⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-20 更新
Leveraging Semantic Asymmetry for Precise Gross Tumor Volume Segmentation of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Planning CT
Authors:Zi Li, Ying Chen, Zeli Chen, Yanzhou Su, Tai Ma, Tony C. W. Mok, Yan-Jie Zhou, Yunhai Bai, Zhinlin Zheng, Le Lu, Yirui Wang, Jia Ge, Xianghua Ye, Senxiang Yan, Dakai Jin
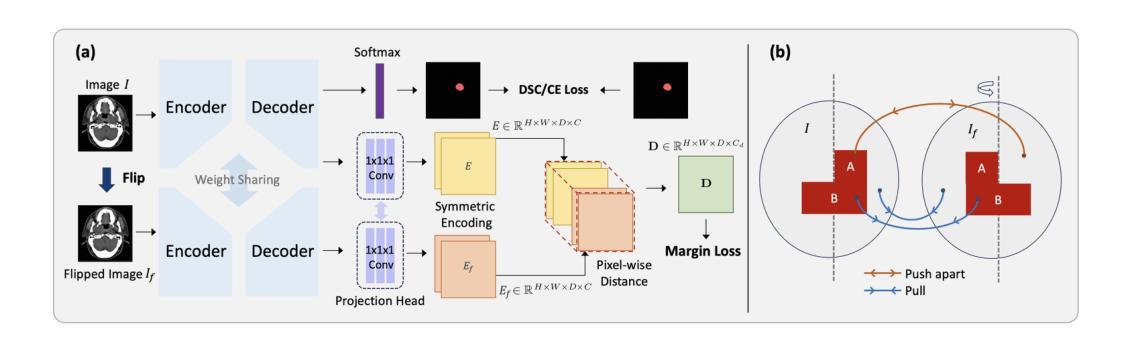
In the radiation therapy of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC), clinicians typically delineate the gross tumor volume (GTV) using non-contrast planning computed tomography to ensure accurate radiation dose delivery. However, the low contrast between tumors and adjacent normal tissues necessitates that radiation oncologists manually delineate the tumors, often relying on diagnostic MRI for guidance. % In this study, we propose a novel approach to directly segment NPC gross tumors on non-contrast planning CT images, circumventing potential registration errors when aligning MRI or MRI-derived tumor masks to planning CT. To address the low contrast issues between tumors and adjacent normal structures in planning CT, we introduce a 3D Semantic Asymmetry Tumor segmentation (SATs) method. Specifically, we posit that a healthy nasopharyngeal region is characteristically bilaterally symmetric, whereas the emergence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma disrupts this symmetry. Then, we propose a Siamese contrastive learning segmentation framework that minimizes the voxel-wise distance between original and flipped areas without tumor and encourages a larger distance between original and flipped areas with tumor. Thus, our approach enhances the sensitivity of features to semantic asymmetries. % Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed SATs achieves the leading NPC GTV segmentation performance in both internal and external testing, \emph{e.g.}, with at least 2% absolute Dice score improvement and 12% average distance error reduction when compared to other state-of-the-art methods in the external testing.
在鼻咽癌(NPC)的放射治疗过程中,临床医生通常使用非对比规划计算机断层扫描(CT)来界定大体肿瘤体积(GTV),以确保准确的辐射剂量传递。然而,肿瘤与相邻正常组织之间的对比度较低,迫使放疗科医生手动界定肿瘤,通常依赖诊断磁共振成像(MRI)进行引导。本研究提出了一种直接在非对比规划CT图像上分割鼻咽癌大体肿瘤的新方法,避免了将MRI或MRI衍生的肿瘤掩膜与规划CT对齐时可能出现的注册错误。为了解决规划CT中肿瘤与相邻正常结构之间的低对比度问题,我们引入了3D语义不对称肿瘤分割(SATs)方法。具体来说,我们认为健康的鼻咽区域具有双侧对称性,而鼻咽癌的出现会破坏这种对称性。然后,我们提出了一种Siamese对比学习分割框架,该框架最小化原始和翻转的无肿瘤区域之间的体素距离,同时鼓励原始和翻转的带肿瘤区域之间的距离更大。因此,我们的方法提高了对语义不对称性的特征敏感性。大量的实验表明,所提出的SATs在内部和外部测试中均实现了领先的NPC GTV分割性能,例如与外部测试中的其他最新方法相比,至少提高了2%的绝对Dice得分,平均距离误差减少了12%。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出了一种新的鼻咽癌(NPC)粗肿瘤体积(GTV)分割方法,直接在非对比规划计算机断层扫描图像上进行,避免了MRI或MRI衍生的肿瘤掩膜与规划CT对齐时可能出现的注册错误。该方法利用健康的鼻咽区域通常具有的双侧对称性特征来检测肿瘤的语义不对称性,并通过Siamese对比学习分割框架来提高对语义不对称性的敏感度。实验证明,该方法在内部和外部测试中的NPC GTV分割性能均居领先地位。相较于其他最先进的方法,该方法在外部测试中绝对Dice得分提高了至少2%,平均距离误差减少了12%。
Key Takeaways
- 鼻咽癌辐射疗法中,肿瘤与邻近正常组织对比度低,需放射肿瘤学家手动分割肿瘤,通常依赖诊断MRI进行引导。
- 提出了一种新的鼻咽癌粗肿瘤体积分割方法,直接应用于非对比规划CT图像,避免了MRI注册误差。
- 利用健康的鼻咽区域具有的双侧对称性特征来检测肿瘤的语义不对称性。
- 采用Siamese对比学习分割框架,提高对语义不对称性的敏感度。
- 实验显示,该方法在NPC GTV分割性能上表现领先,相较于其他方法,Dice得分有显著提高,平均距离误差有所减少。
点此查看论文截图

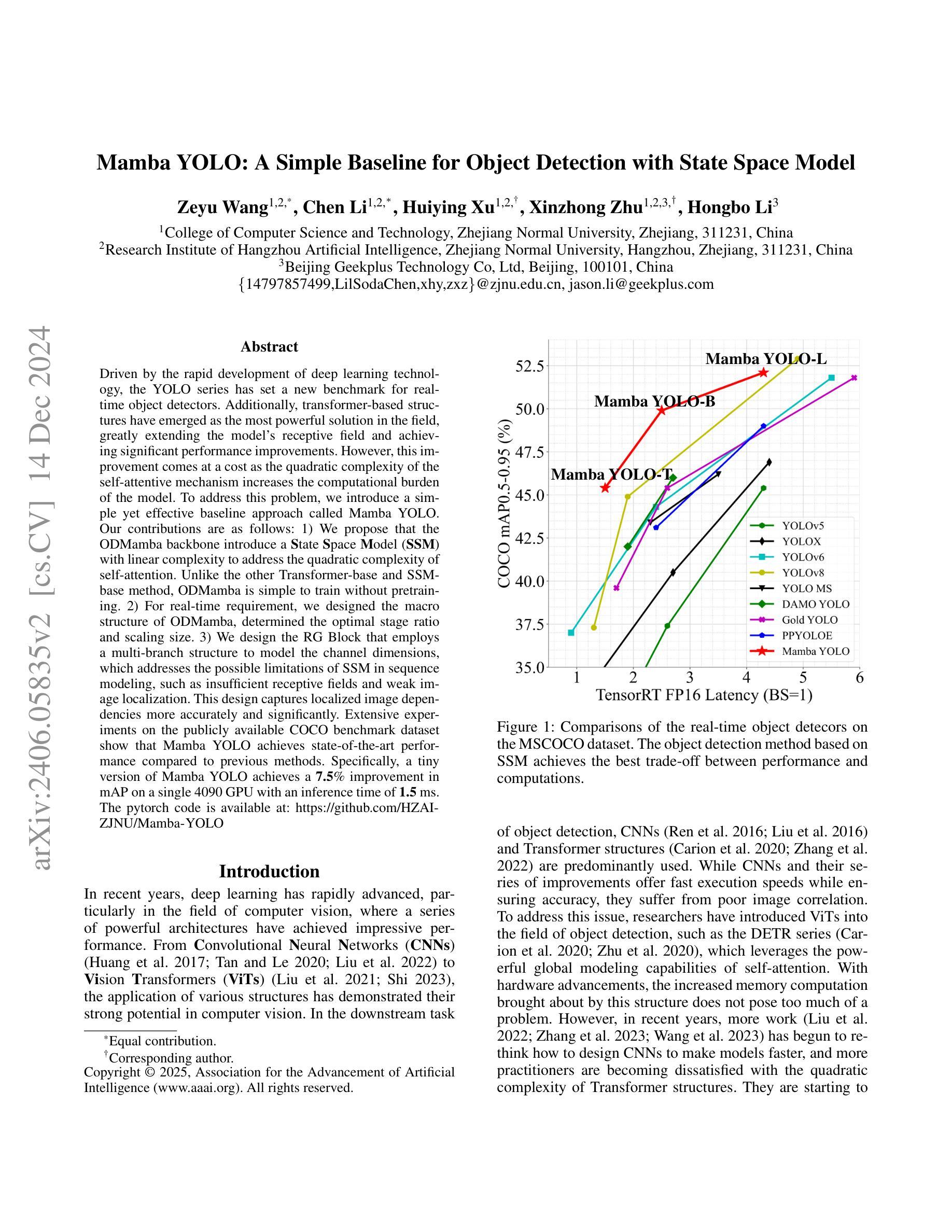
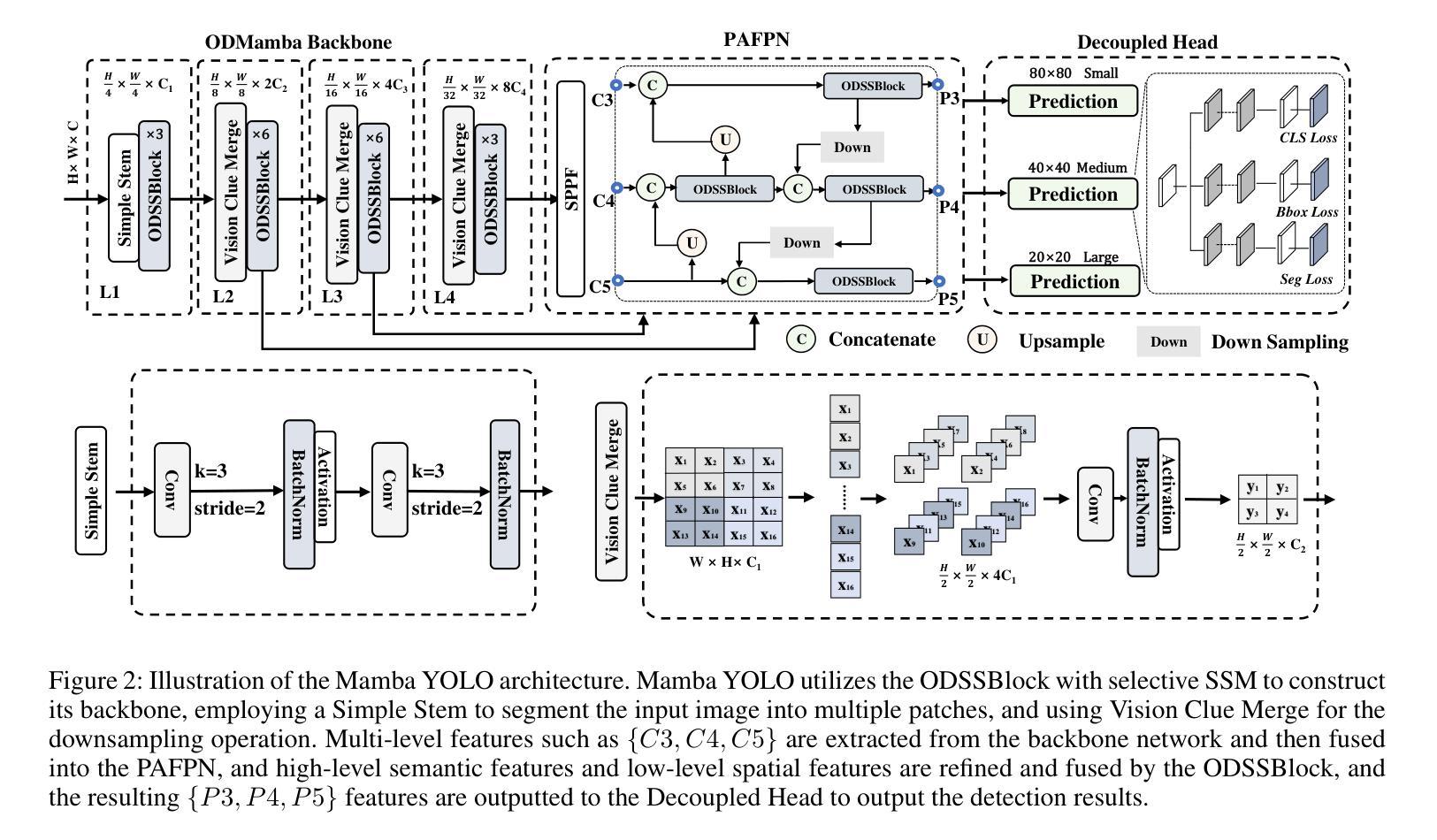
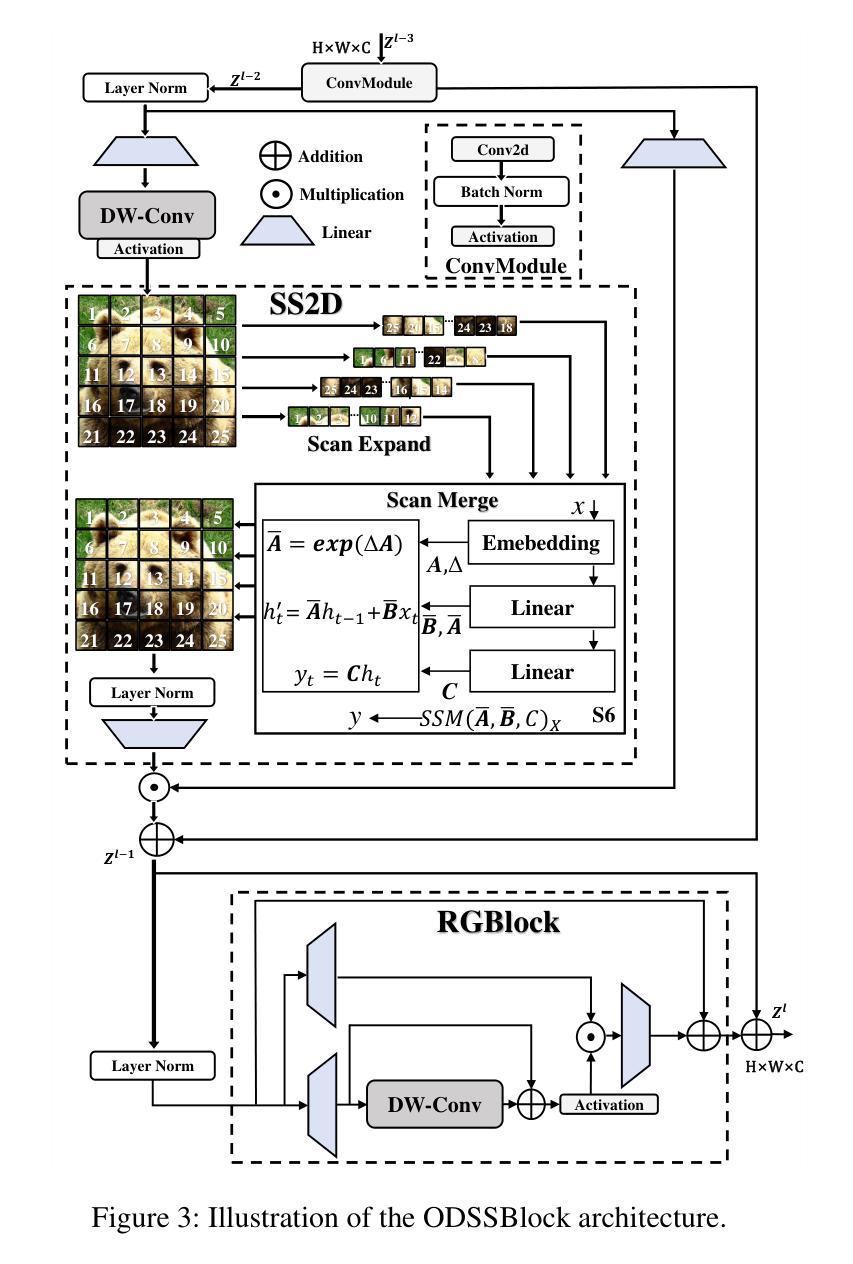
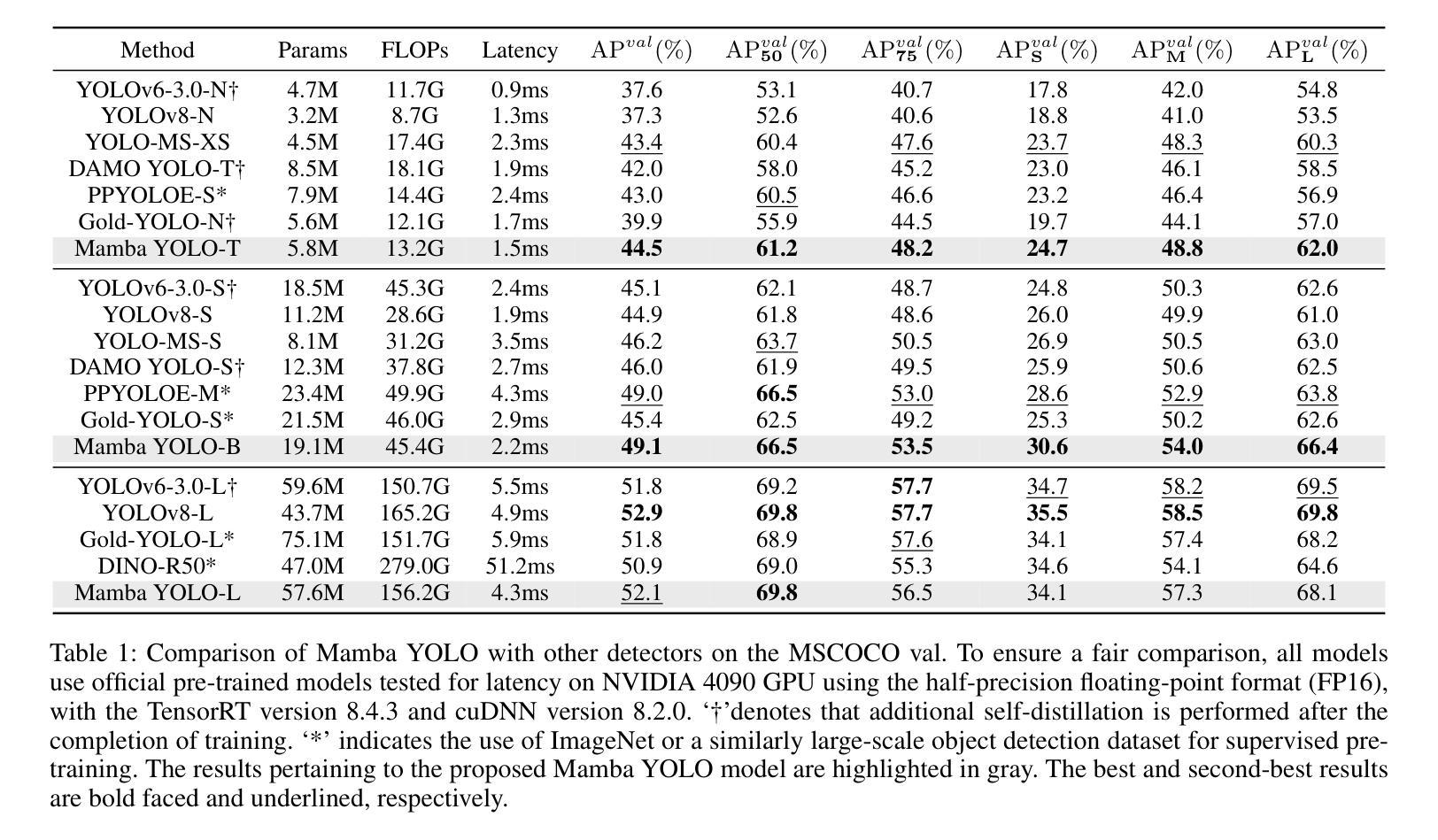
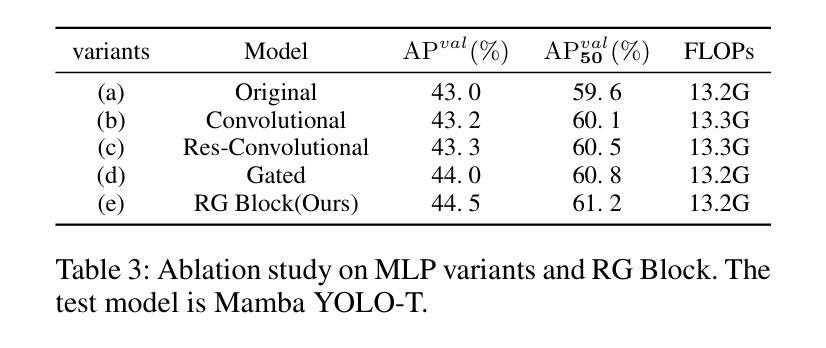
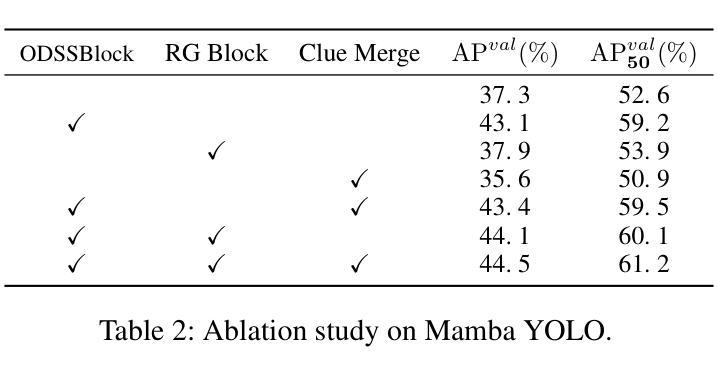
Mamba YOLO: A Simple Baseline for Object Detection with State Space Model
Authors:Zeyu Wang, Chen Li, Huiying Xu, Xinzhong Zhu, Hongbo Li
Driven by the rapid development of deep learning technology, the YOLO series has set a new benchmark for real-time object detectors. Additionally, transformer-based structures have emerged as the most powerful solution in the field, greatly extending the model’s receptive field and achieving significant performance improvements. However, this improvement comes at a cost as the quadratic complexity of the self-attentive mechanism increases the computational burden of the model. To address this problem, we introduce a simple yet effective baseline approach called Mamba YOLO. Our contributions are as follows: 1) We propose that the ODMamba backbone introduce a \textbf{S}tate \textbf{S}pace \textbf{M}odel (\textbf{SSM}) with linear complexity to address the quadratic complexity of self-attention. Unlike the other Transformer-base and SSM-base method, ODMamba is simple to train without pretraining. 2) For real-time requirement, we designed the macro structure of ODMamba, determined the optimal stage ratio and scaling size. 3) We design the RG Block that employs a multi-branch structure to model the channel dimensions, which addresses the possible limitations of SSM in sequence modeling, such as insufficient receptive fields and weak image localization. This design captures localized image dependencies more accurately and significantly. Extensive experiments on the publicly available COCO benchmark dataset show that Mamba YOLO achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to previous methods. Specifically, a tiny version of Mamba YOLO achieves a \textbf{7.5}% improvement in mAP on a single 4090 GPU with an inference time of \textbf{1.5} ms. The pytorch code is available at: \url{https://github.com/HZAI-ZJNU/Mamba-YOLO}
随着深度学习技术的飞速发展,YOLO系列为实时目标检测器设定了新的基准。此外,基于transformer的结构已成为该领域最强大的解决方案,极大地扩展了模型的感受野,并实现了性能的大幅提升。然而,这种提升是有代价的,自注意力机制的二次复杂性增加了模型的计算负担。为了解决这一问题,我们引入了一种简单有效的基线方法,称为Mamba YOLO。我们的贡献如下:1)我们提出ODMamba骨干网,引入具有线性复杂性的状态空间模型(SSM),以解决自注意力的二次复杂性。与其他基于Transformer和SSM的方法不同,ODMamba训练简单,无需预训练。2)为了满足实时要求,我们设计了ODMamba的宏观结构,确定了最佳阶段比例和缩放大小。3)我们设计了RG块,采用多分支结构对通道维度进行建模,解决了SSM在序列建模中可能存在的局限性,如感受野不足和图像定位较弱。这一设计更准确地捕捉了局部图像依赖关系,并带来了显著的提升。在公开的COCO基准数据集上进行的大量实验表明,Mamba YOLO相较于以前的方法实现了最先进的性能。具体来说,Mamba YOLO的微小版本在单个4090 GPU上实现了7.5%的mAP提升,推理时间为1.5毫秒。PyTorch代码可在以下网址找到:[https://github.com/HZAI-ZJNU/Mamba-YOLO]
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
基于深度学习技术的快速发展,YOLO系列为实时目标检测器设立了新基准。为应对Transformer结构带来的计算负担问题,我们提出了简单有效的基线方法Mamba YOLO,主要贡献包括:引入具有线性复杂度的SSM(State Space Model)解决自注意力的二次复杂度问题;设计ODMamba的宏观结构,确定最佳阶段比例和缩放尺寸;设计RG块,采用多分支结构建模通道维度,解决SSM在序列建模中的潜在局限性。在COCO基准数据集上的实验表明,Mamba YOLO相比之前的方法取得了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- YOLO系列利用深度学习技术为实时目标检测设立了新标准。
- Mamba YOLO被引入作为解决Transformer结构计算负担问题的基线方法。
- SSM(State Space Model)具有线性复杂度,解决自注意力的二次复杂度问题。
- ODMamba的宏观结构经过设计,以确定最佳阶段比例和缩放尺寸,满足实时要求。
- RG块采用多分支结构建模通道维度,解决SSM在序列建模中的局限性。
- Mamba YOLO在COCO数据集上的性能达到了最新水平,其中小型版本在单个4090 GPU上实现了7.5%的mAP改进,推理时间为1.5毫秒。
点此查看论文截图
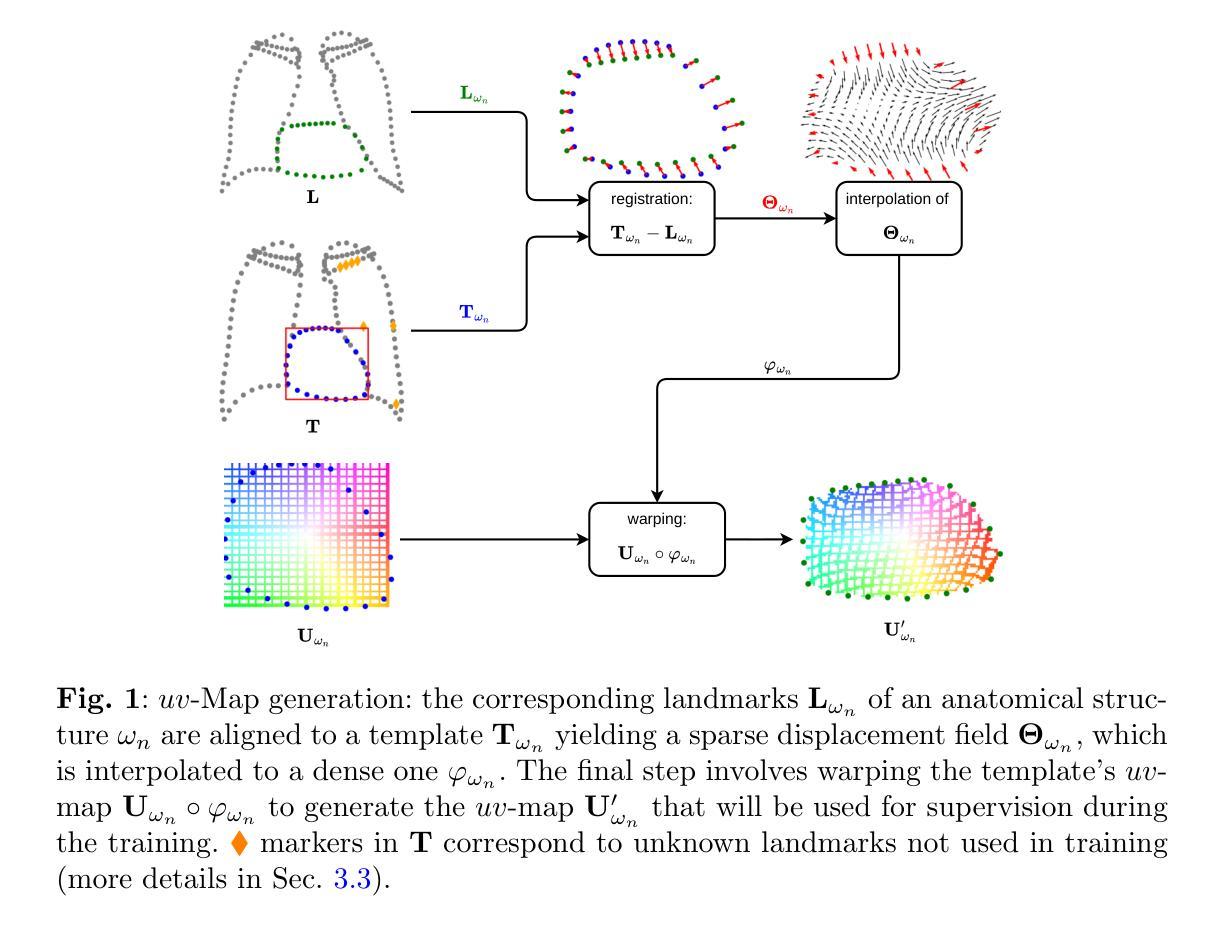
DenseSeg: Joint Learning for Semantic Segmentation and Landmark Detection Using Dense Image-to-Shape Representation
Authors:Ron Keuth, Lasse Hansen, Maren Balks, Ronja Jäger, Anne-Nele Schröder, Ludger Tüshaus, Mattias Heinrich
Purpose: Semantic segmentation and landmark detection are fundamental tasks of medical image processing, facilitating further analysis of anatomical objects. Although deep learning-based pixel-wise classification has set a new-state-of-the-art for segmentation, it falls short in landmark detection, a strength of shape-based approaches. Methods: In this work, we propose a dense image-to-shape representation that enables the joint learning of landmarks and semantic segmentation by employing a fully convolutional architecture. Our method intuitively allows the extraction of arbitrary landmarks due to its representation of anatomical correspondences. We benchmark our method against the state-of-the-art for semantic segmentation (nnUNet), a shape-based approach employing geometric deep learning and a convolutional neural network-based method for landmark detection. Results: We evaluate our method on two medical dataset: one common benchmark featuring the lungs, heart, and clavicle from thorax X-rays, and another with 17 different bones in the paediatric wrist. While our method is on pair with the landmark detection baseline in the thorax setting (error in mm of $2.6\pm0.9$ vs $2.7\pm0.9$), it substantially surpassed it in the more complex wrist setting ($1.1\pm0.6$ vs $1.9\pm0.5$). Conclusion: We demonstrate that dense geometric shape representation is beneficial for challenging landmark detection tasks and outperforms previous state-of-the-art using heatmap regression. While it does not require explicit training on the landmarks themselves, allowing for the addition of new landmarks without necessitating retraining.}
目的:语义分割和关键点检测是医学图像处理中的基本任务,有助于对解剖对象进行进一步分析。尽管基于深度学习的像素级分类为分割任务创造了新的技术高度,但在关键点检测方面仍有所不足,而基于形状的方法在这方面具有优势。方法:在这项工作中,我们提出了一种密集图像到形状的表示方法,它通过采用全卷积架构实现了关键点和语义分割的联合学习。我们的方法直观地允许提取任意关键点,因为它表示了解剖结构对应关系。我们将方法与最先进的语义分割方法(nnUNet)进行基准测试比较,这是一种采用几何深度学习的基于形状的方法,以及与用于关键点检测的卷积神经网络方法进行基准测试比较。结果:我们在两个医学数据集上评估了我们的方法:一个是常见的包含胸部X射线中的肺、心脏和锁骨的基准数据集,另一个是包含儿童手腕的17块不同骨骼的数据集。虽然我们的方法在胸部设置中的关键点检测基线表现相当(以毫米为单位的误差为$2.6±0.9$与$2.7±0.9$),但在更复杂的腕部设置中却大大超过了它(误差为$1.1±0.6$与$1.9±0.5$)。结论:我们证明了密集几何形状表示对于具有挑战性的关键点检测任务是有益的,并且在使用热图回归的先前技术中表现更好。我们的方法不需要对关键点本身进行明确的训练,允许添加新的关键点而无需重新训练。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
本文提出了一种基于深度学习的密集图像到形状表示方法,能够联合学习地标和语义分割。该方法采用全卷积架构,能够直观地提取任意地标,并通过对解剖对应关系的表示实现这一功能。实验结果表明,该方法在医学图像分割和地标检测任务上取得了优异性能,特别是在具有挑战性的地标检测任务中表现出优势。该方法不需要针对地标本身进行明确的训练,可以方便地添加新的地标而无需重新训练。
关键见解
- 语义分割和地标检测是医学图像处理中的基本任务,有助于进一步分析解剖对象。
- 虽然基于深度学习的像素级分类在分割方面处于领先地位,但在地标检测方面仍存在短板。
- 本文提出了一种密集图像到形状表示的方法,通过全卷积架构联合学习地标和语义分割。
- 该方法能够直观地提取任意地标,通过对解剖对应关系的表示实现这一功能。
- 实验结果表明,该方法在多个医学数据集上取得了优异性能,特别是在具有挑战性的地标检测任务中表现出优势。
- 与目前最先进的语义分割方法(如nnUNet)相比,本文提出的方法在特定数据集上具有竞争优势。
点此查看论文截图

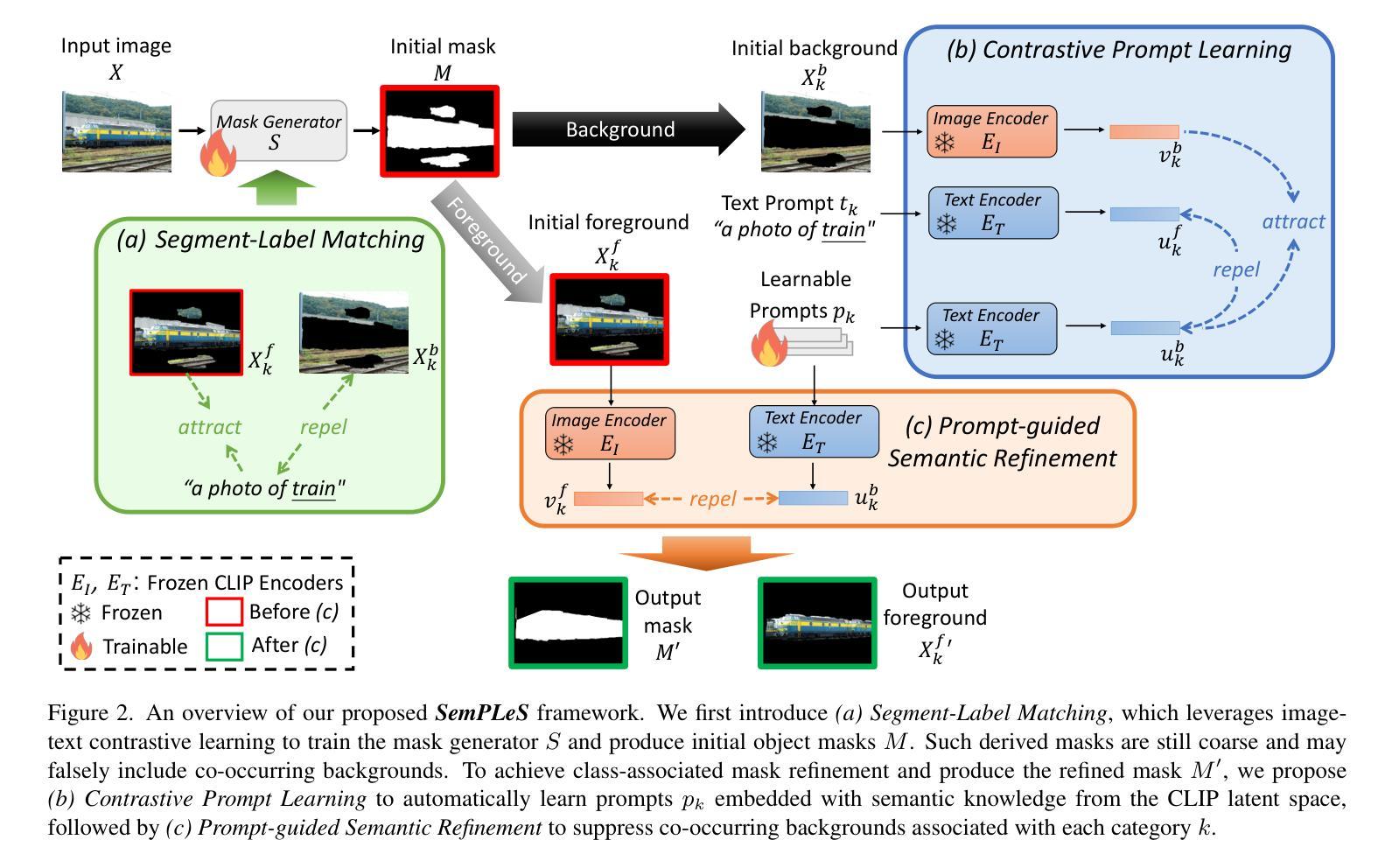
Semantic Prompt Learning for Weakly-Supervised Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Ci-Siang Lin, Chien-Yi Wang, Yu-Chiang Frank Wang, Min-Hung Chen
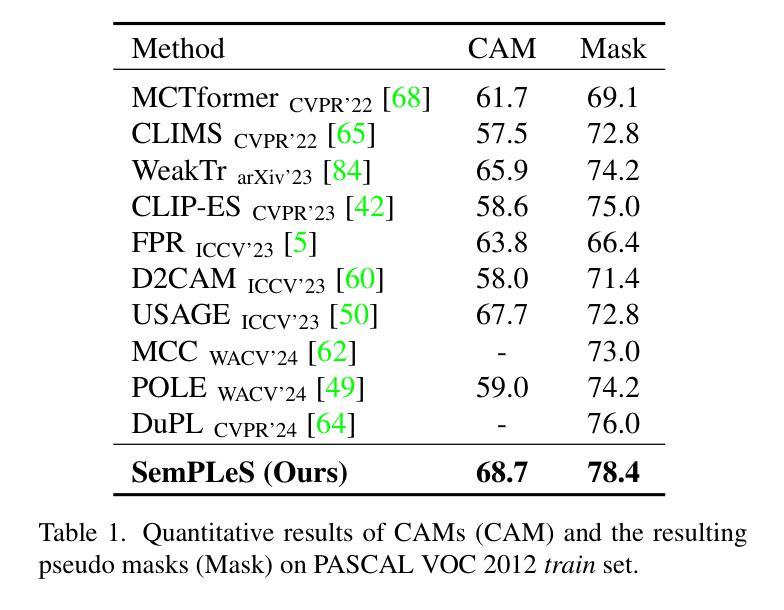
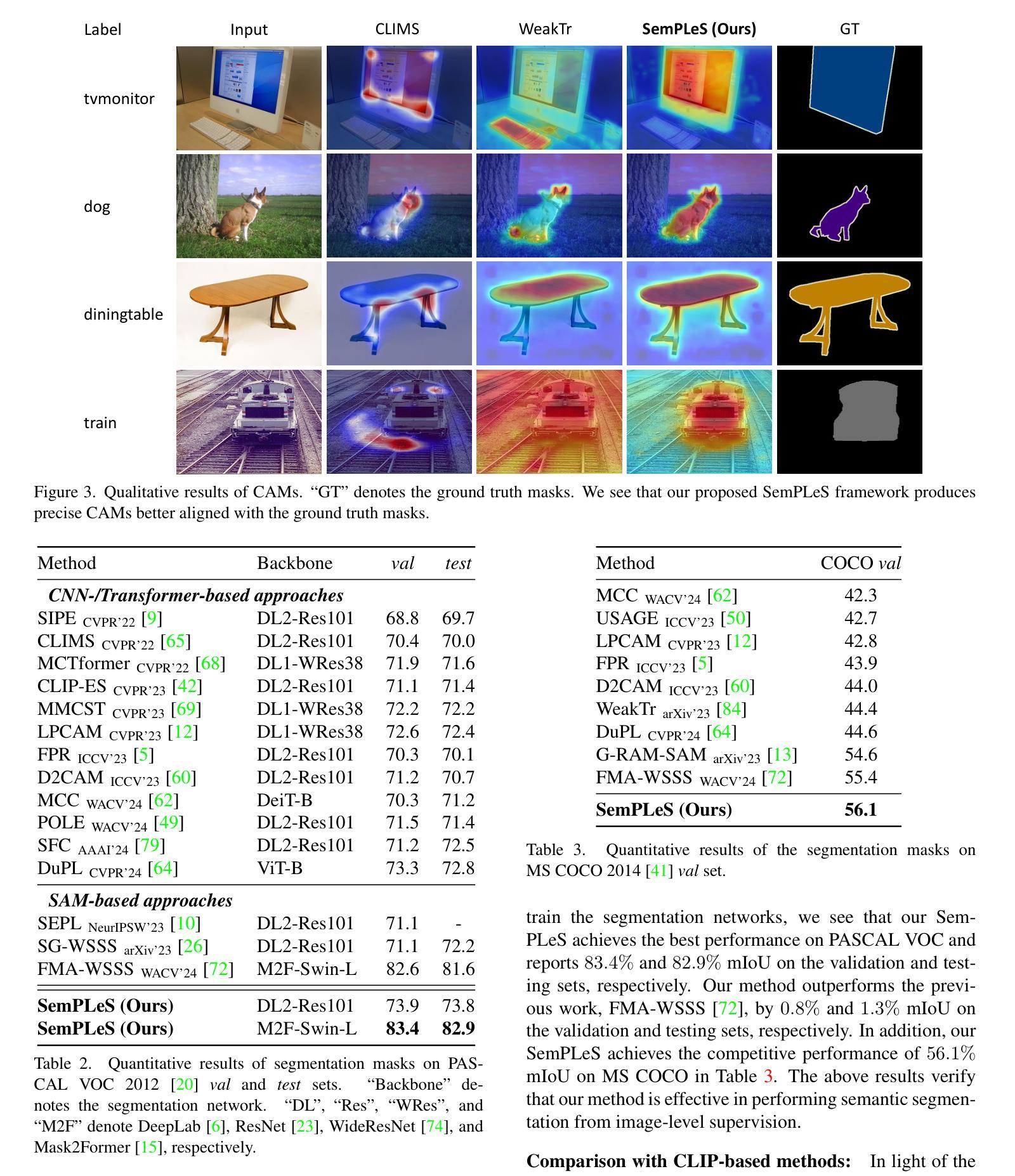
Weakly-Supervised Semantic Segmentation (WSSS) aims to train segmentation models using image data with only image-level supervision. Since precise pixel-level annotations are not accessible, existing methods typically focus on producing pseudo masks for training segmentation models by refining CAM-like heatmaps. However, the produced heatmaps may capture only the discriminative image regions of object categories or the associated co-occurring backgrounds. To address the issues, we propose a Semantic Prompt Learning for WSSS (SemPLeS) framework, which learns to effectively prompt the CLIP latent space to enhance the semantic alignment between the segmented regions and the target object categories. More specifically, we propose Contrastive Prompt Learning and Prompt-guided Semantic Refinement to learn the prompts that adequately describe and suppress the co-occurring backgrounds associated with each object category. In this way, SemPLeS can perform better semantic alignment between object regions and class labels, resulting in desired pseudo masks for training segmentation models. The proposed SemPLeS framework achieves competitive performance on standard WSSS benchmarks, PASCAL VOC 2012 and MS COCO2014, and shows compatibility with other WSSS methods.
弱监督语义分割(WSSS)旨在使用仅带有图像级监督的图像数据来训练分割模型。由于无法获取精确的像素级注释,现有方法通常通过改进CAM类热图来生成用于训练分割模型的伪掩码。然而,生成的热图可能只捕获对象类别的判别性图像区域或相关的共发生背景。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了WSSS的语义提示学习(SemPLeS)框架,该框架学习有效地提示CLIP潜在空间,以增强分割区域与目标对象类别之间的语义对齐。更具体地说,我们提出了对比提示学习和提示引导语义细化,以学习足够描述并抑制与每个对象类别相关的共发生背景的提示。通过这种方式,SemPLeS可以在对象区域和类别标签之间实现更好的语义对齐,从而产生用于训练分割模型的理想伪掩码。所提出的SemPLeS框架在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO2014标准WSSS基准测试上取得了有竞争力的性能,并显示出与其他WSSS方法的兼容性。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF WACV 2025. Project page: https://projectdisr.github.io/semples
Summary
本文介绍了弱监督语义分割(WSSS)的挑战,并提出了一个新的框架SemPLeS来解决这一问题。SemPLeS通过学习在CLIP潜在空间中的提示来增强分割区域与目标对象类别之间的语义对齐。它采用对比提示学习和提示引导语义细化来学习描述和抑制与每个对象类别相关的共发生背景的提示。这提高了语义对齐的准确性,为训练分割模型生成了理想的伪掩膜。SemPLeS在PASCAL VOC 2012和MS COCO2014等标准WSSS基准测试中表现优异,且与其他WSSS方法兼容。
Key Takeaways
- 弱监督语义分割(WSSS)利用仅带有图像级监督的图像数据训练分割模型。
- 现有方法主要通过生成伪掩膜来训练分割模型,通过细化CAM热力图实现。
- 现有方法存在的问题是生成的伪掩膜可能只覆盖对象的判别区域或相关背景。
- SemPLeS框架通过有效提示CLIP潜在空间来解决上述问题,增强语义对齐。
- SemPLeS采用对比提示学习和提示引导语义细化来学习描述和抑制与对象类别相关的共发生背景。
- SemPLeS在标准WSSS基准测试中表现优异,并与其他方法兼容。
点此查看论文截图
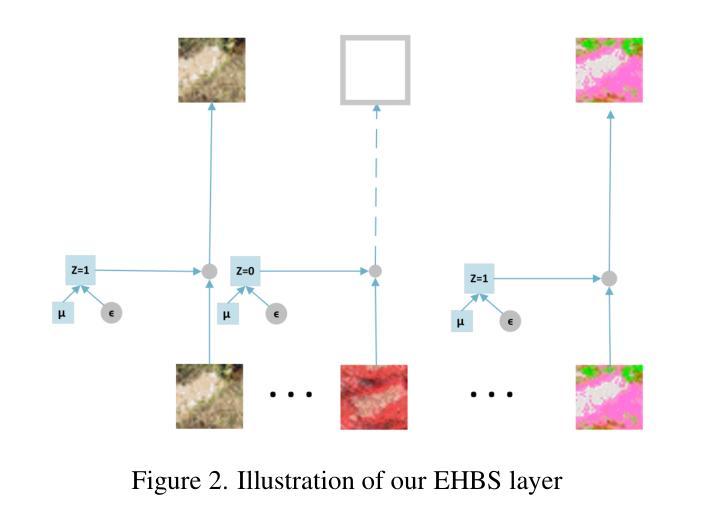
Embedded Hyperspectral Band Selection with Adaptive Optimization for Image Semantic Segmentation
Authors:Yaniv Zimmer, Oren Glickman
The selection of hyperspectral bands plays a pivotal role in remote sensing and image analysis, with the aim of identifying the most informative spectral bands while minimizing computational overhead. This paper introduces a pioneering approach for hyperspectral band selection that offers an embedded solution, making it well-suited for resource-constrained or real-time applications. Our proposed method, embedded hyperspectral band selection (EHBS), excels in selecting the best bands without needing prior processing, seamlessly integrating with the downstream task model. This is achieved through stochastic band gates along with an approximation of the $l0$ norm on the number of selected bands as the regularization term and the integration of a dynamic optimizer, DoG, which removes the need for the required tuning of the learning rate. We conduct experiments on two distinct semantic-segmentation hyperspectral benchmark datasets, demonstrating their superiority in terms of accuracy and ease of use compared to many common and state-of-the-art methods. Furthermore, our contributions extend beyond hyperspectral band selection. Our approach’s adaptability to other tasks, especially those involving grouped features, opens promising avenues for broader applications within the realm of deep learning, such as feature selection for feature groups.
高光谱波段的选择在遥感与图像分析中扮演着至关重要的角色,其目标是在减少计算开销的同时,确定最具信息量的光谱波段。本文介绍了一种高光谱波段选择的前沿方法,它提供了一种嵌入式解决方案,非常适合资源受限或实时应用。我们提出的方法——嵌入式高光谱波段选择(EHBS)能够在无需预先处理的情况下选择最佳波段,并与下游任务模型无缝集成。这是通过随机波段门以及近似$l0$范数作为正则化项来实现的,正则化项的作用在于限制选定波段的数量,并整合了动态优化器DoG,它无需调整学习率。我们在两个不同的语义分割高光谱基准数据集上进行了实验,相较于许多常见和最新方法,该方法在精度和易用性方面表现出卓越性能。此外,我们的贡献不仅局限于高光谱波段选择。我们的方法对其他任务的适应性,特别是涉及分组特征的任务,为深度学习领域内的更广泛应用开辟了充满希望的途径,例如特征组特征选择。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
超光谱波段选择在遥感与图像分析中至关重要,旨在识别最具信息量的光谱波段并最小化计算开销。本文介绍了一种嵌入式超光谱波段选择方法,无需预先处理即可选择最佳波段,并与下游任务模型无缝集成。该方法通过随机波段门选择波段,并采用对所选波段数量的l0范数近似作为正则化项,同时集成了动态优化器DoG,无需调整学习率。实验显示该方法在语义分割超光谱基准数据集上的准确性和易用性优于许多常见和最先进的方法。此外,其可适应于其他任务,尤其是在涉及分组特征方面展示出潜力巨大的应用前景。该嵌入式方法可对深度学习领域的特征组选择方法有所启发。
Key Takeaways
- 超光谱波段选择在遥感与图像分析中十分重要,本文提出一种创新的嵌入式超光谱波段选择方法(EHBS)。
- EHBS方法无需预先处理即可选择最佳波段,与下游任务模型无缝集成。
- EHBS通过随机波段门进行选择,并采用对所选波段数量的l0范数近似作为正则化项进行优化。
- 动态优化器DoG的集成使得该方法无需调整学习率。
- 实验证明EHBS在语义分割超光谱基准数据集上的准确性和易用性优于其他方法。
- EHBS方法具有适应于其他任务的能力,特别是在涉及分组特征方面展示出潜力巨大的应用前景。
点此查看论文截图


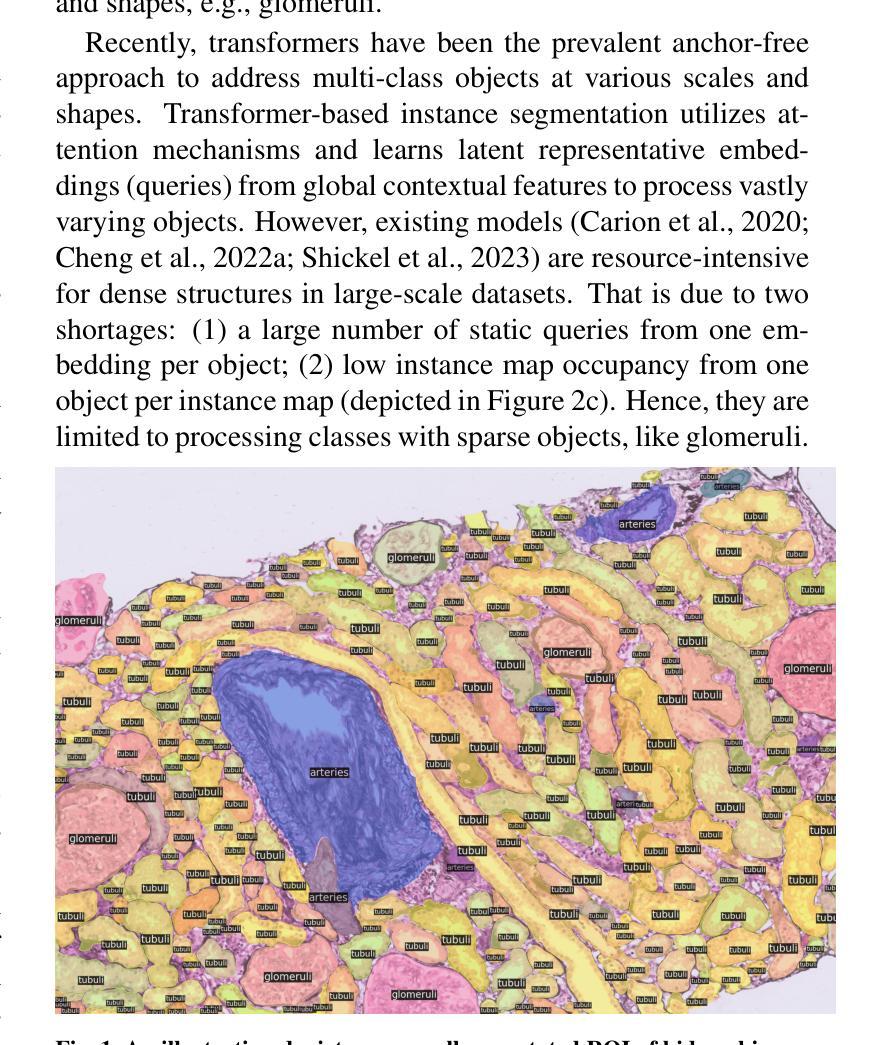
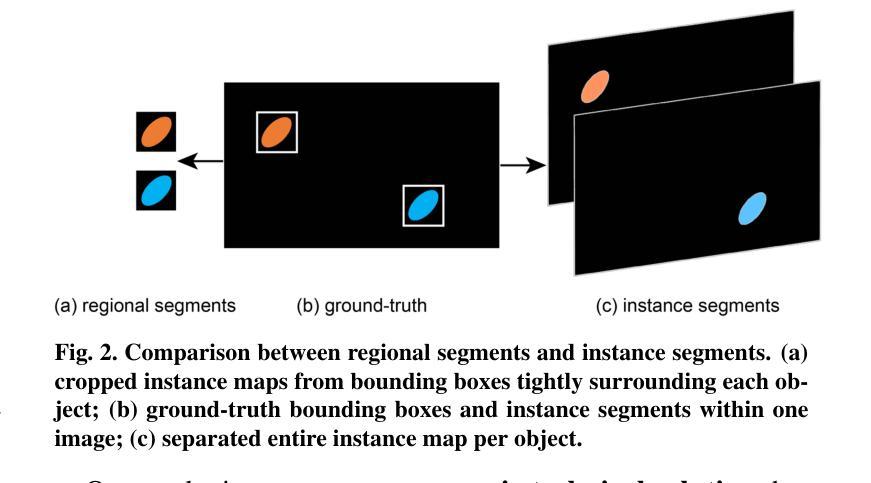
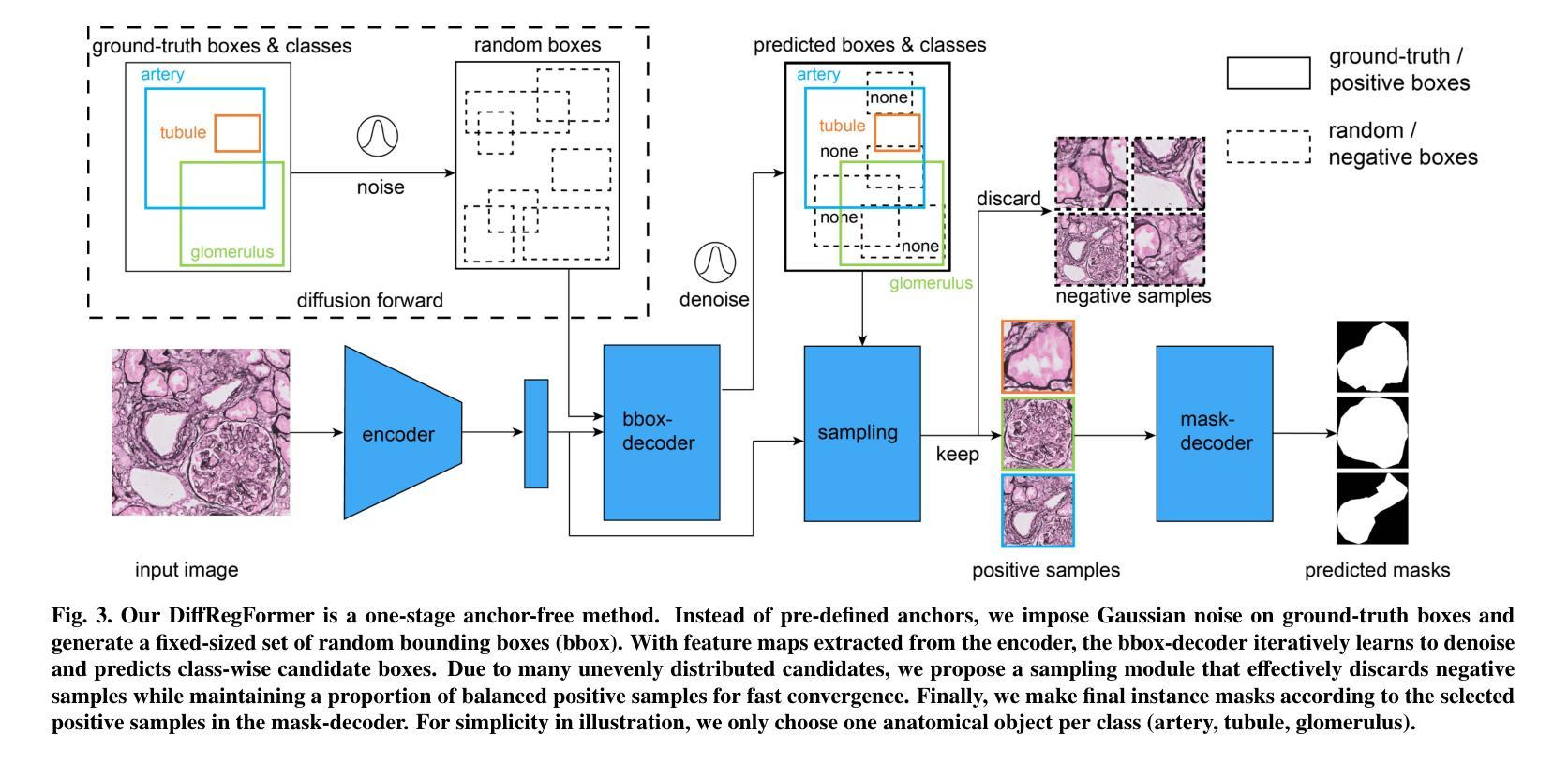
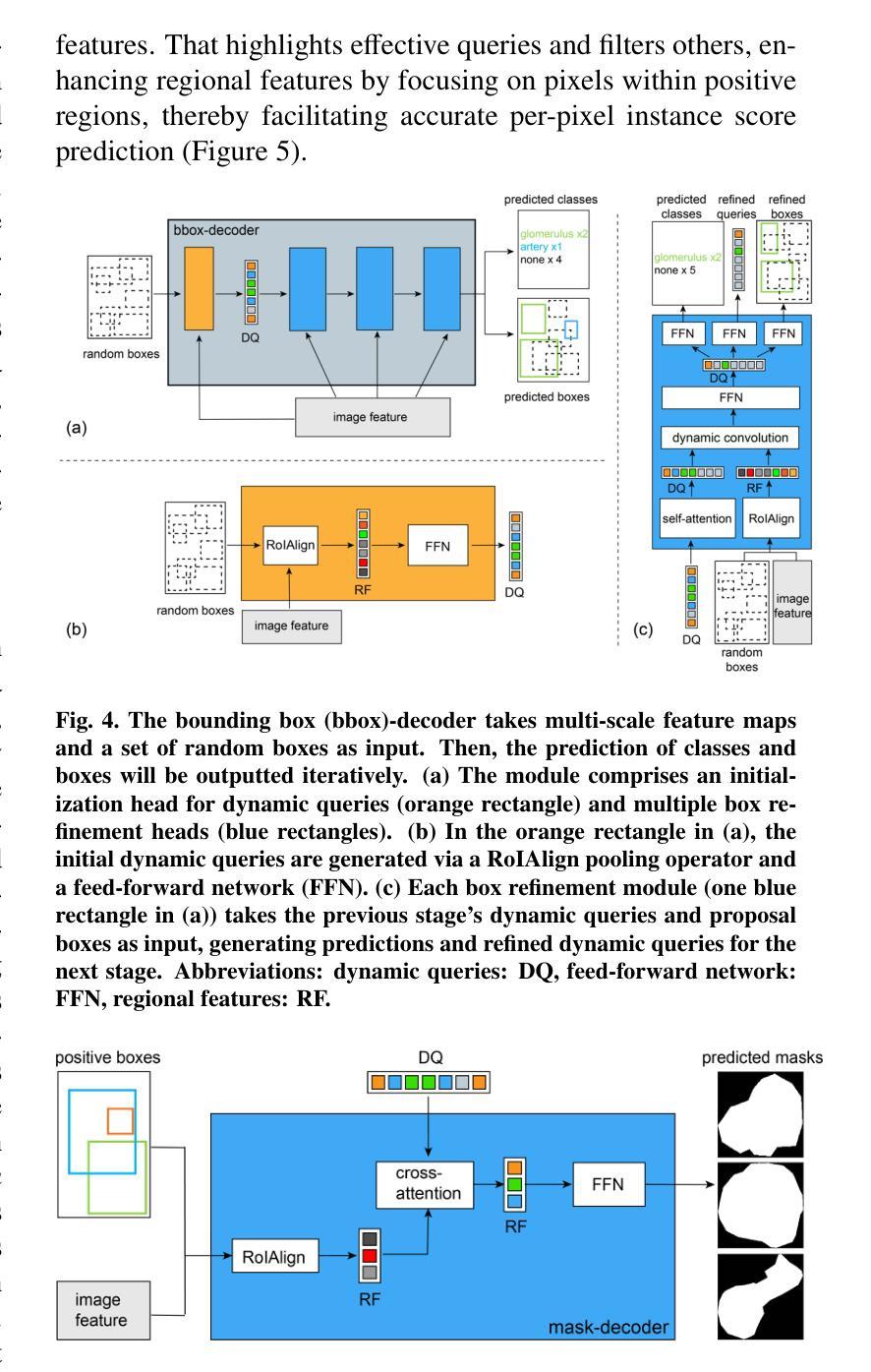
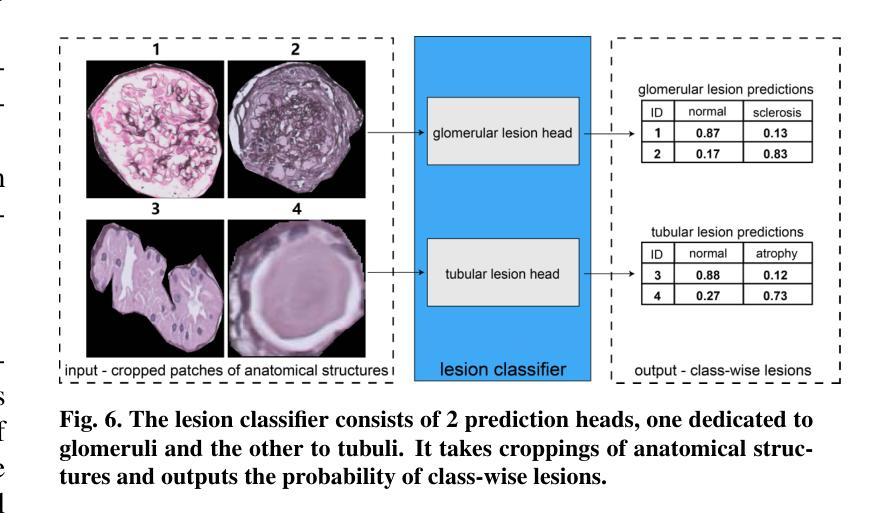
Advances in Kidney Biopsy Lesion Assessment through Dense Instance Segmentation
Authors:Zhan Xiong, Junling He, Pieter Valkema, Tri Q. Nguyen, Maarten Naesens, Jesper Kers, Fons J. Verbeek
Renal biopsies are the gold standard for the diagnosis of kidney diseases. Lesion scores made by renal pathologists are semi-quantitative and exhibit high inter-observer variability. Automating lesion classification within segmented anatomical structures can provide decision support in quantification analysis, thereby reducing inter-observer variability. Nevertheless, classifying lesions in regions-of-interest (ROIs) is clinically challenging due to (a) a large amount of densely packed anatomical objects, (b) class imbalance across different compartments (at least 3), (c) significant variation in size and shape of anatomical objects and (d) the presence of multi-label lesions per anatomical structure. Existing models cannot address these complexities in an efficient and generic manner. This paper presents an analysis for a \textbf{generalized solution} to datasets from various sources (pathology departments) with different types of lesions. Our approach utilizes two sub-networks: dense instance segmentation and lesion classification. We introduce \textbf{DiffRegFormer}, an end-to-end dense instance segmentation sub-network designed for multi-class, multi-scale objects within ROIs. Combining diffusion models, transformers, and RCNNs, DiffRegFormer {is a computational-friendly framework that can efficiently recognize over 500 objects across three anatomical classes, i.e., glomeruli, tubuli, and arteries, within ROIs.} In a dataset of 303 ROIs from 148 Jones’ silver-stained renal Whole Slide Images (WSIs), our approach outperforms previous methods, achieving an Average Precision of 52.1% (detection) and 46.8% (segmentation). Moreover, our lesion classification sub-network achieves 89.2% precision and 64.6% recall on 21889 object patches out of the 303 ROIs. Lastly, our model demonstrates direct domain transfer to PAS-stained renal WSIs without fine-tuning.
肾活检是诊断肾脏疾病的金标准。肾病理学家进行的病变评分属于半定量评估,表现出较高的观察者间变异性。在分割的解剖结构内自动进行病变分类,可以为定量分析提供决策支持,从而减少观察者间的变异性。然而,在感兴趣区域(ROI)进行病变分类在临床上具有挑战性,原因包括(a)大量密集排列的解剖对象,(b)不同部位(至少3个部位)的类别不平衡,(c)解剖对象的大小和形状存在显著差异,以及(d)每个解剖结构中存在多标签病变。现有模型无法以高效且通用的方式处理这些复杂性。本文旨在为来自不同来源(病理科)和不同病变类型的数据集提供一种通用解决方案。我们的方法利用两个子网络:密集实例分割和病变分类。我们引入了DiffRegFormer,这是一个端到端的密集实例分割子网络,专为ROI内的多类、多尺度对象设计。结合扩散模型、转换器和RCNNs,DiffRegFormer是一个计算友好的框架,可以高效地识别ROI内的三个解剖类(即肾小球、肾小管和动脉)中的超过500个对象。在包含148个琼斯银染肾全幻灯片图像(WSI)的303个ROI数据集中,我们的方法优于以前的方法,达到平均精度检测为52.1%,分割为46.8%。此外,我们的病变分类子网络在303个ROI中的21889个对象斑块上达到了89.2%的精确度和64.6%的召回率。最后,我们的模型证明可以无需微调直接转移到PAS染色的肾WSI上。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary:
本文介绍了一种针对肾脏疾病诊断中病灶分类的自动化解决方案。通过利用密集实例分割和病灶分类两个子网络,提出了一种名为DiffRegFormer的端到端框架,用于识别ROI内的多类、多尺度对象。在肾脏全切片图像数据集上的实验表明,该方法在病灶检测和分类方面表现出优异的性能,并可直接应用于其他染色方法的肾脏图像而无需微调。
Key Takeaways:
- 肾活检是诊断肾脏疾病的金标准,但病灶评分存在半定量和高观察者间变异性的问题。
- 自动化病灶分类在量化分析中提供决策支持,有助于减少观察者间变异性。
- 病灶分类在临床上面临多个挑战,如密集的对象、类别不平衡、对象大小和形状的变化以及多标签病灶。
- 本文提出了一种结合密集实例分割和病灶分类的广义解决方案。
- DiffRegFormer框架结合了扩散模型、变压器和RCNNs,可高效识别ROI内的多类、多尺度对象。
- 在肾脏全切片图像数据集上的实验表明,DiffRegFormer在病灶检测和分类方面表现出优异性能。
点此查看论文截图