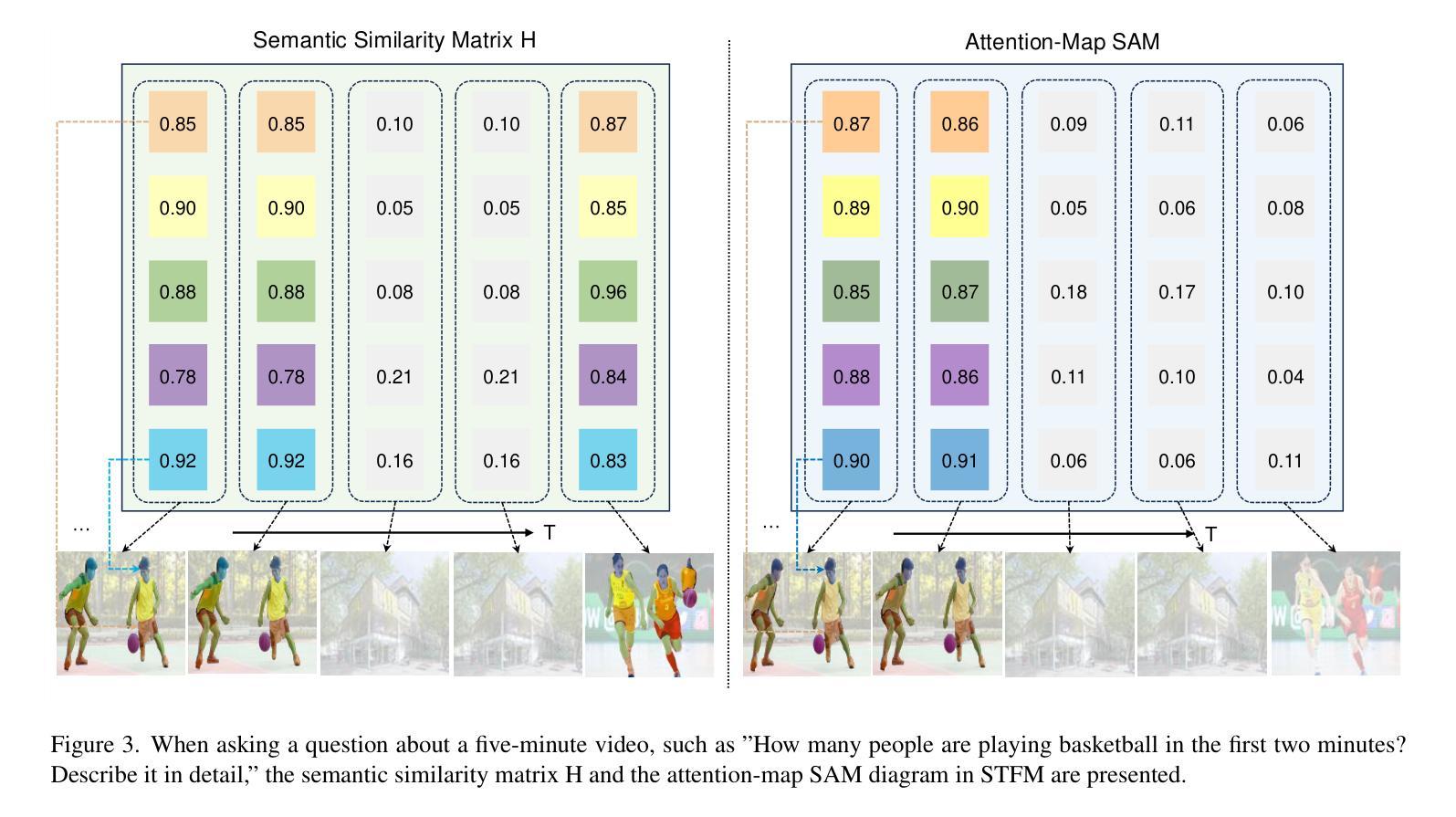
Recently, multi-modal large language models have made significant progress. However, visual information lacking of guidance from the user’s intention may lead to redundant computation and involve unnecessary visual noise, especially in long, untrimmed videos. To address this issue, we propose FocusChat, a text-guided multi-modal large language model (LLM) that emphasizes visual information correlated to the user’s prompt. In detail, Our model first undergoes the semantic extraction module, which comprises a visual semantic branch and a text semantic branch to extract image and text semantics, respectively. The two branches are combined using the Spatial-Temporal Filtering Module (STFM). STFM enables explicit spatial-level information filtering and implicit temporal-level feature filtering, ensuring that the visual tokens are closely aligned with the user’s query. It lowers the essential number of visual tokens inputted into the LLM. FocusChat significantly outperforms Video-LLaMA in zero-shot experiments, using an order of magnitude less training data with only 16 visual tokens occupied. It achieves results comparable to the state-of-the-art in few-shot experiments, with only 0.72M pre-training data.
最近,多模态大型语言模型取得了显著进展。然而,缺乏用户意图指导的视觉信息可能导致冗余计算并引入不必要的视觉噪声,特别是在长而无剪辑的视频中。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了FocusChat,这是一个文本引导的多模态大型语言模型(LLM),它强调与用户提示相关的视觉信息。具体来说,我们的模型首先经过语义提取模块,该模块包括一个视觉语义分支和一个文本语义分支,分别提取图像和文本语义。两个分支通过时空滤波模块(STFM)进行结合。STFM实现了显式的空间级别信息滤波和隐式的特征时间级别滤波,确保视觉令牌与用户查询紧密对齐。它降低了输入到LLM中的必要视觉令牌数量。FocusChat在零样本实验中显著优于Video-LLaMA,使用数量级更少的训练数据,仅占用16个视觉令牌。在少量样本实验中,它实现了与国家最新技术相当的结果,仅有0.72M的预训练数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 4 figures
Summary
多媒体大语言模型有所进展,但仍存在冗余计算和视觉噪音问题。为此,提出FocusChat模型,结合文本和用户意图引导多模态大型语言模型。FocusChat有语义提取模块、空间时间过滤模块(STFM)等技术实现图像与文本的协同作用,并提高了实验效果。对于Zero Shot和少样本训练,此模型也取得了优秀的成果。此项技术的成果或有望成为业界里程碑式的成就。目前其已经大幅减少了冗余计算和数据量,并在特定任务上表现出优异的性能。其成果将为未来多模态大语言模型的发展奠定坚实基础。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型在处理长视频时存在冗余计算和视觉噪音问题。
- FocusChat是一个文本引导的多模态大型语言模型,强调与用户意图相关的视觉信息。
- FocusChat通过语义提取模块和空间时间过滤模块等技术,实现图像和文本的协同作用。
- 该模型在零样本和少样本实验中表现出色,预训练数据量仅为同类技术的十分之一左右。相较于业界前沿技术,其效果相当可观。
点此查看论文截图

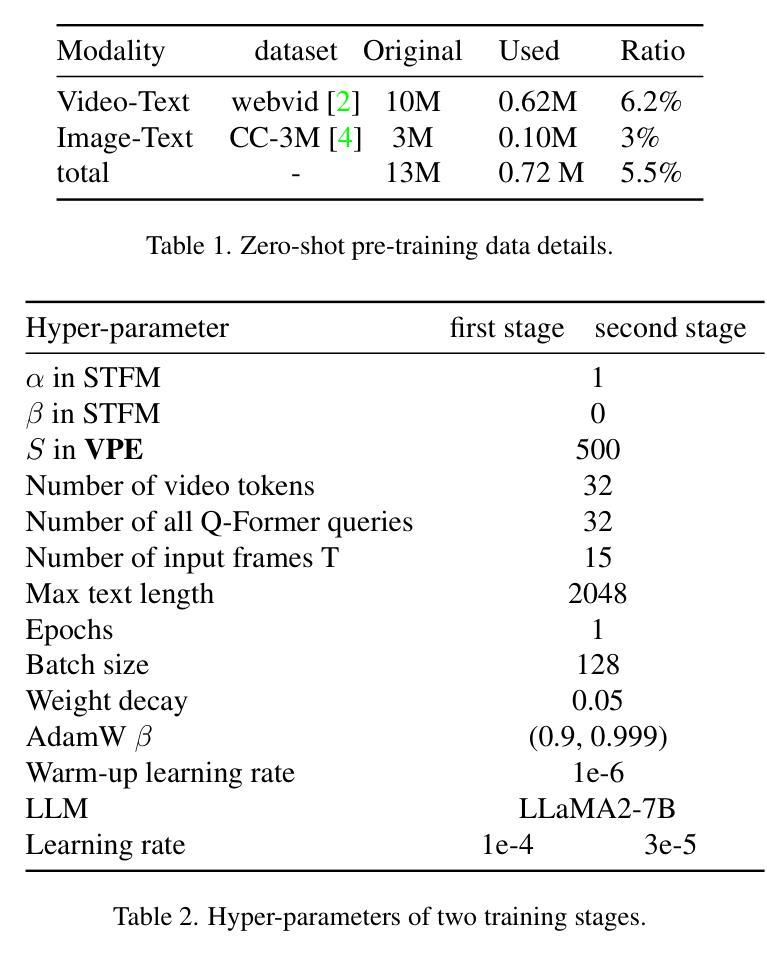
CG-Bench: Clue-grounded Question Answering Benchmark for Long Video Understanding
Authors:Guo Chen, Yicheng Liu, Yifei Huang, Yuping He, Baoqi Pei, Jilan Xu, Yali Wang, Tong Lu, Limin Wang
Most existing video understanding benchmarks for multimodal large language models (MLLMs) focus only on short videos. The limited number of benchmarks for long video understanding often rely solely on multiple-choice questions (MCQs). However, because of the inherent limitation of MCQ-based evaluation and the increasing reasoning ability of MLLMs, models can give the current answer purely by combining short video understanding with elimination, without genuinely understanding the video content. To address this gap, we introduce CG-Bench, a novel benchmark designed for clue-grounded question answering in long videos. CG-Bench emphasizes the model’s ability to retrieve relevant clues for questions, enhancing evaluation credibility. It features 1,219 manually curated videos categorized by a granular system with 14 primary categories, 171 secondary categories, and 638 tertiary categories, making it the largest benchmark for long video analysis. The benchmark includes 12,129 QA pairs in three major question types: perception, reasoning, and hallucination. Compensating the drawbacks of pure MCQ-based evaluation, we design two novel clue-based evaluation methods: clue-grounded white box and black box evaluations, to assess whether the model generates answers based on the correct understanding of the video. We evaluate multiple closed-source and open-source MLLMs on CG-Bench. Results indicate that current models significantly underperform in understanding long videos compared to short ones, and a significant gap exists between open-source and commercial models. We hope CG-Bench can advance the development of more trustworthy and capable MLLMs for long video understanding. All annotations and video data are released at https://cg-bench.github.io/leaderboard/.
针对多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的视频理解基准测试大多数只关注短视频。针对长视频理解的基准测试数量有限,通常只依赖于多项选择题(MCQs)。然而,由于基于MCQ的评估的固有局限性以及MLLMs日益增强的推理能力,模型可以通过结合短视频理解与排除法给出当前答案,而无需真正了解视频内容。为了解决这一差距,我们引入了CG-Bench,这是一个专为长视频中的线索导向问答设计的新型基准测试。CG-Bench强调模型检索与问题相关的线索的能力,提高评估的可信度。它包含1219个手动整理的视频,这些视频由一个精细的系统分为14个主要类别、171个次要类别和638个三级类别,成为最大的长视频分析基准测试。该基准测试包含三种主要类型的问答对,共12,129个:感知、推理和幻觉。为了弥补纯基于MCQ评估的缺陷,我们设计了两种新的基于线索的评估方法:线索基础的白盒和黑盒评估,以评估模型是否基于对视频的正确理解生成答案。我们在CG-Bench上评估了多个封闭源代码和开源的MLLMs。结果表明,与短视频相比,当前模型在长视频理解方面存在显著不足,并且开源与商业模型之间存在明显差距。我们希望CG-Bench能够促进更可靠、更强大的长视频理解MLLMs的发展。所有注释和视频数据已发布在https://cg-bench.github.io/leaderboard/上。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 9 figures
摘要
本文介绍了针对多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的视频理解基准测试,重点指出当前大多数基准测试只关注短视频的问题。对于长视频理解的基准测试通常仅依赖于多项选择题(MCQs),但这种方式存在局限性。因此,本文提出了CG-Bench,一个用于长视频中线索引导问答的新型基准测试。CG-Bench强调模型检索与问题相关的线索的能力,提高评估的可信度。它包含1,219个手动整理的视频,分为14个主要类别、171个次要类别和638个三级类别,成为最大的长视频分析基准测试。该基准测试包括三种主要问题的12,129个问答对:感知、推理和幻觉。为弥补纯MCQ评估的不足,我们设计了两种新型基于线索的评估方法:线索引导的白盒和黑盒评估,以评估模型是否基于正确理解视频生成答案。我们对多个封闭源代码和开源的MLLMs进行了CG-Bench评估。结果表明,当前模型在长视频理解方面相较于短视频存在显著不足,并且开源模型和商业模型之间存在显著差距。我们希望CG-Bench能够促进更可靠和更具能力MLLMs的长视频理解发展。
关键见解
- 当前视频理解基准测试主要关注短视频,缺乏针对长视频理解的全面基准测试。
- 现有长视频理解基准测试主要依赖多项选择题(MCQs),这限制了模型的评估效果。
- CG-Bench作为一种新型基准测试,旨在评估模型在长视频中的线索检索能力,提高评估可信度。
- CG-Bench包含大量手动整理的视频数据,并采用多种类型的问题进行评估。
- CG-Bench引入了两种新的线索基础评估方法:线索引导的白盒和黑盒评估,以更准确地评估模型性能。
- 当前模型在长视频理解方面显著落后于短视频理解,且不同模型之间存在显著性能差异。
点此查看论文截图


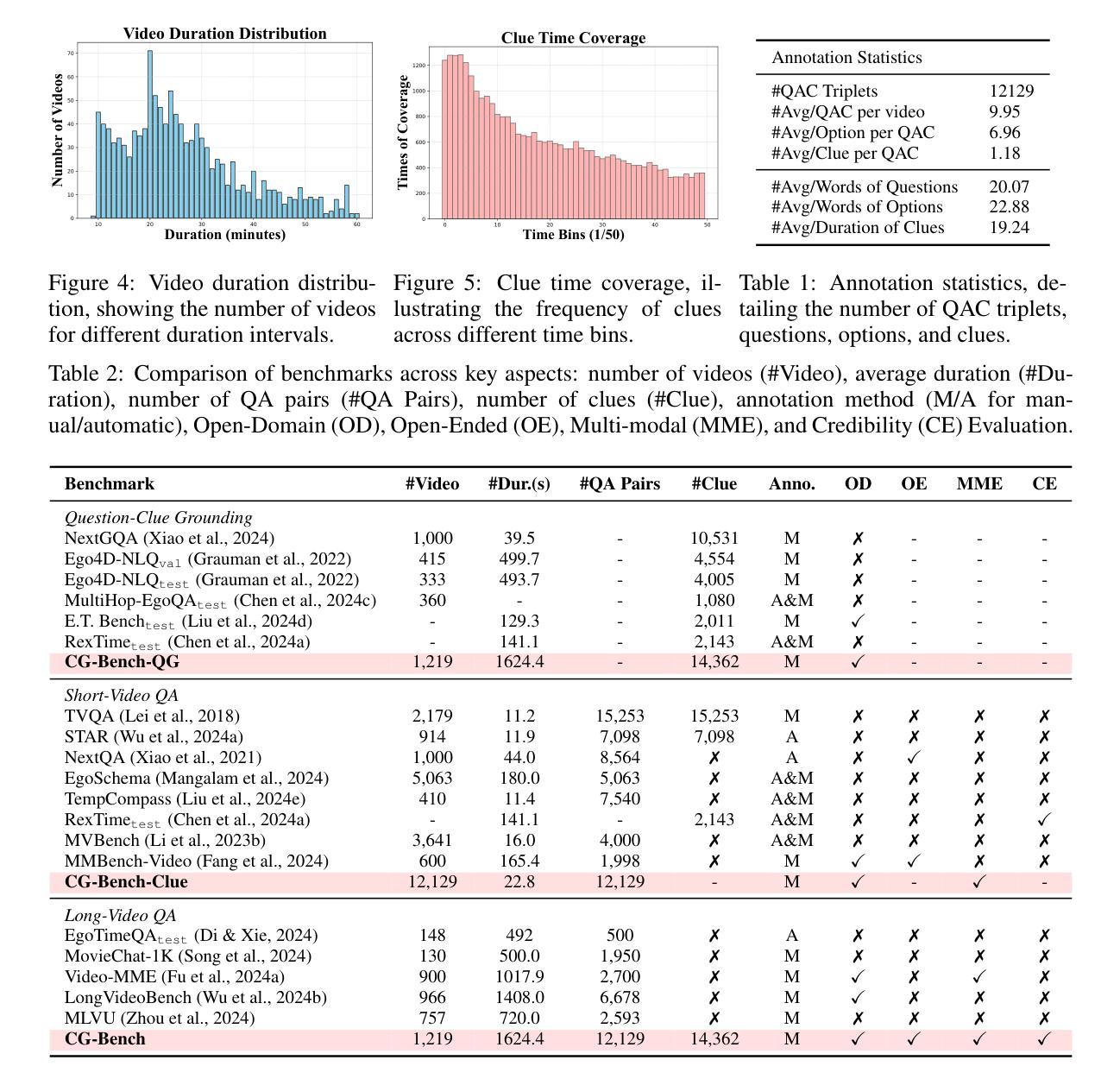
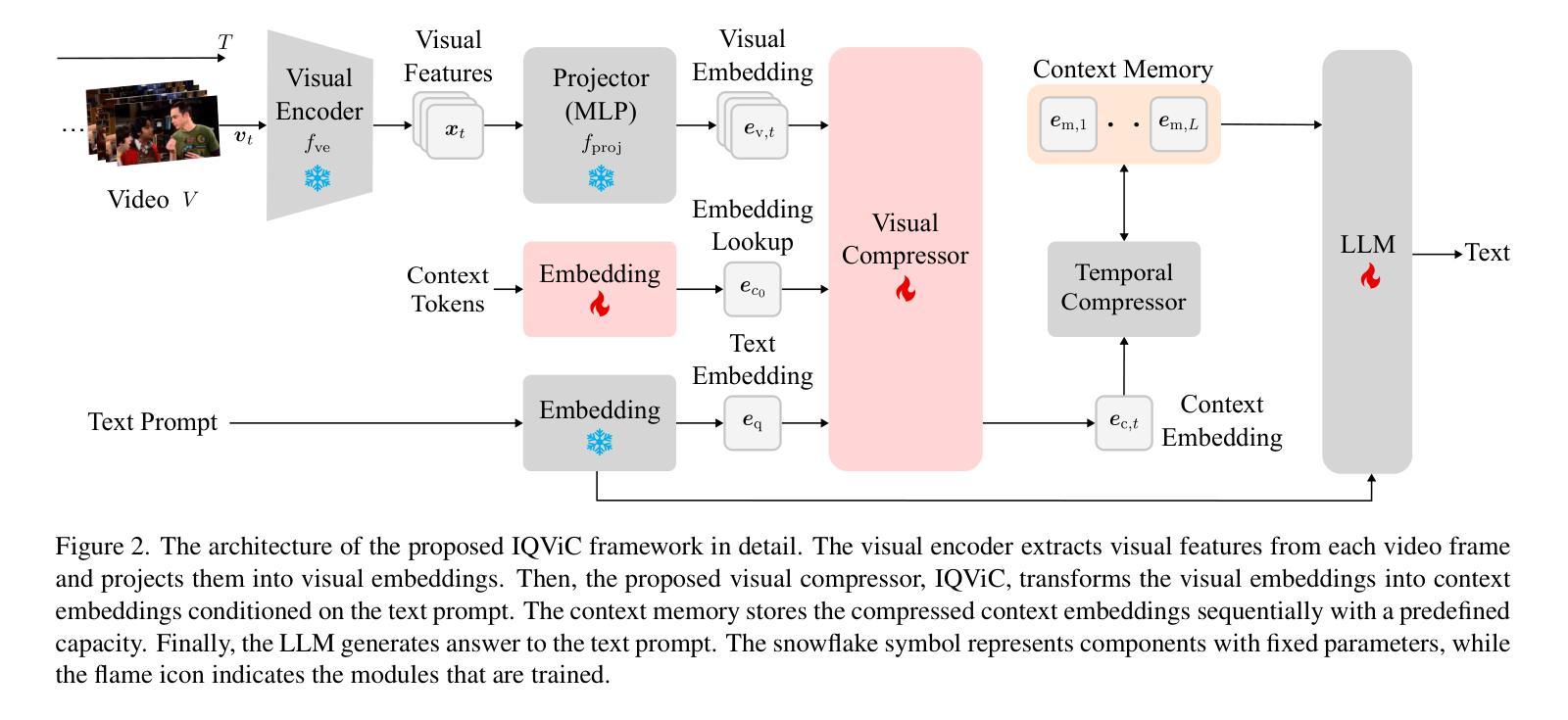
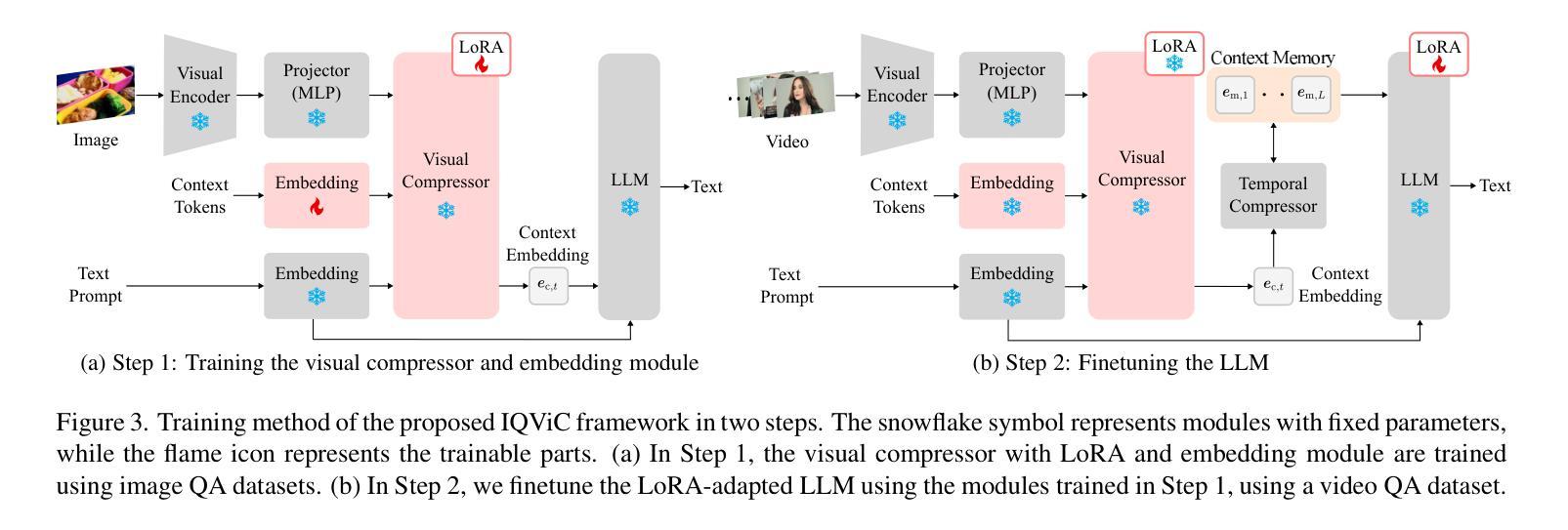
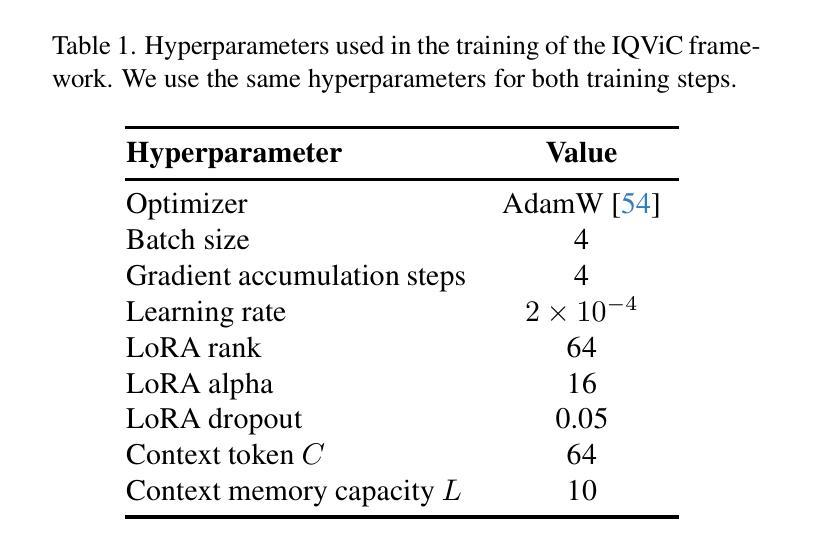
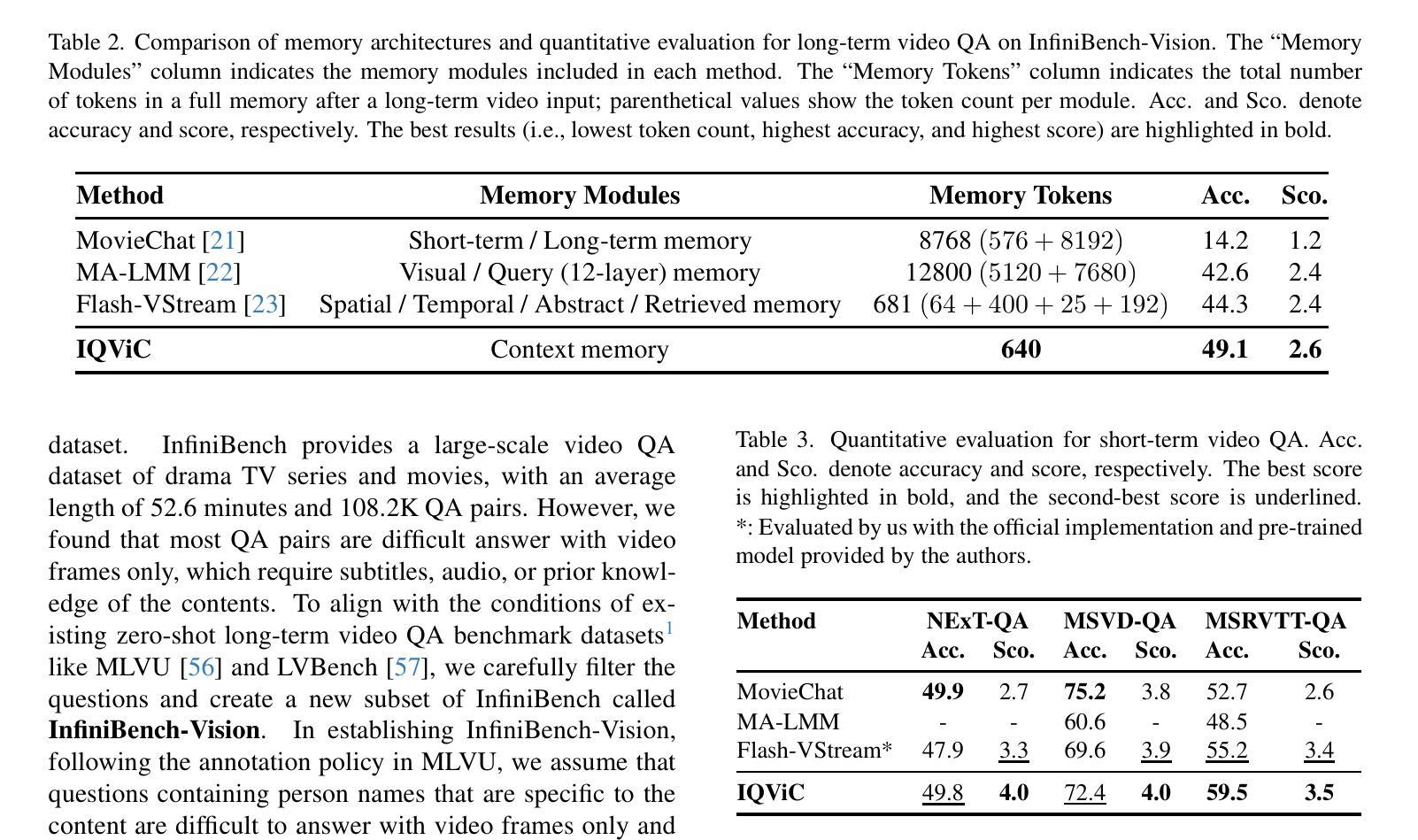
IQViC: In-context, Question Adaptive Vision Compressor for Long-term Video Understanding LMMs
Authors:Sosuke Yamao, Natsuki Miyahara, Yuki Harazono, Shun Takeuchi
With the increasing complexity of video data and the need for more efficient long-term temporal understanding, existing long-term video understanding methods often fail to accurately capture and analyze extended video sequences. These methods typically struggle to maintain performance over longer durations and to handle the intricate dependencies within the video content. To address these limitations, we propose a simple yet effective large multi-modal model framework for long-term video understanding that incorporates a novel visual compressor, the In-context, Question Adaptive Visual Compressor (IQViC). The key idea, inspired by humans’ selective attention and in-context memory mechanisms, is to introduce a novel visual compressor and incorporate efficient memory management techniques to enhance long-term video question answering. Our framework utilizes IQViC, a transformer-based visual compressor, enabling question-conditioned in-context compression, unlike existing methods that rely on full video visual features. This selectively extracts relevant information, significantly reducing memory token requirements. Through extensive experiments on a new dataset based on InfiniBench for long-term video understanding, and standard benchmarks used for existing methods’ evaluation, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed IQViC framework and its superiority over state-of-the-art methods in terms of video understanding accuracy and memory efficiency.
随着视频数据的复杂性不断增加和对更高效长期时间理解的需求,现有的长期视频理解方法往往无法准确地捕获和分析扩展的视频序列。这些方法通常在维持长时间性能和处理视频内容内部的复杂依赖关系方面遇到困难。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种简单有效的长期视频理解大型多模态模型框架,该框架融入了一种新型视觉压缩机——上下文问题自适应视觉压缩机(IQViC)。该关键理念受到人类选择性注意力和上下文记忆机制的启发,旨在引入新型视觉压缩机并融入高效的内存管理技术,以提升长期视频问答。我们的框架利用基于变压器的IQViC进行上下文内的压缩,不同于现有方法依赖于全视频视觉特征。这能够选择性提取相关信息,从而极大地减少内存令牌需求。我们在基于InfiniBench的长期视频理解的新数据集以及用于现有方法评估的标准基准测试集上进行了广泛的实验,证明了我们所提出的IQViC框架的有效性,其在视频理解准确性和内存效率方面优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first and second authors contributed equally to this work
Summary
针对长期视频理解任务的复杂性,现有方法难以准确捕捉和分析延长视频序列。为此,我们提出一个简单有效的大型多模态模型框架,引入了一种新型视觉压缩机——基于上下文的问题自适应视觉压缩机(IQViC),以提高长期视频问答的性能。该框架通过选择性提取相关信息,显著减少内存令牌需求,并在新的基于InfiniBench的长期视频理解数据集和现有方法评估标准基准测试上展示了IQViC框架的有效性和优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 现有长期视频理解方法难以准确捕捉和分析延长视频序列。
- 提出了一个大型多模态模型框架,用于长期视频理解。
- 引入了基于上下文的问题自适应视觉压缩机(IQViC)。
- IQViC能够选择性提取视频中的相关信息。
- IQViC框架显著减少了内存令牌需求。
- 在基于InfiniBench的长期视频理解数据集上进行了广泛实验。
点此查看论文截图
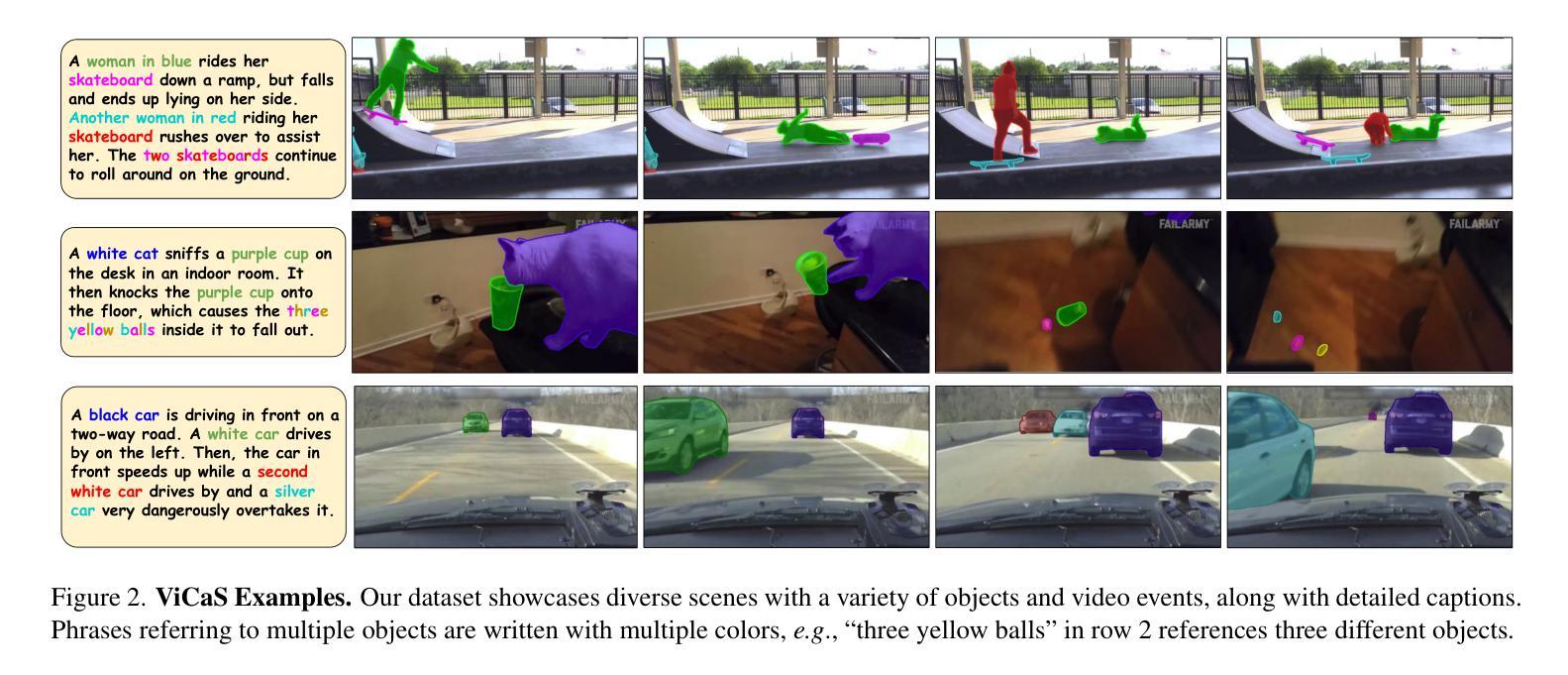
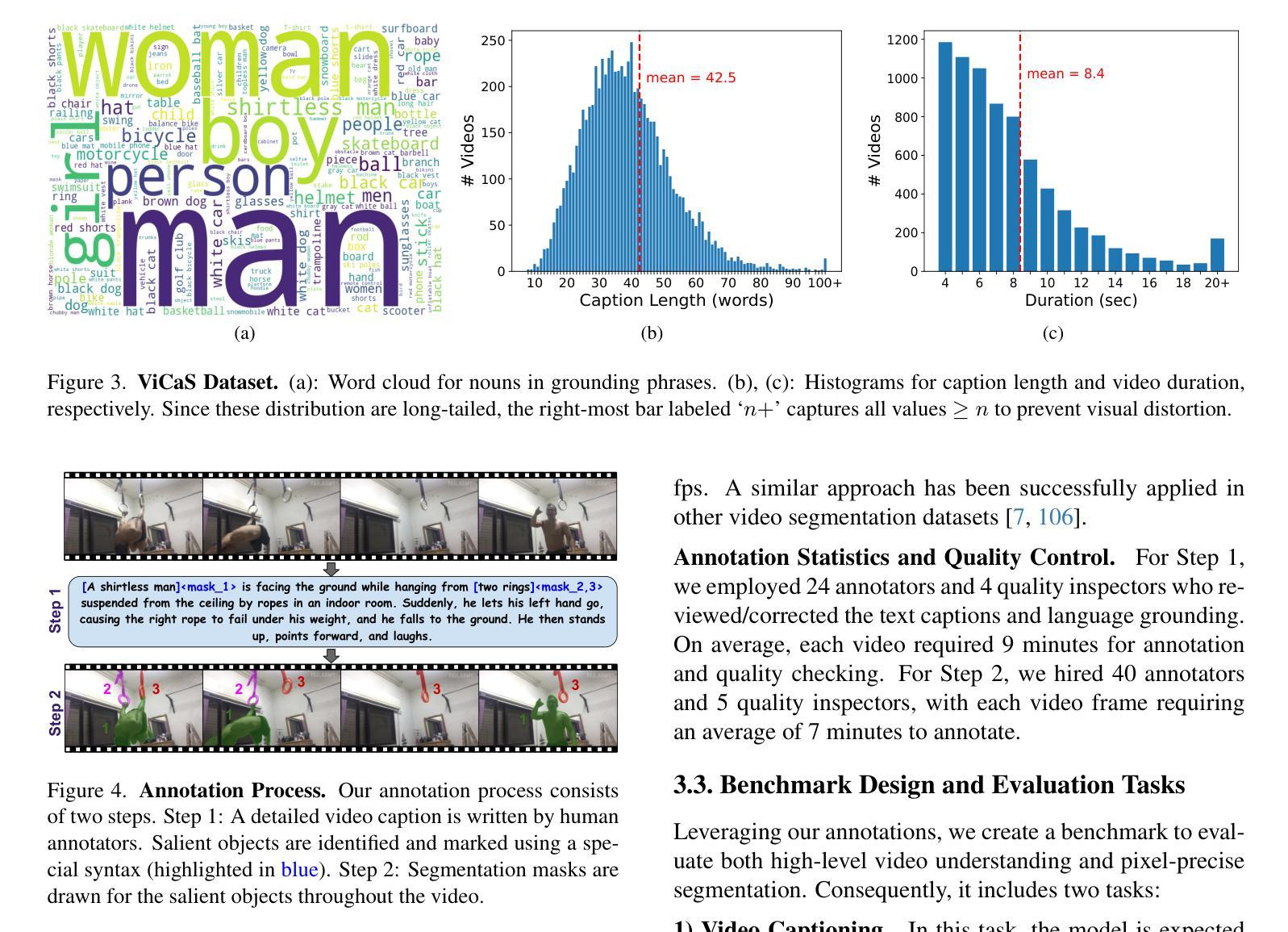
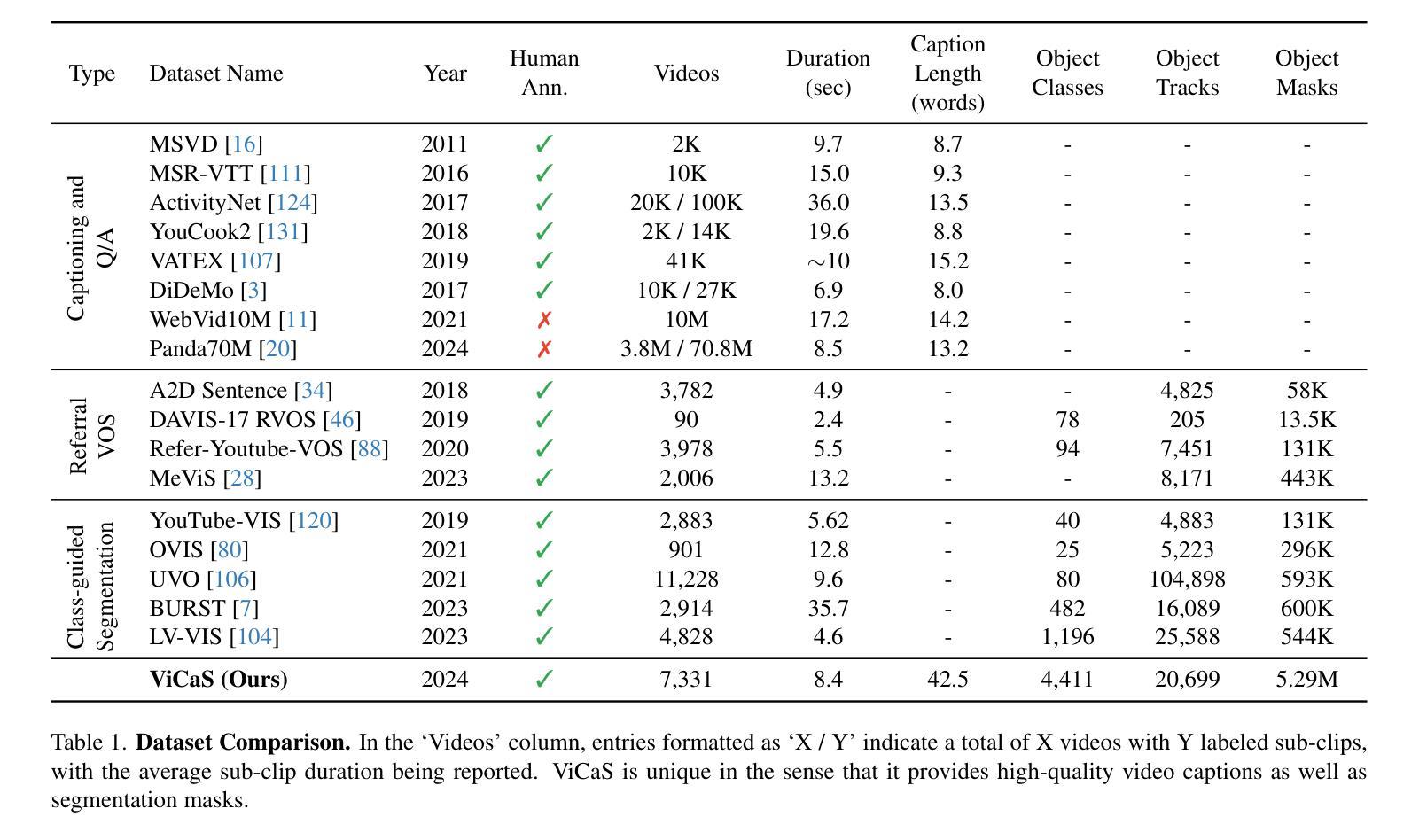
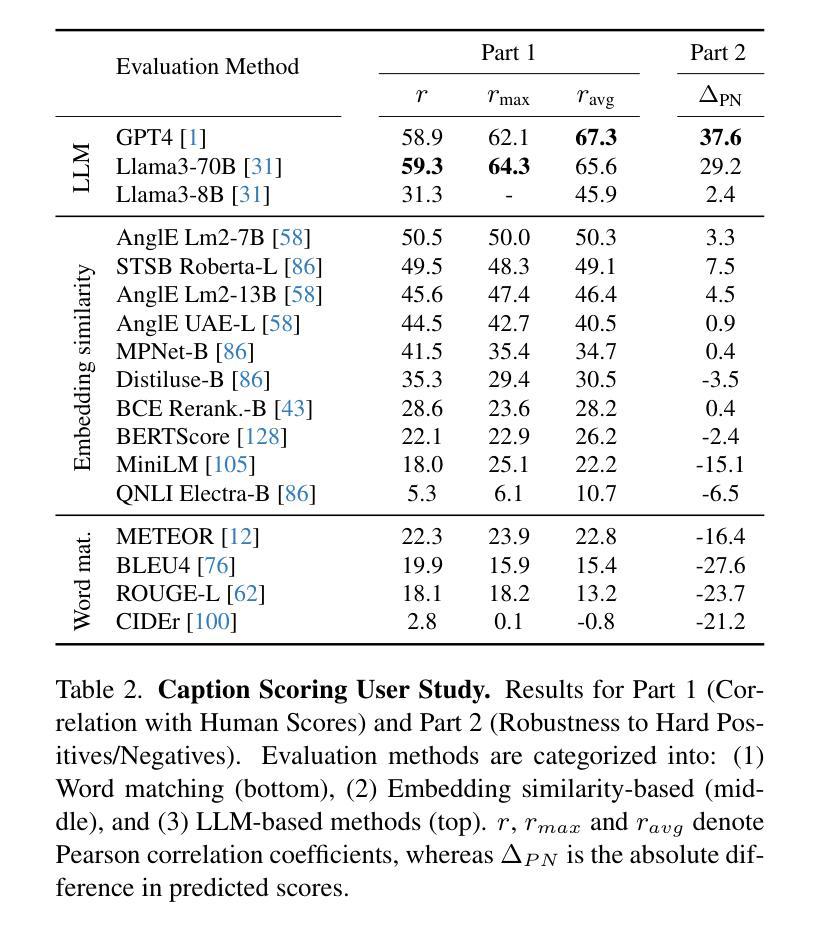
ViCaS: A Dataset for Combining Holistic and Pixel-level Video Understanding using Captions with Grounded Segmentation
Authors:Ali Athar, Xueqing Deng, Liang-Chieh Chen
Recent advances in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have expanded research in video understanding, primarily focusing on high-level tasks such as video captioning and question-answering. Meanwhile, a smaller body of work addresses dense, pixel-precise segmentation tasks, which typically involve category-guided or referral-based object segmentation. Although both research directions are essential for developing models with human-level video comprehension, they have largely evolved separately, with distinct benchmarks and architectures. This paper aims to unify these efforts by introducing ViCaS, a new dataset containing thousands of challenging videos, each annotated with detailed, human-written captions and temporally consistent, pixel-accurate masks for multiple objects with phrase grounding. Our benchmark evaluates models on both holistic/high-level understanding and language-guided, pixel-precise segmentation. We also present carefully validated evaluation measures and propose an effective model architecture that can tackle our benchmark. The project page is at https://ali2500.github.io/vicas-project/
近年来,多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)的进步推动了视频理解研究的发展,主要集中于高级任务,如视频描述和问答。与此同时,一小部分工作涉及密集、像素精确的分割任务,通常涉及类别指导或基于引用的对象分割。虽然这两个研究方向对于开发具有人类水平视频理解能力的模型都至关重要,但它们大多独立发展,具有不同的基准和架构。本文旨在通过引入ViCaS数据集来统一这些努力,该数据集包含数千个具有挑战性的视频,每个视频都经过详细的人类书写描述和与时间一致的像素精确掩膜进行注释,用于多个对象的短语定位。我们的基准测试对整体/高级理解和语言指导的像素精确分割进行评估。我们还提供了经过仔细验证的评价指标,并提出了可以有效应对我们基准测试模型架构。项目页面为:https://ali2500.github.io/vicas-project/(请按照实际网站链接进行替换) 。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视频理解领域的最新进展,主要关注高级任务,如视频描述和问答。同时,也有少量工作涉及密集、像素精确的分割任务。本文旨在通过引入ViCaS数据集统一这些研究方向,该数据集包含数千个具有挑战的视频,每个视频都经过详细的人类注释,包含标题和基于语言的像素精确分割掩膜。该数据集评估模型对整体高级理解和语言指导的像素精确分割能力,并提供了有效的模型架构来解决这一基准测试。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态大型语言模型(MLLMs)在视频理解领域取得进展,主要关注高级任务和密集像素精确分割任务。
- ViCaS数据集旨在统一这两个方向的研究,包含详细注释的视频和基于语言的像素精确分割掩膜。
- ViCaS数据集评估模型对整体高级理解和语言指导的像素精确分割能力。
- 该论文还提出了一种有效的模型架构来解决这一基准测试。
- 数据集具有挑战性,需要模型同时具备高级理解和精确分割能力。
- 该数据集为视频理解研究提供了新的评估标准和方法。
点此查看论文截图