⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-20 更新
Idea23D: Collaborative LMM Agents Enable 3D Model Generation from Interleaved Multimodal Inputs
Authors:Junhao Chen, Xiang Li, Xiaojun Ye, Chao Li, Zhaoxin Fan, Hao Zhao
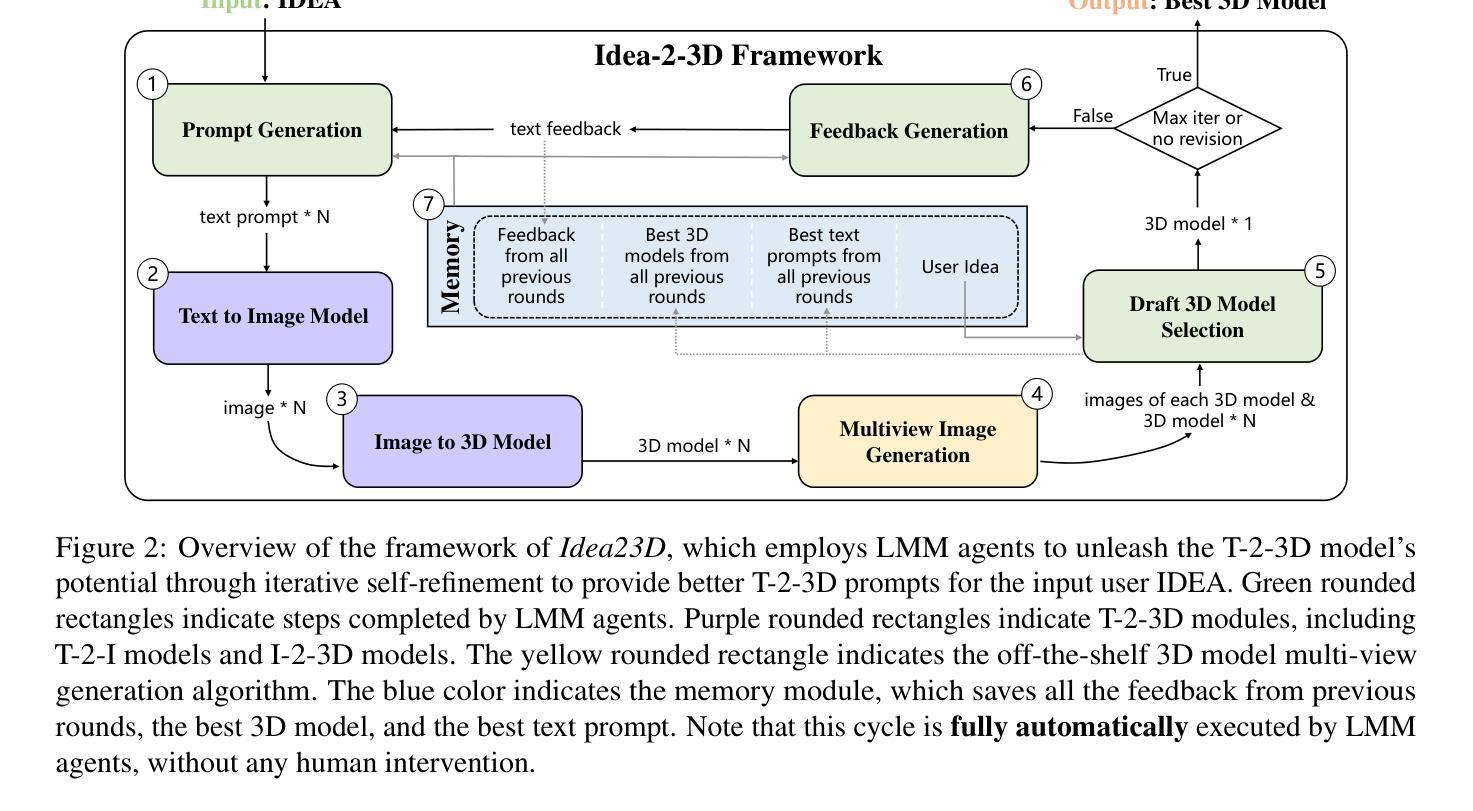
With the success of 2D diffusion models, 2D AIGC content has already transformed our lives. Recently, this success has been extended to 3D AIGC, with state-of-the-art methods generating textured 3D models from single images or text. However, we argue that current 3D AIGC methods still do not fully unleash human creativity. We often imagine 3D content made from multimodal inputs, such as what it would look like if my pet bunny were eating a doughnut on the table. In this paper, we explore a novel 3D AIGC approach: generating 3D content from IDEAs. An IDEA is a multimodal input composed of text, image, and 3D models. To our knowledge, this challenging and exciting 3D AIGC setting has not been studied before. We propose the new framework Idea23D, which combines three agents based on large multimodal models (LMMs) and existing algorithmic tools. These three LMM-based agents are tasked with prompt generation, model selection, and feedback reflection. They collaborate and critique each other in a fully automated loop, without human intervention. The framework then generates a text prompt to create 3D models that align closely with the input IDEAs. We demonstrate impressive 3D AIGC results that surpass previous methods. To comprehensively assess the 3D AIGC capabilities of Idea23D, we introduce the Eval3DAIGC-198 dataset, containing 198 multimodal inputs for 3D generation tasks. This dataset evaluates the alignment between generated 3D content and input IDEAs. Our user study and quantitative results show that Idea23D significantly improves the success rate and accuracy of 3D generation, with excellent compatibility across various LMM, Text-to-Image, and Image-to-3D models. Code and dataset are available at \url{https://idea23d.github.io/}.
随着二维扩散模型的成功,二维AIGC内容已经改变了我们的生活。最近,这一成功已经扩展到三维AIGC,最先进的的方法可以从单一图像或文本生成纹理化的三维模型。然而,我们认为当前的三维AIGC方法还没有完全释放人类的创造力。我们经常想象由多模态输入创建的三维内容,比如我的宠物兔子在桌子上吃甜甜圈会是什么样子。在本文中,我们探索了一种新颖的三维AIGC方法:从IDEA生成三维内容。IDEA是由文本、图像和三维模型组成的多模态输入。据我们所知,这一充满挑战和令人兴奋的三维AIGC场景之前尚未被研究过。我们提出了全新的框架Idea23D,它结合了基于大型多模态模型(LMM)和现有算法工具的三个代理。这三个基于LMM的代理负责提示生成、模型选择和反馈反思。它们在全自动循环中相互协作和批判,无需人工干预。该框架随后生成一个文本提示来创建与输入IDEA紧密对齐的三维模型。我们展示了令人印象深刻的三维AIGC结果,超过了以前的方法。为了全面评估Idea23D的三维AIGC能力,我们引入了Eval3DAIGC-198数据集,包含用于三维生成任务的198个多模态输入。该数据集评估生成的三维内容与输入IDEA的对齐程度。我们的用户研究和定量结果表明,Idea23D显著提高了三维生成的成功率和准确性,与各种LMM、文本到图像和图像到三维模型具有良好的兼容性。代码和数据集可在[https://idea23d.github.io/]找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by COLING 2025 (The 31st International Conference on Computational Linguistics) Project Page: https://idea23d.github.io/ Code: https://github.com/yisuanwang/Idea23D
Summary
本文探讨了基于IDEA(文本、图像和三维模型的多模态输入)的3D AIGC新方法。提出了一种新型框架Idea23D,结合基于大型多模态模型(LMM)的代理和现有算法工具,实现全自动化的3D内容生成。通过引入Eval3DAIGC-198数据集,全面评估了Idea23D的3D AIGC能力,并展示了令人印象深刻的生成结果。
Key Takeaways
- 3D AIGC已成功扩展至基于大型多模态模型(LMM)的新方法,可从单一图像或文本生成高质量纹理的3D模型。
- 当前方法未能充分释放人类创造力,本文首次提出了基于IDEA的多模态输入的3D AIGC设置。
- Idea23D框架结合了三个基于大型多模态模型的代理,负责提示生成、模型选择和反馈反思,它们之间协作并相互评价。
- 引入Eval3DAIGC-198数据集用于全面评估Idea23D的3D生成能力,该数据集包含用于3D生成任务的198个多模态输入。
- Idea23D显著提高了3D生成的成功率和准确性,并具有良好的跨不同LMM、文本到图像和图像到3D模型的兼容性。
- Idea23D框架能够实现全自动化的3D内容生成,无需人工干预。
点此查看论文截图

AGFSync: Leveraging AI-Generated Feedback for Preference Optimization in Text-to-Image Generation
Authors:Jingkun An, Yinghao Zhu, Zongjian Li, Enshen Zhou, Haoran Feng, Xijie Huang, Bohua Chen, Yemin Shi, Chengwei Pan
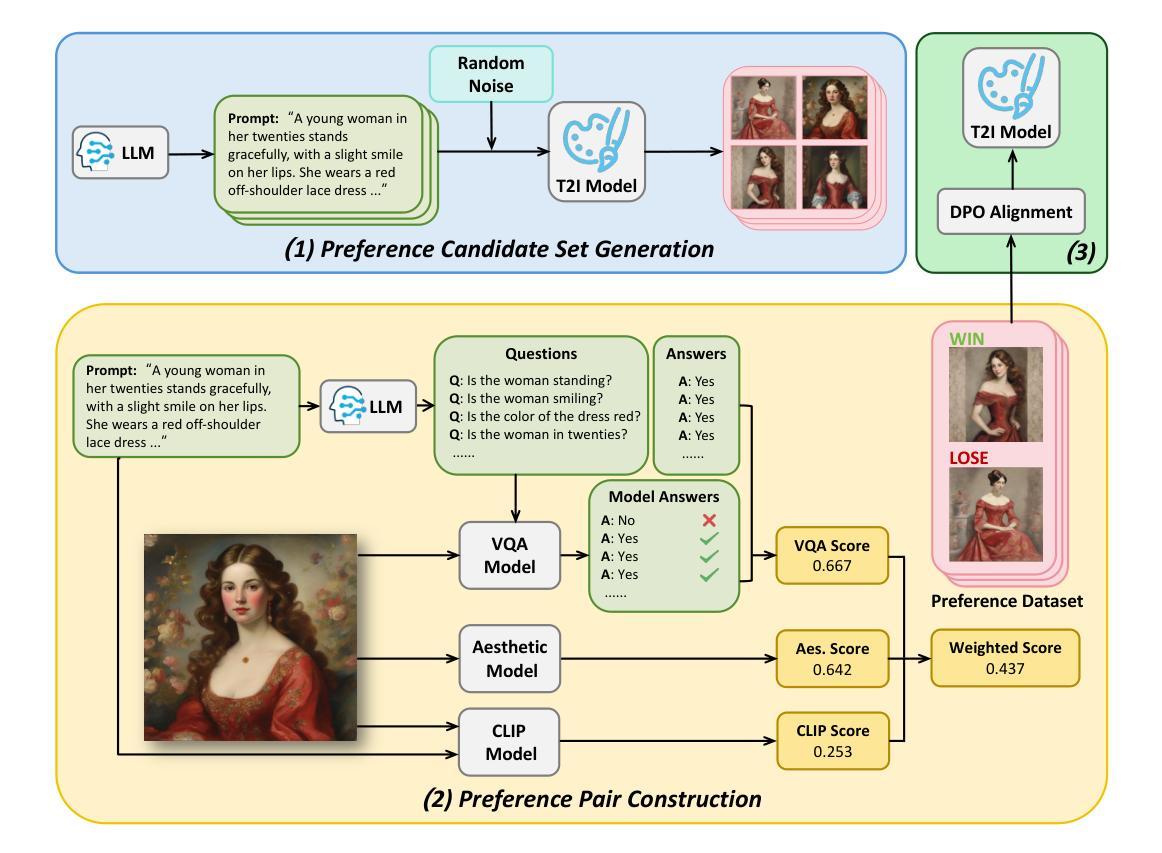
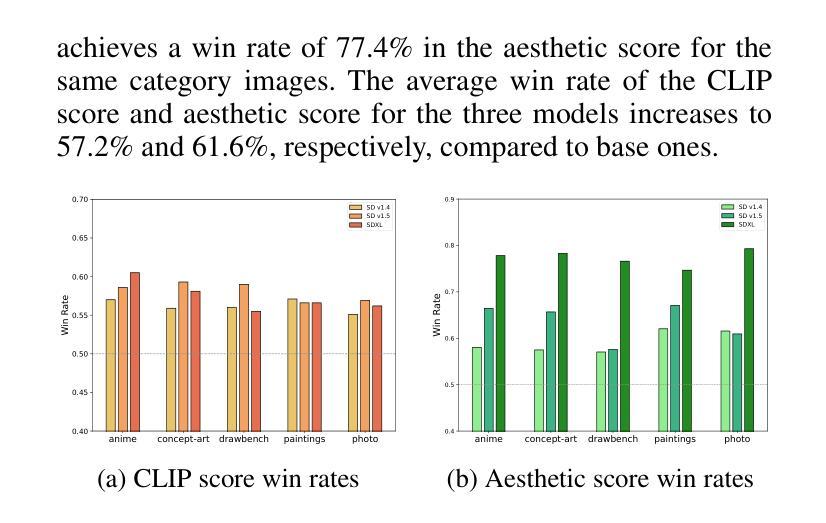
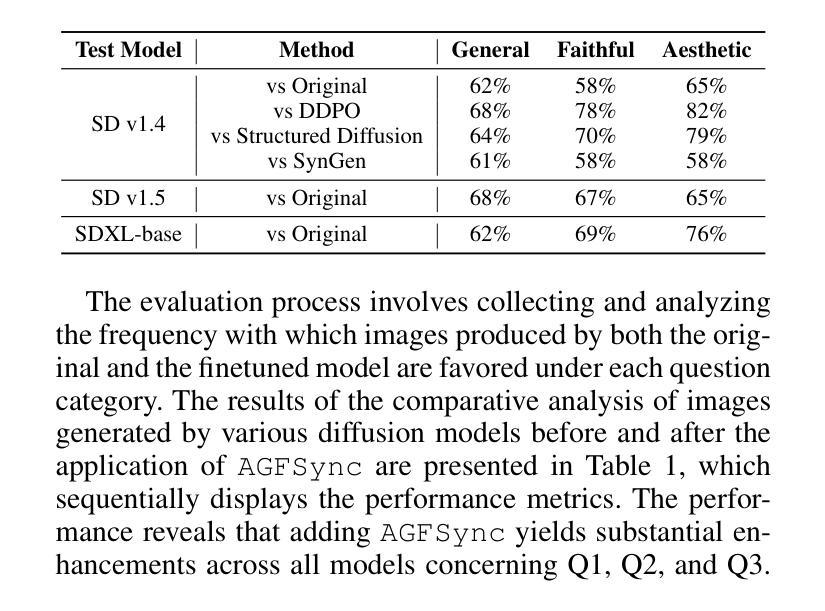
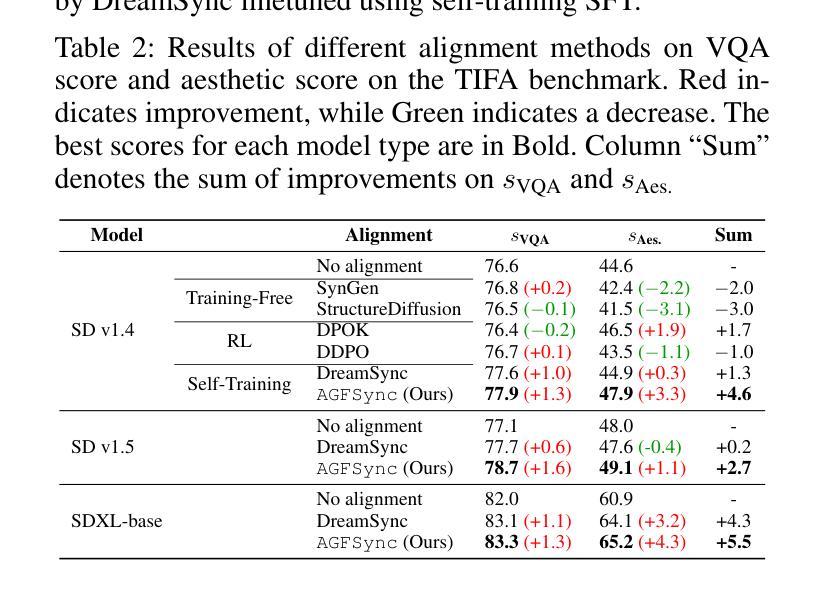
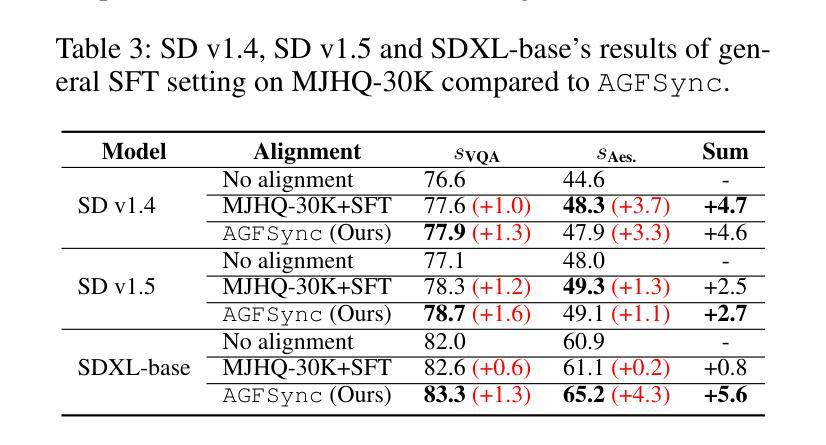
Text-to-Image (T2I) diffusion models have achieved remarkable success in image generation. Despite their progress, challenges remain in both prompt-following ability, image quality and lack of high-quality datasets, which are essential for refining these models. As acquiring labeled data is costly, we introduce AGFSync, a framework that enhances T2I diffusion models through Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) in a fully AI-driven approach. AGFSync utilizes Vision-Language Models (VLM) to assess image quality across style, coherence, and aesthetics, generating feedback data within an AI-driven loop. By applying AGFSync to leading T2I models such as SD v1.4, v1.5, and SDXL-base, our extensive experiments on the TIFA dataset demonstrate notable improvements in VQA scores, aesthetic evaluations, and performance on the HPSv2 benchmark, consistently outperforming the base models. AGFSync’s method of refining T2I diffusion models paves the way for scalable alignment techniques. Our code and dataset are publicly available at https://anjingkun.github.io/AGFSync.
文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型在图像生成方面取得了显著的成功。尽管有所进展,但在提示遵循能力、图像质量以及缺乏高质量数据集等方面仍然存在挑战,这些挑战对于完善这些模型至关重要。由于获取标记数据成本高昂,我们引入了AGFSync框架,它通过完全AI驱动的方法直接优化偏好(DPO)来增强T2I扩散模型。AGFSync利用视觉语言模型(VLM)来评估跨风格、连贯性和美学的图像质量,在AI驱动的循环中生成反馈数据。通过将AGFSync应用于领先的T2I模型,如SD v1.4、v1.5和SDXL-base,我们在TIFA数据集上的广泛实验表明,VQA分数、美学评价和HPSv2基准测试的性能均有显著提高,始终优于基础模型。AGFSync完善T2I扩散模型的方法为可扩展的对齐技术铺平了道路。我们的代码和数据集可在https://anjingkun.github.io/AGFSync上公开访问。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by AAAI-2025
Summary
文本介绍了文本到图像(T2I)扩散模型面临的挑战以及如何通过AGFSync框架进行改进。AGFSync采用直接偏好优化(DPO)方法,利用视觉语言模型(VLM)评估图像质量,生成反馈数据在人工智能驱动的循环中优化模型。通过在不同T2I模型上的实验验证,AGFSync显著提高了模型性能,提高了VQA分数、美学评价以及HPSv2基准测试的表现。该框架为可扩展的对齐技术铺平了道路。其代码和数据集已公开。
Key Takeaways
- T2I扩散模型虽然取得显著进展,但仍面临遵循提示能力、图像质量和缺乏高质量数据集等挑战。
- AGFSync框架通过直接偏好优化(DPO)方法解决这些问题,该方法在人工智能循环中生成反馈数据以改进模型性能。
- AGFSync使用视觉语言模型(VLM)来评估图像质量,涉及风格、连贯性和美学方面的考量。
- 在SD v1.4、v1.5和SDXL-base等主流T2I模型上的实验验证了AGFSync的有效性。
- AGFSync提高了模型的VQA分数、美学评价以及HPSv2基准测试表现,并优于基础模型。
- AGFSync的方法为可扩展的对齐技术开辟了道路,提高了T2I扩散模型的性能上限。
点此查看论文截图

Advances in Kidney Biopsy Lesion Assessment through Dense Instance Segmentation
Authors:Zhan Xiong, Junling He, Pieter Valkema, Tri Q. Nguyen, Maarten Naesens, Jesper Kers, Fons J. Verbeek
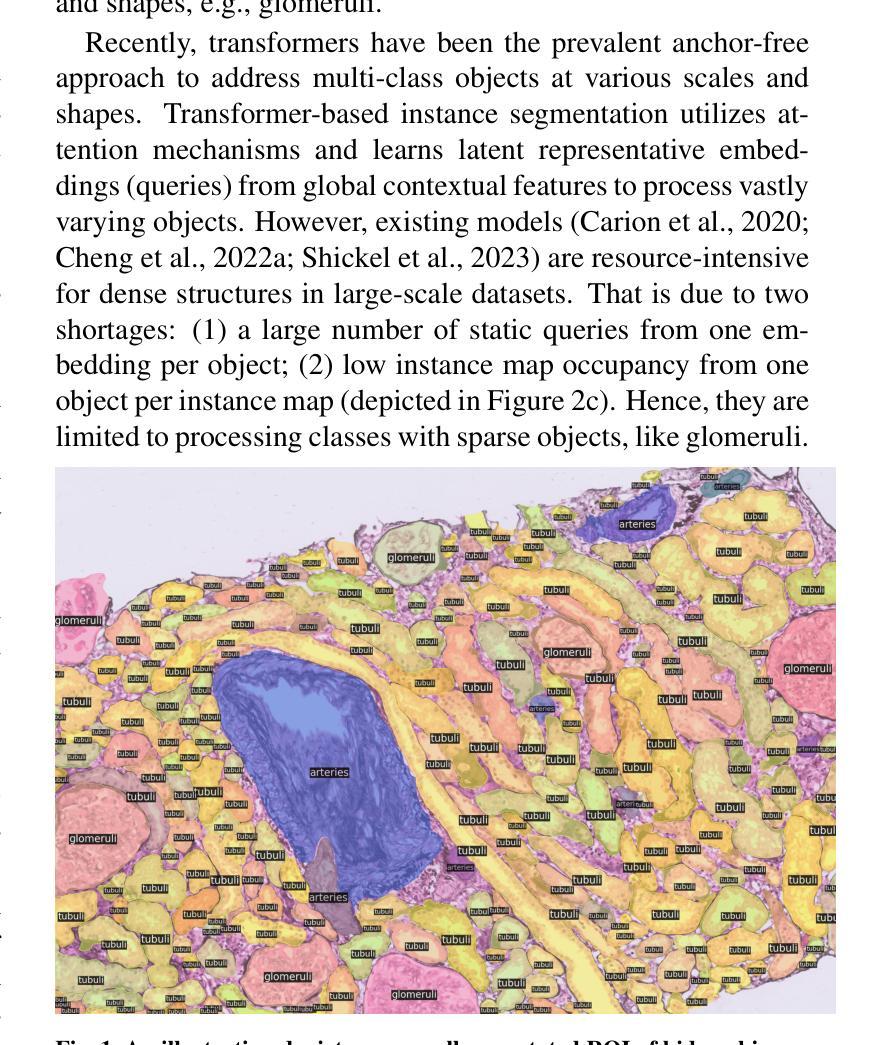
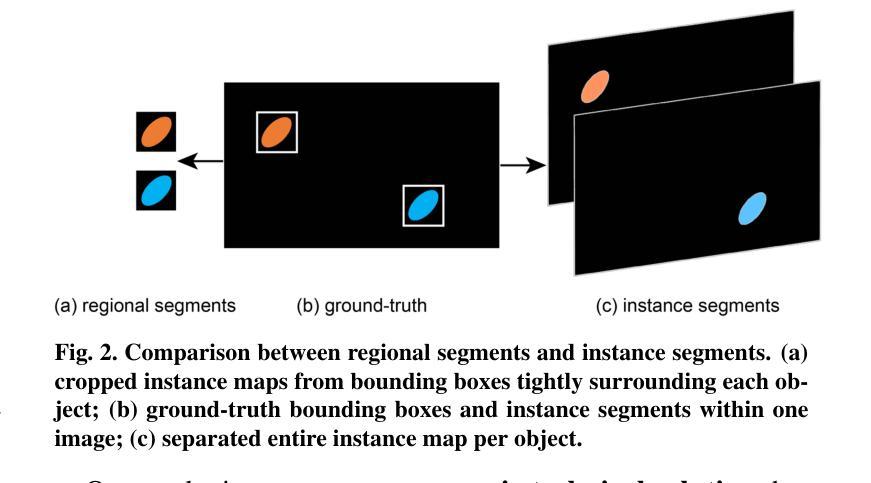
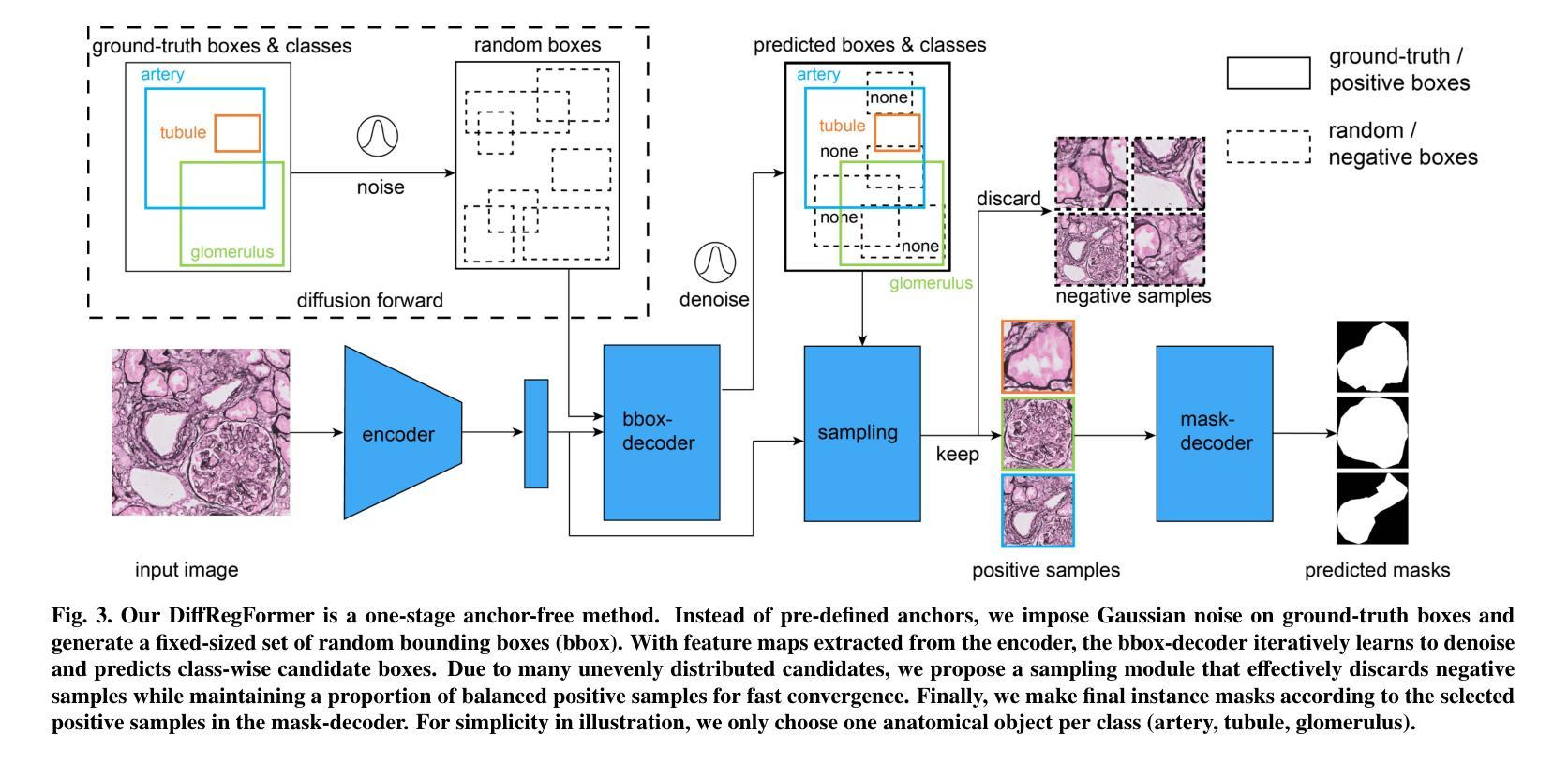
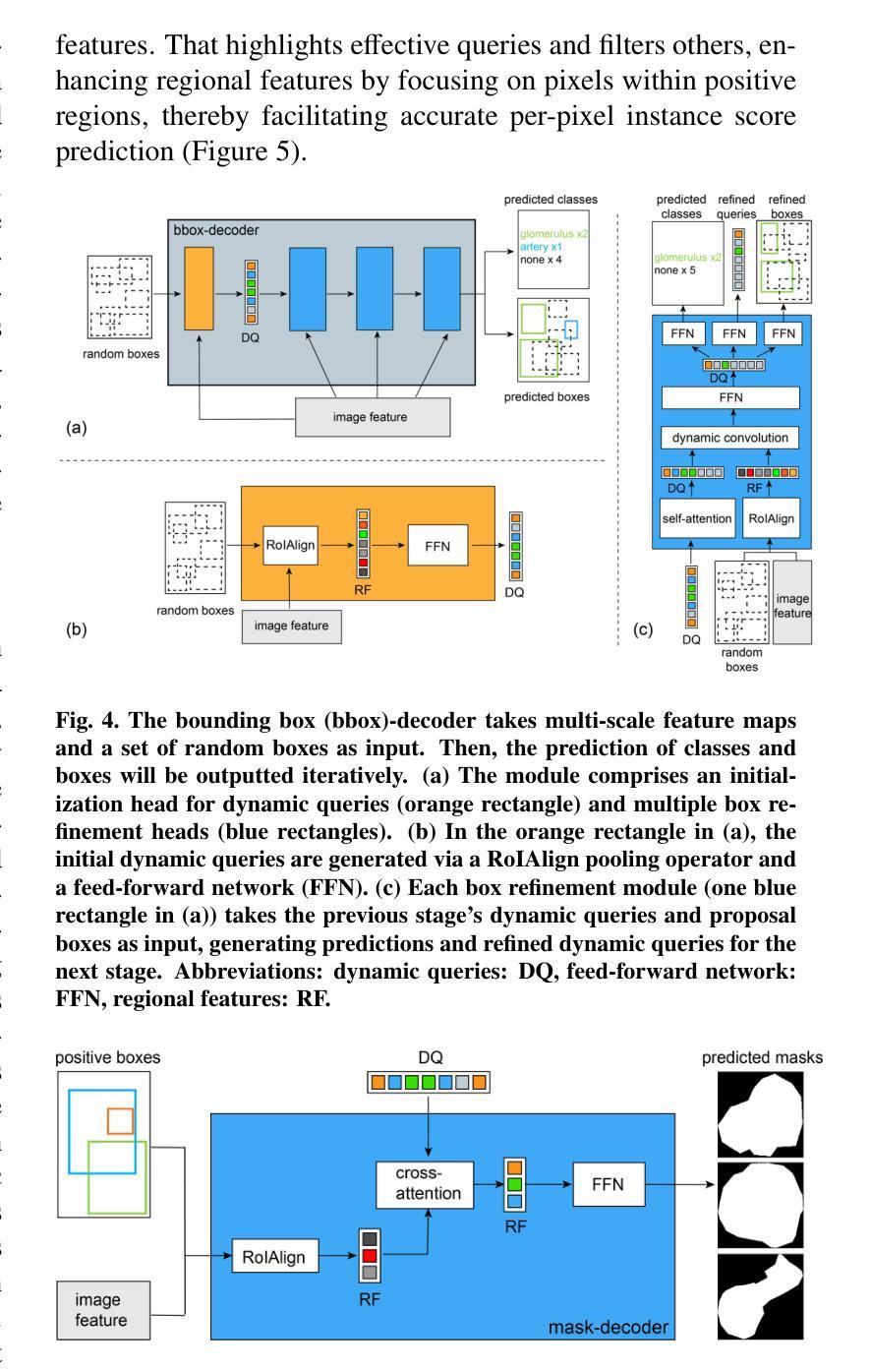
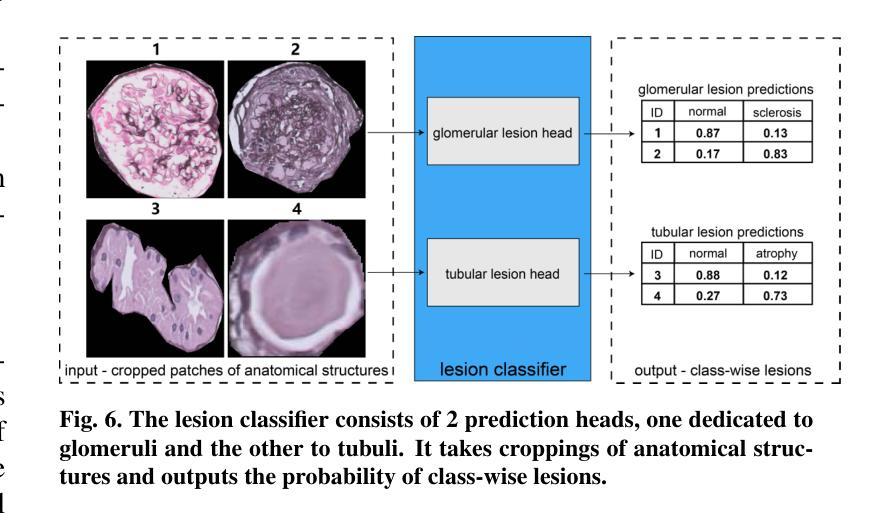
Renal biopsies are the gold standard for the diagnosis of kidney diseases. Lesion scores made by renal pathologists are semi-quantitative and exhibit high inter-observer variability. Automating lesion classification within segmented anatomical structures can provide decision support in quantification analysis, thereby reducing inter-observer variability. Nevertheless, classifying lesions in regions-of-interest (ROIs) is clinically challenging due to (a) a large amount of densely packed anatomical objects, (b) class imbalance across different compartments (at least 3), (c) significant variation in size and shape of anatomical objects and (d) the presence of multi-label lesions per anatomical structure. Existing models cannot address these complexities in an efficient and generic manner. This paper presents an analysis for a \textbf{generalized solution} to datasets from various sources (pathology departments) with different types of lesions. Our approach utilizes two sub-networks: dense instance segmentation and lesion classification. We introduce \textbf{DiffRegFormer}, an end-to-end dense instance segmentation sub-network designed for multi-class, multi-scale objects within ROIs. Combining diffusion models, transformers, and RCNNs, DiffRegFormer {is a computational-friendly framework that can efficiently recognize over 500 objects across three anatomical classes, i.e., glomeruli, tubuli, and arteries, within ROIs.} In a dataset of 303 ROIs from 148 Jones’ silver-stained renal Whole Slide Images (WSIs), our approach outperforms previous methods, achieving an Average Precision of 52.1% (detection) and 46.8% (segmentation). Moreover, our lesion classification sub-network achieves 89.2% precision and 64.6% recall on 21889 object patches out of the 303 ROIs. Lastly, our model demonstrates direct domain transfer to PAS-stained renal WSIs without fine-tuning.
肾活检是诊断肾脏疾病的金标准。肾病理学家进行的病变评分是半定量的,并且表现出较高的观察者间变异性。在分割的解剖结构内自动进行病变分类可以为定量分析提供决策支持,从而减少观察者间的变异性。然而,在感兴趣区域(ROI)内进行病变分类在临床上具有挑战性,原因包括(a)大量密集排列的解剖对象,(b)不同部位(至少3个部位)的类别不平衡,(c)解剖对象的大小和形状变化很大,以及(d)每个解剖结构中存在多标签病变。现有模型无法以高效且通用的方式处理这些复杂性。本文为来自不同来源(病理科)的各种类型病变的数据集提供了一种通用解决方案的分析。我们的方法利用两个子网络:密集实例分割和病变分类。我们引入了DiffRegFormer,这是一个端到端的密集实例分割子网络,专为ROI内的多类、多尺度对象设计。结合扩散模型、变压器和RCNN,DiffRegFormer是一个计算友好的框架,可以高效地识别ROI内的三个解剖类(即肾小球、肾小管和动脉)的500多个对象。在包含148个琼斯银染肾全切片图像(WSI)的303个ROI数据集中,我们的方法优于以前的方法,检测的平均精度达到52.1%(检测)和46.8%(分割)。此外,我们的病变分类子网络在303个ROI中的21889个对象补丁上达到了89.2%的精确度和64.6%的召回率。最后,我们的模型演示了无需微调即可直接转移到PAS染色的肾WSI领域。
论文及项目相关链接
摘要
肾活检是诊断肾脏疾病的金标准。病理学家对病灶的评分是半定量的,且存在较高的观察者间变异性。自动化病灶在分割解剖结构内的分类可以提供量化分析的支持,从而减少观察者间的变异性。然而,在感兴趣区域(ROI)进行病灶分类具有临床挑战性,包括解剖对象密集、各类别比例不平衡、解剖对象尺寸和形态差异大以及单个解剖结构存在多标签病灶等问题。现有模型无法以高效且通用的方式应对这些复杂性。本文提出一种通用解决方案,适用于不同来源(病理科)的数据集和不同类型的病灶。我们的方法利用两个子网络:密集实例分割和病灶分类。我们引入DiffRegFormer,这是一个专为ROI内多类、多尺度对象设计的端到端密集实例分割子网络。结合扩散模型、变压器和RCNN,DiffRegFormer是一个计算友好的框架,可高效识别超过500个对象跨越三个解剖类,即肾小球、肾小管和动脉。在包含来自148张琼斯银染肾全切片图像(WSI)的303个ROI的数据集中,我们的方法优于以前的方法,检测平均精度为52.1%,分割平均精度为46.8%。此外,我们的病灶分类子网络在来自这些ROI的21889个对象补丁上达到了89.2%的精确度和64.6%的召回率。最后,我们的模型展示了对PAS染色肾WSI的直接域迁移能力,无需微调。
要点摘要
- 肾活检是诊断肾脏疾病的金标准,但病理学家对病灶的评分存在半定量和高度的观察者间变异性。
- 自动化病灶分类在减少观察者间变异性方面提供决策支持。
- 现有模型面临临床挑战,如解剖对象密集、类别不平衡、形态和尺寸差异大以及多标签病灶等问题。
- 本文提出一种结合扩散模型、变压器和RCNN的通用解决方案DiffRegFormer,用于多类、多尺度对象的密集实例分割。
- DiffRegFormer在包含不同肾区域的数据集中表现优异,检测平均精度为52.1%,分割平均精度为46.8%。
- 病灶分类子网络在病灶对象补丁上表现出高精确度(89.2%)和召回率(64.6%)。
点此查看论文截图