⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-20 更新
Fibottention: Inceptive Visual Representation Learning with Diverse Attention Across Heads
Authors:Ali Khaleghi Rahimian, Manish Kumar Govind, Subhajit Maity, Dominick Reilly, Christian Kümmerle, Srijan Das, Aritra Dutta
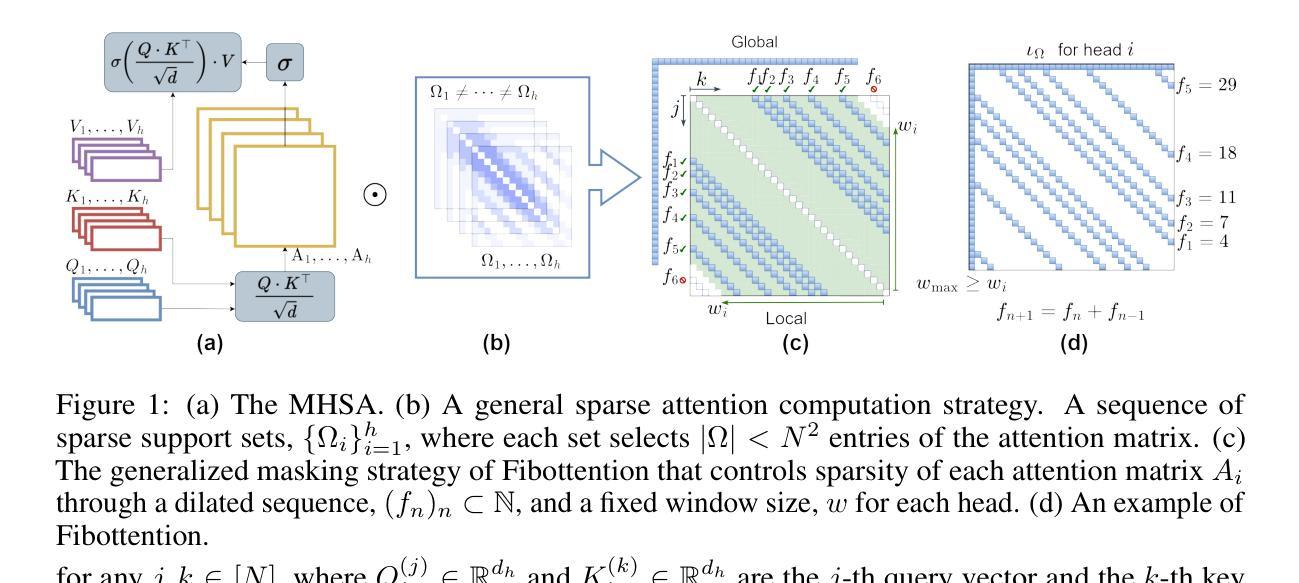
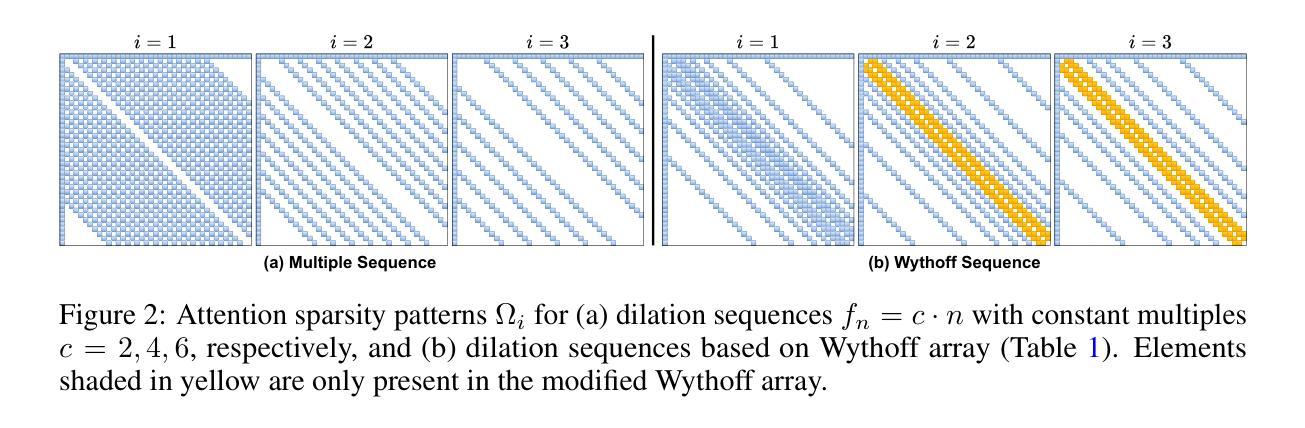
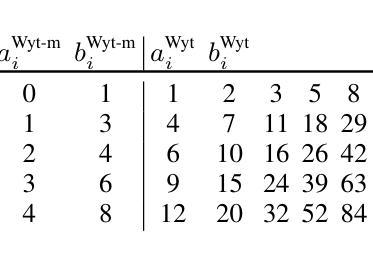
Transformer architectures such as Vision Transformers (ViT) have proven effective for solving visual perception tasks. However, they suffer from two major limitations; first, the quadratic complexity of self-attention limits the number of tokens that can be processed, and second, Transformers often require large amounts of training data to attain state-of-the-art performance. In this paper, we propose a new multi-head self-attention (MHSA) variant named Fibottention, which can replace MHSA in Transformer architectures. Fibottention is data-efficient and computationally more suitable for processing large numbers of tokens than the standard MHSA. It employs structured sparse attention based on dilated Fibonacci sequences, which, uniquely, differ across attention heads, resulting in inception-like diverse features across heads. The spacing of the Fibonacci sequences follows the Wythoff array, which minimizes the redundancy of token interactions aggregated across different attention heads, while still capturing sufficient complementary information through token pair interactions. These sparse attention patterns are unique among the existing sparse attention and lead to an $O(N \log N)$ complexity, where $N$ is the number of tokens. Leveraging only 2-6% of the elements in the self-attention heads, Fibottention embedded into popular, state-of-the-art Transformer architectures can achieve significantly improved predictive performance for domains with limited data such as image classification, video understanding, and robot learning tasks, and render reduced computational complexity. We further validated the improved diversity of feature representations resulting from different self-attention heads, and our model design against other sparse attention mechanisms.
Vision Transformer(ViT)等Transformer架构已被证明在解决视觉感知任务方面非常有效。然而,它们存在两个主要局限性:首先,自注意力的二次复杂性限制了可以处理的令牌数量;其次,Transformer通常需要大量训练数据才能达到最新性能。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的多头自注意力(MHSA)变体,名为Fibottention,它可以替代Transformer架构中的MHSA。Fibottention具有数据高效性,并且与标准MHSA相比,在计算上更适合处理大量令牌。它采用基于膨胀斐波那契序列的结构化稀疏注意力,这在各个注意力头是独特的,从而在头之间产生类似于inception的多样化特征。斐波那契序列的间隔遵循怀托夫阵列,这最小化了不同注意力头聚集的令牌交互的冗余,同时通过令牌对交互捕获足够的互补信息。这些稀疏注意力模式在现有的稀疏注意力中是独一无二的,并导致O(N log N)的复杂性,其中N是令牌的数量。仅利用自注意力头中2-6%的元素,Fibottention嵌入到流行且最新的Transformer架构中,就可以实现对数据有限领域的预测性能显著改善,如图像分类、视频理解和机器人学习任务,并降低了计算复杂性。我们进一步验证了不同自注意力头产生的特征表示改进多样性,以及我们的模型设计与其他稀疏注意力机制的区别。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF The complete implementation, including source code and evaluation scripts, is publicly available at: https://github.com/Charlotte-CharMLab/Fibottention
Summary:本文提出一种新的多头自注意力(MHSA)变体,名为Fibottention,适用于处理大量标记的视觉任务。它采用基于斐波那契序列的结构化稀疏注意力,不同注意力头之间具有不同的序列,形成多样化的特征。Fibottention具有数据高效性和计算优势,能在有限数据领域如图像分类、视频理解和机器人学习任务中实现显著改进的预测性能,并降低计算复杂度。
Key Takeaways:
- Vision Transformers (ViT) 在解决视觉感知任务时表现出色,但存在两个主要限制:自注意力的二次复杂度和需要大量训练数据。
- 提出了一种新的多头自注意力(MHSA)变体Fibottention,用于替换Transformer架构中的MHSA。
- Fibottention采用基于斐波那契序列的结构化稀疏注意力,不同注意力头之间具有独特的序列。
- Fibottention具有数据效率和计算优势,能在处理大量标记时表现出良好的性能。
- Fibottention能在有限数据领域如图像分类、视频理解和机器人学习任务中实现显著改进的预测性能。
- Fibottention具有O(N log N)的复杂度,其中N是标记的数量,且仅利用自注意力头中2-6%的元素。
点此查看论文截图

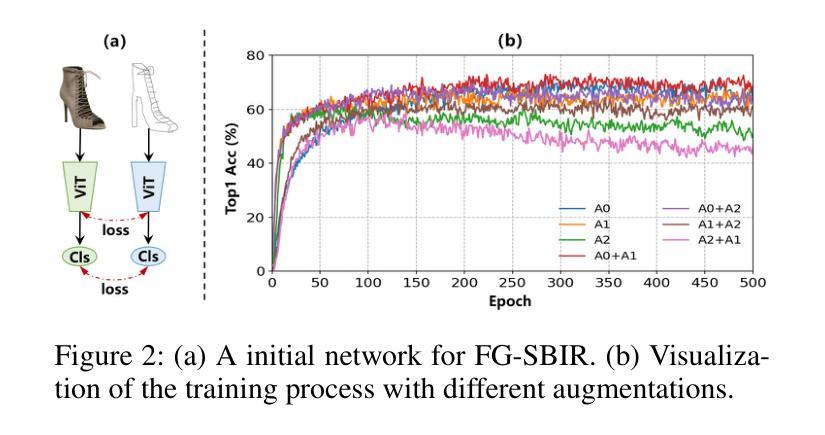
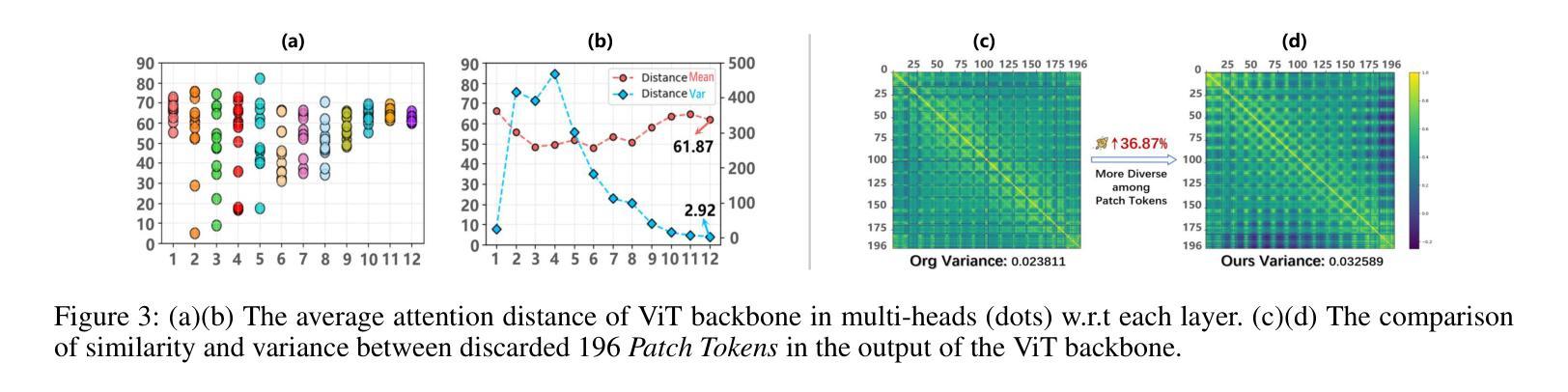
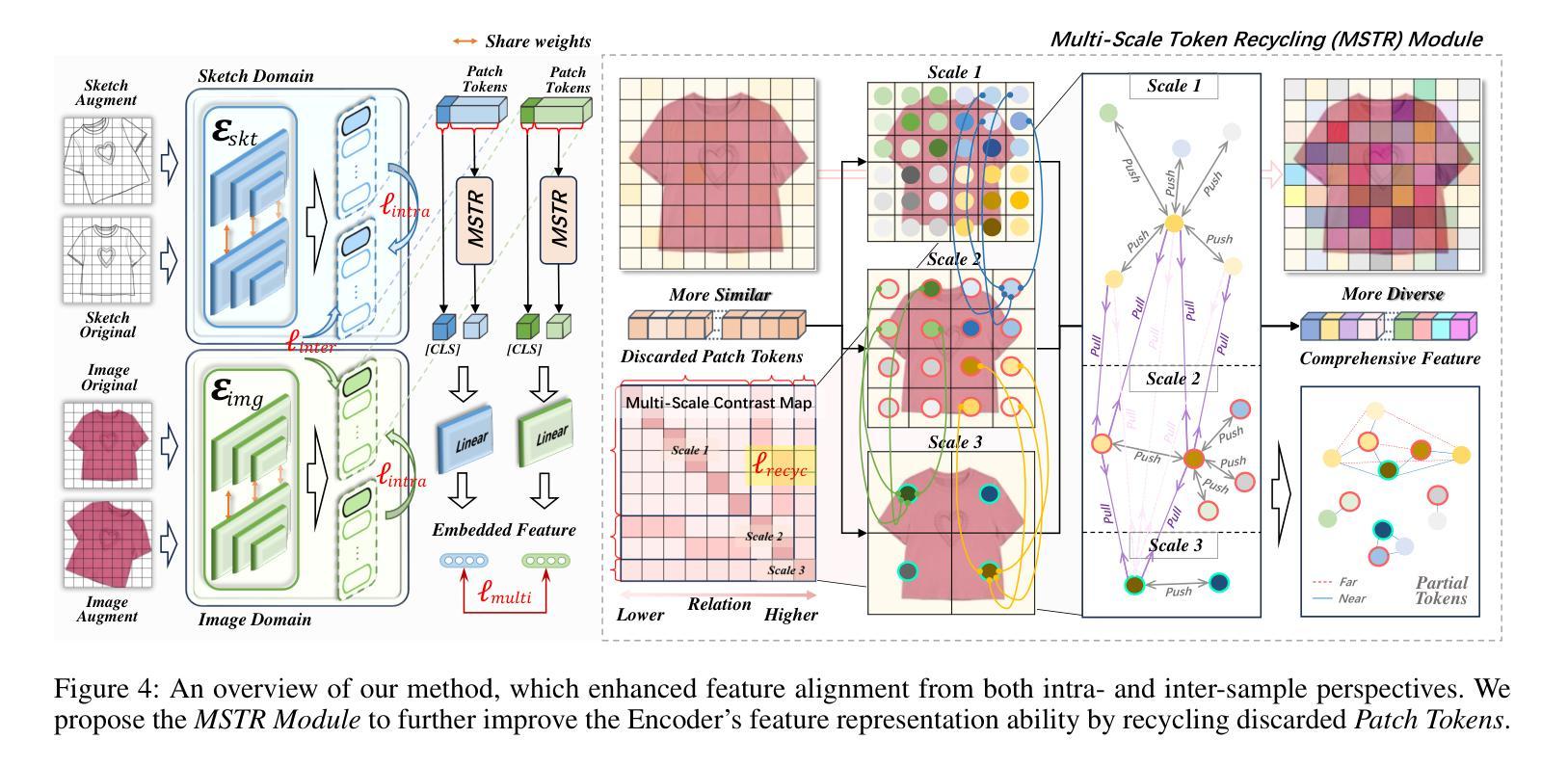
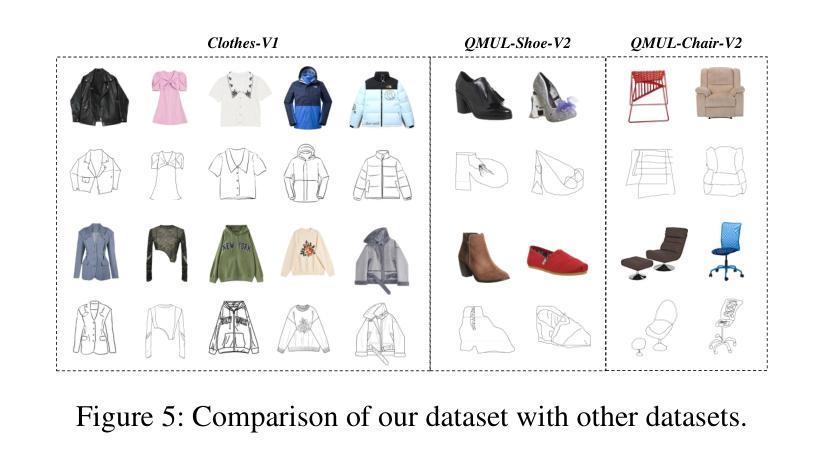
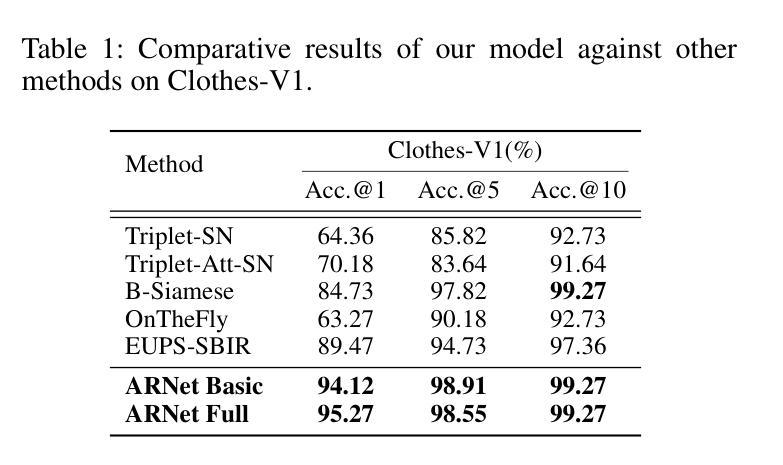
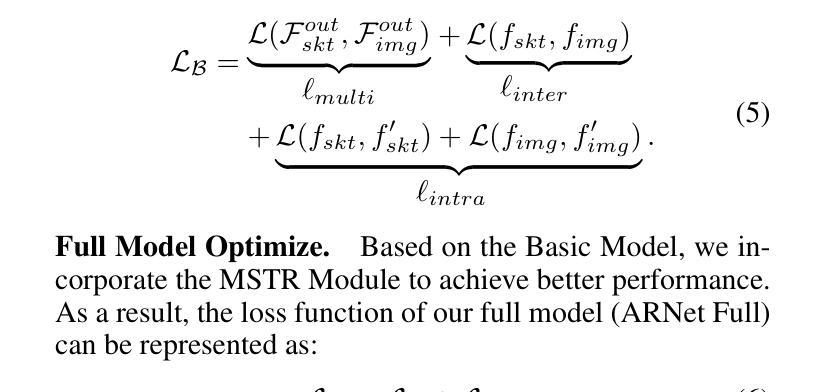
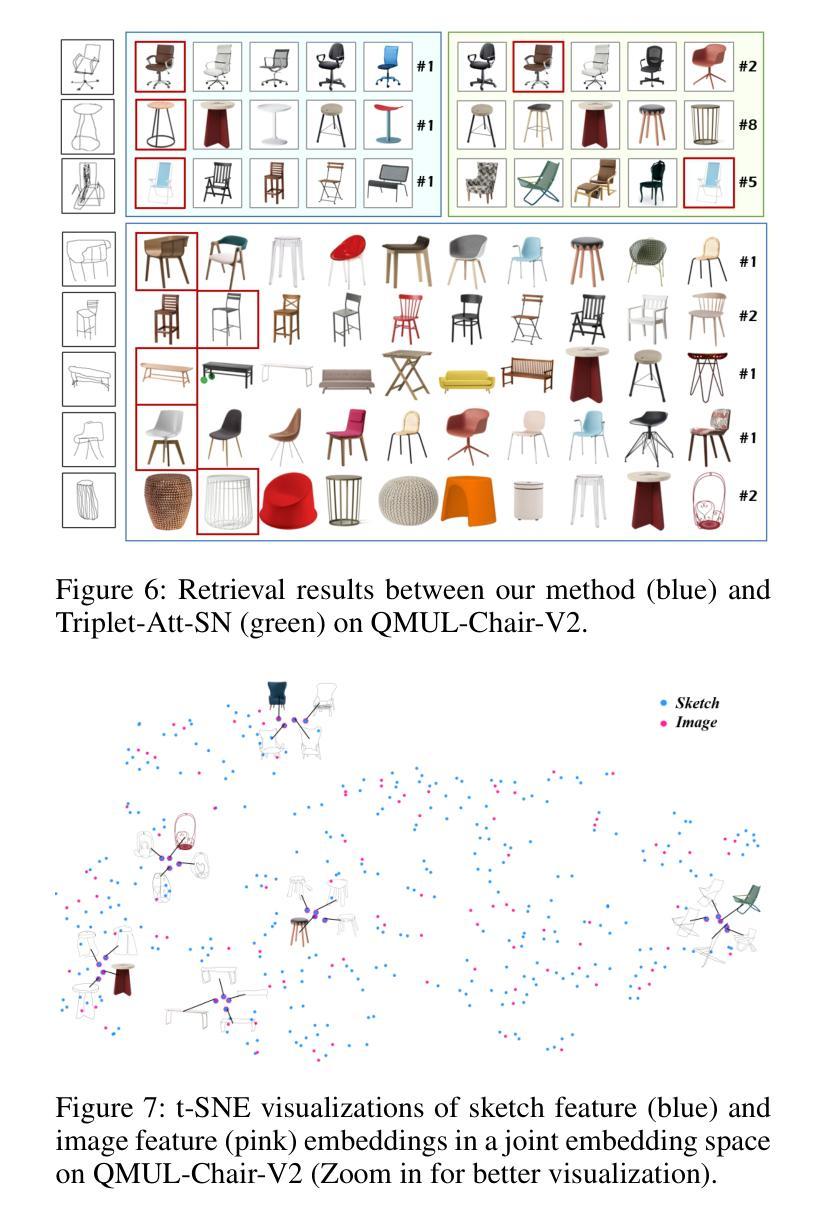
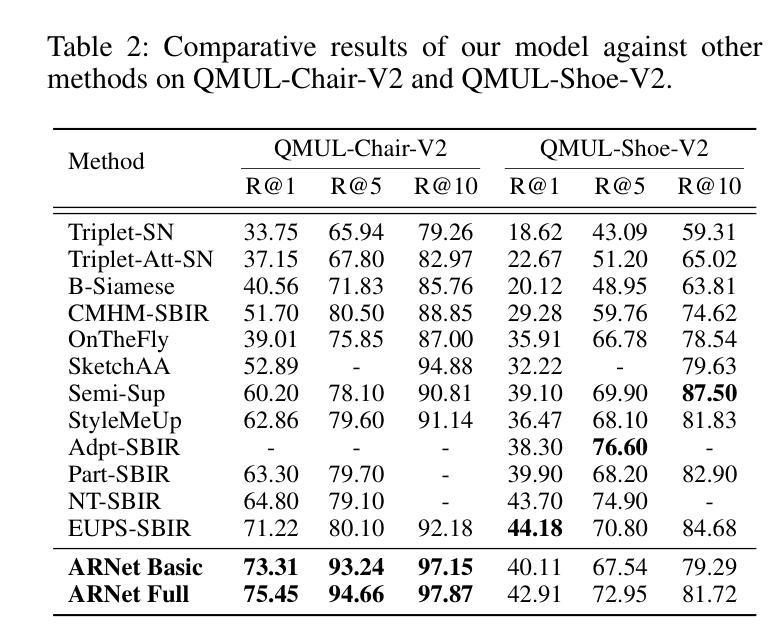
ARNet: Self-Supervised FG-SBIR with Unified Sample Feature Alignment and Multi-Scale Token Recycling
Authors:Jianan Jiang, Hao Tang, Zhilin Jiang, Weiren Yu, Di Wu
Fine-Grained Sketch-Based Image Retrieval (FG-SBIR) aims to minimize the distance between sketches and corresponding images in the embedding space. However, scalability is hindered by the growing complexity of solutions, mainly due to the abstract nature of fine-grained sketches. In this paper, we propose an effective approach to narrow the gap between the two domains. It mainly facilitates unified mutual information sharing both intra- and inter-samples, rather than treating them as a single feature alignment problem between modalities. Specifically, our approach includes: (i) Employing dual weight-sharing networks to optimize alignment within the sketch and image domain, which also effectively mitigates model learning saturation issues. (ii) Introducing an objective optimization function based on contrastive loss to enhance the model’s ability to align features in both intra- and inter-samples. (iii) Presenting a self-supervised Multi-Scale Token Recycling (MSTR) Module featured by recycling discarded patch tokens in multi-scale features, further enhancing representation capability and retrieval performance. Our framework achieves excellent results on CNN- and ViT-based backbones. Extensive experiments demonstrate its superiority over existing methods. We also introduce Cloths-V1, the first professional fashion sketch-image dataset, utilized to validate our method and will be beneficial for other applications.
细粒度草图基于图像检索(FG-SBIR)旨在最小化嵌入空间中草图与对应图像之间的距离。然而,解决方案的日益复杂性阻碍了其可扩展性,这主要是因为细粒度草图具有抽象性。在本文中,我们提出了一种有效的方法来缩小两个领域之间的差距。它主要通过促进跨样本内和跨样本的统一信息共享,而不是将它们视为不同模态之间的单一特征对齐问题。具体来说,我们的方法包括:(i)采用双权重共享网络来优化草图域和图像域内的对齐,这也可以有效地缓解模型学习饱和问题。(ii)引入基于对比损失的客观优化函数,以提高模型在跨样本内和跨样本中对齐特征的能力。(iii)提出了一种自我监督的多尺度令牌回收(MSTR)模块,该模块以回收多尺度特征中的丢弃补丁令牌为特征,进一步提高了表示能力和检索性能。我们的框架在基于CNN和ViT的骨干网上取得了良好效果。大量实验证明了其优于现有方法。我们还介绍了Cloths-V1数据集,这是第一个专业时尚草图图像数据集,用于验证我们的方法,并将对其他应用有益。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by the 39th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-25)
Summary
针对细粒度草图基础图像检索(FG-SBIR)问题,本文提出了一种有效的解决方案,旨在缩小草图与图像之间的差距。通过统一跨样本和跨模态的信息共享,解决抽象草图带来的复杂性挑战。引入双权重共享网络优化内部对齐,并基于对比损失进行目标优化,同时提出多尺度令牌回收模块进一步增强性能。该框架在CNN和ViT骨干网上均表现优异,并公开了首个专业时尚草图图像数据集Cloths-V1以验证方法价值。
Key Takeaways
- 针对细粒度草图基础图像检索(FG-SBIR)的挑战,文章提出了一种缩小草图与图像领域差距的有效方法。
- 通过统一跨样本和跨模态的信息共享来解决抽象草图带来的复杂性。
- 采用双权重共享网络优化内部对齐,有效缓解模型学习饱和问题。
- 引入基于对比损失的目标优化函数,增强模型在跨样本内的特征对齐能力。
- 提出多尺度令牌回收模块(MSTR),通过回收多尺度特征中的丢弃补丁令牌,进一步提高表示能力和检索性能。
- 该框架在CNN和ViT骨干网络上均有卓越表现。
点此查看论文截图

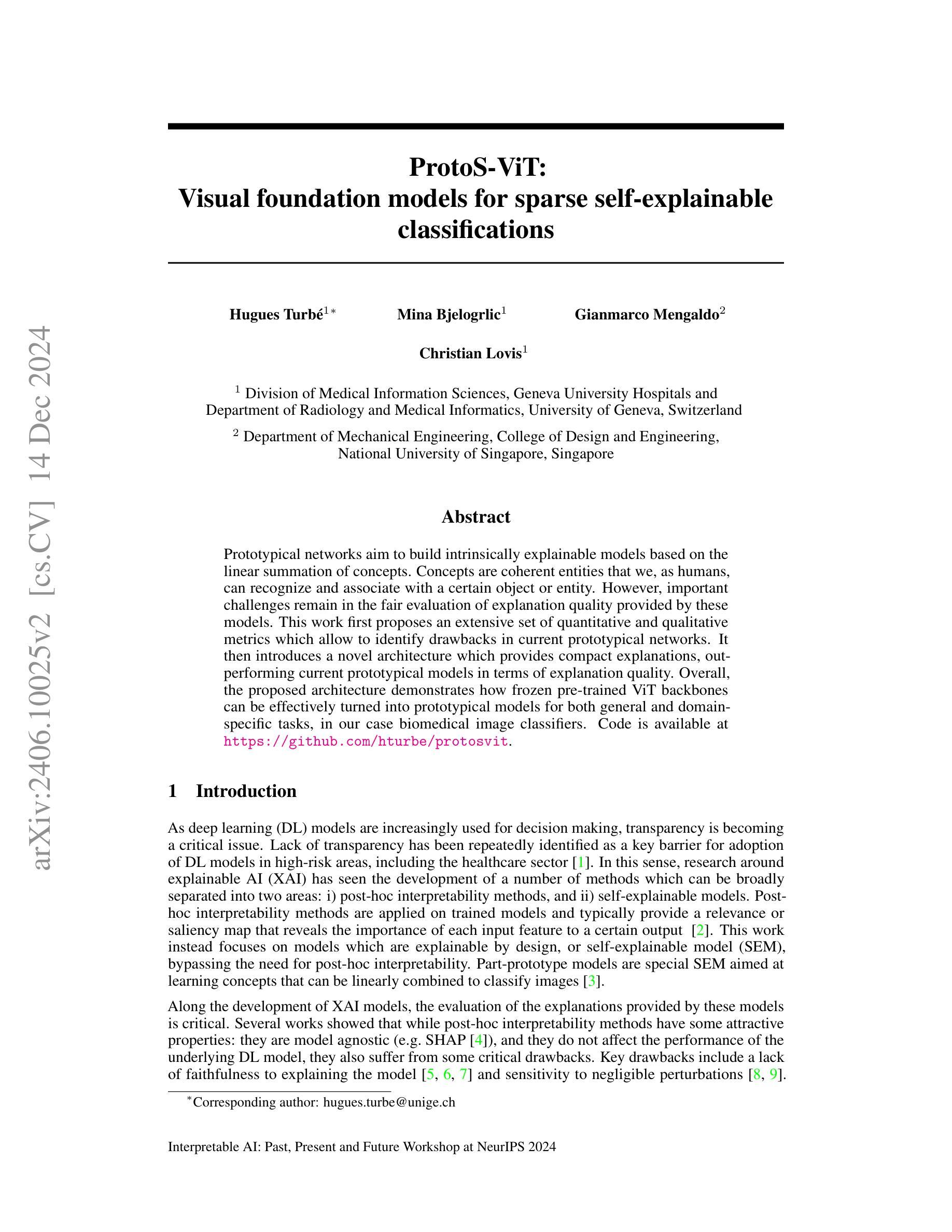
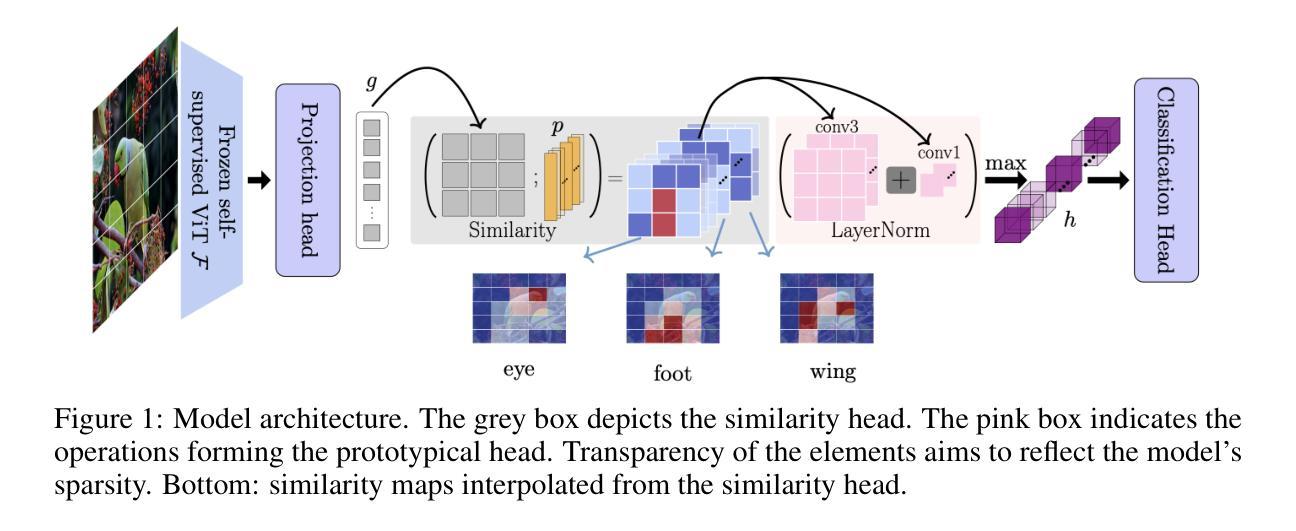
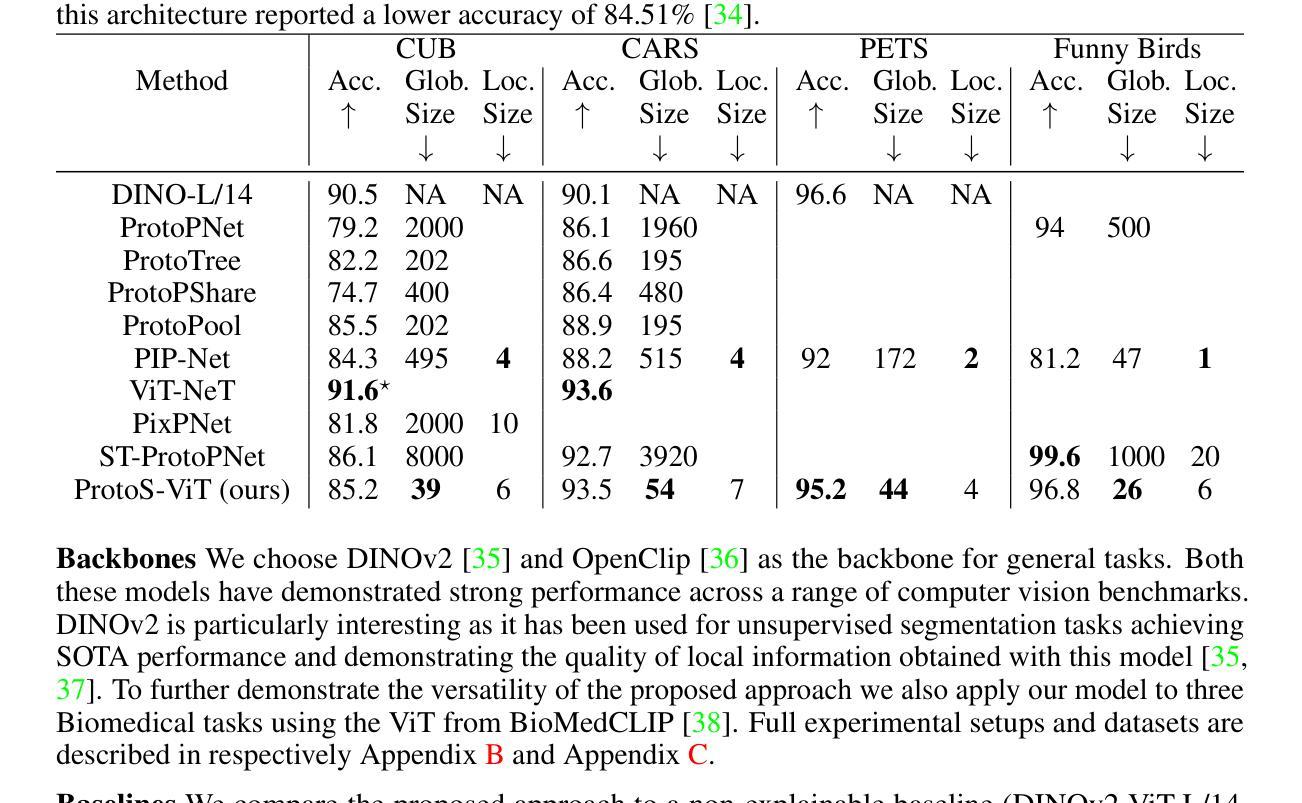
ProtoS-ViT: Visual foundation models for sparse self-explainable classifications
Authors:Hugues Turbé, Mina Bjelogrlic, Gianmarco Mengaldo, Christian Lovis
Prototypical networks aim to build intrinsically explainable models based on the linear summation of concepts. Concepts are coherent entities that we, as humans, can recognize and associate with a certain object or entity. However, important challenges remain in the fair evaluation of explanation quality provided by these models. This work first proposes an extensive set of quantitative and qualitative metrics which allow to identify drawbacks in current prototypical networks. It then introduces a novel architecture which provides compact explanations, outperforming current prototypical models in terms of explanation quality. Overall, the proposed architecture demonstrates how frozen pre-trained ViT backbones can be effectively turned into prototypical models for both general and domain-specific tasks, in our case biomedical image classifiers. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/hturbe/protosvit}.
原型网络旨在基于概念的线性总和建立内在可解释性的模型。概念是人类可以识别并与某个对象或实体相关联的连贯实体。然而,在公平评估这些模型提供的解释质量方面仍然存在重要挑战。这项工作首先提出了一套广泛的定量和定性指标,可以识别当前原型网络中的缺点。然后它引入了一种新型架构,该架构提供了简洁的解释,在解释质量方面优于当前的原型模型。总的来说,所提出的架构展示了如何将冻结的预训练ViT骨干网有效地转化为原型模型,用于通用和特定领域的任务,在我们的情况下是生物医学图像分类器。代码可在https://github.com/hturbe/protosvit找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Update publication to match paper presented at the Interpretable AI: Past, Present and Future Workshop at NeurIPS 2024
Summary
本文介绍了原型网络旨在构建基于概念线性叠加的内在可解释模型。文章指出当前原型网络在解释质量评估上存在的挑战,并提出一系列定量和定性指标来识别现有原型网络的不足。随后,文章引入了一种新型架构,该架构能够提供简洁的解释,在解释质量方面优于当前的原型模型。整体而言,该架构展示了如何将冻结的预训练ViT骨干有效转化为原型模型,用于一般和特定领域的任务,例如生物医学图像分类器。
Key Takeaways
- 原型网络基于概念的线性叠加构建内在可解释模型。
- 当前原型网络在解释质量评估上面临挑战。
- 文章提出一系列定量和定性指标来评估原型网络的不足。
- 新型架构提供简洁的解释,优于现有的原型模型在解释质量方面。
- 冻结的预训练ViT骨干可以转化为原型模型,适用于一般和特定领域任务。
- 文章展示的架构特别适用于生物医学图像分类器等任务。
点此查看论文截图
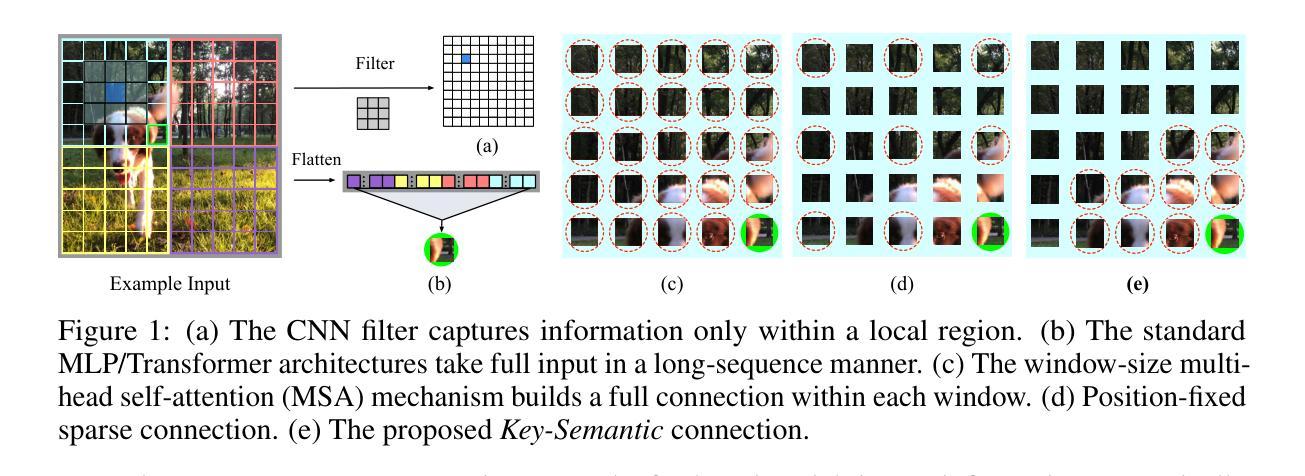
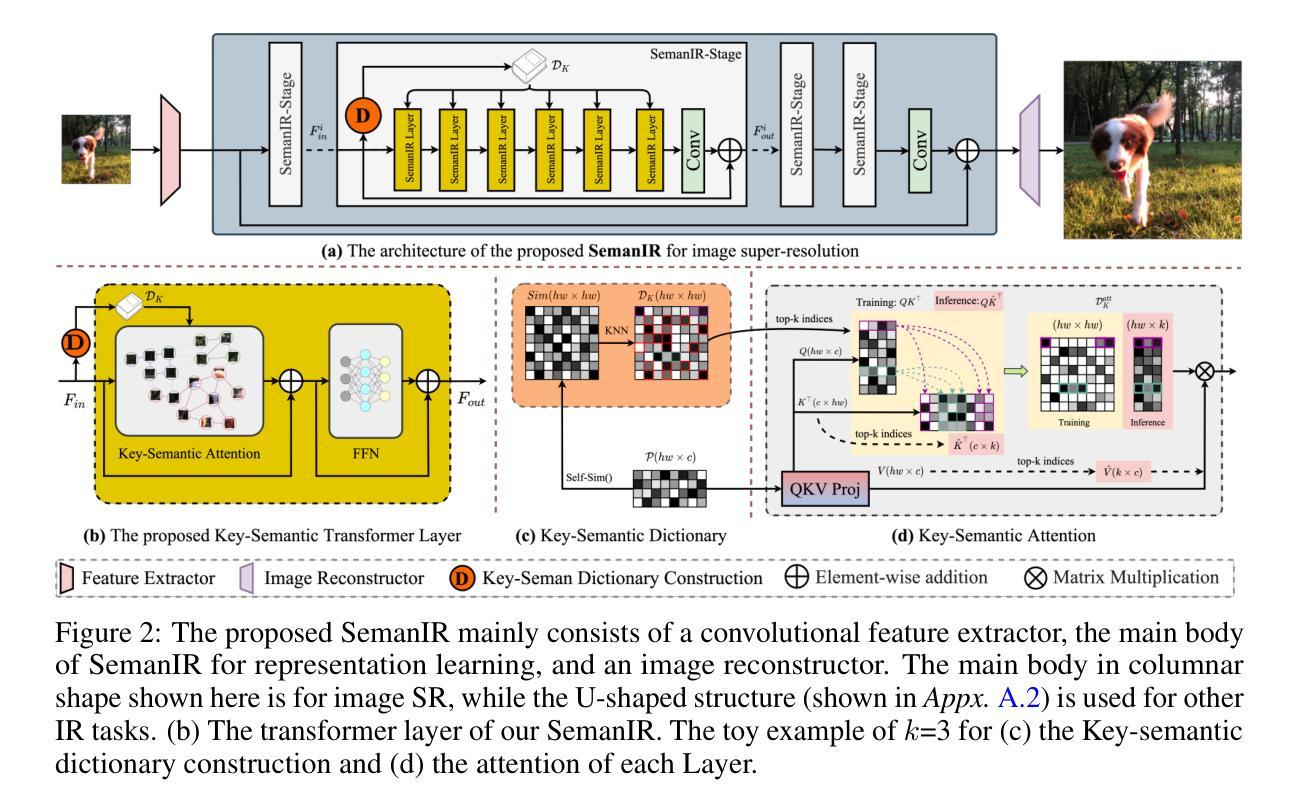
Sharing Key Semantics in Transformer Makes Efficient Image Restoration
Authors:Bin Ren, Yawei Li, Jingyun Liang, Rakesh Ranjan, Mengyuan Liu, Rita Cucchiara, Luc Van Gool, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Nicu Sebe
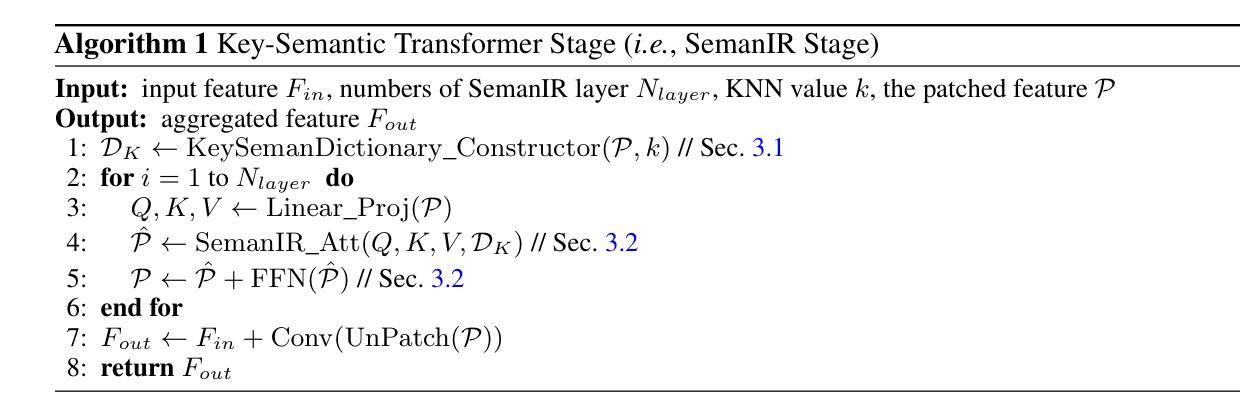
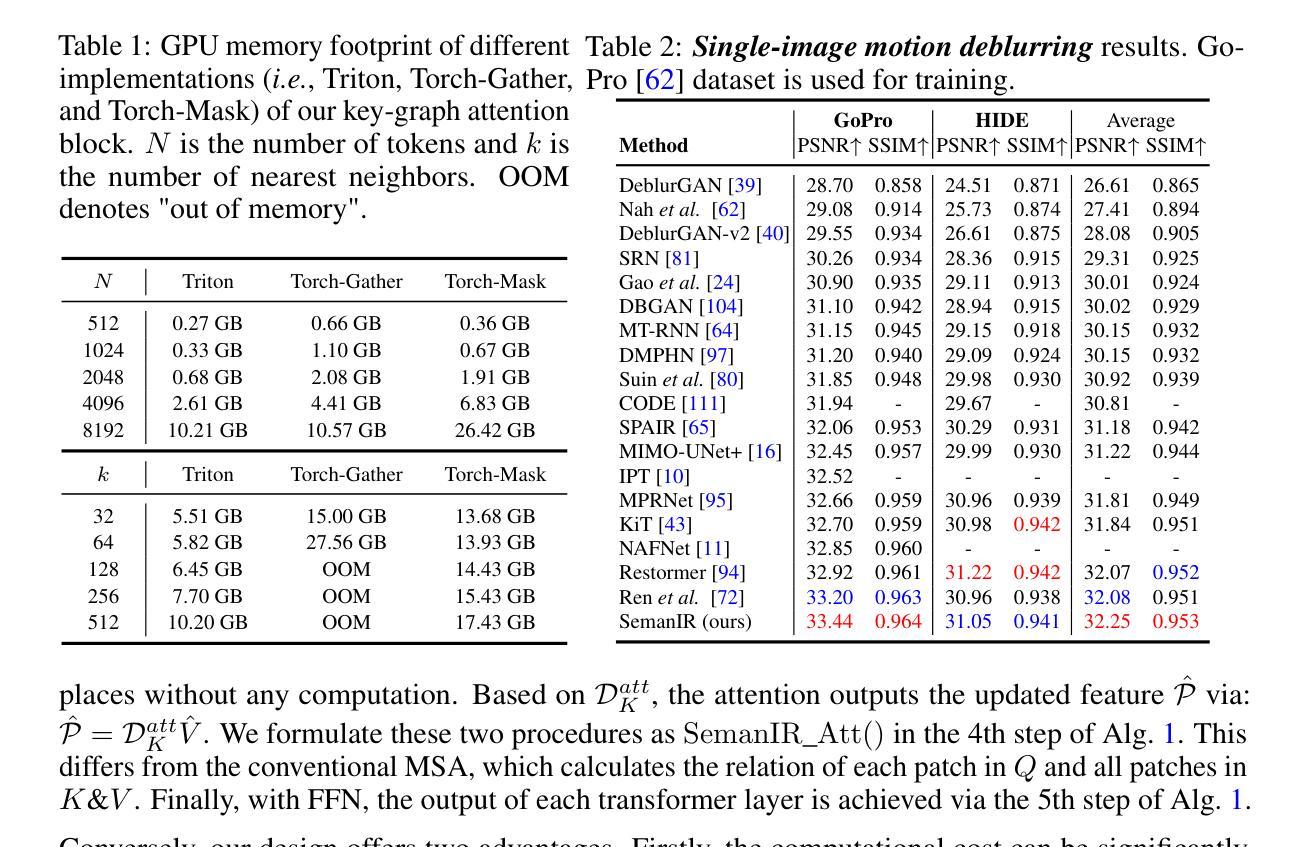
Image Restoration (IR), a classic low-level vision task, has witnessed significant advancements through deep models that effectively model global information. Notably, the emergence of Vision Transformers (ViTs) has further propelled these advancements. When computing, the self-attention mechanism, a cornerstone of ViTs, tends to encompass all global cues, even those from semantically unrelated objects or regions. This inclusivity introduces computational inefficiencies, particularly noticeable with high input resolution, as it requires processing irrelevant information, thereby impeding efficiency. Additionally, for IR, it is commonly noted that small segments of a degraded image, particularly those closely aligned semantically, provide particularly relevant information to aid in the restoration process, as they contribute essential contextual cues crucial for accurate reconstruction. To address these challenges, we propose boosting IR’s performance by sharing the key semantics via Transformer for IR (\ie, SemanIR) in this paper. Specifically, SemanIR initially constructs a sparse yet comprehensive key-semantic dictionary within each transformer stage by establishing essential semantic connections for every degraded patch. Subsequently, this dictionary is shared across all subsequent transformer blocks within the same stage. This strategy optimizes attention calculation within each block by focusing exclusively on semantically related components stored in the key-semantic dictionary. As a result, attention calculation achieves linear computational complexity within each window. Extensive experiments across 6 IR tasks confirm the proposed SemanIR’s state-of-the-art performance, quantitatively and qualitatively showcasing advancements. The visual results, code, and trained models are available at https://github.com/Amazingren/SemanIR.
图像恢复(IR)是经典低级视觉任务之一,通过有效建模全局信息的深度模型取得了显著进展。值得注意的是,视觉转换器(ViTs)的出现进一步推动了这些进展。在计算过程中,ViTs的核心自注意力机制往往包含所有全局线索,即使来自语义上不相关的对象或区域。这种包容性带来了计算效率低下的问题,特别是在高输入分辨率下更为明显,因为它需要处理不相关的信息,从而影响了效率。此外,对于图像恢复任务,人们通常注意到退化图像的小片段,尤其是那些语义上紧密对齐的片段,提供了特别相关的信息,有助于恢复过程,因为它们提供了对准确重建至关重要的上下文线索。针对这些挑战,本文提出了通过Transformer共享关键语义来提高图像恢复性能的方法(即SemanIR)。具体来说,SemanIR首先通过在每个transformer阶段建立每个退化图块的必要语义连接来构建稀疏而全面的关键语义词典。随后,该词典在同一阶段的后续transformer块之间共享。此策略通过专注于关键语义词典中语义相关的组件来优化每个块内的注意力计算。因此,每个窗口内的注意力计算实现了线性计算复杂性。在6个图像恢复任务上的大量实验证实了所提出的SemanIR的卓越性能,在数量和质量上均展示了其进展。视觉结果、代码和训练模型可在https://github.com/Amazingren/SemanIR上找到。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NeurIPS2024
Summary
图像修复(IR)任务在深度模型的推动下取得了显著进展,特别是引入了Vision Transformers(ViTs)后。ViTs中的自注意力机制虽然能有效建模全局信息,但在处理图像修复任务时存在计算效率低下的问题,因为它包含了所有全局线索,包括来自语义上不相关对象或区域的线索。为了提升性能并优化计算效率,本文提出了通过Transformer进行IR的关键语义共享方法(即SemanIR)。SemanIR在每个transformer阶段内建立稀疏但全面的关键语义字典,并在同一阶段的后续transformer块之间共享此字典。此方法优化了注意力计算,使其专注于语义相关的组件,从而提高了计算效率并在六个IR任务上达到了最先进的性能。
Key Takeaways
- Vision Transformers (ViTs) 的引入对图像修复(IR)任务产生了显著影响。
- 自注意力机制在处理图像修复任务时存在计算效率低下的问题,因为它包含了所有全局线索,包括语义上不相关的内容。
- SemanIR方法旨在通过共享关键语义信息来解决这一问题,从而提高计算效率和图像修复性能。
- SemanIR在每个transformer阶段内建立关键语义字典,并在同一阶段的后续transformer块之间共享此字典。
- 该策略优化了注意力计算,使其专注于语义相关的组件,从而提高了图像修复的准确性。
- 广泛实验表明,SemanIR在六个图像修复任务上达到了最先进的性能。
点此查看论文截图