⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-19 更新
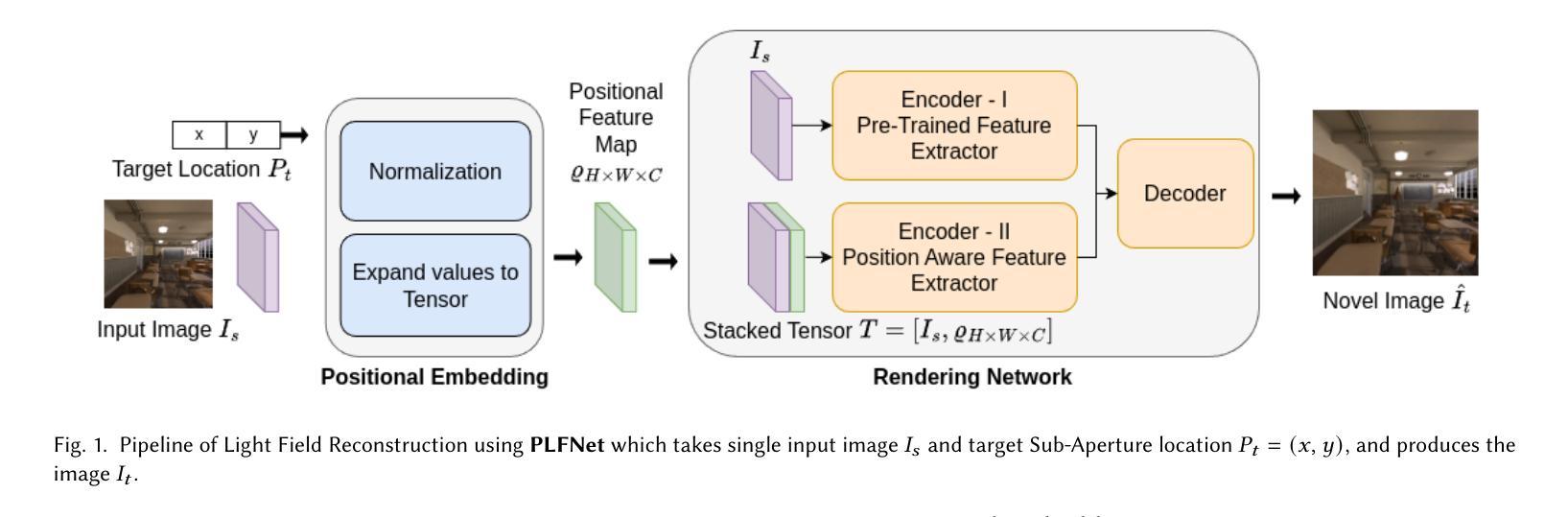
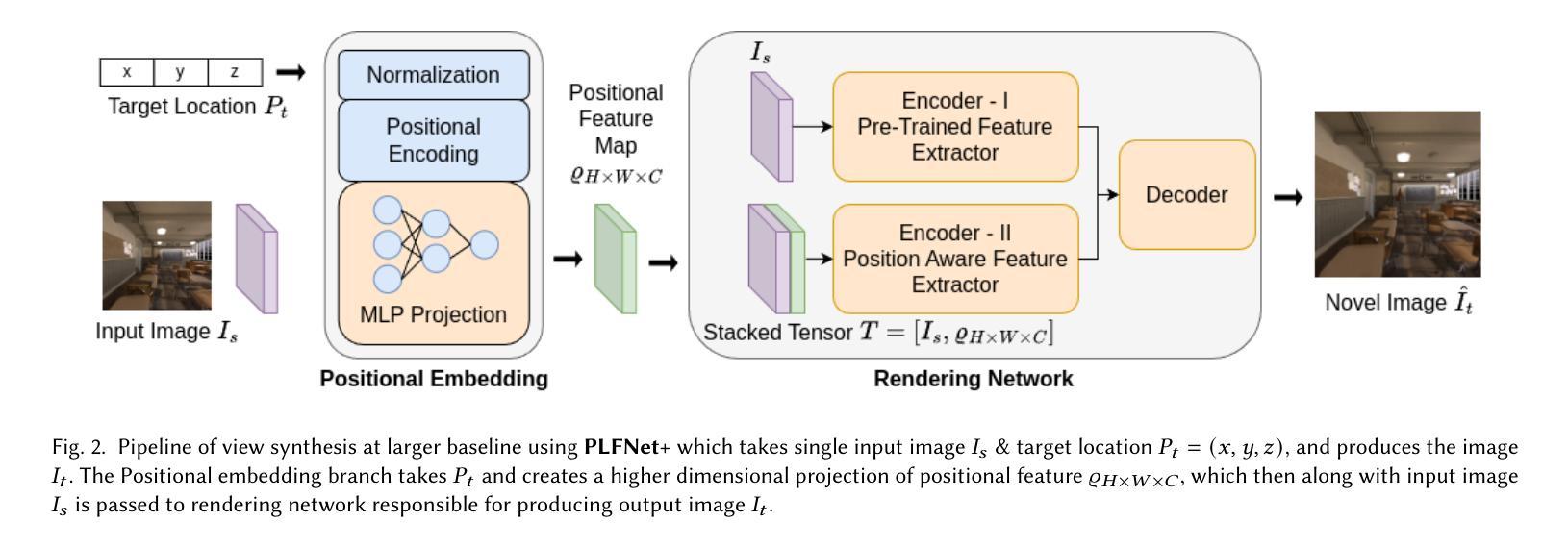
Real-Time Position-Aware View Synthesis from Single-View Input
Authors:Manu Gond, Emin Zerman, Sebastian Knorr, Mårten Sjöström
Recent advancements in view synthesis have significantly enhanced immersive experiences across various computer graphics and multimedia applications, including telepresence, and entertainment. By enabling the generation of new perspectives from a single input view, view synthesis allows users to better perceive and interact with their environment. However, many state-of-the-art methods, while achieving high visual quality, face limitations in real-time performance, which makes them less suitable for live applications where low latency is critical. In this paper, we present a lightweight, position-aware network designed for real-time view synthesis from a single input image and a target camera pose. The proposed framework consists of a Position Aware Embedding, modeled with a multi-layer perceptron, which efficiently maps positional information from the target pose to generate high dimensional feature maps. These feature maps, along with the input image, are fed into a Rendering Network that merges features from dual encoder branches to resolve both high level semantics and low level details, producing a realistic new view of the scene. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves superior efficiency and visual quality compared to existing approaches, particularly in handling complex translational movements without explicit geometric operations like warping. This work marks a step toward enabling real-time view synthesis from a single image for live and interactive applications.
近期视图合成技术的进展在各类计算机图形和多媒体应用中大幅提升了沉浸式体验,包括远程存在和娱乐。视图合成能够通过单个输入视图生成新的视角,使用户更好地感知和与其环境进行交互。然而,许多最先进的方法虽然视觉质量很高,但在实时性能方面存在局限性,这使得它们在低延迟至关重要的实时应用中不太适用。在本文中,我们提出了一种用于实时视图合成的轻量级、位置感知网络,该网络从单个输入图像和目标相机姿态进行视图合成。所提出的框架由一个位置感知嵌入组成,通过多层感知器进行建模,能够高效地将目标姿态的位置信息映射到生成高维特征图。这些特征图与输入图像一起输入到渲染网络中,该网络合并来自双编码器分支的特征以解决高级语义和低级细节问题,从而生成场景的现实新视图。实验结果表明,与现有方法相比,我们的方法在效率和视觉质量方面实现了优越性,特别是在处理复杂的平移运动而无需明确的几何操作(如扭曲)方面。这项工作标志着为实时应用和交互式应用的单图像视图合成迈出了重要一步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
随着计算机图形学和多媒体应用的快速发展,视图合成技术不断进步,极大地提升了沉浸式体验。本文提出了一种轻量级、位置感知的网络,用于从单张输入图像和目标相机姿态进行实时视图合成。该网络通过位置感知嵌入和多层感知器有效地映射目标姿态的位置信息,生成高维特征图。实验结果表明,该方法与现有方法相比,在效率和视觉质量方面表现优越,尤其擅长处理复杂的平移运动。
Key Takeaways
- 视图合成技术增强了沉浸式体验,允许从单一视角生成新的视角。
- 现有方法虽然视觉质量高,但实时性能有限,不适合低延迟的实时应用。
- 本文提出了一种轻量级、位置感知的网络,用于实时视图合成。
- 该网络通过位置感知嵌入和多层感知器映射目标姿态的位置信息。
- 网络生成高维特征图,与输入图像一起输入渲染网络。
- 渲染网络合并来自两个编码器分支的特征,解决高级语义和低级细节,生成逼真的新视图。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在效率和视觉质量方面表现优越,尤其擅长处理复杂的平移运动。
点此查看论文截图

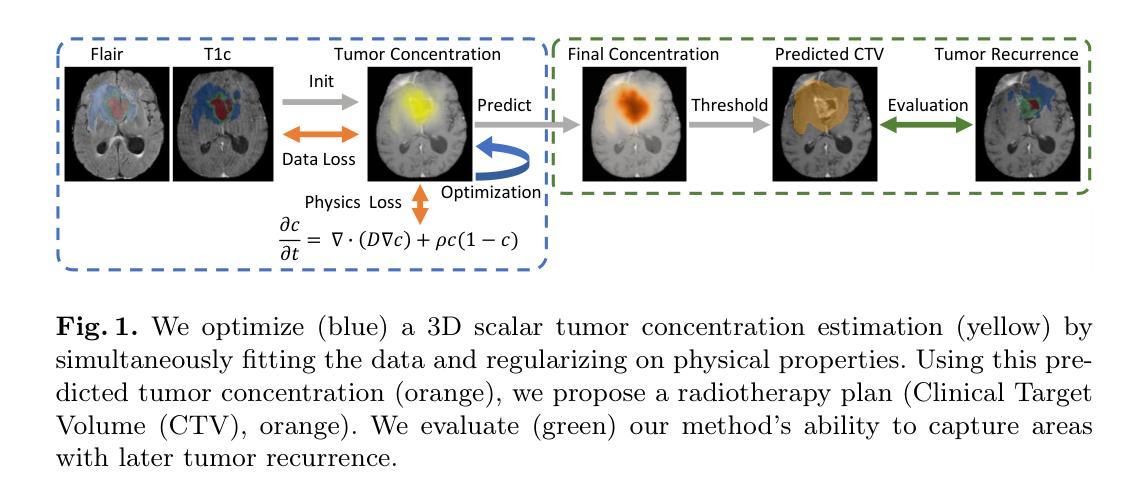
Spatial Brain Tumor Concentration Estimation for Individualized Radiotherapy Planning
Authors:Jonas Weidner, Michal Balcerak, Ivan Ezhov, André Datchev, Laurin Lux, Lucas Zimmerand Daniel Rueckert, Björn Menze, Benedikt Wiestler
Biophysical modeling of brain tumors has emerged as a promising strategy for personalizing radiotherapy planning by estimating the otherwise hidden distribution of tumor cells within the brain. However, many existing state-of-the-art methods are computationally intensive, limiting their widespread translation into clinical practice. In this work, we propose an efficient and direct method that utilizes soft physical constraints to estimate the tumor cell concentration from preoperative MRI of brain tumor patients. Our approach optimizes a 3D tumor concentration field by simultaneously minimizing the difference between the observed MRI and a physically informed loss function. Compared to existing state-of-the-art techniques, our method significantly improves predicting tumor recurrence on two public datasets with a total of 192 patients while maintaining a clinically viable runtime of under one minute - a substantial reduction from the 30 minutes required by the current best approach. Furthermore, we showcase the generalizability of our framework by incorporating additional imaging information and physical constraints, highlighting its potential to translate to various medical diffusion phenomena with imperfect data.
脑肿瘤的生物物理建模已成为一种有前途的策略,通过估计脑内肿瘤细胞的隐蔽分布来个性化放射治疗计划。然而,许多现有的最先进的方法计算量大,限制了它们在临床实践中的广泛应用。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种高效且直接的方法,利用软物理约束来估计脑肿瘤患者的术前MRI中的肿瘤细胞浓度。我们的方法通过同时最小化观察到的MRI和一个物理信息损失函数之间的差异来优化三维肿瘤浓度场。与现有的最先进技术相比,我们的方法在两个公共数据集上对192名患者的肿瘤复发预测进行了显著改善,同时保持了一分钟以内的临床可行运行时间——这大大减少了当前最佳方法所需的30分钟。此外,我们通过融入额外的成像信息和物理约束来展示我们框架的普遍性,突显其在具有不完美数据的各种医学扩散现象中的翻译潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种高效且直接的方法,利用软物理约束,通过脑肿瘤患者的术前MRI来估计肿瘤细胞浓度。该方法优化了一个三维肿瘤浓度场,同时最小化观察到的MRI与物理信息损失函数之间的差异。相较于现有的先进技术,该方法在预测肿瘤复发方面表现更优,同时在维持临床可行的运行时间(少于一分钟)的同时,显著减少了计算时间(从当前最佳方法的三十分钟减少到一分钟)。此外,该研究展示了该框架的通用性,可融入额外的成像信息和物理约束,突显其在不完美数据下的医学扩散现象翻译潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了一种利用软物理约束直接估计脑肿瘤细胞浓度的方法。
- 通过优化三维肿瘤浓度场,最小化观察到的MRI与物理信息损失函数之间的差异。
- 方法显著提高了在公共数据集上预测肿瘤复发的准确性。
- 维持了临床可行的运行时间,显著减少了计算时间。
- 框架具有通用性,可融入额外的成像信息和物理约束。
- 该方法有望为临床放射治疗计划提供个性化策略。
点此查看论文截图

Towards Automatic Evaluation for Image Transcreation
Authors:Simran Khanuja, Vivek Iyer, Claire He, Graham Neubig
Beyond conventional paradigms of translating speech and text, recently, there has been interest in automated transcreation of images to facilitate localization of visual content across different cultures. Attempts to define this as a formal Machine Learning (ML) problem have been impeded by the lack of automatic evaluation mechanisms, with previous work relying solely on human evaluation. In this paper, we seek to close this gap by proposing a suite of automatic evaluation metrics inspired by machine translation (MT) metrics, categorized into: a) Object-based, b) Embedding-based, and c) VLM-based. Drawing on theories from translation studies and real-world transcreation practices, we identify three critical dimensions of image transcreation: cultural relevance, semantic equivalence and visual similarity, and design our metrics to evaluate systems along these axes. Our results show that proprietary VLMs best identify cultural relevance and semantic equivalence, while vision-encoder representations are adept at measuring visual similarity. Meta-evaluation across 7 countries shows our metrics agree strongly with human ratings, with average segment-level correlations ranging from 0.55-0.87. Finally, through a discussion of the merits and demerits of each metric, we offer a robust framework for automated image transcreation evaluation, grounded in both theoretical foundations and practical application. Our code can be found here: https://github.com/simran-khanuja/automatic-eval-transcreation
在传统语音和文本翻译的范式之外,最近人们对自动创建图像以推动不同文化间的视觉内容本地化产生了兴趣。将这一领域定义为正式的机器学习(ML)问题的尝试受到了缺乏自动评估机制的阻碍,早期的工作完全依赖于人工评估。在本文中,我们试图通过借鉴机器翻译(MT)指标提出一套自动评估指标来填补这一空白,这些指标可分为三类:a)基于对象的,b)基于嵌入的,以及c)基于视觉语言模型(VLM)的。我们从翻译研究理论和现实世界的图像转创实践出发,确定了图像转创的三个关键维度:文化相关性、语义等价性和视觉相似性,并设计了我们的指标来沿着这些轴评估系统。我们的结果表明,专有视觉语言模型在识别文化相关性和语义等价性方面表现最佳,而视觉编码器表示在衡量视觉相似性方面很在行。在7个国家的元评估显示,我们的指标与人类评分高度一致,平均分段相关性在0.55-0.87之间。最后,通过对每种指标的优缺点进行讨论,我们提供了一个既基于理论也适用于实际应用的稳健框架,用于自动化图像转创评估。我们的代码可以在这里找到:https://github.com/simran-khanuja/automatic-eval-transcreation
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文旨在解决图像转创(Image Transcreation)的自动评估问题,提出了一系列基于机器翻译(MT)的自动评估指标,包括对象基础、嵌入基础和VLM基础三种类型。这些指标旨在从文化相关性、语义等价性和视觉相似性三个关键维度评估图像转创系统。实验结果表明,专有VLMs在识别文化相关性和语义等价性方面表现最佳,而视觉编码器表示在测量视觉相似性方面表现良好。此外,对七个国家的元评估显示,本文提出的指标与人类评分高度一致,平均分段相关性在0.55至0.87之间。最后,本文讨论了各项指标的优缺点,为基于理论和实践的自动化图像转创评估提供了稳健框架。
Key Takeaways
- 图像转创(Image Transcreation)是翻译领域的新发展方向,旨在实现不同文化背景下视觉内容的本地化。
- 现有研究中缺乏图像转创的自动评估机制,因此本文提出了一系列基于机器翻译的自动评估指标。
- 这些指标从文化相关性、语义等价性和视觉相似性三个关键维度对图像转创系统进行评估。
- 实验表明,专有VLMs在识别文化相关性和语义等价性方面表现最佳,视觉编码器擅长测量视觉相似性。
- 跨七国的元评估证实,本文提出的指标与人类评分高度一致。
- 本文详细讨论了各项指标的优缺点,为未来的研究提供了方向。
点此查看论文截图



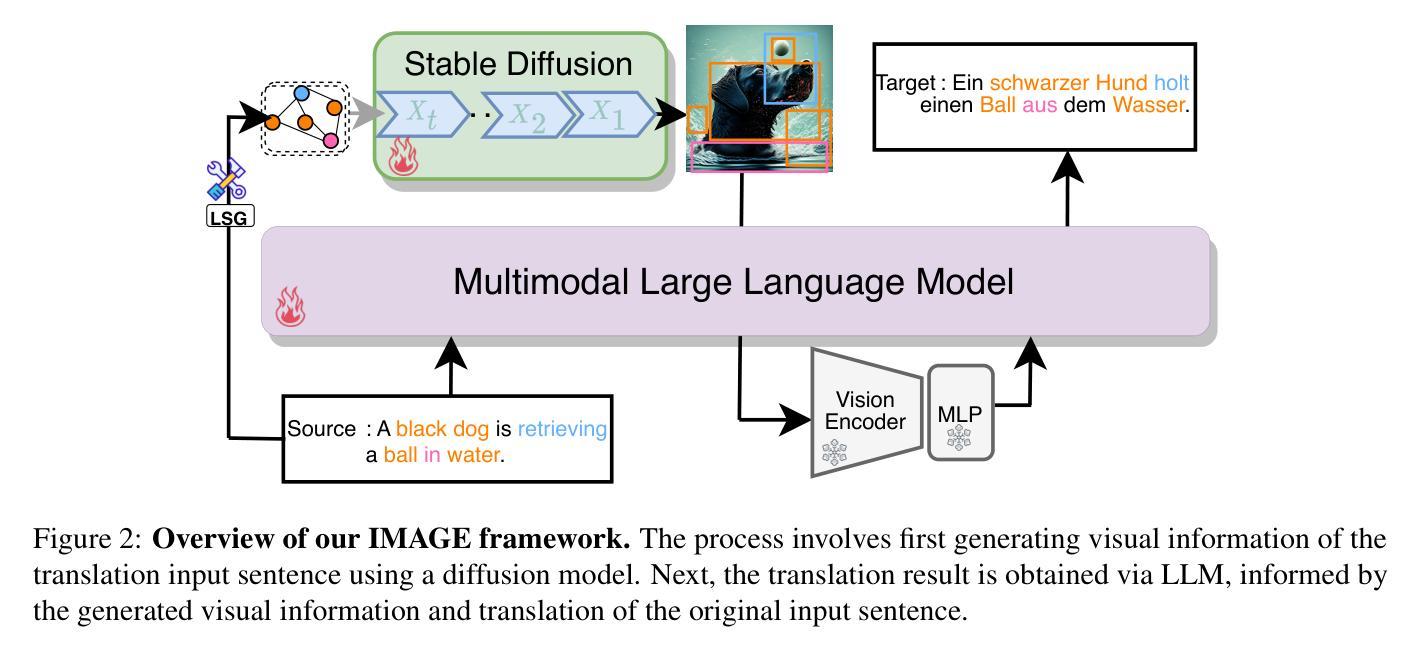
Make Imagination Clearer! Stable Diffusion-based Visual Imagination for Multimodal Machine Translation
Authors:Andong Chen, Yuchen Song, Kehai Chen, Muyun Yang, Tiejun Zhao, Min Zhang
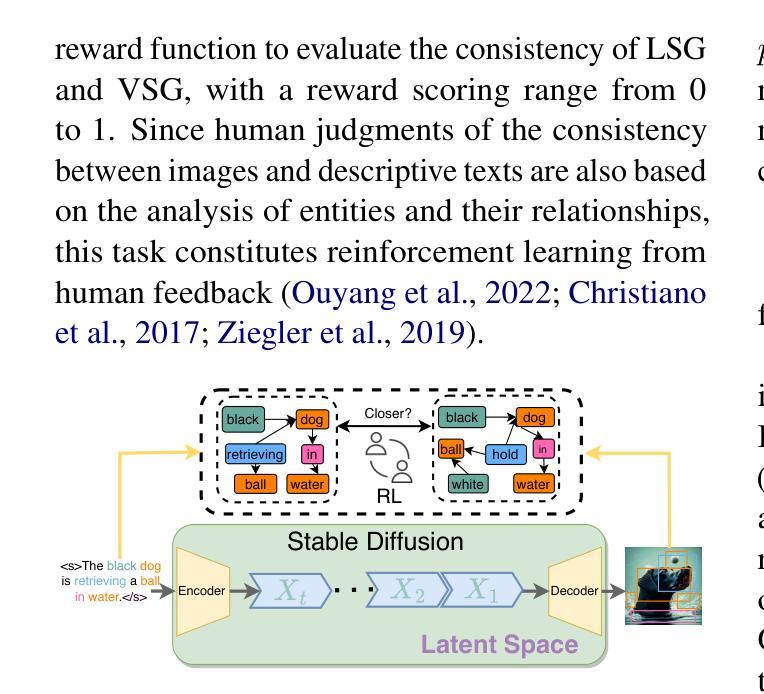
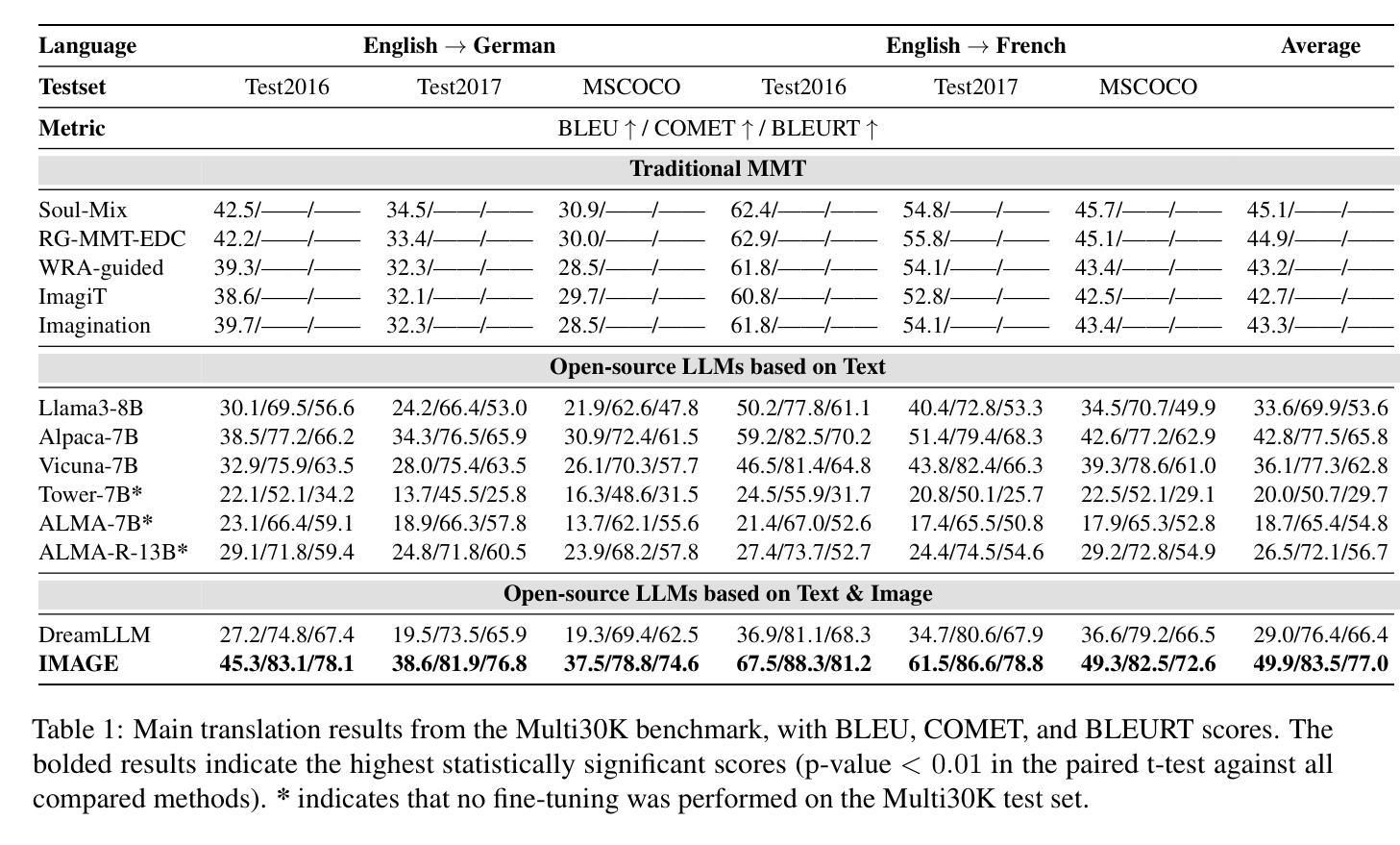
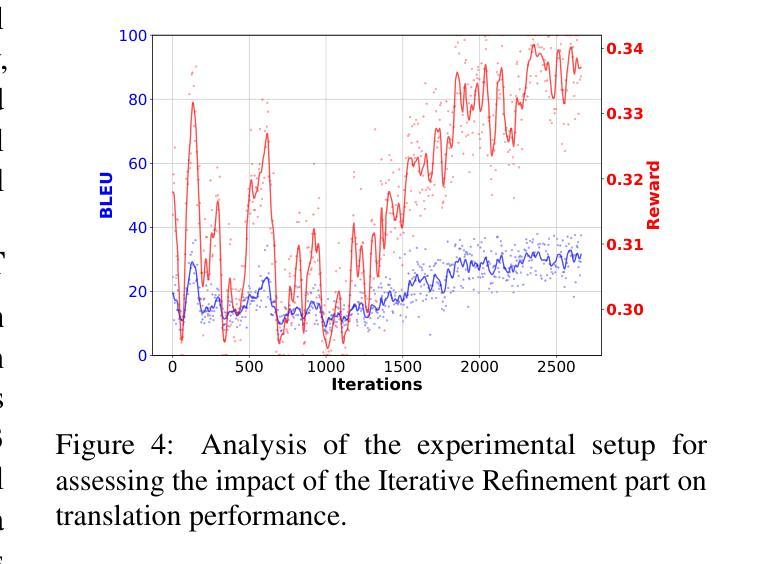
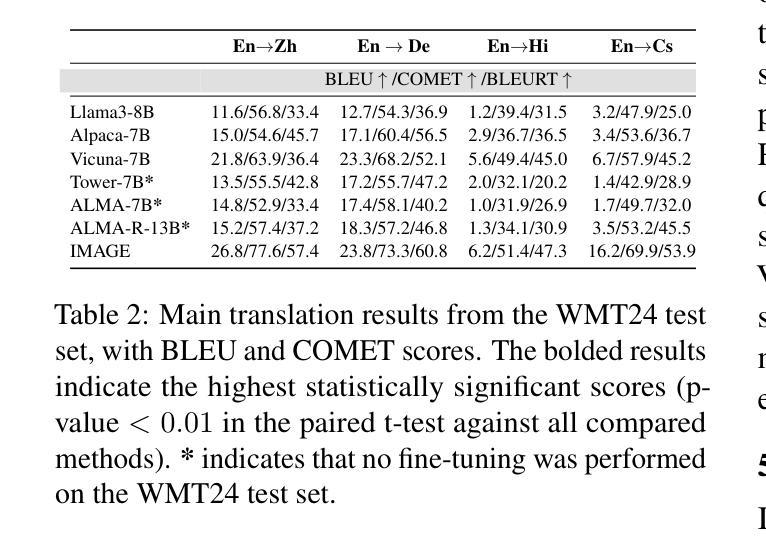
Visual information has been introduced for enhancing machine translation (MT), and its effectiveness heavily relies on the availability of large amounts of bilingual parallel sentence pairs with manual image annotations. In this paper, we introduce a stable diffusion-based imagination network into a multimodal large language model (MLLM) to explicitly generate an image for each source sentence, thereby advancing the multimodel MT. Particularly, we build heuristic human feedback with reinforcement learning to ensure the consistency of the generated image with the source sentence without the supervision of image annotation, which breaks the bottleneck of using visual information in MT. Furthermore, the proposed method enables imaginative visual information to be integrated into large-scale text-only MT in addition to multimodal MT. Experimental results show that our model significantly outperforms existing multimodal MT and text-only MT, especially achieving an average improvement of more than 14 BLEU points on Multi30K multimodal MT benchmarks.
将视觉信息引入机器翻译(MT)以增强其功能,其有效性在很大程度上依赖于大量带有手动图像注释的双语平行句子对。在本文中,我们将基于稳定扩散的想象网络引入多模态大型语言模型(MLLM),以明确为每句源句生成相应的图像,从而促进多模态机器翻译的发展。特别地,我们利用强化学习构建启发式人类反馈,确保生成的图像与源句的一致性,无需图像注释的监督,从而突破了机器翻译中使用视觉信息的瓶颈。此外,该方法除了多模态MT之外,还可以将想象性视觉信息集成到大规模纯文本MT中。实验结果表明,我们的模型在现有的多模态MT和纯文本MT上表现优越,特别是在Multi30K多模态MT基准测试上平均提高了超过14个BLEU点。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Work in progress
Summary
本文引入了一种基于稳定扩散的想象网络到多模态大型语言模型中,能够针对每个源句子生成对应的图像,从而推进多模态机器翻译的发展。通过结合启发式人工反馈和强化学习,确保生成图像与源句子的一致性,无需手动图像注释的监督,打破了机器翻译中使用视觉信息的瓶颈。此外,该方法不仅能够应用于多模态机器翻译,还能够将想象性的视觉信息集成到大规模的纯文本机器翻译中。实验结果表明,该模型在多模态机器翻译方面显著优于现有技术,特别是在Multi30K多模态机器翻译基准测试上平均提高了超过14个BLEU点。
Key Takeaways
- 引入稳定扩散基于想象网络的模型以增强机器翻译。
- 通过生成与源句子相对应的图片推进多模态机器翻译的发展。
- 结合启发式人工反馈和强化学习,确保生成图像与源句子的一致性。
- 该方法无需手动图像注释的监督,打破使用视觉信息在机器翻译中的瓶颈。
- 想象性的视觉信息可集成到大规模的纯文本机器翻译中。
- 模型在多模态机器翻译方面表现优异,特别是Multi30K基准测试。
点此查看论文截图

LineArt: A Knowledge-guided Training-free High-quality Appearance Transfer for Design Drawing with Diffusion Model
Authors:Xi Wang, Hongzhen Li, Heng Fang, Yichen Peng, Haoran Xie, Xi Yang, Chuntao Li
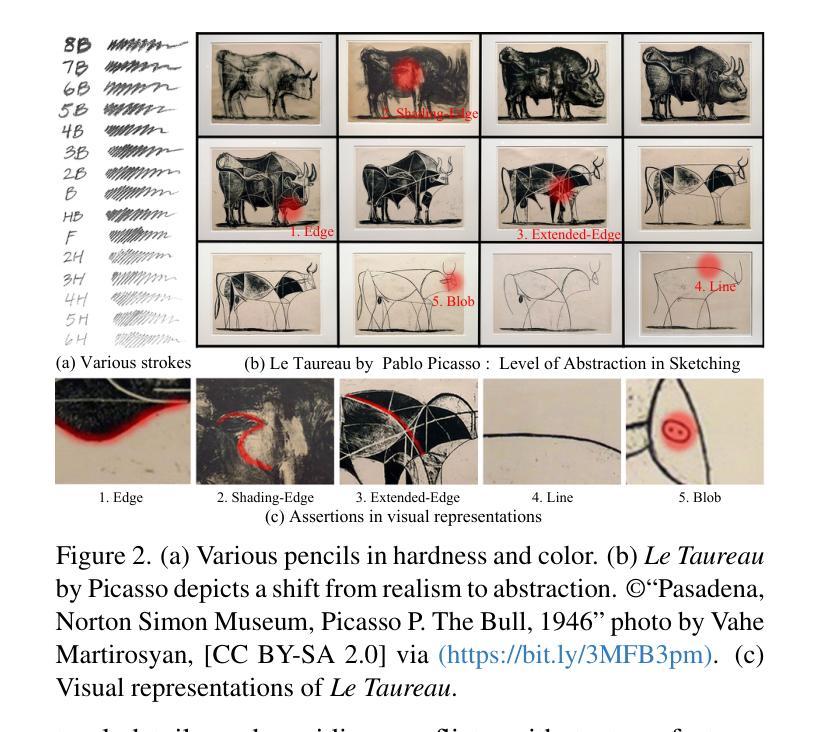
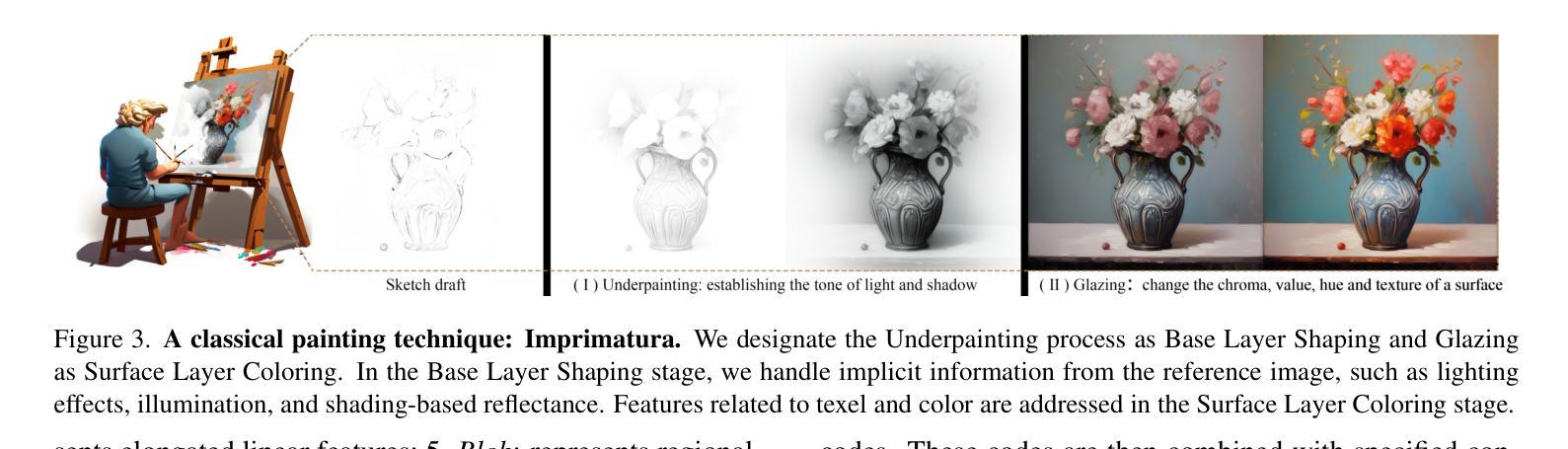
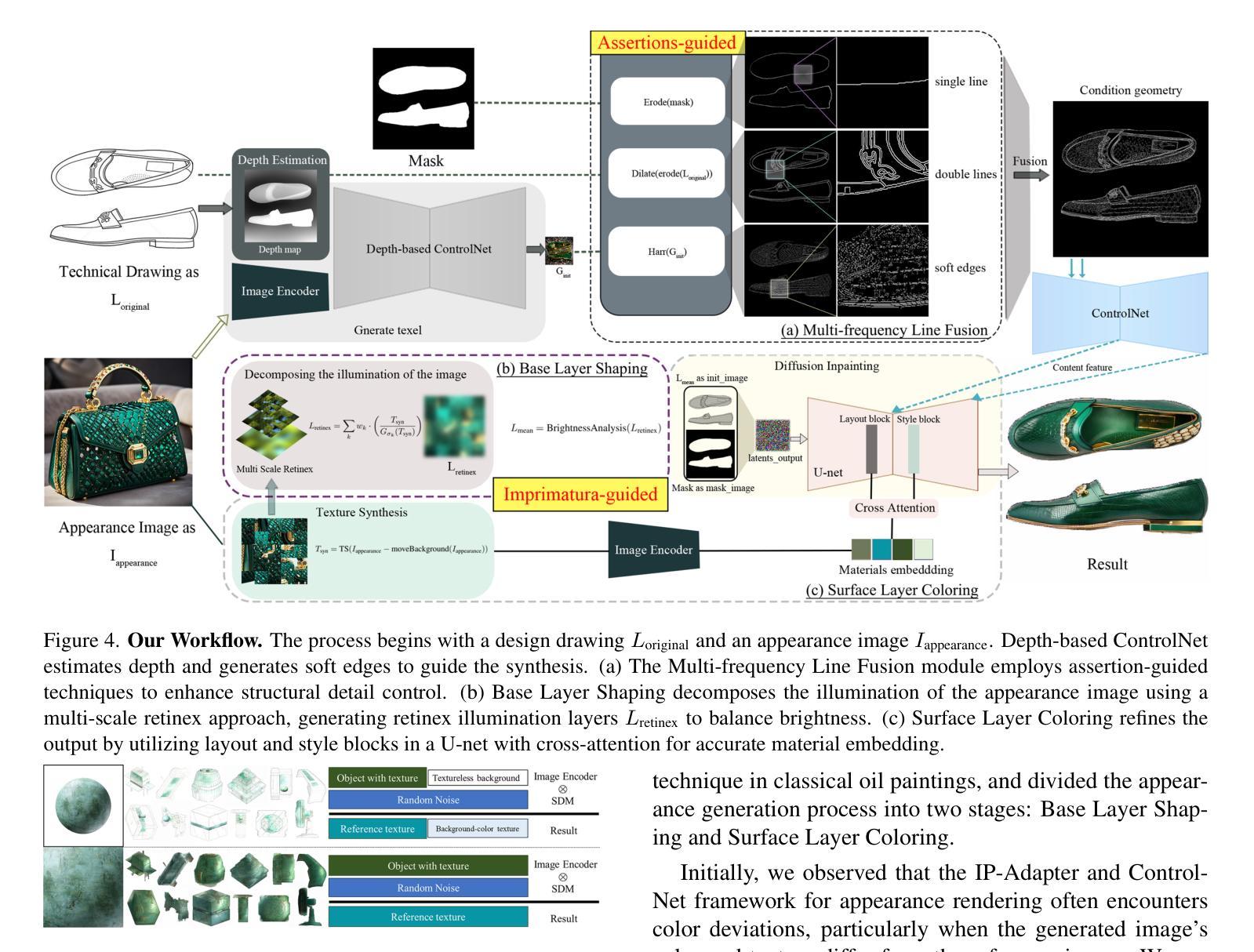
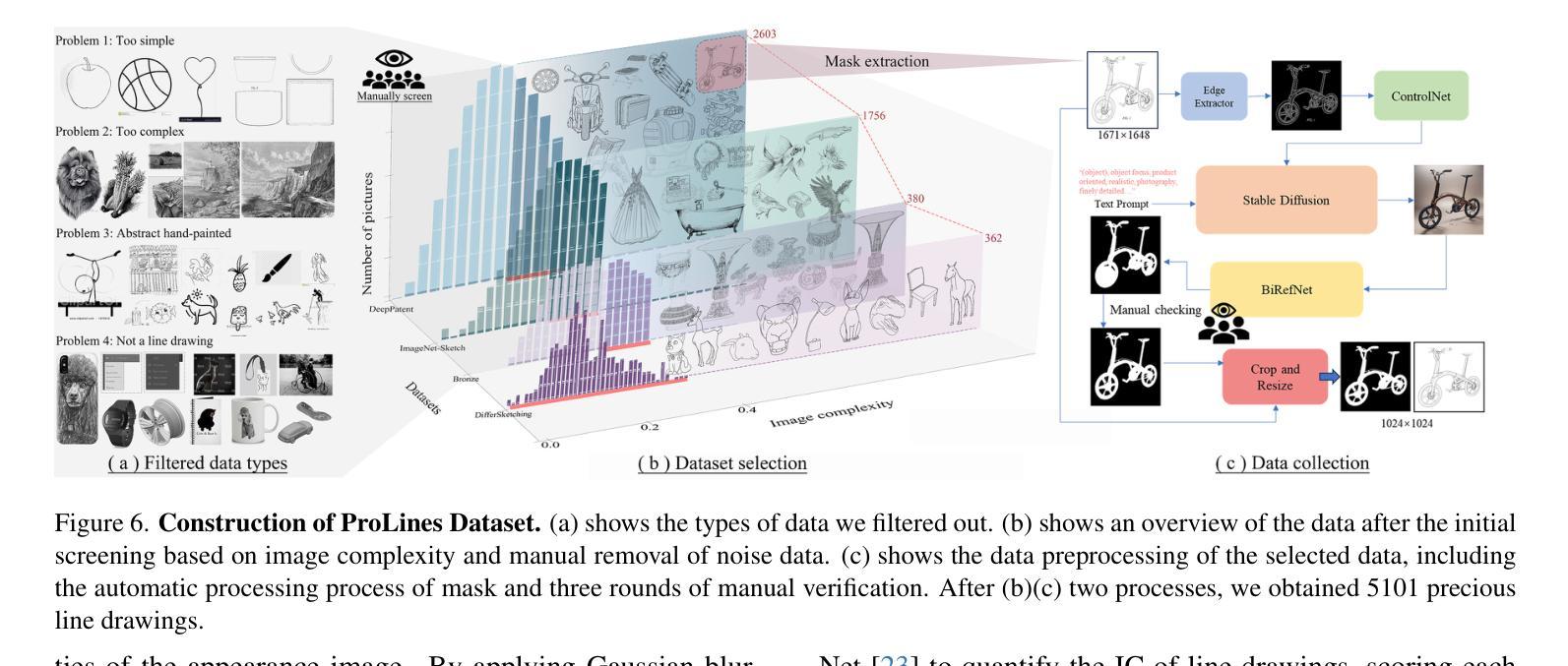
Image rendering from line drawings is vital in design and image generation technologies reduce costs, yet professional line drawings demand preserving complex details. Text prompts struggle with accuracy, and image translation struggles with consistency and fine-grained control. We present LineArt, a framework that transfers complex appearance onto detailed design drawings, facilitating design and artistic creation. It generates high-fidelity appearance while preserving structural accuracy by simulating hierarchical visual cognition and integrating human artistic experience to guide the diffusion process. LineArt overcomes the limitations of current methods in terms of difficulty in fine-grained control and style degradation in design drawings. It requires no precise 3D modeling, physical property specs, or network training, making it more convenient for design tasks. LineArt consists of two stages: a multi-frequency lines fusion module to supplement the input design drawing with detailed structural information and a two-part painting process for Base Layer Shaping and Surface Layer Coloring. We also present a new design drawing dataset ProLines for evaluation. The experiments show that LineArt performs better in accuracy, realism, and material precision compared to SOTAs.
从线条图像中呈现图像在设计及图像生成技术中至关重要,该技术可以降低生产成本,然而专业的线条图像需要保留复杂的细节。文本提示在准确性方面存在困难,图像翻译在一致性和精细控制方面也存在挑战。我们提出了LineArt框架,该框架能够将复杂的外观转移到详细的设计图纸上,促进设计和艺术创作。它通过模拟分层视觉认知并整合人类艺术经验来指导扩散过程,从而在保留结构准确性的同时生成高保真外观。LineArt克服了当前方法在精细控制方面的难度和设计图纸中的风格退化等局限性。它不需要精确的三维建模、物理属性规格或网络训练,为设计任务提供了便利。LineArt由两个阶段组成:一个多频线条融合模块,用于为输入的设计图纸补充详细的结构信息,以及分为两部分的上色过程,即基础层塑形和表层着色。我们还提供了一个新的设计图纸数据集ProLines,用于评估。实验表明,与最新技术相比,LineArt在准确性、真实感和材料精度方面表现更佳。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project Page: https://meaoxixi.github.io/LineArt/
Summary
线画图在设计和图像生成技术中扮演着至关重要的角色,但专业线画图需要保留复杂的细节。当前技术面临文本提示准确性不足和图像翻译一致性及精细控制方面的问题。为此,我们提出了LineArt框架,它能将复杂的外观转移到详细的设计图纸上,促进了设计和艺术创作。该框架通过模拟分层视觉认知并整合人类艺术经验来指导扩散过程,能在保持结构准确性的同时生成高保真外观,克服了现有方法的缺点。LineArt无需精确的3D建模、物理属性规格或网络训练,更适合用于设计任务。它由多频线条融合模块和两层绘画流程组成,分别为基础层塑形和表层着色。我们还推出了新的设计绘图数据集ProLines进行评估。实验表明,LineArt在准确性、逼真度和材料精度方面表现优于现有技术。
Key Takeaways
- 线画图在设计及图像生成技术中至关重要,且需保留复杂细节。
- 当前技术面临文本提示准确性及图像翻译一致性、精细控制难题。
- LineArt框架能通过模拟分层视觉认知指导扩散过程,生成高保真外观。
- LineArt在保持结构准确性的同时,克服了现有方法的缺点。
- LineArt无需精确的3D建模、物理属性规格或网络训练,适用于设计任务。
- LineArt由多频线条融合模块和两层绘画流程构成,包括基础层塑形和表层着色。
- 新推出的设计绘图数据集ProLines为LineArt提供了评估标准,实验表明其表现优于现有技术。
点此查看论文截图

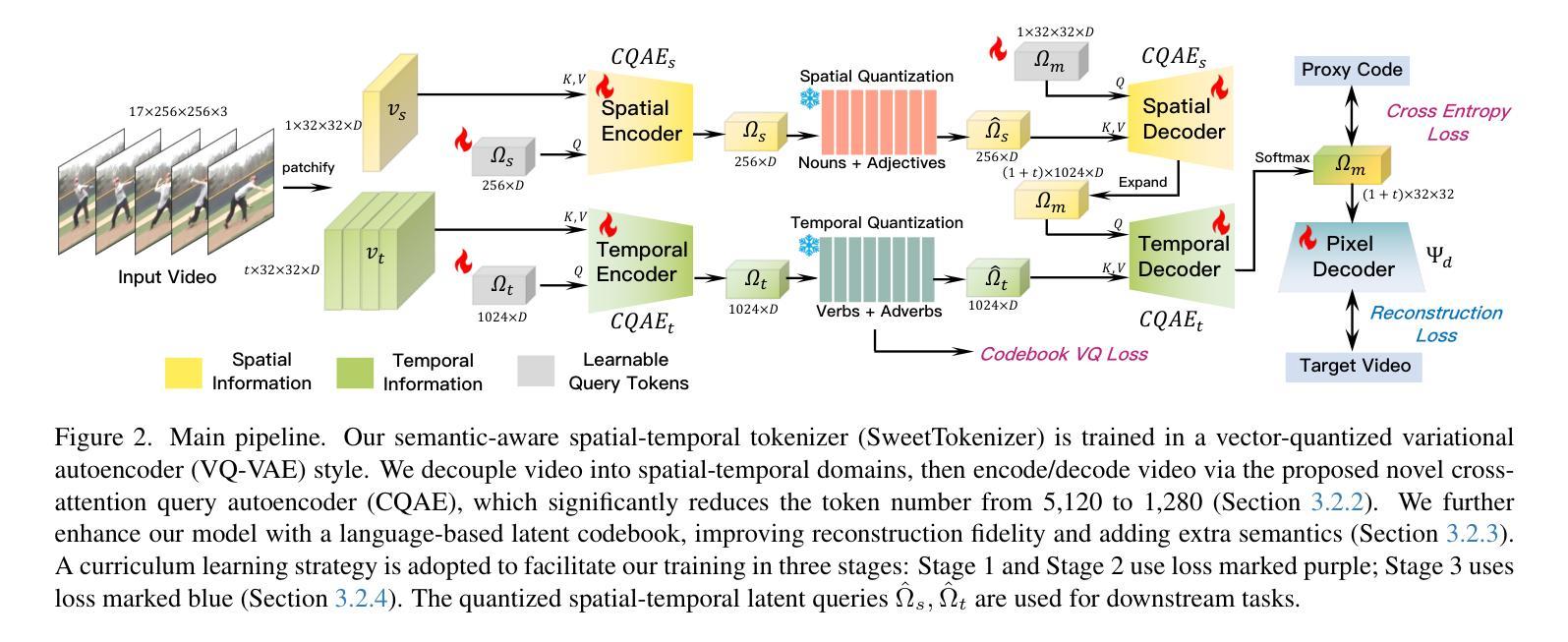
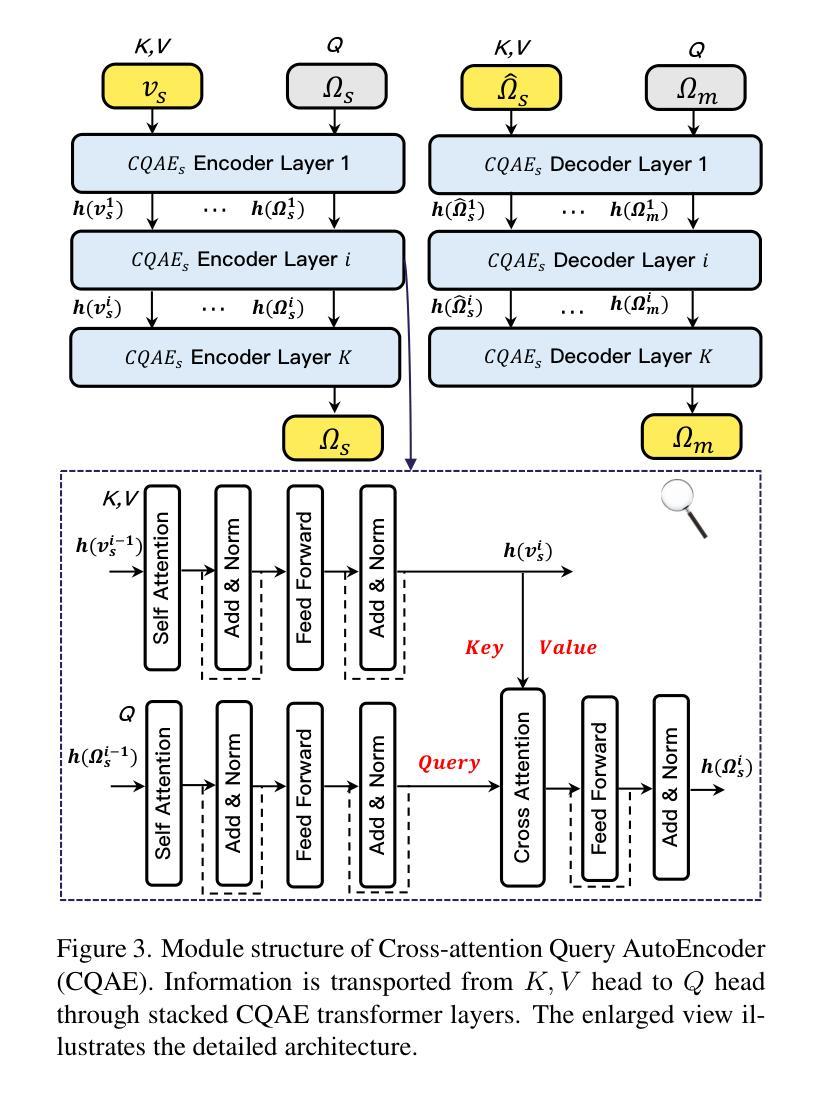
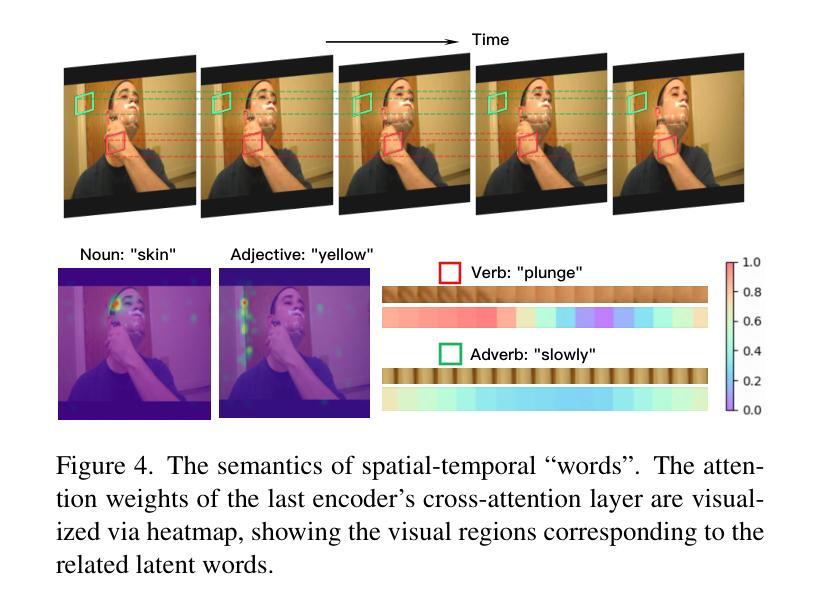
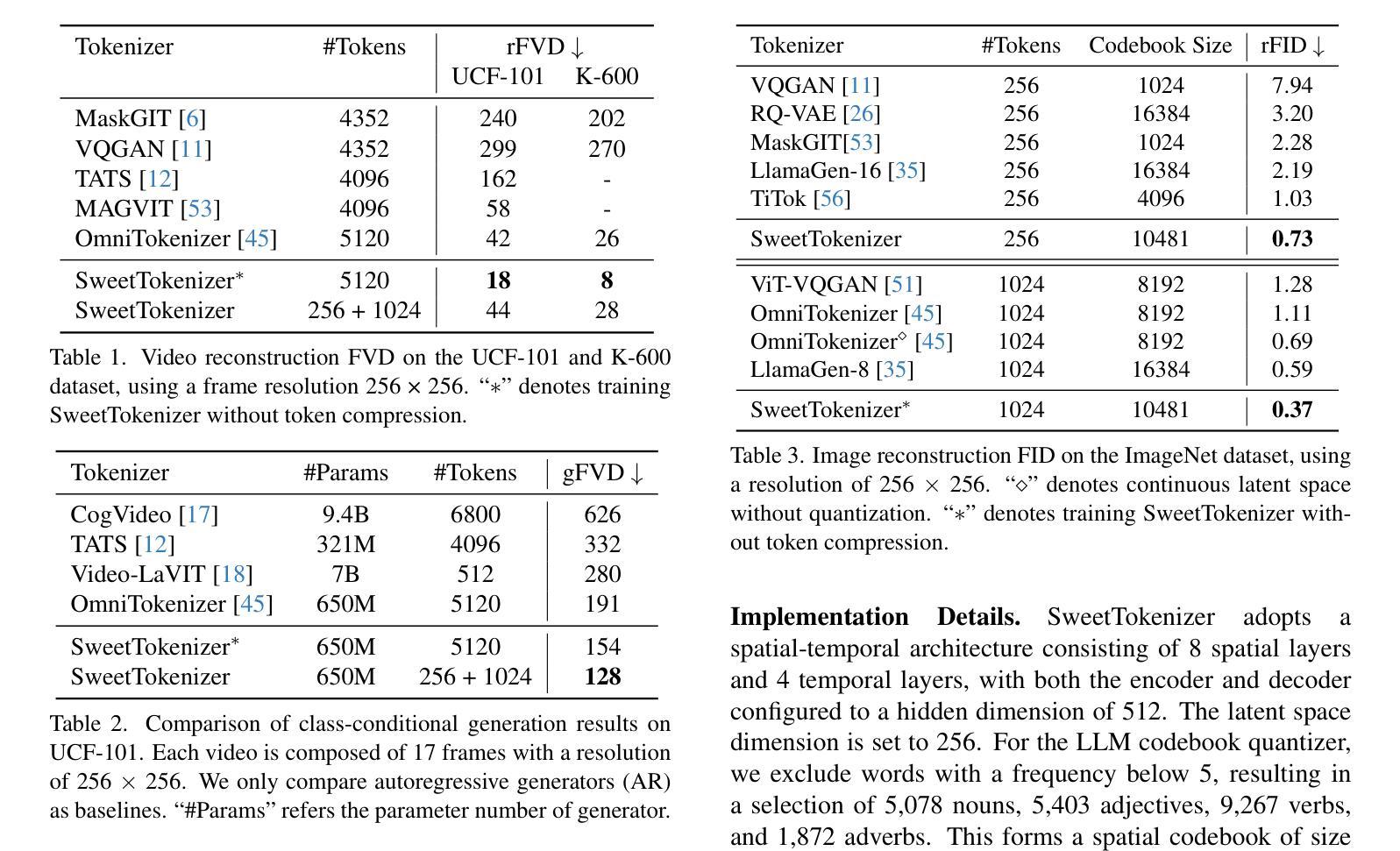
SweetTokenizer: Semantic-Aware Spatial-Temporal Tokenizer for Compact Visual Discretization
Authors:Zhentao Tan, Ben Xue, Jian Jia, Junhao Wang, Wencai Ye, Shaoyun Shi, Mingjie Sun, Wenjin Wu, Quan Chen, Peng Jiang
This paper presents the \textbf{S}emantic-a\textbf{W}ar\textbf{E} spatial-t\textbf{E}mporal \textbf{T}okenizer (SweetTokenizer), a compact yet effective discretization approach for vision data. Our goal is to boost tokenizers’ compression ratio while maintaining reconstruction fidelity in the VQ-VAE paradigm. Firstly, to obtain compact latent representations, we decouple images or videos into spatial-temporal dimensions, translating visual information into learnable querying spatial and temporal tokens through a \textbf{C}ross-attention \textbf{Q}uery \textbf{A}uto\textbf{E}ncoder (CQAE). Secondly, to complement visual information during compression, we quantize these tokens via a specialized codebook derived from off-the-shelf LLM embeddings to leverage the rich semantics from language modality. Finally, to enhance training stability and convergence, we also introduce a curriculum learning strategy, which proves critical for effective discrete visual representation learning. SweetTokenizer achieves comparable video reconstruction fidelity with only \textbf{25%} of the tokens used in previous state-of-the-art video tokenizers, and boost video generation results by \textbf{32.9%} w.r.t gFVD. When using the same token number, we significantly improves video and image reconstruction results by \textbf{57.1%} w.r.t rFVD on UCF-101 and \textbf{37.2%} w.r.t rFID on ImageNet-1K. Additionally, the compressed tokens are imbued with semantic information, enabling few-shot recognition capabilities powered by LLMs in downstream applications.
本文介绍了Semantic-Aware空间时序令牌化器(SweetTokenizer),这是一种紧凑且有效的针对视觉数据的离散化方法。我们的目标是在VQ-VAE范式中提高令矢量化器的压缩率,同时保持重建保真度。首先,为了获取紧凑的潜在表示,我们将图像或视频解耦为空间时间维度,通过跨注意力查询自动编码器(CQAE)将视觉信息转换为可学习的查询空间和时间令牌。其次,为了在压缩过程中补充视觉信息,我们通过从现成的LLM嵌入中派生出的专用代码本对这些令牌进行量化,以利用语言模态的丰富语义。最后,为了提高训练稳定性和收敛性,我们还引入了一种课程学习策略,这对于有效的离散视觉表示学习至关重要。SweetTokenizer在仅使用现有最先技术视频令牌化器中使用的25%令牌的情况下,实现了相当的视频重建保真度,并将视频生成结果提高了32.9%,以GFVD为准。在使用相同令牌数量的情况下,我们在UCF-101上的视频重建结果和ImageNet-1K上的图像重建结果分别提高了57.1%和37.2%,以rFVD和rFID为准。此外,压缩的令牌被赋予了语义信息,可在下游应用中借助LLM实现少量的识别功能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了基于语义战争编码(SweetTokenizer)的紧凑且有效的离散化方法,用于处理视觉数据。该方法旨在提高VQ-VAE框架中的压缩比并保持重建保真度。它通过解耦图像或视频的空间时间维度获得紧凑的潜在表示,并通过跨注意力查询自动编码器(CQAE)将视觉信息转换为可学习的查询空间和时间令牌。此外,通过利用从语言模态中获得的丰富语义信息,通过专用代码本对这些令牌进行量化。最后,引入课程学习策略以增强训练和收敛。SweetTokenizer实现了与现有技术相比的视频重建保真度,并提高了视频生成结果。此外,压缩的令牌具有语义信息,可在下游应用中实现由大型语言模型驱动的少样本识别功能。
Key Takeaways
- SweetTokenizer是一种针对视觉数据的紧凑且有效的离散化方法。
- 它通过解耦图像或视频的空间时间维度来提高压缩比并保持重建保真度。
- 使用跨注意力查询自动编码器(CQAE)将视觉信息转换为令牌。
- 通过使用专用代码本和语言模态的丰富语义信息来量化这些令牌。
- 引入课程学习策略以增强训练和收敛。
- SweetTokenizer实现了高视频重建保真度和改进的视频生成结果。
点此查看论文截图

herakoi: a sonification experiment for astronomical data
Authors:Michele Ginolfi, Luca Di Mascolo, Anita Zanella
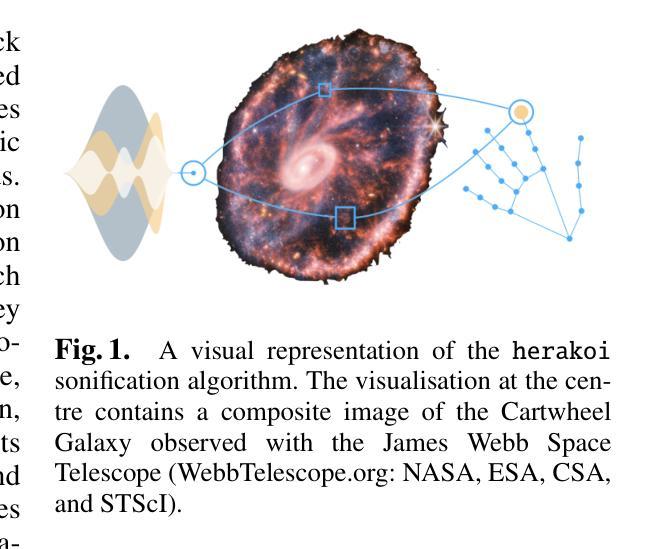
Recent research is revealing data-sonification as a promising complementary approach to vision, benefiting both data perception and interpretation. We present herakoi, a novel open-source software that uses machine learning to allow real-time image sonification, with a focus on astronomical data. By tracking hand movements via a webcam and mapping them to image coordinates, herakoi translates visual properties into sound, enabling users to “hear” images. Its swift responsiveness allows users to access information in astronomical images with short training, demonstrating high reliability and effectiveness. The software has shown promise in educational and outreach settings, making complex astronomical concepts more engaging and accessible to diverse audiences, including blind and visually impaired individuals. We also discuss future developments, such as the integration of large language and vision models to create a more interactive experience in interpreting astronomical data.
最近的研究表明,数据可视化作为一种有前景的补充方法,有益于数据感知和解释。我们推出了herakoi,这是一款新型开源软件,利用机器学习实现实时图像可视化,重点处理天文数据。herakoi通过追踪通过网络摄像头的手部动作并将其映射到图像坐标,将视觉属性转换为声音,使用户能够“听到”图像。其快速响应能力使用户在短暂训练后就能访问天文图像中的信息,表现出高度的可靠性和有效性。该软件在教育普及和宣传领域展现出潜力,使复杂的天文概念更加引人入胜,更容易被不同受众接受,包括盲人和视觉障碍人士。我们还讨论了未来发展,如整合大型语言和视觉模型,为解释天文数据创造更加互动的体验。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF to be published in the proceedings of “Various Innovative Technological Experiences - VITE II” by MemSAIt
Summary
数据音频化是一种有前景的补充视觉方法,可助力数据感知和解读。推出新型开源软件herakoi,运用机器学习实现实时图像音频化,专注于天文数据。软件通过追踪通过摄像头的手部动作并映射图像坐标,将视觉特性转化为声音,使用户能够“听”图像。软件响应迅速,短时间内培训后,用户就能快速获取天文图像信息,表现出高可靠性和有效性。在教育普及和对外宣传方面表现出巨大潜力,让复杂的天文概念更加引人入胜,易于受众理解,包括盲人和视障人士。未来还将开发大型语言和视觉模型集成,创造更加互动的天文数据解读体验。
Key Takeaways
- 数据音频化是一种新兴的视觉辅助方法,有助于提高数据感知和解读能力。
- herakoi软件是一种新型开源工具,可将图像实时转化为声音。
- herakoi软件专注于天文数据的音频化处理。
- 软件通过追踪手部动作并映射图像坐标来实现图像音频化。
- herakoi软件响应迅速,用户可快速获取天文图像信息。
- 软件在教育普及和对盲人和视障人士的宣传方面具有巨大潜力。
点此查看论文截图

Go With the Flow: Fast Diffusion for Gaussian Mixture Models
Authors:George Rapakoulias, Ali Reza Pedram, Panagiotis Tsiotras
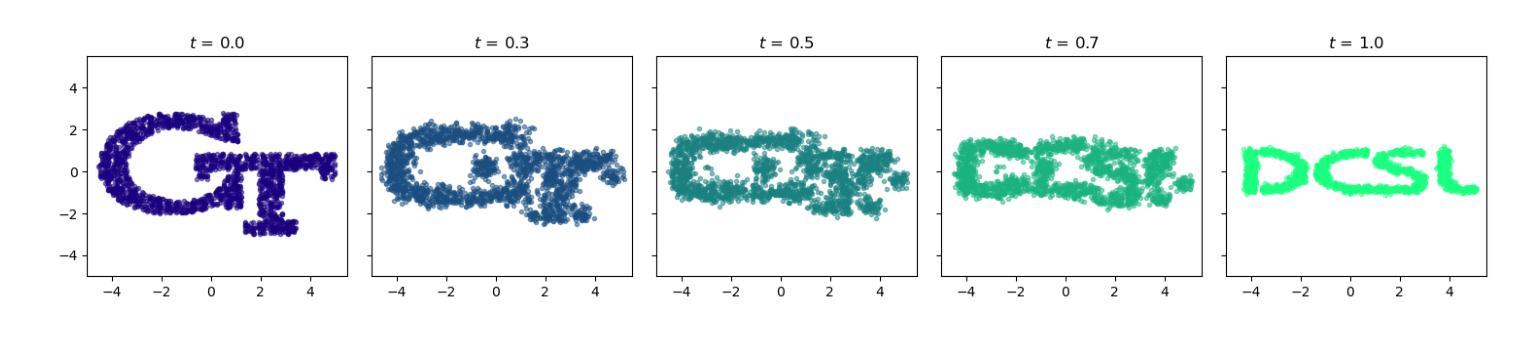
Schr"{o}dinger Bridges (SB) are diffusion processes that steer, in finite time, a given initial distribution to another final one while minimizing a suitable cost functional. Although various methods for computing SBs have recently been proposed in the literature, most of these approaches require computationally expensive training schemes, even for solving low-dimensional problems. In this work, we propose an analytic parametrization of a set of feasible policies for steering the distribution of a dynamical system from one Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) to another. Instead of relying on standard non-convex optimization techniques, the optimal policy within the set can be approximated as the solution of a low-dimensional linear program whose dimension scales linearly with the number of components in each mixture. Furthermore, our method generalizes naturally to more general classes of dynamical systems such as controllable Linear Time-Varying systems that cannot currently be solved using traditional neural SB approaches. We showcase the potential of this approach in low-to-moderate dimensional problems such as image-to-image translation in the latent space of an autoencoder, and various other examples. We also benchmark our approach on an Entropic Optimal Transport (EOT) problem and show that it outperforms state-of-the-art methods in cases where the boundary distributions are mixture models while requiring virtually no training.
薛定谔桥(Schrödinger Bridges,简称SB)是一种扩散过程,能够在有限时间内将给定的初始分布引导到另一个最终分布,同时最小化适当的成本函数。尽管最近在文献中提出了多种计算SB的方法,但大多数这些方法都需要计算昂贵的训练方案,即使对于解决低维问题也是如此。在这项工作中,我们提出了一组可行策略的解析参数化,以引导动力系统从一个高斯混合模型(GMM)分布转向另一个GMM分布。我们并没有依赖标准的非凸优化技术,而是将集合中的最佳策略近似为低维线性程序的解,其维度与每个混合中的组件数量呈线性关系。此外,我们的方法自然地推广到了更一般的动力系统类,如目前无法用传统神经SB方法解决的可控线性时变系统。我们通过低维到中维的问题展示了该方法的潜力,例如在自动编码器的潜在空间中的图像到图像翻译以及其他各种示例。我们还用熵最优传输(EOT)问题来评估我们的方法,并表明它在边界分布为混合模型的情况下优于现有技术,而几乎不需要进行训练。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种基于高斯混合模型(GMM)的Schrödinger桥(SB)分布转换方法。通过解析参数化方法求解线性规划问题,能在较低计算成本下实现SB的计算,适用于低维到中等维度的动态系统问题。该方法可自然推广到更一般的可控线性时变系统,在图像翻译等任务中展现潜力,且在边界分布为混合模型的情况下优于现有方法。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍Schrödinger桥(SB)是一种分布转换的扩散过程,能够在有限时间内将初始分布导向另一个最终分布,同时最小化合适的成本函数。但现有的计算方法通常计算量大且成本高昂。
- 提出了一种基于高斯混合模型(GMM)的解析参数化方法计算SBs,可实现高效求解。对于具有少量组件的混合模型特别有效。此方法克服了标准非凸优化技术的困难。
- 通过低维线性规划近似最优策略的计算过程较为简便。问题的维度会随着每个混合模型中组件数量的增加而线性增长。
- 该方法适用于更广泛的动态系统类型,包括可控线性时变系统,无法用传统的神经网络SB方法解决的系统也可以处理。此方法具有一定的通用性。
- 方法在实际应用如图像到图像的潜空间翻译以及包括更高维度任务上的潜力和能力有所体现。在不同维度的任务中展示了良好的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

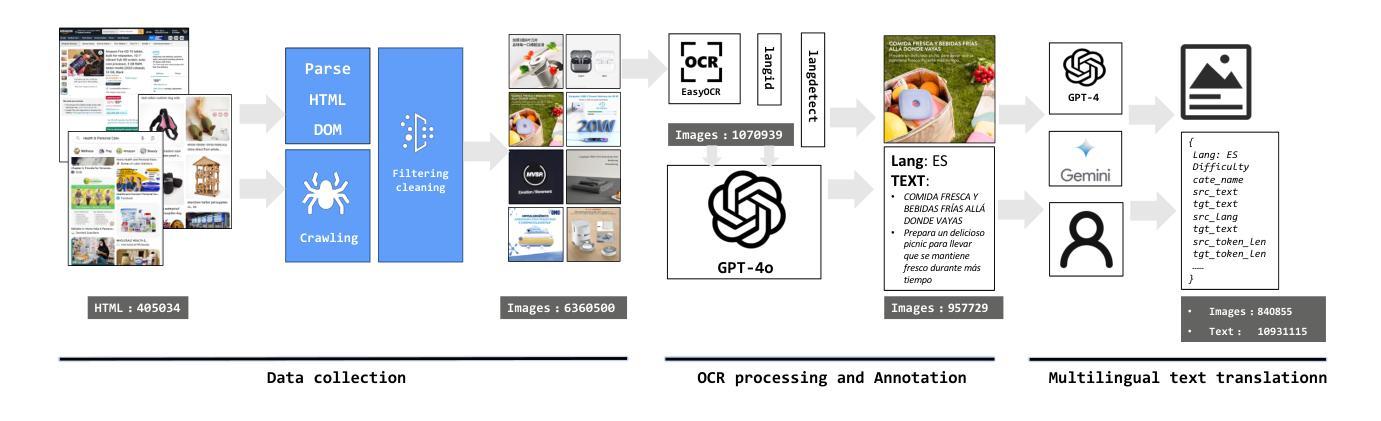
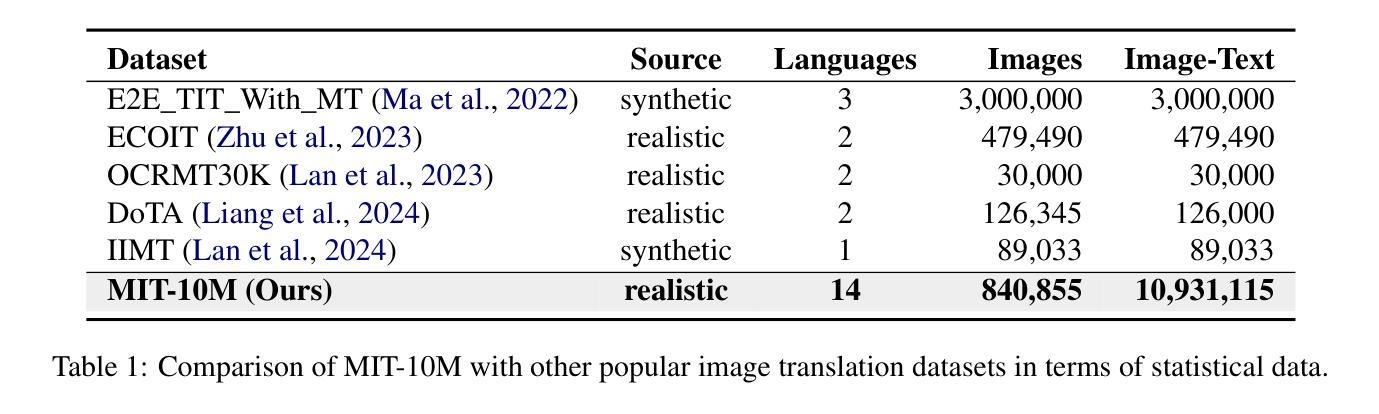
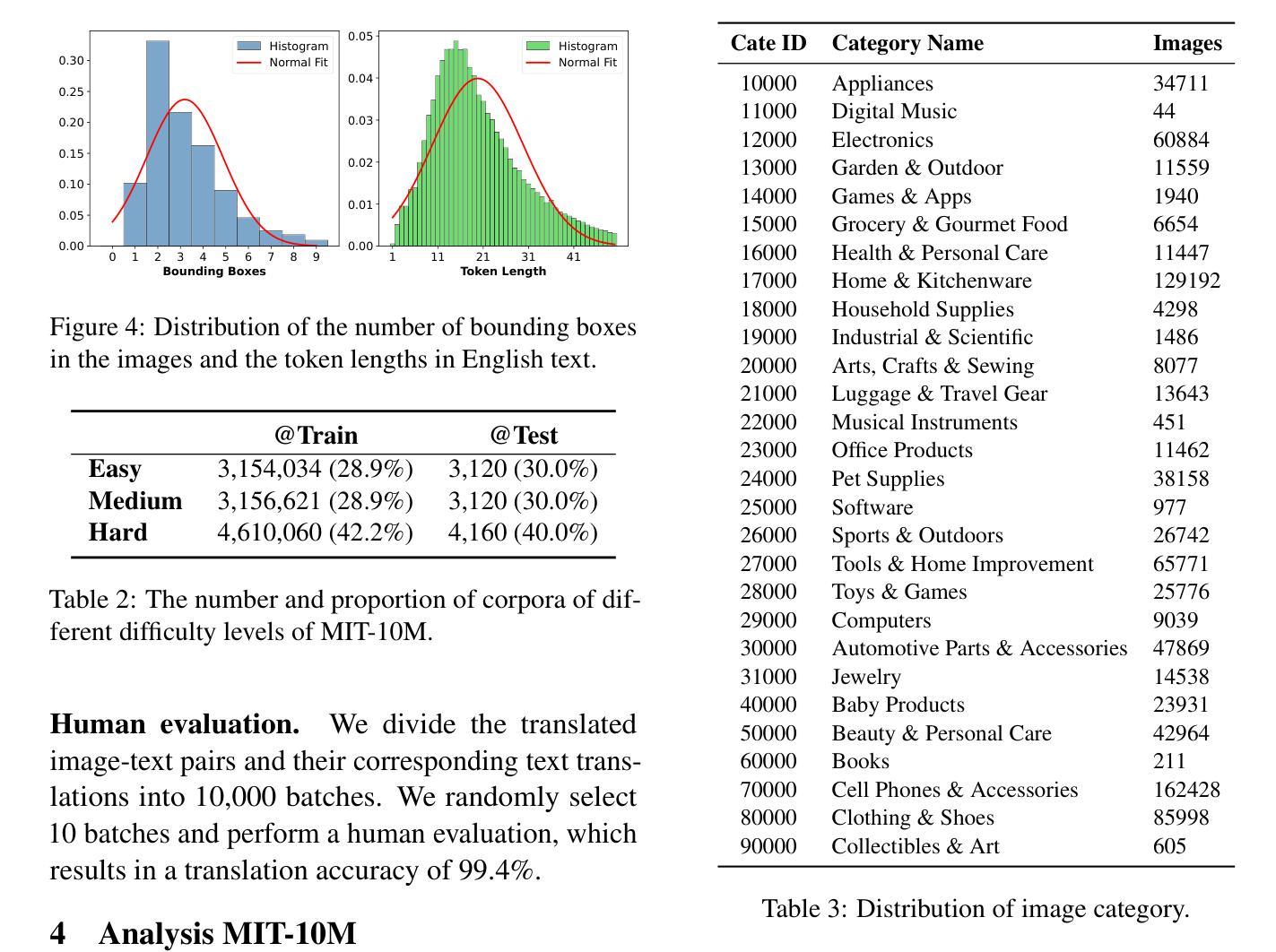
MIT-10M: A Large Scale Parallel Corpus of Multilingual Image Translation
Authors:Bo Li, Shaolin Zhu, Lijie Wen
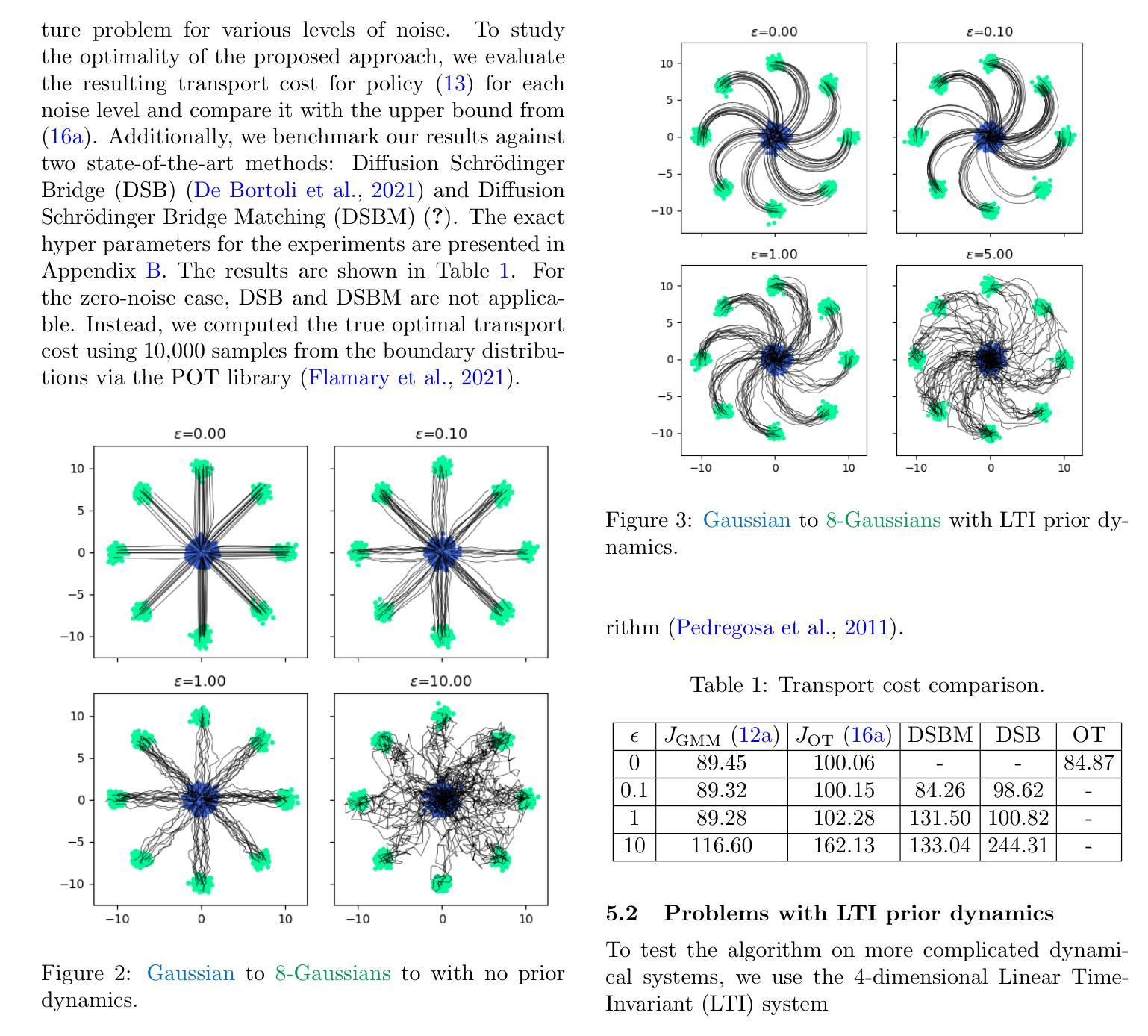
Image Translation (IT) holds immense potential across diverse domains, enabling the translation of textual content within images into various languages. However, existing datasets often suffer from limitations in scale, diversity, and quality, hindering the development and evaluation of IT models. To address this issue, we introduce MIT-10M, a large-scale parallel corpus of multilingual image translation with over 10M image-text pairs derived from real-world data, which has undergone extensive data cleaning and multilingual translation validation. It contains 840K images in three sizes, 28 categories, tasks with three levels of difficulty and 14 languages image-text pairs, which is a considerable improvement on existing datasets. We conduct extensive experiments to evaluate and train models on MIT-10M. The experimental results clearly indicate that our dataset has higher adaptability when it comes to evaluating the performance of the models in tackling challenging and complex image translation tasks in the real world. Moreover, the performance of the model fine-tuned with MIT-10M has tripled compared to the baseline model, further confirming its superiority.
图像翻译(IT)在各个领域具有巨大的潜力,能够实现图像内文本内容的跨语言翻译。然而,现有数据集在规模、多样性和质量方面存在诸多局限,阻碍了IT模型的开发与评估。为了解决这个问题,我们推出了MIT-10M,这是一个大规模的多语言图像翻译平行语料库,包含超过1000万个图像文本对,这些数据均来源于现实世界,并经过了严格的数据清洗和多语言翻译验证。它包含3种尺寸、28个类别的84万个图像,任务难度分为3个级别,以及14种语言的图像文本对,相较于现有数据集,这是一个显著的改进。我们在MIT-10M上进行了大量的实验来评估和训练模型。实验结果清楚地表明,我们的数据集在评估模型应对现实世界中具有挑战性和复杂性的图像翻译任务的性能时具有更高的适应性。此外,与基线模型相比,使用MIT-10M进行微调后的模型性能提高了三倍,进一步证明了其优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in COLING 2025
Summary
图像翻译(IT)在多个领域具有巨大潜力,可实现图像内文本的跨语言翻译。然而,现有数据集在规模、多样性和质量方面存在局限性,阻碍了IT模型的开发和评估。为此,我们推出了MIT-10M,这是一个包含超过1000万张图像文本对的大型多语言图像翻译平行语料库,源于现实世界数据,并经过严格的数据清洗和多语言翻译验证。它在图像大小、类别、任务难度和语言多样性方面都有显著改进。实验表明,MIT-10M在应对现实世界中的复杂图像翻译任务时表现出更高的适应性,使用MIT-10M微调的模型性能是基线模型的三倍。
Key Takeaways
- 图像翻译(IT)在多个领域具有巨大的应用潜力,特别是在跨语言翻译方面。
- 现有数据集存在规模、多样性和质量问题,限制了IT模型的发展。
- MIT-10M是一个大型多语言图像翻译平行语料库,包含超过10M张图像文本对,源于现实数据并经过严格验证。
- MIT-10M在图像大小、类别、任务难度和语言方面都有显著改进,增强了数据集的多样性。
- 实验表明,MIT-10M在评估模型性能和处理复杂图像翻译任务方面表现出更高的适应性。
- 使用MIT-10M微调的模型性能是基线模型的三倍,证实了其优越性。
- MIT-10M的推出为IT领域的研究和发展提供了重要的数据集支持。
点此查看论文截图


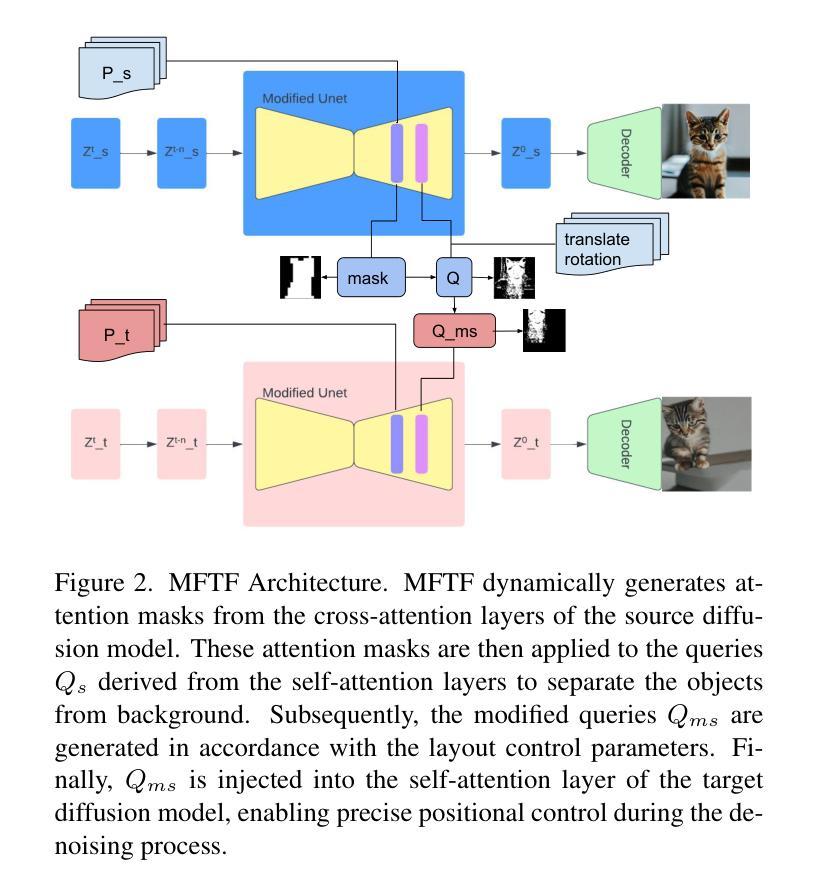
MFTF: Mask-free Training-free Object Level Layout Control Diffusion Model
Authors:Shan Yang
Text-to-image generation models have revolutionized content creation, but diffusion-based vision-language models still face challenges in precisely controlling the shape, appearance, and positional placement of objects in generated images using text guidance alone. Existing global image editing models rely on additional masks or images as guidance to achieve layout control, often requiring retraining of the model. While local object-editing models allow modifications to object shapes, they lack the capability to control object positions. To address these limitations, we propose the Mask-free Training-free Object-Level Layout Control Diffusion Model (MFTF), which provides precise control over object positions without requiring additional masks or images. The MFTF model supports both single-object and multi-object positional adjustments, such as translation and rotation, while enabling simultaneous layout control and object semantic editing. The MFTF model employs a parallel denoising process for both the source and target diffusion models. During this process, attention masks are dynamically generated from the cross-attention layers of the source diffusion model and applied to queries from the self-attention layers to isolate objects. These queries, generated in the source diffusion model, are then adjusted according to the layout control parameters and re-injected into the self-attention layers of the target diffusion model. This approach ensures accurate and precise positional control of objects. Project source code available at https://github.com/syang-genai/MFTF.
文本到图像生成模型已经彻底改变了内容创作的方式,但是基于扩散的视语言模型在仅使用文本指导来精确控制生成图像中物体的形状、外观和位置放置方面仍然面临挑战。现有的全局图像编辑模型依赖于额外的蒙版或图像作为指导来实现布局控制,通常需要重新训练模型。虽然局部物体编辑模型允许修改物体形状,但它们缺乏控制物体位置的能力。为了解决这些限制,我们提出了无需蒙版训练的对象级布局控制扩散模型(MFTF),该模型无需额外的蒙版或图像即可精确控制物体位置。MFTF模型支持单物体和多物体的位置调整,如平移和旋转,同时实现布局控制和物体语义编辑。MFTF模型对源和目标扩散模型进行并行去噪处理。在此过程中,从源扩散模型的交叉注意层动态生成注意力蒙版,并应用于自我注意层的查询以隔离物体。这些在源扩散模型中生成的查询会根据布局控制参数进行调整,然后重新注入目标扩散模型的自我注意层。这种方法确保了物体的精确位置控制。项目源代码可在https://github.com/syang-genai/MFTF找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 8 pages, 7 figures
Summary
文本转图像生成模型已革新内容创作,但基于扩散的视语言模型在用文本指导生成图像时,仍面临精确控制物体形状、外观和位置放置的挑战。现有全局图像编辑模型需额外蒙版或图像指导以实现布局控制,且常需重新训练模型。局部物体编辑模型虽可修改物体形状,但无法控制物体位置。为解决这些局限,我们提出无需蒙版训练的Mask-free Training-free Object-Level Layout Control Diffusion Model(MFTF)。该模型无需额外蒙版或图像即可精确控制物体位置,支持单物体和多物体的位置调整,如平移和旋转,同时实现布局控制和物体语义编辑。该模型采用源和目标扩散模型的并行去噪过程,通过动态生成注意力蒙版并应用于查询,以隔离物体,并根据布局控制参数调整查询,再注入目标扩散模型的自注意力层,确保物体的精确位置控制。
Key Takeaways
- 文本转图像生成模型在内容创作领域具有革命性影响。
- 现有扩散模型在精确控制物体形状、外观和位置方面存在挑战。
- 全局图像编辑模型依赖额外的蒙版或图像进行布局控制,并常需重新训练模型。
- 局部物体编辑模型虽然可以修改物体形状,但无法控制物体位置。
- Mask-free Training-free Object-Level Layout Control Diffusion Model(MFTF)提出解决上述问题。
- MFTF模型无需额外蒙版或图像即可实现精确的对象位置控制。
点此查看论文截图

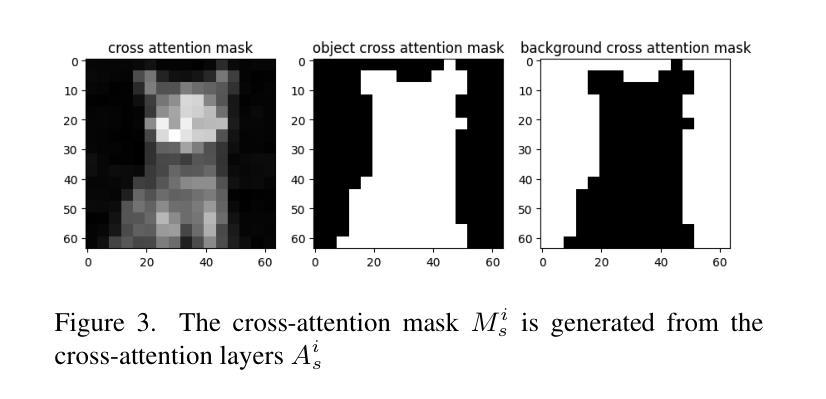
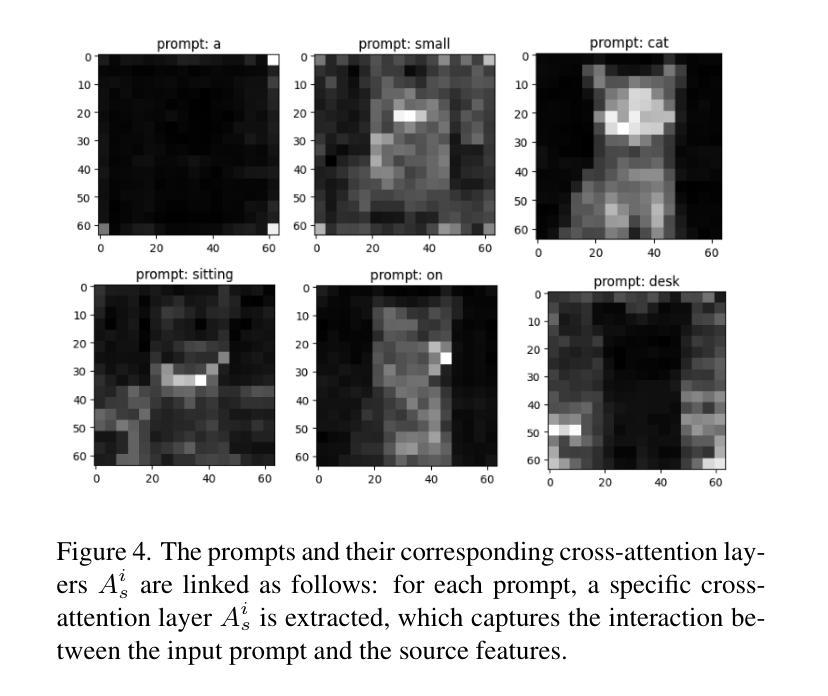

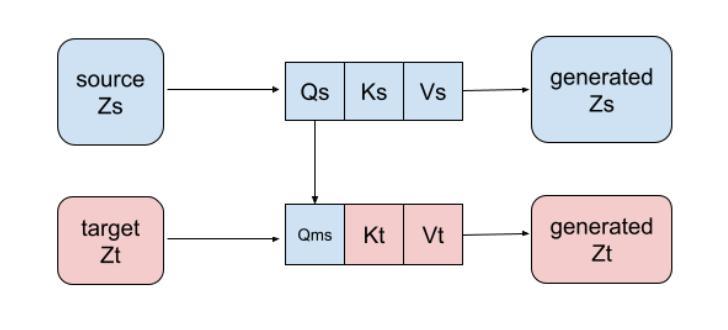
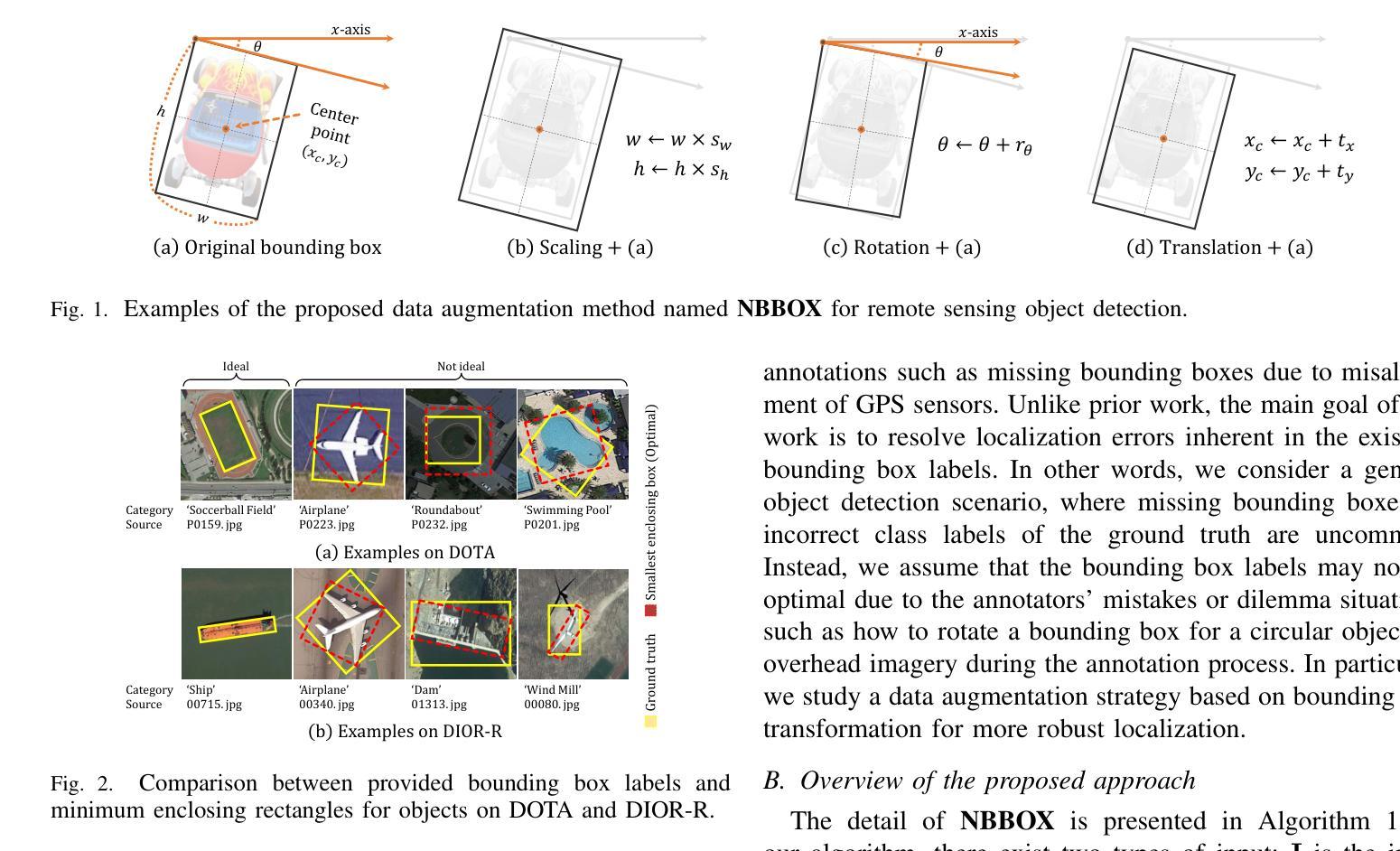
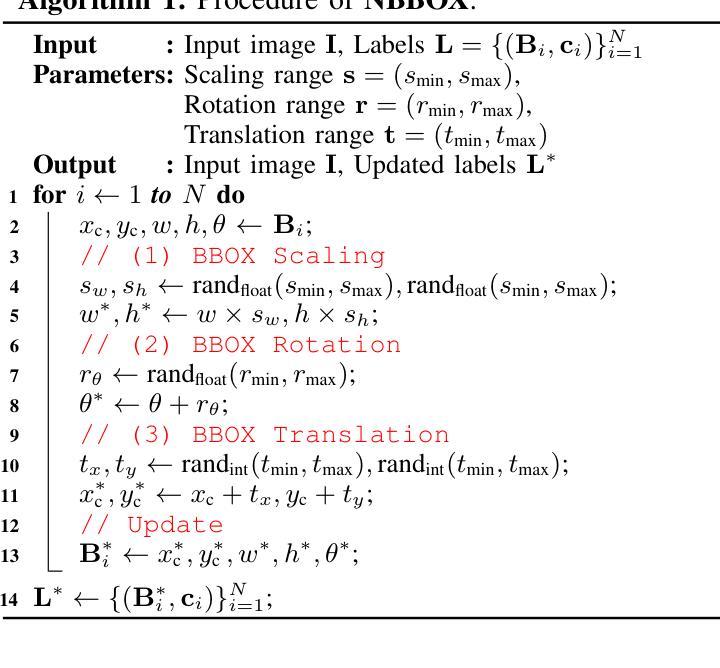
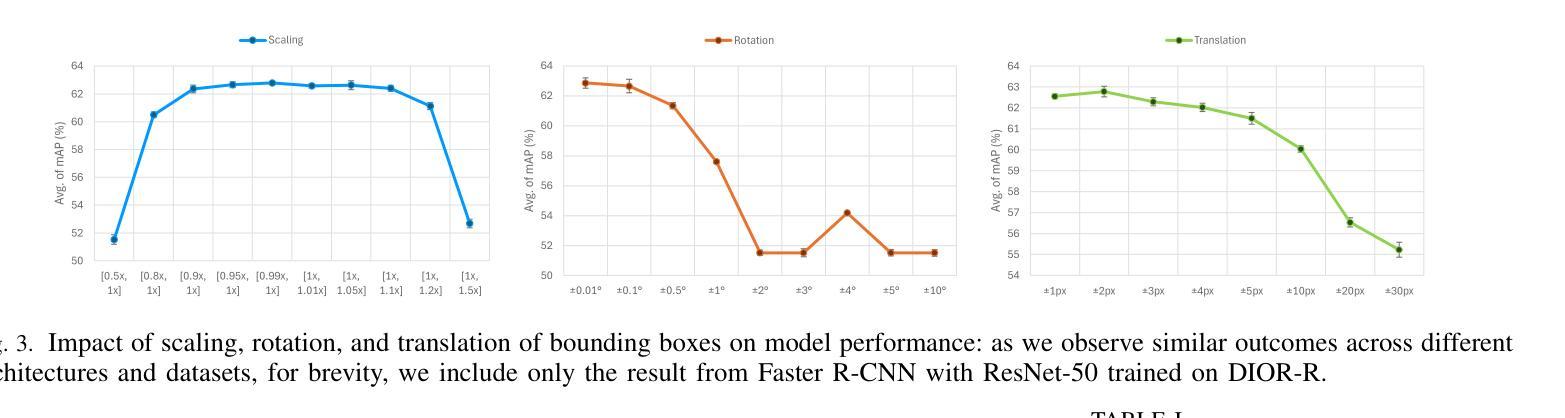
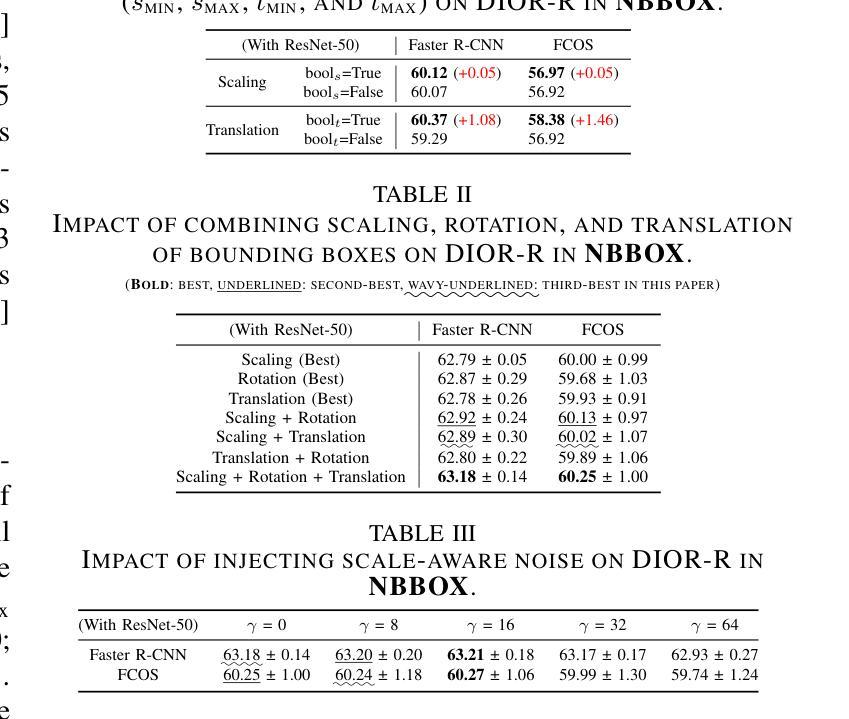
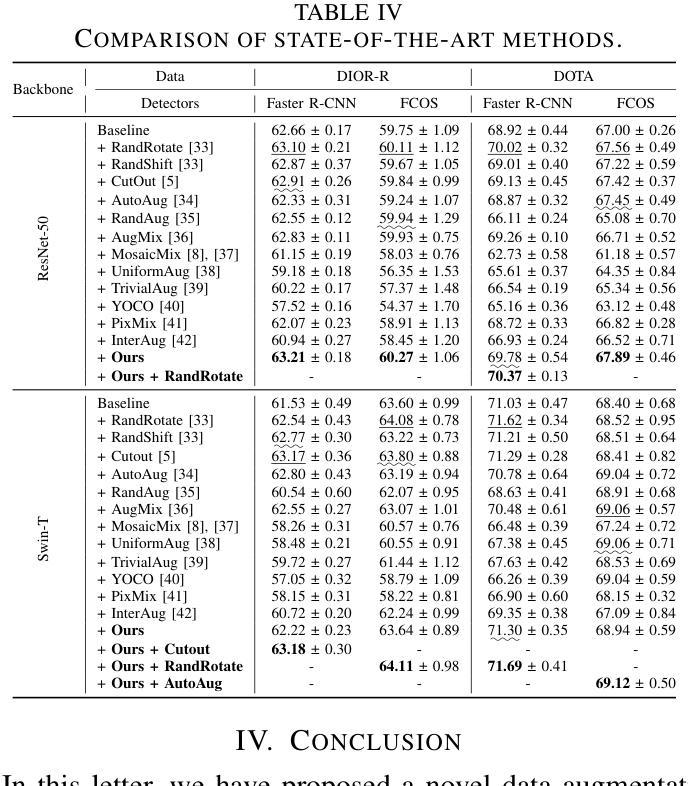
NBBOX: Noisy Bounding Box Improves Remote Sensing Object Detection
Authors:Yechan Kim, SooYeon Kim, Moongu Jeon
Data augmentation has shown significant advancements in computer vision to improve model performance over the years, particularly in scenarios with limited and insufficient data. Currently, most studies focus on adjusting the image or its features to expand the size, quality, and variety of samples during training in various tasks including object detection. However, we argue that it is necessary to investigate bounding box transformations as a data augmentation technique rather than image-level transformations, especially in aerial imagery due to potentially inconsistent bounding box annotations. Hence, this letter presents a thorough investigation of bounding box transformation in terms of scaling, rotation, and translation for remote sensing object detection. We call this augmentation strategy NBBOX (Noise Injection into Bounding Box). We conduct extensive experiments on DOTA and DIOR-R, both well-known datasets that include a variety of rotated generic objects in aerial images. Experimental results show that our approach significantly improves remote sensing object detection without whistles and bells and it is more time-efficient than other state-of-the-art augmentation strategies.
数据增强在计算机视觉领域已展现出显著进展,多年来一直在提高模型性能,特别是在数据有限和不足的场景下。目前,大多数研究集中在调整图像或其特征以扩大样本大小、质量和多样性,用于包括目标检测在内的各种任务的训练。然而,我们认为有必要研究边界框变换作为一种数据增强技术,而不是图像级别的变换,尤其是在航空图像中,因为边界框注释可能存在潜在的不一致性。因此,本文全面研究了边界框变换在缩放、旋转和翻译方面的应用,用于遥感目标检测。我们将这种增强策略称为NBBOX(噪声注入边界框)。我们在DOTA和DIOR-R这两个包含航空图像中各种旋转通用对象的数据集上进行了大量实验。实验结果表明,我们的方法在不使用任何花哨技巧的情况下显著提高了遥感目标检测的精度,并且比其他最先进的增强策略更加省时。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
数据增强技术在计算机视觉领域已取得显著进展,特别是在数据有限和不足的情况下,能够提高模型性能。目前研究主要集中在图像或其特征的调整上,以扩大样本的大小、质量和种类。本文提出研究边界框转换作为数据增强技术,特别是在航空图像中,因为边界框注释可能存在不一致的情况。本文对边界框转换的缩放、旋转和翻译进行了深入研究,用于遥感目标检测。我们称这种增强策略为NBBOX(噪声注入边界框)。在DOTA和DIOR-R两个包含航空图像中旋转通用对象的大型数据集上进行了大量实验。实验结果表明,我们的方法在不增加额外时间和成本的情况下显著提高了遥感目标检测的准确性。
Key Takeaways
- 数据增强技术在计算机视觉领域的重要性:特别是在数据有限和不足时,有助于提高模型性能。
- 当前研究主要集中在图像级别的数据增强上,通过调整图像或其特征来扩大样本规模、提高质量和多样性。
- 论文主张研究边界框转换作为数据增强技术,特别是在航空图像中,因为存在边界框注释不一致的问题。
- 论文介绍了NBBOX策略,这是一种将噪声注入边界框的数据增强方法,包括缩放、旋转和翻译的研究。
- 实验在DOTA和DIOR-R两个数据集上进行,这两个数据集包含航空图像中的旋转通用对象。
- 实验结果表明,NBBOX策略在遥感目标检测中具有显著的优势,并且比一些先进的增强策略更加高效。
点此查看论文截图


AllWeatherNet:Unified Image Enhancement for Autonomous Driving under Adverse Weather and Lowlight-conditions
Authors:Chenghao Qian, Mahdi Rezaei, Saeed Anwar, Wenjing Li, Tanveer Hussain, Mohsen Azarmi, Wei Wang
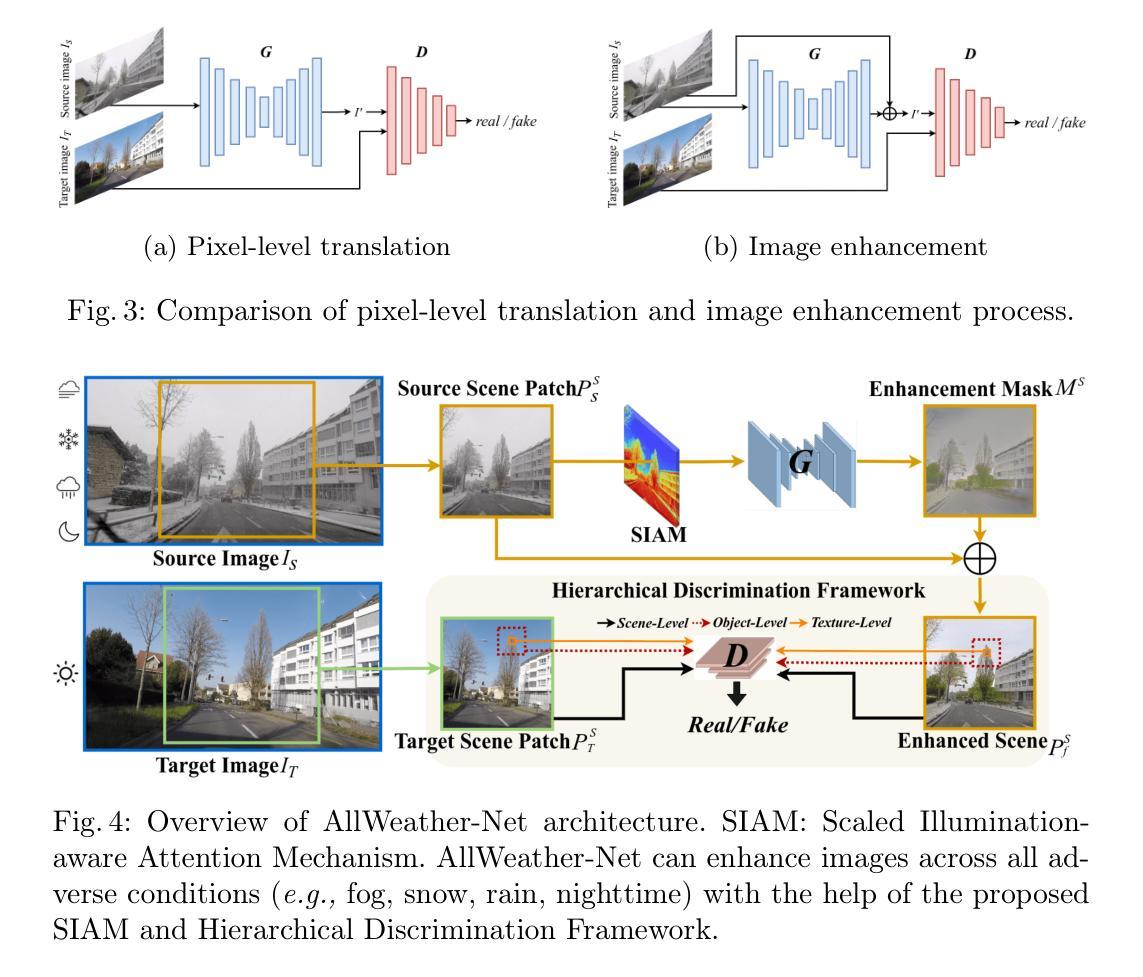
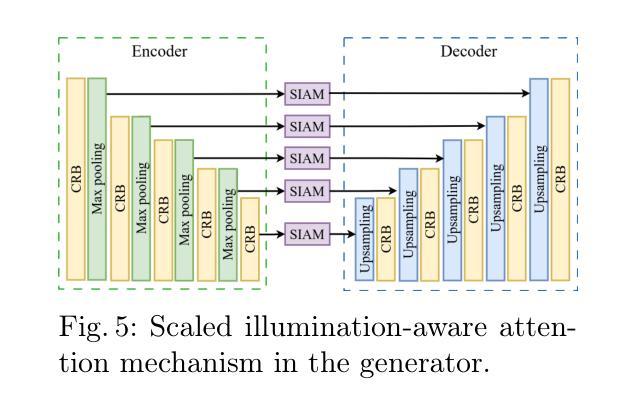
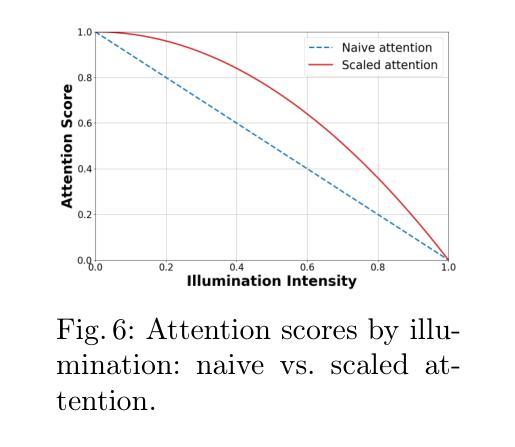
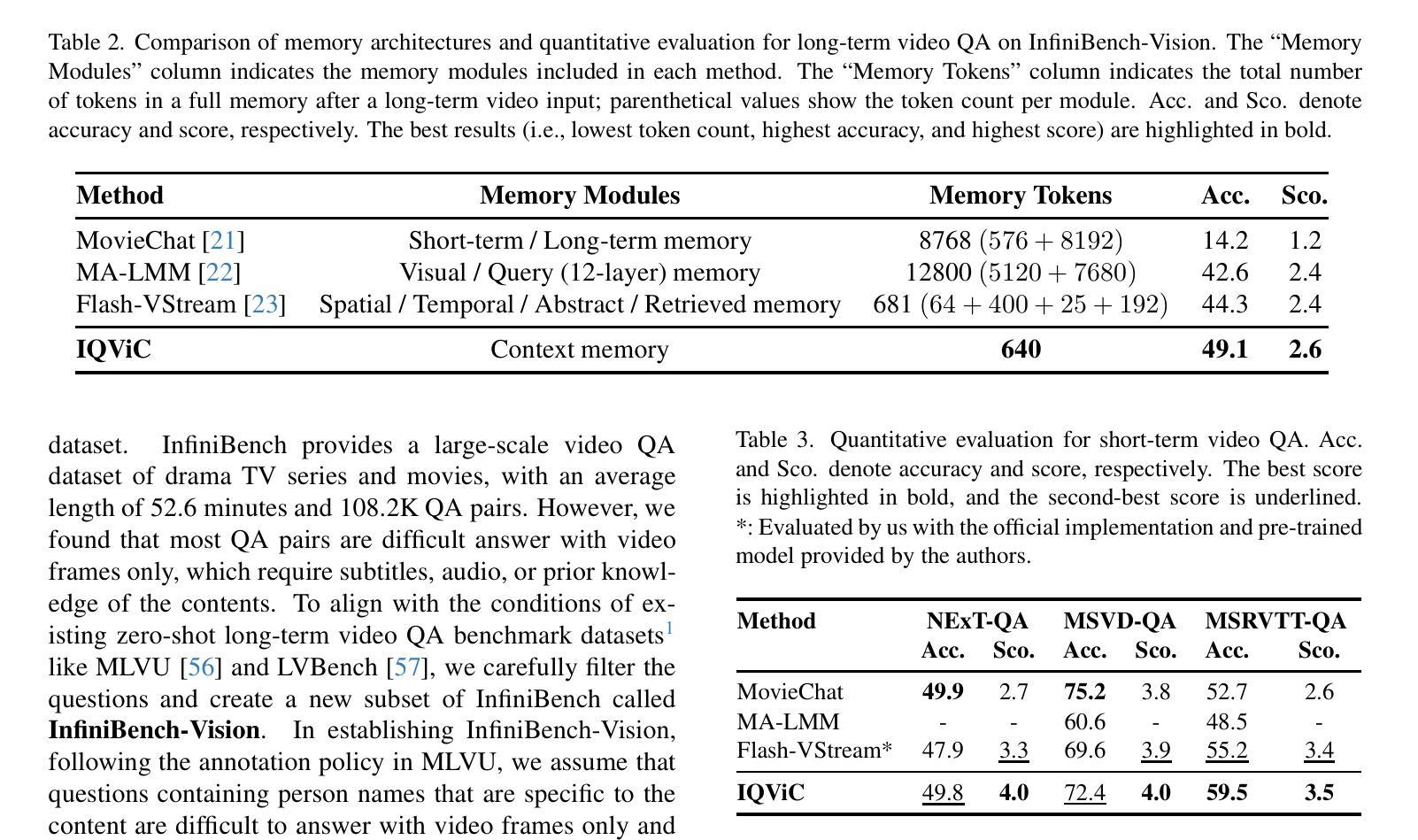
Adverse conditions like snow, rain, nighttime, and fog, pose challenges for autonomous driving perception systems. Existing methods have limited effectiveness in improving essential computer vision tasks, such as semantic segmentation, and often focus on only one specific condition, such as removing rain or translating nighttime images into daytime ones. To address these limitations, we propose a method to improve the visual quality and clarity degraded by such adverse conditions. Our method, AllWeather-Net, utilizes a novel hierarchical architecture to enhance images across all adverse conditions. This architecture incorporates information at three semantic levels: scene, object, and texture, by discriminating patches at each level. Furthermore, we introduce a Scaled Illumination-aware Attention Mechanism (SIAM) that guides the learning towards road elements critical for autonomous driving perception. SIAM exhibits robustness, remaining unaffected by changes in weather conditions or environmental scenes. AllWeather-Net effectively transforms images into normal weather and daytime scenes, demonstrating superior image enhancement results and subsequently enhancing the performance of semantic segmentation, with up to a 5.3% improvement in mIoU in the trained domain. We also show our model’s generalization ability by applying it to unseen domains without re-training, achieving up to 3.9% mIoU improvement. Code can be accessed at: https://github.com/Jumponthemoon/AllWeatherNet.
恶劣条件,如雪、雨、夜晚和雾,给自动驾驶感知系统带来了挑战。现有方法在改善重要的计算机视觉任务(如语义分割)方面的效果有限,而且通常只关注一种特定条件,例如去雨或将夜间图像转换为日间图像。为了解决这些局限性,我们提出了一种方法,用以改善由这些恶劣条件造成的视觉质量和清晰度下降的问题。我们的方法,AllWeather-Net,利用一种新型分层架构,提升各种恶劣条件下的图像。该架构通过区分三个语义级别的信息(场景、物体和纹理)来增强图像。此外,我们引入了一种缩放照明感知注意机制(SIAM),引导学习面向对自动驾驶感知至关重要的道路元素。SIAM表现出稳健性,不受天气条件或环境场景变化的影响。AllWeather-Net能有效地将图像转换为正常天气和日间场景,显示出卓越的图像增强效果,进而提升语义分割的性能,在训练域内平均交并比(mIoU)提高5.3%。我们还通过将在未见域的应用展示了我们模型的泛化能力,无需重新训练即可实现高达3.9%的mIoU改善。相关代码可访问:https://github.com/Jumponthemoon/AllWeatherNet。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ICPR 2024, Piero Zamperoni Overall Best Student Paper Award
Summary
本文提出一种应对恶劣天气条件挑战的方法,名为AllWeather-Net。该方法采用分层架构,通过场景、物体和纹理三个语义层次的信息处理来改善图像质量。引入的缩放光照感知注意力机制(SIAM)能指导学习关注对自动驾驶感知至关重要的道路元素。AllWeather-Net可将图像转化为正常天气和白天场景,提升语义分割性能,并在训练和未训练领域均表现出优异的图像增强效果。
Key Takeaways
- 恶劣条件如雨雪、夜晚和雾对自动驾驶感知系统构成挑战。
- 现有方法改善计算机视觉任务(如语义分割)的效果有限,通常只针对单一条件。
- AllWeather-Net采用分层架构,处理场景、物体和纹理三个语义层次的信息,改善图像质量。
- 引入缩放光照感知注意力机制(SIAM),指导学习关注自动驾驶感知中重要的道路元素。
- AllWeather-Net可将图像转化为正常天气和白天场景,显著提升语义分割性能。
- 该方法在训练和未训练领域均展现出优异的图像增强效果。
点此查看论文截图