⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-19 更新
A New Adversarial Perspective for LiDAR-based 3D Object Detection
Authors:Shijun Zheng, Weiquan Liu, Yu Guo, Yu Zang, Siqi Shen, Cheng Wang
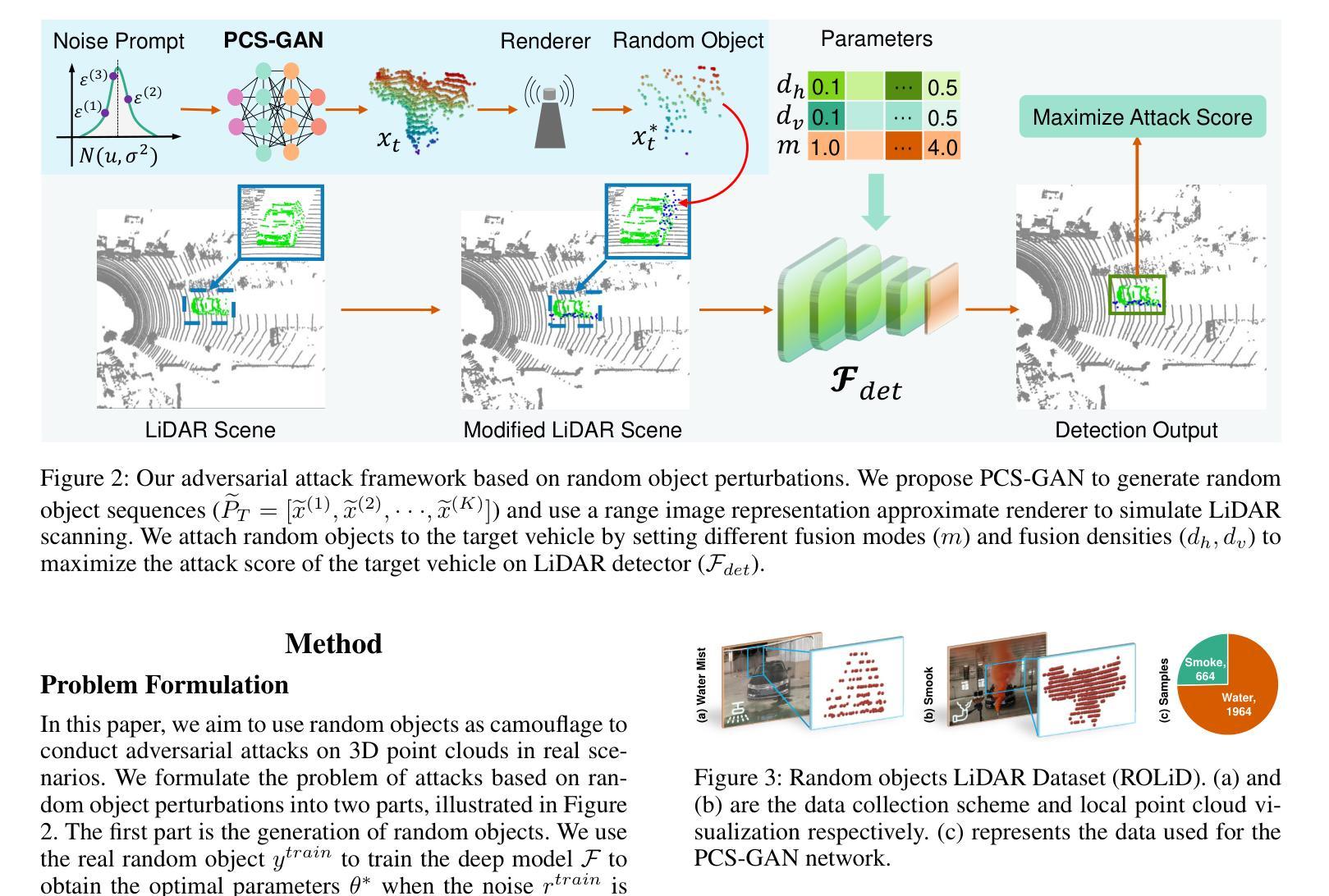
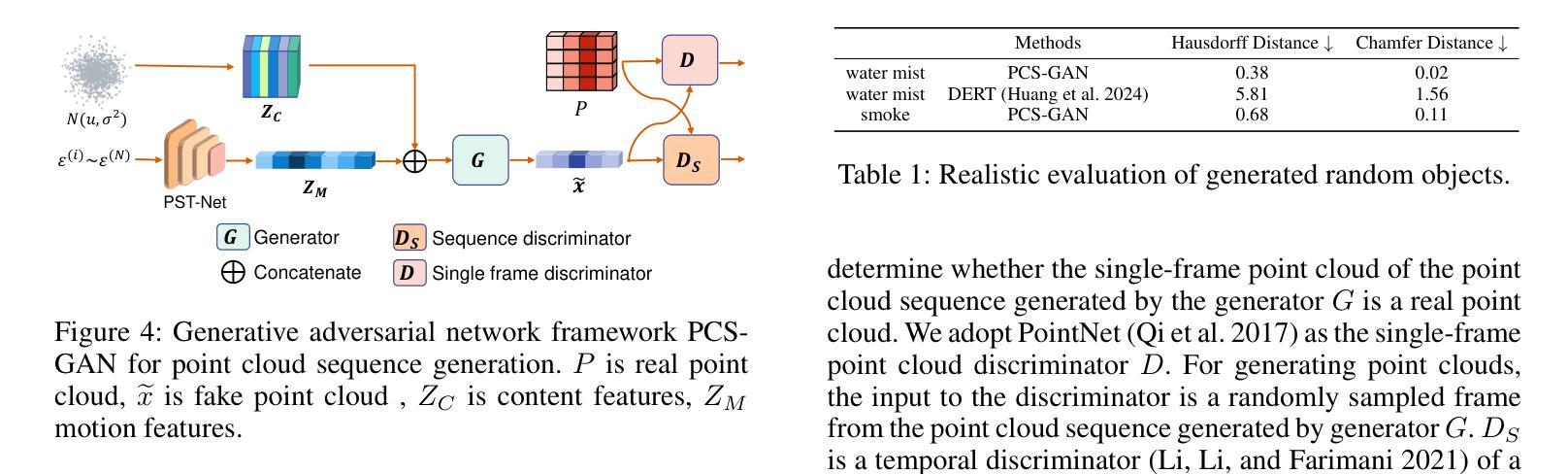
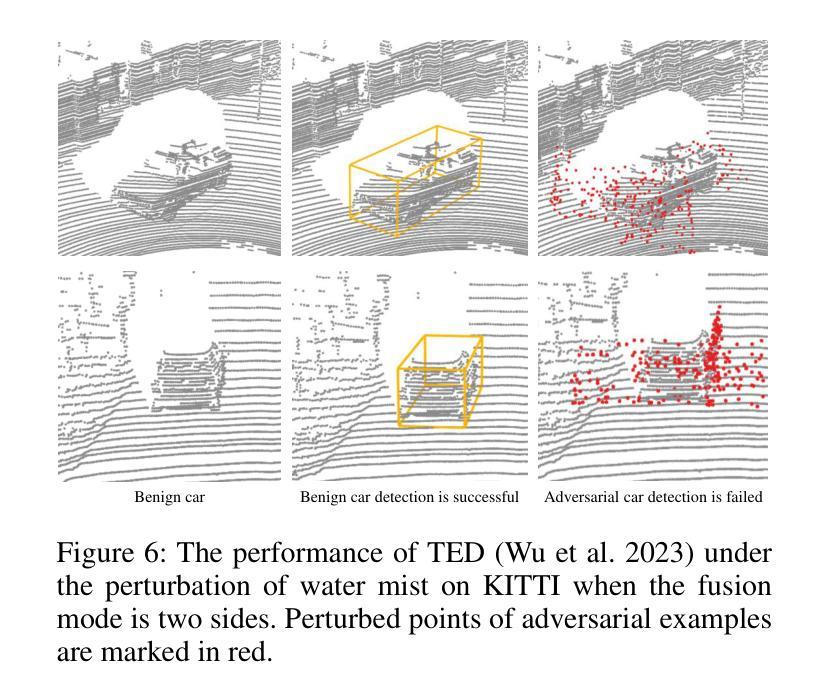
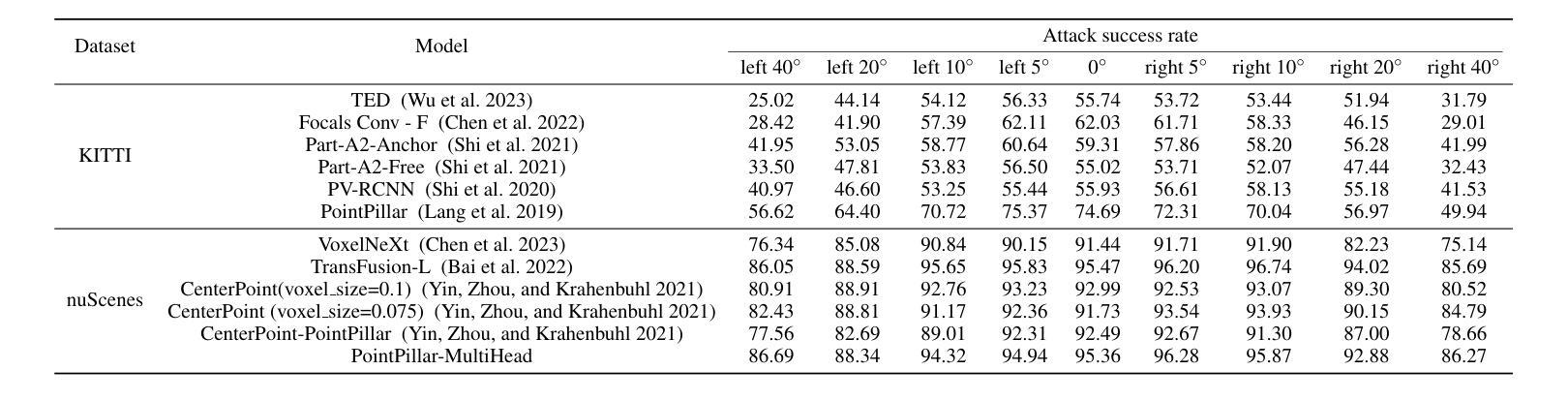
Autonomous vehicles (AVs) rely on LiDAR sensors for environmental perception and decision-making in driving scenarios. However, ensuring the safety and reliability of AVs in complex environments remains a pressing challenge. To address this issue, we introduce a real-world dataset (ROLiD) comprising LiDAR-scanned point clouds of two random objects: water mist and smoke. In this paper, we introduce a novel adversarial perspective by proposing an attack framework that utilizes water mist and smoke to simulate environmental interference. Specifically, we propose a point cloud sequence generation method using a motion and content decomposition generative adversarial network named PCS-GAN to simulate the distribution of random objects. Furthermore, leveraging the simulated LiDAR scanning characteristics implemented with Range Image, we examine the effects of introducing random object perturbations at various positions on the target vehicle. Extensive experiments demonstrate that adversarial perturbations based on random objects effectively deceive vehicle detection and reduce the recognition rate of 3D object detection models.
自动驾驶车辆(AVs)在驾驶场景中依赖于激光雷达传感器进行环境感知和决策。然而,在复杂环境中确保AVs的安全性和可靠性仍然是一个紧迫的挑战。为了解决这个问题,我们引入了一个真实世界数据集(ROLiD),它包括激光雷达扫描的两个随机对象的点云:水雾和烟雾。在本文中,我们通过提出一个利用水雾和烟雾模拟环境干扰的攻击框架,引入了一种新的对抗性视角。具体来说,我们提出了一种使用名为PCS-GAN的运动和内容分解生成对抗网络来点云序列生成方法,以模拟随机对象的分布。此外,借助模拟激光雷达扫描特性并通过范围图像实现,我们研究了在目标车辆的不同位置引入随机对象扰动的影响。大量实验表明,基于随机对象的对抗性扰动可以有效地欺骗车辆检测并降低3D对象检测模型的识别率。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 7 figures, AAAI2025
Summary
在自动驾驶车辆(AVs)的感知和决策过程中,激光雷达传感器扮演着关键角色。然而,在复杂环境下确保AVs的安全性和可靠性是一项亟待解决的挑战。为解决这一问题,本研究创建了一个真实世界数据集(ROLiD),包含了激光雷达扫描到的两种随机物体——水雾和烟雾的点云。本文提出了一种新的对抗性视角,通过构建一个攻击框架来模拟环境干扰,利用水雾和烟雾来模拟随机物体的干扰。具体来说,本研究提出了一种名为PCS-GAN的基于运动和内容的分解生成对抗网络,用于生成点云序列来模拟随机物体的分布。此外,结合模拟的激光雷达扫描特性和范围图像,本研究探讨了在不同位置引入随机物体扰动对目标车辆的影响。实验表明,基于随机物体的对抗性扰动可有效欺骗车辆检测并降低三维物体检测模型的识别率。
Key Takeaways
- 自动驾驶车辆(AVs)依赖激光雷达传感器进行环境感知和驾驶决策。
- 在复杂环境下确保AVs的安全性和可靠性是一大挑战。
- 创建了真实世界数据集(ROLiD),包含水雾和烟雾的点云数据。
- 提出了一种新的对抗性视角,通过模拟环境干扰来模拟随机物体的影响。
- 使用了名为PCS-GAN的生成对抗网络来模拟随机物体的分布和点云序列生成。
- 模拟实验表明,随机物体的对抗性扰动能有效欺骗车辆检测。
点此查看论文截图


Ensemble Learning and 3D Pix2Pix for Comprehensive Brain Tumor Analysis in Multimodal MRI
Authors:Ramy A. Zeineldin, Franziska Mathis-Ullrich
Motivated by the need for advanced solutions in the segmentation and inpainting of glioma-affected brain regions in multi-modal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), this study presents an integrated approach leveraging the strengths of ensemble learning with hybrid transformer models and convolutional neural networks (CNNs), alongside the innovative application of 3D Pix2Pix Generative Adversarial Network (GAN). Our methodology combines robust tumor segmentation capabilities, utilizing axial attention and transformer encoders for enhanced spatial relationship modeling, with the ability to synthesize biologically plausible brain tissue through 3D Pix2Pix GAN. This integrated approach addresses the BraTS 2023 cluster challenges by offering precise segmentation and realistic inpainting, tailored for diverse tumor types and sub-regions. The results demonstrate outstanding performance, evidenced by quantitative evaluations such as the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC), Hausdorff Distance (HD95) for segmentation, and Structural Similarity Index Measure (SSIM), Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), and Mean-Square Error (MSE) for inpainting. Qualitative assessments further validate the high-quality, clinically relevant outputs. In conclusion, this study underscores the potential of combining advanced machine learning techniques for comprehensive brain tumor analysis, promising significant advancements in clinical decision-making and patient care within the realm of medical imaging.
针对多模态磁共振成像(MRI)中胶质母细胞瘤受影响脑区的分割和修复需求,本研究提出了一种结合集成学习、混合变压器模型和卷积神经网络(CNN)优势的综合方法,并创新性地应用了3D Pix2Pix生成对抗网络(GAN)。我们的方法结合了强大的肿瘤分割能力,利用轴向注意力和变压器编码器进行增强的空间关系建模,以及通过3D Pix2Pix GAN合成生物上合理的脑组织的能力。这一综合方法通过提供精确的分割和逼真的修复,解决了BraTS 2023集群挑战,适用于多种肿瘤类型和子区域。结果表现出色,通过定量评估(如Dice相似系数(DSC)、Hausdorff距离(HD95)进行分割评估,以及结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)和均方误差(MSE)进行修复评估)证明了其性能。定性评估进一步验证了其高质量、临床相关的输出。总之,本研究强调了结合先进机器学习技术进行全面的脑肿瘤分析潜力,有望在医学成像领域的临床决策和患者护理中取得重大进展。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at the MICCAI BraTS Challenge 2023
Summary:
本研究针对多模态磁共振成像(MRI)中胶质瘤影响的大脑区域分割和修复的需求,提出了一种结合集成学习、混合变压器模型、卷积神经网络(CNN)和3D Pix2Pix生成对抗网络(GAN)的集成方法。该方法不仅利用轴向注意力和变压器编码器进行精确肿瘤分割,而且通过3D Pix2Pix GAN合成生物上合理的大脑组织。该研究为BraTS 2023集群挑战提供了精确的分割和逼真的修复,针对各种肿瘤类型和子区域进行定制,显示出优异的性能。
Key Takeaways:
- 本研究提出了一种结合多种先进机器学习技术的集成方法,用于分割和修复多模态MRI中的胶质瘤影响区域。
- 利用集成学习、混合变压器模型、CNN和3D Pix2Pix GAN等技术,提高了肿瘤分割的精确性和修复的真实感。
- 通过轴向注意力和变压器编码器增强空间关系建模,提高了肿瘤分割的鲁棒性。
- 定量评估结果,如Dice相似系数(DSC)、Hausdorff距离(HD95)等,显示了该方法在分割方面的出色性能。
- 对于修复效果的评估指标,如结构相似性指数度量(SSIM)、峰值信噪比(PSNR)和均方误差(MSE),验证了输出的高质量和临床相关性。
- 该方法针对BraTS 2023集群挑战提供了解决方案,适用于不同类型的肿瘤和子区域的分割和修复。
点此查看论文截图

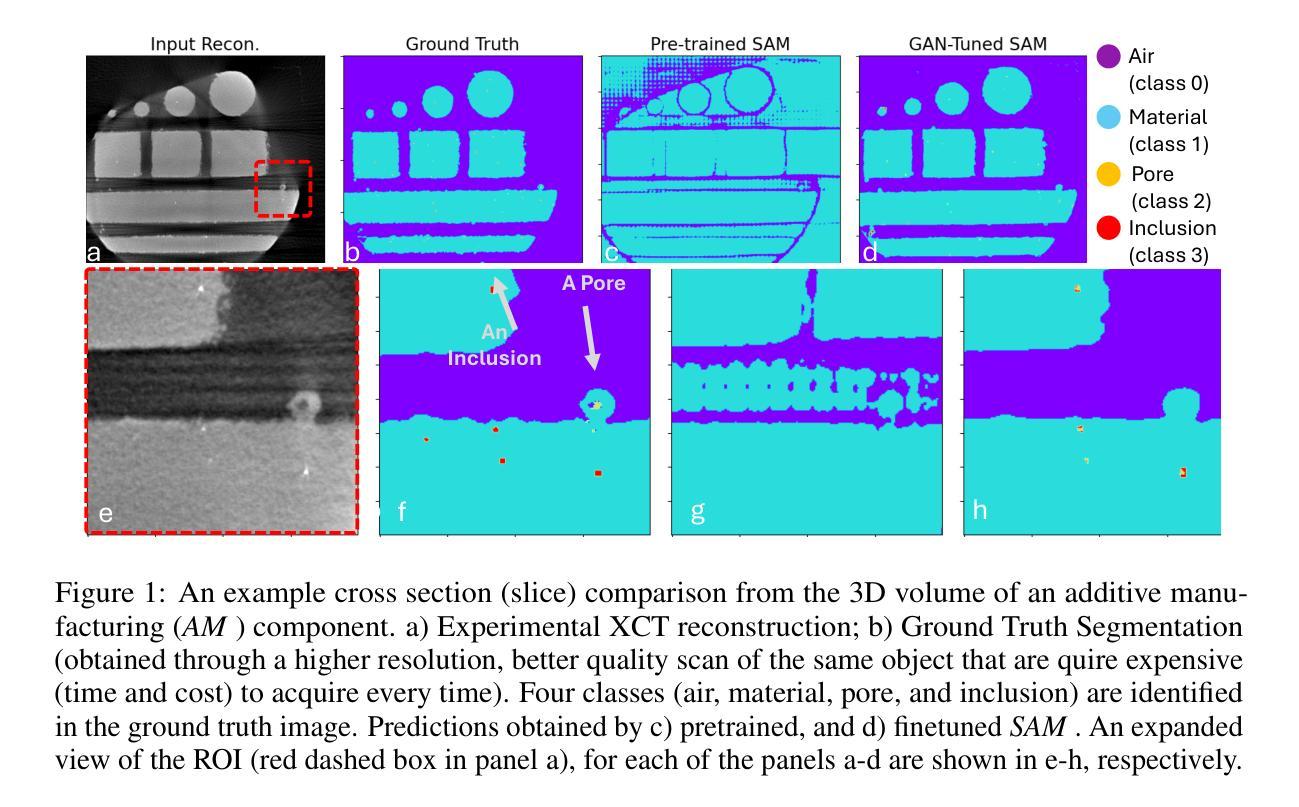
Adapting Segment Anything Model (SAM) to Experimental Datasets via Fine-Tuning on GAN-based Simulation: A Case Study in Additive Manufacturing
Authors:Anika Tabassum, Amirkoushyar Ziabari
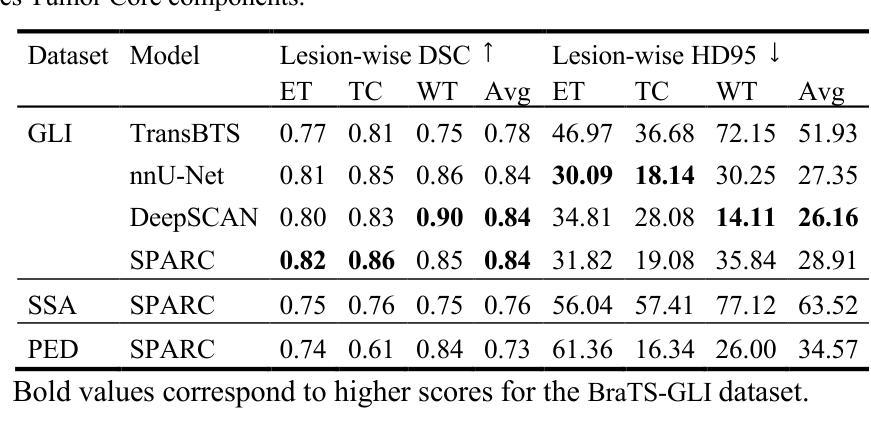
Industrial X-ray computed tomography (XCT) is a powerful tool for non-destructive characterization of materials and manufactured components. XCT commonly accompanied by advanced image analysis and computer vision algorithms to extract relevant information from the images. Traditional computer vision models often struggle due to noise, resolution variability, and complex internal structures, particularly in scientific imaging applications. State-of-the-art foundational models, like the Segment Anything Model (SAM)-designed for general-purpose image segmentation-have revolutionized image segmentation across various domains, yet their application in specialized fields like materials science remains under-explored. In this work, we explore the application and limitations of SAM for industrial X-ray CT inspection of additive manufacturing components. We demonstrate that while SAM shows promise, it struggles with out-of-distribution data, multiclass segmentation, and computational efficiency during fine-tuning. To address these issues, we propose a fine-tuning strategy utilizing parameter-efficient techniques, specifically Conv-LoRa, to adapt SAM for material-specific datasets. Additionally, we leverage generative adversarial network (GAN)-generated data to enhance the training process and improve the model’s segmentation performance on complex X-ray CT data. Our experimental results highlight the importance of tailored segmentation models for accurate inspection, showing that fine-tuning SAM on domain-specific scientific imaging data significantly improves performance. However, despite improvements, the model’s ability to generalize across diverse datasets remains limited, highlighting the need for further research into robust, scalable solutions for domain-specific segmentation tasks.
工业X射线计算机断层扫描(XCT)是非破坏性表征材料和制造部件的强大工具。XCT通常与先进的图像分析和计算机视觉算法相结合,从图像中提取相关信息。传统计算机视觉模型由于噪声、分辨率变化和复杂内部结构的影响而常常表现挣扎,特别是在科学成像应用中。最新的基础模型,如用于通用图像分割的Segment Anything Model(SAM)已经彻底改变了各种领域的图像分割,但其在材料科学等特定领域的应用仍然被探索不足。在这项工作中,我们探索了SAM在增材制造部件的工业X射线CT检测中的应用和局限性。我们证明,虽然SAM显示出潜力,但在处理分布外数据、多类分割和微调过程中的计算效率方面存在挑战。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种利用参数高效技术的微调策略,特别是Conv-LoRa,以适应特定材料的数据集。此外,我们还利用生成对抗网络(GAN)生成的数据来增强训练过程,提高模型在复杂X射线CT数据上的分割性能。我们的实验结果强调了为准确检查量身定制分割模型的重要性,并表明在特定领域的科学成像数据上微调SAM可以显著提高性能。然而,尽管有所改进,该模型在不同数据集上的泛化能力仍然有限,这突显了需要进一步研究用于特定领域分割任务的稳健、可扩展解决方案的必要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:本文探讨了将Segment Anything Model(SAM)应用于工业X射线计算机断层扫描(XCT)检测增材制造部件的潜力与局限性。研究发现,虽然SAM模型显示出一定的潜力,但在处理离群数据、多类别分割和计算效率方面存在挑战。为解决这些问题,研究人员提出了一种利用Conv-LoRa技术的精细调整策略,并借助生成对抗网络(GAN)生成的数据增强训练过程,以提高模型在复杂X射线CT数据上的分割性能。实验结果表明,针对特定领域的科学成像数据对SAM进行微调可显著提高性能,但模型的泛化能力仍有待提高,需要进一步研究具有针对性的稳健解决方案。
Key Takeaways:
- 工业X射线计算机断层扫描(XCT)是材料和非破坏性检测的重要工具,常与先进的图像分析和计算机视觉算法相结合提取信息。
- 传统计算机视觉模型在处理噪声、分辨率变化和复杂内部结构方面存在困难,特别是在科学成像应用中。
- Segment Anything Model(SAM)在各个领域的图像分割中取得了革命性的进展,但在材料科学等特定领域的应用仍待探索。
- SAM在处理离群数据、多类别分割和计算效率方面存在挑战。
- 通过利用Conv-LoRa技术的精细调整策略和生成对抗网络(GAN)生成的数据,增强了模型在复杂X射线CT数据上的分割性能。
- 实验结果指出针对特定领域的科学成像数据对SAM进行微调的重要性,可显著提高性能。
点此查看论文截图


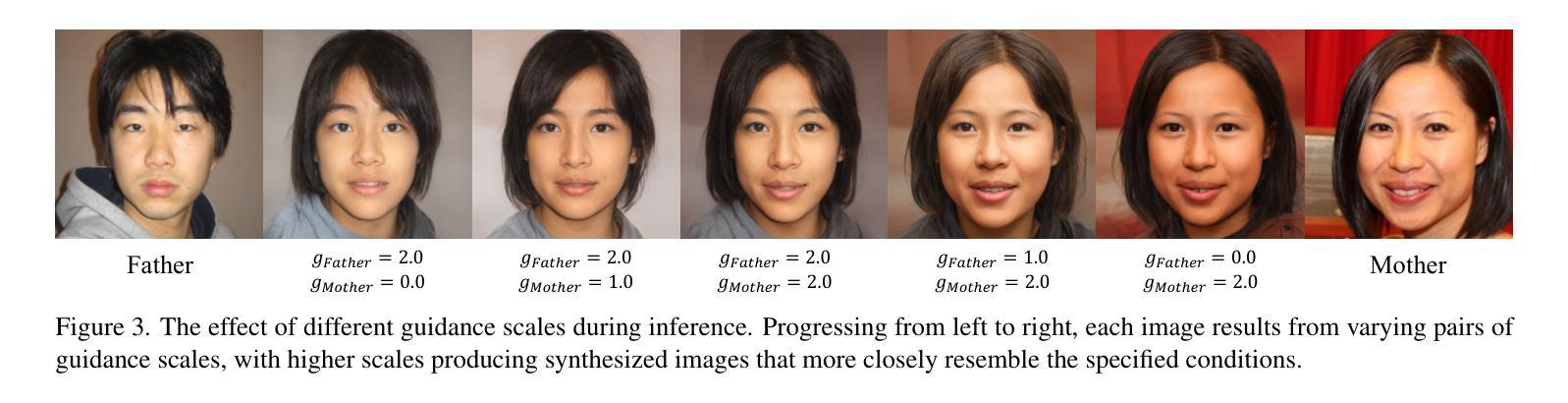
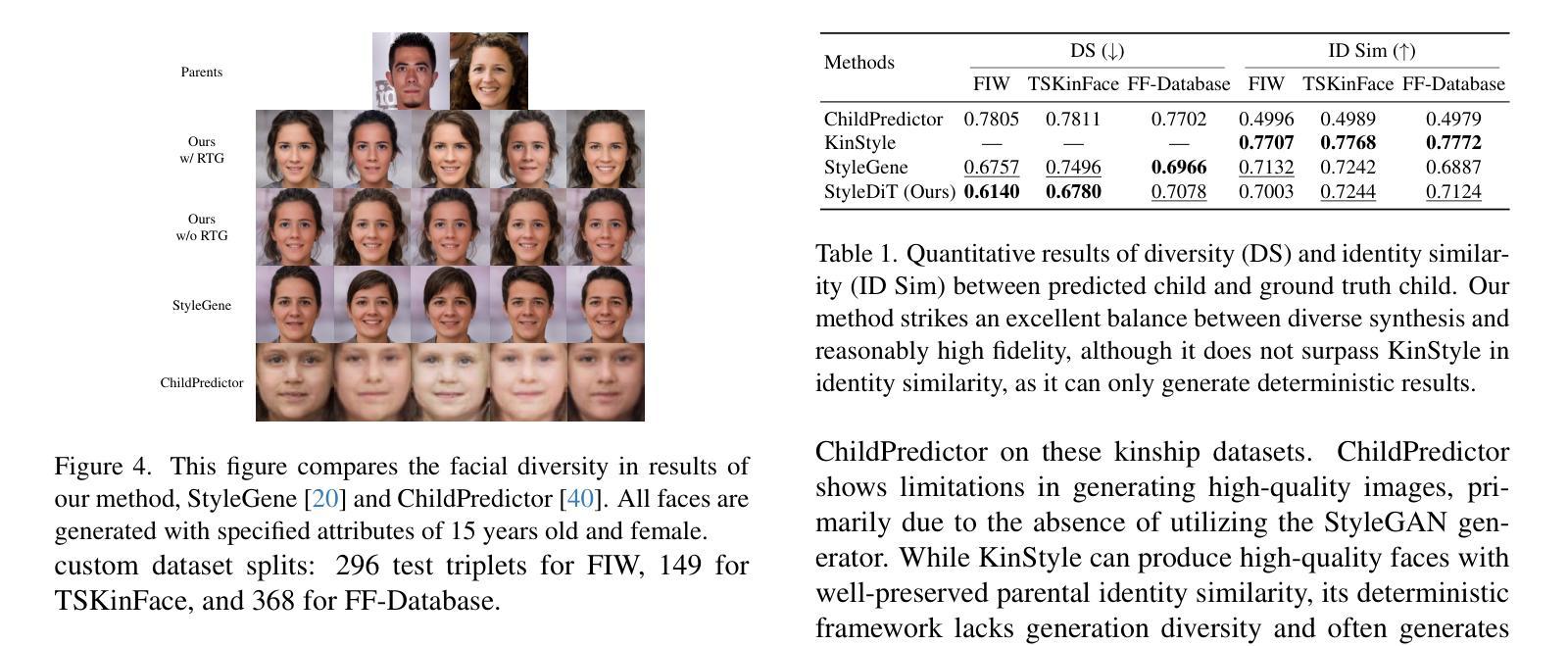
StyleDiT: A Unified Framework for Diverse Child and Partner Faces Synthesis with Style Latent Diffusion Transformer
Authors:Pin-Yen Chiu, Dai-Jie Wu, Po-Hsun Chu, Chia-Hsuan Hsu, Hsiang-Chen Chiu, Chih-Yu Wang, Jun-Cheng Chen
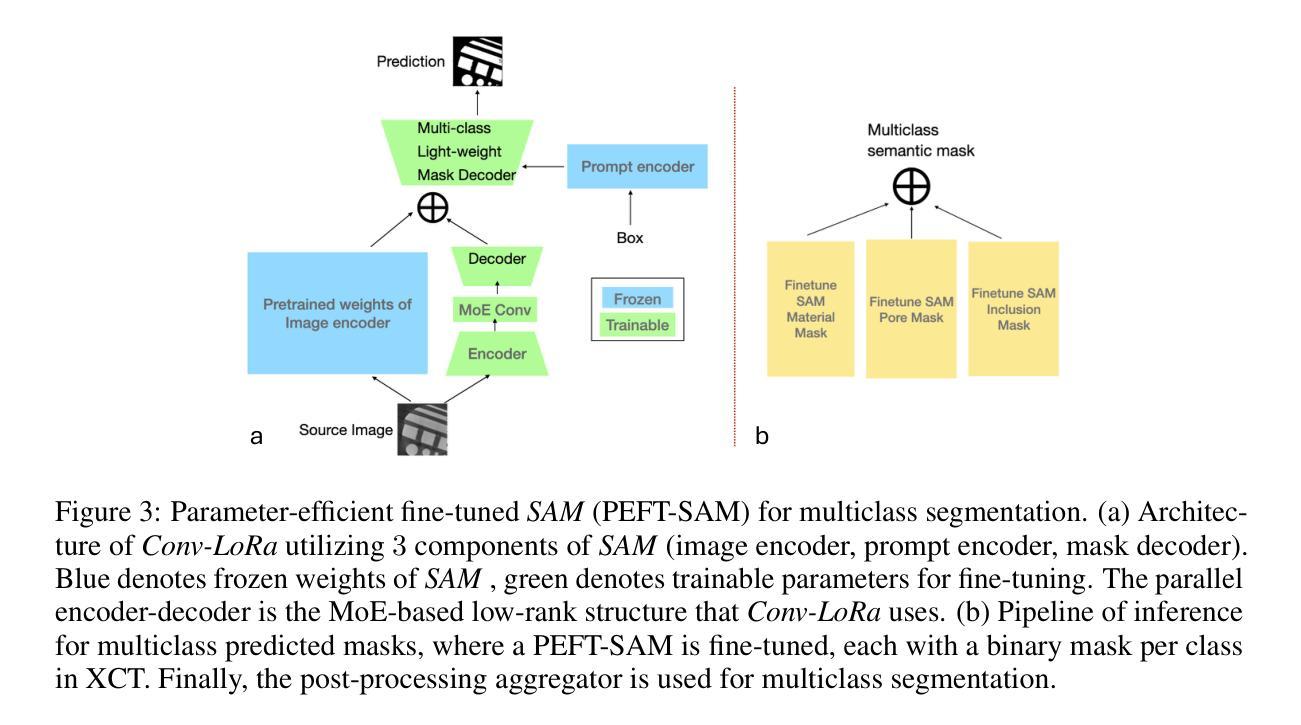
Kinship face synthesis is a challenging problem due to the scarcity and low quality of the available kinship data. Existing methods often struggle to generate descendants with both high diversity and fidelity while precisely controlling facial attributes such as age and gender. To address these issues, we propose the Style Latent Diffusion Transformer (StyleDiT), a novel framework that integrates the strengths of StyleGAN with the diffusion model to generate high-quality and diverse kinship faces. In this framework, the rich facial priors of StyleGAN enable fine-grained attribute control, while our conditional diffusion model is used to sample a StyleGAN latent aligned with the kinship relationship of conditioning images by utilizing the advantage of modeling complex kinship relationship distribution. StyleGAN then handles latent decoding for final face generation. Additionally, we introduce the Relational Trait Guidance (RTG) mechanism, enabling independent control of influencing conditions, such as each parent’s facial image. RTG also enables a fine-grained adjustment between the diversity and fidelity in synthesized faces. Furthermore, we extend the application to an unexplored domain: predicting a partner’s facial images using a child’s image and one parent’s image within the same framework. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our StyleDiT outperforms existing methods by striking an excellent balance between generating diverse and high-fidelity kinship faces.
亲属关系面部合成是一项具有挑战性的任务,因为可用的亲属关系数据稀缺且质量低下。现有方法往往难以生成具有高度多样性和保真度的后代,同时难以精确控制面部属性,如年龄和性别。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Style Latent Diffusion Transformer(StyleDiT)这一新型框架,它结合了StyleGAN和扩散模型的优点,用于生成高质量和多样化的亲属关系面部。在该框架中,StyleGAN的丰富面部先验知识能够实现细粒度的属性控制,而我们的条件扩散模型则利用建模复杂的亲属关系分布的优势,对与条件图像相符的StyleGAN潜在向量进行采样。然后,StyleGAN处理潜在解码以生成最终面部。此外,我们引入了Relational Trait Guidance(RTG)机制,实现对影响条件(如每个父母的面部图像)的独立控制。RTG还能够在合成面部的多样性和保真度之间进行精细调整。此外,我们将应用扩展到了一个未被探索的领域:在同一框架内,使用孩子的图像和父母的图像来预测伴侣的面部图像。大量实验表明,我们的StyleDiT在生成多样化和高保真度的亲属关系面部方面取得了出色的平衡,超越了现有方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一个名为StyleDiT的新框架,结合了StyleGAN和扩散模型的优点,用于生成高质量、多样化的亲属关系面孔。该框架利用StyleGAN的丰富面部先验信息实现精细的属性控制,通过条件扩散模型对与条件图像相符的StyleGAN潜在向量进行采样,并利用亲属关系分布建模的优势。此外,还引入了关系特征引导(RTG)机制,实现对影响条件如父母面部图像的独立控制,并在合成面部的多样性和逼真度之间进行精细调整。该框架还扩展到了预测配偶面部图像的应用,使用孩子的图像和父母的图像。实验表明,StyleDiT在生成多样化和高保真度的亲属关系面孔方面优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- StyleDiT结合了StyleGAN和扩散模型的优点,用于生成亲属关系面孔。
- StyleGAN的丰富面部先验信息实现了精细的属性控制。
- 条件扩散模型用于采样与条件图像相符的StyleGAN潜在向量。
- 引入了关系特征引导(RTG)机制,实现了影响条件的独立控制。
- RTG机制可以在多样性和逼真度之间进行精细调整。
- StyleDiT框架扩展到了预测配偶面部图像的应用。
点此查看论文截图


Fine-grained Text to Image Synthesis
Authors:Xu Ouyang, Ying Chen, Kaiyue Zhu, Gady Agam
Fine-grained text to image synthesis involves generating images from texts that belong to different categories. In contrast to general text to image synthesis, in fine-grained synthesis there is high similarity between images of different subclasses, and there may be linguistic discrepancy among texts describing the same image. Recent Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN), such as the Recurrent Affine Transformation (RAT) GAN model, are able to synthesize clear and realistic images from texts. However, GAN models ignore fine-grained level information. In this paper we propose an approach that incorporates an auxiliary classifier in the discriminator and a contrastive learning method to improve the accuracy of fine-grained details in images synthesized by RAT GAN. The auxiliary classifier helps the discriminator classify the class of images, and helps the generator synthesize more accurate fine-grained images. The contrastive learning method minimizes the similarity between images from different subclasses and maximizes the similarity between images from the same subclass. We evaluate on several state-of-the-art methods on the commonly used CUB-200-2011 bird dataset and Oxford-102 flower dataset, and demonstrated superior performance.
细粒度文本到图像合成涉及从不同类别的文本生成图像。与一般的文本到图像合成相比,在细粒度合成中,不同子类的图像之间具有高度相似性,描述同一图像的文本之间可能存在语言差异。最近的生成对抗网络(GAN),如循环仿射变换(RAT)GAN模型,能够从文本中合成清晰和现实的图像。然而,GAN模型忽略了细粒度级别的信息。在本文中,我们提出了一种方法,该方法在鉴别器中结合了辅助分类器,并采用对比学习方法来提高由RAT GAN合成图像的细粒度细节的准确性。辅助分类器帮助鉴别器对图像进行分类,并帮助生成器合成更准确的细粒度图像。对比学习方法最小化不同子类图像之间的相似性,并最大化同一子类图像之间的相似性。我们在常用的CUB-200-2011鸟类数据集和Oxford-102花卉数据集上对一些最先进的方法进行了评估,并展示了优越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于文本的精细粒度图像合成使用文本生成不同类别的图像。与一般的文本到图像合成相比,精细粒度合成中不同子类的图像高度相似,描述同一图像的文本之间可能存在语言差异。尽管最近的生成对抗网络(GAN)如循环仿射变换(RAT)GAN模型能够生成清晰逼真的图像,但它们忽略了精细级别的信息。本文提出了一种方法,在鉴别器中引入辅助分类器,并采用对比学习方法来提高由RAT GAN合成的图像中精细级别信息的准确性。辅助分类器帮助鉴别器对图像进行分类,并帮助生成器生成更精确的精细粒度图像。对比学习方法减少了不同子类图像之间的相似性并增加了同一子类图像之间的相似性。我们在常用的CUB-200-2011鸟类数据集和Oxford-102花卉数据集上进行了评估,并展示了优越的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 文本到图像合成可以分为精细粒度合成和一般合成,其中精细粒度合成涉及不同类别的图像生成。
- 现有GAN模型如RAT GAN在生成图像时忽略了精细级别的信息。
- 本文提出了一种在鉴别器中引入辅助分类器的方法,以提高图像合成的准确性。
- 辅助分类器有助于鉴别器对图像进行分类,同时帮助生成器生成更精确的精细粒度图像。
- 采用对比学习方法,减少不同子类图像之间的相似性,增加同一子类图像之间的相似性。
- 方法在CUB-200-2011鸟类数据集和Oxford-102花卉数据集上的评估表现优越。
点此查看论文截图

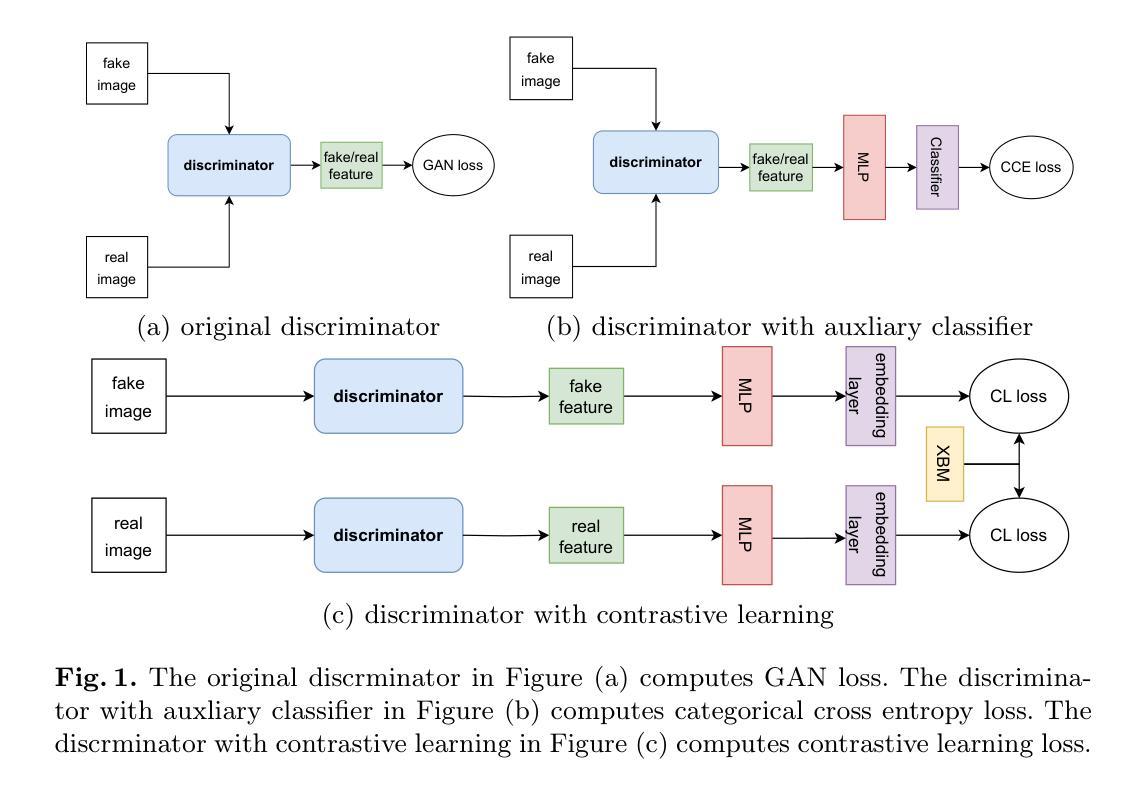
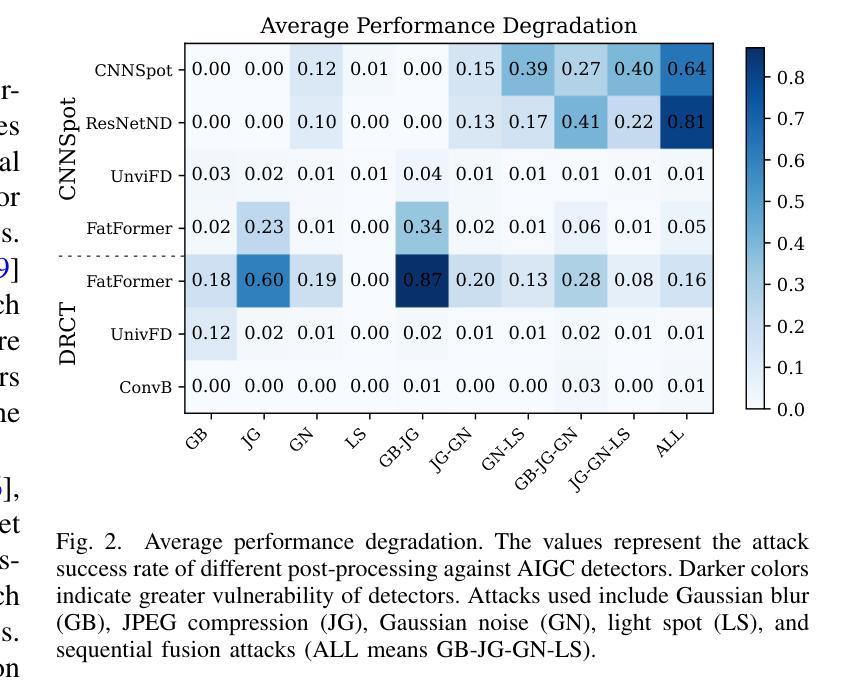
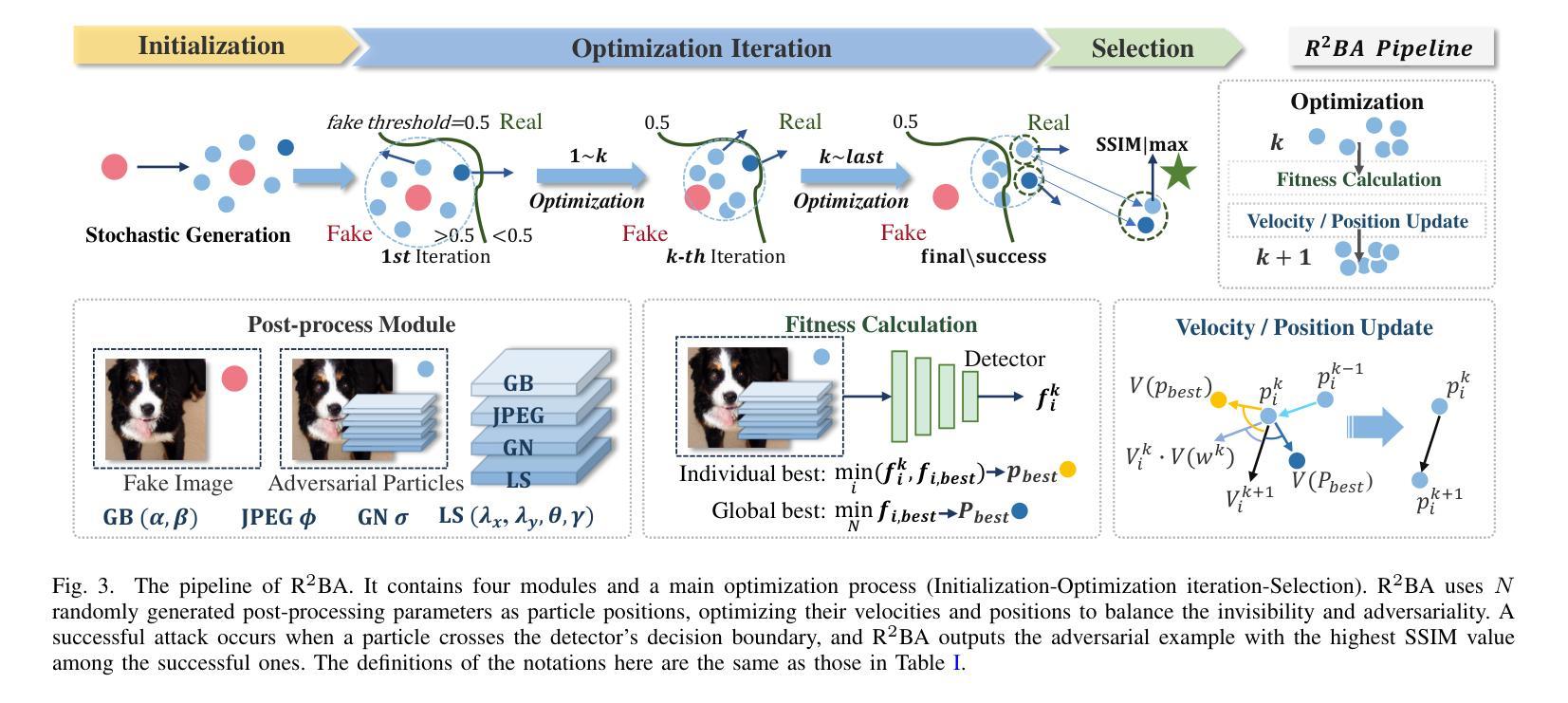
Take Fake as Real: Realistic-like Robust Black-box Adversarial Attack to Evade AIGC Detection
Authors:Caiyun Xie, Dengpan Ye, Yunming Zhang, Long Tang, Yunna Lv, Jiacheng Deng, Jiawei Song
The security of AI-generated content (AIGC) detection is crucial for ensuring multimedia content credibility. To enhance detector security, research on adversarial attacks has become essential. However, most existing adversarial attacks focus only on GAN-generated facial images detection, struggle to be effective on multi-class natural images and diffusion-based detectors, and exhibit poor invisibility. To fill this gap, we first conduct an in-depth analysis of the vulnerability of AIGC detectors and discover the feature that detectors vary in vulnerability to different post-processing. Then, considering that the detector is agnostic in real-world scenarios and given this discovery, we propose a Realistic-like Robust Black-box Adversarial attack (R$^2$BA) with post-processing fusion optimization. Unlike typical perturbations, R$^2$BA uses real-world post-processing, i.e., Gaussian blur, JPEG compression, Gaussian noise and light spot to generate adversarial examples. Specifically, we use a stochastic particle swarm algorithm with inertia decay to optimize post-processing fusion intensity and explore the detector’s decision boundary. Guided by the detector’s fake probability, R$^2$BA enhances/weakens the detector-vulnerable/detector-robust post-processing intensity to strike a balance between adversariality and invisibility. Extensive experiments on popular/commercial AIGC detectors and datasets demonstrate that R$^2$BA exhibits impressive anti-detection performance, excellent invisibility, and strong robustness in GAN-based and diffusion-based cases. Compared to state-of-the-art white-box and black-box attacks, R$^2$BA shows significant improvements of 15%–72% and 21%–47% in anti-detection performance under the original and robust scenario respectively, offering valuable insights for the security of AIGC detection in real-world applications.
人工智能生成内容(AIGC)检测的的安全性对于确保多媒体内容可信度至关重要。为了提升检测器安全性,对抗性攻击的研究变得至关重要。然而,现有大多数对抗性攻击仅专注于生成对抗网络(GAN)生成的面部图像检测,对于多类自然图像和基于扩散的检测器的效果欠佳,隐形性也较差。为了填补这一空白,我们首先对AIGC检测器的脆弱性进行了深入分析,并发现了检测器对不同后处理的脆弱性存在差异。基于此发现,考虑到检测器在现实场景中的不可知特性,我们提出了一种具有后处理融合优化的类似现实的鲁棒黑盒对抗性攻击(R$^2$BA)。不同于典型的扰动,R$^2$BA使用现实世界的后处理,例如高斯模糊、JPEG压缩、高斯噪声和光斑来生成对抗样本。具体来说,我们使用带有惯性衰减的随机粒子群算法来优化后处理融合强度并探索检测器的决策边界。在流行的/商业AIGC检测器和数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,R$^2$BA具有令人印象深刻的反检测性能、出色的隐形性和强烈的稳健性,在基于GAN和基于扩散的情况下均表现良好。与最先进的白盒和黑盒攻击相比,R$^2$BA在原场景和稳健场景下的反检测性能分别提高了15%–72%和21%–47%,为AIGC检测在现实世界应用中的安全性提供了宝贵的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于人工智能生成的内容(AIGC)检测的安全对于确保多媒体内容可信度至关重要。为提高检测器安全性,对抗性攻击的研究变得至关重要。针对现有对抗性攻击在GAN生成的面部图像检测上的局限性,本文深入分析了AIGC检测器的脆弱性,并提出了一种名为R²BA的逼真型鲁棒黑盒对抗性攻击方法,通过优化后处理融合策略,能够在多类自然图像和扩散检测器上实现有效攻击,同时保持良好的隐蔽性。
Key Takeaways
- AIGC检测安全对多媒体内容可信度至关重要。
- 对抗性攻击是提高AIGC检测器安全性的关键。
- 现有对抗性攻击在GAN生成的面部图像检测上表现出局限性,缺乏在多类自然图像和扩散检测器上的有效性及隐蔽性。
- 本文分析了AIGC检测器的脆弱性,发现不同后处理对检测器的影响存在差异。
- 提出了R²BA攻击方法,利用现实世界的后处理生成对抗样本,如高斯模糊、JPEG压缩等。
- R²BA通过优化后处理融合策略,实现了在检测器决策边界的探索和平衡对抗性与隐蔽性。
- 实验结果表明,R²BA在主流和商业AIGC检测器及数据集上表现出卓越的抗检测性能、高度的隐蔽性和强大的鲁棒性。
点此查看论文截图


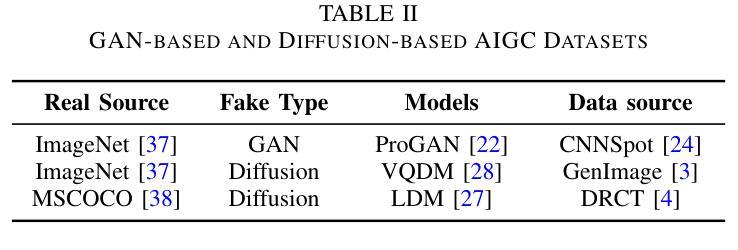
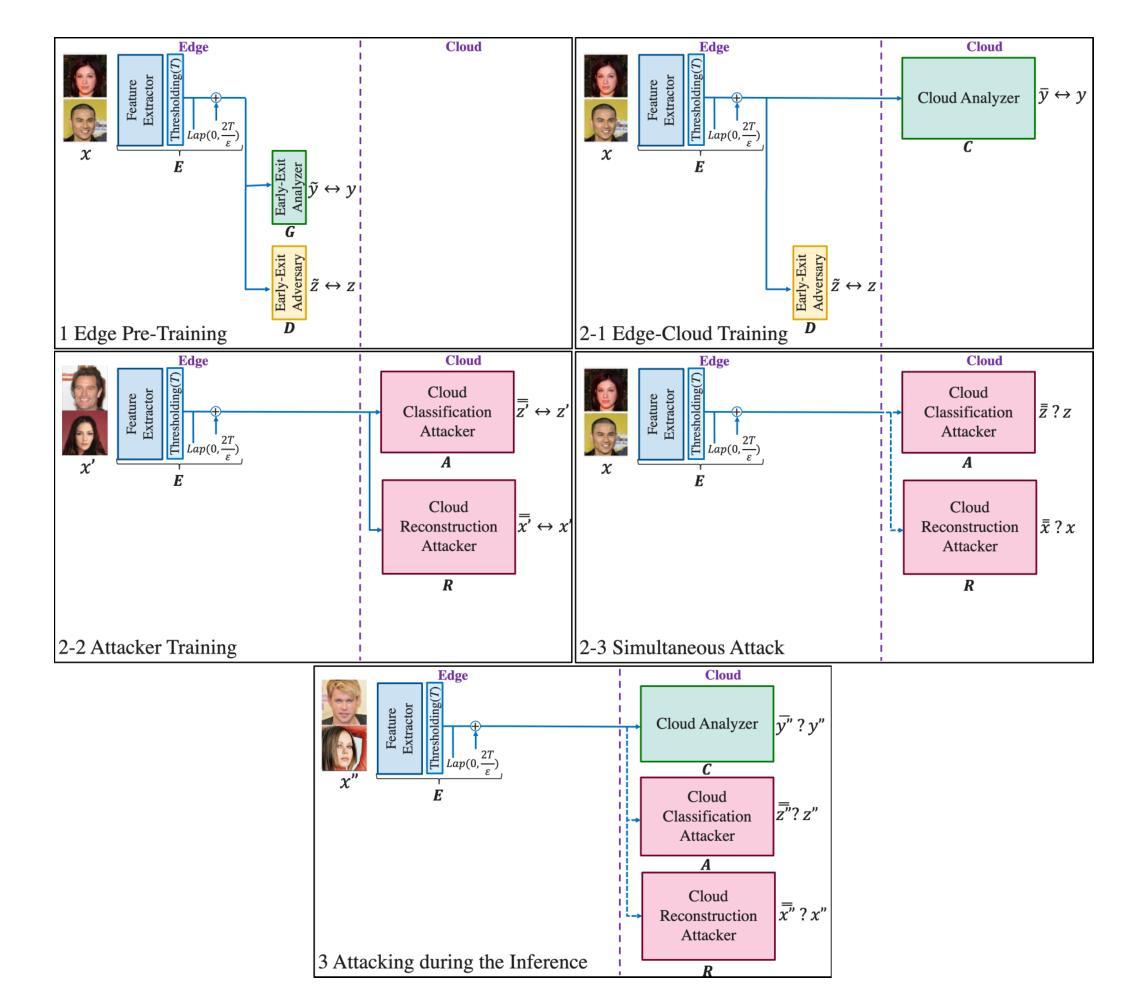
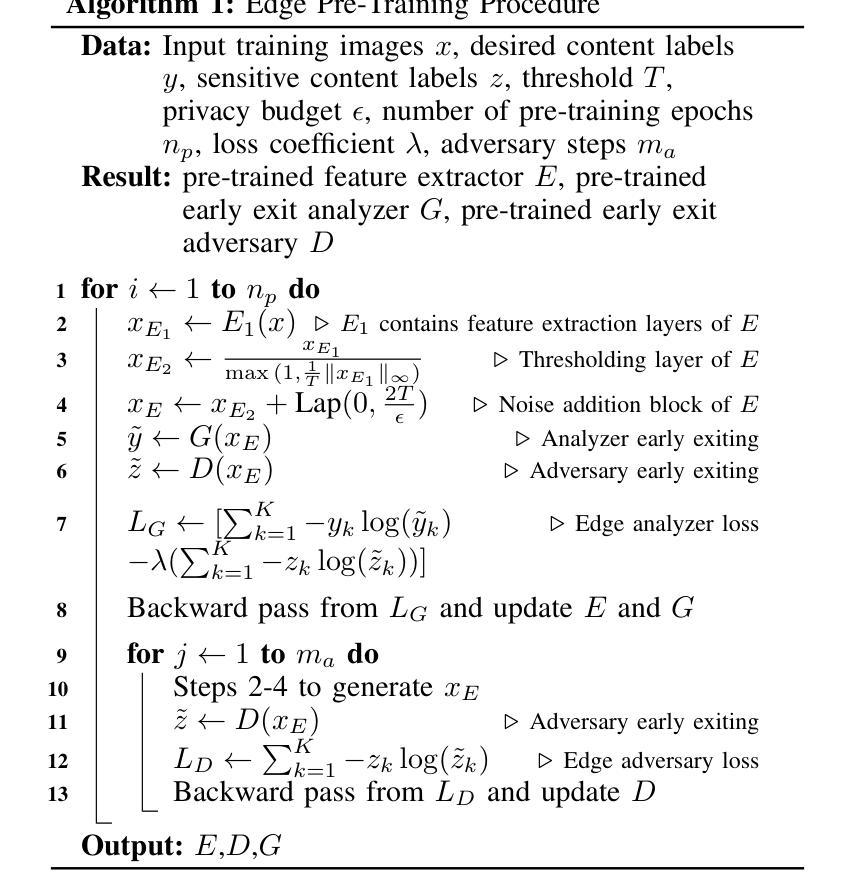
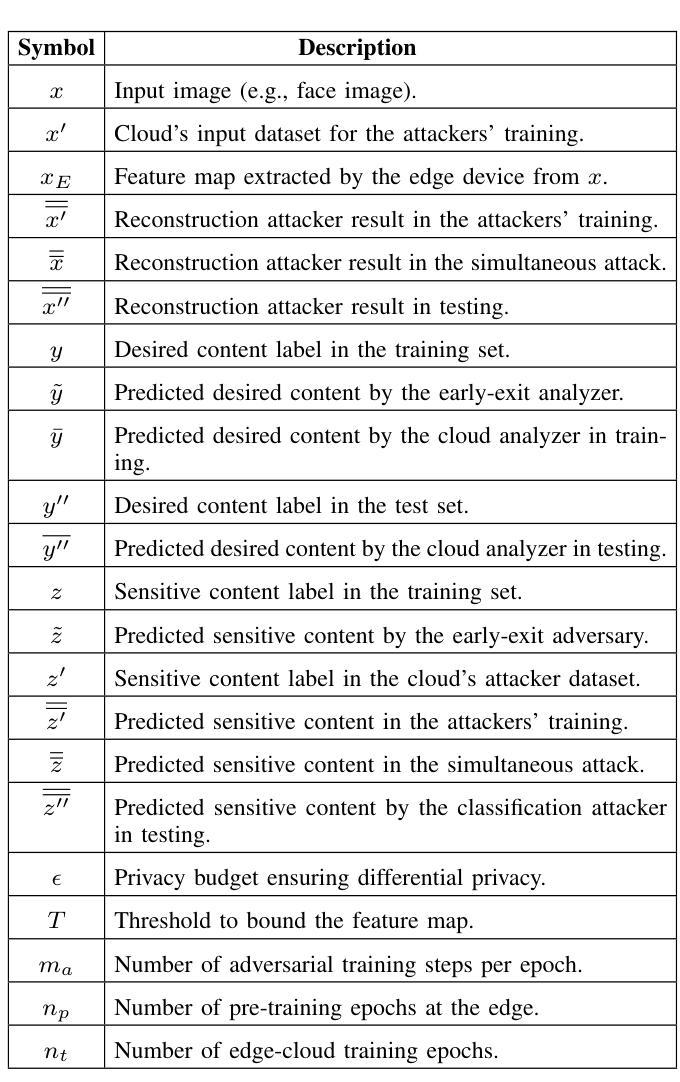
PriPHiT: Privacy-Preserving Hierarchical Training of Deep Neural Networks
Authors:Yamin Sepehri, Pedram Pad, Pascal Frossard, L. Andrea Dunbar
The training phase of deep neural networks requires substantial resources and as such is often performed on cloud servers. However, this raises privacy concerns when the training dataset contains sensitive content, e.g., facial or medical images. In this work, we propose a method to perform the training phase of a deep learning model on both an edge device and a cloud server that prevents sensitive content being transmitted to the cloud while retaining the desired information. The proposed privacy-preserving method uses adversarial early exits to suppress the sensitive content at the edge and transmits the task-relevant information to the cloud. This approach incorporates noise addition during the training phase to provide a differential privacy guarantee. We extensively test our method on different facial and medical datasets with diverse attributes using various deep learning architectures, showcasing its outstanding performance. We also demonstrate the effectiveness of privacy preservation through successful defenses against different white-box, deep and GAN-based reconstruction attacks. This approach is designed for resource-constrained edge devices, ensuring minimal memory usage and computational overhead.
深度神经网络训练阶段需要大量的资源,因此通常会在云服务器上执行。然而,当训练数据集包含敏感内容时,例如面部或医疗图像,这引发了隐私担忧。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种在边缘设备和云服务器上执行深度学习模型训练阶段的方法,该方法可防止敏感内容传输到云,同时保留所需的信息。所提出的隐私保护方法使用对抗性早期退出策略来抑制边缘的敏感内容,并将与任务相关的信息传输到云中。这种方法在训练阶段添加了噪声,以提供差分隐私保证。我们在具有不同属性的各种面部和医疗数据集上,使用各种深度学习架构对我们的方法进行了广泛测试,展示了其出色的性能。我们还通过成功防御各种白盒、深度以及基于GAN的重建攻击来证明了隐私保护的有效性。该方法专为资源受限的边缘设备设计,确保最小的内存使用和计算开销。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 19 figures, 11 tables
Summary
深度学习模型的训练阶段需要大量的资源,通常在云服务器上进行。但当训练数据集包含敏感内容时,如面部或医疗图像,这会引起隐私担忧。为此,我们提出了一种在边缘设备和云服务器上进行深度学习模型训练的方法,可防止敏感内容传输到云端,同时保留所需的信息。该方法使用对抗性早期退出策略在边缘设备抑制敏感内容,并将任务相关信息传输到云端。该方法在训练阶段添加噪声,提供差分隐私保证。我们已经在不同的面部和医疗数据集以及各种深度学习架构上进行了广泛测试,展示了其卓越的性能。我们还通过成功的防御各种白盒、深度和网络生成对抗攻击证明了隐私保护的有效性。此方法专为资源受限的边缘设备设计,确保低内存使用和计算开销。
Key Takeaways
- 深度学习模型的训练需要大量资源,通常于云服务器上进行。
- 训练包含敏感内容的数据集(如面部或医疗图像)会引发隐私担忧。
- 提出一种在边缘设备和云服务器上进行深度学习模型训练的方法,能防止敏感内容传输到云端。
- 使用对抗性早期退出策略在边缘设备抑制敏感内容。
- 该方法在训练阶段添加噪声,以提供差分隐私保证。
- 方法已在多种数据集和深度学习架构上进行了广泛测试,表现出卓越性能。
点此查看论文截图


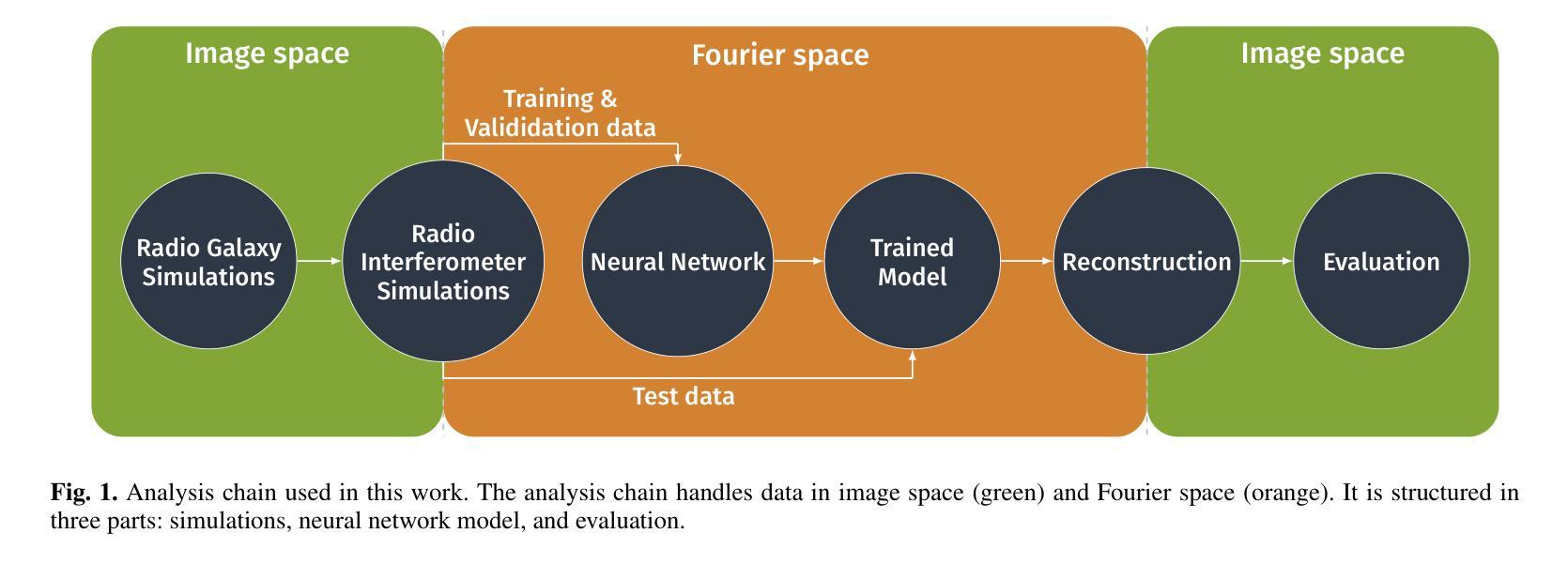
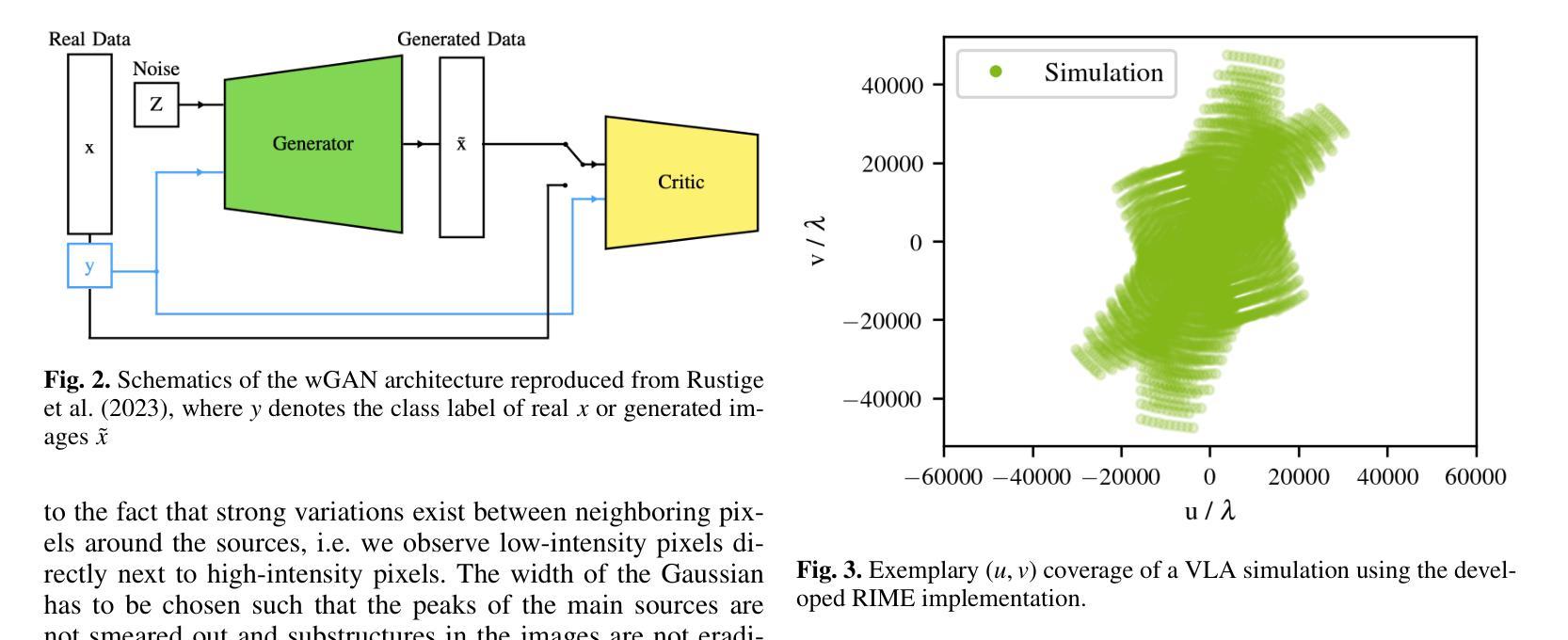
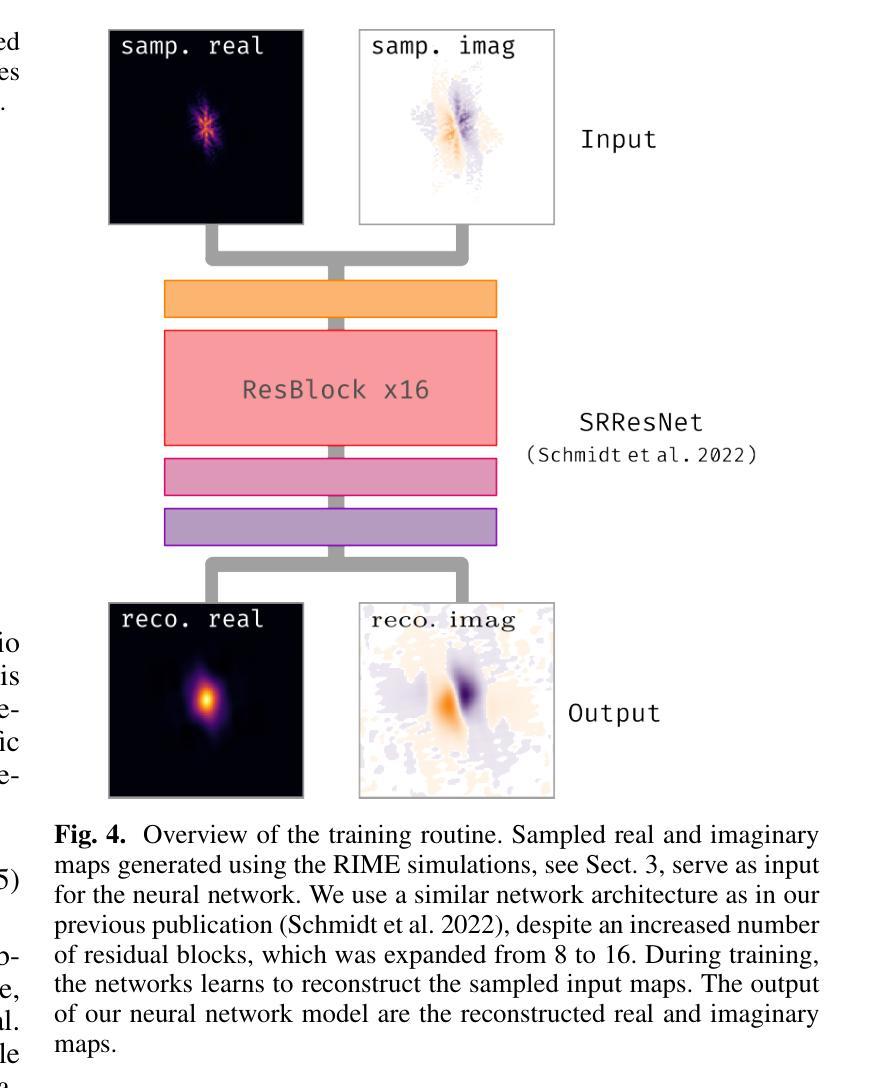
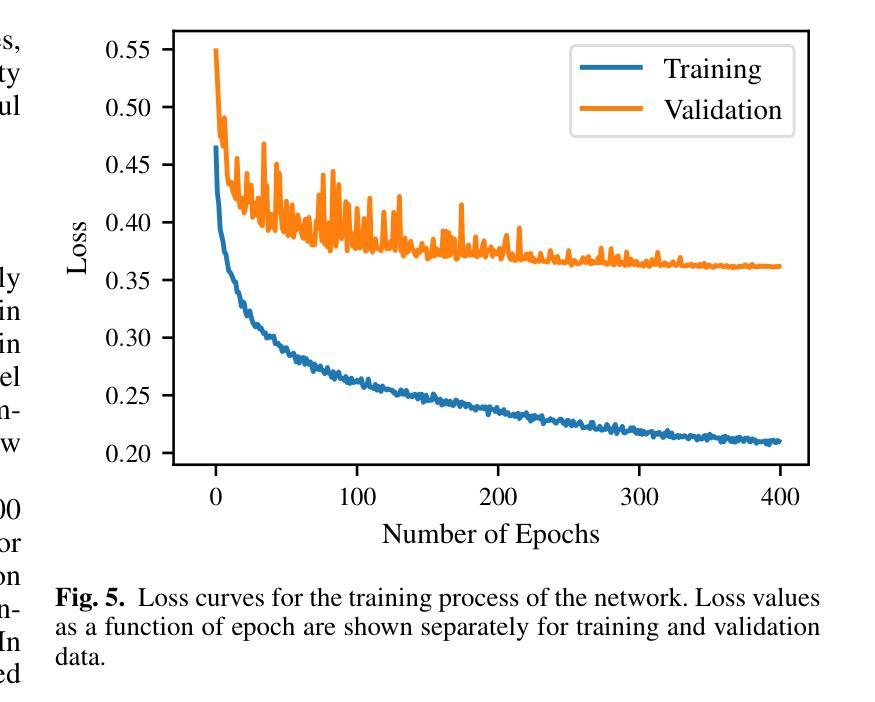
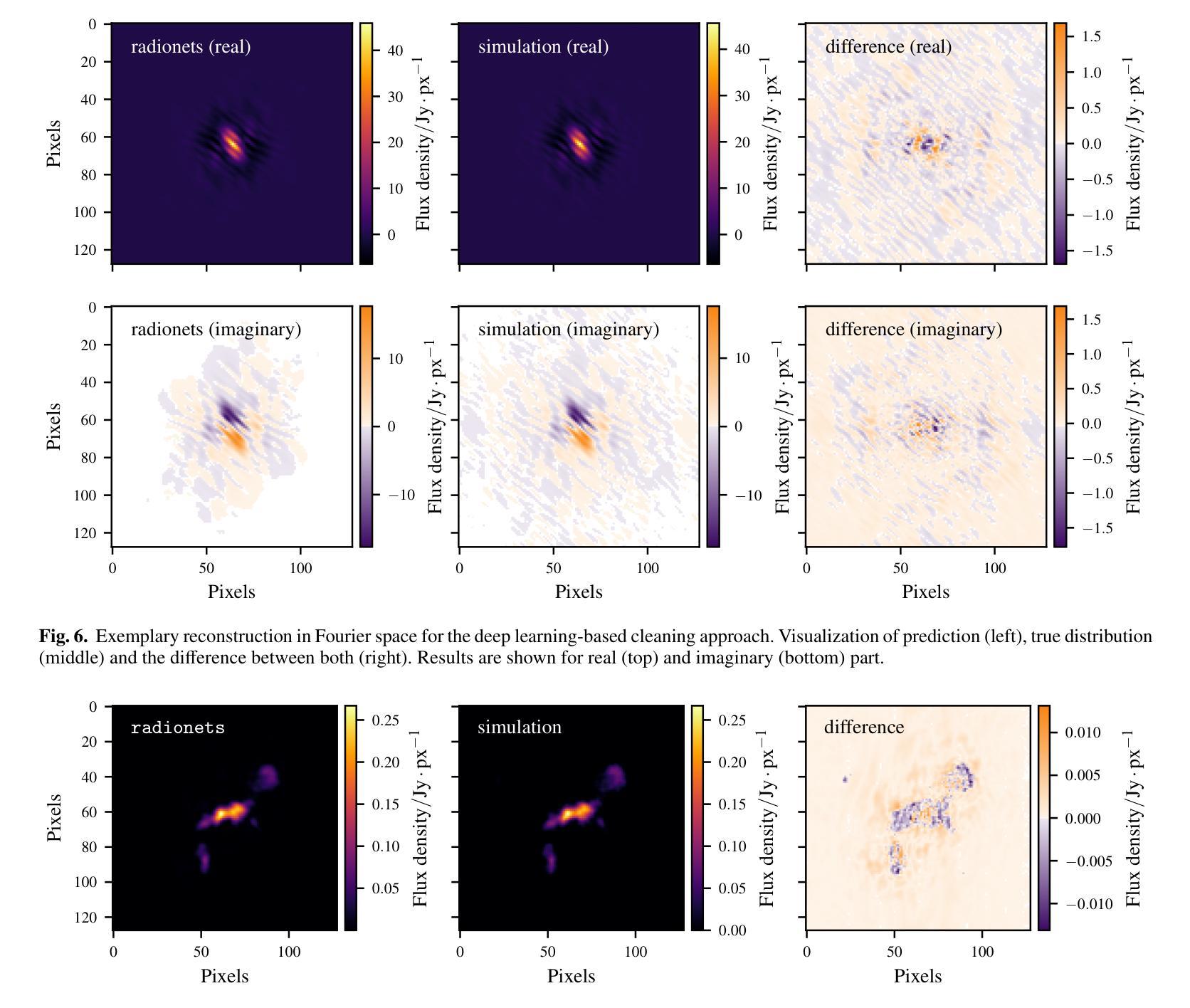
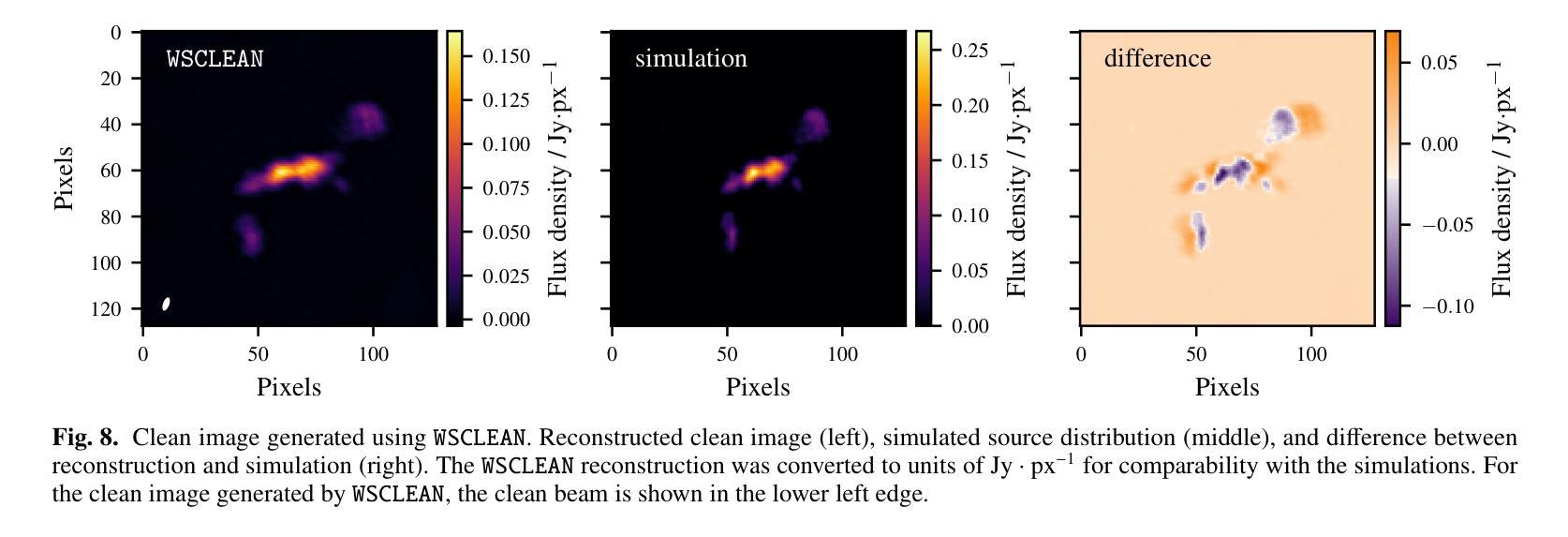
Deep learning-based radiointerferometric imaging with GAN-aided training
Authors:F. Geyer, K. Schmidt, J. Kummer, M. Brüggen, H. W. Edler, D. Elsässer, F. Griese, A. Poggenpohl, L. Rustige, W. Rhode
Radio interferometry invariably suffers from an incomplete coverage of the spatial Fourier space, which leads to imaging artifacts. The current state-of-the-art technique is to create an image by Fourier-transforming the incomplete visibility data and to clean the systematic effects originating from incomplete data in Fourier space. Previously, we have shown how super-resolution methods based on convolutional neural networks can reconstruct sparse visibility data. Our previous work has suffered from a low realism of the training data. The aim of this work is to build a whole simulation chain for realistic radio sources that then leads to a vastly improved neural net for the reconstruction of missing visibilities. This method offers considerable improvements in terms of speed, automatization and reproducibility over the standard techniques. Here we generate large amounts of training data by creating images of radio galaxies with a generative adversarial network (GAN) that has been trained on radio survey data. Then, we applied the Radio Interferometer Measurement Equation (RIME) in order to simulate the measurement process of a radio interferometer. We show that our neural network can reconstruct faithfully images of realistic radio galaxies. The reconstructed images agree well with the original images in terms of the source area, integrated flux density, peak flux density, and the multi-scale structural similarity index. Finally, we show how the neural net can be adapted to estimate the uncertainties in the imaging process.
射电干涉仪通常会面临空间傅里叶变换覆盖不完全的问题,从而导致成像失真。目前最先进的技术是通过傅里叶变换不完整可见度数据来创建图像,并清除由傅里叶空间中不完整数据引起的系统效应。之前,我们已经展示了基于卷积神经网络的超分辨率方法如何重建稀疏可见度数据。我们之前的工作受到训练数据低真实性的影响。这项工作的目的是为真实射电源建立一个完整的仿真链,然后建立一个改进型神经网络,用于重建缺失的可见度。该方法在速度、自动化和可重复性方面为标准技术提供了相当大的改进。在这里,我们通过使用生成对抗网络(GAN)创建射电星系图像来生成大量训练数据,该网络已经在射电调查数据上进行了训练。然后,我们应用了射电干涉仪测量方程(RIME),以模拟射电干涉仪的测量过程。我们证明我们的神经网络能够忠实重建真实射电星系的图像。重建的图像在源区域、积分流量密度、峰值流量密度和多尺度结构相似性指数方面与原始图像吻合良好。最后,我们展示了神经网络如何适应以估计成像过程中的不确定性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in Astronomy & Astrophysics
Summary
本摘要基于提供的文本,概括其主要信息:通过使用生成对抗网络(GAN)模拟生成逼真的射电星系图像作为训练数据,应用于射电干涉仪的测量过程模拟,构建的神经网络能够以大幅提高的速度和自动化程度重建缺失的可见度数据,并能准确地重建射电星系的图像。该神经网络还可以适应估计成像过程中的不确定性。总结简洁有力,准确无误地传达了文本的核心内容。
Key Takeaways
以下是从文本中提取出的七个关键要点:
- 射电干涉仪存在空间傅里叶变换覆盖不完整的问题,导致成像出现伪影。
- 当前主流技术是通过傅里叶变换处理不完全的可见度数据并清除系统性效应。
- 基于卷积神经网络的超分辨率方法能够重建稀疏可见度数据。
- 之前的工作在训练数据的真实感方面存在不足。
- 使用生成对抗网络(GAN)模拟生成逼真的射电星系图像作为训练数据。
- 神经网络应用于射电干涉仪测量模拟过程,大幅提高了速度、自动化程度和可重复性。
点此查看论文截图