⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-19 更新
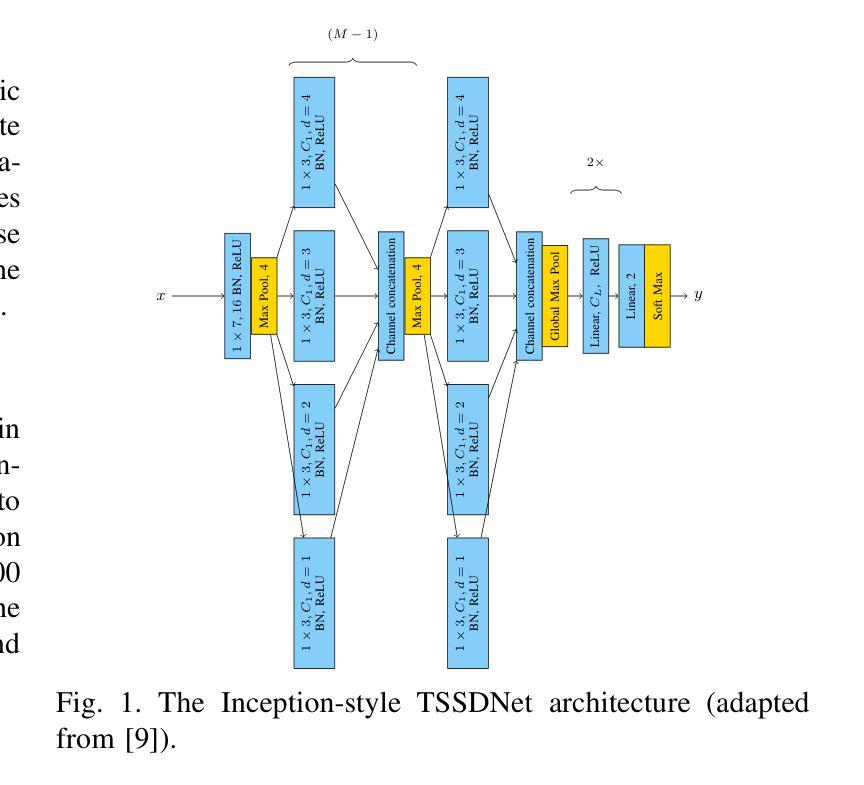
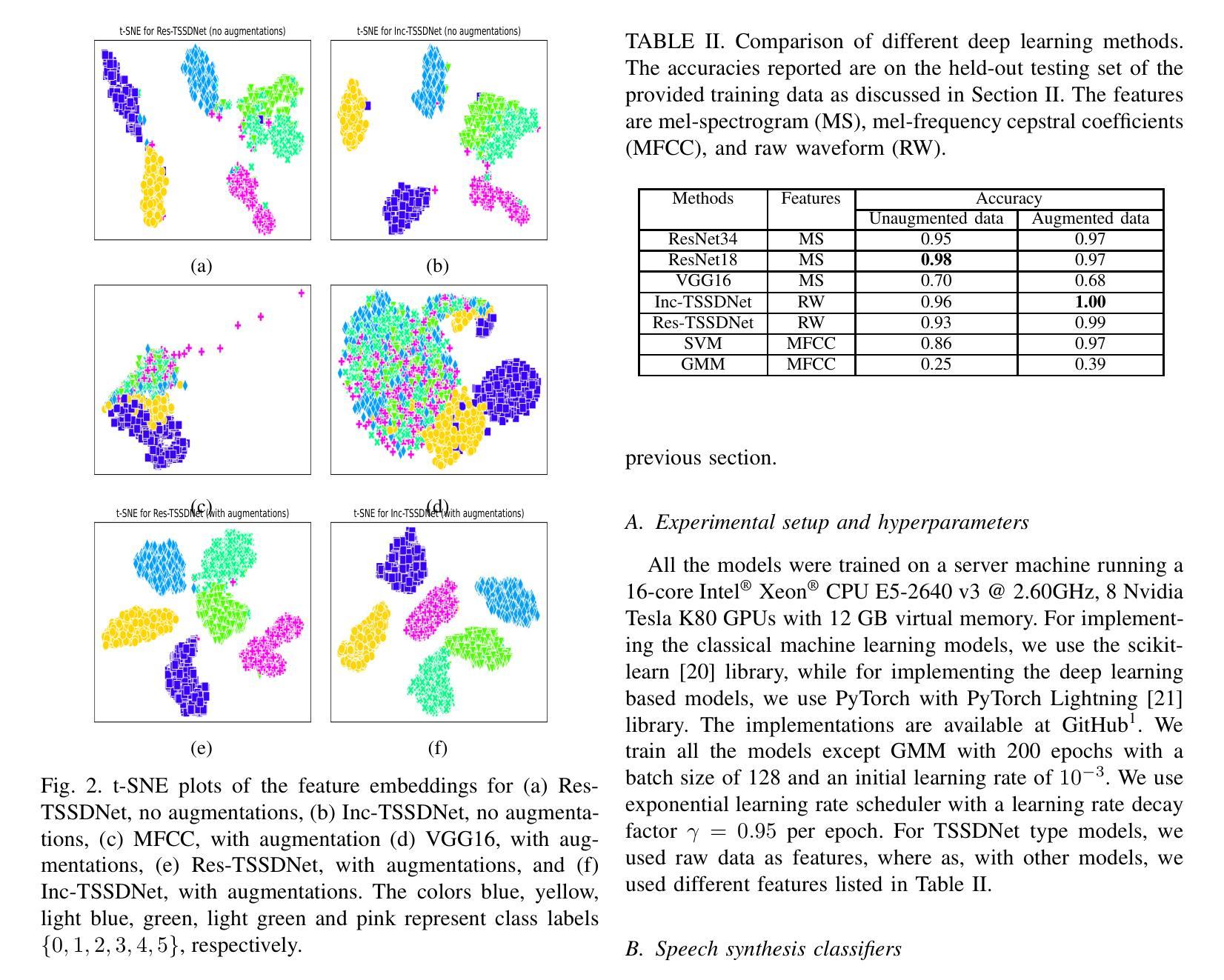
Synthetic Speech Classification: IEEE Signal Processing Cup 2022 challenge
Authors:Mahieyin Rahmun, Rafat Hasan Khan, Tanjim Taharat Aurpa, Sadia Khan, Zulker Nayeen Nahiyan, Mir Sayad Bin Almas, Rakibul Hasan Rajib, Syeda Sakira Hassan
The aim of this project is to implement and design arobust synthetic speech classifier for the IEEE Signal ProcessingCup 2022 challenge. Here, we learn a synthetic speech attributionmodel using the speech generated from various text-to-speech(TTS) algorithms as well as unknown TTS algorithms. Weexperiment with both the classical machine learning methodssuch as support vector machine, Gaussian mixture model, anddeep learning based methods such as ResNet, VGG16, and twoshallow end-to-end networks. We observe that deep learningbased methods with raw data demonstrate the best performance.
此项目的目标是针对IEEE信号处理杯2022挑战赛,设计和实现一个稳健的合成语音分类器。在这里,我们使用各种文本到语音(TTS)算法以及未知TTS算法生成的语音来学习合成语音归属模型。我们尝试使用经典的机器学习方法和深度学习的方法,比如支持向量机、高斯混合模型以及ResNet、VGG16和两个浅层端到端网络。我们发现基于深度学习和原始数据的方案表现出最佳性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该项目旨在针对IEEE信号处理杯2022挑战赛设计和实现一个稳健的合成语音分类器。该项目使用各种文本到语音(TTS)算法生成的语音以及未知TTS算法来学习合成语音属性模型。实验包括使用经典机器学习方法和深度学习方法的对比实验,结果显示深度学习方法的性能最佳。
Key Takeaways
- 项目目标是设计和实现一个针对IEEE信号处理杯2022挑战赛的稳健合成语音分类器。
- 项目使用多种TTS算法生成的语音作为数据来训练模型。
- 项目对比了经典机器学习方法(如支持向量机和高斯混合模型)和深度学习方法(如ResNet和VGG16)。
- 实验结果表明深度学习方法的性能最佳。
- 直接使用原始数据能够提高深度学习模型的性能。
- 该项目为合成语音的识别提供了有效方法和思路。
点此查看论文截图

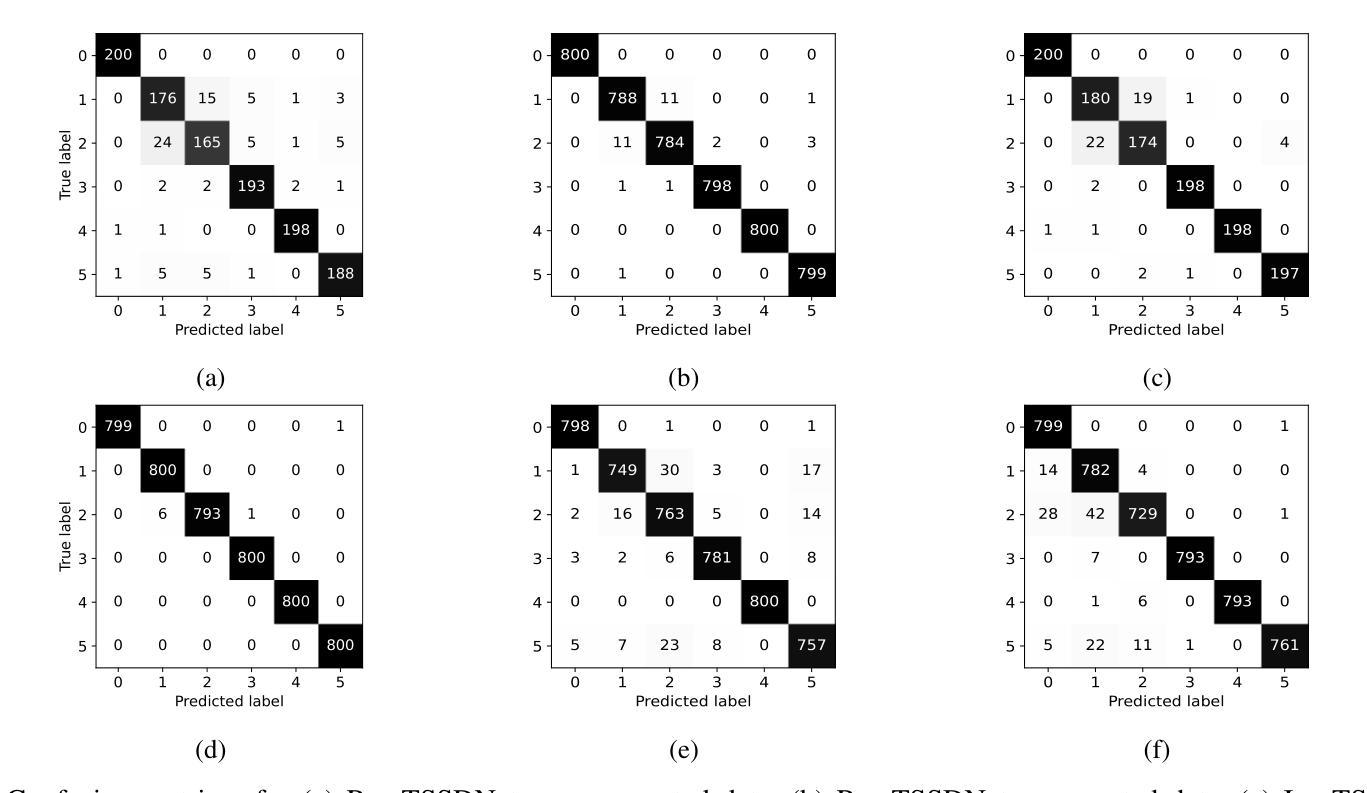
Phoneme-Level Feature Discrepancies: A Key to Detecting Sophisticated Speech Deepfakes
Authors:Kuiyuan Zhang, Zhongyun Hua, Rushi Lan, Yushu Zhang, Yifang Guo
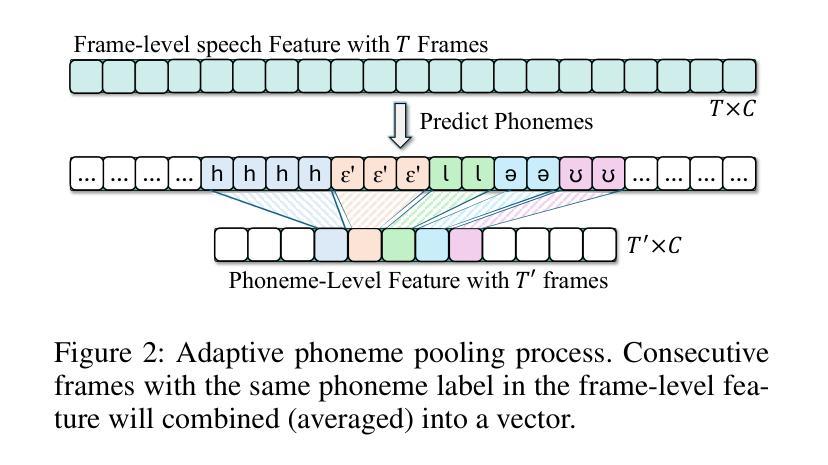
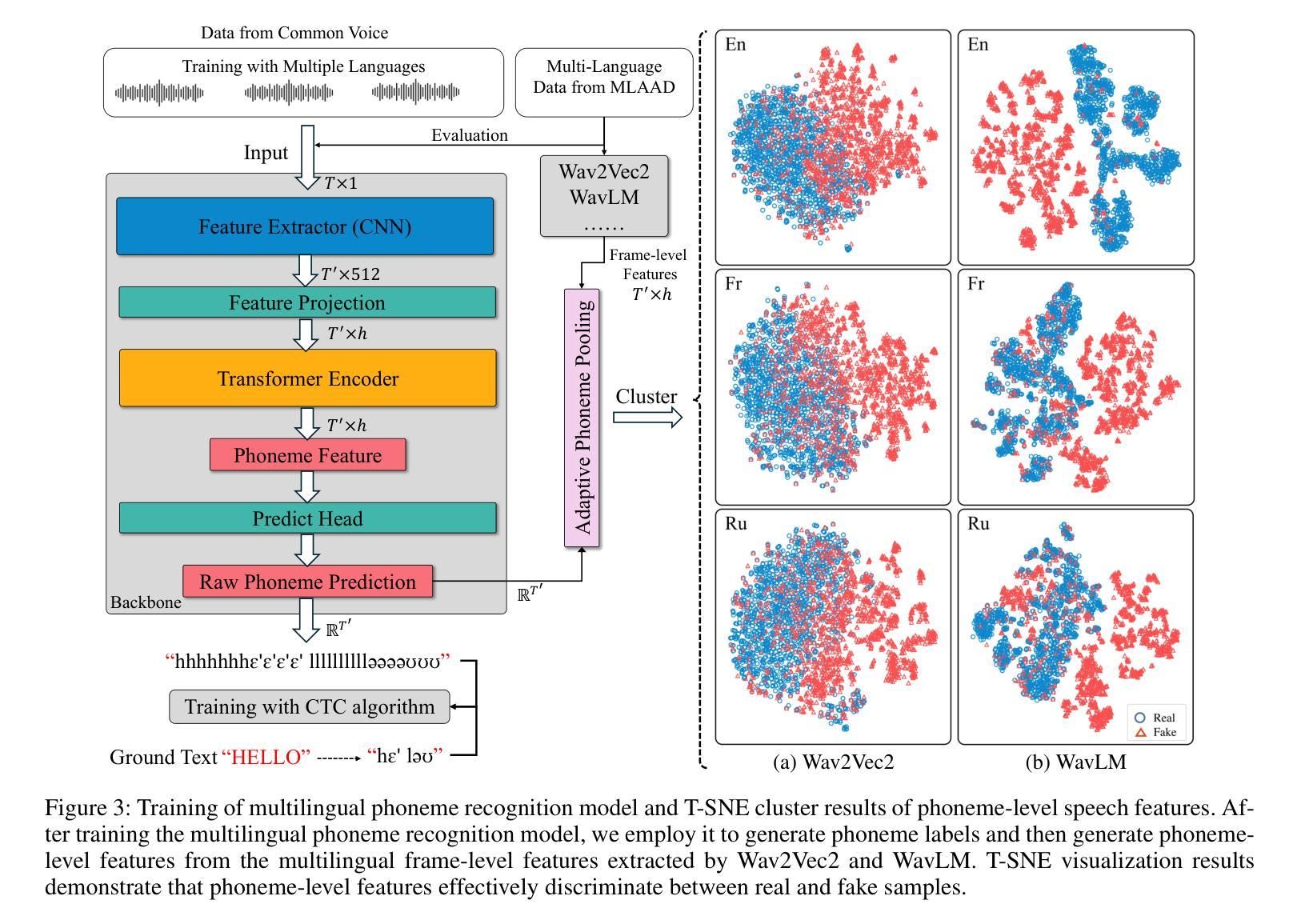
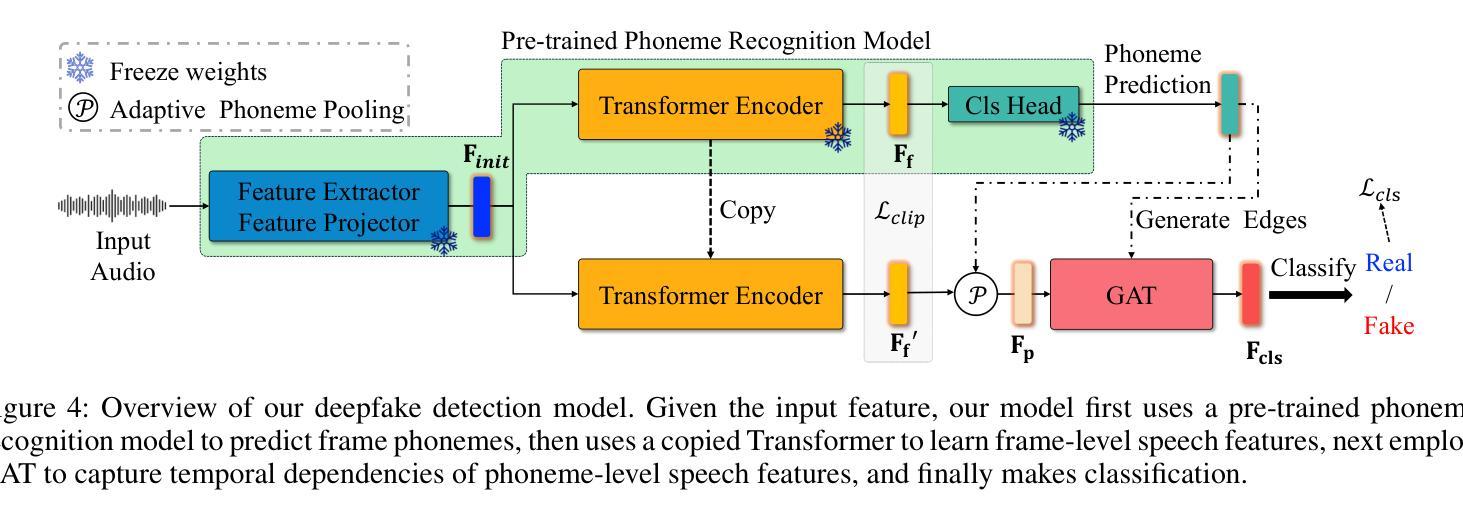
Recent advancements in text-to-speech and speech conversion technologies have enabled the creation of highly convincing synthetic speech. While these innovations offer numerous practical benefits, they also cause significant security challenges when maliciously misused. Therefore, there is an urgent need to detect these synthetic speech signals. Phoneme features provide a powerful speech representation for deepfake detection. However, previous phoneme-based detection approaches typically focused on specific phonemes, overlooking temporal inconsistencies across the entire phoneme sequence. In this paper, we develop a new mechanism for detecting speech deepfakes by identifying the inconsistencies of phoneme-level speech features. We design an adaptive phoneme pooling technique that extracts sample-specific phoneme-level features from frame-level speech data. By applying this technique to features extracted by pre-trained audio models on previously unseen deepfake datasets, we demonstrate that deepfake samples often exhibit phoneme-level inconsistencies when compared to genuine speech. To further enhance detection accuracy, we propose a deepfake detector that uses a graph attention network to model the temporal dependencies of phoneme-level features. Additionally, we introduce a random phoneme substitution augmentation technique to increase feature diversity during training. Extensive experiments on four benchmark datasets demonstrate the superior performance of our method over existing state-of-the-art detection methods.
近期文本到语音和语音转换技术的进展使得创建高度逼真的合成语音成为可能。虽然这些创新提供了许多实际好处,但它们在恶意滥用时也带来了重大的安全挑战。因此,急需检测这些合成语音信号。音素特征为深度伪造检测提供了强大的语音表征。然而,以前的基于音素的检测方法通常专注于特定音素,忽略了整个音素序列中的时间不一致性。在本文中,我们开发了一种通过识别音素级语音特征的不一致性来检测语音深度伪造的新机制。我们设计了一种自适应的音素池化技术,从帧级语音数据中提取样本特定的音素级特征。通过将这项技术应用在从先前未见过的深度伪造数据集上预训练的音频模型所提取的特征上,我们证明与真实语音相比,深度伪造样本在音素级上通常表现出不一致性。为了进一步提高检测精度,我们提出了一种使用图注意力网络对音素级特征的时间依赖性进行建模的深度伪造检测器。此外,我们还引入了一种随机音素替换增强技术,以增加训练过程中的特征多样性。在四个基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法优于现有的最先进的检测方法。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
近期文本转语音和语音转换技术的进展使得创建高度逼真的合成语音成为可能。虽然这些创新提供了许多实际利益,但当它们被恶意误用时,也会带来重大安全挑战。因此,迫切需要检测这些合成语音信号。本文提出了一种通过识别音素级语音特征的不一致性来检测语音深度伪造的新机制。我们设计了一种自适应的音素池化技术,从帧级语音数据中提取样本特定的音素级特征。通过将此技术应用于预训练音频模型提取的特征之前未见过的深度伪造数据集上,我们证明深度伪造样本与真实语音相比,往往表现出音素级的不一致性。为进一步提高检测精度,我们提出了一种使用图注意力网络对音素级特征的时间依赖性进行建模的深度伪造检测器。此外,我们还引入了一种随机音素替换增强技术,以增加训练过程中的特征多样性。在四个基准数据集上的广泛实验表明,我们的方法优于现有的最先进的检测方法。
Key Takeaways
- 合成语音技术的进展带来了实用性和安全性挑战。
- 检测合成语音信号的需求迫切。
- 音素级特征在深度伪造检测中起到重要作用。
- 提出了一种自适应的音素池化技术,用于提取样本特定的音素级特征。
- 通过图注意力网络对音素级特征的时间依赖性进行建模,提高检测精度。
- 引入随机音素替换增强技术,增加训练特征多样性。
点此查看论文截图

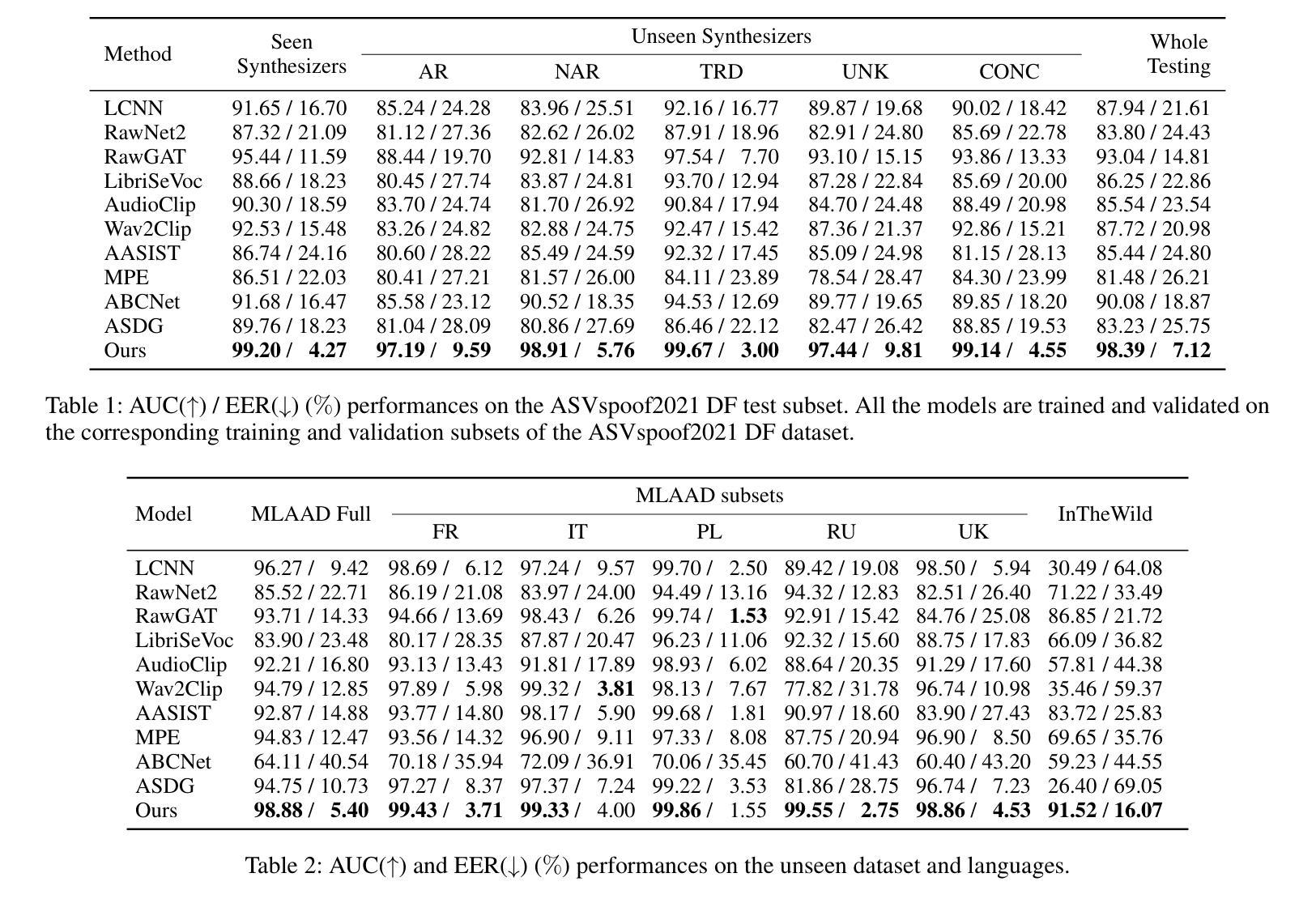
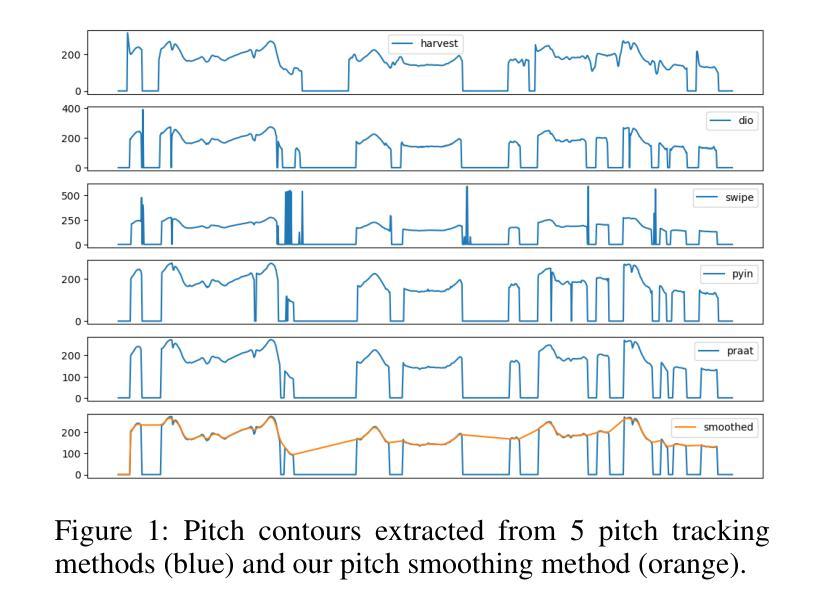
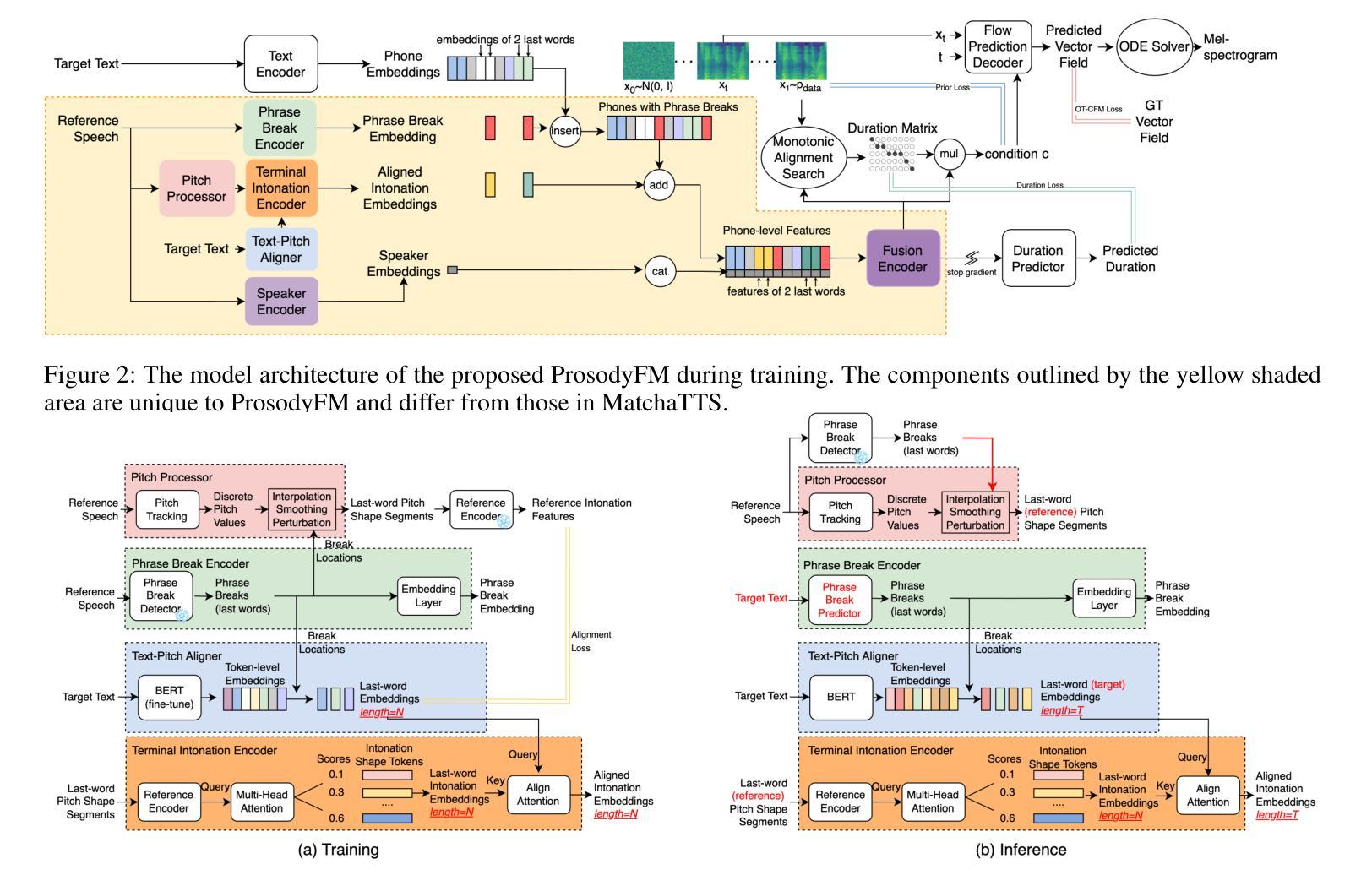
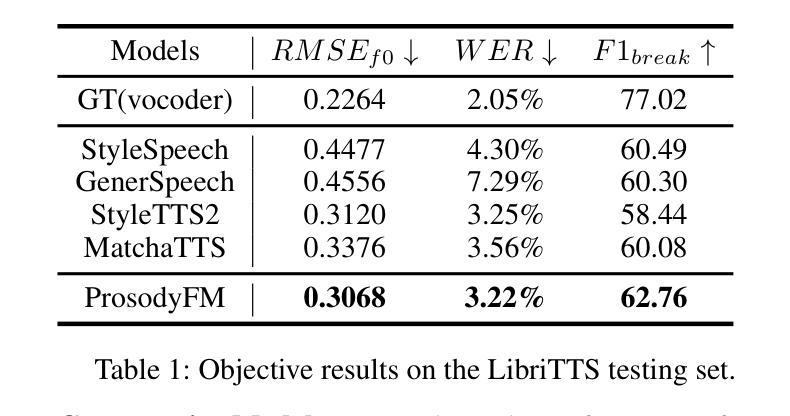
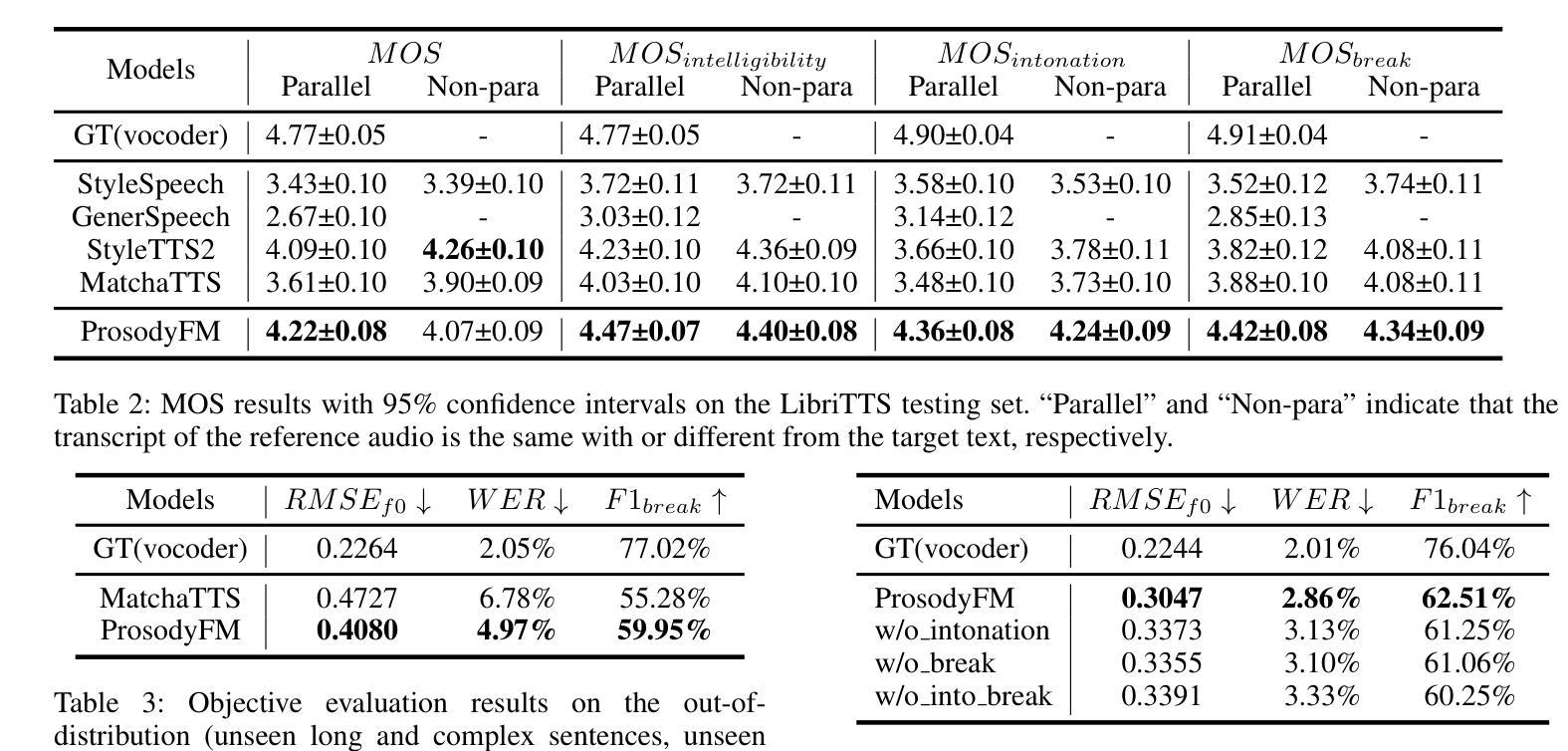
ProsodyFM: Unsupervised Phrasing and Intonation Control for Intelligible Speech Synthesis
Authors:Xiangheng He, Junjie Chen, Zixing Zhang, Björn W. Schuller
Prosody contains rich information beyond the literal meaning of words, which is crucial for the intelligibility of speech. Current models still fall short in phrasing and intonation; they not only miss or misplace breaks when synthesizing long sentences with complex structures but also produce unnatural intonation. We propose ProsodyFM, a prosody-aware text-to-speech synthesis (TTS) model with a flow-matching (FM) backbone that aims to enhance the phrasing and intonation aspects of prosody. ProsodyFM introduces two key components: a Phrase Break Encoder to capture initial phrase break locations, followed by a Duration Predictor for the flexible adjustment of break durations; and a Terminal Intonation Encoder which integrates a set of intonation shape tokens combined with a novel Pitch Processor for more robust modeling of human-perceived intonation change. ProsodyFM is trained with no explicit prosodic labels and yet can uncover a broad spectrum of break durations and intonation patterns. Experimental results demonstrate that ProsodyFM can effectively improve the phrasing and intonation aspects of prosody, thereby enhancing the overall intelligibility compared to four state-of-the-art (SOTA) models. Out-of-distribution experiments show that this prosody improvement can further bring ProsodyFM superior generalizability for unseen complex sentences and speakers. Our case study intuitively illustrates the powerful and fine-grained controllability of ProsodyFM over phrasing and intonation.
韵律包含超越词汇字面意义的丰富信息,这对于语音的清晰度至关重要。当前模型在短语和语调方面仍有不足;它们在合成具有复杂结构的长句子时,不仅会遗漏或错位断点,还会产生不自然的语调。我们提出了ProsodyFM,这是一个具有韵律感知的文本到语音合成(TTS)模型,它采用流匹配(FM)作为主干,旨在增强韵律的短语和语调方面。ProsodyFM引入了两个关键组件:Phrase Break Encoder用于捕捉初始短语断点位置,然后是Duration Predictor用于灵活调整断句持续时间;Terminal Intonation Encoder则整合了一组语调形状标记,并结合新型Pitch Processor,以更稳健地模拟人类感知的语调变化。ProsodyFM无需明确的韵律标签即可进行训练,但能够揭示广泛的断句持续时间和语调模式。实验结果表明,ProsodyFM可以有效改善韵律的短语和语调方面,从而与四种最先进模型相比提高整体清晰度。分布外实验表明,这种韵律改进可以进一步提高ProsodyFM对未见过的复杂句子和说话人的泛化能力。我们的案例研究直观地说明了ProsodyFM在短语和语调上的强大和精细可控性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
文本中的信息指出,语音中的韵律(Prosody)包含超越单词字面意义的丰富信息,这对语音的可懂度至关重要。当前的语音合成模型在表达和语调方面仍存在不足,无法正确或自然地处理长句复杂结构中的停顿和语调。为此,我们提出了一个带有流匹配(FM)背骨的韵律感知文本到语音合成(TTS)模型——ProsodyFM,旨在增强韵律的语调和表达方面。ProsodyFM引入了两个关键组件:一个短语断句编码器,用于捕捉初始断句位置,随后是一个时长预测器,用于灵活地调整断句时长;还有一个终端语调编码器,它结合了语调形状标记和一种新的音调处理器,以更稳健地模拟人类感知的语调变化。ProsodyFM无需明确的韵律标签即可进行训练,但可以揭示广泛的断句时长和语调模式。实验结果表明,与四种最先进模型相比,ProsodyFM可以有效地改善韵律的表达和语调方面,从而提高整体的可懂度。此外,针对未见过的复杂句子和说话者的实验表明,ProsodyFM在泛化能力上具有优势。我们的案例研究直观地展示了ProsodyFM在表达和语调方面的强大和精细可控性。
Key Takeaways
- 文本中的韵律信息对语音的可懂度至关重要。
- 当前语音合成模型在表达和语调方面存在不足。
- 提出了一种新的韵律感知文本到语音合成模型——ProsodyFM。
- ProsodyFM包含短语断句编码器、时长预测器和终端语调编码器三个关键组件。
- ProsodyFM无需明确的韵律标签即可进行训练,并能揭示广泛的断句时长和语调模式。
- 实验结果表明,ProsodyFM在表达和语调方面优于其他先进模型,提高了语音的整体可懂度。
点此查看论文截图

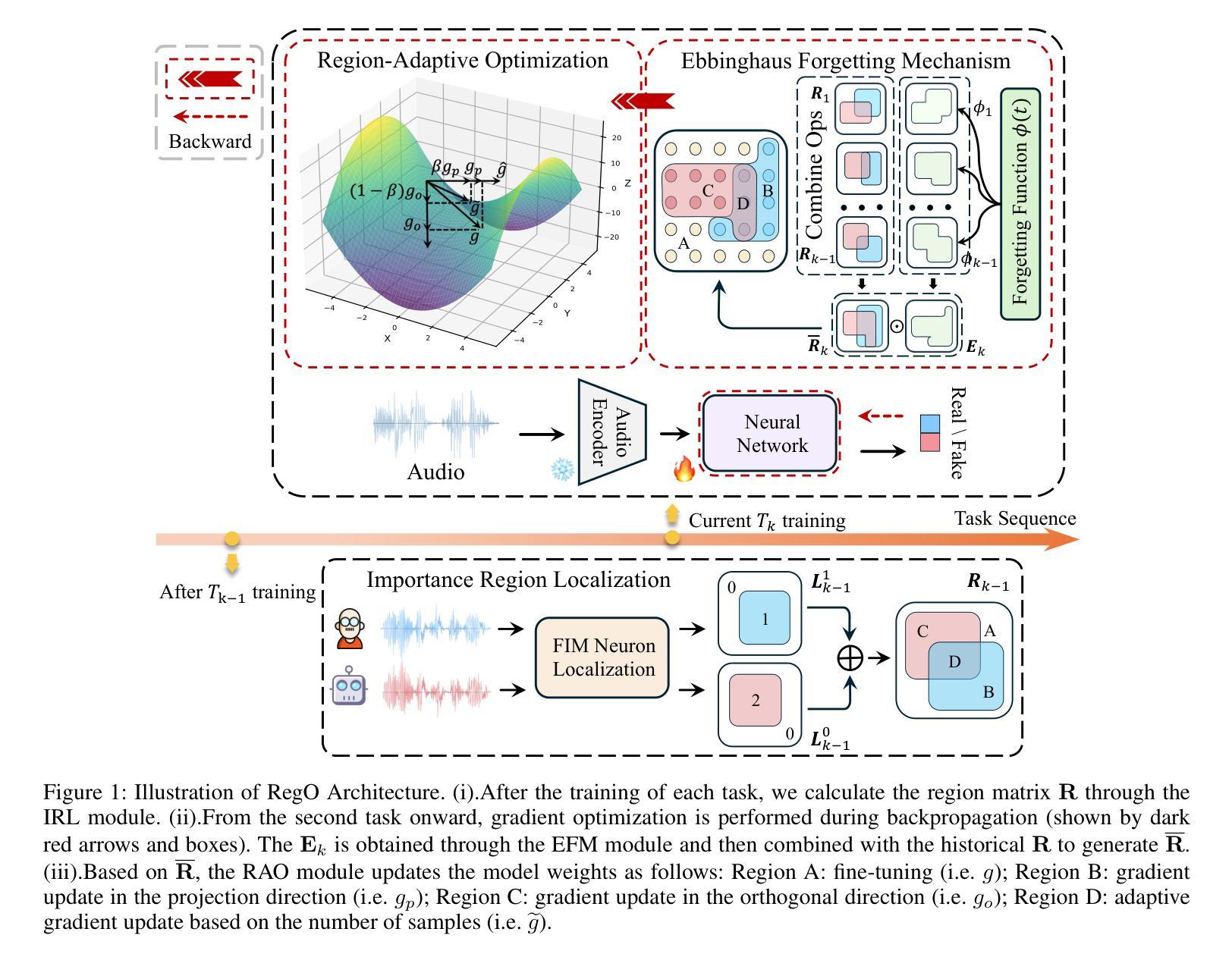
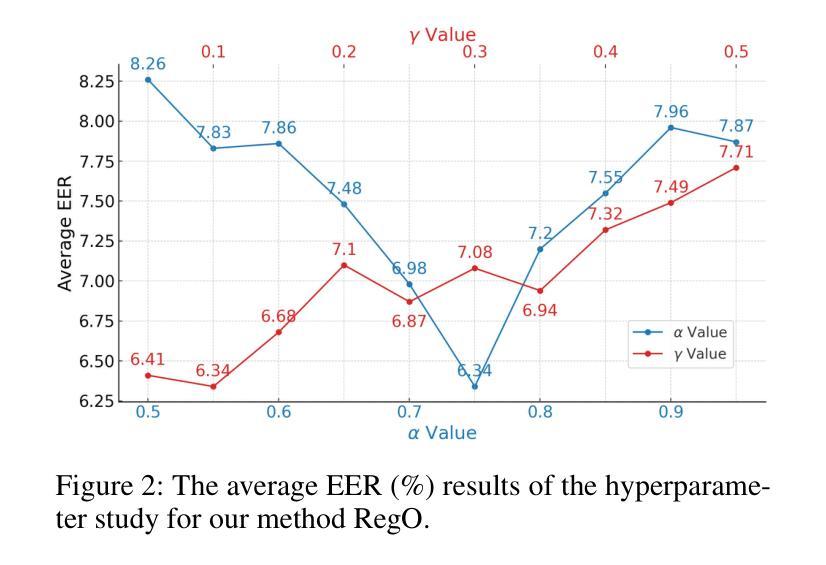
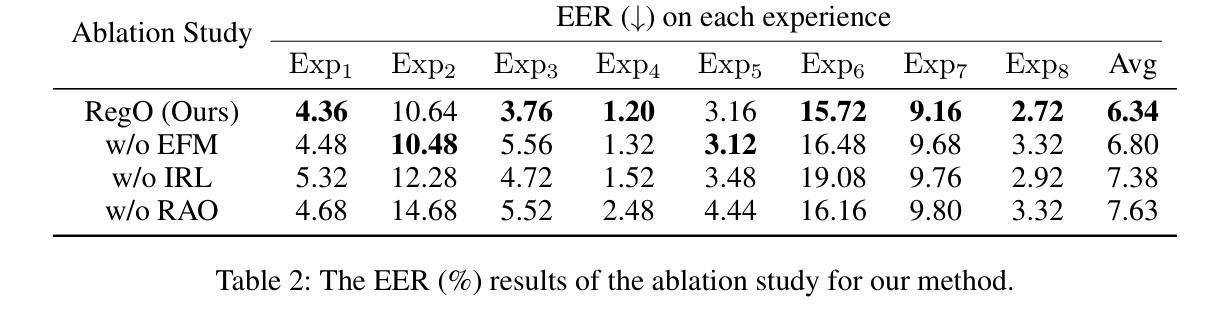
Region-Based Optimization in Continual Learning for Audio Deepfake Detection
Authors:Yujie Chen, Jiangyan Yi, Cunhang Fan, Jianhua Tao, Yong Ren, Siding Zeng, Chu Yuan Zhang, Xinrui Yan, Hao Gu, Jun Xue, Chenglong Wang, Zhao Lv, Xiaohui Zhang
Rapid advancements in speech synthesis and voice conversion bring convenience but also new security risks, creating an urgent need for effective audio deepfake detection. Although current models perform well, their effectiveness diminishes when confronted with the diverse and evolving nature of real-world deepfakes. To address this issue, we propose a continual learning method named Region-Based Optimization (RegO) for audio deepfake detection. Specifically, we use the Fisher information matrix to measure important neuron regions for real and fake audio detection, dividing them into four regions. First, we directly fine-tune the less important regions to quickly adapt to new tasks. Next, we apply gradient optimization in parallel for regions important only to real audio detection, and in orthogonal directions for regions important only to fake audio detection. For regions that are important to both, we use sample proportion-based adaptive gradient optimization. This region-adaptive optimization ensures an appropriate trade-off between memory stability and learning plasticity. Additionally, to address the increase of redundant neurons from old tasks, we further introduce the Ebbinghaus forgetting mechanism to release them, thereby promoting the capability of the model to learn more generalized discriminative features. Experimental results show our method achieves a 21.3% improvement in EER over the state-of-the-art continual learning approach RWM for audio deepfake detection. Moreover, the effectiveness of RegO extends beyond the audio deepfake detection domain, showing potential significance in other tasks, such as image recognition. The code is available at https://github.com/cyjie429/RegO
随着语音合成和语音转换的快速发展,虽然现有的模型在音频深度伪造检测方面表现良好,但当面对现实世界中多样且不断演变的音频深度伪造时,其有效性会降低,这既带来了便利也带来了新的安全风险,从而迫切需要有效的音频深度伪造检测技术。为了解决这一问题,我们提出了一种用于音频深度伪造检测的持续学习方法,称为基于区域的优化(RegO)。具体来说,我们使用Fisher信息矩阵来衡量真实和伪造音频检测中重要的神经元区域,并将其分为四个区域。首先,我们直接微调不太重要的区域以快速适应新任务。接下来,我们对仅对真实音频检测重要的区域进行并行梯度优化,而对仅对伪造音频检测重要的区域进行正交方向上的梯度优化。对于两者都重要的区域,我们使用基于样本比例的适应性梯度优化。这种区域自适应优化确保了内存稳定性和学习可塑性之间的适当权衡。此外,为了解决旧任务中冗余神经元的增加问题,我们进一步引入了艾宾浩斯遗忘机制来释放它们,从而促进模型学习更通用的判别特征的能力。实验结果表明,我们的方法在音频深度伪造检测的EER上比最新持续学习方法RWM提高了21.3%。而且,RegO的有效性不仅局限于音频深度伪造检测领域,在图像识别等其他任务中也显示出潜在的重要性。相关代码可通过https://github.com/cyjie429/RegO获取。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
本文介绍了音频深度伪造检测的新挑战和解决方案。针对现有模型在应对真实世界深度伪造时效果下降的问题,提出了一种基于区域优化的持续学习方法(RegO)。该方法使用Fisher信息矩阵对音频真实与伪造检测中的重要神经元区域进行划分,采用不同优化策略。实验结果显示,该方法在音频深度伪造检测上的性能较最新持续学习方法RWM提高了21.3%。同时,RegO方法在其他任务如图像识别中也显示出潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 语音合成和语音转换的快速发展带来了便利,同时也带来了新的安全风险,对音频深度伪造检测提出了迫切需求。
- 当前模型在应对真实世界深度伪造时面临挑战,需要更有效的解决方案。
- 提出的RegO方法使用Fisher信息矩阵划分重要神经元区域,并采用不同优化策略来提高音频深度伪造检测的性能。
- RegO方法通过直接微调次要区域、对真实音频检测重要区域应用梯度优化、释放冗余神经元等机制,实现了记忆稳定性与学习可塑性之间的平衡。
- Ebbinghaus忘记机制被引入以释放冗余神经元,提高模型学习更通用判别特征的能力。
- 实验结果显示,RegO方法在音频深度伪造检测上的性能较RWM有显著提高。
点此查看论文截图


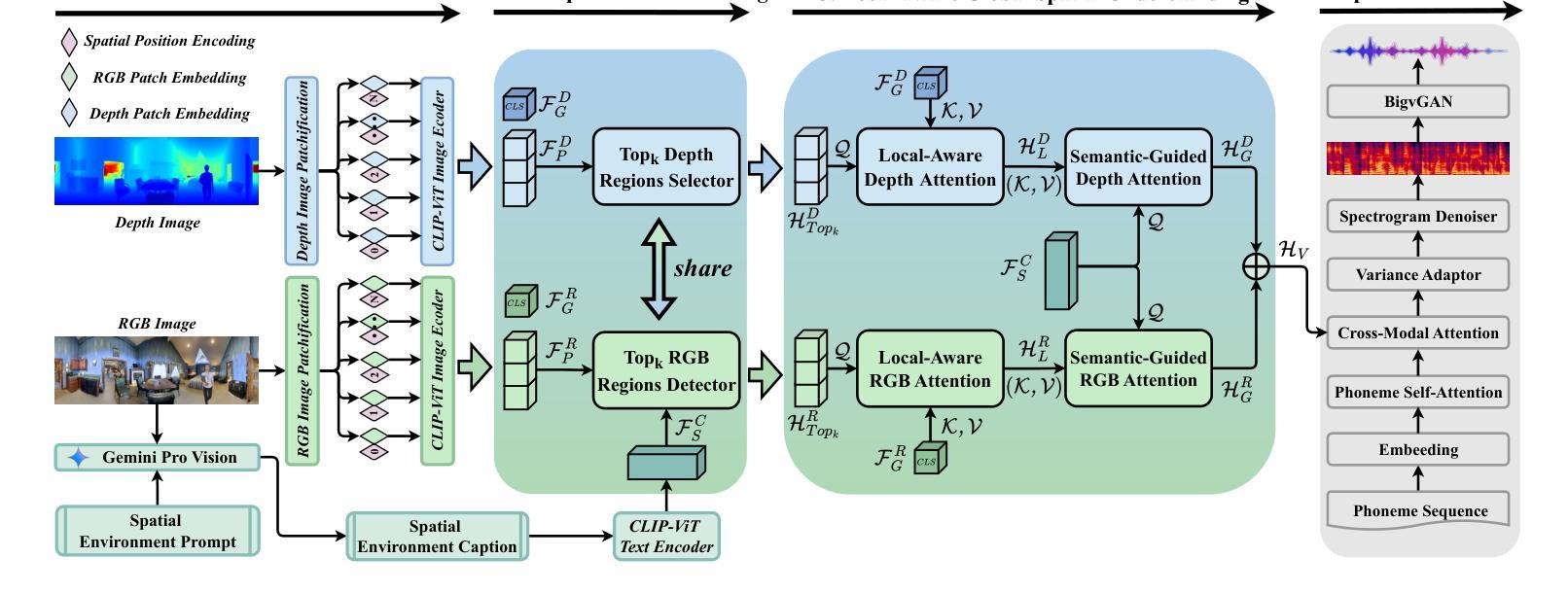
Multi-modal and Multi-scale Spatial Environment Understanding for Immersive Visual Text-to-Speech
Authors:Rui Liu, Shuwei He, Yifan Hu, Haizhou Li
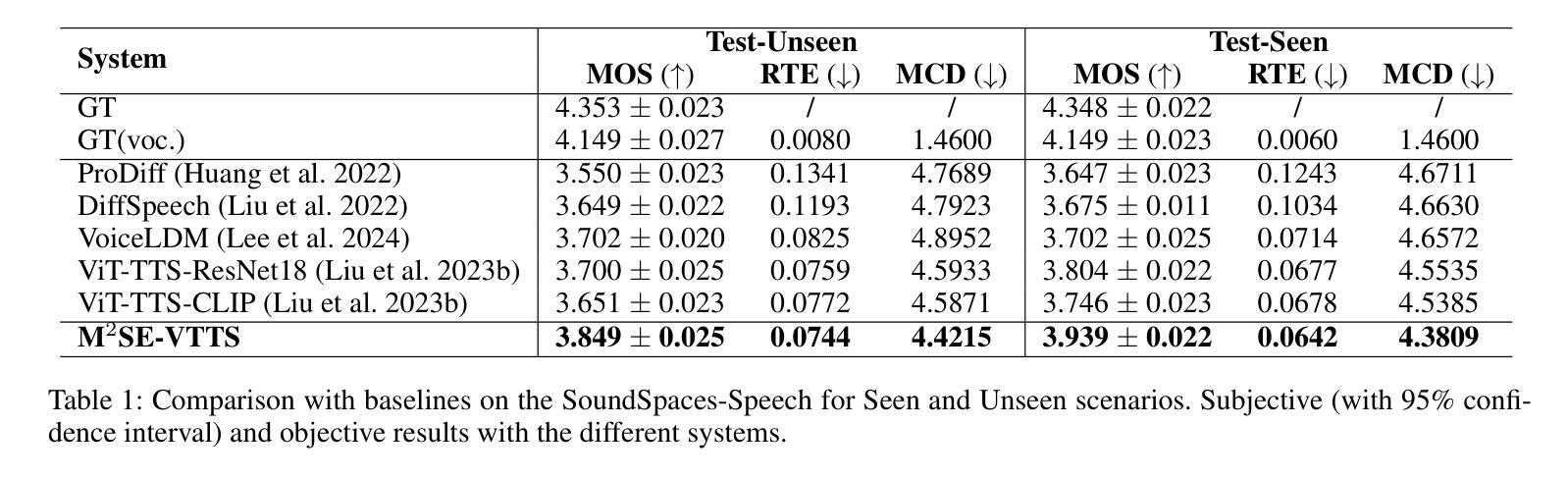
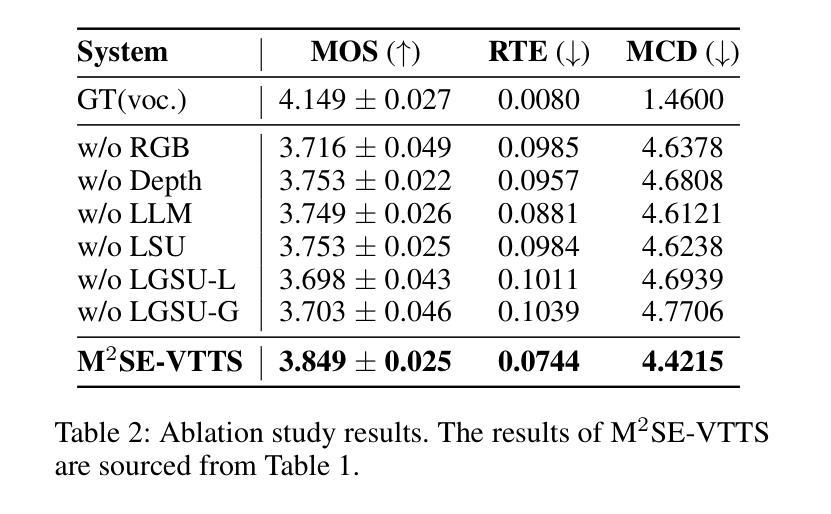
Visual Text-to-Speech (VTTS) aims to take the environmental image as the prompt to synthesize the reverberant speech for the spoken content. The challenge of this task lies in understanding the spatial environment from the image. Many attempts have been made to extract global spatial visual information from the RGB space of an spatial image. However, local and depth image information are crucial for understanding the spatial environment, which previous works have ignored. To address the issues, we propose a novel multi-modal and multi-scale spatial environment understanding scheme to achieve immersive VTTS, termed M2SE-VTTS. The multi-modal aims to take both the RGB and Depth spaces of the spatial image to learn more comprehensive spatial information, and the multi-scale seeks to model the local and global spatial knowledge simultaneously. Specifically, we first split the RGB and Depth images into patches and adopt the Gemini-generated environment captions to guide the local spatial understanding. After that, the multi-modal and multi-scale features are integrated by the local-aware global spatial understanding. In this way, M2SE-VTTS effectively models the interactions between local and global spatial contexts in the multi-modal spatial environment. Objective and subjective evaluations suggest that our model outperforms the advanced baselines in environmental speech generation. The code and audio samples are available at: https://github.com/AI-S2-Lab/M2SE-VTTS.
视觉文本到语音(VTTS)旨在以环境图像为提示,合成与语音内容相符的回响语音。该任务面临的挑战在于从图像中理解空间环境。许多尝试都试图从空间图像的RGB空间中提取全局空间视觉信息。然而,局部和深度图像信息对于理解空间环境至关重要,而以前的工作却忽略了这一点。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新颖的多模式、多尺度的空间环境理解方案,以实现沉浸式VTTS,称为M2SE-VTTS。多模式旨在利用空间图像的RGB和深度空间来学习更全面的空间信息,而多尺度则旨在同时建模局部和全局空间知识。具体来说,我们首先将RGB和深度图像分割成斑块,并采用Gemini生成的环境字幕来指导局部空间理解。之后,通过局部感知全局空间理解,将多模式和多尺度特征相结合。这样,M2SE-VTTS有效地建模了多模式空间环境中局部和全局空间上下文之间的交互。客观和主观评估表明,我们的模型在环境语音生成方面优于先进的基线模型。代码和音频样本可在:https://github.com/AI-S2-Lab/M2SE-VTTS找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages,2 figures, Accepted by AAAI’2025
Summary
视觉文本到语音(VTTS)以环境图像为提示合成语音内容。其挑战在于从图像理解空间环境。为更好地了解空间环境,我们提出一种新颖的多模式多尺度空间环境理解方案,实现沉浸式VTTS,称为M2SE-VTTS。该方案旨在同时利用图像的RGB和深度空间学习更全面的空间信息,并同时建模局部和全局空间知识。通过分割RGB和深度图像成补丁并采用Gemini生成的环境字幕来指导局部空间理解,然后整合多模式多尺度特征。这种方式有效地建模了多模式空间环境中局部和全局空间上下文之间的交互。客观和主观评估表明,我们的模型在环境语音生成方面优于先进基线。
Key Takeaways
- VTTS以环境图像为提示合成语音内容。
- 理解空间环境是VTTS的核心挑战。
- 提出一种新颖的多模式多尺度空间环境理解方案M2SE-VTTS。
- M2SE-VTTS同时利用图像的RGB和深度空间。
- M2SE-VTTS通过分割图像并整合多模式多尺度特征来实现局部和全局空间知识的建模。
- M2SE-VTTS有效地建模了多模式空间环境中局部和全局空间上下文的交互。
点此查看论文截图

Efficient Generative Modeling with Residual Vector Quantization-Based Tokens
Authors:Jaehyeon Kim, Taehong Moon, Keon Lee, Jaewoong Cho
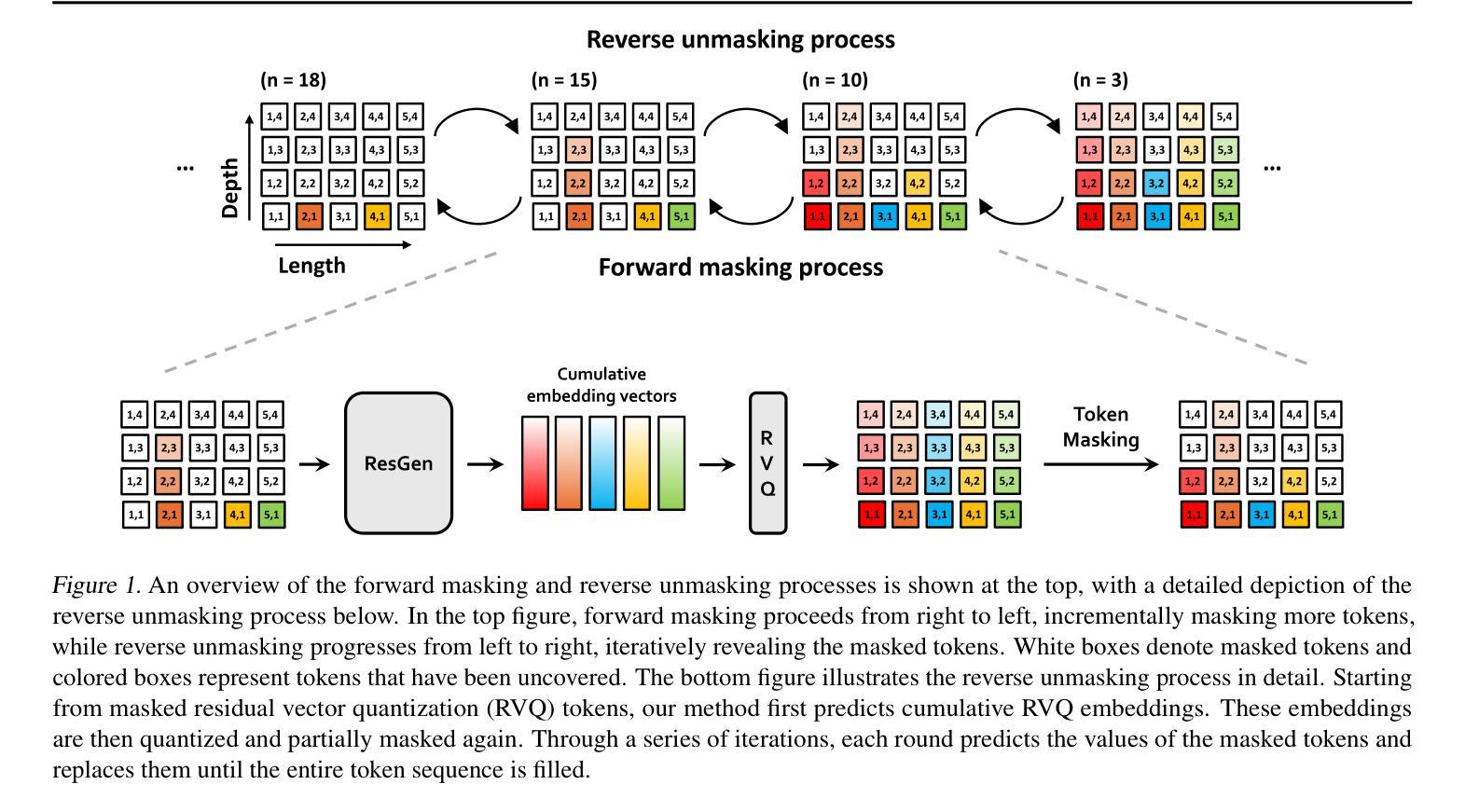
We explore the use of Residual Vector Quantization (RVQ) for high-fidelity generation in vector-quantized generative models. This quantization technique maintains higher data fidelity by employing more in-depth tokens. However, increasing the token number in generative models leads to slower inference speeds. To this end, we introduce ResGen, an efficient RVQ-based discrete diffusion model that generates high-fidelity samples without compromising sampling speed. Our key idea is a direct prediction of vector embedding of collective tokens rather than individual ones. Moreover, we demonstrate that our proposed token masking and multi-token prediction method can be formulated within a principled probabilistic framework using a discrete diffusion process and variational inference. We validate the efficacy and generalizability of the proposed method on two challenging tasks across different modalities: conditional image generation} on ImageNet 256x256 and zero-shot text-to-speech synthesis. Experimental results demonstrate that ResGen outperforms autoregressive counterparts in both tasks, delivering superior performance without compromising sampling speed. Furthermore, as we scale the depth of RVQ, our generative models exhibit enhanced generation fidelity or faster sampling speeds compared to similarly sized baseline models. The project page can be found at https://resgen-genai.github.io
我们探讨了残差向量量化(RVQ)在高保真生成向量量化生成模型中的应用。这种量化技术通过采用更深入的标记来保持更高的数据保真度。然而,在生成模型中增加标记数量会导致推理速度变慢。为此,我们引入了ResGen,这是一个基于RVQ的高效离散扩散模型,能够在不牺牲采样速度的情况下生成高保真样本。我们的关键想法是预测集体标记的向量嵌入而不是单个标记。此外,我们证明,我们提出的标记掩码和多标记预测方法可以使用离散扩散过程和变分推断在原则性概率框架内制定。我们在两个不同模态的挑战性任务上验证了所提出方法的有效性和通用性:ImageNet 256x256上的条件图像生成和零样本文本到语音合成。实验结果表明,ResGen在这两项任务中都优于自回归方法,在不牺牲采样速度的情况下实现了卓越的性能。此外,随着我们扩大RVQ的深度,我们的生成模型与类似规模的基准模型相比,表现出更高的生成保真度或更快的采样速度。项目页面可在https://resgen-genai.github.io找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本摘要介绍了Residual Vector Quantization(RVQ)在向量量化生成模型中的应用,并探讨如何通过保持更高数据保真度的同时提高效率来解决生成模型的推断速度问题。研究人员引入了ResGen模型,这是一个基于RVQ的离散扩散模型,可以在不牺牲采样速度的情况下生成高质量样本。其核心思想是对集体向量嵌入的直接预测,并采用了一种有原则的随机过程和变分推断来表述所提出的方法。实验结果证明,ResGen在条件图像生成和零样本文本到语音合成等任务上优于自回归模型,且随着RVQ深度的增加,其生成质量和采样速度都有所提升。
Key Takeaways
以下是该文本的关键见解:
- Residual Vector Quantization(RVQ)用于提高向量量化生成模型的数据保真度。
- 生成模型中增加token数量会导致推断速度下降。
- ResGen是一个高效的基于RVQ的离散扩散模型,能同时实现高保真度样本生成和快速采样。
- 核心思想是对集体token向量嵌入的直接预测而非单个token的预测。
- 提出的方法在条件图像生成和零样本文本到语音合成任务上表现优异。
- 与自回归模型相比,ResGen展现出优越的性能。
点此查看论文截图

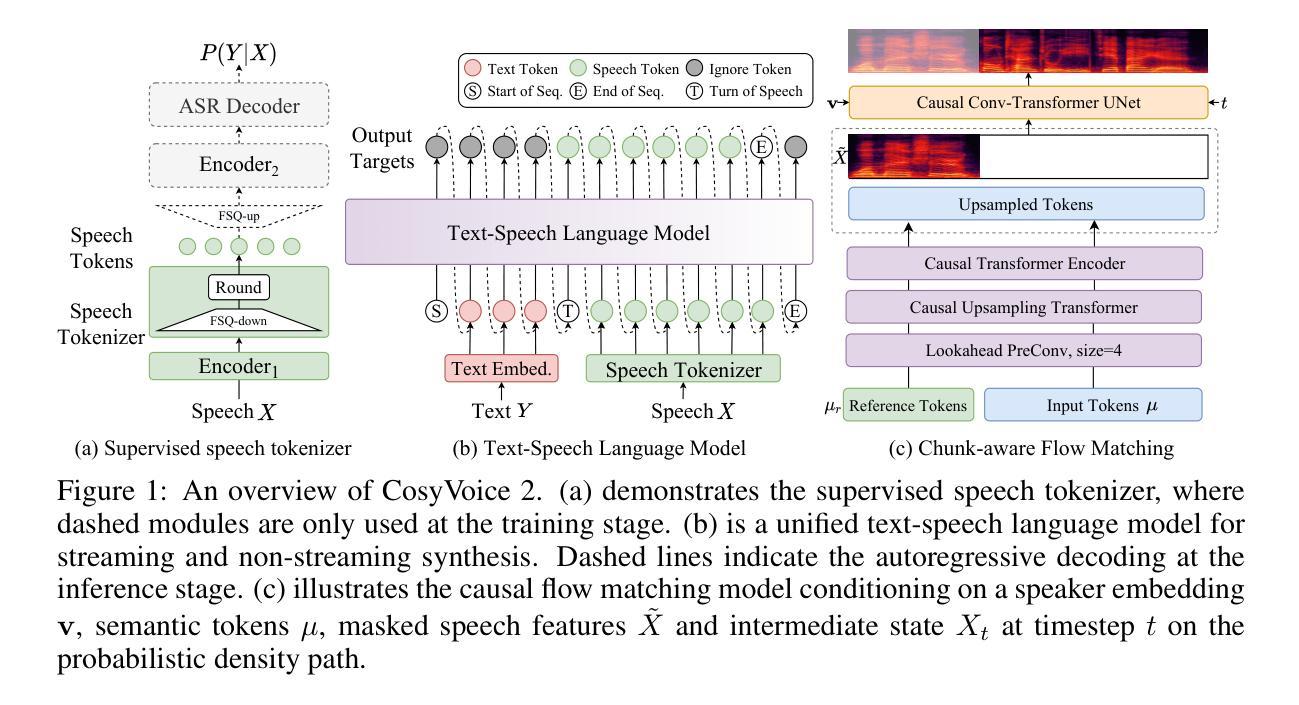
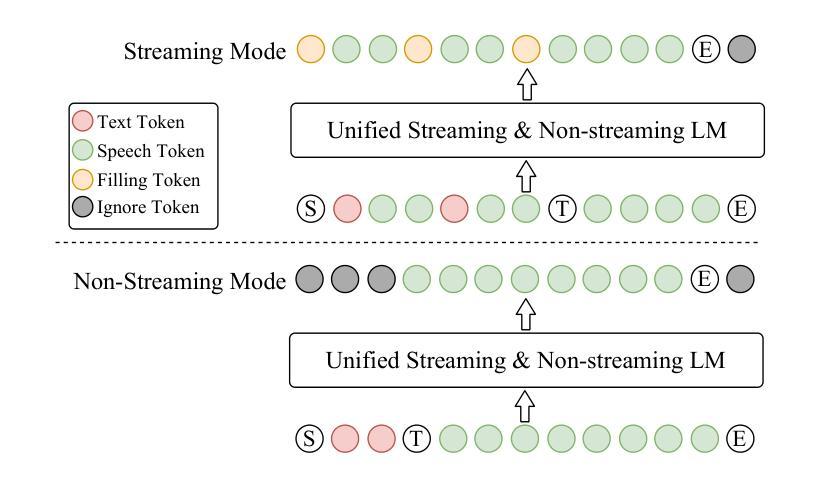
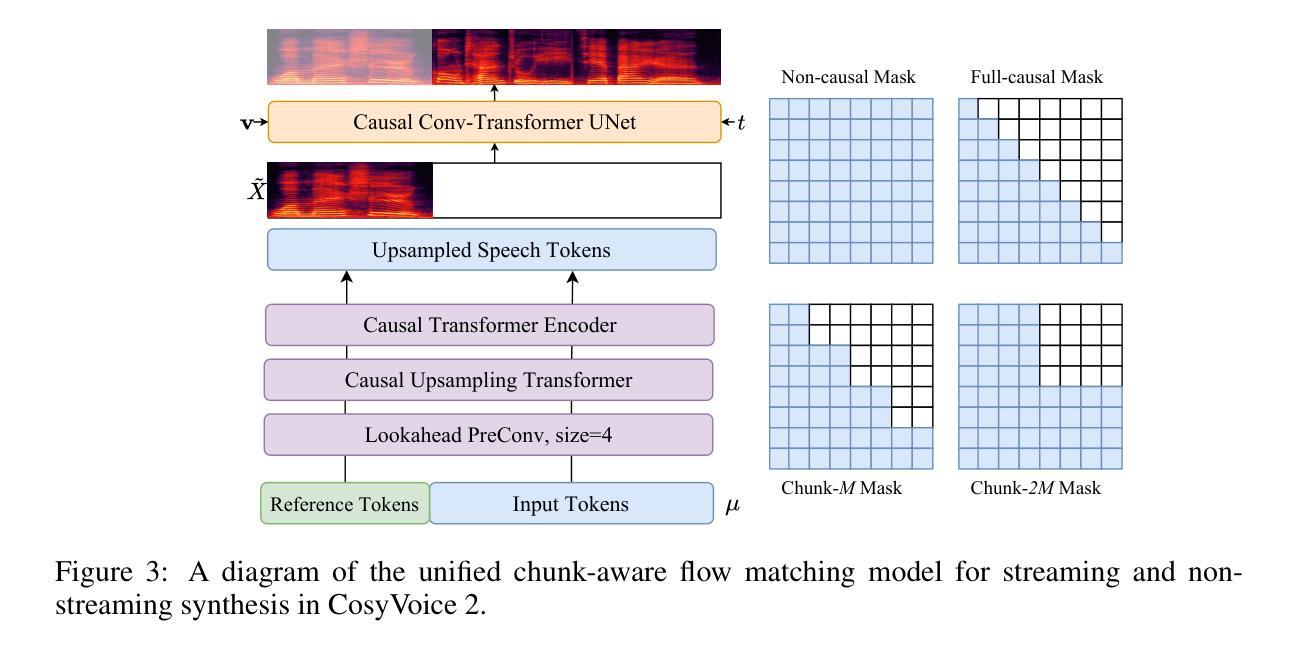
CosyVoice 2: Scalable Streaming Speech Synthesis with Large Language Models
Authors:Zhihao Du, Yuxuan Wang, Qian Chen, Xian Shi, Xiang Lv, Tianyu Zhao, Zhifu Gao, Yexin Yang, Changfeng Gao, Hui Wang, Fan Yu, Huadai Liu, Zhengyan Sheng, Yue Gu, Chong Deng, Wen Wang, Shiliang Zhang, Zhijie Yan, Jingren Zhou
In our previous work, we introduced CosyVoice, a multilingual speech synthesis model based on supervised discrete speech tokens. By employing progressive semantic decoding with two popular generative models, language models (LMs) and Flow Matching, CosyVoice demonstrated high prosody naturalness, content consistency, and speaker similarity in speech in-context learning. Recently, significant progress has been made in multi-modal large language models (LLMs), where the response latency and real-time factor of speech synthesis play a crucial role in the interactive experience. Therefore, in this report, we present an improved streaming speech synthesis model, CosyVoice 2, which incorporates comprehensive and systematic optimizations. Specifically, we introduce finite-scalar quantization to improve the codebook utilization of speech tokens. For the text-speech LM, we streamline the model architecture to allow direct use of a pre-trained LLM as the backbone. In addition, we develop a chunk-aware causal flow matching model to support various synthesis scenarios, enabling both streaming and non-streaming synthesis within a single model. By training on a large-scale multilingual dataset, CosyVoice 2 achieves human-parity naturalness, minimal response latency, and virtually lossless synthesis quality in the streaming mode. We invite readers to listen to the demos at https://funaudiollm.github.io/cosyvoice2.
在之前的工作中,我们介绍了CosyVoice,这是一个基于监督离散语音标记的多语种语音合成模型。通过采用两种流行的生成模型——语言模型和流匹配,进行渐进式语义解码,CosyVoice在语境中学习语音时,表现出高度的语调自然性、内容一致性和说话人相似性。最近,多模态大型语言模型(LLMs)取得了重大进展,其中语音合成的响应延迟和实时因素在交互体验中发挥了关键作用。因此,在这份报告中,我们提出了一种改进的流式语音合成模型CosyVoice 2,它包含了全面和系统的优化。具体来说,我们引入有限标量量化来提高语音标记的码本利用率。对于文本-语音LM,我们简化了模型架构,允许直接使用预训练的大型语言模型作为骨干。此外,我们开发了一种块感知因果流匹配模型,以支持各种合成场景,能在单个模型中实现流式和非流式合成。通过在大规模多语种数据集上进行训练,CosyVoice 2达到了与人类相当的自然度、极短的响应延迟,以及在流式模式下的几乎无损的合成质量。我们邀请读者在https://funaudiollm.github.io/cosyvoice
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Tech report, work in progress
摘要
基于先前的工作,我们推出了CosyVoice 2,一个优化的流式语音合成模型。该模型采用有限标量量化改进语音令牌的码本利用率,简化文本-语音LM模型架构以直接使用预训练LLM作为骨干。此外,我们开发了块感知因果流匹配模型,支持各种合成场景,在单个模型内实现流和非流合成。通过大规模多语种数据集进行训练,CosyVoice 2达到了人类自然水平的自然度、极低的响应延迟和几乎无损的合成质量。
要点
- CosyVoice 2是改进的流式语音合成模型,基于之前的工作CosyVoice。
- 引入有限标量量化改进语音令牌的码本利用率,提高合成质量。
- 简化文本-语音LM模型架构,允许直接使用预训练LLM作为骨干,增强模型的通用性和灵活性。
- 开发块感知因果流匹配模型,支持多种合成场景,实现流和非流合成。
- 模型在大规模多语种数据集上进行训练,具有强大的泛化能力。
- CosyVoice 2达到了人类自然水平的自然度,合成质量高。
点此查看论文截图

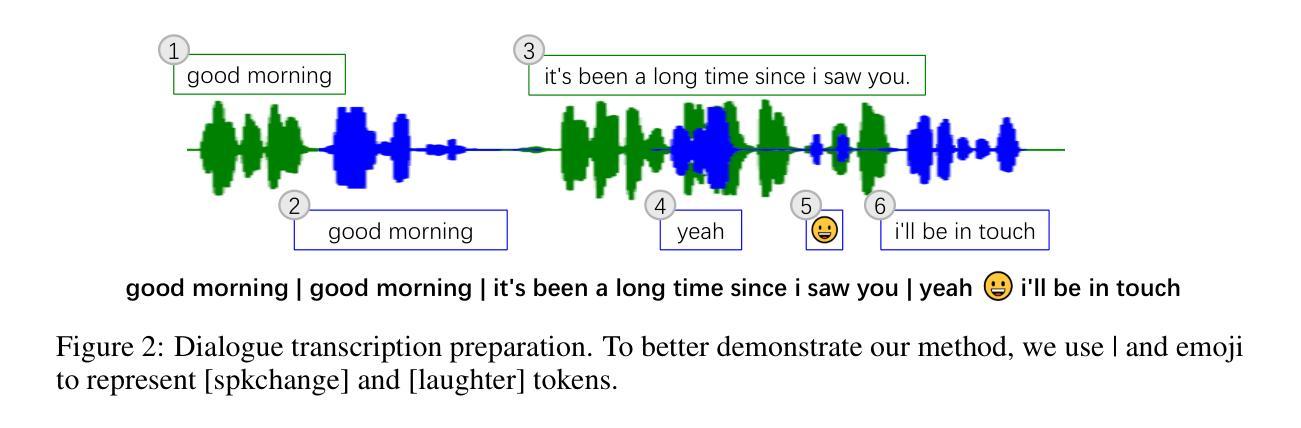
CoVoMix: Advancing Zero-Shot Speech Generation for Human-like Multi-talker Conversations
Authors:Leying Zhang, Yao Qian, Long Zhou, Shujie Liu, Dongmei Wang, Xiaofei Wang, Midia Yousefi, Yanmin Qian, Jinyu Li, Lei He, Sheng Zhao, Michael Zeng
Recent advancements in zero-shot text-to-speech (TTS) modeling have led to significant strides in generating high-fidelity and diverse speech. However, dialogue generation, along with achieving human-like naturalness in speech, continues to be a challenge. In this paper, we introduce CoVoMix: Conversational Voice Mixture Generation, a novel model for zero-shot, human-like, multi-speaker, multi-round dialogue speech generation. CoVoMix first converts dialogue text into multiple streams of discrete tokens, with each token stream representing semantic information for individual talkers. These token streams are then fed into a flow-matching based acoustic model to generate mixed mel-spectrograms. Finally, the speech waveforms are produced using a HiFi-GAN model. Furthermore, we devise a comprehensive set of metrics for measuring the effectiveness of dialogue modeling and generation. Our experimental results show that CoVoMix can generate dialogues that are not only human-like in their naturalness and coherence but also involve multiple talkers engaging in multiple rounds of conversation. This is exemplified by instances generated in a single channel where one speaker’s utterance is seamlessly mixed with another’s interjections or laughter, indicating the latter’s role as an attentive listener. Audio samples are available at https://aka.ms/covomix.
近期零样本文本到语音(TTS)建模的进展为生成高保真和多样化的语音迈出了重要的一步。然而,对话生成以及实现语音的人类自然性仍然是一个挑战。在本文中,我们介绍了CoVoMix:会话语音混合生成,这是一种用于零样本、人类、多发言人、多轮对话语音生成的新型模型。CoVoMix首先将对对话文本转换为多个离散令牌流,每个令牌流代表个别发言者的语义信息。这些令牌流然后被输入基于流匹配的声学模型,以生成混合的梅尔频谱图。最后,使用HiFi-GAN模型生成语音波形。此外,我们设计了一套综合指标来评估对话建模和生成的有效性。我们的实验结果表明,CoVoMix可以生成不仅自然连贯且人性化,而且涉及多个发言者进行多轮对话的语音。这体现在单通道生成的实例中,一个发言人的话语可以无缝地与其他发言人的插话或笑声混合,这表明后者作为倾听者的角色。音频样本可在https://aka.ms/covomix找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Neural Information Processing Systems 2024, poster
Summary
本文介绍了CoVoMix模型,一种用于零样本、人类般的、多说话者、多轮对话语音生成的新模型。该模型通过将对话文本转换为多个离散令牌流,再利用基于流匹配的声学模型生成混合梅尔频谱图,最后使用HiFi-GAN模型生成语音波形,实现对话生成。此外,本文还提出了一套全面的度量标准来衡量对话建模和生成的有效性。实验结果表明,CoVoMix不仅可以生成人类般自然和连贯的对话,而且可以涉及多个说话者在单一通道中进行多轮对话。
Key Takeaways
- CoVoMix是一种用于零样本、人类般的、多说话者、多轮对话语音生成的新模型。
- 该模型通过将对话文本转换为多个离散令牌流来处理多说话者对话。
- CoVoMix利用基于流匹配的声学模型生成混合梅尔频谱图。
- HiFi-GAN模型用于生成语音波形。
- 提出了一套全面的度量标准来衡量对话建模和生成的有效性。
- 实验结果表明,CoVoMix可以生成自然、连贯的多轮对话,涉及多个说话者。
点此查看论文截图

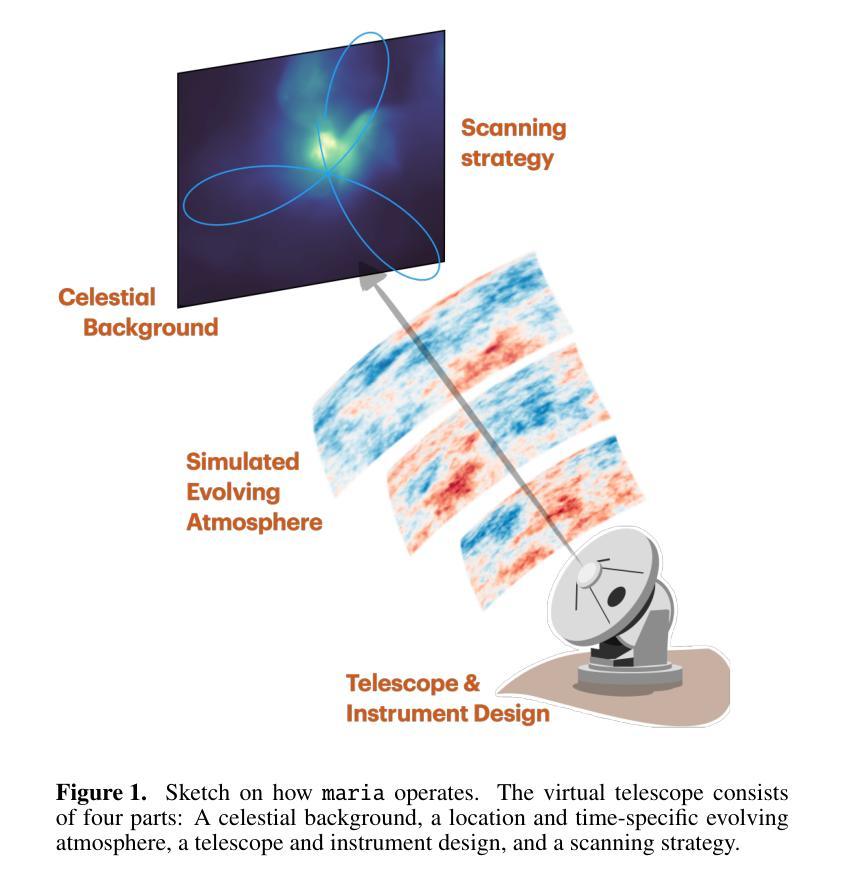
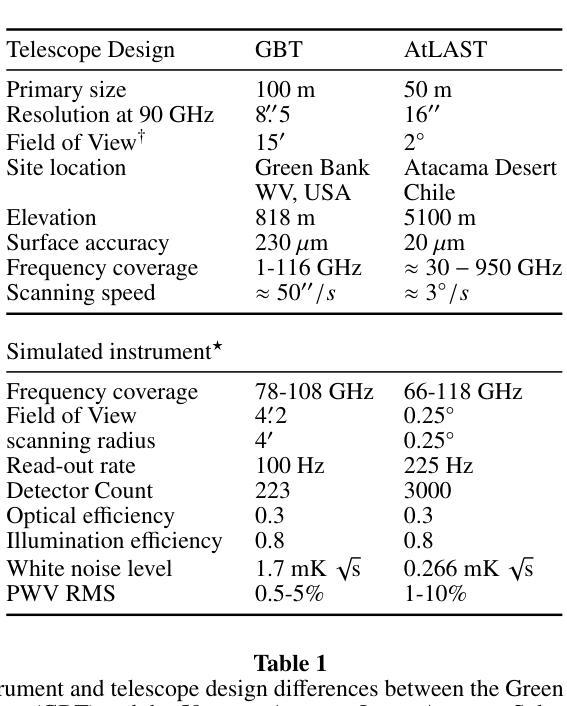
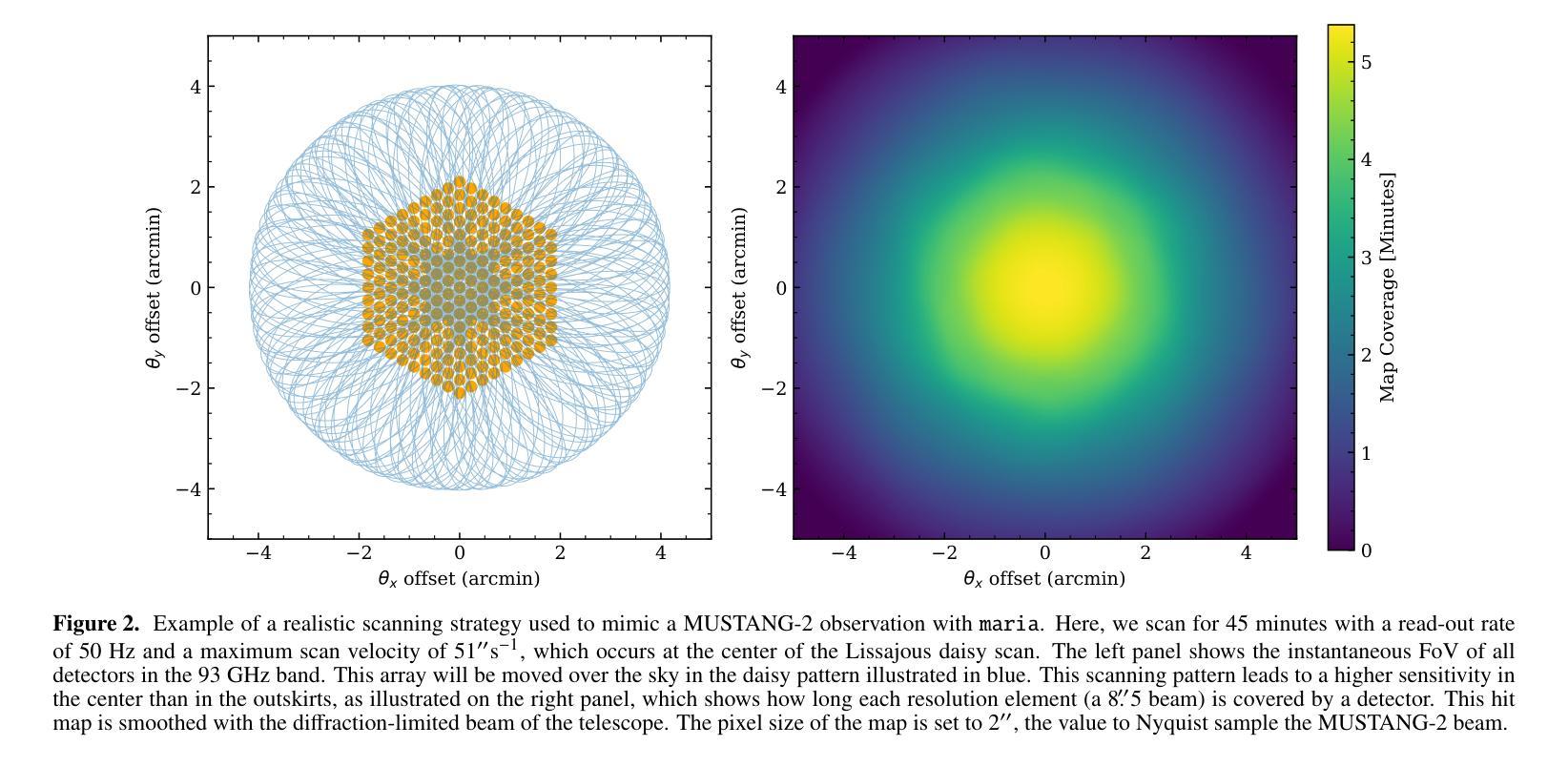
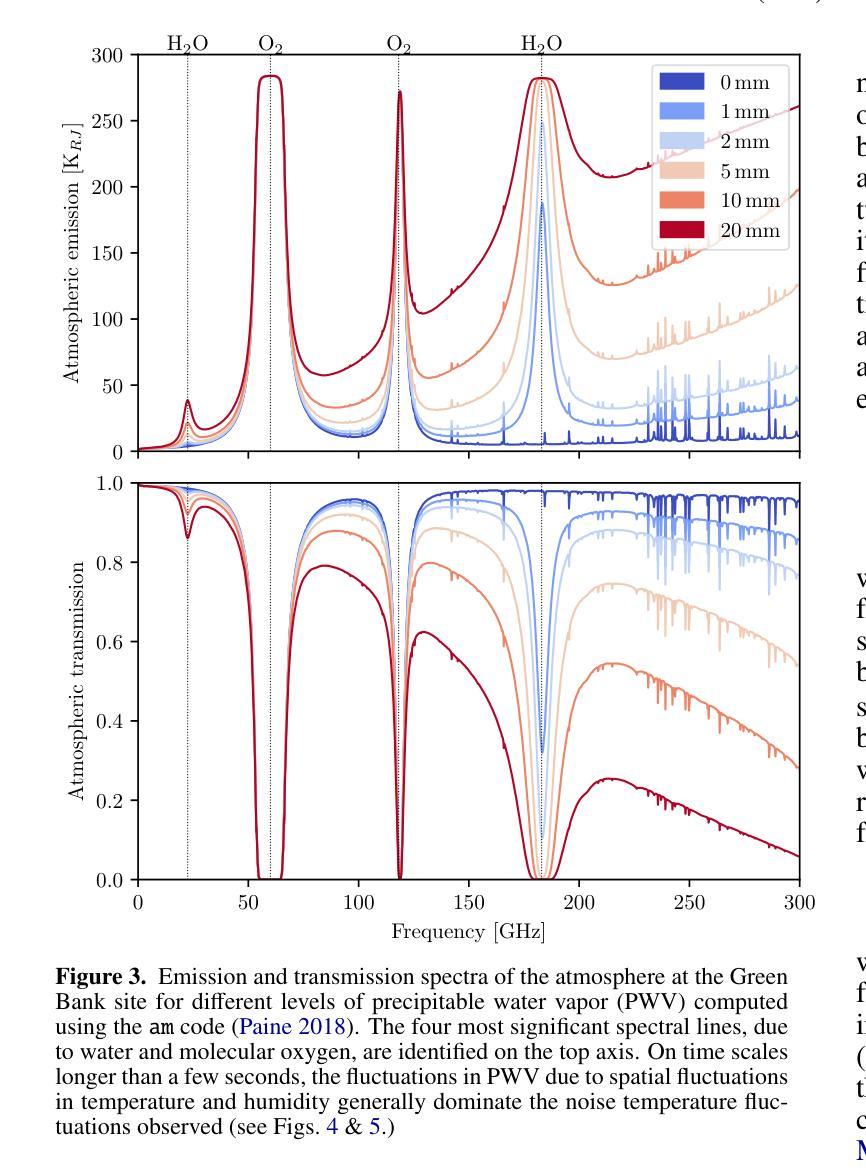
maria: A novel simulator for forecasting (sub-)mm observations
Authors:J. van Marrewijk, T. W. Morris, T. Mroczkowski, C. Cicone, S. Dicker, L. Di Mascolo, S. K. Haridas, J. Orlowski-Scherer, E. Rasia, C. Romero, J. Würzinger
Millimeter-wave single-dish telescopes offer two key advantages compared to interferometers: they can efficiently map larger portions of the sky, and they can recover larger spatial scales. Nonetheless, fluctuations in the atmosphere limit the accurate retrieval of signals from astronomical sources. To efficiently reduce atmospheric noise and filtering effects in current and future facilities, we introduce {\tt maria}, a versatile and user-friendly multi-purpose telescope simulator that optimizes scanning strategies and instrument designs, produces synthetic time-ordered data, time streams, and maps from hydrodynamical simulations, thereby enabling a fair comparison between theory and observations. Each mock observatory scans through the atmosphere in a configurable pattern over the celestial object. We generate evolving and location-and-time-specific weather for each of the fiducial sites using a combination of satellite and ground-based measurements. While {\tt maria} is a generic virtual telescope, this study specifically focuses on mimicking broadband bolometers observing at 100 GHz. We compare the mock time streams with real MUSTANG-2 observations and find that they are quantitatively similar by conducting a k-sample Anderson-Darling test resulting in a p-value of p<0.001. Subsequently, we image the TODs to create noise maps and realistic mock observations of clusters of galaxies for both MUSTANG-2 and an instrument concept for the 50m Atacama Large Aperture Submillimeter Telescope (AtLAST). Furthermore, using {\tt maria}, we find that a 50m dish provides the highest levels of correlation of atmospheric signals across adjacent detectors compared to smaller apertures (e.g., 42-cm and 6-m), facilitating removal of atmospheric signal on large scales.
毫米波单盘望远镜与干涉仪相比具有两大优势:它们可以有效地映射天空的更大部分,并且可以恢复更大的空间尺度。然而,大气波动限制了从天文源准确检索信号。为了在当前和未来的设施中有效地减少大气噪声和滤波效应,我们引入了{\tt maria},这是一个通用且用户友好的多功能望远镜模拟器,它优化扫描策略和仪器设计,从流体动力学模拟中产生合成时间顺序数据、时间流和地图,从而实现理论与观察之间的公平比较。每个模拟天文台都以可配置的模式通过大气扫描天体对象。我们结合卫星和地面测量,为每个基准点生成不断发展和特定地点和时间的天气。虽然{\tt maria}是一个通用的虚拟望远镜,但这项研究特别侧重于模拟在100 GHz观测的宽带测辐射仪。我们将模拟的时间流与现实中的MUSTANG-2观测结果进行比较,并通过进行k样本安德森-达林测试得出p值为p<0.001,发现它们在数量上是相似的。随后,我们将时间序列图像化为噪声图,并为MUSTANG-2和50米阿塔卡马大口径亚毫米波望远镜(AtLAST)的概念仪器制作逼真的模拟观测星系团图像。此外,通过{\tt maria},我们发现与较小的孔径(例如42厘米和6米)相比,50米的盘子在大范围上提供最高水平的大气信号相关性,有助于消除大气信号。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
毫米波单盘望远镜与干涉仪相比具有两大优势:能够高效地映射天空更大区域,并能恢复更大的空间尺度。然而,大气波动限制了从天文源准确检索信号。为了在当前和未来的设施中有效地减少大气噪声和过滤效应,我们引入了{\tt maria},这是一个通用且用户友好的多功能望远镜模拟器,可以优化扫描策略和仪器设计,从流体动力学模拟中产生合成时序数据、时间流和地图,从而实现理论与观测之间的公平比较。每个模拟观测站都以可配置的模式穿过大气层对天体进行扫描。我们结合卫星和地面测量,为每一个基准点生成不断发展和特定于地点和时间的天气。虽然{\tt maria}是一个通用的虚拟望远镜,但这项研究特别关注模仿在100 GHz观测的宽带 bolo仪。我们将模拟的时间流与实际的MUSTANG-2观测结果进行比较,发现它们在数量上是相似的,通过进行k样本安德森-达林测试得出p值小于0.001。随后,我们对TOD进行成像以创建噪声图和现实的模拟星系团观测结果,这些结果适用于MUSTANG-2和50米阿塔卡马大型孔径亚毫米望远镜(AtLAST)的仪器概念。此外,通过{\tt maria},我们发现与较小的孔径(例如42厘米和6米)相比,50米的盘子提供的大气信号相邻探测器之间的最高水平相关性,有助于在大尺度上消除大气信号。
要点掌握
- 毫米波单盘望远镜相比干涉仪具有映射天空区域更广、恢复空间尺度更大的两大优势。
- 大气波动对从天文学源接收信号产生影响,需要减少大气噪声和过滤效应。
- {\tt maria}是一个多功能望远镜模拟器,能够优化扫描策略和仪器设计,并生成合成数据、时间流和地图。
- {\tt maria}模拟观测站以特定模式扫描天体,同时考虑大气层的影响。
- 通过结合卫星和地面测量,生成特定地点和时间的天气数据。
- {\tt maria}模拟结果与MUSTANG-2实际观测在数量上相似,经过严格统计测试验证。
点此查看论文截图