⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-19 更新
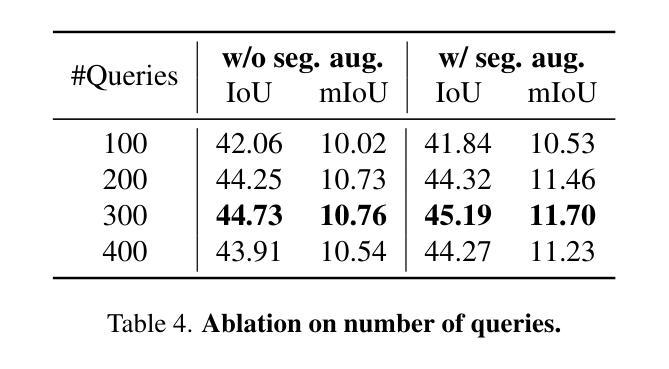
GraphAvatar: Compact Head Avatars with GNN-Generated 3D Gaussians
Authors:Xiaobao Wei, Peng Chen, Ming Lu, Hui Chen, Feng Tian
Rendering photorealistic head avatars from arbitrary viewpoints is crucial for various applications like virtual reality. Although previous methods based on Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) can achieve impressive results, they lack fidelity and efficiency. Recent methods using 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have improved rendering quality and real-time performance but still require significant storage overhead. In this paper, we introduce a method called GraphAvatar that utilizes Graph Neural Networks (GNN) to generate 3D Gaussians for the head avatar. Specifically, GraphAvatar trains a geometric GNN and an appearance GNN to generate the attributes of the 3D Gaussians from the tracked mesh. Therefore, our method can store the GNN models instead of the 3D Gaussians, significantly reducing the storage overhead to just 10MB. To reduce the impact of face-tracking errors, we also present a novel graph-guided optimization module to refine face-tracking parameters during training. Finally, we introduce a 3D-aware enhancer for post-processing to enhance the rendering quality. We conduct comprehensive experiments to demonstrate the advantages of GraphAvatar, surpassing existing methods in visual fidelity and storage consumption. The ablation study sheds light on the trade-offs between rendering quality and model size. The code will be released at: https://github.com/ucwxb/GraphAvatar
从任意视角渲染逼真的头像对于虚拟现实等应用至关重要。尽管基于神经辐射场(NeRF)的先前方法可以实现令人印象深刻的结果,但它们缺乏真实感和效率。使用三维高斯平铺(3DGS)的最近方法提高了渲染质量和实时性能,但仍然需要很大的存储开销。在本文中,我们介绍了一种名为GraphAvatar的方法,该方法利用图神经网络(GNN)生成头像的3D高斯分布。具体来说,GraphAvatar训练了一个几何GNN和一个外观GNN,从跟踪的网格中产生3D高斯分布的属性。因此,我们的方法可以存储GNN模型而不是3D高斯分布,将存储开销大幅降低到仅10MB。为了减少面部跟踪误差的影响,我们还提供了一个新型的图引导优化模块,用于在训练过程中优化面部跟踪参数。最后,我们引入了一个用于后处理的3D感知增强器,以提高渲染质量。我们进行了全面的实验,展示了GraphAvatar的优势,在视觉真实感和存储消耗方面超越了现有方法。消融研究揭示了渲染质量和模型大小之间的权衡。代码将在https://github.com/ucwxb/GraphAvatar发布。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted by AAAI2025
摘要
采用图神经网络(GNN)生成头显人物模型,实现高保真度渲染。通过几何GNN和外观GNN生成三维高斯分布属性,降低存储需求至仅10MB。引入图引导优化模块,减少面部跟踪误差对渲染质量的影响,并提出三维感知增强器用于后期处理以提升渲染质量。实验证明GraphAvatar在视觉保真度和存储消耗方面优于现有方法。
关键见解
- 利用图神经网络(GNN)生成三维高斯分布,实现高质量的头显人物渲染。
- 通过几何和外观GNN模型生成属性,大幅降低存储需求至仅10MB。
- 图引导优化模块减少了面部跟踪误差对渲染效果的影响。
- 提出一种新型的三维感知增强器进行后处理以提升渲染质量。
- 实验证明GraphAvatar在视觉保真度和存储消耗方面优于现有方法。
- 消融研究揭示了渲染质量和模型大小之间的权衡关系。
点此查看论文截图

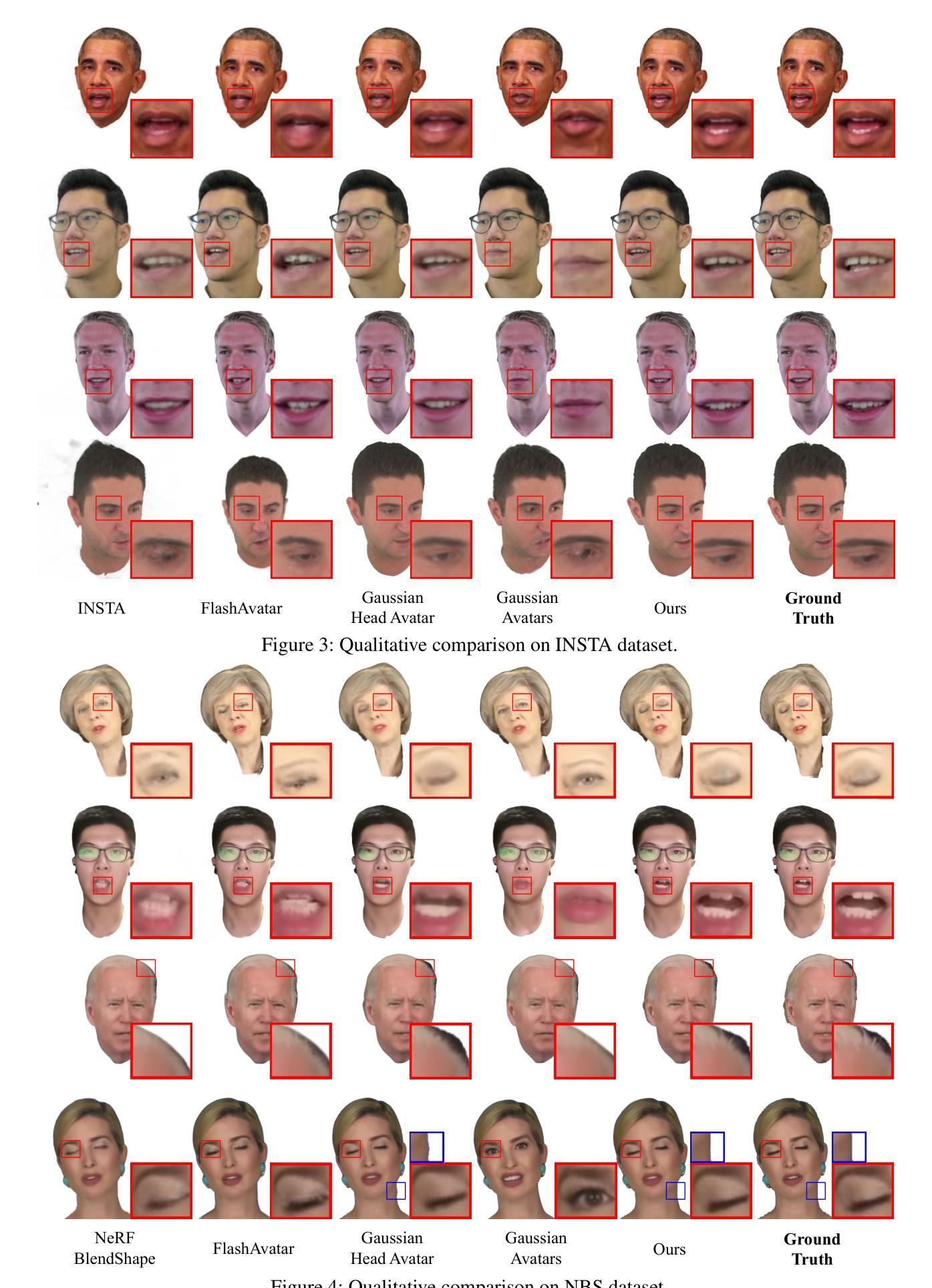
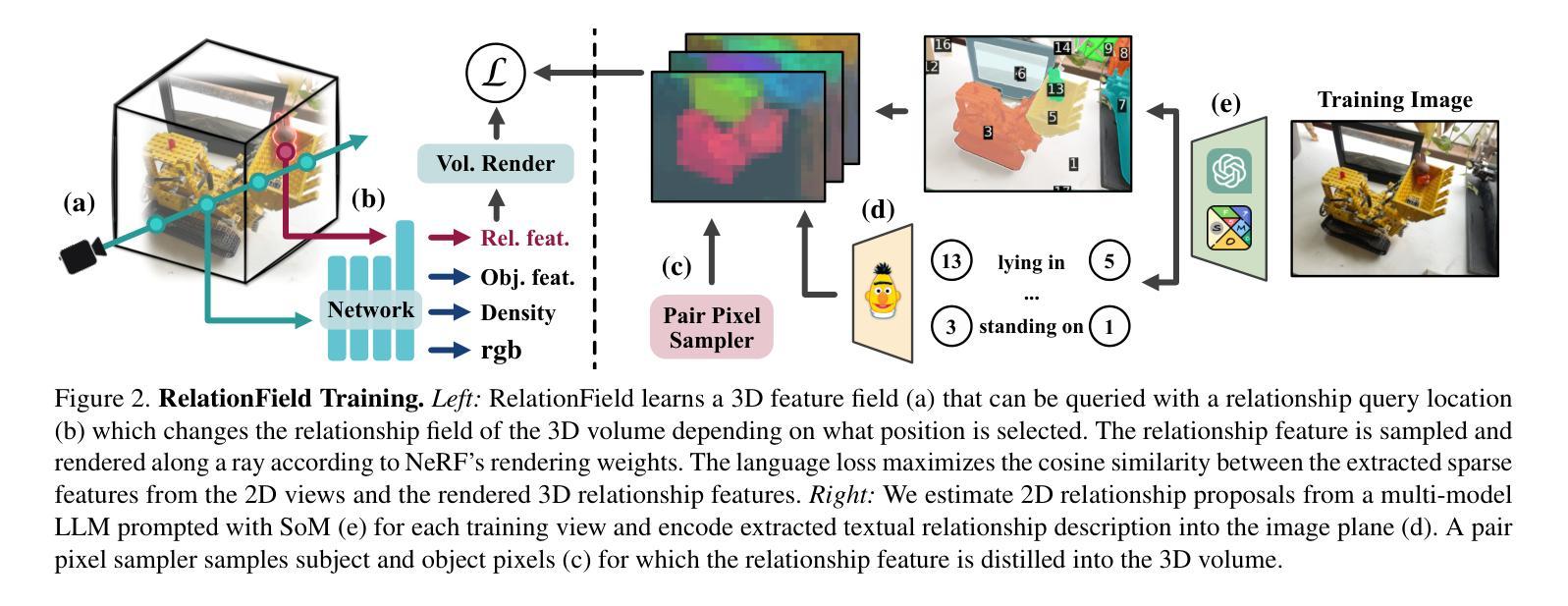
RelationField: Relate Anything in Radiance Fields
Authors:Sebastian Koch, Johanna Wald, Mirco Colosi, Narunas Vaskevicius, Pedro Hermosilla, Federico Tombari, Timo Ropinski
Neural radiance fields are an emerging 3D scene representation and recently even been extended to learn features for scene understanding by distilling open-vocabulary features from vision-language models. However, current method primarily focus on object-centric representations, supporting object segmentation or detection, while understanding semantic relationships between objects remains largely unexplored. To address this gap, we propose RelationField, the first method to extract inter-object relationships directly from neural radiance fields. RelationField represents relationships between objects as pairs of rays within a neural radiance field, effectively extending its formulation to include implicit relationship queries. To teach RelationField complex, open-vocabulary relationships, relationship knowledge is distilled from multi-modal LLMs. To evaluate RelationField, we solve open-vocabulary 3D scene graph generation tasks and relationship-guided instance segmentation, achieving state-of-the-art performance in both tasks. See the project website at https://relationfield.github.io.
神经辐射场是一种新兴的3D场景表示方法,最近甚至被扩展为通过学习特征来用于场景理解,通过从视觉语言模型中提炼开放词汇特征。然而,当前的方法主要集中在面向对象的表示上,支持对象分割或检测,而理解对象之间的语义关系仍然在很大程度上未被探索。为了弥补这一空白,我们提出了RelationField,这是第一种直接从神经辐射场中提取对象间关系的方法。RelationField将对象之间的关系表示为神经辐射场内的射线对,有效地将其公式扩展为包括隐式关系查询。为了教导RelationField复杂且开放的词汇关系,关系知识是从多模态大型语言模型中提炼出来的。为了评估RelationField的性能,我们解决了开放式词汇的3D场景图生成任务和关系导向的实例分割任务,在这两项任务中都达到了最先进的性能。更多详情可见项目网站:https://relationfield.github.io。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://relationfield.github.io
Summary
神经网络辐射场(NeRF)是一种新兴的三维场景表示方法,最近被扩展用于学习场景理解的特征。当前的方法主要关注对象中心的表示,支持对象分割或检测,但在理解对象之间的语义关系方面仍存在很大差距。针对这一问题,我们提出RelationField,这是第一种直接从神经网络辐射场中提取对象间关系的方法。RelationField将对象间的关系表示为神经辐射场内的成对射线,有效地将其公式扩展为包含隐式关系查询。为了教授RelationField复杂、开放词汇的关系,我们从多模态大型语言模型(LLM)中提炼关系知识。在开放词汇3D场景图生成任务和关系引导实例分割任务中,RelationField取得了最佳性能。有关详细信息,请访问项目网站:https://relationfield.github.io。
Key Takeaways
- 当前NeRF主要用于对象中心的表示,支持对象分割和检测。
- 对象间的语义关系在NeRF中的理解仍然是一个未被充分探索的领域。
- RelationField是第一个直接从NeRF提取对象间关系的方法。
- RelationField通过将对象间的关系表示为NeRF内的成对射线来有效地处理隐式关系查询。
- RelationField从多模态大型语言模型中提炼复杂、开放词汇的关系知识。
- 在开放词汇3D场景图生成任务和关系引导实例分割任务中,RelationField达到了最佳性能。
点此查看论文截图

EOGS: Gaussian Splatting for Earth Observation
Authors:Luca Savant Aira, Gabriele Facciolo, Thibaud Ehret
Recently, Gaussian splatting has emerged as a strong alternative to NeRF, demonstrating impressive 3D modeling capabilities while requiring only a fraction of the training and rendering time. In this paper, we show how the standard Gaussian splatting framework can be adapted for remote sensing, retaining its high efficiency. This enables us to achieve state-of-the-art performance in just a few minutes, compared to the day-long optimization required by the best-performing NeRF-based Earth observation methods. The proposed framework incorporates remote-sensing improvements from EO-NeRF, such as radiometric correction and shadow modeling, while introducing novel components, including sparsity, view consistency, and opacity regularizations.
最近,高斯涂抹(Gaussian splatting)作为一种强大的NeRF替代方法崭露头角,展现出令人印象深刻的3D建模能力,同时仅需一小部分训练和渲染时间。在本文中,我们展示了如何适应标准高斯涂抹框架进行遥感,同时保持其高效率。这使得我们能够在几分钟内达到最新技术水平,而无需使用基于NeRF的地球观测方法中表现最佳的长时间优化方法。所提出的框架融入了遥感改进的内容,例如EO-NeRF的辐射校正和阴影建模,同时引入了新颖组件,包括稀疏性、视图一致性和不透明度正则化。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
近期,高斯涂抹技术成为NeRF的有力替代方案,展现了强大的3D建模能力,且只需一小部分训练和渲染时间。本文展示了如何将标准高斯涂抹框架适应于遥感领域,同时保持其高效率。这使我们在短短几分钟内即可实现卓越性能,而最佳性能的NeRF地球观测方法则需要一整天的优化。所提框架融入了EO-NeRF的遥感改进,如辐射校正和阴影建模,同时引入了新颖组件,包括稀疏性、视图一致性和不透明度正则化。
要点
- 高斯涂抹技术作为NeRF的替代方案,展现出强大的3D建模能力,且效率更高。
- 提出的框架适应于遥感领域,实现了高效性能。
- 与最佳性能的NeRF地球观测方法相比,该框架在几分钟内即可实现卓越性能,无需长时间的优化。
- 融合了EO-NeRF的遥感改进,如辐射校正和阴影建模。
- 引入了新颖组件,包括稀疏性处理、视图一致性以及不透明度正则化。
- 所提框架具有广泛的应用前景,可应用于遥感领域的不同场景。
点此查看论文截图

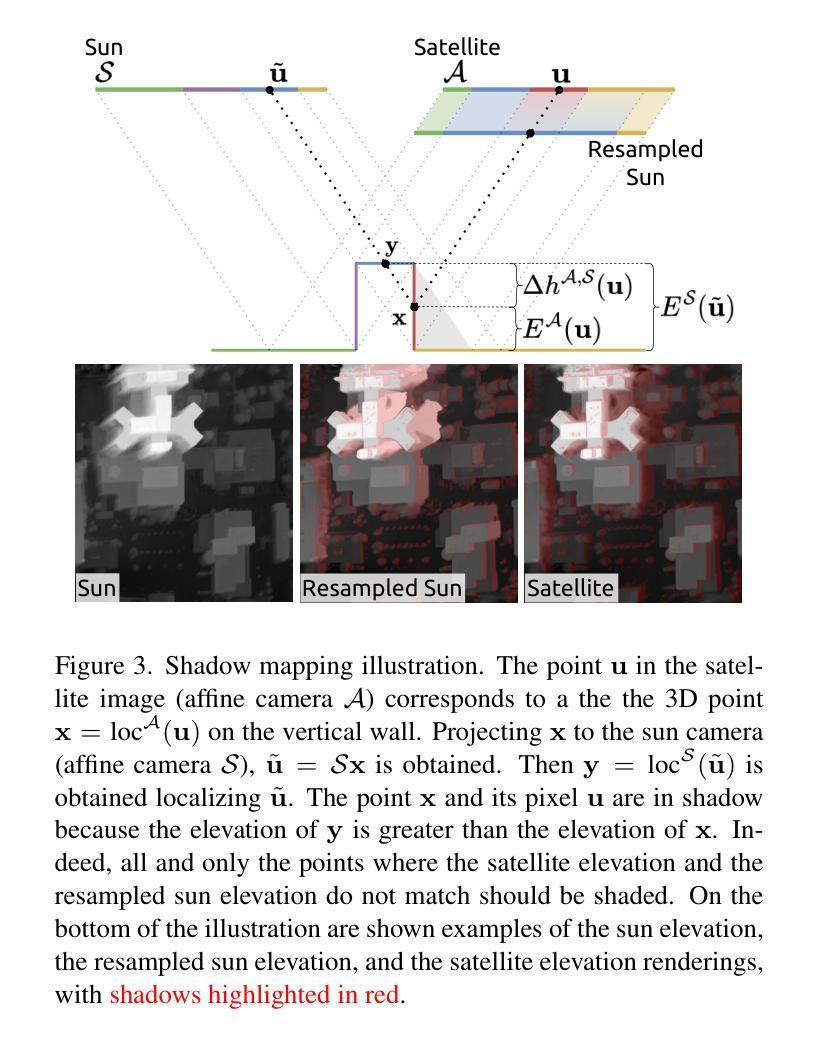

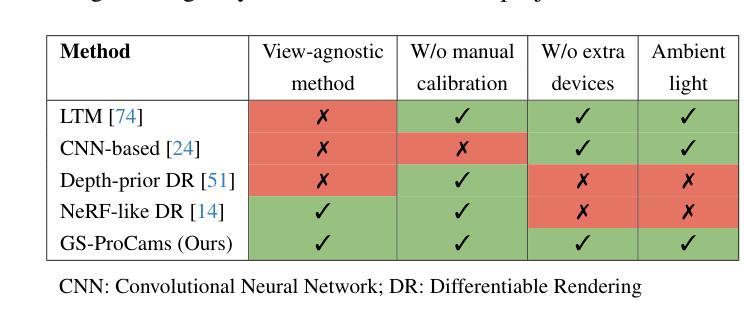
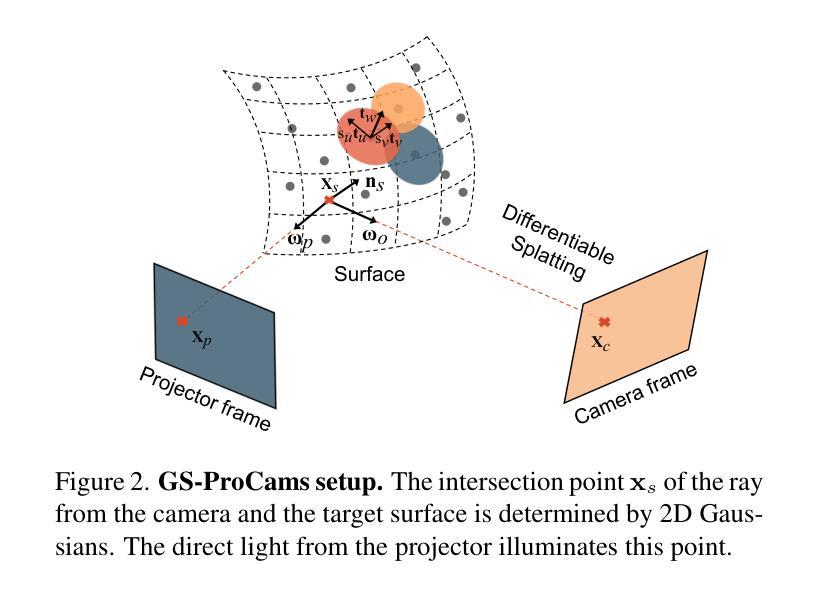
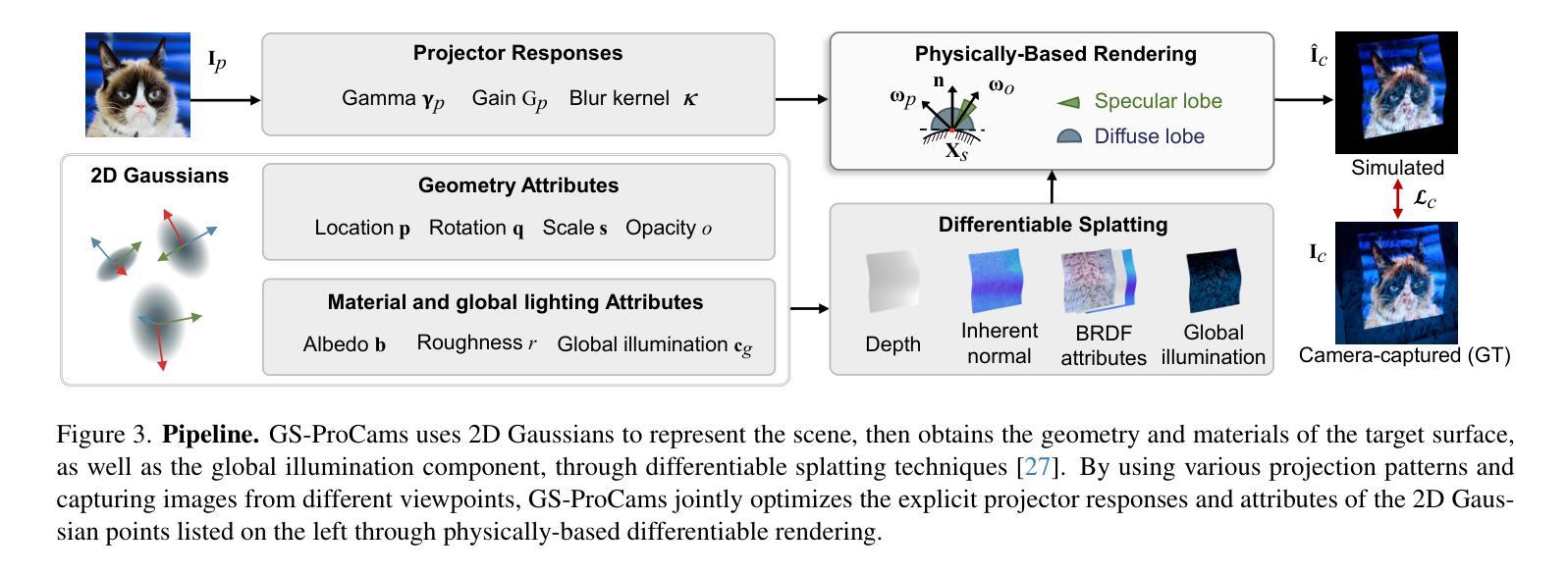
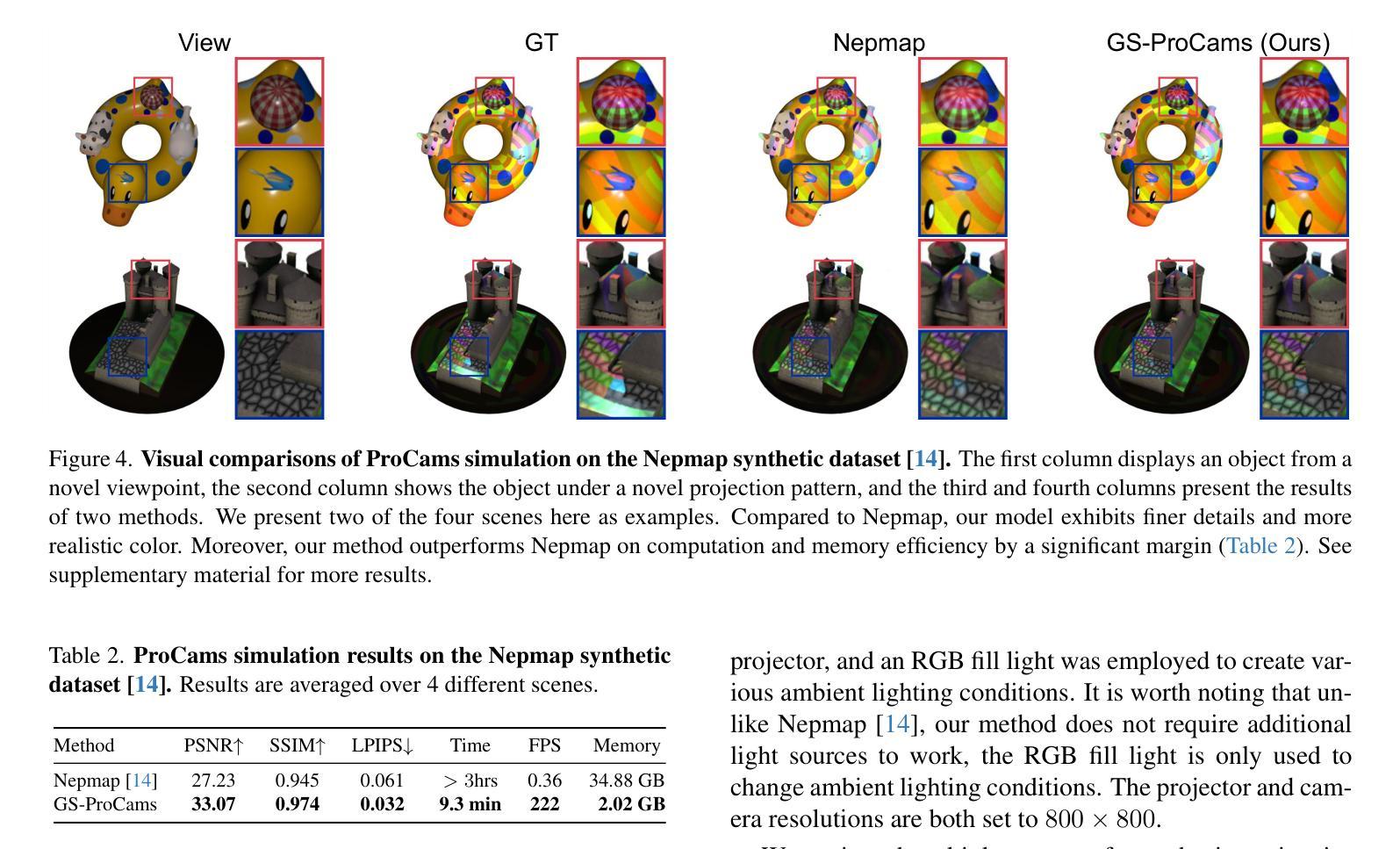
GS-ProCams: Gaussian Splatting-based Projector-Camera Systems
Authors:Qingyue Deng, Jijiang Li, Haibin Ling, Bingyao Huang
We present GS-ProCams, the first Gaussian Splatting-based framework for projector-camera systems (ProCams). GS-ProCams significantly enhances the efficiency of projection mapping (PM) that requires establishing geometric and radiometric mappings between the projector and the camera. Previous CNN-based ProCams are constrained to a specific viewpoint, limiting their applicability to novel perspectives. In contrast, NeRF-based ProCams support view-agnostic projection mapping, however, they require an additional colocated light source and demand significant computational and memory resources. To address this issue, we propose GS-ProCams that employs 2D Gaussian for scene representations, and enables efficient view-agnostic ProCams applications. In particular, we explicitly model the complex geometric and photometric mappings of ProCams using projector responses, the target surface’s geometry and materials represented by Gaussians, and global illumination component. Then, we employ differentiable physically-based rendering to jointly estimate them from captured multi-view projections. Compared to state-of-the-art NeRF-based methods, our GS-ProCams eliminates the need for additional devices, achieving superior ProCams simulation quality. It is also 600 times faster and uses only 1/10 of the GPU memory.
我们提出了GS-ProCams,这是基于高斯拼贴技术的投影仪相机系统(ProCams)的首个框架。GS-ProCams极大地提高了投影映射(PM)的效率,该映射需要在投影仪和相机之间建立几何和辐射度量映射。之前的基于CNN的ProCams受限于特定的视角,限制了其在新型视角的应用。相比之下,基于NeRF的ProCams支持视角无关的投影映射,但它们需要额外的共置光源,并需要大量的计算和内存资源。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了GS-ProCams,它采用二维高斯进行场景表示,并实现了高效的视角无关ProCams应用。特别是,我们通过投影仪响应、由高斯表示的目标表面的几何形状和材料以及全局照明组件,明确地建模了ProCams复杂的几何和光度映射。然后,我们采用基于物理的、可微分的渲染方法,从捕获的多视角投影联合估计它们。与最先进的基于NeRF的方法相比,我们的GS-ProCams不需要额外的设备,实现了卓越的ProCams模拟质量。其速度也更快(高达600倍),并且只使用十分之一的GPU内存。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于GS-ProCams的高效投影仪相机系统研究摘要:该研究提出了一种基于高斯混合的GS-ProCams框架,用于投影仪相机系统(ProCams)。该方法提高了投影映射的效率,并解决了CNN基ProCams视角限制的问题,支持无视角投影映射。此外,它利用二维高斯进行场景表示,并利用基于物理的渲染技术估计几何和光度映射。相比现有NeRF基方法,GS-ProCams无需额外设备即可实现高质量模拟,同时速度快600倍且使用GPU内存仅十分之一。
Key Takeaways
- GS-ProCams是基于高斯混合的投影仪相机系统框架,提高了投影映射效率。
- 该方法解决了CNN基ProCams的视角限制问题,支持无视角投影映射。
- GS-ProCams使用二维高斯进行场景表示。
- 通过基于物理的渲染技术估计几何和光度映射。
- 与现有NeRF基方法相比,GS-ProCams实现高质量模拟,速度快且使用内存少。
点此查看论文截图

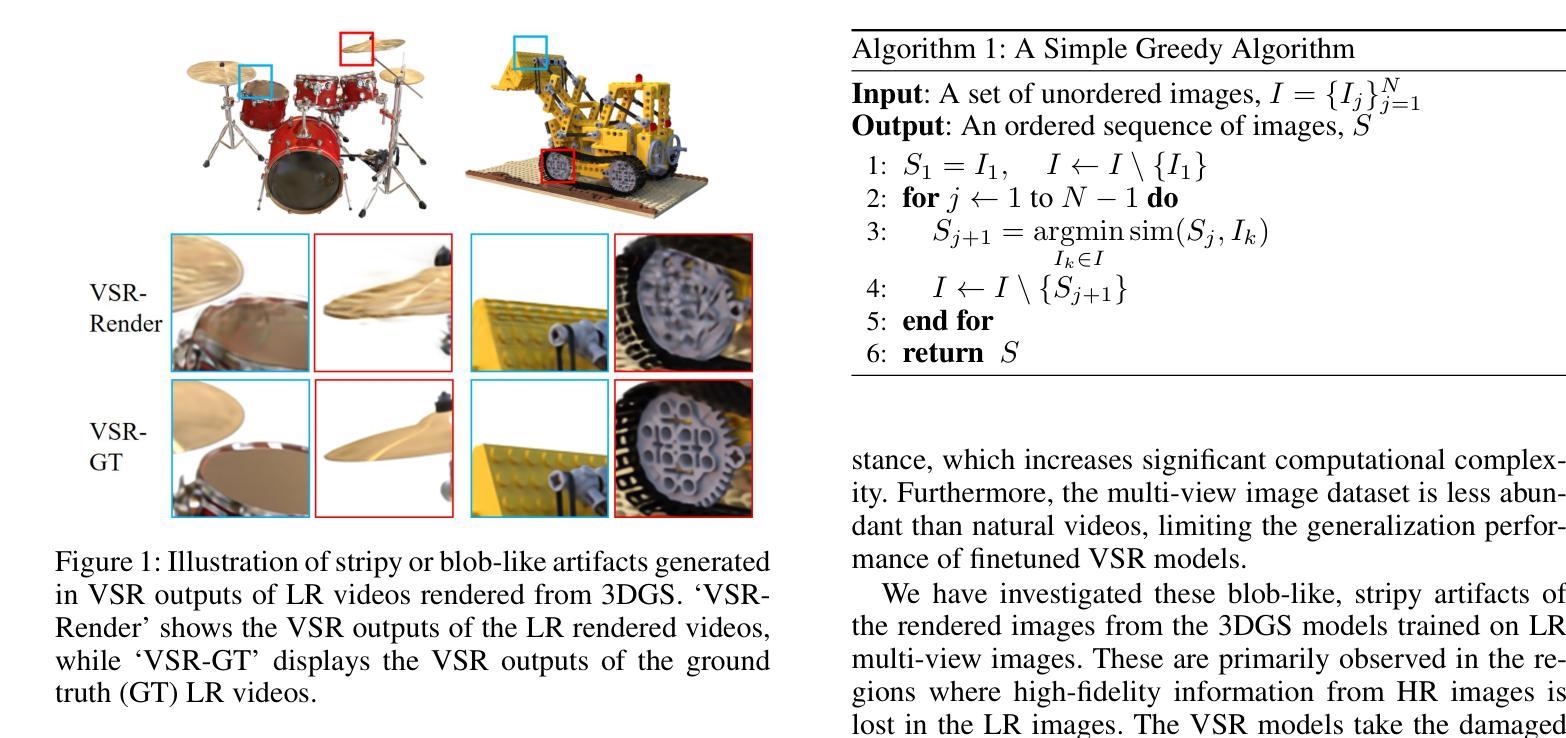
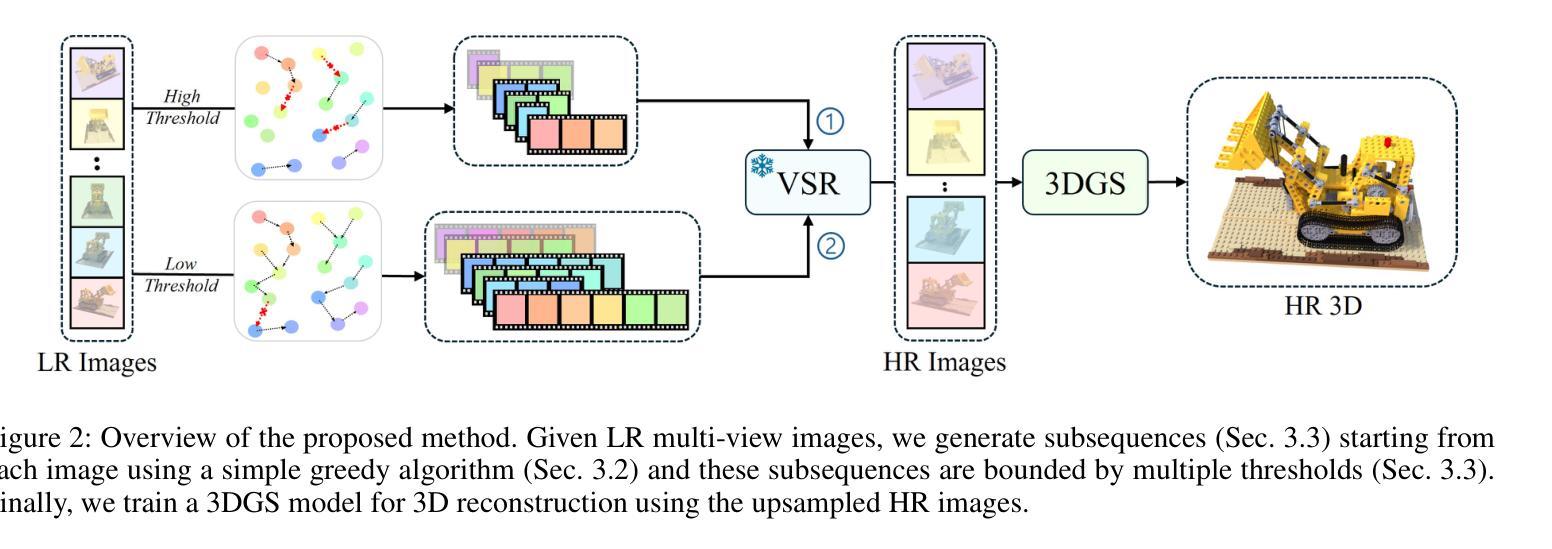
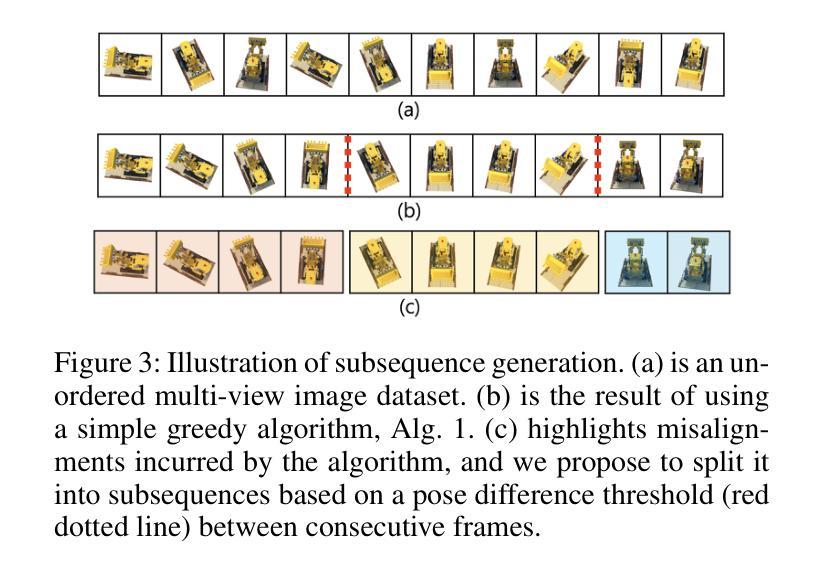
Sequence Matters: Harnessing Video Models in 3D Super-Resolution
Authors:Hyun-kyu Ko, Dongheok Park, Youngin Park, Byeonghyeon Lee, Juhee Han, Eunbyung Park
3D super-resolution aims to reconstruct high-fidelity 3D models from low-resolution (LR) multi-view images. Early studies primarily focused on single-image super-resolution (SISR) models to upsample LR images into high-resolution images. However, these methods often lack view consistency because they operate independently on each image. Although various post-processing techniques have been extensively explored to mitigate these inconsistencies, they have yet to fully resolve the issues. In this paper, we perform a comprehensive study of 3D super-resolution by leveraging video super-resolution (VSR) models. By utilizing VSR models, we ensure a higher degree of spatial consistency and can reference surrounding spatial information, leading to more accurate and detailed reconstructions. Our findings reveal that VSR models can perform remarkably well even on sequences that lack precise spatial alignment. Given this observation, we propose a simple yet practical approach to align LR images without involving fine-tuning or generating ‘smooth’ trajectory from the trained 3D models over LR images. The experimental results show that the surprisingly simple algorithms can achieve the state-of-the-art results of 3D super-resolution tasks on standard benchmark datasets, such as the NeRF-synthetic and MipNeRF-360 datasets. Project page: https://ko-lani.github.io/Sequence-Matters
三维超分辨率旨在从低分辨率(LR)多视角图像重建高保真三维模型。早期研究主要集中在单图像超分辨率(SISR)模型上,将LR图像上采样为高分辨率图像。然而,这些方法通常缺乏视角一致性,因为它们独立地处理每张图像。尽管已经广泛探索了各种后处理技术来缓解这些不一致性,但它们尚未完全解决这些问题。
在本文中,我们通过对视频超分辨率(VSR)模型的利用,对三维超分辨率进行了全面的研究。通过利用VSR模型,我们确保了更高的空间一致性,并且可以引用周围的空间信息,从而导致更精确和详细的重建。我们的研究发现,即使在缺乏精确空间对齐的序列上,VSR模型也可以表现得非常出色。鉴于此观察,我们提出了一种简单而实用的方法来对齐LR图像,而无需涉及精细调整或从训练的3D模型在LR图像上生成“平滑”轨迹。实验结果表明,这些出人意料的简单算法可以在标准基准数据集上实现最先进的三维超分辨率任务的结果,如NeRF-synthetic和MipNeRF-360数据集。项目页面:https://ko-lani.github.io/Sequence-Matters
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://ko-lani.github.io/Sequence-Matters
Summary
本文研究了如何利用视频超分辨率(VSR)模型进行3D超分辨率重建。通过对VSR模型的利用,确保了较高的空间一致性,并能参考周围的空间信息,从而得到更准确、更详细的重建结果。实验表明,即使在缺乏精确空间对齐的序列上,VSR模型也能表现出优异的性能。本研究提出了一种简单实用的方法,无需微调或生成平滑轨迹,即可对低分辨率图像进行对齐。在标准数据集上,该算法实现了令人惊讶的3D超分辨率任务的最佳结果。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究利用视频超分辨率(VSR)模型进行3D超分辨率重建,确保空间一致性和详细性。
- VSR模型能参考周围的空间信息,从而得到更准确、更详细的重建结果。
- 实验表明,VSR模型在缺乏精确空间对齐的序列上也能表现出优异的性能。
- 提出一种简单实用的方法,无需微调或生成平滑轨迹,即可对低分辨率图像进行对齐。
- 该方法在标准数据集上实现了3D超分辨率任务的最佳结果。
- 本研究不仅对3D超分辨率技术做出了重要贡献,而且推动了视频超分辨率模型的进一步应用和发展。
点此查看论文截图


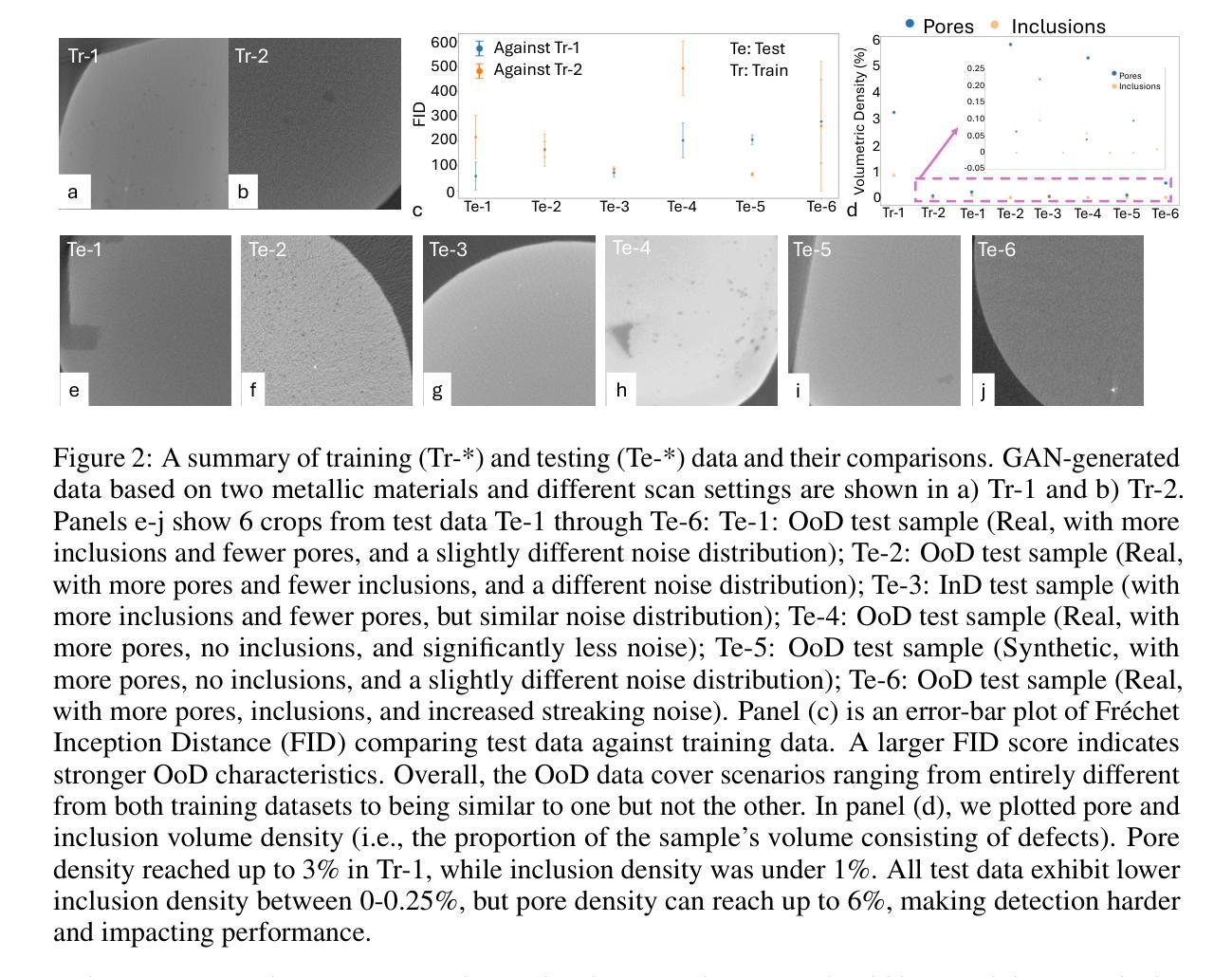
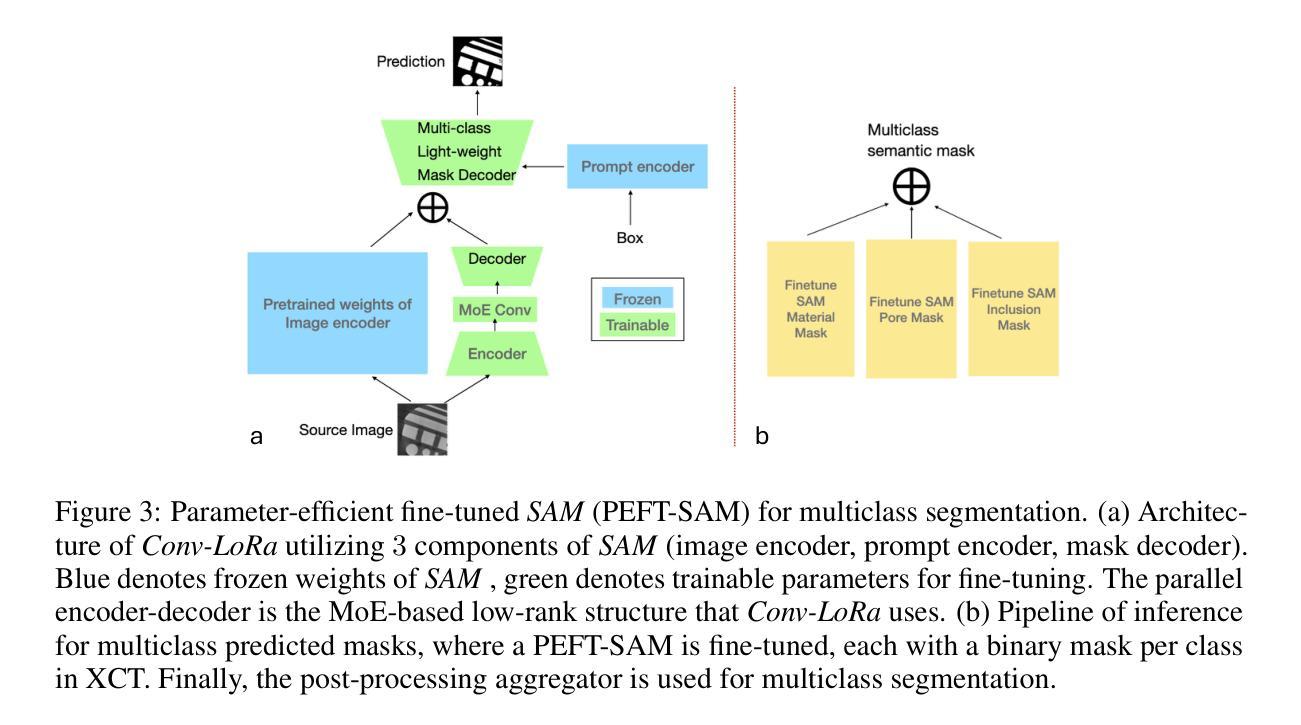
Adapting Segment Anything Model (SAM) to Experimental Datasets via Fine-Tuning on GAN-based Simulation: A Case Study in Additive Manufacturing
Authors:Anika Tabassum, Amirkoushyar Ziabari
Industrial X-ray computed tomography (XCT) is a powerful tool for non-destructive characterization of materials and manufactured components. XCT commonly accompanied by advanced image analysis and computer vision algorithms to extract relevant information from the images. Traditional computer vision models often struggle due to noise, resolution variability, and complex internal structures, particularly in scientific imaging applications. State-of-the-art foundational models, like the Segment Anything Model (SAM)-designed for general-purpose image segmentation-have revolutionized image segmentation across various domains, yet their application in specialized fields like materials science remains under-explored. In this work, we explore the application and limitations of SAM for industrial X-ray CT inspection of additive manufacturing components. We demonstrate that while SAM shows promise, it struggles with out-of-distribution data, multiclass segmentation, and computational efficiency during fine-tuning. To address these issues, we propose a fine-tuning strategy utilizing parameter-efficient techniques, specifically Conv-LoRa, to adapt SAM for material-specific datasets. Additionally, we leverage generative adversarial network (GAN)-generated data to enhance the training process and improve the model’s segmentation performance on complex X-ray CT data. Our experimental results highlight the importance of tailored segmentation models for accurate inspection, showing that fine-tuning SAM on domain-specific scientific imaging data significantly improves performance. However, despite improvements, the model’s ability to generalize across diverse datasets remains limited, highlighting the need for further research into robust, scalable solutions for domain-specific segmentation tasks.
工业X射线计算机断层扫描(XCT)是非破坏性表征材料和制造部件的强大工具。XCT通常与先进的图像分析和计算机视觉算法相结合,从图像中提取相关信息。由于噪声、分辨率变化和复杂内部结构的影响,传统计算机视觉模型在科学成像应用中经常面临挑战。最先进的基础模型,如用于通用图像分割的Segment Anything Model(SAM),已经推动了各个领域图像分割的革命,但它们在材料科学等特定领域的应用仍然被探索不足。在这项工作中,我们探索了SAM在增材制造部件的工业X射线CT检测中的应用和局限性。我们证明,虽然SAM显示出潜力,但在微调过程中,它在处理离群数据、多类分割和计算效率方面存在困难。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种利用参数高效技术的微调策略,特别是Conv-LoRa,来适应材料特定的数据集。此外,我们还利用生成对抗网络(GAN)生成的数据来增强训练过程,提高模型在复杂X射线CT数据上的分割性能。我们的实验结果强调了定制分割模型对于准确检测的重要性,并表明在特定领域的科学成像数据上微调SAM可以显著提高性能。然而,尽管有所改进,模型在不同数据集上的泛化能力仍然有限,这凸显了对针对特定领域的分割任务的稳健、可扩展解决方案的进一步研究的必要性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了将先进的计算机视觉模型,如Segment Anything Model(SAM),应用于工业X射线计算机断层扫描(XCT)技术,用于分析制造部件的材料特性。研究展示了SAM在应对复杂内部结构、噪声和分辨率变化时的潜力与局限性,并提出了通过利用Conv-LoRa等参数高效技术进行微调,以及使用生成对抗网络(GAN)生成数据以增强训练过程的方法。实验结果表明,针对特定领域的科学成像数据微调SAM可显著提高性能,但模型的泛化能力仍有待提高。
Key Takeaways
- Segment Anything Model (SAM) 在工业X射线CT检测中显示出潜力,尤其在分析制造部件的材料特性方面。
- SAM在面对噪声、分辨率变化和复杂内部结构时存在挑战。
- 通过利用参数高效技术(如Conv-LoRa)进行微调,可适应材料特定数据集。
- 利用生成对抗网络(GAN)生成数据可以增强训练过程,提高模型在复杂X射线CT数据上的分割性能。
- 实验表明,针对特定领域的科学成像数据微调SAM能显著提高性能。
- 尽管有所改进,但模型的泛化能力仍然有限,需要在不同数据集上进行更多研究以寻找更稳健、可扩展的解决方案。
点此查看论文截图


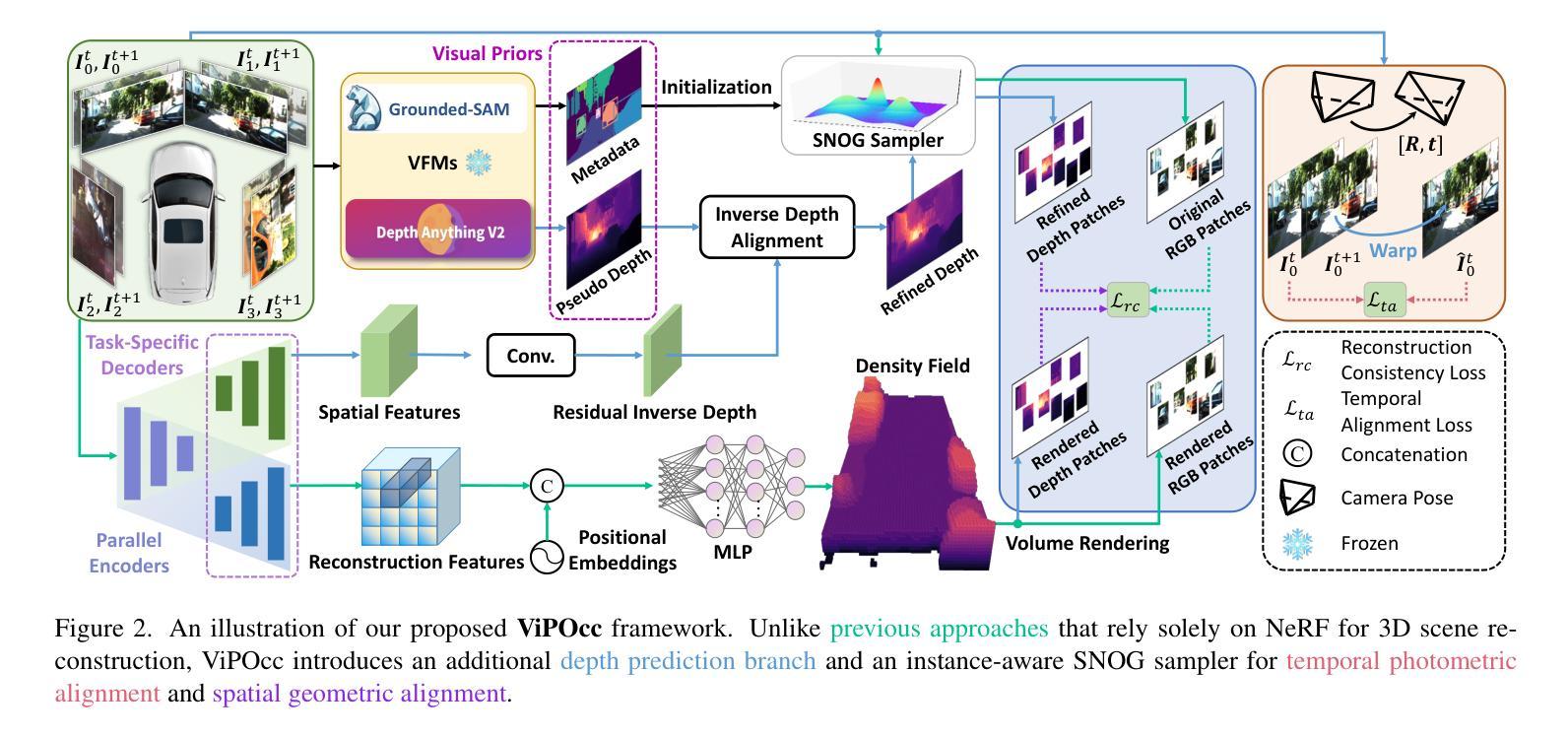
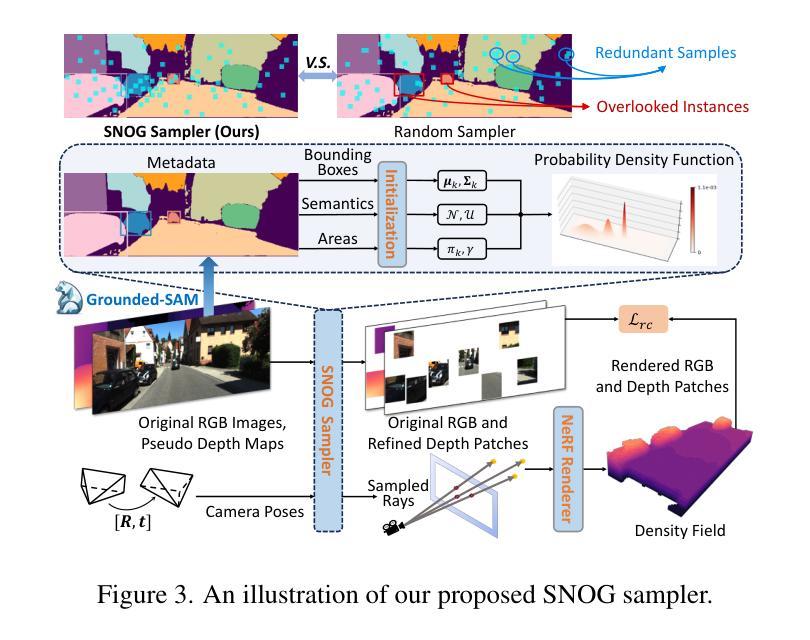
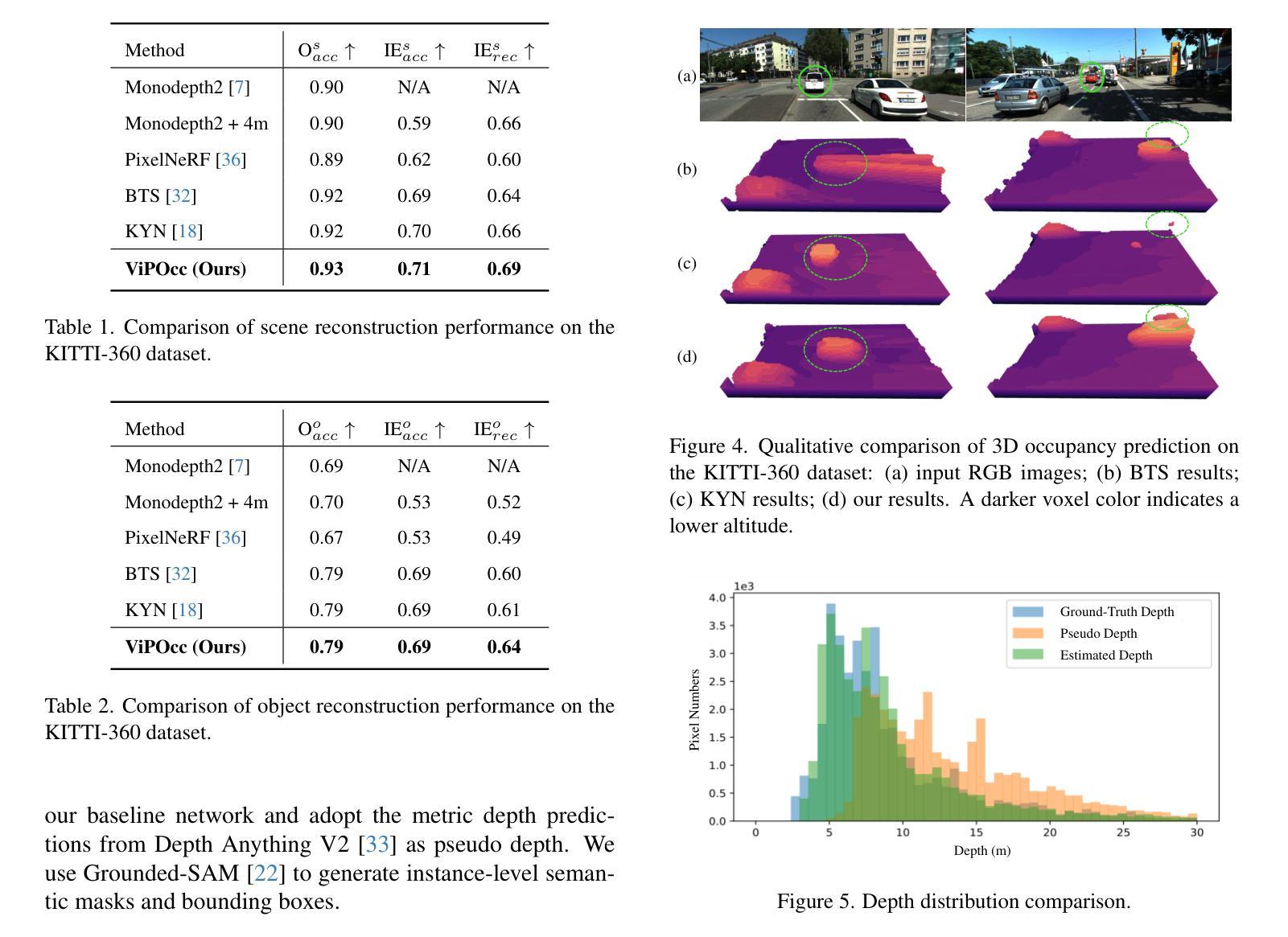
ViPOcc: Leveraging Visual Priors from Vision Foundation Models for Single-View 3D Occupancy Prediction
Authors:Yi Feng, Yu Han, Xijing Zhang, Tanghui Li, Yanting Zhang, Rui Fan
Inferring the 3D structure of a scene from a single image is an ill-posed and challenging problem in the field of vision-centric autonomous driving. Existing methods usually employ neural radiance fields to produce voxelized 3D occupancy, lacking instance-level semantic reasoning and temporal photometric consistency. In this paper, we propose ViPOcc, which leverages the visual priors from vision foundation models (VFMs) for fine-grained 3D occupancy prediction. Unlike previous works that solely employ volume rendering for RGB and depth image reconstruction, we introduce a metric depth estimation branch, in which an inverse depth alignment module is proposed to bridge the domain gap in depth distribution between VFM predictions and the ground truth. The recovered metric depth is then utilized in temporal photometric alignment and spatial geometric alignment to ensure accurate and consistent 3D occupancy prediction. Additionally, we also propose a semantic-guided non-overlapping Gaussian mixture sampler for efficient, instance-aware ray sampling, which addresses the redundant and imbalanced sampling issue that still exists in previous state-of-the-art methods. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superior performance of ViPOcc in both 3D occupancy prediction and depth estimation tasks on the KITTI-360 and KITTI Raw datasets. Our code is available at: \url{https://mias.group/ViPOcc}.
从单幅图像推断场景的三维结构是视觉自主驾驶领域中一个设置不当且具有挑战性的课题。现有方法通常采用神经辐射场来生成体素化的三维占用信息,但缺乏实例级别的语义推理和时间上的光度一致性。在本文中,我们提出了ViPOcc,它利用视觉先验知识从视觉基础模型(VFMs)进行精细粒度的三维占用预测。与仅使用体积渲染进行RGB和深度图像重建的先前工作不同,我们引入了度量深度估计分支,其中提出了逆深度对齐模块来弥合视觉基础模型预测和真实值之间深度分布的域差距。然后利用恢复的度量深度进行时间光度对齐和空间几何对齐,以确保准确且一致的三维占用预测。此外,我们还提出了一种语义引导的非重叠高斯混合采样器,用于高效、实例感知的射线采样,解决了先前最先进的方法中仍然存在的不必要的和不平衡的采样问题。大量实验表明,ViPOcc在KITTI-360和KITTI Raw数据集上的三维占用预测和深度估计任务中均表现出卓越的性能。我们的代码可在:https://mias.group/ViPOcc。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF accepted to AAAI25
Summary
本文提出一种基于视觉先验的精细粒度三维占用预测方法ViPOcc,利用视觉基础模型(VFMs)进行单图像三维场景推断。方法包括引入度量深度估计分支和逆深度对齐模块,以缩小VFM预测与真实值之间的深度分布域差距。此外,还提出了语义引导的非重叠高斯混合采样器,解决之前的冗余和不平衡采样问题。在KITTI-360和KITTI Raw数据集上的实验表明,ViPOcc在三维占用预测和深度估计任务上表现优越。
Key Takeaways
- ViPOcc利用视觉基础模型(VFMs)进行精细粒度的三维占用预测。
- 引入度量深度估计分支和逆深度对齐模块以改善深度预测的准确性。
- 语义引导的非重叠高斯混合采样器解决了之前的冗余和不平衡采样问题。
- ViPOcc在KITTI-360和KITTI Raw数据集上的实验表现出优越性能。
- 方法结合了视觉先验、深度估计和语义信息,提高了三维占用预测的准确性。
- ViPOcc代码已公开可用。
点此查看论文截图

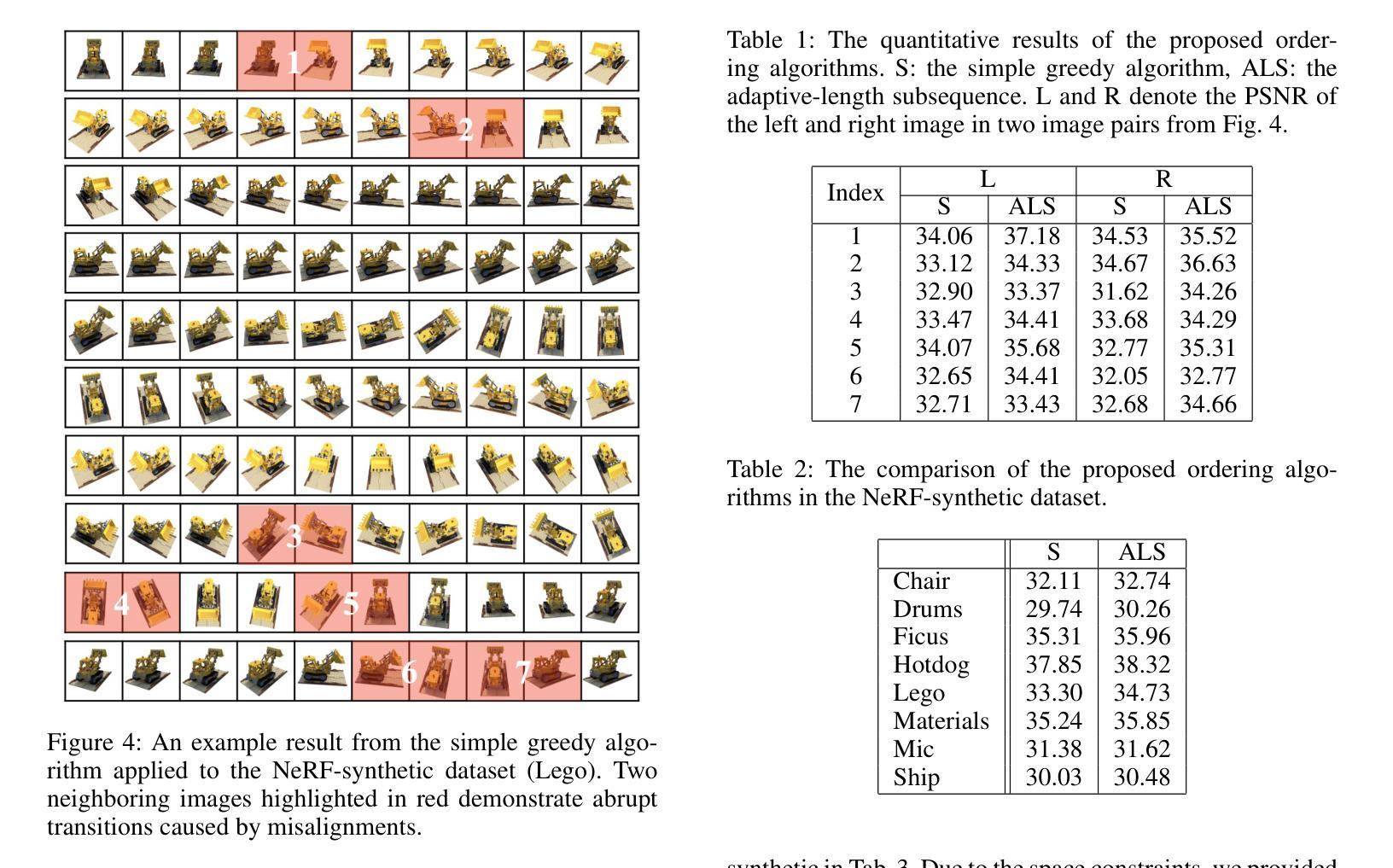
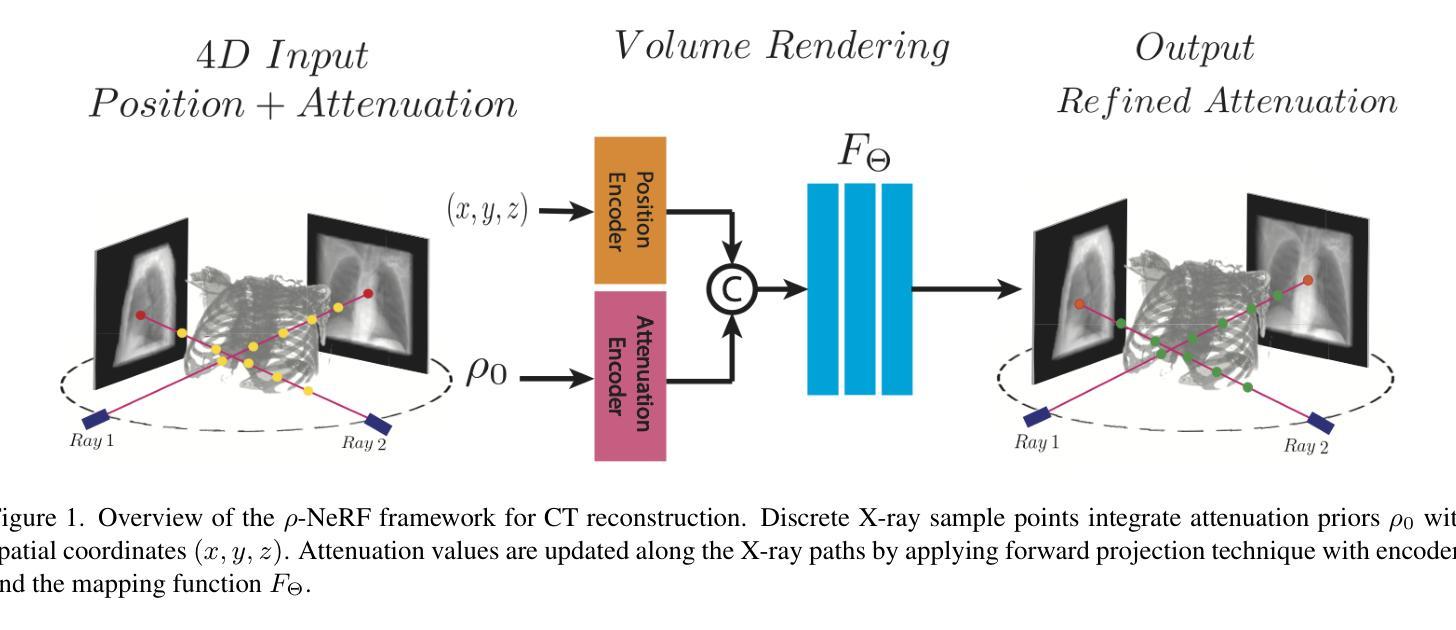
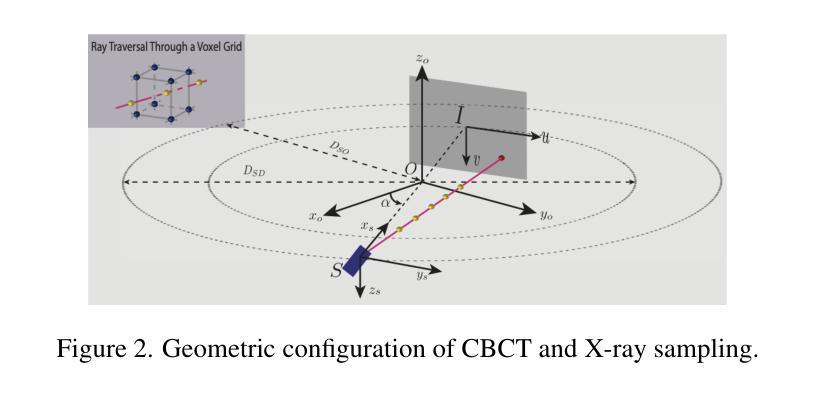
$ρ$-NeRF: Leveraging Attenuation Priors in Neural Radiance Field for 3D Computed Tomography Reconstruction
Authors:Li Zhou, Changsheng Fang, Bahareh Morovati, Yongtong Liu, Shuo Han, Yongshun Xu, Hengyong Yu
This paper introduces $\rho$-NeRF, a self-supervised approach that sets a new standard in novel view synthesis (NVS) and computed tomography (CT) reconstruction by modeling a continuous volumetric radiance field enriched with physics-based attenuation priors. The $\rho$-NeRF represents a three-dimensional (3D) volume through a fully-connected neural network that takes a single continuous four-dimensional (4D) coordinate, spatial location $(x, y, z)$ and an initialized attenuation value ($\rho$), and outputs the attenuation coefficient at that position. By querying these 4D coordinates along X-ray paths, the classic forward projection technique is applied to integrate attenuation data across the 3D space. By matching and refining pre-initialized attenuation values derived from traditional reconstruction algorithms like Feldkamp-Davis-Kress algorithm (FDK) or conjugate gradient least squares (CGLS), the enriched schema delivers superior fidelity in both projection synthesis and image recognition.
本文介绍了$\rho$-NeRF,这是一种自监督方法,通过建立一个基于物理衰减先验的连续体积辐射场,为新型视图合成(NVS)和计算机断层扫描(CT)重建设定了新的标准。$\rho$-NeRF通过全连接神经网络代表一个三维(3D)体积,该网络接收一个连续的四维(4D)坐标(空间位置$(x, y, z)$和初始化的衰减值$\rho$),并输出该位置的衰减系数。通过沿着X射线路径查询这些四维坐标,采用经典的前向投影技术将衰减数据集成到三维空间中。通过匹配和细化源自传统重建算法的预初始化衰减值(如Feldkamp-Davis-Kress算法(FDK)或共轭梯度最小二乘法(CGLS)),丰富了模式在投影合成和图像识别方面均实现了较高的保真度。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The paper was submitted to CVPR 2025
摘要
本文介绍了ρ-NeRF,这是一种自监督方法,通过建立一个包含物理衰减先验的连续体积辐射场,为新型视图合成(NVS)和计算机断层扫描(CT)重建设定了新的标准。ρ-NeRF通过全连接神经网络代表一个三维体积,该网络接受一个连续的四维坐标(包括空间位置(x,y,z)和一个初始化的衰减值ρ),并输出该位置的衰减系数。通过沿着X射线路径查询这些四维坐标,采用经典的前向投影技术来整合三维空间中的衰减数据。通过匹配和细化从传统的重建算法(如Feldkamp-Davis-Kress算法(FDK)或共轭梯度最小二乘法(CGLS))得出的预初始化衰减值,丰富的模式在投影合成和图像识别方面都提供了更高的保真度。
要点
- $\rho$-NeRF是一种自监督方法,用于新型视图合成(NVS)和计算机断层扫描(CT)重建。
- 通过建立一个包含物理衰减先验的连续体积辐射场,提升了质量。
- 使用全连接神经网络代表三维体积,网络输入四维坐标和初始化衰减值来输出衰减系数。
- 采用经典的前向投影技术整合四维坐标上的衰减数据。
- ρ-NeRF匹配并改进了从传统的重建算法获得的预初始化衰减值。
- 在投影合成和图像识别方面都表现出了更高的保真度。
- 这种方法有助于提升CT图像的质量并改善诊断的准确性。
点此查看论文截图

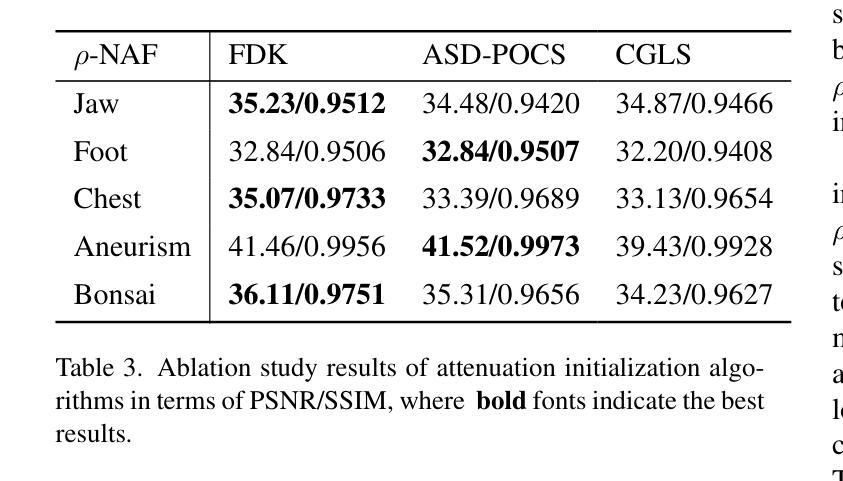
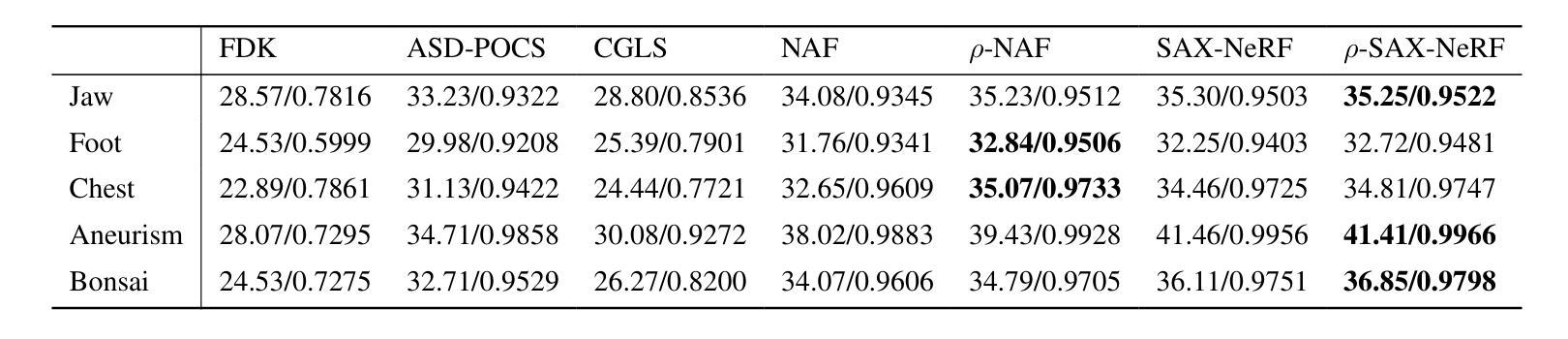
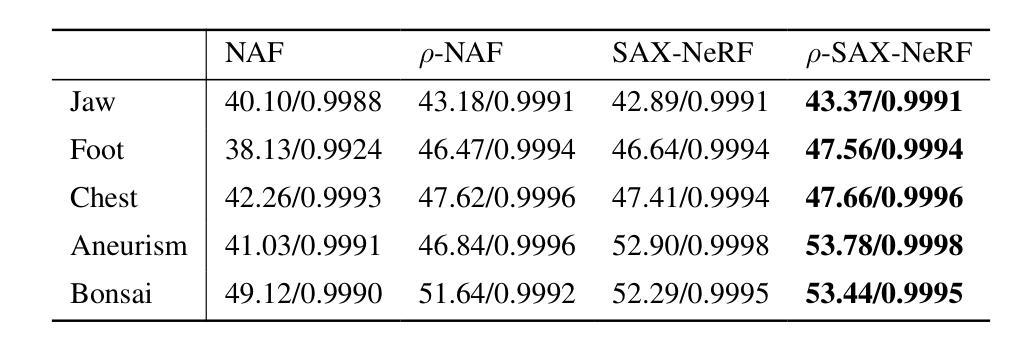
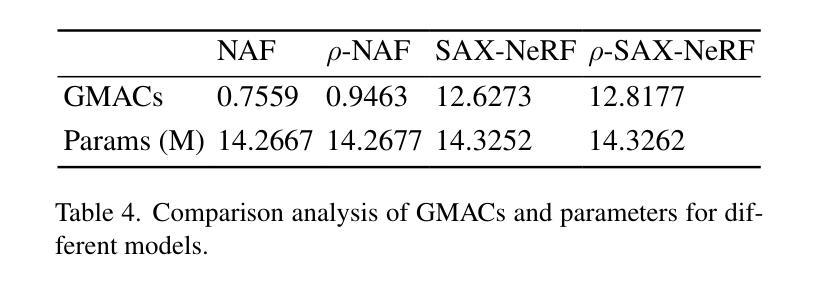
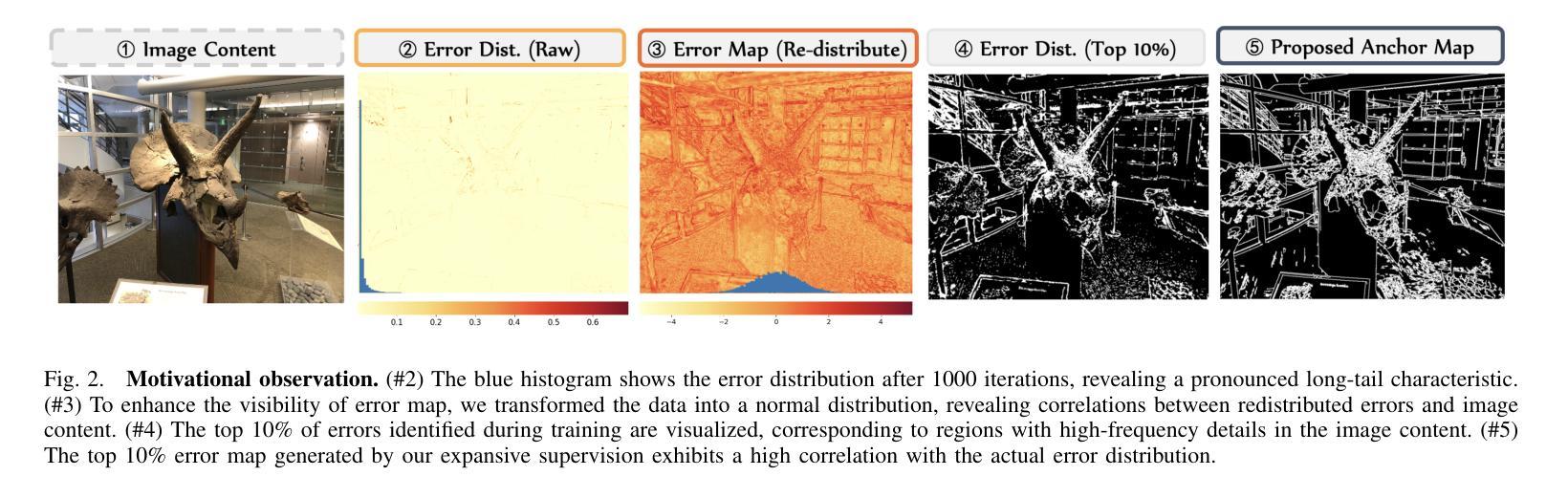
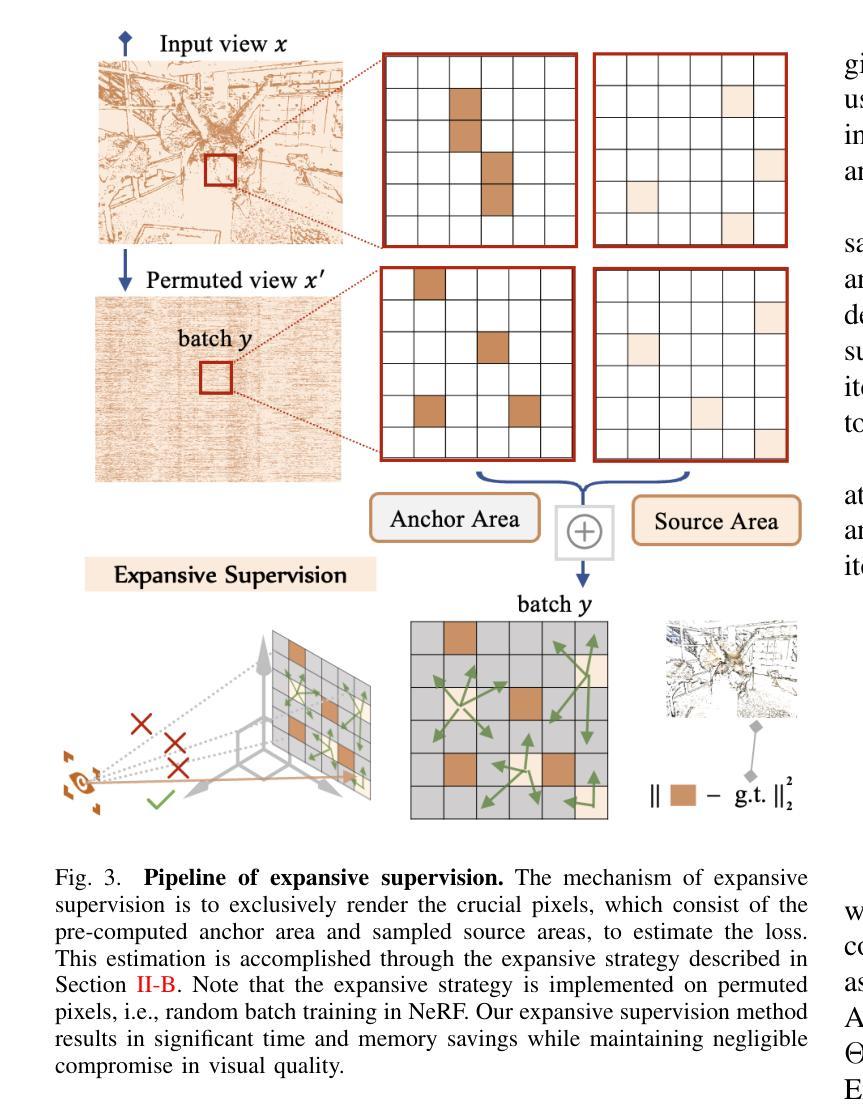
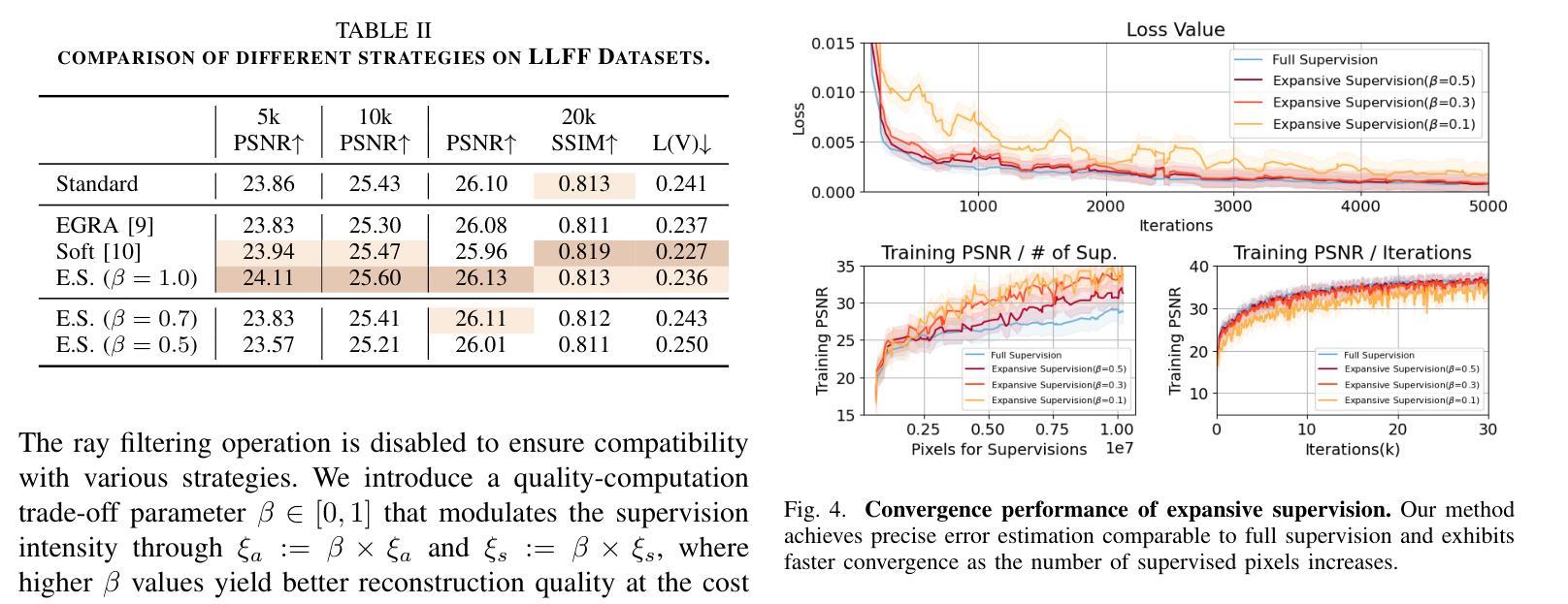
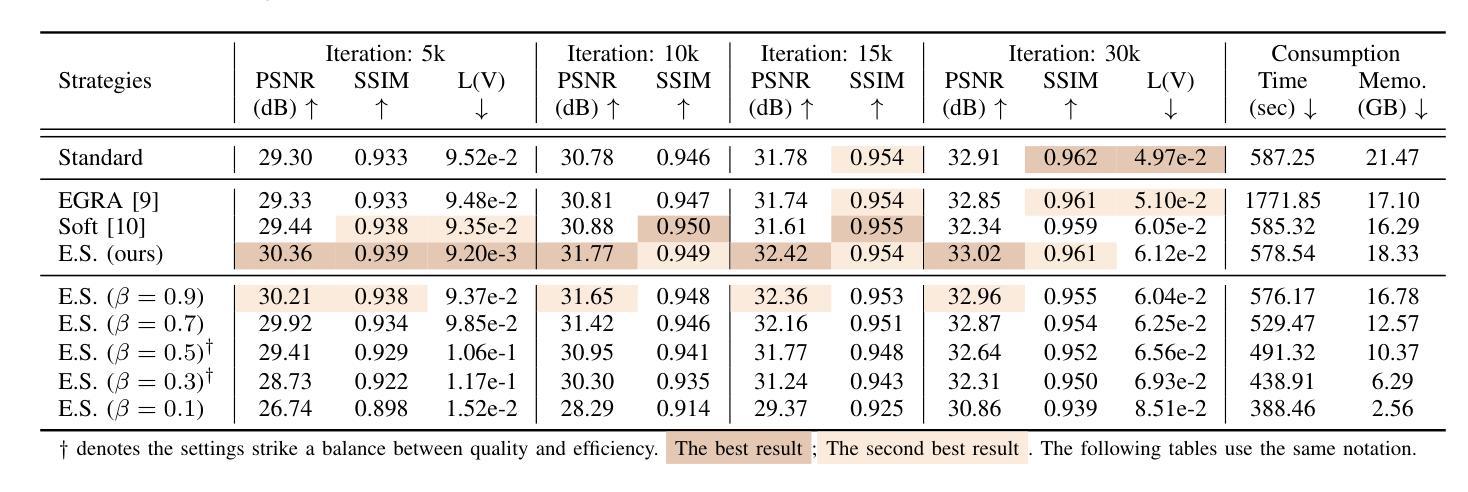
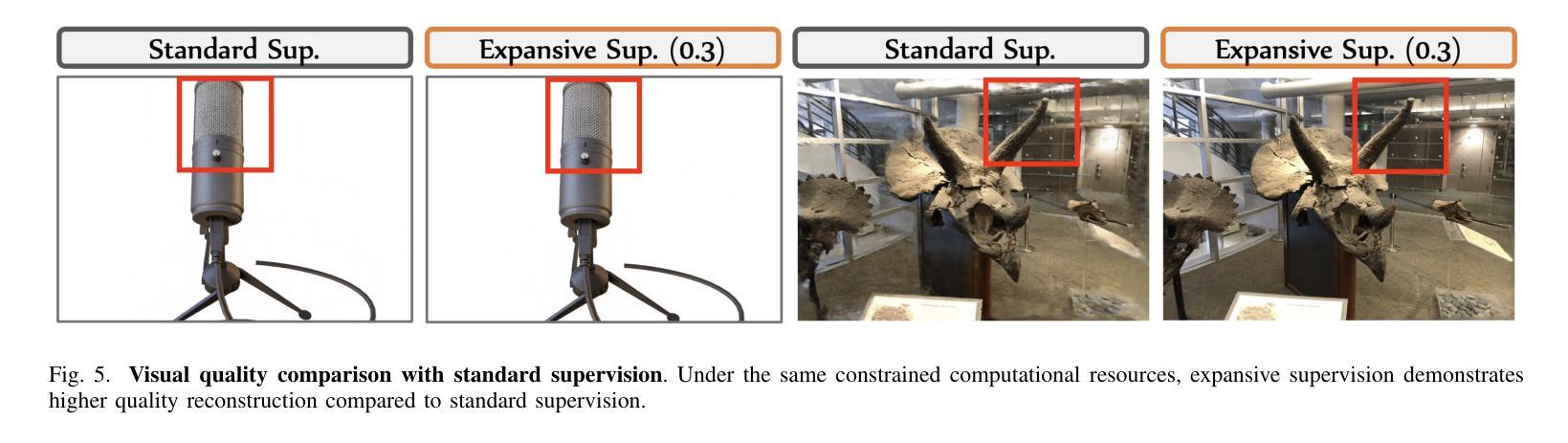
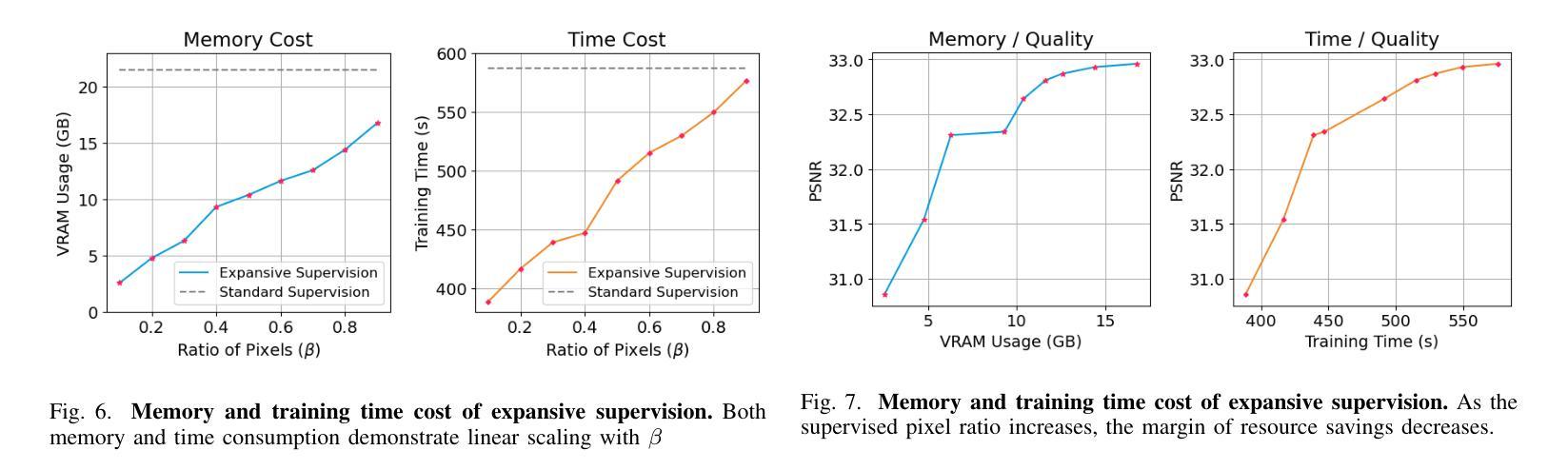
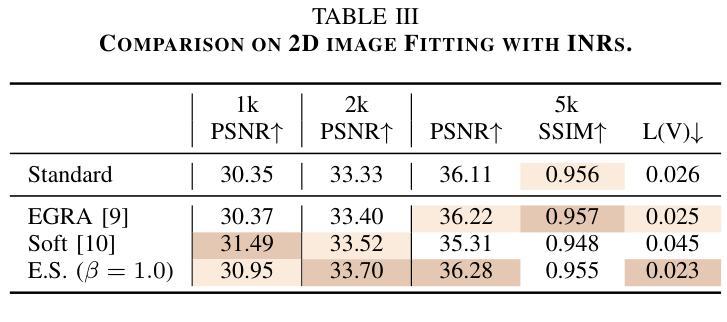
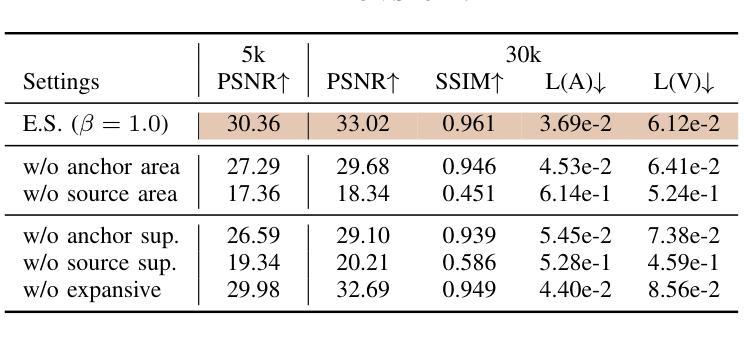
Expansive Supervision for Neural Radiance Field
Authors:Weixiang Zhang, Shuzhao Xie, Shijia Ge, Wei Yao, Chen Tang, Zhi Wang
Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) has achieved remarkable success in creating immersive media representations through its exceptional reconstruction capabilities. However, the computational demands of dense forward passes and volume rendering during training continue to challenge its real-world applications. In this paper, we introduce Expansive Supervision to reduce time and memory costs during NeRF training from the perspective of partial ray selection for supervision. Specifically, we observe that training errors exhibit a long-tail distribution correlated with image content. Based on this observation, our method selectively renders a small but crucial subset of pixels and expands their values to estimate errors across the entire area for each iteration. Compared to conventional supervision, our approach effectively bypasses redundant rendering processes, resulting in substantial reductions in both time and memory consumption. Experimental results demonstrate that integrating Expansive Supervision within existing state-of-the-art acceleration frameworks achieves 52% memory savings and 16% time savings while maintaining comparable visual quality.
神经辐射场(NeRF)凭借其出色的重建能力,在创建沉浸式媒体表示方面取得了显著的成功。然而,训练过程中的密集前向传递和体积渲染的计算需求仍然对其实际应用提出了挑战。本文引入扩张监督(Expansive Supervision)从部分射线选择监督的角度减少NeRF训练的时间和内存成本。具体来说,我们观察到训练错误与图像内容呈长尾分布相关。基于此观察,我们的方法选择渲染一小部分但至关重要的像素,并扩大它们的值来估计每次迭代的整个区域的误差。与传统的监督方法相比,我们的方法有效地绕过了冗余的渲染过程,导致时间和内存消耗大幅减少。实验结果证明,将扩张监督集成到最先进的加速框架中,可以实现52%的内存节省和16%的时间节省,同时保持相当的可视质量。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
神经网络辐射场(NeRF)在创建沉浸式媒体表示方面取得了显著的成功,但其训练过程中的密集正向传递和体积渲染的计算需求仍然挑战其实际应用。本文引入扩展监督(Expansive Supervision)方法,从部分射线选择的监督角度减少NeRF训练的时间和内存成本。通过选择性渲染一小部分关键像素并扩展其值来估算每个迭代中的整体误差,实现时间和内存的显著减少。实验结果表明,在现有最先进的加速框架内整合扩展监督方法可实现52%的内存节省和16%的时间节省,同时保持相当的可视质量。
Key Takeaways
- NeRF在创建沉浸式媒体表示方面表现出卓越的重构能力。
- 训练过程中的密集正向传递和体积渲染是NeRF面临的实际应用挑战。
- 扩展监督方法通过部分射线选择的监督来减少NeRF训练的时间和内存成本。
- 该方法通过选择性渲染一小部分关键像素并扩展其值来估算整体误差。
- 扩展监督方法实现了时间和内存的显著减少。
- 与现有最先进的加速框架结合,扩展监督方法可在保持相当可视质量的同时实现52%的内存节省和16%的时间节省。
点此查看论文截图

FisherRF: Active View Selection and Uncertainty Quantification for Radiance Fields using Fisher Information
Authors:Wen Jiang, Boshu Lei, Kostas Daniilidis
This study addresses the challenging problem of active view selection and uncertainty quantification within the domain of Radiance Fields. Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have greatly advanced image rendering and reconstruction, but the cost of acquiring images poses the need to select the most informative viewpoints efficiently. Existing approaches depend on modifying the model architecture or hypothetical perturbation field to indirectly approximate the model uncertainty. However, selecting views from indirect approximation does not guarantee optimal information gain for the model. By leveraging Fisher Information, we directly quantify observed information on the parameters of Radiance Fields and select candidate views by maximizing the Expected Information Gain(EIG). Our method achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple tasks, including view selection, active mapping, and uncertainty quantification, demonstrating its potential to advance the field of Radiance Fields.
本研究旨在解决Radiance Fields领域内主动视图选择和不确定性量化这一具有挑战性的问题。Neural Radiance Fields(NeRF)在图像渲染和重建方面取得了巨大的进步,但获取图像的成本促使我们需要高效地选择最具有信息量的视角。现有方法依赖于修改模型架构或假设扰动场来间接地近似模型的不确定性。然而,从间接近似中选择视图并不能保证模型获得最优的信息增益。通过利用Fisher信息,我们直接量化Radiance Fields参数上的观测信息,并通过最大化预期信息增益(EIG)选择候选视图。我们的方法在多个任务上实现了最先进的成果,包括视图选择、主动映射和不确定性量化,证明了其在Radiance Fields领域的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://jiangwenpl.github.io/FisherRF/
摘要
本研究探讨了活动视角选择与不确定性量化在光场领域中的难题。神经光场(NeRF)极大地推动了图像渲染和重建的发展,但获取图像的成本促使需要有效选择最具信息量的视角。现有方法依赖于修改模型架构或假设扰动场来间接近似模型不确定性。然而,从间接近似中选择视图并不能保证模型的最佳信息增益。本研究利用Fisher信息直接量化光场参数上的观测信息,通过最大化预期信息增益(EIG)选择候选视图。该方法在多任务上均达到了最新技术水准,包括视角选择、活动映射和不确定性量化,显示了其推动光场领域的潜力。
关键见解
- 研究聚焦于光场领域的活动视角选择和不确定性量化难题。
- 现有方法间接近似模型不确定性,可能导致信息增益不足。
- 利用Fisher信息直接量化光场参数观测信息。
- 通过最大化预期信息增益选择候选视角。
- 方法在多项任务上表现优异,包括视角选择、活动映射和不确定性量化。
- 研究结果推动了光场领域的发展。
点此查看论文截图


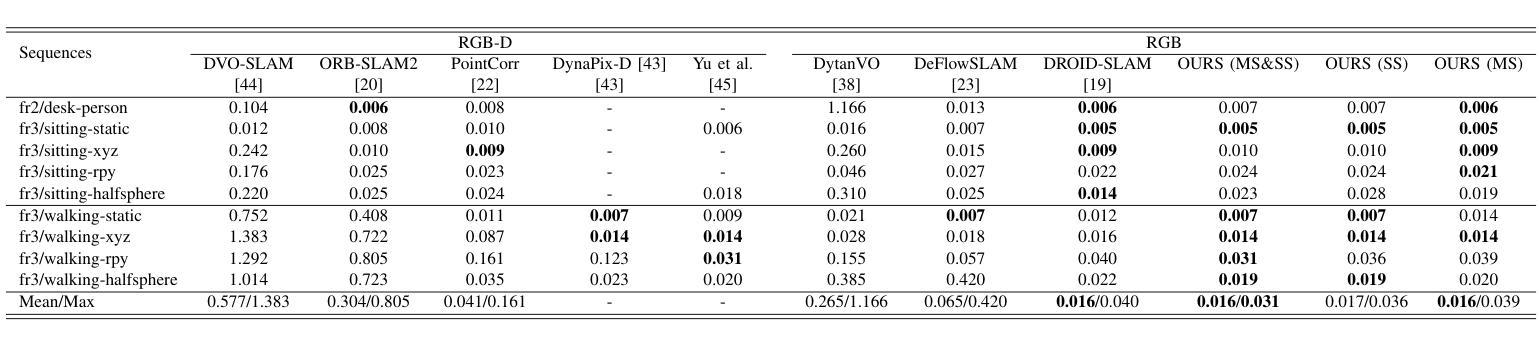
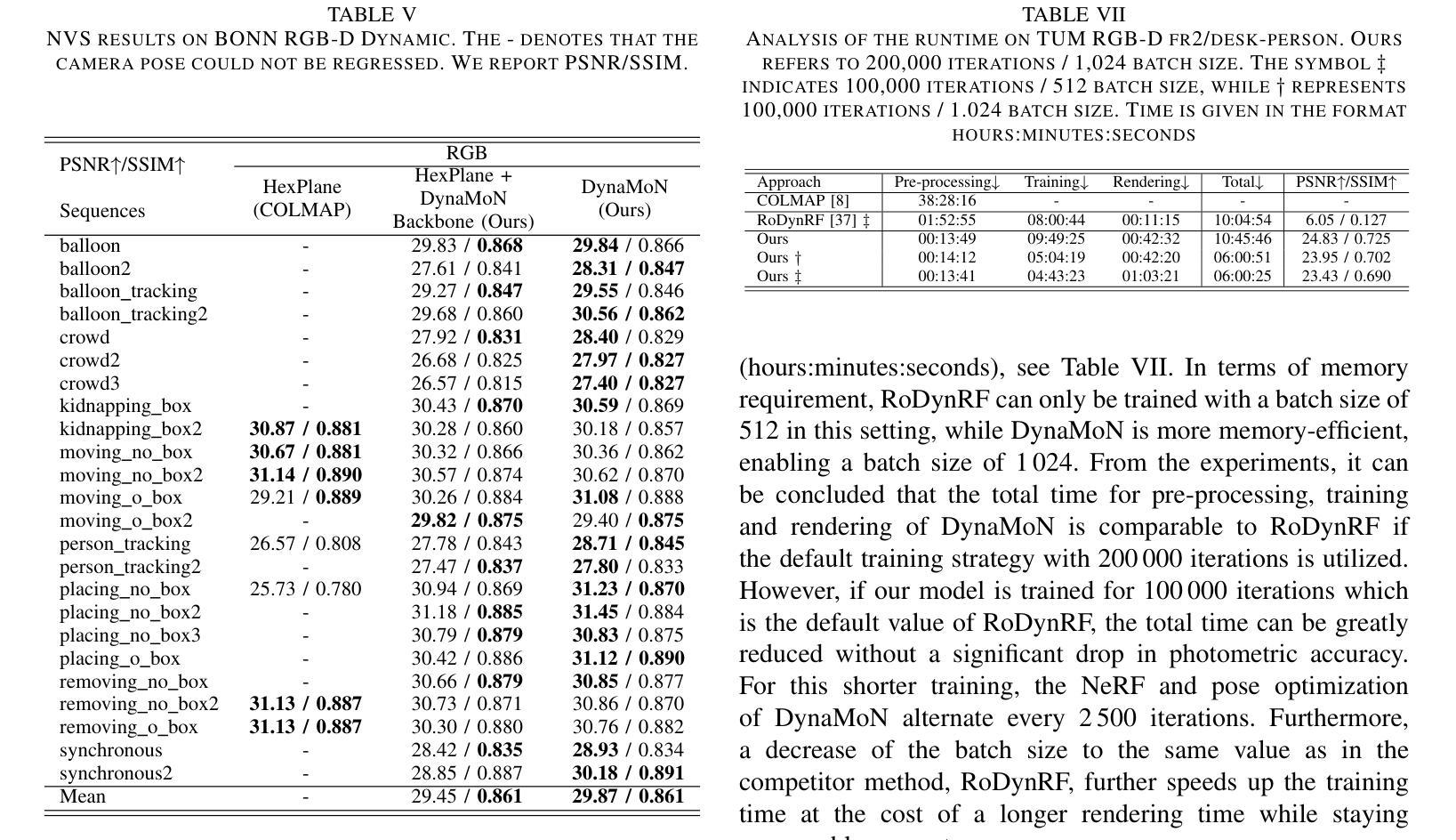
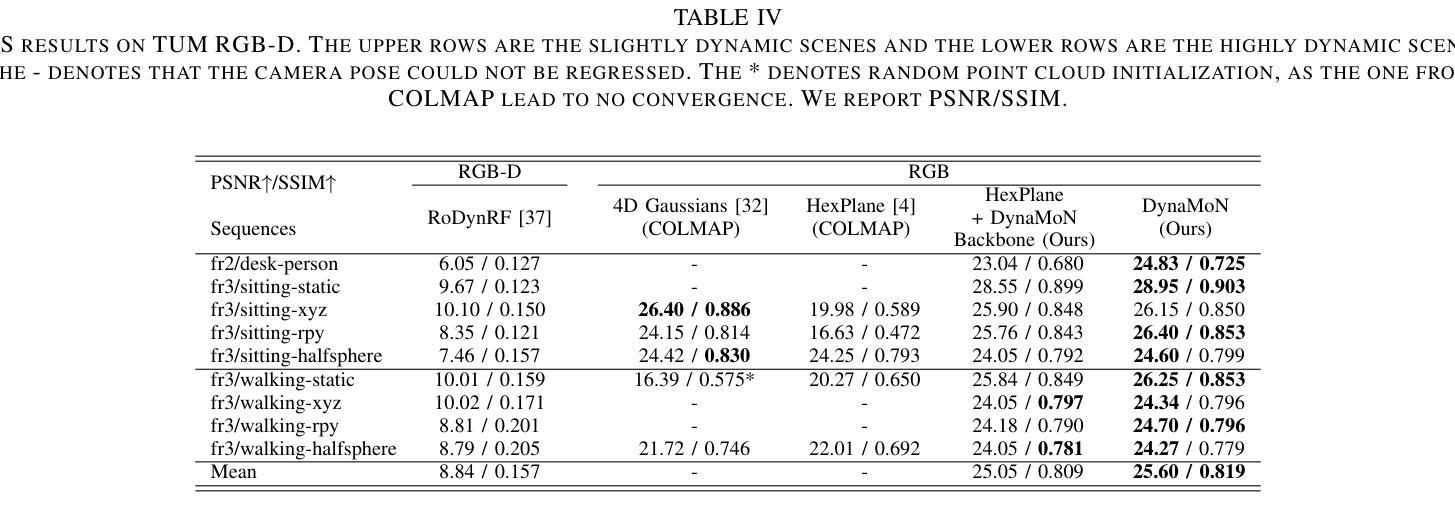
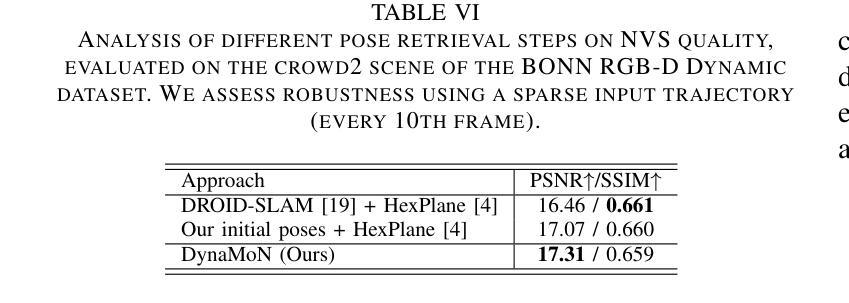
DynaMoN: Motion-Aware Fast and Robust Camera Localization for Dynamic Neural Radiance Fields
Authors:Nicolas Schischka, Hannah Schieber, Mert Asim Karaoglu, Melih Görgülü, Florian Grötzner, Alexander Ladikos, Daniel Roth, Nassir Navab, Benjamin Busam
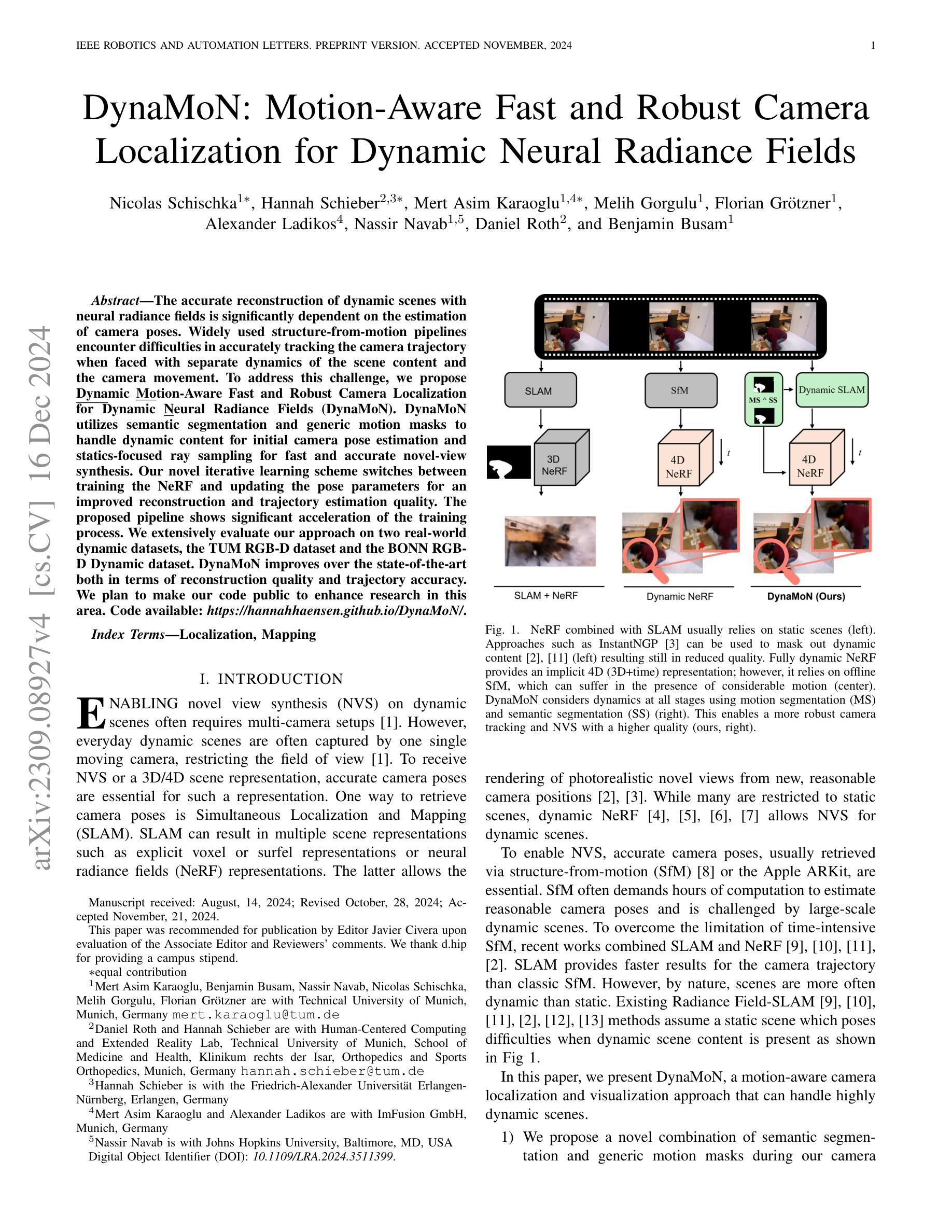
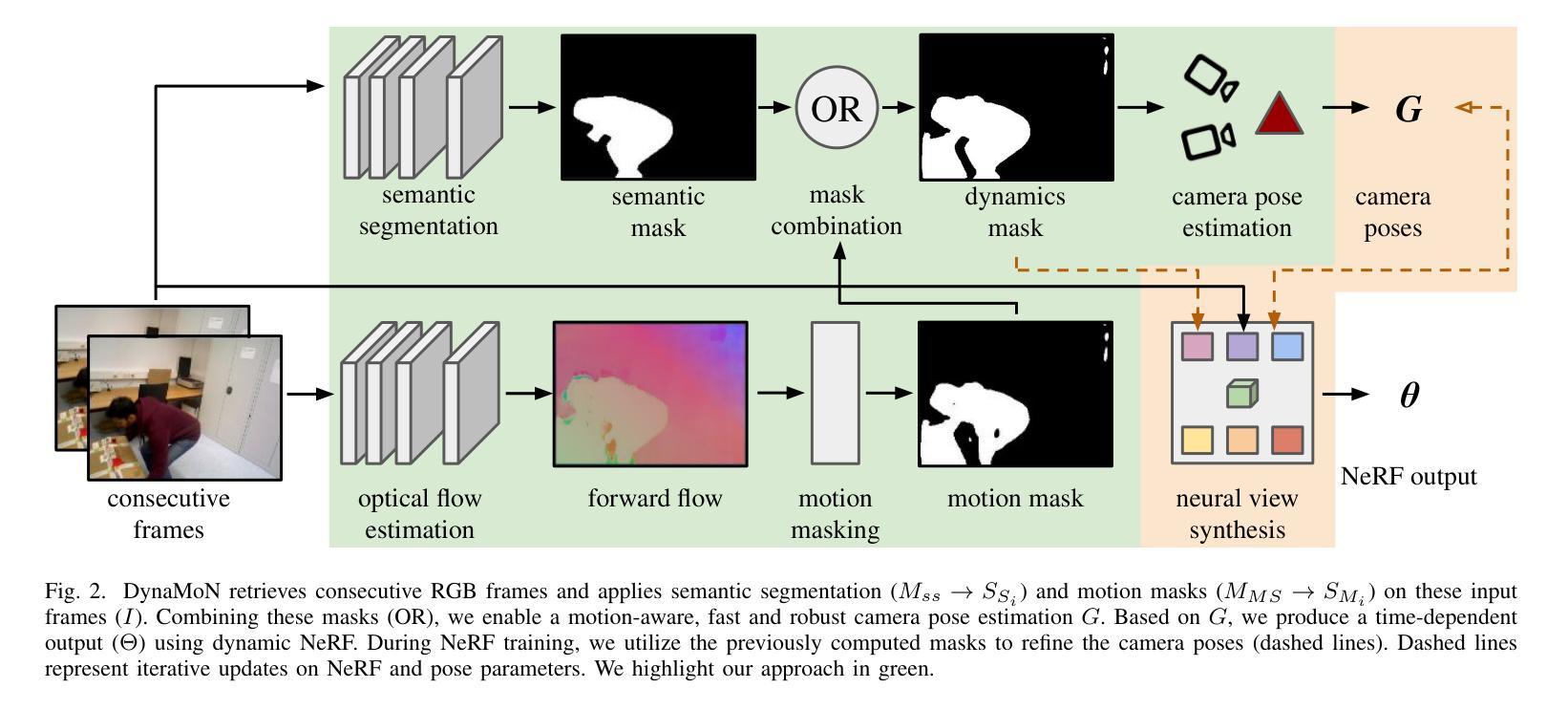
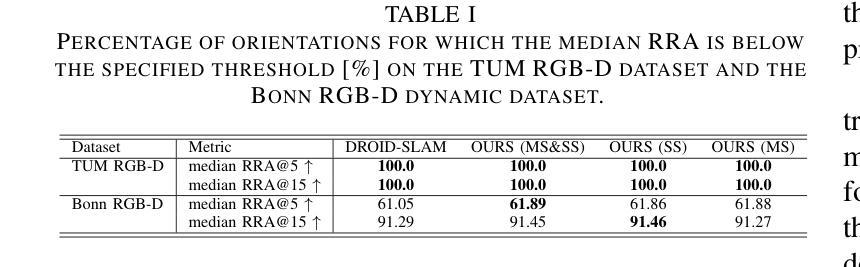
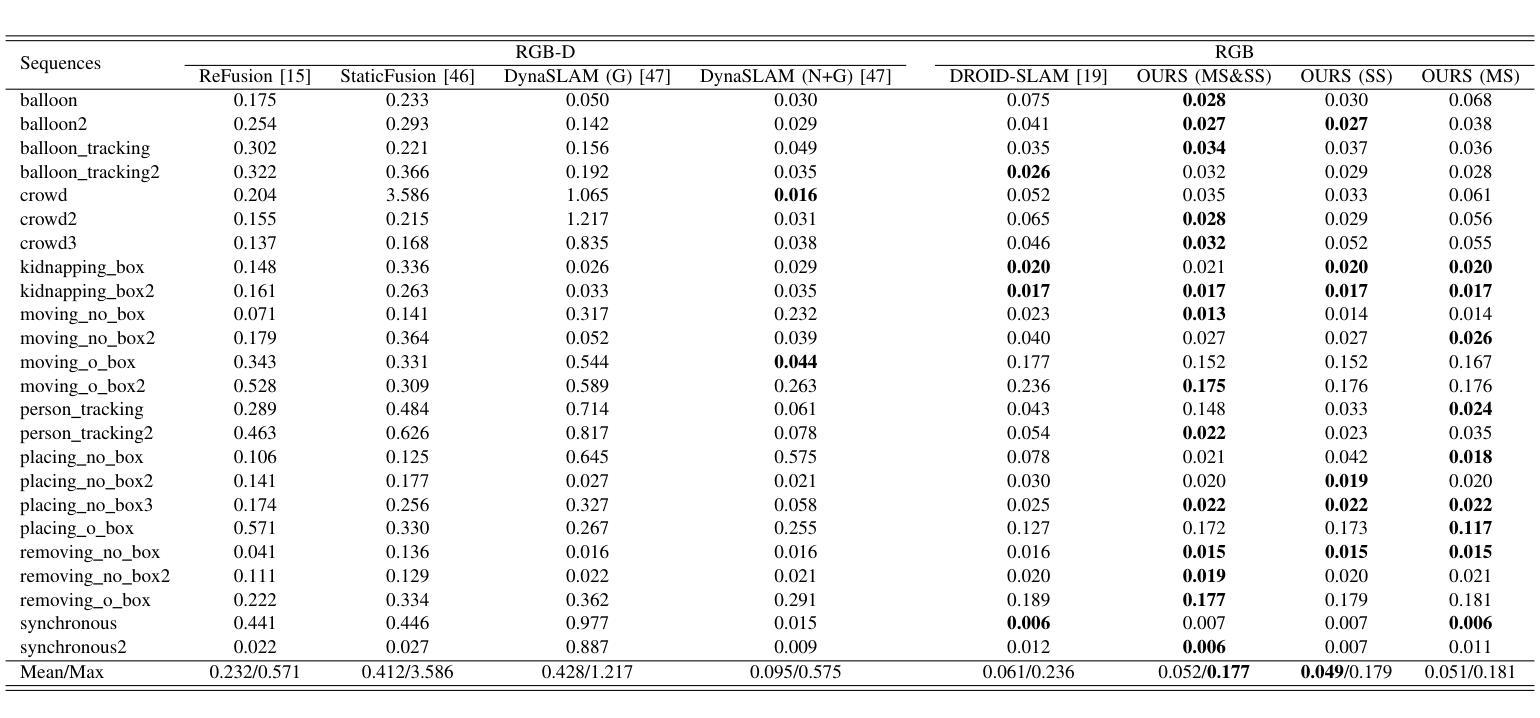
The accurate reconstruction of dynamic scenes with neural radiance fields is significantly dependent on the estimation of camera poses. Widely used structure-from-motion pipelines encounter difficulties in accurately tracking the camera trajectory when faced with separate dynamics of the scene content and the camera movement. To address this challenge, we propose Dynamic Motion-Aware Fast and Robust Camera Localization for Dynamic Neural Radiance Fields (DynaMoN). DynaMoN utilizes semantic segmentation and generic motion masks to handle dynamic content for initial camera pose estimation and statics-focused ray sampling for fast and accurate novel-view synthesis. Our novel iterative learning scheme switches between training the NeRF and updating the pose parameters for an improved reconstruction and trajectory estimation quality. The proposed pipeline shows significant acceleration of the training process. We extensively evaluate our approach on two real-world dynamic datasets, the TUM RGB-D dataset and the BONN RGB-D Dynamic dataset. DynaMoN improves over the state-of-the-art both in terms of reconstruction quality and trajectory accuracy. We plan to make our code public to enhance research in this area.
利用神经辐射场对动态场景的精确重建在很大程度上依赖于相机姿态的估计。广泛使用的结构运动管道在面对场景内容的独立动态和相机运动时的轨迹跟踪时遇到困难。为了应对这一挑战,我们提出了动态运动感知快速稳健相机定位用于动态神经辐射场(DynaMoN)。DynaMoN利用语义分割和通用运动蒙版来处理动态内容来进行初始相机姿态估计,并侧重于静态射线采样以快速准确地合成新视角。我们的新颖迭代学习方案在训练NeRF和更新姿态参数之间切换,以提高重建和轨迹估计的质量。所提的管道显著加速了训练过程。我们在两个真实世界的动态数据集——TUM RGB-D数据集和BONN RGB-D动态数据集上广泛评估了我们的方法。DynaMoN在重建质量和轨迹准确性方面都超过了现有技术。我们计划公开我们的代码以促进该领域的研究。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于动态场景神经辐射场重建中相机姿态估计的重要性,提出一种动态运动感知的快速稳健相机定位方法(DynaMoN)。该方法采用语义分割和通用运动掩膜处理动态内容,进行初始相机姿态估计,并采用静态聚焦射线采样实现快速准确的新视角合成。其迭代学习方案在训练NeRF和更新姿态参数之间切换,提高了重建和轨迹估计质量。DynaMoN显著加速了训练过程,并在两个真实动态数据集上进行了广泛评估,提升了重建质量和轨迹准确性。计划公开代码以促进该领域研究。
Key Takeaways
- 动态场景重建中相机姿态估计的重要性。
- DynaMoN方法利用语义分割和通用运动掩膜处理动态内容,用于初始相机姿态估计。
- DynaMoN采用静态聚焦射线采样实现快速准确的新视角合成。
- 迭代学习方案在训练NeRF和更新姿态参数之间切换,提升重建和轨迹估计质量。
- DynaMoN显著加速了训练过程。
- 在两个真实动态数据集上进行了广泛评估,表现出优秀的性能。
点此查看论文截图
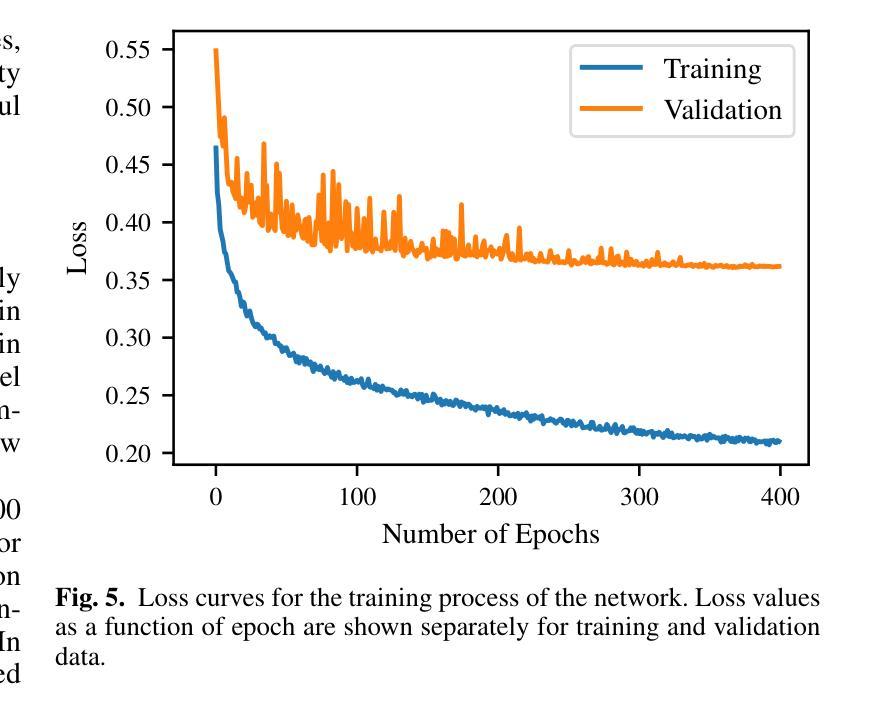
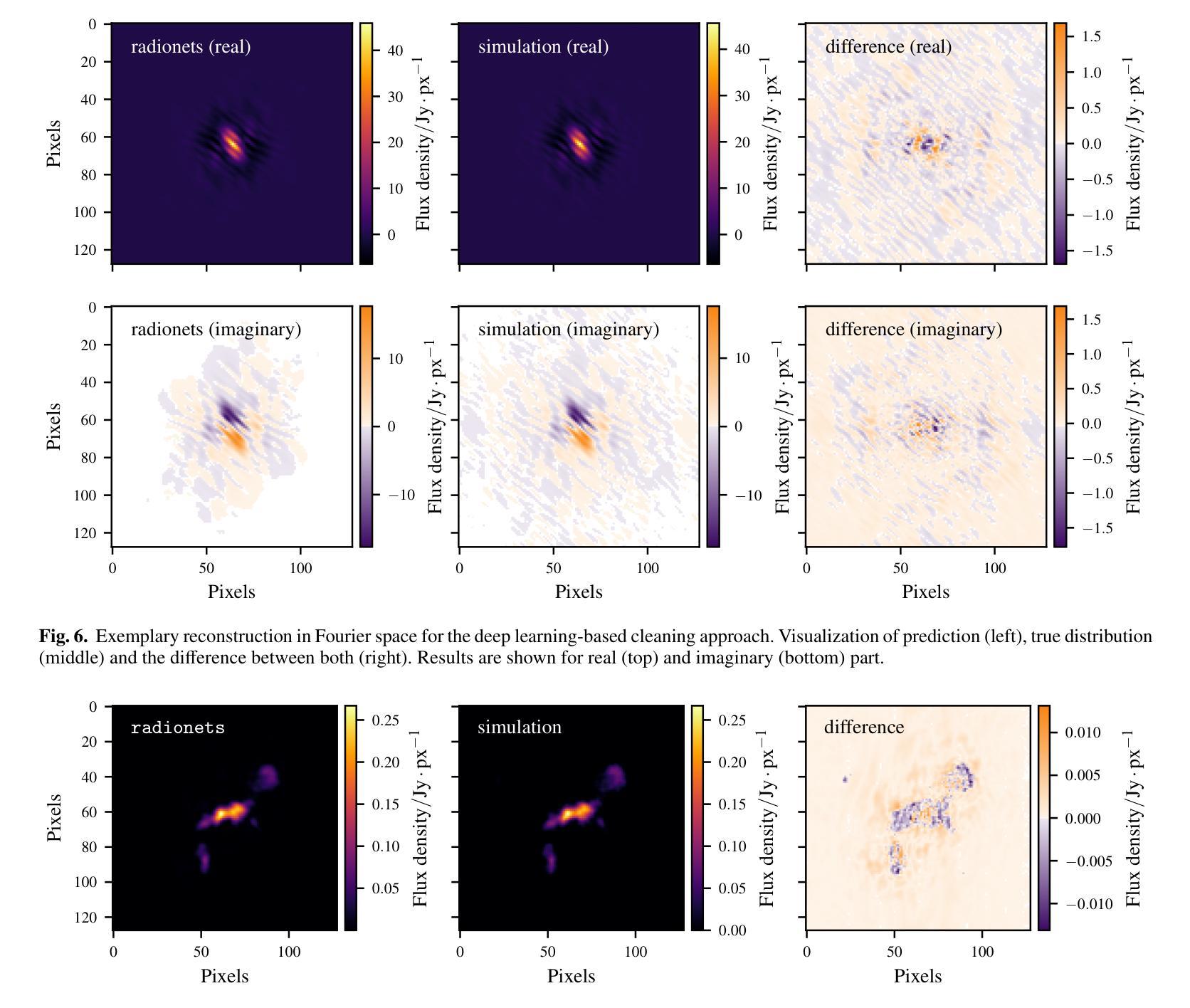
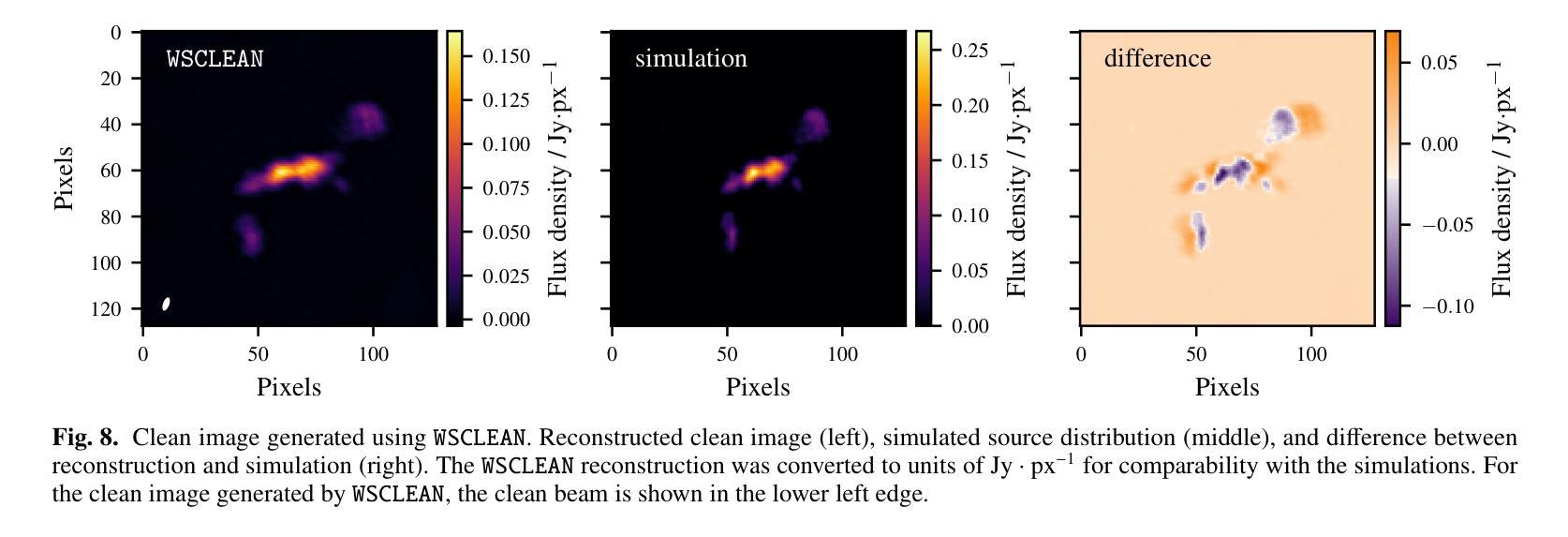
Deep learning-based radiointerferometric imaging with GAN-aided training
Authors:F. Geyer, K. Schmidt, J. Kummer, M. Brüggen, H. W. Edler, D. Elsässer, F. Griese, A. Poggenpohl, L. Rustige, W. Rhode
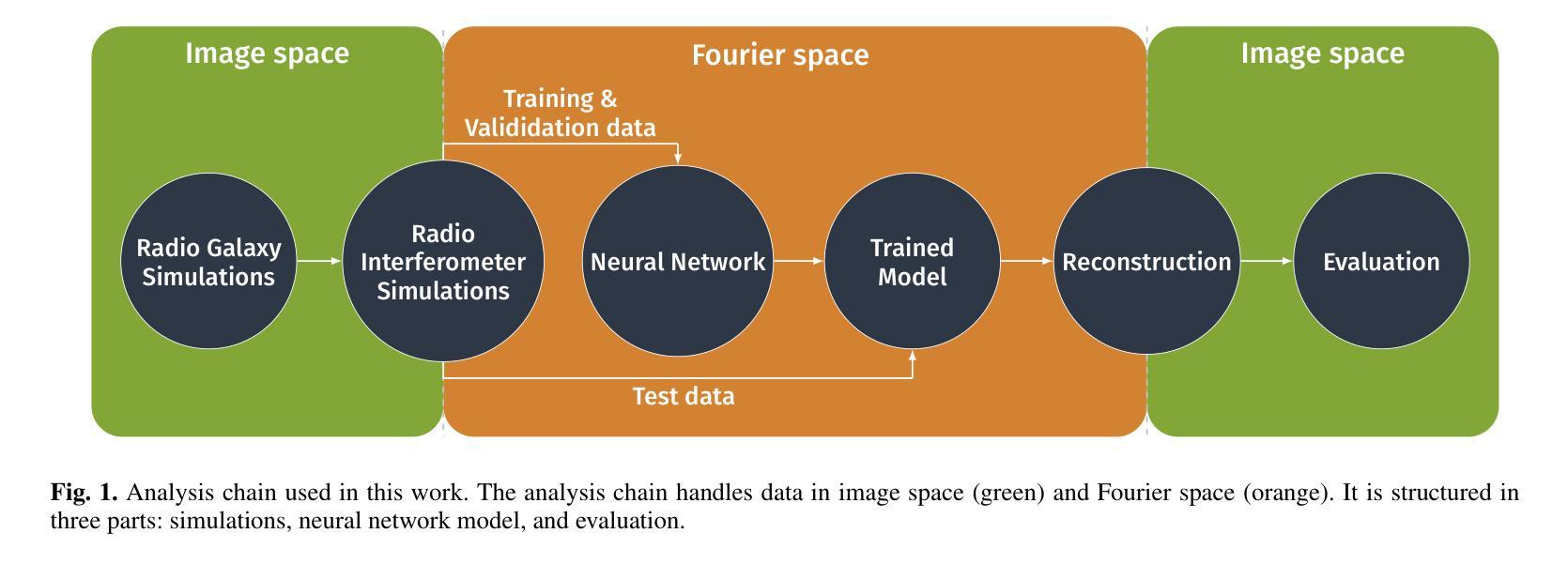
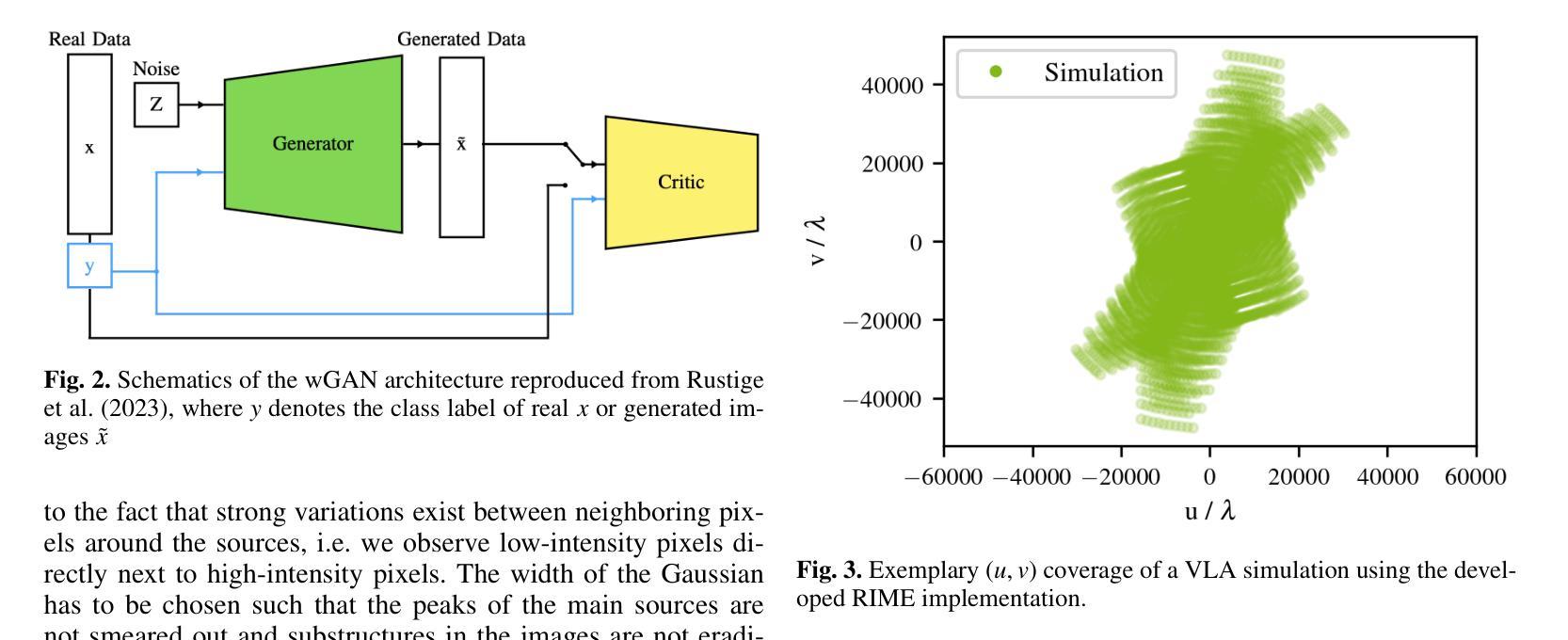
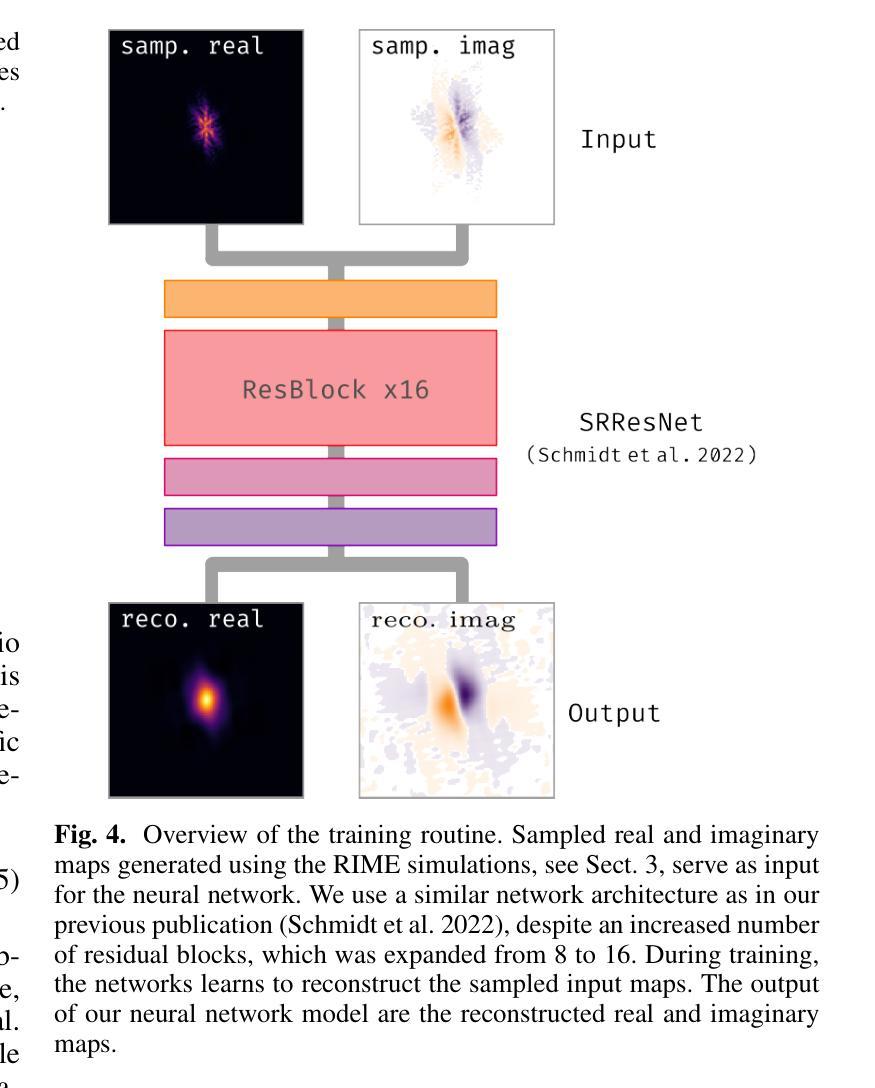
Radio interferometry invariably suffers from an incomplete coverage of the spatial Fourier space, which leads to imaging artifacts. The current state-of-the-art technique is to create an image by Fourier-transforming the incomplete visibility data and to clean the systematic effects originating from incomplete data in Fourier space. Previously, we have shown how super-resolution methods based on convolutional neural networks can reconstruct sparse visibility data. Our previous work has suffered from a low realism of the training data. The aim of this work is to build a whole simulation chain for realistic radio sources that then leads to a vastly improved neural net for the reconstruction of missing visibilities. This method offers considerable improvements in terms of speed, automatization and reproducibility over the standard techniques. Here we generate large amounts of training data by creating images of radio galaxies with a generative adversarial network (GAN) that has been trained on radio survey data. Then, we applied the Radio Interferometer Measurement Equation (RIME) in order to simulate the measurement process of a radio interferometer. We show that our neural network can reconstruct faithfully images of realistic radio galaxies. The reconstructed images agree well with the original images in terms of the source area, integrated flux density, peak flux density, and the multi-scale structural similarity index. Finally, we show how the neural net can be adapted to estimate the uncertainties in the imaging process.
射电干涉仪经常面临空间傅里叶变换覆盖不全的问题,从而导致成像失真。目前最先进的技术是通过傅里叶变换不完整可见度数据来创建图像,并清理由傅里叶空间不完整数据引起的系统效应。以前,我们已经展示了基于卷积神经网络的超分辨率方法如何重建稀疏可见度数据。我们之前的工作受到了训练数据真实度低的影响。这项工作的目标是建立一个针对真实射电源的整体仿真链,从而建立一个大大改进的神经网络,用于重建缺失的可见度。这种方法在速度、自动化和可重复性方面提供了对标准技术的重大改进。在这里,我们通过使用生成对抗网络(GAN)创建射电星系图像来生成大量训练数据,该网络已经在射电调查数据上进行了训练。然后,我们应用射电干涉仪测量方程(RIME)来模拟射电干涉仪的测量过程。我们证明了我们的神经网络能够忠实地重建真实的射电星系的图像。重建的图像在源区域、积分流量密度、峰值流量密度和多尺度结构相似性指数方面与原始图像吻合良好。最后,我们展示了如何调整神经网络以估计成像过程中的不确定性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in Astronomy & Astrophysics
Summary
本文介绍了射电干涉仪在成像时存在空间傅里叶变换不完全的问题,导致成像出现伪影。为解决此问题,本文构建了一个完整的模拟链以生成真实的射电源,进而使用基于卷积神经网络的方法重建缺失的可见度数据。该方法使用生成对抗网络(GAN)生成射电波源图像,并利用射电干涉仪测量方程模拟测量过程。实验表明,神经网络能够重建真实的射电波源图像,与原始图像在源面积、积分流量密度、峰值流量密度和多尺度结构相似指数等方面达成良好共识。此外,本文还展示了如何调整神经网络以估计成像过程中的不确定性。
Key Takeaways
- 射电干涉仪存在空间傅里叶变换不完全的问题,导致成像伪影。
- 当前先进的方法是通过傅里叶变换生成图像并清理由不完全数据引起的系统性影响。
- 之前基于卷积神经网络的方法虽能重建稀疏可见度数据,但训练数据缺乏真实感。
- 本文旨在构建一个完整的模拟链来生成真实的射电源,进而提高神经网络对缺失可见度的重建能力。
- 使用生成对抗网络(GAN)生成射电波源图像,并模拟测量过程。
- 神经网络能够重建真实的射电波源图像,与原始图像在多个方面达成良好共识。
点此查看论文截图