⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-19 更新
FarExStance: Explainable Stance Detection for Farsi
Authors:Majid Zarharan, Maryam Hashemi, Malika Behroozrazegh, Sauleh Eetemadi, Mohammad Taher Pilehvar, Jennifer Foster
We introduce FarExStance, a new dataset for explainable stance detection in Farsi. Each instance in this dataset contains a claim, the stance of an article or social media post towards that claim, and an extractive explanation which provides evidence for the stance label. We compare the performance of a fine-tuned multilingual RoBERTa model to several large language models in zero-shot, few-shot, and parameter-efficient fine-tuned settings on our new dataset. On stance detection, the most accurate models are the fine-tuned RoBERTa model, the LLM Aya-23-8B which has been fine-tuned using parameter-efficient fine-tuning, and few-shot Claude-3.5-Sonnet. Regarding the quality of the explanations, our automatic evaluation metrics indicate that few-shot GPT-4o generates the most coherent explanations, while our human evaluation reveals that the best Overall Explanation Score (OES) belongs to few-shot Claude-3.5-Sonnet. The fine-tuned Aya-32-8B model produced explanations most closely aligned with the reference explanations.
我们介绍了FarExStance数据集,这是一个用于波斯语的可解释立场检测的新数据集。该数据集中的每个实例都包含一个声明、一篇文章或社交媒体帖子对该声明的立场以及提供立场标签证据的解释性摘要。我们在新的数据集上对比了微调的多语言RoBERTa模型与多种大型语言模型在零样本、少样本和参数高效微调设置中的表现。在立场检测方面,表现最准确的模型是微调的RoBERTa模型、经过参数高效微调的大型语言模型Aya-23-8B和少样本的Claude-3.5-Sonnet。关于解释的质量,我们的自动评估指标显示,少样本的GPT-4o生成的解释最为连贯,而我们的人工评估显示,最好的整体解释得分(OES)属于少样本的Claude-3.5-Sonnet。经过微调的Aya-32-8B模型生成的解释与参考解释最为一致。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in COLING 2025
Summary
FarExStance数据集用于波斯语的解释性立场检测。研究对比了微调过的多语言RoBERTa模型、大型语言模型在零样本、少样本和参数高效微调设置上的表现。在立场检测方面,微调的RoBERTa模型、经过参数高效调教的LLM aya-23-8B和少样本的Claude-3.5-Sonnet表现最准确。在解释质量方面,GPT-4o的自动评估指标显示其解释最连贯,而人工评估显示最好的整体解释分数来自少样本的Claude-3.5-Sonnet。同时,经过微调的aya-32-8B模型生成的解释与参考解释最为接近。
Key Takeaways
- FarExStance是一个用于波斯语解释性立场检测的新数据集。
- 研究对比了多种模型在FarExStance数据集上的表现。
- 在立场检测方面,微调的RoBERTa模型、LLM aya-23-8B(参数高效微调)和少样本的Claude-3.5-Sonnet表现最佳。
- 在解释质量方面,GPT-4o的自动评估指标显示其解释最连贯。
- 人工评估显示最好的整体解释分数来自少样本的Claude-3.5-Sonnet模型。
- 相比其他模型,aya-32-8B模型生成的解释与参考解释最为接近。
点此查看论文截图

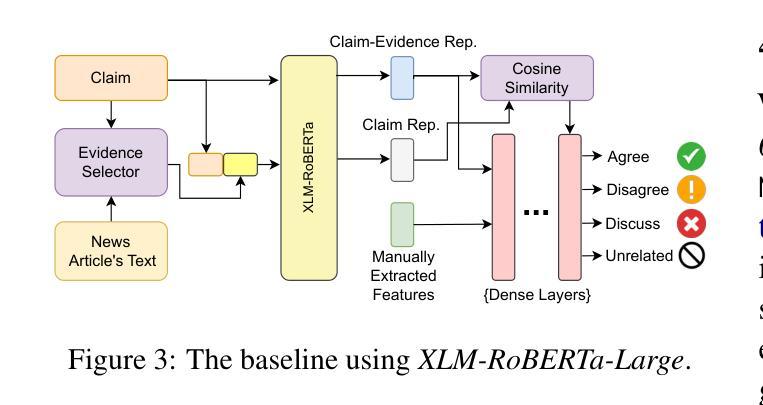
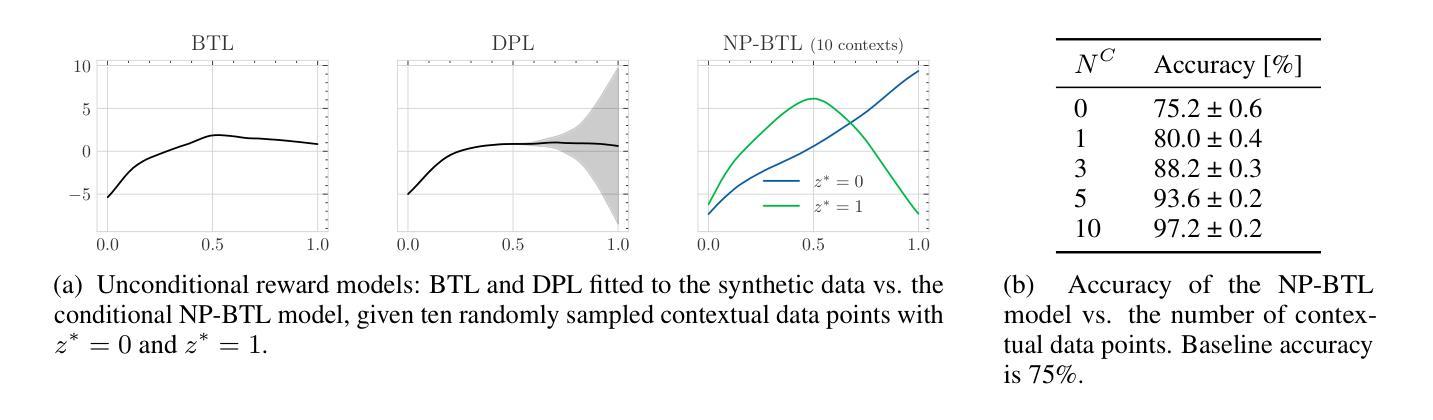
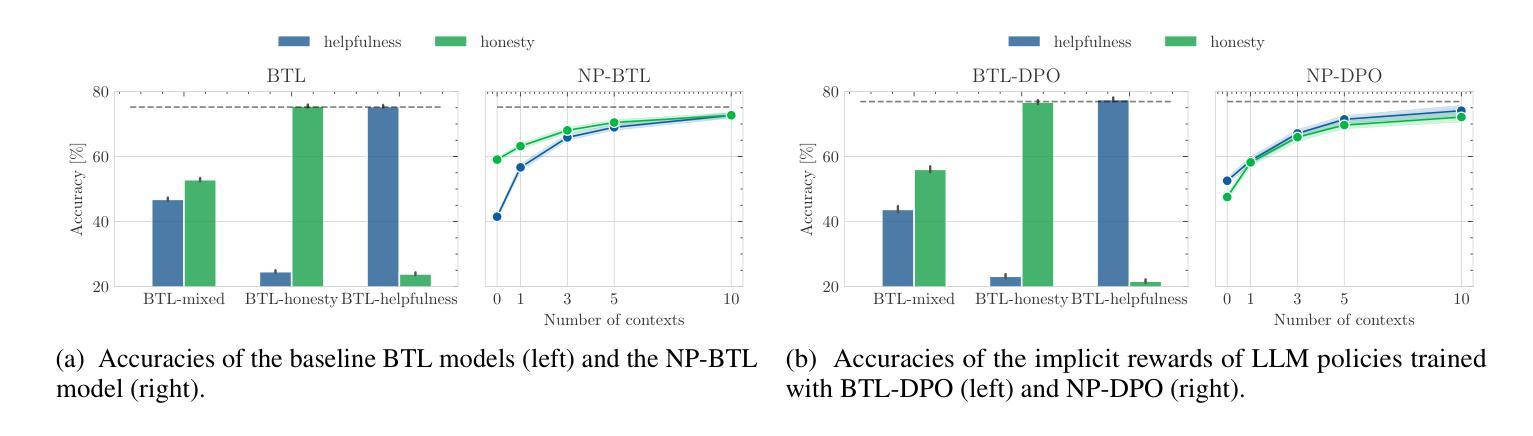
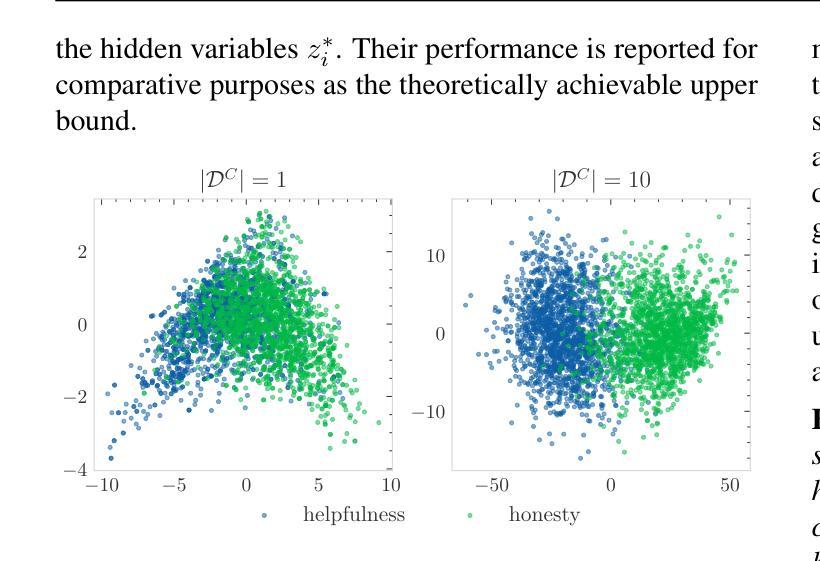
Few-shot Steerable Alignment: Adapting Rewards and LLM Policies with Neural Processes
Authors:Katarzyna Kobalczyk, Claudio Fanconi, Hao Sun, Mihaela van der Schaar
As large language models (LLMs) become increasingly embedded in everyday applications, ensuring their alignment with the diverse preferences of individual users has become a critical challenge. Currently deployed approaches typically assume homogeneous user objectives and rely on single-objective fine-tuning. However, human preferences are inherently heterogeneous, influenced by various unobservable factors, leading to conflicting signals in preference data. Existing solutions addressing this diversity often require costly datasets labelled for specific objectives and involve training multiple reward models or LLM policies, which is computationally expensive and impractical. In this work, we present a novel framework for few-shot steerable alignment, where users’ underlying preferences are inferred from a small sample of their choices. To achieve this, we extend the Bradley-Terry-Luce model to handle heterogeneous preferences with unobserved variability factors and propose its practical implementation for reward modelling and LLM fine-tuning. Thanks to our proposed approach of functional parameter-space conditioning, LLMs trained with our framework can be adapted to individual preferences at inference time, generating outputs over a continuum of behavioural modes. We empirically validate the effectiveness of methods, demonstrating their ability to capture and align with diverse human preferences in a data-efficient manner. Our code is made available at: https://github.com/kasia-kobalczyk/few-shot-steerable-alignment.
随着大型语言模型(LLM)在日常应用中的嵌入程度越来越高,确保它们与个别用户的多样化偏好保持一致已成为一项关键挑战。当前部署的方法通常假设用户目标是均质的,并依赖于单目标微调。然而,人类偏好本质上是异质的,受到各种不可观察因素的影响,导致偏好数据中的冲突信号。解决这种多样性的现有解决方案通常需要为特定目标标记的昂贵数据集,并涉及训练多个奖励模型或LLM策略,这在计算上很昂贵且不切实际。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种用于少样本可控对齐的新型框架,其中用户的潜在偏好是从其选择的小样本中推断出来的。为了实现这一点,我们扩展了Bradley-Terry-Luce模型以处理具有未观察到的变异性因素的异质偏好,并提出了其用于奖励建模和LLM调参的实际实现。由于我们提出的功能参数空间调节方法,使用我们的框架训练的LLM可以在推理时适应个人偏好,在连续的行为模式上生成输出。我们通过实证验证了方法的有效性,证明了它们在数据高效的方式下捕捉和与人类多样化偏好保持一致的能力。我们的代码可在:https://github.com/kasia-kobalczyk/few-shot-steerable-alignment找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型(LLM)在日常应用中的普及对确保其与用户多样化偏好的对齐提出了巨大挑战。现有方法假设用户目标的一致性并依赖于单一目标的微调。然而,人类偏好本质上是多样化的,受到各种不可观察因素的影响,导致偏好数据中的冲突信号。为解决这一多样性,现有解决方案通常需要针对特定目标进行昂贵的标注数据集,并涉及训练多个奖励模型或LLM策略,计算成本高且不切实际。本研究提出了一种新的少样本可操控对齐框架,通过少量用户选择样本推断用户的潜在偏好。我们扩展了Bradley-Terry-Luce模型以处理具有未观察到的变异因素的异质偏好,并提出了其实用于奖励建模和LLM微调的实际实现。借助我们的功能参数空间条件处理方法,用我们的框架训练的LLM可以在推理时间适应个人偏好,生成一系列行为模式的输出。我们验证了方法的有效性,并展示了其在数据高效方式下捕捉和与人类多样化偏好对齐的能力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型(LLM)与用户的多样化偏好对齐是一个关键挑战。
- 现有方法通常基于假设用户目标的同质性并依赖单一目标微调,但这并不适用于人类偏好的多样性。
- 人类偏好受到多种不可观察因素的影响,导致偏好数据中的冲突信号。
- 解决此问题需要适应少量用户选择的样本数据。
- 本研究提出了一种新的少样本可操控对齐框架,扩展了Bradley-Terry-Luce模型以处理具有未观察到的变异因素的异质偏好。
- 提出了一种实际实现用于奖励建模和LLM微调的方法。
点此查看论文截图

Zero-Shot Prompting and Few-Shot Fine-Tuning: Revisiting Document Image Classification Using Large Language Models
Authors:Anna Scius-Bertrand, Michael Jungo, Lars Vögtlin, Jean-Marc Spat, Andreas Fischer
Classifying scanned documents is a challenging problem that involves image, layout, and text analysis for document understanding. Nevertheless, for certain benchmark datasets, notably RVL-CDIP, the state of the art is closing in to near-perfect performance when considering hundreds of thousands of training samples. With the advent of large language models (LLMs), which are excellent few-shot learners, the question arises to what extent the document classification problem can be addressed with only a few training samples, or even none at all. In this paper, we investigate this question in the context of zero-shot prompting and few-shot model fine-tuning, with the aim of reducing the need for human-annotated training samples as much as possible.
分类扫描文档是一个涉及图像、布局和文本分析以理解文档的挑战性问题。然而,对于某些基准数据集(尤其是RVL-CDIP),考虑到数十万个训练样本,当前技术的状态正在接近近乎完美的性能。随着大型语言模型(LLM)的出现,这些模型是出色的少样本学习者,因此出现的问题是,仅使用少量训练样本,甚至完全不使用样本,可以在多大程度上解决文档分类问题。在本文中,我们在零样本提示和少样本模型微调的背景下调查了这个问题,旨在尽可能减少对人工注释训练样本的需求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICPR 2024
Summary
本文探讨了使用大型语言模型(LLMs)进行文档分类的问题,尤其是在零样本提示和少量模型微调的环境下。文章旨在通过减少对人类注释训练样本的需求来解决文档分类问题,对零样本学习和少量训练样本的场景进行深入分析。通过此方式提升机器学习模型的效率与准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 文档分类是一个涉及图像、布局和文本分析的问题。随着大型语言模型(LLMs)的出现,尤其是其作为优秀的少样本学习者,人们开始探讨文档分类问题是否可以通过少量或零训练样本解决。
- 该论文旨在减少文档分类对大量人工标注训练样本的依赖,探究在零样本提示和少样本模型微调情境下的解决方案。其中“零样本学习”技术至关重要,机器能理解和推断人类语言的间接意图与概念转移知识,从而实现跨场景学习与理解任务迁移能力。这也符合少样本学习的思想精髓——使用有限样本完成复杂的任务学习。这也是当前人工智能研究的重要趋势之一。这一方法有望进一步推进机器学习的实际应用,尤其是在需要大量人工标注训练样本的领域如文档分类等。
点此查看论文截图


Extreme Multi-label Completion for Semantic Document Labelling with Taxonomy-Aware Parallel Learning
Authors:Julien Audiffren, Christophe Broillet, Ljiljana Dolamic, Philippe Cudré-Mauroux
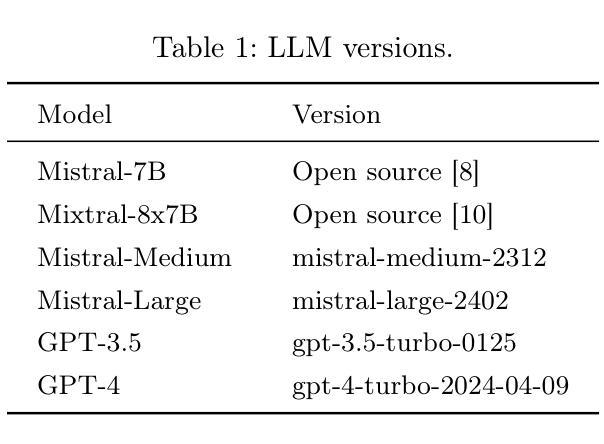
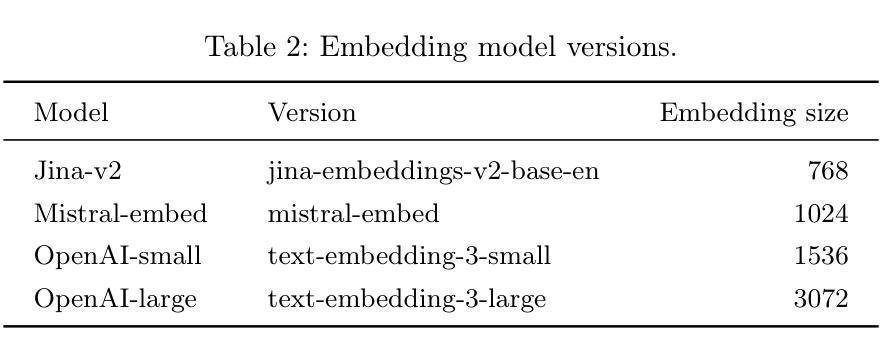
In Extreme Multi Label Completion (XMLCo), the objective is to predict the missing labels of a collection of documents. Together with XML Classification, XMLCo is arguably one of the most challenging document classification tasks, as the very high number of labels (at least ten of thousands) is generally very large compared to the number of available labelled documents in the training dataset. Such a task is often accompanied by a taxonomy that encodes the labels organic relationships, and many methods have been proposed to leverage this hierarchy to improve the results of XMLCo algorithms. In this paper, we propose a new approach to this problem, TAMLEC (Taxonomy-Aware Multi-task Learning for Extreme multi-label Completion). TAMLEC divides the problem into several Taxonomy-Aware Tasks, i.e. subsets of labels adapted to the hierarchical paths of the taxonomy, and trains on these tasks using a dynamic Parallel Feature sharing approach, where some parts of the model are shared between tasks while others are task-specific. Then, at inference time, TAMLEC uses the labels available in a document to infer the appropriate tasks and to predict missing labels. To achieve this result, TAMLEC uses a modified transformer architecture that predicts ordered sequences of labels on a Weak-Semilattice structure that is naturally induced by the tasks. This approach yields multiple advantages. First, our experiments on real-world datasets show that TAMLEC outperforms state-of-the-art methods for various XMLCo problems. Second, TAMLEC is by construction particularly suited for few-shots XML tasks, where new tasks or labels are introduced with only few examples, and extensive evaluations highlight its strong performance compared to existing methods.
在极端多标签补全(XMLCo)中,目标是预测一组文档中的缺失标签。与XML分类一起,XMLCo可以说是最具挑战性的文档分类任务之一,因为标签数量(至少数万)通常比训练数据集中可用的带标签文档的数量要大得多。此类任务通常伴随着对标签有机关系进行编码的分类法,已经提出了许多方法来利用这个层次结构来改善XMLCo算法的结果。在本文中,我们针对这个问题提出了一种新方法:TAMLEC(用于极端多标签补全的分层感知多任务学习)。TAMLEC将问题分为多个层次感知任务,即适应分类层次路径的标签子集,并使用动态并行特征共享方法在这些任务上进行训练,其中模型的部分组件在任务之间是共享的,而其他一些是特定于任务的。然后,在推理时,TAMLEC使用文档中可用的标签来推断适当的任务并预测缺失的标签。为了实现这一结果,TAMLEC使用了一种改进的转换器架构,该架构在弱半格结构上预测标签的有序序列,该结构自然是由任务引起的。这种方法具有多个优点。首先,我们在真实数据集上的实验表明,TAMLEC优于各种XMLCo问题的最新方法。其次,TAMLEC在构建时特别适合小样本的XML任务,其中引入的新任务或标签只有少数几个示例,并且广泛的评估突出了其与现有方法的强大性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该文本介绍了针对极端多标签补全任务(XMLCo)的新方法TAMLEC。TAMLEC将问题分为多个与税收等级相符的子任务,并利用动态并行特征共享方法对其进行训练。在推断时,TAMLEC利用文档中的现有标签来推断适当的任务并预测缺失的标签。该方法在真实数据集上的实验表现优于其他先进方法,尤其适用于只有少量示例的新任务或标签的XML任务。
Key Takeaways
- Extreme Multi Label Completion (XMLCo)旨在预测一组文档缺失的标签,是极具挑战性的文档分类任务之一。
2.TAMLEC(Taxonomies-Aware Multi-task Learning for Extreme multi-label Completion)是一种新的解决方法,它将问题划分为多个与税收等级相符的子任务。
3.TAMLEC利用动态并行特征共享方法进行训练,部分模型部件是共享任务,而其他部件是特定任务的。
4.在推断时,TAMLEC使用文档中的现有标签来推断适当的任务并预测缺失的标签。
5.TAMLEC采用修改后的转换器架构,在弱半格结构上预测标签的有序序列,这是由任务自然引发的。
6.实验表明,TAMLEC在真实数据集上的表现优于其他最先进的方法。
点此查看论文截图

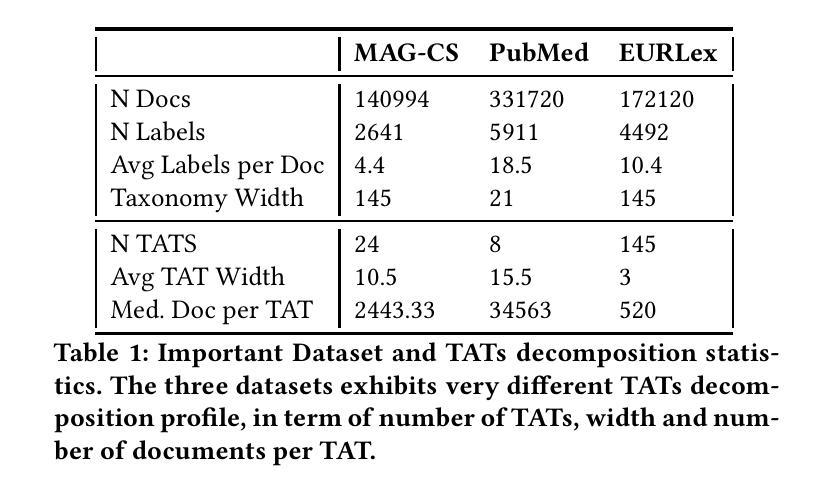
Modelling Multi-modal Cross-interaction for ML-FSIC Based on Local Feature Selection
Authors:Kun Yan, Zied Bouraoui, Fangyun Wei, Chang Xu, Ping Wang, Shoaib Jameel, Steven Schockaert
The aim of multi-label few-shot image classification (ML-FSIC) is to assign semantic labels to images, in settings where only a small number of training examples are available for each label. A key feature of the multi-label setting is that images often have several labels, which typically refer to objects appearing in different regions of the image. When estimating label prototypes, in a metric-based setting, it is thus important to determine which regions are relevant for which labels, but the limited amount of training data and the noisy nature of local features make this highly challenging. As a solution, we propose a strategy in which label prototypes are gradually refined. First, we initialize the prototypes using word embeddings, which allows us to leverage prior knowledge about the meaning of the labels. Second, taking advantage of these initial prototypes, we then use a Loss Change Measurement~(LCM) strategy to select the local features from the training images (i.e.\ the support set) that are most likely to be representative of a given label. Third, we construct the final prototype of the label by aggregating these representative local features using a multi-modal cross-interaction mechanism, which again relies on the initial word embedding-based prototypes. Experiments on COCO, PASCAL VOC, NUS-WIDE, and iMaterialist show that our model substantially improves the current state-of-the-art.
多标签小样本图像分类(ML-FSIC)的目标是在每个标签只有少量训练样本的情况下,为图像分配语义标签。多标签设置的一个关键特点是图像通常具有多个标签,这些标签通常指的是图像中不同区域出现的对象。在基于度量的环境中估计标签原型时,确定哪些区域与哪些标签相关非常重要,但训练数据的有限性和局部特征的噪声性质使得这极具挑战性。作为一种解决方案,我们提出了一种逐渐完善标签原型的策略。首先,我们使用词嵌入来初始化原型,这使我们能够利用有关标签含义的先验知识。其次,利用这些初始原型,我们采用损失变化测量(LCM)策略来选择训练图像(即支持集)中最可能代表给定标签的局部特征。第三,我们通过多模态交叉交互机制聚合这些代表性局部特征,构建标签的最终原型,这同样依赖于最初的基于词嵌入的原型。在COCO、PASCAL VOC、NUS-WIDE和iMaterialist上的实验表明,我们的模型大幅提升了当前的最佳水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in Transactions on Multimedia Computing Communications and Applications
Summary
本文介绍了多标签少样本图像分类(ML-FSIC)的目标,即在每个标签只有少量训练样本的情况下,对图像进行语义标签分配。文章提出了一种基于度量方法的标签原型估计策略,通过逐步优化标签原型来解决训练数据有限和局部特征噪声的问题。首先,使用词嵌入初始化标签原型以利用标签的先验知识;其次,利用损失变化测量(LCM)策略选择最可能代表给定标签的训练图像局部特征;最后,通过多模态交叉交互机制聚合这些代表性局部特征来构建最终的标签原型。实验结果表明,该方法在COCO、PASCAL VOC、NUS-WIDE和iMaterialist数据集上显著提高了当前技术水平。
Key Takeaways
- 多标签少样本图像分类(ML-FSIC)的目标是在有限的训练样本下,为图像分配多个语义标签。
- 标签原型估计在ML-FSIC中至关重要,因为图像通常具有多个标签,这些标签通常指代图像不同区域的物体。
- 提出的策略通过逐步优化标签原型来解决训练数据限制和局部特征噪声问题。
- 初始化标签原型时使用词嵌入,以利用标签的先验知识。
- 采用损失变化测量(LCM)策略选择最可能代表给定标签的训练图像局部特征。
- 通过多模态交叉交互机制聚合代表性局部特征来构建最终的标签原型。
点此查看论文截图

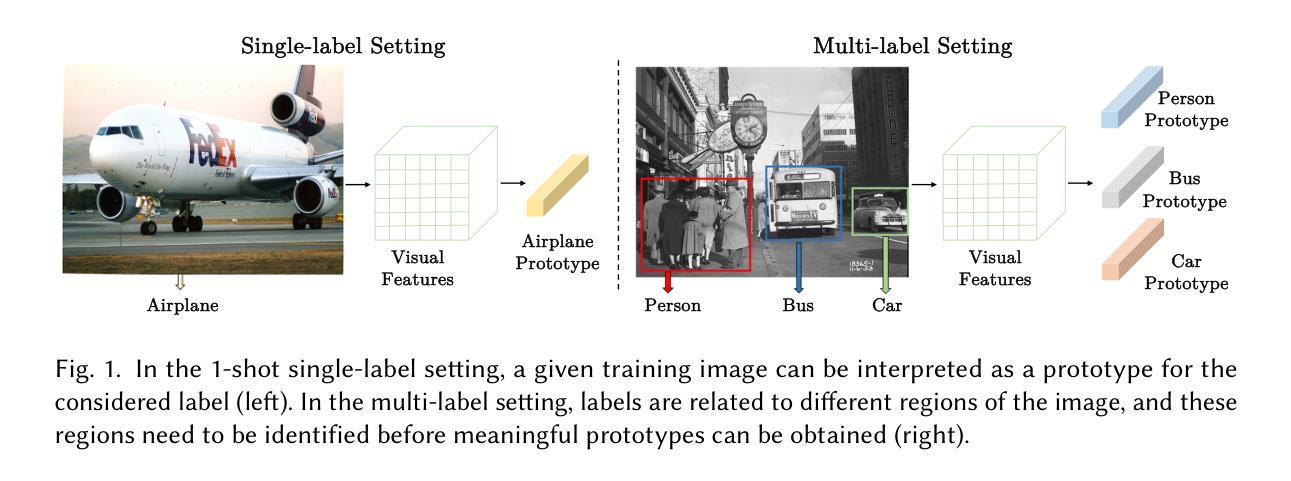
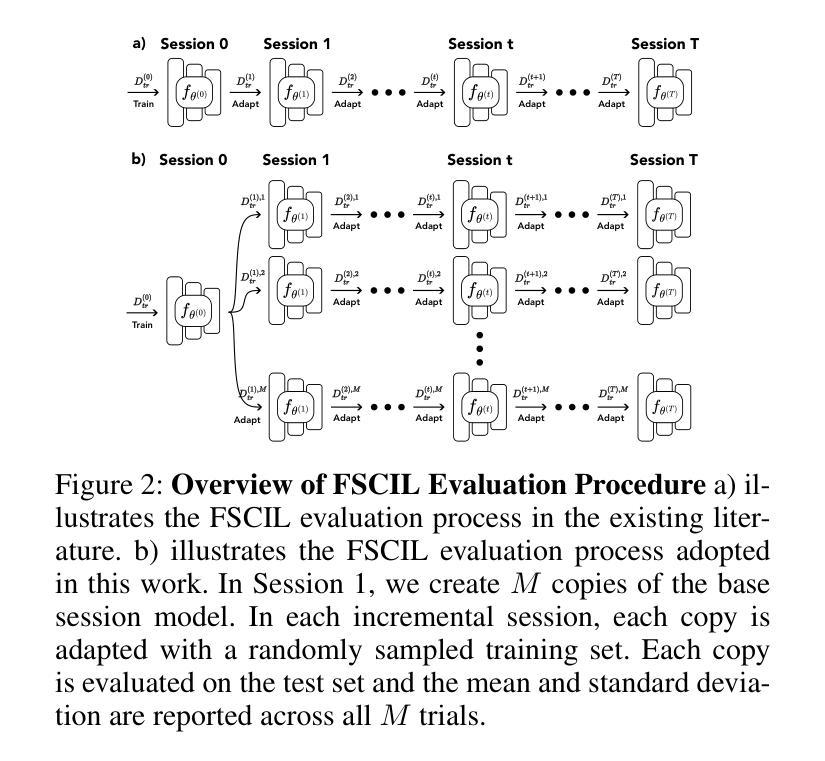
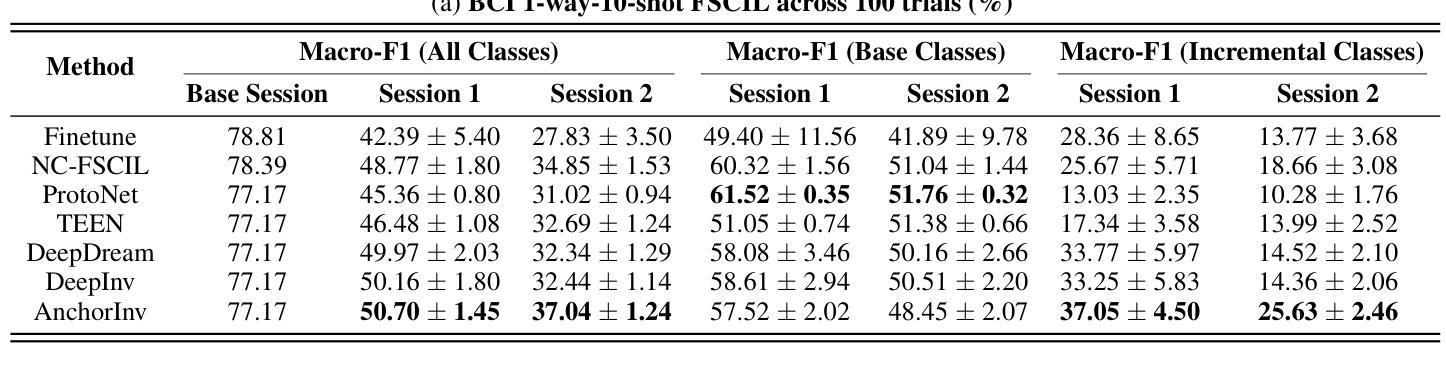
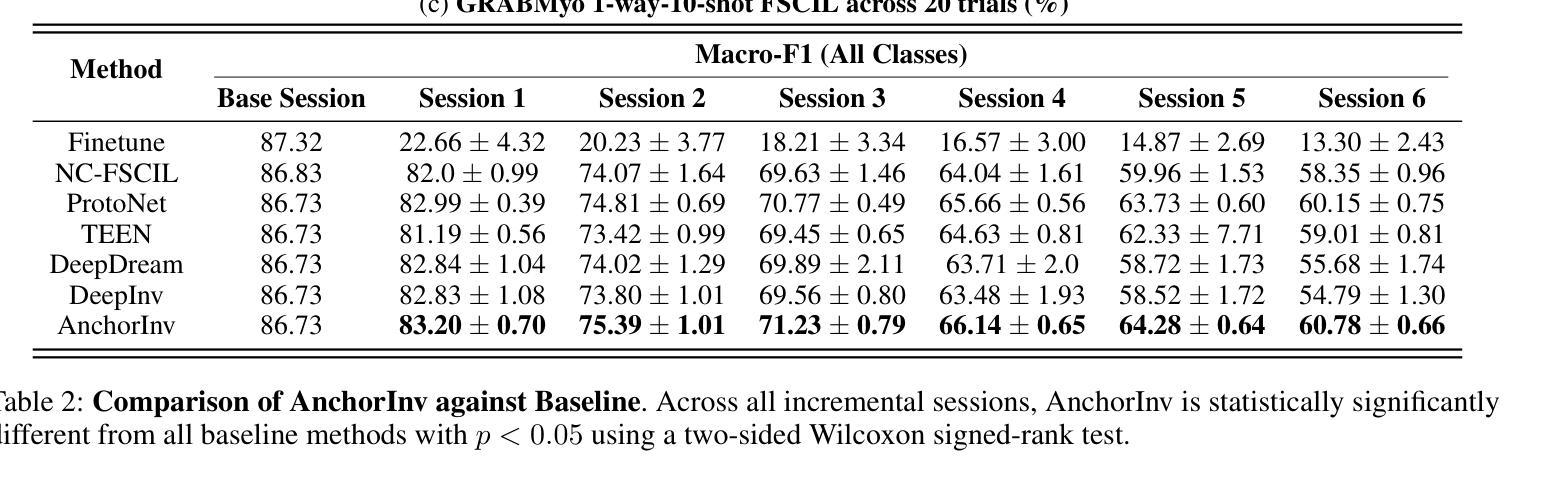
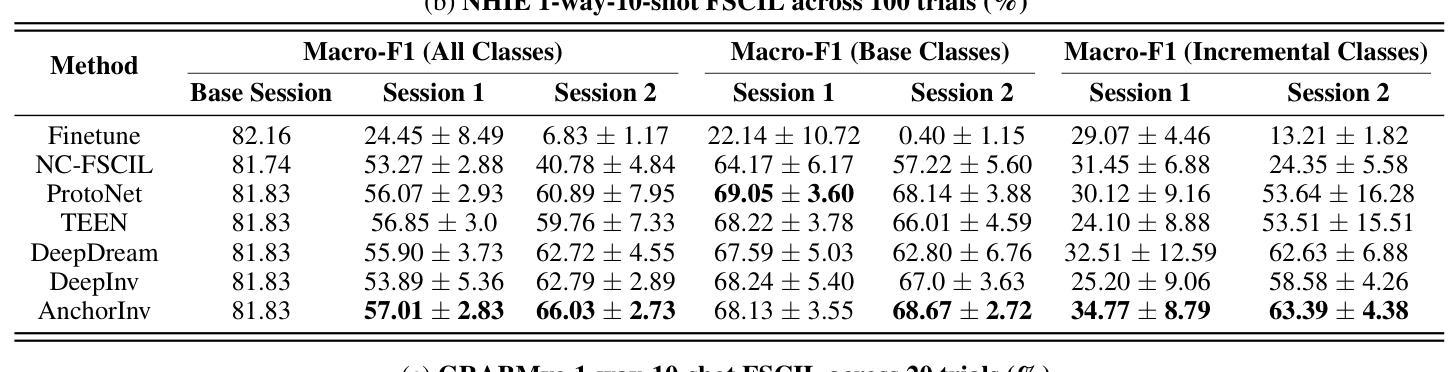
AnchorInv: Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning of Physiological Signals via Representation Space Guided Inversion
Authors:Chenqi Li, Boyan Gao, Gabriel Jones, Timothy Denison, Tingting Zhu
Deep learning models have demonstrated exceptional performance in a variety of real-world applications. These successes are often attributed to strong base models that can generalize to novel tasks with limited supporting data while keeping prior knowledge intact. However, these impressive results are based on the availability of a large amount of high-quality data, which is often lacking in specialized biomedical applications. In such fields, models are usually developed with limited data that arrive incrementally with novel categories. This requires the model to adapt to new information while preserving existing knowledge. Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) methods offer a promising approach to addressing these challenges, but they also depend on strong base models that face the same aforementioned limitations. To overcome these constraints, we propose AnchorInv following the straightforward and efficient buffer-replay strategy. Instead of selecting and storing raw data, AnchorInv generates synthetic samples guided by anchor points in the feature space. This approach protects privacy and regularizes the model for adaptation. When evaluated on three public physiological time series datasets, AnchorInv exhibits efficient knowledge forgetting prevention and improved adaptation to novel classes, surpassing state-of-the-art baselines.
深度学习模型在多种实际应用中表现出了卓越的性能。这些成功往往归功于能够推广到新型任务且保持先验知识不变的强大基础模型。然而,这些令人印象深刻的结果是基于大量高质量数据的可用性,这在专门的生物医学应用中往往缺乏。在这些领域中,模型通常是在有限的数据上开发的,这些数据会随着时间的推移陆续出现新的类别。这要求模型在适应新信息的同时保持现有知识。小样本类增量学习(FSCIL)方法为解决这些挑战提供了一种有前途的解决思路,但它们同样依赖于上述提到的强大基础模型。为了克服这些限制,我们提出了基于简单高效缓冲回放策略的AnchorInv。AnchorInv不选择和存储原始数据,而是根据特征空间中的锚点生成合成样本。这种方法保护了隐私并促进了模型的适应。在三个公共生理时间序列数据集上进行评估时,AnchorInv表现出了有效的知识遗忘预防和对新类别的良好适应能力,超越了现有的最佳基线。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI-25 Extended Version
Summary
深度学习模型在多种实际应用中展现出卓越性能,这归功于能够在有限数据支持下泛化到新任务并保留先验知识的强大基础模型。然而,这些成果建立在大量高质量数据可用性的基础上,这在专门的生物医学应用中往往缺乏。在这些领域,模型通常使用有限且陆续到来的新类别数据进行开发,这要求模型在适应新信息的同时保留现有知识。针对这些挑战,Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning(FSCIL)方法提供了一个有前景的解决方案,但它们也依赖于面临相同限制的强大基础模型。为了克服这些制约因素,提出了AnchorInv方法,采用简单高效的缓冲区回放策略。AnchorInv通过特征空间中的锚点生成合成样本,而不是选择和存储原始数据,这种方法保护了隐私并促进了模型的适应性调整。在三个公共生理时间序列数据集上的评估表明,AnchorInv有效地防止了知识遗忘,并提高了对新类别的适应能力,超越了最新的基线方法。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习模型在多种应用中表现出卓越性能,归功于强大的基础模型。
- 在生物医学等特定领域,数据有限且陆续到来,要求模型能适应新信息并保留现有知识。
- Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning(FSCIL)方法用于解决此挑战。
- AnchorInv方法采用缓冲区回放策略,通过特征空间中的锚点生成合成样本,以保护隐私并促进模型适应性调整。
- AnchorInv在生理时间序列数据集上的评估表现优越,有效防止知识遗忘,提高对新类别的适应能力。
- AnchorInv方法依赖于强大基础模型,但仍存在数据限制的问题。
点此查看论文截图

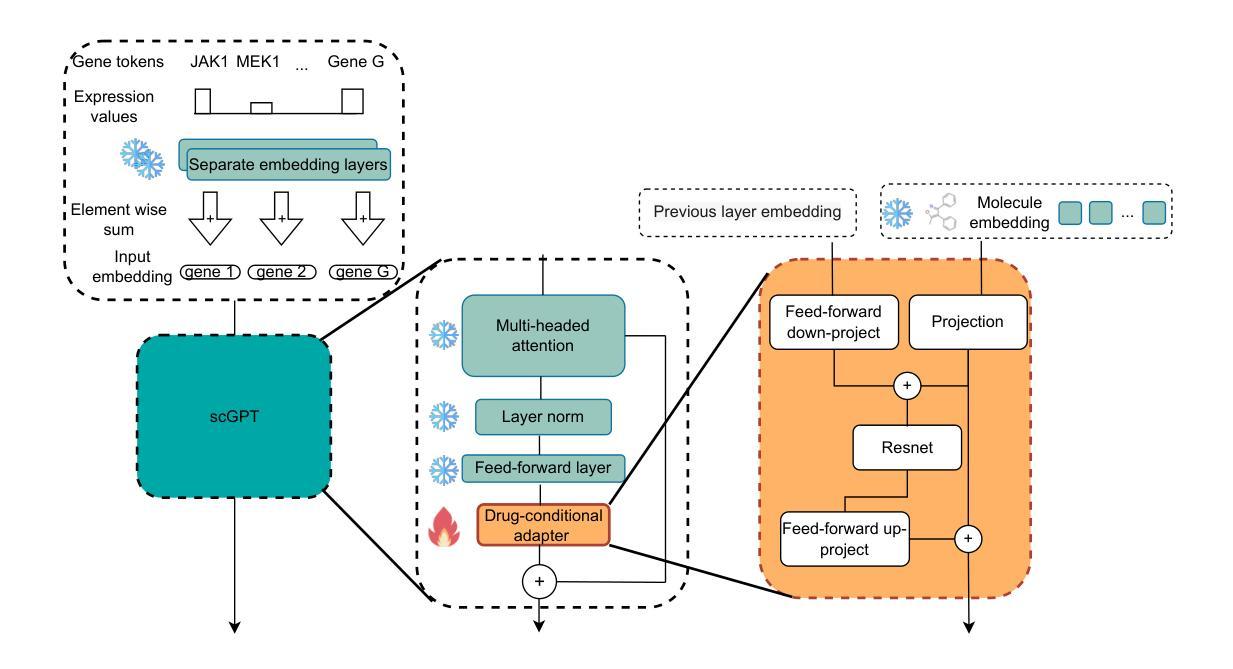
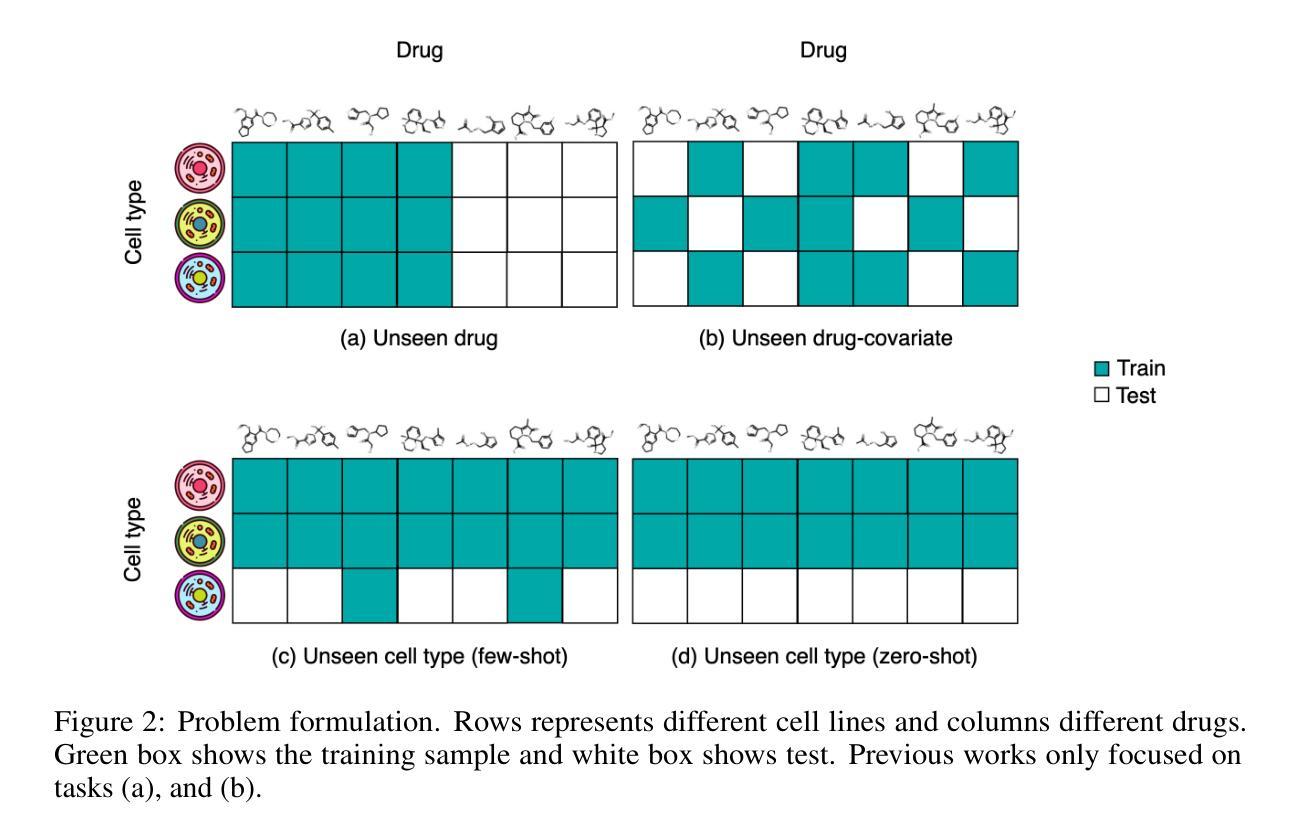
Efficient Fine-Tuning of Single-Cell Foundation Models Enables Zero-Shot Molecular Perturbation Prediction
Authors:Sepideh Maleki, Jan-Christian Huetter, Kangway V. Chuang, Gabriele Scalia, Tommaso Biancalani
Predicting transcriptional responses to novel drugs provides a unique opportunity to accelerate biomedical research and advance drug discovery efforts. However, the inherent complexity and high dimensionality of cellular responses, combined with the extremely limited available experimental data, makes the task challenging. In this study, we leverage single-cell foundation models (FMs) pre-trained on tens of millions of single cells, encompassing multiple cell types, states, and disease annotations, to address molecular perturbation prediction. We introduce a drug-conditional adapter that allows efficient fine-tuning by training less than 1% of the original foundation model, thus enabling molecular conditioning while preserving the rich biological representation learned during pre-training. The proposed strategy allows not only the prediction of cellular responses to novel drugs, but also the zero-shot generalization to unseen cell lines. We establish a robust evaluation framework to assess model performance across different generalization tasks, demonstrating state-of-the-art results across all settings, with significant improvements in the few-shot and zero-shot generalization to new cell lines compared to existing baselines.
预测新型药物的转录反应为加速生物医学研究和推进药物发现努力提供了独特的机会。然而,细胞反应的固有复杂性和高维性,以及可用的实验数据极为有限,使得这一任务具有挑战性。在这项研究中,我们利用基于单细胞的预训练模型(FMs),该模型基于数千万个单细胞进行预训练,涵盖多种细胞类型、状态和疾病注释,来解决分子扰动预测问题。我们引入了一种药物条件适配器,通过训练不到原始预训练模型的1%,实现了高效的微调,从而在保持预训练期间学习的丰富生物学表征的同时,实现了分子调节。所提出的策略不仅允许预测新型药物的细胞反应,而且可以在未见过的细胞系中实现零样本泛化。我们建立了一个稳健的评估框架,以评估模型在不同泛化任务上的性能,在所有设置中都取得了最先进的结果,与现有基线相比,在新细胞系的少样本和零样本泛化方面取得了显著改进。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
预测新型药物的转录反应为加速生物医学研究和推动药物发现提供了独特的机会。本研究利用基于单细胞预训练模型应对分子扰动预测的挑战,通过引入药物条件适配器实现高效微调,只需训练原预训练模型的不到百分之一,从而在保留预训练丰富生物学表征的同时实现分子条件化。该策略不仅可预测新型药物的细胞反应,还可实现零样本泛化至未见过的细胞系。我们建立了稳健的评估框架以评估模型在不同泛化任务中的性能,显示在各种设置中均达到最新结果,与新细胞系的零样本和少样本泛化方面较现有基线有显著改善。
Key Takeaways
- 利用单细胞预训练模型预测新型药物的转录反应,加速生物医学研究和药物发现。
- 引入药物条件适配器,实现高效微调并保留预训练的丰富生物学表征。
- 该策略不仅能预测新型药物的细胞反应,还能实现零样本泛化至未见过的细胞系。
- 建立稳健的评估框架以评估模型性能。
- 模型在各种设置下均表现出最新结果。
- 与现有基线相比,在新细胞系的零样本和少样本泛化方面有明显改善。
点此查看论文截图

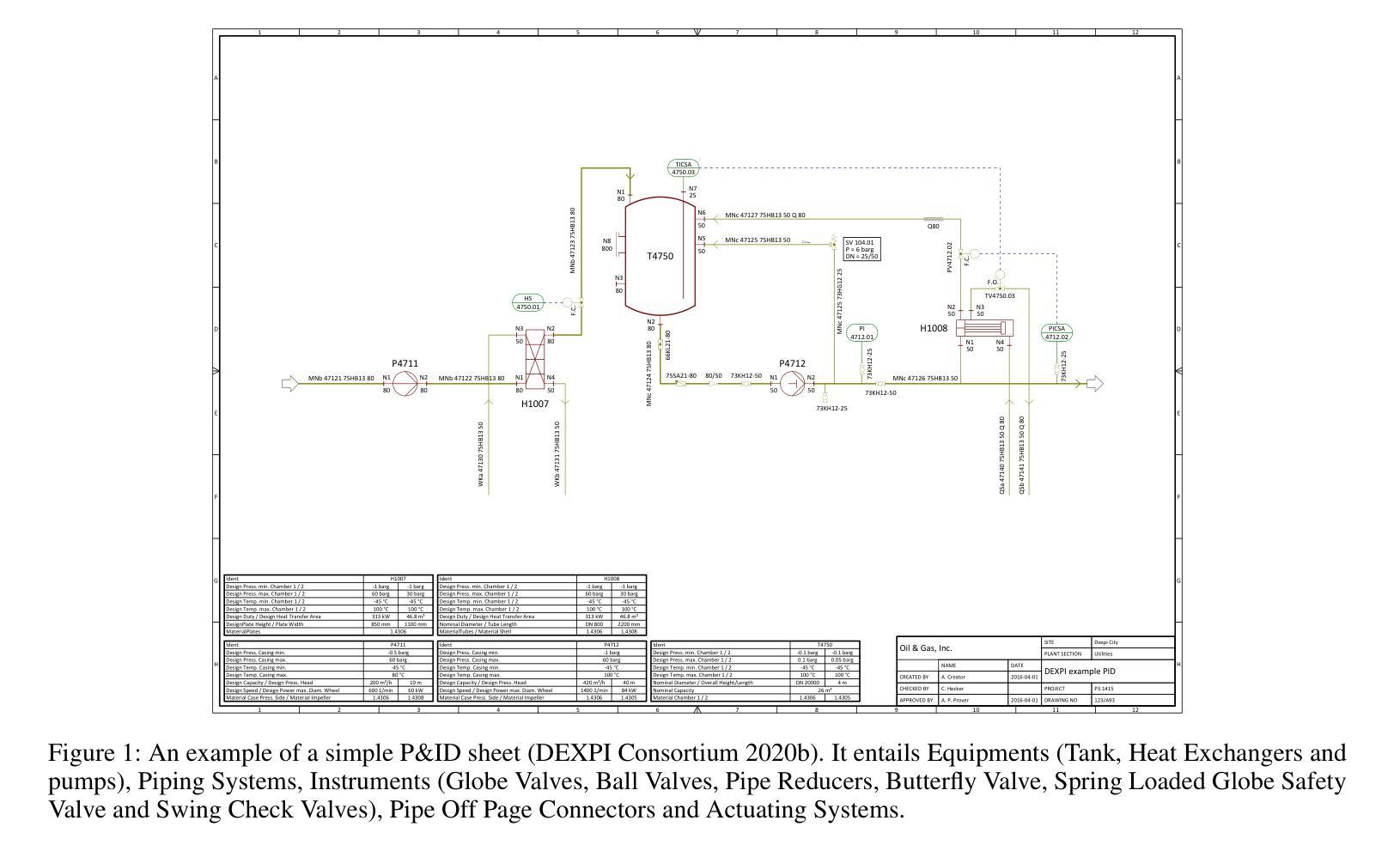
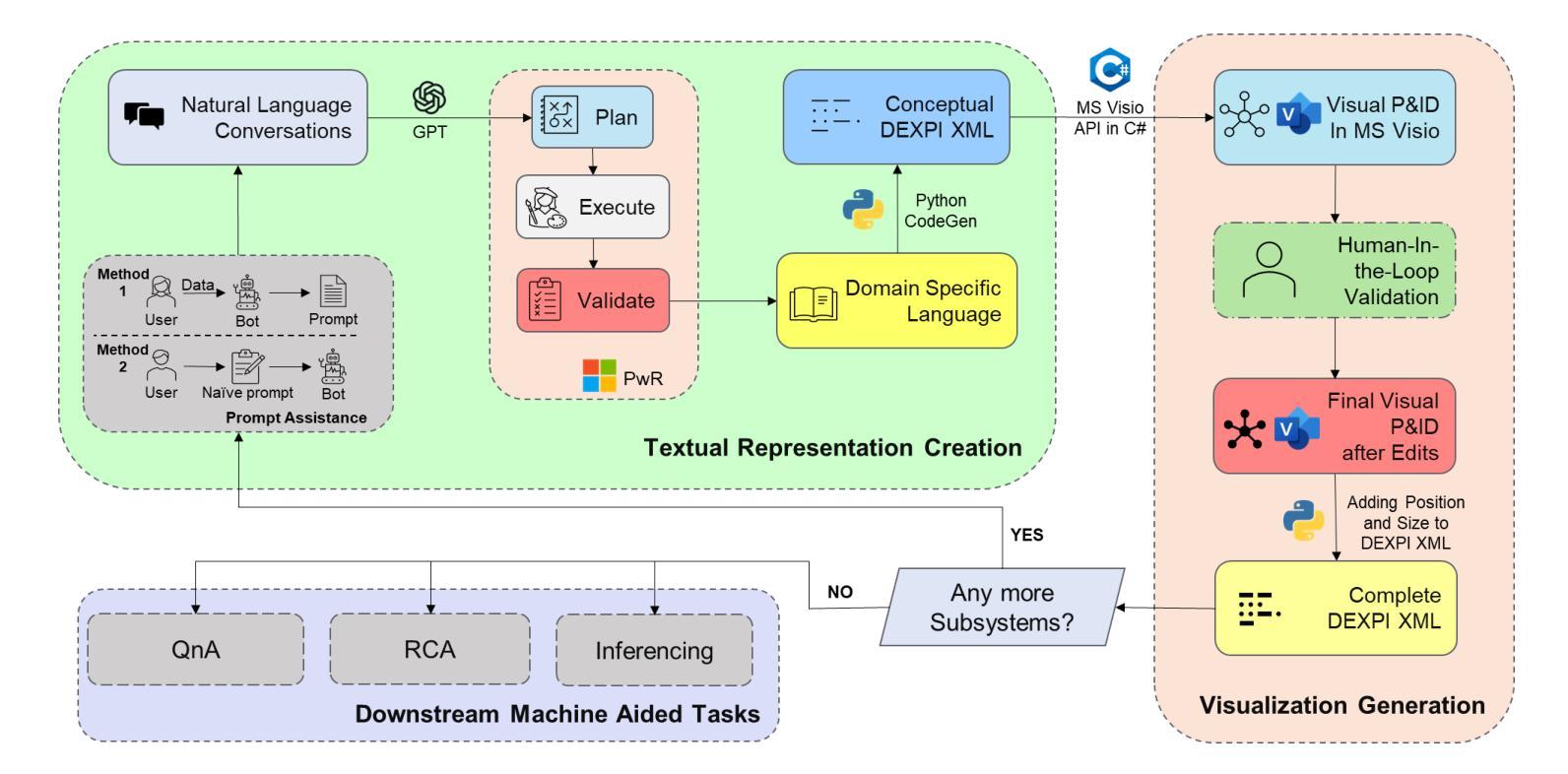
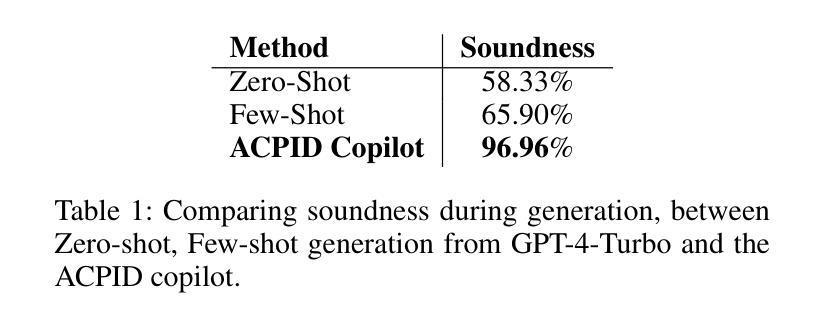
An Agentic Approach to Automatic Creation of P&ID Diagrams from Natural Language Descriptions
Authors:Shreeyash Gowaikar, Srinivasan Iyengar, Sameer Segal, Shivkumar Kalyanaraman
The Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams (P&IDs) are foundational to the design, construction, and operation of workflows in the engineering and process industries. However, their manual creation is often labor-intensive, error-prone, and lacks robust mechanisms for error detection and correction. While recent advancements in Generative AI, particularly Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vision-Language Models (VLMs), have demonstrated significant potential across various domains, their application in automating generation of engineering workflows remains underexplored. In this work, we introduce a novel copilot for automating the generation of P&IDs from natural language descriptions. Leveraging a multi-step agentic workflow, our copilot provides a structured and iterative approach to diagram creation directly from Natural Language prompts. We demonstrate the feasibility of the generation process by evaluating the soundness and completeness of the workflow, and show improved results compared to vanilla zero-shot and few-shot generation approaches.
管道与仪表图(P&IDs)是工程和工艺行业工作流程设计、构建和运营的基础。然而,其手动创建往往劳动强度大、易出错,且缺乏稳健的误差检测和校正机制。虽然最近生成式人工智能的进展,特别是大型语言模型(LLMs)和视觉语言模型(VLMs)已经在各个领域展现出显著潜力,但它们在自动化生成工程工作流程方面的应用仍然被探索得不够深入。在这项工作中,我们引入了一种新型助手,用于根据自然语言描述自动生成管道与仪表图。通过利用多步骤代理工作流程,我们的助手提供了结构化、迭代化的方法,直接从自然语言提示生成图表。我们通过评估工作流程的健全性和完整性来验证生成过程的可行性,并展示了相较于普通零样本和少样本生成方法,我们的方法具有更好的结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the AAAI’25 Workshop on AI to Accelerate Science and Engineering (AI2ASE)
Summary
工程流程图和仪器流程图(P&IDs)是工程和工艺行业工作流程设计、构建和运营的基础。然而,其手动创建往往劳动强度大、易出错,且缺乏可靠的错误检测和纠正机制。最近,生成式人工智能(尤其是大型语言模型和视觉语言模型)在各领域展现出巨大潜力,但在自动化生成工程工作流程方面的应用仍被忽视。本研究引入了一种新型P&IDs自动生成助手,它能直接从自然语言描述中生成流程图。借助多步骤的代理工作流程,该助手提供结构化和迭代式的图表创建方法。通过评估工作流程的健全性和完整性,展示了生成过程的可行性,并表现出相较于零样本和少样本生成方法的改进结果。
Key Takeaways
- P&IDs在工程和工艺行业中至关重要,但其手动创建过程劳动强度大、易出错。
- 生成式人工智能,特别是大型语言模型和视觉语言模型,在自动化生成工程工作流程方面的应用潜力巨大,但相关研究仍有限。
- 研究提出了一种新型的P&IDs自动生成助手,能直接从自然语言描述中生成流程图。
- 该助手采用多步骤的代理工作流程,提供结构化和迭代式的图表创建方法。
- 该自动生成助手的可行性通过评估工作流程的健全性和完整性得以验证。
- 与零样本和少样本生成方法相比,该助手展现出明显的改进。
- 这一研究为工程和工艺行业的自动化和智能化发展开辟了新的道路。
点此查看论文截图


Question: How do Large Language Models perform on the Question Answering tasks? Answer:
Authors:Kevin Fischer, Darren Fürst, Sebastian Steindl, Jakob Lindner, Ulrich Schäfer
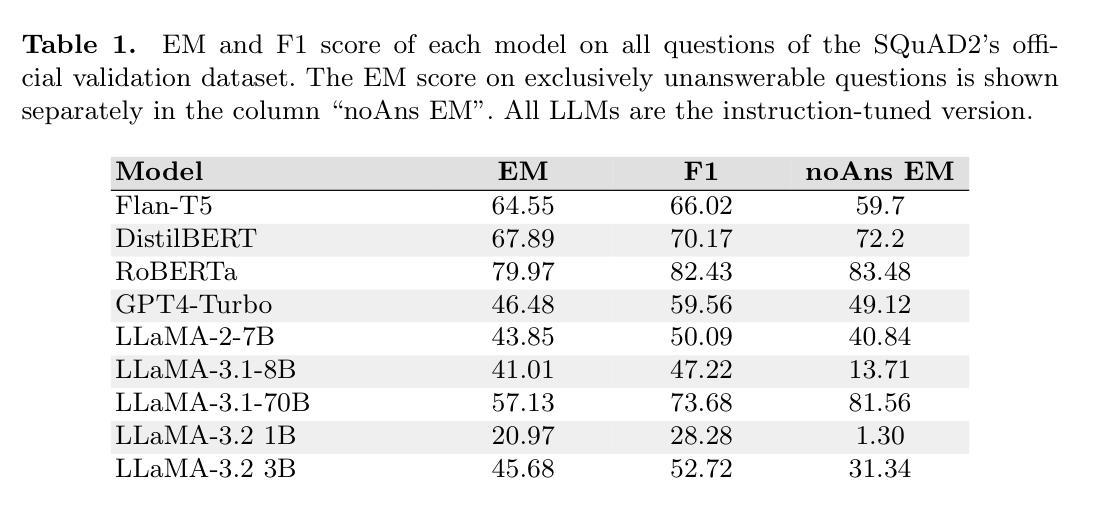
Large Language Models (LLMs) have been showing promising results for various NLP-tasks without the explicit need to be trained for these tasks by using few-shot or zero-shot prompting techniques. A common NLP-task is question-answering (QA). In this study, we propose a comprehensive performance comparison between smaller fine-tuned models and out-of-the-box instruction-following LLMs on the Stanford Question Answering Dataset 2.0 (SQuAD2), specifically when using a single-inference prompting technique. Since the dataset contains unanswerable questions, previous work used a double inference method. We propose a prompting style which aims to elicit the same ability without the need for double inference, saving compute time and resources. Furthermore, we investigate their generalization capabilities by comparing their performance on similar but different QA datasets, without fine-tuning neither model, emulating real-world uses where the context and questions asked may differ from the original training distribution, for example swapping Wikipedia for news articles. Our results show that smaller, fine-tuned models outperform current State-Of-The-Art (SOTA) LLMs on the fine-tuned task, but recent SOTA models are able to close this gap on the out-of-distribution test and even outperform the fine-tuned models on 3 of the 5 tested QA datasets.
大型语言模型(LLM)在多种NLP任务中展现出令人瞩目的结果,这些任务无需通过少量样本或零样本提示技术进行特定训练。一个常见的NLP任务是问答(QA)。在这项研究中,我们对经过微调的小型模型与即插即用的指令遵循型LLM在Stanford Question Answering Dataset 2.0(SQuAD2)上的综合性能进行了全面比较,特别是当使用单一推理提示技术时。由于该数据集包含无法回答的问题,之前的工作使用了双重推理方法。我们提出了一种提示风格,旨在在不使用双重推理的情况下激发相同的能力,从而节省计算时间和资源。此外,我们通过比较他们在类似但不同的QA数据集上的性能来调查他们的泛化能力,且无需对任何模型进行微调,以模拟现实世界的使用情况,其中上下文和所提问题可能与原始训练分布有所不同,例如将Wikipedia替换为新闻文章。我们的结果表明,经过微调的小型模型在当前先进的大型语言模型在微调任务上的表现更出色,但最近先进的大型语言模型能够在超出分布测试上缩小这一差距,甚至在五个测试问答数据集的三个上表现超过经过微调的小型模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at SAI Computing Conference 2025
Summary
LLM在问答任务上的性能表现全面比较。研究发现在特定任务上,精细调整的小型模型表现优于当前先进的LLM,但在脱离分布测试的环境下,先进的LLM能够缩小差距,甚至在三个测试中的五个问答数据集上表现优于精细调整模型。提出新的提示风格以简化推理过程。
Key Takeaways
- LLM在多种NLP任务中表现出色,可通过少样本或零样本提示技术无需特定训练即可完成。
- 在Stanford Question Answering Dataset 2.0(SQuAD2)上进行了小型精细调整模型与即插即用型LLM的性能比较。
- 提出了一种新的提示风格,旨在无需双重推理即可引出相同能力,从而节省计算时间和资源。
- 分析了LLM在类似但不同的问答数据集上的泛化能力,模拟了真实世界的使用情况,其中上下文和所提问题可能与原始训练分布不同。
- 精细调整的小型模型在特定任务上表现优于当前先进的LLM。
- 在脱离分布测试的环境下,先进的LLM能够缩小与精细调整模型的性能差距,甚至在多个数据集上表现更优。
点此查看论文截图

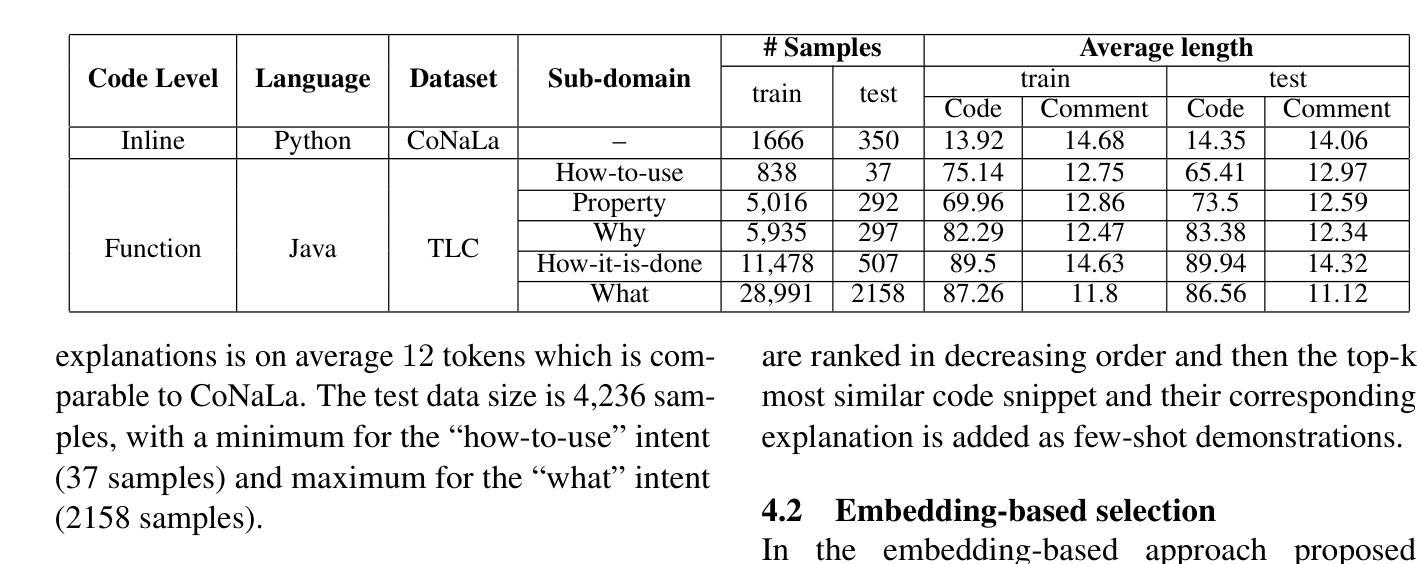
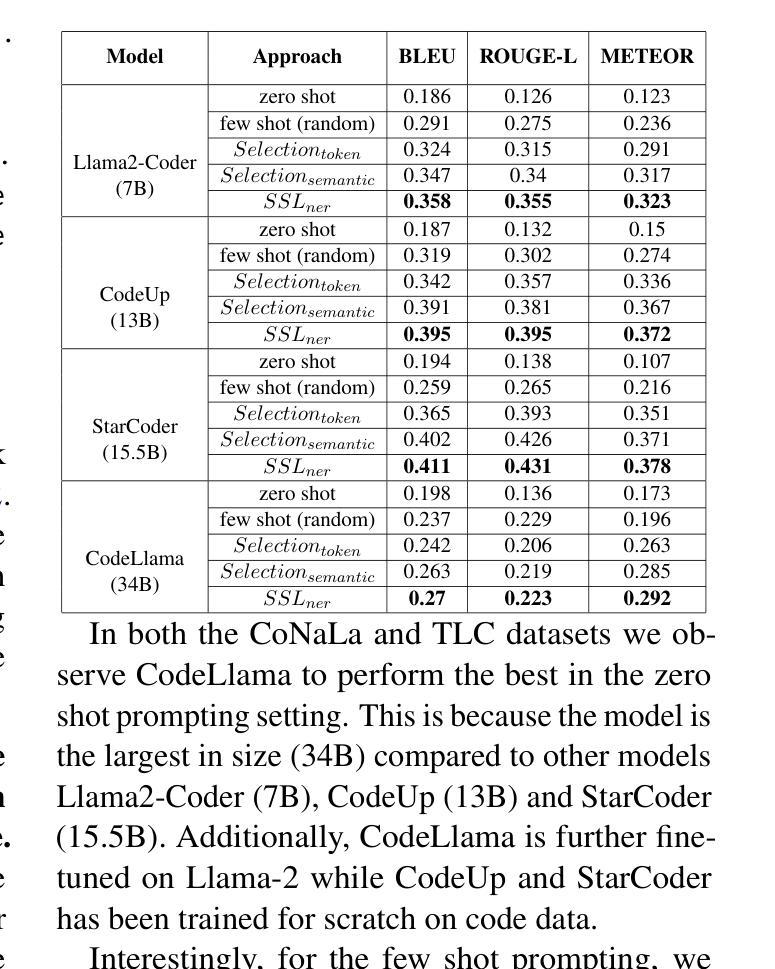
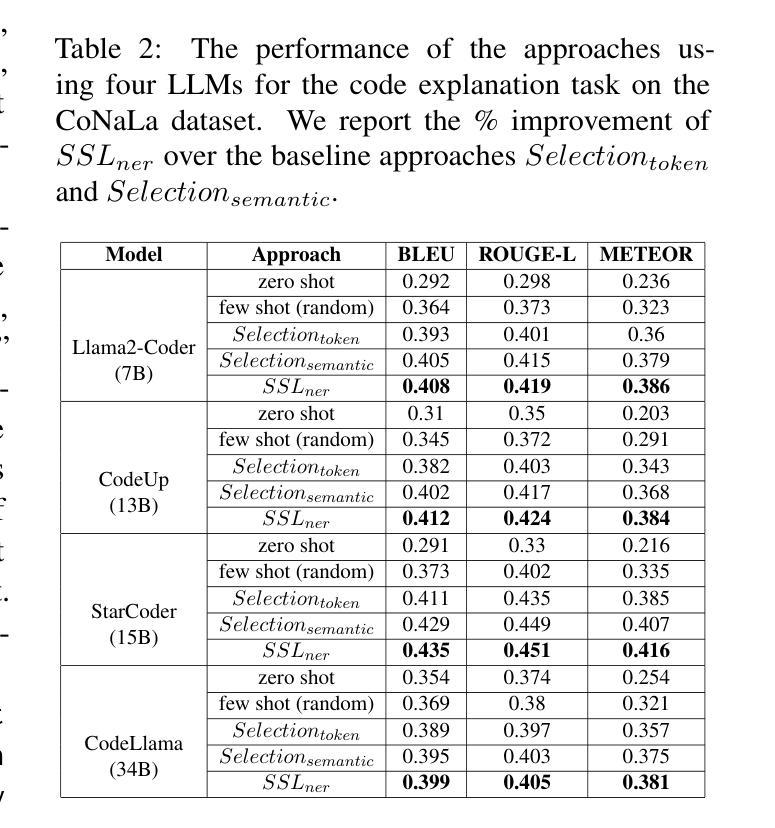
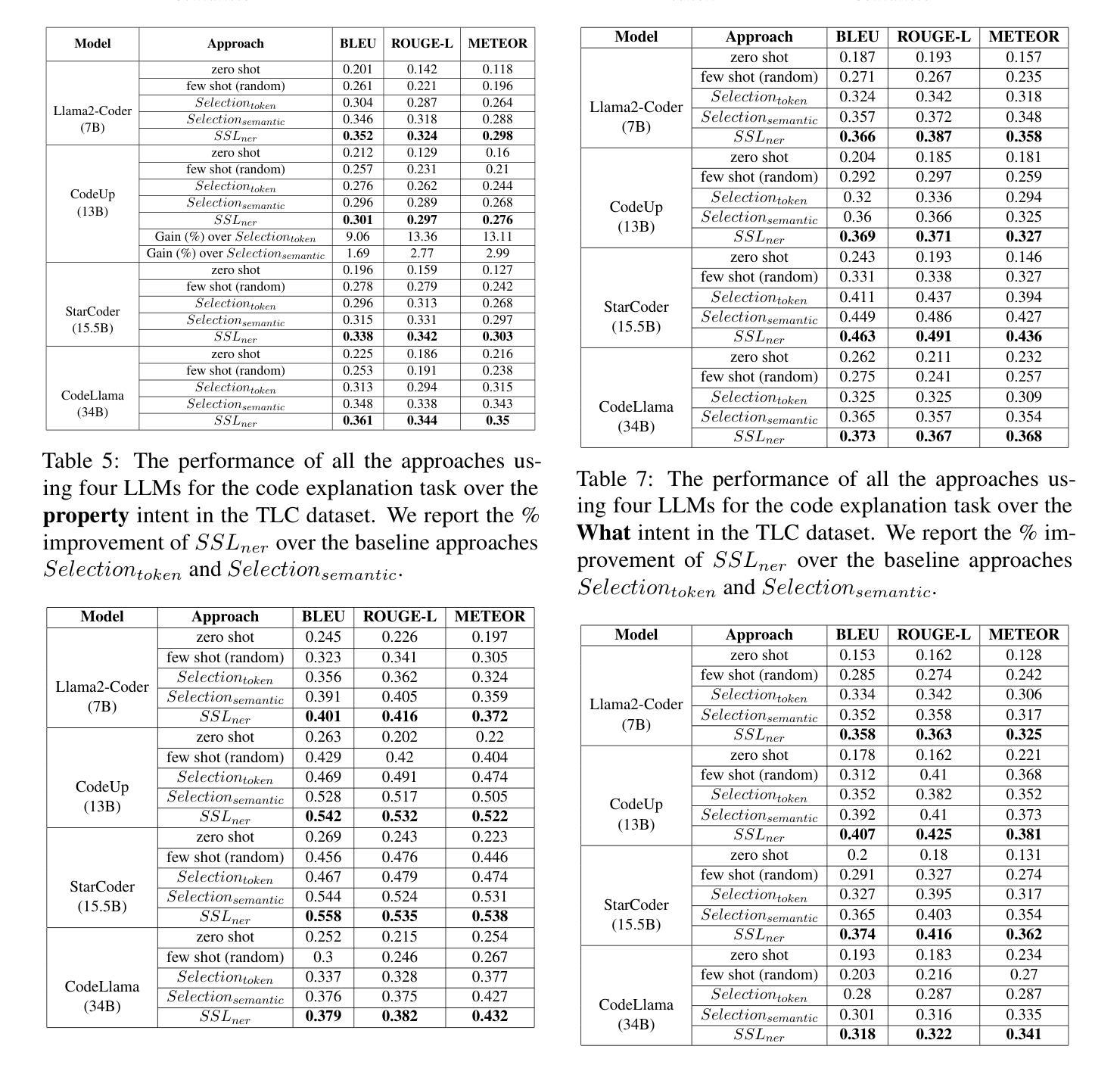
Selective Shot Learning for Code Explanation
Authors:Paheli Bhattacharya, Rishabh Gupta
Code explanation plays a crucial role in the software engineering domain, aiding developers in grasping code functionality efficiently. Recent work shows that the performance of LLMs for code explanation improves in a few-shot setting, especially when the few-shot examples are selected intelligently. State-of-the-art approaches for such Selective Shot Learning (SSL) include token-based and embedding-based methods. However, these SSL approaches have been evaluated on proprietary LLMs, without much exploration on open-source Code-LLMs. Additionally, these methods lack consideration for programming language syntax. To bridge these gaps, we present a comparative study and propose a novel SSL method (SSL_ner) that utilizes entity information for few-shot example selection. We present several insights and show the effectiveness of SSL_ner approach over state-of-the-art methods across two datasets. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first systematic benchmarking of open-source Code-LLMs while assessing the performances of the various few-shot examples selection approaches for the code explanation task.
代码解释在软件工程领域扮演着至关重要的角色,它帮助开发者高效地掌握代码功能。最近的研究表明,大型语言模型(LLMs)在少量样本场景下的代码解释性能有所提升,尤其是当选择的少量样本是明智的时候。针对此类选择性射击学习(SSL)的最新方法包括基于令牌和基于嵌入的方法。然而,这些SSL方法主要是在专有的大型语言模型上进行了评估,而对开源代码的大型语言模型(Code-LLMs)的探索并不多。此外,这些方法没有考虑到编程语言的语法。为了弥补这些差距,我们进行了一项比较研究,并提出了一种新的SSL方法(SSL_ner),该方法利用实体信息进行少量样本选择。我们获得了一些见解,并展示了SSL_ner方法在两个数据集上的性能优于最新方法。据我们所知,这是在对各种少量样本选择方法进行性能评估的同时,首次对开源代码的大型语言模型进行系统的基准测试。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于软件工程领域中的代码解释的重要性,LLMs(大型预训练语言模型)在少数样本下的表现提升受到关注。近期工作表明,合理选择少数样本对于提升LLMs在代码解释任务中的性能尤为关键。本研究针对开源Code-LLMs进行系统性评估,并提出一种利用实体信息的新型Selective Shot Learning(SSL_ner)方法。该方法在考虑编程语言的语法结构基础上,实现了对SSL方法的改进。研究提供了丰富的见解,并在两个数据集上验证了SSL_ner方法的有效性。这是首个针对开源Code-LLMs评估不同少数样本选择方法在代码解释任务上的表现的基准测试。
Key Takeaways
- 代码解释在软件工程中扮演着至关重要的角色,有助于开发者高效理解代码功能。
- LLMs在少数样本下的性能提升受到关注,尤其是合理选择少数样本的重要性。
- 现有的SSL方法在评估中主要针对私有LLMs,而较少探索开源Code-LLMs。
- SSL方法在考虑编程语言的语法结构上存在不足。
- 研究提出了一种新的SSL方法——SSL_ner,该方法利用实体信息进行少数样本选择。
- 研究在多个数据集上验证了SSL_ner方法的有效性,表明其相较于现有方法的优势。
点此查看论文截图

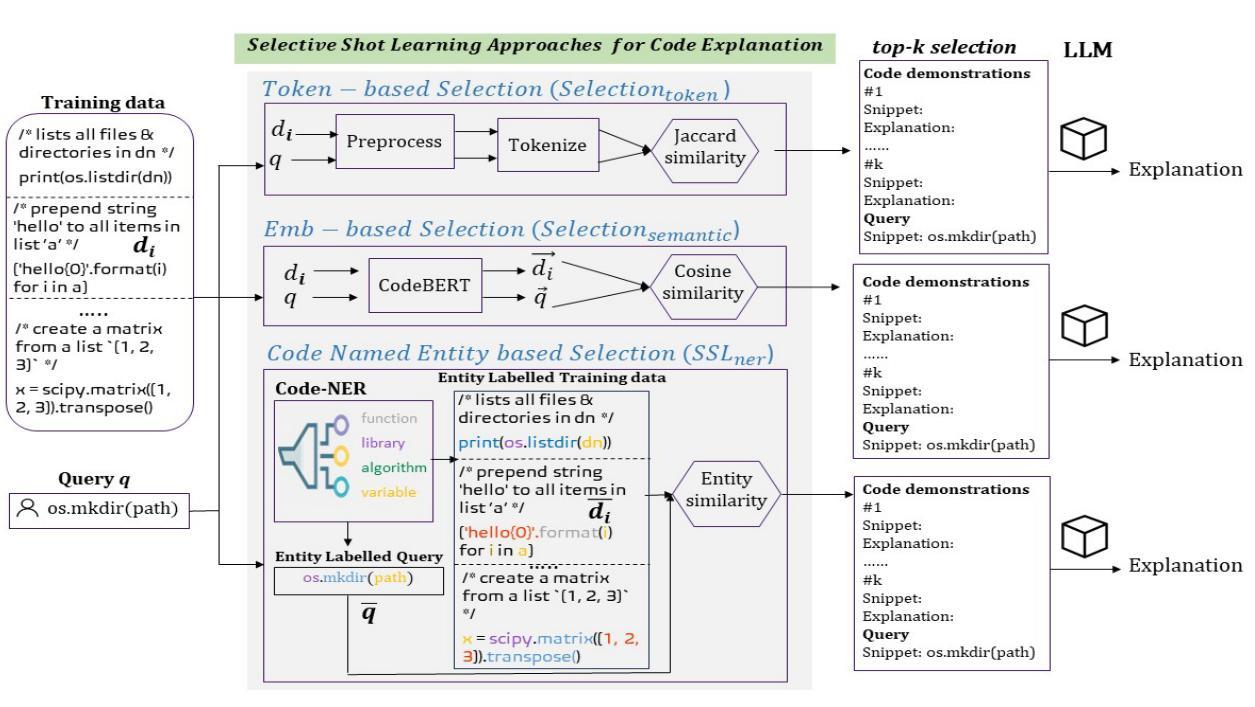
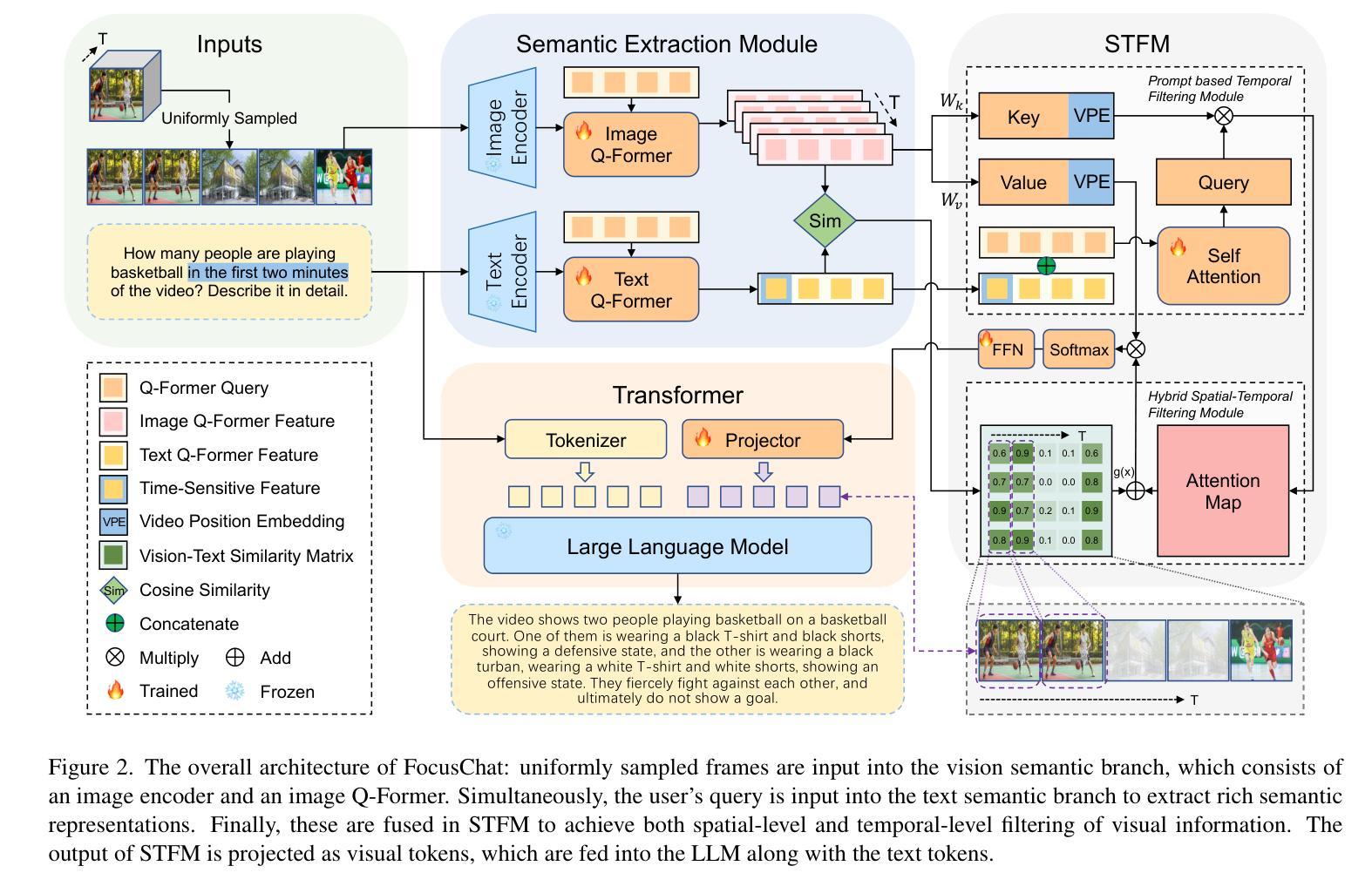
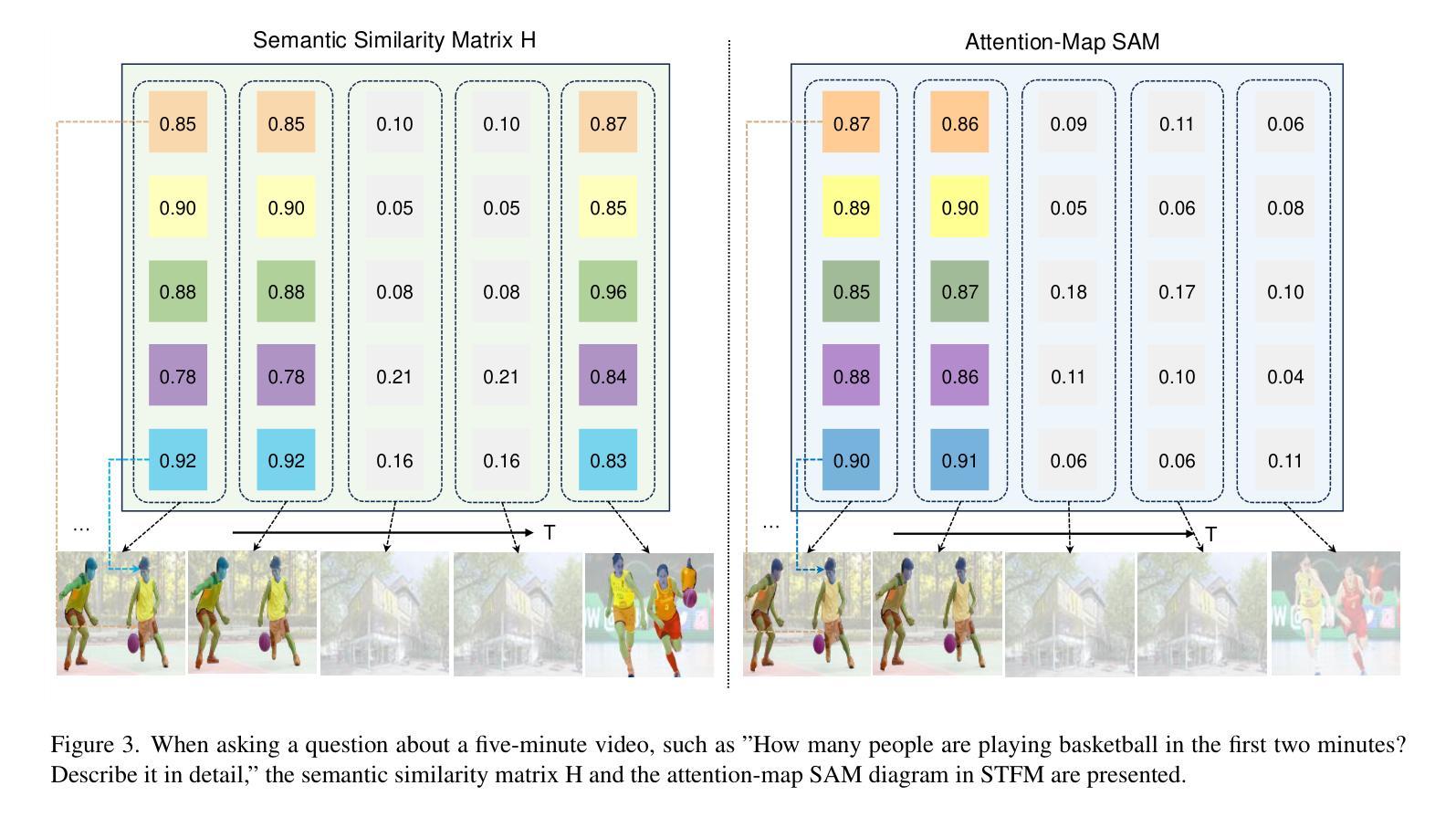
FocusChat: Text-guided Long Video Understanding via Spatiotemporal Information Filtering
Authors:Zheng Cheng, Rendong Wang, Zhicheng Wang
Recently, multi-modal large language models have made significant progress. However, visual information lacking of guidance from the user’s intention may lead to redundant computation and involve unnecessary visual noise, especially in long, untrimmed videos. To address this issue, we propose FocusChat, a text-guided multi-modal large language model (LLM) that emphasizes visual information correlated to the user’s prompt. In detail, Our model first undergoes the semantic extraction module, which comprises a visual semantic branch and a text semantic branch to extract image and text semantics, respectively. The two branches are combined using the Spatial-Temporal Filtering Module (STFM). STFM enables explicit spatial-level information filtering and implicit temporal-level feature filtering, ensuring that the visual tokens are closely aligned with the user’s query. It lowers the essential number of visual tokens inputted into the LLM. FocusChat significantly outperforms Video-LLaMA in zero-shot experiments, using an order of magnitude less training data with only 16 visual tokens occupied. It achieves results comparable to the state-of-the-art in few-shot experiments, with only 0.72M pre-training data.
近期,多模态大型语言模型取得了显著进展。然而,缺乏用户意图指导的视觉信息可能导致冗余计算并引入不必要的视觉噪声,特别是在长且未修剪的视频中。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了FocusChat,这是一个文本引导的多模态大型语言模型(LLM),它强调与用户提示相关的视觉信息。具体来说,我们的模型首先经过语义提取模块,该模块包括视觉语义分支和文本语义分支,分别提取图像和文本语义。这两个分支通过时空滤波模块(STFM)进行组合。STFM实现了显式的空间级信息滤波和隐式的时间级特征滤波,确保视觉令牌与用户查询紧密对齐。它降低了输入到LLM中的必要视觉令牌数量。FocusChat在零样本实验中显著优于Video-LLaMA,使用数量级更少的训练数据,仅占用16个视觉令牌。在少量样本实验中,它达到了与国家最新技术相当的结果,仅有0.72M的预训练数据。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 4 figures
Summary
文本提出了一种名为FocusChat的文本引导式多模态大型语言模型,该模型强调与用户提示相关的视觉信息。它通过语义提取模块和空间时间过滤模块,降低了输入到语言模型中的视觉标记数量,从而提高效率并减少冗余计算。FocusChat在零射击实验中的表现显著优于Video-LLaMA,使用的训练数据量减少了一个数量级,同时在少击实验中取得了与最新技术相当的结果,仅使用0.72M的预训练数据。
Key Takeaways
- FocusChat是一个文本引导的多模态大型语言模型,旨在解决在视频处理中由于用户意图缺乏指导而导致的冗余计算和视觉噪音问题。
- 该模型通过语义提取模块和空间时间过滤模块来强调与用户提示相关的视觉信息。
- FocusChat通过降低输入到语言模型中的视觉标记数量来提高效率。
- FocusChat在零射击实验中的表现优于Video-LLaMA,使用的训练数据量大大减少。
- 该模型在少击实验中取得了与最新技术相当的结果。
- FocusChat的预训练数据量仅为0.72M。
点此查看论文截图

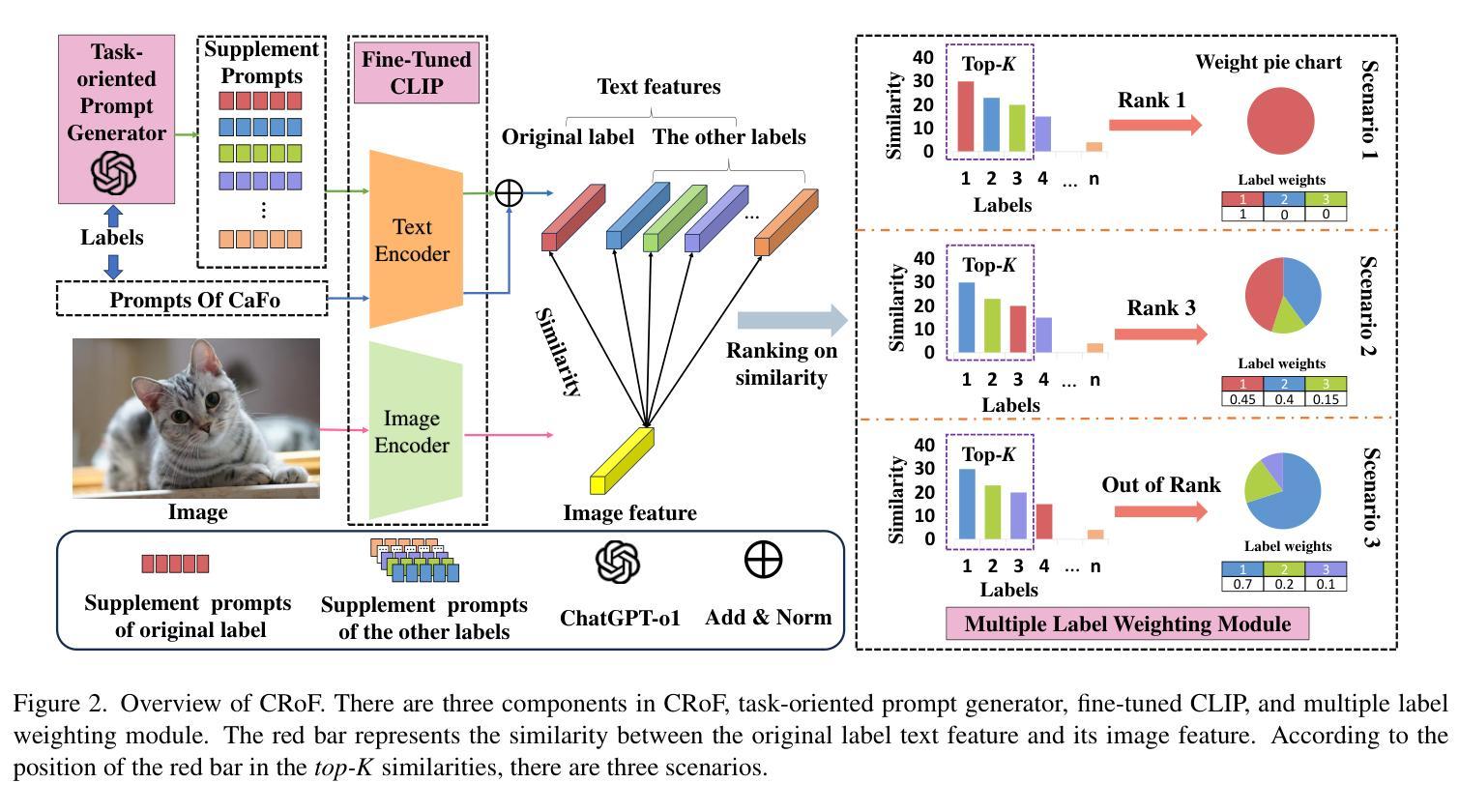
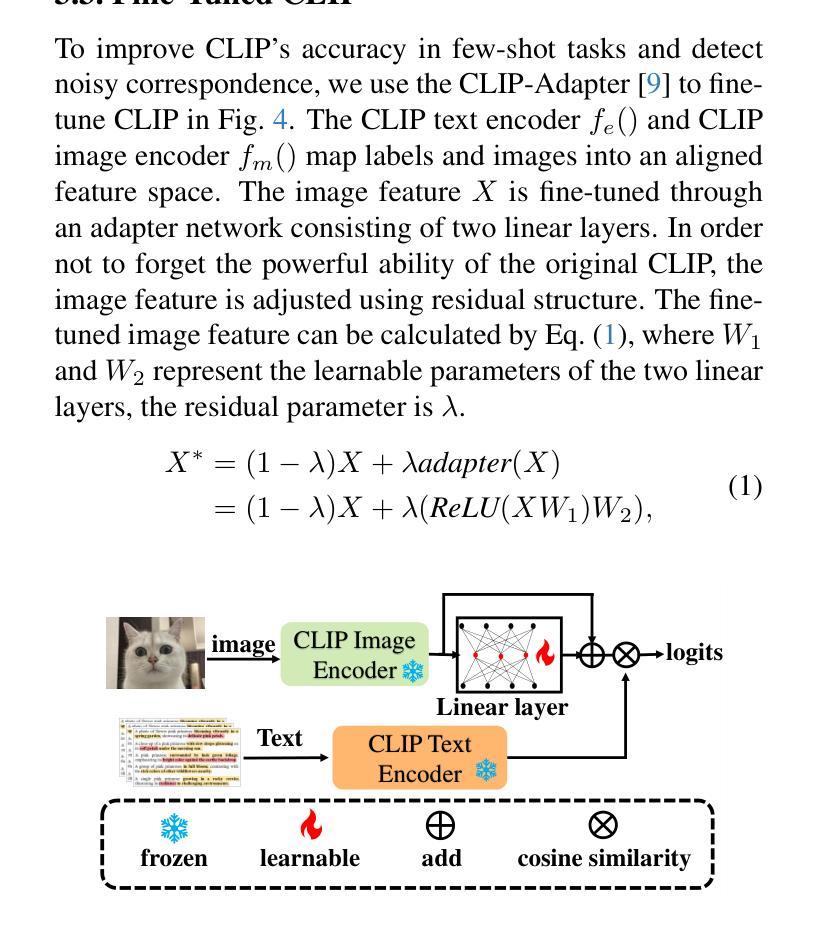
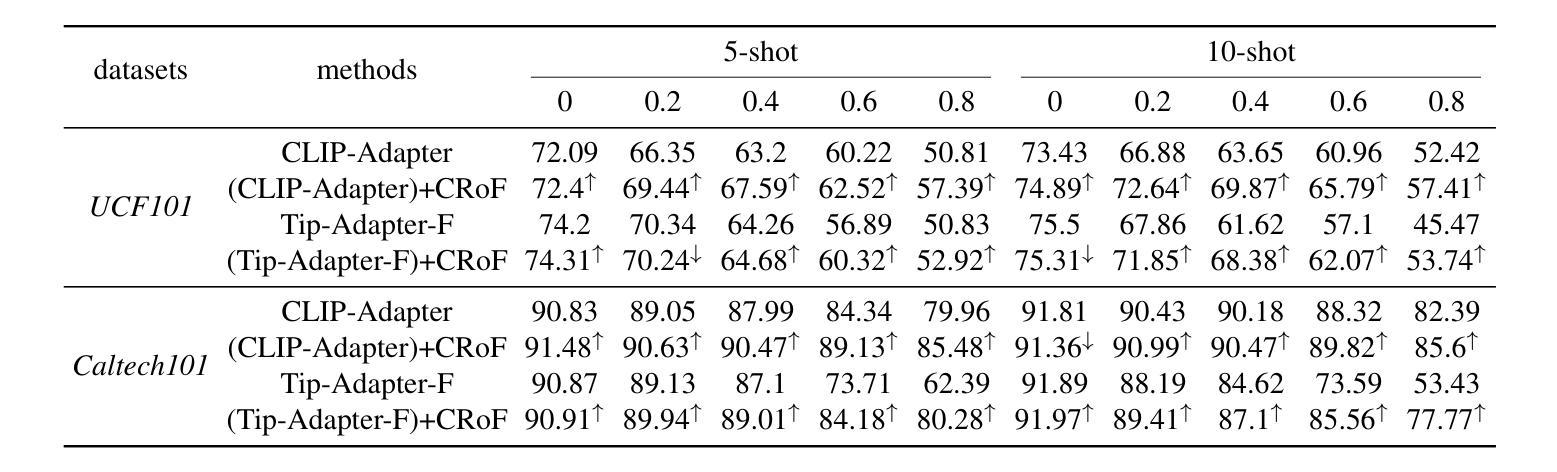
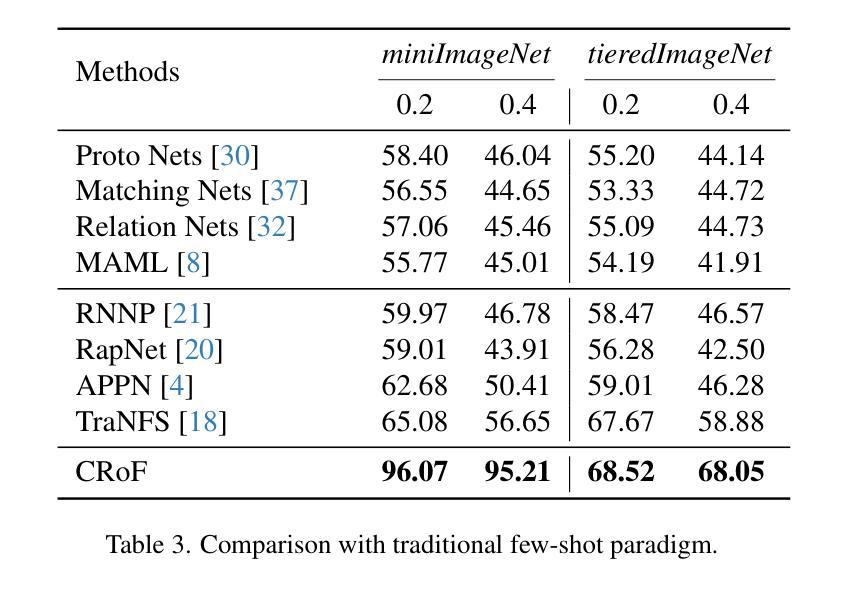
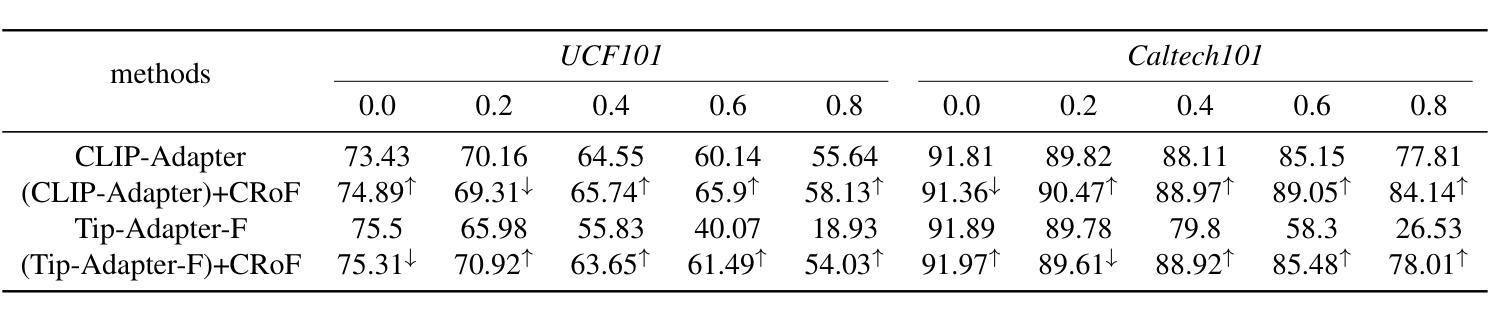
CRoF: CLIP-based Robust Few-shot Learning on Noisy Labels
Authors:Shizhuo Deng, Bowen Han, Jiaqi Chen, Hao Wang, Dongyue Chen, Tong Jia
Noisy labels threaten the robustness of few-shot learning (FSL) due to the inexact features in a new domain. CLIP, a large-scale vision-language model, performs well in FSL on image-text embedding similarities, but it is susceptible to misclassification caused by noisy labels. How to enhance domain generalization of CLIP on noisy data within FSL tasks is a critical challenge. In this paper, we provide a novel view to mitigate the influence of noisy labels, CLIP-based Robust Few-shot learning (CRoF). CRoF is a general plug-in module for CLIP-based models. To avoid misclassification and confused label embedding, we design the few-shot task-oriented prompt generator to give more discriminative descriptions of each category. The proposed prompt achieves larger distances of inter-class textual embedding. Furthermore, rather than fully trusting zero-shot classification by CLIP, we fine-tune CLIP on noisy few-shot data in a new domain with a weighting strategy like label-smooth. The weights for multiple potentially correct labels consider the relationship between CLIP’s prior knowledge and original label information to ensure reliability. Our multiple label loss function further supports robust training under this paradigm. Comprehensive experiments show that CRoF, as a plug-in, outperforms fine-tuned and vanilla CLIP models on different noise types and noise ratios.
带噪声的标签由于新领域的特征不准确而威胁少样本学习(FSL)的稳健性。CLIP是一种大规模的视觉语言模型,在图像文本嵌入相似性方面,FSL中表现良好,但它容易受到带噪声标签导致的误分类影响。如何在FSL任务中带噪声数据上增强CLIP的领域泛化是一个关键挑战。在本文中,我们提供了减轻带噪声标签影响的全新观点,即基于CLIP的鲁棒少样本学习(CRoF)。CRoF是一个适用于CLIP模型的通用插件模块。为了避免误分类和混淆标签嵌入,我们设计了面向少样本任务的提示生成器,为每个类别提供更具区分度的描述。所提出的提示实现了较大的类间文本嵌入距离。此外,我们不是完全信任CLIP的零样本分类,而是使用标签平滑等加权策略对新领域中的带噪声少样本数据进行微调。多个可能正确的标签的权重考虑了CLIP的先验知识和原始标签信息之间的关系,以确保可靠性。我们的多标签损失函数进一步支持此模式下的稳健训练。综合实验表明,作为插件的CRoF在不同噪声类型和噪声比率上优于经过精细调整和原始的CLIP模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
CLIP模型在少量样本学习(FSL)中因新域的不精确特征而受到噪声标签的威胁。本文提出了一种新型的CRoF模块来减少噪声标签的影响,它增强了CLIP模型的域泛化能力。CRoF是一种针对CLIP模型的通用插件模块,它通过设计面向任务的少量提示生成器来避免误分类和混淆标签嵌入。此外,CRoF还采用了一种加权策略对CLIP进行微调,以适应新域的噪声数据。通过综合实验证明,CRoF作为插件在不同噪声类型和噪声比率上均优于微调后的CLIP模型和原始CLIP模型。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP在少量样本学习(FSL)中易受噪声标签影响,导致性能下降。
- CRoF作为一种新型插件模块,旨在提高CLIP模型在新域的泛化能力。
- CRoF通过设计面向任务的少量提示生成器,减少误分类和混淆标签嵌入的问题。
- CRoF采用加权策略对CLIP进行微调,以适应新域的噪声数据,提高模型的可靠性。
- CRoF利用多重标签损失函数进行稳健训练。
- 综合实验表明,CRoF在多种噪声类型和比率下性能优于原始CLIP模型和微调后的CLIP模型。
点此查看论文截图


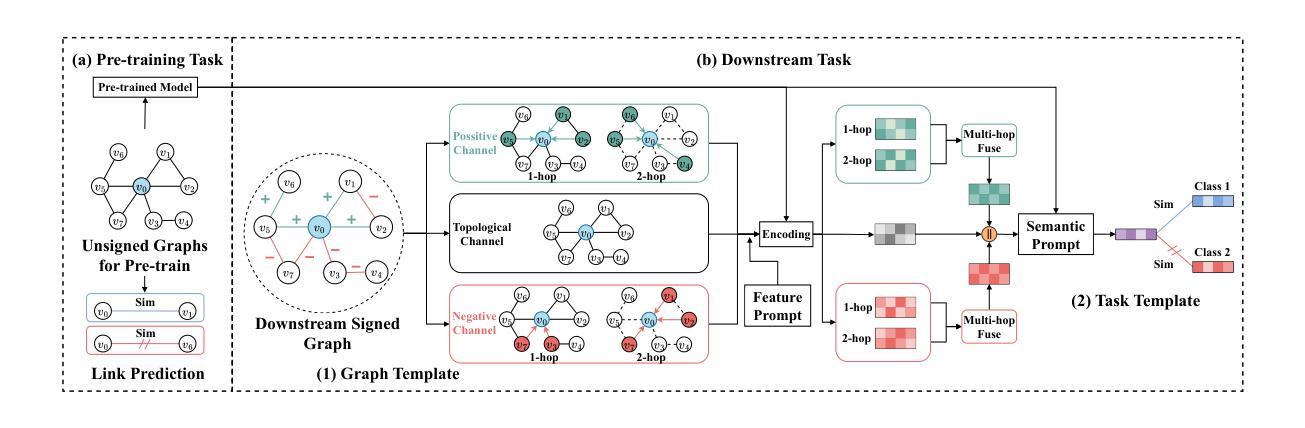
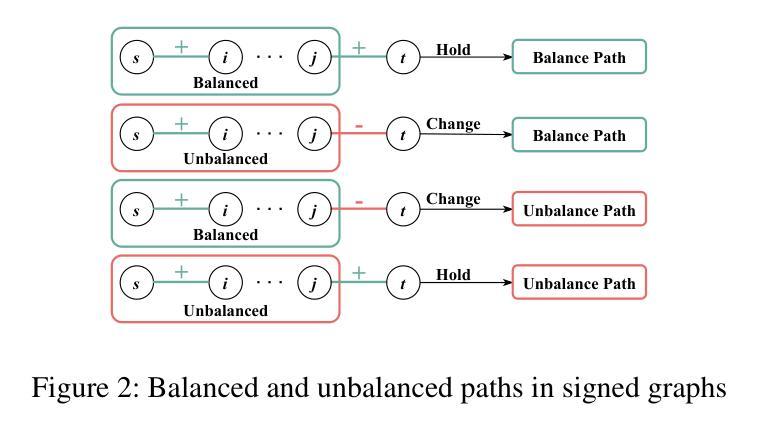
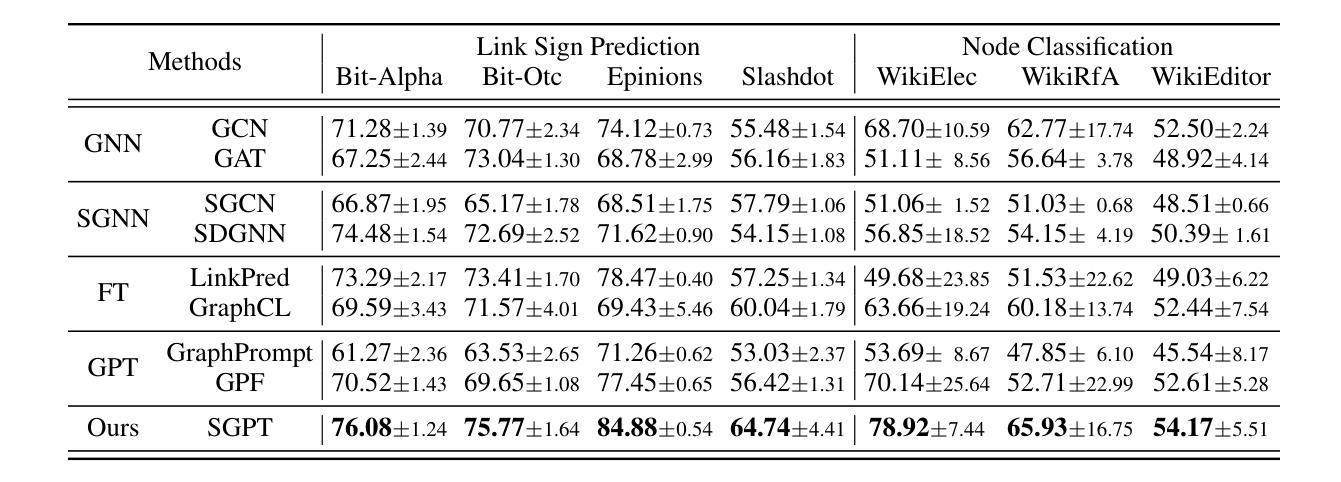
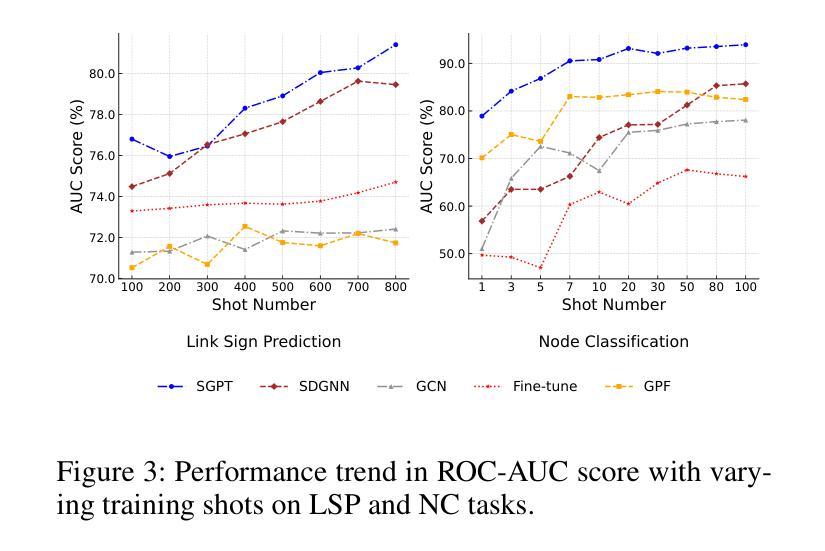
Adapting Unsigned Graph Neural Networks for Signed Graphs: A Few-Shot Prompt Tuning Approach
Authors:Zian Zhai, Sima Qing, Xiaoyang Wang, Wenjie Zhang
Signed Graph Neural Networks (SGNNs) are powerful tools for signed graph representation learning but struggle with limited generalization and heavy dependence on labeled data. While recent advancements in “graph pre-training and prompt tuning” have reduced label dependence in Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) and improved their generalization abilities by leveraging pre-training knowledge, these efforts have focused exclusively on unsigned graphs. The scarcity of publicly available signed graph datasets makes it essential to transfer knowledge from unsigned graphs to signed graph tasks. However, this transfer introduces significant challenges due to the graph-level and task-level divergences between the pre-training and downstream phases. To address these challenges, we propose Signed Graph Prompt Tuning (SGPT) in this paper. Specifically, SGPT employs a graph template and a semantic prompt to segregate mixed link semantics in the signed graph and then adaptively integrate the distinctive semantic information according to the needs of downstream tasks, thereby unifying the pre-training and downstream graphs. Additionally, SGPT utilizes a task template and a feature prompt to reformulate the downstream signed graph tasks, aligning them with pre-training tasks to ensure a unified optimization objective and consistent feature space across tasks. Finally, extensive experiments are conducted on popular signed graph datasets, demonstrating the superiority of SGPT over state-of-the-art methods.
有符号图神经网络(SGNNs)是有符号图表示学习的强大工具,但在泛化有限和严重依赖标签数据方面存在挑战。虽然最近的“图预训练和提示调整”进展减少了图神经网络(GNNs)对标签的依赖,并利用预训练知识提高了其泛化能力,但这些努力都集中在无符号图上。有符号图数据集公开可用的稀缺性使得从无符号图向有符号图任务转移知识变得至关重要。然而,由于预训练和下流阶段之间的图级别和任务级别差异,这种转移引入了重大挑战。为了应对这些挑战,我们在本文中提出了有符号图提示调整(SGPT)。具体来说,SGPT采用图模板和语义提示来分离有符号图中的混合链接语义,然后根据下游任务的需求自适应地集成不同的语义信息,从而统一预训练和下流图。此外,SGPT利用任务模板和特征提示来重新制定下游有符号图任务,使它们与预训练任务对齐,以确保统一优化目标和任务之间一致的特征空间。最后,在流行的有符号图数据集上进行了大量实验,证明了SGPT优于最先进的方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
SGNN的强大工具用于有符号图表示学习,但存在泛化受限和依赖大量标签数据的问题。最近图预训练和提示调整技术的进步减少了图神经网络对标签的依赖,利用预训练知识提高了泛化能力,但这些努力主要集中在无符号图上。有符号图数据集的稀缺性使得从无符号图向有符号图任务转移知识变得至关重要,但由于预训练和下游阶段的图级别和任务级别的差异,这种转移引入了重大挑战。本文提出了有符号图提示调整(SGPT)来解决这些挑战。SGPT使用图模板和语义提示来分离混合链接语义,并根据下游任务的需要自适应地集成不同的语义信息,从而统一预训练和下游图。此外,SGPT还使用任务模板和特征提示来重新制定下游有符号图任务,使其与预训练任务对齐,确保统一的优化目标和跨任务的一致特征空间。在流行的有符号图数据集上进行了广泛实验,证明SGPT优于最新方法。
Key Takeaways
- Signed Graph Neural Networks (SGNNs) 面临泛化有限和依赖大量标签数据的问题。
- 最近图预训练和提示调整技术的进步已应用于无符号图上,以提高泛化能力和减少标签依赖。
- 有符号图数据集的稀缺性导致需要从无符号图向有符号图任务转移知识。
- 这种转移面临预训练和下游阶段的图级别和任务级别的差异带来的挑战。
- Signed Graph Prompt Tuning (SGPT) 被提出来解决这些挑战,通过图模板和语义提示来分离混合链接语义并集成不同的语义信息。
- SGPT还使用任务模板和特征提示来重新制定下游有符号图任务,确保统一的优化目标和一致的特征空间。
点此查看论文截图

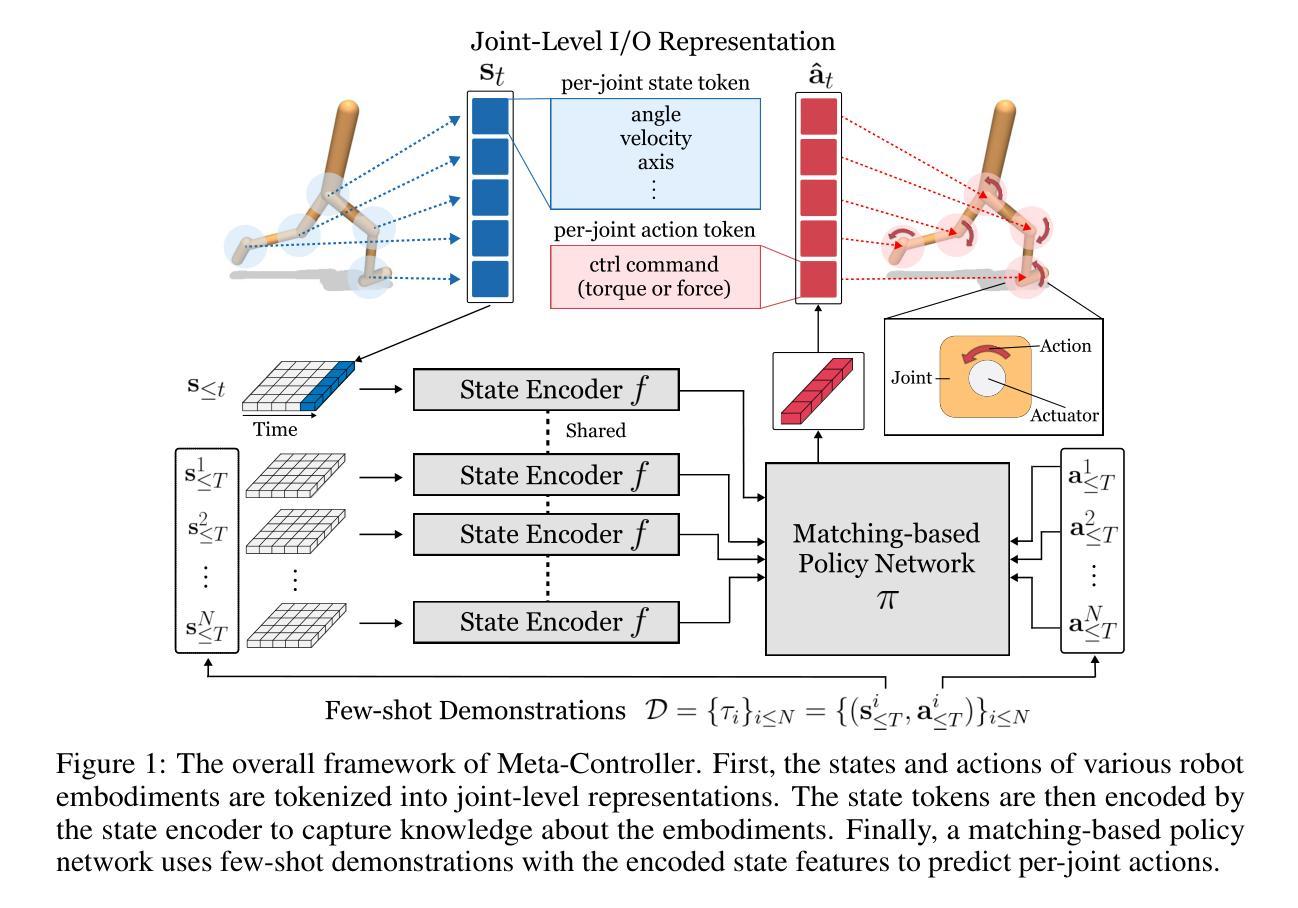
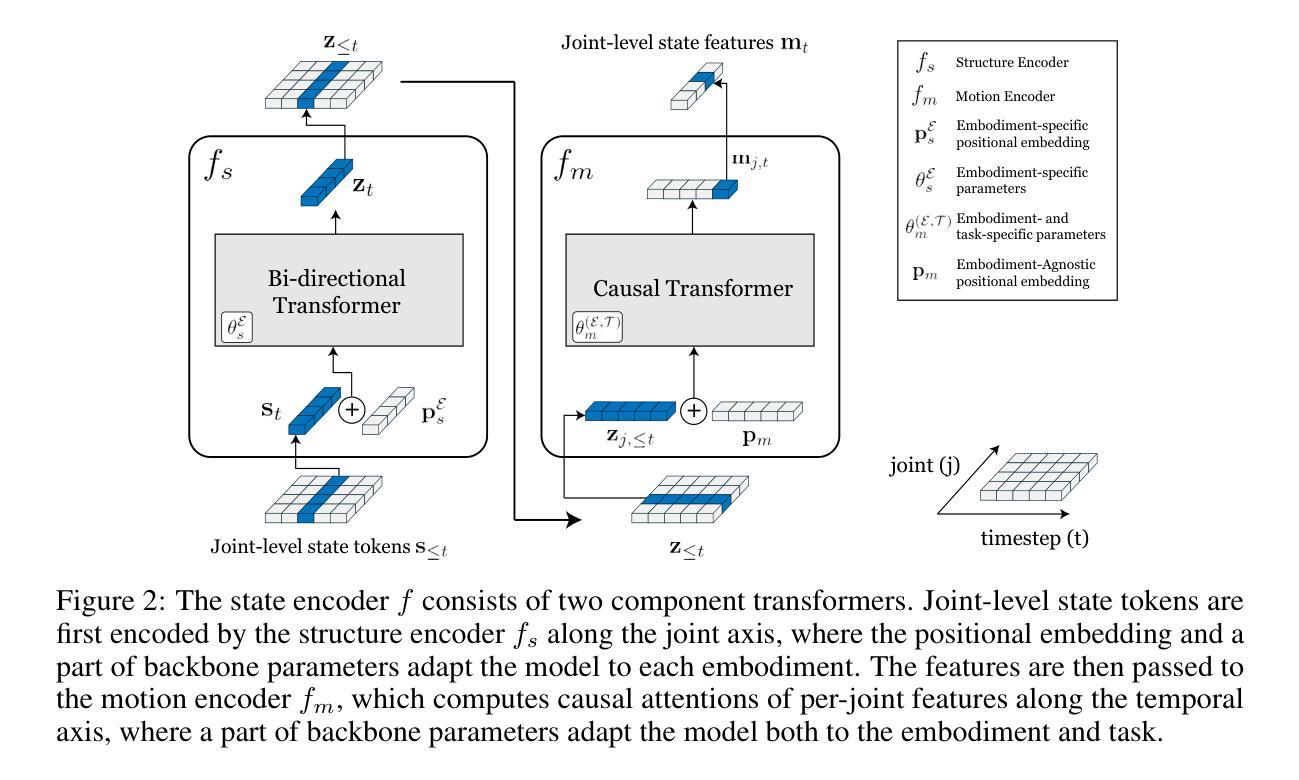
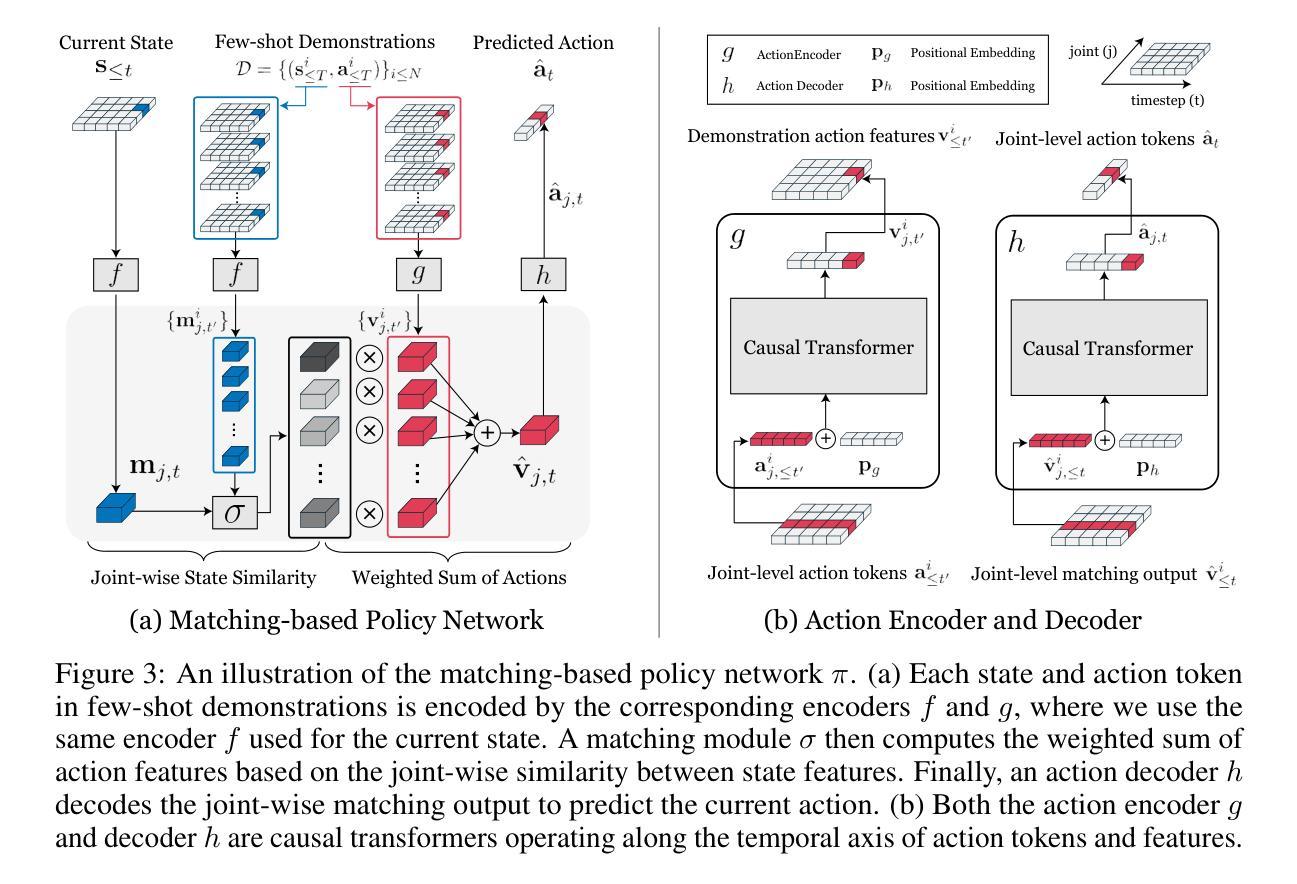
Meta-Controller: Few-Shot Imitation of Unseen Embodiments and Tasks in Continuous Control
Authors:Seongwoong Cho, Donggyun Kim, Jinwoo Lee, Seunghoon Hong
Generalizing across robot embodiments and tasks is crucial for adaptive robotic systems. Modular policy learning approaches adapt to new embodiments but are limited to specific tasks, while few-shot imitation learning (IL) approaches often focus on a single embodiment. In this paper, we introduce a few-shot behavior cloning framework to simultaneously generalize to unseen embodiments and tasks using a few (\emph{e.g.,} five) reward-free demonstrations. Our framework leverages a joint-level input-output representation to unify the state and action spaces of heterogeneous embodiments and employs a novel structure-motion state encoder that is parameterized to capture both shared knowledge across all embodiments and embodiment-specific knowledge. A matching-based policy network then predicts actions from a few demonstrations, producing an adaptive policy that is robust to over-fitting. Evaluated in the DeepMind Control suite, our framework termed \modelname{} demonstrates superior few-shot generalization to unseen embodiments and tasks over modular policy learning and few-shot IL approaches. Codes are available at \href{https://github.com/SeongwoongCho/meta-controller}{https://github.com/SeongwoongCho/meta-controller}.
对于自适应机器人系统来说,跨机器人实体和任务的一般化至关重要。模块化策略学习方法能够适应新的实体,但仅限于特定任务,而少样本模仿学习(IL)方法通常侧重于单一实体。在本文中,我们引入了一种少样本行为克隆框架,该框架能够利用少量(例如五个)无奖励示范来同时推广到未见过的实体和任务。我们的框架利用关节级输入输出表示来统一异质实体的状态和行为空间,并采用新型结构运动状态编码器,该编码器经过参数化设置,能够捕捉所有实体之间的共享知识以及针对实体的特定知识。然后,基于匹配的策略网络从少数示范中预测行为,产生能够适应过度拟合的稳健策略。在DeepMind Control套件中进行评估,我们的框架(称为\modelname)在未见过的实体和任务上表现出优于模块化策略学习和少样本IL方法的少样本泛化能力。代码可在https://github.com/SeongwoongCho/meta-controller中找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文提出了一种基于行为克隆的框架,能够在少量奖励无关演示的基础上,同时推广到未见过的机器人实体和任务。该框架利用关节级输入输出表示来统一不同实体的状态和行为空间,并采用新型结构运动状态编码器捕捉跨实体的共享知识和特定实体的知识。匹配策略网络根据少量演示预测行为,产生适应性策略,减少过度拟合。在DeepMind控制套件中评估,该框架展现出出色的未见实体和任务的少样本泛化能力,优于模块化政策学习和少样本模仿学习的方法。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种基于行为克隆的框架,可以推广到未见过的机器人实体和任务。
- 利用关节级输入输出表示来统一不同实体的状态和行为空间。
- 采用新型结构运动状态编码器捕捉跨实体的共享知识和特定实体的知识。
- 通过匹配策略网络预测行为,产生适应性策略,减少过度拟合。
- 在DeepMind控制套件中评估,展现出出色的未见实体和任务的少样本泛化能力。
- 该框架优于模块化政策学习和少样本模仿学习的方法。
点此查看论文截图

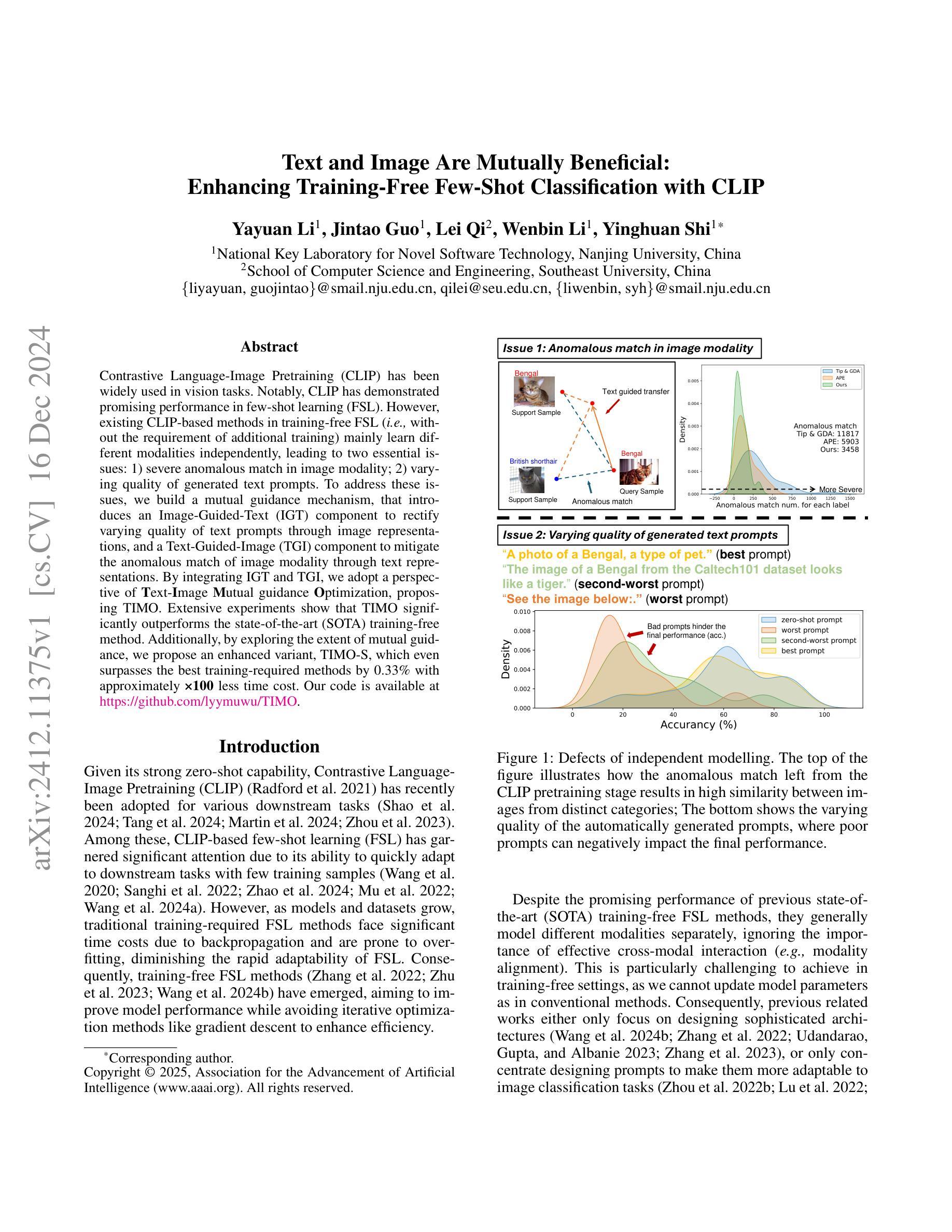
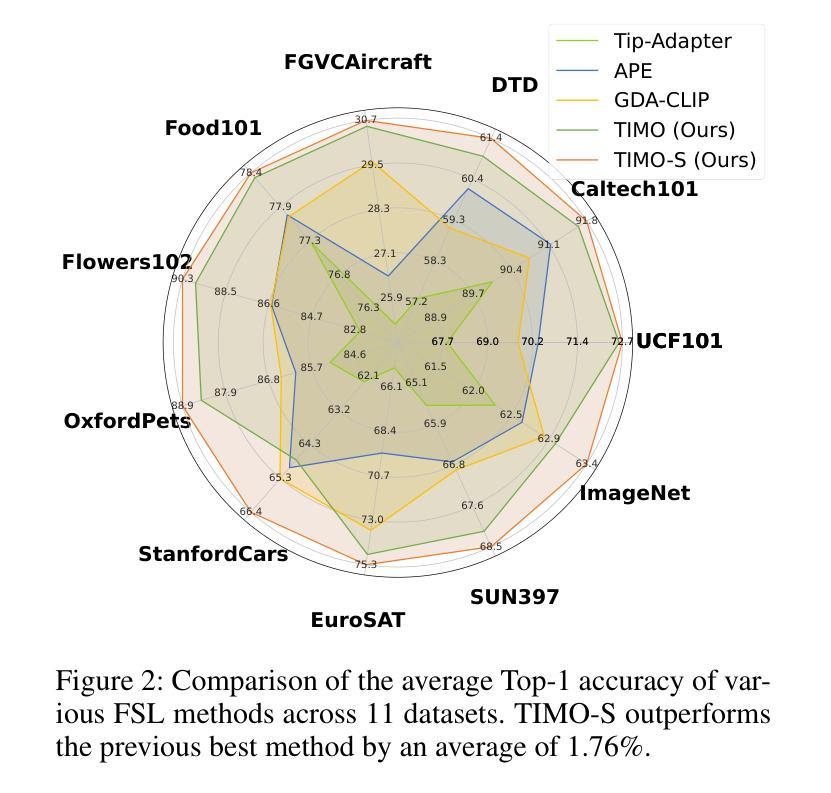
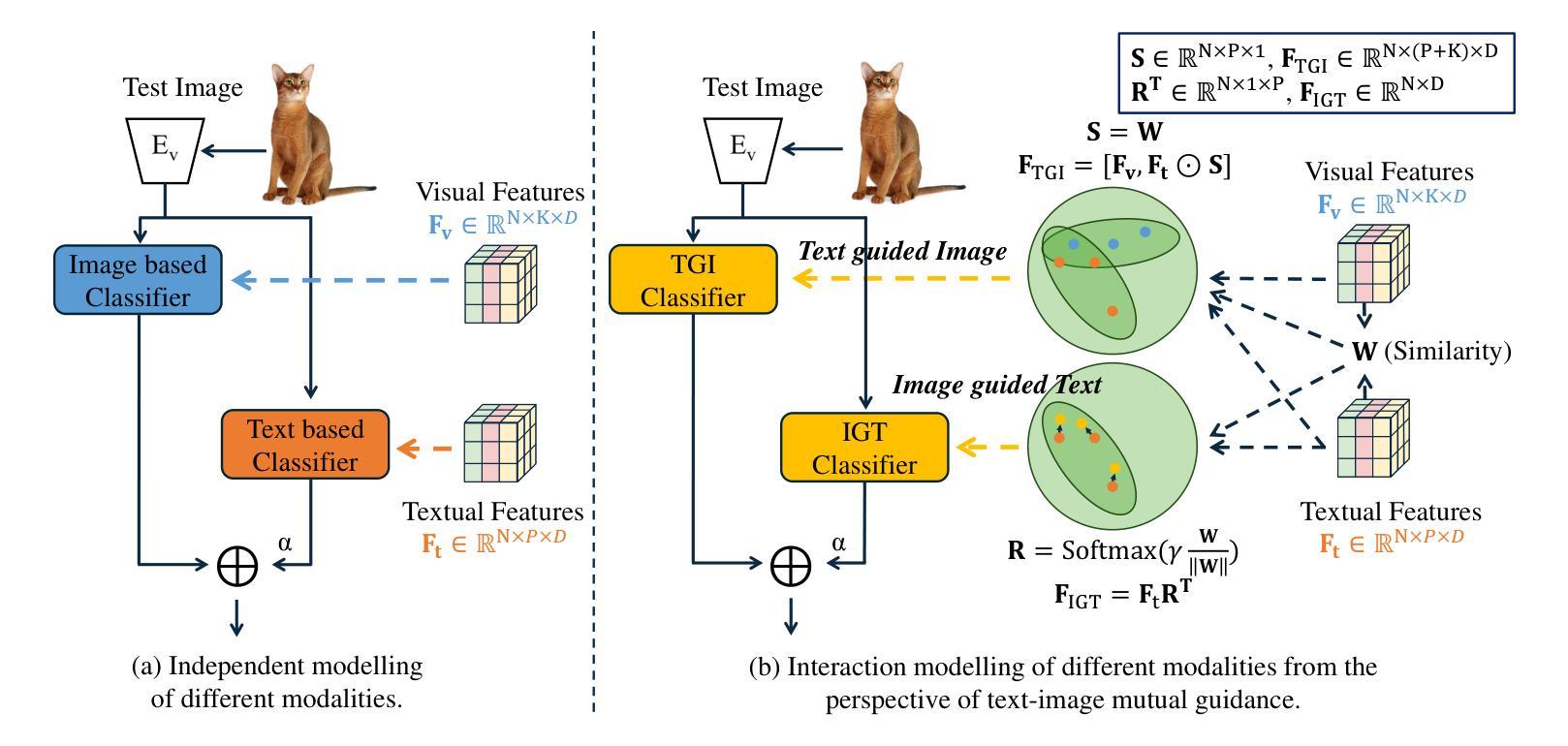
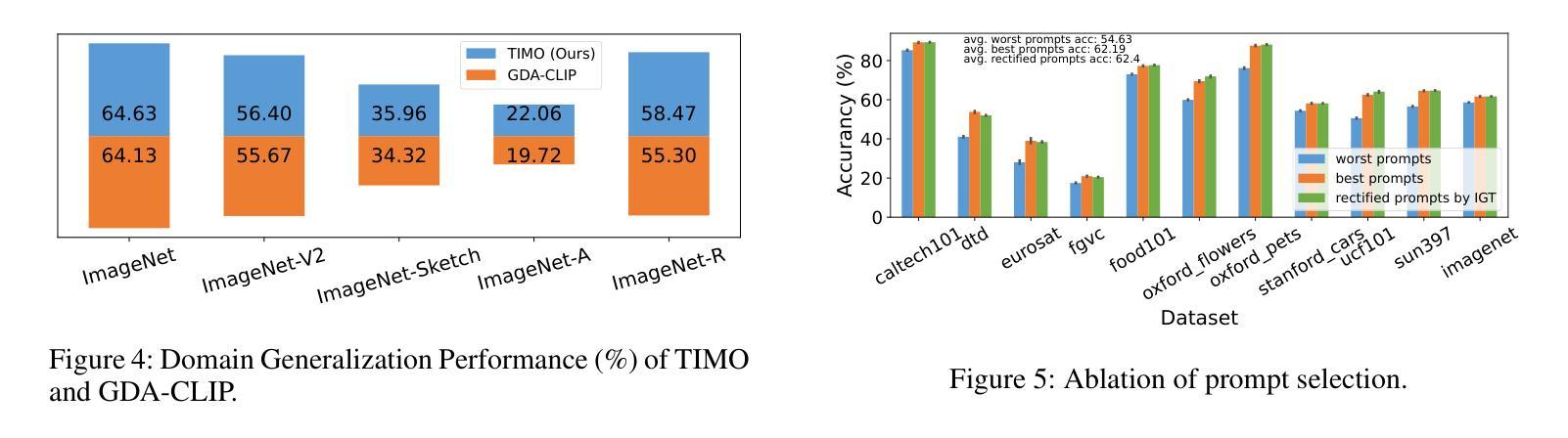
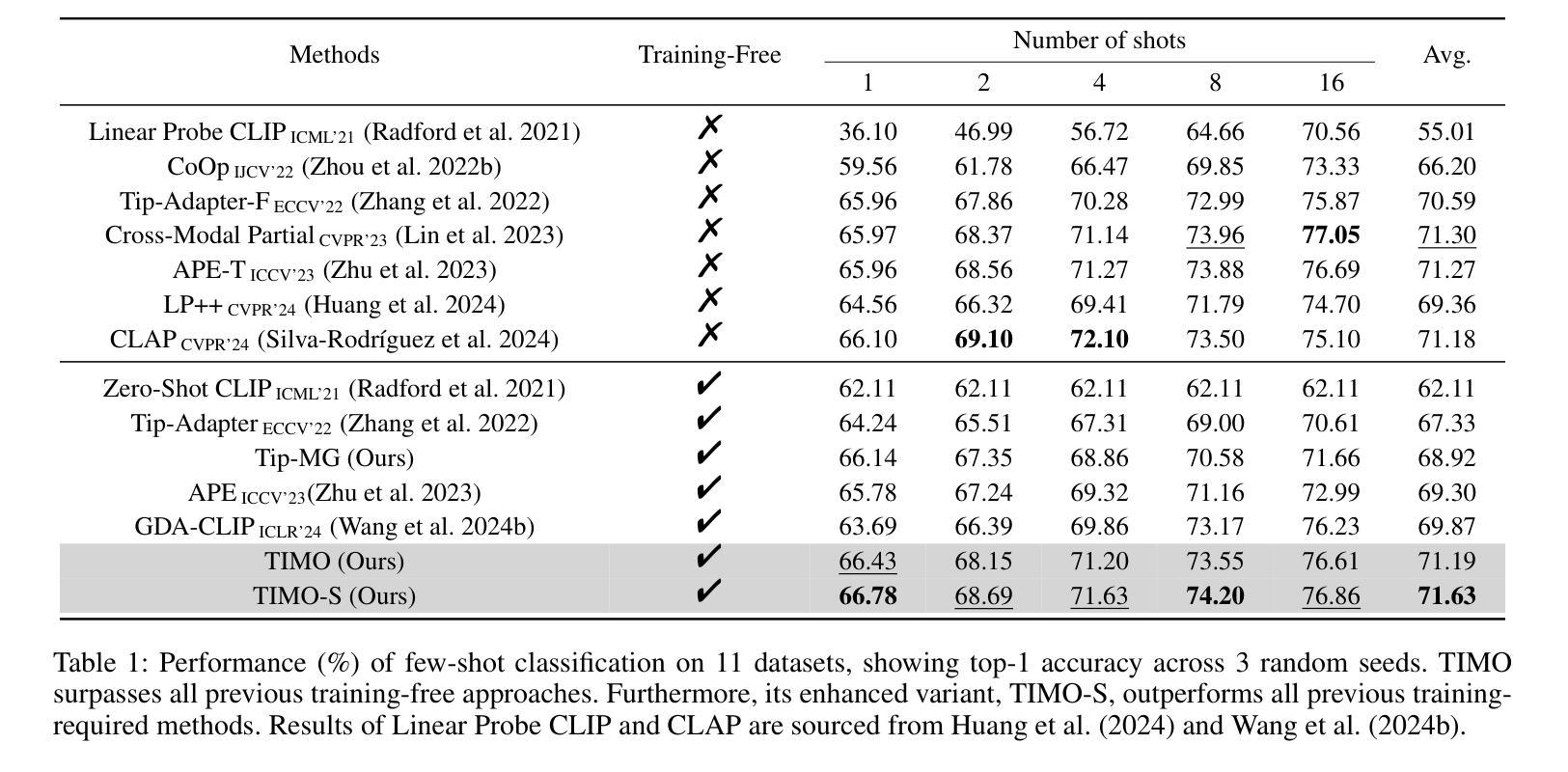
Text and Image Are Mutually Beneficial: Enhancing Training-Free Few-Shot Classification with CLIP
Authors:Yayuan Li, Jintao Guo, Lei Qi, Wenbin Li, Yinghuan Shi
Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) has been widely used in vision tasks. Notably, CLIP has demonstrated promising performance in few-shot learning (FSL). However, existing CLIP-based methods in training-free FSL (i.e., without the requirement of additional training) mainly learn different modalities independently, leading to two essential issues: 1) severe anomalous match in image modality; 2) varying quality of generated text prompts. To address these issues, we build a mutual guidance mechanism, that introduces an Image-Guided-Text (IGT) component to rectify varying quality of text prompts through image representations, and a Text-Guided-Image (TGI) component to mitigate the anomalous match of image modality through text representations. By integrating IGT and TGI, we adopt a perspective of Text-Image Mutual guidance Optimization, proposing TIMO. Extensive experiments show that TIMO significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art (SOTA) training-free method. Additionally, by exploring the extent of mutual guidance, we propose an enhanced variant, TIMO-S, which even surpasses the best training-required methods by 0.33% with approximately 100 times less time cost. Our code is available at https://github.com/lyymuwu/TIMO.
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)已在视觉任务中得到广泛应用。特别是,CLIP在少样本学习(FSL)中表现出了有前景的性能。然而,在无需额外训练的少样本学习(Free-training Few-Shot Learning, FT-FSL)中,现有的基于CLIP的方法主要独立学习不同的模态,导致两个关键问题:1)图像模态中存在严重的异常匹配;2)生成的文本提示质量不一。为了解决这些问题,我们建立了一种相互引导机制,该机制引入了一个图像引导文本(IGT)组件,通过图像表示来校正文本提示的质量不一问题,以及一个文本引导图像(TGI)组件,通过文本表示来缓解图像模态的异常匹配问题。通过整合IGT和TGI,我们从文本图像相互引导优化的角度入手,提出了TIMO。大量实验表明,TIMO显著优于最新的无需训练的方法。此外,通过探索相互引导的程度,我们提出了增强型TIMO-S,其甚至以约100倍的时间成本超越了最佳需要训练的方法,准确率提高了0.33%。我们的代码可在https://github.com/lyymuwu/TIMO找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
基于对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)的技术在视觉任务中广泛应用,特别是在小样学习(FSL)中表现优异。然而,现有的CLIP在零训练小样学习(无额外训练需求)的方法主要独立学习不同模态,导致图像模态的异常匹配和生成文本提示的质量不一。为解决这些问题,本文提出了文本图像相互引导优化(TIMO)的方法,通过图像引导文本(IGT)组件纠正文本提示的质量,以及文本引导图像(TGI)组件减轻图像模态的异常匹配。实验显示,TIMO显著优于现有零训练方法,其增强版TIMO-S甚至超越了最佳需训练方法的性能,同时时间成本大幅降低。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP技术在视觉任务和小样学习中表现优异。
- 现有CLIP在零训练小样学习中存在图像模态异常匹配和文本提示质量不一的问题。
- TIMO通过文本图像相互引导机制解决上述问题。
- IGT组件用于纠正文本提示的质量,TGI组件减轻图像模态的异常匹配。
- TIMO显著优于现有零训练方法。
- TIMO的增强版TIMO-S在时间成本大幅降低的同时,性能超越最佳需训练方法。
点此查看论文截图
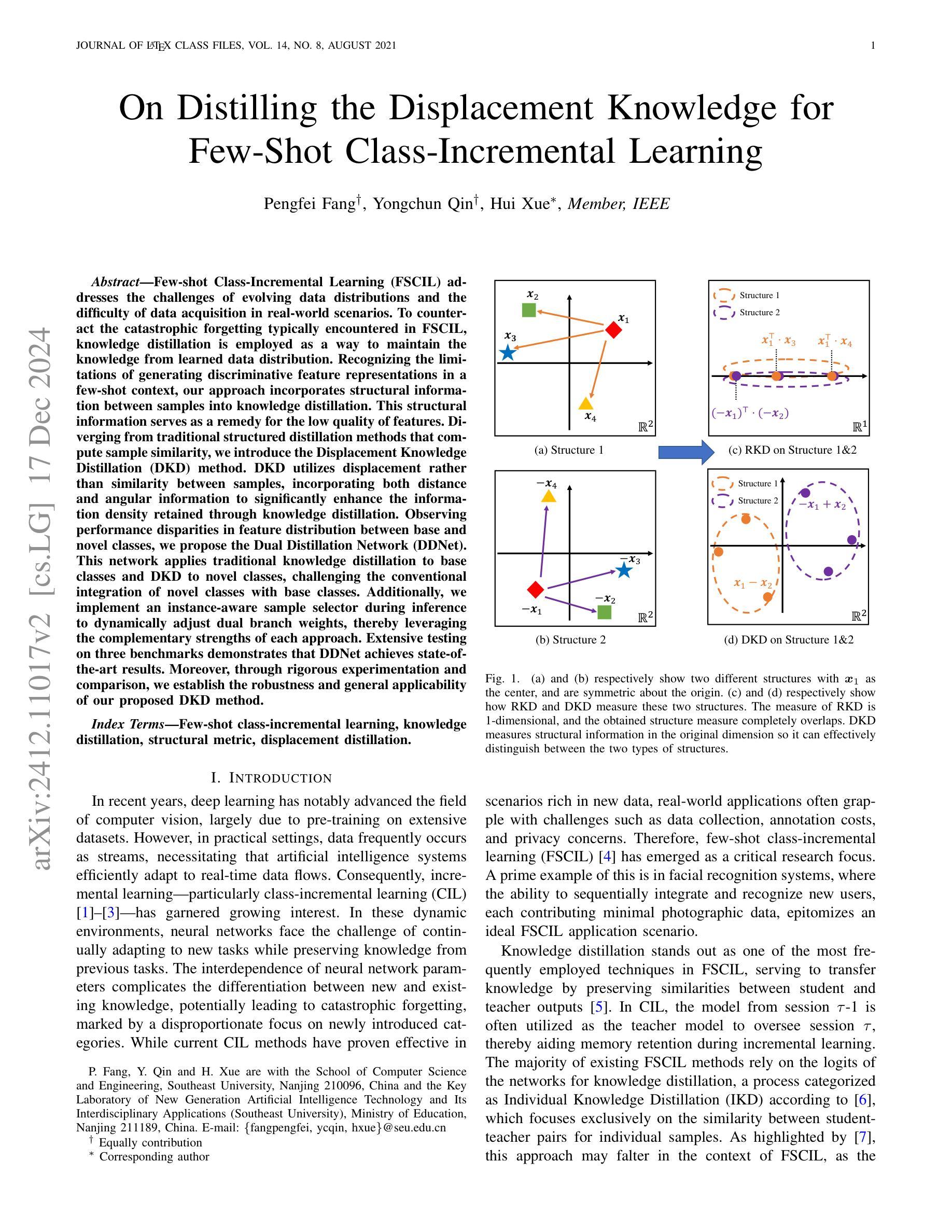
On Distilling the Displacement Knowledge for Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Authors:Pengfei Fang, Yongchun Qin, Hui Xue
Few-shot Class-Incremental Learning (FSCIL) addresses the challenges of evolving data distributions and the difficulty of data acquisition in real-world scenarios. To counteract the catastrophic forgetting typically encountered in FSCIL, knowledge distillation is employed as a way to maintain the knowledge from learned data distribution. Recognizing the limitations of generating discriminative feature representations in a few-shot context, our approach incorporates structural information between samples into knowledge distillation. This structural information serves as a remedy for the low quality of features. Diverging from traditional structured distillation methods that compute sample similarity, we introduce the Displacement Knowledge Distillation (DKD) method. DKD utilizes displacement rather than similarity between samples, incorporating both distance and angular information to significantly enhance the information density retained through knowledge distillation. Observing performance disparities in feature distribution between base and novel classes, we propose the Dual Distillation Network (DDNet). This network applies traditional knowledge distillation to base classes and DKD to novel classes, challenging the conventional integration of novel classes with base classes. Additionally, we implement an instance-aware sample selector during inference to dynamically adjust dual branch weights, thereby leveraging the complementary strengths of each approach. Extensive testing on three benchmarks demonstrates that DDNet achieves state-of-the-art results. Moreover, through rigorous experimentation and comparison, we establish the robustness and general applicability of our proposed DKD method.
少量样本类增量学习(FSCIL)解决了数据分布演变和现实世界场景中数据获取困难的问题。为了抵消FSCIL中通常遇到的灾难性遗忘,采用知识蒸馏作为一种保持已学习数据分布知识的方法。我们的方法认识到在少量样本情况下生成判别特征表示的局限性,将样本之间的结构信息纳入知识蒸馏中。这种结构信息作为对特征质量低的补救措施。我们引入了位移知识蒸馏(DKD)方法,该方法利用样本之间的位移而不是相似性,结合距离和角度信息,通过知识蒸馏显著增强保留的信息密度。观察到基础类和新颖类之间特征分布的性能差异,我们提出了双蒸馏网络(DDNet)。该网络对基础类应用传统知识蒸馏,对新颖类应用DKD,挑战了新颖类与基础类的传统融合方式。此外,我们在推理过程中实现了实例感知样本选择器,以动态调整双分支权重,从而充分利用每种方法的互补优势。在三个基准测试上的广泛测试表明,DDNet达到了最新技术水平。而且,通过严格的实验和比较,我们确定了我们所提出的DKD方法的稳健性和通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了Few-shot类增量学习(FSCIL)面临的挑战,包括数据分布的变化和真实场景中数据获取的困难。为解决灾难性遗忘问题,采用知识蒸馏技术保留已学习数据分布的知识。针对少样本情境下生成判别特征表示的限制,结合样本间的结构信息改进知识蒸馏。引入位移知识蒸馏(DKD)方法,利用样本间的位移而非相似性,结合距离和角度信息,显著提高通过知识蒸馏保留的信息密度。为解决基础类和新型类在特征分布上的性能差异,提出双蒸馏网络(DDNet),该网络对基础类应用传统知识蒸馏,对新型类应用DKD,并动态调整双分支权重。在三个基准测试上的测试表明DDNet取得了最新成果。
Key Takeaways
- Few-shot类增量学习(FSCIL)面临数据分布变化和真实场景数据获取困难等挑战。
- 知识蒸馏技术用于解决FSCIL中的灾难性遗忘问题,保留已学习数据分布的知识。
- 引入位移知识蒸馏(DKD)方法,结合距离和角度信息,提高信息密度。
- 双蒸馏网络(DDNet)针对基础类和新型类在特征分布上的性能差异,实施不同的蒸馏策略。
- DDNet通过在动态调整双分支权重的方法中融合传统知识蒸馏与DKD的优势。
- 实验表明DDNet在三个基准测试上取得了最新成果。
点此查看论文截图
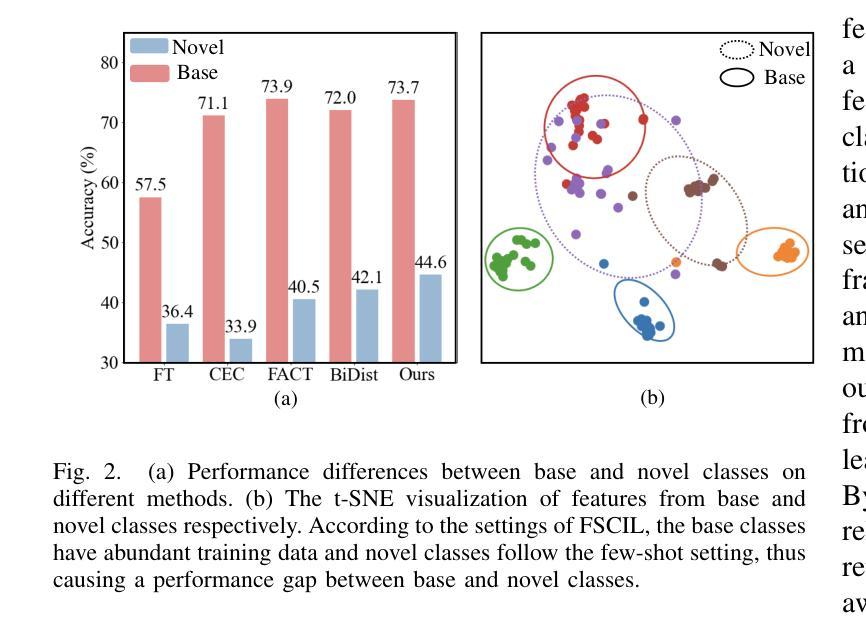
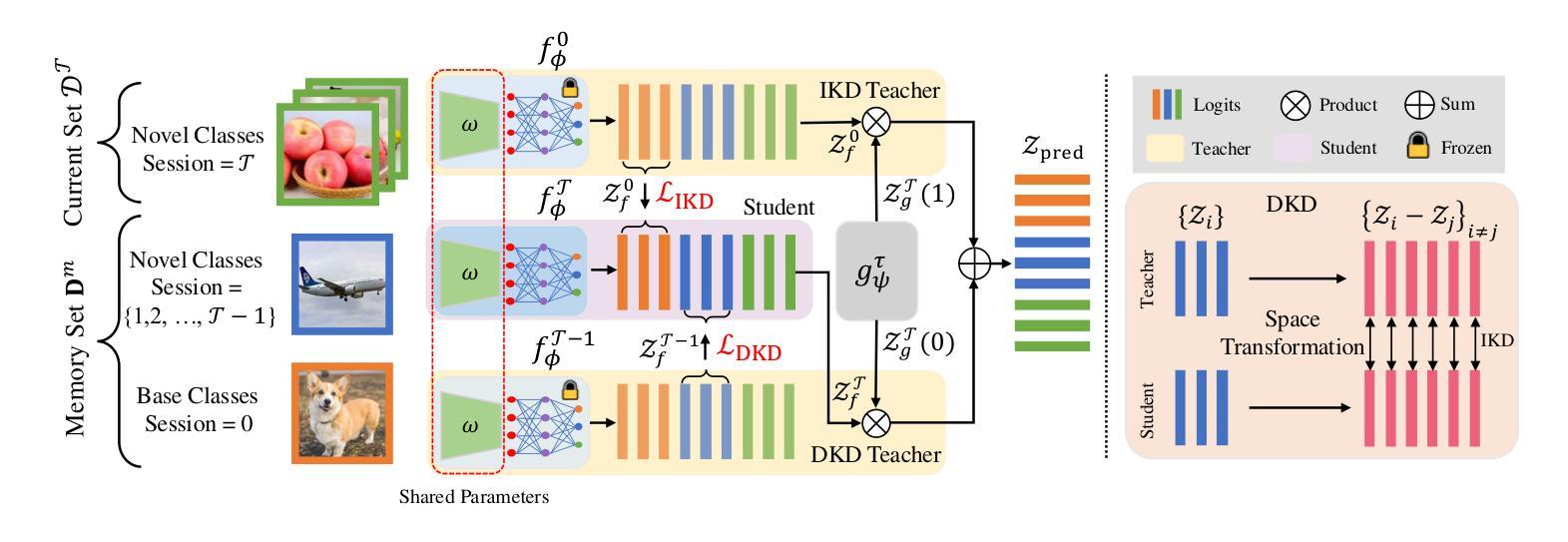
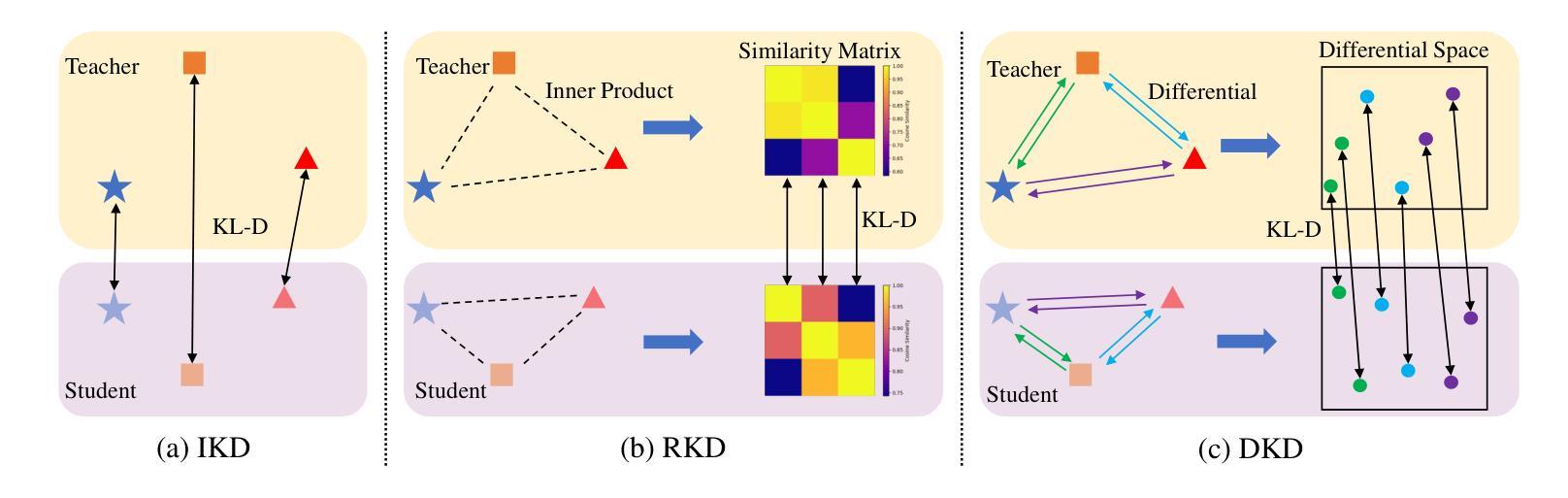
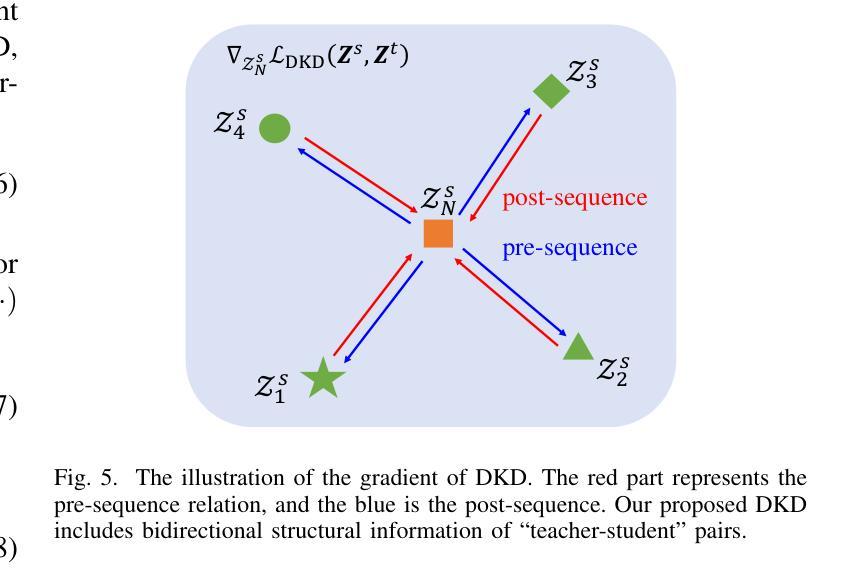
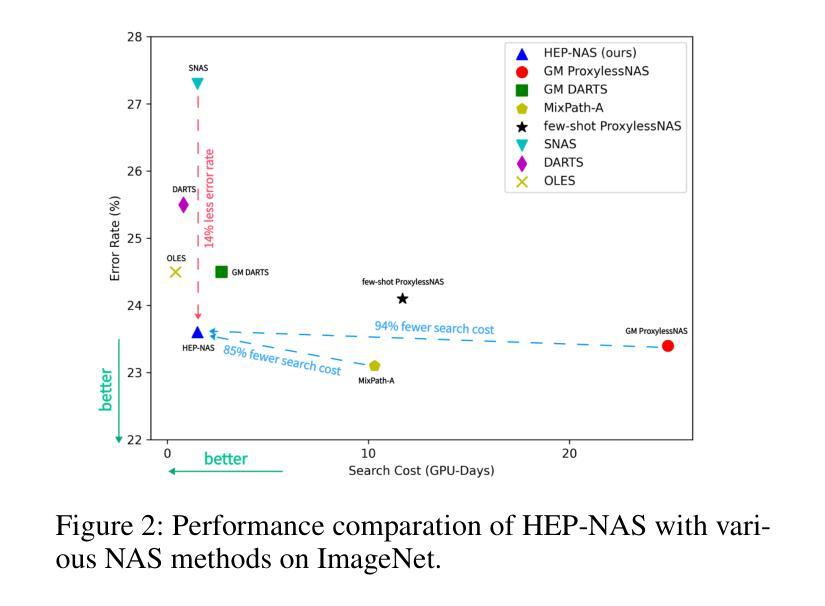
HEP-NAS: Towards Efficient Few-shot Neural Architecture Search via Hierarchical Edge Partitioning
Authors:Jianfeng Li, Jiawen Zhang, Feng Wang, Lianbo Ma
One-shot methods have significantly advanced the field of neural architecture search (NAS) by adopting weight-sharing strategy to reduce search costs. However, the accuracy of performance estimation can be compromised by co-adaptation. Few-shot methods divide the entire supernet into individual sub-supernets by splitting edge by edge to alleviate this issue, yet neglect relationships among edges and result in performance degradation on huge search space. In this paper, we introduce HEP-NAS, a hierarchy-wise partition algorithm designed to further enhance accuracy. To begin with, HEP-NAS treats edges sharing the same end node as a hierarchy, permuting and splitting edges within the same hierarchy to directly search for the optimal operation combination for each intermediate node. This approach aligns more closely with the ultimate goal of NAS. Furthermore, HEP-NAS selects the most promising sub-supernet after each segmentation, progressively narrowing the search space in which the optimal architecture may exist. To improve performance evaluation of sub-supernets, HEP-NAS employs search space mutual distillation, stabilizing the training process and accelerating the convergence of each individual sub-supernet. Within a given budget, HEP-NAS enables the splitting of all edges and gradually searches for architectures with higher accuracy. Experimental results across various datasets and search spaces demonstrate the superiority of HEP-NAS compared to state-of-the-art methods.
一shot方法通过采用权重共享策略来降低搜索成本,从而显著推动了神经网络架构搜索(NAS)领域的发展。然而,协同适应可能会损害性能估计的准确性。Few-shot方法通过逐边分割将整个超网分成单个的子超网来缓解这个问题,但却忽视了边之间的关系,并在巨大的搜索空间上导致性能下降。在本文中,我们介绍了HEP-NAS,这是一种层次划分算法,旨在进一步提高准确性。首先,HEP-NAS将共享相同末端节点的边视为一个层次结构,对同一层次内的边进行排列和分割,以直接搜索每个中间节点的最佳操作组合。这种方法更贴近NAS的最终目标。此外,HEP-NAS会在每次分割后选择最有希望的子超网,逐步缩小可能存在最优架构的搜索空间。为了改进子超网的性能评估,HEP-NAS采用搜索空间相互蒸馏技术,稳定训练过程并加速每个子超网的收敛。在给定预算内,HEP-NAS能够实现所有边的分割并逐步搜索更高精度的架构。在不同数据集和搜索空间上的实验结果证明了HEP-NAS相较于最新技术方法的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经网络架构搜索(NAS)领域已经通过采用一次性方法取得了显著进展,这些方法通过采用权重共享策略来降低搜索成本。然而,性能估计的准确性可能会受到协同适应性的威胁。本文提出了一种层次划分算法——HEP-NAS,旨在进一步提高准确性。它通过边缘层次划分,更直接地搜索每个中间节点的最佳操作组合,以缩小搜索空间并找到最具潜力的子超网络。此外,它采用搜索空间相互蒸馏技术,稳定训练过程并加速每个子超网络的收敛。实验结果表明,在有限的预算内,HEP-NAS能够在各种数据集和搜索空间中实现更高的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 一键式方法在神经网络架构搜索领域取得显著进展,通过权重共享策略降低搜索成本。
- 性能估计的准确性可能受到协同适应性的威胁。
- HEP-NAS是一种层次划分算法,通过在同一层次内对边缘进行排列和分割,更直接地搜索最佳操作组合。
- HEP-NAS在分割后选择最有前途的子超网络,逐步缩小可能包含最佳架构的搜索空间。
- HEP-NAS采用搜索空间相互蒸馏技术,稳定训练过程并加速子超网络的收敛。
- HEP-NAS能够在有限的预算内实现更高的准确性,并在各种数据集和搜索空间中表现出优越性。
点此查看论文截图

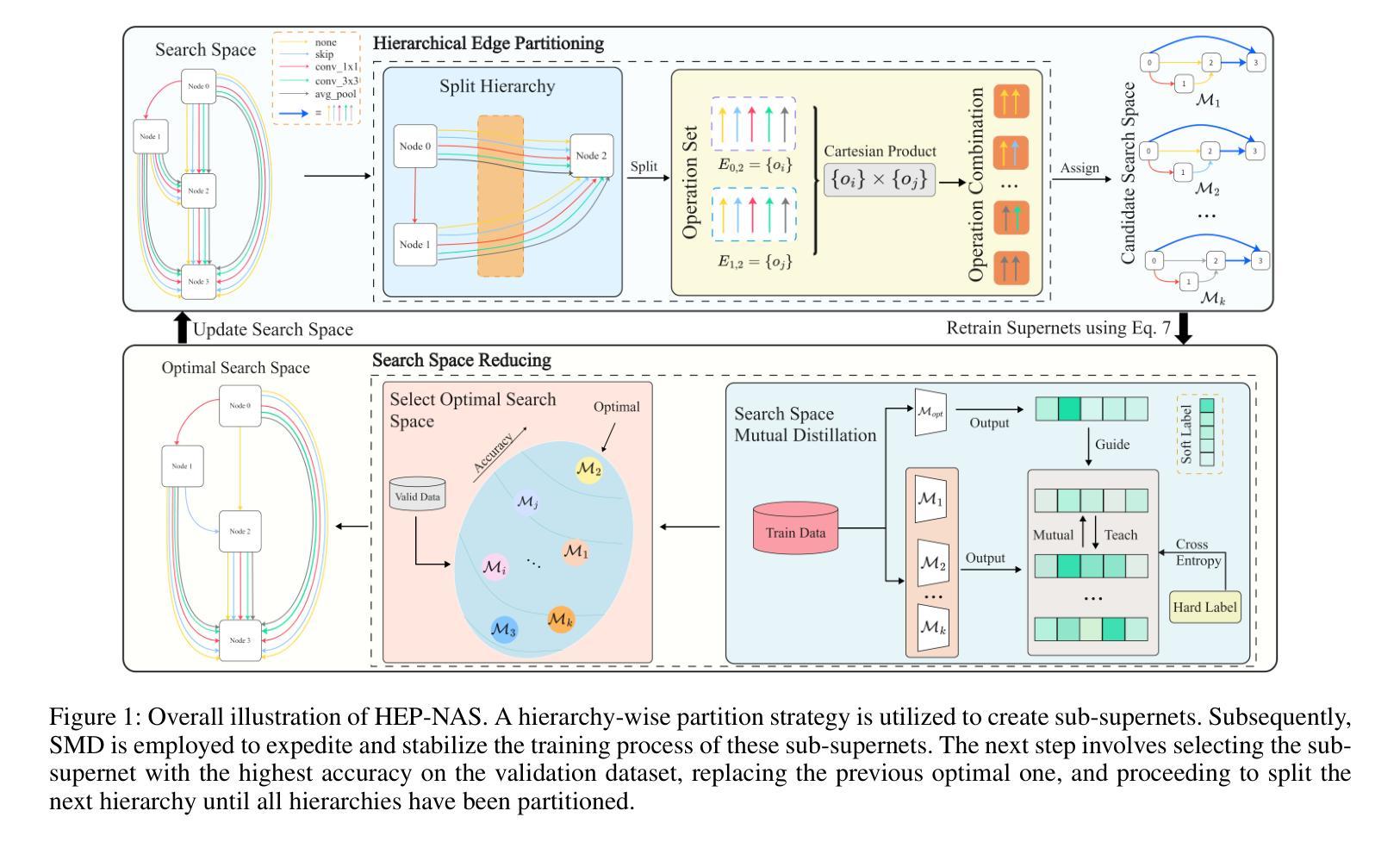
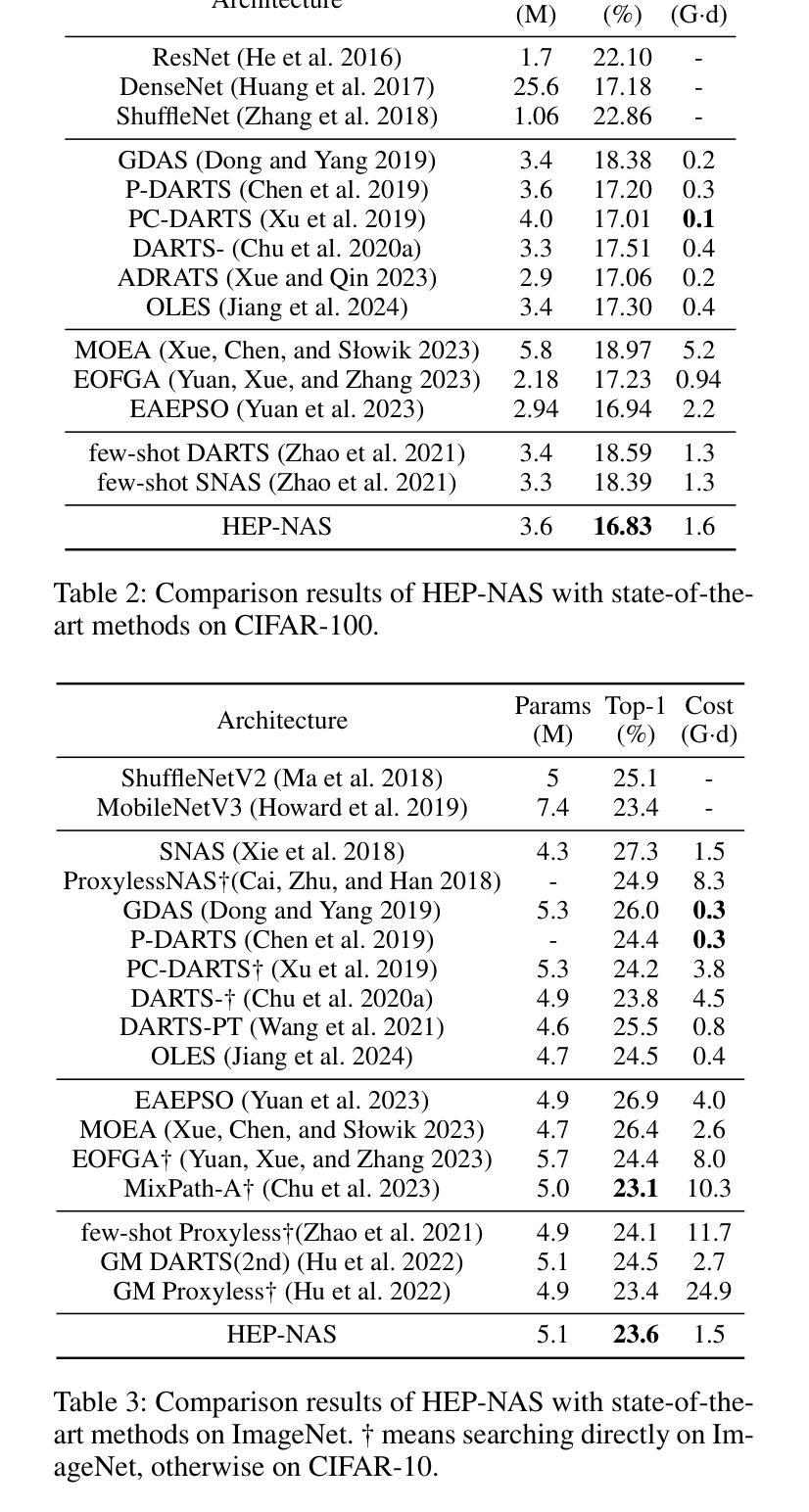
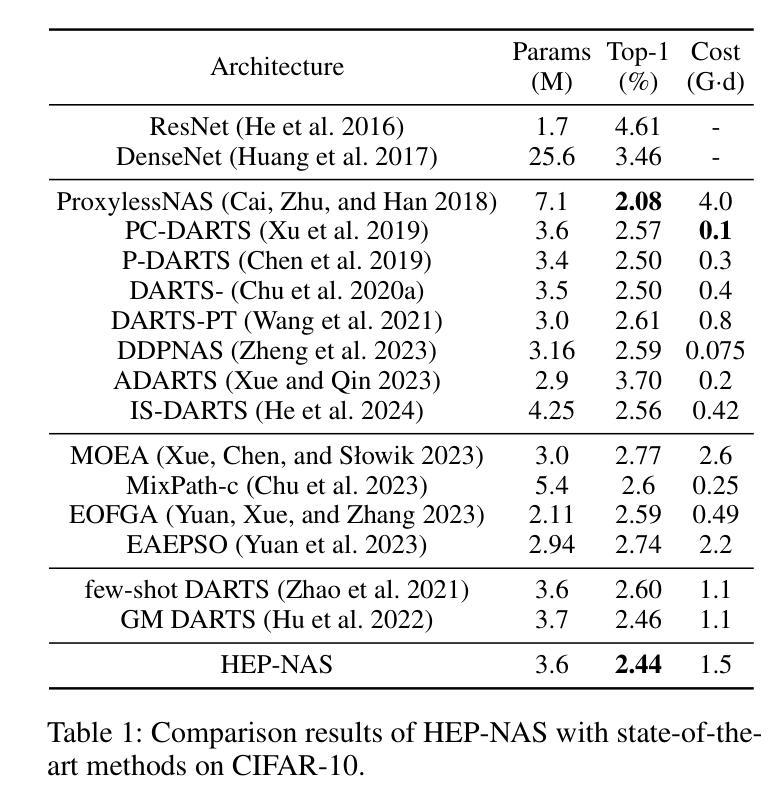
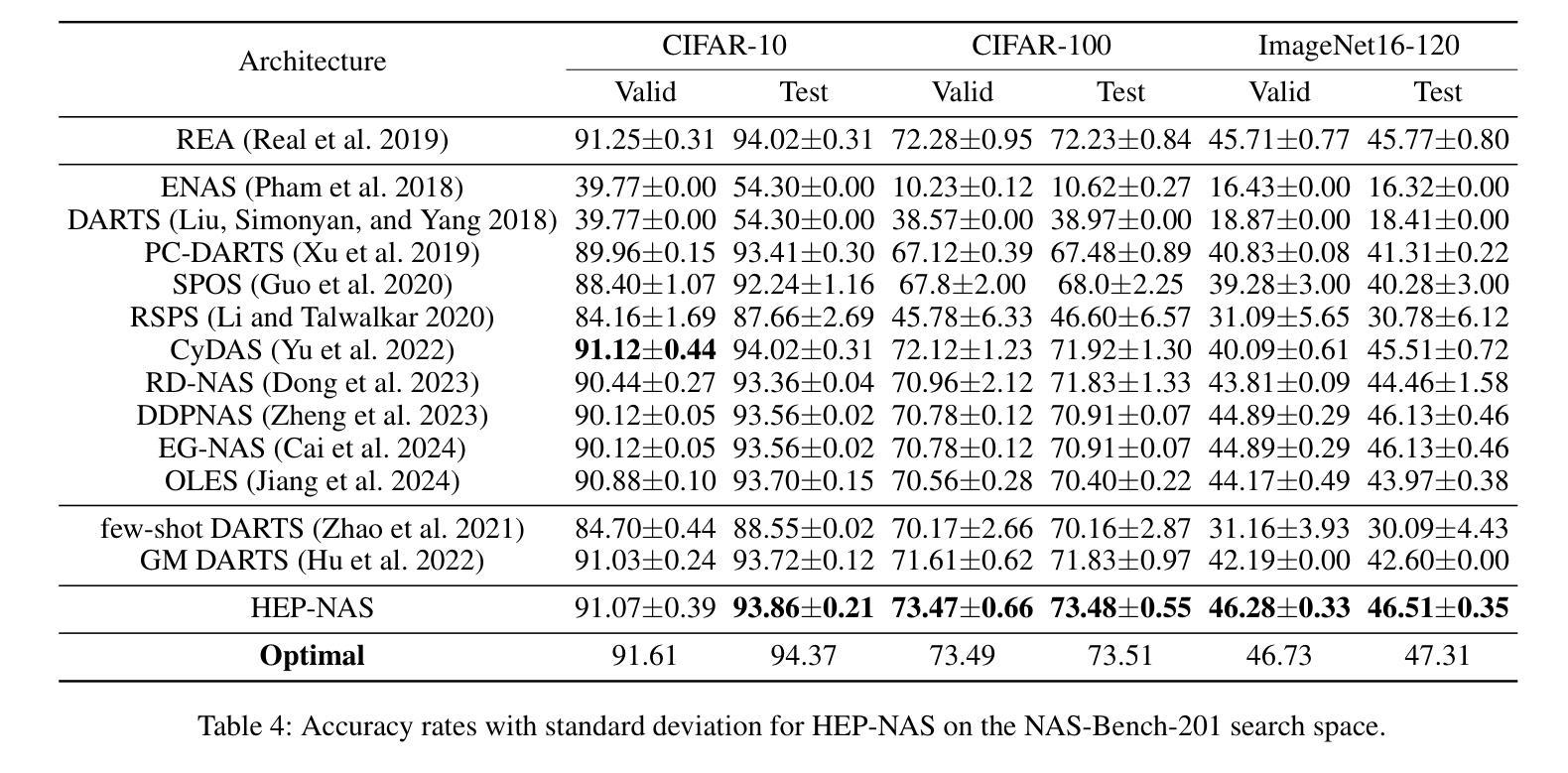
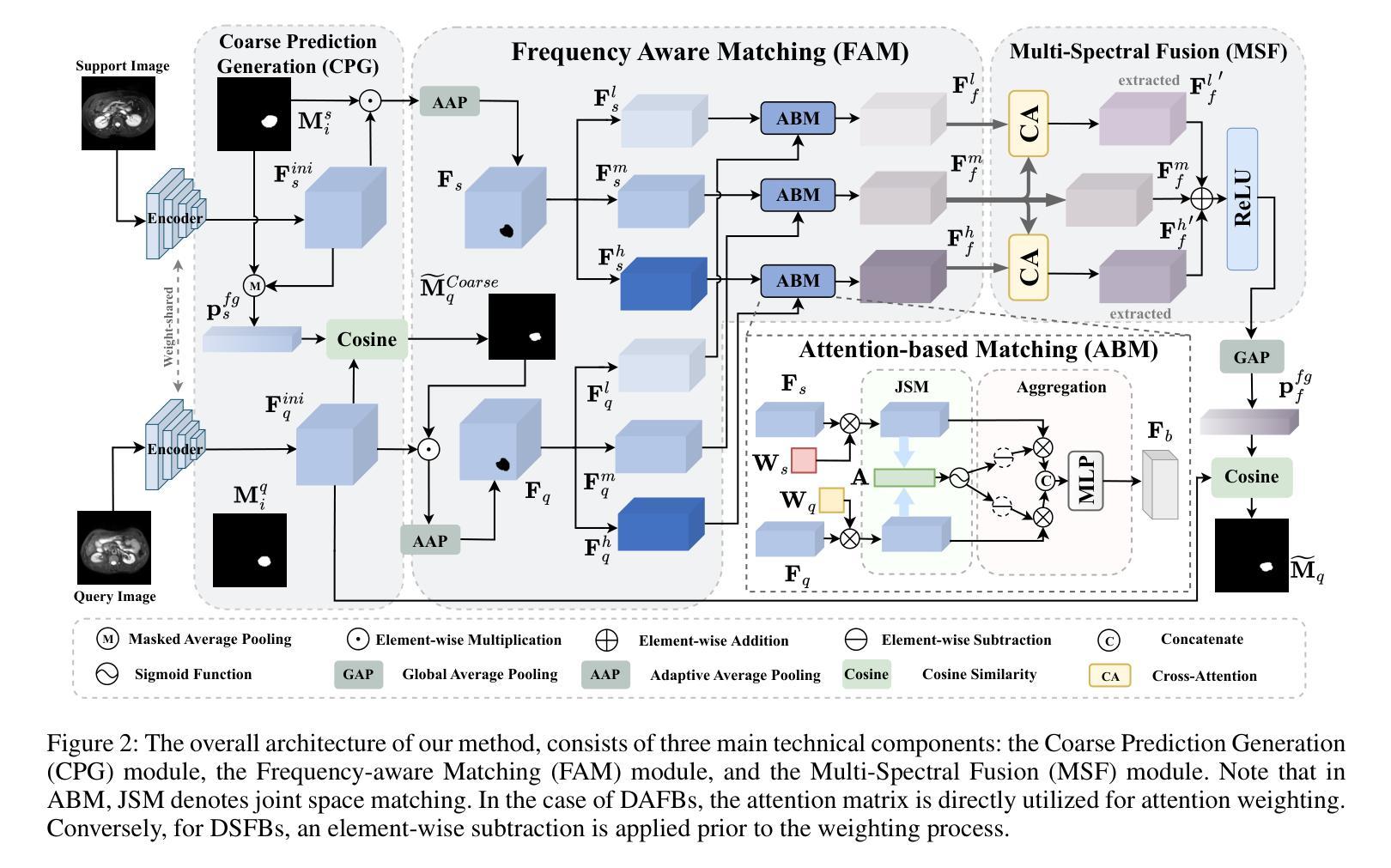
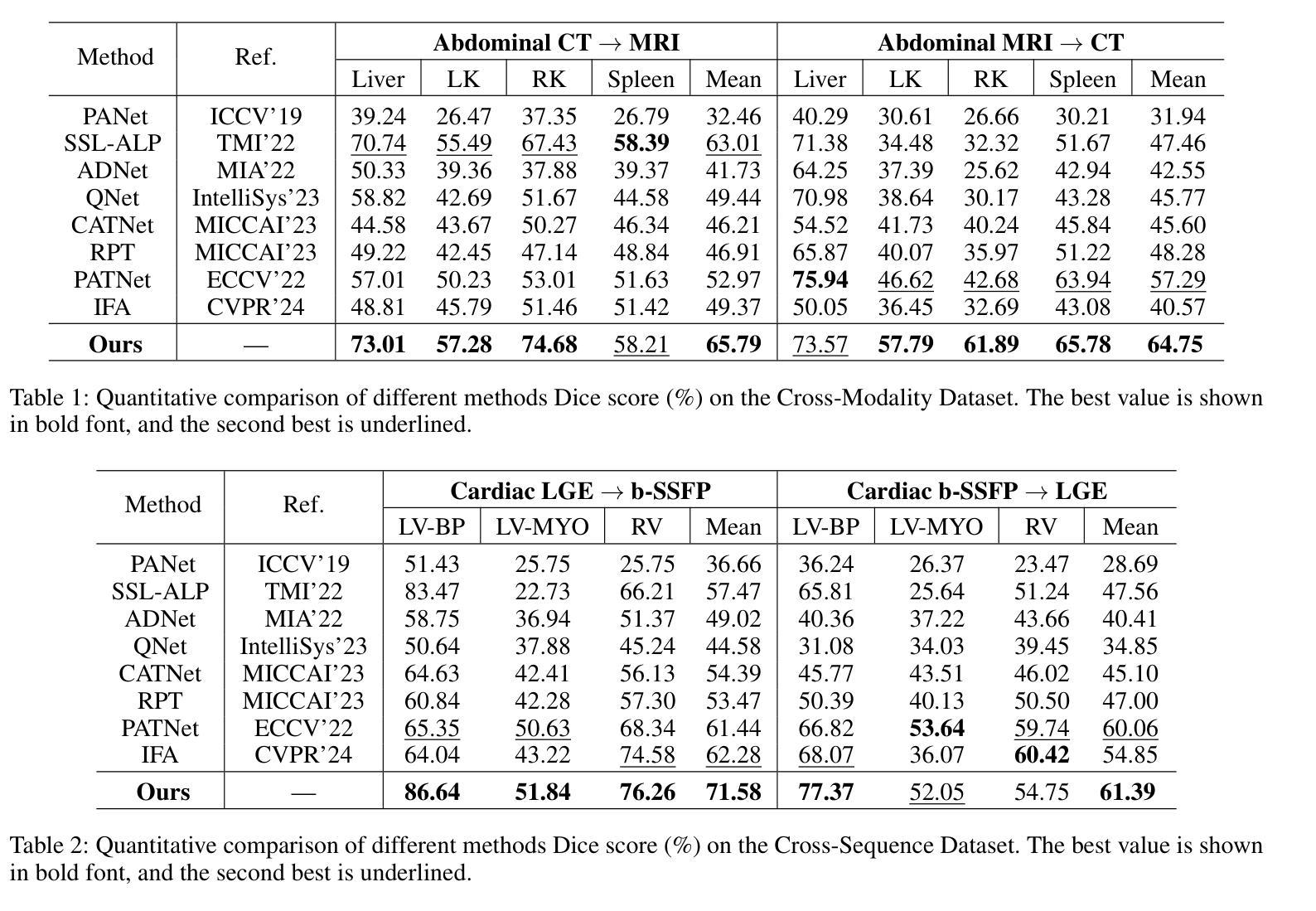
FAMNet: Frequency-aware Matching Network for Cross-domain Few-shot Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Yuntian Bo, Yazhou Zhu, Lunbo Li, Haofeng Zhang
Existing few-shot medical image segmentation (FSMIS) models fail to address a practical issue in medical imaging: the domain shift caused by different imaging techniques, which limits the applicability to current FSMIS tasks. To overcome this limitation, we focus on the cross-domain few-shot medical image segmentation (CD-FSMIS) task, aiming to develop a generalized model capable of adapting to a broader range of medical image segmentation scenarios with limited labeled data from the novel target domain. Inspired by the characteristics of frequency domain similarity across different domains, we propose a Frequency-aware Matching Network (FAMNet), which includes two key components: a Frequency-aware Matching (FAM) module and a Multi-Spectral Fusion (MSF) module. The FAM module tackles two problems during the meta-learning phase: 1) intra-domain variance caused by the inherent support-query bias, due to the different appearances of organs and lesions, and 2) inter-domain variance caused by different medical imaging techniques. Additionally, we design an MSF module to integrate the different frequency features decoupled by the FAM module, and further mitigate the impact of inter-domain variance on the model’s segmentation performance. Combining these two modules, our FAMNet surpasses existing FSMIS models and Cross-domain Few-shot Semantic Segmentation models on three cross-domain datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance in the CD-FSMIS task.
现有的少样本医学图像分割(FSMIS)模型无法解决医学成像中的一个实际问题:由不同成像技术引起的域偏移,这限制了其在当前FSMIS任务中的应用。为了克服这一局限性,我们专注于跨域少样本医学图像分割(CD-FSMIS)任务,旨在开发一种通用模型,能够在有限的新目标域的标记数据下,适应更广泛的医学图像分割场景。我们受到不同域之间频率域相似性特征的启发,提出了一种频率感知匹配网络(FAMNet),它包括两个关键组件:频率感知匹配(FAM)模块和多光谱融合(MSF)模块。FAM模块解决了元学习阶段的两个问题:1)由于器官和病变的不同外观导致的域内方差,这是固有的支持查询偏见的结果;2)由不同的医学成像技术引起的域间方差。此外,我们设计了一个MSF模块,以整合FAM模块解耦的不同频率特征,并进一步减轻域间方差对模型分割性能的影响。结合这两个模块,我们的FAMNet在三个跨域数据集上超越了现有的FSMIS模型和跨域少样本语义分割模型,在CD-FSMIS任务中达到了最先进的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-25)
Summary
本文关注跨域少样本医疗图像分割(CD-FSMIS)任务,旨在开发一个能够适应更广泛医疗图像分割场景、解决不同成像技术引起的领域偏移问题的通用模型。为此,提出了频率感知匹配网络(FAMNet),包括频率感知匹配(FAM)模块和多光谱融合(MSF)模块,提高了模型在元学习阶段的性能。这些创新点使模型在跨域数据集上的表现超越了现有的FSMIS模型和跨域少样本语义分割模型,实现了在CD-FSMIS任务中的最佳性能。
Key Takeaways
- 跨域少样本医疗图像分割(CD-FSMIS)是医疗图像处理领域的一个重要问题,涉及到不同成像技术的领域偏移问题。
- 本文提出了频率感知匹配网络(FAMNet)来解决CD-FSMIS任务,包括频率感知匹配(FAM)模块和多光谱融合(MSF)模块。
- FAM模块解决了元学习阶段的两个主要问题:由器官和病变不同外观引起的内部领域差异和不同医学成像技术引起的跨领域差异。
- MSF模块用于整合由FAM模块分离的不同频率特征,进一步减轻跨领域差异对模型分割性能的影响。
- FAMNet模型在三个跨域数据集上的表现超越了现有的FSMIS模型和跨域少样本语义分割模型。
- 该研究为医疗图像分割领域提供了一种新的解决方案,能够应对有限的标签数据和不同的成像技术。
点此查看论文截图

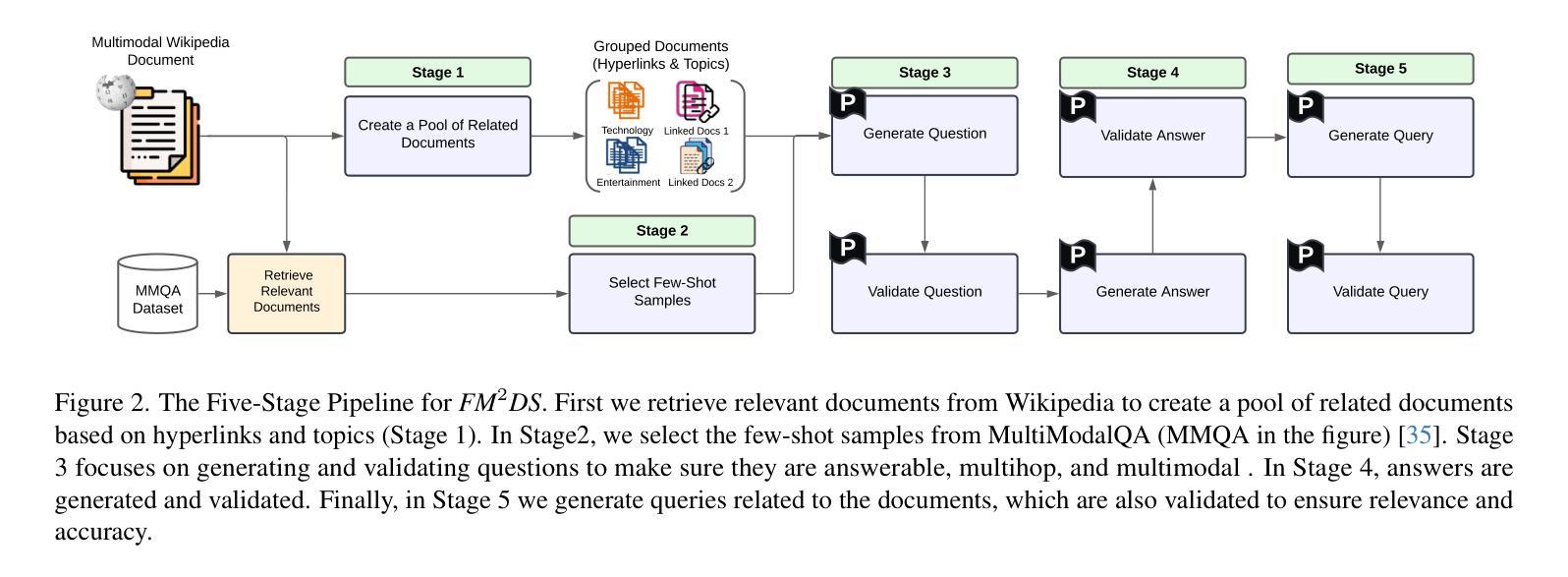
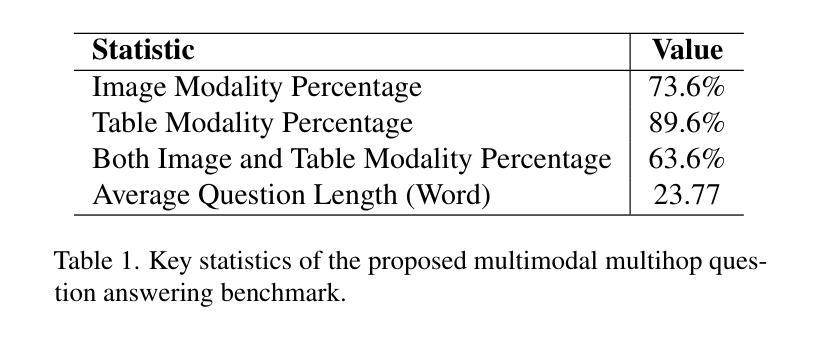
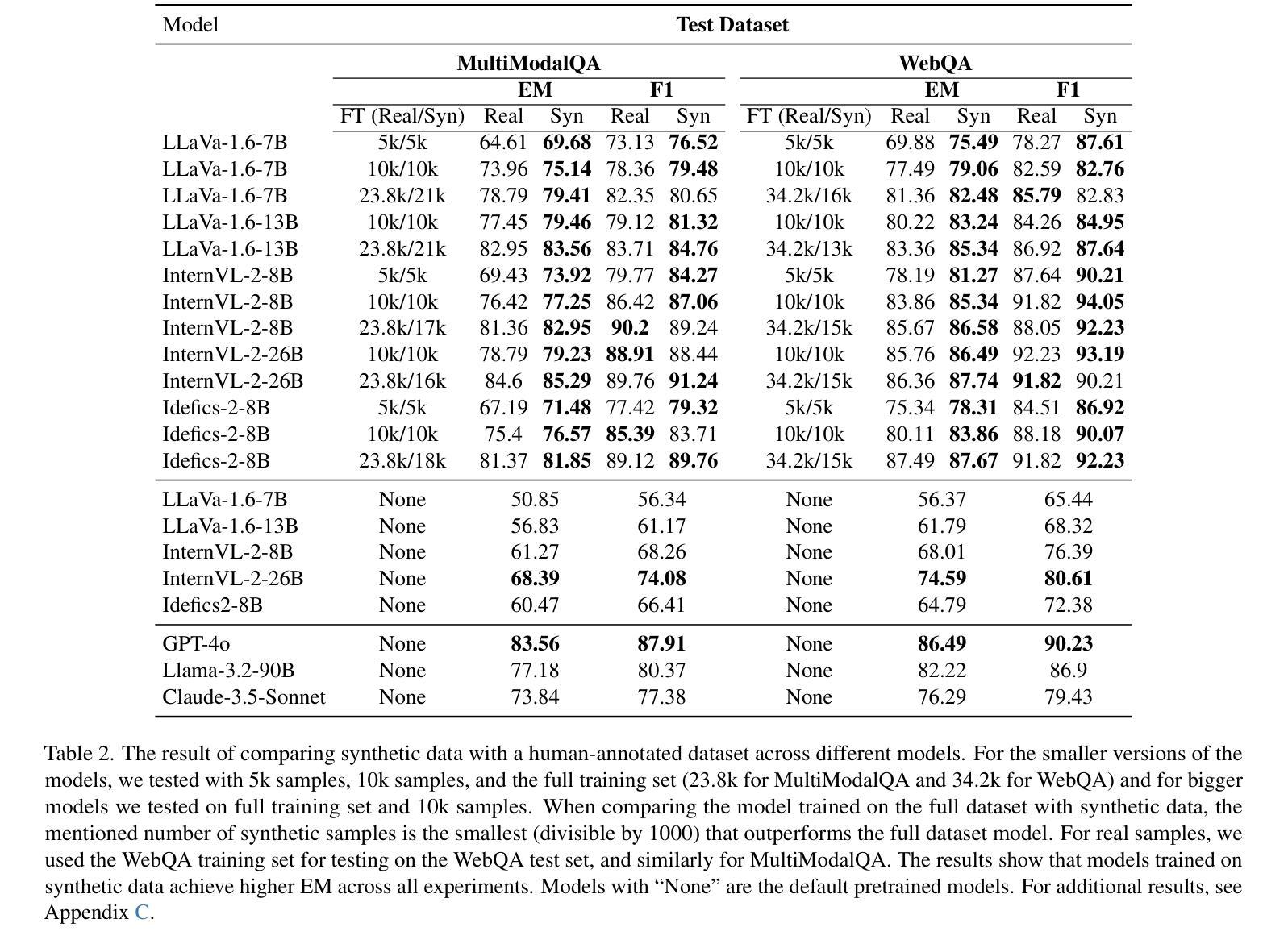
FM2DS: Few-Shot Multimodal Multihop Data Synthesis with Knowledge Distillation for Question Answering
Authors:Amirhossein Abaskohi, Spandana Gella, Giuseppe Carenini, Issam H. Laradji
Multimodal multihop question answering is a complex task that requires reasoning over multiple sources of information, such as images and text, to answer questions. While there has been significant progress in visual question answering, the multihop setting remains unexplored due to the lack of high-quality datasets. Current methods focus on single-hop question answering or a single modality, which makes them unsuitable for real-world scenarios such as analyzing multimodal educational materials, summarizing lengthy academic articles, or interpreting scientific studies that combine charts, images, and text. To address this gap, we propose a novel methodology, introducing the first framework for creating a high-quality dataset that enables training models for multimodal multihop question answering. Our approach consists of a 5-stage pipeline that involves acquiring relevant multimodal documents from Wikipedia, synthetically generating high-level questions and answers, and validating them through rigorous criteria to ensure quality data. We evaluate our methodology by training models on our synthesized dataset and testing on two benchmarks, our results demonstrate that, with an equal sample size, models trained on our synthesized data outperform those trained on human-collected data by 1.9 in exact match (EM) on average. We believe our data synthesis method will serve as a strong foundation for training and evaluating multimodal multihop question answering models.
多模态多跳问答是一项复杂的任务,它要求在多源信息上进行推理,如图像和文本,以回答问题。尽管视觉问答已经取得了重大进展,但由于缺乏高质量的数据集,多跳设置仍然未被探索。当前的方法侧重于单跳问答或单一模态,这使得它们不适合现实场景,如分析多模态教育材料、总结冗长的学术论文或解释结合图表、图像和文本的科学研究。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了一种新的方法,并引入了创建高质量数据集的第一个框架,该框架能够训练多模态多跳问答模型。我们的方法包括一个涉及从维基百科获取相关多模态文档、合成生成高级问题和答案、并通过严格标准验证以确保数据质量的五个阶段的管道。我们通过在我们的合成数据集上训练模型并在两个基准上进行测试来评估我们的方法。结果表明,在样本大小相同的情况下,在我们的合成数据上训练的模型在平均精确匹配(EM)上比在人类收集的数据上训练的模型高出1.9。我们相信我们的数据合成方法将为训练和评估多模态多跳问答模型提供坚实的基础。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 20 pages, 11 figures, 10 tables, Submitted to CVPR 2025
Summary
该文本介绍了多模态多跳问答任务的重要性,其需要融合图像和文字等多种信息来源进行推理。尽管视觉问答任务已取得了重要进展,但由于缺乏高质量数据集,多跳设置仍未被探索。当前方法主要关注单跳问答或单一模态,不适用于分析多模态教育材料、总结冗长学术论文或解读结合图表、文字和图像的科学研究等现实场景。为弥补这一空白,我们提出了一种新方法,首次构建了高质量数据集,为训练多模态多跳问答模型提供了可能。我们的方法包括一个涉及从维基百科获取相关多模态文档、合成高级问题和答案、并通过严格标准验证数据质量的五个阶段管道。通过在我们的合成数据集上训练模型并在两个基准上进行测试,结果表明,在样本大小相等的情况下,我们的合成数据训练的模型在人收集的基准数据上的平均精确匹配得分高出1.9分。我们相信我们的数据合成方法将为训练和评估多模态多跳问答模型提供坚实的基础。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态多跳问答是一个跨越图像和文本等多个信息源的复杂任务,需要强大的推理能力。
- 当前缺乏高质量数据集限制了多跳问答任务的进展。
- 当前方法主要关注单模态和单跳问答,不适用于现实世界的复杂场景。
- 提出了一种新的方法,构建了高质量数据集以支持多模态多跳问答的训练和评估。
- 该方法包括五个阶段的管道,涉及从维基百科获取多模态文档、合成高级问题和答案等步骤。
- 实验结果表明,在样本大小相同的情况下,合成数据训练的模型性能优于在人收集的基准数据上训练的模型。
点此查看论文截图

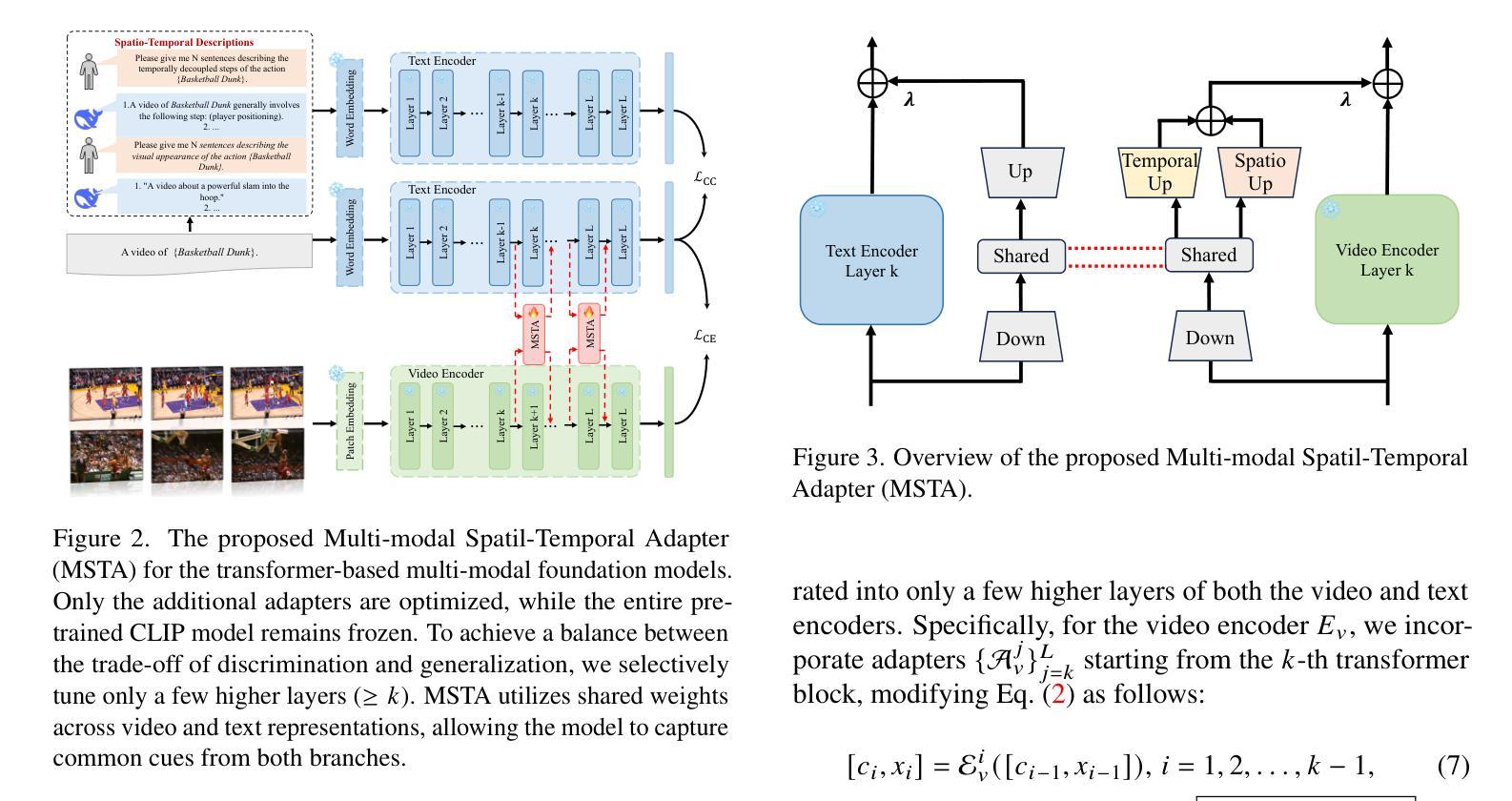
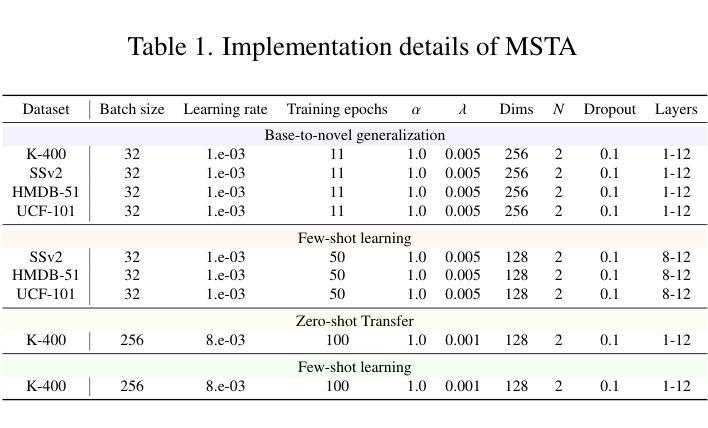
Efficient Transfer Learning for Video-language Foundation Models
Authors:Haoxing Chen, Zizheng Huang, Yan Hong, Yanshuo Wang, Zhongcai Lyu, Zhuoer Xu, Jun Lan, Zhangxuan Gu
Pre-trained vision-language models provide a robust foundation for efficient transfer learning across various downstream tasks. In the field of video action recognition, mainstream approaches often introduce additional parameter modules to capture temporal information. While the increased model capacity brought by these additional parameters helps better fit the video-specific inductive biases, existing methods require learning a large number of parameters and are prone to catastrophic forgetting of the original generalizable knowledge. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective Multi-modal Spatio-Temporal Adapter (MSTA) to improve the alignment between representations in the text and vision branches, achieving a balance between general knowledge and task-specific knowledge. Furthermore, to mitigate over-fitting and enhance generalizability, we introduce a spatio-temporal description-guided consistency constraint. This constraint involves feeding template inputs (i.e., ``a video of ${\textbf{cls}}$’’) into the trainable language branch, while LLM-generated spatio-temporal descriptions are input into the pre-trained language branch, enforcing consistency between the outputs of the two branches. This mechanism prevents over-fitting to downstream tasks and improves the distinguishability of the trainable branch within the spatio-temporal semantic space. We evaluate the effectiveness of our approach across four tasks: zero-shot transfer, few-shot learning, base-to-novel generalization, and fully-supervised learning. Compared to many state-of-the-art methods, our MSTA achieves outstanding performance across all evaluations, while using only 2-7% of the trainable parameters in the original model. Code will be avaliable at https://github.com/chenhaoxing/ETL4Video.
预训练过的视觉语言模型为高效迁移学习在各种下游任务中的迁移提供了坚实的基础。在视频动作识别领域,主流方法通常引入额外的参数模块来捕获时间信息。虽然这些额外参数带来的模型容量增加有助于更好地适应视频特定的归纳偏见,但现有方法需要学习大量参数,并容易遗忘原始的通用知识。在本文中,我们提出了一种简单有效的多模态时空适配器(MSTA),以提高文本和视觉分支之间表示的对齐,在通用知识和任务特定知识之间取得平衡。此外,为了缓解过拟合并增强通用性,我们引入了一种受时空描述引导的一致性约束。该约束涉及将模板输入(例如,“一个视频中的${\textbf{cls}}$”)输入到可训练的语言分支,同时将LLM生成的时空描述输入到预训练的语言分支,强制两个分支的输出保持一致。这种机制防止了对下游任务的过度拟合,提高了可训练分支在时空语义空间中的可区分性。我们在四种任务上评估了我们的方法的有效性:零样本迁移、小样学习、基础到新颖的泛化和全监督学习。与许多先进的方法相比,我们的MSTA在所有评估中都取得了出色的性能,同时只使用了原始模型中2-7%的可训练参数。代码将在https://github.com/chenhaoxing/ETL4Video上提供。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个简单有效的多模态时空适配器(MSTA),用于改善文本和视觉分支之间的表示对齐,实现了通用知识和任务特定知识之间的平衡。为提高模型的泛化能力并减轻过拟合问题,引入了时空描述引导的一致性约束。在四个任务上的评估表明,MSTA在零样本迁移、少样本学习、基础到新颖泛化以及全监督学习方面都取得了出色的性能,并且仅使用原始模型中2-7%的可训练参数。
Key Takeaways
- 多模态时空适配器(MSTA)增强了预训练视觉语言模型的表示对齐,提高了在各种下游任务中的迁移学习效率。
- MSTA实现了通用知识和任务特定知识之间的平衡,通过引入少量额外参数模块来捕捉时空信息。
- 引入的时空描述引导的一致性约束提高了模型的泛化能力,并减轻了过拟合问题。
- 通过使用模板输入和LLM生成的时空描述,增强了模型在时空语义空间中的可辨识性。
- MSTA在四个任务上的性能均优于许多最新方法,且仅使用原始模型的很小部分可训练参数。
- 该方法具有广泛的应用潜力,适用于零样本迁移、少样本学习、基础到新颖泛化以及全监督学习等任务。
点此查看论文截图

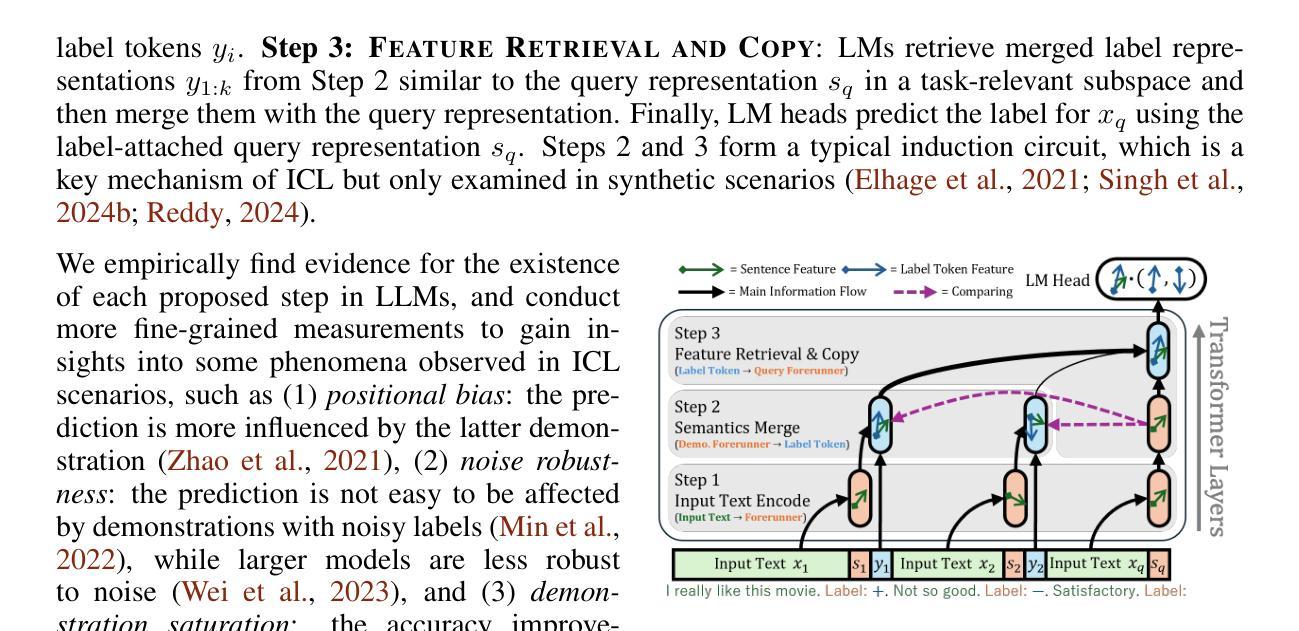
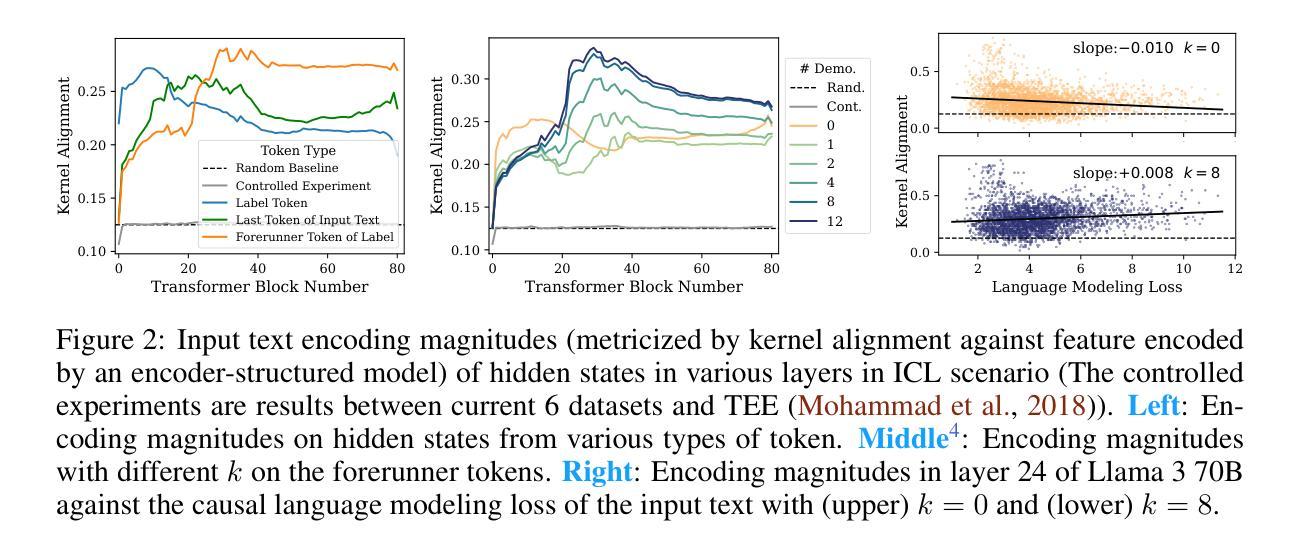
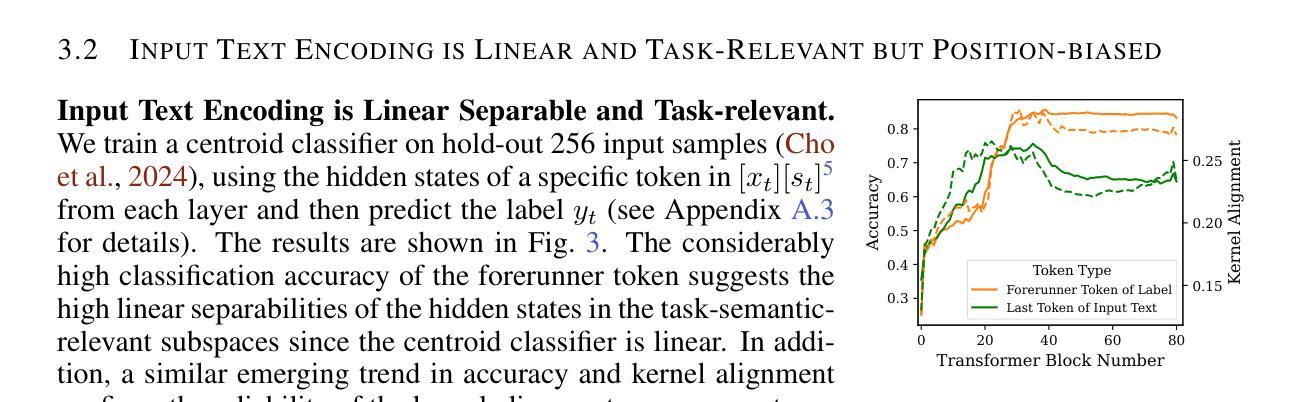
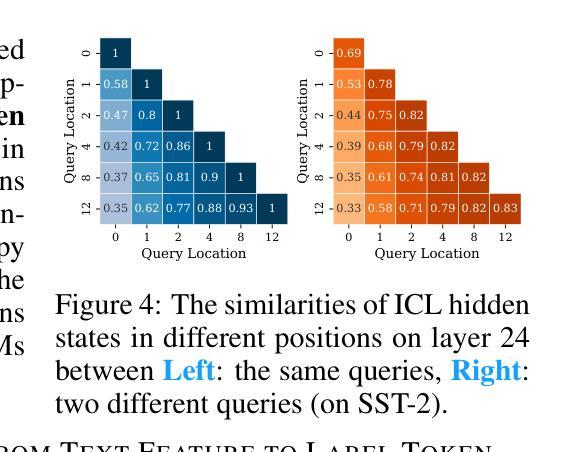
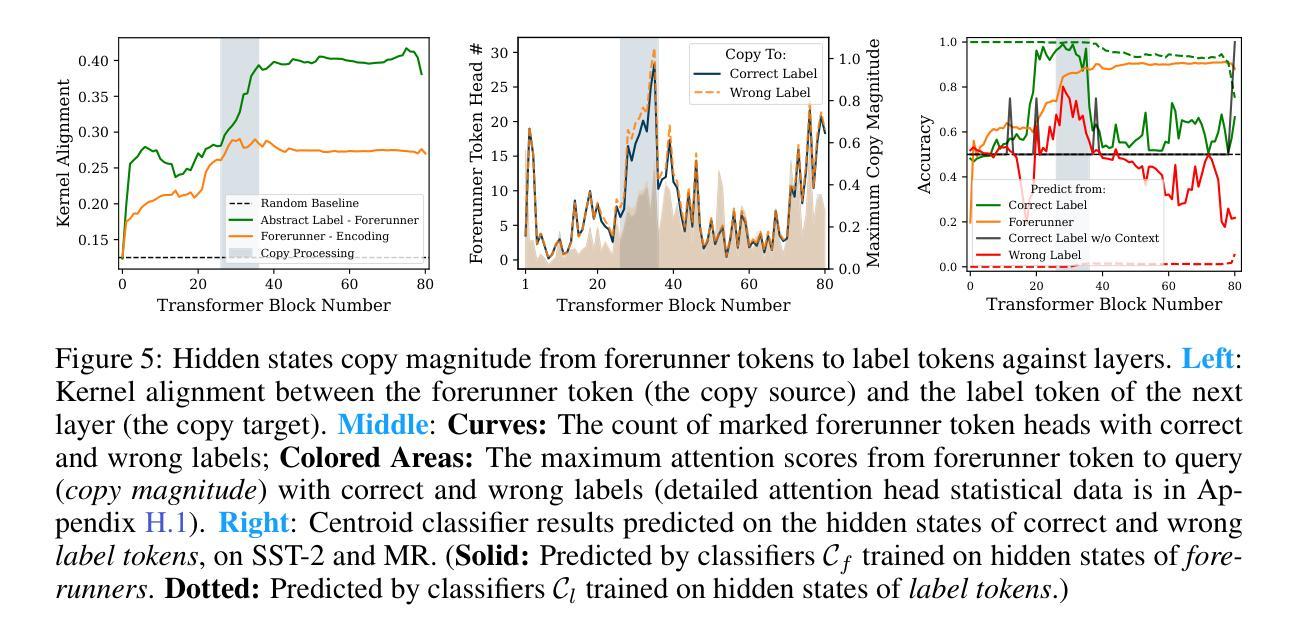
Revisiting In-context Learning Inference Circuit in Large Language Models
Authors:Hakaze Cho, Mariko Kato, Yoshihiro Sakai, Naoya Inoue
In-context Learning (ICL) is an emerging few-shot learning paradigm on Language Models (LMs) with inner mechanisms un-explored. There are already existing works describing the inner processing of ICL, while they struggle to capture all the inference phenomena in large language models. Therefore, this paper proposes a comprehensive circuit to model the inference dynamics and try to explain the observed phenomena of ICL. In detail, we divide ICL inference into 3 major operations: (1) Input Text Encode: LMs encode every input text (demonstrations and queries) into linear representation in the hidden states with sufficient information to solve ICL tasks. (2) Semantics Merge: LMs merge the encoded representations of demonstrations with their corresponding label tokens to produce joint representations of labels and demonstrations. (3) Feature Retrieval and Copy: LMs search the joint representations similar to the query representation on a task subspace, and copy the searched representations into the query. Then, language model heads capture these copied label representations to a certain extent and decode them into predicted labels. The proposed inference circuit successfully captured many phenomena observed during the ICL process, making it a comprehensive and practical explanation of the ICL inference process. Moreover, ablation analysis by disabling the proposed steps seriously damages the ICL performance, suggesting the proposed inference circuit is a dominating mechanism. Additionally, we confirm and list some bypass mechanisms that solve ICL tasks in parallel with the proposed circuit.
上下文学习(ICL)是一种新兴的语言模型(LM)小样本学习范式,其内部机制尚未被探索。已有工作描述了ICL的内部处理过程,但很难捕捉大型语言模型中的所有推理现象。因此,本文提出了一个综合电路来模拟推理动态,并试图解释观察到的ICL现象。具体来说,我们将ICL推理过程分为三大操作:(1)输入文本编码:LM将每个输入文本(演示和查询)编码为隐藏状态中的线性表示,其中包含解决ICL任务所需的信息。(2)语义合并:LM将演示的编码表示与其相应的标签令牌合并,以产生标签和演示的联合表示。(3)特征检索和复制:LM在任务子空间中搜索与查询表示相似的联合表示,并将所搜索的表示复制到查询中。然后,语言模型头部在一定程度上捕获这些复制的标签表示,并将其解码为预测标签。所提出的推理电路成功地捕捉到了ICL过程中观察到的许多现象,是对ICL推理过程的全面和实际解释。此外,通过禁用所提出的步骤进行的分析严重损害了ICL的性能,这表明所提出的推理电路是主导机制。另外,我们确认并列出了一些与所提出的电路并行解决ICL任务的旁路机制。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 37 pages, 41 figures, 8 tables
Summary
本论文针对语言模型中的In-context Learning(ICL)提出了一种全面的推理电路模型,用以解释ICL过程中的推理现象。该电路将ICL推理分为三大操作:输入文本编码、语义合并以及特征检索与复制。该模型成功捕捉了ICL过程中的许多现象,为ICL提供了全面而实用的解释。此外,通过去除该电路中的某些步骤,ICL性能受到严重影响,证明了该电路的主导作用。同时,论文还确认了与电路并行解决ICL任务的某些旁路机制。
Key Takeaways
- In-context Learning(ICL)是一种新兴的语言模型中的小样本学习范式,其内部机制尚未被完全探索。
- 现有研究在描述ICL的内部处理方面已有成果,但难以捕捉大型语言模型中的所有推理现象。
- 本论文提出了一种全面的推理电路模型,用以解释ICL过程中的推理现象,包括输入文本编码、语义合并以及特征检索与复制三大操作。
- 该电路模型成功捕捉了ICL过程中的许多现象,为理解这一过程提供了全面而实用的解释。
- 通过去除电路中的某些步骤,ICL性能受到严重影响,证明了该电路的主导作用。
- 论文还确认了与电路并行解决ICL任务的某些旁路机制。
点此查看论文截图