⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-19 更新
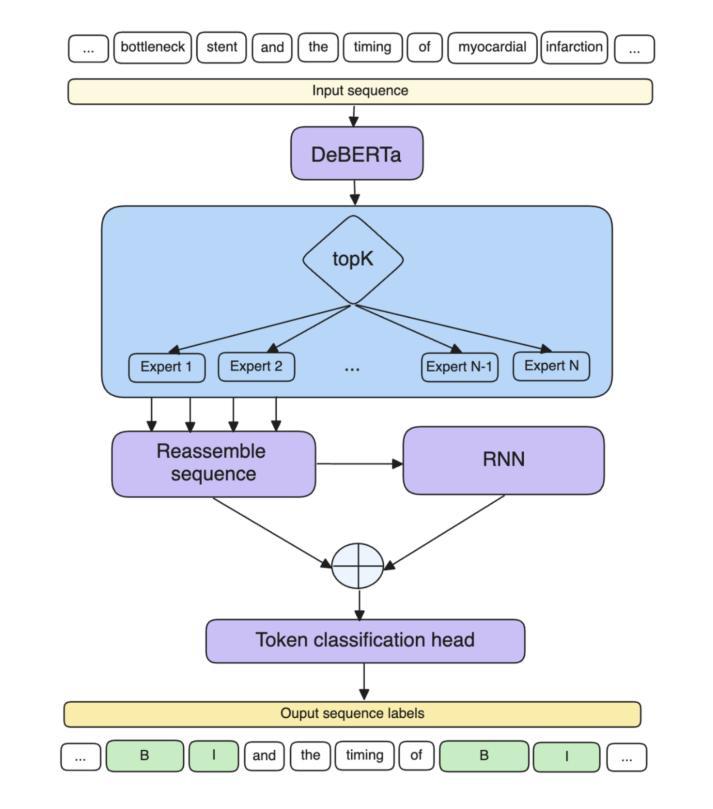
SEKE: Specialised Experts for Keyword Extraction
Authors:Matej Martinc, Hanh Thi Hong Tran, Senja Pollak, Boshko Koloski
Keyword extraction involves identifying the most descriptive words in a document, allowing automatic categorisation and summarisation of large quantities of diverse textual data. Relying on the insight that real-world keyword detection often requires handling of diverse content, we propose a novel supervised keyword extraction approach based on the mixture of experts (MoE) technique. MoE uses a learnable routing sub-network to direct information to specialised experts, allowing them to specialize in distinct regions of the input space. SEKE, a mixture of Specialised Experts for supervised Keyword Extraction, uses DeBERTa as the backbone model and builds on the MoE framework, where experts attend to each token, by integrating it with a recurrent neural network (RNN), to allow successful extraction even on smaller corpora, where specialisation is harder due to lack of training data. The MoE framework also provides an insight into inner workings of individual experts, enhancing the explainability of the approach. We benchmark SEKE on multiple English datasets, achieving state-of-the-art performance compared to strong supervised and unsupervised baselines. Our analysis reveals that depending on data size and type, experts specialize in distinct syntactic and semantic components, such as punctuation, stopwords, parts-of-speech, or named entities. Code is available at: https://github.com/matejMartinc/SEKE_keyword_extraction
关键词提取涉及识别文档中最具描述性的单词,从而实现大量不同文本数据的自动分类和摘要。我们依赖于一种见解,即现实世界中的关键词检测通常需要处理多样化的内容,因此,我们提出了一种基于专家混合(MoE)技术的新型监督关键词提取方法。MoE使用一个可学习的路由子网络来指导信息流向专业专家,使他们能够专注于输入空间的特定区域。SEKE(用于监督关键词提取的专用专家混合)使用DeBERTa作为骨干模型,基于MoE框架构建,其中的专家会关注每个标记,并通过将其与循环神经网络(RNN)集成,即使在较小的语料库上也能实现成功的提取。由于缺乏训练数据,使得专业化变得更加困难。MoE框架还提供了对个别专家内部工作的深入了解,增强了该方法的可解释性。我们在多个英文数据集上对SEKE进行了基准测试,与强大的有监督和无监督基准相比,实现了最先进的性能。我们的分析表明,根据数据的大小和类型,专家会在不同的句法和语义成分上专业化,如标点符号、停用词、短语成分或命名实体。相关代码可通过以下链接获取:https://github.com/matejMartinc/SEKE_keyword_extraction
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于关键词提取的重要性,提出了一种新型的基于混合专家(MoE)技术的关键词提取方法。结合多种模型的优势,使用监督学习方法识别描述性词汇以进行大规模文本的自动分类和摘要。该方法在多个英语数据集上取得了卓越性能,且专家模型能够针对不同类型的文本进行专业处理,提高了解释性。代码已公开。
Key Takeaways
- 关键词提取是通过识别文档中最具描述性的词汇,实现对大规模多样文本数据的自动分类和摘要。
- 提出了一种基于混合专家(MoE)技术的关键词提取方法,结合多种模型优势进行更准确的分析。
点此查看论文截图

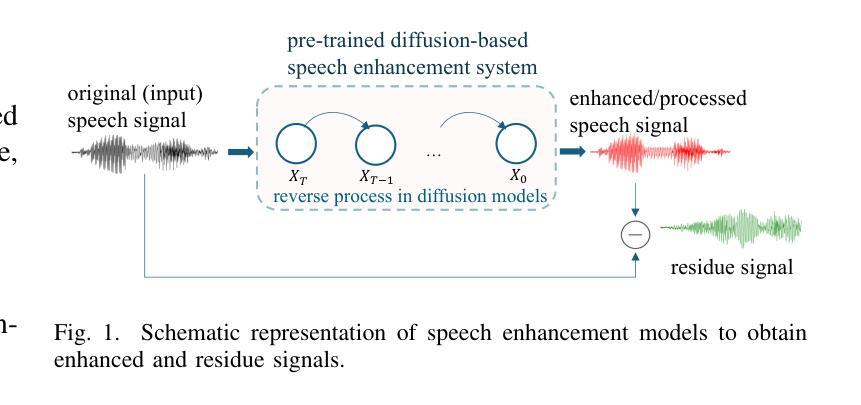
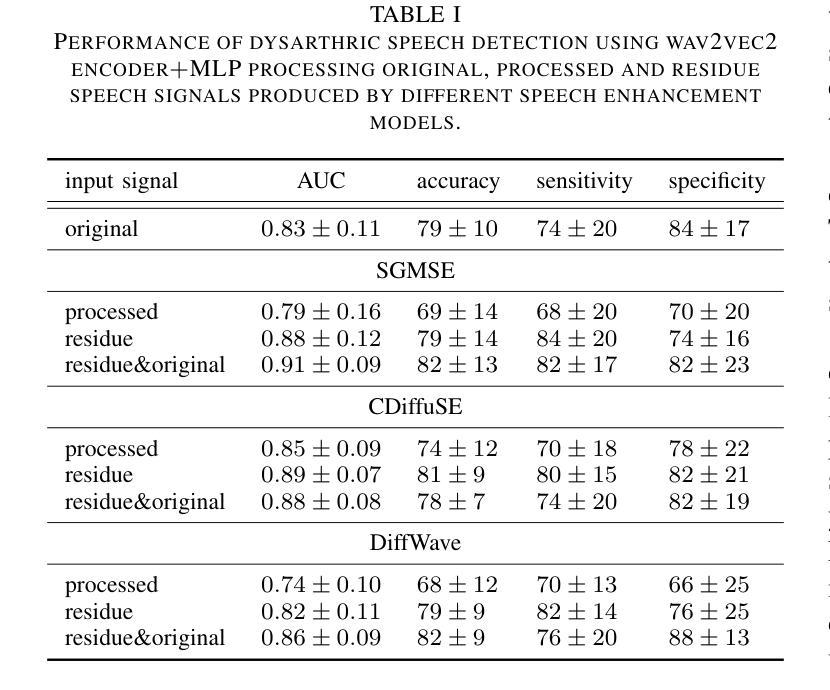
Investigating the Effects of Diffusion-based Conditional Generative Speech Models Used for Speech Enhancement on Dysarthric Speech
Authors:Joanna Reszka, Parvaneh Janbakhshi, Tilak Purohit, Sadegh Mohammadi
In this study, we aim to explore the effect of pre-trained conditional generative speech models for the first time on dysarthric speech due to Parkinson’s disease recorded in an ideal/non-noisy condition. Considering one category of generative models, i.e., diffusion-based speech enhancement, these models are previously trained to learn the distribution of clean (i.e, recorded in a noise-free environment) typical speech signals. Therefore, we hypothesized that when being exposed to dysarthric speech they might remove the unseen atypical paralinguistic cues during the enhancement process. By considering the automatic dysarthric speech detection task, in this study, we experimentally show that during the enhancement process of dysarthric speech data recorded in an ideal non-noisy environment, some of the acoustic dysarthric speech cues are lost. Therefore such pre-trained models are not yet suitable in the context of dysarthric speech enhancement since they manipulate the pathological speech cues when they process clean dysarthric speech. Furthermore, we show that the removed acoustics cues by the enhancement models in the form of residue speech signal can provide complementary dysarthric cues when fused with the original input speech signal in the feature space.
在这项研究中,我们首次探索了预训练的条件生成语音模型对帕金森病引起的构音障碍语音的影响,这些语音是在理想/无噪音的条件下录制的。考虑到一类生成模型,即基于扩散的语音增强模型,这些模型之前接受过训练,学习清洁(即在无噪音环境中录制的)典型语音信号的分布。因此,我们假设当暴露于构音障碍语音时,它们可能会在增强过程中消除未见过的非语言提示。通过考虑自动构音障碍语音检测任务,本研究实验表明,在理想无噪音环境下录制的构音障碍语音数据的增强过程中,一些声学构音障碍语音线索会丢失。因此,这样的预训练模型在构音障碍语音增强方面尚不适用,因为它们在处理干净的构音障碍语音时会操作病理语音线索。此外,我们还表明,增强模型以残留语音信号的形式去除的声学线索,当与原始输入语音信号融合在特征空间时,可以提供补充的构音障碍线索。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted at ICASSP 2025 Satellite Workshop: Workshop on Speech Pathology Analysis and DEtection (SPADE)
Summary
本研究旨在探索在非噪声环境下预训练的基于条件的生成语音模型对帕金森氏病引起的言语障碍(又称言语困难症)的影响。先前已训练过这些模型以学习干净(即在无噪声环境中录制)的典型语音信号的分布。我们假设,当这些模型接触到言语障碍语音时,它们可能会在增强过程中消除未观察到的异常副语言线索。本研究通过实验表明,在理想非噪声环境下录制的言语障碍语音数据的增强过程中,部分声学障碍线索会丢失。因此,这种预训练的模型尚不适用于增强言语障碍语音的背景,因为它们在处理干净的言语障碍语音时会干扰病理语音线索。然而,我们还发现,增强模型以残留语音信号的形式去除的声学线索可以与原始输入语音信号融合,为识别言语障碍提供额外的线索。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究首次探讨了预训练的基于条件的生成语音模型对帕金森氏病导致的言语障碍语音的影响。
- 这些预训练模型旨在学习干净(无噪声环境中录制的)典型语音信号的分布。
- 在非噪声环境下录制的言语障碍语音数据的增强过程中,这些模型会消除一些声学障碍线索。
- 预训练的模型尚不适用于增强言语障碍语音,因为它们会干扰病理语音线索。
- 增强模型去除的声学线索(以残留语音信号的形式)与原始输入语音信号融合后,可为识别言语障碍提供额外的信息。
- 研究结果表明,这些预训练模型需要进一步调整和优化,以更有效地处理言语障碍语音。
点此查看论文截图

Typhoon 2: A Family of Open Text and Multimodal Thai Large Language Models
Authors:Kunat Pipatanakul, Potsawee Manakul, Natapong Nitarach, Warit Sirichotedumrong, Surapon Nonesung, Teetouch Jaknamon, Parinthapat Pengpun, Pittawat Taveekitworachai, Adisai Na-Thalang, Sittipong Sripaisarnmongkol, Krisanapong Jirayoot, Kasima Tharnpipitchai
This paper introduces Typhoon 2, a series of text and multimodal large language models optimized for the Thai language. The series includes models for text, vision, and audio. Typhoon2-Text builds on state-of-the-art open models, such as Llama 3 and Qwen2, and we perform continual pre-training on a mixture of English and Thai data. We employ various post-training techniques to enhance Thai language performance while preserving the base models’ original capabilities. We release text models across a range of sizes, from 1 to 70 billion parameters, available in both base and instruction-tuned variants. Typhoon2-Vision improves Thai document understanding while retaining general visual capabilities, such as image captioning. Typhoon2-Audio introduces an end-to-end speech-to-speech model architecture capable of processing audio, speech, and text inputs and generating both text and speech outputs simultaneously.
本文介绍了台风2系列,这是一系列针对泰语优化的文本和多模态大型语言模型。该系列包括文本、视觉和音频模型。Typhoon2-Text建立在最前沿的开放模型上,如Llama 3和Qwen2,我们对英语和泰语数据的混合进行持续预训练。我们采用各种后训练技术,在提高泰语性能的同时,保留基础模型的原始功能。我们发布了一系列文本模型,参数从1亿到70亿不等,既有基础模型也有指令调优的变体。Typhoon2-Vision在保留通用视觉功能(如图像标题)的同时,提高了对泰语文档的理解能力。Typhoon2-Audio引入了一种端到端的语音到语音的模型架构,能够处理音频、语音和文本输入,并同时生成文本和语音输出。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF technical report, 55 pages
Summary:
本文介绍了Typhoon 2系列大型语言模型,该系列模型针对泰语进行了优化,包括文本、视觉和音频模型。Typhoon2-Text基于最前沿的开放模型进行构建,如Llama 3和Qwen2,并在混合的英语和泰语数据上进行持续预训练。通过采用各种后训练技术,提高了泰语性能,同时保留了基础模型的原始能力。此外,还发布了不同规模的文本模型,包括基础模型和指令微调模型。Typhoon2-Vision提高了对泰语文档的理解能力,同时保留了通用的视觉功能,如图像标题生成。Typhoon2-Audio则引入了端到端的语音到语音模型架构,能够处理音频、语音和文本输入,并同时生成文本和语音输出。
Key Takeaways:
- Typhoon 2系列模型是针对泰语优化的文本、视觉和音频大型语言模型。
- Typhoon2-Text基于Llama 3和Qwen2构建,并在混合语言数据上进行预训练。
- 通过后训练技术提高泰语性能,同时保留基础模型的原始能力。
- 发布不同规模的文本模型,包括基础模型和指令微调模型。
- Typhoon2-Vision提高了对泰语文档的理解能力,同时保留通用的视觉功能。
- Typhoon2-Audio具备端到端的语音到语音生成能力,能处理多种输入并生成多种输出。
- 模型具备强大的多模态处理能力,可以应用于多种场景。
点此查看论文截图

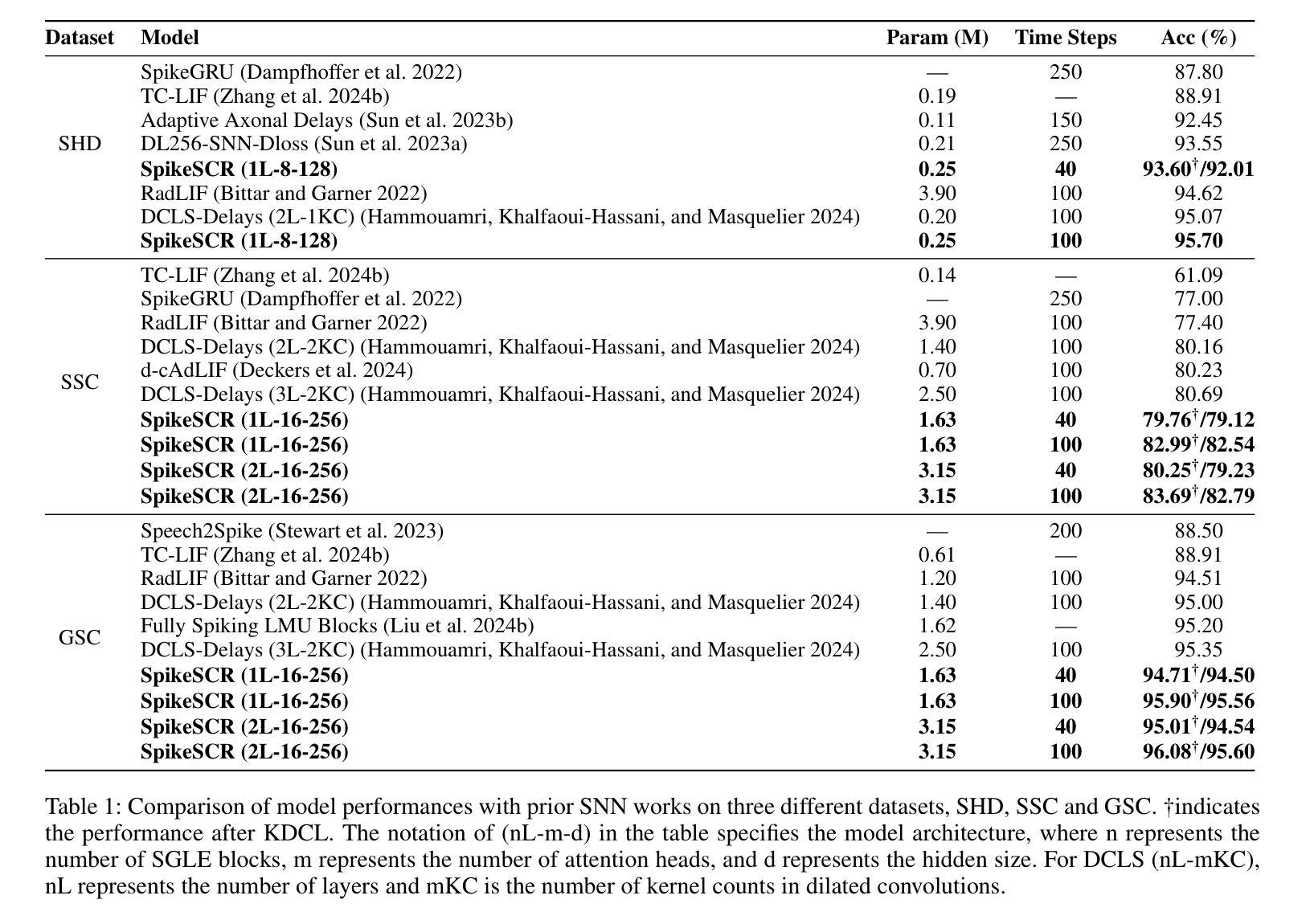
Efficient Speech Command Recognition Leveraging Spiking Neural Network and Curriculum Learning-based Knowledge Distillation
Authors:Jiaqi Wang, Liutao Yu, Liwei Huang, Chenlin Zhou, Han Zhang, Zhenxi Song, Min Zhang, Zhengyu Ma, Zhiguo Zhang
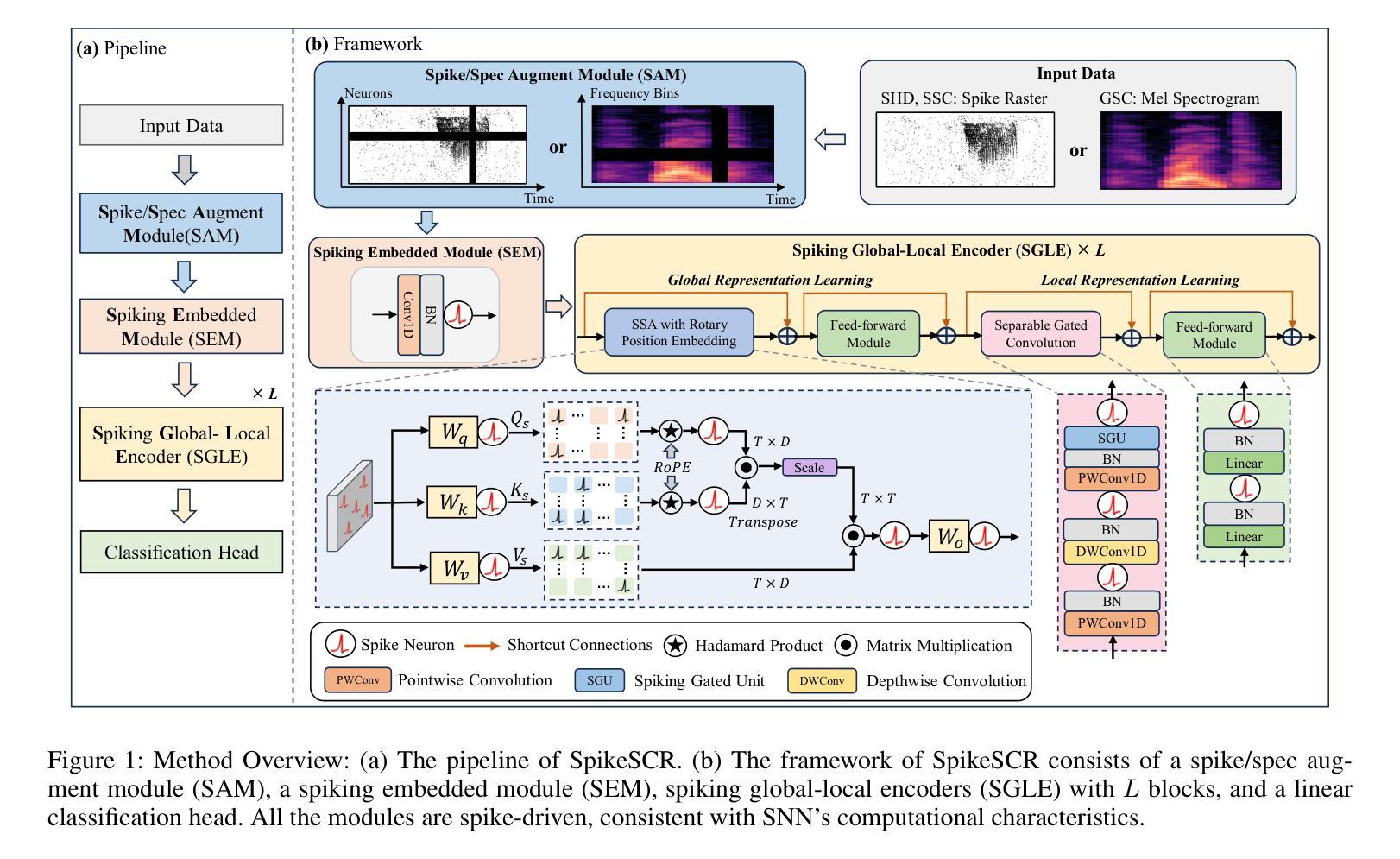
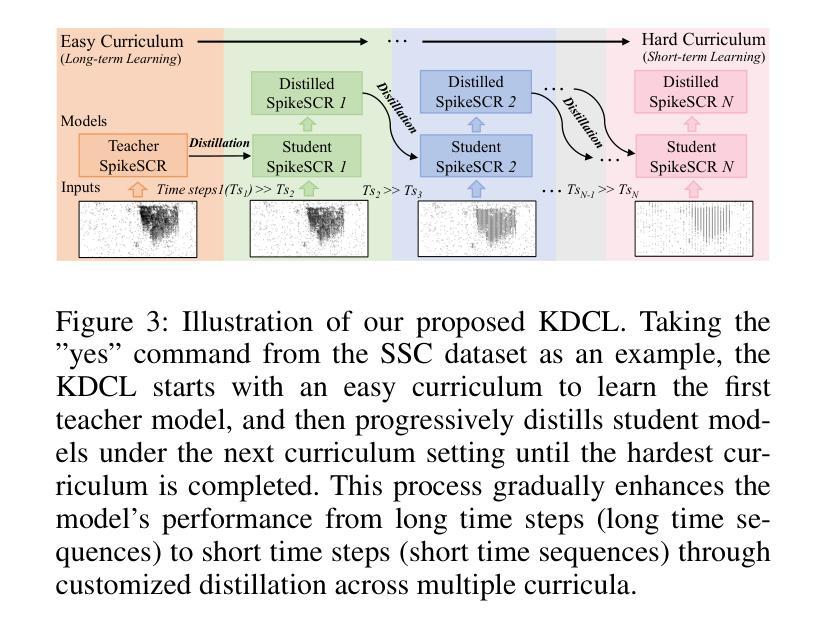
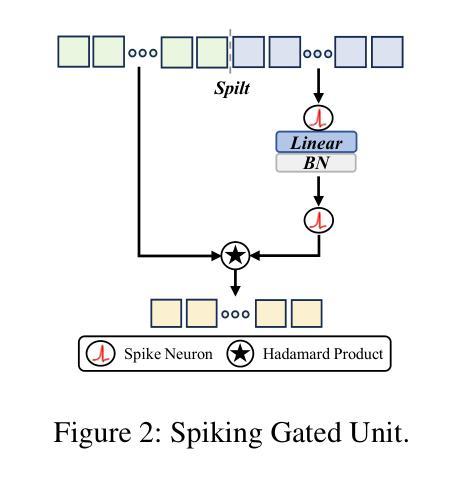
The intrinsic dynamics and event-driven nature of spiking neural networks (SNNs) make them excel in processing temporal information by naturally utilizing embedded time sequences as time steps. Recent studies adopting this approach have demonstrated SNNs’ effectiveness in speech command recognition, achieving high performance by employing large time steps for long time sequences. However, the large time steps lead to increased deployment burdens for edge computing applications. Thus, it is important to balance high performance and low energy consumption when detecting temporal patterns in edge devices. Our solution comprises two key components. 1). We propose a high-performance fully spike-driven framework termed SpikeSCR, characterized by a global-local hybrid structure for efficient representation learning, which exhibits long-term learning capabilities with extended time steps. 2). To further fully embrace low energy consumption, we propose an effective knowledge distillation method based on curriculum learning (KDCL), where valuable representations learned from the easy curriculum are progressively transferred to the hard curriculum with minor loss, striking a trade-off between power efficiency and high performance. We evaluate our method on three benchmark datasets: the Spiking Heidelberg Dataset (SHD), the Spiking Speech Commands (SSC), and the Google Speech Commands (GSC) V2. Our experimental results demonstrate that SpikeSCR outperforms current state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods across these three datasets with the same time steps. Furthermore, by executing KDCL, we reduce the number of time steps by 60% and decrease energy consumption by 54.8% while maintaining comparable performance to recent SOTA results. Therefore, this work offers valuable insights for tackling temporal processing challenges with long time sequences in edge neuromorphic computing systems.
脉冲神经网络(SNNs)的内在动态和事件驱动特性使它们能够自然地利用嵌入的时间序列作为时间步长,从而擅长处理时序信息。最近采用这种方法的研究已经证明了SNNs在语音命令识别中的有效性,通过采用大的时间步长来处理长时间序列,实现了高性能。然而,大步长给边缘计算应用的部署带来了更大的负担。因此,在边缘设备中检测时序模式时,平衡高性能和低能耗是至关重要的。我们的解决方案包含两个关键组成部分。1. 我们提出了一个高性能的全脉冲驱动框架,名为SpikeSCR,其特点是具有全局-局部混合结构,用于有效表示学习,具有长期学习能力并扩展时间步长。2. 为了进一步拥抱低能耗,我们提出了一种基于课程学习的有效知识蒸馏方法(KDCL),从简单的课程中学习到的有价值表示逐步转移到困难的课程中,几乎没有损失,在功率效率与高性能之间取得了平衡。我们在三个基准数据集上评估了我们的方法:斯派克海德堡数据集(SHD)、斯派克语音命令(SSC)和谷歌语音命令(GSC)V2。我们的实验结果表明,SpikeSCR在这三个数据集上的性能优于当前的最先进方法。此外,通过执行KDCL,我们将时间步长减少了60%,能量消耗降低了54.8%,同时保持与最近的最先进结果相当的性能。因此,这项工作为解决边缘神经形态计算系统中长时间序列的时序处理挑战提供了有价值的见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Under Review
摘要
脉冲神经网络(SNNs)的内在动态和事件驱动特性使其能够利用嵌入的时间序列作为时间步长,在时序信息处理方面表现出卓越的能力。近期采用此方法的研究在语音命令识别中展示了SNNs的有效性,通过使用大的时间步长来处理长时间序列,实现了高性能。然而,大时间步长给边缘计算应用带来了部署负担。因此,在边缘设备上检测时序模式时,需要平衡高性能与低能耗。本研究解决方案包含两个关键组成部分:1)我们提出了一种高性能的全脉冲驱动框架SpikeSCR,具有全局-局部混合结构,用于高效表示学习,具有长时间步长的长期学习能力。2)为了进一步实现低能耗,我们提出了一种基于课程学习的有效知识蒸馏方法(KDCL),从简单课程中学习的有价值表示逐步转移到困难课程,实现了功率效率与高性能之间的平衡。我们在三个基准数据集上评估了我们的方法:Spiking Heidelberg Dataset(SHD)、Spiking Speech Commands(SSC)和Google Speech Commands(GSC)V2。实验结果表明,SpikeSCR在这三个数据集上的性能优于当前最先进的方法,通过执行KDCL,我们将时间步长减少了60%,并降低了54.8%的能耗,同时保持与最新先进结果的相当性能。因此,这项工作为解决边缘神经形态计算系统中长时间序列的时序处理挑战提供了有价值的见解。
关键见解
- 脉冲神经网络(SNNs)能利用时间序列进行高效时序信息处理。
- SNNs在语音命令识别方面表现出色,但大时间步长增加了边缘计算的部署负担。
- 提出了一种高性能全脉冲驱动框架SpikeSCR,具有全局-局部混合结构,实现长期学习。
- 通过知识蒸馏方法(KDCL)减少时间步长和能量消耗,同时保持高性能。
- 在三个基准数据集上的实验结果表明SpikeSCR优于当前最先进的方法。
- KDCL方法能有效平衡功率效率与高性能。
点此查看论文截图

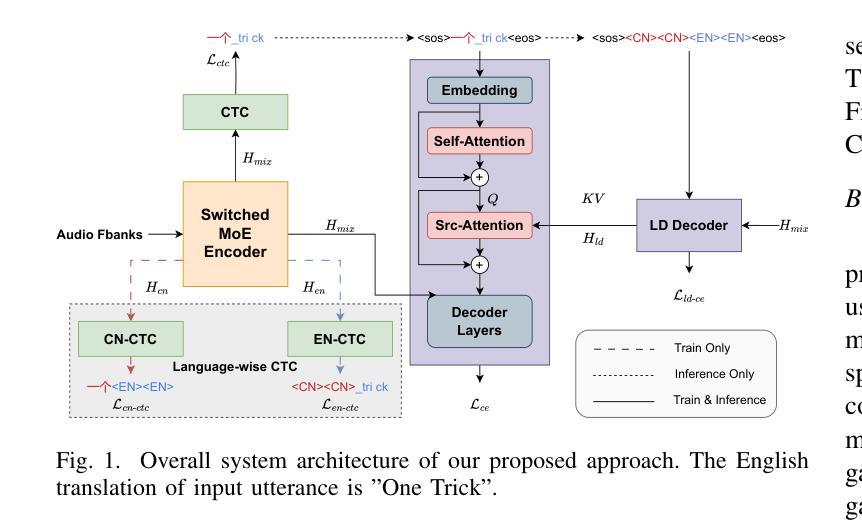
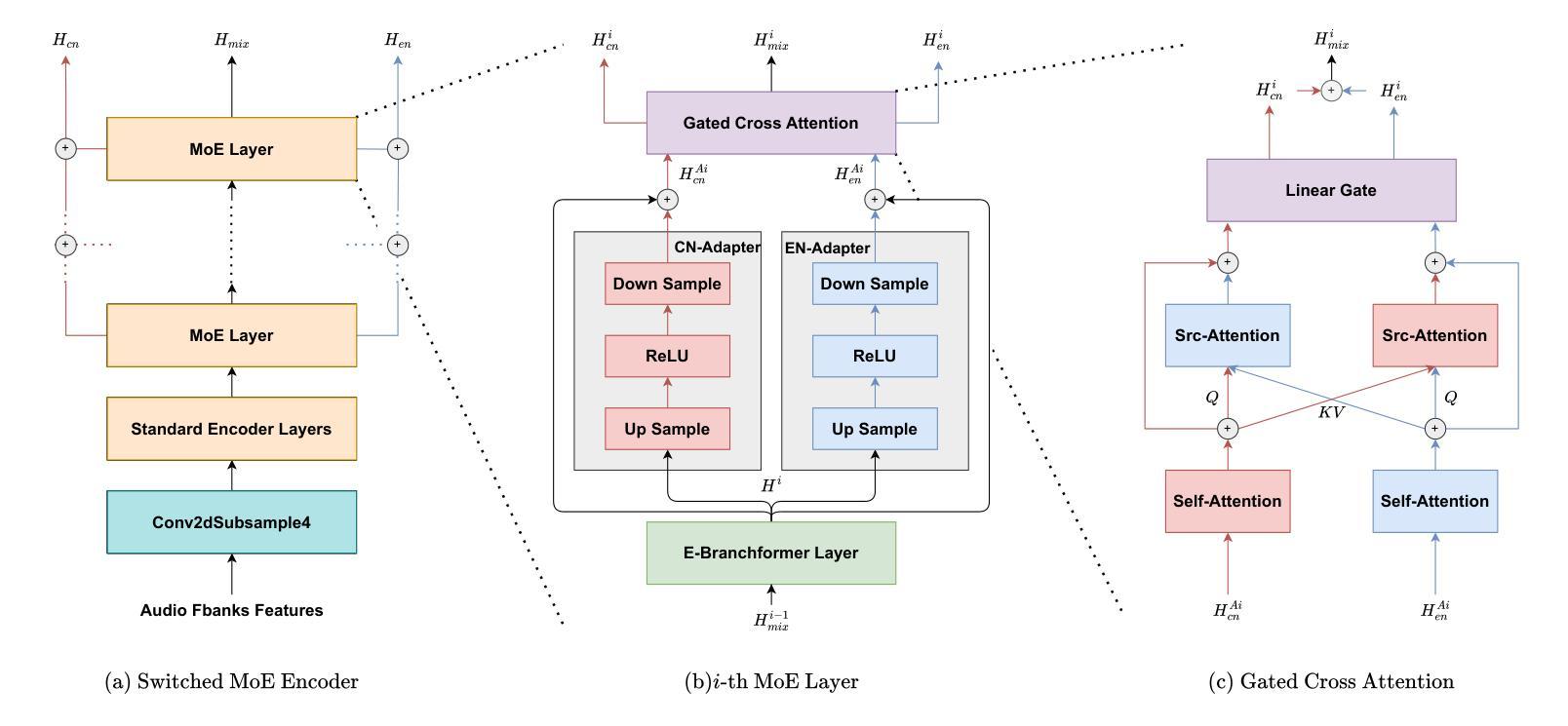
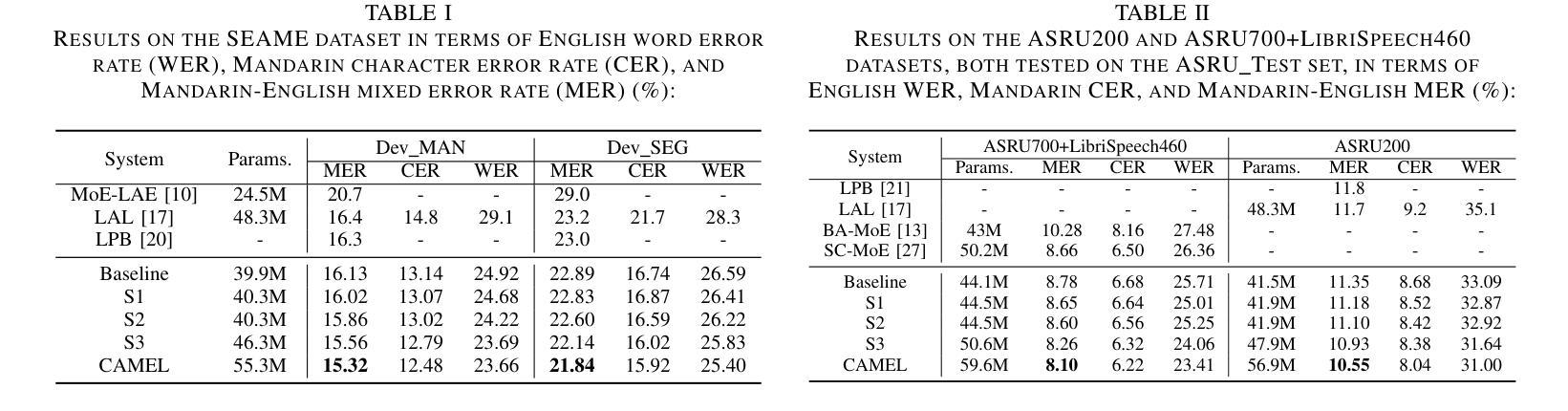
CAMEL: Cross-Attention Enhanced Mixture-of-Experts and Language Bias for Code-Switching Speech Recognition
Authors:He Wang, Xucheng Wan, Naijun Zheng, Kai Liu, Huan Zhou, Guojian Li, Lei Xie
Code-switching automatic speech recognition (ASR) aims to transcribe speech that contains two or more languages accurately. To better capture language-specific speech representations and address language confusion in code-switching ASR, the mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture and an additional language diarization (LD) decoder are commonly employed. However, most researches remain stagnant in simple operations like weighted summation or concatenation to fuse language-specific speech representations, leaving significant opportunities to explore the enhancement of integrating language bias information. In this paper, we introduce CAMEL, a cross-attention-based MoE and language bias approach for code-switching ASR. Specifically, after each MoE layer, we fuse language-specific speech representations with cross-attention, leveraging its strong contextual modeling abilities. Additionally, we design a source attention-based mechanism to incorporate the language information from the LD decoder output into text embeddings. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on the SEAME, ASRU200, and ASRU700+LibriSpeech460 Mandarin-English code-switching ASR datasets.
代码切换自动语音识别(ASR)旨在准确转录包含两种或多种语言的语音。为了更好地捕获特定语言的语音表示并解决代码切换ASR中的语言混淆问题,通常采用专家混合(MoE)架构和额外的语言日记化(LD)解码器。然而,大多数研究仍然停留在加权求和或串联等简单操作来融合特定语言的语音表示,这留下了探索整合语言偏向信息以增强性能的巨大机会。在本文中,我们介绍了CAMEL,这是一种基于交叉注意力的MoE和语言偏向方法,用于代码切换ASR。具体来说,在每个MoE层之后,我们利用交叉注意力融合特定语言的语音表示,利用其强大的上下文建模能力。此外,我们设计了一种基于源注意力的机制,将LD解码器的语言信息融入文本嵌入。实验结果表明,我们的方法在SEAME、ASRU200、ASRU700+LibriSpeech460的汉语-英语代码切换ASR数据集上达到了最新性能水平。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by ICASSP 2025. 5 pages, 2 figures
Summary
本文介绍了针对双语或多语言自动语音识别(ASR)的代码切换问题,提出了一种基于交叉注意力和语言偏好的混合专家(MoE)架构方法CAMEL。该方法通过交叉注意力融合语言特定语音表示,并将语言信息从语言日记解码器输出融入文本嵌入中。实验结果表明,CAMEL在SEAME、ASRU200和ASRU700+LibriSpeech460的普通话-英语代码切换ASR数据集上达到了最新性能。
Key Takeaways
- 代码切换自动语音识别(ASR)旨在准确转录包含两种或多种语言的语音。
- 目前研究在融合语言特定语音表示时仍停留在简单操作,如加权求和或拼接,存在探索增强整合语言偏见信息的空间。
- 引入CAMEL方法,结合混合专家(MoE)架构和交叉注意力机制,以改进代码切换ASR的性能。
- CAMEL利用交叉注意力融合语言特定语音表示,并在每个MoE层后进行。
- CAMEL设计了一种基于源注意力的机制,将语言信息从语言日记解码器输出融入文本嵌入。
- 实验结果表明,CAMEL在多个普通话-英语代码切换ASR数据集上达到了最新性能。
点此查看论文截图

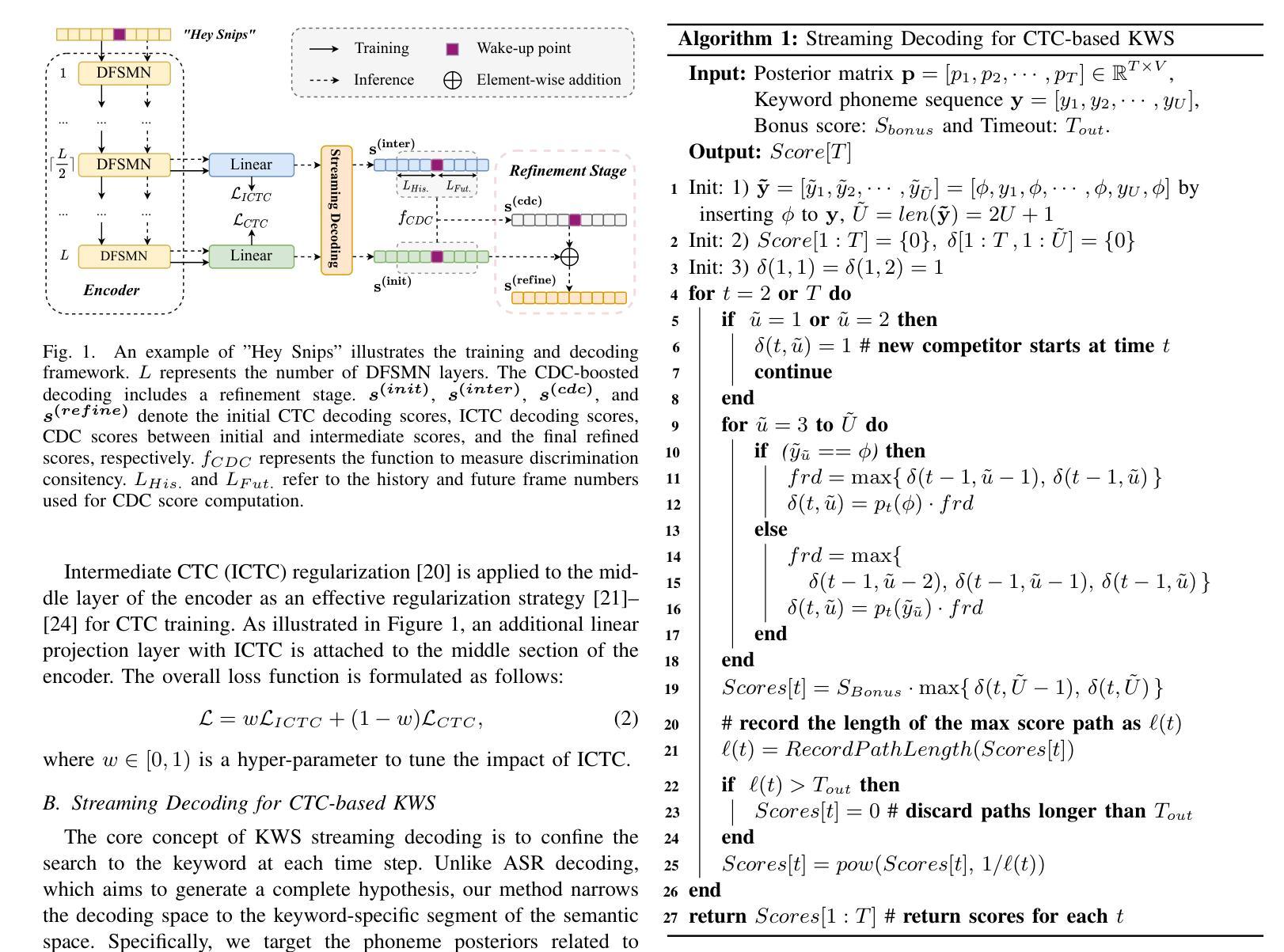
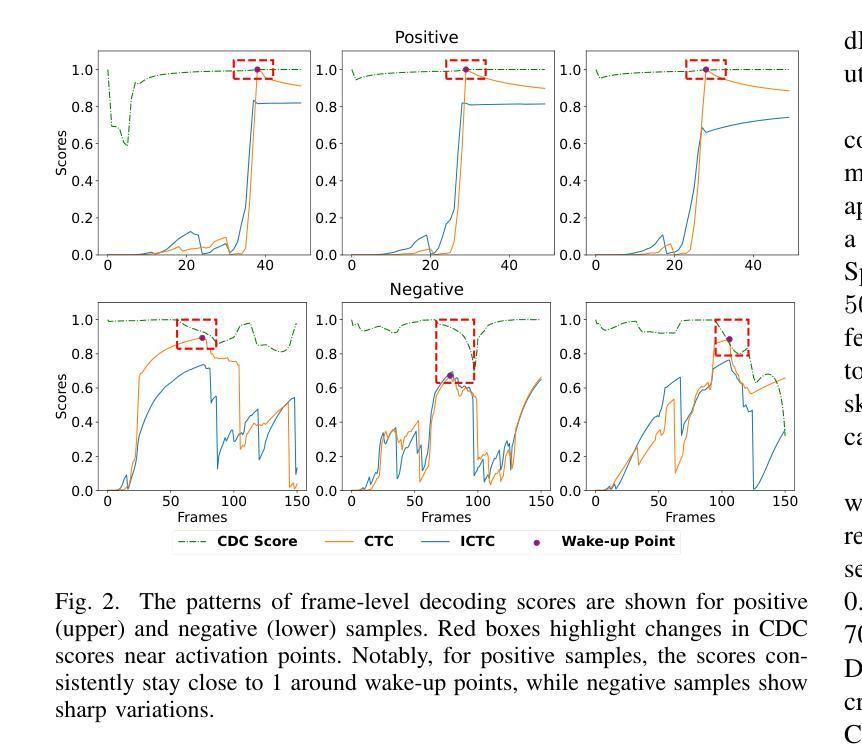
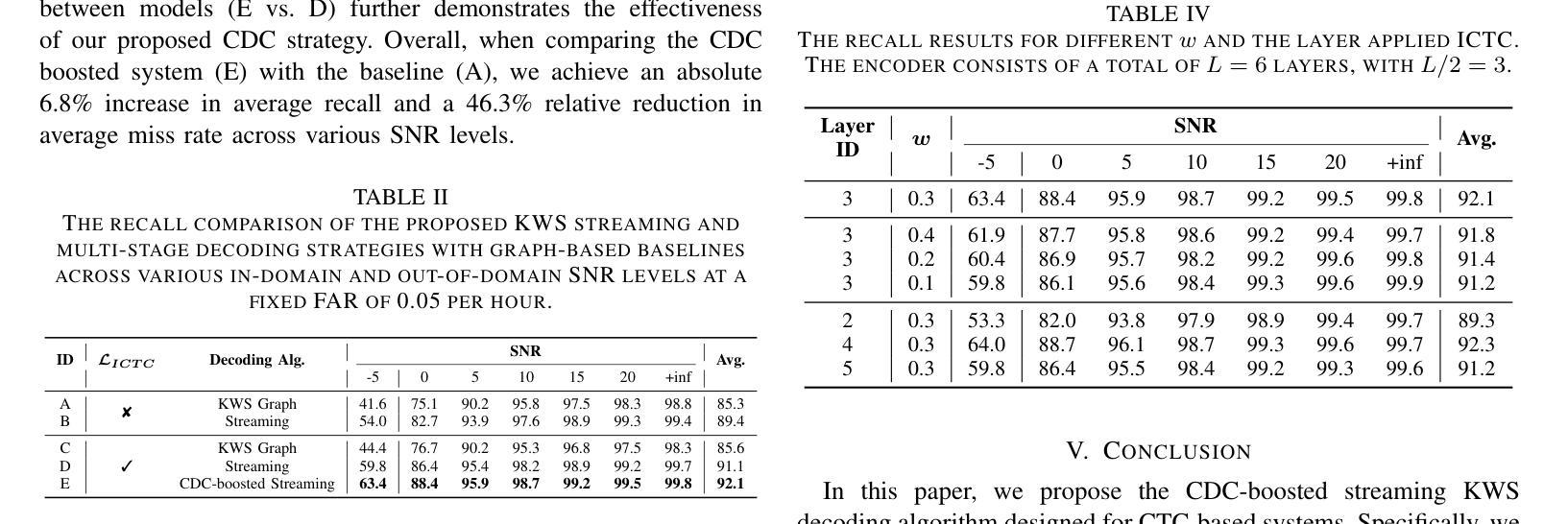
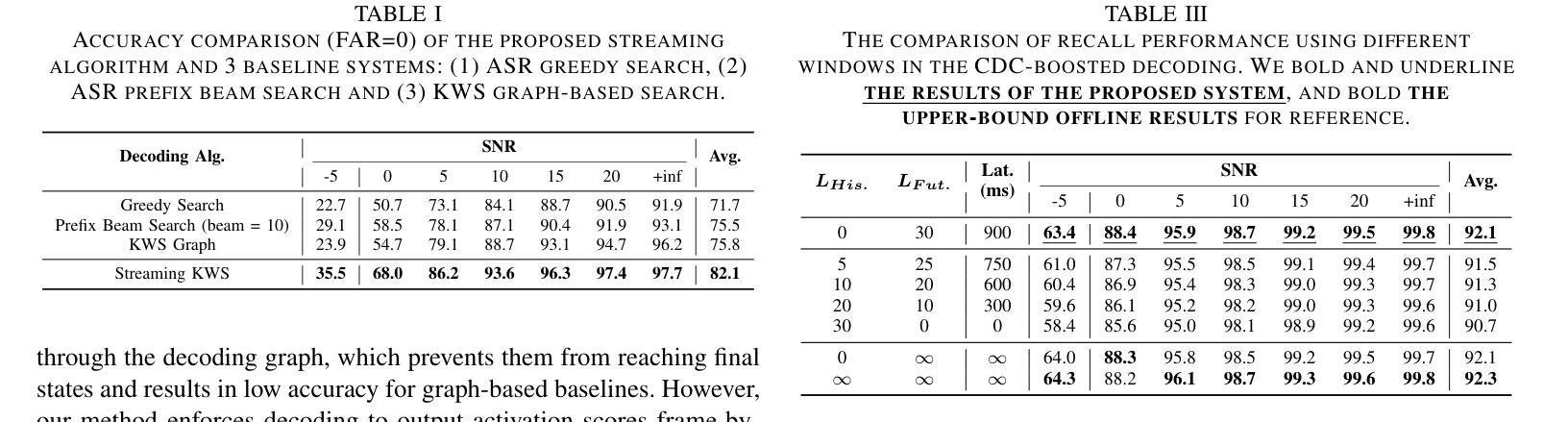
Streaming Keyword Spotting Boosted by Cross-layer Discrimination Consistency
Authors:Yu Xi, Haoyu Li, Xiaoyu Gu, Hao Li, Yidi Jiang, Kai Yu
Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC), a non-autoregressive training criterion, is widely used in online keyword spotting (KWS). However, existing CTC-based KWS decoding strategies either rely on Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), which performs suboptimally due to its broad search over the acoustic space without keyword-specific optimization, or on KWS-specific decoding graphs, which are complex to implement and maintain. In this work, we propose a streaming decoding algorithm enhanced by Cross-layer Discrimination Consistency (CDC), tailored for CTC-based KWS. Specifically, we introduce a streamlined yet effective decoding algorithm capable of detecting the start of the keyword at any arbitrary position. Furthermore, we leverage discrimination consistency information across layers to better differentiate between positive and false alarm samples. Our experiments on both clean and noisy Hey Snips datasets show that the proposed streaming decoding strategy outperforms ASR-based and graph-based KWS baselines. The CDC-boosted decoding further improves performance, yielding an average absolute recall improvement of 6.8% and a 46.3% relative reduction in the miss rate compared to the graph-based KWS baseline, with a very low false alarm rate of 0.05 per hour.
连接时序分类(CTC)是一种非自回归训练准则,广泛应用于在线关键词识别(KWS)。然而,现有的基于CTC的KWS解码策略要么依赖于自动语音识别(ASR),由于其在声学空间上的广泛搜索而没有针对关键词的特定优化,导致性能不佳;要么依赖于特定的KWS解码图,这些图复杂且难以实施和维护。在这项工作中,我们提出了一种通过跨层鉴别一致性(CDC)增强的流式解码算法,适用于基于CTC的KWS。具体来说,我们引入了一种简洁有效的解码算法,能够在任意位置检测关键词的开始。此外,我们利用跨层的鉴别一致性信息来更好地区分正负样本。我们在干净和嘈杂的Hey Snips数据集上的实验表明,所提出的流式解码策略优于基于ASR和基于图的KWS基线。通过CDC增强的解码进一步提高了性能,与基于图的KWS基线相比,平均绝对召回率提高了6.8%,漏报率相对降低了46.3%,且每小时误报率非常低,为0.05。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Submitted to ICASSP2025
Summary
CTC(连接时序分类)在非自回归训练准则中广泛应用于在线关键词识别(KWS)。然而,现有的CTC-based KWS解码策略依赖于自动语音识别(ASR),性能不佳,因为它在声学空间进行广泛搜索而没有关键词特定优化。或依赖于复杂的KWS特定解码图。本研究提出了一种由跨层鉴别一致性(CDC)增强的流式解码算法,适用于CTC-based KWS。该算法能有效检测关键词的起始位置,并借助跨层的鉴别一致性信息,更好地区分正样本和误警样本。在Hey Snips数据集上的实验表明,所提流式解码策略优于基于ASR和基于图的KWS基线方法。CDC增强的解码进一步提高了性能,与基于图的KWS基线相比,平均绝对召回率提高了6.8%,误报率降低了46.3%,且每小时误警率很低,为每小时0.05次。
Key Takeaways
- CTC在非自回归训练准则中广泛用于在线关键词识别(KWS)。
- 现有CTC-based KWS解码策略存在依赖自动语音识别(ASR)和复杂实施的KWS特定解码图的问题。
- 本研究提出了一种由跨层鉴别一致性(CDC)增强的流式解码算法,有效检测关键词起始位置并区分正、误警样本。
- 所提流式解码策略优于基于ASR和基于图的KWS基线方法。
- CDC增强的解码提高了性能,平均绝对召回率提高,误报率降低。
- 该方法在Hey Snips数据集上的实验验证具有较低误警率。
点此查看论文截图

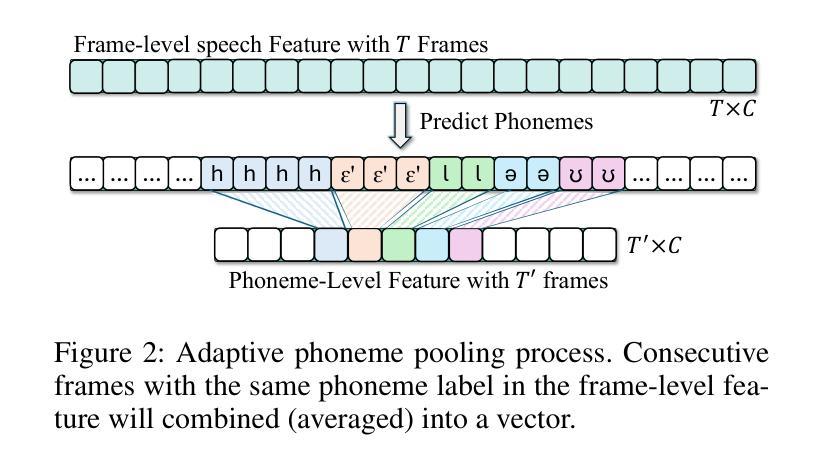
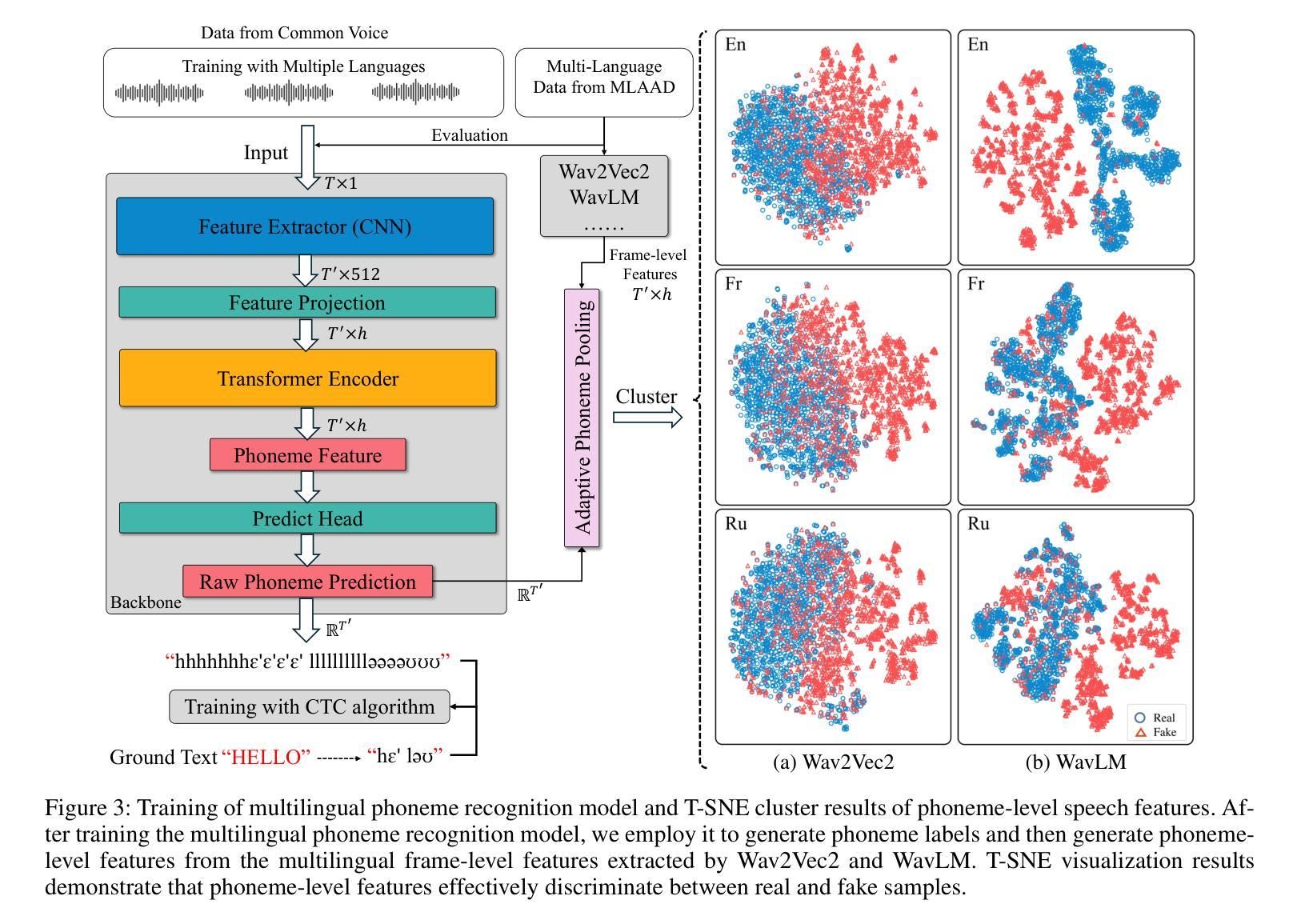
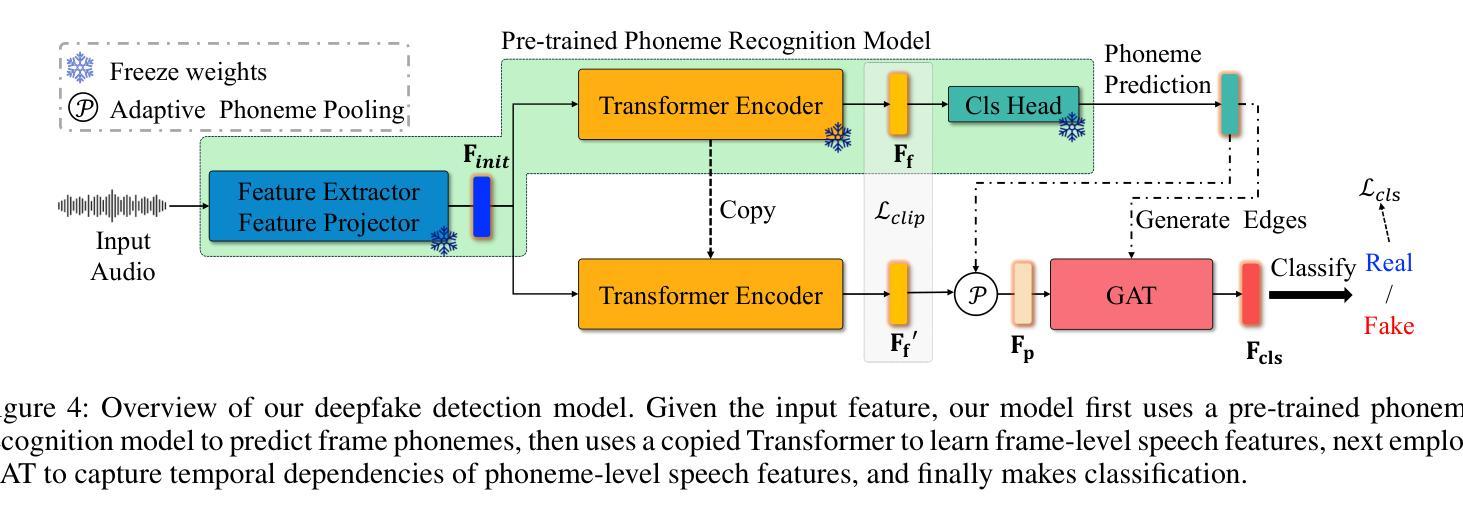
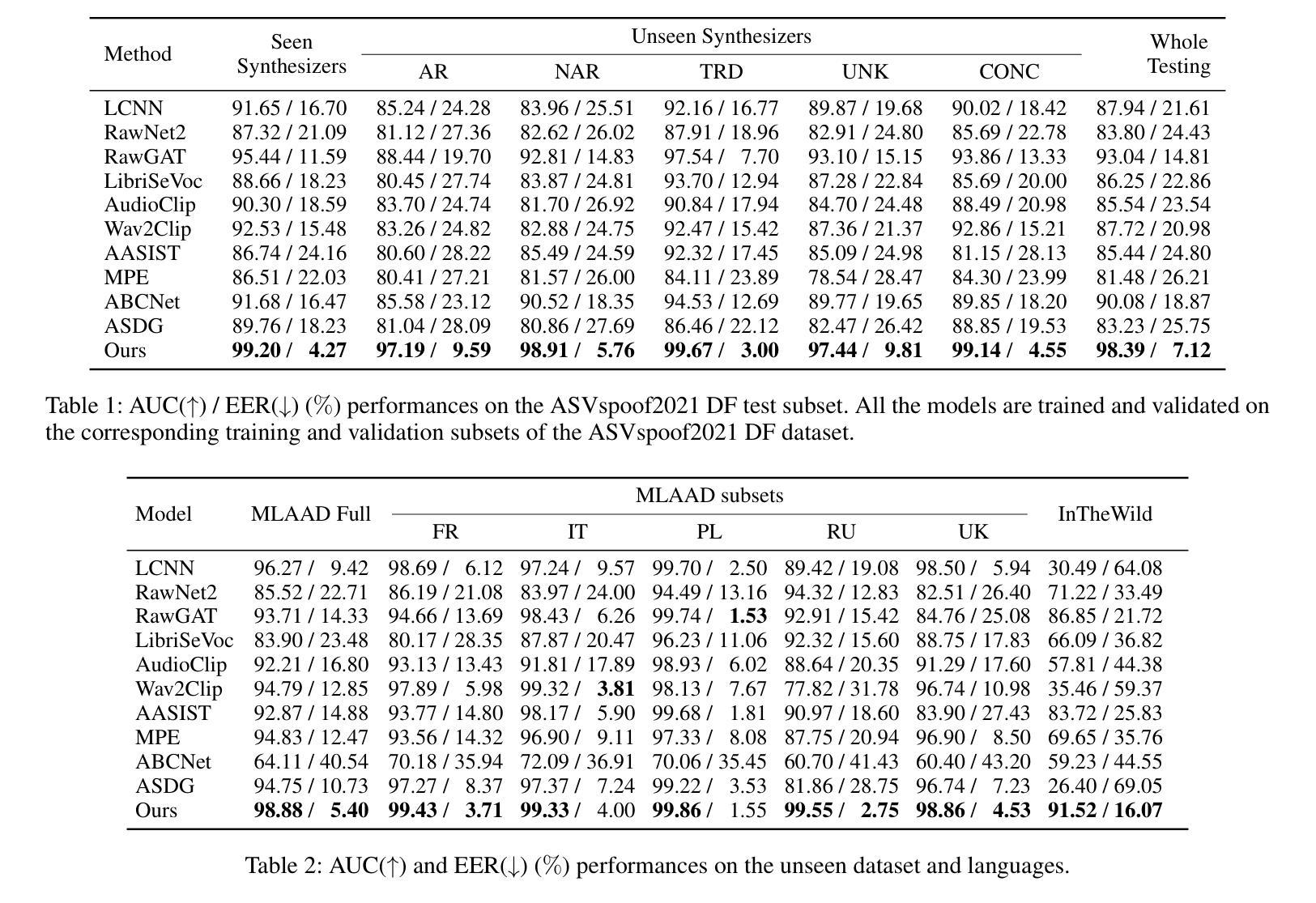
Phoneme-Level Feature Discrepancies: A Key to Detecting Sophisticated Speech Deepfakes
Authors:Kuiyuan Zhang, Zhongyun Hua, Rushi Lan, Yushu Zhang, Yifang Guo
Recent advancements in text-to-speech and speech conversion technologies have enabled the creation of highly convincing synthetic speech. While these innovations offer numerous practical benefits, they also cause significant security challenges when maliciously misused. Therefore, there is an urgent need to detect these synthetic speech signals. Phoneme features provide a powerful speech representation for deepfake detection. However, previous phoneme-based detection approaches typically focused on specific phonemes, overlooking temporal inconsistencies across the entire phoneme sequence. In this paper, we develop a new mechanism for detecting speech deepfakes by identifying the inconsistencies of phoneme-level speech features. We design an adaptive phoneme pooling technique that extracts sample-specific phoneme-level features from frame-level speech data. By applying this technique to features extracted by pre-trained audio models on previously unseen deepfake datasets, we demonstrate that deepfake samples often exhibit phoneme-level inconsistencies when compared to genuine speech. To further enhance detection accuracy, we propose a deepfake detector that uses a graph attention network to model the temporal dependencies of phoneme-level features. Additionally, we introduce a random phoneme substitution augmentation technique to increase feature diversity during training. Extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our method over existing state-of-the-art detection methods.
近期文本转语音和语音转换技术的进展使得创建高度逼真的合成语音成为可能。虽然这些创新提供了许多实际好处,但它们在被恶意误用时也会带来巨大的安全挑战。因此,检测这些合成语音信号变得极为迫切。音素特征为深度伪造检测提供了强大的语音表示。然而,基于音素的检测方法通常侧重于特定的音素,忽略了整个音素序列的时间不一致性。在本文中,我们开发了一种通过识别音素级语音特征的不一致性来检测语音深度伪造的新机制。我们设计了一种自适应的音素池技术,从帧级语音数据中提取样本特定的音素级特征。我们将该技术应用于在之前未见过的深度伪造数据集上预训练的音频模型所提取的特征,结果表明,与真实语音相比,深度伪造样本在音素级上通常表现出不一致性。为了进一步提高检测精度,我们提出了一种使用图注意力网络对音素级特征的时间依赖性进行建模的深度伪造检测器。此外,我们还引入了一种随机音素替换增强技术,以增加训练过程中的特征多样性。在四个基准数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的方法优于现有的最先进的检测方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期文本转语音和语音转换技术的进展为创建高度逼真的合成语音提供了可能。这些技术带来诸多实用优势的同时,也存在恶意滥用带来的重大安全隐患。因此,检测合成语音信号变得至关重要。本文提出一种基于音素级语音特征不一致性的新型深度伪造检测机制。设计自适应音素池化技术,从帧级语音数据中提取样本特定的音素级特征。通过将此项技术应用于预训练音频模型提取的特征上,我们证明与真实语音相比,深度伪造样本的音素级存在不一致性。为提高检测准确性,我们提出使用图注意力网络的深度伪造检测器,对音素级特征的时序依赖性进行建模。此外,引入随机音素替换增强技术以提高训练过程中的特征多样性。在四个基准数据集上的实验表明,我们的方法优于现有最先进的检测方法。
Key Takeaways
- 近期文本转语音技术带来实用优势,但也存在安全隐患。
- 检测合成语音信号的重要性。
- 提出一种新型深度伪造检测机制,基于音素级语音特征的不一致性。
- 设计自适应音素池化技术,提取样本特定的音素级特征。
- 深度伪造样本与真实语音在音素级存在不一致性。
- 使用图注意力网络对音素级特征的时序依赖性进行建模,提高检测准确性。
- 引入随机音素替换增强技术,增加训练过程中的特征多样性。
点此查看论文截图

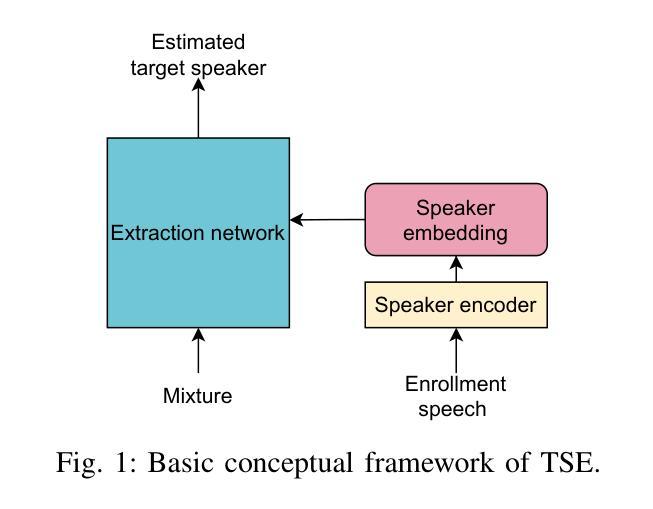
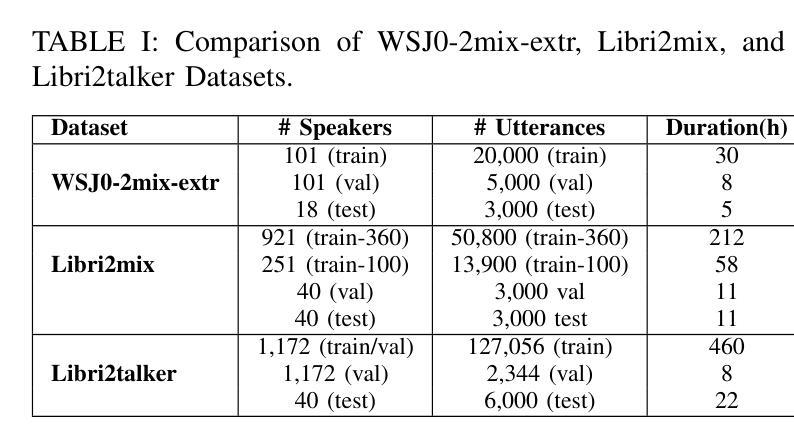
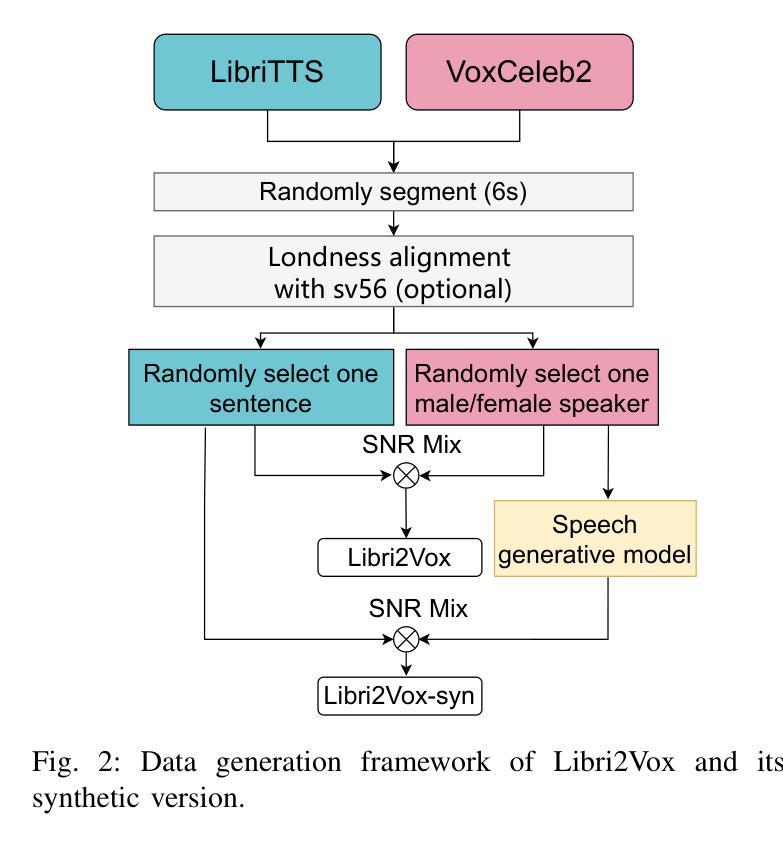
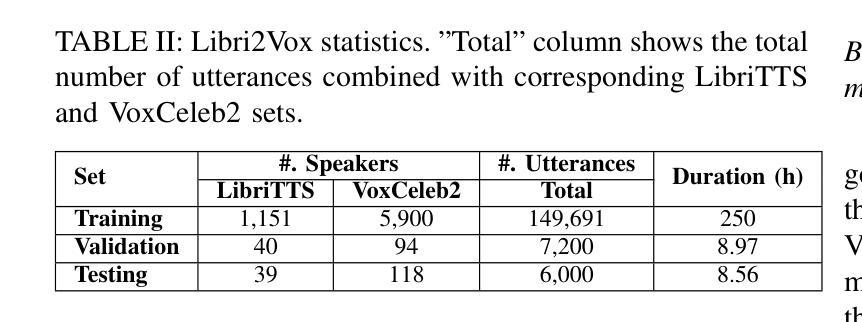
Libri2Vox Dataset: Target Speaker Extraction with Diverse Speaker Conditions and Synthetic Data
Authors:Yun Liu, Xuechen Liu, Xiaoxiao Miao, Junichi Yamagishi
Target speaker extraction (TSE) is essential in speech processing applications, particularly in scenarios with complex acoustic environments. Current TSE systems face challenges in limited data diversity and a lack of robustness in real-world conditions, primarily because they are trained on artificially mixed datasets with limited speaker variability and unrealistic noise profiles. To address these challenges, we propose Libri2Vox, a new dataset that combines clean target speech from the LibriTTS dataset with interference speech from the noisy VoxCeleb2 dataset, providing a large and diverse set of speakers under realistic noisy conditions. We also augment Libri2Vox with synthetic speakers generated using state-of-the-art speech generative models to enhance speaker diversity. Additionally, to further improve the effectiveness of incorporating synthetic data, curriculum learning is implemented to progressively train TSE models with increasing levels of difficulty. Extensive experiments across multiple TSE architectures reveal varying degrees of improvement, with SpeakerBeam demonstrating the most substantial gains: a 1.39 dB improvement in signal-to-distortion ratio (SDR) on the Libri2Talker test set compared to baseline training. Building upon these results, we further enhanced performance through our speaker similarity-based curriculum learning approach with the Conformer architecture, achieving an additional 0.78 dB improvement over conventional random sampling methods in which data samples are randomly selected from the entire dataset. These results demonstrate the complementary benefits of diverse real-world data, synthetic speaker augmentation, and structured training strategies in building robust TSE systems.
目标说话人提取(TSE)在语音处理应用中至关重要,特别是在复杂声学环境场景中。当前的TSE系统面临数据多样性有限和在实际环境中的稳健性不足的挑战,主要是因为它们是在人工混合数据集上训练的,具有有限的说话人变体和不太现实的噪声分布。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了Libri2Vox数据集,该数据集将LibriTTS的干净目标语音与VoxCeleb2的干扰语音相结合,在真实噪声条件下提供了大量且多样的说话人数据。我们还使用最先进的语音生成模型生成的合成说话人来增强Libri2Vox的说话人多样性。此外,为了进一步提高合成数据的有效性,我们实施了课程学习,以逐步训练具有不同难度的TSE模型。跨多个TSE架构的广泛实验显示出了不同程度的改进,其中SpeakerBeam的改进最为显著:与基线训练相比,在Libri2Talker测试集上,信号失真率(SDR)提高了1.39分贝。基于这些结果,我们进一步采用基于说话人相似性的课程学习方法,采用Conformer架构,相较于传统的随机采样方法,在数据样本从整个数据集中随机选择的情况下,实现了额外的0.78分贝的改进。这些结果证明了现实世界的多样数据、合成说话人增强和结构化训练策略在构建稳健的TSE系统中的互补效益。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出一个新的数据集Libri2Vox,用于解决目标说话人提取(TSE)在复杂声学环境下的挑战。Libri2Vox结合了LibriTTS的干净目标语音和VoxCeleb2的干扰语音,提供了大量真实噪声条件下的不同说话人数据。此外,还使用先进的语音生成模型生成合成说话人来增强说话人的多样性。为了进一步提高合成数据的有效性,实施课程学习逐步训练不同难度的TSE模型。实验表明,SpeakerBeam表现最佳,在Libri2Talker测试集上信号失真比(SDR)提高了1.39分贝。在此基础上,采用基于说话人相似性的课程学习方法与Conformer架构进一步提高了性能,与传统随机采样方法相比,实现了额外的0.78分贝的改进。结果表明,多样现实数据、合成说话人增强和结构化训练策略在构建稳健的TSE系统中具有互补优势。
关键见解
- 引入Libri2Vox数据集,结合真实噪声条件下的干净目标语音和干扰语音,提高目标说话人提取(TSE)的鲁棒性。
- 通过结合先进的语音生成模型,增强说话人多样性。
- 实施课程学习,逐步训练TSE模型,提高模型的有效性。
- 实验显示SpeakerBeam在Libri2Talker测试集上的SDR有显著改善。
- 基于说话人相似性的课程学习方法与Conformer架构结合,实现了性能的提升。
- 对比传统随机采样方法,基于说话人相似性的采样展现出更好的效果。
- 多样化的现实数据、合成说话人增强和结构化训练策略在构建稳健TSE系统中具有关键作用。
点此查看论文截图

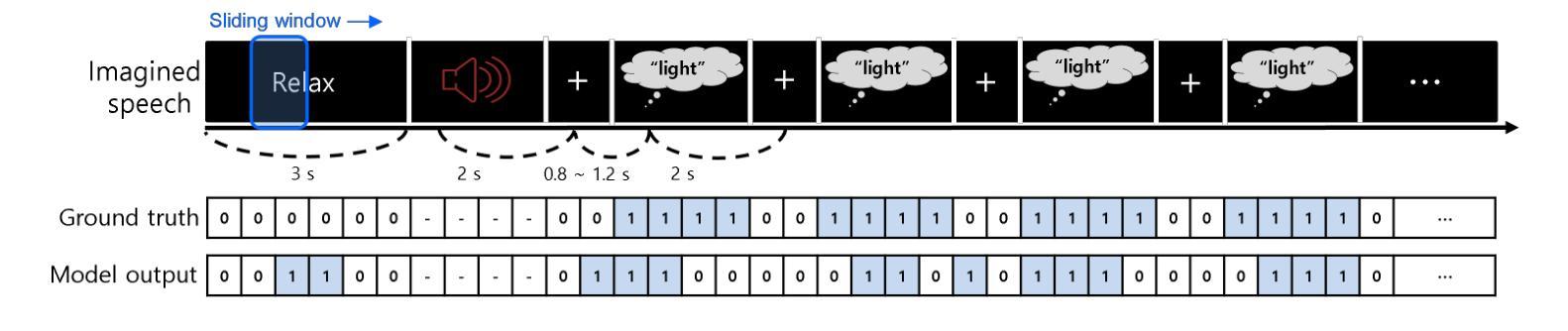
Imagined Speech State Classification for Robust Brain-Computer Interface
Authors:Byung-Kwan Ko, Jun-Young Kim, Seo-Hyun Lee
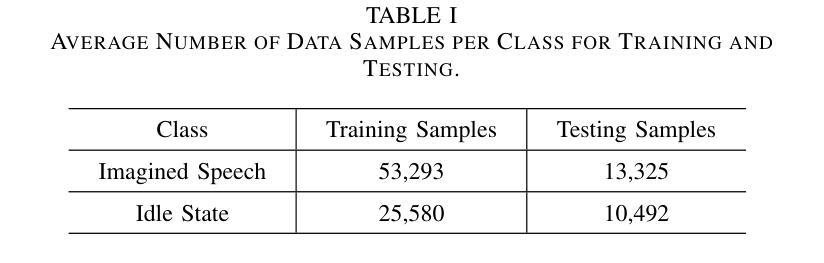
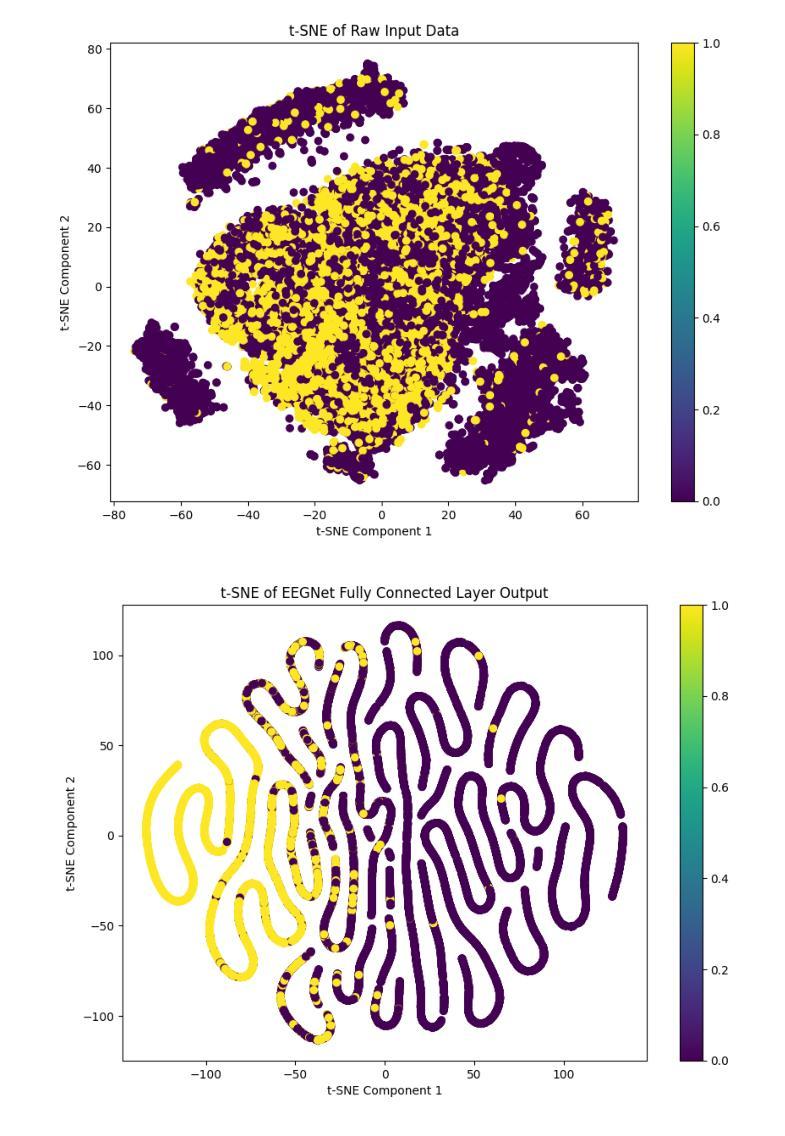
This study examines the effectiveness of traditional machine learning classifiers versus deep learning models for detecting the imagined speech using electroencephalogram data. Specifically, we evaluated conventional machine learning techniques such as CSP-SVM and LDA-SVM classifiers alongside deep learning architectures such as EEGNet, ShallowConvNet, and DeepConvNet. Machine learning classifiers exhibited significantly lower precision and recall, indicating limited feature extraction capabilities and poor generalization between imagined speech and idle states. In contrast, deep learning models, particularly EEGNet, achieved the highest accuracy of 0.7080 and an F1 score of 0.6718, demonstrating their enhanced ability in automatic feature extraction and representation learning, essential for capturing complex neurophysiological patterns. These findings highlight the limitations of conventional machine learning approaches in brain-computer interface (BCI) applications and advocate for adopting deep learning methodologies to achieve more precise and reliable classification of detecting imagined speech. This foundational research contributes to the development of imagined speech-based BCI systems.
本研究探讨了传统机器学习分类器与深度学习模型在利用脑电图数据检测想象中的语音方面的有效性。具体来说,我们评估了传统的机器学习技术,如CSP-SVM和LDA-SVM分类器,以及深度学习架构,如EEGNet、ShallowConvNet和DeepConvNet。机器学习分类器的精度和召回率明显较低,表明其在特征提取能力方面有限,且在想象语言和空闲状态之间的泛化能力较差。相比之下,深度学习模型,尤其是EEGNet,达到了最高的0.7080的准确率和0.6718的F1分数,证明了其在自动特征提取和表示学习方面的增强能力,这对于捕捉复杂的神经生理模式至关重要。这些发现突显了传统机器学习方法在脑机接口(BCI)应用中的局限性,并提倡采用深度学习方法来实现更精确、更可靠的想象语言检测分类。这项基础研究为基于想象语言的BCI系统的发展做出了贡献。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文探讨了传统机器学习分类器与深度学习模型在利用脑电图数据检测想象语言方面的有效性对比。研究评估了传统机器学习技术(如CSP-SVM和LDA-SVM分类器)和深度学习架构(如EEGNet、ShallowConvNet和DeepConvNet)的表现。结果显示,机器学习分类器的精度和召回率较低,表明其在特征提取和想象语言与静止状态间的泛化能力有限。相比之下,深度学习模型,尤其是EEGNet,达到了最高的0.7080的准确率和0.6718的F1分数,证明了其在自动特征提取和表示学习方面的优势,这对于捕捉复杂的神经生理模式至关重要。研究强调了传统机器学习方法在脑机接口(BCI)应用中的局限性,并主张采用深度学习方法以实现更精确、可靠的想象语言检测分类。该研究为基于想象语言的BCI系统发展奠定了基础。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究对比了传统机器学习分类器和深度学习模型在想象语言检测中的表现。
- 机器学习分类器在特征提取和泛化能力上表现有限。
- 深度学习模型,尤其是EEGNet,表现出较高的准确率和F1分数。
- 深度学习模型具有自动特征提取和表示学习的优势,能捕捉复杂的神经生理模式。
- 传统机器学习方法在脑机接口(BCI)应用中存在局限性。
- 研究主张采用深度学习方法以实现更精确、可靠的想象语言检测分类。
点此查看论文截图

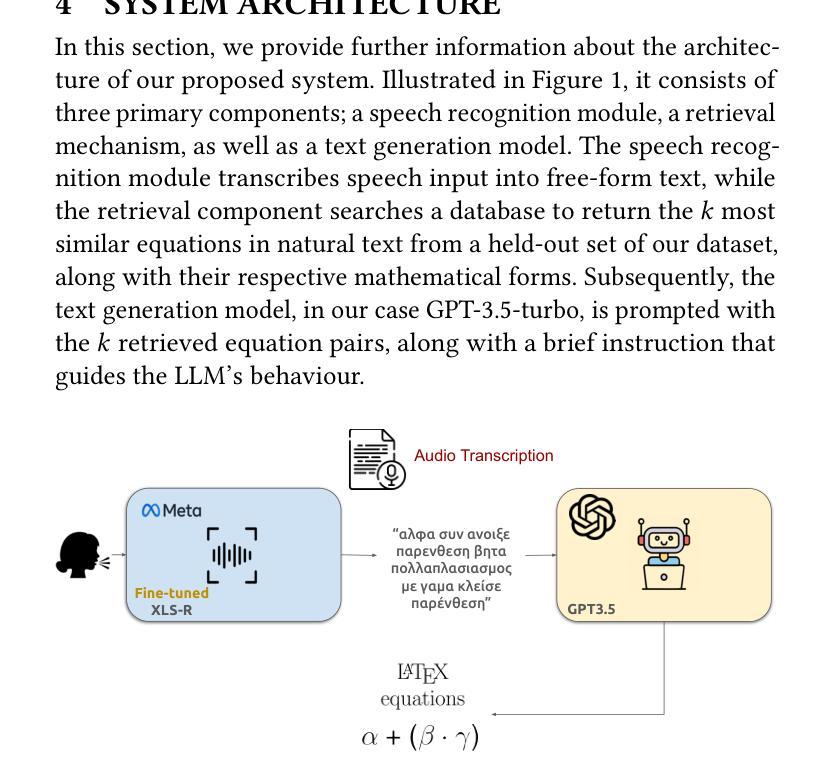
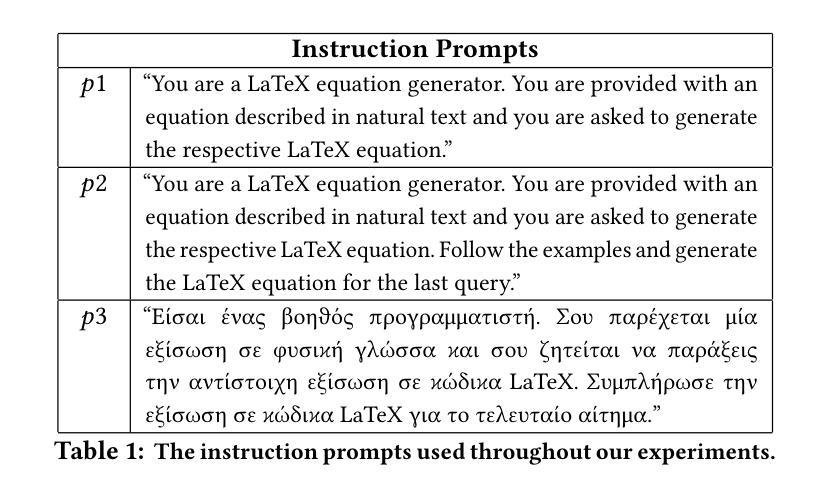
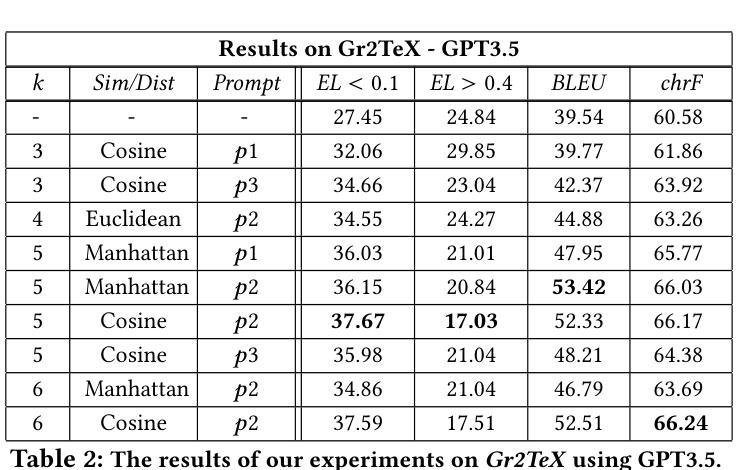
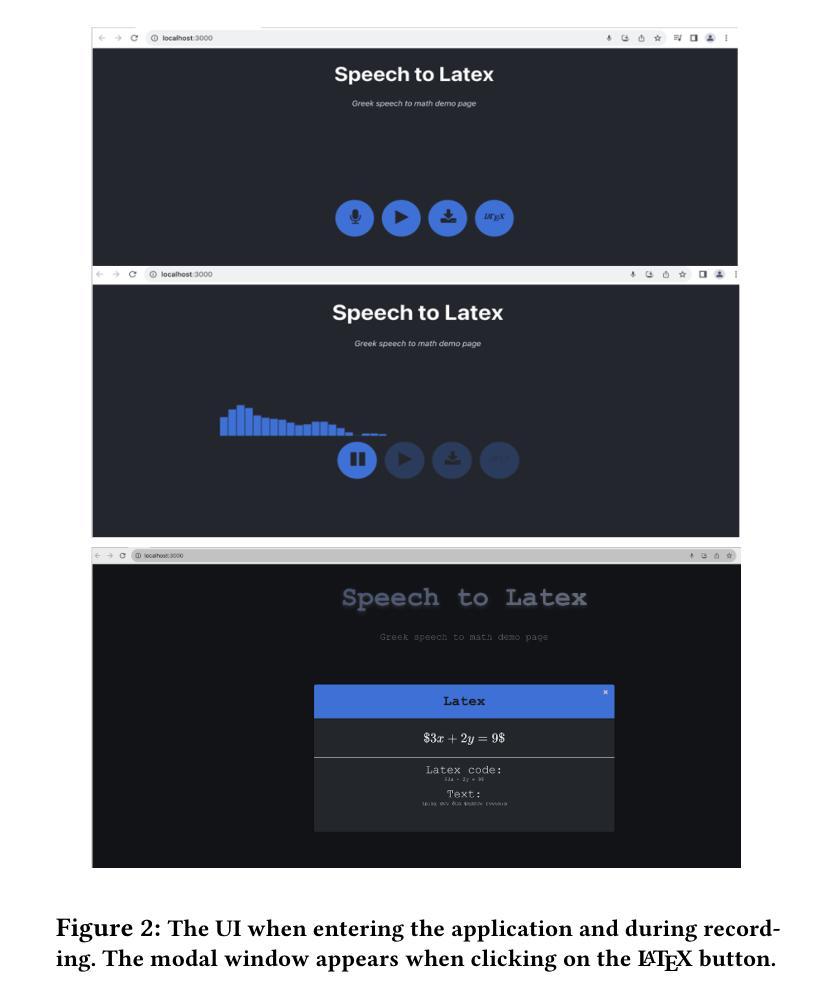
Greek2MathTex: A Greek Speech-to-Text Framework for LaTeX Equations Generation
Authors:Evangelia Gkritzali, Panagiotis Kaliosis, Sofia Galanaki, Elisavet Palogiannidi, Theodoros Giannakopoulos
In the vast majority of the academic and scientific domains, LaTeX has established itself as the de facto standard for typesetting complex mathematical equations and formulae. However, LaTeX’s complex syntax and code-like appearance present accessibility barriers for individuals with disabilities, as well as those unfamiliar with coding conventions. In this paper, we present a novel solution to this challenge through the development of a novel speech-to-LaTeX equations system specifically designed for the Greek language. We propose an end-to-end system that harnesses the power of Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to enable users to verbally dictate mathematical expressions and equations in natural language, which are subsequently converted into LaTeX format. We present the architecture and design principles of our system, highlighting key components such as the ASR engine, the LLM-based prompt-driven equations generation mechanism, as well as the application of a custom evaluation metric employed throughout the development process. We have made our system open source and available at https://github.com/magcil/greek-speech-to-math.
在学术和科学领域的绝大多数场景中,LaTeX已确立了自己在排版复杂的数学方程和公式方面的实际标准地位。然而,LaTeX的复杂语法和类似于代码的界面为残疾人以及不熟悉编码规范的人设置了访问障碍。在本文中,我们针对这一挑战提出了一种新颖的解决方案,开发了一种专门用于希腊语的新型语音到LaTeX方程系统。我们提出了一种端到端的系统,它利用自动语音识别(ASR)和自然语言处理(NLP)技术的力量,使用户能够用自然语言口头表述数学表达式和方程,随后将其转换为LaTeX格式。我们介绍了系统的架构和设计原则,重点介绍了关键组件,如ASR引擎、基于LLM的提示驱动方程生成机制,以及开发过程中使用的自定义评估指标的应用。我们的系统已开源,可在https://github.com/magcil/greek-speech-to-math找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 4 pages, 2 figures, SETN2024: 13th EETN Conference on Artificial Intelligence
Summary
本文介绍了一个针对希腊语的新型语音到LaTeX方程系统。此系统利用自动语音识别(ASR)和自然语言处理(NLP)技术,使用户能够用自然语言口述数学表达式和方程,并将其转换为LaTeX格式。文中介绍了系统的架构和设计原则,包括ASR引擎、基于LLM的提示驱动方程生成机制以及自定义评估指标的应用。
Key Takeaways
- LaTeX是学术和科学领域中用于排版复杂数学方程和公式的标准。
- LaTeX的复杂语法和类似代码的外观对残障人士和不熟悉编码规范的人造成了访问障碍。
- 针对这一问题,提出了一种新型语音到LaTeX方程系统,特别适用于希腊语。
- 系统利用自动语音识别(ASR)和自然语言处理(NLP)技术,使用户能够用自然语言表述数学方程。
- 系统将用户的口语数学表达式和方程转换为LaTeX格式。
- 介绍了系统的架构、设计原则、关键组件(如ASR引擎和基于LLM的提示驱动方程生成机制)。
- 系统已开源,并可通过特定链接进行访问。
点此查看论文截图

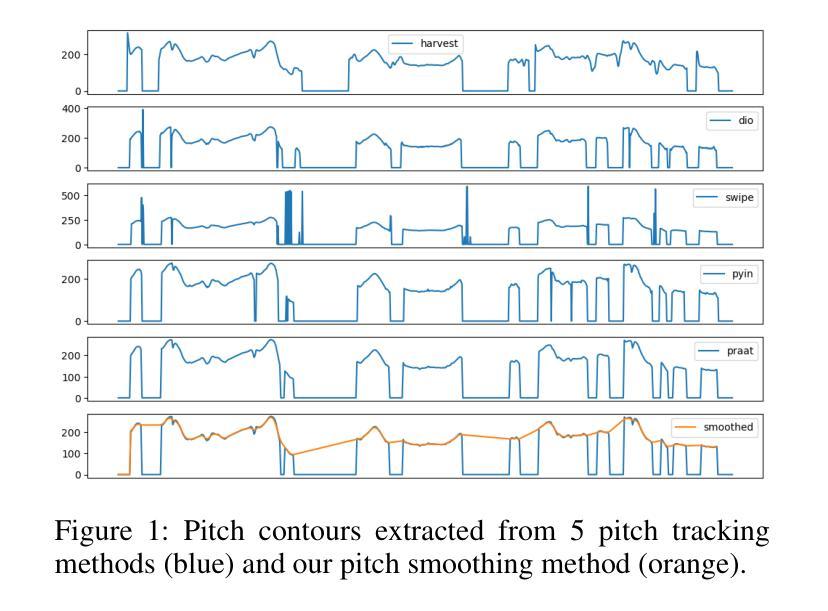
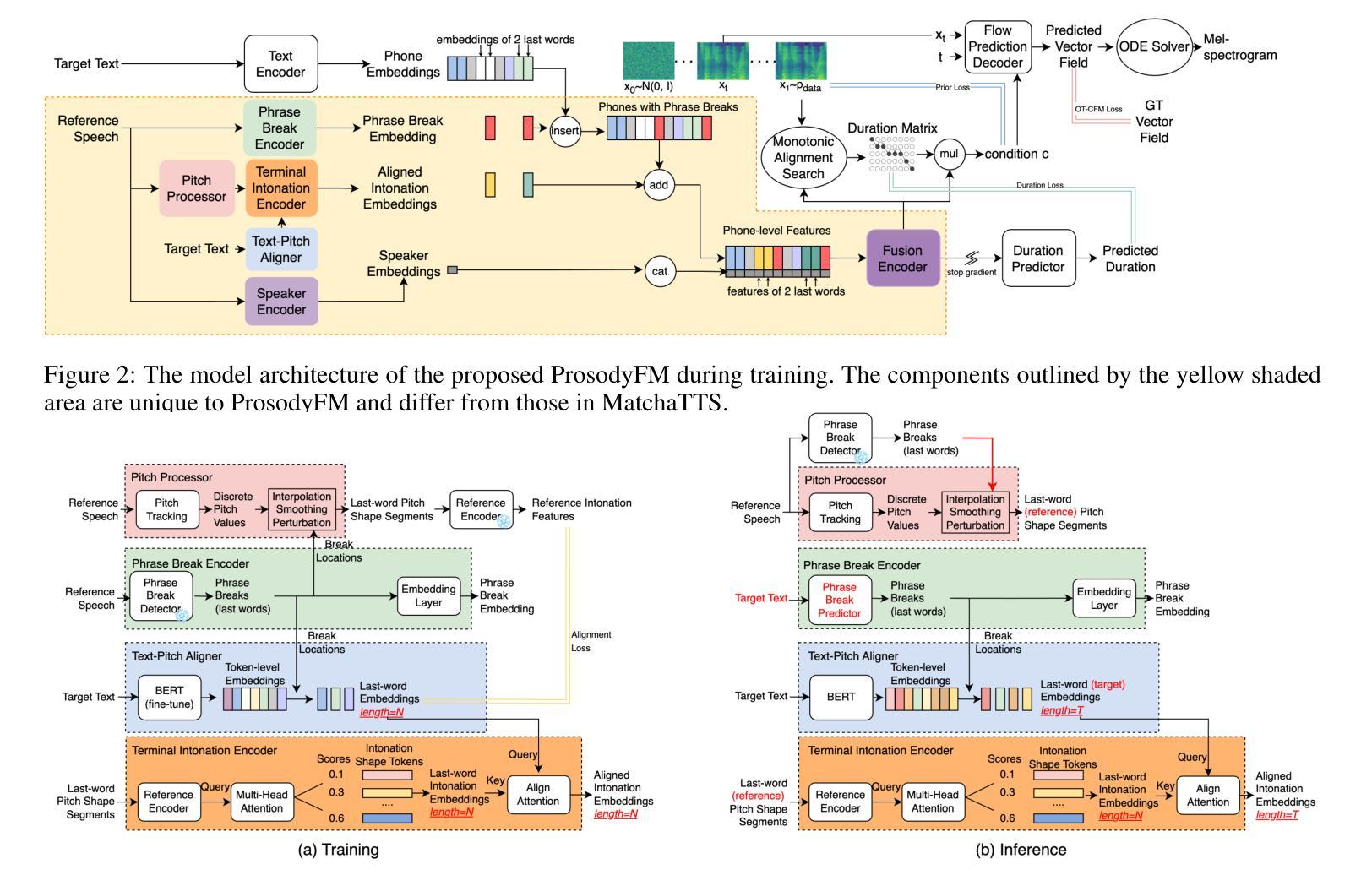
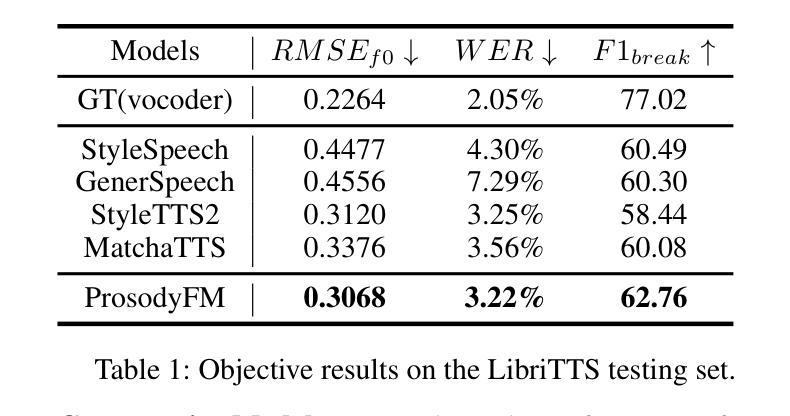
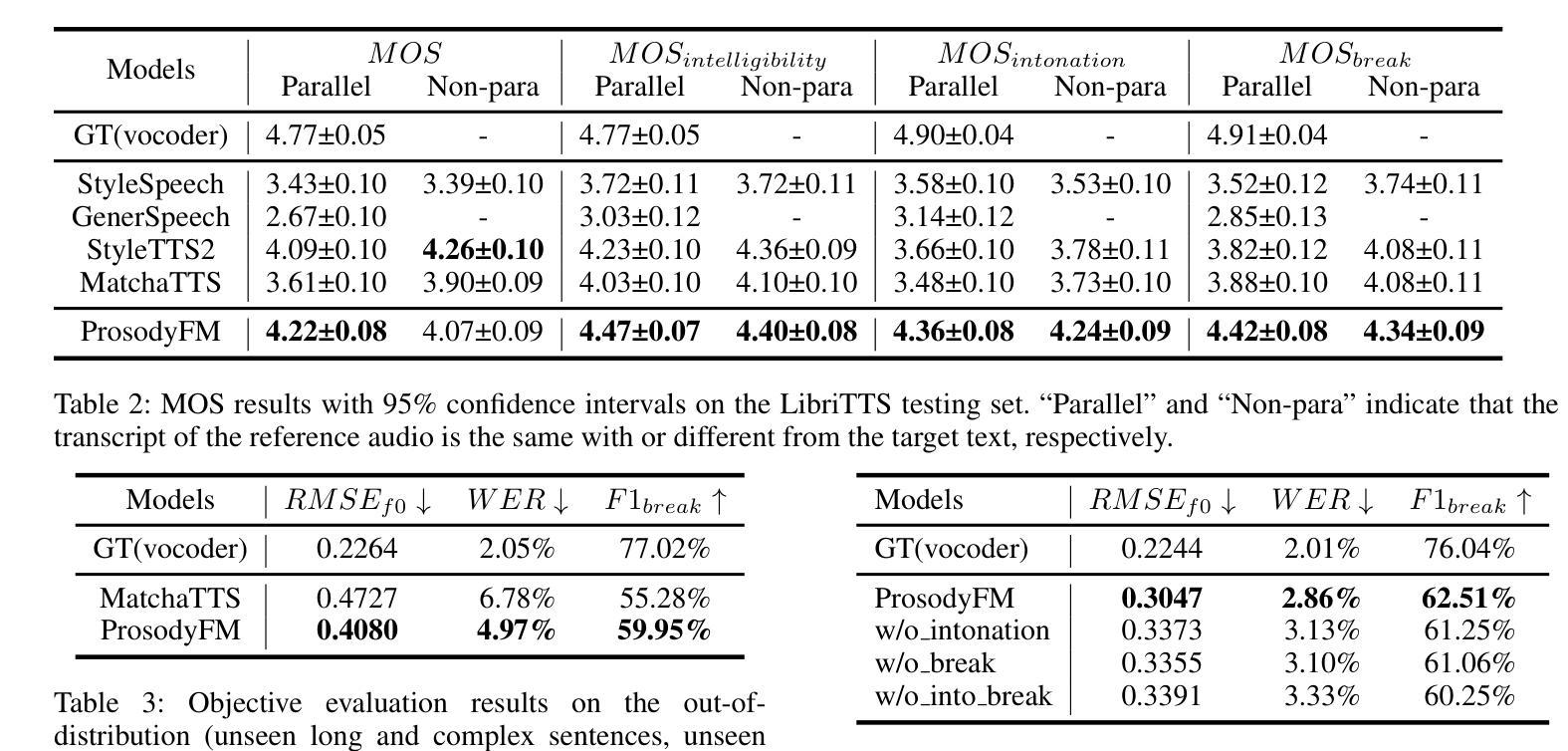
ProsodyFM: Unsupervised Phrasing and Intonation Control for Intelligible Speech Synthesis
Authors:Xiangheng He, Junjie Chen, Zixing Zhang, Björn W. Schuller
Prosody contains rich information beyond the literal meaning of words, which is crucial for the intelligibility of speech. Current models still fall short in phrasing and intonation; they not only miss or misplace breaks when synthesizing long sentences with complex structures but also produce unnatural intonation. We propose ProsodyFM, a prosody-aware text-to-speech synthesis (TTS) model with a flow-matching (FM) backbone that aims to enhance the phrasing and intonation aspects of prosody. ProsodyFM introduces two key components: a Phrase Break Encoder to capture initial phrase break locations, followed by a Duration Predictor for the flexible adjustment of break durations; and a Terminal Intonation Encoder which integrates a set of intonation shape tokens combined with a novel Pitch Processor for more robust modeling of human-perceived intonation change. ProsodyFM is trained with no explicit prosodic labels and yet can uncover a broad spectrum of break durations and intonation patterns. Experimental results demonstrate that ProsodyFM can effectively improve the phrasing and intonation aspects of prosody, thereby enhancing the overall intelligibility compared to four state-of-the-art (SOTA) models. Out-of-distribution experiments show that this prosody improvement can further bring ProsodyFM superior generalizability for unseen complex sentences and speakers. Our case study intuitively illustrates the powerful and fine-grained controllability of ProsodyFM over phrasing and intonation.
韵律包含超越单词字面意义的丰富信息,这对于语音的清晰度至关重要。当前模型在短语和语调方面仍然不足;它们在合成具有复杂结构的长句子时,不仅会遗漏或错误放置断点,而且会产生不自然的语调。我们提出了ProsodyFM,这是一种具有流匹配(FM)骨干的韵律感知文本到语音(TTS)合成模型,旨在增强韵律的短语和语调方面。ProsodyFM引入了两个关键组件:一个短语断裂编码器,用于捕捉初始短语断裂位置,随后是一个持续时间预测器,用于灵活地调整断裂持续时间;以及一个终端语调编码器,它结合了语调形状标记和一种新的音调处理器,以更稳健地模拟人类感知到的语调变化。ProsodyFM不需要明确的韵律标签进行训练,但能够发现广泛的断裂持续时间和语调模式。实验结果表明,与四种最先进模型相比,ProsodyFM可以有效地改善韵律的短语和语调方面,从而提高整体清晰度。分布外实验表明,这种韵律改进可以进一步提高ProsodyFM对未见过的复杂句子和说话人的泛化能力。我们的案例研究直观地说明了ProsodyFM在短语和语调上的强大和精细可控性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
文本强调了在语音中,除了字面意义外,韵律还包含丰富的信息,这对语音的可懂度至关重要。当前模型在合成具有复杂结构的长句子时,存在断句和语调上的不足。为此,提出了ProsodyFM,一个基于韵律感知的文本到语音合成(TTS)模型,旨在增强断句和语调方面的韵律。该模型引入了两个关键组件:短语断句编码器用于捕捉初始断句位置,持续时间预测器用于灵活调整断句持续时间;终端语调编码器集成了语调形状标记和新颖的音调处理器,以更稳健地模拟人类感知的语调变化。实验结果表明,与四种最新技术模型相比,ProsodyFM能有效改善断句和语调方面的韵律,从而提高整体可懂度。此外,该模型在未见复杂句子和说话人的实验中显示出良好的通用性。我们的案例研究直观地展示了ProsodyFM在断句和语调上的强大和精细可控性。
Key Takeaways
- 语音中的韵律包含超越单词字面意义的信息,对语音的可懂度至关重要。
- 当前文本到语音合成模型在断句和语调方面存在不足,尤其在处理复杂长句时。
- 提出了一种新的TTS模型——ProsodyFM,旨在解决上述问题,提高语音的断句和语调表现。
- ProsodyFM引入短语断句编码器和持续时间预测器,用于捕捉和调整断句位置和持续时间。
- 终端语调编码器集成了语调形状标记和音调处理器,模拟人类语调变化感知。
- 实验结果显示ProsodyFM能提高语音的智听性和整体可懂度,相较于其他模型具有优势。
点此查看论文截图

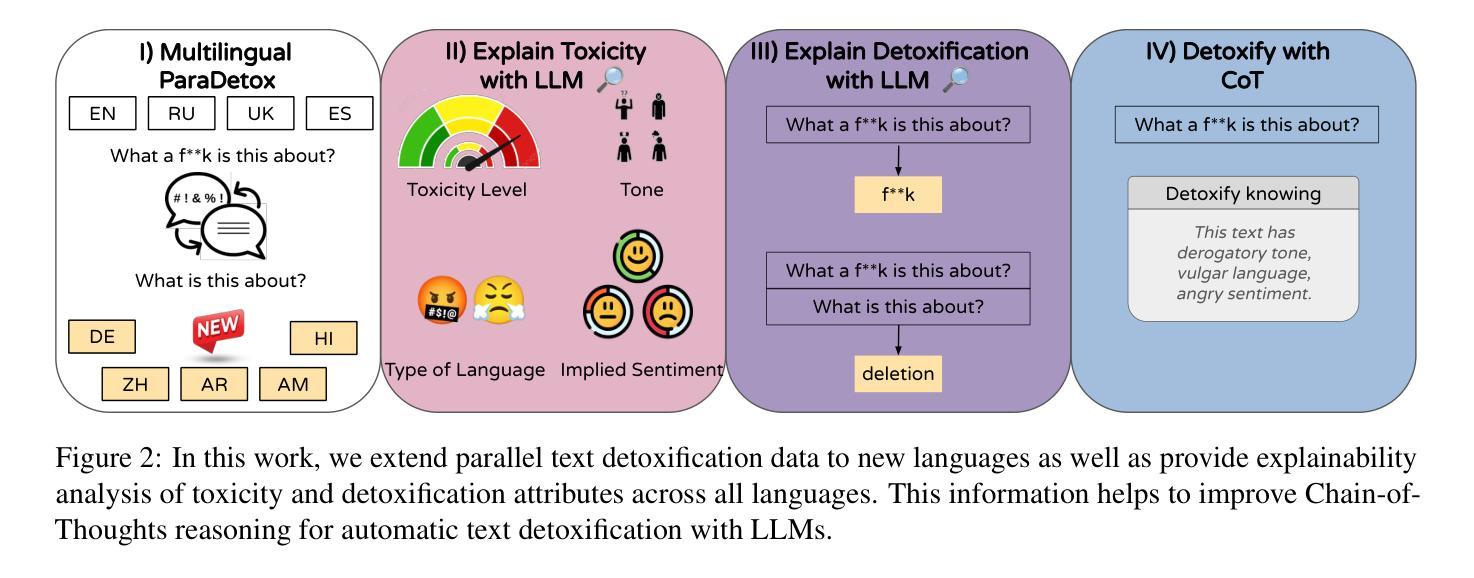
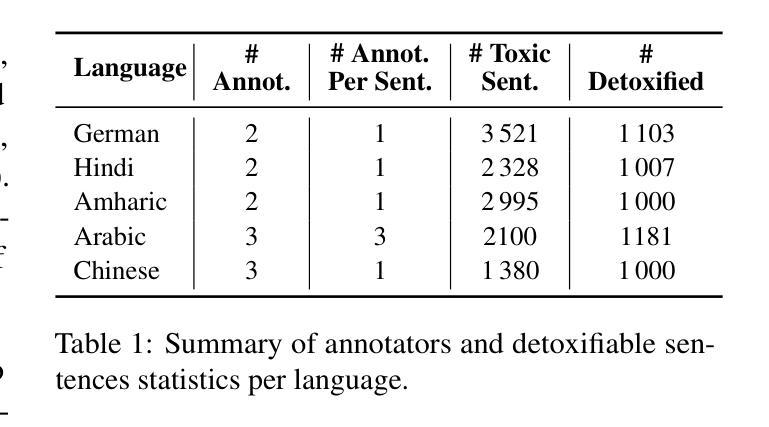
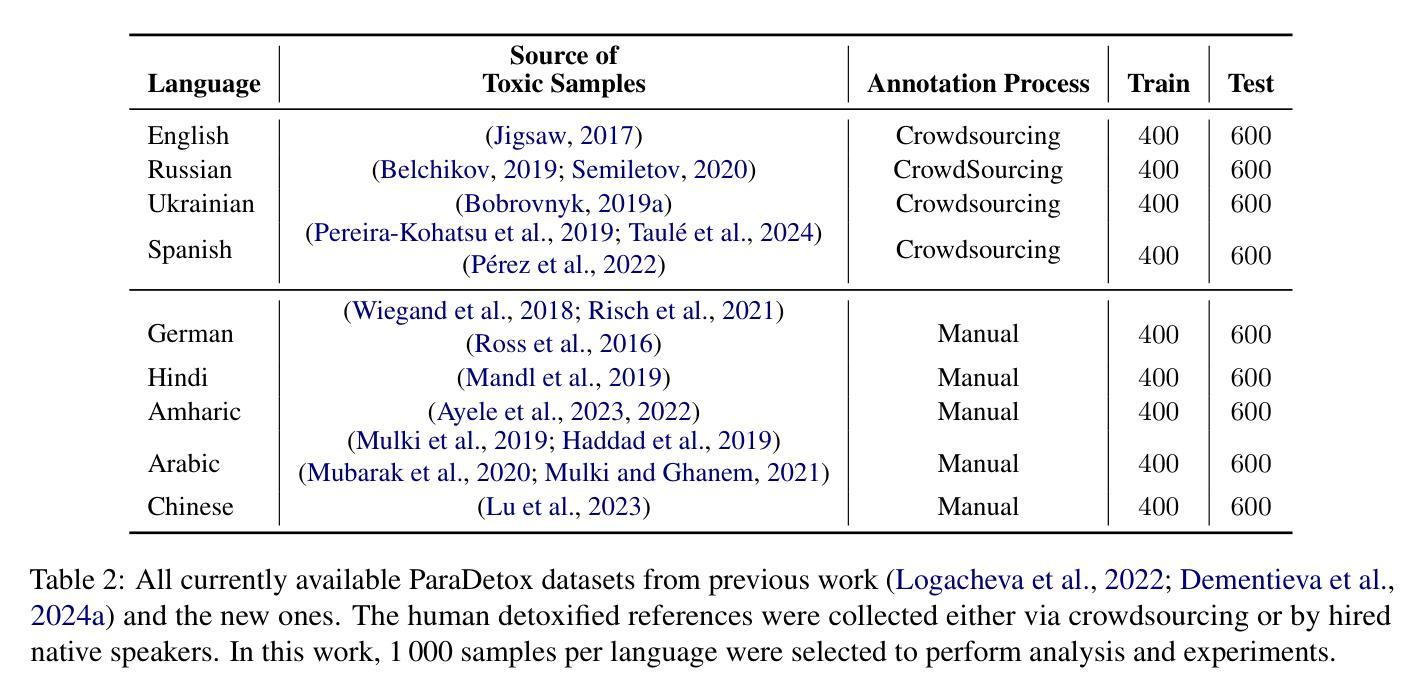
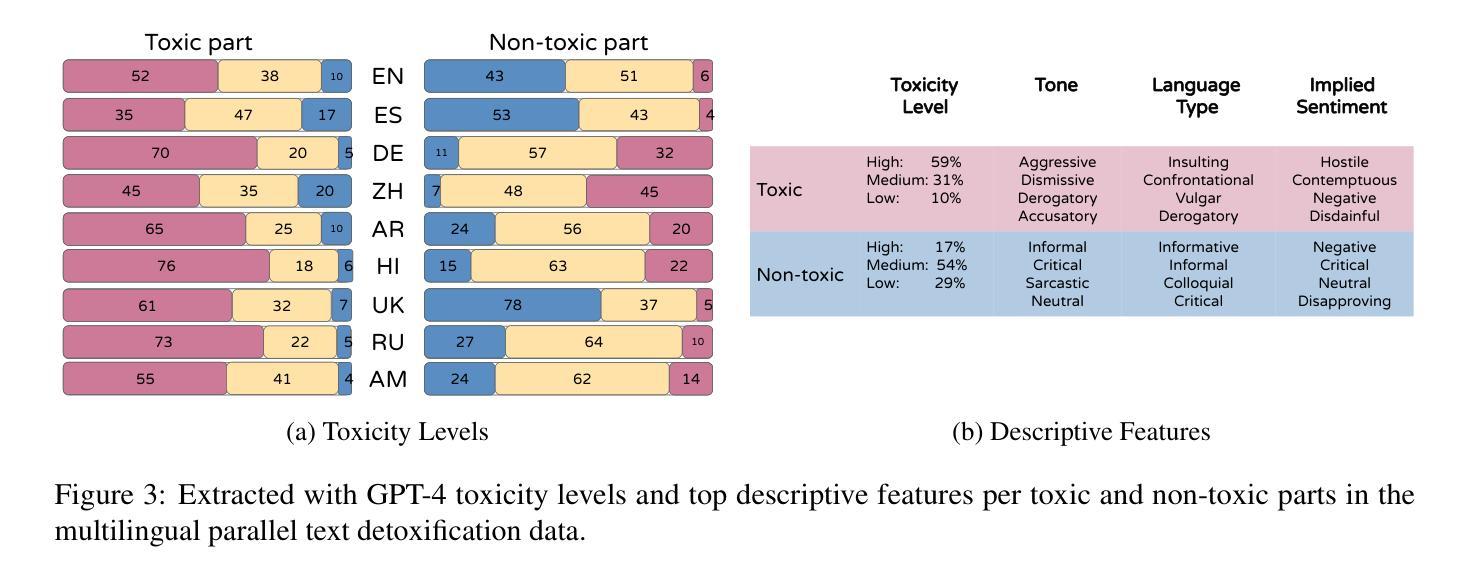
Multilingual and Explainable Text Detoxification with Parallel Corpora
Authors:Daryna Dementieva, Nikolay Babakov, Amit Ronen, Abinew Ali Ayele, Naquee Rizwan, Florian Schneider, Xintong Wang, Seid Muhie Yimam, Daniil Moskovskiy, Elisei Stakovskii, Eran Kaufman, Ashraf Elnagar, Animesh Mukherjee, Alexander Panchenko
Even with various regulations in place across countries and social media platforms (Government of India, 2021; European Parliament and Council of the European Union, 2022, digital abusive speech remains a significant issue. One potential approach to address this challenge is automatic text detoxification, a text style transfer (TST) approach that transforms toxic language into a more neutral or non-toxic form. To date, the availability of parallel corpora for the text detoxification task (Logachevavet al., 2022; Atwell et al., 2022; Dementievavet al., 2024a) has proven to be crucial for state-of-the-art approaches. With this work, we extend parallel text detoxification corpus to new languages – German, Chinese, Arabic, Hindi, and Amharic – testing in the extensive multilingual setup TST baselines. Next, we conduct the first of its kind an automated, explainable analysis of the descriptive features of both toxic and non-toxic sentences, diving deeply into the nuances, similarities, and differences of toxicity and detoxification across 9 languages. Finally, based on the obtained insights, we experiment with a novel text detoxification method inspired by the Chain-of-Thoughts reasoning approach, enhancing the prompting process through clustering on relevant descriptive attributes.
尽管各国和社交媒体平台(印度政府,2021年;欧洲议会和欧洲联盟理事会,2022年)已经制定了各种规定,网络欺凌言论仍然是一个重大问题。解决这一挑战的一种潜在方法是自动文本净化,这是一种文本风格转换(TST)方法,可以将有毒语言转换为更中性或非有毒的形式。迄今为止,文本净化任务的平行语料库的可用性(Logachevavet等人,2022年;Atwell等人,2022年;Dementievavet等人,2024a)已被证明对最新方法至关重要。在这项工作中,我们将平行文本净化语料库扩展到新语言——德语、简体中文、阿拉伯语、印地语和阿姆哈拉语——并在广泛的多语言设置TST基准上进行测试。接下来,我们进行了首例自动化、可解释性分析,研究有毒和无毒句子的描述性特征,深入探究9种语言中毒性和净化之间的细微差别、相似性和差异性。最后,基于所获得的见解,我们尝试了一种受思维链推理方法启发的新型文本净化方法,通过聚类相关的描述性属性来增强提示过程。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF COLING 2025, main conference, long
Summary
本文指出数字滥用言论仍然是一个重大问题,尽管不同国家和社交媒体平台已经实施了各种规定。为解决这一挑战,提出了一种自动文本净化方法,即文本风格转移(TST),将有毒语言转化为更中性或非有毒的形式。本文扩展了平行文本净化语料库,支持多种新语言,并进行了有毒和非常有毒句子的描述特征的自动化和可解释性分析。最后,基于所得见解,尝试了一种受思维链启发的新型文本净化方法,通过聚类相关描述属性来增强提示过程。
Key Takeaways
- 数字滥用言论仍然是一个普遍存在的问题,尽管各个国家和社交媒体平台已经实施了相关法规。
- 自动文本净化是一种有效的解决策略,其中文本风格转移(TST)是将有毒语言转化为中性语言的方法。
- 平行语料库对于文本净化任务至关重要,本文扩展了支持多种新语言的平行文本净化语料库。
- 对有毒和非常有毒句子的描述特征进行了自动化和可解释性分析。
- 深入研究了不同语言中毒性和净化细微差别和相似之处。
- 基于所得见解,尝试了一种新型文本净化方法,该方法受思维链启发,增强了提示过程。
点此查看论文截图

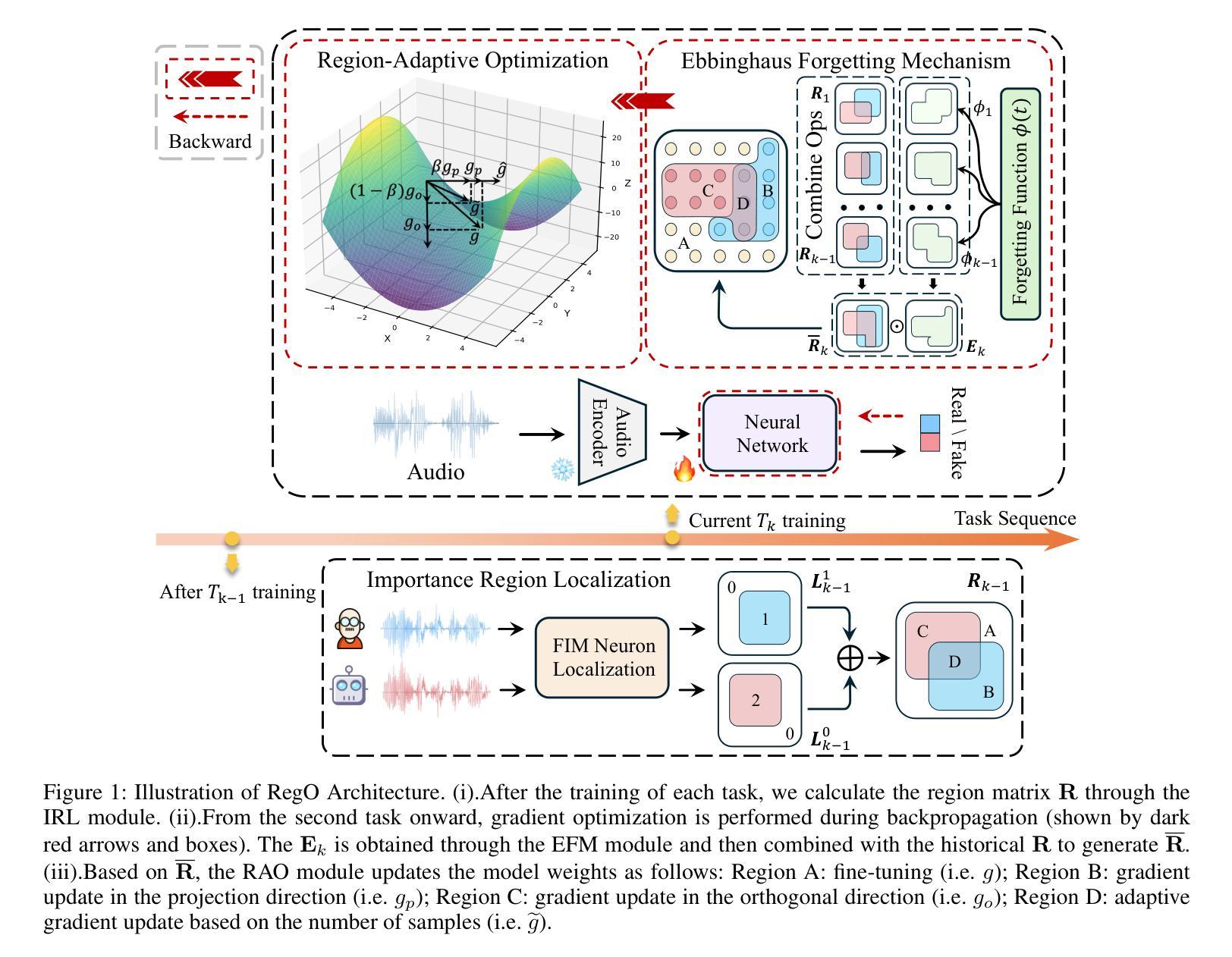
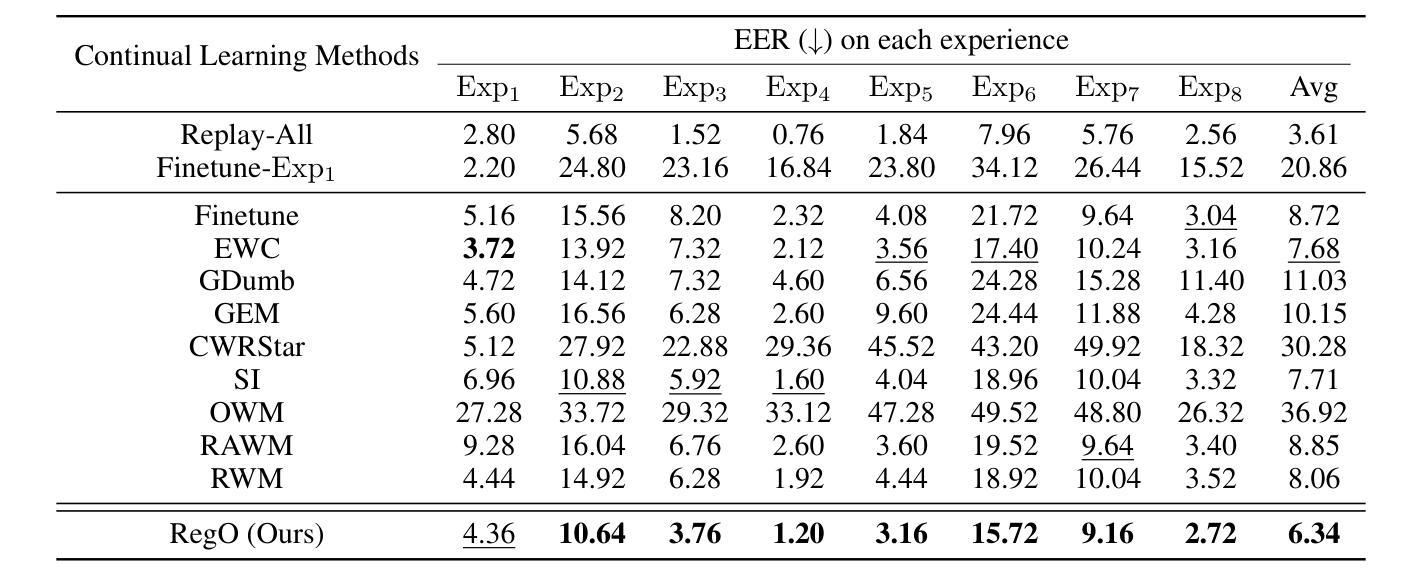
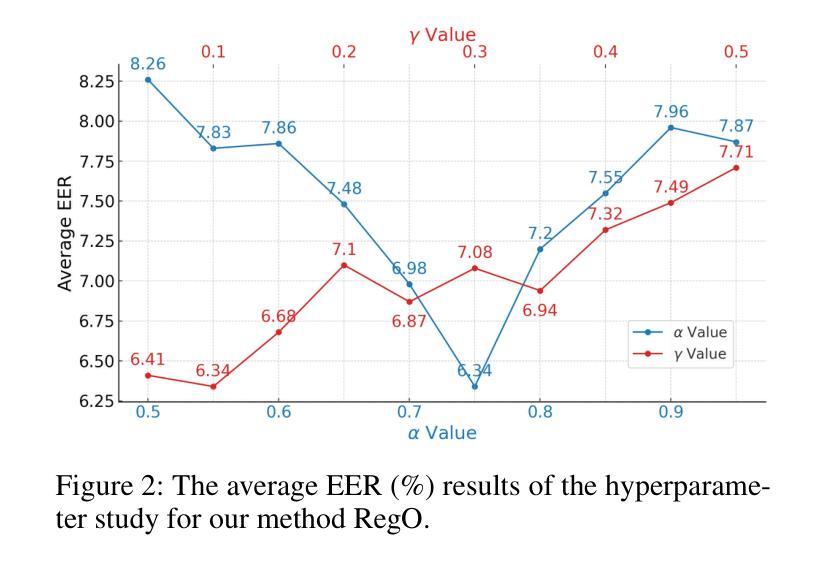
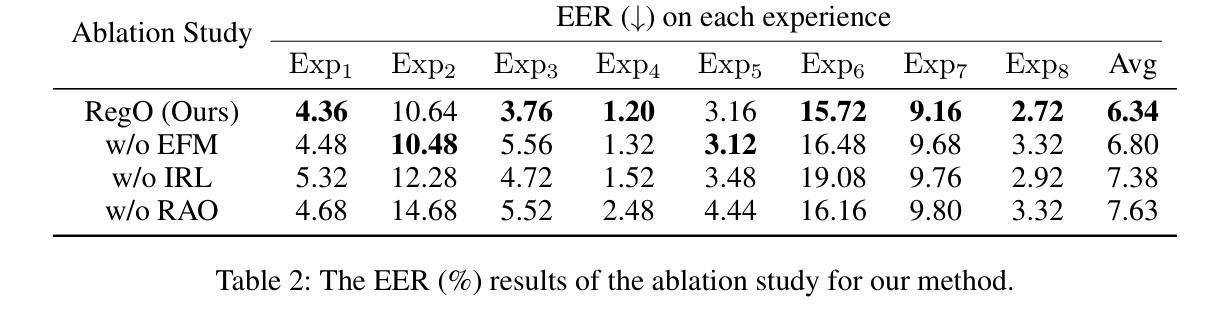
Region-Based Optimization in Continual Learning for Audio Deepfake Detection
Authors:Yujie Chen, Jiangyan Yi, Cunhang Fan, Jianhua Tao, Yong Ren, Siding Zeng, Chu Yuan Zhang, Xinrui Yan, Hao Gu, Jun Xue, Chenglong Wang, Zhao Lv, Xiaohui Zhang
Rapid advancements in speech synthesis and voice conversion bring convenience but also new security risks, creating an urgent need for effective audio deepfake detection. Although current models perform well, their effectiveness diminishes when confronted with the diverse and evolving nature of real-world deepfakes. To address this issue, we propose a continual learning method named Region-Based Optimization (RegO) for audio deepfake detection. Specifically, we use the Fisher information matrix to measure important neuron regions for real and fake audio detection, dividing them into four regions. First, we directly fine-tune the less important regions to quickly adapt to new tasks. Next, we apply gradient optimization in parallel for regions important only to real audio detection, and in orthogonal directions for regions important only to fake audio detection. For regions that are important to both, we use sample proportion-based adaptive gradient optimization. This region-adaptive optimization ensures an appropriate trade-off between memory stability and learning plasticity. Additionally, to address the increase of redundant neurons from old tasks, we further introduce the Ebbinghaus forgetting mechanism to release them, thereby promoting the capability of the model to learn more generalized discriminative features. Experimental results show our method achieves a 21.3% improvement in EER over the state-of-the-art continual learning approach RWM for audio deepfake detection. Moreover, the effectiveness of RegO extends beyond the audio deepfake detection domain, showing potential significance in other tasks, such as image recognition. The code is available at https://github.com/cyjie429/RegO
随着语音合成和语音转换的快速发展,虽然为人们的生活带来了便利,但同时也带来了新的安全风险,这引发了对于有效音频深度伪造检测技术的迫切需求。当前模型在实际应对多样化且不断发展的深伪造音频时,其效果有所减弱。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种用于音频深度伪造检测的持续学习方法,名为基于区域的优化(RegO)。具体来说,我们使用Fisher信息矩阵来衡量真实和伪造音频检测的重要神经元区域,并将其划分为四个区域。首先,我们直接微调不太重要的区域,以快速适应新任务。接着,我们对仅对真实音频检测重要的区域进行并行梯度优化,而对仅对伪造音频检测重要的区域进行正交方向上的梯度优化。对于两者都重要的区域,我们使用基于样本比例的自适应梯度优化。这种区域自适应优化确保了内存稳定性和学习可塑性之间的适当平衡。此外,为了解决旧任务中冗余神经元的增加问题,我们进一步引入了艾宾浩斯遗忘机制来释放它们,从而促进模型学习更通用的辨别特征的能力。实验结果表明,我们的方法在音频深度伪造检测方面比最新的持续学习方法RWM在EER上提高了21.3%。此外,RegO的有效性不仅适用于音频深度伪造检测领域,在图像识别等其他任务中也显示出潜在的重要性。代码可在https://github.com/cyjie429/RegO找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
随着语音合成和语音转换技术的快速发展,音频深度伪造检测面临新的挑战。为解决现有模型面对多样化和不断发展的现实深度伪造时效果不佳的问题,提出一种名为Region-Based Optimization(RegO)的持续学习方法。该方法通过Fisher信息矩阵衡量真实和伪造音频检测的重要神经元区域,并对其进行分区优化。实验结果显示,相较于最新持续学习方法RWM,RegO在音频深度伪造检测上的EER降低了21.3%,并且在图像识别等其他任务中也展现出潜在的重要性。相关代码已公开于GitHub上。
Key Takeaways
- 语音合成和语音转换技术的快速发展带来了音频深度伪造检测的新挑战。
- 当前音频深度伪造检测模型面对不断演变的伪造技术时效果有待提高。
- Region-Based Optimization(RegO)是一种针对音频深度伪造检测提出的持续学习方法。
- RegO使用Fisher信息矩阵衡量真实和伪造音频检测的重要神经元区域,并进行分区优化。
- RegO在音频深度伪造检测上的性能较最新持续学习方法有所提升,代码已公开于GitHub上。
- RegO的效能不仅限于音频深度伪造检测,还可能应用于其他任务如图像识别等。
点此查看论文截图

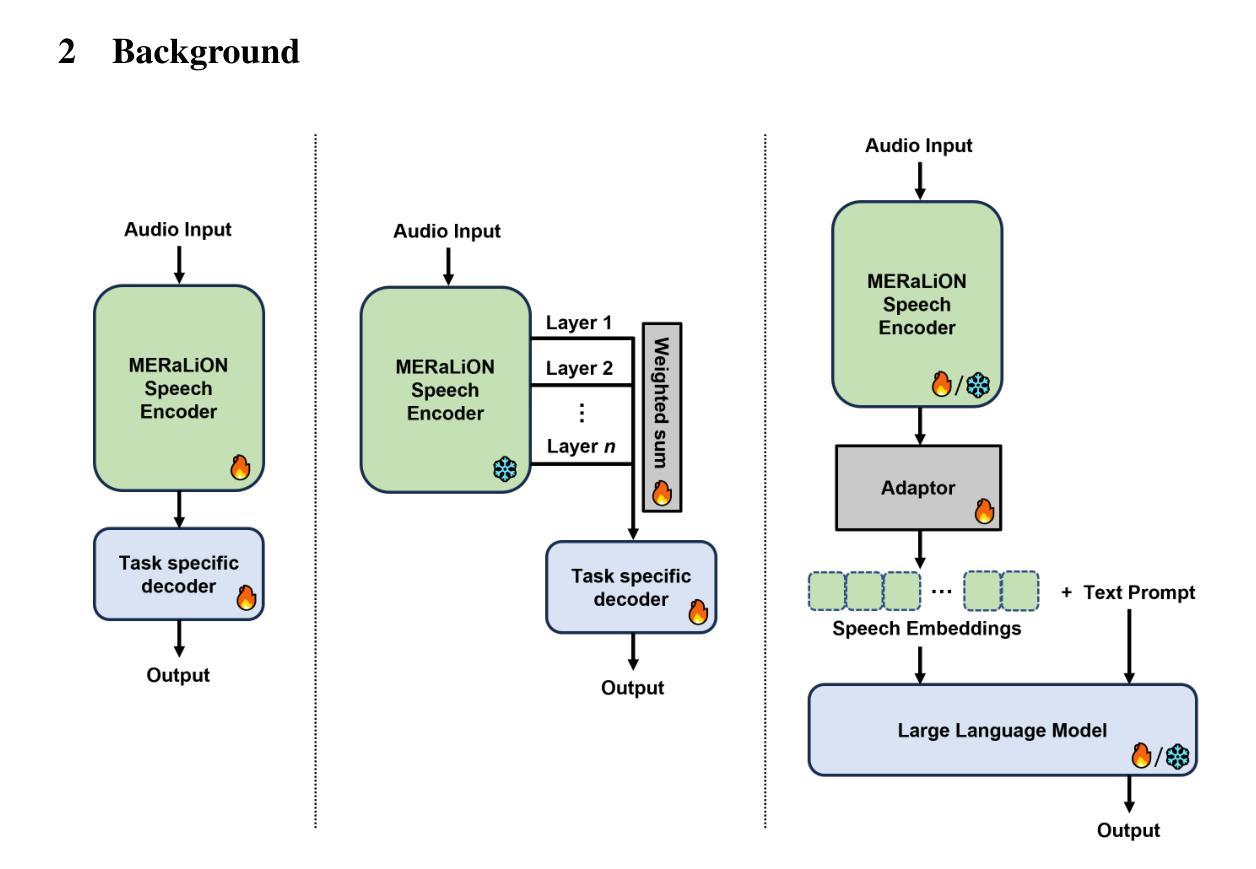
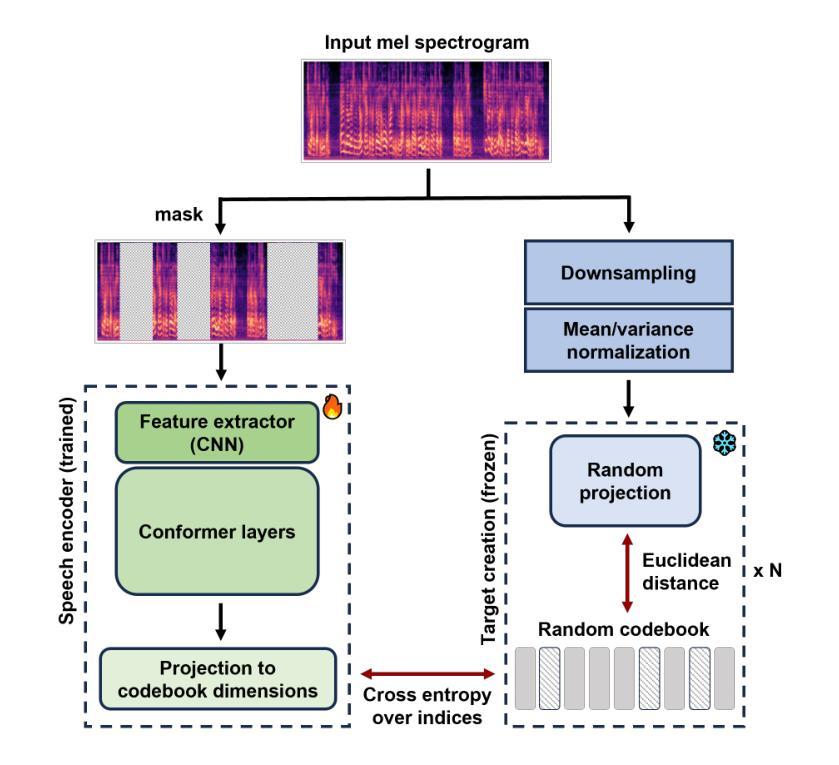
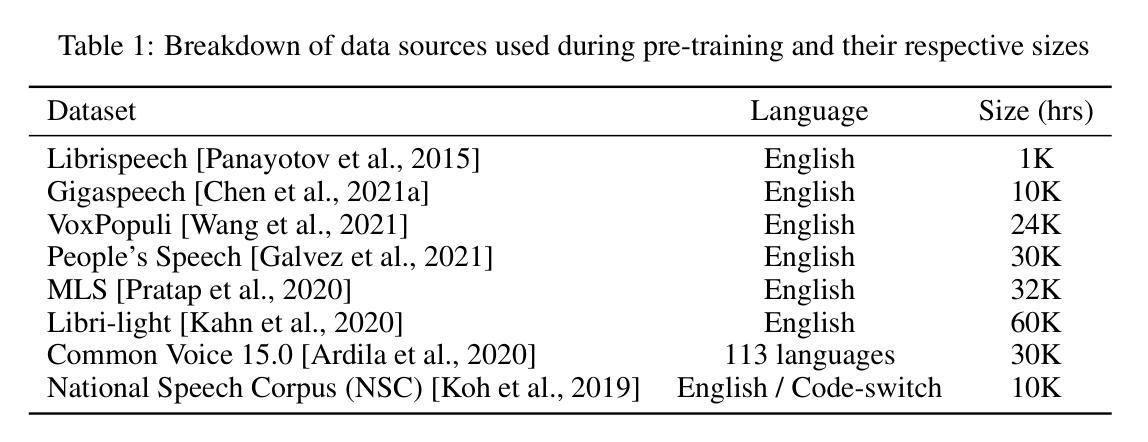
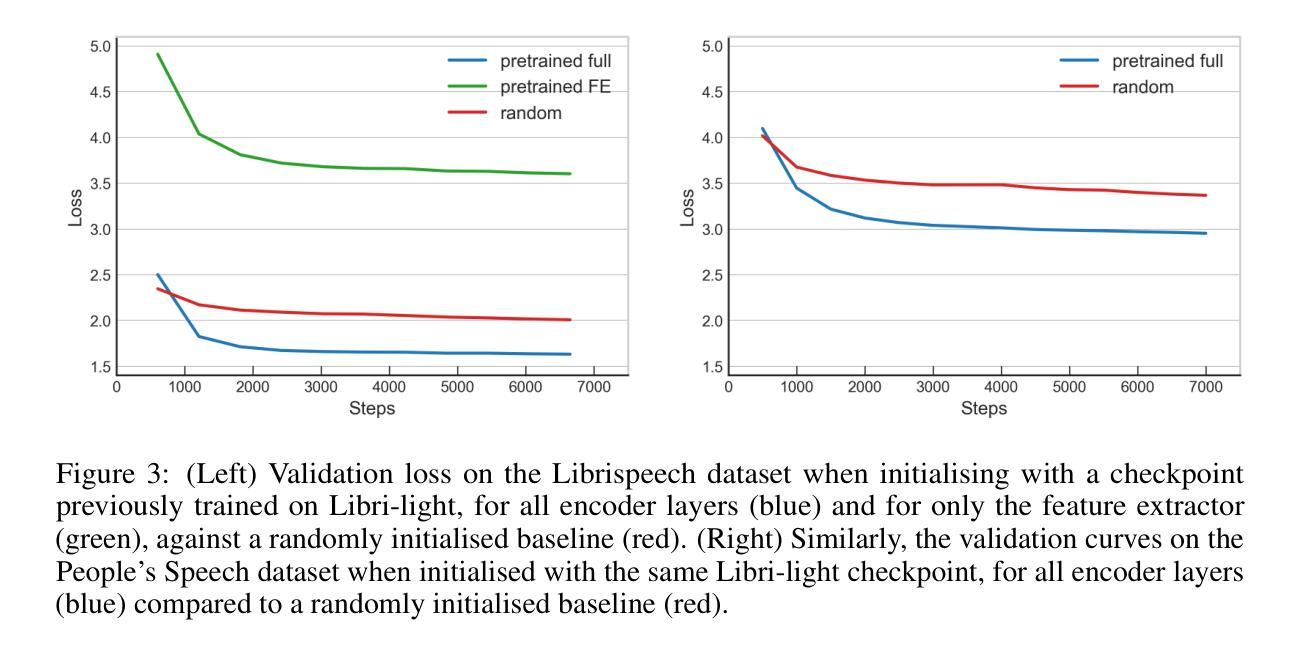
Towards a Speech Foundation Model for Singapore and Beyond
Authors:Muhammad Huzaifah, Tianchi Liu, Hardik B. Sailor, Kye Min Tan, Tarun K. Vangani, Qiongqiong Wang, Jeremy H. M. Wong, Nancy F. Chen, Ai Ti Aw
This technical report describes the MERaLiON Speech Encoder, a foundation model designed to support a wide range of downstream speech applications. Developed as part of Singapore’s National Multimodal Large Language Model Programme, the MERaLiON Speech Encoder is tailored to address the speech processing needs in Singapore and the surrounding Southeast Asian region. The model currently supports mainly English, including the variety spoken in Singapore. We are actively expanding our datasets to gradually cover other languages in subsequent releases. The MERaLiON Speech Encoder was pre-trained from scratch on 200K hours of unlabelled speech data using a self-supervised learning approach based on masked language modelling. We describe our training procedure and hyperparameter tuning experiments in detail below. Our evaluation demonstrates improvements to spontaneous and Singapore speech benchmarks for speech recognition, while remaining competitive to other state-of-the-art speech encoders across ten other speech tasks. We commit to releasing our model, supporting broader research endeavours, both in Singapore and beyond.
本技术报告介绍了MERaLiON语音编码器,这是一个基础模型,旨在支持广泛的下游语音应用程序。作为新加坡国家多模态大型语言模型计划的一部分而开发,MERaLiON语音编码器针对新加坡及周边东南亚地区的语音处理需求进行了定制。该模型目前主要支持英语,包括新加坡所说的英语。我们正在积极扩充数据集,在后续版本中逐步覆盖其他语言。MERaLiON语音编码器使用基于掩码语言建模的自我监督学习方法,在20万小时的无标签语音数据上进行从头训练。我们下面详细描述了我们的训练过程和超参数调整实验。我们的评估表明,在语音识别方面,对自发语音和新加坡语音基准测试有了改进,同时在其他十个语音任务上与其他最先端的语音编码器保持竞争力。我们致力于发布我们的模型,以支持新加坡内外的更广泛研究努力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
MERaLiON语音编码器是一款基础模型,旨在支持各种下游语音应用。该模型专为新加坡及周边东南亚地区的语音处理需求设计,目前主要支持英语,包括新加坡英语。模型采用自我监督学习方法,基于掩码语言建模,在20万小时的无标签语音数据上进行预训练。评估结果表明,该模型在语音识别方面对自然和新加坡语音基准测试有所改善,同时在其他十个语音任务上保持竞争力。我们承诺发布模型,以支持新加坡及全球更广泛的研究工作。
Key Takeaways
- MERaLiON语音编码器是一个为新加坡和东南亚地区设计的语音处理基础模型。
- 模型主要支持英语,并正在积极扩展以覆盖其他语言。
- 采用自我监督学习方法,基于掩码语言建模进行预训练,使用大量无标签语音数据。
- 模型在语音识别方面表现出色,对自然和新加坡语音基准测试有所改善。
- 在其他十个语音任务上,该模型具有竞争力。
- MERaLiON语音编码器将公开发布,以支持更广泛的研究工作。
点此查看论文截图

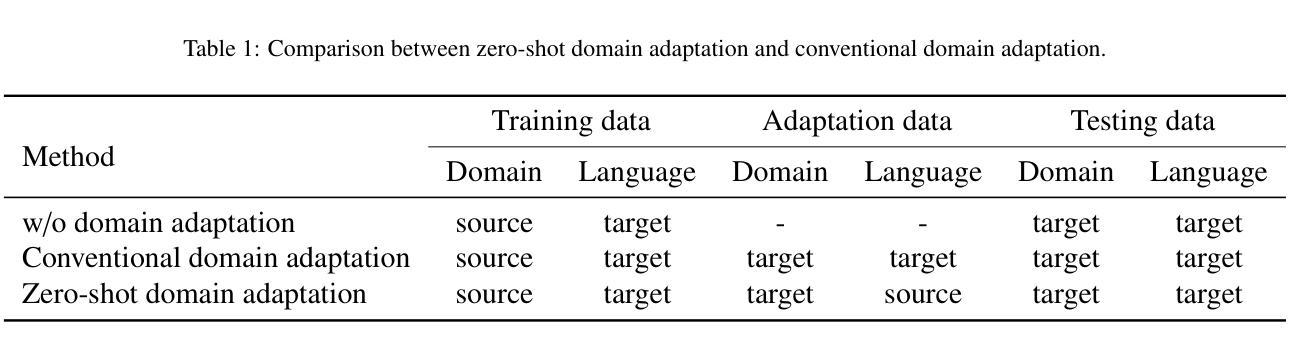
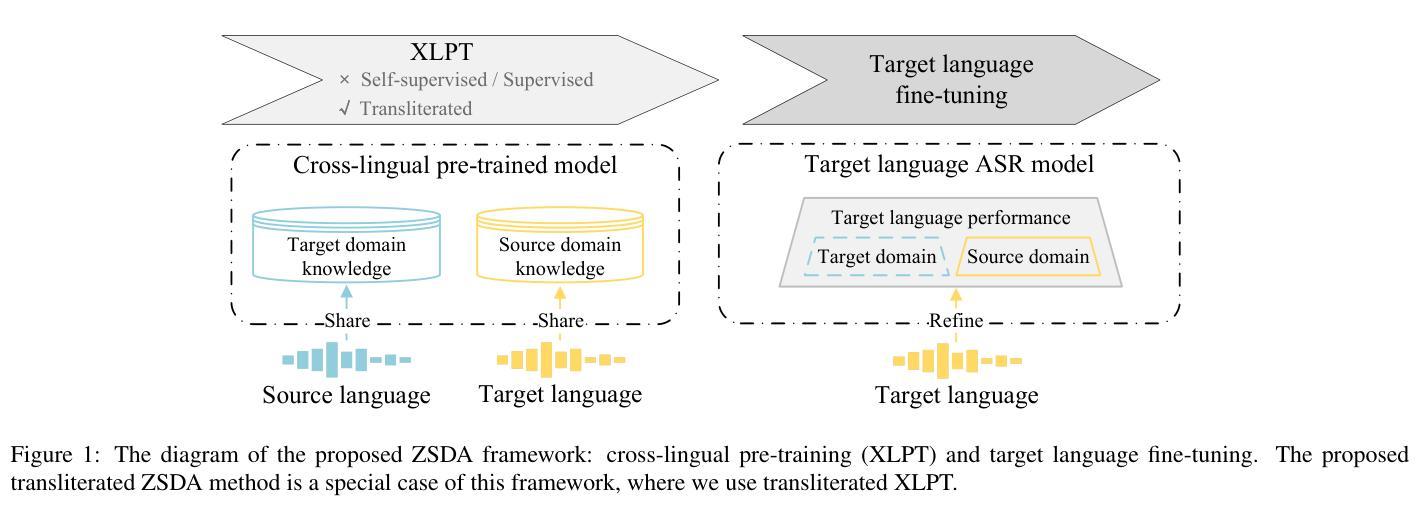
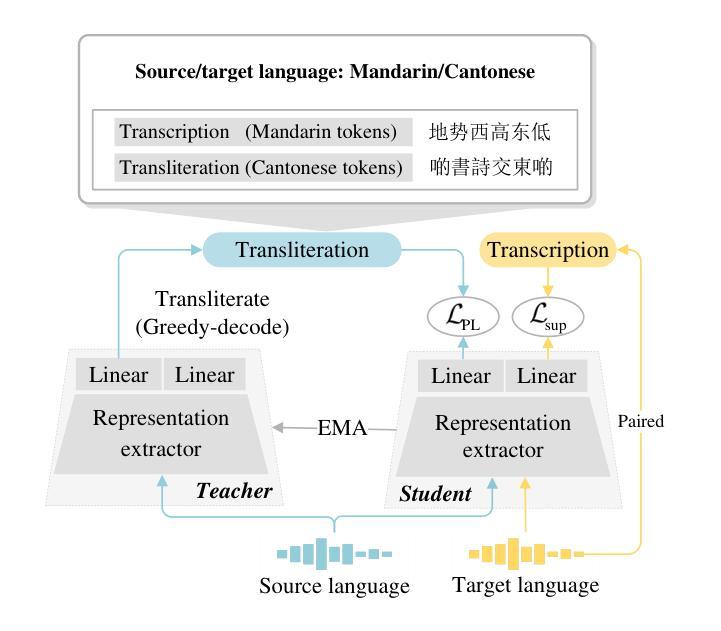
Transliterated Zero-Shot Domain Adaptation for Automatic Speech Recognition
Authors:Han Zhu, Gaofeng Cheng, Qingwei Zhao, Pengyuan Zhang
The performance of automatic speech recognition models often degenerates on domains not covered by the training data. Domain adaptation can address this issue, assuming the availability of the target domain data in the target language. However, such assumption does not stand in many real-world applications. To make domain adaptation more applicable, we address the problem of zero-shot domain adaptation (ZSDA), where target domain data is unavailable in the target language. Instead, we transfer the target domain knowledge from another source language where the target domain data is more accessible. To do that, we first perform cross-lingual pre-training (XLPT) to share domain knowledge across languages, then use target language fine-tuning to build the final model. One challenge in this practice is that the pre-trained knowledge can be forgotten during fine-tuning, resulting in sub-optimal adaptation performance. To address this issue, we propose transliterated ZSDA to achieve consistent pre-training and fine-tuning labels, leading to maximum preservation of the pre-trained knowledge. Experimental results show that transliterated ZSDA relatively decreases the word error rate by 9.2% compared with a wav2vec 2.0 baseline. Moreover, transliterated ZSDA consistently outperforms self-supervised ZSDA and performs on par with supervised ZSDA, proving the superiority of transliteration-based pre-training labels.
自动语音识别模型在训练数据未涵盖的领域上的性能往往会退化。领域适配(Domain Adaptation)可以解决此问题,前提是目标领域数据以目标语言的形式可用。然而,这一假设并不适用于许多现实世界的应用场景。为了使领域适配更具适用性,我们解决了零射击领域适配(Zero-Shot Domain Adaptation,ZSDA)的问题,其中目标领域的数据在目标语言中无法使用。相反,我们从另一种源语言中转移目标领域的知识,其中目标领域的数据更容易获得。为此,我们首先要执行跨语言预训练(Cross-Lingual Pre-Training,XLPT),以跨语言共享领域知识,然后使用目标语言微调来构建最终模型。这一实践中的一个挑战是,预训练知识可能会在微调过程中被遗忘,导致次优的适配性能。为解决这一问题,我们提出音译ZSDA方法,以实现预训练和微调标签的一致性,最大限度地保留预训练知识。实验结果表明,与wav2vec 2.0基线相比,音译ZSDA相对降低了9.2%的单词错误率。此外,音译ZSDA始终优于自监督ZSDA,并与监督ZSDA表现相当,证明了基于音译的预训练标签的优越性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
跨领域语音识别模型在未被训练数据覆盖的领域性能会退化。为解决此问题,研究提出零样本领域自适应(ZSDA)方法,通过另一种源语言转移目标领域知识,当目标领域数据在该源语言中更容易获取时。通过跨语言预训练(XLPT)共享领域知识,然后针对目标语言进行微调构建最终模型。预训练知识在微调过程中可能会遗忘的问题是一大挑战,导致适应性能不佳。为解决这一问题,研究提出采用音译ZSDA方法,实现预训练和微调标签的一致性,最大限度地保留预训练知识。实验结果表明,音译ZSDA相较于wav2vec 2.0基线降低了9.2%的词错误率。此外,音译ZSDA表现优于自监督ZSDA,与监督ZSDA表现相当,证明了音译预训练标签的优越性。
Key Takeaways
- 自动语音识别模型在未知领域性能退化问题可通过领域自适应解决。
- ZSDA方法旨在解决目标领域数据在目标语言中不可用的问题,通过另一种源语言转移知识。
- 跨语言预训练(XLPT)被用于在不同语言间共享领域知识。
- 微调过程中的预训练知识遗忘是ZSDA实践中的一个挑战。
- 提出的音译ZSDA方法能最大程度上保留预训练知识,提高适应性能。
- 实验结果显示音译ZSDA相比基线降低了词错误率。
点此查看论文截图

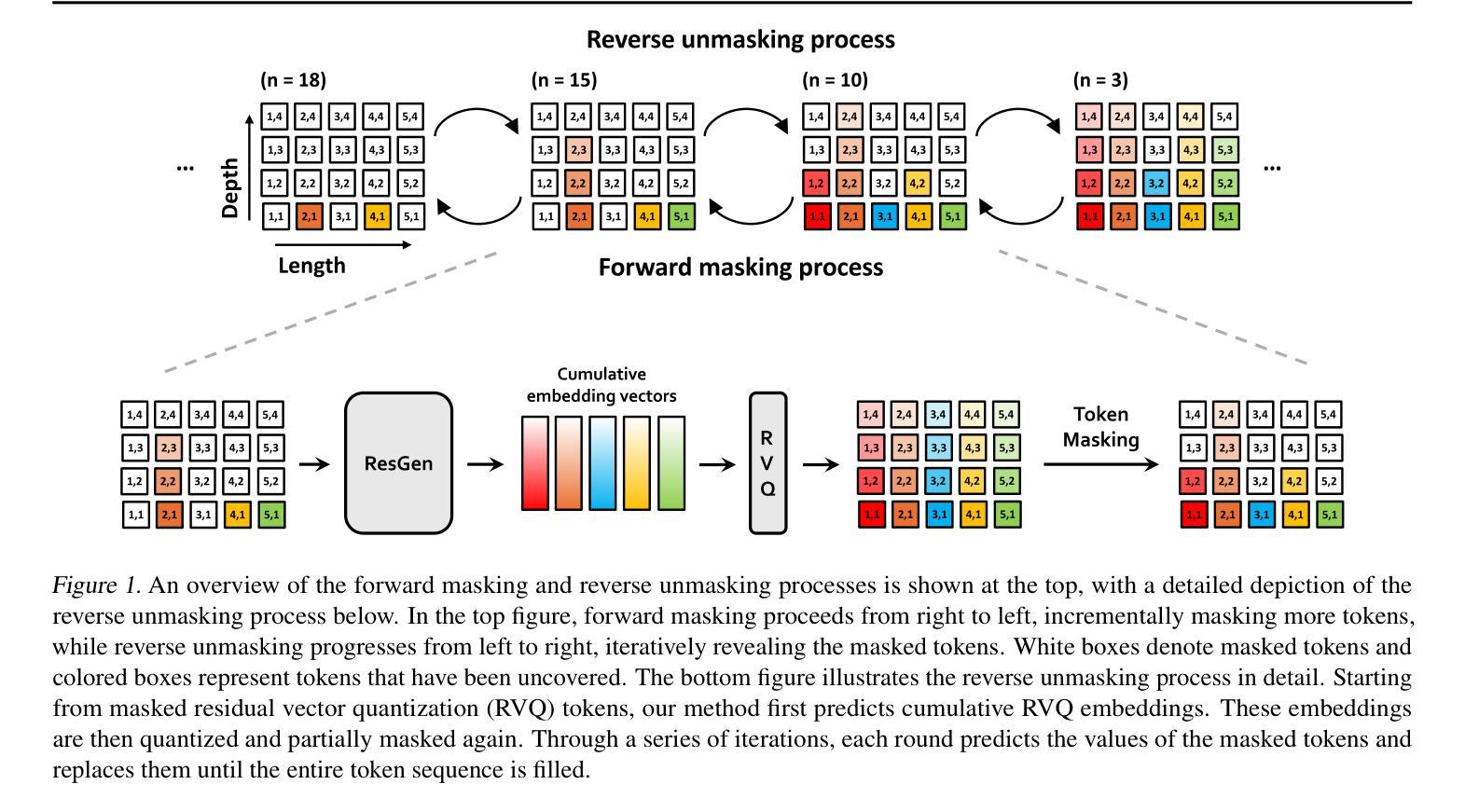
Efficient Generative Modeling with Residual Vector Quantization-Based Tokens
Authors:Jaehyeon Kim, Taehong Moon, Keon Lee, Jaewoong Cho
We explore the use of Residual Vector Quantization (RVQ) for high-fidelity generation in vector-quantized generative models. This quantization technique maintains higher data fidelity by employing more in-depth tokens. However, increasing the token number in generative models leads to slower inference speeds. To this end, we introduce ResGen, an efficient RVQ-based discrete diffusion model that generates high-fidelity samples without compromising sampling speed. Our key idea is a direct prediction of vector embedding of collective tokens rather than individual ones. Moreover, we demonstrate that our proposed token masking and multi-token prediction method can be formulated within a principled probabilistic framework using a discrete diffusion process and variational inference. We validate the efficacy and generalizability of the proposed method on two challenging tasks across different modalities: conditional image generation} on ImageNet 256x256 and zero-shot text-to-speech synthesis. Experimental results demonstrate that ResGen outperforms autoregressive counterparts in both tasks, delivering superior performance without compromising sampling speed. Furthermore, as we scale the depth of RVQ, our generative models exhibit enhanced generation fidelity or faster sampling speeds compared to similarly sized baseline models. The project page can be found at https://resgen-genai.github.io
我们探索了残差向量量化(RVQ)在向量量化生成模型中的高保真生成应用。这种量化技术通过采用更深入的令牌来保持更高的数据保真度。然而,在生成模型中增加令牌数量会导致推理速度变慢。为此,我们引入了ResGen,这是一个基于RVQ的高效离散扩散模型,能够在不牺牲采样速度的情况下生成高保真样本。我们的关键想法是预测集体令牌的向量嵌入,而不是单个令牌。此外,我们证明,通过离散扩散过程和变分推断,我们提出的令牌掩码和多令牌预测方法可以在有原则的概率框架内制定。我们在不同模态的两个具有挑战性的任务上验证了所提出方法的有效性和通用性:在ImageNet 256x256上进行条件图像生成和零样本文本到语音合成。实验结果表明,ResGen在这两项任务中的表现都优于自回归模型,实现了卓越的性能,同时没有牺牲采样速度。此外,随着我们扩大RVQ的深度,我们的生成模型与类似规模的基准模型相比,表现出更高的生成保真度或更快的采样速度。项目页面可在https://resgen-genai.github.io找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于Residual Vector Quantization(RVQ)的高保真生成在向量量化生成模型中得到了探索。该技术通过采用更深入的令牌来保持更高的数据保真度,但增加生成模型中的令牌数量会导致推理速度变慢。为此,我们引入了ResGen,这是一种基于RVQ的高效离散扩散模型,可在不牺牲采样速度的情况下生成高保真样本。我们的关键想法是预测集体令牌的向量嵌入,而不是单独的令牌。我们在离散扩散过程和变分推理的概率框架下,证明了所提出的方法可以有效地用于跨不同模态的两种挑战任务:在ImageNet 256x256上进行条件图像生成和零样本文本到语音合成。实验结果表明,ResGen在两项任务中的表现均优于自回归模型,且在不牺牲采样速度的情况下实现了卓越的性能。随着RVQ深度的增加,我们的生成模型的生成保真度得到了提高或采样速度得到了加快,与类似规模的基准模型相比具有优势。
Key Takeaways
- Residual Vector Quantization(RVQ)被用于向量量化生成模型中以实现高保真生成。
- 增加令牌数量可以提高数据保真度,但会导致推理速度下降。
- ResGen是一种基于RVQ的离散扩散模型,旨在在不牺牲采样速度的情况下生成高保真样本。
- ResGen通过预测集体令牌的向量嵌入来提高效率。
- 所提出的方法在条件图像生成和零样本文本到语音合成两项任务中表现出色。
- ResGen相较于自回归模型有优越的表现。
点此查看论文截图

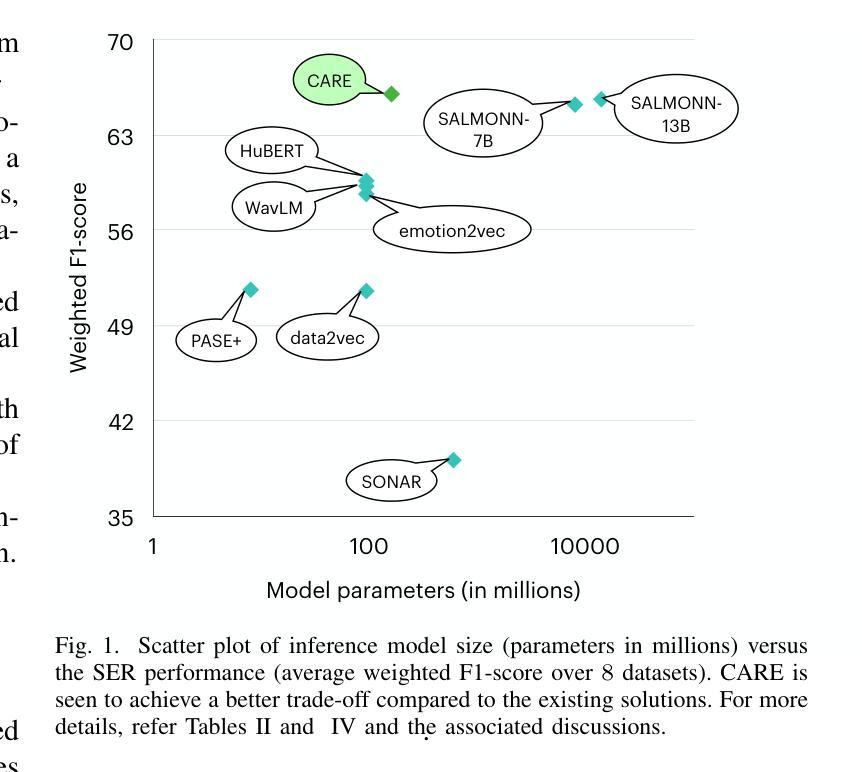
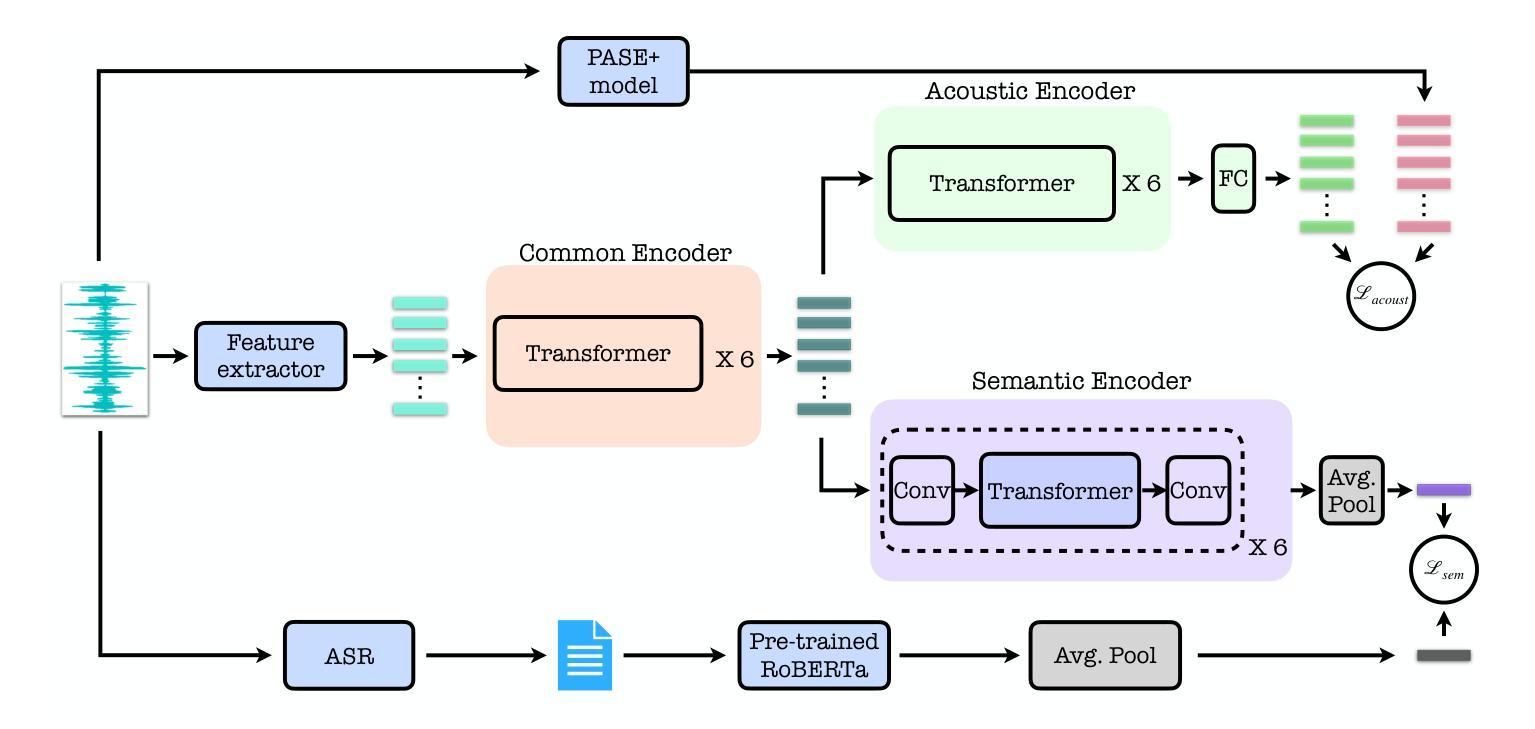
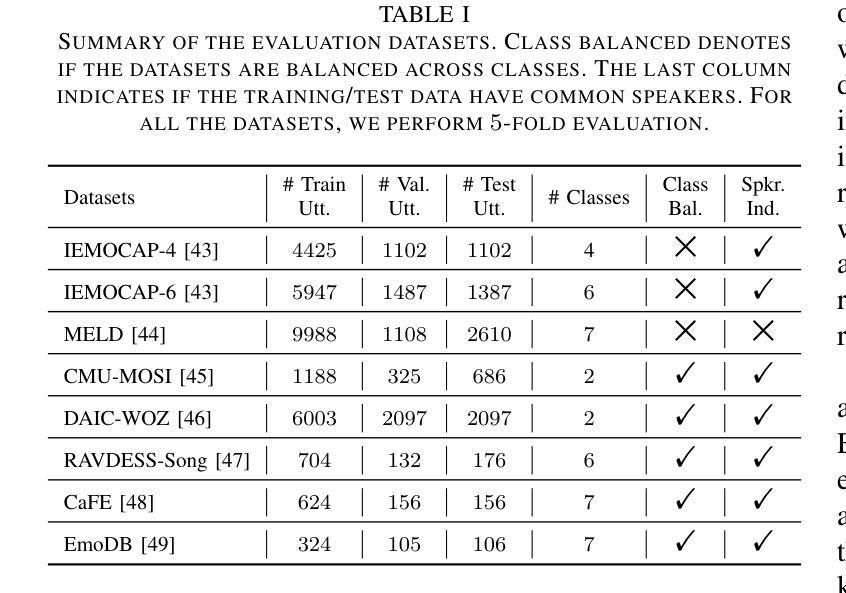
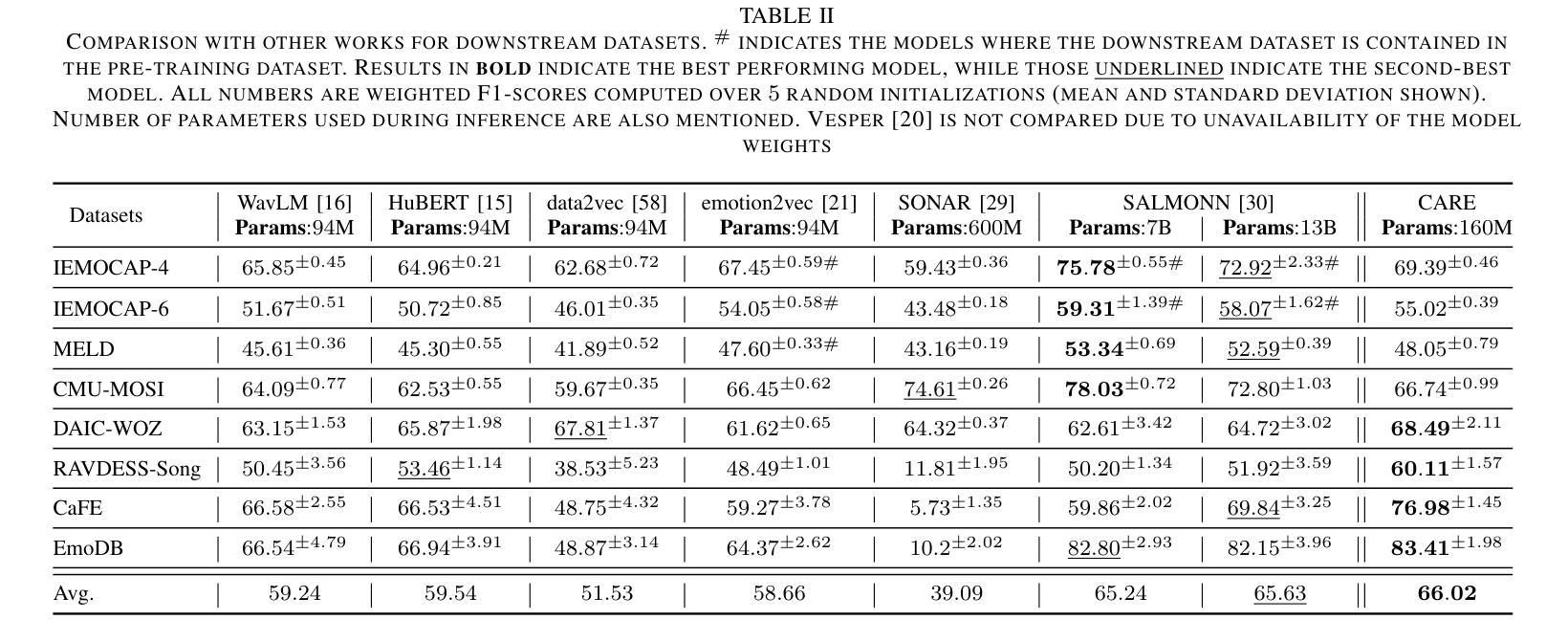
Leveraging Content and Acoustic Representations for Speech Emotion Recognition
Authors:Soumya Dutta, Sriram Ganapathy
Speech emotion recognition (SER), the task of identifying the expression of emotion from spoken content, is challenging due to the difficulty in extracting representations that capture emotional attributes from speech. The scarcity of labeled datasets further complicates the challenge where large models are prone to over-fitting. In this paper, we propose CARE (Content and Acoustic Representations of Emotions), where we design a dual encoding scheme which emphasizes semantic and acoustic factors of speech. While the semantic encoder is trained using distillation from utterance-level text representations, the acoustic encoder is trained to predict low-level frame-wise features of the speech signal. The proposed dual encoding scheme is a base-sized model trained only on unsupervised raw speech. With a simple light-weight classification model trained on the downstream task, we show that the CARE embeddings provide effective emotion recognition on a variety of datasets. We compare the proposal with several other self-supervised models as well as recent large-language model based approaches. In these evaluations, the proposed CARE is shown to be the best performing model based on average performance across 8 diverse datasets. We also conduct several ablation studies to analyze the importance of various design choices.
语音情感识别(SER)是从口语内容中识别情感表达的任务,由于从语音中提取能捕捉情感属性的表示形式具有挑战性,因此这一任务具有挑战性。标记数据集的稀缺进一步加剧了这一挑战,大型模型容易过度拟合。在本文中,我们提出CARE(情感的内容和声学表示),设计了一种双编码方案,该方案侧重于语音的语义和声学因素。语义编码器使用蒸馏法从话语级别的文本表示中进行训练,而声学编码器则经过训练以预测语音信号的低级帧级特征。所提出的双编码方案是一个基础大小的模型,仅在有监督的原始语音上进行训练。使用在下游任务上训练的简单轻量级分类模型,我们证明了CARE嵌入在各种数据集上提供了有效的情感识别。我们将提案与其他自监督模型以及最近的大型语言模型方法进行了比较。在这些评估中,CARE被证明是在8个不同数据集上表现最好的模型。我们还进行了几项消融研究,以分析各种设计选择的重要性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 5 figures, 6 tables
Summary
语音情感识别(SER)是从口语内容中识别情感表达的任务,由于从语音中提取能捕捉情感属性的表示形式具有挑战性,因此该任务充满艰辛。此外,缺乏标记数据集也使这一挑战更加复杂,大型模型容易过度拟合。本文提出了CARE(情感的内容和声学表示),设计了一种双编码方案,强调语音的语义和声学因素。语义编码器通过蒸馏的方式使用话语级别的文本表示进行训练,而声学编码器则训练用于预测语音信号的低级帧级特征。所提出的双编码方案是一个基础模型,仅使用无监督的原始语音进行训练。使用简单的轻量级分类模型对下游任务进行训练,我们展示了CARE嵌入在多个数据集上的有效情感识别。我们将提案与其他的自我监督模型以及最近的大型语言模型方法进行了比较。在这些评估中,所提出的CARE被证明是在8个不同数据集上的最佳性能模型。我们还进行了几项废除研究,以分析各种设计选择的重要性。
Key Takeaways
- 语音情感识别(SER)面临从语音中提取情感属性表示的困难。
- 缺乏标记数据集使SER任务更加复杂,大型模型容易过度拟合。
- 本文提出了CARE(情感的内容和声学表示),采用双编码方案结合语义和声音因素。
- 语义编码器通过蒸馏方式使用文本表示进行训练,声学编码器则预测语音信号的帧级特征。
- CARE模型在多个数据集上表现出有效的情感识别能力。
- 与其他自我监督模型和大型语言模型相比,CARE在多个数据集上的性能最佳。
点此查看论文截图

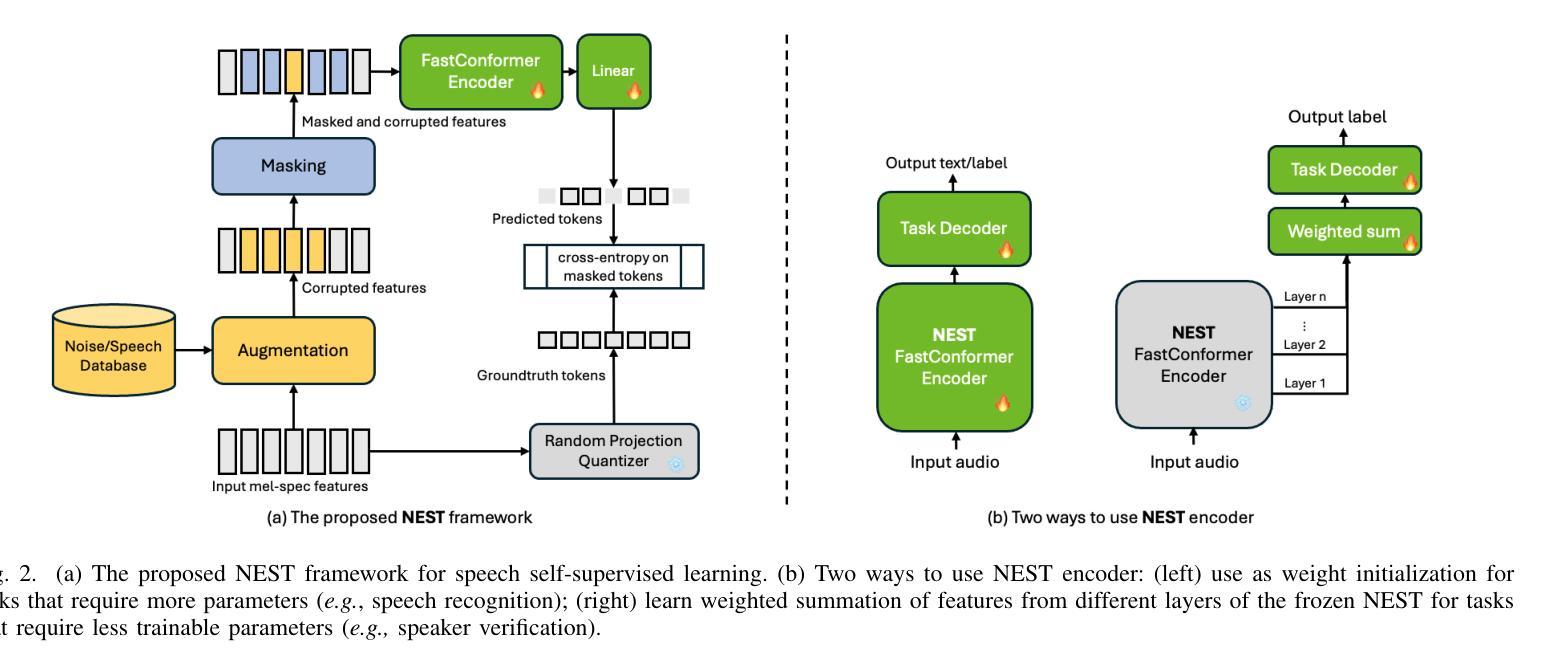
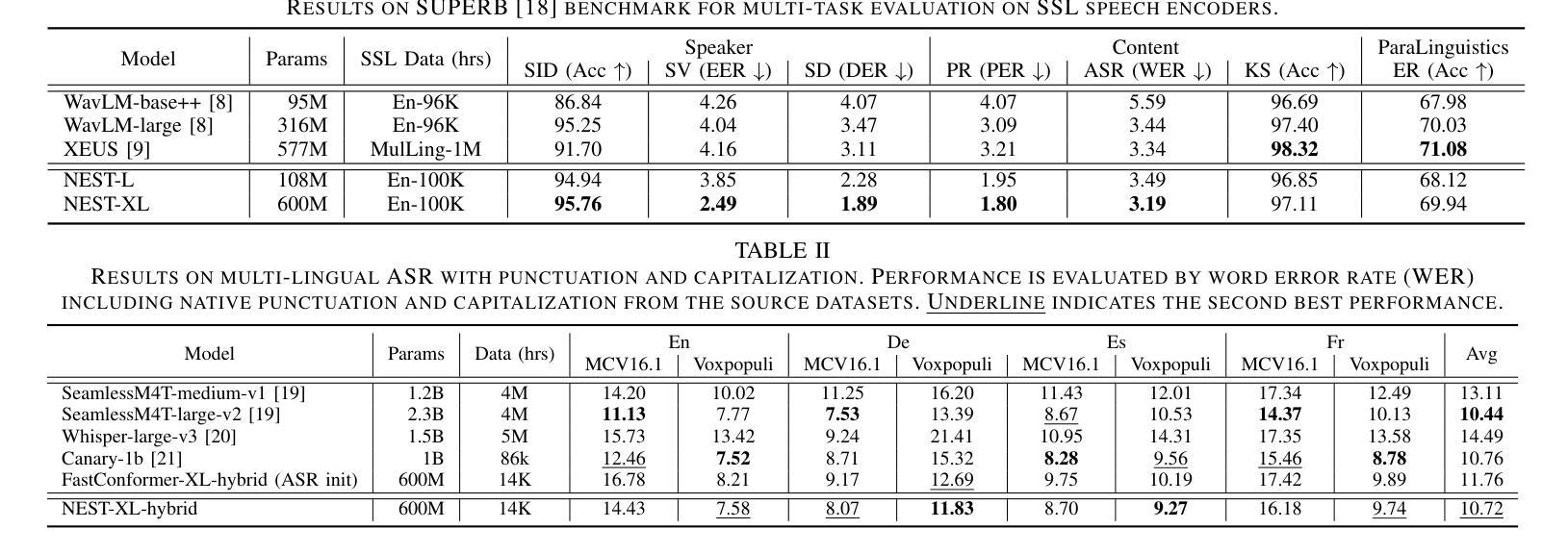
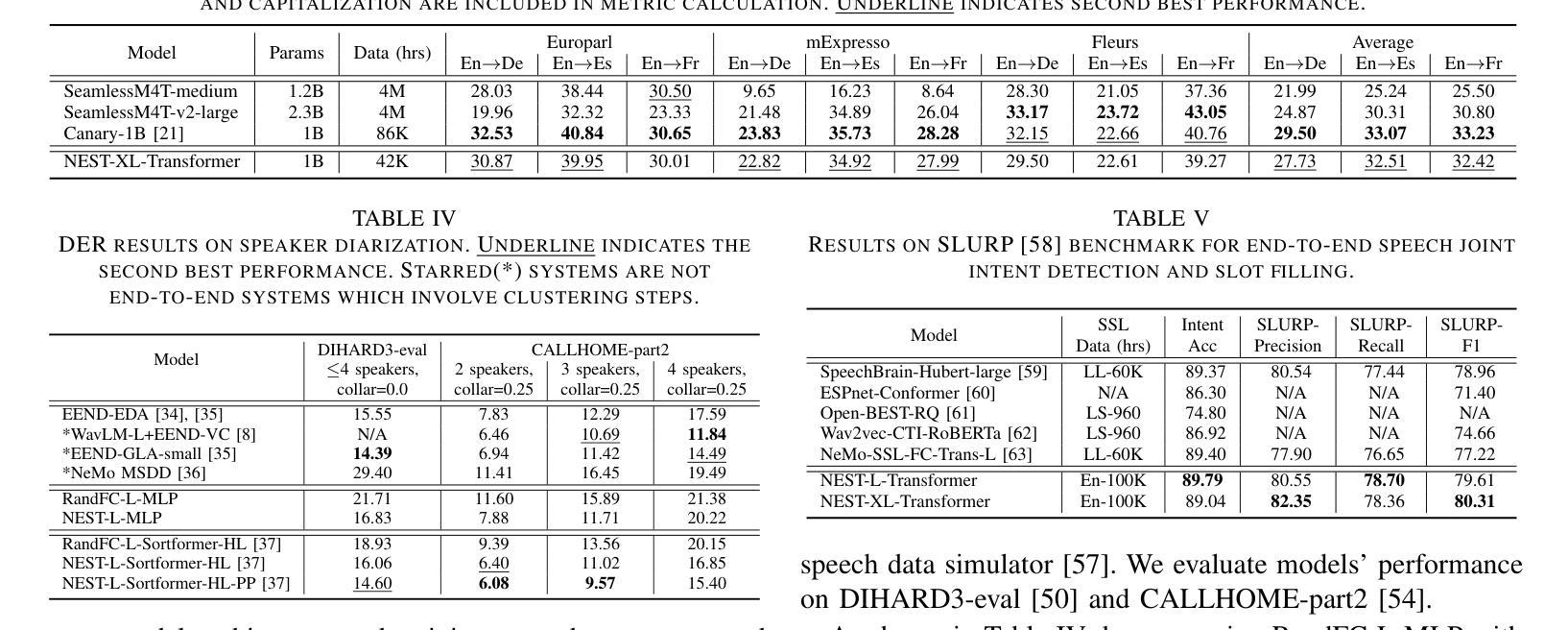
NEST: Self-supervised Fast Conformer as All-purpose Seasoning to Speech Processing Tasks
Authors:He Huang, Taejin Park, Kunal Dhawan, Ivan Medennikov, Krishna C. Puvvada, Nithin Rao Koluguri, Weiqing Wang, Jagadeesh Balam, Boris Ginsburg
Self-supervised learning has been proved to benefit a wide range of speech processing tasks, such as speech recognition/translation, speaker verification and diarization, etc. However, most of current approaches are computationally expensive. In this paper, we propose a simplified and more efficient self-supervised learning framework termed as NeMo Encoder for Speech Tasks (NEST). Specifically, we adopt the FastConformer architecture with 8x sub-sampling rate, which is faster than Transformer or Conformer architectures. Instead of clustering-based quantization, we use fixed random projection for its simplicity and effectiveness. We also implement a generalized noisy speech augmentation that teaches the model to disentangle the main speaker from noise or other speakers. Experiments show that \model improves over existing self-supervised models and achieves new state-of-the-art performance on a variety of speech processing tasks, such as speech recognition/translation, speaker diarization, spoken language understanding, etc. Code and checkpoints are publicly available via NVIDIA NeMo framework.
自监督学习已被证明对多种语音处理任务(如语音识别/翻译、说话人验证和日记化等)都有益。然而,当前大多数方法的计算成本都很高。在本文中,我们提出了一种简化且更高效的自监督学习框架,称为用于语音任务的NeMo编码器(NEST)。具体来说,我们采用了具有8倍子采样率的FastConformer架构,其速度比Transformer或Conformer架构更快。我们没有使用基于聚类的量化方法,而是采用简单有效的固定随机投影法。我们还实现了一种通用的噪声语音增强方法,以训练模型从噪声或其他说话人中分离出主说话人的声音。实验表明,该模型在多种语音处理任务上超越了现有的自监督模型,并实现了最新的最佳性能,包括语音识别/翻译、说话人日记化、语音语言理解等任务。模型和检查点可通过NVIDIA NeMo框架公开获取。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种简化且高效的自监督学习框架,名为NeMo Encoder for Speech Tasks (NEST)。采用FastConformer架构,实现8倍子采样率,比Transformer或Conformer架构更快。使用固定随机投影代替聚类量化,并实现了通用的噪声语音增强技术,旨在使模型能够区分主要说话者的声音。实验表明,该模型在多种语音处理任务上超过了现有的自监督模型,并达到了最新技术水平。代码和检查点可通过NVIDIA NeMo框架公开获取。
Key Takeaways
- 提出了简化的自监督学习框架NEST,针对语音处理任务高效运行。
- 使用FastConformer架构实现了较高的采样率与更快的运算速度。
- 采用固定随机投影方法替代了复杂的聚类量化过程。
- 引入了一种通用的噪声语音增强技术,以提高模型的鲁棒性。
- 在多个语音处理任务上表现出优于现有自监督模型的性能。
- NEST框架达到了最新技术水平,并成功应用于多种语音处理任务,如语音识别、翻译、说话人分析等。
点此查看论文截图

Towards High-Quality and Efficient Speech Bandwidth Extension with Parallel Amplitude and Phase Prediction
Authors:Ye-Xin Lu, Yang Ai, Hui-Peng Du, Zhen-Hua Ling
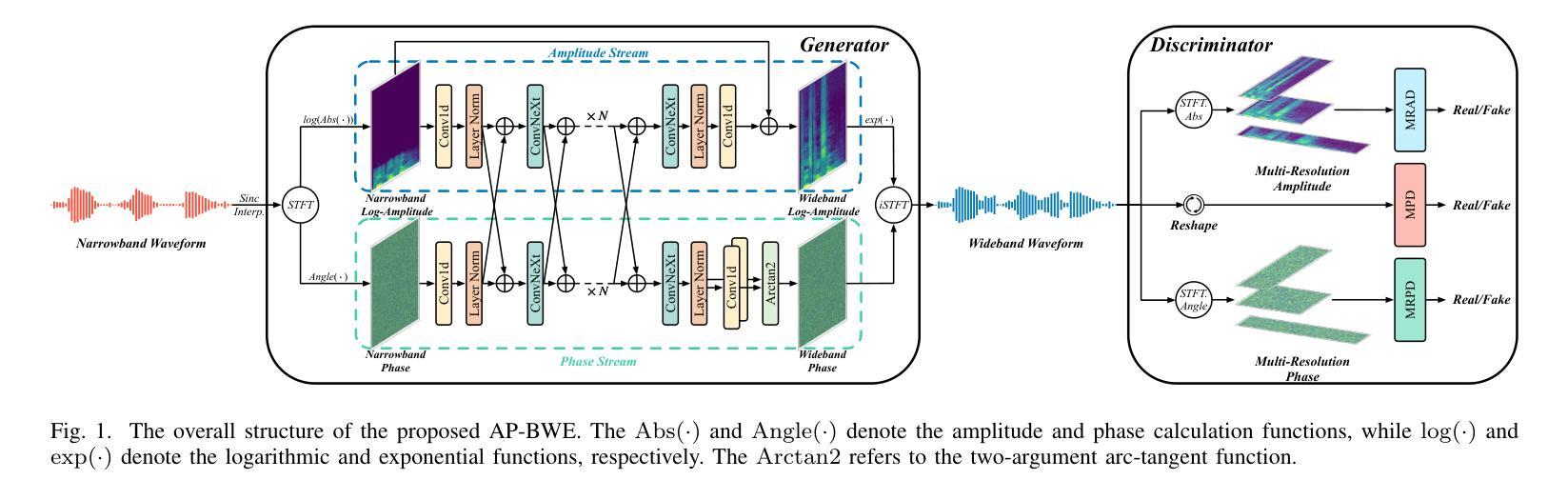
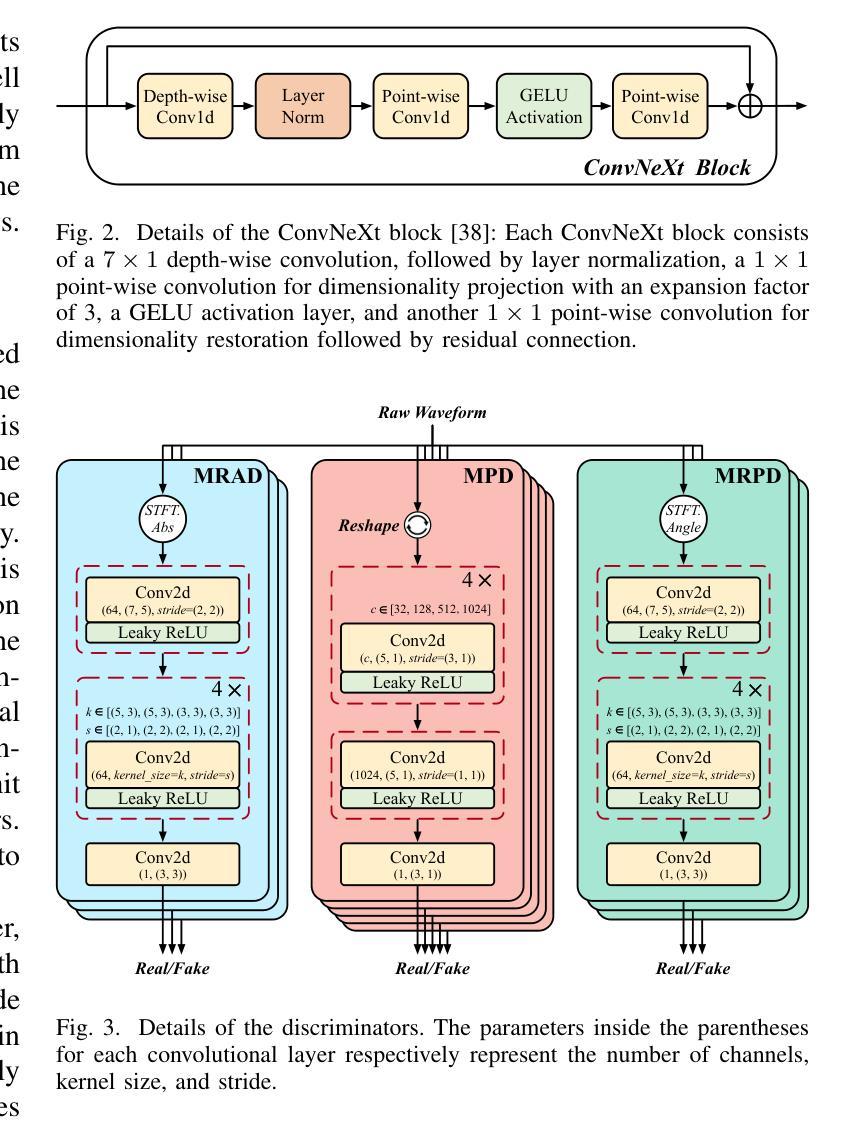
Speech bandwidth extension (BWE) refers to widening the frequency bandwidth range of speech signals, enhancing the speech quality towards brighter and fuller. This paper proposes a generative adversarial network (GAN) based BWE model with parallel prediction of Amplitude and Phase spectra, named AP-BWE, which achieves both high-quality and efficient wideband speech waveform generation. The proposed AP-BWE generator is entirely based on convolutional neural networks (CNNs). It features a dual-stream architecture with mutual interaction, where the amplitude stream and the phase stream communicate with each other and respectively extend the high-frequency components from the input narrowband amplitude and phase spectra. To improve the naturalness of the extended speech signals, we employ a multi-period discriminator at the waveform level and design a pair of multi-resolution amplitude and phase discriminators at the spectral level, respectively. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed AP-BWE achieves state-of-the-art performance in terms of speech quality for BWE tasks targeting sampling rates of both 16 kHz and 48 kHz. In terms of generation efficiency, due to the all-convolutional architecture and all-frame-level operations, the proposed AP-BWE can generate 48 kHz waveform samples 292.3 times faster than real-time on a single RTX 4090 GPU and 18.1 times faster than real-time on a single CPU. Notably, to our knowledge, AP-BWE is the first to achieve the direct extension of the high-frequency phase spectrum, which is beneficial for improving the effectiveness of existing BWE methods.
语音带宽扩展(BWE)是指扩大语音信号的频率带宽范围,提高语音质量,使其更加明亮和丰满。本文针对语音信号的宽带波形生成问题,提出了一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的BWE模型,该模型可以同时预测振幅和相位谱,称为AP-BWE。该模型实现了高质量且高效的宽带语音波形生成。提出的AP-BWE生成器完全基于卷积神经网络(CNNs)。它采用双流传输架构,相互交互,其中振幅流和相位流相互通信,分别从输入的窄带振幅和相位谱扩展高频分量。为了提高扩展语音信号的自然性,我们在波形级别采用了多周期鉴别器,并在光谱级别设计了一对多分辨率振幅和相位鉴别器。实验结果表明,我们提出的AP-BWE在针对16kHz和48kHz采样率的BWE任务时,语音质量达到了最新水平。在提高生成效率方面,由于采用了全卷积架构和帧级操作,AP-BWE在单个RTX 4090 GPU上生成48kHz波形样本的速度是实时速度的292.3倍,在单个CPU上是实时速度的18.1倍。据我们所知,AP-BWE首次实现了高频相位谱的直接扩展,这有利于提高现有BWE方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing
摘要
本文提出一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的语音带宽扩展(BWE)模型,该模型可实现振幅和相位谱的并行预测,称为AP-BWE。它完全基于卷积神经网络(CNNs),具有双流传感器架构,实现振幅和相位传感器之间的相互交流,分别从输入窄带振幅和相位谱扩展高频分量。为提高扩展语音信号的自然性,采用波形级别的多周期鉴别器和光谱级别的多分辨率振幅与相位鉴别器。实验结果表明,针对采样率为16kHz和48kHz的BWE任务,所提出的AP-BWE在语音质量方面达到最新技术水平。在生成效率方面,由于全卷积架构和帧级操作,AP-BWE在单个RTX 4090 GPU上生成48kHz波形样本的速度是实时速度的292.3倍,在单个CPU上是实时的18.1倍。据我们所知,AP-BWE首次实现了高频相位谱的直接扩展,这有助于提高现有BWE方法的有效性。
关键见解
- 本文提出了一种基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的语音带宽扩展(BWE)模型AP-BWE,旨在增强语音质量并扩展频率带宽范围。
- AP-BWE采用卷积神经网络(CNNs)完全构建,具有双流架构,实现振幅和相位传感器间的相互交流。
- 通过采用多周期鉴别器和多分辨率振幅与相位鉴别器,提高了扩展语音信号的自然性。
- 实验结果显示,AP-BWE在语音质量和生成效率方面达到最新技术水平。
- AP-BWE实现了高频相位谱的直接扩展,有助于提高现有BWE方法的效果。
- AP-BWE能够在单个高性能GPU上实现快速语音波形生成,显著提高了实时性能。
点此查看论文截图