⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-20 更新
CAD-Recode: Reverse Engineering CAD Code from Point Clouds
Authors:Danila Rukhovich, Elona Dupont, Dimitrios Mallis, Kseniya Cherenkova, Anis Kacem, Djamila Aouada
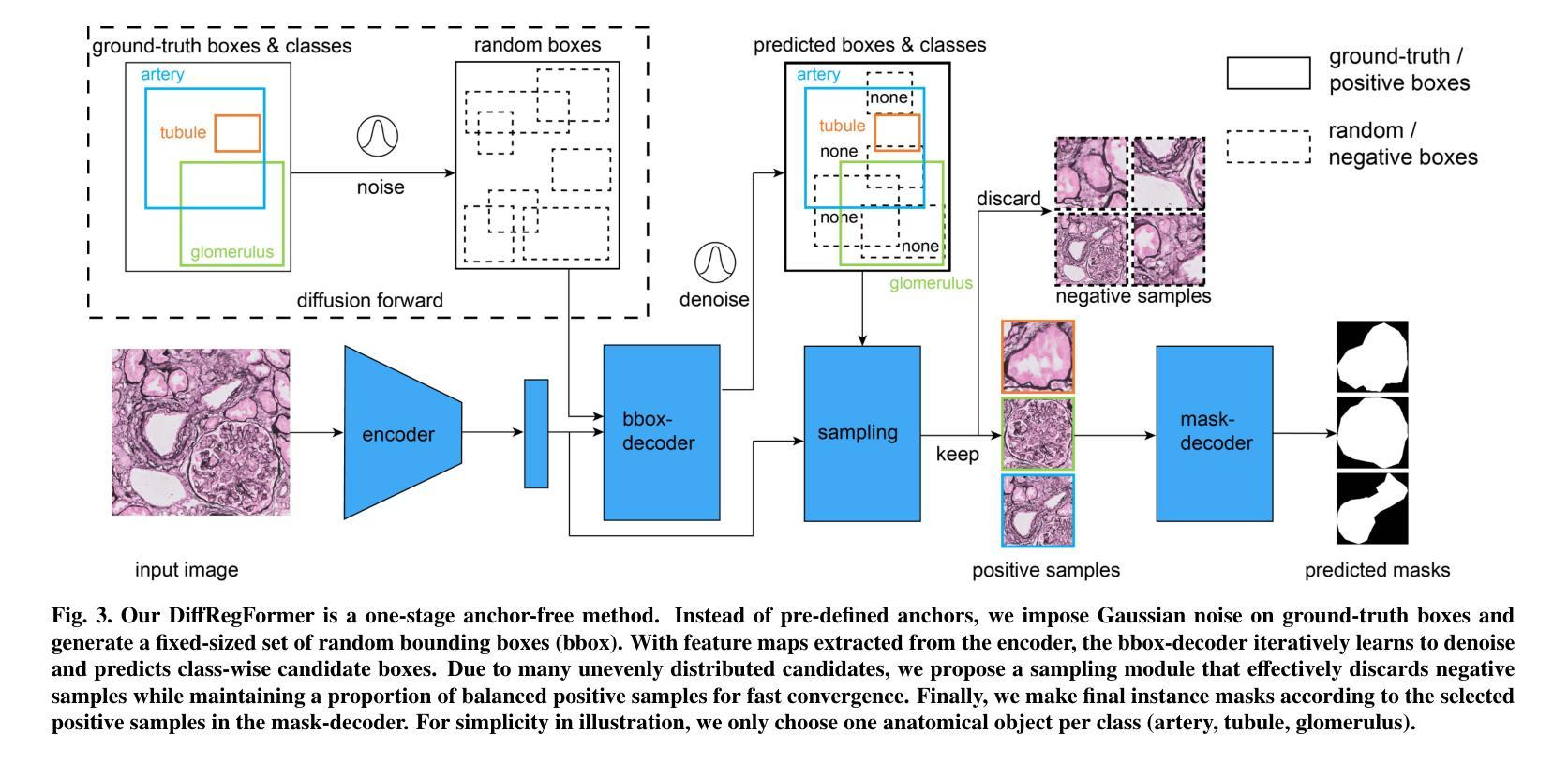
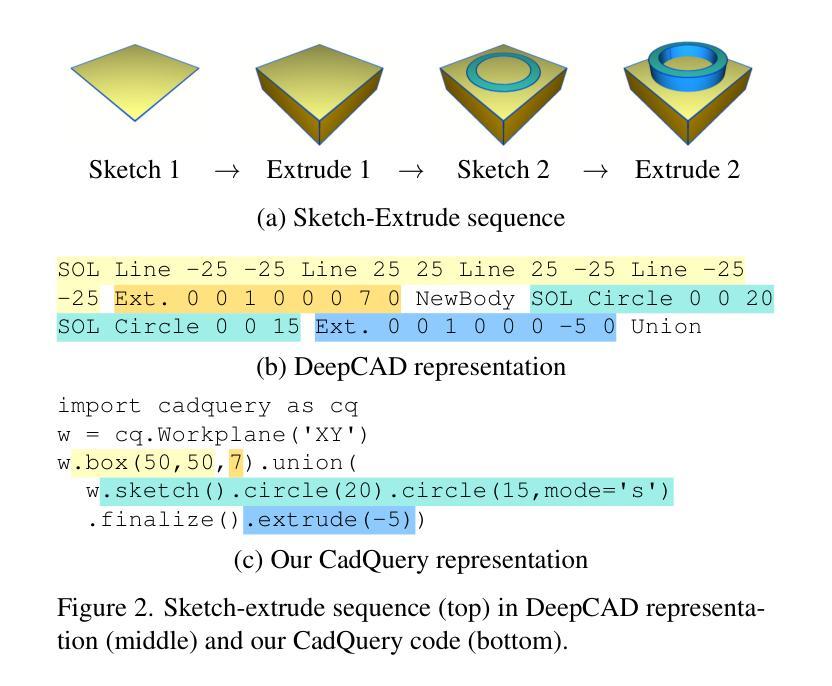
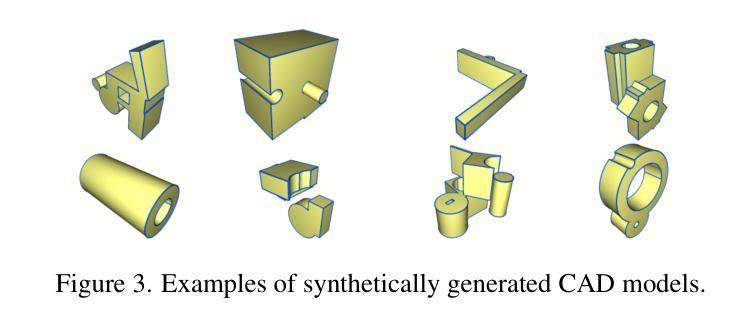
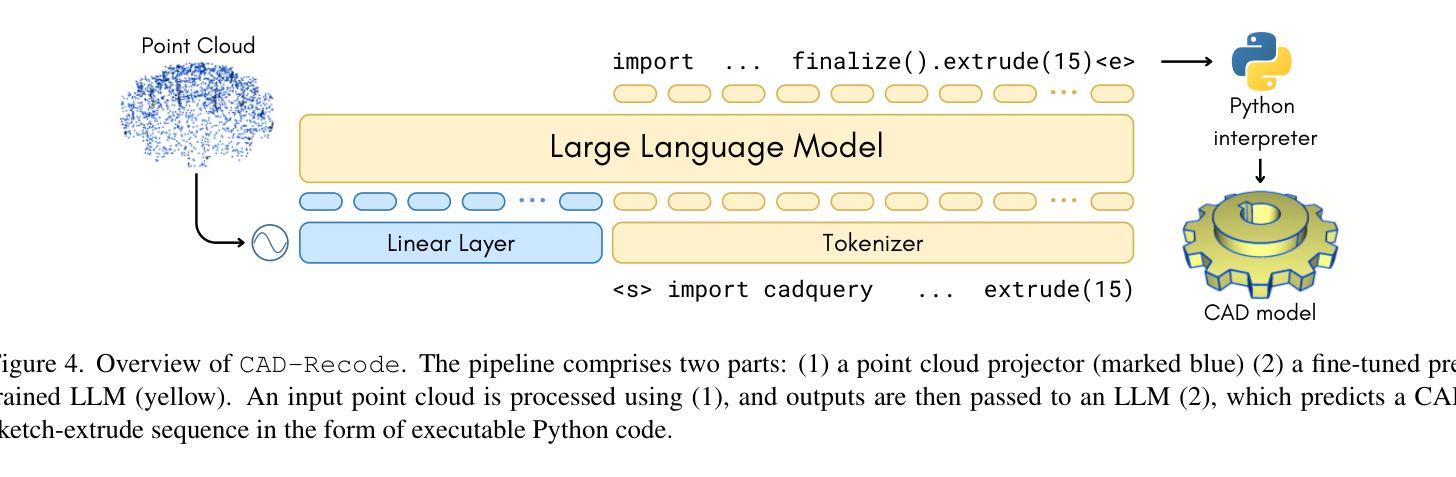
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) models are typically constructed by sequentially drawing parametric sketches and applying CAD operations to obtain a 3D model. The problem of 3D CAD reverse engineering consists of reconstructing the sketch and CAD operation sequences from 3D representations such as point clouds. In this paper, we address this challenge through novel contributions across three levels: CAD sequence representation, network design, and dataset. In particular, we represent CAD sketch-extrude sequences as Python code. The proposed CAD-Recode translates a point cloud into Python code that, when executed, reconstructs the CAD model. Taking advantage of the exposure of pre-trained Large Language Models (LLMs) to Python code, we leverage a relatively small LLM as a decoder for CAD-Recode and combine it with a lightweight point cloud projector. CAD-Recode is trained solely on a proposed synthetic dataset of one million diverse CAD sequences. CAD-Recode significantly outperforms existing methods across three datasets while requiring fewer input points. Notably, it achieves 10 times lower mean Chamfer distance than state-of-the-art methods on DeepCAD and Fusion360 datasets. Furthermore, we show that our CAD Python code output is interpretable by off-the-shelf LLMs, enabling CAD editing and CAD-specific question answering from point clouds.
计算机辅助设计(CAD)模型通常是通过依次绘制参数草图并应用CAD操作来获得的三维模型。3D CAD逆向工程的问题在于从点云等3D表示重建草图和CAD操作序列。在本文中,我们通过三个层次的全新贡献来解决这一挑战:CAD序列表示、网络设计和数据集。特别是,我们将CAD草图挤压序列表示为Python代码。所提出的CAD-Recode将点云转换为Python代码,执行时可重建CAD模型。我们利用预训练的的大型语言模型(LLM)对Python代码的暴露,利用一个相对较小的LLM作为CAD-Recode的解码器,并与轻量级的点云投影仪相结合。CAD-Recode仅在一个包含一百万多个CAD序列的合成数据集上进行训练。在三个数据集中,CAD-Recode显著优于现有方法,且所需的输入点数更少。值得注意的是,它在DeepCAD和Fusion360数据集上实现了比最新技术低10倍的平均Chamfer距离。此外,我们展示了我们的CAD Python代码输出可以通过市面上的LLM进行解释,从而能够有点云进行CAD编辑和特定的问答。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文解决了计算机三维CAD模型的逆向工程问题,通过三个层次的贡献:CAD序列表示、网络设计和数据集。提出一种名为CAD-Recode的方法,将点云转化为Python代码,执行后可重建CAD模型。利用预训练的少量大型语言模型(LLMs)解码CAD-Recode并与轻量级点云投影仪结合。仅在提出的百万级合成CAD序列数据集上进行训练,CAD-Recode在三个数据集上的表现均优于现有方法,且输入点更少。此外,它的输出是易于理解的CAD Python代码,使点云能够进行CAD编辑和问答。
Key Takeaways
- CAD-Recode解决了计算机三维CAD模型的逆向工程问题。
- CAD-Recode将点云转化为Python代码进行重建CAD模型。
- 利用大型语言模型(LLMs)解码CAD-Recode。
- CAD-Recode在合成数据集上进行训练,表现优于现有方法。
- CAD-Recode输入点需求更少,且实现了更低的Chamfer距离。
点此查看论文截图

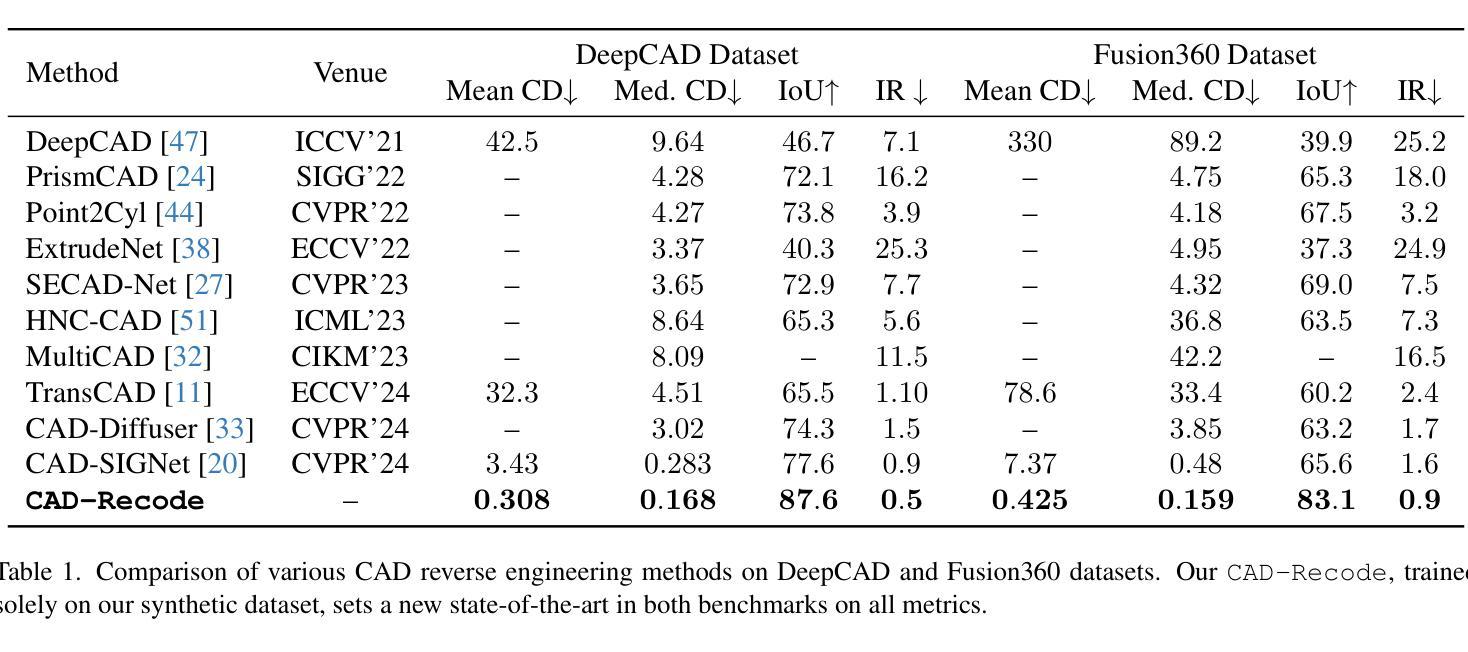
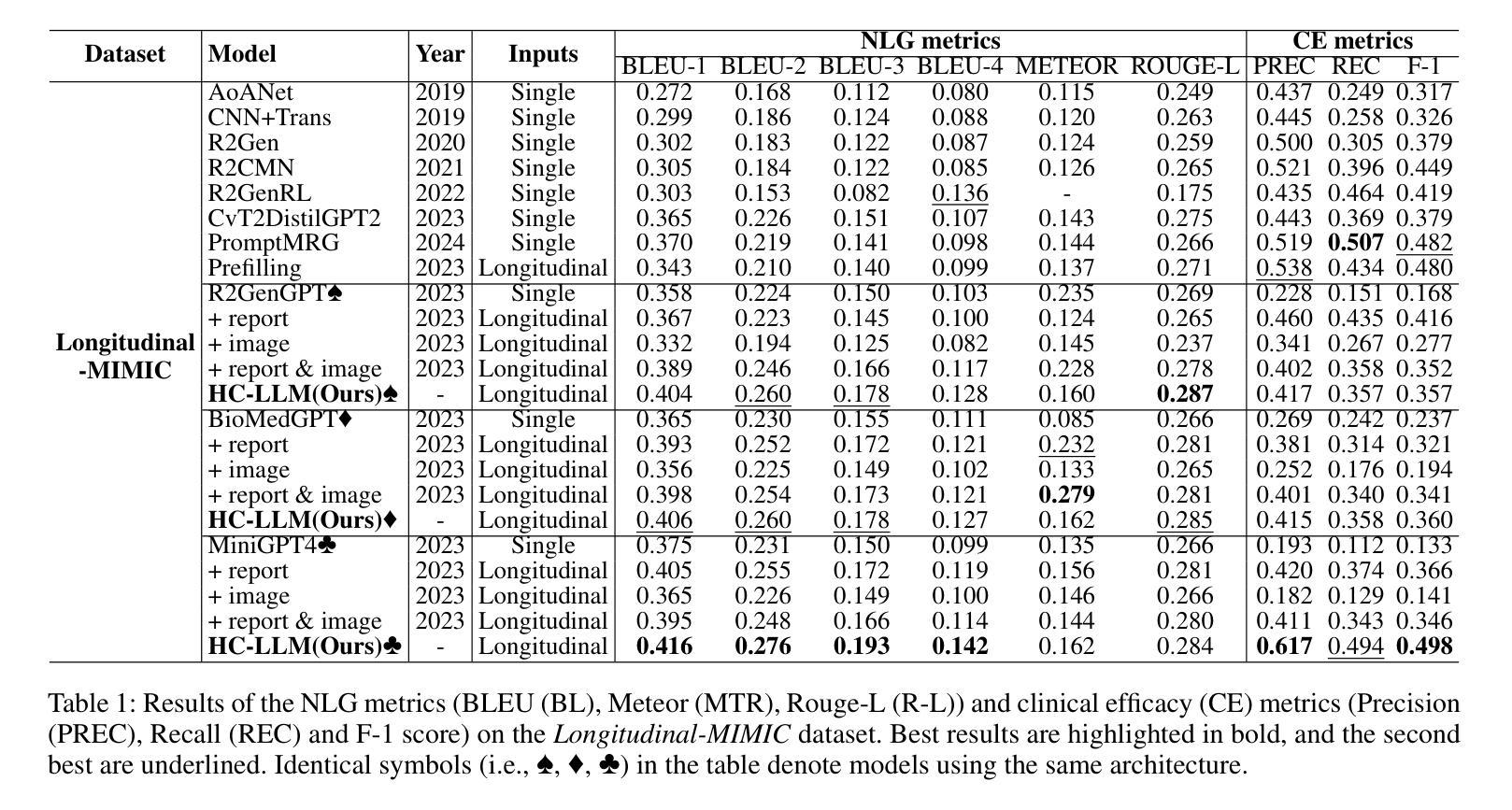
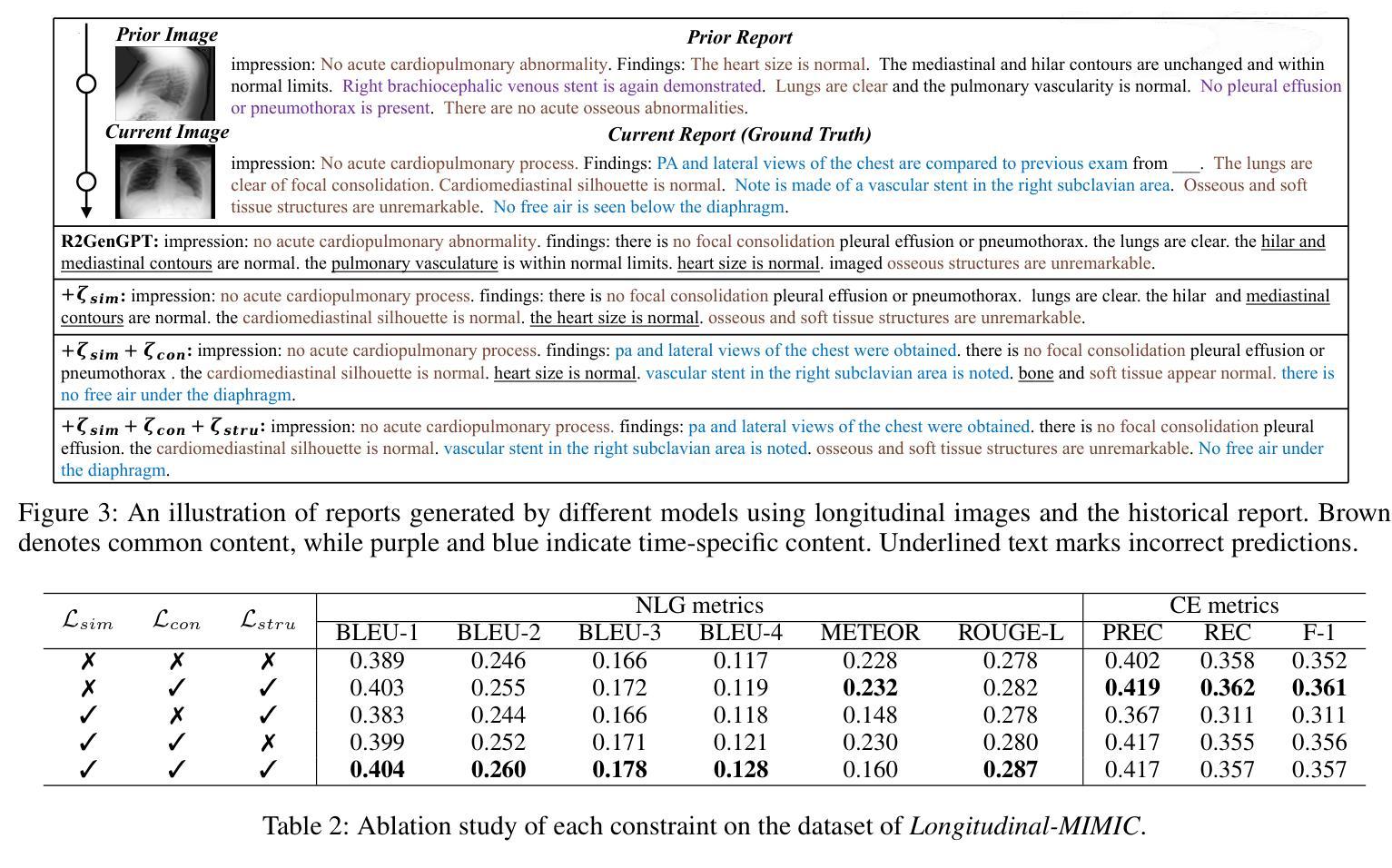
HC-LLM: Historical-Constrained Large Language Models for Radiology Report Generation
Authors:Tengfei Liu, Jiapu Wang, Yongli Hu, Mingjie Li, Junfei Yi, Xiaojun Chang, Junbin Gao, Baocai Yin
Radiology report generation (RRG) models typically focus on individual exams, often overlooking the integration of historical visual or textual data, which is crucial for patient follow-ups. Traditional methods usually struggle with long sequence dependencies when incorporating historical information, but large language models (LLMs) excel at in-context learning, making them well-suited for analyzing longitudinal medical data. In light of this, we propose a novel Historical-Constrained Large Language Models (HC-LLM) framework for RRG, empowering LLMs with longitudinal report generation capabilities by constraining the consistency and differences between longitudinal images and their corresponding reports. Specifically, our approach extracts both time-shared and time-specific features from longitudinal chest X-rays and diagnostic reports to capture disease progression. Then, we ensure consistent representation by applying intra-modality similarity constraints and aligning various features across modalities with multimodal contrastive and structural constraints. These combined constraints effectively guide the LLMs in generating diagnostic reports that accurately reflect the progression of the disease, achieving state-of-the-art results on the Longitudinal-MIMIC dataset. Notably, our approach performs well even without historical data during testing and can be easily adapted to other multimodal large models, enhancing its versatility.
放射学报告生成(RRG)模型通常关注个别检查,往往忽略了历史视觉或文本数据的整合,这对于患者随访至关重要。传统方法在整合历史信息时通常难以处理长序列依赖问题,而大型语言模型(LLM)擅长上下文学习,非常适合分析纵向医疗数据。鉴于此,我们提出了一个新的历史约束大型语言模型(HC-LLM)框架,用于RRG,通过约束纵向图像与其相应报告之间的一致性和差异,增强LLM的纵向报告生成能力。具体地说,我们的方法从纵向的胸部X射线和诊断报告中提取时间共享和时间特定的特征,以捕捉疾病的进展。然后,我们通过应用模态内相似性约束并跨模态对齐各种特征,使用多模态对比和结构约束来确保一致表示。这些组合约束有效地指导了LLM生成能准确反映疾病进展的诊断报告,在Longitudinal-MIMIC数据集上达到了最新结果。值得注意的是,我们的方法即使在测试时没有历史数据也能表现良好,并且可以轻松适应其他多模态大型模型,增强了其通用性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI2025
Summary
本文提出一种基于历史约束的大型语言模型(HC-LLM)框架,用于放射报告生成(RRG)。该框架能够从纵向的胸部X射线和诊断报告中提取时间共享和时间特定的特征,以捕捉疾病的进展,并通过多种约束确保报告的准确性。此框架在Longitudinal-MIMIC数据集上取得了最佳结果。
Key Takeaways
- RRG模型通常关注个体检查,但忽略历史视觉或文本数据的整合,这对患者随访至关重要。
- 传统方法在整合历史信息时面临长期序列依赖问题。
- 大型语言模型(LLMs)擅长上下文学习,适合分析纵向医疗数据。
- HC-LLM框架结合了纵向报告生成能力,通过约束纵向图像与相应报告之间的一致性和差异来实现。
- HC-LLM从纵向胸部X射线和诊断报告中提取时间共享和时间特定的特征,以捕捉疾病进展。
- 通过应用内部模态相似性约束和跨模态多模态对比和结构约束,确保一致性的表示。
点此查看论文截图

Mask Enhanced Deeply Supervised Prostate Cancer Detection on B-mode Micro-Ultrasound
Authors:Lichun Zhang, Steve Ran Zhou, Moon Hyung Choi, Jeong Hoon Lee, Shengtian Sang, Adam Kinnaird, Wayne G. Brisbane, Giovanni Lughezzani, Davide Maffei, Vittorio Fasulo, Patrick Albers, Sulaiman Vesal, Wei Shao, Ahmed N. El Kaffas, Richard E. Fan, Geoffrey A. Sonn, Mirabela Rusu
Prostate cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths among men. The recent development of high frequency, micro-ultrasound imaging offers improved resolution compared to conventional ultrasound and potentially a better ability to differentiate clinically significant cancer from normal tissue. However, the features of prostate cancer remain subtle, with ambiguous borders with normal tissue and large variations in appearance, making it challenging for both machine learning and humans to localize it on micro-ultrasound images. We propose a novel Mask Enhanced Deeply-supervised Micro-US network, termed MedMusNet, to automatically and more accurately segment prostate cancer to be used as potential targets for biopsy procedures. MedMusNet leverages predicted masks of prostate cancer to enforce the learned features layer-wisely within the network, reducing the influence of noise and improving overall consistency across frames. MedMusNet successfully detected 76% of clinically significant cancer with a Dice Similarity Coefficient of 0.365, significantly outperforming the baseline Swin-M2F in specificity and accuracy (Wilcoxon test, Bonferroni correction, p-value<0.05). While the lesion-level and patient-level analyses showed improved performance compared to human experts and different baseline, the improvements did not reach statistical significance, likely on account of the small cohort. We have presented a novel approach to automatically detect and segment clinically significant prostate cancer on B-mode micro-ultrasound images. Our MedMusNet model outperformed other models, surpassing even human experts. These preliminary results suggest the potential for aiding urologists in prostate cancer diagnosis via biopsy and treatment decision-making.
前列腺癌是男性癌症相关死亡的主要原因之一。最近开发的高频微超声成像与常规超声相比具有更高的分辨率,并可能具有更好的能力来区分临床重要的癌症和正常组织。然而,前列腺癌的特征仍然很微妙,与正常组织的边界模糊,外观变化很大,无论是机器学习还是人类都很难在微超声图像上定位它。我们提出了一种新型掩膜增强深度监督微超声网络,称为MedMusNet,可以自动更准确地分割前列腺癌,用作活检程序的潜在目标。MedMusNet利用预测的前列腺癌掩膜在网络内逐层强制学习特征,减少噪声的影响,提高帧间整体一致性。MedMusNet成功检测到了76%的临床重要癌症,Dice相似系数为0.365,在特异性和准确性方面显著优于基线Swin-M2F(Wilcoxon检验,Bonferroni校正,p值<0.05)。虽然病灶水平和患者水平分析显示与人类专家和不同基线相比性能有所提高,但提高并未达到统计学意义,这可能是由于队列人数较少。我们提出了一种在B模式微超声图像上自动检测和分割临床重要前列腺癌的新方法。我们的MedMusNet模型优于其他模型,甚至超越了人类专家。这些初步结果表明,该模型有潜力辅助泌尿科医生进行前列腺癌诊断、活检和治疗决策。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种名为MedMusNet的新颖的前列腺癌自动检测与分割方法,该方法在B模式微超声图像上表现优异。通过利用预测的癌症掩膜,在网络内逐层强化学习特征,减少噪声影响,提高帧间一致性。相较于基线模型Swin-M2F,MedMusNet在特异性及准确度上有所提升,尤其是在临床显著癌症检测方面表现突出。虽然相对于人类专家的性能提升尚未达到统计学意义,但初步结果仍显示出其在辅助泌尿科医生进行前列腺癌诊断和制定治疗方案方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 高频微超声成像技术相较于传统超声具有更高的分辨率,能更好地区分临床显著癌症与正常组织。
- 前列腺癌的特征微妙,与正常组织边界模糊且外观变化大,使得机器学习和人类都难以定位。
- MedMusNet模型利用预测的癌症掩膜,强化学习特征并减少噪声影响,提高分割准确性。
- MedMusNet成功检测出76%的临床显著癌症,Dice相似系数为0.365。相较于基线模型Swin-M2F,其在特异性和准确度上有所提升。
- 虽然相对于人类专家的性能提升未达统计学意义,但MedMusNet的初步结果仍显示出其在辅助前列腺癌诊断方面的潜力。
- MedMusNet模型在B模式微超声图像上的自动检测与分割技术有助于医生进行前列腺癌的诊断、活检和治疗决策。
点此查看论文截图

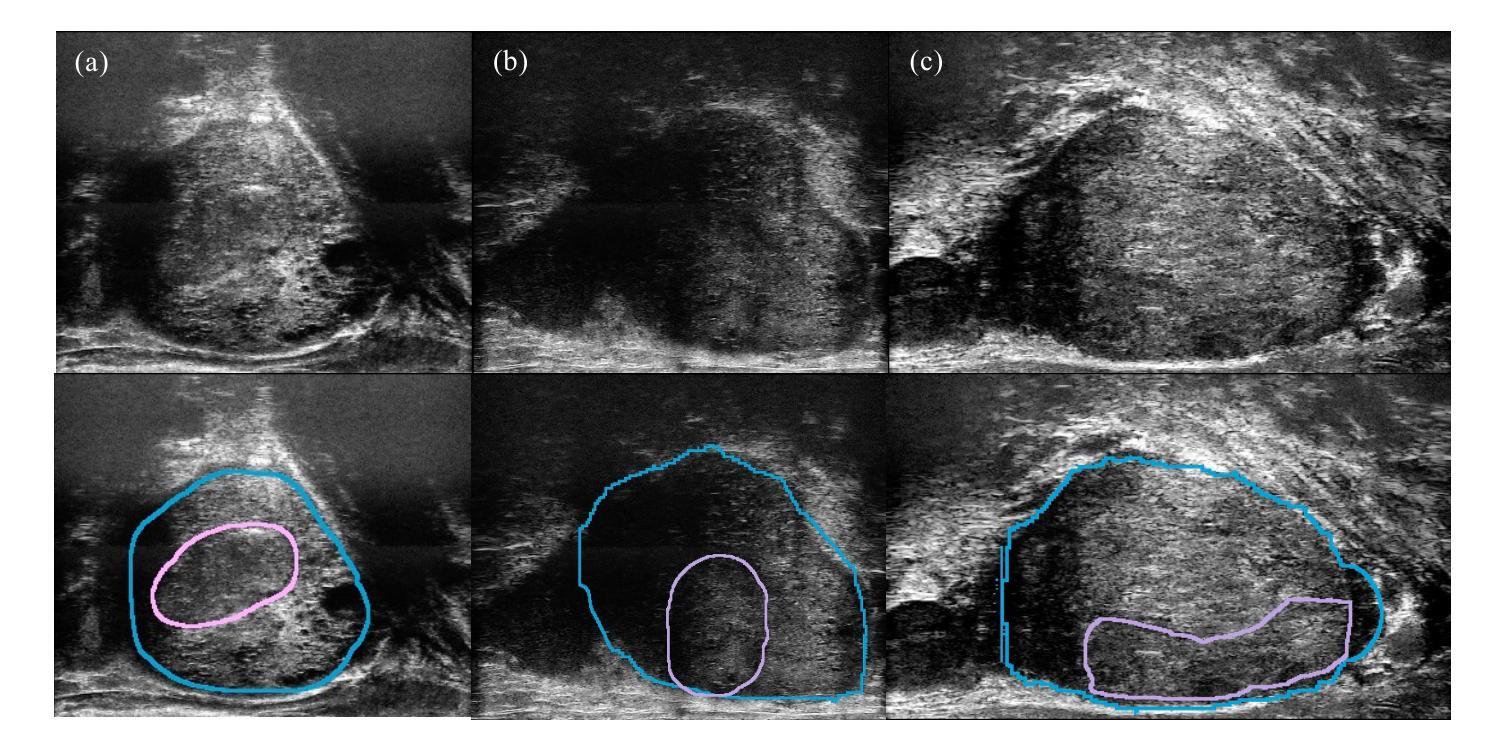
Biological and Radiological Dictionary of Radiomics Features: Addressing Understandable AI Issues in Personalized Prostate Cancer; Dictionary Version PM1.0
Authors:Mohammad R. Salmanpour, Sajad Amiri, Sara Gharibi, Ahmad Shariftabrizi, Yixi Xu, William B Weeks, Arman Rahmim, Ilker Hacihaliloglu
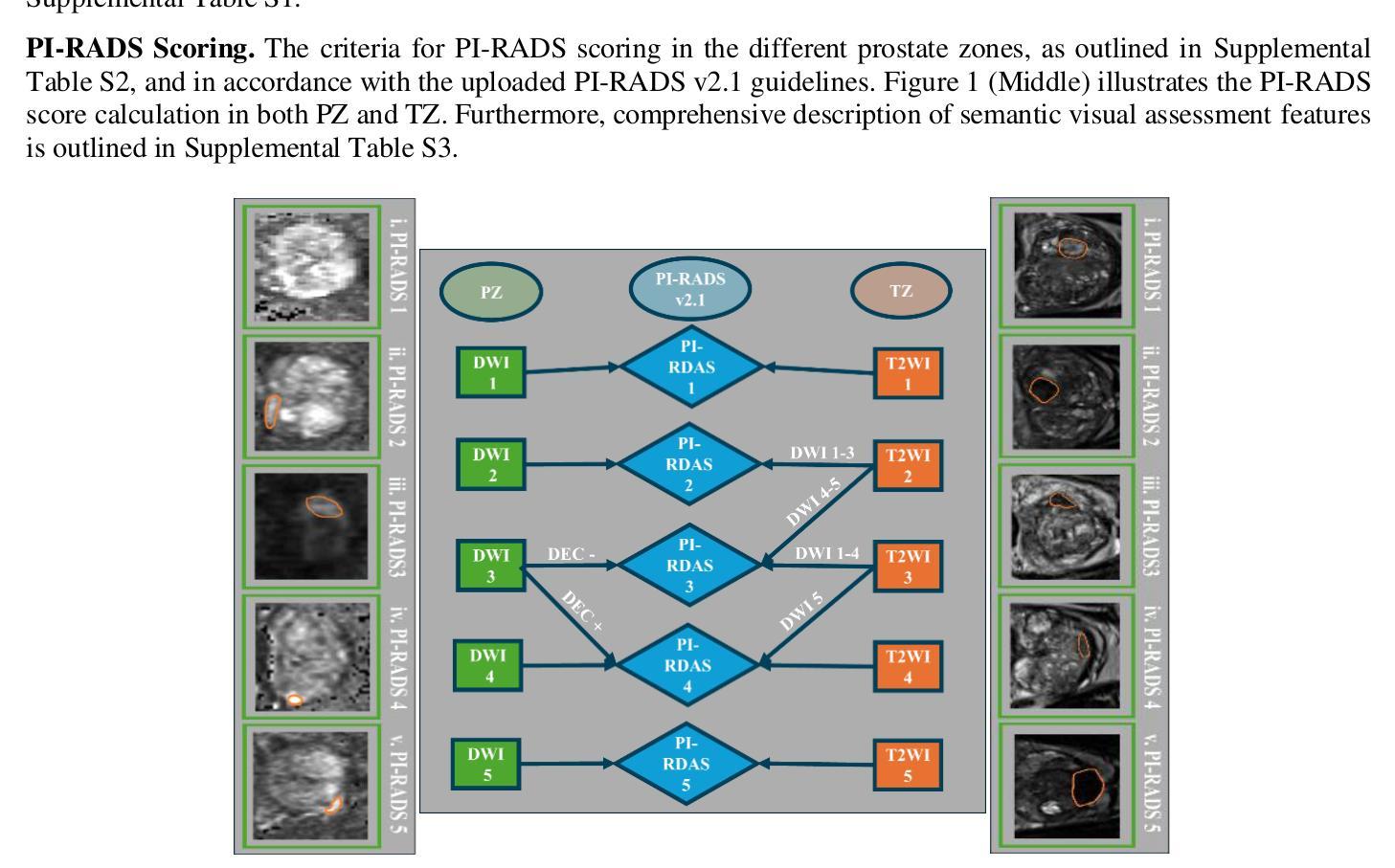
We investigate the connection between visual semantic features defined in PI-RADS and associated risk factors, moving beyond abnormal imaging findings, establishing a shared framework between medical and AI professionals by creating a standardized dictionary of biological/radiological RFs. Subsequently, 6 interpretable and seven complex classifiers, linked with nine interpretable feature selection algorithms (FSA) applied to risk factors, were extracted from segmented lesions in T2-weighted imaging (T2WI), diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) multiparametric-prostate MRI sequences to predict the UCLA scores. We then utilized the created dictionary to interpret the best-predictive models. Combining T2WI, DWI, and ADC with FSAs including ANOVA F-test, Correlation Coefficient, and Fisher Score, and utilizing logistic regression, identified key features: The 90th percentile from T2WI, which captures hypo-intensity related to prostate cancer risk; Variance from T2WI, indicating lesion heterogeneity; shape metrics including Least Axis Length and Surface Area to Volume ratio from ADC, describing lesion shape and compactness; and Run Entropy from ADC, reflecting texture consistency. This approach achieved the highest average accuracy of 0.78, significantly outperforming single-sequence methods (p-value<0.05). The developed dictionary for Prostate-MRI (PM1.0) serves as a common language, fosters collaboration between clinical professionals and AI developers to advance trustworthy AI solutions that support reliable/interpretable clinical decisions.
我们研究了PI-RADS中定义的视觉语义特征和相关风险因素之间的联系,不仅关注异常成像结果,还通过创建生物学/放射学RF的标准字典,在医疗和人工智能专业人士之间建立共享框架。随后,我们从T2加权成像(T2WI)、扩散加权成像(DWI)和表观扩散系数(ADC)多参数前列腺MRI序列中分割的病灶中提取了6个可解释和七个复杂分类器,这些分类器与应用于风险因素的九个可解释特征选择算法(FSA)相关联,以预测UCLA评分。然后,我们利用创建的字典来解释最佳预测模型。结合T2WI、DWI和ADC与FSA,包括ANOVA F检验、相关系数和费舍尔得分,并利用逻辑回归,确定了关键特征:T2WI的90th百分位数,捕捉与前列腺癌风险相关的低强度;表示病变异质性的T2WI方差;来自ADC的形状度量指标,包括最小轴长、表面积与体积比,描述病变的形状和紧凑度;以及反映纹理一致性的ADC的Run Entropy。该方法达到了最高的平均准确率0.78,显著优于单序列方法(p值<0.05)。所开发的前列腺MRI字典(PM1.0)作为一种通用语言,促进了临床专业人士和人工智能开发者之间的合作,推动了可信赖的人工智能解决方案的发展,支持可靠/可解释的临床决策。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 24 pages, 3 Figures, 2 Tables
Summary
本文研究了PI-RADS定义的视觉语义特征与相关风险因素之间的关系,并创建了一个标准化词典来描述生物学/放射学中的风险因素。利用该词典并结合特征选择算法(FSA),对T2加权成像(T2WI)、扩散加权成像(DWI)和表观扩散系数(ADC)的多参数前列腺MRI序列进行特征提取和模型预测,实现对UCLA评分的预测。该方法成功构建了平均准确率为0.78的预测模型,且显著优于单序列方法。所开发的PM1.0词典作为临床专业人士与人工智能开发者之间的共同语言,有助于推动可靠且可解释的人工智能解决方案的发展,以支持可信的临床决策。
Key Takeaways
- 研究了PI-RADS视觉语义特征与风险因素的关联,并超越了异常成像发现,建立了医学和AI专业人士之间的共享框架。
- 创建了一个标准化词典来描述生物学/放射学中的风险因素(PM1.0)。
- 使用了多种特征选择算法(FSA)来从多参数前列腺MRI序列中提取关键特征。
- 结合T2WI、DWI和ADC数据预测UCLA评分,构建了平均准确率为0.78的预测模型。
- 模型成功识别了与前列腺癌风险相关的关键特征,如T2WI的90th百分位数的低强度、T2WI的方差表示的病变异质性等。
- 该模型显著优于单序列方法(p值<0.05)。
- PM1.0词典为临床专业人士和人工智能开发者提供了共同语言,促进了可靠且可解释的人工智能解决方案的发展。
点此查看论文截图

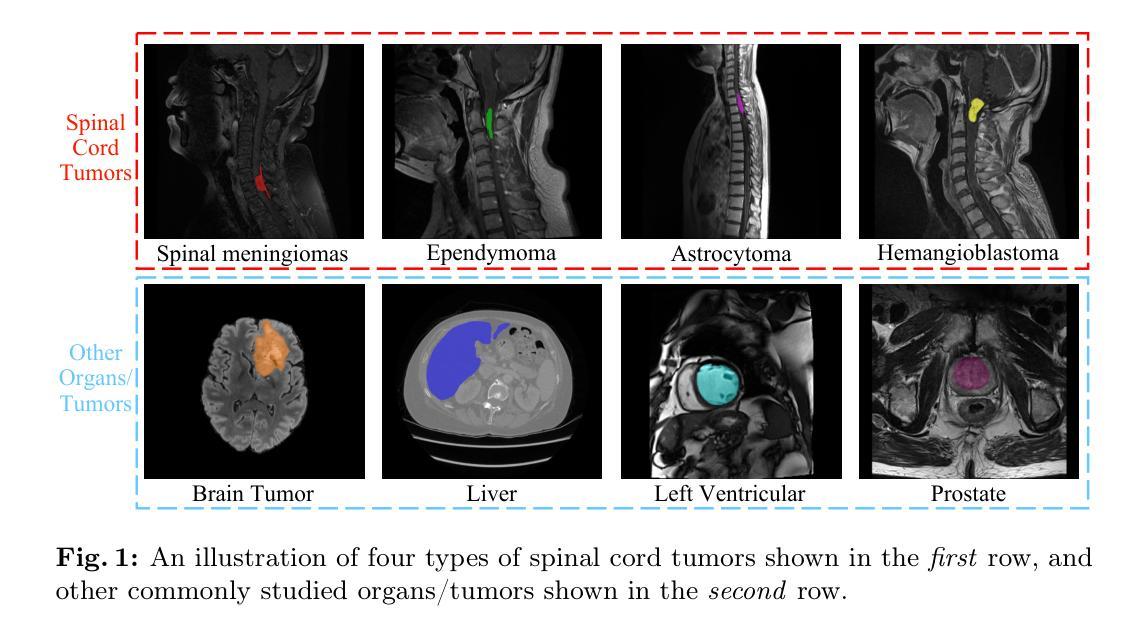
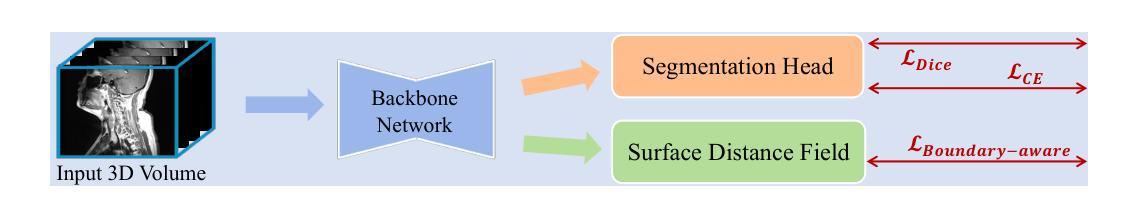
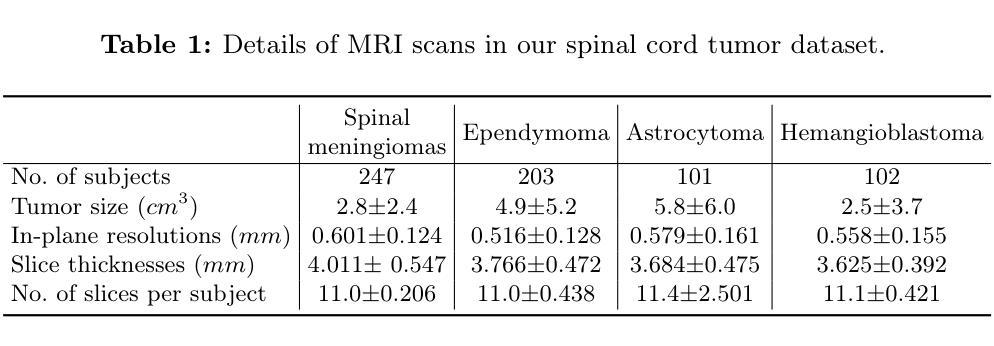
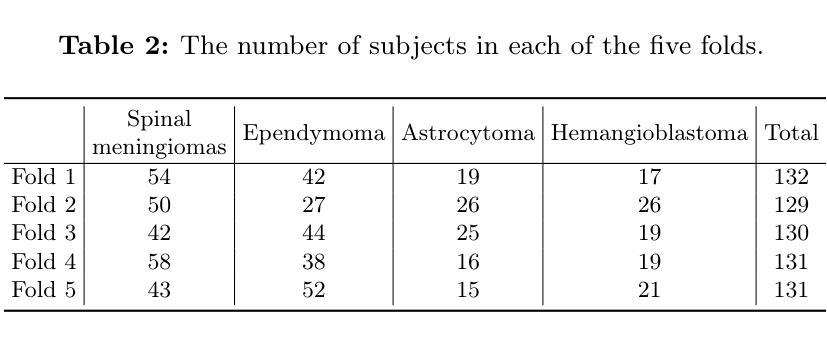
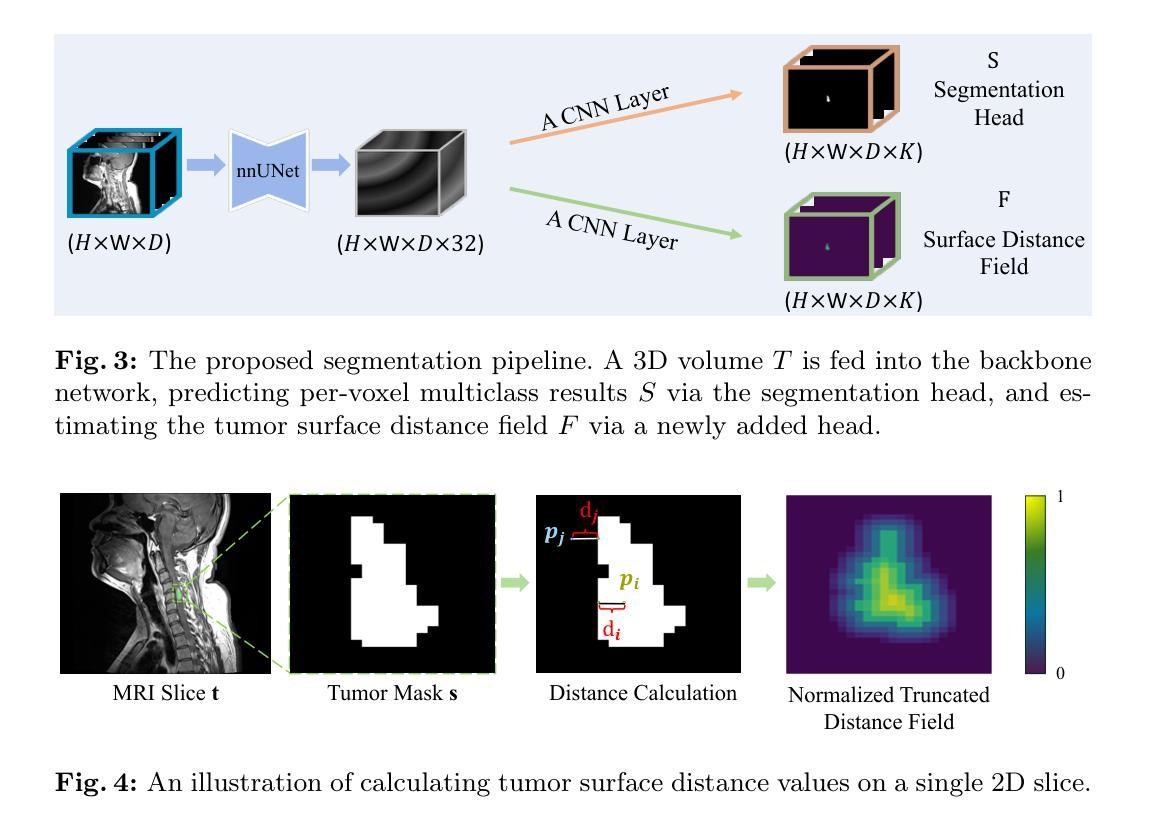
BATseg: Boundary-aware Multiclass Spinal Cord Tumor Segmentation on 3D MRI Scans
Authors:Hongkang Song, Zihui Zhang, Yanpeng Zhou, Jie Hu, Zishuo Wang, Hou Him Chan, Chon Lok Lei, Chen Xu, Yu Xin, Bo Yang
Spinal cord tumors significantly contribute to neurological morbidity and mortality. Precise morphometric quantification, encompassing the size, location, and type of such tumors, holds promise for optimizing treatment planning strategies. Although recent methods have demonstrated excellent performance in medical image segmentation, they primarily focus on discerning shapes with relatively large morphology such as brain tumors, ignoring the challenging problem of identifying spinal cord tumors which tend to have tiny sizes, diverse locations, and shapes. To tackle this hard problem of multiclass spinal cord tumor segmentation, we propose a new method, called BATseg, to learn a tumor surface distance field by applying our new multiclass boundary-aware loss function. To verify the effectiveness of our approach, we also introduce the first and large-scale spinal cord tumor dataset. It comprises gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted 3D MRI scans from 653 patients and contains the four most common spinal cord tumor types: astrocytomas, ependymomas, hemangioblastomas, and spinal meningiomas. Extensive experiments on our dataset and another public kidney tumor segmentation dataset show that our proposed method achieves superior performance for multiclass tumor segmentation.
脊髓肿瘤对神经系统的发病率和死亡率有显著影响。精确的形态计量量化,包括肿瘤的大小、位置和类型,有望优化治疗规划策略。尽管最近的方法在医学图像分割中表现出了卓越的性能,但它们主要关注辨别形态相对较大的肿瘤,如脑肿瘤,而忽略了识别脊髓肿瘤的难题,这些肿瘤往往尺寸小、位置多样、形态各异。为了解决多类脊髓肿瘤分割这一难题,我们提出了一种新方法,称为BATseg,通过应用我们新的多类边界感知损失函数来学习肿瘤表面距离场。为了验证我们的方法的有效性,我们还介绍了第一个大规模的脊髓肿瘤数据集。它包含653例患者的钆增强T1加权3D MRI扫描,包含四种最常见的脊髓肿瘤类型:星形细胞瘤、室管膜瘤、血管母细胞瘤和脊髓脑膜瘤。在我们数据集和另一个公共肾脏肿瘤分割数据集上的大量实验表明,我们提出的方法在多类肿瘤分割方面取得了优越的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF ECCV 2024 Workshop on BioImage Computing. Code and data are available at: https://github.com/vLAR-group/BATseg
Summary
基于精确形态学测量的新方法,对于优化脊髓肿瘤治疗策略具有巨大潜力。然而,现有方法难以解决多类脊髓肿瘤分割问题。为此,我们提出了一种名为BATseg的新方法,通过应用新的多类边界感知损失函数来学习肿瘤表面距离场。同时,我们还引入了首个大规模脊髓肿瘤数据集,包含来自653位患者的钆增强T1加权三维MRI扫描数据,并证明该方法在多类肿瘤分割上具有优越性能。该数据集包括最常见的四种脊髓肿瘤类型:神经胶质瘤、神经纤维瘤病、内皮样细胞囊样细胞瘤和脊髓脊膜瘤。此项研究的目的是更精准地治疗脊髓肿瘤患者,缓解他们神经受损程度严重的现象,甚至是防治进一步加剧患者的神经问题以提高生活质量等现实生存需求压力的情况出现。所研发的该数据库将对精准治疗具有推动作用。经过试验证明其方法对于分割尺寸小、位置多样且形态各异的脊髓肿瘤有明显优势。此方法有助于提升治疗精准度与预后效果。该数据集也可用于未来对多类肿瘤分割算法进行更深入的评估和优化。该研究的成果对于提高医学图像分割技术的实际应用价值和推进相关领域的科研进展具有重要意义。简而言之,研究为脊髓肿瘤的治疗提供了新的视角和方法。
Key Takeaways
点此查看论文截图

Leveraging Semantic Asymmetry for Precise Gross Tumor Volume Segmentation of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Planning CT
Authors:Zi Li, Ying Chen, Zeli Chen, Yanzhou Su, Tai Ma, Tony C. W. Mok, Yan-Jie Zhou, Yunhai Bai, Zhinlin Zheng, Le Lu, Yirui Wang, Jia Ge, Xianghua Ye, Senxiang Yan, Dakai Jin
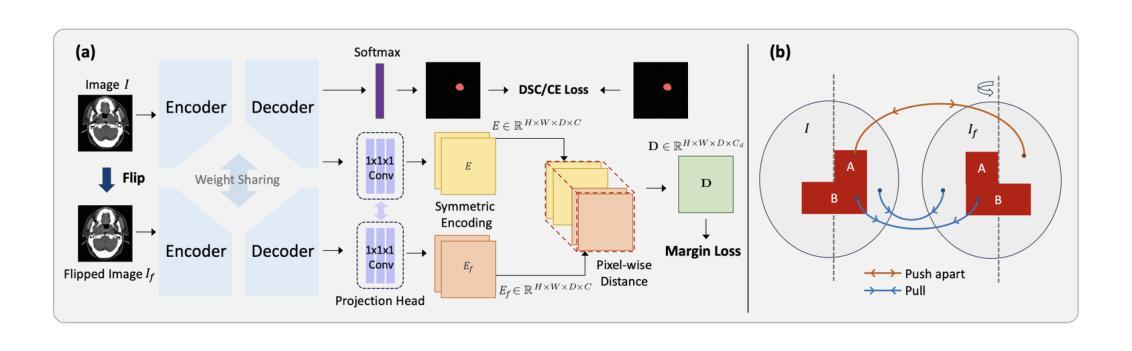
In the radiation therapy of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), clinicians typically delineate the gross tumor volume (GTV) using non-contrast planning computed tomography to ensure accurate radiation dose delivery. However, the low contrast between tumors and adjacent normal tissues necessitates that radiation oncologists manually delineate the tumors, often relying on diagnostic MRI for guidance. % In this study, we propose a novel approach to directly segment NPC gross tumors on non-contrast planning CT images, circumventing potential registration errors when aligning MRI or MRI-derived tumor masks to planning CT. To address the low contrast issues between tumors and adjacent normal structures in planning CT, we introduce a 3D Semantic Asymmetry Tumor segmentation (SATs) method. Specifically, we posit that a healthy nasopharyngeal region is characteristically bilaterally symmetric, whereas the emergence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma disrupts this symmetry. Then, we propose a Siamese contrastive learning segmentation framework that minimizes the voxel-wise distance between original and flipped areas without tumor and encourages a larger distance between original and flipped areas with tumor. Thus, our approach enhances the sensitivity of features to semantic asymmetries. % Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed SATs achieves the leading NPC GTV segmentation performance in both internal and external testing, \emph{e.g.}, with at least 2% absolute Dice score improvement and 12% average distance error reduction when compared to other state-of-the-art methods in the external testing.
在鼻咽癌(NPC)的放射治疗过程中,临床医生通常使用非对比计划计算机断层扫描(CT)来精确描绘大体肿瘤体积(GTV),以确保准确的辐射剂量传递。然而,肿瘤与邻近正常组织之间的对比度较低,这使得放射肿瘤学家必须手动描绘肿瘤,通常依赖诊断性磁共振成像(MRI)进行引导。在本研究中,我们提出了一种在非对比计划CT图像上直接分割鼻咽癌大体肿瘤的新方法,从而避免了将MRI或MRI衍生的肿瘤掩膜与计划CT进行对齐时可能出现的潜在注册误差。为了解决规划CT中肿瘤与邻近正常结构之间对比度低的问题,我们引入了3D语义不对称肿瘤分割(SATs)方法。具体来说,我们认为健康的鼻咽区域具有典型的双侧对称性,而鼻咽癌的出现会破坏这种对称性。然后,我们提出了一种Siamese对比学习分割框架,该框架可以最小化原始区域和翻转区域(无肿瘤)之间的体素距离,同时鼓励原始区域和翻转区域(有肿瘤)之间的距离增大。因此,我们的方法提高了对语义不对称性的特征敏感性。大量实验表明,所提出SATs在内部和外部测试中均实现了领先的NPC GTV分割性能,例如与外部测试中的其他最先进的方法相比,至少提高了2%的绝对Dice得分和降低了12%的平均距离误差。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种新型方法,直接在非对比剂规划计算机断层扫描(CT)图像上分割鼻咽癌(NPC)的肿瘤体积,避免了MRI或MRI衍生的肿瘤掩膜与规划CT对齐时可能出现的注册误差。该方法通过利用健康的鼻咽区域具有典型的双侧对称性,而鼻咽癌的出现会破坏这种对称性这一特性,引入了一种名为语义不对称肿瘤分割(SATs)的3D分割方法。实验表明,SATs在内部和外部测试中均实现了领先的鼻咽癌GTV分割性能。
Key Takeaways
- 本研究提出了一种新型的鼻咽癌肿瘤体积分割方法,该方法直接应用于非对比剂规划CT图像。
- 方法的核心在于利用健康鼻咽区域的双侧对称性以及鼻咽癌对此对称性的破坏来进行肿瘤分割。
- 研究中引入了名为语义不对称肿瘤分割(SATs)的3D分割方法,以处理肿瘤与相邻正常组织之间对比度低的问题。
- SATs方法通过最小化原始和翻转区域(无肿瘤)之间的体素距离,并鼓励原始和翻转区域(有肿瘤)之间保持较大的距离,从而提高特征对语义不对称的敏感性。
- 实验结果显示,SATs方法相较于其他先进方法,在外部测试中实现了至少2%的绝对Dice分数提高和12%的平均距离误差降低。
点此查看论文截图

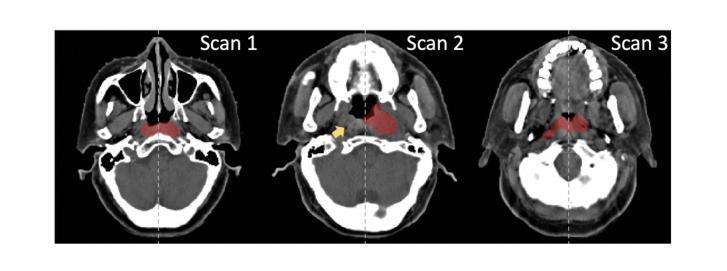
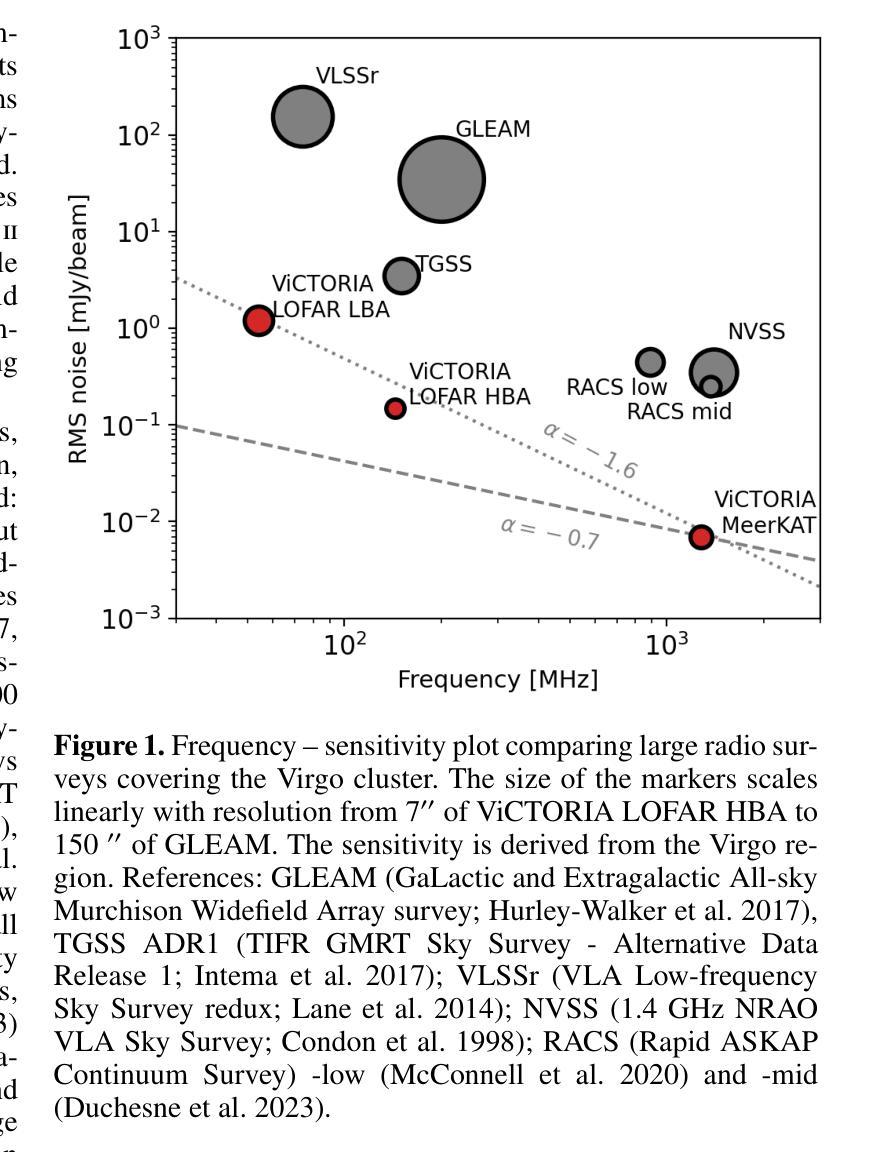
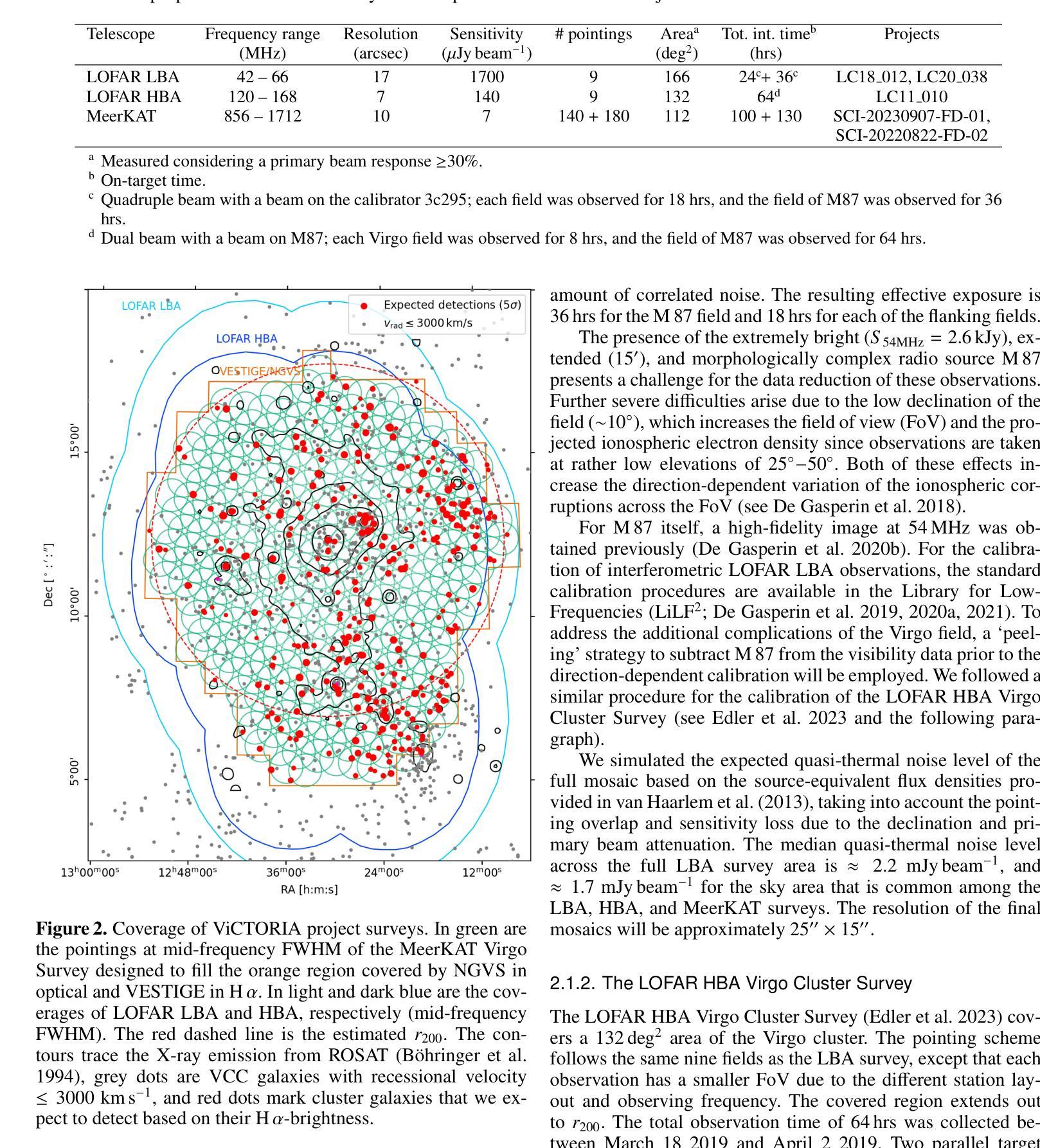
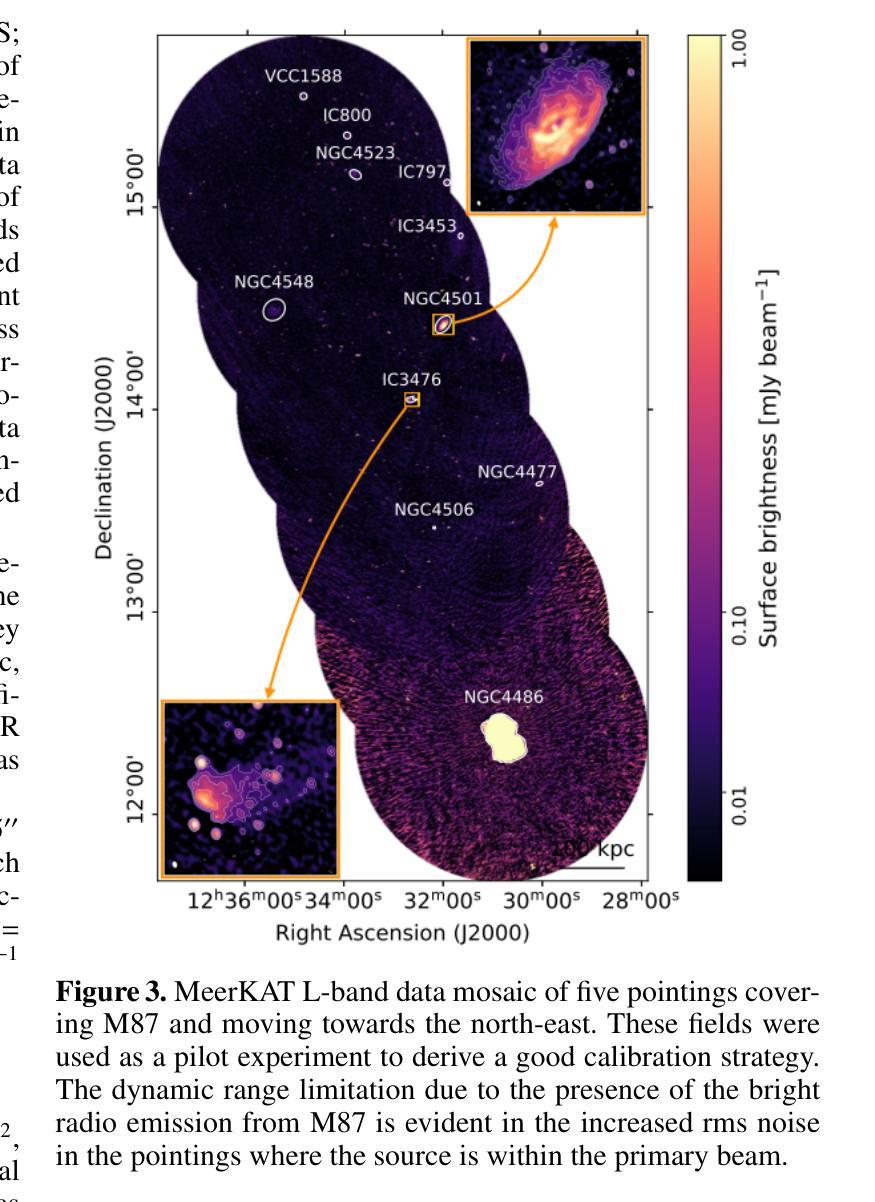
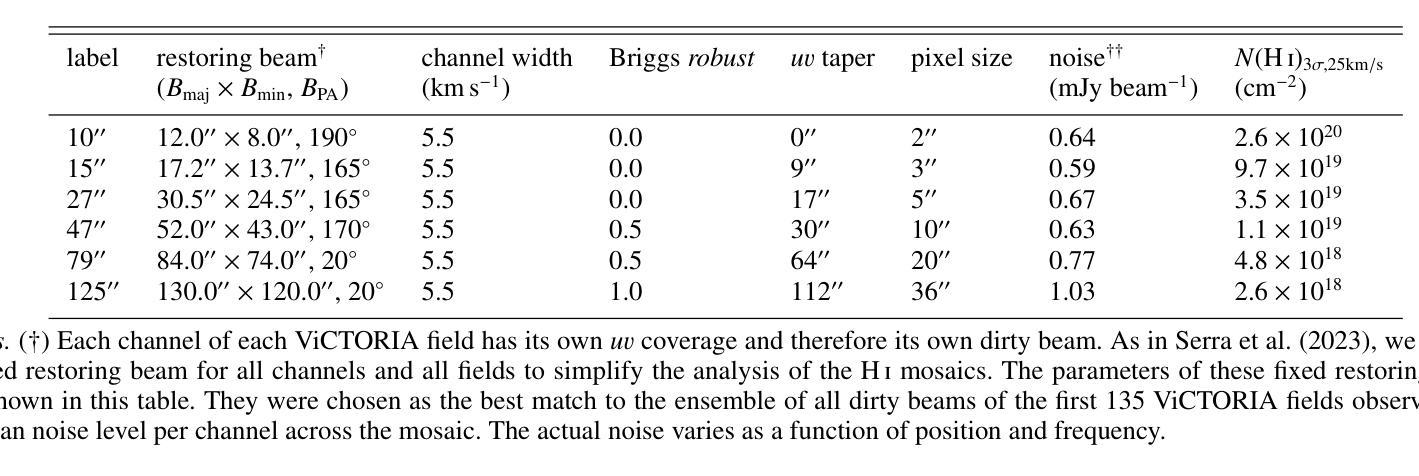
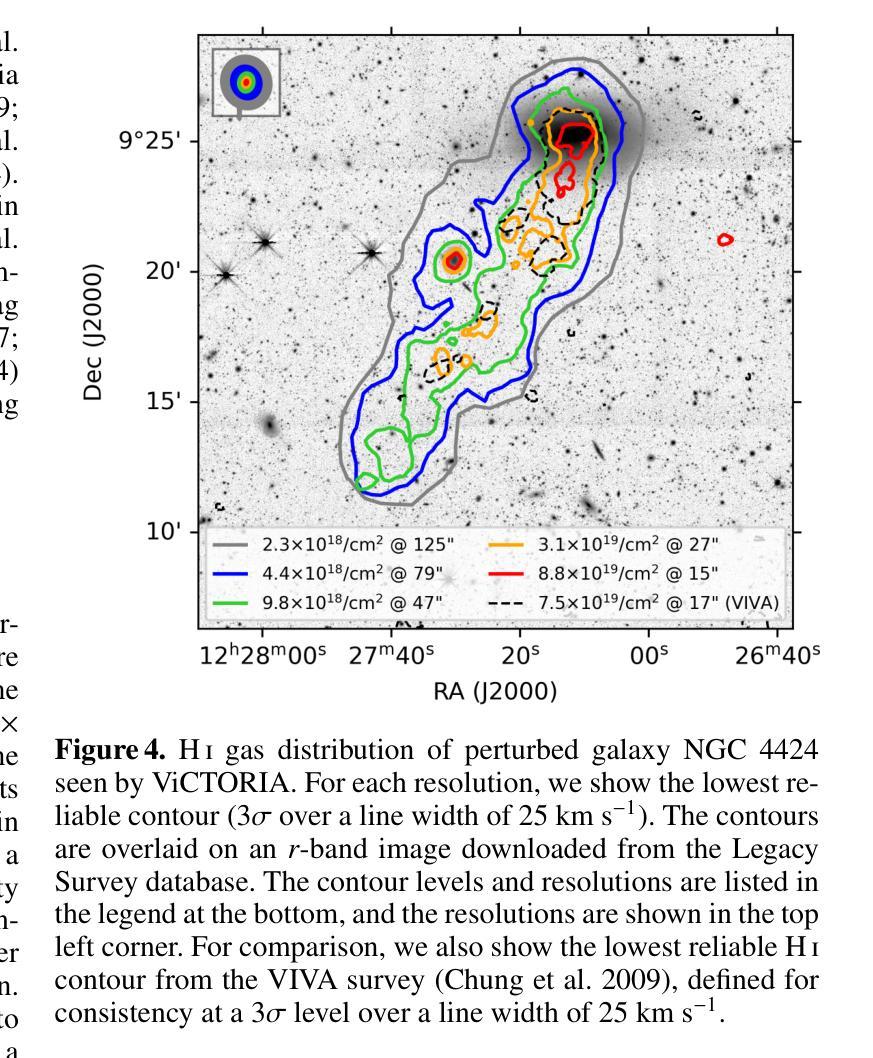
The ViCTORIA project: description of a multi-frequency radio survey of the Virgo galaxy cluster
Authors:F. de Gasperin, H. W. Edler, A. Boselli, P. Serra, M. Fossati, V. Heesen, A. Merloni, M. Murgia, T. H. Reiprich, A. Spasic, N. Zabel
The Virgo cluster is the closest richest nearby galaxy cluster. It is in the formation process, with a number of sub-clusters undergoing merging and interactions. Although a great laboratory to study galaxy evolution and cluster formation, its large apparent size and the severe dynamic range limitations due to the presence of the bright radio source Virgo A (M 87) reduced the ability of past wide-area radio surveys to image the region with high sensitivity and fidelity. In this paper we describe the “Virgo Cluster multi-Telescope Observations in Radio of Interacting galaxies and AGN” (ViCTORIA) project. The survey and its data reduction strategy are designed to mitigate the challenges of this field and deliver: images from 42 MHz to 1.7 GHz frequencies of the Virgo cluster, about 60 times deeper than existing data, in full polarisation, and including a blind HI survey that aims at mapping seven times more galaxies than previous experiments and without selection biases. Data have been collected with the Low-Frequency Array (LOFAR) and with MeerKAT in L-band, including polarisation and enough frequency resolution to conduct local HI studies. At the distance of Virgo, current radio instruments have the resolution to probe scales of ~500 pc and the sensitivity to study dwarf galaxies, the most fragile systems given their shallow gravitational potential wells, making Virgo a unique laboratory to study galaxy evolution and AGN feedback in a rich environment. In this work, we present some preliminary results, including high resolution images of the radio emission surrounding M 87, that show that the lobes are filled with filamentary structures. The combination of the presented radio surveys with state-of-the-art optical, UV, X-ray surveys will massively increase the scientific output from the studies of the Virgo cluster, making the ViCTORIA Project’s legacy value outstanding.
处女座星系团是附近最丰富且距离最近的天体星系团之一。它正处于形成过程中,多个子星系团正在合并和互动。尽管它是一个研究星系演化和星系团形成的重要实验室,但由于其巨大的表面大小以及明亮无线电源处女座A(M 87)产生的动态范围严重限制因素,过去的大型区域无线电调查很难以高度敏感性和保真度来呈现该区域。在这篇论文中,我们介绍了“处女座星系团交互星系和活跃星系核的无线电多望远镜观测”(ViCTORIA)项目。我们的调查及其数据缩减策略旨在缓解该领域的挑战,并带来以下成果:从42兆赫到1.7千兆赫频率的处女座星团的图像,其深度大约是现有数据的60倍,以全极化形式呈现,并包括一个旨在映射比先前实验更多的星系的盲HI调查,目标是没有偏见地映射出比先前实验更多的七倍星系。我们使用低频阵列(LOFAR)和MeerKAT在L波段收集数据,包括极化以及足够的频率分辨率来进行局部HI研究。在处女座的范围内,当前的无线电仪器具有探测约500个天文单位的尺度的分辨率,并具有研究矮星系等的灵敏度,这些矮星系由于其较浅的引力势井而成为最脆弱的系统之一,这使得处女座成为一个独特的实验室来研究丰富的环境中星系演化以及活动星系核反馈。在这项工作中,我们介绍了一些初步结果,包括围绕M 87的高分辨率图像显示其瓣由纤维状结构填充。结合最新的光学、紫外线和X射线调查与本次呈现的无线电调查将大大提高从处女座星团的研究中获得的科学产出,从而突显出ViCTORIA项目的杰出价值。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted for publication in A&A
Summary
Virgo星系团是附近最丰富的星系团,正处于形成过程中,包含许多正在合并和交互的子星系团。由于Virgo A(M 87)的影响,过去的大范围无线电调查难以在此区域进行高灵敏度和保真度的成像。本文介绍了“Virgo星系团多望远镜观测交互星系和活跃星系核的无线电”(ViCTORIA)项目,旨在克服这一难题,并提供从42 MHz到1.7 GHz频率的处女座星系团图像,深度约为现有数据的60倍,包括全极化以及旨在比先前实验多映射七倍星系的盲HI调查。初步结果显示M 87周围的无线电发射高分辨率图像,显示细丝状结构。结合最新的光学、紫外线和X射线调查,ViCTORIA项目将大大提高处女座星系团的研究产出,具有杰出的遗产价值。
Key Takeaways
- Virgo星系团是附近最丰富的星系团,正在形成过程中,包含多个子星系团间的合并和交互作用。
- 由于Virgo A的影响,过去对Virgo星系团进行大范围无线电调查存在挑战。
- ViCTORIA项目旨在克服这些挑战,提供前所未有的深度和高分辨率的无线电图像。
- ViCTORIA项目首次进行了包括全极化的无线电调查,涵盖从42 MHz到1.7 GHz的频率范围。
- 项目包括盲HI调查,旨在映射更多星系,减少选择偏见。
- 使用最新技术获得的初步结果显示M 87周围的无线电发射高分辨率图像具有细丝状结构。
点此查看论文截图

Panning for gold with the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory: an optimal strategy for finding the counterparts to gravitational wave events
Authors:R. A. J. Eyles-Ferris, P. A. Evans, A. A. Breeveld, S. B. Cenko, S. Dichiara, J. A. Kennea, N. J. Klingler, N. P. M. Kuin, F. E. Marshall, S. R. Oates, M. J. Page, S. Ronchini, M. H. Siegel, A. Tohuvavohu, S. Campana, V. D’Elia, J. P. Osborne, K. L. Page, M. De Pasquale, E. Troja
The LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA gravitational wave observatories are currently undertaking their O4 observing run offering the opportunity to discover new electromagnetic counterparts to gravitational wave events. We examine the capability of the Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory (Swift) to respond to these triggers, primarily binary neutron star mergers, with both the UV/Optical Telescope (UVOT) and the X-ray Telescope (XRT). We simulate Swift’s response to a trigger under different strategies using model skymaps, convolving these with the 2MPZ catalogue to produce an ordered list of observing fields, deriving the time taken for Swift to reach the correct field and simulating the instrumental responses to modelled kilonovae and short gamma-ray burst afterglows. We find that UVOT using the $u$ filter with an exposure time of order 120 s is optimal for most follow-up observations and that we are likely to detect counterparts in $\sim6$% of all binary neutron star triggers detectable by LVK in O4. We find that the gravitational wave 90% error area and measured distance to the trigger allow us to select optimal triggers to follow-up. Focussing on sources less than 300 Mpc away or 500 Mpc if the error area is less than a few hundred square degrees, distances greater than previously assumed, offer the best opportunity for discovery by Swift with $\sim5 - 30$% of triggers having detection probabilities $\geq 0.5$. At even greater distances, we can further optimise our follow-up by adopting a longer 250 s or 500 s exposure time.
LIGO、Virgo和KAGRA引力波观测站目前正在开展O4观测运行,有机会发现引力波事件的新电磁对应体。我们研究了尼尔·盖尔尔斯·斯威夫特观测站(Swift)对这些触发事件的响应能力,主要是双中子星合并事件,包括紫外线/光学望远镜(UVOT)和X射线望远镜(XRT)。我们采用不同策略模拟Swift对触发的响应,使用模型星图并结合2MPZ目录生成有序观测场列表,推算Swift到达正确观测场的时间,并模拟仪器对模拟的千新星和短伽马射线暴余辉的响应。我们发现,使用u滤镜曝光时间约为120秒的UVOT最适合大多数后续观测,我们可能检测到LVK在O4中可检测到的所有双中子星触发事件的约6%。我们发现引力波的90%误差区域和到触发的测量距离有助于我们选择最佳触发事件进行后续观测。对于距离小于300Mpc或如果误差面积小于几百平方度则距离为500Mpc的源,比以往假设的更远的距离提供了Swift发现的新机会,约有5-30%的触发事件检测概率≥0.5。在更大的距离上,我们可以通过采用更长的250秒或500秒曝光时间来进一步优化我们的后续观测。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 13 figures. Final version accepted by MNRAS
摘要
LIGO、Virgo和KAGRA引力波观测站正在进行O4观测运行,寻找与引力波事件相对应的新电磁对应物。本文研究了尼尔·盖尔尔斯·斯威夫特天文台(Swift)对这些触发事件(主要是双中子星合并)的响应能力,包括紫外/光学望远镜(UVOT)和X射线望远镜(XRT)。通过模拟斯威夫特对不同策略的响应,结合模型星图与2MPZ目录,生成观测场清单,并推算斯威夫特到达正确观测场的时间。同时模拟仪器对模拟的千新星和短伽马射线暴余辉的响应。研究发现,UVOT使用u滤镜,曝光时间约120秒,最适合大多数后续观测,在O4期间,我们可能会检测到LVK可检测到的双中子星触发事件的约6%。我们发现引力波的90%误差区域和触发源的距离有助于我们选择最佳触发事件进行后续观测。聚焦距离小于300Mpc或误差面积小于几百平方度时距离大于以前假设的来源,提供最佳的发现机会。斯威夫特有约5-30%的触发事件检测概率大于或等于0.5。即使在更大的距离上,通过采用更长的250秒或500秒曝光时间,我们也可以进一步优化后续观测。
关键见解
- LIGO、Virgo和KAGRA引力波观测站正在进行O4观测运行,目标是发现新的电磁对应体。
- 研究了Swift天文台对引力波触发事件的响应能力,包括UVOT和XRT的响应。
- UVOT使用u滤镜,曝光时间约120秒,最适合进行后续观测。
- 在O4期间,预计能检测到约6%的LVK可检测到的双中子星触发事件。
- 引力波的90%误差区域和触发源的距离是选择最佳触发事件进行后续观测的关键因素。
- 最佳发现机会出现在距离小于300Mpc或特定误差区域的来源,并考虑更长的曝光时间以提高检测概率。
点此查看论文截图

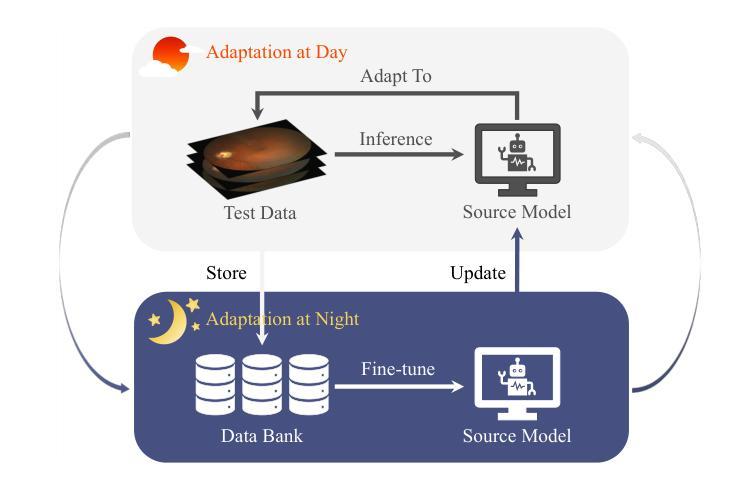
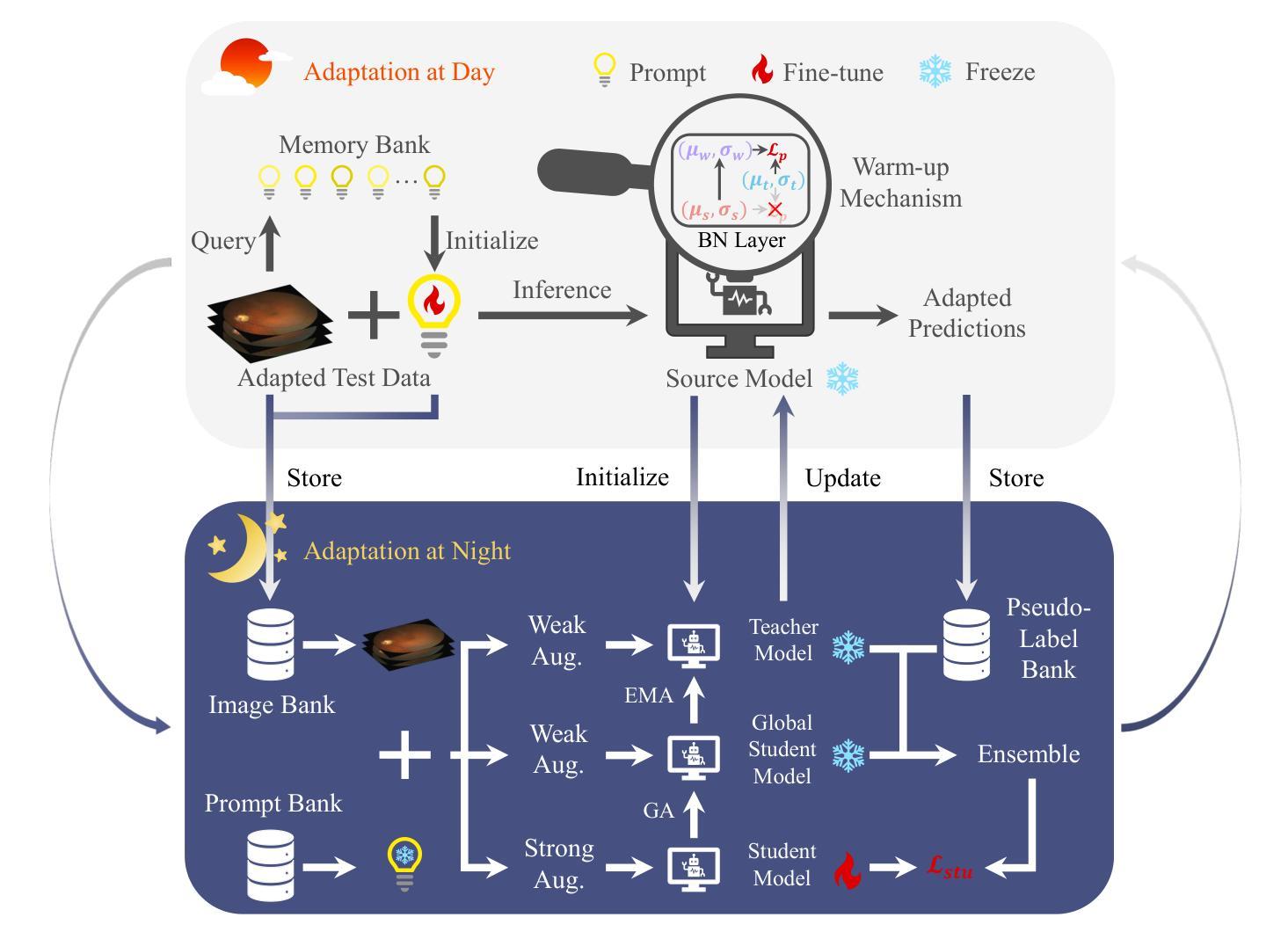
Day-Night Adaptation: An Innovative Source-free Adaptation Framework for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Ziyang Chen, Yiwen Ye, Yongsheng Pan, Jingfeng Zhang, Yanning Zhang, Yong Xia
Distribution shifts widely exist in medical images acquired from different medical centres, hindering the deployment of semantic segmentation models trained on one centre (source domain) to another (target domain). While unsupervised domain adaptation has shown significant promise in mitigating these shifts, it poses privacy risks due to sharing data between centres. To facilitate adaptation while preserving data privacy, source-free domain adaptation (SFDA) and test-time adaptation (TTA) have emerged as effective paradigms, relying solely on target domain data. However, SFDA requires a pre-collected target domain dataset before deployment. TTA insufficiently exploit the potential value of test data, as it processes the test data only once. Considering that most medical centres operate during the day and remain inactive at night in clinical practice, we propose a novel adaptation framework called Day-Night Adaptation (DyNA) with above insights, which performs adaptation through day-night cycles without requiring access to source data. During the day, a low-frequency prompt is trained to adapt the frozen model to each test sample. We construct a memory bank for prompt initialization and develop a warm-up mechanism to enhance prompt training. During the night, we reuse test data collected from the day and introduce a global student model to bridge the knowledge between teacher and student models, facilitating model fine-tuning while ensuring training stability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our DyNA outperforms existing TTA and SFDA methods on two benchmark medical image segmentation tasks. Code will be available after the paper is published.
医学图像在不同医学中心采集时存在广泛的分布转移问题,这阻碍了在一个中心(源域)训练的语义分割模型在另一个中心(目标域)的应用部署。尽管无监督域自适应在缓解这些转移方面显示出巨大潜力,但由于需要在中心之间共享数据,因此存在隐私风险。为了在适应过程中保护数据隐私,出现了无源域自适应(SFDA)和测试时自适应(TTA)这两种有效的范式,它们仅依赖于目标域数据。然而,SFDA需要在部署前预先收集目标域数据集。而TTA未能充分利用测试数据的潜在价值,因为它仅处理一次测试数据。考虑到大多数医学中心的日常运营情况,即在白天运行而在夜间临床实践中处于非活跃状态,我们结合上述见解提出了一个名为“昼夜适应”(DyNA)的新型自适应框架。该框架通过昼夜循环进行自适应,无需访问源数据。在白天,我们训练低频提示来适应每个测试样本的冻结模型。我们构建了用于提示初始化的内存银行,并开发了一种预热机制以增强提示训练。在夜间,我们重复使用白天收集的测试数据,并引入全局学生模型来桥接教师和学学生模型之间的知识,从而帮助进行模型微调并确保训练稳定性。大量实验表明,我们的DyNA在两项基准医学图像分割任务上的表现优于现有的TTA和SFDA方法。代码将在论文发表后提供。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 16 pages, 4 figures, 6 tables
Summary
本文主要探讨医学图像在不同医学中心间的分布差异导致的领域适应性问题。针对无监督领域适应方法存在的数据共享隐私问题,提出了源无关领域适应(SFDA)和测试时间适应(TTA)两大有效模式。在此基础上,结合医学中心的日常运营特点,本文提出了一种新颖的领域适应框架——Day-Night Adaptation(DyNA),它通过日夜周期进行模型适应,无需访问源数据。该框架在日间采用低频提示对冻结模型进行适应训练,并建立提示初始化记忆库和预热机制来增强提示训练效果。夜间则利用日间收集的测试数据进行模型微调,并引入全局学生模型以桥接教师和学生的知识,确保训练稳定性。实验证明,DyNA在两项基准医学图像分割任务上的表现优于现有的TTA和SFDA方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像在不同医学中心间存在分布差异,影响模型应用。
- 无监督领域适应方法虽有助于缓解分布差异,但存在数据共享隐私问题。
- 源无关领域适应(SFDA)和测试时间适应(TTA)是两种有效保护隐私的适应模式。
- 提出的Day-Night Adaptation(DyNA)框架结合医学中心的日常运营特点,通过日夜周期进行模型适应,无需访问源数据。
- DyNA采用低频提示进行日间模型适应训练,并建立提示初始化记忆库和预热机制。
- 夜间利用测试数据进行模型微调,引入全局学生模型以确保训练稳定性和知识桥接。
点此查看论文截图

Invertible ResNets for Inverse Imaging Problems: Competitive Performance with Provable Regularization Properties
Authors:Clemens Arndt, Judith Nickel
Learning-based methods have demonstrated remarkable performance in solving inverse problems, particularly in image reconstruction tasks. Despite their success, these approaches often lack theoretical guarantees, which are crucial in sensitive applications such as medical imaging. Recent works by Arndt et al (2023 Inverse Problems 39 125018, 2024 Inverse Problems 40 045021) addressed this gap by analyzing a data-driven reconstruction method based on invertible residual networks (iResNets). They revealed that, under reasonable assumptions, this approach constitutes a convergent regularization scheme. However, the performance of the reconstruction method was only validated on academic toy problems and small-scale iResNet architectures. In this work, we address this gap by evaluating the performance of iResNets on two real-world imaging tasks: a linear blurring operator and a nonlinear diffusion operator. To do so, we extend some of the theoretical results from Arndt et al to encompass nonlinear inverse problems and offer insights for the design of large-scale performant iResNet architectures. Through numerical experiments, we compare the performance of our iResNet models against state-of-the-art neural networks, confirming their efficacy. Additionally, we numerically investigate the theoretical guarantees of this approach and demonstrate how the invertibility of the network enables a deeper analysis of the learned forward operator and its learned regularization.
基于学习的方法在解决反问题方面表现出了显著的性能,特别是在图像重建任务中。尽管这些方法取得了成功,但它们通常缺乏理论保证,这在医疗成像等敏感应用中至关重要。Arndt等人近期的工作(2023年逆向问题39 125018;2024年逆向问题40 045021)通过分析基于可逆残差网络(iResNets)的数据驱动重建方法,填补了这一空白。他们证明,在合理的假设下,这种方法构成了一种收敛的正则化方案。然而,重建方法的性能仅在学术玩具问题和小型iResNet架构上得到了验证。在这项工作中,我们通过评估iResNets在现实世界成像任务(线性模糊算子和非线性扩散算子)上的性能来解决这一差距。为此,我们扩展了Arndt等人的一些理论结果,以涵盖非线性反问题,并为设计大规模高性能iResNet架构提供了见解。通过数值实验,我们将iResNet模型的性能与最先进的神经网络进行了比较,证实了其有效性。此外,我们还从数值上研究了该方法的理论保证,并展示了网络的可逆性如何使我们能够更深入地分析学习到的正向算子和其学习的正则化。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于学习的方法在解决反问题,特别是在图像重建任务中表现出卓越的性能。然而,这些方法往往缺乏理论保证,这在医疗成像等敏感应用中至关重要。最近的研究分析了基于可逆残差网络(iResNets)的数据驱动重建方法,并揭示了其在合理假设下构成收敛正则化方案的可能性。然而,该重建方法的性能仅在学术玩具问题和小规模iResNet架构上得到验证。本研究通过评估iResNets在真实世界成像任务(线性模糊算子和非线性扩散算子)上的性能来弥补这一不足。研究扩展了之前的理论结果,涵盖了非线性反问题,并为设计高性能的大规模iResNet架构提供了见解。数值实验证实iResNet模型与最新神经网络相比具有优越性能,并对网络的可逆性如何促进对所学前向算子和正则化的深入分析进行了数值探讨。
Key Takeaways
- 学习方法在图像重建中表现优秀。
- 对于敏感应用如医疗成像,理论保证至关重要。
- 基于可逆残差网络(iResNets)的数据驱动重建方法构成收敛正则化方案。
- 之前的研究仅在学术玩具问题和小规模架构上验证了iResNets的性能。
- 本研究评估了iResNets在真实世界成像任务(如线性模糊和非线性扩散)上的性能。
- 研究扩展了理论结果以涵盖非线性反问题。
点此查看论文截图

MGH Radiology Llama: A Llama 3 70B Model for Radiology
Authors:Yucheng Shi, Peng Shu, Zhengliang Liu, Zihao Wu, Quanzheng Li, Tianming Liu, Ninghao Liu, Xiang Li
In recent years, the field of radiology has increasingly harnessed the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance diagnostic accuracy, streamline workflows, and improve patient care. Large language models (LLMs) have emerged as particularly promising tools, offering significant potential in assisting radiologists with report generation, clinical decision support, and patient communication. This paper presents an advanced radiology-focused large language model: MGH Radiology Llama. It is developed using the Llama 3 70B model, building upon previous domain-specific models like Radiology-GPT and Radiology-Llama2. Leveraging a unique and comprehensive dataset from Massachusetts General Hospital, comprising over 6.5 million de-identified medical reports across various imaging modalities, the model demonstrates significant improvements in generating accurate and clinically relevant radiology impressions given the corresponding findings. Our evaluation, incorporating both traditional metrics and a GPT-4-based assessment, highlights the enhanced performance of this work over general-purpose LLMs.
近年来,放射学领域越来越多地利用人工智能(AI)的力量,以提高诊断准确性、优化工作流程和改善患者护理。大型语言模型(LLM)作为特别有前景的工具,在辅助放射科医生生成报告、临床决策支持和患者沟通方面显示出巨大潜力。本文介绍了一款专注于放射学的大型语言模型:MGH放射学拉马模型。它是以拉马3 70B模型为基础开发的,建立在之前的特定领域模型上,如放射学-GPT和放射学拉马2。该模型利用来自麻省总医院(Massachusetts General Hospital)的独特且全面的数据集,该数据集包含超过650万份去标识化的医学报告,涵盖各种成像模式,根据相应的检查结果生成准确且临床相关的放射学印象。我们的评估结合了传统指标和基于GPT-4的评估,突出了这项工作相较于通用大型语言模型的性能提升。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages, 3 figures, 1 table
Summary
医学领域越来越多地利用人工智能(AI)提高诊断准确性、优化工作流程和改善患者护理。本文介绍了一款先进的针对放射科的的大型语言模型:MGH放射科拉玛(Llama)。它利用马萨诸塞州综合医院的大规模脱密医疗报告数据集,在各种成像模式上表现出显著的优势,能生成准确且临床相关的放射学印象。评估结果表明,该模型在通用大型语言模型上的性能有所提升。
Key Takeaways
- 医学领域日益依赖人工智能提高诊断准确性、优化工作流程和改善患者护理。
- 大型语言模型在放射科领域具有显著潜力,可辅助放射科医生进行报告生成、临床决策支持和患者沟通。
- MGH放射科拉玛模型是基于Llama 3 70B模型开发的先进放射科大型语言模型。
- 该模型使用马萨诸塞州综合医院的综合数据集进行训练,包含超过650万份脱密医疗报告。
- 模型能生成准确且临床相关的放射学印象,在多种成像模式上表现优异。
- 评估结果证明,该模型在性能上优于通用大型语言模型。
点此查看论文截图



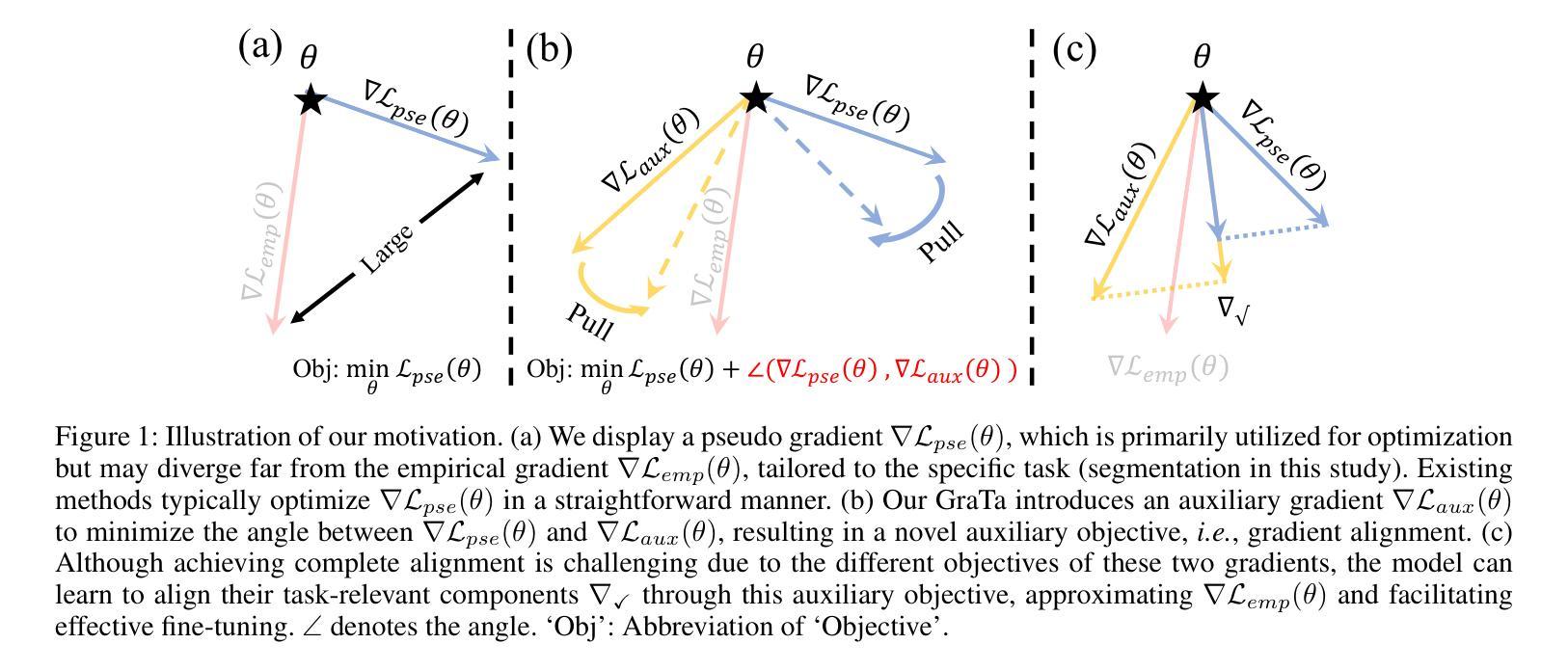
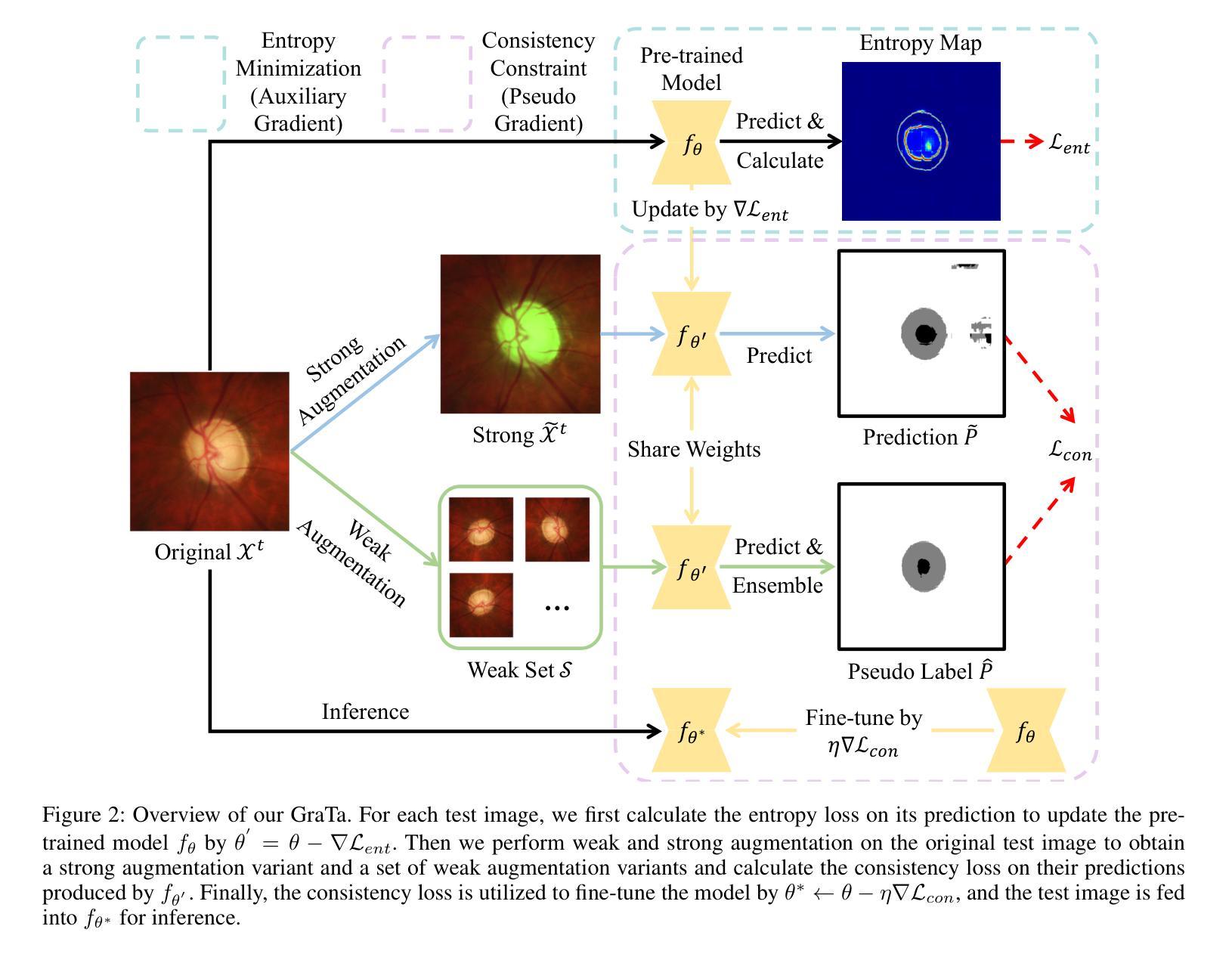
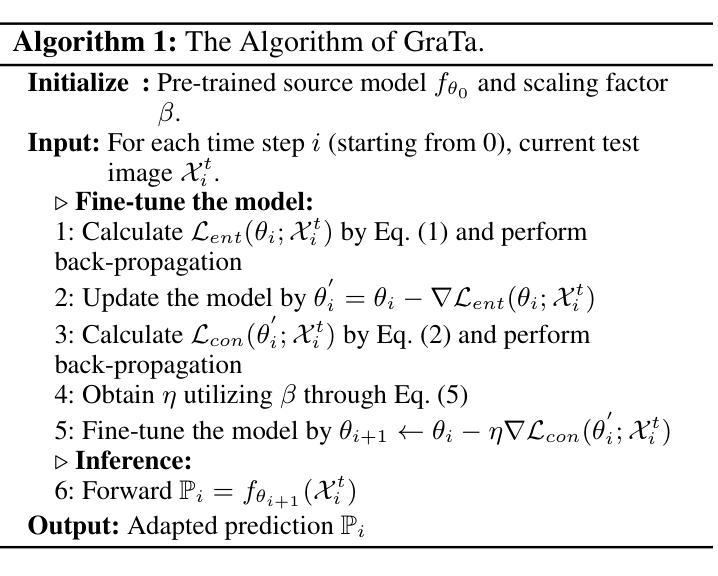
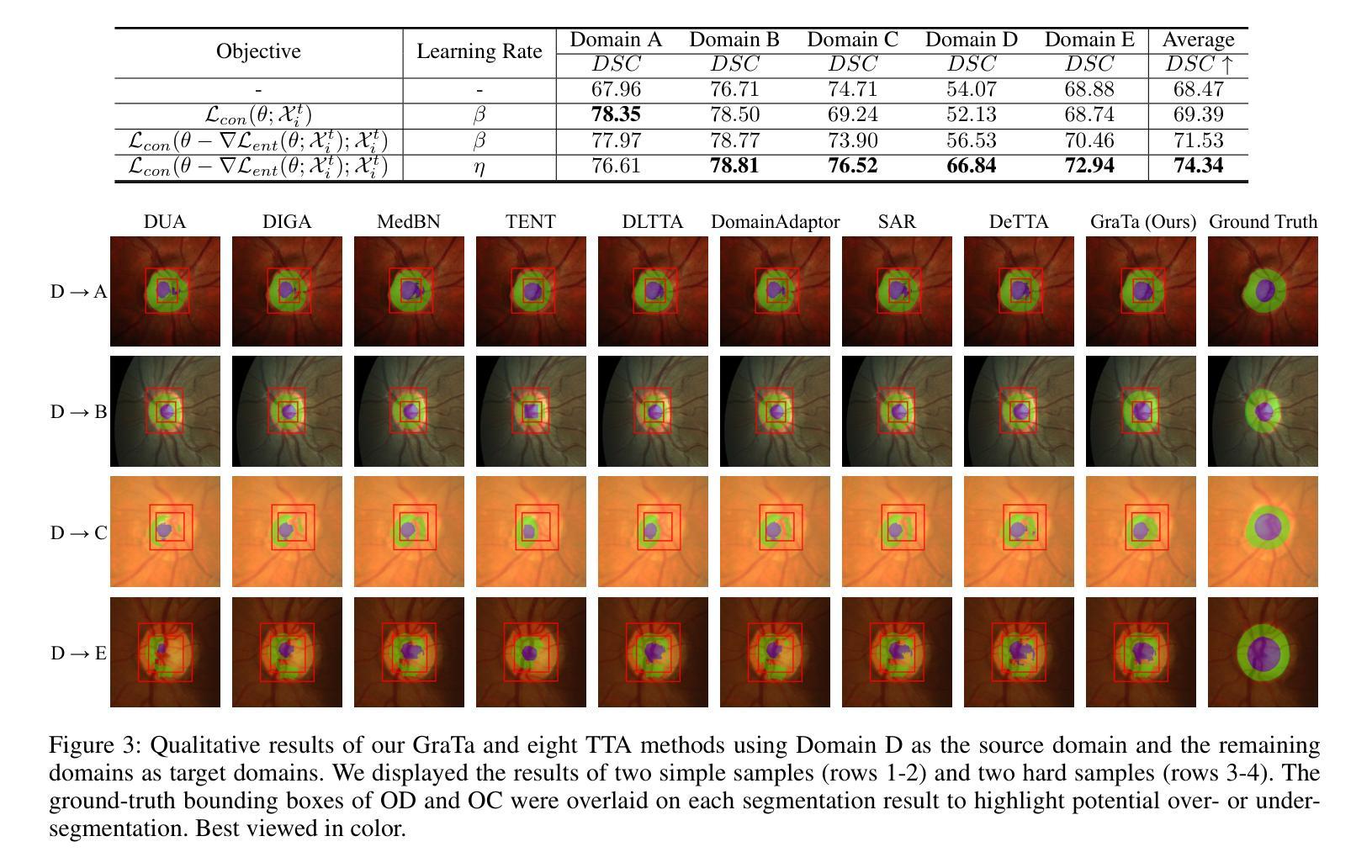
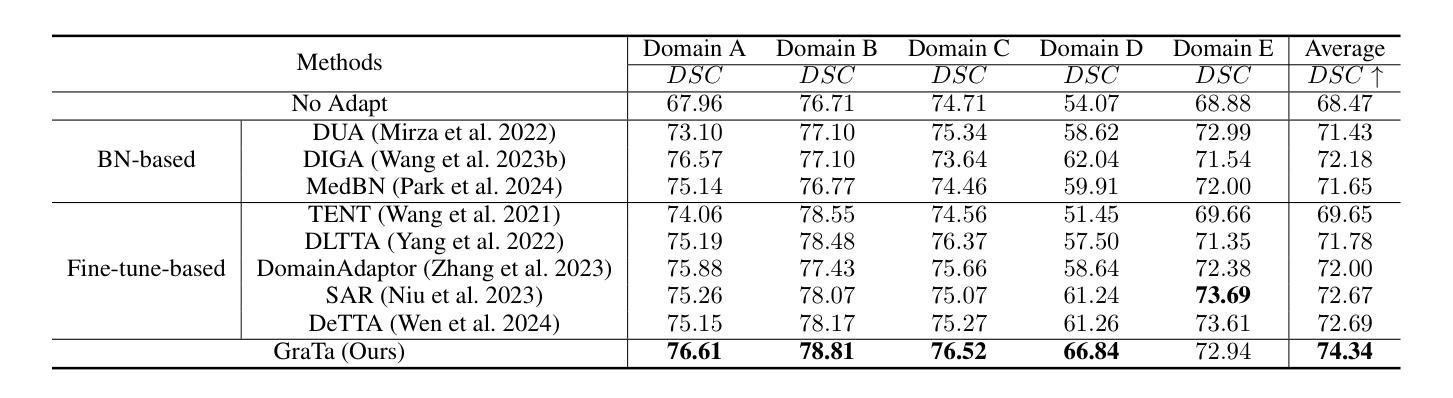
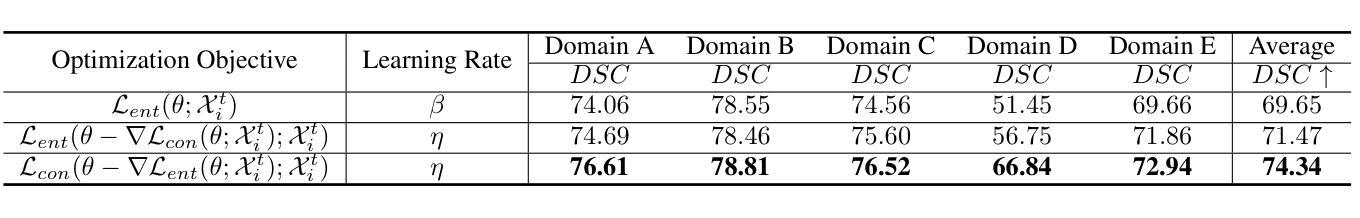
Gradient Alignment Improves Test-Time Adaptation for Medical Image Segmentation
Authors:Ziyang Chen, Yiwen Ye, Yongsheng Pan, Yong Xia
Although recent years have witnessed significant advancements in medical image segmentation, the pervasive issue of domain shift among medical images from diverse centres hinders the effective deployment of pre-trained models. Many Test-time Adaptation (TTA) methods have been proposed to address this issue by fine-tuning pre-trained models with test data during inference. These methods, however, often suffer from less-satisfactory optimization due to suboptimal optimization direction (dictated by the gradient) and fixed step-size (predicated on the learning rate). In this paper, we propose the Gradient alignment-based Test-time adaptation (GraTa) method to improve both the gradient direction and learning rate in the optimization procedure. Unlike conventional TTA methods, which primarily optimize the pseudo gradient derived from a self-supervised objective, our method incorporates an auxiliary gradient with the pseudo one to facilitate gradient alignment. Such gradient alignment enables the model to excavate the similarities between different gradients and correct the gradient direction to approximate the empirical gradient related to the current segmentation task. Additionally, we design a dynamic learning rate based on the cosine similarity between the pseudo and auxiliary gradients, thereby empowering the adaptive fine-tuning of pre-trained models on diverse test data. Extensive experiments establish the effectiveness of the proposed gradient alignment and dynamic learning rate and substantiate the superiority of our GraTa method over other state-of-the-art TTA methods on a benchmark medical image segmentation task. The code and weights of pre-trained source models are available at https://github.com/Chen-Ziyang/GraTa.
尽管近年来医学图像分割领域取得了显著进展,但来自不同中心的医学图像存在的领域偏移问题仍然阻碍着预训练模型的有效部署。许多测试时适应(TTA)方法已被提出,通过推理过程中的测试数据对预训练模型进行微调来解决这个问题。然而,这些方法往往由于优化方向不佳(由梯度决定)和固定步长(基于学习率)而优化效果不佳。在本文中,我们提出了基于梯度对齐的测试时适应(GraTa)方法,以改进优化过程中的梯度方向和学习率。不同于主要优化自监督目标所派生出的伪梯度的传统TTA方法,我们的方法结合了辅助梯度和伪梯度,以实现梯度对齐。这种梯度对齐使模型能够挖掘不同梯度之间的相似性,并纠正梯度方向以逼近与当前分割任务相关的经验梯度。此外,我们基于伪梯度和辅助梯度之间的余弦相似性设计了一种动态学习率,从而实现对不同测试数据的预训练模型的自适应微调。大量实验验证了所提出的梯度对齐和动态学习率的有效性,并证实我们的GraTa方法在基准医学图像分割任务上优于其他最先进的TTA方法。预训练模型的代码和权重可在https://github.com/Chen-Ziyang/GraTa找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 9 pages, 3 figures, 5 tables
Summary
本文主要介绍了针对医学图像分割领域中的域迁移问题,提出了一种基于梯度对齐的测试时自适应(GraTa)方法。该方法通过结合伪梯度和辅助梯度来实现梯度对齐,并设计了一种基于余弦相似度的动态学习率,以自适应微调预训练模型。实验证明,该方法在基准医学图像分割任务上优于其他最先进的TTA方法。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像分割领域存在域迁移问题,影响预训练模型的有效部署。
- 测试时自适应(TTA)方法旨在通过测试数据在推理过程中对预训练模型进行微调。
- 现有TTA方法常常因优化方向不佳和固定学习率而优化效果不佳。
- GraTa方法结合伪梯度和辅助梯度实现梯度对齐,优化梯度方向和学习率。
- GraTa方法通过挖掘不同梯度之间的相似性,校正梯度方向以逼近当前分割任务的实证梯度。
- GraTa方法设计了一种基于余弦相似度的动态学习率,实现自适应微调。
点此查看论文截图

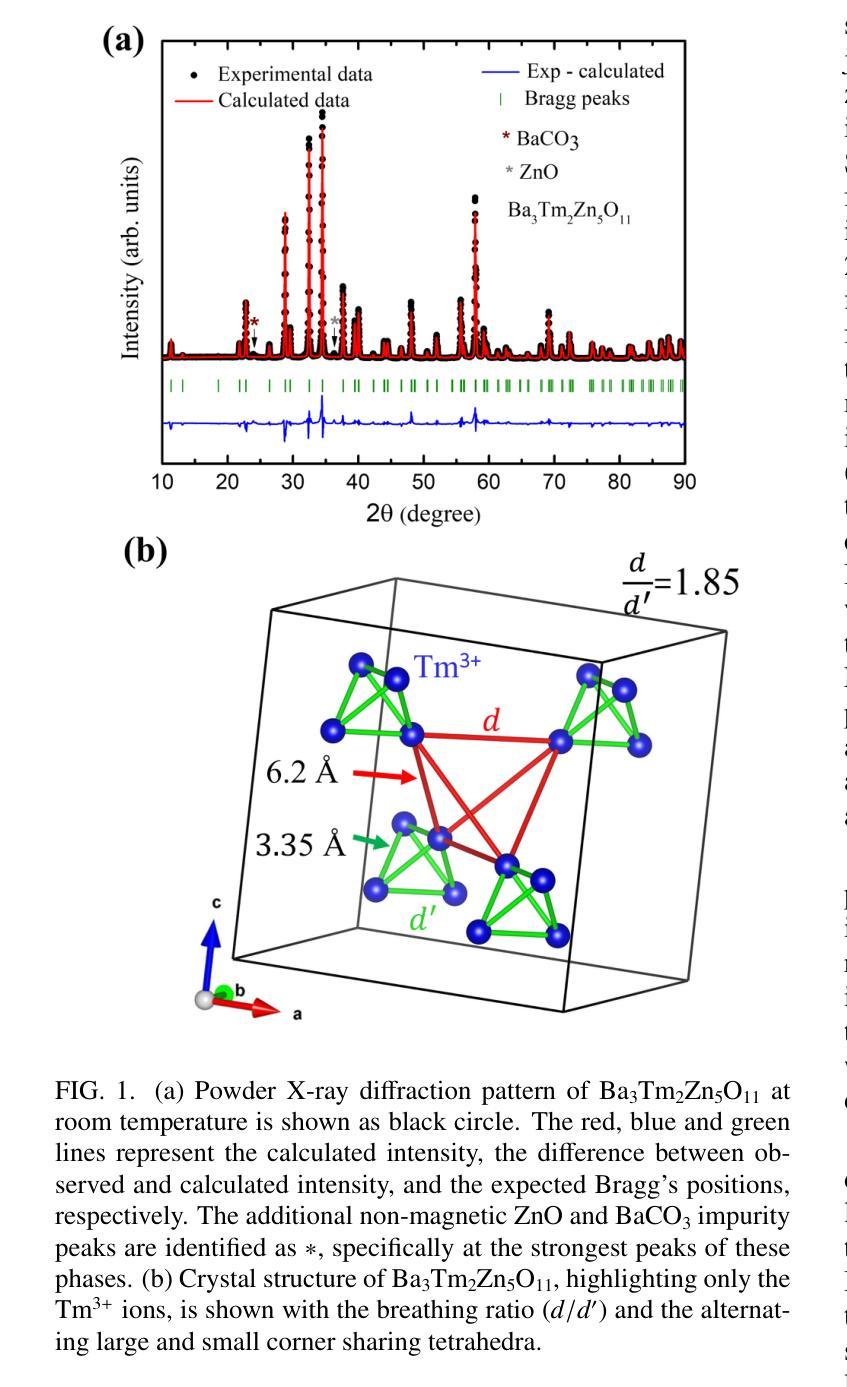
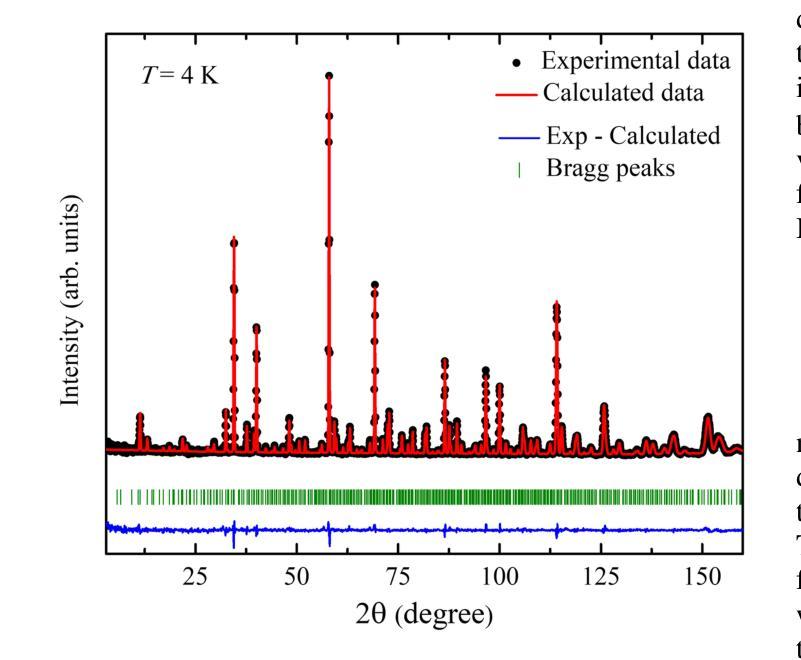
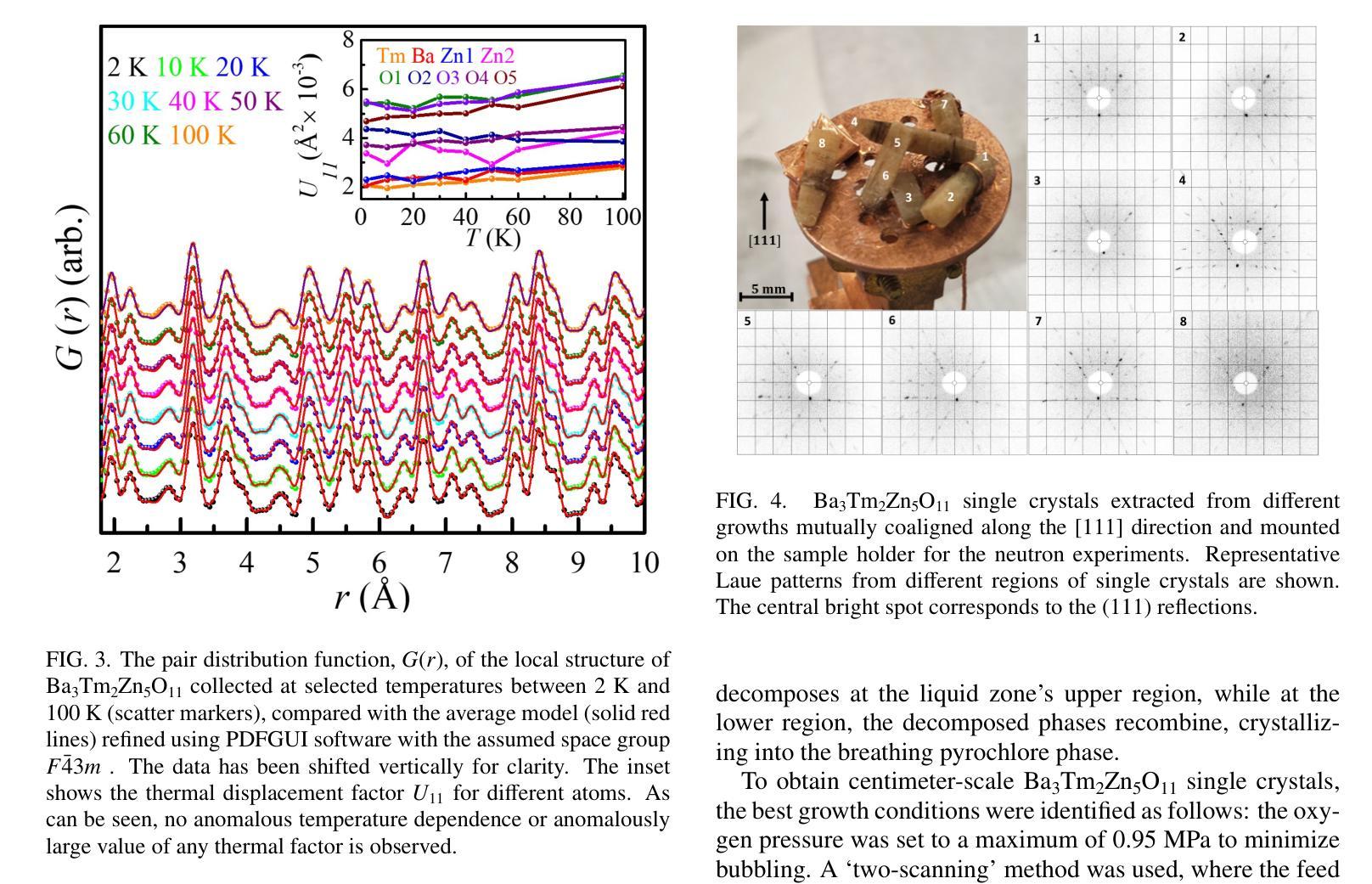
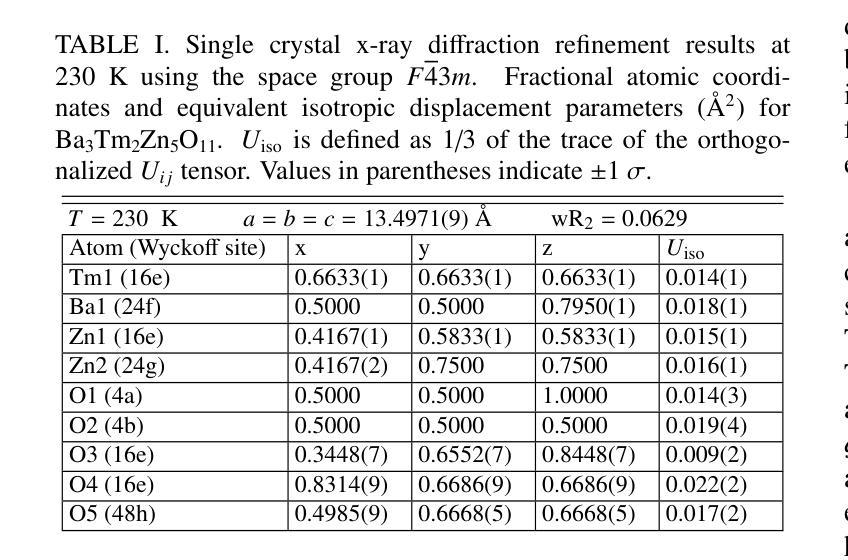
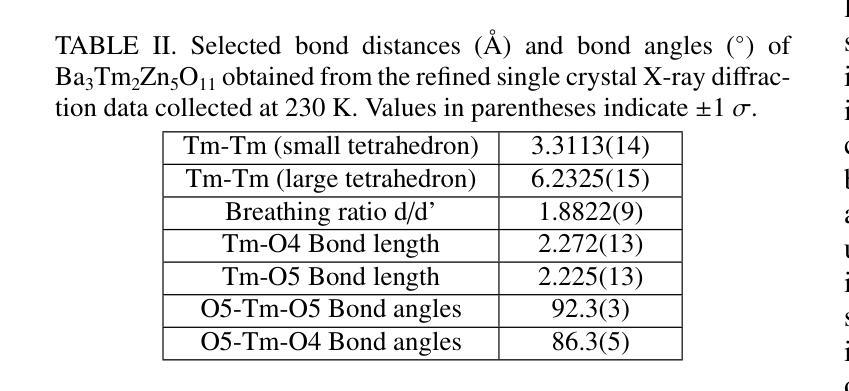
Synthesis and characterization of the novel breathing pyrochlore compound Ba3Tm2Zn5O11
Authors:Lalit Yadav, Rabindranath Bag, Ramesh Dhakal, Stephen M. Winter, Jeffrey G. Rau, Sachith E. Dissanayake, Alexander I. Kolesnikov, Andrey A. Podlesnyak, Craig M. Brown, Nicholas P. Butch, David Graf, Michel J. P. Gingras, Sara Haravifard
In this study, a novel material from the rare-earth based breathing pyrochlore family, Ba3Tm2Zn5O11, was successfully synthesized. Powder x-ray diffraction and high-resolution powder neutron diffraction confirmed phase purity and the F-43m breathing pyrochlore crystal structure, while thermogravimetric analysis revealed incongruent melting behavior compared to its counterpart, Ba3Yb2Zn5O11. High-quality single crystals of Ba3Tm2Zn5O11 were grown using the traveling solvent floating zone technique and assessed using Laue x-ray diffraction and single crystal x-ray diffraction. Thermodynamic characterization indicated paramagnetic behavior down to 0.05 K, and inelastic neutron scattering measurements identified distinct dispersionless crystal electric field energy bands, with the fitted crystal electric field model predicting a single-ion singlet ground state and an energy gap of ~9 meV separating it from the first excited (singlet) state. Additional low-energy excitation studies on single crystals revealed dispersionless bands at 0.8 and 1 meV. Computed phonon dispersions from first-principles calculations ruled out phonons as the origin of these modes, further illustrating the puzzling and unique properties of Ba3Tm2Zn5O11.
在这项研究中,成功合成了一种来自稀土基呼吸型烧绿石家族的新型材料Ba3Tm2Zn5O11。通过粉末X射线衍射和高分辨率粉末中子衍射证实了其相纯度和F-43m呼吸型烧绿石晶体结构。热重分析显示其熔融行为与另一种材料Ba3Yb2Zn5O11不一致。使用流动溶剂浮区技术生长了Ba3Tm2Zn5O11的高质量单晶,并使用劳厄X射线衍射和单晶X射线衍射进行了评估。热力学表征表明,其表现至0.05K仍为顺磁性行为。非弹性中子散射测量确定了无散射晶体电场能带的特征,拟合的晶体电场模型预测了单离子基态为单重态,与第一激发单重态之间存在约9meV的能隙。对单晶进行的额外低能激发研究表明,在0.8和1meV处存在无散射带。基于第一原理计算得出的声子散射排除了声子是这些模式的起源,进一步展示了Ba3Tm2Zn5O11独特且令人困惑的特性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
此研究成功合成了一种来自稀土基呼吸金锰石家族的新材料Ba3Tm2Zn5O11。通过粉末X射线衍射和高分辨率粉末中子衍射确认其相纯度和F-43m呼吸金锰石晶体结构。热重分析显示其与Ba3Yb2Zn5O11相比具有不相融的熔化行为。利用浮动区熔法生长高质量单晶,并通过劳厄X射线衍射和单晶X射线衍射进行评估。热力学表征显示至0.05K表现出顺磁性行为,非弹性中子散射测量识别出无发散晶体电场能带,拟合晶体电场模型预测单离子基态单重态和约9meV的能隙与第一激发(单重态)状态分离。单晶的低能激发研究显示出在0.8和1meV时的无发散带。第一性原理计算得出的声子分散排除了声子是这些模式的起源,进一步展示了Ba3Tm2Zn5O11独特且神秘的特性。
Key Takeaways
- 成功合成新型材料Ba3Tm2Zn5O11,属于稀土基呼吸金锰石家族。
- 通过多种衍射技术确认了其相纯度和晶体结构。
- 热重分析显示该材料与对比材料Ba3Yb2Zn5O11的熔化行为不同。
- 利用旅行溶剂浮动区熔技术生长了高质量单晶。
- 材料表现出顺磁性行为,且非弹性中子散射测量揭示了特定的晶体电场特征。
- 单晶的低能激发研究显示存在无发散带。
点此查看论文截图

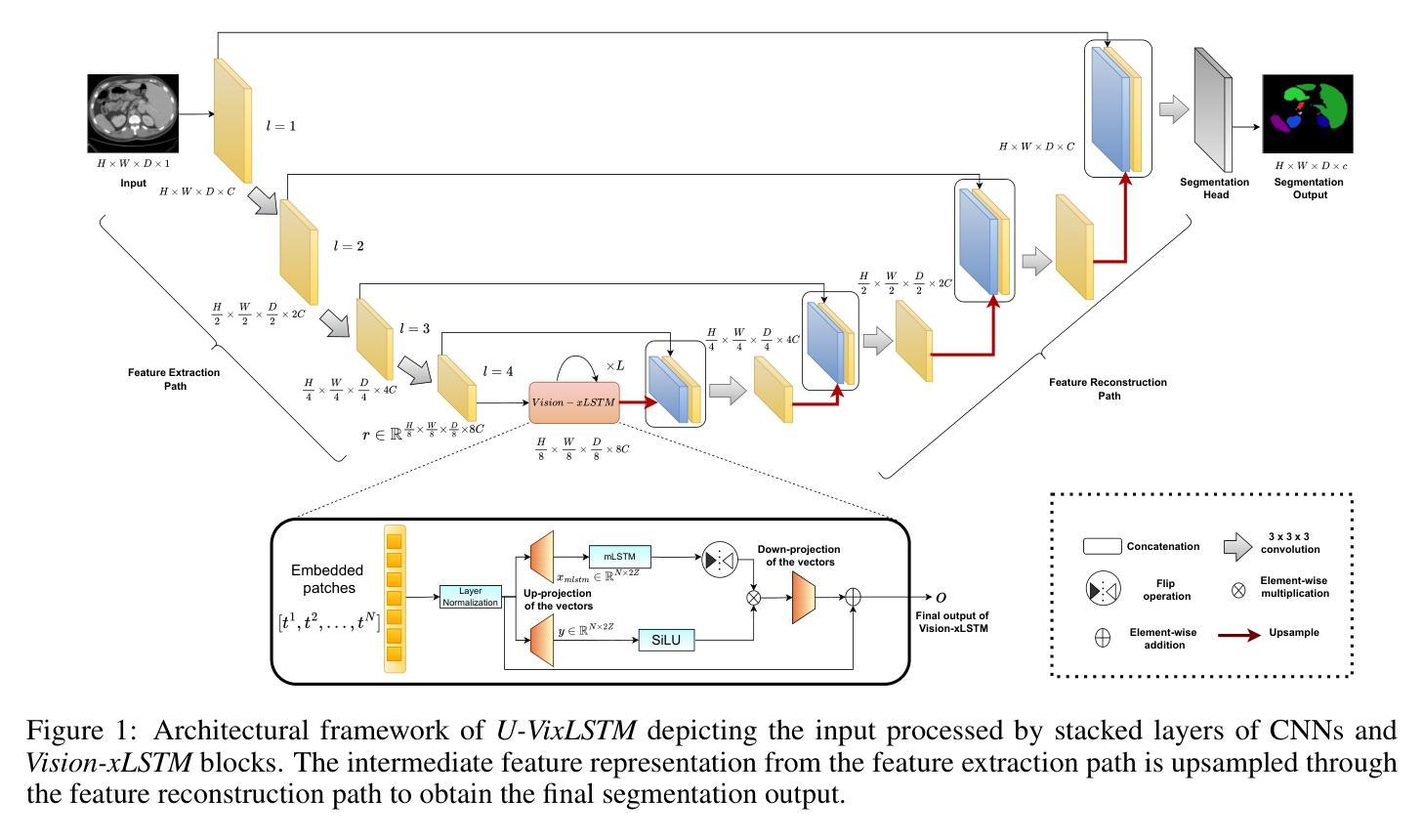
Are Vision xLSTM Embedded UNet More Reliable in Medical 3D Image Segmentation?
Authors:Pallabi Dutta, Soham Bose, Swalpa Kumar Roy, Sushmita Mitra
The development of efficient segmentation strategies for medical images has evolved from its initial dependence on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to the current investigation of hybrid models that combine CNNs with Vision Transformers. There is an increasing focus on creating architectures that are both high-performance and computationally efficient, able to be deployed on remote systems with limited resources. Although transformers can capture global dependencies in the input space, they face challenges from the corresponding high computational and storage expenses involved. This paper investigates the integration of CNNs with Vision Extended Long Short-Term Memory (Vision-xLSTM)s by introducing the novel {\it \textbf{U-VixLSTM}}. The Vision-xLSTM blocks capture temporal and global relationships within the patches, as extracted from the CNN feature maps. The convolutional feature reconstruction path upsamples the output volume from the Vision-xLSTM blocks, to produce the segmentation output. Our primary objective is to propose that Vision-xLSTM forms an appropriate backbone for medical image segmentation, offering excellent performance with reduced computational costs. The U-VixLSTM exhibits superior performance, compared to the state-of-the-art networks in the publicly available Synapse, ISIC and ACDC datasets. Code provided: https://github.com/duttapallabi2907/U-VixLSTM
医学影像的高效分割策略发展从最初依赖卷积神经网络(CNN)到当前对结合CNN与视觉变压器的混合模型的探索。目前,人们越来越关注创建高性能且计算效率高的架构,能够部署在资源有限的远程系统上。虽然变压器可以捕获输入空间中的全局依赖性,但它们也面临着相应的计算和存储成本高昂的挑战。本文通过将CNN与视觉扩展长短时记忆(Vision-xLSTM)网络相结合,引入新型U-VixLSTM模型进行研究。Vision-xLSTM块捕获从CNN特征图中提取的补丁内的临时和全局关系。卷积特征重建路径对Vision-xLSTM块的输出体积进行上采样,以产生分割输出。我们的主要目标是提出Vision-xLSTM可作为医学影像分割的合适骨干网,在降低计算成本的同时提供出色的性能。与公开可用的Synapse、ISIC和ACDC数据集中最先进的网络相比,U-VixLSTM表现出卓越的性能。代码提供:https://github.com/duttapallabi2907/U-VixLSTM
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于卷积神经网络(CNNs)的传统医学影像分割策略正逐渐融合视线转模型,以适应更加高效且具有高性能计算要求的医疗图像处理需求。该论文创新性提出了结合CNN和扩展的视域长短期记忆(Vision-xLSTM)模型的U-VixLSTM网络架构。这一模型能够有效捕捉图像块中的时序和全局关系,并在公开数据集Synapse、ISIC和ACDC中展现出卓越性能,显著优于当前主流网络。其计算成本较低,适用于资源受限的远程系统部署。
Key Takeaways
- 医疗图像分割策略正从依赖卷积神经网络向混合模型转变,结合CNN与视线转模型。
- U-VixLSTM结合了CNN和Vision-xLSTM模型,形成新颖架构。
- Vision-xLSTM块能捕捉图像中的时序和全局关系。
- U-VixLSTM在公开数据集上表现出卓越性能,优于现有主流网络。
- U-VixLSTM计算成本低,适合部署在资源受限的远程系统上。
- 该论文提供了U-VixLSTM网络的代码实现。
- 该研究为医疗图像分割提供了一个新的高效策略方向。
点此查看论文截图

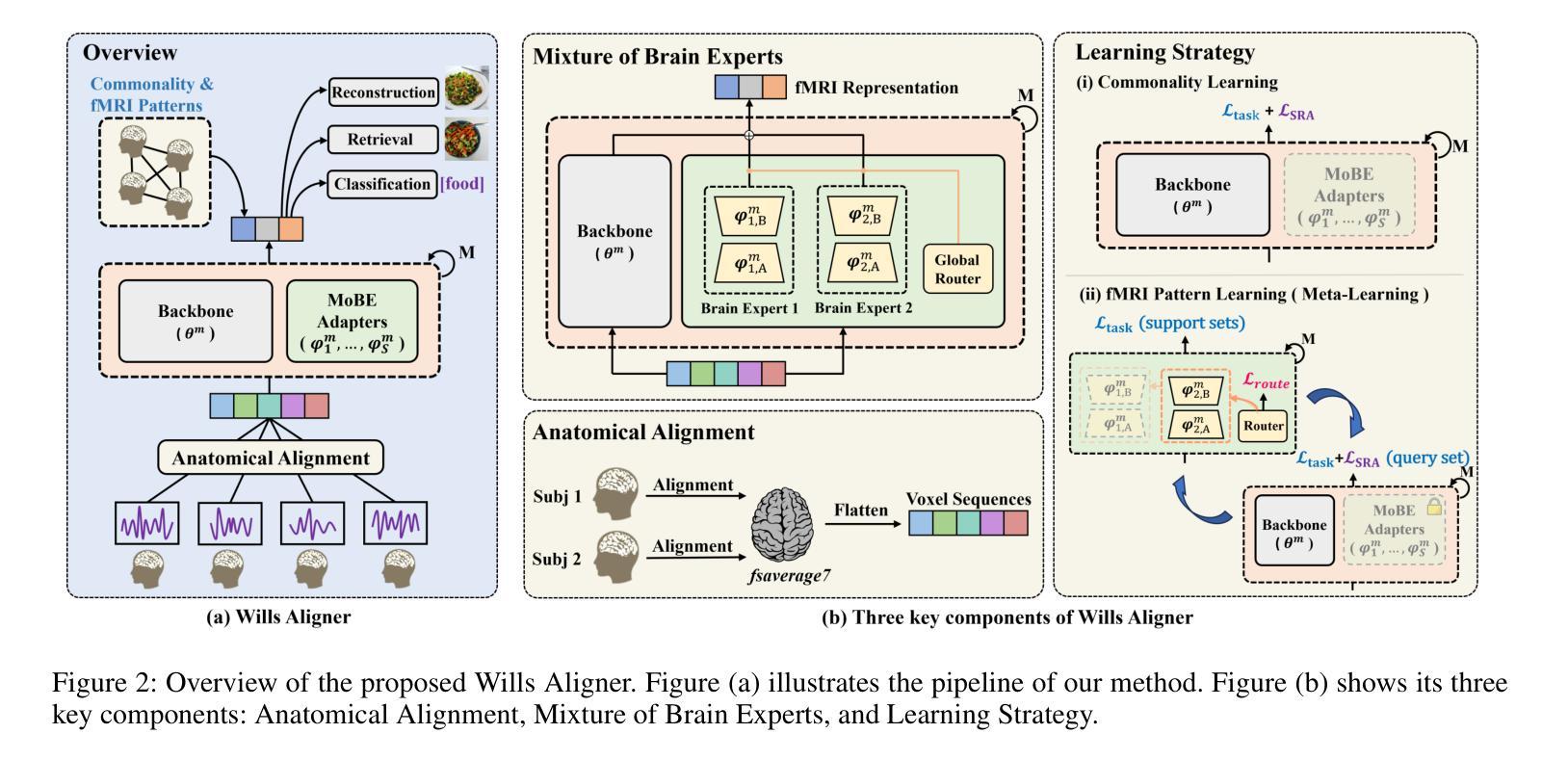
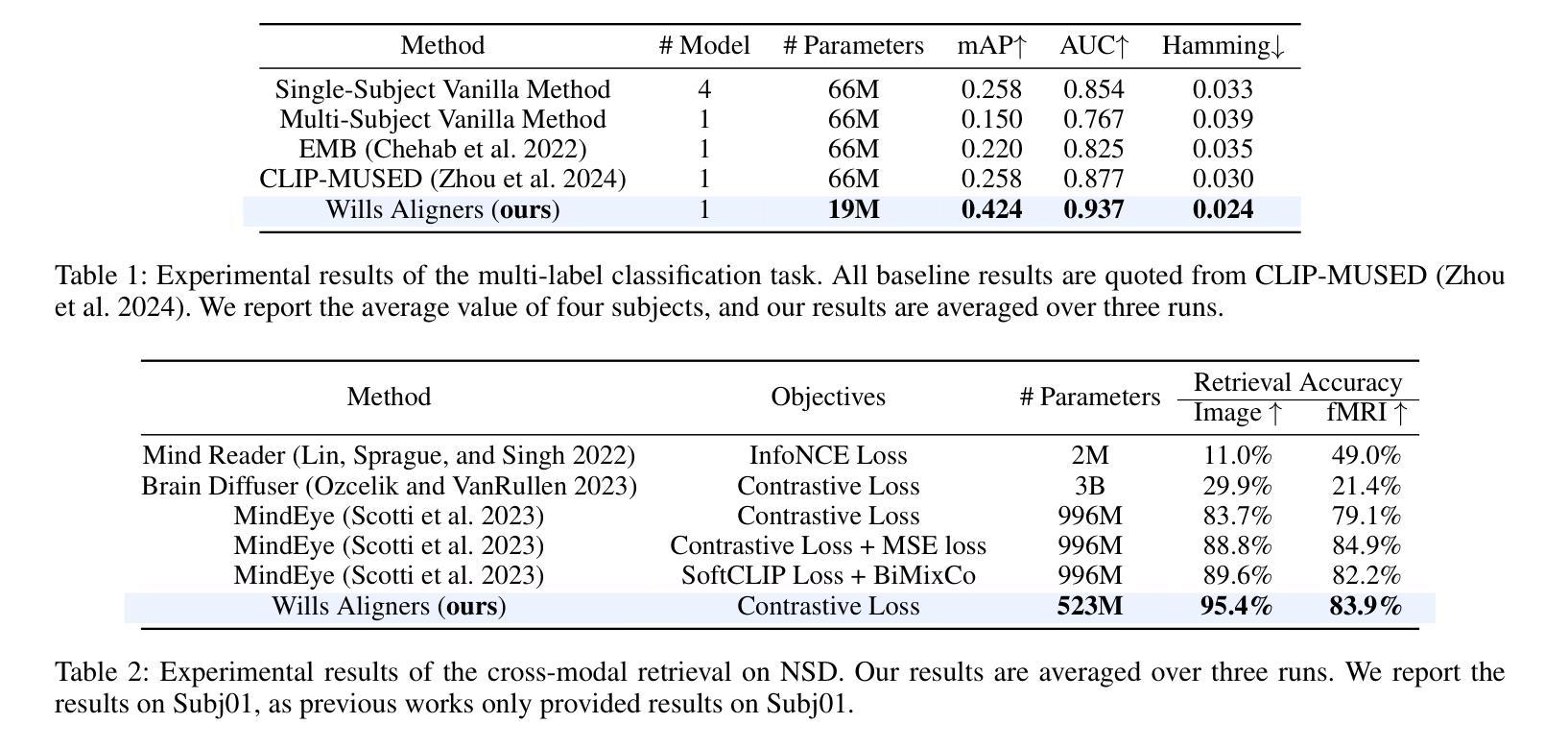
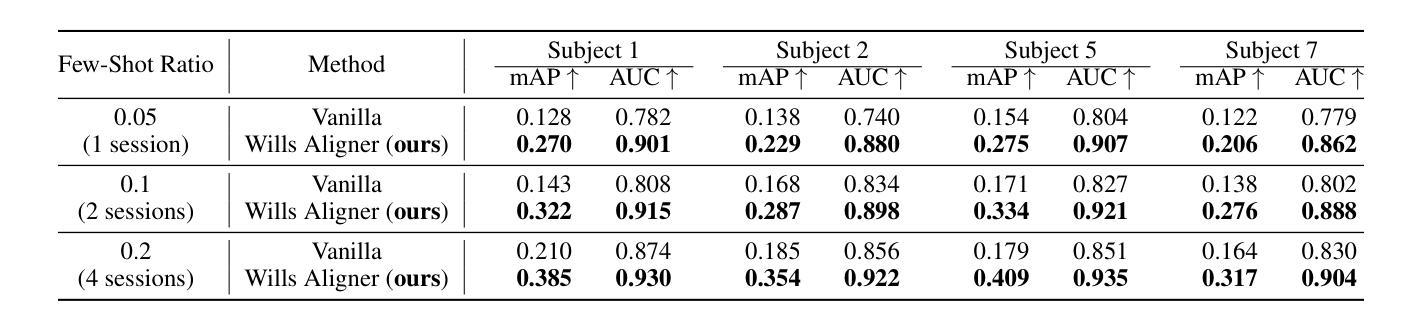
Wills Aligner: Multi-Subject Collaborative Brain Visual Decoding
Authors:Guangyin Bao, Qi Zhang, Zixuan Gong, Jialei Zhou, Wei Fan, Kun Yi, Usman Naseem, Liang Hu, Duoqian Miao
Decoding visual information from human brain activity has seen remarkable advancements in recent research. However, the diversity in cortical parcellation and fMRI patterns across individuals has prompted the development of deep learning models tailored to each subject. The personalization limits the broader applicability of brain visual decoding in real-world scenarios. To address this issue, we introduce Wills Aligner, a novel approach designed to achieve multi-subject collaborative brain visual decoding. Wills Aligner begins by aligning the fMRI data from different subjects at the anatomical level. It then employs delicate mixture-of-brain-expert adapters and a meta-learning strategy to account for individual fMRI pattern differences. Additionally, Wills Aligner leverages the semantic relation of visual stimuli to guide the learning of inter-subject commonality, enabling visual decoding for each subject to draw insights from other subjects’ data. We rigorously evaluate our Wills Aligner across various visual decoding tasks, including classification, cross-modal retrieval, and image reconstruction. The experimental results demonstrate that Wills Aligner achieves promising performance.
从人类大脑活动中解码视觉信息的研究在近段时间取得了显著的进步。然而,不同个体间皮质分区和功能性磁共振成像(fMRI)模式的多样性促使了针对每个个体量身定制的深度学习模型的发展。个人化限制了脑视觉解码在真实世界场景中的更广泛应用。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了Wills Aligner,这是一种旨在实现多主体协作脑视觉解码的新型方法。Wills Aligner首先通过解剖层面将不同主体的fMRI数据进行对齐。然后,它采用精细的混合脑专家适配器和元学习策略来应对个体fMRI模式差异。此外,Wills Aligner还利用视觉刺激之间的语义关系来指导跨主体共同性的学习,使每个主体的视觉解码都能从其他主体的数据中获取洞见。我们在各种视觉解码任务中对Wills Aligner进行了严格评估,包括分类、跨模态检索和图像重建。实验结果表明,Wills Aligner表现出良好的性能。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025, 16 pages
Summary
医学图像解码领域的新进展通过引入个性化深度学习模型,应对了脑部皮质细分和功能性磁共振成像模式在个体间的差异性问题。为扩大应用范围,我们提出了Wills Aligner新方法,它通过解剖学层级对齐不同个体的fMRI数据,利用精细的混合脑专家适配器和元学习策略来解决个体差异问题。此外,Wills Aligner还利用视觉刺激的语义关系来指导跨主体共同性的学习,使每个主体的视觉解码都能从其他主体的数据中获益。经过分类、跨模态检索和图像重建等多种视觉解码任务的严格评估,实验结果表明Wills Aligner表现出良好的性能。
Key Takeaways
- 医学图像解码领域面临个体差异导致的挑战。
- 深度学习模型在解码过程中需要根据个体进行定制。
- Wills Aligner通过解剖学层级对齐fMRI数据来解决个体差异问题。
- Wills Aligner使用混合脑专家适配器和元学习策略来处理个体差异。
- Wills Aligner利用视觉刺激的语义关系指导跨主体共同性学习。
- Wills Aligner在各种视觉解码任务中表现出良好性能。
点此查看论文截图

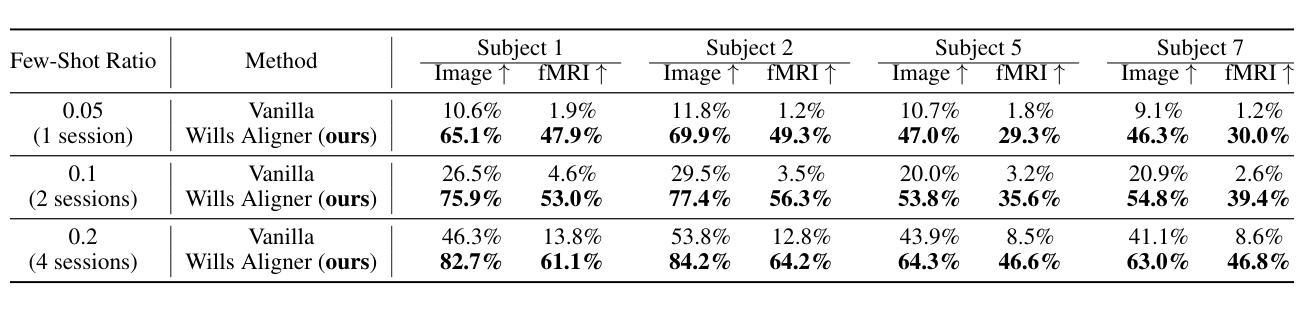
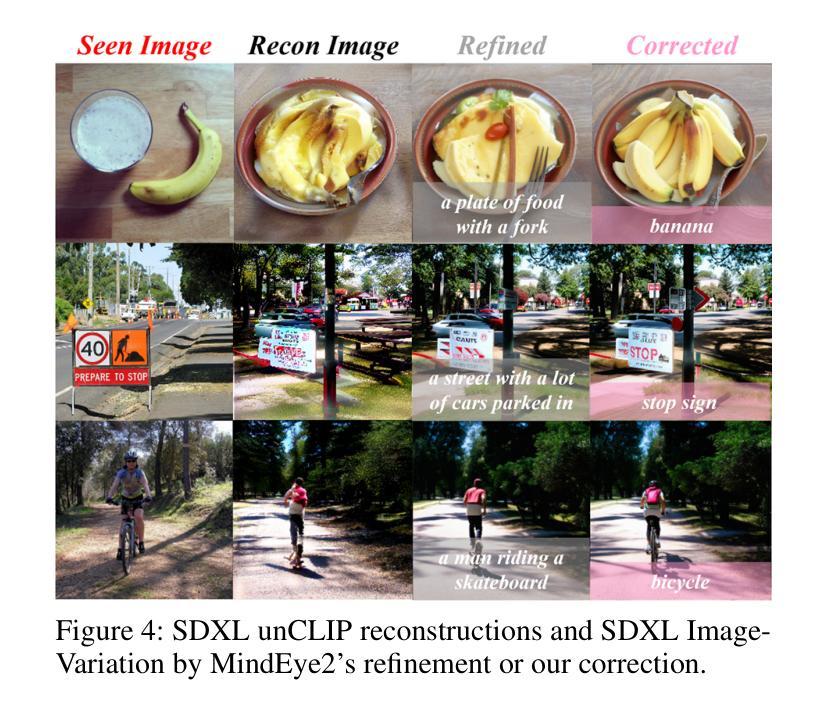
MindTuner: Cross-Subject Visual Decoding with Visual Fingerprint and Semantic Correction
Authors:Zixuan Gong, Qi Zhang, Guangyin Bao, Lei Zhu, Ke Liu, Liang Hu, Duoqian Miao
Decoding natural visual scenes from brain activity has flourished, with extensive research in single-subject tasks and, however, less in cross-subject tasks. Reconstructing high-quality images in cross-subject tasks is a challenging problem due to profound individual differences between subjects and the scarcity of data annotation. In this work, we proposed MindTuner for cross-subject visual decoding, which achieves high-quality and rich semantic reconstructions using only 1 hour of fMRI training data benefiting from the phenomena of visual fingerprint in the human visual system and a novel fMRI-to-text alignment paradigm. Firstly, we pre-train a multi-subject model among 7 subjects and fine-tune it with scarce data on new subjects, where LoRAs with Skip-LoRAs are utilized to learn the visual fingerprint. Then, we take the image modality as the intermediate pivot modality to achieve fMRI-to-text alignment, which achieves impressive fMRI-to-text retrieval performance and corrects fMRI-to-image reconstruction with fine-tuned semantics. The results of both qualitative and quantitative analyses demonstrate that MindTuner surpasses state-of-the-art cross-subject visual decoding models on the Natural Scenes Dataset (NSD), whether using training data of 1 hour or 40 hours.
解码自然视觉场景的研究已经从单一任务的研究扩展到了多个任务的研究,而在跨任务研究中仍有许多工作要做。在跨任务中重构高质量图像是一个具有挑战性的问题,因为不同个体之间存在巨大差异,并且数据标注稀缺。在这项工作中,我们提出了用于跨任务视觉解码的MindTuner,它仅使用1小时的fMRI训练数据就能实现高质量和丰富的语义重构,这得益于人类视觉系统中的视觉指纹现象以及一种新的fMRI到文本的对齐范式。首先,我们在7个主体之间预训练了一个多主体模型,并使用稀缺数据对新主体进行微调,其中使用LoRAs和Skip-LoRAs来学习视觉指纹。然后,我们以图像模式作为中间中心模式来实现fMRI到文本的对齐,实现了令人印象深刻的fMRI到文本的检索性能,并通过微调语义校正了fMRI到图像的重建。定性和定量分析的结果均表明,无论是在使用1小时或40小时的训练数据的情况下,MindTuner在自然场景数据集(NSD)上的跨任务视觉解码性能均超过了最先进的模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF AAAI 2025, 14 pages
Summary
解码自然视觉场景研究活跃于针对单个主体的任务上,跨主体任务上的研究较少。利用跨主体任务中的脑神经影像数据进行高质量图像重建极具挑战性,原因在于不同个体间存在显著差异且数据标注稀缺。本研究提出MindTuner用于跨主体视觉解码,仅使用一小时的fMRI训练数据便实现了高质量且丰富的语义重建,得益于人类视觉系统中的视觉指纹现象以及新颖的fMRI-文本对齐范式。通过预训练多主体模型并在新主体上微调,利用LoRAs与Skip-LoRAs学习视觉指纹。此外,以图像模态作为中间枢纽模态实现fMRI-文本对齐,取得了令人印象深刻的fMRI-文本检索性能,并修正了具有精细语义的fMRI-图像重建。定性与定量分析结果显示,无论是在使用一小时还是四十小时的训练数据情况下,MindTuner在天然场景数据集上的跨主体视觉解码表现均超越现有顶尖模型。
Key Takeaways
- 研究关注跨主体任务中脑神经影像数据的高质量图像重建挑战。
- MindTuner方法仅使用一小时的fMRI训练数据实现高质量和丰富的语义重建。
- 利用视觉指纹现象和新颖的fMRI-文本对齐范式促进解码。
- 通过预训练多主体模型并在新主体上微调,使用LoRAs与Skip-LoRAs学习视觉指纹。
- 以图像模态作为中间枢纽实现fMRI-文本对齐,提高fMRI-文本检索性能。
- MindTuner在天然场景数据集上的跨主体视觉解码表现超越现有顶尖模型。
点此查看论文截图

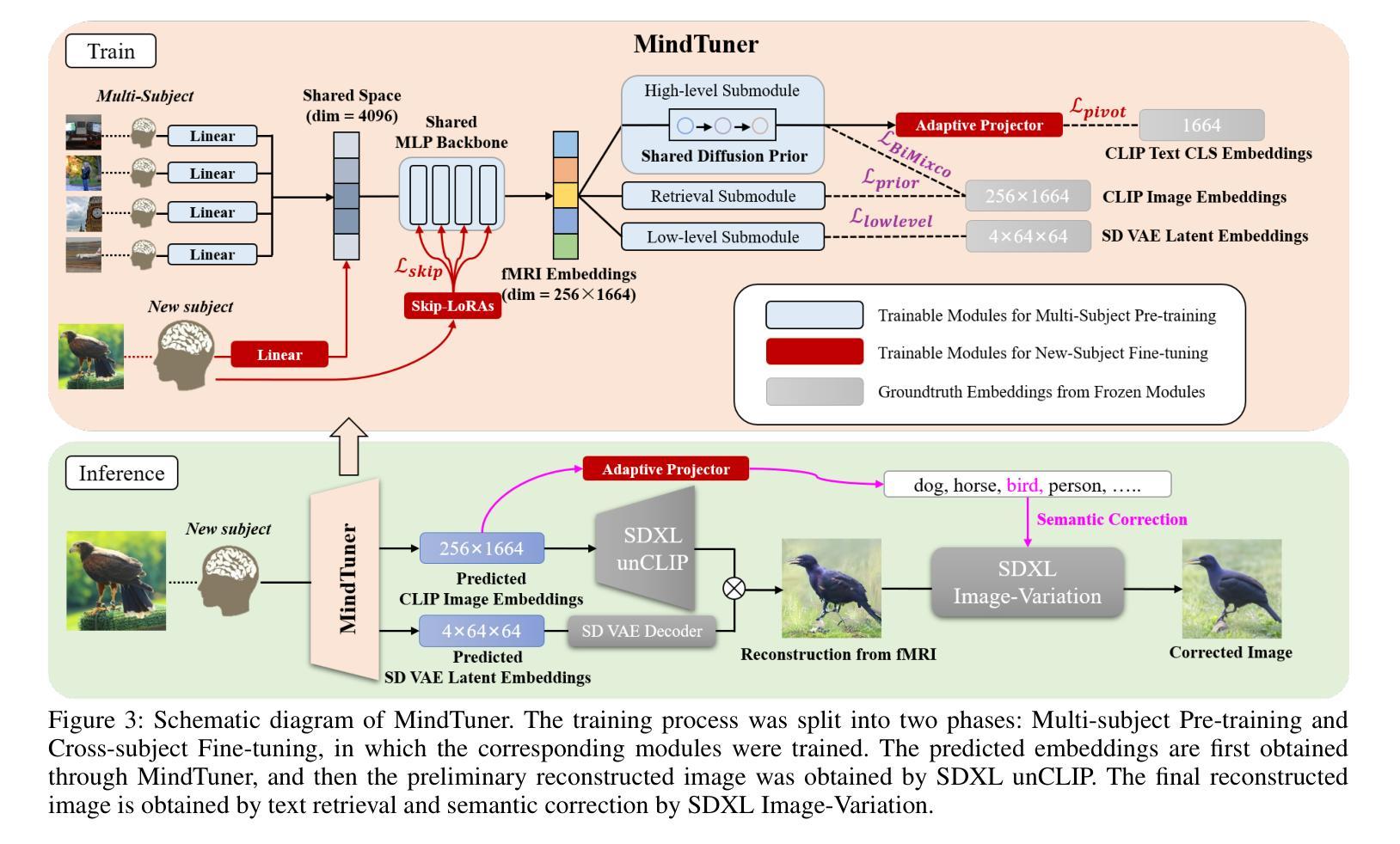

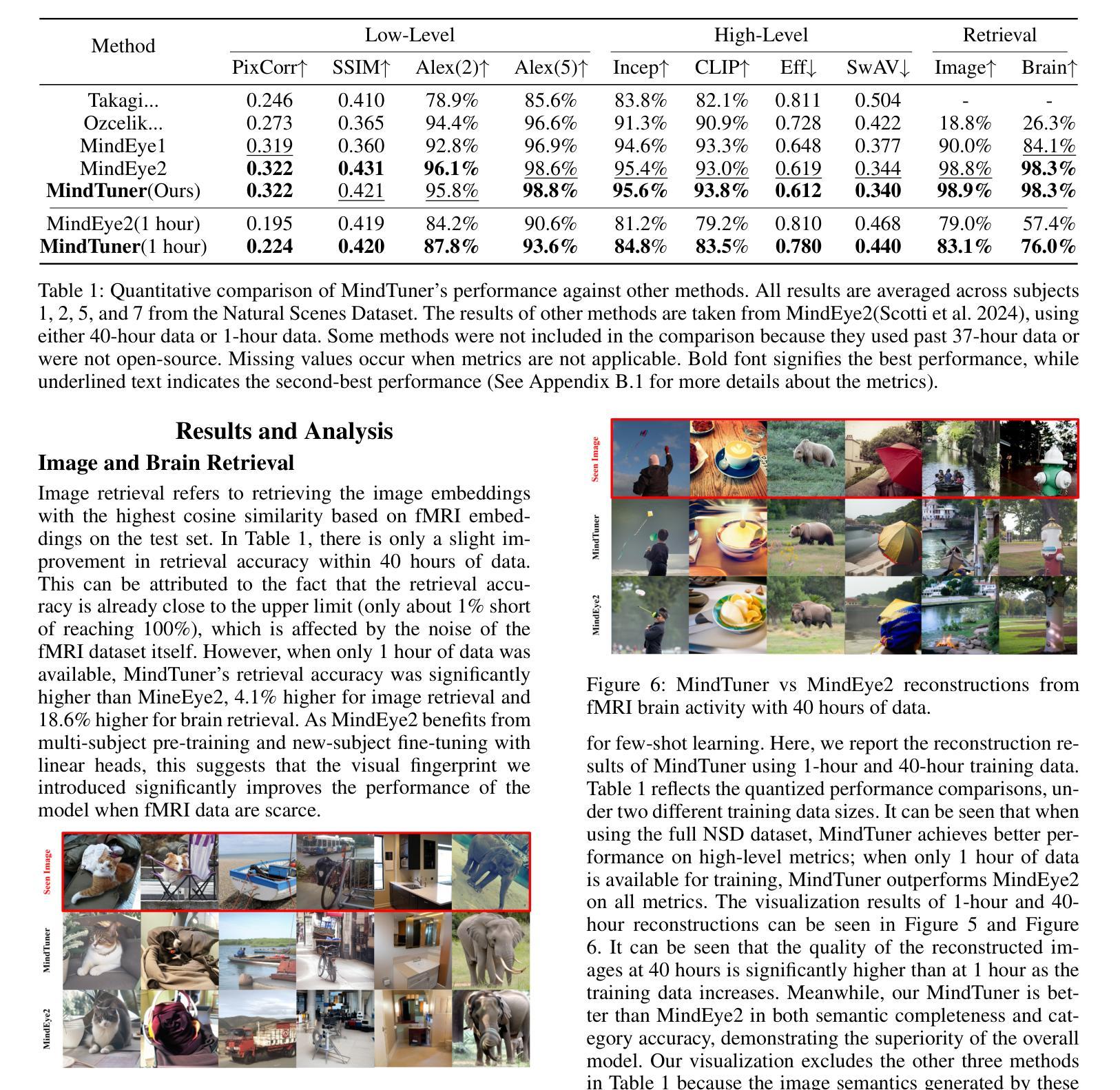
Towards a Comprehensive, Efficient and Promptable Anatomic Structure Segmentation Model using 3D Whole-body CT Scans
Authors:Heng Guo, Jianfeng Zhang, Jiaxing Huang, Tony C. W. Mok, Dazhou Guo, Ke Yan, Le Lu, Dakai Jin, Minfeng Xu
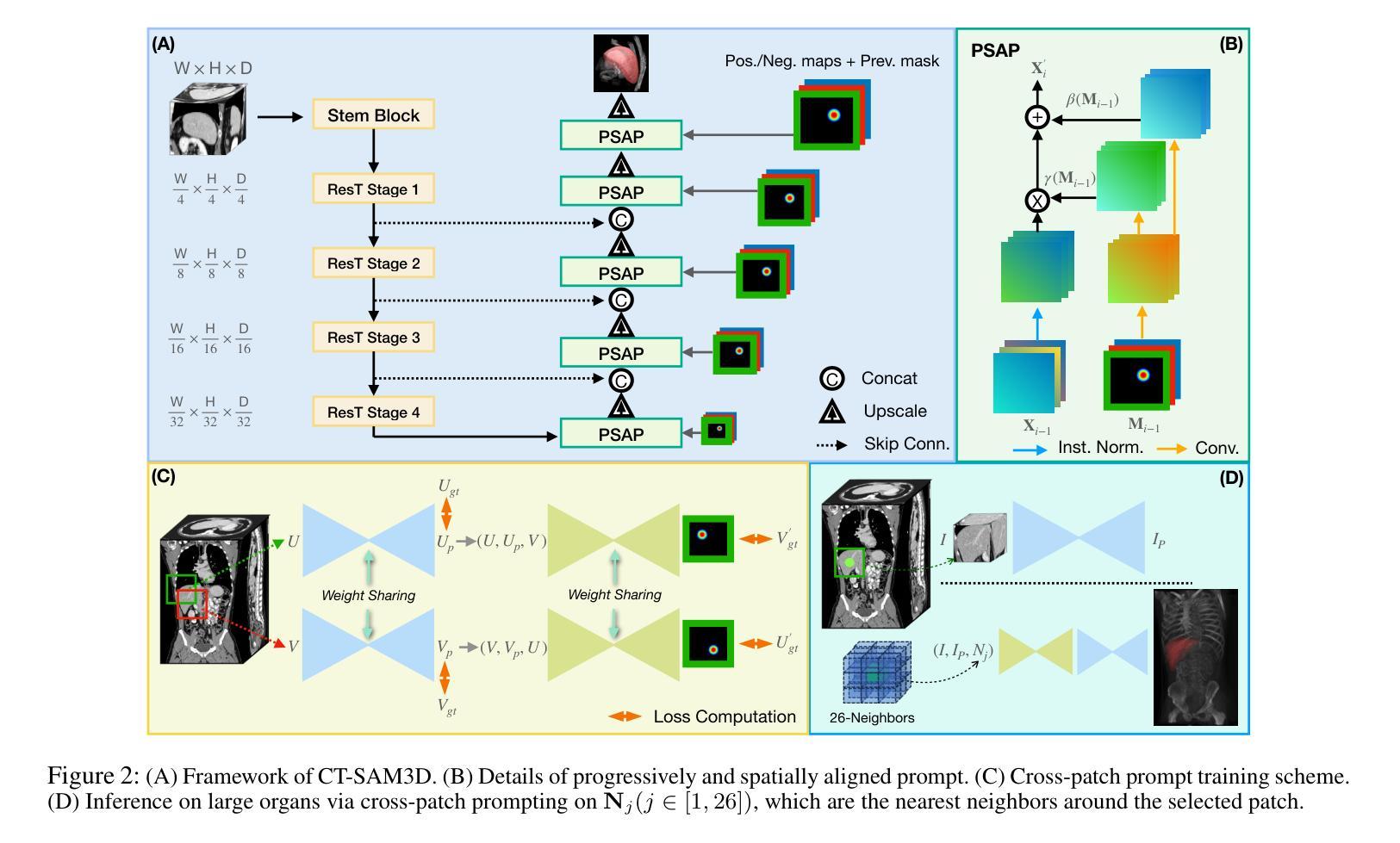
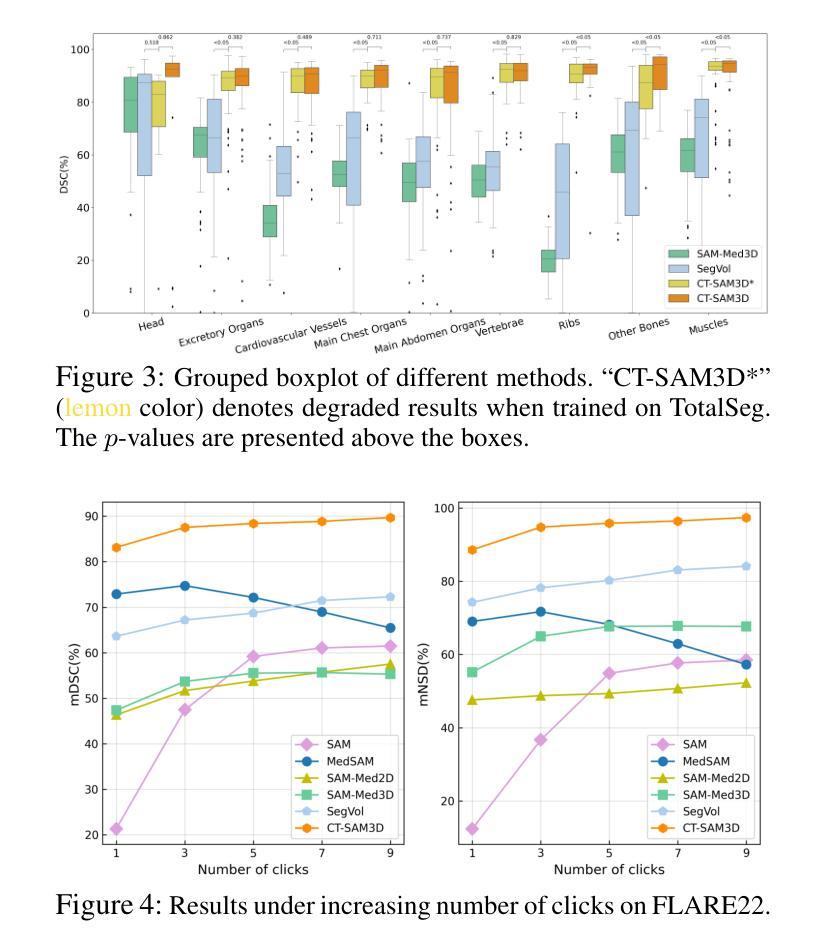
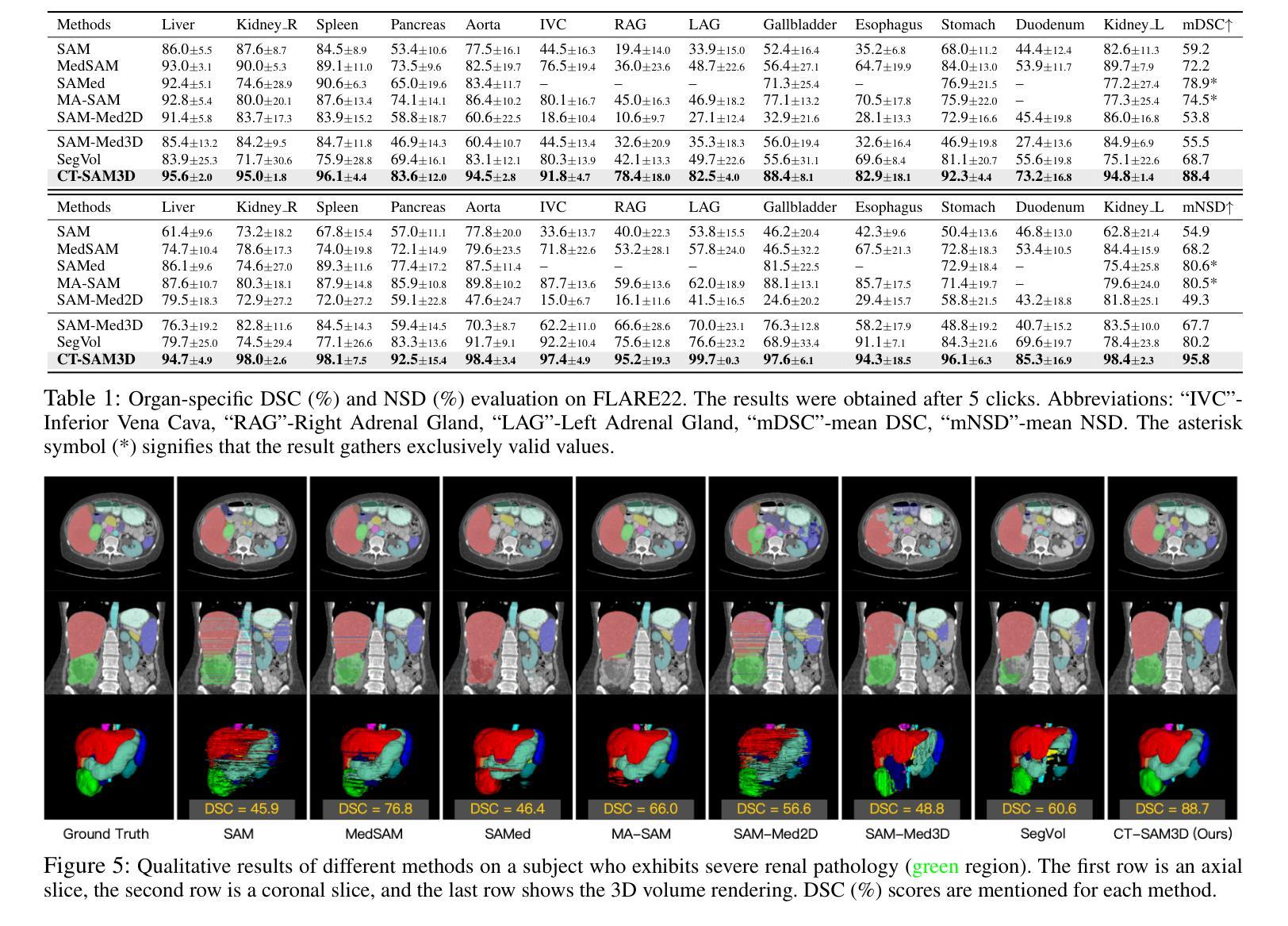
Segment anything model (SAM) demonstrates strong generalization ability on natural image segmentation. However, its direct adaptation in medical image segmentation tasks shows significant performance drops. It also requires an excessive number of prompt points to obtain a reasonable accuracy. Although quite a few studies explore adapting SAM into medical image volumes, the efficiency of 2D adaptation methods is unsatisfactory and 3D adaptation methods are only capable of segmenting specific organs/tumors. In this work, we propose a comprehensive and scalable 3D SAM model for whole-body CT segmentation, named CT-SAM3D. Instead of adapting SAM, we propose a 3D promptable segmentation model using a (nearly) fully labeled CT dataset. To train CT-SAM3D effectively, ensuring the model’s accurate responses to higher-dimensional spatial prompts is crucial, and 3D patch-wise training is required due to GPU memory constraints. Therefore, we propose two key technical developments: 1) a progressively and spatially aligned prompt encoding method to effectively encode click prompts in local 3D space; and 2) a cross-patch prompt scheme to capture more 3D spatial context, which is beneficial for reducing the editing workloads when interactively prompting on large organs. CT-SAM3D is trained using a curated dataset of 1204 CT scans containing 107 whole-body anatomies and extensively validated using five datasets, achieving significantly better results against all previous SAM-derived models. Code, data, and our 3D interactive segmentation tool with quasi-real-time responses are available at https://github.com/alibaba-damo-academy/ct-sam3d.
分段任何事情模型(SAM)在自然图像分割上展现出强大的泛化能力。然而,在医学图像分割任务中直接应用SAM会使其性能大幅下降。它还需要大量的提示点才能获得合理的精度。尽管有一些研究尝试将SAM适应到医学图像体积中,但2D适应方法效率不高,而3D适应方法只能对特定器官/肿瘤进行分割。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个全面且可扩展的3D SAM模型,用于全身CT分割,名为CT-SAM3D。我们并不是去适应SAM,而是提出使用(近乎)全标记CT数据集的一个3D可提示分割模型。为了有效地训练CT-SAM3D,确保模型对更高维度空间提示的准确响应至关重要,并且由于GPU内存限制,需要进行3D补丁式训练。因此,我们提出了两项关键技术发展:1)一种渐进且空间对齐的提示编码方法,可以有效地在局部3D空间中编码点击提示;2)一种跨补丁提示方案,以捕获更多的3D空间上下文,这对于在大型器官上进行交互式提示时减少编辑工作量是有益的。CT-SAM3D是使用包含107个全身解剖结构的1204个CT扫描的精选数据集进行训练的,并在五个数据集上进行了广泛验证,与所有先前的SAM衍生模型相比取得了显著更好的结果。代码、数据以及我们的具有准实时响应的3D交互式分割工具可在https://github.com/alibaba-damo-academy/ct-sam3d找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI 2025
摘要
本文提出一种用于全身CT图像分割的综合、可扩展的3D SAM模型——CT-SAM3D。相较于SAM和其他模型,CT-SAM3D展现出更高的性能和适用性。该研究在有效训练模型的同时,提出了两种关键技术改进,以实现更高的响应准确性并降低内存限制带来的干扰。这些方法包括空间对齐提示编码技术和跨区块提示方案,旨在提高模型在三维空间中的感知能力并减少编辑工作量。此外,CT-SAM3D在多个数据集上的表现均优于先前的SAM衍生模型。相关代码和数据集可通过链接访问。
关键见解
- SAM在自然图像分割中表现出良好的泛化能力,但在医学图像分割任务中性能显著下降。
- 直接将SAM应用于医学图像分割需要大量提示点才能获得合理的准确度。
- 虽然已有研究尝试将SAM适应于医学图像体积,但效率不足且对某些器官/肿瘤的适应性有限。
- 提出一种全面的三维CT图像分割模型CT-SAM3D,适用于全身CT图像分割。
- CT-SAM3D通过两种关键技术改进来确保对更高维度空间提示的准确响应并克服GPU内存限制:空间对齐提示编码方法和跨区块提示方案。
- CT-SAM3D在多个数据集上的表现优于所有先前的SAM衍生模型。
点此查看论文截图

Signal Reconstruction from Samples at Unknown Locations with Application to 2D Unknown View Tomography
Authors:Sheel Shah, Kaishva Shah, Karthik S. Gurumoorthy, Ajit Rajwade
It is well known that a band-limited signal can be reconstructed from its uniformly spaced samples if the sampling rate is sufficiently high. More recently, it has been proved that one can reconstruct a 1D band-limited signal even if the exact sample locations are unknown, but given a uniform distribution of the sample locations and their ordering in 1D. In this work, we extend the analytical error bounds in such scenarios for quasi-bandlimited (QBL) signals, and for the case of arbitrary but known sampling distributions. We also prove that such reconstruction methods are resilient to a certain proportion of errors in the specification of the sample location ordering. We then express the problem of tomographic reconstruction of 2D images from 1D Radon projections under unknown angles (2D UVT) with known angle distribution, as a special case for reconstruction of QBL signals from samples at unknown locations with known distribution. Building upon our theoretical background, we present asymptotic bounds for 2D QBL image reconstruction from 1D Radon projections in the unknown angles setting, and present an extensive set of simulations to verify these bounds in varied parameter regimes. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first piece of work to perform such an analysis for 2D UVT and explicitly relate it to advances in sampling theory, even though the associated reconstruction algorithms have been known for a long time.
众所周知,如果采样率足够高,带限信号可以从其均匀间隔的样本中重建。最近,已经证明即使不知道确切的样本位置,但只要给定样本位置的一维均匀分布和它们的排序,也可以重建一维带限信号。在这项工作中,我们扩展了此类场景下准带限(QBL)信号的分析误差界限,以及任意但已知的采样分布的情况。我们还证明了这种重建方法对指定样本位置排序中的一定比例的误差具有韧性。然后,我们将二维图像从未知角度的一维 Radon 投影(2D UVT)的层析成像重建问题表达为从未知位置的样本重建QBL信号的特殊案例,已知其分布。基于我们的理论背景,我们为未知角度设置下从二维QBL图像的一维Radon投影重建提供了渐近界限,并通过大量的模拟验证了在各种参数环境下的这些界限。据我们所知,尽管相关的重建算法已经存在很长时间了,但这是首次进行此类分析关于二维UVT的工作并将其与采样理论的进展明确联系起来。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF This is a preprint of a paper accepted to Signal Processing (Elsevier)
Summary
该文本讨论了从均匀分布的样本中重建一维带限信号的方法,并扩展到准带限信号和任意但已知的采样分布的情况。研究还表明,此类重建方法对样本位置排序的特定错误比例具有弹性。此外,将二维图像从未知角度的一维Radon投影重建问题表述为从具有已知分布的未知样本位置重建QBL信号的特例。基于理论背景,为二维QBL图像从未知角度的一维Radon投影重建提供了渐近边界,并通过大量模拟验证了这些边界在不同参数条件下的有效性。这是首次将二维未知角度变换与采样理论进展相结合进行分析,并明确关联起来。
Key Takeaways
- 带限信号可以从其均匀间隔的样本中重建出来,前提是采样率足够高。
- 一维带限信号可以从未知确切样本位置中重建,只要给定样本位置的均匀分布和它们在一维中的排序。
- 对于准带限信号和任意但已知的采样分布,研究扩展了分析误差边界。
- 此类重建方法对样本位置排序的特定错误比例具有鲁棒性。
- 二维图像的Radon投影重建问题可视为从具有已知分布的未知样本位置重建QBL信号的特例。
- 研究为二维QBL图像从未知角度的一维Radon投影重建提供了渐近边界。
点此查看论文截图