⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-19 更新
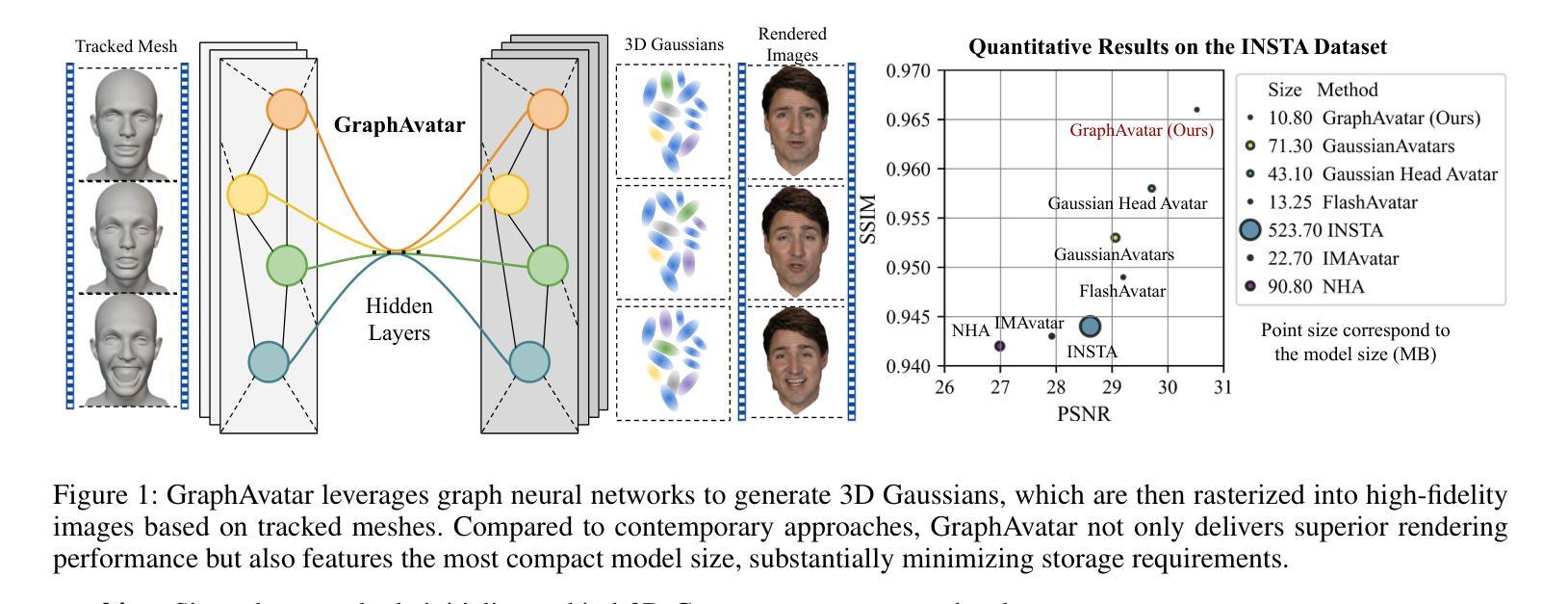
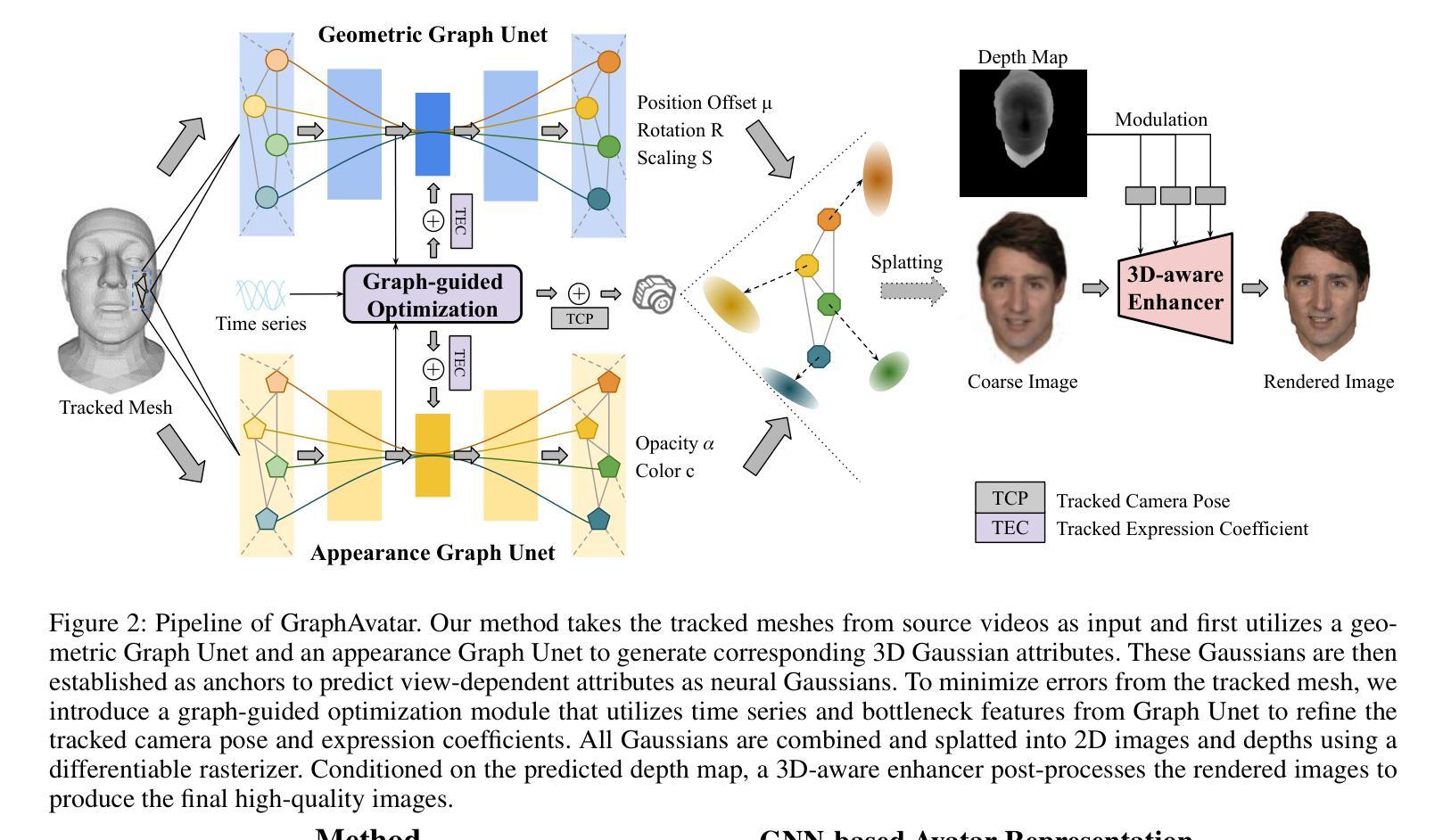
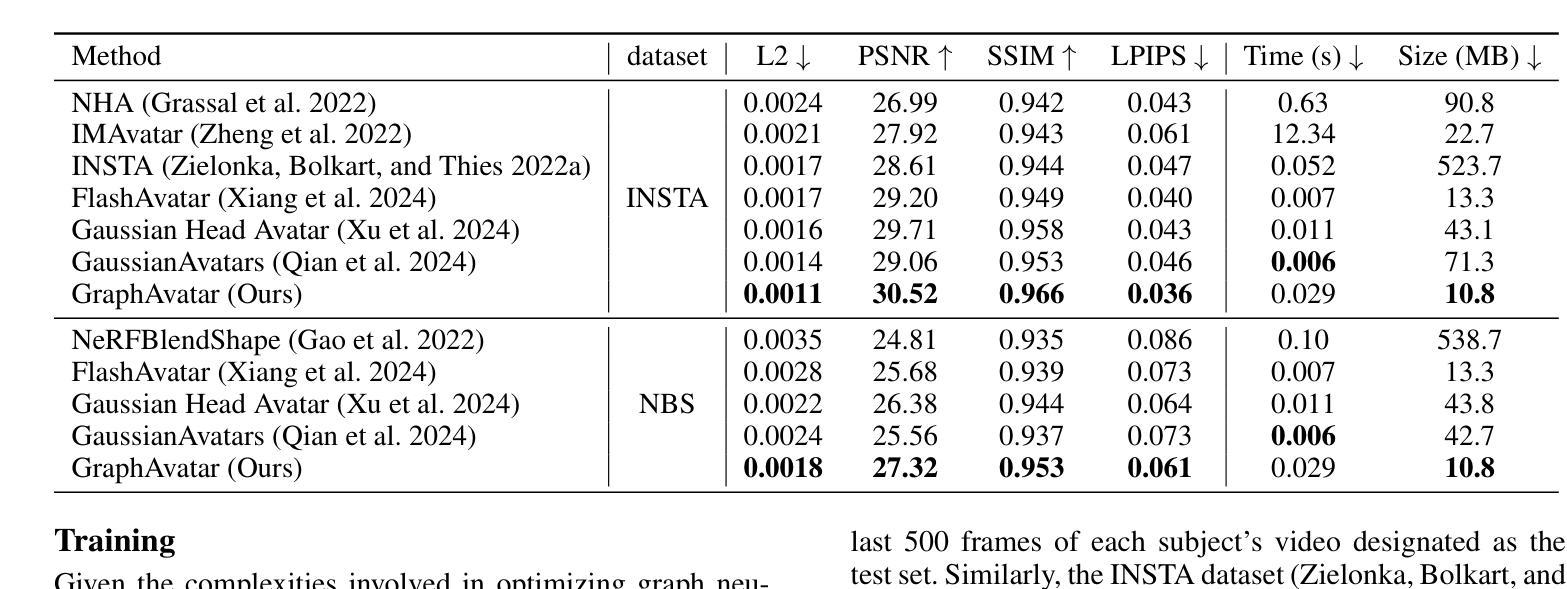
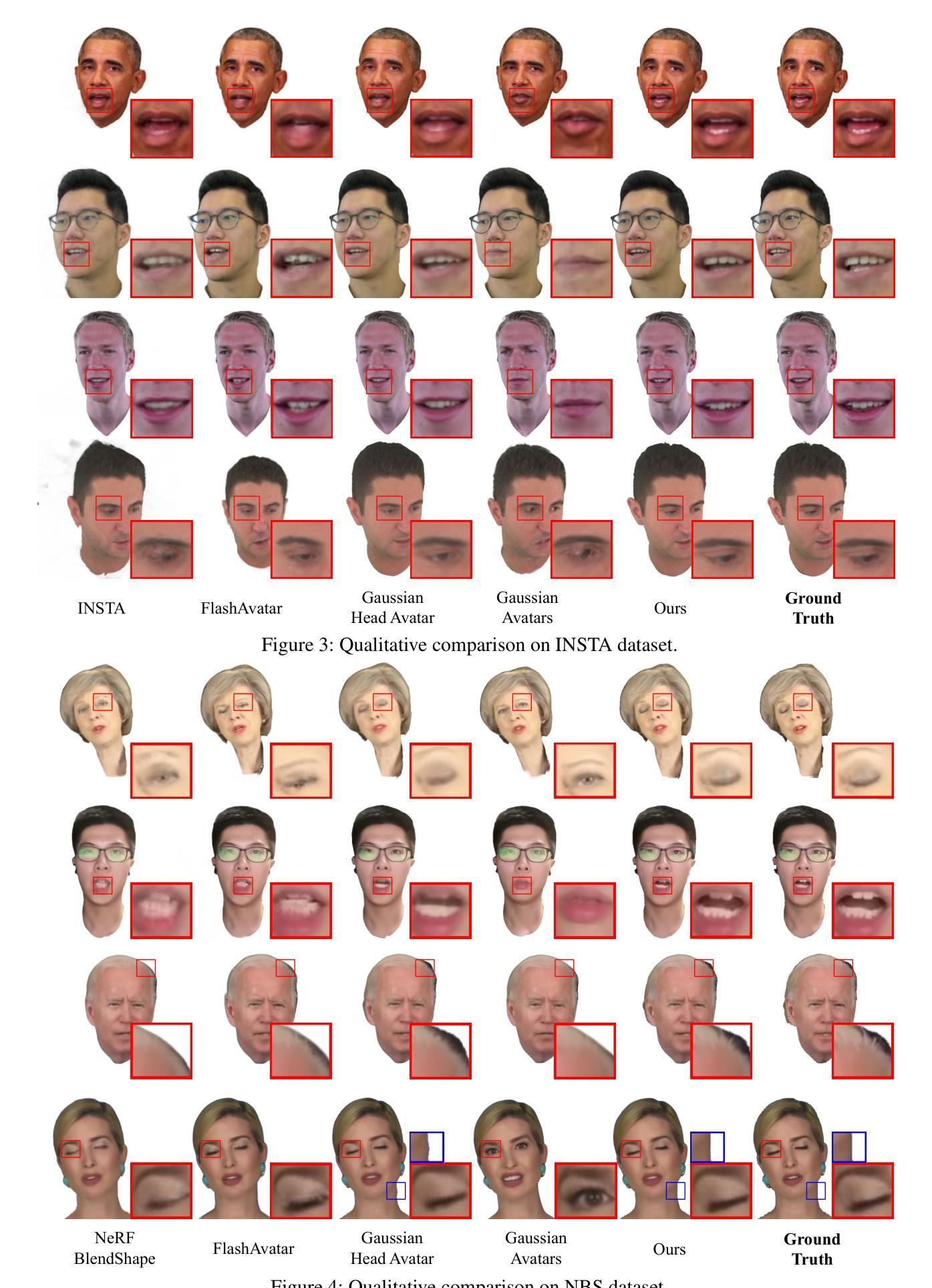
GraphAvatar: Compact Head Avatars with GNN-Generated 3D Gaussians
Authors:Xiaobao Wei, Peng Chen, Ming Lu, Hui Chen, Feng Tian
Rendering photorealistic head avatars from arbitrary viewpoints is crucial for various applications like virtual reality. Although previous methods based on Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) can achieve impressive results, they lack fidelity and efficiency. Recent methods using 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have improved rendering quality and real-time performance but still require significant storage overhead. In this paper, we introduce a method called GraphAvatar that utilizes Graph Neural Networks (GNN) to generate 3D Gaussians for the head avatar. Specifically, GraphAvatar trains a geometric GNN and an appearance GNN to generate the attributes of the 3D Gaussians from the tracked mesh. Therefore, our method can store the GNN models instead of the 3D Gaussians, significantly reducing the storage overhead to just 10MB. To reduce the impact of face-tracking errors, we also present a novel graph-guided optimization module to refine face-tracking parameters during training. Finally, we introduce a 3D-aware enhancer for post-processing to enhance the rendering quality. We conduct comprehensive experiments to demonstrate the advantages of GraphAvatar, surpassing existing methods in visual fidelity and storage consumption. The ablation study sheds light on the trade-offs between rendering quality and model size. The code will be released at: https://github.com/ucwxb/GraphAvatar
从任意视角渲染逼真的头部化身对于虚拟现实等应用至关重要。尽管基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的先前方法可以达到令人印象深刻的效果,但它们缺乏真实性和效率。最近使用3D高斯摊铺(3DGS)的方法提高了渲染质量和实时性能,但仍然需要巨大的存储开销。在本文中,我们介绍了一种名为GraphAvatar的方法,它利用图神经网络(GNN)生成头部化身的3D高斯。具体来说,GraphAvatar训练了一个几何GNN和一个外观GNN,从跟踪的网格生成3D高斯属性。因此,我们的方法可以存储GNN模型,而不是3D高斯,将存储开销大幅降低到仅10MB。为了减少面部跟踪误差的影响,我们还提出了一种新型的图引导优化模块,在训练过程中对面部跟踪参数进行微调。最后,我们引入了一个用于后处理的3D感知增强器,以提高渲染质量。我们进行了全面的实验,展示了GraphAvatar的优势,在视觉逼真度和存储消耗方面超越了现有方法。消融研究揭示了渲染质量和模型大小之间的权衡。代码将在以下网址发布:https://github.com/ucwxb/GraphAvatar
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by AAAI2025
Summary
本文介绍了一种利用图神经网络(GNN)生成头部角色三维高斯渲染的方法,称为GraphAvatar。该方法通过训练几何GNN和外观GNN生成三维高斯属性,从追踪网格中生成头像。相比传统方法,GraphAvatar显著减少了存储需求,仅需要存储GNN模型,大大减少了存储开销。此外,为了减轻面部跟踪误差的影响,引入了新型的图引导优化模块用于在训练过程中优化面部跟踪参数。最后通过综合实验证明了GraphAvatar在视觉保真度和存储消耗方面的优势。
Key Takeaways
- GraphAvatar利用图神经网络(GNN)生成头部角色的三维高斯渲染。
- 通过训练几何GNN和外观GNN生成三维高斯属性。
- 仅需存储GNN模型,显著减少存储需求。
- 引入图引导优化模块以优化面部跟踪参数,减轻面部跟踪误差的影响。
- 提供了综合实验证明GraphAvatar在视觉保真度和存储消耗方面的优势。
- 公开了代码以供研究使用。
点此查看论文截图

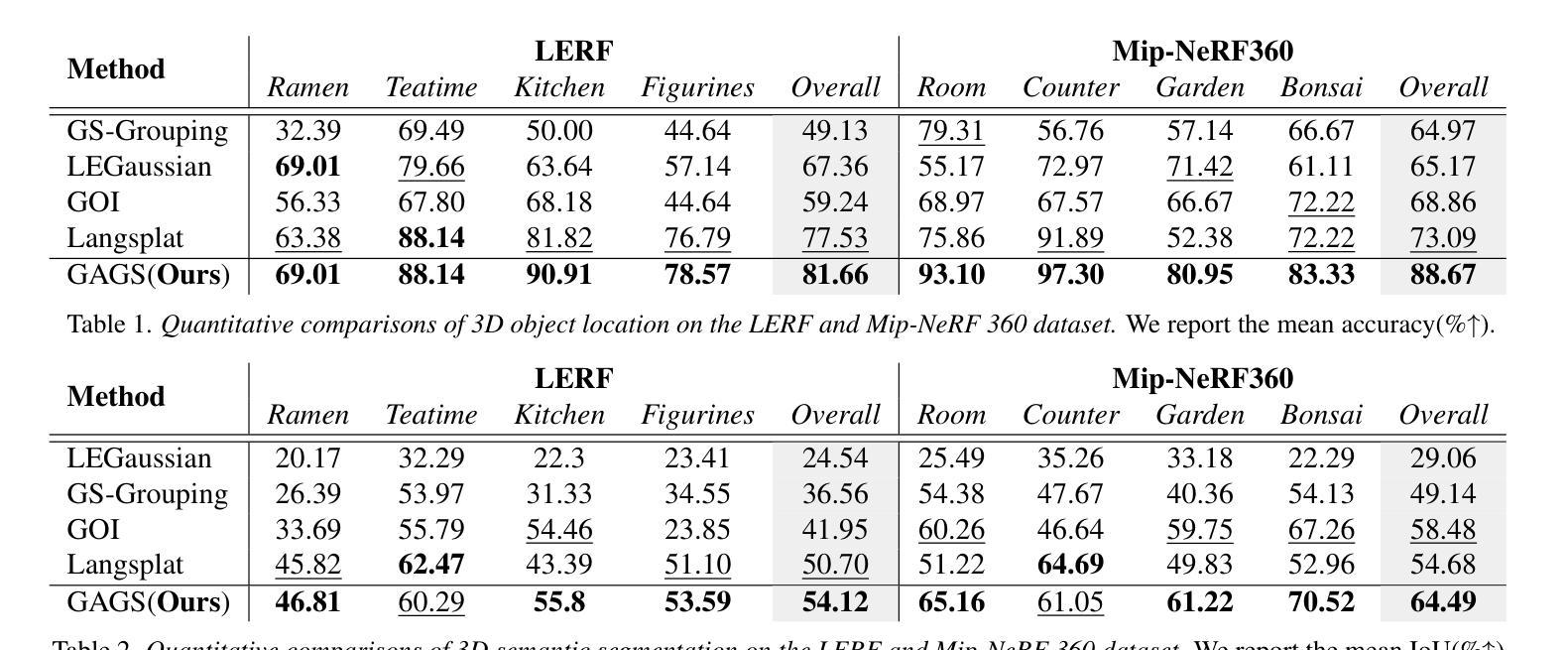
GAGS: Granularity-Aware Feature Distillation for Language Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Yuning Peng, Haiping Wang, Yuan Liu, Chenglu Wen, Zhen Dong, Bisheng Yang
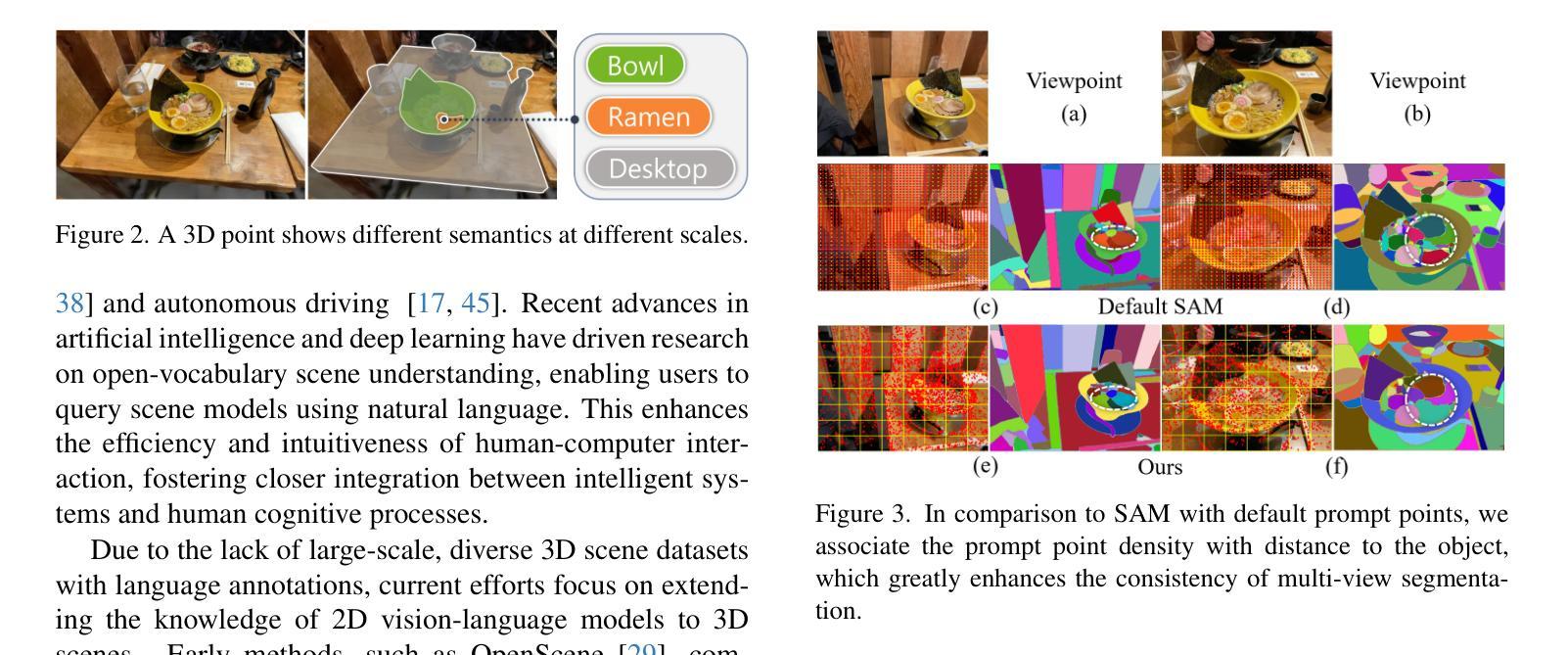
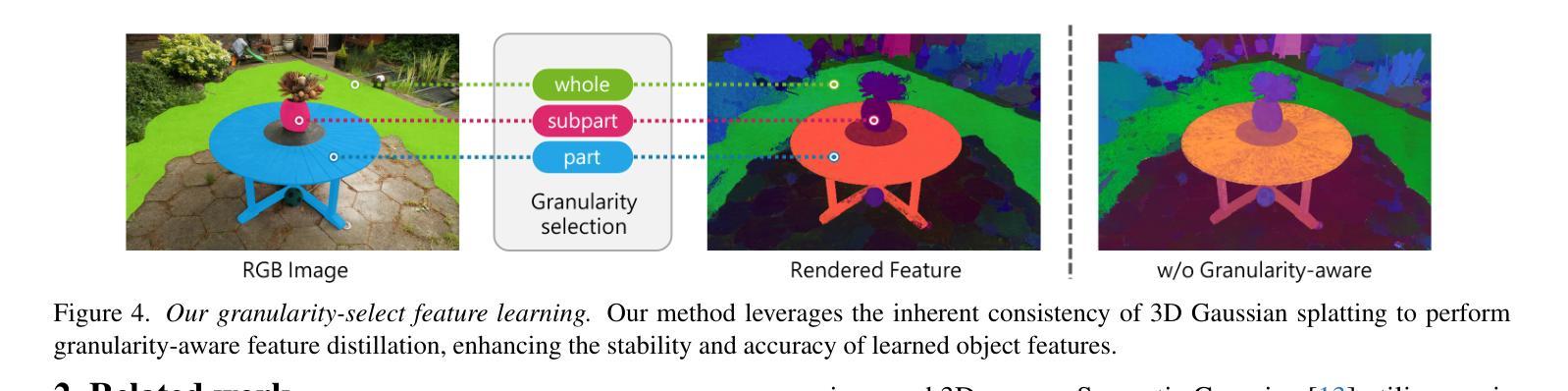
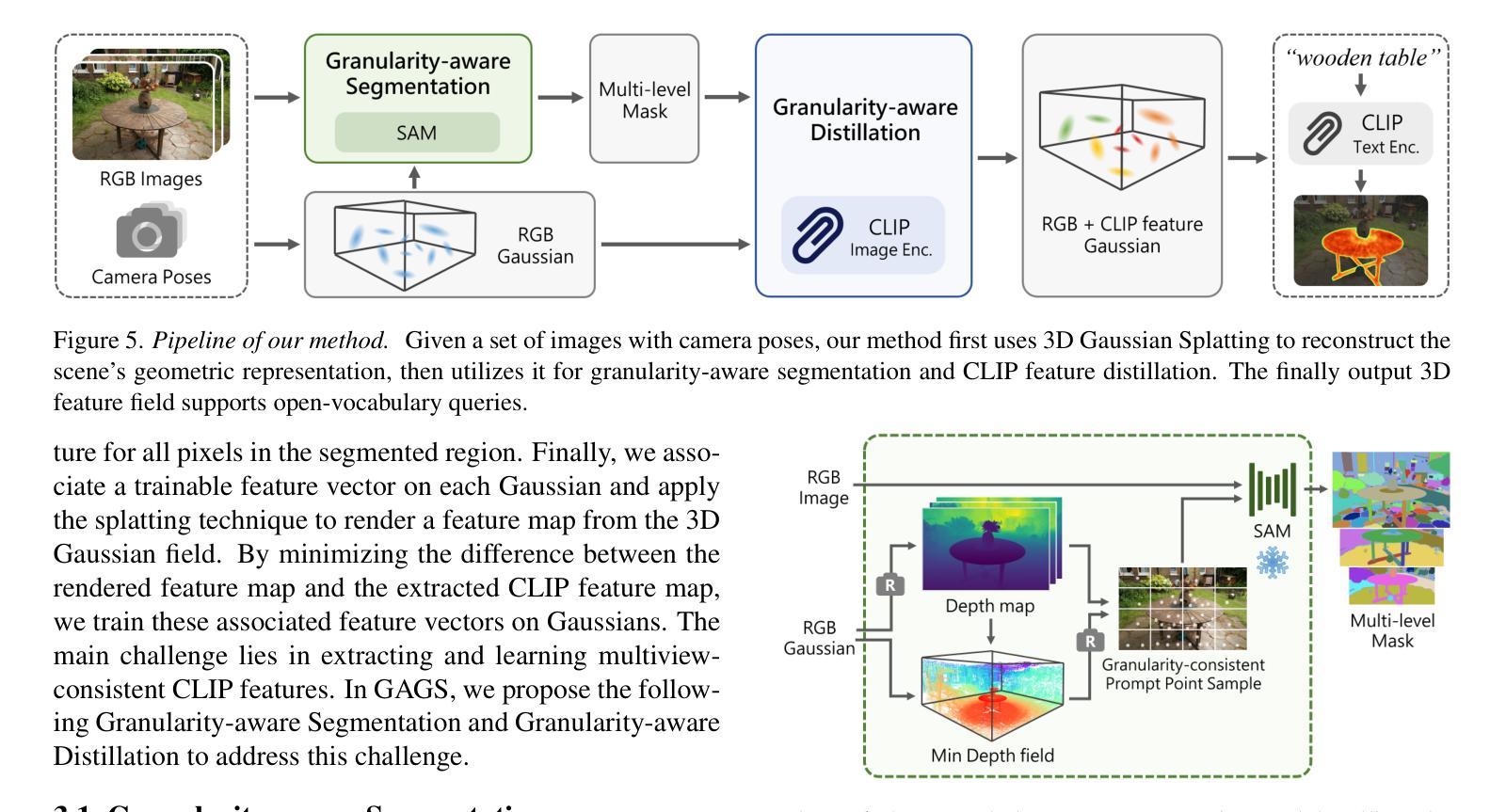
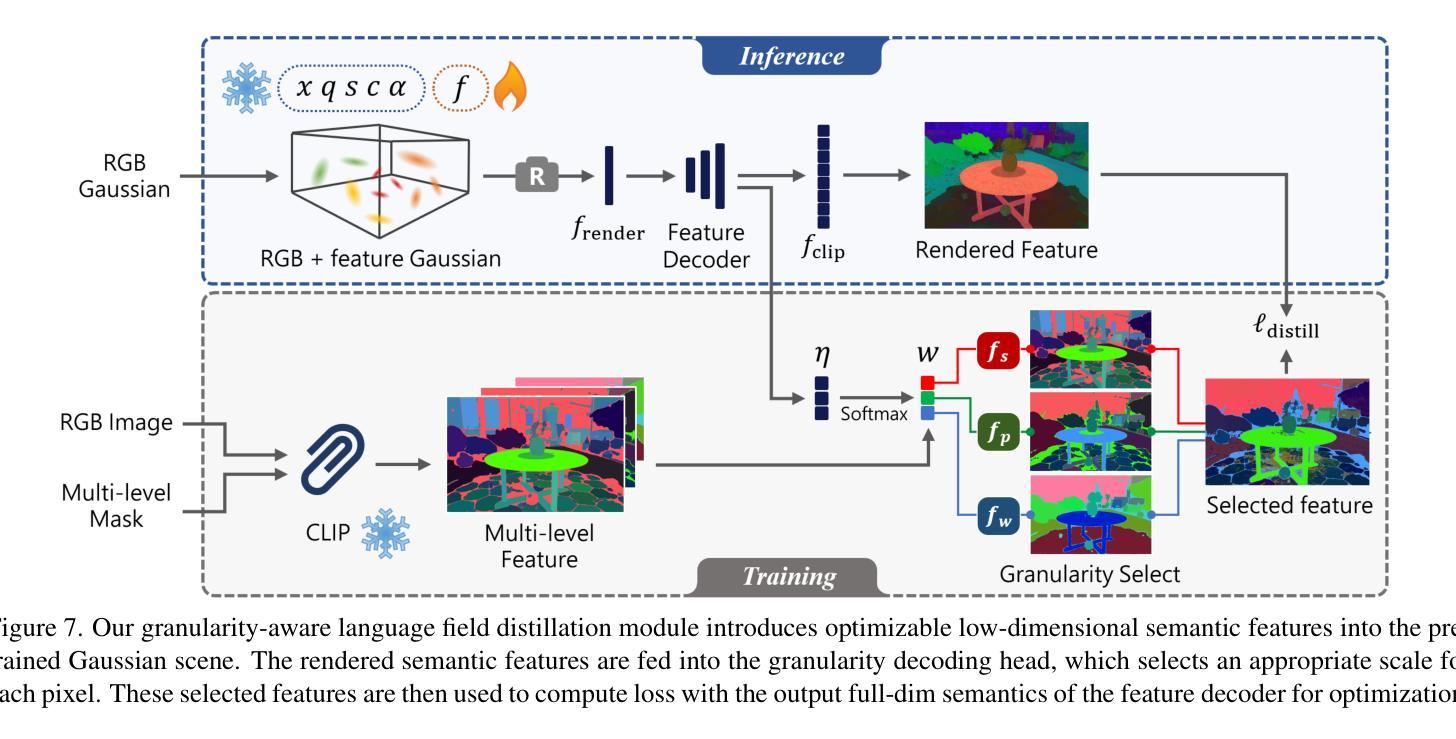
3D open-vocabulary scene understanding, which accurately perceives complex semantic properties of objects in space, has gained significant attention in recent years. In this paper, we propose GAGS, a framework that distills 2D CLIP features into 3D Gaussian splatting, enabling open-vocabulary queries for renderings on arbitrary viewpoints. The main challenge of distilling 2D features for 3D fields lies in the multiview inconsistency of extracted 2D features, which provides unstable supervision for the 3D feature field. GAGS addresses this challenge with two novel strategies. First, GAGS associates the prompt point density of SAM with the camera distances, which significantly improves the multiview consistency of segmentation results. Second, GAGS further decodes a granularity factor to guide the distillation process and this granularity factor can be learned in a unsupervised manner to only select the multiview consistent 2D features in the distillation process. Experimental results on two datasets demonstrate significant performance and stability improvements of GAGS in visual grounding and semantic segmentation, with an inference speed 2$\times$ faster than baseline methods. The code and additional results are available at https://pz0826.github.io/GAGS-Webpage/ .
近年来,能够准确感知空间中物体复杂语义属性的三维开放词汇场景理解引起了广泛的关注。在本文中,我们提出了GAGS框架,它将二维CLIP特征转化为三维高斯融合技术,为任意视角的渲染实现开放词汇查询。蒸馏二维特征用于三维领域的挑战在于提取的二维特征的多视角不一致性,这为三维特征领域提供了不稳定的监督。GAGS通过两种新策略来解决这一挑战。首先,GAGS将SAM的提示点密度与相机距离相关联,这大大提高了分割结果的多视角一致性。其次,GAGS进一步解码粒度因子来指导蒸馏过程,该粒度因子可以以无监督的方式学习,仅在蒸馏过程中选择多视角一致的二维特征。在两个数据集上的实验结果表明,在视觉定位和目标分割方面,GAGS的性能和稳定性显著提高,其推理速度比基线方法快两倍。代码和更多结果可在https://pz0826.github.io/GAGS-Webpage/获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://pz0826.github.io/GAGS-Webpage/
Summary
本文提出一种名为GAGS的框架,它将二维CLIP特征转化为三维高斯混合表示,实现对任意视角渲染的三维场景进行开放词汇查询的任务。该框架解决了二维特征在三维场景中蒸馏面临的多视角不一致性问题,提高了语义分割和视觉定位的性能及稳定性。其创新性在于通过关联采样点密度与相机距离、解码粒度因子等策略改善多视角一致性。相关代码和额外结果已发布于网站:https://pz0826.github.io/GAGS-Webpage/。
Key Takeaways
- GAGS框架实现了二维CLIP特征到三维高斯混合表示的转化,为三维场景理解带来新思路。
- 解决了二维特征在三维场景蒸馏过程中的多视角不一致性问题。
- 通过关联采样点密度与相机距离的策略,提高了分割结果的多视角一致性。
- 引入粒度因子以指导蒸馏过程,能够选择多视角一致的二维特征。
- 在两个数据集上的实验结果显示,GAGS在视觉定位与语义分割任务中实现了显著的性能提升。
- GAGS框架的推理速度比基准方法快两倍。
点此查看论文截图

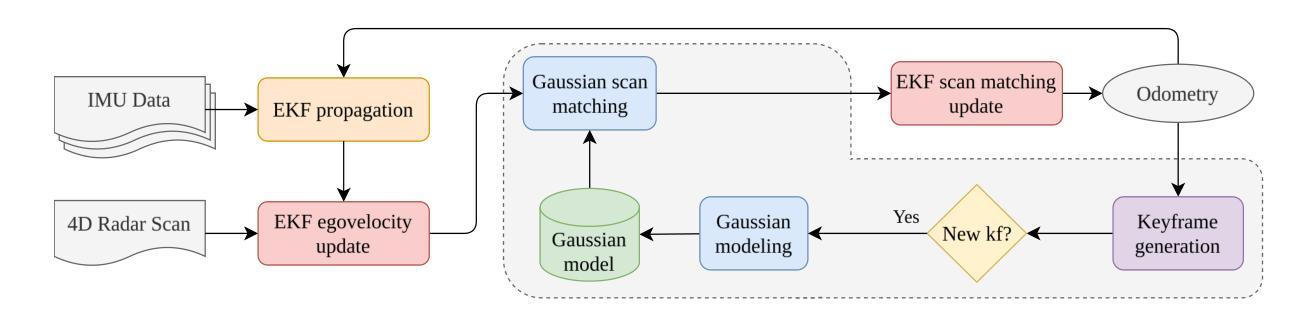
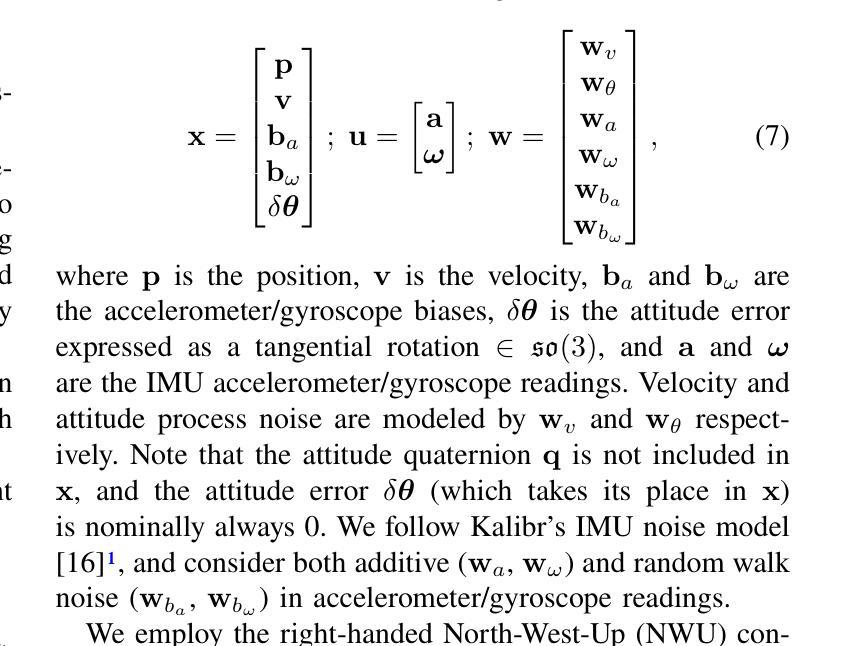
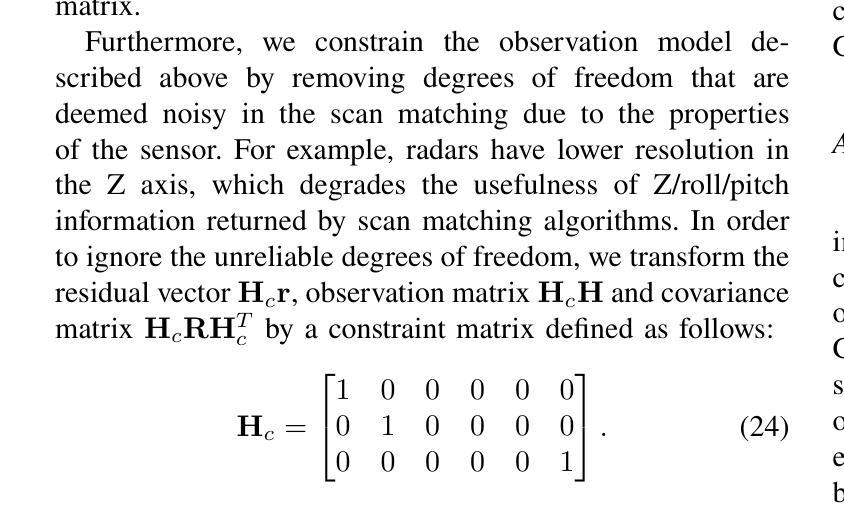
4D Radar-Inertial Odometry based on Gaussian Modeling and Multi-Hypothesis Scan Matching
Authors:Fernando Amodeo, Luis Merino, Fernando Caballero
4D millimeter-wave (mmWave) radars are sensors that provide robustness against adverse weather conditions (rain, snow, fog, etc.), and as such they are increasingly being used for odometry and SLAM applications. However, the noisy and sparse nature of the returned scan data proves to be a challenging obstacle for existing point cloud matching based solutions, especially those originally intended for more accurate sensors such as LiDAR. Inspired by visual odometry research around 3D Gaussian Splatting, in this paper we propose using freely positioned 3D Gaussians to create a summarized representation of a radar point cloud tolerant to sensor noise, and subsequently leverage its inherent probability distribution function for registration (similar to NDT). Moreover, we propose simultaneously optimizing multiple scan matching hypotheses in order to further increase the robustness of the system against local optima of the function. Finally, we fuse our Gaussian modeling and scan matching algorithms into an EKF radar-inertial odometry system designed after current best practices. Experiments show that our Gaussian-based odometry is able to outperform current baselines on a well-known 4D radar dataset used for evaluation.
四维毫米波雷达传感器在恶劣天气条件下(如雨、雪、雾等)表现出稳健性,因此越来越多地用于测距和SLAM应用。然而,返回的扫描数据具有噪声大和稀疏性的特点,证明这对现有的基于点云匹配的解决方案构成了一项具有挑战性的障碍,尤其是那些最初为激光雷达等更精确传感器设计的解决方案。受围绕三维高斯喷溅的视觉测距研究启发,本文提出使用自由定位的3D高斯来创建一种对传感器噪声具有容忍度的雷达点云摘要表示,然后利用其固有的概率分布函数进行注册(类似于NDT)。此外,我们还提出同时优化多个扫描匹配假设,以进一步提高系统对函数局部最优解的稳健性。最后,我们将高斯建模和扫描匹配算法融合到一个借鉴当前最佳实践的雷达惯性测距系统的扩展卡尔曼滤波器中。实验表明,我们基于高斯模型的测距系统在众所周知的四维雷达数据集上的性能优于当前基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Our code and results can be publicly accessed at: https://github.com/robotics-upo/gaussian-rio
Summary
基于三维高斯技术的雷达点云摘要表示可抗干扰传感器噪声,并利用其固有概率分布函数进行注册,类似于NDT。同时优化多个扫描匹配假设,提高系统对局部最优解的稳健性。融合高斯建模和扫描匹配算法,构建雷达惯性里程计系统,在4D雷达数据集上的表现优于当前基线。
Key Takeaways
- 4D毫米波雷达能在恶劣天气条件下稳健运行,适用于里程计和SLAM应用。
- 雷达返回扫描数据具有噪声大和稀疏性,对点云匹配解决方案构成挑战。
- 灵感来自视觉里程计中的三维高斯展开研究,提出使用自由定位的三维高斯对雷达点云进行摘要表示,以抗干扰传感器噪声。
- 利用概率分布函数进行注册,类似于NDT方法。
- 同时优化多个扫描匹配假设,增强系统稳健性,减少局部最优解干扰。
- 将高斯建模和扫描匹配算法融合进EKF雷达惯性里程计系统。
点此查看论文截图

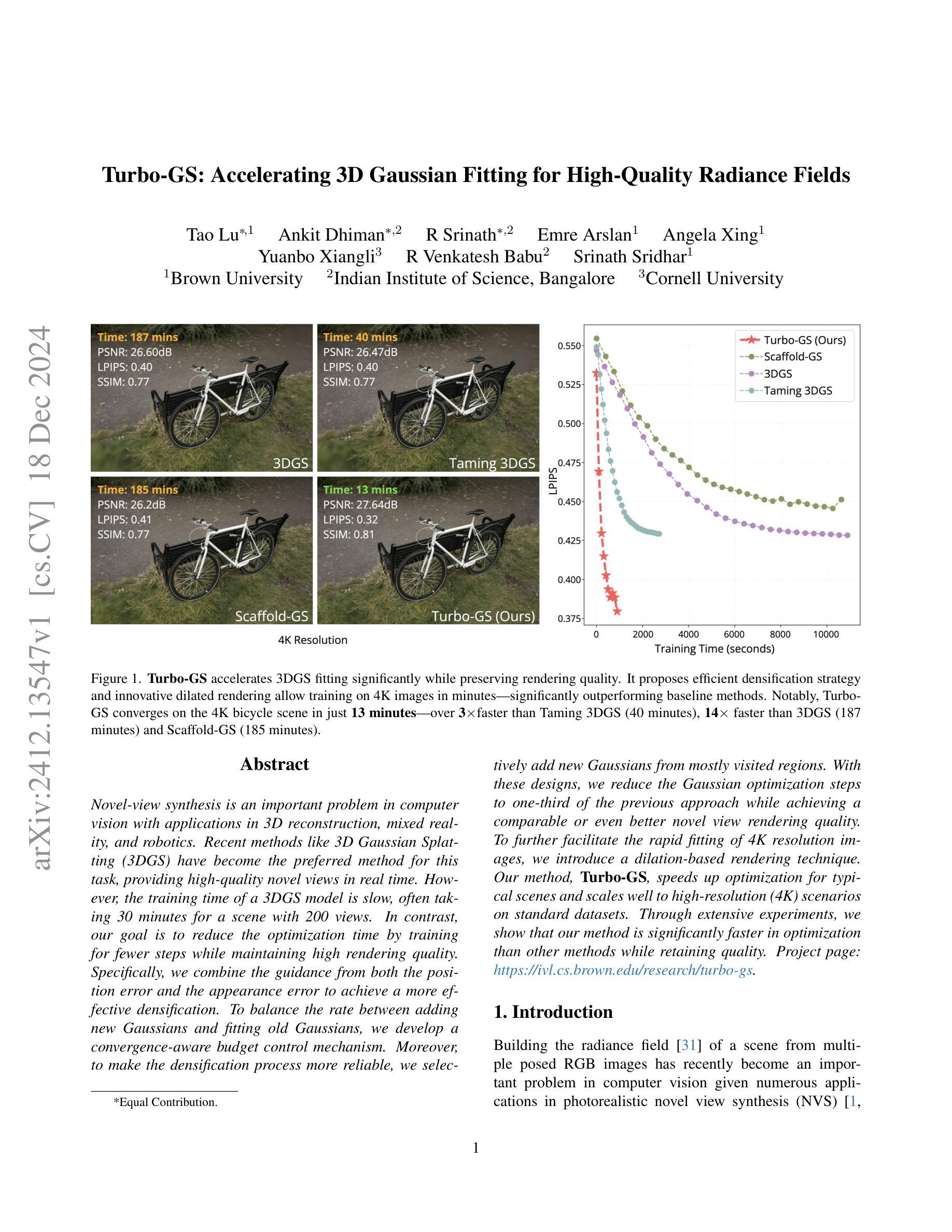
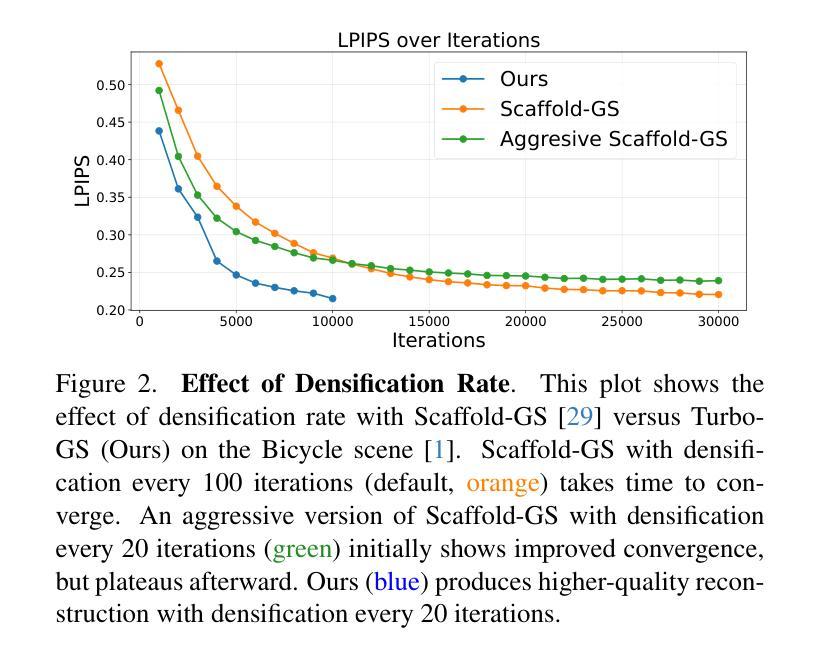
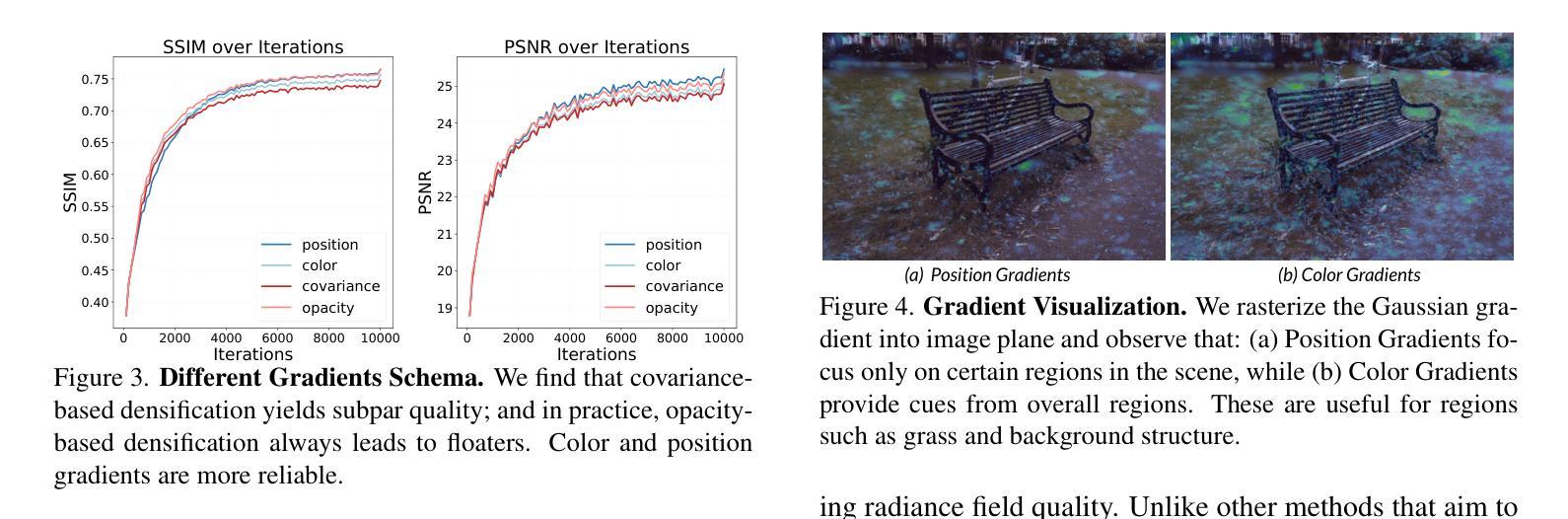
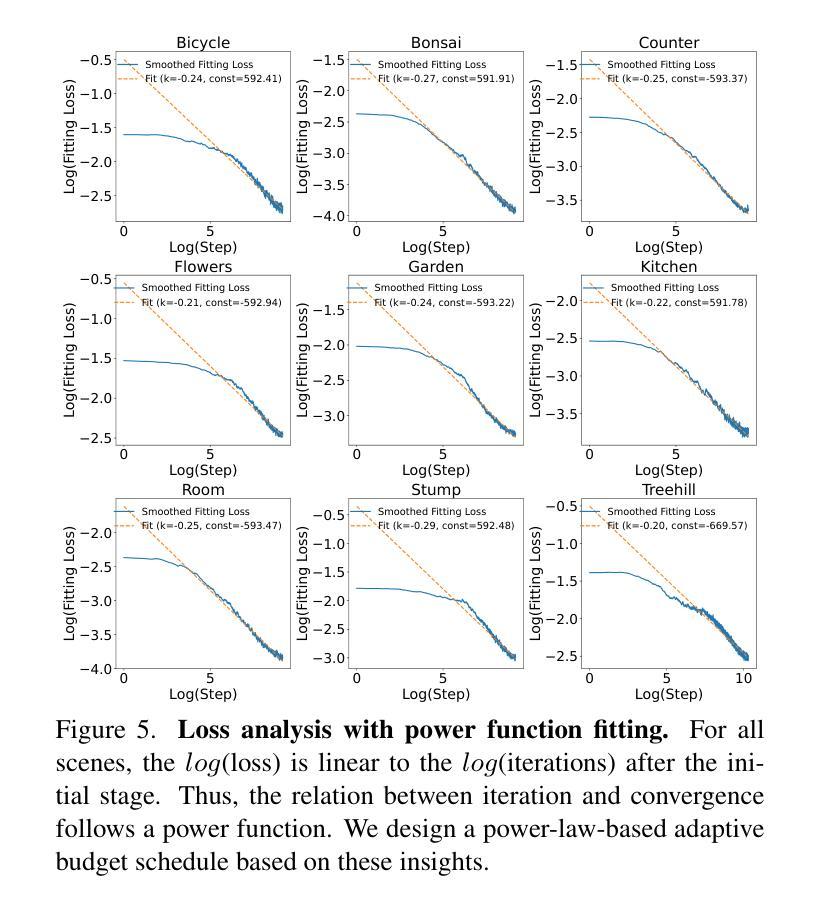
Turbo-GS: Accelerating 3D Gaussian Fitting for High-Quality Radiance Fields
Authors:Tao Lu, Ankit Dhiman, R Srinath, Emre Arslan, Angela Xing, Yuanbo Xiangli, R Venkatesh Babu, Srinath Sridhar
Novel-view synthesis is an important problem in computer vision with applications in 3D reconstruction, mixed reality, and robotics. Recent methods like 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have become the preferred method for this task, providing high-quality novel views in real time. However, the training time of a 3DGS model is slow, often taking 30 minutes for a scene with 200 views. In contrast, our goal is to reduce the optimization time by training for fewer steps while maintaining high rendering quality. Specifically, we combine the guidance from both the position error and the appearance error to achieve a more effective densification. To balance the rate between adding new Gaussians and fitting old Gaussians, we develop a convergence-aware budget control mechanism. Moreover, to make the densification process more reliable, we selectively add new Gaussians from mostly visited regions. With these designs, we reduce the Gaussian optimization steps to one-third of the previous approach while achieving a comparable or even better novel view rendering quality. To further facilitate the rapid fitting of 4K resolution images, we introduce a dilation-based rendering technique. Our method, Turbo-GS, speeds up optimization for typical scenes and scales well to high-resolution (4K) scenarios on standard datasets. Through extensive experiments, we show that our method is significantly faster in optimization than other methods while retaining quality. Project page: https://ivl.cs.brown.edu/research/turbo-gs.
新颖视角合成是计算机视觉中的一个重要问题,在3D重建、混合现实和机器人技术等领域有广泛应用。最近的方法如3D高斯喷涂(3DGS)已成为该任务的首选方法,能够在实时生成高质量的新颖视角。然而,3DGS模型的训练时间较慢,对于包含200个视角的场景通常需要30分钟。相比之下,我们的目标是通过减少训练步骤来缩短优化时间,同时保持高渲染质量。具体来说,我们结合了位置误差和外观误差的指导来实现更有效的密集化。为了平衡添加新高斯和拟合旧高斯之间的比率,我们开发了一种收敛感知预算控制机制。此外,为了使密集化过程更加可靠,我们从访问较多的区域中选择性地添加新的高斯值。通过这些设计,我们将高斯优化步骤减少到先前方法的三分之一,同时实现相当或更好的新颖视角渲染质量。为了进一步促进4K分辨率图像的快速拟合,我们引入了一种基于膨胀的渲染技术。我们的方法Turbo-GS加速典型场景的优化,在标准数据集上很好地扩展到高分辨率(4K)场景。通过大量实验,我们证明与其他方法相比,我们的方法在优化过程中显著更快且保留质量。项目页面:https://ivl.cs.brown.edu/research/turbo-gs。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://ivl.cs.brown.edu/research/turbo-gs
摘要
本文探讨了计算机视觉领域中的新型视图合成问题,特别是在3D重建、混合现实和机器人技术中的应用。针对当前方法如3D高斯拼贴(3DGS)训练时间长的问题,提出了一种新的优化方法Turbo-GS。该方法通过结合位置误差和外观误差的指导,实现更有效的密集化。同时,通过开发收敛感知预算控制机制和选择性添加新高斯的方式,将高斯优化步骤减少至原方法的三分之一,实现了相当或更好的新型视图渲染质量。此外,还引入了一种基于膨胀的渲染技术,以加快4K分辨率图像的快速拟合。实验表明,该方法在优化速度上显著快于其他方法,同时保持高质量。
关键见解
- 新型视图合成是计算机视觉中的重要问题,应用于3D重建、混合现实和机器人技术。
- 3DGS等方法虽然能提供高质量的新型视图,但训练时间长。
- Turbo-GS方法通过结合位置误差和外观误差指导,实现更有效的密集化。
- 收敛感知预算控制机制和选择性添加新高斯的方式,大幅减少优化步骤。
- Turbo-GS方法实现相当或更好的新型视图渲染质量,同时显著加快优化速度。
- 引入基于膨胀的渲染技术,以加快4K分辨率图像的快速拟合。
点此查看论文截图

GaussTR: Foundation Model-Aligned Gaussian Transformer for Self-Supervised 3D Spatial Understanding
Authors:Haoyi Jiang, Liu Liu, Tianheng Cheng, Xinjie Wang, Tianwei Lin, Zhizhong Su, Wenyu Liu, Xinggang Wang
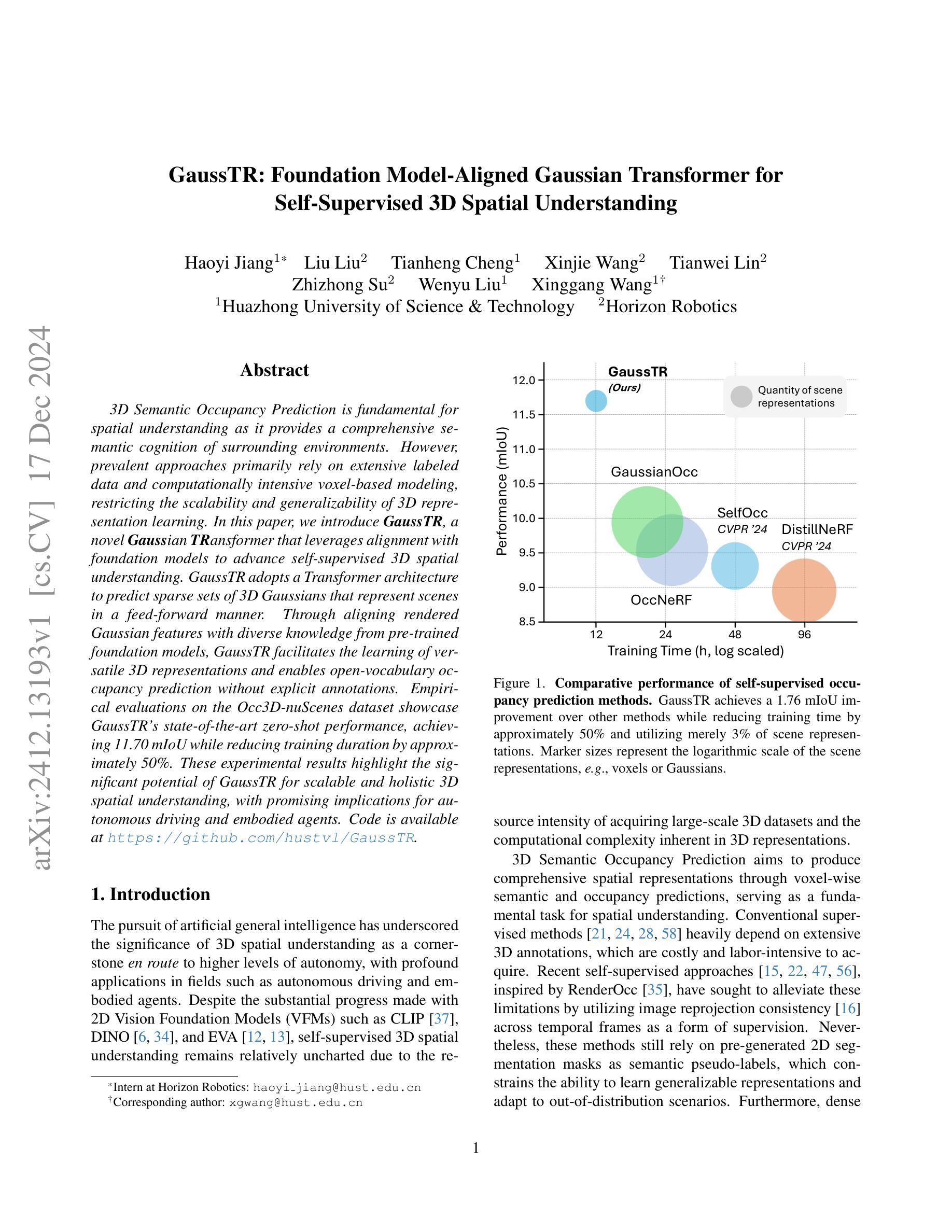
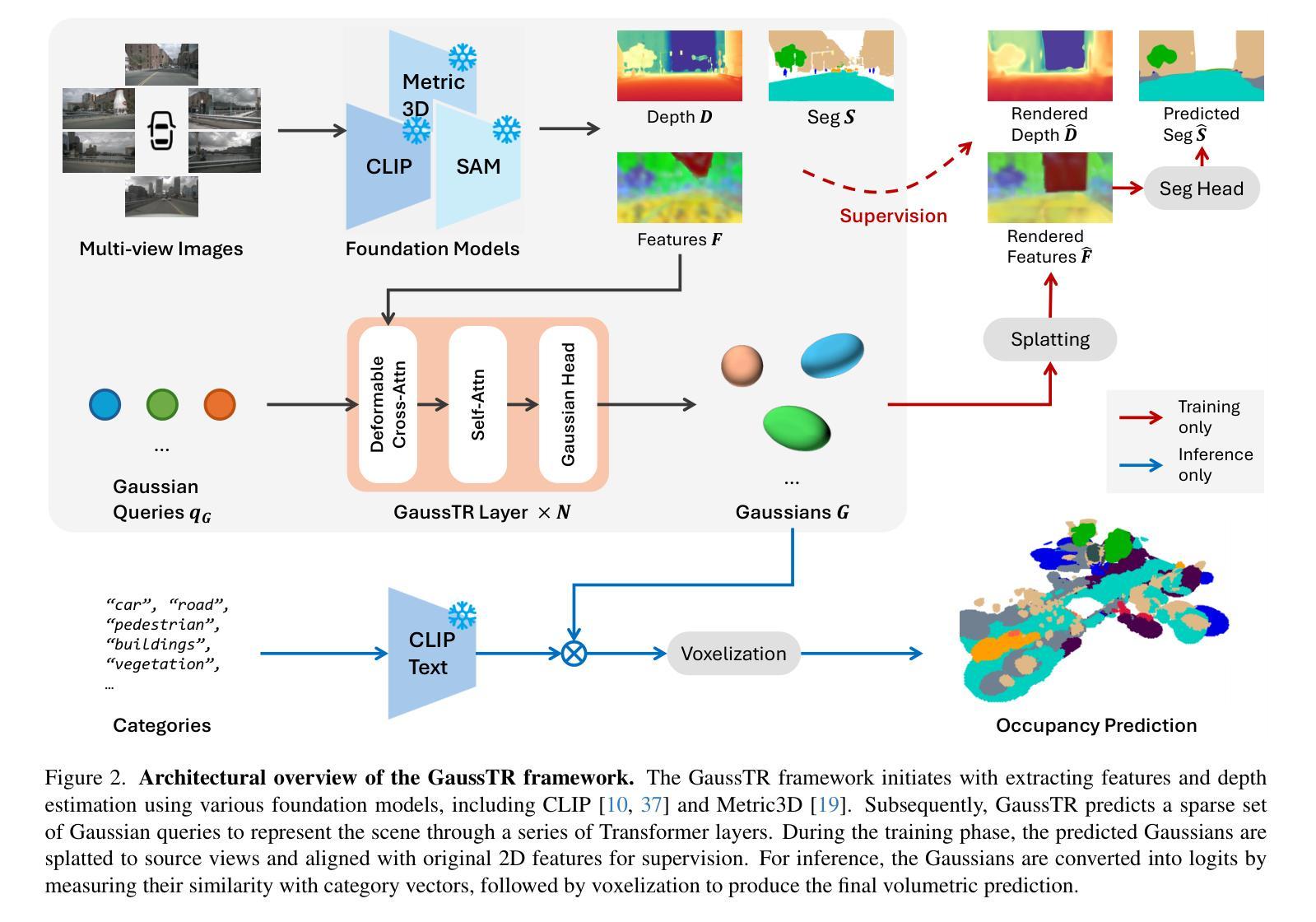
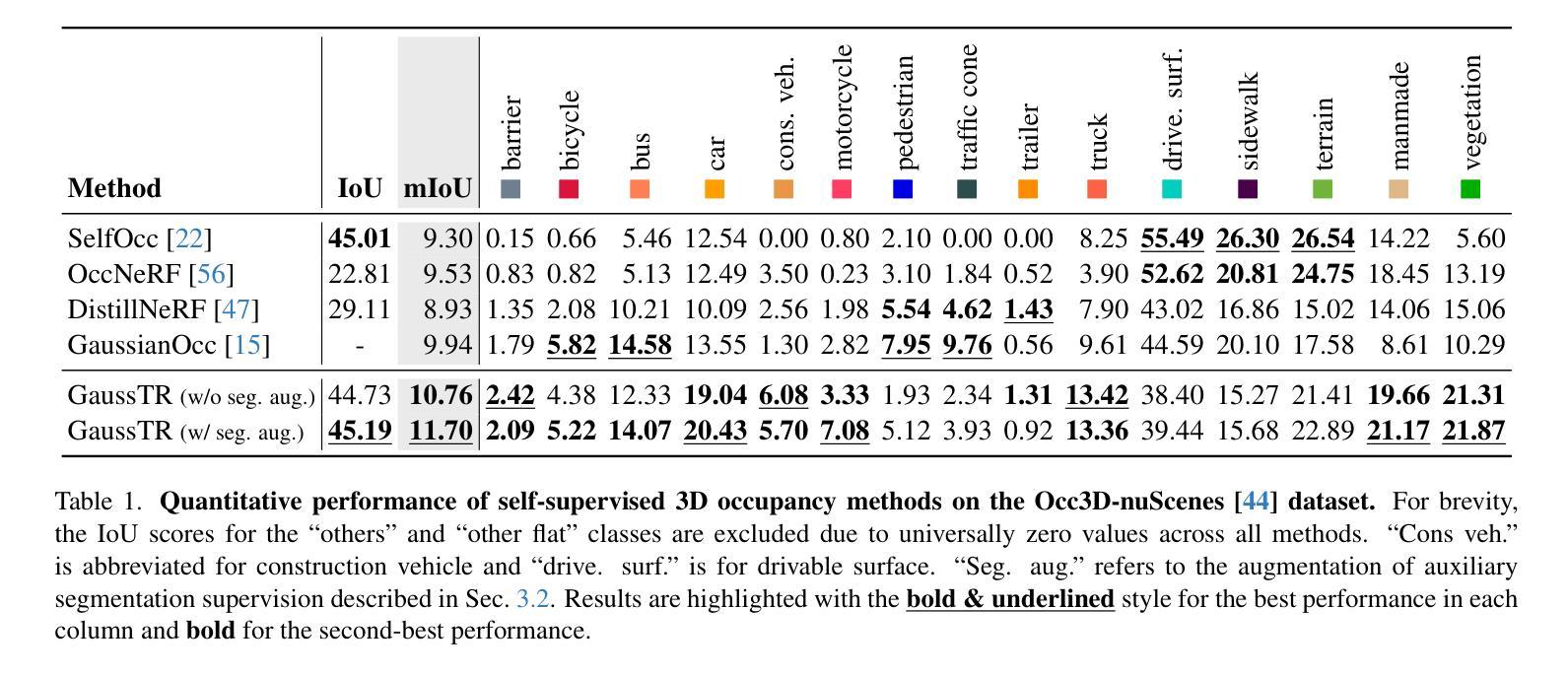
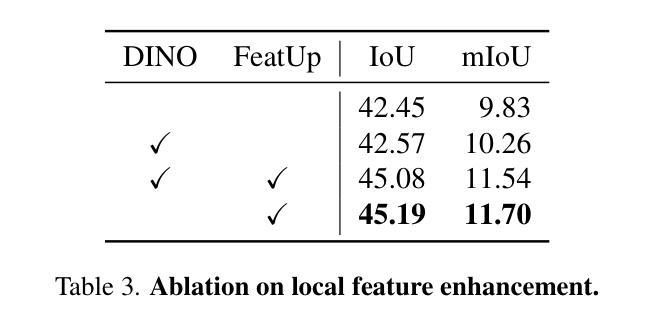
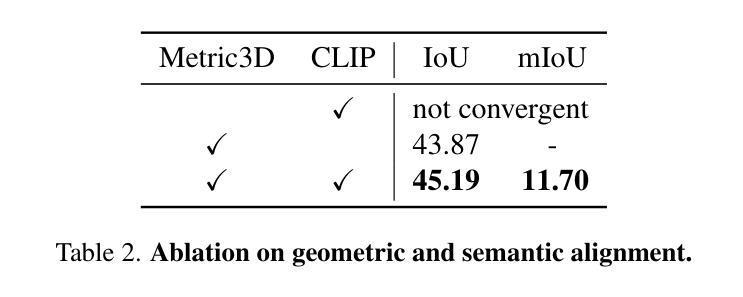
3D Semantic Occupancy Prediction is fundamental for spatial understanding as it provides a comprehensive semantic cognition of surrounding environments. However, prevalent approaches primarily rely on extensive labeled data and computationally intensive voxel-based modeling, restricting the scalability and generalizability of 3D representation learning. In this paper, we introduce GaussTR, a novel Gaussian Transformer that leverages alignment with foundation models to advance self-supervised 3D spatial understanding. GaussTR adopts a Transformer architecture to predict sparse sets of 3D Gaussians that represent scenes in a feed-forward manner. Through aligning rendered Gaussian features with diverse knowledge from pre-trained foundation models, GaussTR facilitates the learning of versatile 3D representations and enables open-vocabulary occupancy prediction without explicit annotations. Empirical evaluations on the Occ3D-nuScenes dataset showcase GaussTR’s state-of-the-art zero-shot performance, achieving 11.70 mIoU while reducing training duration by approximately 50%. These experimental results highlight the significant potential of GaussTR for scalable and holistic 3D spatial understanding, with promising implications for autonomous driving and embodied agents. Code is available at https://github.com/hustvl/GaussTR.
3D语义占用预测对于空间理解至关重要,因为它提供了对周围环境的全面语义认知。然而,流行的方法主要依赖于大量的标记数据和计算密集型的基于体素(voxel-based)建模,这限制了3D表示学习的可扩展性和通用性。在本文中,我们介绍了GaussTR,这是一种新型的高斯变换器(Gaussian Transformer),它利用与基础模型的对齐来推进自我监督的3D空间理解。GaussTR采用Transformer架构,以前馈方式预测代表场景的稀疏3D高斯集。通过使渲染的高斯特征与来自预训练基础模型的多样化知识对齐,GaussTR促进了多种3D表示的学习,并能够在没有显式注释的情况下实现开放词汇表的占用预测。在Occ3D-nuScenes数据集上的实证评估展示了GaussTR的零样本性能处于最新水平,实现了11.70 mIoU,同时训练时间缩短了约50%。这些实验结果突出了GaussTR在可扩展和全面的3D空间理解方面的巨大潜力,对自动驾驶和实体代理具有广阔的应用前景。代码可在https://github.com/hustvl/GaussTR获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了GaussTR模型,这是一种利用高斯变换器进行三维语义占用预测的方法。该模型通过预测稀疏三维高斯集来以自适应方式呈现场景,并结合预训练基础模型的丰富知识实现自我监督的三维空间理解。高斯TR模型无需明确注释即可进行开放式词汇占用预测,并在Occ3D-nuScenes数据集上实现了最先进的零样本性能,实现了11.70 mIoU,同时减少了大约50%的训练时间。这为可扩展和全面的三维空间理解提供了显著潜力,对自动驾驶和智能体具有重要影响。
Key Takeaways
- GaussTR模型利用高斯变换器进行三维语义占用预测,为周围环境提供全面的语义认知。
- 模型采用Transformer架构预测稀疏三维高斯集来呈现场景。
- GaussTR通过与预训练基础模型对齐来丰富其知识,并实现自我监督的三维表示学习。
- GaussTR支持开放式词汇占用预测,无需明确注释。
- GaussTR在Occ3D-nuScenes数据集上实现了最先进的零样本性能,达到了11.70 mIoU。
- GaussTR模型减少了大约50%的训练时间,提高了效率。
点此查看论文截图
Real-time Free-view Human Rendering from Sparse-view RGB Videos using Double Unprojected Textures
Authors:Guoxing Sun, Rishabh Dabral, Heming Zhu, Pascal Fua, Christian Theobalt, Marc Habermann
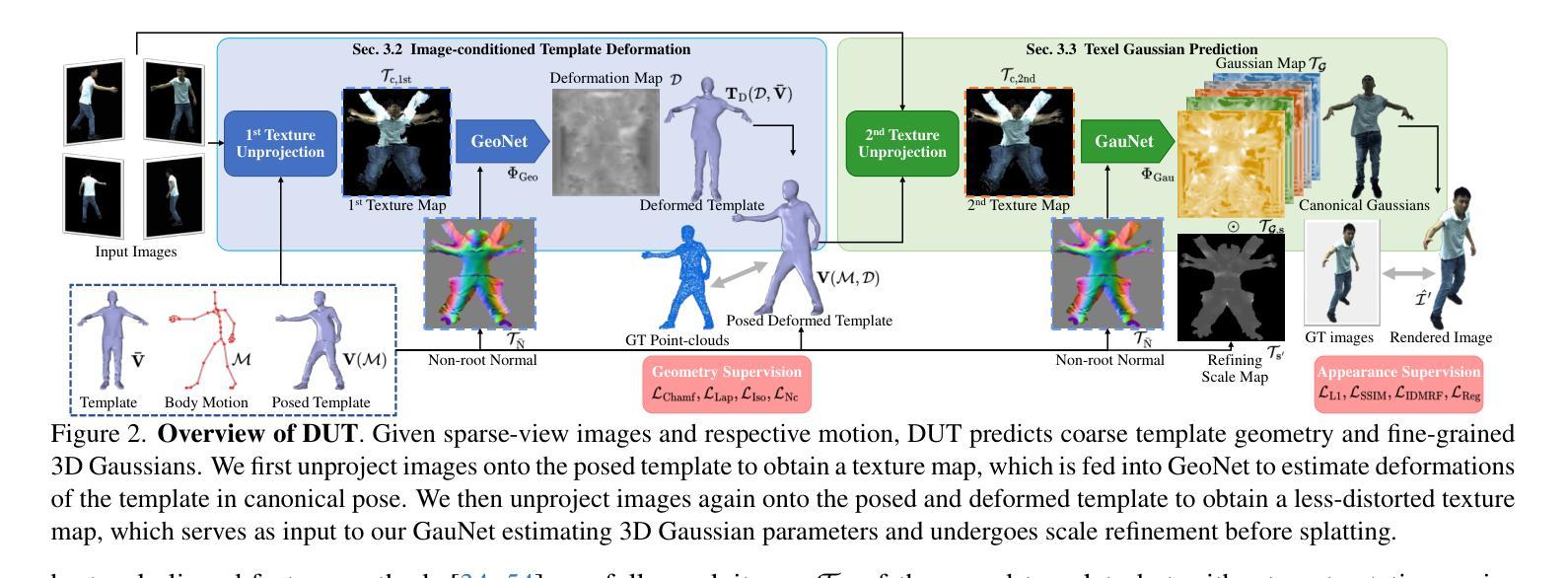
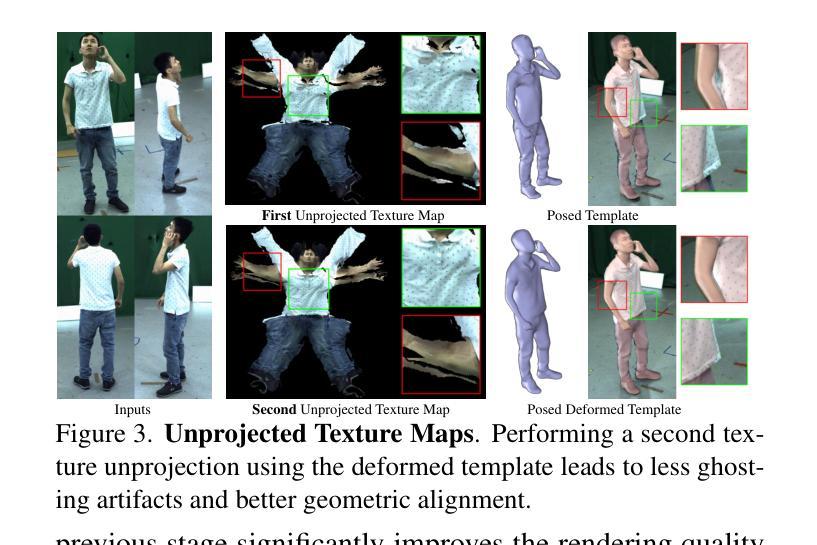
Real-time free-view human rendering from sparse-view RGB inputs is a challenging task due to the sensor scarcity and the tight time budget. To ensure efficiency, recent methods leverage 2D CNNs operating in texture space to learn rendering primitives. However, they either jointly learn geometry and appearance, or completely ignore sparse image information for geometry estimation, significantly harming visual quality and robustness to unseen body poses. To address these issues, we present Double Unprojected Textures, which at the core disentangles coarse geometric deformation estimation from appearance synthesis, enabling robust and photorealistic 4K rendering in real-time. Specifically, we first introduce a novel image-conditioned template deformation network, which estimates the coarse deformation of the human template from a first unprojected texture. This updated geometry is then used to apply a second and more accurate texture unprojection. The resulting texture map has fewer artifacts and better alignment with input views, which benefits our learning of finer-level geometry and appearance represented by Gaussian splats. We validate the effectiveness and efficiency of the proposed method in quantitative and qualitative experiments, which significantly surpasses other state-of-the-art methods.
从稀疏视图RGB输入进行实时自由视角人类渲染是一项具有挑战性的任务,这主要是由于传感器稀缺和严格的时间预算限制。为了保证效率,最近的方法利用在纹理空间操作的2D卷积神经网络来学习渲染原理。然而,它们要么联合学习几何和外观,要么完全忽略稀疏图像信息进行几何估计,这严重损害了视觉质量和对未见姿态的鲁棒性。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了双未投影纹理(Double Unprojected Textures)方法,该方法的核心是将粗糙的几何变形估计从外观合成中分离出来,实现实时、稳健和逼真的4K渲染。具体来说,我们首先引入了一种新型图像条件模板变形网络,该网络从第一个未投影纹理估计人类模板的粗糙变形。然后,使用这个更新的几何来应用第二个更加精确的纹理反投影。结果得到的纹理贴图具有较少的伪影并且与输入视图对齐更好,这有利于我们学习由高斯点表示的更精细级别的几何和外观。我们在定量和定性实验中都验证了所提出方法的有效性和效率,该方法显著超越了其他最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://vcai.mpi-inf.mpg.de/projects/DUT/
Summary
实时从稀疏视角RGB输入进行自由视角人类渲染是一项具有挑战性的任务。为提高效率,近期方法利用二维卷积神经网络在纹理空间学习渲染原理。然而,这些方法要么联合学习几何和外观,要么在估计几何时完全忽略稀疏图像信息,严重损害视觉质量和对未见姿态的鲁棒性。为解决这些问题,我们提出Double Unprojected Textures方法,该方法核心将粗略几何变形估计与外观合成解耦,实现实时鲁棒且逼真的4K渲染。具体来说,我们首先引入图像条件模板变形网络,从第一次未投影纹理估计人类模板的粗略变形。更新的几何再用于应用第二次更准确纹理的未投影。结果纹理图具有较少的伪影并与输入视图对齐更好,这有利于我们学习由高斯斑表示的更精细级别的几何和外观。
Key Takeaways
- 实时自由视角人类渲染是项艰巨任务,得益于二维卷积神经网络在纹理空间的学习。
- 现有方法联合学习几何和外观或忽略稀疏图像信息,导致视觉质量和鲁棒性受损。
- 提出Double Unprojected Textures方法,将几何变形与外观合成解耦,实现更准确、逼真的渲染。
- 引入图像条件模板变形网络,从第一次未投影纹理估计粗略变形。
- 更新几何用于第二次更准确纹理未投影,减少伪影并与输入视图对齐更好。
- 结果纹理图有助于学习更精细级别的几何和外观表示。
点此查看论文截图



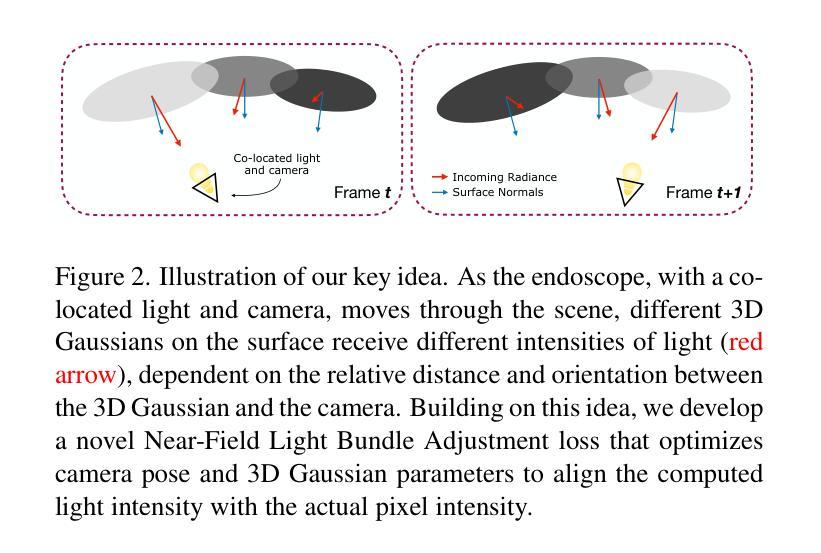
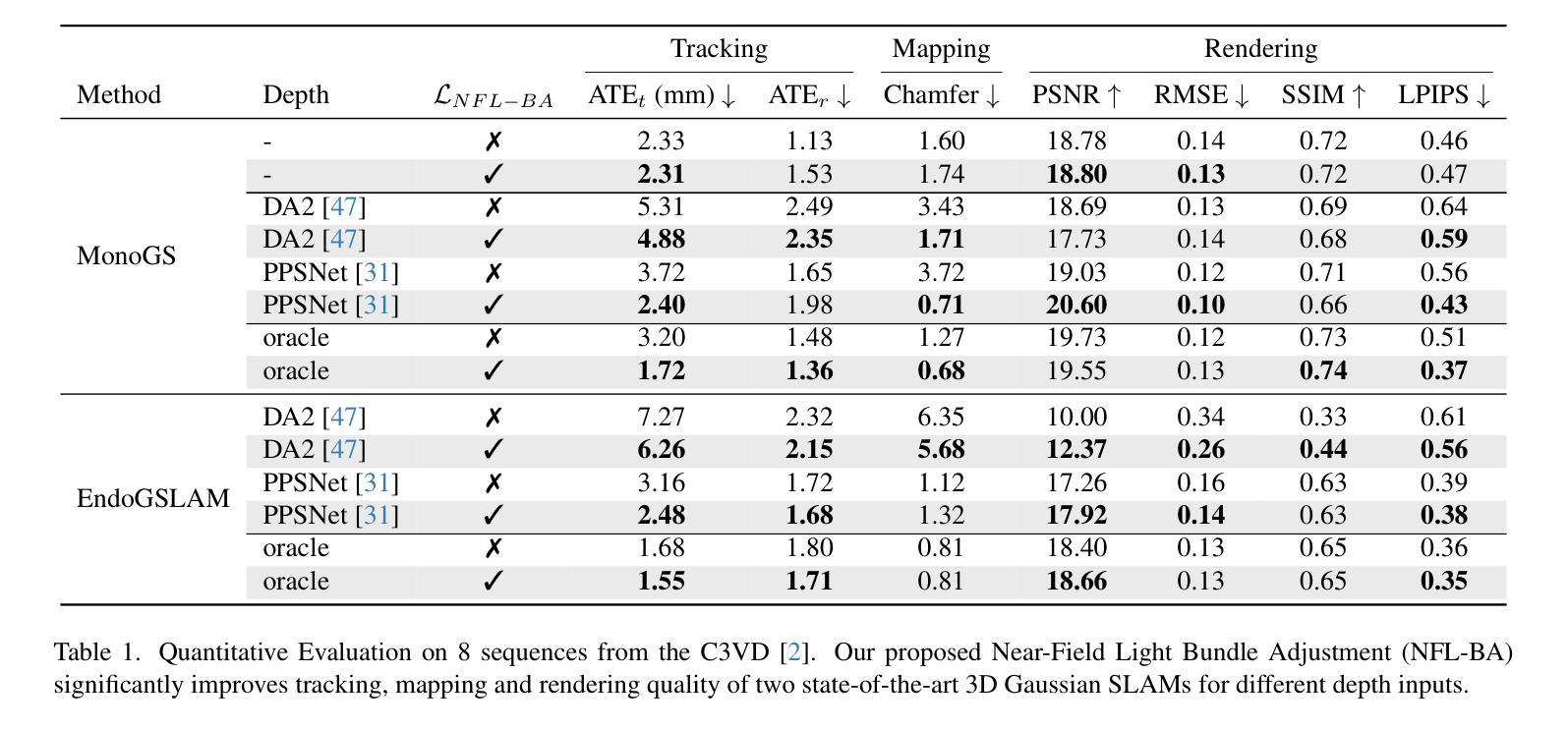
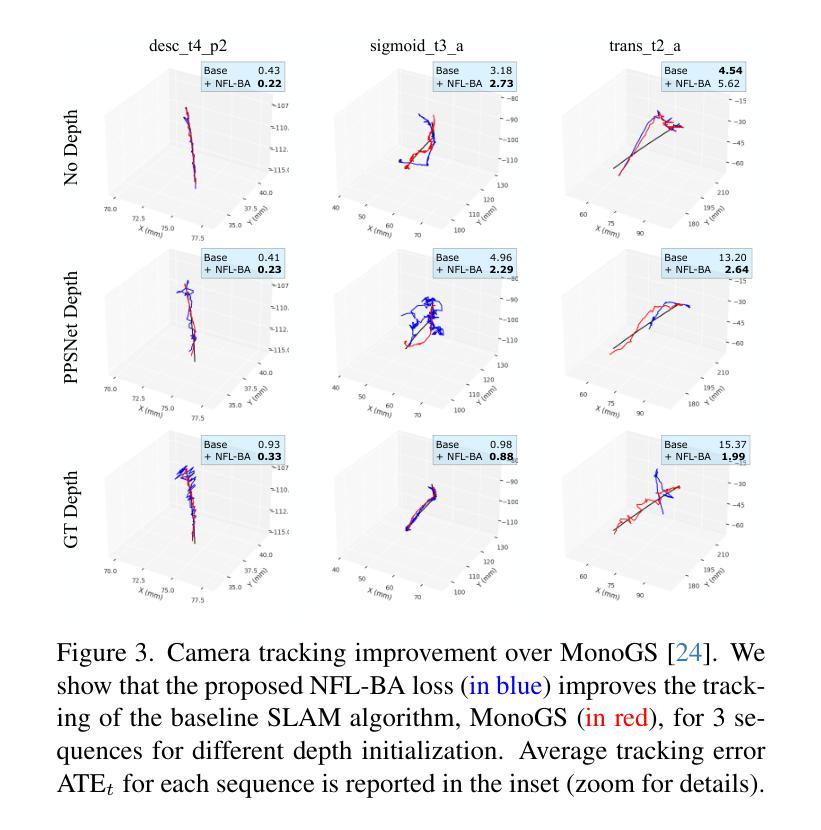
NFL-BA: Improving Endoscopic SLAM with Near-Field Light Bundle Adjustment
Authors:Andrea Dunn Beltran, Daniel Rho, Marc Niethammer, Roni Sengupta
Simultaneous Localization And Mapping (SLAM) from a monocular endoscopy video can enable autonomous navigation, guidance to unsurveyed regions, and 3D visualizations, which can significantly improve endoscopy experience for surgeons and patient outcomes. Existing dense SLAM algorithms often assume distant and static lighting and textured surfaces, and alternate between optimizing scene geometry and camera parameters by minimizing a photometric rendering loss, often called Photometric Bundle Adjustment. However, endoscopic environments exhibit dynamic near-field lighting due to the co-located light and camera moving extremely close to the surface, textureless surfaces, and strong specular reflections due to mucus layers. When not considered, these near-field lighting effects can cause significant performance reductions for existing SLAM algorithms from indoor/outdoor scenes when applied to endoscopy videos. To mitigate this problem, we introduce a new Near-Field Lighting Bundle Adjustment Loss $(L_{NFL-BA})$ that can also be alternatingly optimized, along with the Photometric Bundle Adjustment loss, such that the captured images’ intensity variations match the relative distance and orientation between the surface and the co-located light and camera. We derive a general NFL-BA loss function for 3D Gaussian surface representations and demonstrate that adding $L_{NFL-BA}$ can significantly improve the tracking and mapping performance of two state-of-the-art 3DGS-SLAM systems, MonoGS (35% improvement in tracking, 48% improvement in mapping with predicted depth maps) and EndoGSLAM (22% improvement in tracking, marginal improvement in mapping with predicted depths), on the C3VD endoscopy dataset for colons. The project page is available at https://asdunnbe.github.io/NFL-BA/
从单目内窥镜视频进行的同步定位与地图构建(SLAM)可以实现自主导航、对未勘测区域的指导以及3D可视化,这可以显著改善外科医生的内窥镜体验并改善患者结果。现有的密集SLAM算法通常假设光照距离较远且静态,表面有纹理,并通过最小化光度渲染损失来优化场景几何和相机参数,这通常被称为光度捆绑调整。然而,内窥镜环境表现出由于光源和相机极近距离表面而产生的动态近场光照、无纹理的表面以及由于粘液层产生的强烈镜面反射。当不考虑这些因素时,这些近场照明效果会对应用于内窥镜视频时的室内/室外场景的现有SLAM算法造成显著的性能下降。为了缓解这个问题,我们引入了一种新的近场照明捆绑调整损失(L_NFL-BA),它可以与光度捆绑调整损失交替优化,以使捕获的图像强度变化与表面与协同定位的光源和相机之间的相对距离和方向相匹配。我们为3D高斯表面表示法推导了一个通用的NFL-BA损失函数,并证明添加L_NFL-BA可以显着提高两种最新3DGS-SLAM系统(MonoGS(跟踪提高35%,使用预测深度图进行映射提高48%)和EndoGSLAM(跟踪提高22%,使用预测深度进行映射轻微改进))的跟踪和映射性能。项目页面可在https://asdunnbe.github.io/NFL-BA/访问。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了在单目内窥镜视频中利用同步定位与地图构建(SLAM)技术实现自主导航、未勘测区域引导和三维可视化。针对内窥镜环境中的近场照明效应,引入了一种新的近场照明捆绑调整损失(L_{NFL-BA}),并与光度捆绑调整损失交替优化,以匹配图像强度变化与表面与协同照明和相机之间的距离和方位。该损失函数可显著提高两种最先进的3DGS-SLAM系统(MonoGS和EndoGSLAM)在C3VD结肠内窥镜数据集上的跟踪和映射性能。
Key Takeaways
- SLAM技术应用于单目内窥镜视频,能提升自主导航、未勘测区域引导和三维可视化。
- 内窥镜环境存在动态近场照明、无纹理表面和粘液层引起的强镜面反射,对现有的SLAM算法性能造成严重影响。
- 引入新的近场照明捆绑调整损失(L_{NFL-BA}),以应对内窥镜视频的近场照明效应。
- L_{NFL-BA}可交替优化,与光度捆绑调整损失相结合,匹配图像强度变化与表面和相机之间的距离和方位。
- L_{NFL-BA}的引入显著提高了MonoGS和EndoGSLAM两种3DGS-SLAM系统在C3VD结肠内窥镜数据集上的跟踪和映射性能。
- 近场照明效应对SLAM算法性能的影响,揭示了未来研究中需要更多考虑内窥镜环境的特殊性质。
点此查看论文截图

EOGS: Gaussian Splatting for Earth Observation
Authors:Luca Savant Aira, Gabriele Facciolo, Thibaud Ehret
Recently, Gaussian splatting has emerged as a strong alternative to NeRF, demonstrating impressive 3D modeling capabilities while requiring only a fraction of the training and rendering time. In this paper, we show how the standard Gaussian splatting framework can be adapted for remote sensing, retaining its high efficiency. This enables us to achieve state-of-the-art performance in just a few minutes, compared to the day-long optimization required by the best-performing NeRF-based Earth observation methods. The proposed framework incorporates remote-sensing improvements from EO-NeRF, such as radiometric correction and shadow modeling, while introducing novel components, including sparsity, view consistency, and opacity regularizations.
最近,高斯涂斑技术作为NeRF的有力替代方案崭露头角,它在只需一小部分训练和渲染时间的情况下表现出了令人印象深刻的3D建模能力。在本文中,我们展示了如何将标准的高斯涂斑框架适应于遥感领域,同时保持其高效率。这使得我们能够在几分钟内实现最先进的性能表现,相比之下,表现最佳的基于NeRF的地球观测方法则需要一整天的优化时间。所提出的框架纳入了EO-NeRF的遥感改进内容,例如辐射校正和阴影建模,同时引入了新颖组件,包括稀疏性、视图一致性和不透明度正则化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了高斯贴图技术,该技术作为NeRF的替代方案展现出强大的3D建模能力,且训练与渲染时间大幅减少。文章展示了如何将标准高斯贴图框架适应于遥感领域,并保持其高效率。相较于现有领先的NeRF地球观测方法,新框架可在几分钟内达到最佳性能,无需长时间的优化。该框架结合了EO-NeRF的遥感改进技术,如辐射校正和阴影建模,并引入了稀疏性、视图一致性和透明度正则化等新颖组件。
Key Takeaways
- 高斯贴图技术作为NeRF的替代方案展现出强大的3D建模能力,且训练与渲染时间大幅减少。
- 文章将标准高斯贴图框架适应于遥感领域,并保持其高效率。
- 新框架可在几分钟内达到最佳性能,无需长时间的优化。
- 该框架结合了EO-NeRF的遥感改进技术,如辐射校正和阴影建模。
- 新框架引入了稀疏性、视图一致性和透明度正则化等新颖组件。
- 高斯贴图技术在3D建模领域的优势在于其高效性和广泛的应用潜力。
点此查看论文截图

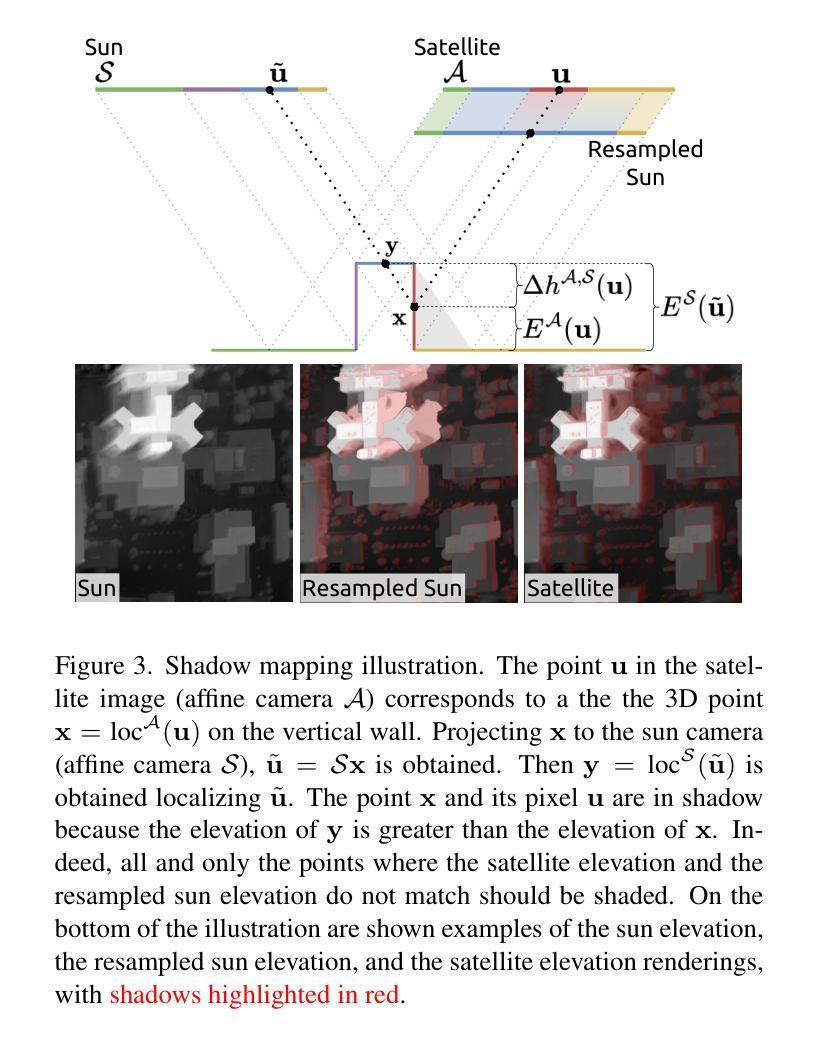

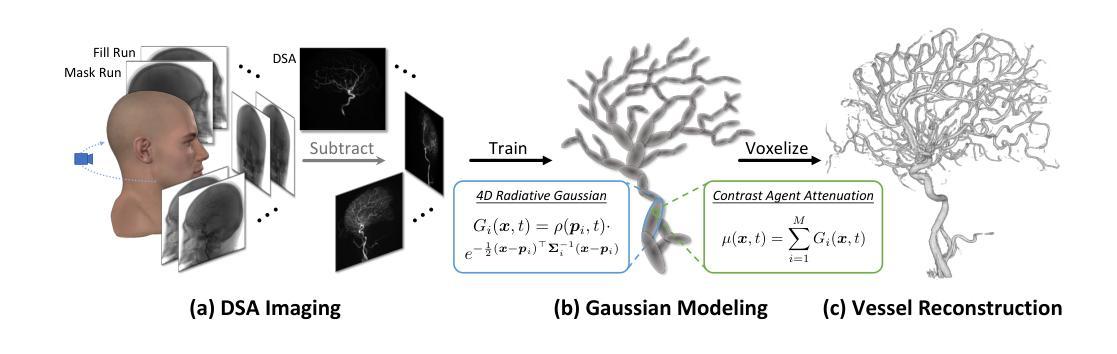
4DRGS: 4D Radiative Gaussian Splatting for Efficient 3D Vessel Reconstruction from Sparse-View Dynamic DSA Images
Authors:Zhentao Liu, Ruyi Zha, Huangxuan Zhao, Hongdong Li, Zhiming Cui
Reconstructing 3D vessel structures from sparse-view dynamic digital subtraction angiography (DSA) images enables accurate medical assessment while reducing radiation exposure. Existing methods often produce suboptimal results or require excessive computation time. In this work, we propose 4D radiative Gaussian splatting (4DRGS) to achieve high-quality reconstruction efficiently. In detail, we represent the vessels with 4D radiative Gaussian kernels. Each kernel has time-invariant geometry parameters, including position, rotation, and scale, to model static vessel structures. The time-dependent central attenuation of each kernel is predicted from a compact neural network to capture the temporal varying response of contrast agent flow. We splat these Gaussian kernels to synthesize DSA images via X-ray rasterization and optimize the model with real captured ones. The final 3D vessel volume is voxelized from the well-trained kernels. Moreover, we introduce accumulated attenuation pruning and bounded scaling activation to improve reconstruction quality. Extensive experiments on real-world patient data demonstrate that 4DRGS achieves impressive results in 5 minutes training, which is 32x faster than the state-of-the-art method. This underscores the potential of 4DRGS for real-world clinics.
从稀疏视角动态数字减法血管造影(DSA)图像重建3D血管结构,可以实现准确的医学评估,同时减少辐射暴露。现有方法往往产生不理想的结果或需要过多的计算时间。在这项工作中,我们提出4D辐射高斯展开(4DRGS)以实现高效的高质量重建。具体来说,我们用4D辐射高斯核表示血管。每个核都具有时间不变的几何参数,包括位置、旋转和尺度,以模拟静态血管结构。每个核的时间相关中心衰减由紧凑神经网络预测,以捕捉造影剂流动的暂时变化响应。我们通过X射线光栅化展开这些高斯核来合成DSA图像,并用真实捕获的图像优化模型。最终的3D血管体积是由训练良好的核体素化得到的。此外,我们引入了累积衰减修剪和有界缩放激活来提高重建质量。在真实患者数据上的大量实验表明,4DRGS在5分钟内训练即可取得令人印象深刻的结果,比现有最佳方法快32倍。这突出了4DRGS在真实世界临床应用中的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Zhentao Liu and Ruyi Zha made equal contributions
Summary
本文提出一种基于四维辐射高斯展开(4DRGS)的方法,用于从稀疏视角动态数字减影血管造影(DSA)图像重建三维血管结构。通过用四维辐射高斯核表示血管,结合神经网络预测对比剂流动的时间依赖中心衰减,高效合成DSA图像,从而实现了高质量的三维重建。方法能够在五分钟内完成训练,速度远超现有技术,展现了在实际临床应用中的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 使用四维辐射高斯展开(4DRGS)方法从稀疏视角的DSA图像重建三维血管结构。
- 通过时间不变的几何参数(位置、旋转、尺度)建模静态血管结构。
- 利用神经网络预测对比剂流动的时间依赖中心衰减,捕捉动态响应。
- 利用X射线光栅化技术将高斯核展开以合成DSA图像。
- 通过真实捕获的图像优化模型,将训练良好的高斯核体素化为最终的3D血管体积。
- 引入累积衰减修剪和边界缩放激活技术提高重建质量。
点此查看论文截图

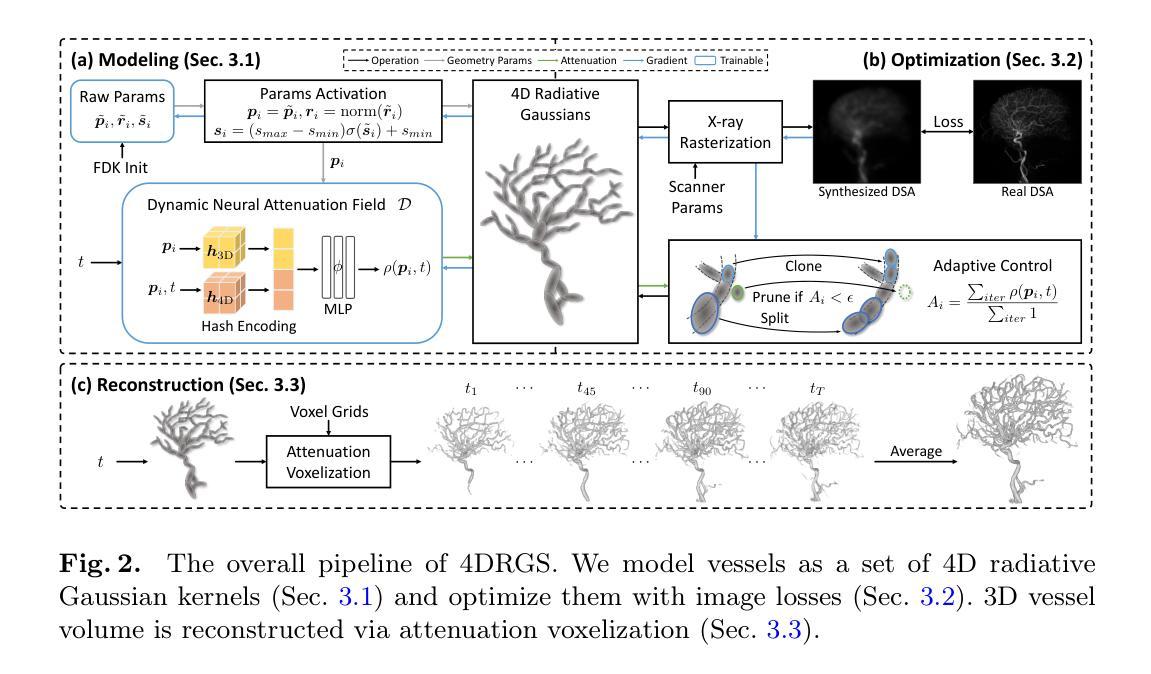
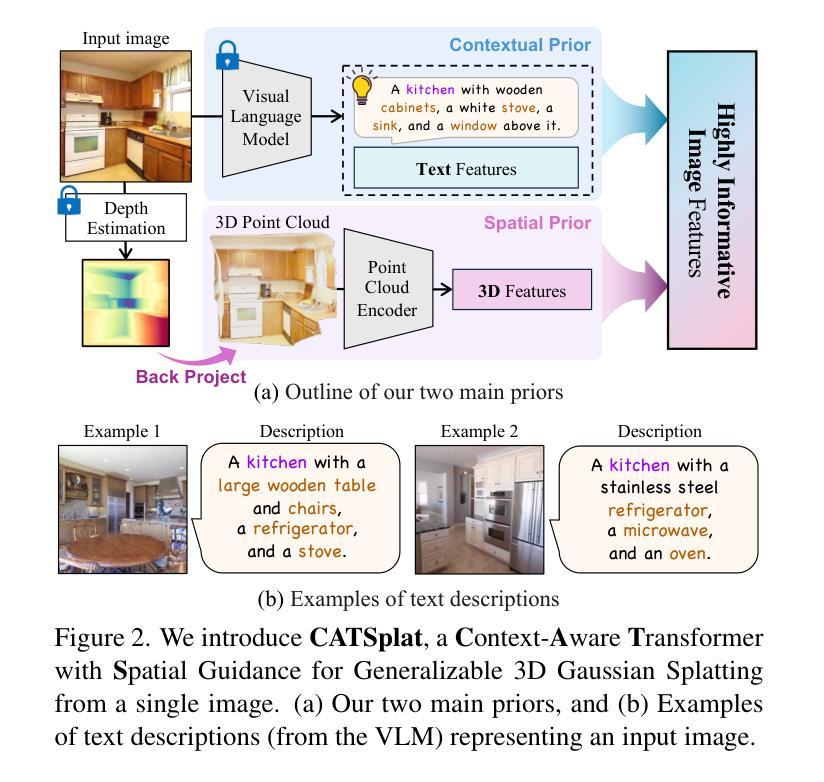
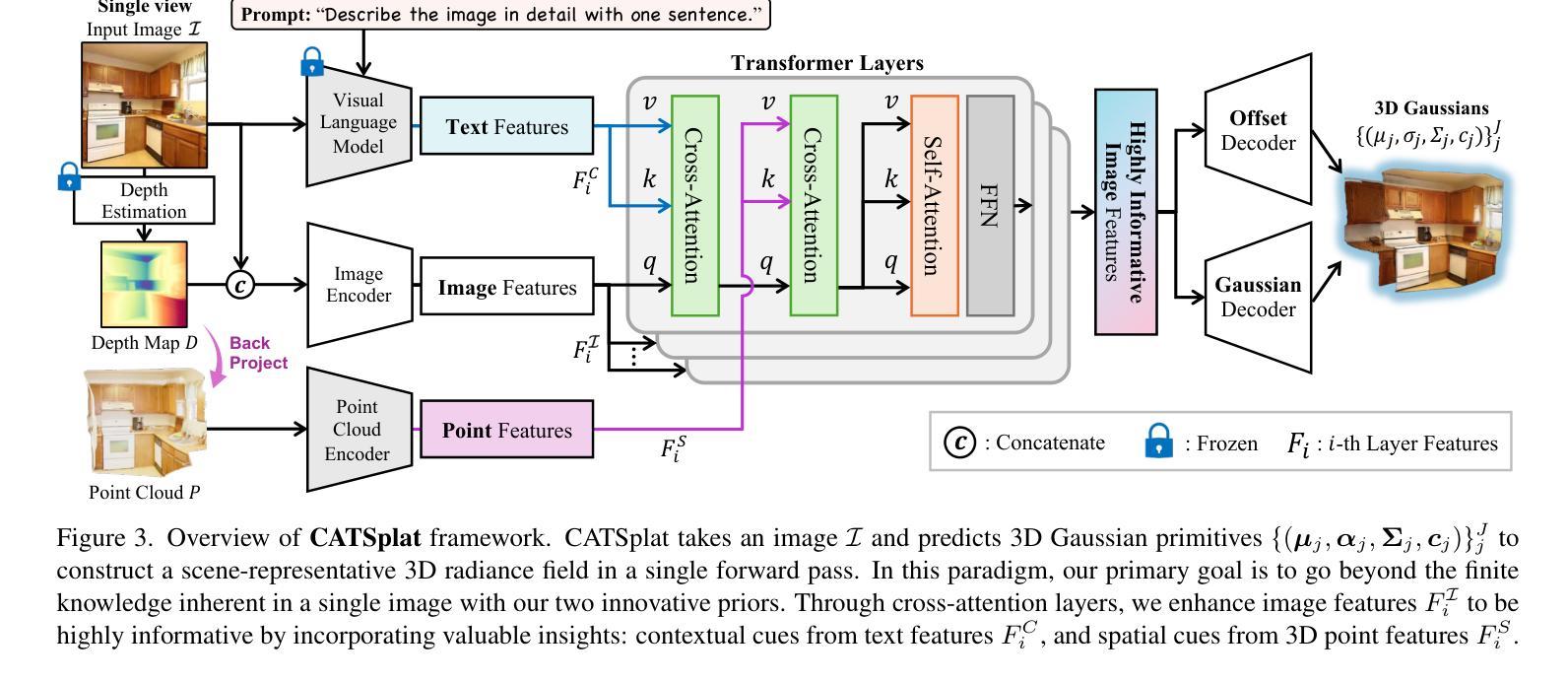
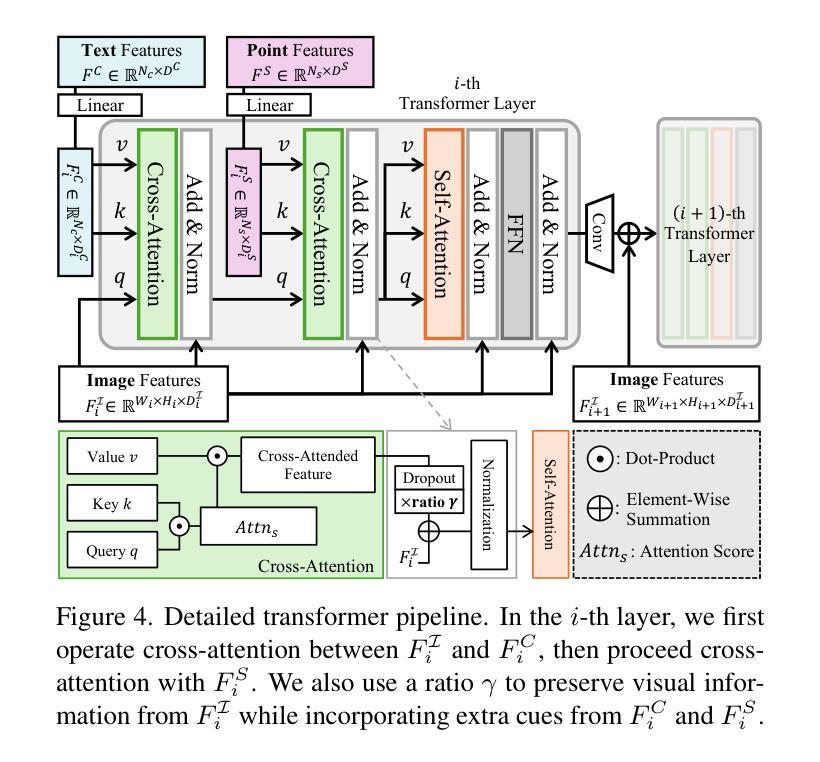
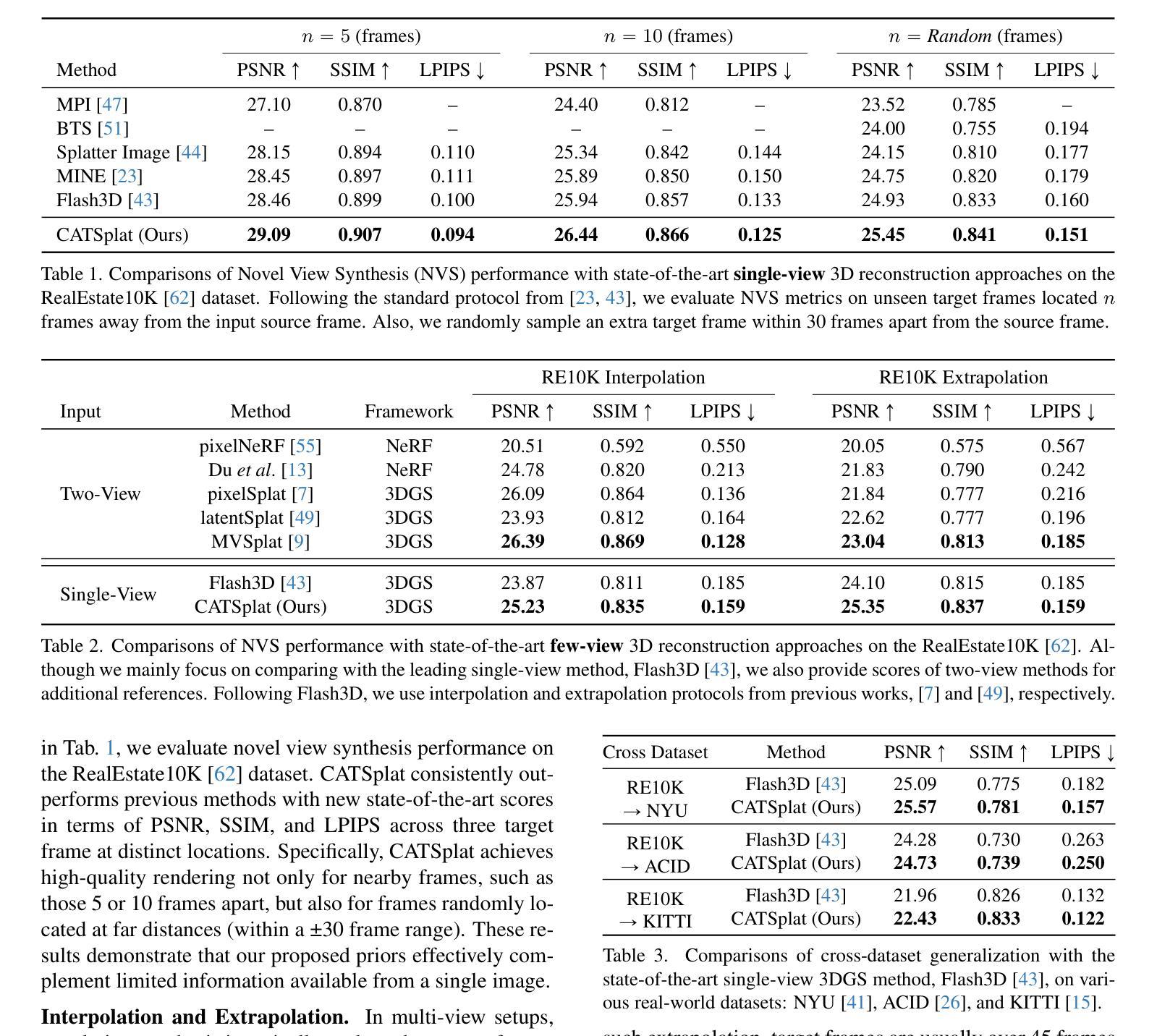
CATSplat: Context-Aware Transformer with Spatial Guidance for Generalizable 3D Gaussian Splatting from A Single-View Image
Authors:Wonseok Roh, Hwanhee Jung, Jong Wook Kim, Seunggwan Lee, Innfarn Yoo, Andreas Lugmayr, Seunggeun Chi, Karthik Ramani, Sangpil Kim
Recently, generalizable feed-forward methods based on 3D Gaussian Splatting have gained significant attention for their potential to reconstruct 3D scenes using finite resources. These approaches create a 3D radiance field, parameterized by per-pixel 3D Gaussian primitives, from just a few images in a single forward pass. However, unlike multi-view methods that benefit from cross-view correspondences, 3D scene reconstruction with a single-view image remains an underexplored area. In this work, we introduce CATSplat, a novel generalizable transformer-based framework designed to break through the inherent constraints in monocular settings. First, we propose leveraging textual guidance from a visual-language model to complement insufficient information from a single image. By incorporating scene-specific contextual details from text embeddings through cross-attention, we pave the way for context-aware 3D scene reconstruction beyond relying solely on visual cues. Moreover, we advocate utilizing spatial guidance from 3D point features toward comprehensive geometric understanding under single-view settings. With 3D priors, image features can capture rich structural insights for predicting 3D Gaussians without multi-view techniques. Extensive experiments on large-scale datasets demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of CATSplat in single-view 3D scene reconstruction with high-quality novel view synthesis.
最近,基于三维高斯拼贴(3D Gaussian Splatting)的通用前馈方法因其利用有限资源重建三维场景的潜力而受到广泛关注。这些方法通过单次前向传递仅从几张图像中创建一个三维辐射场,该场由像素级三维高斯基元参数化。然而,不同于受益于跨视图对应关系的多视图方法,单视图图像的三维场景重建仍然是一个未被充分研究的领域。在这项工作中,我们引入了CATSplat,这是一种新型的可泛化、基于Transformer的框架,旨在突破单目视觉设置中的固有约束。首先,我们提出利用视觉语言模型的文本指导来补充单幅图像中的信息不足。通过跨注意力融入特定场景的上下文细节和文本嵌入,我们为仅依赖视觉线索的上下文感知三维场景重建铺平了道路。此外,我们主张利用三维点特征的空间指导,以实现单视图设置下的全面几何理解。借助三维先验知识,图像特征可以捕捉到丰富的结构洞察力,无需多视图技术即可预测三维高斯分布。大规模数据集上的大量实验表明,CATSplat在单视图三维场景重建中具有最先进的性能,并能进行高质量的新视角合成。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于3D高斯拼贴技术的通用前馈方法,在有限的资源下重建3D场景已受到广泛关注。但单视图重建仍是一个未充分研究的领域。本研究提出基于文本引导的上下文感知的重建方法,通过引入视觉语言模型与空间引导3D点特征进行单视图场景的重建,提高了对场景的丰富几何理解。实验证明,CATSplat在单视图重建和高质量新视角合成方面具有卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 基于通用前馈方法的重建技术使用有限资源通过单视图图像重建3D场景。
- 使用视觉语言模型提供文本指导,以弥补单视图信息的不足。
- 通过跨注意力机制引入场景特定的上下文细节,实现上下文感知的重建。
- 使用空间指导技术通过单点特征的坐标和空间特征了解综合几何。
- 结合先进的实验,展示了在单视图重建和高质量新视角合成方面的最新性能。
- CATSplat框架具有突破固有约束的能力,有助于推进单视图场景重建研究。
点此查看论文截图
HyperGS: Hyperspectral 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Christopher Thirgood, Oscar Mendez, Erin Chao Ling, Jon Storey, Simon Hadfield
We introduce HyperGS, a novel framework for Hyperspectral Novel View Synthesis (HNVS), based on a new latent 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) technique. Our approach enables simultaneous spatial and spectral renderings by encoding material properties from multi-view 3D hyperspectral datasets. HyperGS reconstructs high-fidelity views from arbitrary perspectives with improved accuracy and speed, outperforming currently existing methods. To address the challenges of high-dimensional data, we perform view synthesis in a learned latent space, incorporating a pixel-wise adaptive density function and a pruning technique for increased training stability and efficiency. Additionally, we introduce the first HNVS benchmark, implementing a number of new baselines based on recent SOTA RGB-NVS techniques, alongside the small number of prior works on HNVS. We demonstrate HyperGS’s robustness through extensive evaluation of real and simulated hyperspectral scenes with a 14db accuracy improvement upon previously published models.
我们引入了HyperGS,这是一个基于新型潜在三维高斯拼贴(3DGS)技术的高光谱新型视图合成(HNVS)的新框架。我们的方法通过编码多视角三维高光谱数据集的材料属性,实现了空间和光谱的同时渲染。HyperGS能够从任意视角重建高保真视图,提高了准确性和速度,超越了现有的方法。为了解决高维数据的挑战,我们在学习到的潜在空间进行视图合成,结合像素级自适应密度函数和修剪技术,以提高训练的稳定性和效率。此外,我们建立了首个HNVS基准测试,基于最新的RGB-NVS技术实现了一系列新基线,以及少数现有的HNVS工作。我们通过真实和模拟高光谱场景的广泛评估,证明了HyperGS的稳健性,其准确性相较于已发布的模型提高了14db。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
HyperGS是一个基于新的潜在三维高斯溅射技术(3DGS)的用于超光谱新颖视角合成(HNVS)的新框架。它采用编码多视角三维超光谱数据集的材料属性,实现空间和光谱的同时渲染,能重建出高保真度的任意视角视图,并提高了准确性与速度,超越了现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- HyperGS是一个基于潜在三维高斯溅射技术(3DGS)的新框架,用于超光谱新颖视角合成(HNVS)。
- 该框架能同时实现空间和光谱的渲染。
- 通过编码多视角三维超光谱数据集的材料属性,HyperGS能够重建高保真度的任意视角视图。
- 与现有方法相比,HyperGS提高了准确性和速度。
- 为了解决高维数据的挑战,HyperGS在学习的潜在空间进行视角合成。
- 该框架采用了像素级的自适应密度函数和修剪技术,以提高训练稳定性和效率。
点此查看论文截图

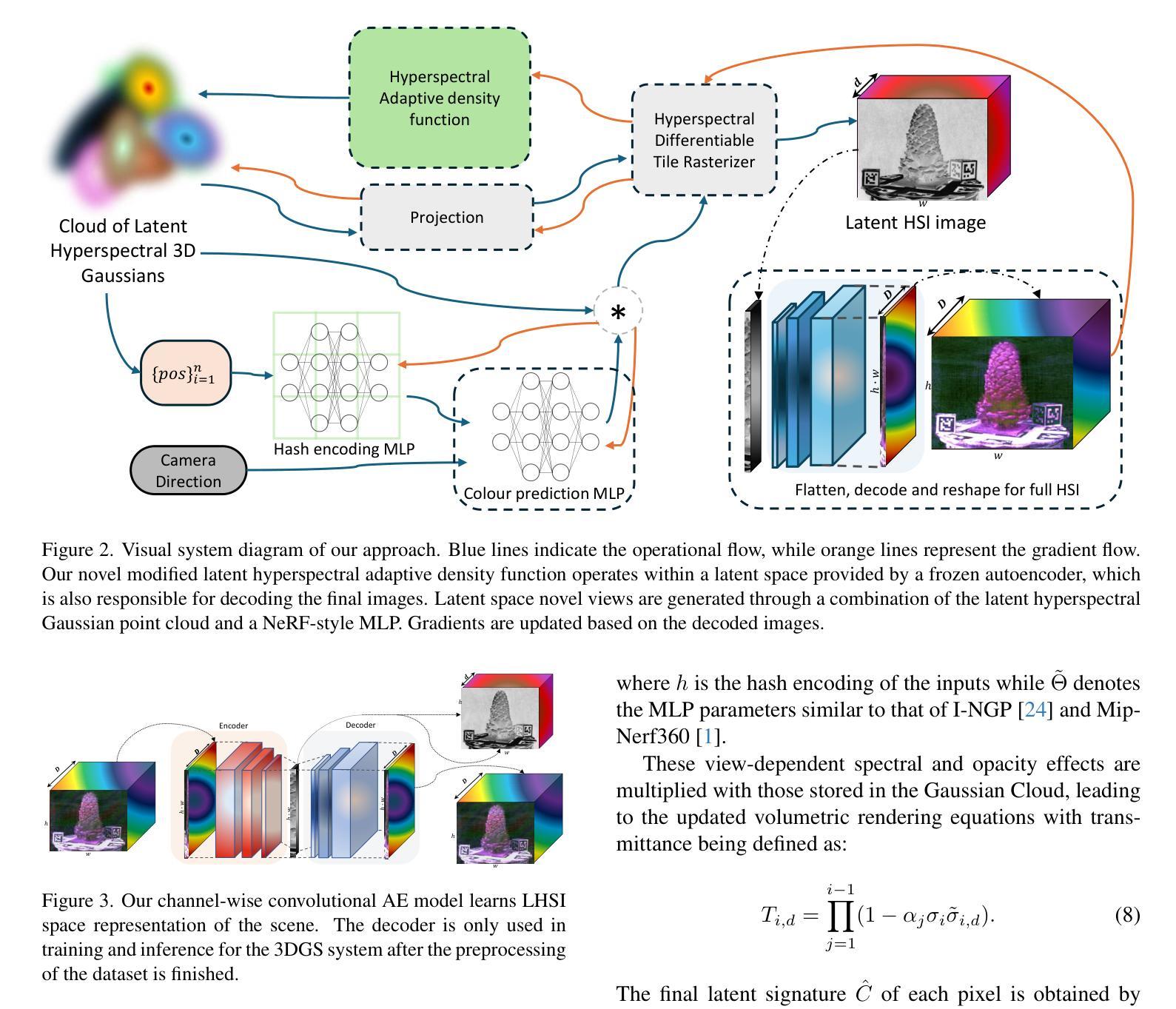

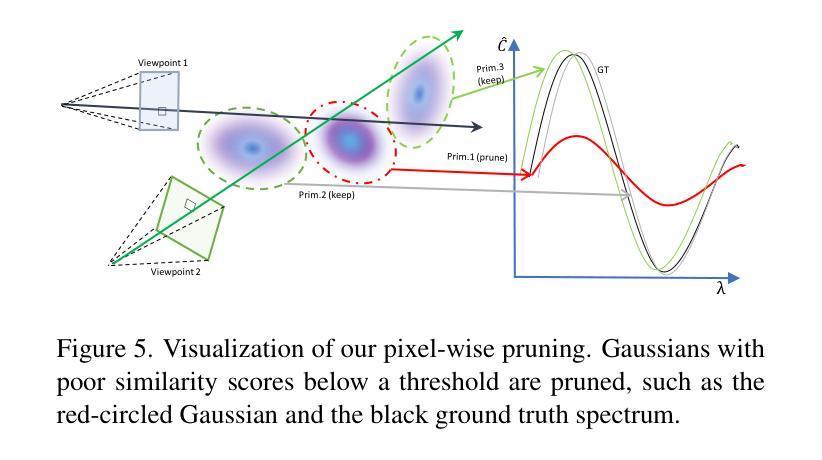
PanSplat: 4K Panorama Synthesis with Feed-Forward Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Cheng Zhang, Haofei Xu, Qianyi Wu, Camilo Cruz Gambardella, Dinh Phung, Jianfei Cai
With the advent of portable 360{\deg} cameras, panorama has gained significant attention in applications like virtual reality (VR), virtual tours, robotics, and autonomous driving. As a result, wide-baseline panorama view synthesis has emerged as a vital task, where high resolution, fast inference, and memory efficiency are essential. Nevertheless, existing methods are typically constrained to lower resolutions (512 $\times$ 1024) due to demanding memory and computational requirements. In this paper, we present PanSplat, a generalizable, feed-forward approach that efficiently supports resolution up to 4K (2048 $\times$ 4096). Our approach features a tailored spherical 3D Gaussian pyramid with a Fibonacci lattice arrangement, enhancing image quality while reducing information redundancy. To accommodate the demands of high resolution, we propose a pipeline that integrates a hierarchical spherical cost volume and Gaussian heads with local operations, enabling two-step deferred backpropagation for memory-efficient training on a single A100 GPU. Experiments demonstrate that PanSplat achieves state-of-the-art results with superior efficiency and image quality across both synthetic and real-world datasets. Code will be available at \url{https://github.com/chengzhag/PanSplat}.
随着便携式360°相机的出现,全景技术在虚拟现实(VR)、虚拟游览、机器人和自动驾驶等领域的应用中受到了广泛关注。因此,宽基线全景视图合成成为了一项重要任务,其中高分辨率、快速推理和内存效率都是至关重要的。然而,由于内存和计算需求较高,现有方法通常局限于较低分辨率(512×1024)。在本文中,我们提出了PanSplat,这是一种通用的前馈方法,有效地支持高达4K(2048×4096)的分辨率。我们的方法采用定制的球形3D高斯金字塔,具有斐波那契格子排列,提高了图像质量,同时减少了信息冗余。为了满足高分辨率的需求,我们提出了一种结合分层球形成本量和高斯头与当地操作的流程,实现两步延迟反向传播,可在单个A100 GPU上进行内存高效训练。实验表明,PanSplat在合成和真实世界数据集上实现了卓越的结果、效率和图像质量。代码将在https://github.com/chengzhag/PanSplat上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://chengzhag.github.io/publication/pansplat/ Code: https://github.com/chengzhag/PanSplat
Summary
全景技术随着便携式360°相机的出现,在虚拟现实、虚拟游览、机器人和自动驾驶等领域受到广泛关注。为满足高分辨率、快速推理和内存效率的要求,宽基线全景视图合成成为重要任务。然而,现有方法受限于较低分辨率(如512×1024)。本文提出PanSplat,一种通用前馈方法,支持高达4K(2048×4096)的分辨率。通过定制球形3D高斯金字塔和斐波那契格子布局,提高图像质量并减少信息冗余。为满足高分辨率需求,我们设计了一个集成分层球形成本量和高斯头部的管道,进行本地操作,实现单A100 GPU上的高效内存训练的两步延迟反向传播。实验表明,PanSplat在合成和真实世界数据集上实现了卓越的结果、高效能和图像质量。
Key Takeaways
- 全景技术在多个领域受到关注,尤其是随着便携式相机的普及。
- 宽基线全景视图合成要求高分辨率、快速推理和内存效率。
- 现有方法受限于较低分辨率,而PanSplat支持高达4K的分辨率。
- PanSplat使用定制球形3D高斯金字塔和斐波那契格子布局提高图像质量。
- 通过集成分层球形成本量和高斯头部的管道,实现高效训练。
- PanSplat采用两步延迟反向传播以适应高分辨率并优化内存使用。
点此查看论文截图

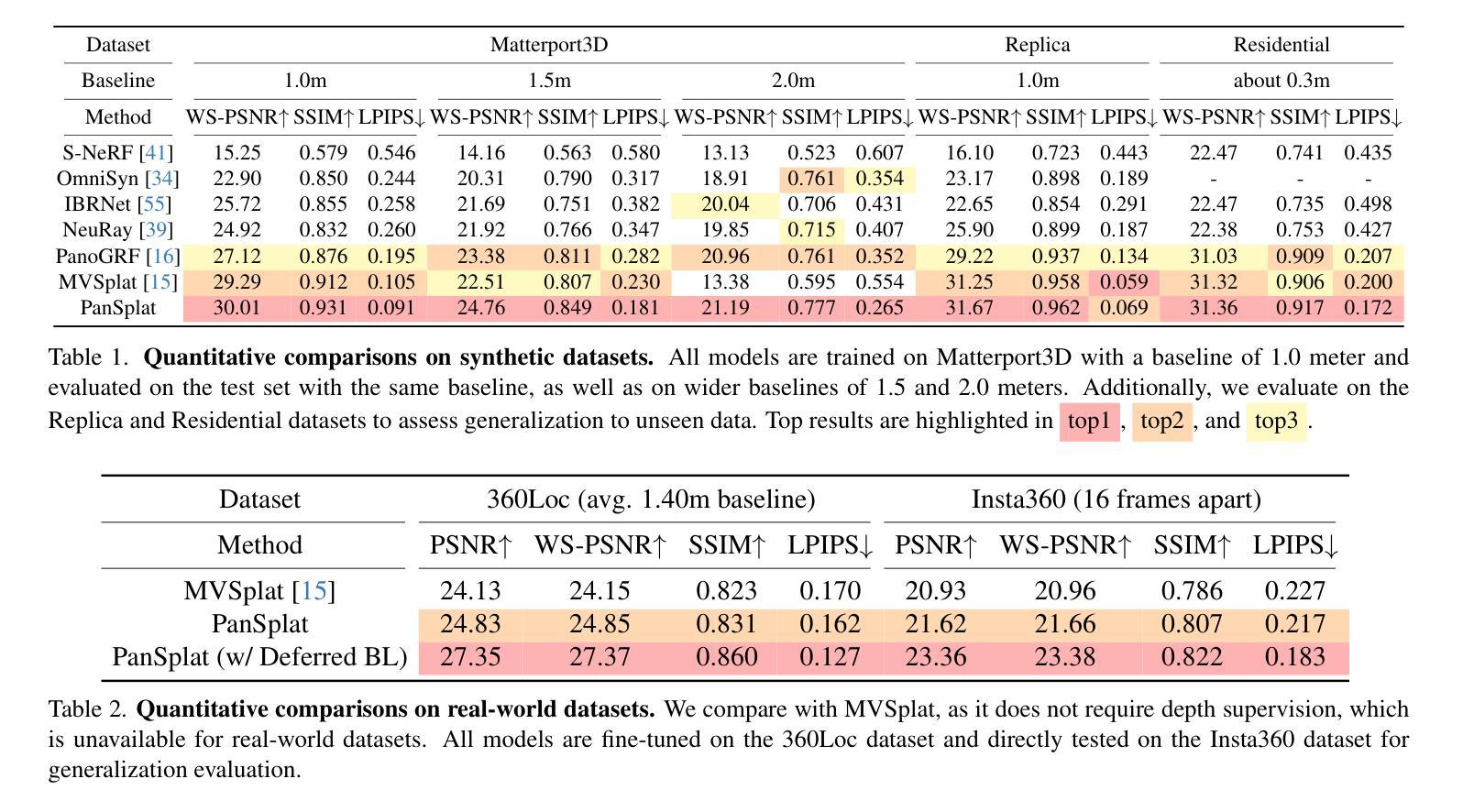
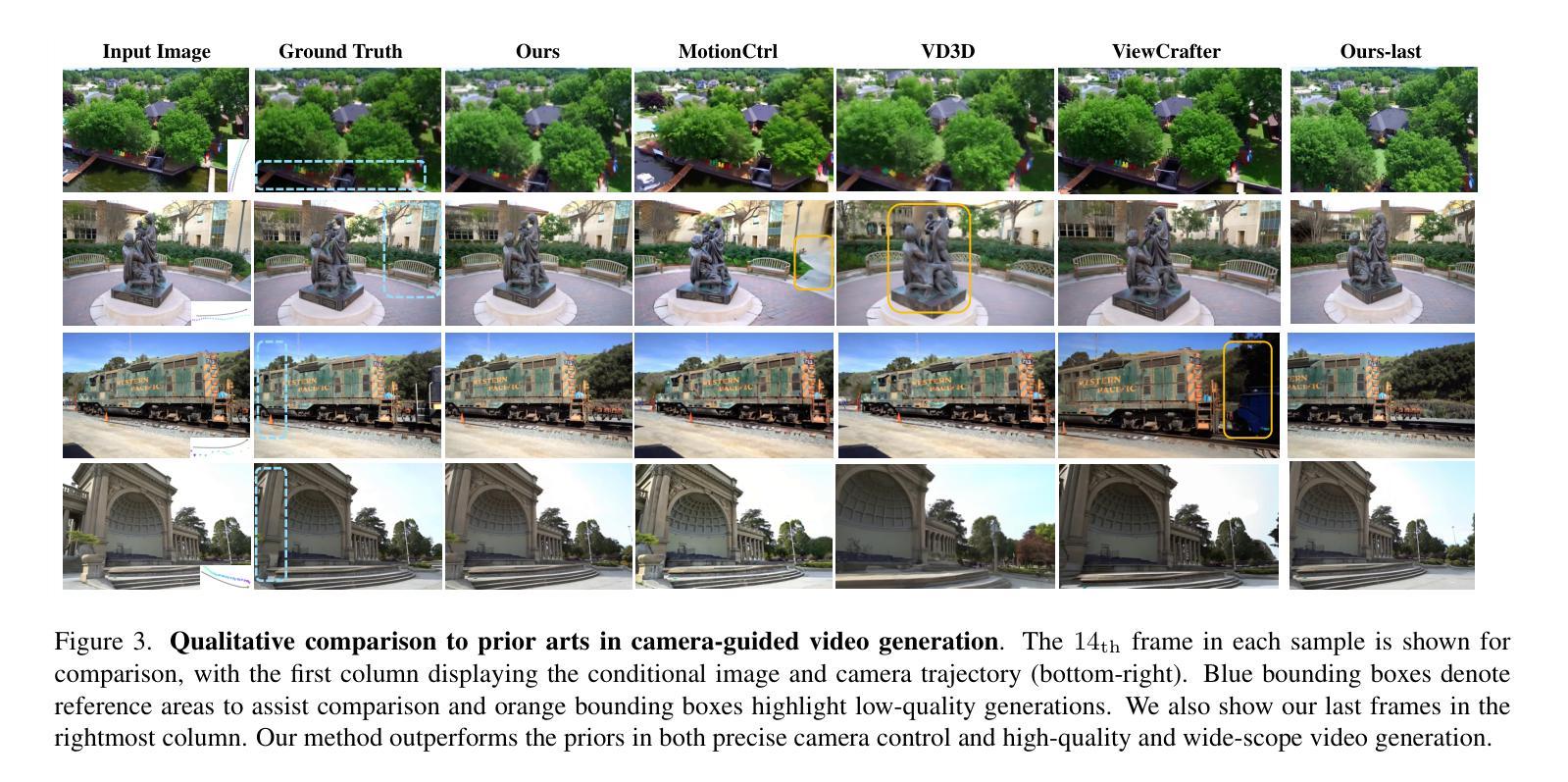
Wonderland: Navigating 3D Scenes from a Single Image
Authors:Hanwen Liang, Junli Cao, Vidit Goel, Guocheng Qian, Sergei Korolev, Demetri Terzopoulos, Konstantinos N. Plataniotis, Sergey Tulyakov, Jian Ren
This paper addresses a challenging question: How can we efficiently create high-quality, wide-scope 3D scenes from a single arbitrary image? Existing methods face several constraints, such as requiring multi-view data, time-consuming per-scene optimization, low visual quality in backgrounds, and distorted reconstructions in unseen areas. We propose a novel pipeline to overcome these limitations. Specifically, we introduce a large-scale reconstruction model that uses latents from a video diffusion model to predict 3D Gaussian Splattings for the scenes in a feed-forward manner. The video diffusion model is designed to create videos precisely following specified camera trajectories, allowing it to generate compressed video latents that contain multi-view information while maintaining 3D consistency. We train the 3D reconstruction model to operate on the video latent space with a progressive training strategy, enabling the efficient generation of high-quality, wide-scope, and generic 3D scenes. Extensive evaluations across various datasets demonstrate that our model significantly outperforms existing methods for single-view 3D scene generation, particularly with out-of-domain images. For the first time, we demonstrate that a 3D reconstruction model can be effectively built upon the latent space of a diffusion model to realize efficient 3D scene generation.
本文提出了一个具有挑战性的问题:如何从一张任意图像高效创建高质量、大范围的三维场景?现有方法面临多重限制,如需要多视角数据、耗时的场景优化、背景视觉质量低下以及未见区域的失真重建。我们提出了一种新的流程来克服这些限制。具体来说,我们引入了一种大规模重建模型,该模型使用视频扩散模型的潜在特征来以正向方式预测场景的三维高斯Splattings。视频扩散模型被设计为精确地遵循指定的相机轨迹来创建视频,从而生成压缩的视频潜在特征,这些特征包含多视角信息,同时保持三维一致性。我们采用渐进的训练策略来训练三维重建模型,使其能够在视频潜在空间上运行,从而能够高效生成高质量、大范围、通用的三维场景。在多个数据集上的广泛评估表明,我们的模型在单视图三维场景生成方面显著优于现有方法,特别是在域外图像上。我们首次证明,可以在扩散模型的潜在空间上构建三维重建模型,以实现高效的三维场景生成。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://snap-research.github.io/wonderland/
Summary
该文提出了一种解决如何从单一任意图像高效创建高质量、大范围3D场景的问题。针对现有方法的局限性,如需要多视角数据、耗时的场景优化、背景视觉质量低以及在未见区域的重建失真等,该文提出了一种新的流程。具体来说,引入了一种大规模重建模型,该模型利用视频扩散模型的潜在特征来预测场景的3D高斯Splattings,并以前馈方式进行。视频扩散模型被设计为遵循指定的相机轨迹创建视频,能够生成包含多视角信息的压缩视频潜在特征,同时保持3D一致性。通过渐进的训练策略,对3D重建模型在视频潜在空间进行操作,能够高效生成高质量、大范围、通用的3D场景。在多个数据集上的评估表明,对于单视图3D场景生成,特别是域外图像,我们的模型显著优于现有方法。首次实现了在扩散模型的潜在空间上建立有效的3D重建模型,实现了高效的3D场景生成。
Key Takeaways
- 该论文解决了从单一图像高效创建高质量3D场景的挑战。
- 现有方法存在多视角数据需求、耗时优化、背景视觉质量低和未见区域重建失真等问题。
- 论文提出了一种新的流程,包括使用视频扩散模型的潜在特征进行3D高斯Splattings预测。
- 视频扩散模型能生成包含多视角信息的压缩视频潜在特征,并维持3D一致性。
- 采用渐进的训练策略,使得模型能在视频潜在空间操作,生成高质量、大范围、通用的3D场景。
- 在多个数据集上的评估显示,该模型在单视图3D场景生成上显著优于现有方法,特别是处理域外图像。
点此查看论文截图


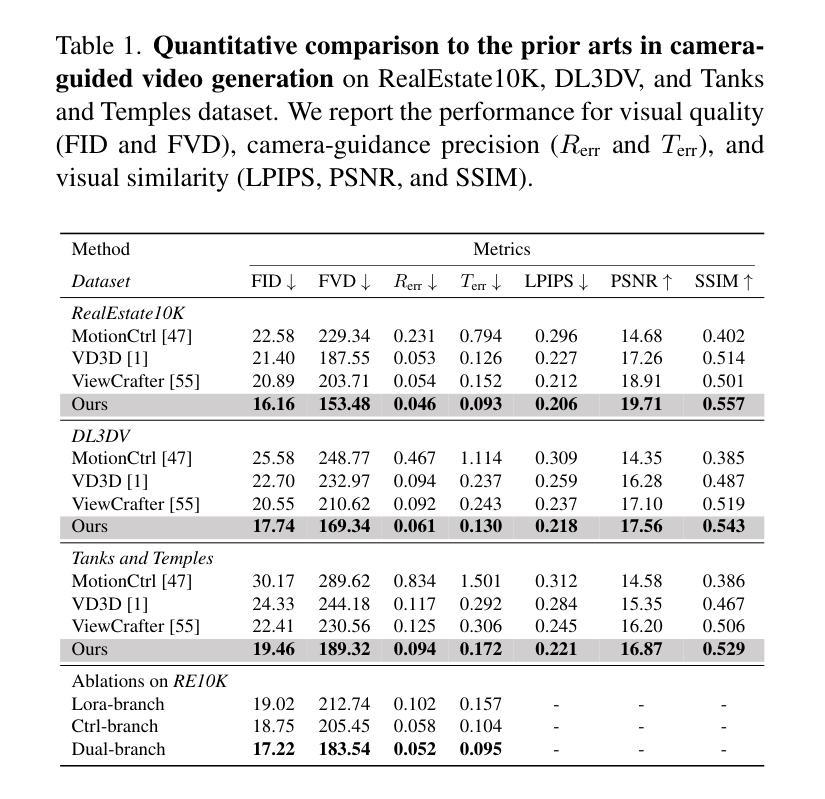
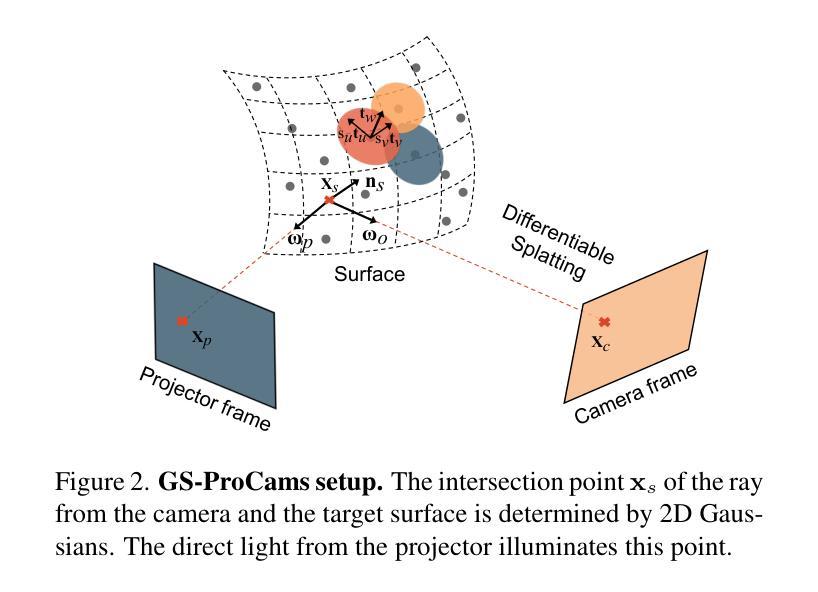
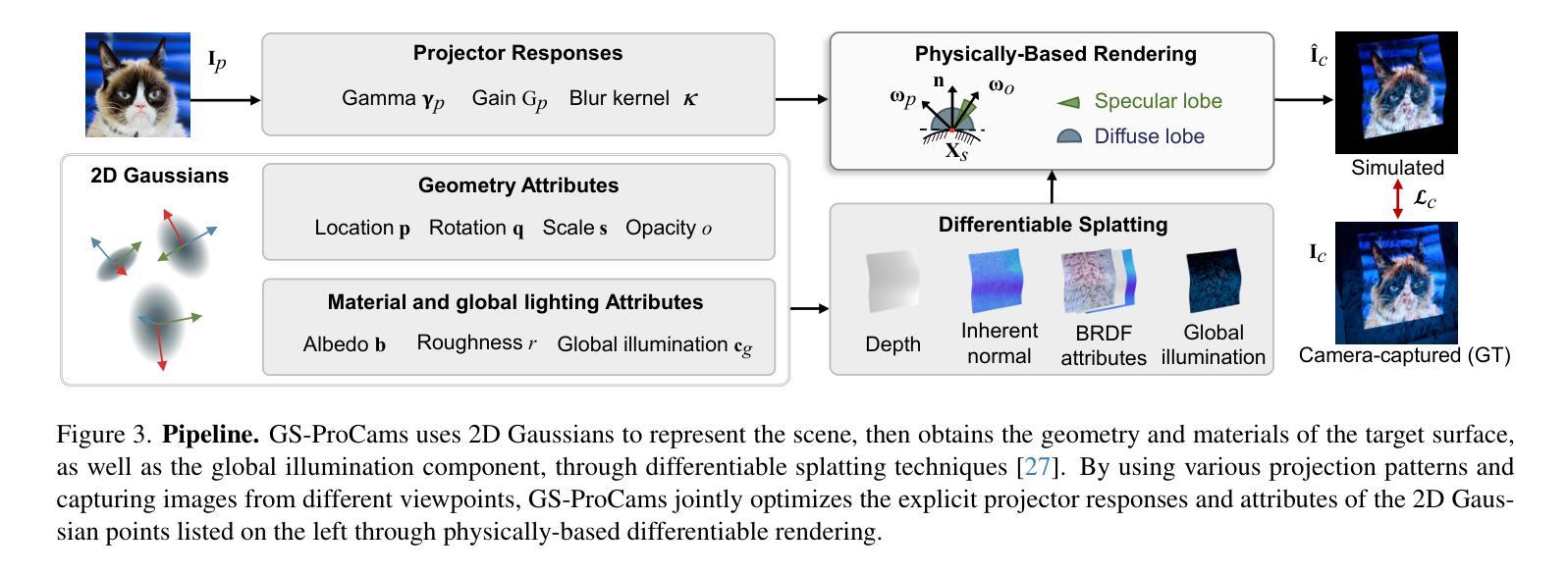
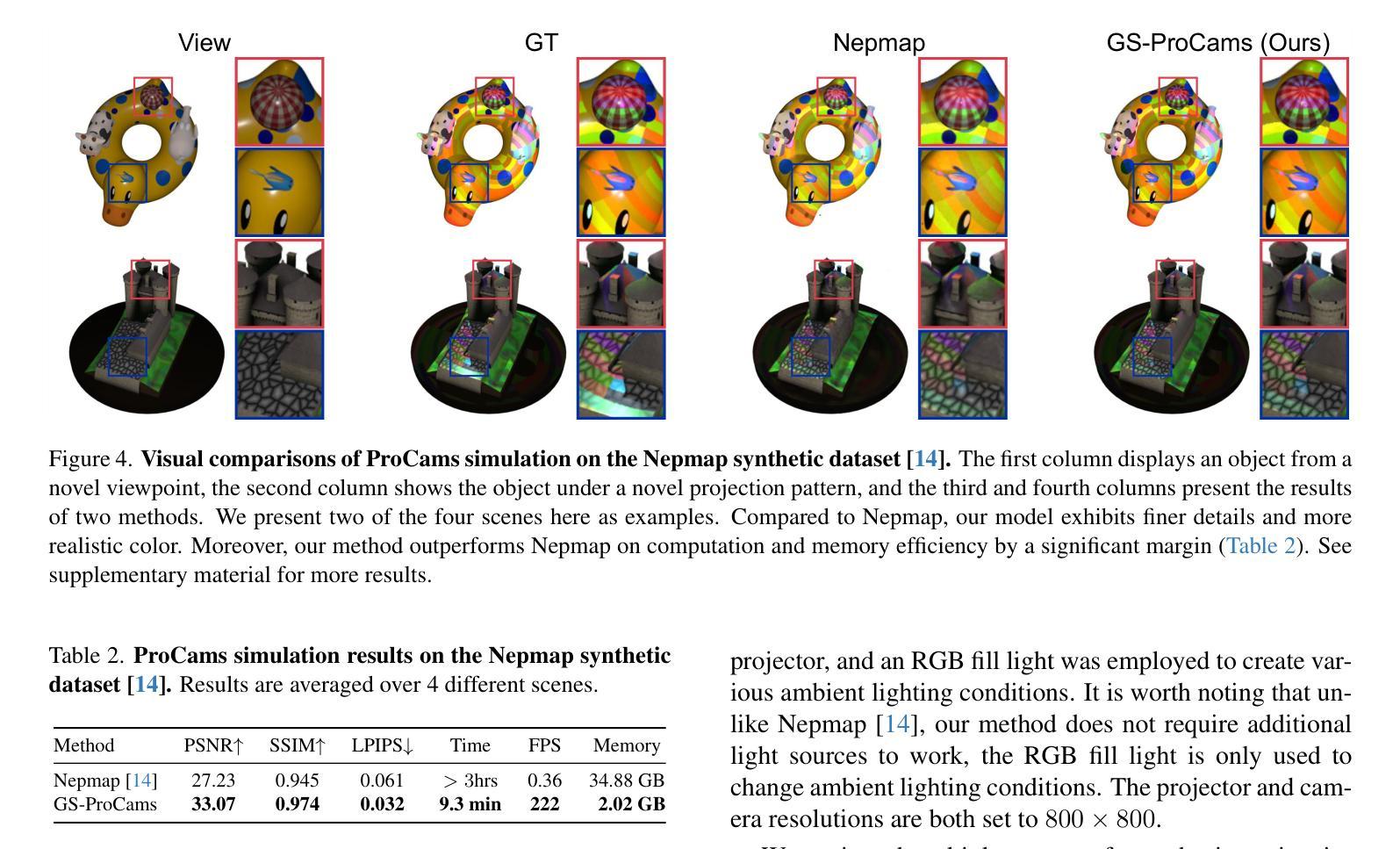
GS-ProCams: Gaussian Splatting-based Projector-Camera Systems
Authors:Qingyue Deng, Jijiang Li, Haibin Ling, Bingyao Huang
We present GS-ProCams, the first Gaussian Splatting-based framework for projector-camera systems (ProCams). GS-ProCams significantly enhances the efficiency of projection mapping (PM) that requires establishing geometric and radiometric mappings between the projector and the camera. Previous CNN-based ProCams are constrained to a specific viewpoint, limiting their applicability to novel perspectives. In contrast, NeRF-based ProCams support view-agnostic projection mapping, however, they require an additional colocated light source and demand significant computational and memory resources. To address this issue, we propose GS-ProCams that employs 2D Gaussian for scene representations, and enables efficient view-agnostic ProCams applications. In particular, we explicitly model the complex geometric and photometric mappings of ProCams using projector responses, the target surface’s geometry and materials represented by Gaussians, and global illumination component. Then, we employ differentiable physically-based rendering to jointly estimate them from captured multi-view projections. Compared to state-of-the-art NeRF-based methods, our GS-ProCams eliminates the need for additional devices, achieving superior ProCams simulation quality. It is also 600 times faster and uses only 1/10 of the GPU memory.
我们提出了GS-ProCams,这是基于高斯拼贴技术的投影仪摄像头系统(ProCams)的首个框架。GS-ProCams大大提高了投影映射(PM)的效率,该效率需要建立投影仪和摄像头之间的几何和辐射度量映射。以前的基于CNN的ProCams受限于特定视角,限制了其在新颖视角的应用。相比之下,基于NeRF的ProCams支持独立于视图的投影映射,然而,它们需要额外的共置光源,并需要巨大的计算和内存资源。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了GS-ProCams,它采用2D高斯进行场景表示,并实现了高效的独立于视图的ProCams应用程序。特别是,我们使用投影仪响应、由高斯表示的目标表面的几何形状和材料以及全局照明组件来显式建模ProCams的复杂几何和光度映射。然后,我们采用基于物理的可微分渲染来联合估计从捕获的多视角投影。与最新的基于NeRF的方法相比,我们的GS-ProCams不需要额外的设备,实现了卓越的ProCams仿真质量。其速度也更快(高达600倍),并且只使用1/10的GPU内存。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
GS-ProCams是首个基于高斯展开技术的投影仪相机系统框架,它能显著提升投影映射的效率。与仅适用于特定视角的CNN模型相比,GS-ProCams实现了不受视角限制的投影映射,并且不需要额外的光源设备。通过建模复杂几何和光度映射关系,结合物理渲染技术,GS-ProCams实现了高质量的投影模拟,计算速度提升600倍,GPU内存使用减少十分之九。
Key Takeaways
- GS-ProCams是首个基于高斯展开技术的投影仪相机系统框架。
- GS-ProCams提高了投影映射的效率。
- 相比于CNN模型,GS-ProCams支持更广泛的视角。
- GS-ProCams不需要额外的光源设备。
- GS-ProCams通过建模复杂几何和光度映射关系实现高质量的投影模拟。
- GS-ProCams利用物理渲染技术来提升性能。
点此查看论文截图

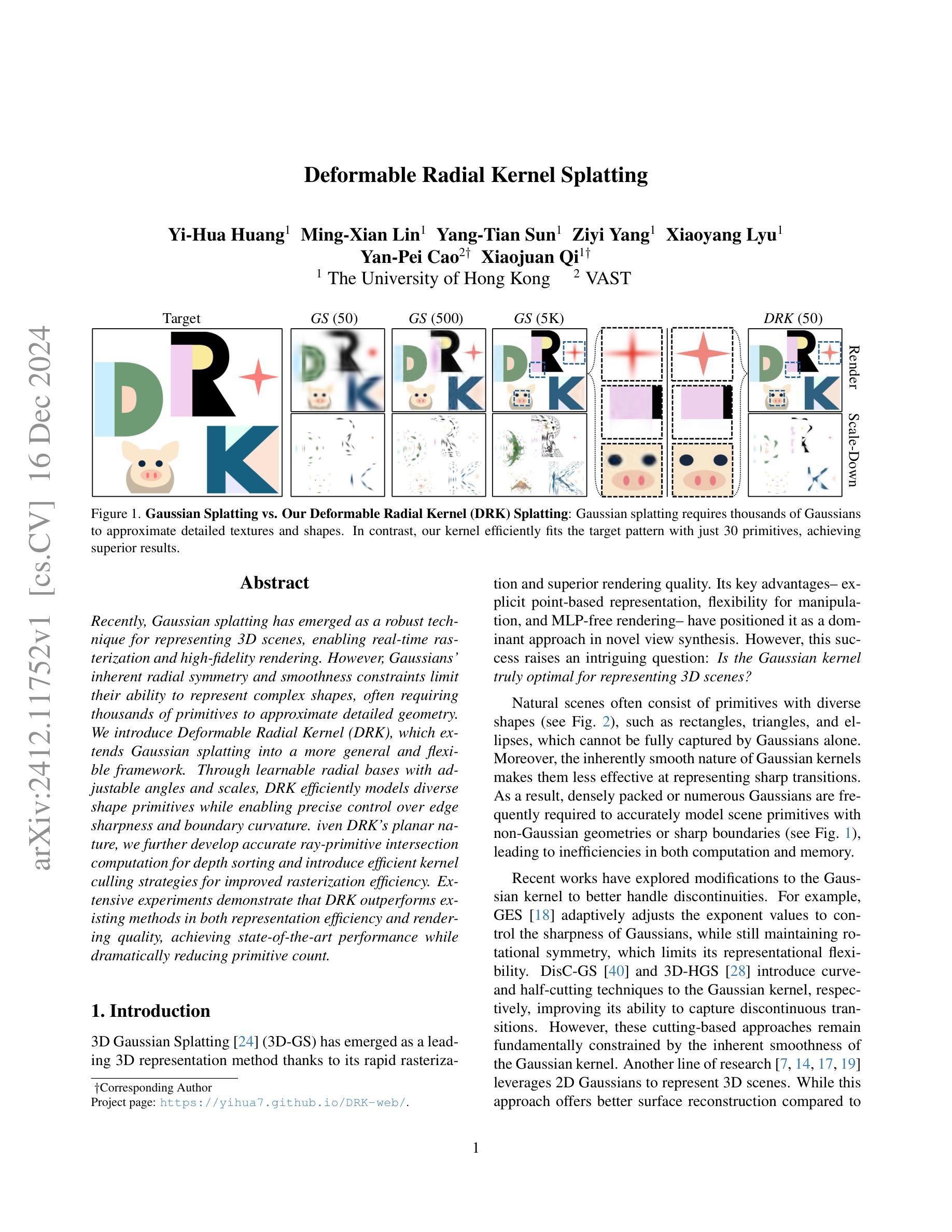
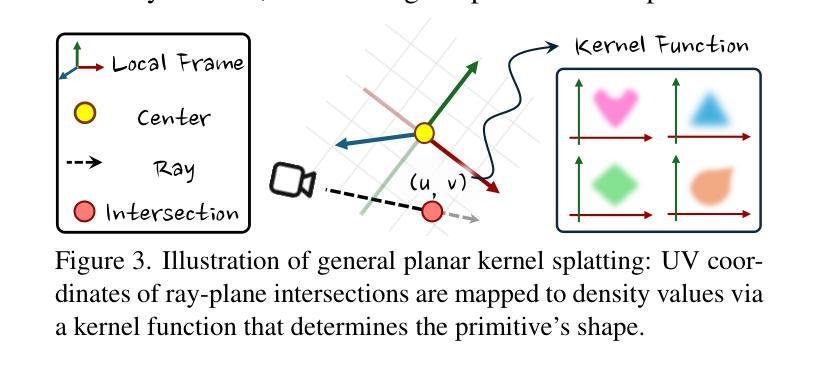
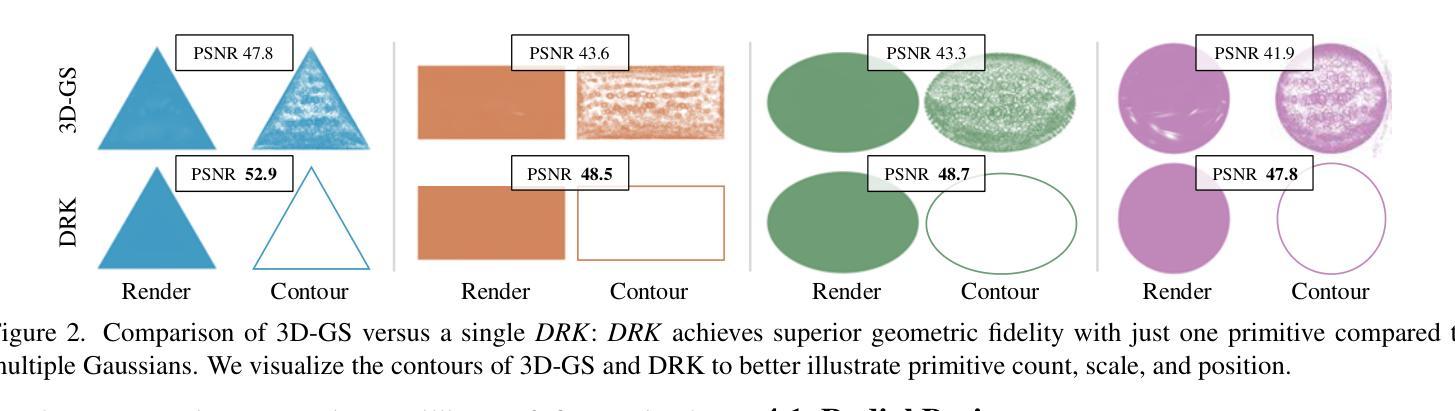
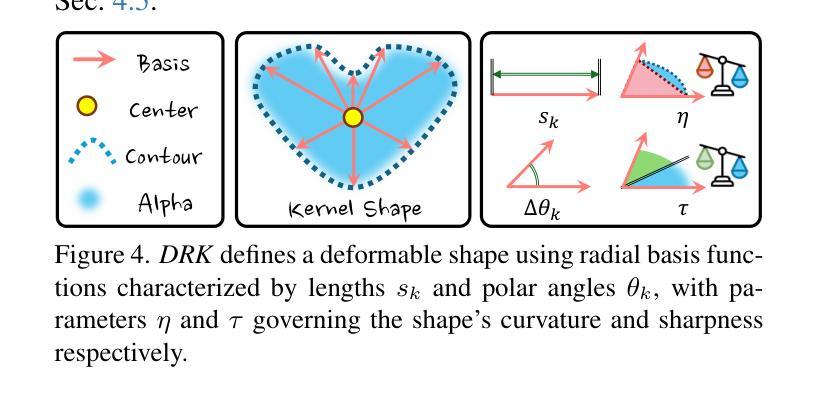
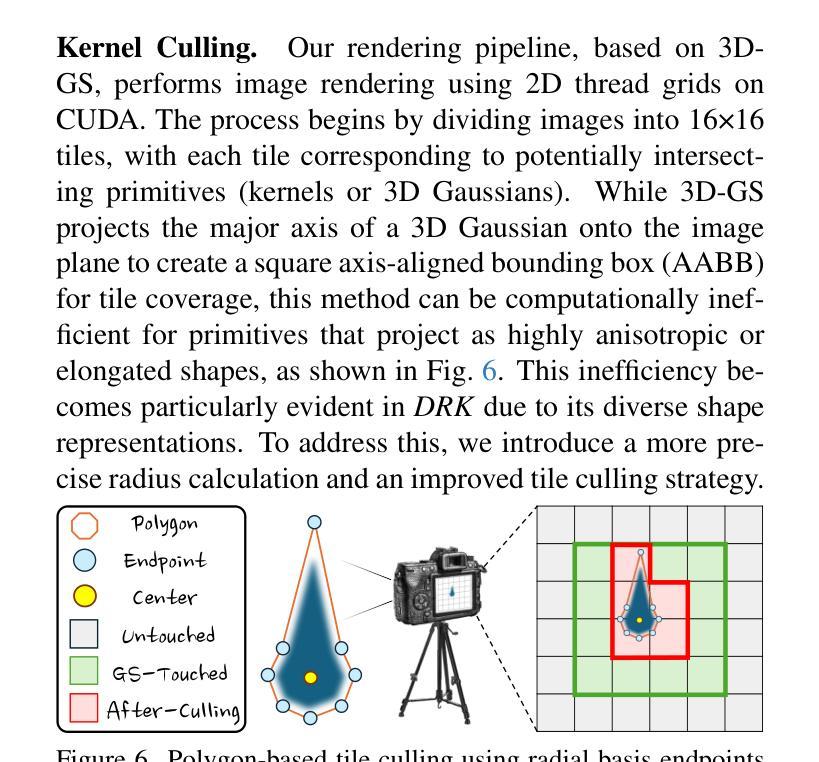
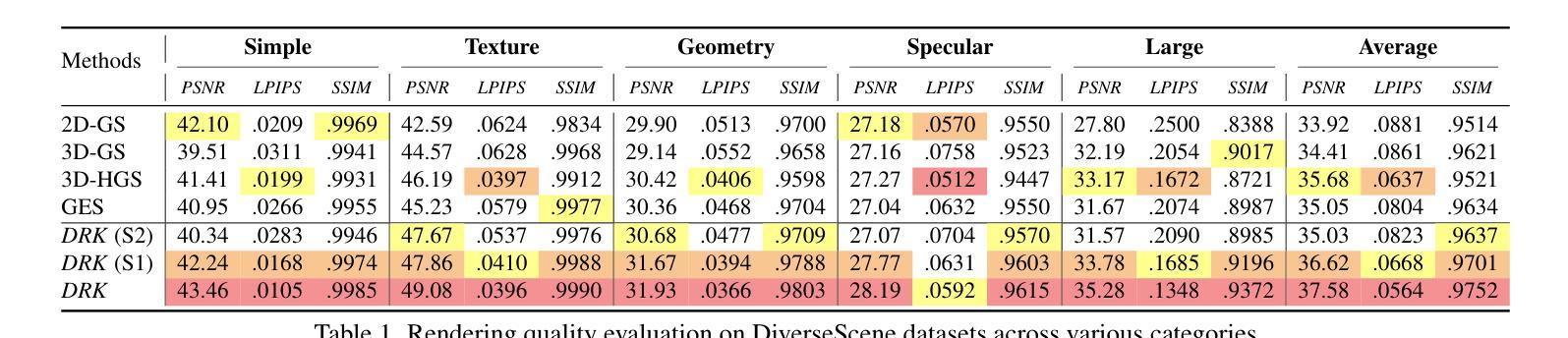
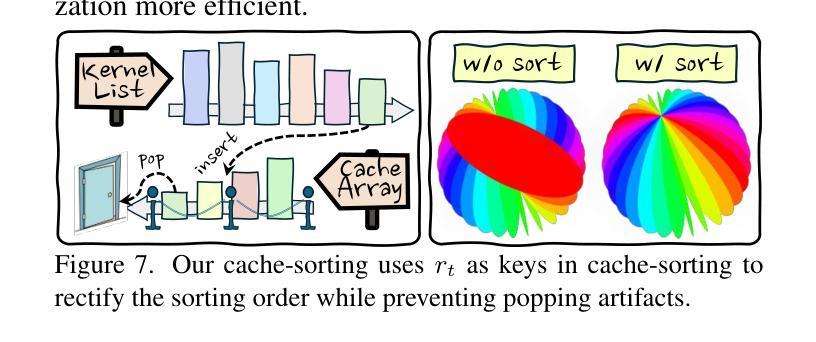
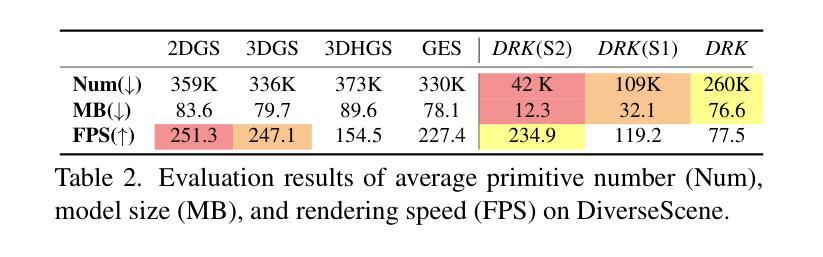
Deformable Radial Kernel Splatting
Authors:Yi-Hua Huang, Ming-Xian Lin, Yang-Tian Sun, Ziyi Yang, Xiaoyang Lyu, Yan-Pei Cao, Xiaojuan Qi
Recently, Gaussian splatting has emerged as a robust technique for representing 3D scenes, enabling real-time rasterization and high-fidelity rendering. However, Gaussians’ inherent radial symmetry and smoothness constraints limit their ability to represent complex shapes, often requiring thousands of primitives to approximate detailed geometry. We introduce Deformable Radial Kernel (DRK), which extends Gaussian splatting into a more general and flexible framework. Through learnable radial bases with adjustable angles and scales, DRK efficiently models diverse shape primitives while enabling precise control over edge sharpness and boundary curvature. iven DRK’s planar nature, we further develop accurate ray-primitive intersection computation for depth sorting and introduce efficient kernel culling strategies for improved rasterization efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DRK outperforms existing methods in both representation efficiency and rendering quality, achieving state-of-the-art performance while dramatically reducing primitive count.
近期,高斯涂斑技术已成为表示3D场景的一种稳健技术,可实现实时光线追踪和高保真渲染。然而,高斯固有的径向对称性和平滑性约束限制了其表示复杂形状的能力,通常需要数千个基本图形来近似详细的几何形状。我们引入了可变形径向核(DRK),将高斯涂斑扩展为一个更通用和灵活的平台。通过具有可调整角度和比例的可学习径向基,DRK能够高效地建模各种形状基本图形,同时能够精确控制边缘锐度和边界曲率。鉴于DRK的平面特性,我们进一步开发了精确的射线与基本图形相交计算以实现深度排序,并引入了高效的核剔除策略以提高光线追踪效率。大量实验表明,DRK在表示效率和渲染质量方面都优于现有方法,实现了卓越的性能,同时显著减少了基本图形的数量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期,高斯贴图技术已成为表示三维场景的稳健方法,可实现实时渲染和高保真渲染。然而,高斯本身的径向对称性和平滑性约束限制了其表示复杂形状的能力,通常需要数千个基本形状来近似详细的几何形状。本研究介绍了一种可扩展的高斯贴图技术——可变形径向核(DRK),它构建一个更通用和灵活的平台。通过具有可调角度和比例的可学习径向基,DRK能够高效地模拟各种形状基本形状,同时实现对边缘锐度和边界曲率的精确控制。此外,鉴于DRK的平面特性,本研究还开发了精确的射线与基本形状的交点计算深度排序方法,并引入了高效的核剔除策略以提高渲染效率。大量实验表明,DRK在表示效率和渲染质量方面均优于现有方法,实现了卓越的性能,同时大大降低了基本形状的数量。
Key Takeaways
- 高斯贴图技术已用于表示三维场景,具有实时渲染和高保真渲染的能力。
- 传统高斯方法存在局限性,难以表示复杂形状,需要大量基本形状来近似。
- 研究提出了可变形径向核(DRK)技术,扩展了高斯贴图的通用性和灵活性。
- DRK通过可学习径向基,能高效模拟多种形状,并精确控制边缘锐度和边界曲率。
- DRK具有平面特性,开发了精确的射线与基本形状交点计算深度排序方法。
- 研究还引入了高效的核剔除策略,以提高DRK的渲染效率。
点此查看论文截图
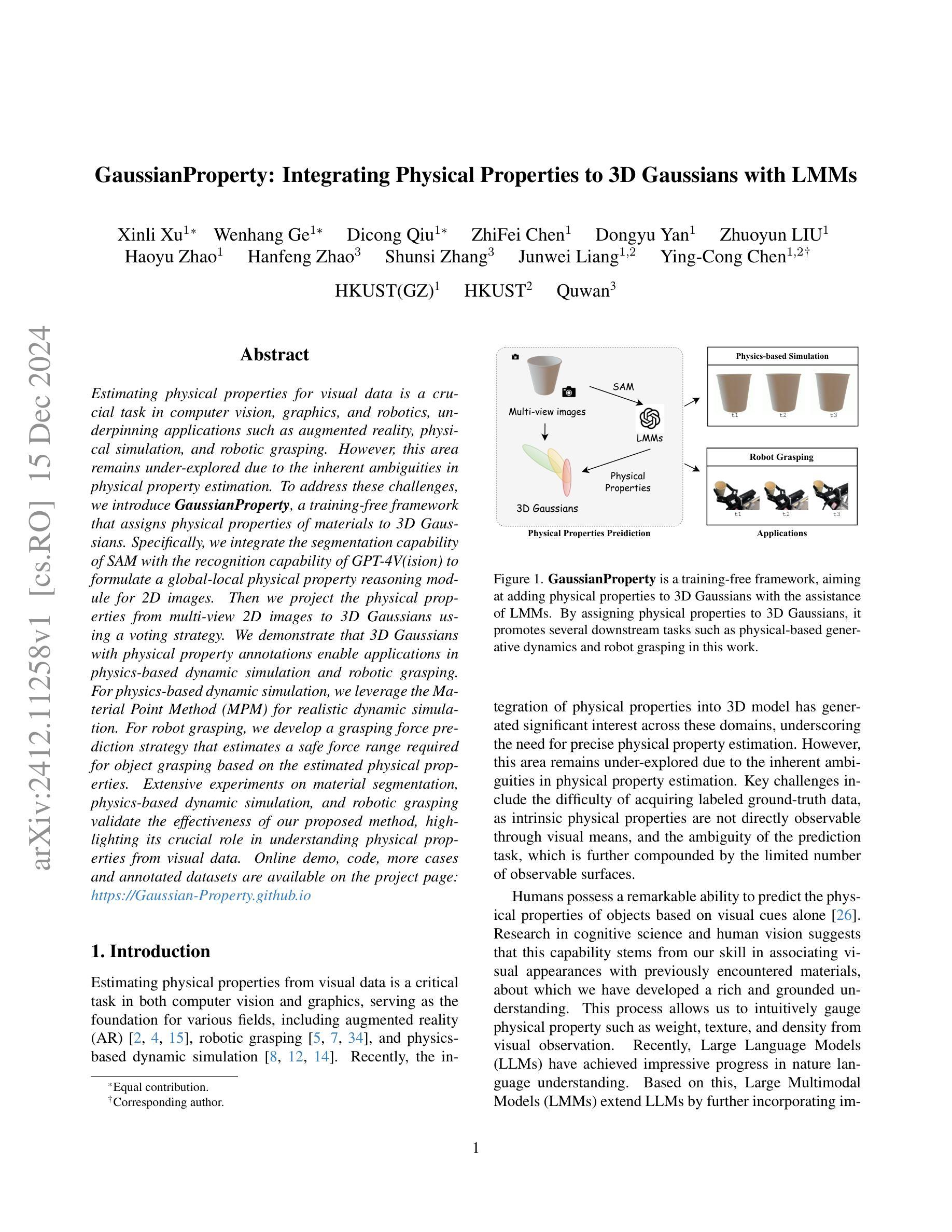
GaussianProperty: Integrating Physical Properties to 3D Gaussians with LMMs
Authors:Xinli Xu, Wenhang Ge, Dicong Qiu, ZhiFei Chen, Dongyu Yan, Zhuoyun Liu, Haoyu Zhao, Hanfeng Zhao, Shunsi Zhang, Junwei Liang, Ying-Cong Chen
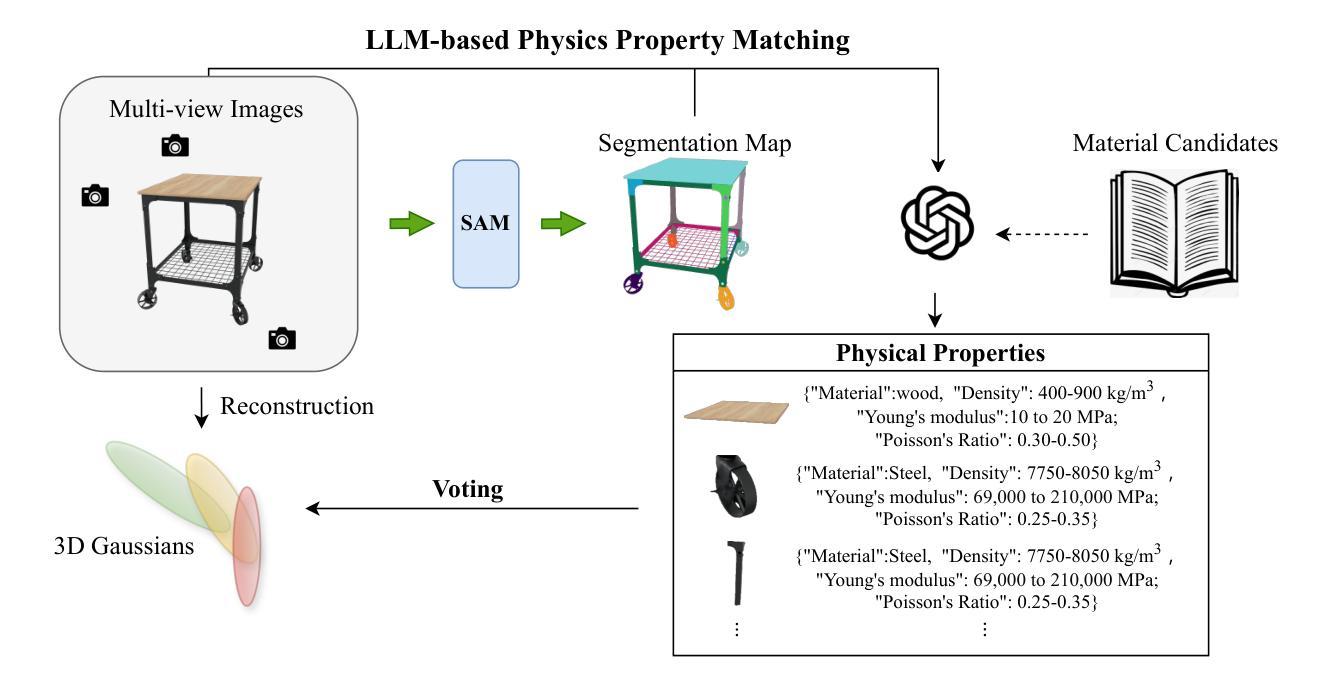
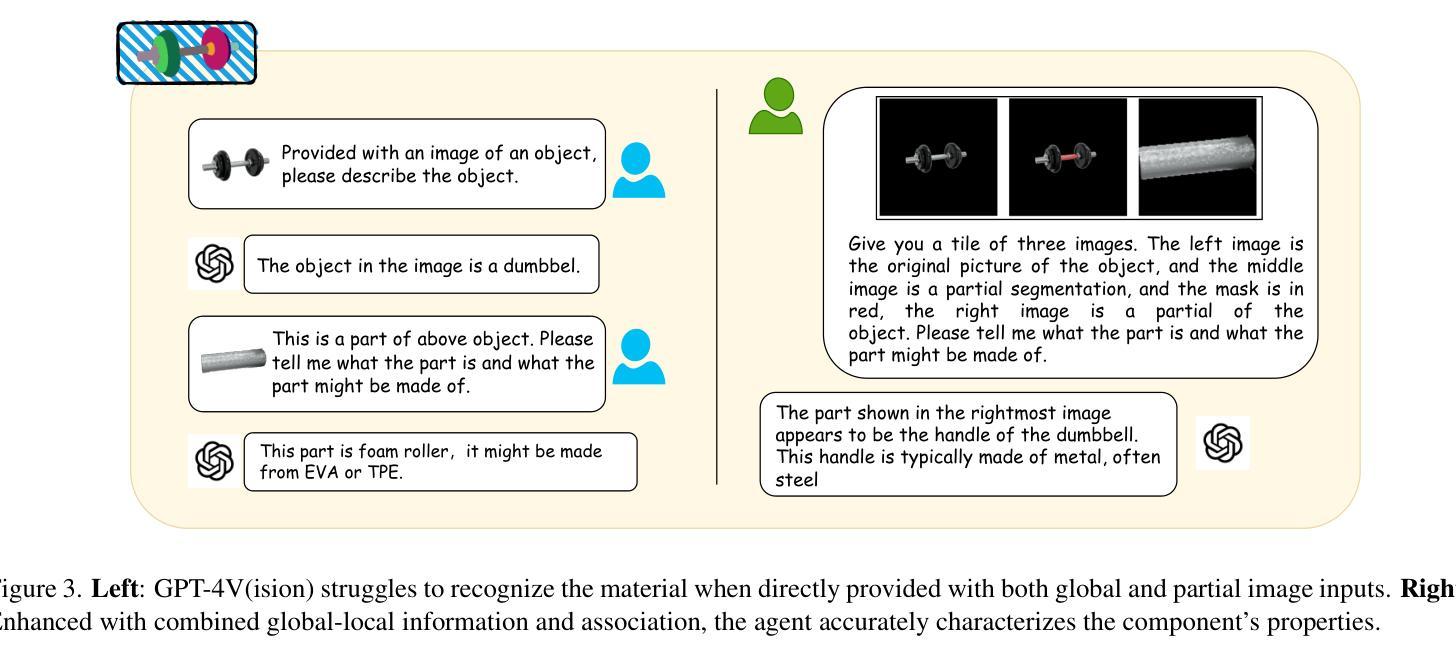
Estimating physical properties for visual data is a crucial task in computer vision, graphics, and robotics, underpinning applications such as augmented reality, physical simulation, and robotic grasping. However, this area remains under-explored due to the inherent ambiguities in physical property estimation. To address these challenges, we introduce GaussianProperty, a training-free framework that assigns physical properties of materials to 3D Gaussians. Specifically, we integrate the segmentation capability of SAM with the recognition capability of GPT-4V(ision) to formulate a global-local physical property reasoning module for 2D images. Then we project the physical properties from multi-view 2D images to 3D Gaussians using a voting strategy. We demonstrate that 3D Gaussians with physical property annotations enable applications in physics-based dynamic simulation and robotic grasping. For physics-based dynamic simulation, we leverage the Material Point Method (MPM) for realistic dynamic simulation. For robot grasping, we develop a grasping force prediction strategy that estimates a safe force range required for object grasping based on the estimated physical properties. Extensive experiments on material segmentation, physics-based dynamic simulation, and robotic grasping validate the effectiveness of our proposed method, highlighting its crucial role in understanding physical properties from visual data. Online demo, code, more cases and annotated datasets are available on \href{https://Gaussian-Property.github.io}{this https URL}.
估算视觉数据的物理属性在计算机视觉、图形和机器人技术中是一项至关重要的任务,它为增强现实、物理模拟和机器人抓取等应用提供了支持。然而,由于物理属性估算固有的模糊性,这个领域仍然有待探索。为了应对这些挑战,我们引入了GaussianProperty这一无需训练的框架,该框架将材料的物理属性分配给3D高斯分布。具体来说,我们将SAM的分割能力与GPT-4V(视觉)的识别能力相结合,形成了针对2D图像的全局-局部物理属性推理模块。然后,我们使用投票策略将多视图2D图像的物理属性投影到3D高斯分布上。我们证明,带有物理属性注释的3D高斯分布可用于基于物理的动态模拟和机器人抓取应用。在基于物理的动态模拟方面,我们利用物质点法(MPM)进行逼真的动态模拟。在机器人抓取方面,我们开发了一种抓取力预测策略,该策略根据估计的物理属性来估计抓取物体所需的安全力范围。在材料分割、基于物理的动态模拟和机器人抓取方面的广泛实验验证了我们的方法的有效性,凸显了其在理解视觉数据物理属性方面的关键作用。在线演示、代码、更多案例和注释数据集可在this https URL上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 17 pages, 17 figures
Summary
本文介绍了一种无需训练的框架——GaussianProperty,该框架可为3D高斯分配材料物理属性。通过结合SAM的分割能力和GPT-4V(ision)的识别能力,形成用于2D图像的全局-局部物理属性推理模块。采用投票策略将多视角2D图像的物理属性投影到3D高斯上。该框架在基于物理的动态模拟和机器人抓取等方面有广泛应用。对于基于物理的动态模拟,利用物质点法(MPM)进行逼真的动态模拟;对于机器人抓取,开发了一种基于估计物理属性的安全力范围预测策略。实验验证了该方法在材料分割、基于物理的动态模拟和机器人抓取中的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- GaussianProperty是一种无需训练的框架,用于为3D高斯分配材料物理属性,如弹性、硬度等。
- 结合SAM的分割能力和GPT-4V(ision)的识别能力,形成2D图像的物理属性推理模块。
- 采用投票策略将2D图像的物理属性投影到3D空间的高斯分布上。
- 该框架可应用于基于物理的动态模拟和机器人抓取。
- 在动态模拟方面,利用物质点法(MPM)进行逼真的模拟。
- 在机器人抓取应用中,提出了基于估计物理属性的安全力范围预测策略。
点此查看论文截图
SplineGS: Robust Motion-Adaptive Spline for Real-Time Dynamic 3D Gaussians from Monocular Video
Authors:Jongmin Park, Minh-Quan Viet Bui, Juan Luis Gonzalez Bello, Jaeho Moon, Jihyong Oh, Munchurl Kim
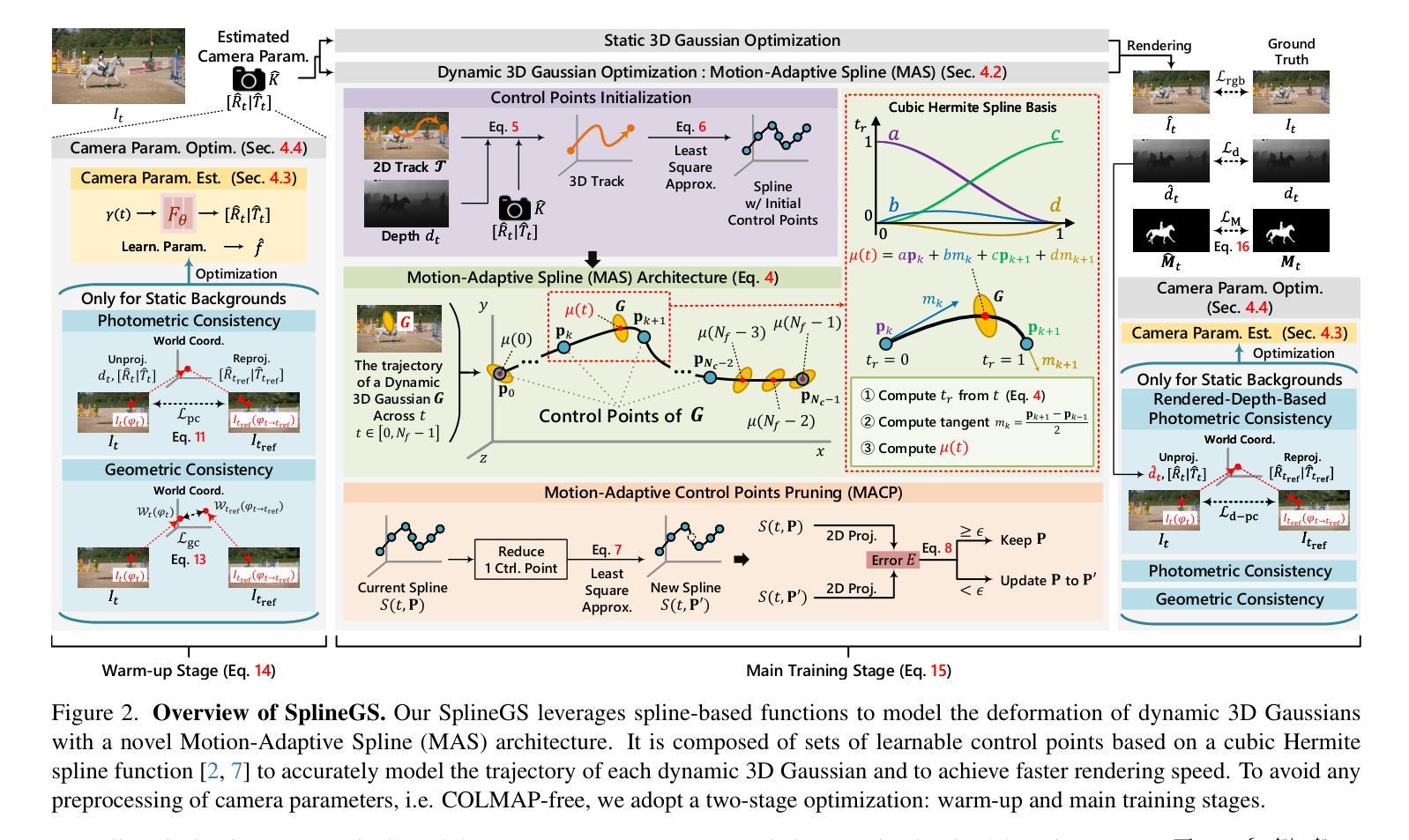
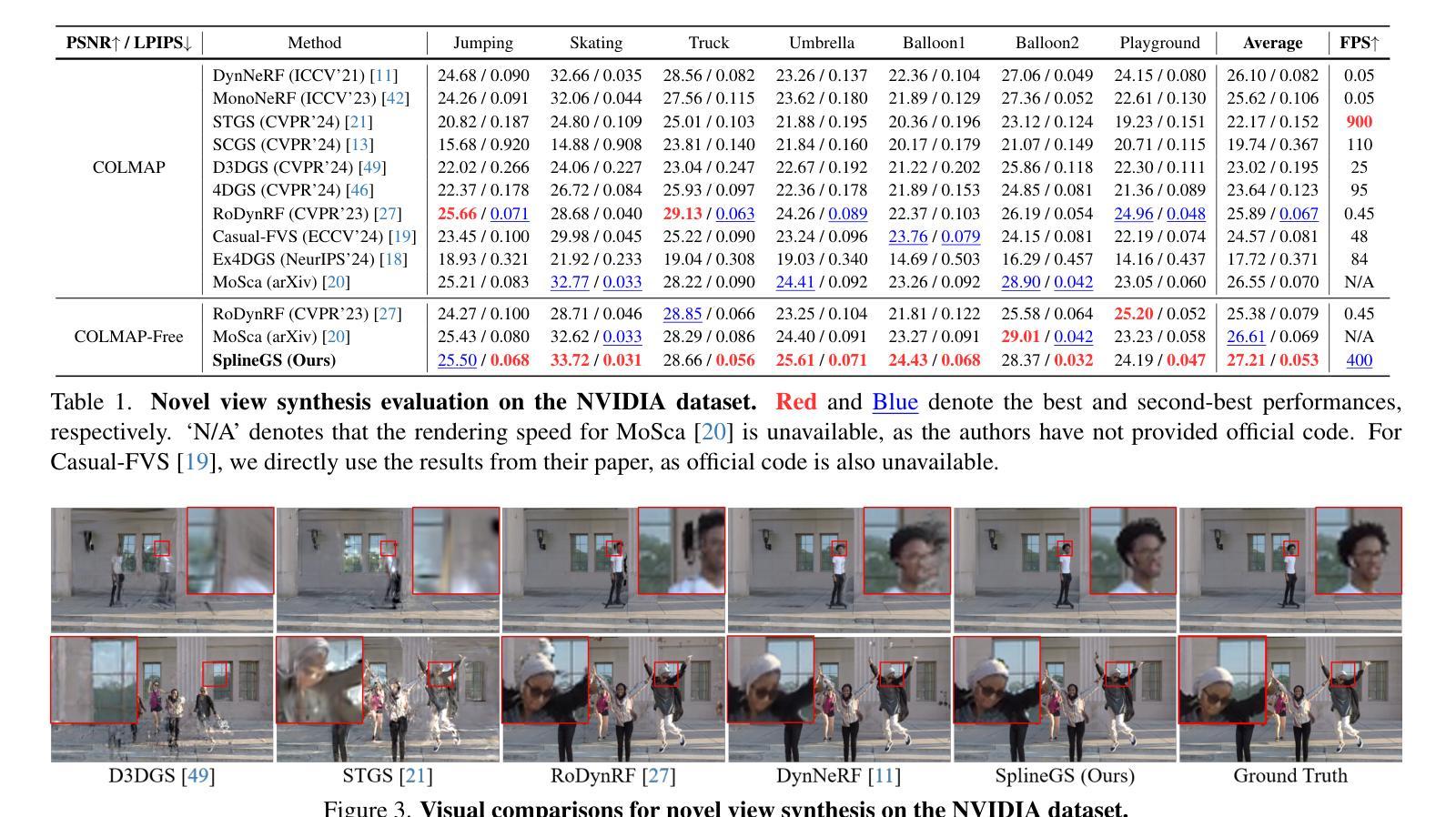
Synthesizing novel views from in-the-wild monocular videos is challenging due to scene dynamics and the lack of multi-view cues. To address this, we propose SplineGS, a COLMAP-free dynamic 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) framework for high-quality reconstruction and fast rendering from monocular videos. At its core is a novel Motion-Adaptive Spline (MAS) method, which represents continuous dynamic 3D Gaussian trajectories using cubic Hermite splines with a small number of control points. For MAS, we introduce a Motion-Adaptive Control points Pruning (MACP) method to model the deformation of each dynamic 3D Gaussian across varying motions, progressively pruning control points while maintaining dynamic modeling integrity. Additionally, we present a joint optimization strategy for camera parameter estimation and 3D Gaussian attributes, leveraging photometric and geometric consistency. This eliminates the need for Structure-from-Motion preprocessing and enhances SplineGS’s robustness in real-world conditions. Experiments show that SplineGS significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in novel view synthesis quality for dynamic scenes from monocular videos, achieving thousands times faster rendering speed.
从野生单目视频中合成新型视角是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为场景动态变化和缺乏多视角线索。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了SplineGS,这是一个无需COLMAP的动态三维高斯喷绘(3DGS)框架,用于从单目视频中实现高质量重建和快速渲染。其核心是一种新型运动自适应样条(MAS)方法,该方法使用少量控制点,通过三次Hermite样条表示连续动态三维高斯轨迹。对于MAS,我们引入了一种运动自适应控制点修剪(MACP)方法,以模拟不同运动下每个动态三维高斯的变化,在保持动态建模完整性的同时逐步修剪控制点。此外,我们还提出了一种用于相机参数估计和三维高斯属性联合优化的策略,利用光度和几何一致性。这消除了对从运动结构进行预处理的需要,提高了SplineGS在现实条件下的稳健性。实验表明,对于从单目视频中得到的动态场景的新型视角合成质量,SplineGS显著优于最先进的方法,并且实现了数千倍的快速渲染速度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The first two authors contributed equally to this work (equal contribution). The last two authors advised equally to this work. Please visit our project page at this https://kaist-viclab.github.io/splinegs-site/
Summary
本文提出一种名为SplineGS的无需COLMAP的动态3D高斯描画(3DGS)框架,用于从单目视频中实现高质量重建和快速渲染。其核心是新型运动自适应样条(MAS)方法,使用少量控制点,通过三次Hermite样条表示连续的动态3D高斯轨迹。为MAS,引入运动自适应控制点修剪(MACP)方法,以模拟不同运动下每个动态3D高斯的变化,同时保持动态建模的完整性。此外,利用光度和几何一致性,提出相机参数估计和3D高斯属性联合优化策略,无需从运动中重建预处理,提高了SplineGS在现实条件下的稳健性。实验表明,SplineGS在单目视频动态场景的新型视图合成质量方面显著优于最先进的方法,渲染速度提高数千倍。
Key Takeaways
- SplineGS是一个基于动态3D高斯描画(3DGS)的框架,用于从单目视频中实现高质量重建和快速渲染。
- 框架核心为运动自适应样条(MAS)方法,使用Hermite样条表示动态3D高斯轨迹。
- 引入运动自适应控制点修剪(MACP)方法,以模拟不同运动下每个动态3D高斯的变化。
- 提出联合优化策略,用于相机参数估计和3D高斯属性估计。
- 该方法无需结构从运动(Structure-from-Motion)预处理,增强了在现实条件下的稳健性。
- 实验显示,SplineGS在单目视频动态场景的新型视图合成质量方面表现优异。
点此查看论文截图

Diffusion Models with Anisotropic Gaussian Splatting for Image Inpainting
Authors:Jacob Fein-Ashley, Benjamin Fein-Ashley
Image inpainting is a fundamental task in computer vision, aiming to restore missing or corrupted regions in images realistically. While recent deep learning approaches have significantly advanced the state-of-the-art, challenges remain in maintaining structural continuity and generating coherent textures, particularly in large missing areas. Diffusion models have shown promise in generating high-fidelity images but often lack the structural guidance necessary for realistic inpainting. We propose a novel inpainting method that combines diffusion models with anisotropic Gaussian splatting to capture both local structures and global context effectively. By modeling missing regions using anisotropic Gaussian functions that adapt to local image gradients, our approach provides structural guidance to the diffusion-based inpainting network. The Gaussian splat maps are integrated into the diffusion process, enhancing the model’s ability to generate high-fidelity and structurally coherent inpainting results. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art techniques, producing visually plausible results with enhanced structural integrity and texture realism.
图像修复是计算机视觉中的一项基本任务,旨在以逼真的方式恢复图像中缺失或损坏的区域。虽然最近的深度学习方法已经显著提高了最新水平,但在保持结构连续性和生成连贯纹理方面仍然存在挑战,特别是在大面积缺失的情况下。扩散模型在生成高保真图像方面显示出潜力,但往往缺乏用于现实修复所需的结构指导。我们提出了一种结合扩散模型和定向高斯涂布技术的新图像修复方法,以有效地捕捉局部结构和全局上下文。我们使用适应局部图像梯度的定向高斯函数对缺失区域进行建模,为基于扩散的图像修复网络提供结构指导。高斯展平图集成到扩散过程中,增强了模型生成高保真和结构上连贯的修复结果的能力。大量实验表明,我们的方法优于最新技术,能够产生视觉上的可信结果,提高结构完整性和纹理逼真度。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
文中提出一种结合扩散模型与异向高斯混合技术的图像修复新方法。该方法能有效捕捉局部结构和全局上下文信息,通过适应图像局部梯度的异向高斯函数对缺失区域进行建模,为扩散模型提供结构指导。整合高斯混合图到扩散过程中,增强了模型生成高保真和结构上连贯的图像修复结果的能力。实验证明,该方法优于现有技术,能生成视觉效果好、结构完整、纹理逼真的图像修复结果。
Key Takeaways
- 提出一种结合扩散模型和异向高斯混合技术的图像修复方法。
- 该方法通过适应局部图像梯度的异向高斯函数建模缺失区域,为扩散模型提供结构指导。
- 高斯混合图被整合到扩散过程中,增强了生成高保真图像的能力。
- 方法能够捕捉局部结构和全局上下文信息,实现更真实的纹理生成。
- 该方法在大型缺失区域中也能保持结构连续性和纹理连贯性。
- 与现有技术相比,该方法在图像修复任务上表现出更好的性能。
点此查看论文截图

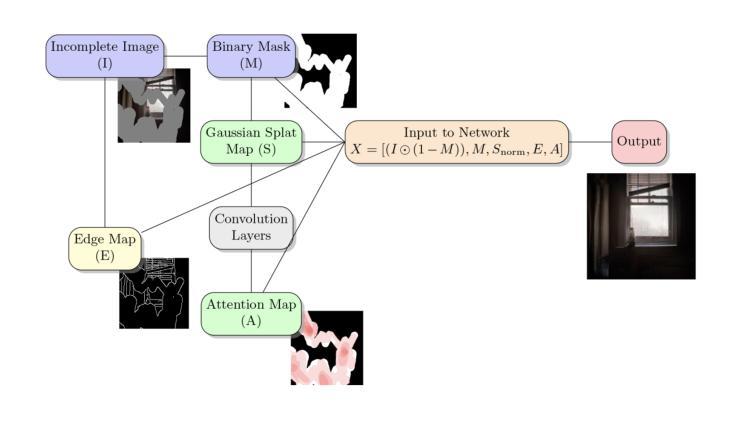
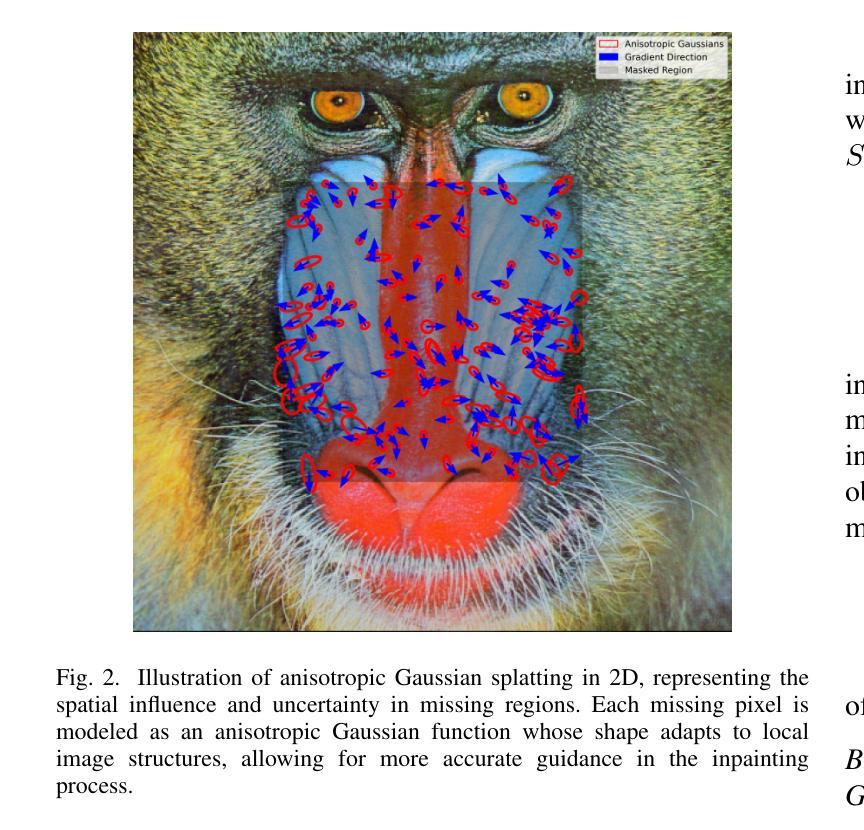
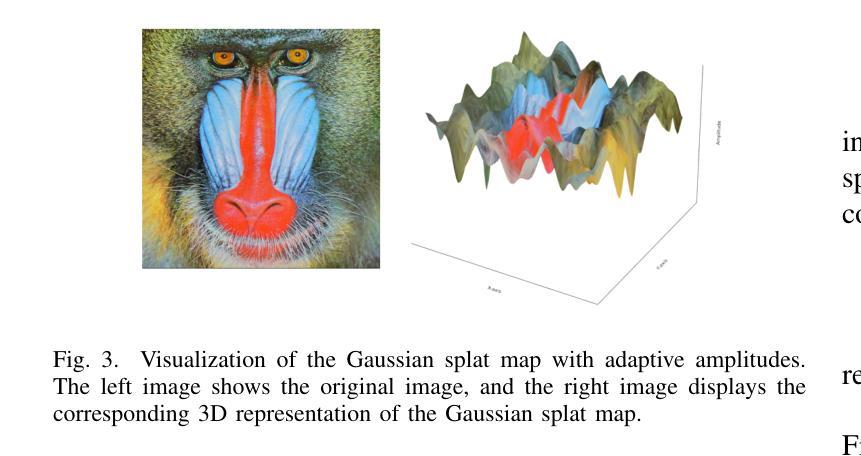
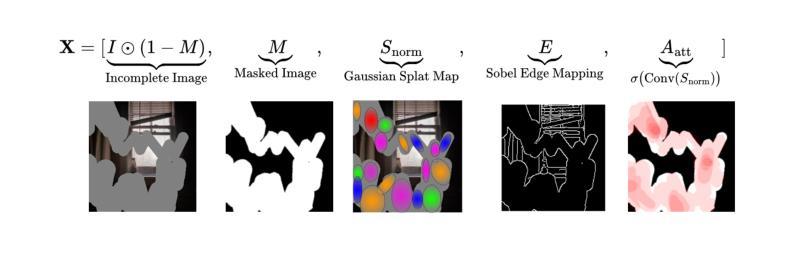
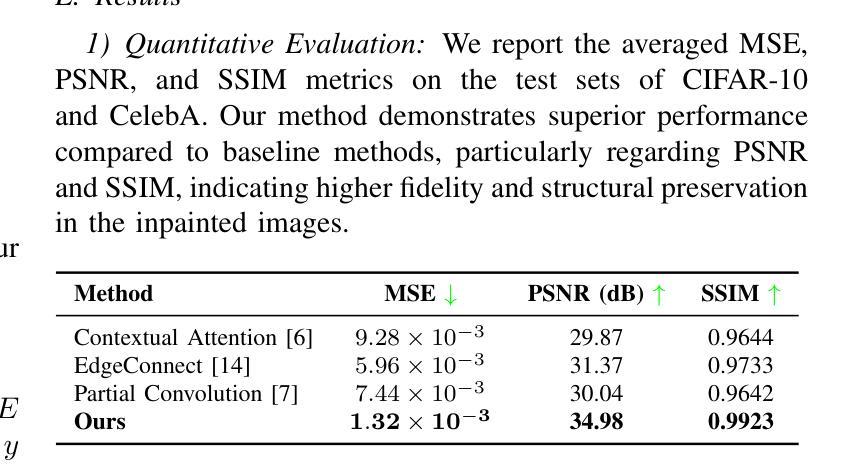
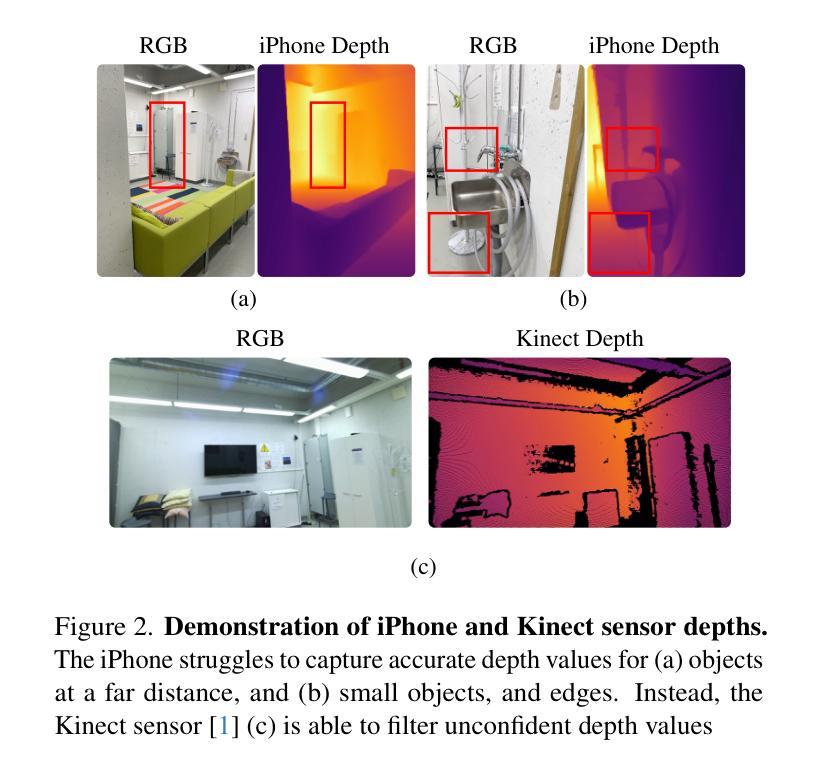
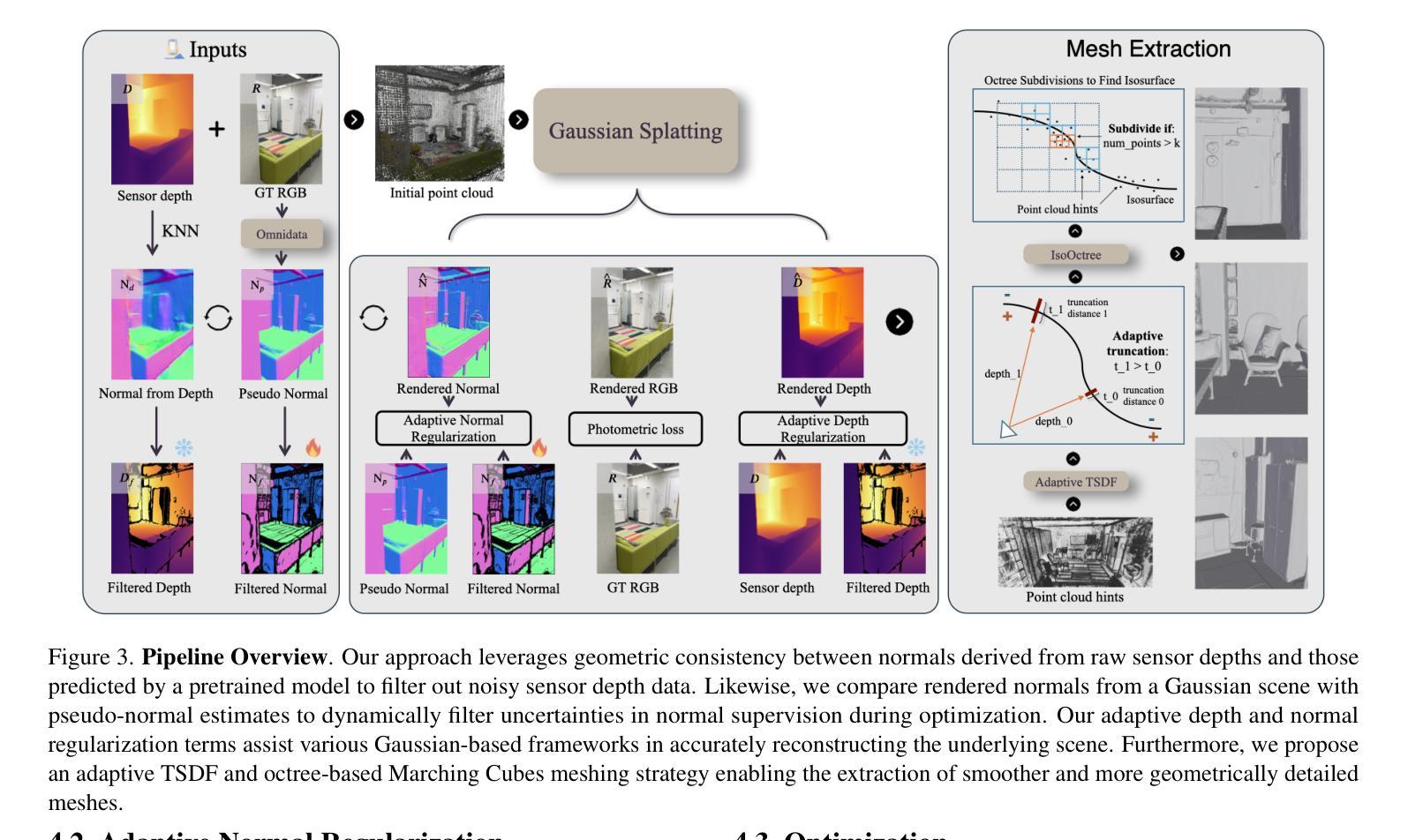
AGS-Mesh: Adaptive Gaussian Splatting and Meshing with Geometric Priors for Indoor Room Reconstruction Using Smartphones
Authors:Xuqian Ren, Matias Turkulainen, Jiepeng Wang, Otto Seiskari, Iaroslav Melekhov, Juho Kannala, Esa Rahtu
Geometric priors are often used to enhance 3D reconstruction. With many smartphones featuring low-resolution depth sensors and the prevalence of off-the-shelf monocular geometry estimators, incorporating geometric priors as regularization signals has become common in 3D vision tasks. However, the accuracy of depth estimates from mobile devices is typically poor for highly detailed geometry, and monocular estimators often suffer from poor multi-view consistency and precision. In this work, we propose an approach for joint surface depth and normal refinement of Gaussian Splatting methods for accurate 3D reconstruction of indoor scenes. We develop supervision strategies that adaptively filters low-quality depth and normal estimates by comparing the consistency of the priors during optimization. We mitigate regularization in regions where prior estimates have high uncertainty or ambiguities. Our filtering strategy and optimization design demonstrate significant improvements in both mesh estimation and novel-view synthesis for both 3D and 2D Gaussian Splatting-based methods on challenging indoor room datasets. Furthermore, we explore the use of alternative meshing strategies for finer geometry extraction. We develop a scale-aware meshing strategy inspired by TSDF and octree-based isosurface extraction, which recovers finer details from Gaussian models compared to other commonly used open-source meshing tools. Our code is released in https://xuqianren.github.io/ags_mesh_website/.
几何先验通常用于增强3D重建。由于许多智能手机配备了低分辨率的深度传感器,以及现成的单目几何估计器的普及,将几何先验作为正则化信号已成为3D视觉任务中的常态。然而,对于高度详细的几何结构,来自移动设备的深度估计精度通常较差,单目估计器通常存在多视角一致性和精度不足的问题。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种联合表面深度和法线精化的高斯平铺方法,用于室内场景的准确3D重建。我们开发了监督策略,通过比较优化过程中先验的一致性,自适应地过滤低质量的深度和法线估计。我们在先验估计存在高不确定性或模糊性的区域减轻正则化。我们的过滤策略和优化设计在具有挑战性的室内房间数据集上,无论是基于3D还是基于2D的高斯平铺方法,在网格估计和新颖视图合成方面都显示出显着改进。此外,我们探索了用于更精细几何提取的替代网格策略。我们受到截断有向距离函数(TSDF)和基于八叉树的等值面提取启发的规模感知网格策略,能够从高斯模型中恢复更精细的细节,与其他常用的开源网格工具相比具有优势。我们的代码发布在https://xuqianren.github.io/ags_mesh_website/。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于几何先验的联合表面深度与法线精细化的方法,用于室内场景的3D重建。通过优化策略,自适应过滤低质量的深度和法线估计,提高网格估计和新颖视角合成的效果。同时,采用尺度感知的网格策略,从高斯模型中恢复更精细的细节。
Key Takeaways
- 几何先验在3D重建中广泛应用,用于增强智能手机低分辨率深度传感器的性能以及使用现成的单眼几何估计器。
- 对高度详细的几何结构,移动设备的深度估计准确性通常较差,单眼估计器在多视角一致性和精度方面常出现问题。
- 提出一种联合表面深度与法线精细化的方法,用于室内场景的3D重建,采用高斯Splatting方法。
- 开发监督策略,自适应过滤低质量的深度和法线估计,通过优化过程中比较先验的一致性来实现。
- 在不确定性或模糊度高的区域减轻正则化。
- 过滤策略和优化设计显著提高了网格估计和新颖视角合成的效果,适用于基于3D和2D高斯Splatting的方法,对具有挑战性的室内数据集。
点此查看论文截图

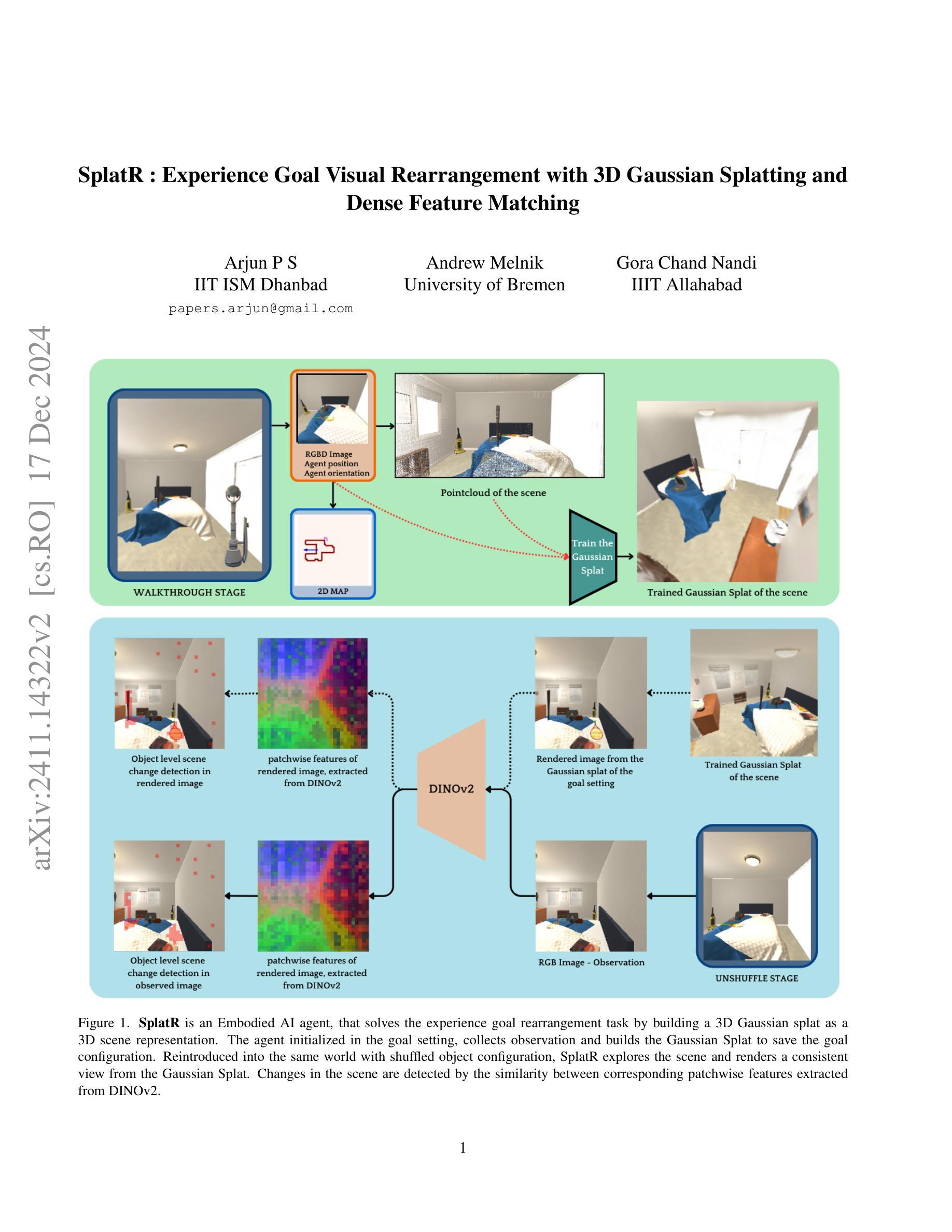
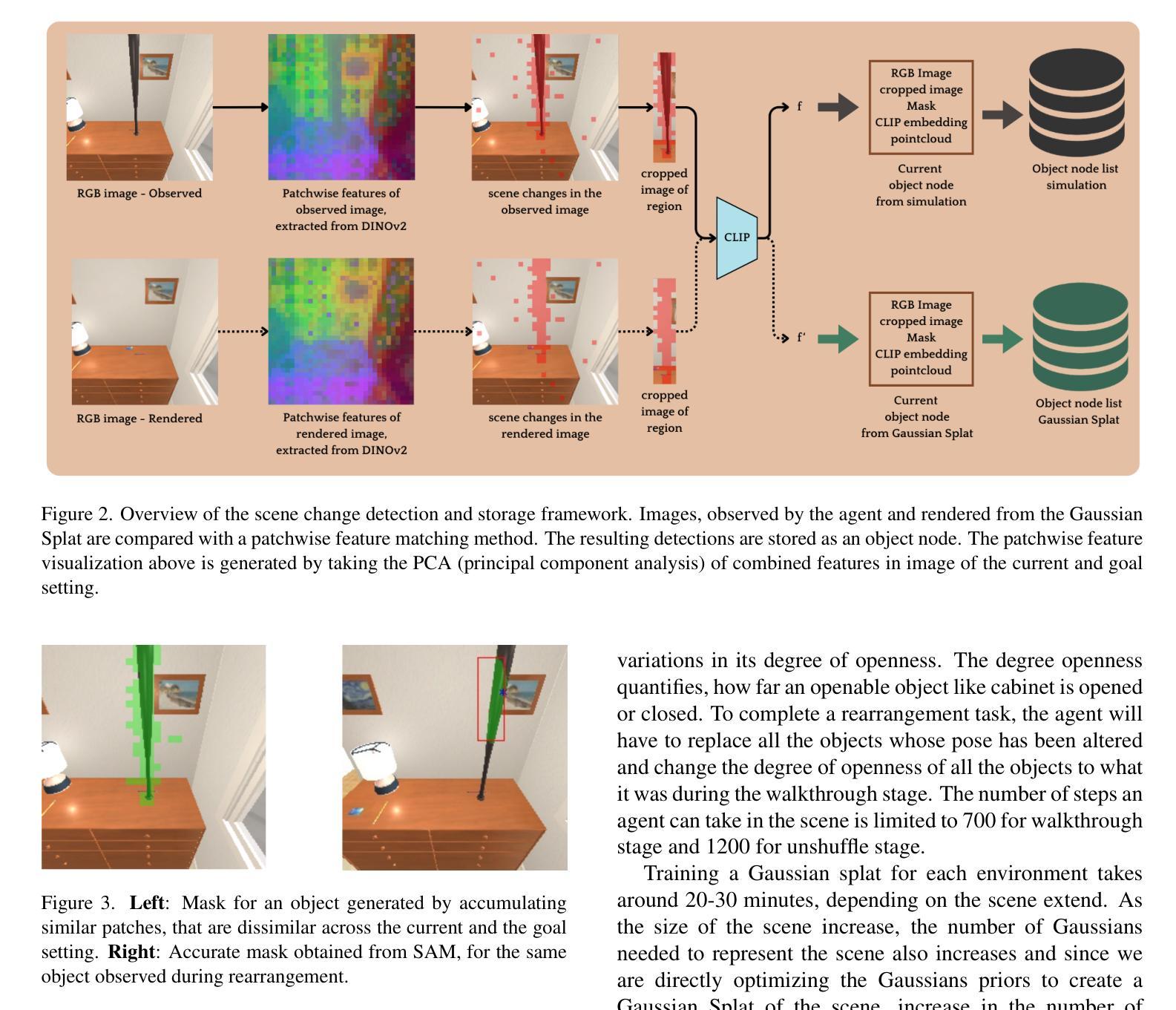
SplatR : Experience Goal Visual Rearrangement with 3D Gaussian Splatting and Dense Feature Matching
Authors:Arjun P S, Andrew Melnik, Gora Chand Nandi
Experience Goal Visual Rearrangement task stands as a foundational challenge within Embodied AI, requiring an agent to construct a robust world model that accurately captures the goal state. The agent uses this world model to restore a shuffled scene to its original configuration, making an accurate representation of the world essential for successfully completing the task. In this work, we present a novel framework that leverages on 3D Gaussian Splatting as a 3D scene representation for experience goal visual rearrangement task. Recent advances in volumetric scene representation like 3D Gaussian Splatting, offer fast rendering of high quality and photo-realistic novel views. Our approach enables the agent to have consistent views of the current and the goal setting of the rearrangement task, which enables the agent to directly compare the goal state and the shuffled state of the world in image space. To compare these views, we propose to use a dense feature matching method with visual features extracted from a foundation model, leveraging its advantages of a more universal feature representation, which facilitates robustness, and generalization. We validate our approach on the AI2-THOR rearrangement challenge benchmark and demonstrate improvements over the current state of the art methods
体验目标视觉重构任务作为嵌入式人工智能领域的一个基础挑战,要求智能体构建一个稳健的世界模型,该模型能够准确捕捉目标状态。智能体使用这个世界模型来恢复随机打乱的场景到其原始配置,因此准确的世界表示对于成功完成任务至关重要。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的框架,它利用三维高斯拼贴作为三维场景表示来解决体验目标视觉重构任务。像三维高斯拼贴这样的体积场景表示的最近进展为高质量和逼真的新视角提供了快速渲染。我们的方法使智能体能够拥有关于重构任务的当前设定和目标设定的统一视角,这使得智能体能够在图像空间中直接比较目标状态和世界的随机状态。为了比较这些视图,我们建议使用一种密集的特征匹配方法,该方法使用从基础模型中提取的视觉特征,利用其更通用的特征表示的优势,有助于增强稳健性和泛化能力。我们在AI2-THOR重构挑战基准测试上验证了我们的方法,并证明了与当前最先进的方法相比有所改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
在Embodied AI领域中的经验目标视觉重构任务中,构建一个准确捕捉目标状态的世界模型是至关重要的。本文提出一种新型框架,利用3D高斯涂斑技术作为该任务的3D场景表示。我们的方法使代理能够具有对当前和重构任务目标设置的一致视图,从而在图像空间中直接比较目标状态和混乱状态的世界。通过密集特征匹配方法和基础模型提取的视觉特征,验证了我们在AI2-THOR重构挑战基准测试上的方法,并展示了相较于当前最先进的方法的改进。
Key Takeaways
- 经验目标视觉重构任务是Embodied AI领域的基础挑战,需要构建准确捕捉目标状态的世界模型。
- 首次提出使用3D高斯涂斑技术作为视觉重构任务的3D场景表示的新型框架。
- 3D高斯涂斑技术等体积场景表示方法能提供高质量、逼真的新型视图快速渲染。
- 通过一致的观点,代理能够直接比较目标状态和混乱状态的世界,有助于更好地完成重构任务。
- 采用密集特征匹配方法与基础模型提取的视觉特征进行比较。
- 方法具有通用特征表示的优越性,增强了鲁棒性和泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图
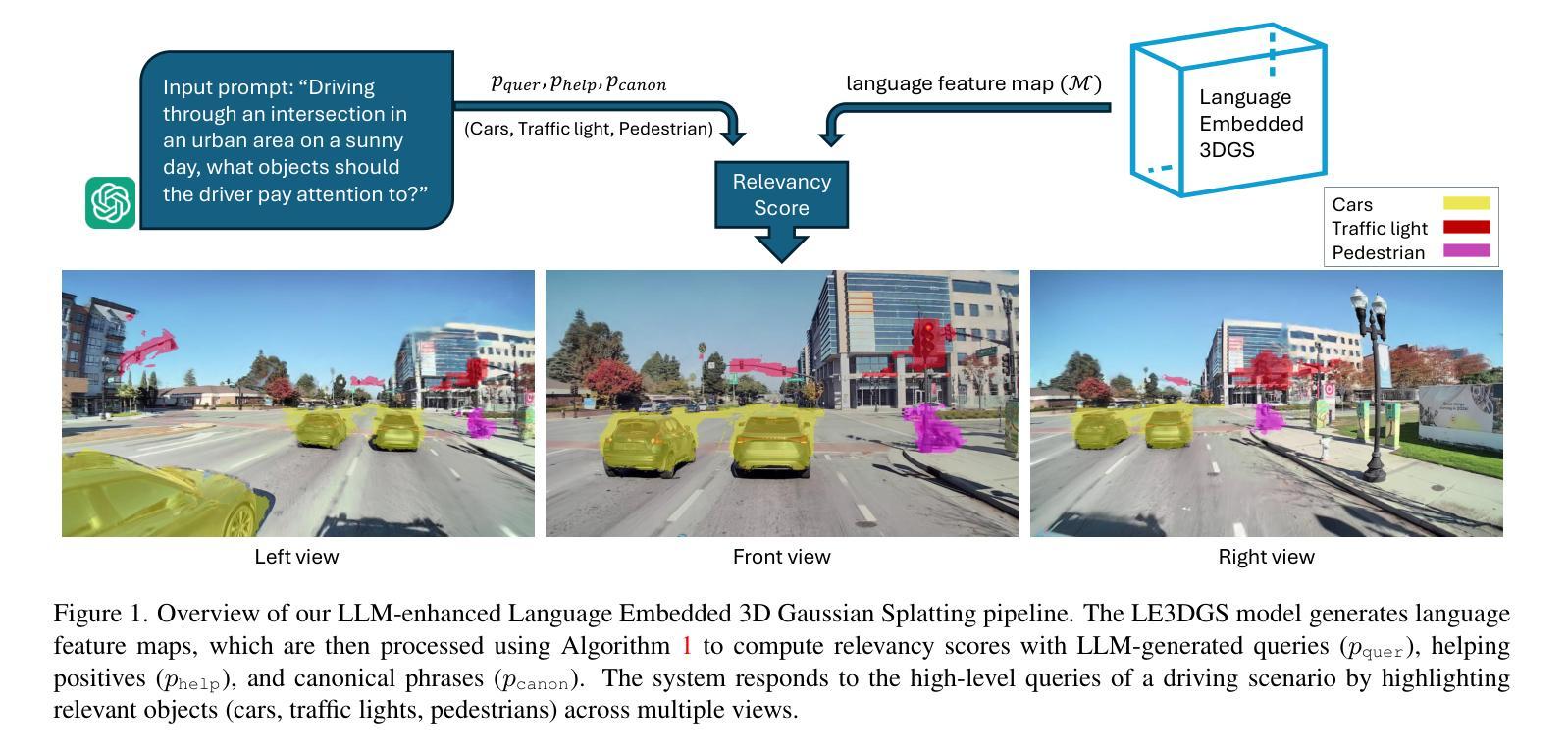
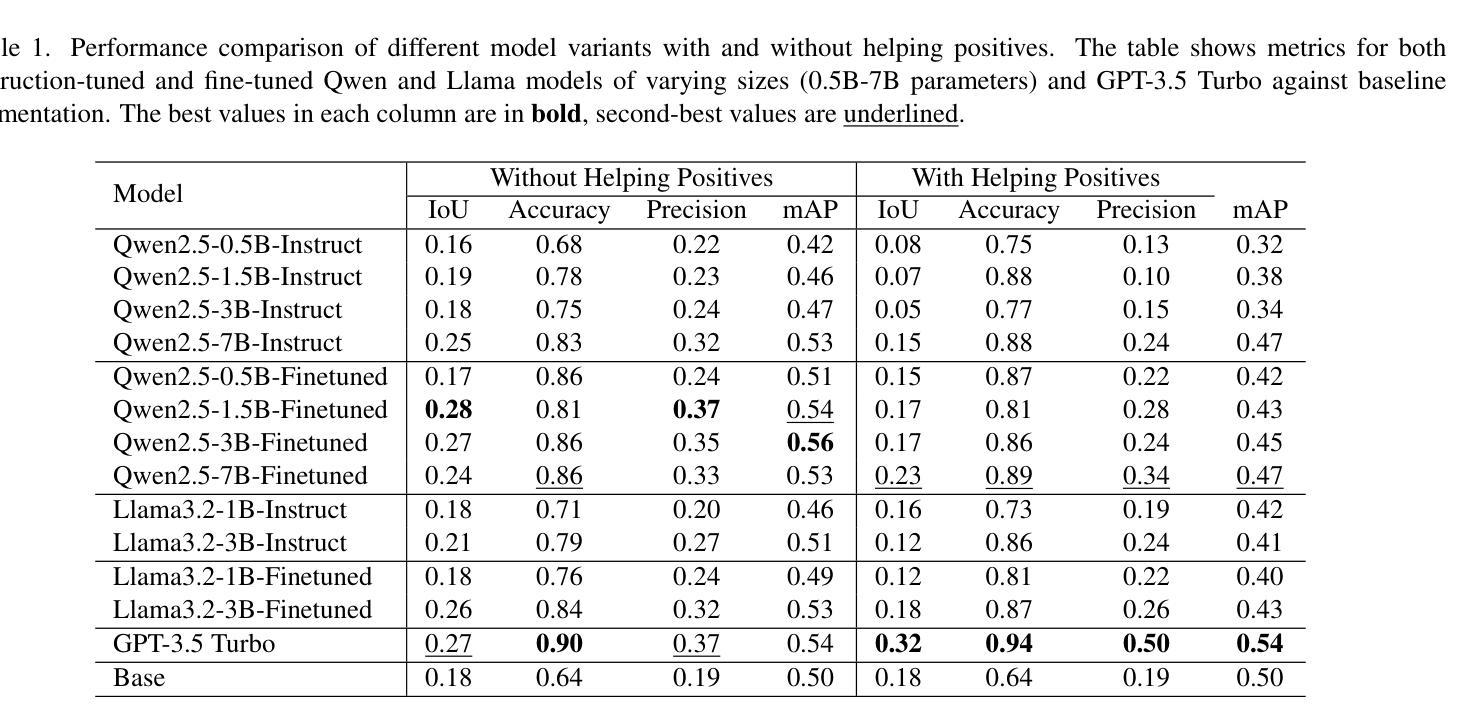
Query3D: LLM-Powered Open-Vocabulary Scene Segmentation with Language Embedded 3D Gaussian
Authors:Amirhosein Chahe, Lifeng Zhou
This paper introduces a novel method for open-vocabulary 3D scene querying in autonomous driving by combining Language Embedded 3D Gaussians with Large Language Models (LLMs). We propose utilizing LLMs to generate both contextually canonical phrases and helping positive words for enhanced segmentation and scene interpretation. Our method leverages GPT-3.5 Turbo as an expert model to create a high-quality text dataset, which we then use to fine-tune smaller, more efficient LLMs for on-device deployment. Our comprehensive evaluation on the WayveScenes101 dataset demonstrates that LLM-guided segmentation significantly outperforms traditional approaches based on predefined canonical phrases. Notably, our fine-tuned smaller models achieve performance comparable to larger expert models while maintaining faster inference times. Through ablation studies, we discover that the effectiveness of helping positive words correlates with model scale, with larger models better equipped to leverage additional semantic information. This work represents a significant advancement towards more efficient, context-aware autonomous driving systems, effectively bridging 3D scene representation with high-level semantic querying while maintaining practical deployment considerations.
本文介绍了一种结合语言嵌入的3D高斯分布与大型语言模型(LLM)进行开放词汇的自动驾驶中3D场景查询的新型方法。我们提出利用LLM生成上下文规范短语和帮助积极词汇,以提高分割和场景解释能力。我们的方法利用GPT-3.5 Turbo作为专家模型来创建高质量的文本数据集,然后我们使用这些数据集对更小、更高效的LLM进行微调,以用于设备部署。我们在WayveScenes101数据集上的全面评估表明,LLM引导的分割显著优于基于预定义规范短语的传统方法。值得注意的是,我们经过微调的小型模型在保持更快的推理时间的同时,实现了与大型专家模型相当的性能。通过消融研究,我们发现帮助积极词汇的有效性与模型规模有关,更大的模型能更好地利用额外的语义信息。这项工作代表了朝着更高效、更面向上下文的自动驾驶系统的重要进展,有效地将3D场景表示与高级语义查询联系起来,同时保持实际的部署考虑。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种结合语言嵌入三维高斯分布和大语言模型(LLM)的开放词汇三维场景查询新方法,用于自动驾驶。文章提出利用LLM生成上下文规范短语和帮助积极词汇,以提高场景分割和解读能力。文章使用GPT-3.5 Turbo作为专家模型创建高质量文本数据集,然后微调更小、更高效的LLM以进行设备部署。在WayveScenes101数据集上的综合评估表明,LLM引导的分割显著优于基于预定义规范短语的传统方法。此外,经过微调的小型模型在保持较快推理速度的同时,实现了与大型专家模型相当的性能。通过消融研究,发现帮助积极词汇的有效性与模型规模相关,较大的模型更能利用额外的语义信息。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了结合语言嵌入三维高斯分布和大语言模型(LLM)的开放词汇三维场景查询新方法。
- 利用LLM生成上下文规范短语和帮助积极词汇以提高场景分割和解读能力。
- 使用GPT-3.5 Turbo作为专家模型创建高质量文本数据集。
- 通过微调更小、更高效的LLM模型,实现了在设备上的部署。
- 在WayveScenes101数据集上的评估显示,LLM引导的分割方法性能优于传统方法。
- 消融研究表明帮助积极词汇的有效性取决于模型规模。
点此查看论文截图



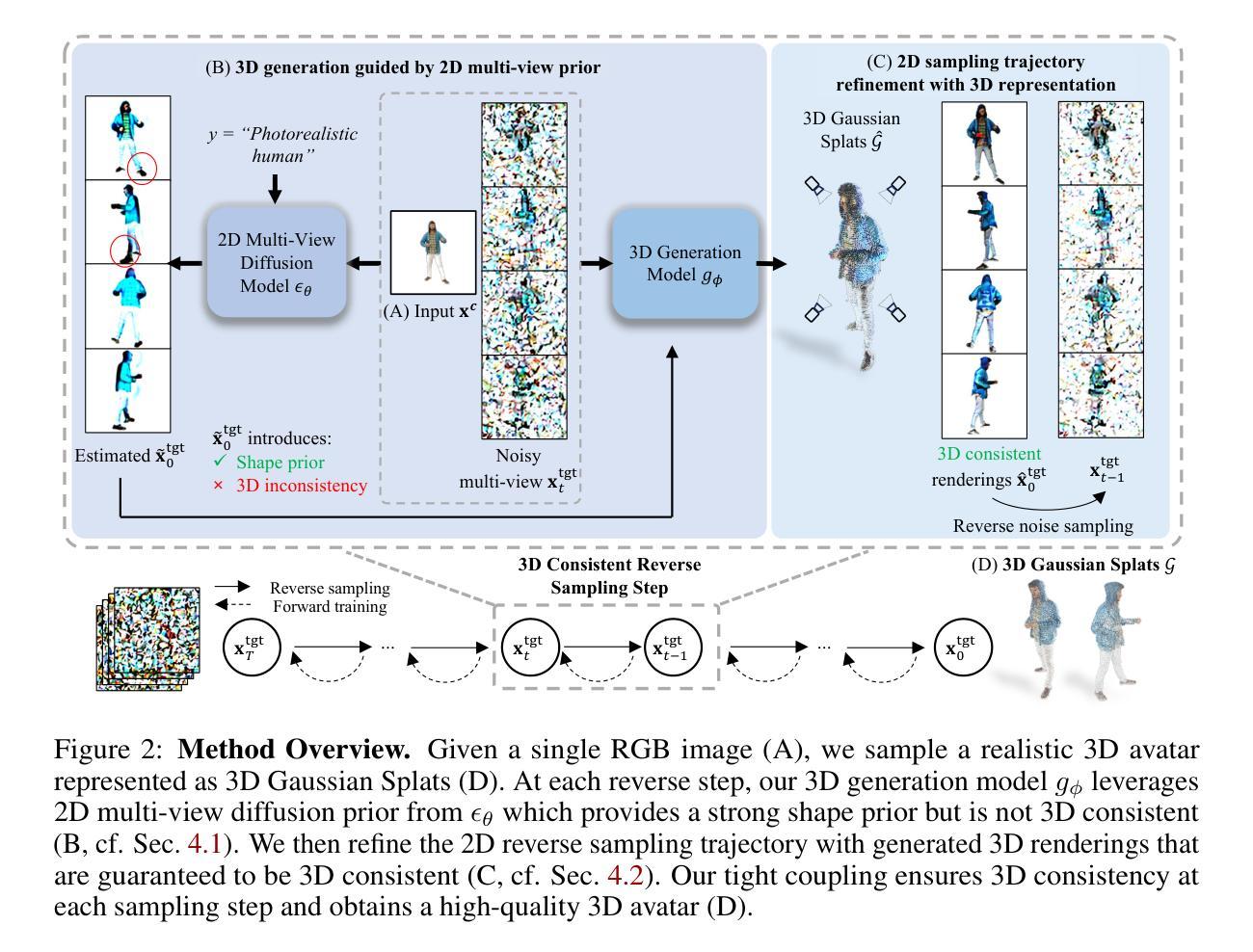
Human-3Diffusion: Realistic Avatar Creation via Explicit 3D Consistent Diffusion Models
Authors:Yuxuan Xue, Xianghui Xie, Riccardo Marin, Gerard Pons-Moll
Creating realistic avatars from a single RGB image is an attractive yet challenging problem. Due to its ill-posed nature, recent works leverage powerful prior from 2D diffusion models pretrained on large datasets. Although 2D diffusion models demonstrate strong generalization capability, they cannot provide multi-view shape priors with guaranteed 3D consistency. We propose Human 3Diffusion: Realistic Avatar Creation via Explicit 3D Consistent Diffusion. Our key insight is that 2D multi-view diffusion and 3D reconstruction models provide complementary information for each other, and by coupling them in a tight manner, we can fully leverage the potential of both models. We introduce a novel image-conditioned generative 3D Gaussian Splats reconstruction model that leverages the priors from 2D multi-view diffusion models, and provides an explicit 3D representation, which further guides the 2D reverse sampling process to have better 3D consistency. Experiments show that our proposed framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods and enables the creation of realistic avatars from a single RGB image, achieving high-fidelity in both geometry and appearance. Extensive ablations also validate the efficacy of our design, (1) multi-view 2D priors conditioning in generative 3D reconstruction and (2) consistency refinement of sampling trajectory via the explicit 3D representation. Our code and models will be released on https://yuxuan-xue.com/human-3diffusion.
创建基于单一RGB图像的真实化身是一个有吸引力但具有挑战性的任务。由于其表述不明确的特点,近期的工作利用从大型数据集上预训练的强大的二维扩散模型的先验知识。虽然二维扩散模型表现出很强的泛化能力,但它们无法提供具有保证的三维一致性多视图形状先验。我们提出了“Human 3Diffusion:通过显式三维一致性扩散创建真实化身”。我们的关键见解是,二维多视图扩散和三维重建模型彼此提供互补信息,通过紧密耦合它们,我们可以充分利用这两个模型的潜力。我们引入了一种新型的图像条件生成三维高斯体素重建模型,该模型利用二维多视图扩散模型的先验知识,并提供了一种显式三维表示,进一步指导二维反向采样过程,以实现更好的三维一致性。实验表明,我们提出的框架优于现有技术方法,能够从单一RGB图像创建逼真的化身,在几何和外观上都实现高保真。广泛的消融实验也验证了我们的设计的有效性,(1)生成三维重建中的多视图二维先验条件;(2)通过显式三维表示对采样轨迹的一致性改进。我们的代码和模型将在[https://yuxuan-xue.com/human-3diffusion]上发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to NeurIPS2024. Project Page: https://yuxuan-xue.com/human-3diffusion
Summary
本文提出一种基于明确的3D一致性扩散模型的真实头像创建方法,通过将二维多视角扩散模型与三维重建模型相结合,引入了一种新的图像条件生成三维高斯splat重建模型。该方法利用二维多视角扩散模型的先验信息,提供明确的三维表示,进一步指导二维逆向采样过程,实现更好的三维一致性。实验结果表明,该方法在几何和外观上都实现了高保真度,并优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 创建真实头像是一个挑战性的问题,需要解决二维扩散模型的局限性。
- 提出了一种新的图像条件生成三维高斯splat重建模型,结合二维多视角扩散模型和三维重建模型的优势。
- 利用二维多视角扩散模型的先验信息,提供明确的三维表示。
- 通过指导二维逆向采样过程,实现了更好的三维一致性。
- 实现了超越现有方法的性能,能够创建逼真的头像。
- 有效的设计包括多视角二维先验条件在生成三维重建中的应用和一致性精炼采样轨迹通过明确的三维表示。
点此查看论文截图

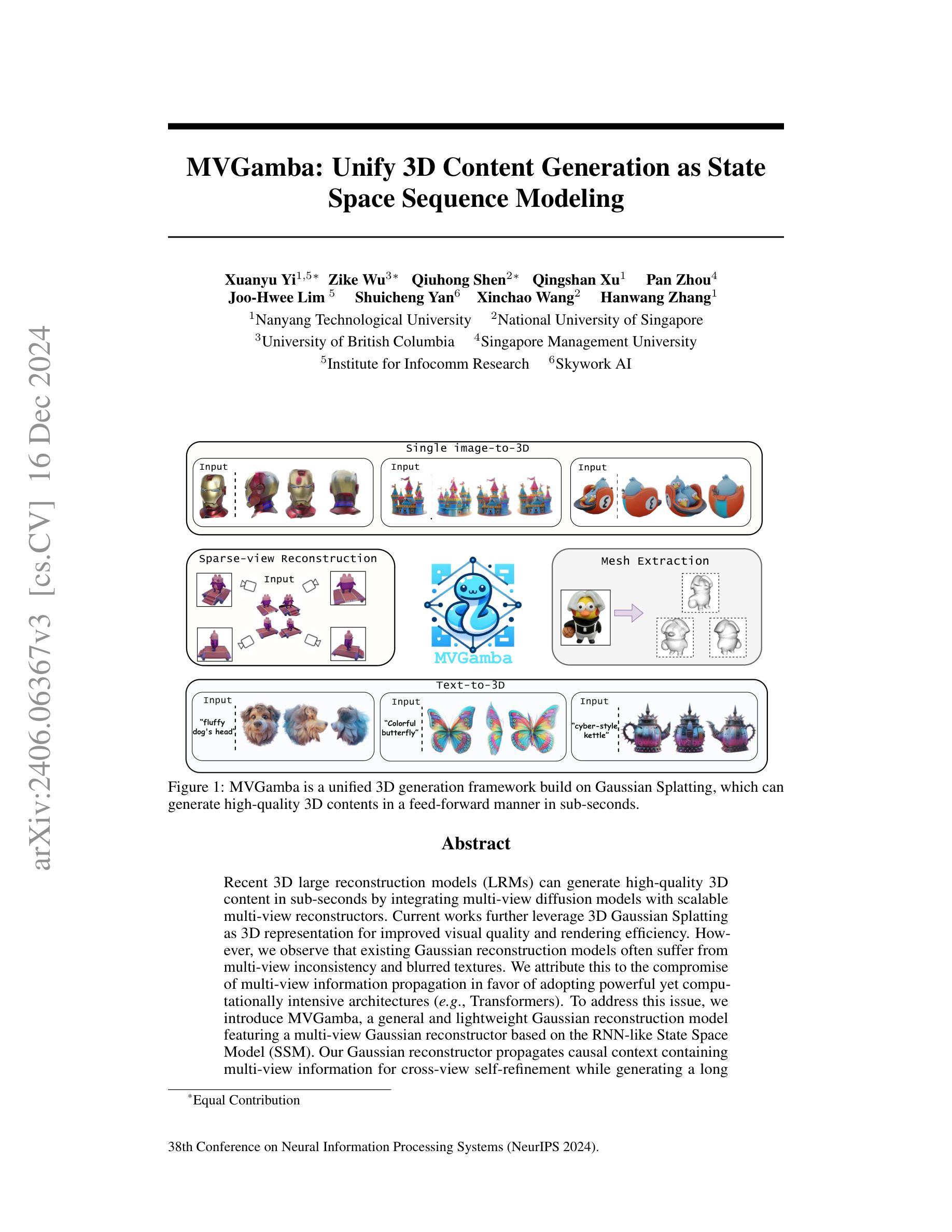
MVGamba: Unify 3D Content Generation as State Space Sequence Modeling
Authors:Xuanyu Yi, Zike Wu, Qiuhong Shen, Qingshan Xu, Pan Zhou, Joo-Hwee Lim, Shuicheng Yan, Xinchao Wang, Hanwang Zhang
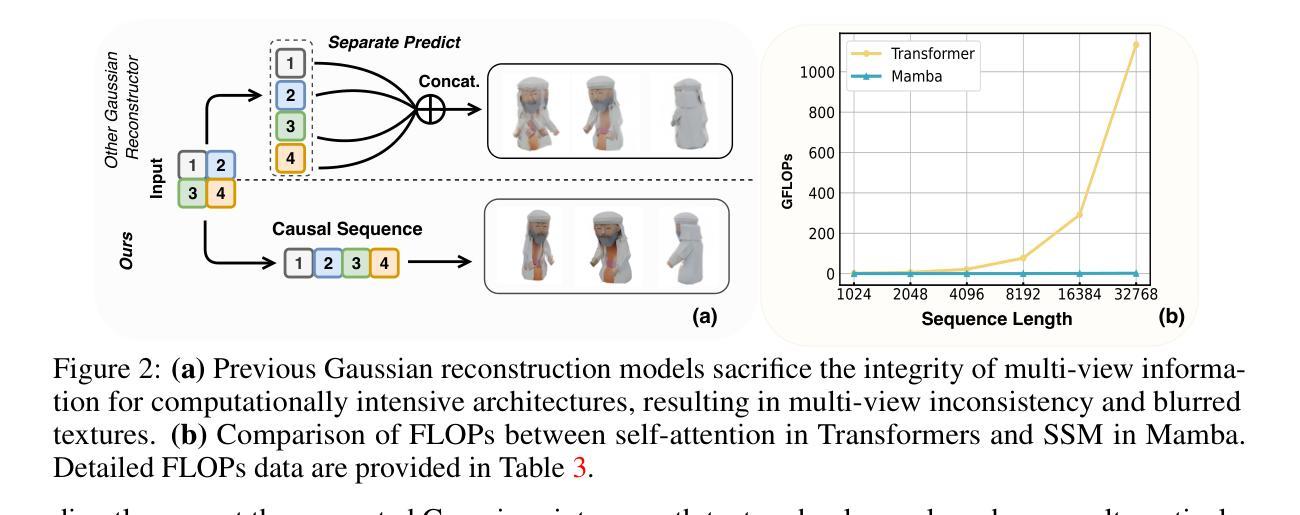
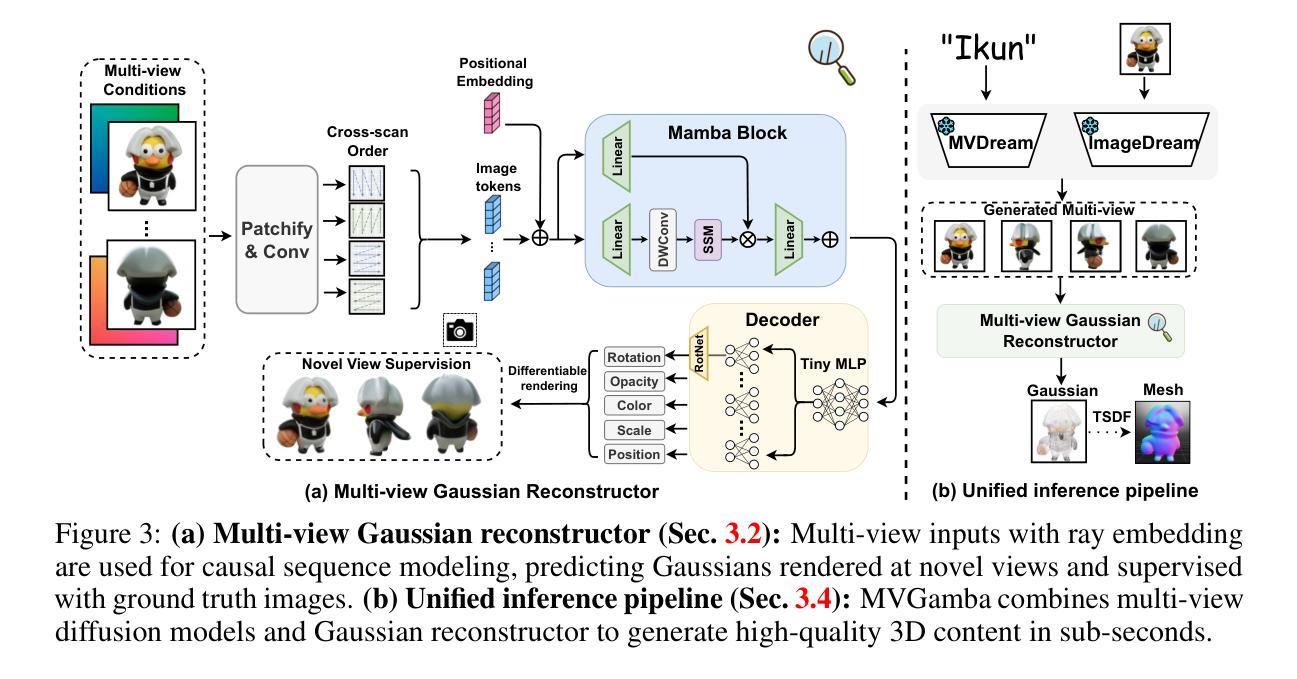
Recent 3D large reconstruction models (LRMs) can generate high-quality 3D content in sub-seconds by integrating multi-view diffusion models with scalable multi-view reconstructors. Current works further leverage 3D Gaussian Splatting as 3D representation for improved visual quality and rendering efficiency. However, we observe that existing Gaussian reconstruction models often suffer from multi-view inconsistency and blurred textures. We attribute this to the compromise of multi-view information propagation in favor of adopting powerful yet computationally intensive architectures (e.g., Transformers). To address this issue, we introduce MVGamba, a general and lightweight Gaussian reconstruction model featuring a multi-view Gaussian reconstructor based on the RNN-like State Space Model (SSM). Our Gaussian reconstructor propagates causal context containing multi-view information for cross-view self-refinement while generating a long sequence of Gaussians for fine-detail modeling with linear complexity. With off-the-shelf multi-view diffusion models integrated, MVGamba unifies 3D generation tasks from a single image, sparse images, or text prompts. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MVGamba outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in all 3D content generation scenarios with approximately only $0.1\times$ of the model size.
最近的三维大重建模型(LRMs)通过整合多视角扩散模型与可扩展的多视角重建器,能够在亚秒内生成高质量的三维内容。当前的研究还进一步利用三维高斯拼贴作为三维表示,以提高视觉质量和渲染效率。然而,我们观察到现有的高斯重建模型经常遭受多视角不一致和纹理模糊的问题。我们将这归因于为了采用强大但计算密集型的架构(例如Transformer)而妥协了多视角信息传播。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了MVGamba,这是一个通用且轻量级的高斯重建模型,它基于RNN类似的状态空间模型(SSM)采用多视角高斯重建器。我们的高斯重建器传播包含多视角信息的因果上下文,用于跨视角自我优化,同时生成一系列高斯数进行精细建模,具有线性复杂度。通过整合现成的多视角扩散模型,MVGamba能够统一从单张图像、稀疏图像或文本提示进行三维生成任务。大量实验表明,在所有的三维内容生成场景中,MVGamba的表现都优于最新的基线模型,并且模型大小只有大约$0.1\times$。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NeurIPS 2024. Code is included in https://github.com/SkyworkAI/MVGamba
Summary
基于多视角扩散模型,新一代三维大型重建模型能够在几秒内生成高质量的三维内容。针对现有高斯重建模型的多视角不一致和纹理模糊问题,提出了MVGamba模型。该模型基于循环神经网络类似的状态空间模型,实现多视角高斯重建器,通过传播包含多视角信息的因果上下文进行跨视角自我优化,并以线性复杂度生成精细的高斯序列进行建模。实验表明,MVGamba在多种三维内容生成场景中均优于最新基线模型,且模型大小仅约为前者的十分之一。
Key Takeaways
- 新型三维大型重建模型可借助多视角扩散模型快速生成高质量三维内容。
- 当前高斯重建模型存在多视角不一致和纹理模糊的问题。
- MVGamba模型通过引入多视角高斯重建器解决上述问题,该重建器基于循环神经网络类似的状态空间模型。
- MVGamba通过传播因果上下文进行跨视角自我优化,包含多视角信息。
- MVGamba能够生成精细的高斯序列用于建模,具有线性复杂度。
- MVGamba在多种三维内容生成场景中表现优异,优于现有最新基线模型。
点此查看论文截图