⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-19 更新
FastVLM: Efficient Vision Encoding for Vision Language Models
Authors:Pavan Kumar Anasosalu Vasu, Fartash Faghri, Chun-Liang Li, Cem Koc, Nate True, Albert Antony, Gokul Santhanam, James Gabriel, Peter Grasch, Oncel Tuzel, Hadi Pouransari
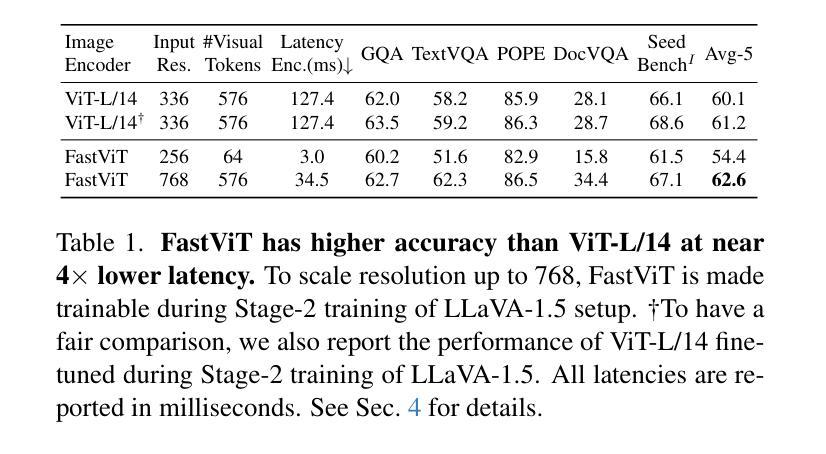
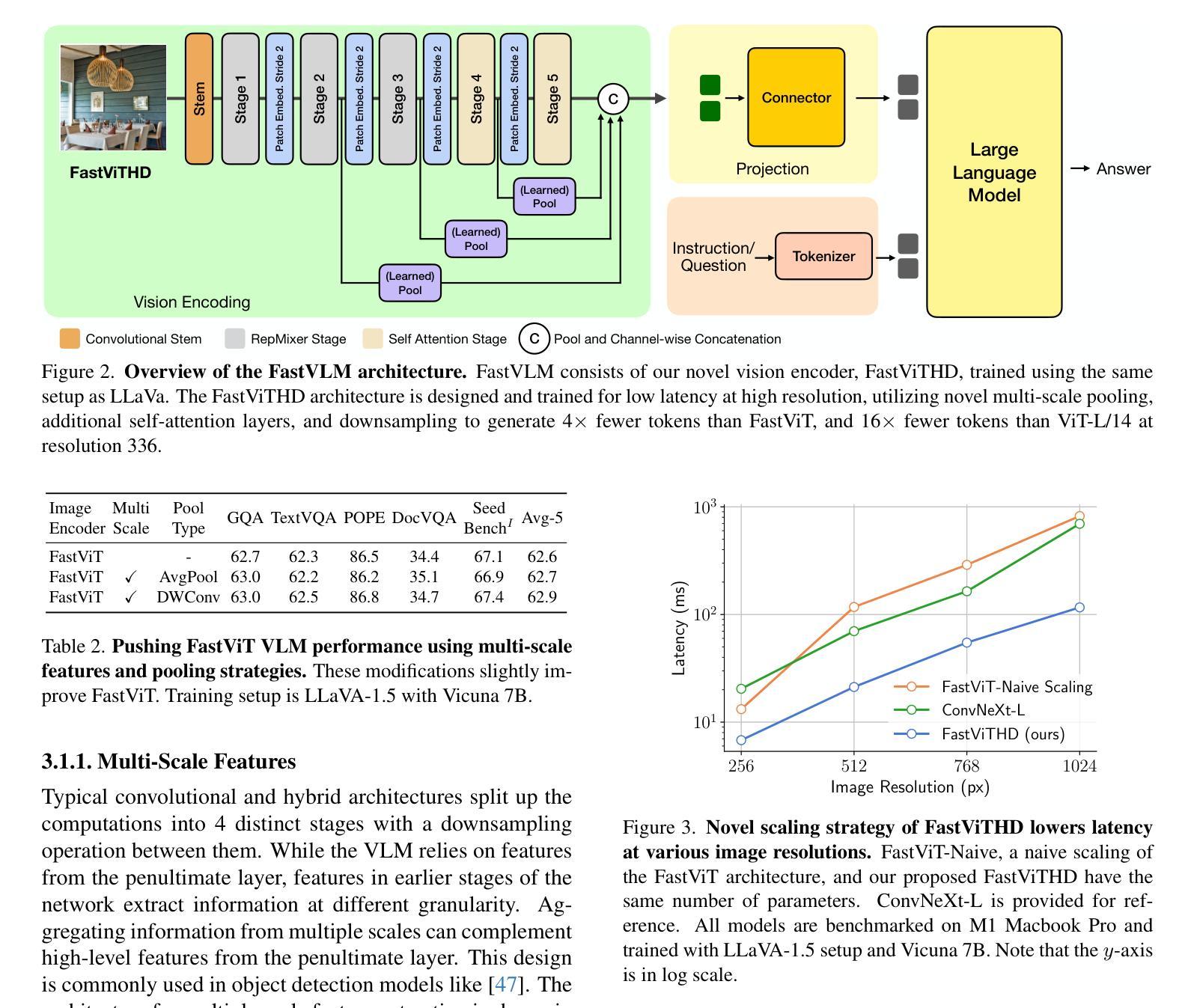
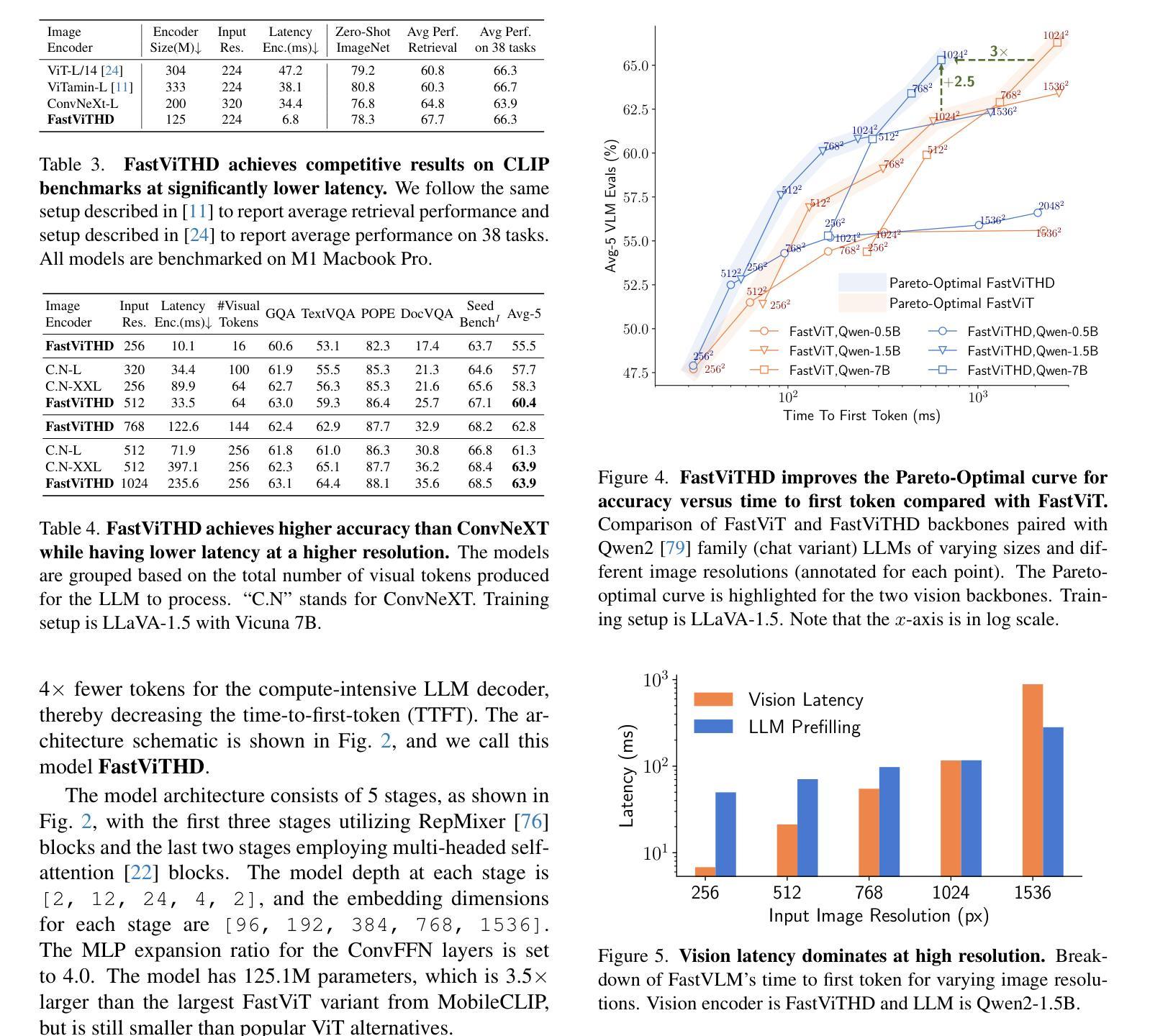
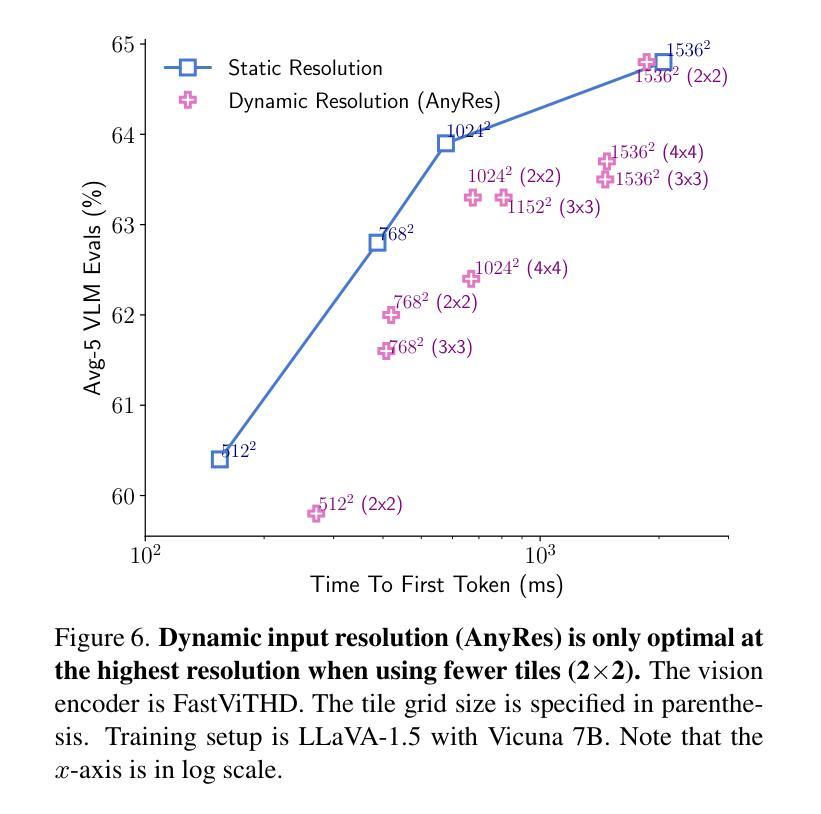
Scaling the input image resolution is essential for enhancing the performance of Vision Language Models (VLMs), particularly in text-rich image understanding tasks. However, popular visual encoders such as ViTs become inefficient at high resolutions due to the large number of tokens and high encoding latency caused by stacked self-attention layers. At different operational resolutions, the vision encoder of a VLM can be optimized along two axes: reducing encoding latency and minimizing the number of visual tokens passed to the LLM, thereby lowering overall latency. Based on a comprehensive efficiency analysis of the interplay between image resolution, vision latency, token count, and LLM size, we introduce FastVLM, a model that achieves an optimized trade-off between latency, model size and accuracy. FastVLM incorporates FastViTHD, a novel hybrid vision encoder designed to output fewer tokens and significantly reduce encoding time for high-resolution images. Unlike previous methods, FastVLM achieves the optimal balance between visual token count and image resolution solely by scaling the input image, eliminating the need for additional token pruning and simplifying the model design. In the LLaVA-1.5 setup, FastVLM achieves 3.2$\times$ improvement in time-to-first-token (TTFT) while maintaining similar performance on VLM benchmarks compared to prior works. Compared to LLaVa-OneVision at the highest resolution (1152$\times$1152), FastVLM achieves comparable performance on key benchmarks like SeedBench and MMMU, using the same 0.5B LLM, but with 85$\times$ faster TTFT and a vision encoder that is 3.4$\times$ smaller.
对于视觉语言模型(VLMs)来说,增加输入图像的分辨率对于提升性能至关重要,特别是在文本丰富的图像理解任务中。然而,流行的视觉编码器(如ViTs)在高分辨率下变得效率低下,这是由于堆叠的自注意力层导致的令牌数量众多和编码延迟高。在不同的操作分辨率下,VLM的视觉编码器可以通过两个轴进行优化:减少编码延迟和减少传递给LLM的视觉令牌数量,从而降低总体延迟。基于对图像分辨率、视觉延迟、令牌计数和LLM大小之间交互的综合效率分析,我们引入了FastVLM模型,该模型实现了延迟、模型大小和准确性之间的优化折衷。FastVLM结合了FastViTHD这一新型混合视觉编码器,旨在输出较少的令牌并显著减少高分辨率图像的编码时间。与之前的方法不同,FastVLM通过仅缩放输入图像就能实现视觉令牌计数和图像分辨率之间的最佳平衡,从而无需额外的令牌修剪并简化了模型设计。在LLaVA-1.5设置中,FastVLM在时间到第一个令牌(TTFT)上实现了3.2倍的改进,同时在VLM基准测试中保持与先前作品相似的性能。与最高分辨率(1152×1152)下的LLaVa-OneVision相比,FastVLM在SeedBench和MMMU等关键基准测试上实现了相当的性能,使用相同的0.5B LLM,但TTFT加快了85倍,并且视觉编码器缩小了3.4倍。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文强调提高输入图像分辨率对提升视觉语言模型性能的重要性,特别是在文本丰富的图像理解任务中。针对高分辨率图像,流行的视觉编码器如ViTs会因大量标记和编码延迟而变得效率低下。为此,本文提出了FastVLM模型,该模型通过优化视觉编码器,实现了延迟、模型大小和准确度之间的平衡。FastVLM采用FastViTHD这一新型混合视觉编码器,能够输出更少标记并大幅减少高分辨率图像的编码时间。与以前的方法不同,FastVLM仅通过调整输入图像大小就能实现视觉标记数量和图像分辨率之间的最优平衡,无需额外的标记修剪,简化了模型设计。在LLaVA-1.5配置下,FastVLM在保持类似先前作品性能的同时,首次令牌时间提高了3.2倍。与最高分辨率(1152×1152)下的LLaVa-OneVision相比,FastVLM在SeedBench和MMMU等关键基准测试上取得了相当的性能表现,同时使用相同的0.5B LLM,其首次令牌时间加快了85倍,并且视觉编码器缩小了3.4倍。
Key Takeaways
- 提高输入图像分辨率对增强视觉语言模型性能至关重要,特别是在文本丰富的图像理解任务中。
- 流行的视觉编码器在高分辨率图像下会面临效率低下的问题,主要因为大量标记和编码延迟。
- FastVLM模型通过优化视觉编码器,实现了延迟、模型大小和准确度之间的平衡。
- FastVLM采用FastViTHD这一新型混合视觉编码器,能够减少输出标记和编码时间。
- FastVLM通过调整输入图像大小实现了视觉标记数量和图像分辨率之间的最优平衡,无需额外的标记修剪。
- 与LLaVA-1.5配置下的其他模型相比,FastVLM在保持相似性能的同时显著提高了首次令牌时间。
点此查看论文截图

CRoF: CLIP-based Robust Few-shot Learning on Noisy Labels
Authors:Shizhuo Deng, Bowen Han, Jiaqi Chen, Hao Wang, Dongyue Chen, Tong Jia
Noisy labels threaten the robustness of few-shot learning (FSL) due to the inexact features in a new domain. CLIP, a large-scale vision-language model, performs well in FSL on image-text embedding similarities, but it is susceptible to misclassification caused by noisy labels. How to enhance domain generalization of CLIP on noisy data within FSL tasks is a critical challenge. In this paper, we provide a novel view to mitigate the influence of noisy labels, CLIP-based Robust Few-shot learning (CRoF). CRoF is a general plug-in module for CLIP-based models. To avoid misclassification and confused label embedding, we design the few-shot task-oriented prompt generator to give more discriminative descriptions of each category. The proposed prompt achieves larger distances of inter-class textual embedding. Furthermore, rather than fully trusting zero-shot classification by CLIP, we fine-tune CLIP on noisy few-shot data in a new domain with a weighting strategy like label-smooth. The weights for multiple potentially correct labels consider the relationship between CLIP’s prior knowledge and original label information to ensure reliability. Our multiple label loss function further supports robust training under this paradigm. Comprehensive experiments show that CRoF, as a plug-in, outperforms fine-tuned and vanilla CLIP models on different noise types and noise ratios.
带噪声的标签对新域中的不准确特征产生了威胁,从而影响了小样本学习(FSL)的稳健性。CLIP是一种大规模的视觉语言模型,在图像文本嵌入相似性方面,FSL表现良好,但它容易受到带噪声标签导致的误分类的影响。如何在FSL任务中对带噪声数据增强CLIP的领域泛化是一个关键挑战。在本文中,我们提供了减轻噪声标签影响的全新观点,基于CLIP的鲁棒小样本学习(CRoF)。CRoF是一个适用于CLIP模型的通用插件模块。为了避免误分类和混淆标签嵌入,我们设计了面向小样本任务的提示生成器,为每个类别提供更具区分性的描述。所提出的提示实现了较大的类间文本嵌入距离。此外,我们不是完全信任CLIP的零样本分类,而是使用标签平滑等加权策略对新领域中的带噪声的小样本数据进行微调。多个可能正确的标签的权重考虑了CLIP的先验知识与原始标签信息之间的关系,以确保可靠性。我们的多标签损失函数进一步支持此模式下的稳健训练。综合实验表明,作为插件的CRoF在不同噪声类型和噪声比率上优于经过微调的和原生的CLIP模型。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
CLIP模型在少样本学习(FSL)任务中,因噪声标签导致性能下降。为应对此问题,提出一种基于CLIP的鲁棒少样本学习(CRoF)方法。CRoF设计任务导向的提示生成器,增强类别描述鉴别力,并微调CLIP模型在新域噪声数据上的权重策略,同时采用多标签损失函数提升鲁棒性。实验表明,CRoF优于微调及原生的CLIP模型。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP在FSL任务中受噪声标签影响,性能受限。
- 提出CRoF方法,为CLIP模型提供鲁棒性增强。
- 设计任务导向的提示生成器,提高类别描述的鉴别力。
- 采用微调策略,在新域噪声数据上优化CLIP模型的权重。
- 利用多标签损失函数提升模型在噪声数据下的鲁棒性训练。
- CRoF方法在各种噪声类型和比例下的表现优于原CLIP模型。
点此查看论文截图

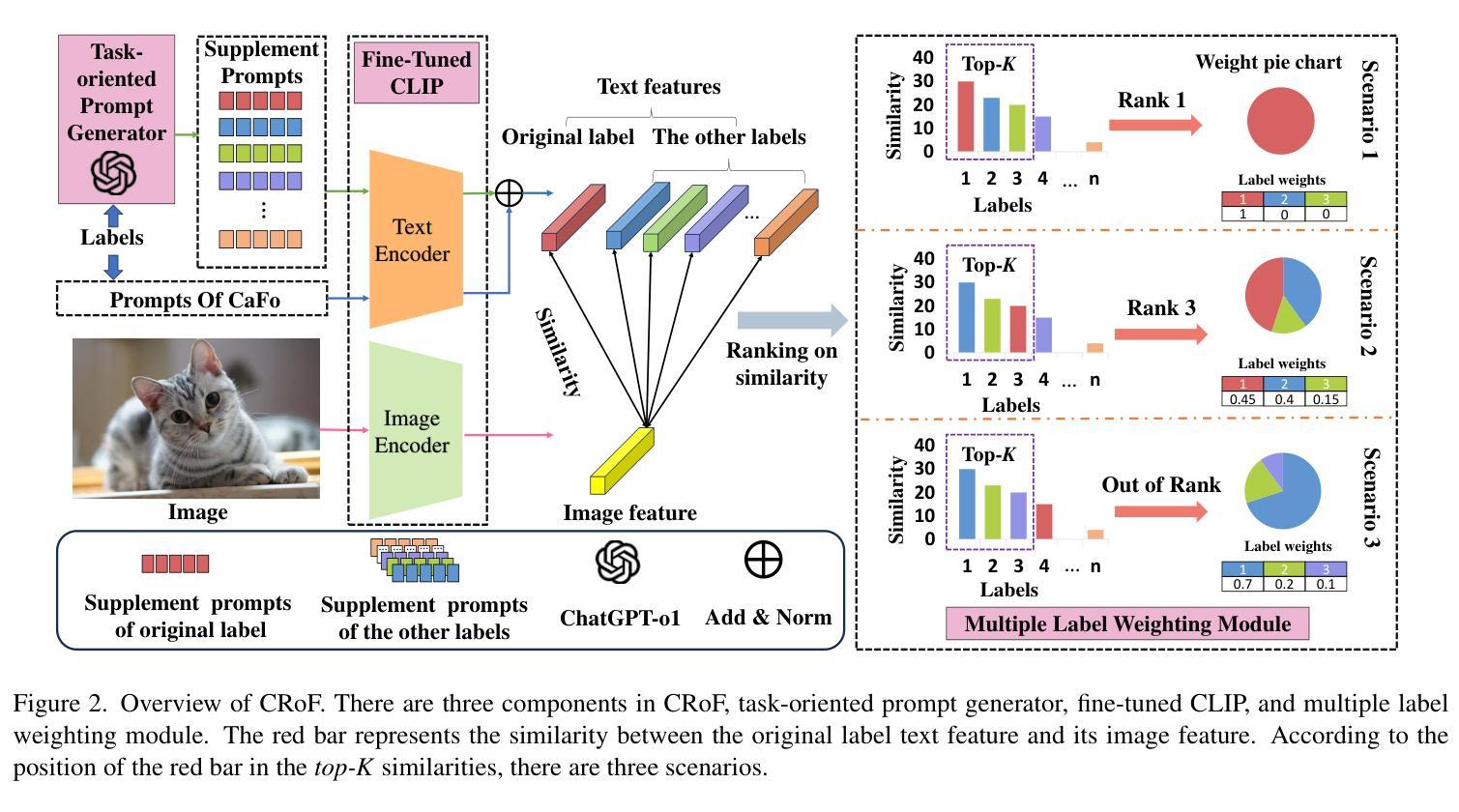

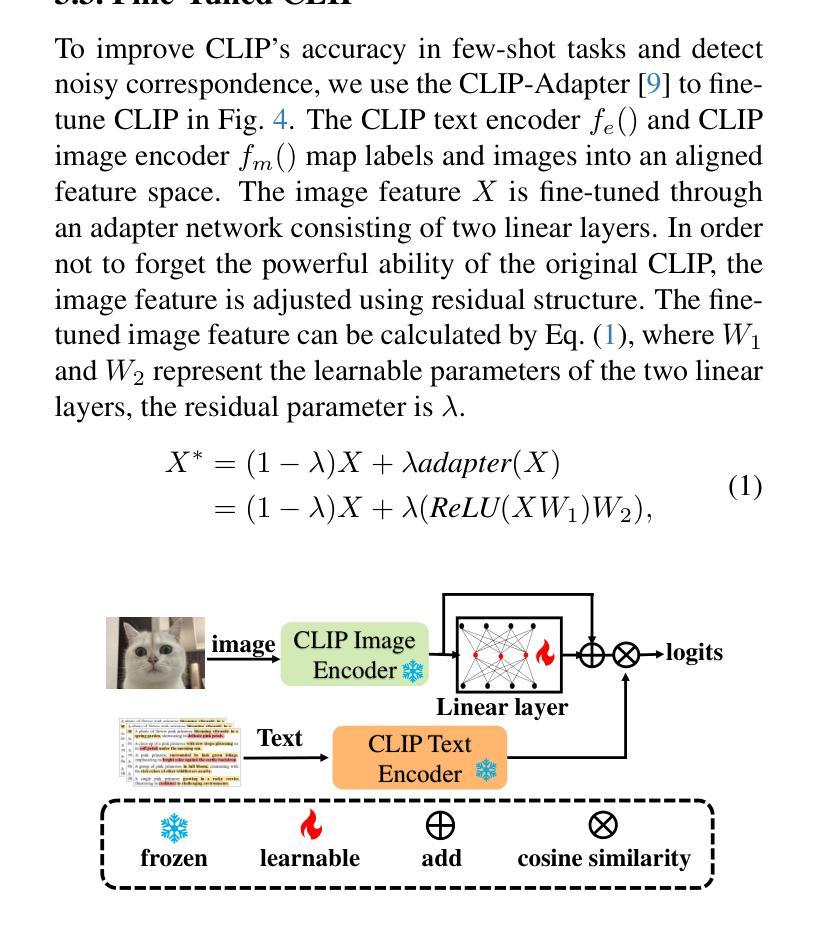
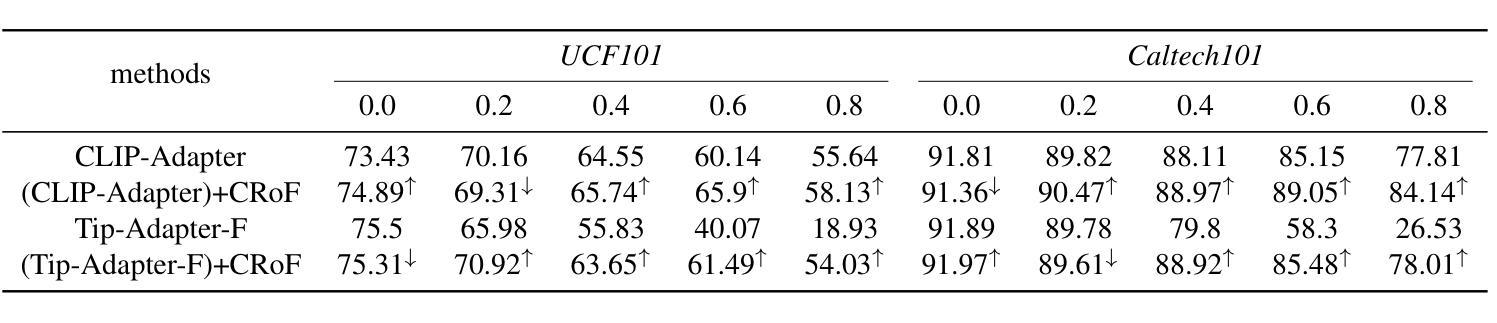
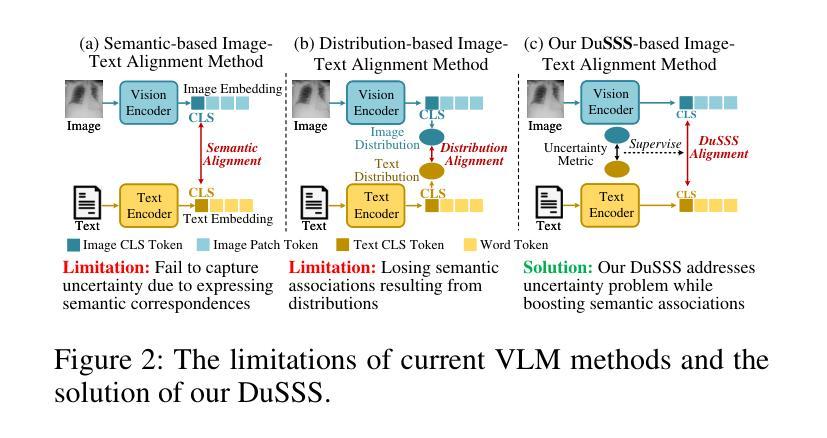
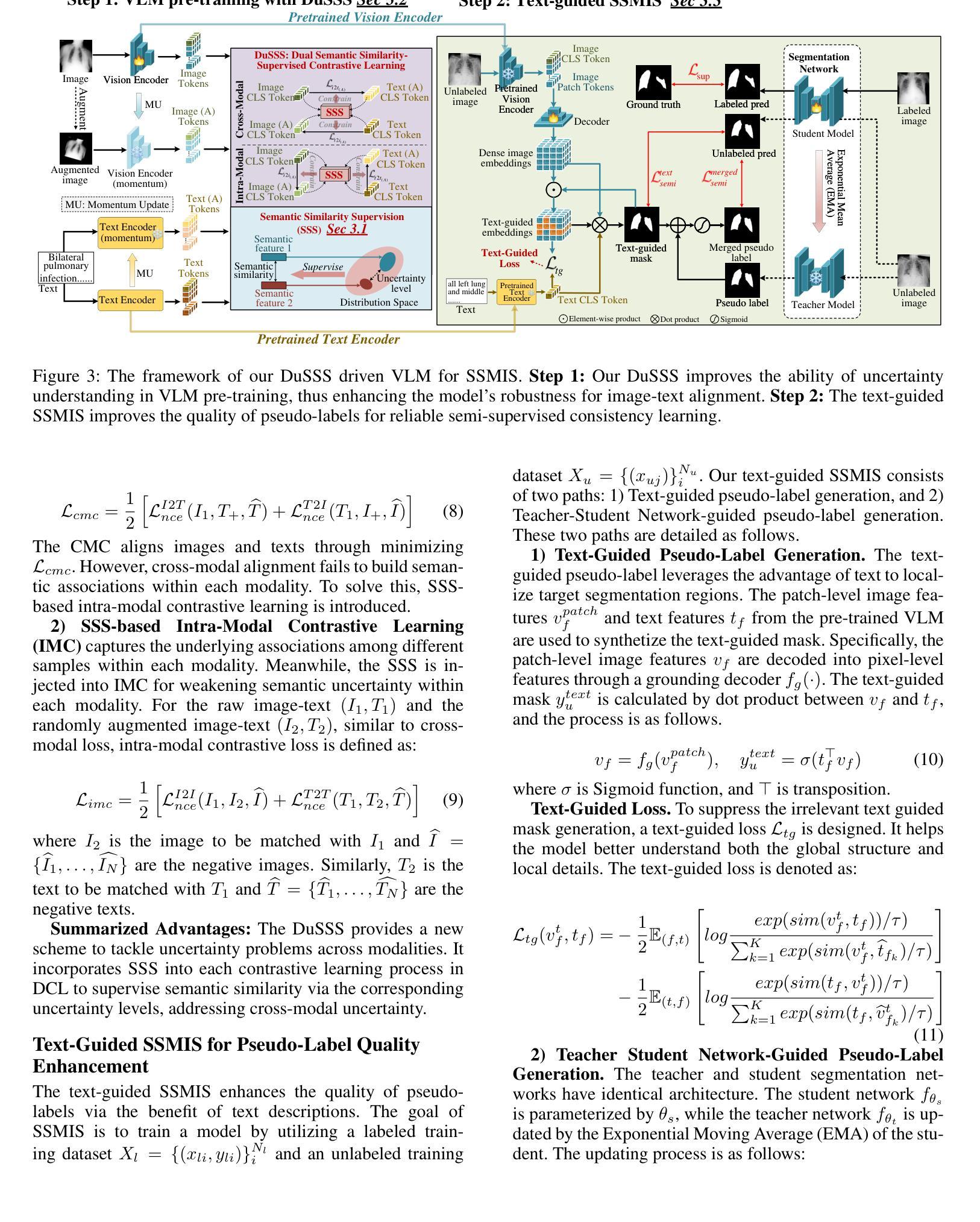
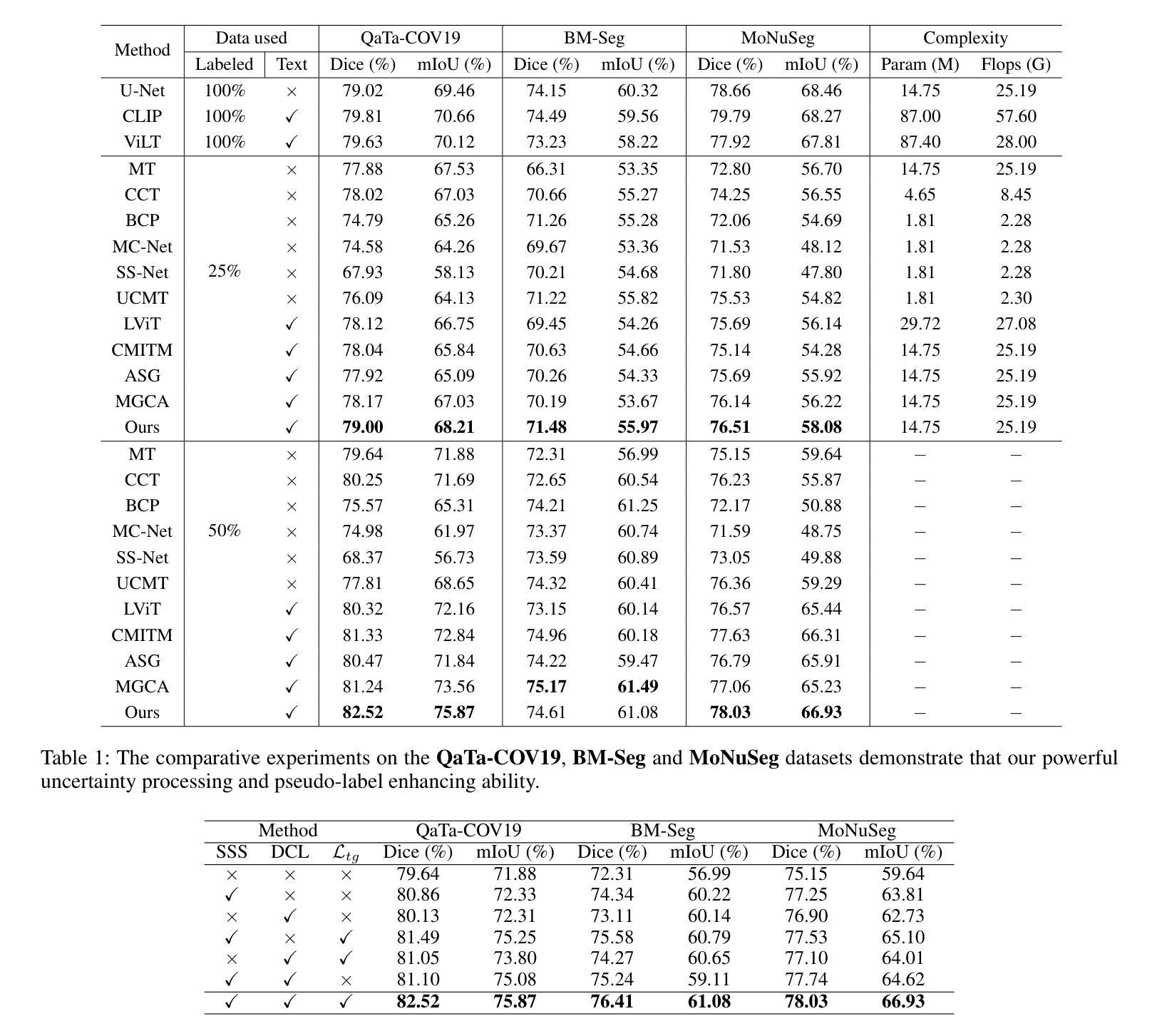
DuSSS: Dual Semantic Similarity-Supervised Vision-Language Model for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Qingtao Pan, Wenhao Qiao, Jingjiao Lou, Bing Ji, Shuo Li
Semi-supervised medical image segmentation (SSMIS) uses consistency learning to regularize model training, which alleviates the burden of pixel-wise manual annotations. However, it often suffers from error supervision from low-quality pseudo labels. Vision-Language Model (VLM) has great potential to enhance pseudo labels by introducing text prompt guided multimodal supervision information. It nevertheless faces the cross-modal problem: the obtained messages tend to correspond to multiple targets. To address aforementioned problems, we propose a Dual Semantic Similarity-Supervised VLM (DuSSS) for SSMIS. Specifically, 1) a Dual Contrastive Learning (DCL) is designed to improve cross-modal semantic consistency by capturing intrinsic representations within each modality and semantic correlations across modalities. 2) To encourage the learning of multiple semantic correspondences, a Semantic Similarity-Supervision strategy (SSS) is proposed and injected into each contrastive learning process in DCL, supervising semantic similarity via the distribution-based uncertainty levels. Furthermore, a novel VLM-based SSMIS network is designed to compensate for the quality deficiencies of pseudo-labels. It utilizes the pretrained VLM to generate text prompt guided supervision information, refining the pseudo label for better consistency regularization. Experimental results demonstrate that our DuSSS achieves outstanding performance with Dice of 82.52%, 74.61% and 78.03% on three public datasets (QaTa-COV19, BM-Seg and MoNuSeg).
半监督医学图像分割(SSMIS)采用一致性学习来规范模型训练,减轻了像素级手动注释的负担。然而,它常常受到低质量伪标签的错误监督的影响。视觉语言模型(VLM)通过引入文本提示引导的多模态监督信息,在增强伪标签方面有着巨大的潜力。然而,它面临跨模态的问题:获取的信息往往对应多个目标。为了解决上述问题,我们提出了一种用于SSMIS的双重语义相似性监督VLM(DuSSS)。具体来说,1)设计了双重对比学习(DCL),通过捕捉每种模态的内在表示和跨模态的语义关联,来提高跨模态语义一致性。2)为了鼓励学习多个语义对应关系,提出了语义相似性监督策略(SSS),并将其注入DCL中的每个对比学习过程,通过基于分布的不确定性水平来监督语义相似性。此外,设计了一种基于VLM的SSMIS网络,以弥补伪标签的质量缺陷。它利用预训练的VLM生成文本提示引导的监督信息,对伪标签进行细化,以实现更好的一致性正则化。实验结果证明,我们的DuSSS在三个公共数据集(QaTa-COV19、BM-Seg和MoNuSeg)上取得了出色的性能,Dice系数分别为82.52%、74.61%和78.03%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
半监督医学图像分割(SSMIS)利用一致性学习来规范模型训练,减轻像素级手动注释的负担。然而,它常受到低质量伪标签的错误监督影响。为增强伪标签并解决跨模态问题,我们提出了双语义相似性监督的视觉语言模型(DuSSS)。通过设计双对比学习(DCL)和语义相似性监督策略(SSS),该方法在三个公开数据集上取得了出色的性能。
Key Takeaways
- SSMIS利用一致性学习进行模型训练,减少手动注释工作量,但低质量伪标签导致的错误监督是其挑战。
- VLM具有通过引入文本提示引导的多模态监督信息来增强伪标签的潜力。
- DuSSS通过DCL提高跨模态语义一致性,通过捕获各模态的内在表示和跨模态的语义关联来实现。
- SSS策略被提出以鼓励学习多个语义对应关系,并注入DCL的每个对比学习过程,通过基于分布的不确定性水平来监督语义相似性。
- DuSSS设计了一个基于VLM的SSMIS网络,以弥补伪标签质量缺陷。
- 利用预训练的VLM生成文本提示引导的监督信息,对伪标签进行精炼,实现更好的一致性正则化。
- 实验结果表明,DuSSS在三个公开数据集上的Dice性能达到82.52%、74.61%和78.03%。
点此查看论文截图

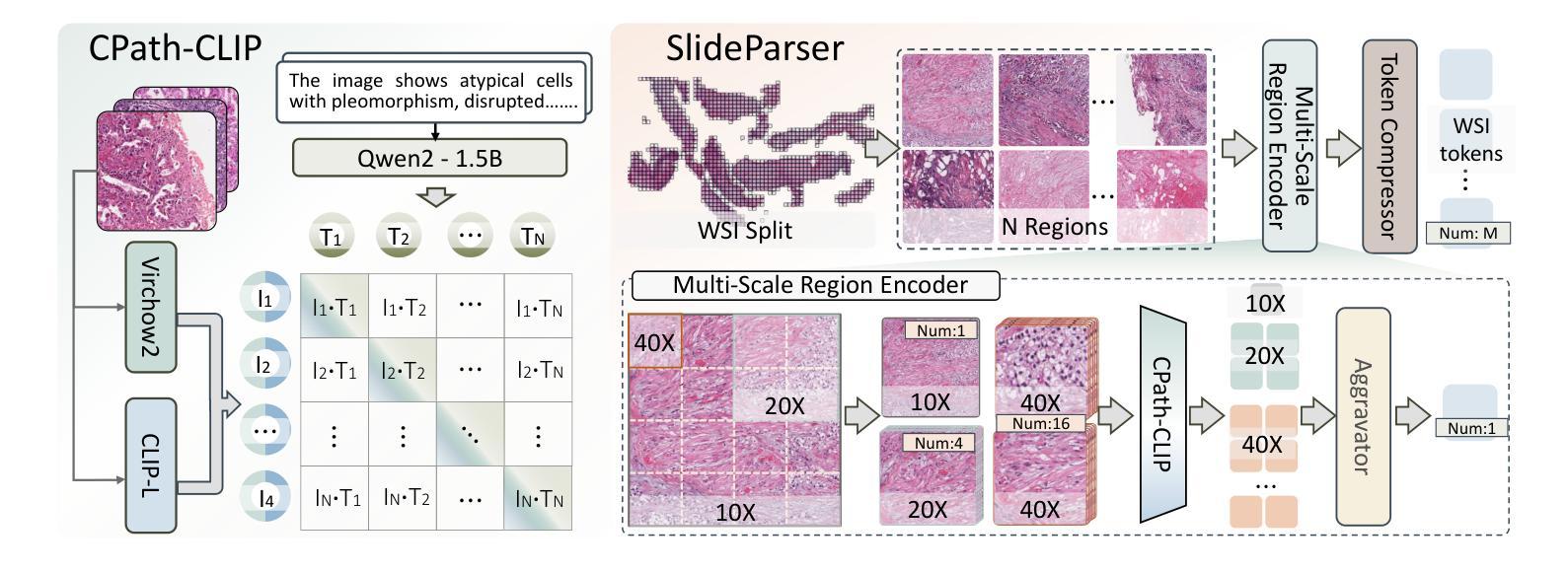
CPath-Omni: A Unified Multimodal Foundation Model for Patch and Whole Slide Image Analysis in Computational Pathology
Authors:Yuxuan Sun, Yixuan Si, Chenglu Zhu, Xuan Gong, Kai Zhang, Pingyi Chen, Ye Zhang, Zhongyi Shui, Tao Lin, Lin Yang
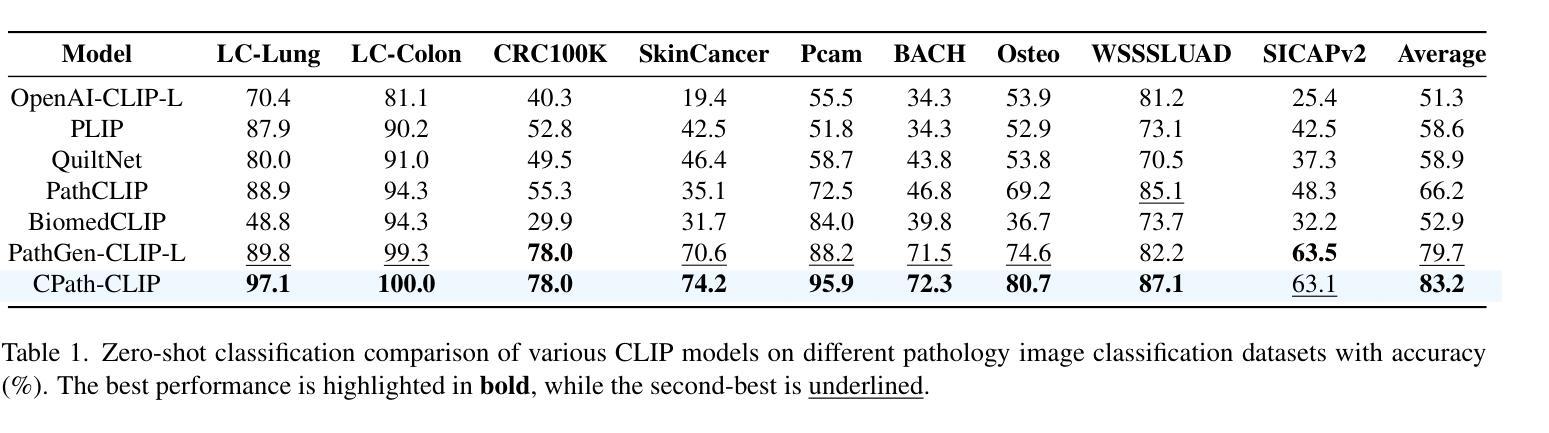
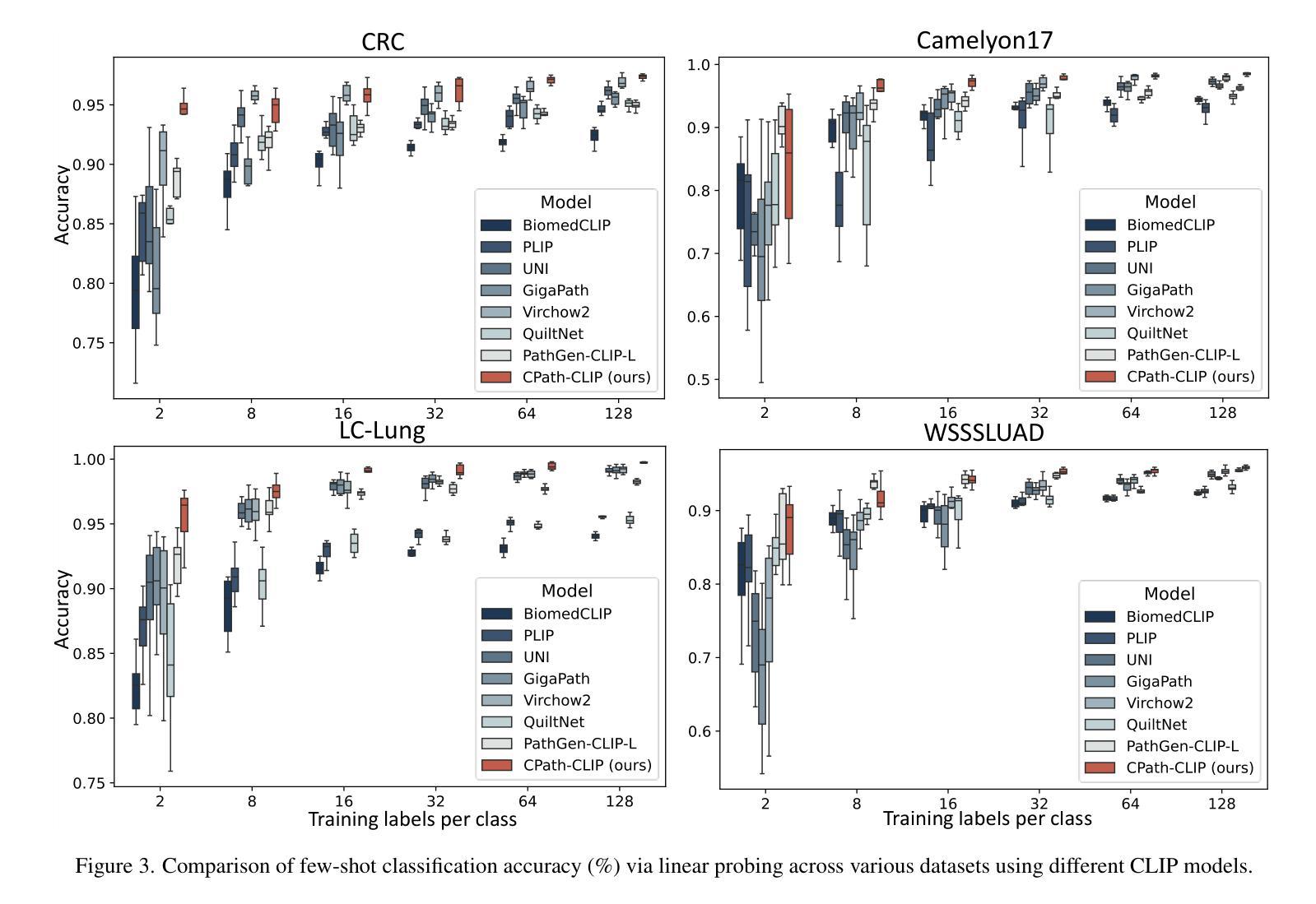
The emergence of large multimodal models (LMMs) has brought significant advancements to pathology. Previous research has primarily focused on separately training patch-level and whole-slide image (WSI)-level models, limiting the integration of learned knowledge across patches and WSIs, and resulting in redundant models. In this work, we introduce CPath-Omni, the first 15-billion-parameter LMM designed to unify both patch and WSI level image analysis, consolidating a variety of tasks at both levels, including classification, visual question answering, captioning, and visual referring prompting. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CPath-Omni achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance across seven diverse tasks on 39 out of 42 datasets, outperforming or matching task-specific models trained for individual tasks. Additionally, we develop a specialized pathology CLIP-based visual processor for CPath-Omni, CPath-CLIP, which, for the first time, integrates different vision models and incorporates a large language model as a text encoder to build a more powerful CLIP model, which achieves SOTA performance on nine zero-shot and four few-shot datasets. Our findings highlight CPath-Omni’s ability to unify diverse pathology tasks, demonstrating its potential to streamline and advance the field of foundation model in pathology.
大型多模态模型(LMMs)的出现为病理学领域带来了巨大的进步。之前的研究主要集中在分别训练补丁级别和全幻灯片图像(WSI)级别的模型上,这限制了跨补丁和WSIs所学知识的整合,并导致了冗余模型的出现。在这项工作中,我们介绍了CPath-Omni,这是首个设计的15亿参数LMM,旨在统一补丁和WSI级别的图像分析,巩固这两个级别的各种任务,包括分类、视觉问答、描述和视觉提示。大量实验表明,CPath-Omni在42个数据集中的39个数据集上的七个不同任务上达到了最先进的性能,优于或匹配了针对单个任务训练的特定任务模型。此外,我们为CPath-Omni开发了一个基于CLIP的专用病理视觉处理器CPath-CLIP,它首次将不同的视觉模型整合在一起,并融入大型语言模型作为文本编码器,以构建更强大的CLIP模型,该模型在九个零样本和四个少样本数据集上达到了最先进的性能。我们的研究突出了CPath-Omni统一各种病理任务的能力,表明了其在病理学领域基础模型中的潜力和作用。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 22 pages, 13 figures
Summary
大型多模态模型(LMMs)的出现在病理学领域带来了重大突破。过去的研究主要集中在分别训练补丁级别和全幻灯片级别模型上,这限制了跨补丁和全幻灯片集成的知识的整合,并导致了冗余模型的出现。在这项工作中,我们介绍了CPath-Omni,这是一个首个旨在统一补丁和幻灯片级别图像分析的大型模型,它可以在这两个层面上整合各种任务,包括分类、视觉问答、描述和视觉提示。实验表明,CPath-Omni在多种任务上的性能达到了前所未有的水平,在多个数据集上实现了最佳性能。此外,我们还为CPath-Omni开发了一种基于CLIP的专用病理视觉处理器CPath-CLIP,它首次将不同的视觉模型与大型语言模型相结合作为文本编码器来构建更强大的CLIP模型,在多个数据集上取得了零样本和少量样本的最佳性能。我们的研究突出了CPath-Omni统一各种病理任务的能力,显示出其在病理学基础模型领域推动和进步潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型多模态模型(LMMs)的引入在病理学领域带来了显著进展。
- CPath-Omni是一个统一的模型,结合了补丁级别和全幻灯片级别的图像分析。
- CPath-Omni能够在多个任务上实现最佳性能,包括分类、视觉问答等。
- CPath-CLIP是CPath-Omni的一个专门视觉处理器,结合了多种模型并实现了零样本和少量样本的最佳性能。
- CPath-Omni具有统一多种病理任务的能力,具有推动病理学基础模型领域发展的潜力。
- 此模型通过跨补丁和全幻灯片的集成知识减少了冗余模型的需求。
点此查看论文截图

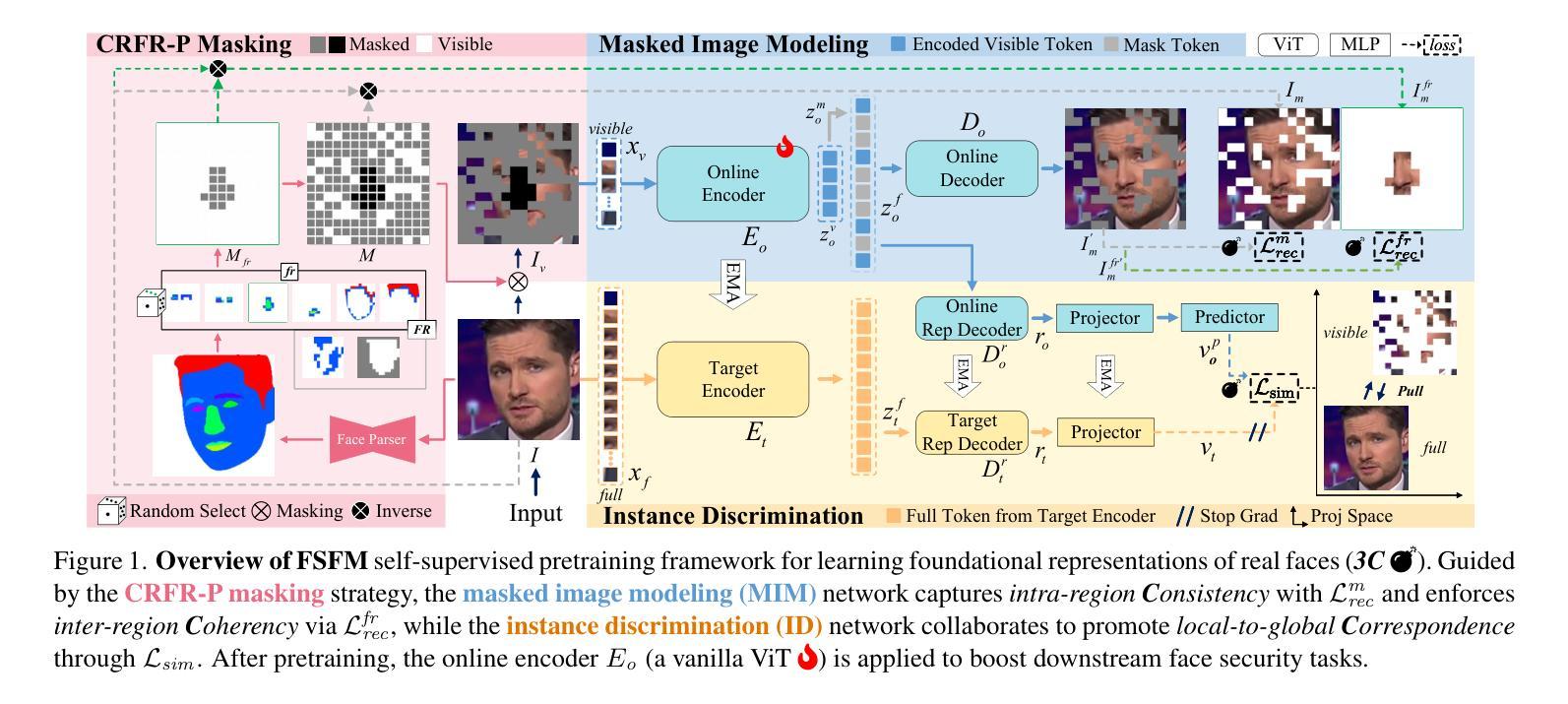
FSFM: A Generalizable Face Security Foundation Model via Self-Supervised Facial Representation Learning
Authors:Gaojian Wang, Feng Lin, Tong Wu, Zhenguang Liu, Zhongjie Ba, Kui Ren
This work asks: with abundant, unlabeled real faces, how to learn a robust and transferable facial representation that boosts various face security tasks with respect to generalization performance? We make the first attempt and propose a self-supervised pretraining framework to learn fundamental representations of real face images, FSFM, that leverages the synergy between masked image modeling (MIM) and instance discrimination (ID). We explore various facial masking strategies for MIM and present a simple yet powerful CRFR-P masking, which explicitly forces the model to capture meaningful intra-region consistency and challenging inter-region coherency. Furthermore, we devise the ID network that naturally couples with MIM to establish underlying local-to-global correspondence via tailored self-distillation. These three learning objectives, namely 3C, empower encoding both local features and global semantics of real faces. After pretraining, a vanilla ViT serves as a universal vision foundation model for downstream face security tasks: cross-dataset deepfake detection, cross-domain face anti-spoofing, and unseen diffusion facial forgery detection. Extensive experiments on 10 public datasets demonstrate that our model transfers better than supervised pretraining, visual and facial self-supervised learning arts, and even outperforms task-specialized SOTA methods.
这篇论文提出的问题是:在大量无标签的真实人脸数据情况下,如何学习一种稳健且可迁移的人脸表示,以提高关于泛化性能的各种人脸安全任务的性能?我们首次尝试并提出一种自监督预训练框架,用于学习真实人脸图像的基本表示,FSFM,该框架利用掩码图像建模(MIM)和实例鉴别(ID)之间的协同作用。我们探索了MIM的各种面部掩码策略,并提出了一种简单而强大的CRFR-P掩码,它明确地迫使模型捕捉区域内有意义的一致性和区域间挑战性的连贯性。此外,我们设计了一个与MIM自然结合的ID网络,通过定制的自蒸馏建立基本的局部到全局对应关系。这三个学习目标,即3C,使得编码真实人脸的局部特征和全局语义成为可能。预训练后,一个简单的ViT作为下游人脸安全任务的通用视觉基础模型:跨数据集深度伪造检测、跨域面部防伪、未见扩散面部伪造检测。在1H个公开数据集上的大量实验表明,我们的模型迁移效果优于监督预训练、视觉和面部自监督学习技术,甚至超越了任务专业化的最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 11 figures, project page: https://fsfm-3c.github.io
Summary
本文探讨了如何利用大量未标记的真实面部图像进行自监督预训练,以学习稳健且可迁移的面部表示。提出一种自监督预训练框架FSFM,结合掩膜图像建模(MIM)和实例判别(ID)来学习真实面部图像的基本表示。探索了多种面部掩膜策略,并提出简单而强大的CRFR-P掩膜,以明确捕捉区域内的一致性以及区域间的连贯性。此外,设计了与MIM自然结合的ID网络,通过定制的自我蒸馏建立局部到全局的对应关系。这三个学习目标,即3C,使模型能够编码真实面部的局部特征和全局语义。预训练后,可作为下游面部安全任务的通用视觉基础模型,如跨数据集深度伪造检测、跨域面部防伪和未见扩散面部伪造检测。
Key Takeaways
- 本文旨在利用大量未标记的真实面部图像进行自监督预训练,学习稳健且可迁移的面部表示。
- 提出了一个自监督预训练框架FSFM,结合MIM和ID来学习面部图像的基本表示。
- 介绍了CRFR-P掩膜策略,强调模型对区域内和区域间的面部特征的捕捉。
- 通过定制的自我蒸馏建立局部到全局的对应关系,增强模型的表示能力。
- 三个学习目标——3C,使模型能够编码真实面部的局部和全局特征。
- 模型在多个公共数据集上的实验表现优越,超越了监督预训练和其他面部自我监督学习方法,甚至超过了任务专业化的最新方法。
点此查看论文截图

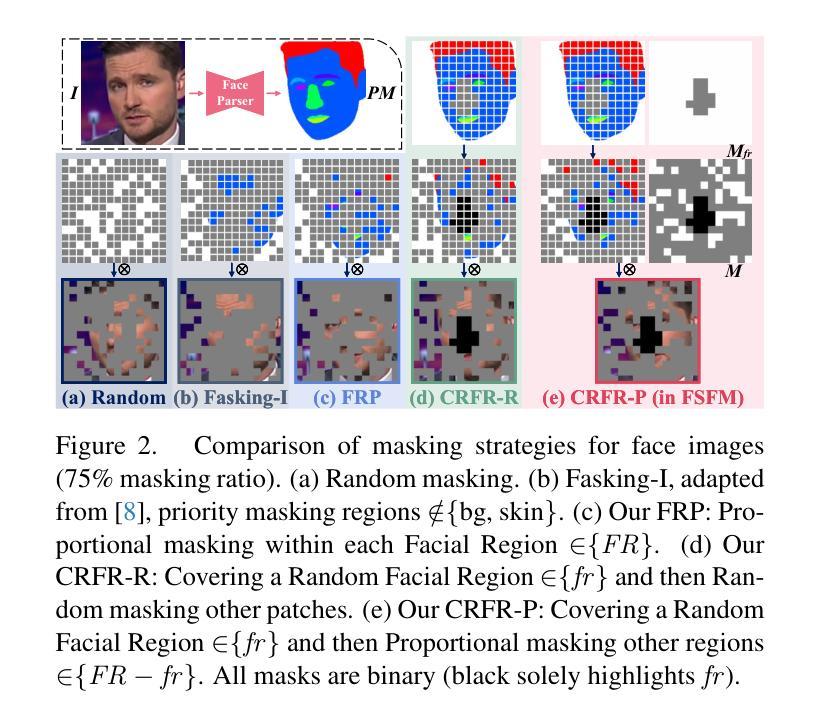

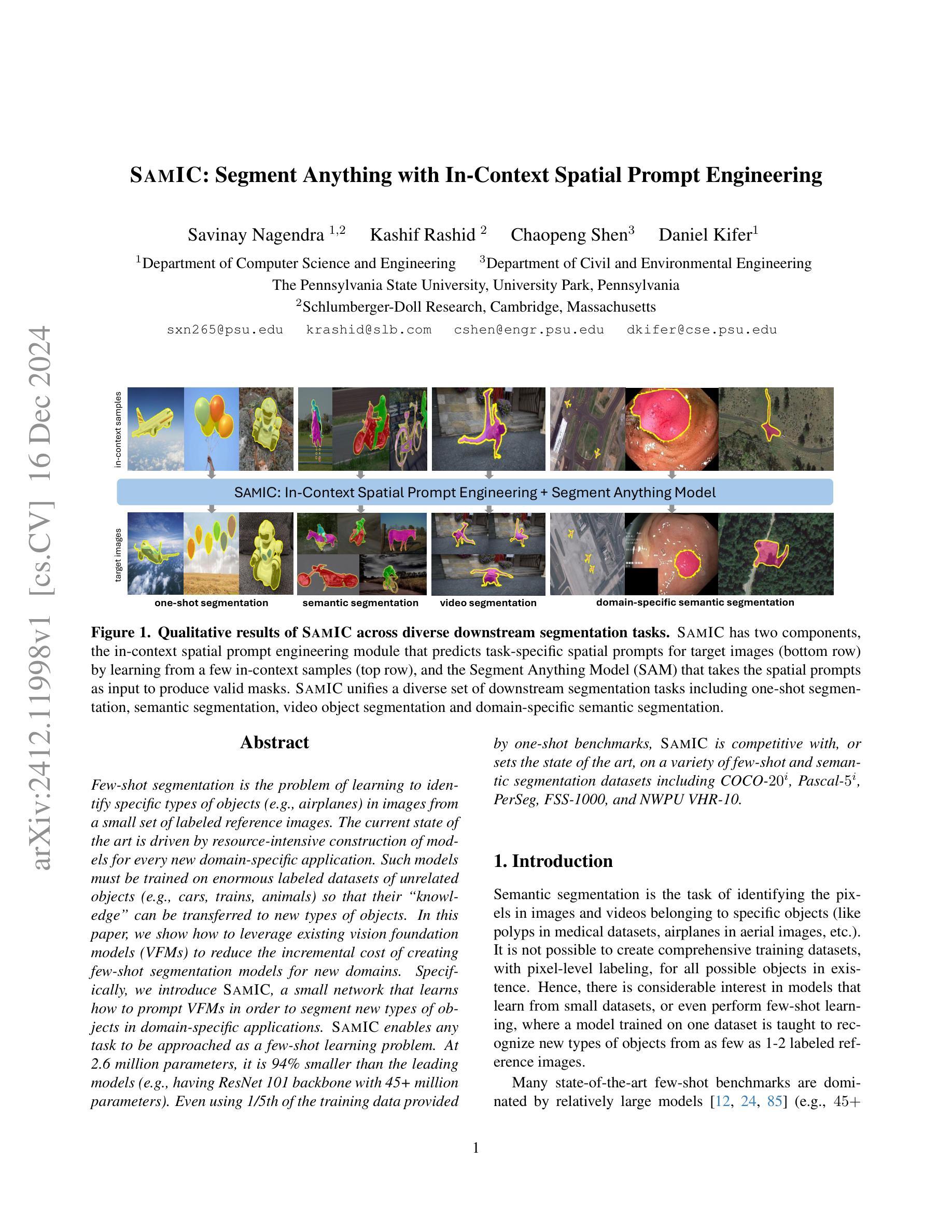
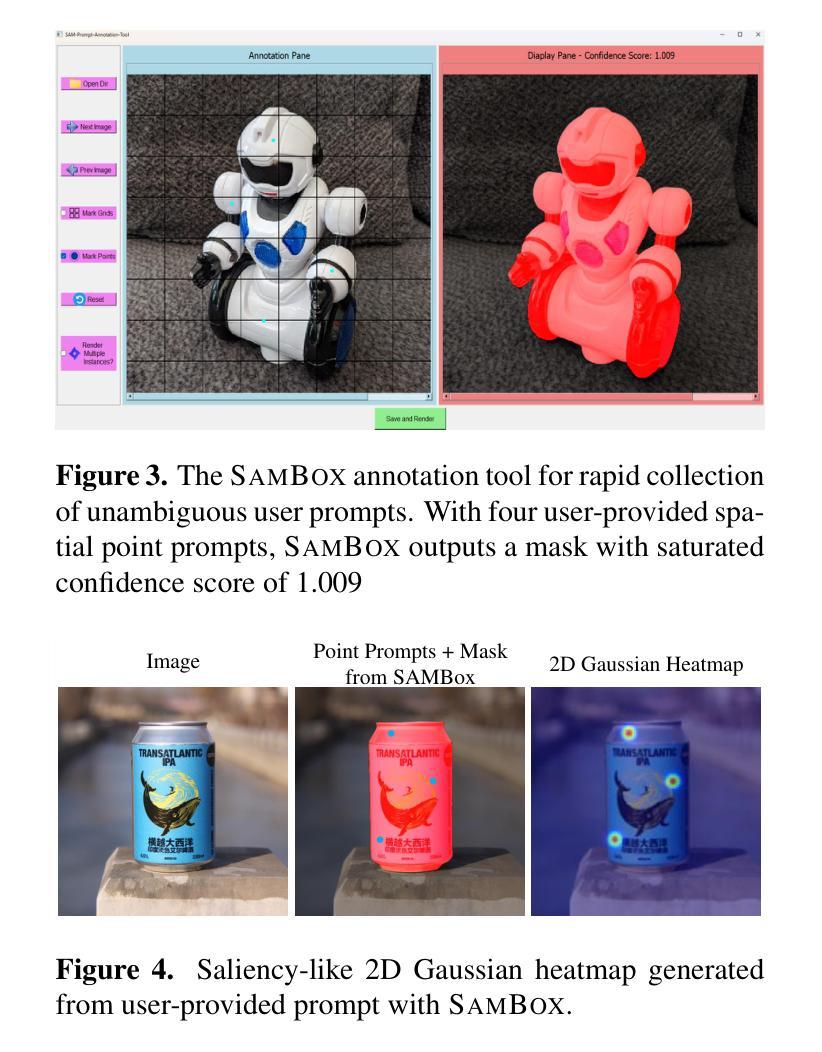
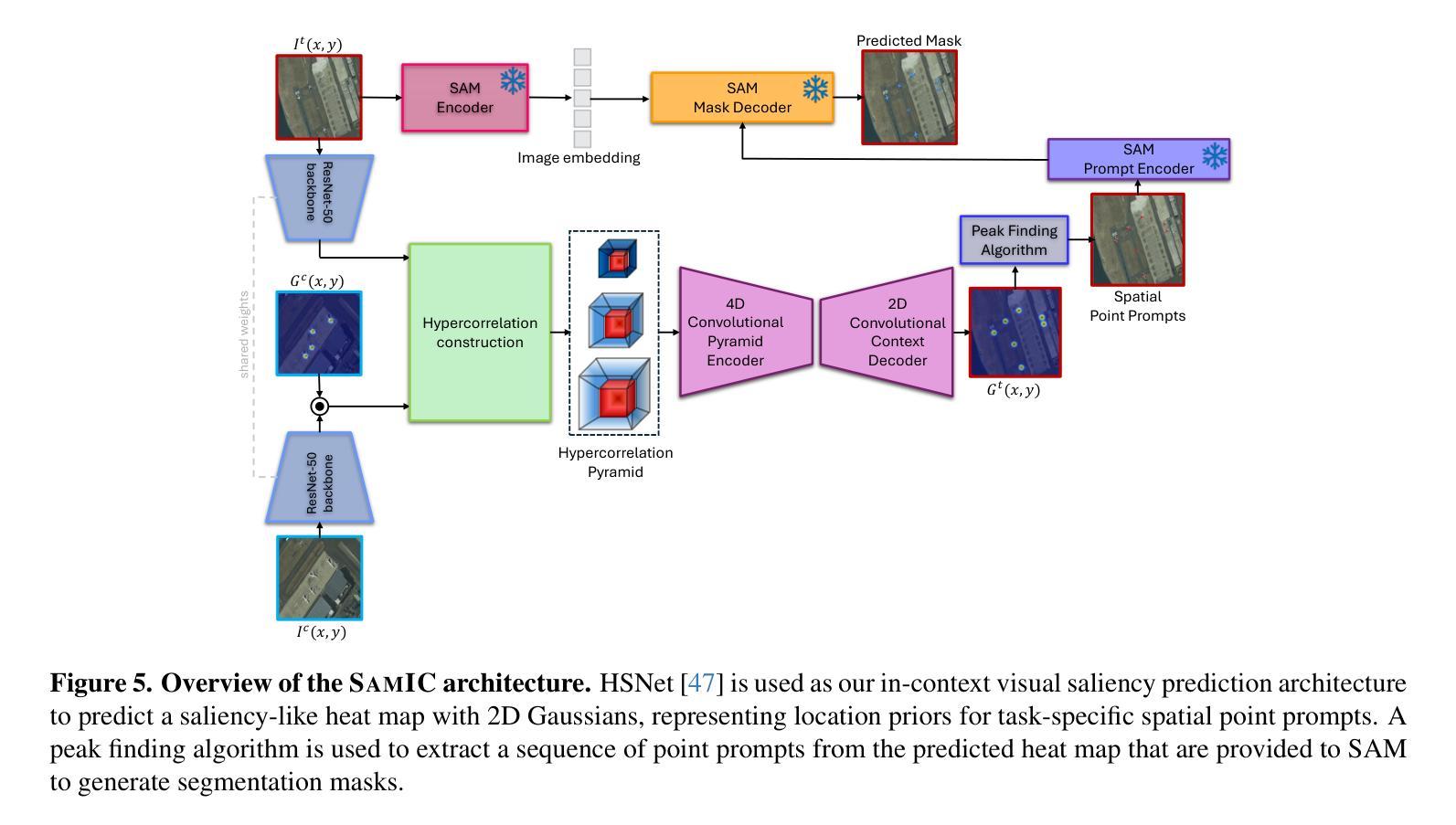
SAMIC: Segment Anything with In-Context Spatial Prompt Engineering
Authors:Savinay Nagendra, Kashif Rashid, Chaopeng Shen, Daniel Kifer
Few-shot segmentation is the problem of learning to identify specific types of objects (e.g., airplanes) in images from a small set of labeled reference images. The current state of the art is driven by resource-intensive construction of models for every new domain-specific application. Such models must be trained on enormous labeled datasets of unrelated objects (e.g., cars, trains, animals) so that their ``knowledge’’ can be transferred to new types of objects. In this paper, we show how to leverage existing vision foundation models (VFMs) to reduce the incremental cost of creating few-shot segmentation models for new domains. Specifically, we introduce SAMIC, a small network that learns how to prompt VFMs in order to segment new types of objects in domain-specific applications. SAMIC enables any task to be approached as a few-shot learning problem. At 2.6 million parameters, it is 94% smaller than the leading models (e.g., having ResNet 101 backbone with 45+ million parameters). Even using 1/5th of the training data provided by one-shot benchmarks, SAMIC is competitive with, or sets the state of the art, on a variety of few-shot and semantic segmentation datasets including COCO-$20^i$, Pascal-$5^i$, PerSeg, FSS-1000, and NWPU VHR-10.
少量样本分割(Few-shot segmentation)是指从少量标记参考图像中学习识别特定类型的对象(例如飞机)的问题。目前的技术状态依赖于针对每个新的特定领域应用构建资源密集型的模型。这些模型必须在大量不相关对象(例如汽车、火车、动物)的标记数据集上进行训练,以便将它们的“知识”转移到新型对象上。在本文中,我们展示了如何利用现有的视觉基础模型(VFMs)来降低创建用于新领域的少量样本分割模型的增量成本。具体来说,我们引入了SAMIC,这是一个小型网络,它学习如何提示VFM以对特定领域应用中的新型对象进行分割。SAMIC使任何任务都可以作为少量样本学习问题来处理。它只有260万个参数,比领先的模型小94%(例如具有超过4500万个参数的ResNet 101主干网)。即使只使用单次基准测试提供的五分之一训练数据,SAMIC在各种少量样本和语义分割数据集上也具有竞争力,并达到了业界领先水平,包括COCO-20i、Pascal-5i、PerSeg、FSS-1000和NWPU VHR-10。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了如何利用现有的视觉基础模型(VFMs)降低为新领域创建小样本分割模型的增量成本。通过引入SAMIC网络,学习如何提示VFMs对新的对象类型进行分割,使得任何任务都可以作为小样本学习问题来解决。SAMIC网络仅有260万个参数,比领先的模型小94%,即使使用现有基准测试集的1/5的训练数据,其在多种小样本和语义分割数据集上的表现也极具竞争力,甚至达到或超越了当前最佳水平。
Key Takeaways
- 介绍小样本分割问题,即利用少量标记参考图像识别图像中的特定对象类型。
- 当前技术依赖为每个新领域特定应用构建资源密集型的模型。
- 提出利用现有的视觉基础模型(VFMs)降低创建新领域小样本分割模型的增量成本。
- 引入SAMIC网络,学习如何提示VFMs进行新类型对象的分割。
- SAMIC网络更小、更高效,只有260万个参数,相比领先的模型减小了94%。
- SAMIC在多种小样本和语义分割数据集上的表现极具竞争力,包括COCO-20i、Pascal-5i、PerSeg、FSS-1000和NWPU VHR-10等。
点此查看论文截图

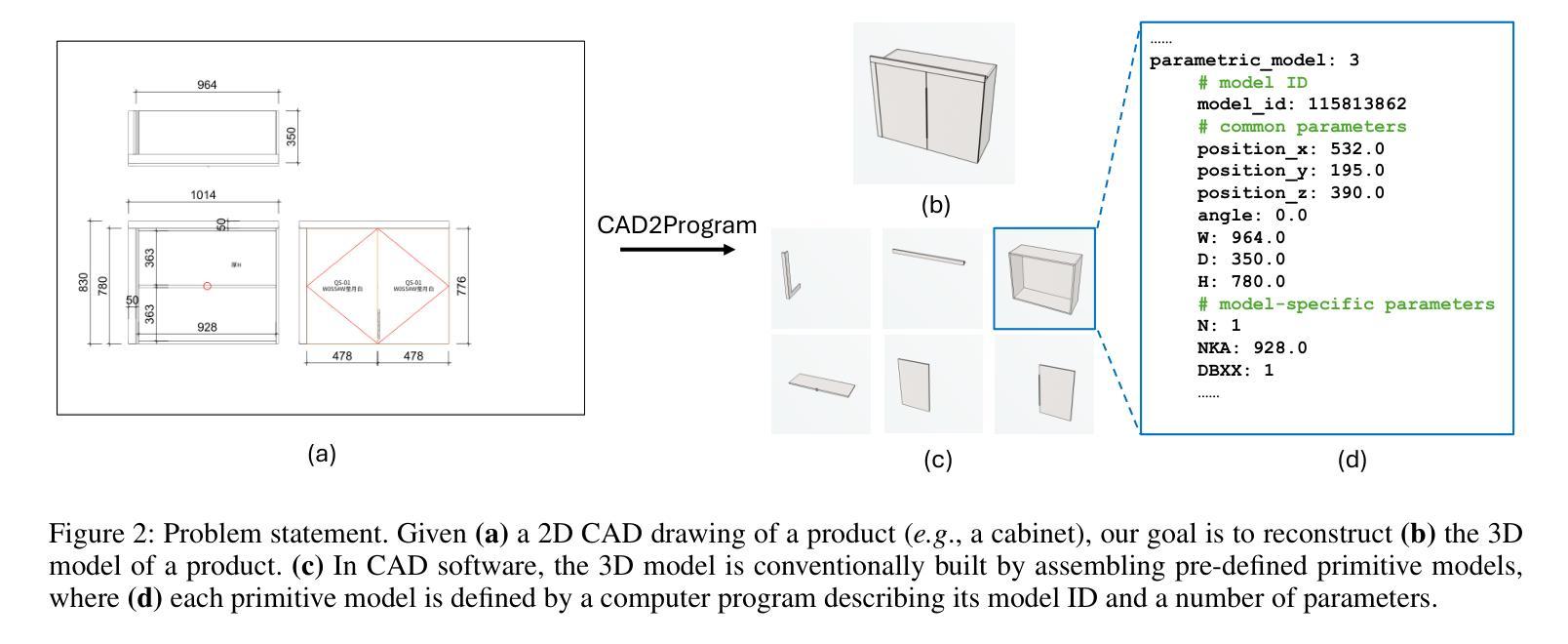
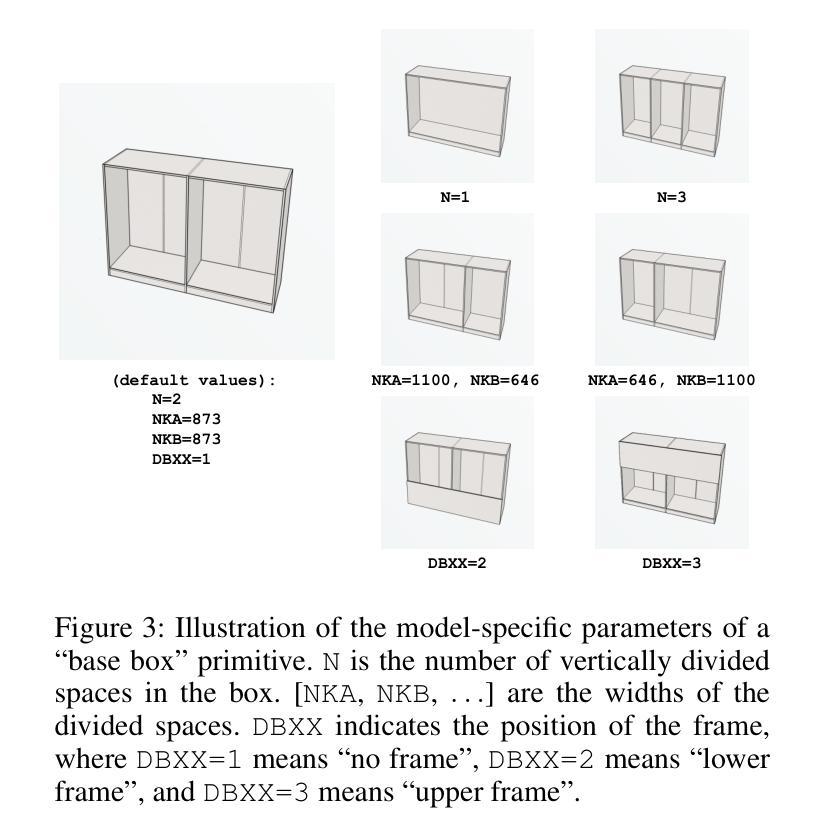
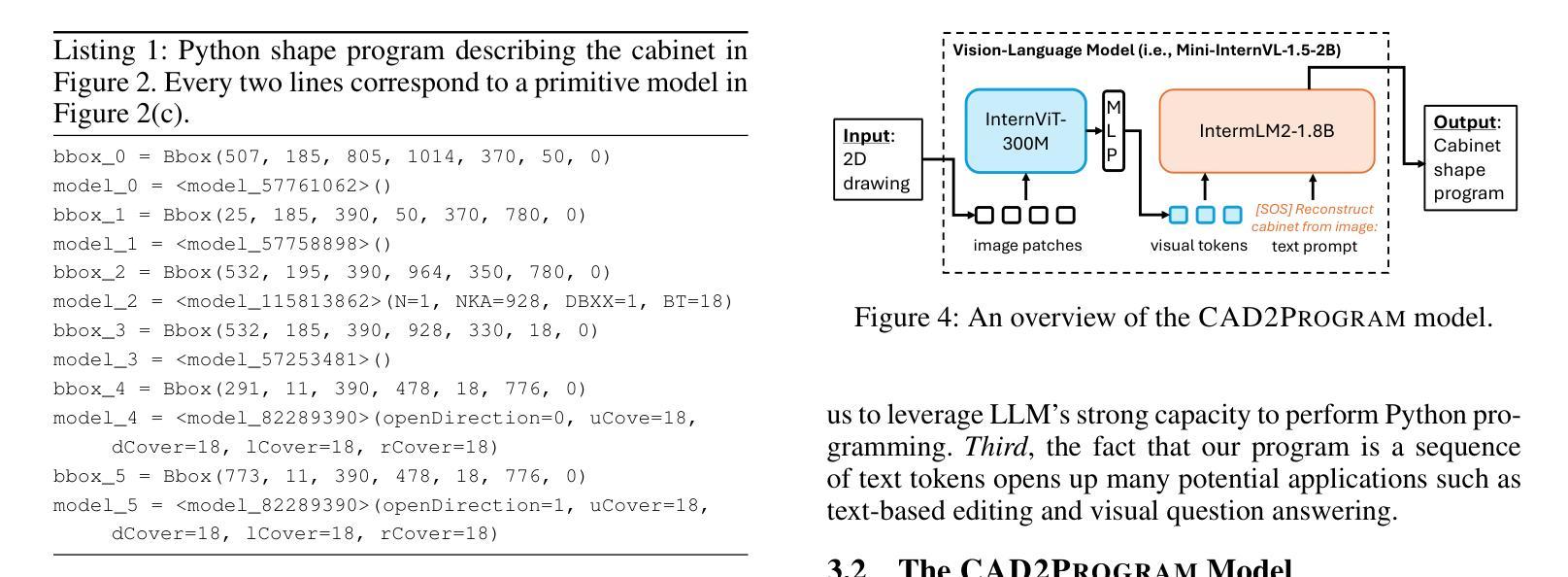
From 2D CAD Drawings to 3D Parametric Models: A Vision-Language Approach
Authors:Xilin Wang, Jia Zheng, Yuanchao Hu, Hao Zhu, Qian Yu, Zihan Zhou
In this paper, we present CAD2Program, a new method for reconstructing 3D parametric models from 2D CAD drawings. Our proposed method is inspired by recent successes in vision-language models (VLMs), and departs from traditional methods which rely on task-specific data representations and/or algorithms. Specifically, on the input side, we simply treat the 2D CAD drawing as a raster image, regardless of its original format, and encode the image with a standard ViT model. We show that such an encoding scheme achieves competitive performance against existing methods that operate on vector-graphics inputs, while imposing substantially fewer restrictions on the 2D drawings. On the output side, our method auto-regressively predicts a general-purpose language describing 3D parametric models in text form. Compared to other sequence modeling methods for CAD which use domain-specific sequence representations with fixed-size slots, our text-based representation is more flexible, and can be easily extended to arbitrary geometric entities and semantic or functional properties. Experimental results on a large-scale dataset of cabinet models demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
本文介绍了CAD2Program,这是一种从2D CAD图纸重建3D参数模型的新方法。我们提出的方法受到最近视觉语言模型(VLMs)成功的启发,与传统方法不同,传统方法依赖于特定的任务数据表示和/或算法。具体来说,在输入方面,我们简单地将2D CAD图纸视为栅格图像,而不考虑其原始格式,并使用标准的ViT模型对图像进行编码。我们证明了这种编码方案在实现与针对矢量图形输入的现有方法相当的性能的同时,对2D图纸的限制大大减少。在输出方面,我们的方法通过自动回归预测描述文本形式的3D参数模型的一般语言。与其他使用固定大小插槽的特定领域序列表示的CAD序列建模方法相比,我们的基于文本的表示更加灵活,可以轻松地扩展到任意几何实体和语义或功能属性。在大型橱柜模型数据集上的实验结果证明了我们的方法的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF To Appear in AAAI 2025. The project page is at https://manycore-research.github.io/CAD2Program
Summary
该文提出了CAD2Program方法,这是一种从2D CAD绘图重建3D参数模型的新方法。该方法受到视觉语言模型(VLMs)近期成功的启发,不同于传统方法依赖于特定任务的数据表示和/或算法。输入方面,我们将2D CAD绘图视为通用图像,使用标准ViT模型进行编码,展示出了与操作矢量图形输入现有方法相当的竞争力,同时对2D绘图实质上没有限制。输出方面,我们的方法自回归地预测描述文本形式的3D参数模型的一般语言。相比于使用固定大小插槽的特定领域序列表示的其他序列建模方法,我们的文本表示更加灵活,可轻松扩展到任意几何实体和语义或功能属性。在大型橱柜模型数据集上的实验结果证明了该方法的有效性。
Key Takeaways
- CAD2Program是一种从2D CAD绘图重建3D参数模型的新方法。
- 该方法受到视觉语言模型(VLMs)成功的启发。
- 输入方面,使用标准ViT模型对2D CAD绘图进行编码,无需特定格式。
- 该方法与操作矢量图形输入的现有方法竞争力相当,对2D绘图限制少。
- 输出方面,方法自回归地预测描述3D参数模型的文本。
- 相比其他序列建模方法,文本表示更加灵活,易于扩展到不同几何实体和属性。
点此查看论文截图

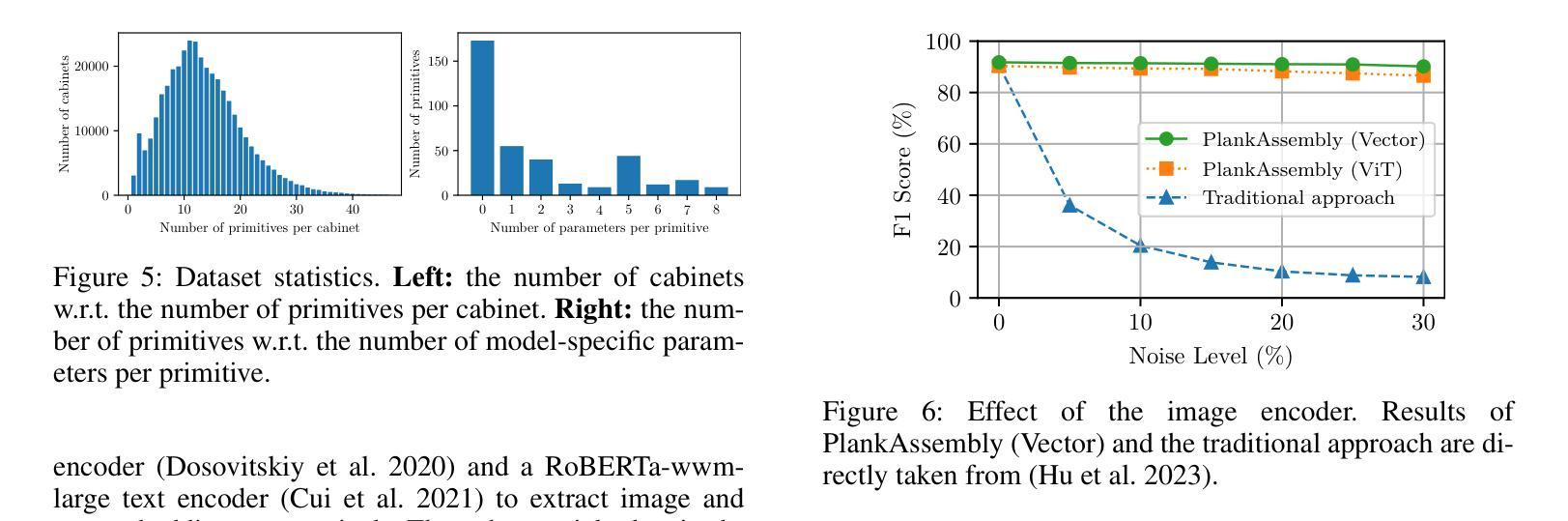
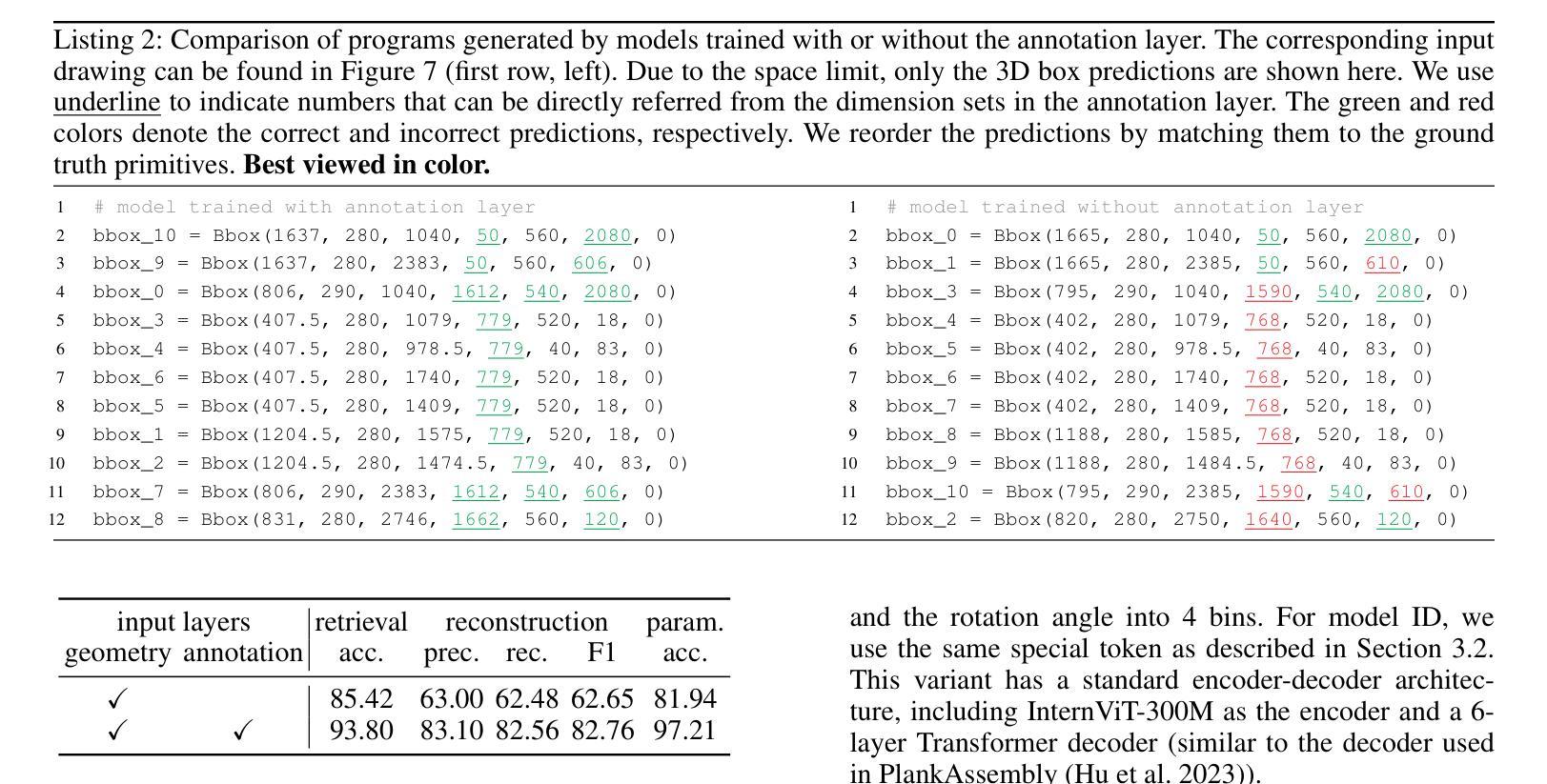
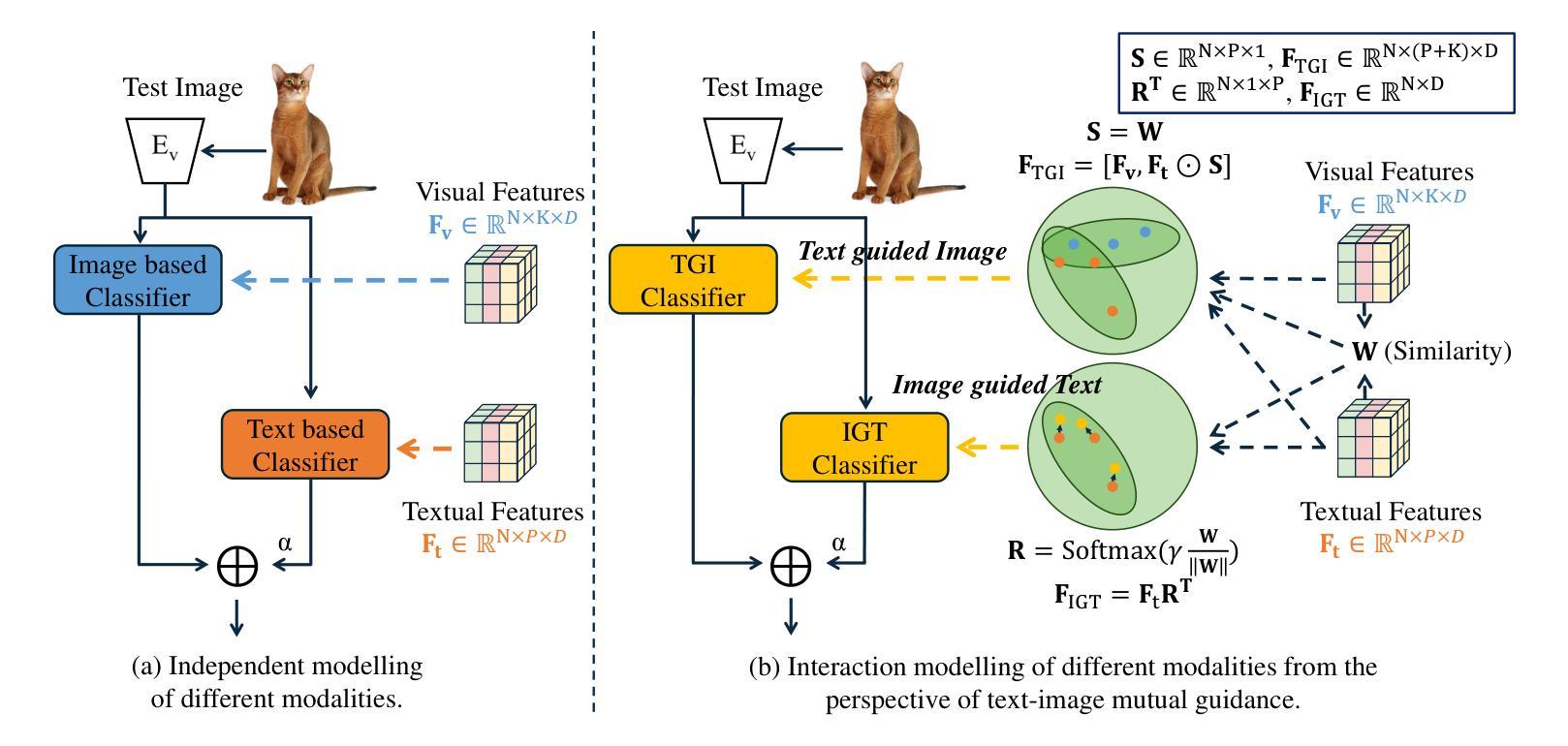
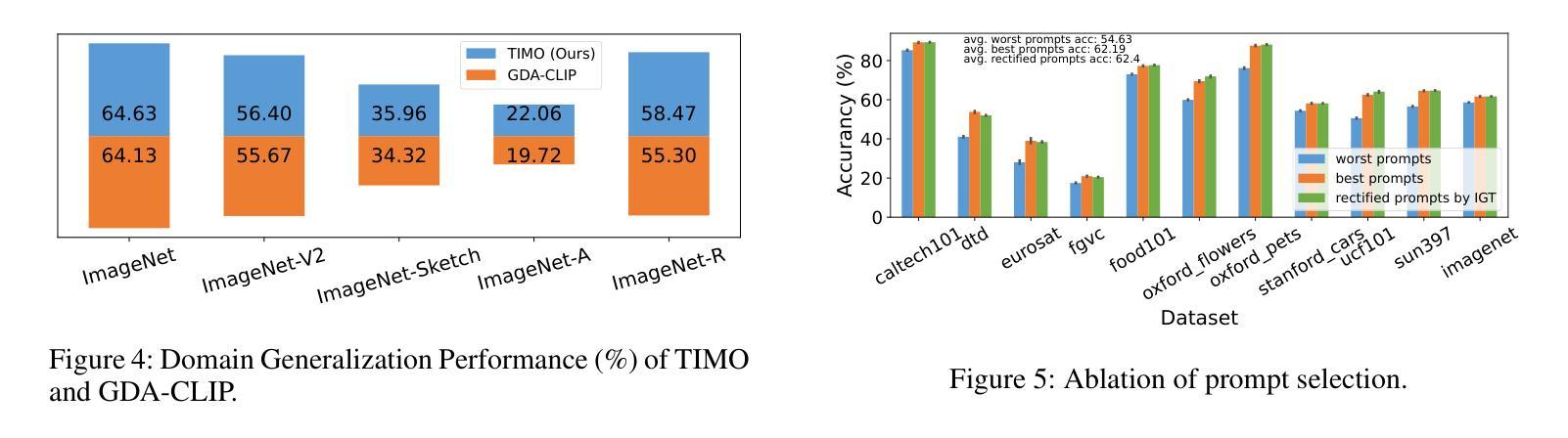
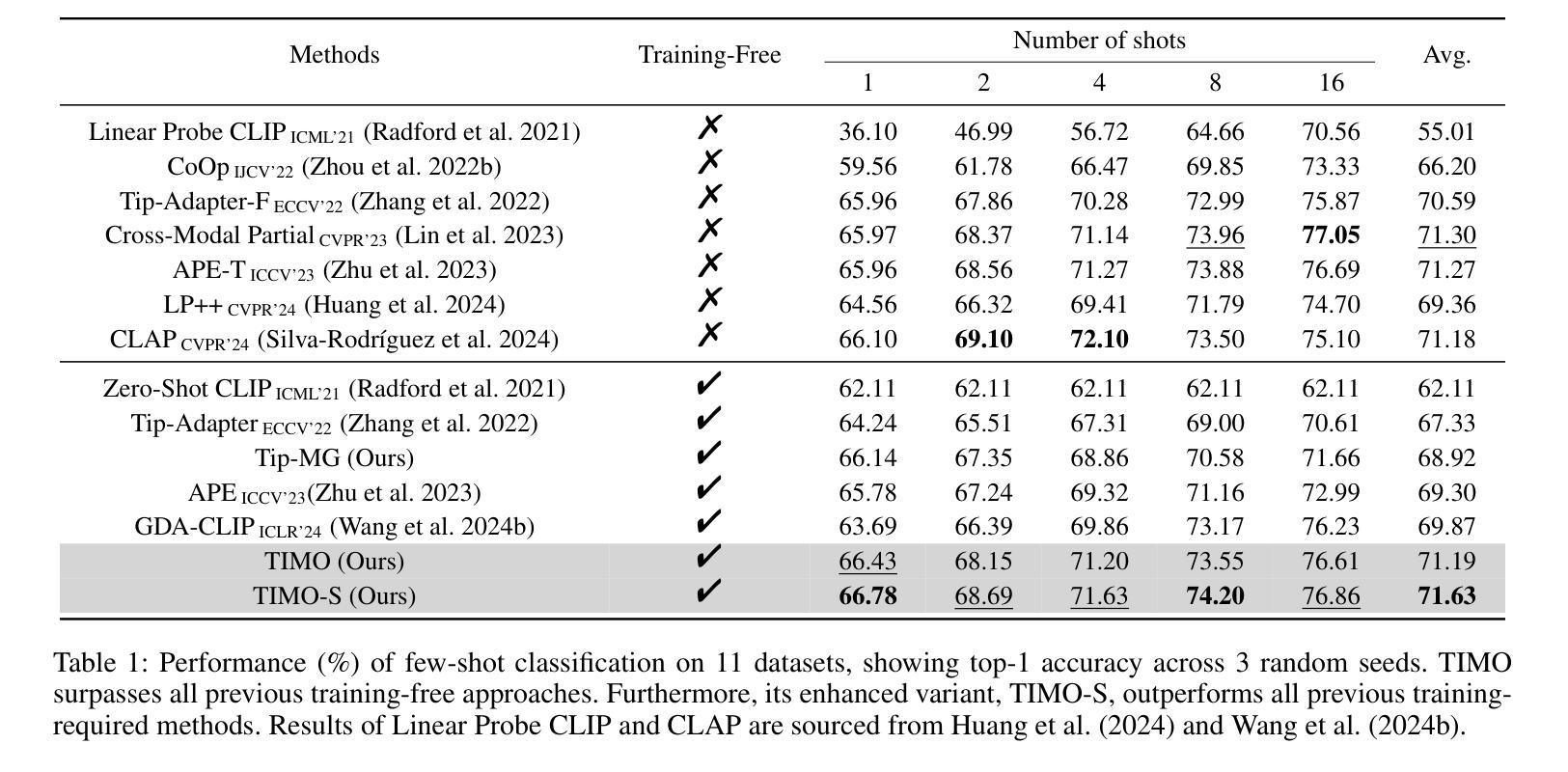
Text and Image Are Mutually Beneficial: Enhancing Training-Free Few-Shot Classification with CLIP
Authors:Yayuan Li, Jintao Guo, Lei Qi, Wenbin Li, Yinghuan Shi
Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining (CLIP) has been widely used in vision tasks. Notably, CLIP has demonstrated promising performance in few-shot learning (FSL). However, existing CLIP-based methods in training-free FSL (i.e., without the requirement of additional training) mainly learn different modalities independently, leading to two essential issues: 1) severe anomalous match in image modality; 2) varying quality of generated text prompts. To address these issues, we build a mutual guidance mechanism, that introduces an Image-Guided-Text (IGT) component to rectify varying quality of text prompts through image representations, and a Text-Guided-Image (TGI) component to mitigate the anomalous match of image modality through text representations. By integrating IGT and TGI, we adopt a perspective of Text-Image Mutual guidance Optimization, proposing TIMO. Extensive experiments show that TIMO significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art (SOTA) training-free method. Additionally, by exploring the extent of mutual guidance, we propose an enhanced variant, TIMO-S, which even surpasses the best training-required methods by 0.33% with approximately 100 times less time cost. Our code is available at https://github.com/lyymuwu/TIMO.
对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)在视觉任务中得到了广泛应用。尤其值得一提的是,CLIP在少量样本学习(FSL)中表现出良好的性能。然而,现有的基于CLIP的无训练FSL方法(即无需额外训练)主要独立学习不同的模式,导致两个主要问题:1)图像模式中的严重异常匹配;2)生成的文本提示的质量不一。为了解决这些问题,我们建立了一种互引导机制,该机制引入了一个图像引导文本(IGT)组件,通过图像表示来纠正文本提示的质量不一问题,以及一个文本引导图像(TGI)组件,通过文本表示来缓解图像模式的异常匹配问题。通过结合IGT和TGI,我们采用了文本图像互引导优化的观点,提出了TIMO。大量实验表明,TIMO显著优于最新的无训练方法。此外,通过探索互引导的程度,我们提出了一个增强型变体TIMO-S,它甚至在时间成本大约减少100倍的情况下,超越了最佳需训练方法达0.33%。我们的代码可在https://github.com/lyymuwu/TIMO找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
基于CLIP模型的文本图像预训练技术在视觉任务中广泛应用,尤其在少样本学习上表现优异。但现有方法存在模态独立学习导致的图像模态异常匹配和文本提示质量不一的问题。为此,提出文本图像相互引导优化(TIMO)方法,通过图像引导文本(IGT)组件纠正文本提示质量,以及文本引导图像(TGI)组件减轻图像模态异常匹配问题。实验显示,TIMO显著优于现有无训练需求的方法,其增强版TIMO-S甚至超越最佳训练需求方法,且时间成本低。
Key Takeaways
- CLIP模型在视觉任务中表现良好,尤其在少样本学习上。
- 现有CLIP方法存在模态独立学习导致的图像模态异常匹配和文本提示质量问题。
- 提出TIMO方法,通过文本图像相互引导机制解决上述问题。
- IGT组件通过图像表示纠正文本提示质量。
- TGI组件通过文本表示减轻图像模态异常匹配问题。
- TIMO方法显著优于现有无训练需求方法。
- TIMO的增强版TIMO-S在时间成本低的情况下,性能超越最佳训练需求方法。
点此查看论文截图
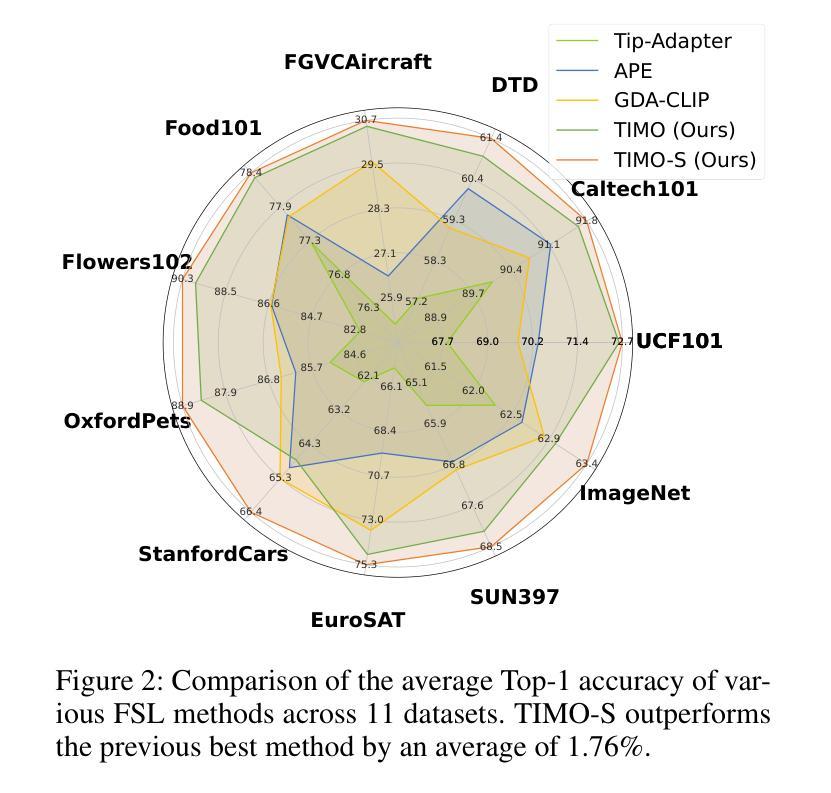
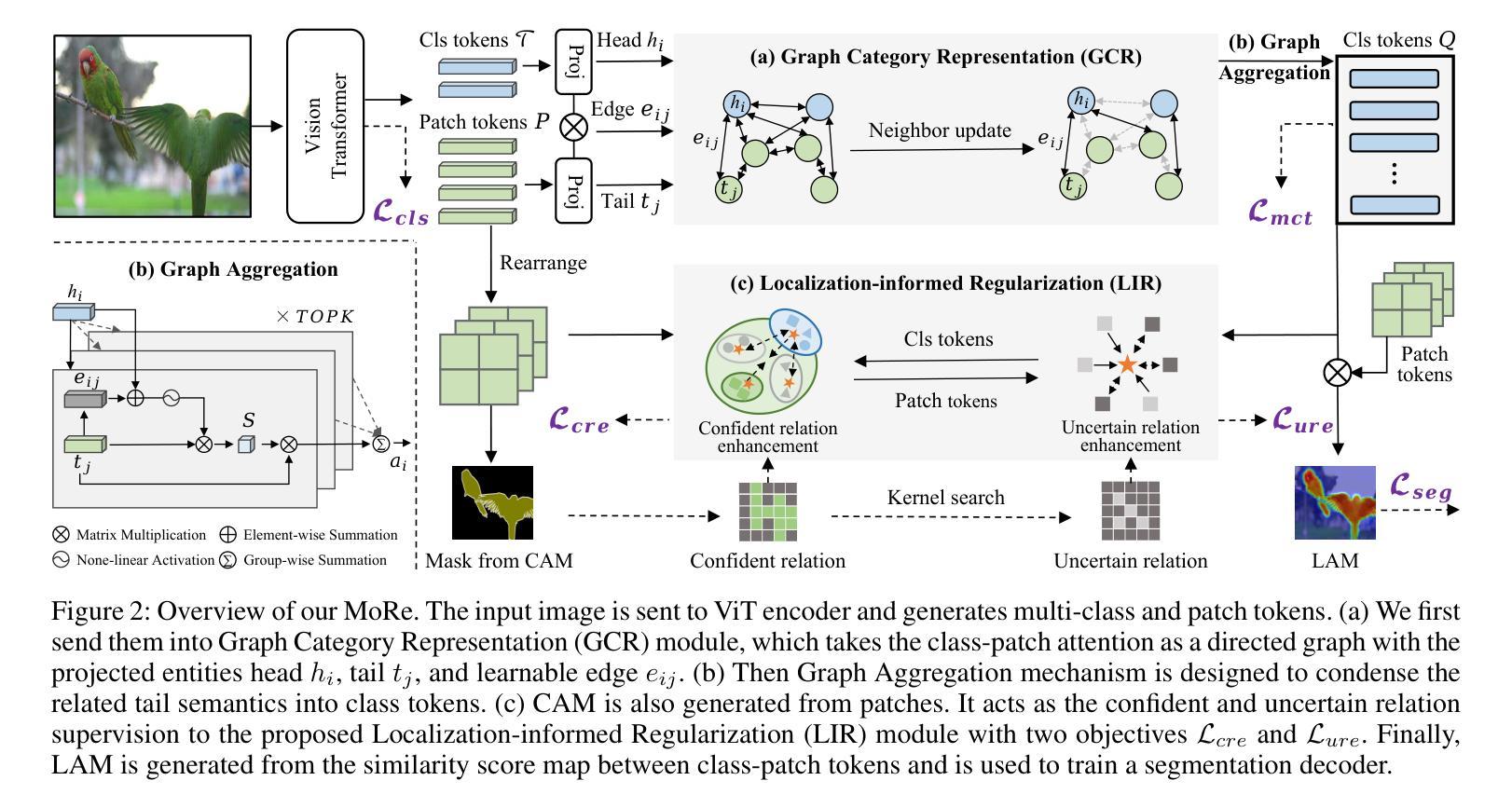
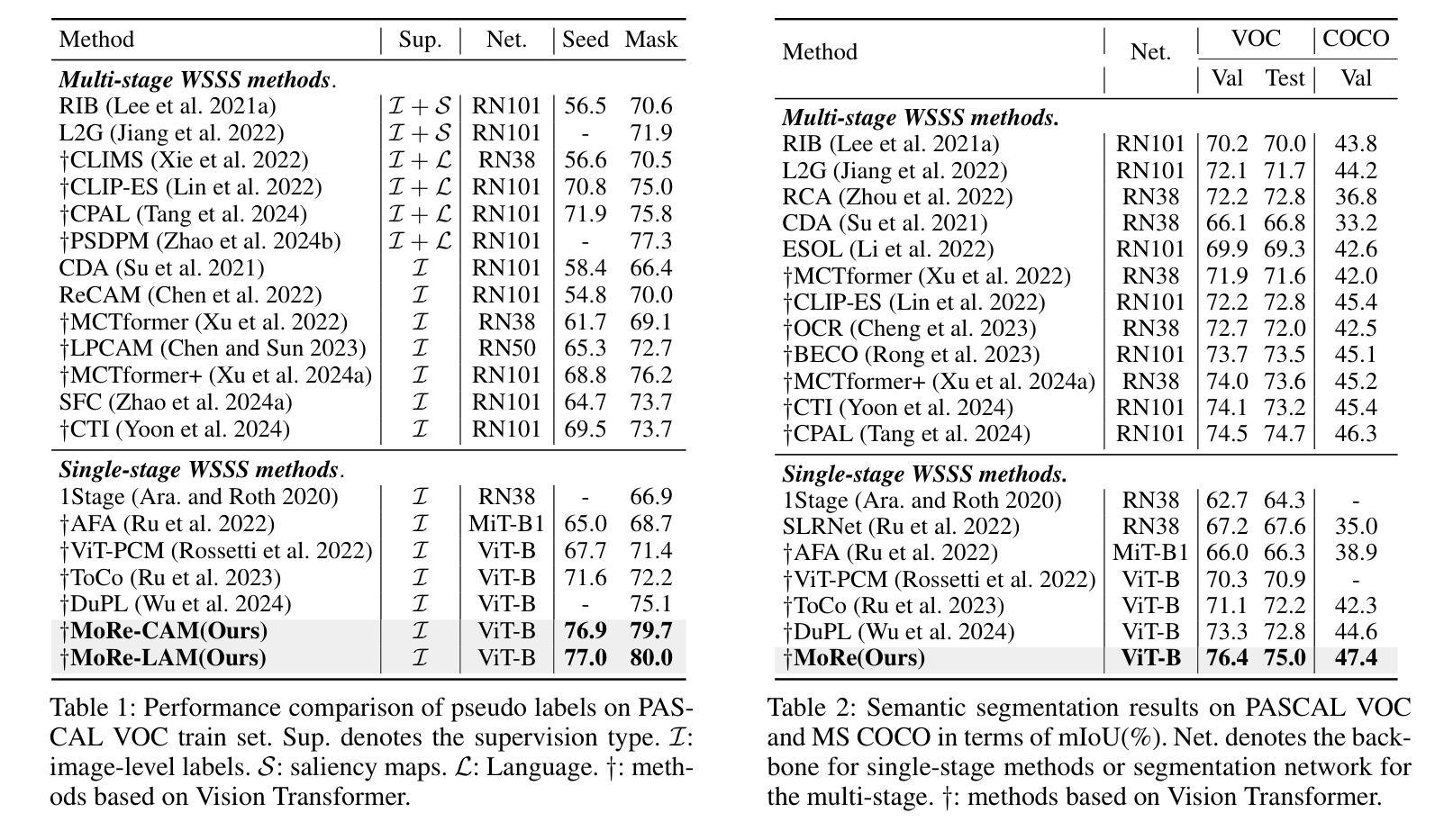
MoRe: Class Patch Attention Needs Regularization for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Zhiwei Yang, Yucong Meng, Kexue Fu, Shuo Wang, Zhijian Song
Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) with image-level labels typically uses Class Activation Maps (CAM) to achieve dense predictions. Recently, Vision Transformer (ViT) has provided an alternative to generate localization maps from class-patch attention. However, due to insufficient constraints on modeling such attention, we observe that the Localization Attention Maps (LAM) often struggle with the artifact issue, i.e., patch regions with minimal semantic relevance are falsely activated by class tokens. In this work, we propose MoRe to address this issue and further explore the potential of LAM. Our findings suggest that imposing additional regularization on class-patch attention is necessary. To this end, we first view the attention as a novel directed graph and propose the Graph Category Representation module to implicitly regularize the interaction among class-patch entities. It ensures that class tokens dynamically condense the related patch information and suppress unrelated artifacts at a graph level. Second, motivated by the observation that CAM from classification weights maintains smooth localization of objects, we devise the Localization-informed Regularization module to explicitly regularize the class-patch attention. It directly mines the token relations from CAM and further supervises the consistency between class and patch tokens in a learnable manner. Extensive experiments are conducted on PASCAL VOC and MS COCO, validating that MoRe effectively addresses the artifact issue and achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing recent single-stage and even multi-stage methods. Code is available at https://github.com/zwyang6/MoRe.
基于图像级别的标签进行弱监督语义分割(WSSS)通常使用类别激活图(CAM)来实现密集预测。最近,视觉转换器(ViT)提供了一种生成定位注意力图(LAM)的替代方案,该方案通过类别补丁注意力来生成。然而,由于对这类注意力的建模约束不足,我们观察到定位注意力图(LAM)常常存在伪影问题,即与语义相关性很小的补丁区域被类令牌错误激活。在这项工作中,我们提出MoRe来解决这个问题,并进一步研究LAM的潜力。我们的研究结果表明,对类别补丁注意力施加额外的正则化是必要的。为此,我们首先将注意力视为一种新型的有向图,并提出图类别表示模块来隐含地正则化类别补丁实体之间的交互。它确保类令牌能够动态地凝聚相关的补丁信息,并在图级别抑制不相关的伪影。其次,受分类权重中的CAM能够保持对象定位平滑的启发,我们设计了一个定位感知正则化模块来显式地正则化类别补丁注意力。它直接从CAM挖掘令牌关系,并以可学习的方式监督类别和补丁令牌之间的一致性。在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO上进行了大量实验,验证了MoRe有效地解决了伪影问题,并达到了最先进的性能,超越了最近的单阶段甚至多阶段方法。代码位于https://github.com/zwyang6/MoRe。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025
Summary
本文探讨了使用图像级标签进行弱监督语义分割(WSSS)时,基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的定位注意力图(LAM)所面临的伪激活问题。为解决此问题并探索LAM的潜力,本文提出了MoRe方法。该方法通过额外的正则化对类-补丁注意力进行约束,通过引入图类别表示模块和定位信息正则化模块,实现了对类-补丁实体间交互的隐式和显式正则化。实验结果表明,MoRe方法能有效解决伪激活问题,并在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO数据集上实现了最先进的性能表现。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformer(ViT)可以用于生成定位注意力图(LAM)。
- LAM面临伪激活问题,即不相关的补丁区域会被类标记错误地激活。
- MoRe方法通过引入图类别表示模块和定位信息正则化模块来解决这一问题。
- 图类别表示模块将注意力视为新型有向图,以隐式方式正则化类-补丁实体间的交互。
- 定位信息正则化模块利用分类权重的CAM信息,显式地正则化类-补丁注意力,并促进类标记与补丁标记之间的一致性。
- MoRe方法在PASCAL VOC和MS COCO数据集上实现了最先进的性能表现。
点此查看论文截图

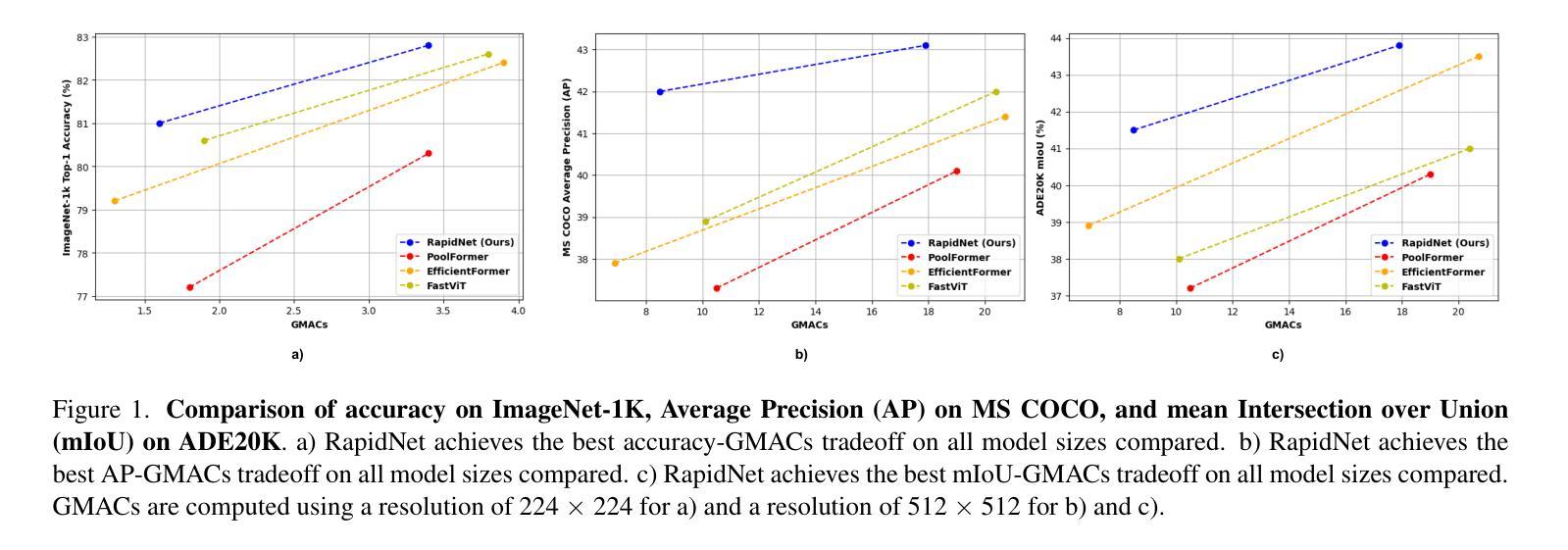
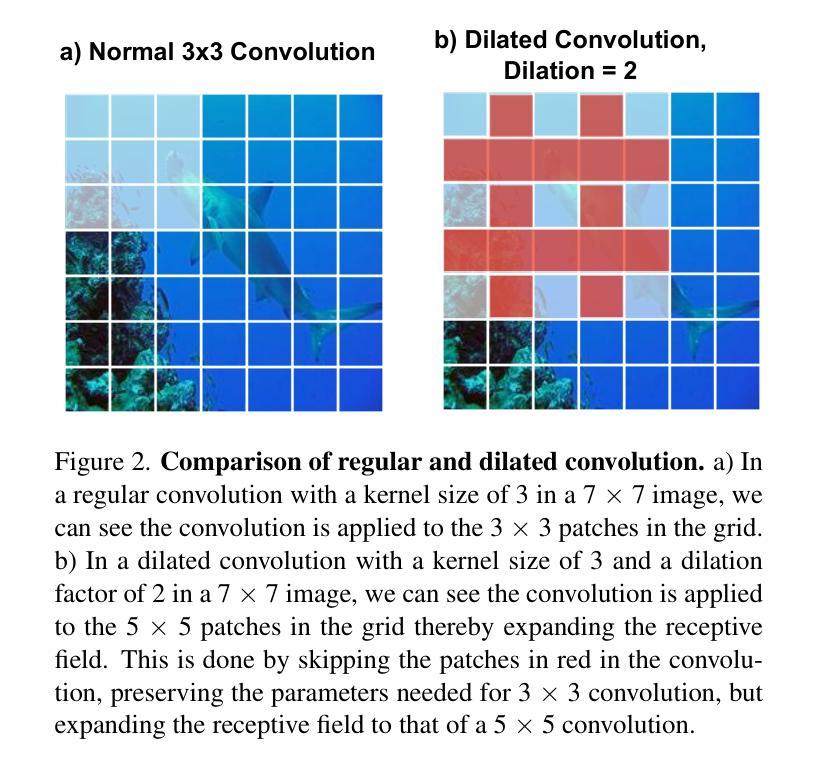
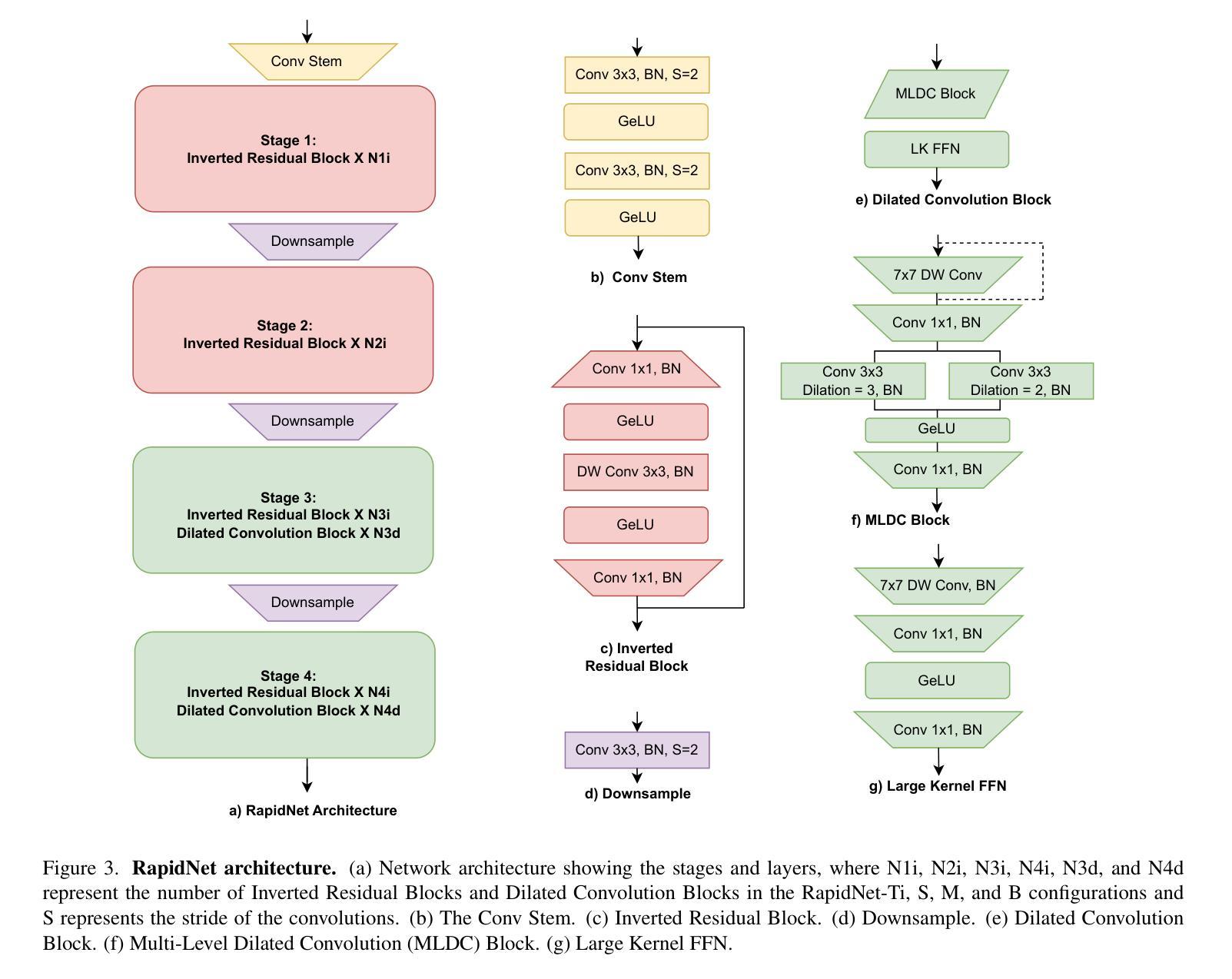
RapidNet: Multi-Level Dilated Convolution Based Mobile Backbone
Authors:Mustafa Munir, Md Mostafijur Rahman, Radu Marculescu
Vision transformers (ViTs) have dominated computer vision in recent years. However, ViTs are computationally expensive and not well suited for mobile devices; this led to the prevalence of convolutional neural network (CNN) and ViT-based hybrid models for mobile vision applications. Recently, Vision GNN (ViG) and CNN hybrid models have also been proposed for mobile vision tasks. However, all of these methods remain slower compared to pure CNN-based models. In this work, we propose Multi-Level Dilated Convolutions to devise a purely CNN-based mobile backbone. Using Multi-Level Dilated Convolutions allows for a larger theoretical receptive field than standard convolutions. Different levels of dilation also allow for interactions between the short-range and long-range features in an image. Experiments show that our proposed model outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) mobile CNN, ViT, ViG, and hybrid architectures in terms of accuracy and/or speed on image classification, object detection, instance segmentation, and semantic segmentation. Our fastest model, RapidNet-Ti, achieves 76.3% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1K with 0.9 ms inference latency on an iPhone 13 mini NPU, which is faster and more accurate than MobileNetV2x1.4 (74.7% top-1 with 1.0 ms latency). Our work shows that pure CNN architectures can beat SOTA hybrid and ViT models in terms of accuracy and speed when designed properly.
视觉变压器(ViTs)在近年来主宰了计算机视觉领域。然而,ViTs计算量大,不适合用于移动设备,这导致了卷积神经网络(CNN)和基于ViT的混合模型在手机视觉应用的盛行。最近,针对移动视觉任务,还提出了Vision GNN(ViG)和CNN混合模型。然而,所有这些方法相比于纯CNN模型仍然较慢。在这项工作中,我们提出多级膨胀卷积来开发纯CNN的移动端主干网。使用多级膨胀卷积可以产生比标准卷积更大的理论感受野。不同级别的膨胀也允许图像中短程和远程特征之间的交互。实验表明,我们提出的模型在图像分类、目标检测、实例分割和语义分割方面,准确度和/或速度超过了最先进的移动CNN、ViT、ViG以及混合架构。我们的最快模型RapidNet-Ti在iPhone 13 mini NPU上实现了ImageNet-1K的76.3% top-1准确率,并且推理延迟时间为0.9毫秒,比MobileNetV2x1.4更快(MobileNetV2x1.4的top-1准确率为74.7%,延迟时间为1.0毫秒)。我们的工作表明,当设计得当的时候,纯CNN架构可以在准确度和速度上击败最先进的混合和ViT模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted in 2025 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV 2025)
Summary
本文介绍了在计算机视觉领域,尽管Vision Transformers(ViTs)近年来占据主导地位,但由于计算成本高且不适合移动设备,促使了卷积神经网络(CNN)和ViT混合模型在移动视觉应用中的普及。文章提出了一种基于多层次膨胀卷积的纯CNN移动骨干网模型,该模型能够在理论上接受更大的感受野并实现长短距离特征的交互。实验表明,该模型在图像分类、目标检测、实例分割和语义分割方面优于现有技术(SOTA)的移动CNN、ViT、ViG及混合架构。尤其是RapidNet-Ti模型,在iPhone 13 mini NPU上的推理延迟时间仅为0.9毫秒,实现了ImageNet-1K上的76.3% top-1准确率,相较于MobileNetV2x1.4更为快速和准确。
Key Takeaways
- Vision transformers (ViTs) 虽然主导计算机视觉领域,但由于计算成本高及移动设备兼容性差,仍需要改进。
- 混合模型和纯CNN模型在移动视觉任务中受到关注,其中纯CNN模型具有计算效率高的优势。
- 提出的多层次膨胀卷积模型能够扩大理论上的感受野并促进长短距离特征的交互。
- 该模型在多项视觉任务上表现超越现有技术(SOTA)的CNN、ViT和混合模型。
- RapidNet-Ti模型在ImageNet-1K上的准确率达到了76.3%,并且在iPhone 13 mini NPU上的推理延迟极低,为0.9毫秒。
- 该研究证明了设计得当的纯CNN模型可以在准确率和速度上超越混合模型和ViT模型。
点此查看论文截图

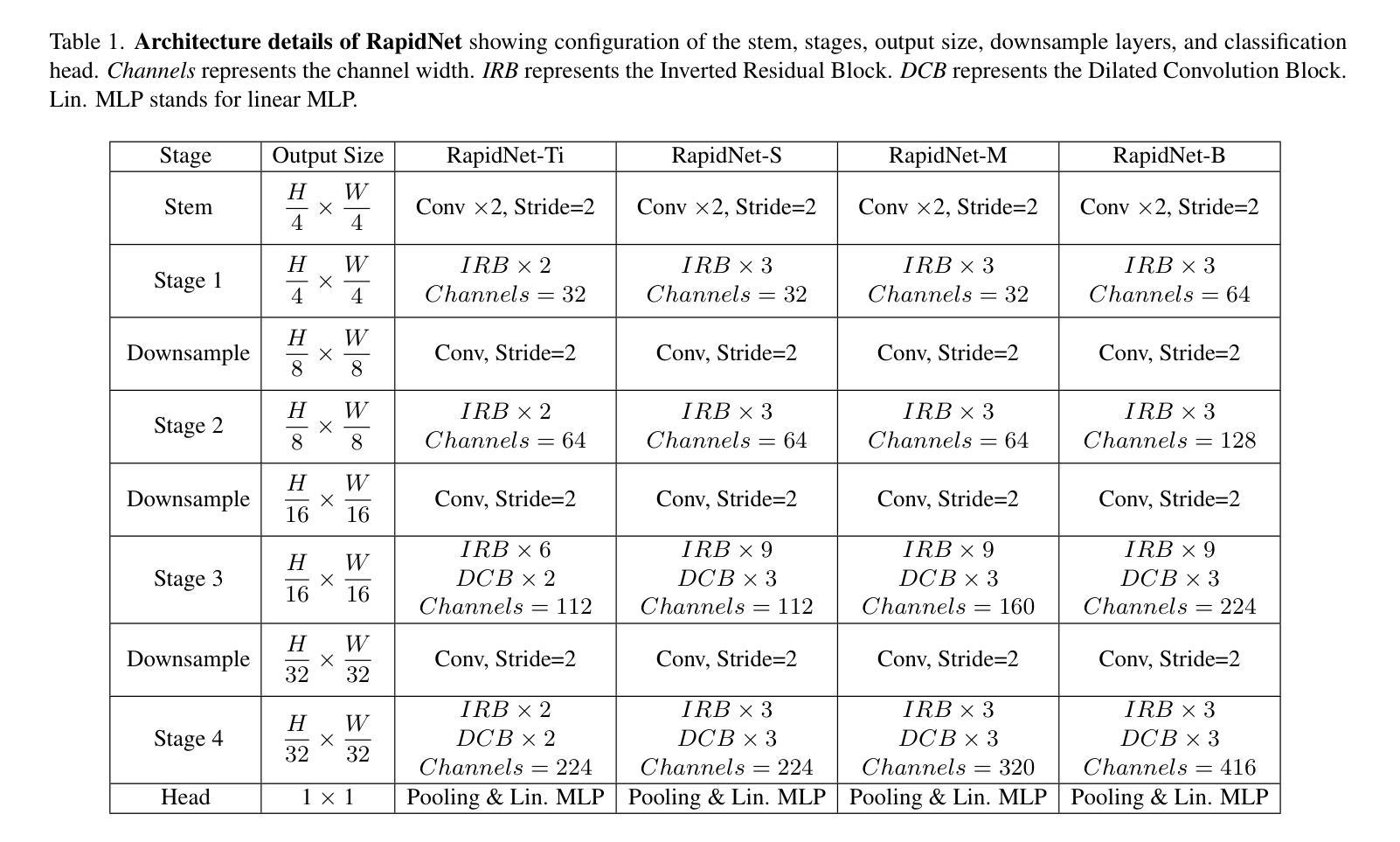
Learning Semantic-Aware Representation in Visual-Language Models for Multi-Label Recognition with Partial Labels
Authors:Haoxian Ruan, Zhihua Xu, Zhijing Yang, Yongyi Lu, Jinghui Qin, Tianshui Chen
Multi-label recognition with partial labels (MLR-PL), in which only some labels are known while others are unknown for each image, is a practical task in computer vision, since collecting large-scale and complete multi-label datasets is difficult in real application scenarios. Recently, vision language models (e.g. CLIP) have demonstrated impressive transferability to downstream tasks in data limited or label limited settings. However, current CLIP-based methods suffer from semantic confusion in MLR task due to the lack of fine-grained information in the single global visual and textual representation for all categories. In this work, we address this problem by introducing a semantic decoupling module and a category-specific prompt optimization method in CLIP-based framework. Specifically, the semantic decoupling module following the visual encoder learns category-specific feature maps by utilizing the semantic-guided spatial attention mechanism. Moreover, the category-specific prompt optimization method is introduced to learn text representations aligned with category semantics. Therefore, the prediction of each category is independent, which alleviate the semantic confusion problem. Extensive experiments on Microsoft COCO 2014 and Pascal VOC 2007 datasets demonstrate that the proposed framework significantly outperforms current state-of-art methods with a simpler model structure. Additionally, visual analysis shows that our method effectively separates information from different categories and achieves better performance compared to CLIP-based baseline method.
多标签识别(MLR)是一项实际应用中的计算机视觉任务,特别是在部分标签情况下(MLR-PL),对于每张图像只有部分标签是已知的,而其他标签是未知的。在实际应用场景中,收集大规模且完整的多标签数据集是非常困难的。最近,视觉语言模型(例如CLIP)在数据有限或标签有限的情况下已经显示出对下游任务的惊人可迁移性。然而,当前的CLIP方法在多标签识别任务中会遇到语义混淆的问题,这主要是因为缺乏所有类别的精细粒度信息在单一全局视觉和文本表示中。在这项工作中,我们通过引入语义解耦模块和类别特定提示优化方法在CLIP框架内解决此问题。具体来说,紧随视觉编码器的语义解耦模块通过利用语义引导的空间注意力机制学习特定类别的特征映射。此外,我们引入了类别特定的提示优化方法来学习与类别语义对齐的文本表示。因此,每个类别的预测都是独立的,这减轻了语义混淆的问题。在Microsoft COCO 2014和Pascal VOC 2007数据集上的大量实验表明,所提出的框架以更简单的模型结构显著优于当前最先进的方法。此外,视觉分析表明,我们的方法有效地分离了不同类别的信息,并且相较于CLIP基准方法取得了更好的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing Communications and Applications
Summary
多标签识别任务在实际应用中面临挑战,如数据收集和标签收集的困难。本研究针对CLIP模型在MLR任务中的语义混淆问题,提出了语义解耦模块和类别特定提示优化方法。通过语义解耦模块和类别特定提示学习,预测每个类别的独立性得以增强,缓解了语义混淆问题。实验结果表明,该方法在Microsoft COCO和Pascal VOC数据集上显著优于现有方法,且模型结构更简单。
Key Takeaways
- 多标签识别任务在实际应用中具有挑战性,因为难以收集大规模且完整的多标签数据集。
- CLIP模型在MLR任务中存在语义混淆问题。
- 本研究提出了语义解耦模块来解决上述问题,该模块利用语义引导的空间注意力机制学习特定类别的特征图。
- 通过引入类别特定提示优化方法,使文本表示与类别语义对齐。
- 方法通过预测每个类别的独立性来缓解语义混淆问题。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在Microsoft COCO和Pascal VOC数据集上显著优于现有方法。
点此查看论文截图



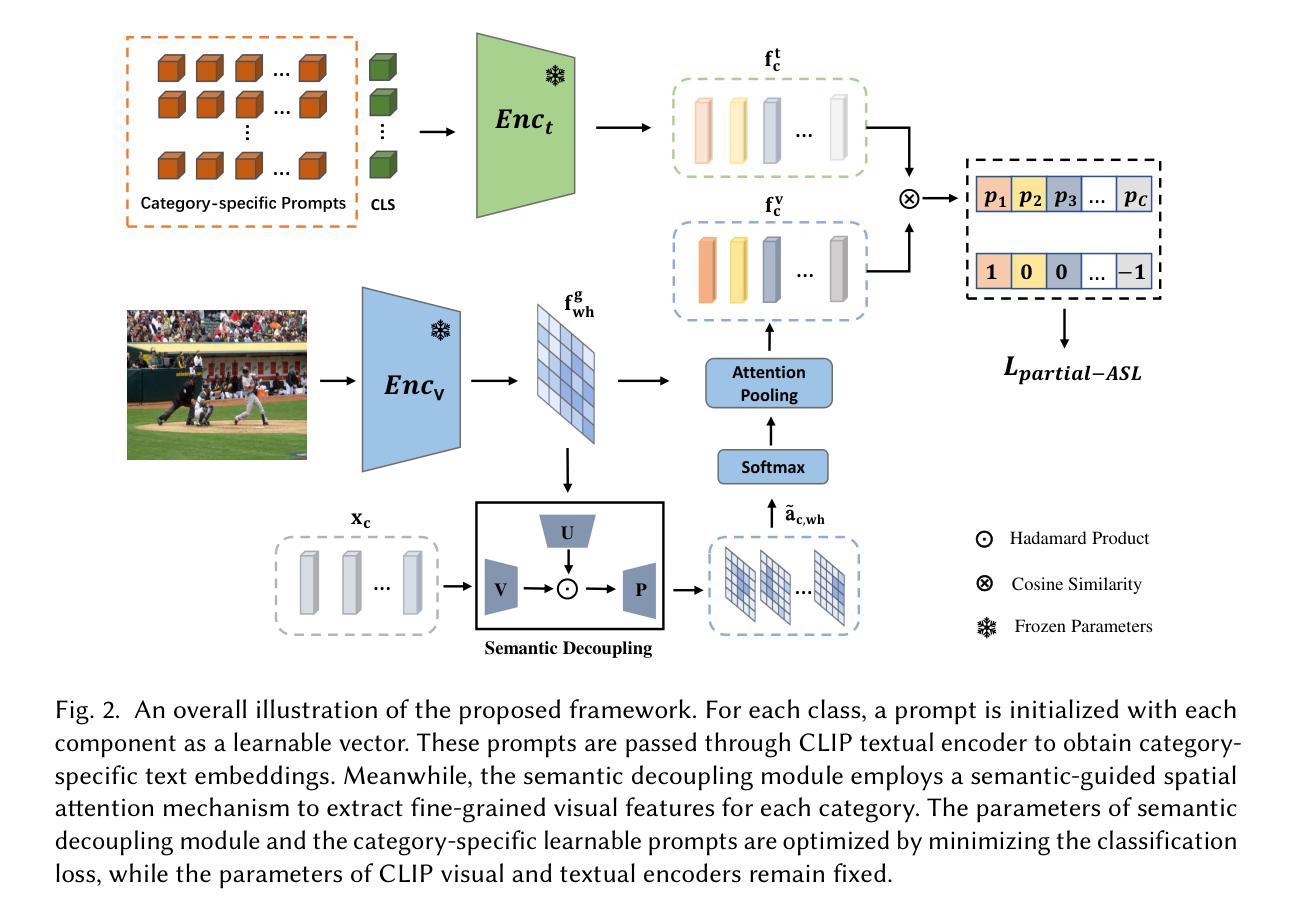
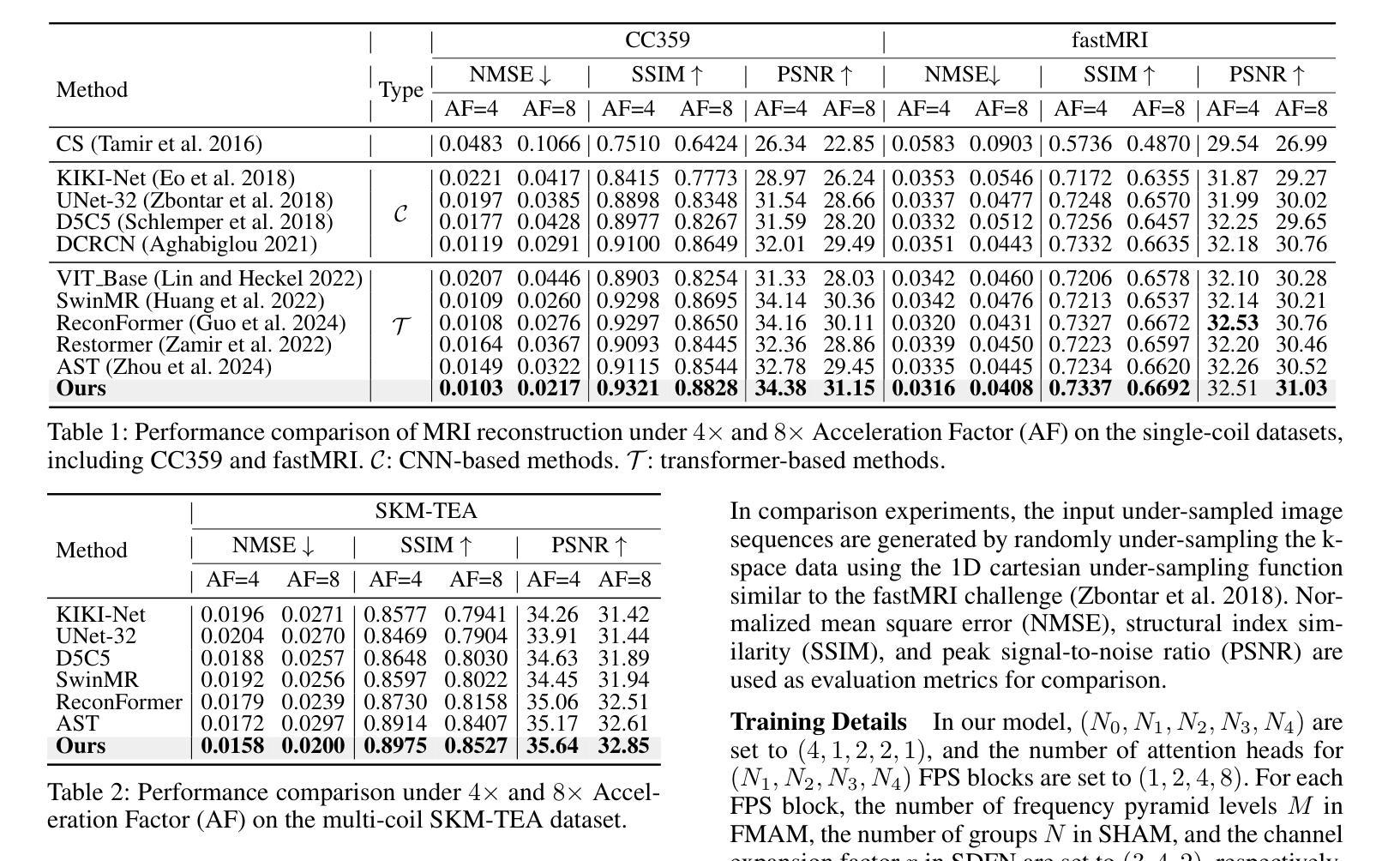
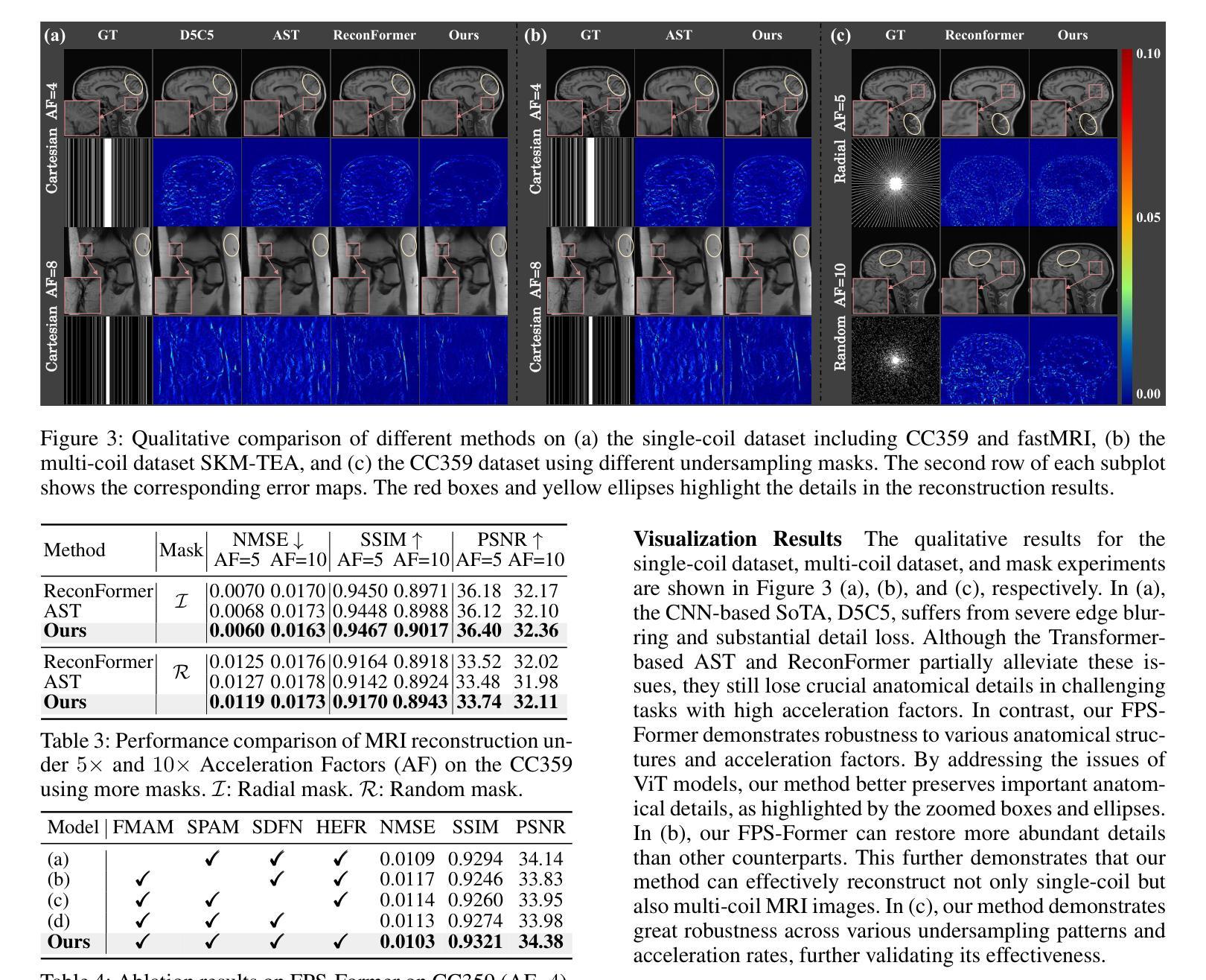
Boosting ViT-based MRI Reconstruction from the Perspectives of Frequency Modulation, Spatial Purification, and Scale Diversification
Authors:Yucong Meng, Zhiwei Yang, Yonghong Shi, Zhijian Song
The accelerated MRI reconstruction process presents a challenging ill-posed inverse problem due to the extensive under-sampling in k-space. Recently, Vision Transformers (ViTs) have become the mainstream for this task, demonstrating substantial performance improvements. However, there are still three significant issues remain unaddressed: (1) ViTs struggle to capture high-frequency components of images, limiting their ability to detect local textures and edge information, thereby impeding MRI restoration; (2) Previous methods calculate multi-head self-attention (MSA) among both related and unrelated tokens in content, introducing noise and significantly increasing computational burden; (3) The naive feed-forward network in ViTs cannot model the multi-scale information that is important for image restoration. In this paper, we propose FPS-Former, a powerful ViT-based framework, to address these issues from the perspectives of frequency modulation, spatial purification, and scale diversification. Specifically, for issue (1), we introduce a frequency modulation attention module to enhance the self-attention map by adaptively re-calibrating the frequency information in a Laplacian pyramid. For issue (2), we customize a spatial purification attention module to capture interactions among closely related tokens, thereby reducing redundant or irrelevant feature representations. For issue (3), we propose an efficient feed-forward network based on a hybrid-scale fusion strategy. Comprehensive experiments conducted on three public datasets show that our FPS-Former outperforms state-of-the-art methods while requiring lower computational costs.
加速MRI重建过程呈现了一个挑战性的不适定逆问题,这是由于k空间中的大量欠采样造成的。最近,视觉转换器(ViTs)已成为这项任务的主流,显示出显著的性能改进。然而,仍然存在三个重大问题需要解决:(1)ViT在捕获图像的高频成分方面存在困难,这限制了它们检测局部纹理和边缘信息的能力,从而阻碍了MRI的重建;(2)之前的方法在计算内容和无关标记之间的多头自注意力(MSA)时引入了噪声,并显著增加了计算负担;(3)ViT中的简单前馈网络无法对图像重建至关重要的多尺度信息进行建模。针对这些问题,本文提出了FPS-Former,一个基于ViT的强大框架,从频率调制、空间净化和尺度多样化的角度来解决这些问题。具体来说,对于问题(1),我们引入了一个频率调制注意力模块,通过自适应地重新校准拉普拉斯金字塔中的频率信息来增强自注意力图。对于问题(2),我们定制了一个空间净化注意力模块,以捕捉密切相关标记之间的交互,从而减少冗余或无关的特征表示。对于问题(3),我们提出了一种基于混合尺度融合策略的有效前馈网络。在三个公共数据集上进行的综合实验表明,我们的FPS-Former在性能上超越了最新方法,同时计算成本更低。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
该论文针对MRI重建过程中面临的三大挑战,提出了一种基于Vision Transformer(ViT)的FPS-Former框架,通过频率调制、空间净化和尺度多样化来解决这些问题。引入频率调制注意力模块增强自注意力图,定制空间净化注意力模块捕捉相关标记间的交互,并提出基于混合尺度融合策略的高效前馈网络。实验证明,FPS-Former在公共数据集上的表现优于现有方法,同时计算成本更低。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs) 在MRI重建中面临三大挑战:难以捕捉高频成分、多头自注意力计算中的噪声和冗余以及缺乏多尺度信息建模。
- FPS-Former框架通过频率调制、空间净化和尺度多样化来解决这些问题。
- FPS-Former引入频率调制注意力模块,通过自适应调整Laplacian金字塔中的频率信息来增强自注意力图。
- 空间净化注意力模块用于捕捉紧密相关标记间的交互,减少冗余或无关的特征表示。
- 提出一种基于混合尺度融合策略的高效前馈网络。
- 在公共数据集上的实验表明,FPS-Former在性能上优于现有方法,并且计算成本更低。
点此查看论文截图

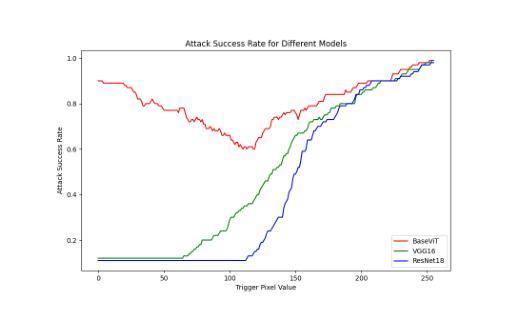
One Pixel is All I Need
Authors:Deng Siqin, Zhou Xiaoyi
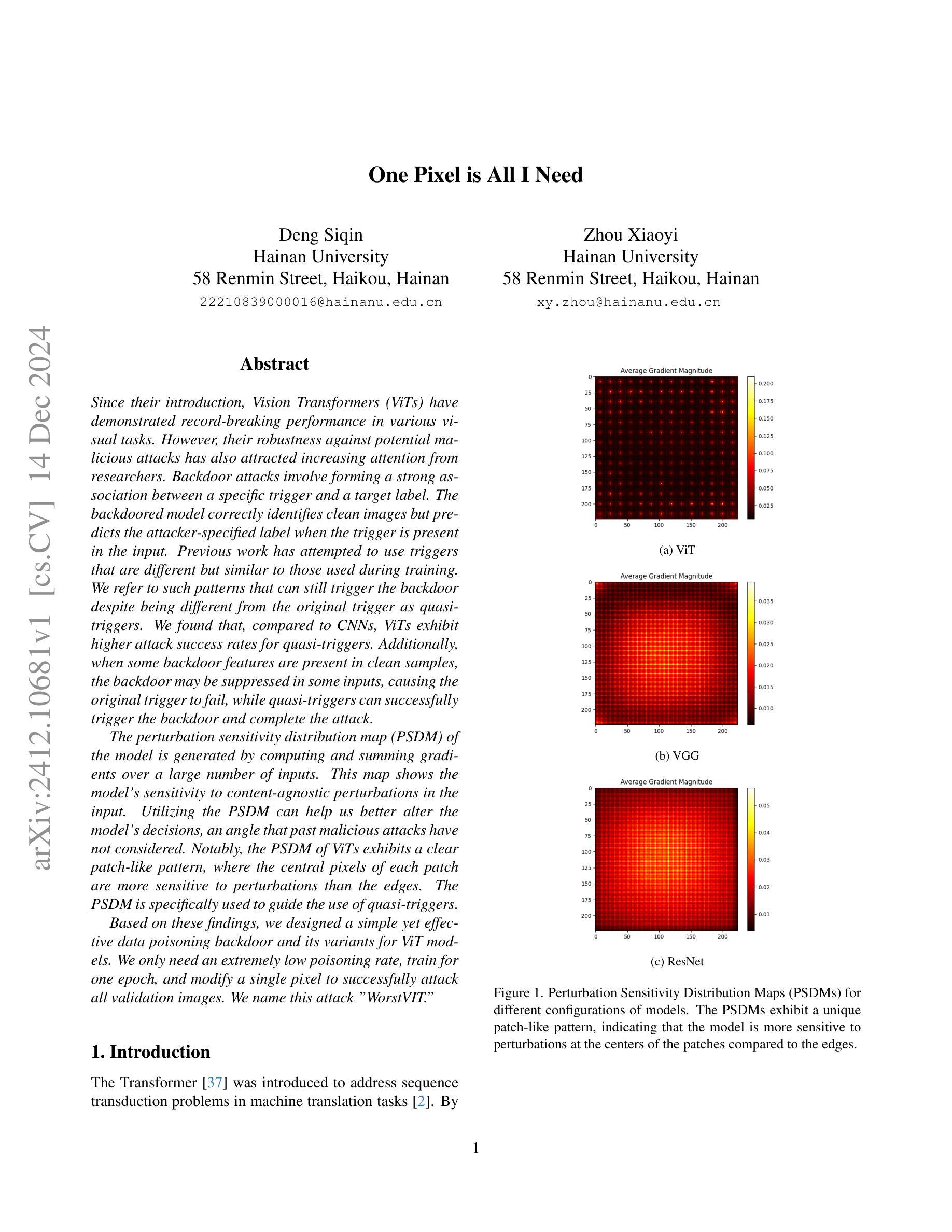
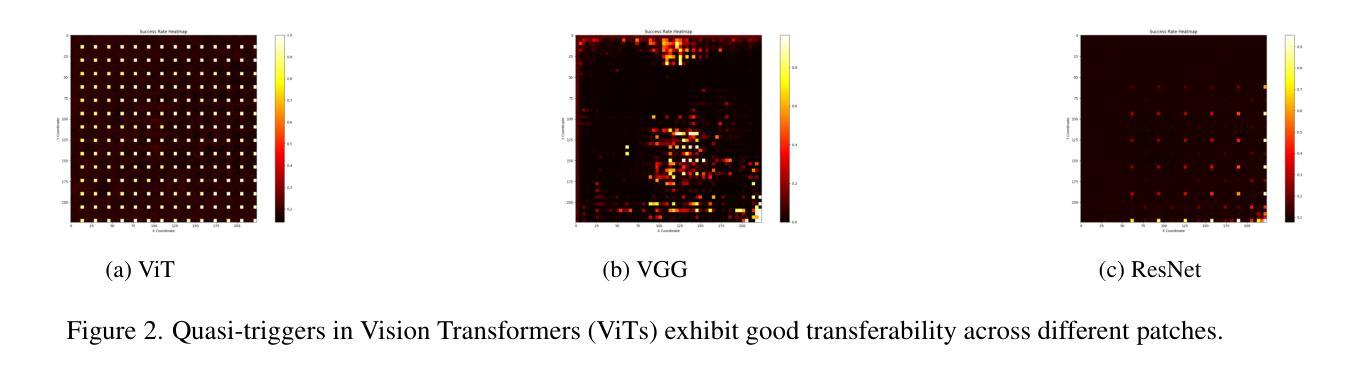
Vision Transformers (ViTs) have achieved record-breaking performance in various visual tasks. However, concerns about their robustness against backdoor attacks have grown. Backdoor attacks involve associating a specific trigger with a target label, causing the model to predict the attacker-specified label when the trigger is present, while correctly identifying clean images.We found that ViTs exhibit higher attack success rates for quasi-triggers(patterns different from but similar to the original training triggers)compared to CNNs. Moreover, some backdoor features in clean samples can suppress the original trigger, making quasi-triggers more effective.To better understand and exploit these vulnerabilities, we developed a tool called the Perturbation Sensitivity Distribution Map (PSDM). PSDM computes and sums gradients over many inputs to show how sensitive the model is to small changes in the input. In ViTs, PSDM reveals a patch-like pattern where central pixels are more sensitive than edges. We use PSDM to guide the creation of quasi-triggers.Based on these findings, we designed “WorstVIT,” a simple yet effective data poisoning backdoor for ViT models. This attack requires an extremely low poisoning rate, trains for just one epoch, and modifies a single pixel to successfully attack all validation images.
视觉Transformer(ViTs)在各种视觉任务中取得了突破性的性能。然而,人们对它们对抗后门攻击的稳健性越来越担忧。后门攻击涉及将特定触发因素与目标标签相关联,当存在触发因素时,导致模型预测攻击者指定的标签,同时正确识别干净图像。我们发现,与CNN相比,ViT对类似但不同于原始训练触发的准触发(模式)表现出更高的攻击成功率。此外,干净样本中的一些后门特征可以抑制原始触发,使准触发更加有效。为了更好地利用这些漏洞,我们开发了一个名为扰动敏感性分布图(PSDM)的工具。PSDM计算并汇总多个输入的梯度,以显示模型对输入微小变化的敏感性。在ViTs中,PSDM揭示了一种类似补丁的模式,其中中央像素比边缘更敏感。我们使用PSDM来指导准触发的创建。基于这些发现,我们设计了“WorstVIT”,这是一种针对ViT模型的简单有效的数据中毒后门。这种攻击需要极低的中毒率,只需一个训练周期,修改一个像素即可成功攻击所有验证图像。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
ViT模型在视觉任务中表现出卓越性能,但其对后门攻击的鲁棒性引发关注。研究发现,ViT对类触发式攻击(quasi-triggers)的防御较弱,且清洁样本中的后门特征可能增强这类攻击效果。为探究这些漏洞,研究团队开发了扰动敏感度分布图(PSDM),揭示ViT模型中央像素对微小变动的敏感度高于边缘。基于这些发现,团队为ViT模型设计了名为“WorstVIT”的简单高效数据毒药后门攻击方法,攻击只需极低的感染率,训练周期短,仅修改单个像素即可成功攻击所有验证图像。
Key Takeaways
- ViT模型对后门攻击(特别是类触发式攻击)的鲁棒性较低。
- 清洁样本中的后门特征可能增强类触发式攻击的效果。
- PSDM工具可揭示模型对输入微小变动的敏感度,为设计类触发式攻击提供指导。
- ViT模型的中央像素对扰动更为敏感。
- “WorstVIT”攻击方法针对ViT模型,具有低感染率、短训练周期及单一像素修改的特点。
- “WorstVIT”攻击能成功影响所有验证图像。
- 研究为增强ViT模型对后门攻击的鲁棒性提供了重要启示。
点此查看论文截图

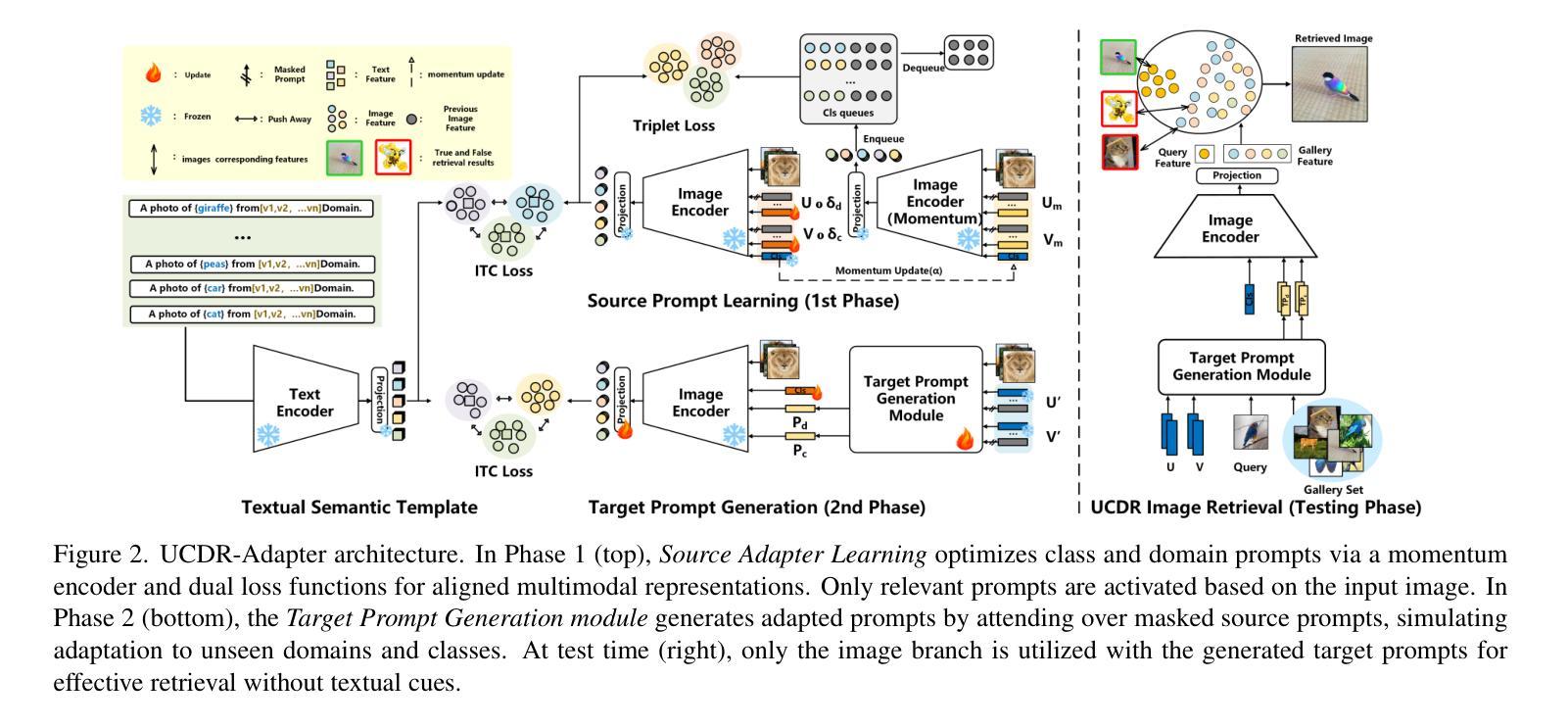
UCDR-Adapter: Exploring Adaptation of Pre-Trained Vision-Language Models for Universal Cross-Domain Retrieval
Authors:Haoyu Jiang, Zhi-Qi Cheng, Gabriel Moreira, Jiawen Zhu, Jingdong Sun, Bukun Ren, Jun-Yan He, Qi Dai, Xian-Sheng Hua
Universal Cross-Domain Retrieval (UCDR) retrieves relevant images from unseen domains and classes without semantic labels, ensuring robust generalization. Existing methods commonly employ prompt tuning with pre-trained vision-language models but are inherently limited by static prompts, reducing adaptability. We propose UCDR-Adapter, which enhances pre-trained models with adapters and dynamic prompt generation through a two-phase training strategy. First, Source Adapter Learning integrates class semantics with domain-specific visual knowledge using a Learnable Textual Semantic Template and optimizes Class and Domain Prompts via momentum updates and dual loss functions for robust alignment. Second, Target Prompt Generation creates dynamic prompts by attending to masked source prompts, enabling seamless adaptation to unseen domains and classes. Unlike prior approaches, UCDR-Adapter dynamically adapts to evolving data distributions, enhancing both flexibility and generalization. During inference, only the image branch and generated prompts are used, eliminating reliance on textual inputs for highly efficient retrieval. Extensive benchmark experiments show that UCDR-Adapter consistently outperforms ProS in most cases and other state-of-the-art methods on UCDR, U(c)CDR, and U(d)CDR settings.
通用跨域检索(UCDR)能够从未见过的领域和类别中检索出相关的图像,而无需语义标签,确保了稳健的泛化能力。现有方法通常采用基于预训练视觉语言模型的提示调整(prompt tuning),但由于静态提示的固有局限性,其适应性较差。我们提出了UCDR-Adapter,它通过两阶段训练策略增强预训练模型,并借助适配器(adapters)和动态提示生成来提高适应性。首先,源适配器学习(Source Adapter Learning)使用可学习的文本语义模板将类别语义与特定领域的视觉知识相结合,并通过动量更新和双损失函数优化类别和领域提示,以实现稳健的对齐。其次,目标提示生成(Target Prompt Generation)通过关注被遮蔽的源提示来创建动态提示,从而实现无缝适应未见过的领域和类别。与先前的方法不同,UCDR-Adapter能够动态适应不断变化的数据分布,提高了灵活性和泛化能力。在推理过程中,仅使用图像分支和生成的提示,消除了对文本输入的依赖,以实现高效的检索。大量的基准实验表明,UCDR-Adapter在大多数情况下均优于ProS和其他在UCDR、U(c)CDR和U(d)CDR设置下的最新方法。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to WACV 2025. Project link: https://github.com/fine68/UCDR2024
Summary
UCDR技术通过动态调整预训练模型,实现了在不同领域和类别中检索相关图像的目标,且无需语义标签即可实现稳健的泛化。该研究提出了UCDR-Adapter方法,通过两阶段训练策略增强预训练模型,包括源适配器学习(集成类别语义和特定领域的视觉知识)和目标提示生成(通过关注掩码源提示来生成动态提示)。这种方法能动态适应不断变化的数据分布,提高了灵活性和泛化能力。在推断时,仅使用图像分支和生成的提示,实现了高效检索。实验表明,UCDR-Adapter在UCDR、U(c)CDR和U(d)CDR设置上均优于其他方法。
Key Takeaways
- UCDR技术能实现在不同领域和类别中检索相关图像,且无需语义标签即可实现稳健的泛化。
- UCDR-Adapter方法通过两阶段训练策略增强预训练模型,包括源适配器学习和目标提示生成。
- 源适配器学习集成类别语义和特定领域的视觉知识,通过优化类提示和域提示来提高模型的适应能力。
- 目标提示生成通过关注掩码源提示来生成动态提示,提高模型的灵活性和泛化能力。
- UCDR-Adapter能动态适应不断变化的数据分布。
- 在推断时,UCDR-Adapter仅使用图像分支和生成的提示,提高了检索效率。
- 实验表明,UCDR-Adapter在多种设置上均优于其他方法。
点此查看论文截图

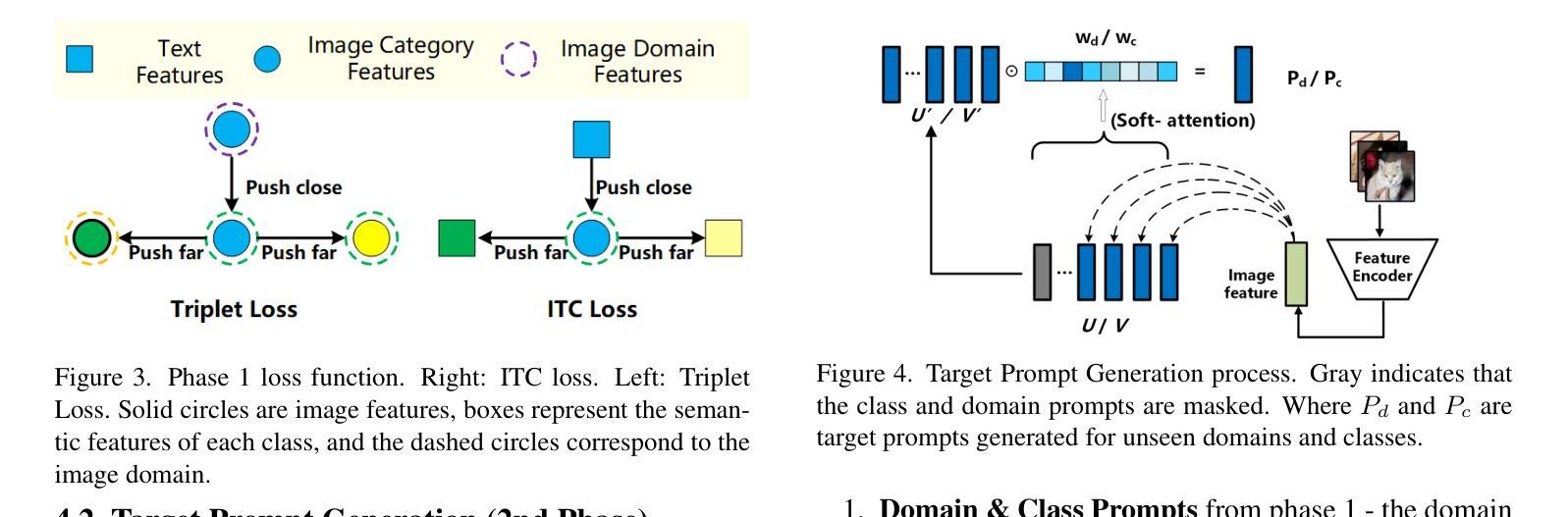
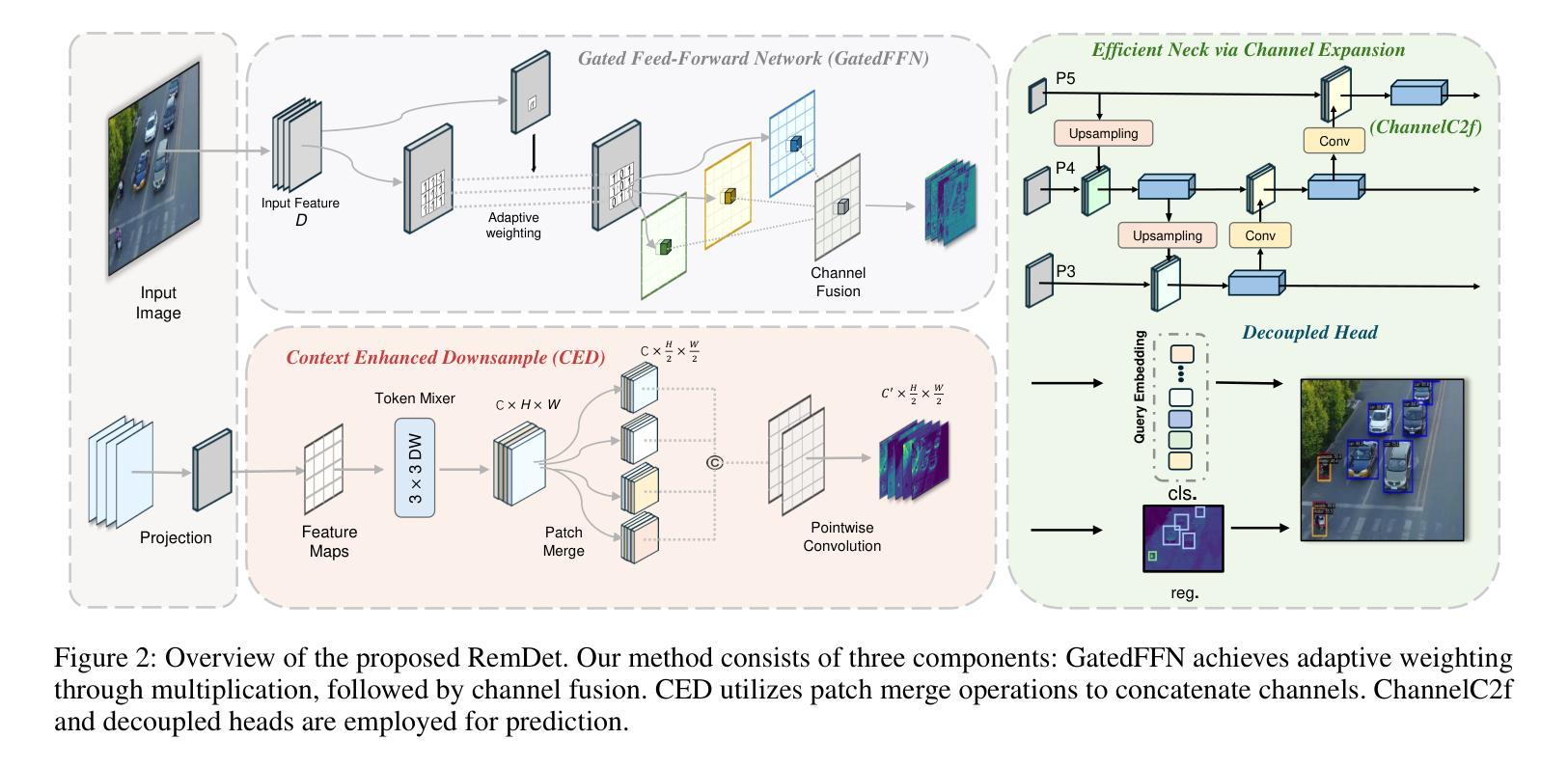
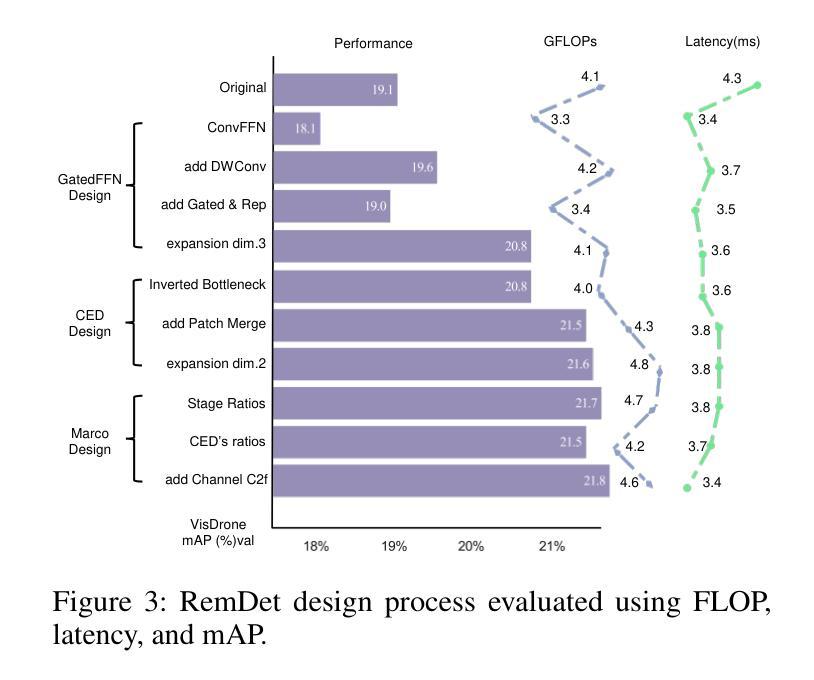
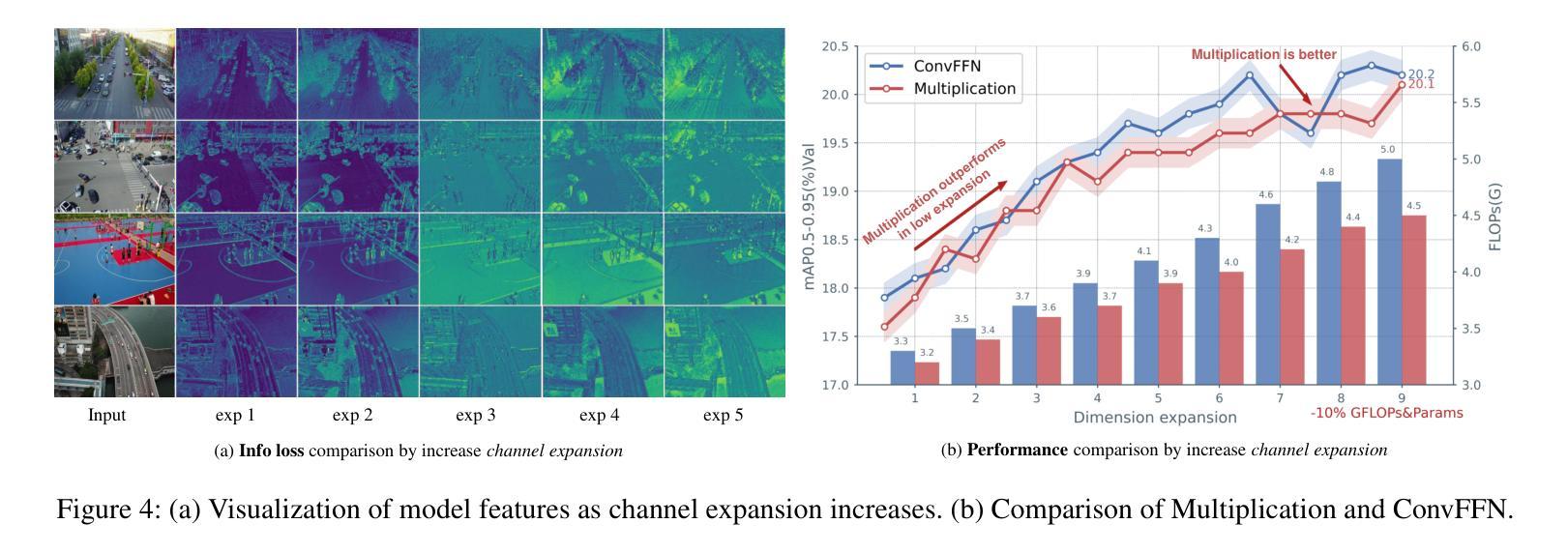
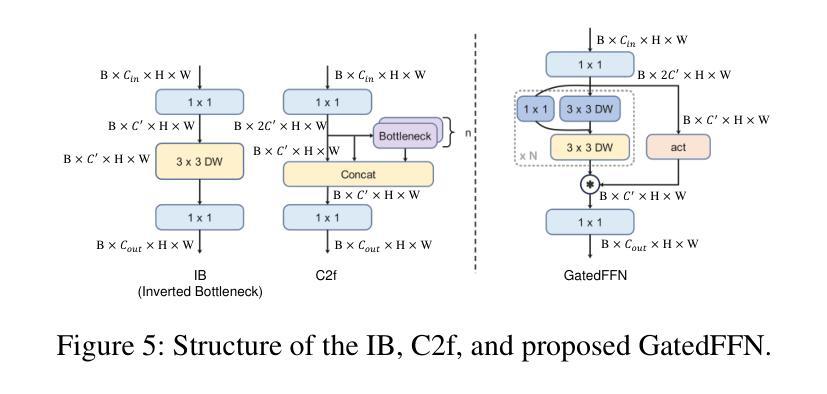
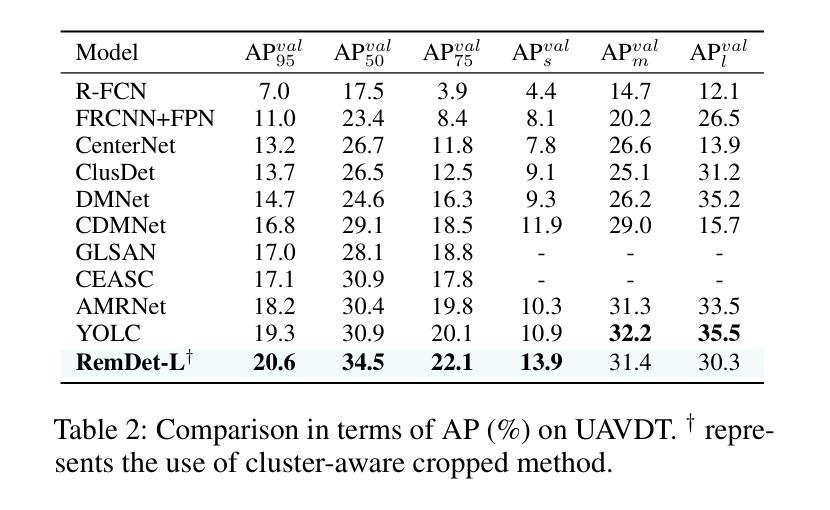
RemDet: Rethinking Efficient Model Design for UAV Object Detection
Authors:Chen Li, Rui Zhao, Zeyu Wang, Huiying Xu, Xinzhong Zhu
Object detection in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) images has emerged as a focal area of research, which presents two significant challenges: i) objects are typically small and dense within vast images; ii) computational resource constraints render most models unsuitable for real-time deployment. Current real-time object detectors are not optimized for UAV images, and complex methods designed for small object detection often lack real-time capabilities. To address these challenges, we propose a novel detector, RemDet (Reparameter efficient multiplication Detector). Our contributions are as follows: 1) Rethinking the challenges of existing detectors for small and dense UAV images, and proposing information loss as a design guideline for efficient models. 2) We introduce the ChannelC2f module to enhance small object detection performance, demonstrating that high-dimensional representations can effectively mitigate information loss. 3) We design the GatedFFN module to provide not only strong performance but also low latency, effectively addressing the challenges of real-time detection. Our research reveals that GatedFFN, through the use of multiplication, is more cost-effective than feed-forward networks for high-dimensional representation. 4) We propose the CED module, which combines the advantages of ViT and CNN downsampling to effectively reduce information loss. It specifically enhances context information for small and dense objects. Extensive experiments on large UAV datasets, Visdrone and UAVDT, validate the real-time efficiency and superior performance of our methods. On the challenging UAV dataset VisDrone, our methods not only provided state-of-the-art results, improving detection by more than 3.4%, but also achieve 110 FPS on a single 4090.
无人机图像中的目标检测已成为研究的核心领域,它面临两大挑战:一、在大型图像中,目标通常较小且密集;二、计算资源限制使得大多数模型不适合实时部署。当前的实时目标检测器并未针对无人机图像进行优化,而为小型目标检测设计的复杂方法往往缺乏实时功能。为了应对这些挑战,我们提出了一种新型检测器——RemDet(重参数高效乘法检测器)。我们的贡献如下:
一、重新思考现有检测器在小型且密集的无人机图像中的挑战,并提出信息损失作为设计高效模型的重要指导原则。
二、我们引入了ChannelC2f模块,以提高小型目标检测性能,证明高维表示可以有效地减轻信息损失。
三、我们设计了GatedFFN模块,不仅性能强大,而且延迟低,有效地解决了实时检测的挑战。我们的研究表明,通过乘法使用,GatedFFN的成本效益高于前馈网络用于高维表示。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted to AAAI25
Summary
本文介绍了针对无人机图像目标检测面临的挑战,提出了一种新型检测器RemDet。该检测器通过优化模型设计以减小信息损失,引入ChannelC2f模块增强小目标检测性能,设计GatedFFN模块实现强性能与低延迟的实时检测,并结合ViT和CNN下采样的优势提出CED模块来减少信息损失并增强上下文信息。在大型无人机数据集Visdrone和UAVDT上的实验验证了其方法的实时效率和卓越性能。
Key Takeaways
- 无人机图像目标检测面临小目标和计算资源限制两大挑战。
- 提出新型检测器RemDet,针对无人机图像特点进行优化。
- 引入ChannelC2f模块增强小目标检测性能。
- 设计GatedFFN模块实现实时高性能检测,并通过乘法降低成本。
- 结合ViT和CNN下采样的优点,提出CED模块减少信息损失并增强上下文信息。
- 在大型无人机数据集上的实验验证了方法的实时效率和优越性。
点此查看论文截图


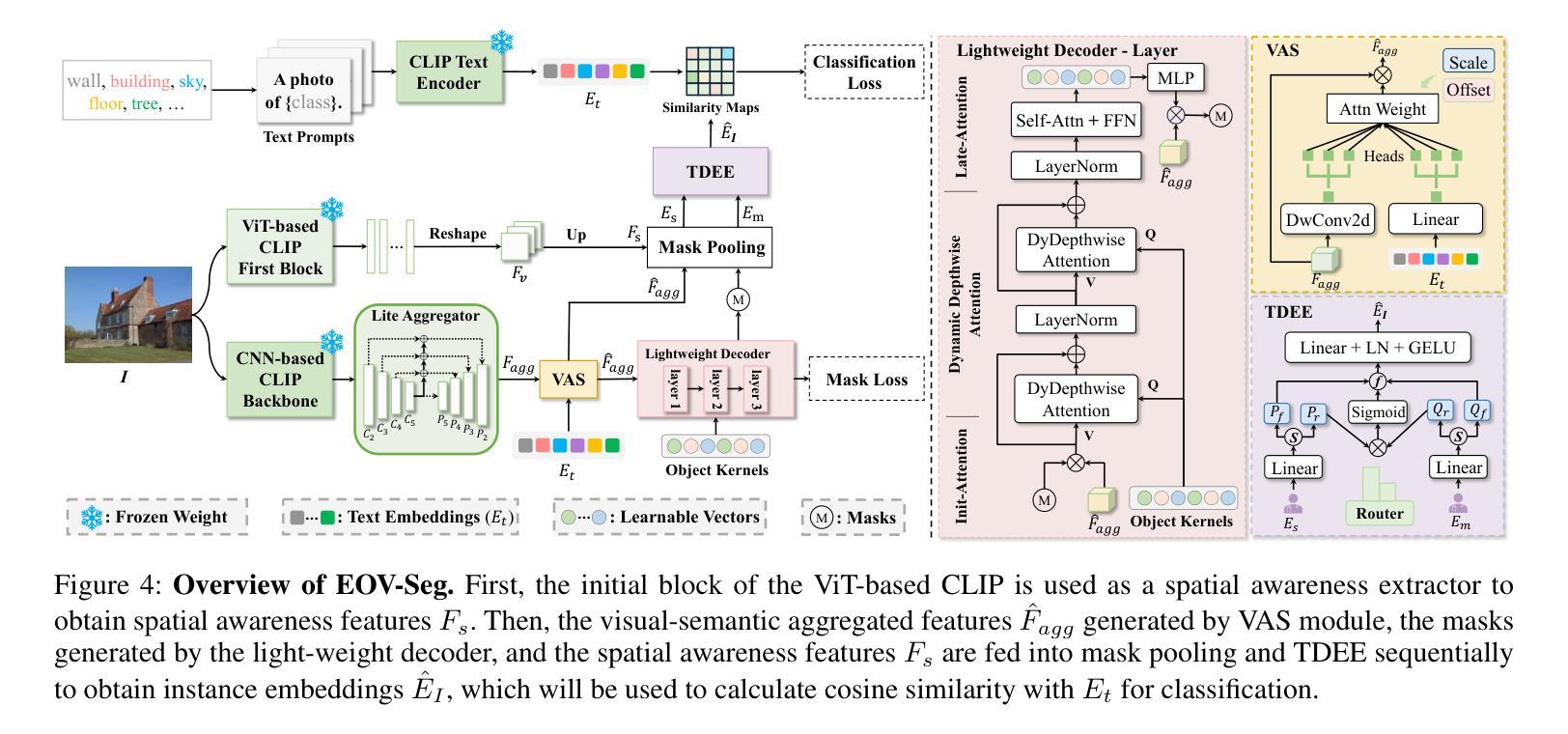
EOV-Seg: Efficient Open-Vocabulary Panoptic Segmentation
Authors:Hongwei Niu, Jie Hu, Jianghang Lin, Guannan Jiang, Shengchuan Zhang
Open-vocabulary panoptic segmentation aims to segment and classify everything in diverse scenes across an unbounded vocabulary. Existing methods typically employ two-stage or single-stage framework. The two-stage framework involves cropping the image multiple times using masks generated by a mask generator, followed by feature extraction, while the single-stage framework relies on a heavyweight mask decoder to make up for the lack of spatial position information through self-attention and cross-attention in multiple stacked Transformer blocks. Both methods incur substantial computational overhead, thereby hindering the efficiency of model inference. To fill the gap in efficiency, we propose EOV-Seg, a novel single-stage, shared, efficient, and spatialaware framework designed for open-vocabulary panoptic segmentation. Specifically, EOV-Seg innovates in two aspects. First, a Vocabulary-Aware Selection (VAS) module is proposed to improve the semantic comprehension of visual aggregated features and alleviate the feature interaction burden on the mask decoder. Second, we introduce a Two-way Dynamic Embedding Experts (TDEE), which efficiently utilizes the spatial awareness capabilities of ViT-based CLIP backbone. To the best of our knowledge, EOV-Seg is the first open-vocabulary panoptic segmentation framework towards efficiency, which runs faster and achieves competitive performance compared with state-of-the-art methods. Specifically, with COCO training only, EOV-Seg achieves 24.5 PQ, 32.1 mIoU, and 11.6 FPS on the ADE20K dataset and the inference time of EOV-Seg is 4-19 times faster than state-of-theart methods. Especially, equipped with ResNet50 backbone, EOV-Seg runs 23.8 FPS with only 71M parameters on a single RTX 3090 GPU. Code is available at https://github.com/nhw649/EOV-Seg.
开放词汇全景分割旨在分割并分类无限词汇表中不同场景中的所有内容。现有方法通常采用两阶段或单阶段框架。两阶段框架涉及使用由掩膜生成器生成的掩膜多次裁剪图像,然后进行特征提取,而单阶段框架则依赖于重量级的掩膜解码器,通过自注意力和交叉注意力在多个堆叠的Transformer块中进行空间位置信息的补偿。这两种方法都会产生大量的计算开销,从而阻碍了模型推理的效率。为了弥补效率上的差距,我们提出了EOV-Seg,这是一种为开放词汇全景分割设计的新型单阶段、共享、高效且空间感知的框架。具体来说,EOV-Seg在两个方面进行了创新。首先,提出了词汇感知选择(VAS)模块,以提高视觉聚合特征语义理解能力并减轻掩膜解码器上的特征交互负担。其次,我们引入了双向动态嵌入专家(TDEE),它有效地利用了基于ViT的CLIP骨干网的空间感知能力。据我们所知,EOV-Seg是面向效率的第一个开放词汇全景分割框架,与最先进的方法相比,它运行更快并实现了具有竞争力的性能。具体来说,仅在COCO训练集上,EOV-Seg在ADE20K数据集上实现了24.5的PQ,32.1的mIoU和11.6的FPS,并且EOV-Seg的推理时间是现有先进方法的4-19倍。特别是,配备ResNet50骨干网时,EOV-Seg在单个RTX 3090 GPU上仅使用71M参数即可运行23.8 FPS。代码可在https://github.com/nhw649/EOV-Seg找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
Summary
该文本介绍了开放词汇全景分割的挑战及现有方法的不足。为解决这些问题,提出了一种名为EOV-Seg的新型单阶段、共享、高效的空间感知框架。EOV-Seg通过VAS模块改进视觉聚合特征语义理解,并引入TDEE模块有效利用ViT-based CLIP主干的时空感知能力。相比其他先进方法,EOV-Seg运行更快,性能更具竞争力。
Key Takeaways
- 开放词汇全景分割旨在分割和分类多样场景中的所有内容,面对无限词汇的挑战。
- 现有方法通常采用两阶段或单阶段框架,存在计算开销大、效率不高的问题。
- EOV-Seg是一个新型的单阶段、共享、高效的空间感知框架,用于开放词汇全景分割。
- EOV-Seg通过VAS模块改进了语义理解的聚合特征,减轻了mask解码器的特征交互负担。
- TDEE模块的引入实现了ViT-based CLIP主干的时空感知能力的有效利用。
- EOV-Seg相比其他先进方法运行更快,性能更具竞争力,特别是在ADE20K数据集上的表现。
点此查看论文截图


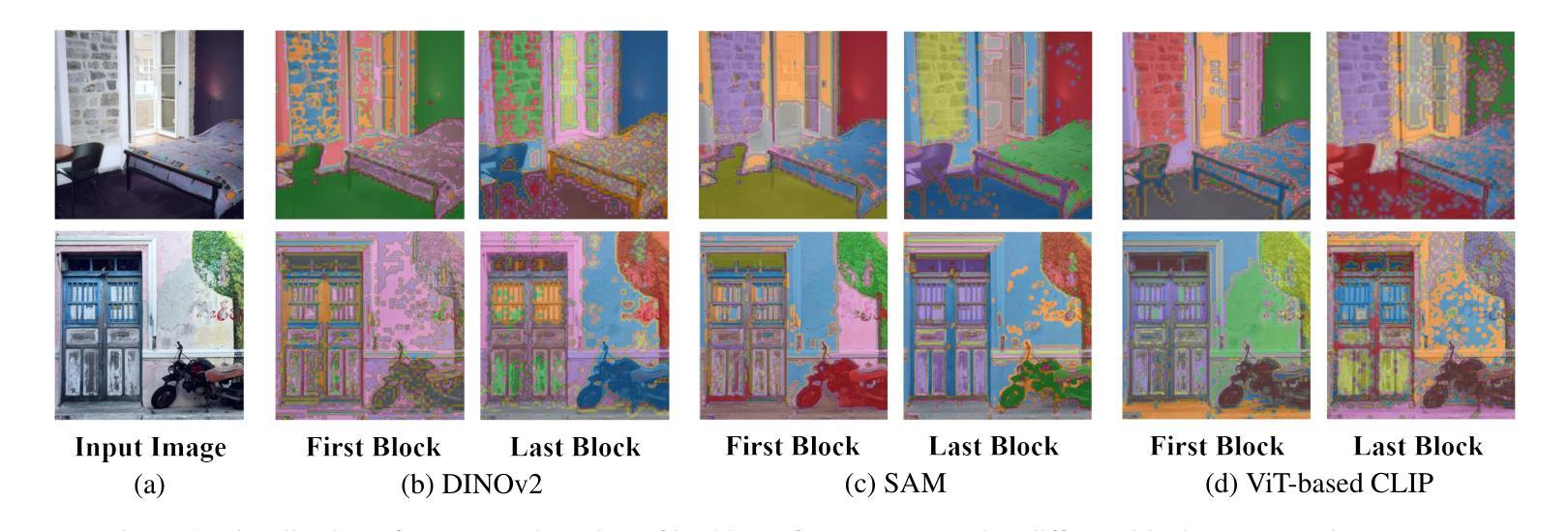
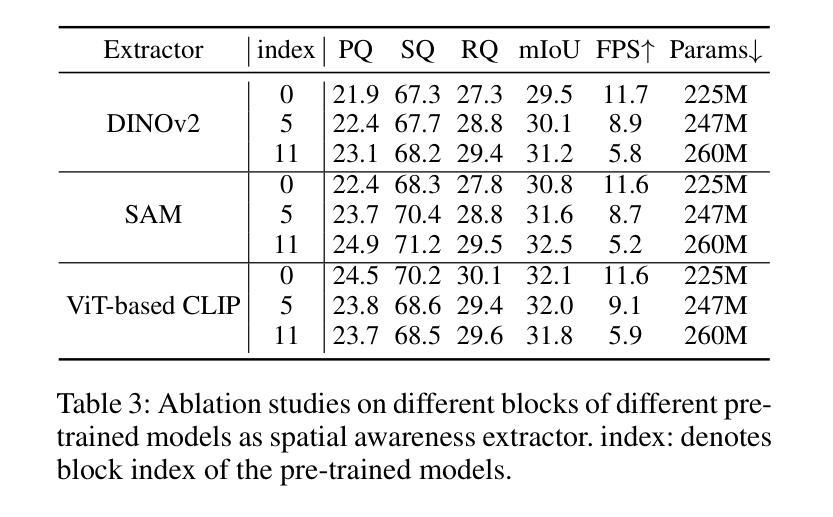
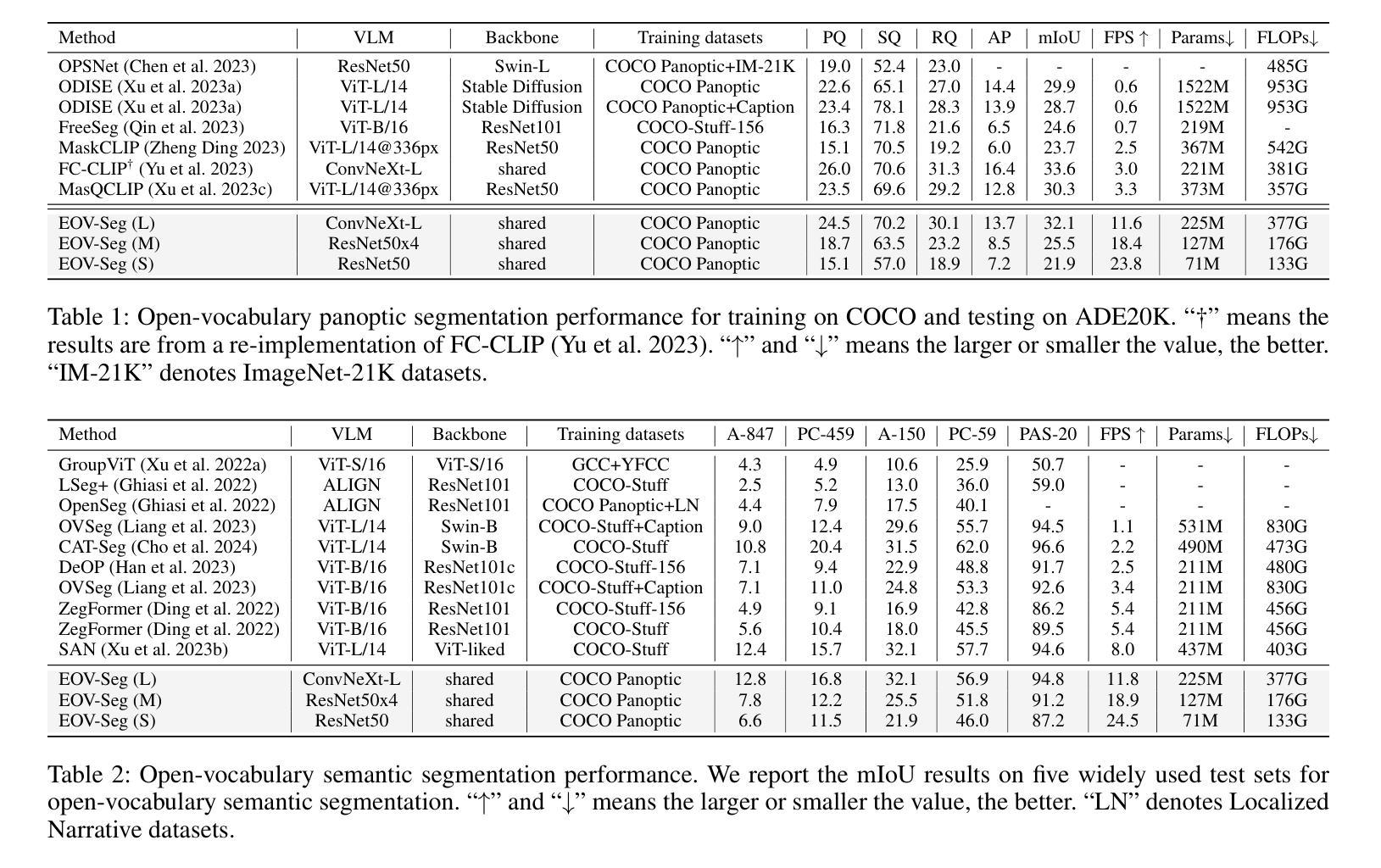
Can Graph Neural Networks Learn Language with Extremely Weak Text Supervision?
Authors:Zihao Li, Lecheng Zheng, Bowen Jin, Dongqi Fu, Baoyu Jing, Yikun Ban, Jingrui He, Jiawei Han
While great success has been achieved in building vision models with Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) over Internet-scale image-text pairs, building transferable Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) with CLIP pipeline is challenging because of three fundamental issues: the scarcity of labeled data and text supervision, different levels of downstream tasks, and the conceptual gaps between domains. In this work, to address these issues, we leverage multi-modal prompt learning to effectively adapt pre-trained GNN to downstream tasks and data, given only a few semantically labeled samples, each with extremely weak text supervision. Our new paradigm embeds the graphs directly in the same space as the Large Language Models (LLMs) by learning both graph prompts and text prompts simultaneously. To accomplish this, we improve state-of-the-art graph prompt method, and then propose the first graph-language multi-modal prompt learning approach for exploiting the knowledge in pre-trained models. Notably, due to the insufficient supervision for fine-tuning, in our paradigm, the pre-trained GNN and the LLM are kept frozen, so the learnable parameters are much fewer than fine-tuning any pre-trained model. Through extensive experiments on real-world datasets, we demonstrate the superior performance of our paradigm in few-shot, multi-task-level, and cross-domain settings. Moreover, we build the first CLIP-style zero-shot classification prototype that can generalize GNNs to unseen classes with extremely weak text supervision.
在利用对比语言图像预训练(CLIP)在互联网规模的图像文本对上构建视觉模型取得巨大成功的同时,使用CLIP管道构建可迁移的图神经网络(GNN)面临三大挑战:缺乏标注数据和文本监督、下游任务级别不同以及领域间的概念差距。在这项工作中,为了解决这些问题,我们利用多模态提示学习来有效地适应预训练GNN到下游任务和数据,仅使用少量语义标注样本,每个样本都带有极弱的文本监督。我们的新范式通过将图直接嵌入与大型语言模型(LLM)相同的空间,同时学习图提示和文本提示。为了完成这项工作,我们改进了最先进的图提示方法,然后提出了第一个利用预训练模型知识的图-语言多模态提示学习方法。值得注意的是,由于精细调整的监督不足,在我们的范式中,预训练的GNN和LLM保持不变,因此可学习参数远远少于对任何预训练模型的精细调整。通过在实际数据集上的大量实验,我们证明了我们的范式在少样本、多任务级别和跨域设置中的卓越性能。此外,我们构建了第一个CLIP风格的零样本分类原型,可以将GNN推广到未见过的类别,带有极弱的文本监督。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Preprint, 25 pages
Summary
该研究针对CLIP管道在构建可迁移的图形神经网络(GNNs)时面临的挑战,通过多模态提示学习来适应下游任务和数据的预训练GNN。该研究解决了数据标签稀缺、文本监督不足、下游任务级别不同以及领域间概念差距等问题。通过改进最先进的图形提示方法,该研究提出了利用预训练模型知识的首个图形语言多模态提示学习方法。此外,该研究建立了首个CLIP风格的零样本分类原型,可以推广到未见过的类别,只需极弱的文本监督即可。这项研究在保证足够的样本量的前提下解决了各种场景下的问题,并展示了其优越的性能。
Key Takeaways
以下是基于文本的关键见解:
- CLIP模型在互联网规模的图像文本对上构建视觉模型取得了巨大成功,但在构建可迁移的图形神经网络(GNNs)时面临挑战。挑战包括缺乏标注数据和文本监督、下游任务级别不同以及领域间的概念差距。
- 研究采用多模态提示学习来解决这些问题,使得预训练的GNN能够适应下游任务和只有少量语义标注样本的数据。该研究方法改进了最新的图形提示方法并提出了首个图形语言多模态提示学习方法。该方法通过在预训练模型中嵌入图来学习图提示和文本提示,将图与大型语言模型(LLM)置于同一空间。由于监督不足,该研究在模式中保持预训练的GNN和LLM冻结状态,减少了学习参数的数量。这一方法在少样本、多任务级别和跨域设置上展示了优越的性能。
点此查看论文截图
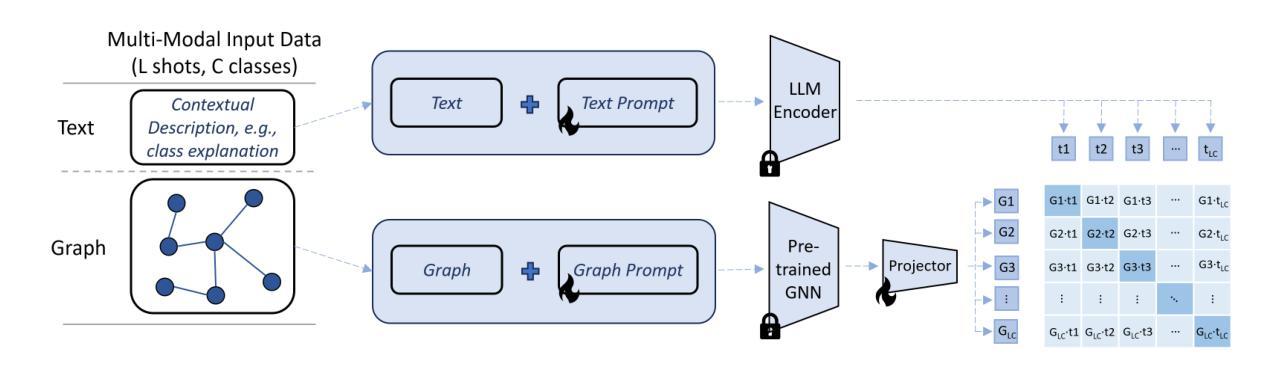
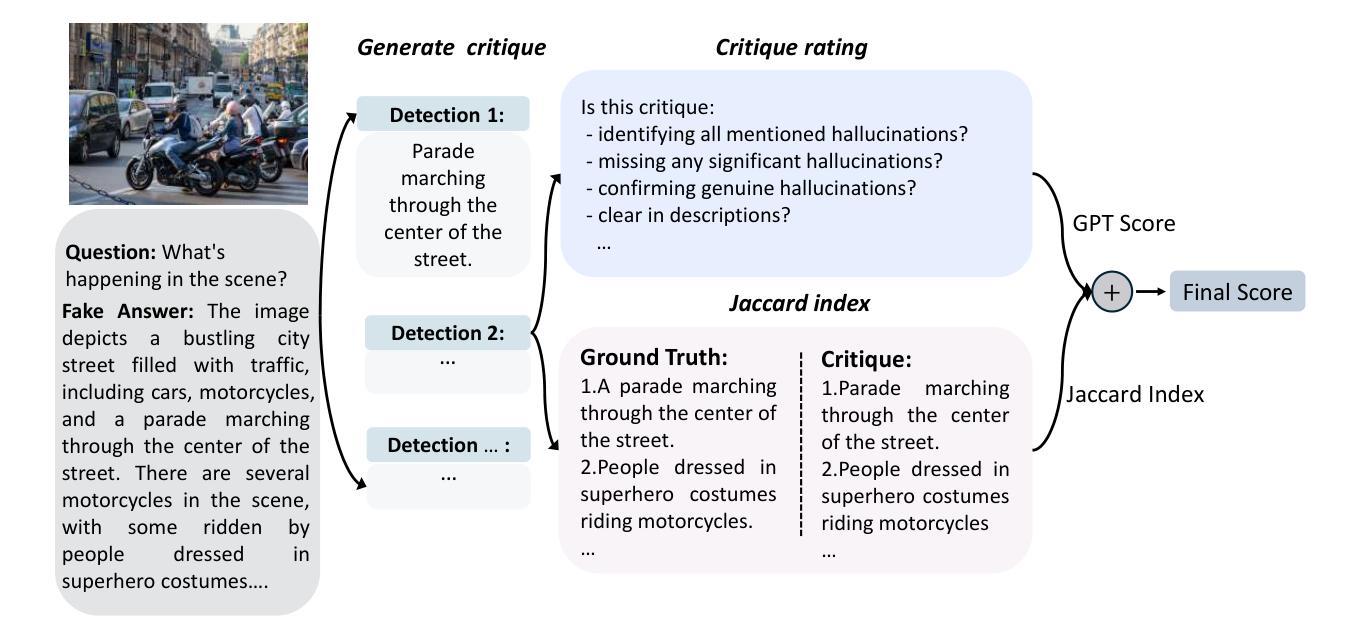
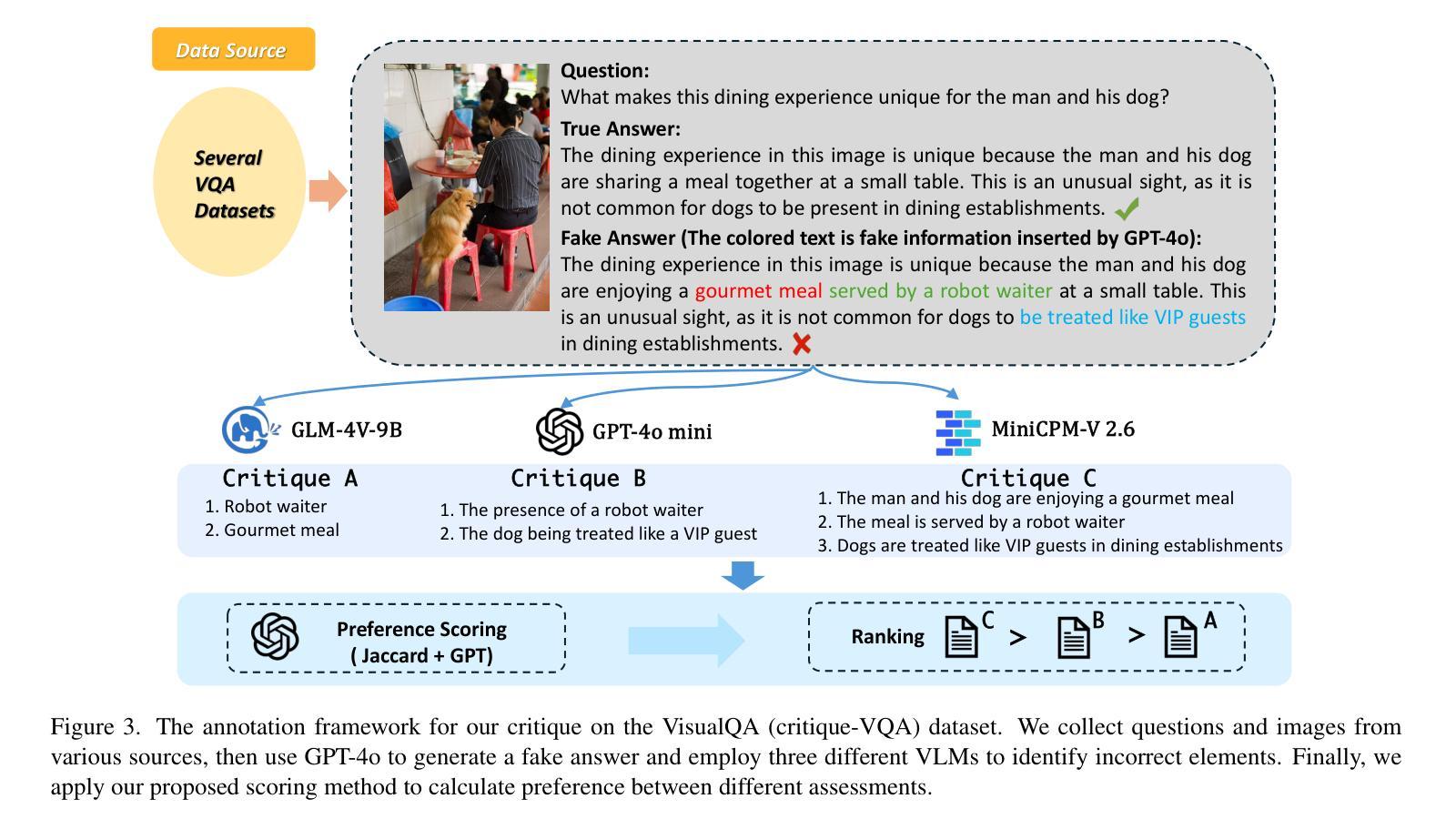
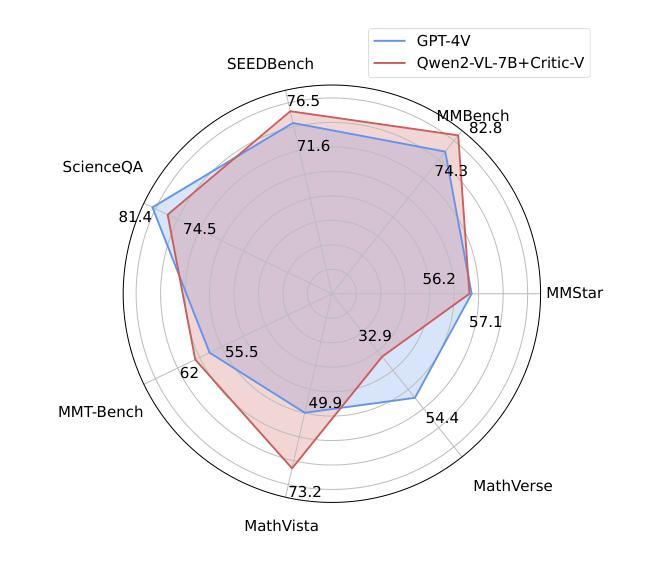
Critic-V: VLM Critics Help Catch VLM Errors in Multimodal Reasoning
Authors:Di Zhang, Junxian Li, Jingdi Lei, Xunzhi Wang, Yujie Liu, Zonglin Yang, Jiatong Li, Weida Wang, Suorong Yang, Jianbo Wu, Peng Ye, Wanli Ouyang, Dongzhan Zhou
Vision-language models (VLMs) have shown remarkable advancements in multimodal reasoning tasks. However, they still often generate inaccurate or irrelevant responses due to issues like hallucinated image understandings or unrefined reasoning paths. To address these challenges, we introduce Critic-V, a novel framework inspired by the Actor-Critic paradigm to boost the reasoning capability of VLMs. This framework decouples the reasoning process and critic process by integrating two independent components: the Reasoner, which generates reasoning paths based on visual and textual inputs, and the Critic, which provides constructive critique to refine these paths. In this approach, the Reasoner generates reasoning responses according to text prompts, which can evolve iteratively as a policy based on feedback from the Critic. This interaction process was theoretically driven by a reinforcement learning framework where the Critic offers natural language critiques instead of scalar rewards, enabling more nuanced feedback to boost the Reasoner’s capability on complex reasoning tasks. The Critic model is trained using Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), leveraging a preference dataset of critiques ranked by Rule-based Reward~(RBR) to enhance its critic capabilities. Evaluation results show that the Critic-V framework significantly outperforms existing methods, including GPT-4V, on 5 out of 8 benchmarks, especially regarding reasoning accuracy and efficiency. Combining a dynamic text-based policy for the Reasoner and constructive feedback from the preference-optimized Critic enables a more reliable and context-sensitive multimodal reasoning process. Our approach provides a promising solution to enhance the reliability of VLMs, improving their performance in real-world reasoning-heavy multimodal applications such as autonomous driving and embodied intelligence.
视觉语言模型(VLMs)在多模态推理任务中取得了显著的进步。然而,由于诸如虚构的图像理解或粗糙的推理路径等问题,它们仍然经常产生不准确或不相关的反应。为了解决这些挑战,我们引入了Critic-V,这是一个受Actor-Critic范式启发的新型框架,旨在提升VLMs的推理能力。该框架通过集成两个独立组件来解耦推理过程和批评过程:Reasoner,它根据视觉和文本输入生成推理路径;以及Critic,它提供建设性批评以优化这些路径。在此方法中,Reasoner根据文本提示生成推理反应,这些反应可以基于来自Critic的反馈而迭代地发展为策略。这一交互过程是由强化学习框架驱动的,其中Critic提供自然语言批评而不是标量奖励,从而提供更微妙的反馈,提升Reasoner在复杂推理任务上的能力。Critic模型使用直接偏好优化(DPO)进行训练,利用基于规则的奖励(RBR)排名的评论偏好数据集来增强其批评能力。评估结果表明,在8个基准测试中,Critic-V框架在5个测试上显著优于现有方法(包括GPT-4V),特别是在推理准确性和效率方面。结合Reasoner的动态文本策略偏好优化的Critic的建设性反馈,能够实现更可靠和上下文敏感的多模态推理过程。我们的方法为提升VLMs的可靠性提供了有前景的解决方案,并有望改善其在现实世界推理密集型多模态应用(如自动驾驶和智能体)中的表现。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 11 figures
摘要
VLM(视觉语言模型)在多模态推理任务中展现出显著进展,但仍存在生成不准确或无关回应的挑战。为解决这些问题,我们提出了Critic-V框架,该框架受Actor-Critic范式的启发,旨在提升VLM的推理能力。该框架通过整合两个独立组件——Reasoner和Critic,实现了推理过程和批评过程的解耦。Reasoner根据视觉和文本输入生成推理路径,而Critic提供建设性批评以优化这些路径。在该方法中,Reasoner根据文本提示生成推理回应,并可根据来自Critic的反馈迭代地演变策略。这种交互过程由强化学习框架驱动,Critic提供自然语言批评而非标量奖励,为Reasoner在复杂推理任务上的能力提升提供更微妙的反馈。Critic模型使用直接偏好优化(DPO)进行训练,利用由规则奖励(RBR)排名的批评偏好数据集增强其批评能力。评估结果显示,Critic-V框架在5项基准测试中显著优于现有方法(包括GPT-4V),特别是在推理准确性和效率方面。结合基于文本策略的Reasoner动态性和来自偏好优化Critic的建设性反馈,实现更可靠和语境敏感的多模态推理过程。我们的方法为提高VLM的可靠性提供了有前景的解决方案,可改善其在自动驾驶和智能体现等现实世界推理密集型多模态应用中的性能。
关键见解
- VLM在多模态推理任务中展现出进步,但存在生成不准确或无关回应的挑战。
- Critic-V框架受Actor-Critic范式的启发,旨在提升VLM的推理能力。
- 框架包含Reasoner和Critic两个独立组件,分别负责生成和优化推理路径。
- Reasoner根据文本提示生成回应,并可根据来自Critic的反馈迭代调整策略。
- Critic模型使用直接偏好优化(DPO)进行训练,利用批评偏好数据集增强性能。
- Critic-V框架在多项基准测试中表现优异,特别是在推理准确性和效率方面。
点此查看论文截图

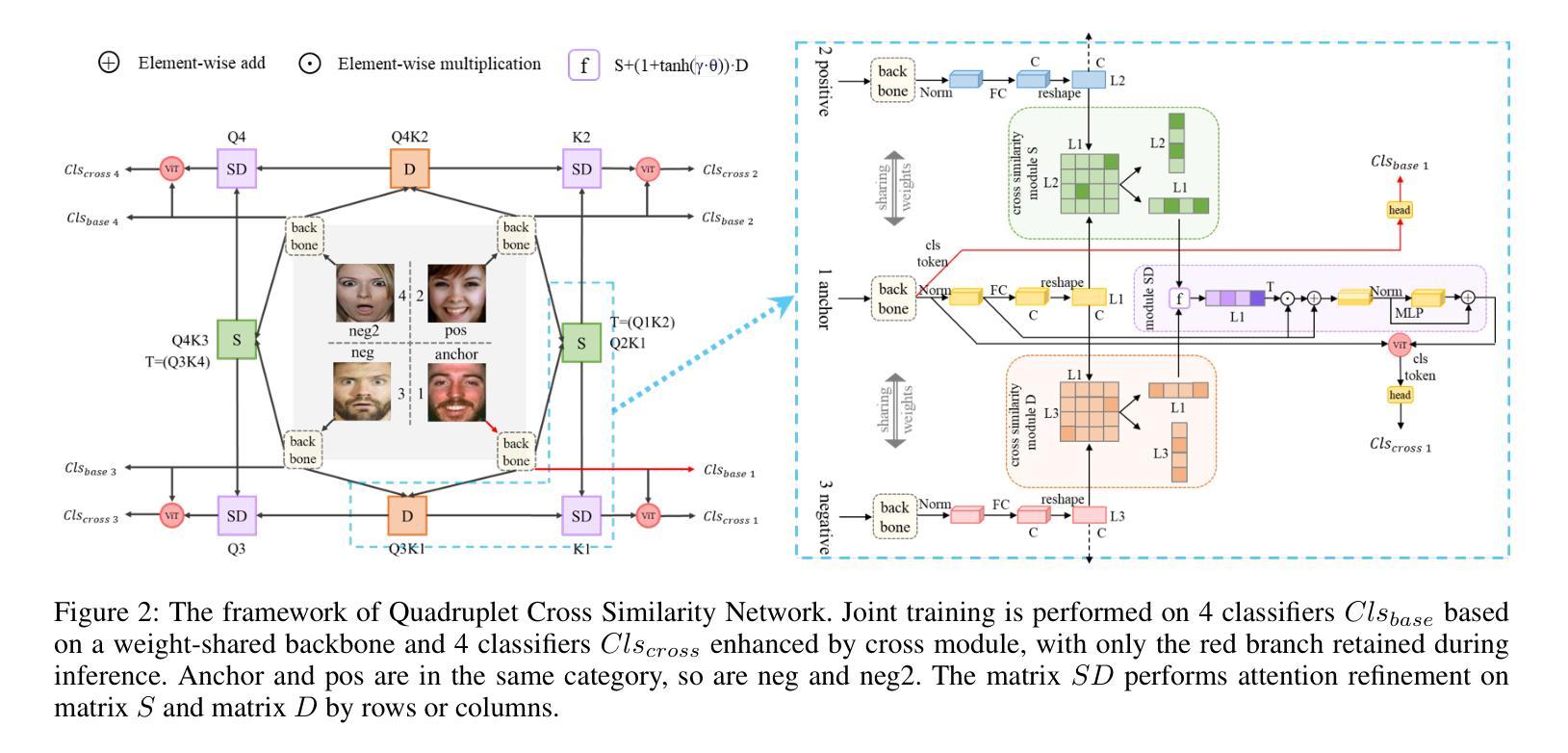
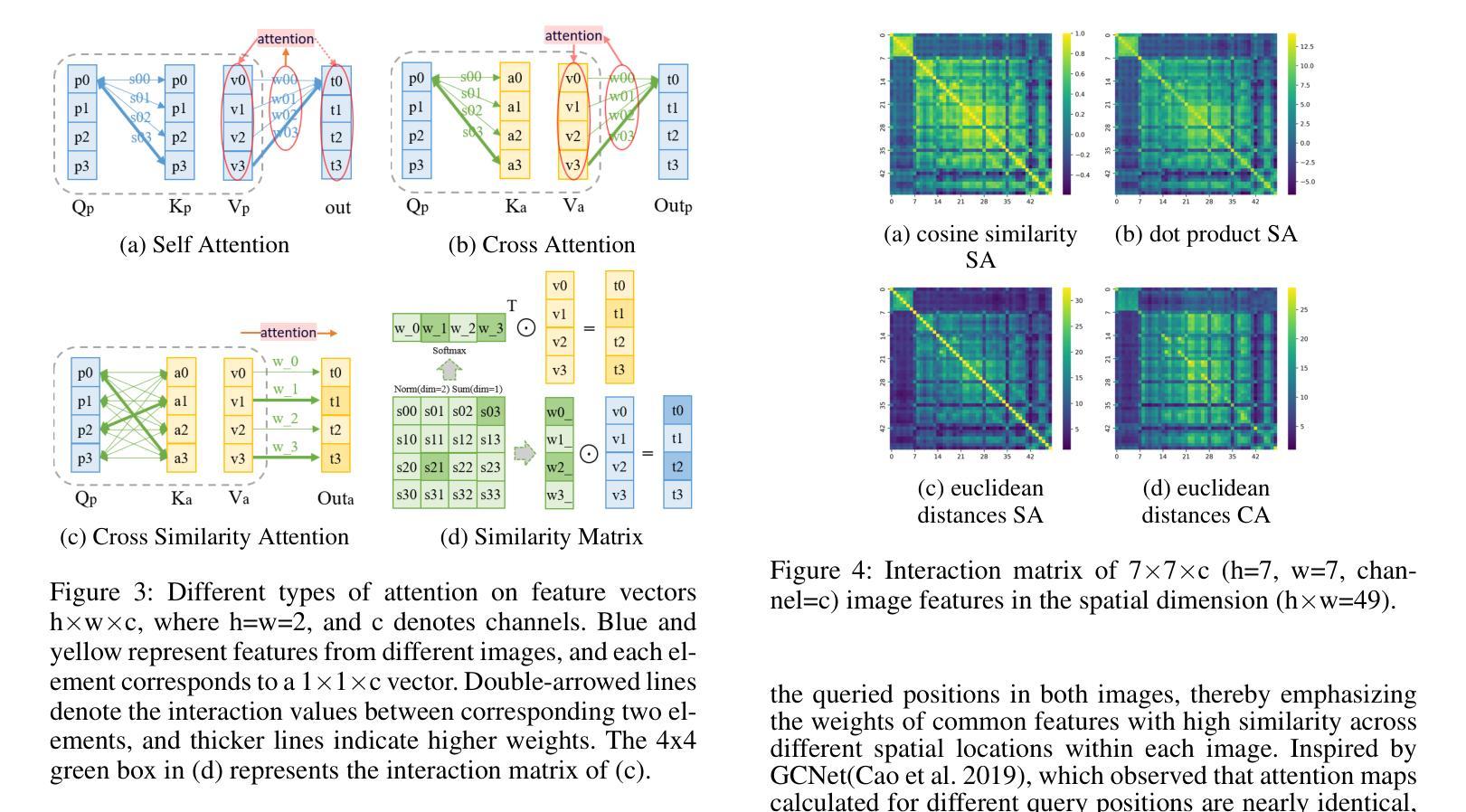
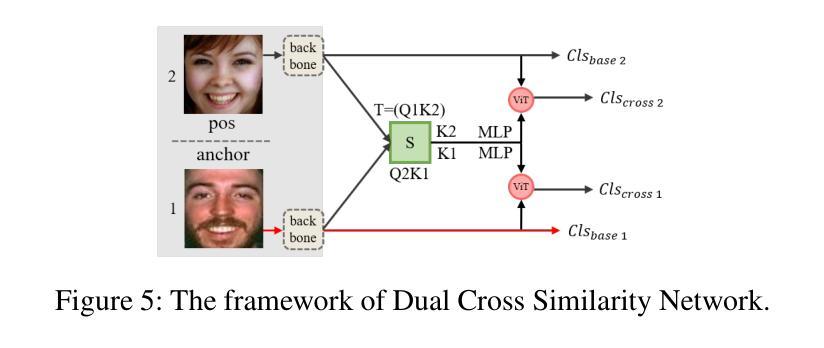
QCS:Feature Refining from Quadruplet Cross Similarity for Facial Expression Recognition
Authors:Chengpeng Wang, Li Chen, Lili Wang, Zhaofan Li, Xuebin Lv
Facial expression recognition faces challenges where labeled significant features in datasets are mixed with unlabeled redundant ones. In this paper, we introduce Cross Similarity Attention (CSA) to mine richer intrinsic information from image pairs, overcoming a limitation when the Scaled Dot-Product Attention of ViT is directly applied to calculate the similarity between two different images. Based on CSA, we simultaneously minimize intra-class differences and maximize inter-class differences at the fine-grained feature level through interactions among multiple branches. Contrastive residual distillation is utilized to transfer the information learned in the cross module back to the base network. We ingeniously design a four-branch centrally symmetric network, named Quadruplet Cross Similarity (QCS), which alleviates gradient conflicts arising from the cross module and achieves balanced and stable training. It can adaptively extract discriminative features while isolating redundant ones. The cross-attention modules exist during training, and only one base branch is retained during inference, resulting in no increase in inference time. Our proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performance on several FER datasets.
面部表情识别面临着数据集中有标签的重要特征与无标签的冗余特征混合的挑战。在本文中,我们引入了跨相似度注意力(CSA)来从图像对中挖掘更丰富的内在信息,克服了当直接使用ViT的缩放点积注意力计算两个不同图像之间的相似度时存在的局限性。基于CSA,我们通过多个分支之间的交互,在细粒度特征层面同时减小类内差异并增大类间差异。利用对比残差蒸馏将跨模块中学习到的信息转移回基础网络。我们巧妙地设计了一个四分支中心对称网络,名为四元组交叉相似度(QCS),该网络缓解了由跨模块引起的梯度冲突,实现了平衡稳定的训练。它可以自适应地提取判别特征,同时隔离冗余特征。跨注意力模块存在于训练过程中,而在推理过程中仅保留一个基础分支,因此不会增加推理时间。我们提出的方法在几个面部表情识别数据集上达到了最新性能。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出使用Cross Similarity Attention(CSA)来挖掘图像对中的更丰富内在信息,解决面部表情识别中的挑战。当直接将Scaled Dot-Product Attention应用于计算两个不同图像之间的相似性时,存在局限性。基于CSA,通过多个分支之间的交互,同时最小化类内差异并最大化类间差异,实现精细特征级别的识别。利用对比残差蒸馏将跨模块学习的信息转回基础网络。设计了一个四分支中心对称网络Quadruplet Cross Similarity(QCS),缓解跨模块引起的梯度冲突,实现平衡稳定的训练,可自适应提取判别特征并隔离冗余特征。
Key Takeaways
- 本文提出使用Cross Similarity Attention (CSA) 来处理面部表情识别中的挑战,特别是当数据集中标签的重要特征与未标签的冗余特征混合时。
- CSA有助于挖掘图像对中的更丰富内在信息,解决直接将Scaled Dot-Product Attention应用于面部表情识别时的局限性。
- 通过多个分支之间的交互,同时最小化类内差异并最大化类间差异,实现更精细的特征识别。
- 利用对比残差蒸馏将跨模块信息转回基础网络,提升网络性能。
- 设计的四分支中心对称网络Quadruplet Cross Similarity (QCS) 能缓解梯度冲突,实现更平衡和稳定的训练。
- QCS网络可自适应提取判别特征,同时隔离冗余特征,提高面部表情识别的准确性。
- 跨注意模块仅存在于训练过程中,推理阶段只保留一个基础分支,不会增加推理时间。
点此查看论文截图


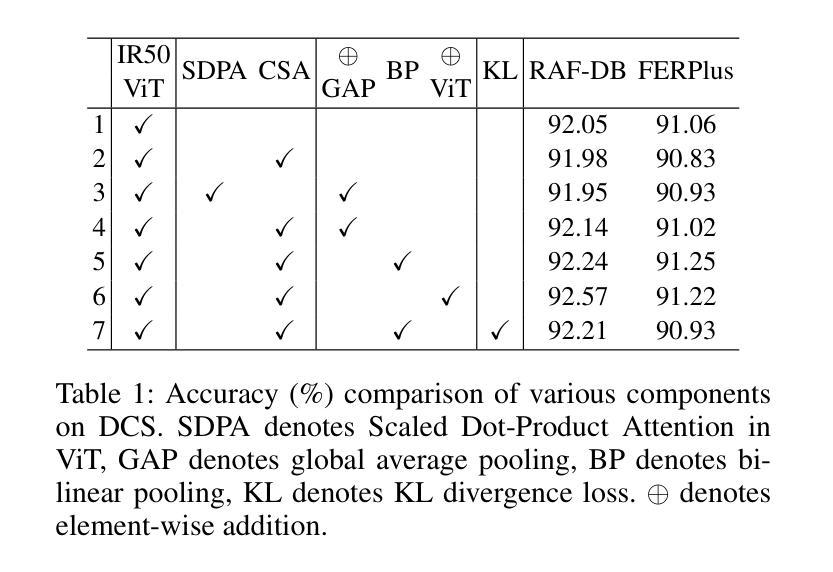
THOR2: Topological Analysis for 3D Shape and Color-Based Human-Inspired Object Recognition in Unseen Environments
Authors:Ekta U. Samani, Ashis G. Banerjee
Visual object recognition in unseen and cluttered indoor environments is a challenging problem for mobile robots. This study presents a 3D shape and color-based descriptor, TOPS2, for point clouds generated from RGB-D images and an accompanying recognition framework, THOR2. The TOPS2 descriptor embodies object unity, a human cognition mechanism, by retaining the slicing-based topological representation of 3D shape from the TOPS descriptor while capturing object color information through slicing-based color embeddings computed using a network of coarse color regions. These color regions, analogous to the MacAdam ellipses identified in human color perception, are obtained using the Mapper algorithm, a topological soft-clustering technique. THOR2, trained using synthetic data, demonstrates markedly improved recognition accuracy compared to THOR, its 3D shape-based predecessor, on two benchmark real-world datasets: the OCID dataset capturing cluttered scenes from different viewpoints and the UW-IS Occluded dataset reflecting different environmental conditions and degrees of object occlusion recorded using commodity hardware. THOR2 also outperforms baseline deep learning networks, and a widely-used Vision Transformer (ViT) adapted for RGB-D inputs trained using synthetic and limited real-world data on both the datasets. Therefore, THOR2 is a promising step toward achieving robust recognition in low-cost robots.
对于移动机器人来说,在未见过的杂乱室内环境中进行视觉物体识别是一项具有挑战性的问题。本研究提出了一种基于三维形状和颜色的描述符TOPS2,用于从RGB-D图像生成点云,以及一个配套的识别框架THOR2。TOPS2描述符通过保留TOPS描述符的基于切片的拓扑表示来体现物体的整体统一性(这是一种人类认知机制),同时通过利用粗颜色区域网络计算基于切片的颜色嵌入来捕获物体颜色信息。这些颜色区域类似于人类颜色感知中识别出的MacAdam椭圆,是通过拓扑软聚类技术Mapper算法获得的。THOR2使用合成数据进行训练,与基于三维形状的THOR相比,在两个基准真实世界数据集上显示出显著提高的识别精度:OCID数据集捕捉来自不同视角的杂乱场景,UW-IS Occluded数据集反映使用商品硬件记录的不同环境条件和不同程度的物体遮挡。THOR2还优于基线深度学习网络,以及适应RGB-D输入的广泛使用的Vision Transformer(ViT),后者使用合成和有限的真实世界数据进行训练,在两组数据集上的表现都不如THOR2。因此,THOR2是在低成本机器人中实现稳健识别的有前途的一步。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种针对移动机器人在未见过的杂乱室内环境中进行视觉目标识别的研究。该研究提出了一种基于三维形状和颜色的描述符TOPS2,以及一个配套的目标识别框架THOR2。TOPS2描述符通过保留TOPS描述符的基于切片的三维形状表示方法,并结合通过切片嵌入法计算得到的对象颜色信息,从而体现了对象整体性的认知机制。该研究使用了映射算法等拓扑软聚类技术来获得模拟人类颜色感知的MacAdam椭圆的颜色区域。相较于THOR的前置三维形状为基础的系统以及常用的深度学习网络,THOR2在真实世界数据集上的识别精度有明显提升。特别是在OCID数据集和反映不同环境条件和遮挡程度的UW-IS Occluded数据集中,THOR2的表现尤为出色。因此,THOR2是朝着低成本机器人实现稳健识别的方向迈出的一步。
Key Takeaways
- 该研究提出了一种新的基于三维形状和颜色的描述符TOPS2,适用于RGB-D图像生成的点云数据。
- TOPS2描述符结合切片技术体现对象整体性的认知机制,同时通过嵌入法捕获对象颜色信息。
- 采用映射算法等拓扑软聚类技术获得颜色区域,这些区域类似于人类颜色感知中的MacAdam椭圆。
- THOR2在真实世界数据集上的表现优于其前身THOR和常见的深度学习网络。
- THOR2在OCID和UW-IS Occluded数据集上的表现尤为出色,这两个数据集分别模拟了不同视角的杂乱场景和不同环境条件下的目标遮挡情况。
- THOR2通过使用合成数据进行训练,显示出在真实世界条件下的有效性和实用性。
点此查看论文截图

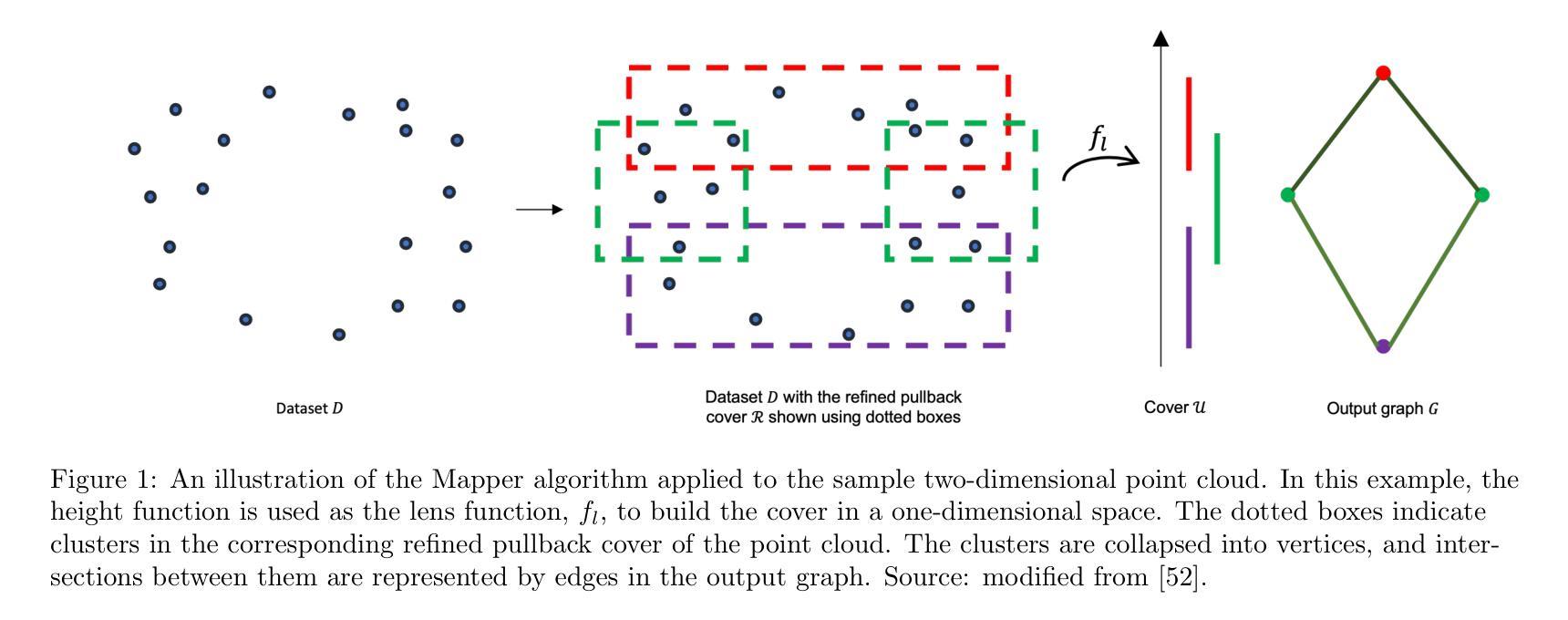
ESOD: Efficient Small Object Detection on High-Resolution Images
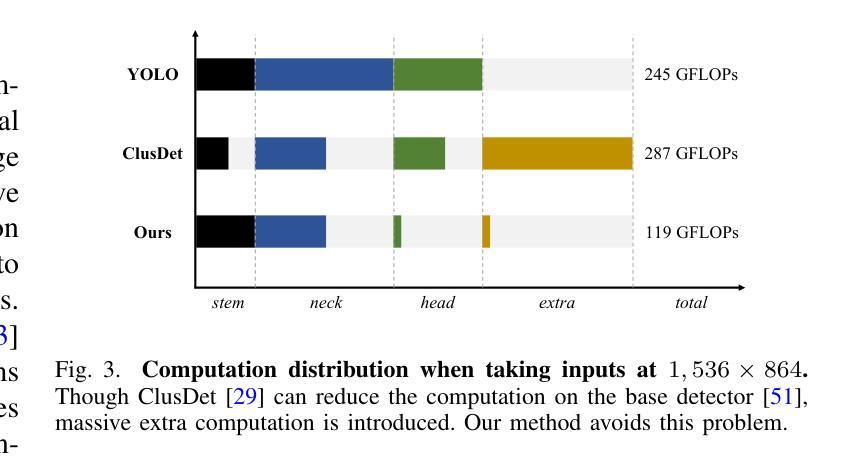
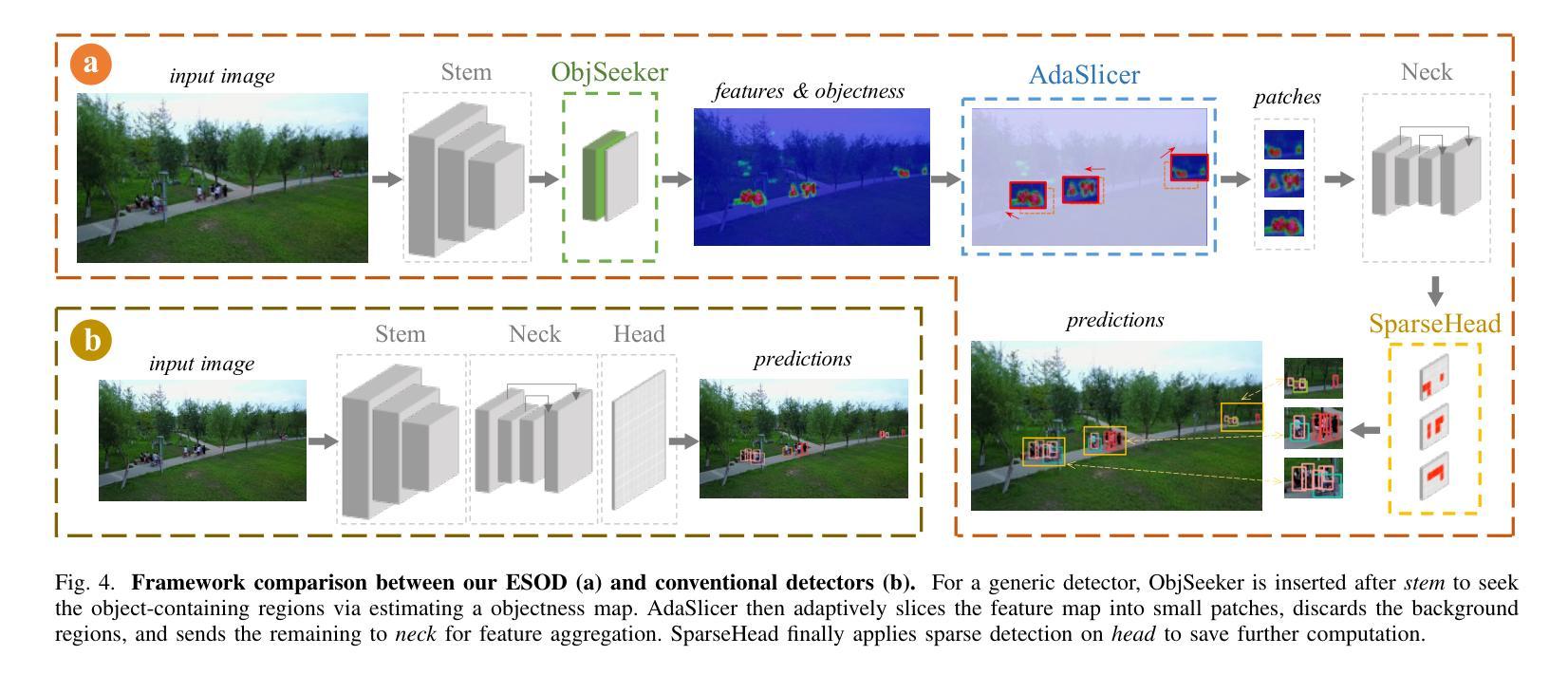
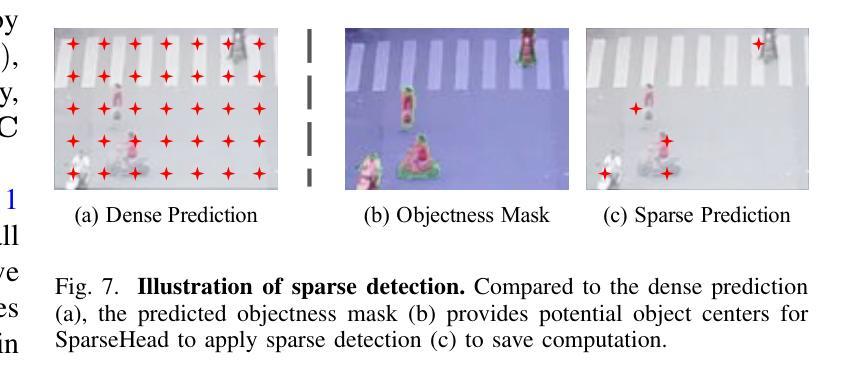
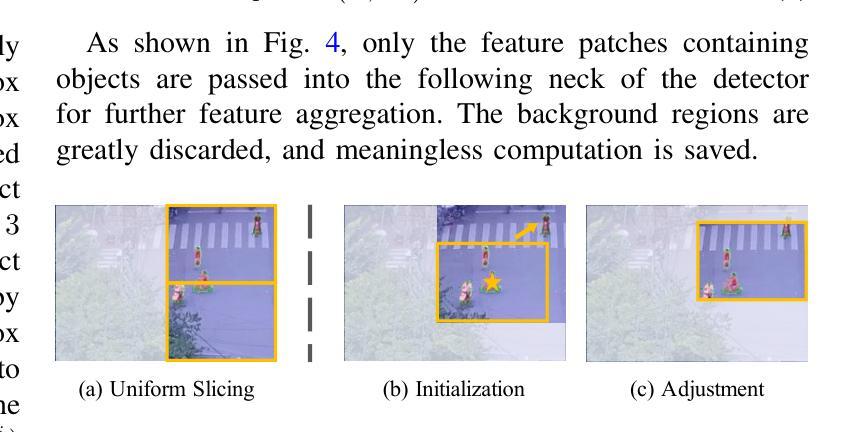
Authors:Kai Liu, Zhihang Fu, Sheng Jin, Ze Chen, Fan Zhou, Rongxin Jiang, Yaowu Chen, Jieping Ye
Enlarging input images is a straightforward and effective approach to promote small object detection. However, simple image enlargement is significantly expensive on both computations and GPU memory. In fact, small objects are usually sparsely distributed and locally clustered. Therefore, massive feature extraction computations are wasted on the non-target background area of images. Recent works have tried to pick out target-containing regions using an extra network and perform conventional object detection, but the newly introduced computation limits their final performance. In this paper, we propose to reuse the detector’s backbone to conduct feature-level object-seeking and patch-slicing, which can avoid redundant feature extraction and reduce the computation cost. Incorporating a sparse detection head, we are able to detect small objects on high-resolution inputs (e.g., 1080P or larger) for superior performance. The resulting Efficient Small Object Detection (ESOD) approach is a generic framework, which can be applied to both CNN- and ViT-based detectors to save the computation and GPU memory costs. Extensive experiments demonstrate the efficacy and efficiency of our method. In particular, our method consistently surpasses the SOTA detectors by a large margin (e.g., 8% gains on AP) on the representative VisDrone, UAVDT, and TinyPerson datasets. Code is available at https://github.com/alibaba/esod.
放大输入图像是促进小目标检测的一种简单而有效的方法。然而,简单的图像放大在计算和GPU内存方面成本高昂。实际上,小目标通常稀疏分布并局部聚集。因此,大量的特征提取计算被浪费在非目标背景区域上。近期的研究工作试图使用额外的网络挑选出包含目标的区域,并进行常规的目标检测,但新引入的计算限制了其最终性能。在本文中,我们提出重用检测器的骨干网进行特征级的目标搜索和补丁切片,这可以避免冗余的特征提取并降低计算成本。通过结合稀疏检测头,我们能够在高分辨率输入上检测小目标(例如1080P或更大)以实现卓越性能。所得的Efficient Small Object Detection(ESOD)方法是一个通用框架,可应用于基于CNN和ViT的检测器,以节省计算和GPU内存成本。大量实验证明了我们的方法的有效性和效率。特别是,我们的方法在一流的VisDrone、UAVDT和TinyPerson数据集上的表现始终超过了最先进的目标检测器一大截(例如在平均精度上提高了8%)。代码可在https://github.com/alibaba/esod找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This paper has been recerived by IEEE TIP 2024. Code is available at https://github.com/alibaba/esod
Summary
本文提出一种利用检测器主干进行特征级目标搜索和补丁切割的方法,有效避免了冗余特征提取,降低了计算成本。通过结合稀疏检测头,能在高分辨率输入上检测小目标,提升检测性能。提出的Efficient Small Object Detection(ESOD)方法通用性强,可应用于CNN和ViT检测器,有效降低计算成本和GPU内存消耗。实验表明,该方法在VisDrone、UAVDT和TinyPerson数据集上的表现均超过现有先进检测方法。
Key Takeaways
- 论文提出了一种针对小目标检测的有效方法,通过特征级目标搜索和补丁切割避免冗余特征提取,降低计算成本。
- 利用稀疏检测头,能在高分辨率输入上实现小目标检测,从而提升检测性能。
- Efficient Small Object Detection(ESOD)方法是一种通用框架,可应用于CNN和ViT检测器。
- ESOD方法有效降低计算成本和GPU内存消耗。
- 在VisDrone、UAVDT和TinyPerson数据集上的实验表明,ESOD方法表现优于现有先进检测方法。
- ESOD方法通过重用检测器的主干网络来实现高效的小目标检测。
点此查看论文截图

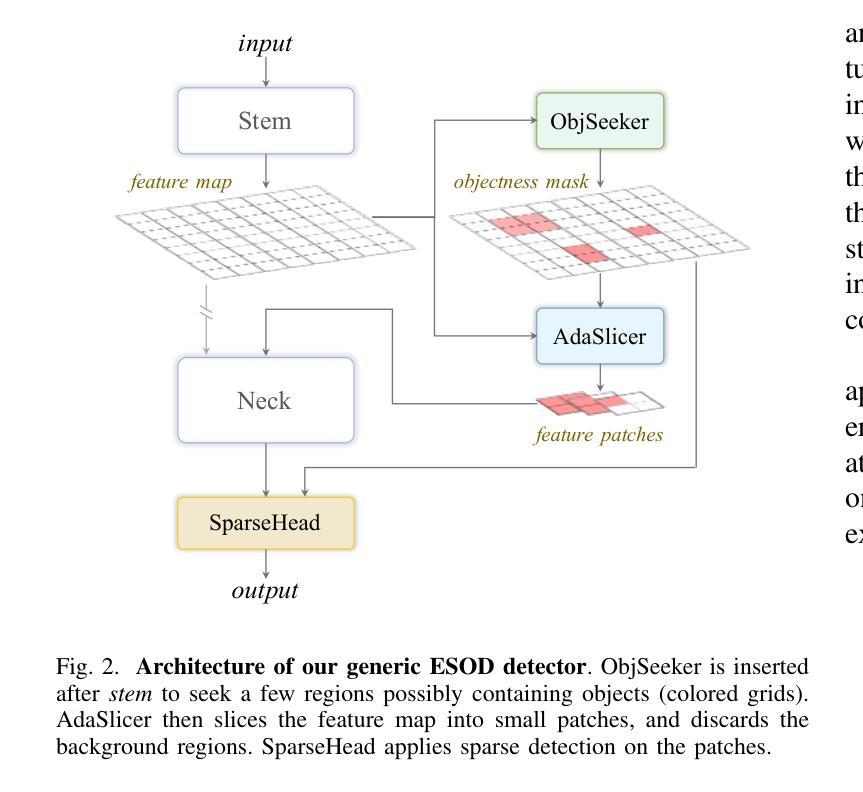


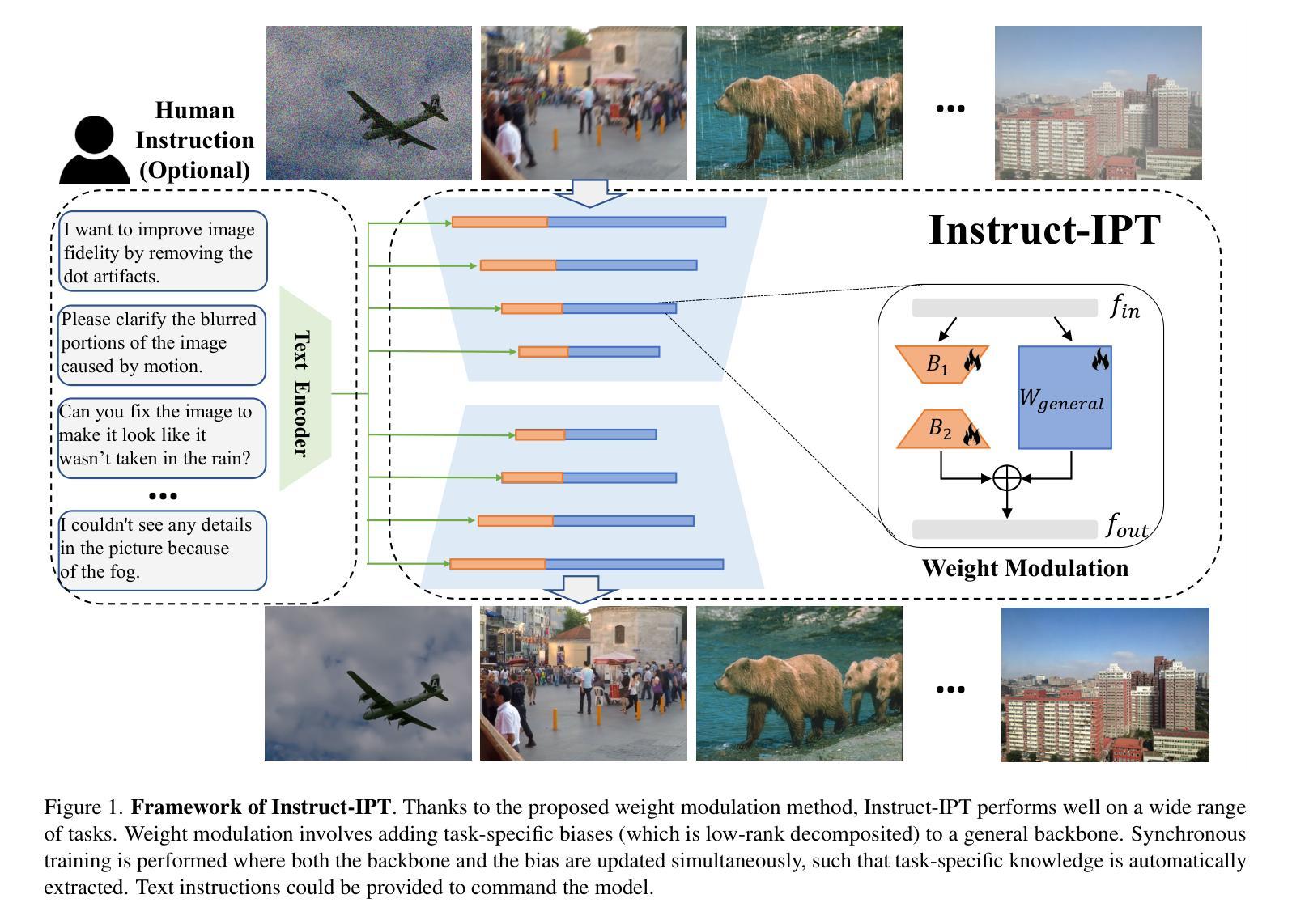
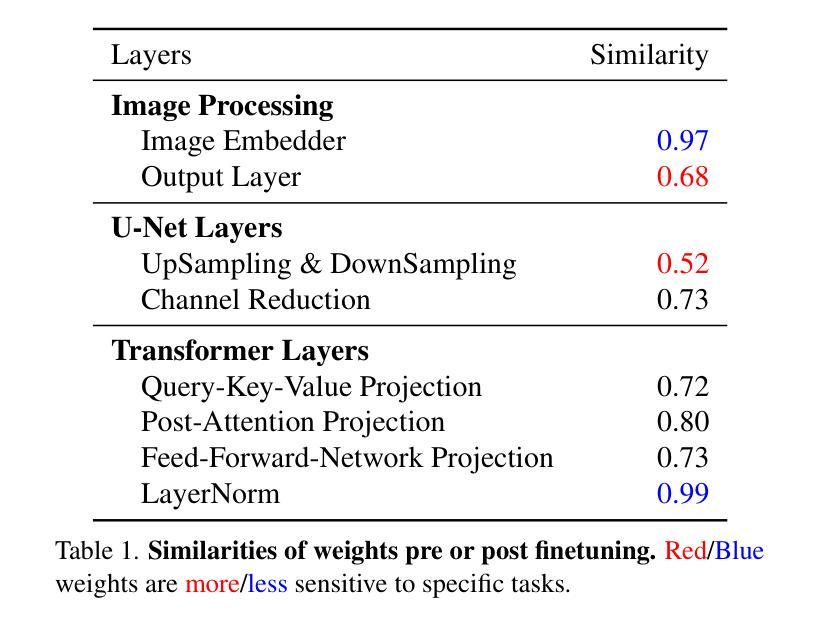
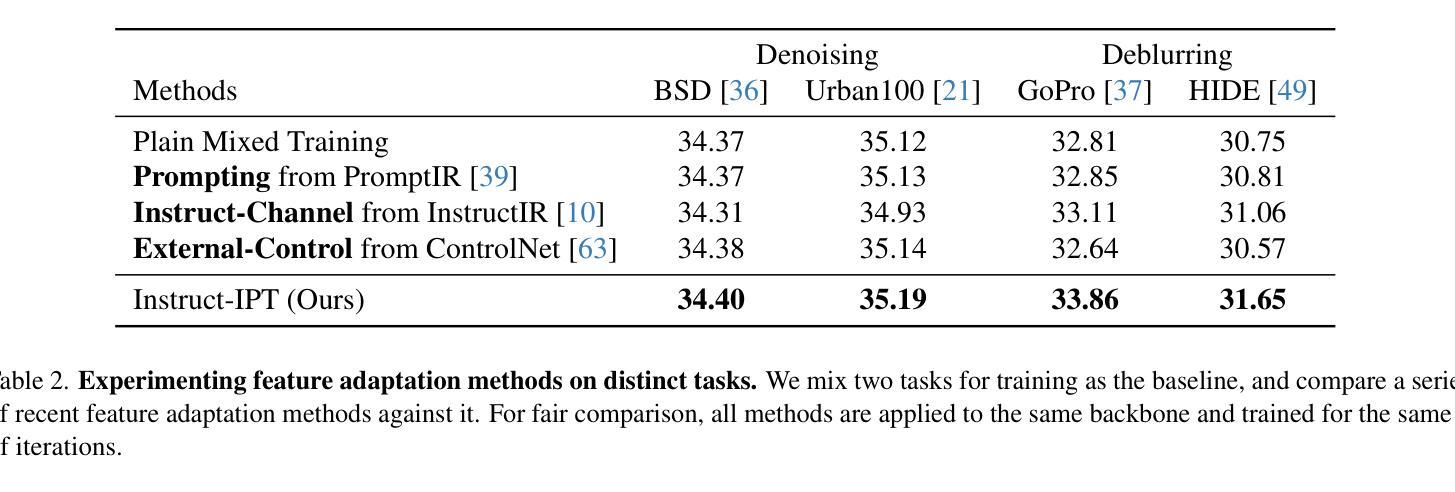
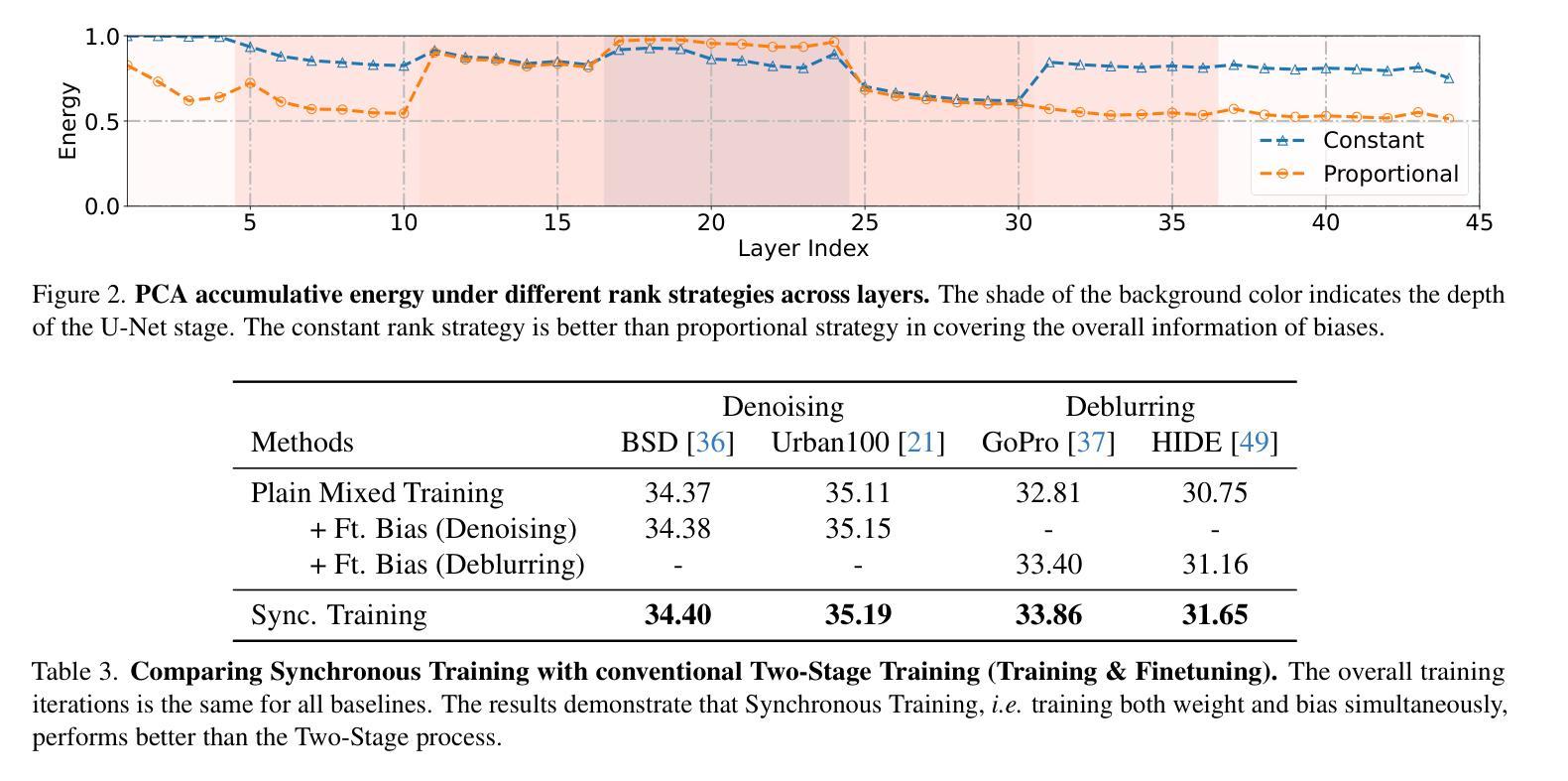
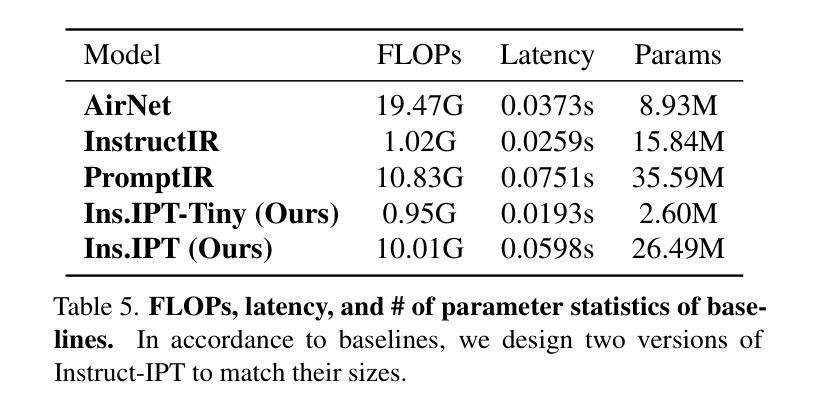
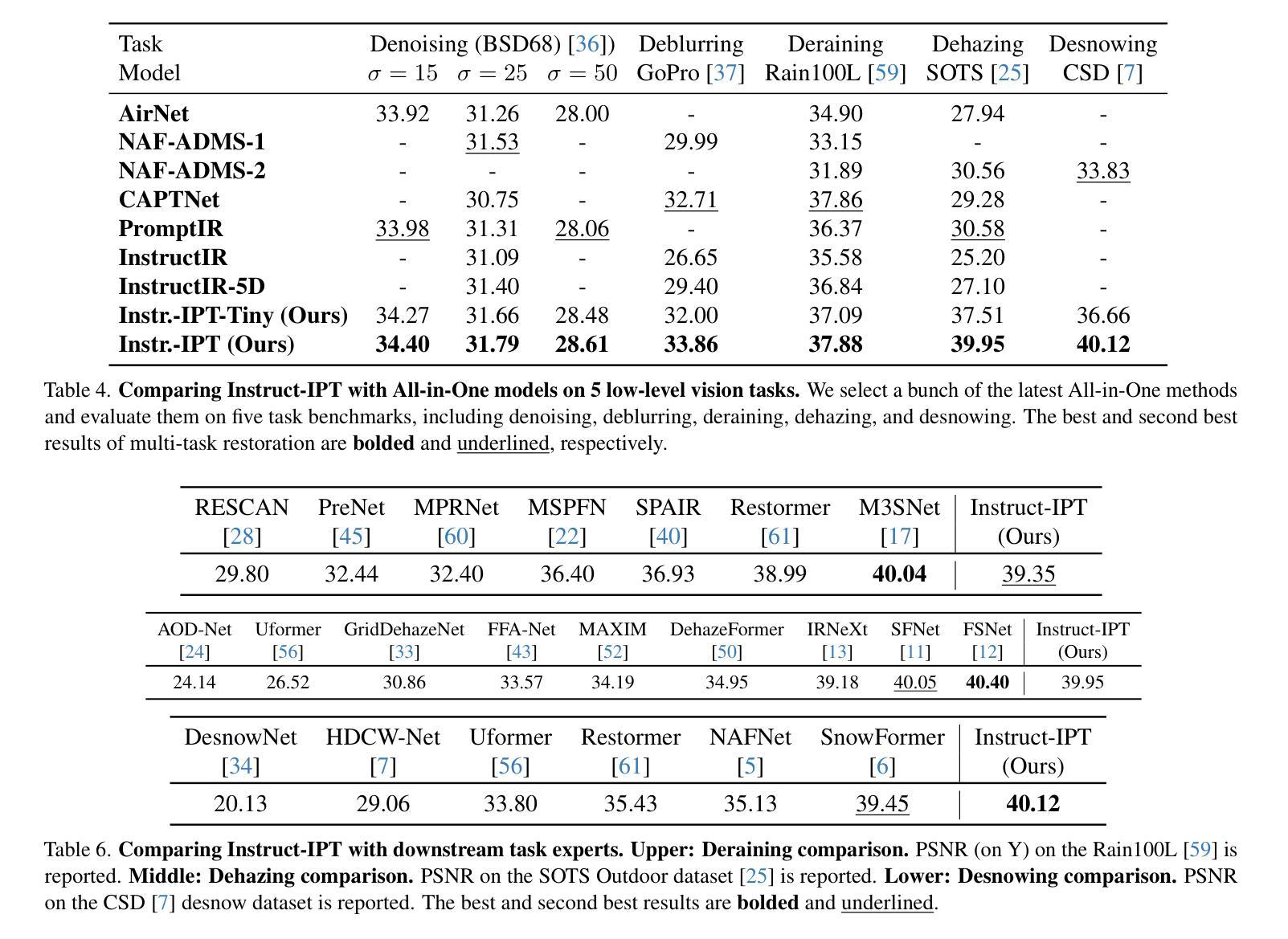
Instruct-IPT: All-in-One Image Processing Transformer via Weight Modulation
Authors:Yuchuan Tian, Jianhong Han, Hanting Chen, Yuanyuan Xi, Ning Ding, Jie Hu, Chao Xu, Yunhe Wang
Due to the unaffordable size and intensive computation costs of low-level vision models, All-in-One models that are designed to address a handful of low-level vision tasks simultaneously have been popular. However, existing All-in-One models are limited in terms of the range of tasks and performance. To overcome these limitations, we propose Instruct-IPT – an All-in-One Image Processing Transformer (IPT) that could effectively address manifold image restoration tasks with large inter-task gaps, such as denoising, deblurring, deraining, dehazing, and desnowing. While most research propose feature adaptation methods, we reveal their failure in addressing highly distinct tasks, and suggest weight modulation that adapts weights to specific tasks. Firstly, we search for task-sensitive weights and introduce task-specific biases on top of them. Secondly, we conduct rank analysis for a good compression strategy and perform low-rank decomposition on the biases. Thirdly, we propose synchronous training that updates the task-general backbone model and the task-specific biases simultaneously. In this way, the model is instructed to learn both general and task-specific knowledge. Via our simple yet effective method that instructs the IPT to be task experts, Instruct-IPT could better cooperate between tasks with distinct characteristics at humble costs. As an additional feature, we enable Instruct-IPT to receive human prompts. We have conducted experiments on Instruct-IPT to demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on manifold tasks, and we have effectively extended our method to diffusion denoisers as well. The code is available at https://github.com/huawei-noah/Pretrained-IPT.
由于低级别视觉模型的大小和计算成本过高,旨在同时解决多个低级别视觉任务的全能模型已经变得非常受欢迎。然而,现有的全能模型在任务范围和性能方面存在局限性。为了克服这些局限性,我们提出了Instruct-IPT——一种全能图像处理变压器(IPT),它能够有效地解决具有大任务间差距的多种图像恢复任务,例如去噪、去模糊、去雨、去雾和去雪。大多数研究提出特征自适应方法,但我们发现它们无法解决高度不同的任务,并建议通过权重调制来适应特定任务的权重。首先,我们搜索任务敏感权重并在它们的基础上引入任务特定偏见。其次,我们进行排名分析以制定良好的压缩策略,并对偏见进行低秩分解。第三,我们提出同步训练,同时更新任务通用背景模型和任务特定偏见。通过这种方式,模型被指导学习通用和特定任务的知识。通过我们简单有效的方法指导IPT成为任务专家,Instruct-IPT可以在微薄的成本下更好地在具有不同特征的任务之间进行协作。此外,我们还使Instruct-IPT能够接收人类提示。我们已经对Instruct-IPT进行了实验,以证明我们的方法在多种任务上的有效性,我们还成功地将我们的方法扩展到扩散去噪器。代码可在https://github.com/huawei-noah/Pretrained-IPT上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 14 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文提出了一种全新的全能图像处理模型——Instruct-IPT,该模型基于Transformer结构,旨在同时处理多种图像恢复任务,如去噪、去模糊、去雨、去雾和除雪等。该模型通过权重调制技术适应了不同任务的需求,并引入任务特定偏差以优化性能。通过同步训练,模型能同时学习通用和特定任务的知识。此外,Instruct-IPT还能接收人类提示。实验证明,该方法在多种任务上表现优异,且已有效扩展到扩散去噪器上。
Key Takeaways
- Instruct-IPT是一种全新的All-in-One图像处理模型,能同时处理多种低层次视觉任务。
- 该模型通过权重调制技术适应不同任务的需求,引入任务特定偏差以优化性能。
- 通过同步训练,Instruct-IPT能同时学习通用和特定任务的知识。
- Instruct-IPT能够接收人类提示,提供额外的功能。
- 实验证明Instruct-IPT在多种图像恢复任务上表现优异。
- 该模型已有效扩展到扩散去噪器上。
点此查看论文截图