⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-19 更新
AniDoc: Animation Creation Made Easier
Authors:Yihao Meng, Hao Ouyang, Hanlin Wang, Qiuyu Wang, Wen Wang, Ka Leong Cheng, Zhiheng Liu, Yujun Shen, Huamin Qu
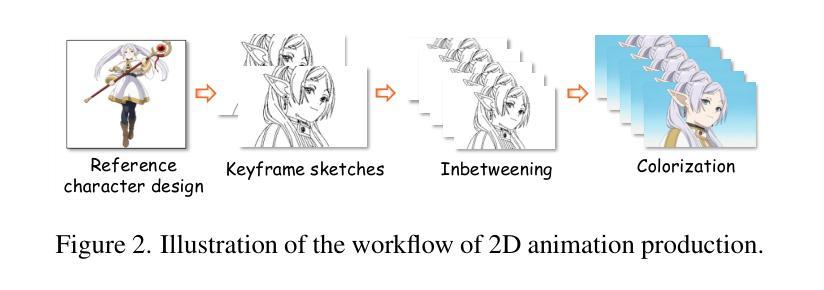
The production of 2D animation follows an industry-standard workflow, encompassing four essential stages: character design, keyframe animation, in-betweening, and coloring. Our research focuses on reducing the labor costs in the above process by harnessing the potential of increasingly powerful generative AI. Using video diffusion models as the foundation, AniDoc emerges as a video line art colorization tool, which automatically converts sketch sequences into colored animations following the reference character specification. Our model exploits correspondence matching as an explicit guidance, yielding strong robustness to the variations (e.g., posture) between the reference character and each line art frame. In addition, our model could even automate the in-betweening process, such that users can easily create a temporally consistent animation by simply providing a character image as well as the start and end sketches. Our code is available at: https://yihao-meng.github.io/AniDoc_demo.
二维动画的制作遵循行业标准的工作流程,包括四个基本阶段:角色设计、关键帧动画、中间帧生成和上色。我们的研究聚焦于利用日益强大的生成式人工智能的潜力,降低上述流程中的劳动力成本。以视频扩散模型为基础,AniDoc作为一种视频线艺术彩色化工具应运而生,它会自动将草图序列转换为彩色动画,并按照参考角色规范进行。我们的模型利用对应匹配作为明确指导,对参考角色与每个线艺术框架之间的变化(例如姿势)具有很强的稳健性。此外,我们的模型甚至可以自动化中间帧生成过程,这样用户只需提供角色图像以及开始和结束的草图,就可以轻松创建时间连贯的动画。我们的代码可在:https://yihao-meng.github.io/AniDoc_demo访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page and code: https://yihao-meng.github.io/AniDoc_demo
Summary
本文介绍了利用视频扩散模型开发的动画生产线工具AniDoc,它能自动将草图序列转化为彩色动画,依据参照角色特性进行色彩填充,并支持自动完成中间过程。工具可实现强鲁棒性,适应角色姿态变化等差异,并简化动画创作流程。相关代码可在指定网址下载。
Key Takeaways
- 使用视频扩散模型开发动画工具AniDoc。
- AniDoc可将草图序列自动转化为彩色动画。
- AniDoc依据参照角色特性进行色彩填充。
4.AniDoc具有强鲁棒性,适应角色姿态变化等差异。 - AniDoc可自动完成中间过程,简化动画创作流程。
- 用户只需提供角色图像以及起始和结束草图,即可轻松创建连贯的动画。
点此查看论文截图

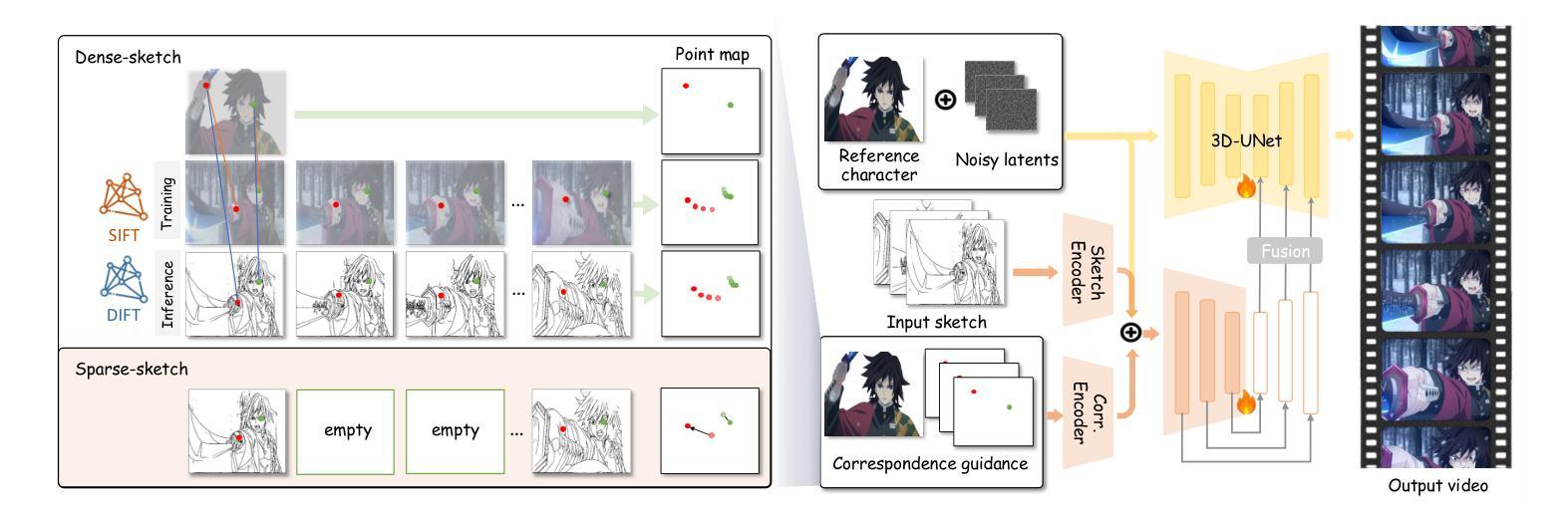
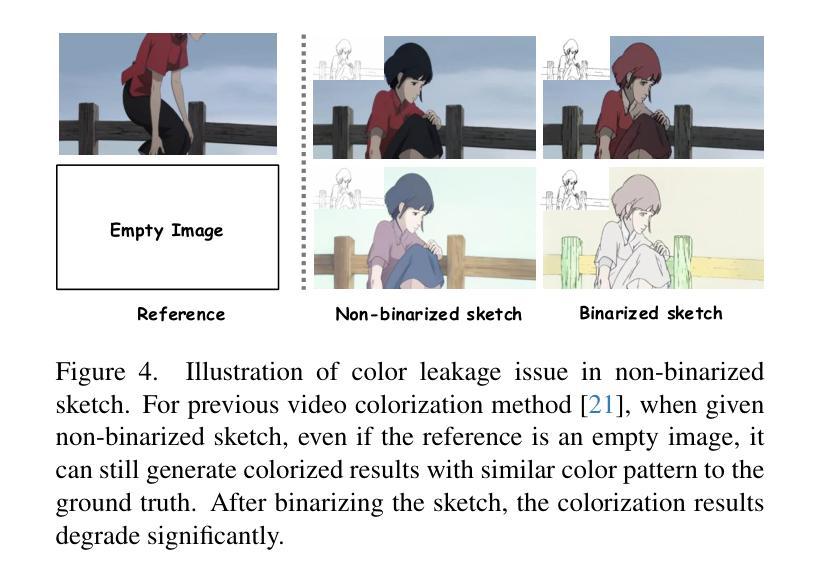

Autoregressive Video Generation without Vector Quantization
Authors:Haoge Deng, Ting Pan, Haiwen Diao, Zhengxiong Luo, Yufeng Cui, Huchuan Lu, Shiguang Shan, Yonggang Qi, Xinlong Wang
This paper presents a novel approach that enables autoregressive video generation with high efficiency. We propose to reformulate the video generation problem as a non-quantized autoregressive modeling of temporal frame-by-frame prediction and spatial set-by-set prediction. Unlike raster-scan prediction in prior autoregressive models or joint distribution modeling of fixed-length tokens in diffusion models, our approach maintains the causal property of GPT-style models for flexible in-context capabilities, while leveraging bidirectional modeling within individual frames for efficiency. With the proposed approach, we train a novel video autoregressive model without vector quantization, termed NOVA. Our results demonstrate that NOVA surpasses prior autoregressive video models in data efficiency, inference speed, visual fidelity, and video fluency, even with a much smaller model capacity, i.e., 0.6B parameters. NOVA also outperforms state-of-the-art image diffusion models in text-to-image generation tasks, with a significantly lower training cost. Additionally, NOVA generalizes well across extended video durations and enables diverse zero-shot applications in one unified model. Code and models are publicly available at https://github.com/baaivision/NOVA.
本文提出了一种新的方法,能够实现高效的自回归视频生成。我们提议将视频生成问题重新表述为未量化的自回归建模,包括时间上的逐帧预测和空间的逐集预测。与先前自回归模型中的扫描预测或扩散模型中固定长度符号的联合分布建模不同,我们的方法保持了GPT风格模型的因果特性,以提供灵活的上下文能力,同时利用单个帧内的双向建模来提高效率。通过这种方法,我们训练了一种名为NOVA的新型视频自回归模型,无需向量量化。结果表明,NOVA在数据效率、推理速度、视觉保真度和视频流畅性方面超越了先前的自回归视频模型,即使其模型容量更小(即0.6B参数)。此外,NOVA在文本到图像生成任务上也超越了最先进的图像扩散模型,并大大降低了训练成本。NOVA还能够适应长时间的视频,在一个统一模型中实现了多样化的零样本应用。代码和模型可在https://github.com/baaivision/NOVA上公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 16 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种新的方法,能够在高效的情况下实现自回归视频生成。该方法重新定义了视频生成问题,采用非量化自回归建模方式,实现了时序逐帧预测和空间逐集预测。该方法保持了GPT风格模型的因果特性,同时利用单个帧内的双向建模来提高效率。所提出的模型称为NOVA,它在数据效率、推理速度、视觉保真度和视频流畅性方面都超越了先前的自回归视频模型,即使模型容量较小(仅为0.6B参数)。此外,NOVA在文本到图像生成任务中也表现出色,训练成本低。它还能够很好地泛化到更长的视频时长,并在统一模型中实现多样化的零样本应用。模型和代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出了一种高效自回归视频生成的新方法。
- 该方法将视频生成问题重新定义为非量化自回归建模问题,实现时序逐帧和空间逐集预测。
- 该方法结合GPT风格模型的因果特性和单个帧内的双向建模来提高效率。
- NOVA模型在数据效率、推理速度、视觉保真度和视频流畅性方面表现优异,超越现有自回归视频模型。
- NOVA在文本到图像生成任务中表现突出,训练成本低。
- NOVA具有良好的泛化能力,可应用于更长的视频时长。
点此查看论文截图

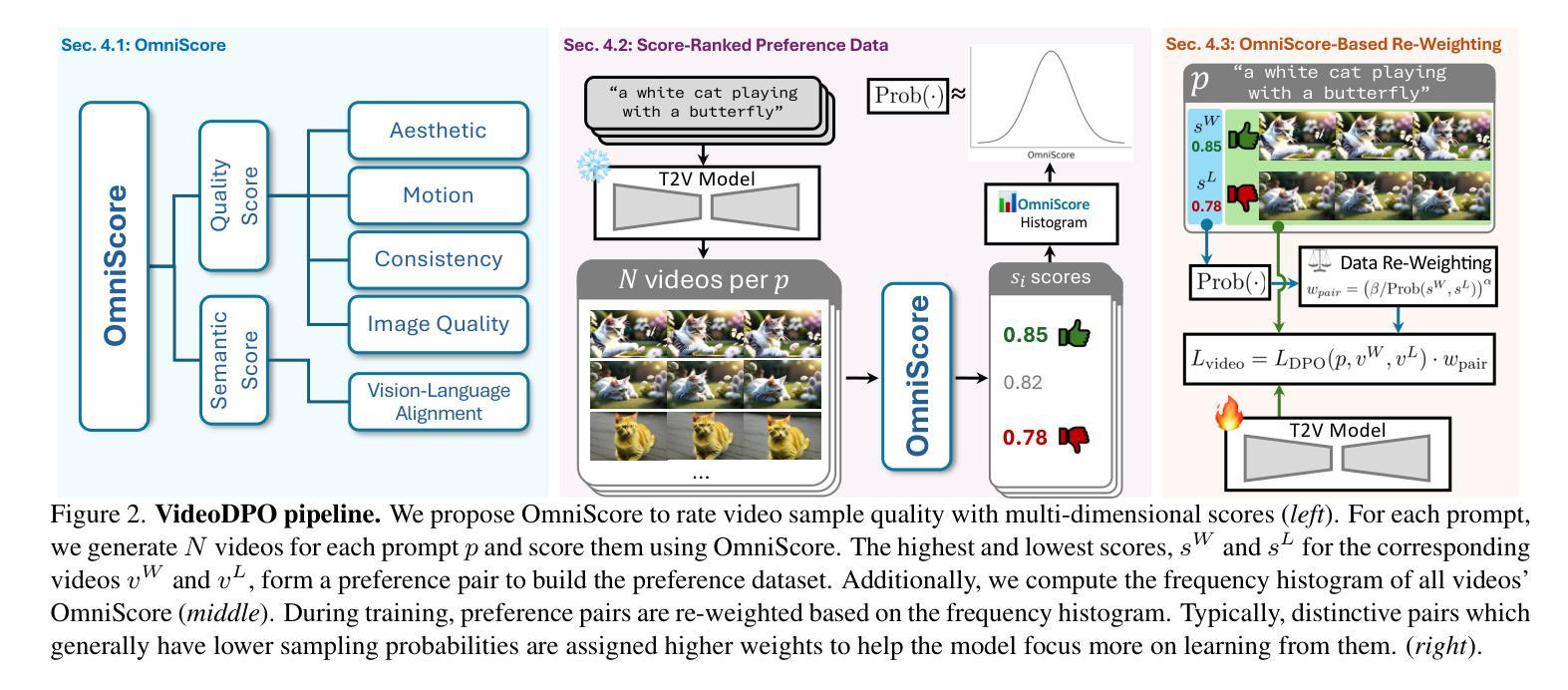
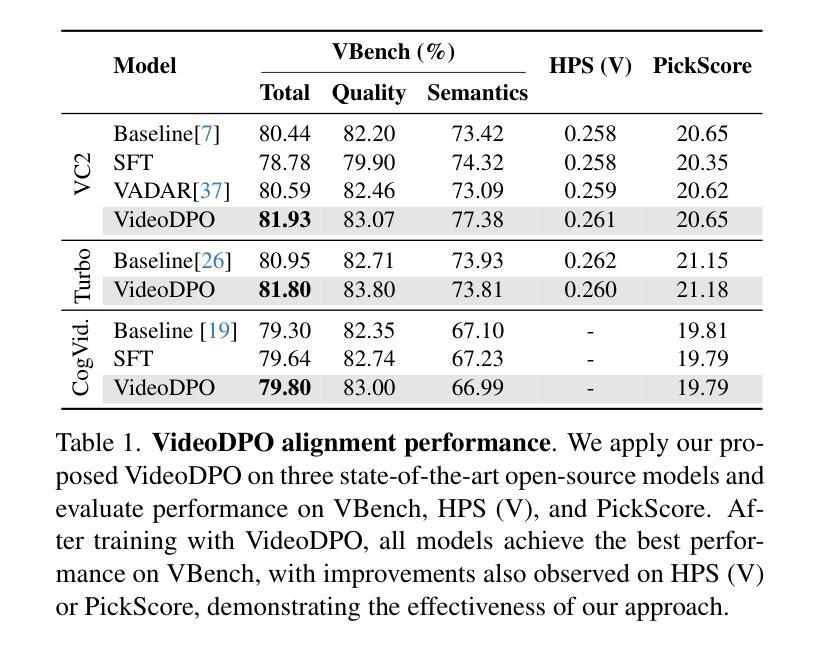
VideoDPO: Omni-Preference Alignment for Video Diffusion Generation
Authors:Runtao Liu, Haoyu Wu, Zheng Ziqiang, Chen Wei, Yingqing He, Renjie Pi, Qifeng Chen
Recent progress in generative diffusion models has greatly advanced text-to-video generation. While text-to-video models trained on large-scale, diverse datasets can produce varied outputs, these generations often deviate from user preferences, highlighting the need for preference alignment on pre-trained models. Although Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) has demonstrated significant improvements in language and image generation, we pioneer its adaptation to video diffusion models and propose a VideoDPO pipeline by making several key adjustments. Unlike previous image alignment methods that focus solely on either (i) visual quality or (ii) semantic alignment between text and videos, we comprehensively consider both dimensions and construct a preference score accordingly, which we term the OmniScore. We design a pipeline to automatically collect preference pair data based on the proposed OmniScore and discover that re-weighting these pairs based on the score significantly impacts overall preference alignment. Our experiments demonstrate substantial improvements in both visual quality and semantic alignment, ensuring that no preference aspect is neglected. Code and data will be shared at https://videodpo.github.io/.
生成式扩散模型的最新进展极大地推动了文本到视频的生成。虽然基于大规模、多样化数据集的文本到视频模型可以产生多样化的输出,但这些生成往往偏离用户偏好,突显了对预训练模型进行偏好对齐的必要性。尽管直接偏好优化(DPO)在语言和图像生成中显示出显着改进,但我们首创将其适应视频扩散模型,并通过几个关键调整提出了VideoDPO管道。与以往仅侧重于(i)视觉质量或(ii)文本和视频之间语义对齐的图像对齐方法不同,我们全面考虑这两个维度,并相应地构建偏好分数,我们称之为OmniScore。我们设计了一个管道,基于提出的OmniScore自动收集偏好对数据,并发现根据该分数重新权重这些对会显著影响整体的偏好对齐。我们的实验表明,在视觉质量和语义对齐方面都有实质性的改进,确保不会忽略任何偏好方面。相关代码和数据将在https://videodpo.github.io/共享。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
生成式扩散模型的最新进展极大地推动了文本到视频的生成。尽管在大型、多样化的数据集上训练的文本到视频模型可以产生多样化的输出,但这些输出常常偏离用户偏好,突显了对预训练模型进行偏好调整的必要性。我们率先将直接偏好优化(DPO)适应到视频扩散模型,并提出VideoDPO管道,通过几个关键调整来实现。不同于之前只关注视觉质量或文本与视频之间语义对齐的图像对齐方法,我们全面考虑这两个维度,并据此构建了一个偏好得分,称为OmniScore。我们设计了一个管道来基于提出的OmniScore自动收集偏好对数据,并发现根据得分重新加权这些对可以显著影响偏好对齐的整体效果。我们的实验表明,在视觉质量和语义对齐方面都有显著改进,确保不会忽略任何偏好方面。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到视频生成领域受益于生成式扩散模型的最新进展。
- 文本到视频模型的输出常偏离用户偏好,需要调整预训练模型的偏好对齐。
- 直接偏好优化(DPO)被首次适应到视频扩散模型中,形成VideoDPO管道。
- VideoDPO通过全面考虑视觉质量和语义对齐来构建OmniScore偏好得分。
- 自动收集基于OmniScore的偏好对数据显示重新加权对可以影响偏好对齐的整体效果。
- 实验证明VideoDPO在视觉质量和语义对齐方面都有显著改进。
点此查看论文截图



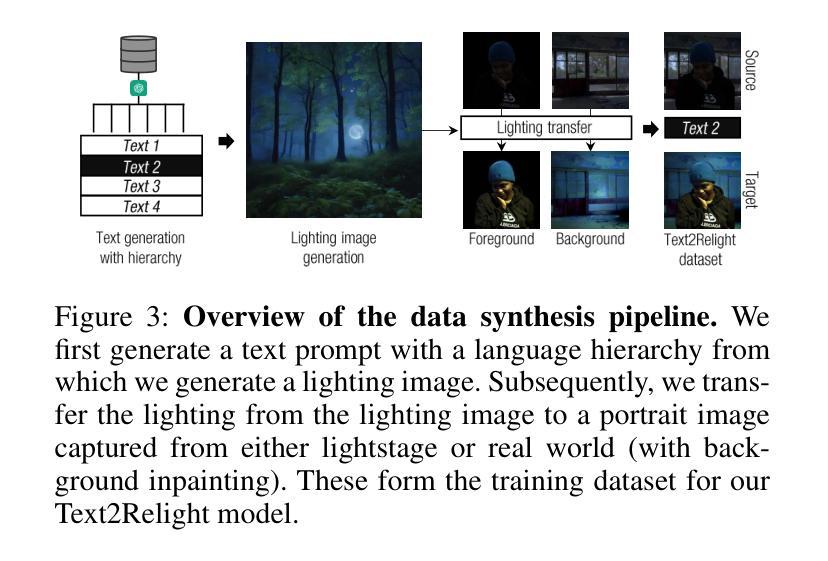
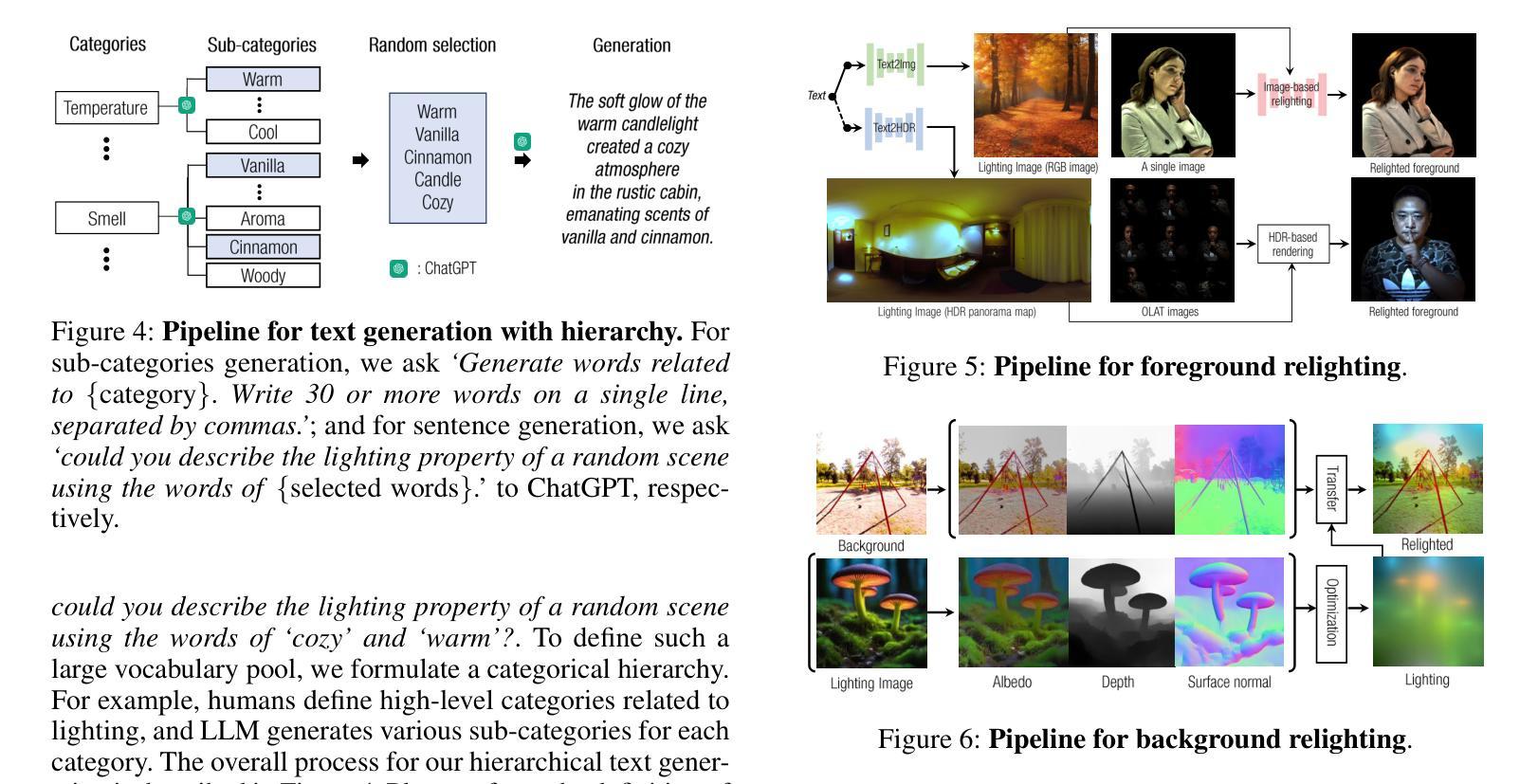
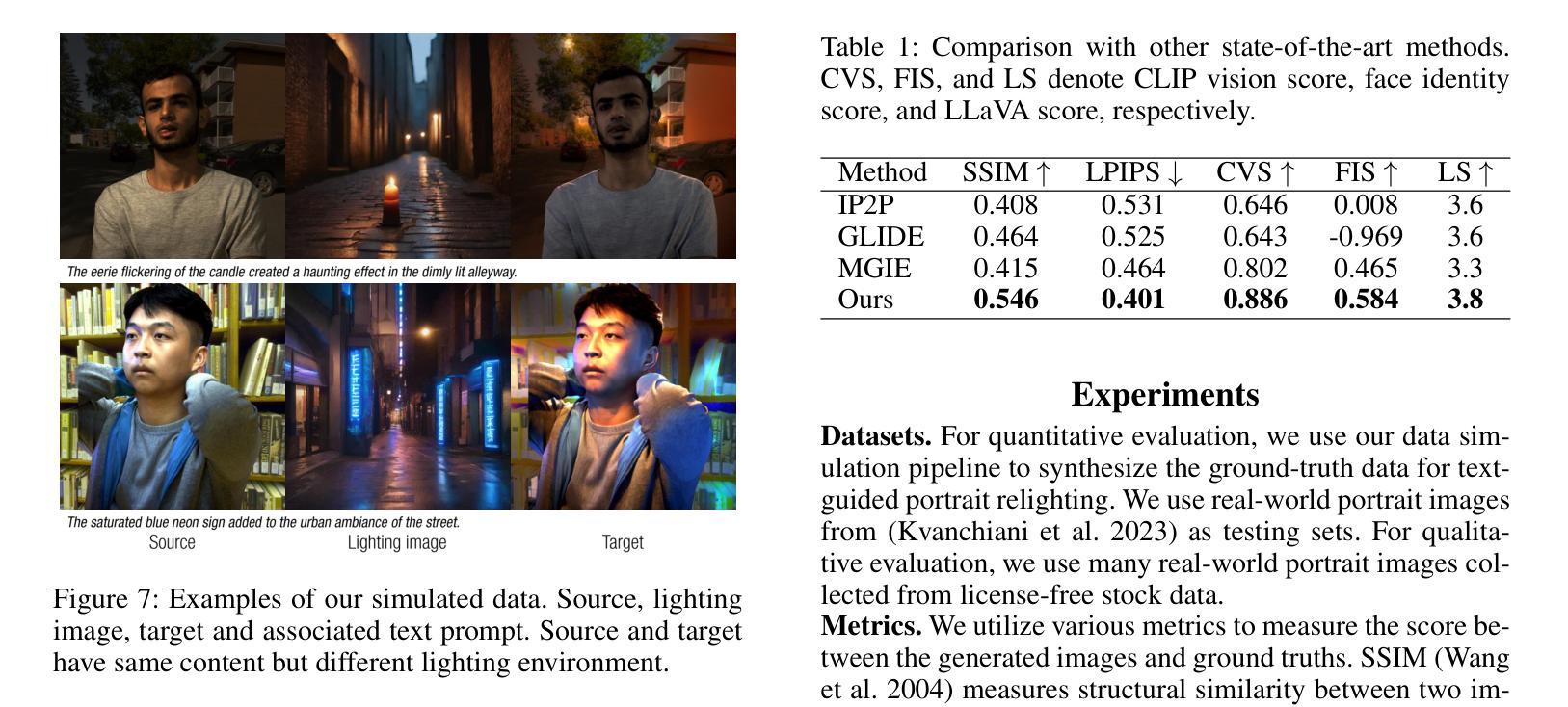
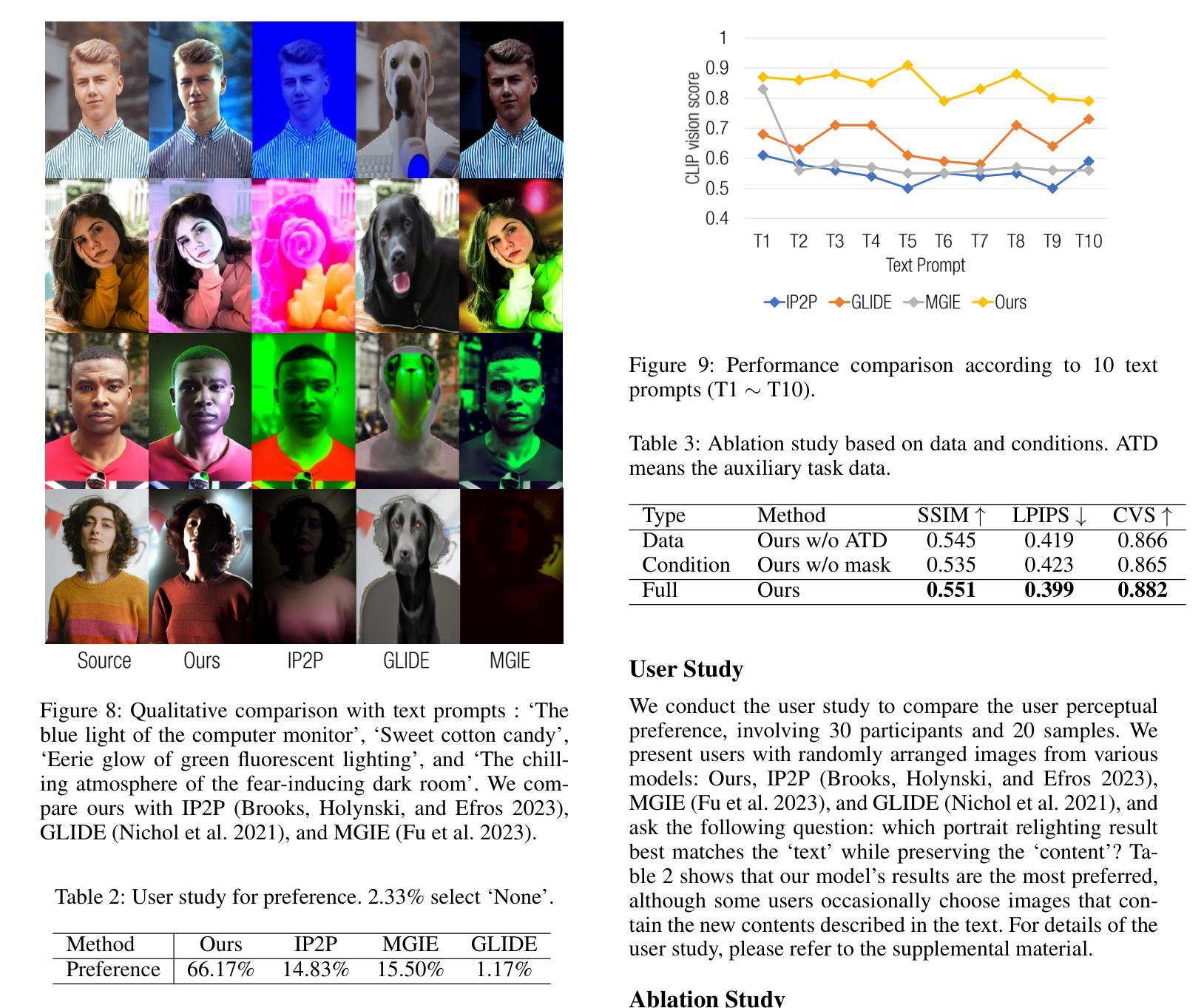
Text2Relight: Creative Portrait Relighting with Text Guidance
Authors:Junuk Cha, Mengwei Ren, Krishna Kumar Singh, He Zhang, Yannick Hold-Geoffroy, Seunghyun Yoon, HyunJoon Jung, Jae Shin Yoon, Seungryul Baek
We present a lighting-aware image editing pipeline that, given a portrait image and a text prompt, performs single image relighting. Our model modifies the lighting and color of both the foreground and background to align with the provided text description. The unbounded nature in creativeness of a text allows us to describe the lighting of a scene with any sensory features including temperature, emotion, smell, time, and so on. However, the modeling of such mapping between the unbounded text and lighting is extremely challenging due to the lack of dataset where there exists no scalable data that provides large pairs of text and relighting, and therefore, current text-driven image editing models does not generalize to lighting-specific use cases. We overcome this problem by introducing a novel data synthesis pipeline: First, diverse and creative text prompts that describe the scenes with various lighting are automatically generated under a crafted hierarchy using a large language model (e.g., ChatGPT). A text-guided image generation model creates a lighting image that best matches the text. As a condition of the lighting images, we perform image-based relighting for both foreground and background using a single portrait image or a set of OLAT (One-Light-at-A-Time) images captured from lightstage system. Particularly for the background relighting, we represent the lighting image as a set of point lights and transfer them to other background images. A generative diffusion model learns the synthesized large-scale data with auxiliary task augmentation (e.g., portrait delighting and light positioning) to correlate the latent text and lighting distribution for text-guided portrait relighting.
我们提出了一种感知照明的图像编辑流程。给定肖像图像和文字提示,该流程可以对单幅图像进行重新照明。我们的模型会修改前景和背景的照明和颜色,以符合提供的文字描述。文本的无界创造性使我们能够描述任何感觉特征的场景照明,包括温度、情感、气味、时间等等。然而,在文本和照明之间进行此类映射的建模极具挑战性,因为缺乏大型数据集提供大量的文本和重新照明配对。因此,当前的文本驱动图像编辑模型并不适用于特定的照明用例。我们通过引入新型数据合成流程来解决这一问题:首先,在一个精心设计的层次结构下,使用大型语言模型(例如ChatGPT)自动生成描述各种照明的场景的各种创意文本提示。文本引导的图像生成模型创建与文本最佳匹配的照明图像。作为照明图像的条件,我们使用单幅肖像图像或从灯光舞台系统捕获的一组OLAT(一次一个灯光)图像对前景和背景进行基于图像的重新照明。特别是针对背景重新照明,我们将照明图像表示为一组点光源并将其转移到其他背景图像上。生成扩散模型通过辅助任务增强(例如肖像照明和灯光定位)来学习合成的大规模数据,从而关联潜在文本和照明分布,实现文本引导的肖像重新照明。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文介绍了一种基于文本提示的图像编辑流程,它可以根据提供的肖像图像和文本提示进行单图像重照明。该模型能够修改前景和背景的光照和颜色,以符合给定的文本描述。文本描述的创意无界性允许我们描述场景的任何感官特征,如温度、情感、气味、时间等。然而,将这种无界的文本与照明之间的映射建模极具挑战性,因为缺乏相应的数据集,现有的文本驱动图像编辑模型无法推广到照明特定的用例。为解决此问题,我们引入了一种新颖的数据合成流程:使用大型语言模型(如ChatGPT)在精心设计的层次结构下自动生成描述场景各种照明的多样化创意文本提示。基于文本指导的图像生成模型创建与文本最佳匹配的照明图像。作为照明图像的条件,我们对前景和背景进行了基于图像的重新照明,使用单个肖像图像或由光舞台系统捕获的一组OLAT(一次一个灯光)图像。特别是针对背景重新照明,我们将照明图像表示为一组点光源并将其转移到其他背景图像上。生成扩散模型通过辅助任务增强(如肖像重照明和灯光定位)来学习合成的大规模数据,从而关联潜在文本和照明分布,以实现文本引导的肖像重新照明。
关键见解
- 介绍了基于文本提示的照明感知图像编辑流程,能够实现单图像重照明。
- 模型能够修改前景和背景的光照和颜色以符合文本描述。
- 创意无界的文本描述允许描述场景的多种感官特征。
- 数据集缺乏是文本与照明映射建模的主要挑战。
- 通过数据合成流程克服此挑战,包括使用大型语言模型自动生成文本提示。
- 使用文本指导的图像生成模型创建与文本匹配的照明图像。
- 通过图像基于条件的重照明技术处理前景和背景,利用生成扩散模型学习大规模数据以实现文本引导的肖像重新照明。
点此查看论文截图


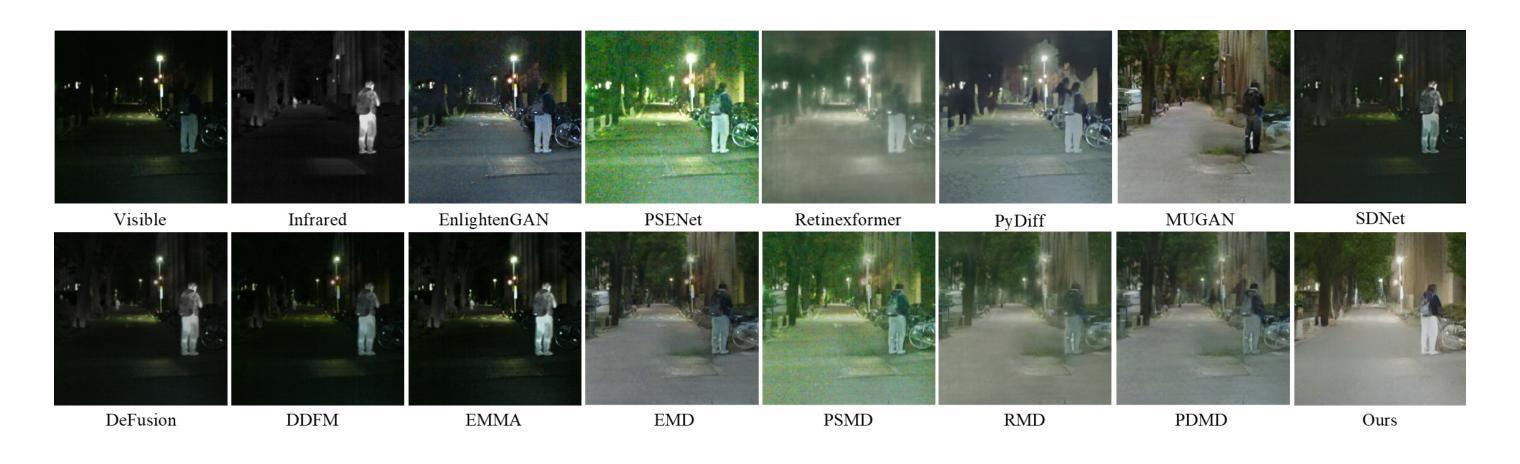
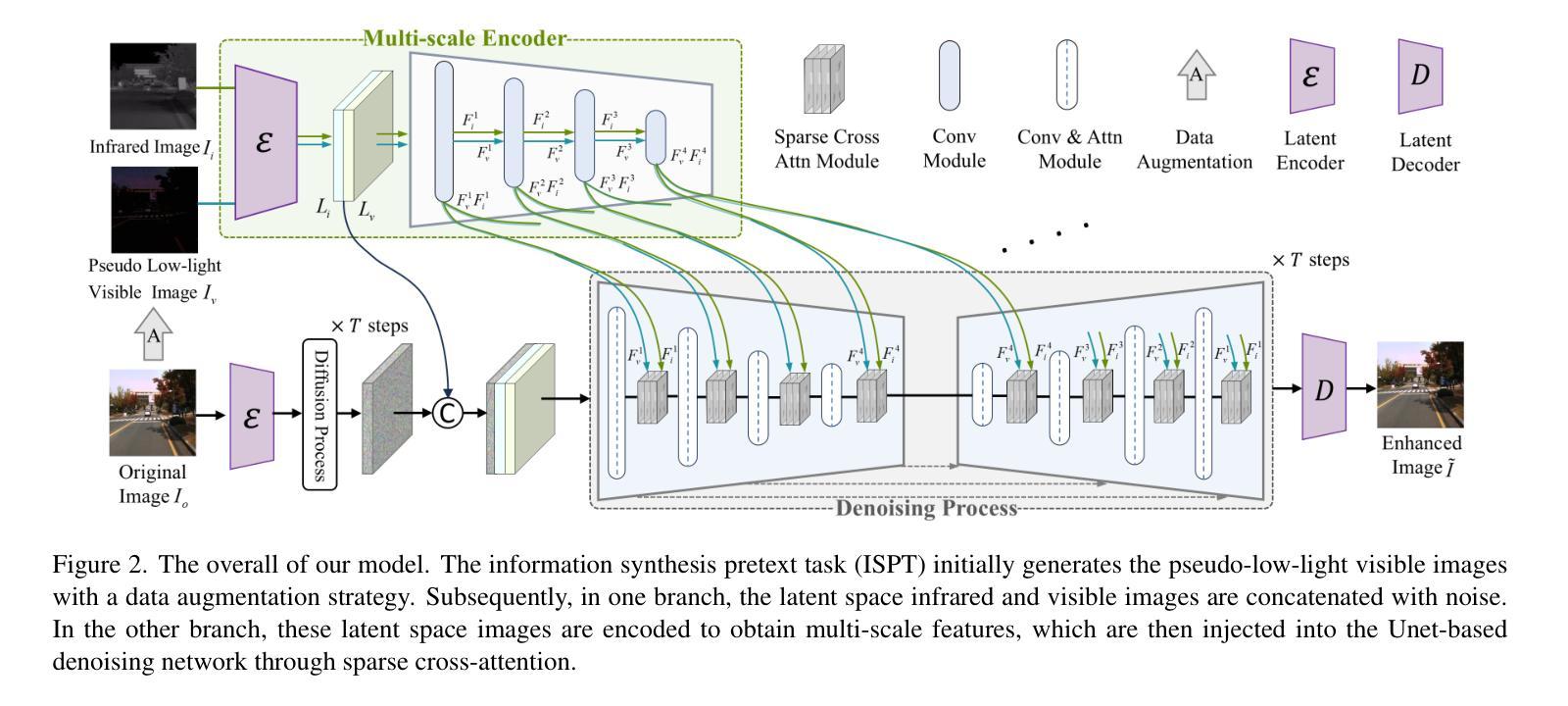
VIIS: Visible and Infrared Information Synthesis for Severe Low-light Image Enhancement
Authors:Chen Zhao, Mengyuan Yu, Fan Yang, Peiguang Jing
Images captured in severe low-light circumstances often suffer from significant information absence. Existing singular modality image enhancement methods struggle to restore image regions lacking valid information. By leveraging light-impervious infrared images, visible and infrared image fusion methods have the potential to reveal information hidden in darkness. However, they primarily emphasize inter-modal complementation but neglect intra-modal enhancement, limiting the perceptual quality of output images. To address these limitations, we propose a novel task, dubbed visible and infrared information synthesis (VIIS), which aims to achieve both information enhancement and fusion of the two modalities. Given the difficulty in obtaining ground truth in the VIIS task, we design an information synthesis pretext task (ISPT) based on image augmentation. We employ a diffusion model as the framework and design a sparse attention-based dual-modalities residual (SADMR) conditioning mechanism to enhance information interaction between the two modalities. This mechanism enables features with prior knowledge from both modalities to adaptively and iteratively attend to each modality’s information during the denoising process. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that our model qualitatively and quantitatively outperforms not only the state-of-the-art methods in relevant fields but also the newly designed baselines capable of both information enhancement and fusion. The code is available at https://github.com/Chenz418/VIIS.
在严重低光环境下捕捉的图像通常缺乏重要信息。现有的单一模态图像增强方法在恢复缺乏有效信息图像区域方面表现困难。通过利用不受光线影响的红外图像,可见光和红外图像融合方法具有揭示隐藏在黑暗中的信息的潜力。然而,它们主要侧重于跨模态互补,而忽略了跨模态内的增强,这限制了输出图像的感知质量。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一个新的任务,称为可见光和红外信息合成(VIIS),旨在实现两个模态的信息增强和融合。考虑到在VIIS任务中获取真实标签的难度,我们基于图像增强设计了一个信息合成预训练任务(ISPT)。我们采用扩散模型作为框架,并设计了一种基于稀疏注意力的双模态残差(SADMR)条件机制,以增强两个模态之间的信息交互。该机制使来自两个模态的先验知识特征能够自适应地迭代关注每个模态的信息去噪过程。我们的大量实验表明,我们的模型不仅在相关领域最先进的方法上表现优越,而且在同时具备信息增强和融合能力的新设计基准上也有出色表现。代码可通过以下网址获取:https://github.com/Chenz418/VIIS 。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to WACV 2025
Summary
针对低光环境下图像信息缺失的问题,现有图像增强方法难以恢复缺失信息。通过结合红外图像,可见光和红外图像融合方法能够揭示隐藏信息。但现有方法主要关注跨模态互补,忽视单模态内增强,影响输出图像感知质量。为此,提出可见光和红外信息合成(VIIS)任务,旨在实现信息增强与双模态融合。针对VIIS任务难以获取真实标注的问题,设计基于图像增强的信息合成预训练任务(ISPT)。采用扩散模型框架,并设计基于稀疏注意力的双模态残差(SADMR)条件机制,增强两模态间的信息交互。实验证明,该模型在相关领域中不仅优于最新方法,而且超越仅具备信息增强和融合功能的新设计基准模型。
Key Takeaways
- 低光环境下的图像存在信息缺失问题,现有图像增强方法难以解决。
- 通过结合红外图像,可见光和红外图像融合方法可以揭示隐藏信息。
- 现有方法主要关注跨模态互补,忽视单模态内的增强,影响输出图像质量。
- 提出可见光和红外信息合成(VIIS)任务,旨在实现信息增强与双模态融合。
- 针对VIIS任务难以获取真实标注的问题,设计基于图像增强的信息合成预训练任务(ISPT)。
- 采用扩散模型框架,并设计SADMR条件机制以增强两模态间的信息交互。
点此查看论文截图





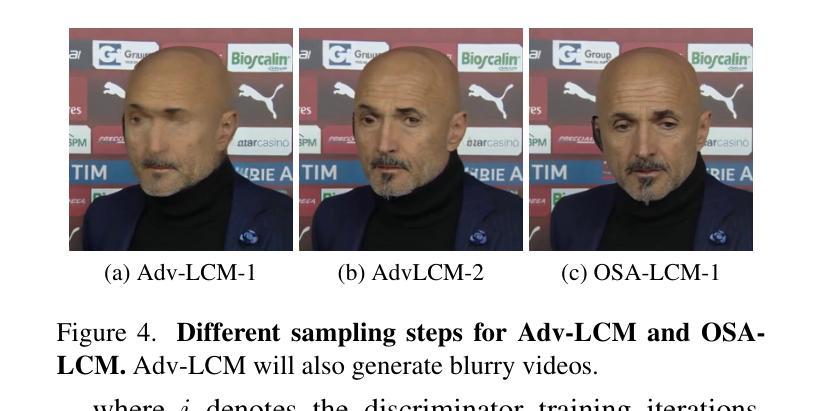
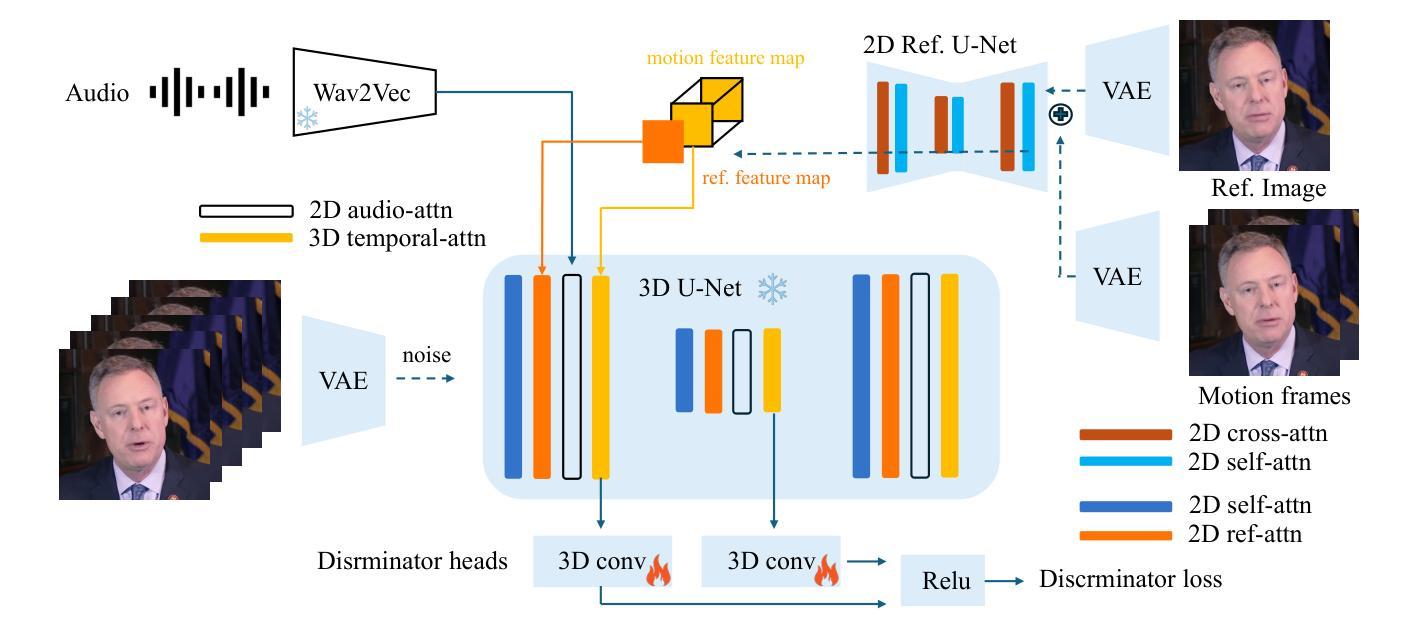
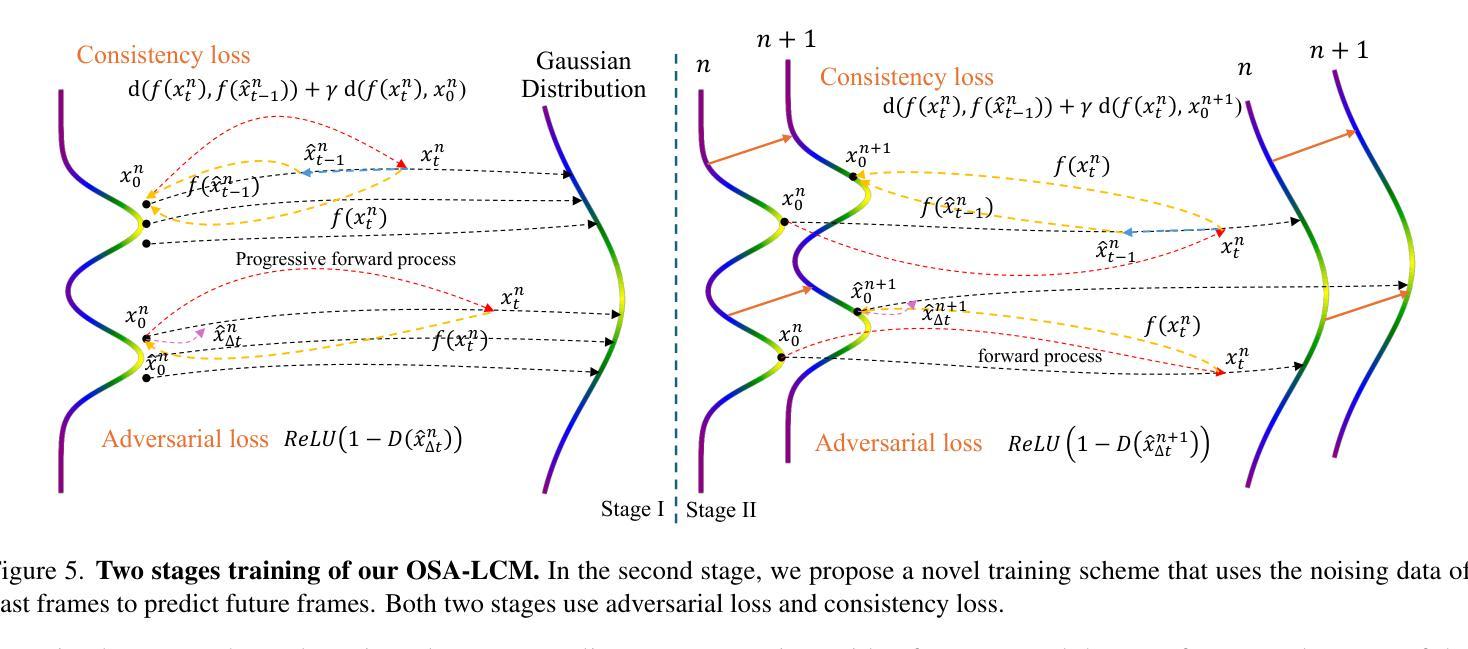
Real-time One-Step Diffusion-based Expressive Portrait Videos Generation
Authors:Hanzhong Guo, Hongwei Yi, Daquan Zhou, Alexander William Bergman, Michael Lingelbach, Yizhou Yu
Latent diffusion models have made great strides in generating expressive portrait videos with accurate lip-sync and natural motion from a single reference image and audio input. However, these models are far from real-time, often requiring many sampling steps that take minutes to generate even one second of video-significantly limiting practical use. We introduce OSA-LCM (One-Step Avatar Latent Consistency Model), paving the way for real-time diffusion-based avatars. Our method achieves comparable video quality to existing methods but requires only one sampling step, making it more than 10x faster. To accomplish this, we propose a novel avatar discriminator design that guides lip-audio consistency and motion expressiveness to enhance video quality in limited sampling steps. Additionally, we employ a second-stage training architecture using an editing fine-tuned method (EFT), transforming video generation into an editing task during training to effectively address the temporal gap challenge in single-step generation. Experiments demonstrate that OSA-LCM outperforms existing open-source portrait video generation models while operating more efficiently with a single sampling step.
潜在扩散模型在利用单一参考图像和音频输入生成表情丰富的肖像视频方面取得了巨大的进步,这些视频具有准确的唇音同步和自然动作。然而,这些模型还远远达不到实时标准,通常需要许多采样步骤,甚至生成一秒钟的视频也需要数分钟的时间,从而极大地限制了其实际使用。我们引入了OSA-LCM(一步式化身潜在一致性模型),为基于扩散的实时化身技术铺平了道路。我们的方法达到了与现有方法相当的视频质量,但仅需一个采样步骤,使其速度超过现有方法十倍以上。为了实现这一点,我们提出了一种新型化身鉴别器设计,该设计用于指导唇音一致性和动作表现力,在有限的采样步骤中提高视频质量。此外,我们采用第二阶段训练架构,使用编辑微调方法(EFT),在训练过程中将视频生成转变为编辑任务,以有效解决单步生成中的时间间隔挑战。实验表明,OSA-LCM在性能上超越了现有的开源肖像视频生成模型,同时凭借单个采样步骤实现了更高效的操作。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages
Summary
基于潜在扩散模型的技术,在仅使用单张参考图像和音频输入的情况下,生成具有精确唇同步和自然动作的表达性肖像视频方面取得了显著进展。然而,这些模型的生成过程并非实时,需要大量采样步骤,甚至生成一秒视频都需要数分钟时间,这极大地限制了其实际使用。我们推出OSA-LCM(一步式化身潜在一致性模型),为基于扩散的实时化身技术铺平了道路。我们的方法实现了与现有方法相当的视频质量,但仅需一个采样步骤,使其速度超过现有技术十倍以上。通过设计新型化身鉴别器,引导唇音频一致性和动作表达性,在有限的采样步骤中提高视频质量。此外,我们采用第二阶段训练架构,使用编辑微调方法(EFT),将视频生成转变为训练过程中的编辑任务,有效解决单步生成中的时间间隔挑战。实验表明,OSA-LCM在肖像视频生成方面优于现有开源模型,同时以单步采样实现更高效的操作。
Key Takeaways
- 潜在扩散模型在生成肖像视频方面取得了显著进展,能够基于单张参考图像和音频输入生成具有精确唇同步和自然动作的视频。
- 现有模型生成过程非实时,需要大量采样步骤,限制了实际应用。
- OSA-LCM模型引入一步式化身潜在一致性模型,实现实时扩散式化身技术。
- OSA-LCM通过设计新型化身鉴别器,提高视频质量,实现与现有方法相当的视频效果。
- OSA-LCM采用编辑微调方法(EFT),将视频生成转变为训练过程中的编辑任务,解决单步生成中的时间间隔挑战。
- 实验证明,OSA-LCM在肖像视频生成方面优于现有开源模型。
点此查看论文截图



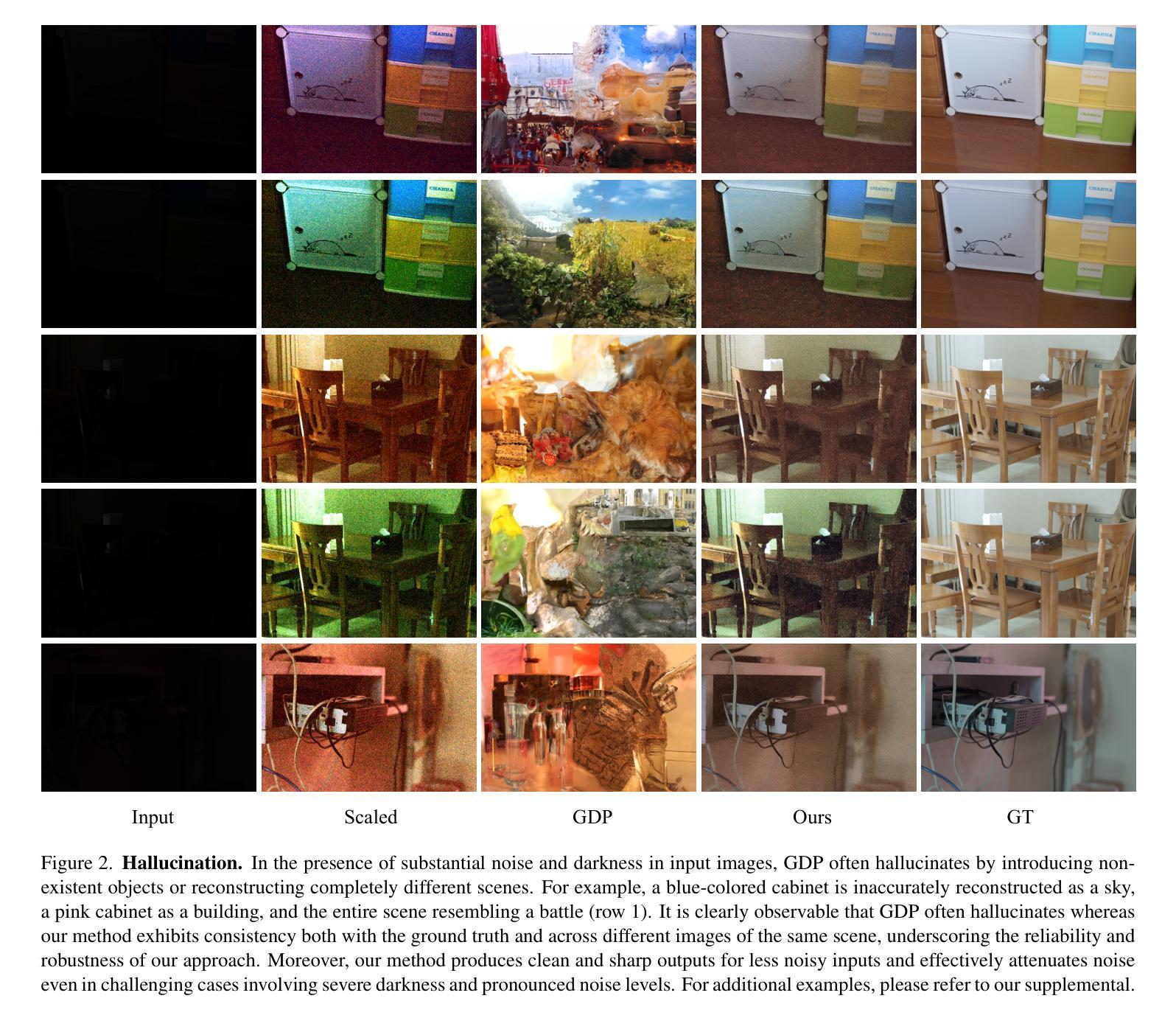
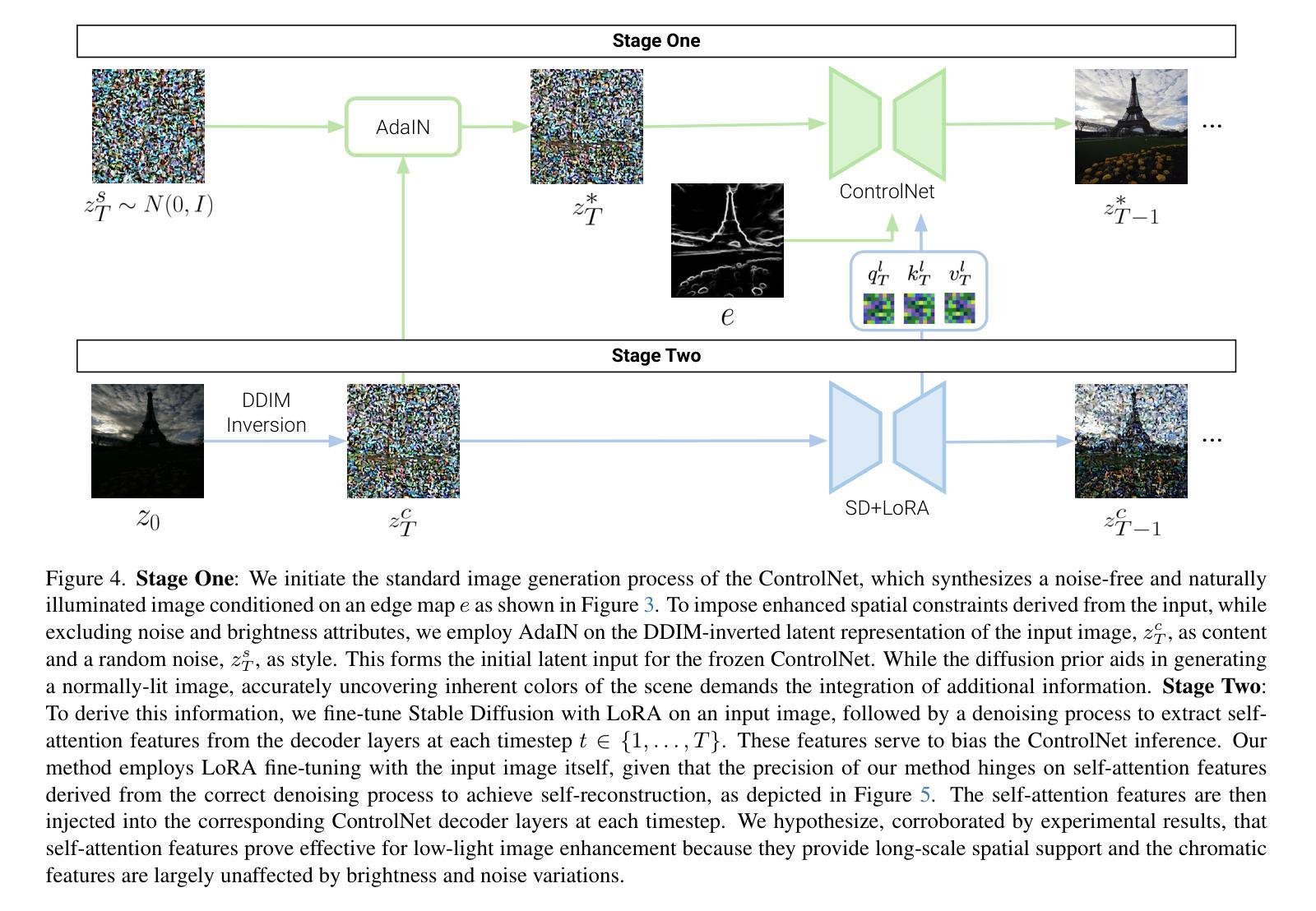
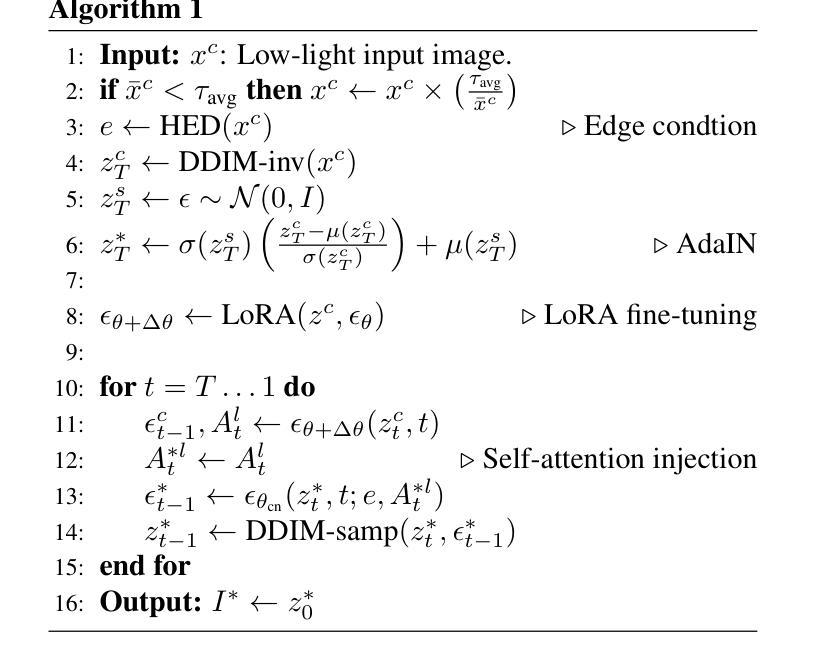
Zero-Shot Low Light Image Enhancement with Diffusion Prior
Authors:Joshua Cho, Sara Aghajanzadeh, Zhen Zhu, D. A. Forsyth
Balancing aesthetic quality with fidelity when enhancing images from challenging, degraded sources is a core objective in computational photography. In this paper, we address low light image enhancement (LLIE), a task in which dark images often contain limited visible information. Diffusion models, known for their powerful image enhancement capacities, are a natural choice for this problem. However, their deep generative priors can also lead to hallucinations, introducing non-existent elements or substantially altering the visual semantics of the original scene. In this work, we introduce a novel zero-shot method for controlling and refining the generative behavior of diffusion models for dark-to-light image conversion tasks. Our method demonstrates superior performance over existing state-of-the-art methods in the task of low-light image enhancement, as evidenced by both quantitative metrics and qualitative analysis.
在计算摄影中,平衡美学质量与保真度,同时对来自具有挑战性的退化源的图像进行增强,是核心目标。本文我们研究低光图像增强(LLIE)问题,暗图像往往包含有限的可视信息。扩散模型以其强大的图像增强能力而著称,因此是此问题的自然选择。然而,它们的深度生成先验也可能导致幻觉,引入不存在的元素或大幅改变原始场景的可视语义。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一种用于控制和细化扩散模型生成行为的新型零样本方法,用于暗到亮的图像转换任务。我们的方法在暗光图像增强任务中的性能优于现有最先进的方法,这由定量指标和定性分析均证明。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文聚焦于低光图像增强任务,旨在平衡美学质量与保真度。虽然扩散模型在图像增强方面表现出强大的能力,但也可能产生幻觉,引入不存在的元素或大幅改变原始场景的视觉语义。本文提出了一种新型的零样本方法,用于控制和优化扩散模型在暗光图像转换任务中的生成行为,并在低光图像增强任务中展现出优于现有先进方法的表现。
Key Takeaways
- 本文关注低光图像增强任务,重点是在挑战性的退化图像源中平衡美学质量与保真度。
- 扩散模型因其强大的图像增强能力而被选为解决此问题的自然选择,但也存在生成幻觉的问题。
- 本文提出了一种新型的零样本方法,用于控制和优化扩散模型在暗光图像转换任务中的生成行为。
- 该方法通过定量指标和定性分析证明了在低光图像增强任务中优于现有先进方法的表现。
- 扩散模型在图像生成方面具有强大的潜力,但也需要进一步研究和改进来控制其生成行为。
- 对于暗光图像转换任务,未来的研究可以探索更多的控制方法和优化策略来提高图像的质量和保真度。
点此查看论文截图



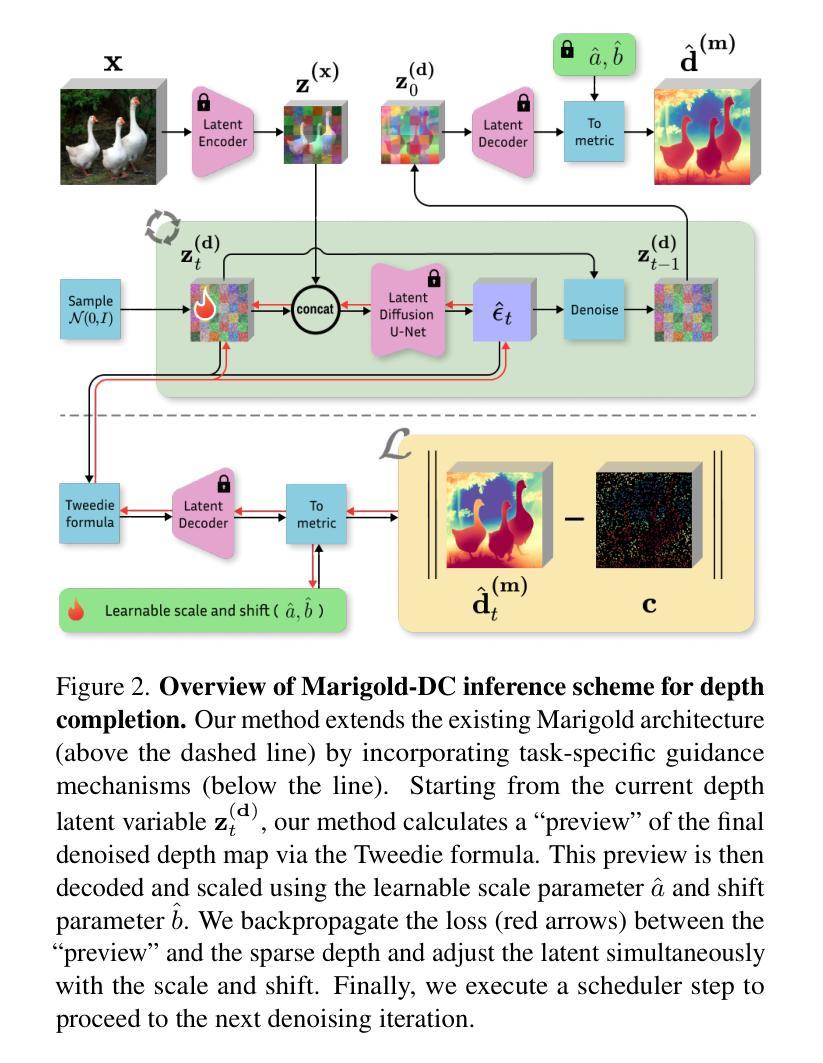
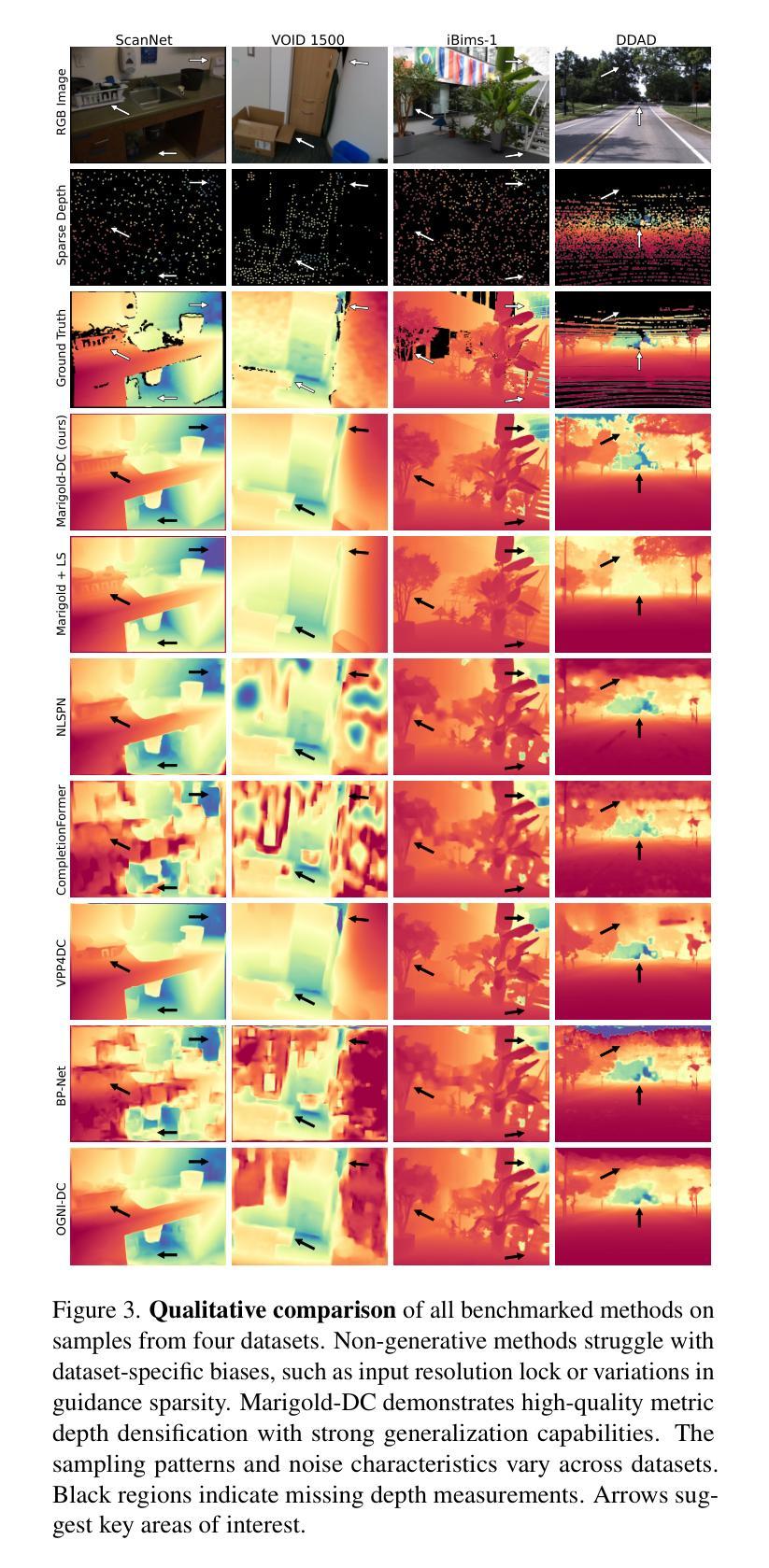
Marigold-DC: Zero-Shot Monocular Depth Completion with Guided Diffusion
Authors:Massimiliano Viola, Kevin Qu, Nando Metzger, Bingxin Ke, Alexander Becker, Konrad Schindler, Anton Obukhov
Depth completion upgrades sparse depth measurements into dense depth maps guided by a conventional image. Existing methods for this highly ill-posed task operate in tightly constrained settings and tend to struggle when applied to images outside the training domain or when the available depth measurements are sparse, irregularly distributed, or of varying density. Inspired by recent advances in monocular depth estimation, we reframe depth completion as an image-conditional depth map generation guided by sparse measurements. Our method, Marigold-DC, builds on a pretrained latent diffusion model for monocular depth estimation and injects the depth observations as test-time guidance via an optimization scheme that runs in tandem with the iterative inference of denoising diffusion. The method exhibits excellent zero-shot generalization across a diverse range of environments and handles even extremely sparse guidance effectively. Our results suggest that contemporary monocular depth priors greatly robustify depth completion: it may be better to view the task as recovering dense depth from (dense) image pixels, guided by sparse depth; rather than as inpainting (sparse) depth, guided by an image. Project website: https://MarigoldDepthCompletion.github.io/
深度补全将稀疏的深度测量值升级为受常规图像引导的密集深度图。针对这一高度不适定的任务,现有方法通常在严格受限的环境中运行,当应用于训练域外的图像或可用的深度测量值稀疏、分布不均或密度不一的情况下,往往会遇到困难。受单目深度估计的最新进展的启发,我们将深度补全重新定位为基于稀疏测量引导的受图像条件控制的深度图生成。我们的方法Marigold-DC建立在用于单目深度估计的预训练潜在扩散模型的基础上,通过一种优化方案在去除噪声扩散的迭代推断过程中注入深度观测值作为测试时的指导。该方法在多种环境中展现出出色的零样本泛化能力,并能有效地处理极其稀疏的指导。我们的结果表明,当代的单目深度先验知识极大地增强了深度补全的稳健性:可能更好的做法是将其视为从(密集)图像像素中恢复密集深度,受稀疏深度引导;而不是将任务视为在图像引导下填充(稀疏)深度。项目网站:https://MarigoldDepthCompletion.github.io/
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为Marigold-DC的深度完成方法,它将深度完成任务重新定义为在稀疏测量指导下,基于图像的深度图生成。该方法利用预训练的潜在扩散模型,通过优化方案在测试时注入深度观测值,与去噪扩散的迭代推理并行运行。该方法具有良好的零样本泛化能力,可处理各种环境,并可有效处理极其稀疏的指导。
Key Takeaways
- Marigold-DC方法将深度完成定义为在稀疏测量指导下,基于图像的深度图生成。
- 它利用预训练的潜在扩散模型,注入深度观测值作为测试时的指导。
- Marigold-DC通过优化方案与去噪扩散的迭代推理并行运行。
- 该方法具有良好的零样本泛化能力,能在各种环境中表现良好。
- Marigold-DC能有效处理极其稀疏的指导情况。
- 现有深度完成方法往往局限于特定环境或训练域,而Marigold-DC具有更强的泛化能力。
点此查看论文截图

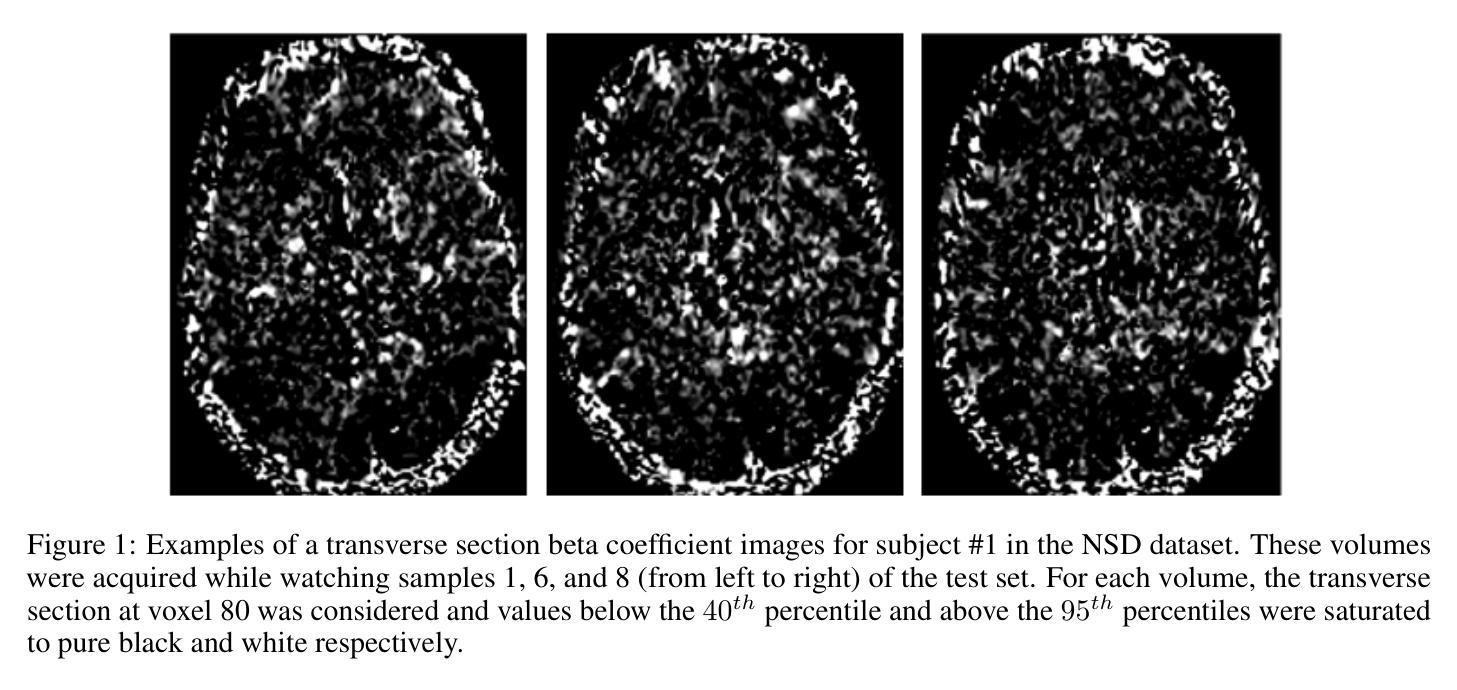
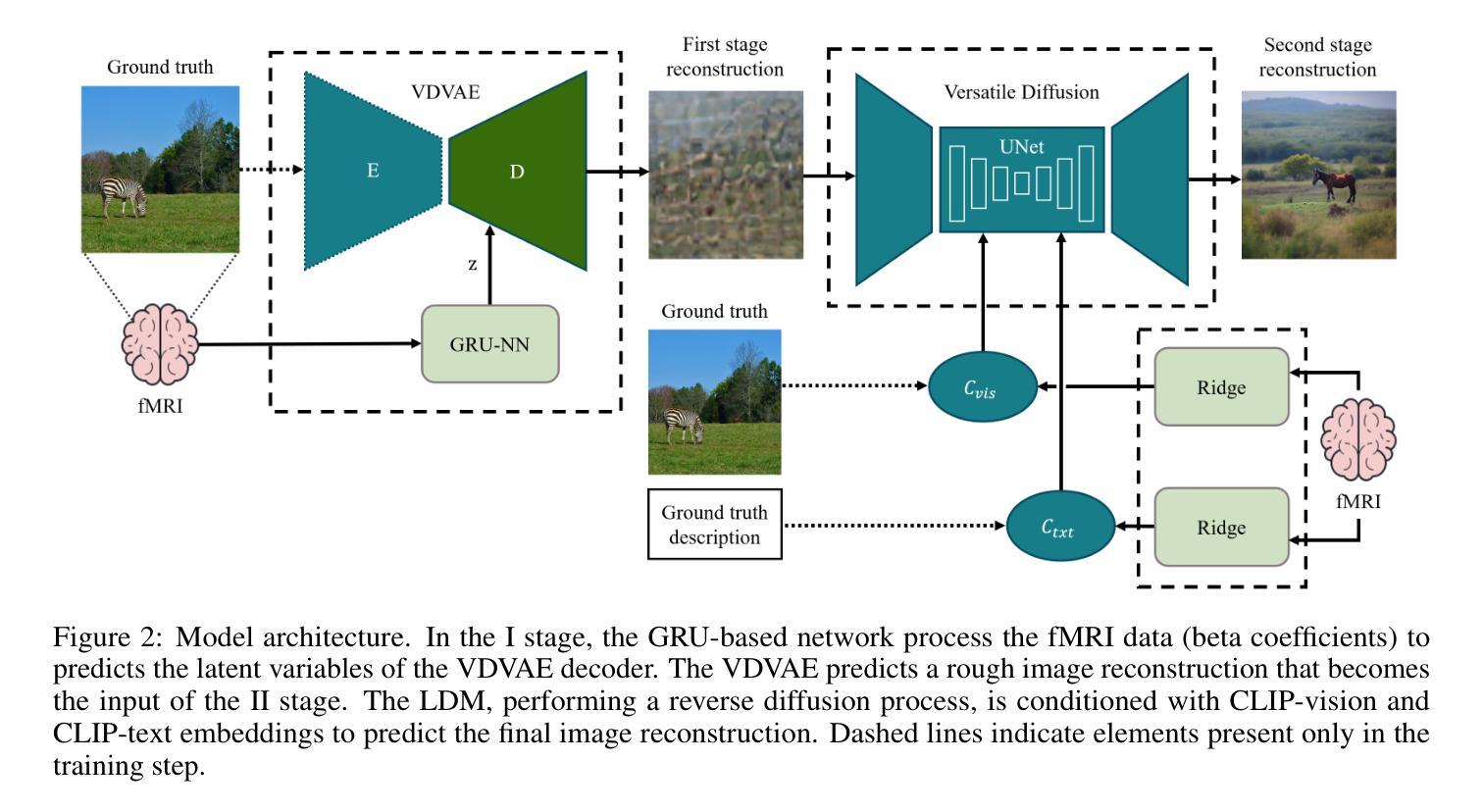
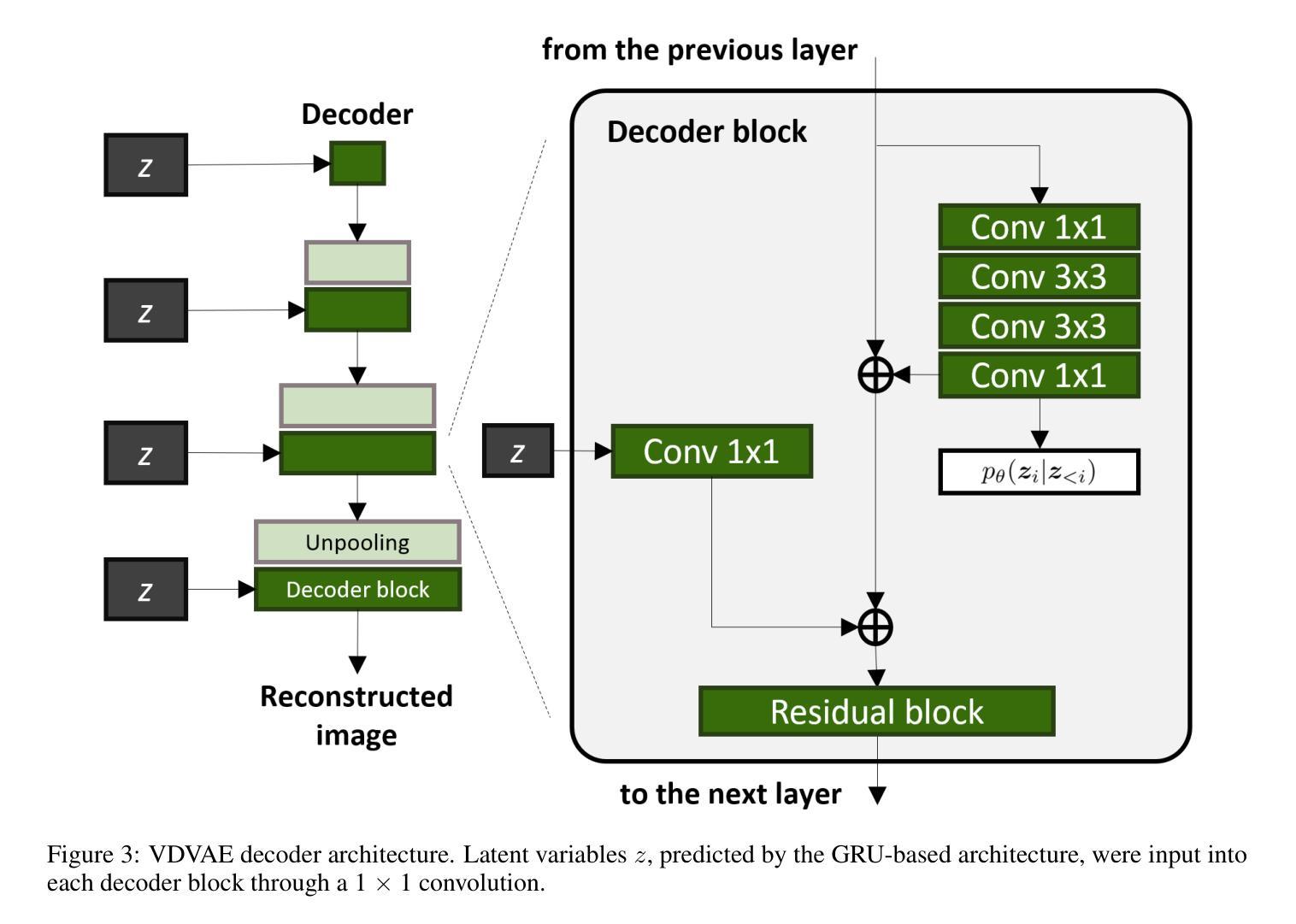
Optimized two-stage AI-based Neural Decoding for Enhanced Visual Stimulus Reconstruction from fMRI Data
Authors:Lorenzo Veronese, Andrea Moglia, Luca Mainardi, Pietro Cerveri
AI-based neural decoding reconstructs visual perception by leveraging generative models to map brain activity, measured through functional MRI (fMRI), into latent hierarchical representations. Traditionally, ridge linear models transform fMRI into a latent space, which is then decoded using latent diffusion models (LDM) via a pre-trained variational autoencoder (VAE). Due to the complexity and noisiness of fMRI data, newer approaches split the reconstruction into two sequential steps, the first one providing a rough visual approximation, the second on improving the stimulus prediction via LDM endowed by CLIP embeddings. This work proposes a non-linear deep network to improve fMRI latent space representation, optimizing the dimensionality alike. Experiments on the Natural Scenes Dataset showed that the proposed architecture improved the structural similarity of the reconstructed image by about 2% with respect to the state-of-the-art model, based on ridge linear transform. The reconstructed image’s semantics improved by about 4%, measured by perceptual similarity, with respect to the state-of-the-art. The noise sensitivity analysis of the LDM showed that the role of the first stage was fundamental to predict the stimulus featuring high structural similarity. Conversely, providing a large noise stimulus affected less the semantics of the predicted stimulus, while the structural similarity between the ground truth and predicted stimulus was very poor. The findings underscore the importance of leveraging non-linear relationships between BOLD signal and the latent representation and two-stage generative AI for optimizing the fidelity of reconstructed visual stimuli from noisy fMRI data.
基于人工智能的神经网络解码通过利用生成模型将功能磁共振成像(fMRI)测量的脑活动映射到潜在层次表示,从而重建视觉感知。传统上,岭线性模型将fMRI转换为潜在空间,然后使用预训练的变分自编码器(VAE)通过潜在扩散模型(LDM)进行解码。由于fMRI数据的复杂性和噪声,更新的方法将重建过程分为两个连续步骤,第一个步骤提供粗略的视觉近似,第二个步骤通过LDM和CLIP嵌入改进刺激预测。这项工作提出了一个非线性深度网络来改善fMRI的潜在空间表示,同时优化维度。在自然场景数据集上的实验表明,与基于岭线性变换的最先进模型相比,所提出的架构改进了重建图像的结构相似性约2%。在感知相似性方面,重建图像的语义改进了约4%。LDM的噪声敏感性分析表明,第一阶段在预测具有高结构相似性的刺激方面起着至关重要的作用。相反,提供大噪声刺激对预测刺激的语义影响较小,而地面真实数据和预测刺激之间的结构相似性非常差。这些发现强调了利用BOLD信号和潜在表示之间的非线性关系以及两阶段生成人工智能在优化从噪声fMRI数据中重建的视觉刺激保真度方面的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 5 figures
摘要
基于人工智能的神经网络解码通过利用生成模型将功能磁共振成像(fMRI)测量的脑活动映射到潜在层次表示中,重建视觉感知。本研究提出一种非线性深度网络,优化fMRI的潜在空间表示,在维度上实现优化。实验表明,与传统的基于岭线性变换的模型相比,该架构提高了重建图像的构造相似性约2%,在感知相似性方面也提高了约4%。对LDM的噪声敏感性分析显示,第一阶段在预测具有高强度构造相似性的刺激时起着至关重要的作用。相反,提供大量噪声刺激对预测刺激的语义影响较小,而地面真实数据与预测刺激之间的构造相似性则较差。研究强调了利用BOLD信号和潜在表现之间的非线性关系以及两阶段生成人工智能在优化从噪声fMRI数据中重建的视觉刺激保真度中的重要性。
关键见解
- AI-based neural decoding利用生成模型映射fMRI数据到潜在层次表示,重建视觉感知。
- 提出非线性深度网络改进fMRI的潜在空间表示,优化维度。
- 与现有模型相比,新架构提高了重建图像的构造相似性约2%,感知相似性约4%。
- LDM的噪声敏感性分析显示第一阶段在预测高强度构造相似性刺激时至关重要。
- 噪声对预测刺激的语义影响较小,但对构造相似性的影响较大。
- 研究强调了利用BOLD信号和潜在表现之间的非线性关系的重要性。
点此查看论文截图

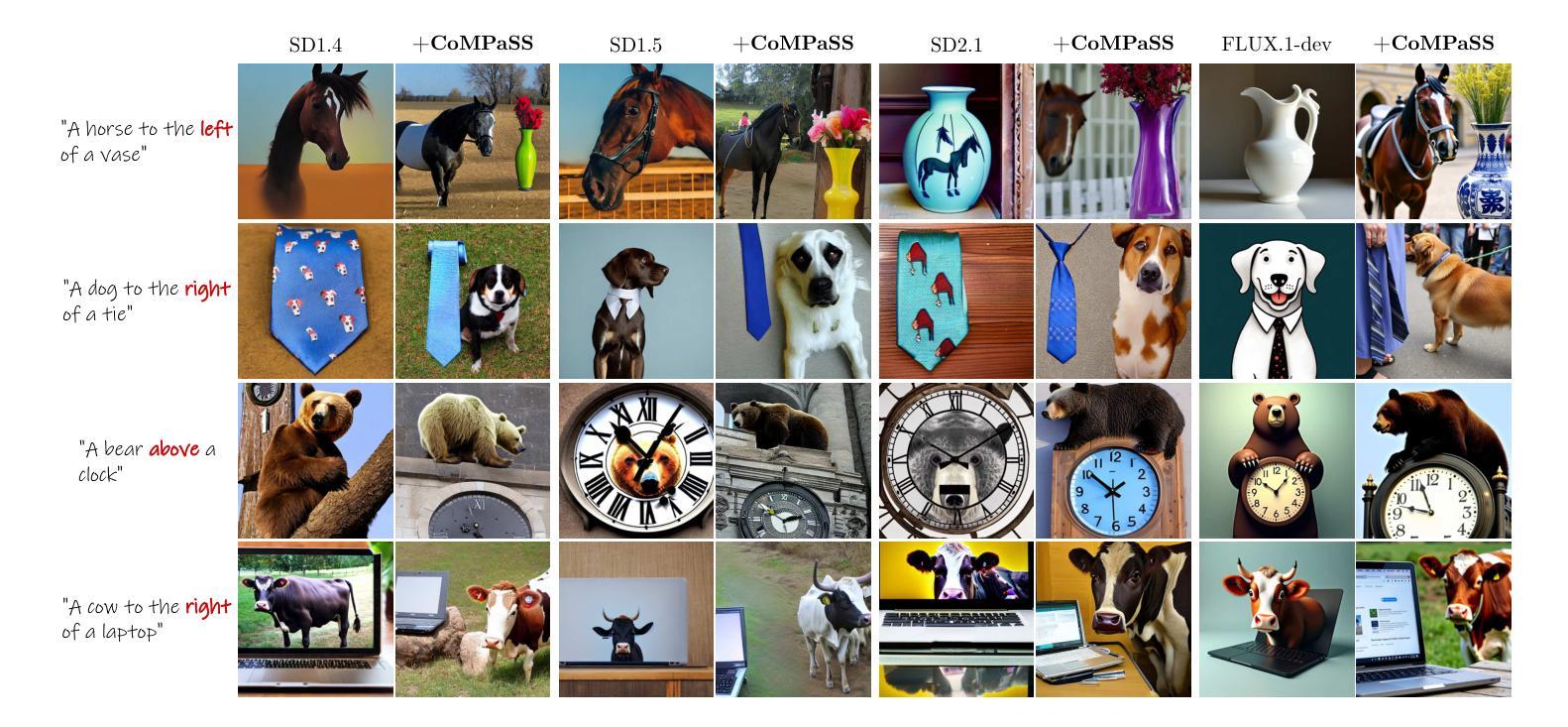
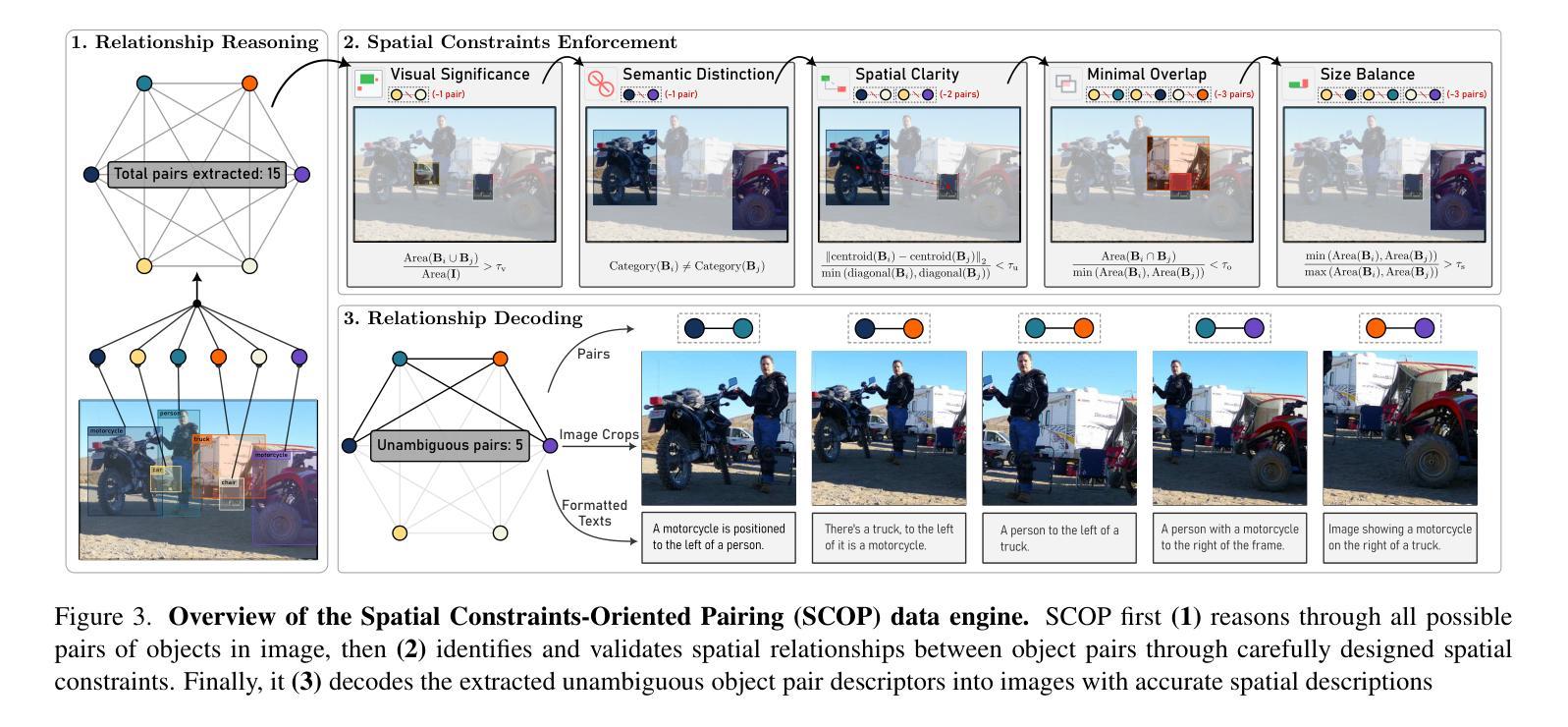
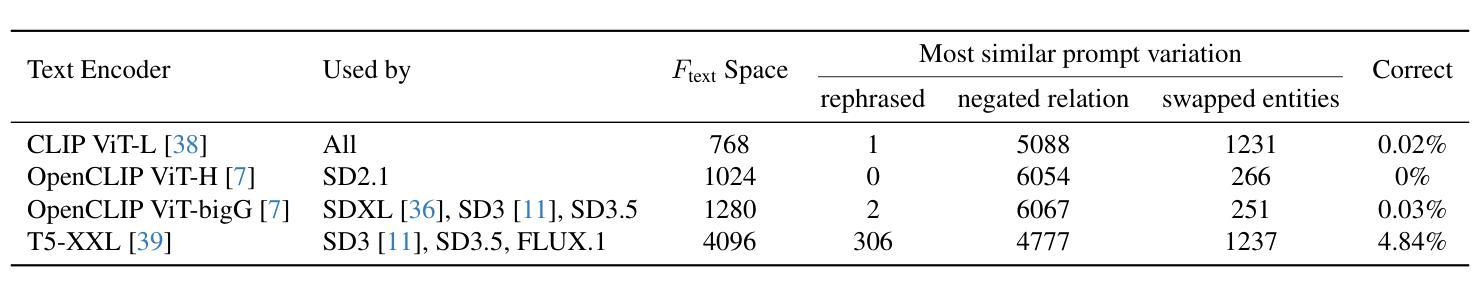
CoMPaSS: Enhancing Spatial Understanding in Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Authors:Gaoyang Zhang, Bingtao Fu, Qingnan Fan, Qi Zhang, Runxing Liu, Hong Gu, Huaqi Zhang, Xinguo Liu
Text-to-image diffusion models excel at generating photorealistic images, but commonly struggle to render accurate spatial relationships described in text prompts. We identify two core issues underlying this common failure: 1) the ambiguous nature of spatial-related data in existing datasets, and 2) the inability of current text encoders to accurately interpret the spatial semantics of input descriptions. We address these issues with CoMPaSS, a versatile training framework that enhances spatial understanding of any T2I diffusion model. CoMPaSS solves the ambiguity of spatial-related data with the Spatial Constraints-Oriented Pairing (SCOP) data engine, which curates spatially-accurate training data through a set of principled spatial constraints. To better exploit the curated high-quality spatial priors, CoMPaSS further introduces a Token ENcoding ORdering (TENOR) module to allow better exploitation of high-quality spatial priors, effectively compensating for the shortcoming of text encoders. Extensive experiments on four popular open-weight T2I diffusion models covering both UNet- and MMDiT-based architectures demonstrate the effectiveness of CoMPaSS by setting new state-of-the-arts with substantial relative gains across well-known benchmarks on spatial relationships generation, including VISOR (+98%), T2I-CompBench Spatial (+67%), and GenEval Position (+131%). Code will be available at https://github.com/blurgyy/CoMPaSS.
文本到图像的扩散模型在生成逼真的图像方面表现出色,但在呈现文本提示中描述的空间关系时通常遇到困难。我们确定了这种常见失败背后的两个核心问题:1)现有数据集中空间相关数据的模糊性质;2)当前文本编码器无法准确解释输入描述的空间语义。我们通过CoMPaSS解决这些问题,这是一种通用的训练框架,可以提高任何T2I扩散模型的空间理解能力。CoMPaSS通过面向空间约束配对(SCOP)数据引擎解决空间相关数据的模糊性问题,该引擎通过一系列有原则的空间约束来策划空间精确的训练数据。为了更好地利用精选的高质量空间先验知识,CoMPaSS还引入了Token ENcoding ORdering(TENOR)模块,允许更有效地利用高质量空间先验知识,有效地弥补了文本编码器的不足。在四个流行的开放权重T2I扩散模型上进行的广泛实验,涵盖了基于UNet和MMDiT的架构,证明了CoMPaSS的有效性。通过在空间关系生成方面设置新的最新技术,并在VISOR(+98%)、T2I-CompBench Spatial(+67%)和GenEval Position(+131%)等基准测试上实现相对较大的提升,证明了其效果。代码将在https://github.com/blurgyy/CoMPaSS上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 11 figures
Summary
文本到图像的扩散模型擅长生成逼真的图像,但在渲染文本提示中描述的空间关系时常常遇到困难。本研究识别出两个核心问题:1)现有数据集中空间相关数据的模糊性;2)当前文本编码器无法准确解释输入描述的空间语义。为了解决这些问题,提出了CoMPaSS,一个通用的训练框架,可增强任何T2I扩散模型的空间理解能力。CoMPaSS通过基于原则的空间约束解决空间相关数据的模糊性,并引入Token ENcoding ORdering(TENOR)模块,以更好地利用高质量的空间先验知识,有效弥补了文本编码器的不足。在四个流行的开放权重T2I扩散模型上的实验表明,CoMPaSS在生成空间关系方面的表现优异,并在VISOR(+98%)、T2I-CompBench Spatial(+67%)和GenEval Position(+131%)等基准测试中取得显著相对增益。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像的扩散模型在生成空间关系时存在困难。
- 现有数据集中空间相关数据的模糊性和文本编码器对空间语义的解读能力是主要挑战。
- CoMPaSS框架通过解决空间相关数据的模糊性和增强空间理解能力来改善模型性能。
- CoMPaSS使用Spatial Constraints-Oriented Pairing(SCOP)数据引擎和Token ENcoding ORdering(TENOR)模块来实现上述目标。
- CoMPaSS在多种测试和基准测试中表现出色,取得显著相对增益。
- 该框架适用于多种T2I扩散模型,包括UNet-和MMDiT-based架构。
点此查看论文截图



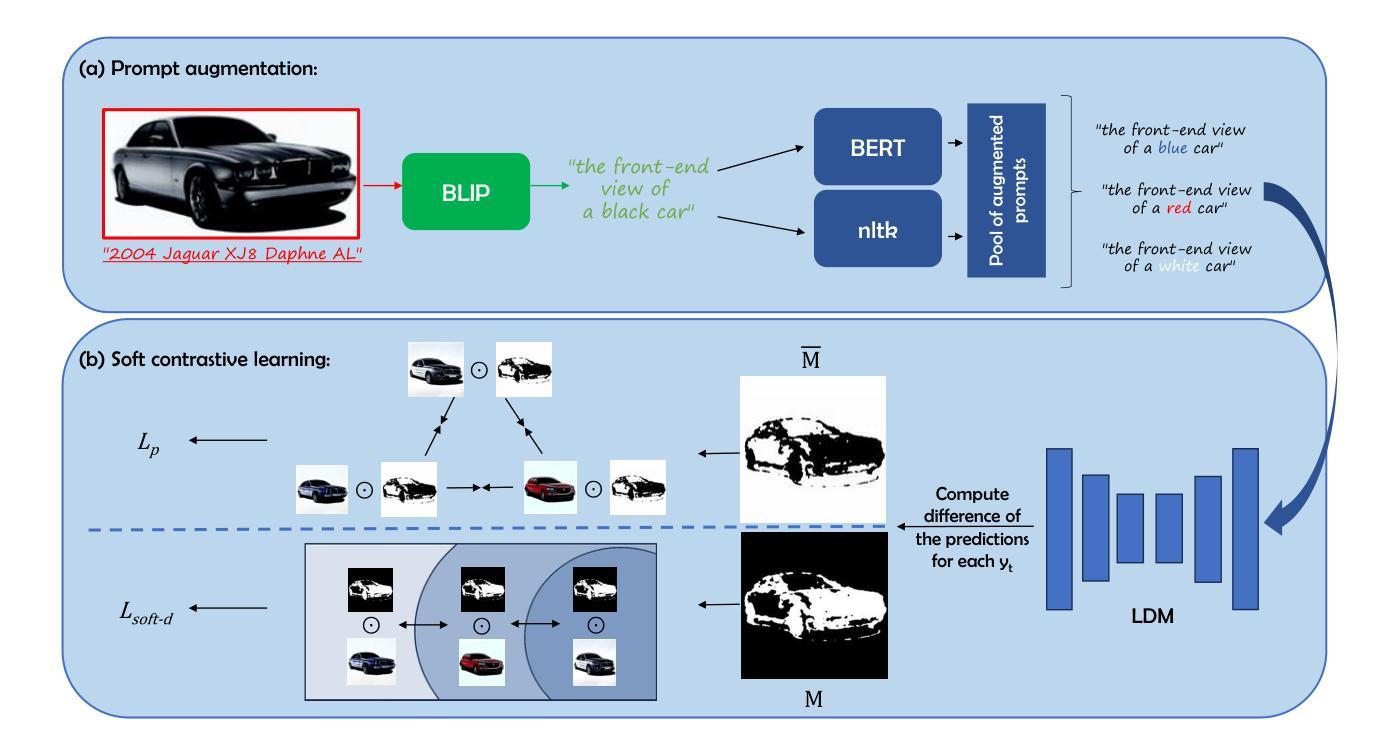
Prompt Augmentation for Self-supervised Text-guided Image Manipulation
Authors:Rumeysa Bodur, Binod Bhattarai, Tae-Kyun Kim
Text-guided image editing finds applications in various creative and practical fields. While recent studies in image generation have advanced the field, they often struggle with the dual challenges of coherent image transformation and context preservation. In response, our work introduces prompt augmentation, a method amplifying a single input prompt into several target prompts, strengthening textual context and enabling localised image editing. Specifically, we use the augmented prompts to delineate the intended manipulation area. We propose a Contrastive Loss tailored to driving effective image editing by displacing edited areas and drawing preserved regions closer. Acknowledging the continuous nature of image manipulations, we further refine our approach by incorporating the similarity concept, creating a Soft Contrastive Loss. The new losses are incorporated to the diffusion model, demonstrating improved or competitive image editing results on public datasets and generated images over state-of-the-art approaches.
文本引导的图像编辑在各种创意和实践领域都有应用。虽然最近的图像生成研究已经推动了该领域的发展,但它们经常面临一致的图像转换和上下文保留的双重挑战。针对这一问题,我们的工作引入了提示增强方法,该方法将单个输入提示放大为多个目标提示,增强了文本上下文并实现了局部图像编辑。具体来说,我们使用增强的提示来描绘预期的操纵区域。我们提出了一种针对驱动有效图像编辑的对比损失,通过位移编辑区域并将保留的区域拉近。考虑到图像操作的连续性,我们通过引入相似度的概念进一步改进了我们的方法,创建了软对比损失。新的损失被纳入到扩散模型中,在公共数据集和生成图像上的图像编辑结果有所改进或具有竞争力,超过了最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了文本引导的图像编辑技术在不同创意和实践领域的应用。针对图像生成中的挑战,本文提出了一种新的方法——提示增强法,通过放大单个输入提示为多个目标提示,强化文本上下文并实现局部图像编辑。具体来说,我们使用增强的提示来描绘预期的修改区域,并提出一种对比损失来驱动有效的图像编辑,通过位移编辑区域并拉近保留区域。考虑到图像操作的连续性,我们进一步通过引入相似性的概念完善了我们的方法,创建了软对比损失。新的损失被纳入扩散模型,在公共数据集和生成图像上展示了改进或具有竞争力的图像编辑结果。
Key Takeaways
- 文本引导的图像编辑技术广泛应用于创意和实践领域。
- 提示增强法能够强化文本上下文并实现局部图像编辑。
- 增强的提示被用于描绘预期的图像修改区域。
- 对比损失被用来驱动有效的图像编辑。
- 位移编辑区域并拉近保留区域以增强图像编辑效果。
- 考虑到图像操作的连续性,引入了相似性的概念以完善方法。
点此查看论文截图


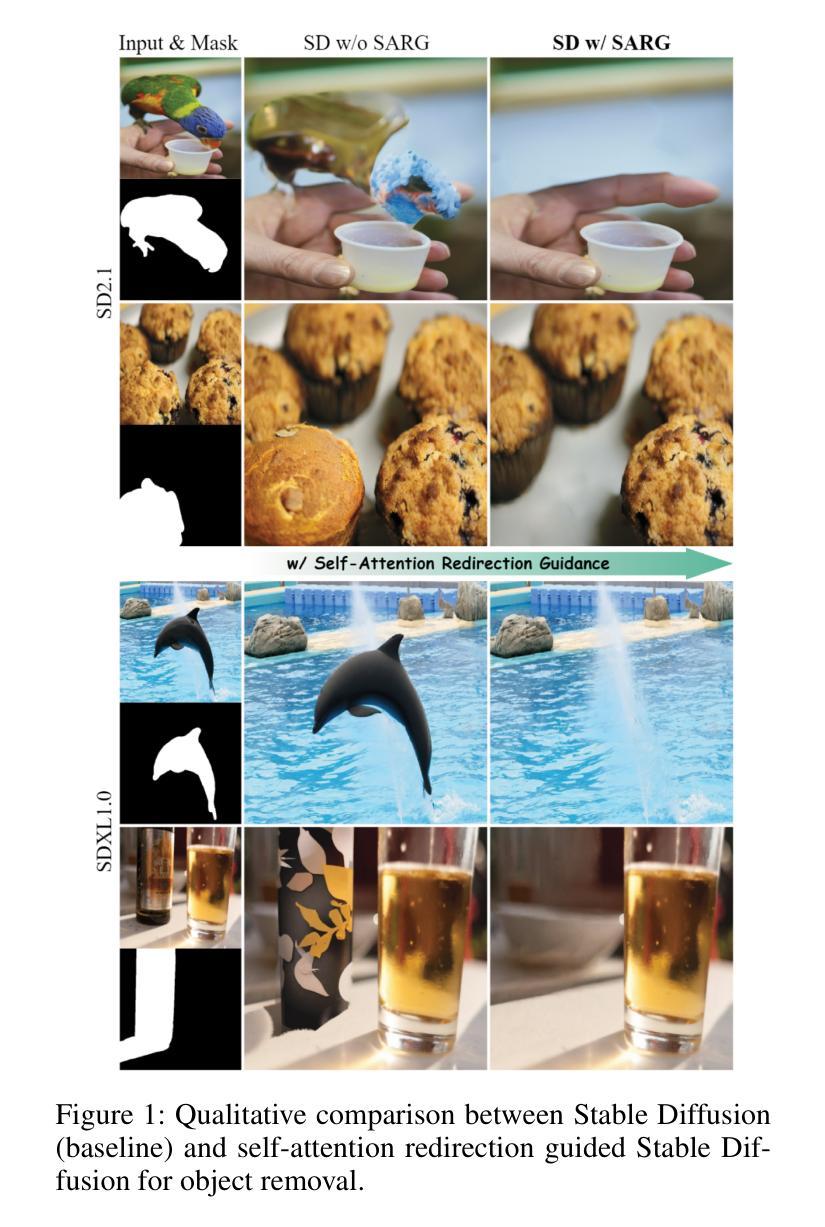
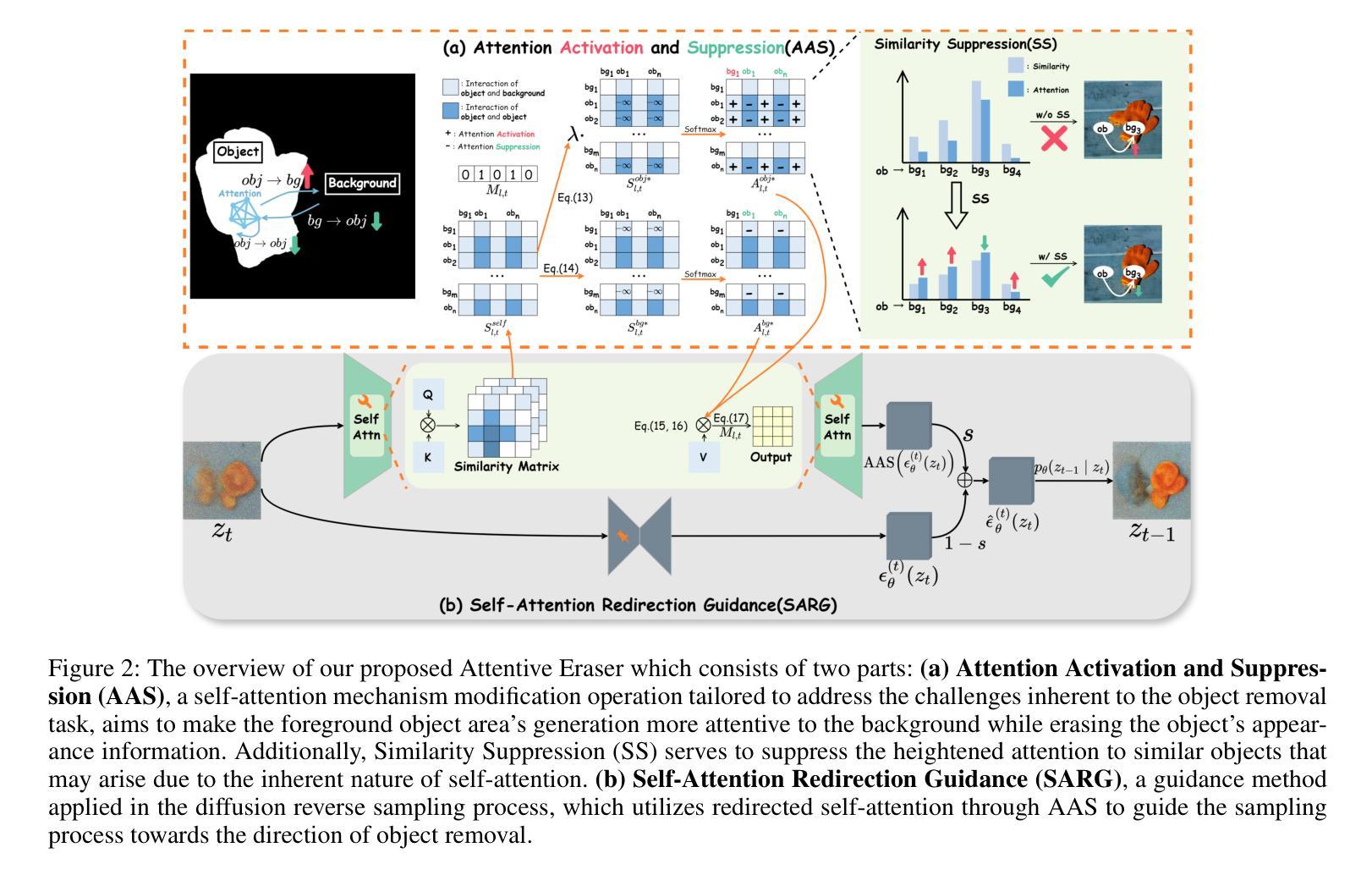
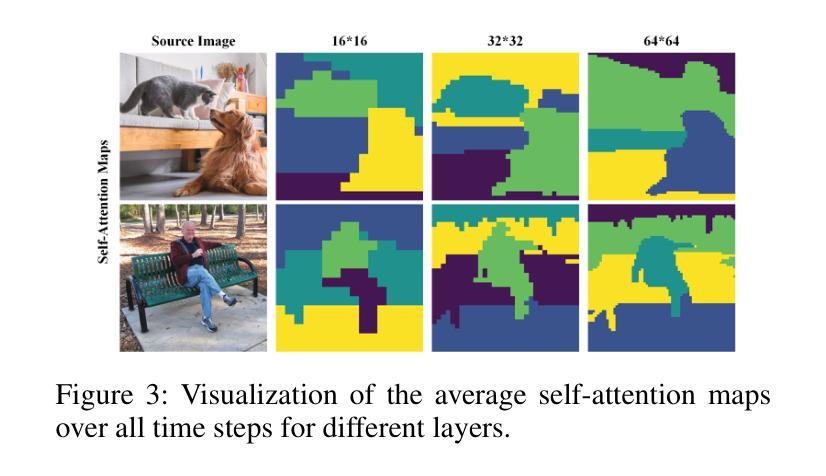
Attentive Eraser: Unleashing Diffusion Model’s Object Removal Potential via Self-Attention Redirection Guidance
Authors:Wenhao Sun, Benlei Cui, Xue-Mei Dong, Jingqun Tang
Recently, diffusion models have emerged as promising newcomers in the field of generative models, shining brightly in image generation. However, when employed for object removal tasks, they still encounter issues such as generating random artifacts and the incapacity to repaint foreground object areas with appropriate content after removal. To tackle these problems, we propose Attentive Eraser, a tuning-free method to empower pre-trained diffusion models for stable and effective object removal. Firstly, in light of the observation that the self-attention maps influence the structure and shape details of the generated images, we propose Attention Activation and Suppression (ASS), which re-engineers the self-attention mechanism within the pre-trained diffusion models based on the given mask, thereby prioritizing the background over the foreground object during the reverse generation process. Moreover, we introduce Self-Attention Redirection Guidance (SARG), which utilizes the self-attention redirected by ASS to guide the generation process, effectively removing foreground objects within the mask while simultaneously generating content that is both plausible and coherent. Experiments demonstrate the stability and effectiveness of Attentive Eraser in object removal across a variety of pre-trained diffusion models, outperforming even training-based methods. Furthermore, Attentive Eraser can be implemented in various diffusion model architectures and checkpoints, enabling excellent scalability. Code is available at https://github.com/Anonym0u3/AttentiveEraser.
最近,扩散模型作为生成模型领域的新晋者表现出色,尤其在图像生成方面。然而,当用于对象去除任务时,它们仍然面临一些问题,例如产生随机伪影和在去除后无法用适当内容重新绘制前景对象区域。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了“Attentive Eraser”,这是一种无需调整的方法,可以为预训练的扩散模型提供稳定有效的对象去除能力。首先,基于观察到自注意力图影响生成图像的结构和形状细节,我们提出了注意力激活和抑制(ASS),它根据给定的掩膜重新设计预训练扩散模型内的自注意力机制,从而在反向生成过程中优先处理背景而非前景对象。此外,我们引入了自注意力重定向指导(SARG),它利用ASS引导的自注意力来指导生成过程,有效地在掩膜内去除前景对象,同时生成既合理又连贯的内容。实验表明,Attentive Eraser在各种预训练的扩散模型中的对象去除表现稳定且有效,甚至超越了基于训练的方法。此外,Attentive Eraser可在各种扩散模型架构和检查点中实现,具有良好的可扩展性。代码可在https://github.com/Anonym0u3/AttentiveEraser处获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
扩散模型在生成模型领域崭露头角,尤其在图像生成方面表现出色。然而,在对象移除任务中,仍存在生成随机瑕疵和移除前景对象后无法重新绘制适当内容的问题。为此,提出无需调整的“Attentive Eraser”方法,使预训练的扩散模型能够进行稳定有效的对象移除。通过利用自我关注地图影响图像结构和形状细节的观察,提出基于给定掩膜的自我关注机制的激活和抑制(ASS),在反向生成过程中优先处理背景而非前景对象。此外,引入自我关注重定向指导(SARG),利用ASS重定向的自我关注来指导生成过程,在掩膜内有效移除前景对象,同时生成既合理又连贯的内容。实验表明,Attentive Eraser在多种预训练扩散模型中的对象移除表现稳定有效,甚至超越基于训练的方法。该方法可在各种扩散模型架构和检查点中实现,展现出卓越的可扩展性。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在图像生成领域展现出巨大潜力。
- 在对象移除任务中,扩散模型面临生成随机瑕疵和重新绘制问题。
- 提出Attentive Eraser方法,无需调整即可增强预训练扩散模型进行稳定有效的对象移除。
- 通过Attention Activation and Suppression (ASS)技术,优先处理背景信息,影响生成图像的结构和形状细节。
- 引入Self-Attention Redirection Guidance (SARG),有效移除前景对象并生成连贯内容。
- 实验证明Attentive Eraser在多种预训练扩散模型中的优异表现。
点此查看论文截图

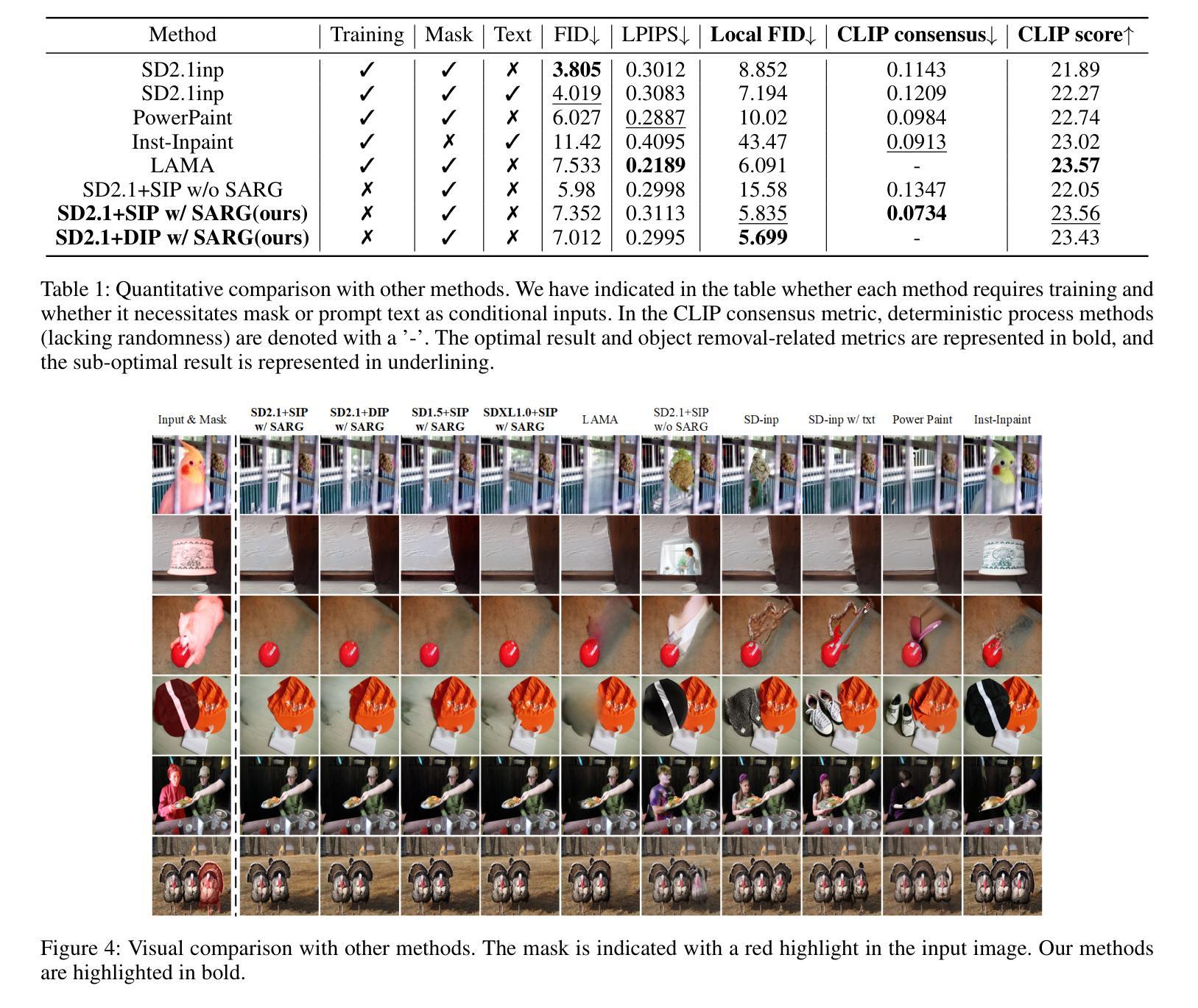

ArtAug: Enhancing Text-to-Image Generation through Synthesis-Understanding Interaction
Authors:Zhongjie Duan, Qianyi Zhao, Cen Chen, Daoyuan Chen, Wenmeng Zhou, Yaliang Li, Yingda Chen
The emergence of diffusion models has significantly advanced image synthesis. The recent studies of model interaction and self-corrective reasoning approach in large language models offer new insights for enhancing text-to-image models. Inspired by these studies, we propose a novel method called ArtAug for enhancing text-to-image models in this paper. To the best of our knowledge, ArtAug is the first one that improves image synthesis models via model interactions with understanding models. In the interactions, we leverage human preferences implicitly learned by image understanding models to provide fine-grained suggestions for image synthesis models. The interactions can modify the image content to make it aesthetically pleasing, such as adjusting exposure, changing shooting angles, and adding atmospheric effects. The enhancements brought by the interaction are iteratively fused into the synthesis model itself through an additional enhancement module. This enables the synthesis model to directly produce aesthetically pleasing images without any extra computational cost. In the experiments, we train the ArtAug enhancement module on existing text-to-image models. Various evaluation metrics consistently demonstrate that ArtAug enhances the generative capabilities of text-to-image models without incurring additional computational costs. The source code and models will be released publicly.
扩散模型的出现极大地推动了图像合成的发展。近期关于大型语言模型的模型交互和自我纠正推理方法的研究,为改进文本到图像的模型提供了新的见解。受这些研究的启发,我们在本文中提出了一种名为ArtAug的新型方法,用于增强文本到图像的模型。据我们所知,ArtAug是通过模型与理解模型的交互来改进图像合成模型的第一种方法。在交互过程中,我们利用图像理解模型隐含地学习人类偏好,为图像合成模型提供精细的建议。这些交互可以修改图像内容,使其具有美学感,例如调整曝光、改变拍摄角度和添加大气效果。通过额外的增强模块,这些交互带来的增强功能被迭代地融合到合成模型本身中。这使得合成模型能够直接生成具有美学感的图像,而无需任何额外的计算成本。在实验中,我们在现有的文本到图像模型上训练了ArtAug增强模块。各种评估指标一致表明,ArtAug在不增加额外计算成本的情况下提高了文本到图像模型的生成能力。源代码和模型将公开发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 18 pages, 8 figures
Summary
本文提出了利用大型语言模型的交互和自修正推理方法,提出一种名为ArtAug的新型图像合成增强方法。ArtAug通过模型交互利用图像理解模型的隐含人类偏好,为图像合成模型提供精细建议。这种交互能够修改图像内容,使其更具审美感,如调整曝光、拍摄角度和添加大气效果等。这种交互增强功能通过额外的增强模块迭代地融入合成模型本身,使得合成模型可直接生成具有美感的图像,无需额外的计算成本。实验证明,ArtAug对现有文本到图像模型的生成能力具有增强效果。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型的兴起已大大推动了图像合成的发展。
- 大型语言模型的交互和自修正推理方法为图像合成模型的改进提供了新的视角。
- ArtAug方法利用图像理解模型隐含的人类偏好,为图像合成模型提供精细建议。
- ArtAug能够通过修改图像内容使其更具审美感,如调整曝光、拍摄角度和大气效果等。
- ArtAug通过额外的增强模块将交互增强功能融入合成模型,无需额外计算成本。
- 实验证明ArtAug能有效提升文本到图像模型的生成能力。
- ArtAug的源代码和模型将公开发布。
点此查看论文截图


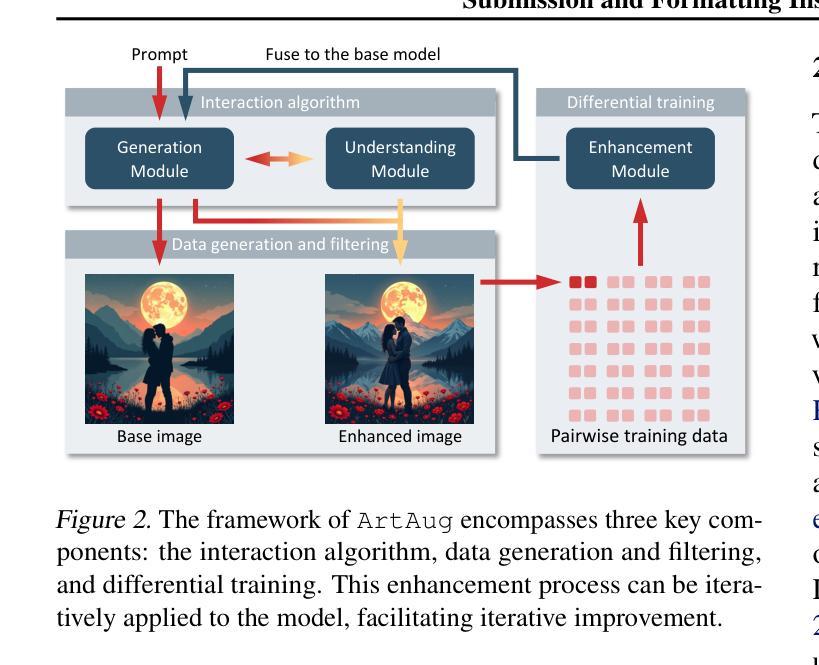

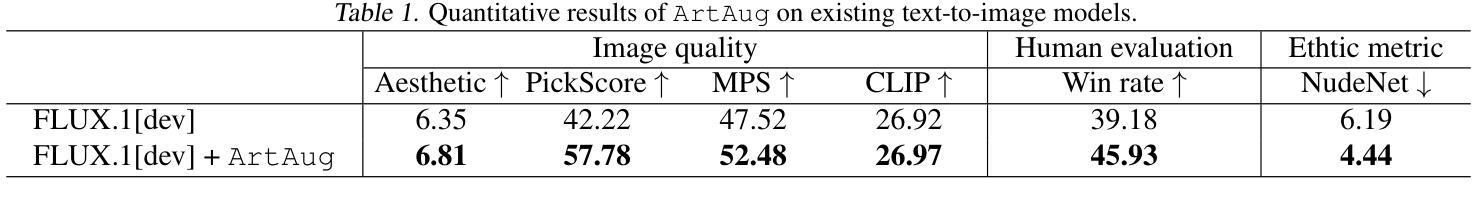
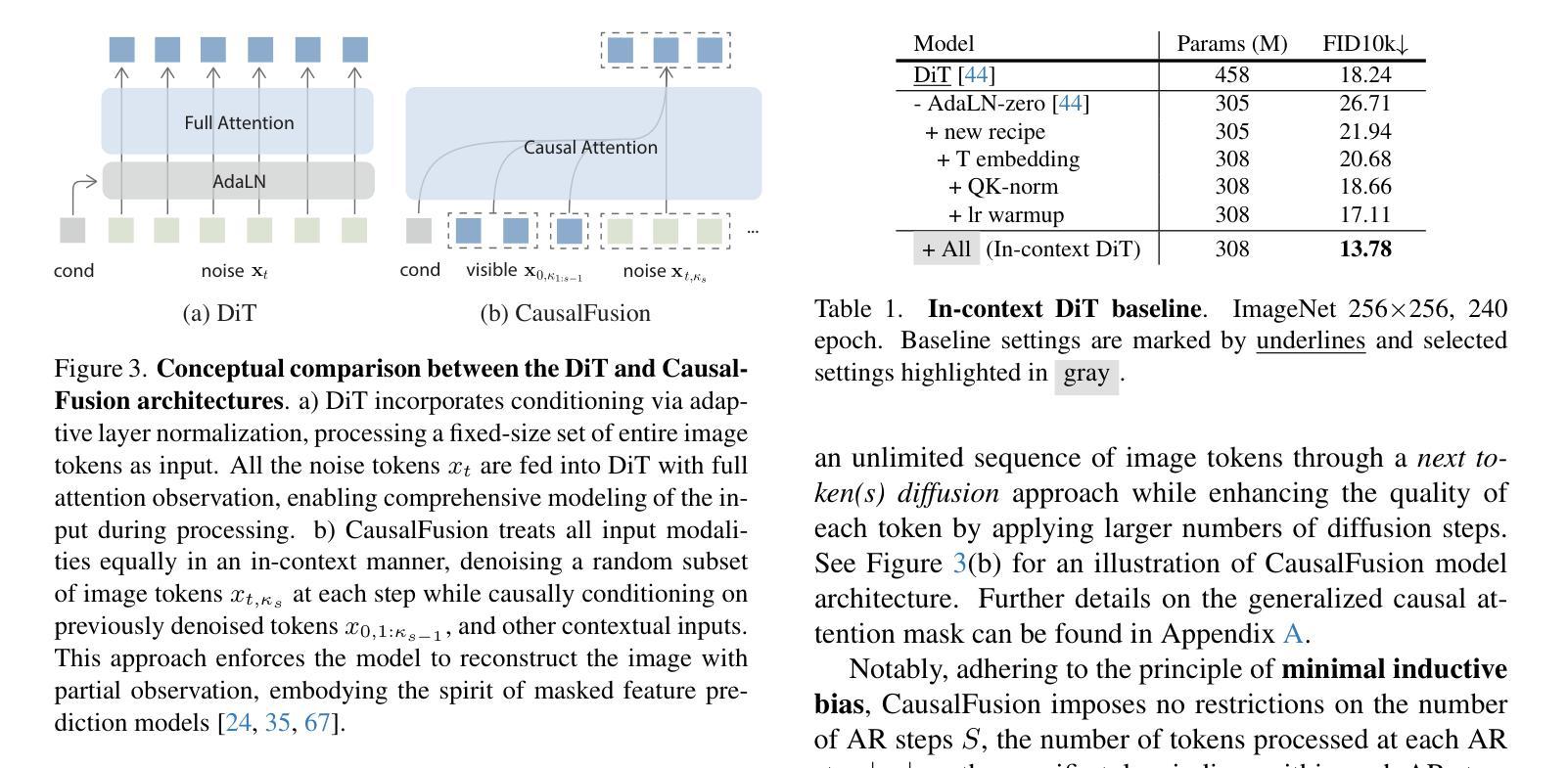
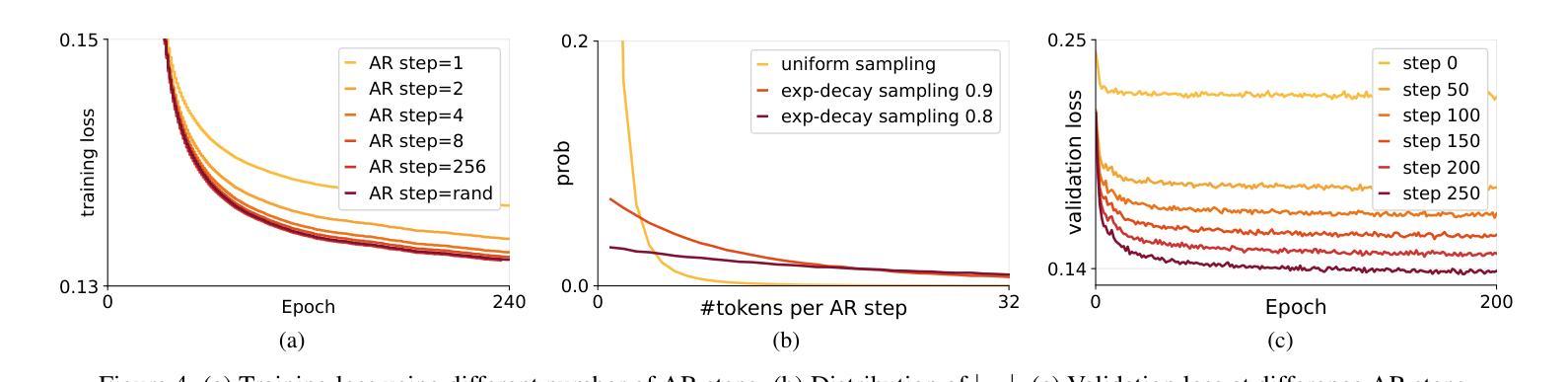
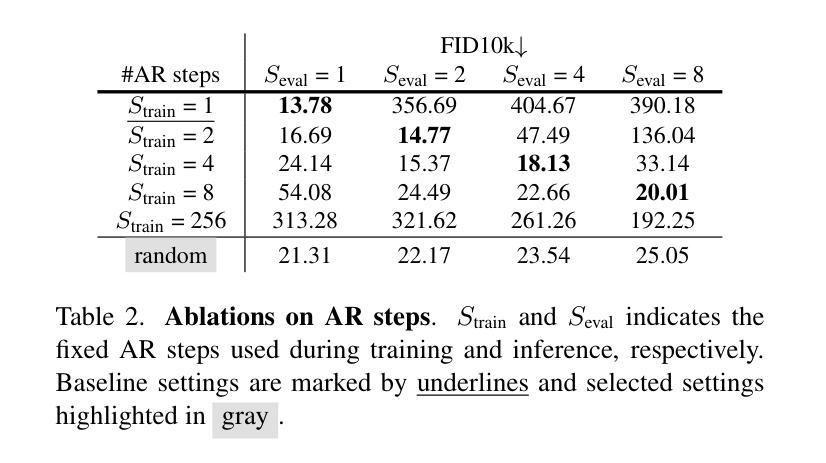
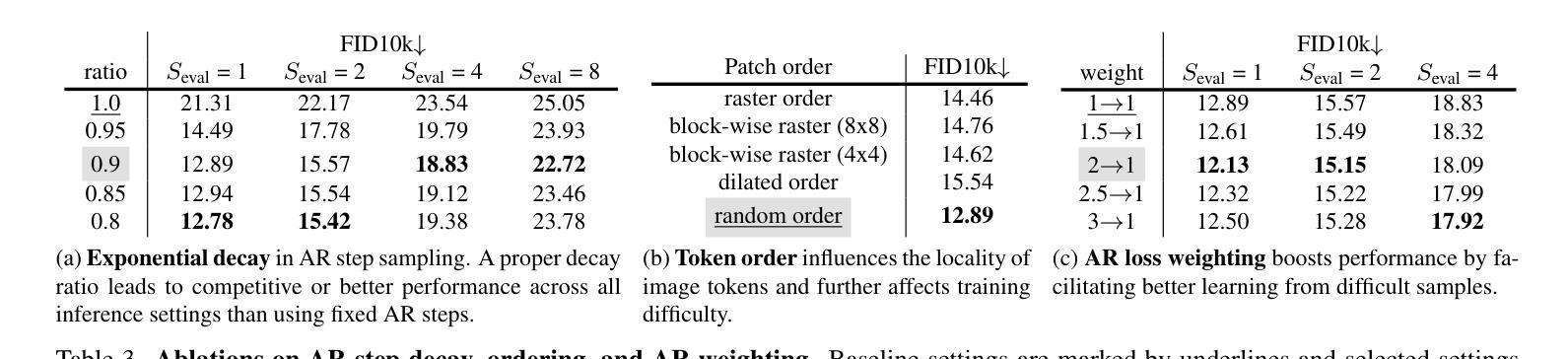
Causal Diffusion Transformers for Generative Modeling
Authors:Chaorui Deng, Deyao Zhu, Kunchang Li, Shi Guang, Haoqi Fan
We introduce Causal Diffusion as the autoregressive (AR) counterpart of Diffusion models. It is a next-token(s) forecasting framework that is friendly to both discrete and continuous modalities and compatible with existing next-token prediction models like LLaMA and GPT. While recent works attempt to combine diffusion with AR models, we show that introducing sequential factorization to a diffusion model can substantially improve its performance and enables a smooth transition between AR and diffusion generation modes. Hence, we propose CausalFusion - a decoder-only transformer that dual-factorizes data across sequential tokens and diffusion noise levels, leading to state-of-the-art results on the ImageNet generation benchmark while also enjoying the AR advantage of generating an arbitrary number of tokens for in-context reasoning. We further demonstrate CausalFusion’s multimodal capabilities through a joint image generation and captioning model, and showcase CausalFusion’s ability for zero-shot in-context image manipulations. We hope that this work could provide the community with a fresh perspective on training multimodal models over discrete and continuous data.
我们引入因果扩散(Causal Diffusion)作为扩散模型的自回归(AR)对应物。它是一种友好的下一个(或多个)令牌预测框架,适用于离散和连续模式,并与现有的下一个令牌预测模型(如LLaMA和GPT)兼容。尽管最近有研究表明尝试将扩散与AR模型相结合,但我们发现对扩散模型引入序列分解可以显著提高性能,并可以在AR和扩散生成模式之间实现平稳过渡。因此,我们提出了因果融合(CausalFusion)——一种仅解码的变压器,它在序列令牌和扩散噪声级别上双重分解数据,从而在ImageNet生成基准测试上取得了最新结果,同时享受AR生成任意数量令牌的上下文推理优势。我们进一步通过联合图像生成和描述模型来展示因果融合的多模式能力,并展示其在零镜头上下文图像操作中的能力。我们希望这项工作能为社区在离散和连续数据上训练多模式模型提供新的视角。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 figures, 21 pages
Summary
本文介绍了因果扩散(Causal Diffusion)作为扩散模型的自回归(AR)对应物。它是一种用于预测下一个或多个符号的框架,适用于离散和连续模态,并与现有的自回归预测模型(如LLaMA和GPT)兼容。本文展示了对扩散模型引入序列分解可以显著提高性能,并在自回归和扩散生成模式之间实现平稳过渡。因此,提出了因果融合(CausalFusion)——一种仅解码的变压器,它在序列标记和扩散噪声级别上双重分解数据,在ImageNet生成基准测试上取得了最新结果,并保留了自回归生成任意数量符号的上下文推理优势。此外,还展示了因果融合的多模式能力和零样本上下文图像操作能力。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍了因果扩散作为自回归模型的扩散模型的对应物。
- 因果扩散是一个用于预测下一个或多个符号的框架,适用于离散和连续模态。
- 现有的自回归预测模型(如LLaMA和GPT)与因果扩散兼容。
- 对扩散模型引入序列分解可以显著提高性能。
- 因果融合是一个仅解码的变压器,它在序列标记和扩散噪声级别上双重分解数据。
- 因果融合在ImageNet生成基准测试上取得了最新结果,同时具有自回归的优势。
- 因果融合具有多模式能力,展示了零样本上下文图像操作能力。
点此查看论文截图

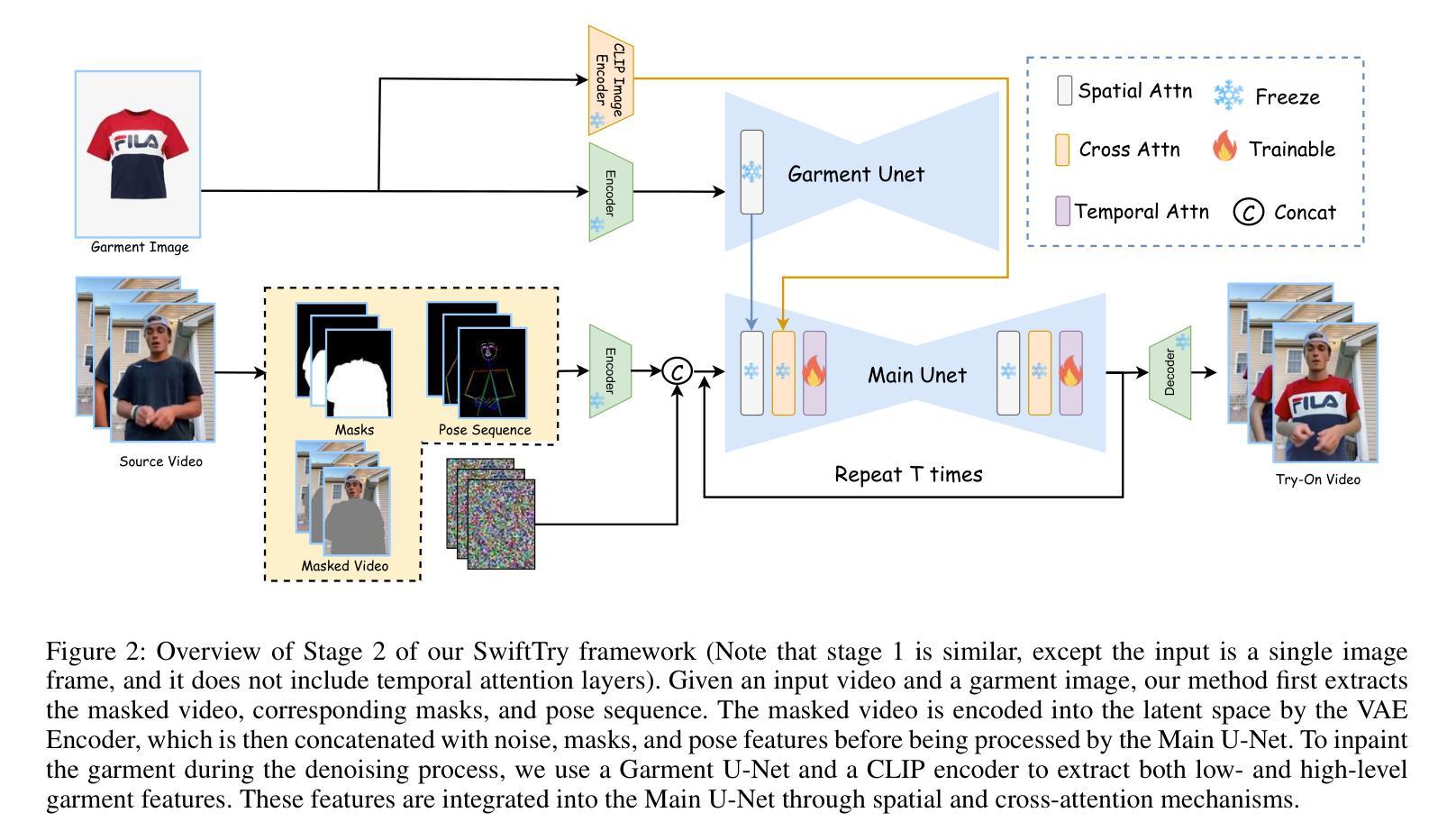
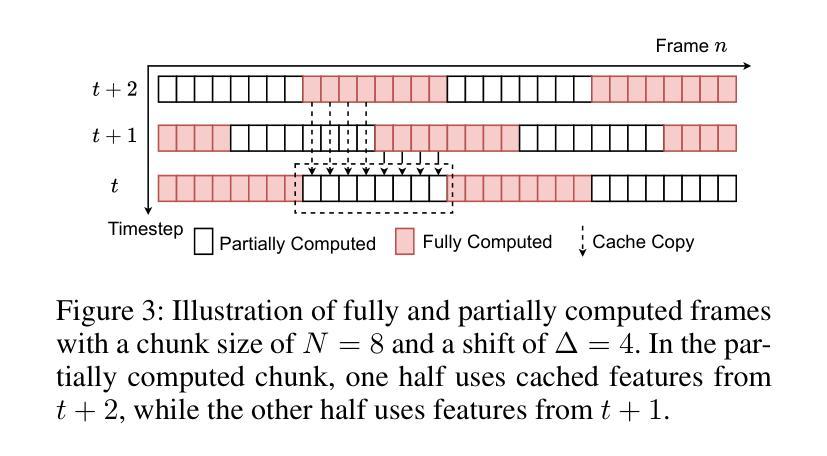
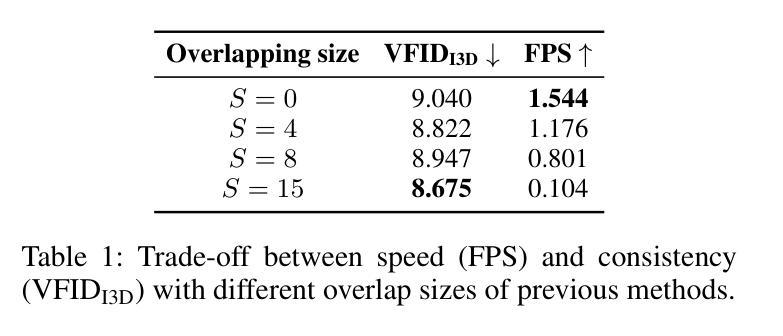
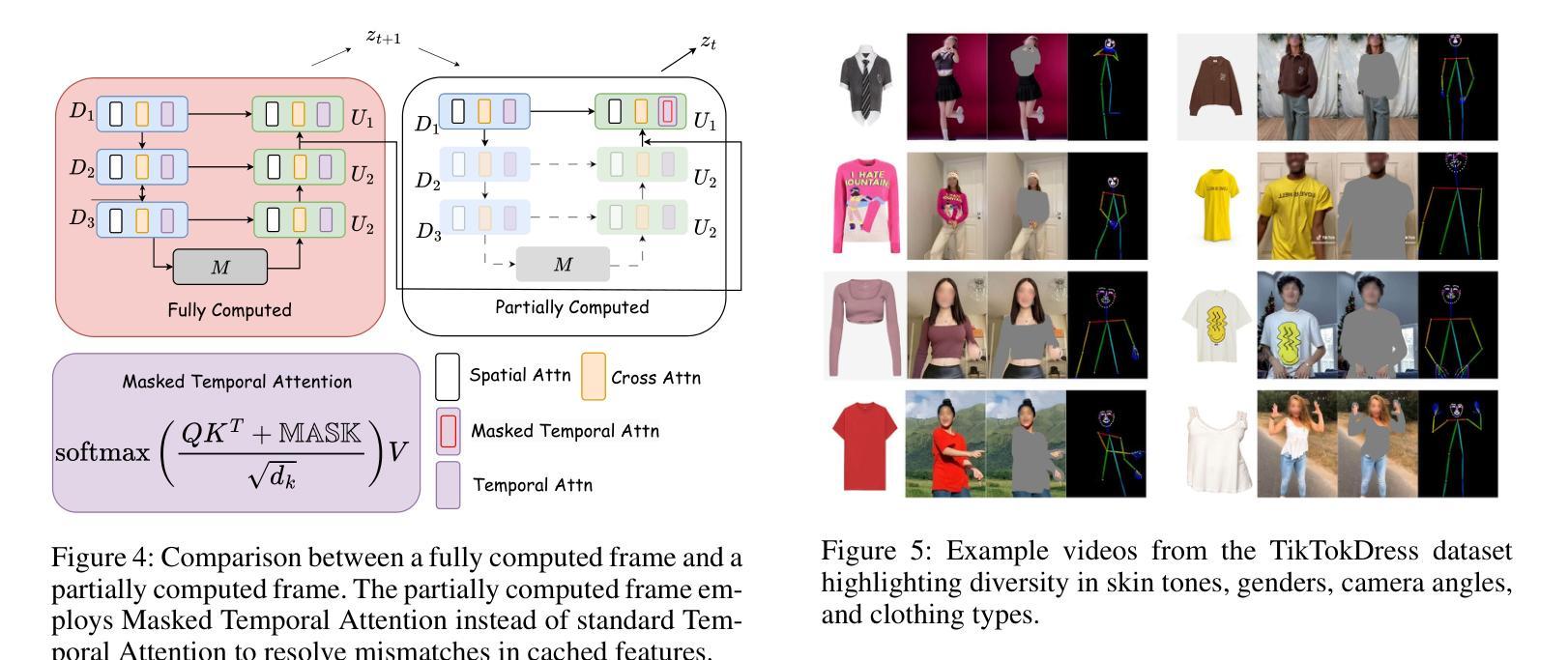
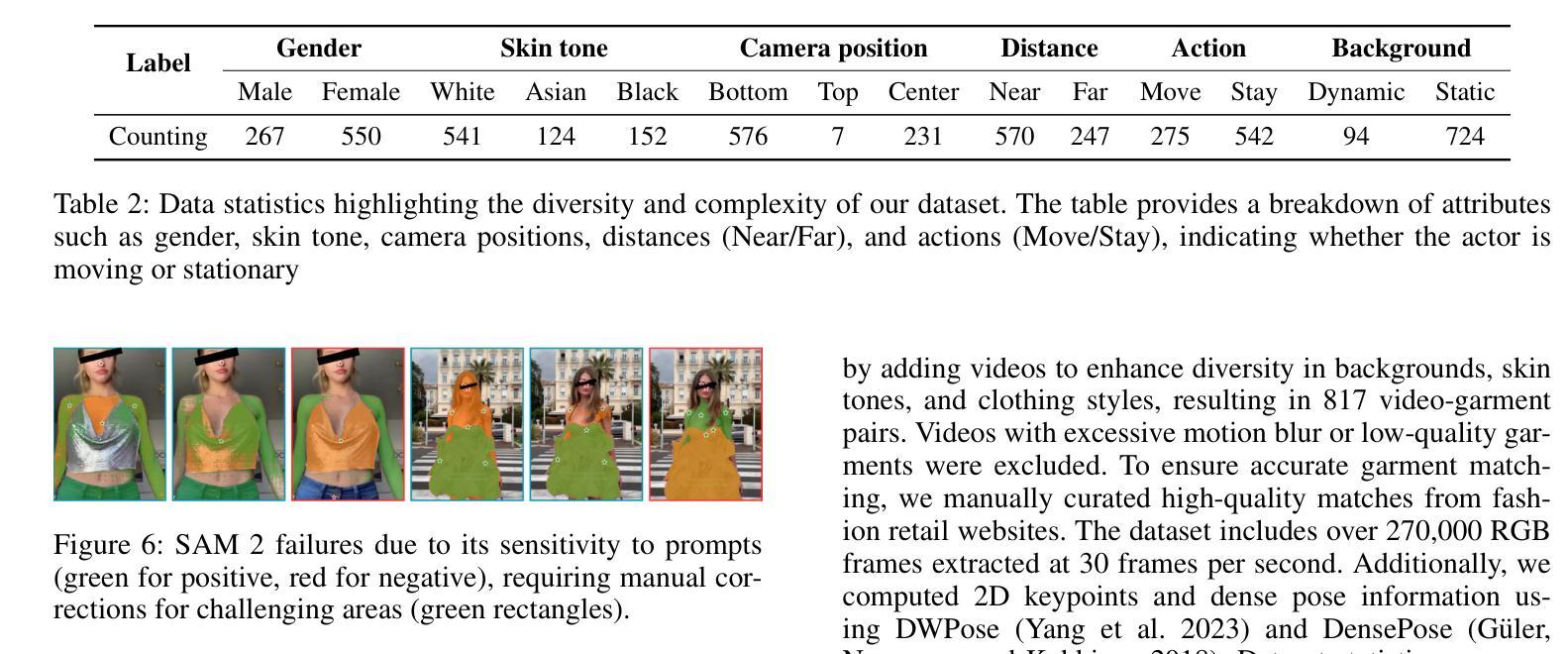
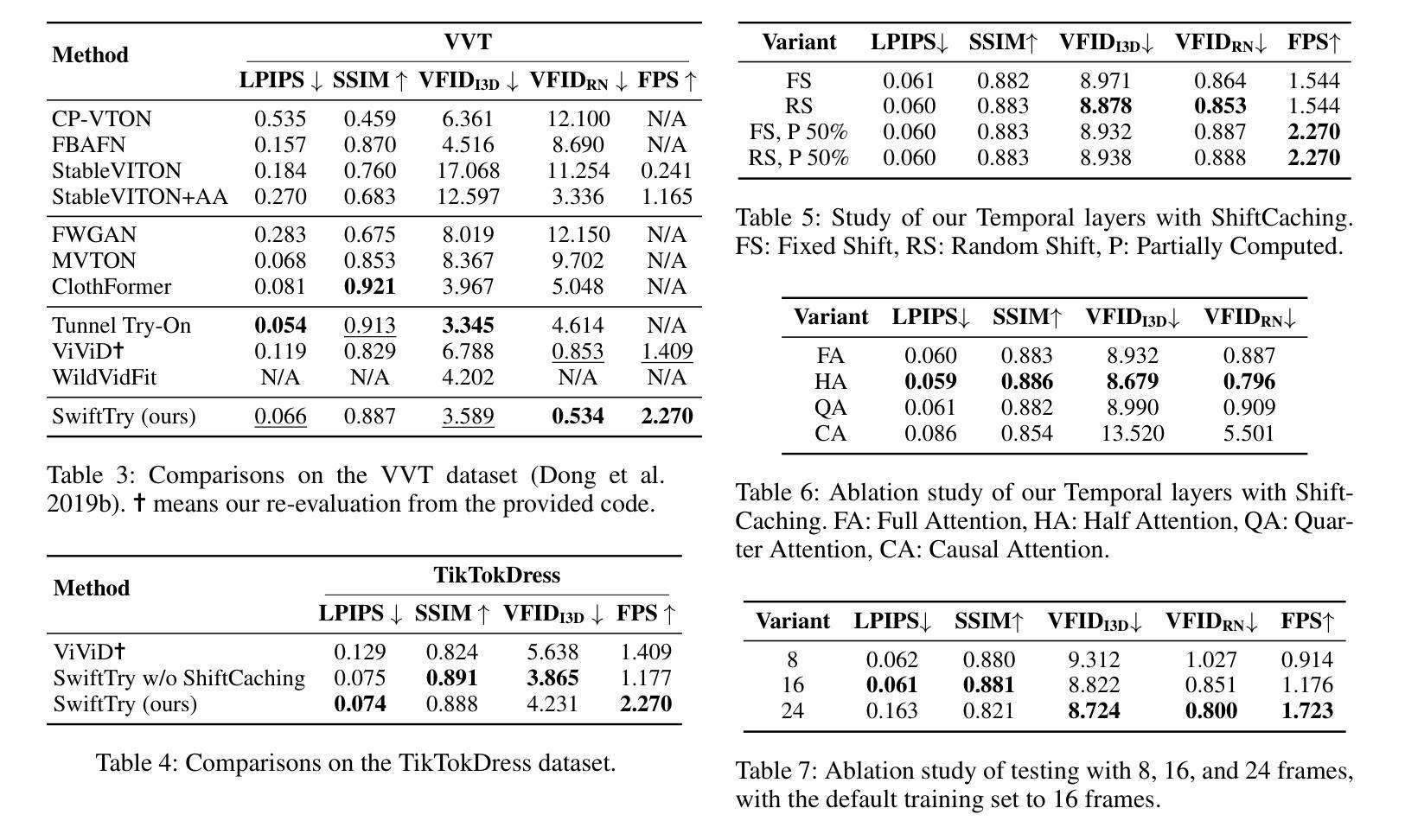
SwiftTry: Fast and Consistent Video Virtual Try-On with Diffusion Models
Authors:Hung Nguyen, Quang Qui-Vinh Nguyen, Khoi Nguyen, Rang Nguyen
Given an input video of a person and a new garment, the objective of this paper is to synthesize a new video where the person is wearing the specified garment while maintaining spatiotemporal consistency. Although significant advances have been made in image-based virtual try-on, extending these successes to video often leads to frame-to-frame inconsistencies. Some approaches have attempted to address this by increasing the overlap of frames across multiple video chunks, but this comes at a steep computational cost due to the repeated processing of the same frames, especially for long video sequences. To tackle these challenges, we reconceptualize video virtual try-on as a conditional video inpainting task, with garments serving as input conditions. Specifically, our approach enhances image diffusion models by incorporating temporal attention layers to improve temporal coherence. To reduce computational overhead, we propose ShiftCaching, a novel technique that maintains temporal consistency while minimizing redundant computations. Furthermore, we introduce the TikTokDress dataset, a new video try-on dataset featuring more complex backgrounds, challenging movements, and higher resolution compared to existing public datasets. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach outperforms current baselines, particularly in terms of video consistency and inference speed. The project page is available at https://swift-try.github.io/.
给定一个输入视频,其中包含一个人和一件新衣服,本文的目标是在保持时空一致性的情况下,合成一个新的视频,其中人物穿着指定的服装。尽管基于图像的虚拟试衣已经取得了重大进展,但这些成功往往难以扩展到视频领域,因为这经常导致帧之间的不一致性。一些方法试图通过增加跨越多个视频片段的帧重叠来解决这个问题,但由于重复处理相同的帧,特别是在处理长视频序列时,这带来了高昂的计算成本。为了应对这些挑战,我们将视频虚拟试衣重新定位为条件视频填充任务,服装作为输入条件。具体来说,我们的方法通过结合时间注意力层来提高图像扩散模型的性能,从而提高时间连贯性。为了减少计算开销,我们提出了ShiftCaching这一新技术,该技术能在保持时间一致性的同时最小化冗余计算。此外,我们还引入了TikTokDress数据集,这是一个新的视频试穿数据集,具有更复杂的背景、更具挑战性的动作和更高的分辨率。大量实验表明,我们的方法优于当前基线方法,特别是在视频一致性和推理速度方面。项目页面可在[https://swift-try.github.io/]上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文旨在合成一个新视频,展示人物穿上指定衣物的同时保持时空一致性。为提高视频连贯性并降低计算成本,研究团队将视频虚拟试衣视为条件视频修复任务,通过引入时间注意力层改进图像扩散模型,并提出ShiftCaching技术减少冗余计算。此外,引入TikTokDress数据集,与现有公开数据集相比,背景更复杂、动作更具挑战性且分辨率更高。实验证明,该方法在视频一致性和推理速度方面均优于当前基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 本文的目标是根据输入的人物视频和新的衣物,合成一个展示人物穿上新衣物的视频,同时保持时空一致性。
- 尽管图像虚拟试衣已经取得了显著进展,但将其扩展到视频时仍面临帧间不一致的问题。
- 研究人员将视频虚拟试衣重新构想为条件视频修复任务,其中衣物作为输入条件。
- 通过引入时间注意力层改进图像扩散模型,以提高视频连贯性。
- 提出ShiftCaching技术来减少冗余计算,提高效率。
- 引入TikTokDress数据集,包含更复杂的背景、挑战性和更高分辨率的视频内容。
点此查看论文截图

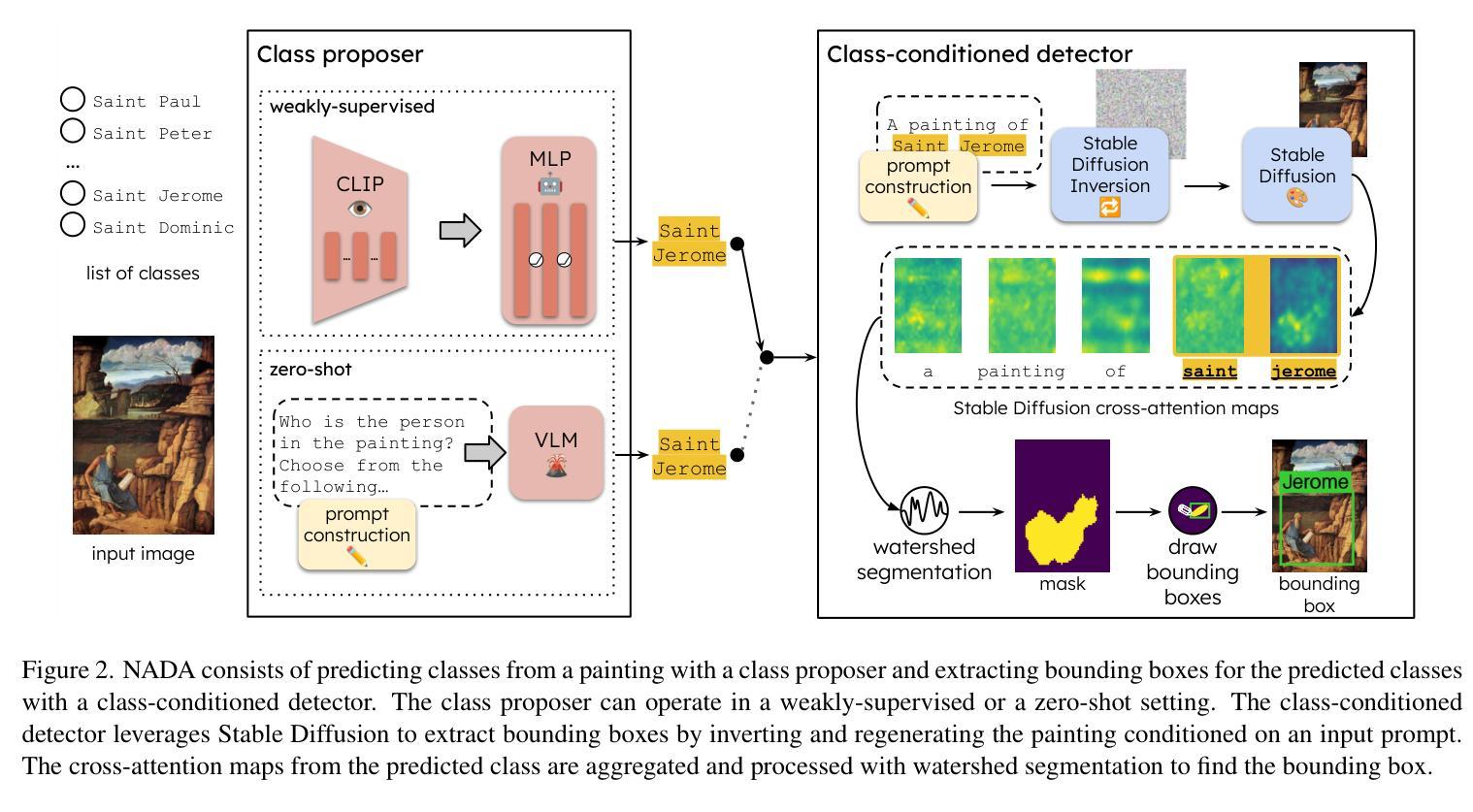
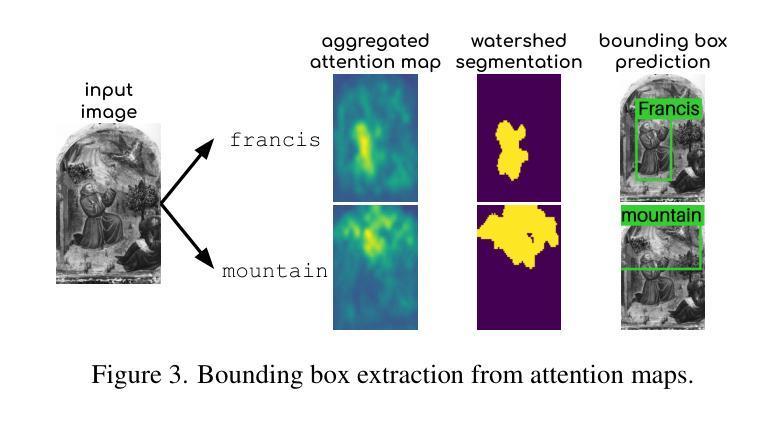
No Annotations for Object Detection in Art through Stable Diffusion
Authors:Patrick Ramos, Nicolas Gonthier, Selina Khan, Yuta Nakashima, Noa Garcia
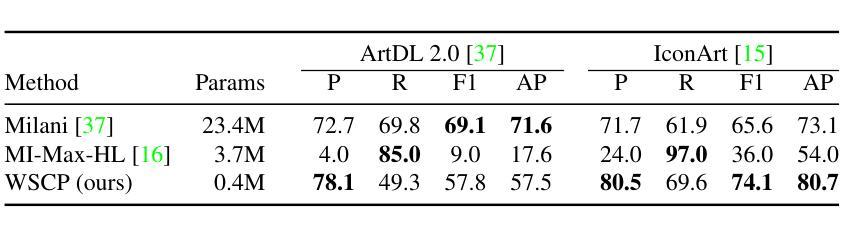
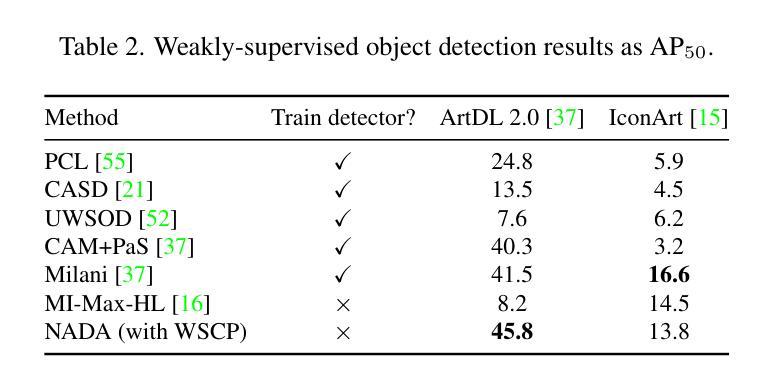
Object detection in art is a valuable tool for the digital humanities, as it allows for faster identification of objects in artistic and historical images compared to humans. However, annotating such images poses significant challenges due to the need for specialized domain expertise. We present NADA (no annotations for detection in art), a pipeline that leverages diffusion models’ art-related knowledge for object detection in paintings without the need for full bounding box supervision. Our method, which supports both weakly-supervised and zero-shot scenarios and does not require any fine-tuning of its pretrained components, consists of a class proposer based on large vision-language models and a class-conditioned detector based on Stable Diffusion. NADA is evaluated on two artwork datasets, ArtDL 2.0 and IconArt, outperforming prior work in weakly-supervised detection, while being the first work for zero-shot object detection in art. Code is available at https://github.com/patrick-john-ramos/nada
艺术品中的目标检测是数字人文领域的一个重要工具,因为它与人类相比,可以更快速地识别艺术和历史图像中的目标。然而,对这些图像进行标注却面临重大挑战,因为需要专业的领域知识。我们提出了NADA(艺术品检测无需标注),这是一种利用扩散模型的与艺术相关的知识,在绘画中进行目标检测,无需完整的边界框监督。我们的方法支持弱监督和无源场景,并且不需要对其预训练组件进行任何微调,它由基于大型视觉语言模型的类提出者和基于Stable Diffusion的类条件检测器组成。NADA在两个艺术品数据集ArtDL 2.0和IconArt上进行了评估,在弱监督检测方面优于先前的工作,同时是艺术品零样本目标检测的首项工作。代码可在https://github.com/patrick-john-ramos/nada找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 6 figures, to be published in WACV 2025
Summary
本文介绍了艺术领域中的物体检测工具的重要性,它能够快速识别艺术和历史图像中的物体。然而,由于需要特定的专业知识,对这类图像进行标注具有挑战性。研究人员提出了一种利用扩散模型的无需全框监督的绘画检测方案——NADA(无需标注进行艺术检测)。该方法支持弱监督和无源场景,无需对其预训练组件进行微调,包括基于大型视觉语言模型的类提出器和基于Stable Diffusion的类条件检测器。在ArtDL 2.0和IconArt两个艺术品数据集上,NADA的表现超越了现有的弱监督检测方法,同时也是第一个在无源艺术领域实现物体检测的。完整代码可以在GitHub上找到。
Key Takeaways
- 艺术领域的物体检测工具可以快速识别艺术和历史图像中的物体,具有实用价值。
- 对艺术图像进行标注需要特定的专业知识,具有挑战性。
- NADA是一种利用扩散模型进行艺术检测的解决方案,无需全框监督。
- NADA支持弱监督和无源场景的应用。
- NADA不需要对其预训练组件进行微调。
- NADA包括基于大型视觉语言模型的类提出器和基于Stable Diffusion的类条件检测器。
点此查看论文截图

MFTF: Mask-free Training-free Object Level Layout Control Diffusion Model
Authors:Shan Yang
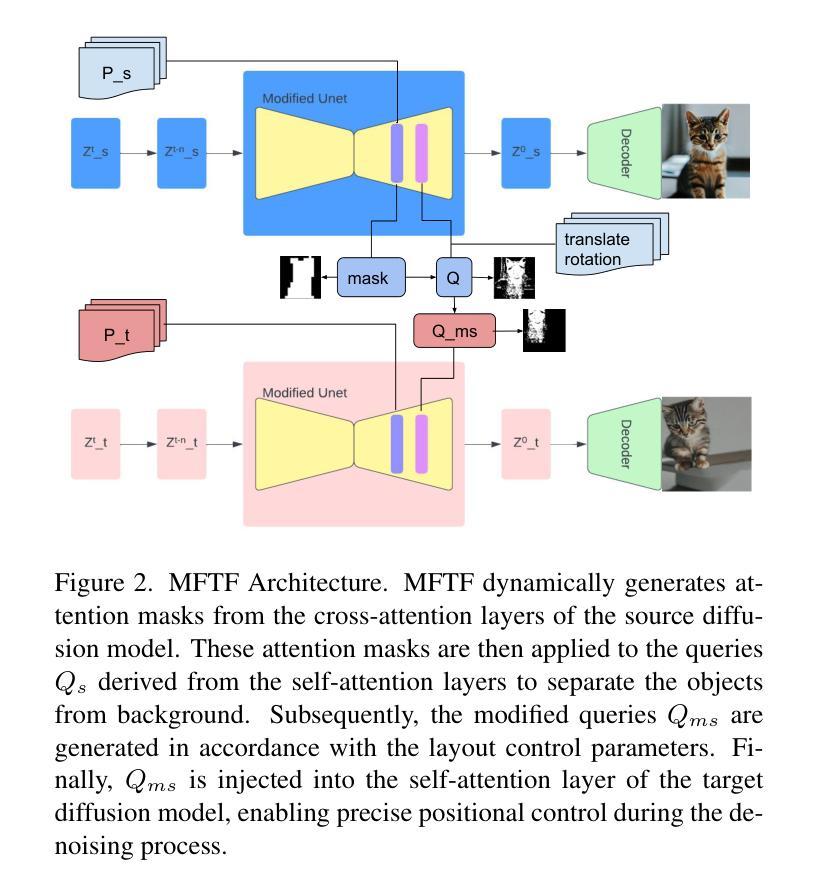
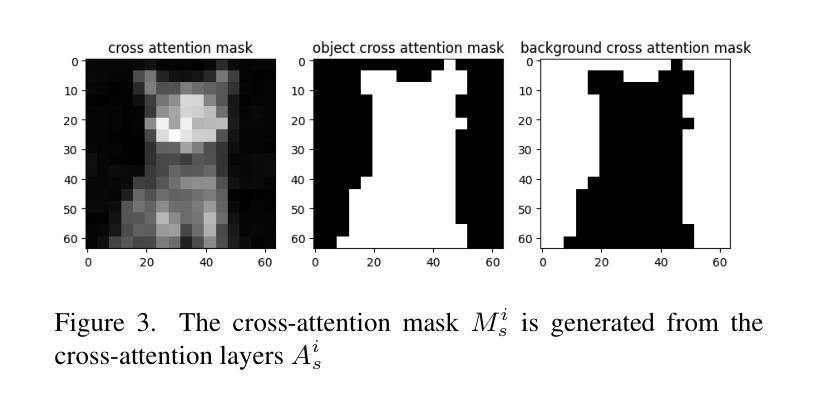
Text-to-image generation models have revolutionized content creation, but diffusion-based vision-language models still face challenges in precisely controlling the shape, appearance, and positional placement of objects in generated images using text guidance alone. Existing global image editing models rely on additional masks or images as guidance to achieve layout control, often requiring retraining of the model. While local object-editing models allow modifications to object shapes, they lack the capability to control object positions. To address these limitations, we propose the Mask-free Training-free Object-Level Layout Control Diffusion Model (MFTF), which provides precise control over object positions without requiring additional masks or images. The MFTF model supports both single-object and multi-object positional adjustments, such as translation and rotation, while enabling simultaneous layout control and object semantic editing. The MFTF model employs a parallel denoising process for both the source and target diffusion models. During this process, attention masks are dynamically generated from the cross-attention layers of the source diffusion model and applied to queries from the self-attention layers to isolate objects. These queries, generated in the source diffusion model, are then adjusted according to the layout control parameters and re-injected into the self-attention layers of the target diffusion model. This approach ensures accurate and precise positional control of objects. Project source code available at https://github.com/syang-genai/MFTF.
文本到图像生成模型已经彻底改变了内容创作的方式,但基于扩散的视语言模型在仅使用文本指导来精确控制生成图像中物体的形状、外观和位置放置方面仍面临挑战。现有的全局图像编辑模型依赖于额外的蒙版或图像作为指导来实现布局控制,通常需要重新训练模型。虽然局部物体编辑模型允许修改物体形状,但它们缺乏控制物体位置的能力。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了无蒙版、无需训练的物体级别布局控制扩散模型(MFTF),该模型能够在无需额外蒙版或图像的情况下,精确控制物体的位置。MFTF模型既支持单物体也支持多物体的位置调整,如平移和旋转,同时实现布局控制和物体语义编辑。MFTF模型采用源和目标扩散模型的并行去噪过程。在此过程中,从源扩散模型的交叉注意层动态生成注意蒙版,并应用于自我注意层的查询以隔离物体。这些在源扩散模型中生成的查询会根据布局控制参数进行调整,然后重新注入目标扩散模型的自我注意层。这种方法确保了物体的精确位置控制。项目源代码可在https://github.com/syang-genai/MFTF找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 7 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种无需掩膜和训练的对象级布局控制扩散模型(MFTF),该模型可在无需额外掩膜或图像的情况下,实现对生成图像中对象的形状、外观和位置进行精确控制。MFTF模型支持单对象和多对象的位置调整,如平移和旋转,同时实现布局控制和对象语义编辑。
Key Takeaways
- 扩散模型在内容创建中实现了文本到图像的生成,但仍面临精确控制对象形状、外观和位置的挑战。
- 现有全局图像编辑模型依赖额外的掩膜或图像作为指导来实现布局控制,需要重训模型。
- 局部对象编辑模型允许修改对象形状,但无法控制对象位置。
- 提出的MFTF模型提供了对对象位置的精确控制,无需额外的掩膜或图像。
- MFTF模型支持单对象和多对象的位置调整,如平移和旋转,同时实现布局控制和对象语义编辑。
- MFTF模型采用并行去噪过程,通过交叉注意层生成注意力掩膜,应用于自我注意层的查询,以隔离对象。
点此查看论文截图


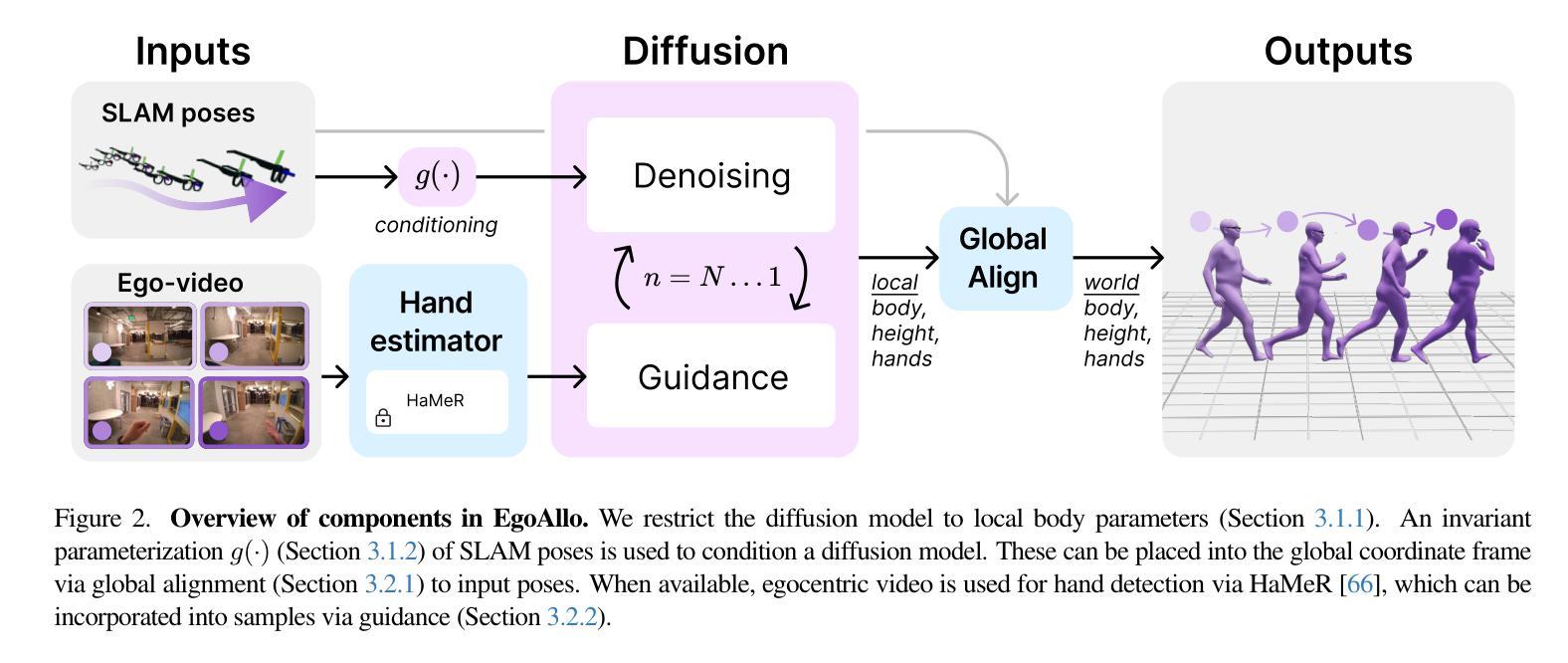
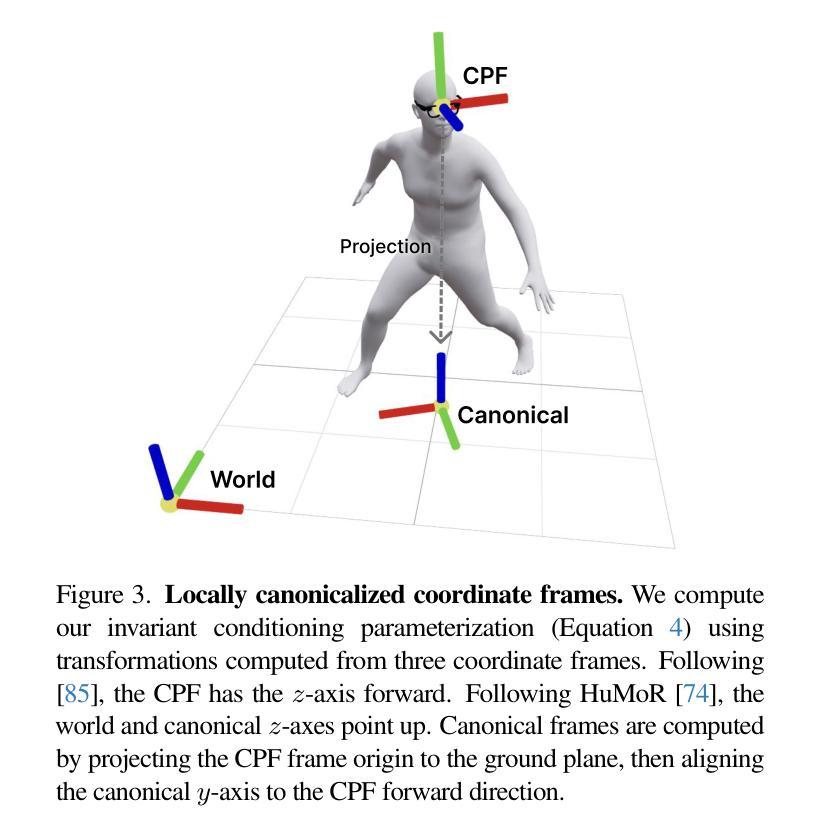
Estimating Body and Hand Motion in an Ego-sensed World
Authors:Brent Yi, Vickie Ye, Maya Zheng, Yunqi Li, Lea Müller, Georgios Pavlakos, Yi Ma, Jitendra Malik, Angjoo Kanazawa
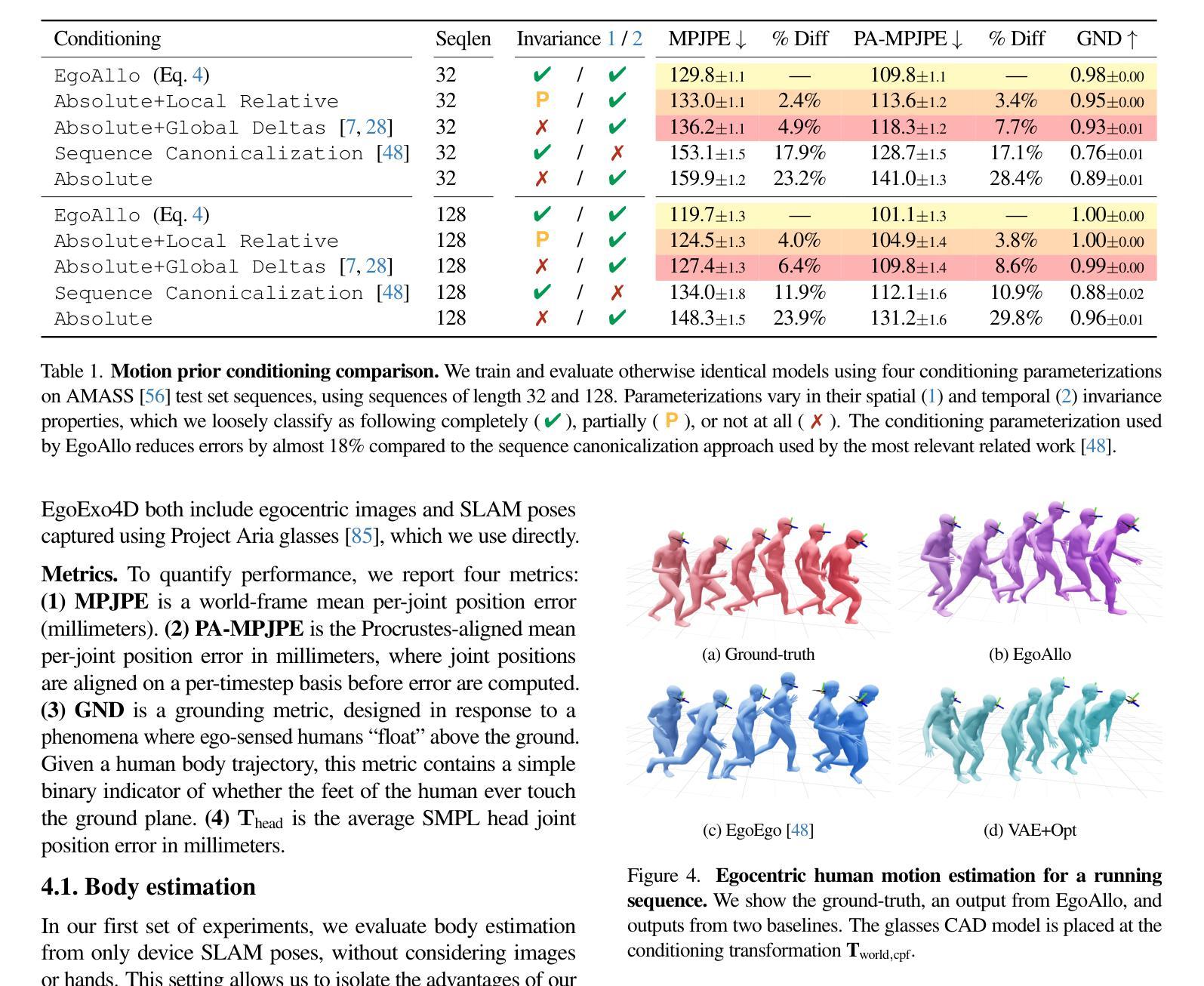
We present EgoAllo, a system for human motion estimation from a head-mounted device. Using only egocentric SLAM poses and images, EgoAllo guides sampling from a conditional diffusion model to estimate 3D body pose, height, and hand parameters that capture a device wearer’s actions in the allocentric coordinate frame of the scene. To achieve this, our key insight is in representation: we propose spatial and temporal invariance criteria for improving model performance, from which we derive a head motion conditioning parameterization that improves estimation by up to 18%. We also show how the bodies estimated by our system can improve hand estimation: the resulting kinematic and temporal constraints can reduce world-frame errors in single-frame estimates by 40%. Project page: https://egoallo.github.io/
我们介绍了EgoAllo系统,该系统通过头戴设备实现人体运动估计。仅使用以自我为中心的SLAM姿势和图像,EgoAllo指导从条件扩散模型中进行采样,以估计三维身体姿势、高度和手部参数,这些参数能够捕获设备佩戴者在场景的中心坐标系中的动作。为实现这一点,我们的关键见解在于表示:我们提出了空间和时间不变性标准以提高模型性能,由此得出头部运动条件参数化,可提高估计精度达18%。我们还展示了我们的系统估计的躯体如何改进手部估计:由此产生的运动学和时间约束可减少单帧估计中的世界框架误差达40%。项目页面:https://egoallo.github.io/
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://egoallo.github.io/
Summary:
我们推出了EgoAllo系统,该系统通过头戴设备实现人体动作估计。仅使用以自我为中心的SLAM姿态和图像,EgoAllo引导从条件扩散模型中进行采样,以估计三维身体姿态、高度以及手部参数,这些参数捕捉设备佩戴者在场景中的以场景为中心的坐标框架中的动作。我们的关键见解在于表示法:我们提出空间和时间不变性标准以提高模型性能,从中得出头部运动条件参数化,可提高估计精度达18%。我们还展示了我们的系统估计的躯体如何改善手部估计:由此产生的运动学和时间约束可减少单帧估计中的世界框架误差达40%。
Key Takeaways:
- EgoAllo系统利用头戴设备实现人体动作估计。
- 仅使用以自我为中心的SLAM姿态和图像进行动作估计。
- 通过条件扩散模型采样来估计三维身体姿态、高度和手部参数。
- 系统的关键在于提出空间和时间不变性标准来提高模型性能。
- 头部运动条件参数化能提高估计精度达18%。
- 躯体估计可改善手部估计。
点此查看论文截图

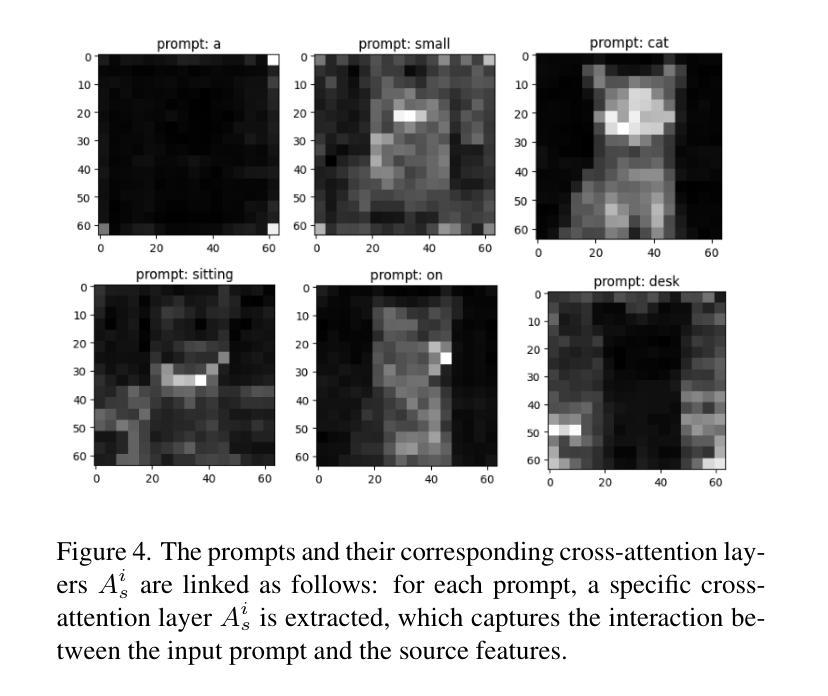
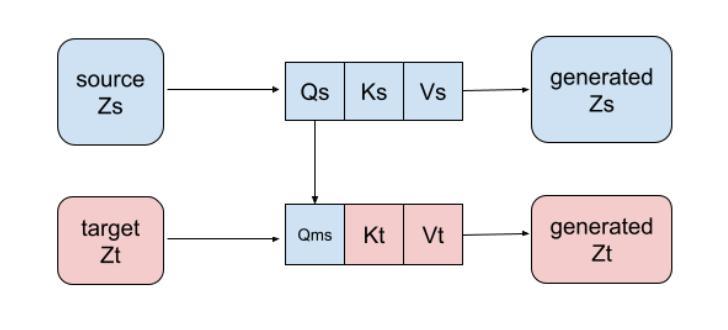
Resolving Multi-Condition Confusion for Finetuning-Free Personalized Image Generation
Authors:Qihan Huang, Siming Fu, Jinlong Liu, Hao Jiang, Yipeng Yu, Jie Song
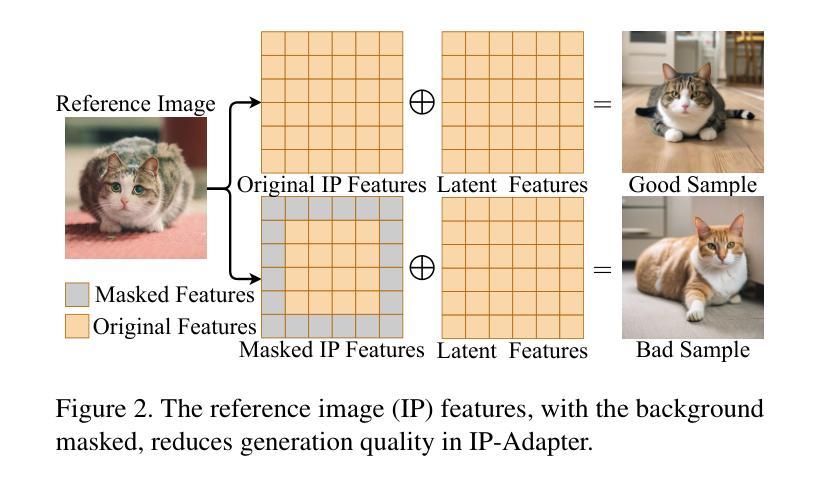
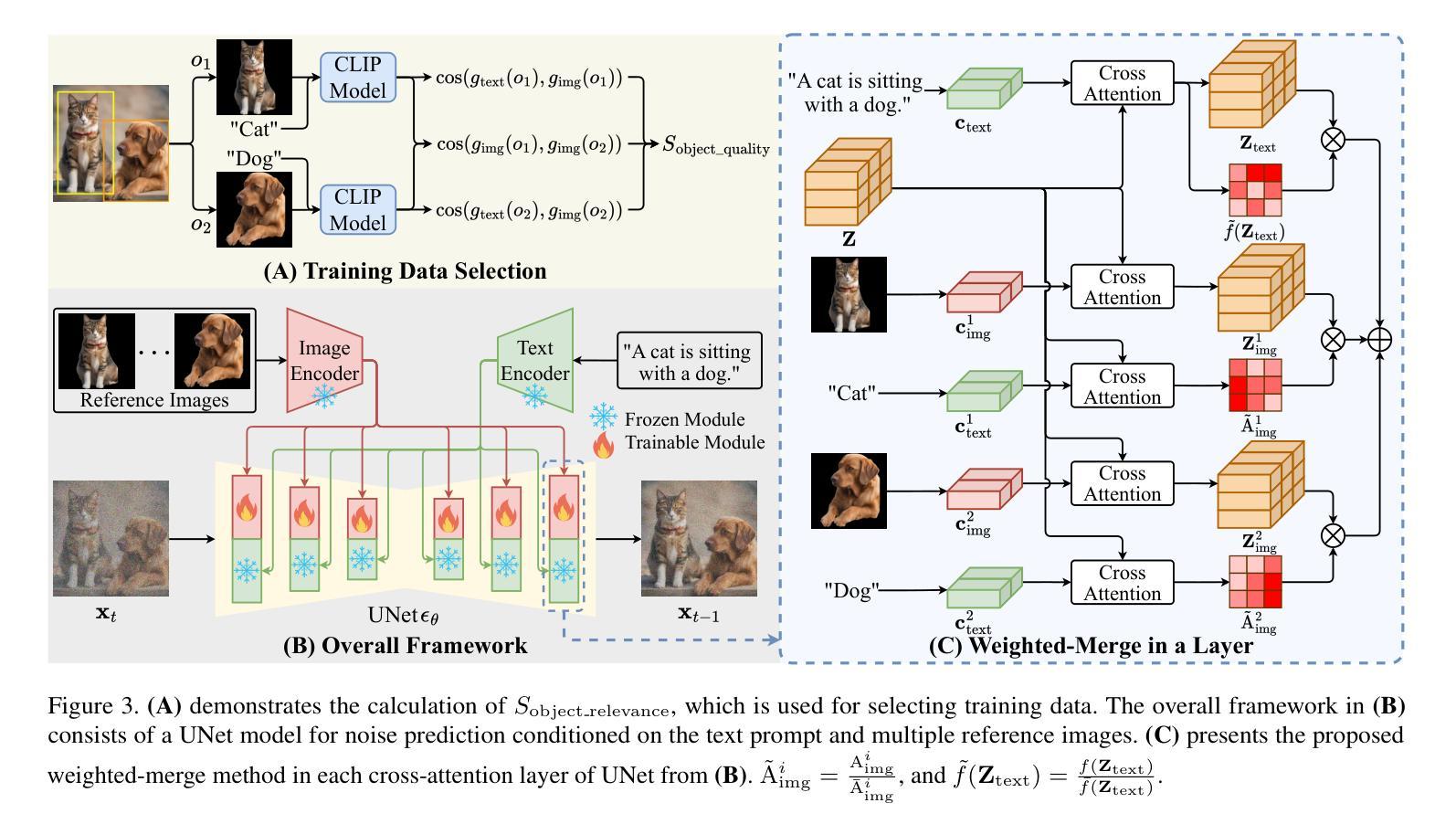
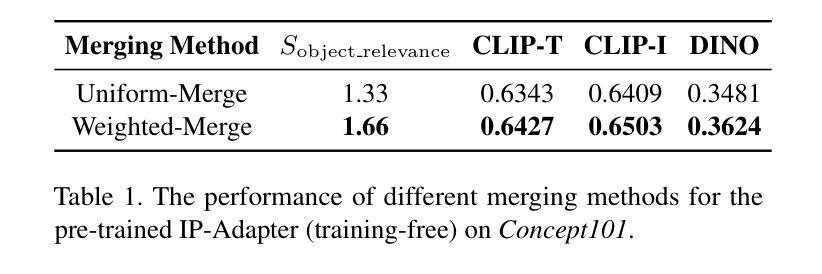
Personalized text-to-image generation methods can generate customized images based on the reference images, which have garnered wide research interest. Recent methods propose a finetuning-free approach with a decoupled cross-attention mechanism to generate personalized images requiring no test-time finetuning. However, when multiple reference images are provided, the current decoupled cross-attention mechanism encounters the object confusion problem and fails to map each reference image to its corresponding object, thereby seriously limiting its scope of application. To address the object confusion problem, in this work we investigate the relevance of different positions of the latent image features to the target object in diffusion model, and accordingly propose a weighted-merge method to merge multiple reference image features into the corresponding objects. Next, we integrate this weighted-merge method into existing pre-trained models and continue to train the model on a multi-object dataset constructed from the open-sourced SA-1B dataset. To mitigate object confusion and reduce training costs, we propose an object quality score to estimate the image quality for the selection of high-quality training samples. Furthermore, our weighted-merge training framework can be employed on single-object generation when a single object has multiple reference images. The experiments verify that our method achieves superior performance to the state-of-the-arts on the Concept101 dataset and DreamBooth dataset of multi-object personalized image generation, and remarkably improves the performance on single-object personalized image generation. Our code is available at https://github.com/hqhQAQ/MIP-Adapter.
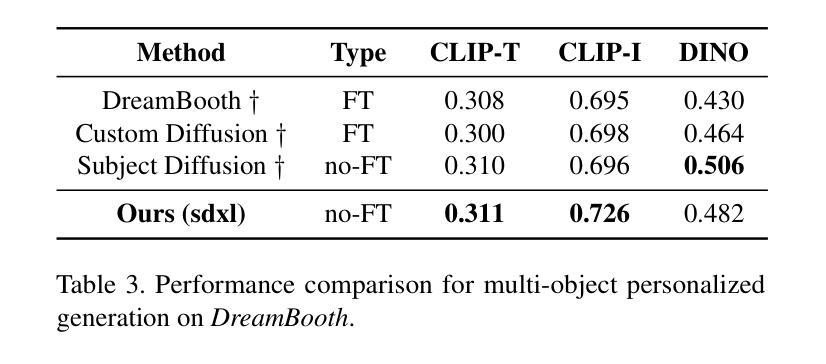
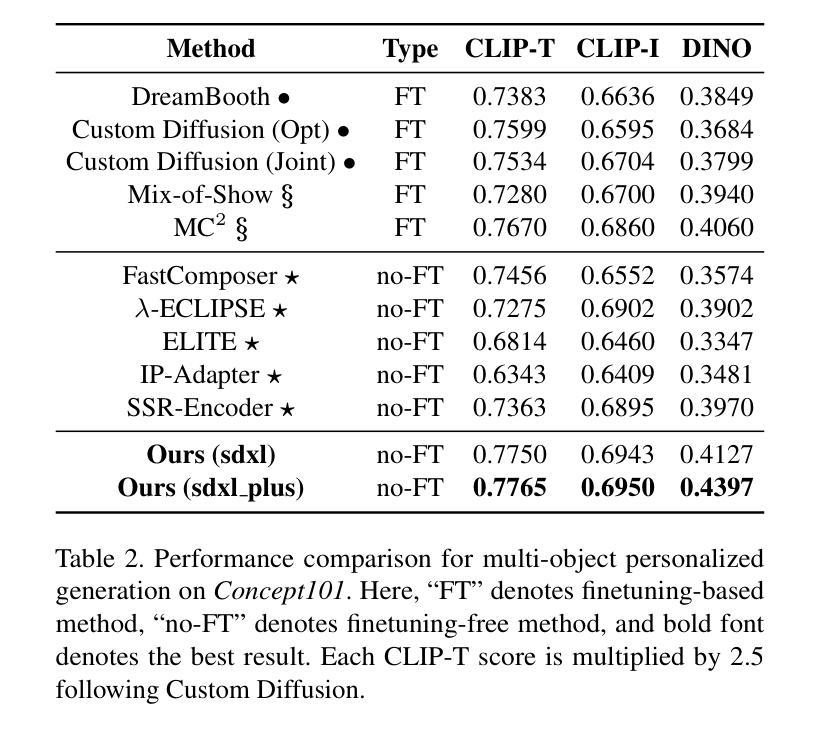
个性化文本到图像生成方法能够根据参考图像生成定制图像,这已引起了广泛的研究兴趣。最近的方法提出了一种无需微调的脱钩交叉注意机制来生成个性化图像,无需测试时的微调。然而,当提供多个参考图像时,当前的脱钩交叉注意机制会遇到对象混淆问题,并且无法将每个参考图像映射到其相应的对象,从而严重限制了其应用范围。为了解决对象混淆问题,在这项工作中,我们研究了潜在图像特征的不同位置与目标对象的相关性,并据此提出了一种加权合并方法,将多个参考图像特征合并到相应的对象中。接下来,我们将这种加权合并方法集成到现有的预训练模型中,并在由开源SA-1B数据集构建的多对象数据集上继续训练模型。为了减轻对象混淆并降低训练成本,我们提出了一种对象质量评分来估计图像质量,以选择高质量的训练样本。此外,我们的加权合并训练框架可以在单个对象有多个参考图像时使用于单个对象的生成。实验验证我们的方法在Concept101数据集和DreamBooth数据集的多对象个性化图像生成方面达到了最新技术的先进水平,并在单对象个性化图像生成方面显著提高了性能。我们的代码可在https://github.com/hqhQAQ/MIP-Adapter找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
针对个性化文本到图像生成方法,研究提出了一种无需微调的解耦跨注意力机制。当提供多个参考图像时,现有方法会遇到对象混淆问题。本研究调查了扩散模型中潜在图像特征与目标对象位置的相关性,并提出加权合并方法将多个参考图像特征合并为对应对象。此外,该研究还构建了多对象数据集,并引入对象质量评分以选择高质量训练样本。实验证明,该方法在多对象个性化图像生成任务上优于现有方法,并在单对象个性化图像生成任务上也有显著提升。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了无需微调的个性化文本到图像生成方法,采用解耦跨注意力机制。
- 当处理多个参考图像时,现有方法存在对象混淆问题。
- 研究了扩散模型中潜在图像特征与目标对象位置的相关性。
- 提出了加权合并方法,将多个参考图像特征合并为对应对象。
- 构建多对象数据集,并引入对象质量评分机制以选择高质量训练样本。
- 方法在多对象个性化图像生成任务上表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

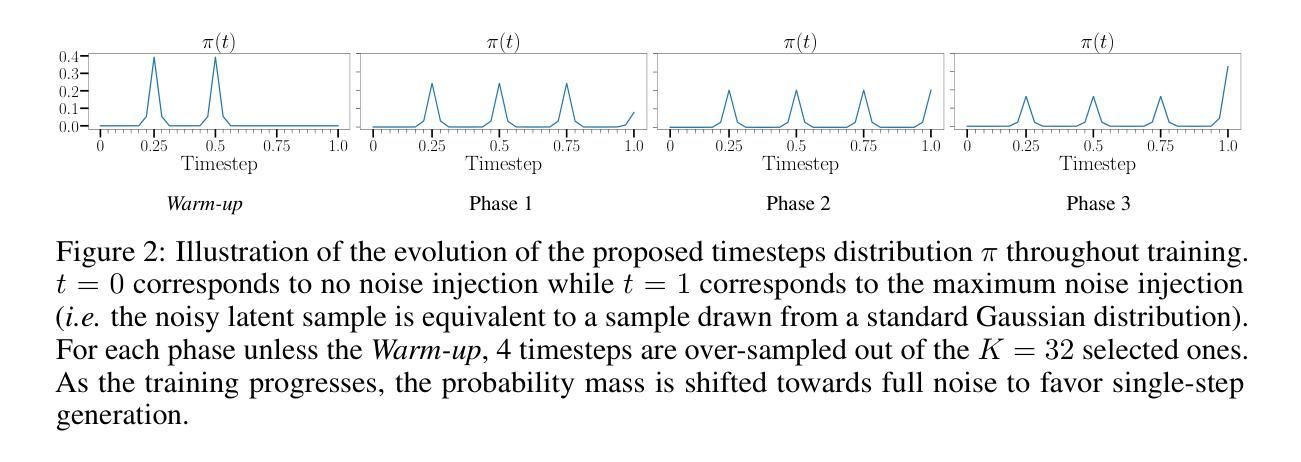
Flash Diffusion: Accelerating Any Conditional Diffusion Model for Few Steps Image Generation
Authors:Clément Chadebec, Onur Tasar, Eyal Benaroche, Benjamin Aubin
In this paper, we propose an efficient, fast, and versatile distillation method to accelerate the generation of pre-trained diffusion models: Flash Diffusion. The method reaches state-of-the-art performances in terms of FID and CLIP-Score for few steps image generation on the COCO2014 and COCO2017 datasets, while requiring only several GPU hours of training and fewer trainable parameters than existing methods. In addition to its efficiency, the versatility of the method is also exposed across several tasks such as text-to-image, inpainting, face-swapping, super-resolution and using different backbones such as UNet-based denoisers (SD1.5, SDXL) or DiT (Pixart-$\alpha$), as well as adapters. In all cases, the method allowed to reduce drastically the number of sampling steps while maintaining very high-quality image generation. The official implementation is available at https://github.com/gojasper/flash-diffusion.
本文提出了一种高效、快速、通用的蒸馏方法来加速预训练扩散模型的生成:Flash Diffusion。该方法在COCO2014和COCO2017数据集上的少量步骤图像生成方面,在FID和CLIP分数上达到了最先进的性能,同时只需几小时的GPU训练时间,并且相较于现有方法需要的可训练参数更少。除了高效性之外,该方法还展现出跨多个任务的灵活性,如文字转图像、图像补全、面部替换、超分辨率以及使用不同的主干网络如基于UNet的去噪器(SD1.5、SDXL)或DiT(Pixart-α),以及适配器等。在所有情况下,该方法在大幅减少采样步骤数量的同时,保持了非常高的图像生成质量。官方实现可访问 https://github.com/gojasper/flash-diffusion 获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to AAAI 2025
Summary
本文提出了一种高效、快速且通用的蒸馏方法,用于加速预训练扩散模型的生成:Flash Diffusion。该方法在COCO2014和COCO2017数据集上进行少量步骤的图像生成时,达到了FID和CLIP-Score的最新性能水平。它只需要几个小时的GPU训练时间,并且相较于现有方法,所需的训练参数更少。除了高效性外,该方法还具有通用性,可用于文本转图像、图像补全、人脸替换、超分辨率处理等多种任务,并支持不同的骨干网络(如基于UNet的降噪器或DiT)和适配器。该方法大幅减少了采样步骤数量,同时保持了高质量图像生成。
Key Takeaways
- Flash Diffusion是一种用于加速预训练扩散模型生成的高效、快速和通用的蒸馏方法。
- 该方法在COCO2014和COCO2017数据集上实现了优异的FID和CLIP-Score性能。
- Flash Diffusion训练时间短,仅需几个小时的GPU时间。
- 相较于其他方法,Flash Diffusion需要的训练参数更少。
- 该方法具有广泛的应用性,可用于多种任务,如文本转图像、图像补全、人脸替换和超分辨率处理。
- Flash Diffusion支持多种骨干网络和适配器,展示了其强大的灵活性。
点此查看论文截图