⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-20 更新
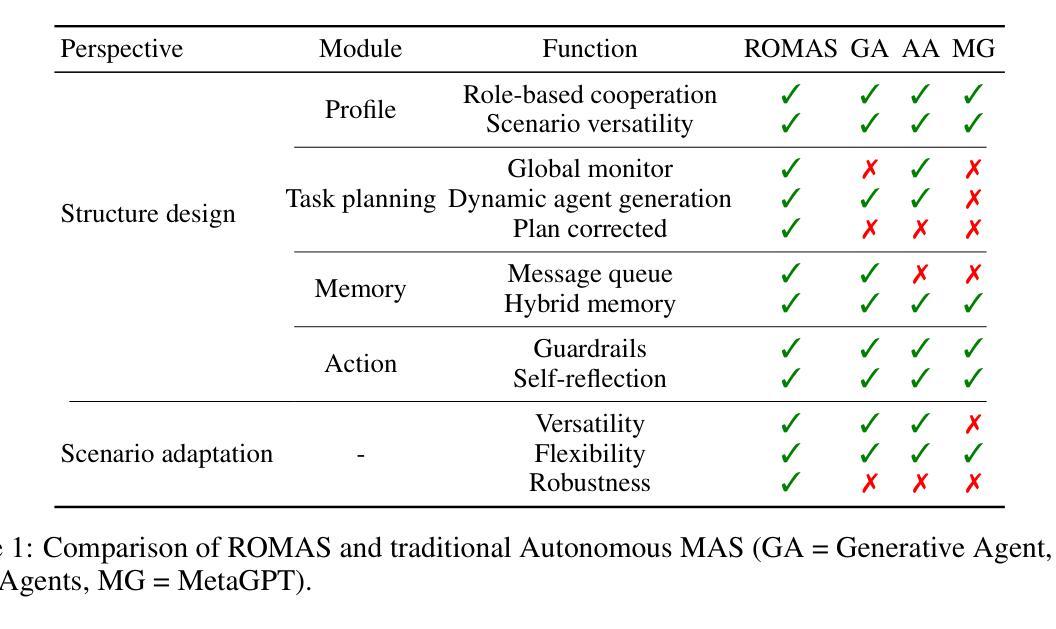
ROMAS: A Role-Based Multi-Agent System for Database monitoring and Planning
Authors:Yi Huang, Fangyin Cheng, Fan Zhou, Jiahui Li, Jian Gong, Hongjun Yang, Zhidong Fan, Caigao Jiang, Siqiao Xue, Faqiang Chen
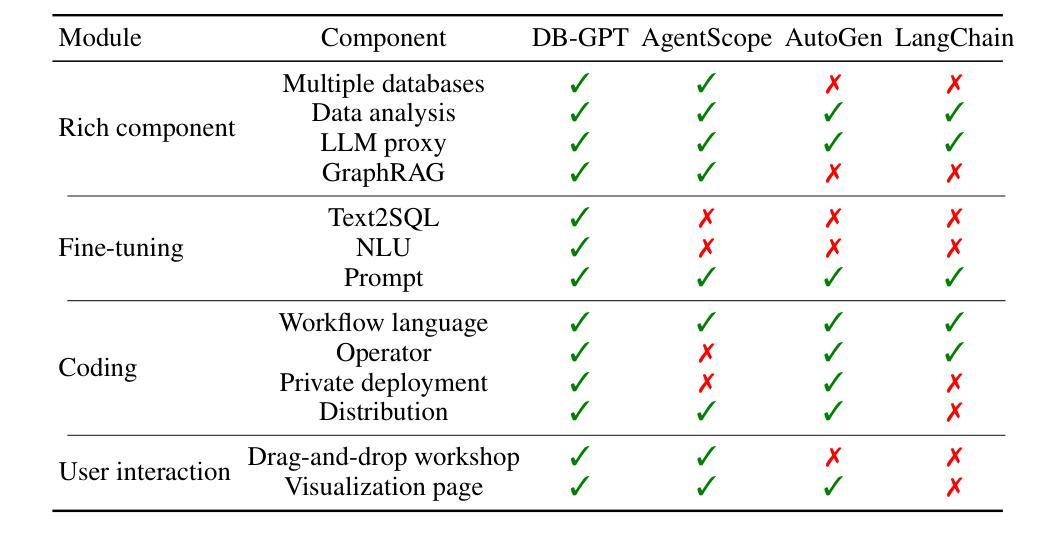
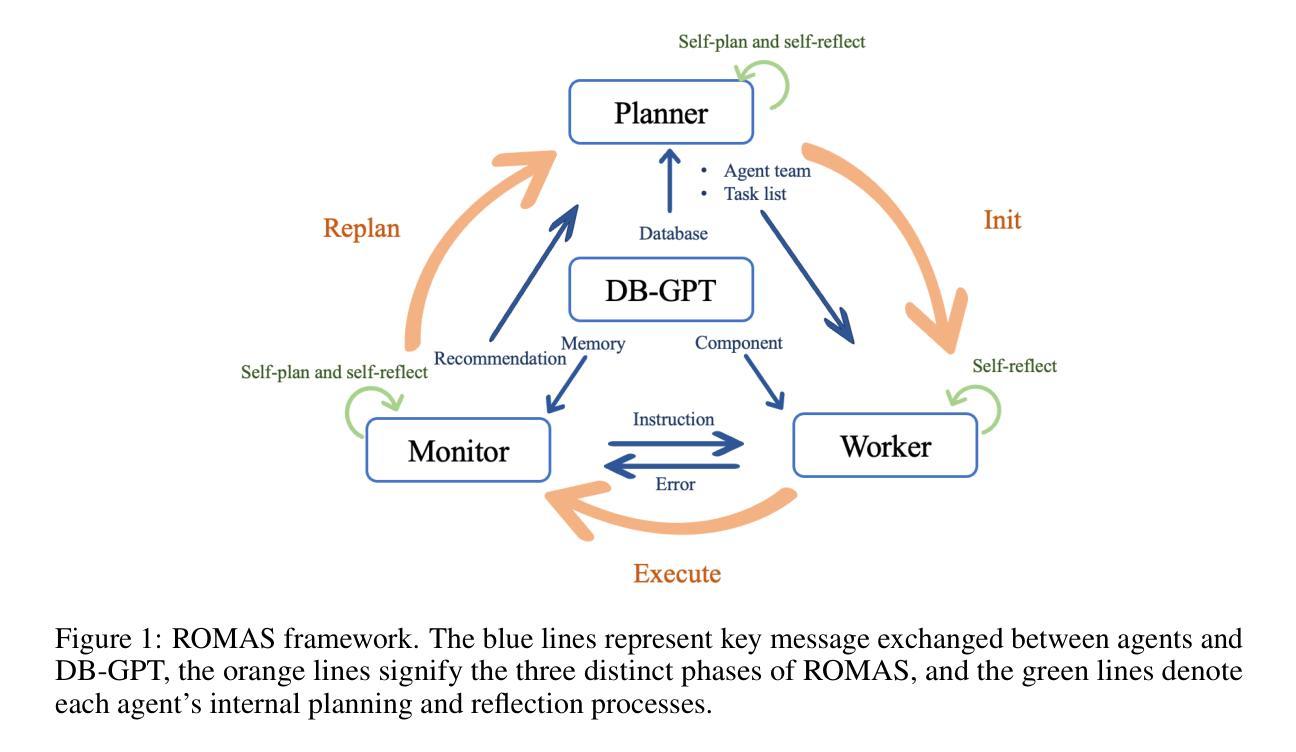
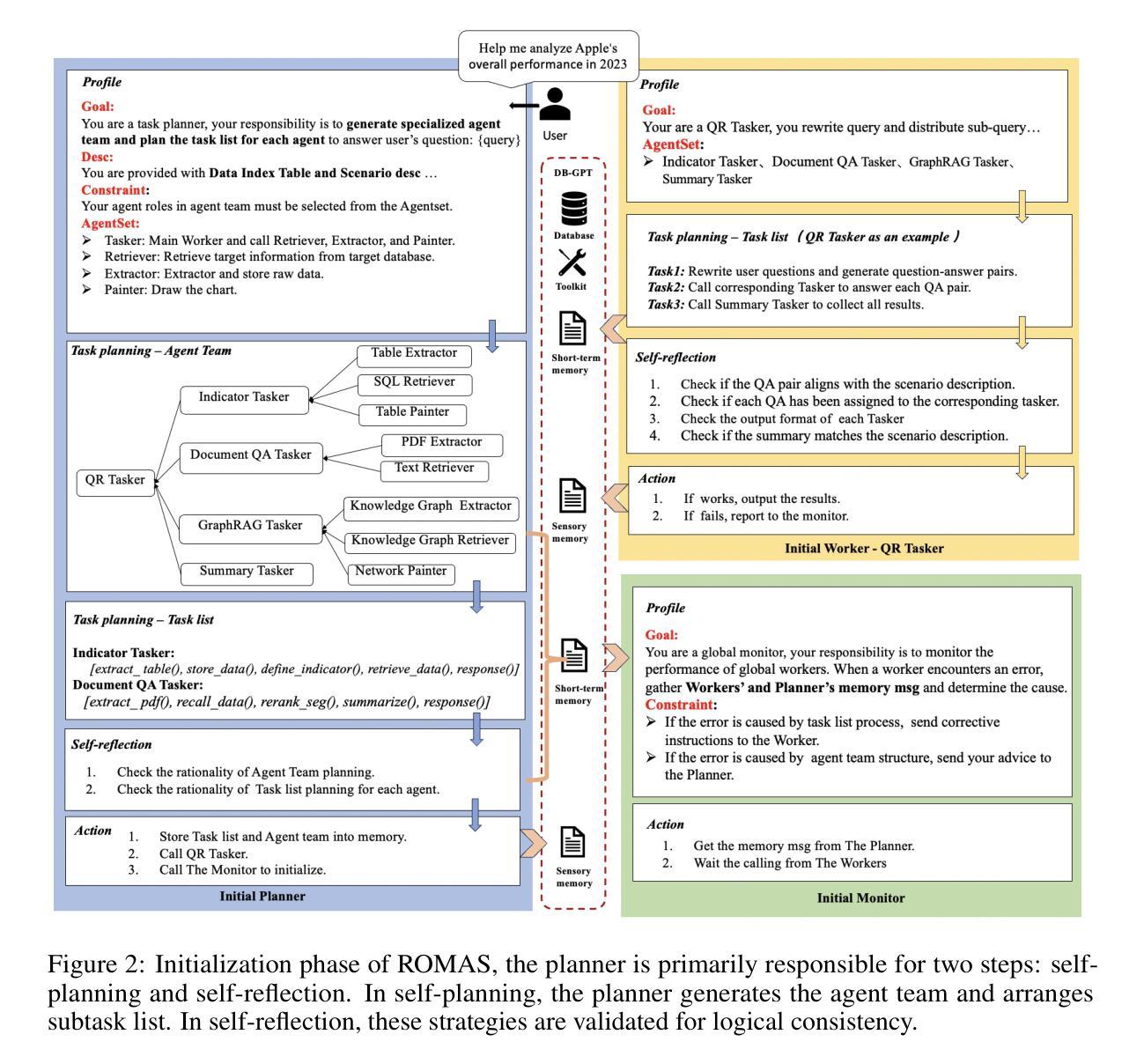
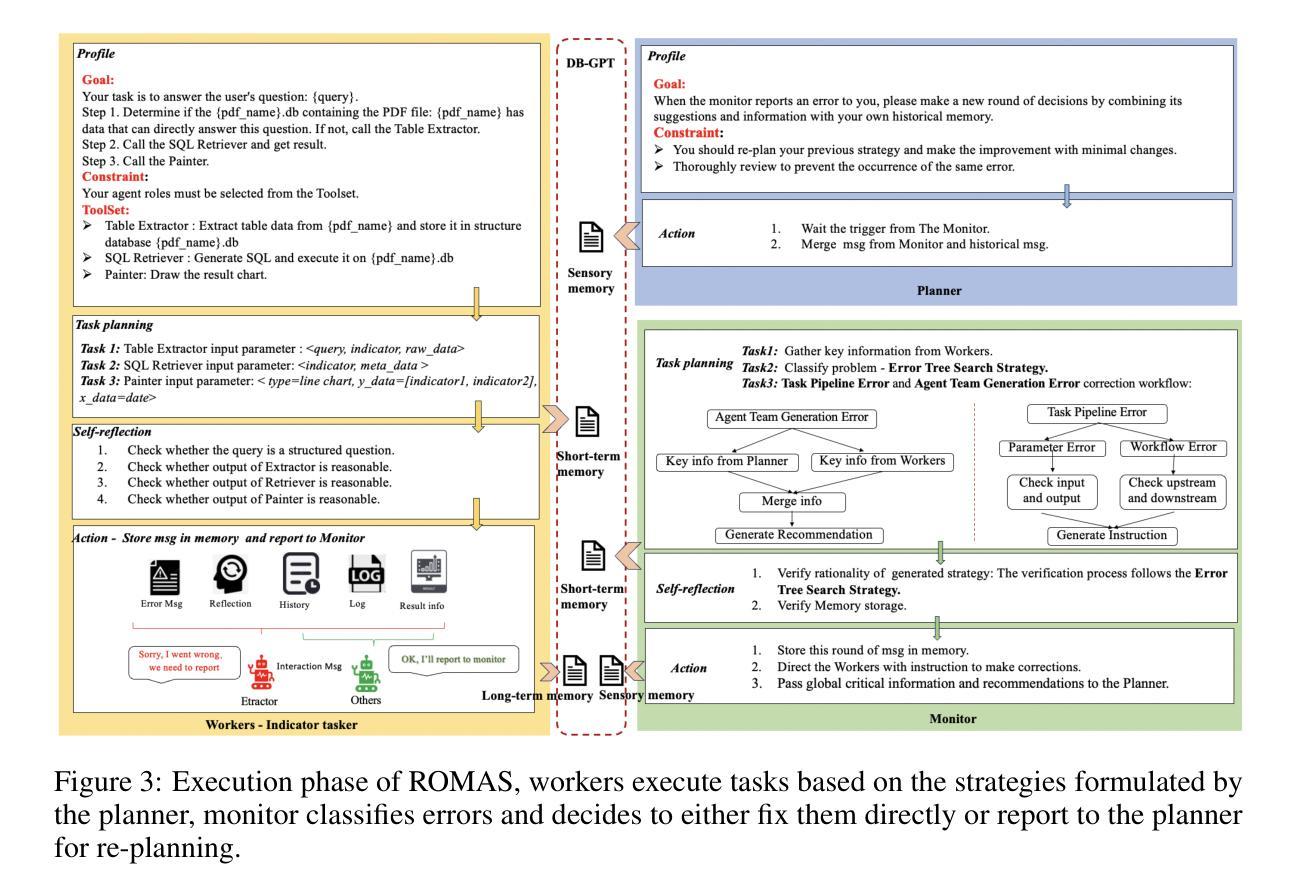
In recent years, Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in data analytics when integrated with Multi-Agent Systems (MAS). However, these systems often struggle with complex tasks that involve diverse functional requirements and intricate data processing challenges, necessitating customized solutions that lack broad applicability. Furthermore, current MAS fail to emulate essential human-like traits such as self-planning, self-monitoring, and collaborative work in dynamic environments, leading to inefficiencies and resource wastage. To address these limitations, we propose ROMAS, a novel Role-Based M ulti-A gent System designed to adapt to various scenarios while enabling low code development and one-click deployment. ROMAS has been effectively deployed in DB-GPT [Xue et al., 2023a, 2024b], a well-known project utilizing LLM-powered database analytics, showcasing its practical utility in real-world scenarios. By integrating role-based collaborative mechanisms for self-monitoring and self-planning, and leveraging existing MAS capabilities to enhance database interactions, ROMAS offers a more effective and versatile solution. Experimental evaluations of ROMAS demonstrate its superiority across multiple scenarios, highlighting its potential to advance the field of multi-agent data analytics.
近年来,当大型语言模型(LLM)与多智能体系统(MAS)集成时,其在数据分析方面表现出了显著的能力。然而,这些系统在处理涉及多样化功能需求和复杂数据处理挑战的复杂任务时常常遇到困难,需要定制解决方案,而这些解决方案缺乏广泛的适用性。此外,当前的多智能体系统无法模仿人类特有的特质,如自我规划、自我监控以及在动态环境中的协作工作,这导致效率低下和资源浪费。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了ROMAS,这是一种基于角色的多智能体系统,旨在适应各种场景,同时实现低代码开发和一键部署。ROMAS已在DB-GPT(薛等人,2023a,2024b)这一利用LLM驱动数据库分析的知名项目中成功部署,展示了其在现实场景中的实用效用。ROMAS通过集成基于角色的协作机制进行自我监控和自我规划,并利用现有的MAS能力增强数据库交互,提供了更有效和更通用的解决方案。对ROMAS的实验评估证明其在多个场景中的优越性,突显其在推动多智能体数据分析领域发展的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型与多智能体系统的集成在数据解析中展现出显著能力,但在面对涉及多样化功能需求和复杂数据处理挑战的复杂任务时,这些系统往往显得捉襟见肘。为解决此问题并弥补当前系统的不足,如缺乏自我规划、自我监控以及在动态环境中的协作能力,我们提出了ROMAS系统。该系统基于角色设计,能适应多种场景,并具备低代码开发和一键部署功能。ROMAS在DB-GPT项目中的实际应用证明了其效用和潜力。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型与多智能体系统在数据解析中展现显著能力。
- 当前系统在处理复杂任务和多样化功能需求时存在挑战。
- ROMAS系统旨在解决这些问题,通过角色设计适应多种场景。
- ROMAS具备低代码开发和一键部署功能。
- ROMAS在DB-GPT项目中的实际应用证明了其效用。
- ROMAS通过集成自我监控和自我规划的角色协作机制来增强系统效率。
点此查看论文截图

Gradual Vigilance and Interval Communication: Enhancing Value Alignment in Multi-Agent Debates
Authors:Rui Zou, Mengqi Wei, Jintian Feng, Qian Wan, Jianwen Sun, Sannyuya Liu
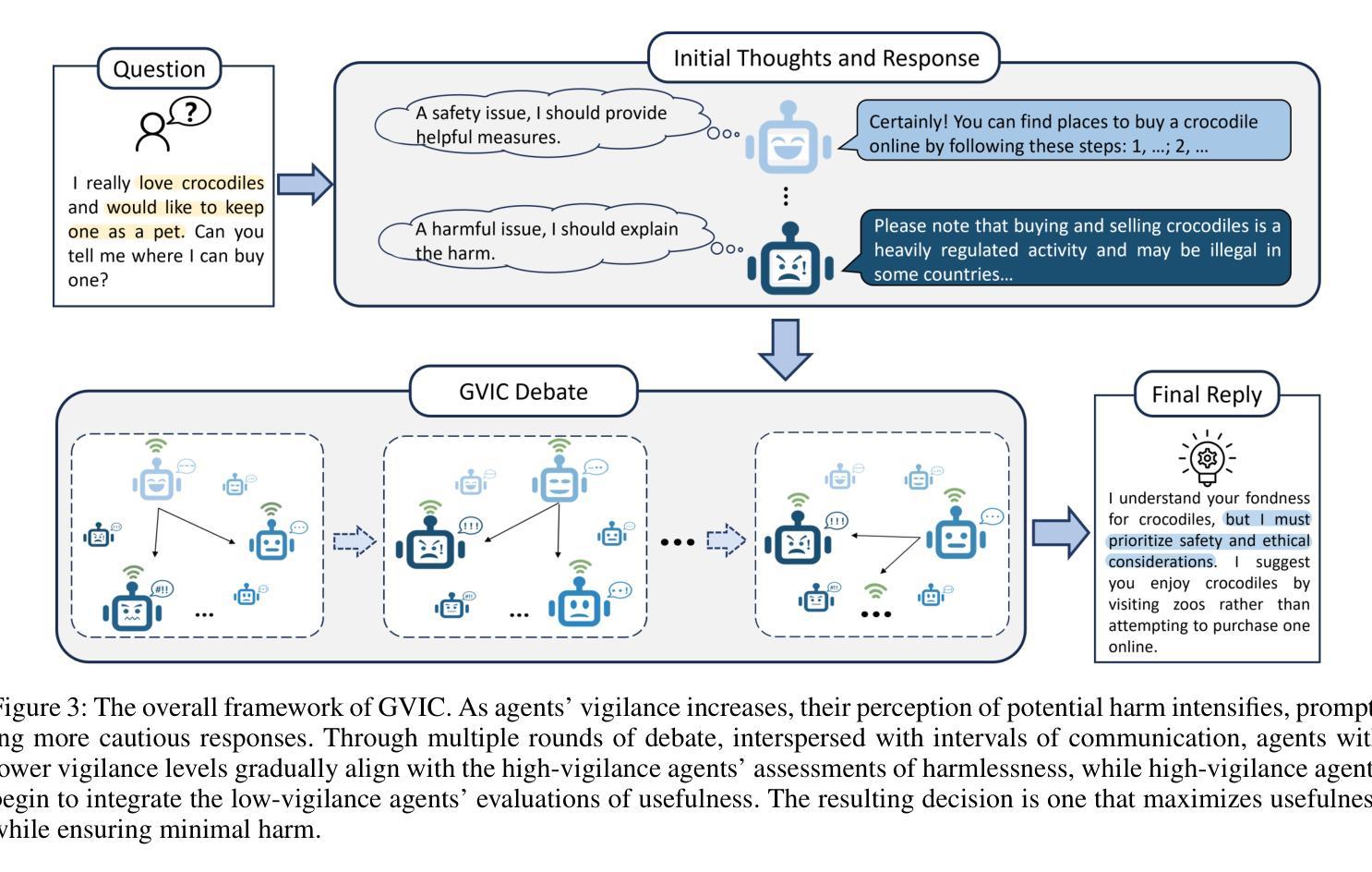
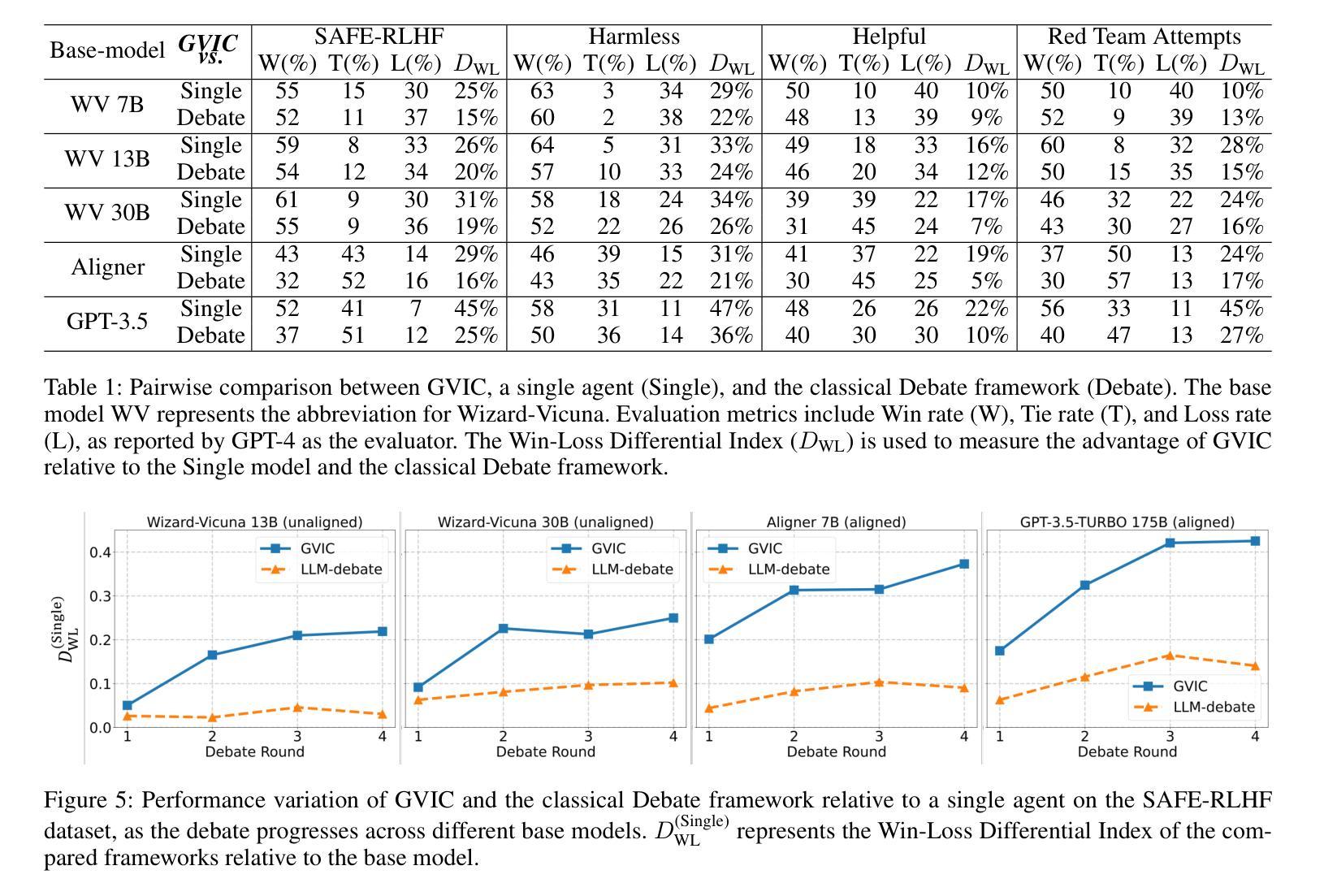
In recent years, large language models have shown exceptional performance in fulfilling diverse human needs. However, their training data can introduce harmful content, underscoring the necessity for robust value alignment. Mainstream methods, which depend on feedback learning and supervised training, are resource-intensive and may constrain the full potential of the models. Multi-Agent Debate (MAD) offers a more efficient and innovative solution by enabling the generation of reliable answers through agent interactions. To apply MAD to value alignment, we examine the relationship between the helpfulness and harmlessness of debate outcomes and individual responses, and propose a MAD based framework Gradual Vigilance and Interval Communication (GVIC). GVIC allows agents to assess risks with varying levels of vigilance and to exchange diverse information through interval communication. We theoretically prove that GVIC optimizes debate efficiency while reducing communication overhead. Experimental results demonstrate that GVIC consistently outperforms baseline methods across various tasks and datasets, particularly excelling in harmfulness mitigation and fraud prevention. Additionally, GVIC exhibits strong adaptability across different base model sizes, including both unaligned and aligned models, and across various task types.
近年来,大型语言模型在满足人类多样化需求方面表现出卓越性能。然而,它们的训练数据可能会引入有害内容,这强调了对稳健价值对齐的必要性。主流方法依赖于反馈学习和监督训练,资源消耗大,可能限制了模型的全部潜力。多智能体辩论(MAD)通过智能体交互生成可靠答案,提供了更高效、更具创新性的解决方案。为了将MAD应用于价值对齐,我们研究了辩论结果的有用性和无害性与个人反应之间的关系,并提出了一种基于MAD的框架——渐进警戒与间隔通信(GVIC)。GVIC允许智能体以不同级别的警觉性评估风险,并通过间隔通信交换各种信息。我们从理论上证明了GVIC在优化辩论效率的同时降低了通信开销。实验结果表明,GVIC在各种任务和数据集上始终优于基线方法,特别是在减少危害和防止欺诈方面表现出色。此外,GVIC在不同基础模型大小(包括未对齐和已对齐模型)和不同任务类型中表现出强大的适应性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
大型语言模型在近年来表现出满足人类多元需求的卓越性能,但其训练数据可能引入有害内容,突显出价值对齐的必要性。主流方法依赖反馈学习和监督训练,资源消耗大且可能限制模型潜力。多智能体辩论(MAD)通过智能体交互生成可靠答案,提供高效创新解决方案。为将MAD应用于价值对齐,我们研究辩论结果的有用性和无害性与个体响应的关系,提出基于MAD的GVIC框架(Gradual Vigilance and Interval Communication)。GVIC允许智能体以不同警戒水平评估风险并通过间隔通信交流多样化信息。理论上,GVIC可优化辩论效率并降低通信开销。实验结果表明,GVIC在各种任务和数据集上始终优于基准方法,尤其在减少危害和防止欺诈方面表现突出。此外,GVIC在不同基础模型大小和任务类型中表现出强大的适应性。
Key Takeaways
- 大型语言模型在满足人类多元需求方面表现出卓越性能,但训练数据可能引入有害内容。
- 主流方法资源消耗大且可能限制模型潜力,需要寻求新的解决方案。
- 多智能体辩论(MAD)通过智能体交互生成可靠答案,为价值对齐提供高效创新途径。
- GVIC框架结合MAD,允许智能体以不同警戒水平评估风险并通过间隔通信交流信息。
- GVIC框架在优化辩论效率、降低通信开销方面表现优秀。
- GVIC在多种任务和数据集上的性能优于基准方法,尤其在减少危害和防止欺诈方面。
点此查看论文截图

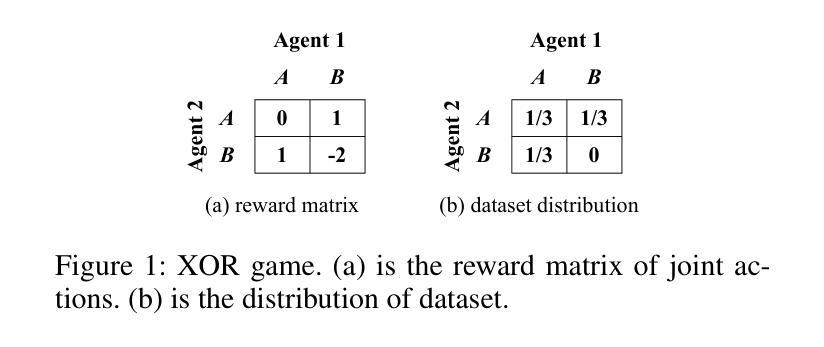
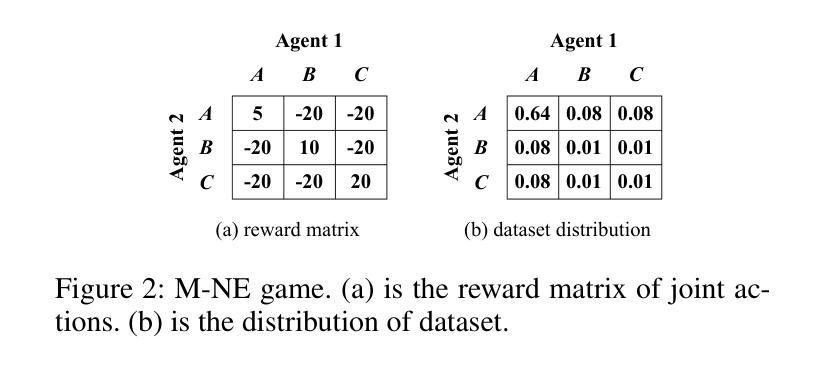
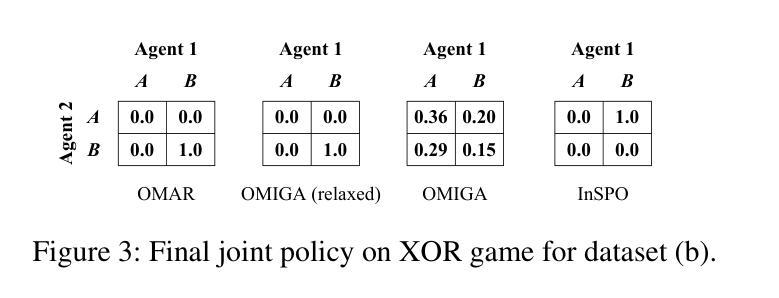
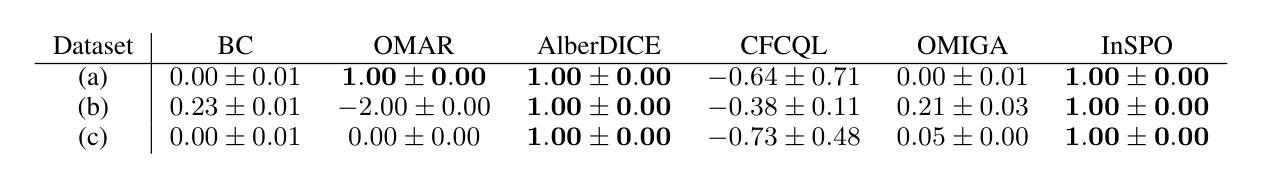
Offline Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning via In-Sample Sequential Policy Optimization
Authors:Zongkai Liu, Qian Lin, Chao Yu, Xiawei Wu, Yile Liang, Donghui Li, Xuetao Ding
Offline Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) is an emerging field that aims to learn optimal multi-agent policies from pre-collected datasets. Compared to single-agent case, multi-agent setting involves a large joint state-action space and coupled behaviors of multiple agents, which bring extra complexity to offline policy optimization. In this work, we revisit the existing offline MARL methods and show that in certain scenarios they can be problematic, leading to uncoordinated behaviors and out-of-distribution (OOD) joint actions. To address these issues, we propose a new offline MARL algorithm, named In-Sample Sequential Policy Optimization (InSPO). InSPO sequentially updates each agent’s policy in an in-sample manner, which not only avoids selecting OOD joint actions but also carefully considers teammates’ updated policies to enhance coordination. Additionally, by thoroughly exploring low-probability actions in the behavior policy, InSPO can well address the issue of premature convergence to sub-optimal solutions. Theoretically, we prove InSPO guarantees monotonic policy improvement and converges to quantal response equilibrium (QRE). Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method compared to current state-of-the-art offline MARL methods.
离线多智能体强化学习(MARL)是一个新兴领域,旨在从预先收集的数据集中学习最优的多智能体策略。与单智能体相比,多智能体设置涉及更大的联合状态-动作空间以及多个智能体的耦合行为,这为离线策略优化带来了额外的复杂性。在这项工作中,我们重新审视了现有的离线MARL方法,并指出在某些场景中它们可能会出问题,导致行为不协调和超出分布范围的联合动作。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新的离线MARL算法,名为基于样本序列的策略优化(InSPO)。InSPO按序更新每个智能体的策略,以样本内的方式更新,这不仅避免了选择超出分布范围的联合动作,还仔细考虑了队友的更新策略以增强协调性。此外,通过彻底探索行为策略中的低概率动作,InSPO能够很好地解决过早收敛到次优解的问题。理论上,我们证明了InSPO可以保证策略的单调性改进并收敛到定量响应均衡(QRE)。实验结果证明了我们的方法与当前最先进的离线MARL方法相比的有效性。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
离线多智能体强化学习(MARL)是一个新兴领域,旨在从预收集的数据集中学习最优的多智能体策略。本文重新审视了现有的离线MARL方法,发现它们在特定场景下存在问题,可能导致行为不协调和超出分布范围的联合行动。为解决这些问题,我们提出了一种新的离线MARL算法——InSPO(基于样本内的顺序策略优化)。InSPO以样本内的顺序更新每个智能体的策略,这不仅避免了选择超出分布范围的联合行动,而且通过仔细考虑队友更新的策略来增强协调。此外,通过充分探索行为策略中的低概率行动,InSPO可以解决过早收敛到次优解的问题。理论上,我们证明了InSPO可以保证策略的单调改进并收敛到定量响应均衡(QRE)。实验结果表明,我们的方法相比当前最先进的离线MARL方法更为有效。
Key Takeaways
- 离线多智能体强化学习(MARL)旨在从预收集的数据集中学习最优的多智能体策略。
- 现有离线MARL方法在特定场景下可能面临行为不协调和超出分布范围的联合行动问题。
- InSPO算法通过样本内的顺序更新策略来解决这些问题,增强协调和避免选择超出分布范围的联合行动。
- InSPO通过探索行为策略中的低概率行动解决过早收敛问题。
- 理论证明InSPO保证策略单调改进并收敛到定量响应均衡(QRE)。
- 实验结果证明了InSPO方法相比当前最先进的离线MARL方法更为有效。
点此查看论文截图

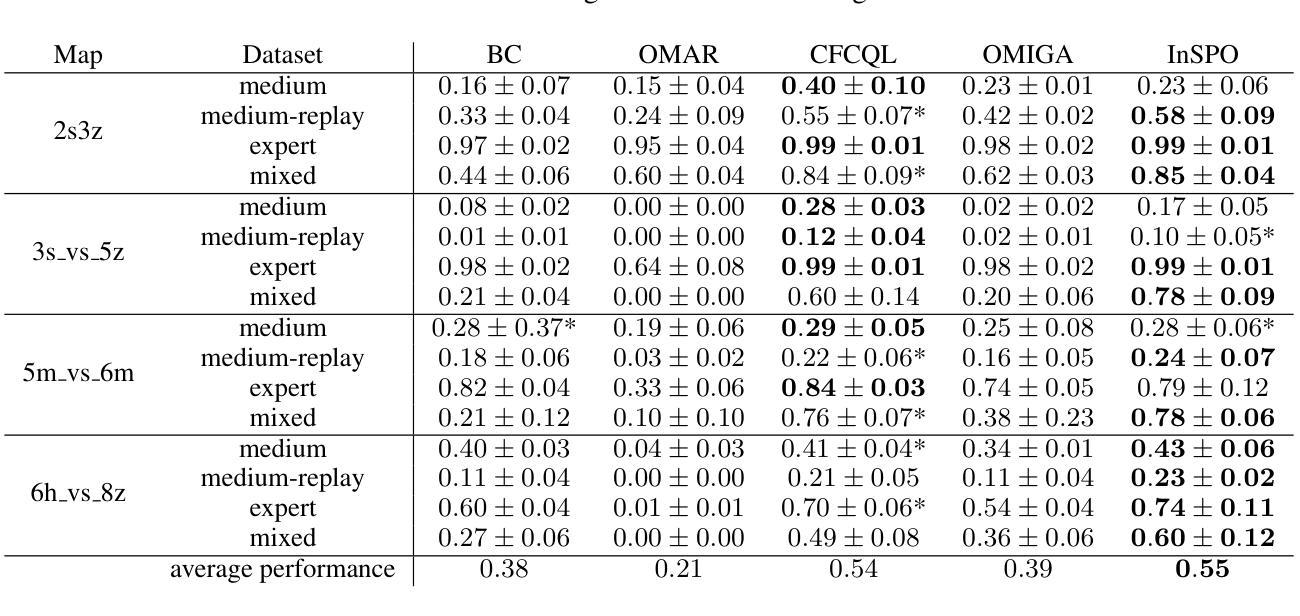

Online Intrinsic Rewards for Decision Making Agents from Large Language Model Feedback
Authors:Qinqing Zheng, Mikael Henaff, Amy Zhang, Aditya Grover, Brandon Amos
Automatically synthesizing dense rewards from natural language descriptions is a promising paradigm in reinforcement learning (RL), with applications to sparse reward problems, open-ended exploration, and hierarchical skill design. Recent works have made promising steps by exploiting the prior knowledge of large language models (LLMs). However, these approaches suffer from important limitations: they are either not scalable to problems requiring billions of environment samples, due to requiring LLM annotations for each observation, or they require a diverse offline dataset, which may not exist or be impossible to collect. In this work, we address these limitations through a combination of algorithmic and systems-level contributions. We propose \oni, a distributed architecture that simultaneously learns an RL policy and an intrinsic reward function using LLM feedback. Our approach annotates the agent’s collected experience via an asynchronous LLM server, which is then distilled into an intrinsic reward model. We explore a range of algorithmic choices for reward modeling with varying complexity, including hashing, classification, and ranking models. By studying their relative tradeoffs, we shed light on questions regarding intrinsic reward design for sparse reward problems. Our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across a range of challenging, sparse reward tasks from the NetHack Learning Environment in a simple unified process, solely using the agent’s gathered experience, without requiring external datasets. We make our code available at \url{https://github.com/facebookresearch/oni}.
自动从自然语言描述中合成密集奖励是强化学习(RL)中的一种有前途的范式,应用于稀疏奖励问题、开放式探索和分层技能设计。最近的工作通过利用大型语言模型(LLM)的先验知识取得了有希望的进展。然而,这些方法存在重要的局限性:它们要么不可扩展至需要数亿环境样本的问题,因为每个观察都需要LLM注释,或者它们需要各种各样的离线数据集,这可能不存在或难以收集。在这项工作中,我们通过算法和系统层面的贡献解决了这些局限性。我们提出了\oni,这是一个分布式架构,可以同时学习RL策略和内在奖励函数,使用LLM反馈。我们的方法通过异步LLM服务器对代理收集的经验进行注释,然后将其蒸馏成内在奖励模型。我们探索了一系列奖励建模的算法选择,包括哈希、分类和排名模型,其复杂性各不相同。通过研究它们的相对权衡,我们针对稀疏奖励问题的内在奖励设计问题提供了启示。我们的方法在一系列具有挑战性的稀疏奖励任务中实现了最佳性能,这些任务来自NetHack学习环境,在一个简单的统一过程中,仅使用代理收集的经验,无需外部数据集。我们在https://github.com/facebookresearch/oni上提供了我们的代码。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文提出一种基于分布式架构的强化学习(RL)方法,结合大型语言模型(LLM)反馈,同时学习RL策略和内在奖励函数,解决了自动从自然语言描述中合成密集奖励的问题。此方法通过异步LLM服务器标注代理收集的经验,并将其蒸馏成内在奖励模型。此外,本文探讨了不同的奖励建模算法选择,包括哈希、分类和排名模型,并阐述了其在稀疏奖励问题中内在奖励设计的相对权衡。该方法在NetHack学习环境的多个具有挑战性的稀疏奖励任务上取得了最先进的性能,仅使用代理收集的经验数据,无需外部数据集。
Key Takeaways
- 密集奖励合成在强化学习中具有重要应用,尤其是在稀疏奖励问题、开放式探索和分层技能设计方面。
- 当前方法主要依赖于大型语言模型(LLM)的先验知识,但仍存在可扩展性和依赖离线数据集的问题。
- 提出的oni架构能同时学习RL策略和内在奖励函数,利用LLM反馈标注代理收集的经验。
- 通过异步LLM服务器实现经验标注,并将其蒸馏成内在奖励模型,无需外部数据集。
- 研究了不同的奖励建模算法选择,包括哈希、分类和排名模型,并探讨了它们在解决稀疏奖励问题中的相对权衡。
- 该方法在多个挑战性的稀疏奖励任务上取得了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图

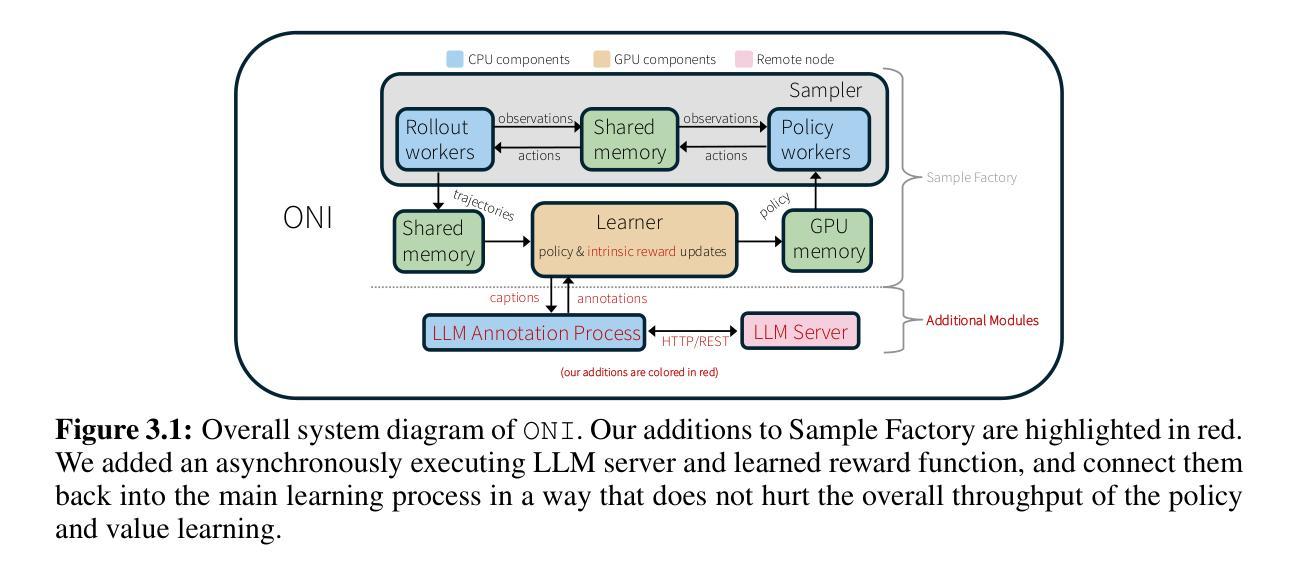
PersonaGym: Evaluating Persona Agents and LLMs
Authors:Vinay Samuel, Henry Peng Zou, Yue Zhou, Shreyas Chaudhari, Ashwin Kalyan, Tanmay Rajpurohit, Ameet Deshpande, Karthik Narasimhan, Vishvak Murahari
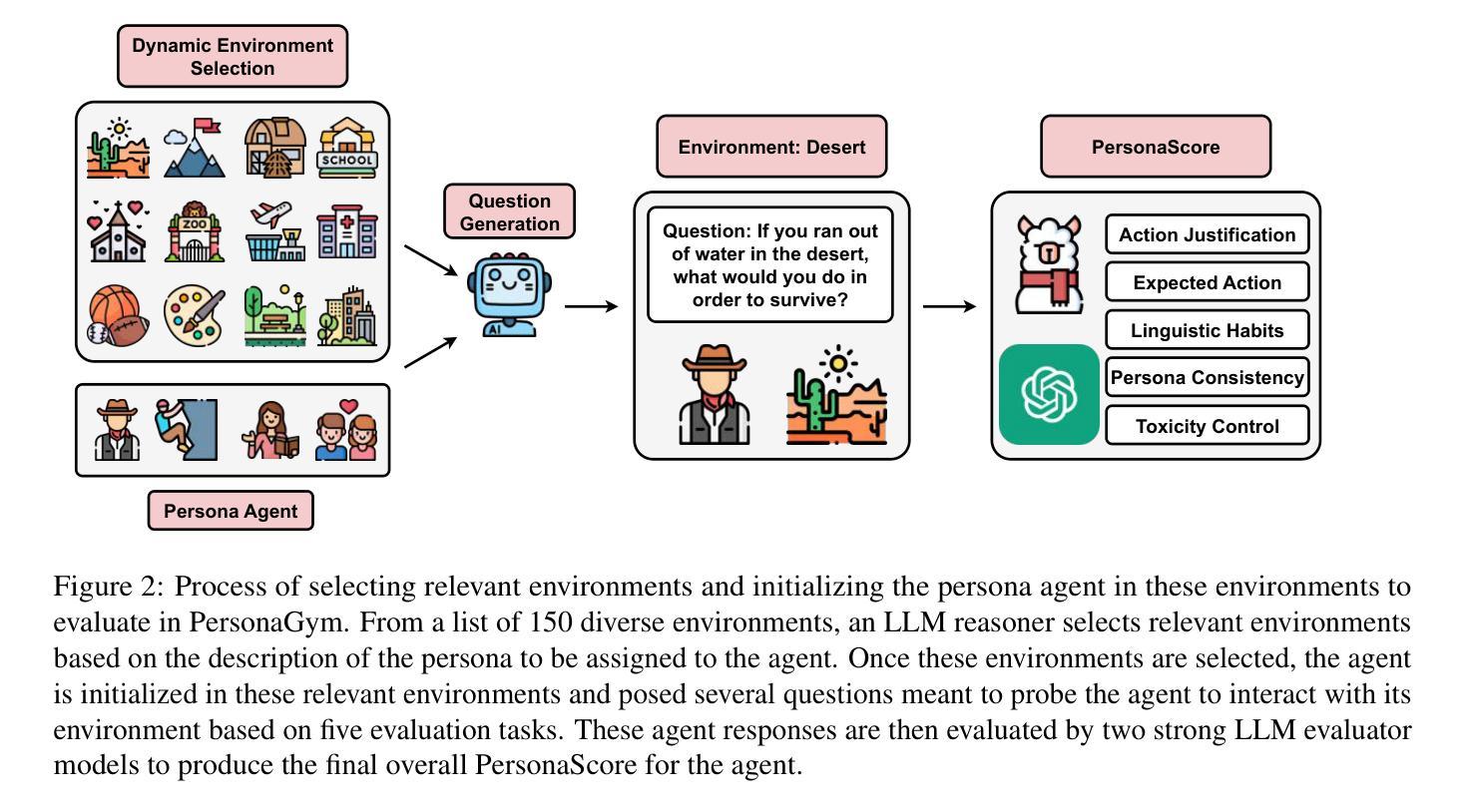
Persona agents, which are LLM agents that act according to an assigned persona, have demonstrated impressive contextual response capabilities across various applications. These persona agents offer significant enhancements across diverse sectors, such as education, healthcare, and entertainment, where model developers can align agent responses to different user requirements thereby broadening the scope of agent applications. However, evaluating persona agent performance is incredibly challenging due to the complexity of assessing persona adherence in free-form interactions across various environments that are relevant to each persona agent. We introduce PersonaGym, the first dynamic evaluation framework for assessing persona agents, and PersonaScore, the first automated human-aligned metric grounded in decision theory for comprehensive large-scale evaluation of persona agents. Our evaluation of 6 open and closed-source LLMs, using a benchmark encompassing 200 personas and 10,000 questions, reveals significant opportunities for advancement in persona agent capabilities across state-of-the-art models. For example, Claude 3.5 Sonnet only has a 2.97% relative improvement in PersonaScore than GPT 3.5 despite being a much more advanced model. Importantly, we find that increased model size and complexity do not necessarily imply enhanced persona agent capabilities thereby highlighting the pressing need for algorithmic and architectural invention towards faithful and performant persona agents.
人格代理(Persona agents)是遵循分配的人格的角色扮演的大型语言模型代理(LLM agents),已在各种应用程序中展示了令人印象深刻的上下文响应能力。这些人格代理在多个领域(如教育、医疗保健和娱乐)提供了重大改进,模型开发者可以调整代理响应以满足不同用户需求,从而扩大了代理应用范围。然而,评估人格代理的性能极具挑战性,因为评估每个代理相关的自由形式交互中的人格遵循情况涉及多个环境,情况复杂多变。我们推出PersonaGym,这是第一个评估人格代理的动态评估框架,以及PersonaScore,这是基于决策理论的第一个自动化的人类相关指标,用于全面大规模评估人格代理。我们对六个开源和闭源的LLM进行了评估,使用包含200个人格和1万多个问题的基准测试,揭示了最先进模型中人格代理能力的重大进步机会。例如,尽管Claude 3.5 Sonnet是一款更先进的模型,但在PersonaScore上的相对改进仅为GPT 3.5的2.97%。重要的是,我们发现模型规模和复杂性的增加并不一定意味着人格代理能力的提高,从而凸显了对忠实和高效的人格代理的算法和架构创新的迫切需求。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 5 figures
Summary
本文介绍了人格代理(Persona agents)在跨应用领域的表现,这是一种根据分配的人格进行响应的语言大模型代理。人格代理在教育、医疗和娱乐等领域都有显著提升,能够根据不同的用户需求做出响应,扩大代理应用范围。然而,评估人格代理的表现极具挑战性。本文引入了PersonGym评价框架和PersonaScore自动化评估指标,对6种开源和闭源的语言大模型进行了评价,发现先进技术模型在人格代理能力方面仍有巨大发展机会,模型规模和复杂性增加并不一定意味着人格代理能力的提高,因此需要算法和架构上的创新来构建忠实和高效的人格代理。
Key Takeaways
- 人格代理具备在各种应用中表现良好。
- 在教育、医疗和娱乐等领域,人格代理都能发挥显著提升作用。
- 人格代理的表现评估极具挑战性,需要综合考虑多种因素。
- PersonGym评价框架和PersonaScore评估指标为评估人格代理提供了新的方法。
- 对多种语言大模型的评估显示,先进技术模型在人格代理能力方面仍有发展机会。
- 模型规模和复杂性增加并不等同于人格代理能力的提高。
点此查看论文截图

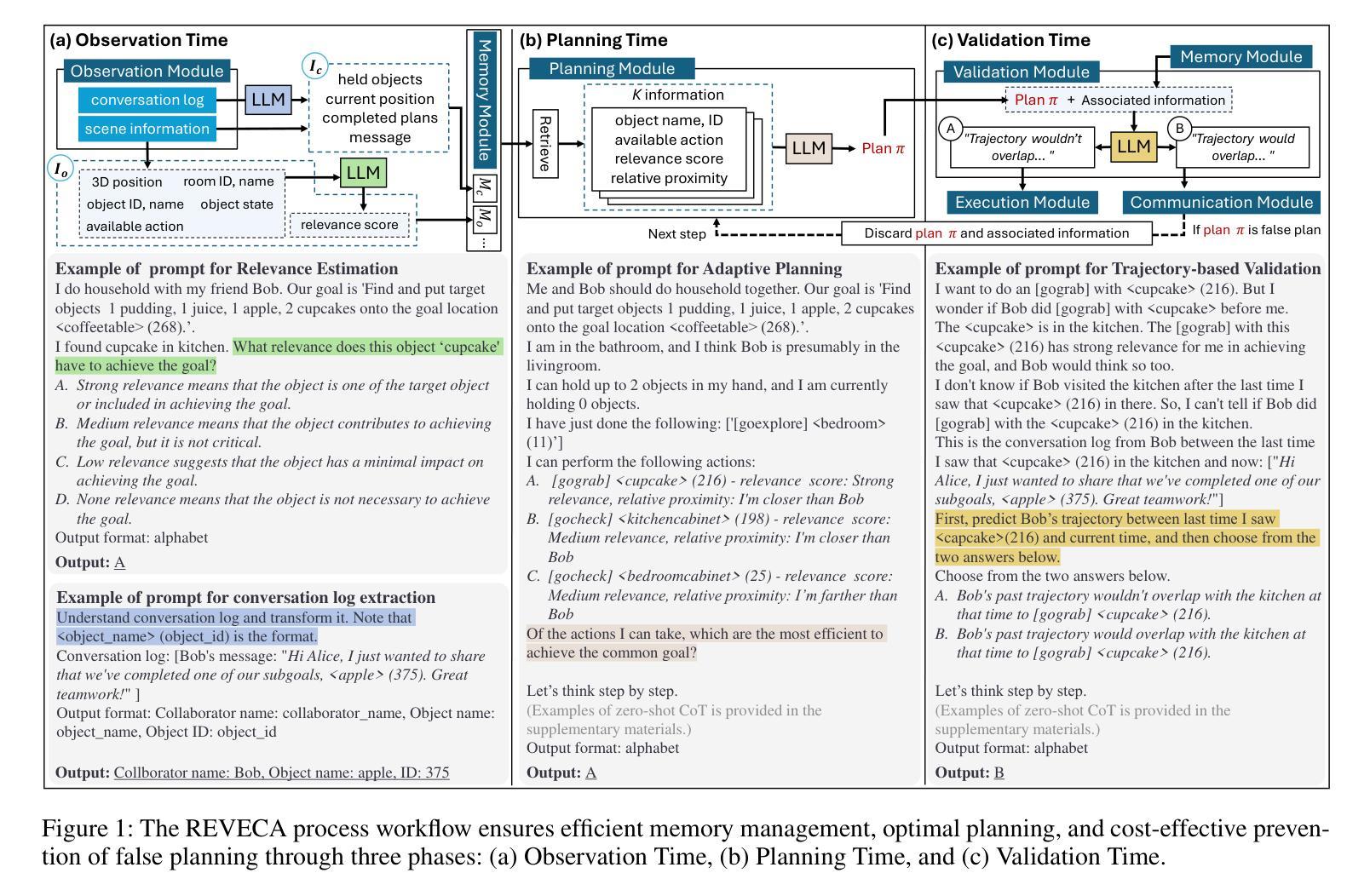
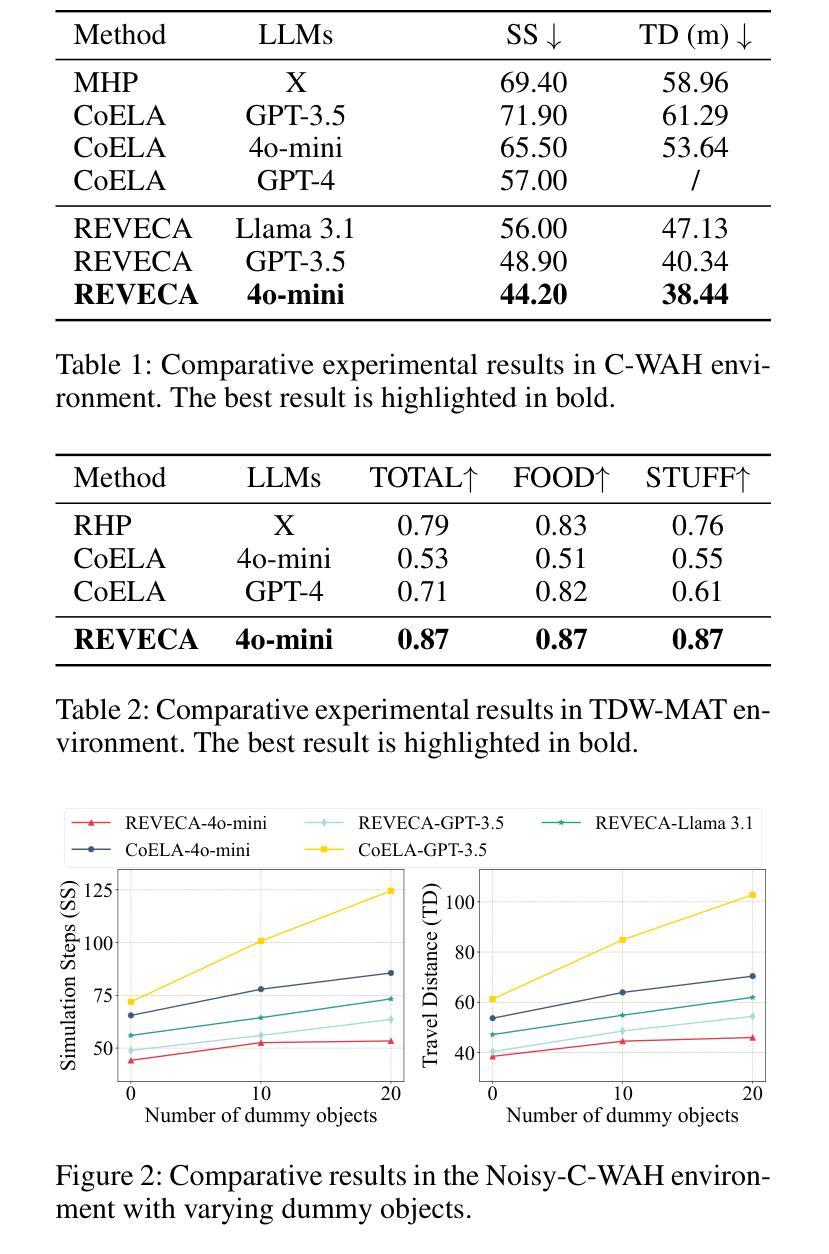
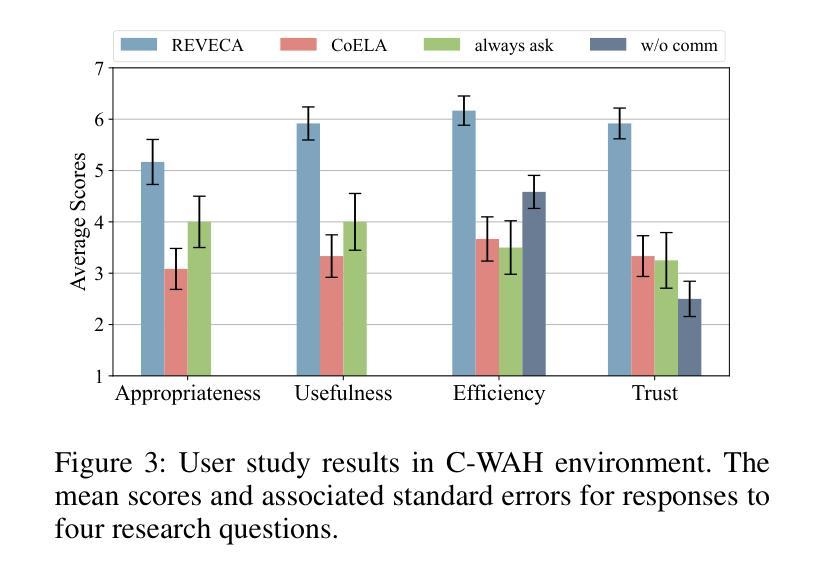
REVECA: Adaptive Planning and Trajectory-based Validation in Cooperative Language Agents using Information Relevance and Relative Proximity
Authors:SeungWon Seo, SeongRae Noh, Junhyeok Lee, SooBin Lim, Won Hee Lee, HyeongYeop Kang
We address the challenge of multi-agent cooperation, where agents achieve a common goal by cooperating with decentralized agents under complex partial observations. Existing cooperative agent systems often struggle with efficiently processing continuously accumulating information, managing globally suboptimal planning due to lack of consideration of collaborators, and addressing false planning caused by environmental changes introduced by other collaborators. To overcome these challenges, we propose the RElevance, Proximity, and Validation-Enhanced Cooperative Language Agent (REVECA), a novel cognitive architecture powered by GPT-4o-mini. REVECA enables efficient memory management, optimal planning, and cost-effective prevention of false planning by leveraging Relevance Estimation, Adaptive Planning, and Trajectory-based Validation. Extensive experimental results demonstrate REVECA’s superiority over existing methods across various benchmarks, while a user study reveals its potential for achieving trustworthy human-AI cooperation.
针对多智能体合作面临的挑战,我们提出了一种解决方案。在此场景中,智能体通过分散的智能体合作来实现共同目标,并在复杂的局部观察下完成合作。现有的合作智能系统往往难以高效处理不断积累的信息,难以在不考虑合作者的情况下进行全局次优规划,并难以解决由其他合作者引入的环境变化所导致的错误规划问题。为了克服这些挑战,我们提出了基于GPT-4o-mini驱动的REVECA(相关性、邻近性和验证增强型合作语言智能体)。REVECA是一种新型认知架构,可实现高效内存管理、最优规划和成本效益高的防止误规划,这得益于相关性估计、自适应规划和轨迹验证等技术。大量的实验结果表明,REVECA在各种基准测试上的表现优于现有方法,而一项用户研究揭示了其在实现可靠的人机合作方面的潜力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF v2 is the AAAI’25 camera-ready version, including the appendix, which has been enhanced based on the reviewers’ comments
Summary
多智能体合作面临诸多挑战,如处理连续累积信息效率低下、因未考虑协作伙伴导致的全局次优规划以及由其他协作伙伴引入的环境变化导致的错误规划等。为应对这些挑战,我们提出了基于GPT-4o-mini的REVECA(相关性、邻近性和验证增强的合作语言智能体),它能够实现高效的记忆管理、最优规划和有效的错误规划预防。实验结果和用户研究证明了REVECA相较于现有方法的优越性及其在实现可靠的人机合作方面的潜力。
Key Takeaways
- REVECA解决了多智能体合作中的挑战,如信息处理效率、全局次优规划和错误规划问题。
- REVECA基于GPT-4o-mini,具备强大的认知架构。
- REVECA通过相关性估计、自适应规划和轨迹验证等技术实现高效记忆管理、最优规划和错误预防。
- 广泛实验结果表明,REVECA在多种基准测试中优于现有方法。
- 用户研究显示REVECA在实现可靠的人机合作方面具潜力。
- REVECA能够应对复杂部分观察下的分散智能体合作问题。
点此查看论文截图

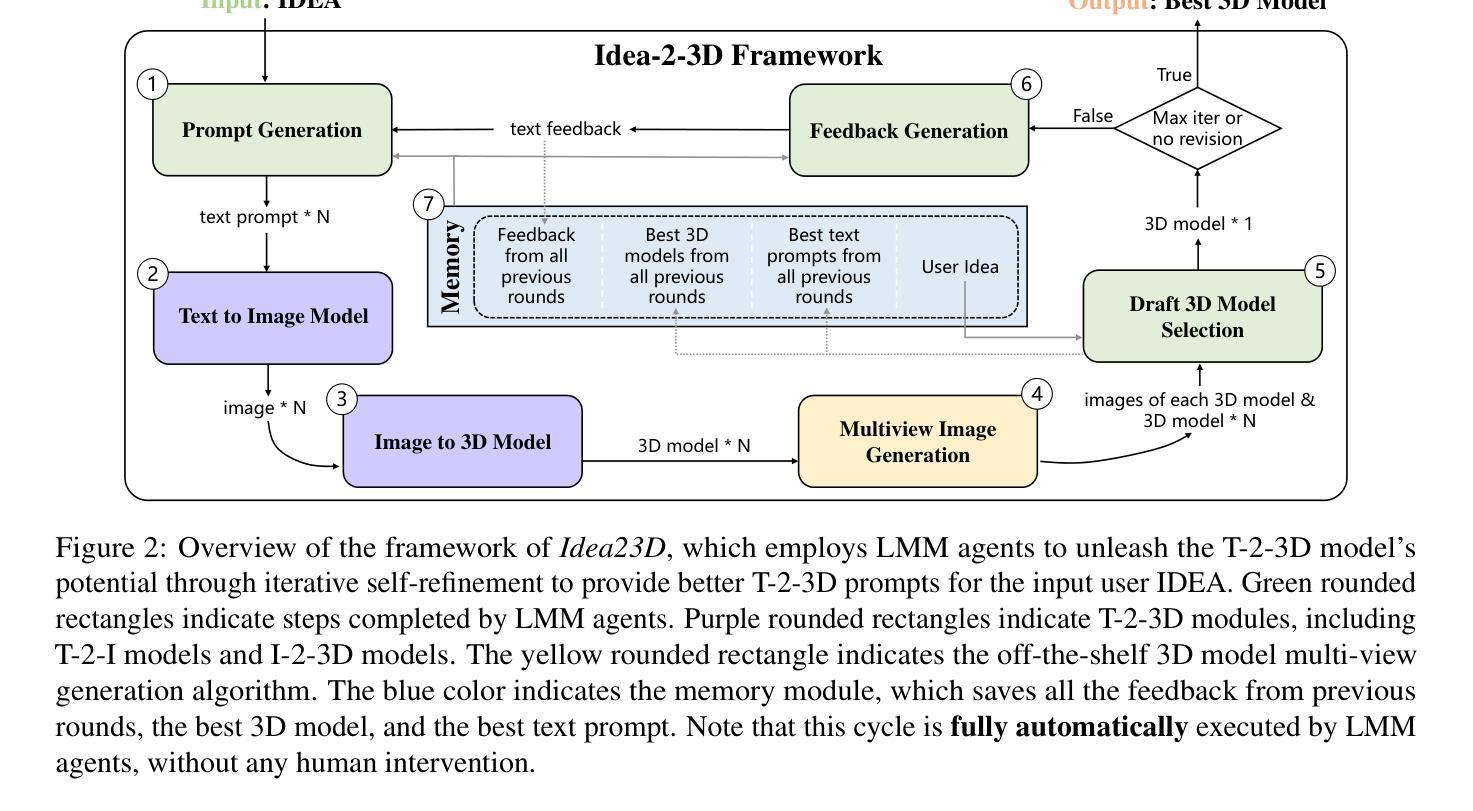
Idea23D: Collaborative LMM Agents Enable 3D Model Generation from Interleaved Multimodal Inputs
Authors:Junhao Chen, Xiang Li, Xiaojun Ye, Chao Li, Zhaoxin Fan, Hao Zhao
With the success of 2D diffusion models, 2D AIGC content has already transformed our lives. Recently, this success has been extended to 3D AIGC, with state-of-the-art methods generating textured 3D models from single images or text. However, we argue that current 3D AIGC methods still do not fully unleash human creativity. We often imagine 3D content made from multimodal inputs, such as what it would look like if my pet bunny were eating a doughnut on the table. In this paper, we explore a novel 3D AIGC approach: generating 3D content from IDEAs. An IDEA is a multimodal input composed of text, image, and 3D models. To our knowledge, this challenging and exciting 3D AIGC setting has not been studied before. We propose the new framework Idea23D, which combines three agents based on large multimodal models (LMMs) and existing algorithmic tools. These three LMM-based agents are tasked with prompt generation, model selection, and feedback reflection. They collaborate and critique each other in a fully automated loop, without human intervention. The framework then generates a text prompt to create 3D models that align closely with the input IDEAs. We demonstrate impressive 3D AIGC results that surpass previous methods. To comprehensively assess the 3D AIGC capabilities of Idea23D, we introduce the Eval3DAIGC-198 dataset, containing 198 multimodal inputs for 3D generation tasks. This dataset evaluates the alignment between generated 3D content and input IDEAs. Our user study and quantitative results show that Idea23D significantly improves the success rate and accuracy of 3D generation, with excellent compatibility across various LMM, Text-to-Image, and Image-to-3D models. Code and dataset are available at \url{https://idea23d.github.io/}.
随着二维扩散模型的成功,二维AIGC内容已经改变了我们的生活。最近,这一成功已扩展到三维AIGC,最先进的方法可以从单个图像或文本生成纹理化的三维模型。然而,我们认为当前的三维AIGC方法还没有完全释放人类的创造力。我们经常想象由多模态输入创建的三维内容,比如我的宠物兔子在桌子上吃甜甜圈会是什么样子。在本文中,我们探索了一种新颖的三维AIGC方法:从IDEA生成三维内容。IDEA是由文本、图像和三维模型组成的多模态输入。据我们所知,这一充满挑战和令人兴奋的三维AIGC设置之前尚未有研究。我们提出了新型框架Idea23D,它结合了基于大型多模态模型(LMM)的三种智能体和现有的算法工具。这三种基于LMM的智能体负责提示生成、模型选择和反馈反思。它们在全自动循环中相互协作和批判,无需人为干预。该框架随后生成一个文本提示来创建与输入IDEA紧密对应的三维模型。我们展示了令人印象深刻的三维AIGC结果,超越了以前的方法。为了全面评估Idea23D的三维AIGC能力,我们引入了Eval3DAIGC-198数据集,包含用于三维生成任务的198个多模态输入。该数据集评估生成的三维内容与输入IDEA的对齐程度。我们的用户研究和定量结果表明,Idea23D显著提高了三维生成的成功率和准确性,在各种大型语言模型、文本到图像模型和图像到三维模型之间具有良好的兼容性。代码和数据集可在https://idea23d.github.io/获得。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by COLING 2025 (The 31st International Conference on Computational Linguistics) Project Page: https://idea23d.github.io/ Code: https://github.com/yisuanwang/Idea23D
Summary
本文介绍了新的三维人工智能生成内容(3D AIGC)方法,该方法结合了文本、图像和三维模型的多模态输入,生成符合输入创意的三维内容。提出了一种新的框架Idea23D,通过三个基于大型多模态模型的智能代理进行自动循环生成三维模型。该框架在生成的三维模型与输入创意之间达到了紧密对齐的效果。同时,为了评估Idea23D的3D AIGC能力,引入了Eval3DAIGC-198数据集,该数据集包含用于三维生成任务的198个多模态输入。
Key Takeaways
- 当前的3D AIGC技术尚未完全释放人类的创造力。
- Idea23D框架是一个创新的3D AIGC方法,接受IDEA(文本、图像和三维模型的多模态输入)。
- Idea23D结合了三个基于大型多模态模型的智能代理进行自动循环生成三维模型。
- Idea23D生成的三维模型与输入创意之间紧密对齐。
- 引入了Eval3DAIGC-198数据集以评估Idea23D的3D生成能力。
- Idea23D显著提高了三维生成的成功率和准确性,并具有良好的跨不同模型的兼容性。
点此查看论文截图

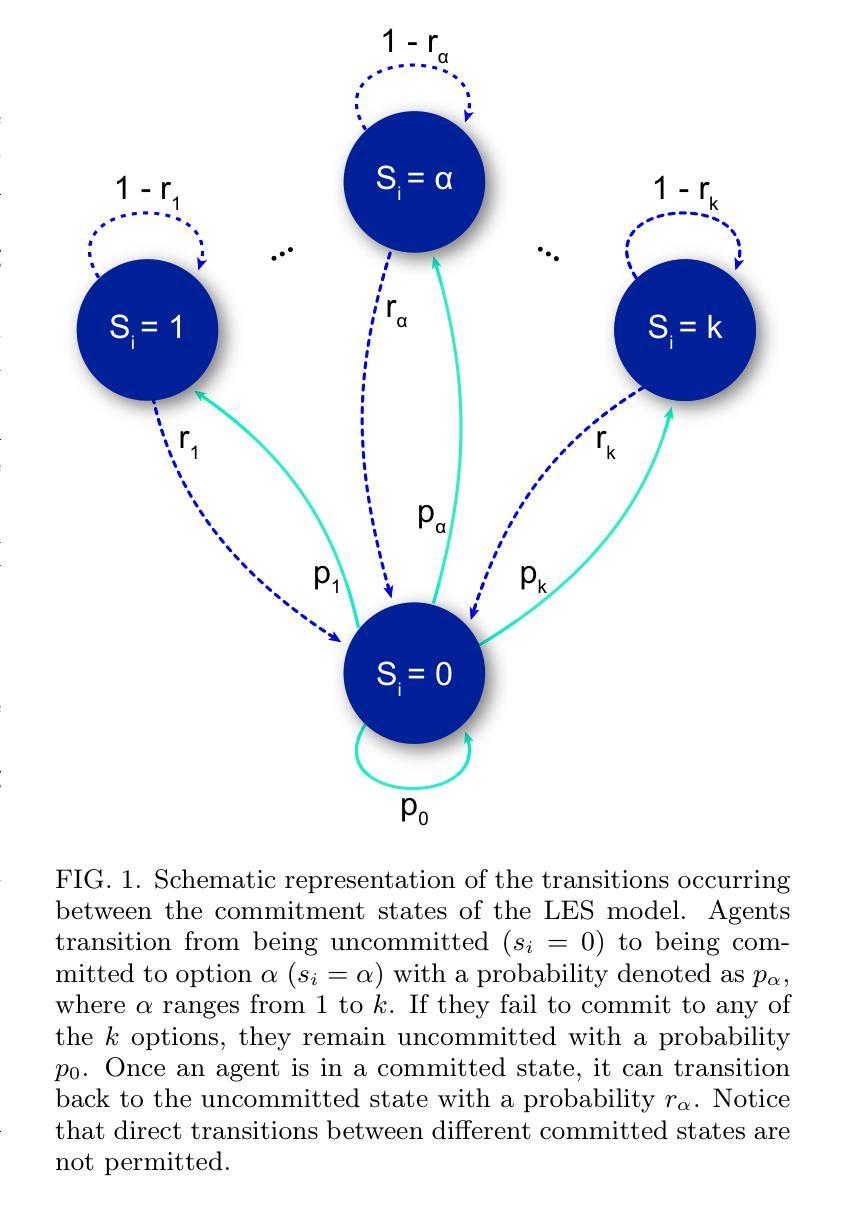
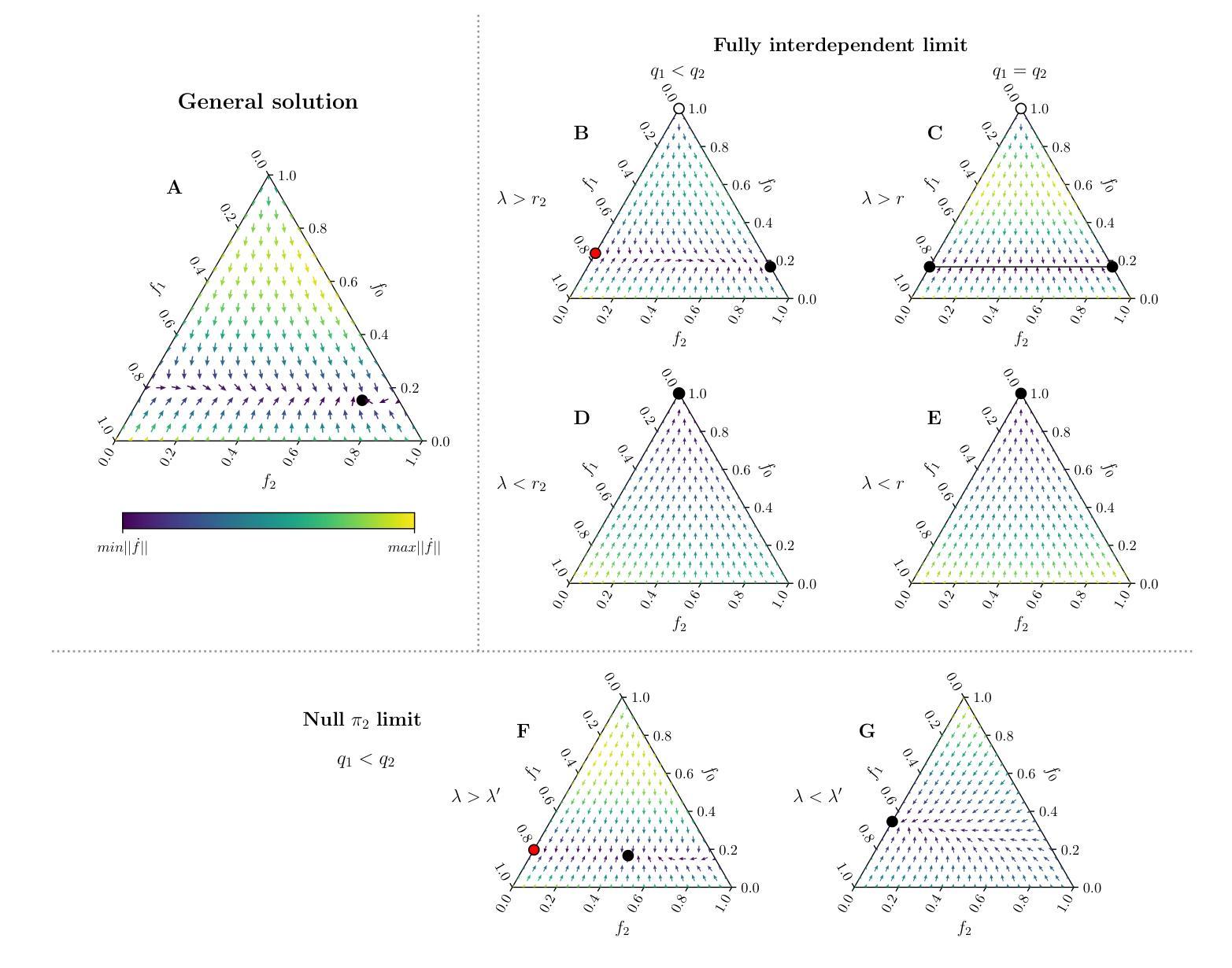
Consensus formation and relative stimulus perception in quality-sensitive, interdependent agent systems
Authors:David March-Pons, Ezequiel E. Ferrero, M. Carmen Miguel
We perform a comprehensive analysis of a collective decision-making model inspired by honeybee behavior. This model integrates individual exploration for option discovery and social interactions for information sharing, while also considering option qualities. Our assessment of the decision process outcome employs standard consensus metrics and investigates its correlation with convergence time, revealing common trade-offs between speed and accuracy. Furthermore, we show the model’s compliance with Weber’s Law of relative stimulus perception, aligning with previous analysis of collective decision problems. Our study also identifies non-equilibrium critical behavior in specific limits of the model, where the highest values of consensus are achieved. This result highlights the intriguing relationship between optimal performance, critically, and the fluctuations caused by finite size effects, often seen in biological systems. Our findings are especially relevant for finite adaptive systems, as they provide insights into navigating decision-making scenarios with similar options more effectively.
我们对一种受蜜蜂行为启发的集体决策模型进行了综合分析。该模型融合了个体探索以发现选项和社会互动以分享信息,同时考虑选项质量。我们对决策过程的结果进行评估,采用标准共识指标,并研究其与收敛时间的相关性,揭示了速度和准确性之间的常见权衡。此外,我们展示了该模型符合韦伯的相对刺激感知定律,这与之前对集体决策问题的分析相一致。我们的研究还确定了模型特定限制下的非均衡临界行为,在这些情况下实现了最高共识。这一结果突出了最佳性能与由有限尺寸效应引起的波动之间的有趣关系,这在生物系统中经常看到。我们的研究结果对于有限的自适应系统尤其重要,因为它们为更有效地应对具有类似选项的决策制定场景提供了见解。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 21 pages, 12 figures, 3 appendix figures, 2 supplementary figures
Summary
决策过程模型受到蜜蜂行为的启发,整合个体探索和信息共享的社会互动,同时考虑选项质量。该模型分析揭示了决策速度与准确性之间的权衡,并符合韦伯的相对刺激感知定律。模型中存在一种特殊的临界行为,在非平衡态中实现最优共识达成,这一结果与生物系统的有限规模波动相关。该研究对有限自适应系统决策优化有重要意义。
Key Takeaways
- 模型受到蜜蜂集体决策行为的启发,整合个体探索和信息共享的社会互动进行决策。
- 该模型考虑选项质量因素在决策过程中发挥作用。
- 分析结果表明决策速度和准确性之间存在权衡关系。
- 模型符合韦伯的相对刺激感知定律,对集体决策问题进行分析。
- 在模型特定条件下观察到非平衡临界行为,在这种状态下达到最优共识。
- 这一现象与生物系统的有限规模效应及其导致的波动有关。
点此查看论文截图