⚠️ 以下所有内容总结都来自于 大语言模型的能力,如有错误,仅供参考,谨慎使用
🔴 请注意:千万不要用于严肃的学术场景,只能用于论文阅读前的初筛!
💗 如果您觉得我们的项目对您有帮助 ChatPaperFree ,还请您给我们一些鼓励!⭐️ HuggingFace免费体验
2024-12-21 更新
SqueezeMe: Efficient Gaussian Avatars for VR
Authors:Shunsuke Saito, Stanislav Pidhorskyi, Igor Santesteban, Forrest Iandola, Divam Gupta, Anuj Pahuja, Nemanja Bartolovic, Frank Yu, Emanuel Garbin, Tomas Simon
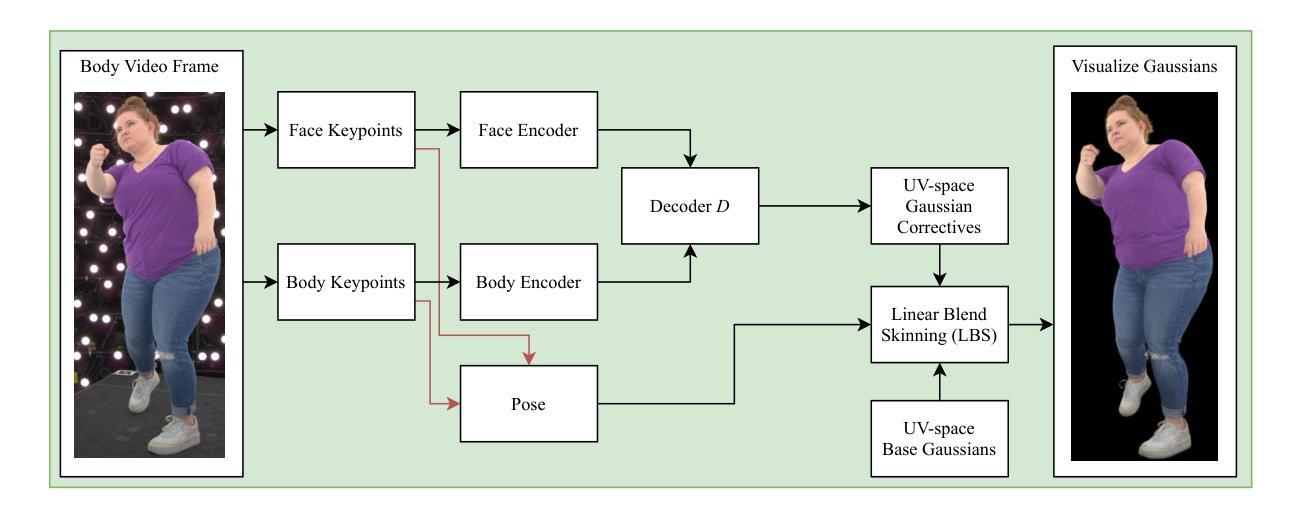
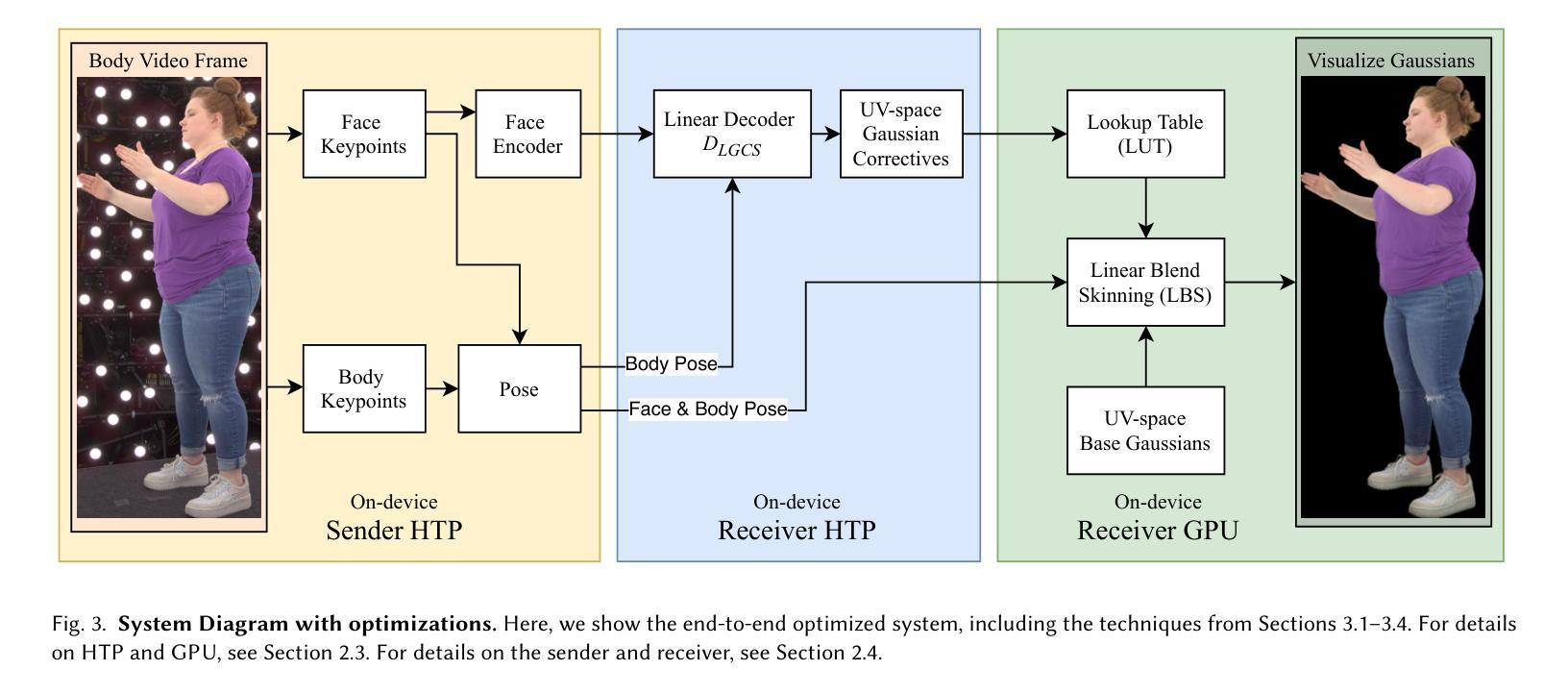
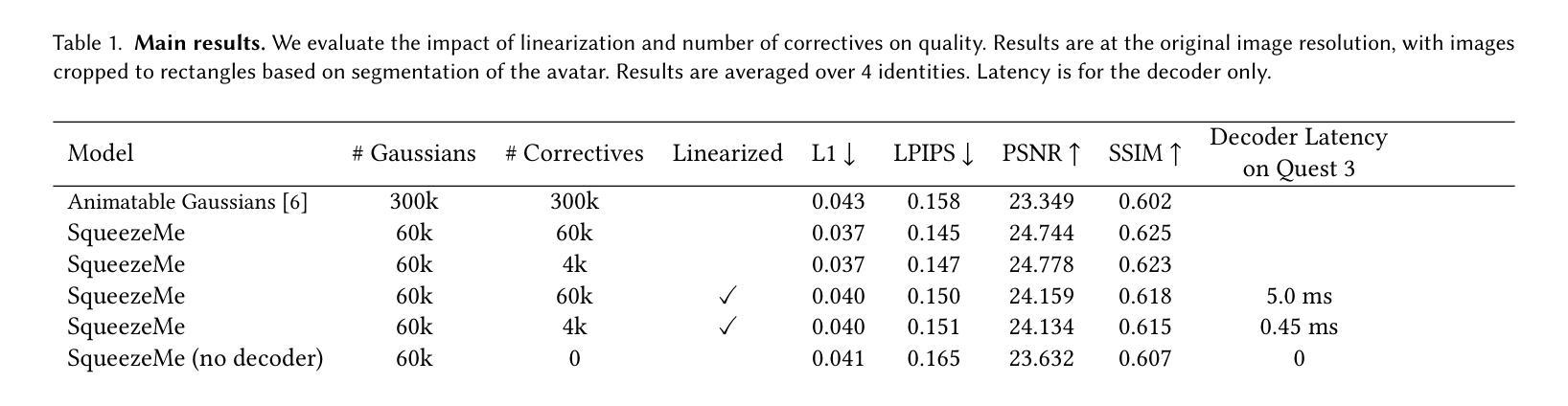
Gaussian Splatting has enabled real-time 3D human avatars with unprecedented levels of visual quality. While previous methods require a desktop GPU for real-time inference of a single avatar, we aim to squeeze multiple Gaussian avatars onto a portable virtual reality headset with real-time drivable inference. We begin by training a previous work, Animatable Gaussians, on a high quality dataset captured with 512 cameras. The Gaussians are animated by controlling base set of Gaussians with linear blend skinning (LBS) motion and then further adjusting the Gaussians with a neural network decoder to correct their appearance. When deploying the model on a Meta Quest 3 VR headset, we find two major computational bottlenecks: the decoder and the rendering. To accelerate the decoder, we train the Gaussians in UV-space instead of pixel-space, and we distill the decoder to a single neural network layer. Further, we discover that neighborhoods of Gaussians can share a single corrective from the decoder, which provides an additional speedup. To accelerate the rendering, we develop a custom pipeline in Vulkan that runs on the mobile GPU. Putting it all together, we run 3 Gaussian avatars concurrently at 72 FPS on a VR headset. Demo videos are at https://forresti.github.io/squeezeme.
高斯涂抹技术已经实现了具有前所未有的视觉品质的真实时3D人类化身。虽然之前的方法需要一个桌面GPU来进行单一化身的实时推理,我们的目标是将多个高斯化身挤压到便携式虚拟现实头盔上,实现可驱动的实时推理。我们首先训练了可动画化的高斯技术(一项之前的工作)在一个用512台相机捕获的高质量数据集上。高斯通过控制基本的高斯集并使用线性混合蒙皮(LBS)运动进行动画,然后通过神经网络解码器进一步调整高斯以校正其外观。当在Meta Quest 3虚拟现实头盔上部署模型时,我们发现两个主要的计算瓶颈:解码器和渲染器。为了加速解码器,我们在UV空间而不是像素空间中训练高斯,并将解码器蒸馏到一个单一的神经网络层。此外,我们发现高斯邻居可以从解码器共享一个修正项,这提供了额外的加速。为了加速渲染器,我们在Vulkan中开发了一个自定义管道,该管道在移动GPU上运行。将所有这些整合在一起,我们在虚拟现实头盔上同时运行三个高斯化身,帧速率为每秒72帧。演示视频位于:[https://forresti.github.io/squeezeme]。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Initial version
Summary
基于高斯混合技术,实现了在虚拟现实头盔上实时驱动多个高质量3D人类角色的能力。通过训练动画化高斯模型并使用神经网络解码器调整外观,在Meta Quest 3 VR头盔上进行部署时,解决了计算瓶颈,提高了渲染速度。展示了一段可以在VR头盔上同时运行三个高斯角色的演示视频。
Key Takeaways
- 高斯混合技术用于创建高质量的实时三维人物模型。
- 研究人员在虚拟头盔设备上实现了多个人物模型的实时推理计算。
- 使用神经网络解码器调整高斯模型的外观,以提高视觉效果。
- 在Meta Quest 3 VR头盔上部署时,解决了计算瓶颈问题。
- 通过在UV空间而非像素空间训练高斯模型,加速了解码过程。
- 通过开发自定义的Vulkan渲染管线,提高了渲染速度。
点此查看论文截图


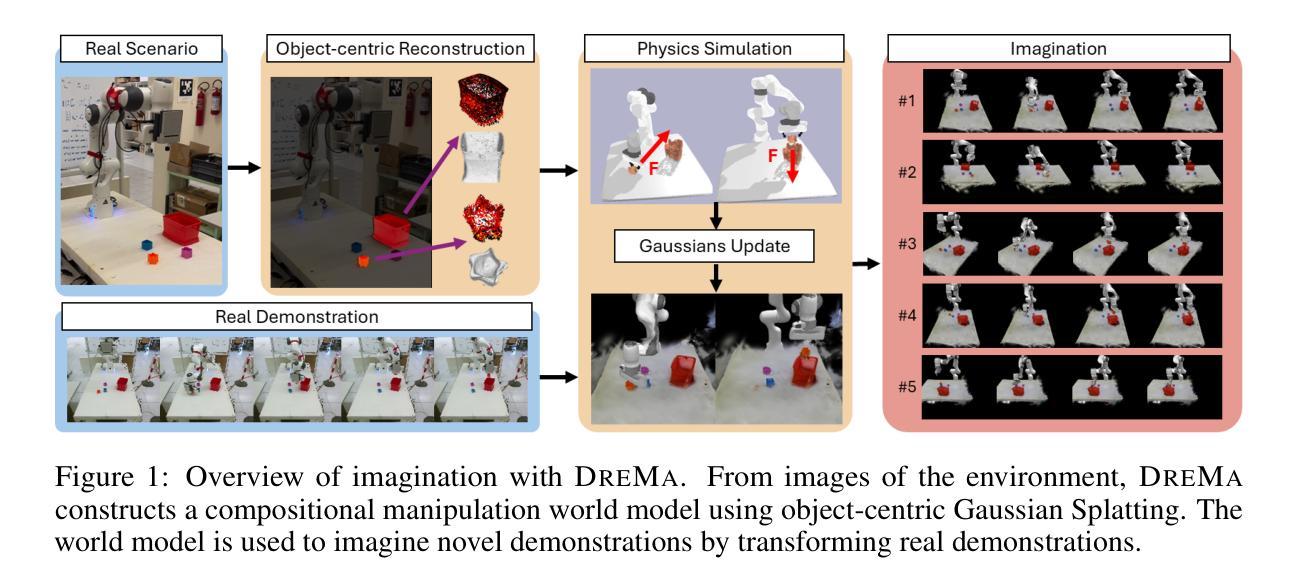
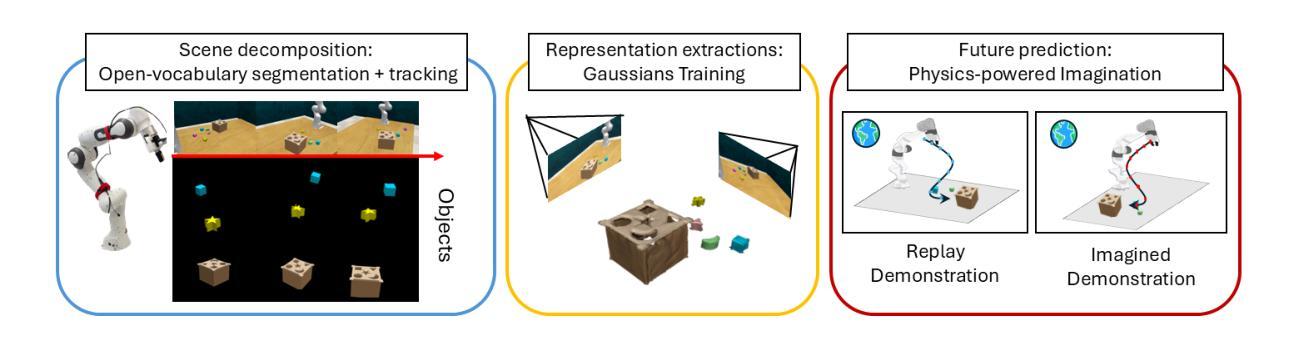
Dream to Manipulate: Compositional World Models Empowering Robot Imitation Learning with Imagination
Authors:Leonardo Barcellona, Andrii Zadaianchuk, Davide Allegro, Samuele Papa, Stefano Ghidoni, Efstratios Gavves
A world model provides an agent with a representation of its environment, enabling it to predict the causal consequences of its actions. Current world models typically cannot directly and explicitly imitate the actual environment in front of a robot, often resulting in unrealistic behaviors and hallucinations that make them unsuitable for real-world applications. In this paper, we introduce a new paradigm for constructing world models that are explicit representations of the real world and its dynamics. By integrating cutting-edge advances in real-time photorealism with Gaussian Splatting and physics simulators, we propose the first compositional manipulation world model, which we call DreMa. DreMa replicates the observed world and its dynamics, allowing it to imagine novel configurations of objects and predict the future consequences of robot actions. We leverage this capability to generate new data for imitation learning by applying equivariant transformations to a small set of demonstrations. Our evaluations across various settings demonstrate significant improvements in both accuracy and robustness by incrementing actions and object distributions, reducing the data needed to learn a policy and improving the generalization of the agents. As a highlight, we show that a real Franka Emika Panda robot, powered by DreMa’s imagination, can successfully learn novel physical tasks from just a single example per task variation (one-shot policy learning). Our project page and source code can be found in https://leobarcellona.github.io/DreamToManipulate/
世界模型为智能体提供其环境的表示,使其能够预测其行为的因果后果。当前的世界模型通常无法直接明确地模仿机器人面前的实际环境,这往往导致不真实的行为和幻觉,使它们不适合真实世界应用。在本文中,我们介绍了一种构建明确表示现实世界及其动态变化的新世界模型的范式。通过整合实时逼真技术与高斯拼贴和物理模拟器的最新进展,我们提出了第一个组合操作世界模型,我们称之为DreMa。DreMa复制了现实世界及其动态变化,能够想象物体的新颖配置并预测机器人行为的未来后果。我们通过应用等价转换来对少数演示进行演示来生成模仿学习的新数据。我们在各种环境中的评估表明,通过增加动作和对象分布,在准确性和稳健性方面实现了显着提高,减少了学习策略的所需数据并提高了智能体的泛化能力。值得一提的是,我们使用DreMa想象的Franka Emika Panda真实机器人可以成功地从每个任务变化只有一个示例(单次策略学习)中学习新的物理任务。我们的项目页面和源代码可以在https://leobarcellona.github.io/DreamToManipulate/找到。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文介绍了一种新的构建世界模型的范式,该模型能够明确表现现实世界及其动态。通过结合最新的实时逼真技术与高斯泼墨和物理模拟器,提出了一种名为DreMa的组成型操作世界模型。DreMa能够复制观察到的世界及其动态,想象物体的新颖配置并预测机器人行动的未来结果。该能力用于生成模仿学习的数据,通过对少量演示应用等价变换实现。评估表明,通过增加动作和物体分布,DreMa在准确性和稳健性方面都有显著提高,减少了学习政策所需的数据并提高了代理的泛化能力。尤其值得一提的是,由DreMa驱动的Franka Emika Panda机器人能够仅通过一个示例学习新的物理任务(一次学习)。
Key Takeaways
- 引入了一种新的世界模型构建方法,能更明确地表现现实世界及其动态。
- 结合了实时逼真技术、高斯泼墨和物理模拟器。
- 提出了组成型操作世界模型DreMa,能复制观察到的世界及其动态。
- DreMa能想象物体的新颖配置并预测机器人行动的未来结果。
- 通过等价变换生成数据,用于模仿学习。
- DreMa提高了机器人学习的准确性和稳健性,减少了学习所需的数据。
点此查看论文截图

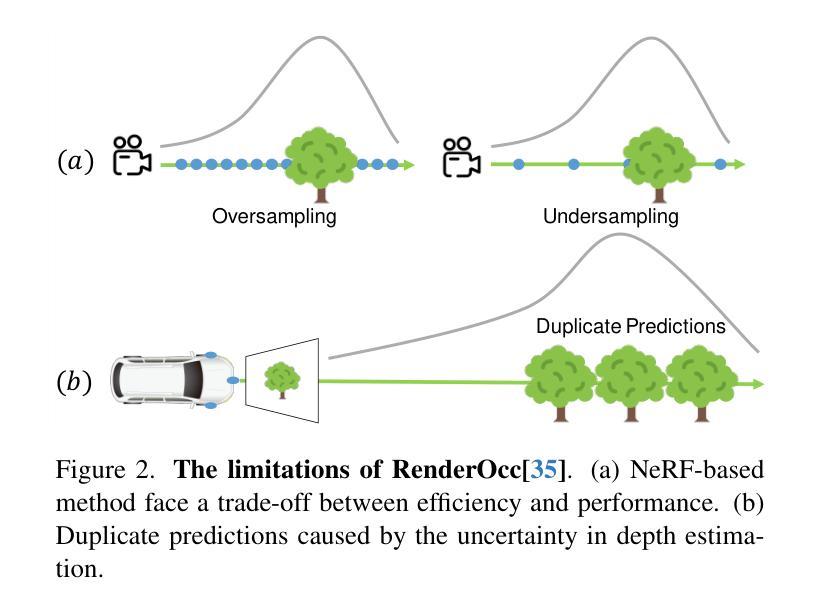
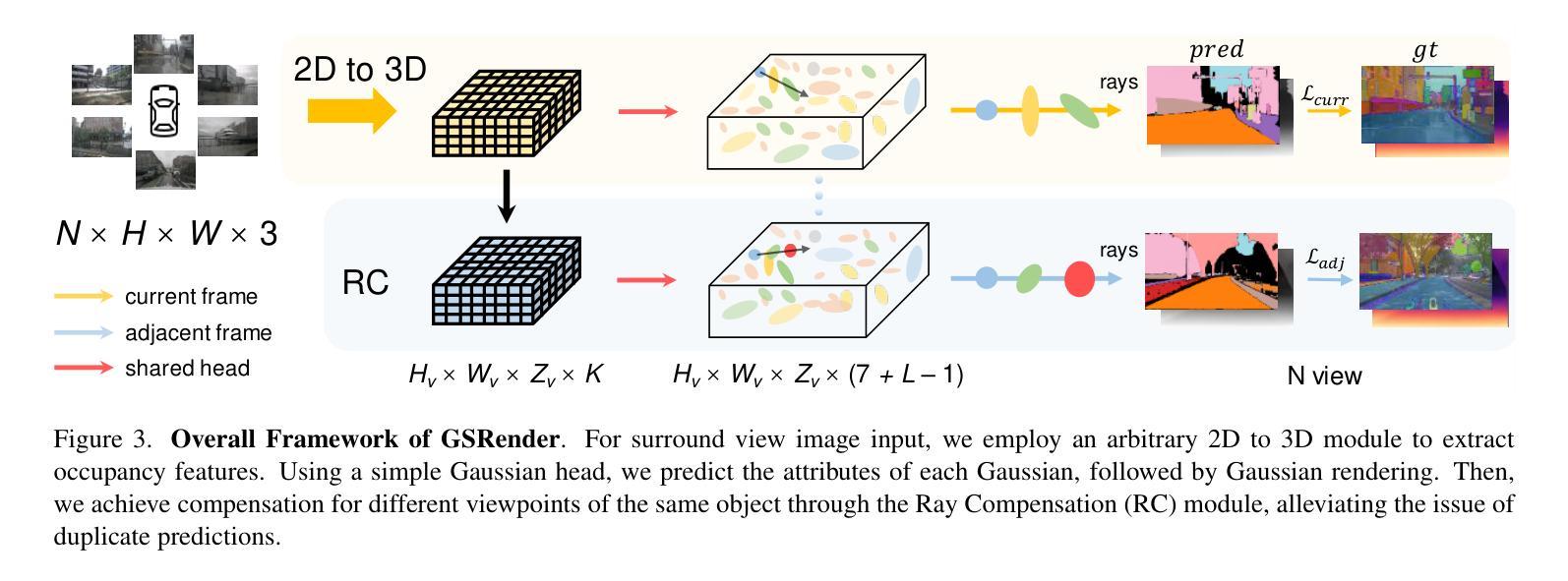
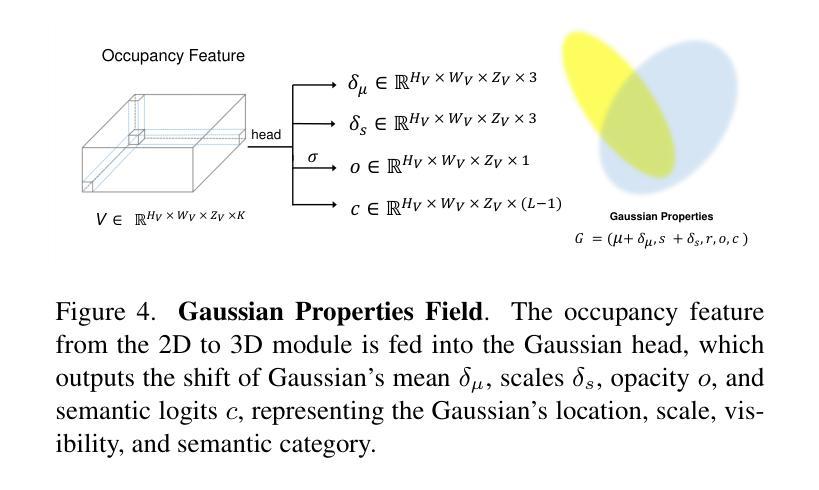
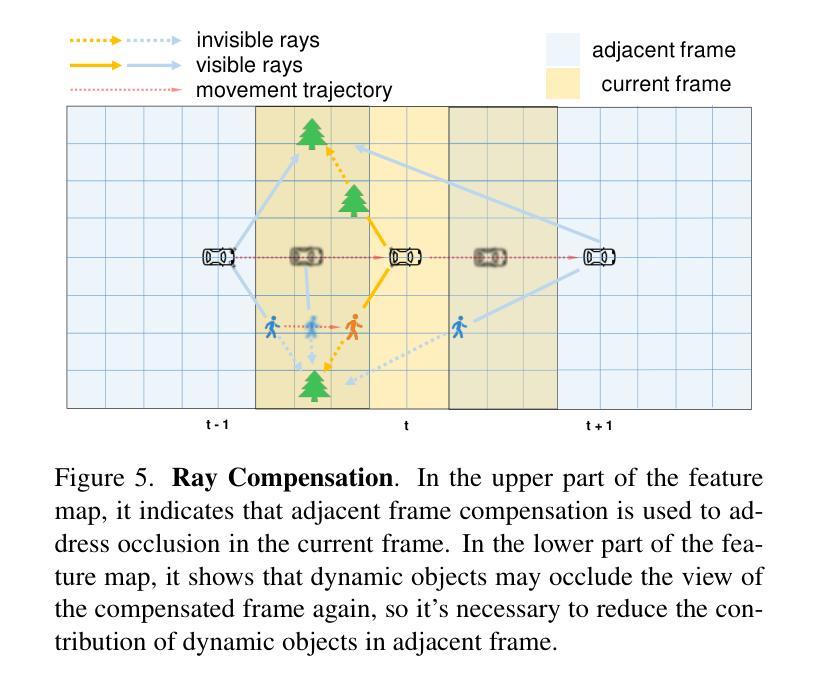
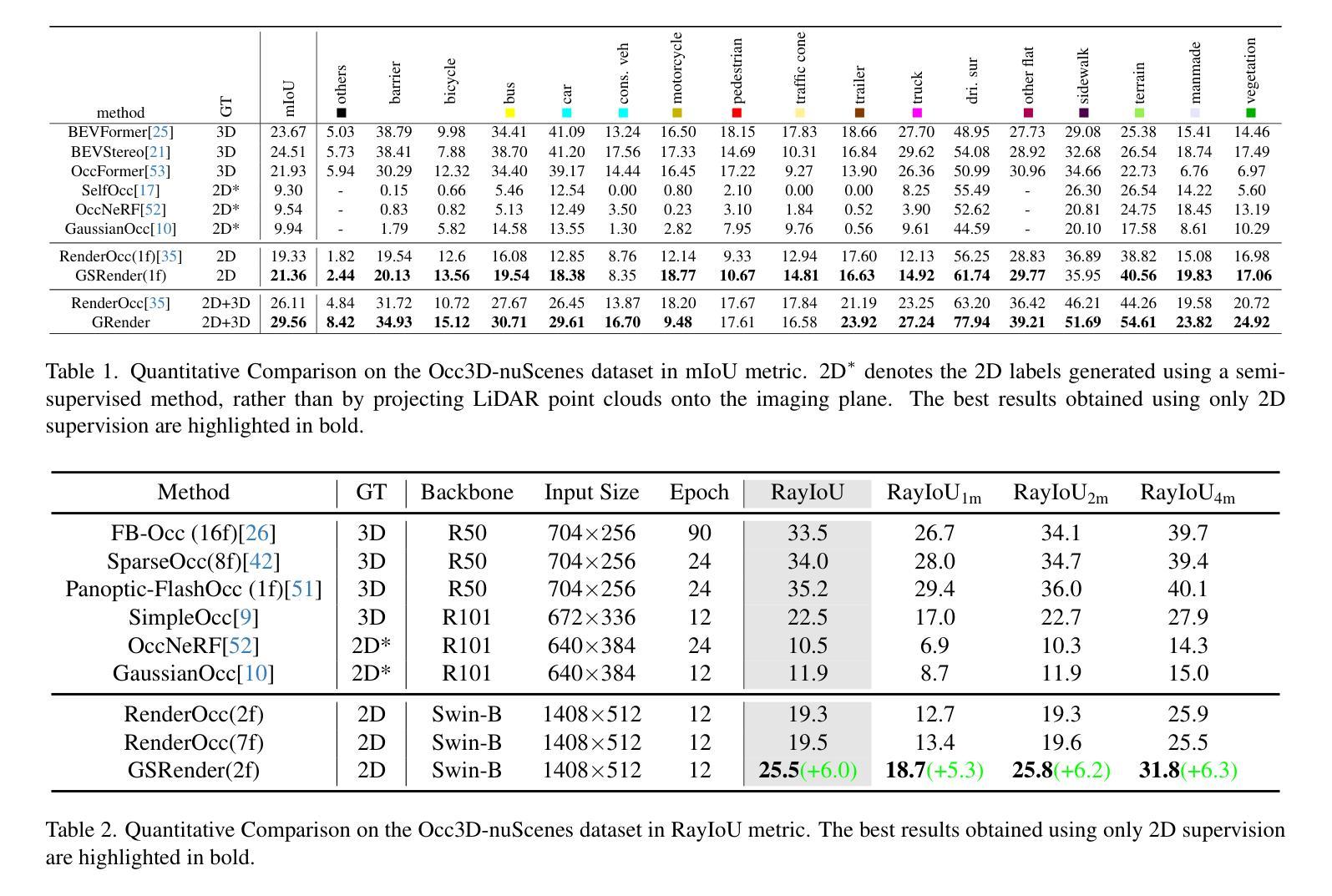
GSRender: Deduplicated Occupancy Prediction via Weakly Supervised 3D Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Qianpu Sun, Changyong Shu, Sifan Zhou, Zichen Yu, Yan Chen, Dawei Yang, Yuan Chun
3D occupancy perception is gaining increasing attention due to its capability to offer detailed and precise environment representations. Previous weakly-supervised NeRF methods balance efficiency and accuracy, with mIoU varying by 5-10 points due to sampling count along camera rays. Recently, real-time Gaussian splatting has gained widespread popularity in 3D reconstruction, and the occupancy prediction task can also be viewed as a reconstruction task. Consequently, we propose GSRender, which naturally employs 3D Gaussian Splatting for occupancy prediction, simplifying the sampling process. In addition, the limitations of 2D supervision result in duplicate predictions along the same camera ray. We implemented the Ray Compensation (RC) module, which mitigates this issue by compensating for features from adjacent frames. Finally, we redesigned the loss to eliminate the impact of dynamic objects from adjacent frames. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves SOTA (state-of-the-art) results in RayIoU (+6.0), while narrowing the gap with 3D supervision methods. Our code will be released soon.
三维占用感知因其能够提供详细且精确的环境表示而越来越受到关注。之前的弱监督NeRF方法在效率和准确性之间取得了平衡,由于沿相机射线的采样数量不同,mIoU(平均交并比)会有5-10个点的变化。最近,实时高斯拼贴在三维重建中得到了广泛的应用,占用预测任务也可以被视为重建任务。因此,我们提出了GSRender,它自然采用三维高斯拼贴进行占用预测,简化了采样过程。此外,由于二维监督的局限性,沿同一相机射线会产生重复的预测。我们实现了光线补偿(RC)模块,通过补偿相邻帧的特征来解决这个问题。最后,我们重新设计了损失函数,以消除相邻帧中动态对象的影响。大量实验表明,我们的方法在RayIoU(+6.0)方面达到了最新水平,并缩小了与三维监督方法的差距。我们的代码将很快发布。
论文及项目相关链接
Summary
本文关注于三维空间中的占据感知问题,提出了一种名为GSRender的方法,该方法利用三维高斯溅射进行占据预测,简化了采样过程。通过引入Ray Compensation(RC)模块解决了因2D监督导致的沿同一相机射线上的重复预测问题,并重新设计了损失函数以消除相邻帧中动态对象的影响。实验表明,该方法在RayIoU上达到了先进水平,并缩小了与三维监督方法的差距。
Key Takeaways
- 3D occupancy perception因能提供详细和精确的环境表示而受到关注。
- 之前的方法如NeRF在效率和准确性之间取得平衡,但采样数量对mIoU影响较大。
3 实时高斯溅射在3D重建中流行,占据预测也可视为重建任务。 - 提出了GSRender方法,利用三维高斯溅射进行占据预测,简化采样过程。
- 引入Ray Compensation(RC)模块解决沿同一相机射线上的重复预测问题。
- 重新设计损失函数以消除相邻帧中动态对象对预测的影响。
点此查看论文截图

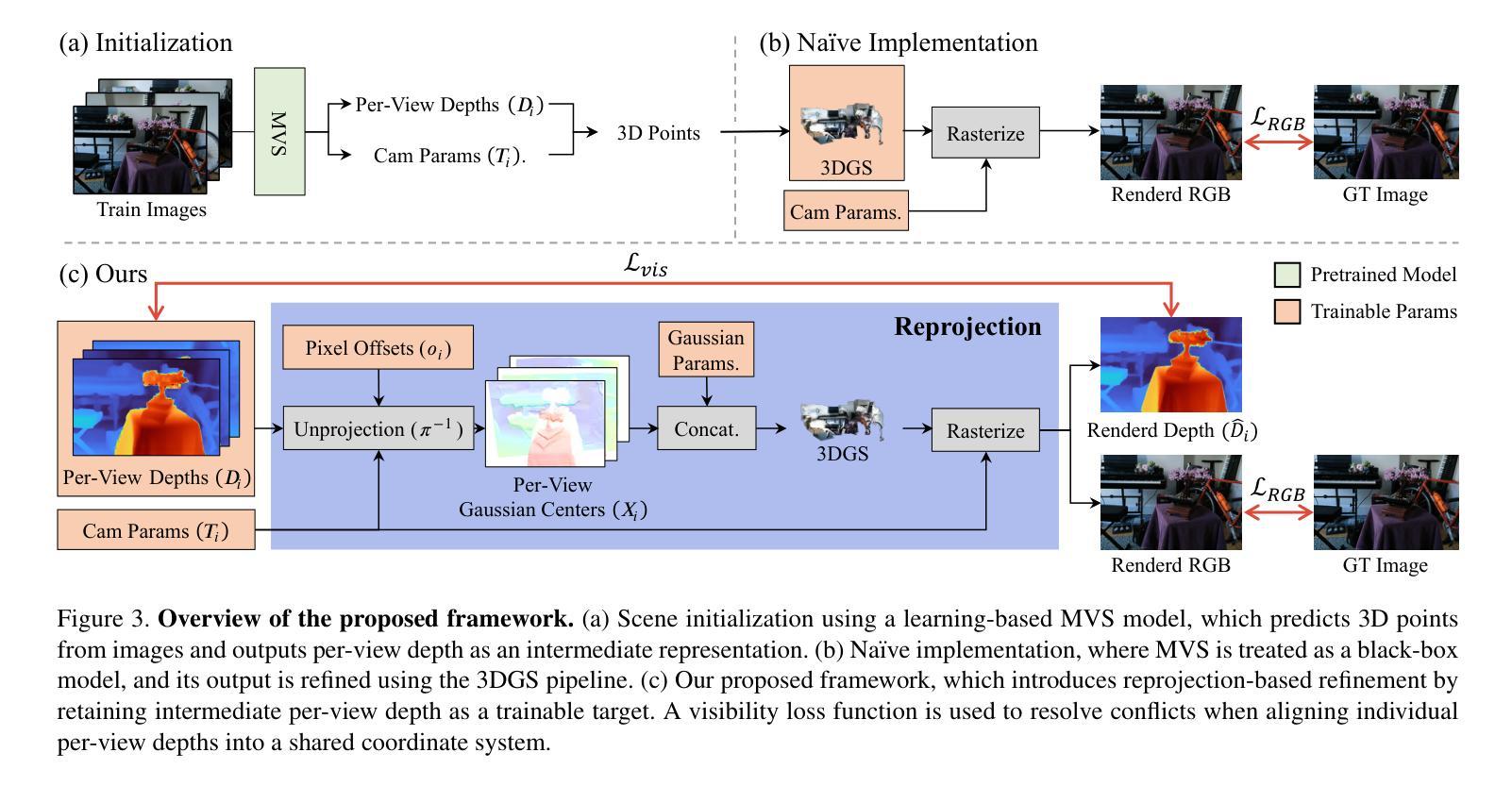
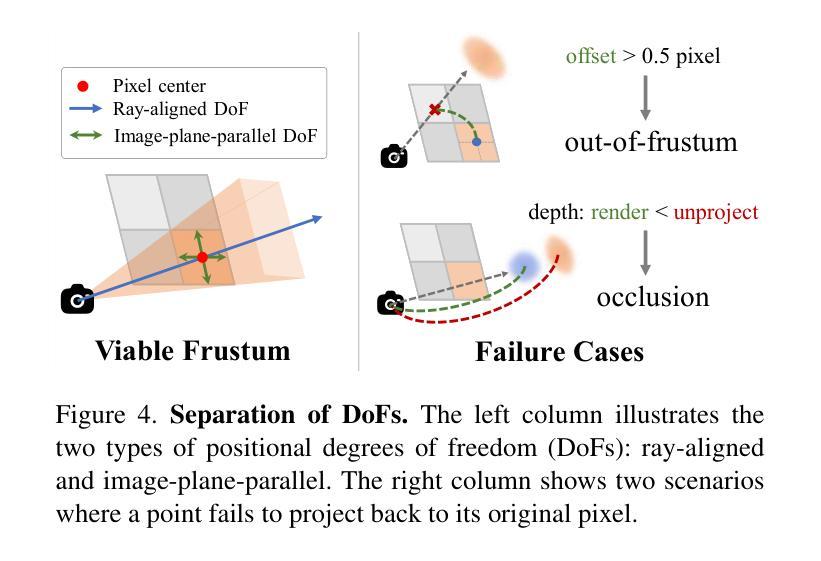
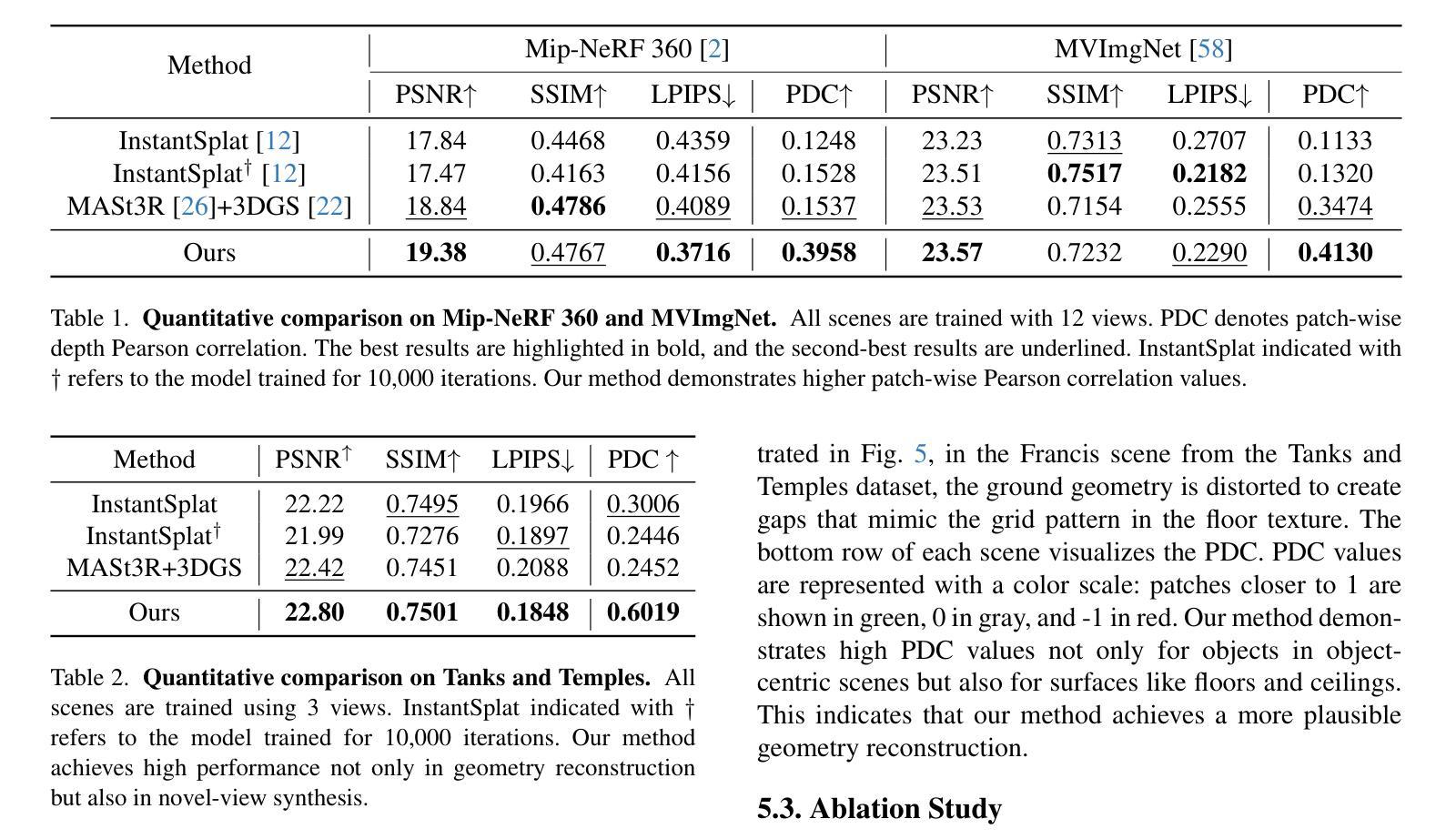
Improving Geometry in Sparse-View 3DGS via Reprojection-based DoF Separation
Authors:Yongsung Kim, Minjun Park, Jooyoung Choi, Sungroh Yoon
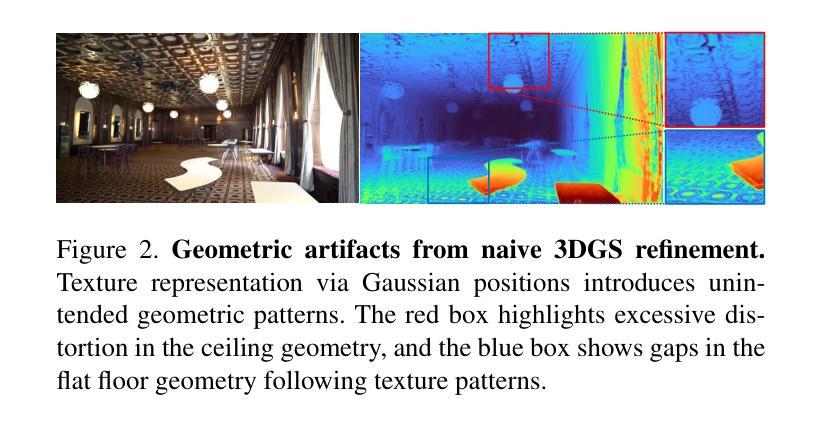
Recent learning-based Multi-View Stereo models have demonstrated state-of-the-art performance in sparse-view 3D reconstruction. However, directly applying 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) as a refinement step following these models presents challenges. We hypothesize that the excessive positional degrees of freedom (DoFs) in Gaussians induce geometry distortion, fitting color patterns at the cost of structural fidelity. To address this, we propose reprojection-based DoF separation, a method distinguishing positional DoFs in terms of uncertainty: image-plane-parallel DoFs and ray-aligned DoF. To independently manage each DoF, we introduce a reprojection process along with tailored constraints for each DoF. Through experiments across various datasets, we confirm that separating the positional DoFs of Gaussians and applying targeted constraints effectively suppresses geometric artifacts, producing reconstruction results that are both visually and geometrically plausible.
最近的学习型多视角立体模型已在稀疏视角的3D重建中展现出最先进的性能。然而,将这些模型应用于直接对3D高斯贴合进行精细调整面临挑战。我们假设高斯中过度的位置自由度会引发几何失真,导致结构忠诚度受到色彩模式的影响。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了基于重新投影的自由度分离方法,该方法通过不确定性来区分位置自由度:图像平面平行自由度和射线对齐自由度。为了独立管理每个自由度,我们引入了重新投影过程并为每个自由度量身定制了约束条件。通过在不同数据集上的实验,我们证实了分离高斯的位置自由度和应用有针对性的约束条件可以有效地抑制几何伪影,产生视觉和几何上合理的重建结果。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 11 pages
Summary
近期基于学习的Multi-View Stereo模型在稀疏视图3D重建中表现卓越。然而,直接应用3D高斯涂抹(3DGS)作为后续优化步骤存在挑战。本研究提出基于再投影的自由度分离(DoF)方法,根据不确定性区分高斯分布中的位置自由度,包括图像平面并行DoF和射线对齐DoF。通过独立管理每个自由度并引入针对每个自由度的定制约束,有效抑制几何伪影,生成视觉和几何上均合理的重建结果。
Key Takeaways
- 学习型Multi-View Stereo模型在稀疏视图3D重建中表现领先。
- 3DGS作为优化步骤存在挑战,主要由于高斯分布中的过多位置自由度引发几何失真。
- 提出基于再投影的自由度分离方法,能有效区分并管理高斯分布中的位置自由度。
- 通过实验验证,自由度分离及针对性约束有助于抑制几何伪影。
- 该方法能生成视觉和几何上均合理的重建结果。
- 再投影过程和定制约束对于管理不同的位置自由度至关重要。
点此查看论文截图

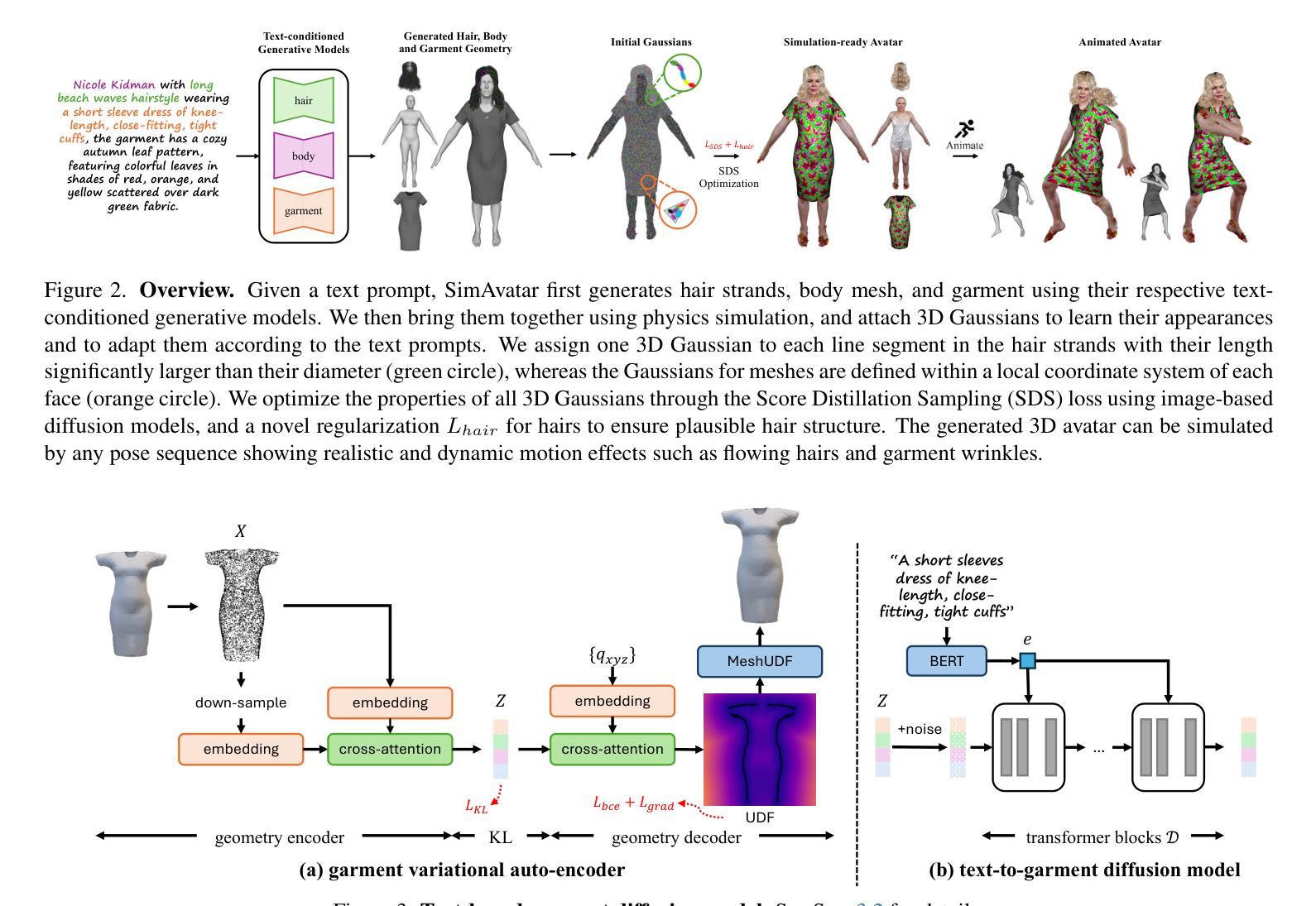
SimAvatar: Simulation-Ready Avatars with Layered Hair and Clothing
Authors:Xueting Li, Ye Yuan, Shalini De Mello, Gilles Daviet, Jonathan Leaf, Miles Macklin, Jan Kautz, Umar Iqbal
We introduce SimAvatar, a framework designed to generate simulation-ready clothed 3D human avatars from a text prompt. Current text-driven human avatar generation methods either model hair, clothing, and the human body using a unified geometry or produce hair and garments that are not easily adaptable for simulation within existing simulation pipelines. The primary challenge lies in representing the hair and garment geometry in a way that allows leveraging established prior knowledge from foundational image diffusion models (e.g., Stable Diffusion) while being simulation-ready using either physics or neural simulators. To address this task, we propose a two-stage framework that combines the flexibility of 3D Gaussians with simulation-ready hair strands and garment meshes. Specifically, we first employ three text-conditioned 3D generative models to generate garment mesh, body shape and hair strands from the given text prompt. To leverage prior knowledge from foundational diffusion models, we attach 3D Gaussians to the body mesh, garment mesh, as well as hair strands and learn the avatar appearance through optimization. To drive the avatar given a pose sequence, we first apply physics simulators onto the garment meshes and hair strands. We then transfer the motion onto 3D Gaussians through carefully designed mechanisms for each body part. As a result, our synthesized avatars have vivid texture and realistic dynamic motion. To the best of our knowledge, our method is the first to produce highly realistic, fully simulation-ready 3D avatars, surpassing the capabilities of current approaches.
我们介绍了SimAvatar框架,该框架旨在从文本提示生成可用于模拟的穿衣3D人类角色。现有的文本驱动的人类角色生成方法要么使用统一的几何图形对头发、服装和人体进行建模,要么生成无法在现有模拟管道中进行模拟的头发和服装。主要挑战在于以一种方式表示头发和服装的几何形状,允许利用基础图像扩散模型(例如Stable Diffusion)的现有先验知识,同时使用物理或神经模拟进行模拟准备。为了解决这一任务,我们提出了一个两阶段的框架,结合了3D高斯值的灵活性和可模拟的头发束和服装网格。具体来说,我们首先采用三个文本控制的3D生成模型,根据给定的文本提示生成服装网格、身体形状和头发束。为了利用基础扩散模型的先验知识,我们将3D高斯值附加到身体网格、服装网格和头发束上,并通过优化学习角色外观。为了在给定的姿势序列驱动下驱动角色,我们首先对服装网格和头发束应用物理模拟器。然后,通过针对每个身体部位精心设计的机制,将运动转移到3D高斯值上。因此,我们合成的角色具有生动的纹理和逼真的动态运动。据我们所知,我们的方法是第一个产生高度逼真、完全模拟准备的3D角色的方法,超越了当前方法的能力。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project website: https://nvlabs.github.io/SimAvatar/
Summary
本文介绍了SimAvatar框架,该框架能够从文本提示生成可用于模拟的穿衣3D人类角色。文章主要讨论了当前文本驱动的人类角色生成方法面临的挑战,并提出了一个两阶段框架来解决这些问题。该框架结合了3D高斯模型的灵活性,可生成逼真的头发和服装网格,并通过物理或神经网络模拟器进行模拟。通过文本提示生成服装网格、人体形态和头发线条,利用基础扩散模型的先验知识,通过优化学习角色外观。此外,该框架还能够根据姿势序列驱动角色动作,将物理模拟的运动转移到每个身体部位的3D高斯模型中。总之,该方法生成的合成角色具有逼真的纹理和动态运动效果。
Key Takeaways
- SimAvatar是一个能够从文本提示生成可用于模拟的穿衣3D人类角色的框架。
- 当前文本驱动的角色生成方法面临的挑战在于如何表示头发和服装几何体,以便利用基础图像扩散模型的先验知识,同时适应物理或神经网络模拟器的模拟。
- SimAvatar采用两阶段框架来解决这个问题,结合3D高斯模型的灵活性,生成逼真的头发和服装网格。
- 通过文本提示生成服装网格、人体形态和头发线条,并利用基础扩散模型的先验知识通过优化学习角色外观。
- SimAvatar能够将物理模拟的运动转移到每个身体部位的3D高斯模型中,实现角色的动态运动效果。
- SimAvatar生成的合成角色具有逼真的纹理和动态运动效果。
点此查看论文截图

CAT4D: Create Anything in 4D with Multi-View Video Diffusion Models
Authors:Rundi Wu, Ruiqi Gao, Ben Poole, Alex Trevithick, Changxi Zheng, Jonathan T. Barron, Aleksander Holynski
We present CAT4D, a method for creating 4D (dynamic 3D) scenes from monocular video. CAT4D leverages a multi-view video diffusion model trained on a diverse combination of datasets to enable novel view synthesis at any specified camera poses and timestamps. Combined with a novel sampling approach, this model can transform a single monocular video into a multi-view video, enabling robust 4D reconstruction via optimization of a deformable 3D Gaussian representation. We demonstrate competitive performance on novel view synthesis and dynamic scene reconstruction benchmarks, and highlight the creative capabilities for 4D scene generation from real or generated videos. See our project page for results and interactive demos: https://cat-4d.github.io/.
我们提出了CAT4D方法,这是一种从单目视频中创建4D(动态3D)场景的方法。CAT4D利用在多种数据集组合上训练的多元视图视频扩散模型,能够在任何指定的相机姿态和时间戳进行新颖视图合成。结合新颖采样方法,此模型能将单一的单目视频转化为多元视图视频,通过优化可变形的3D高斯表示法实现稳健的4D重建。我们在新颖视图合成和动态场景重建基准测试中展示了竞争力,并突出了从真实或生成视频中生成4D场景的创意能力。欲查看结果和交互演示,请访问我们的项目页面:https://cat-4d.github.io/。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Project page: https://cat-4d.github.io/
Summary
本文介绍了CAT4D方法,该方法能够从单目视频中创建4D(动态3D)场景。CAT4D利用在多种数据集上训练的多元视角视频扩散模型,能够在指定的相机姿态和时间戳进行新颖视角的合成。结合新颖的采样方法,该模型能够将单目视频转化为多元视角视频,通过优化可变形的3D高斯表示,实现稳健的4D重建。在新型视角合成和动态场景重建基准测试中表现出竞争力,并展示了从真实或生成的视频中进行4D场景生成的创意能力。更多结果和互动演示请参见项目页面。
Key Takeaways
- CAT4D方法能从单目视频创建4D场景。
- 利用多元视角视频扩散模型进行新颖视角的合成。
- 结合采样方法,将单目视频转化为多元视角视频。
- 通过优化可变形3D高斯表示,实现稳健的4D重建。
- 在新型视角合成和动态场景重建基准测试中表现有竞争力。
- 具备从真实或生成的视频进行4D场景生成的创意能力。
点此查看论文截图


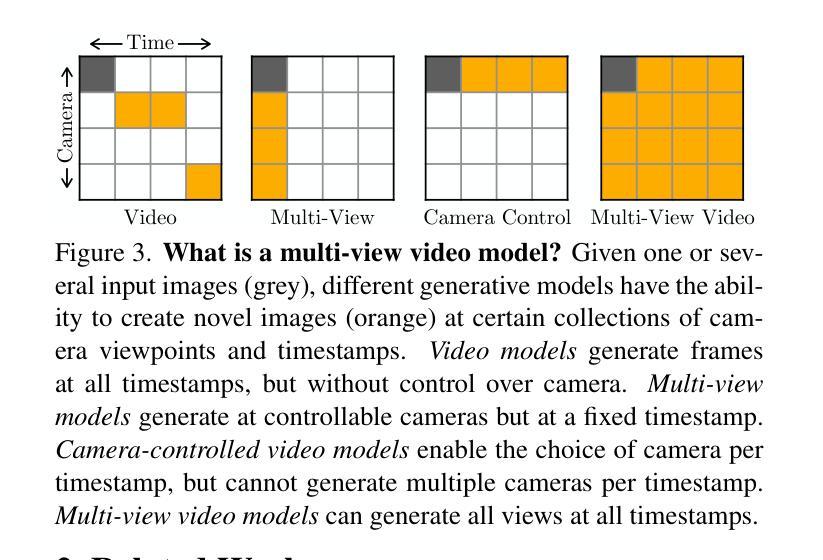
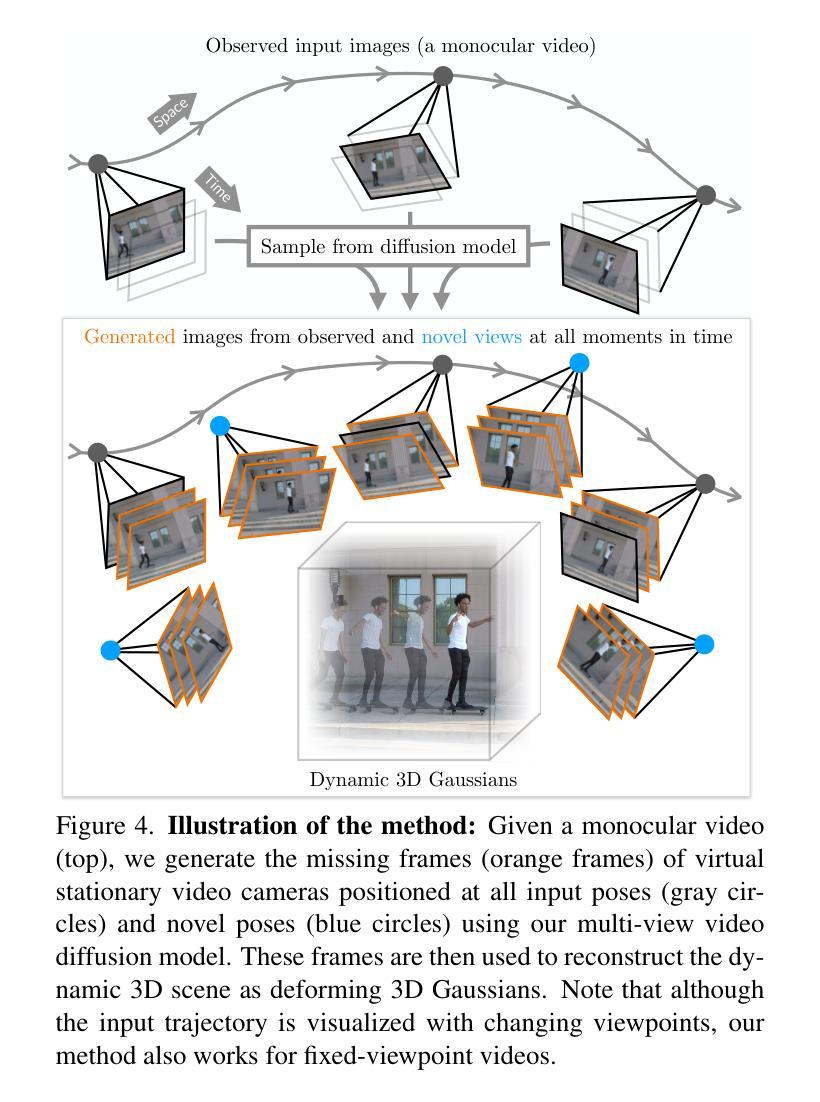
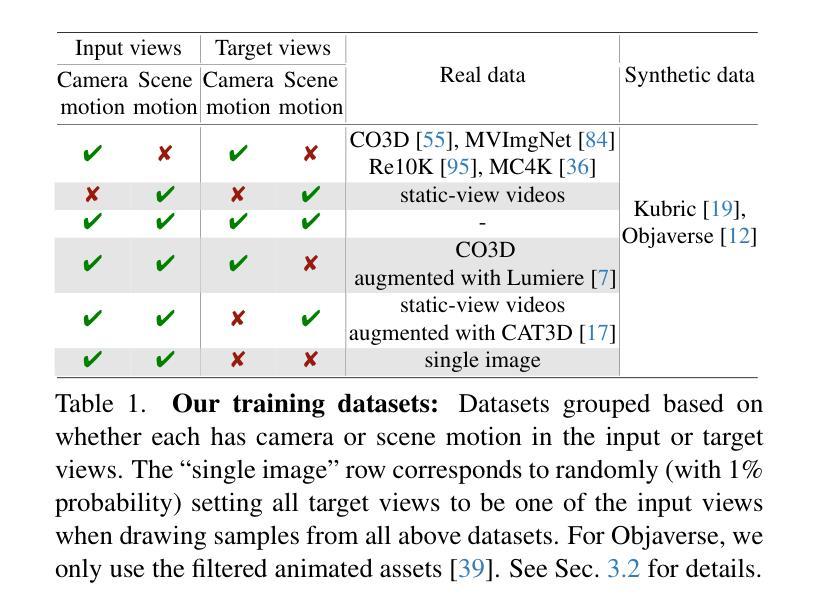
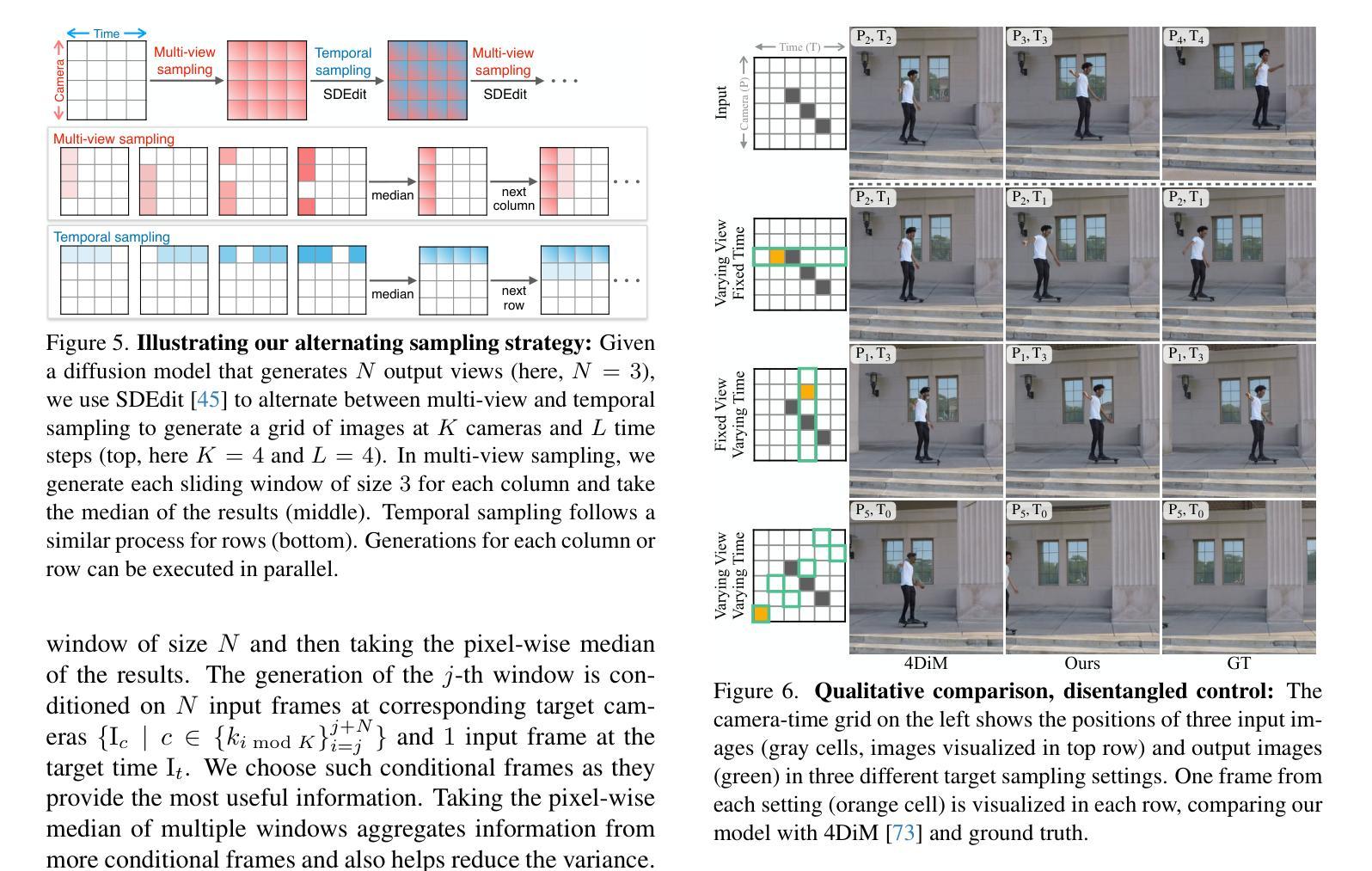
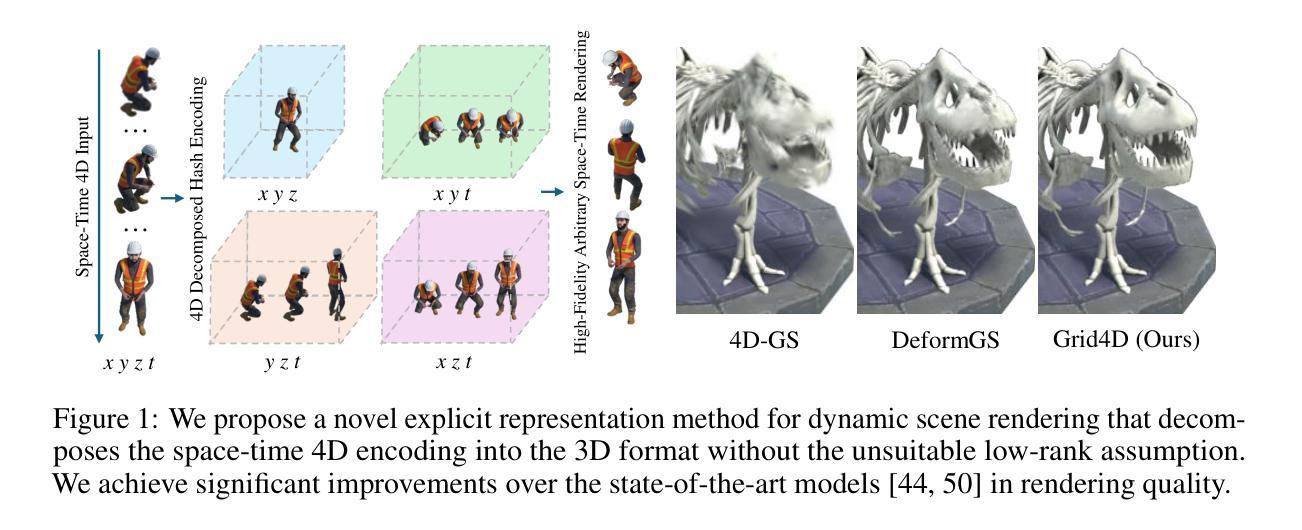
Grid4D: 4D Decomposed Hash Encoding for High-fidelity Dynamic Gaussian Splatting
Authors:Jiawei Xu, Zexin Fan, Jian Yang, Jin Xie
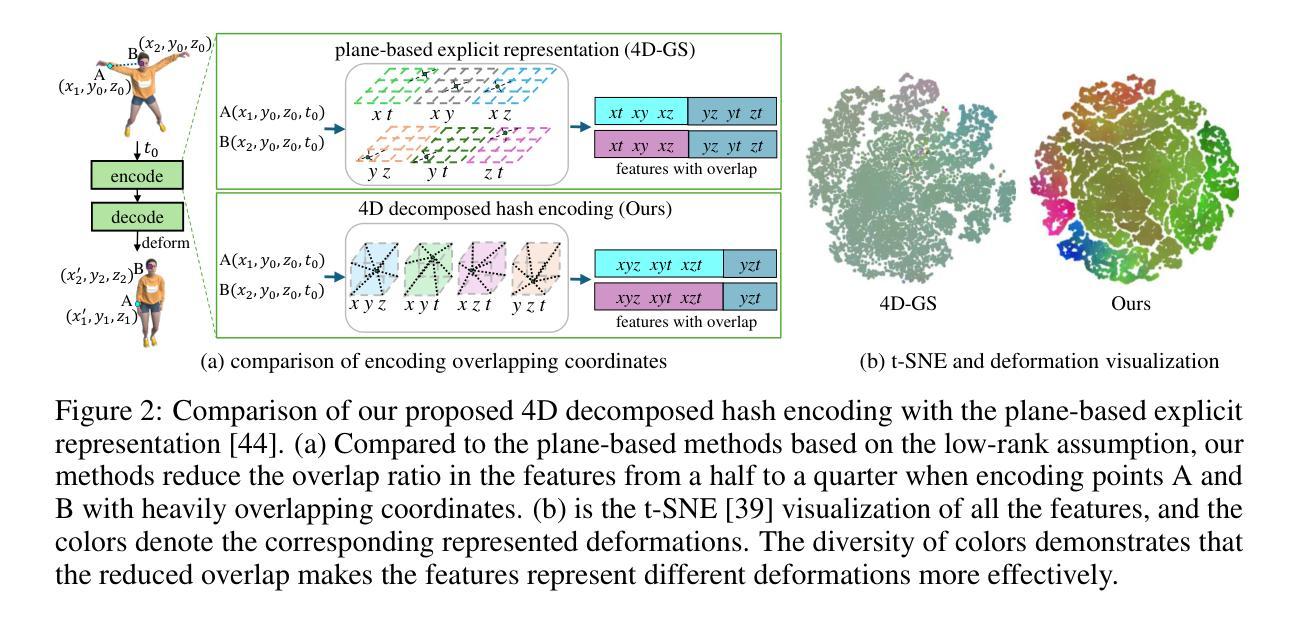
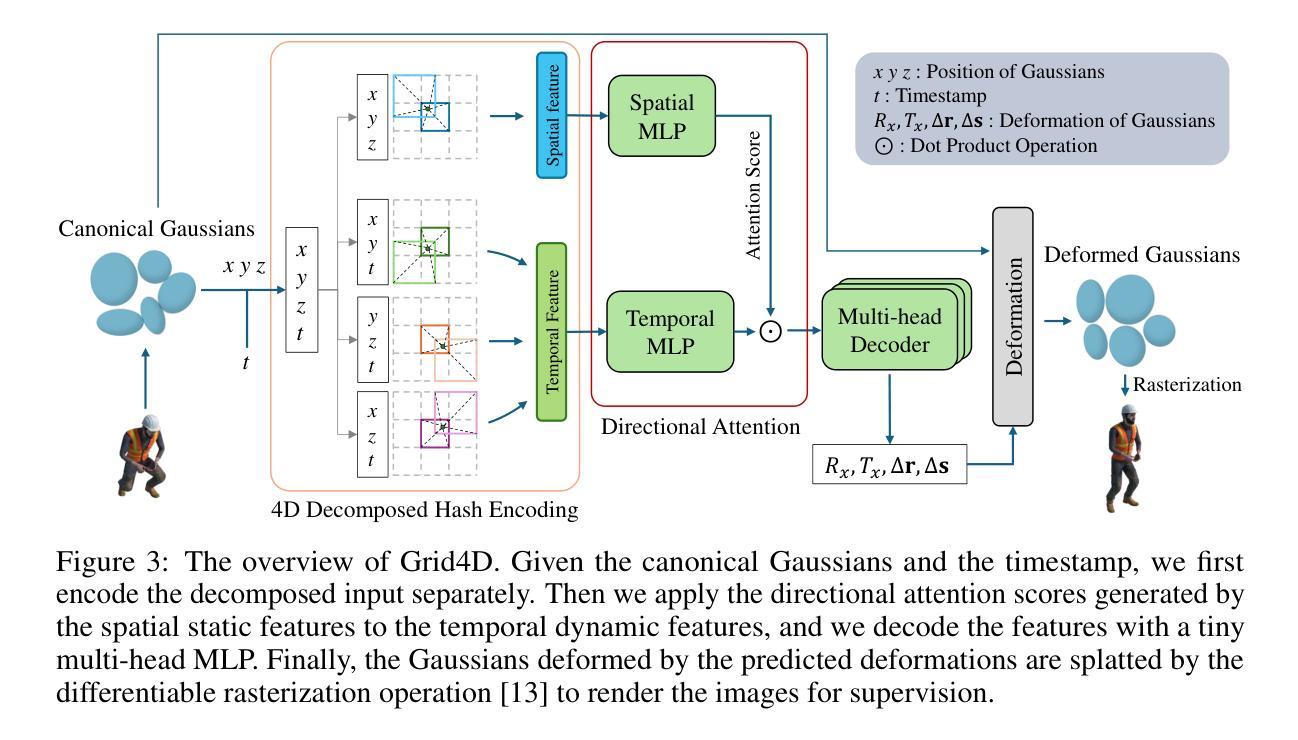
Recently, Gaussian splatting has received more and more attention in the field of static scene rendering. Due to the low computational overhead and inherent flexibility of explicit representations, plane-based explicit methods are popular ways to predict deformations for Gaussian-based dynamic scene rendering models. However, plane-based methods rely on the inappropriate low-rank assumption and excessively decompose the space-time 4D encoding, resulting in overmuch feature overlap and unsatisfactory rendering quality. To tackle these problems, we propose Grid4D, a dynamic scene rendering model based on Gaussian splatting and employing a novel explicit encoding method for the 4D input through the hash encoding. Different from plane-based explicit representations, we decompose the 4D encoding into one spatial and three temporal 3D hash encodings without the low-rank assumption. Additionally, we design a novel attention module that generates the attention scores in a directional range to aggregate the spatial and temporal features. The directional attention enables Grid4D to more accurately fit the diverse deformations across distinct scene components based on the spatial encoded features. Moreover, to mitigate the inherent lack of smoothness in explicit representation methods, we introduce a smooth regularization term that keeps our model from the chaos of deformation prediction. Our experiments demonstrate that Grid4D significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art models in visual quality and rendering speed.
最近,高斯涂斑技术在静态场景渲染领域越来越受到关注。由于显式表示法的计算开销低和内在灵活性,基于平面的显式方法成为预测高斯动态场景渲染模型的变形的流行方式。然而,基于平面的方法依赖于不适当的低秩假设,过度分解了时空4D编码,导致特征重叠过多和渲染质量不满意。为了解决这些问题,我们提出了Grid4D,这是一种基于高斯涂斑的动态场景渲染模型,采用一种新的显式编码方法对4D输入进行哈希编码。不同于基于平面的显式表示方法,我们将4D编码分解为一个空间编码和三个临时3D哈希编码,没有低秩假设。此外,我们设计了一个新型注意力模块,该模块在定向范围内生成注意力分数,以聚合空间和时间特征。定向注意力使Grid4D能够基于空间编码特征更准确地适应不同场景组件的多样变形。此外,为了缓解显式表示方法固有的不光滑性,我们引入了一个平滑正则化项,使我们的模型能够避免变形预测的混乱。我们的实验表明,Grid4D在视觉质量和渲染速度上显著优于最新模型。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF Accepted by NeurIPS 2024
Summary
基于高斯贴图的动态场景渲染中,Grid4D模型采用新型显式编码方法,以4D输入为基础,不使用低阶假设,将空间时间分解为1个空间及三个临时三维哈希编码。模型引入定向注意力模块,提升对场景组件不同变形的拟合精度。此外,为了增强显式表示的平滑性,加入了平滑正则化项。Grid4D在视觉质量和渲染速度上均超越了现有模型。
Key Takeaways
- Gaussian splatting在静态场景渲染中受到关注。
- 平面基于的显式方法是预测高斯动态场景变形的流行方法,但它们依赖于不适当的低阶假设并过度分解空间时间编码。
- Grid4D是一个基于高斯贴图的动态场景渲染模型,采用新型显式编码方法处理4D输入,不使用低阶假设。
- Grid4D将空间时间编码分解为空间与临时三维哈希编码。引入定向注意力模块提升对不同场景组件变形的拟合精度。
- 为了增强显式表示的平滑性,Grid4D加入了平滑正则化项。
点此查看论文截图

Fast and Efficient: Mask Neural Fields for 3D Scene Segmentation
Authors:Zihan Gao, Lingling Li, Licheng Jiao, Fang Liu, Xu Liu, Wenping Ma, Yuwei Guo, Shuyuan Yang
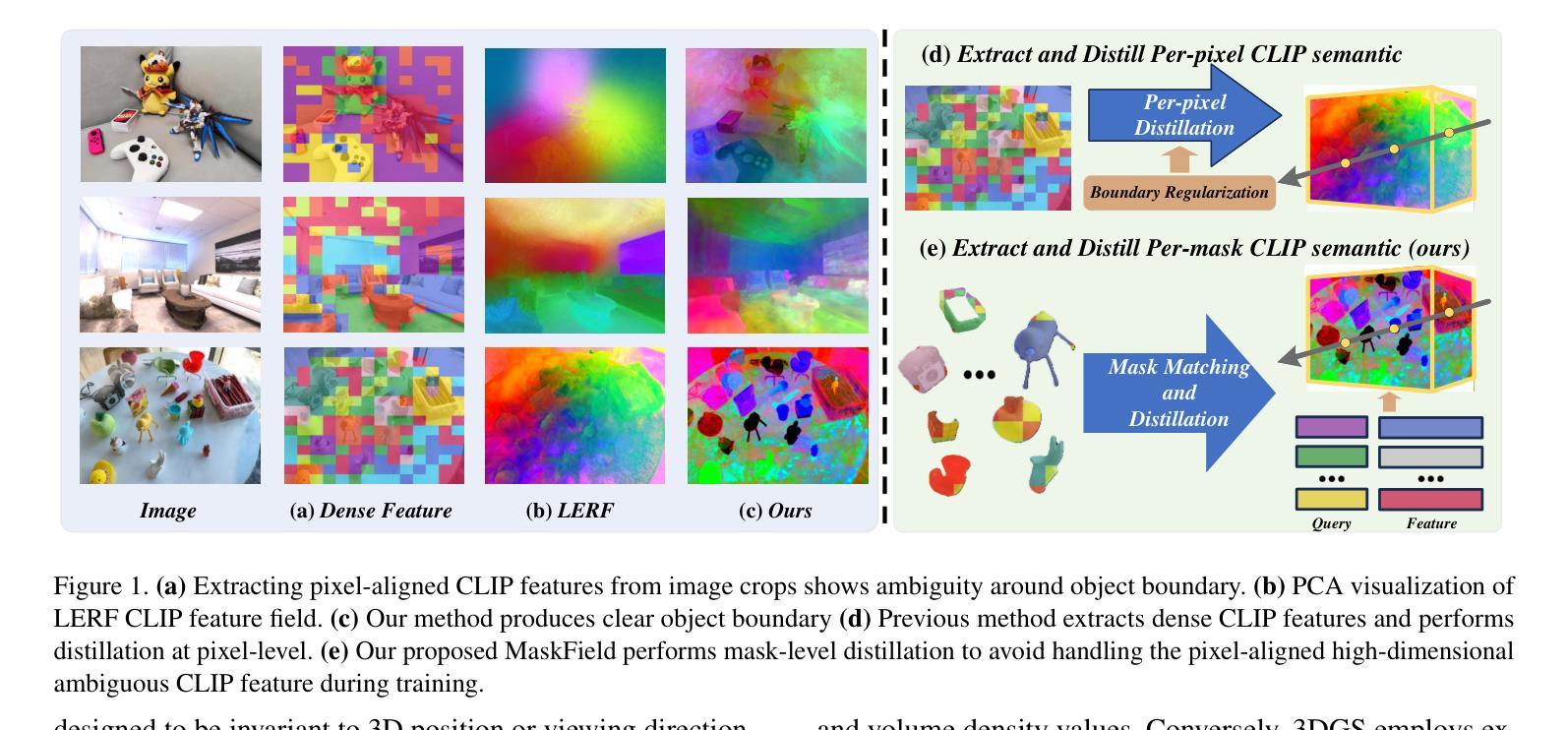
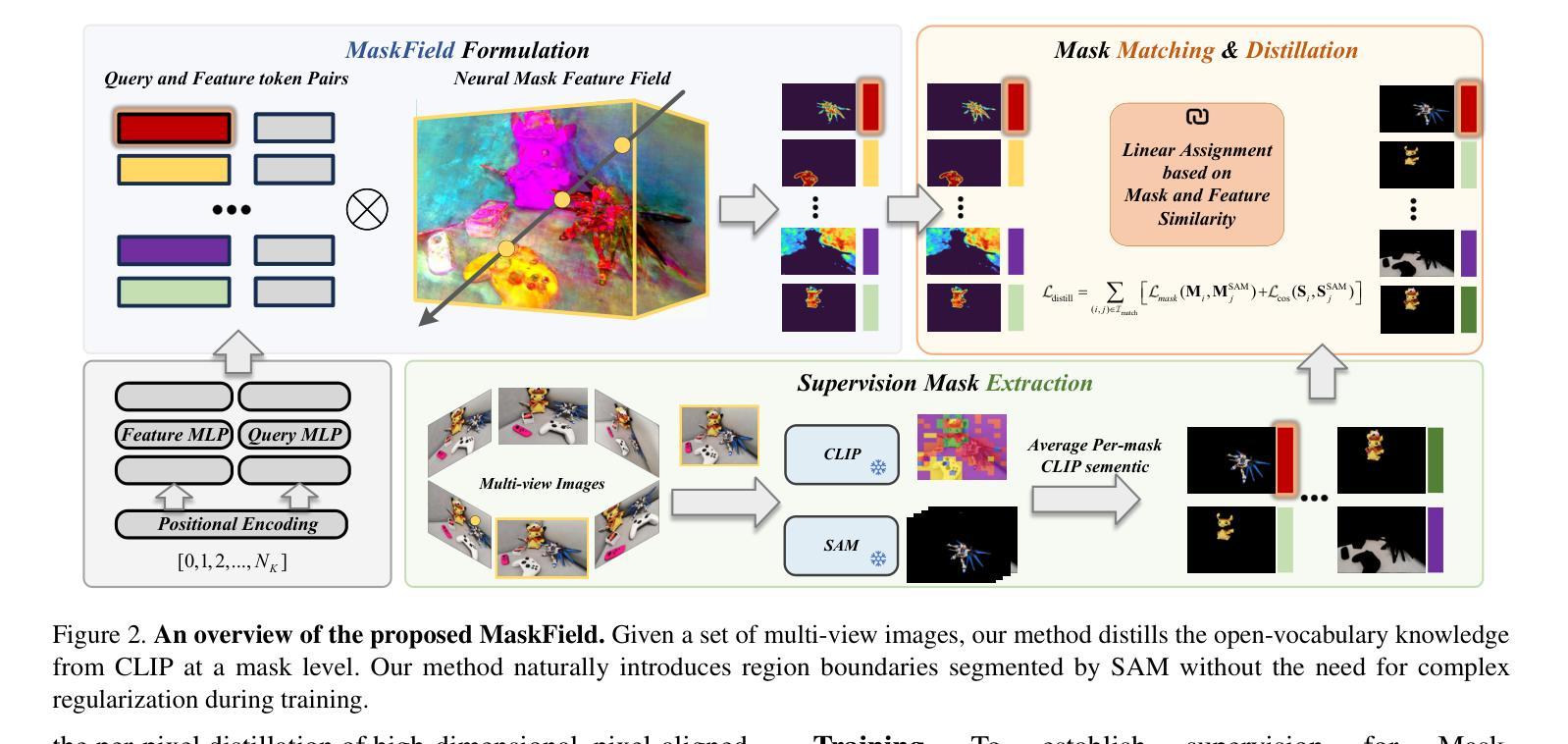
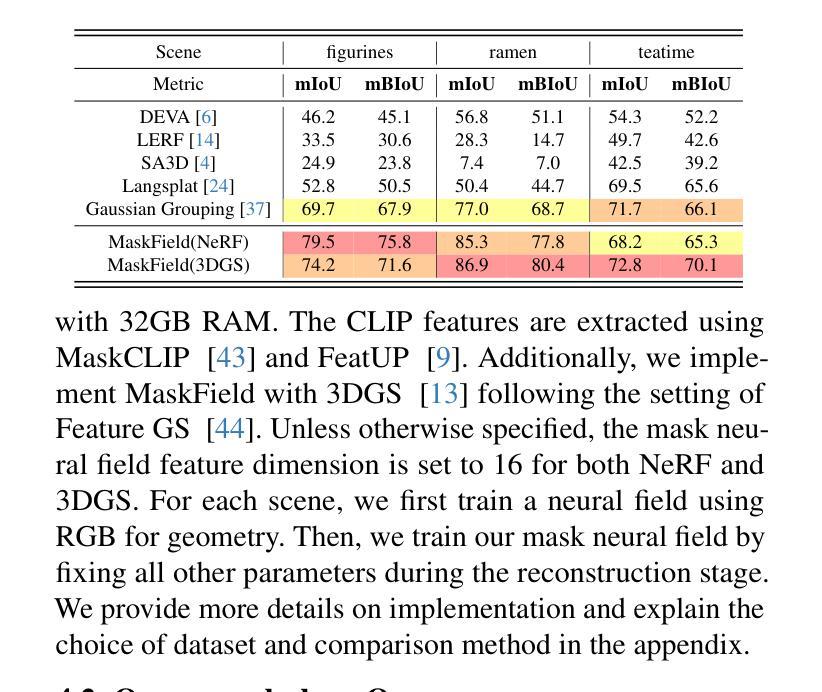
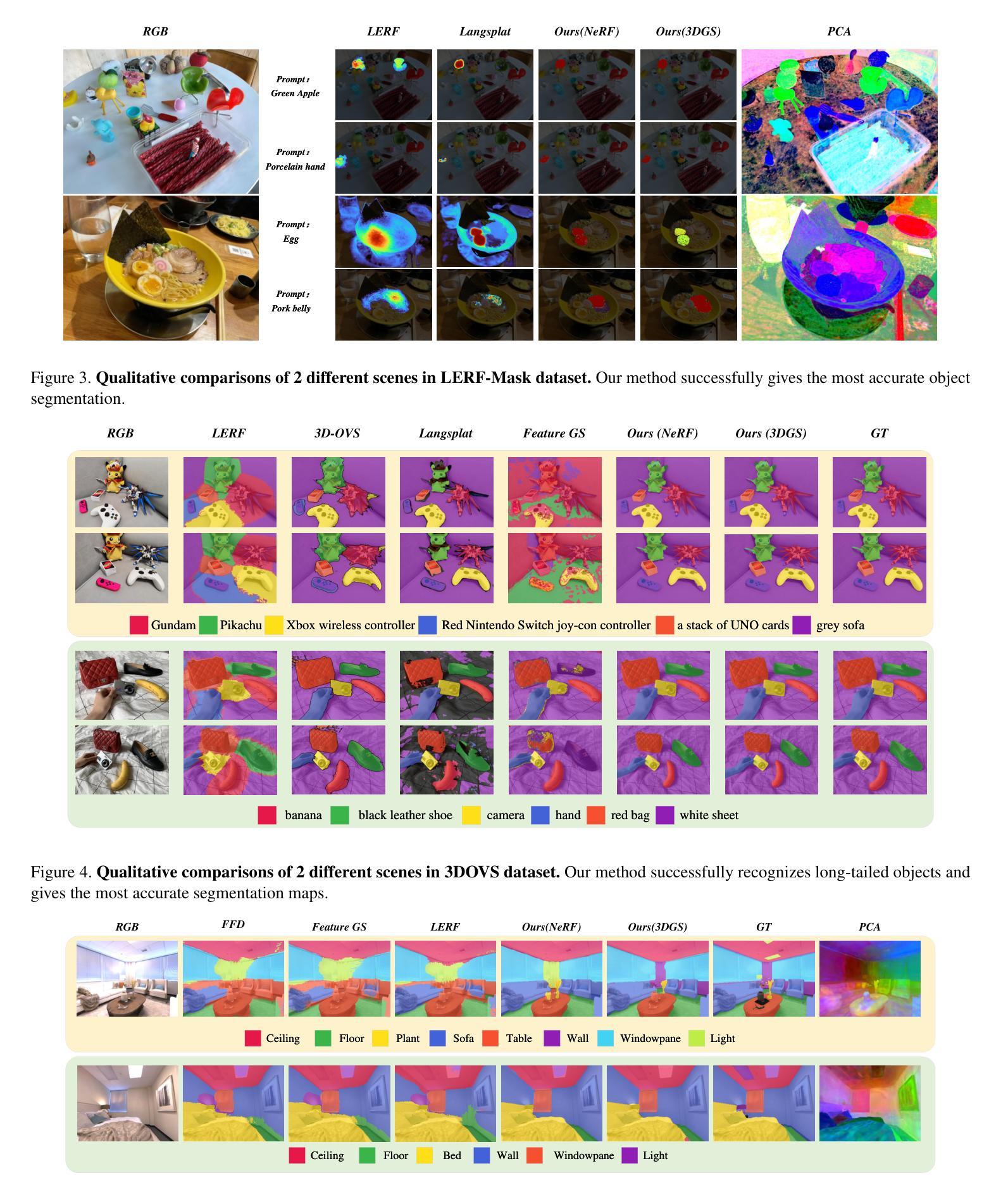
Understanding 3D scenes is a crucial challenge in computer vision research with applications spanning multiple domains. Recent advancements in distilling 2D vision-language foundation models into neural fields, like NeRF and 3DGS, enable open-vocabulary segmentation of 3D scenes from 2D multi-view images without the need for precise 3D annotations. However, while effective, these methods typically rely on the per-pixel distillation of high-dimensional CLIP features, introducing ambiguity and necessitating complex regularization strategies, which adds inefficiency during training. This paper presents MaskField, which enables efficient 3D open-vocabulary segmentation with neural fields from a novel perspective. Unlike previous methods, MaskField decomposes the distillation of mask and semantic features from foundation models by formulating a mask feature field and queries. MaskField overcomes ambiguous object boundaries by naturally introducing SAM segmented object shapes without extra regularization during training. By circumventing the direct handling of dense high-dimensional CLIP features during training, MaskField is particularly compatible with explicit scene representations like 3DGS. Our extensive experiments show that MaskField not only surpasses prior state-of-the-art methods but also achieves remarkably fast convergence. We hope that MaskField will inspire further exploration into how neural fields can be trained to comprehend 3D scenes from 2D models.
理解三维场景是计算机视觉研究中的一项关键挑战,其应用跨越多个领域。最近,在将二维视觉语言基础模型蒸馏为神经场(如NeRF和3DGS)方面的进展,使得无需精确的三维注释,即可从二维多视角图像对三维场景进行开放词汇分割。然而,尽管这些方法很有效,但它们通常依赖于高维度CLIP特征的高像素蒸馏,这引入了歧义并需要复杂的正则化策略,从而增加了训练过程中的不效率。本文提出了MaskField,它可以从一个新的角度,使用神经场实现高效的三维开放词汇分割。不同于以往的方法,MaskField通过制定掩膜特征场和查询,来分解基础模型中的掩膜和语义特征的蒸馏。MaskField通过自然引入SAM分割对象形状,克服了模糊的对象边界问题,而无需在训练过程中进行额外的正则化。通过避免训练过程中直接处理密集的高维度CLIP特征,MaskField特别适合与明确的场景表示(如3DGS)兼容。我们的广泛实验表明,MaskField不仅超越了现有的最先进的方法,还实现了显著的快收敛。我们希望MaskField将激发对如何训练神经场以从二维模型理解三维场景的进一步探索。
论文及项目相关链接
PDF 15 pages, 9 figures, Code:https://github.com/keloee/MaskField
Summary
本文提出了MaskField方法,实现了基于神经场的开放词汇表三维场景分割。MaskField通过分解蒸馏过程中的掩膜和语义特征,引入了掩膜特征场和查询机制,有效地避免了物体边界的模糊性。相比依赖高维CLIP特征的方法,MaskField使用场景明确的三维表示(如3DGS)更加高效,训练速度快,超过了现有的最佳方法。希望MaskField能够激发更多关于如何利用神经场从二维模型理解三维场景的探讨。
Key Takeaways
- MaskField是一种基于神经场的开放词汇表三维场景分割方法。
- MaskField通过分解蒸馏过程中的掩膜和语义特征,解决了物体边界模糊的问题。
- MaskField引入掩膜特征场和查询机制,实现了高效的三维场景分割。
- MaskField方法兼容现有的三维场景表示方法(如3DGS)。
- MaskField在训练过程中避免了直接处理密集的高维CLIP特征,提高了训练效率。
- MaskField方法超越了现有的最佳方法,实现了快速收敛。
点此查看论文截图